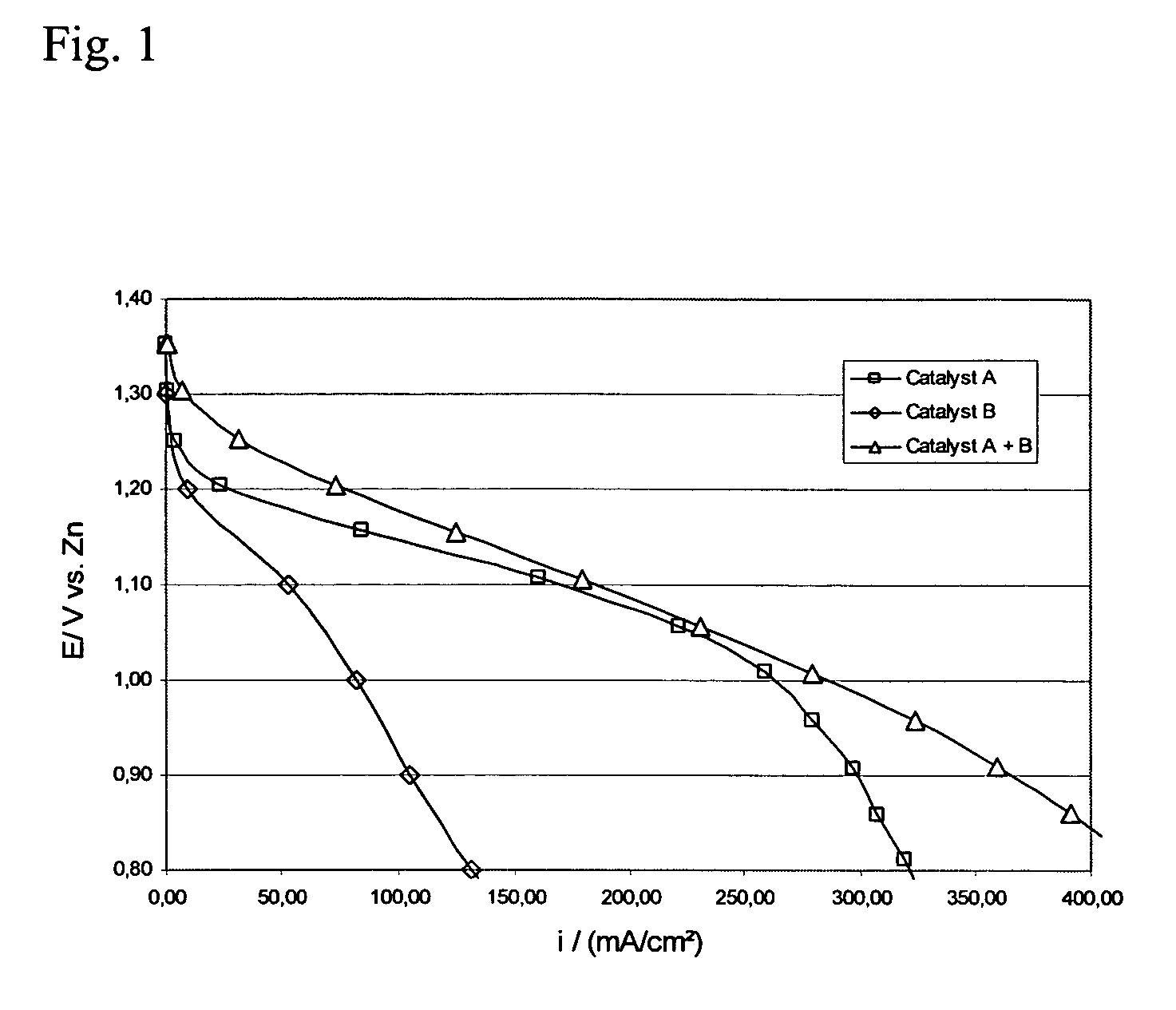
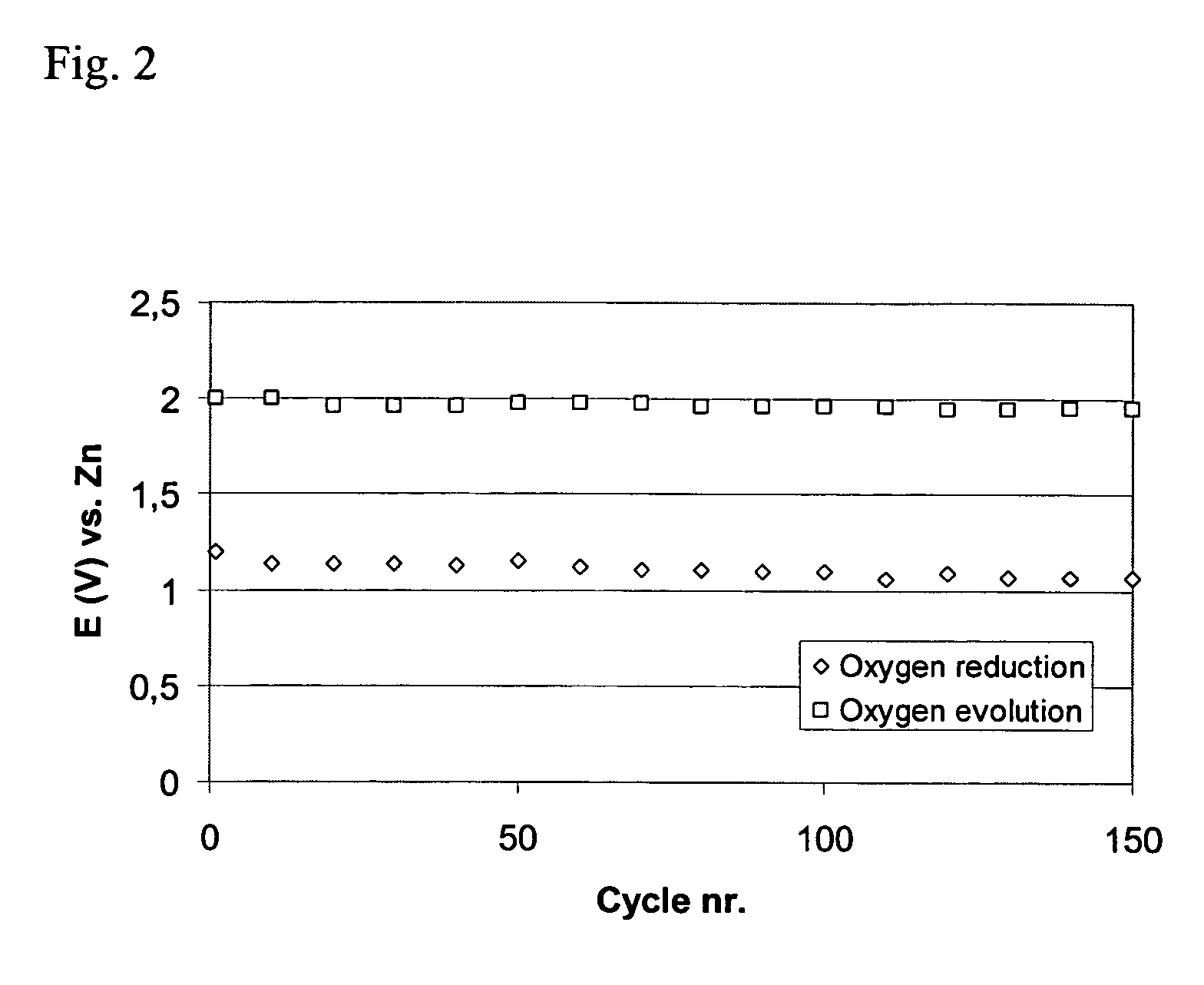
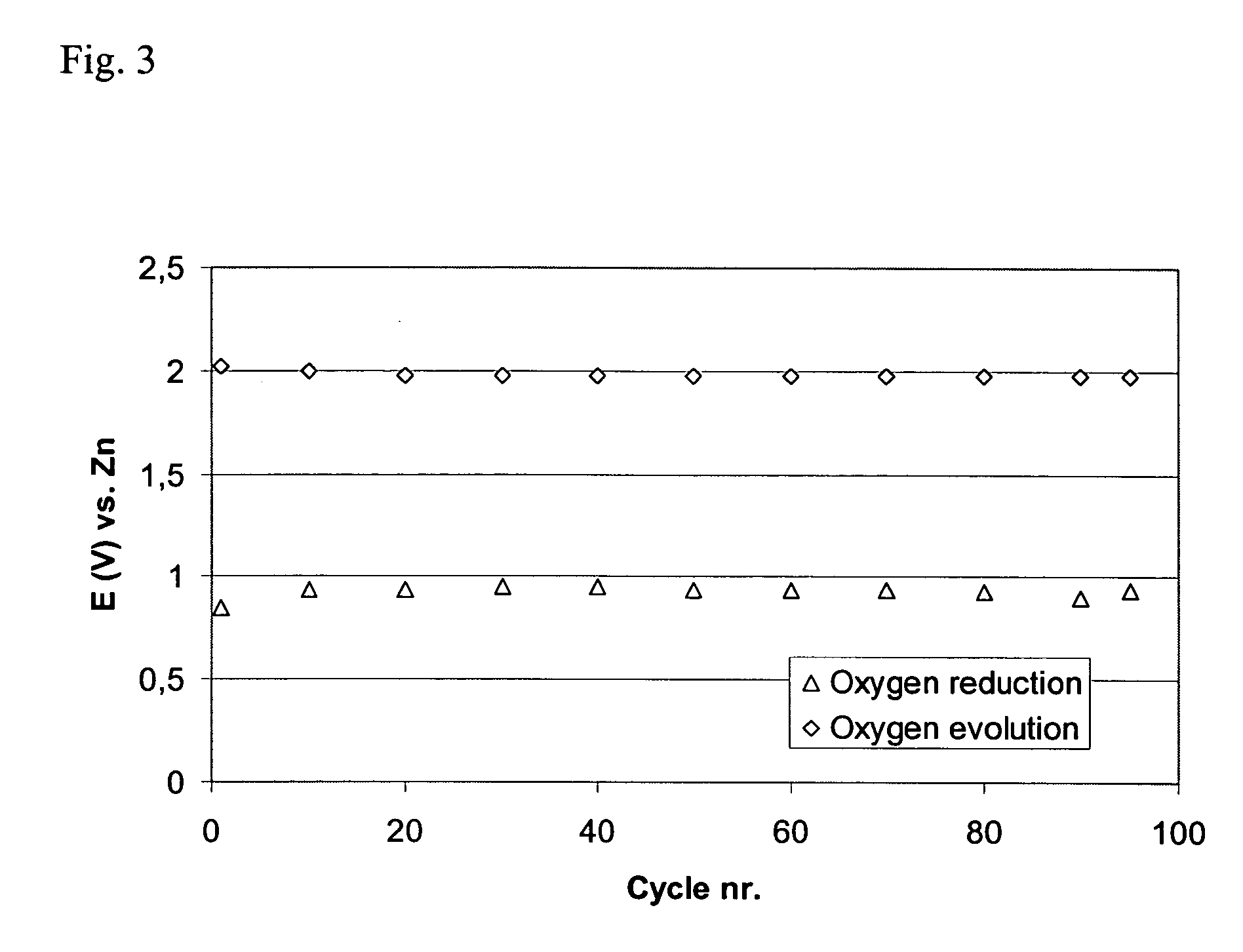
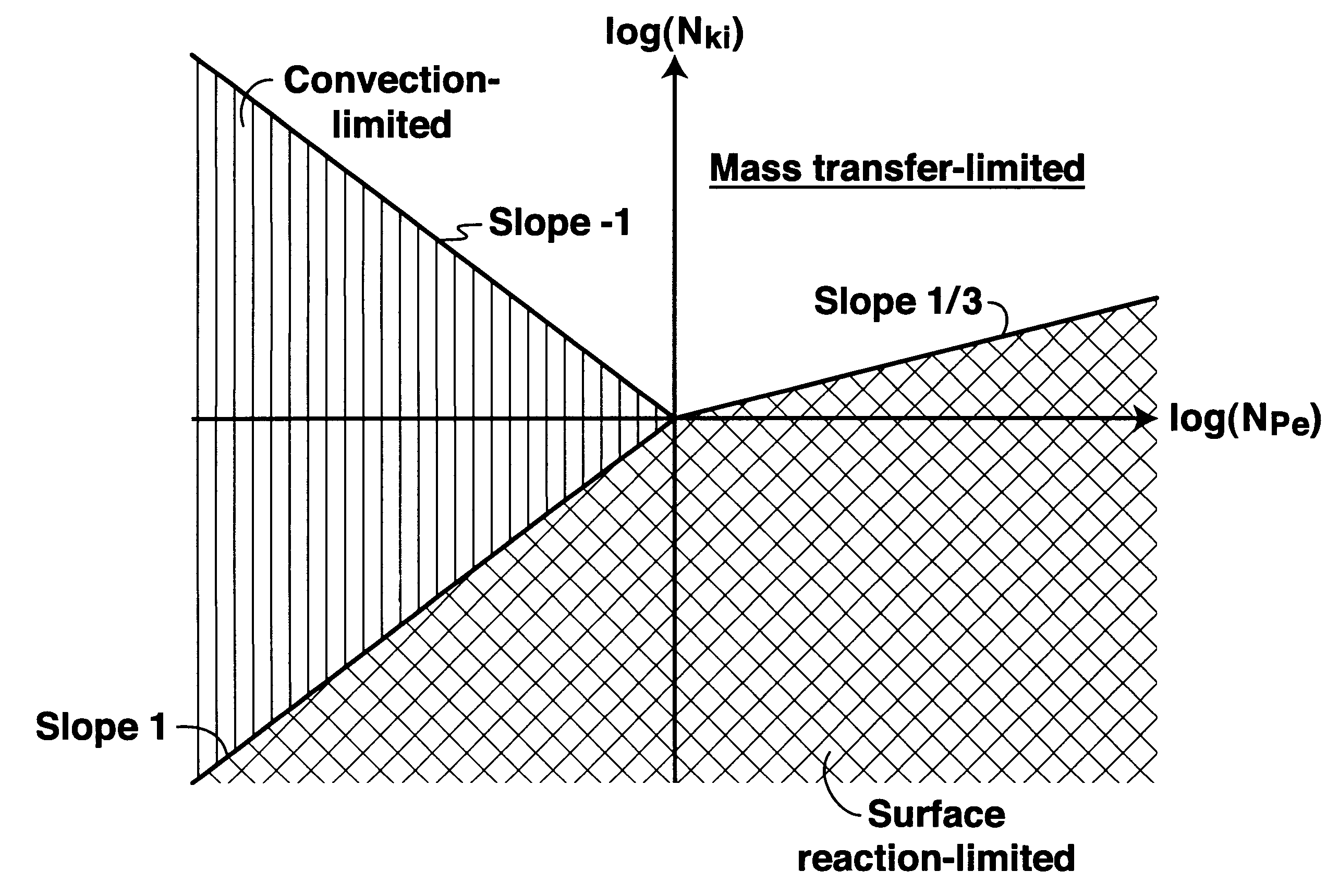
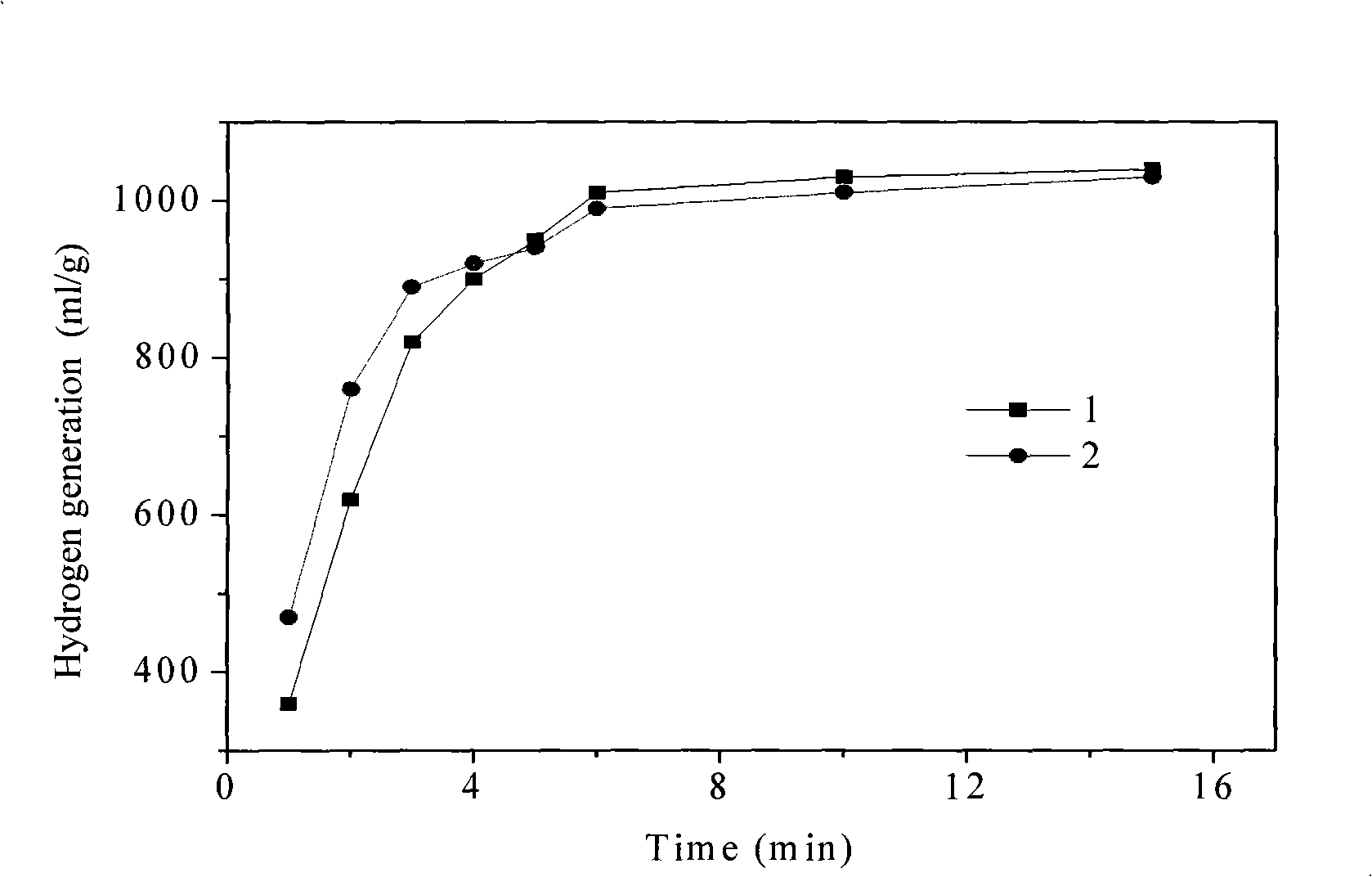
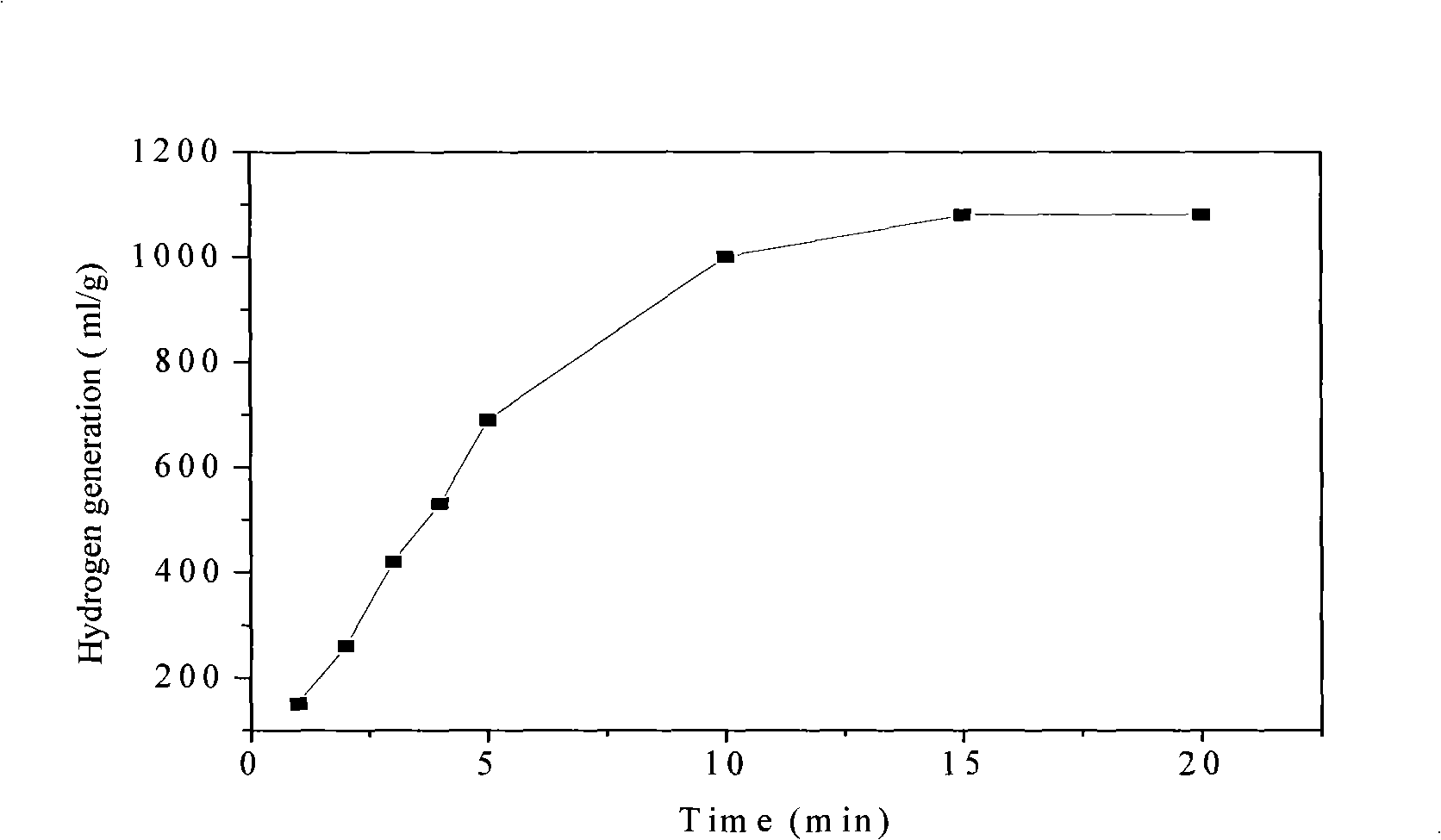
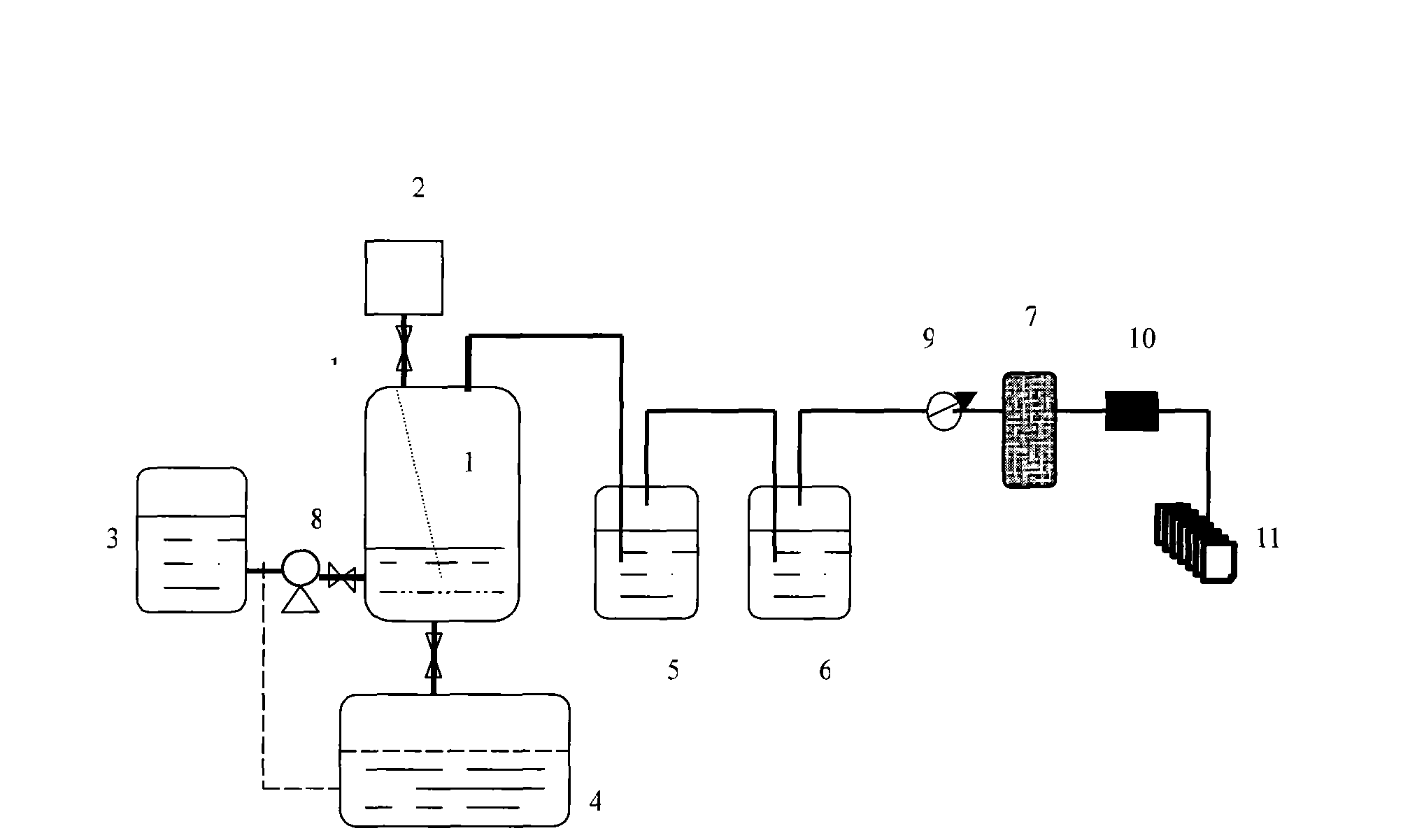
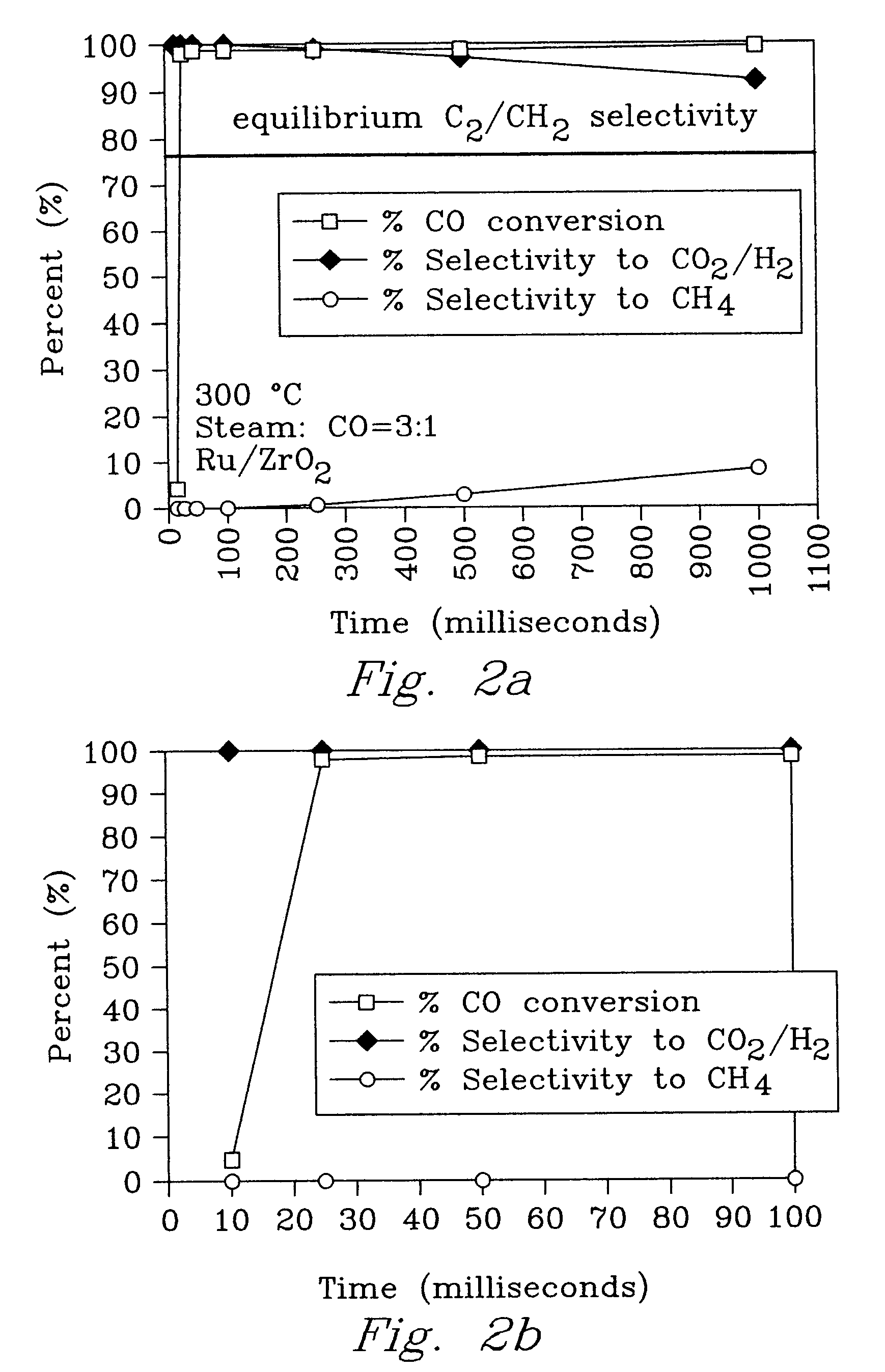
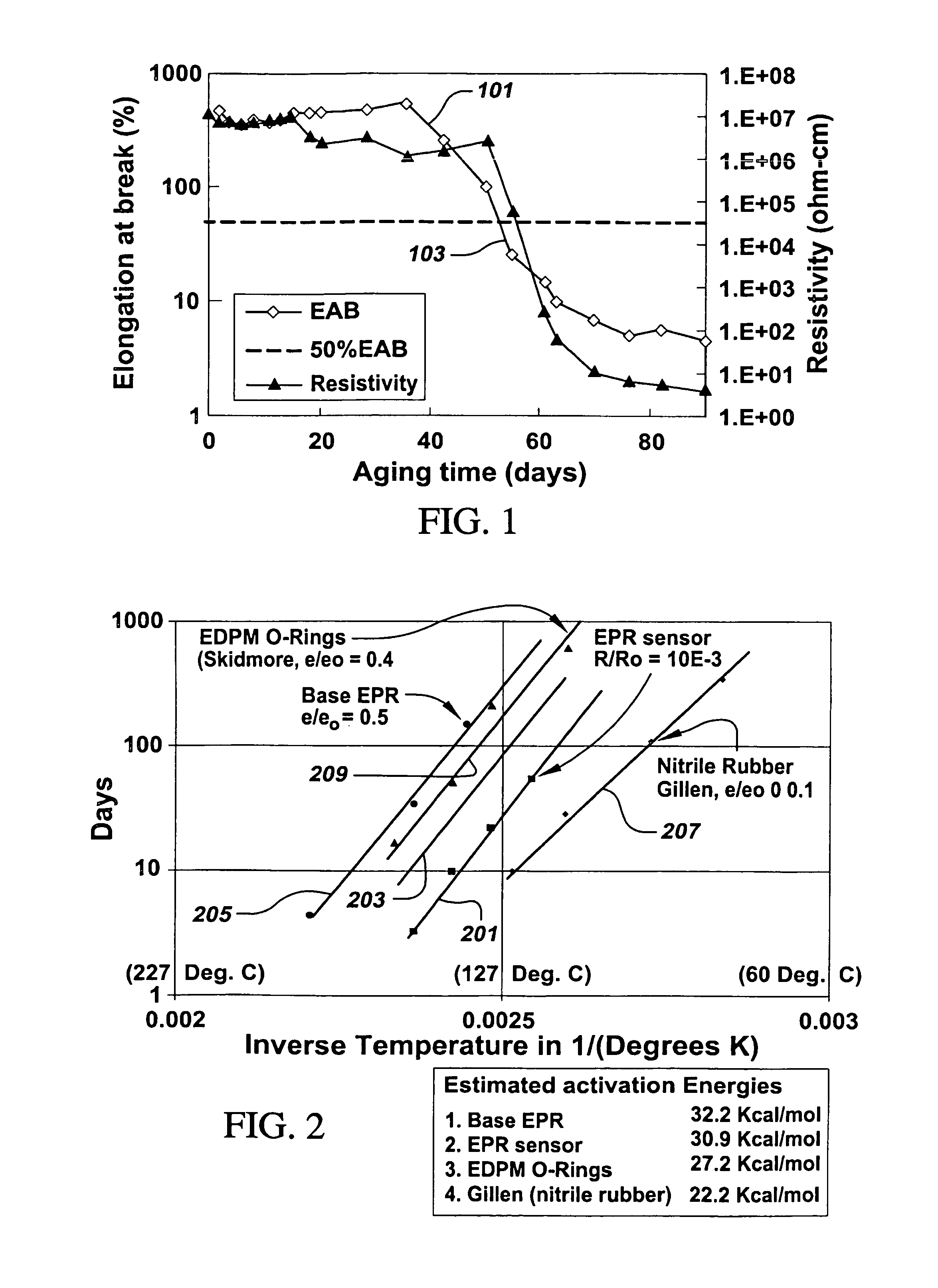
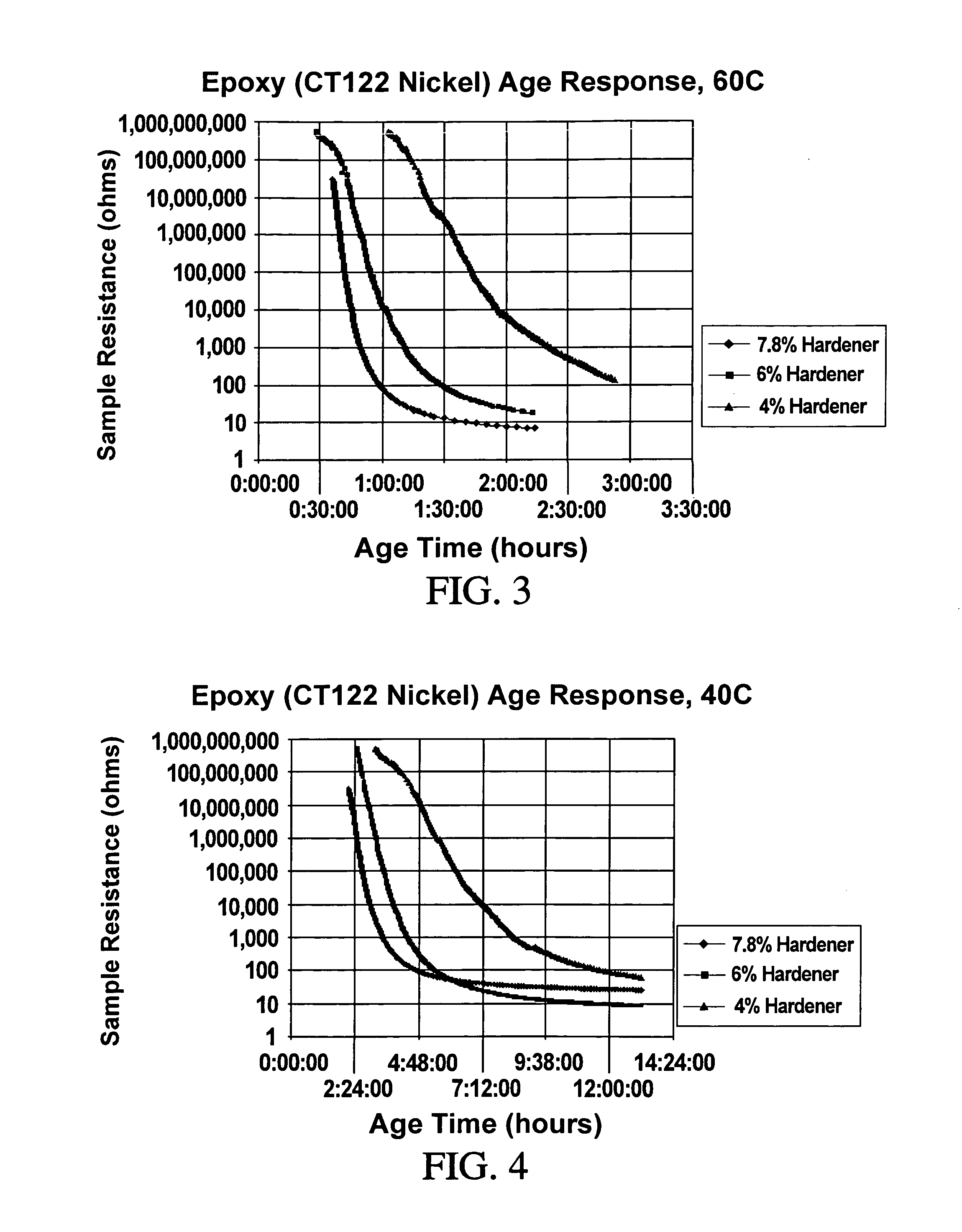
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4418 results about "Reaction rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The reaction rate or rate of reaction is the speed at which reactants are converted into products. For example, the oxidative rusting of iron under Earth's atmosphere is a slow reaction that can take many years, but the combustion of cellulose in a fire is a reaction that takes place in fractions of a second. For most reactions, the rate decreases as the reaction proceeds.
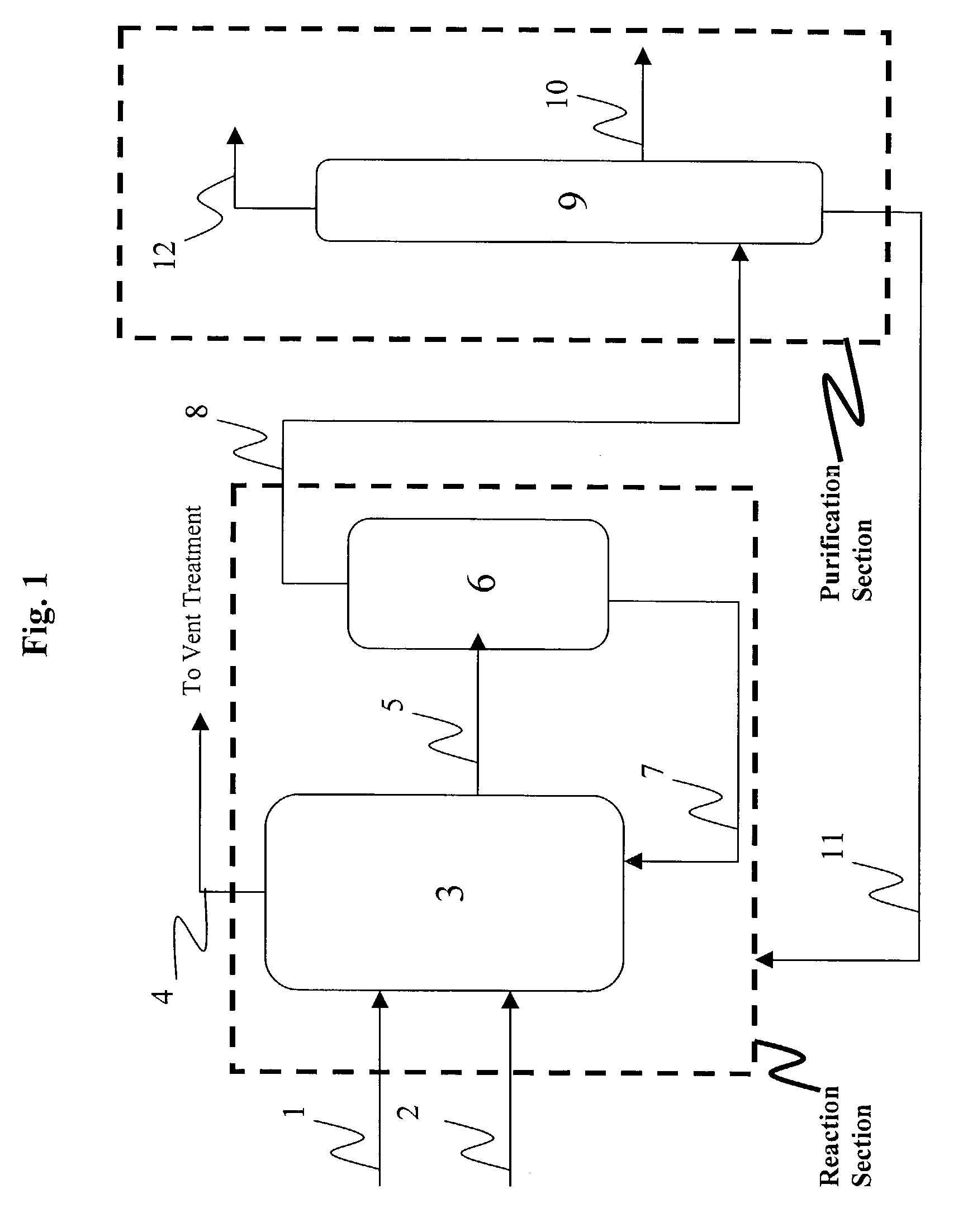
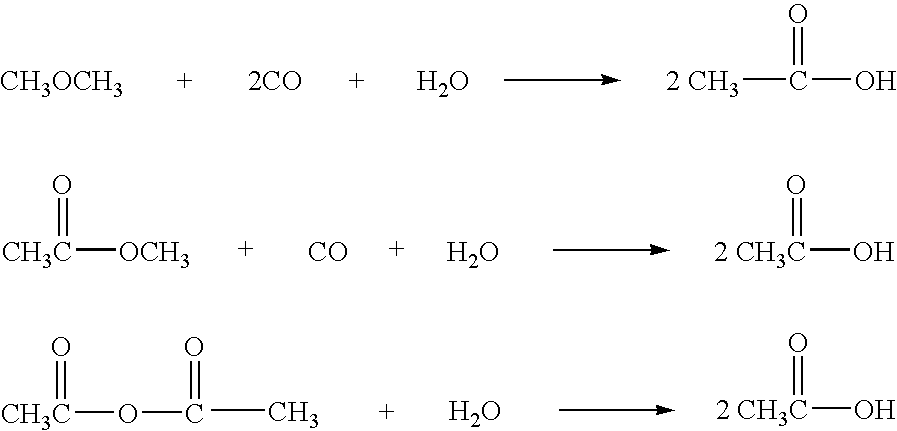
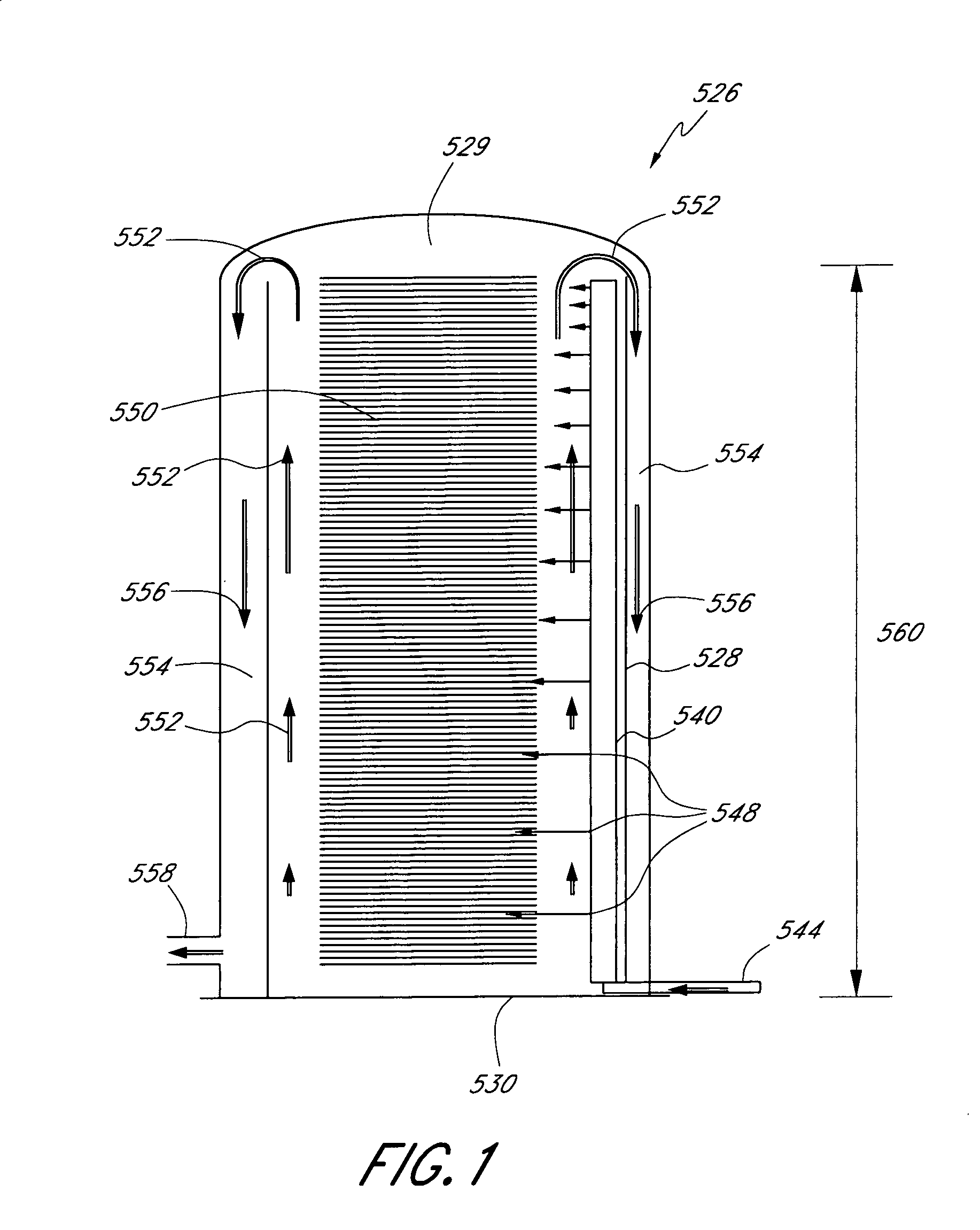
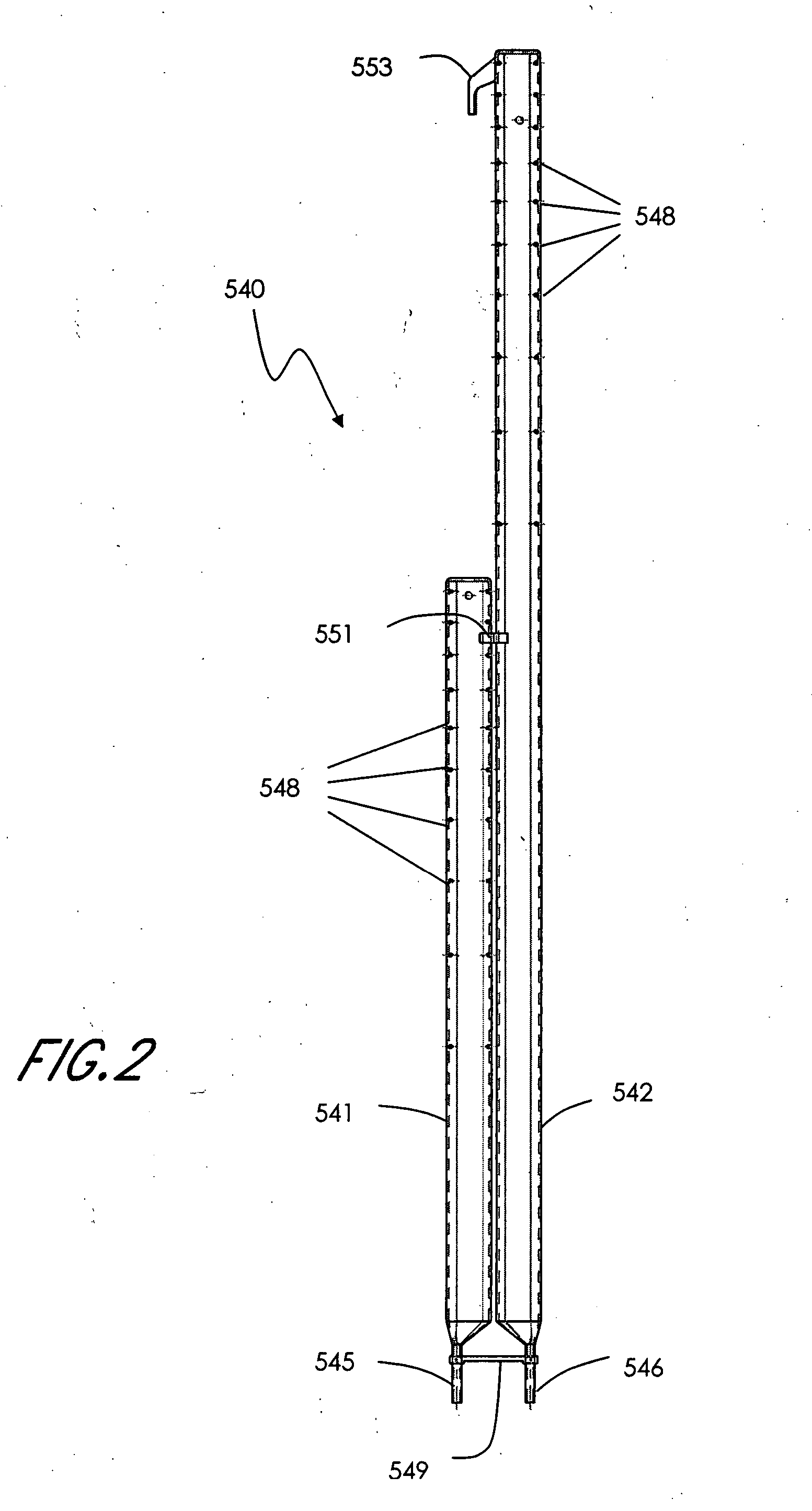
Low water methanol carbonylation process for high acetic acid production and for water balance control
ActiveUS7005541B2High acetic acid production rateIncrease chanceOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionWater methanolAcetic anhydride
The invention relates to a process for the production of acetic acid by carbonylation of methanol, and reactive derivatives thereof, in a reaction mixture using a rhodium-based catalyst in low water conditions. The process is used to achieve reaction rates of at least 15 g mol / l / hr. The high rate reactions proceed at water concentrations of less than 2.0 wt. %. Under certain conditions, the water concentration in the reaction mixture of the process is maintained at a desired concentration by at least one process step including adding a compound such as methyl acetate, dimethyl ether, acetic anhydride, or mixtures of these compounds to the reaction system. The process step of adding the components to the reaction mixture may be combined with other process steps for controlling water concentrations in reaction mixtures for the carbonylation of methanol.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
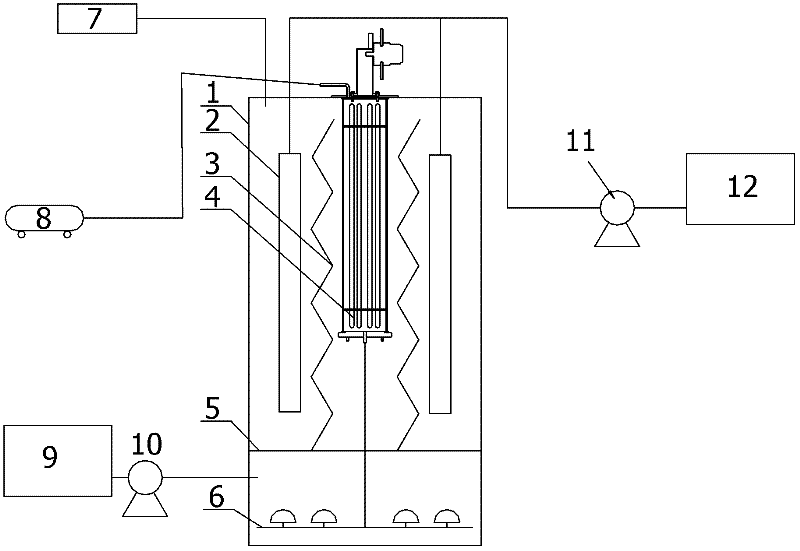
Industrial Wastewater Microwave Electrodeless UV Photocatalysis-Double Membrane Separation Coupling Treatment Device
InactiveCN102260003AAchieve coolingShort wavelengthWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWaste water treatment from animal husbandryIndustrial waste waterDecomposition
The present invention is an industrial waste water microwave electrodeless ultraviolet photocatalysis-dual membrane separation coupling treatment device, the device mainly consists of a reactor (1), a membrane separation system (2), a microwave electrodeless ultraviolet light source system (4), an aeration system, and an ozone tail gas decomposition device (7) connected to the reactor, and an inlet and outlet water system, wherein: the upper and lower parts of the reactor are respectively the reaction zone and the aeration zone, which are separated by a water distribution plate (5); the membrane separation system The microwave electrodeless ultraviolet light source system is located in the reaction zone and is separated by a corrugated partition (3); the aeration system is composed of a microporous aeration head (6) and a blower (8), and the microporous aeration head is located in the aeration At the bottom of the zone, the blower sends air to the aeration zone through the air duct. The invention has the characteristics of high reaction rate, complete degradation of organic matter, long-term operation and the like, and has strong operability and high safety. It is suitable for the treatment of refractory organic industrial wastewater, and it is also suitable for sterilization and disinfection in the field of water supply.
