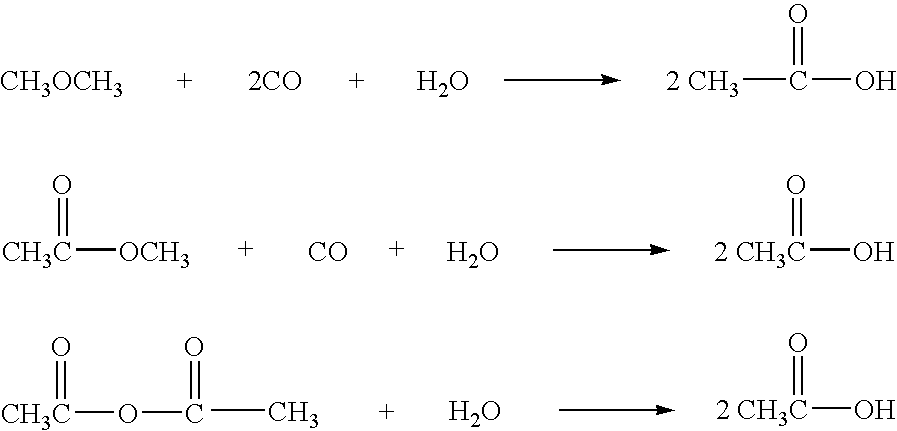
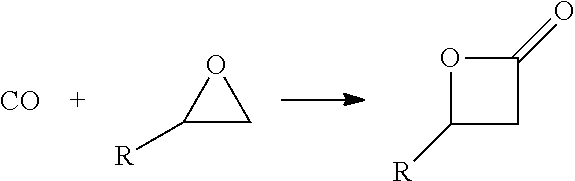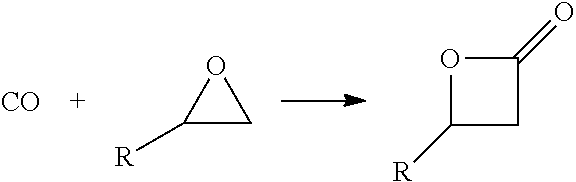Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1091results about "Carboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Low energy carbonylation process
InactiveUS6657078B2Weaken energyHigh purityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsPropanoic acidIodide
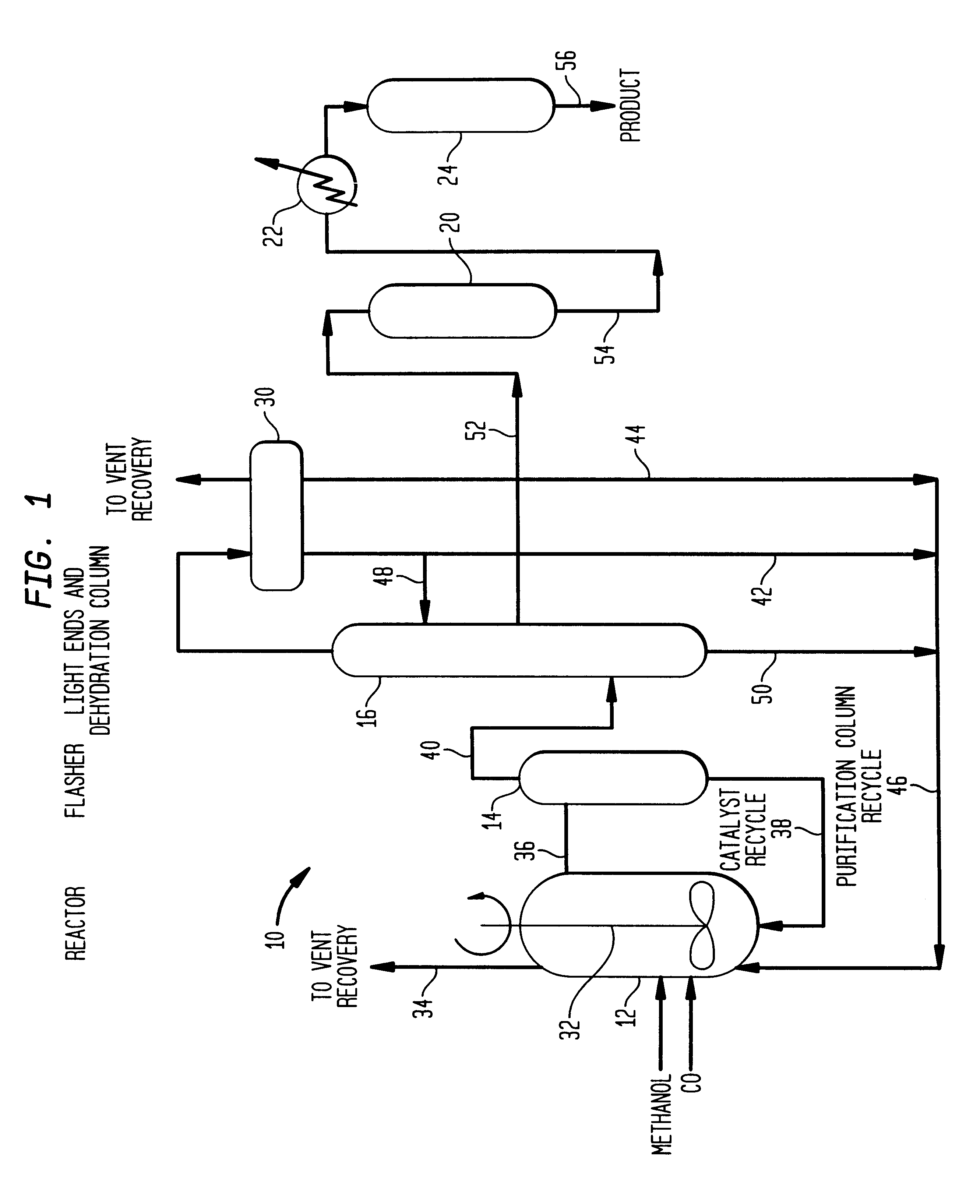
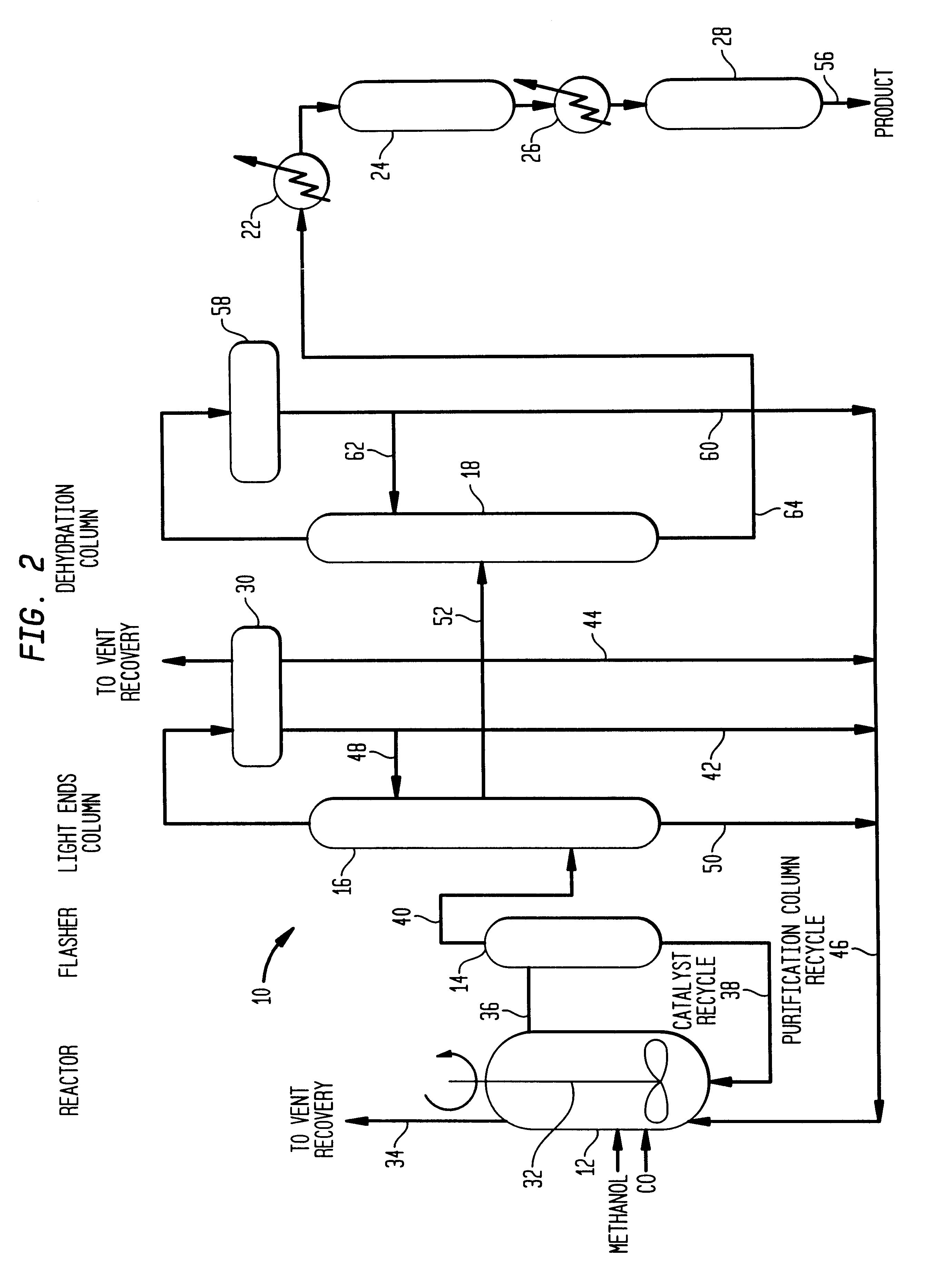
A low energy process for producing acetic acid by the carbonylation of methanol is disclosed. The process involves a rhodium-catalyzed system operated at less than about 14% water utilizing up to 2 distillation columns. The process is preferably controlled such that the product stream has a low level of propionic acid impurity and the level of aldehyde impurities is minimized by way of aldehyde removal or minimizing aldehyde generation. The level of iodides is controlled by contacting the product, at elevated temperatures, with ion exchange resins. In preferred embodiments, at least one silver or mercury exchanged macroreticular strong acid ion exchange resin is used to purify the product. The high temperature treatment provides the added benefit of controlling the Color Value (Pt-Co units) of the product stream.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Low water methanol carbonylation process for high acetic acid production and for water balance control
ActiveUS7005541B2High acetic acid production rateIncrease chanceOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionWater methanolAcetic anhydride
The invention relates to a process for the production of acetic acid by carbonylation of methanol, and reactive derivatives thereof, in a reaction mixture using a rhodium-based catalyst in low water conditions. The process is used to achieve reaction rates of at least 15 g mol / l / hr. The high rate reactions proceed at water concentrations of less than 2.0 wt. %. Under certain conditions, the water concentration in the reaction mixture of the process is maintained at a desired concentration by at least one process step including adding a compound such as methyl acetate, dimethyl ether, acetic anhydride, or mixtures of these compounds to the reaction system. The process step of adding the components to the reaction mixture may be combined with other process steps for controlling water concentrations in reaction mixtures for the carbonylation of methanol.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
