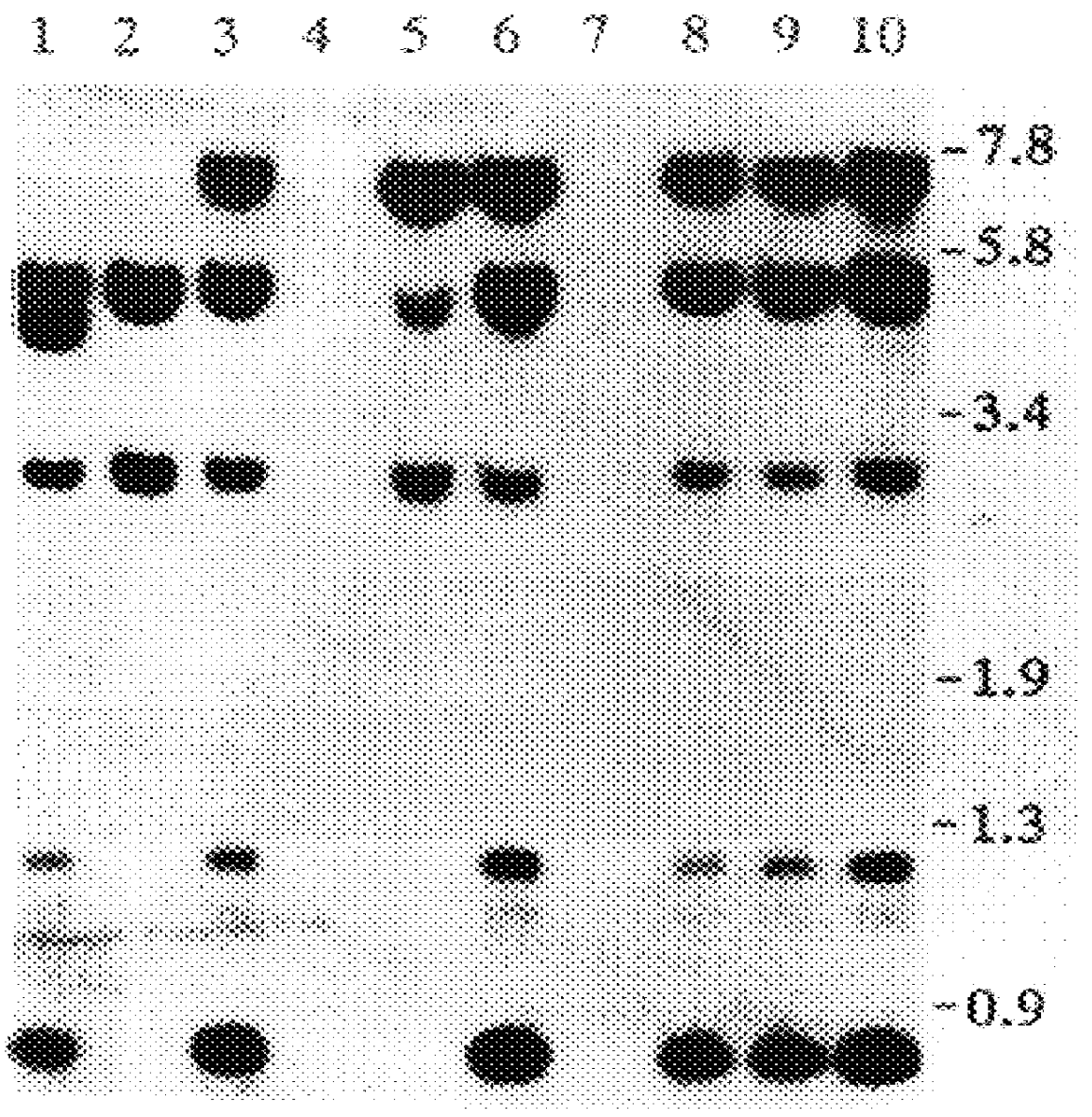
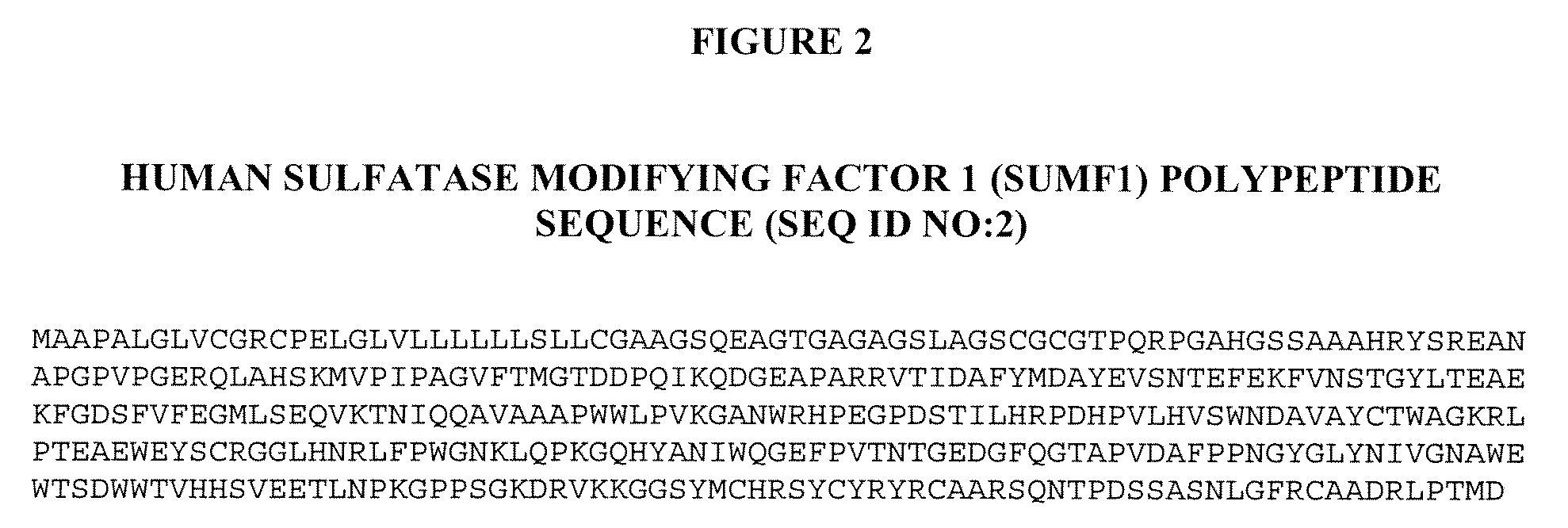
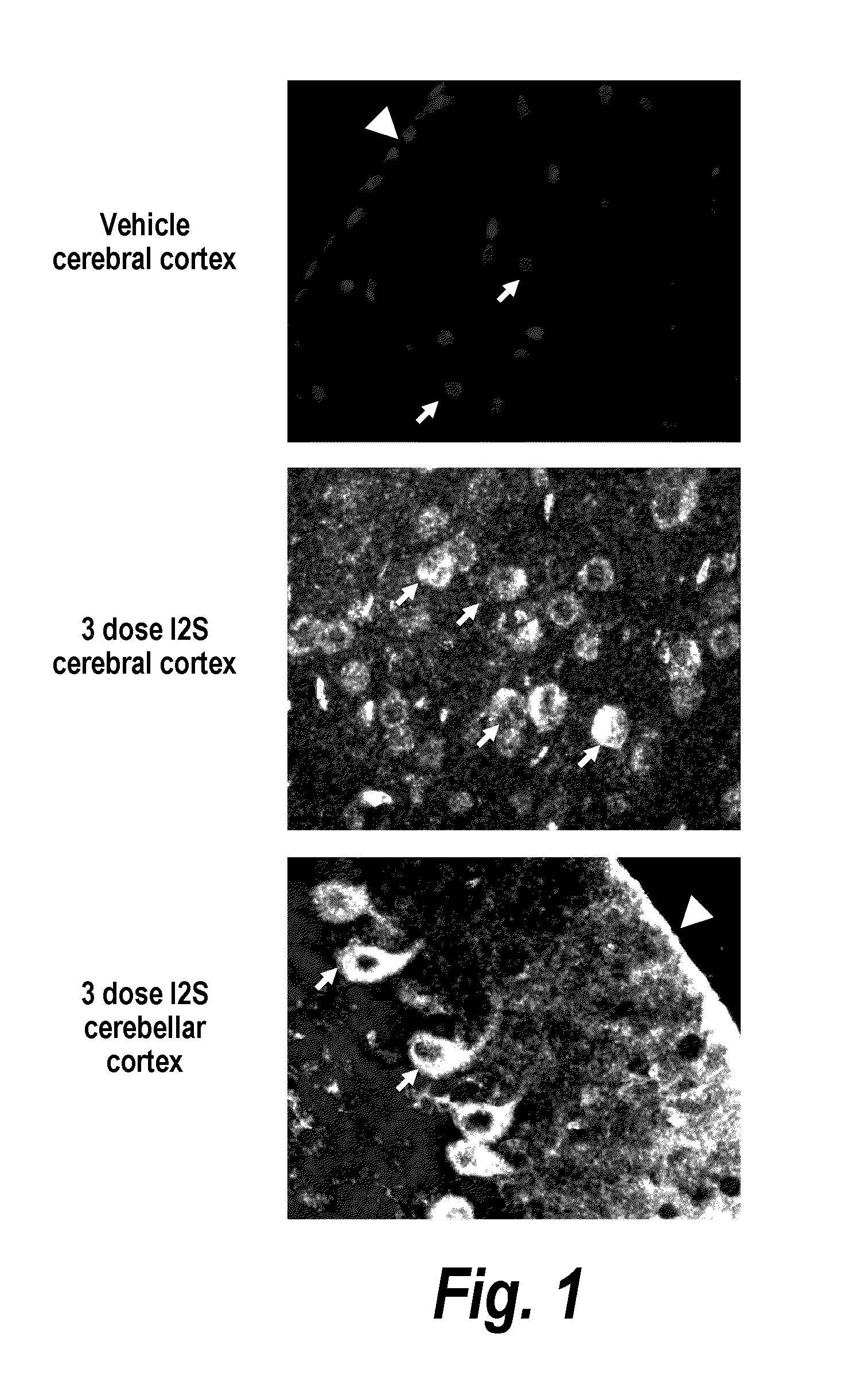
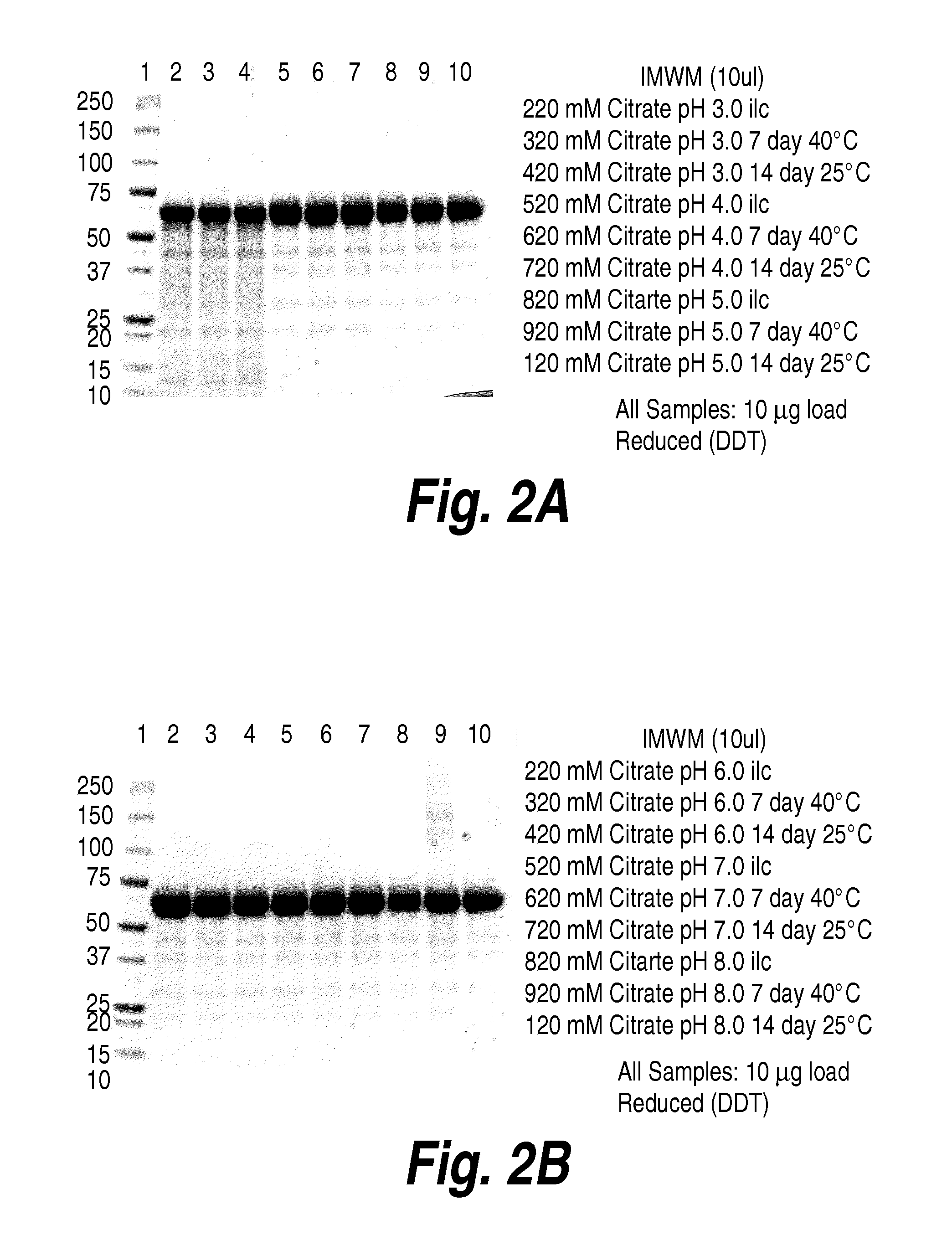
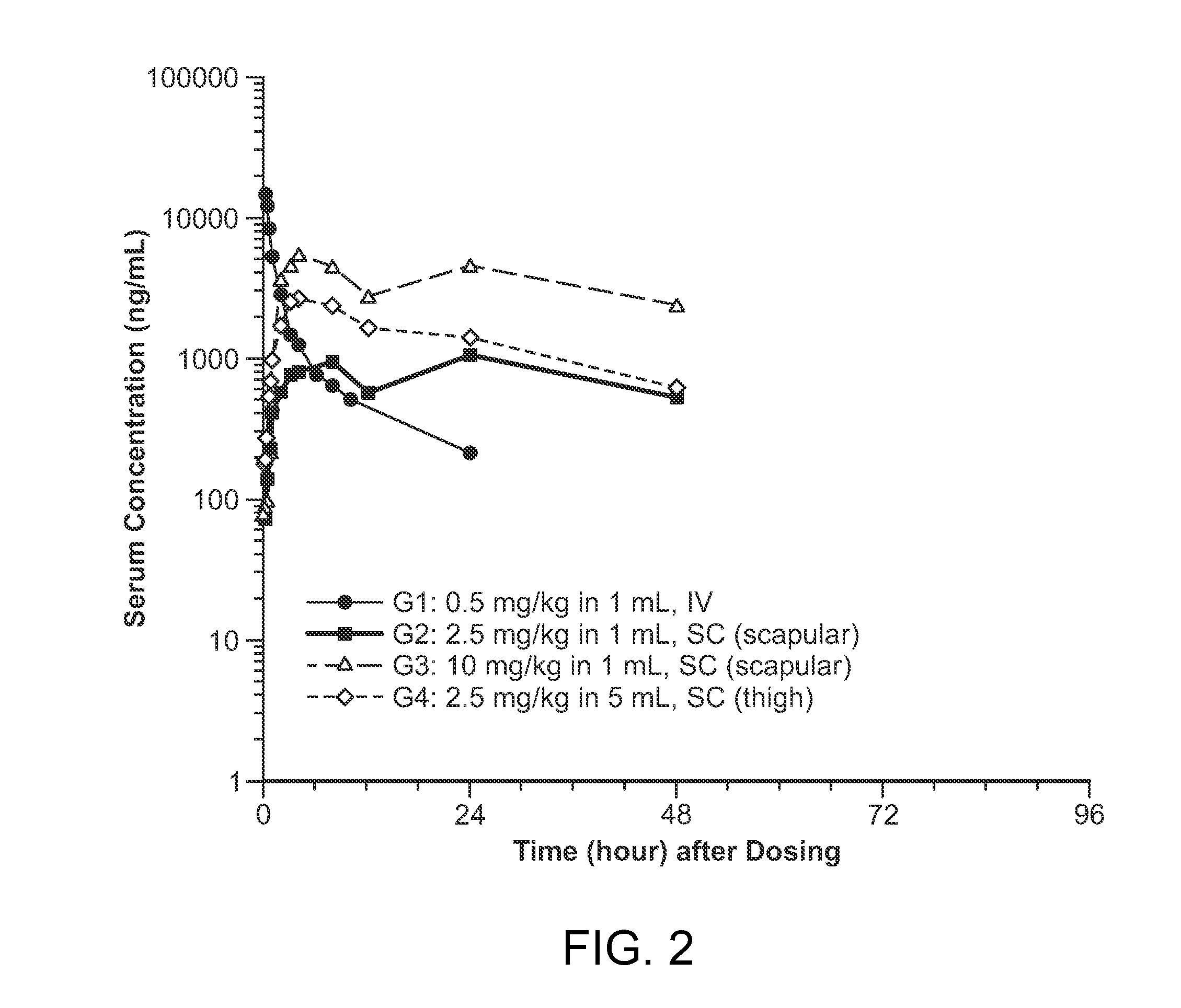
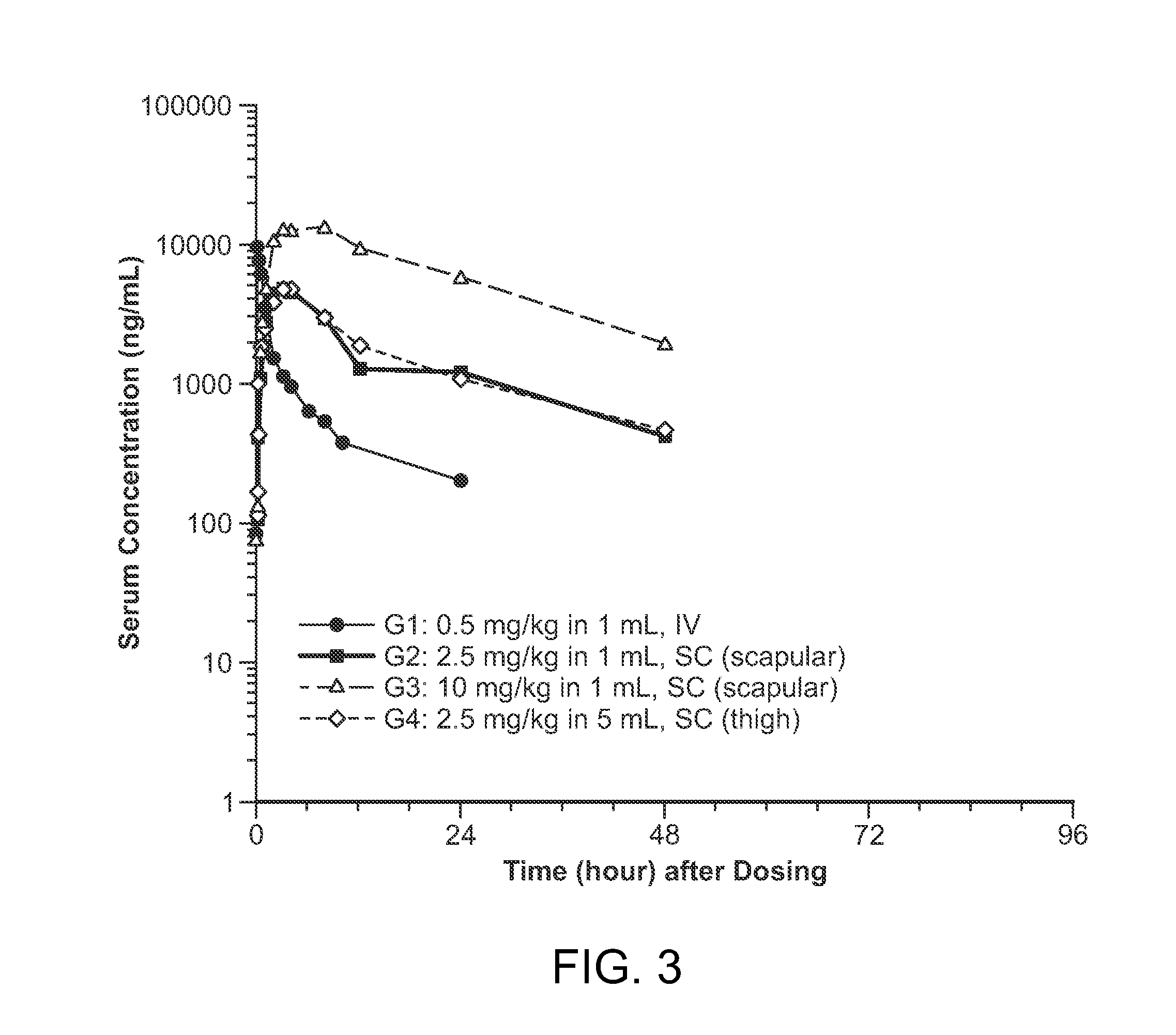
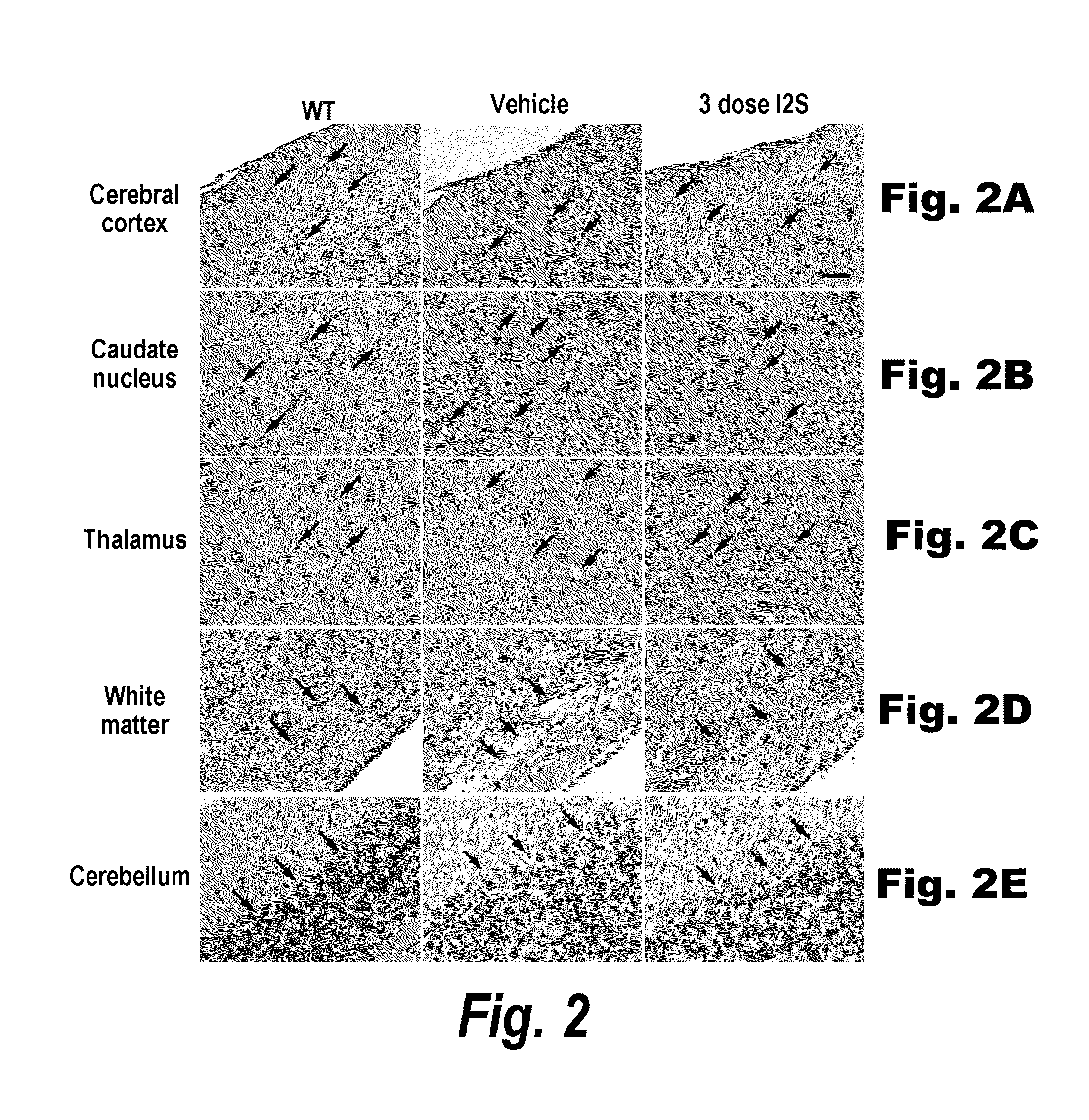
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
168 results about "Sulfatase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sulfatases EC 3.1.6.- are enzymes of the esterase class that catalyze the hydrolysis of sulfate esters. These may be found on a range of substrates, including steroids, carbohydrates and proteins. Sulfate esters may be formed from various alcohols and amines. In the latter case the resultant N-sulfates can also be termed sulfamates.
