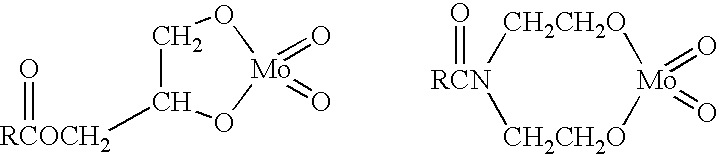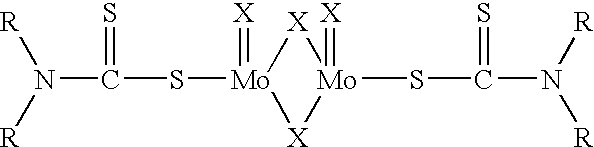Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2125results about How to "Promote oxidation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
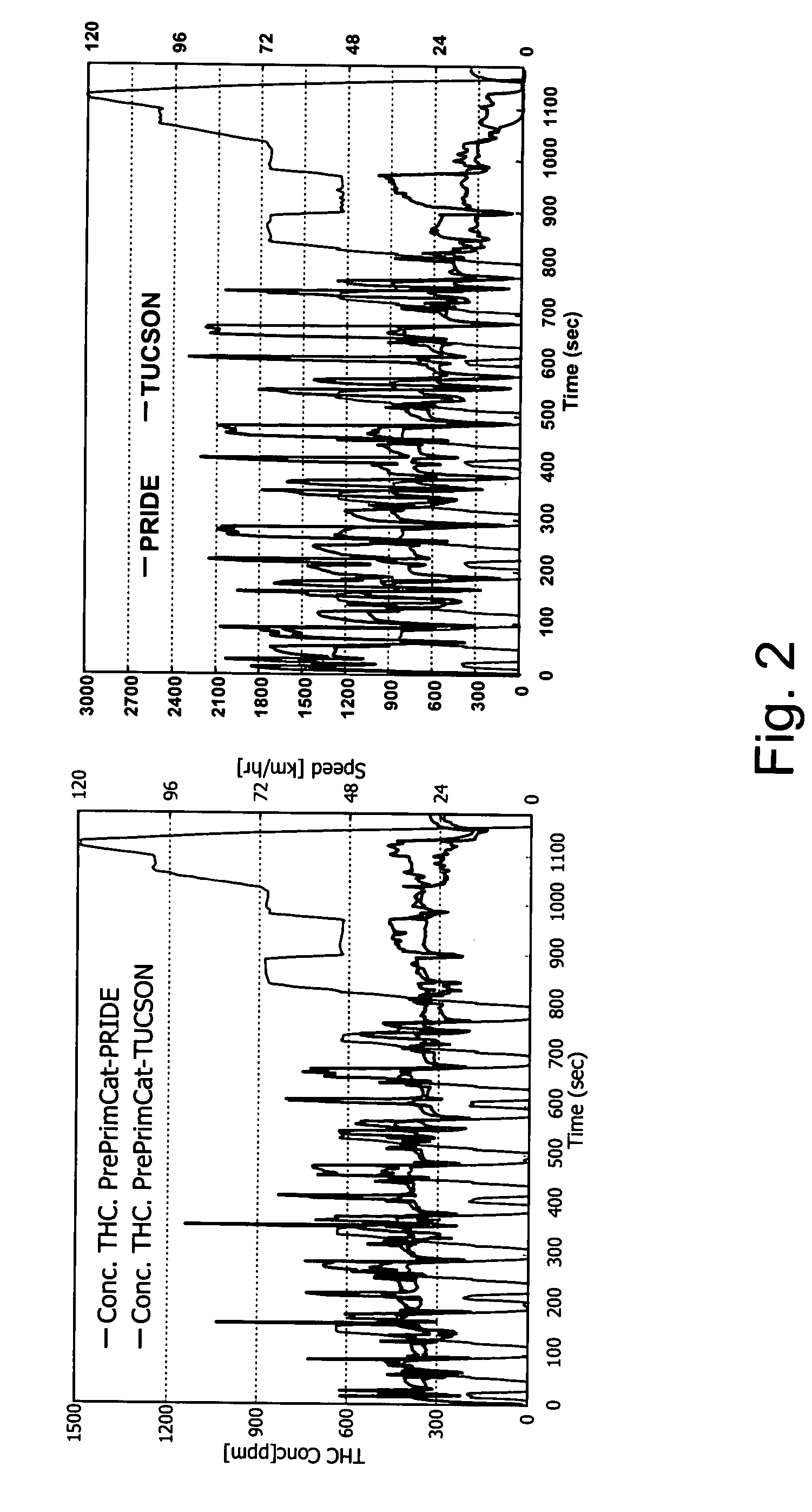
Method for combined removal of mercury and nitrogen oxides from off-gas streams
InactiveUS7118720B1Promote oxidationProcess economyGas treatmentNitrogen compoundsNitrogen dioxideNitrogen oxide
A method for removing elemental Hg and nitric oxide simultaneously from a gas stream is provided whereby the gas stream is reacted with gaseous chlorinated compound to convert the elemental mercury to soluble mercury compounds and the nitric oxide to nitrogen dioxide. The method works to remove either mercury or nitrogen oxide in the absence or presence of each other.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Composite prosthetic bearing having a crosslinked articulating surface and method for making the same
InactiveUS7819925B2Promote oxidationEasy to wearBone implantSynthetic resin layered productsProsthesisCrosslinked polymers
An implantable prosthetic bearing is constructed of a composite material having a first layer and second layer. The first layer has an articulating surface defined therein, whereas the second layer has a engaging surface defined therein for engaging either another prosthetic component or the bone itself The first layer of the implantable prosthetic bearing is constructed of crosslinked polymer such as Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene, whereas the second layer of the implantable prosthetic bearing is constructed of polymer such as Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene that is either non-crosslinked or crosslinked to a lesser degree than the first layer. In such a manner, the first layer possesses mechanical properties which are advantageous in regard to the articulating surface (e.g., enhanced wear and oxidation resistance), whereas the second layer possesses mechanical properties which are advantageous in regard to the engaging surface (e.g., high ductility, toughness, and creep resistance). A method of making a prosthetic bearing is also disclosed.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
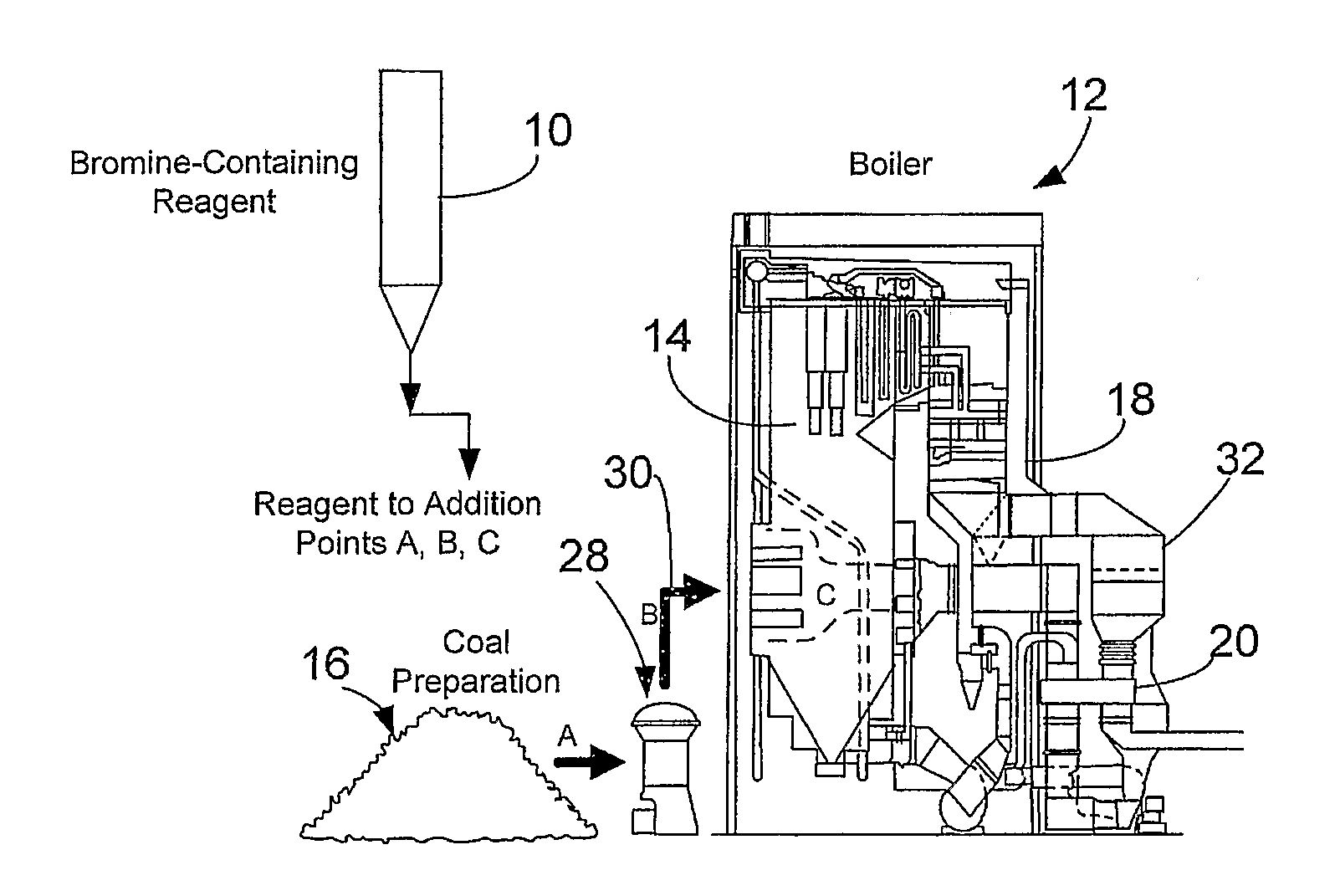
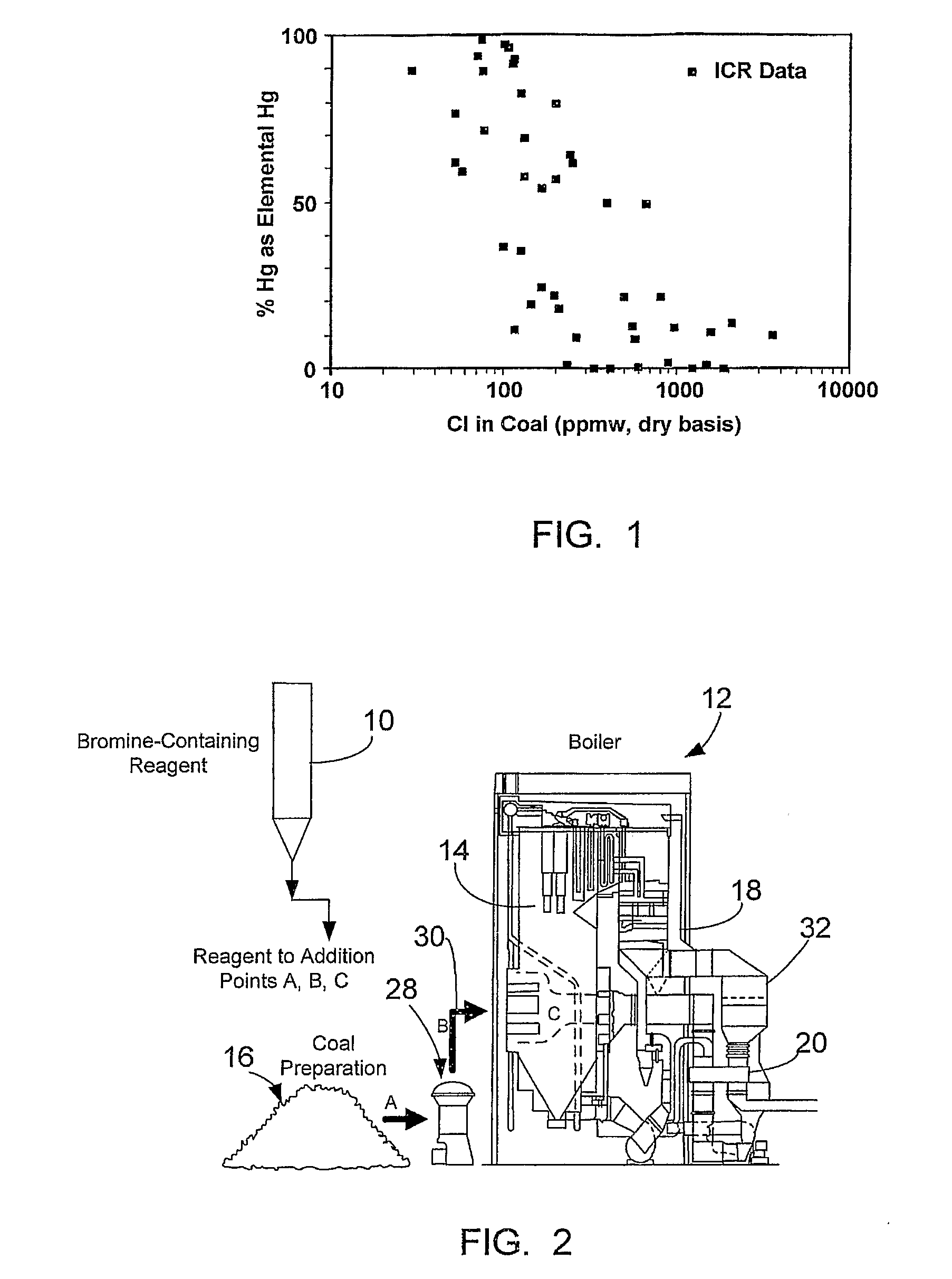
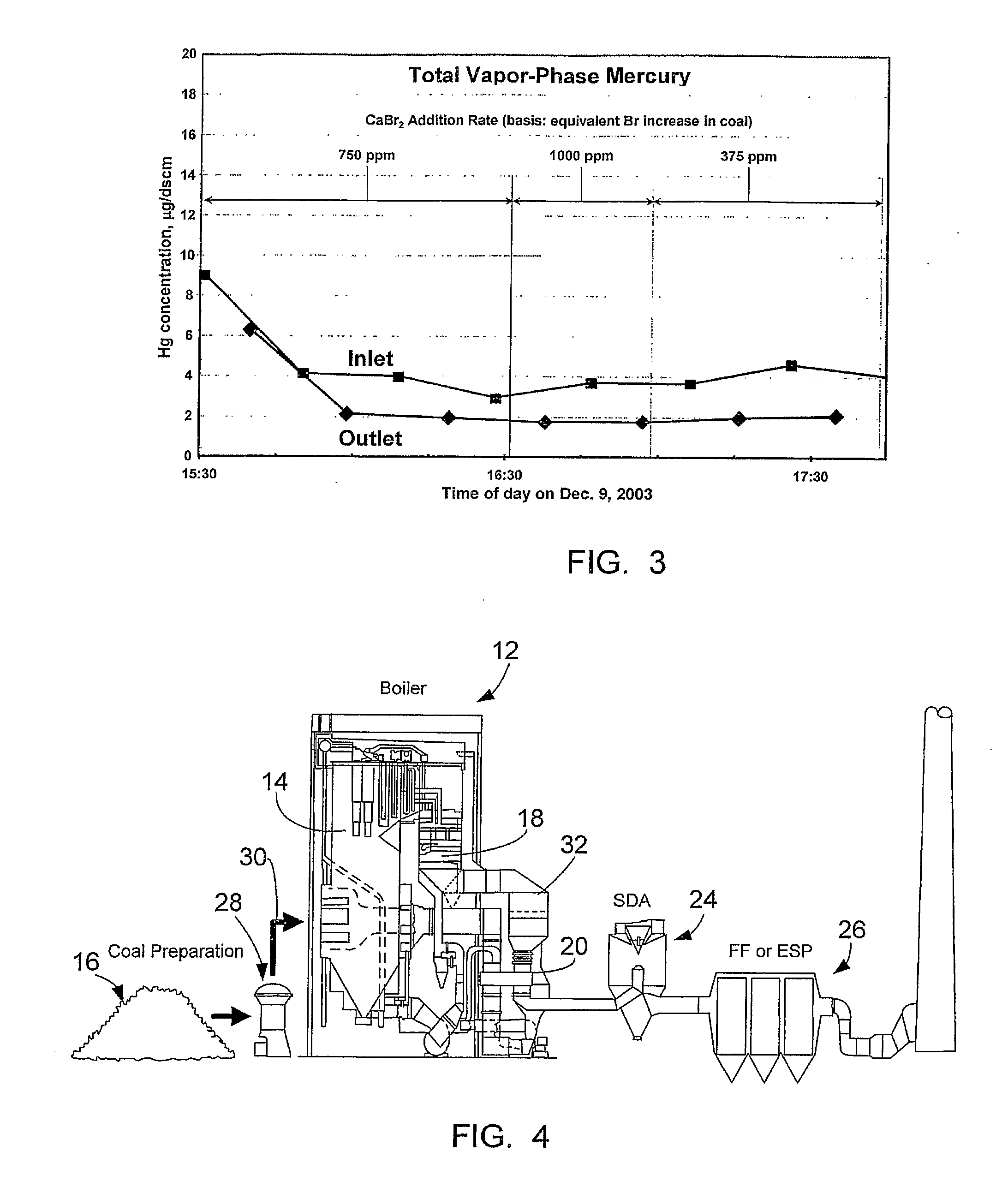
Bromine Addition for the Improved Removal of Mercury from Flue Gas
InactiveUS20080107579A1Significant technicalSignificant commercial advantageGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentCombustionFlue gas
Bromine-containing compounds, added to the coal, or to the boiler combustion furnace, are used to enhance the oxidation of mercury, thereby enhancing the overall removal of mercury in downstream pollution control devices. The method is applicable to utility power plants equipped with wet FGD systems, as well as those plants equipped with spray dryer absorber FGD systems.
