Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45results about How to "Less soluble" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
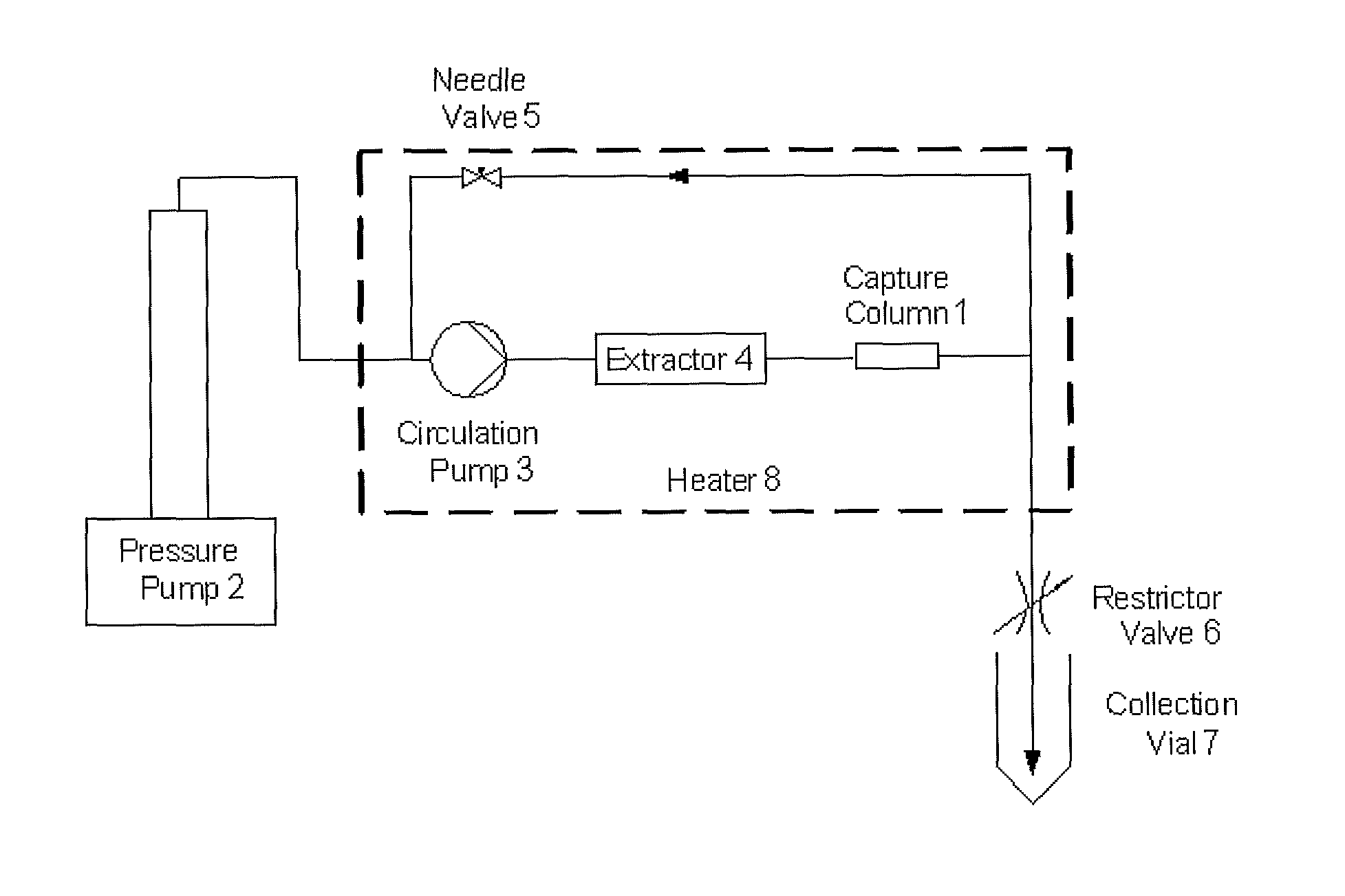
Ultrasound and acoustophoresis for water purification
InactiveUS20110123392A1Low separationEfficiently separateSeawater treatmentBlast furnace detailsStanding waveChemistry
Provided herein are systems and methods for separation of particulate from water using ultrasonically generated acoustic standing waves.
Owner:FLODESIGN SONICS
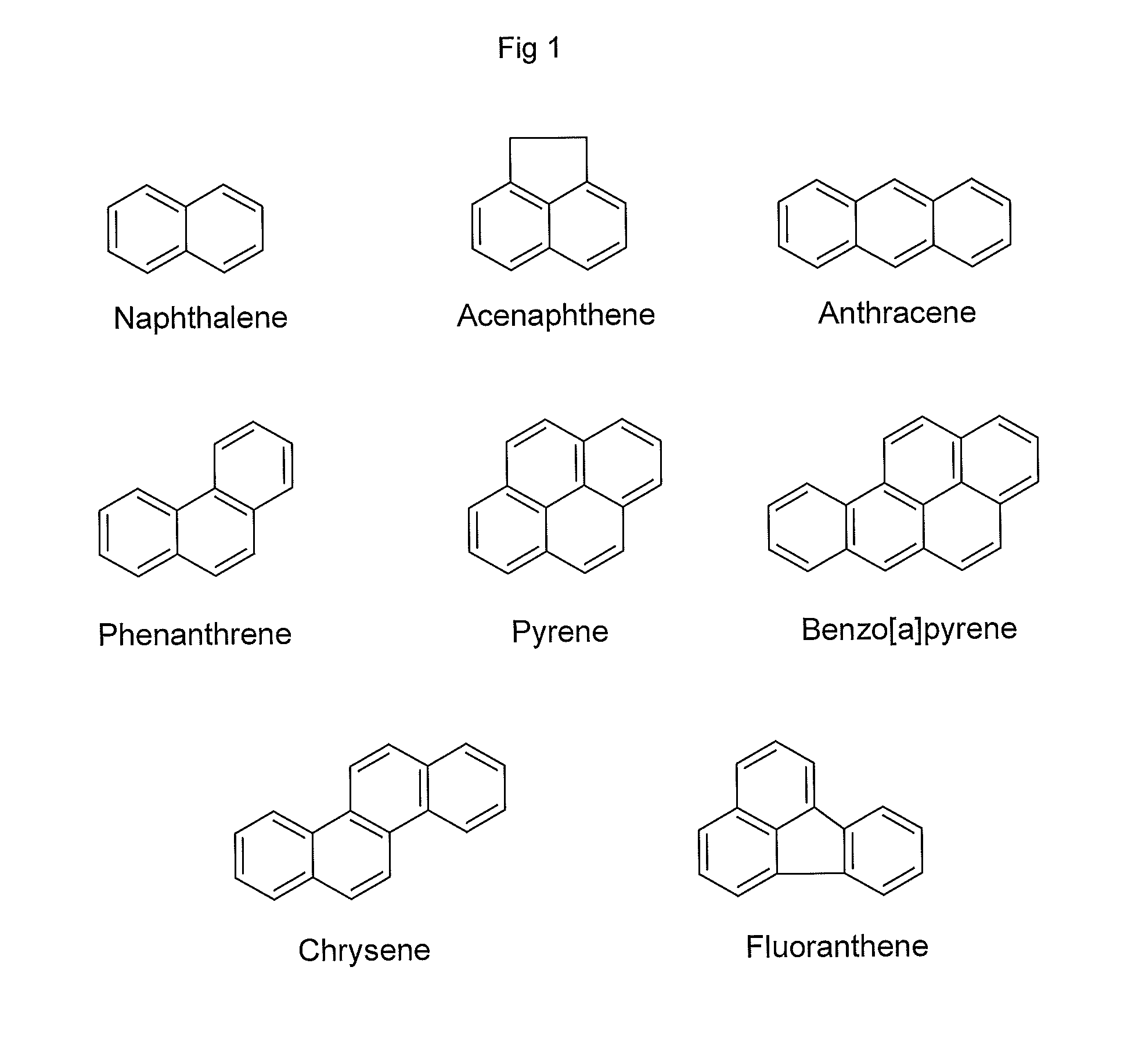
Method for Removing Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons
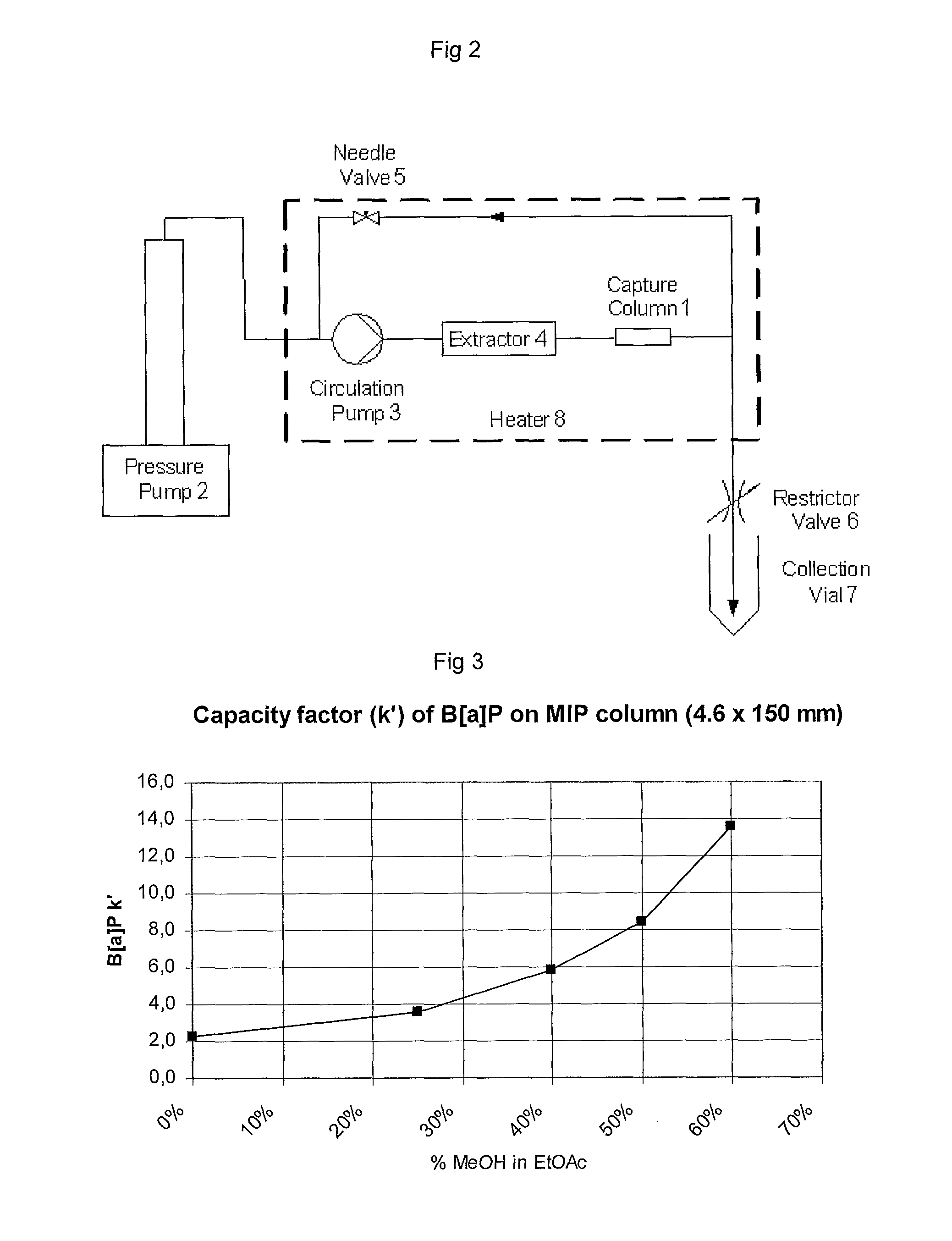
InactiveUS20110159160A1Improve performanceReduce in quantityTobacco treatmentSolvent extractionPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonMolecularly imprinted polymer
A method for extracting a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon from a material such as tobacco or tobacco extracts or other materials comprises treating the material with a molecularly imprinted polymer selective for the hydrocarbon in the presence of a low polarity medium.
Owner:BRITISH AMERICAN TOBACCO (INVESTMENTS) LTD
Tin promoted platinum catalyst for carbonylation of lower alkyl alcohols
InactiveUS6903045B2Not volatileLess solubleIsocyanic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationSolid componentGas phase
A carbonylation catalyst useful for producing esters and carboxylic acids in a vapor phase carbonylation process, wherein the catalyst includes a solid component having a catalytically effective amount of platinum and tin associated with a solid catalyst support material and a vaporous halide promoter component.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
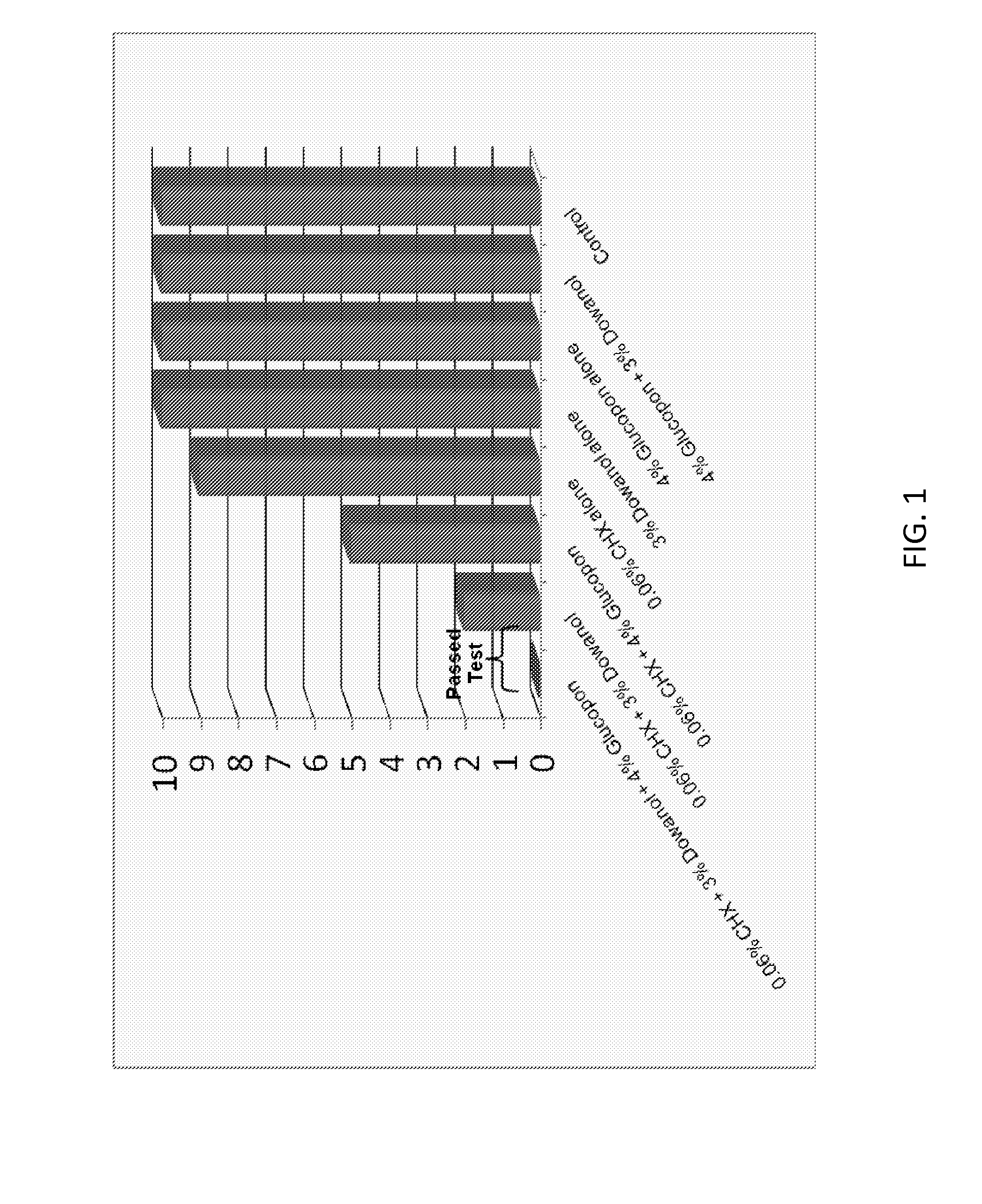
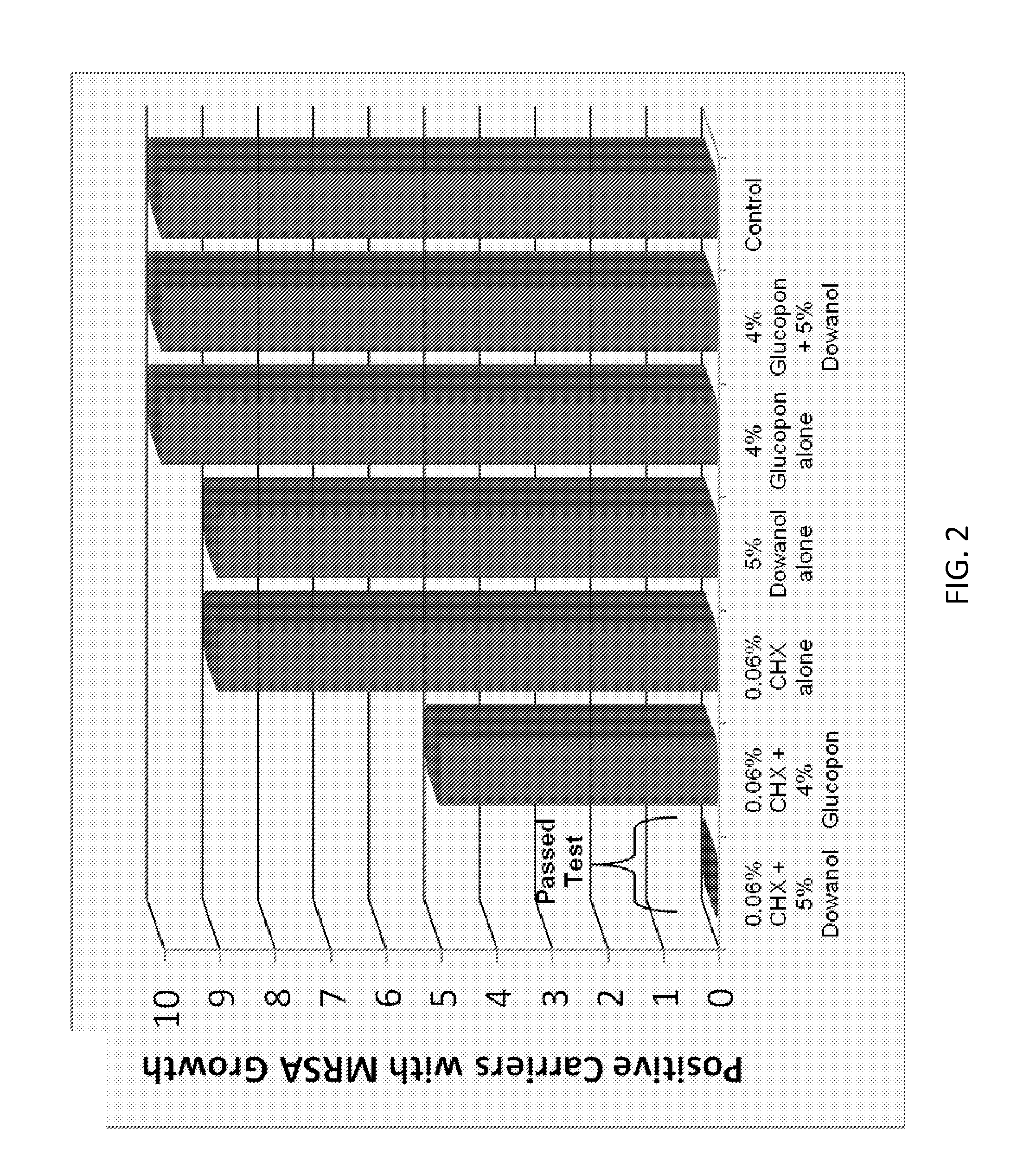
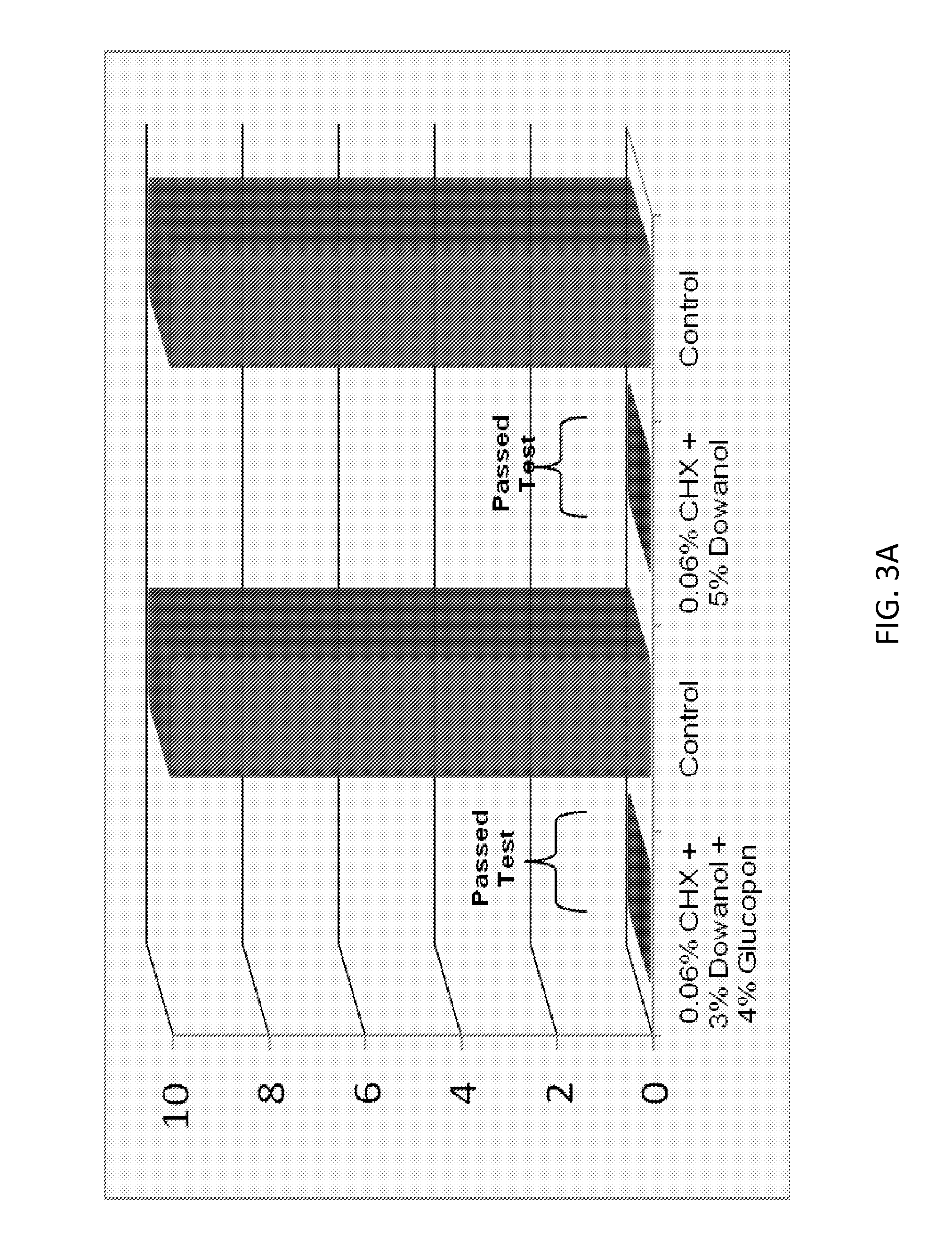
Antimicrobial solutions
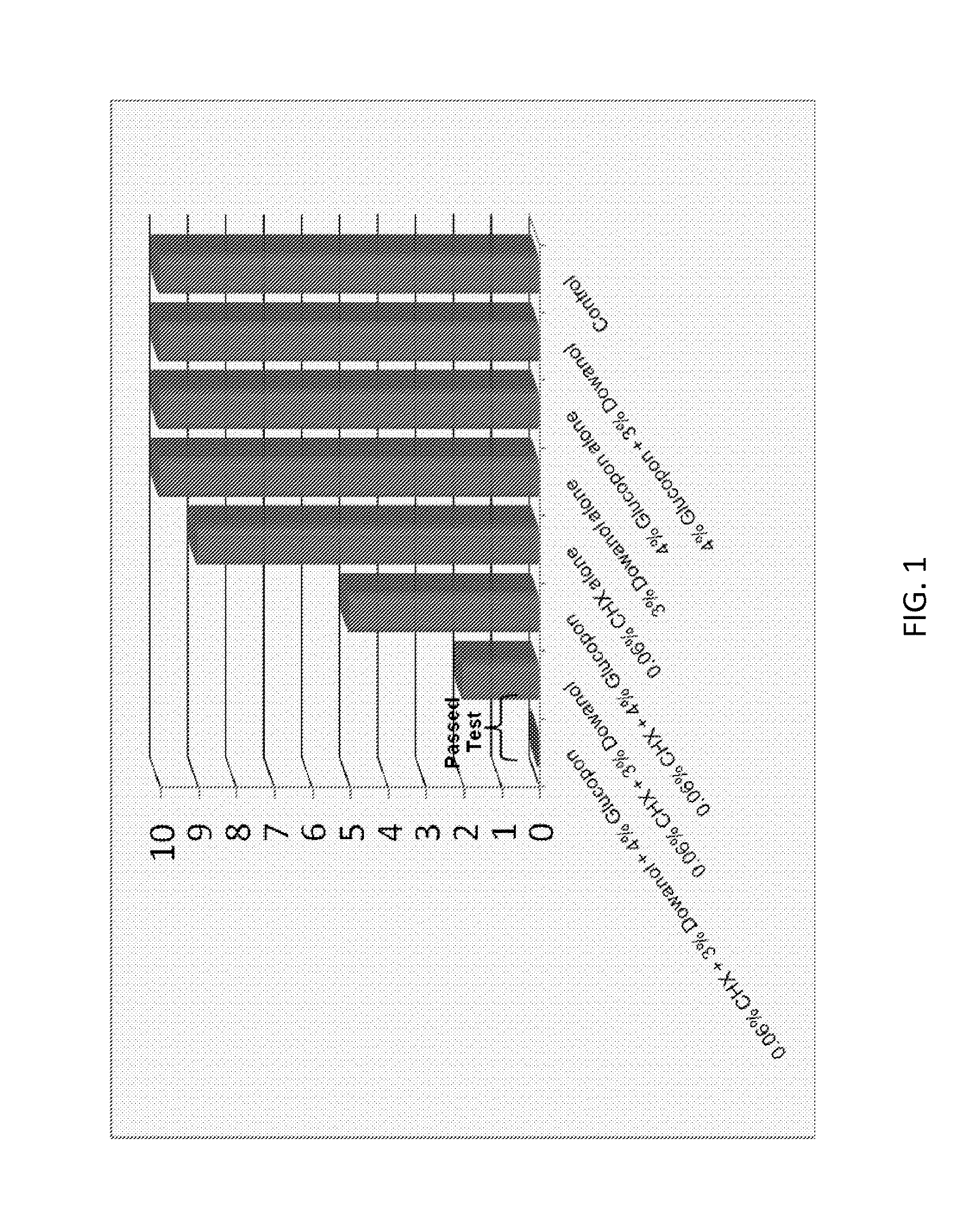
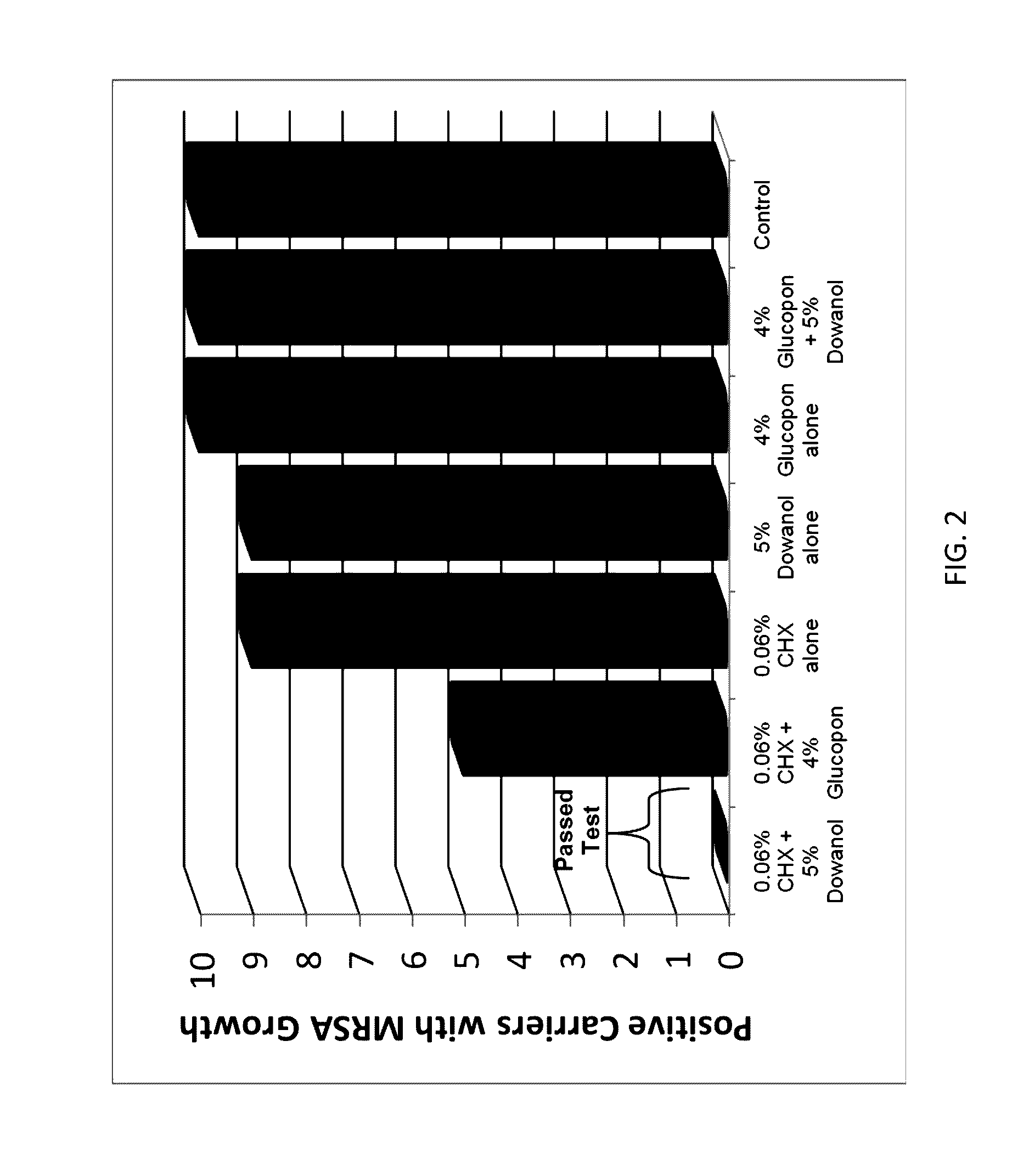
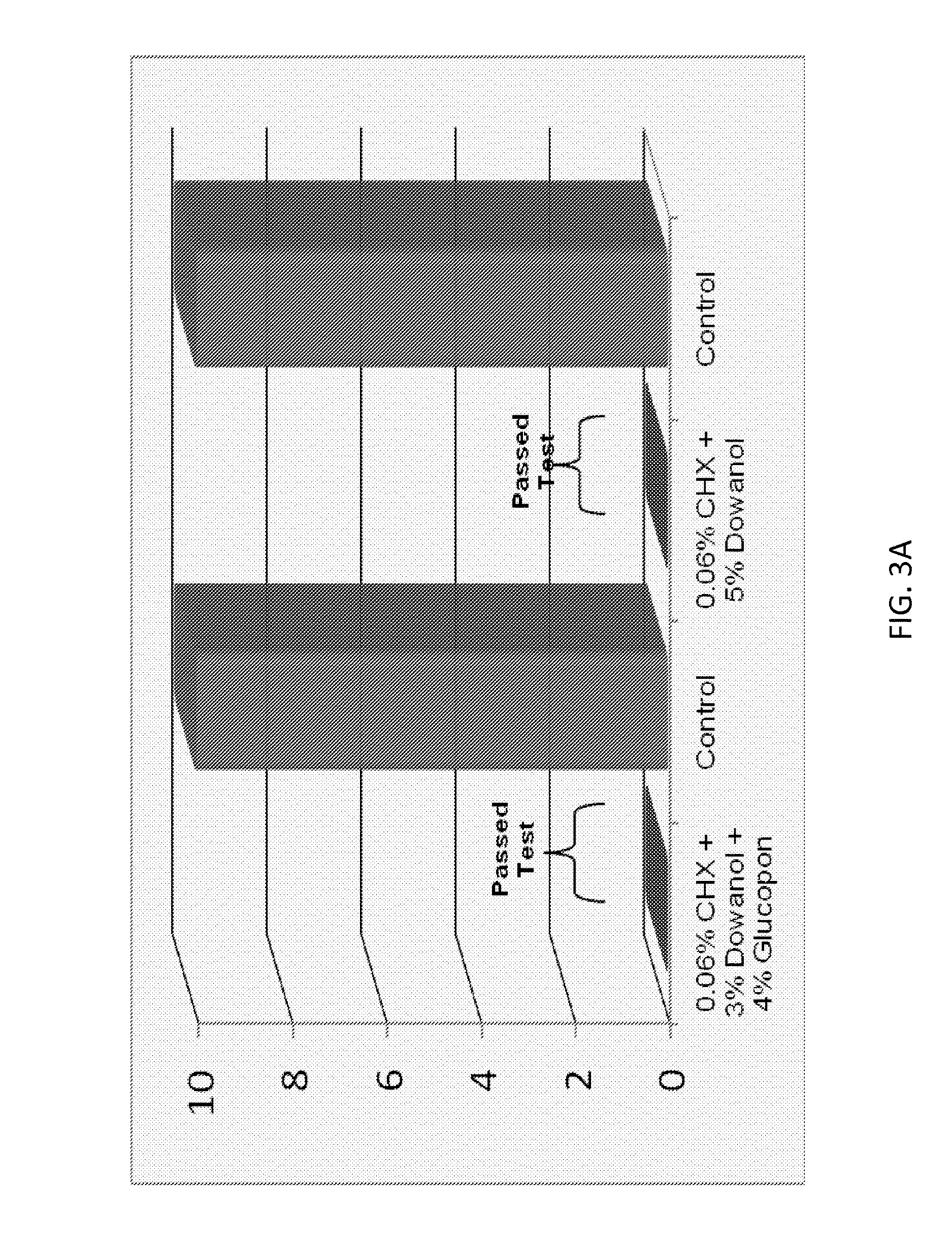