Treatment of central nervous system damage
InactiveUS20050118157A1Decreased inhibitory propertiesImprove plasticityCompound screeningNervous disorderNervous systemChondroitinase ABC
The invention provides a method of promoting neuronal plasticity in the CNS of a mammal, the method comprising administering to the CNS of the mammal an agent that reduces the inhibitory properties of chondroitin sulphate proteoglycans. Preferred agents are chondroitinases and sulfatases, e.g., chondroitinase ABC. Also provided are methods of identifying further agents.
Owner:KING'S COLLEGE LONDON +1
Production and Purification of Recombinant Arylsulftase
ActiveUS20080003211A1Facilitates tight controlHigh and uniform qualityNervous disorderBacteriaNervous systemPurification methods
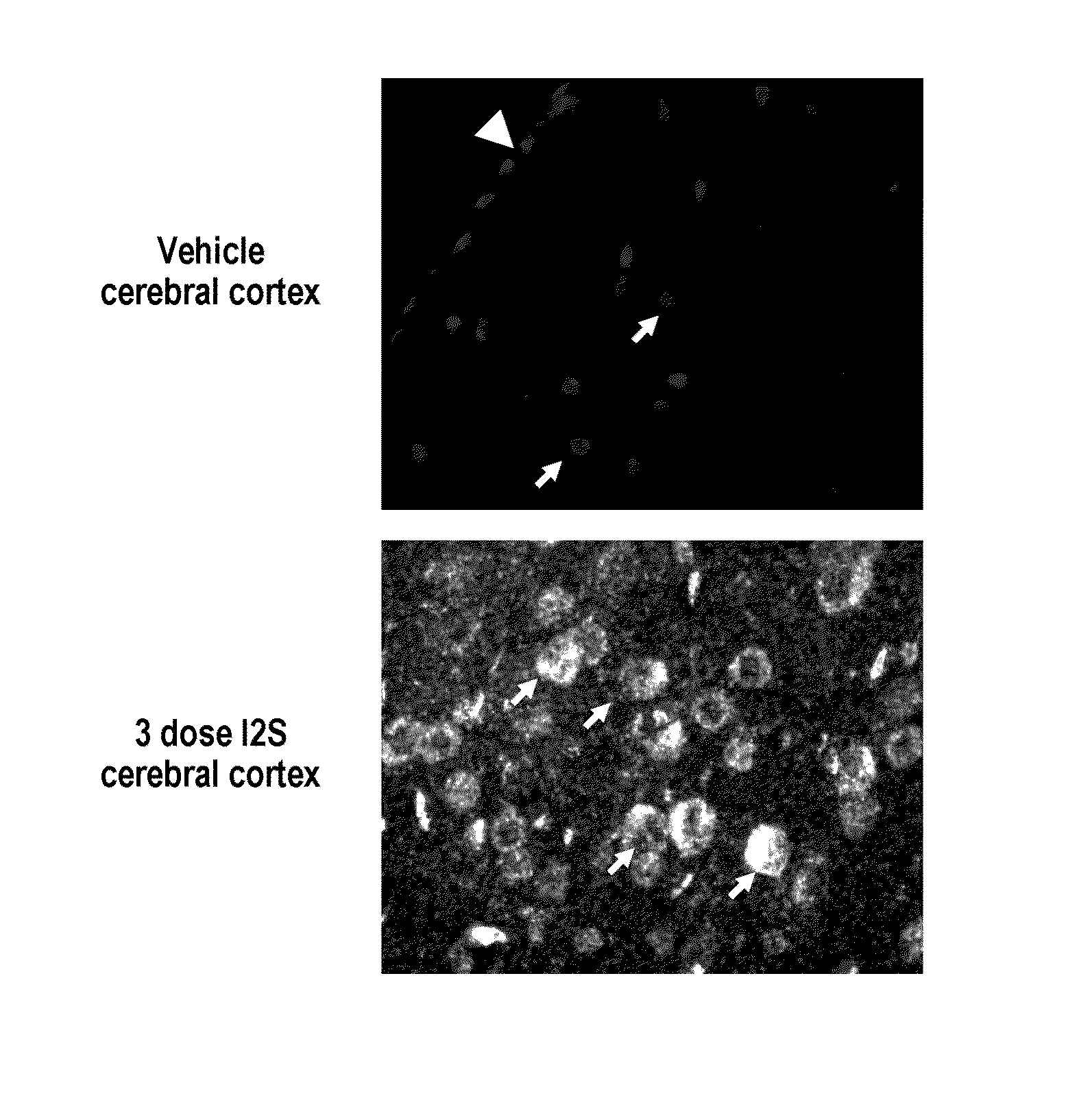
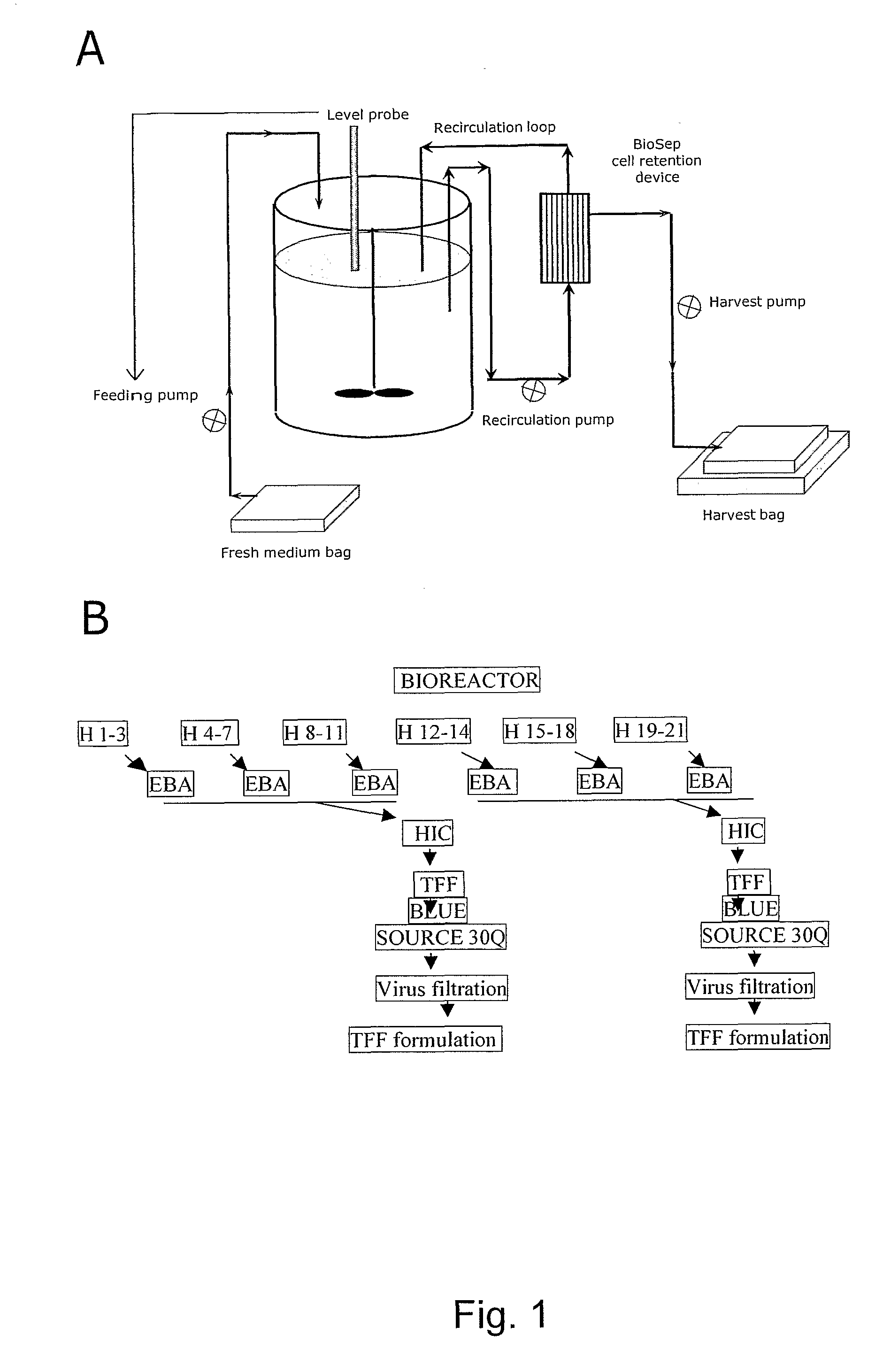
The present invention pertains to a process for production of recombinant arylsulfatase A in a cell culture system, the process comprising culturing a mammalian cell capable of producing rASA in liquid medium in a system comprising one or more bio-reactors; and concentrating, purifying and formulating the rASA by a purification process comprising one or more steps of chromatography. Other aspects of the invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising rASA, which is efficiently endocytosed via the mannose-6-phosphate receptor pathway in vivo as well as a rhASA a medicament and use of a rhASA for the manufacture of a medicament for reducing the galactosyl sulphatide levels within target cells in the peripheral nervous system and / or within the central nervous system in a subject. A final aspect of the invention provides a method of treating a subject in need thereof, said method comprising administering to said subject a pharmaceutical composition comprising a rhASA and thereby obtaining a reduction in the galactosyl sulphatide levels in target cells within said subject.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Cells for producing recombinant iduronate-2-sulfatase
ActiveUS20140004593A1Effective enzyme replacement therapyImprove the level ofAnimal cellsHydrolasesIduronate-2-sulfataseSerum free
The present invention provides, among other things, methods and compositions for production of recombinant I2S protein with improved potency and activity using cells co-express I2S and FGE protein. In some embodiments, cells according to the present invention are engineered to simultaneously over-express recombinant I2S and FGE proteins. Cells according to the invention are adaptable to various cell culture conditions. In some embodiments, cells of the present invention adaptable to a large-scale suspension serum-free culture.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
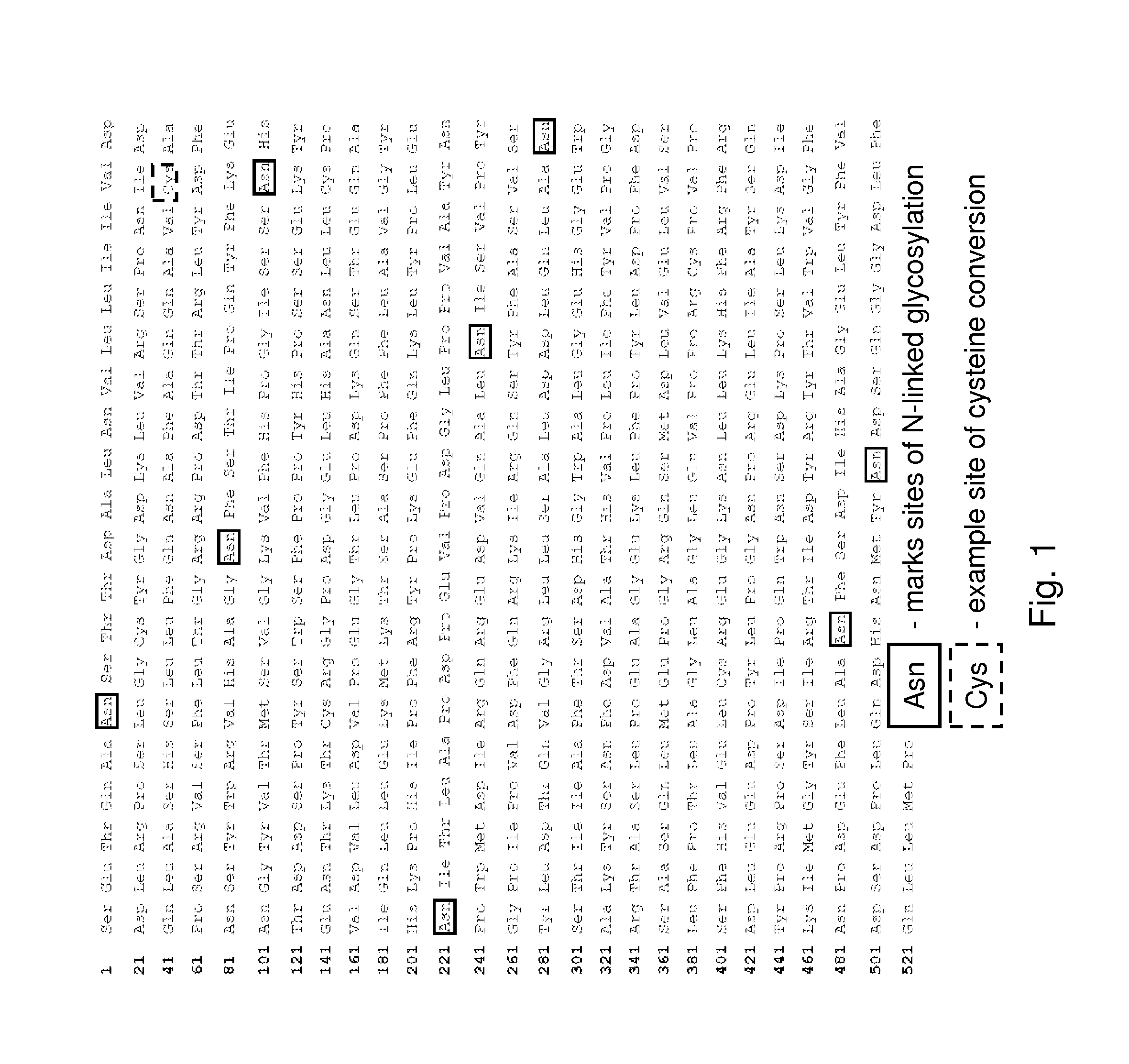
Glycosylation variants of iduronate 2-sulfatase
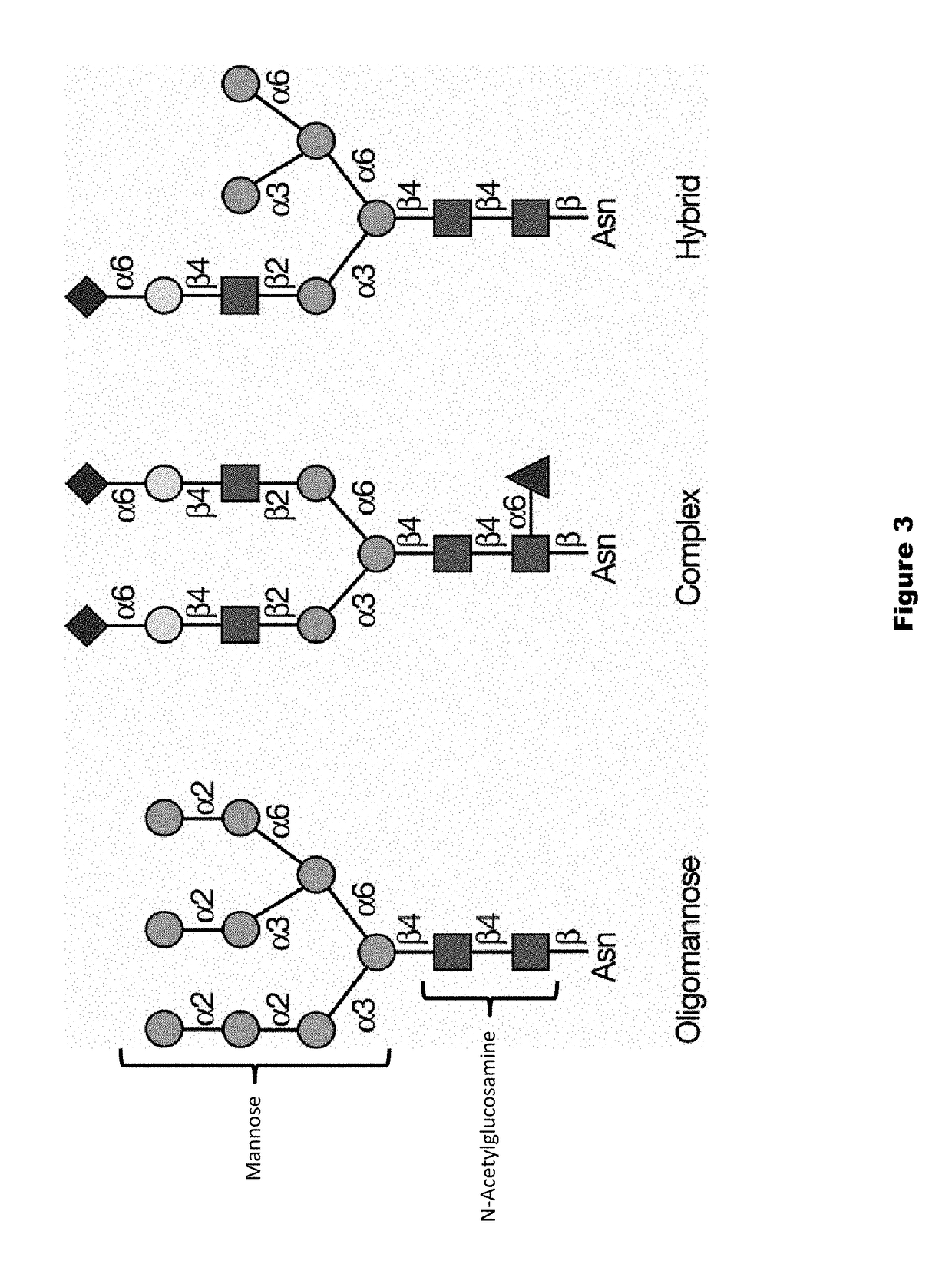
The present invention provides a highly glycosylated iduronate-2-sulfatase enzyme comprising an iduronate-2-sulfatase polypeptide with at least 5 kilodalton (kDa) more sugar than iduronate-2-sulfatase purified from a natural source, e.g. human liver. The present invention also provides an enzymatically active polypeptide fragment or variant of such a highly glycosylated iduronate-2-sulfatase. The present invention further provides an isolated nucleic acid encoding iduronate-2-sulfatase, as well as an expression vector, a host cell and a method for producing the present highly glycosylated iduronate-2-sulfatase enzyme. In one embodiment the present invention is directed to a method for producing a glycosylated iduronate-2-sulfatase enzyme which comprises culturing a host cell containing a nucleic acid encoding an enzymatically active iduronate-2-sulfatase polypeptide wherein the host cell glycosylates the polypeptide to a greater degree than a native iduronate-2-sulfatase polypeptide expressed by a natural human liver cell.