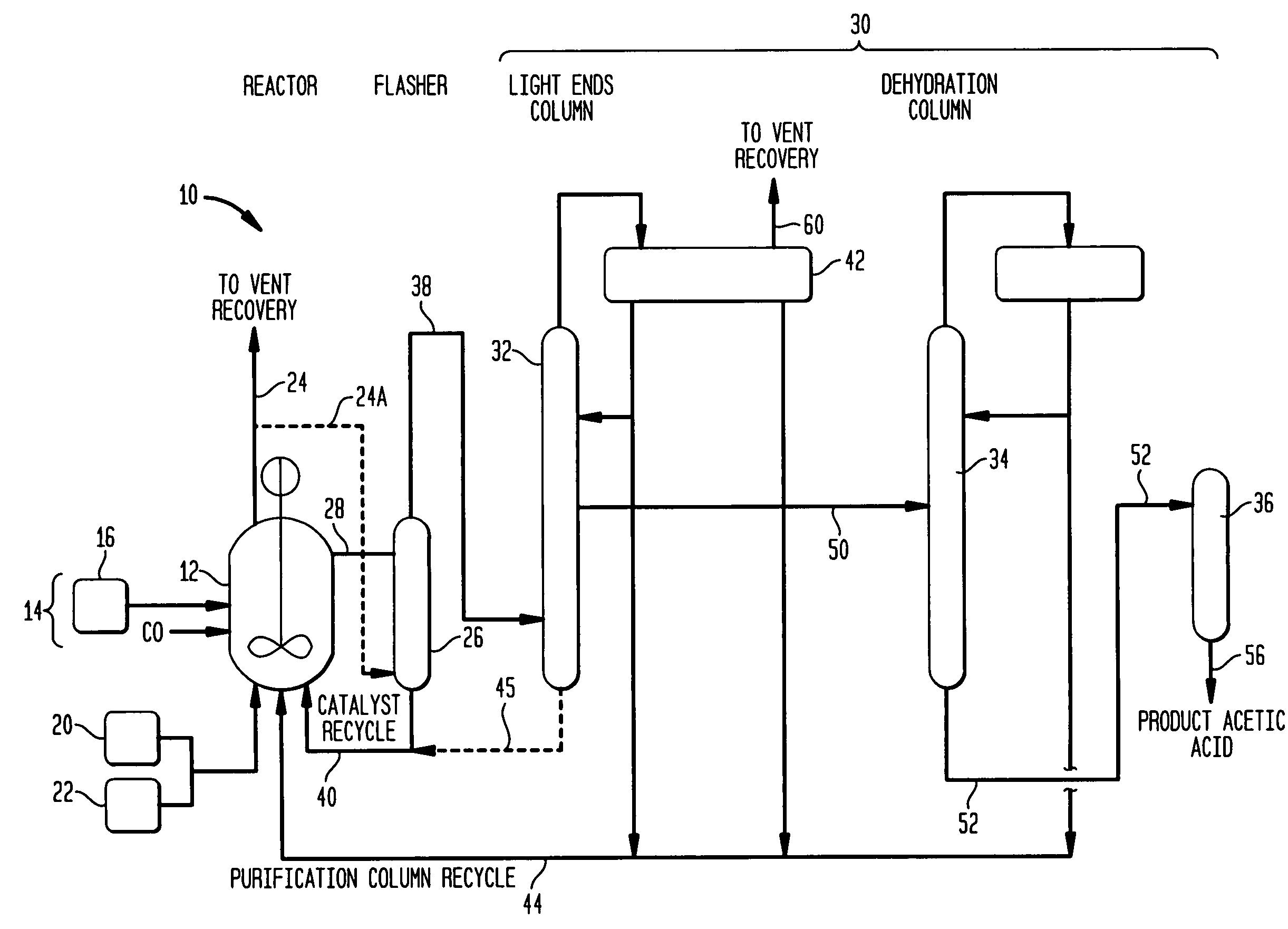
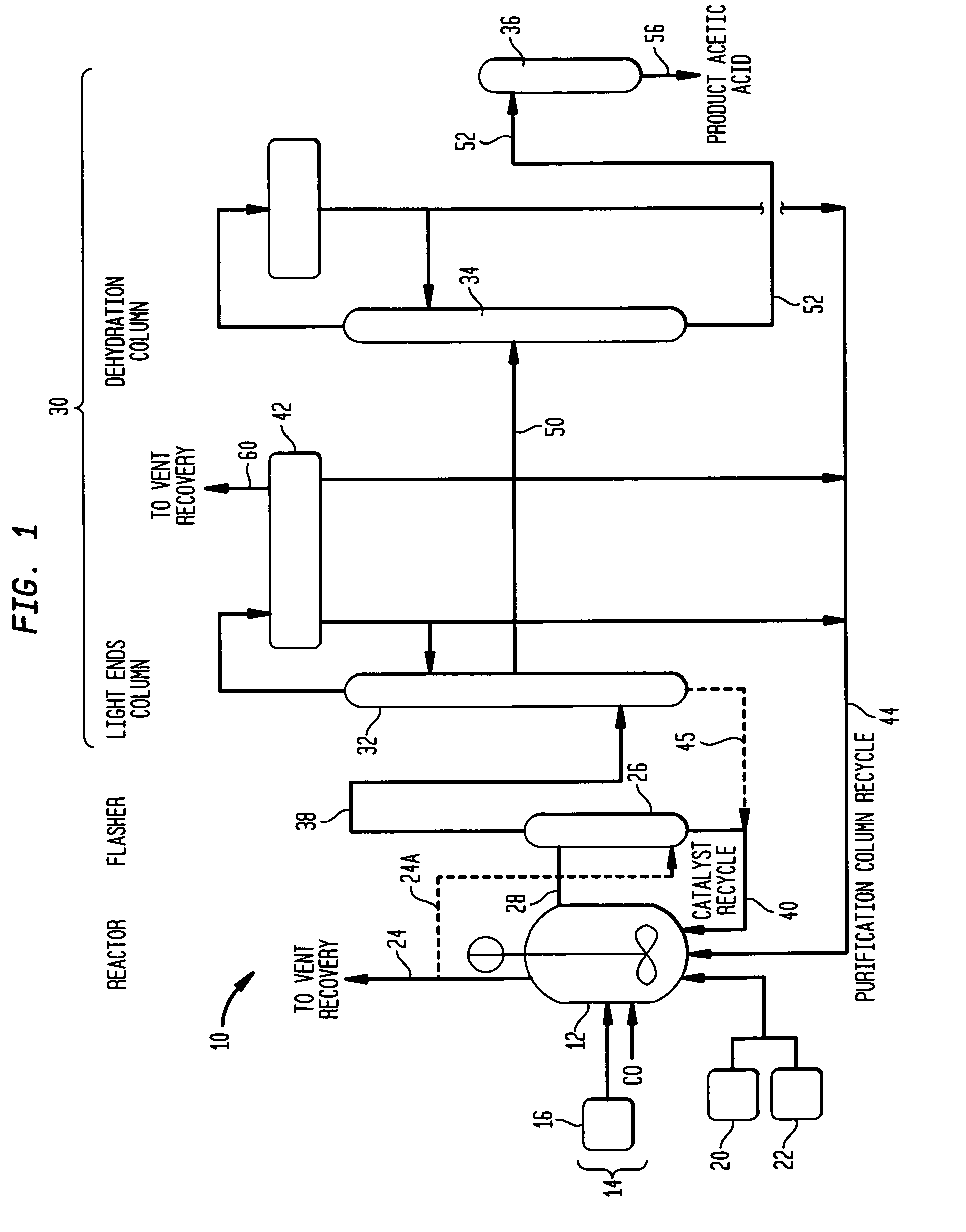
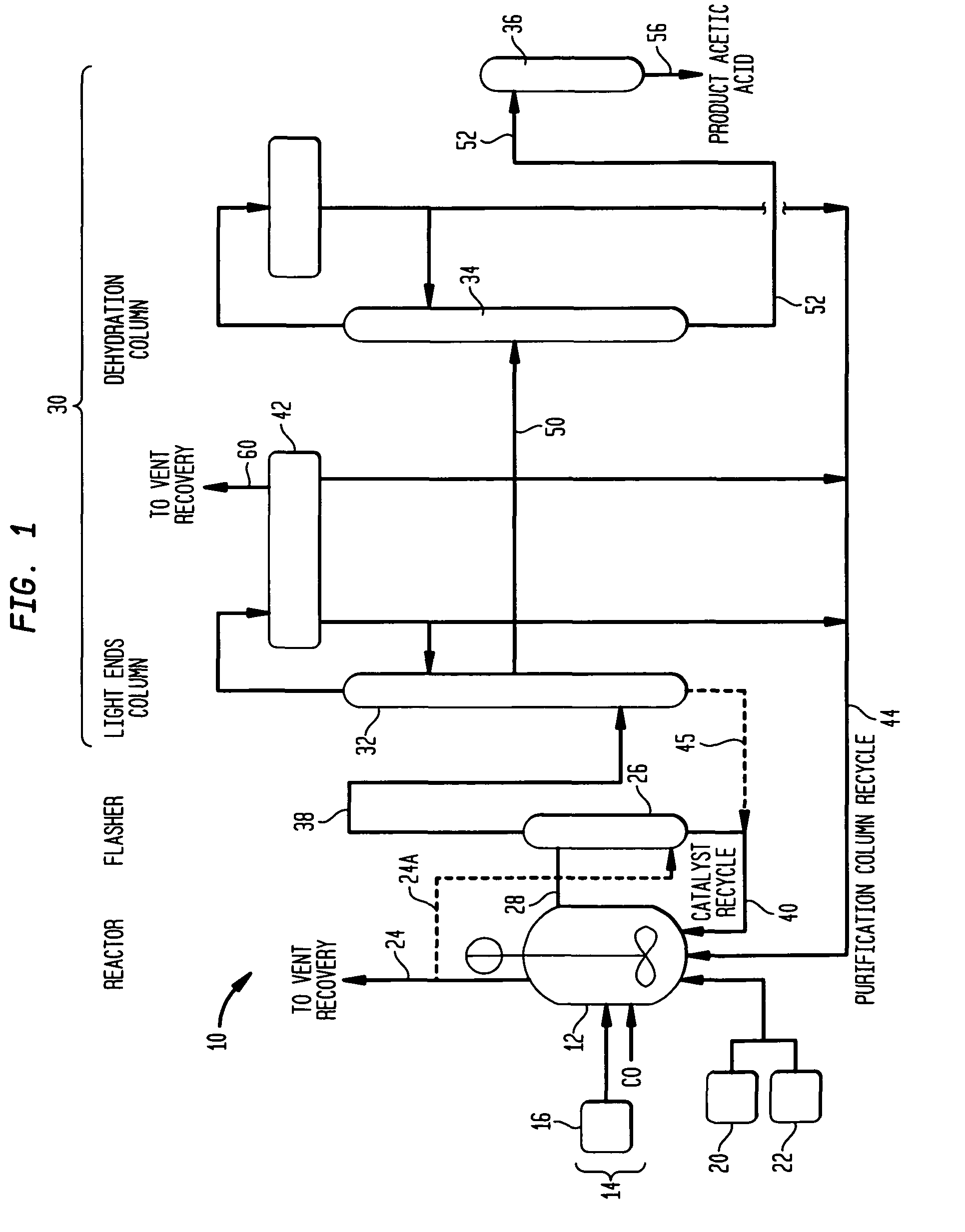
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS7208624B2Easy to separateFacilitate phase separationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionMethyl acetateFormate Esters
An improved process is disclosed for producing acetic acid, including the following steps: reacting a carbonylatable reactant such as methanol, methyl acetate, methyl formate or dimethyl ether with carbon monoxide in a reaction medium containing water, methyl iodide, and a catalyst to produce a reaction product that contains acetic acid; separating the reaction product to provide a volatile phase containing acetic acid, water, and methyl iodide and a less volatile phase; distilling the volatile phase to produce a purified acetic acid product and a first overhead containing water, methyl acetate, and methyl iodide; phase separating the first overhead to provide a first liquid phase containing water and a second liquid phase containing methyl iodide; and adding dimethyl ether to the process in an amount effective to enhance separation of the first overhead to form the first and second liquid phases.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
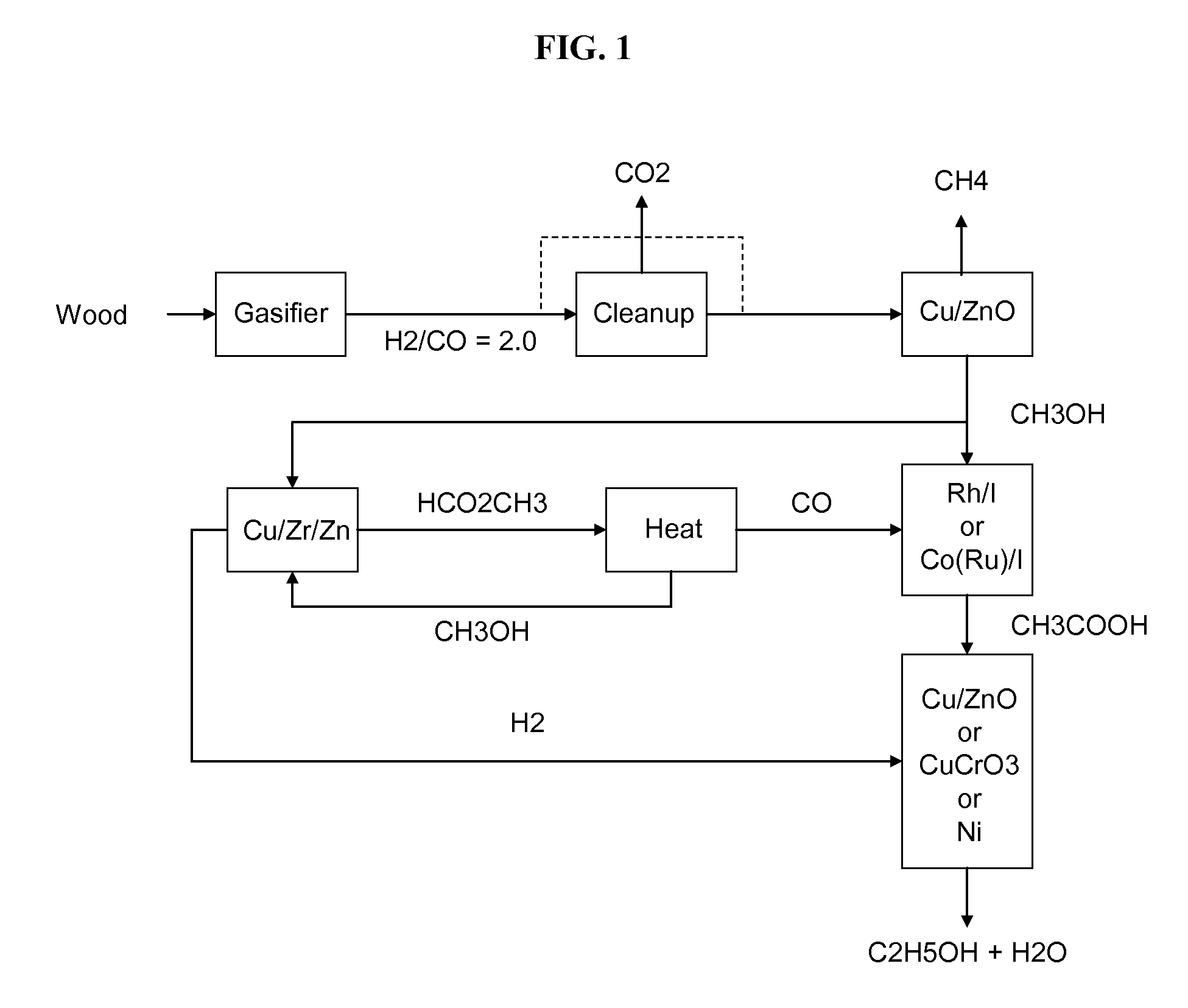
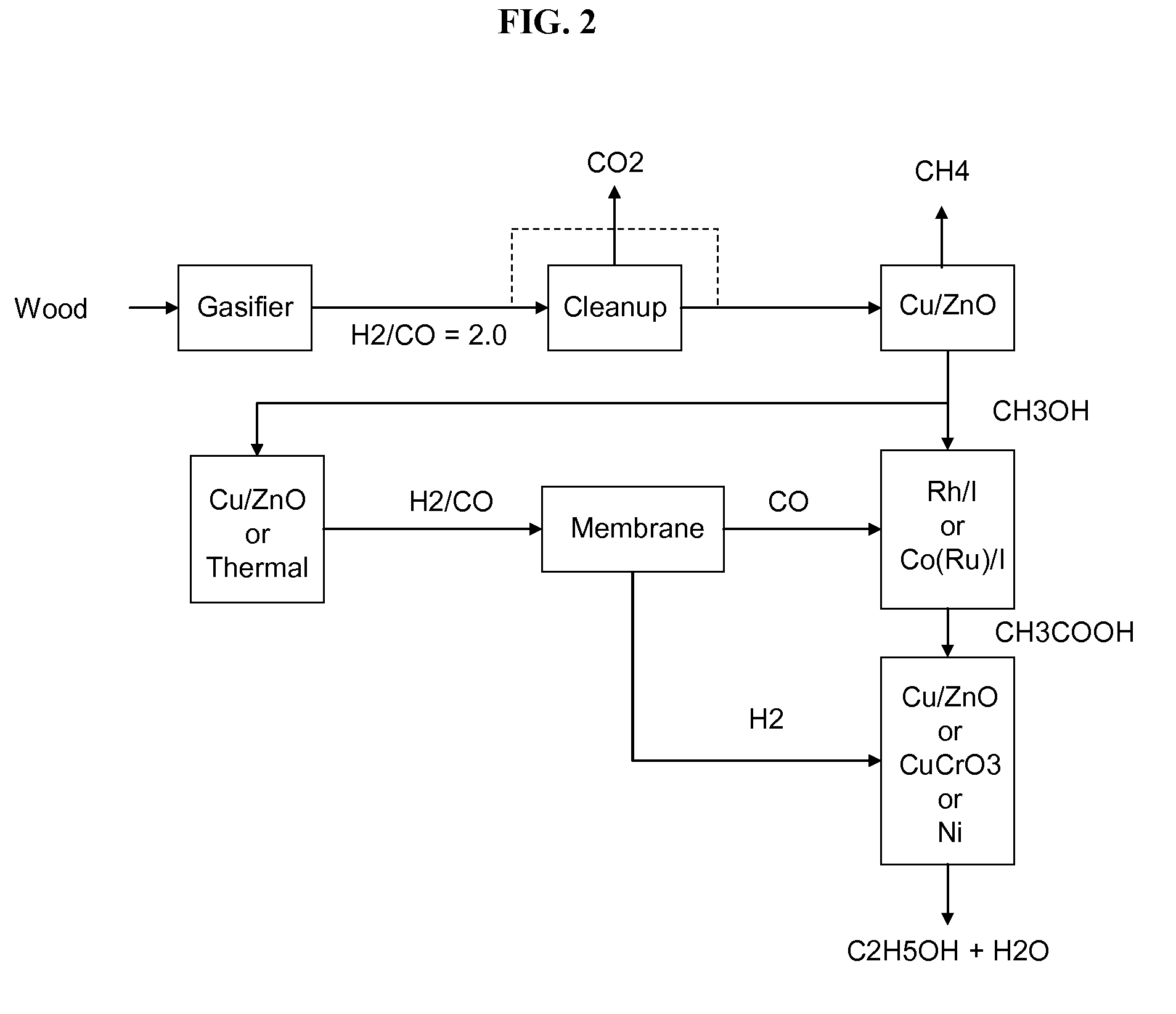
Methods and apparatus for selectively producing ethanol from synthesis gas
The invention provides methods and apparatus for selectively producing ethanol from syngas. As disclosed herein, syngas derived from cellulosic biomass (or other sources) can be catalytically converted into methanol, which in turn can be catalytically converted into acetic acid or acetates. Finally, the acetic acid or acetates can be reduced to ethanol according to several variations. In some embodiments, yields of ethanol from biomass can exceed 100 gallons per dry ton of biomass.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Removal of permanganate reducing compounds from methanol carbonylation process stream