Owner:WUHAN TEXTILE UNIV
Device and technique for producing cyclohexane by benzene hydrogenation
ActiveCN106187660AImprove mass transfer efficiencyIncrease reaction rateHydrocarbon by hydrogenationBenzeneGas phase
The invention discloses a device and technique for producing cyclohexane by benzene hydrogenation. The device for producing cyclohexane by benzene hydrogenation comprises a reactor, a superfine bubble generator and a bubble breaker, wherein the reactor is provided with a first containing cavity; the wall of the first containing cavity is provided with a feed port, a circulation discharge port, a circulation return port and a gas phase outlet; the superfine bubble generator is provided with a second containing cavity; the wall of the second containing cavity is provided with a return port and a gas phase outlet; the return port of the superfine bubble generator communicates with the circulation return port of the reactor; the bubble breaker is arranged in the second containing cavity; the bubble breaker is provided with a gas phase inlet and a liquid phase inlet which communicates with the circulation discharge port of the reactor; and the gas phase inlet of the bubble breaker communicates with the gas phase outlet of the reactor. The device disclosed by the embodiment of the invention has the advantages of high mass transfer efficiency, high reaction rate, short reaction time, low material consumption and energy consumption, simple structure, low manufacturing cost and low maintenance cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Tower-type super fine bubble reactor
ActiveCN106268544AImprove mass transfer efficiencyIncrease reaction rateLiquid-gas reaction processesReaction rateEngineering
The invention discloses a tower-type super fine bubble reactor. The tower-type super fine bubble reactor comprises a body, a primary bubble breaker and a secondary bubble breaker, wherein a reaction cavity is formed in the body, a through hole, a liquid inlet, a circulating liquid outlet, an air inlet and a circulating air outlet are formed in the wall of the reaction cavity, one part of the primary bubble breaker penetrates through the through hole and extends into the reaction cavity, the primary bubble breaker is provided with a circulating liquid inlet, a circulating air inlet and an air-liquid mixture outlet, the circulating liquid inlet is communicated with the circulating liquid outlet, and the circulating air inlet is communicated with the circulating air outlet. The secondary bubble breaker is provided with a feeding port and a discharging port, and the feeding port is communicated with the air-liquid mixture outlet. The tower-type super fine bubble reactor has the advantages of being high in mass transfer efficiency, high in reaction rate, low in energy consumption and the like, the reaction time can be remarkably shortened, and reactor size can be decreased.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Diagnostic device and method
InactiveUS6222619B1Fast resultsImprove the level ofRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationDiagnostic programReaction rate
A method and apparatus of diagnosing a cardiac disease state in as little as two minutes involving the utilization of an evanescent wave assay system in conjunction with a data acquisition and analysis procedure that monitors the precision of assay results in real time (i.e., while data is being acquired). The method includes diagnosing a disease state using a diagnostic procedure (e.g., an immunoassay) wherein the testing device informs the person conducting the test of the results of the test as soon as reliable test data is obtained (generally, <5% variation in the reaction rate of the assay). After which point, the diagnostic procedure may be terminated.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
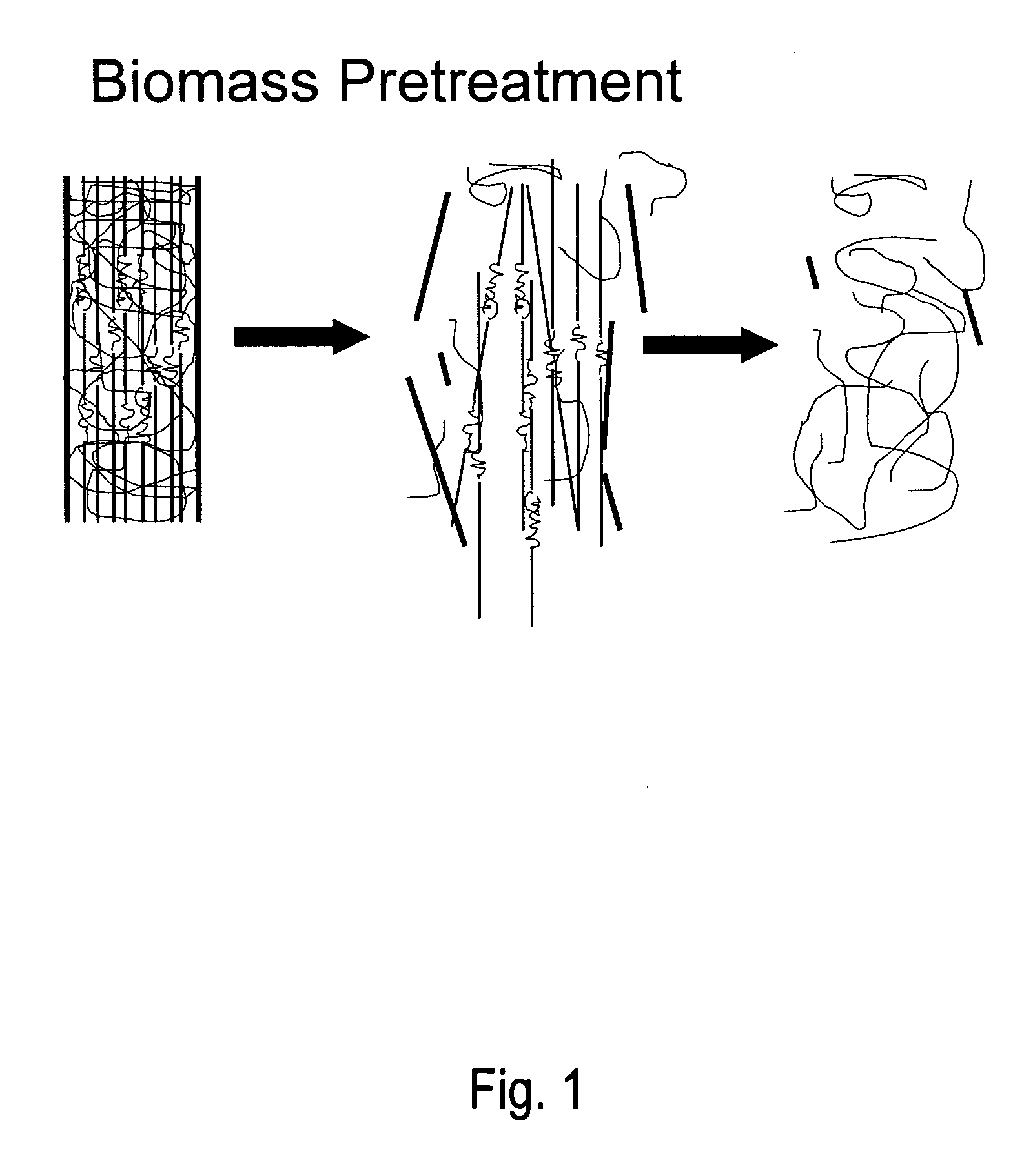
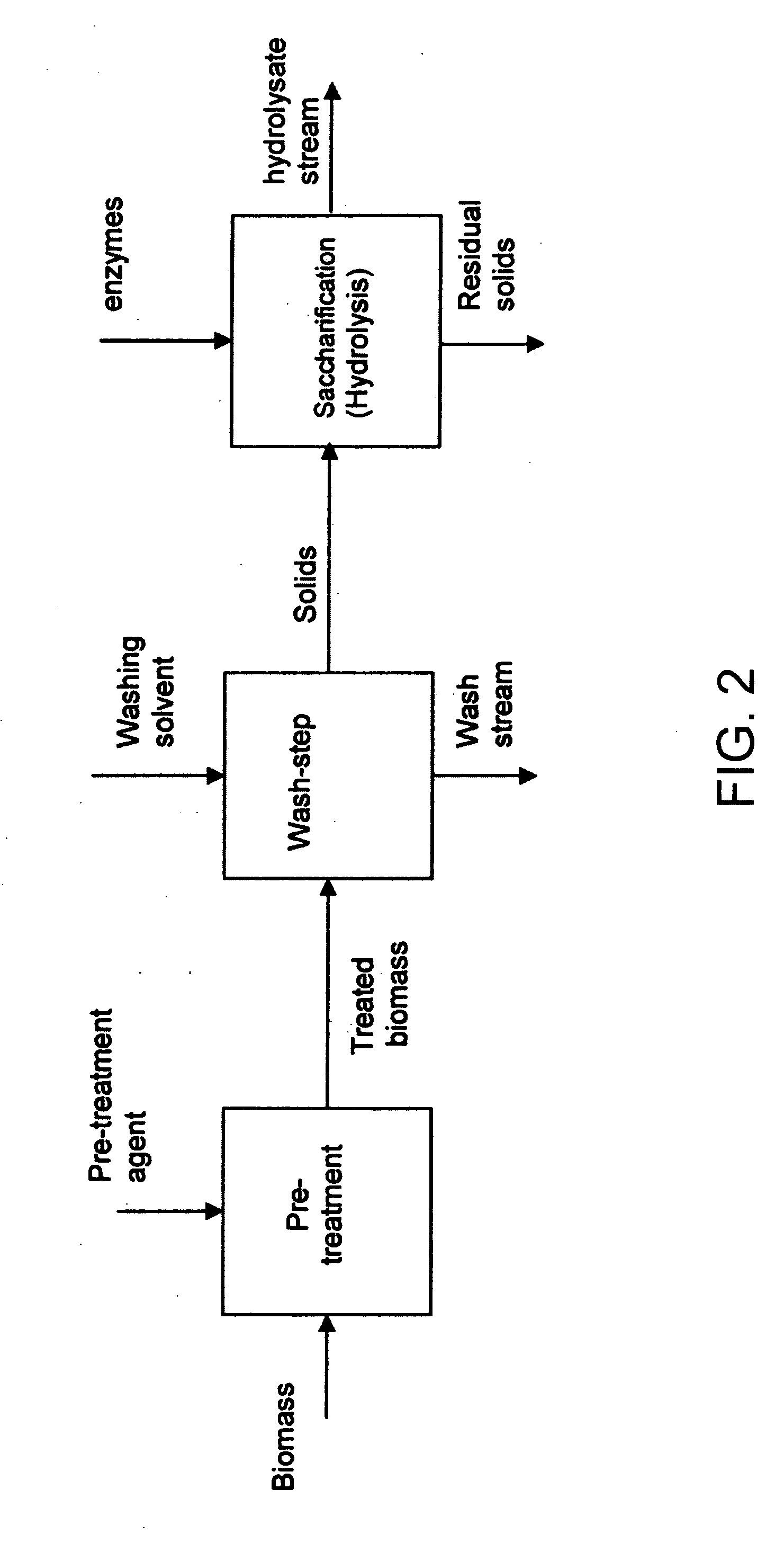
