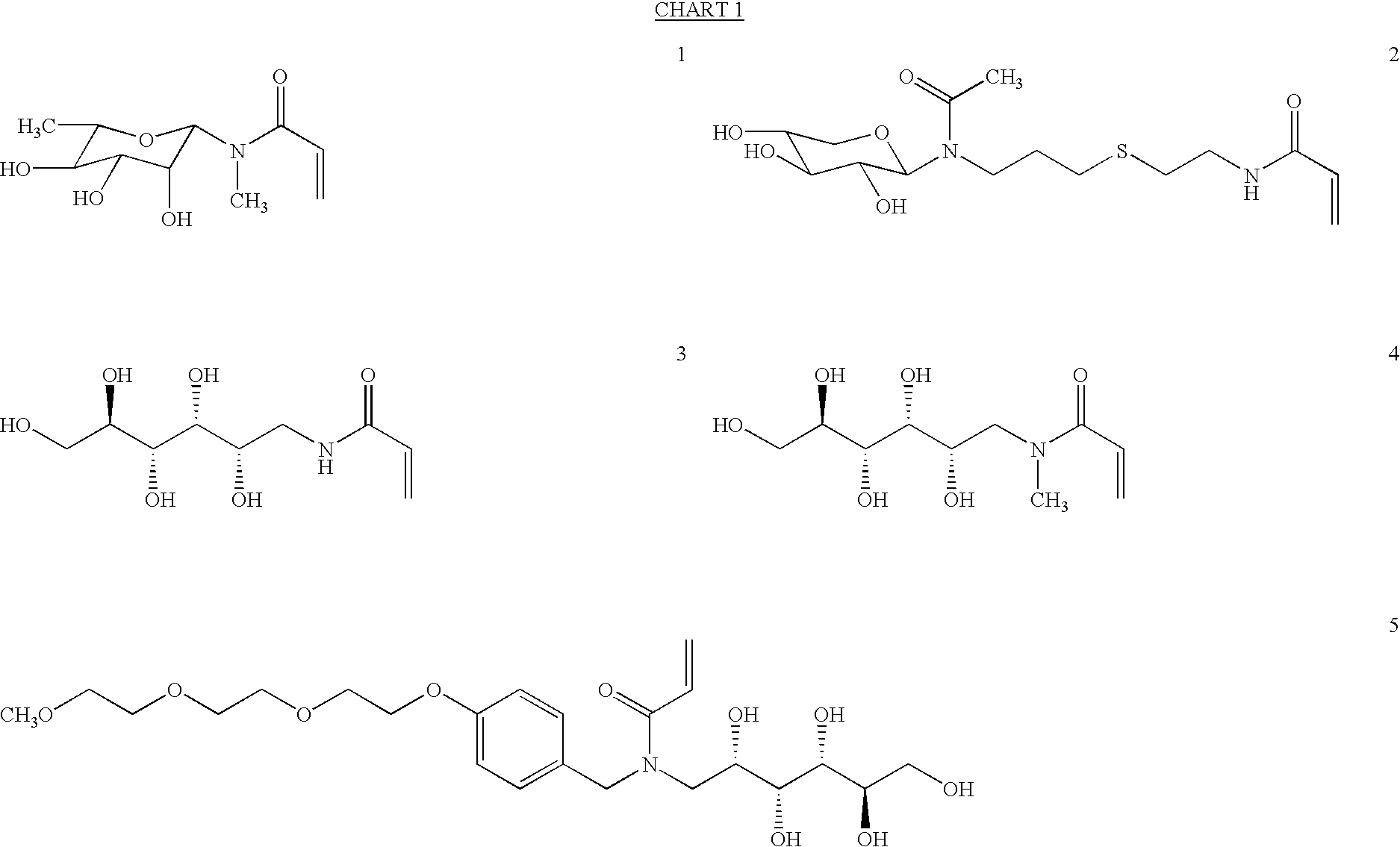
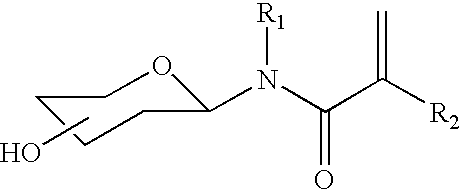
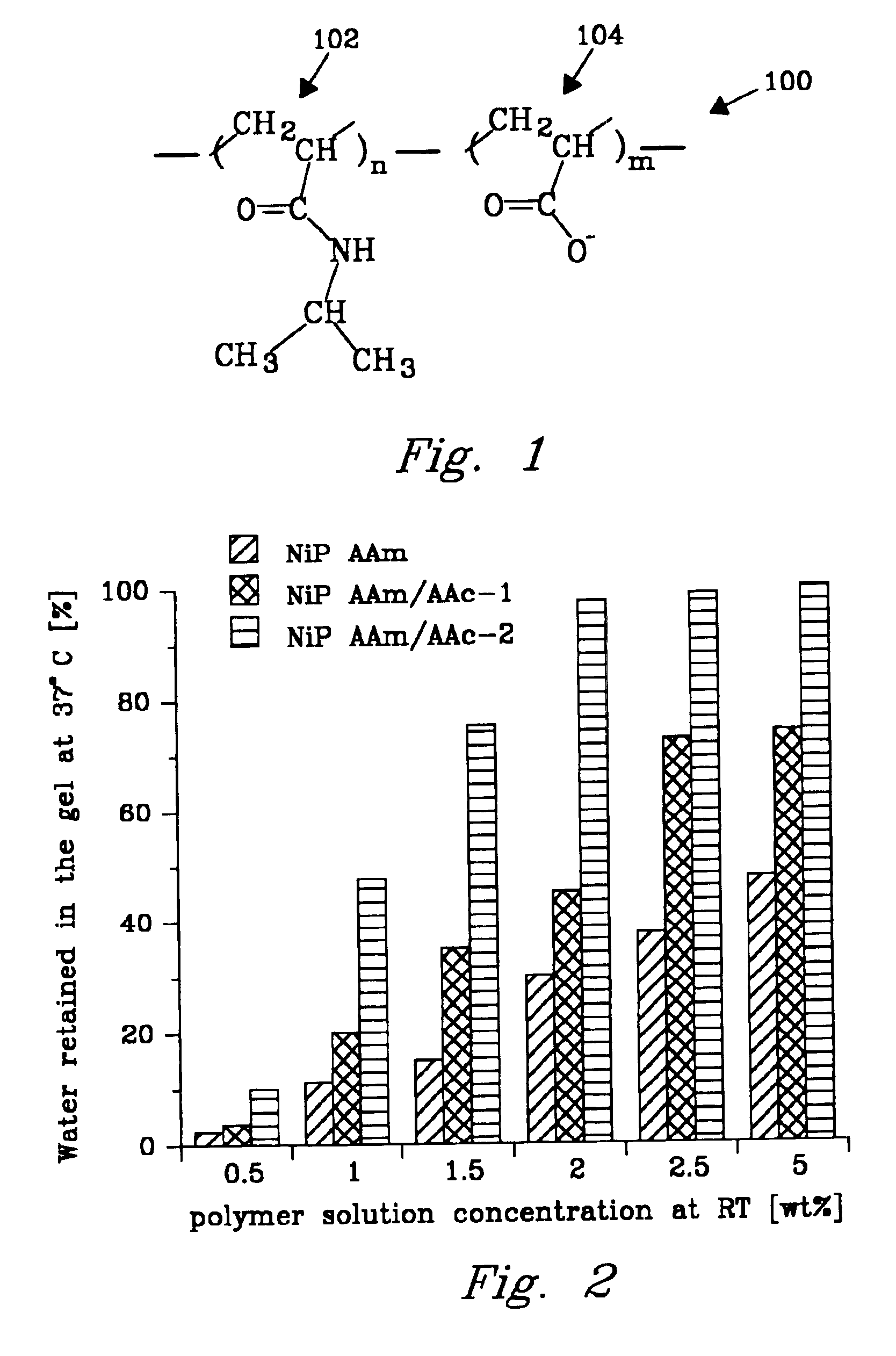
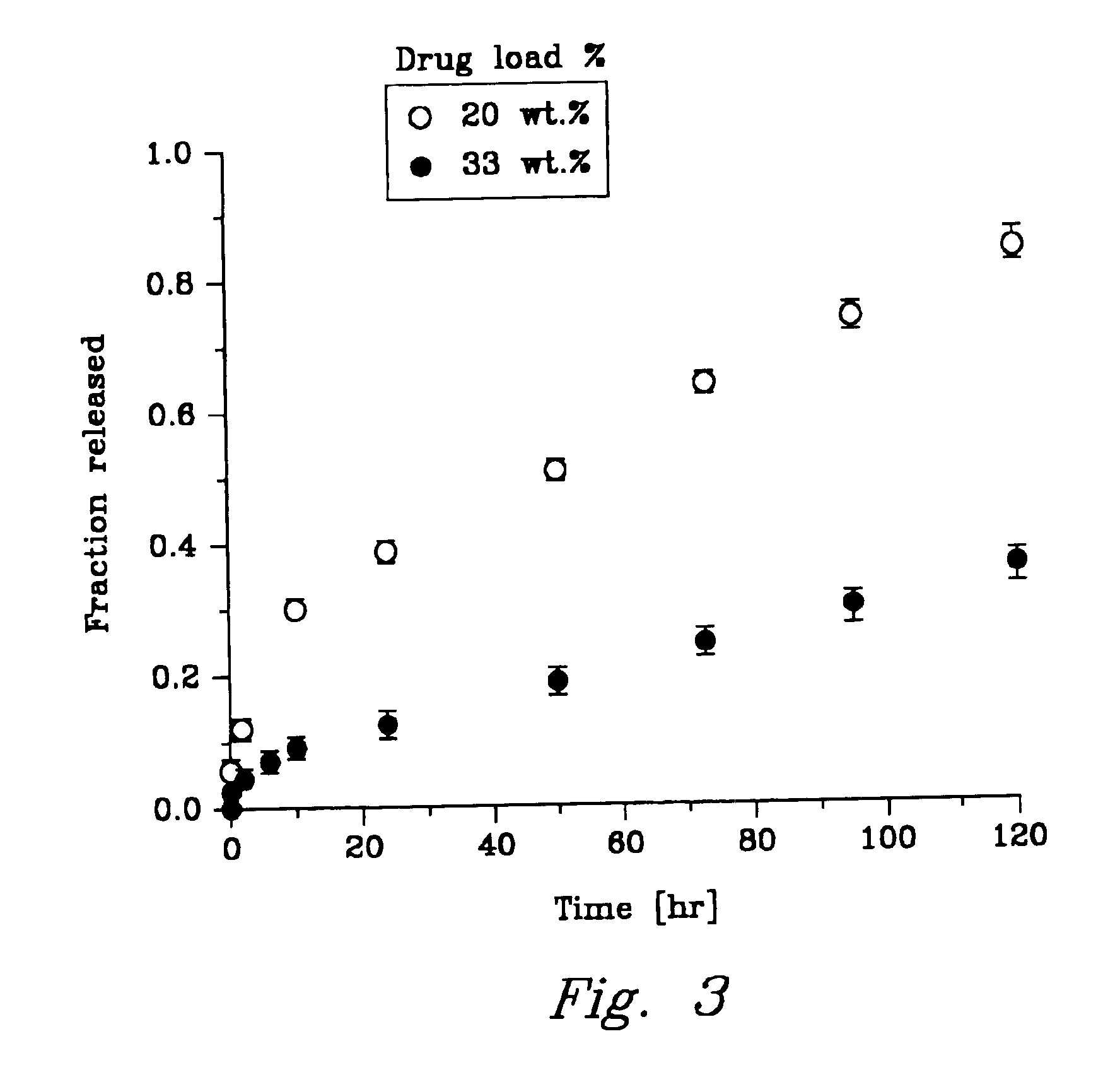
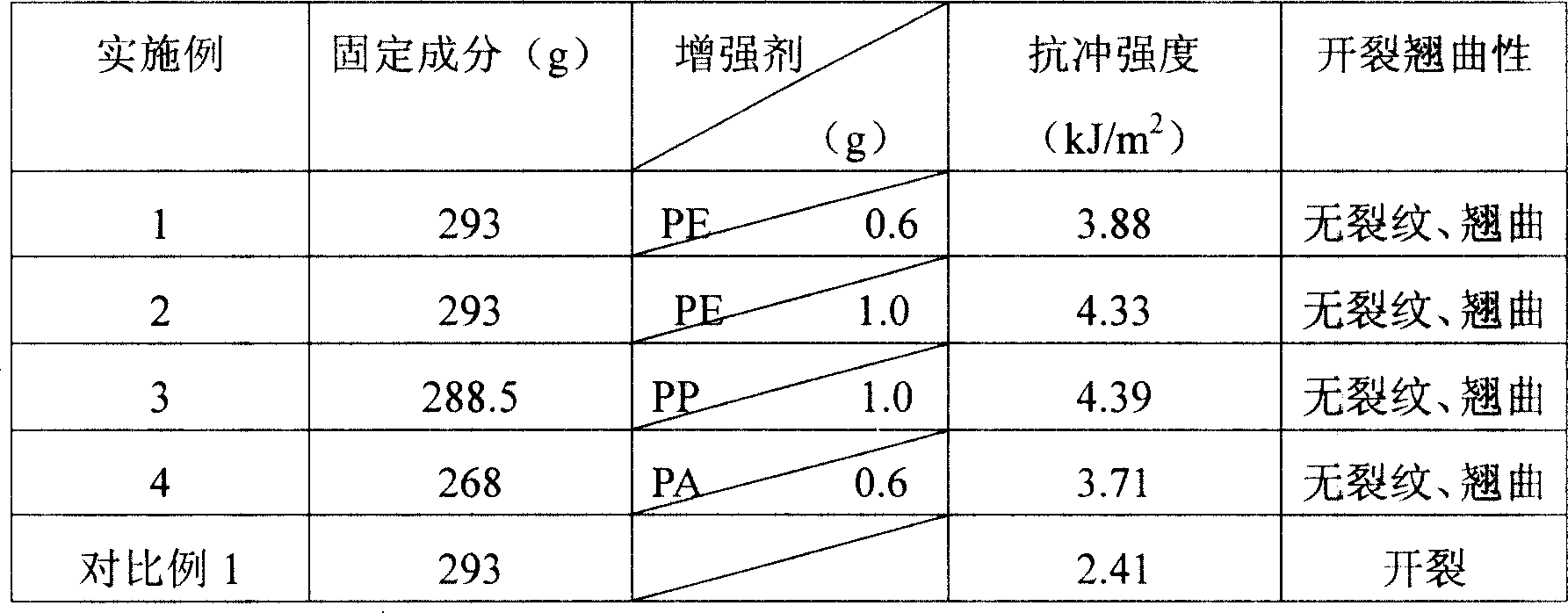
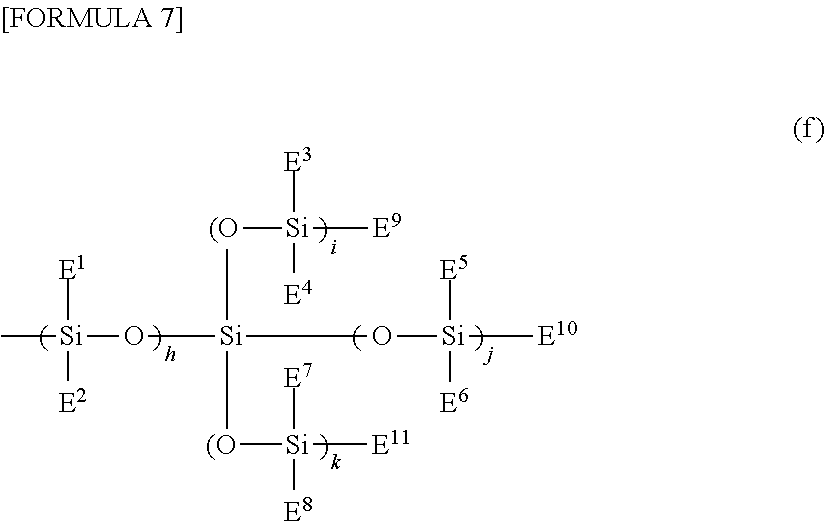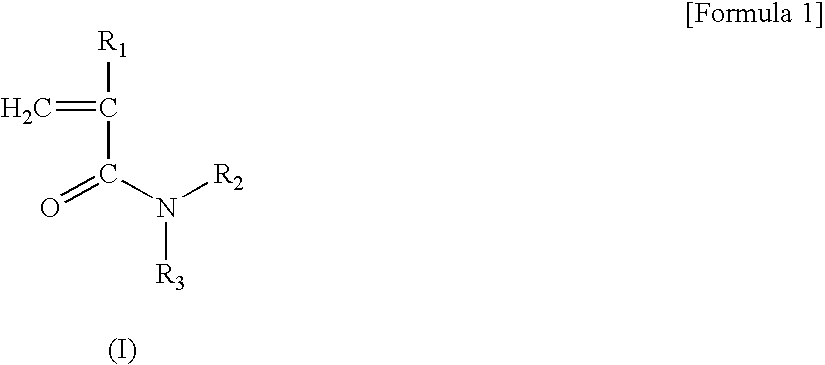Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1963 results about "Methacrylamide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methacrylamide is an industrial chemical used in the production of polymers and copolymers. Methacrylamide is a precursor of methyl methacrylate.
Modified Molecular Arrays
InactiveUS20110059865A1Less reactiveAccelerated programSequential/parallel process reactionsNucleotide librariesMolecular array(Hydroxyethyl)methacrylate
The invention relates to the preparation of a hydrogel surface useful in the formation and manipulation of arrays of molecules, particularly polynucleotides and to the chemical modification of these and other arrays. In particular, the invention relates to a method of preparing a hydrogel immobilised to a solid support comprising polymerising on the support a mixture of a first comonomer which is acrylamide, methacrylamide, hydroxyethyl methacrylate or N-vinyl pyrrolidinone and a second comonomer which is a functionalised acrylamide or acrylate.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Novel Polymers
ActiveUS20080015315A1Sufficient amountReduce the amount requiredOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationHydrophilic monomerPolymer science
The invention relates to novel crosslinkable copolymers which are obtainable by (a) copolymerizing at least two different hydrophilic monomers selected from the group consisting of N,N-dimethyl acrylamide (DMA), 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate (HEA), glycidyl methacrylate (GMA), N-vinylpyrrolidone (NVP), acrylic acid (AA) and a C1-C4-alkoxy polyethylene glycol (meth)acrylate having a weight average molecular weight of from 200 to 1500, and at least one crosslinker comprising two or more ethylenically unsaturated double bonds in the presence of a chain transfer agent having a functional group; and (b) reacting one or more functional groups of the resulting copolymer with an organic compound having an ethylenically unsaturated group.
