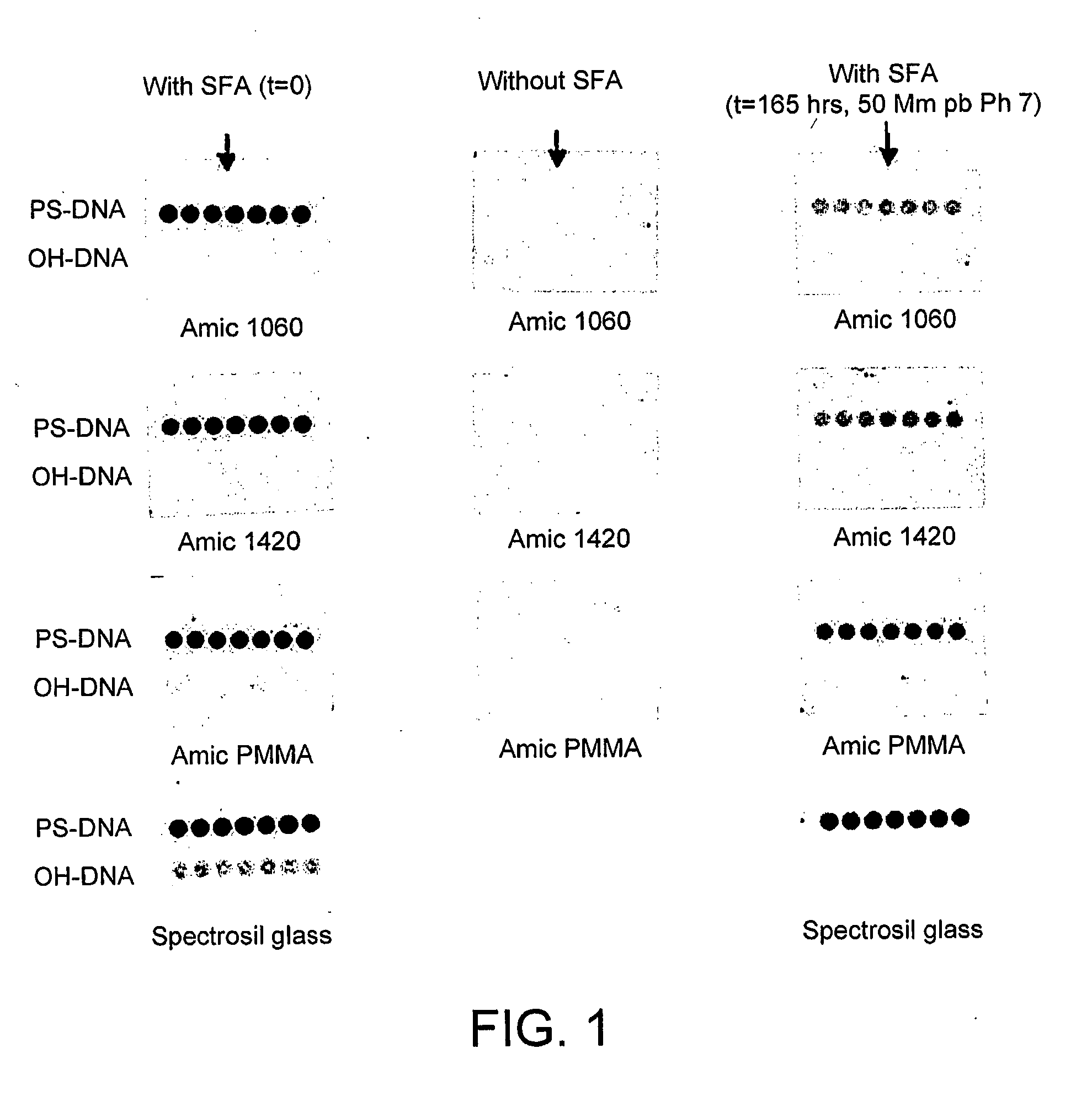
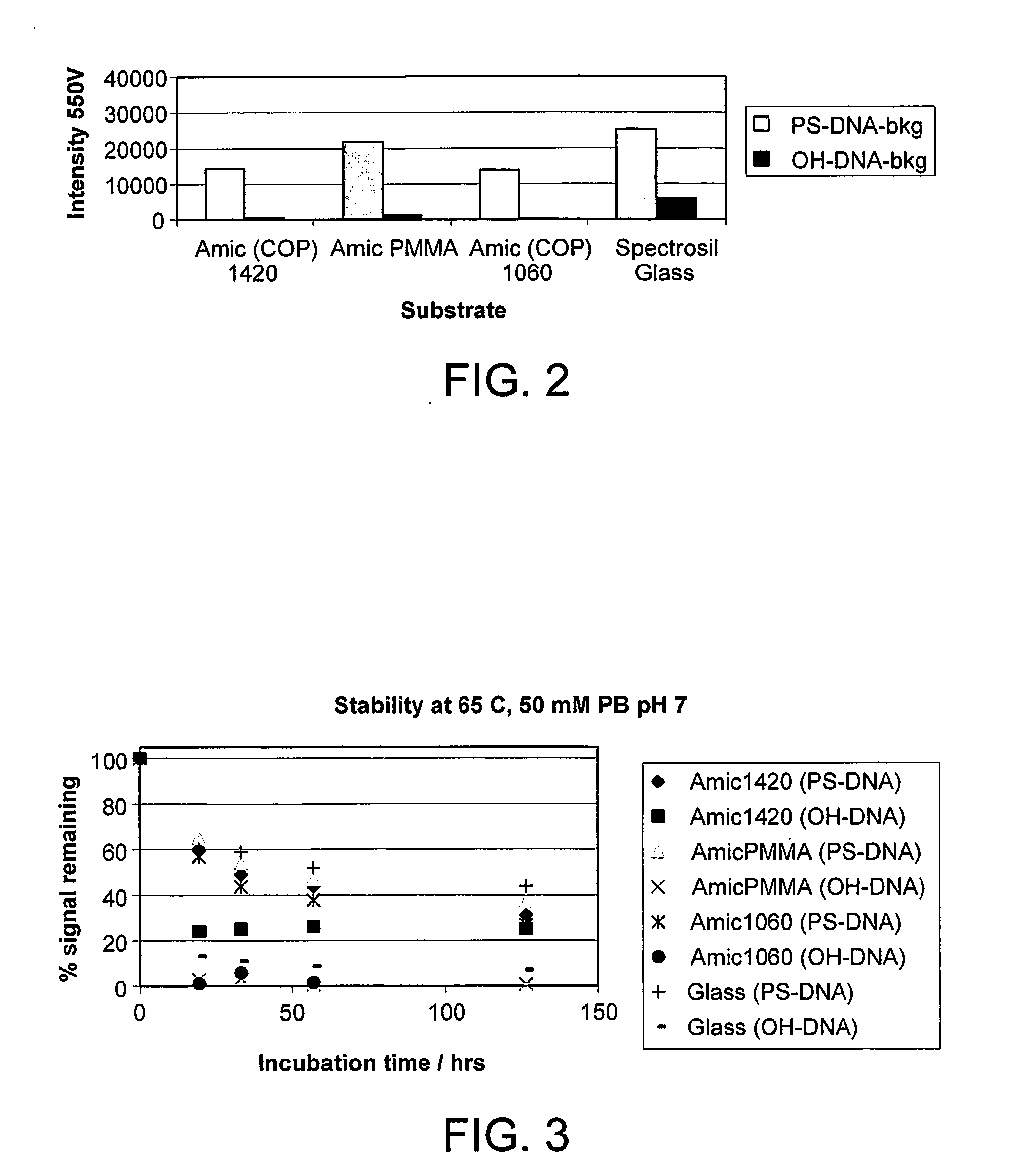
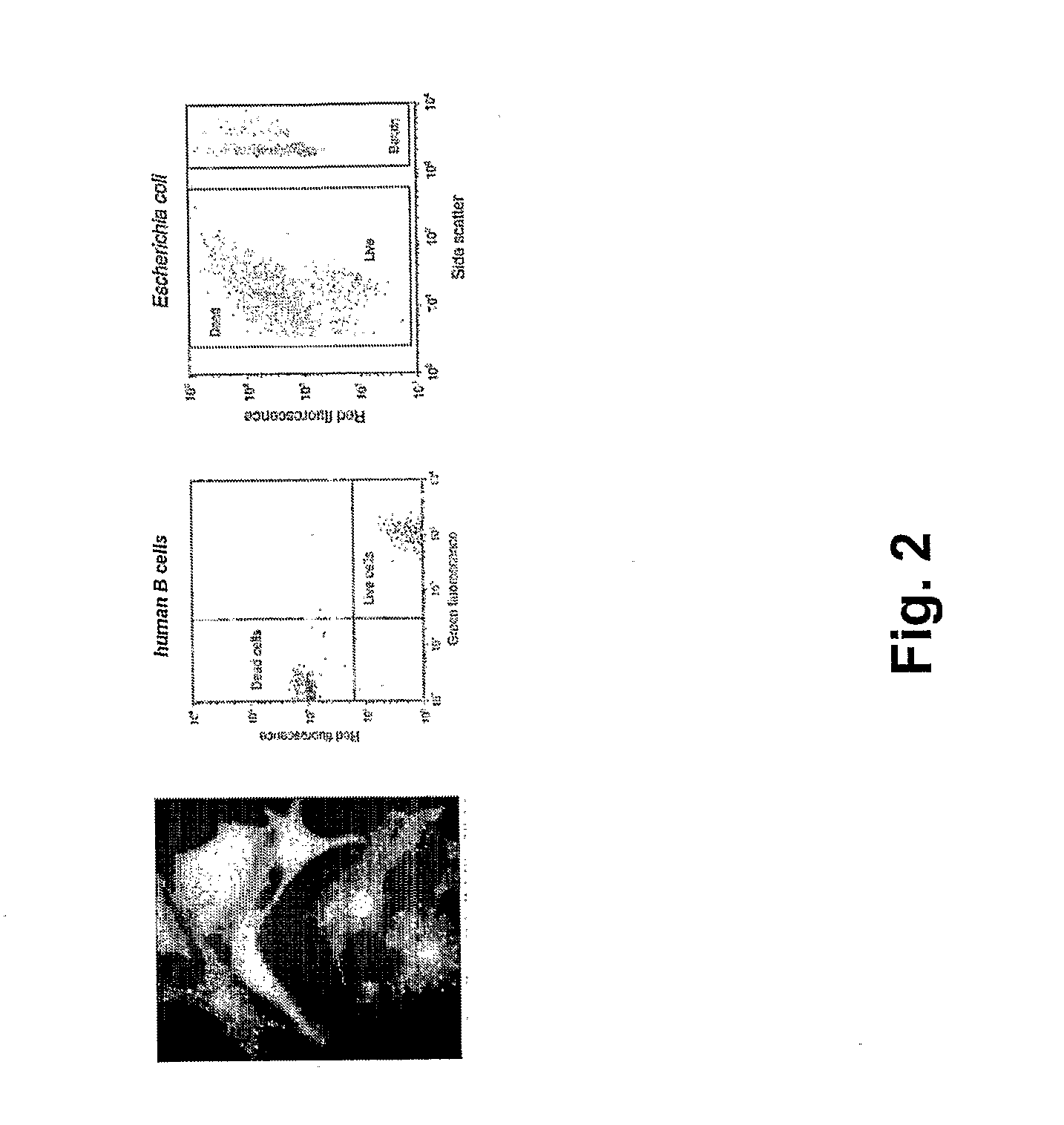
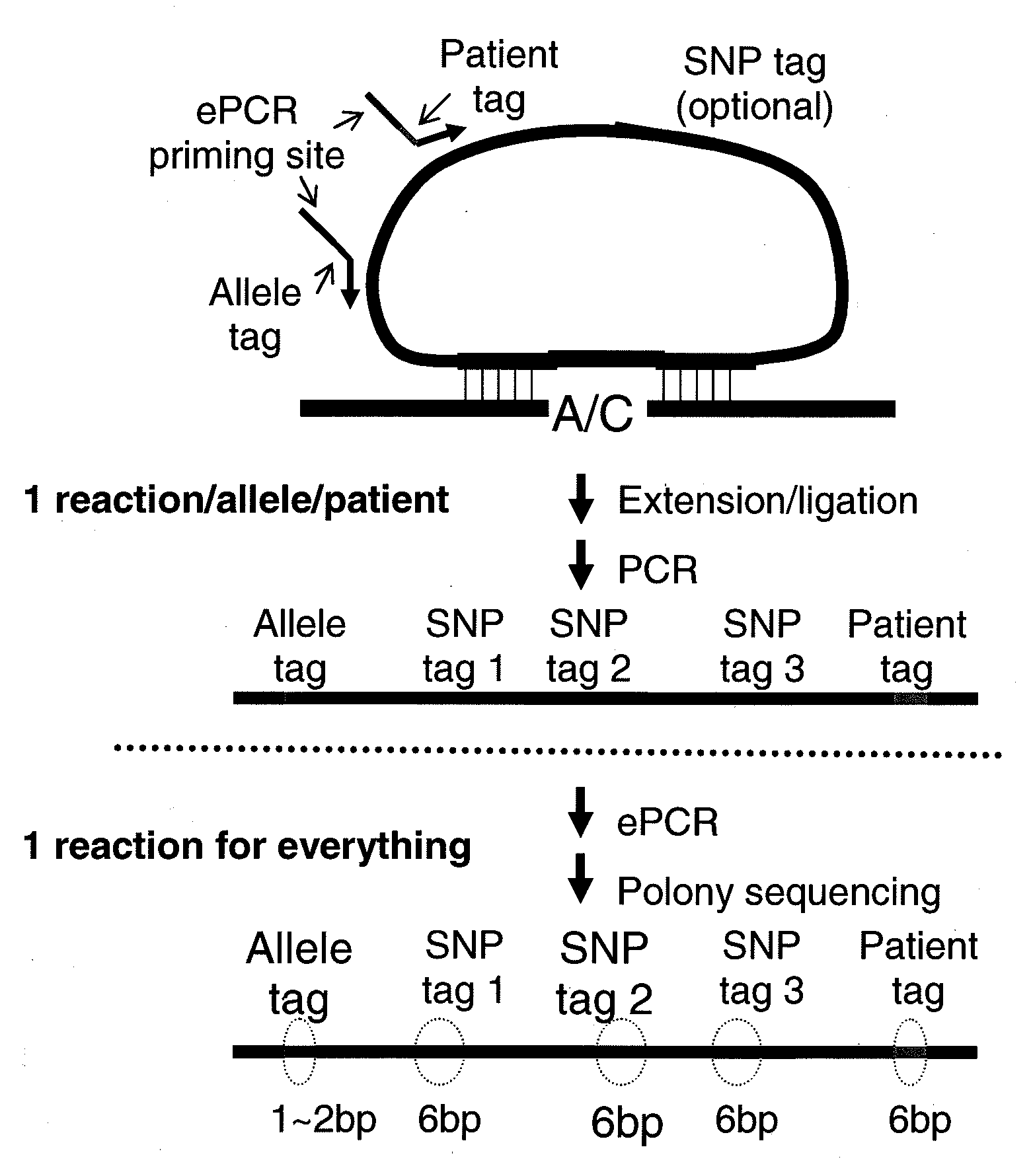
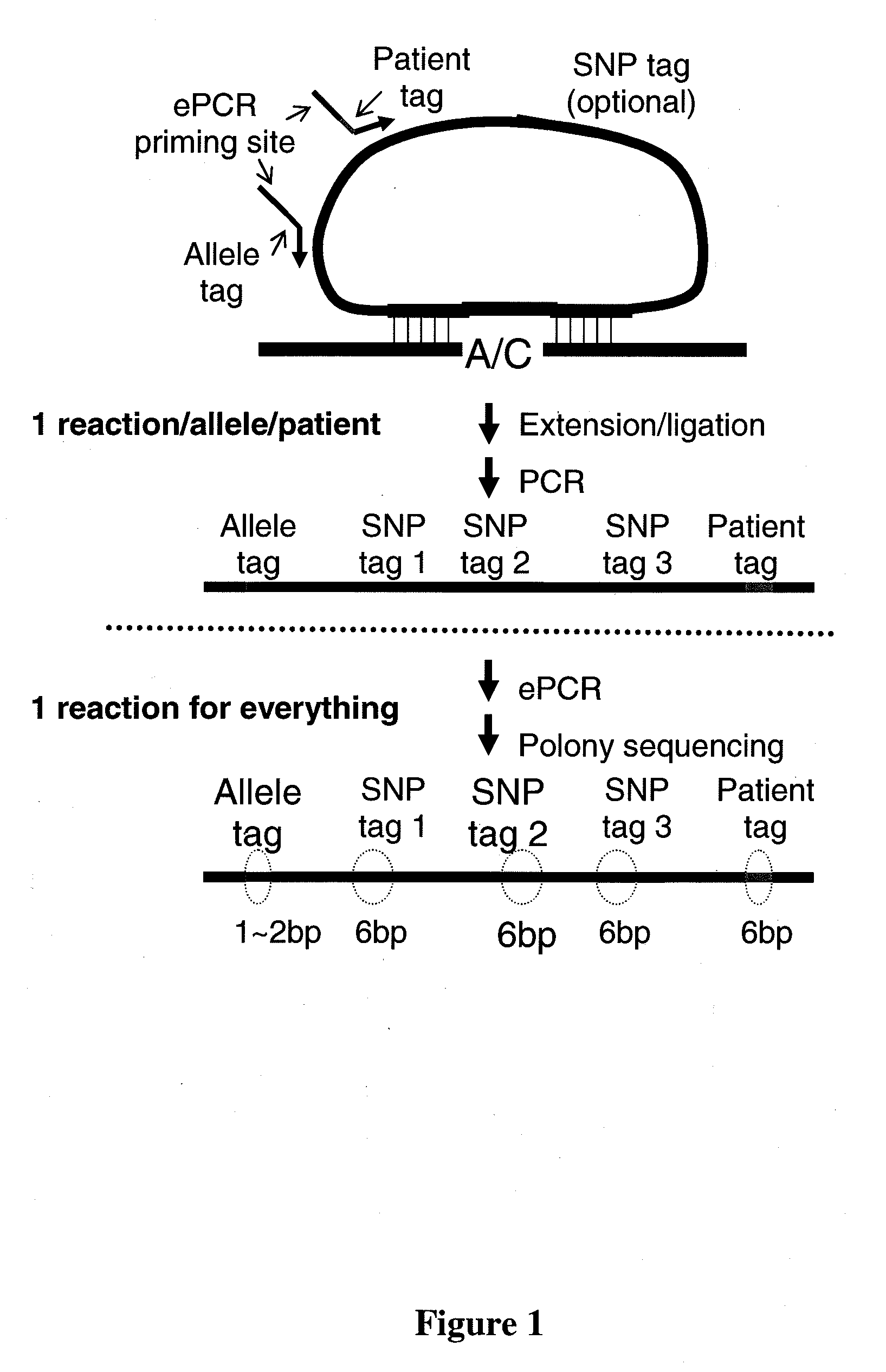
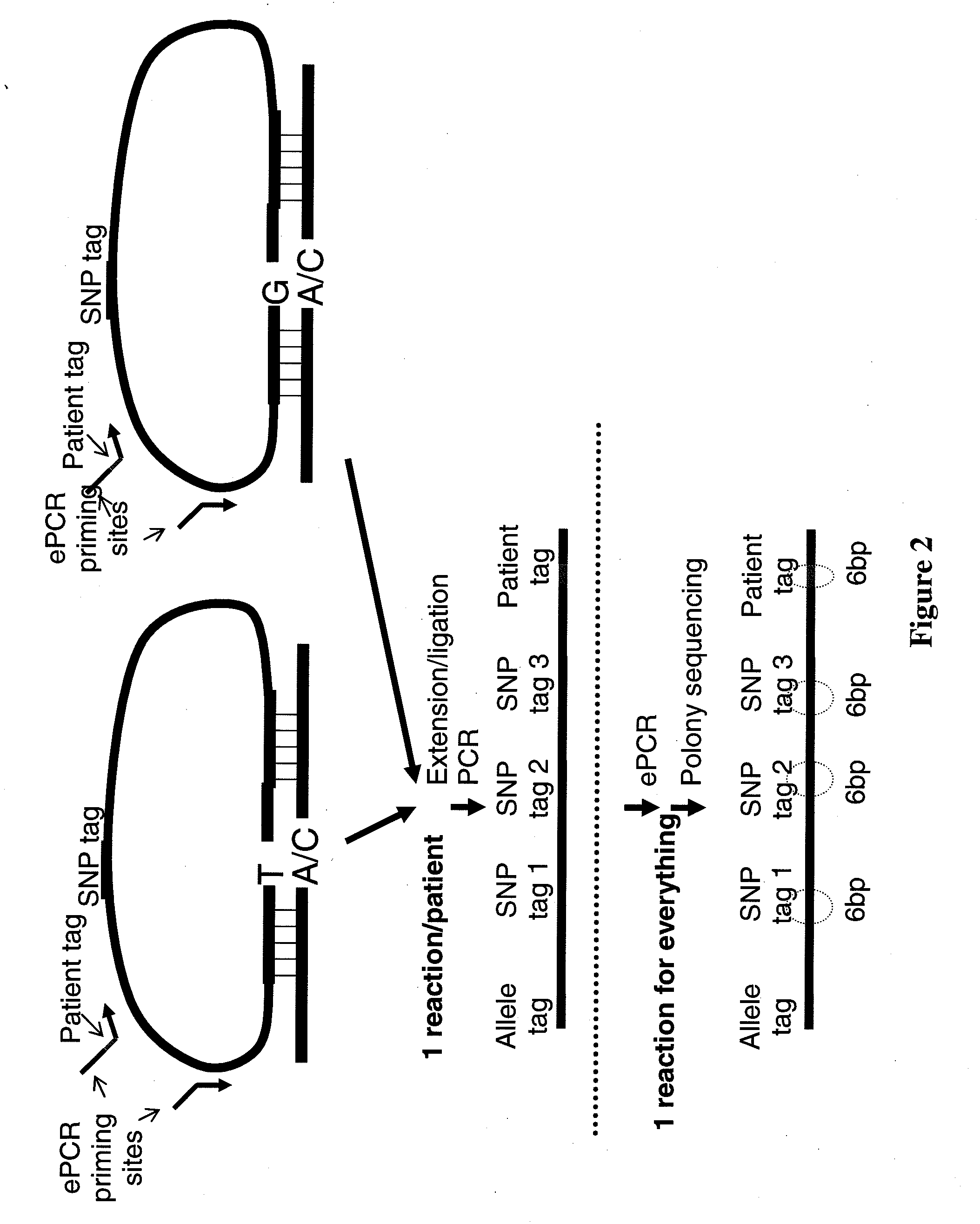
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4538results about "Library creation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
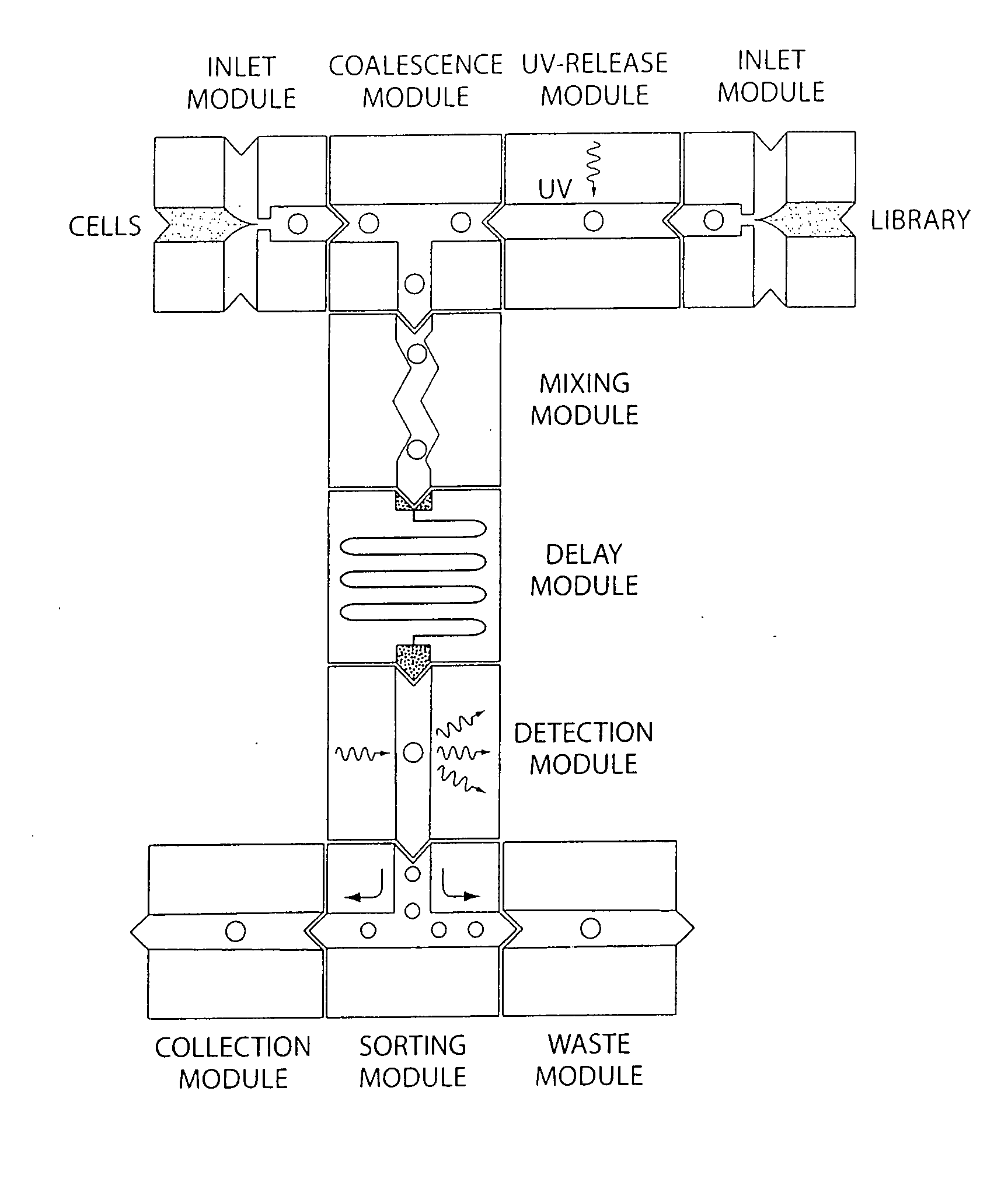
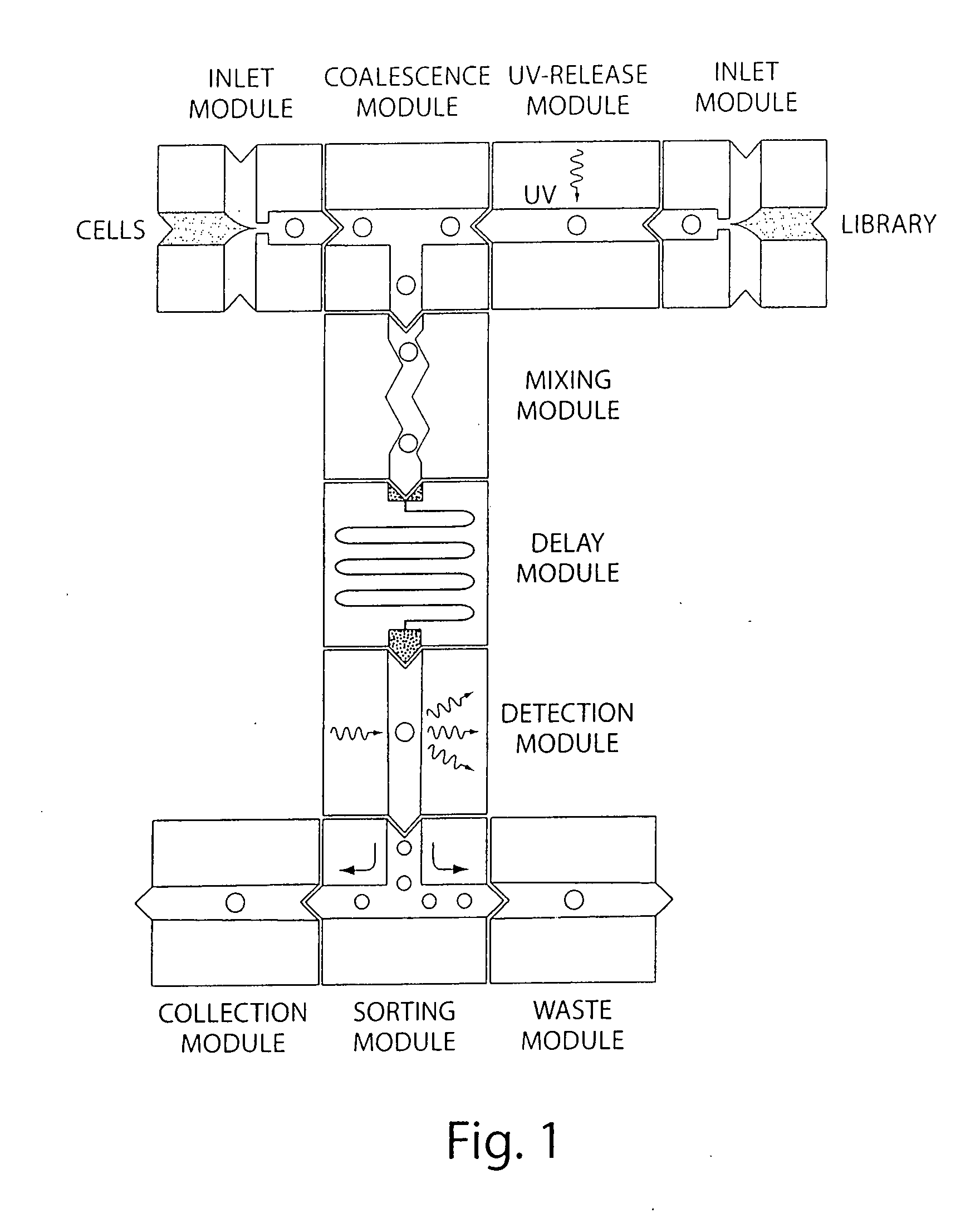
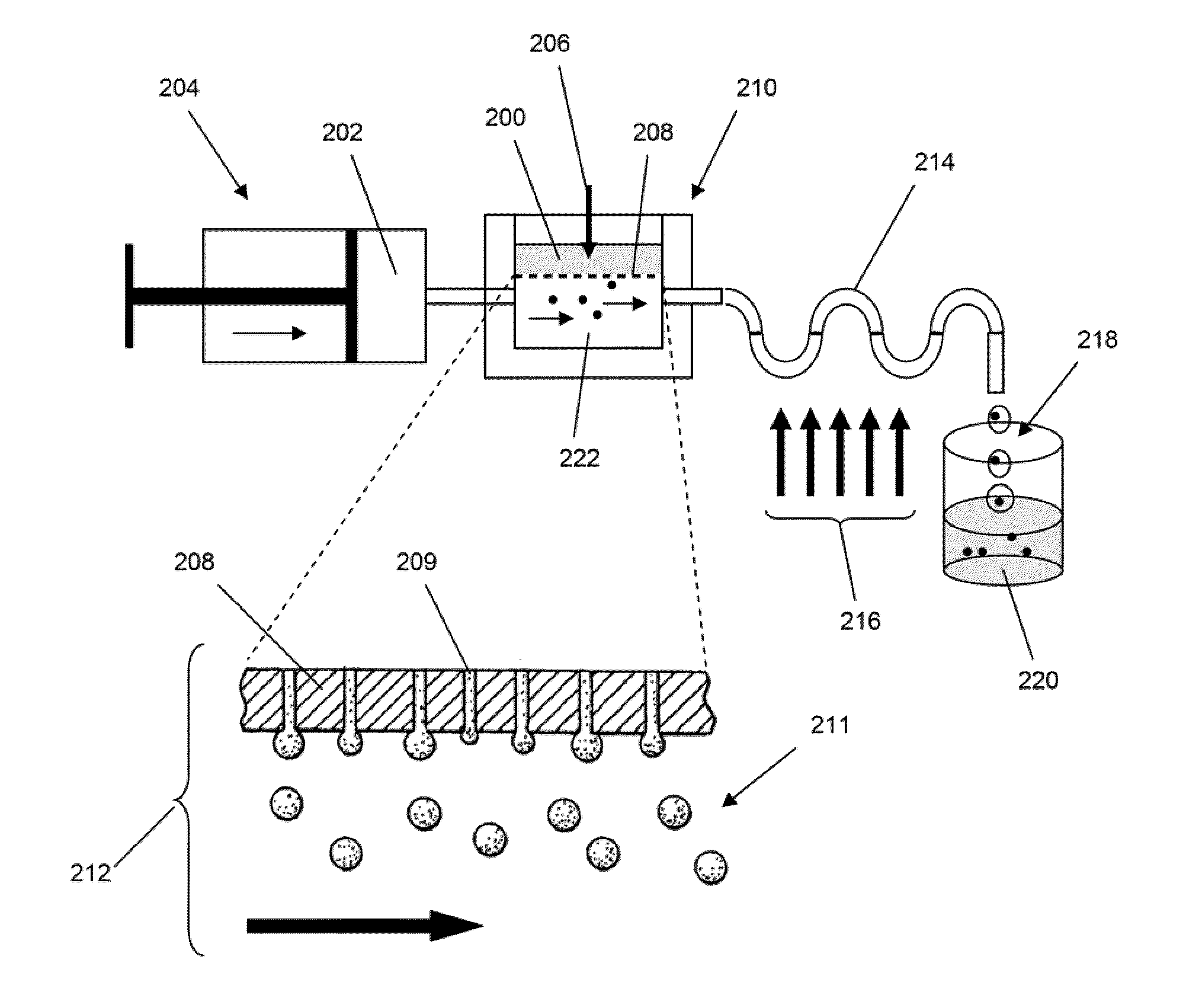
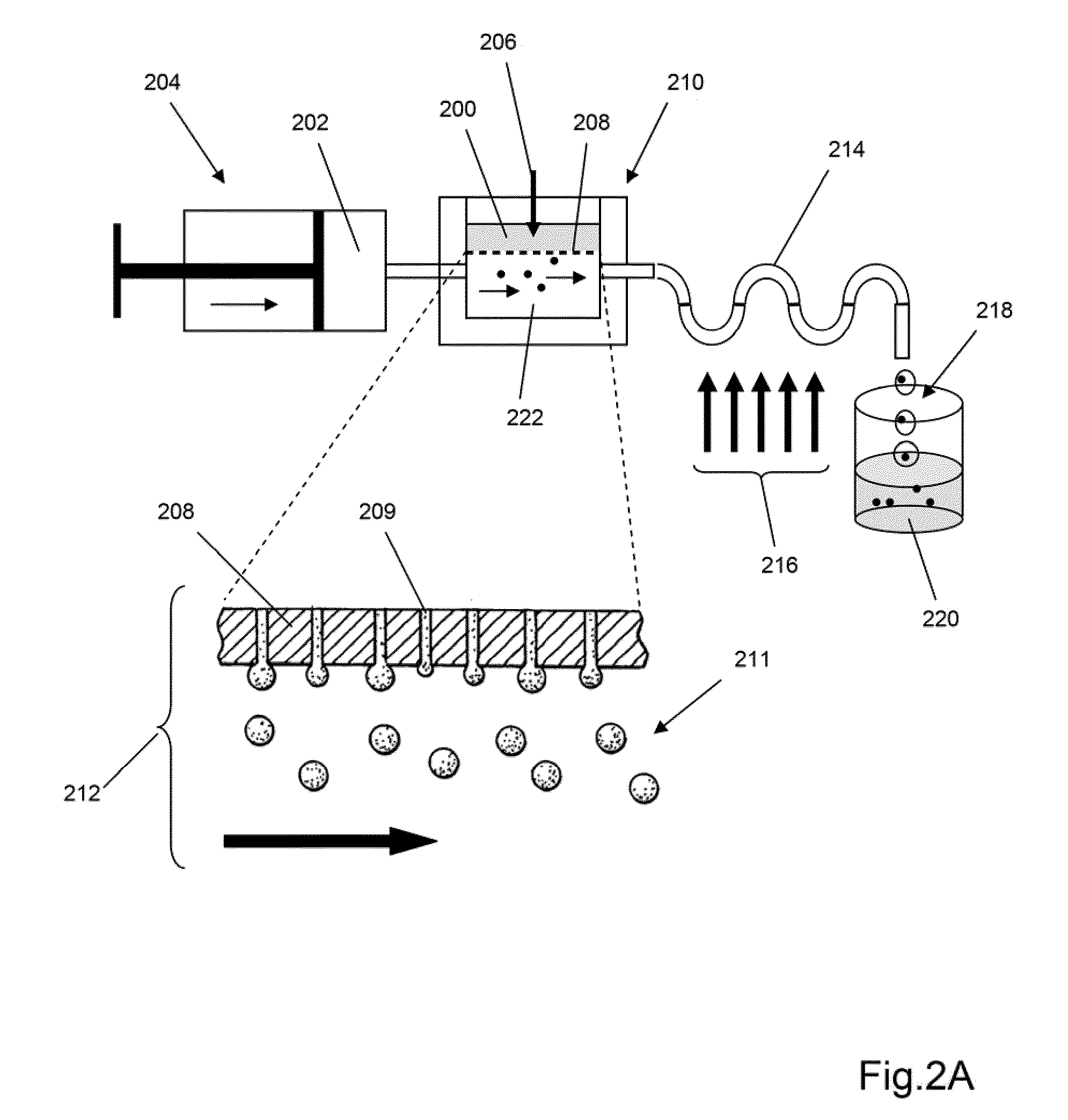
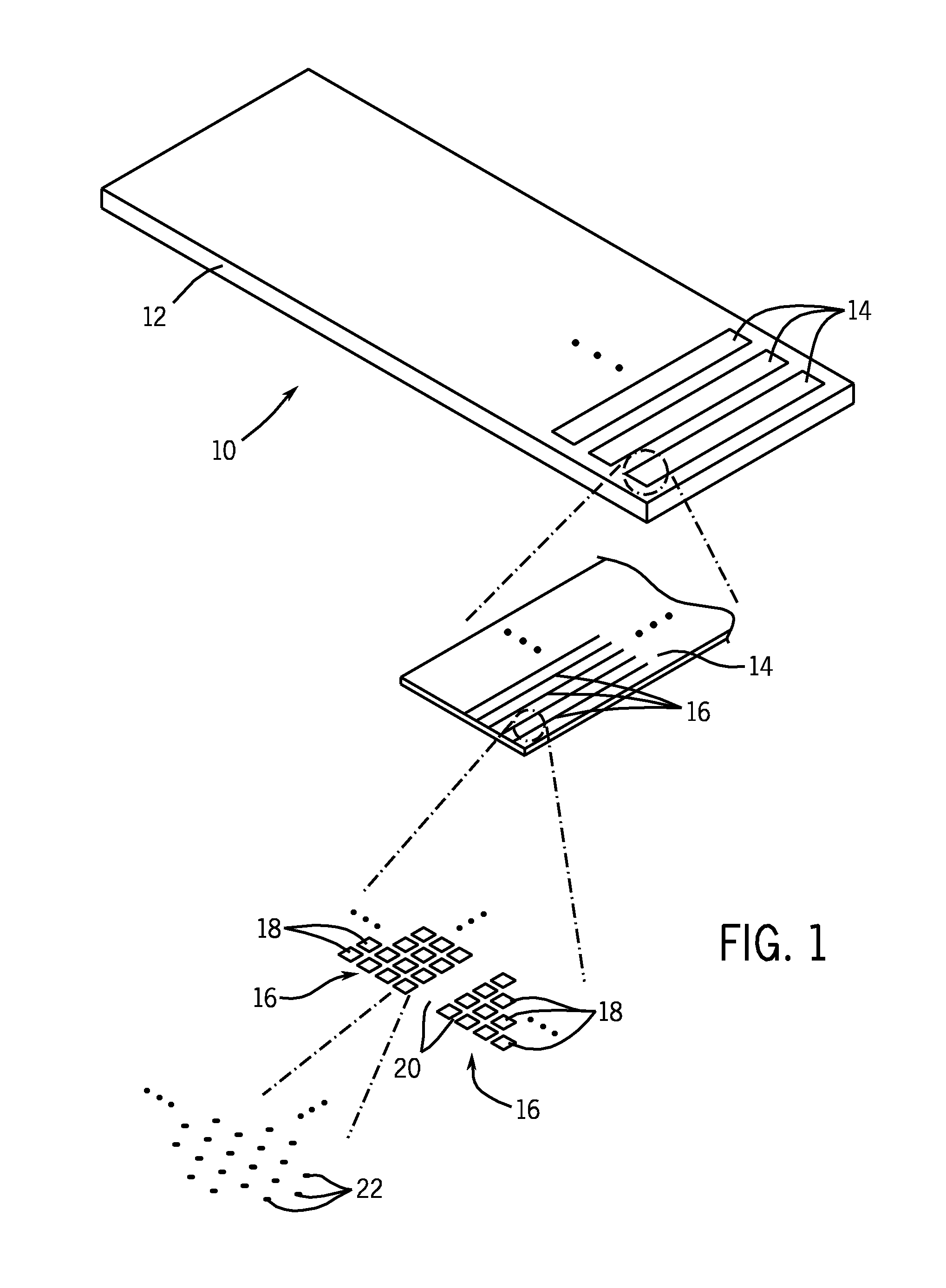
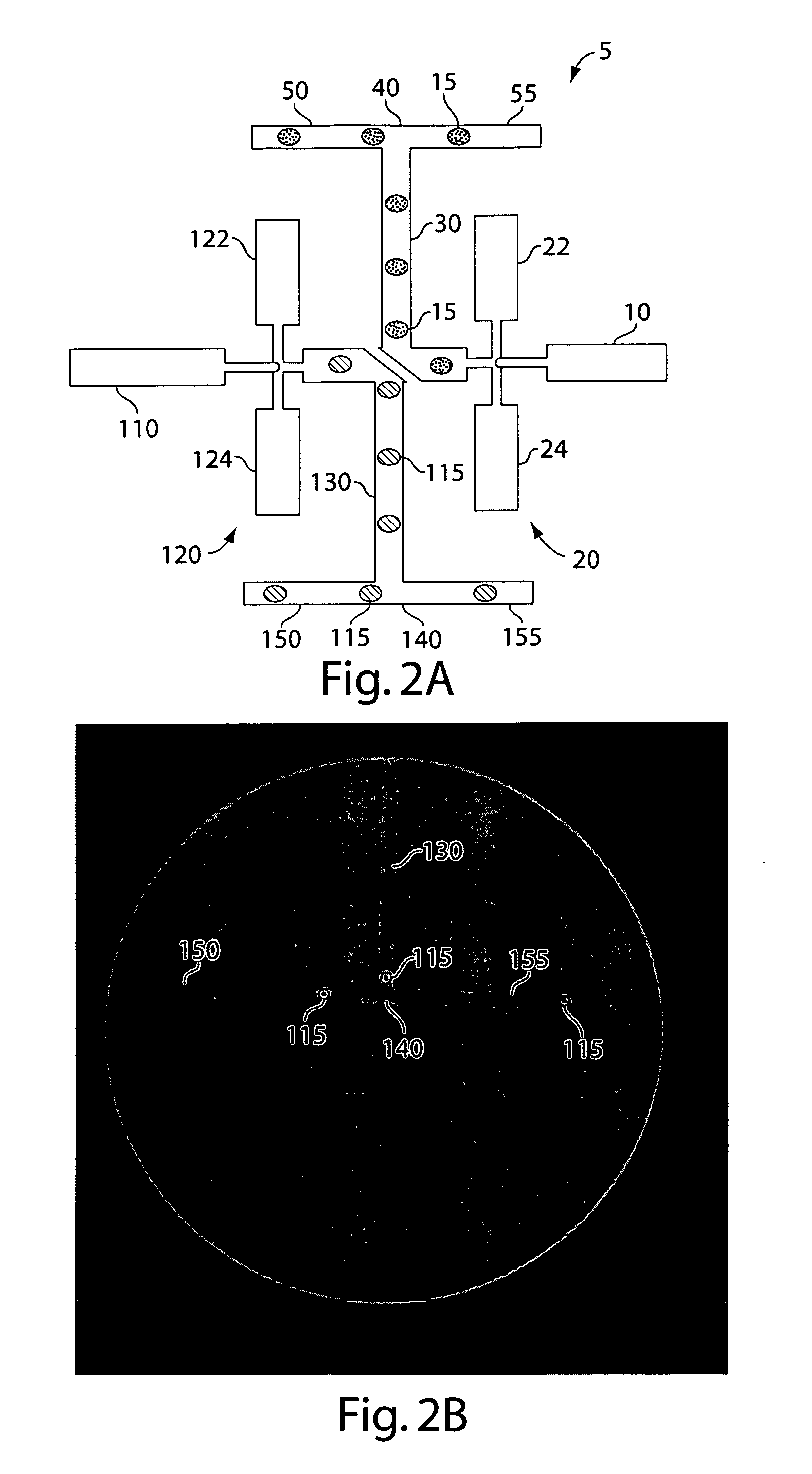
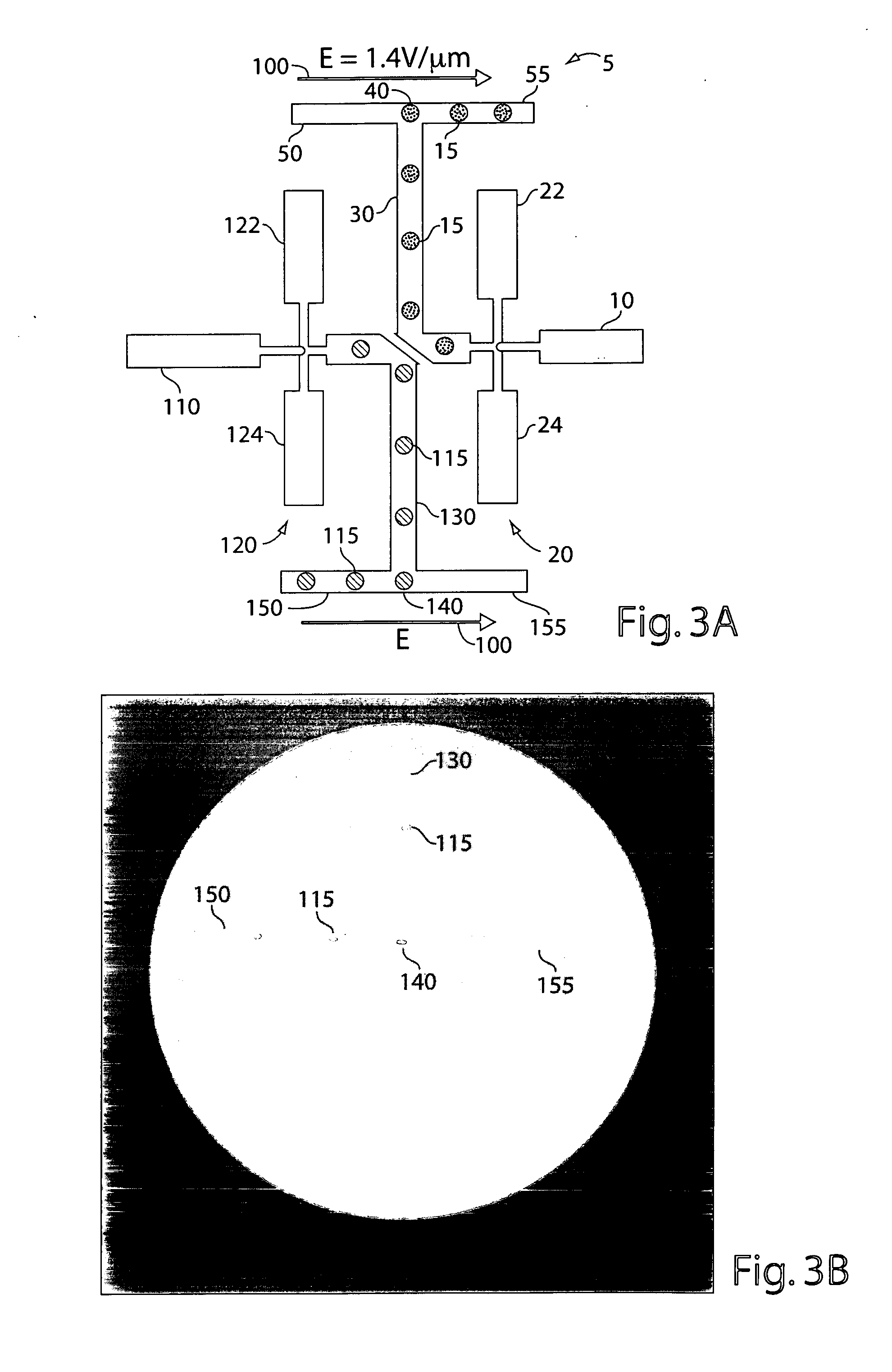
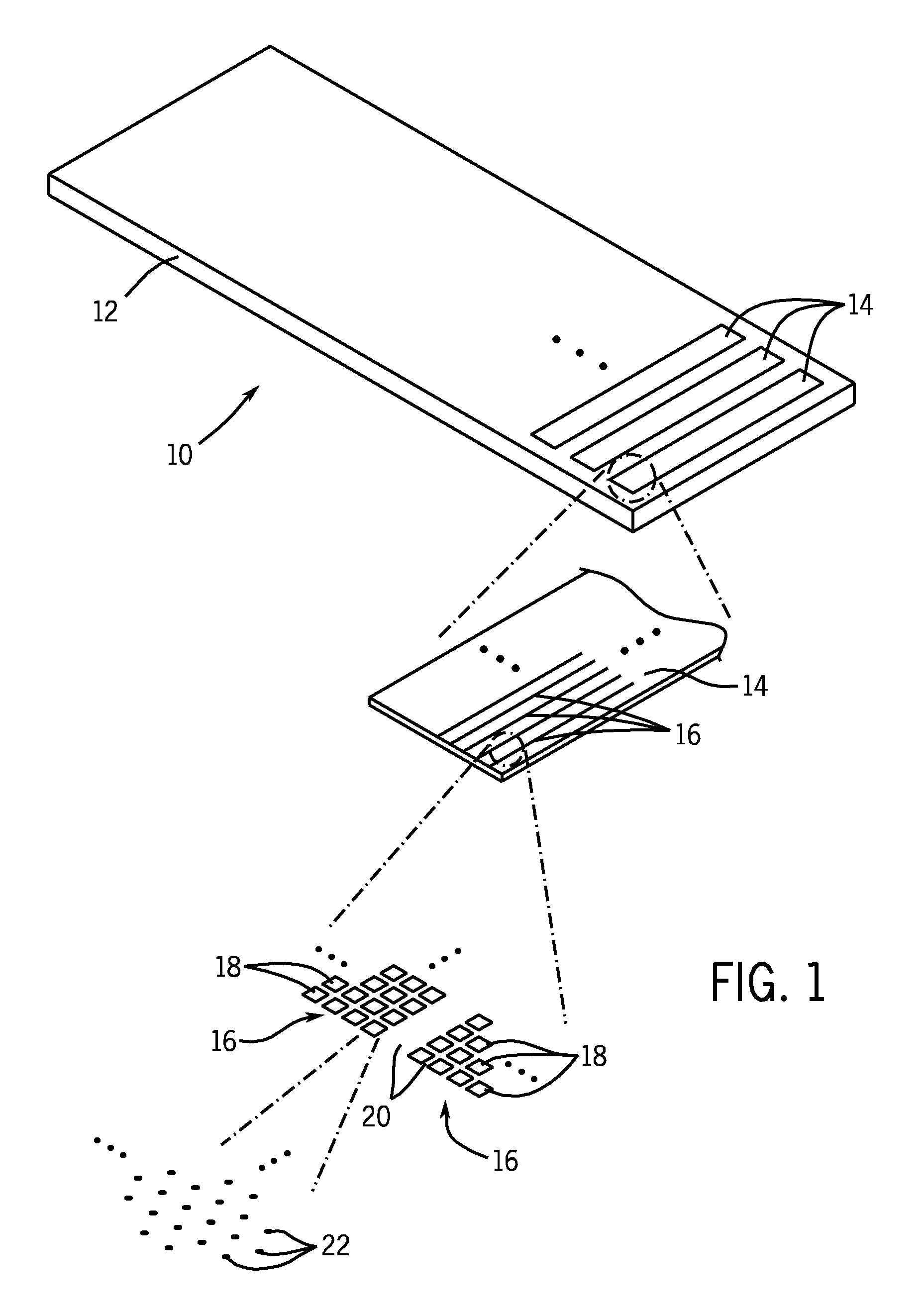
Microfluidic devices and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20080014589A1Eliminates surface wettingDielectrophoresisLiquid separation by electricityComputer moduleBiomedical engineering
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
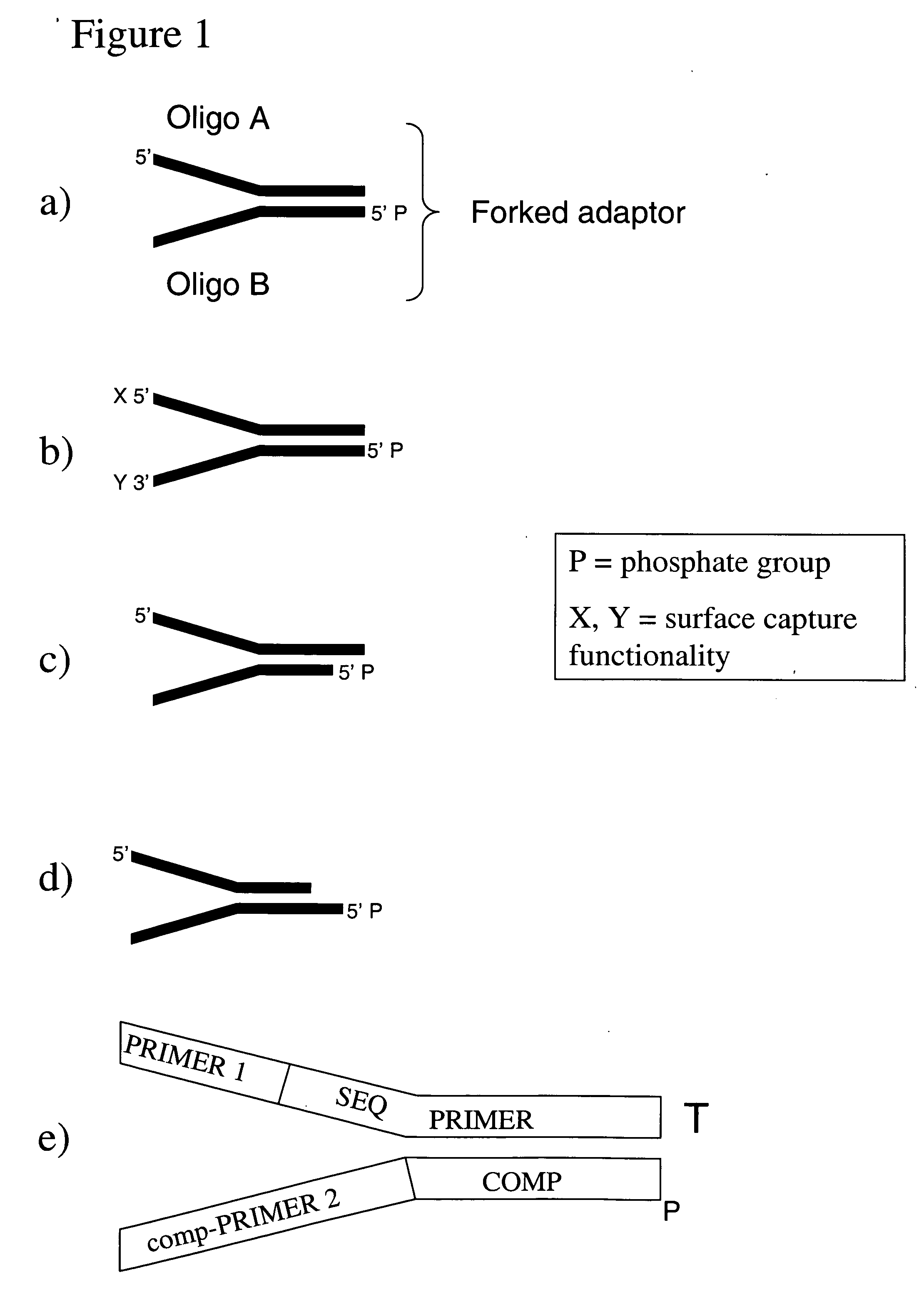
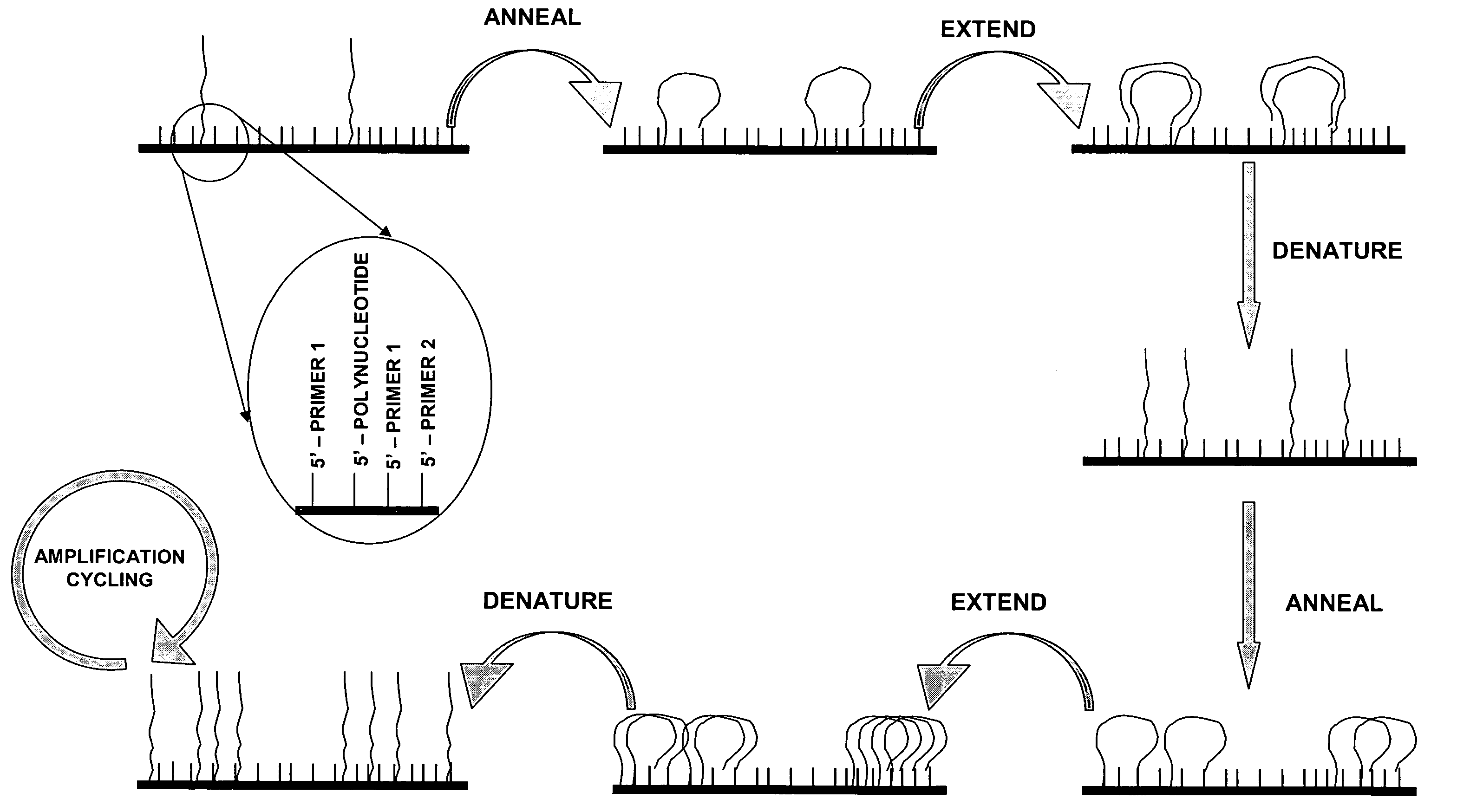
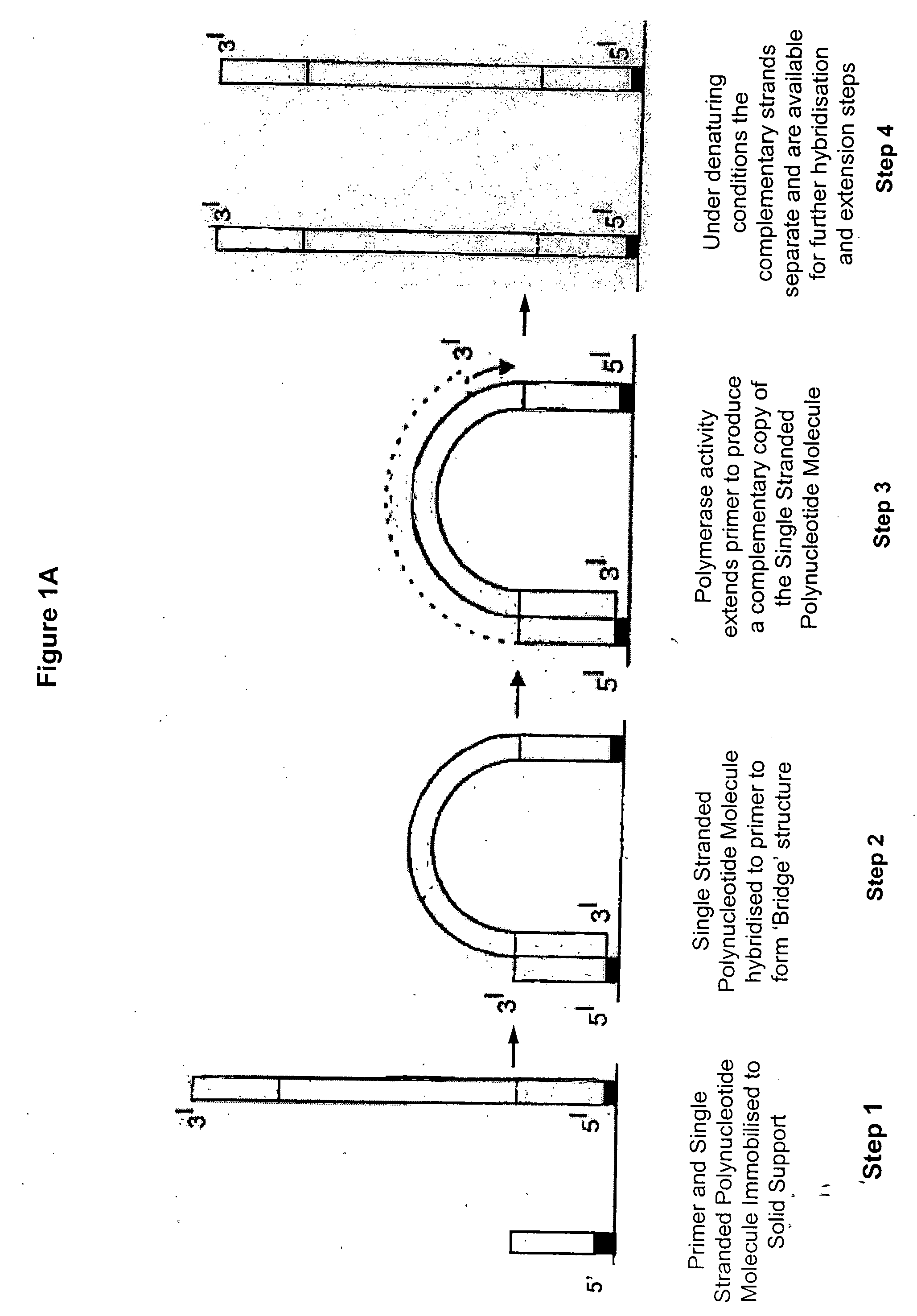
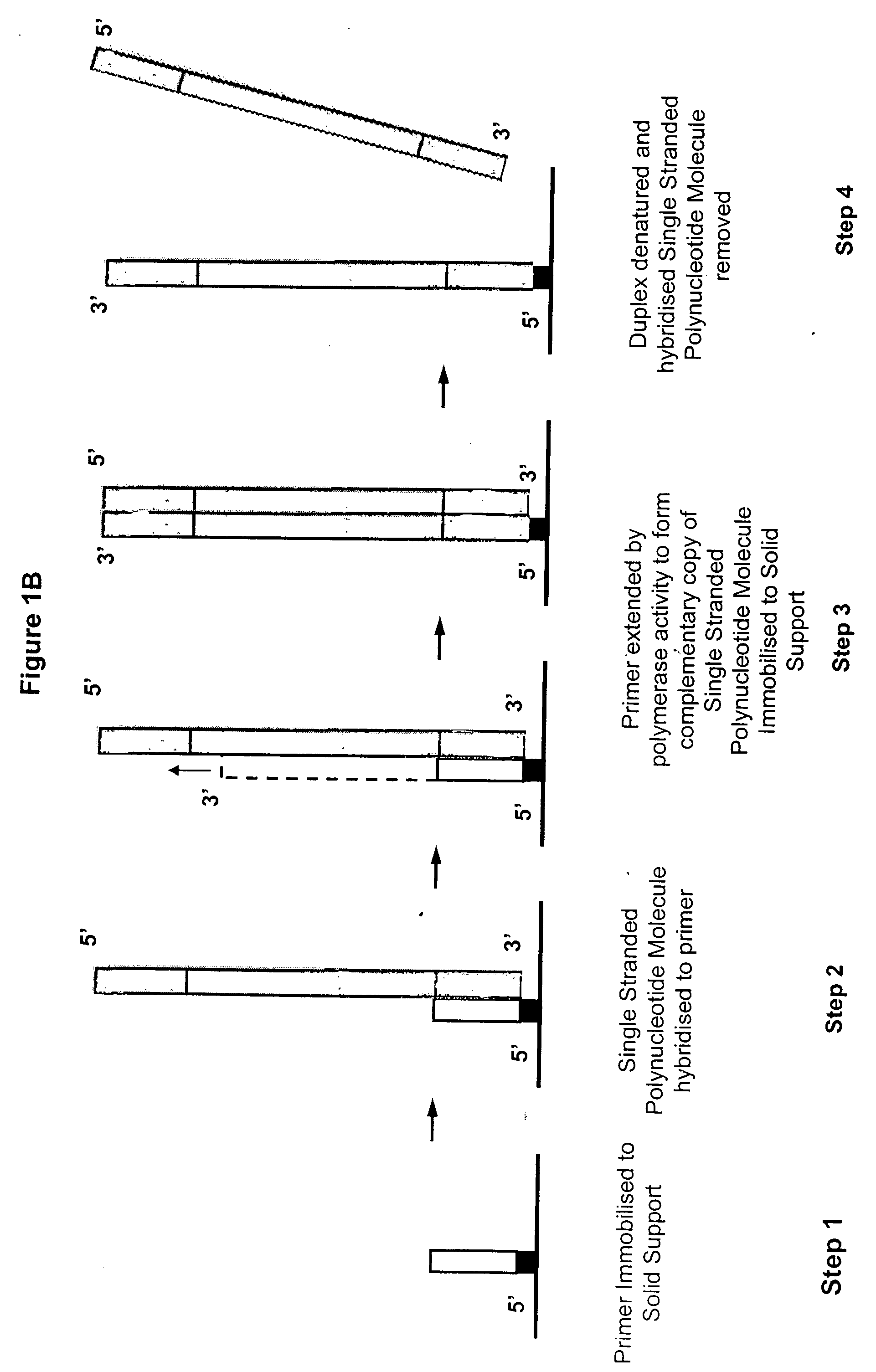
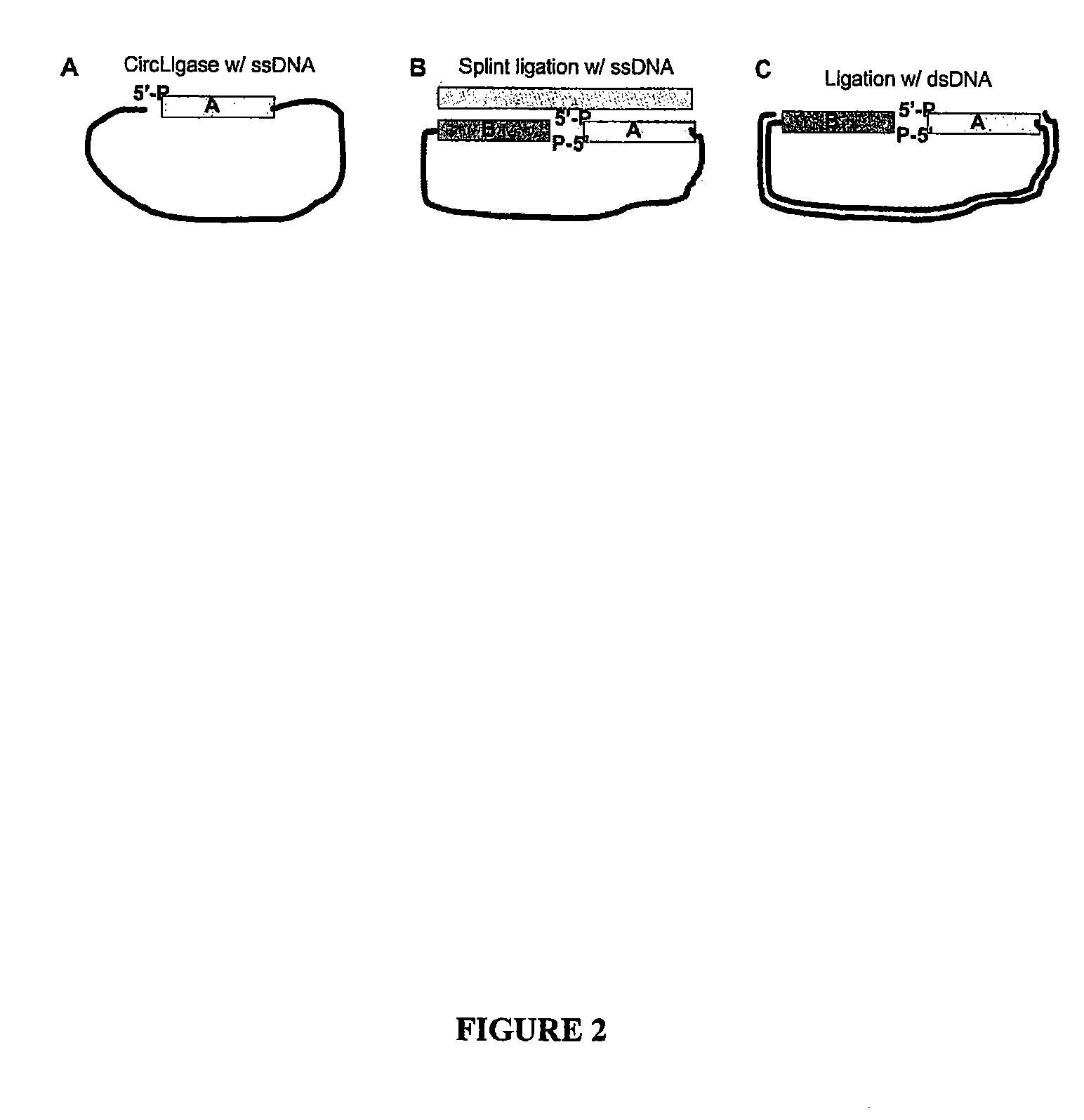
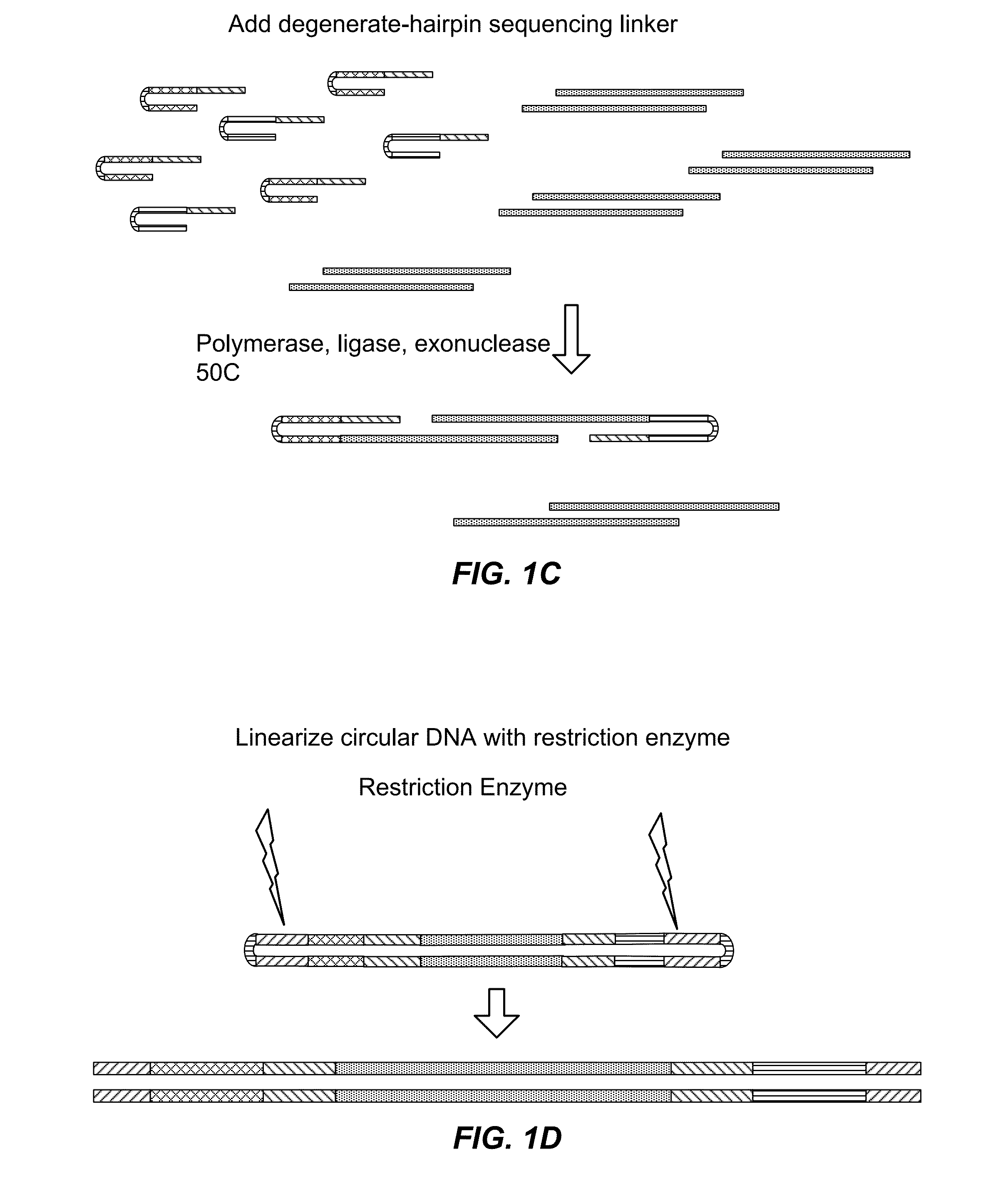
Method of preparing libraries of template polynucleotides
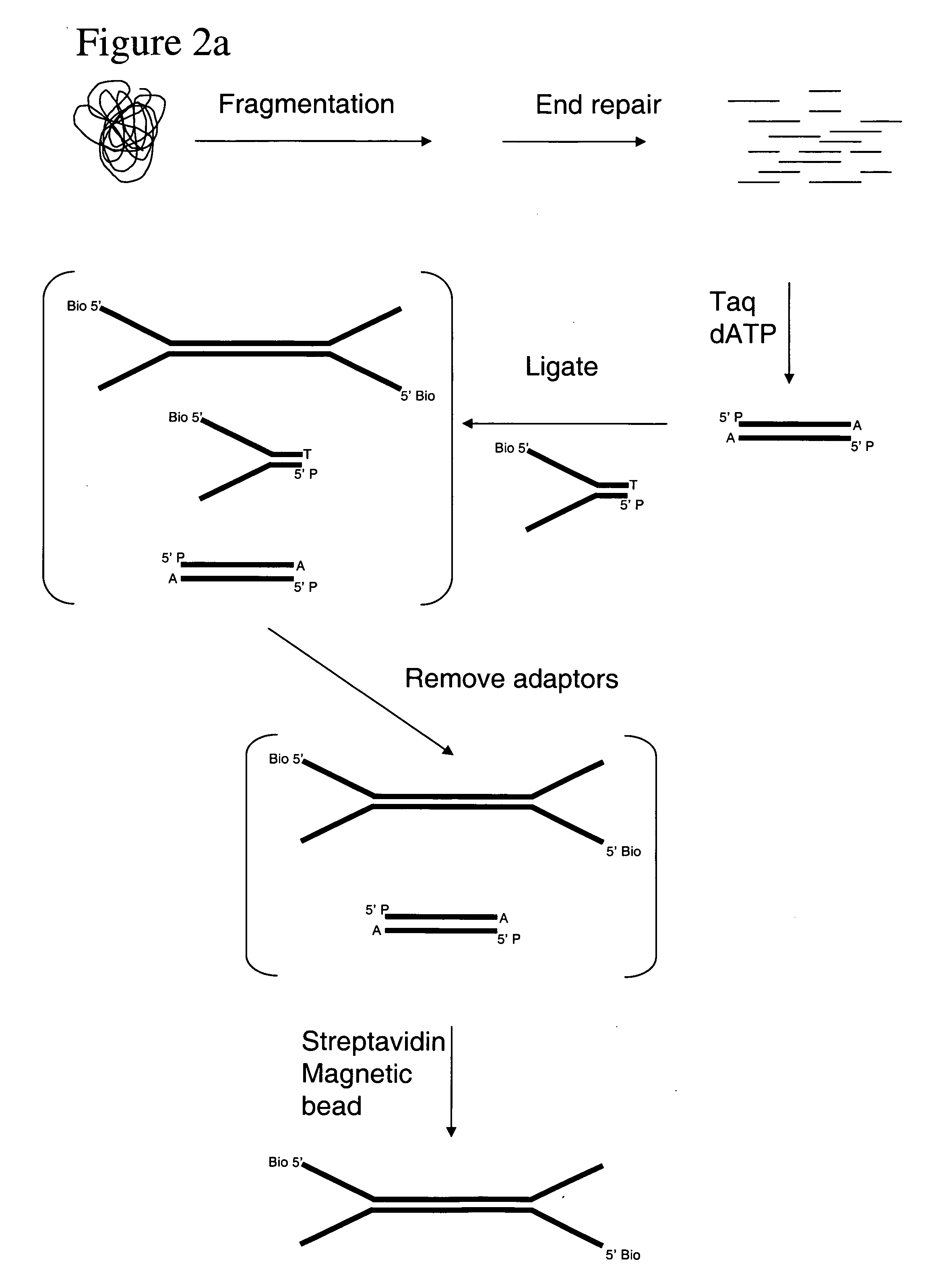
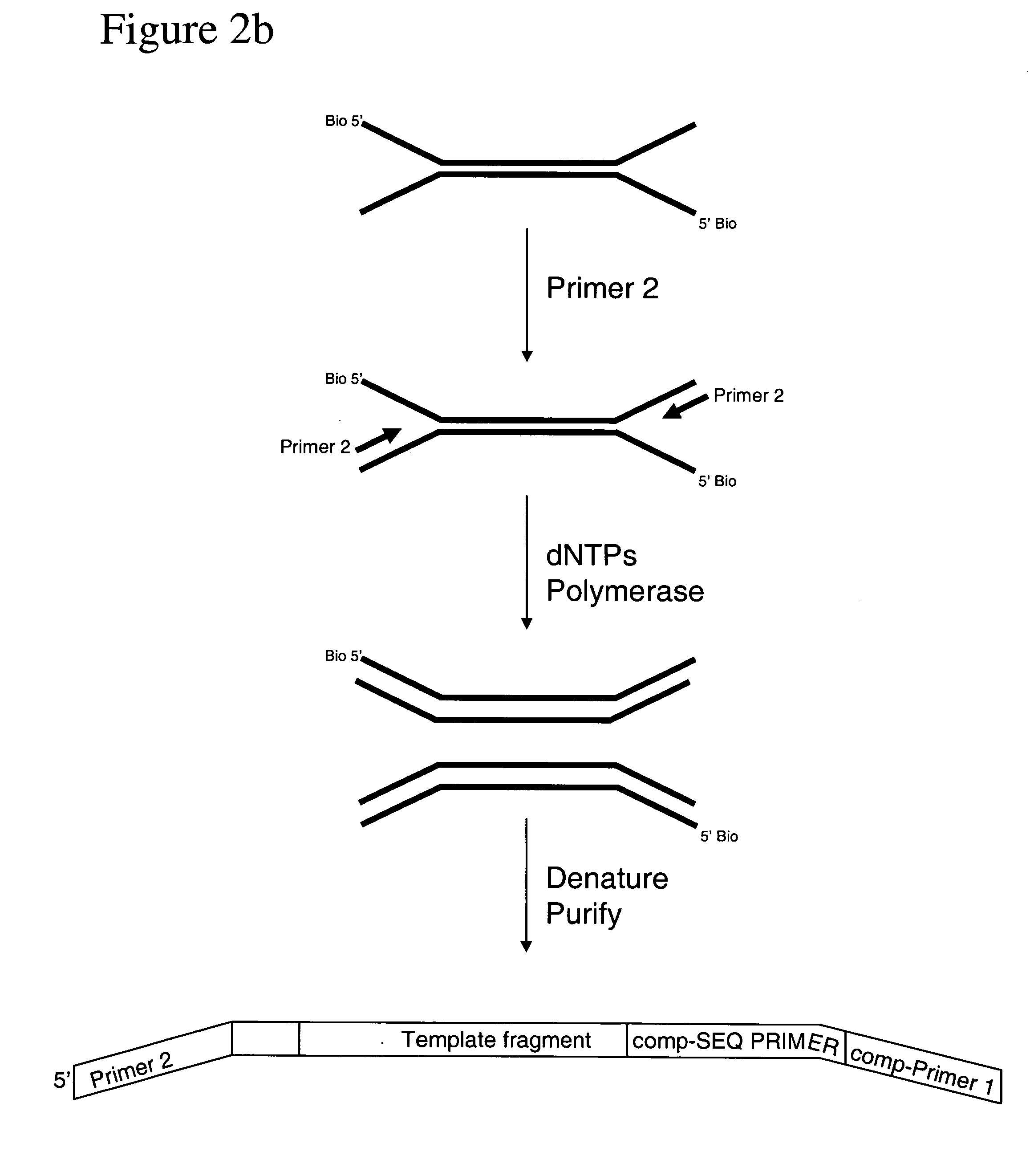
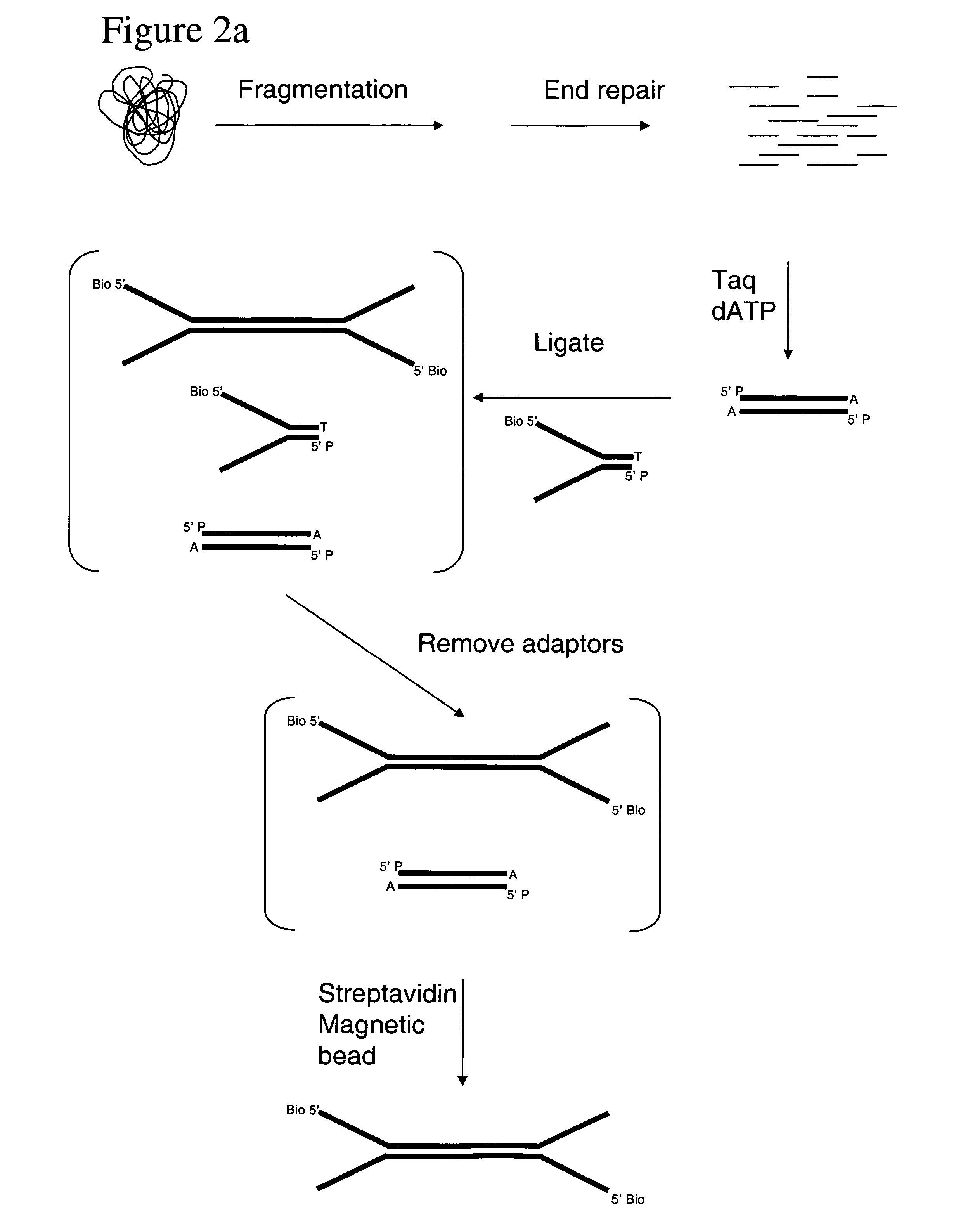
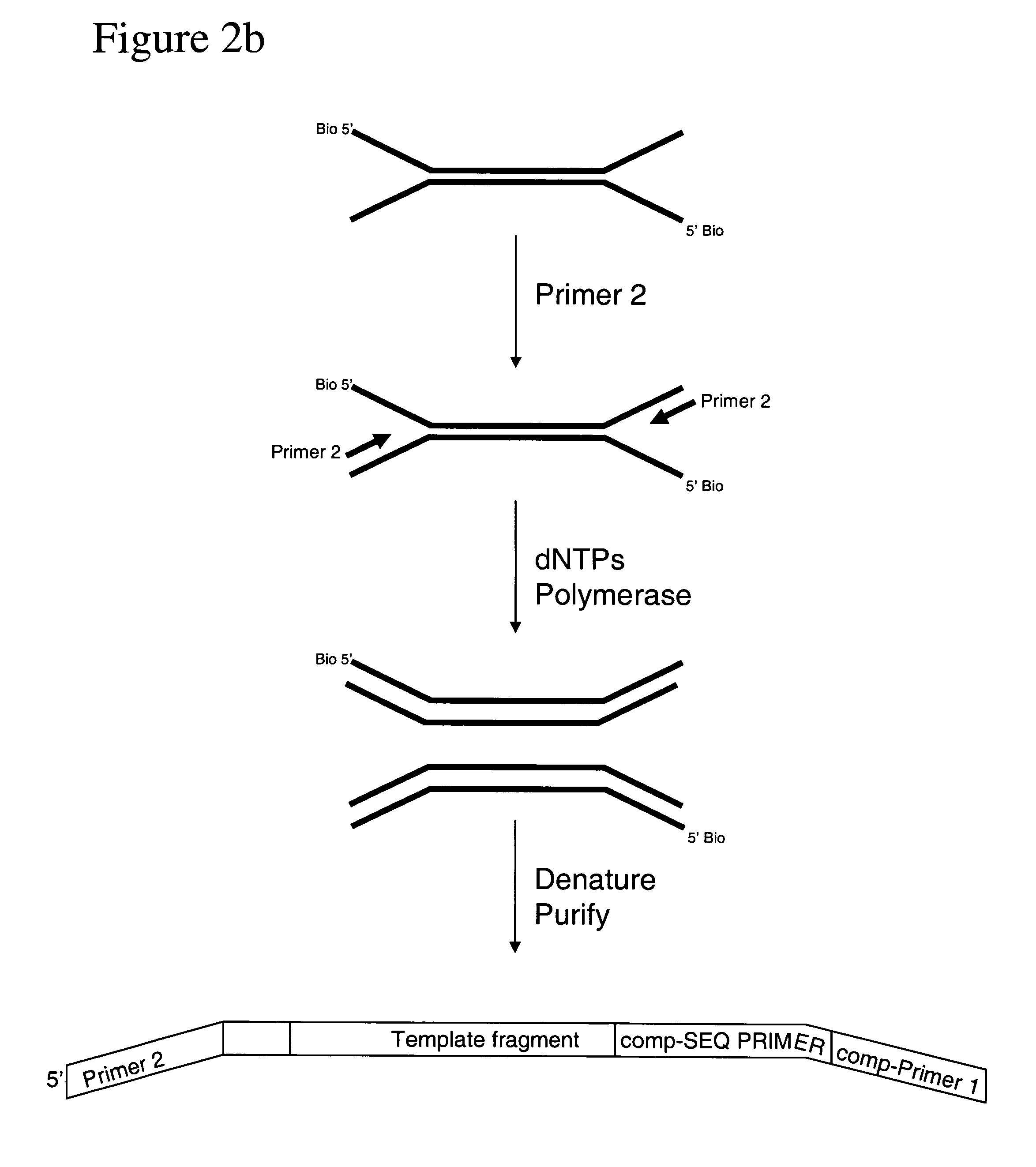
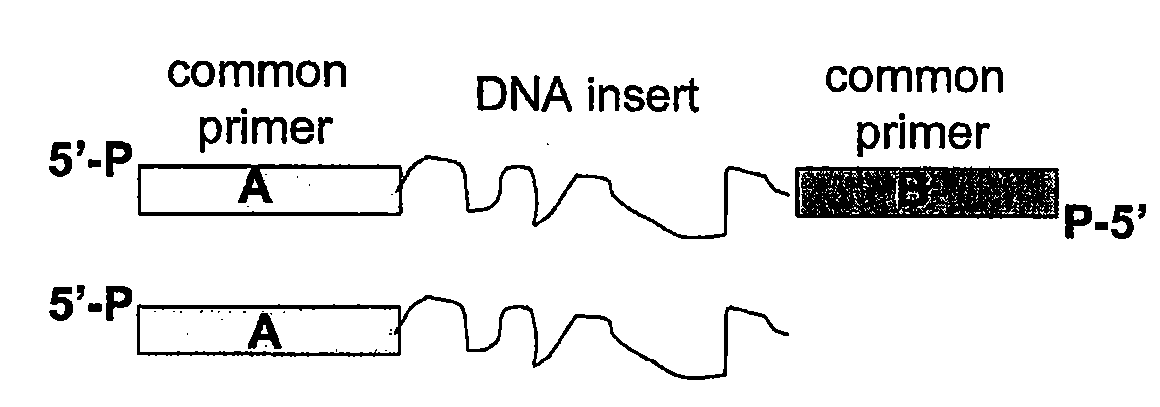
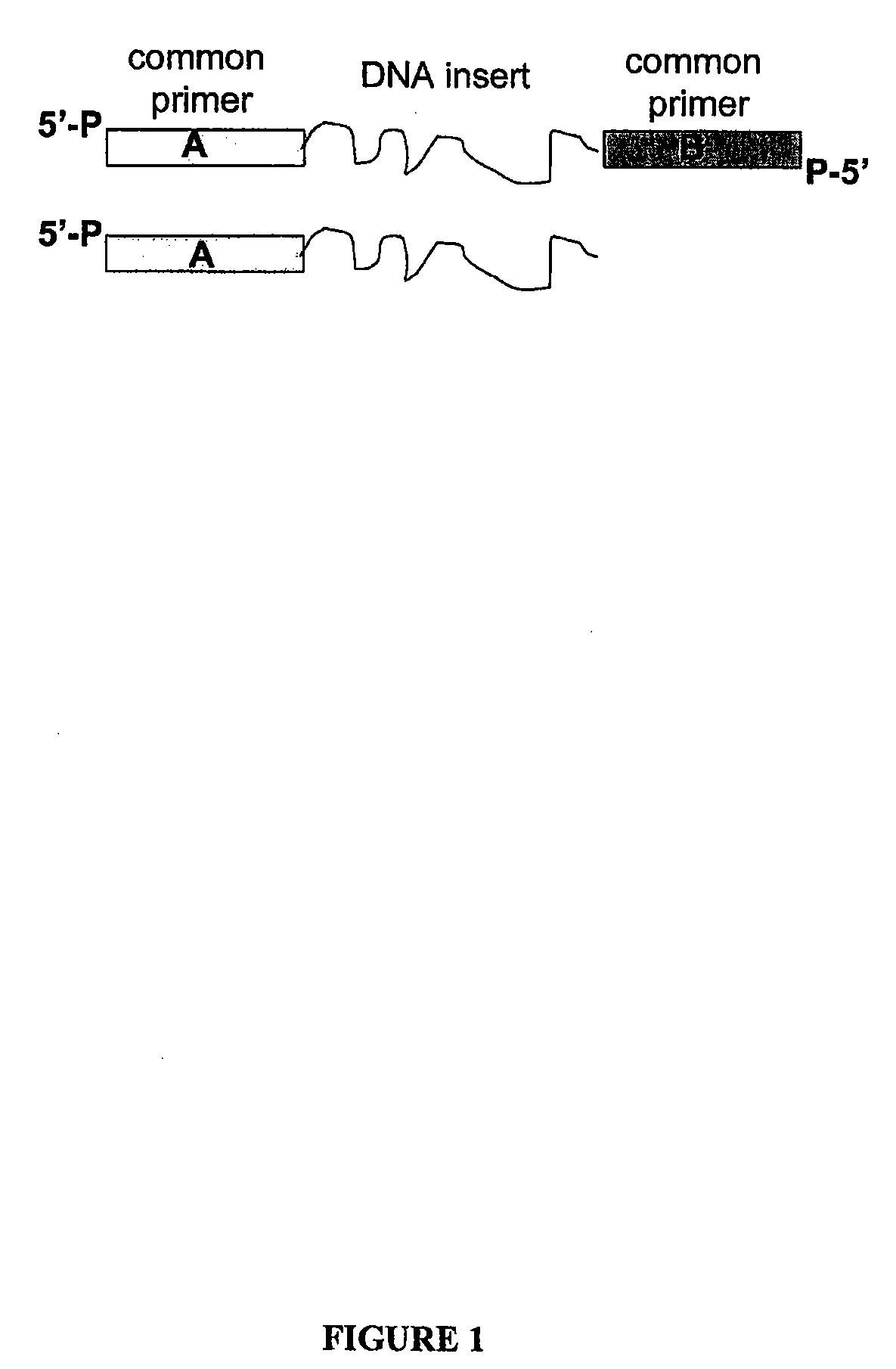
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a library of template polynucleotides and use thereof in methods of solid-phase nucleic acid amplification. More specifically, the invention relates to a method for preparing a library of template polynucleotides that have common sequences at their 5′ ends and at their 3′ ends.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Bead emulsion nucleic acid amplification