Biomass pretreatment
A method for lignocellulose conversion to sugar with improvements in yield and rate of sugar production has been developed by using ionic liquid pretreatment. This new pretreatment strategy substantially improves the efficiency (in terms of yield and reaction rates) of saccharification of lignocellulosic biomass. Cellulose and hemicellulose, when hydrolyzed into their sugars, can be converted into ethanol fuel through well established fermentation technologies. These sugars also form the feedstocks for production of variety of chemicals and polymers. The complex structure of biomass requires proper pretreatment to enable efficient saccharification of cellulose and hemicellulose components to their constituent sugars. Current pretreatment approaches suffer from slow reaction rates of cellulose hydrolysis (by using the enzyme cellulase) and low yields.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO +1
Low temperature silicon compound deposition
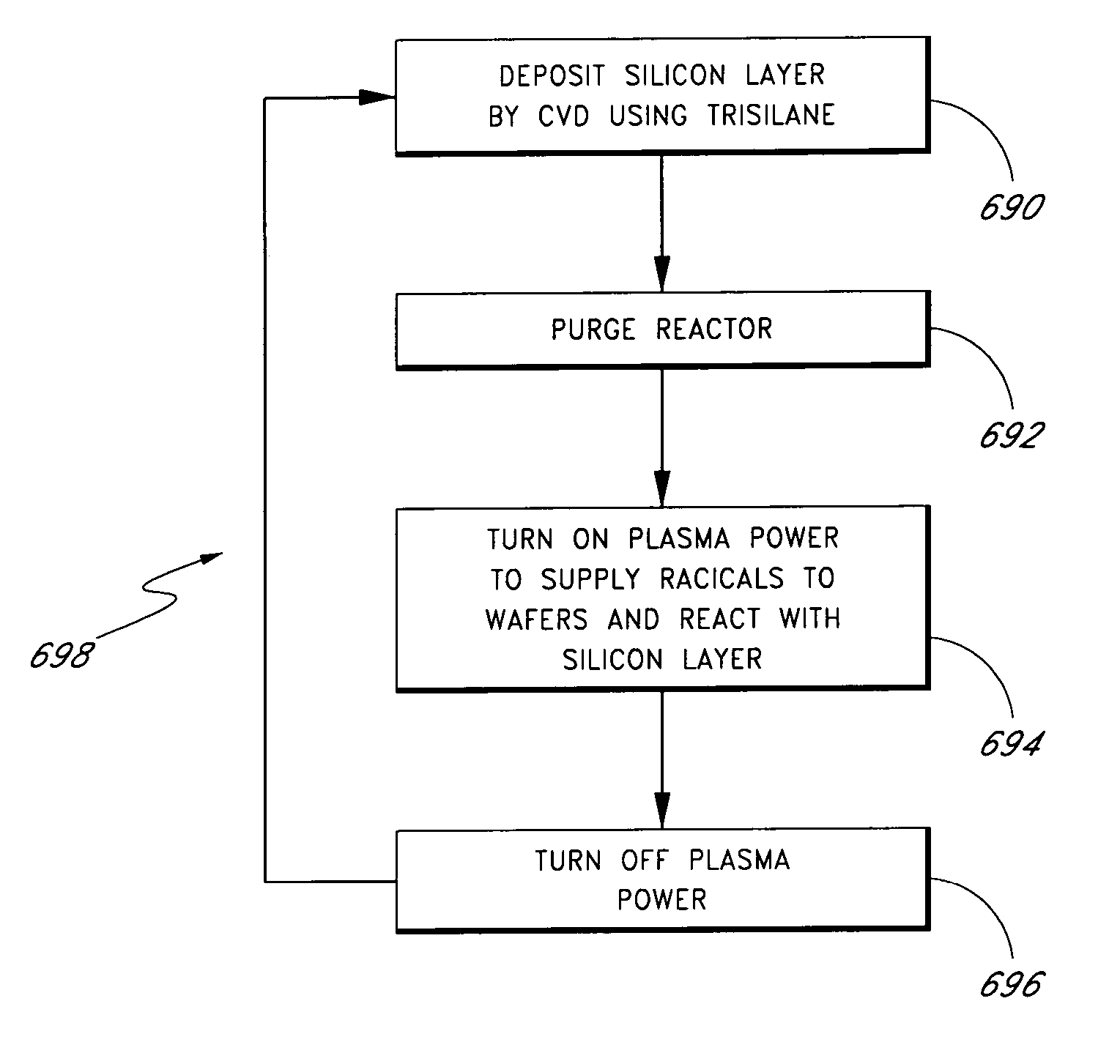
ActiveUS20060088985A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingReaction rateGas phase
Sequential processes are conducted in a batch reaction chamber to form ultra high quality silicon-containing compound layers, e.g., silicon nitride layers, at low temperatures. Under reaction rate limited conditions, a silicon layer is deposited on a substrate using trisilane as the silicon precursor. Trisilane flow is interrupted. A silicon nitride layer is then formed by nitriding the silicon layer with nitrogen radicals, such as by pulsing the plasma power (remote or in situ) on after a trisilane step. The nitrogen radical supply is stopped. Optionally non-activated ammonia is also supplied, continuously or intermittently. If desired, the process is repeated for greater thickness, purging the reactor after each trisilane and silicon compounding step to avoid gas phase reactions, with each cycle producing about 5-7 angstroms of silicon nitride.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
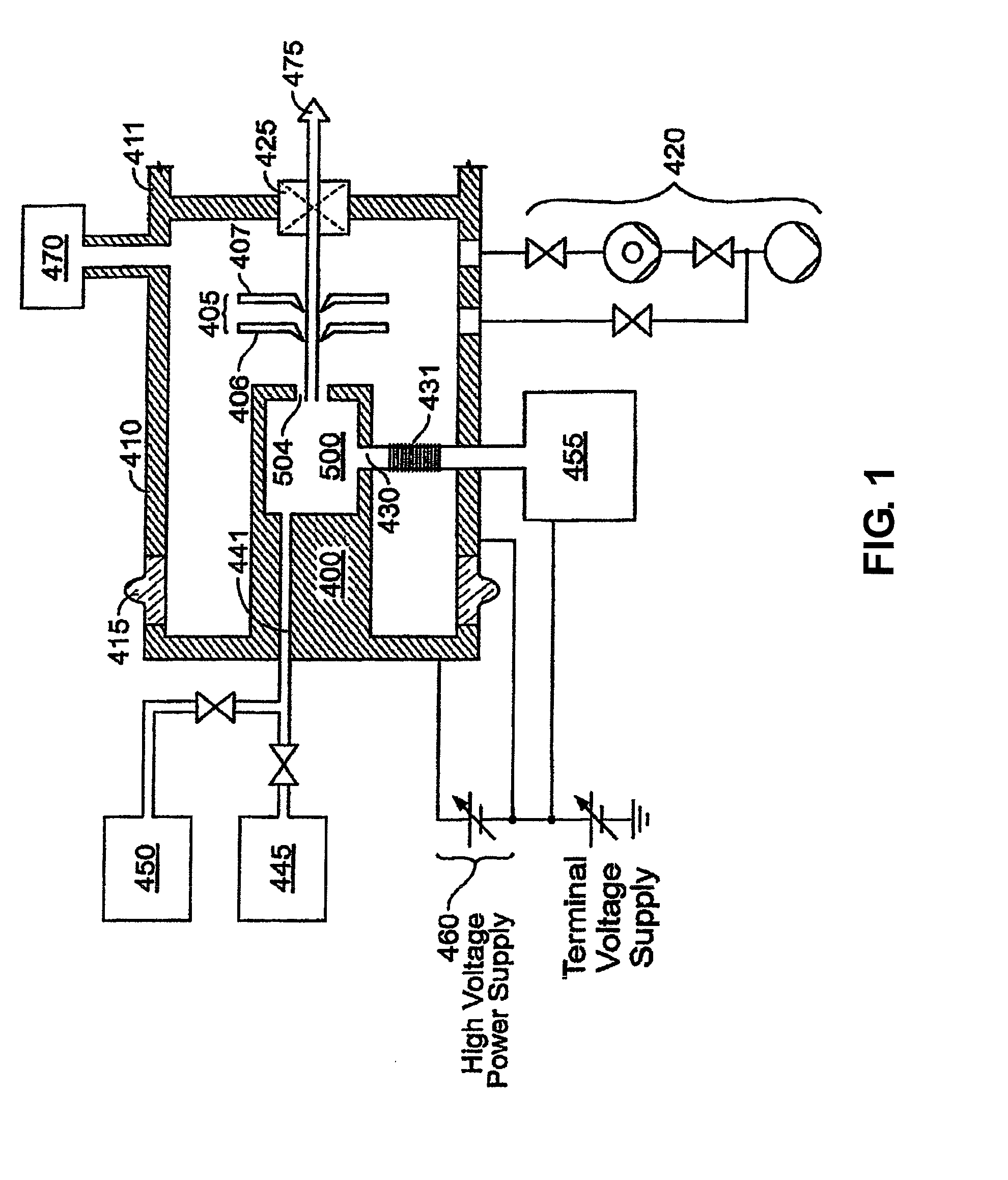
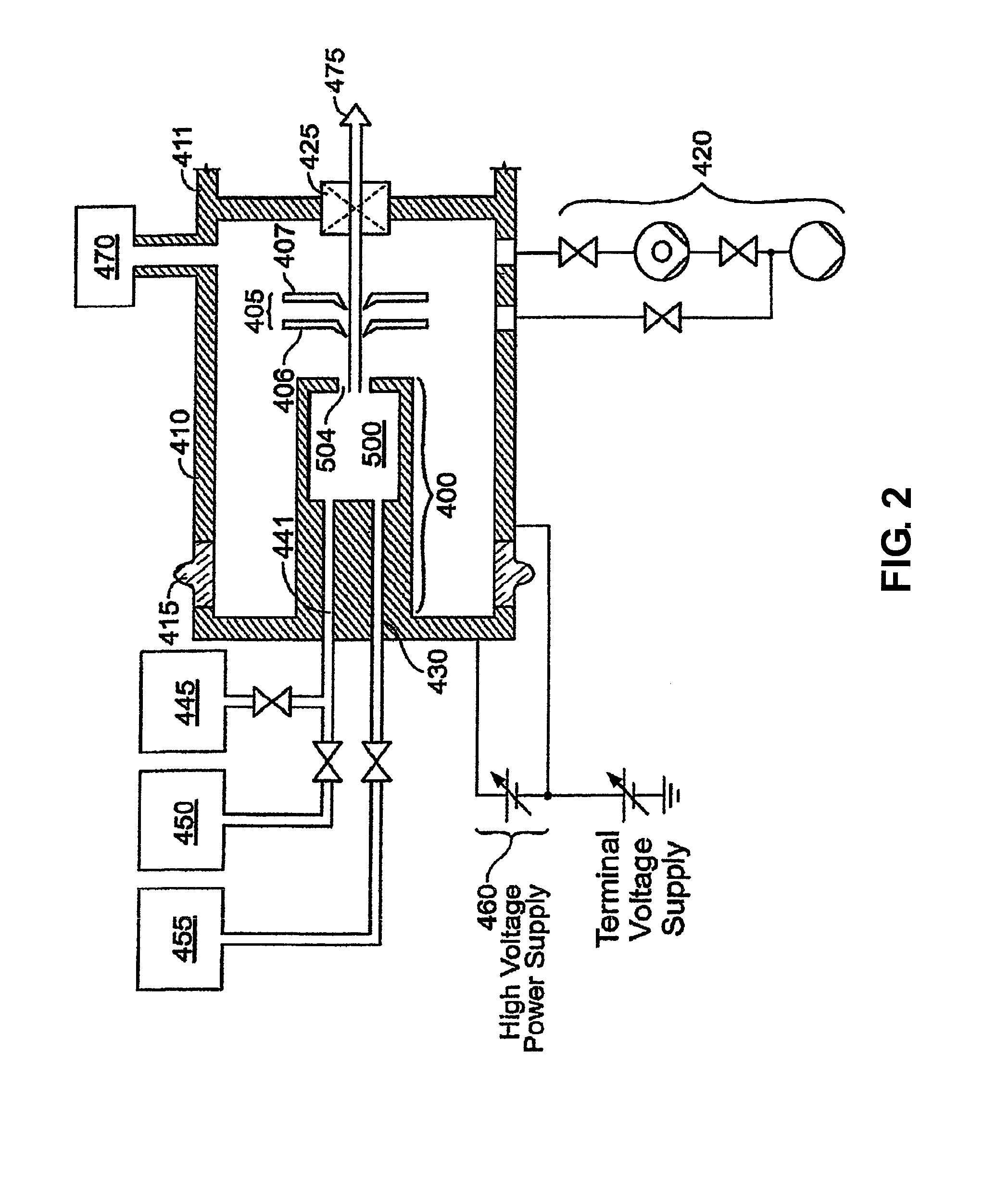
Computer addressable plasma density modification for etch and deposition processes
Disclosed herein are methods of modifying a reaction rate on a semiconductor substrate in a processing chamber which utilize a phased-array of microwave antennas. The methods may include energizing a plasma in a processing chamber, emitting a beam of microwave radiation from a phased-array of microwave antennas, and directing the beam into the plasma so as to cause a change in a reaction rate on the surface of a semiconductor substrate inside the processing chamber. Also disclosed herein are particular embodiments of phased-arrays of microwave antennas, as well as semiconductor processing apparatuses which include a phased-array of microwave antennas configured to emit a beam of microwave radiation into a processing chamber.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Process for producing biodiesel, lubricants, and fuel and lubricant additives in a critical fluid medium
InactiveUS6887283B1Limited mass transferImprove reaction speedFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationBiodieselVegetable oil
A process for producing alkyl esters useful in biofuels and lubricants by transesterifying glyceride- or esterifying free fatty acid-containing substances in a single critical phase medium is disclosed. The critical phase medium provides increased reaction rates, decreases the loss of catalyst or catalyst activity and improves the overall yield of desired product. The process involves the steps of dissolving an input glyceride- or free fatty acid-containing substance with an alcohol or water into a critical fluid medium; reacting the glyceride- or free fatty acid-containing substance with the alcohol or water input over either a solid or liquid acidic or basic catalyst and sequentially separating the products from each other and from the critical fluid medium, which critical fluid medium can then be recycled back in the process. The process significantly reduces the cost of producing additives or alternatives to automotive fuels and lubricants utilizing inexpensive glyceride- or free fatty acid-containing substances, such as animal fats, vegetable oils, rendered fats, and restaurant grease.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