ActiveUS7223886B2Reduce solubilitySimple methodOrganic compound preparationPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionAcetic acidIodide
An improvement of the methanol carbonylation process for manufacturing acetic acid is disclosed. Specifically disclosed is a method for reducing the formation of alkyl iodides and C3-8 carboxylic acids by removing permanganate reducing compounds (“PRC's”) from the light phase of the condensed light ends overhead stream, including (a) distilling the light phase to yield a PRC enriched overhead stream; and (b) extracting the third overhead stream with water in at least two consecutive stages and separating therefrom one or more aqueous streams containing PRC's.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
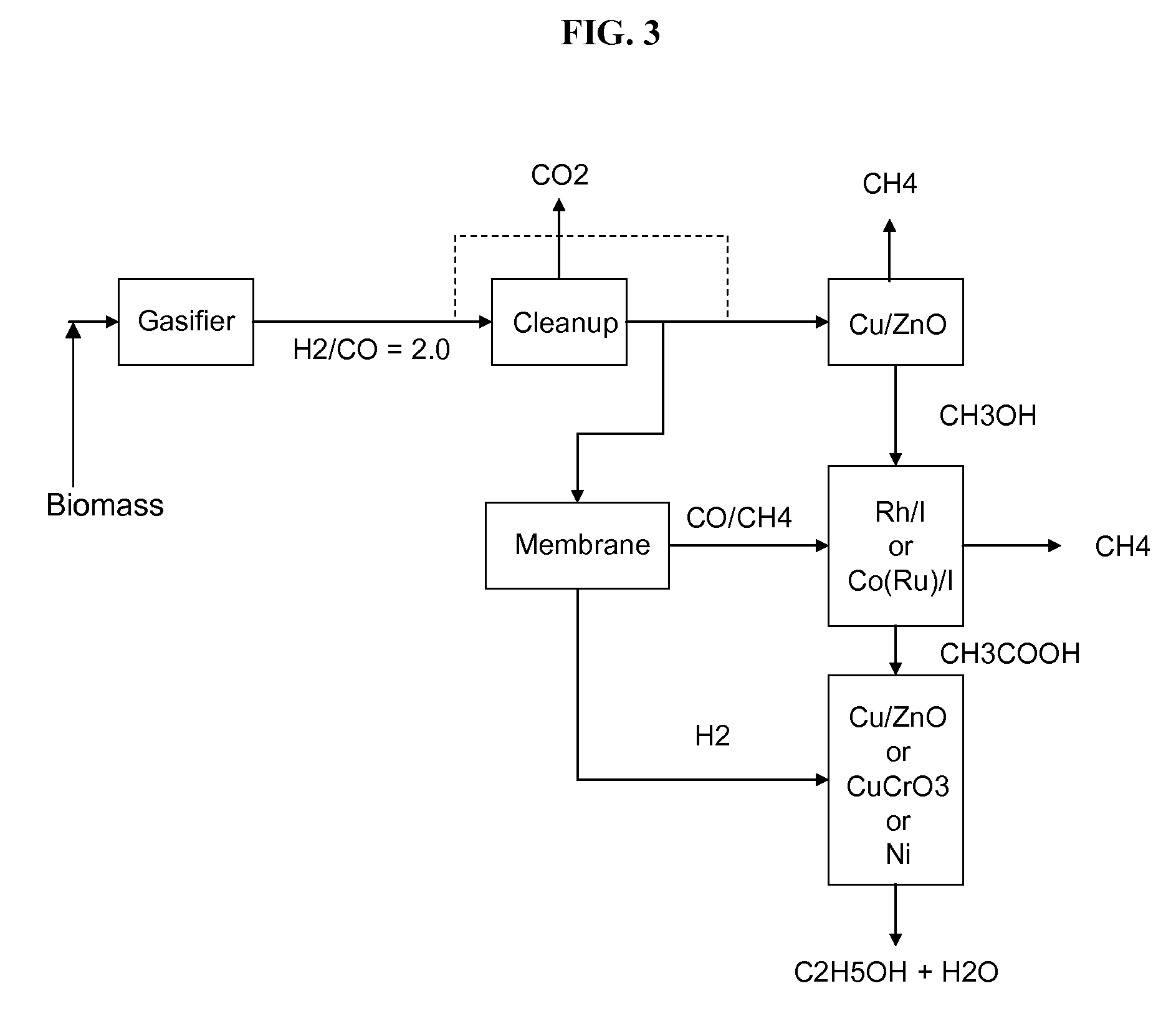
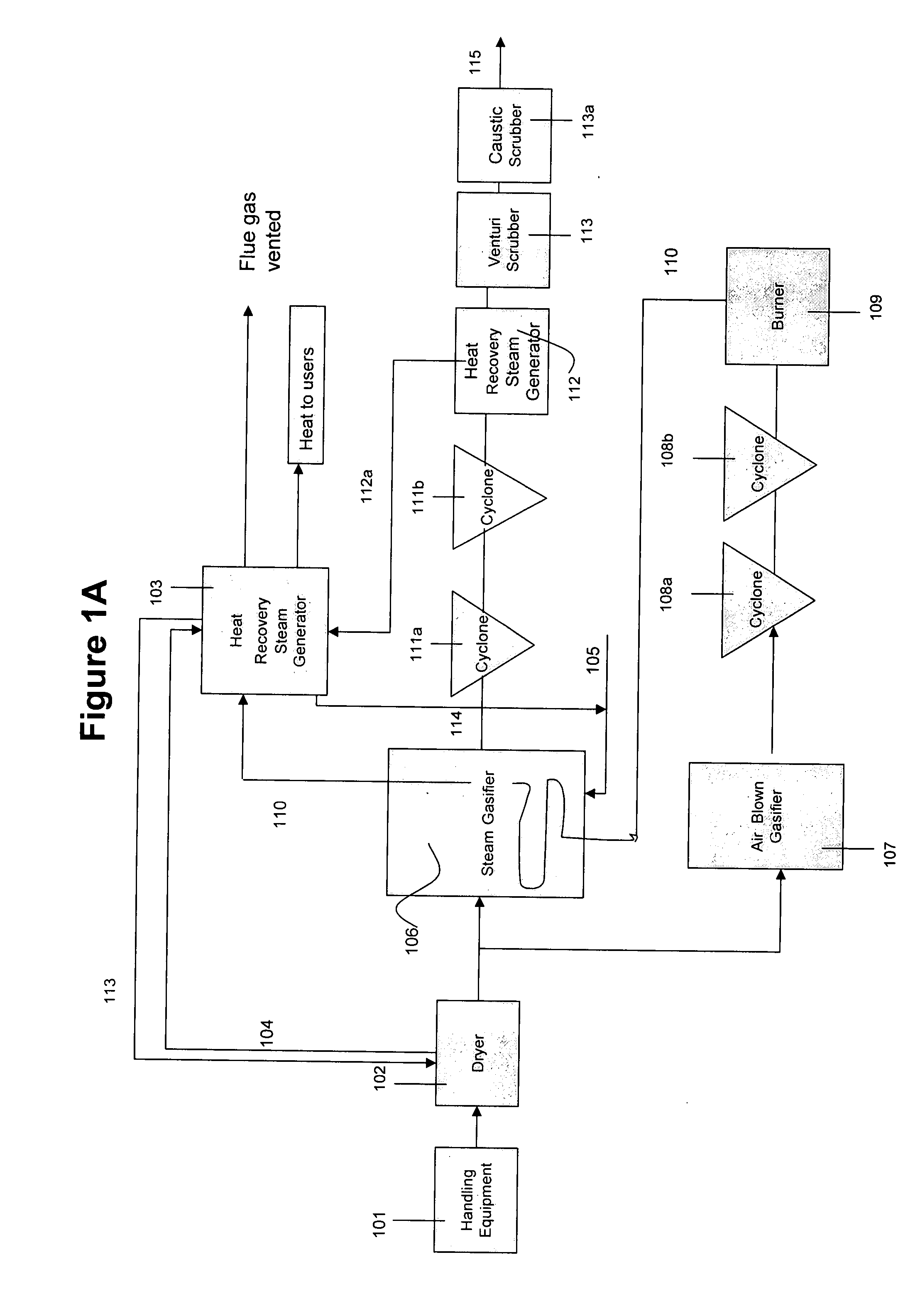
System and method for converting biomass to ethanol via syngas
A method and apparatus for synthesizing ethanol using synthetic routes via synthesis gas are disclosed. A method and apparatus for gasifying biomass, such as biomass, in a steam gasifier that employs a fluidized bed and heating using hot flue gases from the combustion of synthesis gas is described. Methods and apparatus for converting synthesis gas into ethanol are also disclosed, using stepwise catalytic reactions to convert the carbon monoxide and hydrogen into ethanol using catalysts including iridium acetate.
Owner:WOODLAND BIOFUELS
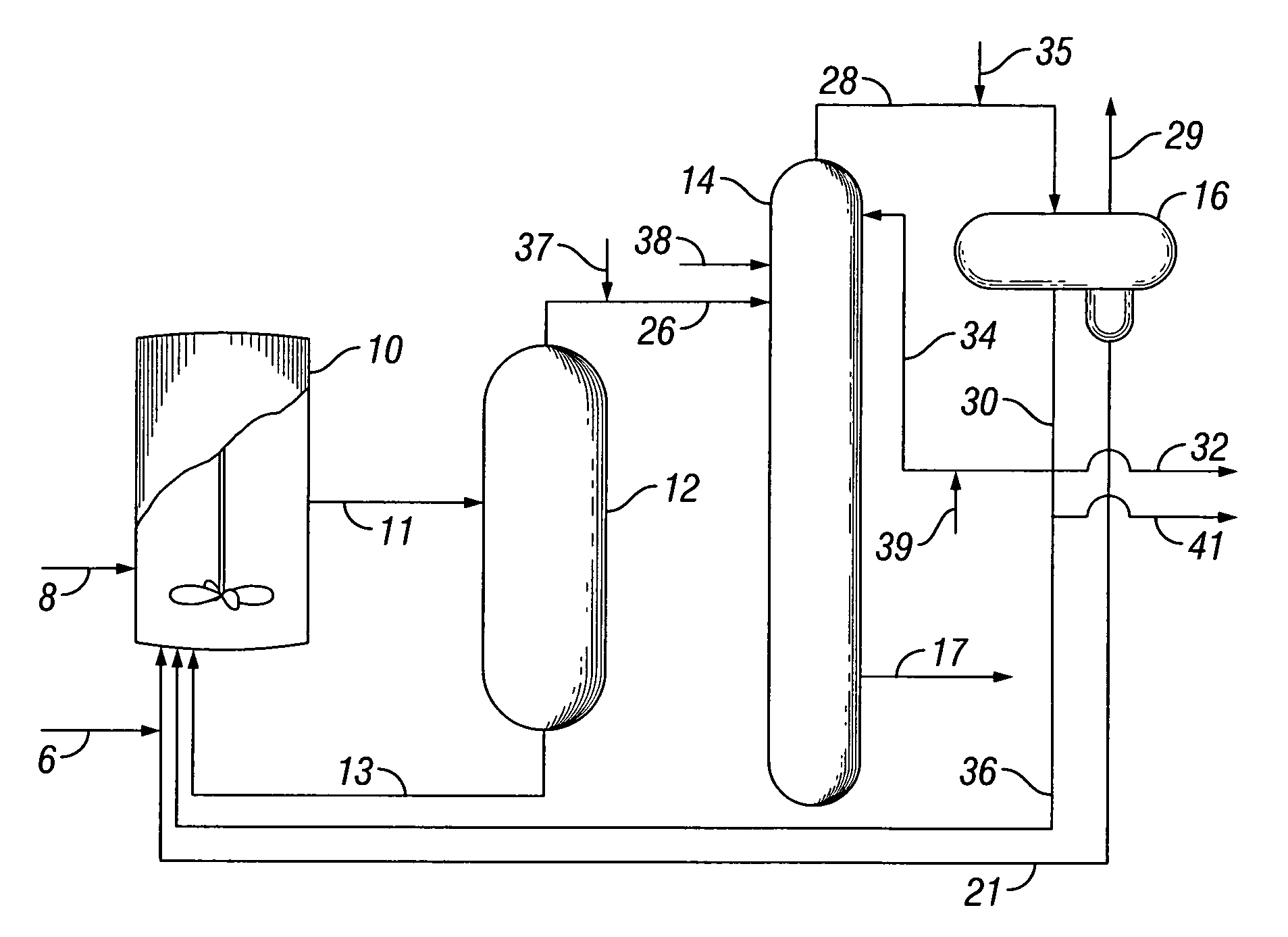
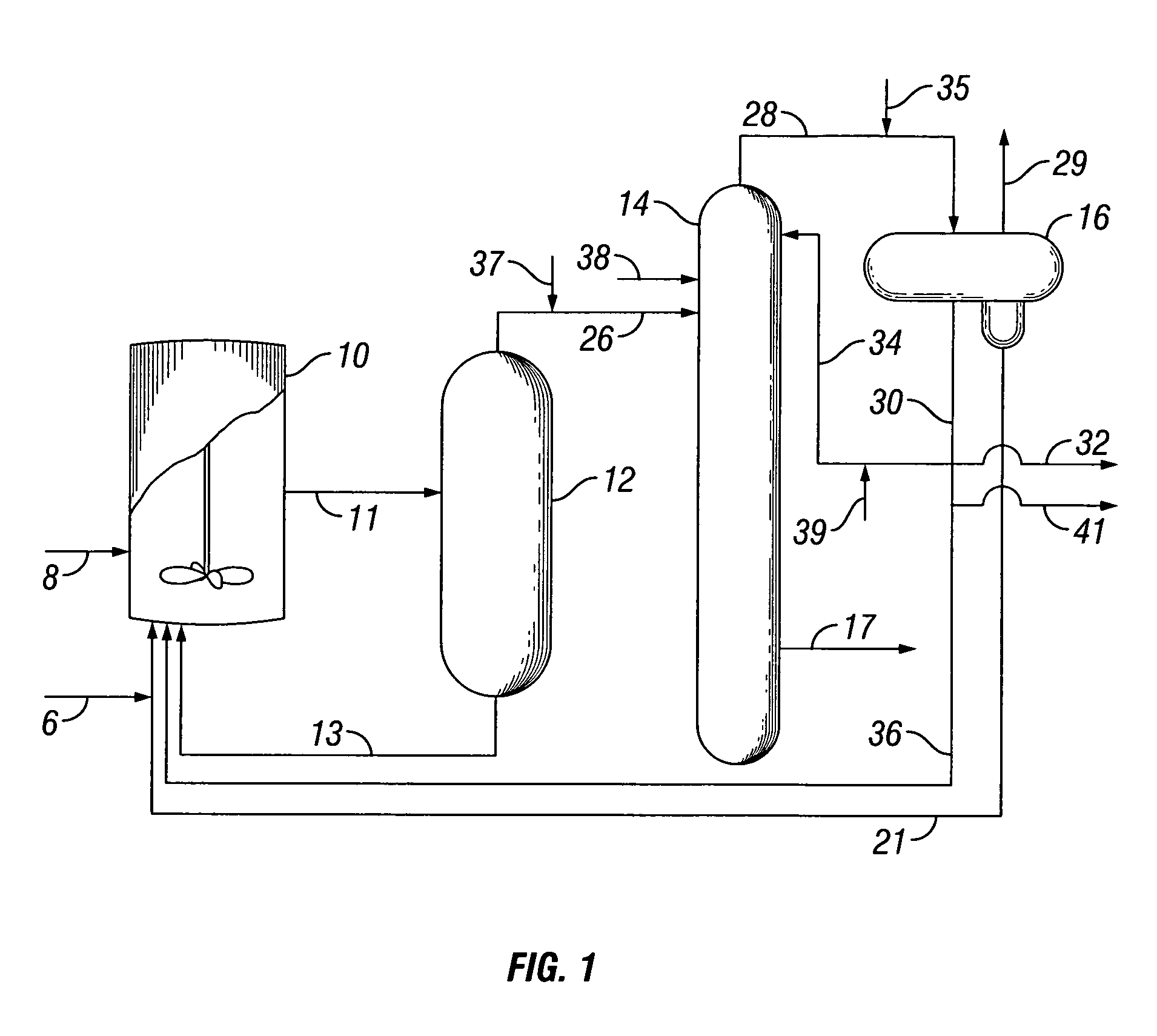
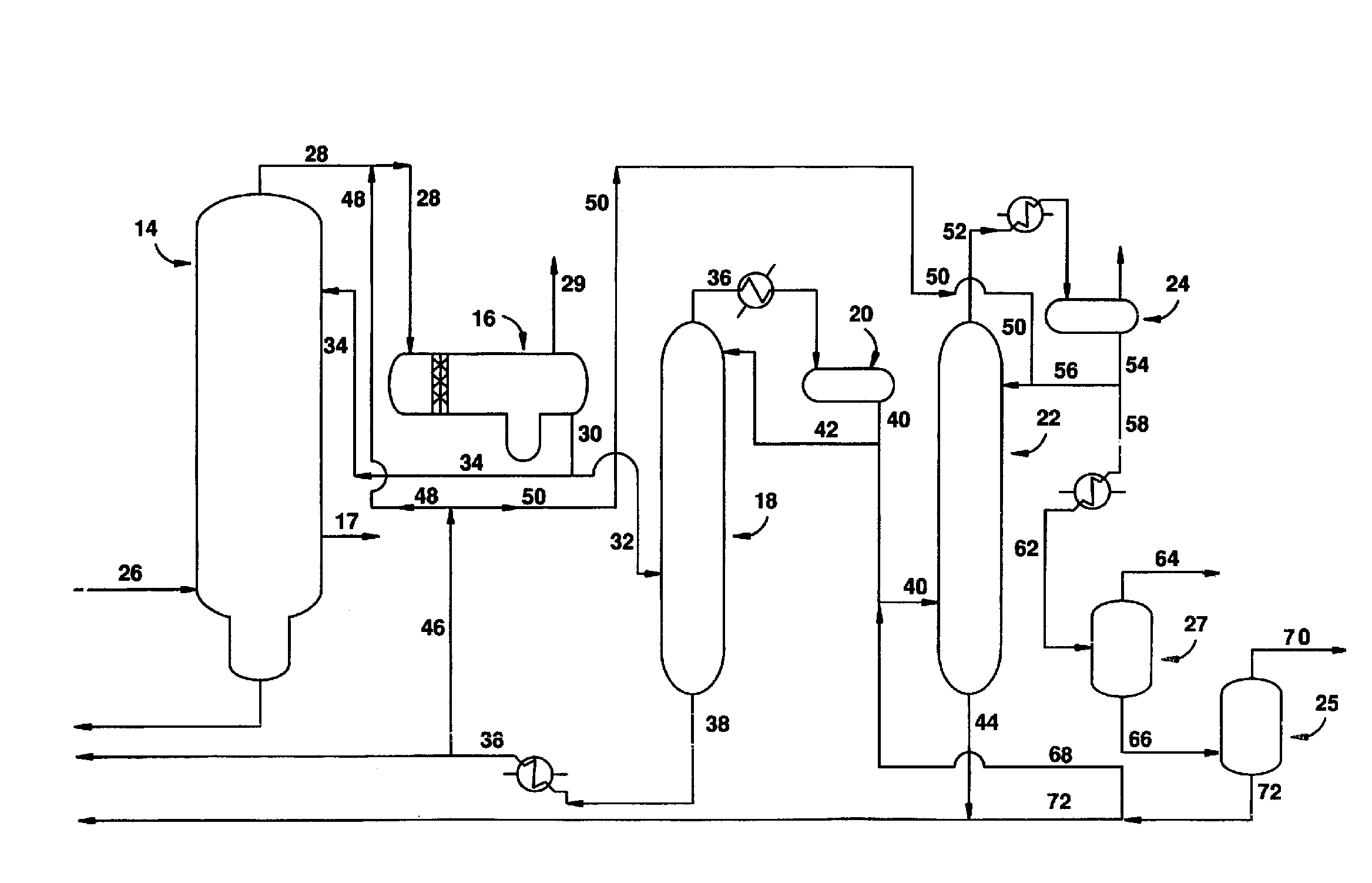
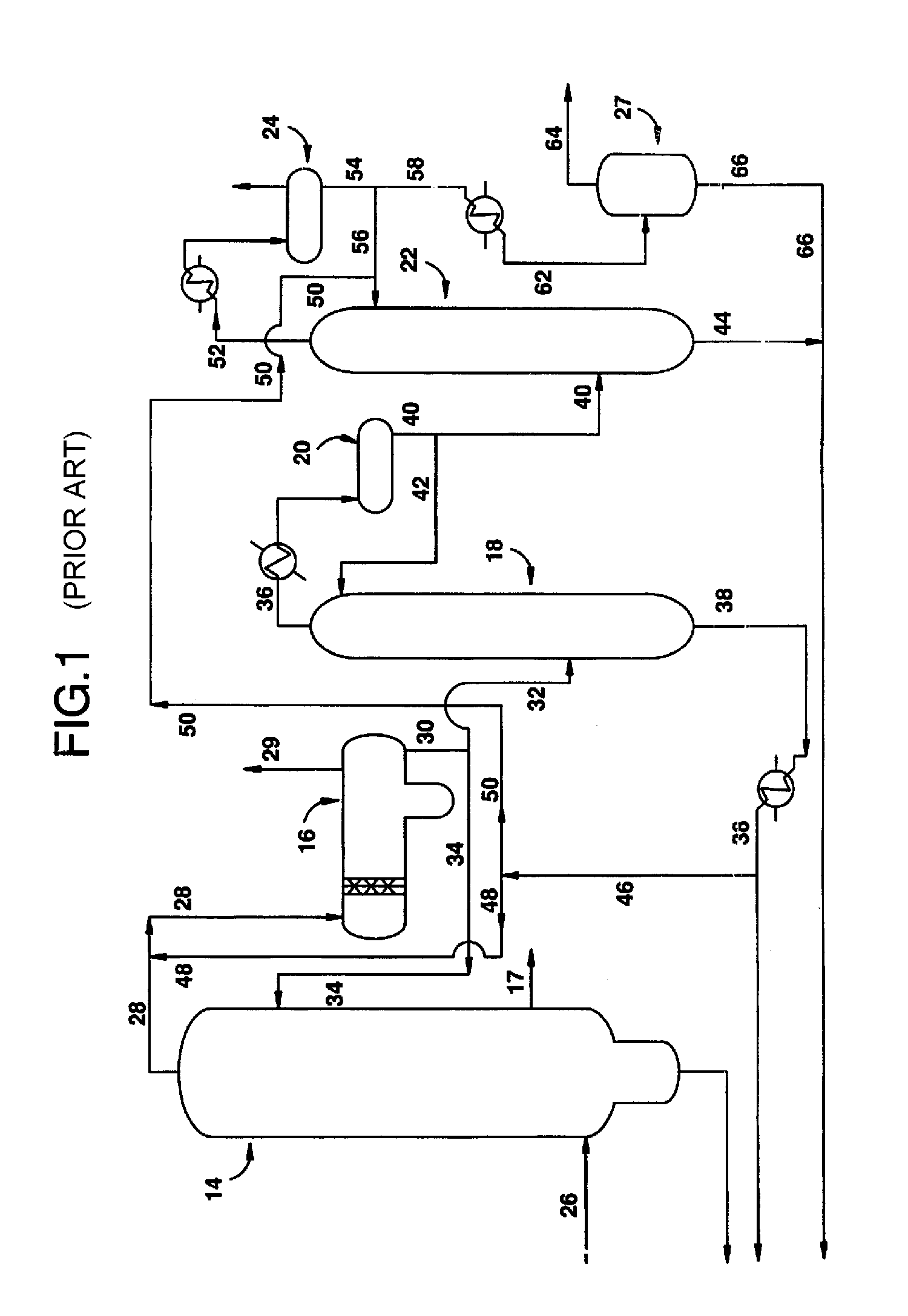
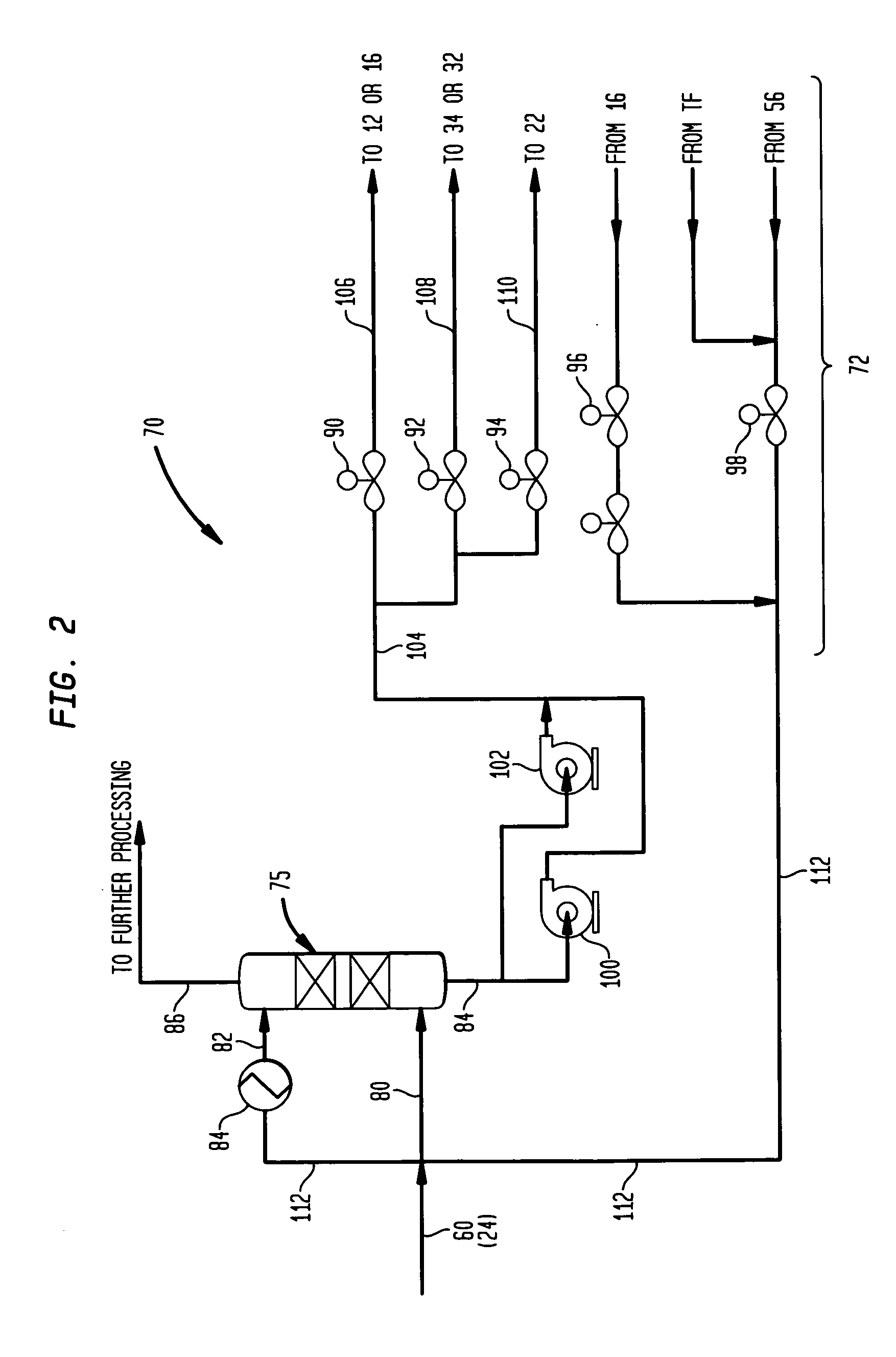
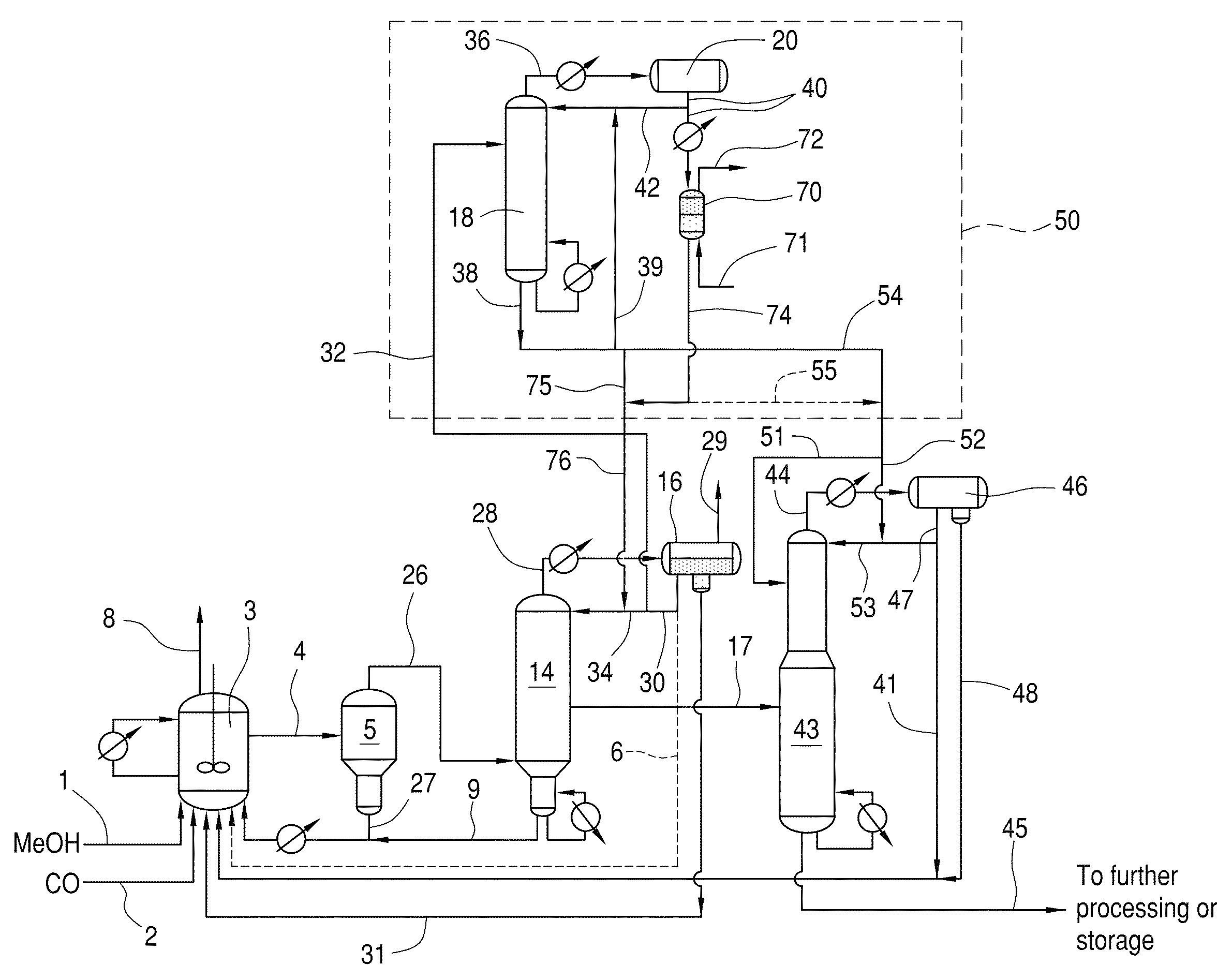
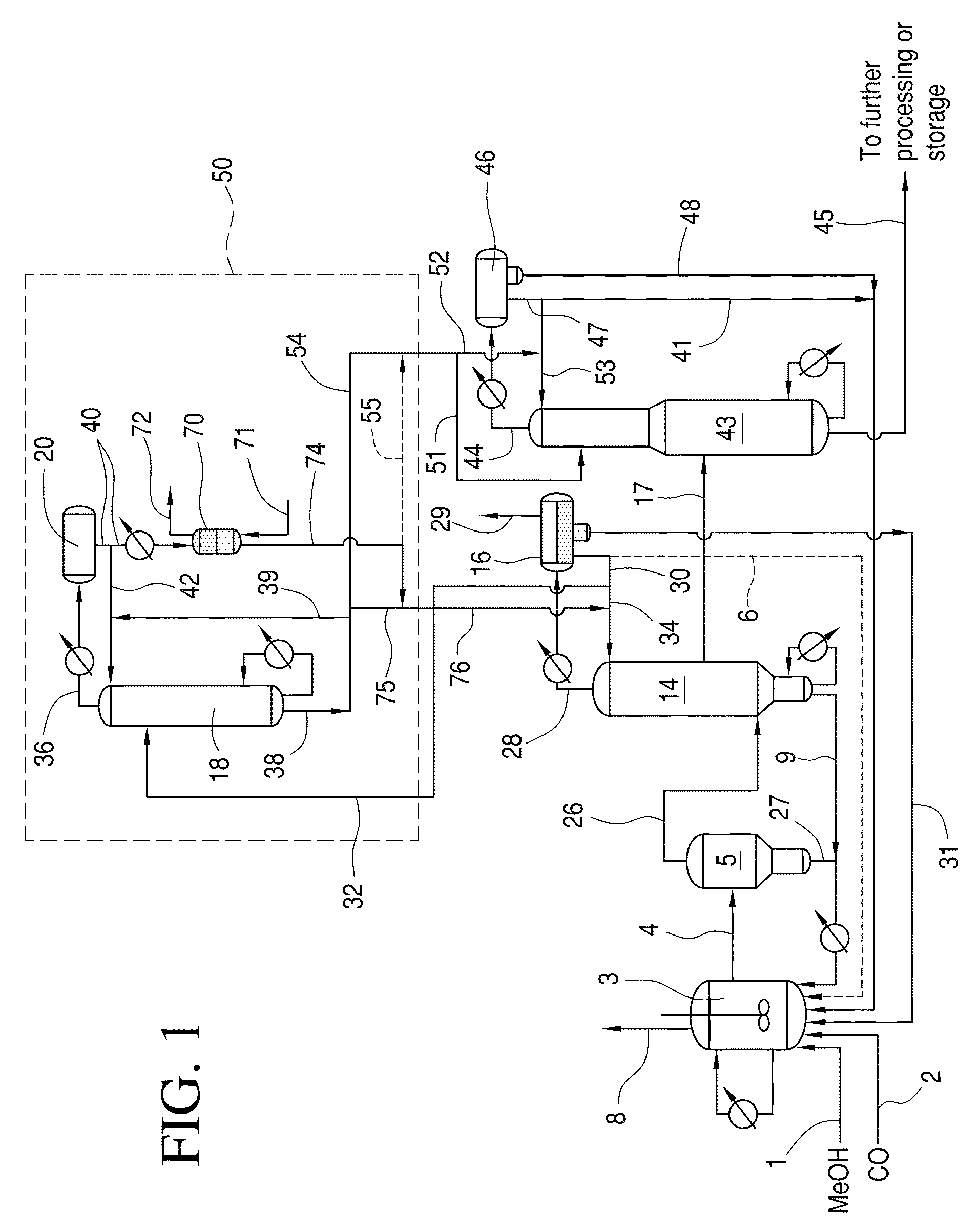
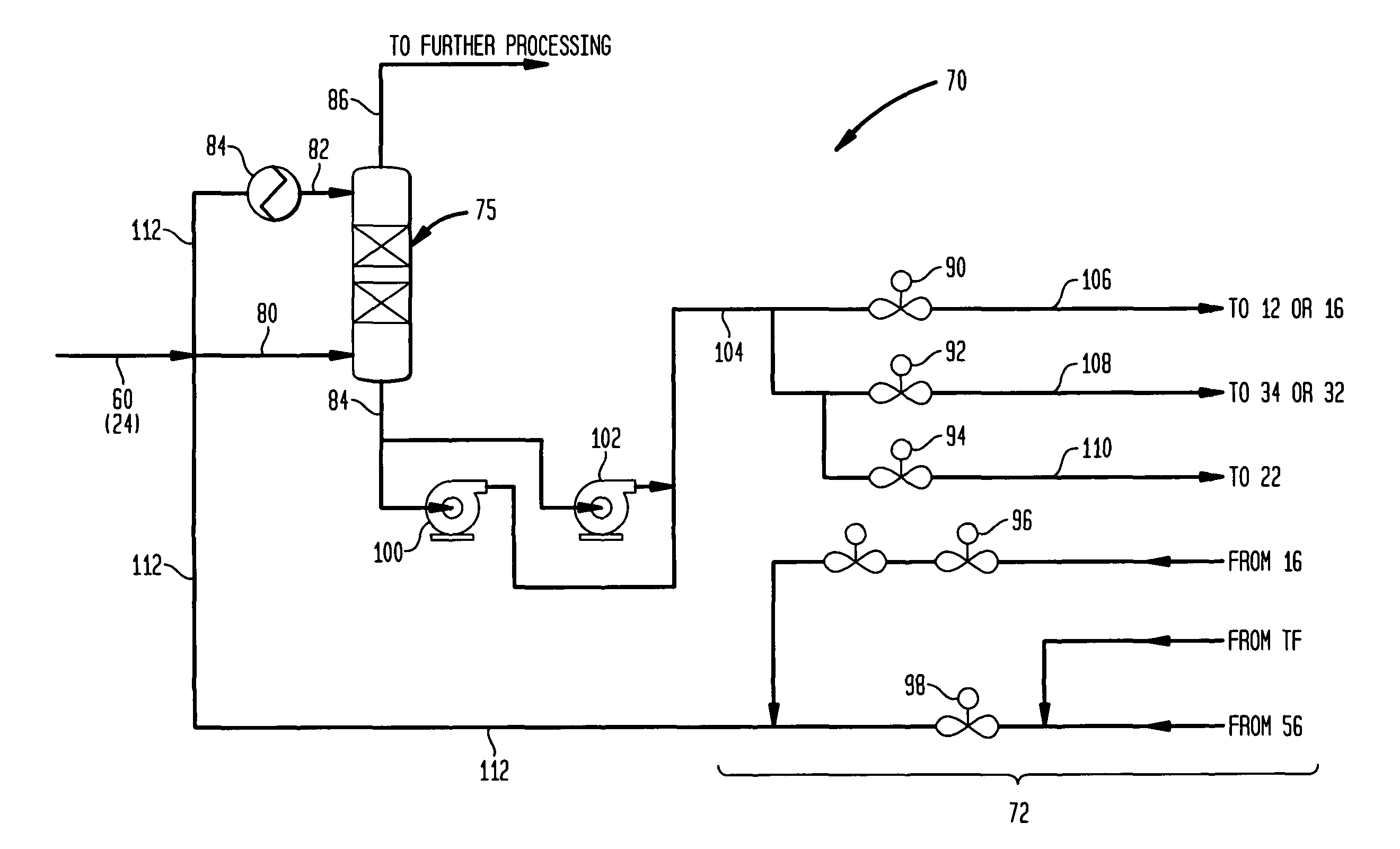
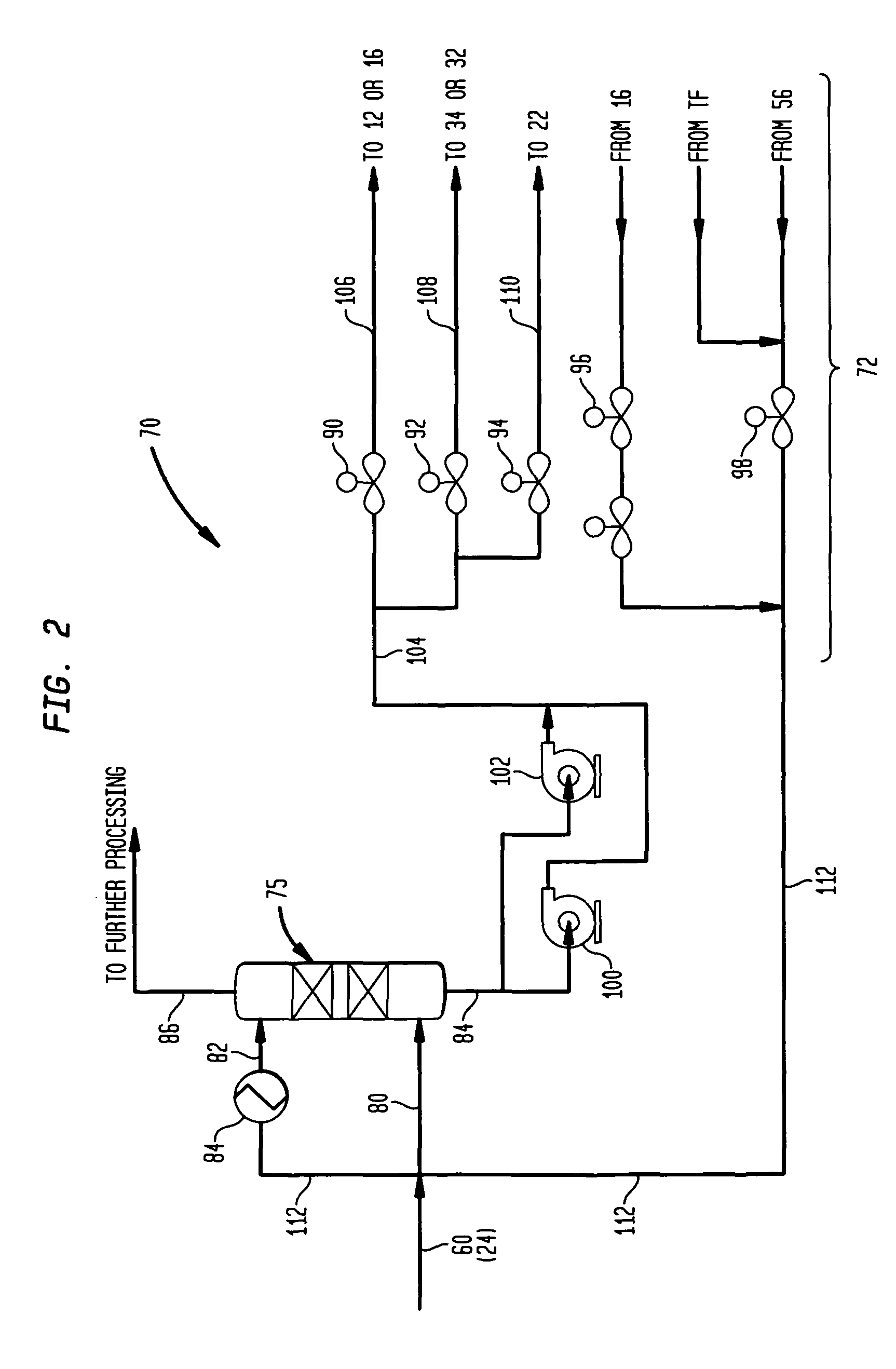
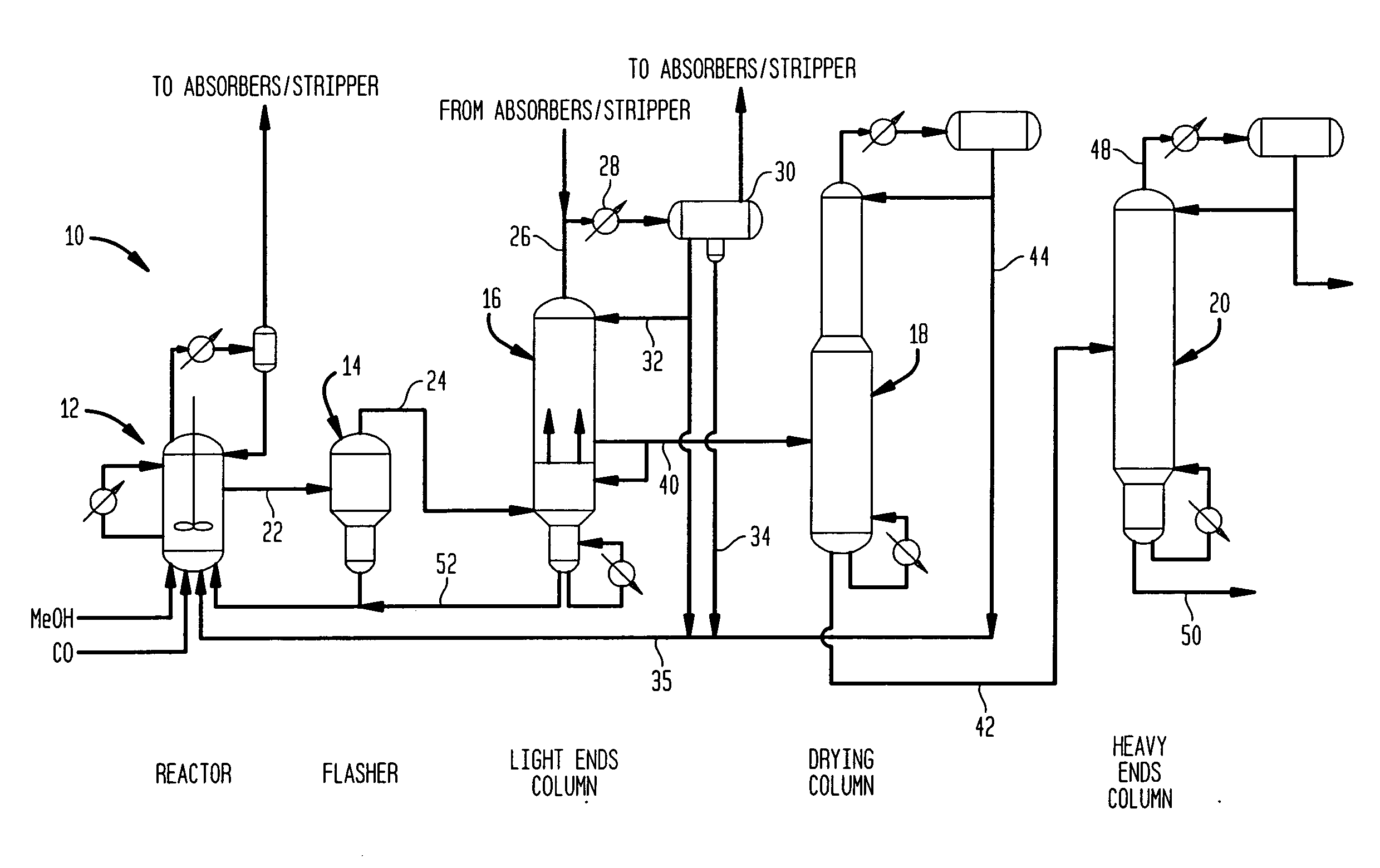
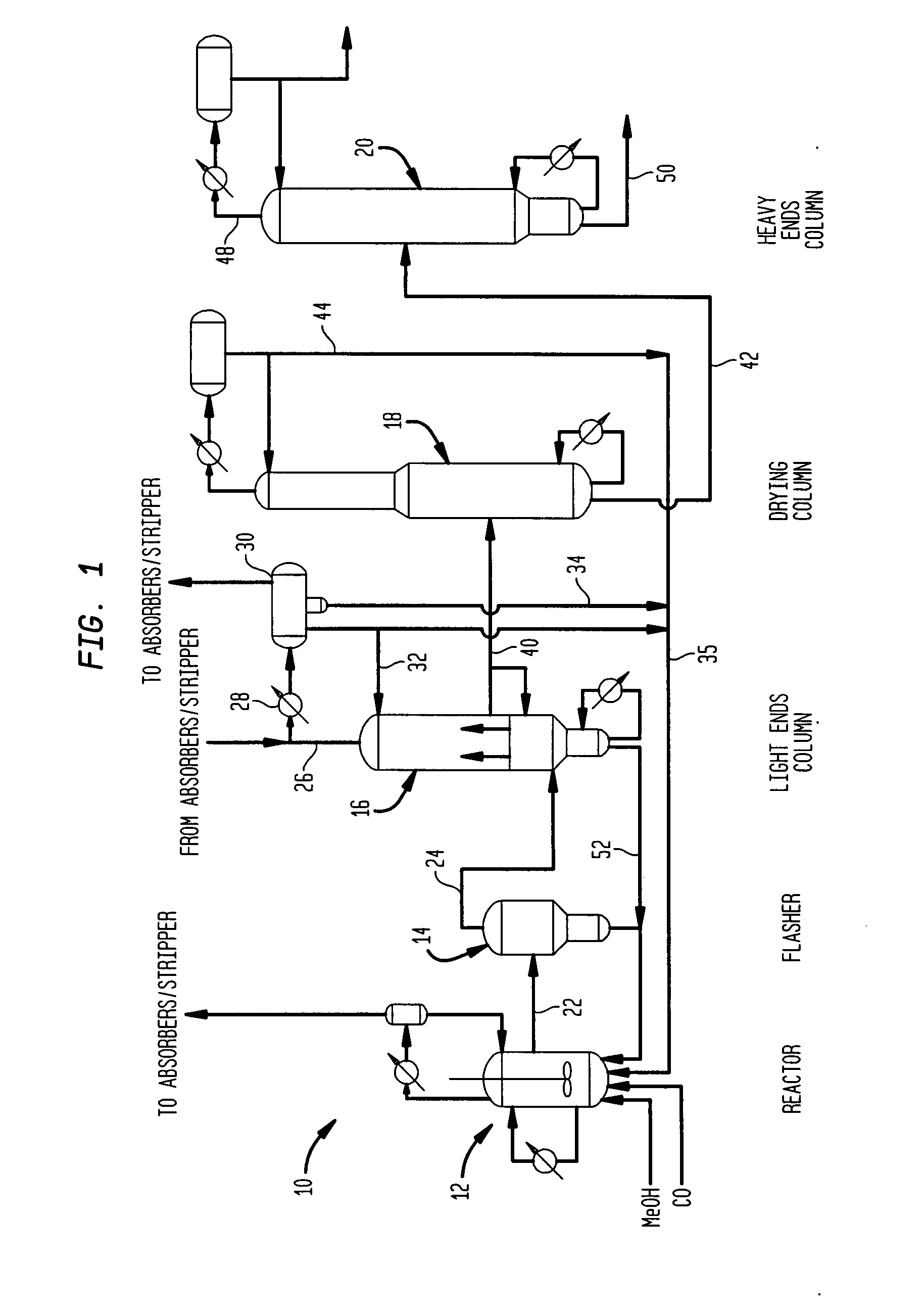
Methanol carbonylation system having absorber with multiple solvent options
A methanol carbonylation system 10 includes an absorber tower 75 adapted for receiving a vent gas stream and removing methyl iodide therefrom with a scrubber solvent, the absorber tower being coupled to first and second scrubber solvent sources 16, 56 which are capable of supplying different first and second scrubber solvents. A switching system including valves 90, 92, 94, 96, 98 alternatively provides first or second scrubber solvents to the absorber tower and returns the used solvent and sorbed material to the carbonylation system to accommodate different operating modes.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
