Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Mucopolysaccharidosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
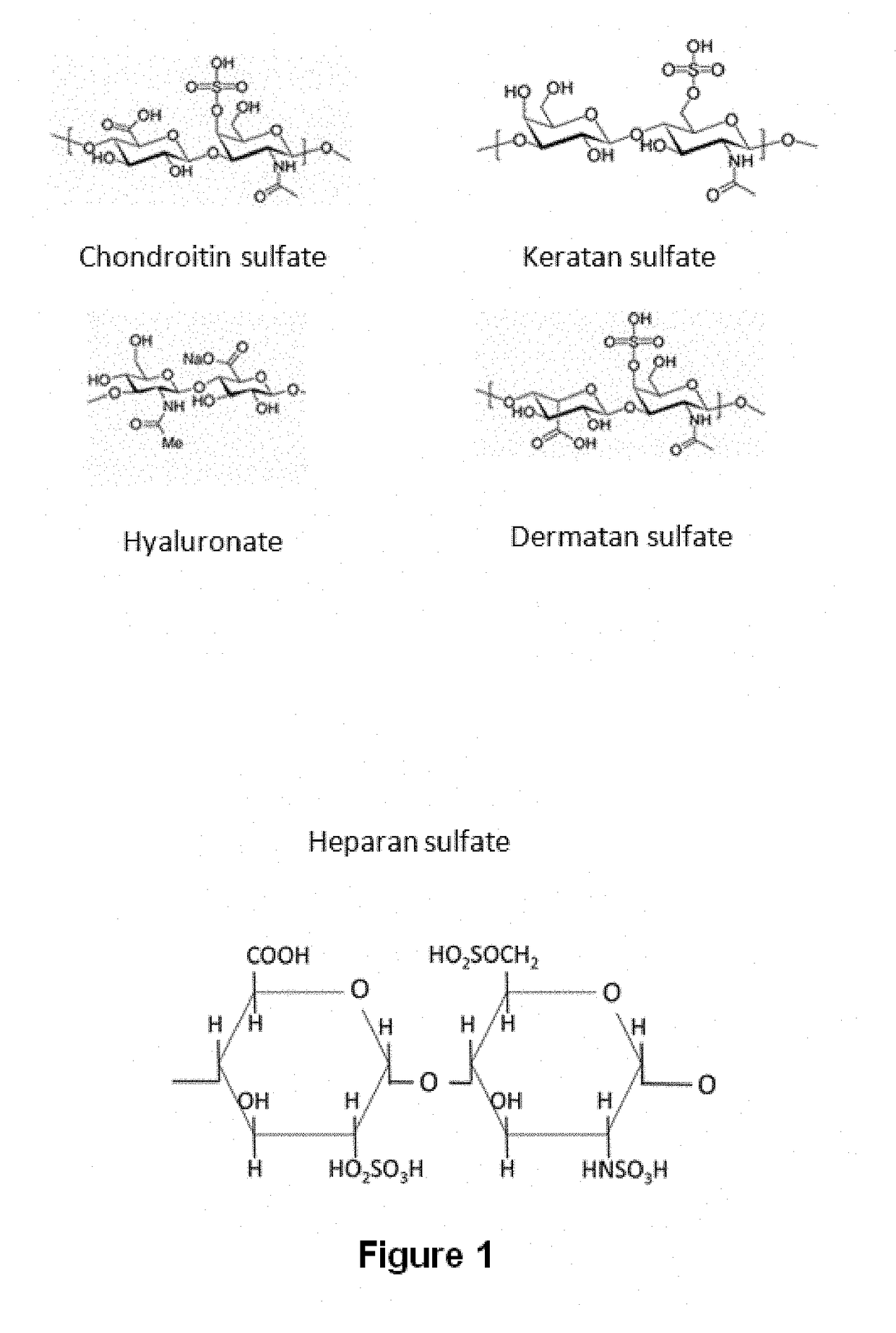
Mucopolysaccharidoses are a group of metabolic disorders caused by the absence or malfunctioning of lysosomal enzymes needed to break down molecules called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). These long chains of sugar carbohydrates occur within the cells that help build bone, cartilage, tendons, corneas, skin and connective tissue. GAGs (formerly called mucopolysaccharides) are also found in the fluids that lubricate joints.
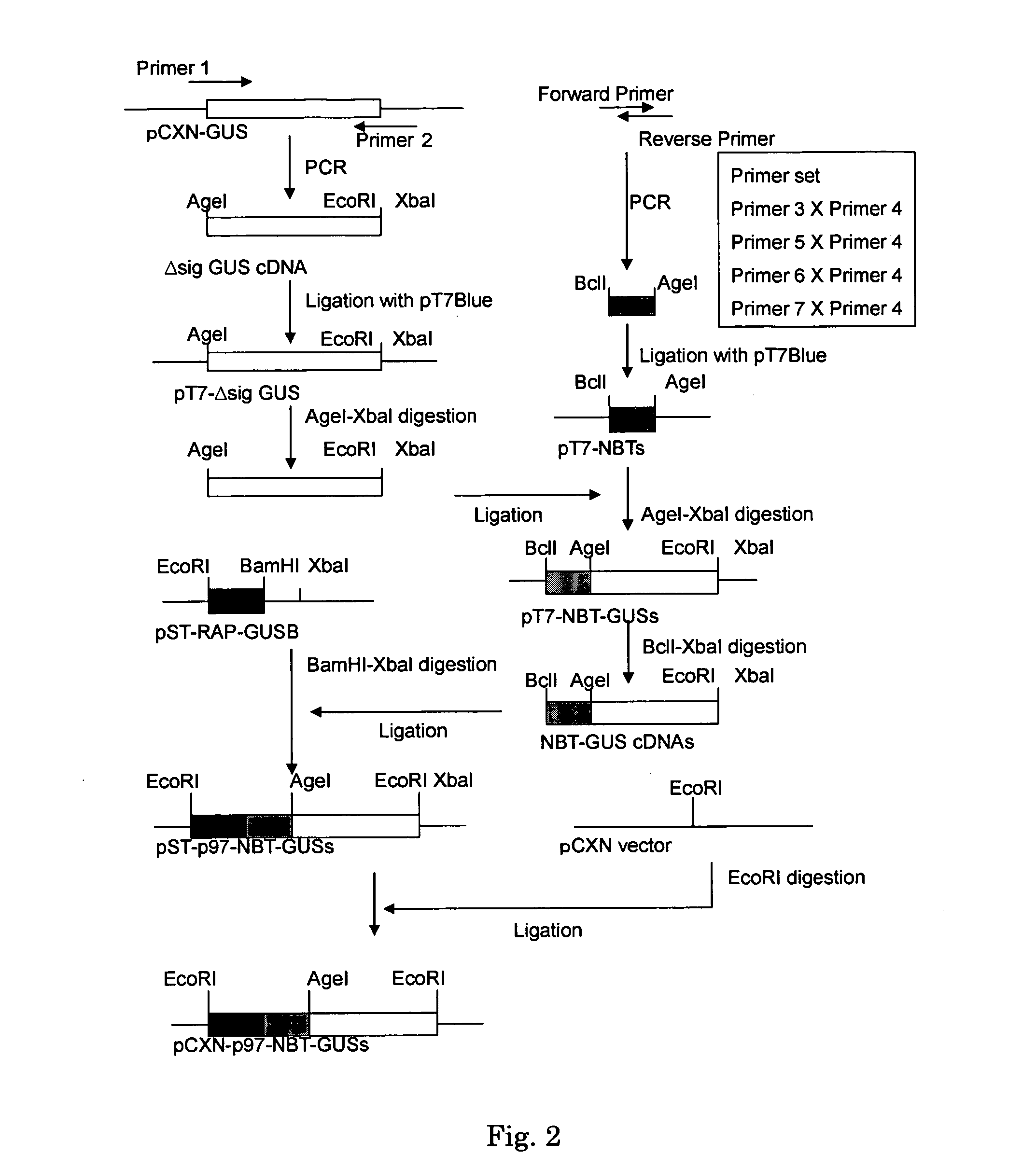
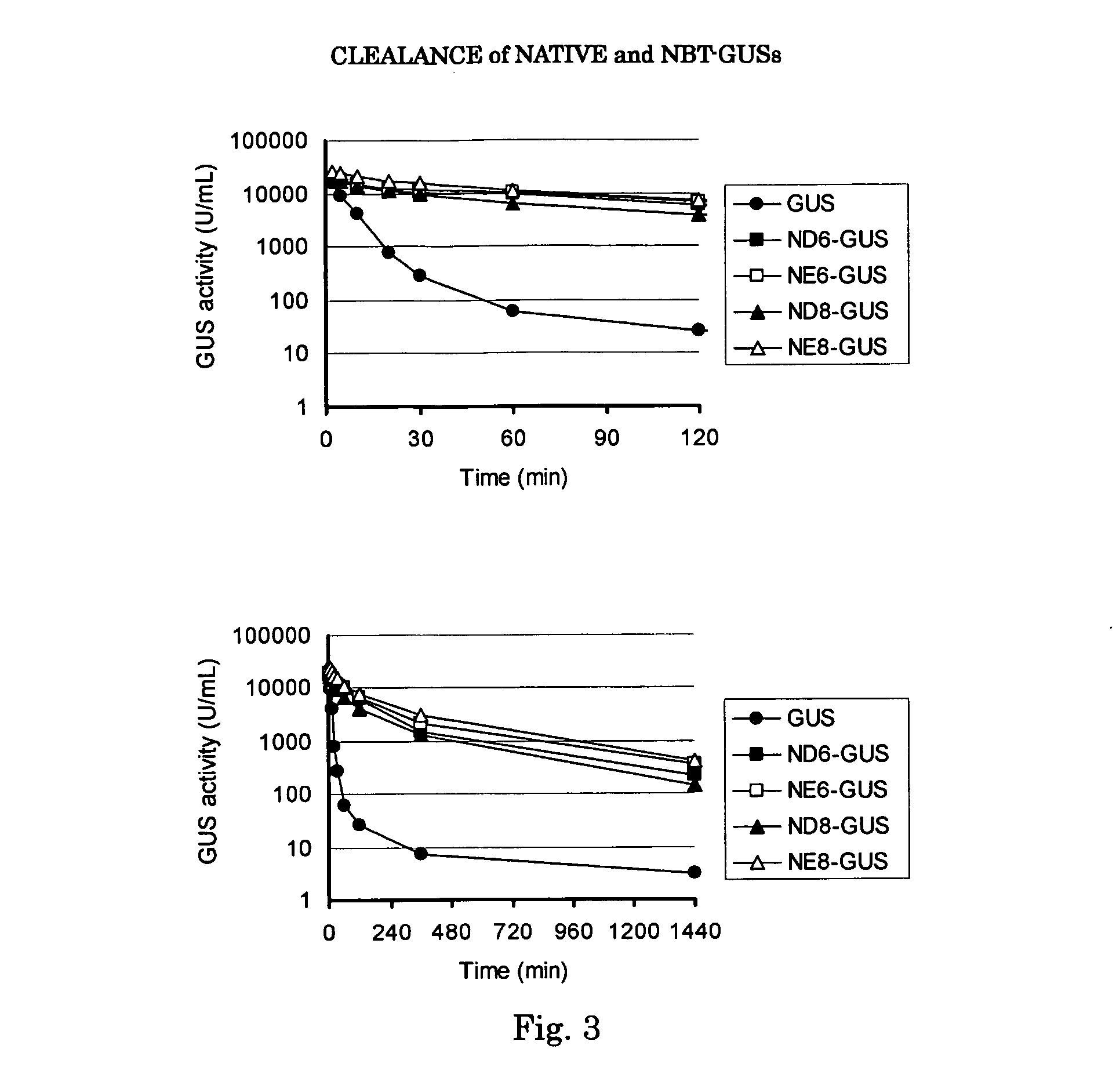
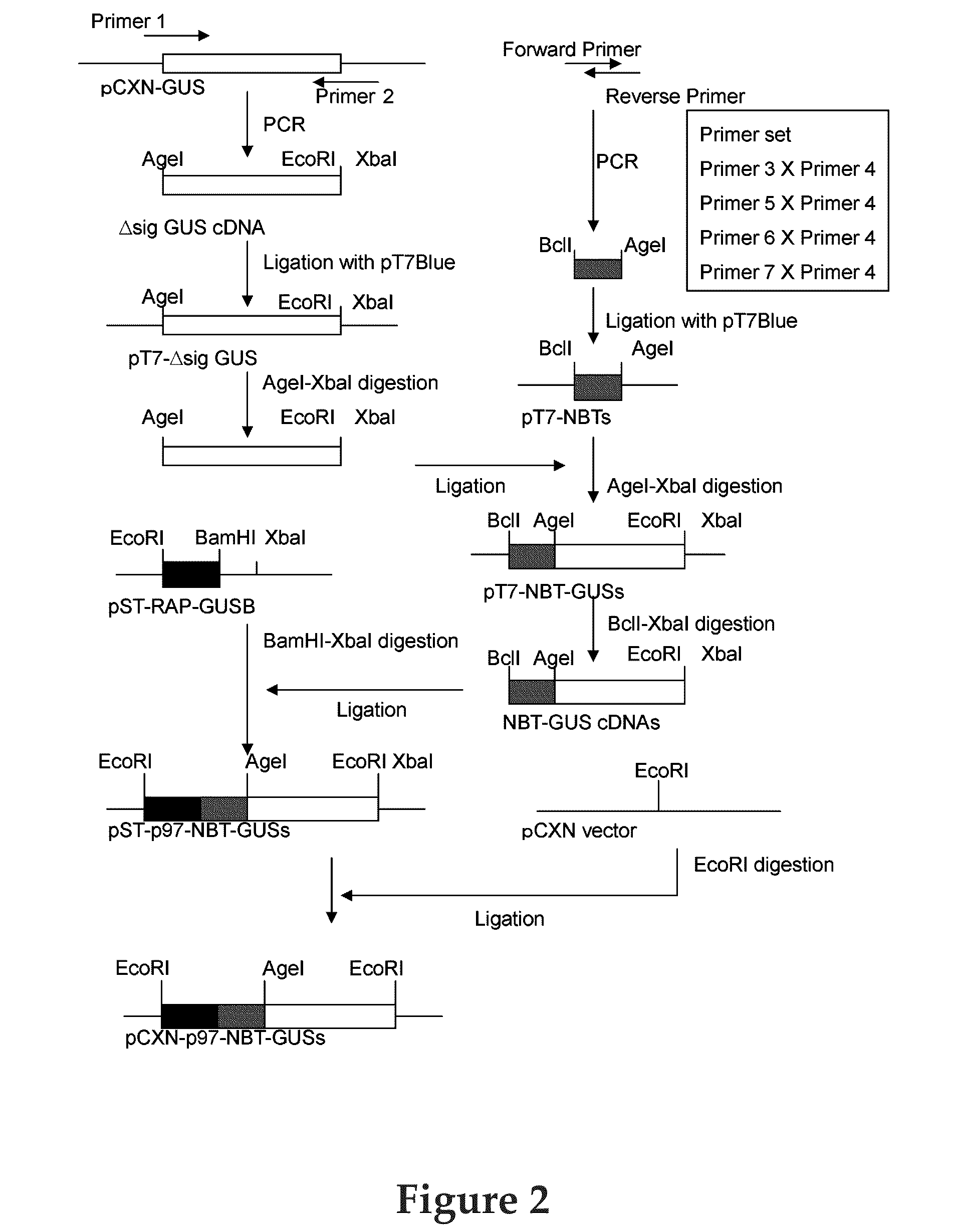
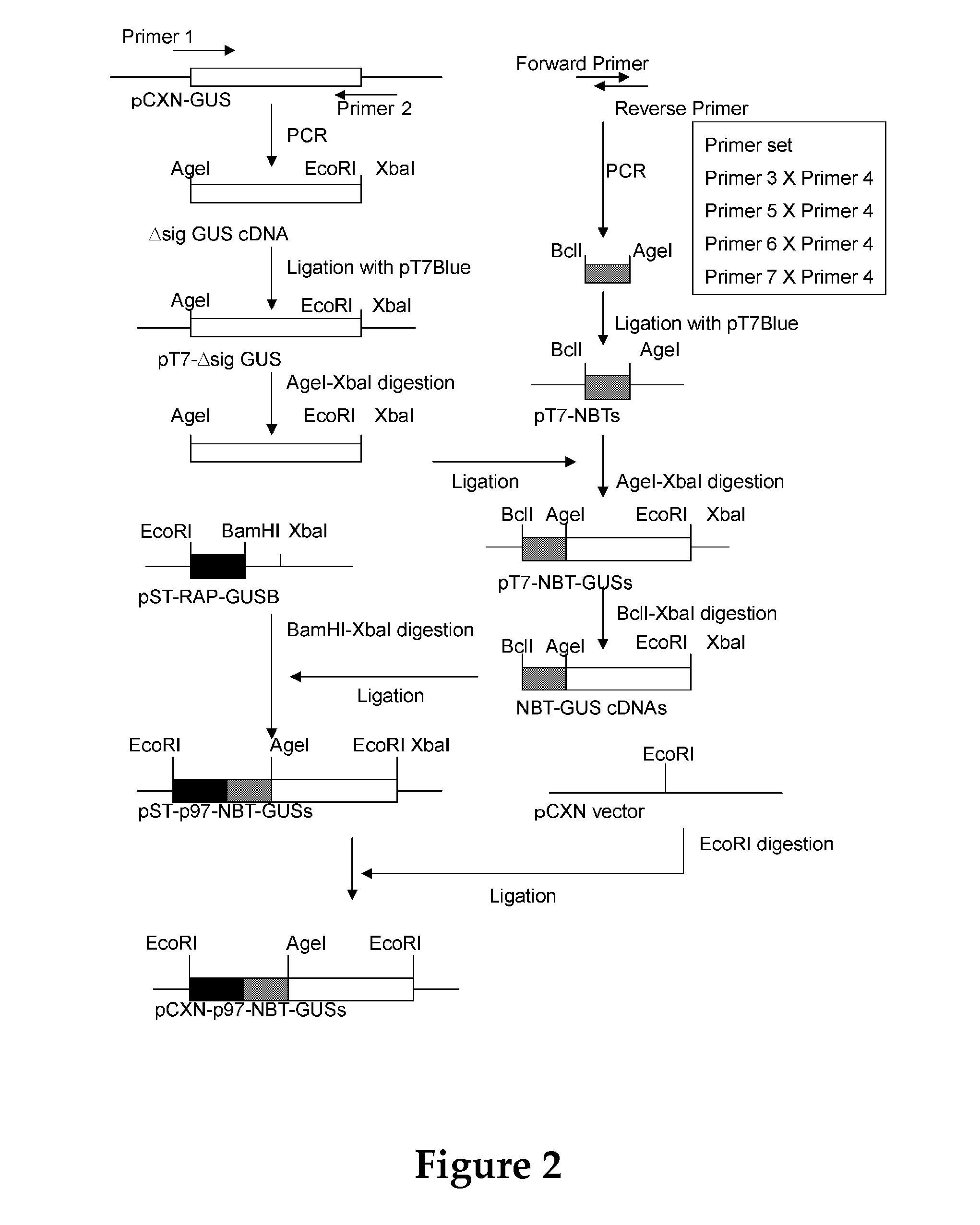
Beta-glucuronidase with an attached short peptide of acidic amino acids
InactiveUS20070081986A1Improve in vivo stabilityImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsEnzyme stabilisationBeta-glucuronidaseAcidic amino acids
Disclosed are a fusion protein comprising enzyme β-glucuronidase and short peptide consisting 4-15 acidic amino acids attached to the enzyme on its N-terminal side, pharmaceutical composition containing the fusion protein, and a method for treatment of type VII mucopolysaccharidosis using the fusion protein. Compared with the native enzyme, the fusion protein exhibits higher stability in the blood.
Owner:TOMATSU SHUNJI +5
Diagnostic method of mucopolysaccharidoses
InactiveUS20070161074A1Accurate and highly sensitive and convenient diagnosisAvoid developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisSpecific enzymeUltrafiltration
Provision of a method for accurate diagnosis of mucopolysaccharidoses, including determining the level of glycosaminoglycan in a biological sample with high sensitivity and with ease. A diagnostic method of mucopolysaccharidoses including the following steps (1) and (2): (1) a step including (a) filtering a biological sample with an ultrafiltration filter, digesting the sample on the filter with a glycosaminoglycan-specific enzyme, centrifuging the digested sample to obtain a filtrate, or (b) digesting a biological sample with a glycosaminoglycan-specific enzym, filtering the sample with an ultrafiltration filter to obtain a filtrate, applying the filtrate obtained by (a) or (b) to a liquid chromatograph / mass spectrometer, and analyzing glycosaminoglycan-derived disaccharides, and (2) a step of diagnosing a subject as having mucopolysaccharidosis, chemically diagnosing effect of treatment of mucopolysaccharidoses, or determining types of mucopolysaccharidoses, on the basis of quantitative concentration data and disaccharide composition obtained in step (1).