Owner:ALCON INC
Dynamic coating with linear polymer mixture for electrophoresis
InactiveUS6787016B2Sludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementCapillary electrophoresisAqueous buffer
Compositions and methods are provided for performing capillary electrophoresis using a composition comprising in combination in an aqueous buffered medium a coating polymer and a sieving polymer, where the sieving polymer is more hydrophilic than the coating polymer and is present in greater amount. Of particular interest are uncrosslinked acrylamide polymer mixtures for coating plastic channels and providing sieving for performing DNA separations in microfluidic devices. Polyacrylamide or N,N-dimethyl acrylamide is used with a N,N-dialkyl acrylamide copolymer, either separately or together for sieving and coating, serving as the medium in capillary electrophoresis DNA separations.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Gel pad and UV-curving production method thereof
The invention relates to a gel pad and a uv-curing production method thereof. This invention, including the gel bag, is characterized in that the gel bag is filled with gel which is prepared from gel monomers, a cross-linking agent and a photoinitiatorandwater prepared from the UV curving. The gel consists of monomers, cross-linking agents, cross-linking agents, photo initiators and water. The said monomer are two or more than two of an acrylic acid alkali metal salt, ester generated by methacrylic acid ,acrylamide ,methacrylamide and AMPS(2-acrylamide-2-methyl-propanesulfonic acid ). The said cross-linking agent is a non-conjugated double bond compound which is polyol(glycerol )N,N'-methylene bisacrylamide. The said photoinitiator is a cracking type initiator or a photosensitive initiator or a cationic initiator. The advantages of the method are that the production process is simple, the gel solidification is fast and the gel pad produced is flattened.
Owner:朱雪兵
Silicone hydrogel, lens for eye and contact lens
ActiveUS20110230589A1Increase contentImprove balanceGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsCoatingsPolymer scienceMeth-
The present invention provides transparent silicone hydrogels with high acrylamide monomer content and an excellent balance between moisture content.The silicone hydrogels may be obtained by polymerizing a monomer mix containing a plurality of monomers, wherein the monomer mix comprises about 30 to about 98% by weight of at least one type of silicone monomer which is, and about 1 to about 50% by weight of at least one type of non-silicone type (meth)acrylamide monomer containing two or more hydroxyl groups within a molecule; wherein the weight percents are based upon the total amount of monomer components and polymer components in the monomer mix.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Biomimetic hydrogel materials
Novel biomimetic hydrogel materials and methods for their preparation. Hydrogels containing acrylamide-functionalized carbohydrate, sulfoxide, sulfide or sulfone copolymerized with a hydrophilic or hydrophobic copolymerizing material selected from the group consisting of an acrylamide, methacrylamide, acrylate, methacrylate, vinyl and a derivative thereof present in concentration from about 1 to about 99 wt %. and methods for their preparation. The method of use of the new hydrogels for fabrication of soft contact lenses and biomedical implants.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Polishing slurry for silicon oxide, additive liquid and polishing method
InactiveUS20070175104A1Increase speedInhibit progressPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesPolyethylene glycolSlurry
The polishing slurry of the invention is a polishing slurry for polishing a silicon oxide film on polysilicon, which contains an abrasive, polysilicon polishing inhibitor, and water. As the polishing inhibitor, it is preferable to use (1) a water-soluble polymer having a N-monosubstituted or N,N-disubstituted skeleton substituted by any member selected from the group consisting of acrylamide, methacrylamide, and α-substituted derivatives thereof, (2) polyethylene glycol, (3) an oxyethylene adduct of an acetylene-based diol, (4) a water-soluble organic compound having an acetylene bond, (5) an alkoxylated linear aliphatic alcohol, or (6) a copolymer containing polyvinyl pyrrolidone or vinyl pyrrolidone. There is provided a polishing method which is capable of polishing a silicon oxide film on a polysilicon film at a high speed, and inhibiting the progress of polishing of a polysilicon film in exposed parts in the manufacturing method for a semiconductor.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
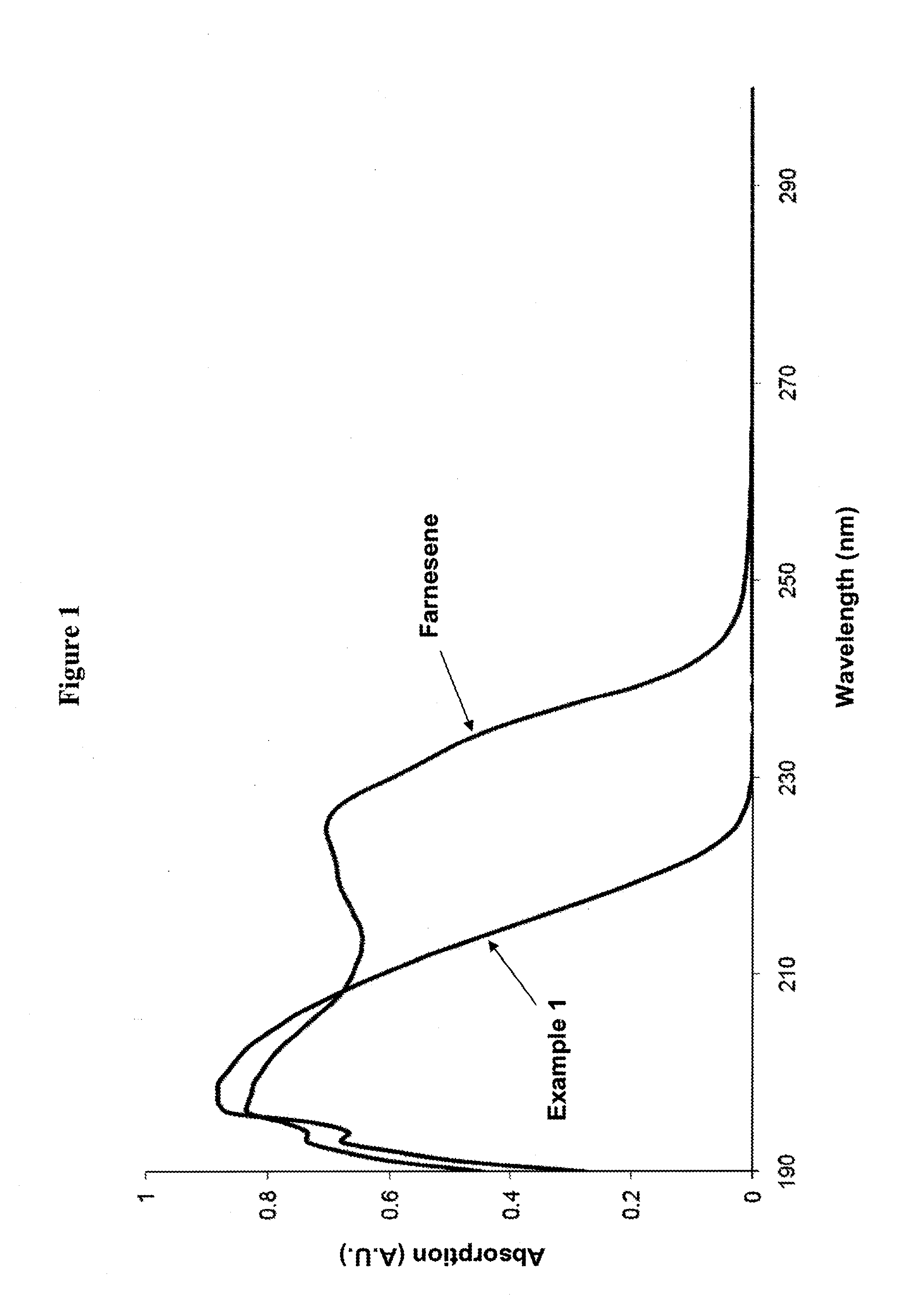
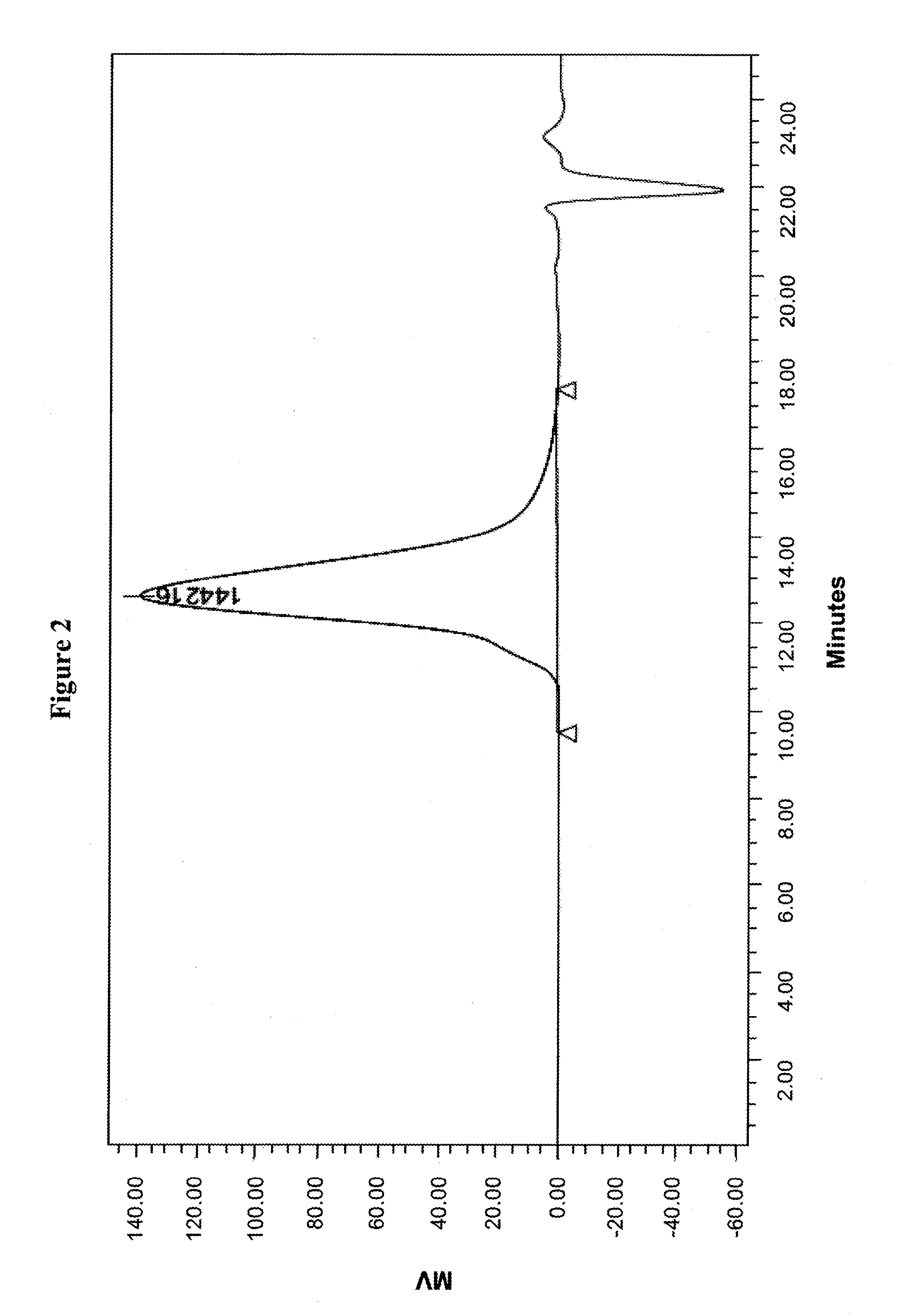
Farnesene interpolymers
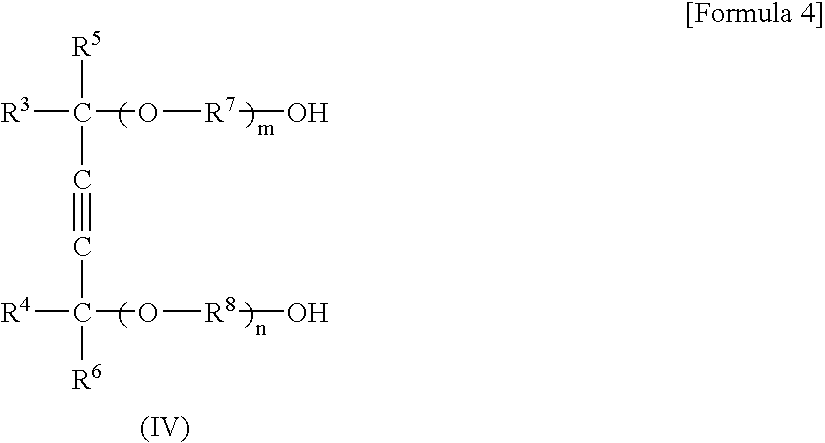
