Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
515results about How to "Improve engine efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
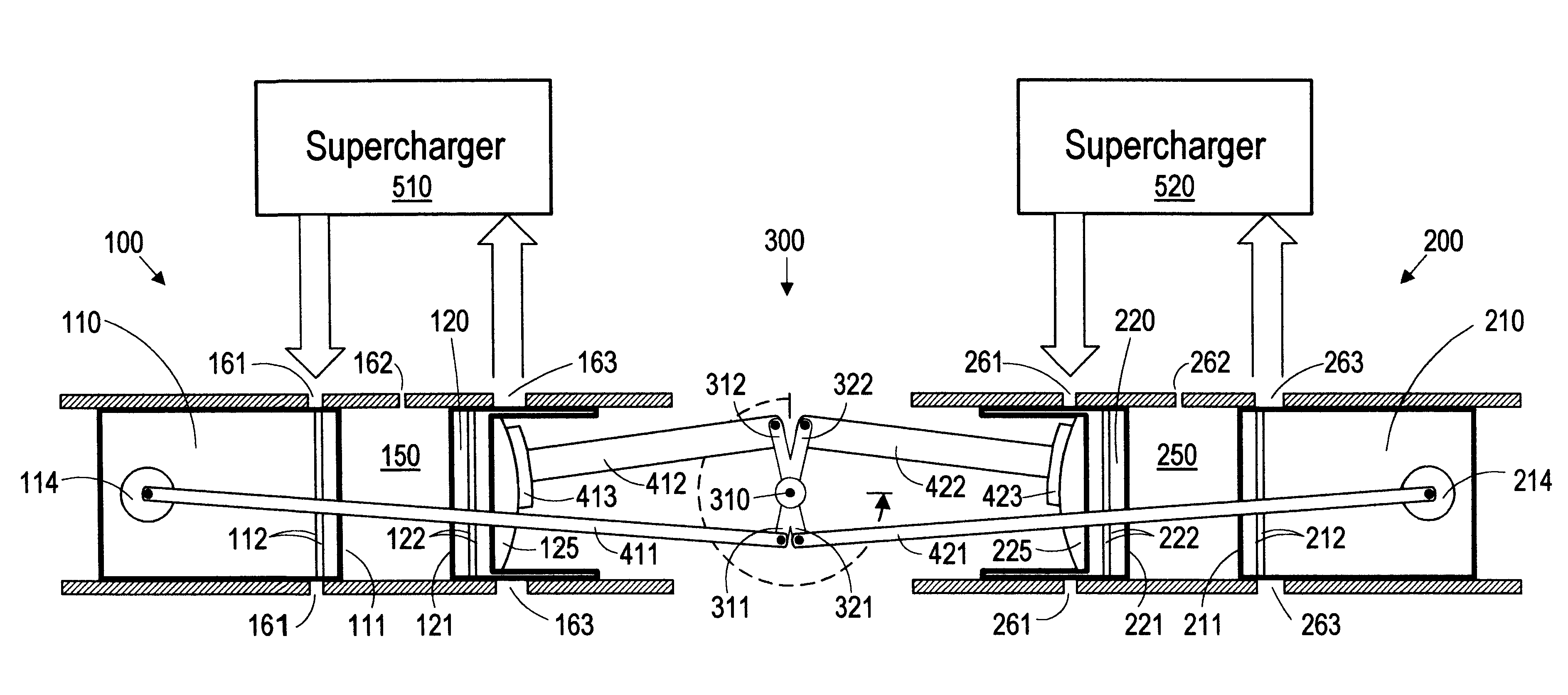
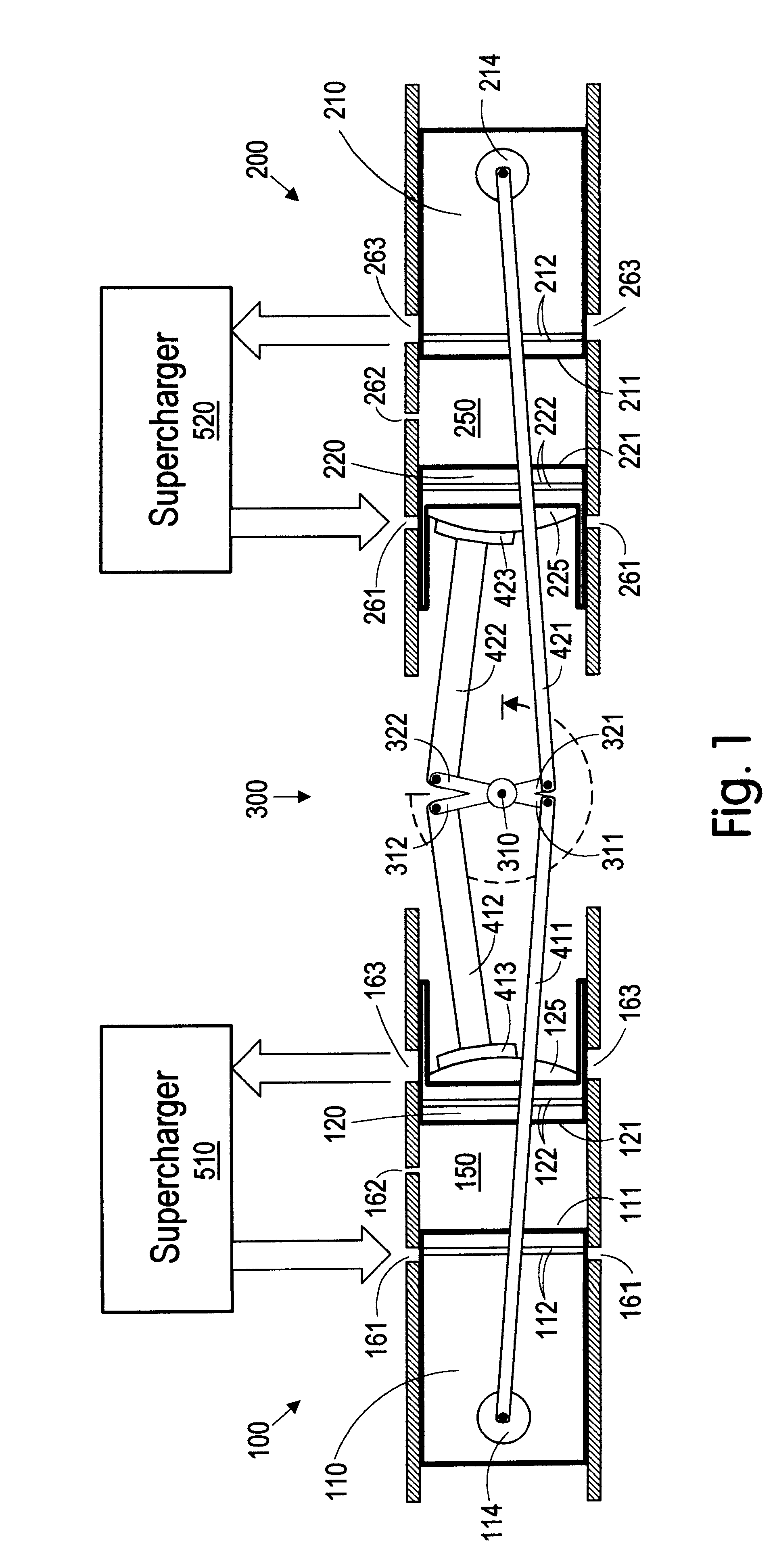
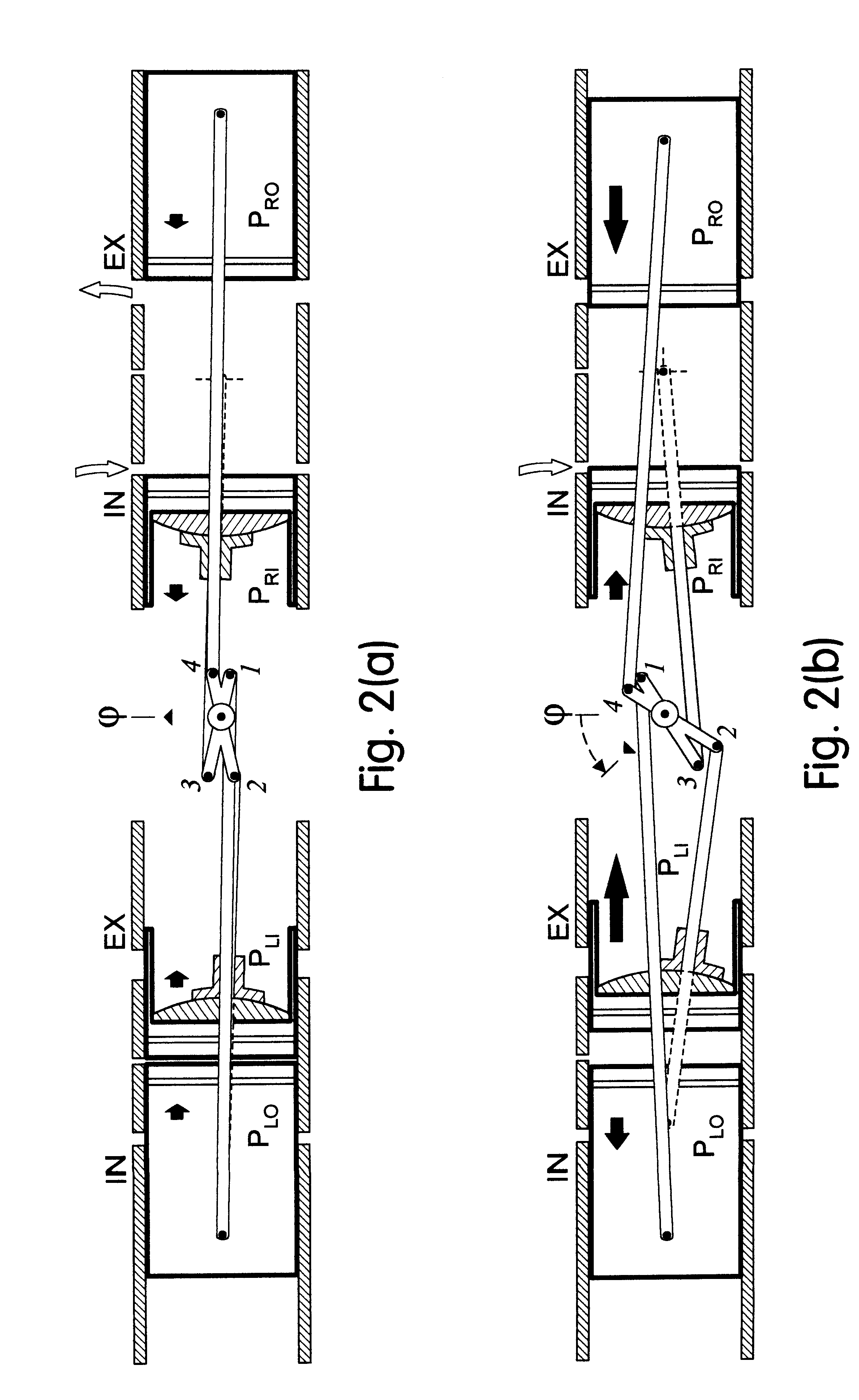
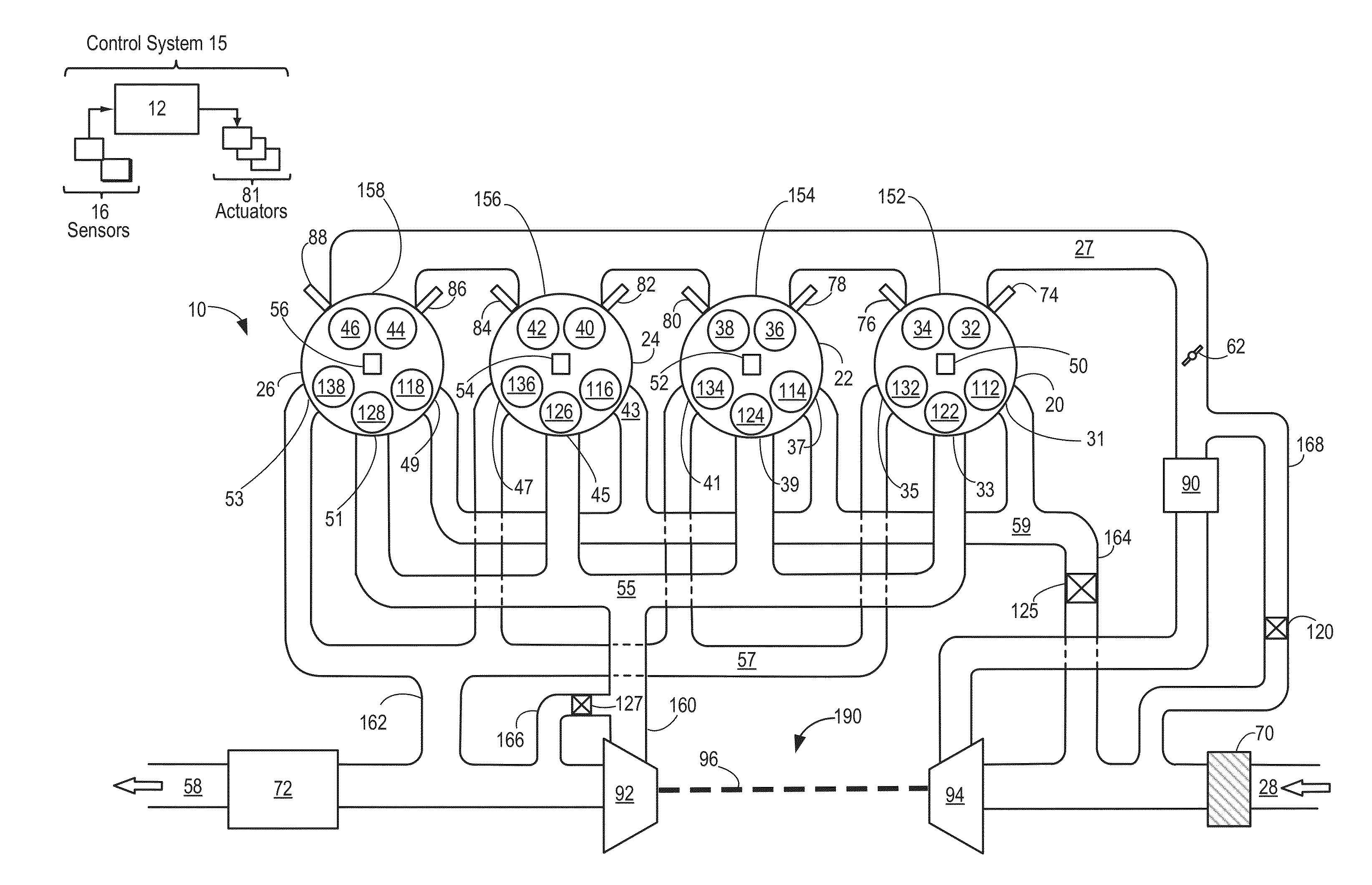