Owner:WOMENS & CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
Manufacture of Active Highly Phosphorylated Human Lysosomal Sulfatase Enzymes and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20090186011A1High yieldAvoid material lossCompound screeningNervous disorderLysosomePhosphorylation
This invention provides compositions of active highly phosphorylated lysosomal sulfatase enzymes, their pharmaceutical compositions, methods of producing and purifying such lysosomal sulfatase enzymes and compositions and their use in the diagnosis, prophylaxis, or treatment of diseases and conditions, including particularly lysosomal storage diseases that are caused by, or associated with, a deficiency in the lysosomal sulfatase enzyme.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
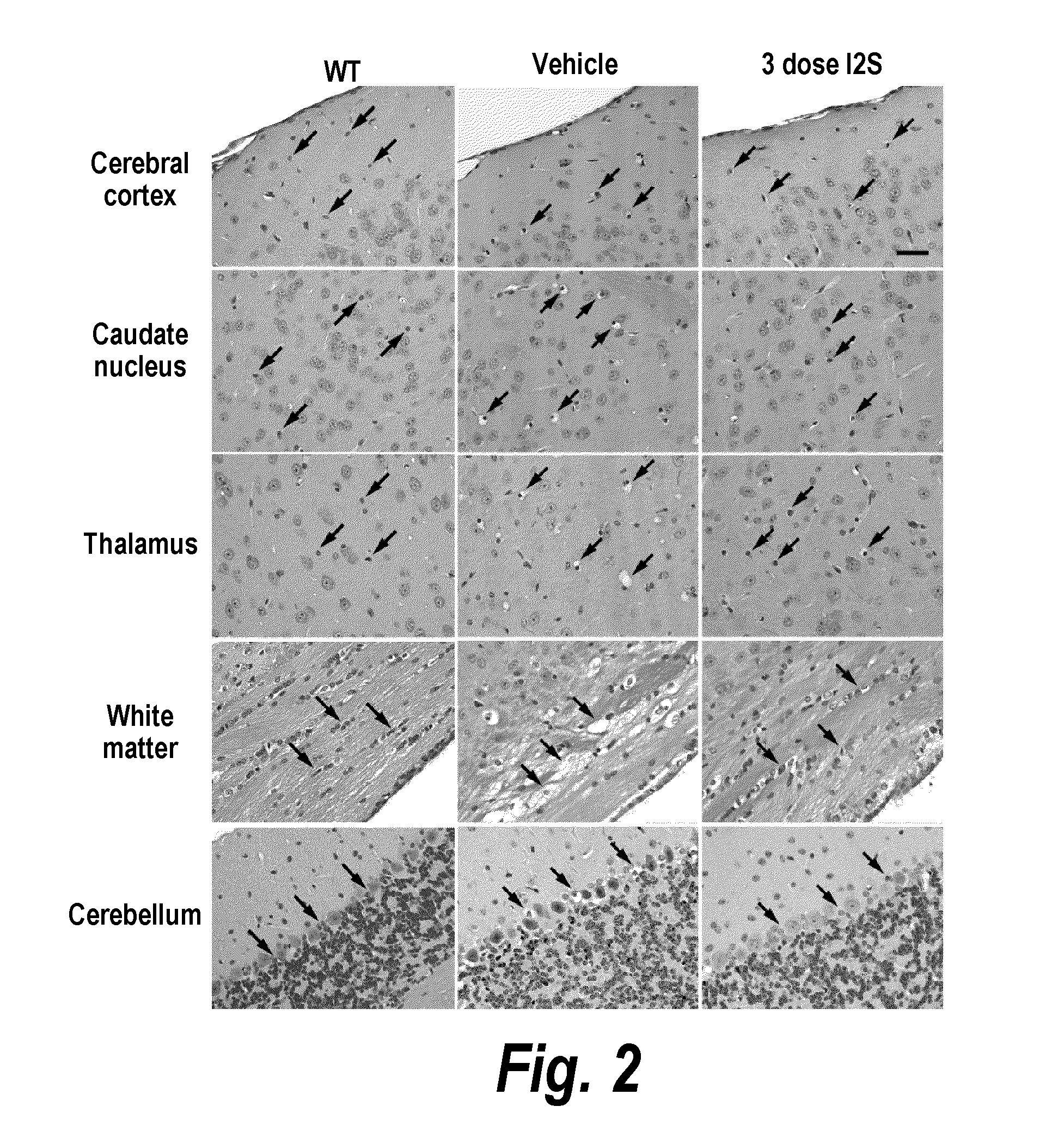
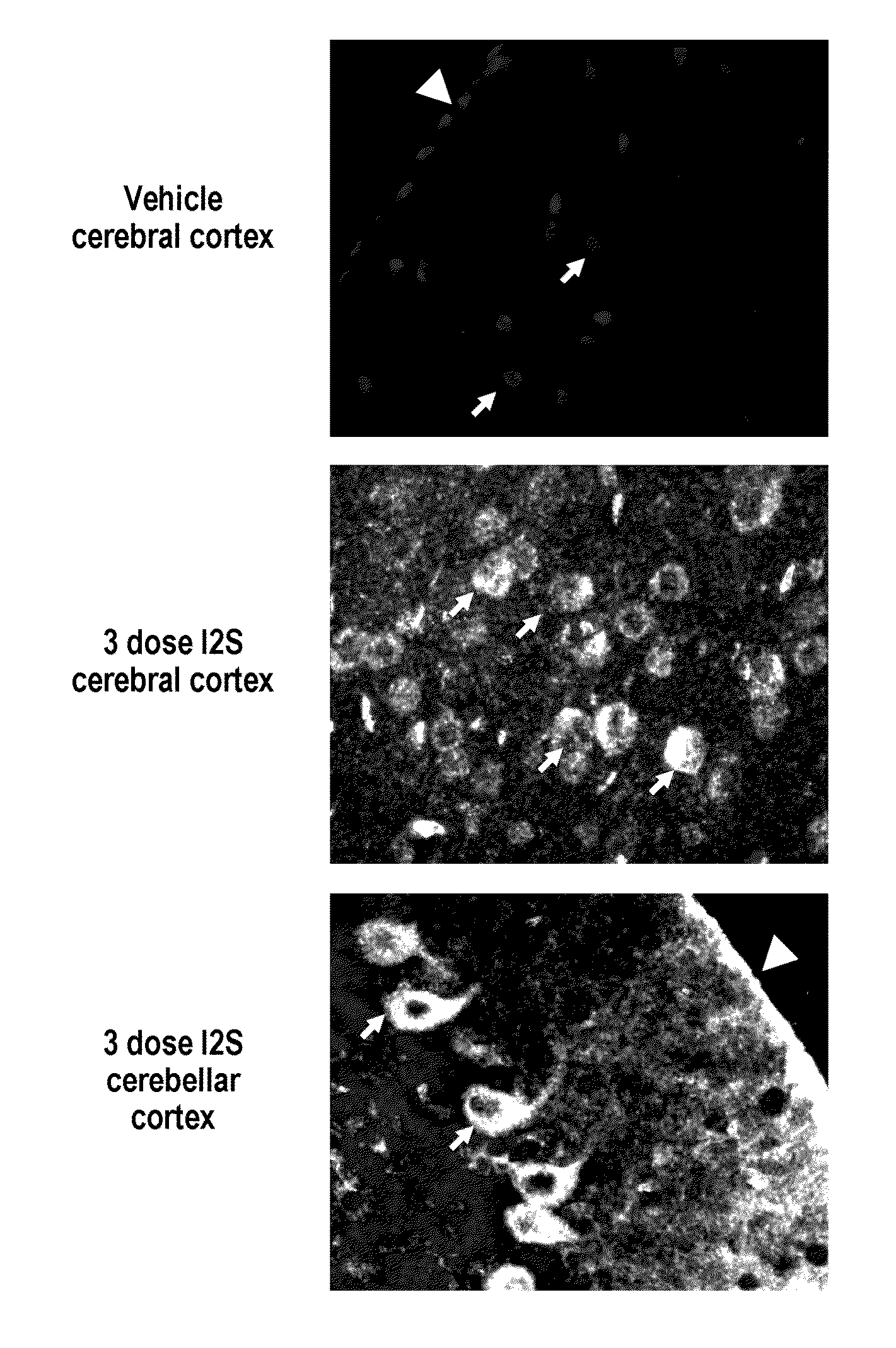
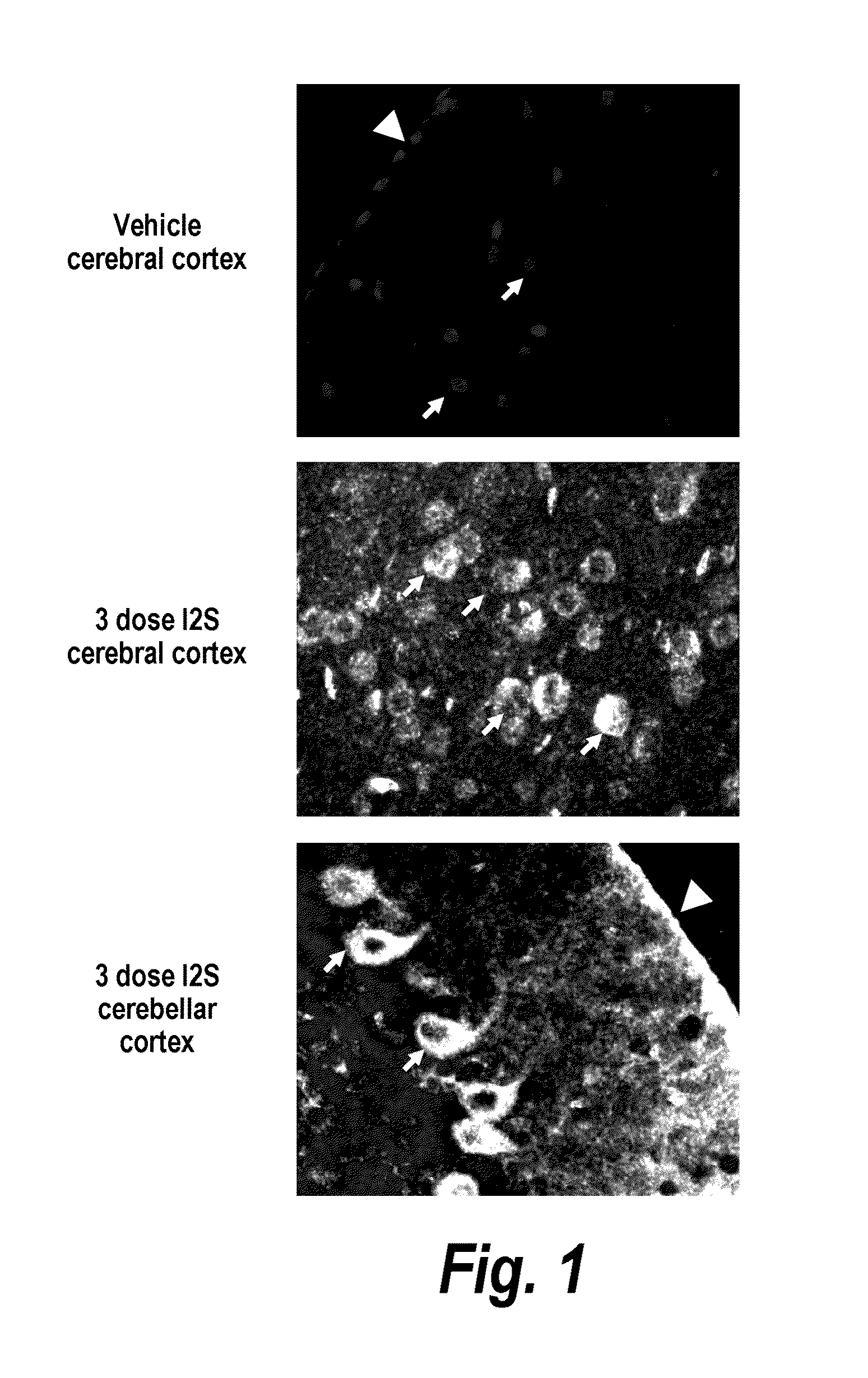
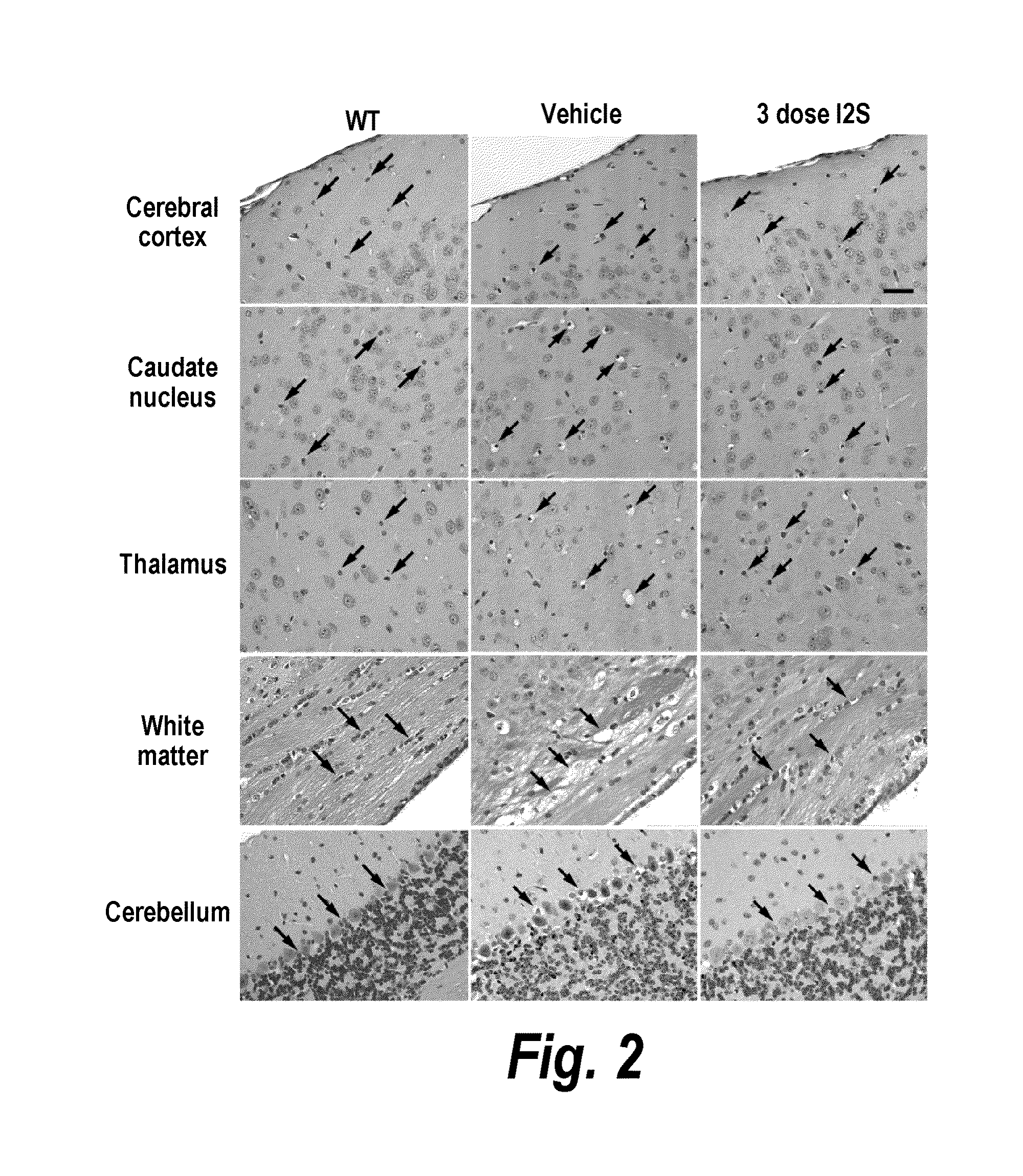
Methods and compositions for CNS delivery of iduronate-2-sulfatase
ActiveUS20110318323A1Effective and less approachEffectively and extensivelyNervous disorderHydrolasesIduronate-2-sulfataseHunter syndrome
The present invention provides, among other things, compositions and methods for CNS delivery of lysosomal enzymes for effective treatment of lysosomal storage diseases. In some embodiments, the present invention includes a stable formulation for direct CNS intrathecal administration comprising an iduronate-2-sulfatase (I2S) protein, salt, and a polysorbate surfactant for the treatment of Hunters Syndrome.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Methods and compositions for CNS delivery of iduronate-2-sulfatase
ActiveUS8545837B2Effective and less invasiveEffectively and extensivelyNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsIduronate-2-sulfataseHunter syndrome
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Manufacture of active highly phosphorylated human lysosomal sulfatase enzymes and uses thereof
ActiveUS8128925B2High yieldAvoid material lossCompound screeningNervous disorderPhosphorylationLysosome
This invention provides compositions of active highly phosphorylated lysosomal sulfatase enzymes, their pharmaceutical compositions, methods of producing and purifying such lysosomal sulfatase enzymes and compositions and their use in the diagnosis, prophylaxis, or treatment of diseases and conditions, including particularly lysosomal storage diseases that are caused by, or associated with, a deficiency in the lysosomal sulfatase enzyme.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Methods and compositions for CNS delivery of heparan n-sulfatase