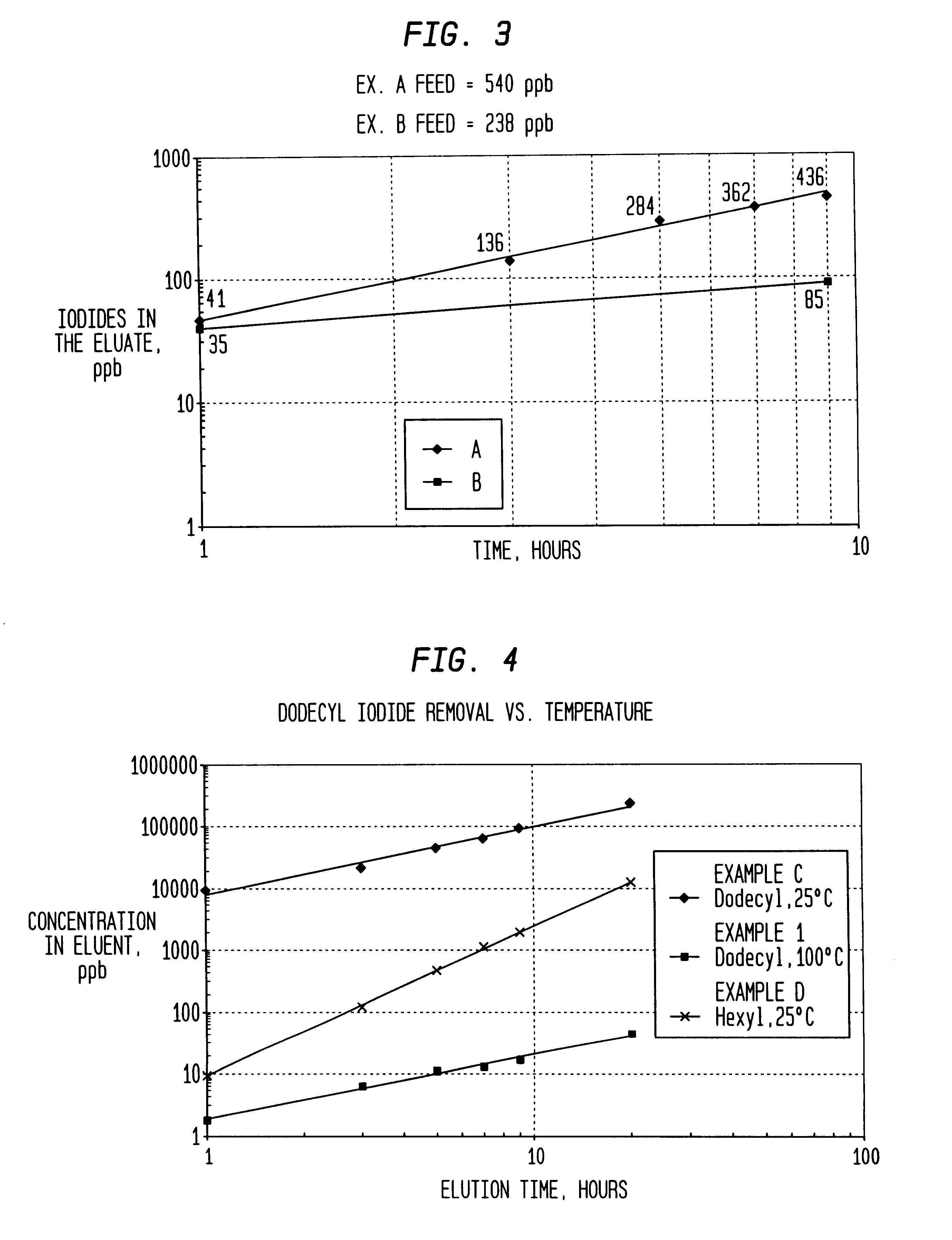
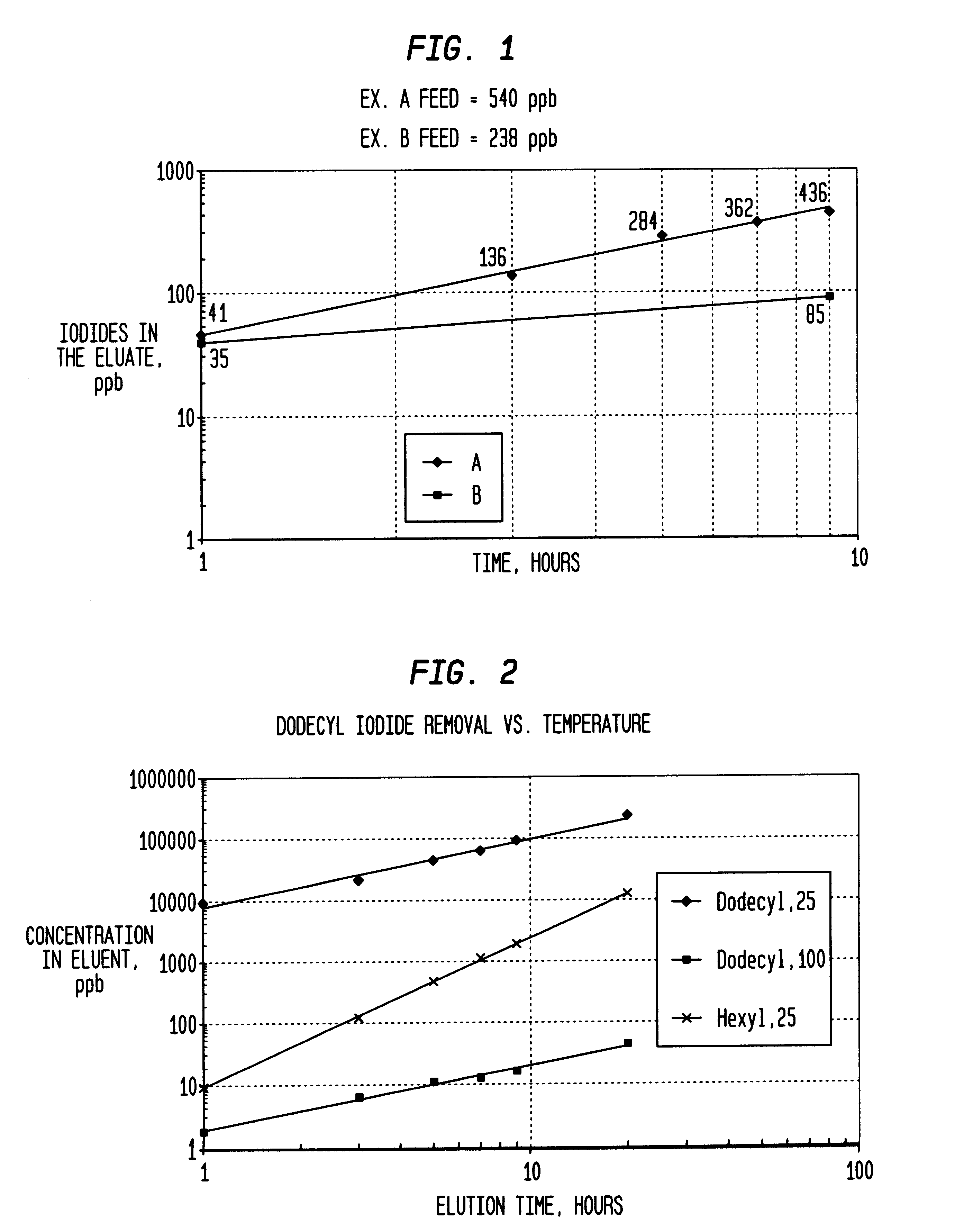
Method of removing organic iodides from organic media
InactiveUS6225498B1Efficient removalCation exchanger materialsOrganic compound preparationAcetic acidAcetic anhydride
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Process for the production of acetic acid
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Control of impurities in reaction product of rhodium-catalyzed methanol carbonylation
InactiveUS20080293966A1Improve the level ofHigh purityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionProtein carbonylCarbonylation
The present invention relates to carbonylation of methanol, methyl acetate, dimethyl ether or mixtures thereof to produce glacial acetic acid, and more specifically to the manufacture of glacial acetic acid by the reaction of methanol, methyl acetate, dimethyl ether or mixtures thereof with carbon monoxide wherein the product glacial acetic acid contains low impurities.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Process for the conversion of hydrocarbons into ethanol
ActiveUS7947746B2Increased formationIncreased purge stepOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionAcetic acidAlcohol
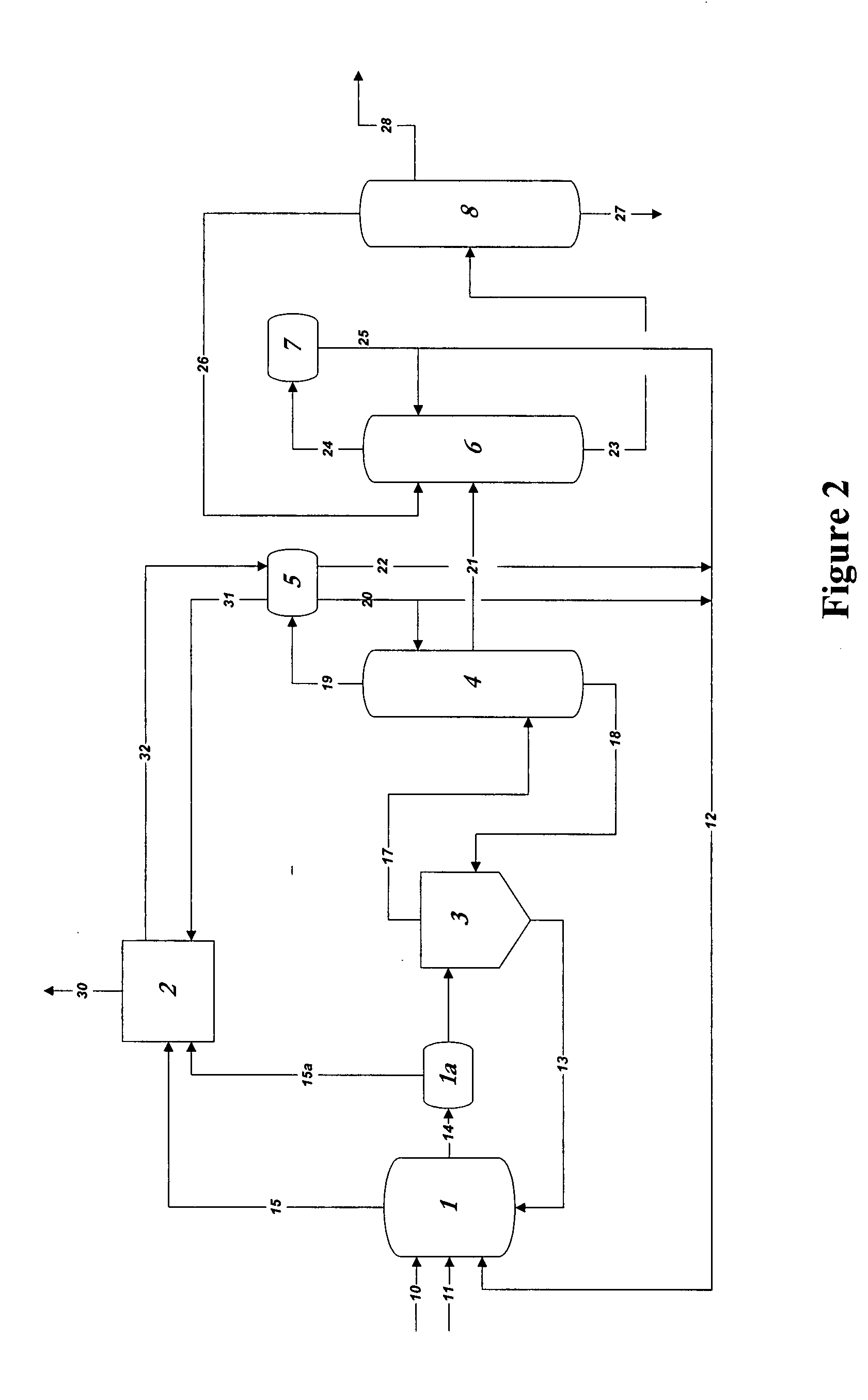
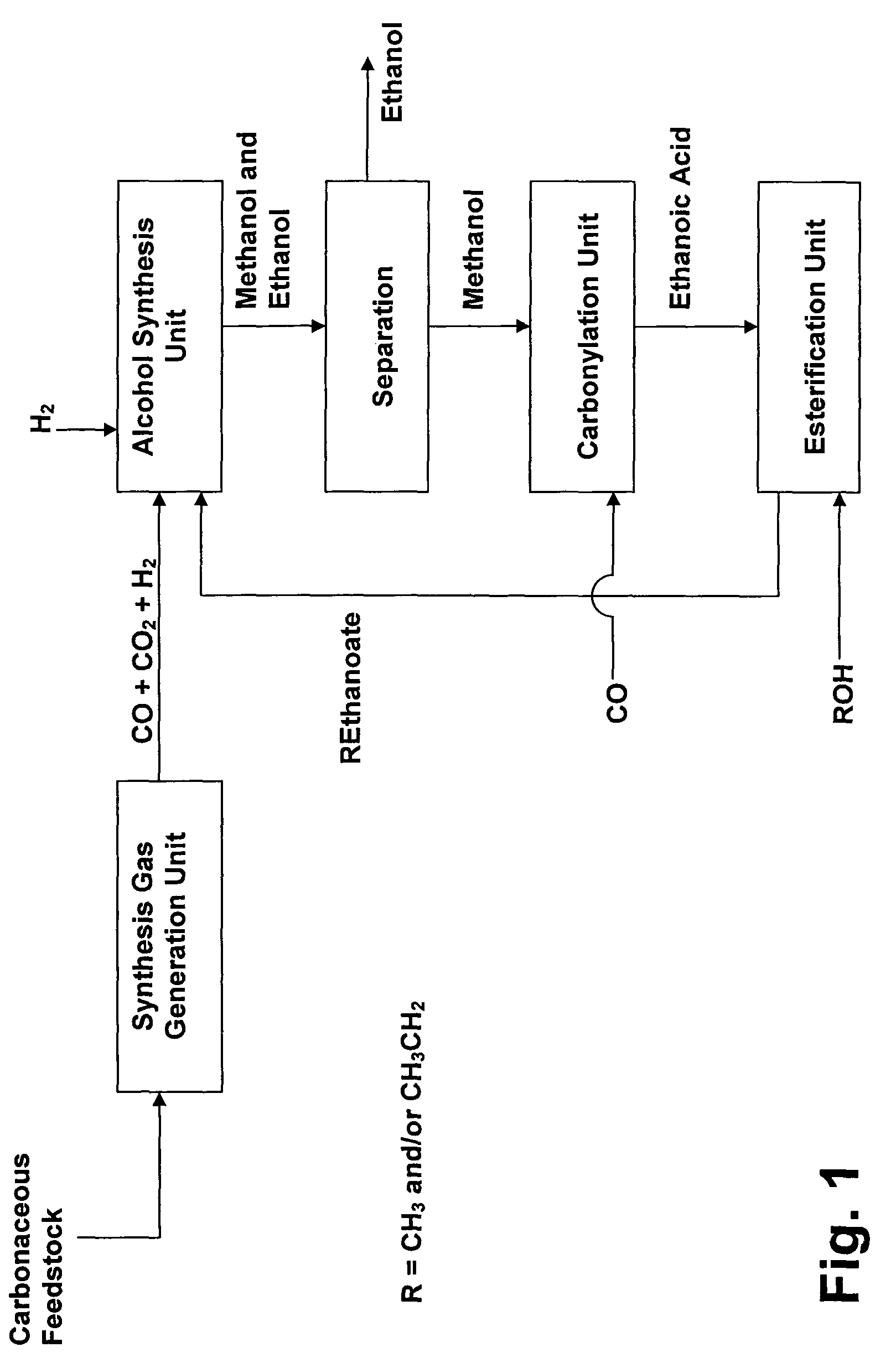
Process for converting synthesis gas to ethanol, including the steps of 1) introducing synthesis gas, together with methyl ethanoate and / or ethyl ethanoate, into an alcohol synthesis unit to produce methanol and ethanol, 2) separating the methanol from the ethanol of step 1, 3) introducing methanol, from step 2, together with CO, into a carbonylation unit in the presence of a methanol carbonylation catalyst, to produce ethanoic acid, and 4) introducing ethanoic acid, from step 3, together with methanol and / or ethanol, into an esterification unit to produce methyl ethanoate and / or ethyl ethanoate. In step 5), methyl ethanoate and / or ethyl ethanoate, produced in step 4, are fed into the alcohol synthesis unit of step 1, and in step 6) ethanol from step 2 is recovered.
