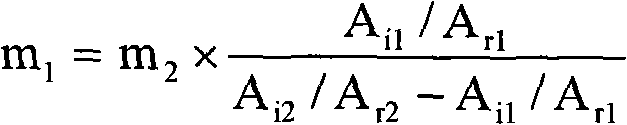Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
113 results about "Dermatan sulfate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dermatan sulfate is a glycosaminoglycan (formerly called a mucopolysaccharide) found mostly in skin, but also in blood vessels, heart valves, tendons, and lungs. It is also referred to as chondroitin sulfate B, although it is no longer classified as a form of chondroitin sulfate by most sources. The formula is C₁₄H₂₁NO₁₅S.
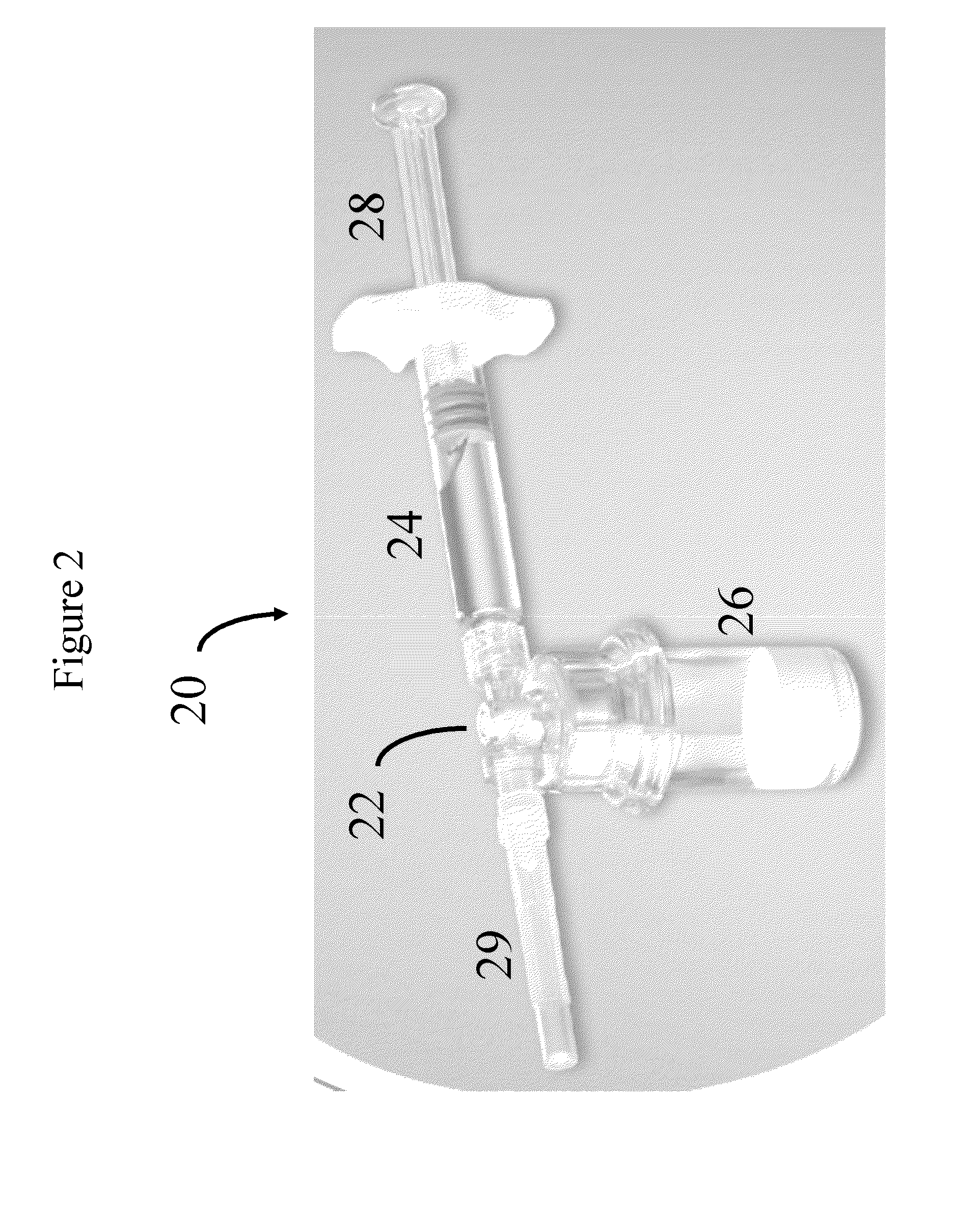
Stabilized Glycosaminoglycan Preparations and Related Methods
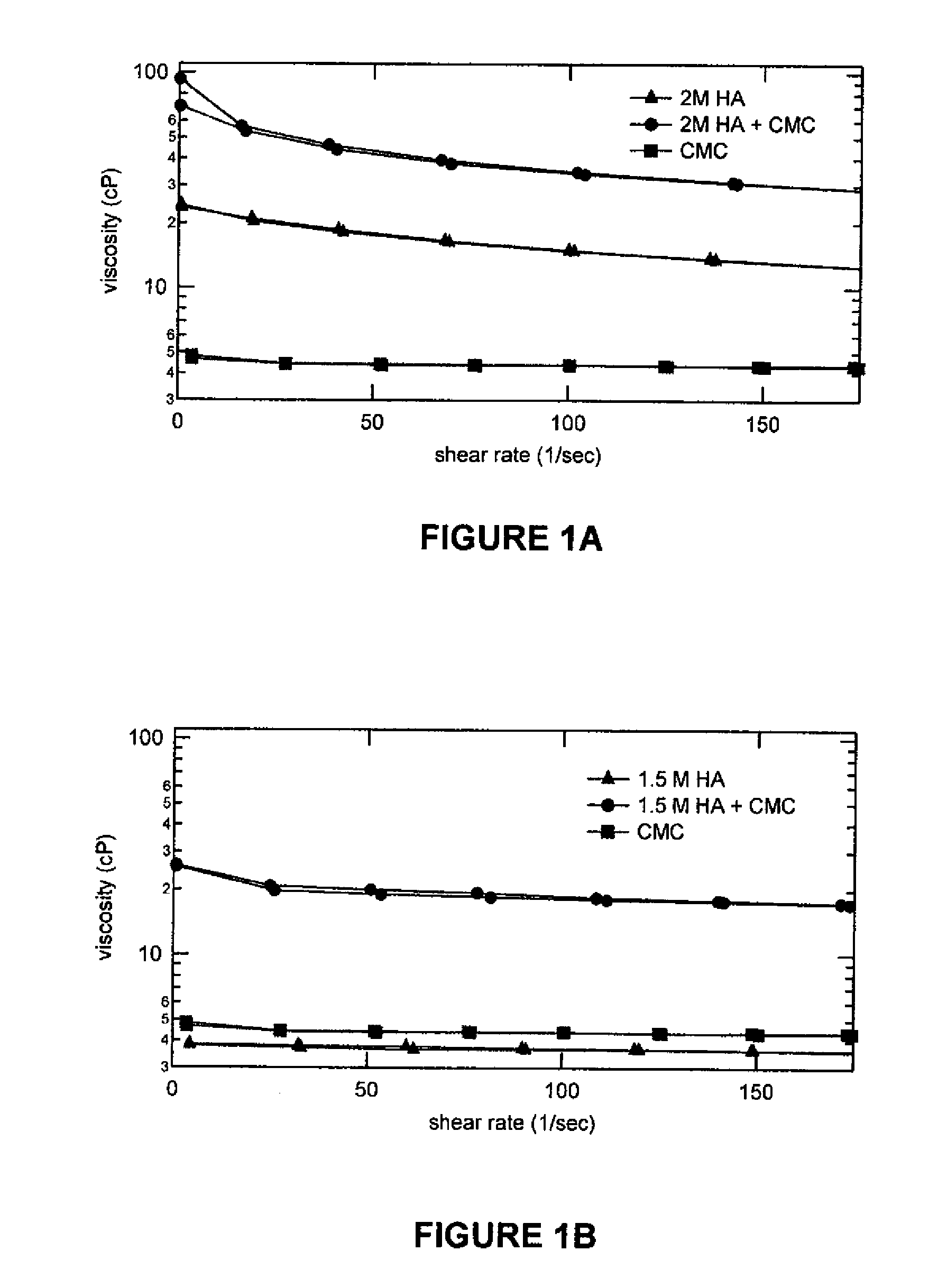
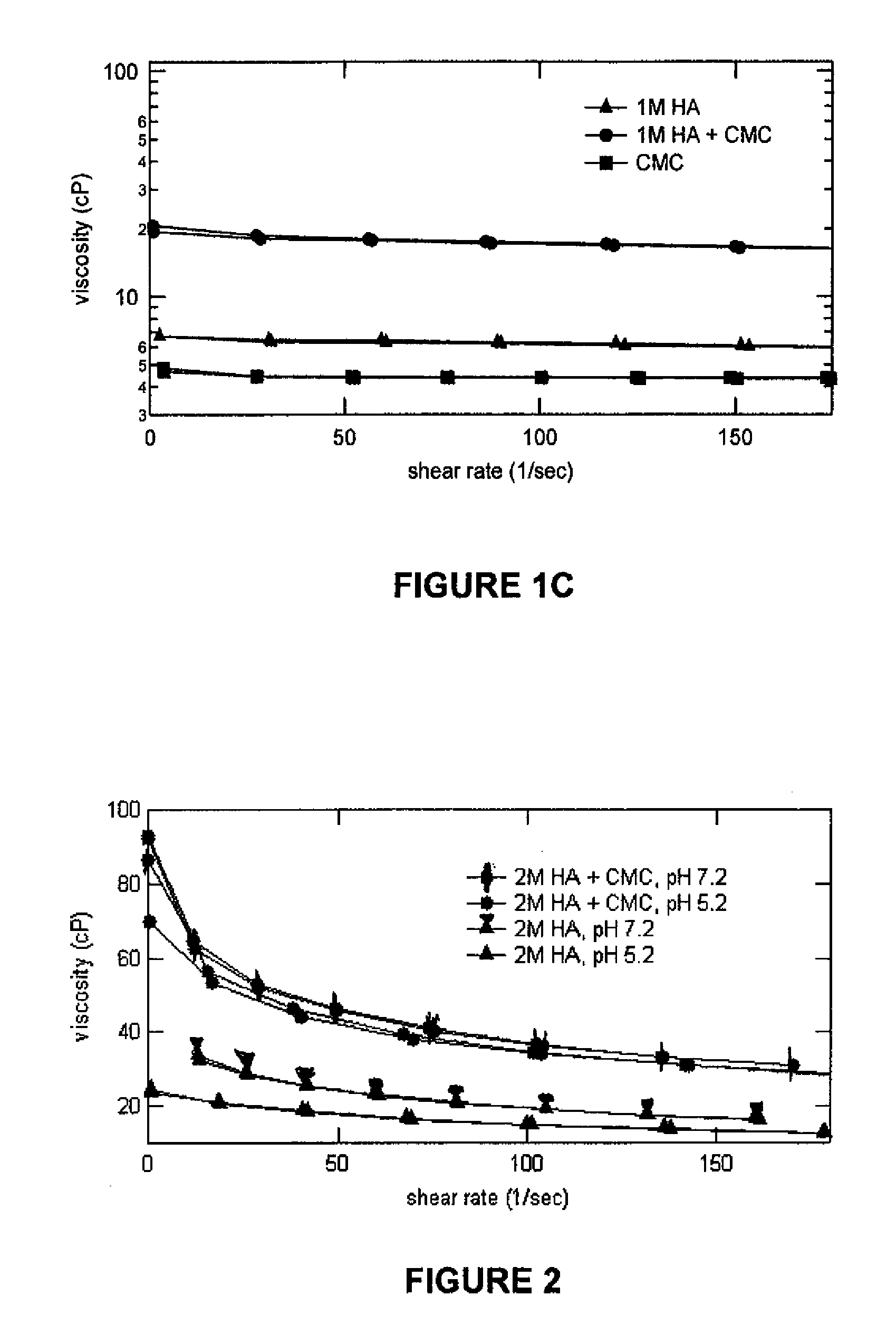
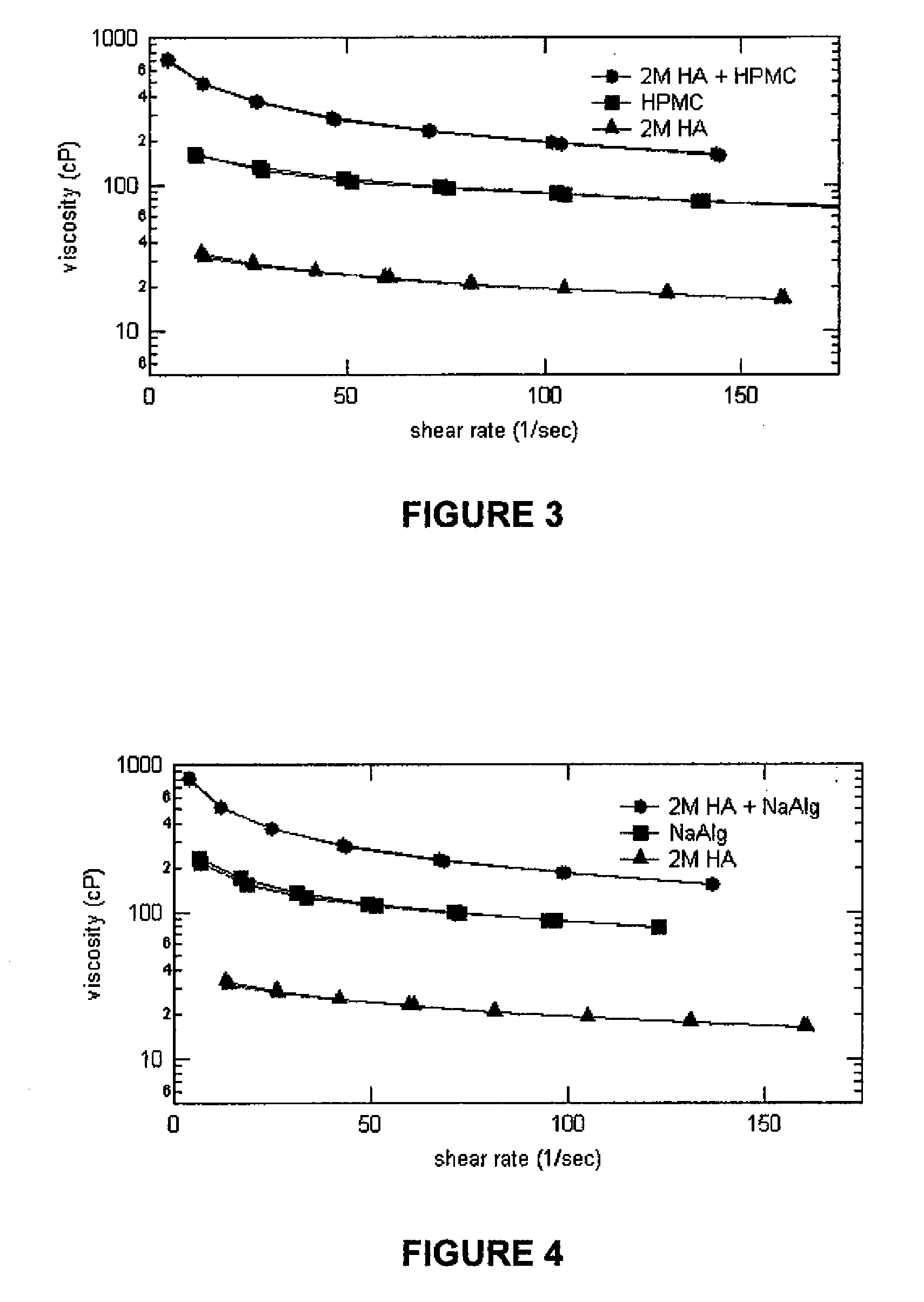
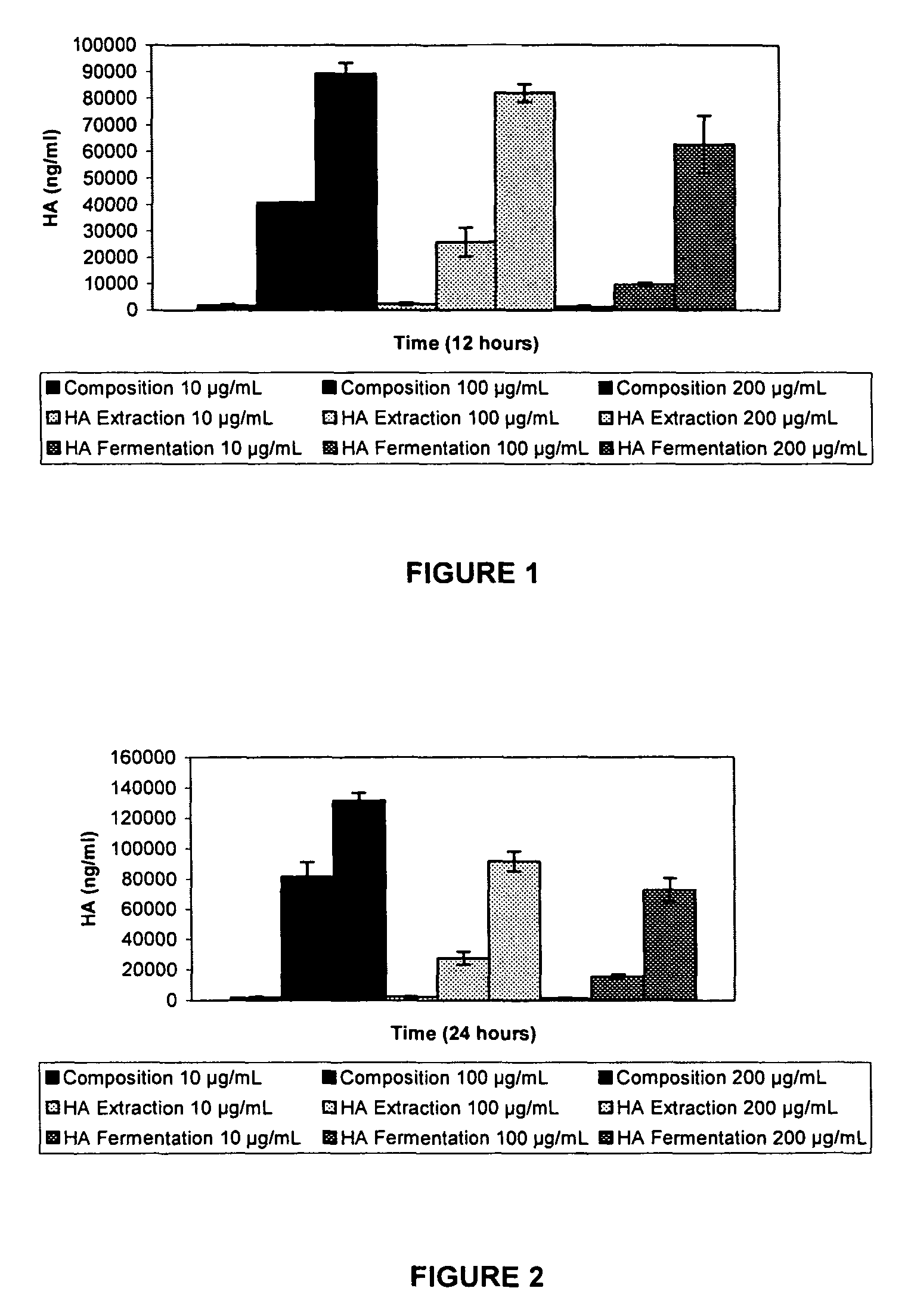
Compositions comprising a glycosaminoglycan (e.g., a hyaluronan, hyaluronic acid, hyaluronate, sodium hyaluronate, dermatan sulfate, karatan sulfate, chondroitin 6-sulfate, heparin, etc.) in combination with at least one component selected from; i) polyglycols (e.g., polyethylene glycol), ii) long chain hydroxy polyanionic polysaccharides (e.g., dextran, sodium alginate, alginic acid, propylene glycol alginate, carboxymethyl cellulose and carboxyethyl cellulose, hydroxyl ethyl starch, hydroxyl propyl methyl cellulose, hydroxy propyl ethyl cellulose, hydroxy propyl cellulose, methyl cellulose, polylysine, polyhistidine, polyhydroxy proline, poly ornithine, polyvinyl pyrolidone, polyvinyl alcohol, chitosan, etc.) and iii) long chain Nitrogen containing polymers (e.g., Polylysine, Polyvinylpyrrolidone, and polyvinyl alcohol). The invention also includes methods for using such compositions (e.g., as substance delivery materials, tissue fillers or bulking agents, as moistening or hydrating agents, etc.)