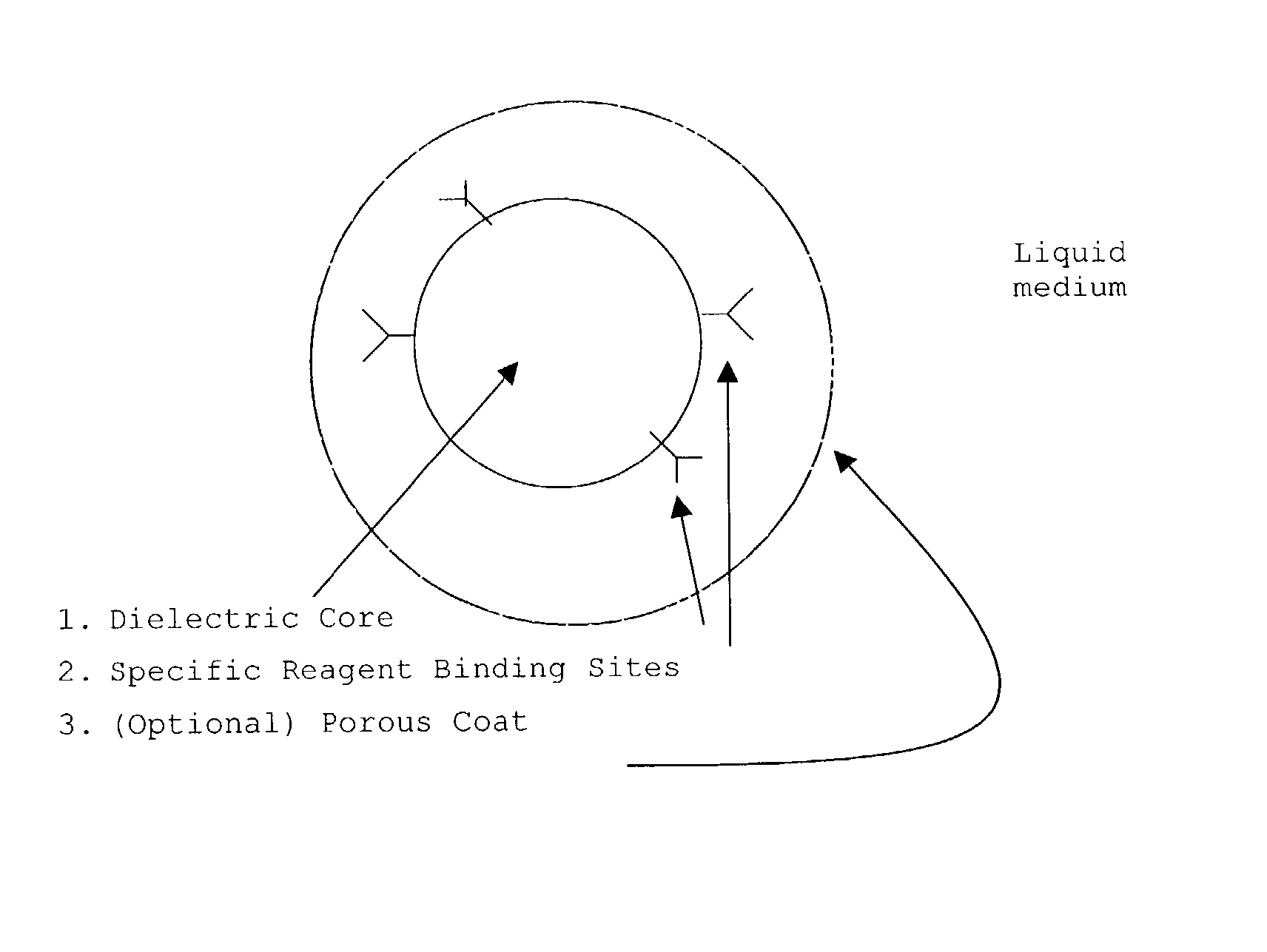
Method for measuring substance and testing piece
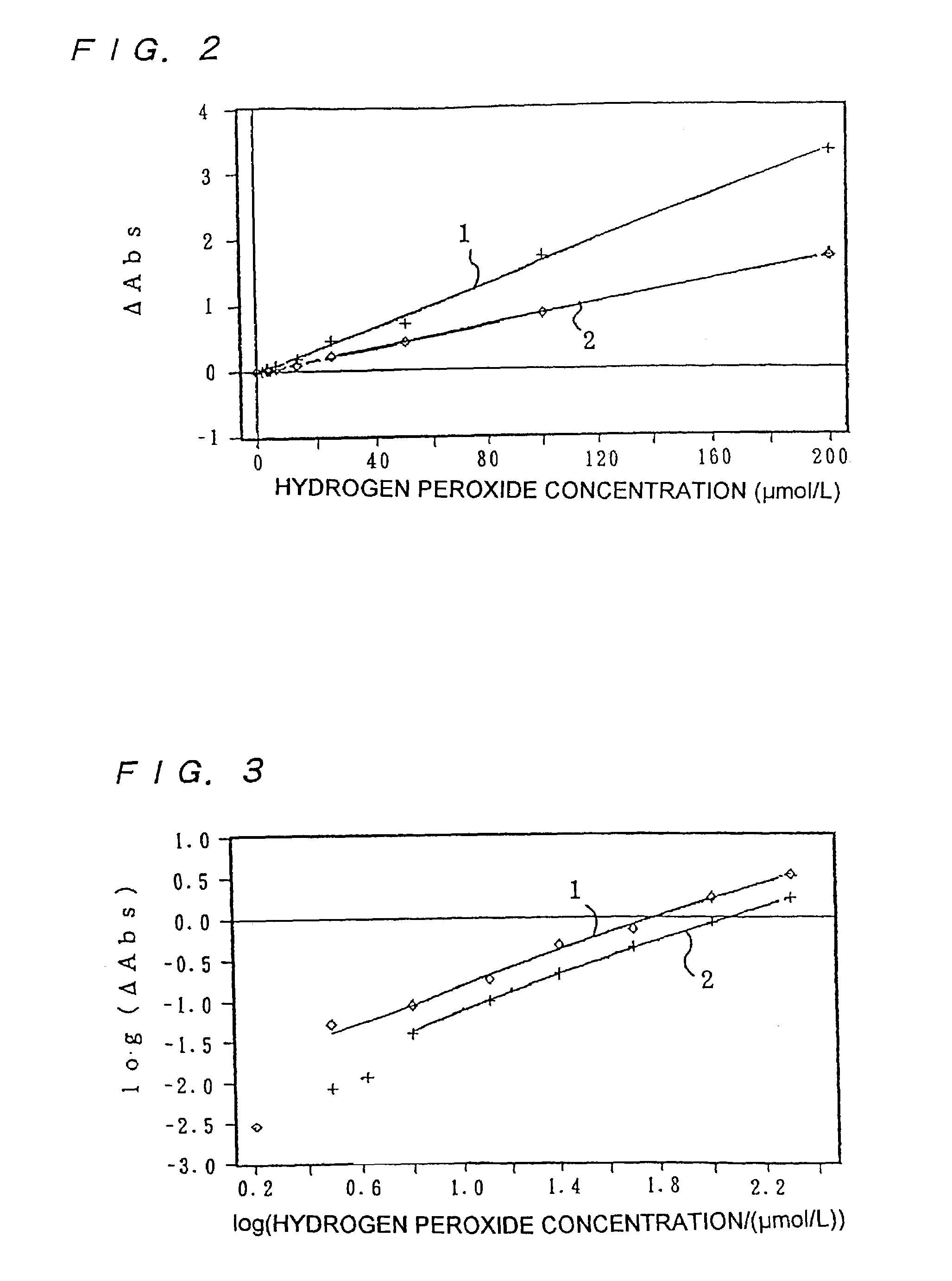
InactiveUS7153696B2High measurement accuracyHigh measurement sensitivityAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDiffusionChemical reaction
A method of measuring an analyte, comprising a step of measuring a detectable substance by using a reaction system including a formation reaction of the detectable substance based on a chemical reaction of the analyte contained in a sample, wherein a layered inorganic compound is caused to exist in the reaction system including the formation reaction of the detectable substance, whereby high-sensitivity measurement is made possible, the detectable substance can be stabilized to improve accuracy of the measurement, a rate of a chemical reaction is increased to enable quick measurement, and high-sensitivity measurement is made possible even in a reaction system which forms an insoluble substance. Also, it can be provided an analytical testing piece for measuring an analyte, by measuring a detectable substance by using a reaction system including a formation reaction of the detectable substance based on a chemical reaction of the analyte contained in a sample, wherein the testing piece comprises at least one test portion having a detection portion for detecting the detectable substance and contains a layered inorganic compound at least in the test portion, whereby diffusion and elution of a dyestuff or the like is prevented, more sensitive and accurate simple analysis is made possible, and easy handling is possible.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Low temperature silicon compound deposition
InactiveUS7294582B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseSilanes
Sequential processes are conducted in a batch reaction chamber to form ultra high quality silicon-containing compound layers, e.g., silicon nitride layers, at low temperatures. Under reaction rate limited conditions, a silicon layer is deposited on a substrate using trisilane as the silicon precursor. Trisilane flow is interrupted. A silicon nitride layer is then formed by nitriding the silicon layer with nitrogen radicals, such as by pulsing the plasma power (remote or in situ) on after a trisilane step. The nitrogen radical supply is stopped. Optionally non-activated ammonia is also supplied, continuously or intermittently. If desired, the process is repeated for greater thickness, purging the reactor after each trisilane and silicon compounding step to avoid gas phase reactions, with each cycle producing about 5-7 angstroms of silicon nitride.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Method for optimizing acid injection rate in carbonate acidizing process
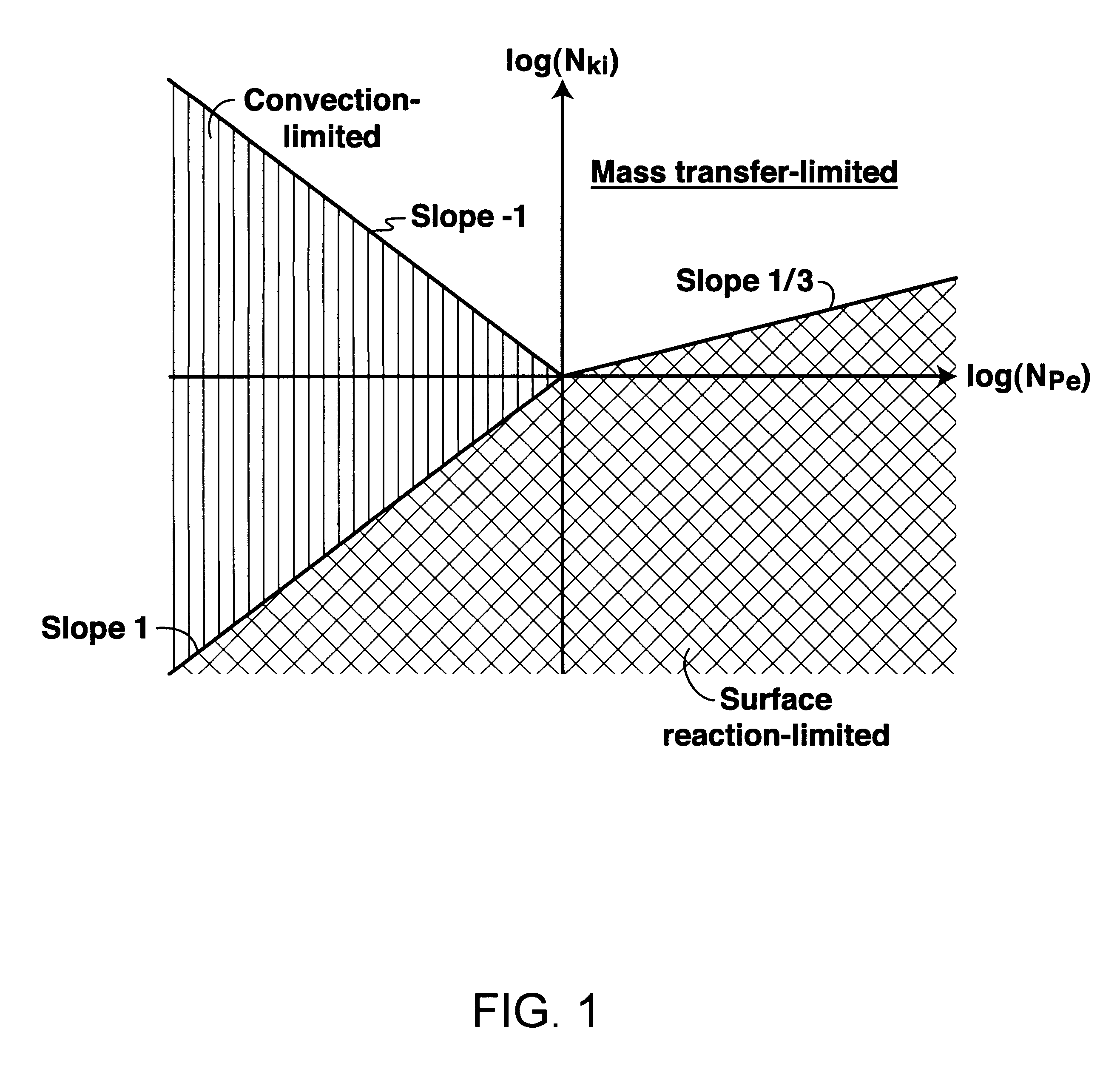
A method for optimizing the rate at which a given acid should be injected into a carbonate-containing rock formation during an acid injection process. The first step of the method calculates the Damkohler numbers for regimes in which kinematic force, diffusion rate and reaction rate control. The Damkohler numbers are then used to calculate the rate of growth of wormholes as a function of flux, taking into account compact dissolution, wormholing, and uniform dissolution. The calculated function is used to calculate an optimum flux for the formation. The optimum flux is then used to calculate an optimum injection rate at a given point in the acid injection process.