Disclosed are methods for nucleic acid amplification wherein nucleic acid templates, beads, and amplification reaction solution are emulsified and the nucleic acid templates are amplified to provide clonal copies of the nucleic acid templates attached to the beads. Also disclosed are kits and apparatuses for performing the methods of the invention.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
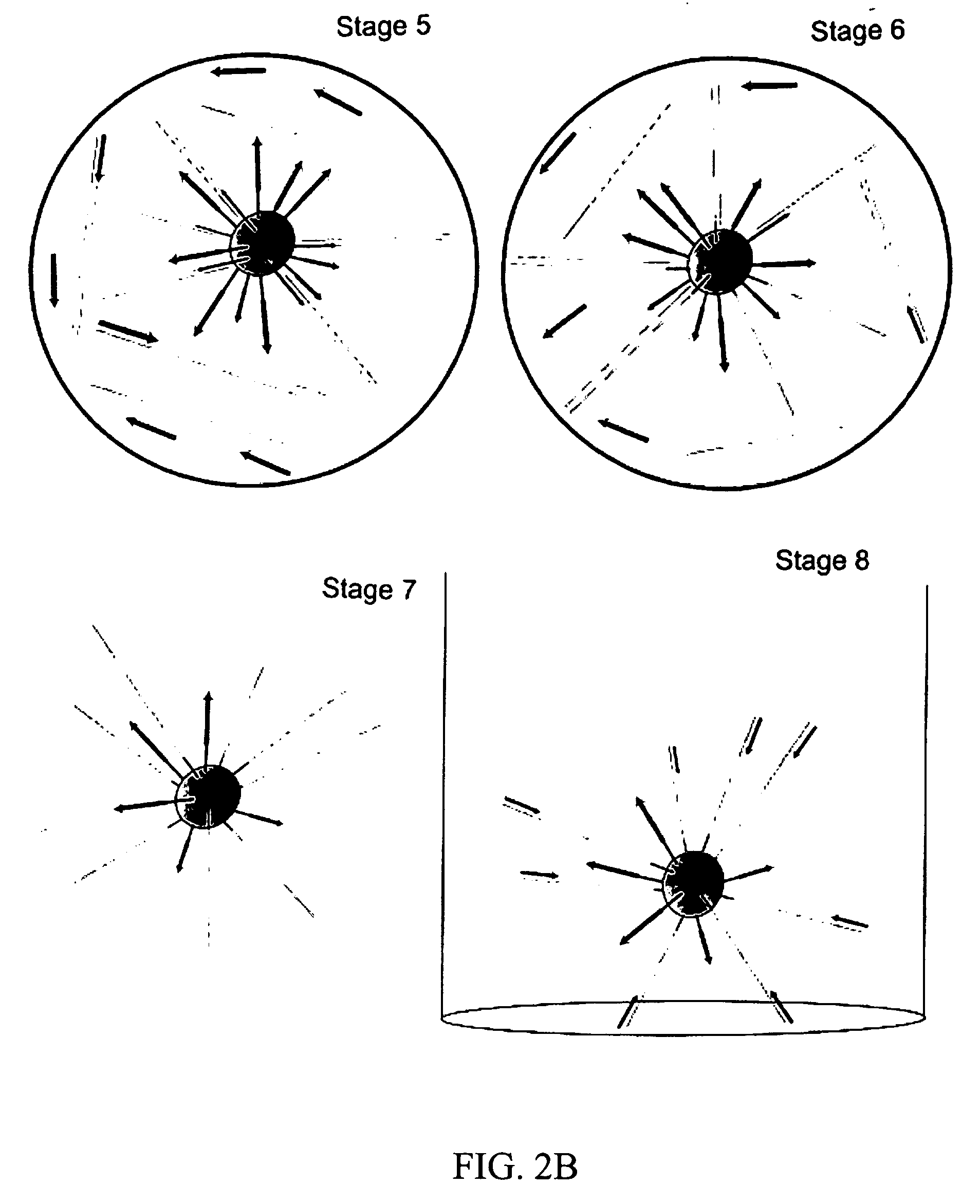
Isothermal methods for creating clonal single molecule arrays
InactiveUS20080009420A1Efficient amplificationIncrease diversityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention is directed to a method for isothermal amplification of a plurality of different target nucleic acids, wherein the different target nucleic acids are amplified using universal primers and colonies produced thereby can be distinguished from each other. The method, therefore, generates distinct colonies of amplified nucleic acid sequences that can be analyzed by various means to yield information particular to each distinct colony.
Owner:SOLEXA
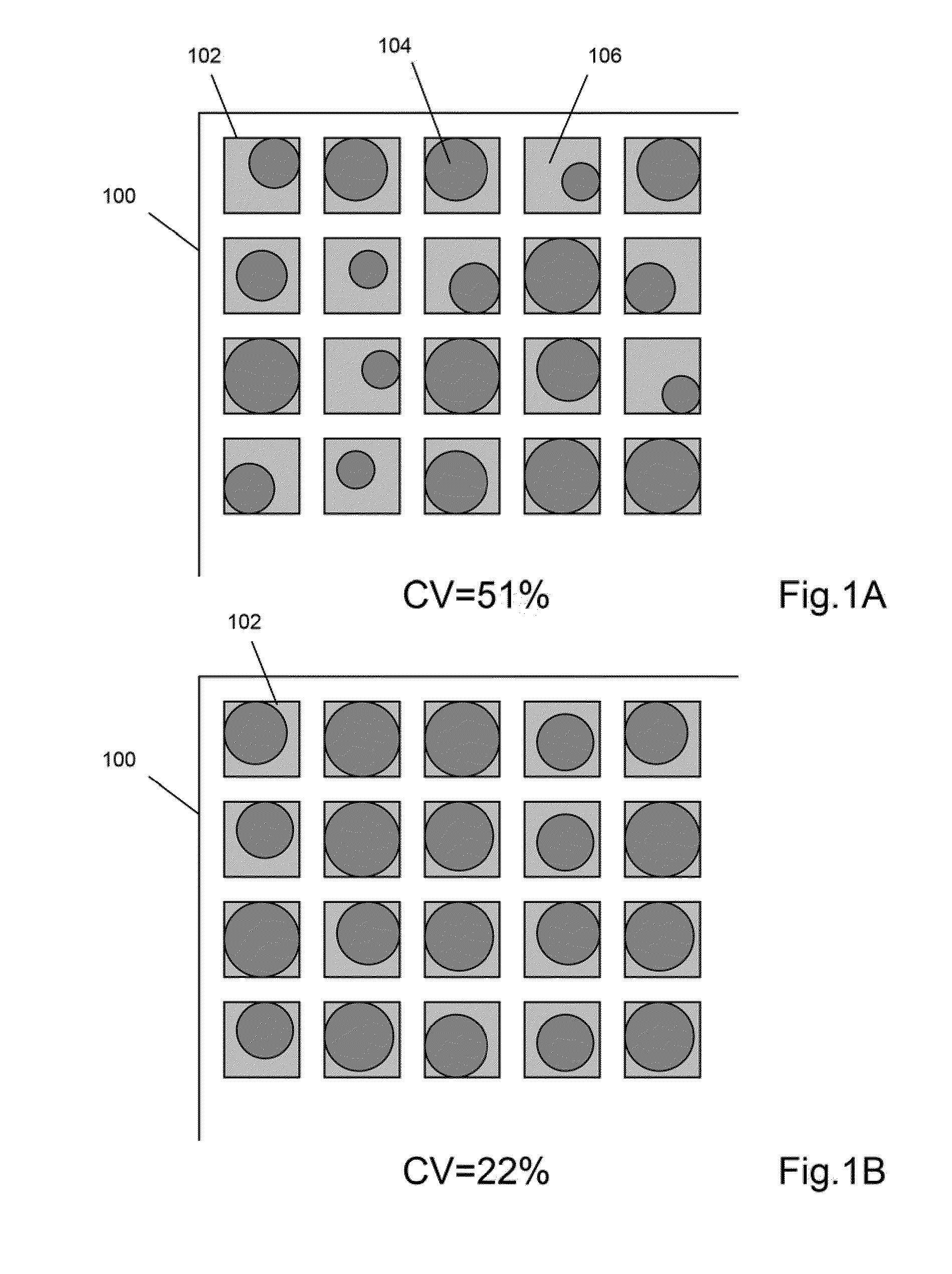
Scaffolded nucleic acid polymer particles and methods of making and using
ActiveUS20100304982A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsParticle compositionPolynucleotide
The invention provides particle compositions having applications in nucleic acid analysis. Nucleic acid polymer particles of the invention allow polynucleotides to be attached throughout their volumes for higher loading capacities than those achievable solely with surface attachment. In one aspect, nucleic acid polymer particles of the invention comprise polyacrylamide particles with uniform size distributions having low coefficients of variations, which result in reduced particle-to-particle variation in analytical assays. Such particle compositions are used in various amplification reactions to make amplicon libraries from nucleic acid fragment libraries.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Support for high performance affinity chromatography and other uses