Owner:INEOS ACETYLS UK LTD
Removal of permanganate reducing compounds from methanol carbonylation process stream
ActiveUS7223883B2Reduce solubilityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionAcetic acidCarbonylation
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Process for carbonylation of alkyl ethers
ActiveUS20070238897A1Organic compound preparationPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesCarboxylic acidCarbonylation
A product comprising a lower alkyl ester of a lower aliphatic carboxylic acid is produced by a process comprising reacting under substantially anhydrous conditions a lower alkyl ether with carbon monoxide in the presence of a zeolite catalyst having an 8-member ring channel which is interconnected with a channel defined by a ring with greater than or equal to 8 members, the 8-member ring having a window size of at least 2.5 Angstroms×at least 3.6 Angstroms and at least one Brønsted acid site and the zeolite having a silica:X2O3 ratio of at least 5, wherein X is selected from aluminum, boron, iron, gallium and mixtures thereof.
Owner:THE BRITISH PETROLEUM CO LTD +1
Tin promoted platinum catalyst for carbonylation of lower alkyl alcohols
InactiveUS6903045B2Not volatileLess solubleIsocyanic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationSolid componentGas phase
A carbonylation catalyst useful for producing esters and carboxylic acids in a vapor phase carbonylation process, wherein the catalyst includes a solid component having a catalytically effective amount of platinum and tin associated with a solid catalyst support material and a vaporous halide promoter component.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Addition of iridium to the rhodium/inorganic iodide catalyst system
InactiveUS6211405B1High rateReduce productionPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationPtru catalystCarboxylic acid
The present invention provides a process for the carbonylation of an alcohol, ether or ester to products comprising a carboxylic acid, the anhydride thereof or coproduction of the carboxylic acid and anhydride. More particularly, the present invention provides a process for the carbonylation of methanol to produce acetic acid by reacting methanol with carbon monoxide in a liquid reaction medium containing a catalyst comprising rhodium, iridium, iodide ion, and said reaction medium further comprising water, acetic acid, methyl iodide, and methyl acetate and subsequently recovering acetic acid from the resulting reaction product.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Processes for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS8889904B2Reduce loadEasy to separateSolvent extractionOrganic compound preparationAcetic acidDistillation
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS20130264186A1Improve concentrationEfficient executionOrganic chemistry methodsDistillation separationBoiling pointFractionating column
Acetic acid is produced while efficiently inhibiting condensation of hydrogen iodide in a distillation column (second distillation column) for purifying crude acetic acid by further distillation.A process for producing acetic acid comprises an acetic acid collection step for feeding a first distillation column with a volatile component at least containing acetic acid, methyl acetate, methyl iodide, water, and hydrogen iodide, separating a first lower boiling point component as an overhead, and collecting a first liquid stream mainly containing acetic acid, and an acetic acid purification step for feeding a second distillation column with the first liquid stream, further separating a second lower boiling point component as an overhead, and collecting a second liquid stream containing acetic acid, wherein an alkali component is added or mixed to the first liquid stream in the manners (1) and / or (2) for distilling a liquid object to be treated containing the first liquid stream and the alkali component in the second column: (1) the alkali component is added to or mixed with the first liquid stream before the first liquid stream is fed to the second column, (2) in the second column, the alkali component is added or mixed at the same height level as or at a height level upper than a height level at which the first liquid stream is fed.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
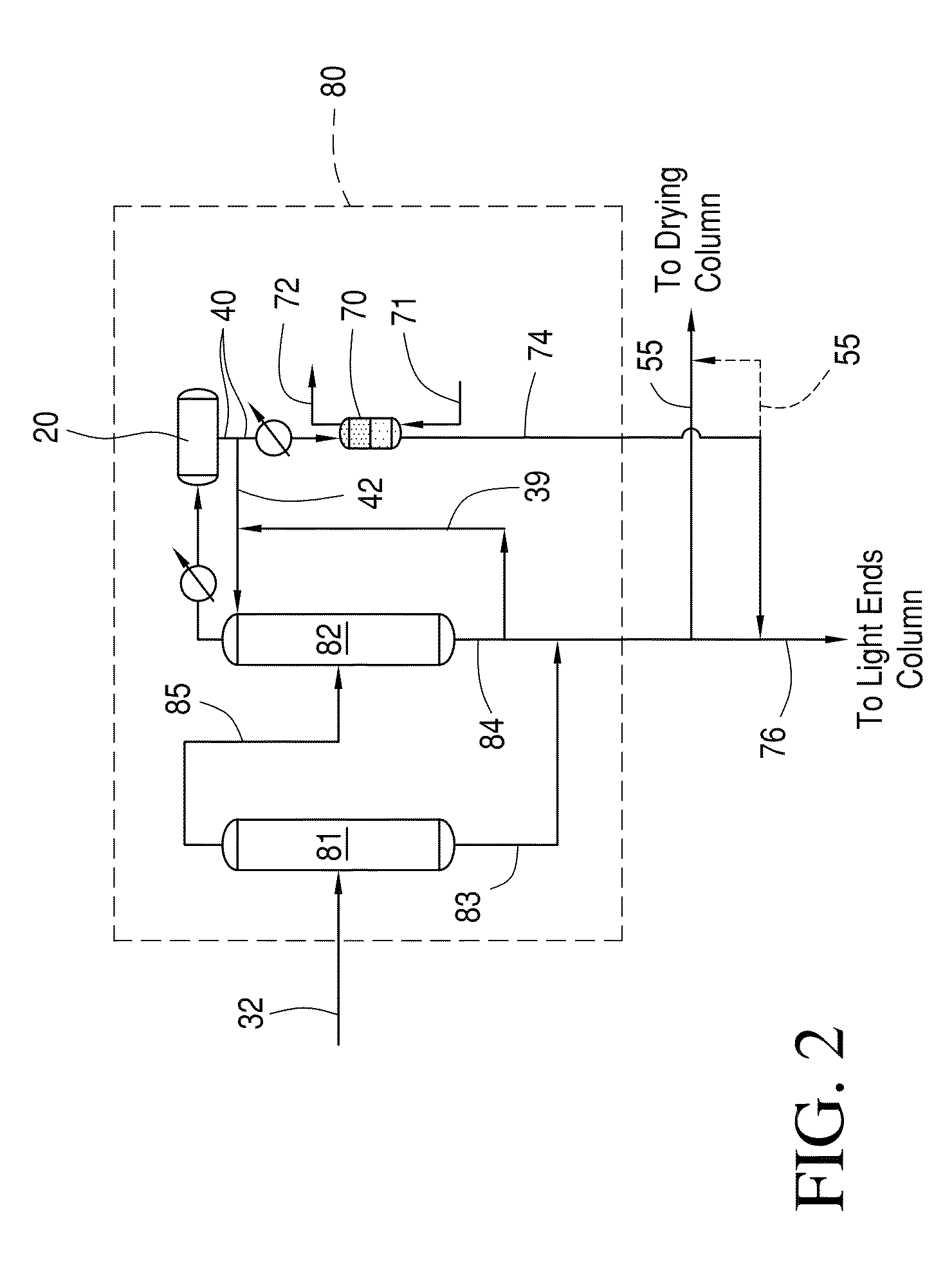
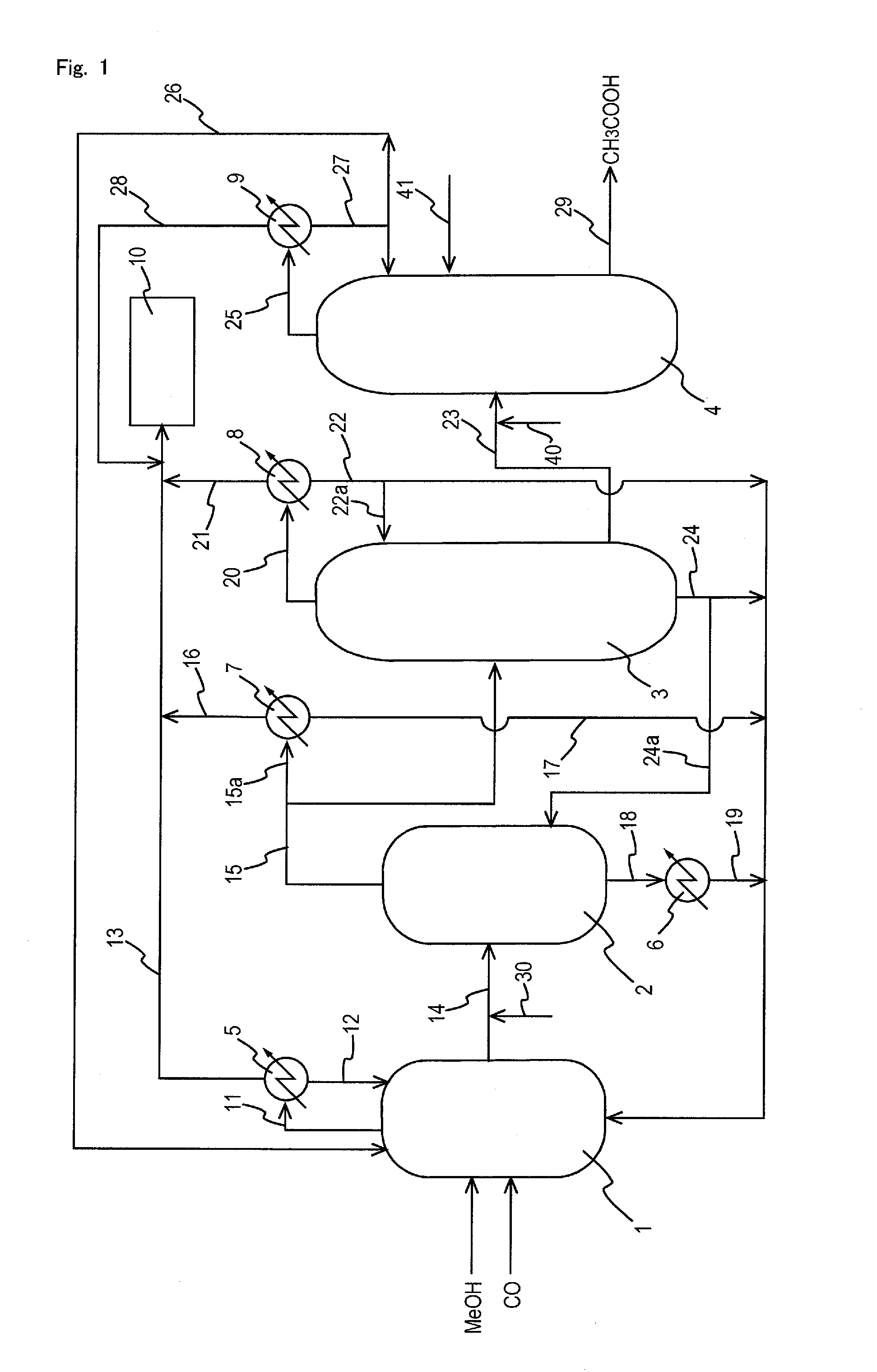
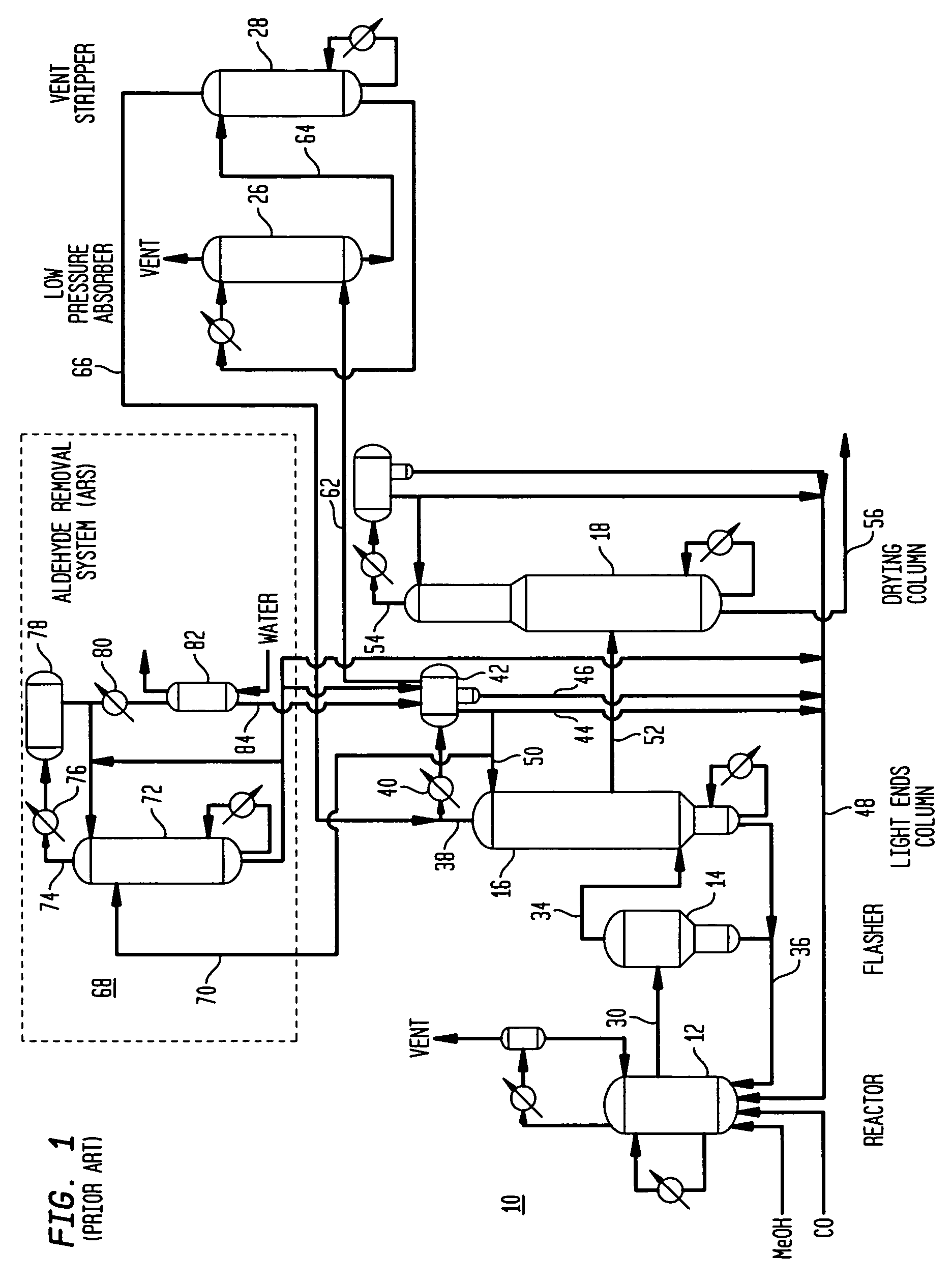
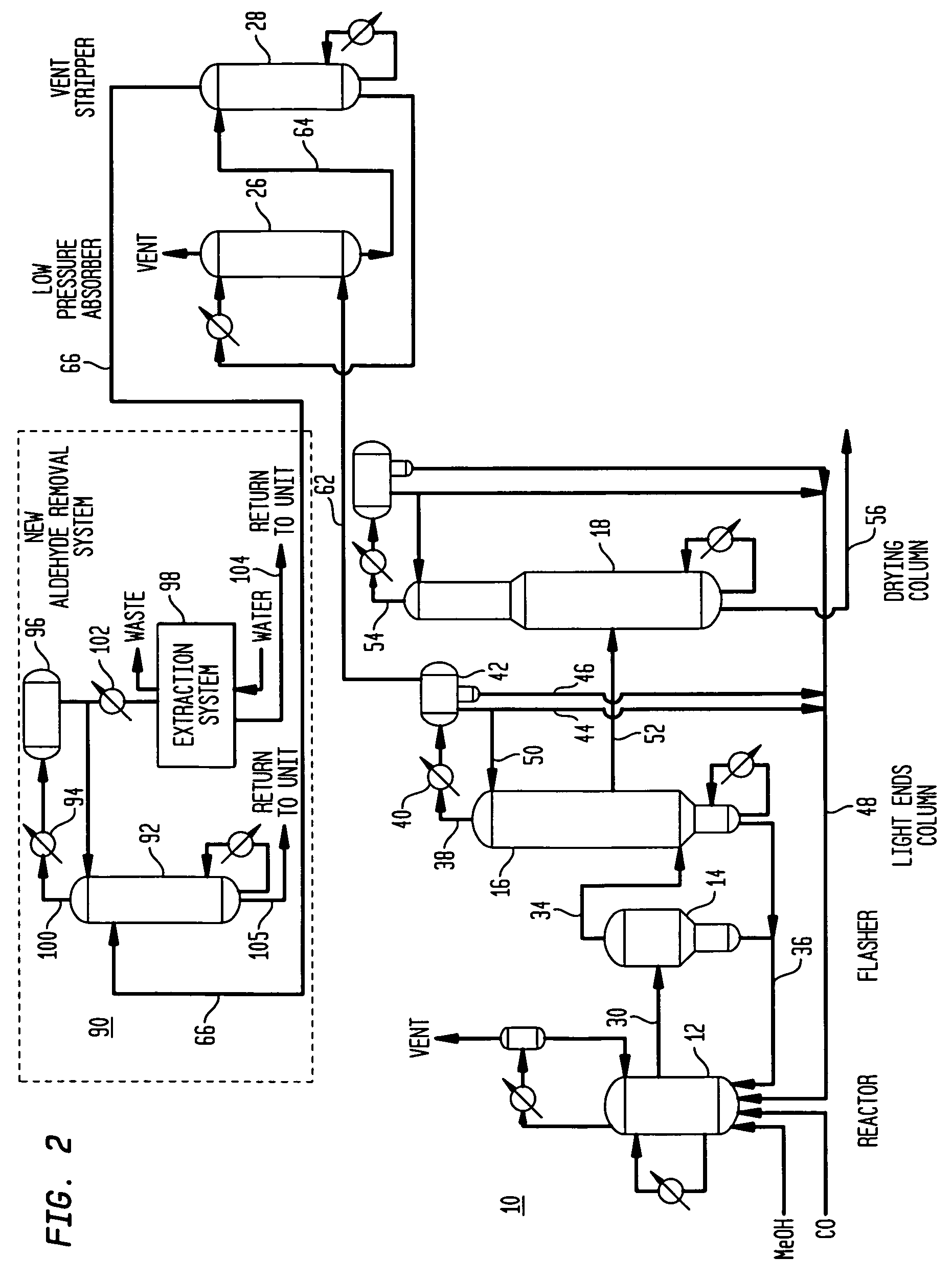
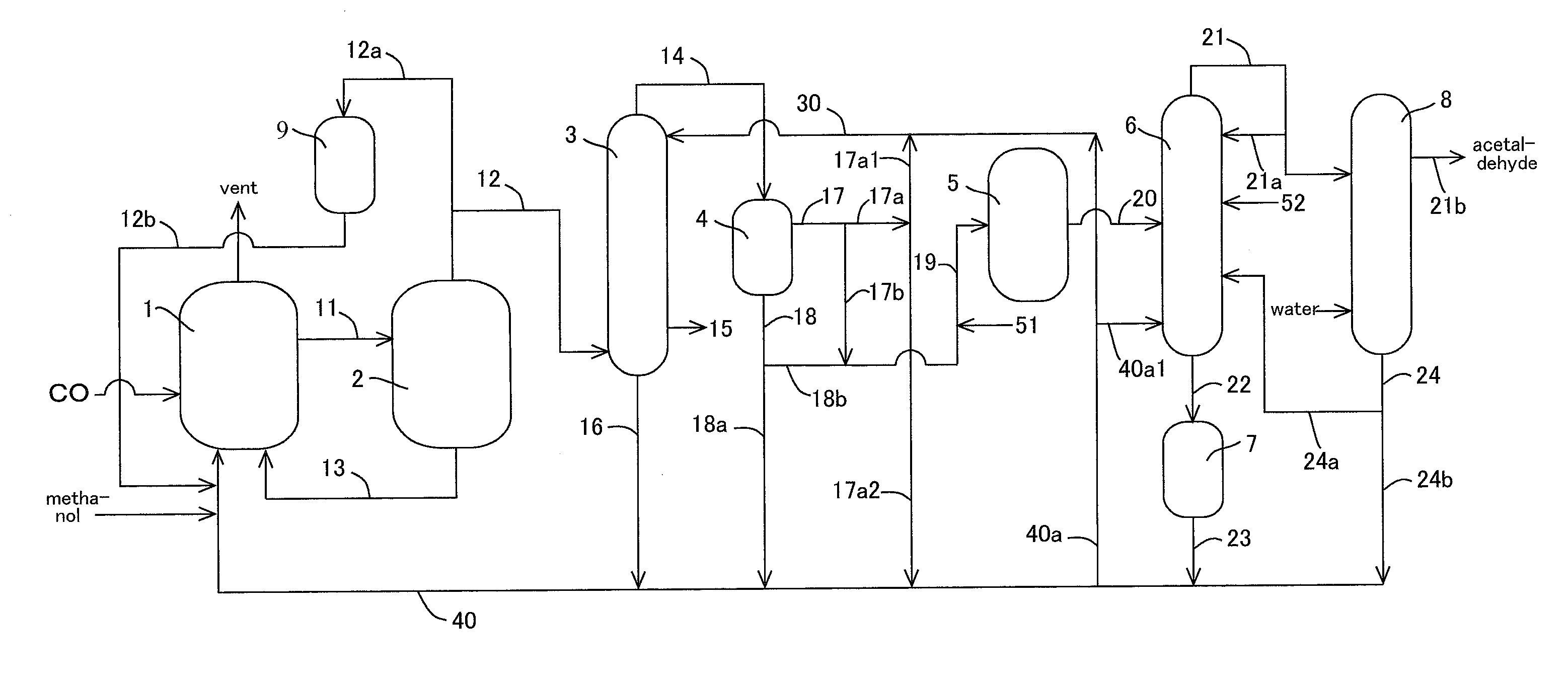
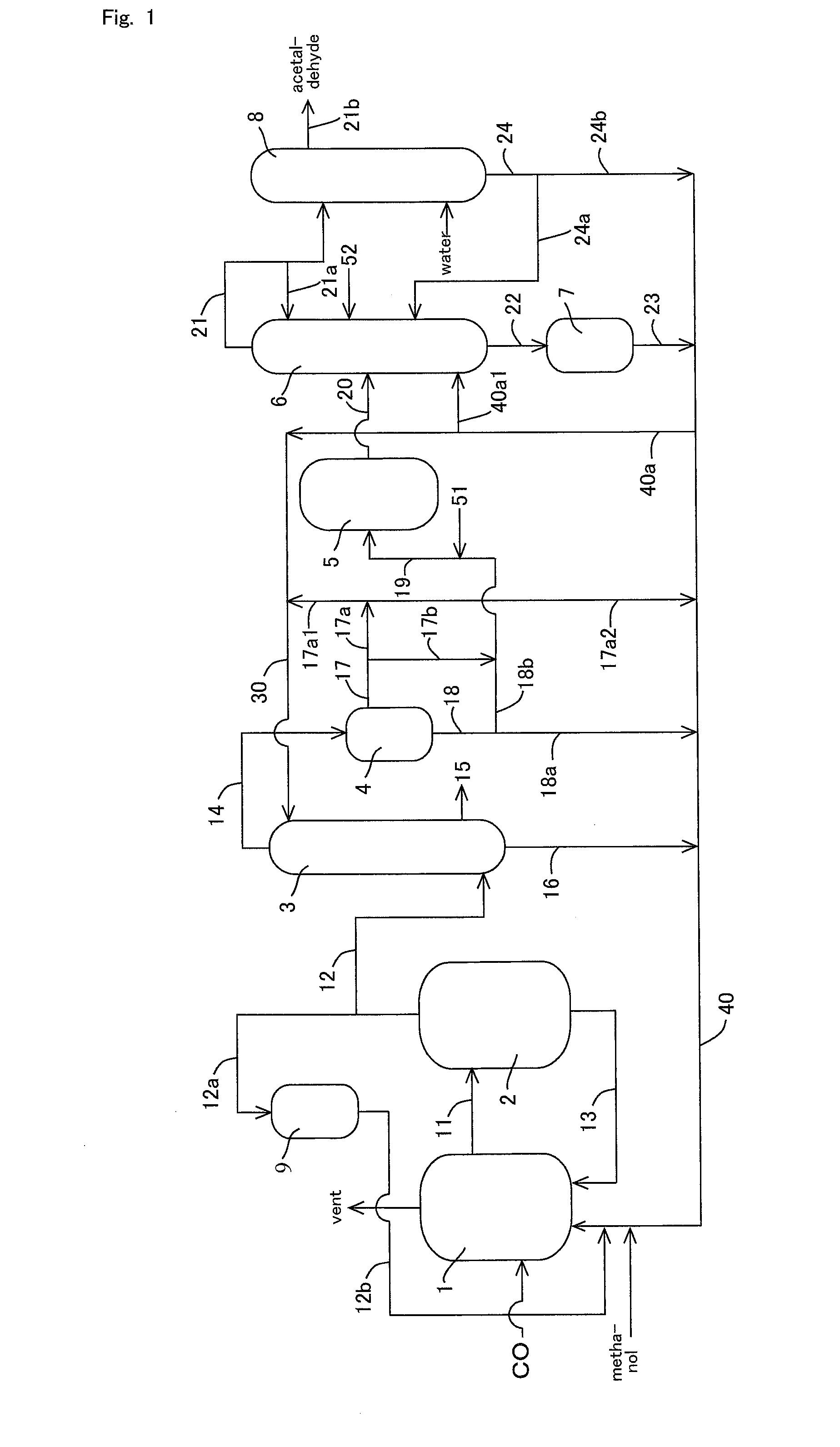
Methanol carbonylation with improved aldehyde removal
ActiveUS7884237B2Operating and capital costLower the volumeOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationOrganic compound preparationCarbonylationSolvent
Methanol carbonylation with improved aldehyde removal includes: (a) scrubbing light ends and aldehyde impurity from vent gas with an absorber solvent; (b) stripping absorbed light ends and aldehyde impurity from the absorber solvent to provide a vent-recovered light ends stream; (c) purifying the vent-recovered light ends stream to remove aldehyde impurity; and (d) recycling purified light ends from the vent-recovered light ends stream to the production system.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Methanol carbonylation system having absorber with multiple solvent options
A methanol carbonylation system 10 includes an absorber tower 75 adapted for receiving a vent gas stream and removing methyl iodide therefrom with a scrubber solvent, the absorber tower being coupled to first and second scrubber solvent sources 16, 56 which are capable of supplying different first and second scrubber solvents. A switching system including valves 90, 92, 94, 96, 98 alternatively provides first or second scrubber solvents to the absorber tower and returns the used solvent and sorbed material to the carbonylation system to accommodate different operating modes.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Process for carbonylation of alkyl ethers
ActiveUS7465822B2Organic compound preparationPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesCarboxylic acidCarbonylation
A product comprising a lower alkyl ester of a lower aliphatic carboxylic acid is produced by a process comprising reacting under substantially anhydrous conditions a lower alkyl ether with carbon monoxide in the presence of a zeolite catalyst having an 8-member ring channel which is interconnected with a channel defined by a ring with greater than or equal to 8 members, the 8-member ring having a window size of at least 2.5 Angstroms×at least 3.6 Angstroms and at least one Brønsted acid site and the zeolite having a silica:X2O3 ratio of at least 5, wherein X is selected from aluminum, boron, iron, gallium and mixtures thereof.