Owner:THE BABCOCK & WILCOX CO
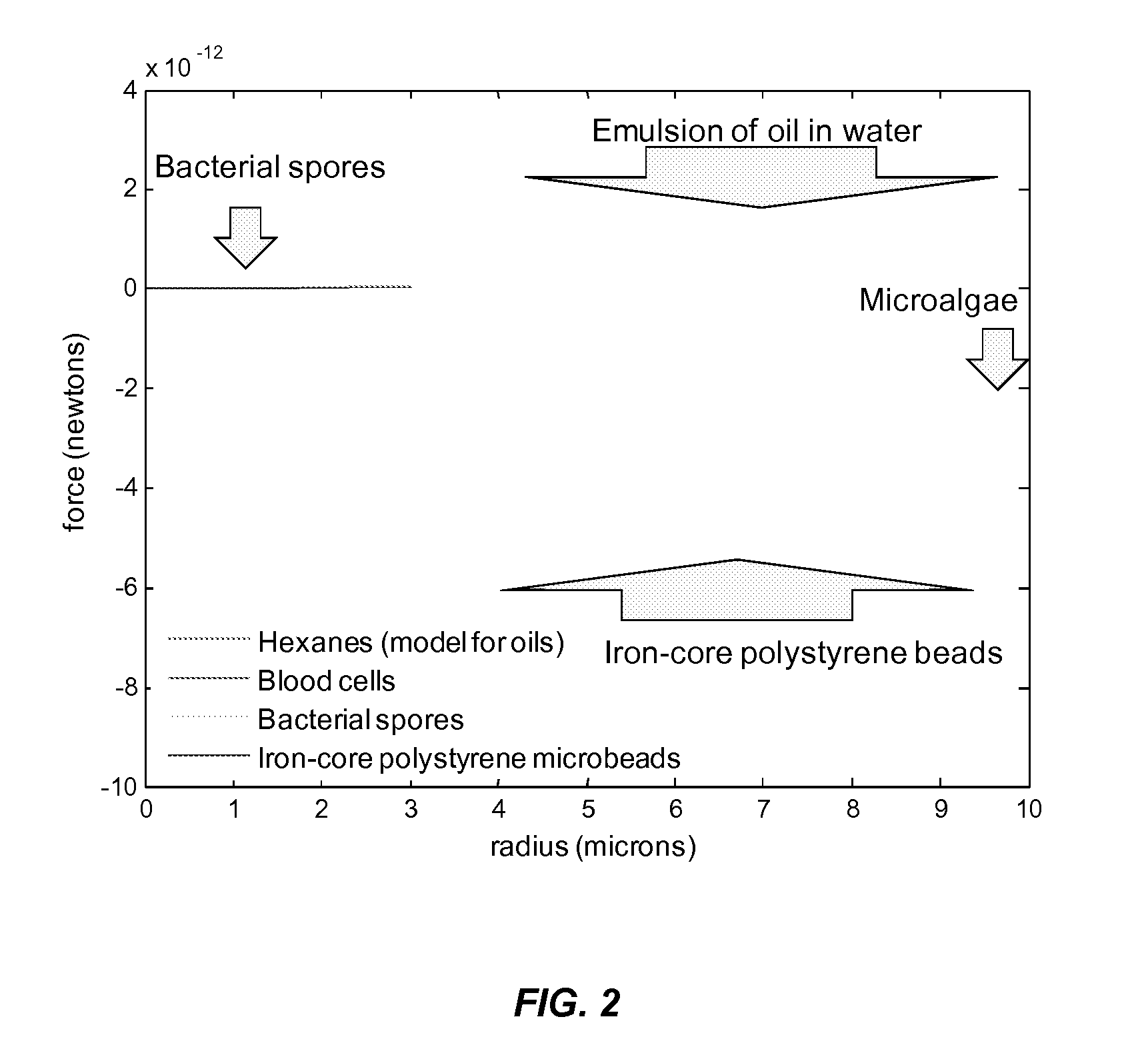
Ultrasound and acoustophoresis for water purification
InactiveUS20110123392A1Low separationEfficiently separateSeawater treatmentBlast furnace detailsStanding waveChemistry
Provided herein are systems and methods for separation of particulate from water using ultrasonically generated acoustic standing waves.
Owner:FLODESIGN SONICS
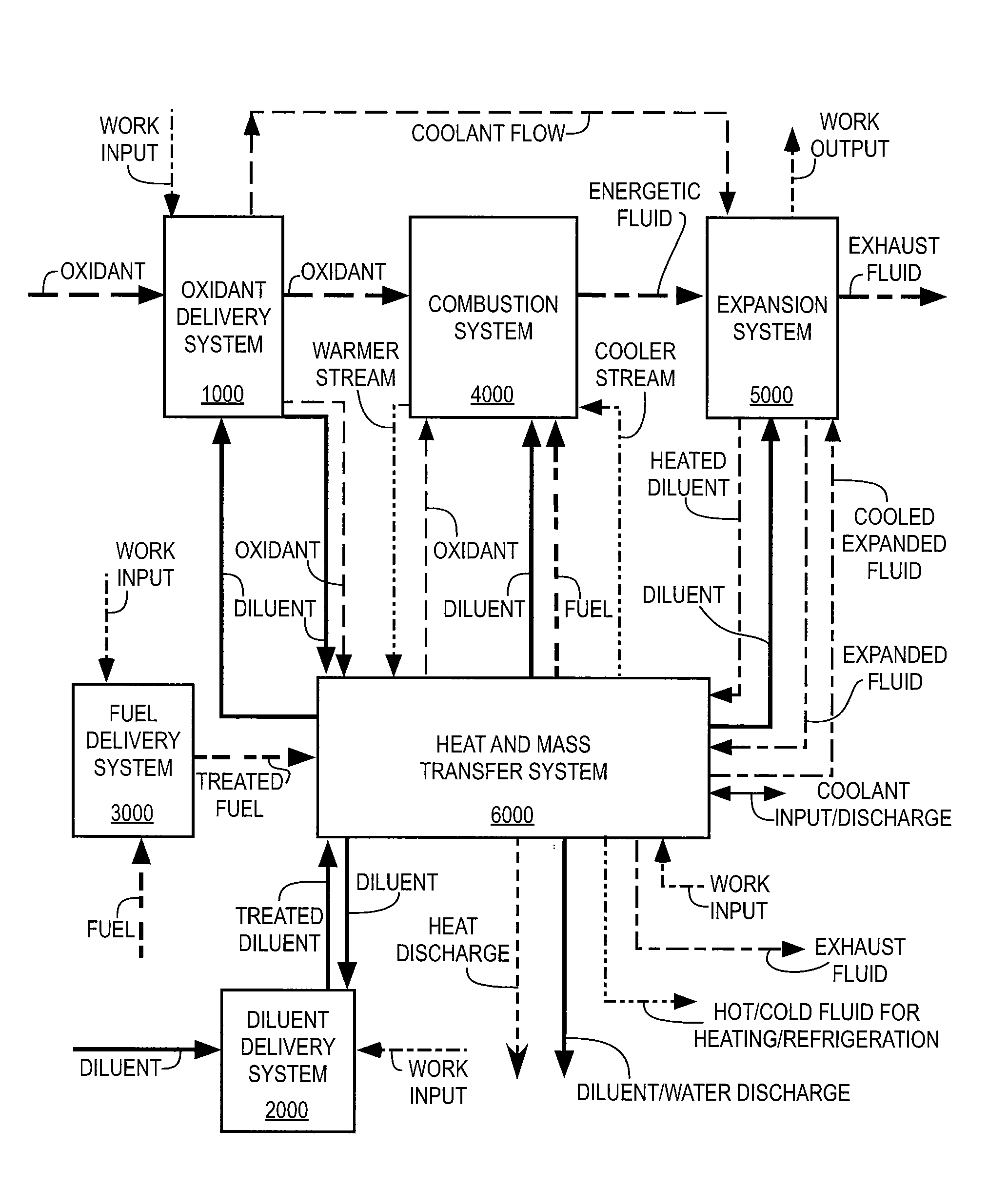
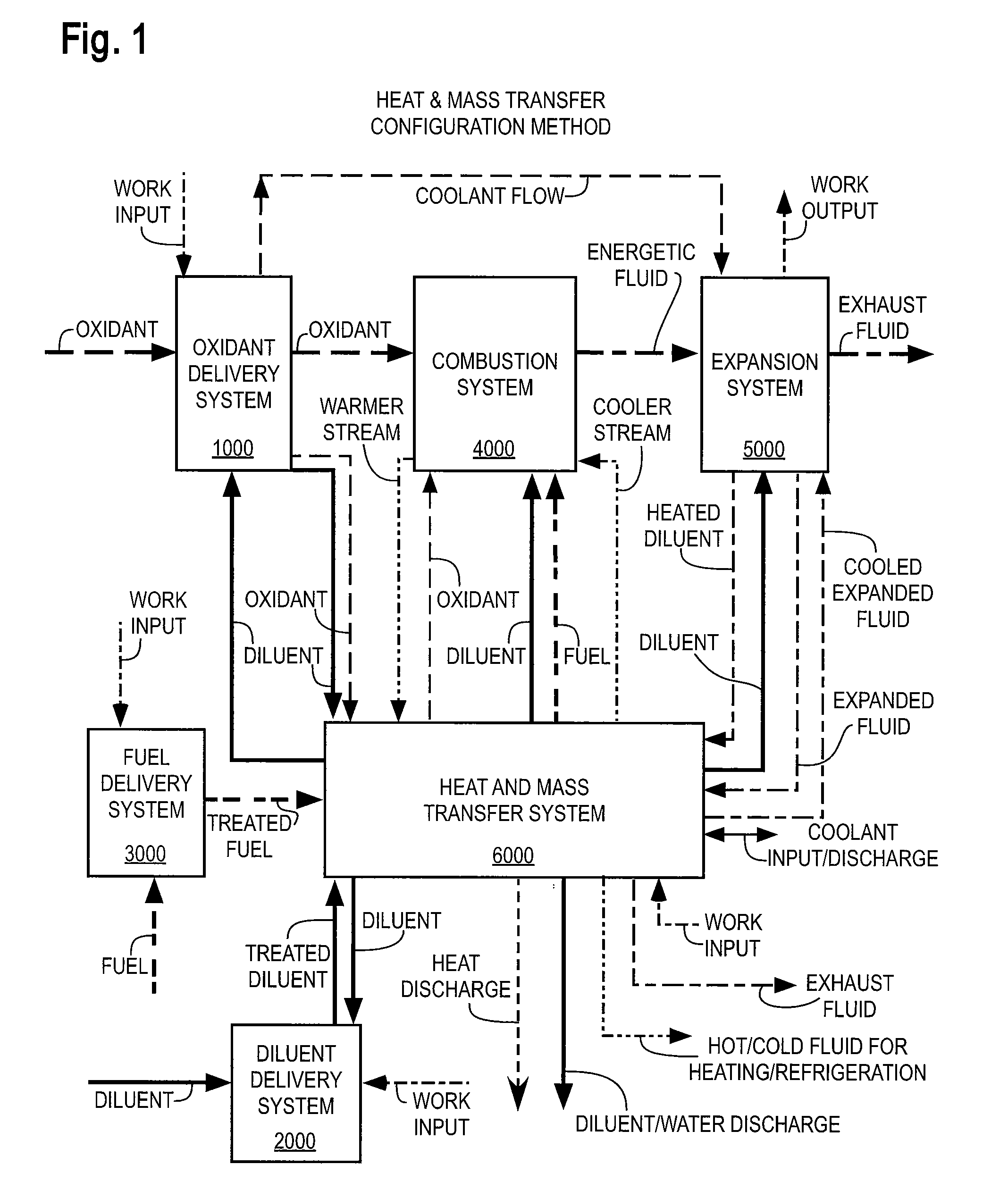
Thermodynamic cycles with thermal diluent
ActiveUS20070234702A1Keeping pollutants lowLow costAir-treating devicesEnergy industryCogenerationThermodynamic cycle
Thermodynamic cycles with diluent that produce mechanical power, electrical power, and / or fluid streams for heating and / or cooling are described. Systems contain a combustion system producing an energetic fluid by combusting fuel with oxidant. Thermal diluent is preferably used in the cycle to improve performance, including one or more of power, efficiency, economics, emissions, dynamic and off-peak load performance, temperature regulation, and / or cooling heated components. Cycles include a heat recovery system and preferably recover and recycle thermal diluent from expanded energetic fluid to improve cycle thermodynamic efficiency and reduce energy conversion costs. Cycles preferably include controls for temperatures, pressures, and flow rates within a combined heat and power (CHP) system, and controls for power, thermal output, efficiency, and / or emissions.