Owner:S K PHARMA INC
Methods of coating a device using anti-thrombin heparin
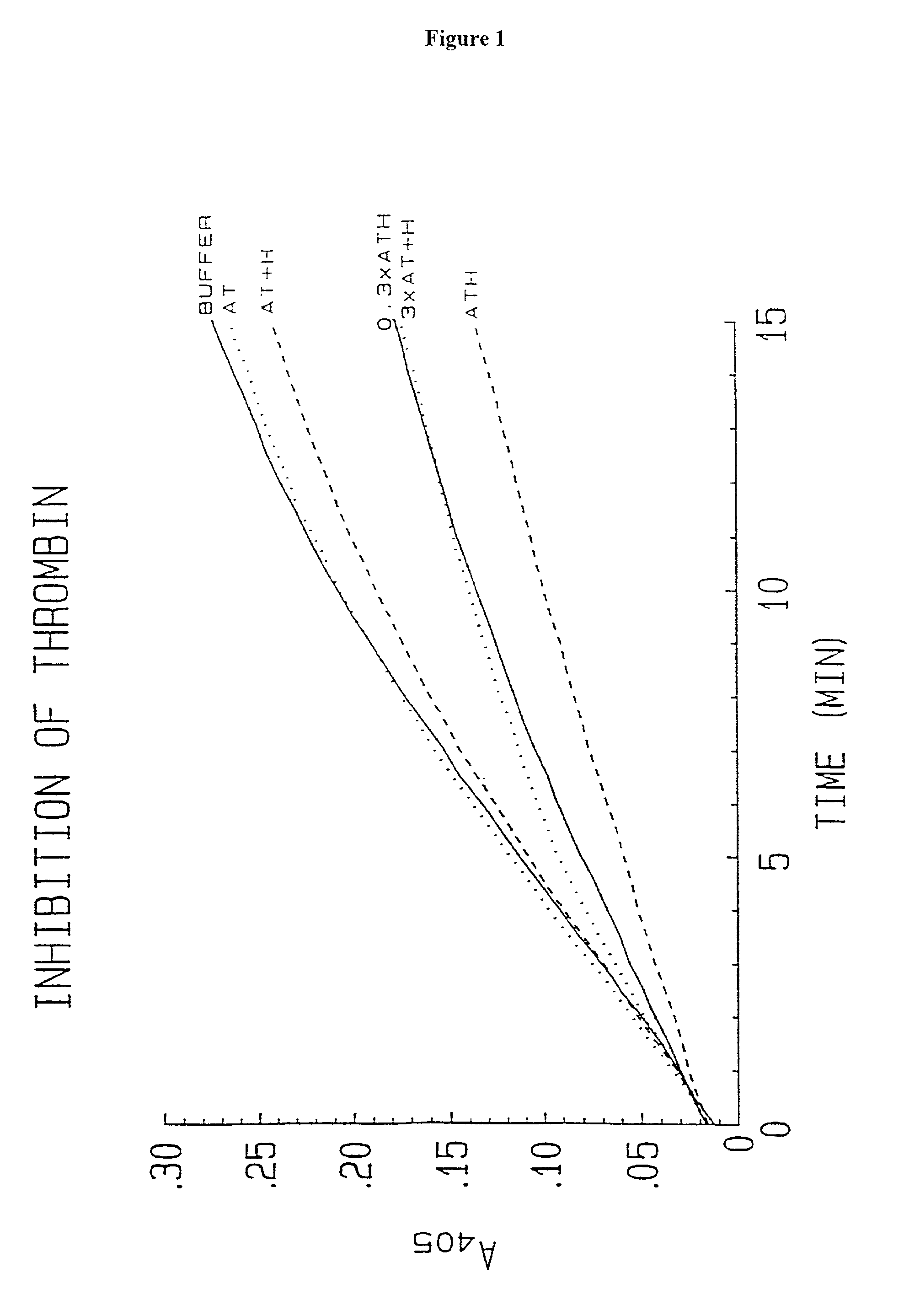
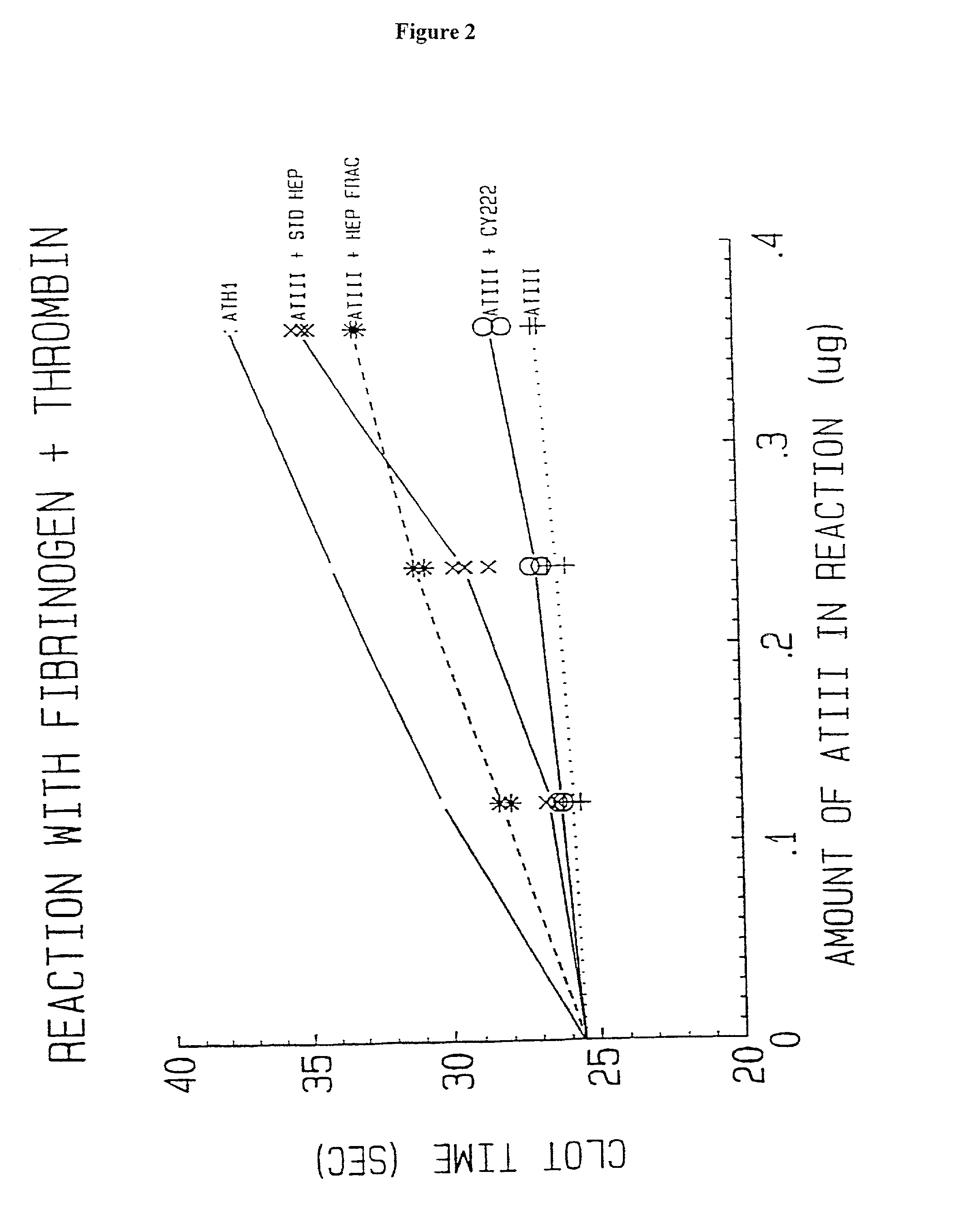
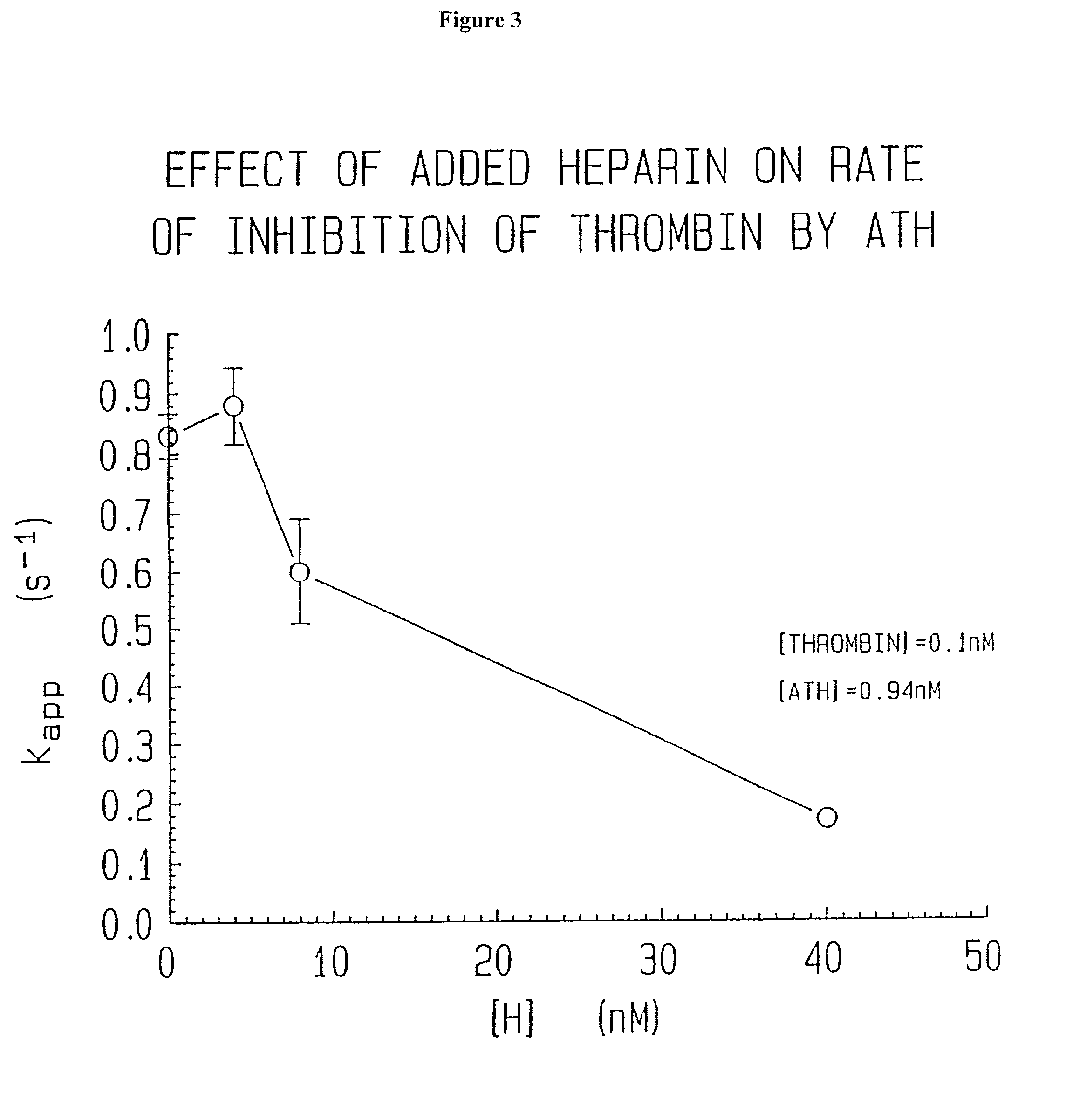
Novel conjugates of glycosaminoglycans, particularly heparin and dermatan sulfate, and amine containing species and therapeutic uses thereof are described. In particular, mild methods of conjugating heparins to proteins, such as antithrombin III and heparin cofactor II, which provide covalent conjugates which retain maximal biological activity are described. Uses of these conjugates to prevent thrombogenesis, in particular in lung airways, such as found in infant and adult respiratory distress syndrome, and on surfaces in contact with blood are also described.