Multilayered particulate materials are formed by coating a particulate substrate with a metal and adsorbing an organic layer comprising a recognition moiety onto the metal film. The recognition moiety interacts with an analyte of interest allowing for its detection, purification, etc. Suitable recognition moieties can be selected from a range of species including, small molecules, polymers and biomolecules and the like. The novel particulate materials of the invention can be utilized in an array of methods including, ion-exchange, ion-selective ion-exchange, assays, affinity dialysis, size exclusion dialysis, as supports in solid phase synthesis, combinatorial synthesis and screening of compound libraries and the like.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods and agents for screening for compounds capable of modulating gene expression
InactiveUS20050048549A1Modulate expressionLibrary screeningTissue cultureRegulator geneProtein level
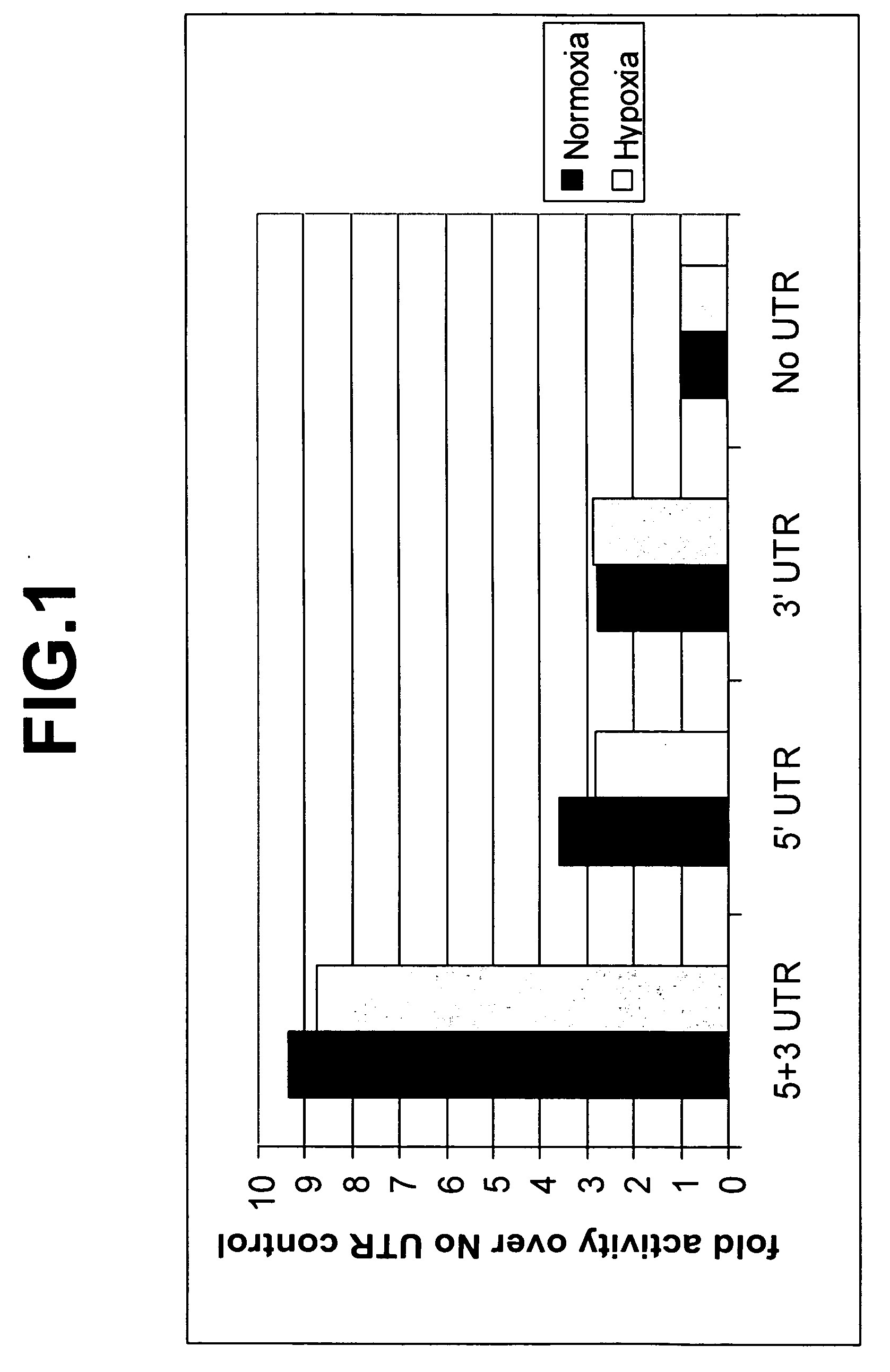
The invention relates to the fields of screening assays, compounds, and methods for altering gene expression and protein levels. In particular, the invention includes assays to screen for agents capable of modulating gene expression in a UTR-dependent manner and agents capable of modulating gene expression.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Modified Molecular Arrays
InactiveUS20110059865A1Less reactiveAccelerated programSequential/parallel process reactionsNucleotide librariesMolecular array(Hydroxyethyl)methacrylate
The invention relates to the preparation of a hydrogel surface useful in the formation and manipulation of arrays of molecules, particularly polynucleotides and to the chemical modification of these and other arrays. In particular, the invention relates to a method of preparing a hydrogel immobilised to a solid support comprising polymerising on the support a mixture of a first comonomer which is acrylamide, methacrylamide, hydroxyethyl methacrylate or N-vinyl pyrrolidinone and a second comonomer which is a functionalised acrylamide or acrylate.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Novel proteins with targeted binding
InactiveUS20050089932A1Stimulate and inhibit activityEasy screeningPeptide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsMonomerComputational biology
Methods for identifying discrete monomer domains and immuno-domains with a desired property are provided. Methods for generating multimers from two or more selected discrete monomer domains are also provided, along with methods for identifying multimers possessing a desired property. Presentation systems are also provided which present the discrete monomer and / or immuno-domains, selected monomer and / or immuno-domains, multimers and / or selected multimers to allow their selection. Compositions, libraries and cells that express one or more library member, along with kits and integrated systems, are also included in the present invention.
Owner:AMGEN MOUNTAIN VIEW
Droplet Libraries
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Methods of Analyzing Nucleic Acids from Individual Cells or Cell Populations
InactiveUS20150376609A1Facilitate hybridizationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationReagentNucleic acid
Methods, compositions and systems for analyzing individual cells or cell populations through the partitioned analysis of contents of individual cells or cell populations. Individual cells or cell populations are co-partitioned with processing reagents for accessing cellular contents, and for uniquely identifying the contents of a given cell or cell population, and subsequently analyzing the cell's contents and characterizing it as having derived from an individual cell or cell population, including analysis and characterization of the cell's nucleic acids through sequencing.