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
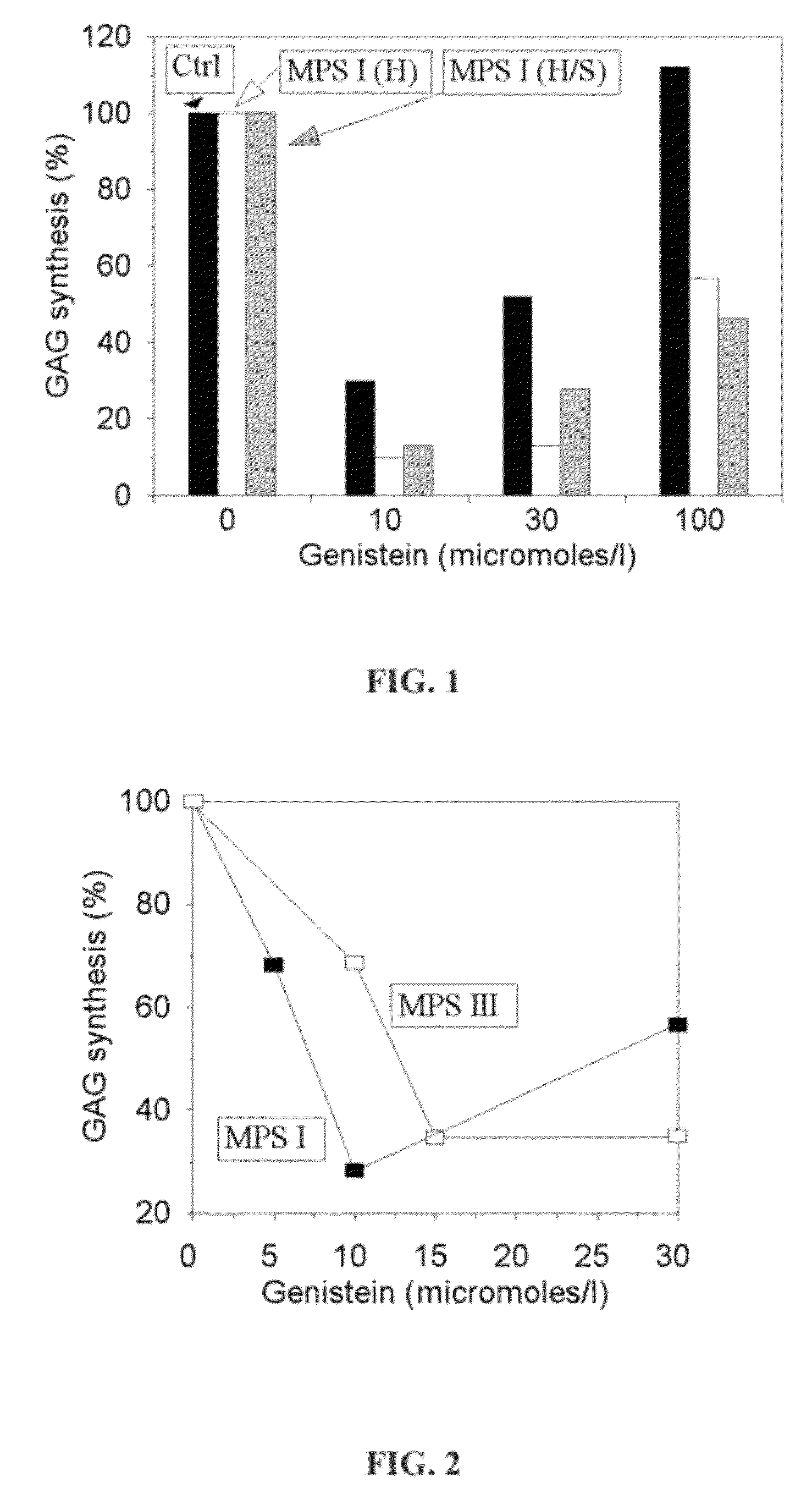
Isoflavones for treating mucopolysaccharidoses
A method of treatment of mucopolysaccharidosis, the method including administering to a patient in the need of such treatment-a therapeutically effective amount of a natural isoflavone of formula (I), a derivative thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. A pharmaceutical composition including a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient; and a natural isoflavone of formula (I), a derivative thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, the natural isoflavone, the derivative thereof, or the pharmaceutically acceptable salt threof being in a therapeutically effective amount for the treatment of mucopolysaccharidosis.
Owner:INSTITUT FARMACEUTYCZNY
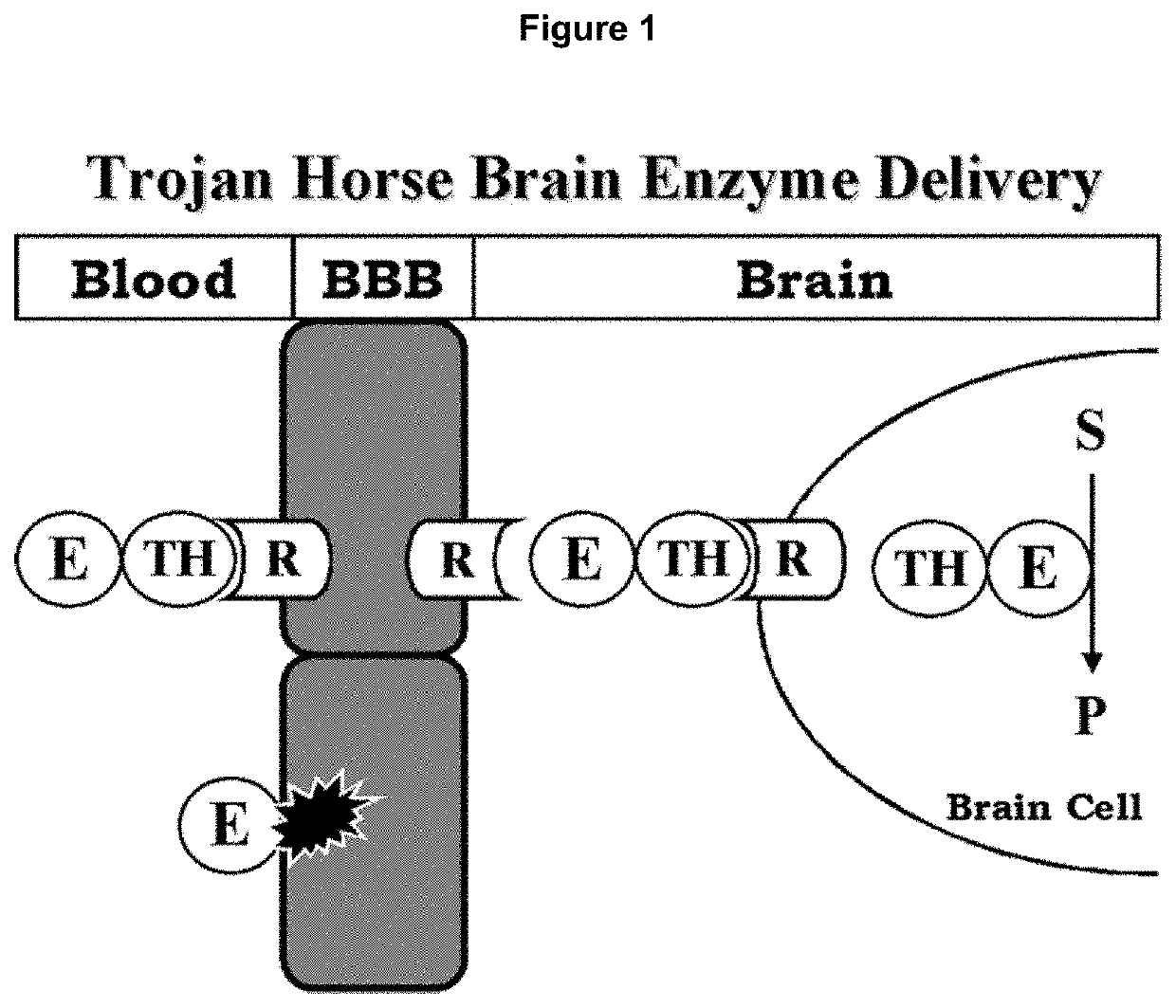
Methods and compositions for delivering enzymes and nucleic acid molecules to brain, bone and other tissues
Disclosed are methods for delivering an enzyme to a subject's brain or bone. The methods include administering a hyaluronidase to the subject and administering the enzyme to the subject. The hyaluronidase and the enzyme are administered to the subject under conditions effective to deliver the enzyme to the subject's brain or bone. Compositions and kits which include hyaluronidase and an enzyme are also disclosed, as are methods for increasing blood-brain barrier permeability in a subject. Also disclosed are methods, compositions, and kits for delivering genes or other nucleic acid molecules to a subject's brain or bone, as well as methods, compositions, and kits for delivering enzymes to a subject's tissues. The methods, compositions, and kits are disclosed as being useful in treating or preventing a variety of enzyme deficiency diseases, such as those affecting brain and / or bone, e.g., as Canavan's disease, Fabry disease, Gaucher's disease, various forms of mucopolysaccharidosis (e.g., Hurler's syndrome, Scheie syndrome, Hurler-Scheie syndrome, Sanfillippo A syndrome, Morquio A syndrome, Morquio B syndrome, etc.), Niemann-Pick disease, Schindler disease, and Pompe disease.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Diagnostic method of mucopolysaccharidoses
InactiveUS20110008810A1Accurate and highly sensitive and convenient diagnosisAvoid developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisSpecific enzymeUltrafiltration
Provision of a method for accurate diagnosis of mucopolysaccharidoses, including determining the level of glycosaminoglycan in a biological sample with high sensitivity and with ease.A diagnostic method of mucopolysaccharidoses including the following steps (1) and (2):(1) a step including (a) filtering a biological sample with an ultrafiltration filter, digesting the sample on the filter with a glycosaminoglycan-specific enzyme, centrifuging the digested sample to obtain a filtrate, or (b) digesting a biological sample with a glycosaminoglycan-specific enzyme, filtering the sample with an ultrafiltration filter to obtain a filtrate, applying the filtrate obtained by (a) or (b) to a liquid chromatograph / mass spectrometer, and analyzing glycosaminoglycan-derived disaccharides, and(2) a step of diagnosing a subject as having mucopolysaccharidosis, chemically diagnosing effect of treatment of mucopolysaccharidoses, or determining types of mucopolysaccharidoses, on the basis of quantitative concentration data and disaccharide composition obtained in step (1).