Owner:MCMASTER UNIV
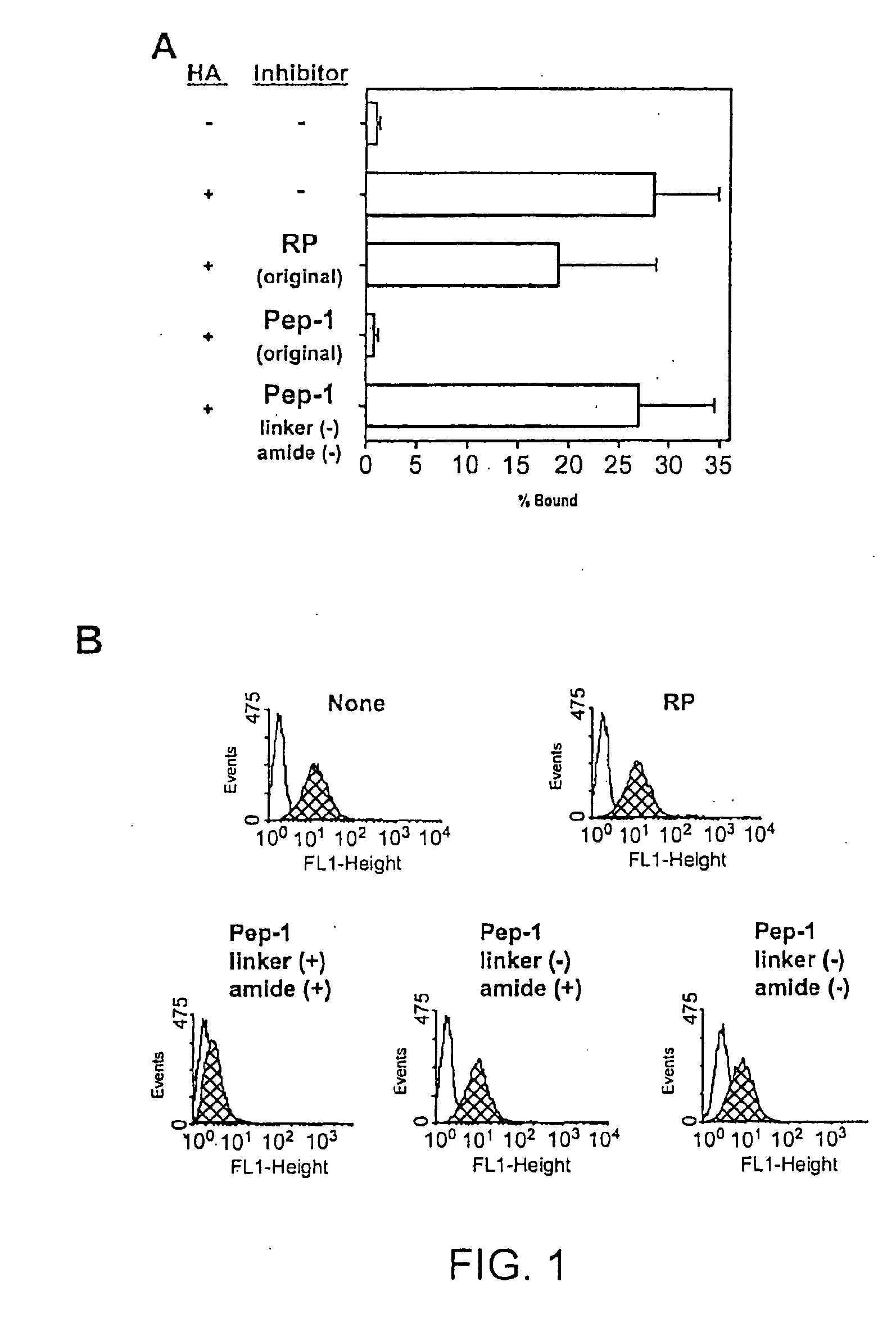
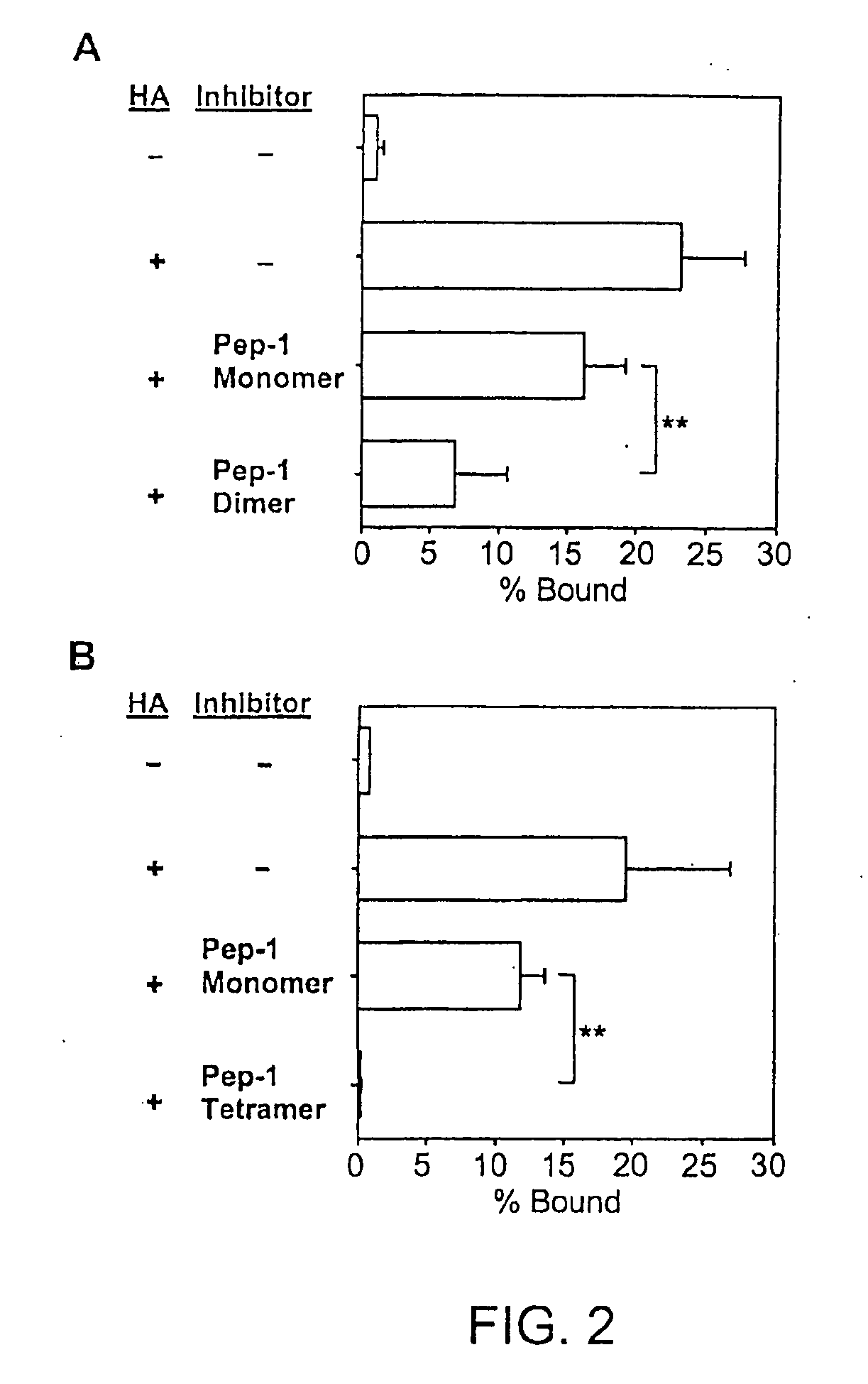
Inhibitors of glycosaminoglycans
InactiveUS20050159343A1Inhibit HA-dependent processInhibit tumorigensis and metastasisConnective tissue peptidesAntipyreticChondroitin Sulfate CAutoimmune condition
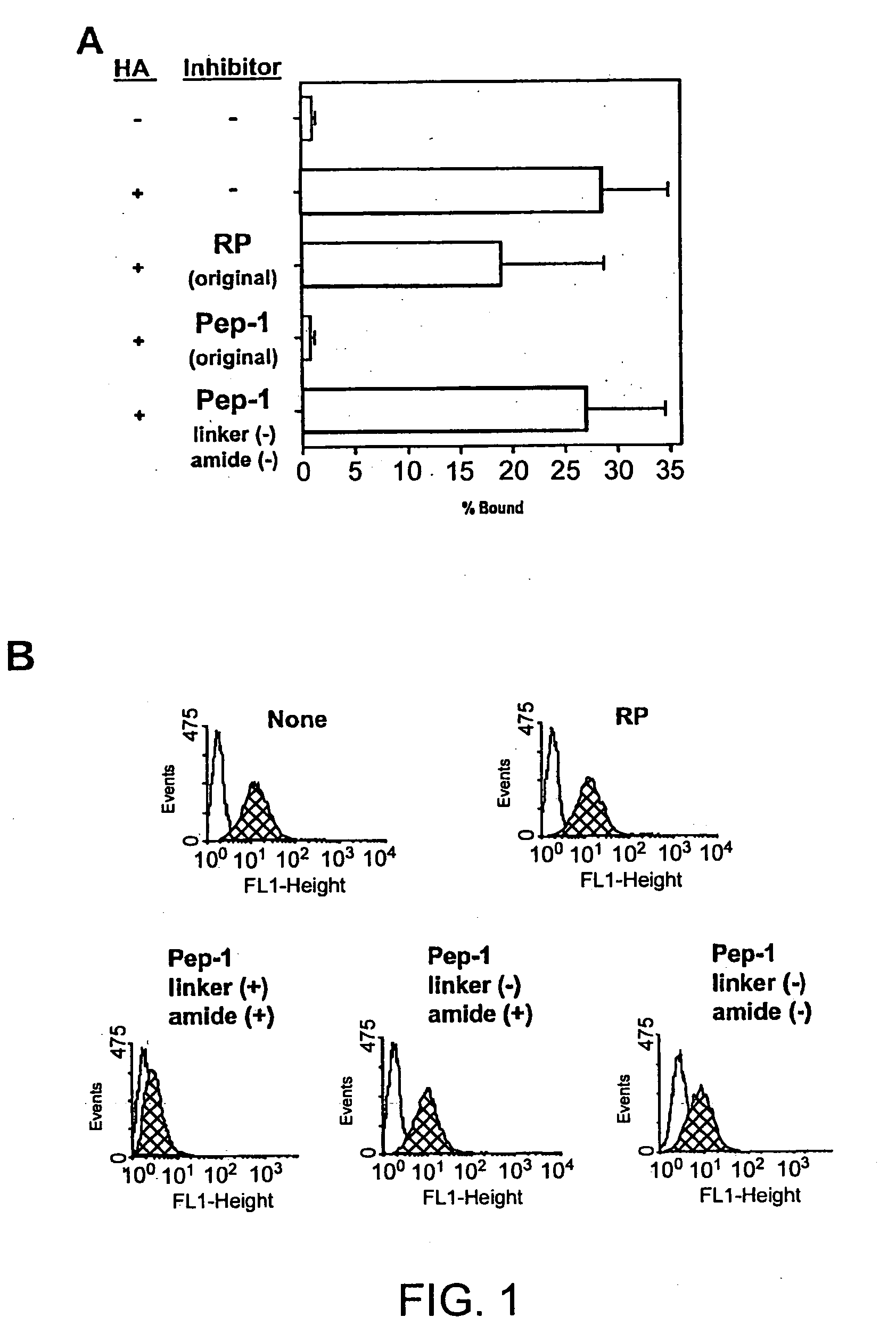
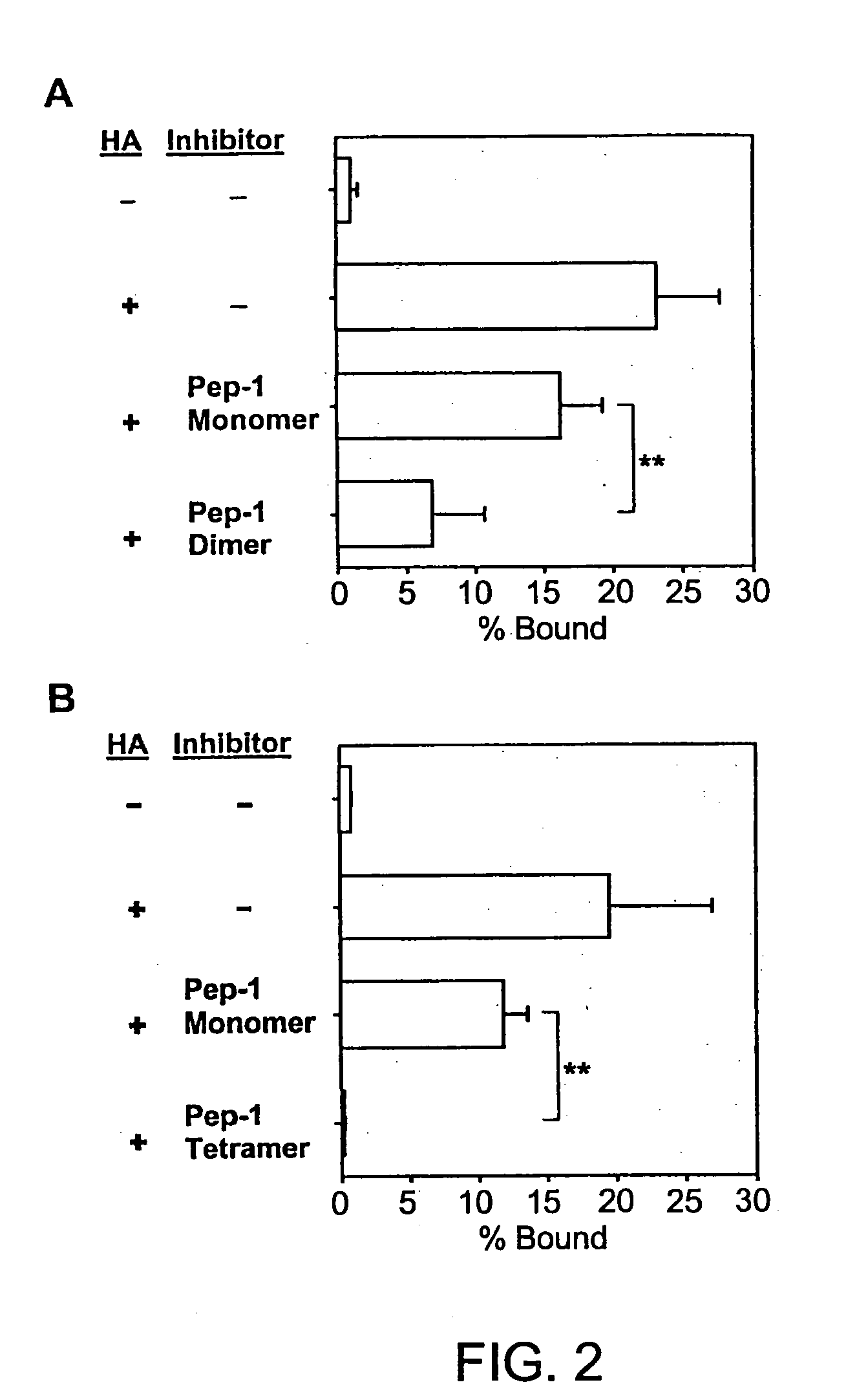
The present invention provides peptide derivatives with a specific affinity for glycosaminoglycan molecules. These peptide derivatives include multimers as well as chemically modified peptides and may be prepared by a variety of methods. The peptides of the invention have numerous functions, including but not limited to use as inhibitors of glycosaminoglycan-mediated signaling events and targeting agents. Peptides of the invention may be directed against any glycosaminoglycan, including hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate A, chondroitin sulfate C, dermatan sulfate, heparin, keratan sulfate, keratosulfate, chitin, chitosan 1, and chitosan 2. The peptide derivatives of the invention also have therapeutic uses in the treatment and prevention of diseases involving inflammatory diseases, cancer, and cancer metastasis, autoimmune diseases, etc.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Cross-linked polysaccharide drug carrier
InactiveUS6953784B2High biodegradation rateControl releasePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsCross-linkDextran