Owner:10X GENOMICS
Microfluidic Devices and Methods of Use in The Formation and Control of Nanoreactors
InactiveUS20100137163A1Material nanotechnologyCompound screeningHigh-Throughput Screening AssaysEmulsion
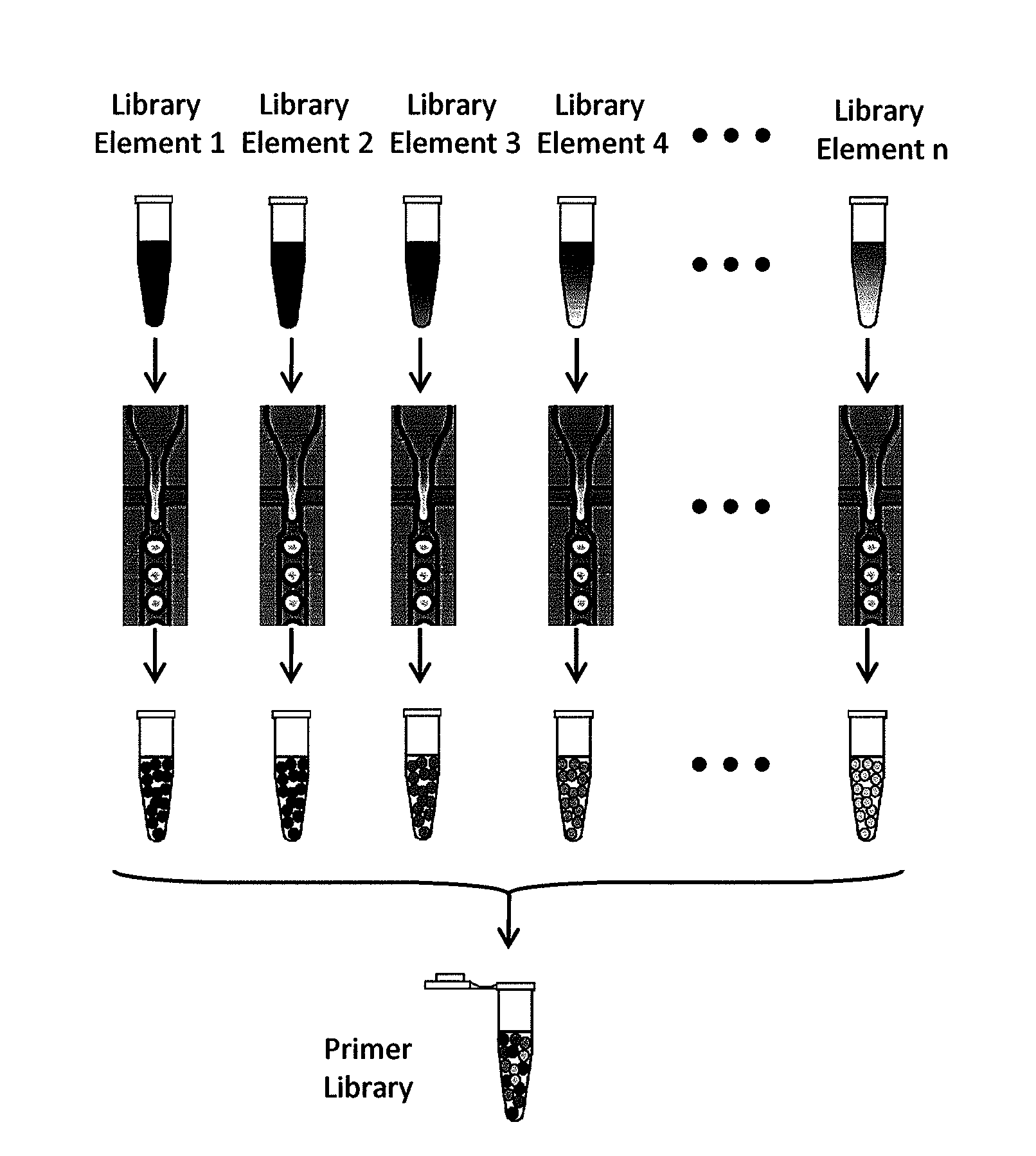
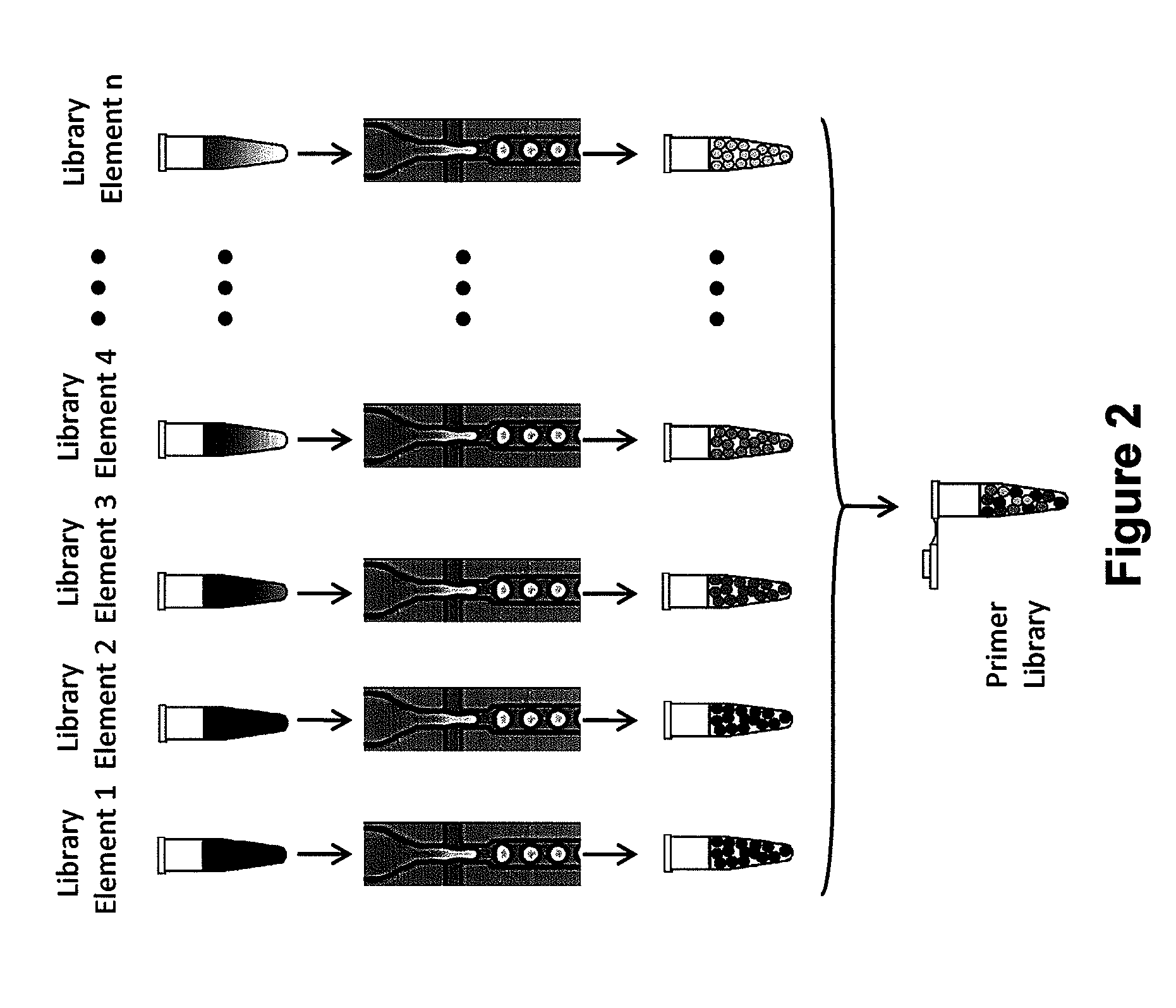
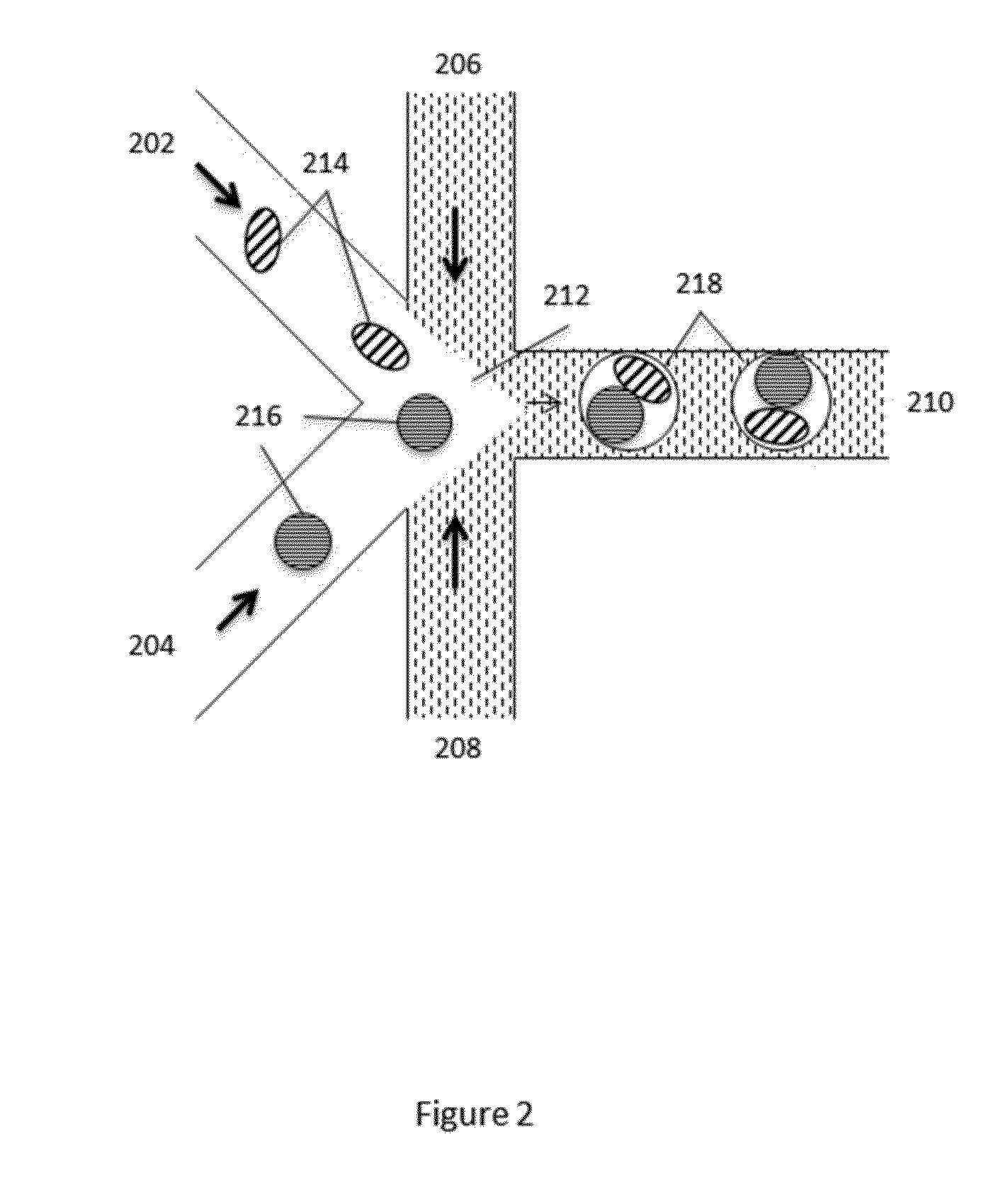
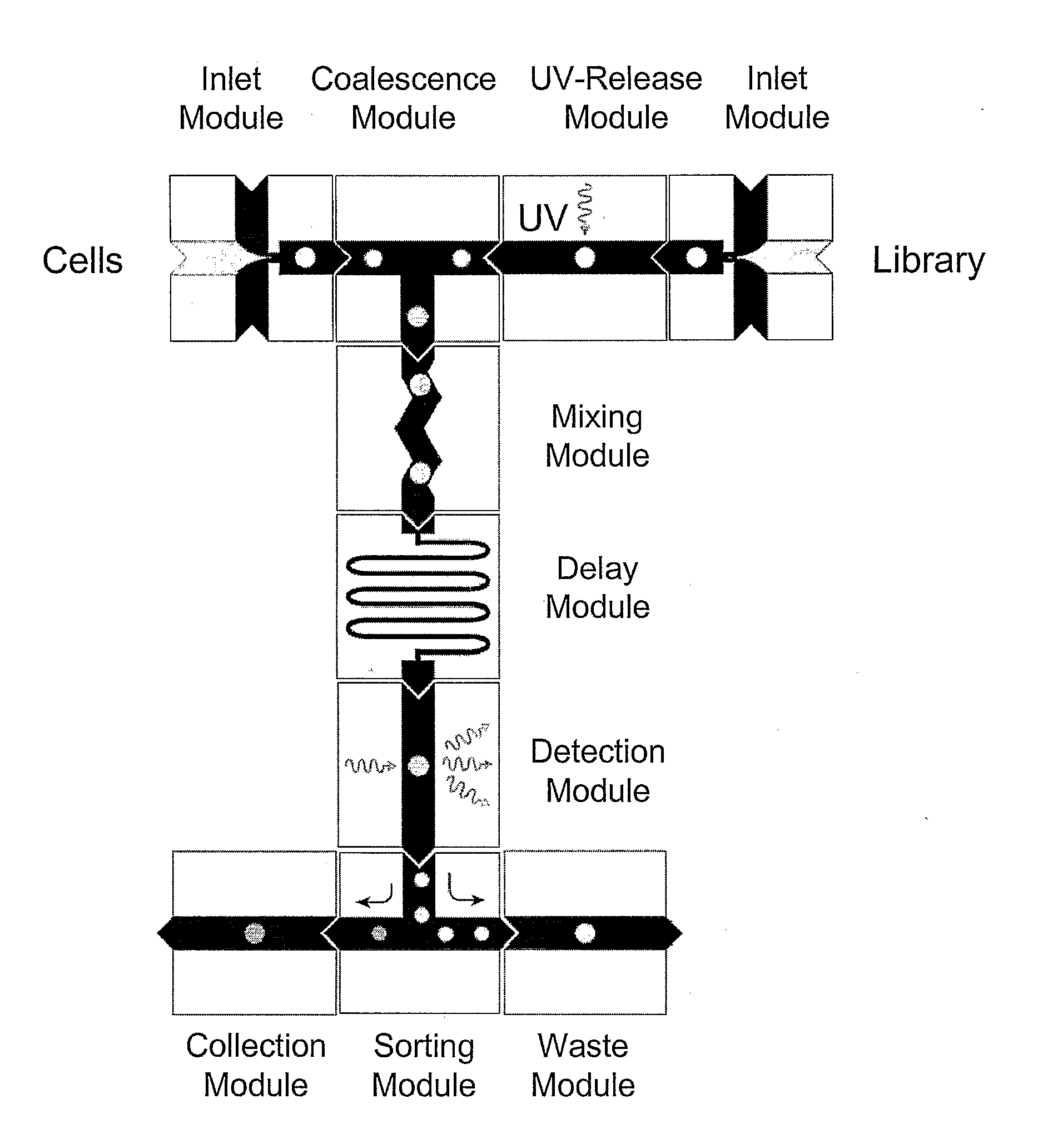
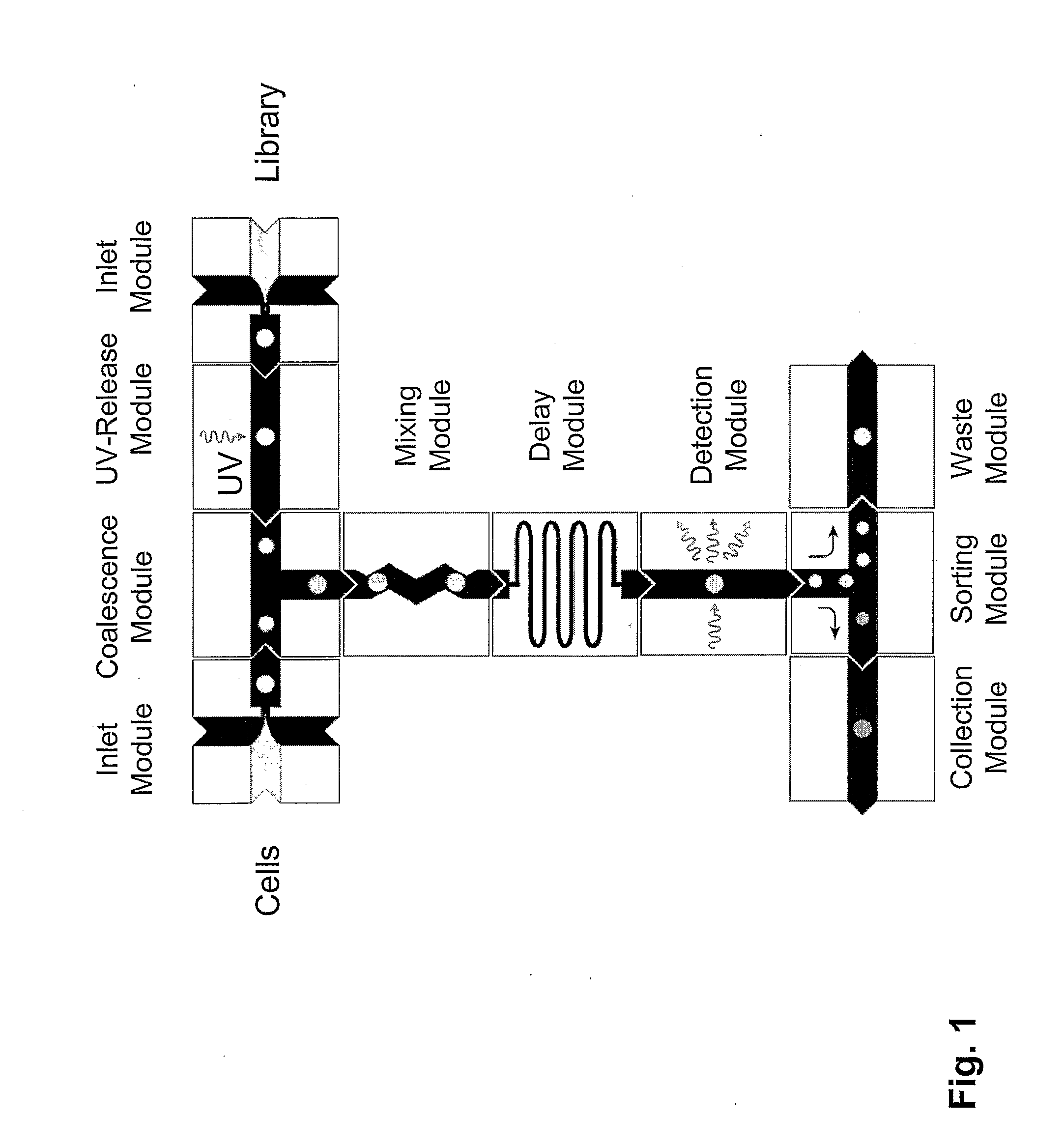
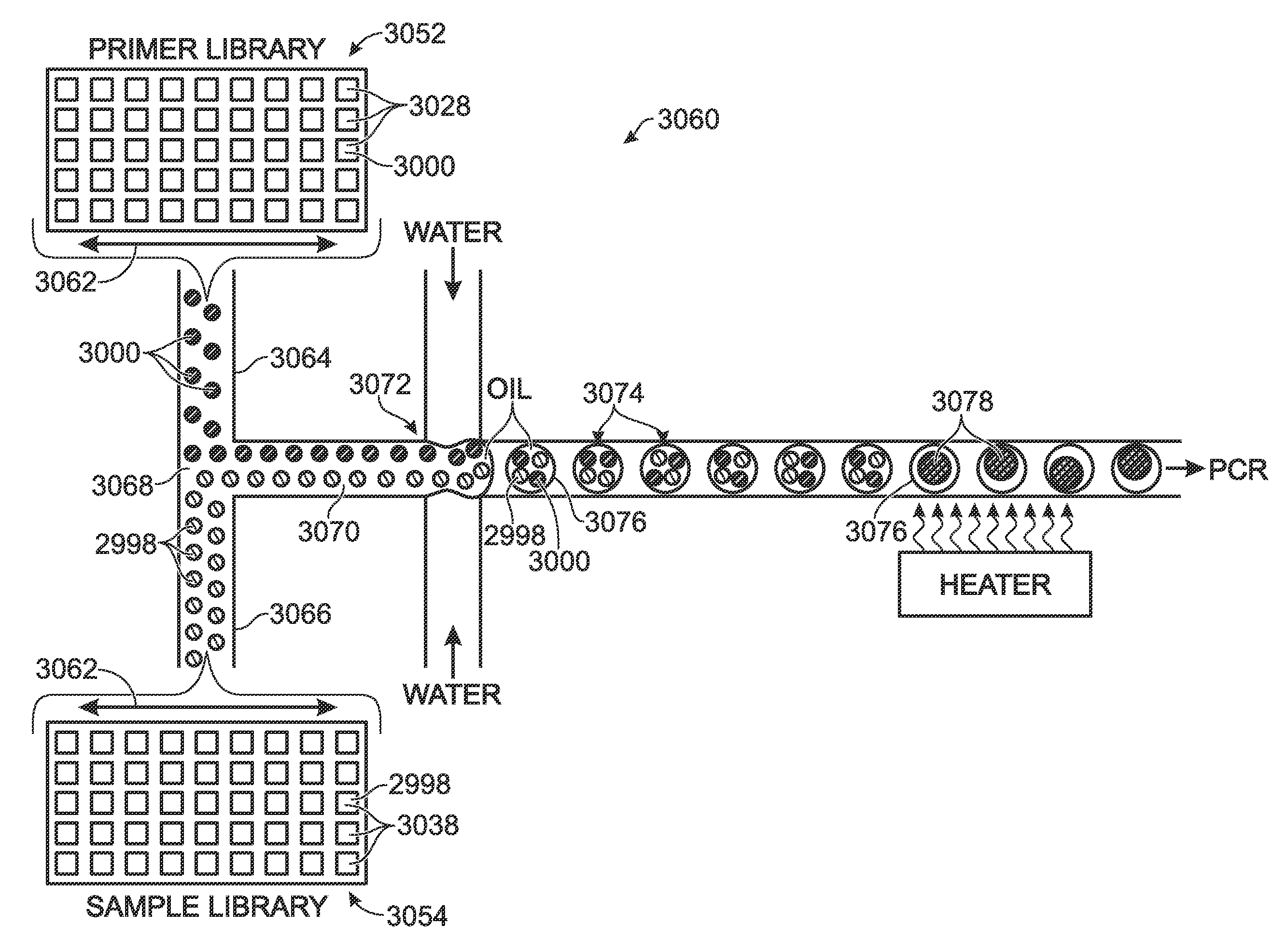
The present invention provides novel microfluidic devices and methods that are useful for performing high-throughput screening assays and combinatorial chemistry. Such methods can include labeling a library of compounds by emulsifying aqueous solutions of the compounds and aqueous solutions of unique liquid labels on a microfluidic device, which includes a plurality of electrically addressable, channel bearing fluidic modules integrally arranged on a microfabricated substrate such that a continuous channel is provided for flow of immiscible fluids, whereby each compound is labeled with a unique liquid label, pooling the labeled emulsions, coalescing the labeled emulsions with emulsions containing a specific cell or enzyme, thereby forming a nanoreactor, screening the nanoreactors for a desirable reaction between the contents of the nanoreactor, and decoding the liquid label, thereby identifying a single compound from a library of compounds.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Methods for making nucleotide probes for sequencing and synthesis
ActiveUS20090099041A1Increase the number ofGuaranteed economic efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideBiology
Compositions and methods for making a plurality of probes for analyzing a plurality of nucleic acid samples are provided. Compositions and methods for analyzing a plurality of nucleic acid samples to obtain sequence information in each nucleic acid sample are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods for making character strings, polynucleotides and polypeptides having desired characteristics
InactiveUS7024312B1Simplifies overall synthesis strategyLow levelPeptide/protein ingredientsBiostatisticsPolynucleotideIn silico
“In silico” nucleic acid recombination methods, related integrated systems utilizing genetic operators and libraries made by in silico shuffling methods are provided.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Stabilized polypeptide compositions
ActiveUS20080050370A1Improved polypeptide compositionImprove methodPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCrystallographyPolypeptide composition
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Compartmentalised screening by microfluidic control
InactiveUS20050221339A1Rapid and high-throughput screeningLow costCompound screeningSequential/parallel process reactionsCompound (substance)Drug development
The invention describes a method for the identification of compounds which bind to a target component of a biochemical system or modulate the activity of the target, comprising the steps of: a) compartmentalising the compounds into microcapsules together with the target, such that only a subset of the repertoire is represented in multiple copies in any one microcapsule; and b) identifying the compound which binds to or modulates the activity of the target; wherein at least one step is performed under microfluidic control. The invention enables the screening of large repertoires of molecules which can serve as leads for drug development.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Method of preparing libraries of template polynucleotides
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a library of template polynucleotides and use thereof in methods of solid-phase nucleic acid amplification. More specifically, the invention relates to a method for preparing a library of template polynucleotides that have common sequences at their 5′ ends and at their 3′ ends.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Methods for generating amplified nucleic acid arrays
InactiveUS20080242560A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
The present invention relates to methods for generating an array of amplified nucleic acid sequences. The methods can utilize amplicons that form nucleic acid balls that can be arrayed on a solid support. The invention additionally provides methods for obtaining targeted nucleic acid sequences.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Antibody specificity transfer using minimal essential binding determinants
The present invention provides methods of making antibodies having the binding specificity of a reference antibody. Antibodies generated by the methods of the inventions have at least one minimal essential binding specificity determinant from a heavy chain or light chain CDR3 from the reference antibody. The method can be used, e.g., in humanization procedures. The invention also provides libraries and antibodies made in accordance with the methods.
Owner:HUMANIGEN INC
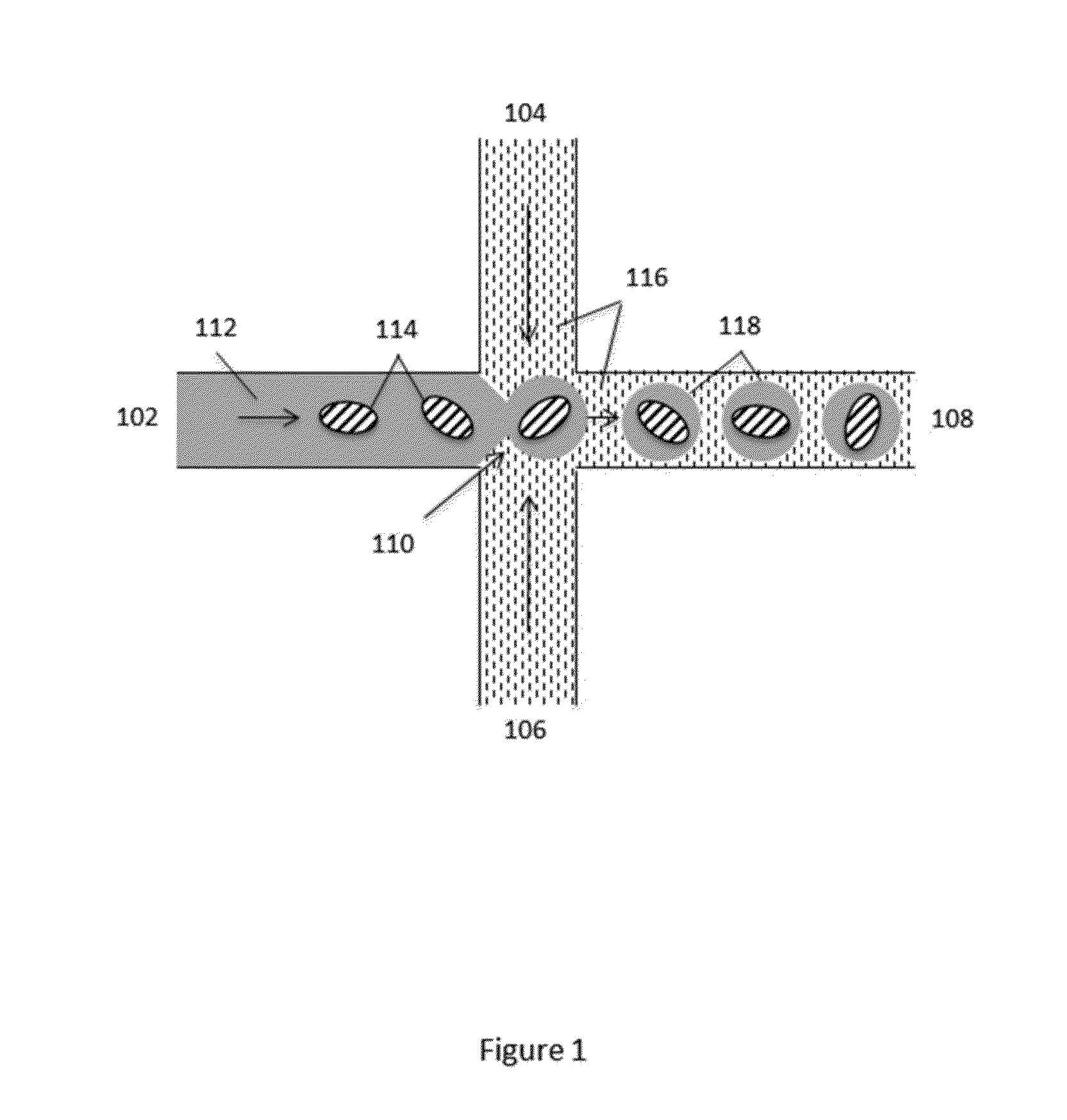
Oligonucleotide arrays and their use for sorting, isolating, sequencing, and manipulating nucleic acids
InactiveUS6322971B1Increase in hybridization specificityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyHybridization ArrayBioinformatics
Ligation methods for manipulating nucleic acid stands and oligonucleotides utilizing hybridization arrays of immobilized oligonucleotides. The oligonucleotide arrays may be plain or sectioned, comprehensive or non-comprehensive. The immobilized oligonucleotides may in some cases be binary oligonucleotides having constant as well as variable segments. Some embodiments include amplification of ligated products.