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
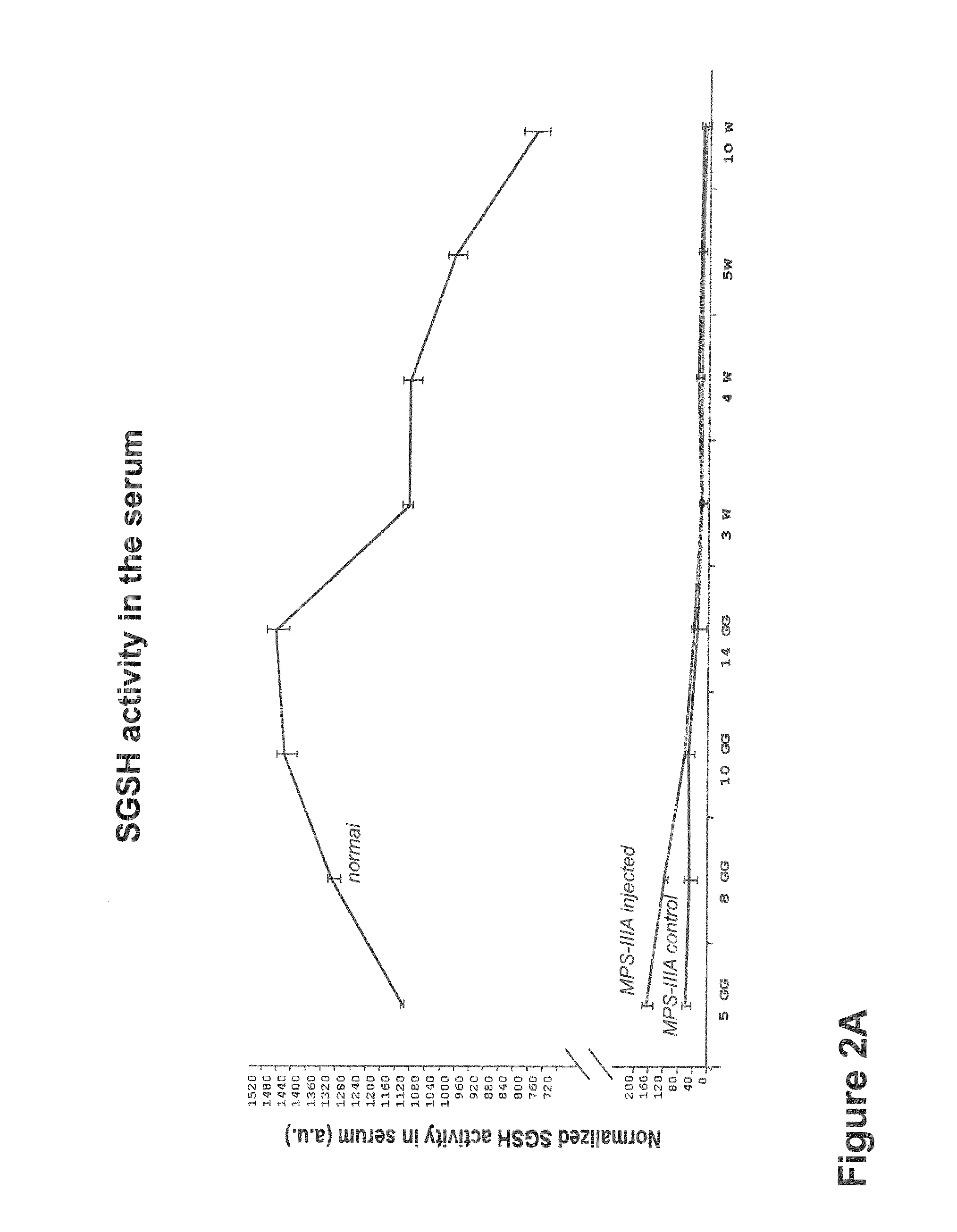
Adeno-associated viral vector for treating III A or III B type mucopolysaccharidosis and application
ActiveCN111718947AEffective treatmentPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderNucleotide sequencingViral vector
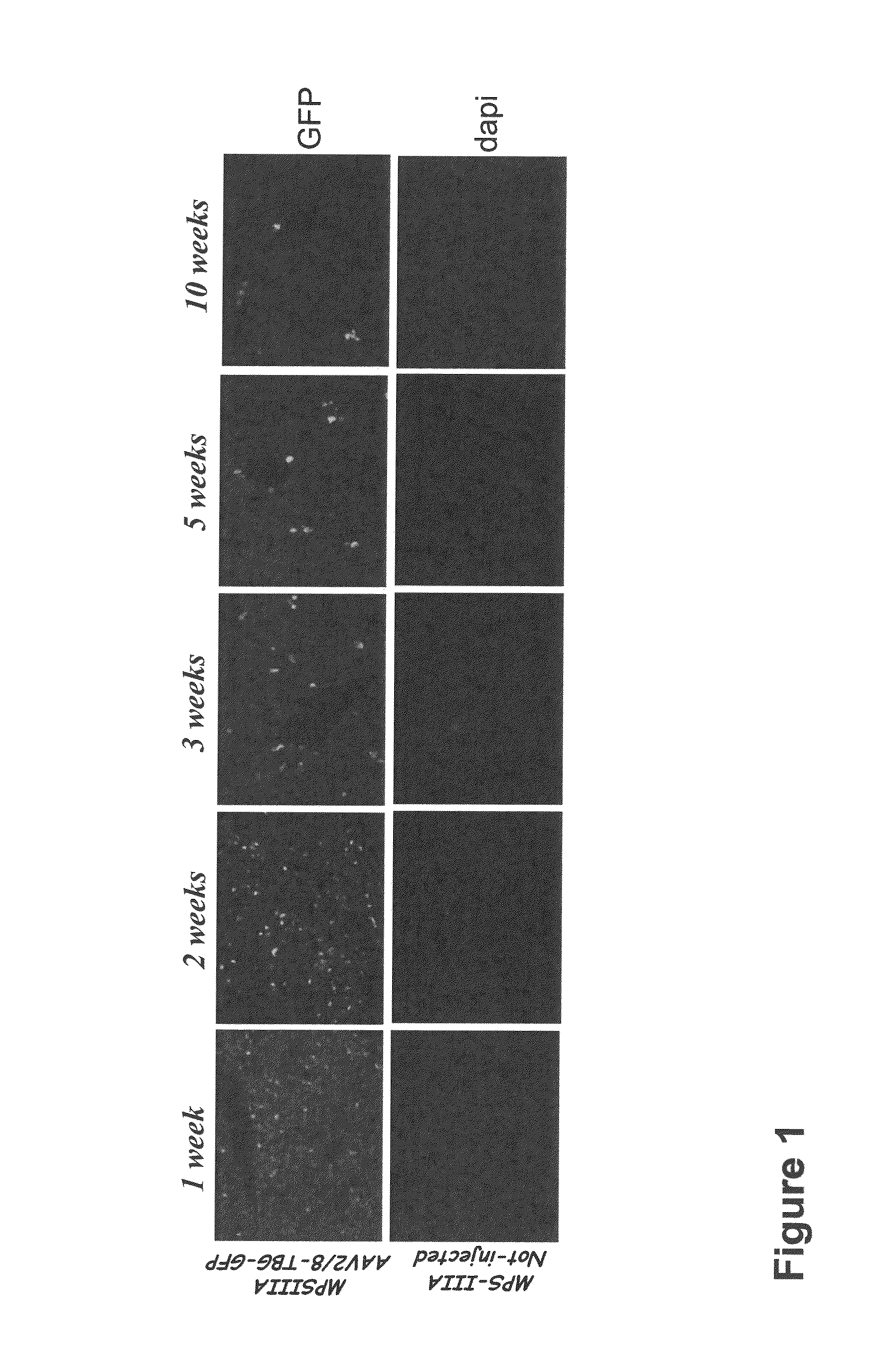
The invention discloses a recombinant nucleic acid molecule. The recombinant nucleic acid molecule comprises a promotor and a nucleotide sequence for coring an SGSH protein or an NAGLU protein, whichare operable and sequentially connected. The invention further discloses a recombinant adeno-associated virus. The recombinant adeno-associated virus comprises an AAV capsid and a carrier genome, wherein the carrier genome comprises a nucleotide sequence for coding a functional SGSH protein or the NAGLU protein, and an expression control sequence for leading the nucleotide sequence of the SGSH protein or the nucleotide sequence of the NAGLU protein to express host cells. The invention further discloses an application of a recombinant adeno-associated virus to effectively treatment of III A orIII B type mucopolysaccharidosis.