Owner:BP CHEM LTD +1
Continuous carbonylation process
InactiveUS6916951B2Improve heat removal efficiencyStable catalyst environmentOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsAcetic acidGas phase
Disclosed is a continuous process wherein carbon monoxide, a carbonylatable reactant, and a halide in the gas phase are contacted with a non-volatile catalyst solution comprising an ionic liquid and a Group VIII metal to produce a carbonylation product in the gas phase. The process is useful for the continuous preparation of acetic acid by the carbonylation of methanol.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
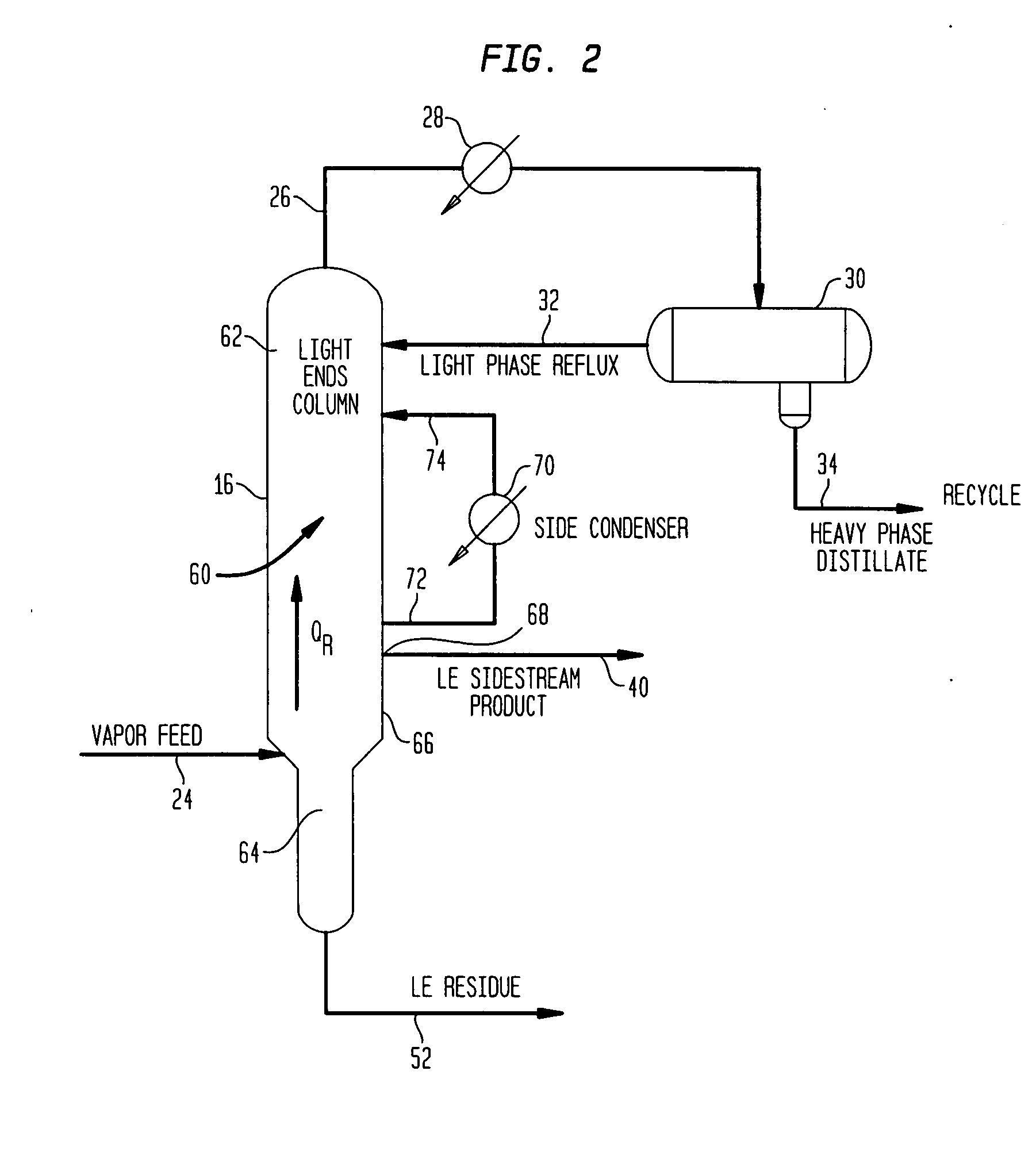
Method and apparatus for making acetic acid with improved light ends column productivity
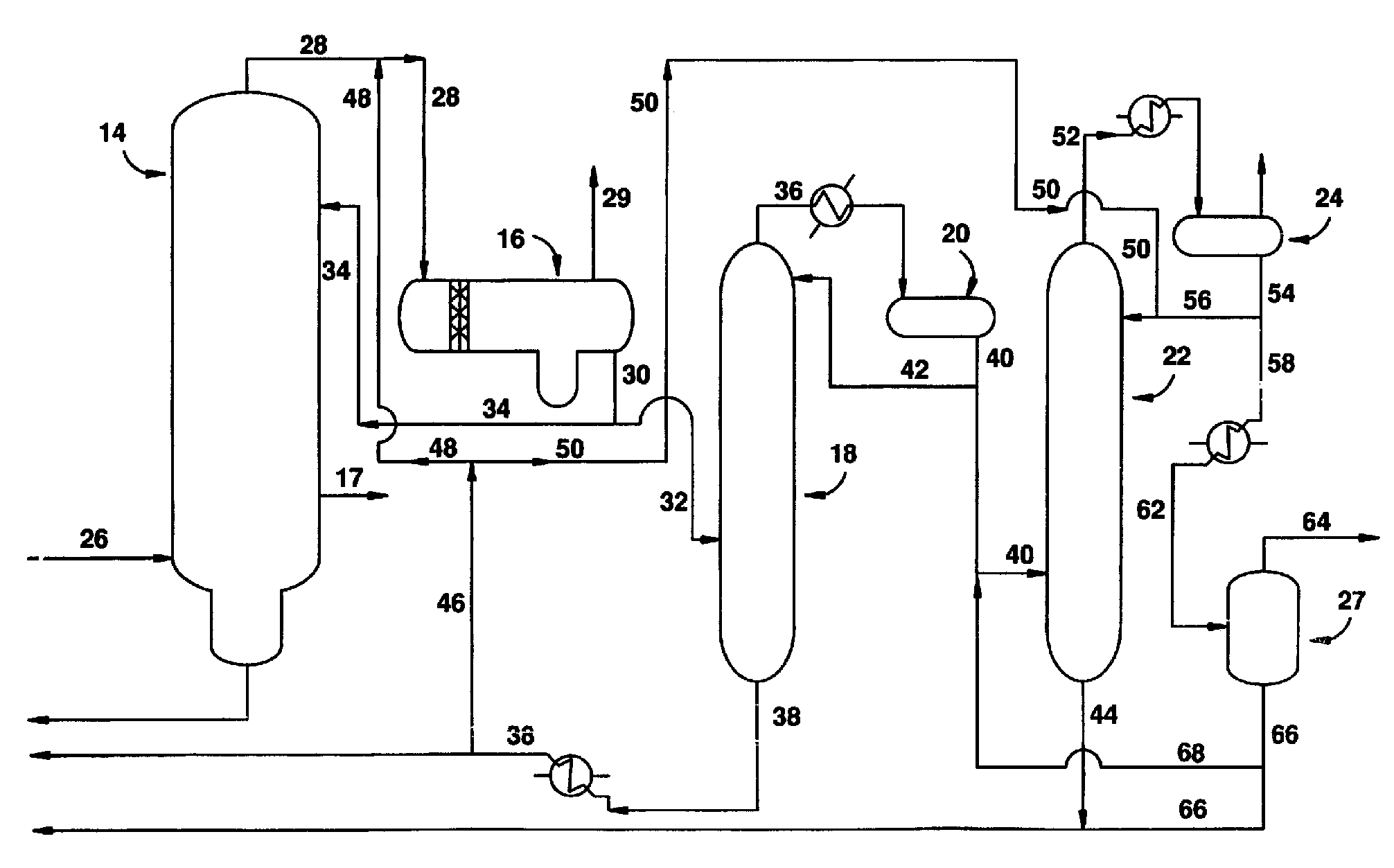
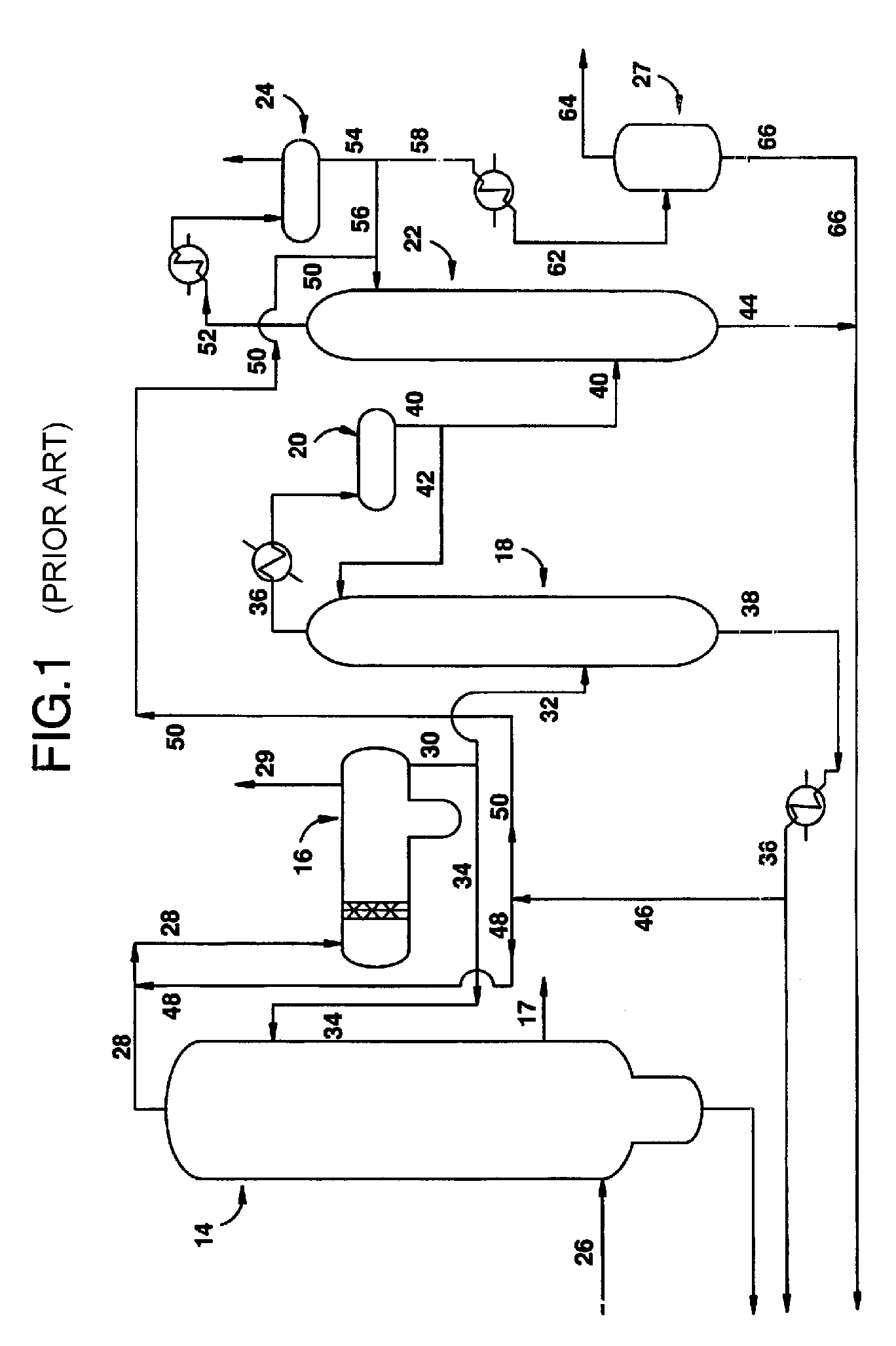
ActiveUS20080287706A1Reduce hydraulic loadLight loadBacterial antigen ingredientsOrganic compound preparationAcetic acidProduction rate
An improved apparatus and method of producing acetic acid includes condensing overhead vapor to provide reflux to the light ends column as well as condensing vapor from a central portion of the light ends column to increase capacity. Throughput or load on the light ends column is substantially reduced without compromising product quality.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
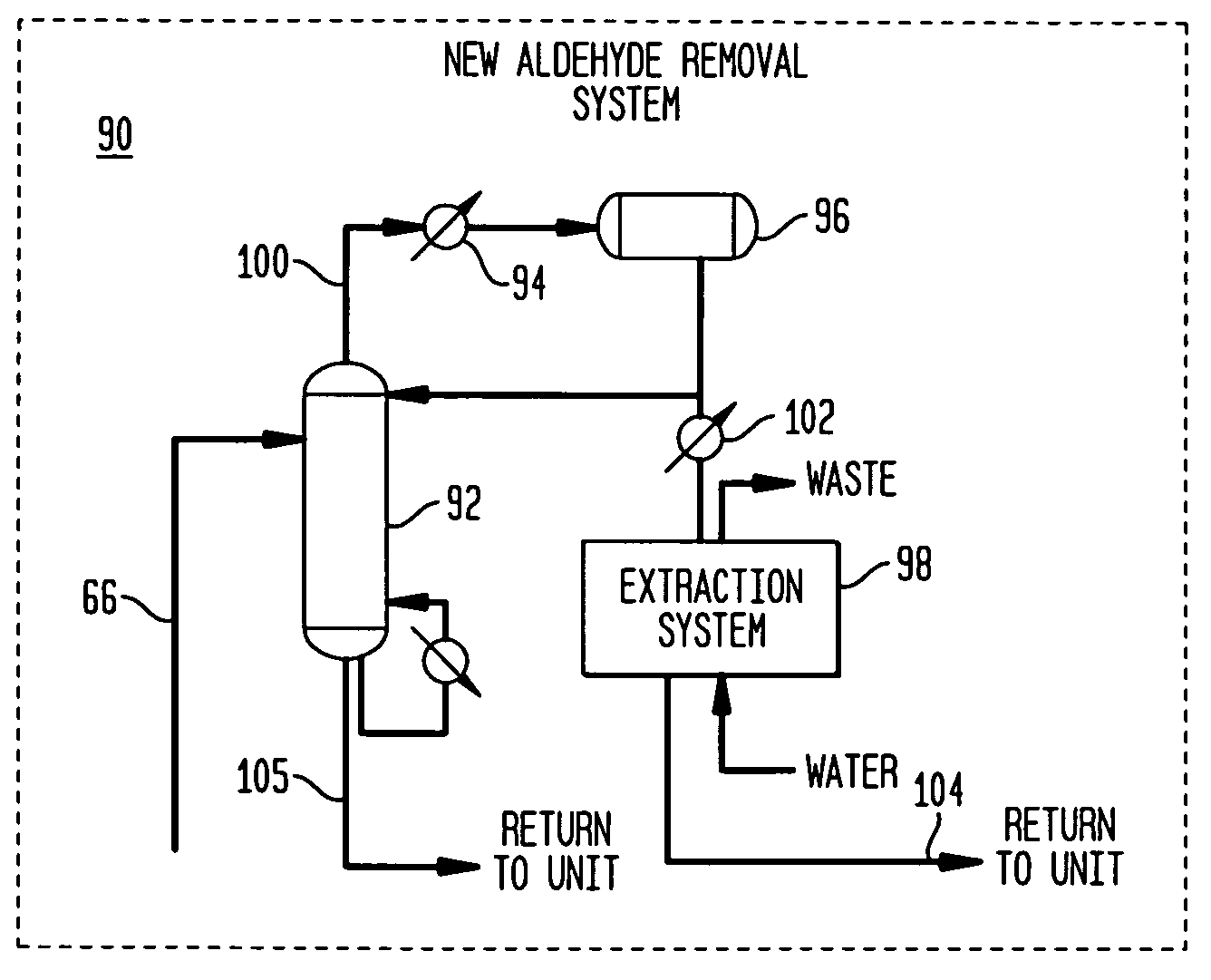
Processes for Producing Acetic Acid
ActiveUS20110288333A1Increase production capacityReduce loadOrganic compound preparationSolvent extractionAcetic acidDistillation
Processes for the reduction and / or removal of permanganate reducing compounds (PRC'S) formed by the carbonylation of methanol in the presence of a Group VIII metal carbonylation catalyst to produce acetic acid are disclosed. More specifically, processes for reducing and / or removing PRC's or their precursors from intermediate streams during the formation of acetic acid by said carbonylation processes are disclosed. In particular, processes in which a low boiling overhead vapor stream from a light ends column is subjected to a distillation to obtain an overhead that is subjected to an extraction to selectively remove and / or reduce PRC's from the process is disclosed. The processes include steps of recycling one or more return streams derived from the distillation step and / or the extraction step to a light ends column and / or a drying column in order to improve water control in the overall reaction system.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
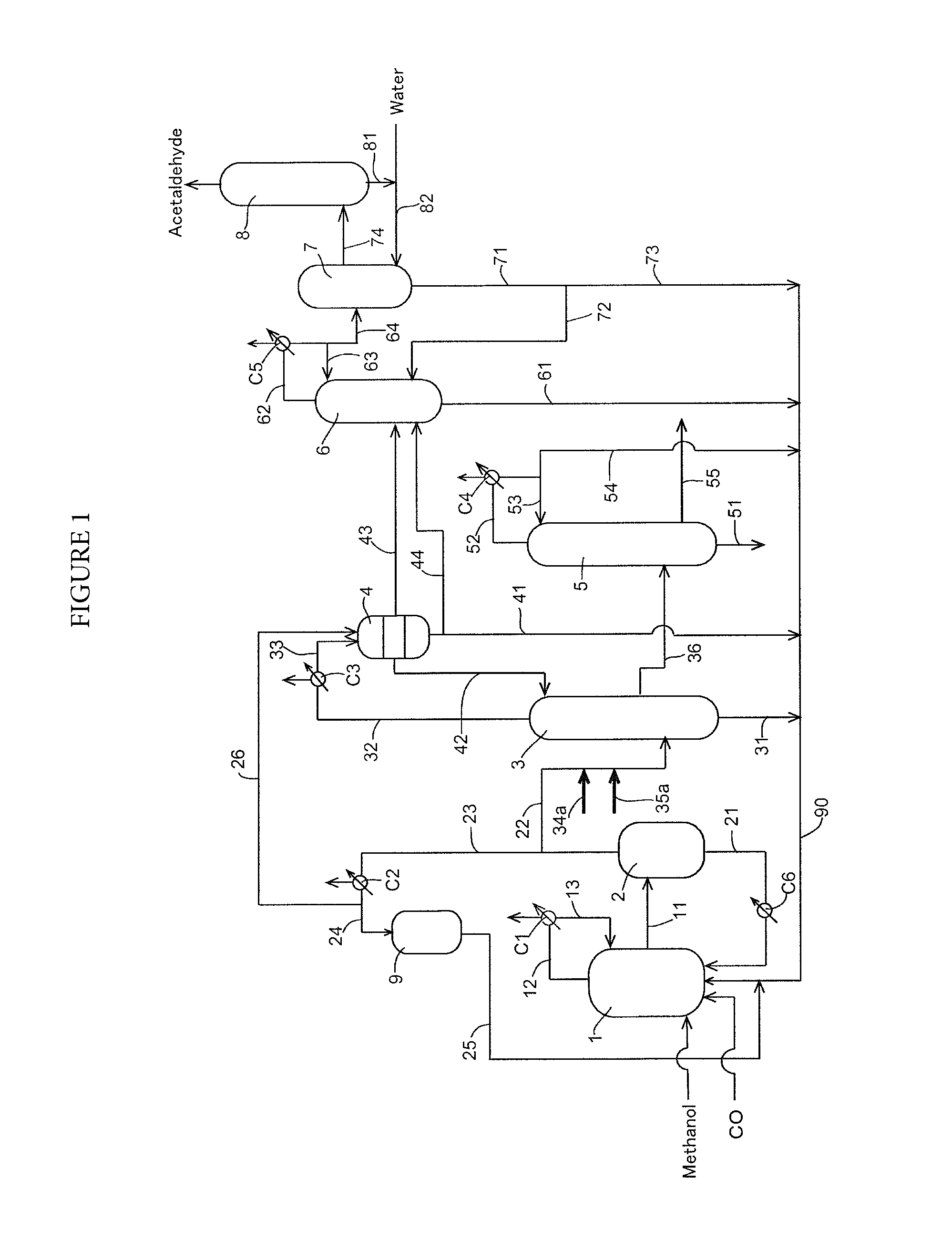
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS20130310603A1Efficient productionEasy to save energyOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsIodideReaction step
Acetic acid is produced while inhibiting an increased concentration or production of hydrogen iodide in a carbonylation reactor or corrosion of the carbonylation reactor.A production process of acetic acid comprises a reaction step for continuously allowing methanol to react with carbon monoxide in the presence of a catalyst system comprising a metal catalyst (e.g., a rhodium catalyst), an ionic iodide (e.g., lithium iodide), and methyl iodide in a carbonylation reactor; and in the process, (i) the concentration of the metal catalyst is maintained at not less than 860 ppm on the basis of weight, the concentration of water is maintained at 0.8 to 15% by weight, the concentration of methyl iodide is maintained at not more than 13.9% by weight, and the concentration of methyl acetate is maintained at not less than 0.1% by weight, in a whole liquid phase in the reactor, and / or (ii) the concentration of the metal catalyst is maintained at not less than 660 ppm on the basis of weight, the concentration of water is maintained at 0.8 to 3.9% by weight, the concentration of the ionic iodide is maintained at not more than 13% by weight, the concentration of methyl iodide is maintained at not more than 13.9% by weight, and the concentration of methyl acetate is maintained at not less than 0.1% by weight, in a whole liquid phase in the reactor.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Process for production of acrylates from epoxides
ActiveUS20140309399A1Low costAvoiding isolation and storageOrganic compound preparationPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionReaction zoneMetal carbonyl
The methods of the present invention comprise the steps of: providing a feedstock stream comprising an epoxide and carbon monoxide; contacting the feedstock stream with a metal carbonyl in a first reaction zone to effect conversion of at least a portion of the provided epoxide to a beta lactone; directing the effluent from the first reaction zone to a second reaction zone where the beta lactone is subjected to conditions that convert it to a compound selected from the group consisting of: an alpha beta unsaturated acid, an alpha beta unsaturated ester, an alpha beta unsaturated amide, and an optionally substituted polypropiolactone polymer; and isolating a final product comprising the alpha-beta unsaturated carboxylic acid, the alpha-beta unsaturated ester, the alpha-beta unsaturated amide or the polypropiolactone.