Owner:VAST HLDG LLC
Meter for use in an improved method of reducing interferences in an electrochemical sensor using two different applied potentials
InactiveUS7655119B2Reduce impactPromote oxidationImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalytePower flow
The present invention is directed to an improved meter that utilizes a method of reducing the effects of interfering compounds in the measurement of analytes and more particularly to a method of reducing the effects of interfering compounds in a system wherein the test strip utilizes two or more working electrodes. In one embodiment of the present invention, a meter is described which applies a first potential to a first working electrode and a second potential, having the same polarity but a greater magnitude than the first potential, is applied to a second working electrode. The meter then measures the generated current and utilizes a predetermined algorithm to correct the measured current to compensate for the presence of interfering compounds in the sample.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Cold start catalyst and its use in exhaust systems
InactiveUS20120308439A1Emission reductionSpeed up the conversion processCombination devicesMolecular sieve catalystsMetal catalystPlatinum group
A cold start catalyst is disclosed. The cold start catalyst comprises a zeolite catalyst and a supported platinum group metal catalyst. The zeolite catalyst comprises a base metal, a noble metal, and a zeolite. The supported platinum group metal catalyst comprises one or more platinum group metals and one or more inorganic oxide carriers. The invention also includes an exhaust system comprising the cold start catalyst. The cold start catalyst and the process result in improved NOx storage and NOx conversion, improved hydrocarbon storage and conversion, and improved CO oxidation through the cold start period.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
Vortexer apparatus
ActiveUS20060180963A1Facilitates submergence and meltingMaintain temperatureStirring devicesCharge manipulationImpellerPositive pressure
The present invention features a vortexer apparatus including a vessel comprising an exterior surface, an interior surface containing fluid and a mouth for receiving material at an upper end portion of the interior surface. In one application the material is metal scrap that is melted in molten metal as the fluid. All components that contact the molten metal are formed of refractory material. An outlet passageway extends downwardly from the interior surface. A vessel inlet opening is located between the exterior and interior surfaces above the outlet passageway. A center line passes through a center of the interior surface and the vessel inlet opening is disposed at a location offset from the center line. A pump is adapted to pump fluid into the vessel effective to form a vortex of fluid in the vessel. The base and impeller are configured and arranged effective to provide molten metal leaving the base outlet with a positive pressure. An outlet conduit extends from the base outlet to near the vessel inlet opening and can be maintained at a temperature above which molten metal solidifies, along its entire length. Instead of the vortexer vessel, the inventive vortexer apparatus may