Owner:STAIDSON BEIJING BIOPHARMACEUTICALS CO LTD +1
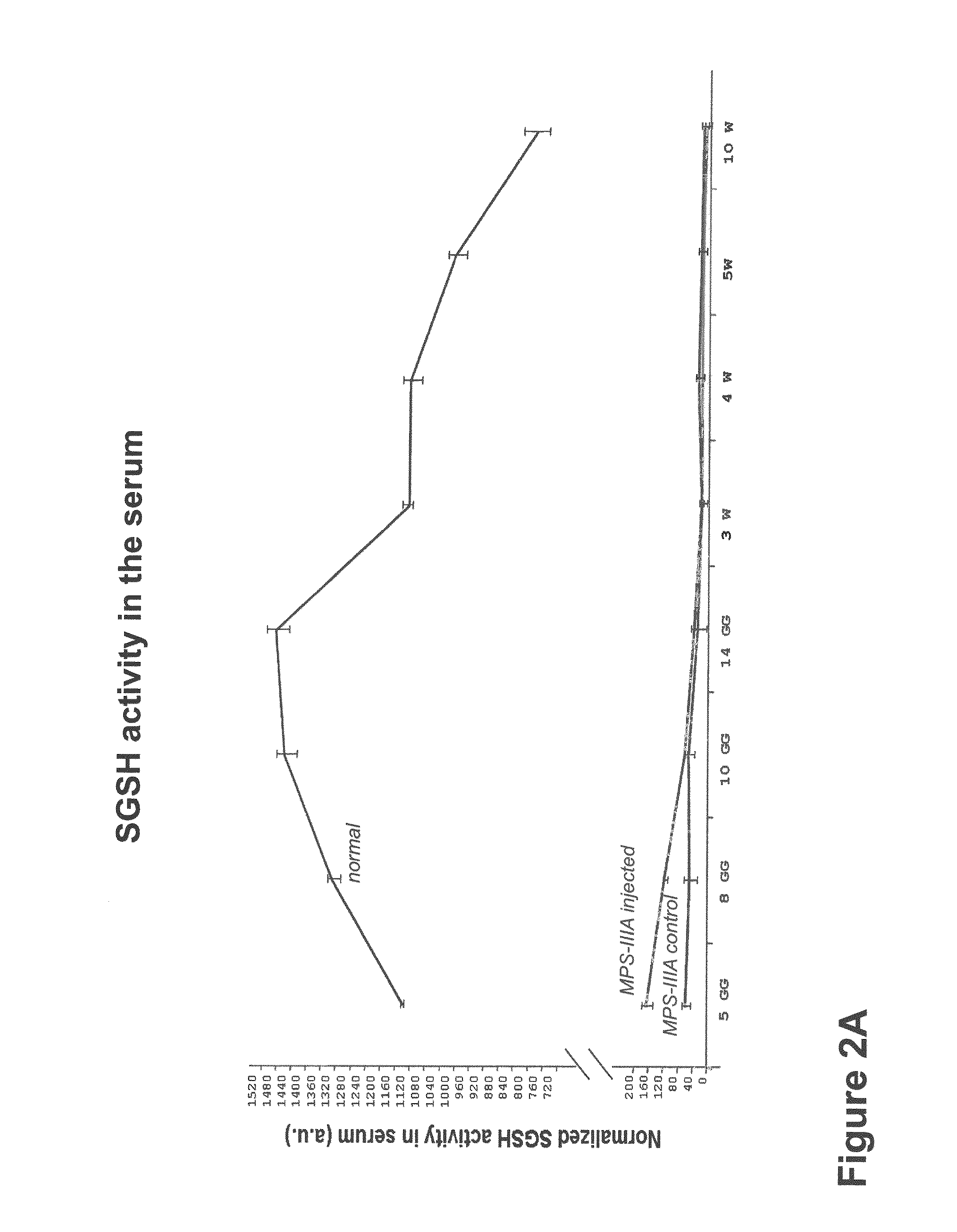
Gene drug construct for treating type 3A mucopolysaccharidosis
The invention provides a novel gene therapy drug construct for treating a type 3A mucopolysaccharidosis. The novel gene therapy drug construct can efficiently express recombinant human heparanase-N-sulfatase (SGSH) for preparation of a gene therapy drug product mediated by an adeno-associated virus vector.
Owner:北京瑞希罕见病基因治疗技术研究所
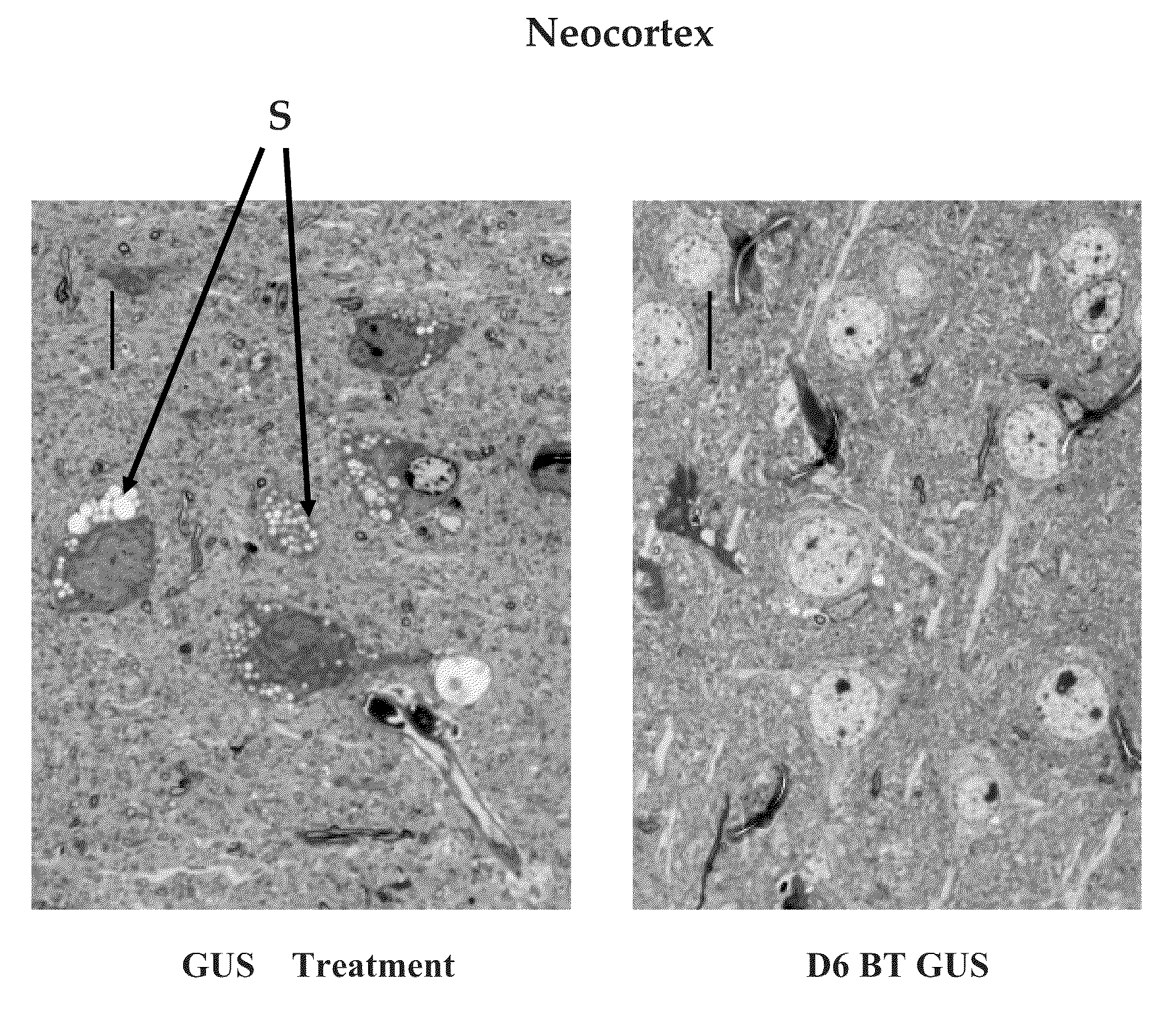
Therapeutic strategies to treat CNS pathology in mucopolysaccharidoses
The invention refers to nucleotide sequence encoding for a chimeric sulfatase, viral vectors expressing such sequences for gene therapy and pharmaceutical uses of the chimeric expressed protein. The invention is particularly applied in the therapy of mucopolysaccharidosis, preferably type IIIA.
Owner:FOND AZIONE TELETHON
Manufacture of active highly phosphorylated human N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase and uses thereof
ActiveUS8765437B2High yieldAvoid material lossNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsPhosphorylationN-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
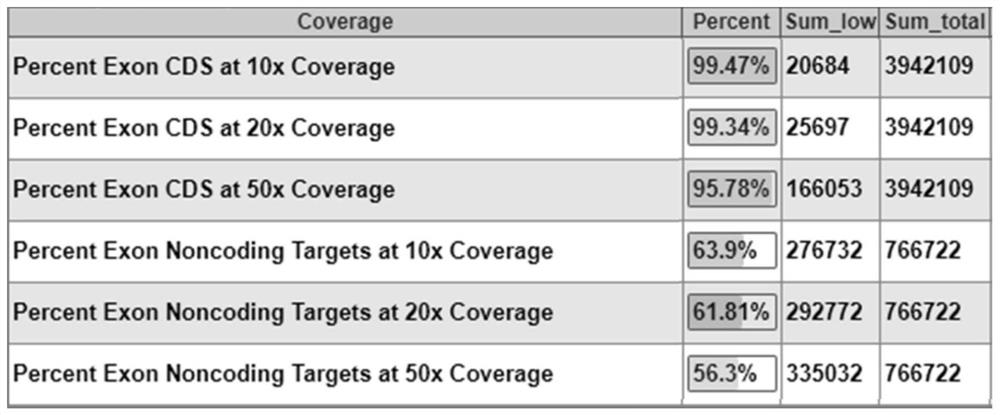
DNA library for detecting and diagnosing pathogenic genes of skeletal development disorders and application thereof
PendingCN112813156AAccurate detectionAids in Clinical Genetic CounselingMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationBone densityA-DNA
The invention relates to a DNA library for detecting and diagnosing pathogenic genes of skeletal development disorders through a targeted high-throughput sequencing technology and application thereof. The library comprises 507 pathogenic genes of skeletal development disorders. According to the invention, 507 pathogenic genes of skeletal development disorders are preferably selected, a probe pool is designed, a target region library for 507 pathogenic genes of skeletal development disorders is established, and the library utilizes the high-throughput sequencing technology for sequencing to find pathogenic mutations, thereby providing genetic and molecular biological bases for clinical diagnosis. The DNA library provided by the invention has the characteristics of accuracy, rapidness, flexibility and low cost. The 507 genes involved in the invention include pathogenic genes of genetic diseases with skeletal development disorders as clinical manifestations, such as collagen dysplasia, metaphysic dysplasia, osteogenesis imperfecta and bone density reduction, mucopolysaccharide storage disease, cartilage dysplasia and the like, and have important significance and clinical value for diagnosis, differential diagnosis and accurate treatment of skeletal development disorders.