Owner:MOBIL OIL CORP
In situ remedial alternative and aquifer properties evaluation probe system
InactiveUS20060046297A1Prevent travelFaster and more easily automatedMicrobiological testing/measurementEarth material testingSoil gasPush technology
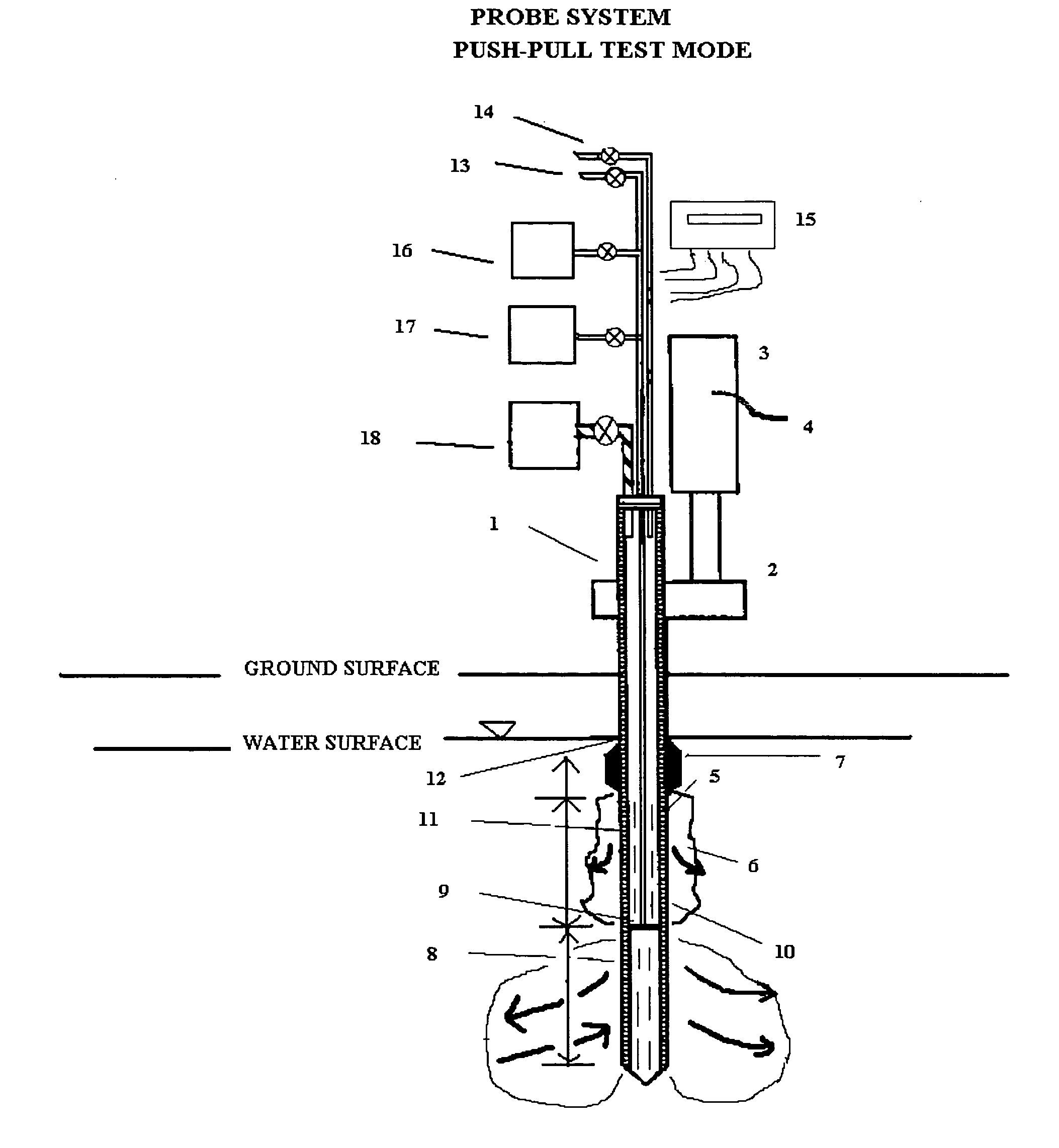
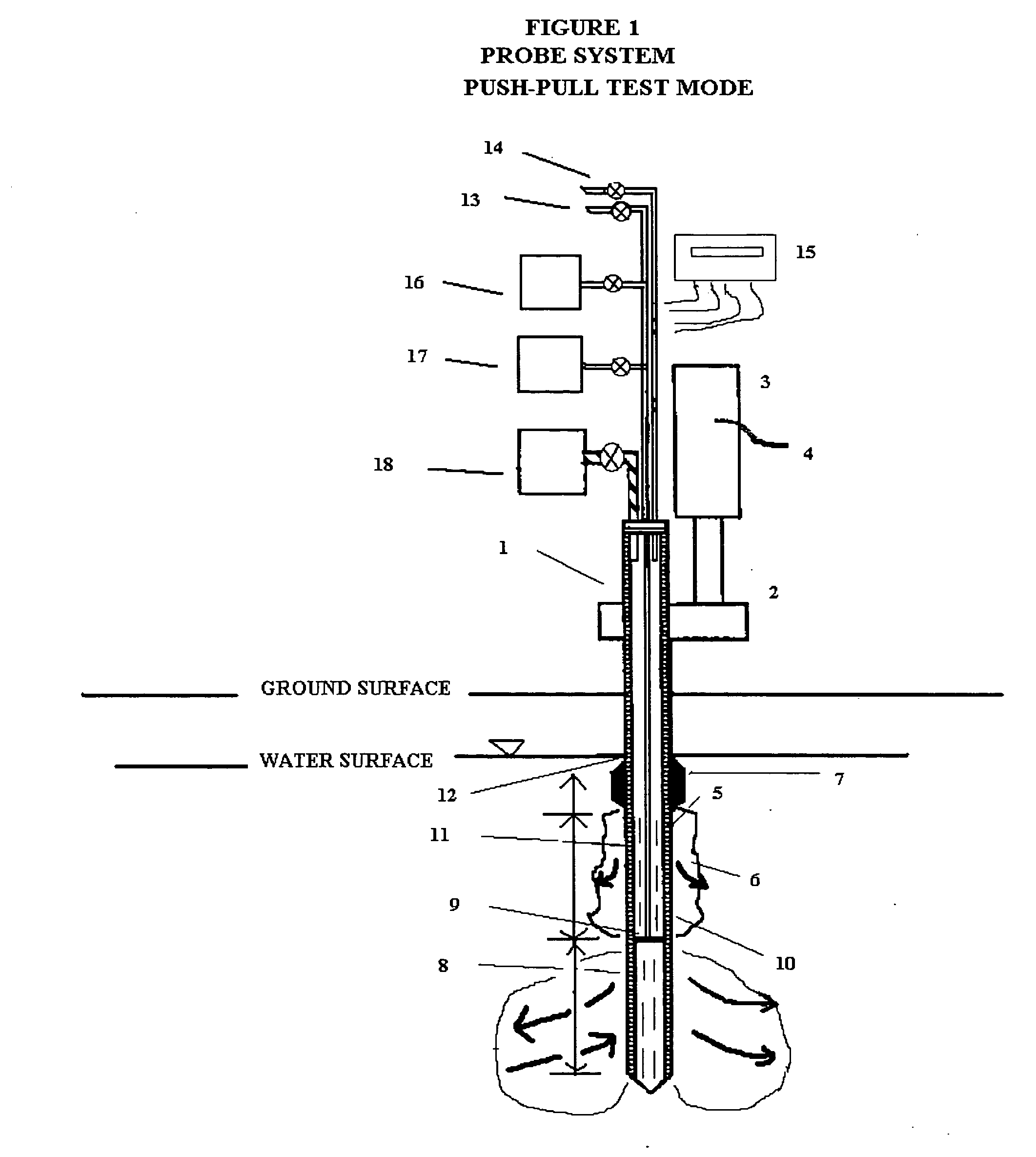
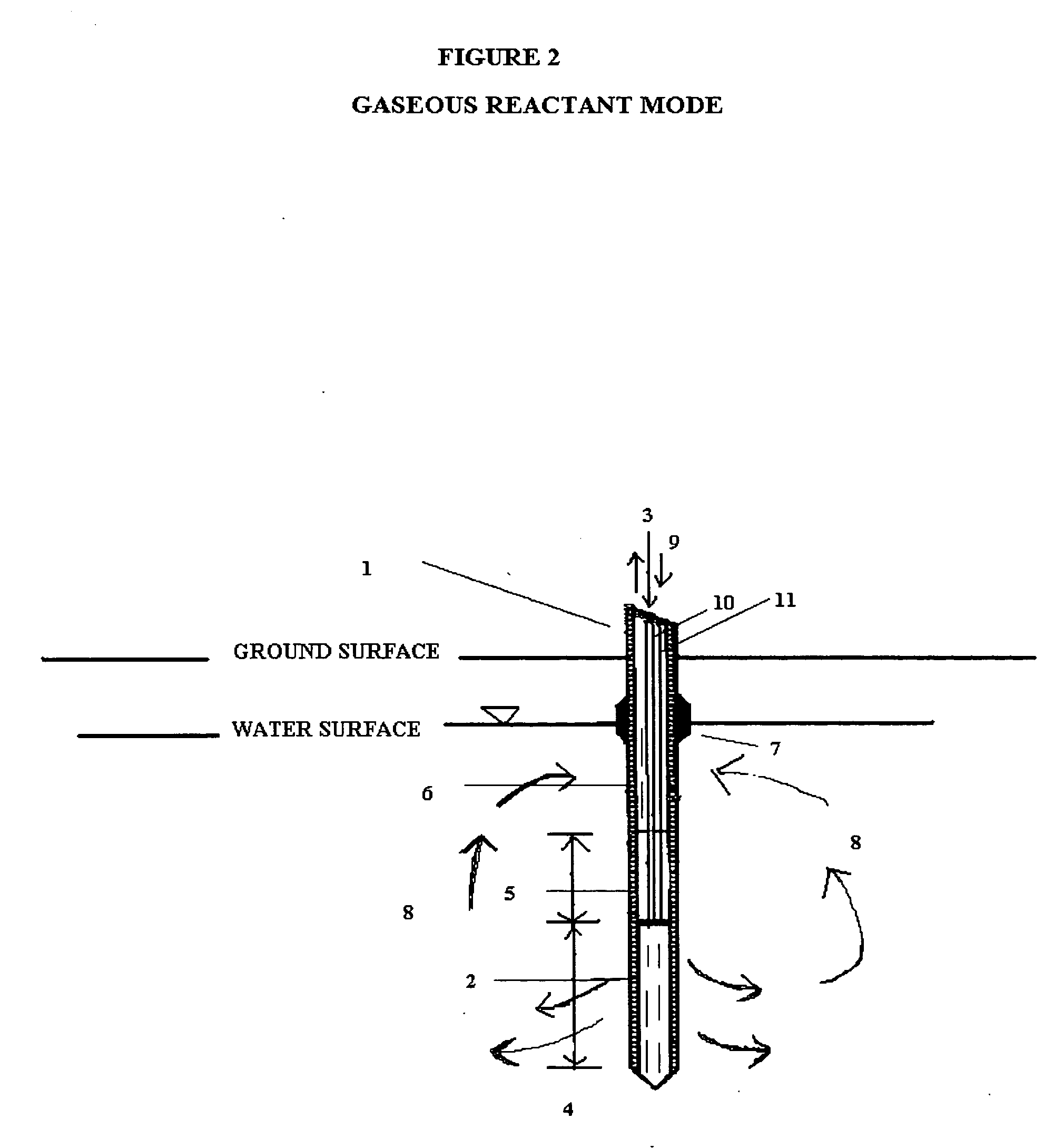
In general, the purpose of the probe system is to provide improved rapid field methods using re-designed direct push technology (DPT) and “push-pull testing” concepts to evaluate in situ chemical, biochemical, surfactant, adsorptive media, and leaching and fixation remediation technologies for hazardous subsurface contaminant(s). The probe system and methods described here when applied to a hazardous waste site being considered for in situ remediation of contaminants (organic or inorganic) by the listed treatment technologies will yield information that greatly reduces the uncertainty with regards to treatment effectiveness for the in situ soil, groundwater, and contaminant(s) conditions affecting dosage requirements and reaction rate(s) for various reactants. The probe system described here is multi-purpose in that it was designed: 1) to measure the relative permeability of the subsurface soil and groundwater to a liquid or gas ejectant, 2) to recover soil gas, soil, or groundwater samples for contaminant analyses, 3) to measure the chemical dosage and reaction, dissolution, adsorption, desorption, leaching, or fixation rate of a reactant such as a chemical or biochemical oxidant, metallic or bimetallic dehalogenating agent, surfactant or emulsifier solution, adsorbent media regenerant, leaching or fixation reagent that is injected into the matrix and withdrawn during a push-pull test, 4) to perform combinations of the above, 5) to measure the in situ adsorption capacity of adsorbent media and subsequently measure the effectiveness of regenerant(s) for the adsorbent media, and (6) to measure the effectiveness of a treated soil column for inorganic contaminant(s) leaching or fixation. In addition to being an in situ remedial alternatives evaluation tool, the probe system can be used as a reactant(s) delivery device after the specific remedial technology has been selected.
Owner:OXYTEC LLC
Directed microwave chemistry
InactiveUS20030082633A1Promote resultsImprove adsorption capacityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsChemical reactionChemical transformation
The present invention concerns a novel means by which chemical preparations can be made. Reactions can be accelerated on special chips using microwave energy. The chips contain materials that efficiently absorb microwave energy causing chemical reaction rate increases. The invention is important in many small scale chemical transformations including those used in protein chemistry and in combinatorial chemistry.
Owner:MIRARI BIOSCI
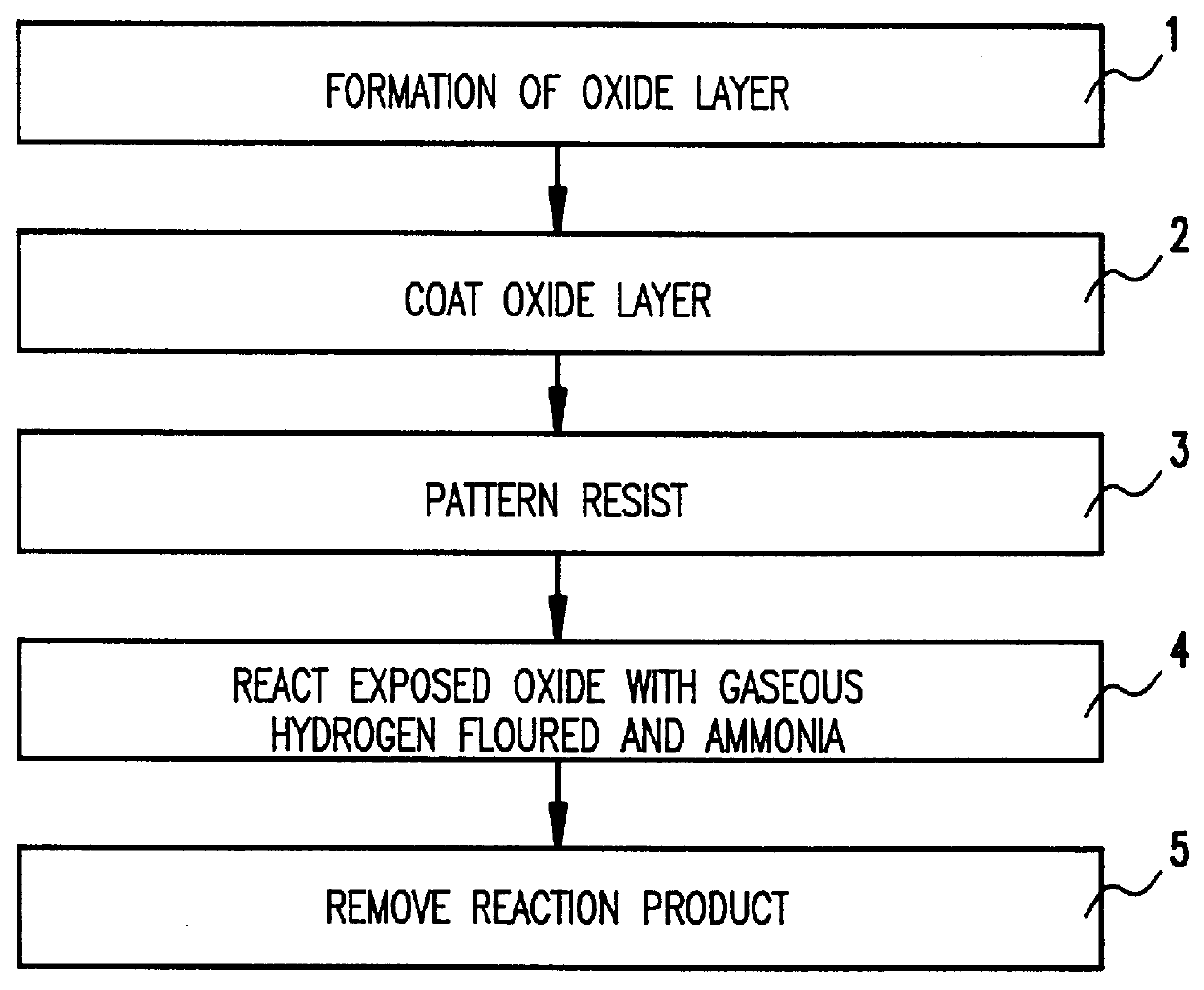
Vapor phase etching of oxide masked by resist or masking material
Hydrogen fluoride undercut of oxide layers may be reduced by using a low pressure mixture of gaseous hydrogen fluoride and gaseous ammonia mixture. Organic photoresists can be used as a masking material when using the gaseous hydrogen fluoride / ammonia mixture without resulting in an enhanced reaction rate. In addition, because of the reaction conditions, the dimensions in the oxide layer being etched can be specifically sized smaller than openings made in the overcoating masking material.