ActiveUS20130231302A1Excellent surface tension lowering activityImprove film qualityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAlcoholMedicine
The present invention provides antimicrobial solutions that in certain cases comprise a biguanide and a glycol ether and, in some cases, optionally also includes combinations of at least one an alcohol, at least one chelator, glycerol, deoxycholate, and / or at least one alkylpolyglucoside. In certain aspects the invention comprises a biguanide and deoxycholate or a combination of chelator, ethanol, and alkylpolyglucoside. Also provided are methods for rapidly killing and / or reducing bacteria, fungi, or virus from surfaces, for example, including surfaces of indwelling medical devices and organic surfaces such as skin and sutures, and inorganic surfaces such as medical equipment, pipelines etc.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Catalysts
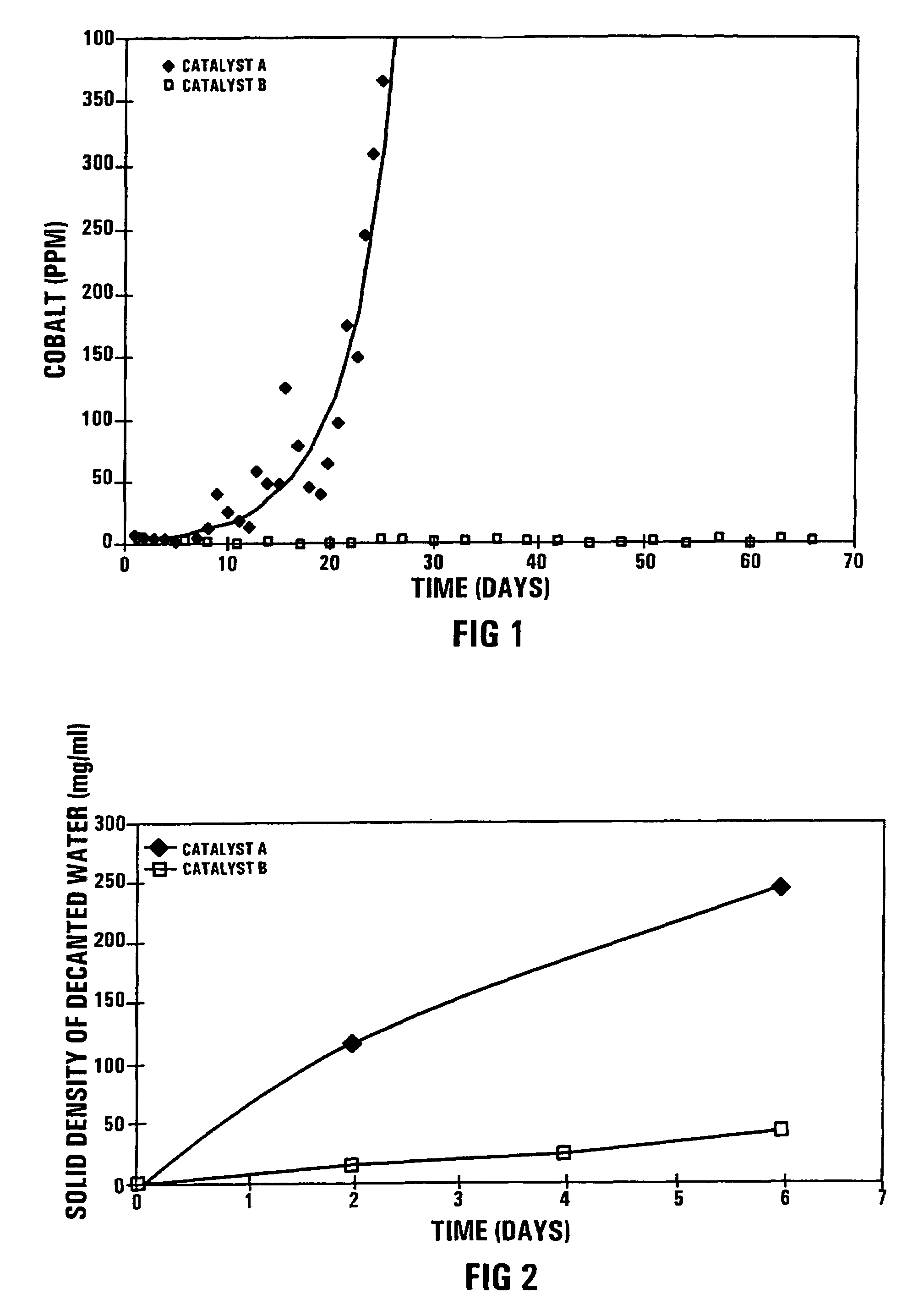
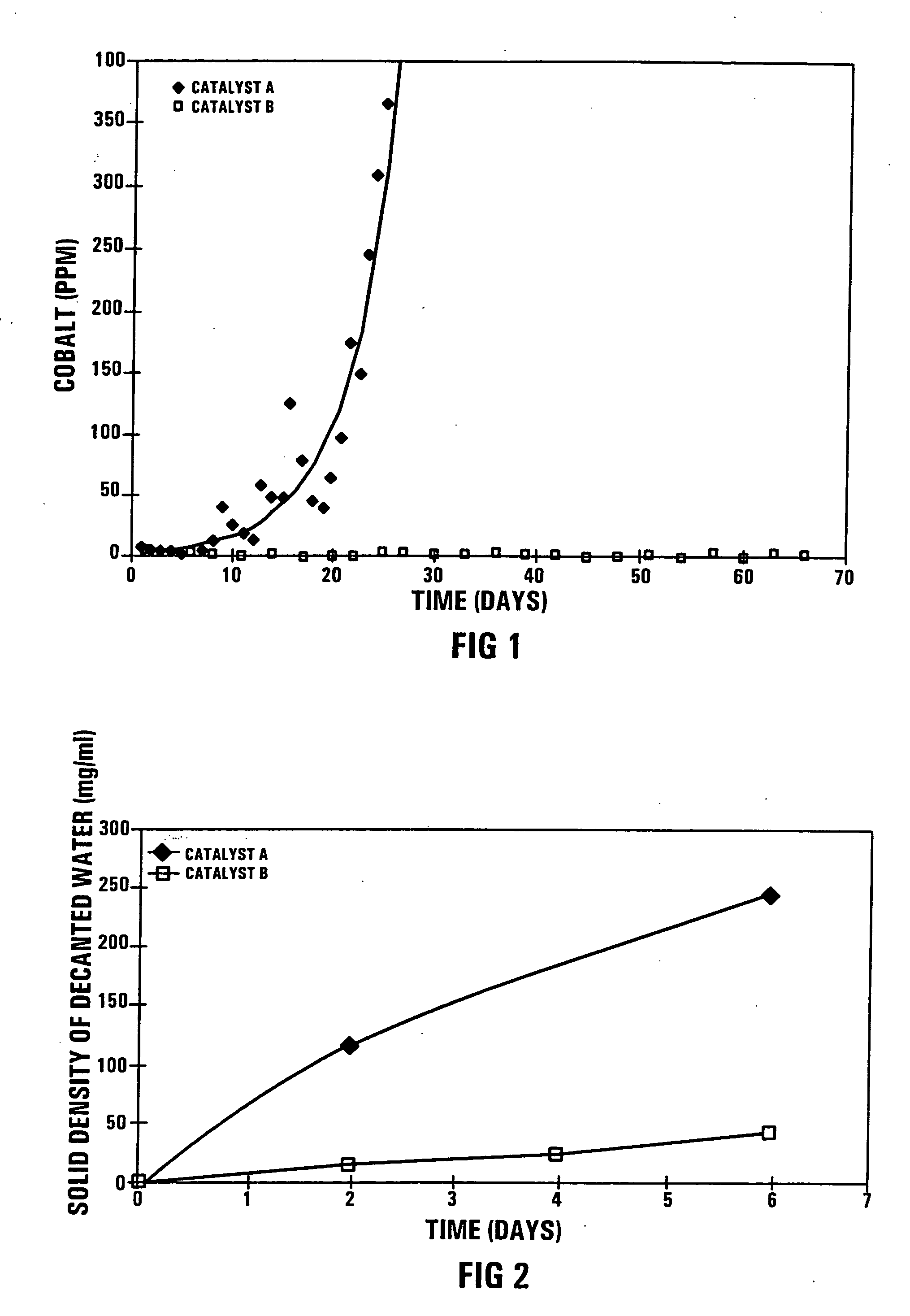
ActiveUS7365040B2Facilitates the eventual dislodging and washingReducing the catalyst precursorLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionHydrocarbon oils refiningPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
A process for preparing a cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst includes introducing a soluble modifying component precursor of the formula Mc(OR)x, where Mc is a modifying component selected from the group comprising Si, Ti, Cu, Zn, Zr, Mn, Ba, Ni, Na, K, Ca, Sn, Cr, Fe, Li, Tl, Sr, Ga, Sb, V, Hf, Th, Ce, Ge, U, Nb, Ta, W or La, R is an alkyl or acyl group, and x is an integer having a value of from 1 to 5, onto and / or into a cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst precursor, which comprises a porous pre-shaped catalyst support supporting cobalt in an oxidized form. The resultant modified cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst precursor is reduced to obtain a cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst.