Owner:UNIV OF MEDICINE & DENTISTRY OF NEW JERSEY
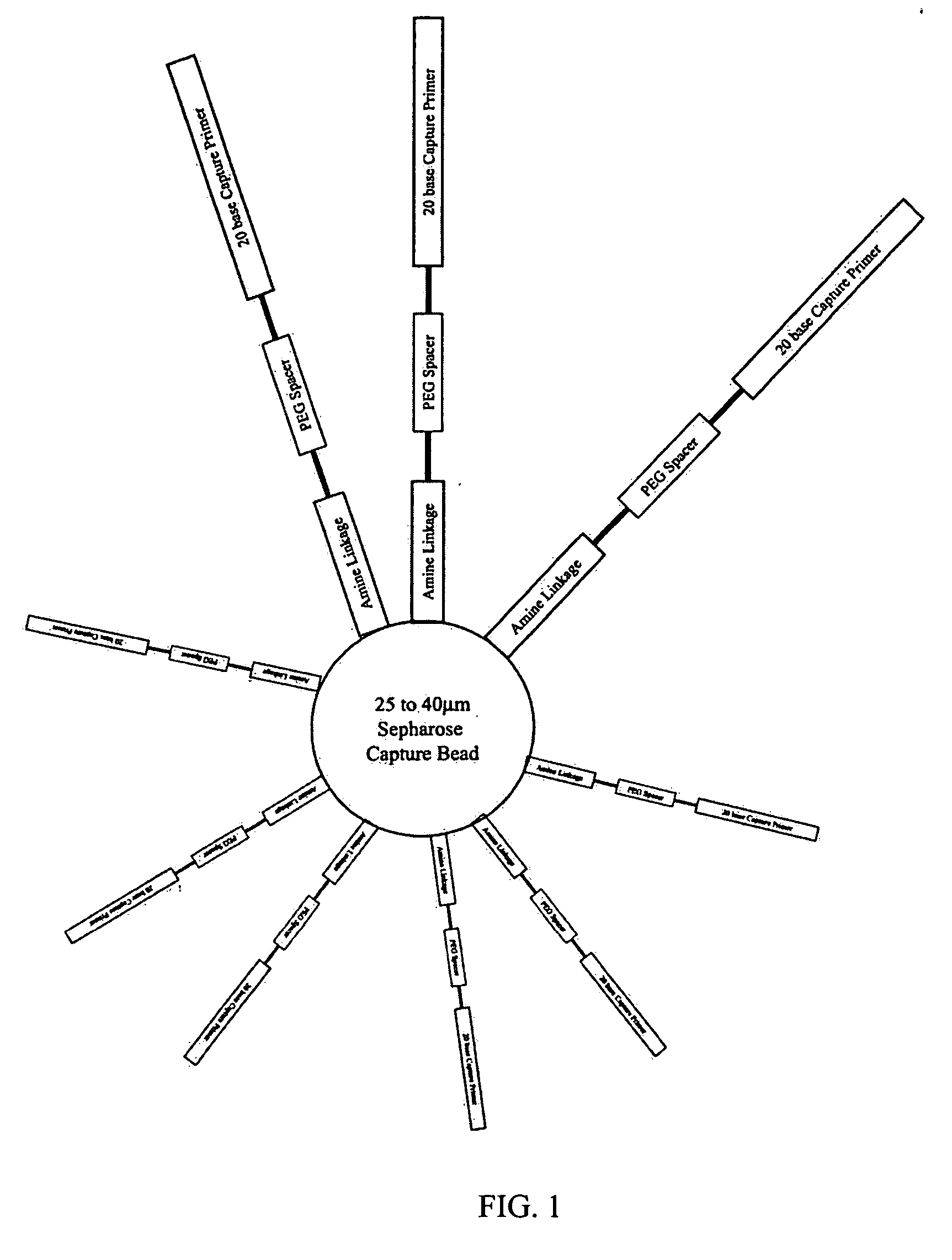
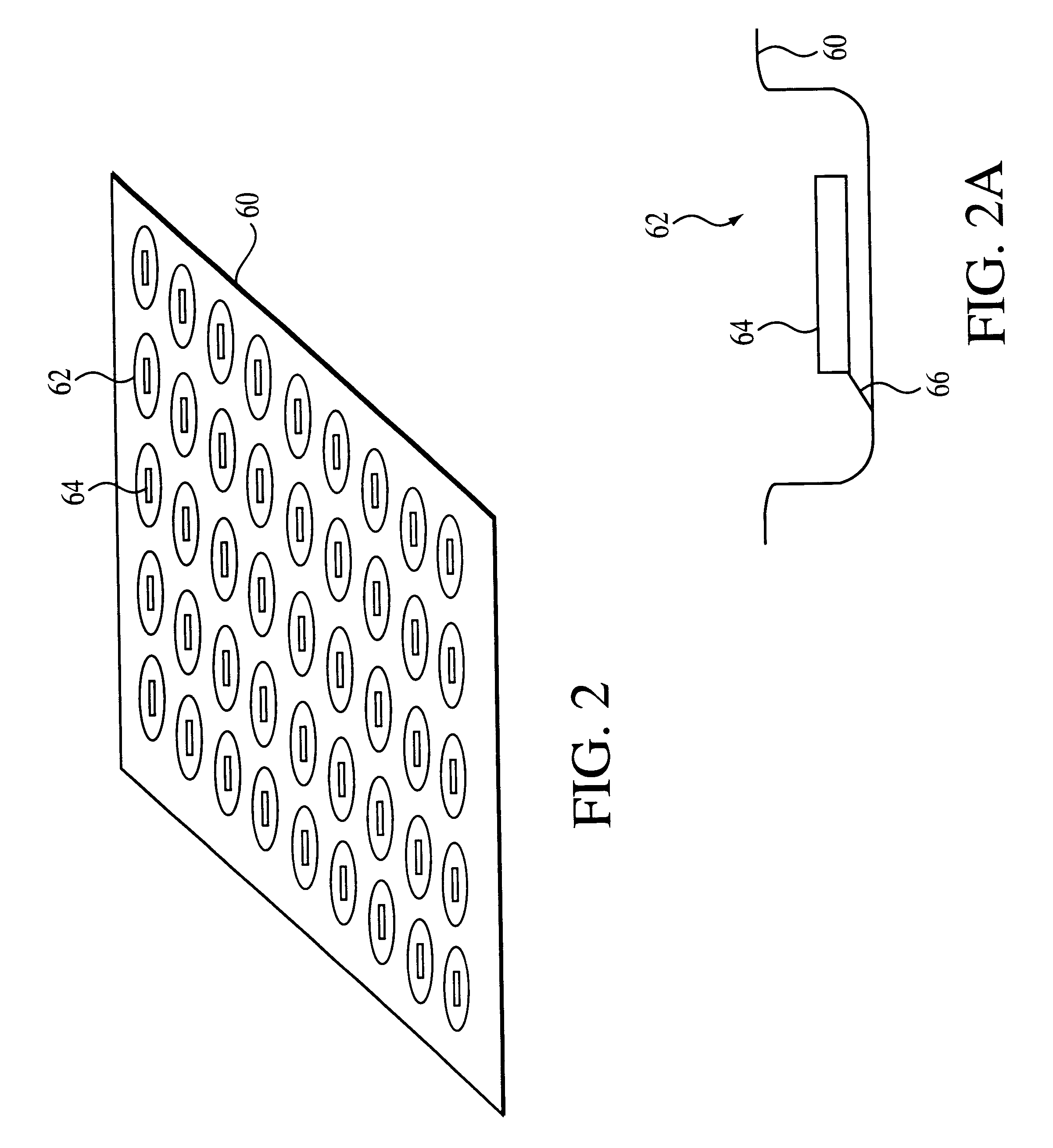
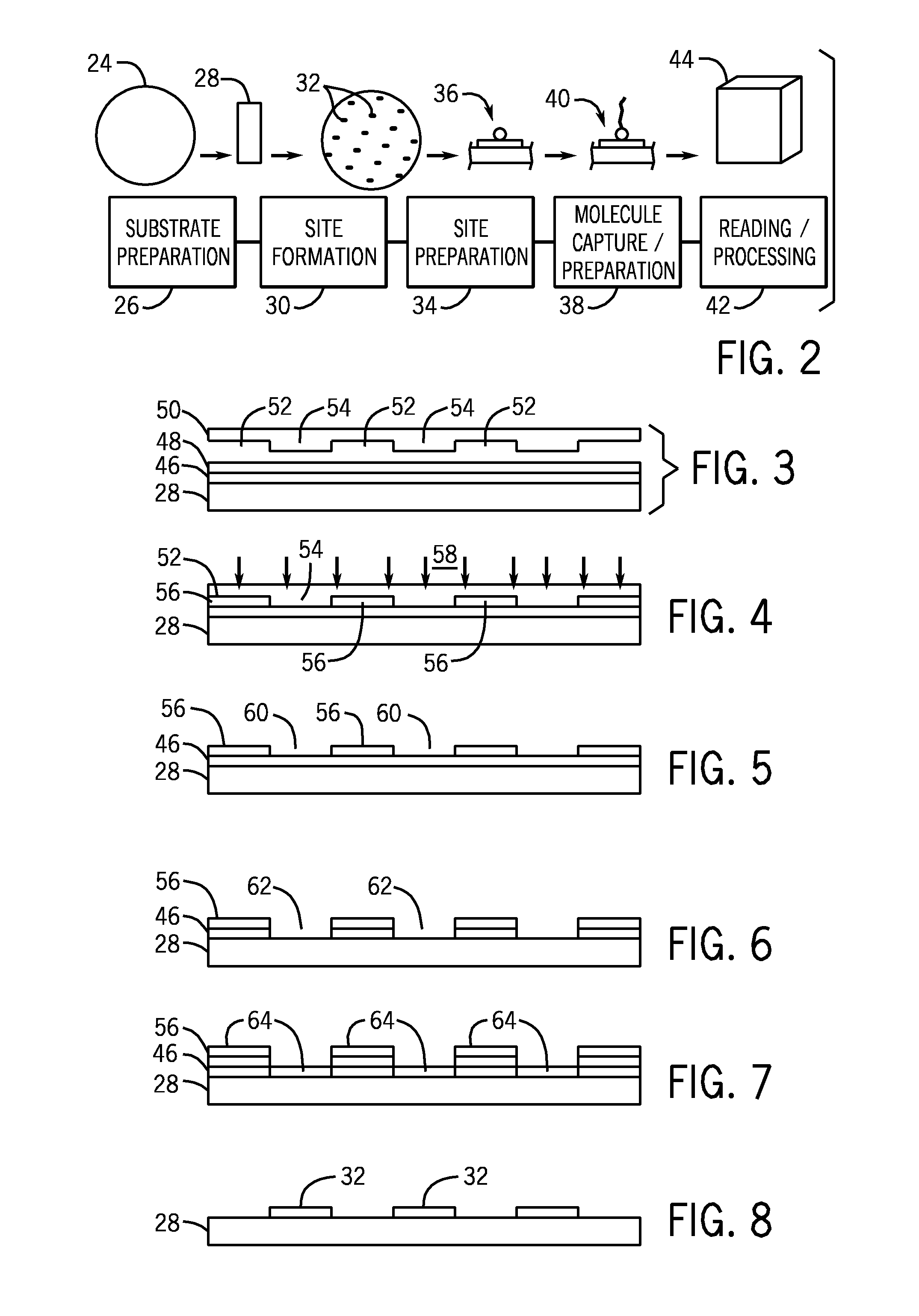
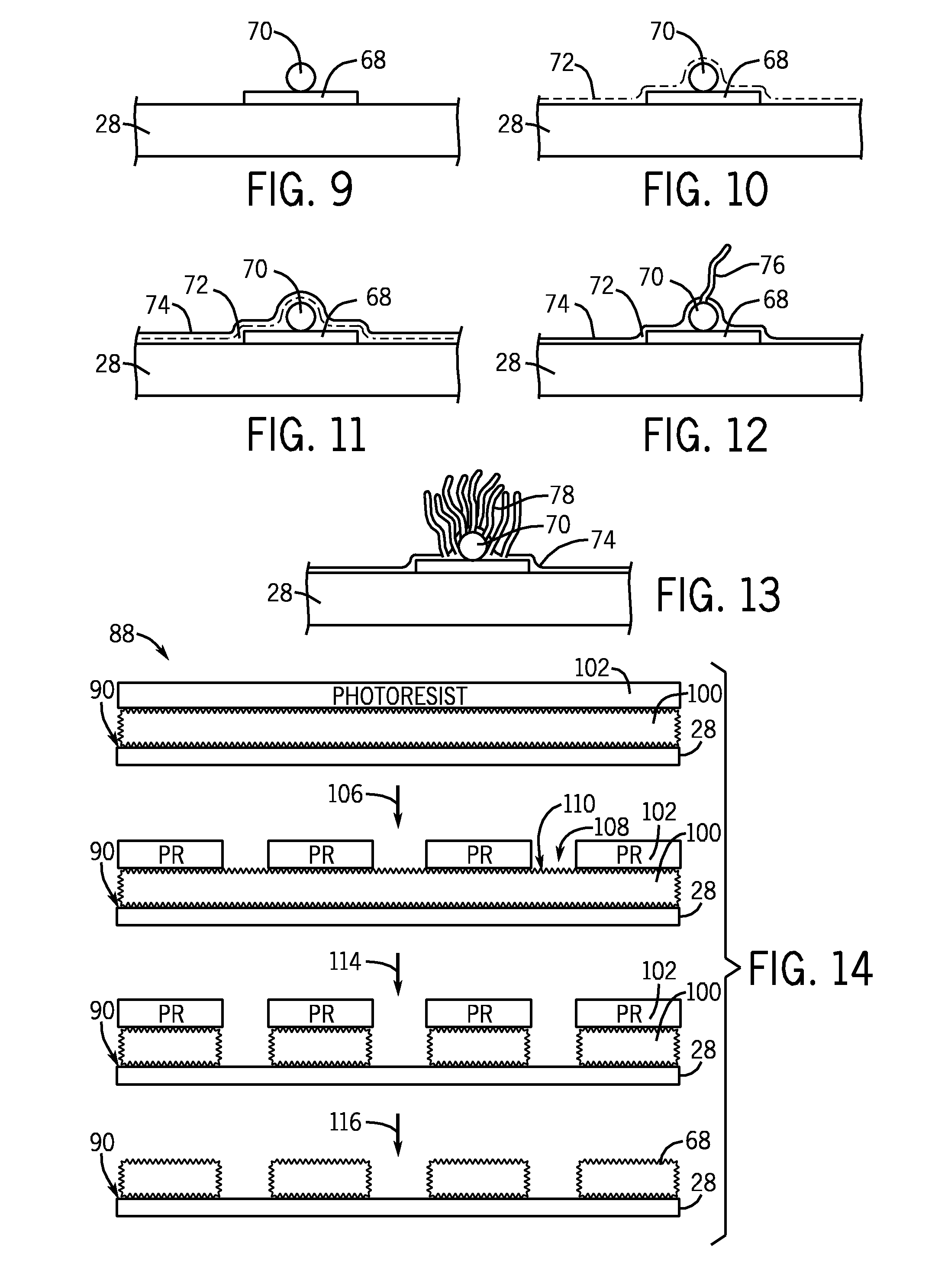
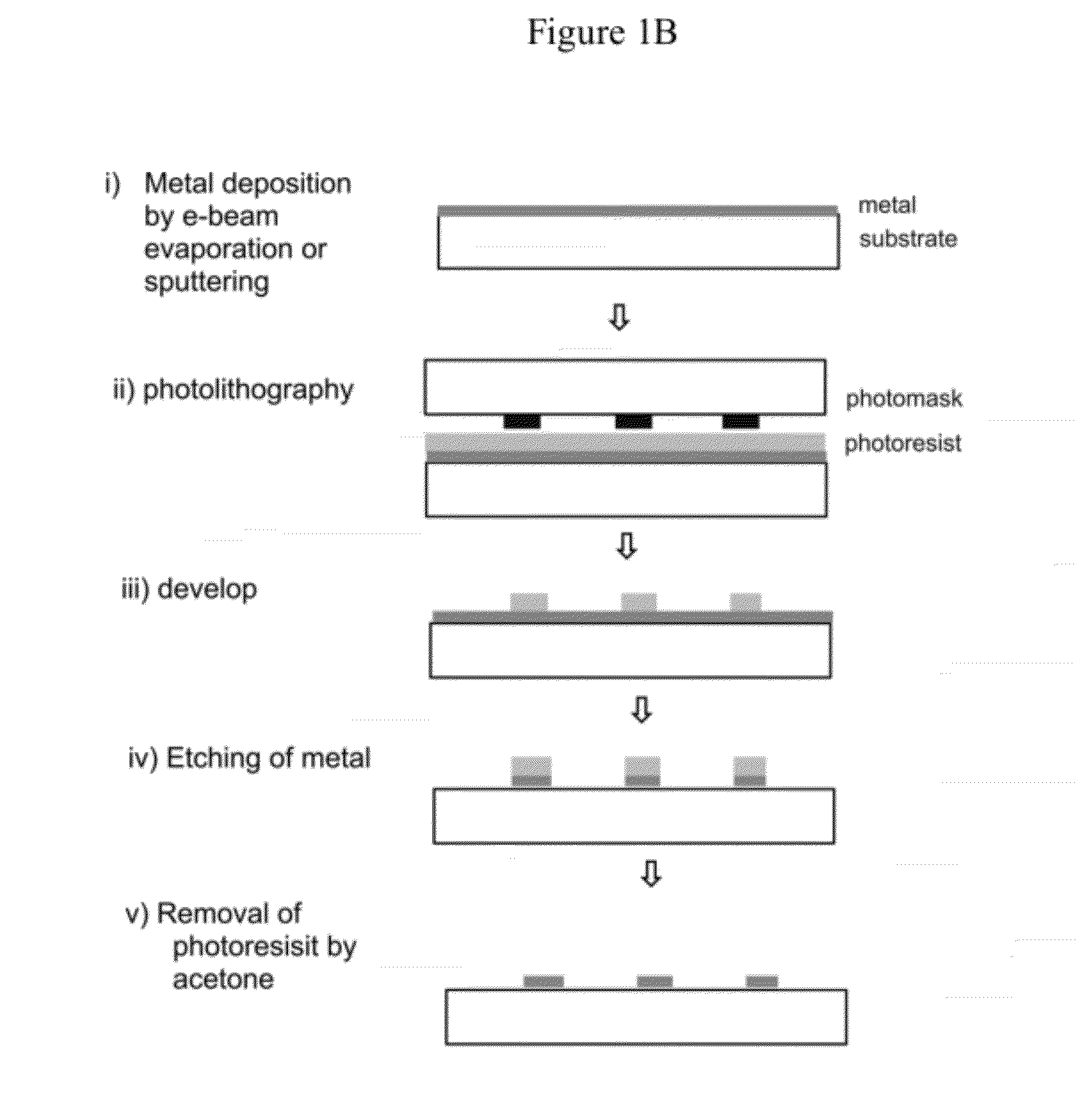
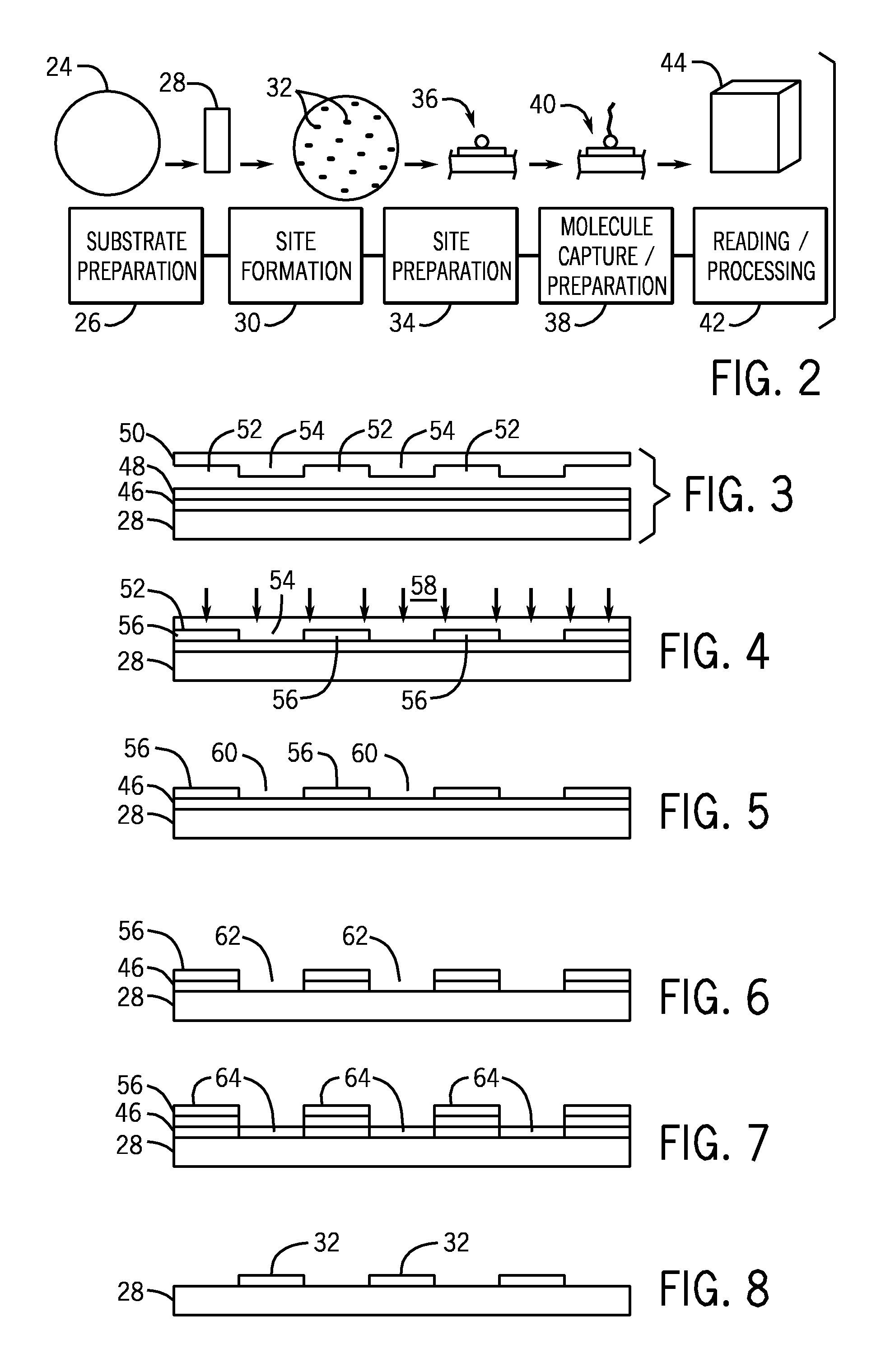
Microarray fabrication system and method
A microarray is designed capture one or more molecules of interest at each of a plurality of sites on a substrate. The sites comprise base pads, such as polymer base pads, that promote the attachment of the molecules at the sites. The microarray may be made by one or more patterning techniques to create a layout of base pads in a desired pattern. Further, the microarrays may include features to encourage clonality at the sites.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
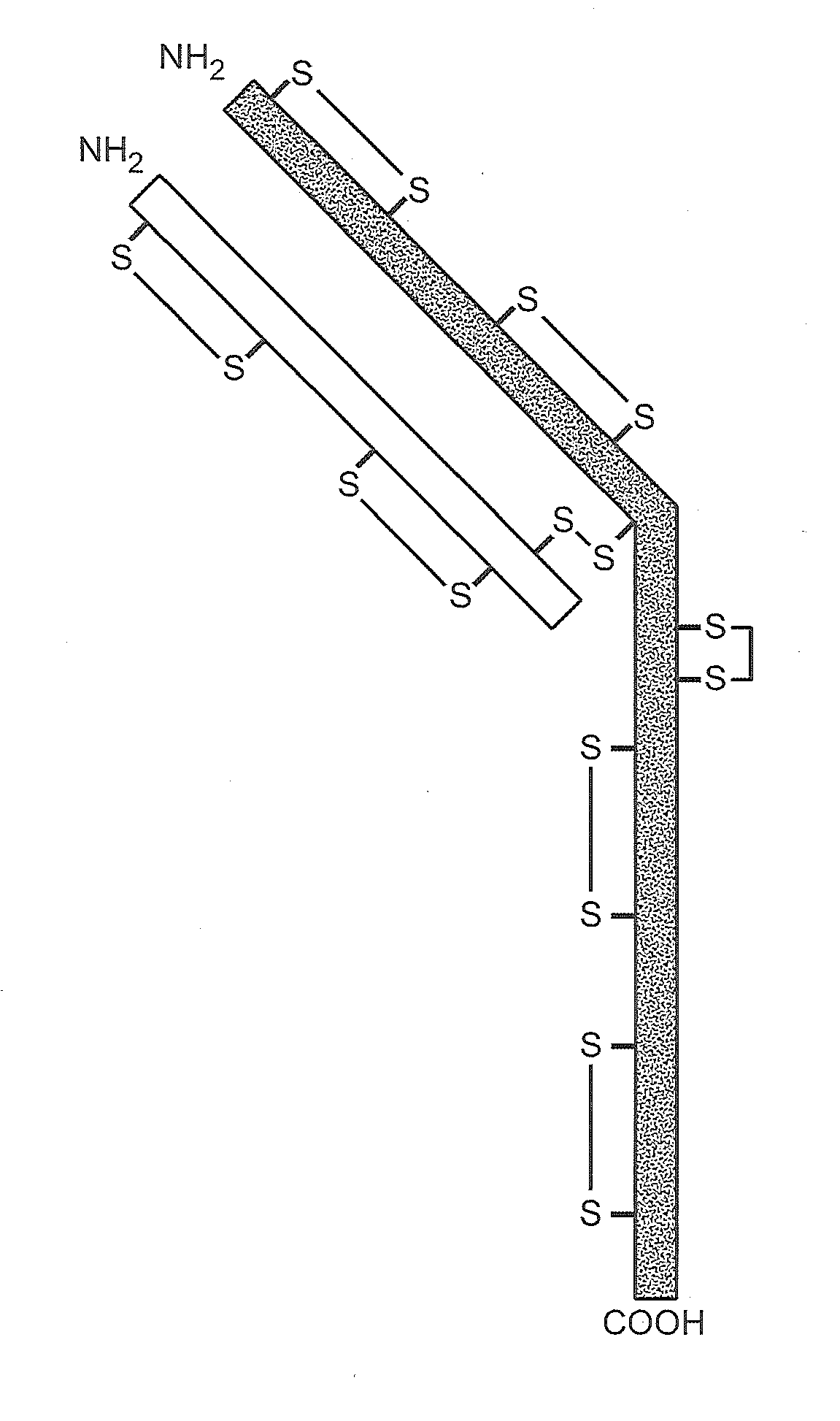
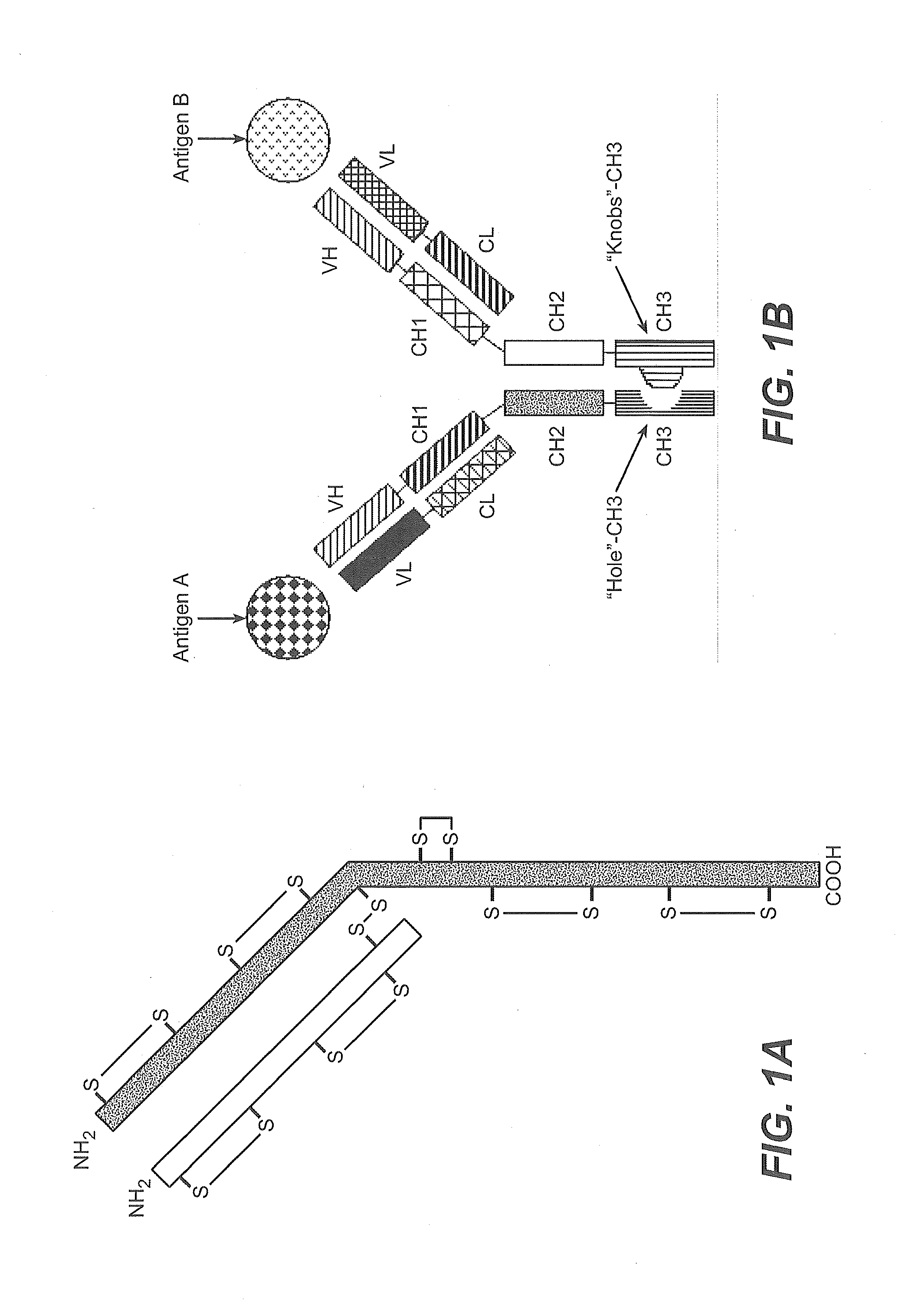
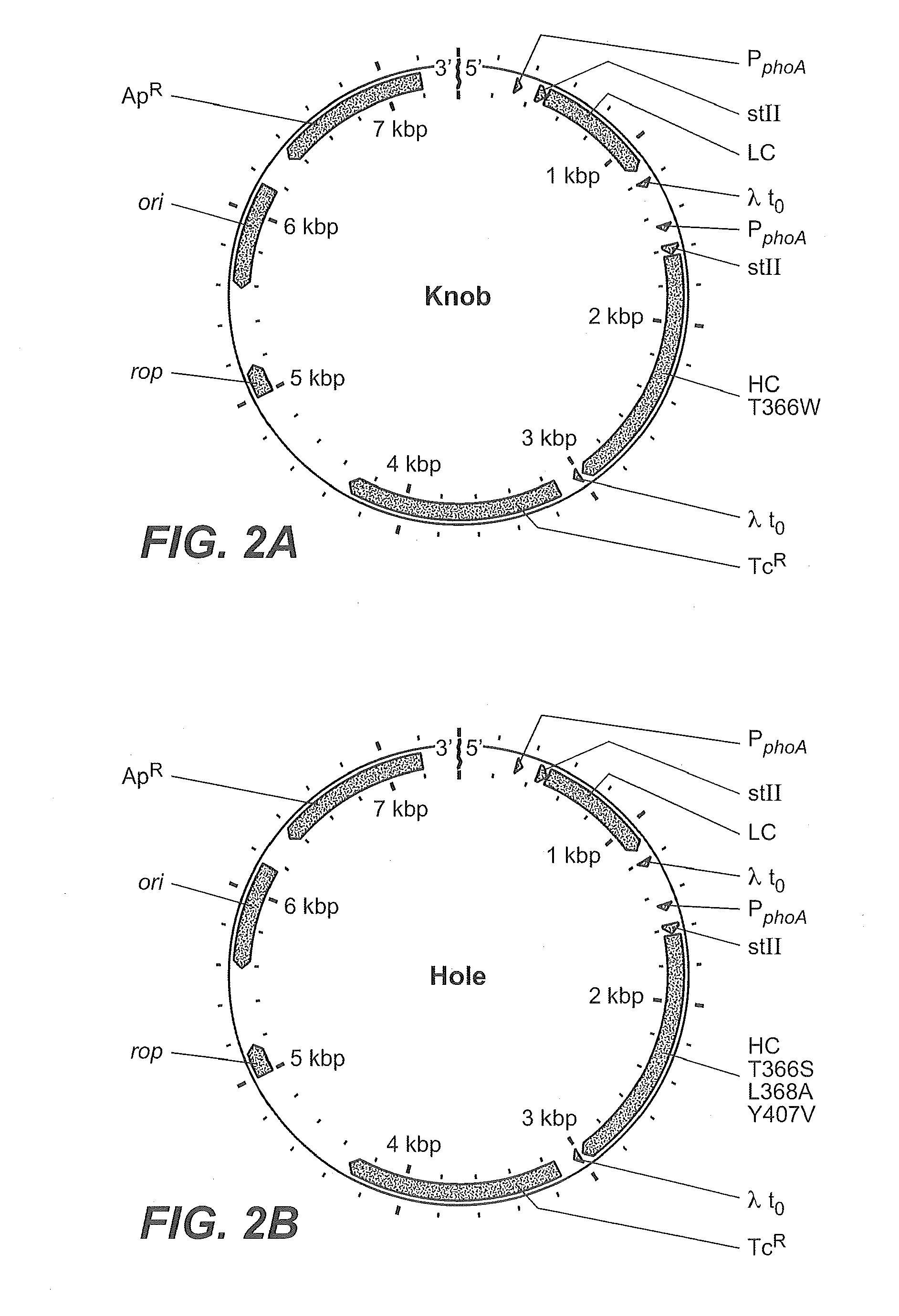
Production of Heteromultimeric Proteins
ActiveUS20110287009A1Reduction in yieldDecreased/elimination of effector functionAntipyreticAnalgesicsEpitopeBiochemistry
Described herein are methods for the efficient production of antibodies and other multimeric protein complexes (collectively referred to herein as heteromultimeric proteins) capable of specifically binding to more than one target. The targets may be, for example, different epitopes on a single molecule or located on different molecules. The methods combine efficient, high gene expression level, appropriate assembly, and ease of purification for the heteromultimeric proteins. The invention also provides methods of using these heteromultimeric proteins, and compositions, kits and articles of manufacture comprising these antibodies.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Nucleic acid encoding reactions
ActiveUS20130005585A1Avoid substantial annealingNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideBarcode
Described herein are methods useful for incorporating one or more adaptors and / or nucleotide tag(s) and / or barcode nucleotide sequence(s) one, or typically more, target nucleotide sequences. In particular embodiments, nucleic acid fragments having adaptors, e.g., suitable for use in high-throughput DNA sequencing are generated. In other embodiments, information about a reaction mixture is encoded into a reaction product. Also described herein are methods and kits useful for amplifying one or more target nucleic acids in preparation for applications such as bidirectional nucleic acid sequencing. In particular embodiments, methods of the invention entail additionally carrying out bidirectional DNA sequencing. Also described herein are methods for encoding and detecting and / or quantifying alleles by primer extension.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
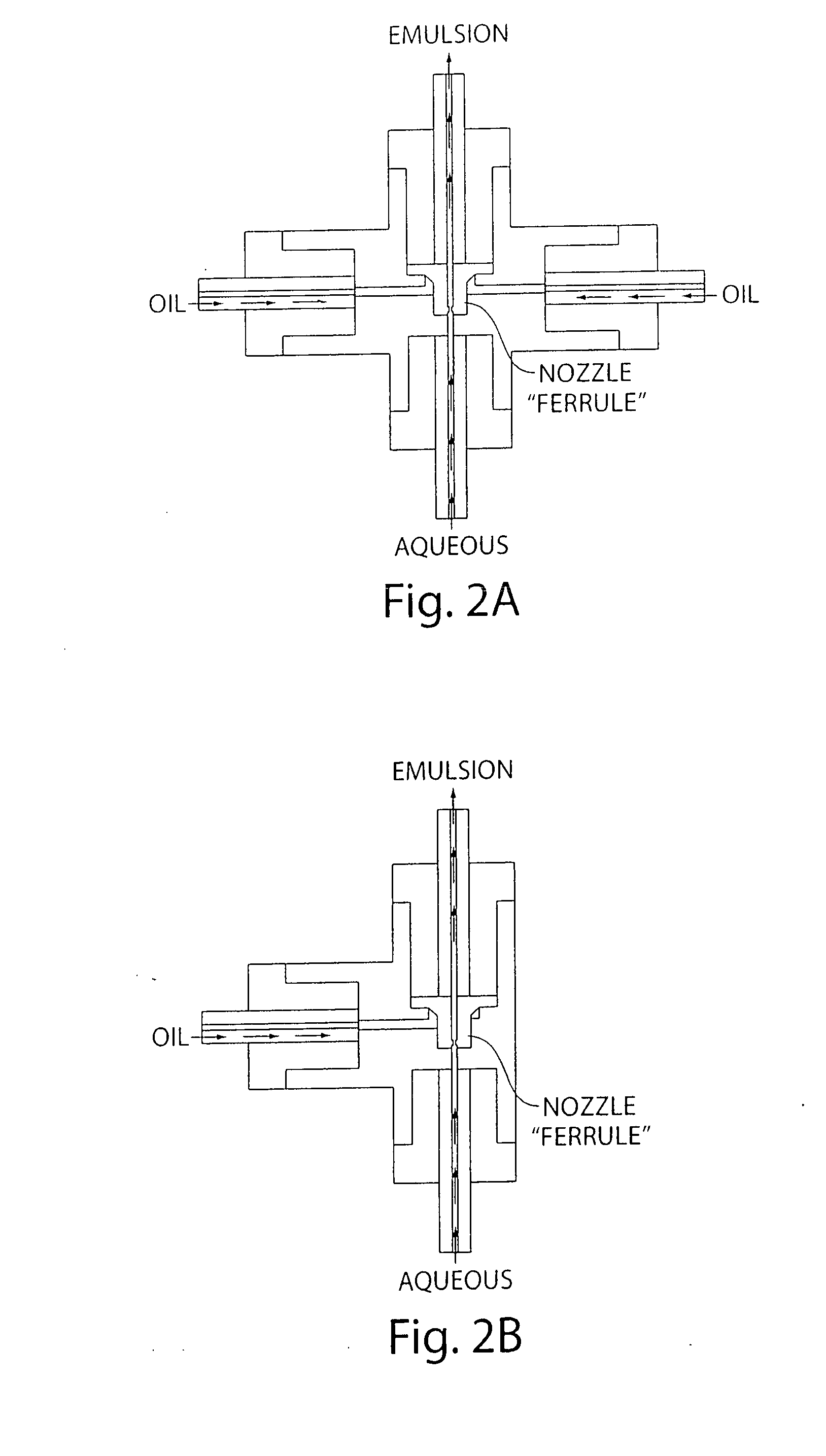
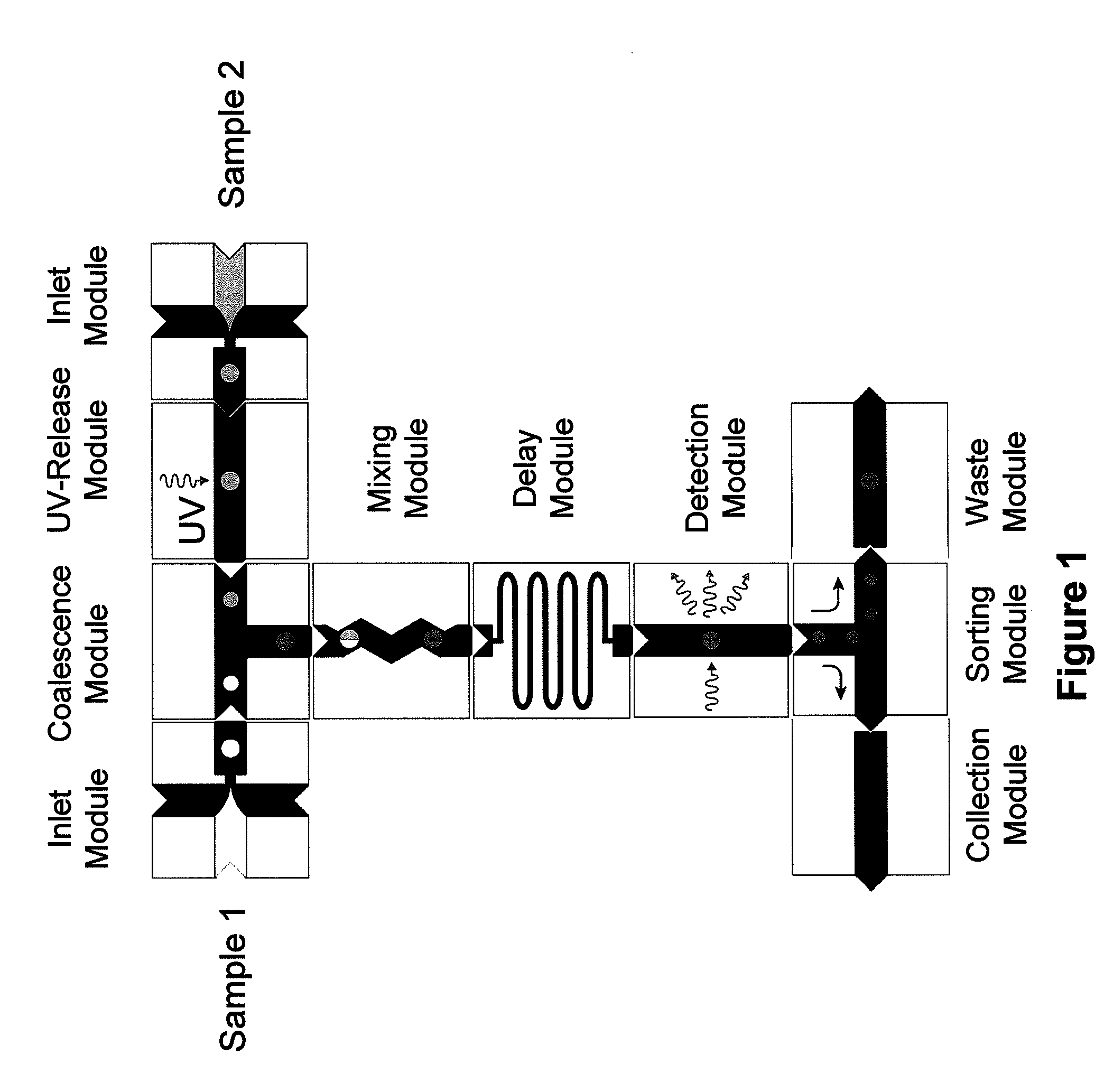
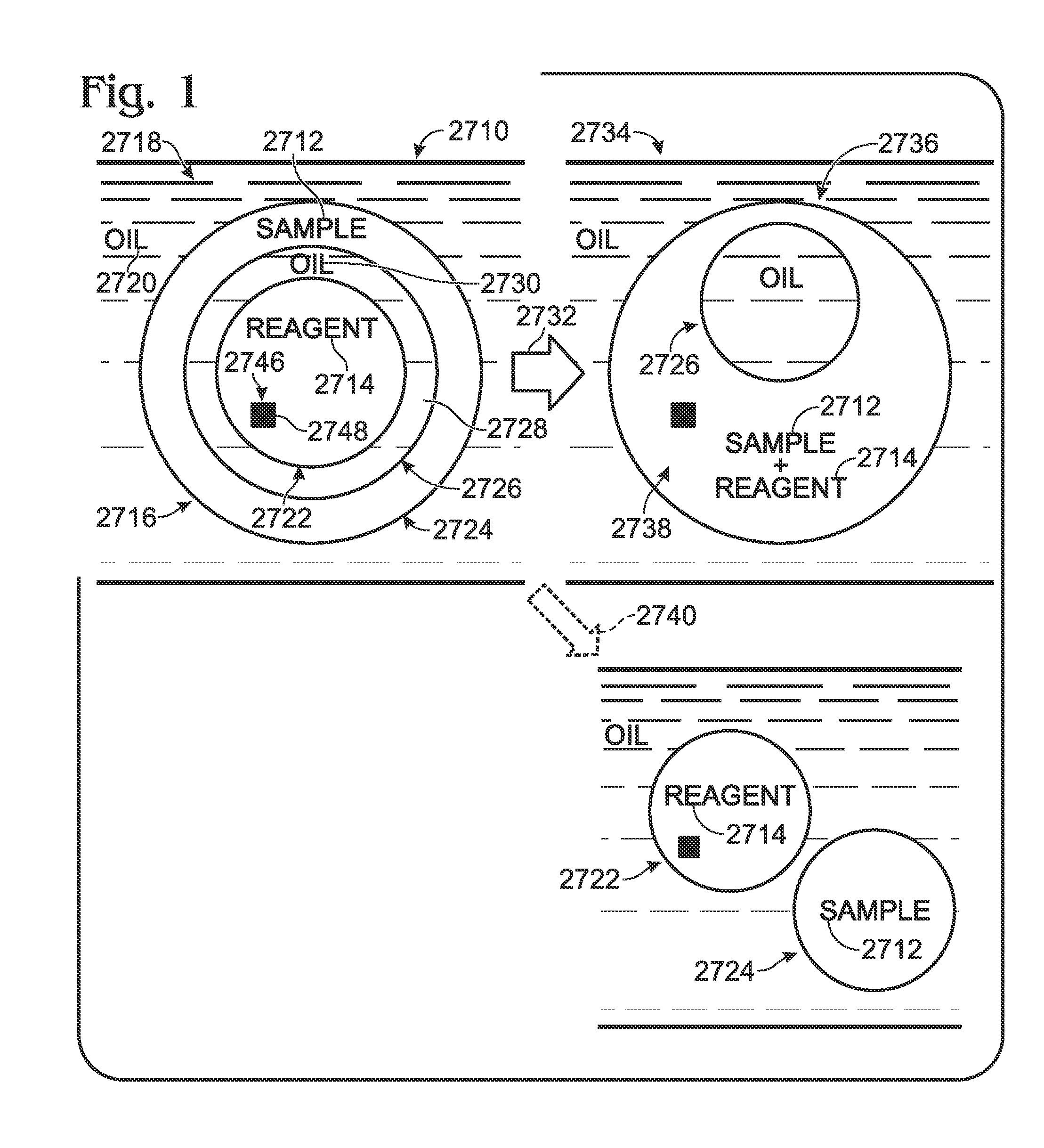