A carrier and a method for preparing it are provided for use in the delivery of therapeutic agents. A polysaccharide is reacted with an oxidizing agent to open sugar rings on the polysaccharide to form aldehyde groups. The aldehyde groups are reacted to form covalent oxime linkages with a second polysaccharide and each of the first and second polysaccharide is selected from the group consisting of hyaluronic acid, dextran, dextran sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, keratan sulfate, heparan, heparan sulfate and alginate.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Method for purifying dermatan sulfate from heparin byproduct
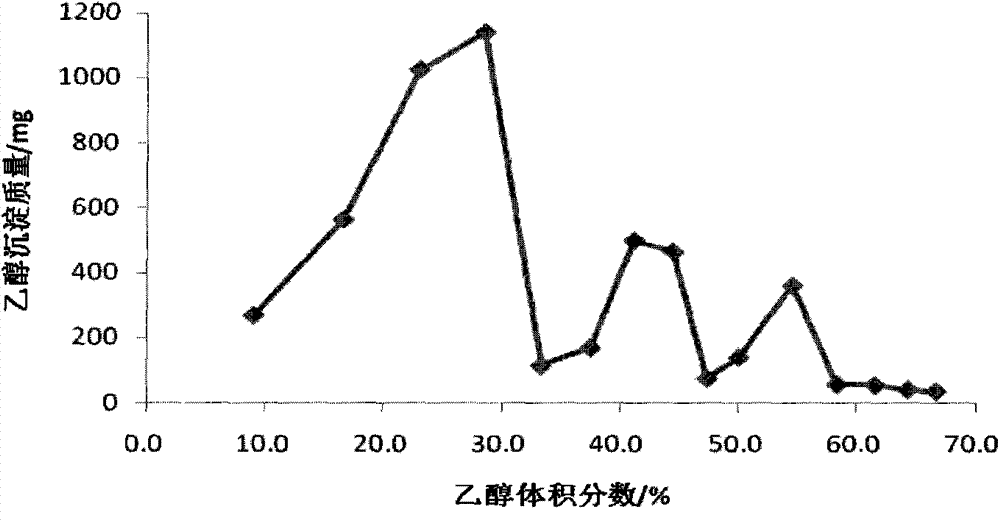
The invention discloses a method for purifying dermatan sulfate from a heparin byproduct. The method comprises the following steps of: using the heparin byproduct as a raw material; dissolving the heparin byproduct, and then adding potassium acetate into the dissolved heparin byproduct; adjusting the pH value of solution by using acetic acid to generate a deposit, wherein clear solution is sulfate polysaccharide solution; adding a Ban's agent and saturated sodium hydroxide solution into the sulfate polysaccharide solution; centrifugally collecting the deposit; performing re-precipitation; dissolving the deposit again; washing away copper ions by using a chromatography column with anion exchange properties and sodium chloride solution; performing linear gradient elution by using the sodium chloride solution; collecting eluant; and evaporating and concentrating the eluant, and depositing the eluant by using ethanol to obtain high-purity dermatan sulfate. The method has the advantages of simple purification process, high purification yield, low cost, easy amplification and suitability for industrial production.