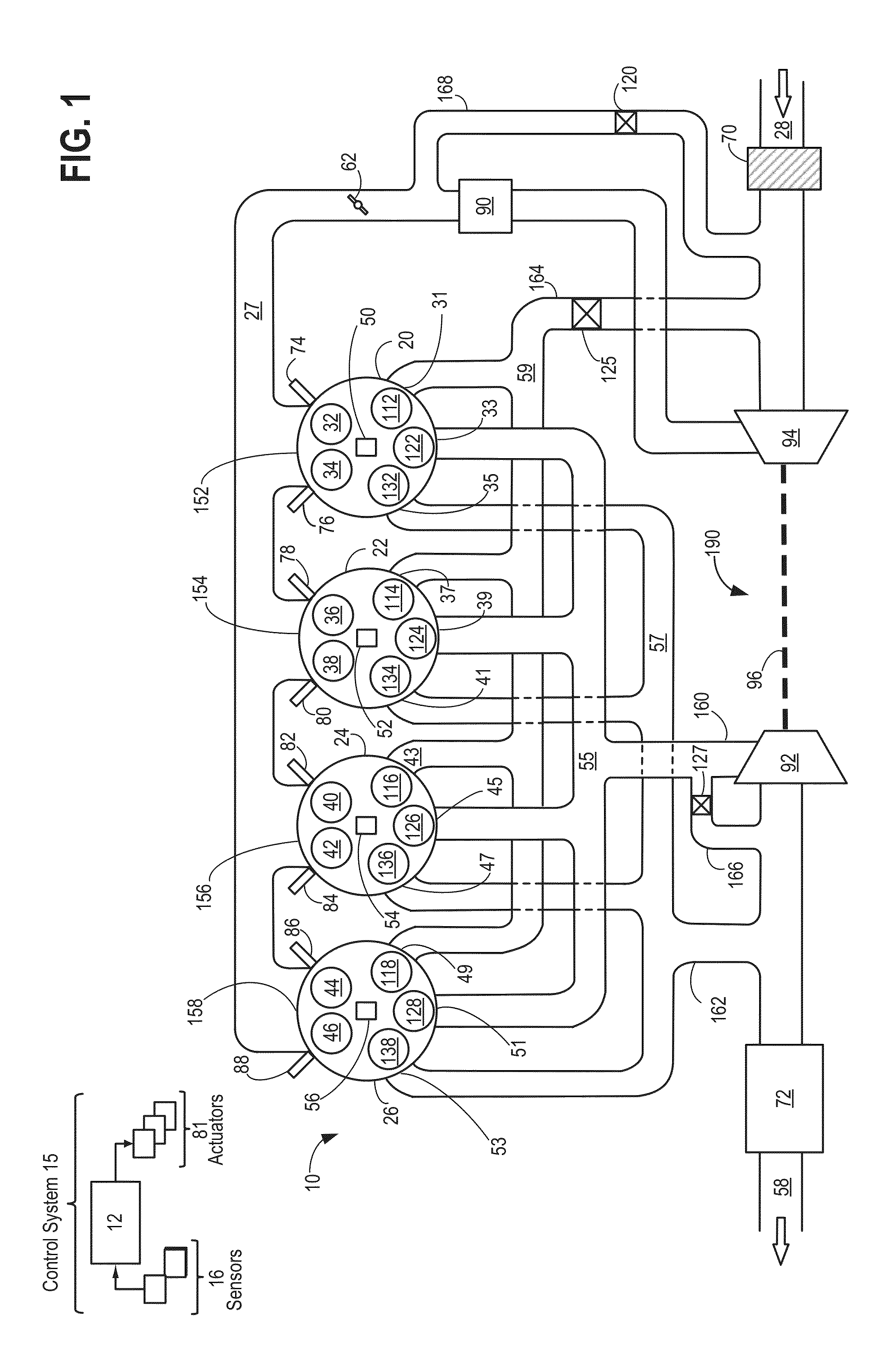
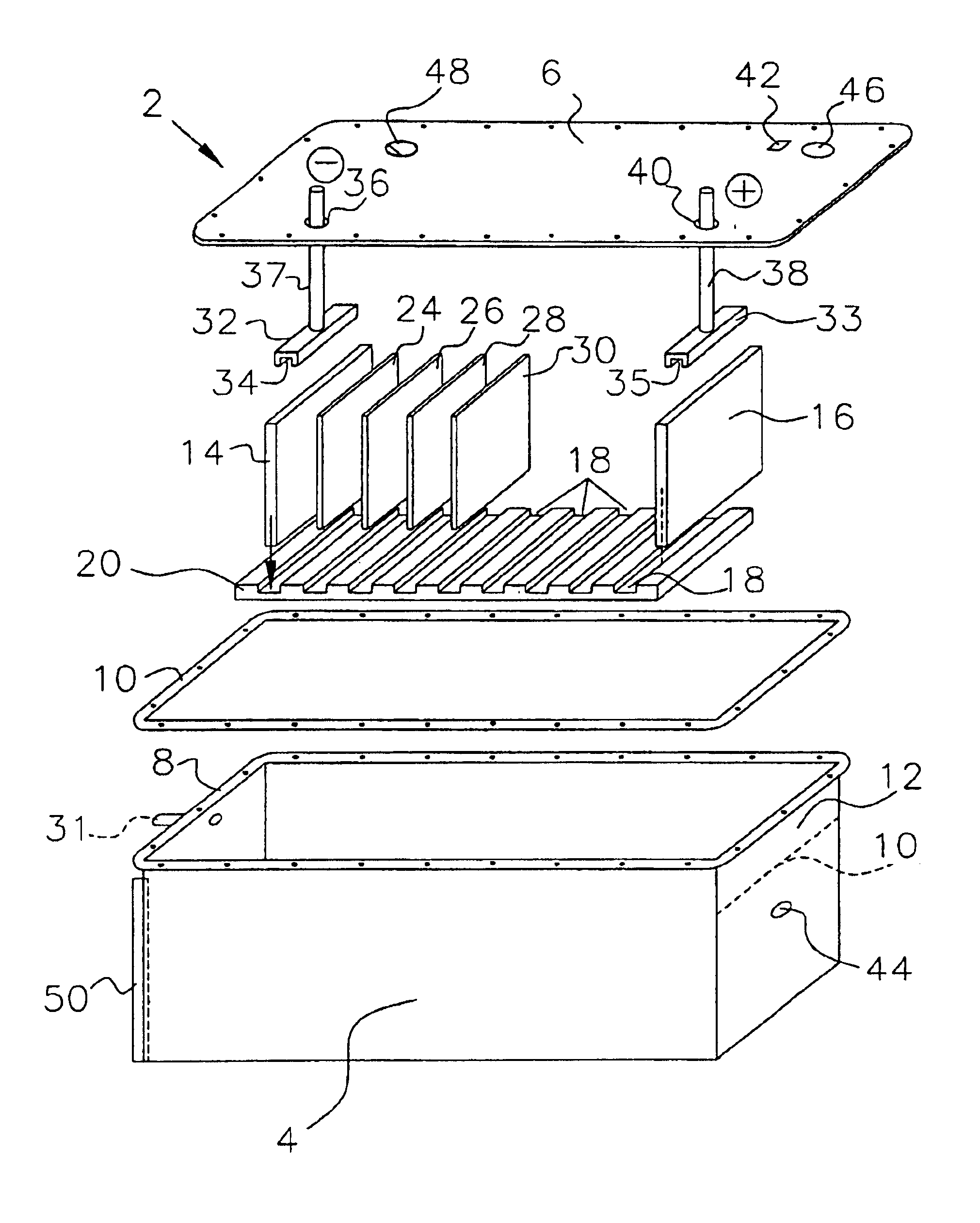
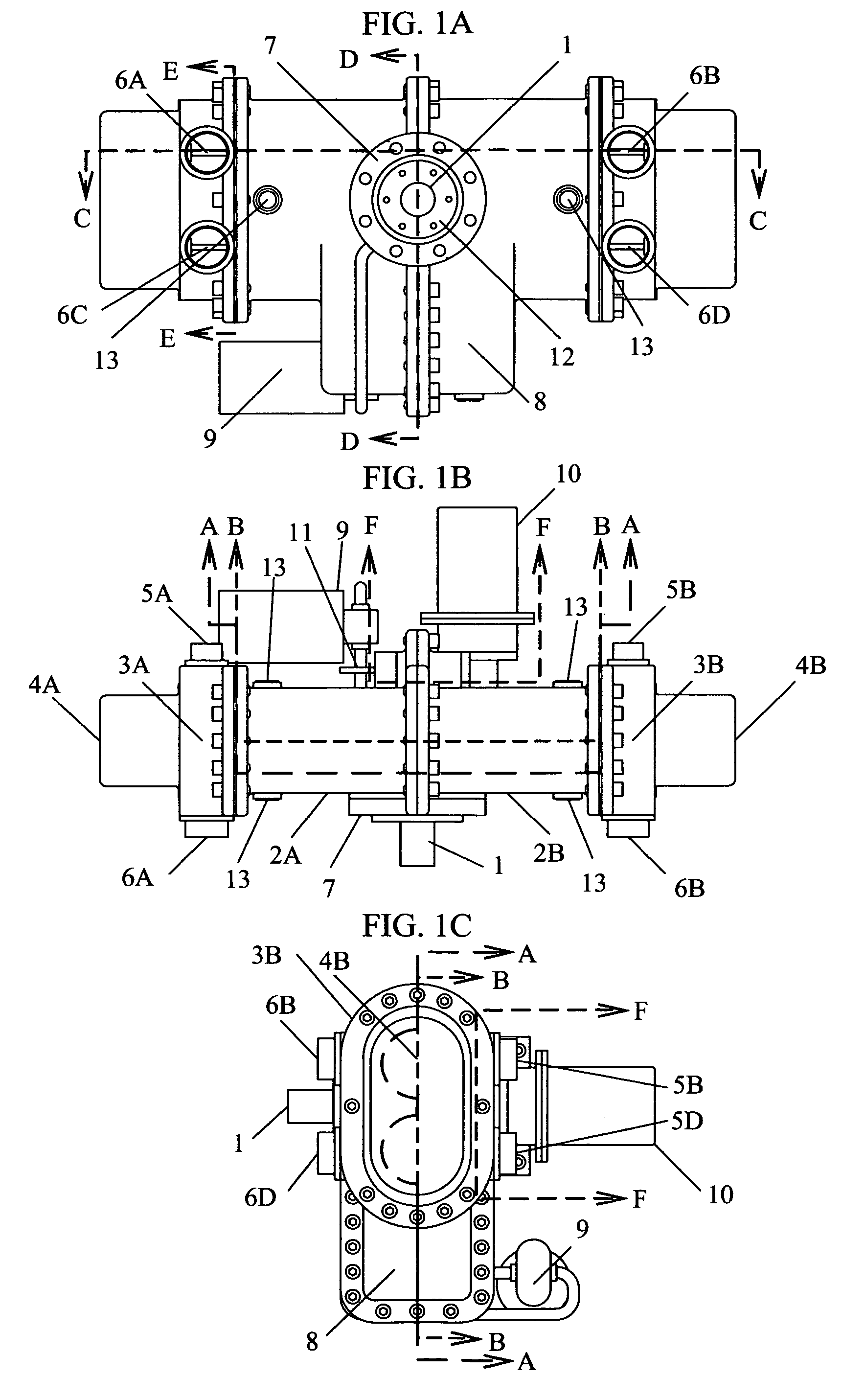
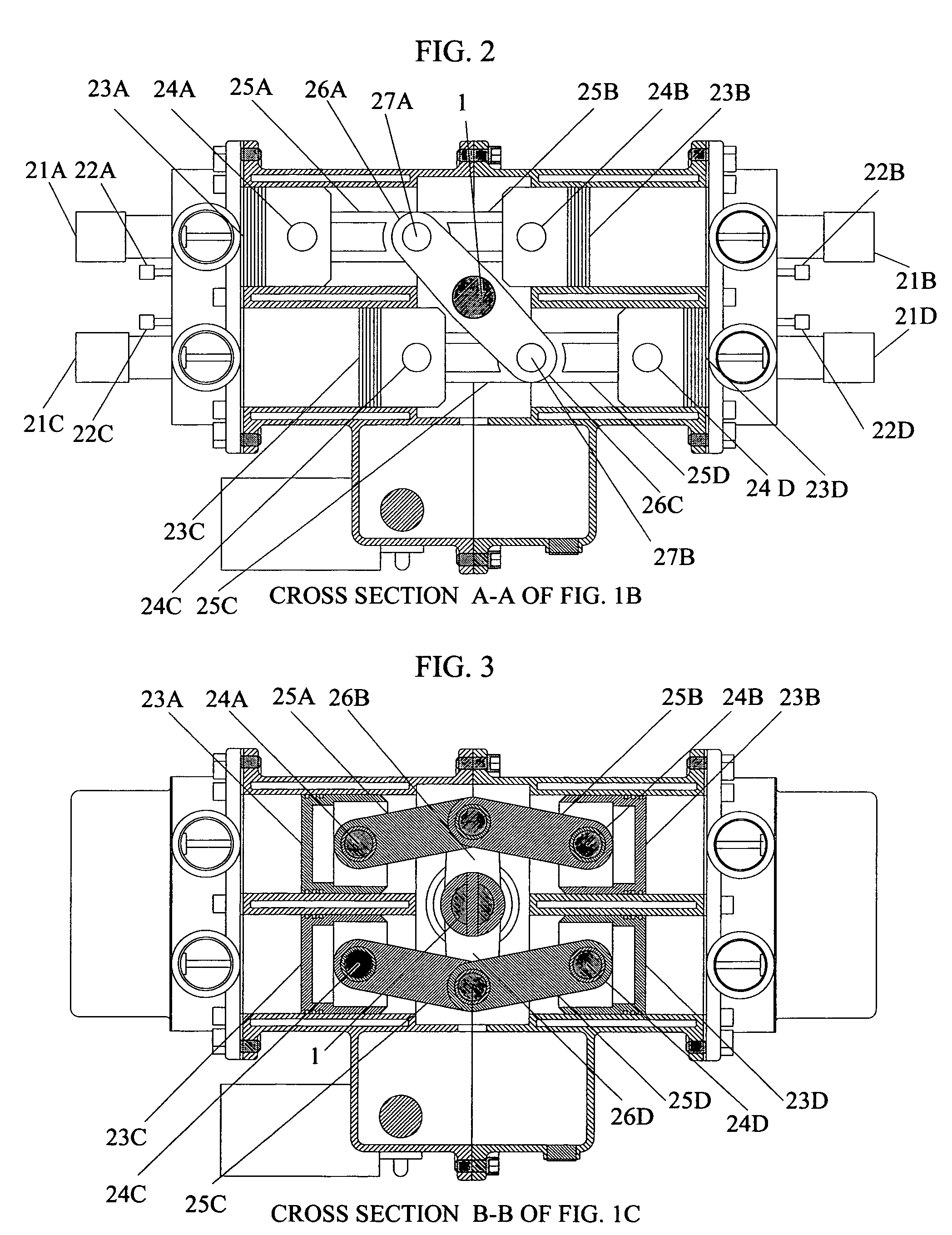
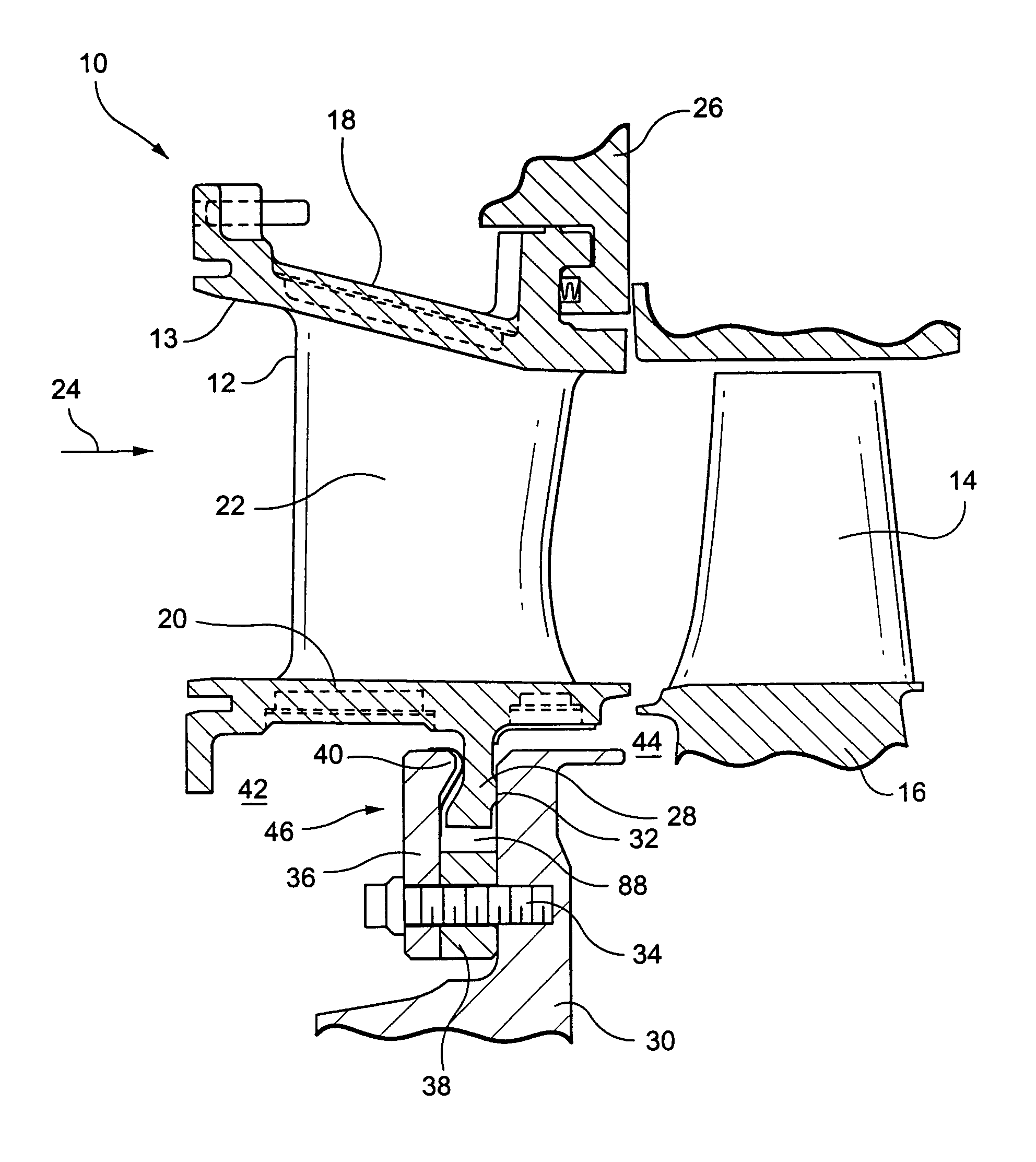
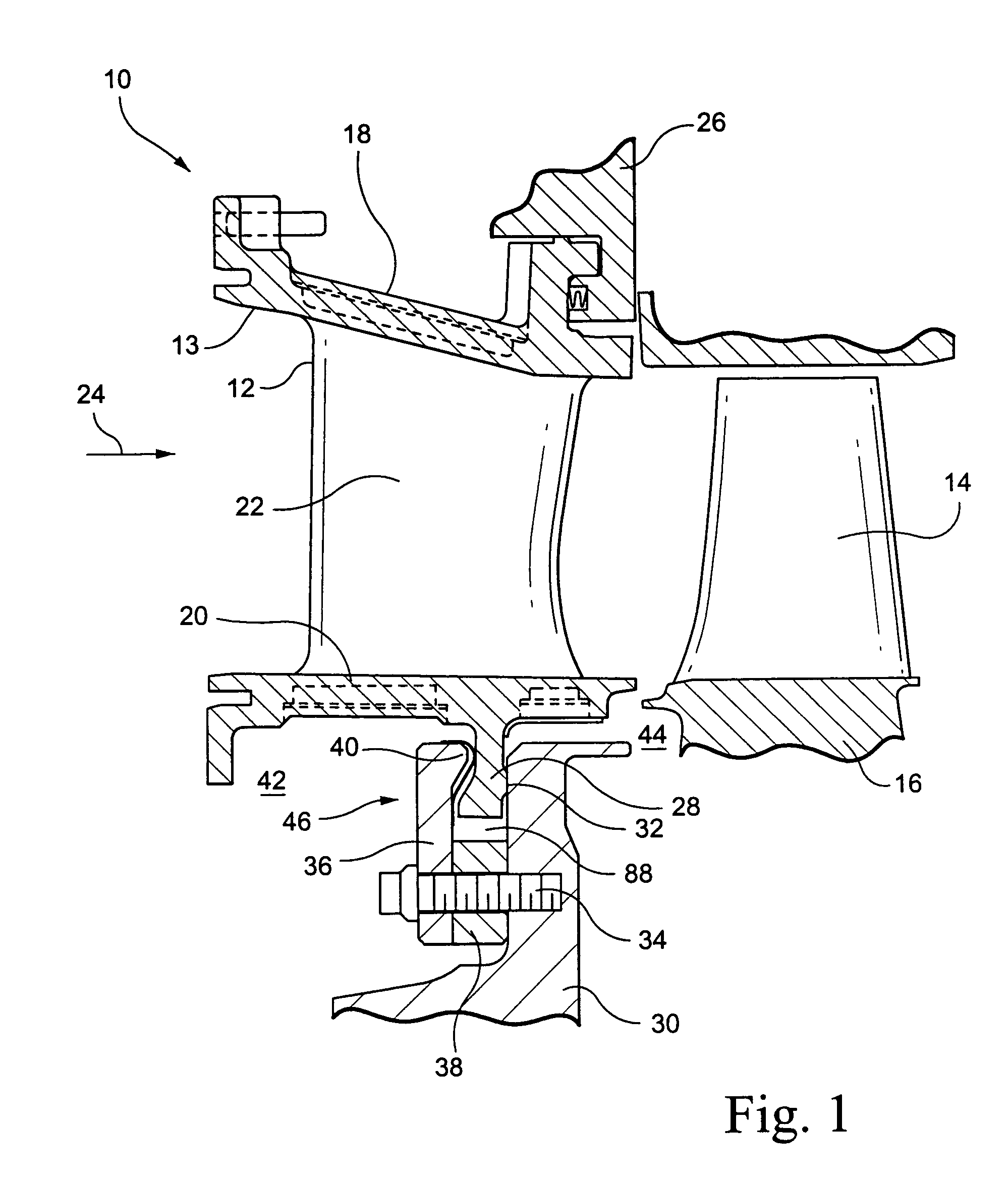
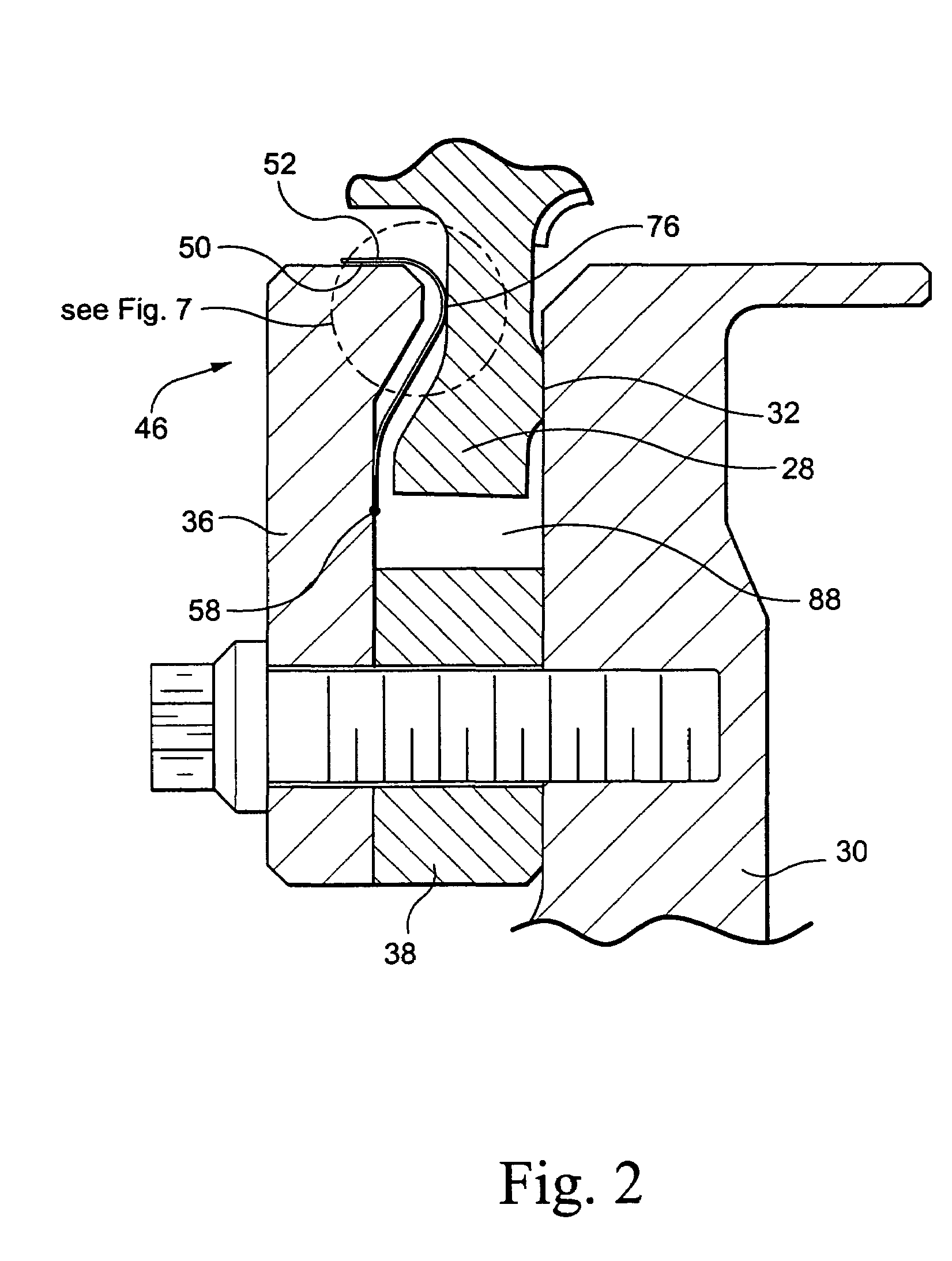
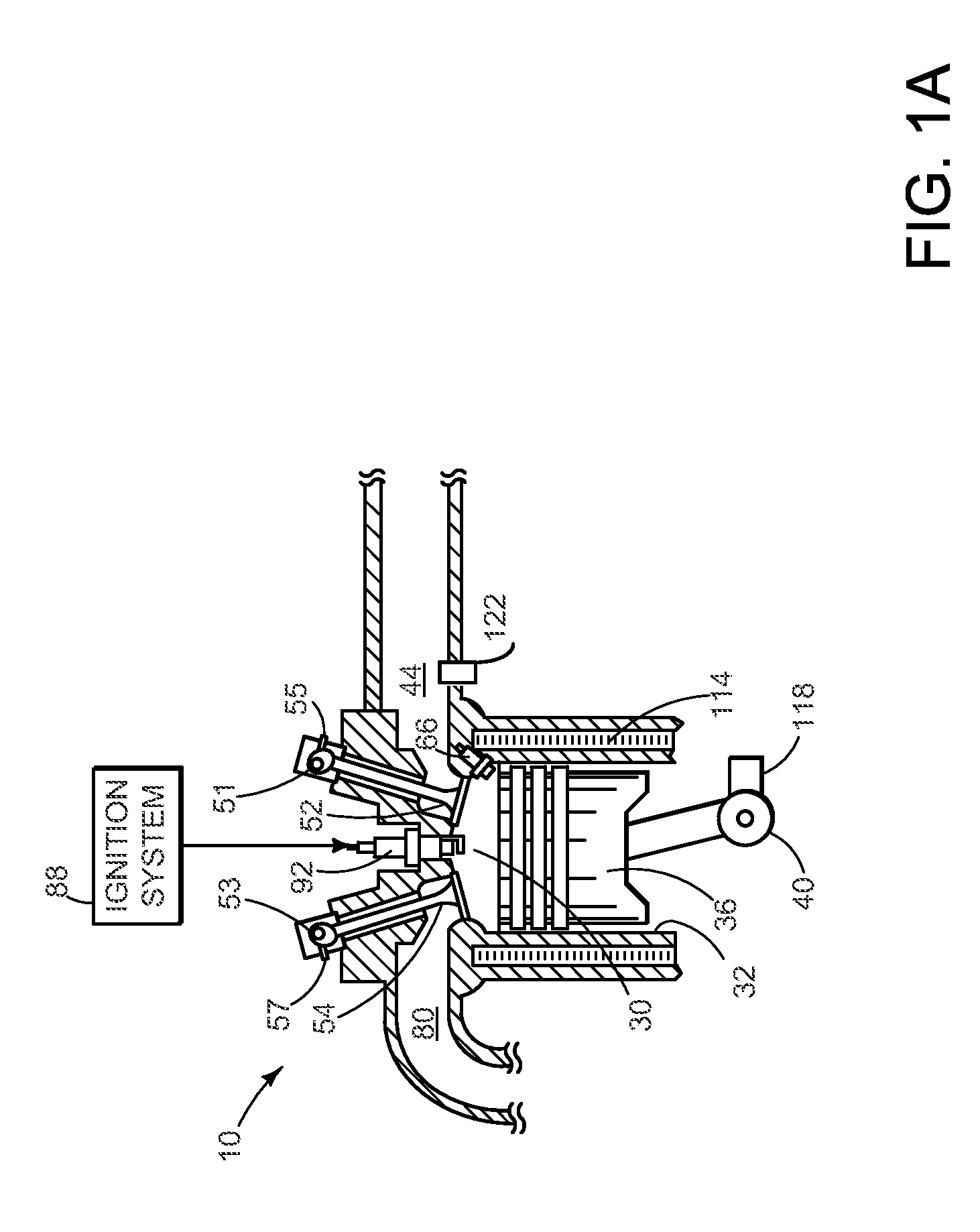