Owner:SASOL TEKHNOLODZHI PROPRIEHJTEHRI LTD
Insulin formulations for insulin release as a function of tissue glucose levels
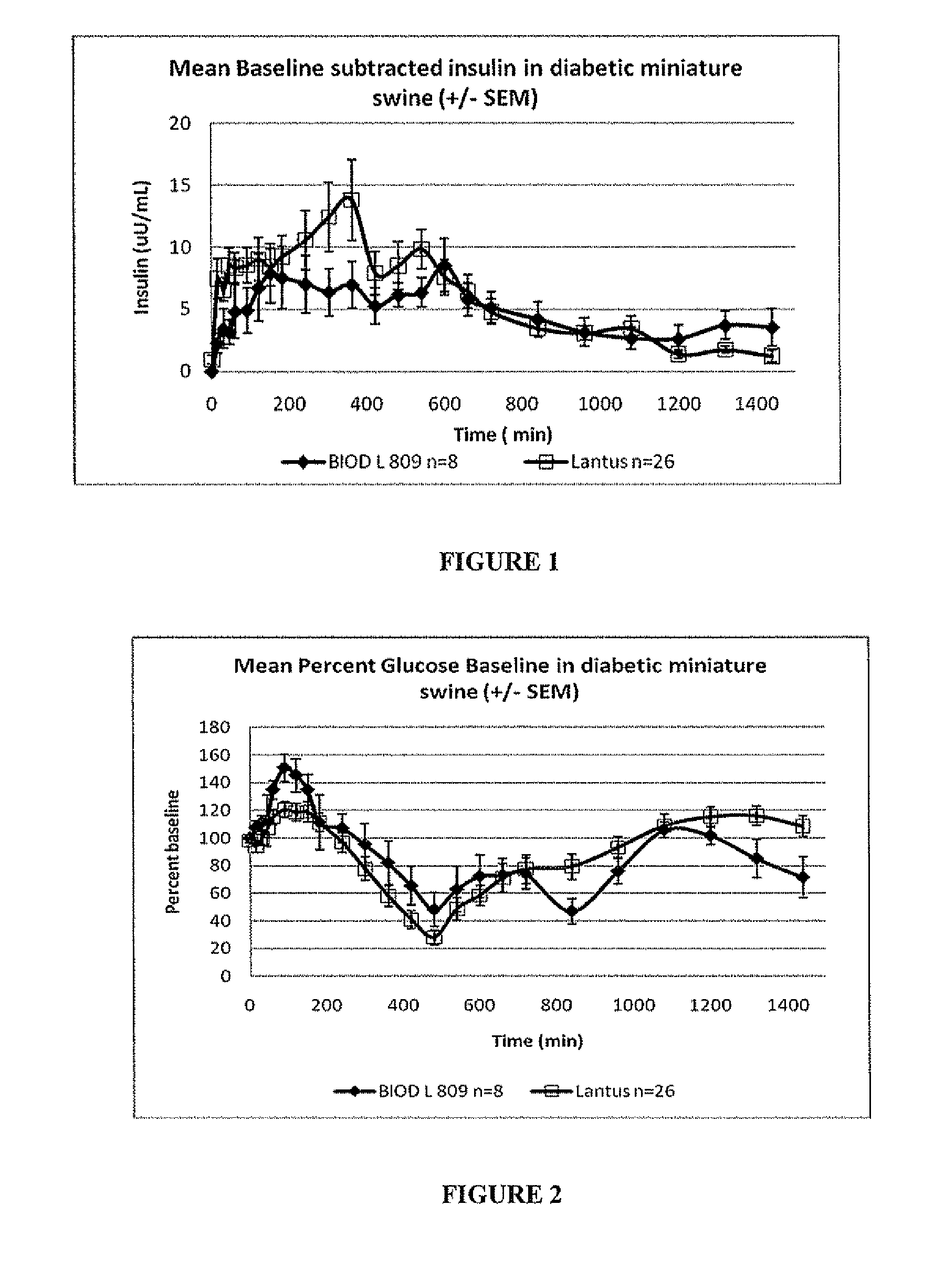
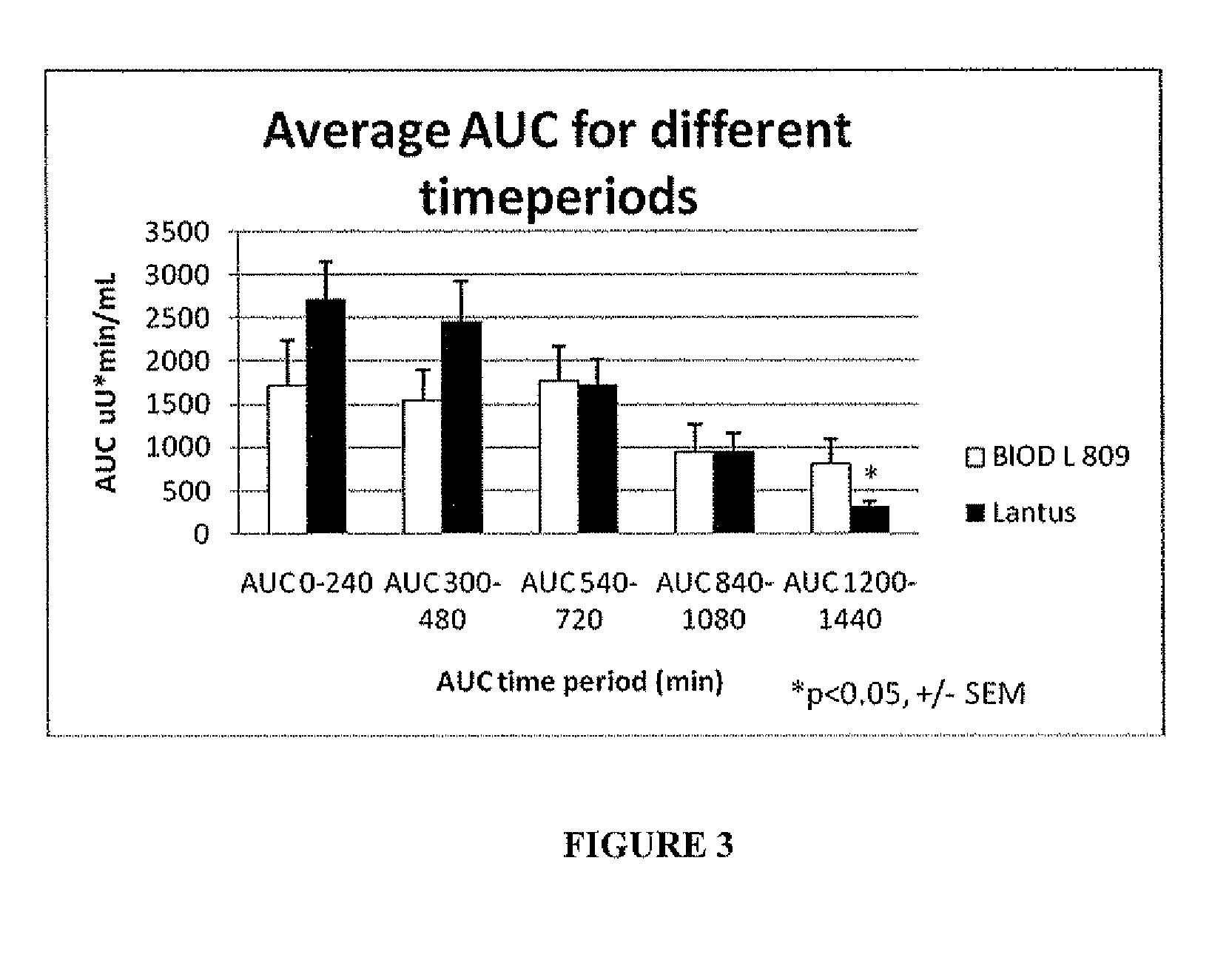
InactiveUS20090175840A1Reduce productionRaise the pHPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInjections insulinReducing agent
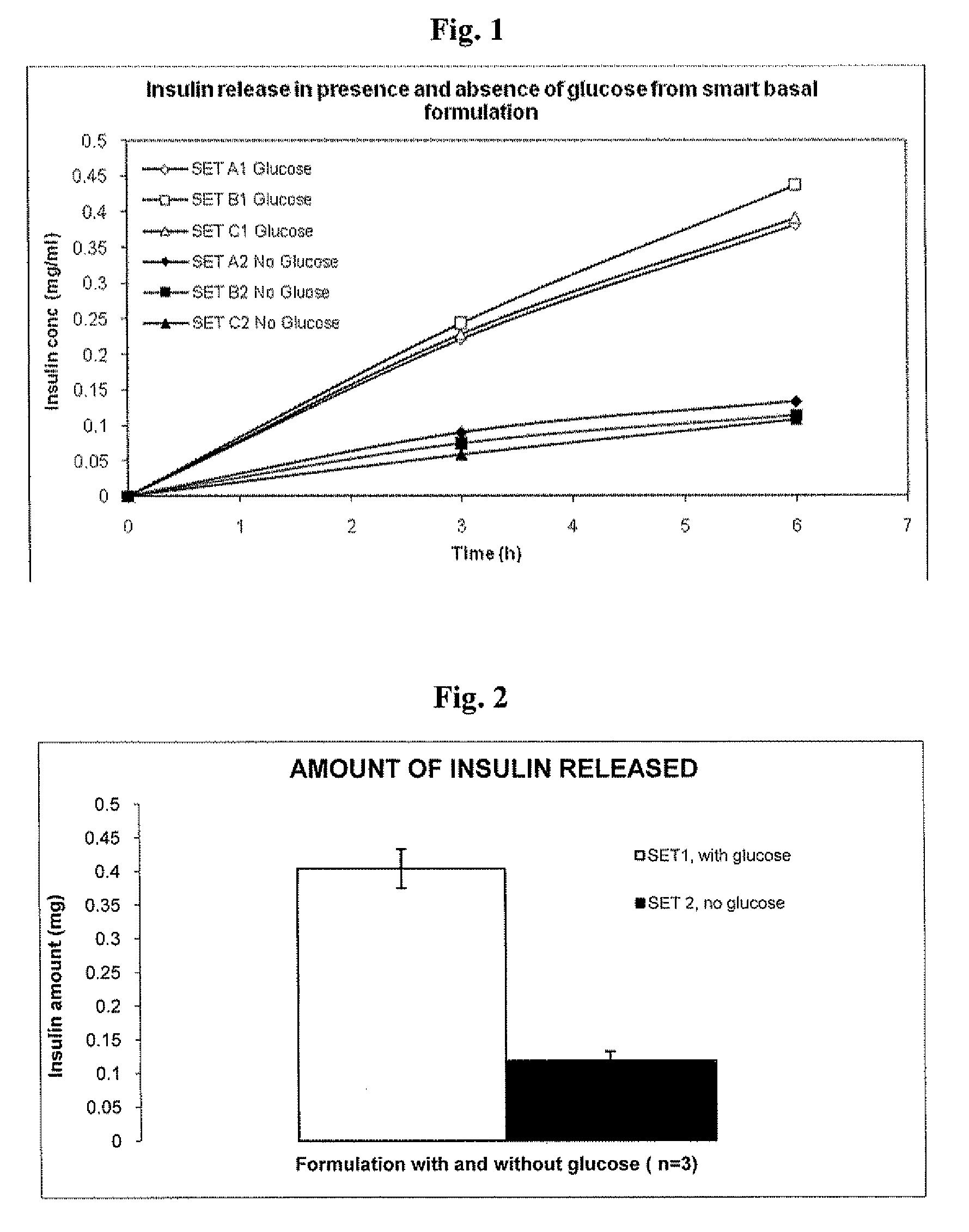
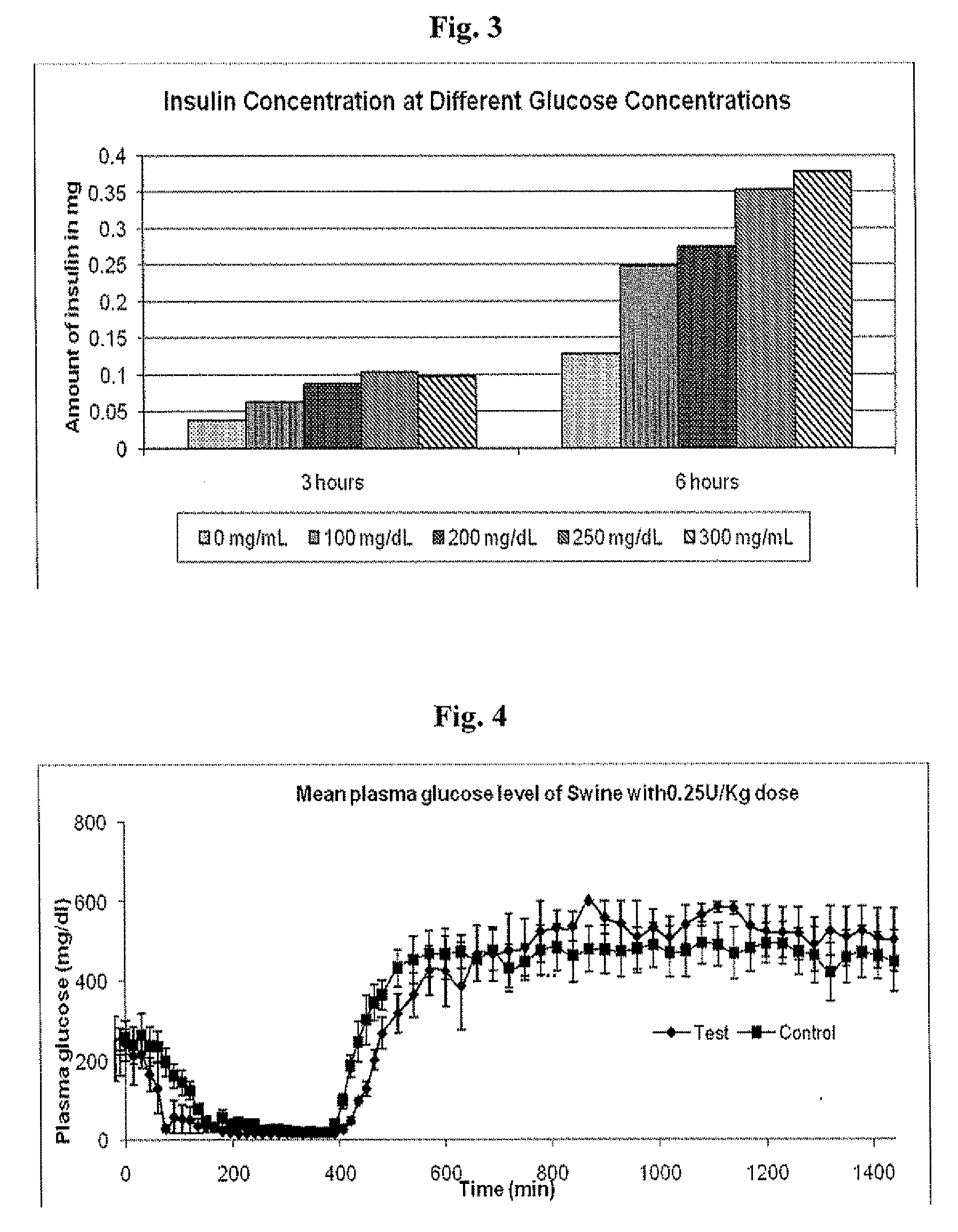
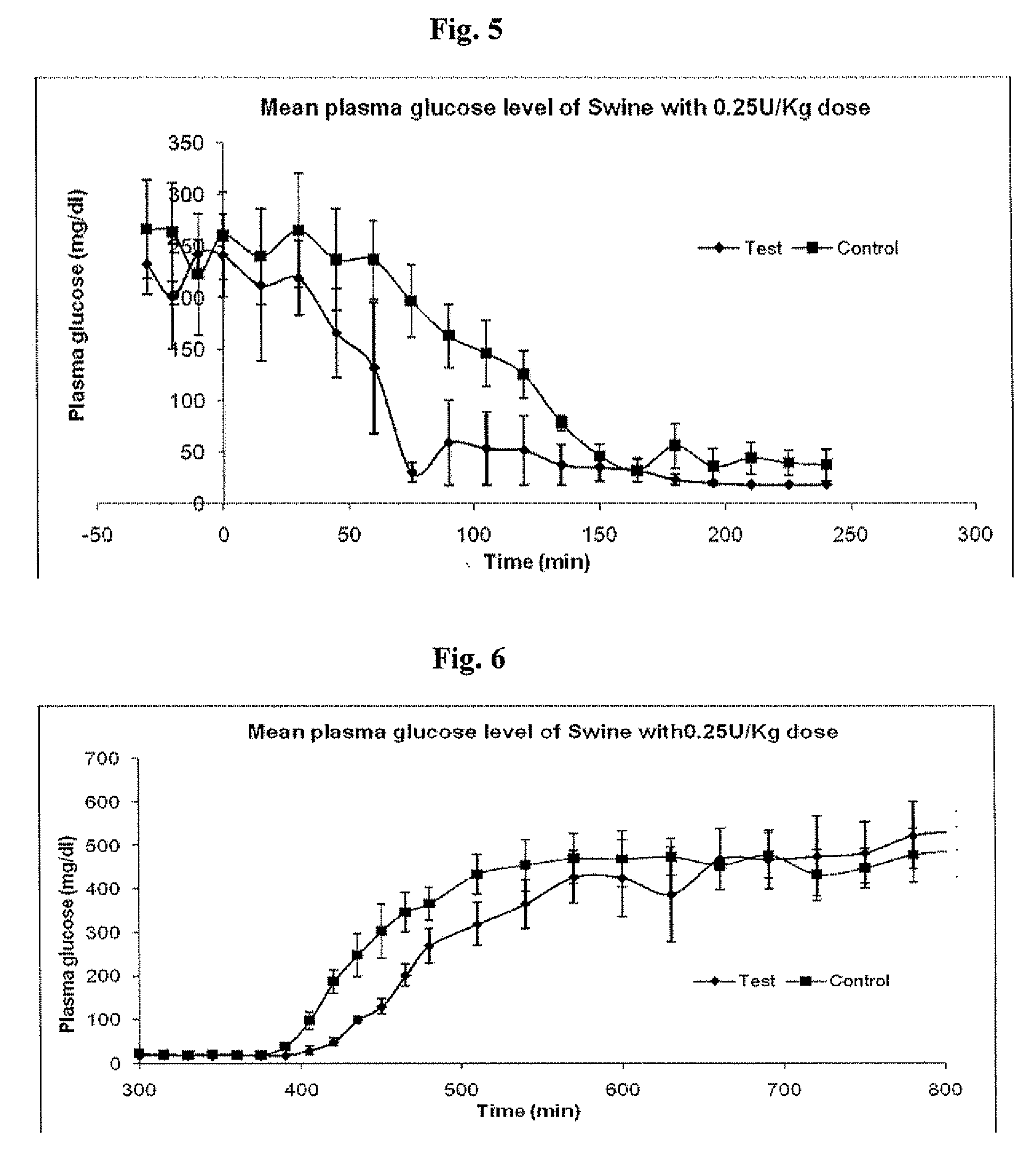
Injectable insulin formulations that are capable of modifying the amount of insulin released based on the patient's tissue glucose levels, methods for making and using these formulations are described herein. The formulation may be administered via subcutaneous, intradermal or intramuscular administration. In one preferred embodiment, the formulations are administered via subcutaneous injection. The formulations contain insulin, an oxidizing agent or enzyme and a reducing agent or enzyme, a diluent and optionally one or more thickening agents. If a thickening agent is present in the formulation, the thickening agent increases the viscosity of the formulation following administration. Preferably the formulation contains an insulin, a diluent, glucose oxidase and peroxidase. Following administration to a patient, the insulin is released from the formulations as a function of the patient's tissue glucose level, which in turn maintains the patient's blood glucose level within an optimum range. The formulation is often referred to as a “smart” formulation since it modifies its release rate of insulin according to the patient's needs at a particular time. In a preferred embodiment, the formulation is designed to release insulin into the systemic circulation over time with a basal release profile following injection in a patient. In another embodiment, the formulation is designed to release insulin into the systemic circulation over time with a non-basal release profile following injection in a patient, such as a regular human insulin release profile or a prandial release profile.
Owner:BIODEL
Integrated fixation systems
InactiveUS6838504B1Barrier to the leaching of environmentally harmful heavy metalsLess solublePrimary cell maintainance/servicingEnergy based wastewater treatmentPhosphatePVA - Polyvinyl alcohol
The invention provides polymeric matrices and films comprising fixation reagents that are capable of reacting with solubilized metals to form less soluble metal compounds. The fixation reagenst may include inorganic sulfides and phosphates, as well as adsorbents. The polymeric matrices may be comprised of polyvinyl alcohols and polyvinyl acetates. In some embodiments, the polymeric matrix is selected to be at least as soluble as the selected fixation reagent, particularly under the conditions in which the matrix is expected to come into contact with the solublized metal.