Owner:NOVOMER INC
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS20130281735A1Efficient removalImprove corrosion resistanceOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsDistillationMethyl acetate
Acetic acid is produced while inhibiting increased concentrations of hydrogen iodide and acetic acid in an acetaldehyde distillation column.A production process of acetic acid comprises a step for allowing methanol to react with carbon monoxide; a step for feeding a flasher with the reaction mixture to separate a volatile component (2A) and a low-volatile component (2B); a step for feeding a distillation column with the volatile component (2A), and separating an overhead (3A) containing methyl iodide, acetic acid, methyl acetate, water, acetaldehyde, and hydrogen iodide, and a stream (3B) containing acetic acid to collect acetic acid; and a separation step for feeding an acetaldehyde distillation column with at least part of the overhead (3A) and separating a liquid object to be treated containing the overhead (3A) into a lower boiling point component (4A) containing acetaldehyde and a higher boiling point component (4B); wherein, in the separation step, the liquid object contains methanol and / or dimethyl ether in a concentration of 0.1 to 50% by weight is subjected to distillation.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS9006483B2Avoid pollutionEnsure stable and continuous operationOrganic compound preparationDistillation separationWater concentrationAcetic acid ear
A production process of acetic acid according to the present invention inhibits concentration of hydrogen iodide and improves a liquid-liquid separation of an overhead from a distillation column. Acetic acid is produced by distilling a mixture containing hydrogen iodide, water, acetic acid and methyl acetate in a first distillation column (3) to form an overhead and a side cut stream or bottom stream containing acetic acid, cooling and condensing the overhead in a condenser (C3) to form separated upper and lower phases in a decanter (4). According to this process, a zone having a high water concentration is formed in the distillation column above the feed position of the mixture by feeding a mixture having a water concentration of not less than an effective amount to not more than 5% by weight (e.g., 0.5 to 4.5% by weight) and a methyl acetate concentration of 0.5 to 9% by weight (e.g., 0.5 to 8% by weight) as the mixture to the distillation column and distilling the mixture. In the zone having a high water concentration, hydrogen iodide is allowed to react with methyl acetate to produce methyl iodide and acetic acid.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
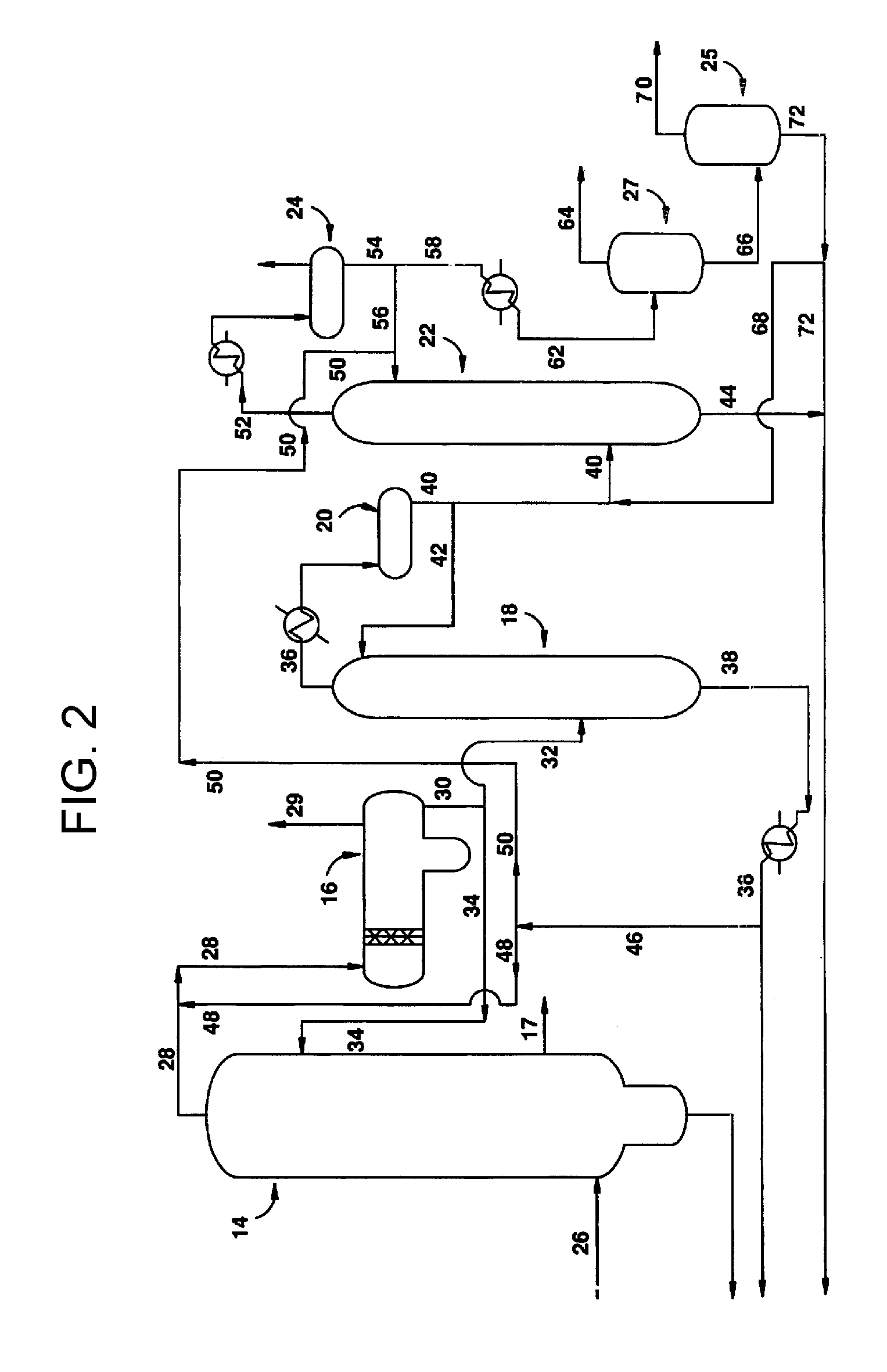
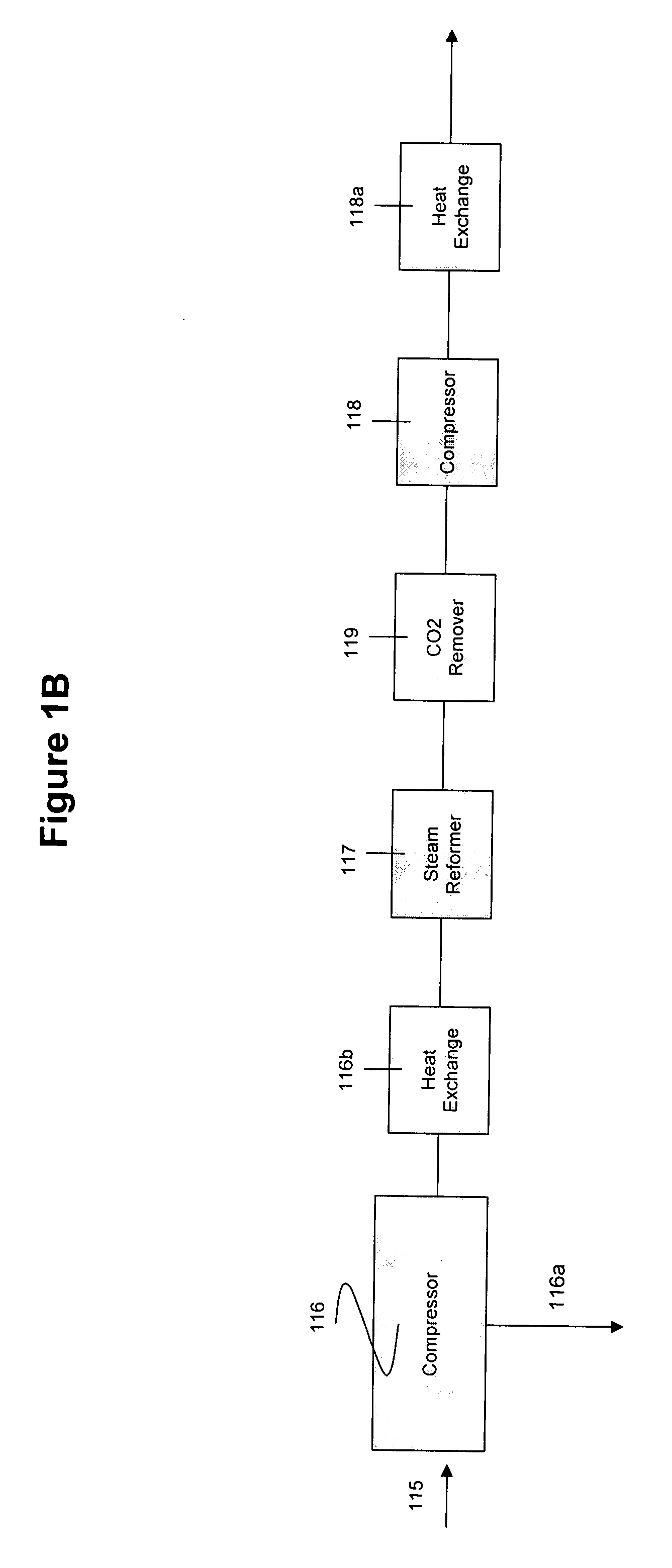
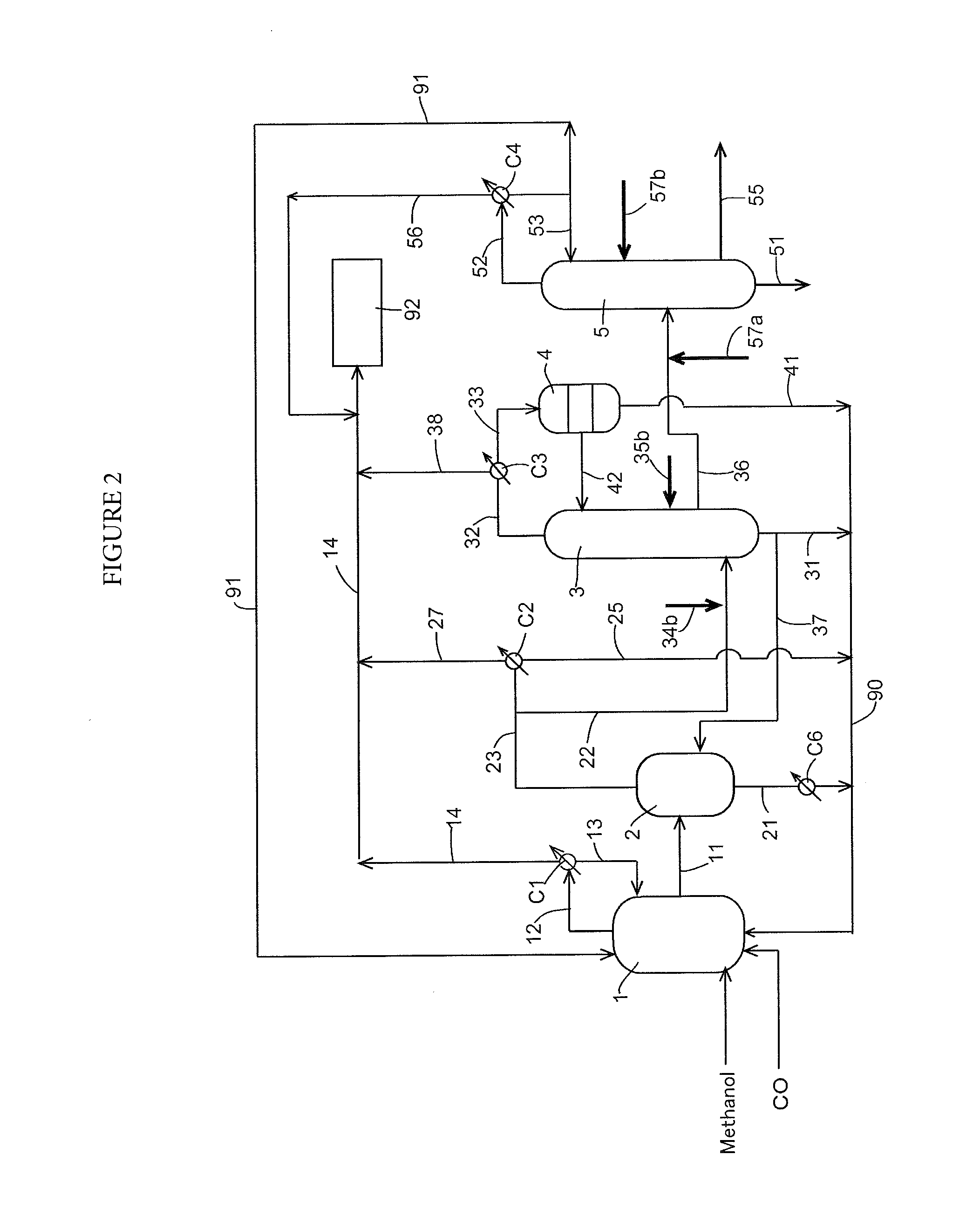
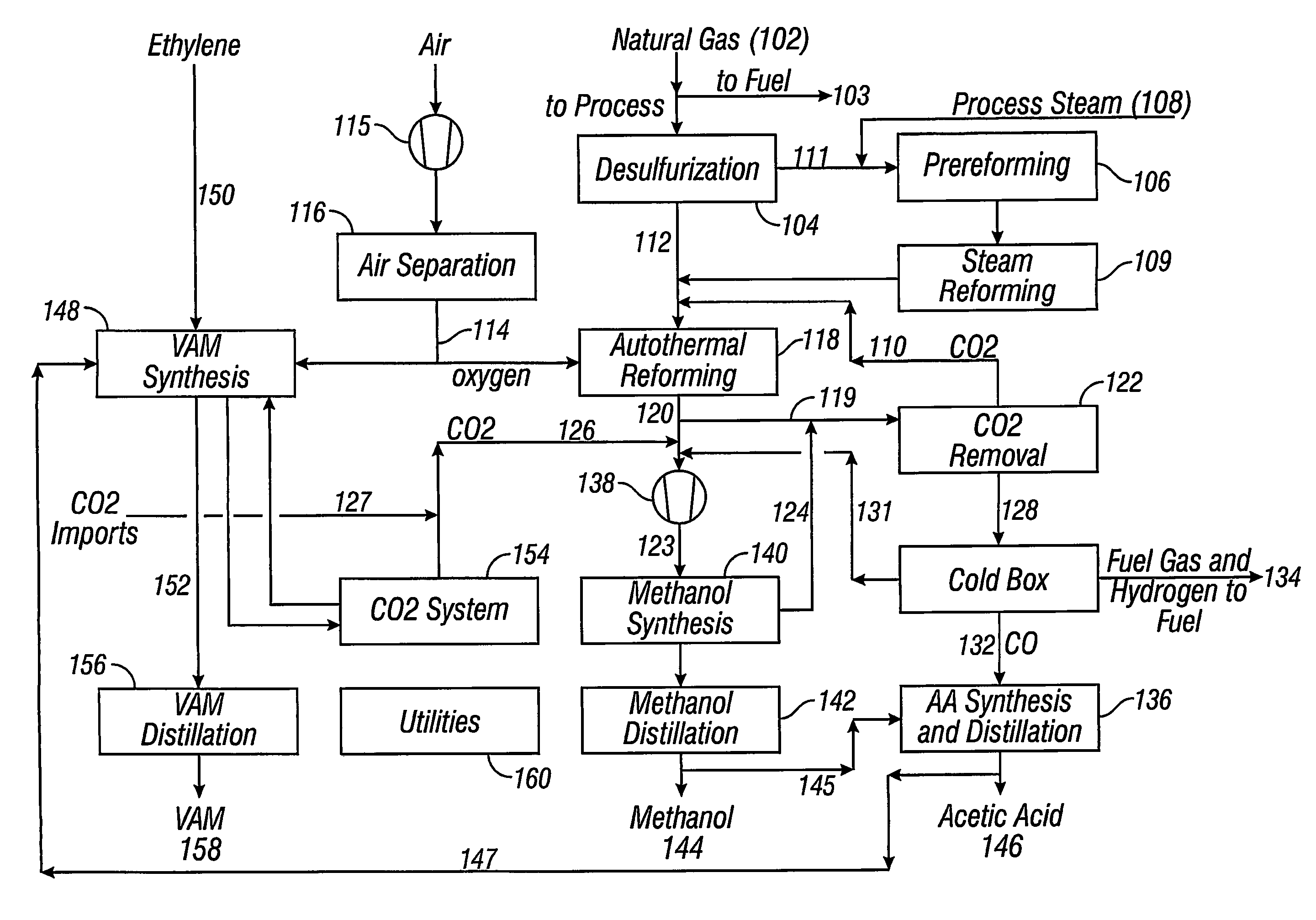
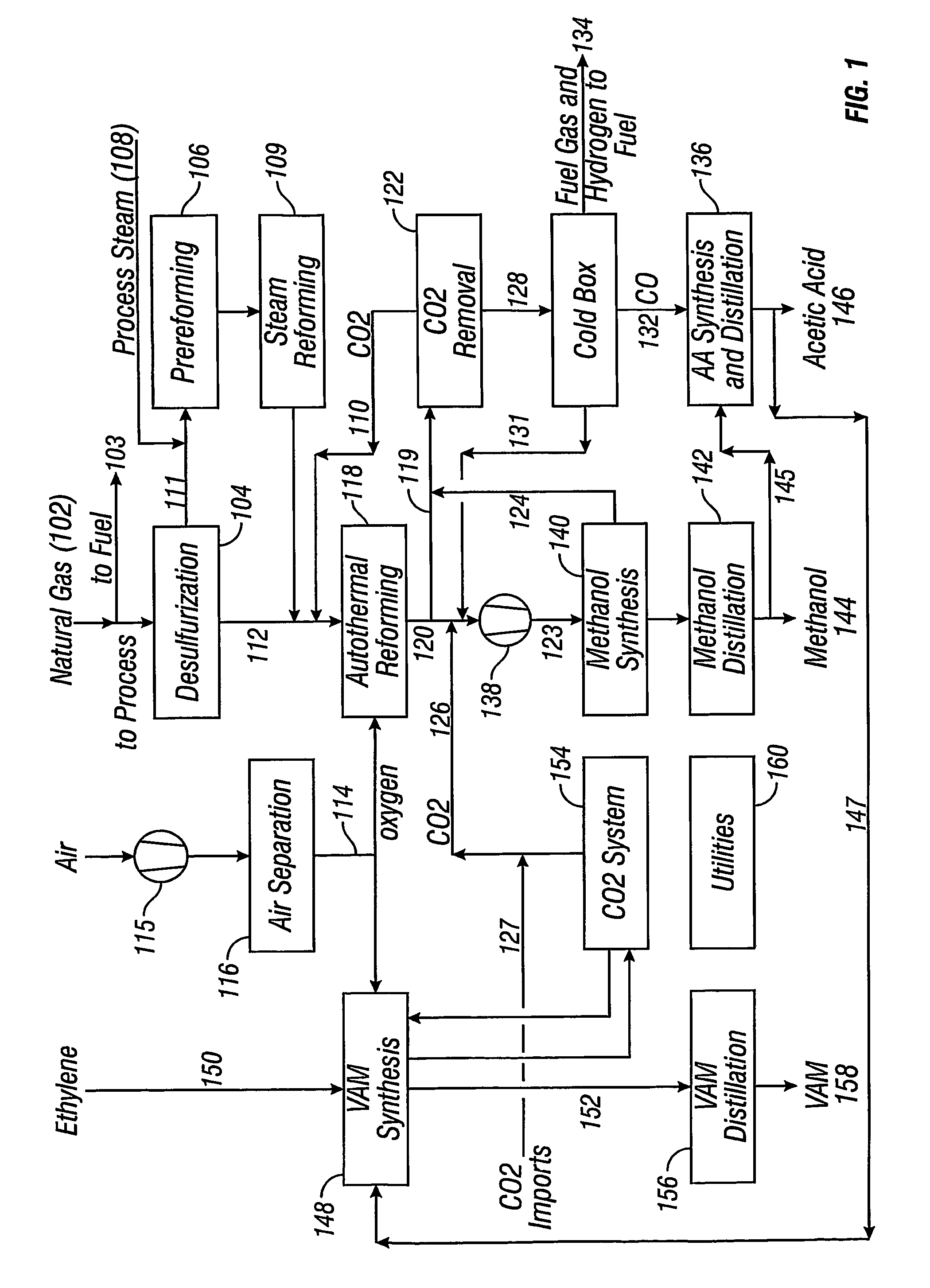
Integrated process for acetic acid and methanol
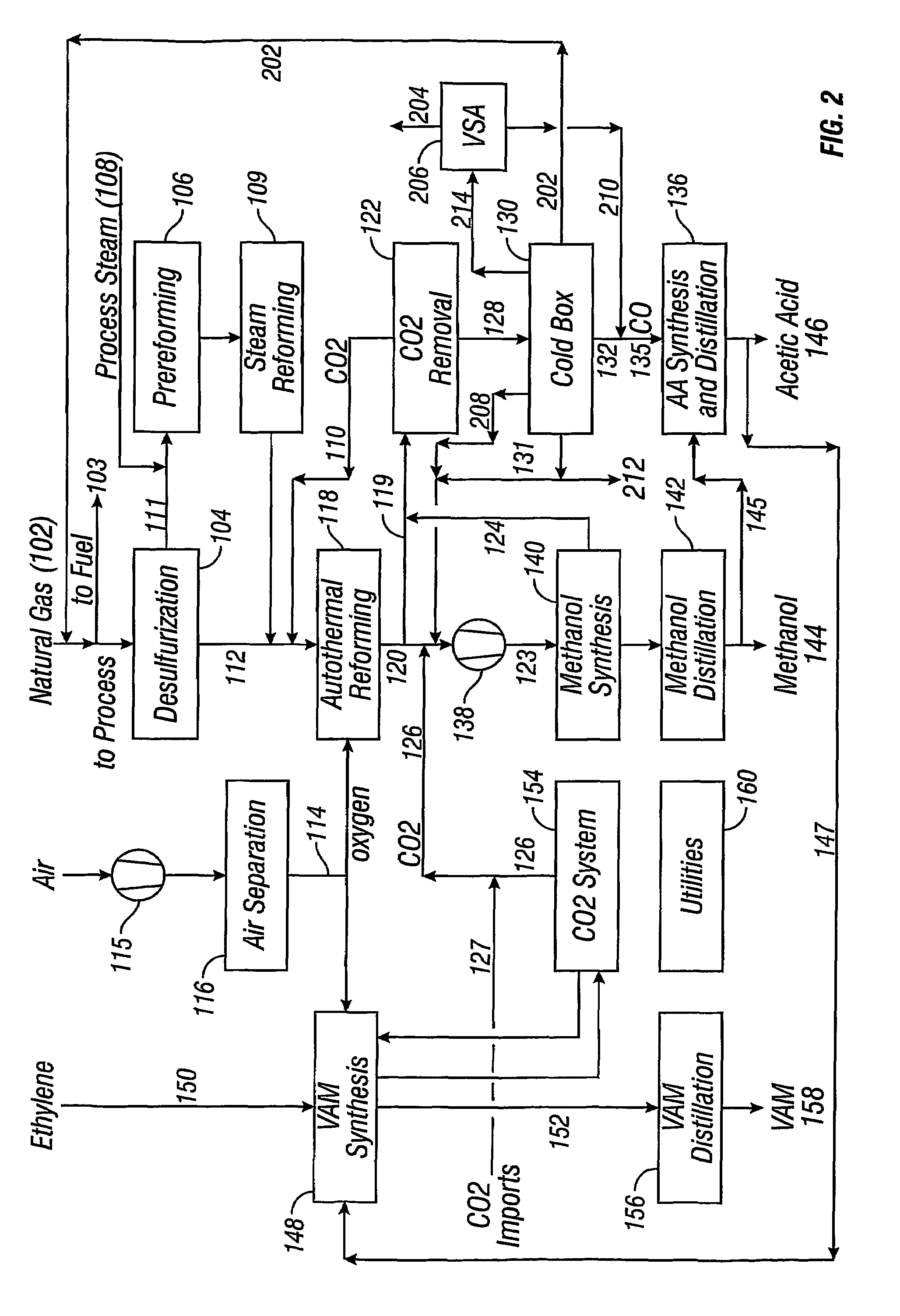
InactiveUS7470811B2Improve matchIncrease productionOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationSteam reformingCo2 removal
Owner:ACETEX
Process for production of acrylates from epoxides
ActiveUS9096510B2Low costAvoiding isolation and storageOrganic compound preparationPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionReaction zoneMetal carbonyl
The methods of the present invention comprise the steps of: providing a feedstock stream comprising an epoxide and carbon monoxide; contacting the feedstock stream with a metal carbonyl in a first reaction zone to effect conversion of at least a portion of the provided epoxide to a beta lactone; directing the effluent from the first reaction zone to a second reaction zone where the beta lactone is subjected to conditions that convert it to a compound selected from the group consisting of: an alpha beta unsaturated acid, an alpha beta unsaturated ester, an alpha beta unsaturated amide, and an optionally substituted polypropiolactone polymer; and isolating a final product comprising the alpha-beta unsaturated carboxylic acid, the alpha-beta unsaturated ester, the alpha-beta unsaturated amide or the polypropiolactone.