ActiveUS20120014936A1Effective and less approachReduce deliverySenses disorderNervous disorderSanfilippo syndrome type aLysosomal enzyme defect
The present invention provides, among other things, compositions and methods for CNS delivery of lysosomal enzymes for effective treatment of lysosomal storage diseases. In some embodiments, the present invention includes a stable formulation for direct CNS intrathecal administration comprising a heparan N-sulfatase (HNS) protein, salt, and a polysorbate surfactant for the treatment of Sanfilippo Syndrome Type A.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
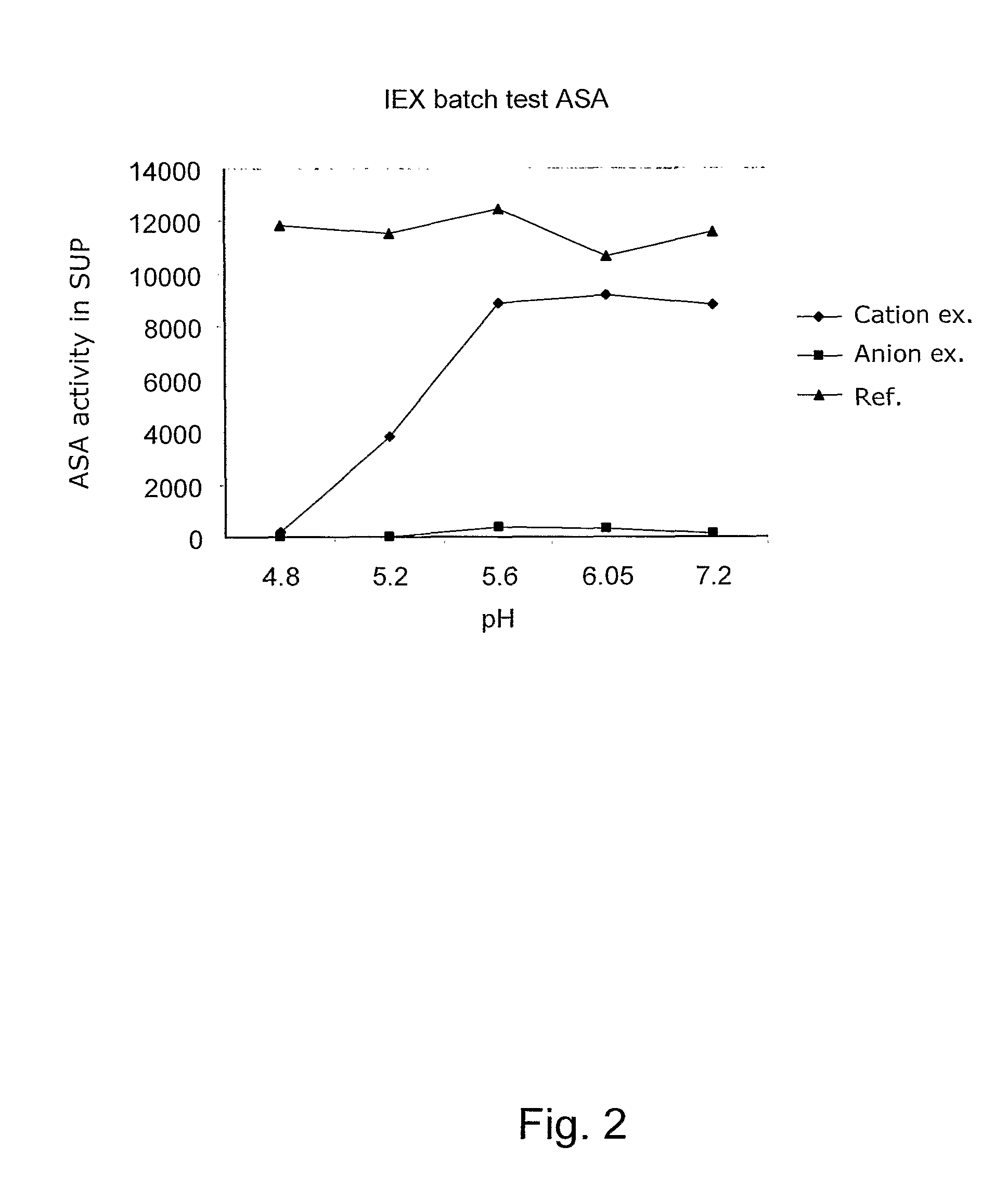
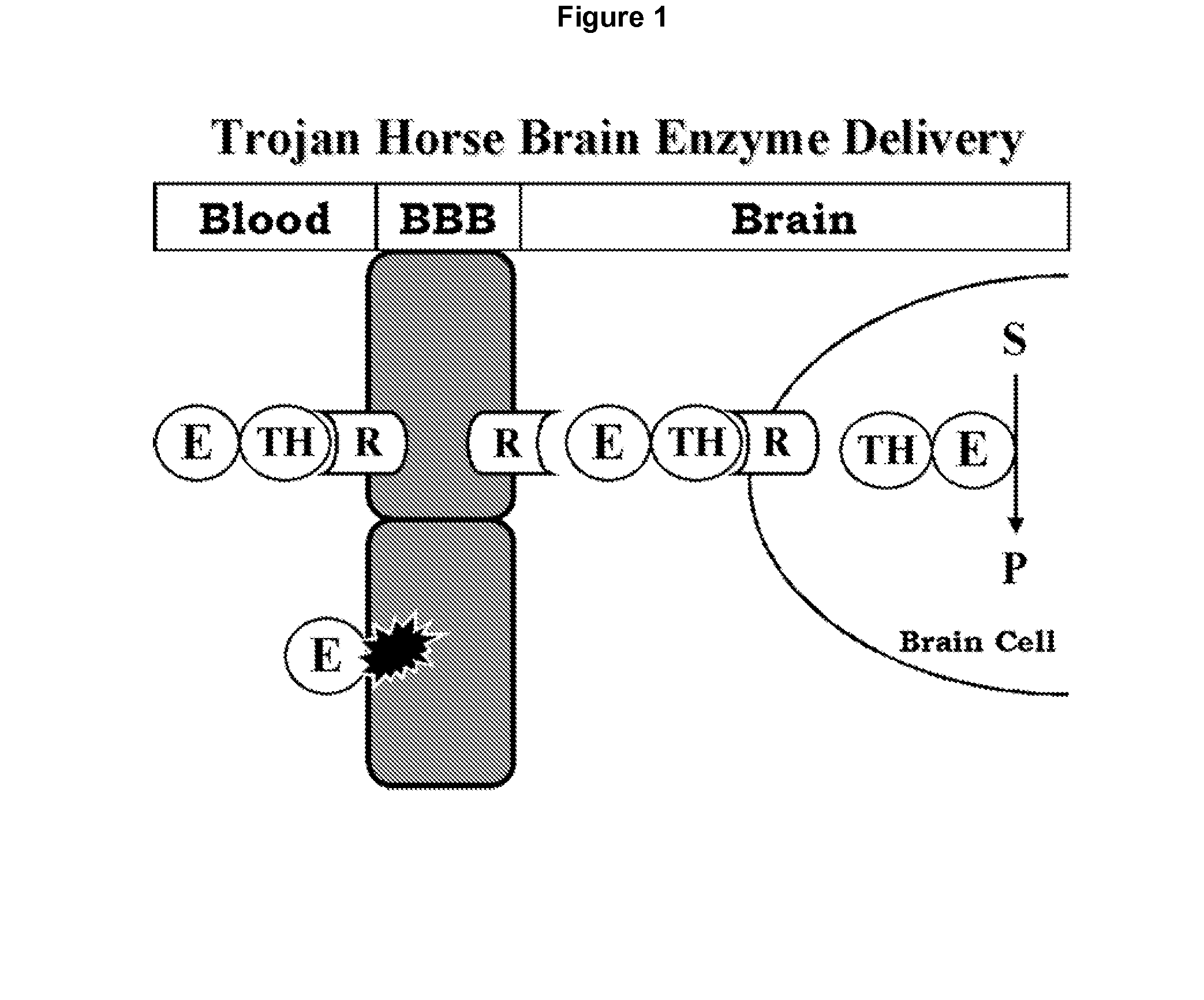
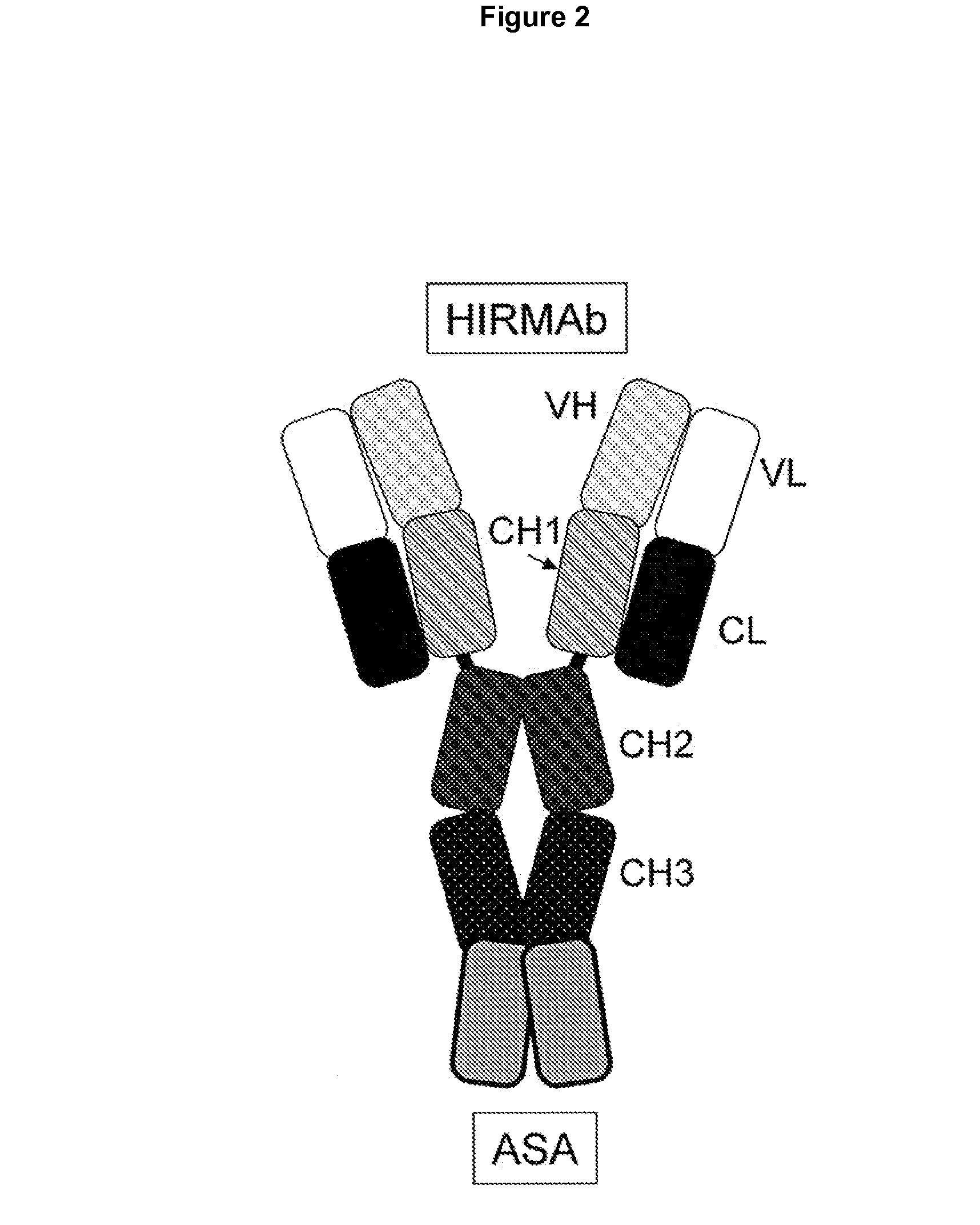
Methods and Compositions for Increasing Arylsulfatase A Activity in the CNS
ActiveUS20130142794A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifNervous disorderArylsulfatase A activityInsulin receptor
Provided herein are methods and compositions for treating a subject suffering from a deficiency in arylsulfatase A in the CNS. The methods include systemic administration of a bifunctional fusion antibody comprising an antibody to a human insulin receptor and an arylsulfatase A.
Owner:JCR PHARMA +1
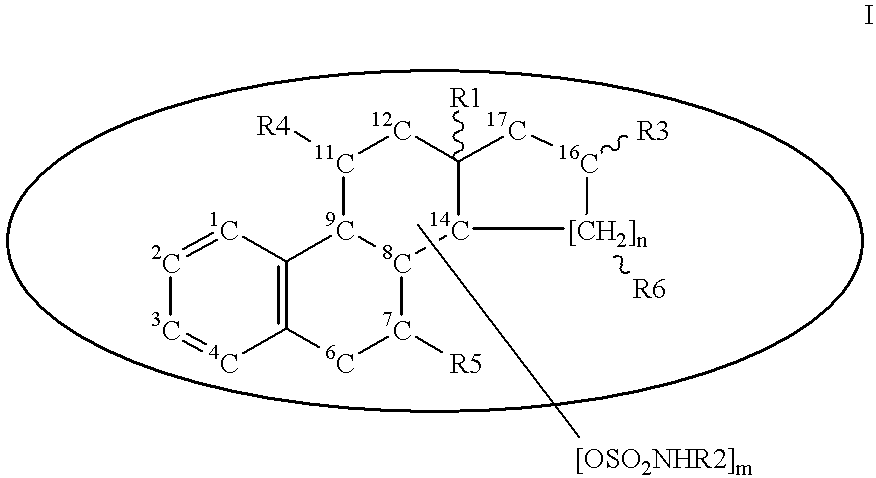
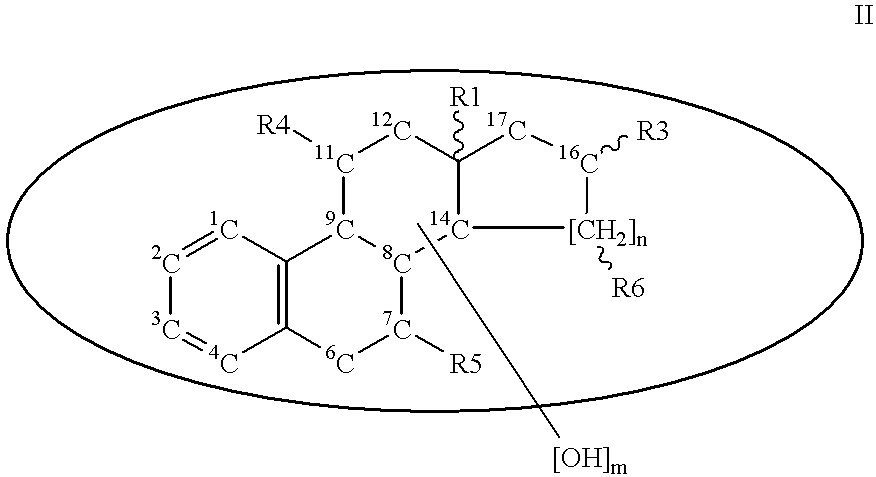
Steroid sulfamates, method for the production and use thereof
InactiveUS6339079B1Improve effectivenessReduced effectivenessBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSterolPharmaceutical industry
A novel class of gonane type and D-homo-gonane type steroids having sulfatase-inhibiting and / or estrogenic activity is presented for application in the pharmaceutical industry. The number and location of sulfamoyloxy groups on the steroids provides for sulfatase inhibiting and estrogenic activities that independently vary over a wide range, allowing the customization of the pharmaceutical for specific purposes, including treatment and diagnosis of estrogen-dependent tumors.
Owner:DR HELMUT KASCH +1
Methods and Compositions for Increasing Arylsulfatase A Activity in the CNS
Provided herein are methods and compositions for treating a subject suffering from a deficiency in arylsulfatase A in the CNS. The methods include systemic administration of a bifunctional fusion antibody comprising an antibody to a human insulin receptor and an arylsulfatase A.