integrate a chamber of a furnace (e.g., a charge well). The chamber may be rectangularor include arcuate portions. Corner inserts may be used to provide the chamber with an oval or generally circular shape that may facilitate the vortex. One feature of the invention is a vortex vessel that includes an offset inlet opening and lower circulation opening. Also featured is a baffle impeller that may be vaned or barrel type. In addition, the invention features a pump having upper and lower impeller chambers separated by a web in the base, and impeller outlets that are isolated from fluid communication with each other.
Owner:THUT BRUNO H
Vortexer apparatus
ActiveUS7497988B2Facilitates submergence and meltingMaintain temperatureStirring devicesCharge manipulationImpellerPositive pressure
Owner:THUT BRUNO H
Composite prosthetic bearing having a crosslinked articulating surface and method for making the same
InactiveUS20030144741A1Easy to wearImprove oxidation resistanceBone implantSynthetic resin layered productsProsthesisCrosslinked polymers
An implantable prosthetic bearing is constructed of a composite material having a first layer and second layer. The first layer has an articulating surface defined therein, whereas the second layer has a engaging surface defined therein for engaging either another prosthetic component or the bone itself. The first layer of the implantable prosthetic bearing is constructed of crosslinked polymer such as UHMWPE, whereas the second layer of the implantable prosthetic bearing is constructed of polymer such as UHMWPE that is either non-crosslinked or crosslinked to a lesser degree than the first layer. In such a manner, the first layer possesses mechanical properties which are advantageous in regard to the articulating surface (e.g., enhanced wear and oxidation resistance), whereas the second layer possesses mechanical properties which are advantageous in regard to the engaging surface (e.g., high ductility, toughness, and creep resistance). A method of making a prosthetic bearing is also disclosed.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
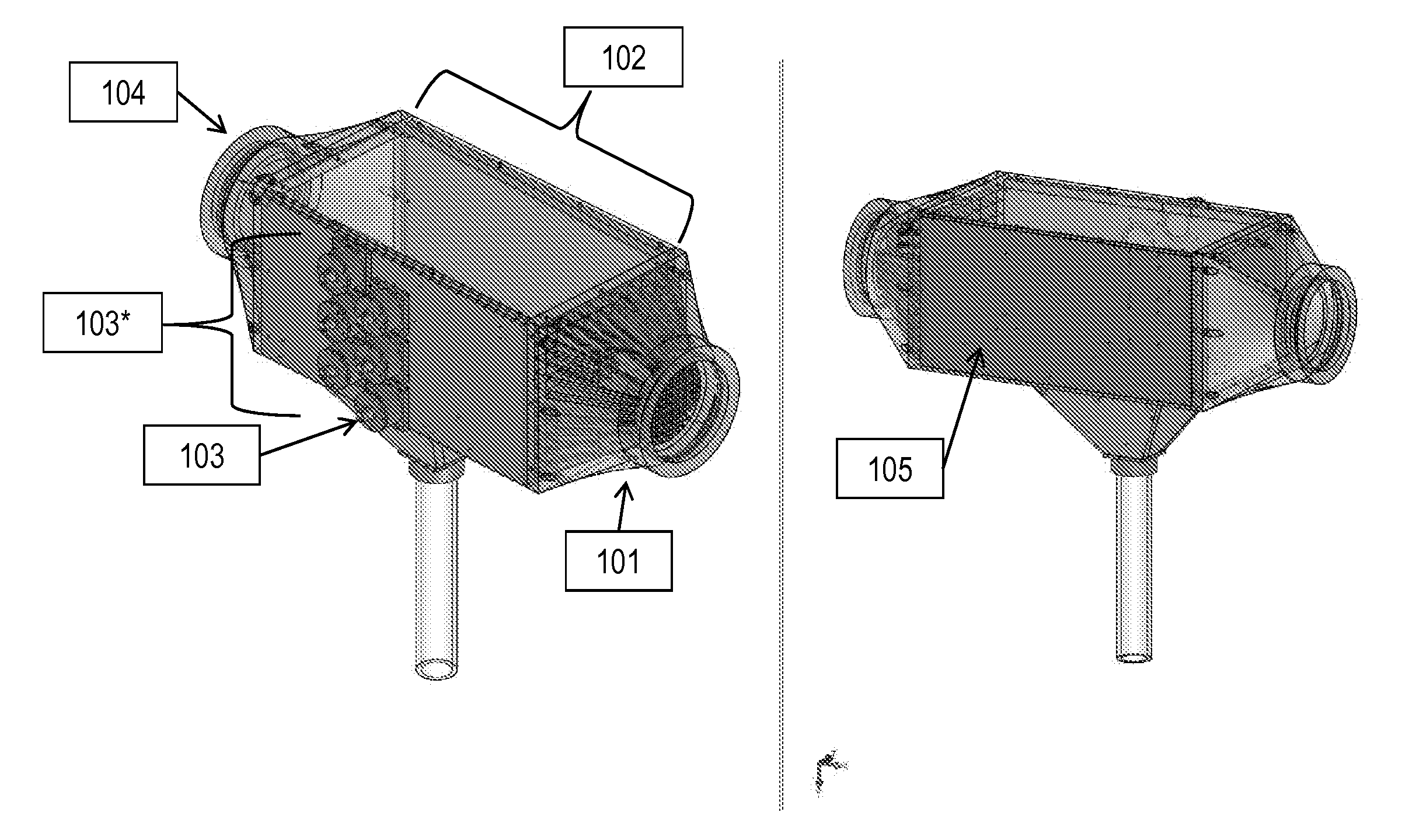
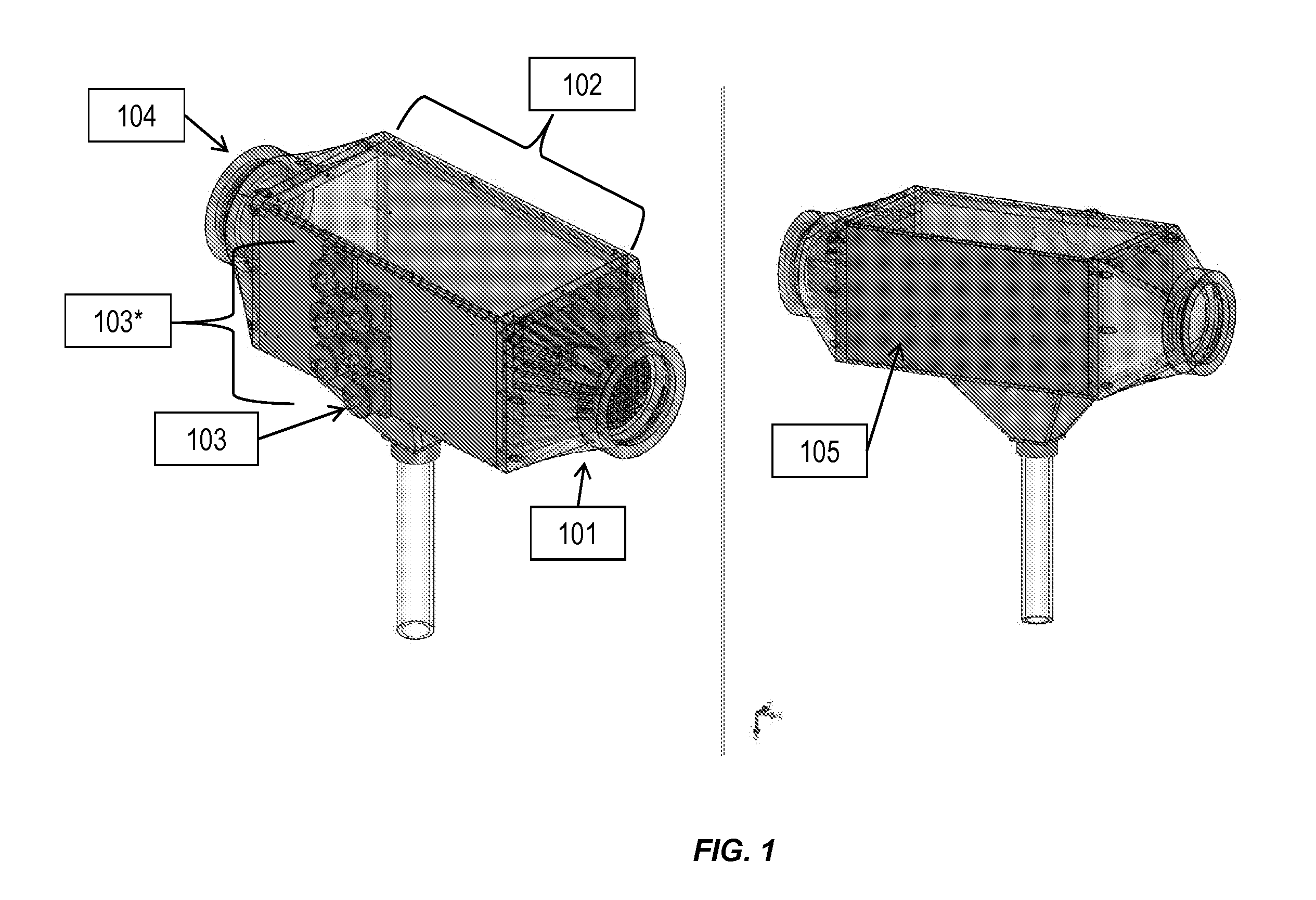
Apparatus for observing combustion conditions in a gas turbine engine
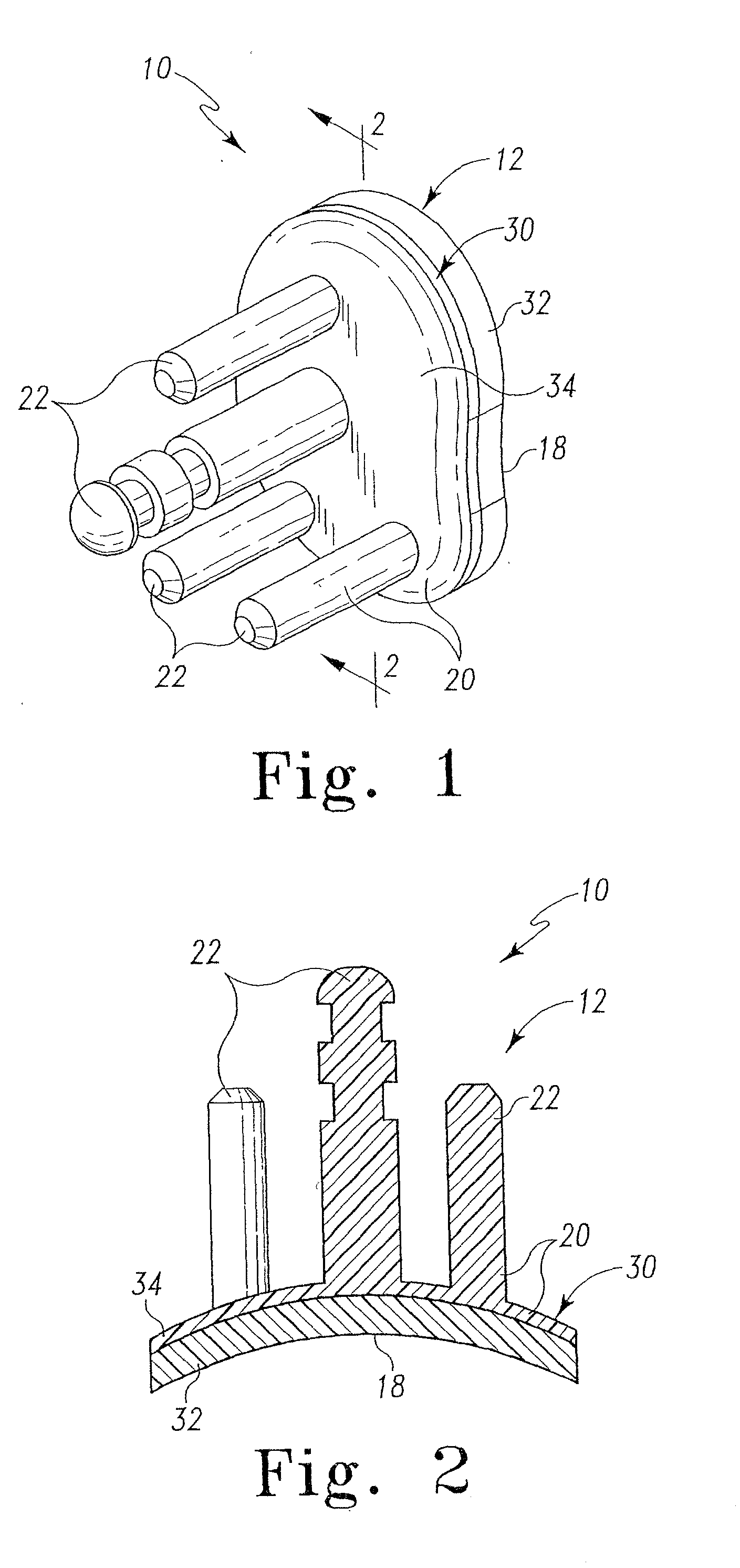
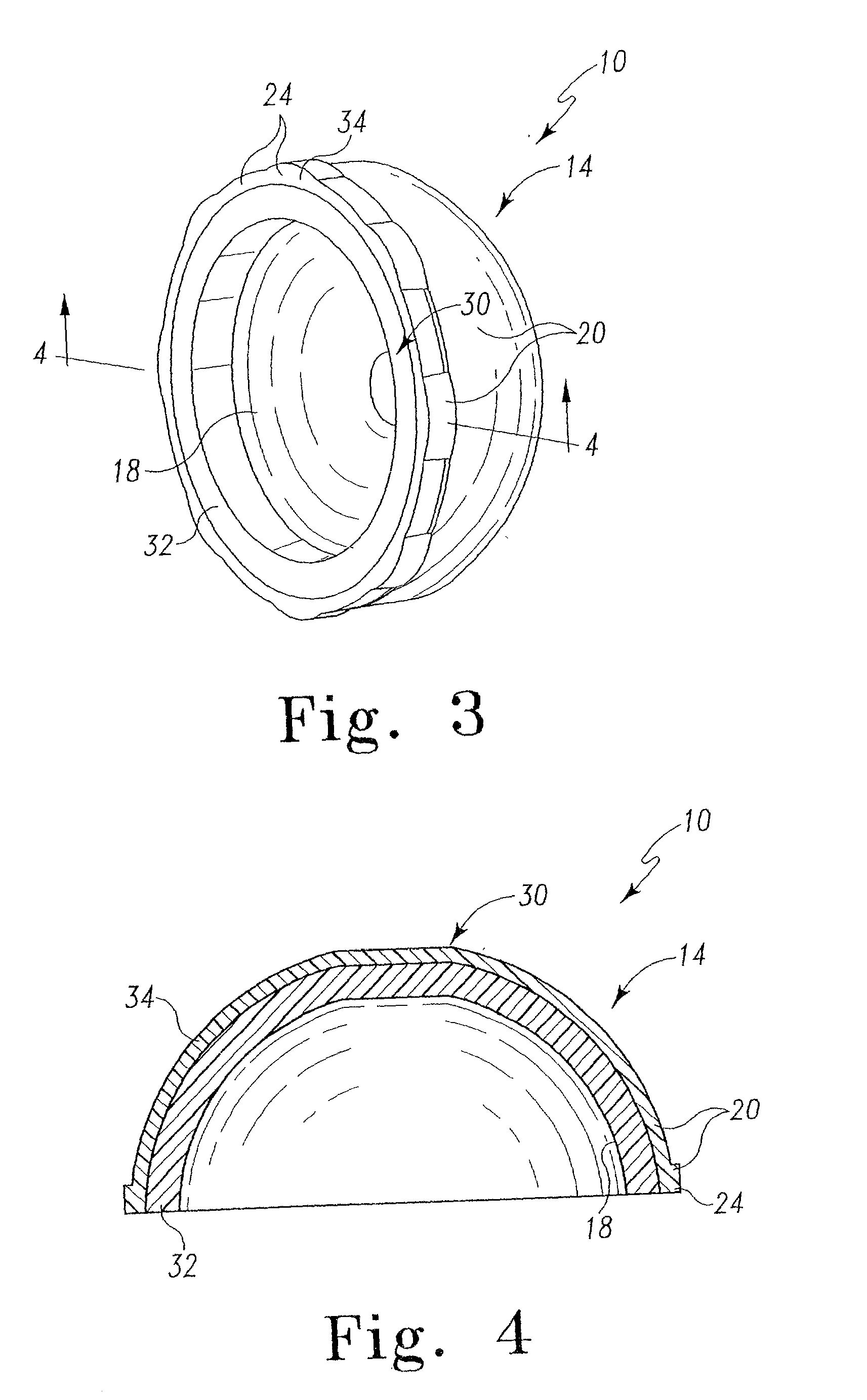
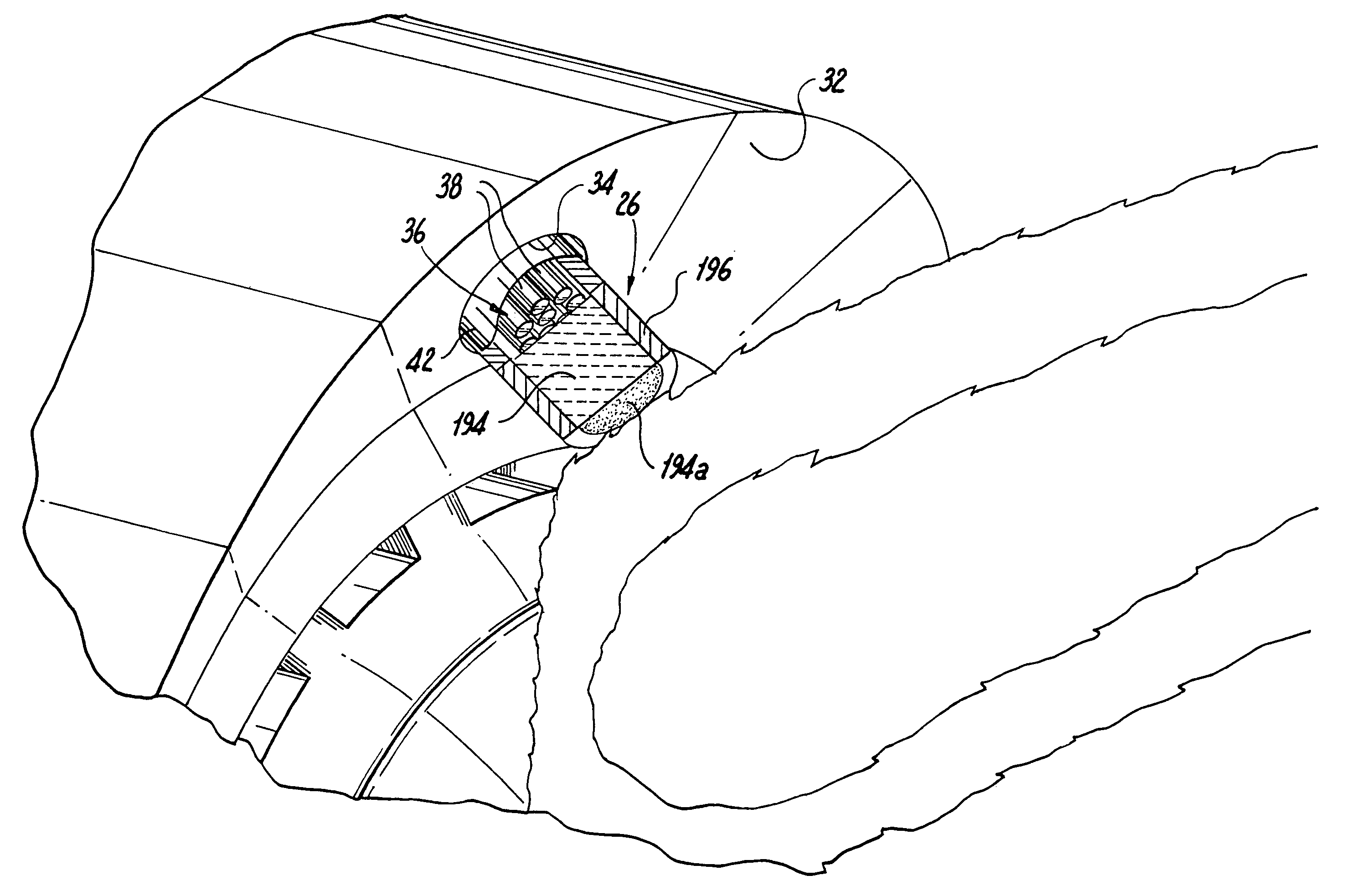
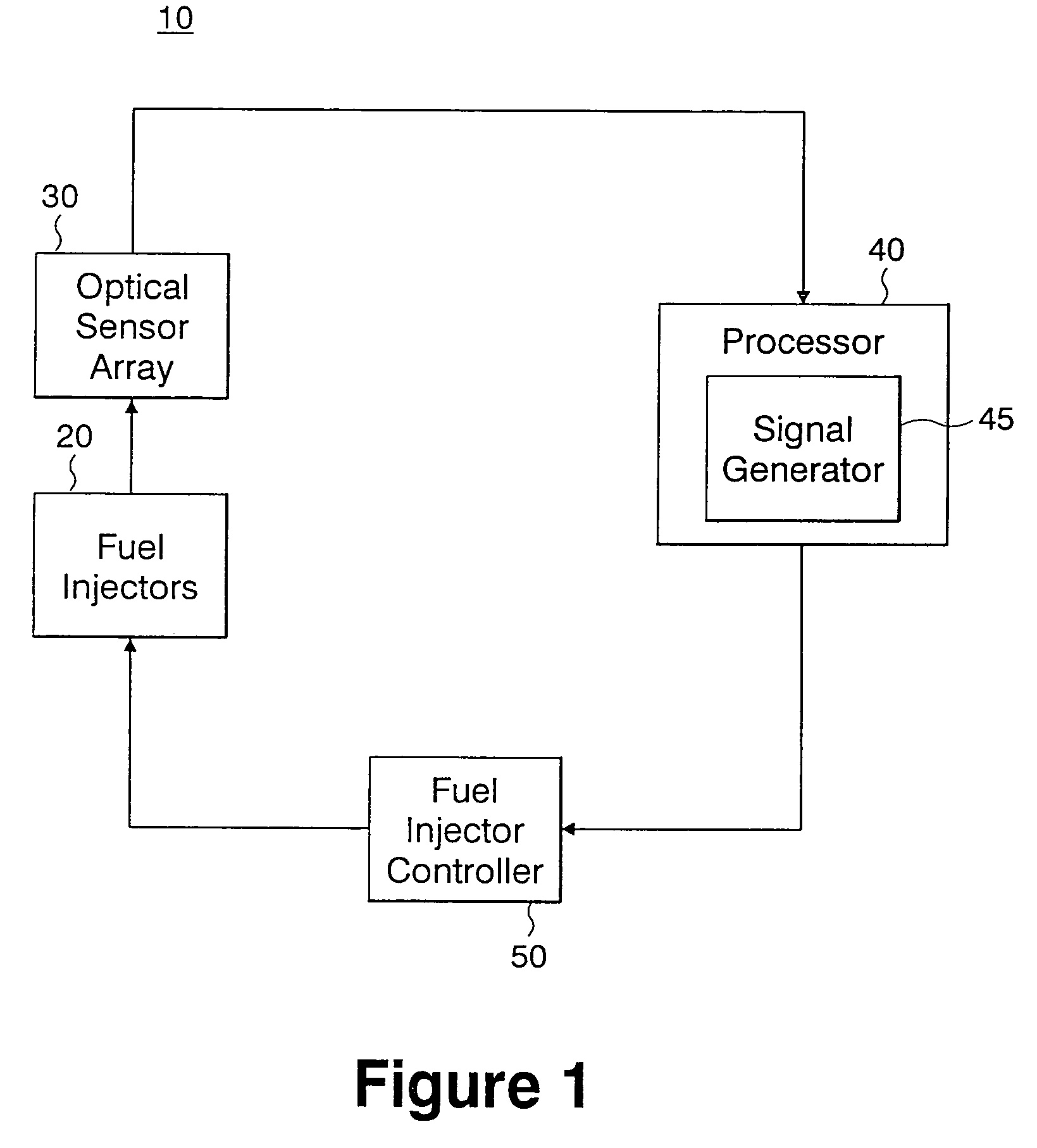
ActiveUS7484369B2Reduce instabilityPromote oxidationContinuous combustion chamberMaterial analysis by optical meansCombustorSoot
A fuel injector for a gas turbine combustor is disclosed which includes a feed arm having a flange for mounting the injector within the combustor and a fuel nozzle depending from the feed arm for injecting fuel into the combustor for combustion. An optical sensor array is operatively associated with the fuel nozzle for observing combustor flame characteristics. The optical sensor array includes a plurality of sapphire rods positioned to be close enough to the combustor flame to oxidize soot deposits thereon.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT AEROSPACE
Membrane electrode assembly for polymer electrolyte fuel cell
InactiveUS20050130006A1Good chemical stabilityImprove heat resistanceElectrolyte holding meansSolid electrolytesCarbon numberPolyelectrolyte