Owner:GEMINI STRATEGIES +2
Insulin with a stable basal release profile
ActiveUS20110281790A1Accelerated precipitationLess solublePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin glargineZinc
A basal insulin formulation composed of insulin, preferably insulin glargine, injectable zinc and injectable iron compounds as precipitating and / or stabilizing agents has been developed for subcutaneous, intradermal or intramuscular administration. The formulation is designed to form a precipitate of insulin following injection, creating a slow releasing “basal insulin” over a period of 12 to 24 hours.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Nonpolar phase-soluble methathesis catalysts
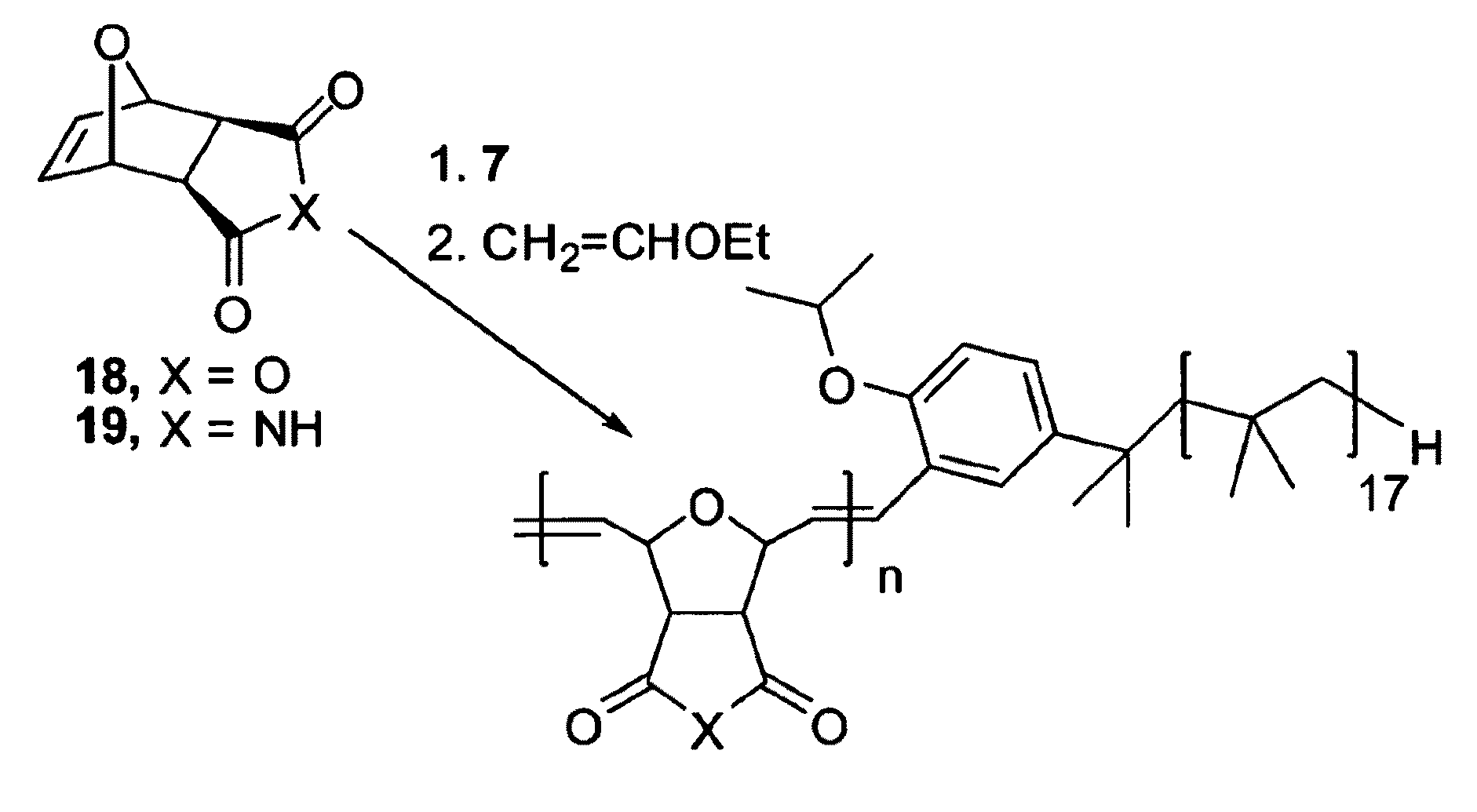
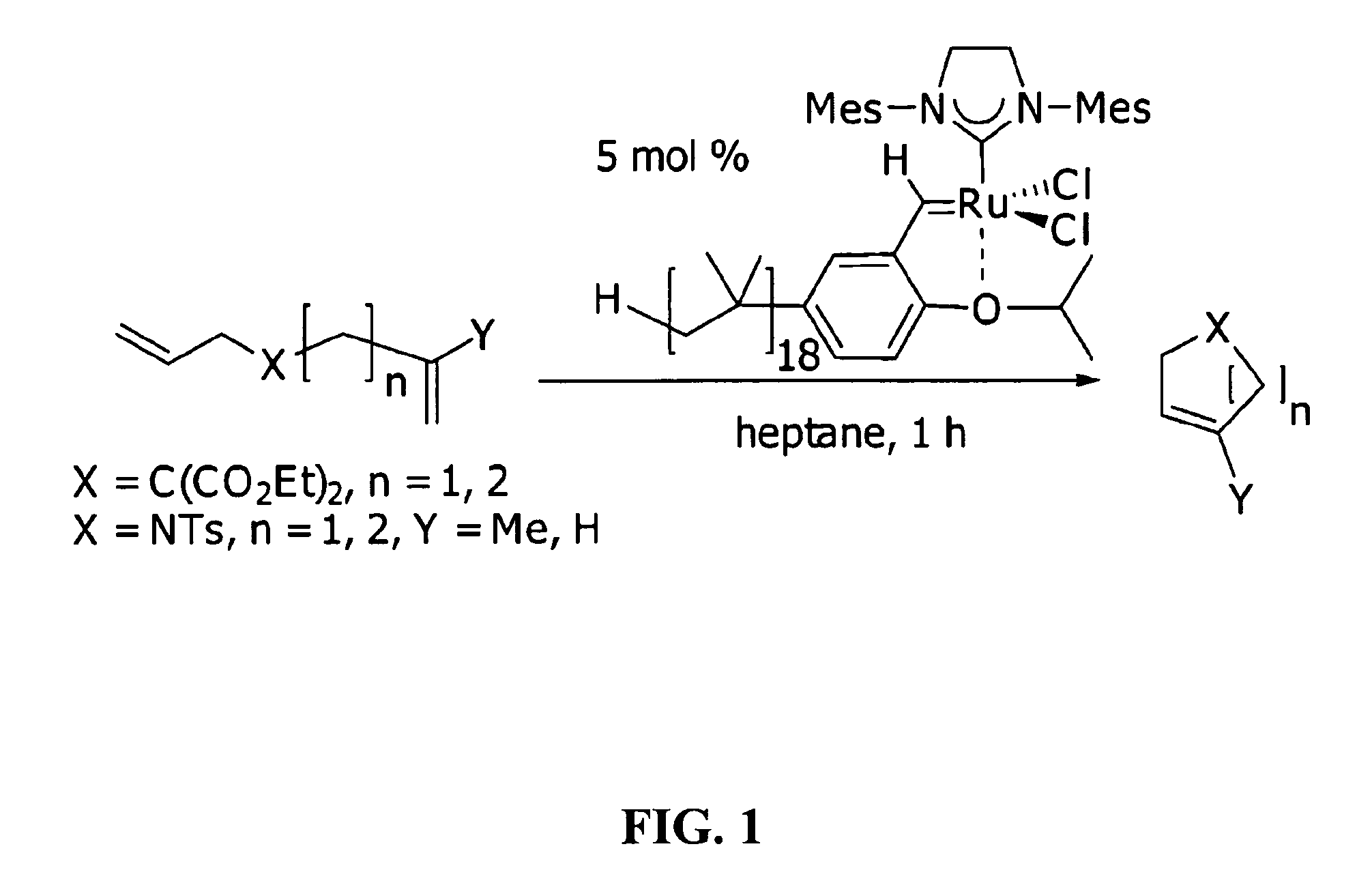
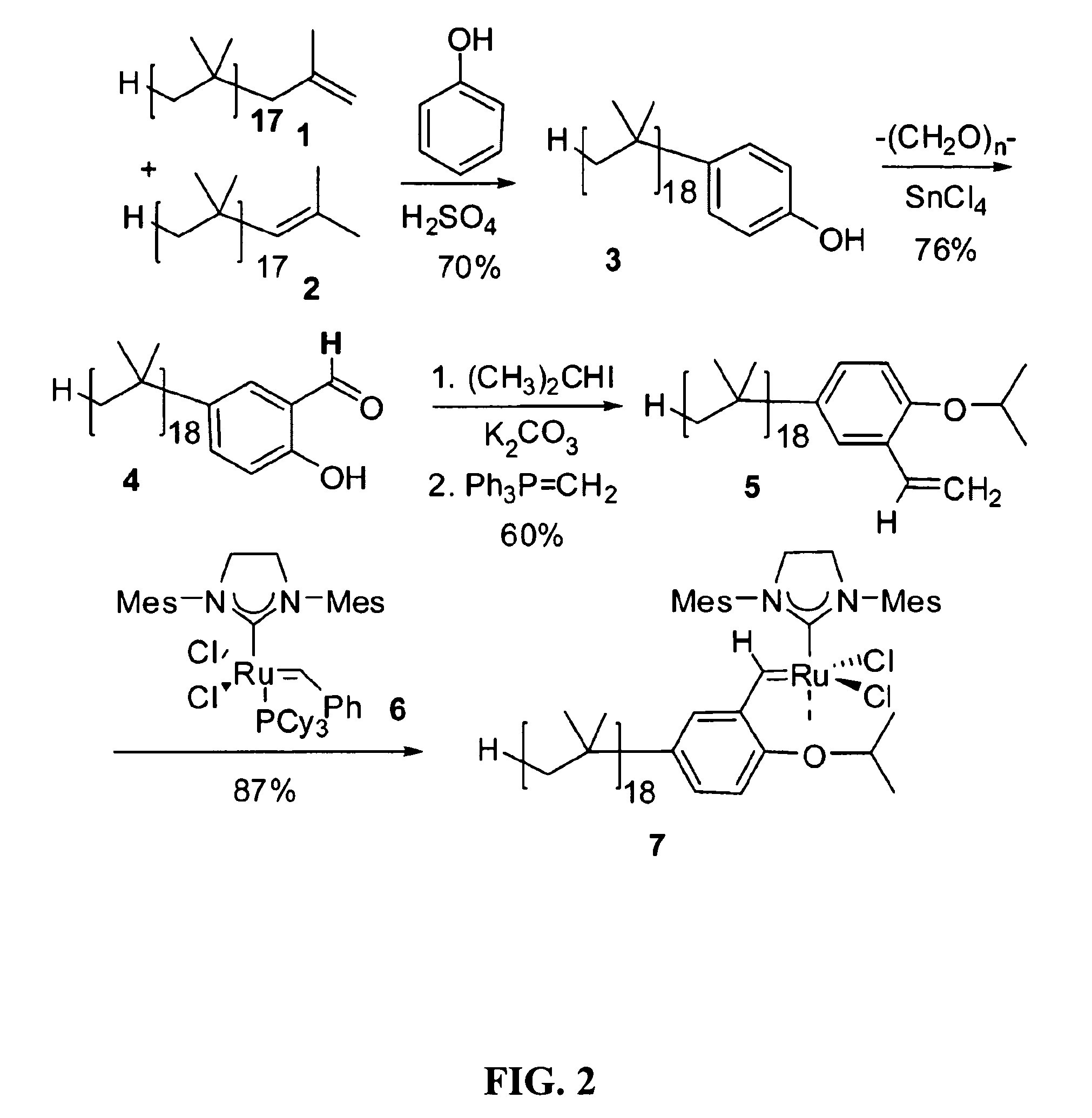
InactiveUS20090203860A1Less solubleLittle and solubilityOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSolubilityOligomer
One embodiment of the invention provides polyisobutylene (PIB) oligomers that are end-functionalized with ruthenium (Ru) catalysts. Such nonpolar catalysts can be dissolved in nonpolar solvents such as heptane, or any other nonpolar solvent that is otherwise not latently biphasic (i.e., if two or more solvent components are present, they remain miscible with each other throughout the entire reaction process, from the addition of substrate through to the removal of product). Substrate that is dissolved in the nonpolar solvent with the catalyst is converted into product. The lower solubility of the product in the nonpolar solvent renders it easily removable, either by extraction with a more polar solvent or by applying physical means in cases where the product precipitates from the nonpolar solvent. In this manner the catalysts are recycled; since the catalysts remain in the nonpolar solvent, a new reaction can be initiated simply by dissolving fresh substrate into the nonpolar solvent.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
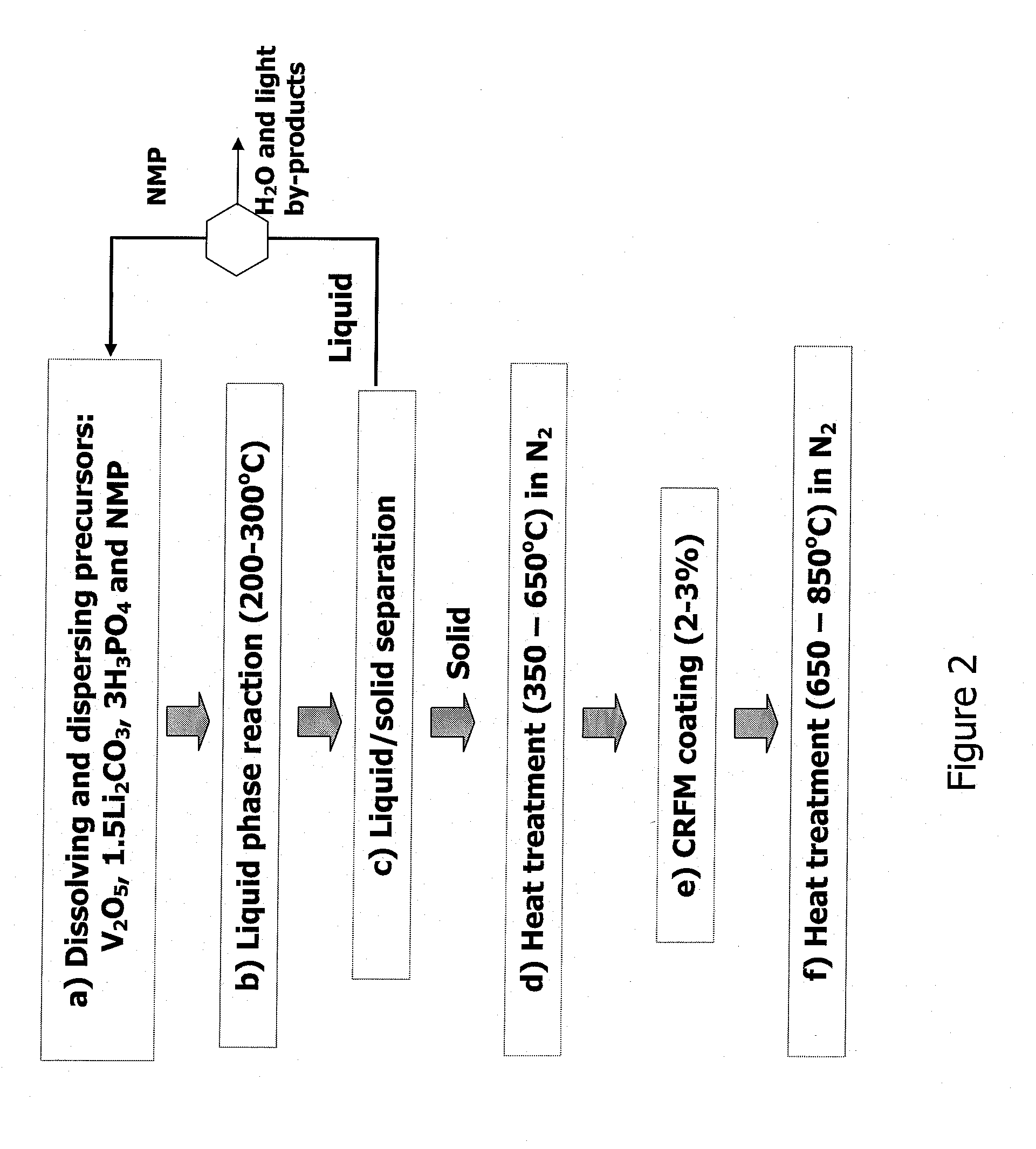
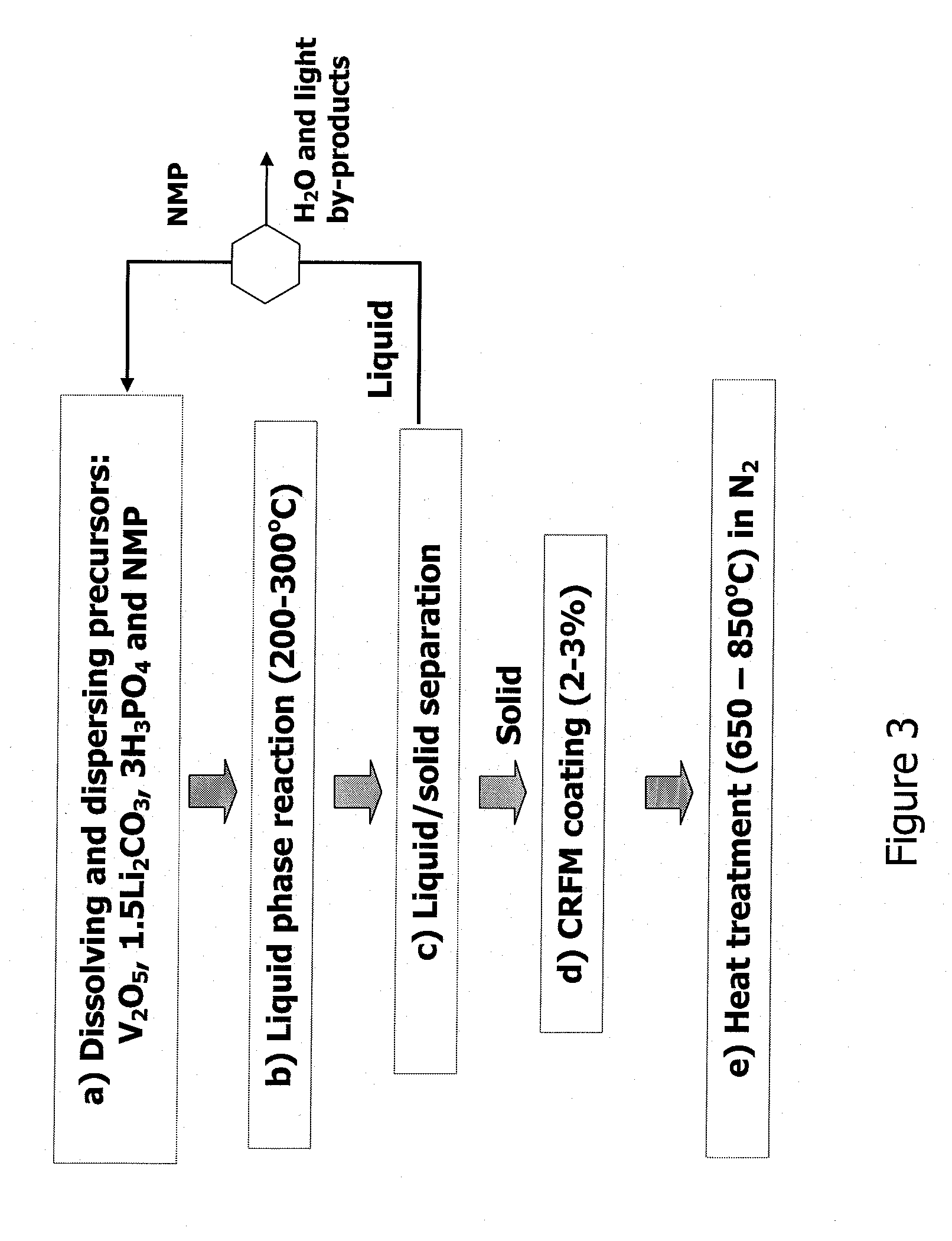
Method for producing lithium vanadium polyanion powders for batteries
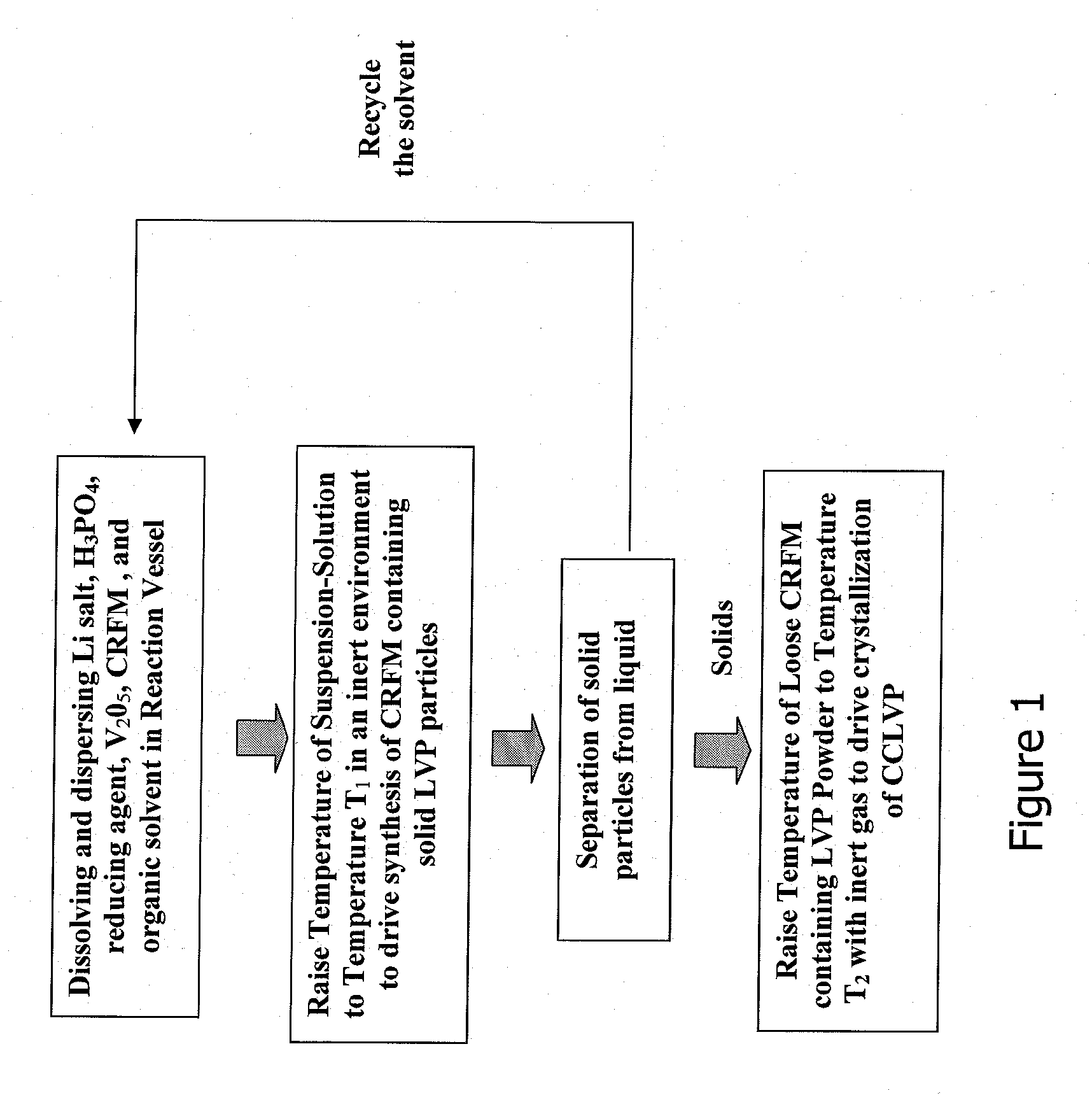
InactiveUS20080305256A1Improve conductivitySufficient electrical conductivityCell electrodesPretreated surfacesSolventLithium-ion battery
This invention relates to a process for producing an improved cathode powder for making lithium ion batteries wherein the powder comprises lithium, vanadium and a polyanion. The process includes forming a solution-suspension of the precursors, which include vanadium pentoxide, with a reducing agent, a solvent, and a carbon-residue-forming material. The reducing agent causes the vanadium in vanadium pentoxide to reduce from V5+ to V3+. The solution-suspension is heated in an inert environment to drive the synthesis of the LVP (Li3V2(PO4)3) such that the carbon-residue-forming material is also oxidized to precipitate in and on the LVP forming carbon-containing LVP or CCLVP. The liquids are separated from the solids and the dry powder is heated to a second higher temperature to drive the crystallization of the product. The resulting product retains a small particle size, includes carbon in the LVP for conductivity and is created with very low cost precursors and avoids the need for milling or other processing to reduce the product to a particle size suitable for use in batteries. It also does not require the addition of carbon black, graphite or other form of carbon to provide the conductivity required for use in batteries.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
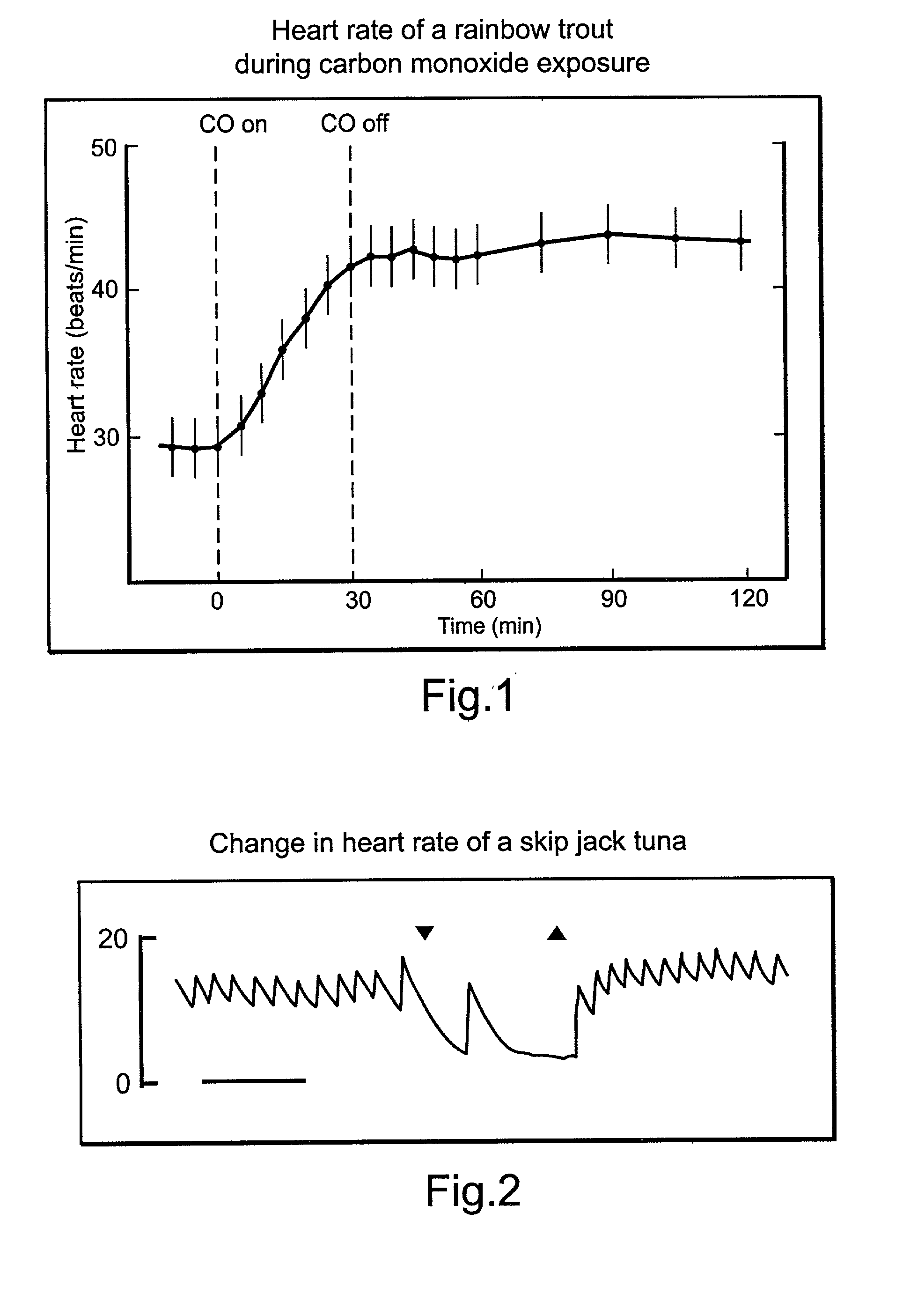
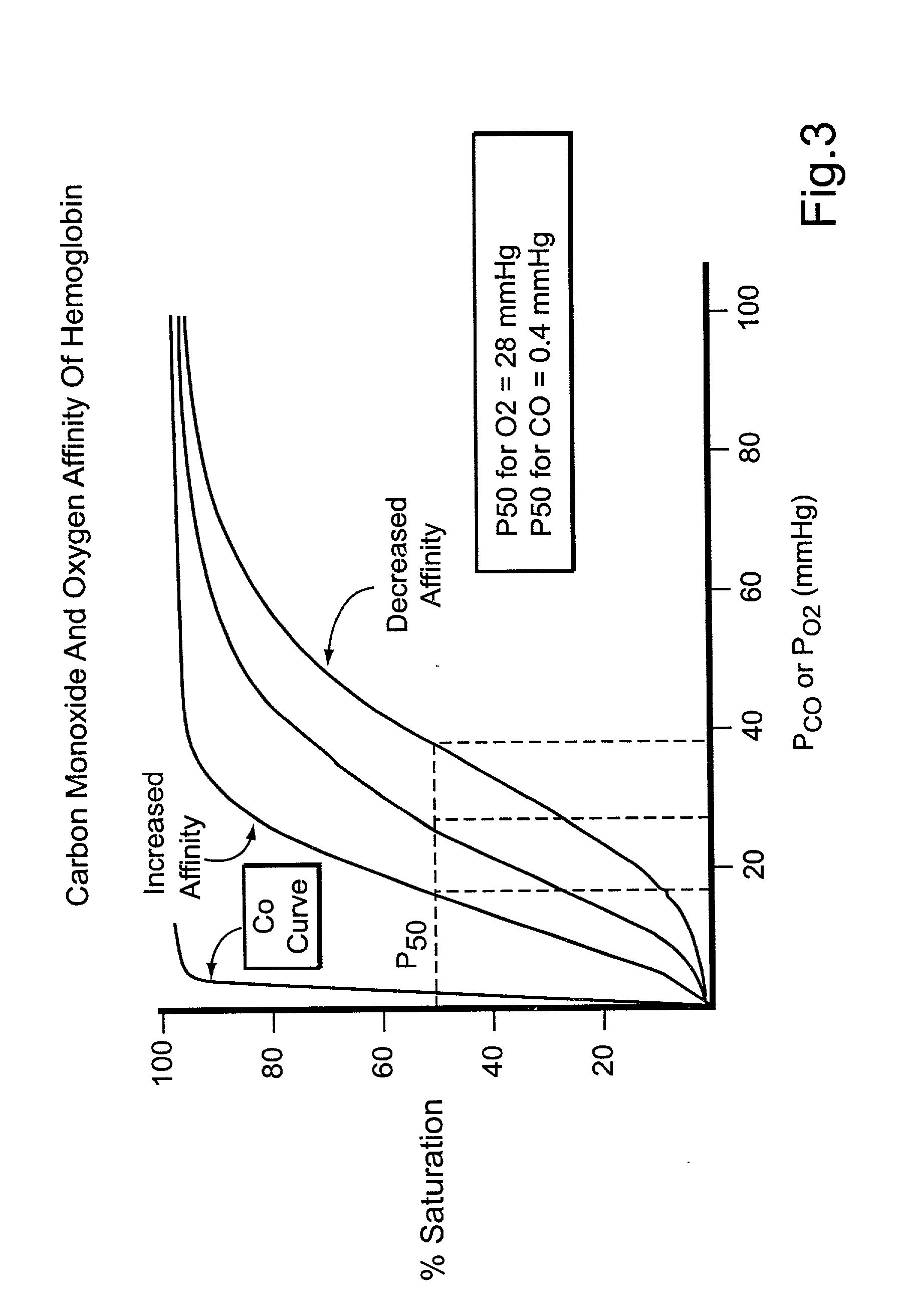
Process to treat fish with tasteless smoke or carbon monoxide through the respiratory and circulatory systems
InactiveUS20030044497A1High activityLight treatment effectOther dairy technologyMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsMuscle tissueSmoke Emission
A process and apparatus for treating fish or other animals by introducing tasteless smoke or carbon monoxide into the respiratory system, so that it is absorbed into the edible muscle tissue through the circulatory system. In one embodiment, tasteless smoke or carbon monoxide is entrained or dissolved in water in which fish are swimming. In another embodiment, tasteless smoke or carbon monoxide is introduced into a foam that is applied to the fish. Devices for entraining or dissolving the tasteless smoke or carbon monoxide into water or foam are also described.