Owner:JCR PHARMA +1
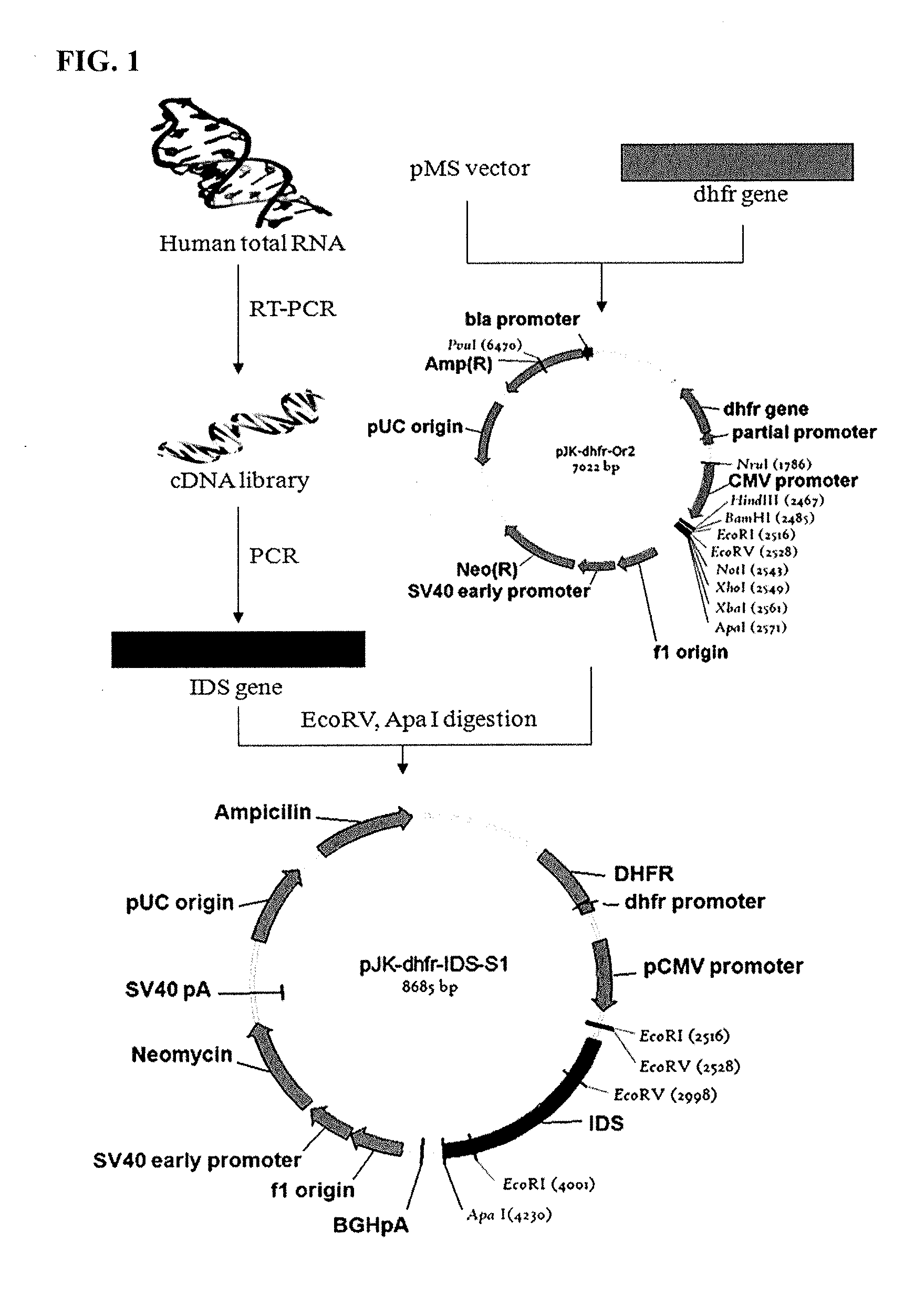
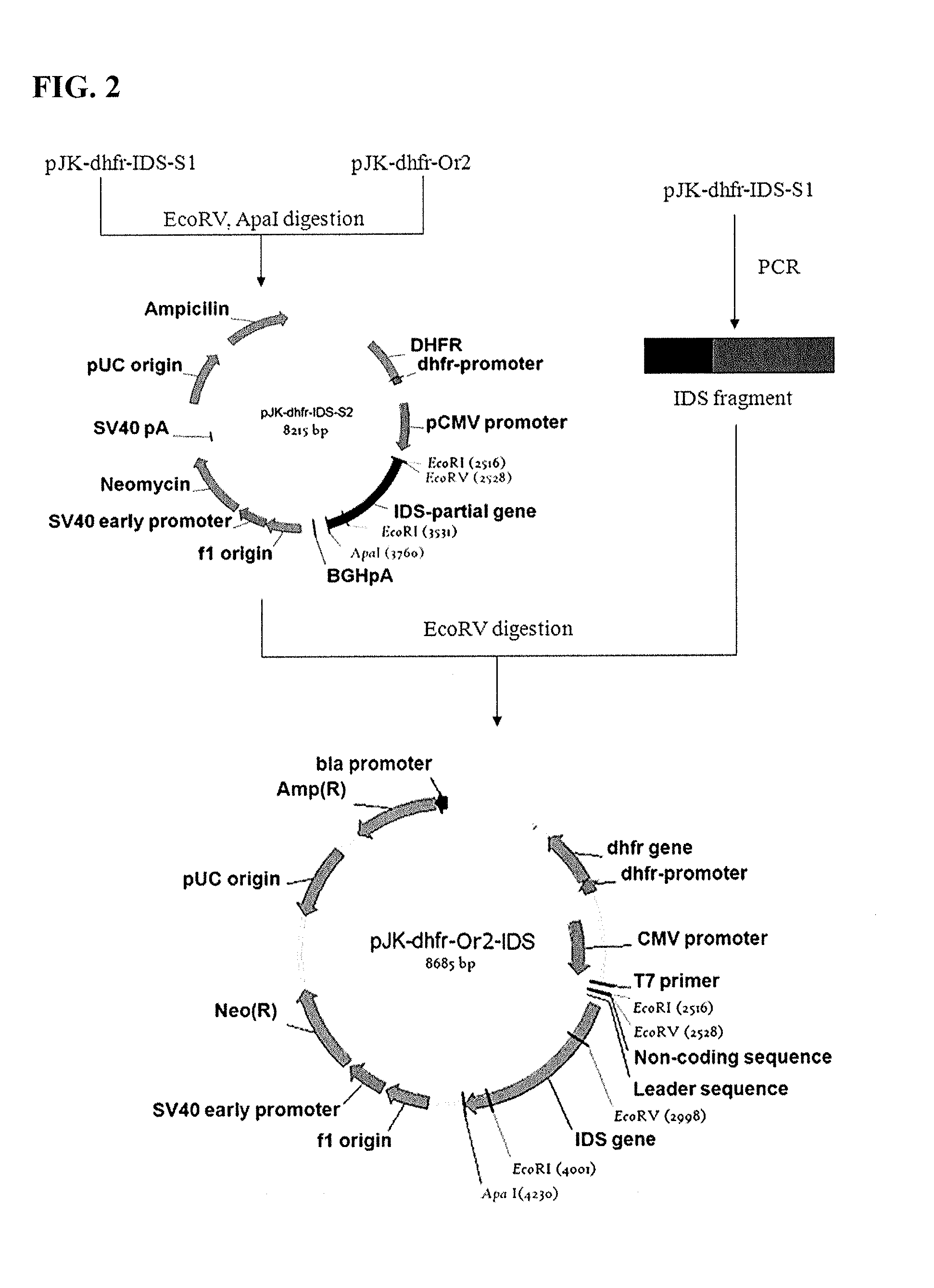
Iduronate-2-sulfatase and use thereof
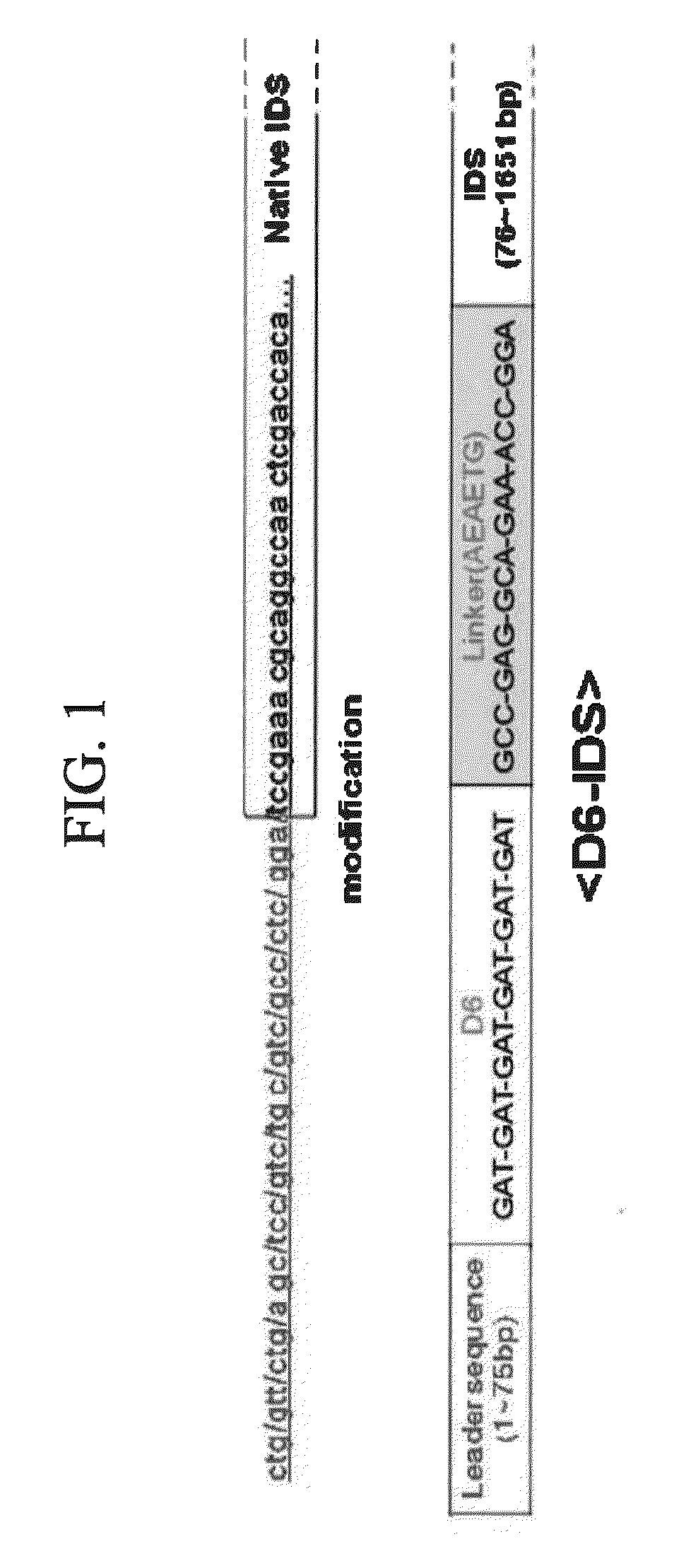
Disclosed is a modified iduronate-2-sulfatase (IDS) gene constructed by inserting the nucleotide of SEQ ID NO: 2 into a wild-type IDS gene. In addition to being negatively charged, the improved IDS enzyme encoded by the modified gene exhibits a sufficient retention time in blood to target the bone, so that it is more effective for treating Hunter syndrome.
Owner:THE GREEN CROSS CORP
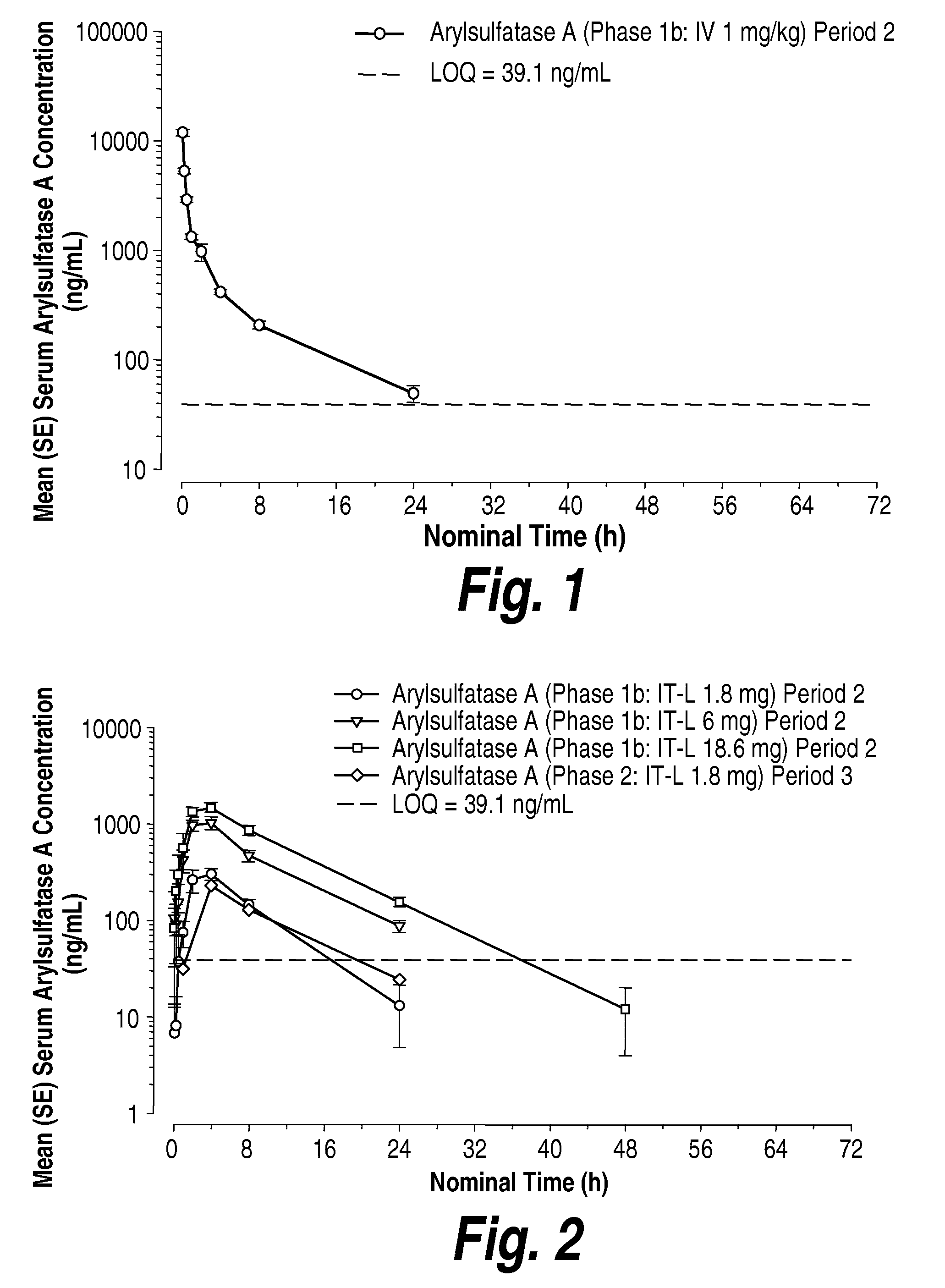
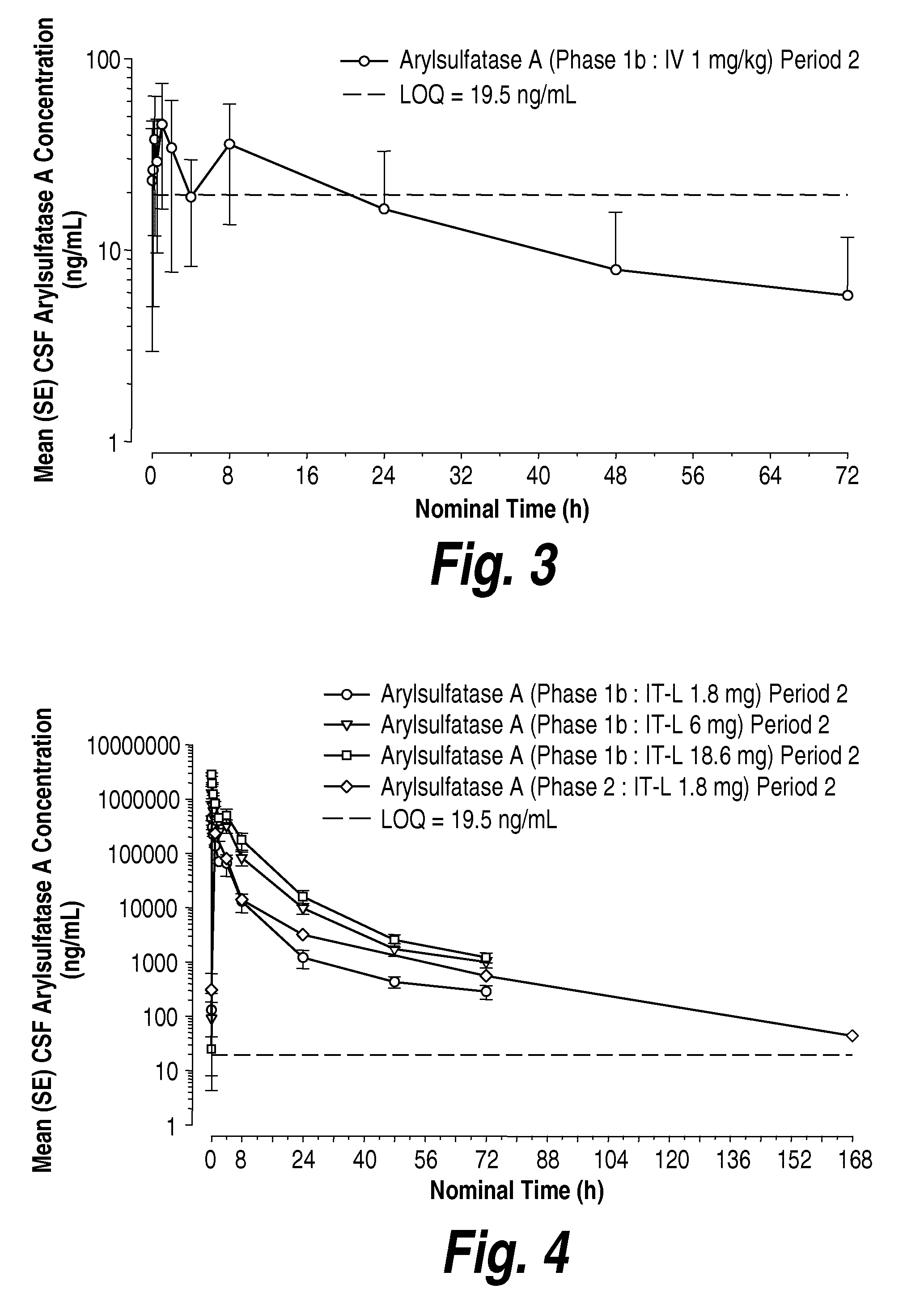
Methods and compositions for CNS delivery of arylsulfatase a
ActiveUS20120009171A1Effective and less approachReduce deliveryNervous disorderHydrolasesMetachromatic leucodystrophyLysosomal enzyme defect
The present invention provides, among other things, compositions and methods for CNS delivery of lysosomal enzymes for effective treatment of lysosomal storage diseases. In some embodiments, the present invention includes a stable formulation for direct CNS intrathecal administration comprising an arylsulfatase A (ASA) protein, salt, and a polysorbate surfactant for the treatment of Metachromatic Leukodystrophy Disease.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Methods and compositions for CNS delivery of iduronate-2-sulfatase
ActiveUS20140271598A1Effective and less approachEffectively and extensivelySenses disorderNervous disorderIduronate-2-sulfataseHunter syndrome
The present invention provides, among other things, compositions and methods for CNS delivery of lysosomal enzymes for effective treatment of lysosomal storage diseases. In some embodiments, the present invention includes a stable formulation for direct CNS intrathecal administration comprising an iduronate-2-sulfatase (I2S) protein, salt, and a polysorbate surfactant for the treatment of Hunters Syndrome.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Methods and compositions for increasing enzyme activity in the CNS
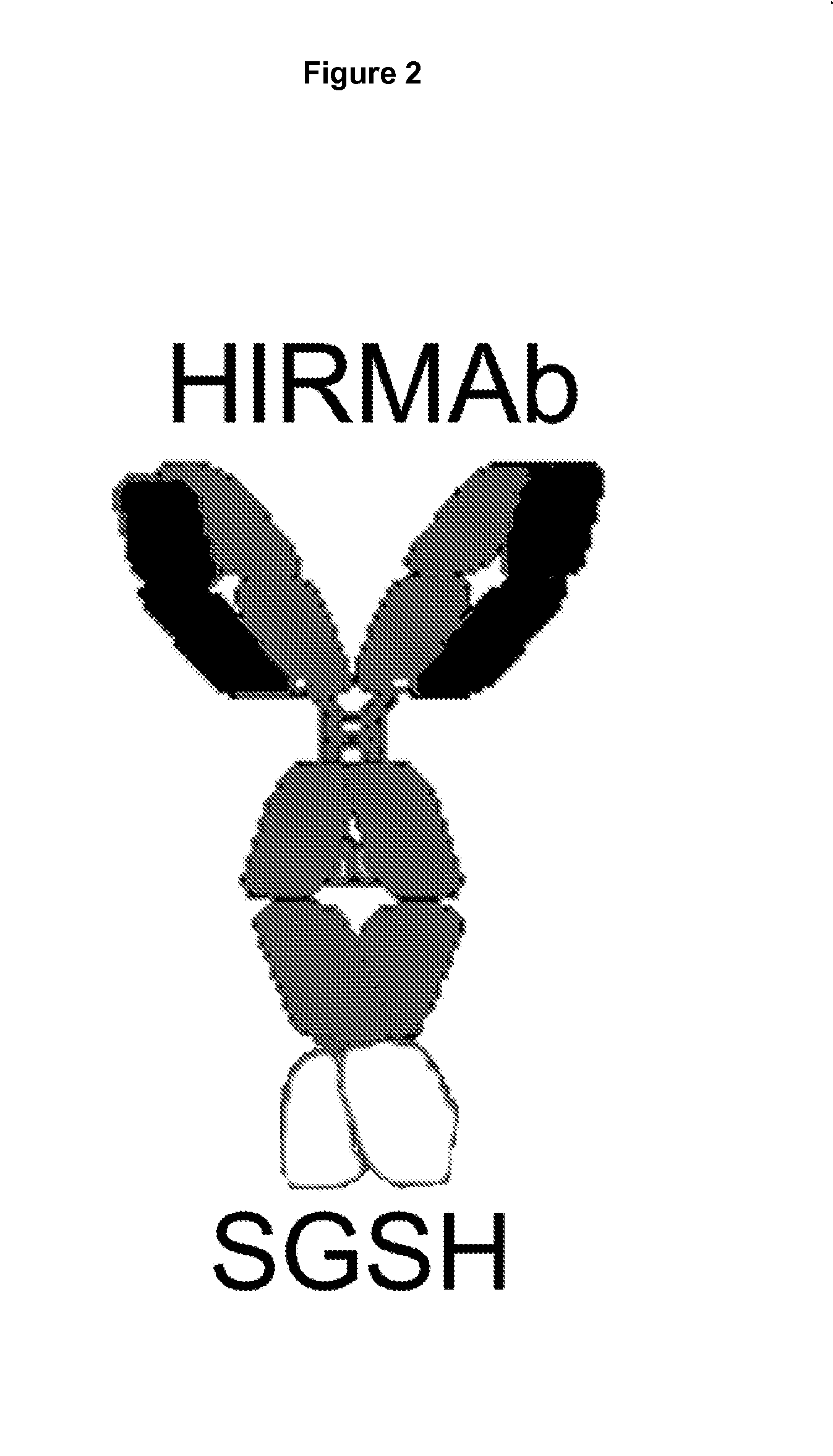
Provided herein are methods and compositions for treating a subject suffering from an enzyme deficiency in the central nervous system (CNS). The bifunctional fusion antibodies provided herein comprise an antibody to an endogenous blood brain barrier (BBB) receptor and an enzyme deficient in mucopolysaccharidosis III (MPS-III). The fusion antibodies provided herein comprise N-sulfoglucosamine sulfohydrolase (SGSH), alpha-N-acetylgulcosaminidase (NAGLU), heparin-alpha-glucosaminide N-acetyltransferase (HGSNAT), or N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfatase (GNS). The methods of treating an enzyme deficiency in the CNS comprise systemic administration of a fusion antibody provided herein.