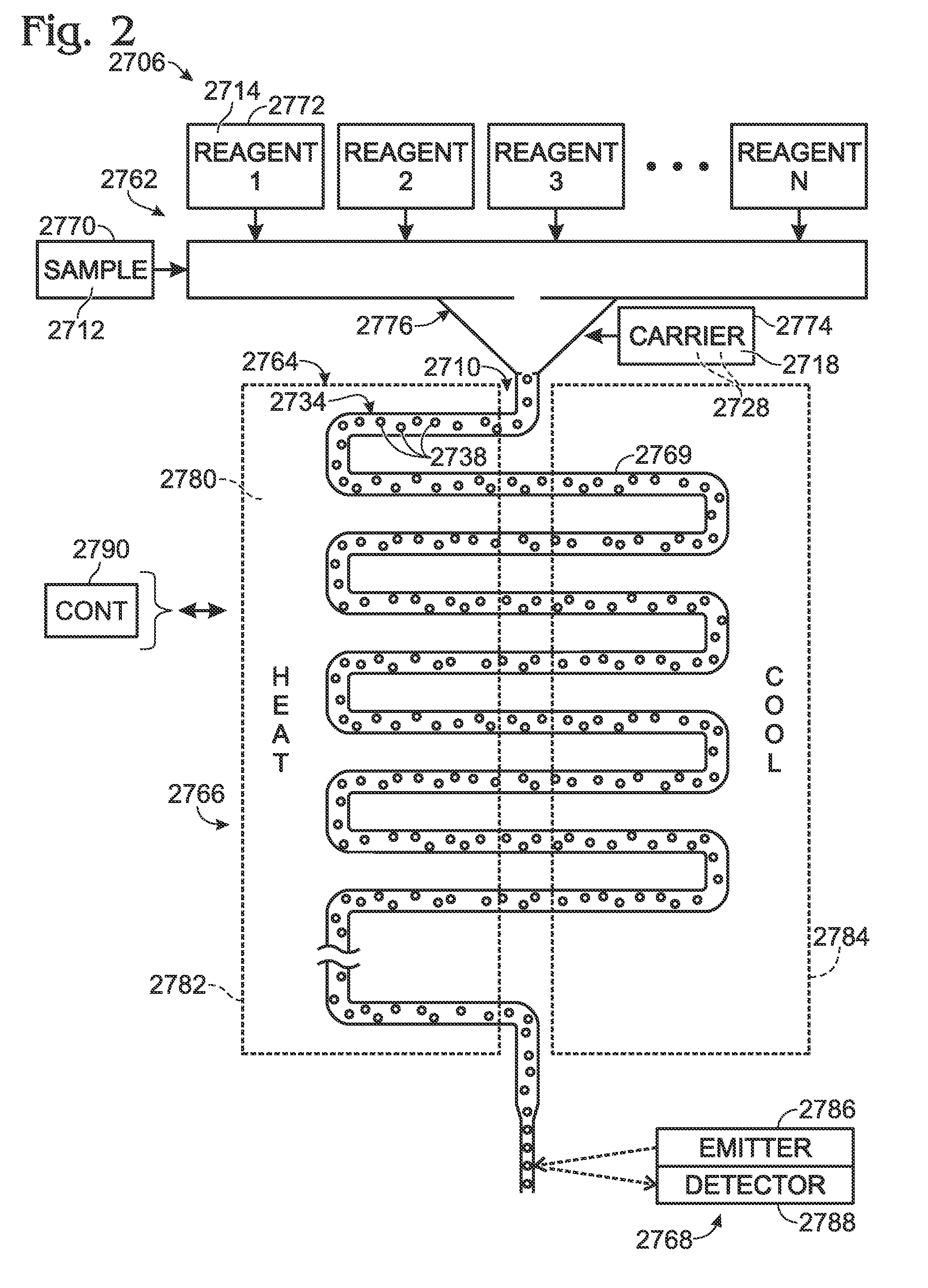
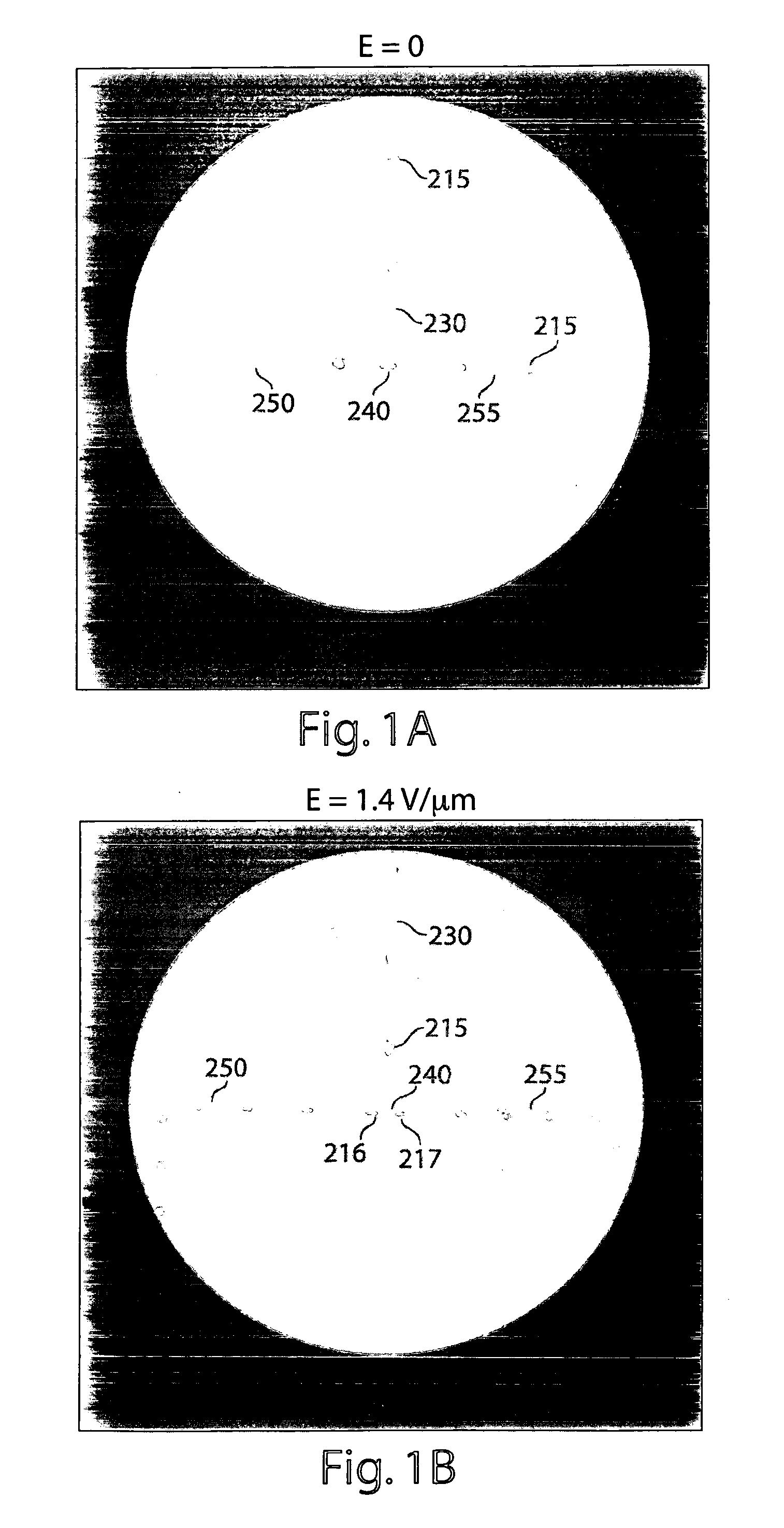
System for mixing fluids by coalescence of multiple emulsions
ActiveUS20110053798A1High-confidence resultLower the volumeSequential/parallel process reactionsHeating or cooling apparatusEmulsionChemistry
System, including methods, apparatus, compositions, and kits, for the mixing of small volumes of fluid by coalescence of multiple emulsions.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Compartmentalised screening by microfluidic control
InactiveUS20070092914A1Rapid and high-throughput screeningLow costCompound screeningSequential/parallel process reactionsCompound (substance)Drug development
The invention describes a method for the identification of compounds which bind to a target component of a biochemical system or modulate the activity of the target, comprising the steps of: a) compartmentalising the compounds into microcapsules together with the target, such that only a subset of the repertoire is represented in multiple copies in any one microcapsule; and b) identifying the compound which binds to or modulates the activity of the target; wherein at least one step is performed under microfluidic control. The invention enables the screening of large repertoires of molecules which can serve as leads for drug development.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
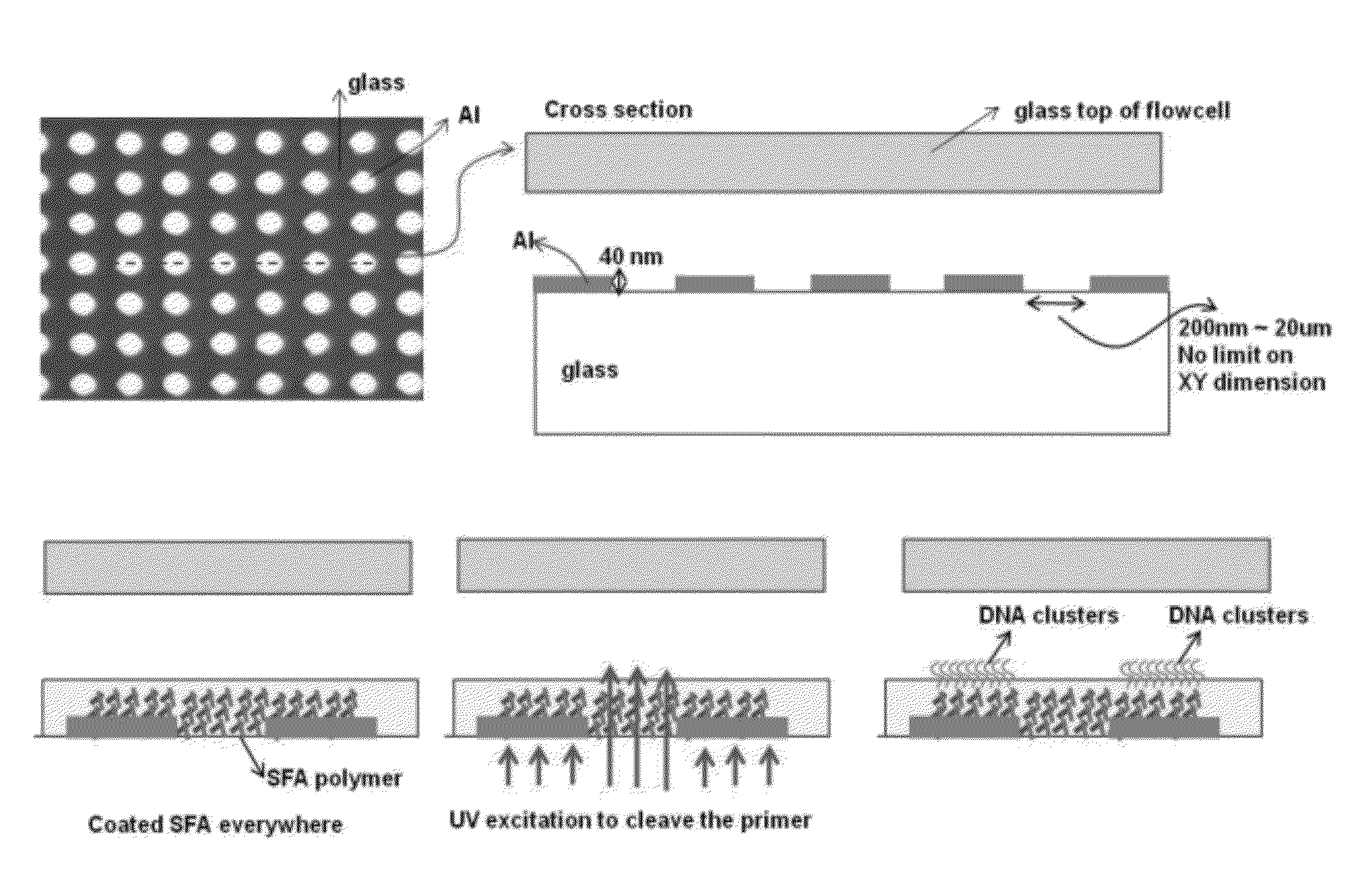
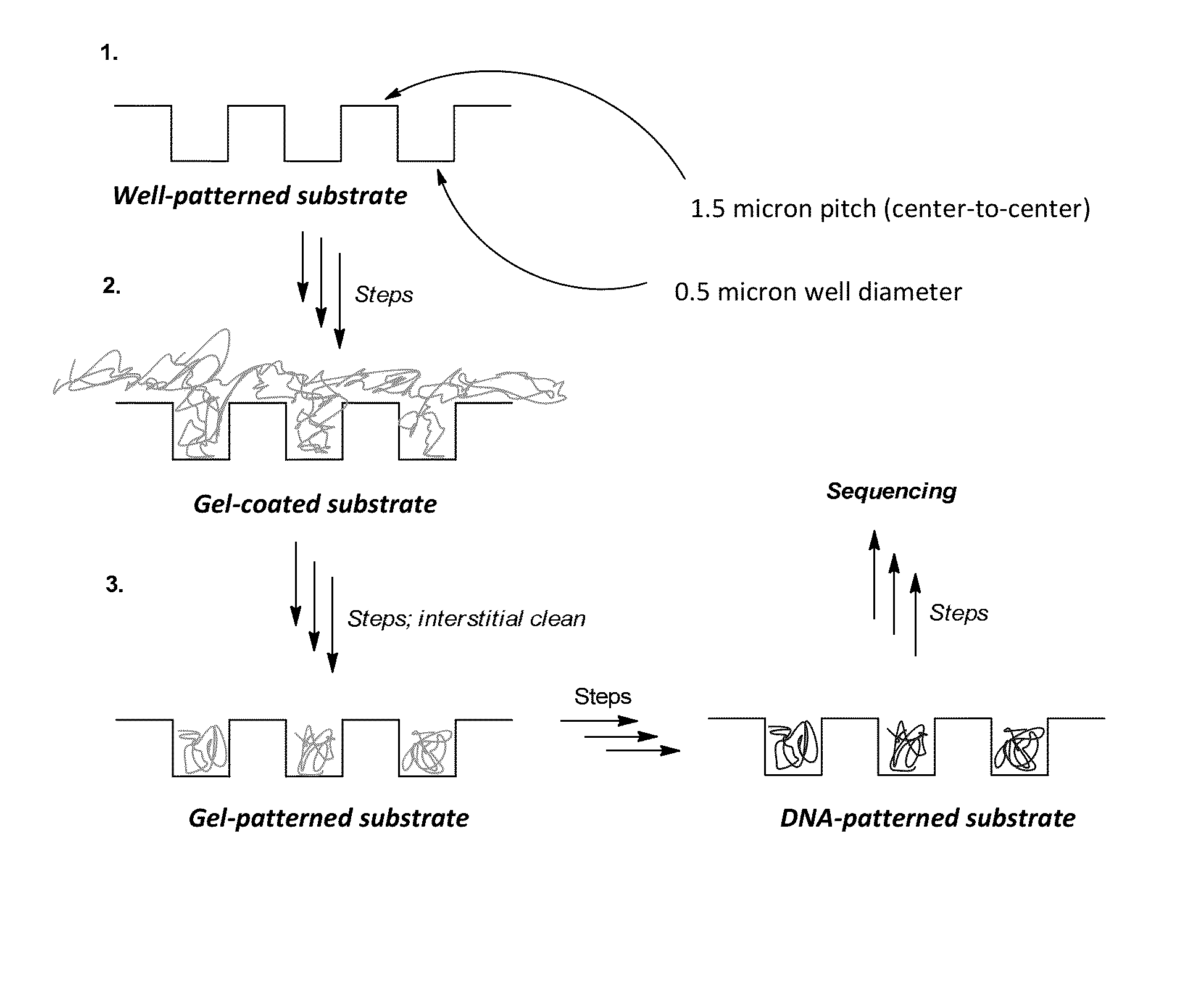
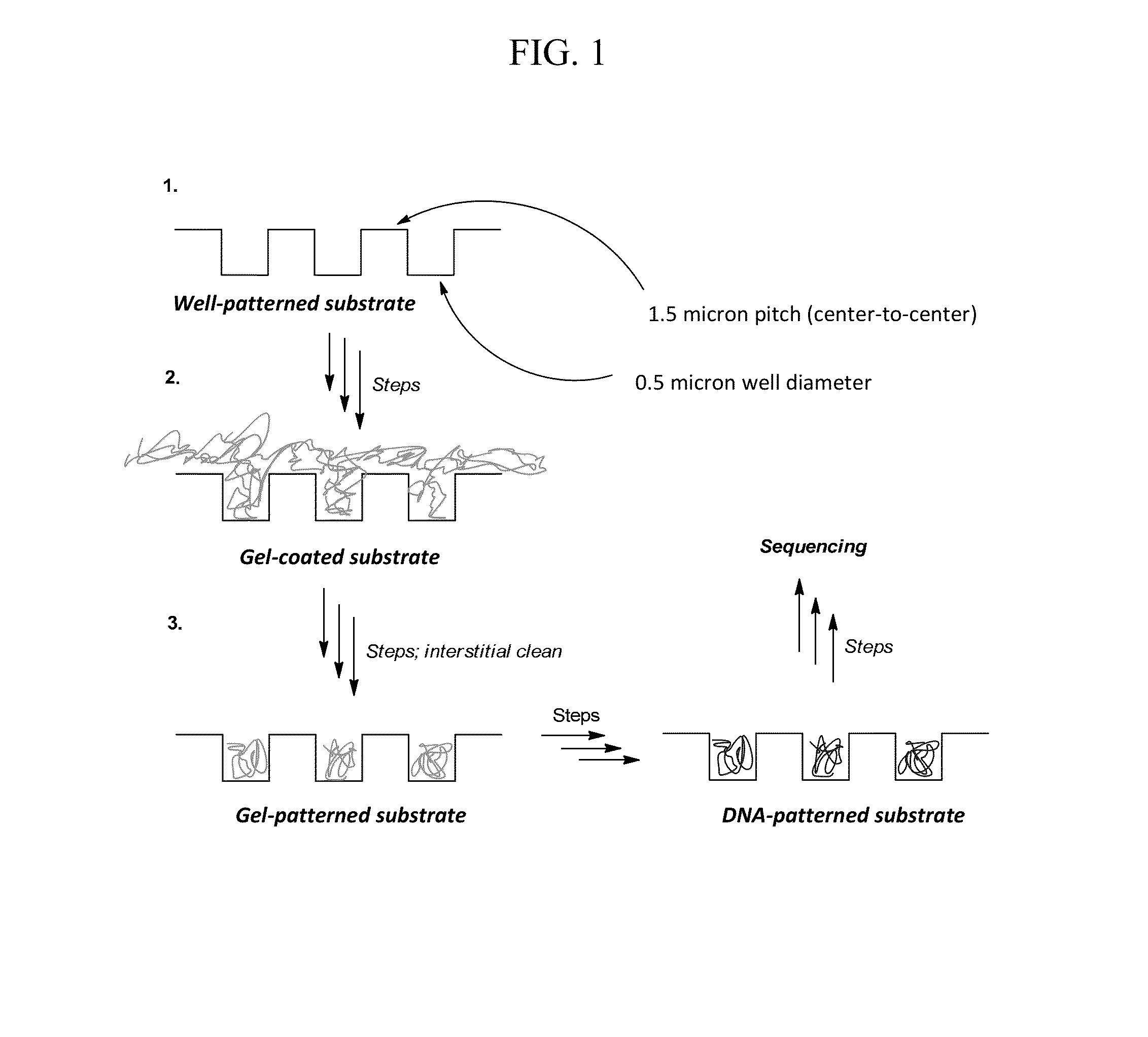
Patterned flow-cells useful for nucleic acid analysis
ActiveUS20120316086A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteFlow cell
Provided is a surface having metal regions and an interstitial region having a composition that differs from the metal regions, wherein a continuous gel layer coats the surface across the metal regions and the interstitial regions. Nucleic acids or other analytes can be attached to the continuous gel layer such that a greater amount is attached over the metal regions than over the interstitial region. Also provided are methods for making such surfaces. Methods are also provided for making an array of nucleic acids or other analytes using such surfaces.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Method and apparatus for transferring and combining reagents
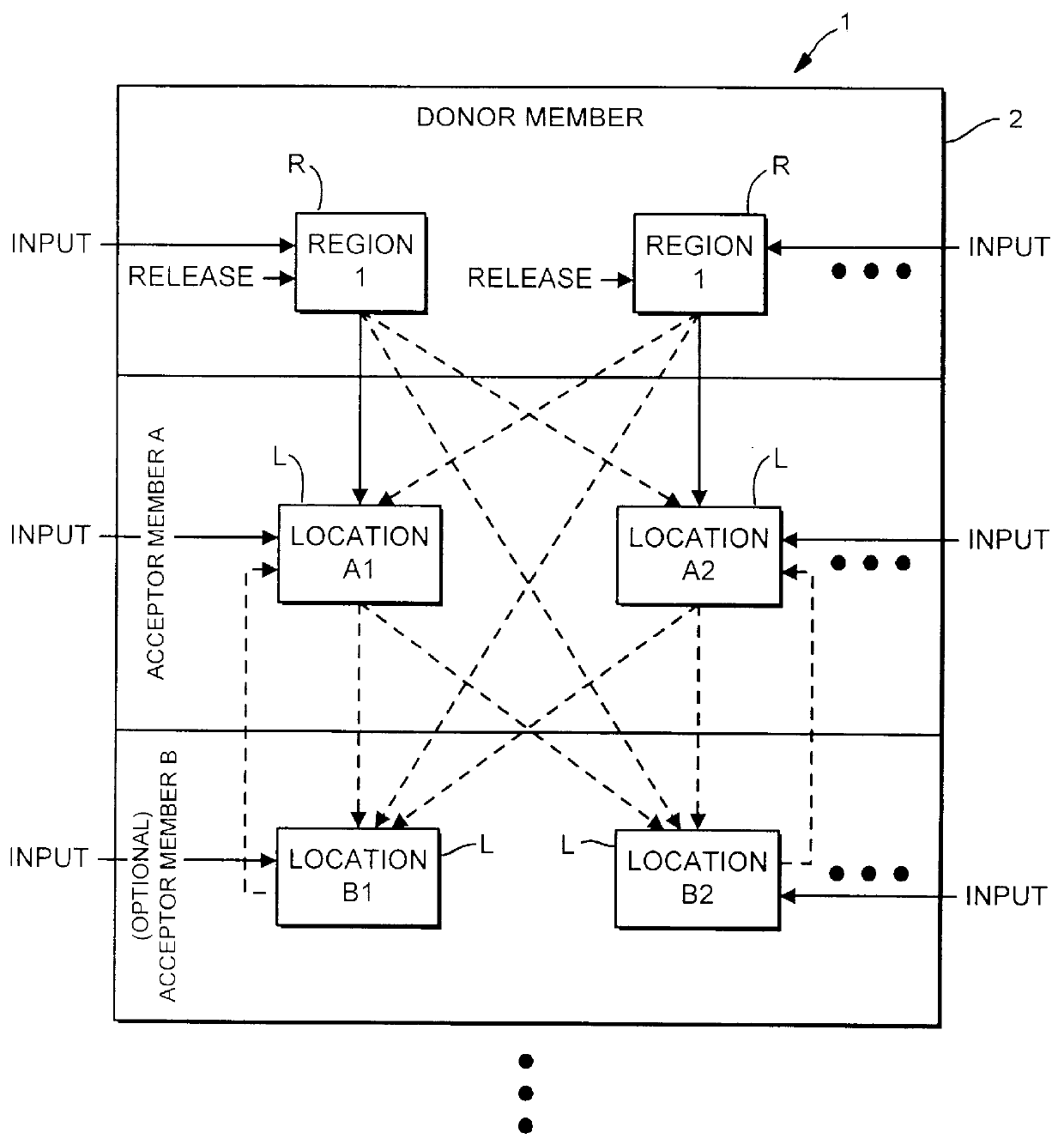
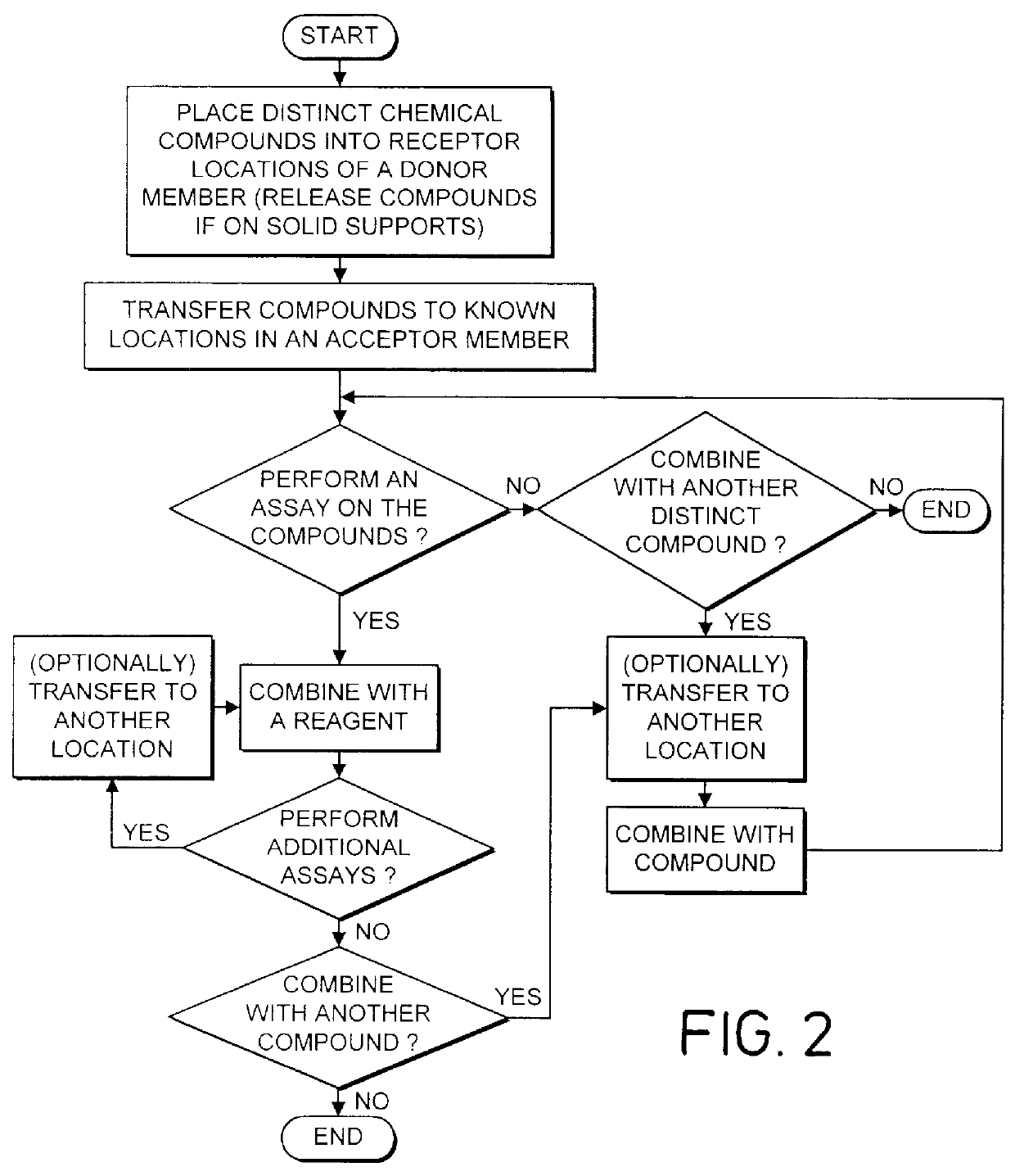
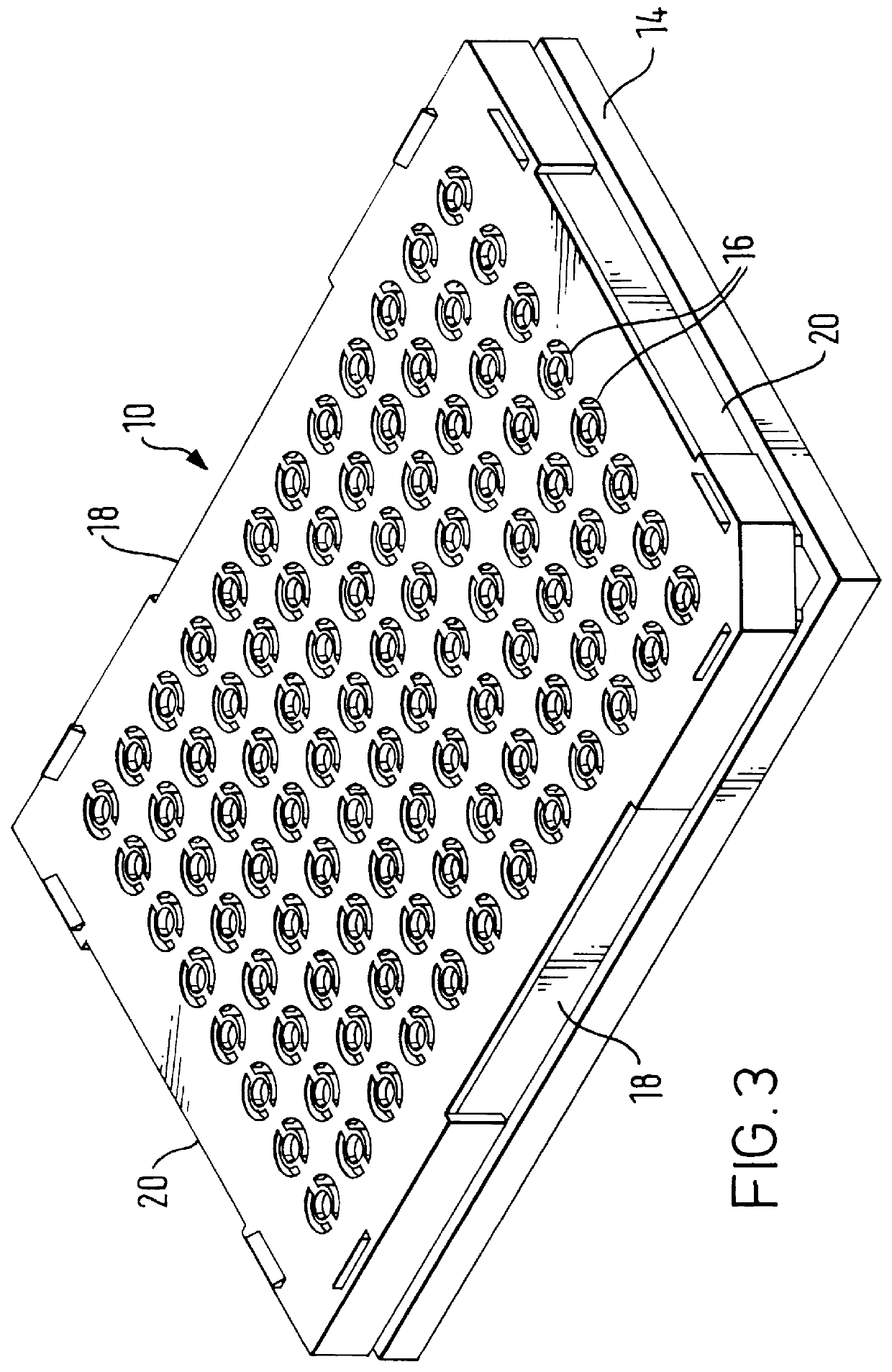
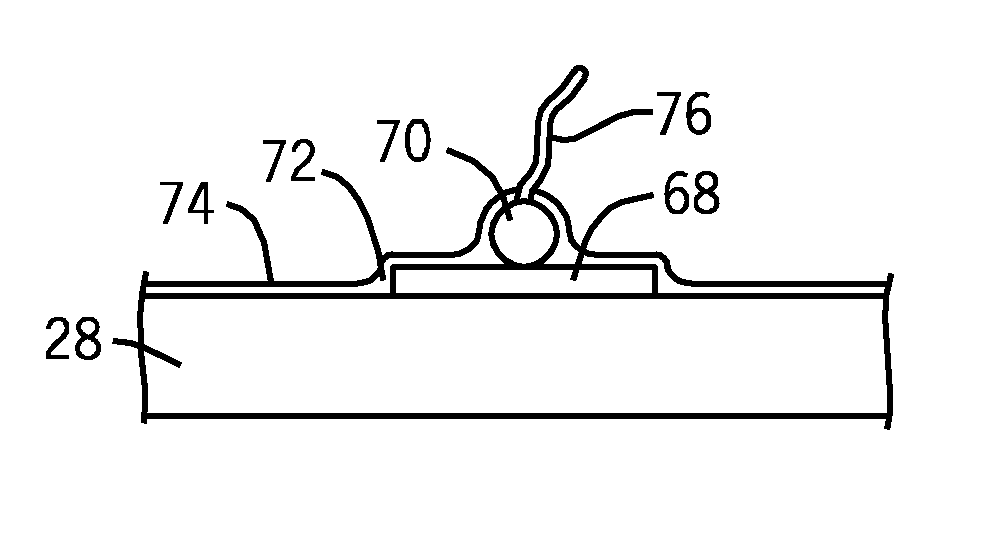
InactiveUS6083761AEasy to carryEfficient transferSequential/parallel process reactionsWithdrawing sample devicesChemical compositionCentrifugation