Farnesene interpolymer comprises units derived from a farnesene (e.g., α-farnesene or β-farnesene) and units derived from at least one vinyl monomer. The farnesene interpolymer can be prepared by copolymerizing the farnesene and at least one vinyl monomer in the presence of a catalyst. In some embodiments, the farnesene is prepared from a sugar by using a microorganism. In other embodiments, the at least one vinyl monomer is ethylene, an α-olefin, or a substituted or unsubstituted vinyl halide, vinyl ether, acrylonitrile, acrylic ester, methacrylic ester, acrylamide or methacrylamide, or a combination thereof.
Owner:AMYRIS INC
Silicone hydrogels for tissue adhesives and tissue dressing applications
InactiveUS20110086077A1Provide strengthFacilitated releaseBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsWound dressingSilanes
A silicone hydrogel formulation may contains random and / or block copolymers or oligomers or macromers. The silicone copolymer is copolymerized or blended with other polymers or monomers or macromers to obtain final formulation. The silicone hydrogel may contain crosslinking groups to provide a complete or partially crosslinked final structure. The silicone hydrogel formulation may be pre-formed as a film or other structure, or it may be polymerized during application as in the case of an adhesive formulation. A wound dressing comprising a silicone hydrogel formed as a film, either prior to application to a wound or in situ on a wound, which film has gas permeability, moisture permeability, and high water content, wherein said silicone hydrogel is formed from a polymerizable silicone such as a difunctional polydimethylsiloxane methacrylate and crosslinking agents such as N,N-dimethyllacrylamide (DMA), 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA), and trimethylsiloxy silane (TRIS).
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Adhesive compositions comprising a polyfarnesene
Adhesive composition comprises a polyfarnesene and a tackifier. The polyfarnesene can be a farnesene homopolymer derived from a farnesene (e.g., α-farnesene or β-farnesene) or a farnesene interpolymer derived from a farnesene and at least a vinyl monomer. In some embodiments, the at least one vinyl monomer is ethylene, an α-olefin such as styrene, or a substituted or unsubstituted vinyl halide, vinyl ether, acrylonitrile, acrylic ester, methacrylic ester, acrylamide or methacrylamide, or a combination thereof. The composition disclosed herein can be used as a hot melt adhesive, a pressure sensitive adhesive or the like.
Owner:AMYRIS INC
Process for producing molded printed material, and molded printed material
A process for producing a molded printed material is provided that includes (A) a step of forming an image by discharging an ink composition on a support by an inkjet method, the ink composition comprising at least 60 wt % relative to the entire ink composition of at least one monofunctional radically polymerizable monomer having only one unsaturated double bond group selected from the group consisting of an acrylate group, a methacrylate group, an acrylamide group, a methacrylamide group, and an N-vinyl group and having at least one cyclic structure-containing group, (B) a step of curing the ink composition by irradiating with actinic radiation the image obtained so as to obtain a printed material having the image cured on the support, and (C) a step of molding the printed material. There is also provided a molded printed material obtained by the process for producing a molded printed material.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Dispersing Sulfide Scales in Oil and Gas Production Systems
ActiveUS20090143252A1Preventing and mitigating formationFluid removalFlushingEthylene HomopolymersPetroleum
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Dynamic coating with linear polymer mixture for electrophoresis
InactiveUS20020029968A1Sludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementCapillary electrophoresisAqueous buffer
Compositions and methods are provided for performing capillary electrophoresis using a composition comprising in combination in an aqueous buffered medium a coating polymer and a sieving polymer, where the sieving polymer is more hydrophilic than the coating polymer and is present in greater amount. Of particular interest are uncrosslinked acrylamide polymer mixtures for coating plastic channels and providing sieving for performing DNA separations in microfluidic devices. Polyacrylamide or N,N-dimethyl acrylamide is used with a N,N-dialkyl acrylamide copolymer, either separately or together for sieving and coating, serving as the medium in capillary electrophoresis DNA separations.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Conductive composition and production method thereof, antistatic coating material, antistatic coating, antistatic film, optical filter, and optical information recording medium, and capacitors and production method thereof