Owner:IBM CORP
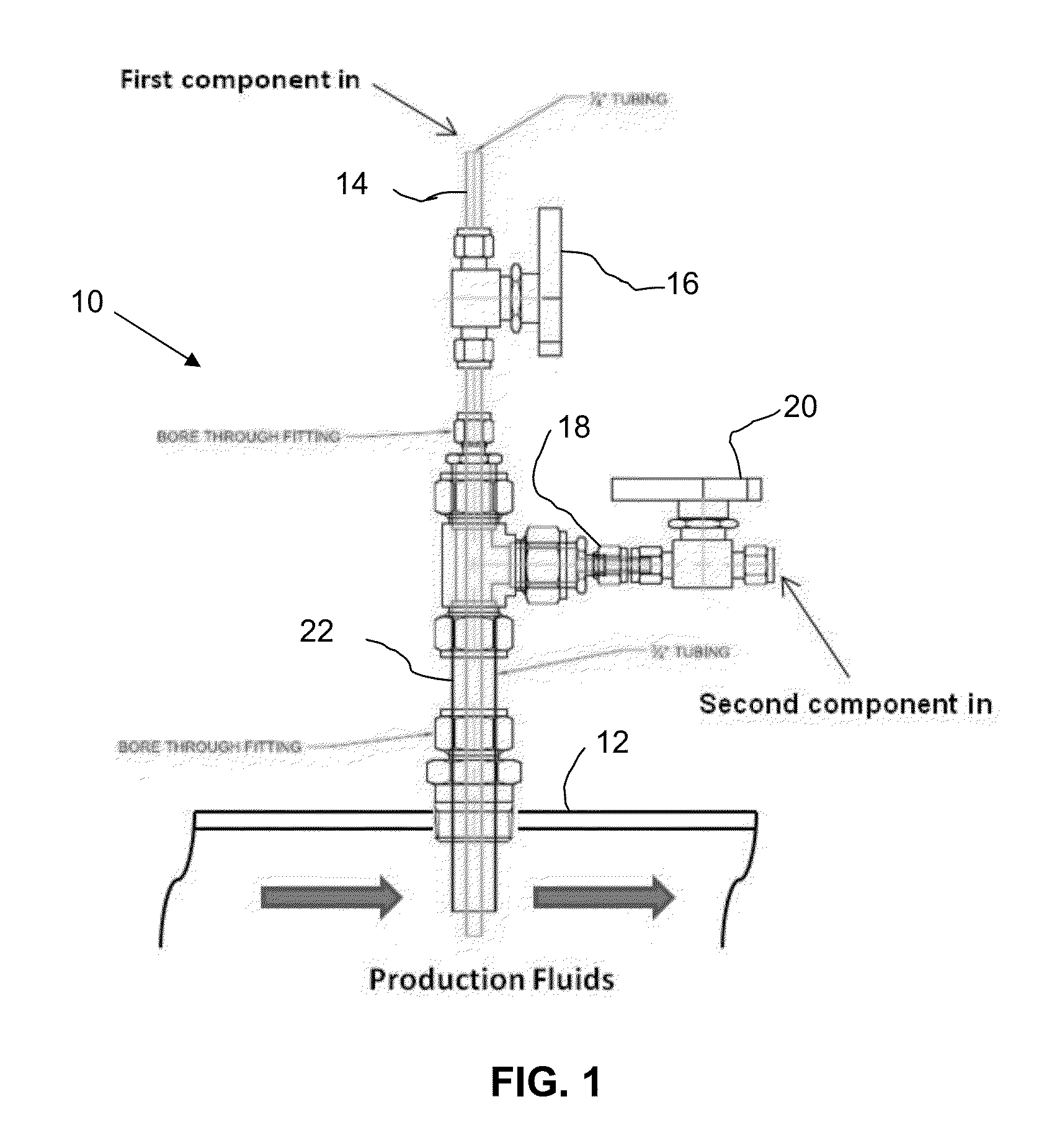
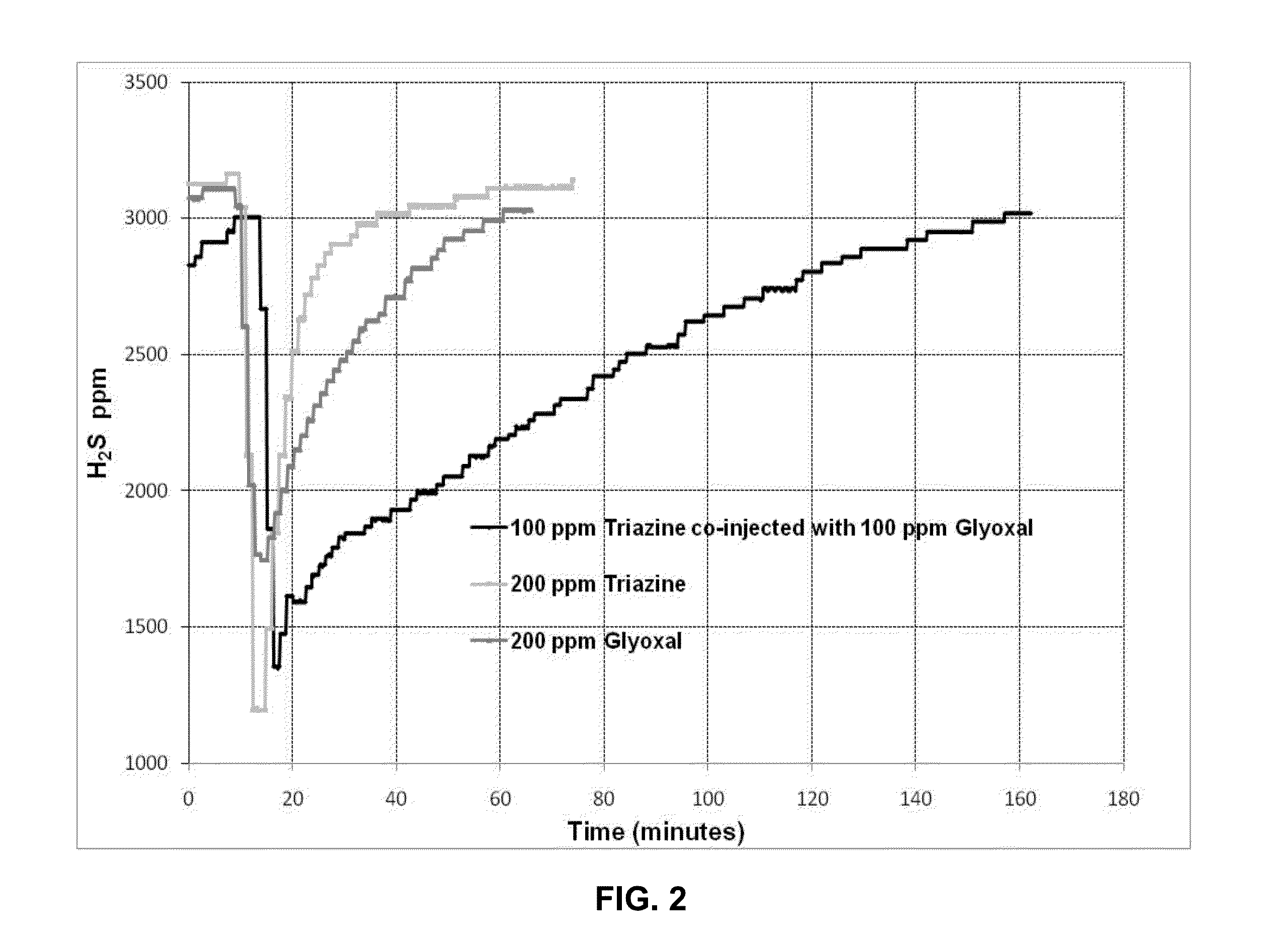
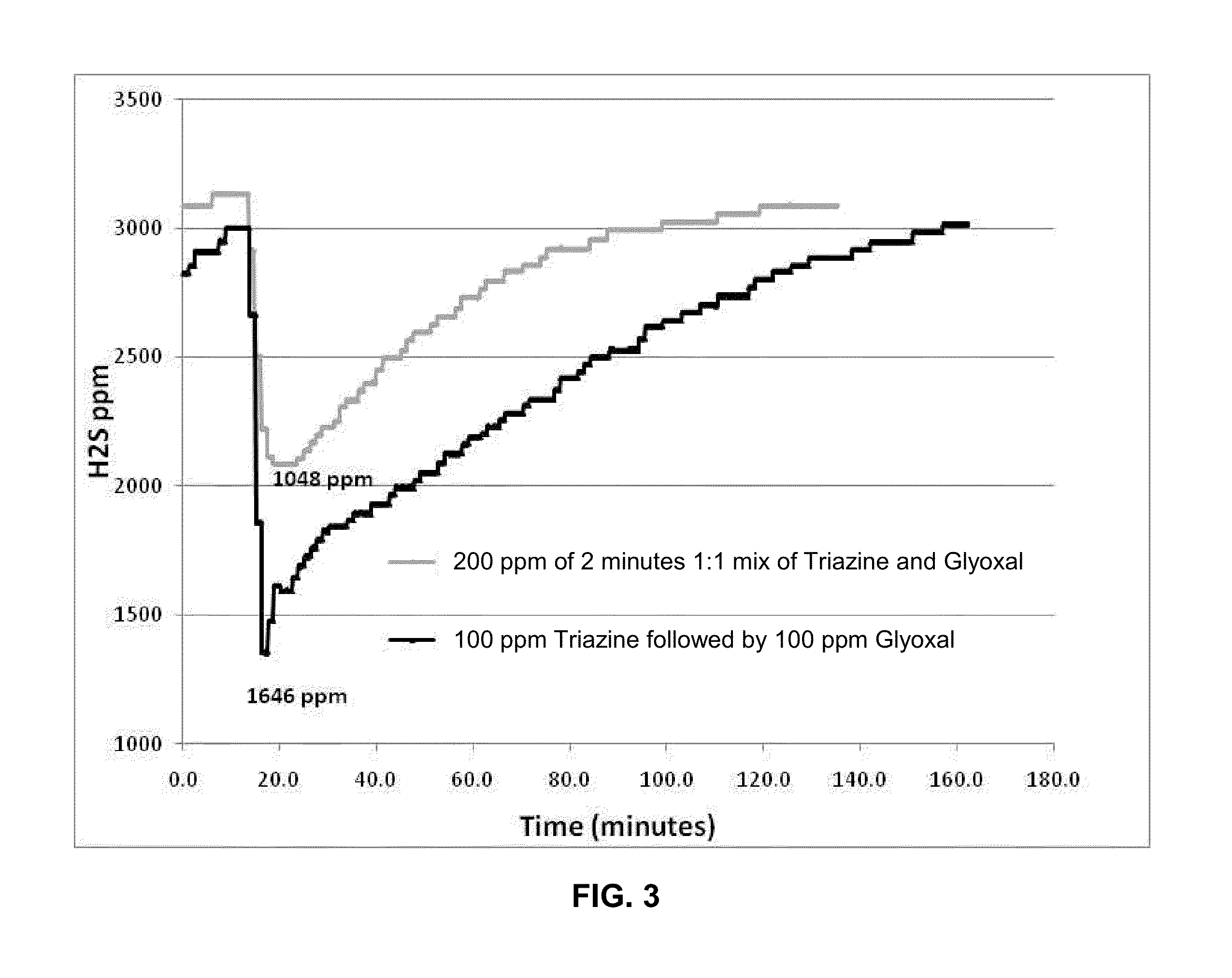
Synergistic Method for Enhanced H2S/Mercaptan Scavenging
The use of a dialdehyde (e.g. glyoxal) and a nitrogen-containing scavenger (e.g. a triazine) when injected separately in media containing hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and / or mercaptans to scavenge H2S and / or mercaptans therefrom gives a synergistically better reaction rate and overall scavenging efficiency, i.e. capacity, over the use of the dialdehyde or the nitrogen-containing scavenger used alone, but in the same total amount of the dialdehyde and nitrogen-containing scavenger. The media may include an aqueous phase, a gas phase, a hydrocarbon phase and mixtures of a gas and / or hydrocarbon phase with an aqueous phase.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Aluminum alloy for preparing hydrogen by hydrolytic decomposition and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101289163ALower the hydrolysis reaction temperatureImprove electrochemical activityHydrogen productionDecompositionReaction rate
The invention relates to a hydrogen preparation method by hydrolyzing aluminum alloy, in particular to an aluminum alloy which can be hydrolyzed to make hydrogen and a preparation method thereof. The alloy consists of simple-substance metal aluminum, metal bismuth, metals with low melting point and water-soluble compound; according to weight percentage, the content of the metal bismuth is 8 to 50 percent, low melting point metal is 0 to 15 percent, water soluble compound is 1 to 40 percent and metal aluminum is 40 to 90 percent. The method of the invention reduces reaction temperature of aluminum hydrolysis, speeds up reaction rate of aluminum hydrolysis, enhances hydrogen yield rate, simplifies reaction devices as well as reduces hydrogen storage cost. The aluminum alloy prepared by the method of the invention is portable easily, is capable of preparing and providing hydrogen at any time and is applicable to providing humid hydrogen for fuel cells.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Water-soluble inorganic zinc-rich paint and preparation method thereof
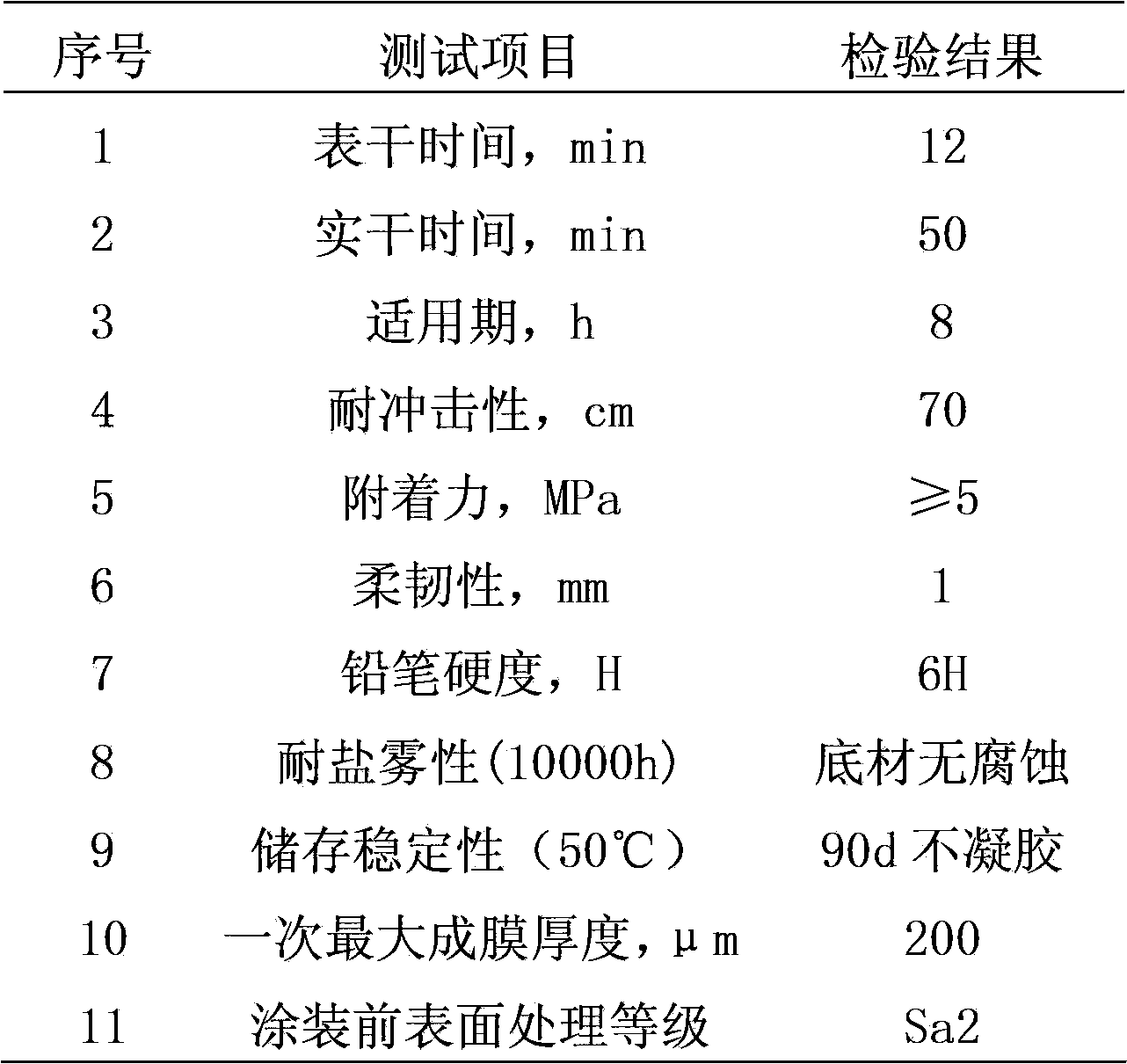
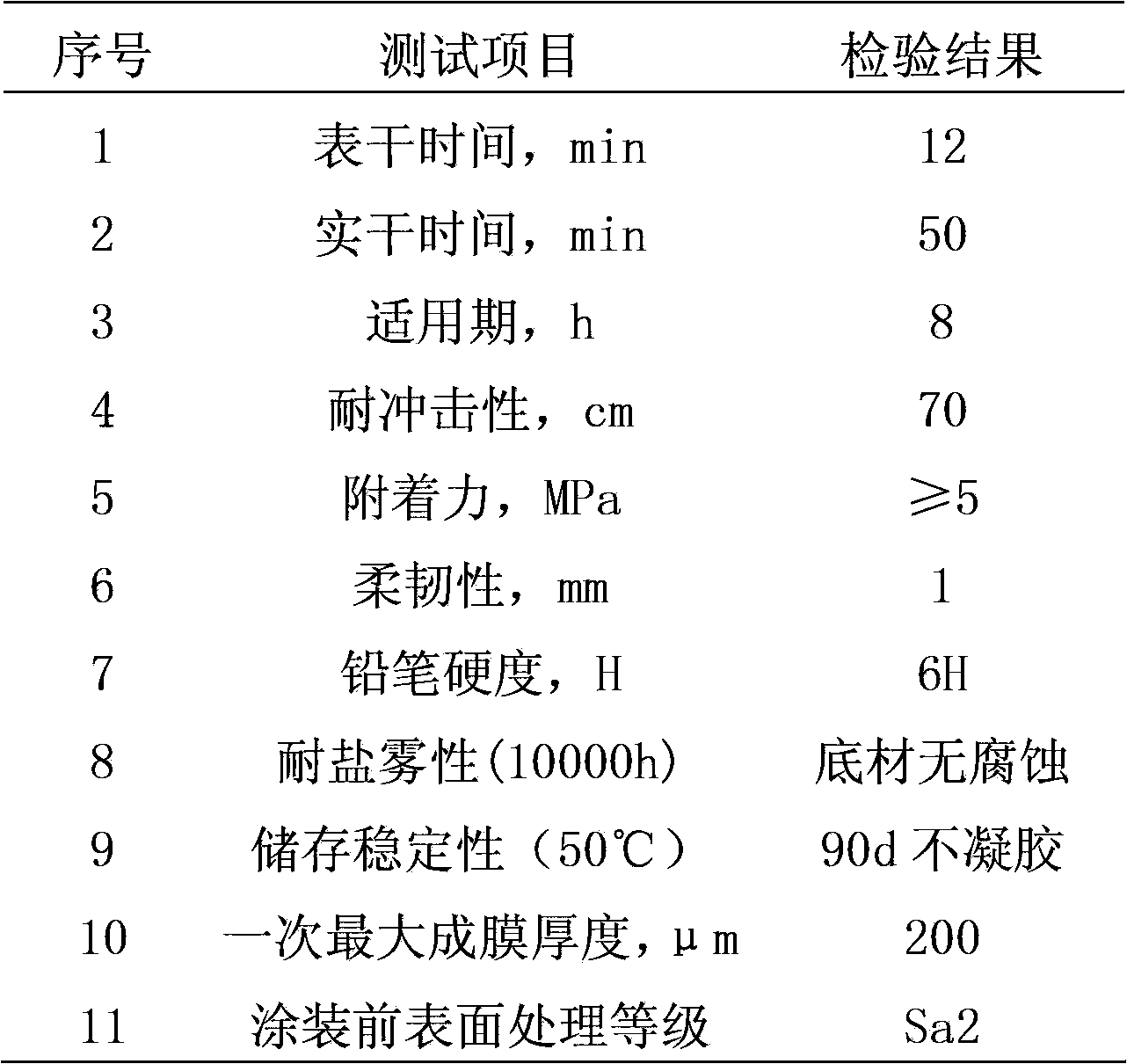
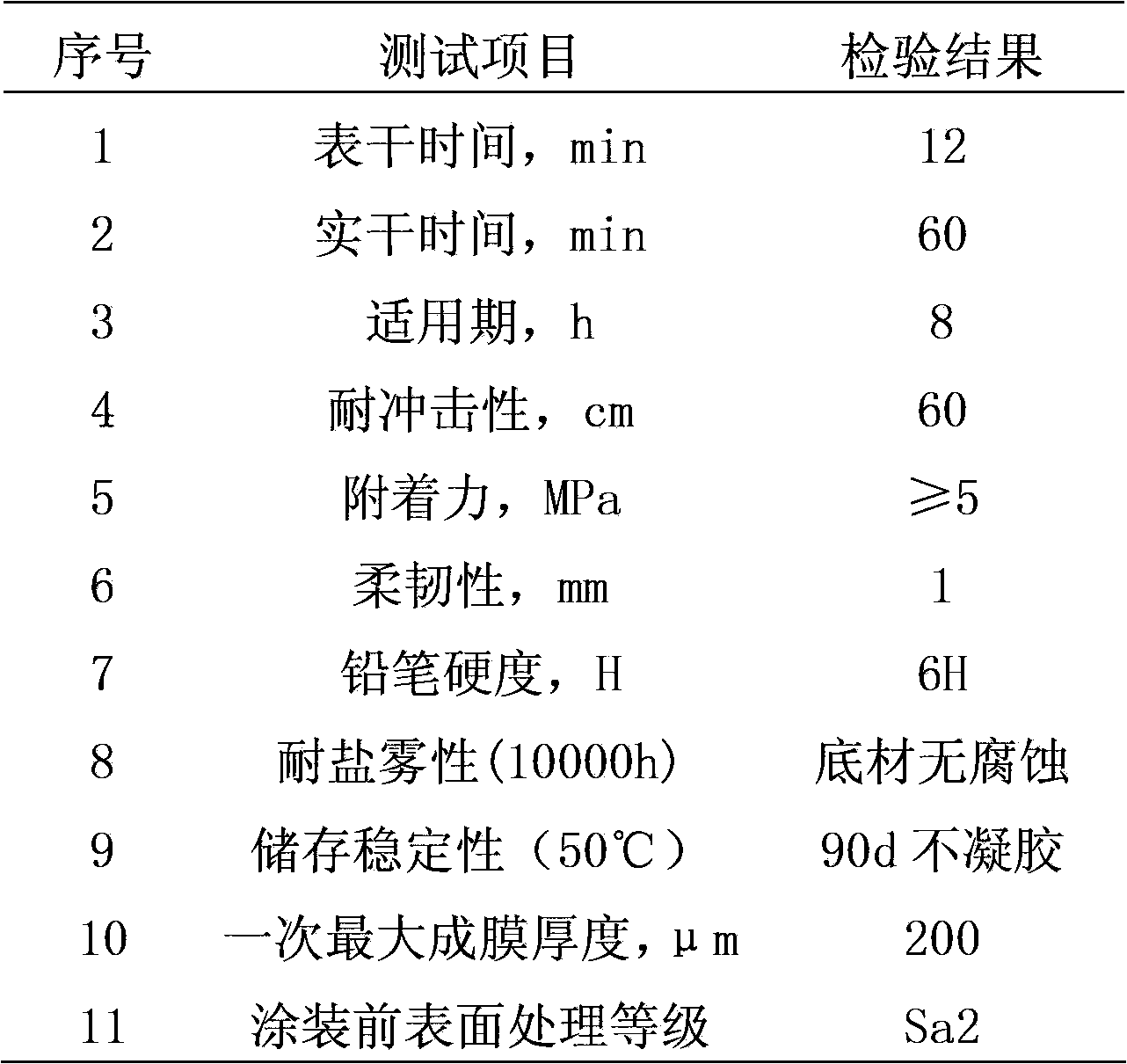
ActiveCN103788734AUniform particle size distributionUniform reaction rateAlkali metal silicate coatingsStress concentrationPowder mixture
The invention provides a water-soluble inorganic zinc-rich paint and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dropwise adding aluminum-modified silica sol into potassium silicate solution with low modulus, so as to obtain a high-modulus potassium silicate solution as a binder; and adding a catalyst, a siloxane oligomer and a modifier to ensure that the high-modulus potassium silicate solution are uniform in size distribution, and does not have gelatinization reaction for a long time, wherein after the high-modulus potassium silicate solution and a zinc powder mixture are stirred uniformly, the zinc-rich paint has the advantages that reaction rates of all parts of a coating are uniform, and no stress concentration phenomenon exist. Proved by experiments, the zinc-rich paint provided by the invention has no gel after being stored for 90 days at 50 DEG C, the thickness of a film formed once can reach 200 mu m, no cracking or bubbling phenomenon exists, construction can be carried out after the treatment level of the steel surface reaches Sa2, and the salt fog resistance of the coating can reach 10000 hours.
Owner:CENT RES INST OF BUILDING & CONSTR CO LTD MCC GRP +2
Method and apparatus for obtaining enhanced production rate of thermal chemical reactions
InactiveUS7045114B2Reduce formationReaction is slowOrganic chemistry methodsChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsSteam reformingChemical reaction
Reactors and processes are disclosed that can utilize high heat fluxes to obtain fast, steady-state reaction rates. Porous catalysts used in conjunction with microchannel reactors to obtain high rates of heat transfer are also disclosed. Reactors and processes that utilize short contact times, high heat flux and low pressure drop are described. Improved methods of steam reforming are also provided.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Electrical sensor for monitoring degradation of products from environmental stressors
InactiveUS7612325B1Material analysis by optical meansCounting objects on conveyorsState dependentReaction rate
An environmental degradation sensor for environmentally sensitive products such as food, pharmaceuticals or cosmetic products provides the degraded state and estimated remaining life of the product. The sensor is made of a polymeric matrix and conductive filler. A control agent, selected to adjust a reaction rate of the sensor to environmental conditions, allows correlation of an electrical property of the sensor to a degraded state of the product. The sensor may be integrated with a passive RFID to provide product identification and degradation status wirelessly via reader. The sensor improves product safety, reduces cost of premature product disposal and, combined with RFIDs, improves the security of products through combined product degradation monitoring and tracking.