Owner:JCR PHARMA +1
Methods and compositions for CNS delivery of heparan N-sulfatase
ActiveUS9320711B2Effective and less invasiveReduce deliveryPowder deliverySenses disorderSanfilippo syndrome type aLysosomal enzyme defect
The present invention provides, among other things, compositions and methods for CNS delivery of lysosomal enzymes for effective treatment of lysosomal storage diseases. In some embodiments, the present invention includes a stable formulation for direct CNS intrathecal administration comprising a heparan N-sulfatase (HNS) protein, salt, and a polysorbate surfactant for the treatment of Sanfilippo Syndrome Type A.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Subcutaneous administration of iduronate- 2-sulfatase
InactiveUS20150086526A1Improved enzyme replacement therapyImprove bioavailabilityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsIduronate-2-sulfataseLysosome
The present invention provides, among other things, compositions, kits and methods for subcutaneous delivery of lysosomal enzymes for effective treatment of lysosomal storage diseases. In some embodiments, the present invention provides methods for treating Hunter syndrome by subcutaneous administration of a replacement iduronate-2-sulfatase (I2S) protein. In some embodiments, the present invention provides a kit comprising an arrangement of components for subcutaneously administering iduronate-2-sulfatase (I2S) protein.
Owner:SHIRE HUMAN GENETIC THERAPIES INC
Manufacture of active highly phosphorylated human lysosomal sulfatase enzymes and uses thereof
ActiveUS7722865B2High yieldAvoid material lossCompound screeningApoptosis detectionPhosphorylationLysosome
This invention provides compositions of active highly phosphorylated lysosomal sulfatase enzymes, their pharmaceutical compositions, methods of producing and purifying such lysosomal sulfatase enzymes and compositions and their use in the diagnosis, prophylaxis, or treatment of diseases and conditions, including particularly lysosomal storage diseases that are caused by, or associated with, a deficiency in the lysosomal sulfatase enzyme.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Methods and compositions for CNS delivery of iduronate-2-sulfatase
ActiveUS9220677B2Effective and less invasiveEffectively and extensivelyPowder deliverySenses disorderIduronate-2-sulfataseHunter syndrome
The present invention provides, among other things, compositions and methods for CNS delivery of lysosomal enzymes for effective treatment of lysosomal storage diseases. In some embodiments, the present invention includes a stable formulation for direct CNS intrathecal administration comprising an iduronate-2-sulfatase (I2S) protein, salt, and a polysorbate surfactant for the treatment of Hunters Syndrome.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
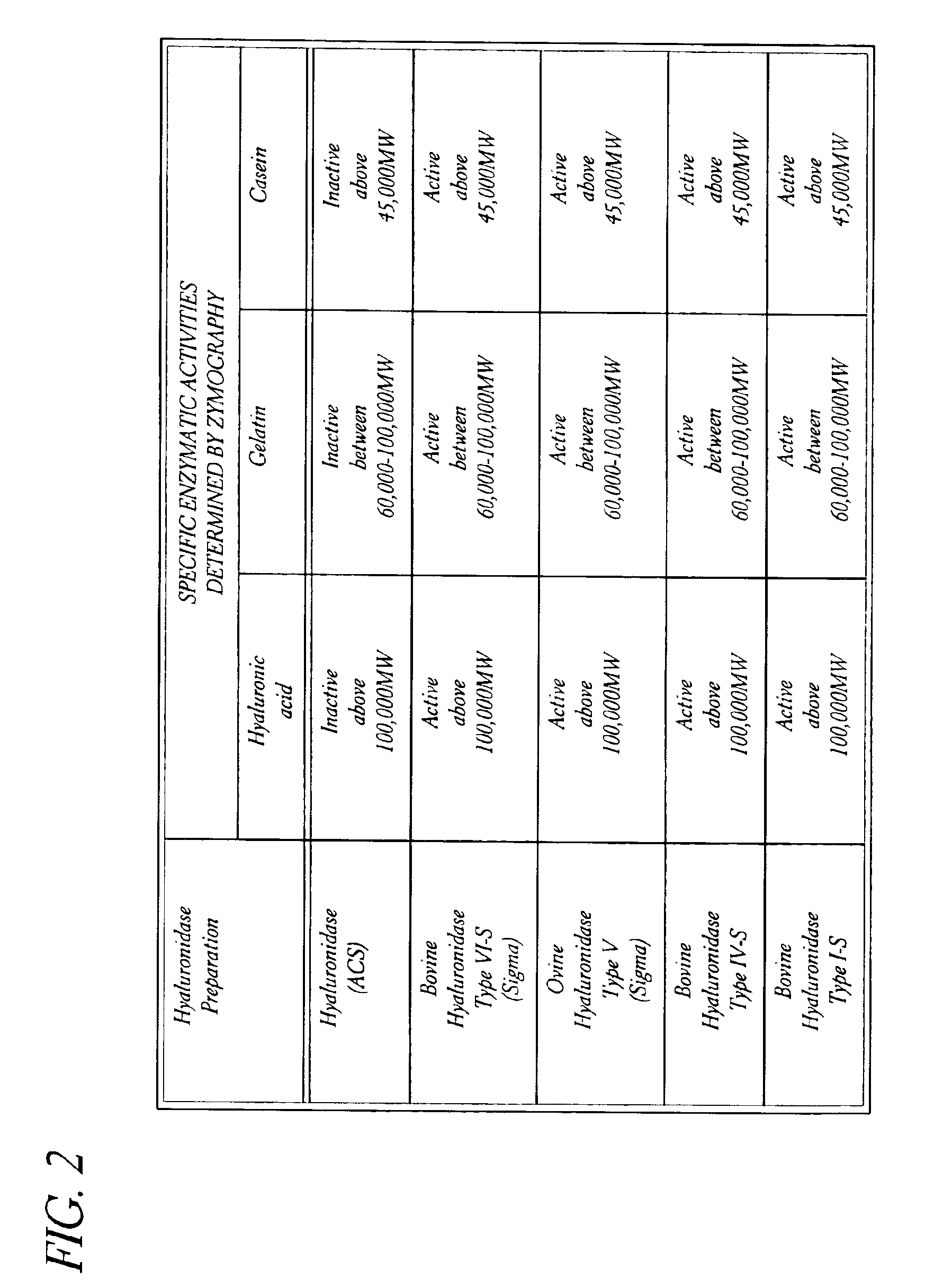
Hyaluronidase preparation for ophthalmic administration and enzymatic methods for accelerating clearance of hemorrhagic blood from the vitreous body of the eye
InactiveUS6939542B2Increase the gapOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderVitreous HumorsBody fluid
A thimerosal-free hyaluronidase preparation wherein the preferred hyaluronidase enzyme is devoid of molecular weight fractions below 40,000 MW, between 60-70,000 MW and above 100,000 MW. Also disclosed is a method for accelerating the clearance of hemorrhagic blood from the vitreous humor of the eye, said method comprising the step of contacting at least one hemorrhage-clearing enzyme (e.g., a β-glucuronidase, matrix metalloproteinase, chondroitinase, chondroitin sulfatase or protein kinase) with the vitreous humor in an amount which is effective to cause accelerated clearance of blood therefrom.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC +1
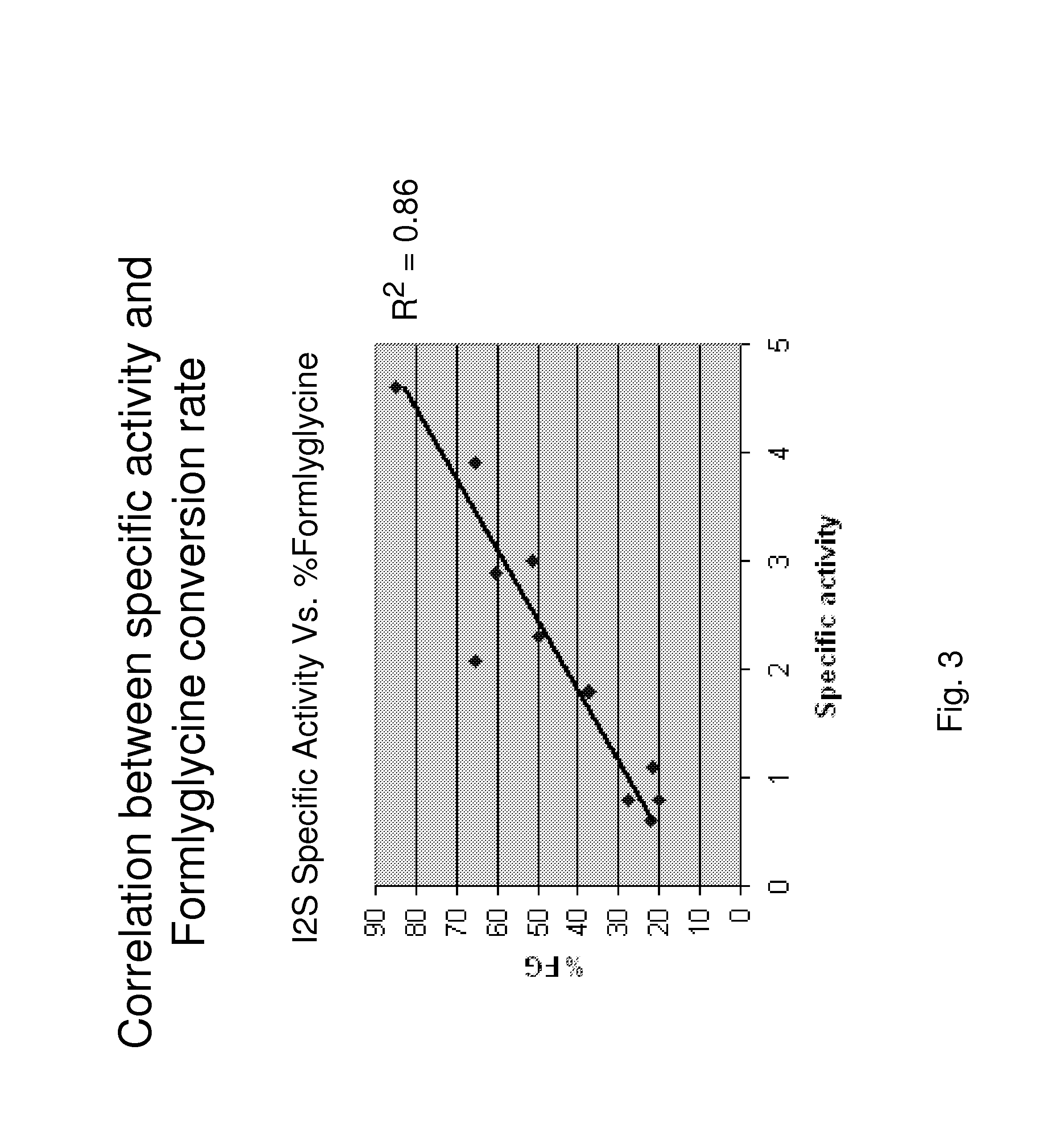
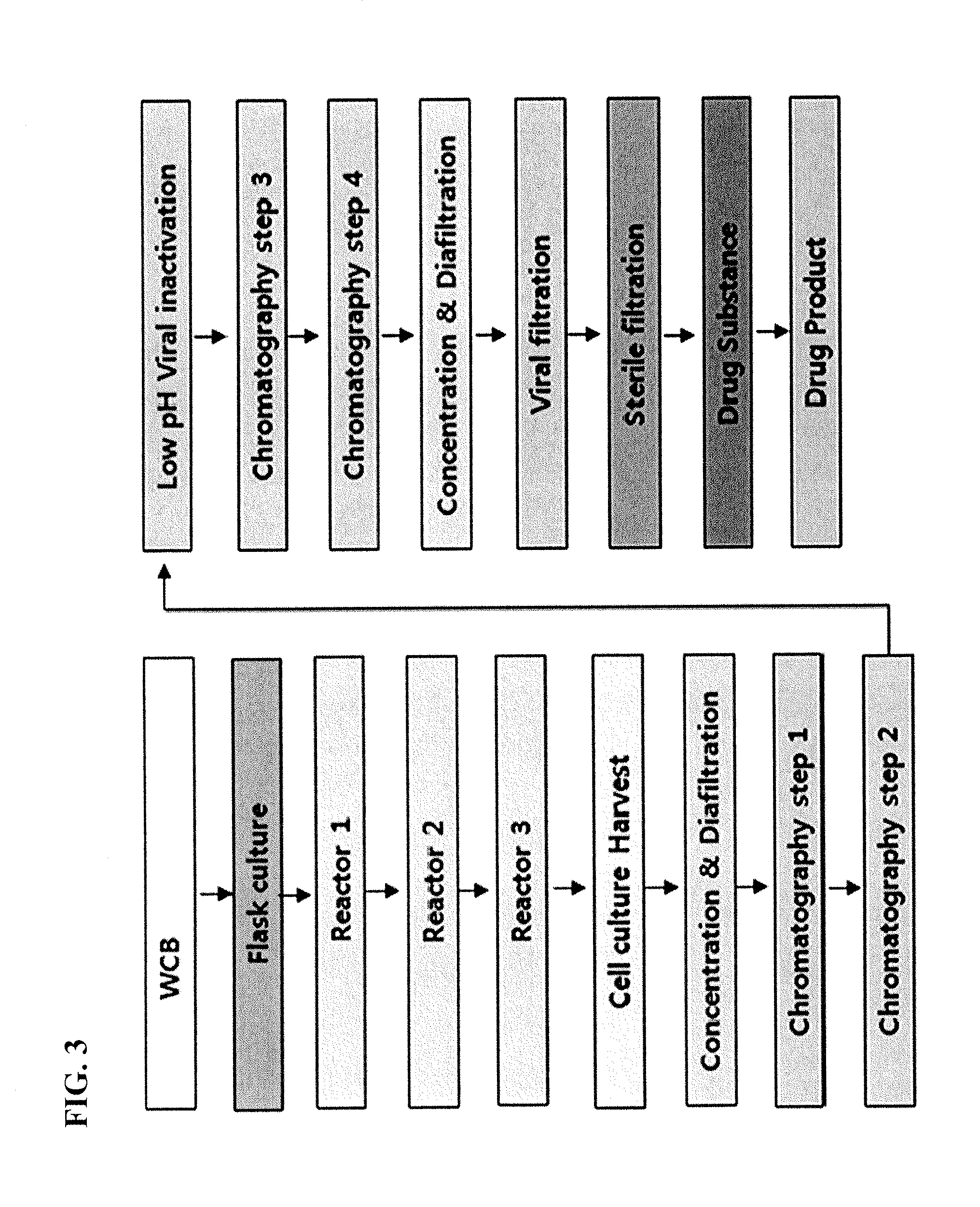
Composition and formulation comprising recombinant human iduronate-2-sulfatase and preparation method thereof
ActiveUS20140242059A1Superior in pharmaceutical efficacyImprove securityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsIduronate-2-sulfataseHunter syndrome
Disclosed is a composition comprising recombinant iduronate-2-sulfatase (IDS). The glycosylation pattern and formylglycine content of the IDS composition are different from those of Elaprase and have superior pharmaceutical efficacy and are safer than the conventional agent and thus can be effectively used for the therapy of Hunter syndrome.
Owner:MEDIGENEBIO CORP +1
Glycosylation variants of iduronate 2-sulfatase
The present invention provides a highly glycosylated iduronate-2-sulfatase enzyme comprising an iduronate-2-sulfatase polypeptide with at least 5 kilodalton (kDa) more sugar than iduronate-2-sulfatase purified from a natural source, e.g. human liver. The present invention also provides an enzymatically active polypeptide fragment or variant of such a highly glycosylated iduronate-2-sulfatase. The present invention further provides an isolated nucleic acid encoding iduronate-2-sulfatase, as well as an expression vector, a host cell and a method for producing the present highly glycosylated iduronate-2-sulfatase enzyme. In one embodiment the present invention is directed to a method for producing a glycosylated iduronate-2-sulfatase enzyme which comprises culturing a host cell containing a nucleic acid encoding an enzymatically active iduronate-2-sulfatase polypeptide wherein the host cell glycosylates the polypeptide to a greater degree than a native iduronate-2-sulfatase polypeptide expressed by a natural human liver cell.