ActiveUS20060062958A1Improve conductivityImprove heat stabilityHybrid capacitor electrolytesHybrid capacitor electrodesVinyl etherConductive polymer
A conductive composition comprises a π conjugated conductive polymer, a dopant composed of polyanion, and at least one crosslinking site forming compound selected from (a) compounds having a glycidyl group and (b) compounds having a hydroxyl group and one selected from the group consisting of allyl, vinyl ether, methacryl, acryl methacrylamide, and acrylamide groups. An antistatic coating material comprises a π conjugated conductive polymer, polyanion, at least one crosslinking site forming compound selected form the above (a) and (b), and a solvent. An antistatic coating is formed by applying the above-mentioned antistatic coating material. In a capacitor comprising an anode composed of a valve metal porous body; a dielectric layer formed by oxidizing the suds of the anode; and a cathode formed on the dielectric lays, the cathode has a solid electrolyte layer formed by crosslinking complexes of a π conjugated conductive polymer and a dopant composed of a polyanion.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU POLYMER CO LTD
Fabric softening laundry detergent
InactiveUS20100190679A1Easy to cleanAvoidingOrganic detergent compounding agentsNon-ionic surface-active compoundsMethacrylamideVinylsulfonic acid
Aqueous laundry detergent compositions containing surfactants and fatty acid, having a pH of from about 6 to about 11 and containing a polymer having a number average molecular weight of from about 700,000 to about 4,000,000 and comprising monomeric units including: nonionic monomers selected from acrylamide, N,N-dialkyl acrylamide, methacrylamide, N,N-dialkylmethacrylamide, hydroxyalkyl acrylate and vinyl pyrrolidone, vinyl acetate, vinyl alcohol, and mixtures thereof; cationic monomers selected from N,N-dialkylaminoalkyl methacrylate, N,N-dialkylaminoalkyl acrylate, N,N-dialkylaminoalkyl acrylamide, N,N-dialkylaminoalkylmethacrylamide, methacylamidoalkyl trialkylammonium chloride, acrylamidoalkylltrialkylammonium chloride, vinylamine, quaternized vinyl imidazole and diallyl dialkyl ammonium chloride, and mixtures thereof; and anionic monomers selected from acrylic acid, methacrylic acid, maleic acid, vinyl sulfonic acid, styrene sulfonic acid, acrylamidopropylmethane sulfonic acid (AMPS), salts thereof, and mixtures thereof; in a specified mole ratio.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Synthesis method of drilling fluid filtrate reducer
InactiveCN101805595ANo pollution in the processFast polymerization rateDrilling compositionSynthesis methodsOil phase
The invention relates to a synthesis method of drilling fluid filtrate reducer. The method comprises: a, nonionic compound emulsifying agent is dissolved in oil and oil phase is made up; a first monomer chosen from fumaric acid, maleic acid, itaconic acid or crylic acid, a second monomer chosen from N, N- dimethylacrylamide, N, N-diethylacrylamide or acrylamide and a third monomer chosen from 4-vinylbenzenesulfonic acid sodium salt, sodium allylsulfonate, 3-allyloxy-2-dydroxy-1-sodium allylsulfonate, 2- methacryloxypropyl-2-methyl propanesulfonic acid, 2-acrylamido-2-methyl propanesulfonic acid or SMAS are dissolved in water with the molar ratio of 1:1 to 5:1 to 5, the pH value of the solution is adjusted to be between 8 and 11, evocating agent is added and water phase solution is made up; and b, the water solution is added to the oil phase solution and the temperature rises to 40 to 70 DEG C for polymerization. The method of the invention has the advantages of fast polymerization speed, high outcome molecular weight and high outcome stability, good filtrate reducing performance, high temperature resistance and high salt resistant performance.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Water-soluble chitosan quaternary ammonium salt antibiotic finishing agent and preparation and application thereof
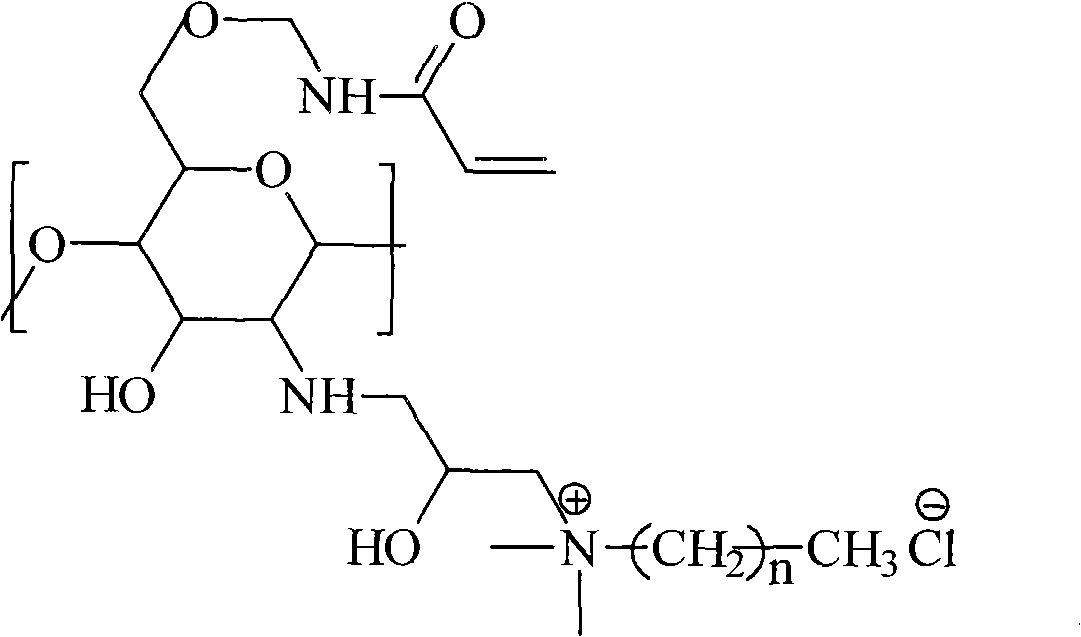
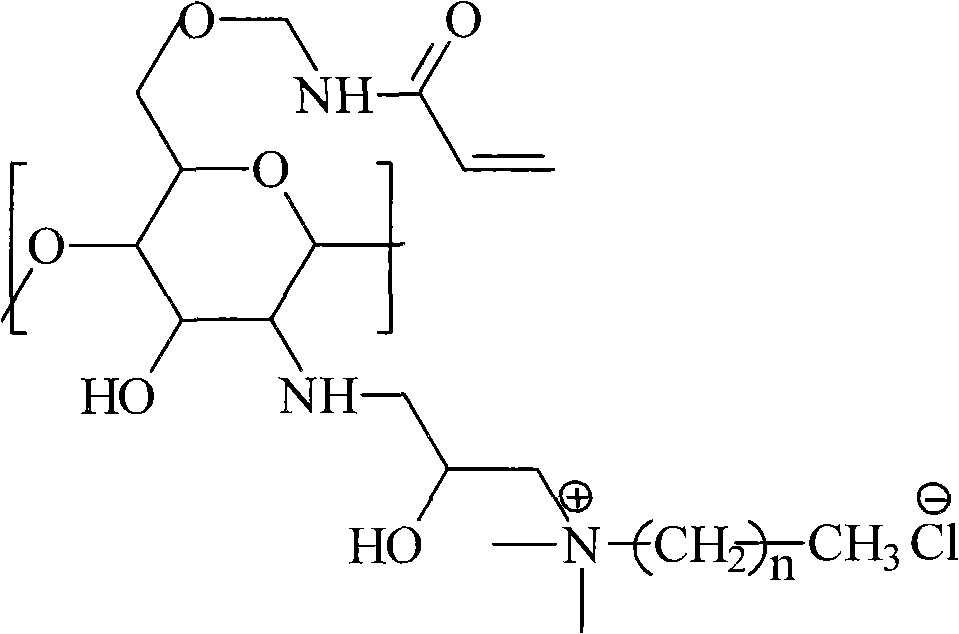