The invention provides exemplary systems, methods, and apparatus for distinctly allocating liquids containing chemical compositions or compounds to known locations in an organized manner so that assays may be performed on the compositions, or so that the chemical compositions may be combined with other distinct chemical compositions or reagents prior to evaluation. In an exemplary embodiment, the invention includes a multiwell plate for handling articles such as resin beads suspended in a liquid. The plate comprises a plurality of wells. The wells in turn have a capillary hole that is adapted to (i) retain articles in the well, and (ii) retain liquid in the well while the liquid is not subjected to extrinsic forces, such as centrifugation or vacuum.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP +1
Microarray fabrication system and method
A microarray is designed capture one or more molecules of interest at each of a plurality of sites on a substrate. The sites comprise base pads, such as polymer base pads, that promote the attachment of the molecules at the sites. The microarray may be made by one or more patterning techniques to create a layout of base pads in a desired pattern. Further, the microarrays may include features to encourage clonality at the sites.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Gel patterned surfaces
ActiveUS20140243224A1Easy to adaptSequential/parallel process reactionsNucleotide librariesBiologyNucleic acid
Provided is an array including a solid support having a surface, the surface having a plurality of wells, the wells containing a gel material, the wells being separated from each other by interstitial regions on the surface, the interstitial regions segregating the gel material in each of the wells from the gel material in other wells of the plurality; and a library of target nucleic acids in the gel material, wherein the gel material in each of the wells comprises a single species of the target nucleic acids of the library. Methods for making and using the array are also provided.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
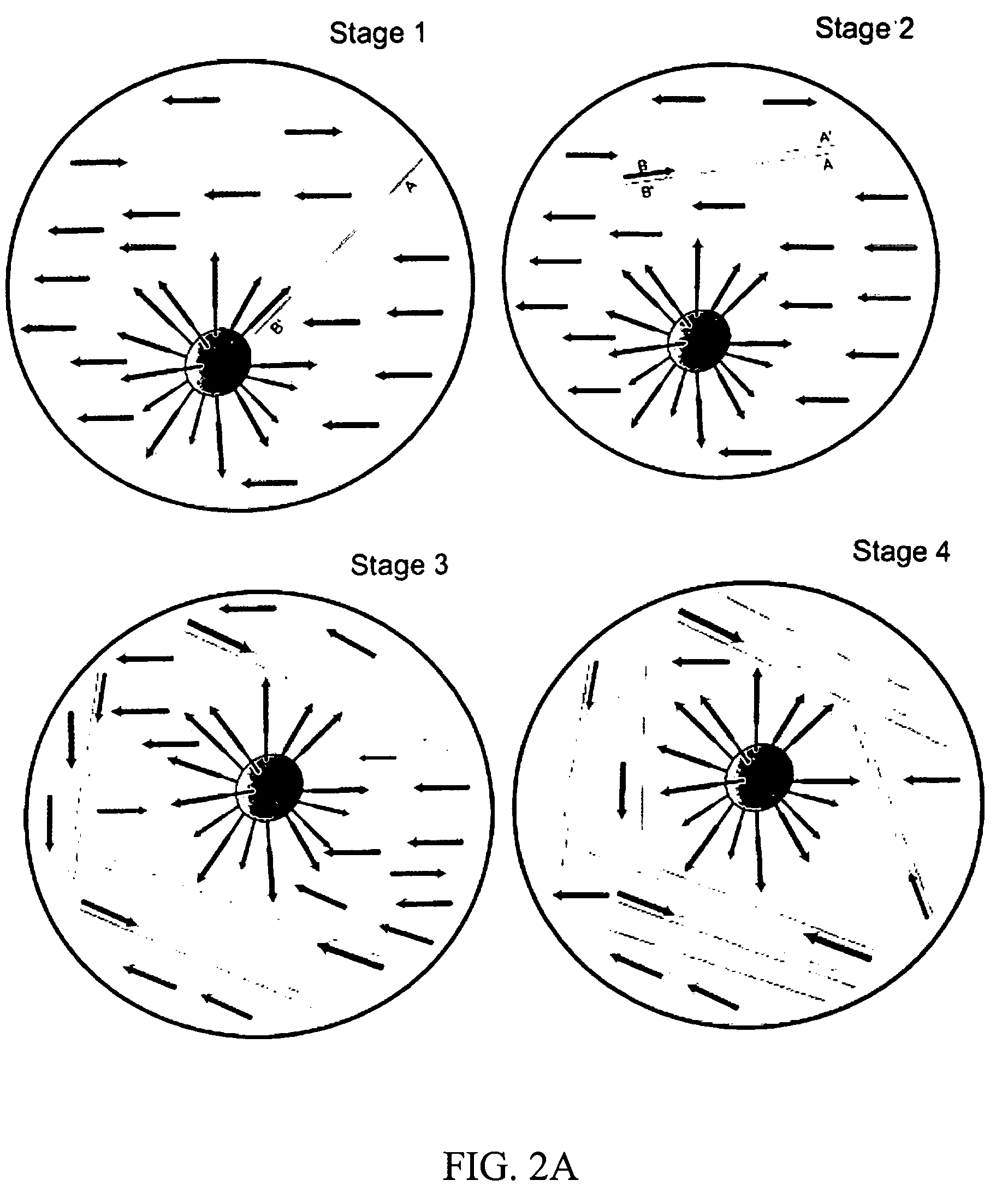
Molecular arrays and single molecule detection
InactiveUS20050244863A1Precision and richness of informationPrecision and richness of and speedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyChemical physicsMolecular array
Methods are provided for producing a molecular array comprising a plurality of molecules immobilized to a solid substrate at a density which allows individual immobilized molecules to be individually resolved, wherein each individual molecule in the array is spatially addressable and the identity of each molecule is known or determined prior to immobilisation. The use of spatially addressable low density molecular arrays in single molecule detection techniques is also provided.
Owner:KALIM MIR +2
Popular searches
Flow mixers Volume/mass flow measurement Chemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactors Fluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elements Isotope separation Biomass after-treatment Fluid speed measurement Optical light guides DNA preparation Water/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fields
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com