Owner:SHENZHEN HEPALINK PHARMA GRP CO LTD
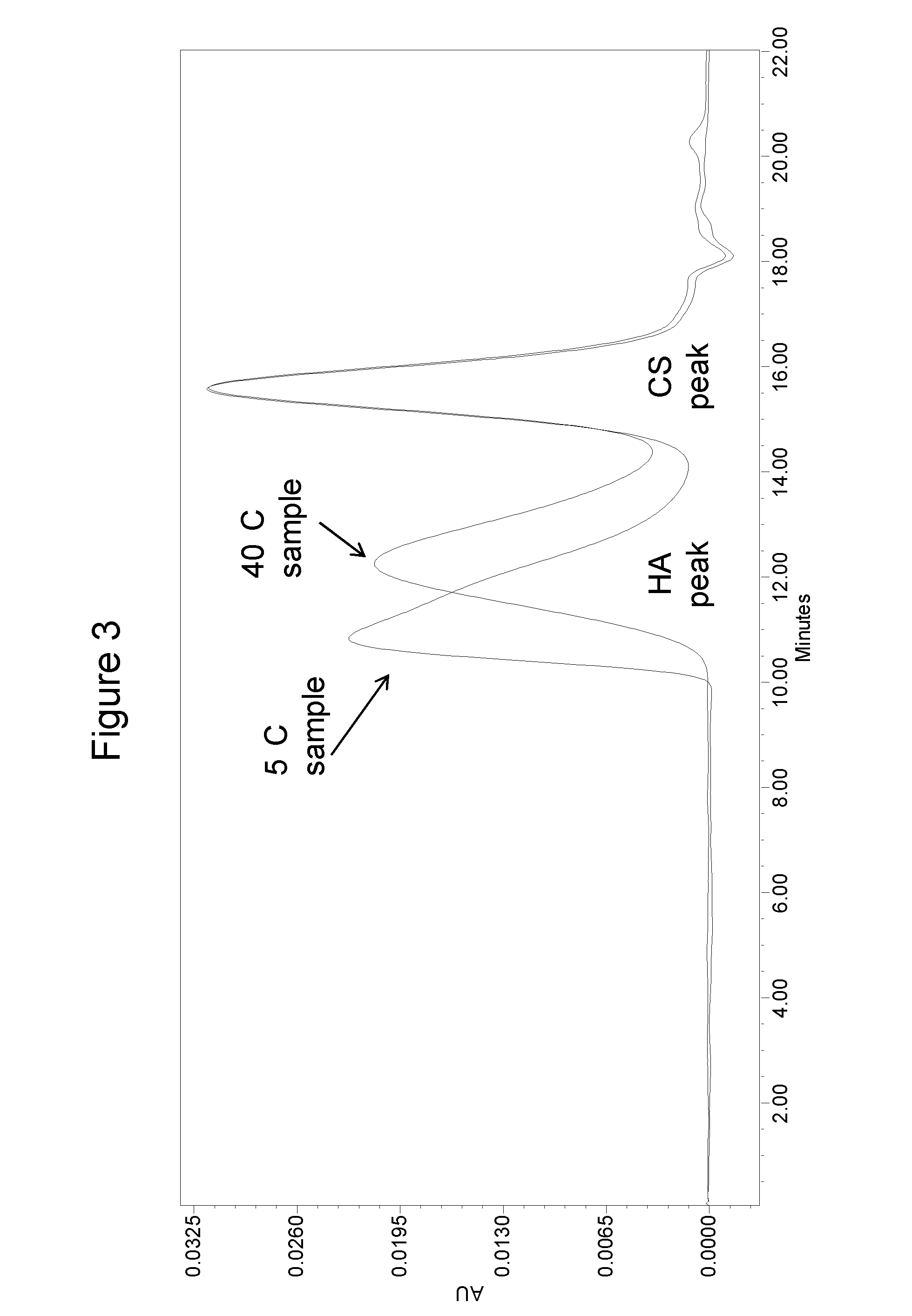
Compositions and methods for stabilized polysaccharide formulations
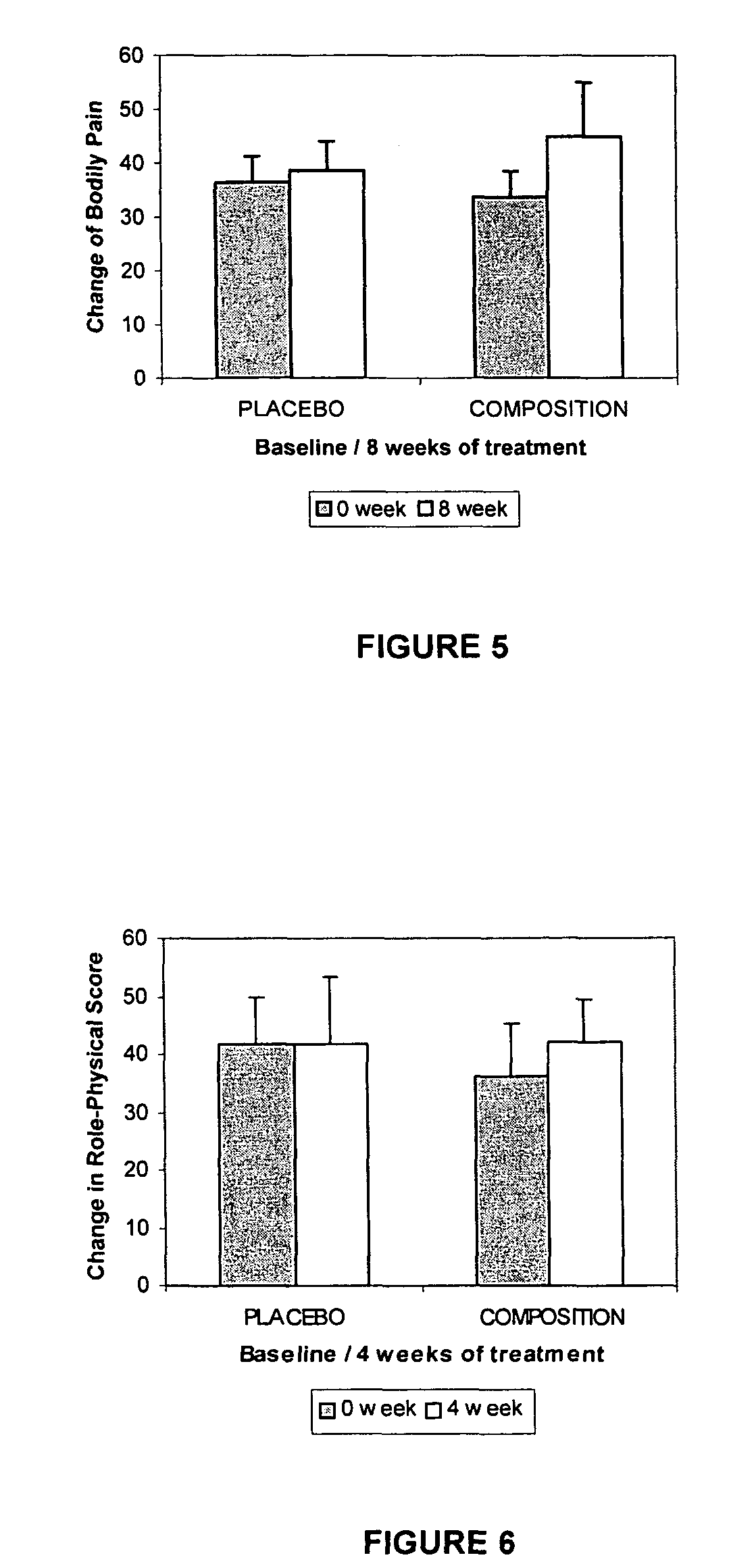
Compositions and methods are provided for treating joint conditions, such as osteoarthritis and / or the pain associated therewith. The compositions and methods utilize a first component, namely hyaluronic acid (“HA”), in combination with at least one stabilizer. The composition can include a stabilizer that increases the stability and shelf-life of the HA. In another embodiment, the compositions and methods can also include an additional component, such as one or more glycosaminoglycans (“GAG”) or GAG precursors. Examples of GAGs or GAG precursors can include chondroitin sulfate (“CS”), dermatan sulfate, heparin, heparan sulfate, keratan sulfate, and glucosamine (“GlcN”).
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Method for separating and purify dermatansulfate and low-molecular heparan sulfate from sodium heparan product
ActiveCN1850864AStable separationImprove solubilityOrganic active ingredientsDermatan sulfateSodium heparin
The invention relates to a method to separate and purify dermatan sulfate and low molecule heparan sulfate from sodium heparin by-product. It uses the by-product of producing sodium heparin as raw material taking fractional precipitation through alcohol to gain raw dermatan sulfate; uses nitrite and nitrous acid ester compounding as oxidant to degrade the heparan sulfate into low molecule heparan sulfate and taking fractional precipitation through alcohol to separate high purity dermatan sulfate and low molecule heparin sulfate.
Owner:NANJING KING FRIEND BIOCHEM PHARMA CO LTD
Inhibitors of glycosaminoglycans
The present invention provides peptide derivatives with a specific affinity for glycosaminoglycan molecules. These peptide derivatives include multimers as well as chemically modified peptides and may be prepared by a variety of methods. The peptides of the invention have numerous functions, including but not limited to use as inhibitors of glycosaminoglycan-mediated signaling events and targeting agents. Peptides of the invention may be directed against any glycosaminoglycan, including hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate A, chondroitin sulfate C, dermatan sulfate, heparin, keratan sulfate, keratosulfate, chitin, chitosan 1, and chitosan 2. The peptide derivatives of the invention also have therapeutic uses in the treatment and prevention of diseases involving inflammatory diseases, cancer, and cancer metastasis, autoimmune diseases, etc.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Comprehensive utilization process for marine fish skins
ActiveCN102676619AEfficient extractionImprove utilization efficiencyConnective tissue peptidesPeptide preparation methodsMarine fishAquatic animal
The invention relates to the field of preparation of marine active substance from byproducts processed by aquatic animals and aims at providing a process for extracting collagen and dermatan sulfate by comprehensively utilizing marine fish skins. The process comprises the steps of fish skin treatment, removal of impure protein of the fish skin, removal of fat of the fish skin, fish skin enzymolysis, collagen salting, collagen collection, collagen dialysis and lyophilization, dermatan sulfate glucosidic bond protection, dermatan sulfate precipitation, dermatan sulfate purification and the like. According to the process disclosed by the invention, the active substances can be extracted from the marine fish skins simply, quickly and efficiently, the aim of cogenerating the collagen with the dermatan sulfate is achieved, the utilization benefits of the fish skins are increased and economic benefits are increased. The process is simple and feasible, high in extraction efficiency and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MARINE DEV RES INST
Compositions and methods for treating joints
Compositions and methods are provided for treating joint conditions, such as osteoarthritis and / or the pain associated therewith. The compositions and methods utilize a first component, namely hyaluraonic acid (“HA”), in combination with a lyophilized second component that is effective to at least temporarily reduce the viscosity of the HA. In an exemplary embodiment, the second component is one or more glycosaminoglycans (“GAG”), such as chondroitin sulfate (“CS”), including CS4 and / or CS6, dermatan sulfate, heparin, heparan sulfate, and keratan sulfate. The composition can optionally include other joint supplements, such as glucosamine (“GlcN”).