Owner:SHANDONG PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANDONG FIRST MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
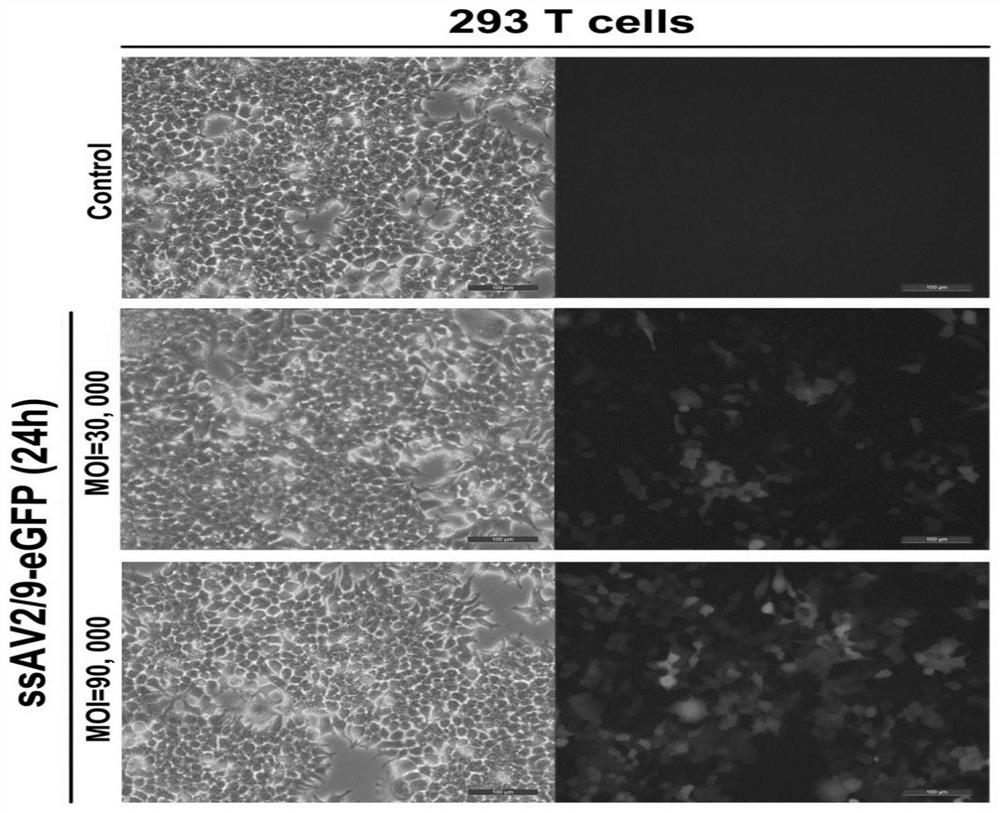
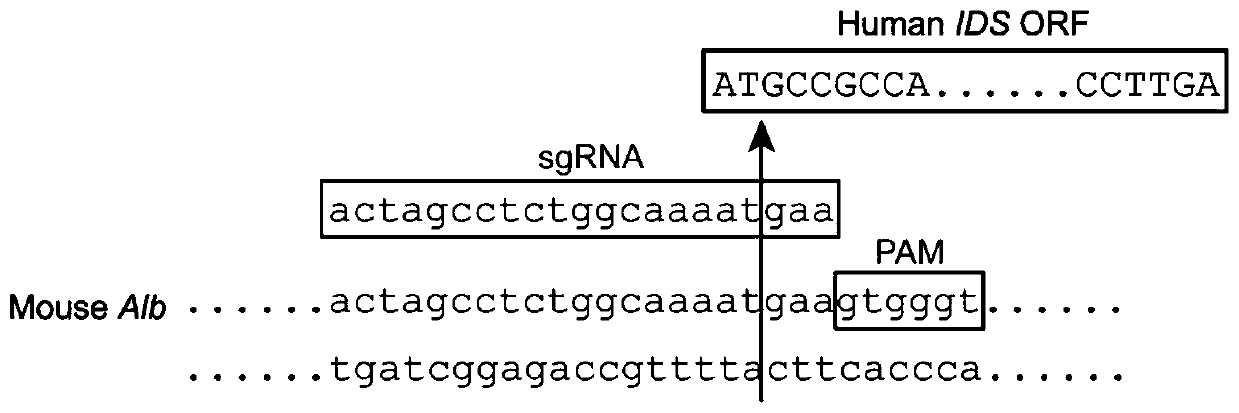
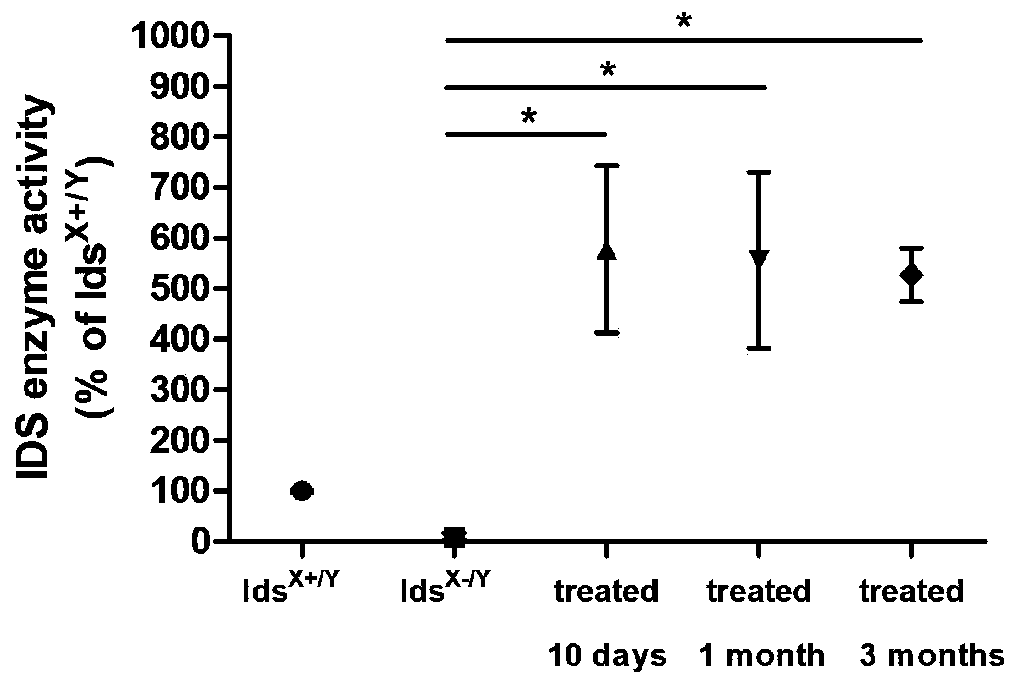
AAV double-vector gene treatment system and application thereof to treatment of type II MPS
PendingCN111110865AShort timeImprove securityDrug compositionsFermentationOpen reading frameIduronate Sulfatase
The invention discloses an AAV (Adeno-Associated Virus) double-vector gene treatment system and application thereof to treatment of type II MPS (Mucopolysaccharidosis). The AAV binary vector gene treatment system consists of a first vector and a second vector, wherein the first vector is an AAV vector carrying specific sgRNA (Small Guide RNA) targeting a human Alb (Albumin) gene cleavage site andan ORF (Open Reading Frame) sequence of a human IDS (Iduronate-2-Sulfatase); the cleavage site is located between a second site basic group and a third site basic group of an Alb gene translation initiation codon atg; and the second vector is an AAV vector carrying Cas9. The AAV double-vector gene treatment system using CRISPR-Cas9 as a gene editing tool has the advantages that the plasma IDS enzyme activity and the liver tissue IDS expression of MPSII model mice can be obviously improved; and after the treatment, the mouse phenotype and bone development are improved. The invention provides aneffective treatment measure for clinic treatment of the type II MPS.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Methods and compositions for increasing N-acetylglucosaminidase (NAGLU) activity in the CNS using a fusion antibody comprising an anti-human insulin receptor antibody and NAGLU
ActiveUS10538589B2Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntiendomysial antibodiesNervous system
Owner:JCR PHARMA +1
Therapeutic strategies to treat CNS pathology in mucopolysaccharidoses
The invention provides for nucleotide sequences encoding for a chimeric sulfatase, viral vectors expressing such sequences for gene therapy and pharmaceutical uses of the chimeric expressed protein. The invention is particularly applied in the therapy of mucopolysaccharidosis, preferably type IIIA.
Owner:FOND AZIONE TELETHON
Methods of treatment using a 1,2,4-oxadiazole benzoic acid
Provided herein are methods of treating, preventing, ameliorating or managing mucopolysaccharidosis (nmMPS) disease, comprising administering a 1,2,4-oxadiazole benzoic acid to a patient having a nmMPS. In particular, provided herein are methods of treating, preventing, ameliorating or managing a MPS.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Method for separating the fraction bound to glycosaminoglycans and applications thereof
ActiveUS20180328939A1Simple and quick and cost-effectiveSmall amount of sampleDisease diagnosisBiological testingLipid formationTreatment effect
The present invention is comprised in the field of glycobiology. In particular, it relates to a method for separating, in biological samples, the fraction bound to or associated with sulfated glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), and the applications thereof in biomedicine, such as for identifying the profile of glycoproteins or the profile of lipids bound to or associated with sulfated GAGs, detecting an alteration in the pattern of glycosylation by sulfated GAGs, identifying biomarkers for the diagnosis, for the prognosis, for monitoring the progression of a disease or of the effect of a therapy, or for identifying compounds suitable for the treatment of a disease. The invention also relates to methods for diagnosing mucopolysaccharidosis and for diagnosing and determining the prognosis of a kidney disease.
Owner:SERVIZO GALEGO DE SAUDESERGAS +3
Gene therapy for mucopolysaccharidosis iiia
Provided herein is a recombinant AAV (rAAV) comprising an AAV capsid and a vector genome packaged therein, wherein the vector genome comprises an AAV 5′ inverted terminal repeat (ITR), an engineered nucleic acid sequence encoding a functional hSGSH, a regulatory sequence which direct expression of hSGSH in a target cell, and an AAV 3′ ITR. Also provided is a pharmaceutical composition comprising a rAAV as described herein in a formulation buffer, and a method of treating a human subject diagnosed with MPS IIIA.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Enhancing the effect of therapeutic proteins on the central nervous system
InactiveUS20100158889A1Improve in vivo stabilityGood treatment effectPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifHormone peptidesNervous systemTherapeutic protein
The present invention provides a polypeptide therapeutic agent, useful in enzyme replacement therapy, with increased therapeutic benefits for the central nervous system. The invention provides a method of enhancing the effect of a polypeptide or protein on the central nervous system by the attachment of a short acidic amino acid sequence. Specifically the inventors disclose the attachment of a 4-15 acidic amino acid sequence to human β-glucuronidase by construction of a fusion protein. This molecule is useful in the treatment of type VII mucopolysaccharidosis when administered to a patient.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
Gene therapy for mucopolysaccharidosis iiib
Provided herein is a recombinant AAV (rAAV) comprising an AAV capsid and a vector genome packaged therein, wherein the vector genome comprises an AAV 5′ inverted terminal repeat (ITR), an engineered nucleic acid sequence encoding a functional human N-acetyl-alpha-glucosaminidase (hNAGLU), a regulatory sequence which direct expression of hNAGLU in a target cell, and an AAV 3′ ITR. Also provided is a pharmaceutical composition comprising a rAAV as described herein in a formulation buffer, and a method of treating a human subject diagnosed with MPS IIIB.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method of treatment of a mucopolysaccharidosis
The present invention relates to the use of 4-methyl-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran-7-yl-5-thio-β-D-xylopyranoside in the treatment of a mucopolysaccharidosis such as type I mucopolysaccharidosis.