The invention relates to a water-soluble chitosan quaternary ammonium salt antibiotic finishing agent. The invention is characterized in that the antibiotic finishing agent is names as O-methacrylamide-N-hydroxypropyl alkyl dimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan and the concrete structural formula is as follows. The preparation thereof includes that: alkyl dimethyl tertiary amide and epichlorohydrin are taken as raw materials to synthesize 2, 3-epoxy alkyl dimethyl ammonium chloride, then the 2, 3-epoxy alkyl dimethyl ammonium chloride is introduce onto the ammonium group of chitosan, so as to obtain N-hydroxypropyl alkyl dimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan HDCC, and then crosslinking is carried out on the HDCC and hydroxymethyl acrylamide is carried out, thus obtaining NMA-HDCC. The quaternary ammonium salt antibiotic finishing agent contains water-soluble group and fibrous reactivity group and has good water solubility, the bacterial inhibition rate of finished cotton fabrics is close to 100%, and the finishing agent can be combined with cellulose fiber by covalent bond and is wash-resistant; and cost is low, raw material is environmental friendly, environmental pollution is less, thus having industrialization application prospect.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
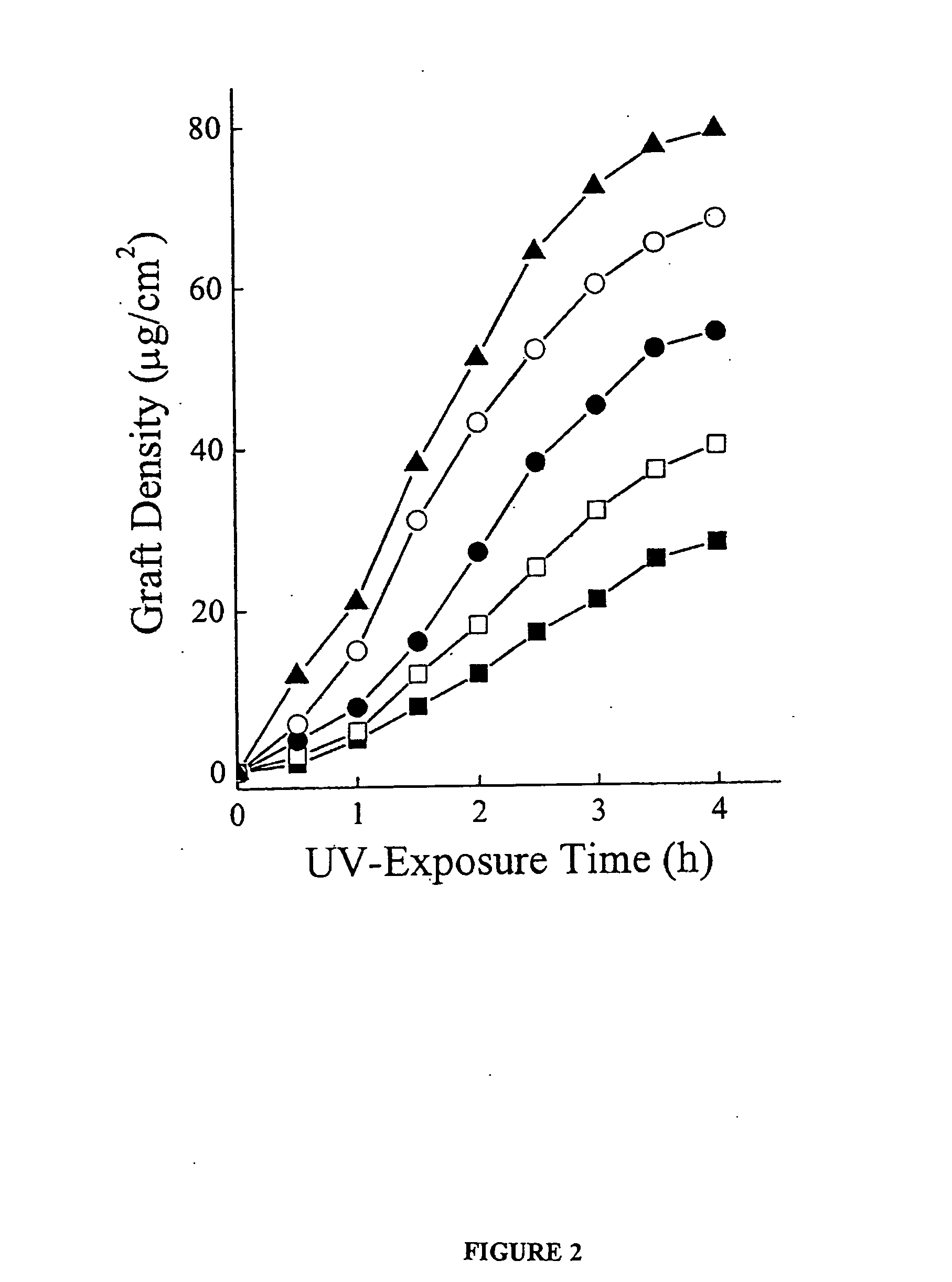
Chemical modifications to polymer surfaces and the application of polymer grafting to biomaterials
InactiveUS20050237480A1Numerous polymerizationQuality improvementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansOptical partsPolymeric surfacePolymer science
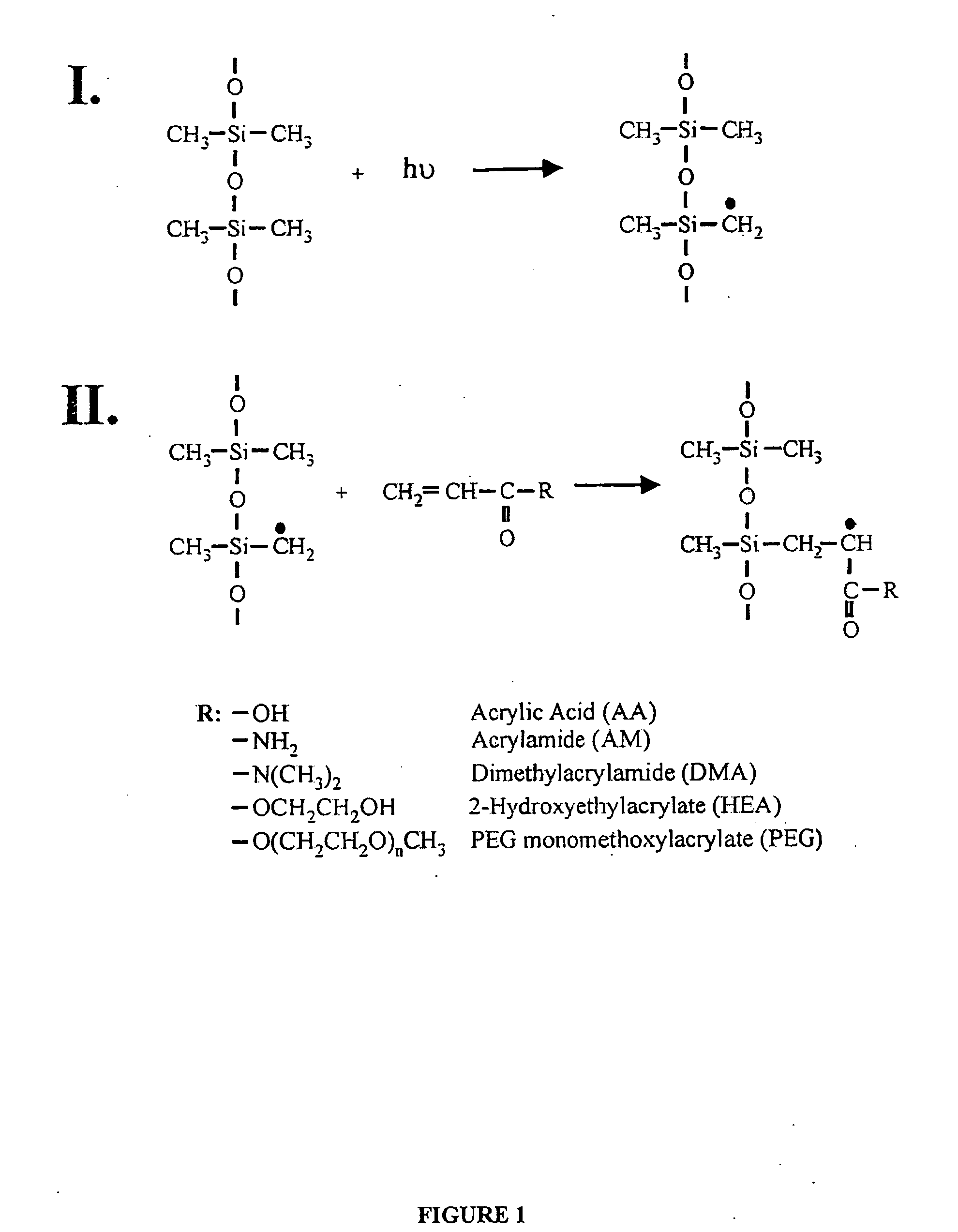
Polymer-based biomaterials are popular due to ease of fabrication and low costs. However, many polymer substrates have undesirable surface properties. The invention provides a procedure to covalently apply a graft polymer to the surface of a polymer substrate by ultraviolet graft polymerization. The graft polymer is formed from monomers such as PEG, AA, monomethoxy acrylate PEG, HEMA, or DMA. Also, mixed monomers may be used to create the graft and the surface properties of the graft may be tailored for different properties, including hydrophobicity, friction coefficient, electroosmotic mobilities and electrophoretic separations. The invention has particular utility in tailoring surface chemistries in ocular lenses and polymer microdevices. I.II.R:—OHAcrylic Acid(AA)—NH2Acrylamide (AM)—N(CH3)2Dimethylacrylamide (DMA)—OCH2CH2OH2-Hydroxyethylacrylate (HEA)—O(CH2CH2O)nCH3PEG monomethyoxylacrylate (PEG)
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Crosslinked acid sand fracturing acid liquor
ActiveCN101724389ALow viscosityCompletely broken glueDrilling compositionReaction rateZirconium oxychloride
The invention relates to crosslinked acid sand fracturing acid liquor, comprising the following components in percentage by weight: 0.7% of thickening agent, 1.5% of cross-linking agent, 1.5% of corrosion inhibitor, 0.5% of surfactant, 0.15% of stabilizing agent, 20% of hydrochloric acid and 75.65% of water, wherein the thickening agent consists of the following components by weight percent: 6.61% of methacrylamidoethyltrimethylamine hydrochloride, 3.22% of acrylamide, 1.25% of acrylic acid, 9.52% of 2-acrylamide-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid, 6.15% of sodium hydroxide and 73.25% of deionized water; and the cross-linking agent consists of the following components in percentage by weight: 1% of zirconium oxychloride, 80% of formaldehyde and 19% of glyoxal. The crosslinked acid sand fracturing acid liquor can be cross-linked in 20% hydrochloric acid, the temperature resistance reaches 100 DEG C, the constant of reaction rate of acid-rock is 1.3744*10-6 (mol / cm<3>)(1-m)*(cm / s), and the viscosity of the gel-breaking liquid is less than 10 mPa.s.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
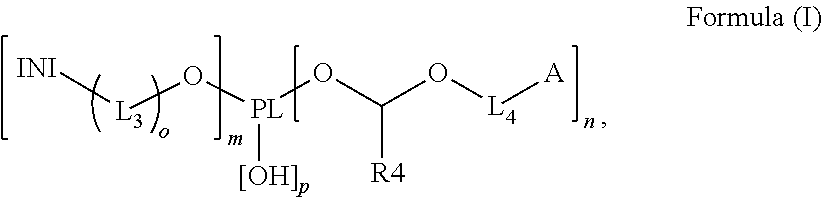
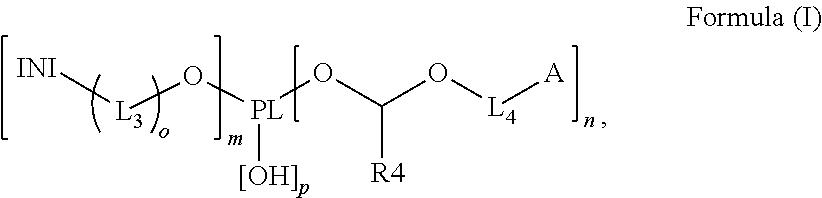
Polymerizable polymeric photoinitiators and radiation curable compositions
InactiveUS20120046376A1Simple and cost efficient procedureAvoiding unecological removal of solventInksVinyl etherPhosphine oxide
A polymerizable polymeric photoinitiator according to Formula (I):wherein:PL represents an n+m+p-functional polymeric core;n and m independently represent an integer from 1 to 30;p represents an integer from 0 to 10;o is 0 or 1;INI represents a group selected from the group consisting of a benzophenone, a thioxanthone, a carbazole, a anthraquinone, a camphor quinone, an α-hydroxyalkylphenone, an α-aminoalkylphenone, an acylphosphine oxide, a bisacyl phosphine oxide, an acylphosphine sulfide, a phenyl glyoxalate, a benzoin ether, a benzyl ketal, an α-dialkoxyacetophenone, a carbazolyl-O-acyl-oxime, an α-haloarylketone and an α-haloaryl sulfone;L3 and L4 represent a substituted or unsubstituted divalent linking group comprising 1 to 14 carbon atoms;A represents a radically polymerizable functional group selected from the group consisting of an acrylate, a methacrylate, a styrene, an acryl amide, a methacryl amide, a maleate, a fumarate, an itaconate, an vinyl ether, an allyl ether, an allyl ester, a maleimide, a vinyl nitrile and a vinyl ester; andR4 represents a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group.Radiation curable compositions containing the polymerizable polymeric photoinitiator and methods for preparing the polymerizable polymeric photoinitiator are also disclosed.