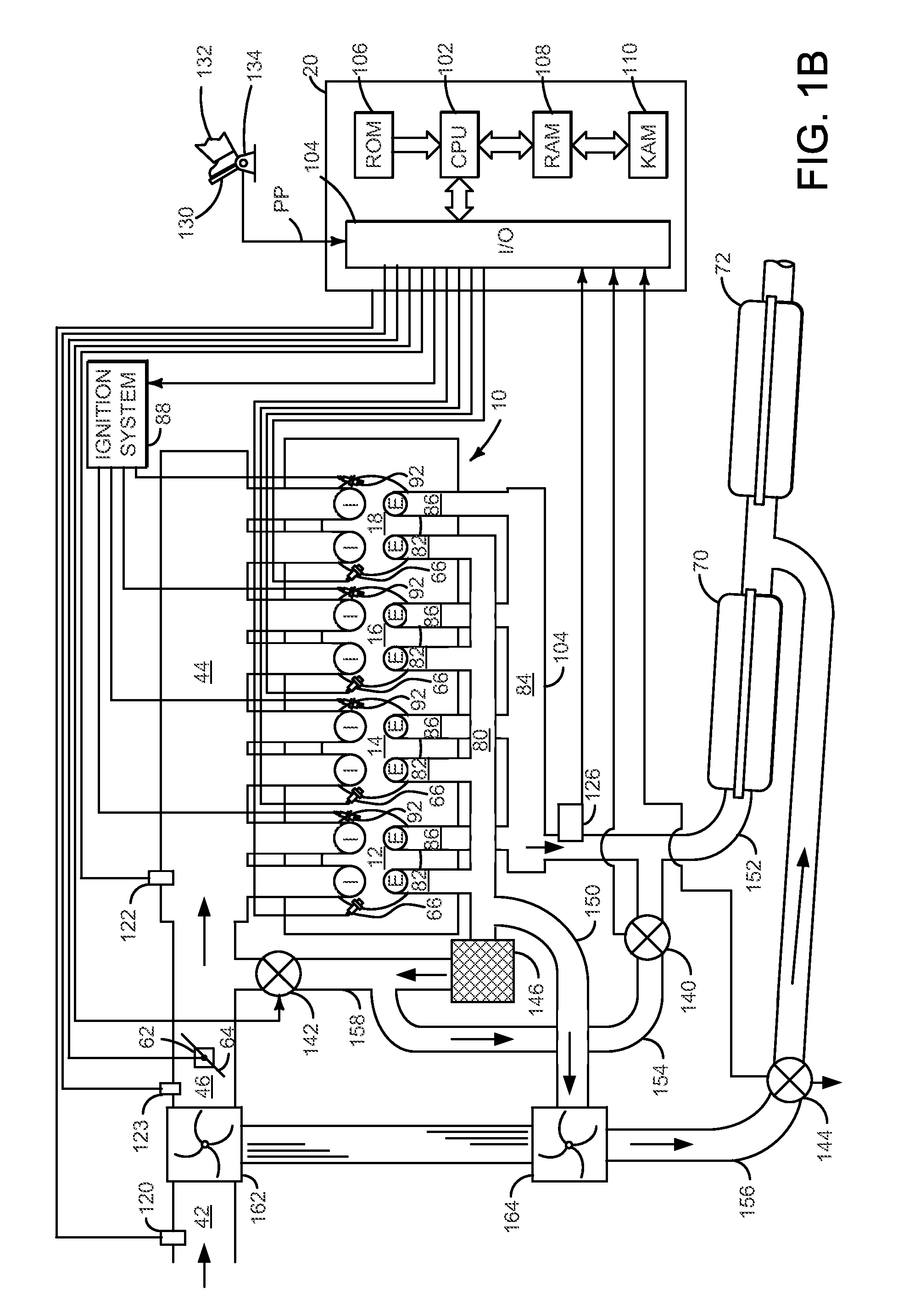
Internal combustion engine with a single crankshaft and having opposed cylinders with opposed pistons
InactiveUS6170443B1MiniaturizationEliminates dynamic imbalanceCombustion enginesReciprocating piston enginesExternal combustion engineEngineering
A two-stroke internal combustion engine is disclosed having opposed cylinders, each cylinder having a pair of opposed pistons, with all the pistons connected to a common central crankshaft. The inboard pistons of each cylinder are connected to the crankshaft with pushrods and the outboard pistons are connected to the crankshaft with pullrods. This configuration results in a compact engine with a very low profile, in which the free mass forces can be essentially totally balanced. The engine configuration also allows for asymmetrical timing of the intake and exhaust ports through independent angular positioning of the eccentrics on the crankshaft, making the engine suitable for supercharging.