Owner:KOWALSKI WILLIAM R
Catalysts
ActiveUS20050245623A1Good resultFacilitates the eventual dislodging and washingLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionHydrocarbon oils refiningChemistryCobalt
A process for preparing a cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst includes introducing a soluble modifying component precursor of the formula Mc(OR)x, where Mc is a modifying component selected from the group comprising Si, Ti, Cu, Zn, Zr, Mn, Ba, Ni, Na, K, Ca, Sn, Cr, Fe, Li, Tl, Sr, Ga, Sb, V, Hf, Th, Ce, Ge, U, Nb, Ta, W or La, R is an alkyl or acyl group, and x is an integer having a value of from 1 to 5, onto and / or into a cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst precursor, which comprises a porous pre-shaped catalyst support supporting cobalt in an oxidized form. The resultant modified cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst precursor is reduced to obtain a cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst.
Owner:SASOL TEKHNOLODZHI PROPRIEHJTEHRI LTD
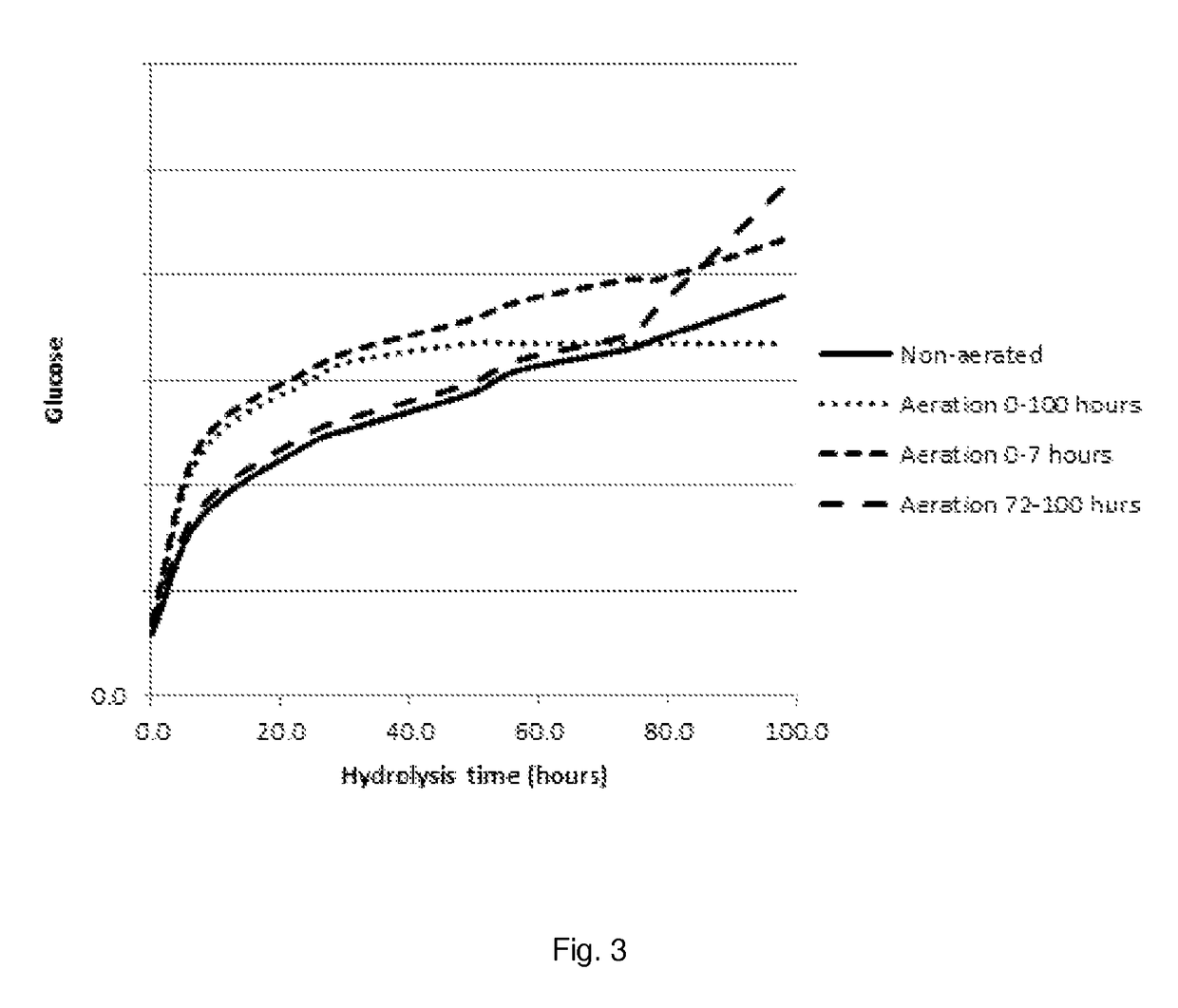
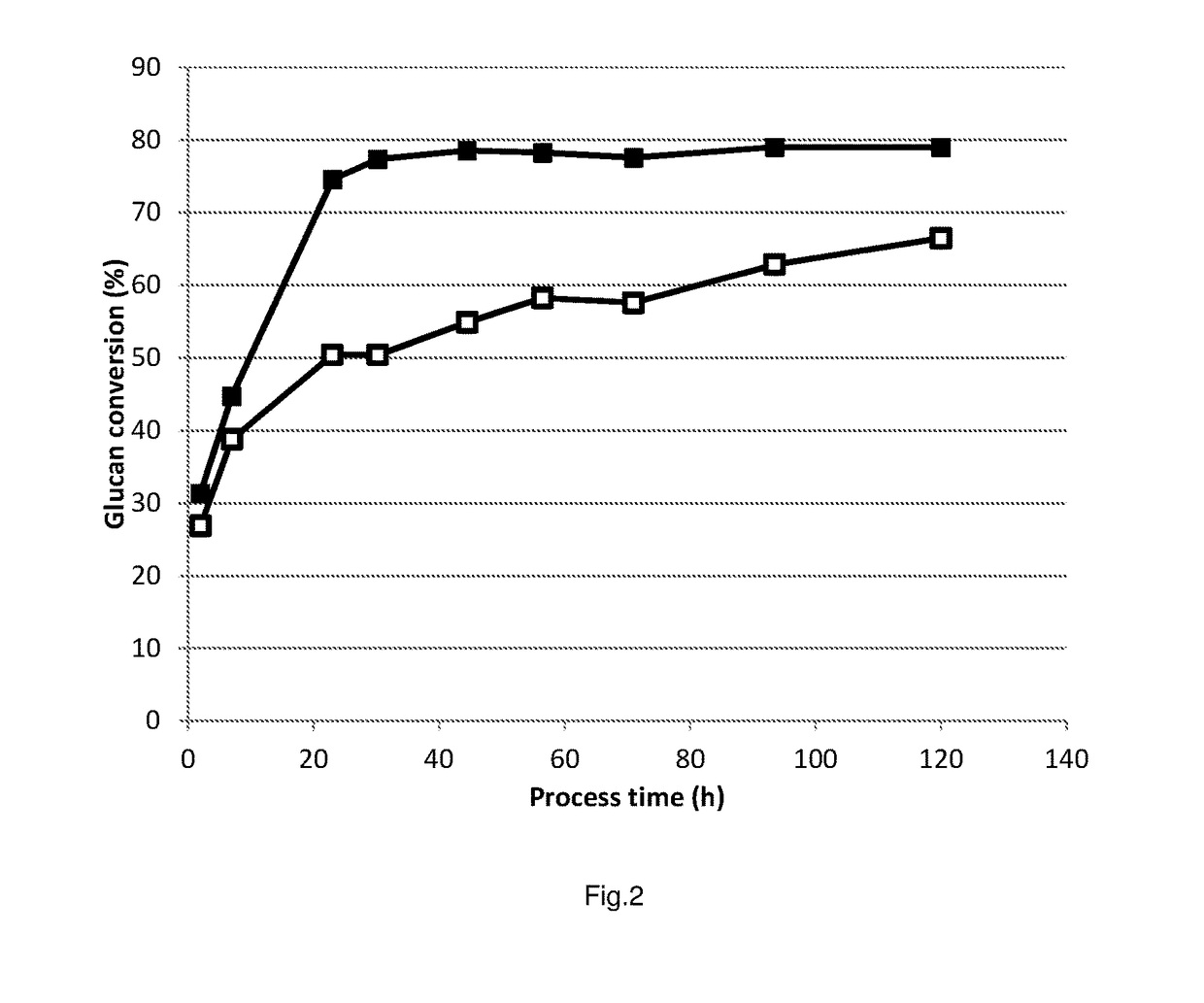
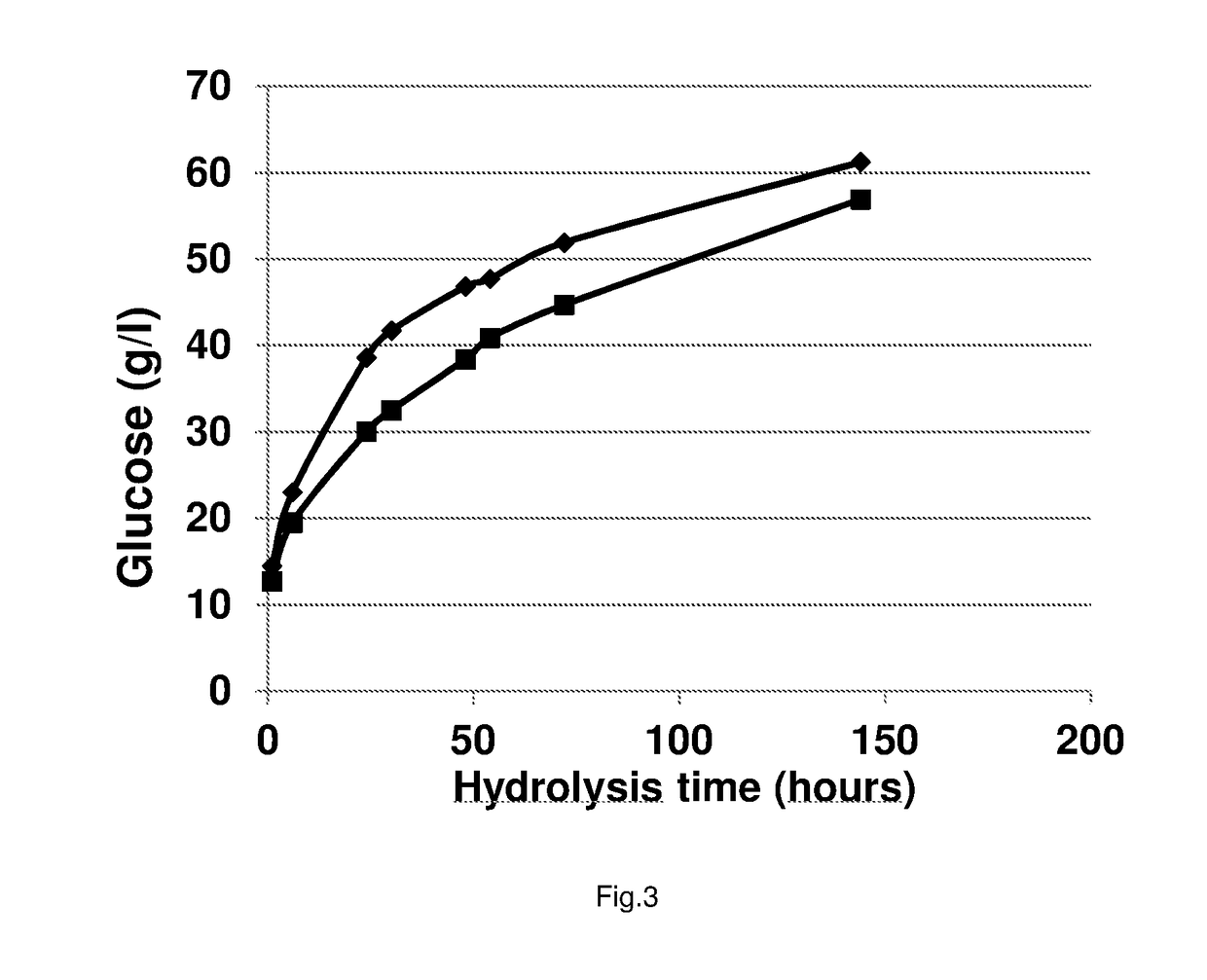
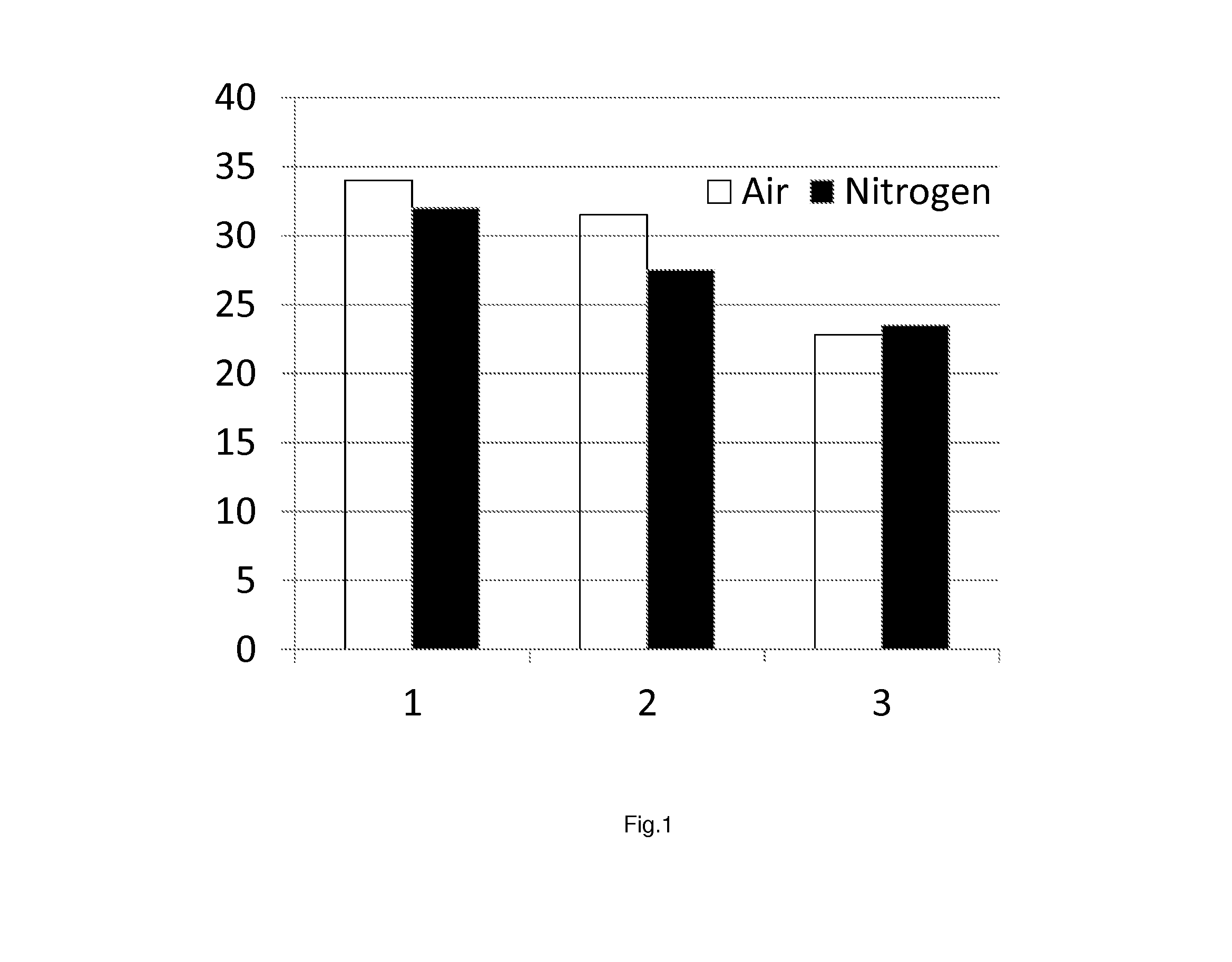
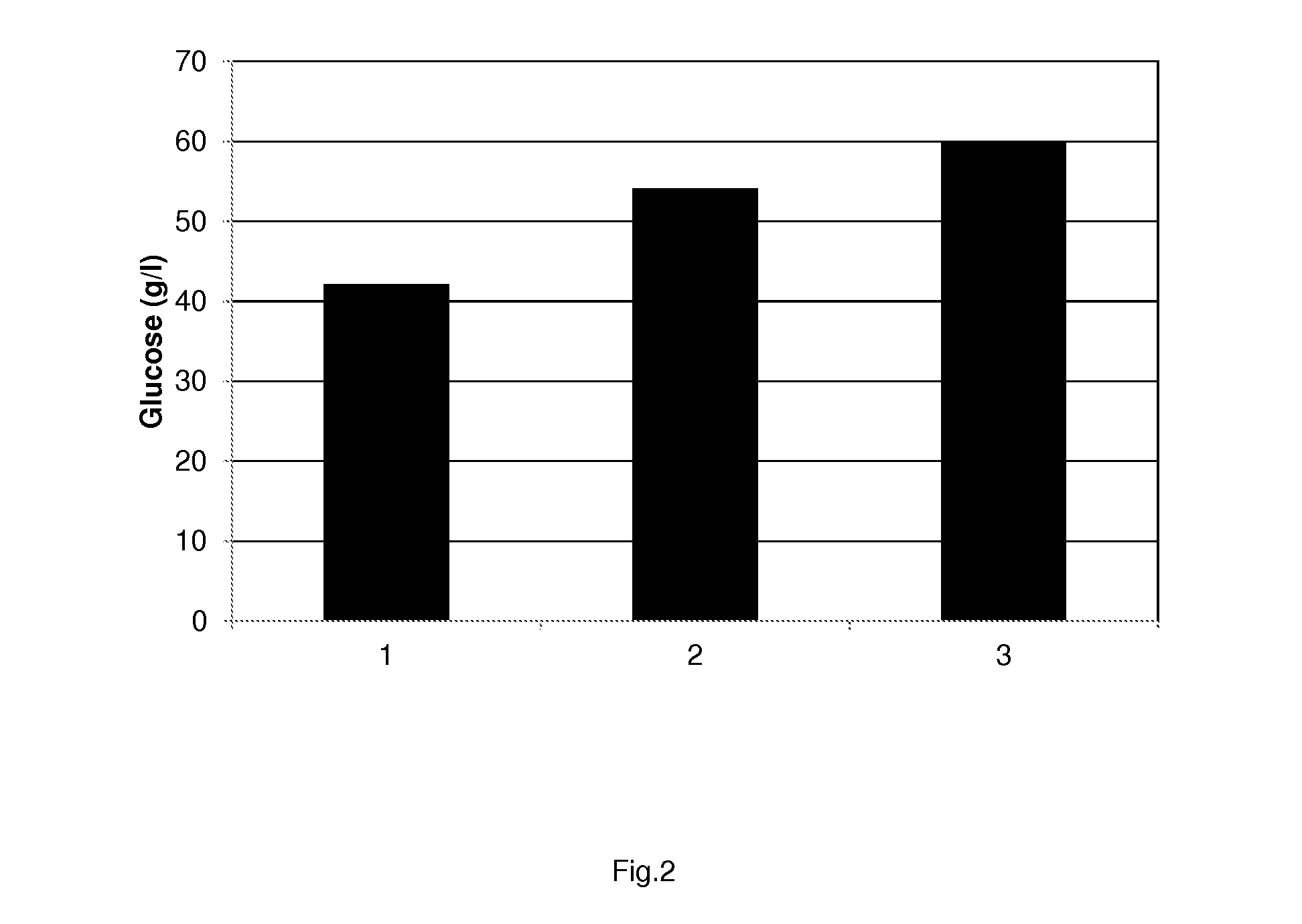
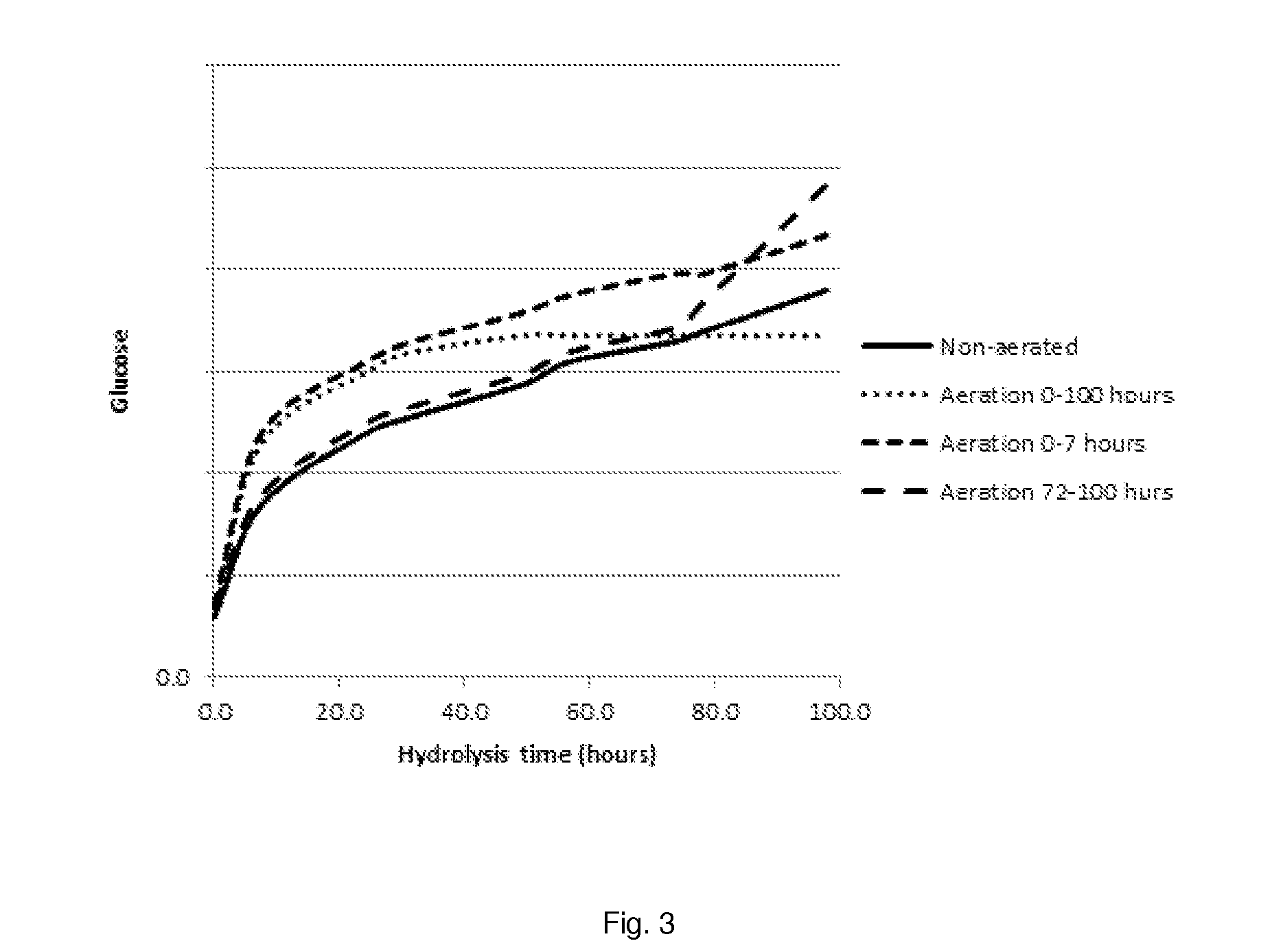
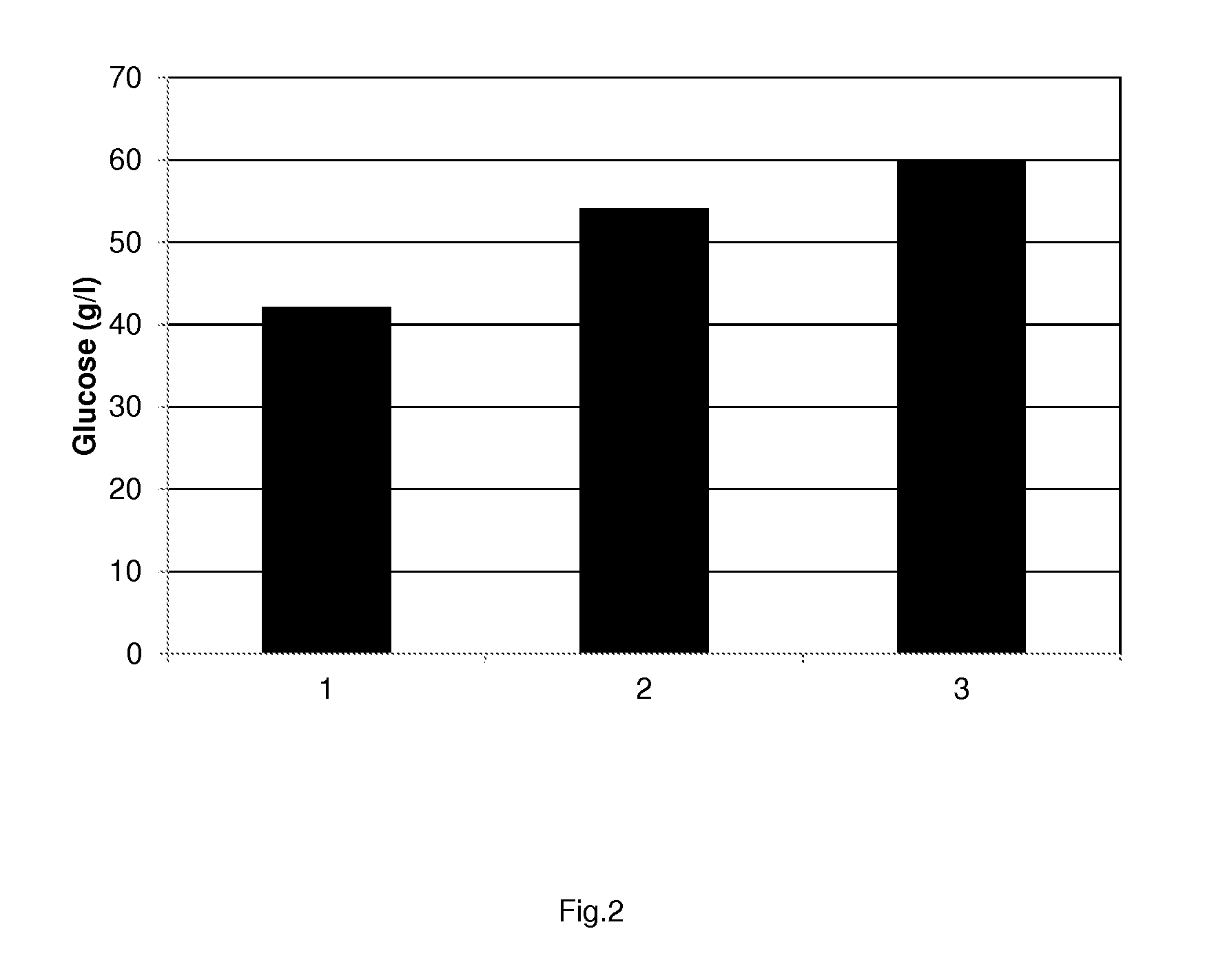
Process for enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic material and fermentation of sugars
ActiveUS9957528B2Reduce processing timeReduce the amount of enzymes usedBiofuelsWaste based fuelEnzymatic hydrolysisCellulase
Owner:VERSALIS SPA
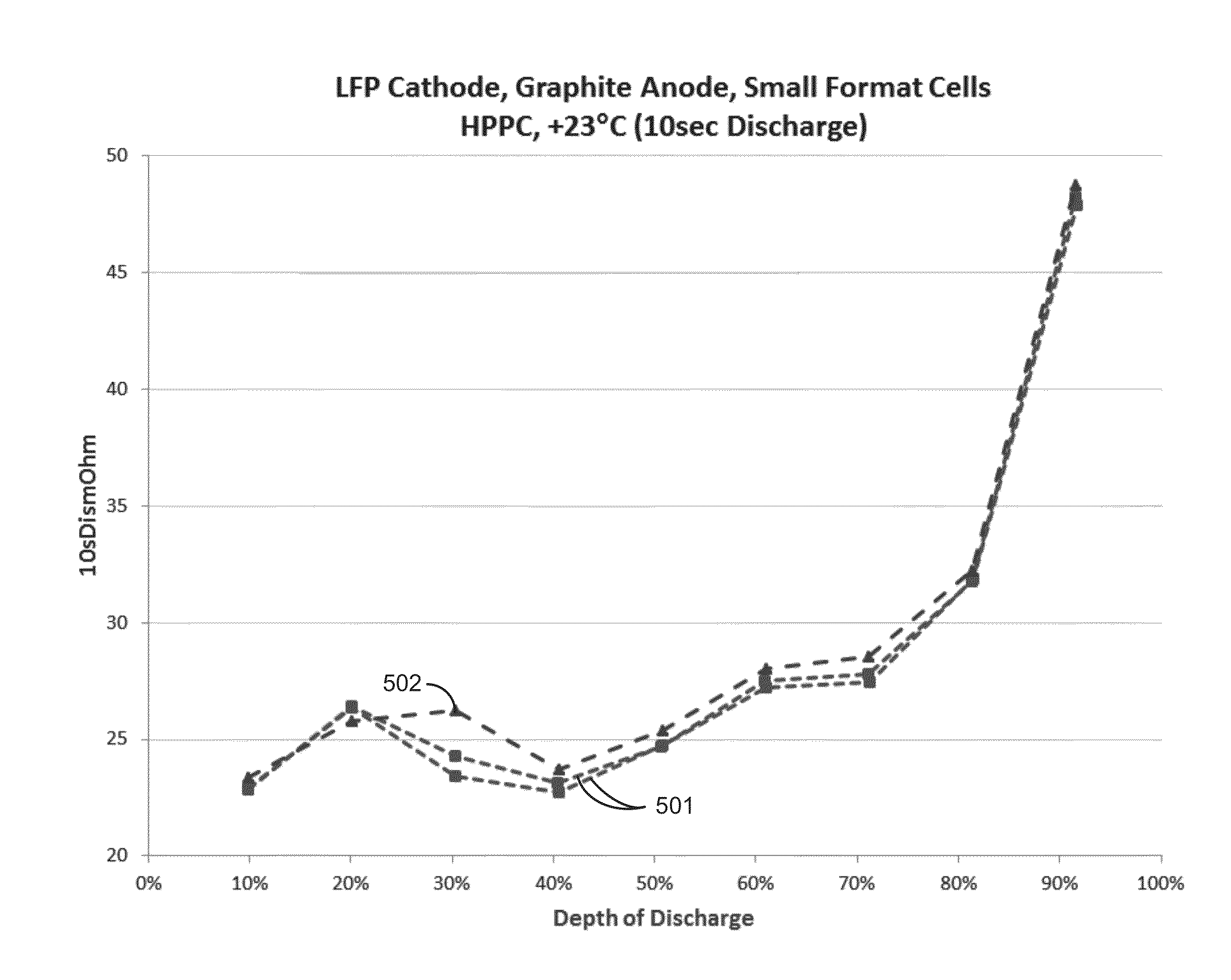
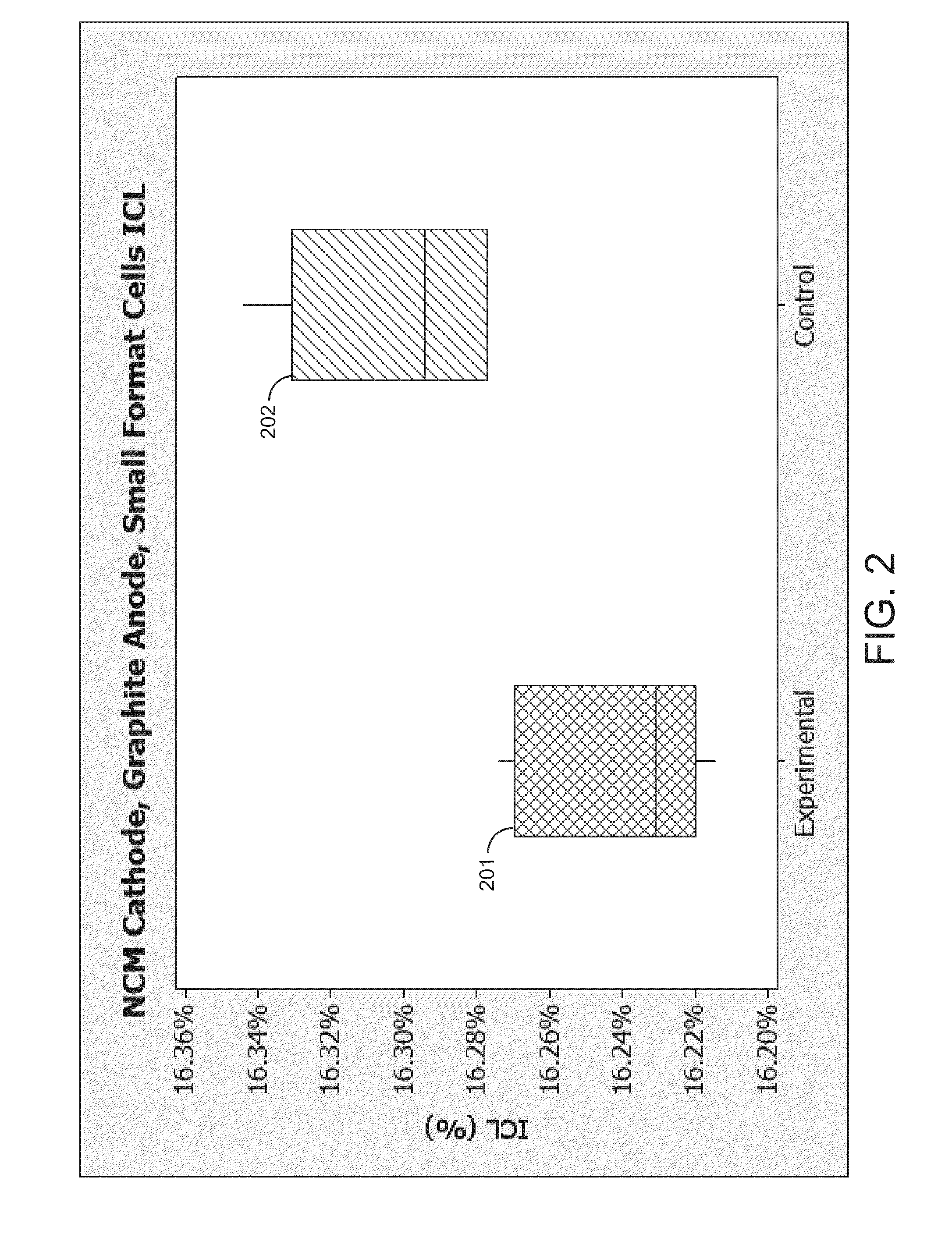
Electrolyte formulation for reduced gassing wide temperature range cycling
ActiveUS20150064549A1Reduce needImprove cycle lifeCell electrodesSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsLithiumBattery cell
A rechargeable battery cell having a specific combination of anode, cathode and electrolyte formulation is provided. The electrolyte formulation includes an additive system and a salt system. The additive system includes a first additive containing a sulfonyl group, an anti-gassing agent, and a second additive. The salt system includes a lithium salt and a co-salt. The disclosed electrolyte formulation has reduced gassing and improved performance over a wide temperature range.
Owner:A123 SYSTEMS LLC
Multivalent metal salts of boronic acids
InactiveUS20040147453A1Low variabilityStable to deboronationBiocideDipeptide ingredientsDivalent metalBoronic acid
Owner:PAION GMBH
Formulations for coated microprojections containing non-volatile counterions
ActiveUS7579013B2Increase volumeLess solubleAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsCounterionPharmacology
Owner:ALZA CORP
Well Buoyancy Elevator and Conveyor Power Apparatus and Method
InactiveUS20120060489A1More power outputLong power cycleCombustion enginesHydro energy generationEngineeringPower apparatus