Owner:WATKINS JR KENNETH S +1
Continuous mass production of carbon nanotubes in a nano-agglomerate fluidized-bed and the reactor
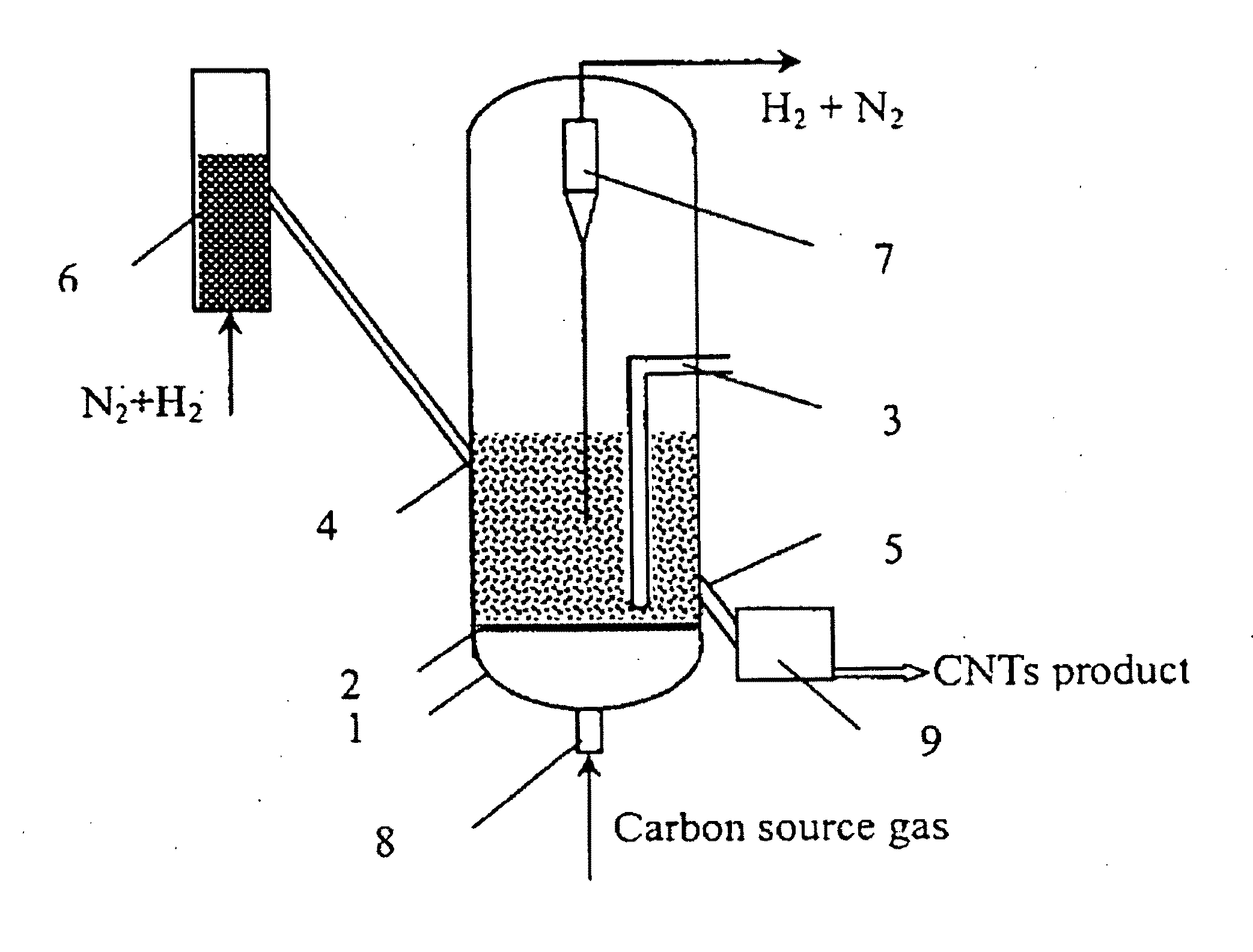
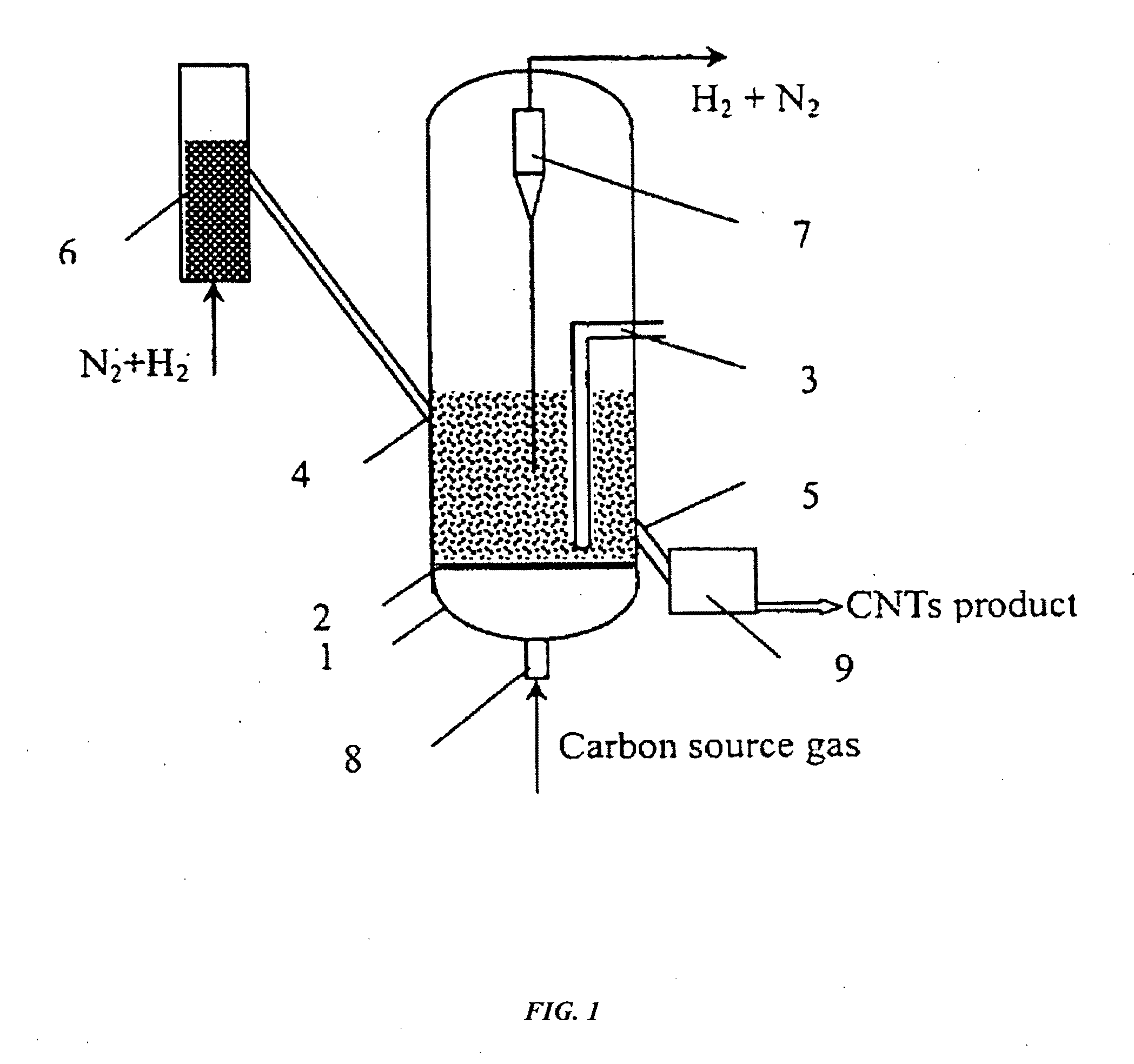
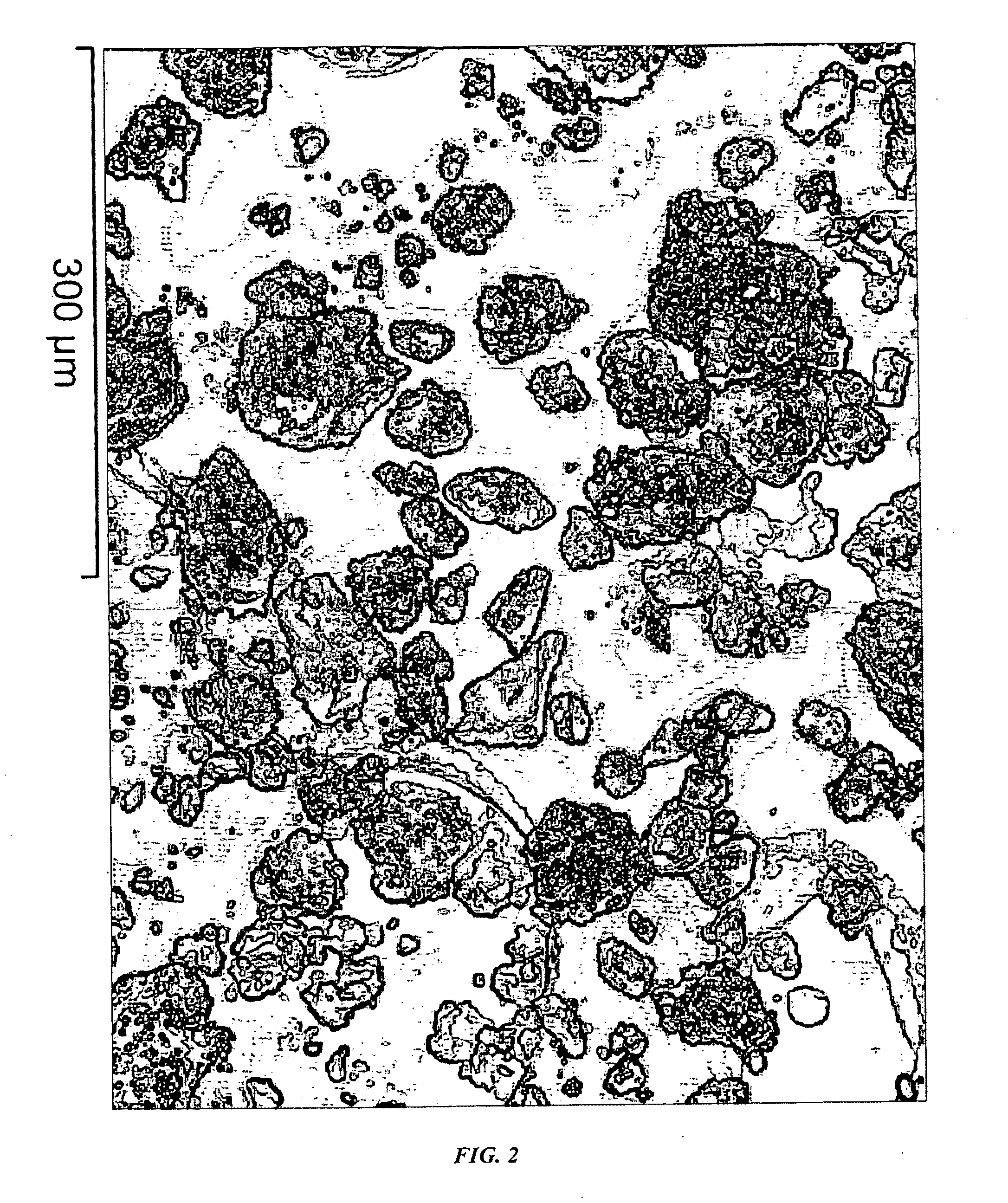
InactiveUS20090286675A1Improve adaptabilityHigh crystallinityMaterial nanotechnologyIndividual molecule manipulationReaction rateCarbon nanotube
The present invention relates to a method for continuous production of carbon nanotubes in a nano-agglomerate fluidized bed, which comprises the following steps: loading transition metal compounds on a support, obtaining supported nanosized metal catalysts by reducing or dissociating, catalytically decomposing a carbon-source gas, and growing carbon nanotubes on the catalyst support by chemical vapor deposition of carbon atoms. The carbon nanotubes are 4˜100 nm in diameter and 0.5˜1000 μm in length. The carbon nanotube agglomerates, ranged between 1˜1000 μm, are smoothly fluidized under 0.005 to 2 m / s superficial gas velocity and 20-800 kg / m3 bed density in the fluidized-bed reactor. The apparatus is simple and easy to operate, has a high reaction rate, and it can be used to produce carbon nanotubes with high degree of crystallization, high purity, and high yield.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and apparatus for extending equipment uptime in ion implantation
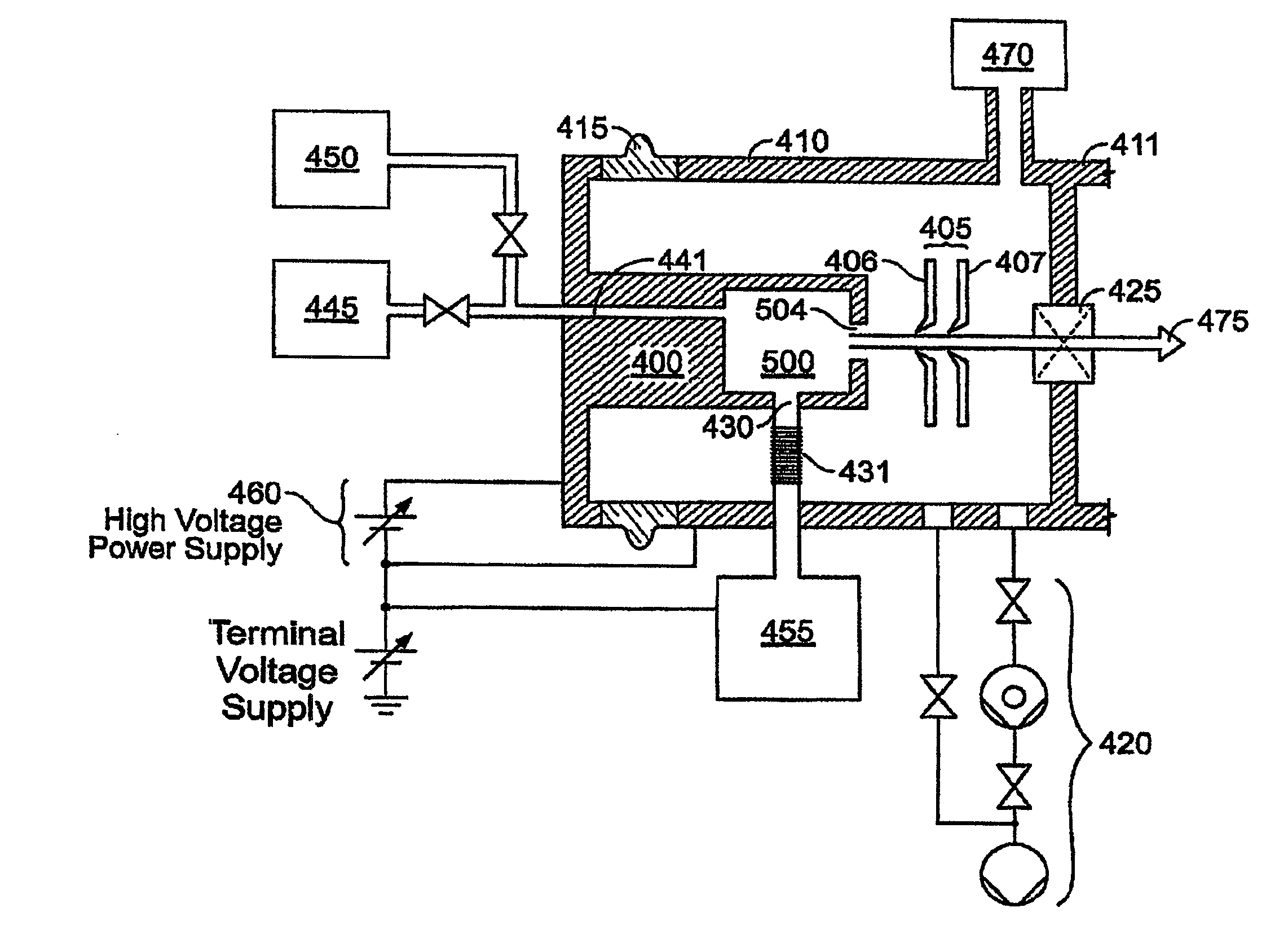
InactiveUS20080223409A1Increasing effective reaction rateReduce pressureElectric discharge tubesHollow article cleaningPressure cycleReaction rate
An in situ cleaning system is disclosed for use with semiconductor processing equipment. In accordance with an important aspect of the invention, the cleaning system provides for dynamic cleaning of the semiconductor processing system by varying the pressure of the cleaning gas over time during a cleaning cycle. In particular, the cleaning gas is applied to the semiconductor processing system in repeated pressure cycles. Each pressure cycle begins with the pressure of the cleaning gas at PMIN. The pressure of the cleaning gas is increased to a maximum pressure PMAX during a fill portion of the pressure cycle and maintained for a dwell time selected to allow the available reactants to generate the desired end products. The pressure in the chamber to be cleaned is then reduced during a vent portion of the pressure cycle to permit venting of the reaction products. As such, each time the chamber to be filled is vented and re-filled, reaction products are removed and new reactants are introduced into the chamber to be cleaned, increasing the effective reaction rate.
Owner:SEMEQUIP
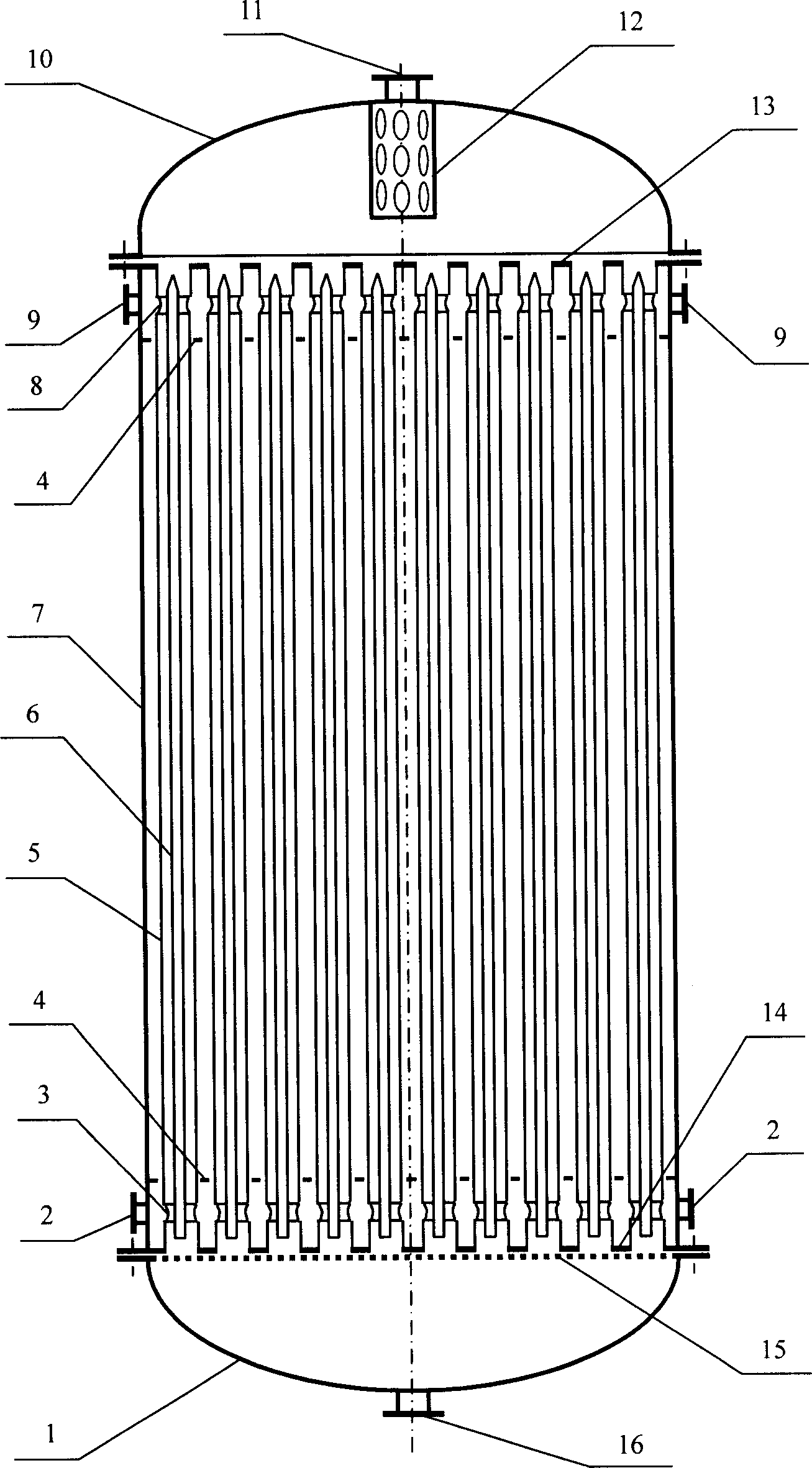
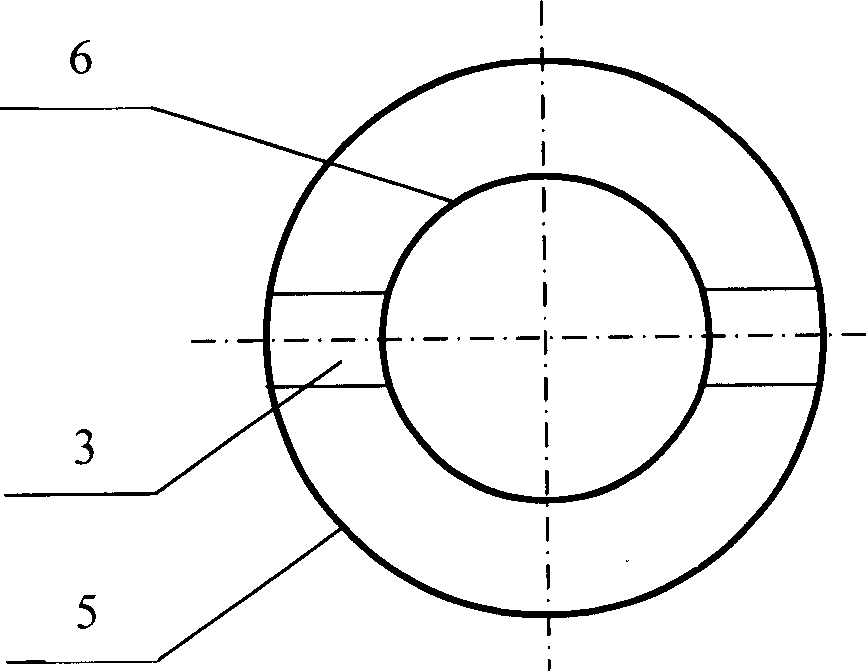
Non-hot spot calandria type fixed bed reactors
InactiveCN1736574AIncrease the heat exchange areaIncrease heat transfer areaChemical/physical processesReaction rateDiameter ratio
Disclosed is a non- thermal point tubular fixed bed reactor, which is technically characterized in that: every tube of the reactor adopts annular tube structure, the inner tubes being closed, the inner tube and outer tube being linked to the shell side of the reactor by canal, the catalyst being filled into the space between tubes to form a catalyst bed layer, the bottom and top of the tubes being equipped with a cooling medium distributing plate. The diameter ratio of the inner tube to outer tube can be regulated according to the reaction rate and the operation temperature to make the reaction heat transfer to the double- side. Dimension of opening of the cooling medium distributing plate and dimension of the opening of the side- wall of double terminals of inner tube can be regulated to control the distribution of cooling medium between inner tube and the shell side of reactor. With the invention, in the condition of no increasing the number of tubes largely, it can increase the heat- exchange area of the tubular fixed bed reactor and decrease the heat- exchange route.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
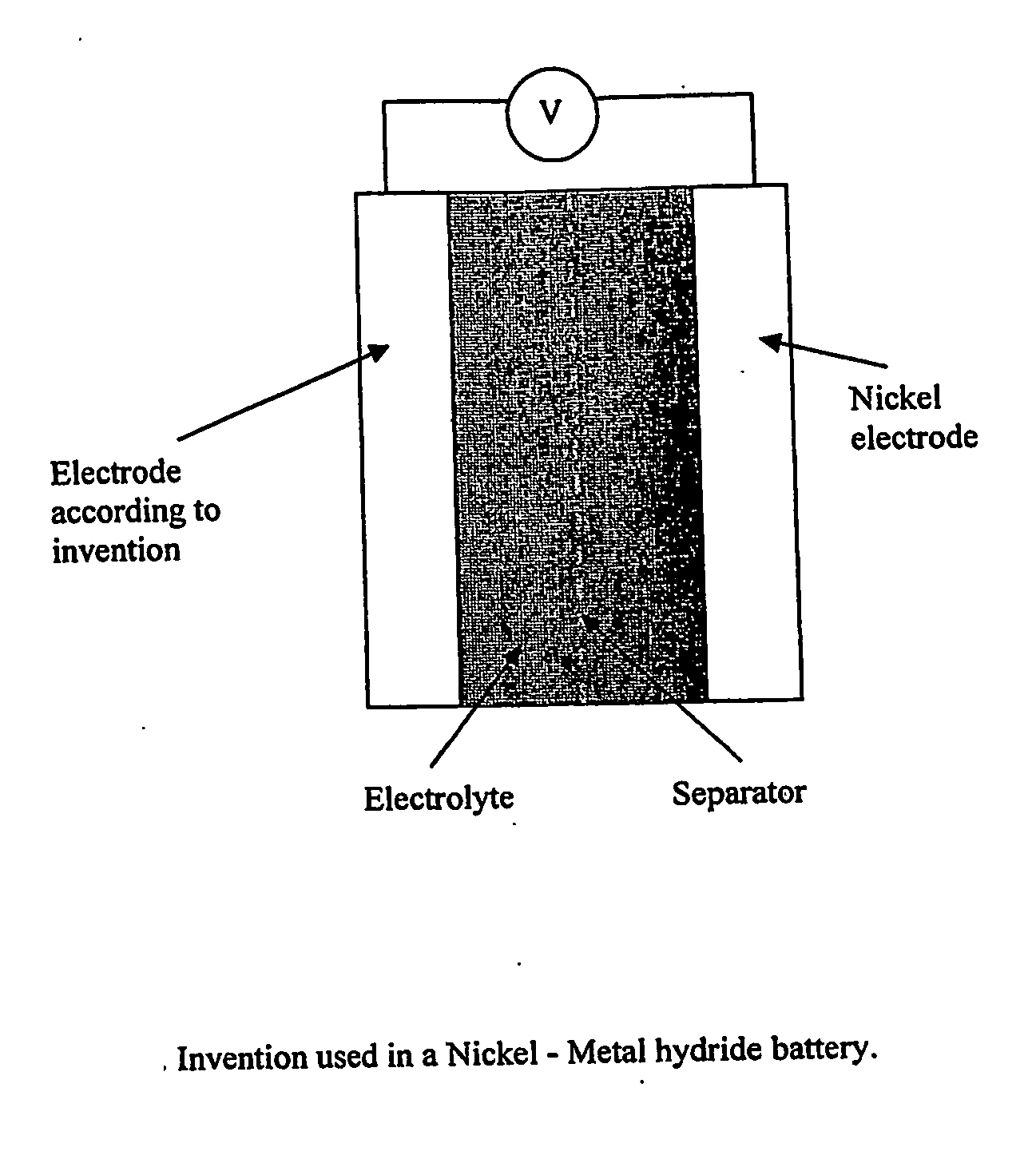
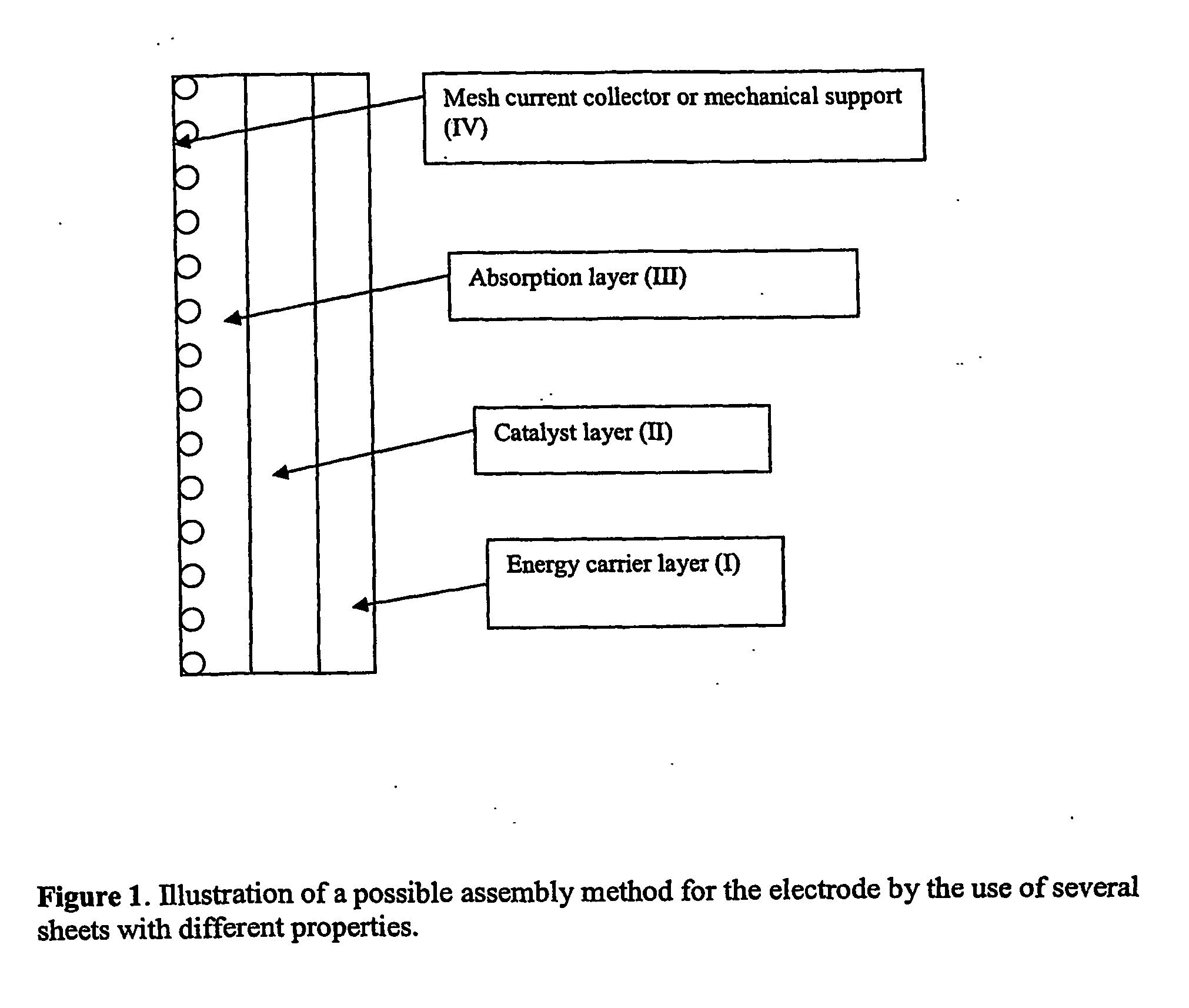
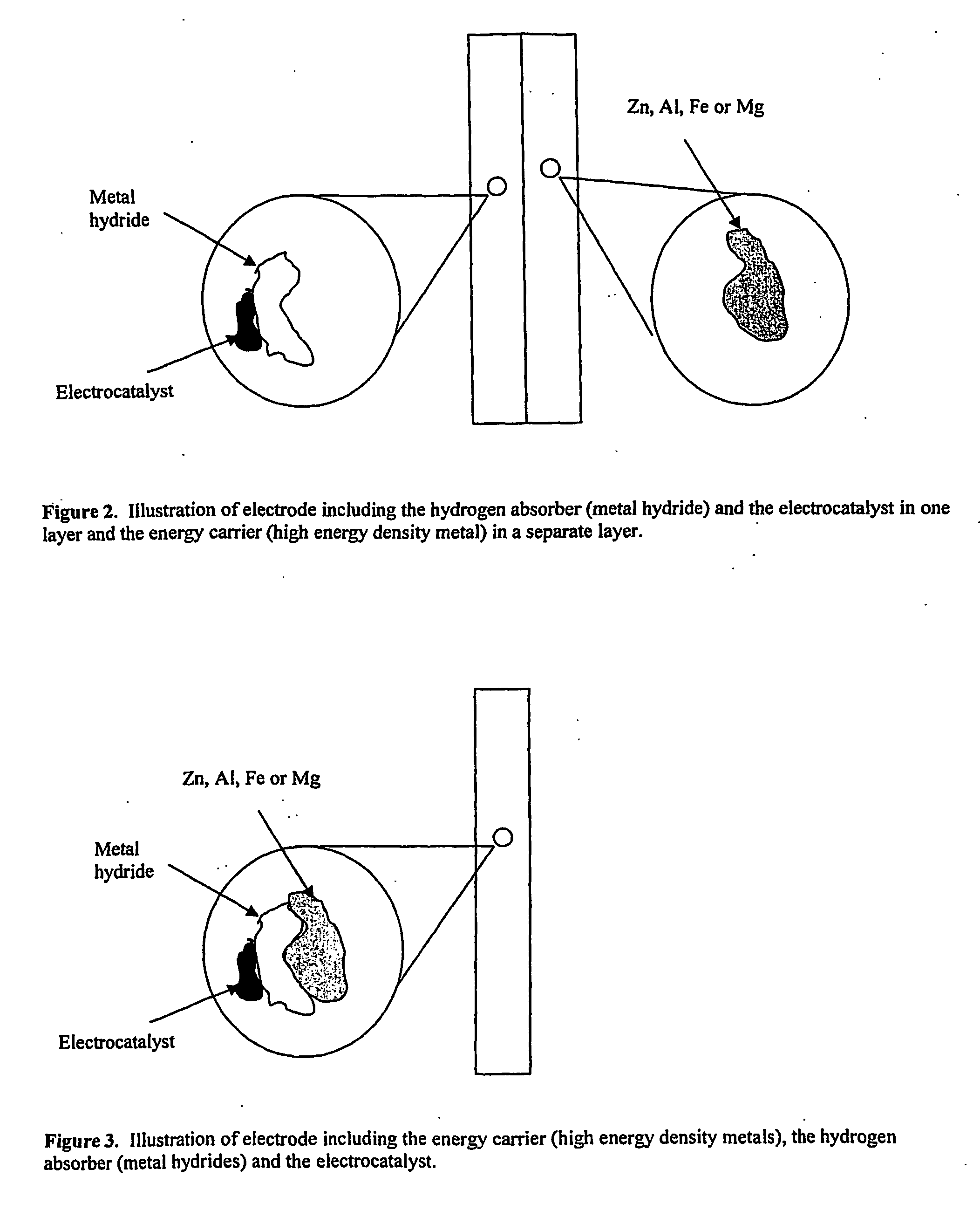
Electrode, method of its production, metal-air fuel cell and metal hydride cell
InactiveUS20070077491A1Improve energy efficiencyHigh energy capacityElectrode rolling/calenderingHydrogenFuel cellsReaction rate
The invention described concerns an anode electrode comprising a hydrogen storage material / alloy and a high energy density metal. In addition a hydrogen electrocatalyst may be added to increase the hydrogen reaction rate. The high energy density metal is selected from a group consisting of Al, Zn, Mg and Fe, or from a combination of these metals. A method of production of an electrode comprising a hydrogen storage alloy and a high energy density metal is also described. The method comprises sintering or binding a high energy density metal powder and / or hydrogen storage alloy into at least one thin street, and calendaring or pressing said sheet forming the electrode. The anode electrode may be used in metal hydride batteries and metal air fuel cells.
Owner:REVOLT TECH LTD
Parallel reactor with sensing of internal properties
InactiveUS7288229B2Minimize gas flowProcess control/regulationSequential/parallel process reactionsReaction rateAmbient pressure
An apparatus and method for carrying out and monitoring the progress and properties of multiple reactions is disclosed. The method and apparatus are especially useful for synthesizing, screening, and characterizing combinatorial libraries, but also offer significant advantages over conventional experimental reactors as well. The apparatus generally includes multiple vessels for containing reaction mixtures, and systems for controlling the stirring rate and temperature of individual reaction mixtures or groups of reaction mixtures. In addition, the apparatus may include provisions for independently controlling pressure in each vessel, and a system for injecting liquids into the vessels at a pressure different than ambient pressure. In situ monitoring of individual reaction mixtures provides feedback for process controllers, and also provides data for determining reaction rates, product yields, and various properties of the reaction products, including viscosity and molecular weight.