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Modulators of polysaccharides and uses thereof
InactiveUS6923965B2Produced cost-effectivelyBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseChondroitin Sulfate C
The present invention provides peptides with a specific affinity for glycosaminoglycan molecules. These peptides may have any number of functions, including but not limited to use as inhibitors of glycosaminoglycan-mediated processes, enhancers of glycosaminoglycan-mediated processes, and as molecular probes to identify the presence of a specific glycosaminoglycan. Peptides of the invention may be directed against any glycosaminoglycan, including hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate A, chondroitin sulfate C, dermatan sulfate, heparin, keratan sulfate, keratosulfate, chitin, chitosan 1, and chitosan 2. These isolated peptides may have therapeutic uses in the treatment or prevention of diseases involving infection, inflammatory diseases, cancer, infections, etc. The peptides may also have other biological functions such as contraception.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Compositions and methods for the treatment of CNS injuries
InactiveUS20140248253A1High degree of recoveryPromotes neurologicalOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAutonomic functionMedicine
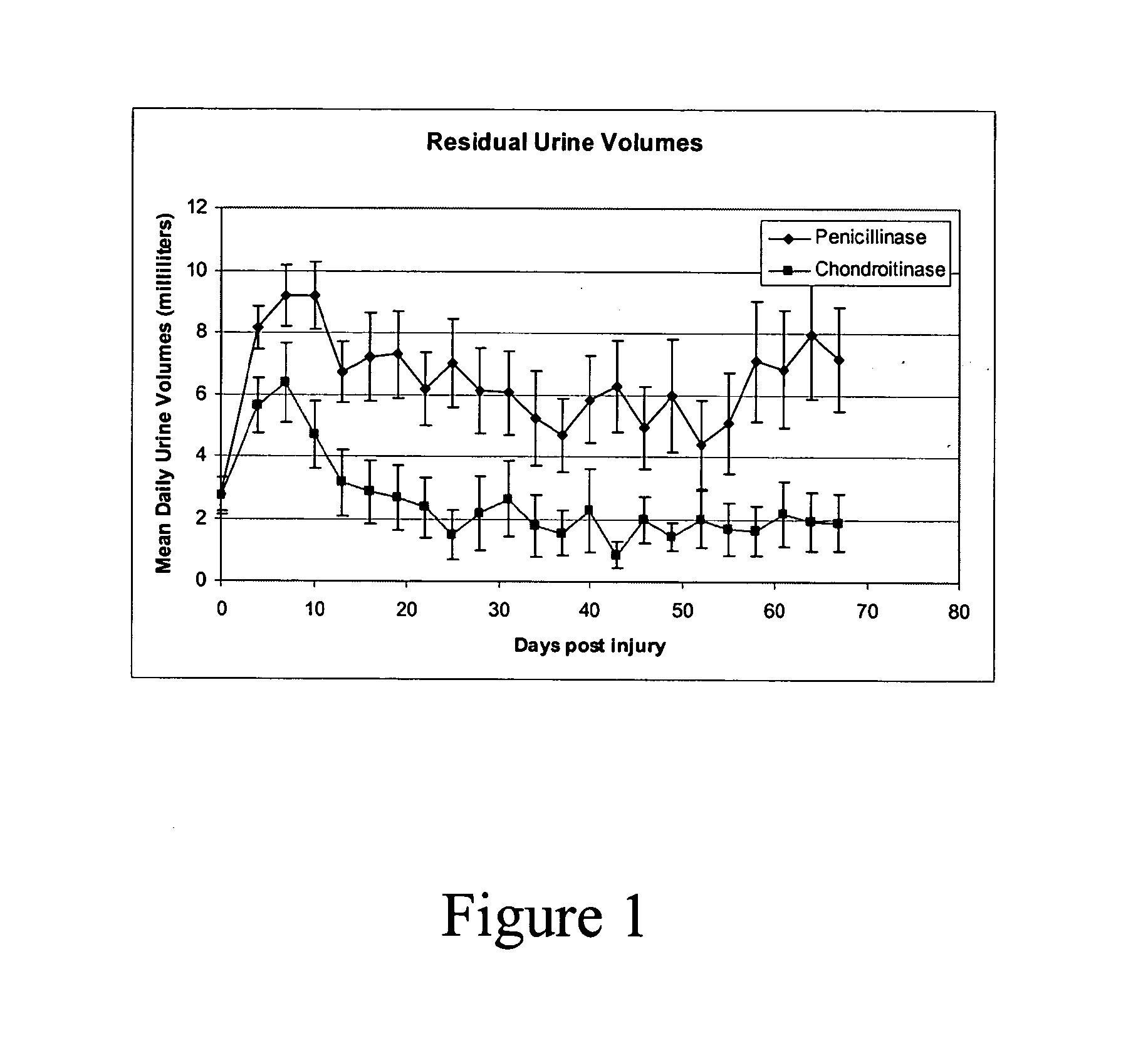
The present invention is directed to a method of improving functional recovery following a central nervous system contusion injury. The method includes administering a therapeutically effective amount of glycosaminoglycan degrading enzyme. The glycosaminoglycan degrading enzyme may be dermatan sulfate or chondroitin sulfate degrading enzymes. The central nervous system contusion injury may include a traumatic brain injury or a spinal cord injury. The functional recovery may include autonomic functions, sensory functions, motor functions or the like.
Owner:ACORDA THERAPEUTICS INC
Heparin derivative polysaccharide mixture and preparation method and medicinal composition thereof
ActiveCN101711771ALow in ingredientsHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderSide effectOrganic base
The invention relates to a heparin derivative polysaccharide mixture and a preparation method and a medicinal composition thereof. Specifically, the heparin derivative polysaccharide mixture of the invention is a degradation product of heparin or heparin ester or heparin ester salt and is characterized in that the weight-average molecular weight is 3,100 to 4,500 Daltons, the activity of anti-coagulation factor Xa is high, and the activity of anti-coagulation factor IIa is low. The heparin derivative polysaccharide mixture of the invention has excellent antithrombotic performance, low side effect, and has no residues of adverse components such as organic base and dermatan sulfate and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI SEANPHARM
Compositions and methods for stabilized polysaccharide formulations
Compositions and methods are provided for treating joint conditions, such as osteoarthritis and / or the pain associated therewith. The compositions and methods utilize a first component, namely hyaluronic acid (“HA”), in combination with at least one stabilizer. The composition can include a stabilizer that increases the stability and shelf-life of the HA. In another embodiment, the compositions and methods can also include an additional component, such as one or more glycosaminoglycans (“GAG”) or GAG precursors. Examples of GAGs or GAG precursors can include chondroitin sulfate (“CS”), dermatan sulfate, heparin, heparan sulfate, keratan sulfate, and glucosamine (“GlcN”).
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Method for quantitatively detecting dermatan sulfate in heparin
ActiveCN101762668AImprove securityControl contentComponent separationSulfateMicrofiltration membrane
The invention relates to a method quantitatively detecting dermatan sulfate in heparin, comprising the following steps according to the technical scheme: preparing detection solution of sample solution in such a way of weighting sample to be detected, dissolving the sample to be detected with ultra-pure water, adding a certain amount of sodium nitrite, adjusting the pH value of the solution to 1.0-1.5 with hydrochloric acid, stirring the solution and making the solution react for a certain time, adjusting the pH value of the solution to 6.5-7.0 with sodium hydroxide, filtering the solution with a microfiltration membrane, removing primary filtrate, and collecting subsequent filtrate; preparing detection solution of reference solution in such a way of weighting a certain amount of standarddermatan sulfate, and adding the sample solution to the standard dermatan sulfate; weighting 10 Mul of sample solution and 10 Mul of reference solution to detect the sample; and calculating the content of the dermatan sulfate with a calculating formula. The invention has the advantages that the dermatan sulfate is separated from the dermatan sulfate from the heparin with the exclusion chromatography, the undegraded dermatan sulfate is detected quantitatively and the content of the dermatan sulfate in the heparin is controlled effectively to improve the safety of the clinical use of the dermatan sulfate.
Owner:DONGYING TIANDONG PHARM CO LTD
Technology for extracting collagen peptide, dermatan sulfate, hydroxyapatite and melanin from black sharkskin
The invention discloses a technology for extracting collagen peptide, dermatan sulfate, hydroxyapatite and melanin from black sharkskin. The technology comprises the following steps: conducting pre-treatment on the black sharkskin; carrying out enzymolysis; carrying out centrifugal separation to separate out a clear liquid and solid sediment; conducting ultrafiltration or resin adsorption on the clear liquid to obtain collagen peptide or dermatan sulfate respectively; treating the solid sediment with NaOH; conducting centrifugal separation on the treated solid sediment to obtain hydroxyapatite and melanin. The technology has the characteristics that collagen peptide, dermatan sulfate, hydroxyapatite and melanin are obtained continuously; the comprehensive utilization of the sharkskin is realized; the discharge of waste materials in the extraction and preparation processes is reduced; the production cost is reduced; the economic efficiency is improved; the technology is simple; industrialization can be realized.
Owner:福州宏东食品有限公司
Compositions and methods for treating joints
Compositions and methods are provided for treating joint conditions, such as osteoarthritis and / or the pain associated therewith. The compositions and methods utilize a first component, namely hyaluraonic acid (“HA”), in combination with a lyophilized second component that is effective to at least temporarily reduce the viscosity of the HA. In an exemplary embodiment, the second component is one or more glycosaminoglycans (“GAG”), such as chondroitin sulfate (“CS”), including CS4 and / or CS6, dermatan sulfate, heparin, heparan sulfate, and keratan sulfate. The composition can optionally include other joint supplements, such as glucosamine (“GlcN”)
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Method for purifying heparitin sulfate from heparin byproduct
The invention discloses a method for purifying heparitin sulfate from a heparin byproduct. The method comprises the following steps of: using the heparin byproduct as a raw material; dissolving the heparin byproduct, and then adding potassium acetate into the dissolved heparin byproduct; adjusting the pH value of solution by using acetic acid; removing a deposit to obtain sulfate polysaccharide solution; adding a Ban's agent and saturated sodium hydroxide solution into the sulfate polysaccharide solution; centrifugally collecting clear solution; adding the Ban's agent and the saturated sodium hydroxide solution into the deposit again, and centrifugally collecting the clear solution; combining the clear solution; washing away copper ions by using a chromatography column with anion exchange properties and sodium chloride solution; performing linear gradient elution by using the sodium chloride solution; collecting eluant; and evaporating and concentrating the eluant, and depositing the eluant by using ethanol to obtain high-purity dermatan sulfate. The method has the advantages of simple purification process, high purification yield, low cost, easy amplification and suitability for industrial production.