Owner:WOMENS & CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
Methods for sterilizing preparations of digestive enzymes
InactiveUS20060115376A1Effective sterilizationAvoid radiationPowder deliverySenses disorderIduronate-2-sulfataseFungal microorganisms
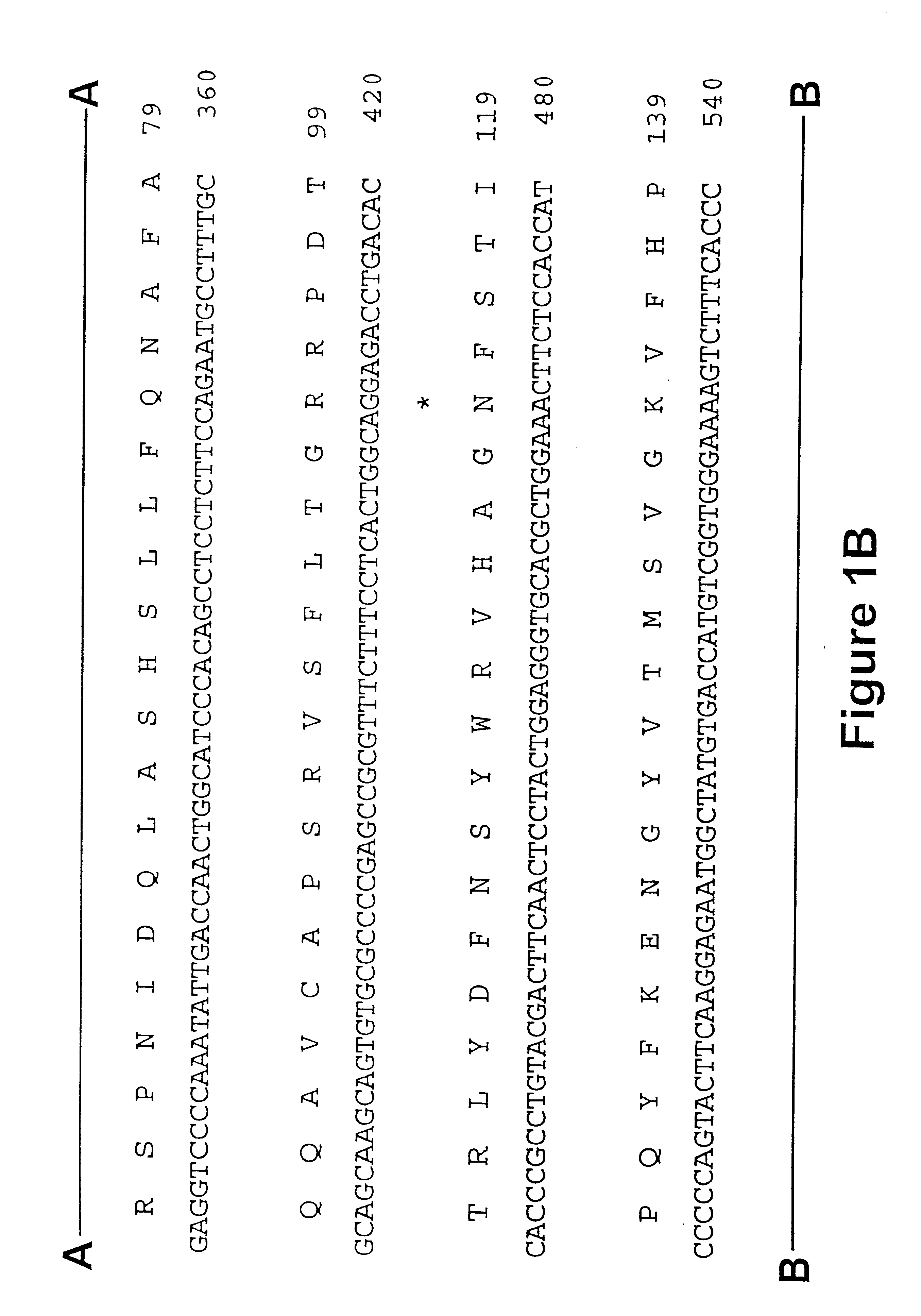
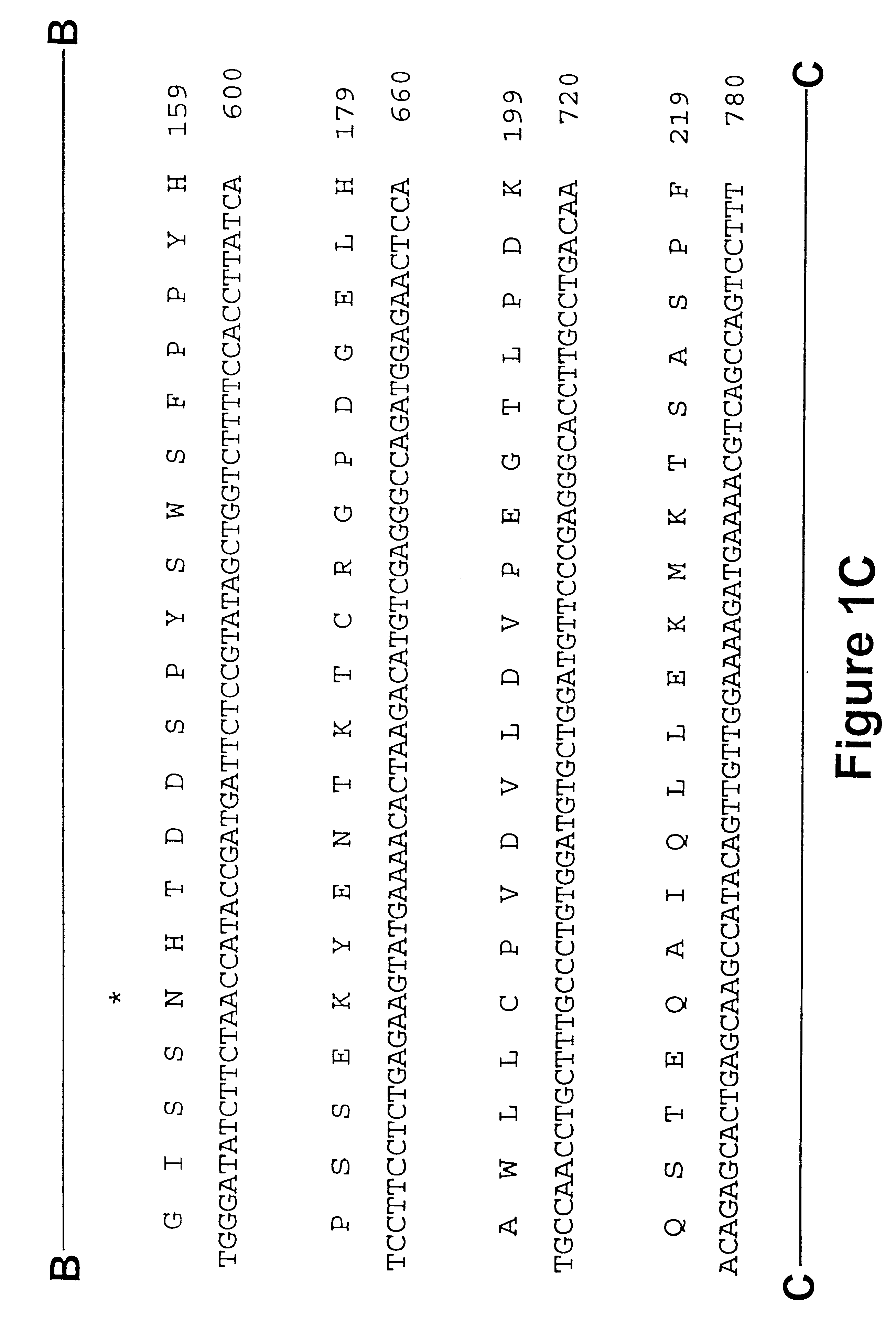
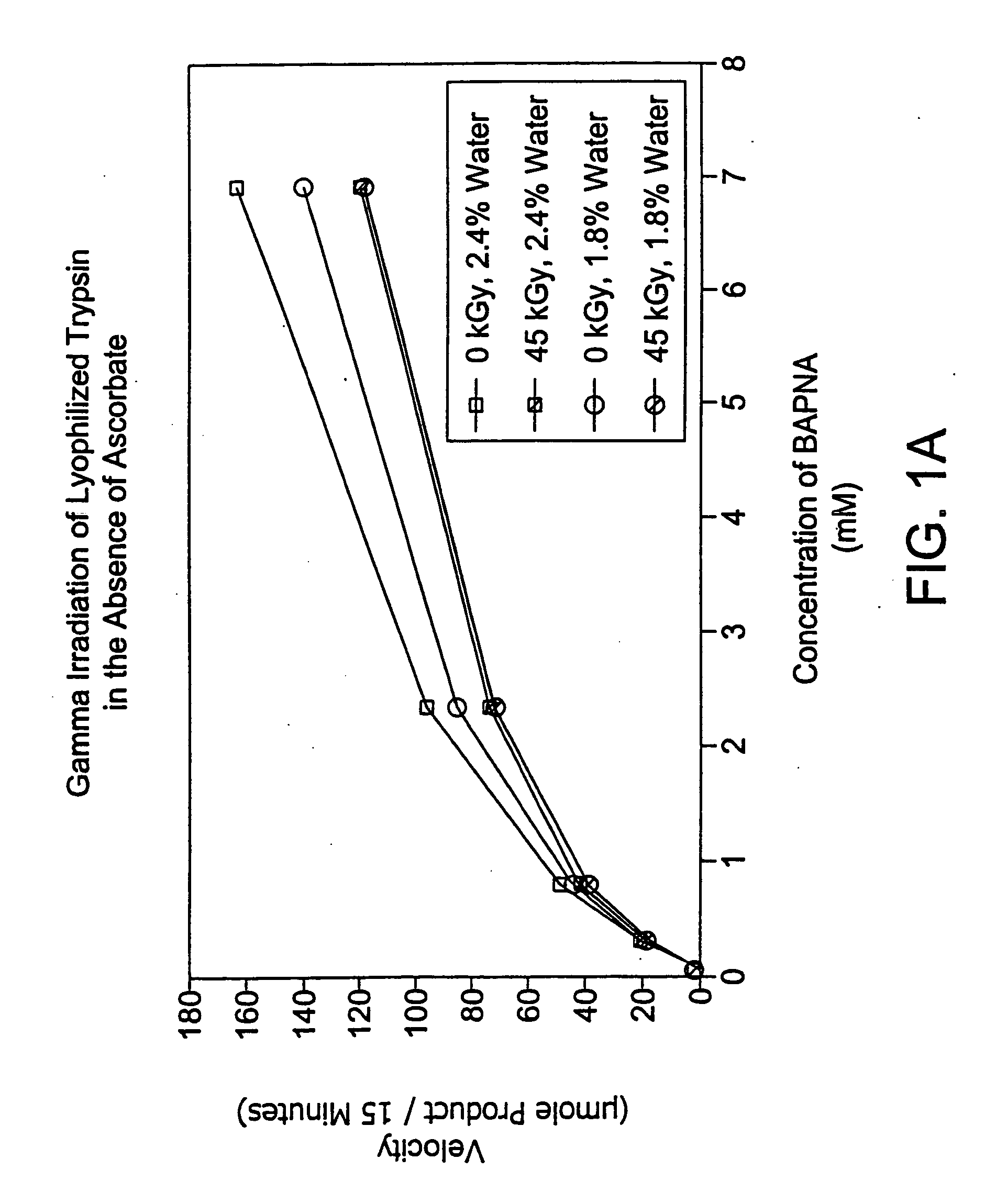
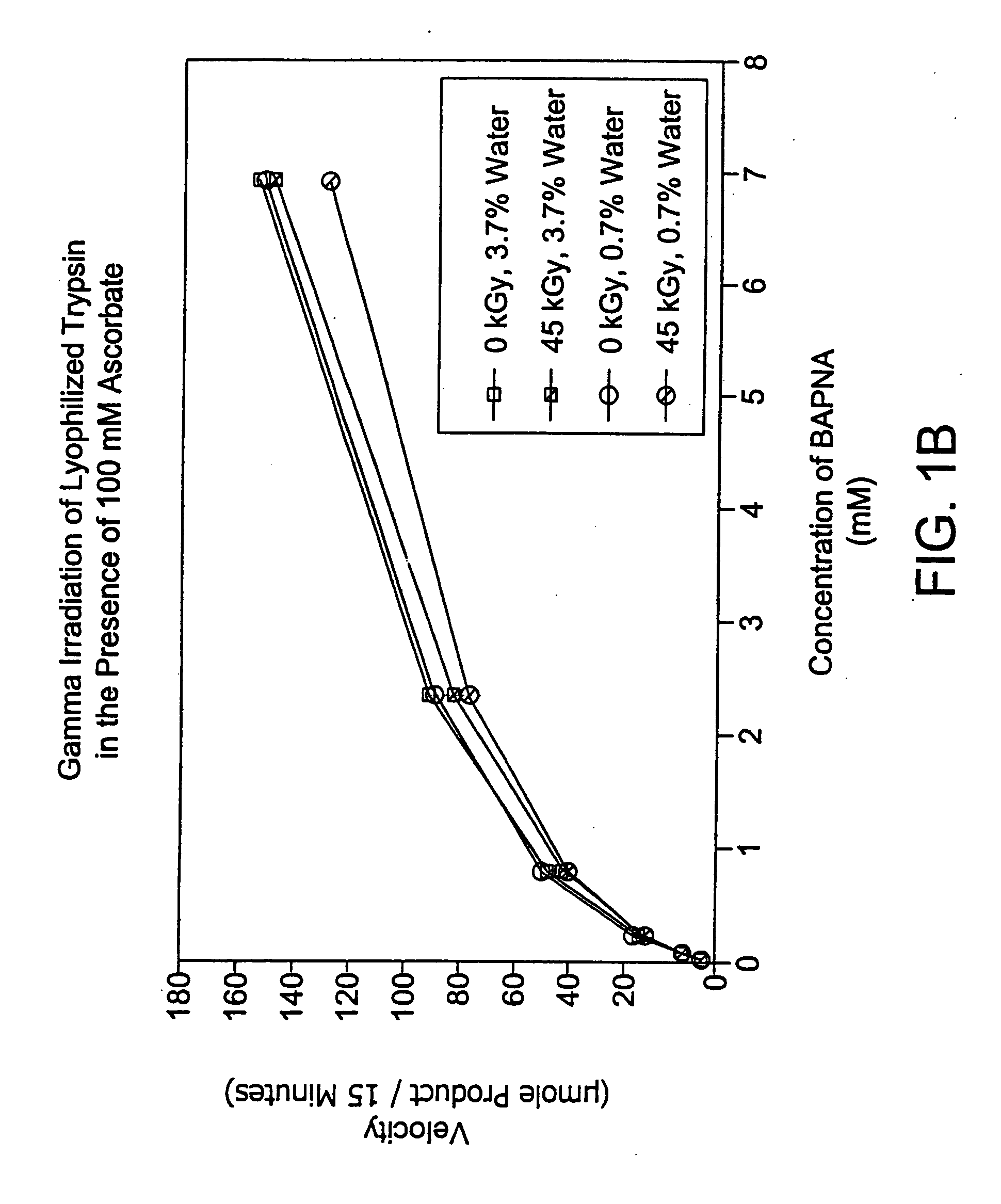
Methods are disclosed for sterilizing preparations of digestive enzymes to reduce the level of one or more active biological contaminants or pathogens therein, such as viruses, bacteria (including inter- and intracellular bacteria, such as mycoplasmas, ureaplasmas, nanobacteria, chlamydia, rickettsias), yeasts, molds, fungi, prions or similar agents responsible, alone or in combination, for TSEs and / or single or multicellular parasites. These methods involve sterilizing preparations of digestive enzymes, such as trypsin, α-galactosidase and iduronate-2-sulfatase, with irradiation.