Systems and methods for generating, converting, and / or storing power under the ground level are disclosed. A well buoyancy power system includes a well adapted to hold a liquid and sealed to hold a pressurize gas, a buoyancy engine that can be a conveyor buoyancy engine or an elevator buoyancy engine, a generator coupled to the buoyancy engine, and an air mover located in the bottom air chamber to transmit the pressurized gas into the liquid at the lower part of the well to drive the buoyancy engine. The system may not be sealed and pressurized for cheaper storage of air when not reused. Because the system utilizes underground space, it is safe, low or no noise, non-polluting, and aesthetically neutral for deployment near where power is to be used such as population centers.
Owner:RIZZI JOSEPH
Stripping and cleaning of organic-containing materials from electronic device substrate surfaces
InactiveUS20070095366A1Reduce odorLess solubleDetergent mixture composition preparationPhotomechanical apparatusPresent methodPropanoic acid
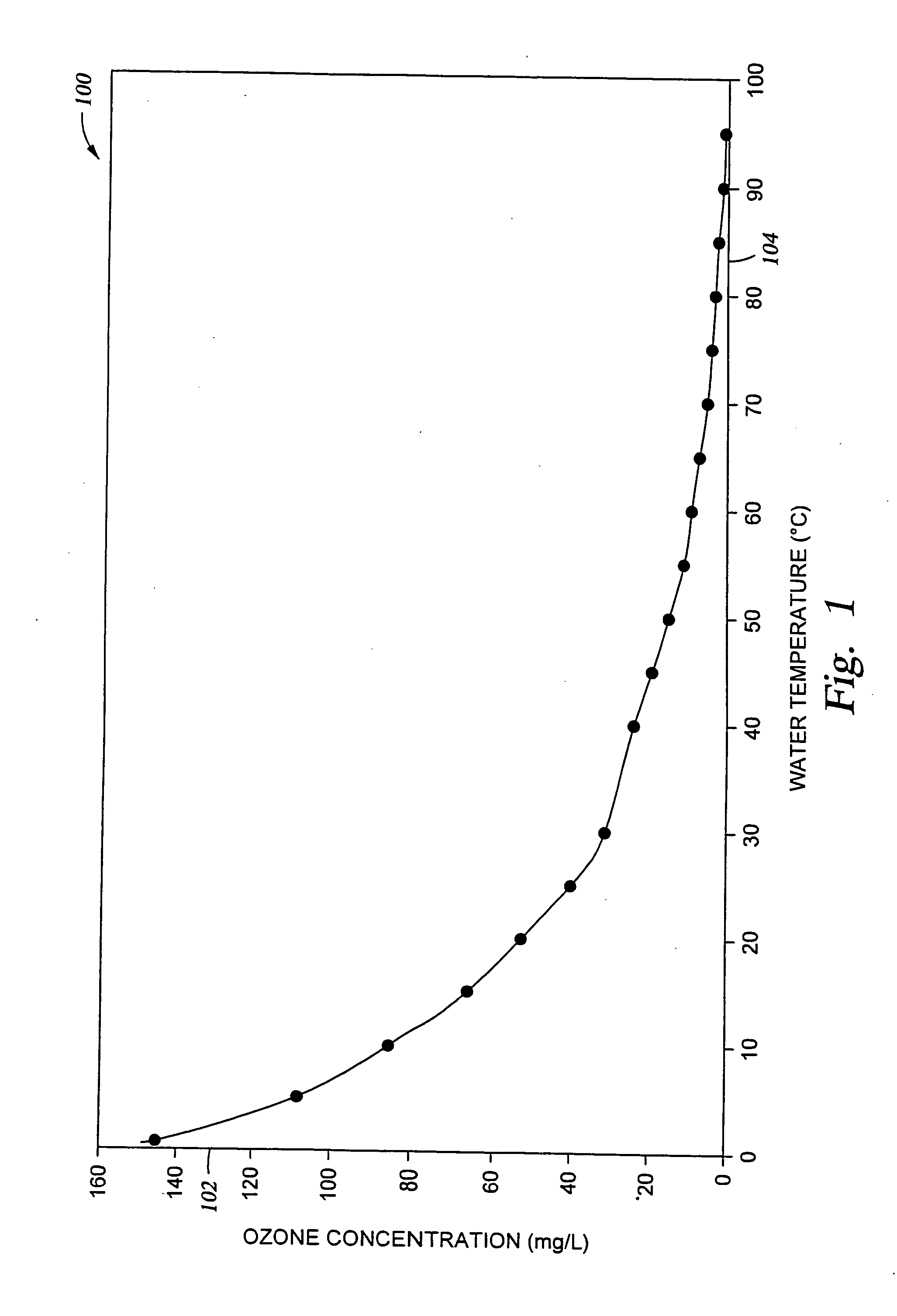
Disclosed herein is a method of removing an organic material from an electronic device substrate surface. The method is particularly useful when the device substrate includes exposed metal. According to the present method, an electronic device substrate surface is exposed to a solution comprising ozone (O3) at a concentration ranging from about 45 ppm to about 600 ppm in a solvent consisting of pure propionic acid or propionic acid in combination with deionized water or a carbonate having from 2 to 4 carbons. The method is particularly useful in the manufacture of large surface areas covered with device structures, such as electronic TFT flat panel displays, solar cell arrays, and structures containing light-emitting diodes. The method is also useful for removing organic materials from the surface of solid state device-containing semiconductor substrates.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
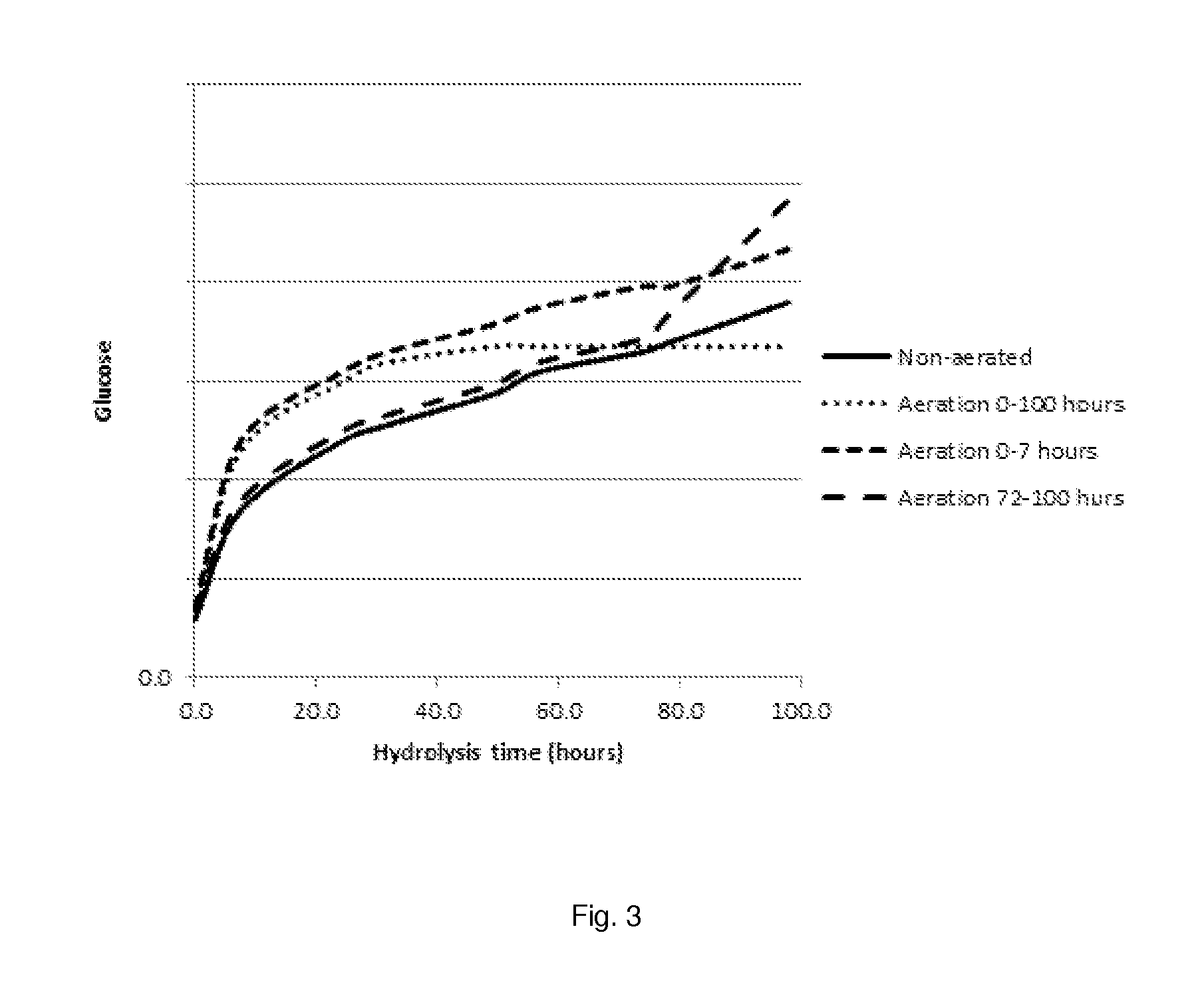
Process for enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic material and fermentation of sugars
ActiveUS20180073048A1Reduce processing timeReduce the amount of enzymes usedBiofuelsFermentationEnzymatic hydrolysisCellulase
The invention relates to a process for the preparation of a fermentation product from ligno-cellulosic material, comprising the following steps:a) optionally pre-treatment of the ligno-cellulosic material;b) optionally washing of the optionally pre-treated ligno-cellulosic material;c) enzymatic hydrolysis of the optionally washed and / or optionally pre-treated ligno-cellulosic material using an enzyme composition comprising at least two cellulase and whereby the enzyme composition at least comprises GH61;d) fermentation of the hydrolysed ligno-cellulosic material to produce a fermentation product; ande) optionally recovery of a fermentation product; wherein before and / or during the enzymatic hydrolysis oxygen is added to the ligno-cellulosic material.