A membrane electrode assembly for a polymer electrolyte fuel cell characterized by using, as solid polyelecrolyte of at least one of a membrane and a catalyst binder, a fluorinated sulfonic acid polymer with a monomer unit represented by the following general formula (3): (wherein Rf1 is a bivalent perfluoro-hydrocarbon group having a carbon number of from 4 to 10), wherein said fluorinated sulfonic acid polymer has melt flow rate (MFR) not higher than 100 g / 10 min at 270° C. when a —SO3H group in said polymer is converted to —SO2F.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
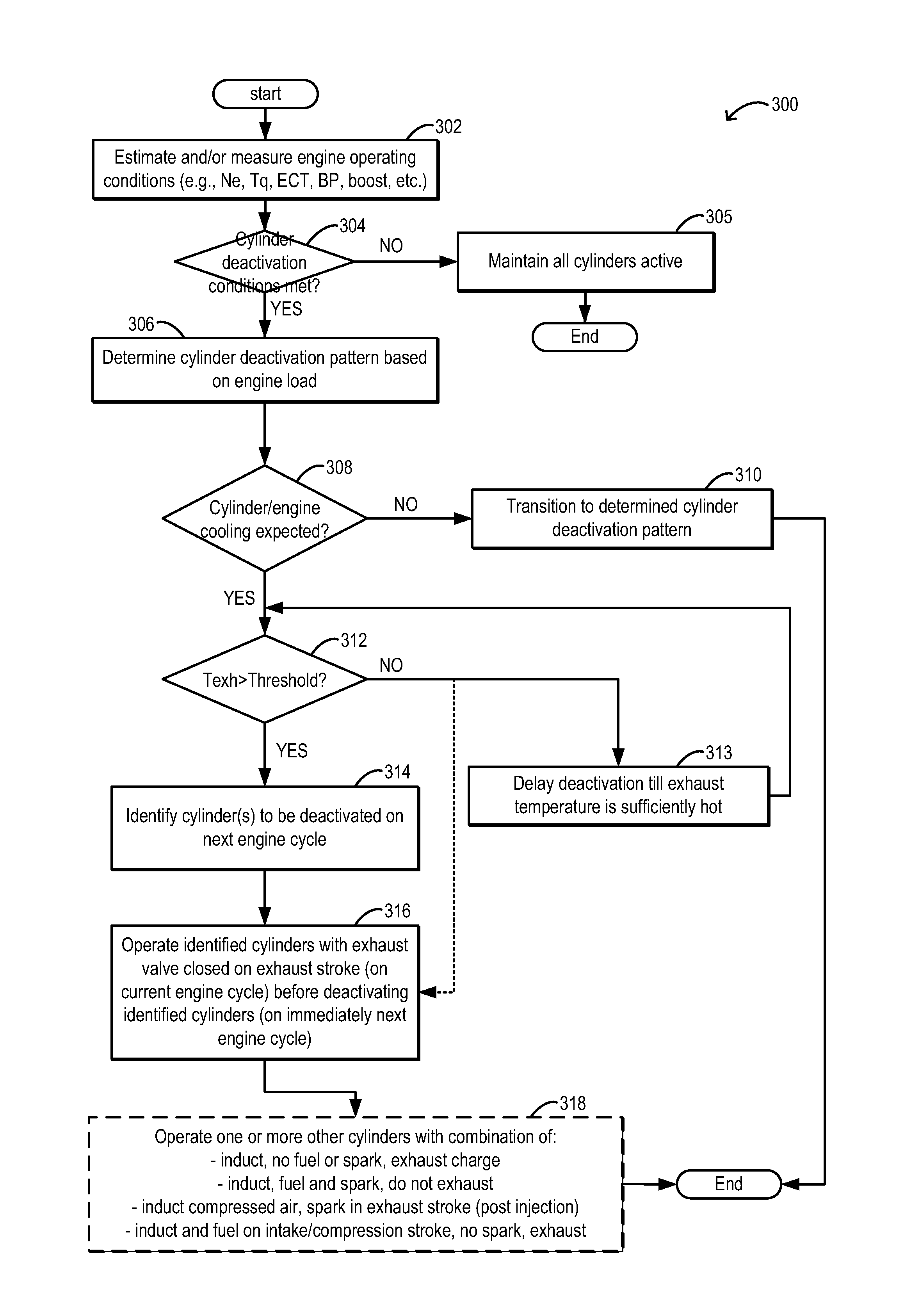
Method and system for engine temperature control
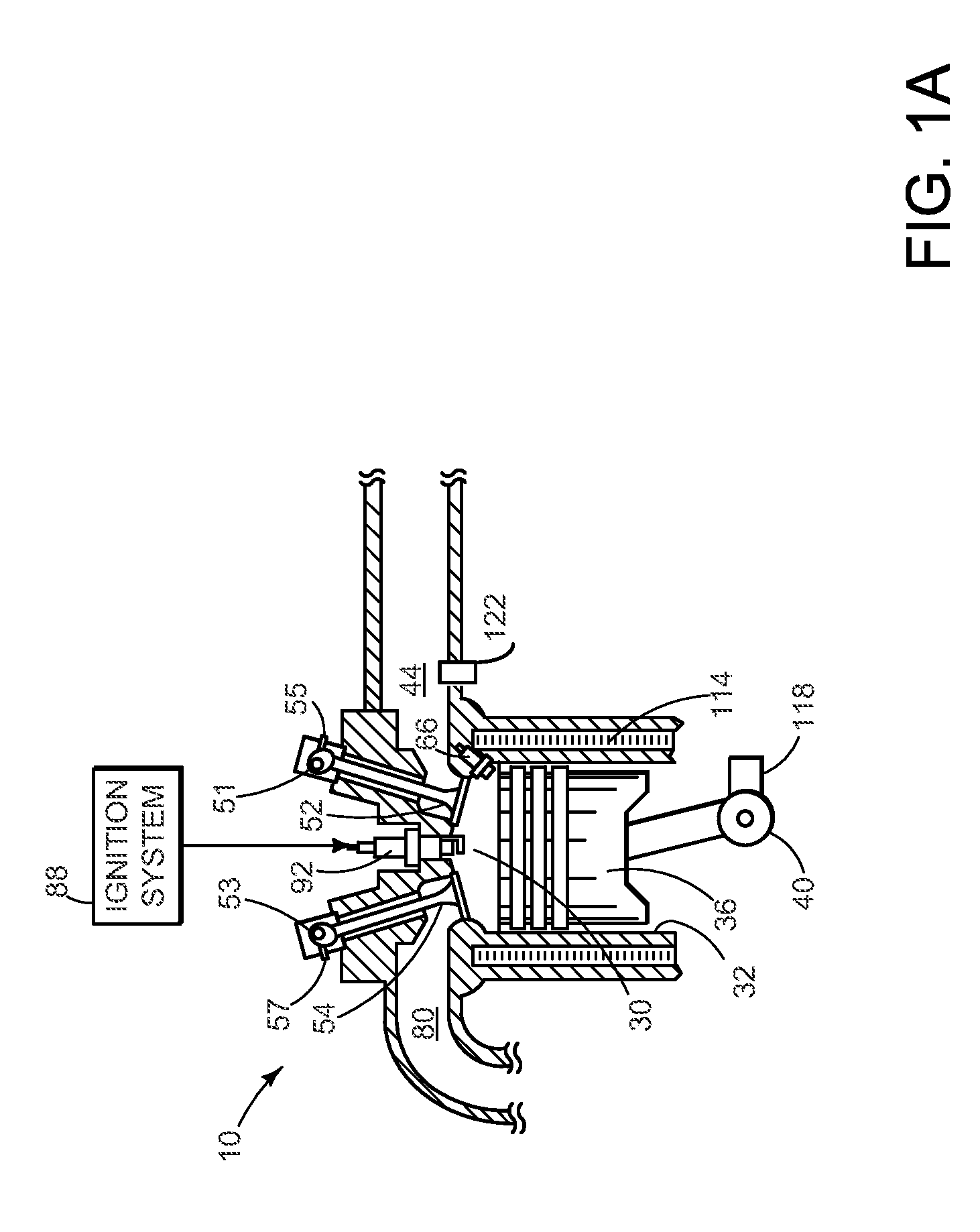
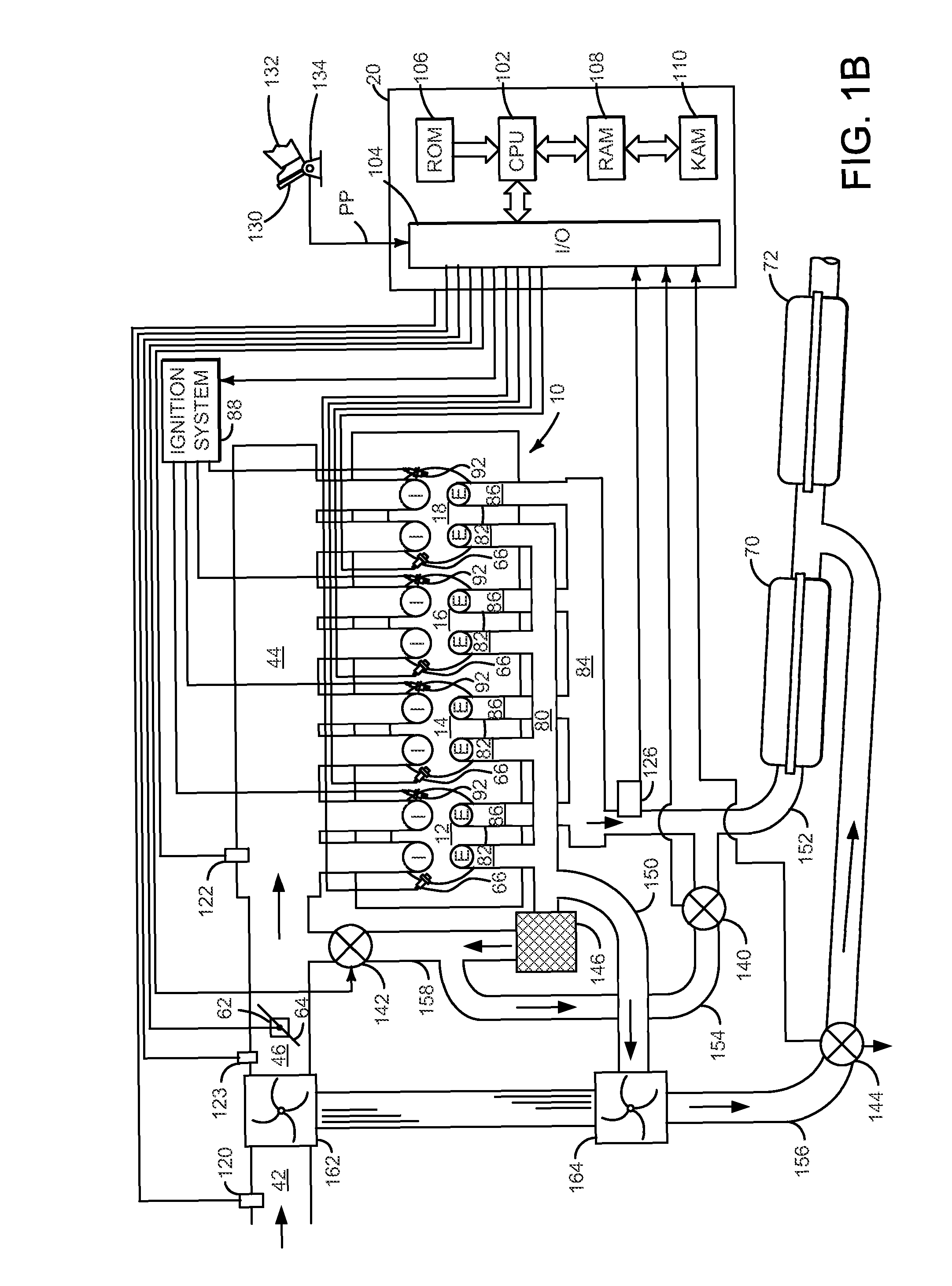
ActiveUS20160115884A1Increased hydrocarbonExhaust emission be highElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesTemperature controlExhaust valve
Methods and systems are provided to improve engine temperature control. Cylinders scheduled for deactivation may have their exhaust retained in the cylinder by holding an exhaust valve closed on the preceding firing cycle. In this way soot emissions on reactivation are reduced.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and system for turbocharging an engine
ActiveUS8069663B2Improve engine efficiencyReduce displacementValve arrangementsElectrical controlEngine efficiencyEngineering
A method for improving operation of a turbocharged engine is presented. In one embodiment, the method may reduce engine emissions and improve engine efficiency during an engine start.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
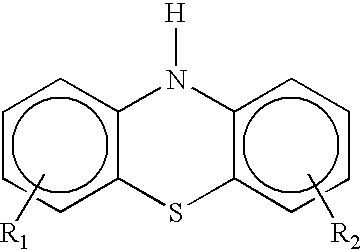
Antioxidant combination for oxidation and deposit control in lubricants containing molybdenum and alkylated phenothiazine
InactiveUS6797677B2Easy to controlPromote oxidationLiquid carbonaceous fuelsAdditivesAntioxidantOxidation resistant
The invention relates to a lubricating oil composition having improved antioxidant properties, and which contains a molybdenum compound and an alkylated phenothiazine. Further, it may also include a secondary diarylamine, preferably an alkylated diphenylamine. This combination of additives provides improved oxidation control and friction modifier performance to the lubricating oil. The composition is particularly suited for use as a crankcase lubricant, or a transmission lubricant, including low levels and zero levels of phosphorus.
Owner:AFTON CHEMICAL +1
Fuel cell with internal combustion chamber
InactiveUS6124053AImprove performanceFacilitate fuel combustionFuel cells groupingFuel cell auxillariesFuel cellsCombustion chamber
A novel fuel cell design is provided having a combustion chamber manifold internal to a fuel cell stack and interfacing one or more anode passage outlets and cathode passage inlets. The combustion chamber is equipped to combine a primary source of oxidant gas with an anode exhaust stream and to combust the mixture, if desired, for use as fuel within the cathode passage. The fuel cell design also provides an external gas manifold for directing carrier gas to the cathode passages upstream of the cathode passage inlets for combining with the combustion chamber exhaust prior to entry into the cathode passages.