Owner:SHENZHEN HEPALINK PHARMA GRP CO LTD
Method for extracting and purifying dermatan sulfate in angler fish skin
InactiveCN101100688AReasonable methodSuitable for industrial productionAntipyreticAnalgesicsSulfate radicalsSide effect
It is concerned with extraction and purification of sulfuric acid skin-lotion from waste skins of angler fish production. It is carried out by: extracting with compounded enzyme of pancreatin and papain, adding NaOH into extracting liquid to cut off glycopeptide bond while protecting glycosidic bond with NaPH4, removing protein by savage process, depositing sulfur acid skin lotion in alcohol, dissolving in water and centrifuging dissoluble substances, dialyzing to remove ions and micro-molecular substances, and frozen drying high purity sulfur acid skin lotion with ratio of sulfate radical to carboxylic radical = 1.07. The product is strong antithrombotic, with less side effect of hemorrhage, has disinfecting activity, and can be used in pharmaceutical field.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
In vitro formation of congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaques to identify anti-plaque therapeutics for the treatment of Alzheimer's and Prion diseases
InactiveUS20020168753A1Test effectivenessCompounds screening/testingNervous disorderCongo redNeuroglycan C
Co-incubation of an amyloid protein with sulfated macromolecules as a method for the formation of amyloid plaques. The amyloid protein may be the beta-amyloid protein or the prion protein or the like. Amyoid plaque formation in one embodiment proceeds in vitro and desireably produces amyloid plaques that stain with Congo red and demonstrate a maltese-cross pattern when viewed under polarized light. The method also produces amyloid plaques that demonstrate an "amyloid star" appearance when viewed by transmission electron microscopy. Sulfated macromolecules include a sulfated proteoglycan selected from the group consisting of perlecan, ~220 kilodalton heparan sulfate proteoglyean, glypican, cerebroglycan, aggrecan, synaptoglycan (SV2PG), syndecan, N-syndecan (also known as syndecan-3), syndecan-1, syndecan-4, neurocan, phosphacan, decorin, biglycan, versican, amphiglycan, lumican, PG-M, PG-M (3), agrin, betaglycan, claustrin, brevican, appican, epican, neuroglycan-C, and fragments thereof. Thw sulfated macromolecule may be a sulfated glycosaminoglycan selected from the group consisting of heparin, heparan sulfate, dermatan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, keratan sulfate, and fragments thereof. An in vivo assay is also presented for selecting a candidate therapeutic agent for inhibiting or disrupting amyloid plaque deposition or persistence. The assay includes a) pre-forming congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaques in vitro following incubation of an amyloid protein and a selected sulfated macromolecule, b) using a first cannula and osmotic pump to continuously infuse for a selected duration the pre-formed congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaques into a tissue or organ, c) changing the first cannulae and osmotic pump with a second cannulae and osmotic pump to administer the candidate therapeutic, and d) detecting the candidate therapeutic's ability to disrupt, reduce, or eliminate congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaque deposition / persistence in the tissue or organ.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Compositions for the treatment of osteoarthritis and to nourish the synovial fluid
Owner:BIOIBI12RICA
Inscribe chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate 4-O-sulfatase as well as encoding gene and application of inscribe chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate 4-O-sulfatase
ActiveCN103952384AHigh endosulfatase activityRegulate metabolismNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsCranial nerve involvementSulfate radicals
The invention relates to inscribe chondroitin sulfate / dermatan sulfate 4-O-sulfatase as well as an encoding gene and an application of the inscribe chondroitin sulfate / dermatan sulfate 4-O-sulfatase. The invention firstly discloses an amino acid sequence of the inscribe chondroitin sulfate / dermatan sulfate 4-O-sulfatase and a nucleotide sequence of the encoding gene of the inscribe chondroitin sulfate / dermatan sulfate 4-O-sulfatase. Found through detection, the enzyme has relatively high inscribe sulfatase activity, plays a role in removing sulfate radicals at the terminal and the inside of polysaccharide and can be effectively acted on polysaccharide, used for modifying and regulating the structure inside polysaccharide and applied to preparation of drugs for restoring cranial nerve involvement, regulating metabolism and treating inflammation and cancer.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate extraction method
InactiveCN105821097AOvercome the source's shortcomingsWide variety of sourcesFermentationDermatan sulfateHyaluronic acid
The invention discloses a chondroitin sulfate / dermatan sulfate extraction method which comprises the following steps: drying the eggshell matrix and grinding to obtain eggshell matrix powder; separating and extracting total glycosaminoglycan from the eggshell matrix powder; and removing heparin / heparan sulfate, keratan sulfate and hyaluronic acid in the total glycosaminoglycan to obtain high-purity chondroitin sulfate / dermatan sulfate.
Owner:刘长国
Method for removing keratan sulfate from chondroitin sulfate crude extract
ActiveCN105777938ABreaking covalent bondsEasy to separateDermatan sulfateElectrical resistivity and conductivity
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and particularly relates to a method for removing keratan sulfate from a chondroitin sulfate crude extract. The method comprises the following steps of adding a sodium hydroxide solution into a chondroitin sulfate crude extract for reaction; then adding hydrochloric acid to regulate the PH value, filtering to obtain a filtrate, and adding sodium chloride into the filtrate to regulate the electrical conductivity of the solution to be 45-48ms / cm; then adding an ethanol solution, controlling the flow velocity of the ethanol solution to be 10-15mL / (L.min), precipitating chondroitin sulfate, and filtering to obtain a precipitate; dehydrating and drying the precipitate obtain a chondroitin sulfate finished product. The method is easy in control over technological conditions, low in cost, simple in operation and low in experimental apparatus requirement, and can be used for thoroughly solving the problems that removal of the keratan sulfate in chondroitin sulfate is difficult and industrial production is difficult to realize.
Owner:RIZHAO LANSHAN BIOCHEM PROD
Method for separating heparan sulfate from animal lungs
The invention discloses a method for separating heparan sulfate from animal lungs, belonging to the technical field of biological pharmacy. The method comprises the following steps: by using animal lungs as the raw material, carrying out composite enzyme degradation on an animal lung brine extract by using hydrolases, adding an oxidizer and activated carbon into the enzymolysis solution to perform oxidative adsorption decolorization, carrying out fractional precipitation on the oxidized solution by using acetone, dehydrating to obtain a heparan sulfate crude product, sequentially carrying out membrane separation and anion exchange chromatography on the crude product heparan sulfate water solution to separate the heparan sulfate from dermatan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, heparin and other impurities, carrying out ultrafiltration concentration on the eluate through a 5000-7000Da ultrafiltration membrane, desalting by gel filtration chromatography, and freeze-drying to obtain the heparan sulfate refined product. The method has advantages of simple technological conditions, accessible raw materials and low cost, and is easy to implement; and the obtained heparan sulfate has high purity.
Owner:SHANDONG CHENZHONG BIOPHARM +1
Process of producing heparan sulfate by using chondrosulphatase
InactiveCN104293866ADoes not affect yieldHigh enzyme efficiencyFermentationUltrafiltrationUnsaturated disaccharide
The invention provides a process of producing heparan sulfate by using chondrosulphatase. The process comprises the following steps: firstly, performing enzymolysis, resin adsorption and sodium chloride solution elution on a heparin sodium crude product to obtain eluate; performing enzymolysis on the eluate by using chondrosulphatase ABC or chondrosulphatase B; exclusively cutting off specificity of 1-4 glucosidic bonds between disaccharide units in a dermatan sulfate structure by virtue of the chondrosulphatase ABC and the chondrosulphatase B to obtain a degradation reaction product unsaturated disaccharide; and then, performing refining steps such as ultrafiltration, heavy metal removal and oxidization to obtain a heparan sulfate fine product. The process not only can be used for overcoming the characteristic that negative charges on the surfaces of the heparan sulfate and the dermatan sulfate are similar in density and difficult to separate, but also can be used for avoiding heavy metal ion impurities brought in heparan sulfate produced according to the conventional route, and thus, the product yield is increased, and the economic benefits are remarkable.
Owner:DONGYING TIANDONG PHARM CO LTD
Method for analyzing mucopolysaccharide with glass-carrying electrophoresis method
ActiveCN101936944AEasy to operateLow production environment requirementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrophoresisQuantitative determination
The invention discloses a method for analyzing mucopolysaccharide with glass-carrying electrophoresis method, comprising the following steps: paving agarose gel on a glass board to form an electrophoresis glue board; arranging the whole glass-carrying board into a proper electrophoresis tank; spotting the sample; performing electrophoresis; taking out the glass-carrying board; drying at the temperature of 60-80 DEG C; dying with toluidine blue; decolouring with tapping water; drying at the temperature of 60-80 DEG C; and finally obtaining the electrophoresis result. The method can store the electrophoresis board for long term; the individual feeding amount is enhanced to 72 from 12-24 in the flat board electrophoresis, which is convenient to perform large-scale analysis; the invention caneffectively separate mucopolysaccharide matters such as heparin, dermatan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate and heparan sulfate and helps to accurately have quantitative determination for the mucopolysaccharide.
Owner:SHENZHEN TECHDOW PHARM CO LTD
Dermatan sulfate with low molecule and its preparing method
InactiveCN1445245ASmall molecular weightRaise the reaction temperatureBlood disorderExtracellular fluid disorderUltrafiltrationThrombus
A low-molecular (3000-8000) dermatan sulfate is prepared from the dermatan sulfate through degradation by hydrogen peroxide, ultrafilter, and gel chromatography. Its advantages are sure thrombus-resistant and thrombolytic functions, easy absorption, long semi-life and high biologic utilization rate.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method of preparing high-purity heparin sodium
The invention discloses a method of preparing high-purity heparin sodium. The method is characterized in that under a room temperature of 298K, an organic precipitation method is adopted to remove heparin sodium-like impurities dermatan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate in the heparin sodium to prepare high-purity heparin sodium, so that the heparin sodium and similar substances thereof are separated according to solubility difference in different polar solvents. The method is suitable for purifying and separating the sodium-like impurities dermatan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate and the like in the heparin sodium to prepare the high-purity heparin sodium, and has remarkable social and beneficial benefits.
Owner:QINGDAO JIULONG BIO PHARMA
Method for extracting hyaluronic acid from eggshell membranes of poultry
The invention provides a method for extracting hyaluronic acid from eggshell membranes of poultry. The method includes steps: separating the eggshell membranes from calcified shells; drying and grinding the eggshell membranes; separating and extracting total glycosaminoglycan from the ground eggshell membranes; removing heparin / heparan sulfate and keratan sulfate from the total glycosaminoglycan, and separating the hyaluronic acid from chondroitin sulfate / dermatan sulfate. By the method, high-purity hyaluronic acid can be separated out, direct extraction of the hyaluronic acid from the eggshell membranes of poultry is realized, extensive sources are available, and the obtained hyaluronic acid which is derived from natural tissues of animals is stable in molecular weight and free of endotoxin.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com