Owner:AGFA NV
Reversible geling co-polymer and method of making
InactiveUS6979464B2Thermally reversible geling copolymer is enhancedInitial viscosityPowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMethyl groupPolymer chemistry
The present invention is a thereapeutic agent carrier having a thermally reversible gel or geling copolymer that is a linear random copolymer of an [meth-]acrylamide derivative and a hydrophilic comonomer, wherein the linear random copolymer is in the form of a plurality of linear chains having a plurality of molecular weights greater than or equal to a minimum geling molecular weight cutoff and a therapeutic agent.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Artwork with modified urea-formaldehyde resin as adhesive and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN101012360AHigh impact strengthImprove cracking performanceDecorative surface effectsOrnamental structuresAqueous solutionPoly methacrylate
The invention discloses a binder and making method of modified urea-formaldehyde resin, which comprises the following steps: adopting urea-formaldehyde resin, fill, reinforcer, deoxidation agent, formaldehyde catching agent, anti-aging agent, anti-shrinking agent, hardener and auxiliary reinforcer; adopting modified copolymer of acrylic acid, sodium acrylate, N, N-dimethylamino propyl methyl acrylamide as anti-shrinking agent; making polyacrylamide solution reacted by acrylamide and ammonium persulphate as formaldehyde catching agent; allocating each component according to proportion; blending evenly; casting; extracting into vacuum; stripping; stewing; drying naturally; coating a layer of polymethacrylate paint on the surface of product; proceeding colorful paint; obtaining the product.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Hair treatment composition containing a combination of at least three different polymers
InactiveUS20060051311A1Without impairing application property and product performanceAttractive consistencyCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsCross-linkMeth-
The hair treatment composition contains a combination of an anionic polysaccharide, a second homopolymer or copolymer, which is built up from acrylamidoalkylsulfonic acids, methacrylamidoalkylsulfonic acids, or their salts, and a third polymer, which is an amphiphilic polymer. Preferably the hair treatment composition is a hair styling gel containing xanthan as a first polymer, ammonium acryloyldimethyltaurate / vinylpyrrolidone copolymer as a second polymer and, as a third polymer, cross-linked copolymers made from (meth)acrylic acid and C10- to C30-alkyl esters of (meth)acrylic acid. The preferred gel has a shaky pudding-like consistency and is suitable as a 2-in-1 gel that can be used as either a hair styling gel for increasing hairstyle volume or as a finishing gel for structuring a hairstyle.
Owner:WELLA GMBH
Preparation method of hydrogel for cartilage repair and with tissue inductivity
InactiveCN105126163AWith dual network structureImprove mechanical propertiesProsthesisDouble bondCartilage repair
The invention discloses a preparation method of hydrogel for cartilage repair and with tissue inductivity. The preparation method comprises the following main steps: A, polysaccharide or protein double bonding, B, hydrogel preparation, and C, adsorption of growth factors. According to the preparation method, double bonded natural polysaccharide / protein and methacrylamide dopamine which are completely degradable are used as the main components, and hydrogel adopting a double network structure can be formed through free radical polymerization of two materials of double bonded polysaccharide / protein and methacrylamide dopamine. Then hydrogel adsorbs biological activity growth factors through the dehydration and reswelling functions, and the growth factors are fixed into hydrogel throguh the dopamine component. The hydrogel obtained according to the preparation method is excellent in biological degradability and cell / tissue affinity, high in activity of the loaded growth factors and good in slow release performance, and can better induce cartilage regeneration and promote cartilage repair.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
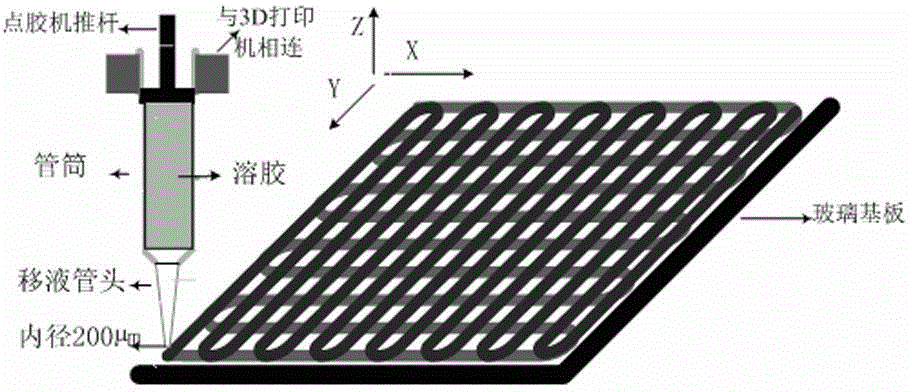
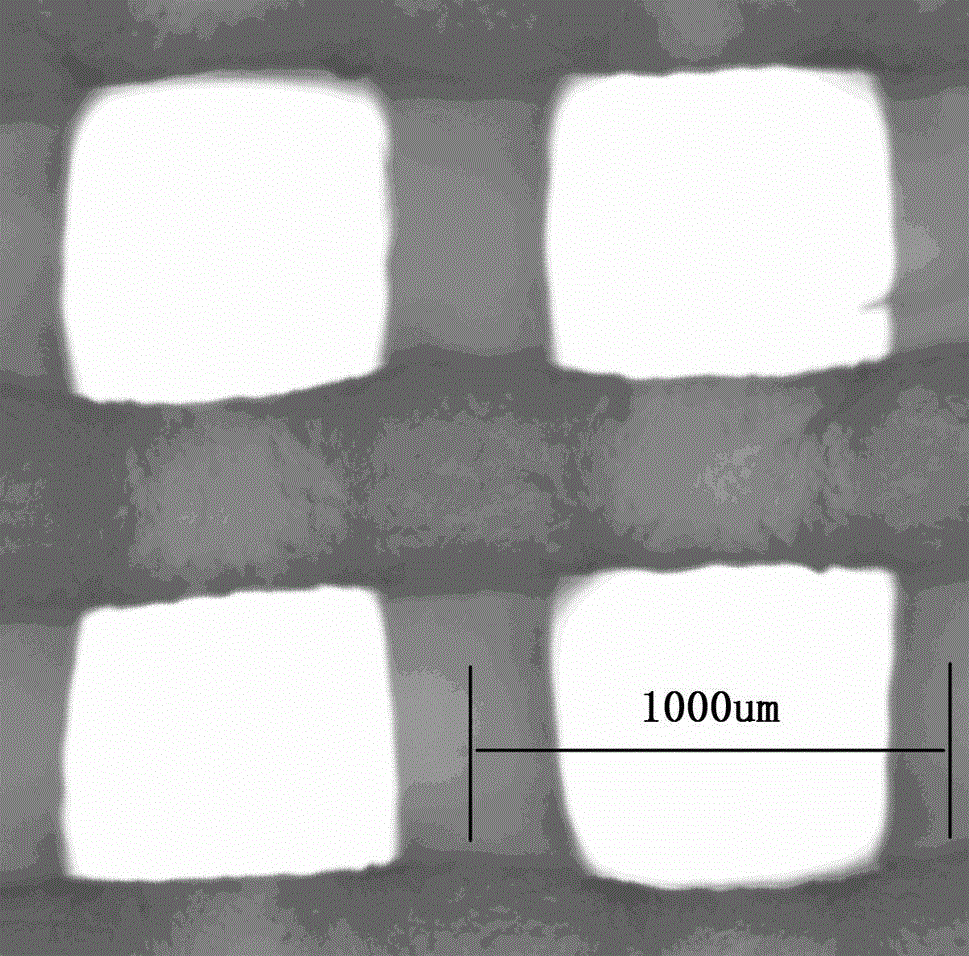
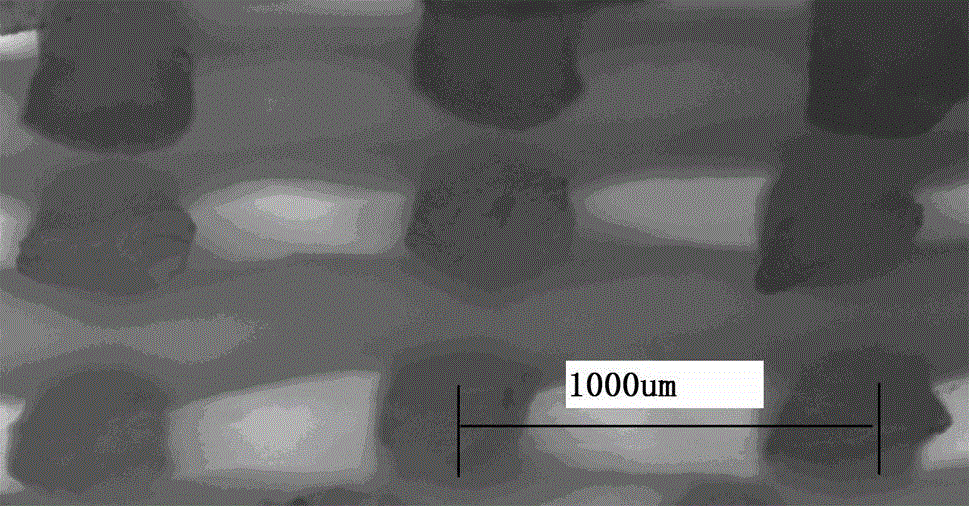
Method for preparing high-strength double-network hydrogel stent by virtue of 3D printing
InactiveCN104628936ANo collapseObvious collapse phenomenonAdditive manufacturing apparatusProsthesisCross-linkUltraviolet lights
The invention discloses a method for preparing a high-strength double-network hydrogel stent by virtue of 3D printing. The method comprises the following steps of adding a polymer monomer N, N-dimethyl acrylamide, an initiator, a crosslinking agent and sodium alginate (SA) into deionized water to form a solution and adding inorganic powder hydroxyapatite to obtain a sol; controlling and extruding the sol by a robot dispenser, and carrying out 3D printing molding to obtain a sol stent; placing the sol stent under ultraviolet light so that the monomer in the stent is subjected to photopolymerization and chemical cross-linking reaction to form a layer of chemically cross-linked network pre-molded hydrogel stent; immersing the pre-molded hydrogel stent into a CaCl2 aqueous solution so that SA in the stent is subjected to physical crosslinking to form a second layer of physically cross-linked network so as to obtain the hydrogel stent having physically and chemically cross-linked double-network. The hydrogel stent prepared by the method has higher mechanical strength and fine internal structure, and the three-dimensional morphology of the stent can be conveniently regulated and controlled to adapt to the complex application requirements of tissue engineering materials.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Orientation film, orientation film material, liquid crystal display having orientation film, and method for forming the same
ActiveUS20110199566A1Suppress image stickingSynthetic resin layered productsCoatingsMethacrylateFilm material
An alignment film material according to the present invention includes: a precursor of a first polyimide (p1); a second polyimide (p2) and a precursor thereof; and a vinyl-type monomer. The vinyl-type monomer is represented by general formula (1) P1-A1-(Z1-A2)n-P2 (in general formula (1), P1 and P2 are, independently, acrylate, methacrylate, acrylamide or methacrylamide; A1 and A2 represent, independently, 1,4-phenylene, 1,4-cyclohexane or 2,5-thiophene, or naphthalene-2,6-diyl or anthracene-2,7-diyl; at least one of A1 and A2 is substituted by at least one fluorine group; and Z1 is a —COO— group, a —OCO— group, a —O— group, a —CONH— group or a single bond, where n is 0 or 1).