Owner:ADVANCED PROPULSION TECH +1
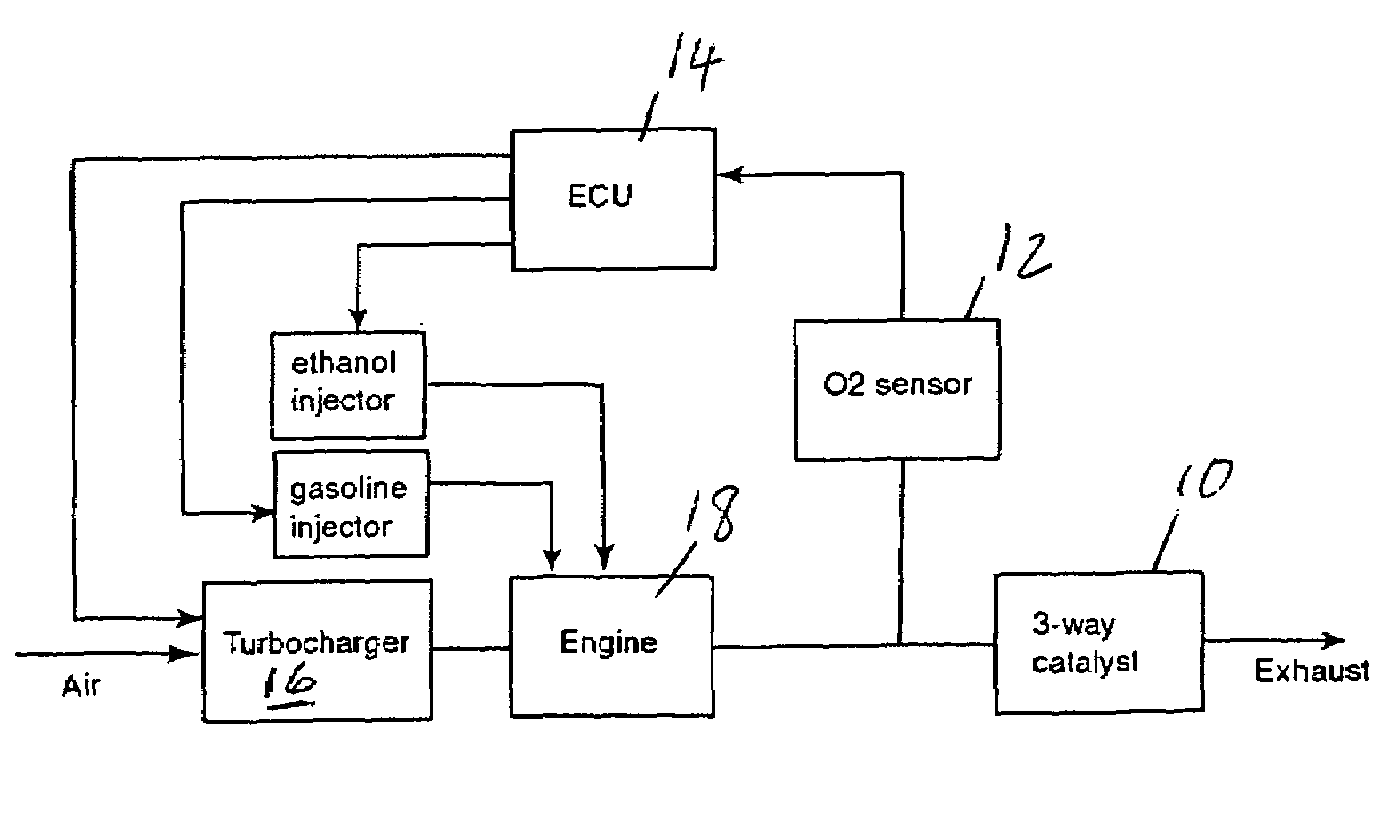
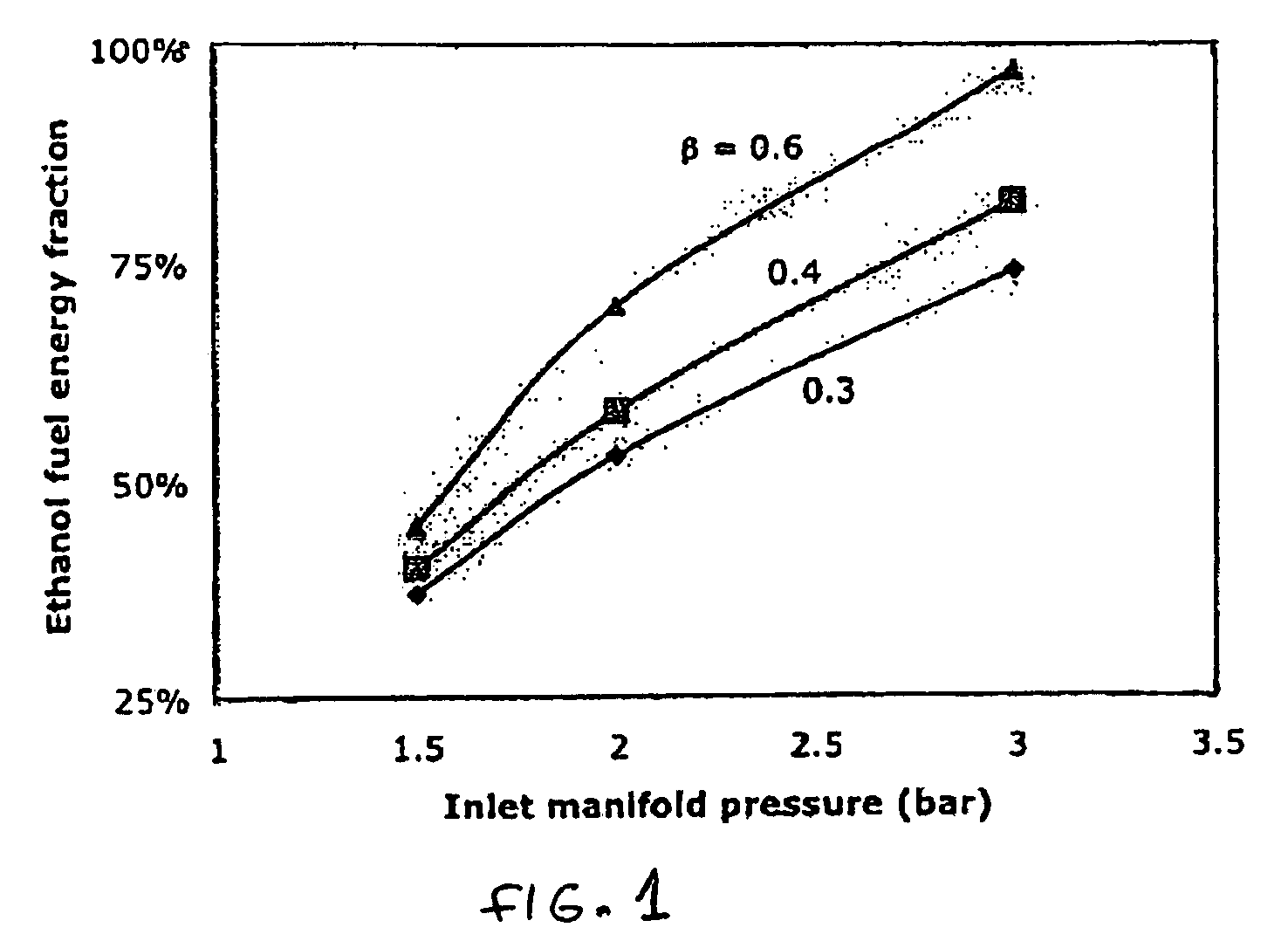
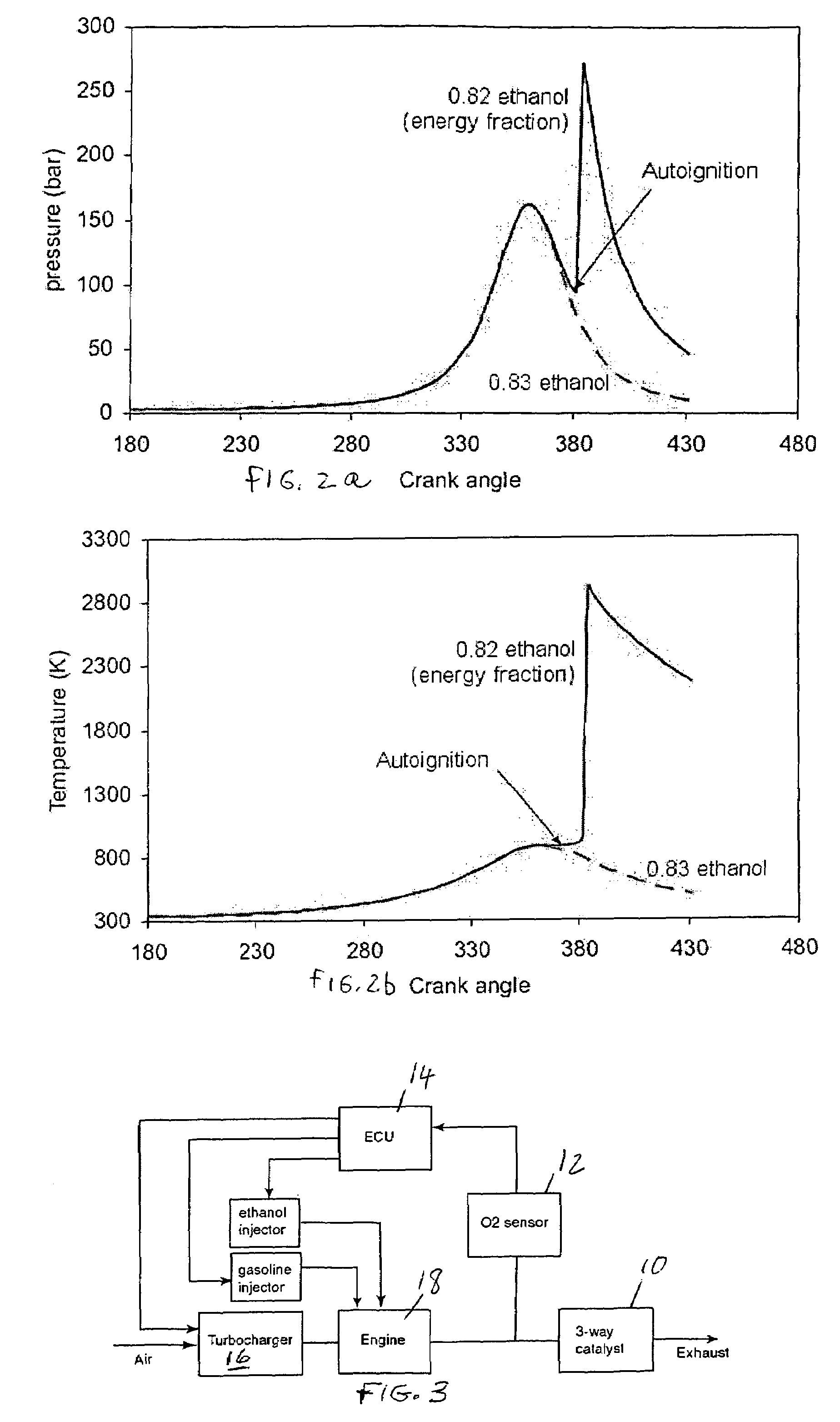
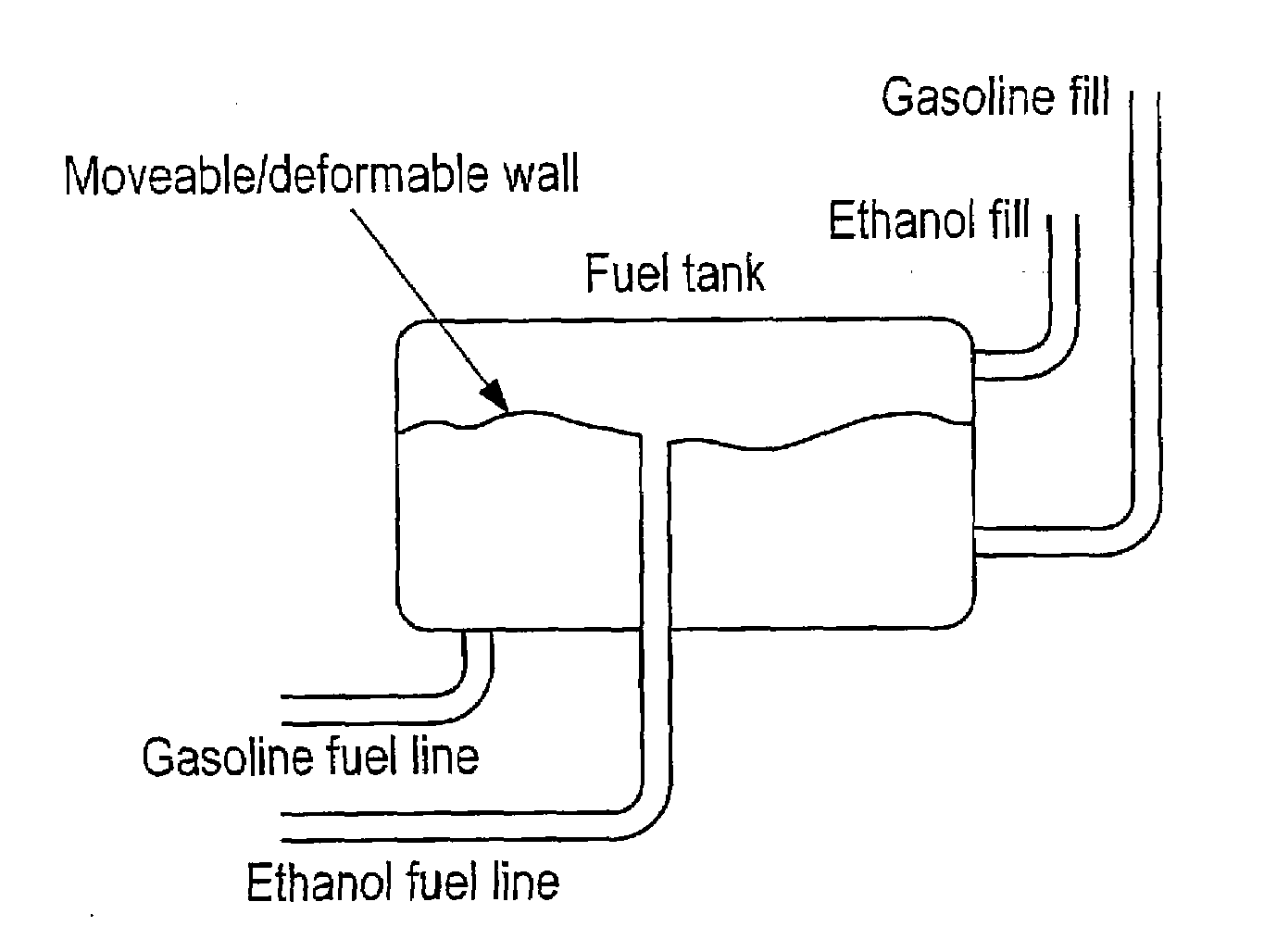
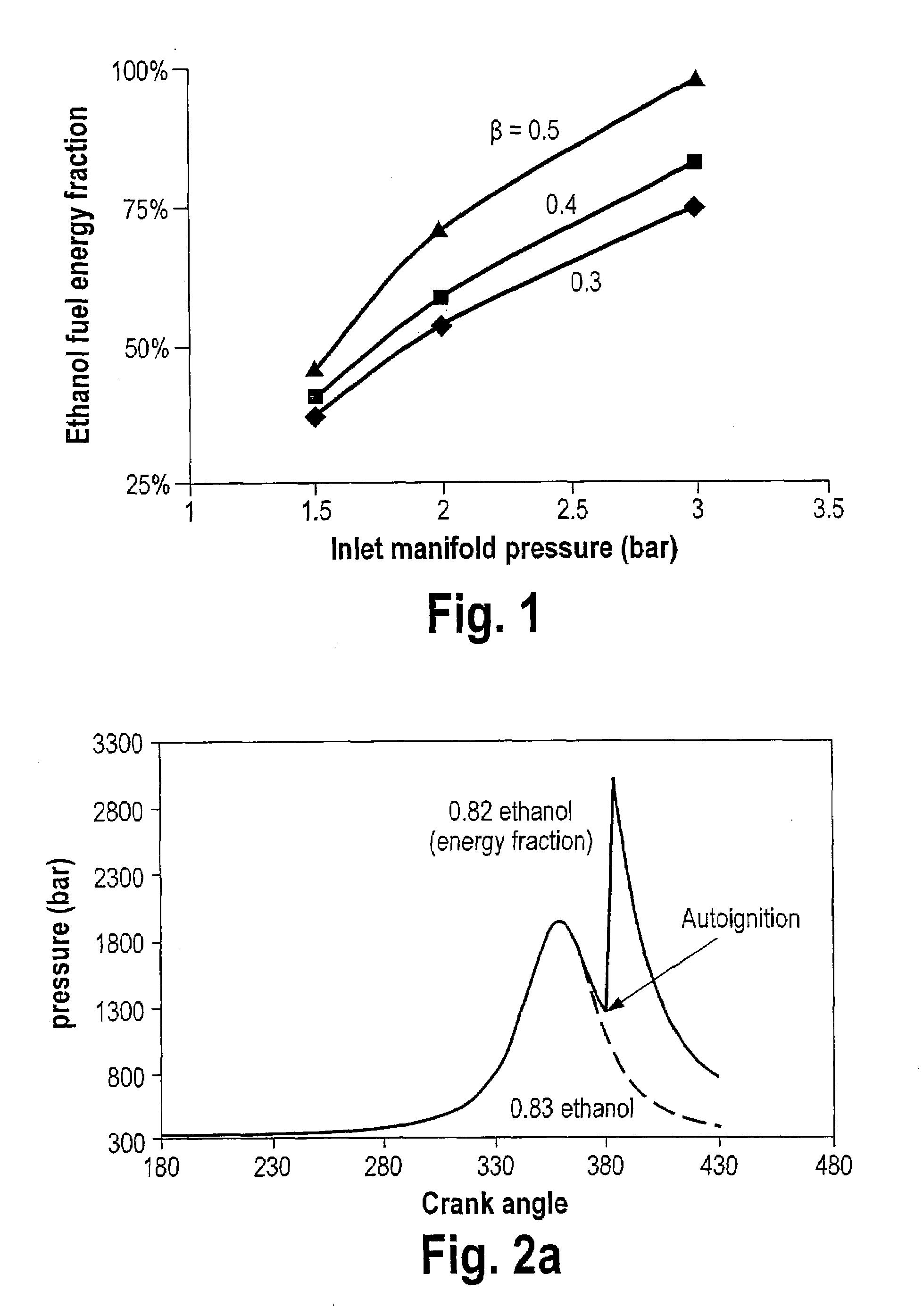
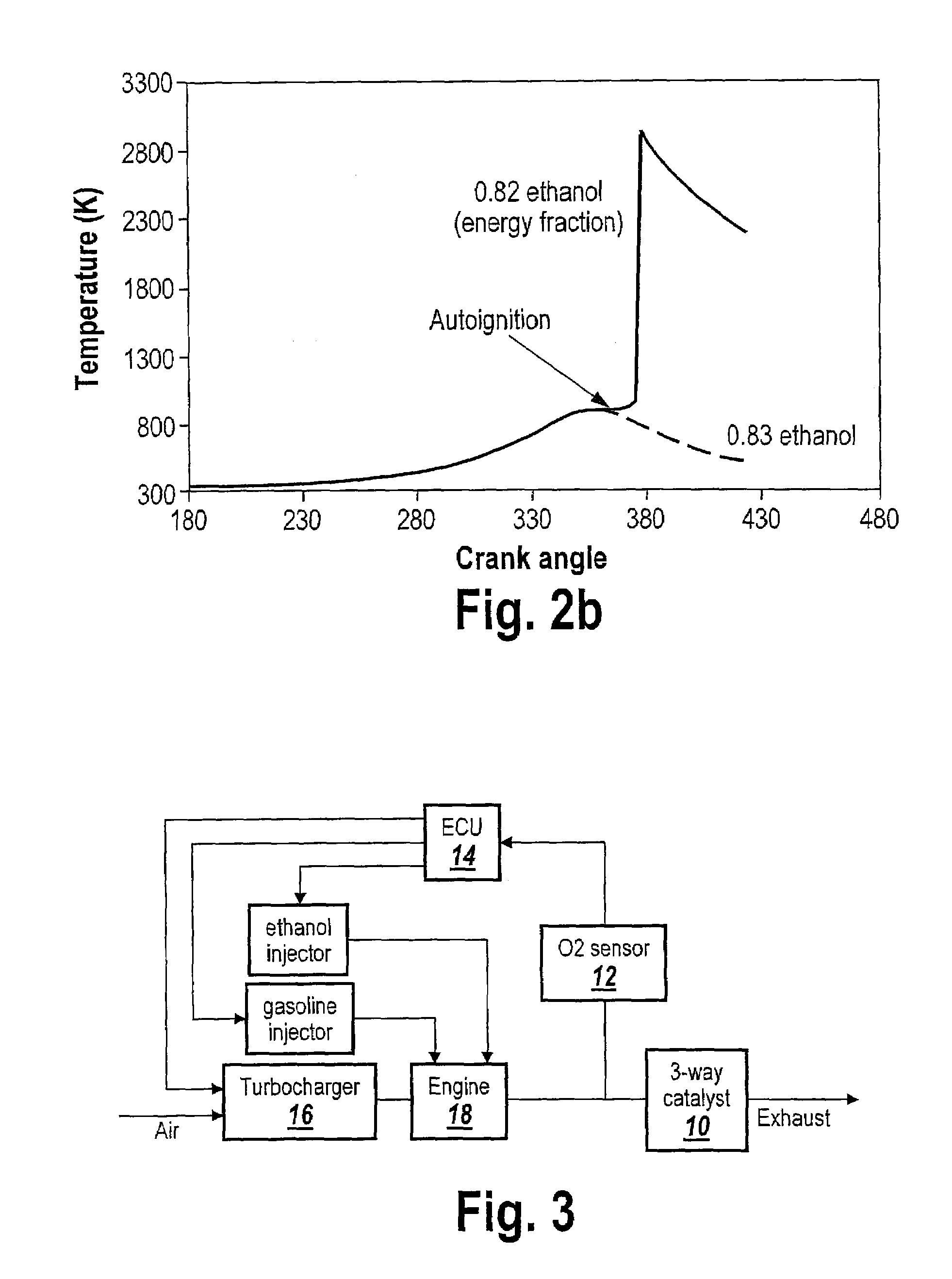
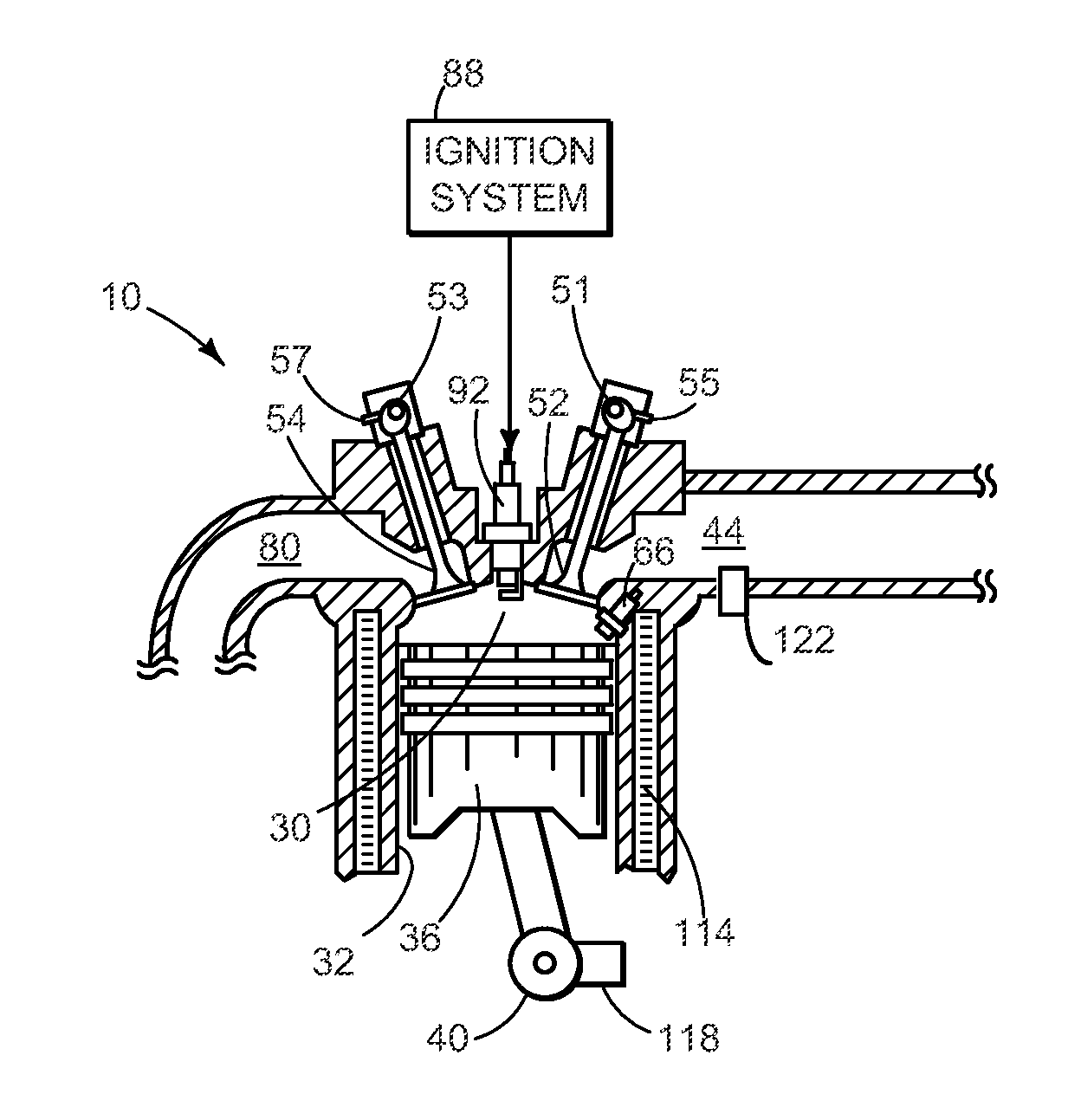
Optimized fuel management system for direct injection ethanol enhancement of gasoline engines
InactiveUS7225787B2Save gasImprove engine efficiencyElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEngineeringProcess engineering
Fuel management system for enhanced operation of a spark ignition gasoline engine. Injectors inject an anti-knock agent such as ethanol directly into a cylinder. It is preferred that the direct injection occur after the inlet valve is closed. It is also preferred that stoichiometric operation with a three way catalyst be used to minimize emissions. In addition, it is also preferred that the anti-knock agents have a heat of vaporization per unit of combustion energy that is at least three times that of gasoline.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
High temperature erosion resistant, abradable thermal barrier composite coating
InactiveUS6235370B1Improve wear resistanceImprove adhesionMolten spray coatingPump componentsCombustorHoneycomb