Owner:VERSALIS SPA
Process for enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic material and fermentation of sugars
ActiveUS20150299749A1Reduce processing timeReduce the amount of enzymes usedHydrolasesTransferasesEnzymatic hydrolysisSugar
The invention relates to a process for the preparation of a sugar product from ligno-cellulosic material, comprising the following steps:a) optionally pre-treatment of the ligno-cellulosic material;b) optionally washing of the optionally pre-treated ligno-cellulosic material;c) enzymatic hydrolysis of the optionally washed and / or optionally pre-treated ligno-cellulosic material using an enzyme composition comprising at least two cellulase and whereby the enzyme composition at least comprises GH61; andd) optionally recovery of a sugar product;wherein during part of the time of the enzymatic hydrolysis, oxygen is added to the ligno-cellulosic material and during part of the time of the enzymatic hydrolysis less oxygen is added to the ligno-cellulosic material compared to the other part of the time of the enzymatic hydrolysis, preferably no oxygen is added to the ligno-cellulosic material.
Owner:VERSALIS SPA
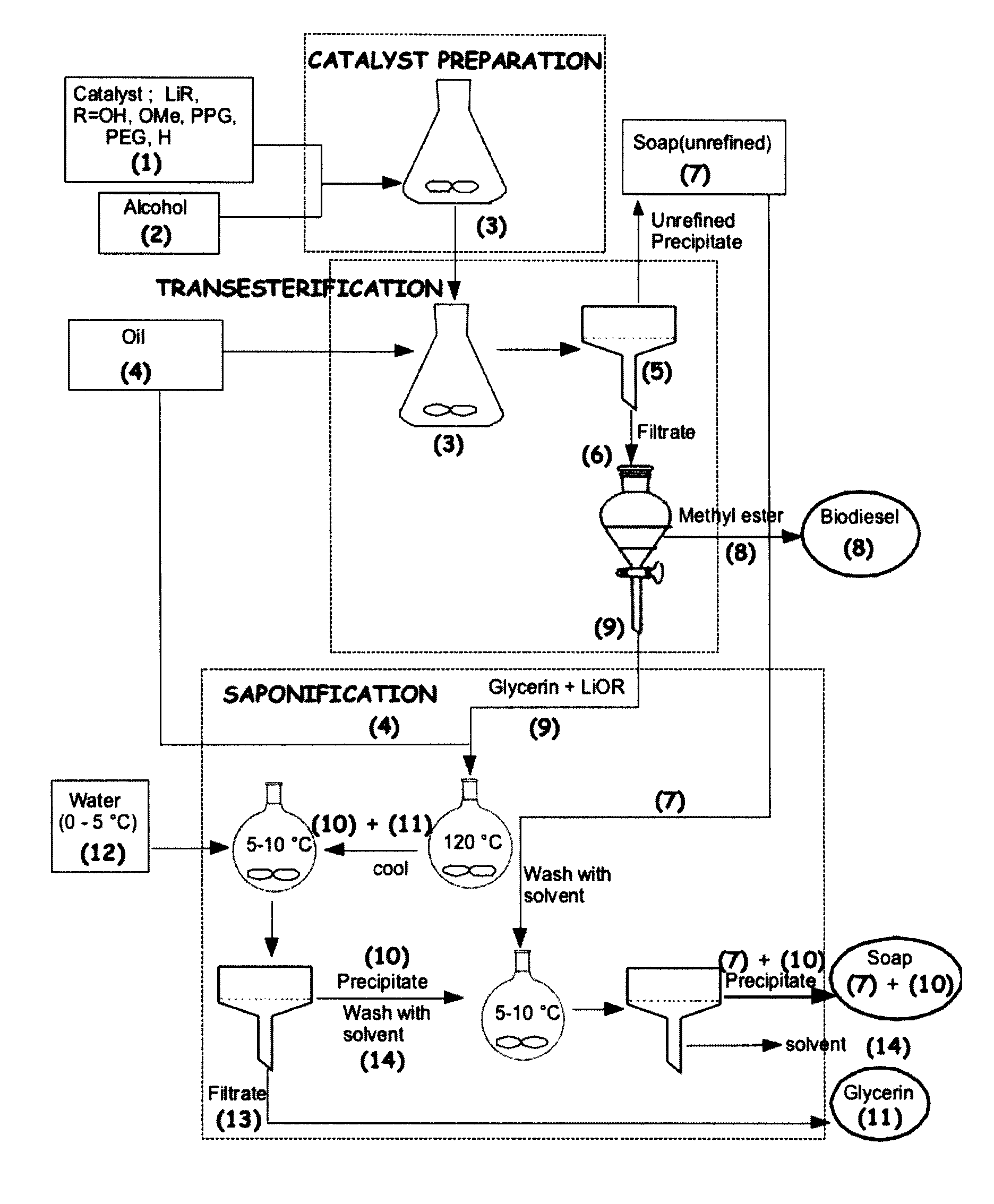
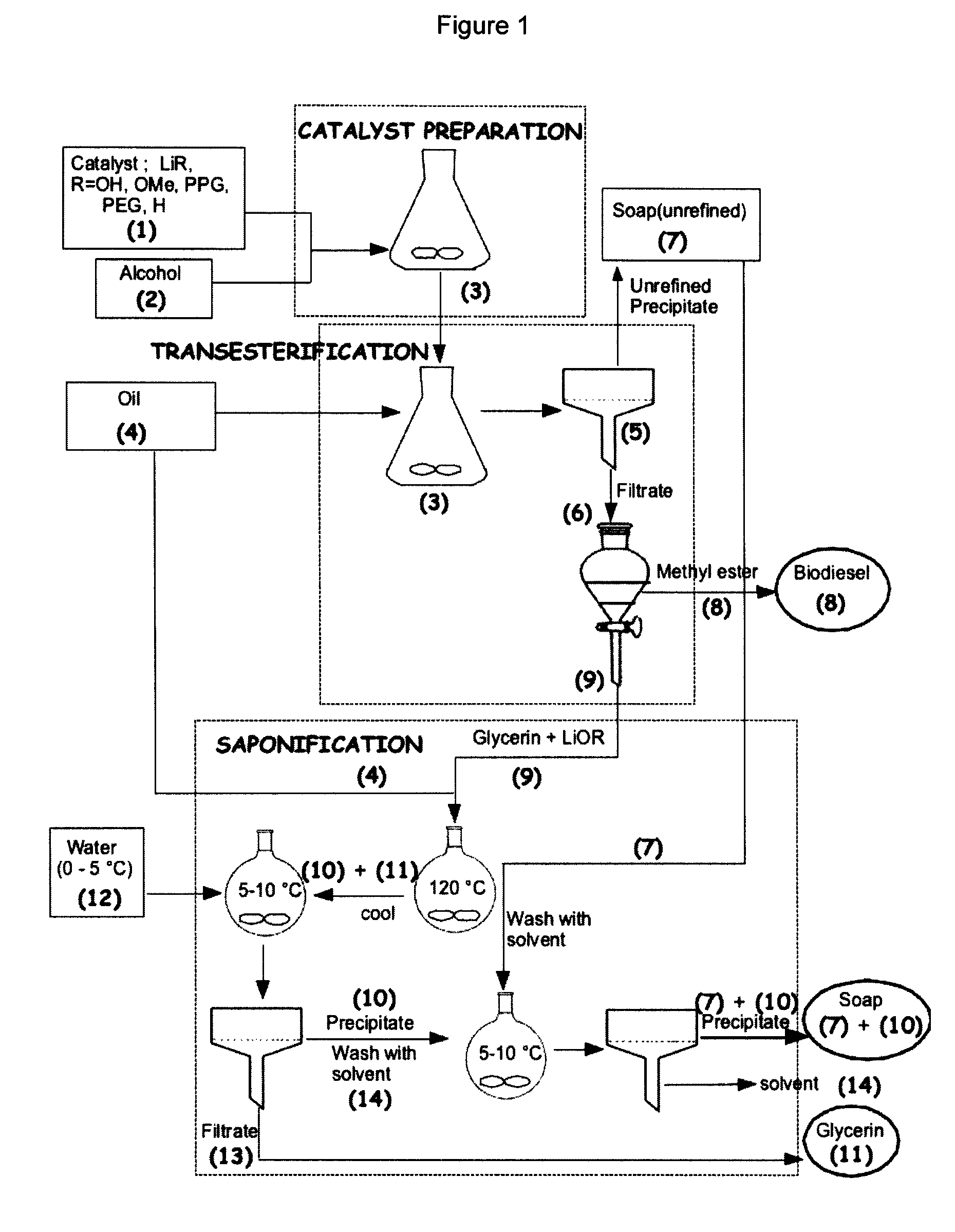
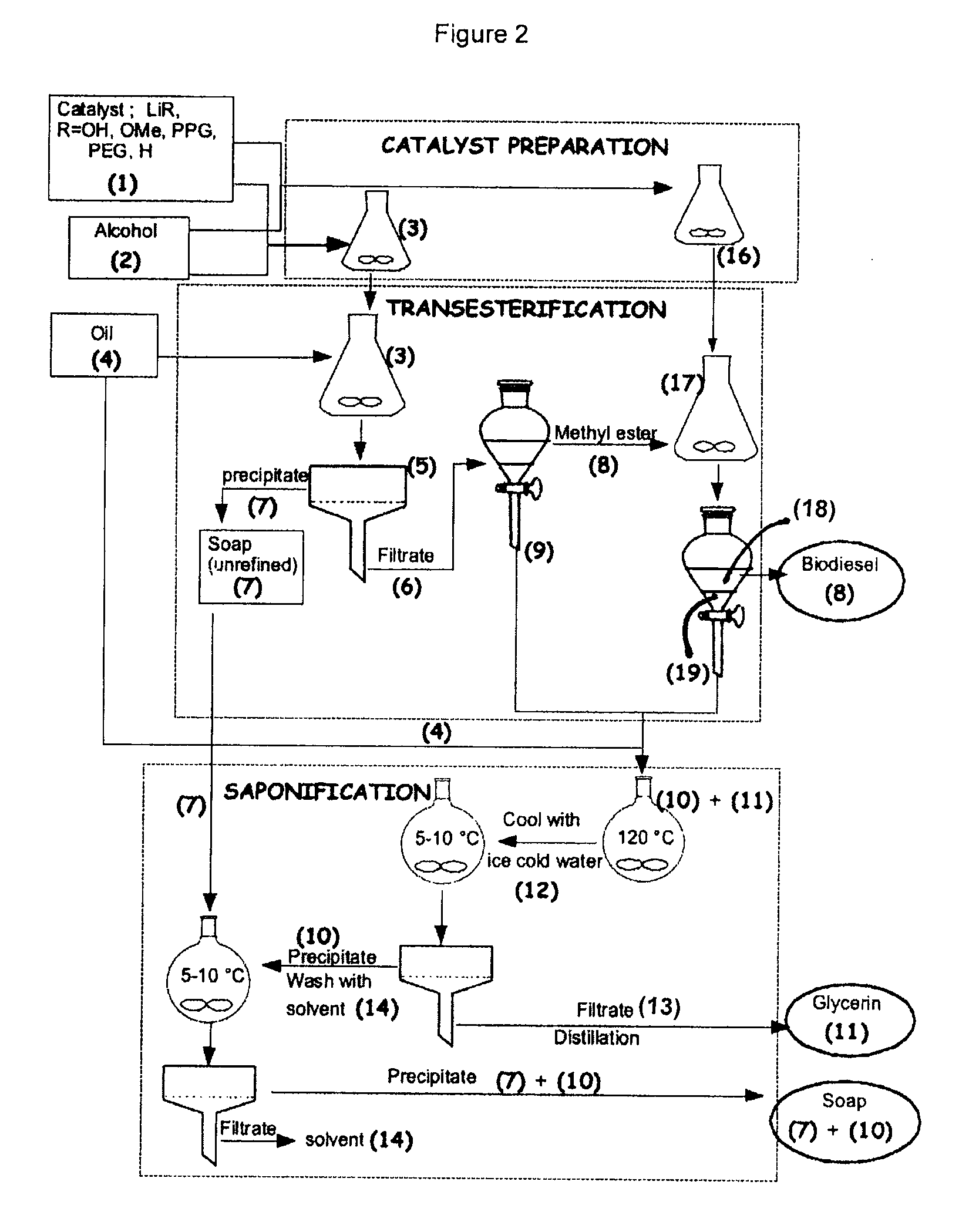
Process for the preparation of biodiesel
ActiveUS7888520B2Easy to disassembleLess solubleFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationLithium soapBiodiesel
The present invention relates to a process of preparing fatty alkyl esters (biodiesel), glycerin and lithium soap comprising: a) transesterifying an oil, fat or grease with a solution of lithium base in a monohydric aliphatic alcohol to produce fatty alkyl esters and a lithium alkaline glycerin; b) separating the fatty alkyl esters and the lithium alkaline glycerin and utilizing the lithium alkaline glycerin to saponify fatty alkyl compounds to produce glycerin and lithium soap; and c) optionally, separating the glycerin and lithium soaps.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN
Ionic Liquids Based on Imidazolium Salts Incorporating a Nitrile Functionality
InactiveUS20090143597A1Increased temperature requirementsDifficult to recycleSilicon organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsHalogenChemical compound
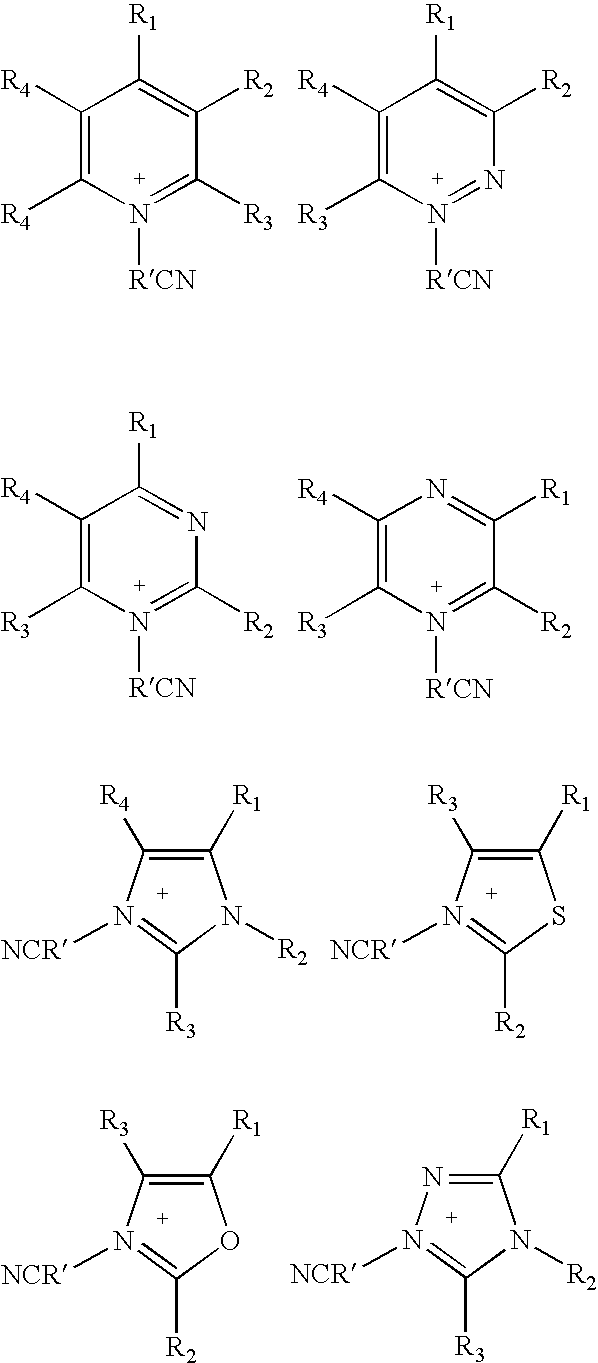
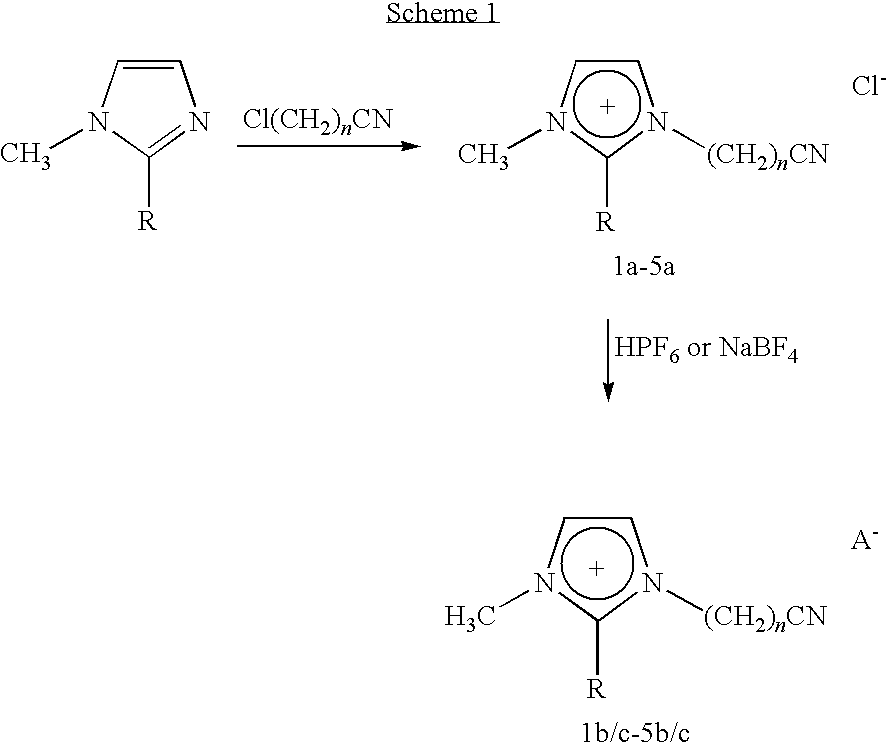
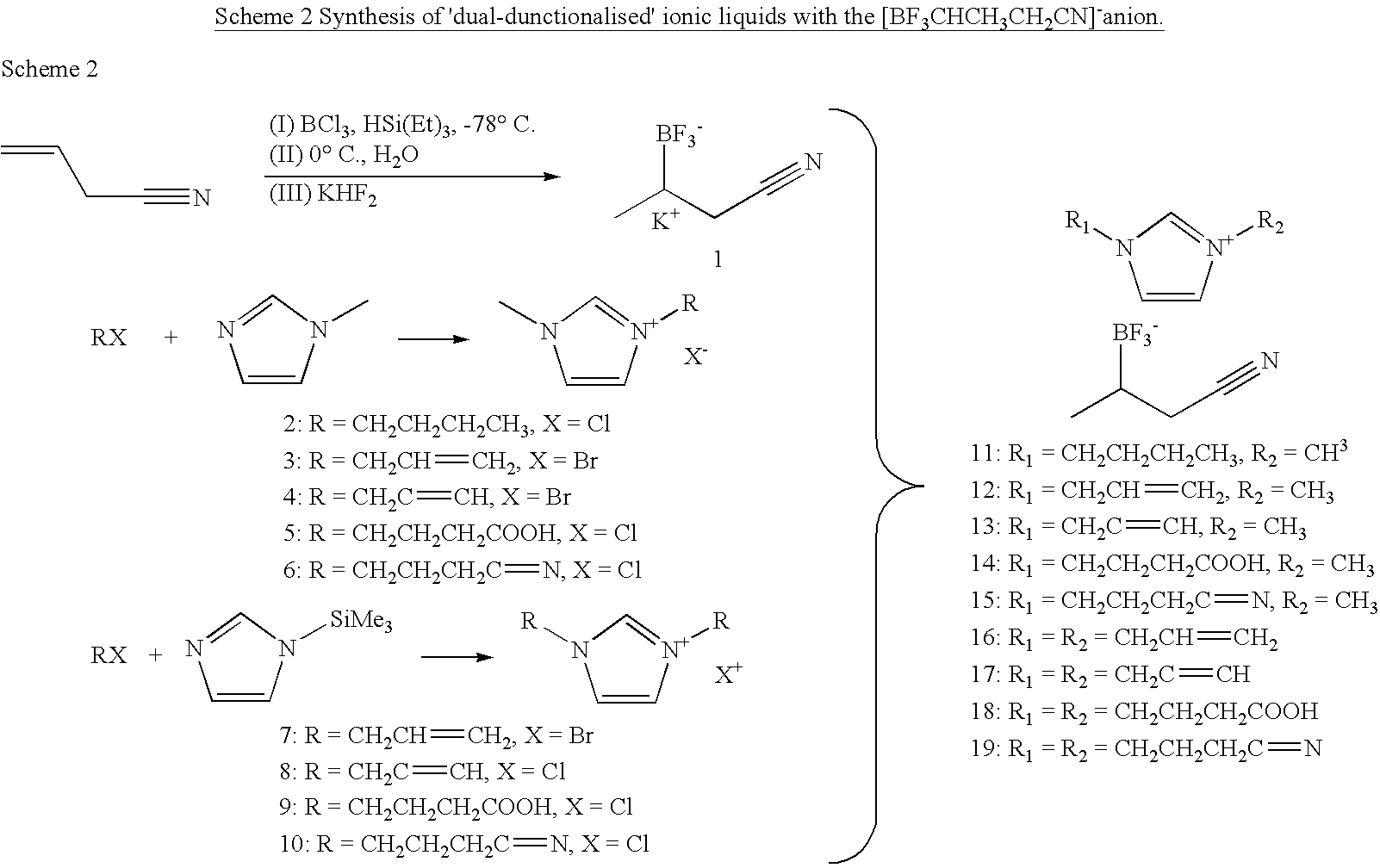
Novel chemical compounds of the general formulaK+A−,in which K+is a 5- or 6-membered heterocyclic ring having 1-3 hetereo atoms, which can be independently N, S, or O;with the proviso that at least one of the hetereo atoms must be a quaternized nitrogen atom having a —R′CN substituent, wherein R′ is alkyl (C1 to C12);the heterocyclic ring having up to 4 or 5 substituents independently chosen from the moieties:(i) H;(ii) halogen or(iii) alkyl (C1 to C12), which is unsubstituted or partially or fully substituted by further groups, preferably F, Cl, N(CnF(2n+1−x)Hx)2, O(CnF(2n+1−x)Hx), SO2(CnF(2n+1−x)Hx)2 or CnF(2n+1−x)Hx where 1<n<6 and 0<x<13; and(iv) a phenyl ring which is unsubstituted or partially or fully substituted by further groups, preferably F, Cl, N(CnF(2n+1−x)Hx)2, O(CnF(2n+1−X)Hx), SO2(CnF(2n+1−x)Hx)2 or CnF(2n+1−x)Hx where 1<n<6 and 0<x≦13; andA− is any anion that provides a salt with a low melting point, below about 100° C.; A can be halide, BF4−, PF6−, NO3−, CH3CO2−, CF3SO3−, (CF3SO2)2N−, (CF3SO2)3C−, CF3CO2− or N(CN)2− or [BF3RCN]These compounds can be used as industrial solvents, especially as ligands for efficient catalyst recycling.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Method of supplementing an edible aqueous liquid composition with two or more mineral salts
InactiveUS20080268102A1Solution clarificationRaise the pHHeavy metal active ingredientsAnimal feeding stuffO-Phosphoric AcidPotassium
One aspect of the invention relates to a method for producing an edible aqueous liquid composition that has been supplemented with a first mineral selected from the group of metals consisting of calcium, magnesium, potassium, zinc, copper, iron, manganese and a second mineral, different from the first mineral, that is selected from the same group of metals.Another aspect of the present inventions relates to a reconstitutable powder containing:0.01-3 mmole of the first mineral per gram of powder;0.02-4 mmole of the second mineral per gram of powder;0.02-8 mmole of acid per gram of powder, said acid being selected from the group consisting of citric acid, tartaric acid, malic acid, phosphoric acid and combinations thereof;0.02-0.99 g of soy protein per gram of powder; andless than 10 wt. % of water.The reconstitutable powder is characterised in that 25 grams of the powder can be reconstituted with 1 kg of water to yield an edible aqueous liquid that will not form a salt sediment of the first and / or second mineral when stored under ambient, quiescent conditions for 3 months or longer.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Process for enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic material and fermentation of sugars
ActiveUS20150307903A1Reduce processing timeReduce the amount of enzymes usedBiofuelsWaste based fuelEnzymatic hydrolysisOxygen
The invention relates to a process for the preparation of a fermentation product from ligno-cellulosic material, comprising the following steps:a) optionally pre-treatment of the ligno-cellulosic material;b) optionally washing of the optionally pre-treated ligno-cellulosic material;c) enzymatic hydrolysis of the optionally washed and / or optionally pre-treated ligno-cellulosic material using an enzyme composition comprising at least two cellulase and whereby the enzyme composition at least comprises GH61;d) whereby less than 7.5 mg enzyme composition / g glucan (on dry matter and enzyme as protein) or less than 3.0 mg enzyme composition / g feedstock (on dry matter and enzyme as protein) is used; ande) fermentation of the hydrolysed ligno-cellulosic material to produce a fermentation product; andf) optionally recovery of a fermentation product;wherein before and / or during the enzymatic hydrolysis oxygen is added to the ligno-cellulosic material.