Owner:FUEL CELL TECH
Polymerization catalyst for polyester, polyester produced with the same, and process for producing polyester
InactiveUS20040058805A1Improve dyeing propertiesPromote oxidationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentChemistryAluminium
A polymerization catalyst for polyester production which contains neither a germanium compound nor an antimony compound as a major component. It contains aluminum as the main metallic ingredient, has excellent catalytic activity, and gives a polyester which is effectively inhibited from suffering thermal degradation, during melt molding, without deactivating or removing the catalyst, and is excellent in thermal stability, stability to thermal oxidation, and hydrolytic resistance. The polymerization catalyst contains as a first metallic ingredient at least one member selected among aluminum and compounds thereof and further contains a phosphorus compound represented by a specific chemical formula. The polyester produced with this catalyst is usable as fibers, films, sheets, various moldings including hollow moldings, etc.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Polycarboxylic acid production system employing oxidative digestion with reduced or eliminated upstream liquor exchange
ActiveUS20070208190A1Reduce formationPromote oxidationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation by oxidationCarboxylic acidSlurry
Disclosed is an optimized system for more efficiently and economically producing terephthalic acid. The system minimizes or eliminates the need for liquor exchange upstream of oxidative digestion and / or upstream of substantial cooling of the TPA-containing slurry.
Owner:ALPEK POLYESTER SA DE CV
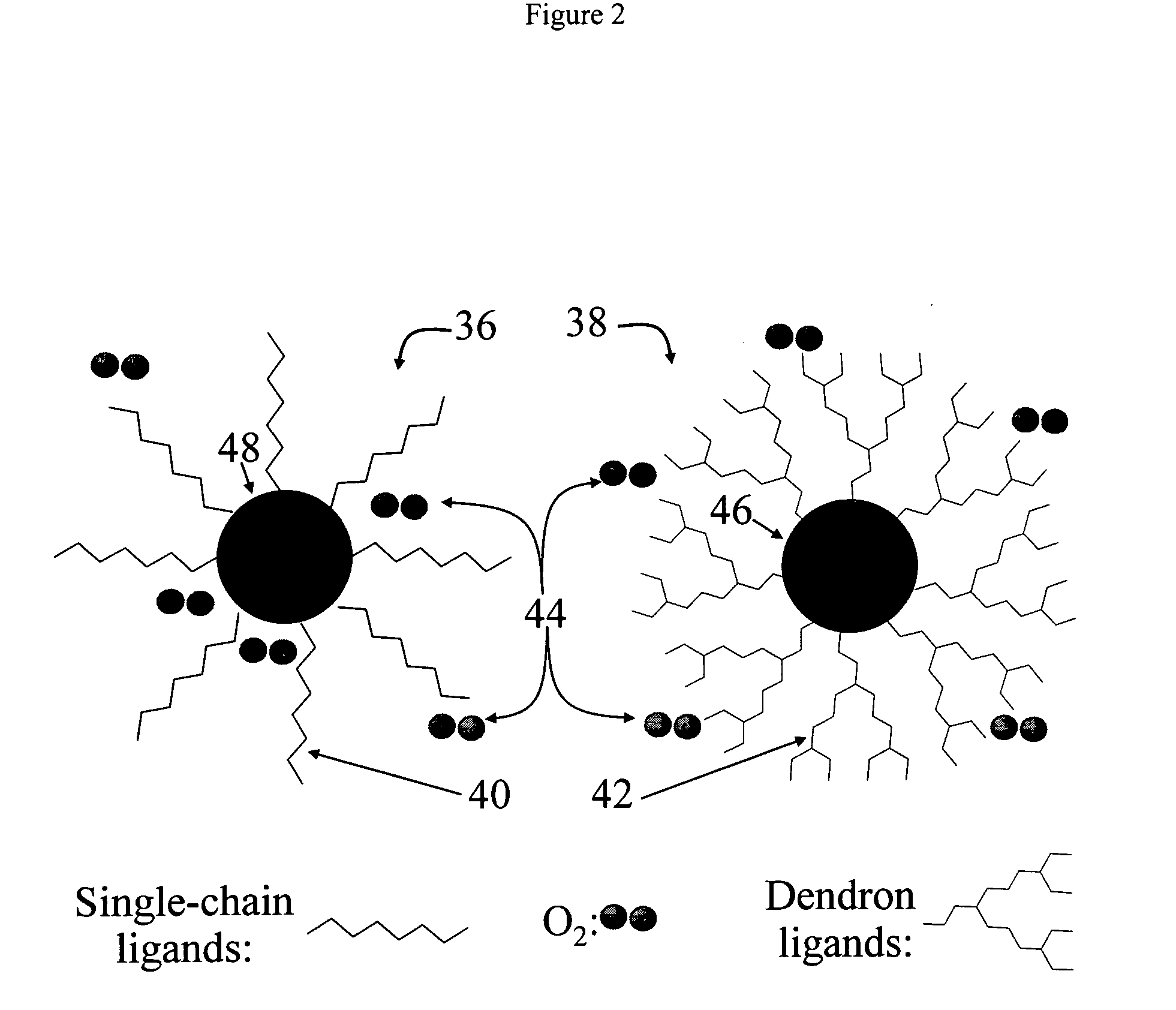
Synthesis of stable colloidal nanocrystals using organic dendrons
ActiveUS7153703B2Enhances protection against oxidationIncrease the number ofFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthCross-linkNanoparticle
A method for stabilizing colloidal suspensions of nanocrystals or nanoparticles in a solvent or solid matrix is provided by coating the nanocrystals with bulky organic molecules, specifically dendrons. By coating nanocrystals with a dense organic dendron coat and further cross-linking the dendron ligands, oxidation of the nanocrystals and dissociation of the ligands are avoided. This invention allows nanocrystals to undergo rigorous purification and processing. It may regularly be applied to a variety of nanocrystals.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS +1
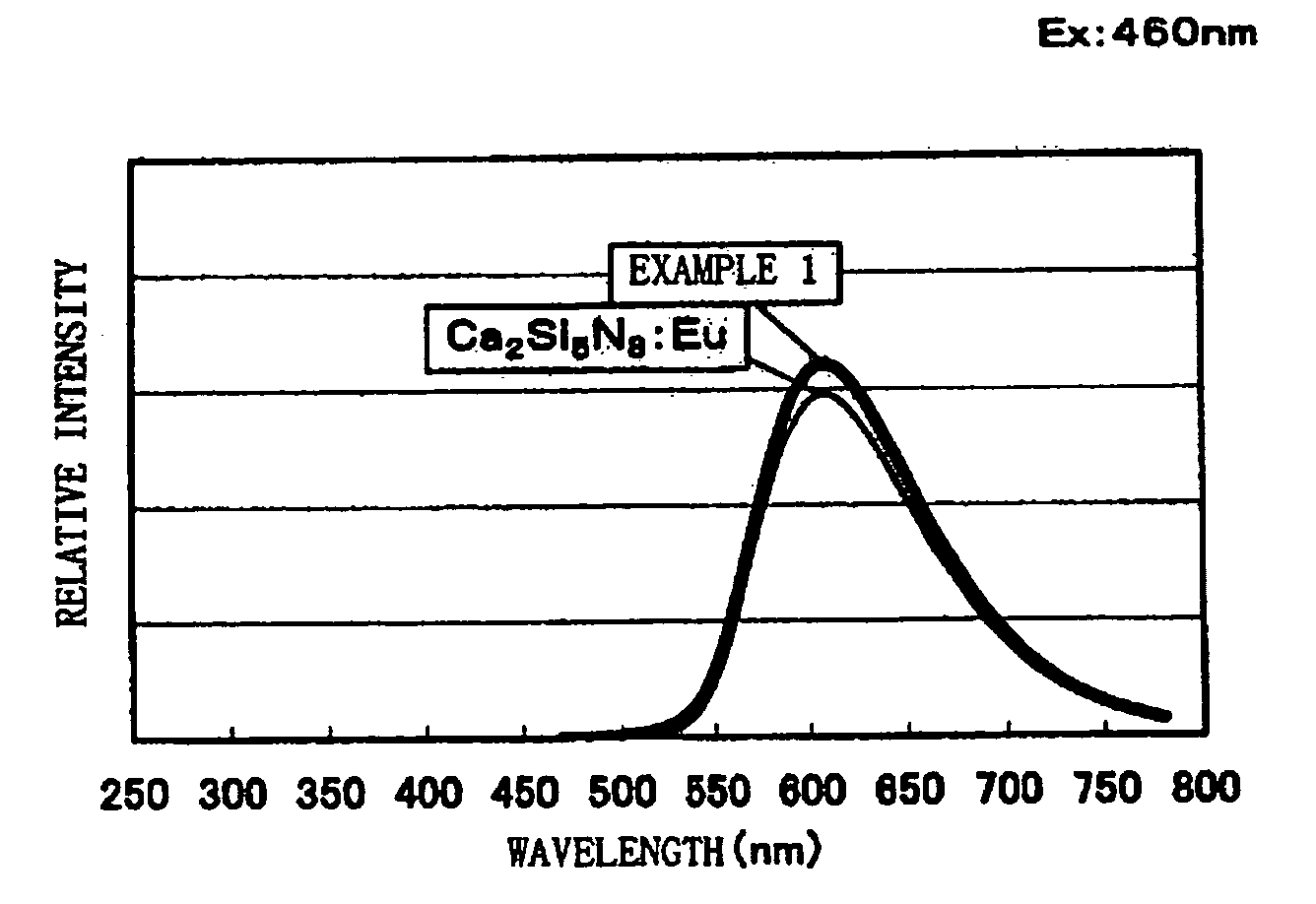
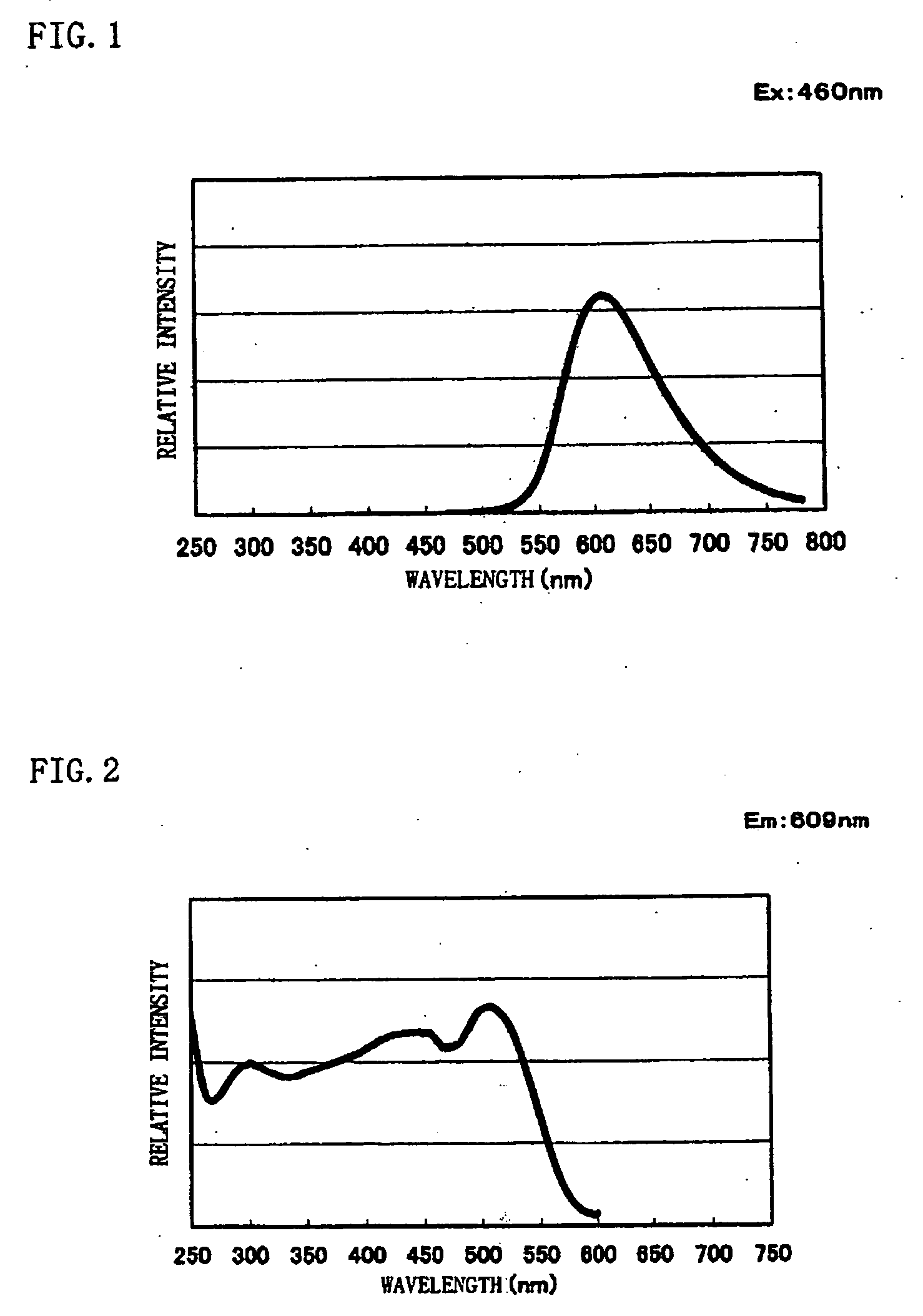
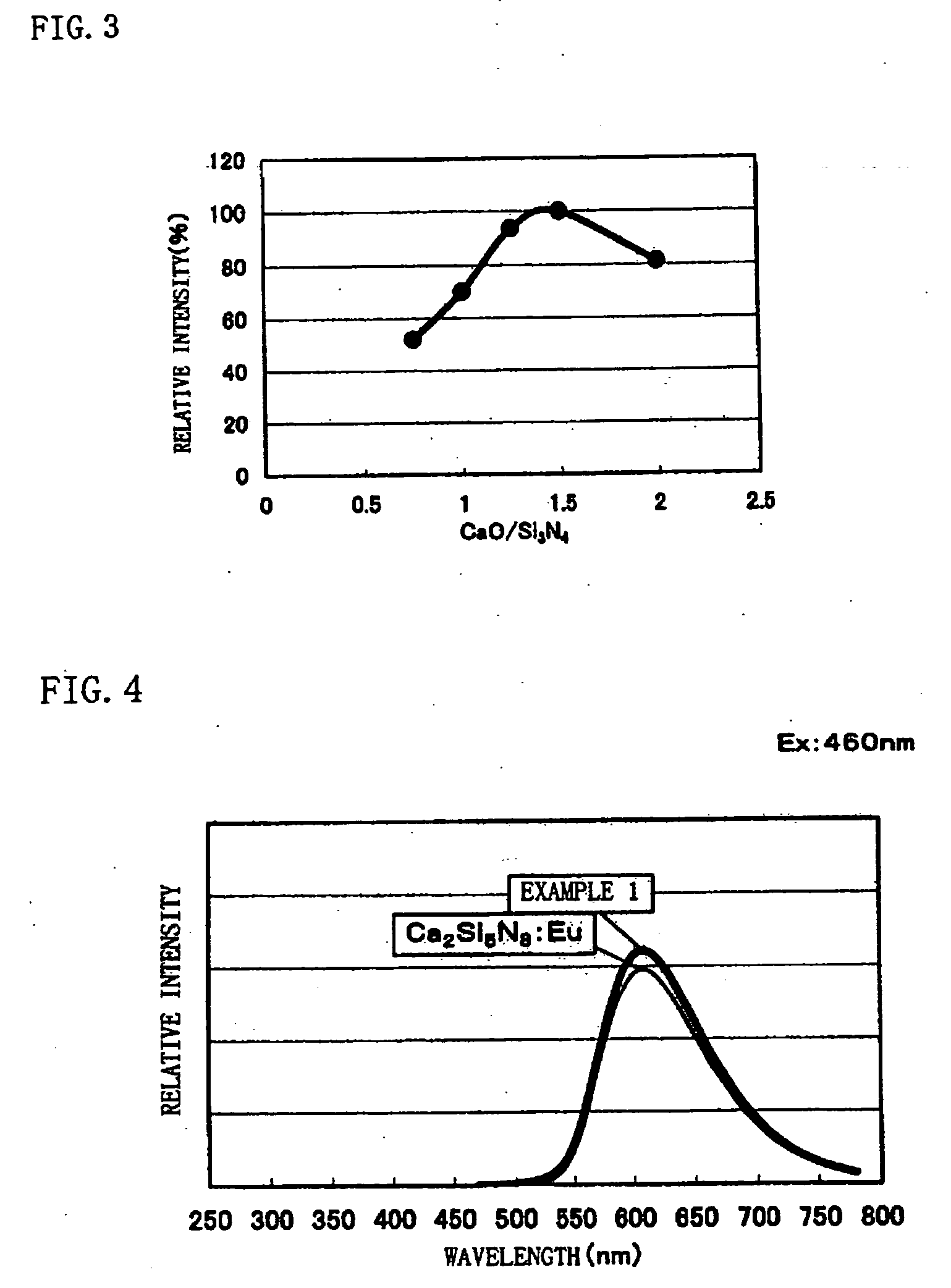
Phosphor and production method of the same and light source and LED using the phosphor
InactiveUS20050253500A1Long life-timeEasy to produceDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesFluorescencePhosphor
A phosphor with high efficiency having an excitation band corresponding to light of the ultraviolet-visible (300 to 550 nm) wavelength region emitted from a light emitting element which emits blue or ultraviolet light is provided. Commercially available CaO [3N], Si3N4 [3N], and Eu2O3 [3N] are prepared, respective materials are weighed and mixed to have a mol ratio of CaO:Si3N4:Eu2O3=1.4775:1:0.01125, and then the mixture is heated to 1600° C. by a heating rate of 15° C. / min under a nitrogen atmosphere and retained and fired at 1600° C. for three hours. Thereafter, the raw materials are cooled down from 1600° C. to 200° C. for an hour to thereby produce a phosphor having a composition formula Ca1.58Si3O1.63N4.35:Eu0.024.