Owner:CLEARANT
Method for producing fucan sulfatase by means of bacteria
InactiveCN1483814AWide Range of Nutritional RequirementsEasy to trainBacteriaEnzymesBacteroidesFreeze-drying
The method for producing fucosan sulfatase by bacterium includes the following steps: inoculating the strain vibrio fluvialis into fermented broth culture medium containing seaweed powder, culturing for a period of time at a certain temp., then adding enzyme-extracting agent, making produced precipitated downward be deposited, making separation, finally freeze-drying so as to obtain the invented product which has two classes of endofucosan sulfatase and exofucosan sulfatase, and can be degraded to obtain its oligosaccharide, disaccharide and monosaccharide. Said enzyme product has high activity and good stability.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Precursor of N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase, methods of treatment using said enzyme and methods for producing and purifying said enzyme
InactiveUS6972124B2High puritySufficient amountBacteriaHydrolasesN-Acetylgalactosamine-4-SulfataseMutant
The present invention provides a highly purified recombinant human precursor N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase and biologically active mutants, fragments and analogs thereof as well as pharmaceutical formulations comprising highly purified recombinant human precursor N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase. The invention also provides methods for treating diseases caused all or in part by deficiencies in human N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase including MPS VI and methods for producing and purifying the recombinant precursor enzyme to a highly purified form.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Engineering colon bacillus for preparing biological gasoline
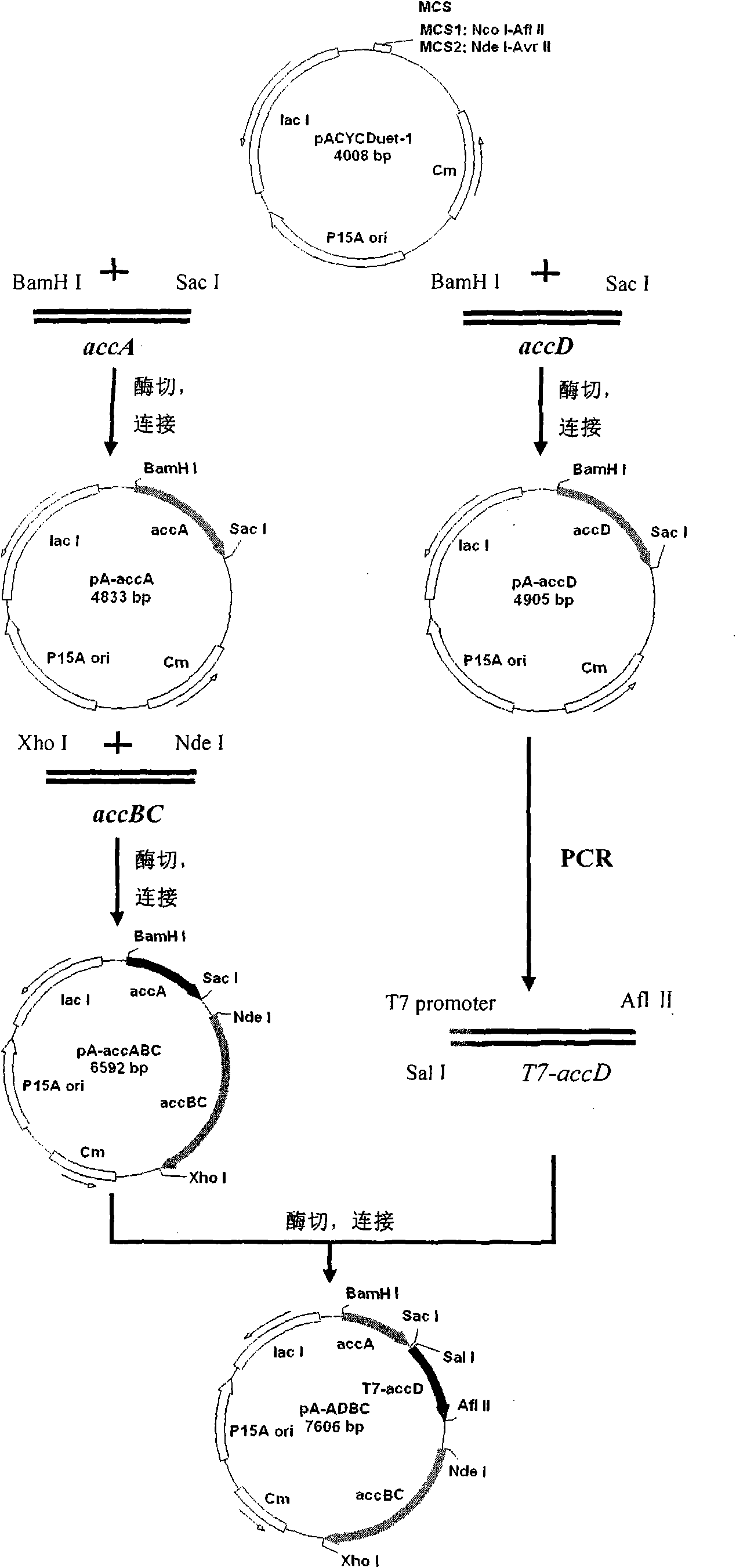
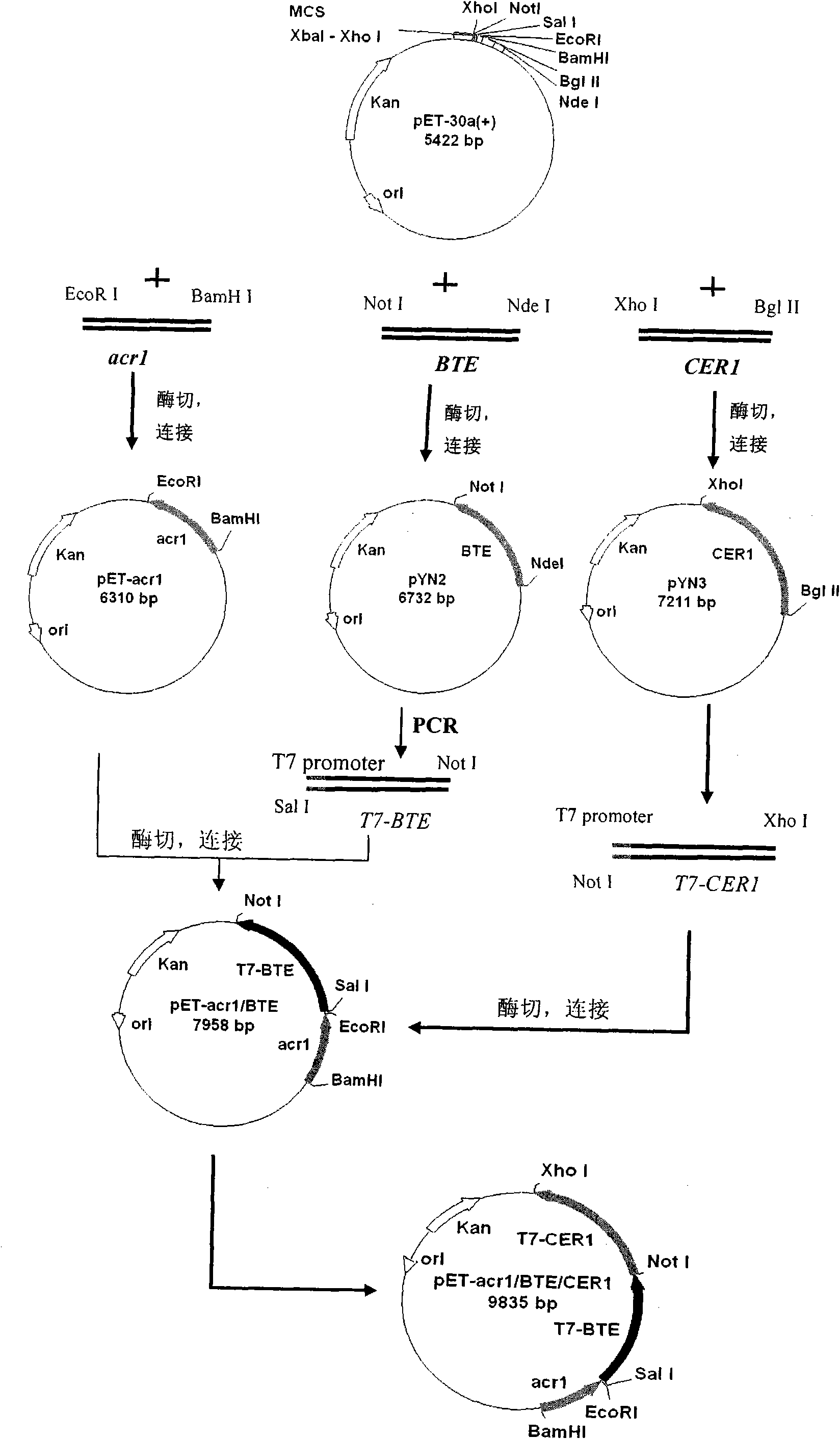
ActiveCN101899412AIncrease concentrationEasy to separateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliSulfatase
The invention discloses engineering colon bacillus for preparing intermediate carbon fatty alcohol and a method for preparing the intermediate carbon fatty alcohol. According to the method, the colon bacillus obtains a capability of producing biological gasoline by excessively expressing sulfatase genes, fatty acyl-CoA reductase genes and fatty aldehyde decarboxylase and the like in the colon bacillus, and the biological gasoline producing capability of the engineering colon bacillus is further improved by combining the excessively expressed acetyl-CoA carboxylase genes and knocking out the fatty acyl-CoA dehydrogenase genes of the colon bacillus. The method can be used for producing the new generation biological gasoline.
Owner:青岛生物能源与过程研究所
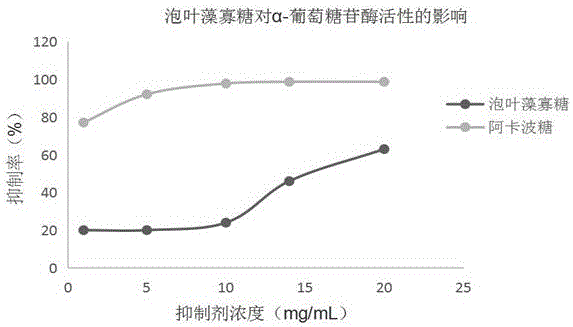
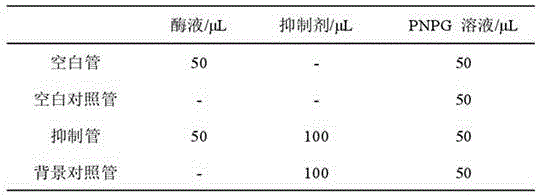
Ascophyllum Nodosum oligosaccharide preparation method and application of Ascophyllum Nodosum oligosaccharide to medicines for reducing blood sugar
ActiveCN105861593AImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyImprove efficiencySugar derivativesMetabolism disorderEnzymatic digestionPectinase
The invention provides an Ascophyllum Nodosum oligosaccharide preparation method and application of Ascophyllum Nodosum oligosaccharide to medicines for reducing blood sugar. The preparation method is characterized by including a technological process of taking degreased, deproteinized and depigmented Ascophyllum Nodosum fucoidin as a raw material, combining microwave-assisted treatment, adding pectinase, cellulose, fucoidanase and sulfatase to subject the fucoidin to enzymolysis, removing the fucoidin not degraded sufficiently and zymoprotein through ethanol precipitation, centrifuging liquid supernatant prior to distillation and concentration, blending the distilled and concentrated liquid supernatant with oligosaccharide generated during polysaccharide extraction prior to sieving by a molecular sieve, and subjecting interception matters to freeze drying so as to obtain the Ascophyllum Nodosum oligosaccharide, wherein ethanol used during preparation is recycled. Through in-vitro and cell tests, the Ascophyllum Nodosum oligosaccharide has a remarkable improvement effect on glycometabolism. The preparation method is an efficient and environment-friendly technological method for preparing the Ascophyllum Nodosum oligosaccharide by microwave-accelerated enzymatic digestion.
Owner:江苏金康神生物科技有限公司
Aryl sulfatase gene, protein encoded by aryl sulfatase gene as well as immobilization method and application of protein
InactiveCN104630248AIncrease vitalityOvercome the problems of low activity and cumbersome enzyme separation and purification processHydrolasesFermentationEscherichia coliSulfatase
The invention discloses an aryl sulfatase gene, a protein encoded by the aryl sulfatase gene as well as an immobilization method and application of the protein. The immobilization method and application comprise the following steps of firstly expressing the aryl sulfatase gene of pseudoalteromonas carrageenovora sp in escherichia coli and purifying to obtain a recombinant aryl sulfatase; by adopting carboxyl-functionalized Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as carriers and glutaraldehyde as a cross-linking reagent and immobilizing the free recombinant aryl sulfatase to obtain the immobilized recombinant aryl sulfatase; treating agar with the immobilized recombinant aryl sulfatase, carrying out shaking reaction for 1 hour at 40 DEG C and measuring the physical properties of agar such as gel strength, the content of sulfate groups and the like. The immobilized recombinant aryl sulfatase disclosed by the invention can be repeatedly used, still maintains more than 60% of the enzyme activity after being repeatedly used for eight times and shows good operating stability and feasibility of practical application.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Dephosphorylated lysosomal storage disease proteins and methods of use thereof
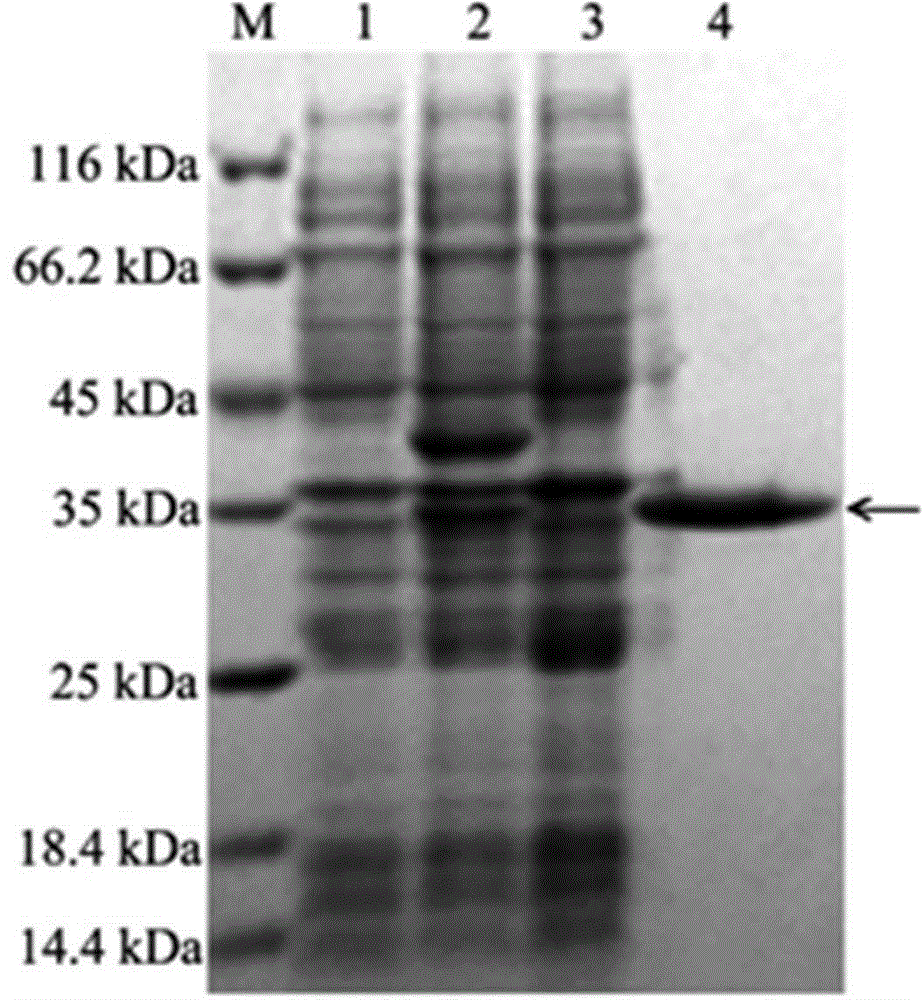
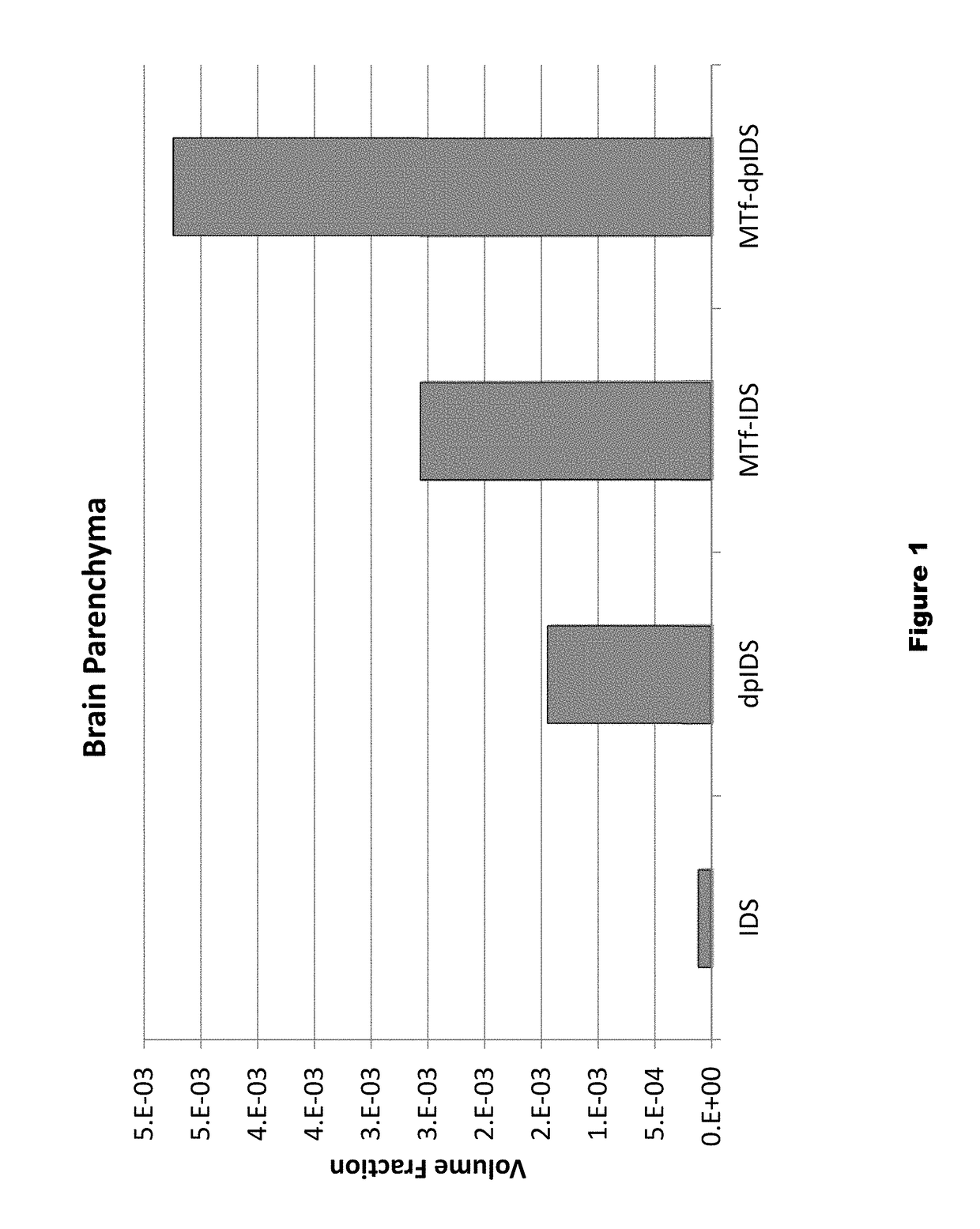
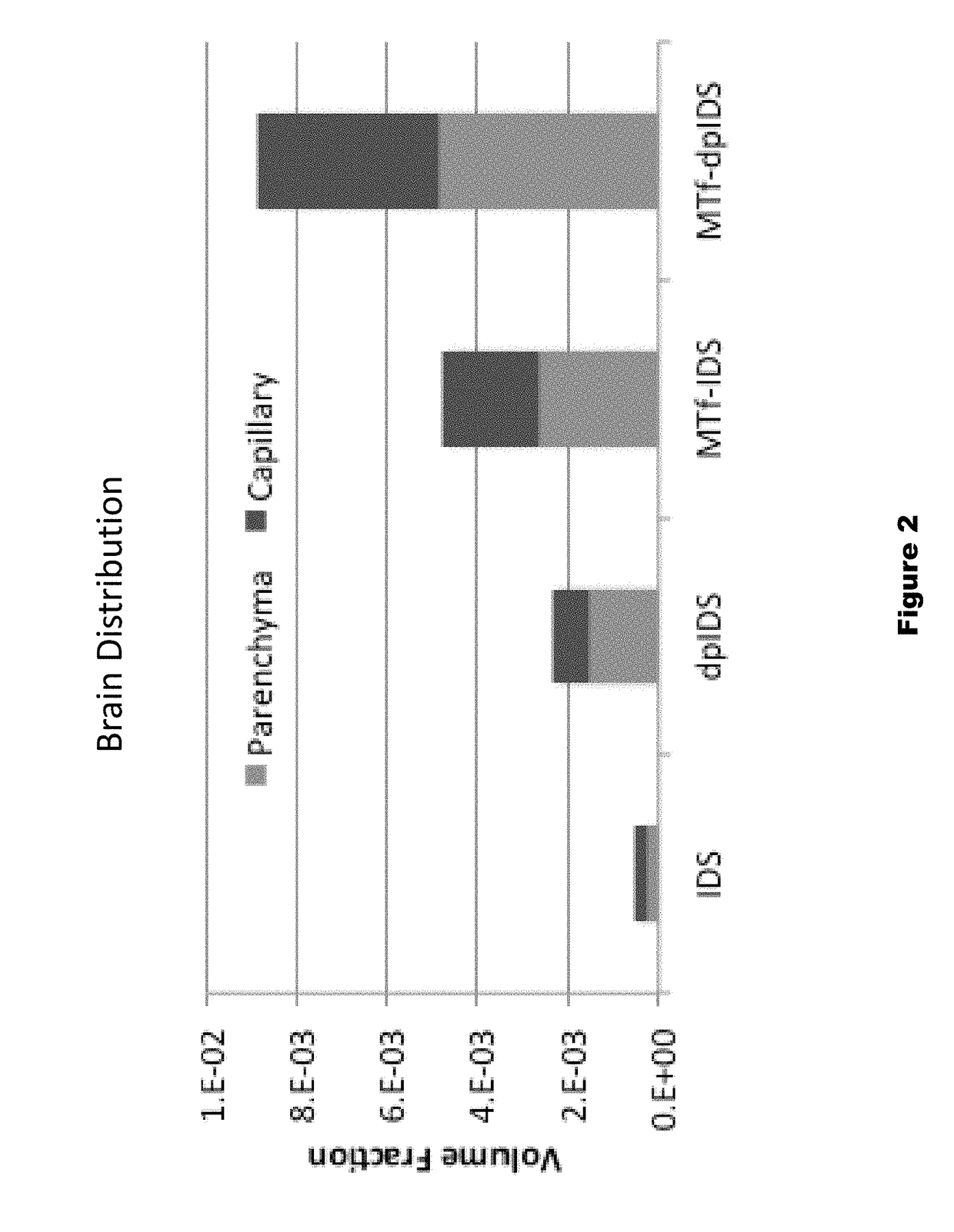
Provided are substantially dephosphorylated forms of lysosomal storage disease (LSD) proteins, including dephosphorylated forms of iduronate-2-sulfatase (IDS, or I2D) and iduronidase (IDU), having increased ability to traverse or penetrate the blood brain barrier (BBB) relative to phosphorylated forms of the protein, and p97 conjugates thereof. Also provided are compositions comprising such dephosphorylated LSD proteins and p97 conjugates, and methods of use thereof, for instance, to treat any one or more lysosomal storage diseases, such as Hunter Syndrome (or MPS Type II).
Owner:BIOASIS TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com