Owner:VERSALIS SPA
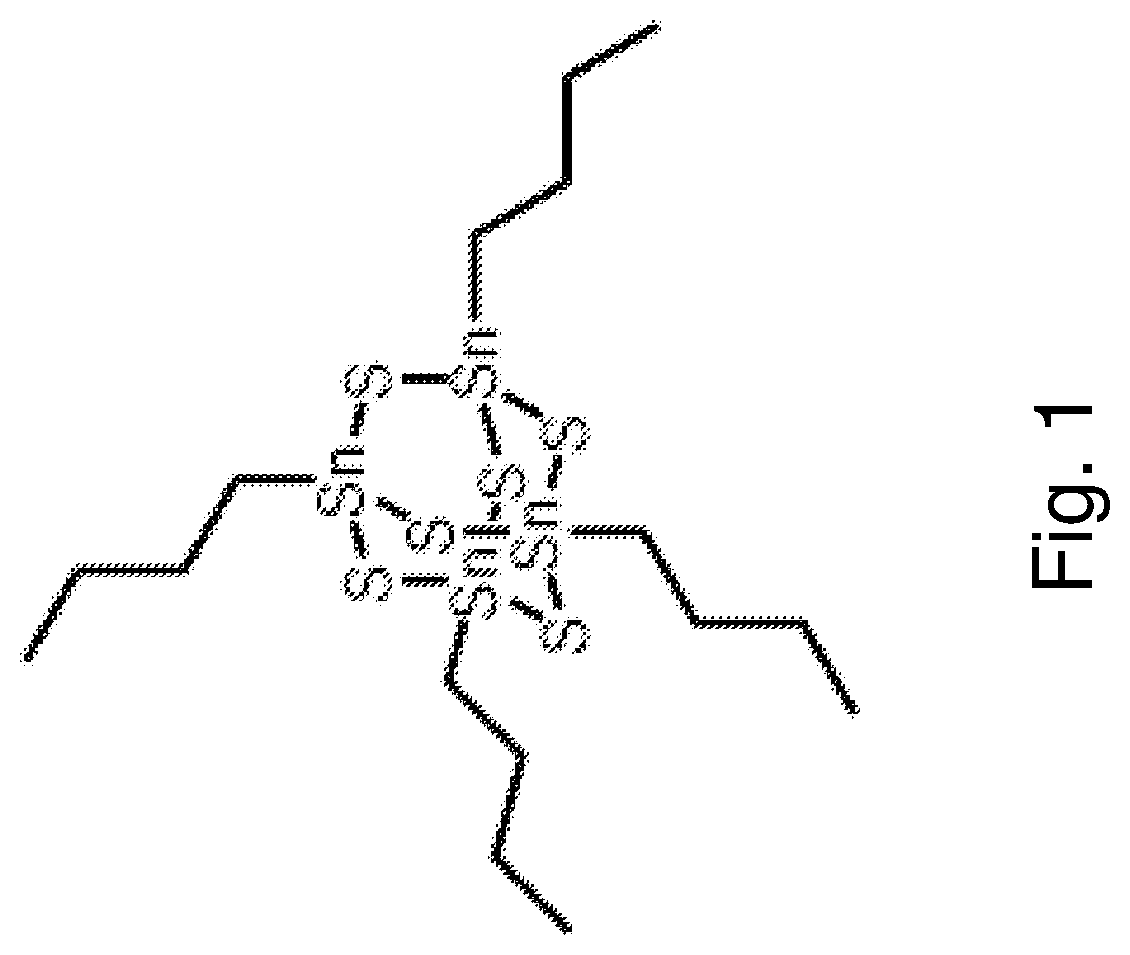
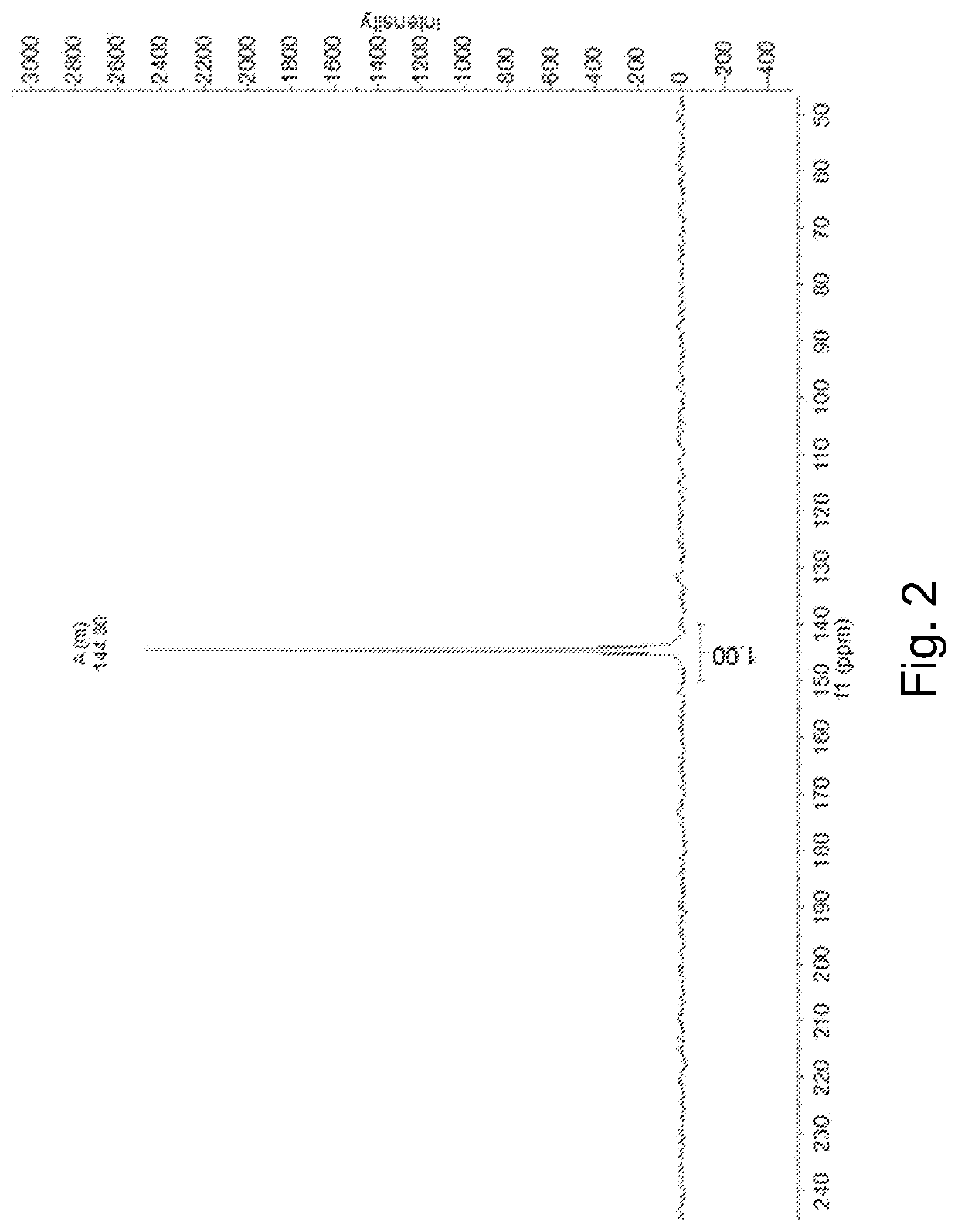
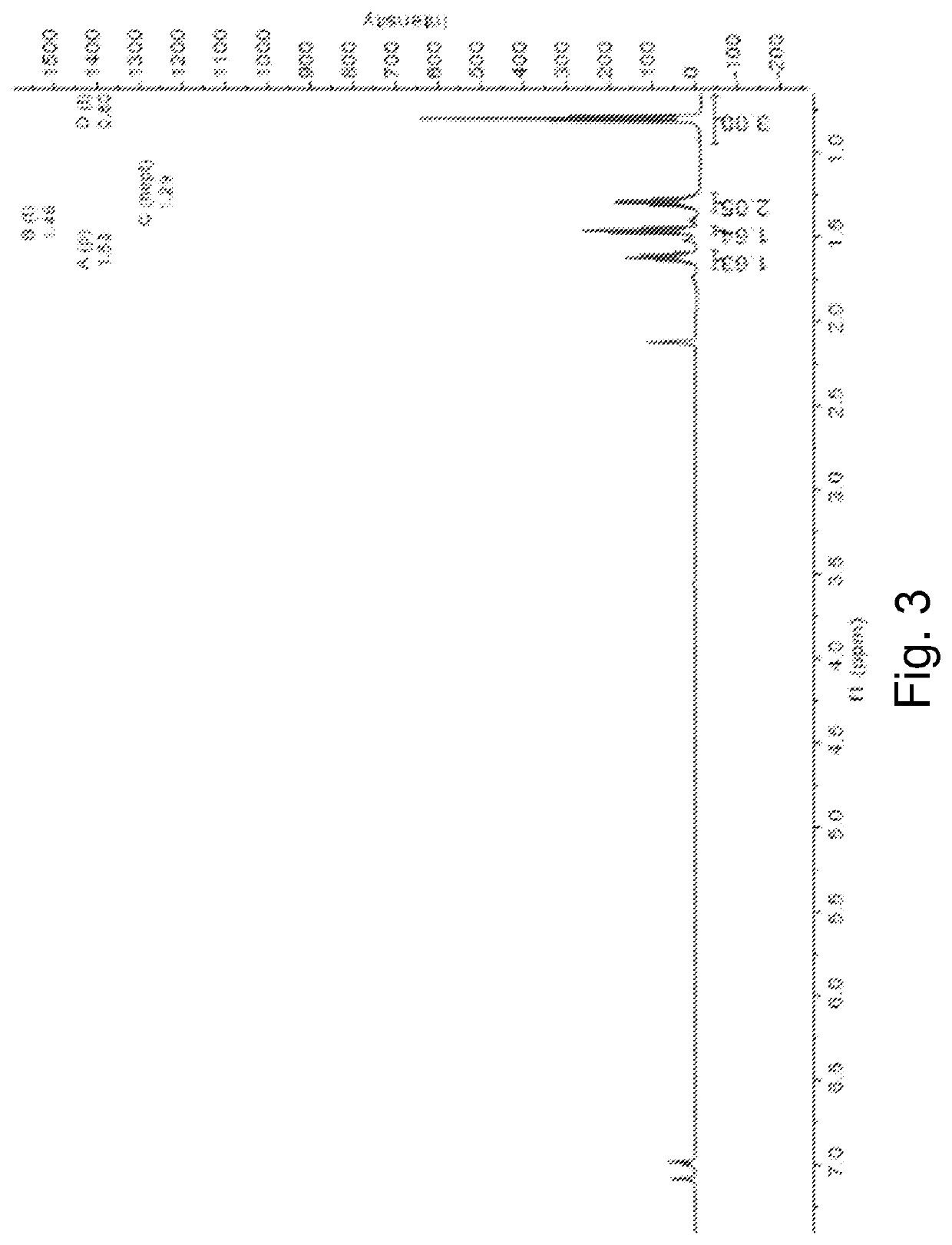
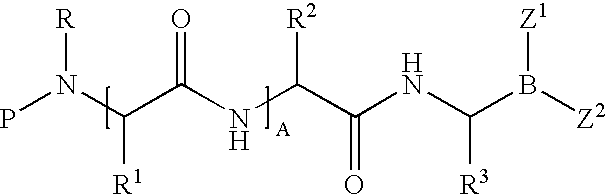
Polymorphs of N-[(6-cyano-2-fluoro)-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-3-(methoxymethyl)-1-({4-[(2-oxopyridin-1-yl)methyl]phenyl}methyl)pyrazole-4-carboxamide as kallikrein inhibitors
ActiveUS10752607B2Easy to processAdvantageousSenses disorderOrganic chemistry methodsMethyl benzeneKinin
The invention provides new polymorphs of N-[(6-cyano-2-fluoro-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-3-(methoxymethyl)-1-({4-[(2-oxopyridin-1-yl)methyl]phenyl}methyl)pyrazole-4-carboxamide, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use in therapy.
Owner:KALVISTA PHARMA
Antimicrobial solutions
ActiveUS9565857B2High activityEnhances the activity of the combination CHXOrganic active ingredientsBiocideGlycerolPharmacology
The present invention provides antimicrobial solutions that in certain cases comprise a biguanide and a glycol ether and, in some cases, optionally also includes combinations of at least one an alcohol, at least one chelator, glycerol, deoxycholate, and / or at least one alkylpolyglucoside. In certain aspects the invention comprises a biguanide and deoxycholate or a combination of chelator, ethanol, and alkylpolyglucoside. Also provided are methods for rapidly killing and / or reducing bacteria, fungi, or virus from surfaces, for example, including surfaces of indwelling medical devices and organic surfaces such as skin and sutures, and inorganic surfaces such as medical equipment, pipelines etc.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Resin compositions, processes for preparing the resin compositions and processes for forming resin films
InactiveUS6927274B2High light transmittanceLess solublePhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical structureSolubility
Polyimide precursors contained in resin compositions of the present invention have a polymer structure unit represented by formula (1) below: wherein chemical structure A2 includes an alicyclic compound but not an aromatic compound such as a benzene ring so that they provide excellent light transmission over a wide wavelength range. The polyimide precursors are imidized at 7.5% or more and 36% or less so that they are less soluble in developing solutions and therefore are not dissolved in the developing solutions at unexposed parts. Thus, the resin compositions of the present invention can be used to form a resin film having a precise pattern by exposure and development.
Owner:DEXERIALS CORP
Insulin with a stable basal release profile
ActiveUS8637458B2Accelerated precipitationLess solublePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin glargineINSULIN PREPARATIONS
A basal insulin formulation composed of insulin, preferably insulin glargine, injectable zinc and injectable iron compounds as precipitating and / or stabilizing agents has been developed for subcutaneous, intradermal or intramuscular administration. The formulation is designed to form a precipitate of insulin following injection, creating a slow releasing “basal insulin” over a period of 12 to 24 hours.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Organometallic metal chalcogenide clusters and application to lithography
PendingUS20210026241A1Less solubleTin organic compoundsPhotomechanical coating apparatusLatent imageMetal chalcogenides
Patterning with UV and EUV light is described with organo tin sulfide (and selenide) clusters. The clusters are solids at room temperature and are soluble in organic solvents that are not too polar. Irradiation can either fragment a carbon metal bond or crosslink unsaturated organic moieties to stabilize the irradiated material. The irradiated material then resists dissolving in organic solvents so that the un-irradiated material can be contacted with an organic solvent to develop the latent image formed with the radiation. Radiation patternable layers can be formed through coating a solution or through vapor deposition. Corresponding precursor solutions, structures and methods are described.
Owner:INPRIA CORP
Inkjet ink reservoir
An ink jet ink reservoir having a part of its members formed of a polyolefin resin is provided which is free from printing defects caused by filter clogging attributable to a compound derived from an antioxidant. An ink jet ink reservoir used in an ink jet recording apparatus, wherein a part of constituent members of the ink jet ink reservoir is formed of a polyolefin resin, wherein the polyolefin resin contains as additive an antioxidant at least with a hindered phenol skeleton and a phosphorus antioxidant more hydrophobic than bis(2,6-di-t-butylphenyl) pentaerythritol diphosphite (denoted by P-6). The members are free from a phosphorus antioxidant having hydrophobicity equal to or lower than the above P-6.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

![Polymorphs of N-[(6-cyano-2-fluoro)-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-3-(methoxymethyl)-1-({4-[(2-oxopyridin-1-yl)methyl]phenyl}methyl)pyrazole-4-carboxamide as kallikrein inhibitors Polymorphs of N-[(6-cyano-2-fluoro)-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-3-(methoxymethyl)-1-({4-[(2-oxopyridin-1-yl)methyl]phenyl}methyl)pyrazole-4-carboxamide as kallikrein inhibitors](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/061222ad-cbe6-44f2-aaa0-ffc6aaed325b/US10752607-D00001.png)
![Polymorphs of N-[(6-cyano-2-fluoro)-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-3-(methoxymethyl)-1-({4-[(2-oxopyridin-1-yl)methyl]phenyl}methyl)pyrazole-4-carboxamide as kallikrein inhibitors Polymorphs of N-[(6-cyano-2-fluoro)-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-3-(methoxymethyl)-1-({4-[(2-oxopyridin-1-yl)methyl]phenyl}methyl)pyrazole-4-carboxamide as kallikrein inhibitors](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/061222ad-cbe6-44f2-aaa0-ffc6aaed325b/US10752607-D00002.png)
![Polymorphs of N-[(6-cyano-2-fluoro)-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-3-(methoxymethyl)-1-({4-[(2-oxopyridin-1-yl)methyl]phenyl}methyl)pyrazole-4-carboxamide as kallikrein inhibitors Polymorphs of N-[(6-cyano-2-fluoro)-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-3-(methoxymethyl)-1-({4-[(2-oxopyridin-1-yl)methyl]phenyl}methyl)pyrazole-4-carboxamide as kallikrein inhibitors](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/061222ad-cbe6-44f2-aaa0-ffc6aaed325b/US10752607-D00003.png)