Owner:DOWA ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CO LTD
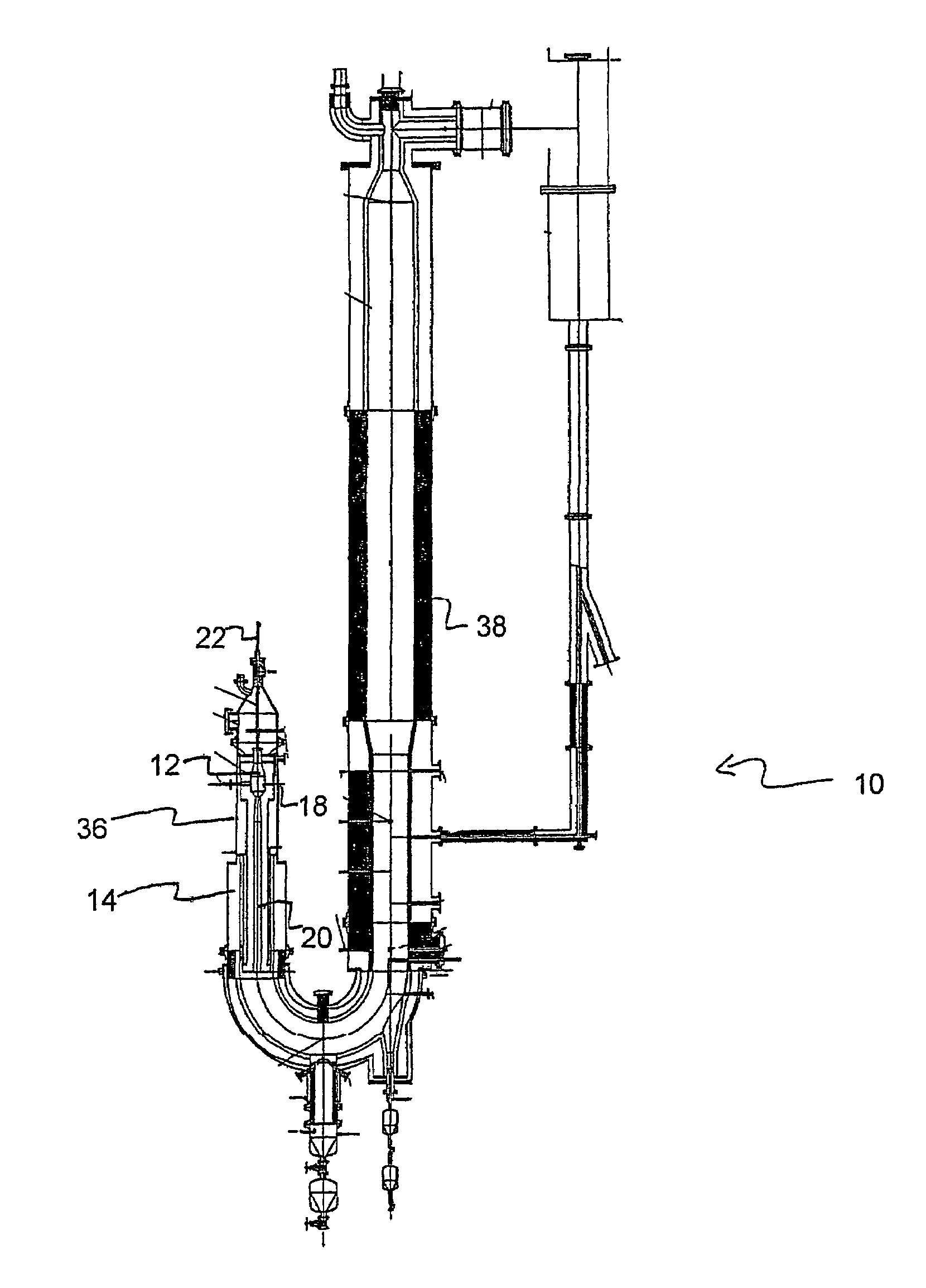
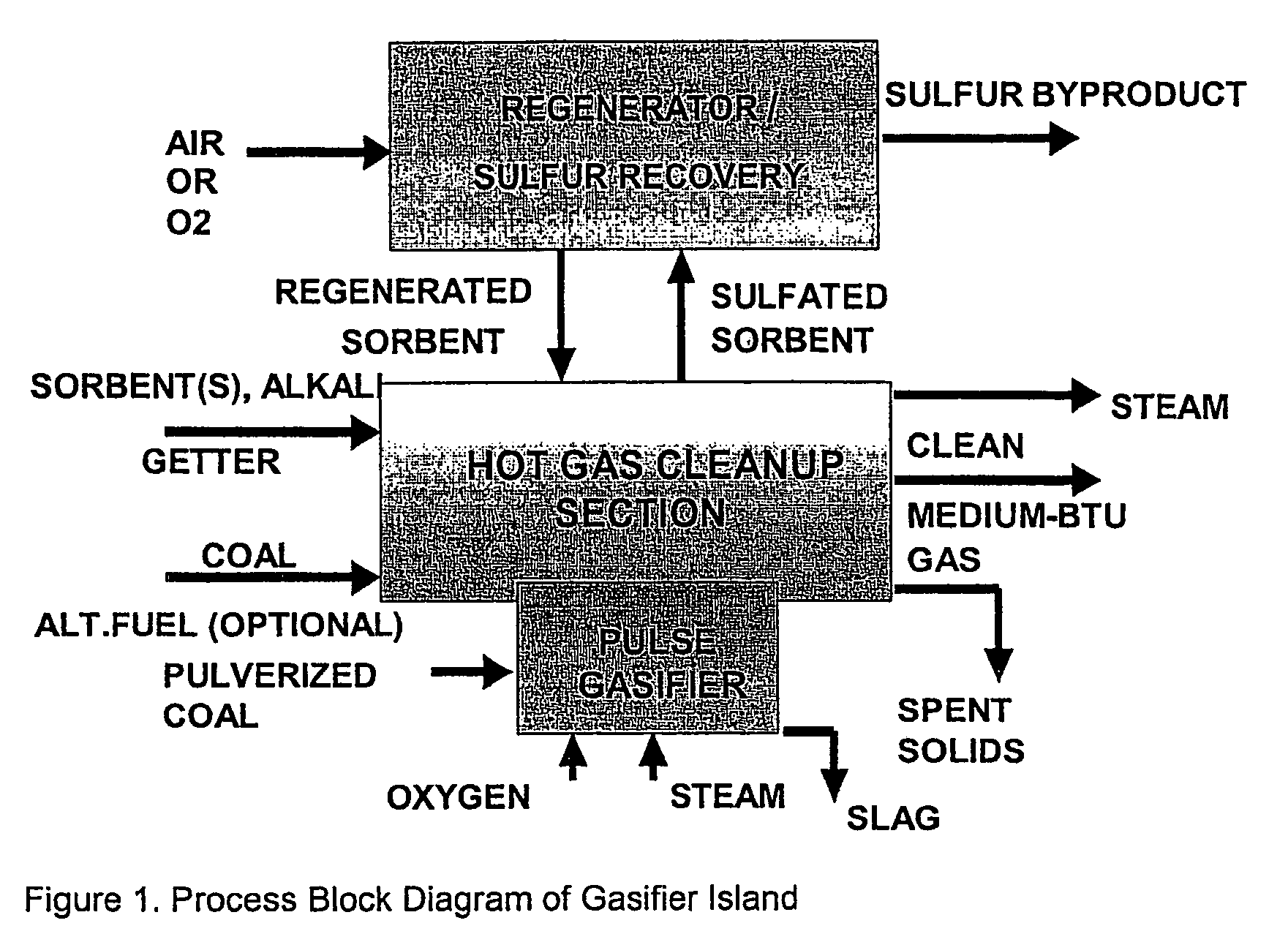
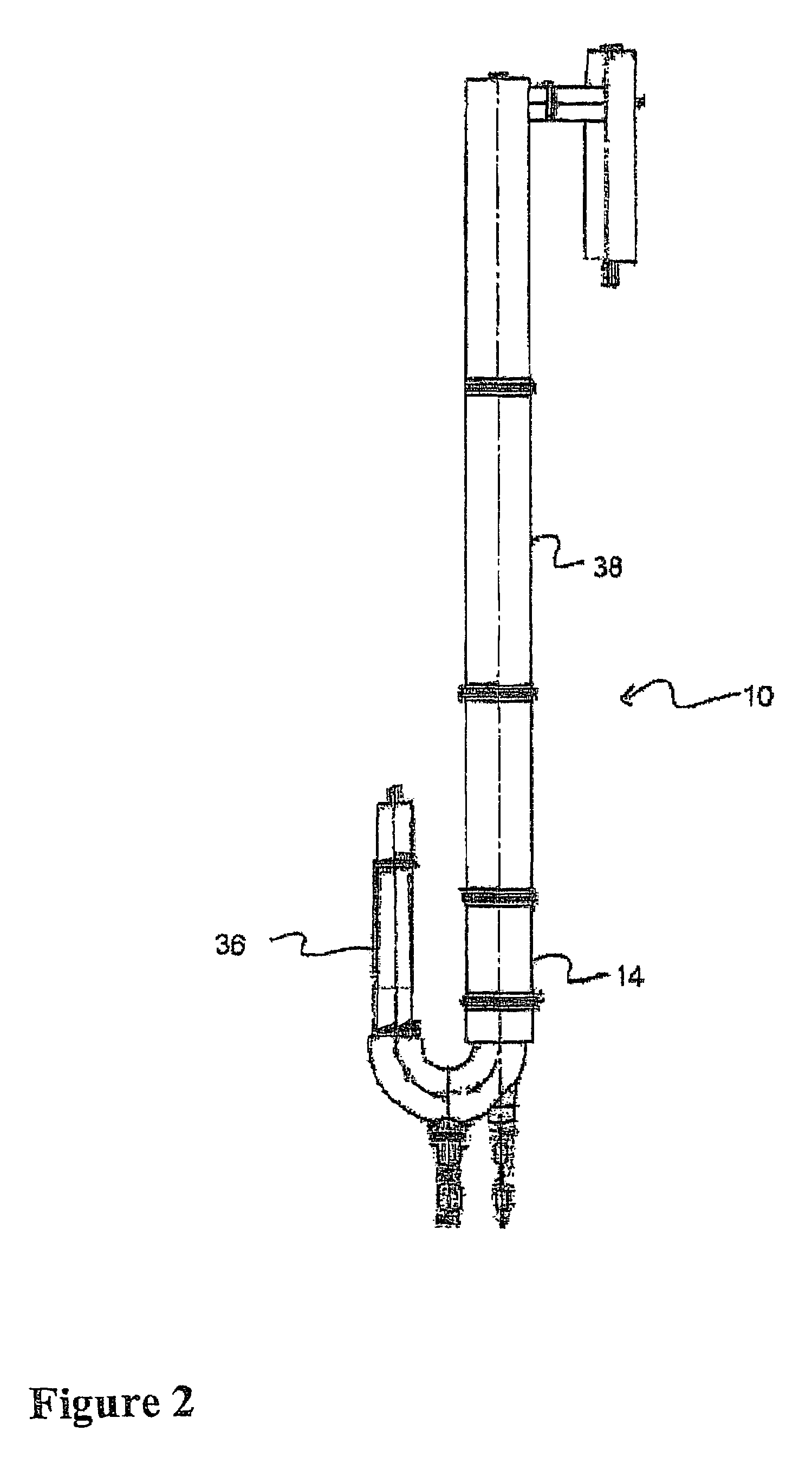
Pulse gasification and hot gas cleanup apparatus and process
InactiveUS6997118B2Easy to useConducive to agglomerationAuxillary pretreatmentGasifier mechanical detailsSteam reformingElectricity
A gasifier system and process comprises a pulse combustion device in communication with a fluid channel for producing a gas stream having heat or fuel value. The pulse combustion device is operated under sub-stoichiometric conditions such that combustion and steam reforming both occur in the fluid channel. The pulse combustion device also produces a pulsating combustion product stream and an acoustic pressure wave. The acoustic pressure wave serves to cause agglomeration of particles contained within the combustion stream for easy removal. In one embodiment, a sulfur capturing agent is injected into the fluid channel for not only removing sulfur from the combustion product stream but for also facilitating particle agglomeration. Ultimately, a gas stream containing hydrogen is produced that may be used in various processes, such as in the production of electricity.