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Preparation method and application of nano-modified PTFE and polyester-based composite film for preventing fan blades from icing
ActiveCN106313811ASolving non-adhesive technical problemsConvenient engineering constructionSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationPolyesterComposite film
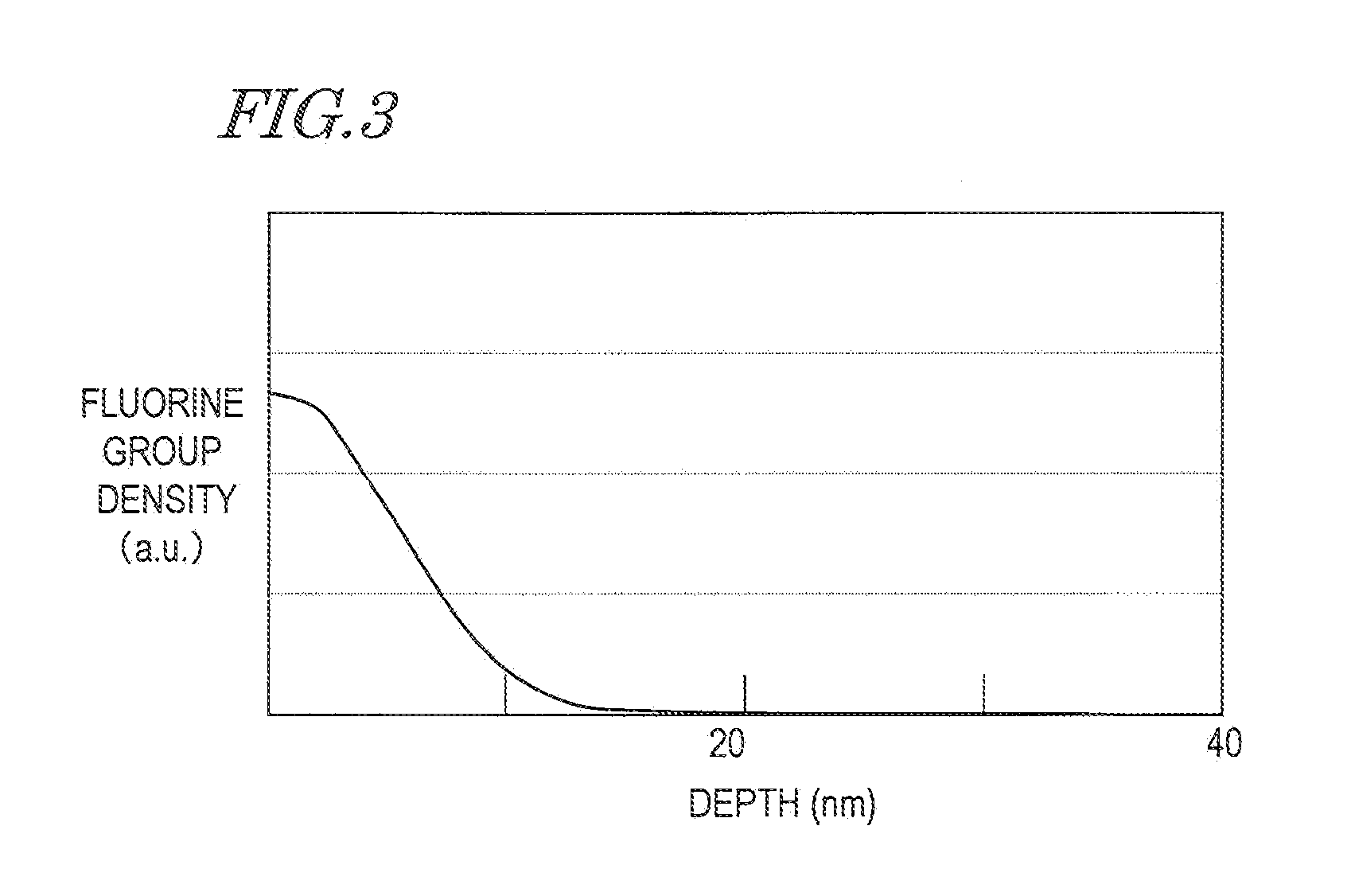
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a nano-modified PTFE and polyester-based composite film for preventing fan blades from icing. The method includes the steps of PTFE film modification, lamination complexing and photo-crosslinked adhesive application. A modifier is prepared from antimony-doped tin oxide nano-crystals, nano-titanium dioxide, nano-silicon carbide, an organic fluorine waterproofing agent and pentaerythritol tri-(3-aziridinyl)-propionate; in lamination complexing, a bonding complexing agent is prepared from 3-isocyanatomethyl-3,5,5-trimethylcyclohexyl isocyanate, vinyl acetate, ethyl carbamate, alpha-linolenic acid, (2)ethoxylated bisphenol A dimethacrylate, trimethylolpropane triacrylate and benzoyl peroxide; a photo-crosslinked adhesive is prepared from a poly[butyl acrylate-glycidyl methacrylate-n-butoxy methacrylamide]copolymer, vinyl acetate, butyl acrylate, an acrylate derivative, a photoinitiator and dimethylformamide. The method and the composite film solve the non-adhesion problem that a PTFE film can not be pasted on the surfaces of fan blades with an adhesive directly.
Owner:NANJING HAOHUI HI TECH CO LTD
High-temperature-resistant dispersed fluid loss agent for oil well cement and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102191027ASolve the problem of poor heat and salt toleranceImprove stabilityDrilling compositionPetroleumMaterials science
The invention provides a high-temperature-resistant dispersed fluid loss agent for oil well cement and a preparation method thereof. The fluid loss agent prepared with the method is used for reducing a fluid loss of cement paste in oil and natural gas well drilling and cementing processes. The fluid loss agent prepared with the method is a quadripolymer; comonomers are 2-acrylamide-2-methyl propanesulfonic acid (AMPS), N,N'-dimethylacrylamide (DMAA), acrylamide (AM), and maleic anhydride (MA); and an initiator is a mixed solution of ammonium persulfate and sodium hydrosulfite. The fluid loss agent provided by the invention has good capacities of controlling fluid loss and improving the rheologic property of the cement paste, and has good temperature-resistant and salt-resistant capabilityand wide application range.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
High-Temperature Crosslinked Polymer for Use in a Well
A method comprising the steps of: (A) forming a fluid comprising a crosslinked polymer, wherein the crosslinked polymer comprises: (i) a first monomeric unit of one or more N-vinyl lactams; and (ii) a crosslinker selected from the group consisting of: divinyl ether, diallyl ether, vinyl or allyl ethers of polyglycols or polyols, divinylbenzene, 1,3-divinylimidazolidin-2-one, divinyltetrahydropyrimidin-2(1H)-one, dienes, allyl amines, N-vinyl-3(E)-ethylidene pyrrolidone, ethylidene bis(N-vinylpyrrolidone), and any combination of any of the foregoing; and (B) introducing the fluid into a portion of a well. The crosslinked polymer may additionally comprise: a second monomeric unit selected from the group consisting of: acrylamide, N-substituted acrylamides, methacrylamide, N-substituted methacrylamides, acrylates, methacrylates, acrylic acid, methacrylic acid, N-vinylamides, N-allyl amides, vinyl alcohol, vinyl ethers, vinyl esters, allyl alcohol, allyl ethers, allyl esters, vinylpyridine, vinyl sulfonates, allyl sulfonates, vinylimidazole, allylimidazole, diallyldimethylammonium chloride, and any combination of any of the foregoing.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Ink composition, inkjet recording method, printed material, and molded printed material
ActiveCN101503587AExcellent curabilityGood flexibilityDuplicating/marking methodsInksMethacrylateDouble bond
An ink composition of the invention is characterized by comprising the following componets: (A) a compound having an ethylenically unsaturated double bond and a silicone chain, (B) a polymerizable monomer, and (C) a radical polymerization initiator, at least 75 wt % of the polymerizable monomer being a monofunctional polymerizable monomer selected from the group consisting of a monofunctional acrylate, a monofunctional methacrylate, a monofunctional vinyloxy compound, a monofunctional N -vinyl compound, a monofunctional ethylenically unsaturated carboxylic acid compound, a monofunctional acrylamide, and a monofunctional methacrylamide. Furthermore, the inkjet recording method, the printed material and molded printed material of the invention uses the ink composition according to the invention.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com