Owner:INVENTIVA
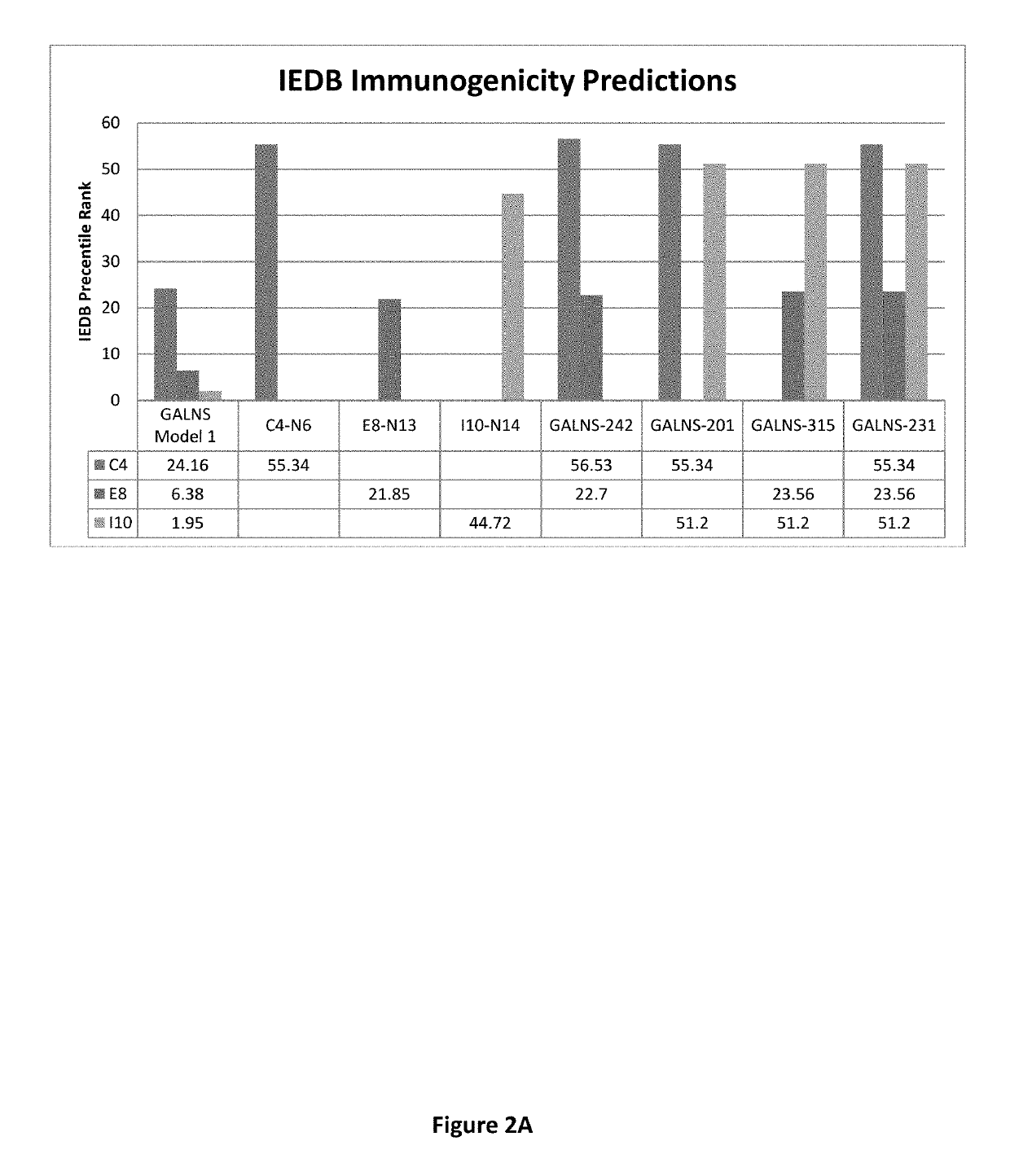
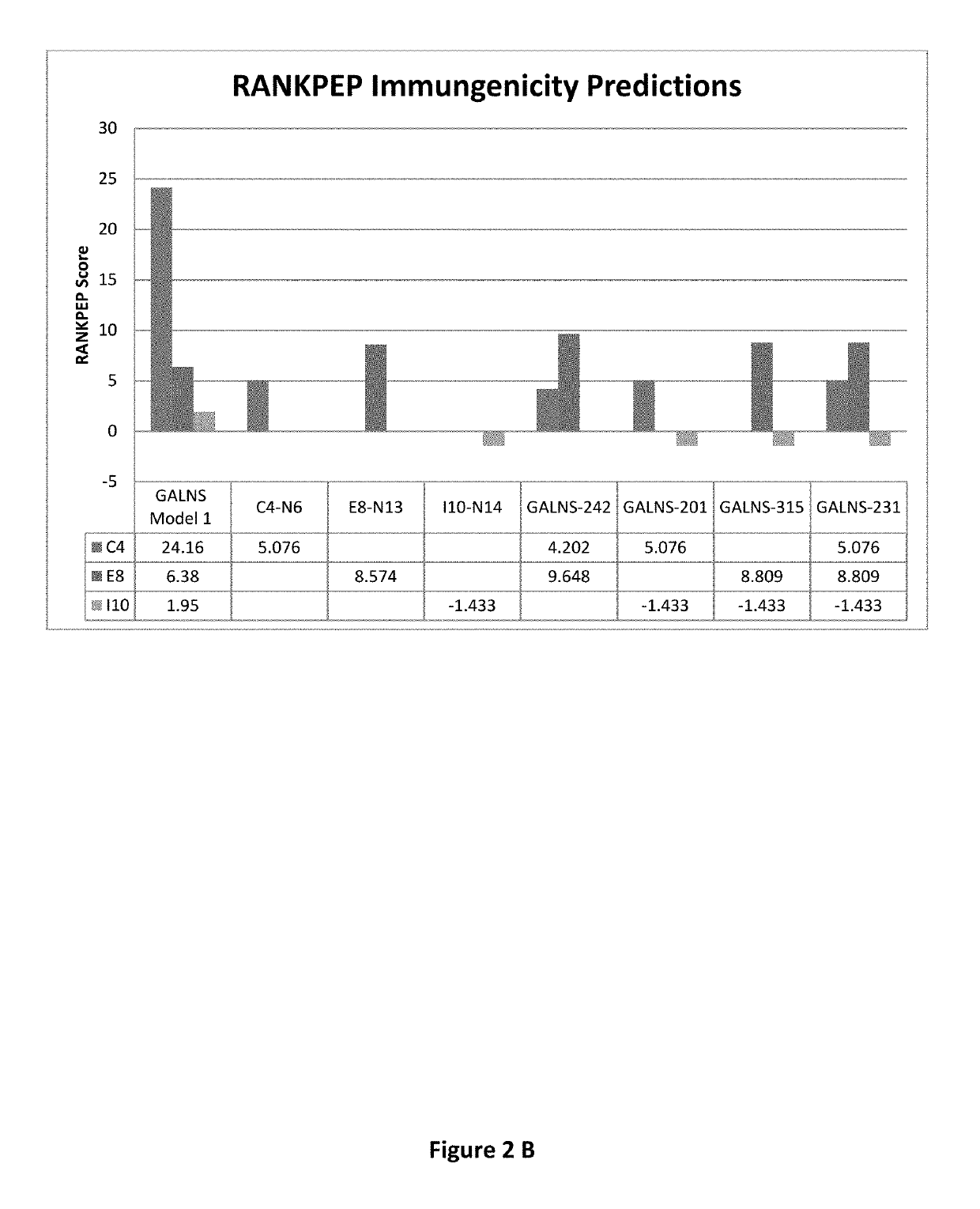
Reduced immunogenic proteins for lysosomal storage disorders
Disclosed are methods and compositions for reduced immunogenic proteins used in enzyme replacement therapy for lysosomal storage disorders. More specifically disclosed are genetically engineered variants of N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase (GALNS), which are less immunogenetic then wild-type GALNS, but maintain enzymatic activity, and may be used to treat Mucopolysaccharidosis IVA (Morquio A disease, MPS IVA).
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
Isoflavones for treating mucopolysaccharidoses
A pharmaceutical composition including a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient; and a natural isoflavone of formula (I), a derivative thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, the natural isoflavone, the derivative thereof, or the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof being in a therapeutically effective amount for the treatment of mucopolysaccharidosis. A method of treatment of mucopolysaccharidosis, the method including administering to a patient in the need of such treatment—a therapeutically effective amount of a natural isoflavone of formula (I), a derivative thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:INSTITUT FARMACEUTYCZNY
Gene therapy for mucopolysaccharidosis, type ii
Owner:BLUEBIRD BIO INC
New use of ebselen
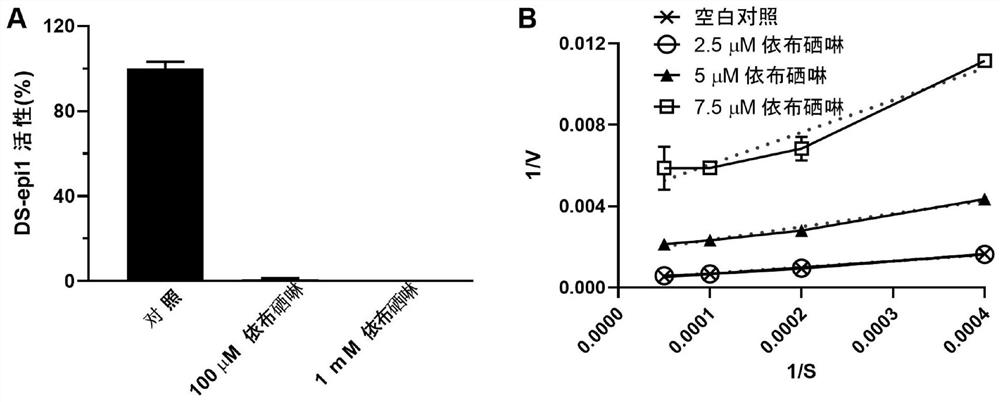
ActiveCN113116888AOvercome various deficiencies that existDrug compositionsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsDiseaseEbselen
The invention relates to a new use of ebselen, and specifically relates to a use of ebselen and a pharmaceutical composition thereof in preparation of a medicine for treating type I mucopolysaccharide storage diseases.