Owner:NOVOMER INC
Process for producing acetic acid
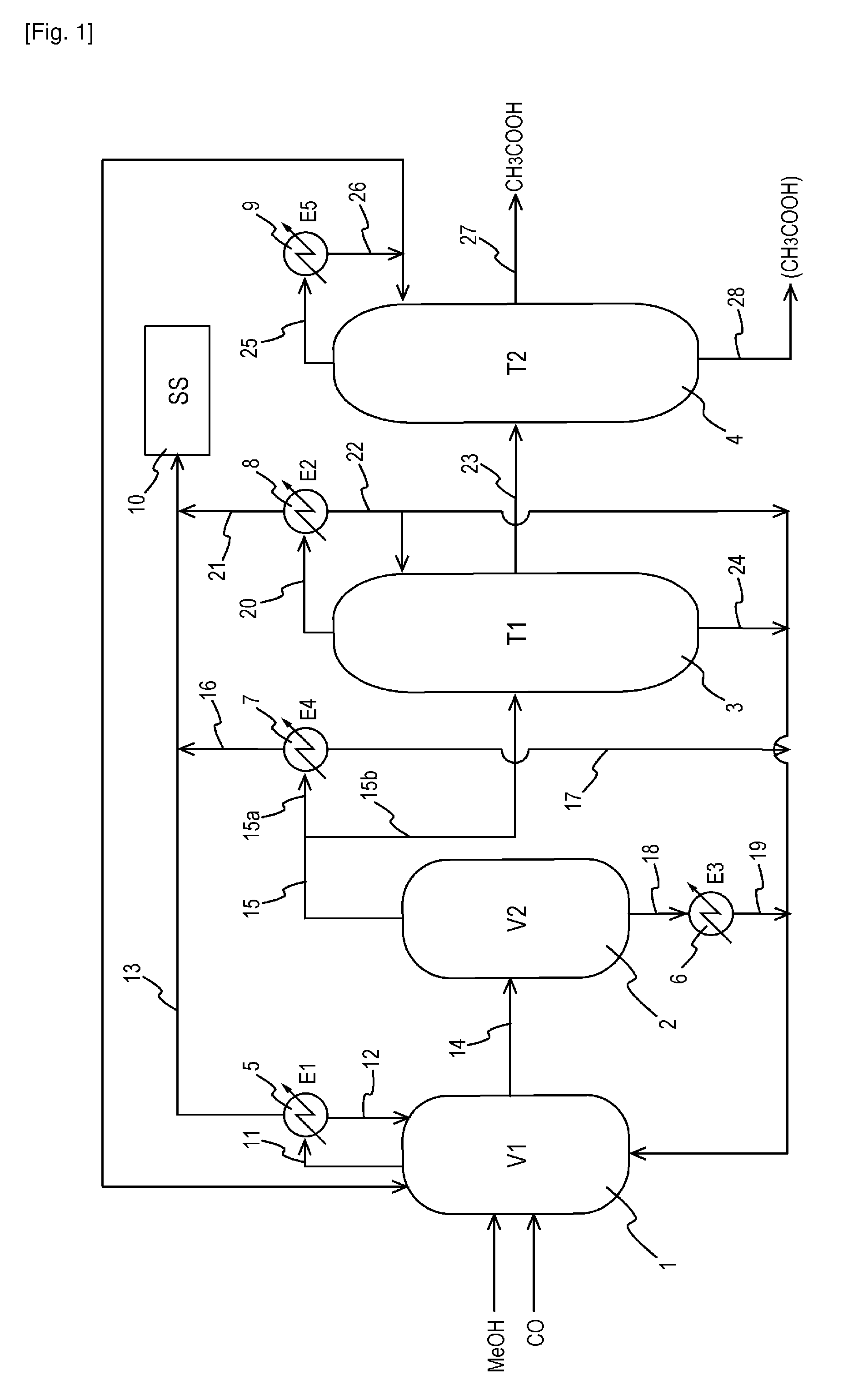
ActiveUS20130116470A1High purityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationChemical industryDistillationResource saving
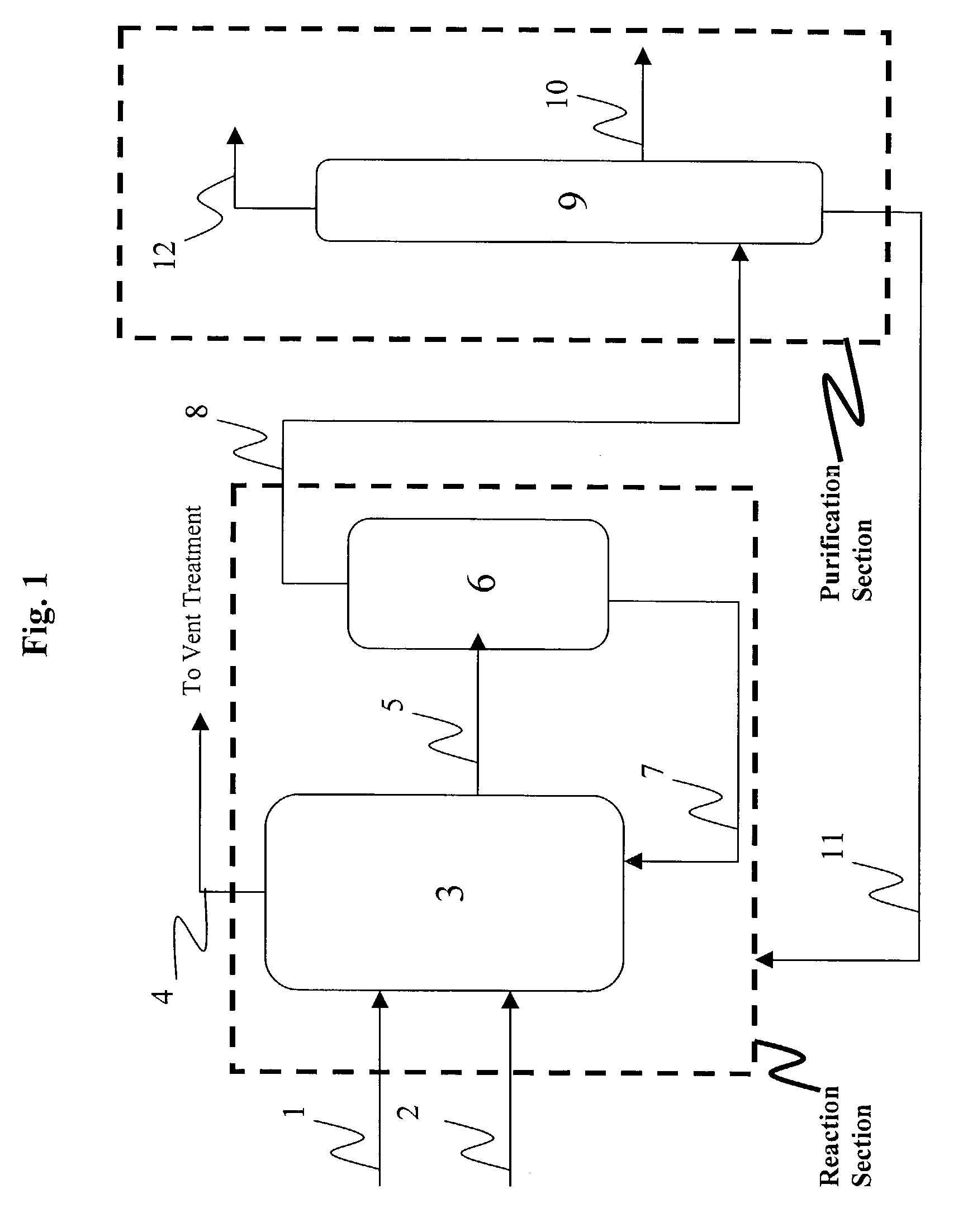
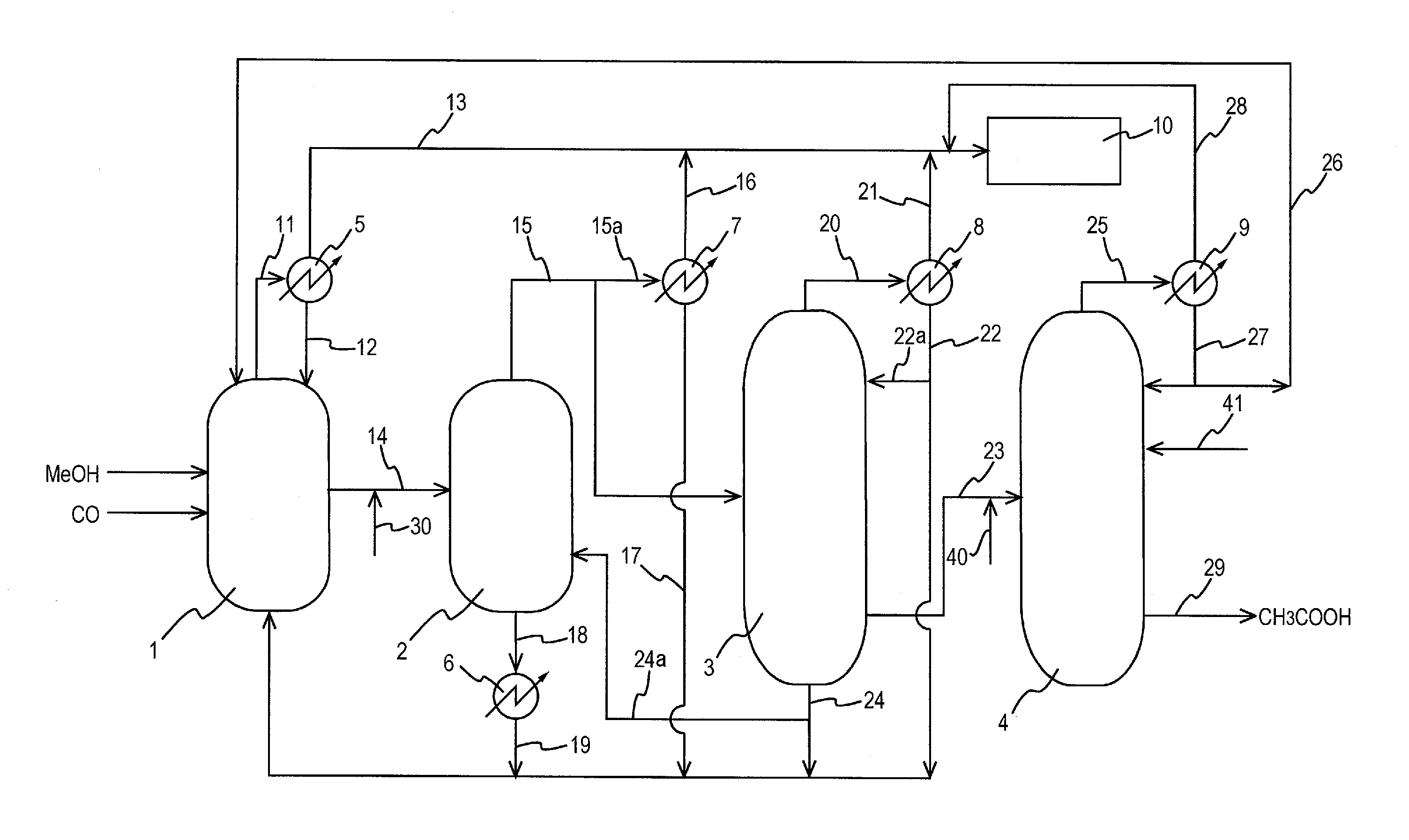
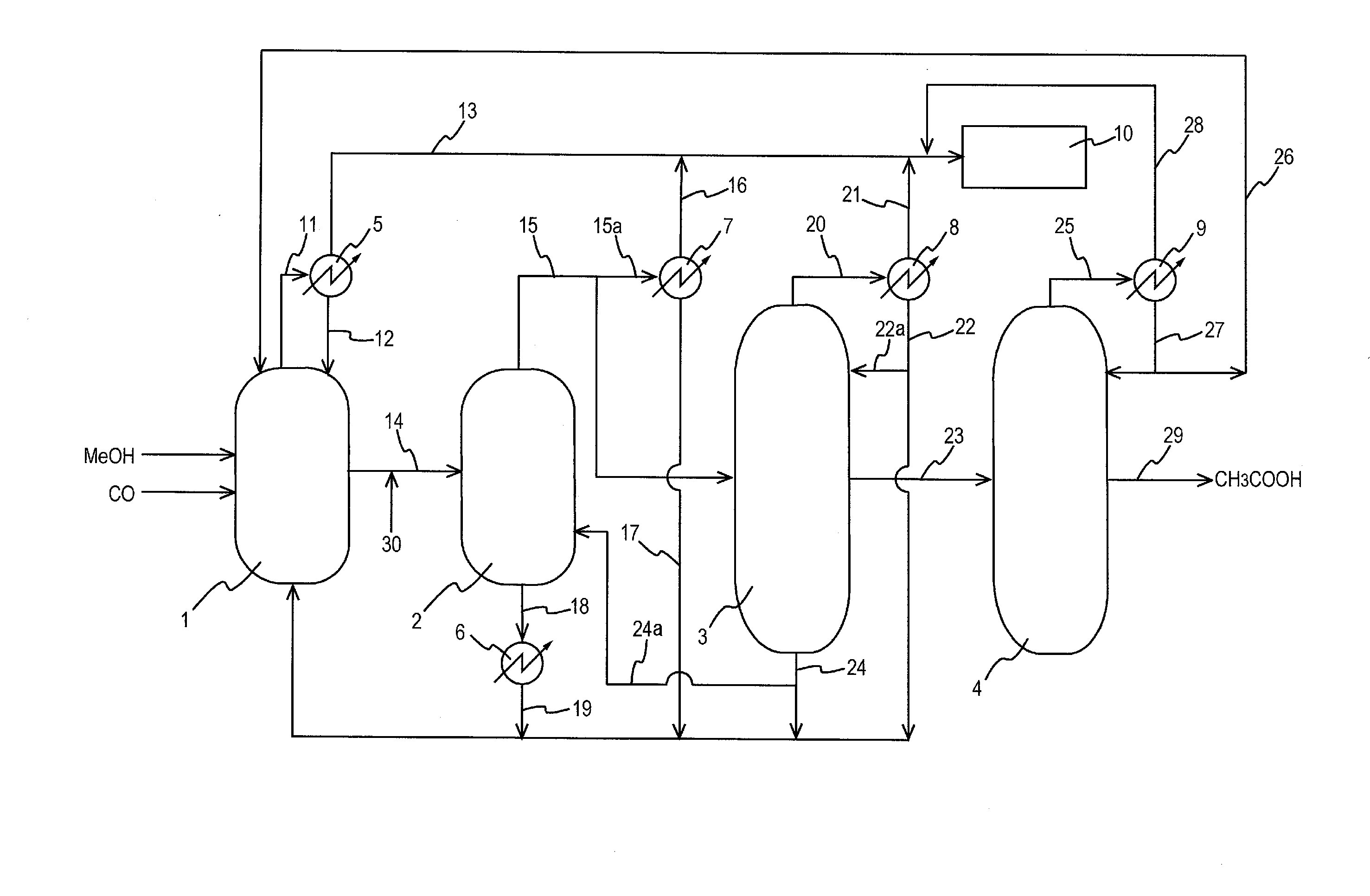
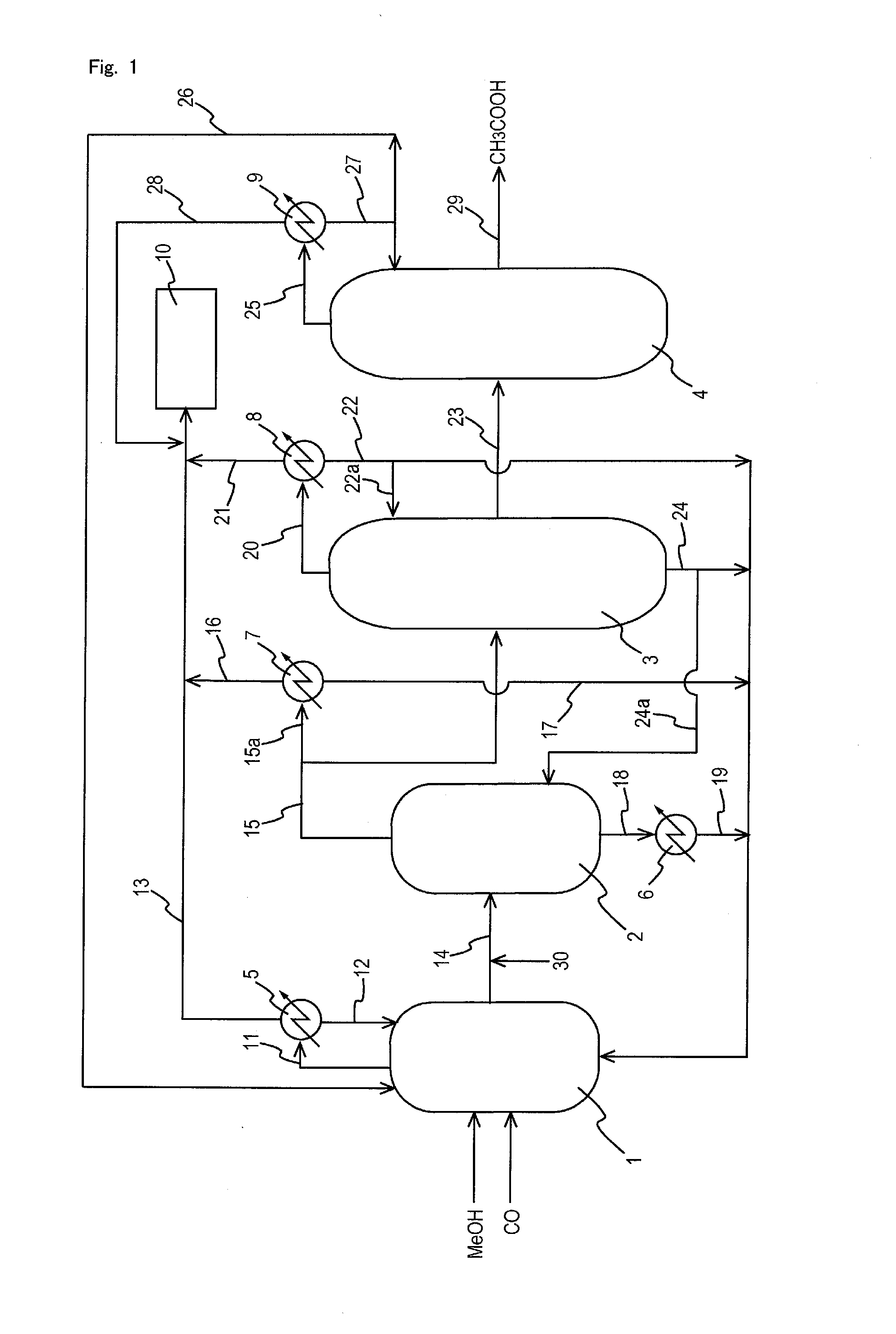
A production process of acetic acid comprises a reaction step for continuously allowing at least one member selected from the group consisting of methanol, dimethyl ether, and methyl acetate to react with carbon monoxide in a catalyst system comprising a rhodium catalyst, an iodide salt, and methyl iodide in the presence of acetic acid and water in a plant compromising a reactor 1; a flasher 2; and a distillation column 3; wherein part of the vaporized stream is introduced into a heat exchanger 7. The process achieves a production of acetic acid with a high purity in a resource-saving and energy-saving equipment by efficiently removing a reaction heat even in a large-sized plant.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com