Owner:MFG & TECH CONVERSION INT
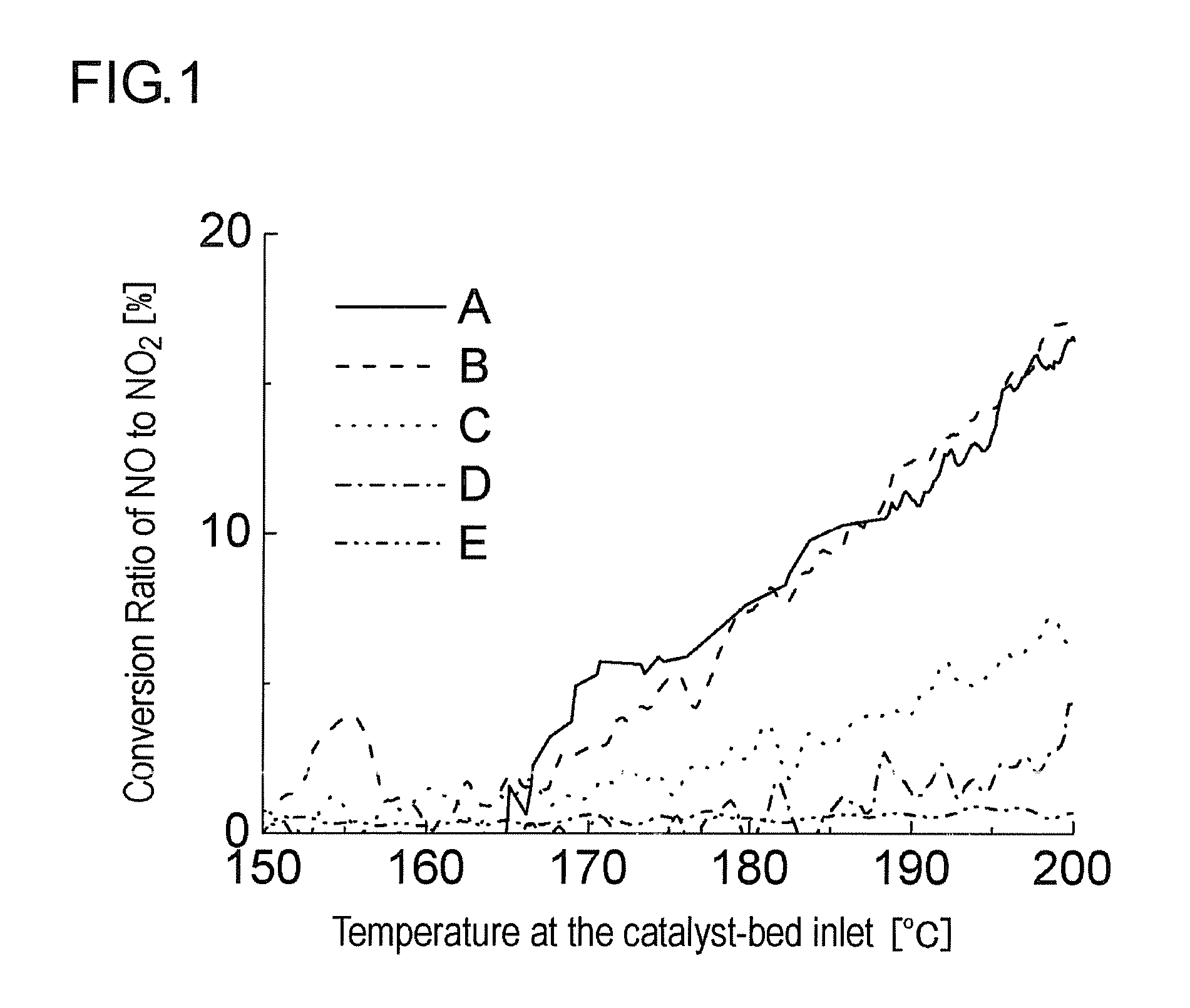
Oxidation Catalyst and Exhaust-Gas Purification System Using the Same
InactiveUS20080124264A1Promote effectiveEfficient removalCombination devicesNitrogen compoundsPlatinumNitrogen monooxide
An oxidation catalyst that efficiently promotes oxidation of NO to NO2 even in a low temperature range, and an exhaust-gas purification system and method that efficiently removes exhaust-gas components even in a low temperature range are provided. This invention provides an oxidation catalyst comprising platinum and palladium as catalytically active components, which promotes oxidation of nitrogen monoxide to nitrogen dioxide, wherein the oxidation catalyst comprises 1 to 55% by weight of the palladium relative to 100% by weight of the platinum.
Owner:ICT CO LTD +1
Three-layered catalyst system for purifying exhaust gases of internal engines
Disclosed herein is a three-layered catalyst system in which layers including predetermined precious metal components are sequentially layered on a substrate, and thus the conversion ratio of HC and CO is increased, thereby improving purification efficiency. The three-layered catalyst system includes a substrate, a lower layer containing a precious metal component of only platinum, an intermediate layer containing a precious metal component of only palladium, and an upper layer containing a precious metal component of only platinum, all of which are sequentially layered.
Owner:HEESUNG CATALYSTS CORP
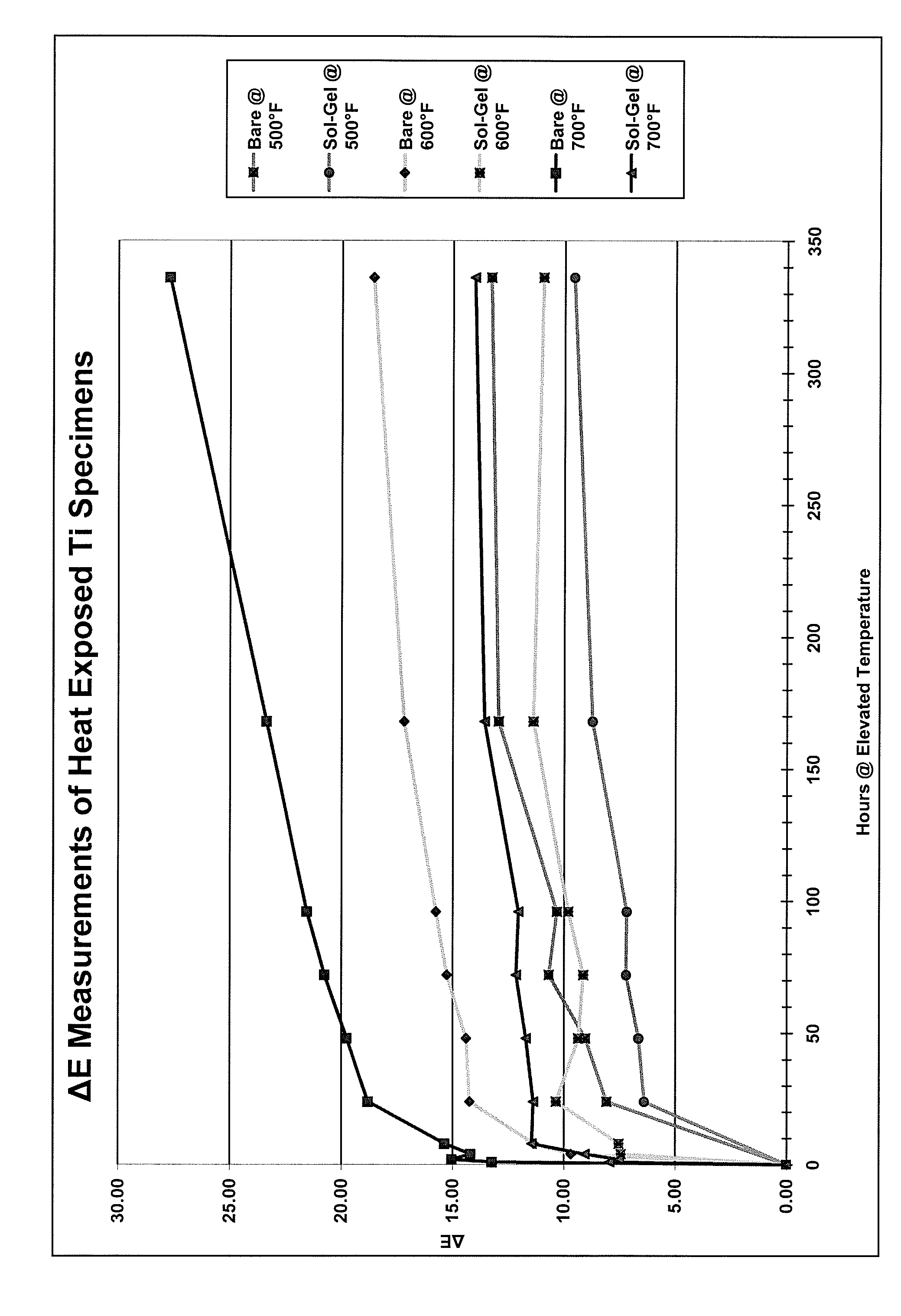
Sol-gel coating method and composition
ActiveUS20080111027A1Excellent protectionReduce airflow obstructionSynthetic resin layered productsPretreated surfacesMetal alkoxideOxidation resistant
A coating composition and a method for coating metallic substrates, such as aircraft components exposed to elevated temperatures and / or oxidative conditions. The coating composition includes an aqueous mixture having about 2 vol % to about 50 vol % organosilane, about 0.3 to about 25 vol % metal alkoxide, and about 0. 1 to about 30 vol % organic complexing agent. The coating composition may be deposited on a metallic substrate and cured to form a sol-gel coating on the surface of the substrate that is adherent to the substrate, and oxidation and discoloration resistant.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Lubricant compositions stabilized with multiple antioxidants
InactiveUS20060128574A1Prevent oxidationPromote oxidationLiquid carbonaceous fuelsAdditivesAntioxidantOxidation stability
A lubricant composition is disclosed that comprises lubricating oil and a mixture of at least two antioxidants, the first antioxidant being a secondary diarylamine and the second antioxidant being a substituted para-phenylenediamine. Also disclosed is a method of increasing the oxidation stability of a lubricating oil comprising adding thereto at least two antioxidants, the first antioxidant being a secondary diarylamine and the second antioxidant being a substituted para-phenylenediamine.
Owner:LANXESS SOLUTIONS US INC
Toner, method for preparing the toner, and developer including the toner
A toner including a binder resin comprising a polyester resin in an amount of from 50 to 100% by weight, wherein the polyester resin includes an unsaturated polyester resin which is preferably a crystalline polyester resin; a colorant; and a fatty acid metal salt which is preferably microencapsulated. A method for preparing a toner including forming particles of a toner composition including at least a binder resin including a polyester resin in an amount of from 50 to 100% by weight and a colorant, in an aqueous medium to prepare a dispersion of a particulate material, wherein the polyester resin includes an unsaturated polyester resin; drying the particulate material; and mixing a fatty acid metal salt with the particulate material to subject double bonds of the unsaturated polyester resin to oxidation polymerization.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method for producing multicrystalline silicon substrate for solar cells
InactiveUS20050101153A1Promote oxidationHigh dissolution rateFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal particleSolar cell
Disclosed is a method for producing a multicrystalline silicon substrate for solar cells comprising: a metal deposition step for depositing such metal particles as platinum and silver on the surface of the substrate by electroless-plating chloroplatinic acid or silver perchlorate; a boring step for subjecting the substrate surface to etching in a solution containing at least one of hydrofluoric acid and hydrogen peroxide; and a step for removing a stain layer by immersing the substrate into an alkaline solution. A multicrystalline silicon substrate having a lower reflectance is provided at a lower cost.
Owner:KANSAI TLO KK
Methods for producing and using a Cu(I)-based wood preservative
Soluble copper(I)-amine complexes, particularly copper(I)-ammonia complexes and copper(I)-monoethanmolamine complexes, are useful injectable wood preservatives. Wood treated with the copper(I)-amine complexes contains less amines, and is less corrosive to metals, than woods treated with the prior art copper(II)-amine complexes. A method of preparing an aqueous wood preservative that includes soluble copper(I) complexes comprises reacting a solution comprising a copper(II)-amine complex with metallic copper to form a copper(I)-amine complex. One aspect of the invention comprises injecting a solution comprising a copper(I)-amine complex into wood and allowing the copper(I)-amine complex to precipitate within the wood.
Owner:OSMOSE
Superalloy article having corrosion resistant coating thereon
InactiveUS20050255329A1Improve adhesionMinimal diffusionPropellersMolten spray coatingCarbideSuperalloy
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
MANGANESE-BASED OXIDES PROMOTED LEAN NOx TRAP (LNT) CATALYST
ActiveUS20120240554A1Reduce usageReduce the environmentGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust gasOxide
MnOx-containing, base-metal oxide mixtures (e.g., MnOx—CeO2) are useful NOx oxidation catalyst materials and NOx storage materials in lean-burn engine exhaust gas treatments using Lean NOx Trap (LNT) systems. These oxidation catalyst materials are used in combination with a NOx storage material and a NOx reduction material. MnOx-containing oxide mixtures can replace platinum (Pt) in LNT systems where the exhaust of the engine is repeatedly varied between a relatively long fuel-lean mode of operation and a relatively short fuel-rich mode of operation. The combination of the MnOx oxidation catalyst, NOx storage material, and NOx reduction catalyst material serves to complete the oxidation of unburned hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide, and to convert NOx to nitrogen.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com