Owner:上海兴糖生物技术有限公司
Methods and compositions for increasing n-acetylglucosaminidase activity in the CNS
InactiveUS20210002379A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntiendomysial antibodiesReceptor
Provided herein are methods and compositions for treating a subject suffering from an enzyme deficiency in the central nervous system (CNS). The bifunctional fusion antibody provided herein comprise an antibody to an endogenous blood brain barrier (BBB) receptor and an enzyme deficient in mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB (MPS-IIIB). The fusion antibodies provided herein comprise alpha-N-acetylgulcosaminidase (NAGLU). The methods of treating an enzyme deficiency in the CNS comprise systemic administration of a fusion antibody provided herein.
Owner:ARMAGEN INC
Enhancing the effect of therapeutic proteins on the central nervous system
InactiveUS20070207139A1Improve in vivo stabilityGood treatment effectPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifNervous disorderNervous systemTherapeutic protein
The present invention provides a polypeptide therapeutic agent, useful in enzyme replacement therapy, with increased therapeutic benefits for the central nervous system. The invention provides a method of enhancing the effect of a polypeptide or protein on the central nervous system by the attachment of a short acidic amino acid sequence. Specifically the inventors disclose the attachment of a 4-15 acidic amino acid sequence to human β-glucuronidase by construction of a fusion protein. This molecule is useful in the treatment of type VII mucopolysaccharidosis when administered to a patient.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
Gene therapy for mucopolysaccharidosis, type I
Owner:BLUEBIRD BIO INC
Gene drug constructs for the treatment of mucopolysaccharidosis type 3a
The invention of this patent provides a novel gene therapy drug construct that can be used for type 3A mucopolysaccharidosis, which can effectively express recombinant human heparan-N-sulfatase (SGSH), and is used to prepare genes mediated by adeno-associated virus vectors Therapeutic pharmaceutical products.
Owner:北京瑞希罕见病基因治疗技术研究所
Method for separating the fraction bound to glycosaminoglycans and applications thereof
ActiveUS10725050B2Simple and quick and cost-effectiveSmall amount of sampleDisease diagnosisBiological testingBiomarker (medicine)Therapeutic effect
The present invention is comprised in the field of glycobiology. In particular, it relates to a method for separating, in biological samples, the fraction bound to or associated with sulfated glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), and the applications thereof in biomedicine, such as for identifying the profile of glycoproteins or the profile of lipids bound to or associated with sulfated GAGs, detecting an alteration in the pattern of glycosylation by sulfated GAGs, identifying biomarkers for the diagnosis, for the prognosis, for monitoring the progression of a disease or of the effect of a therapy, or for identifying compounds suitable for the treatment of a disease. The invention also relates to methods for diagnosing mucopolysaccharidosis and for diagnosing and determining the prognosis of a kidney disease.
Owner:SERVIZO GALEGO DE SAUDESERGAS +3
Gene therapy for mucopolysaccharidosis, type i
Owner:BLUEBIRD BIO INC
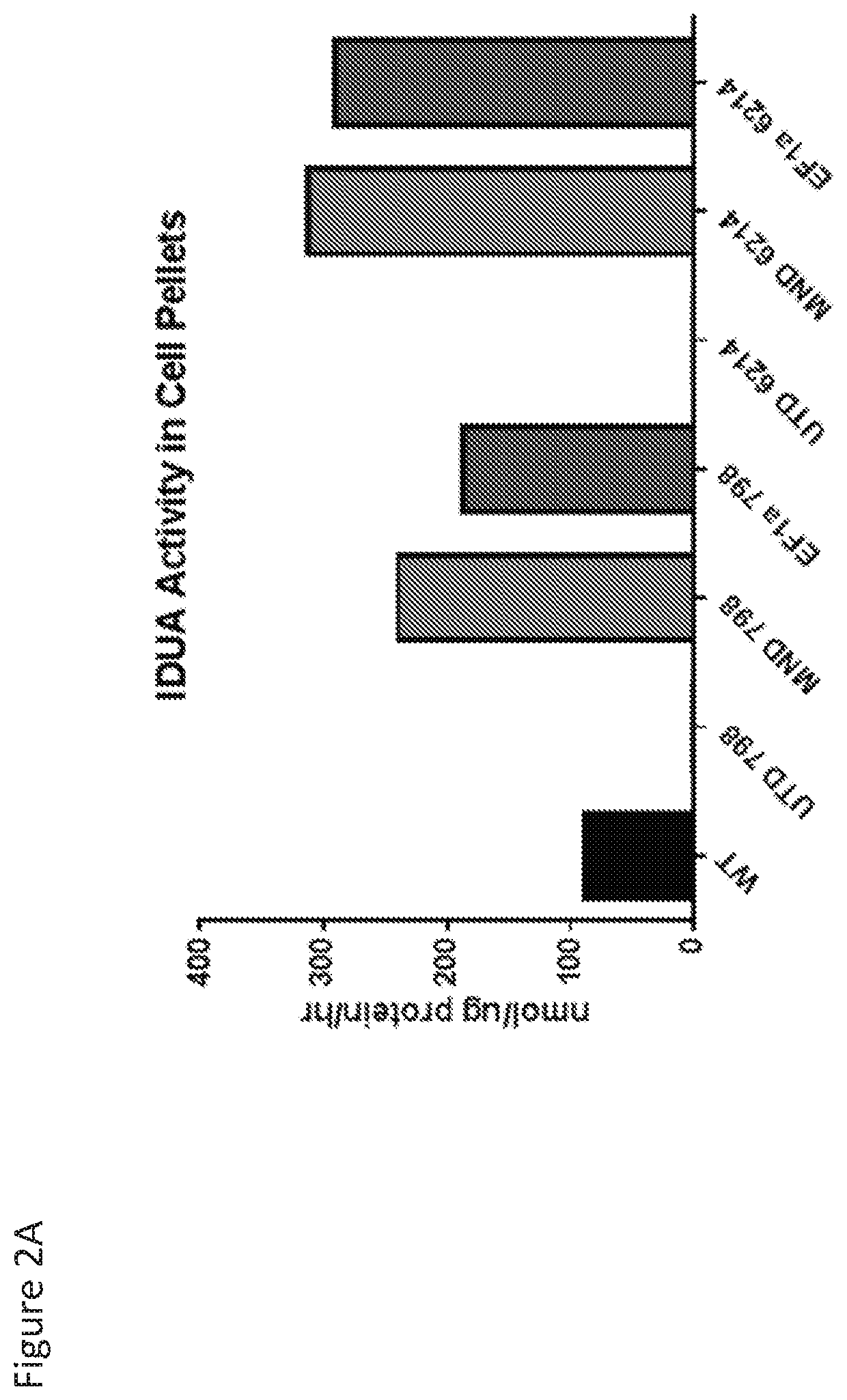
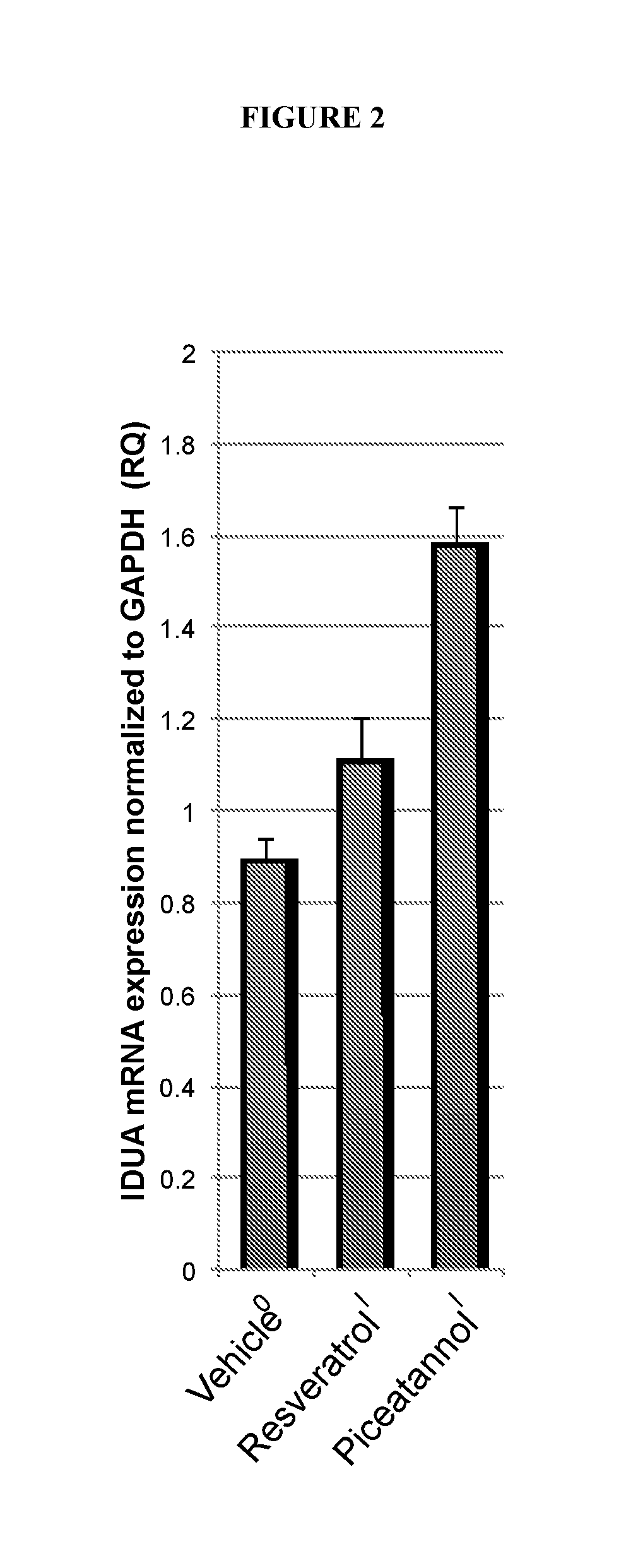
Methods for treating mucopolysaccharidosis
InactiveUS20190076376A1Increasing IDUA activityHigh expressionHalogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsHydroxy compound active ingredientsCancer researchMucopolysaccharidosis
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com