Owner:UNCHAINED LABS
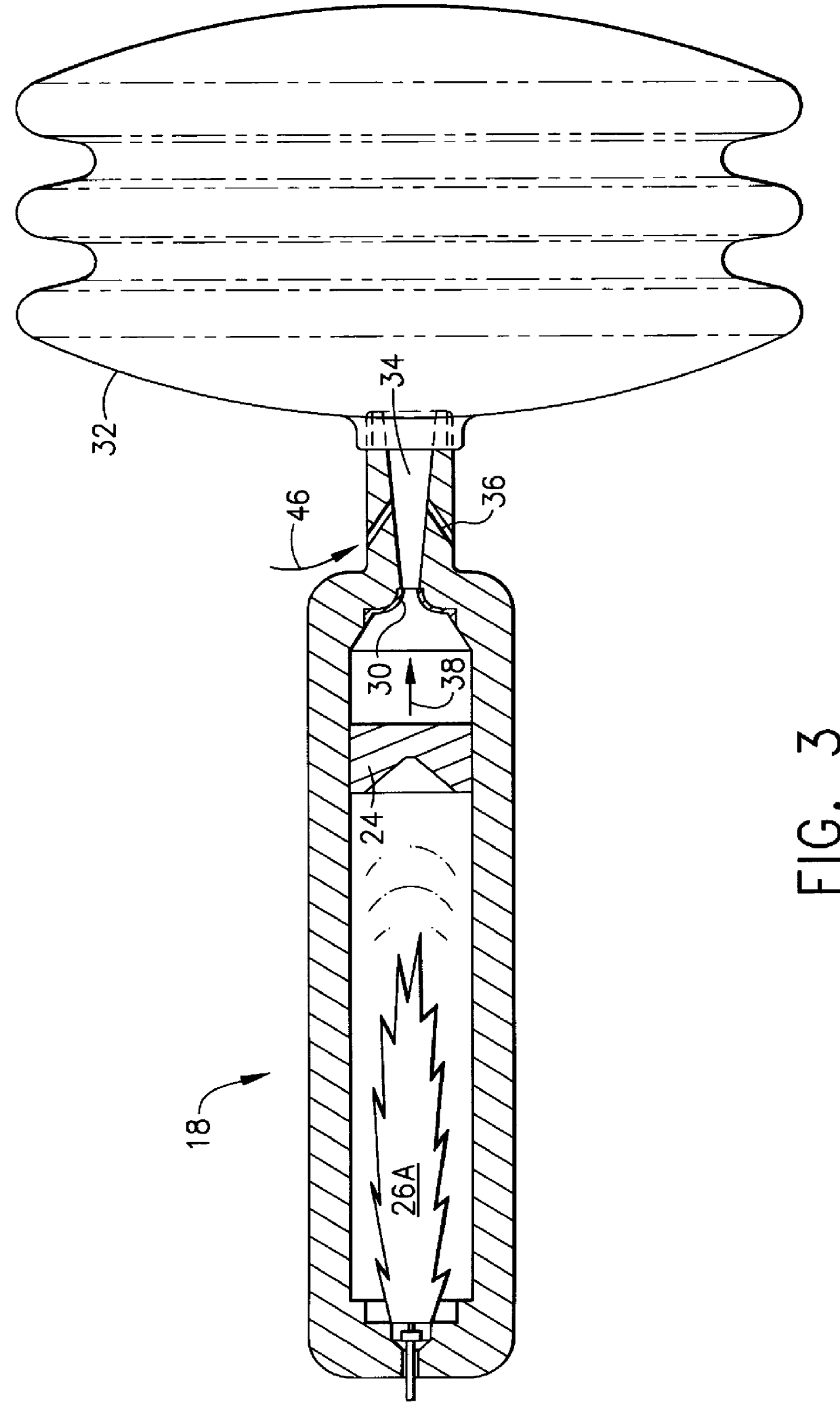
Safety air bag inflation device
InactiveUS6155600AFailure of controlSpeed up the flowPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementLiquid transferring devicesReaction rateGas passing
An air bag inflator providing a source of gas, releasable upon command, to inflate a supplemental inflation restraint (SIR) system commonly known as an automobile air bag. Provided is a pressure vessel containing one or more separate chambers for the purpose of storing gaseous fuel(s) and gaseous oxidizer(s) or liquid fuel(s) and liquid oxidizer(s) under pressure with helium as the primary filler gas. The primary function of the helium gas is to serve as a kinetic damper to modulate and control the reaction rate of the fuel(s) and oxidizer(s). Because of its low mass, high thermal conductivity and high heat capacity for its mass, helium is an excellent filler gas. In the case of the gaseous fuel(s) and oxidizer(s) a single chamber is provided. In the case of liquid fuel(s) and oxidizer(s), two or more separate housings are provided for storing the liquid fuel(s) and oxidizer(s). Along with the liquid fuel(s) and oxidizer(s) housings, two separate chambers containing pressurized helium are provided within the pressure vessel. The first helium chamber rapidly pressurizes upon initiation of a gas producing pyrotechnic igniter. This pressure acts on thin membranes on the first chamber side of the separate liquid storage housings to force the liquid fuel(s) and oxidizer(s) into the second chamber where the materials are atomized and mixed. The mixture is ignited by the arrival of hot gases from the igniter directed into the second chamber via the small diameter tube or orifice. The fuel(s) oxidizer(s) mixture burns to produce gaseous reaction products that are released into the air bag by bursting a controlled rupture burst disc.
Owner:AUTOLIV DEV AB
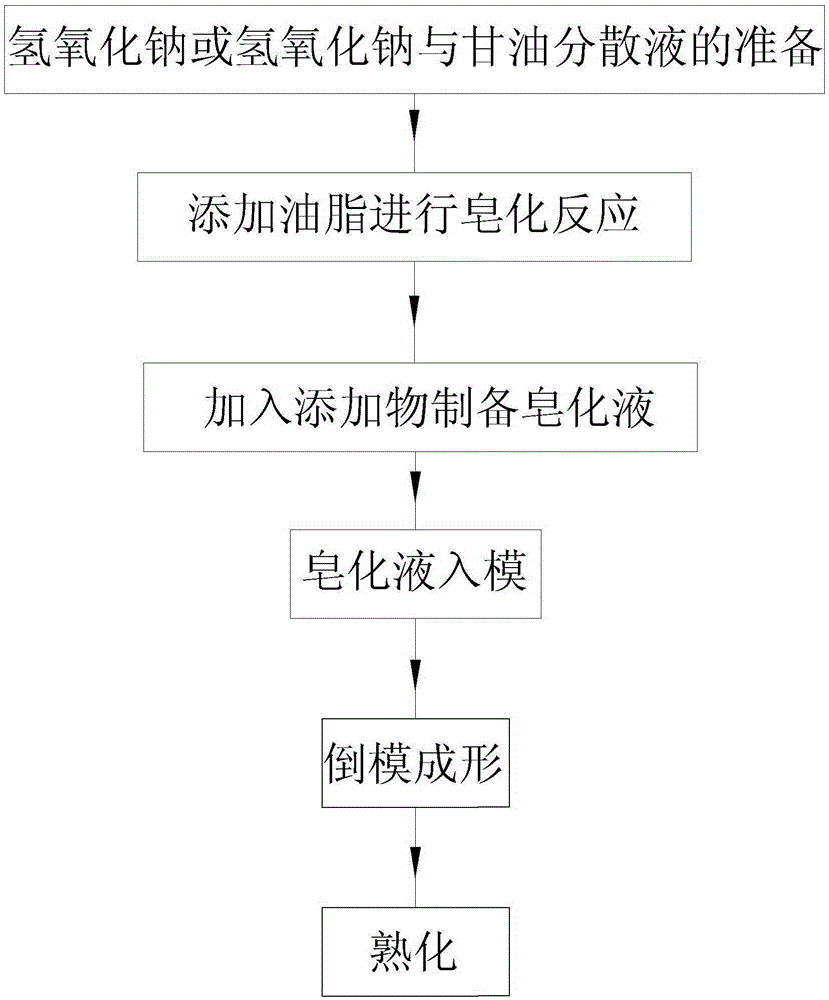
Preparation method of cold-formed soap
ActiveCN105400617AAvoid contact reactionsGive full play to effective functionsShaping soapAlkali/ammonium soap compositionsCold formedReaction rate
The invention relates to a preparation method of a cold-formed soap. The method has simple process steps, and substitutes traditional aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide with sodium hydroxide or a dispersion of sodium hydroxide and glycerol; sodium hydroxide is completely soluble in glycerol but disperses in glycerol, so as to avoid fast reaction after mixing of sodium hydroxide solution with oil too, reduce the initial reaction rate of saponification, and effectively control saponification reaction rate; along with the saponification reaction, the reaction product of glycerol continuously increases to help more fully dispersion of sodium hydroxide, accelerate the reaction rate of sodium hydroxide and the remaining oil. Since the method employs an anhydrous formula, water evaporation process is not needed after soap formation by liquid soap, and the production cycle is significantly shortened; and the nutrition substances are added in solid form powder to effectively prevent the contact reaction of non-alkali-resistant nutrients and alkali hydroxide molecules, so as to retain the active nutrient ingredients in the soap and give full play to the role of skin care of the nutrients.
Owner:NINGBO UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Stratified flow chemical reactor
InactiveUS20030133856A1Maximum effectivenessImprove thermal efficiencyFlow mixersTransportation and packagingReaction rateRates reactions
A polymerization reactor for exothermic liquid phase reactions comprises a reaction zone which is divided into a plurality of channels by thermally conductive heat transfer fins which are conductively mounted on one or more heat pipes for the removal of heat of reaction from reactants and reaction products flowing between the heat transfer fins. The reactor of the invention is capable of maintaining essentially isothermal conditions without the use of complicated and maintenance intensive agitators. The reactor is particularly useful when viscosity of the reactants and / or reaction products is high, when the reaction conducted has a fast reaction rate and when consistent polymer properties are desired.
Owner:SAUDI BASIC IND CORP SA
Stacked semiconductor memory device and control method thereof
ActiveUS20070194455A1High bandwidthReduce the numberSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesReaction rateEngineering
A stacked semiconductor memory device includes an interface chip and a plurality of core chips, in which the interface chip and the plurality of core chips are stacked. The core chips are mutually connected by a plurality of data through electrodes. The core chips each include a plurality of memory arrays. In response to an access request, the plurality of memory arrays corresponding to a predetermined data through electrode are activated, and the plurality of activated memory arrays and the predetermined data through electrode are sequentially connected. Thereby, even though it requires approximately ten-odd ns for transferring the first data, similarly to the conventional case, it is possible to transfer the subsequent data at high speed determined by the reaction rate (1 to 2 ns) of the through electrode. As a result, it becomes possible to increase a bandwidth while suppressing the number of through electrodes.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com