A composite thermal barrier coating system includes a honeycomb metallic structure filled with high thermal expansion ceramic hollow spheres in a phosphate bonded matrix. The composite thermal barrier coating system may be manufactured to thicknesses in excess of current thermal barrier coating systems, thereby imparting greater thermal protection. Superior erosion resistance and abrasion properties are also achieved. The composite thermal barrier coating is useful on combustion turbine components such as ring seal segments, vane segment shrouds, transitions and combustors.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
High efficiency compact gas turbine engine
InactiveUS20120324903A1Improve engine efficiencyThe process is compact and efficientGas turbine plantsEfficient propulsion technologiesWorking fluidCombustor
This disclosure relates to a highly efficient gas turbine engine architecture utilizing multiple stages of intercooling and reheat, ceramic technology, turbocharger technology and high pressure combustion. The approach includes utilizing a conventional dry low NOx combustor for the main combustor and thermal reactors for the reheat apparatuses. In a first configuration, there are three separate turbo-compressor spools and a free power turbine spool. In a second configuration, there are three separate turbo-compressor spools but no free power spool. In a third configuration, all the compressors and turbines are on a single shaft. Each of these configurations can include two stages of intercooling, two stages of reheat and a recuperator to preheat the working fluid before it enters the main combustor.
Owner:ICR TURBINE ENGINE CORP
Method to improve blowthrough and egr via split exhaust
ActiveUS20150316005A1Increase engine power densityReduced fuel economyValve arrangementsElectrical controlAutomotive engineeringTurbine
Methods and systems are provided for a boosted engine having a split exhaust system. In one example, a method comprises directing exhaust from a first cylinder group to one or more of a pre-compressor location, a post-compressor location, and an exhaust turbine, and directing exhaust from a second cylinder group to one or more of the pre-compressor location, and the exhaust turbine. Engine efficiency and knock control may be enhanced by directing exhaust gases to different locations based on engine operating conditions.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
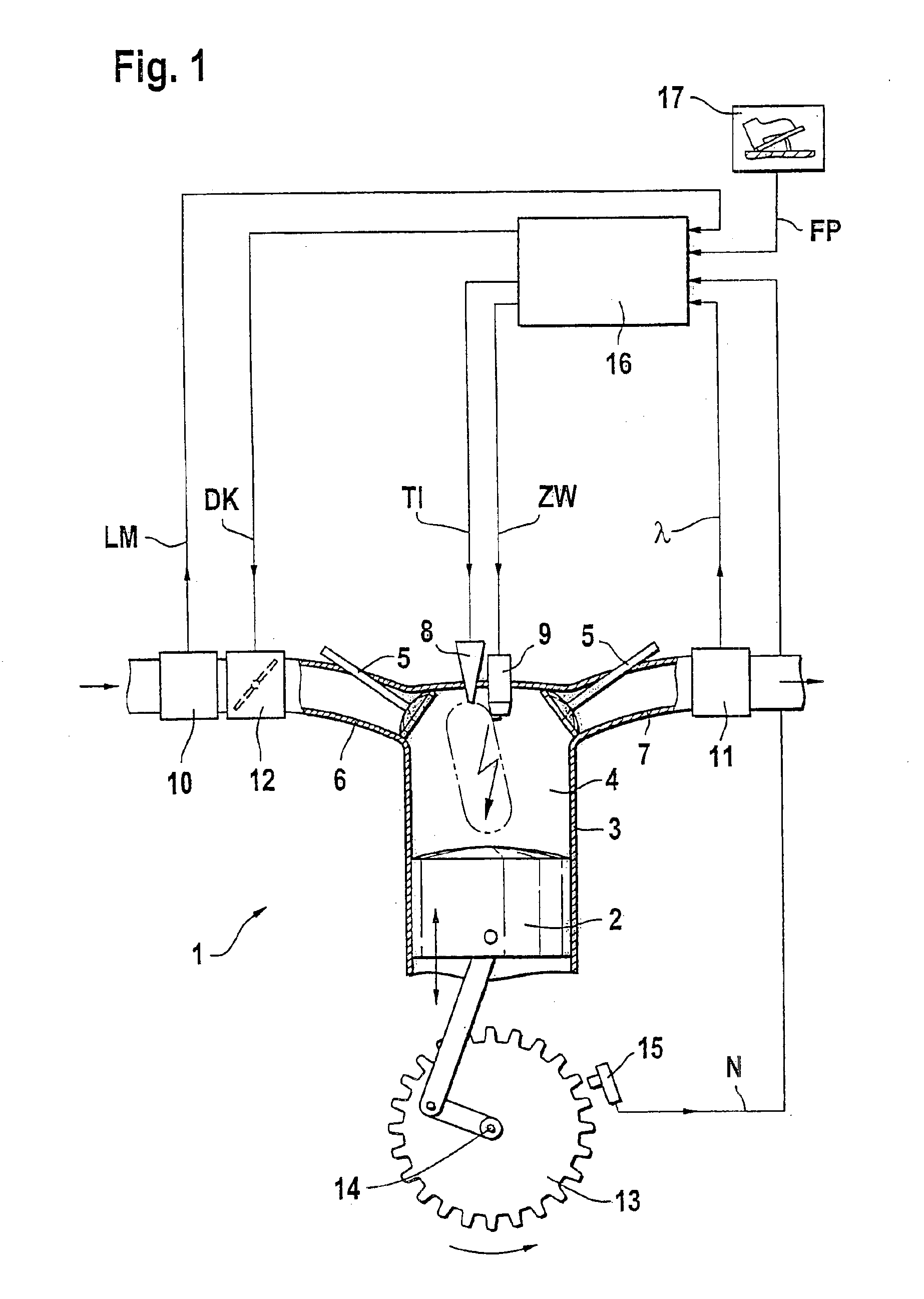
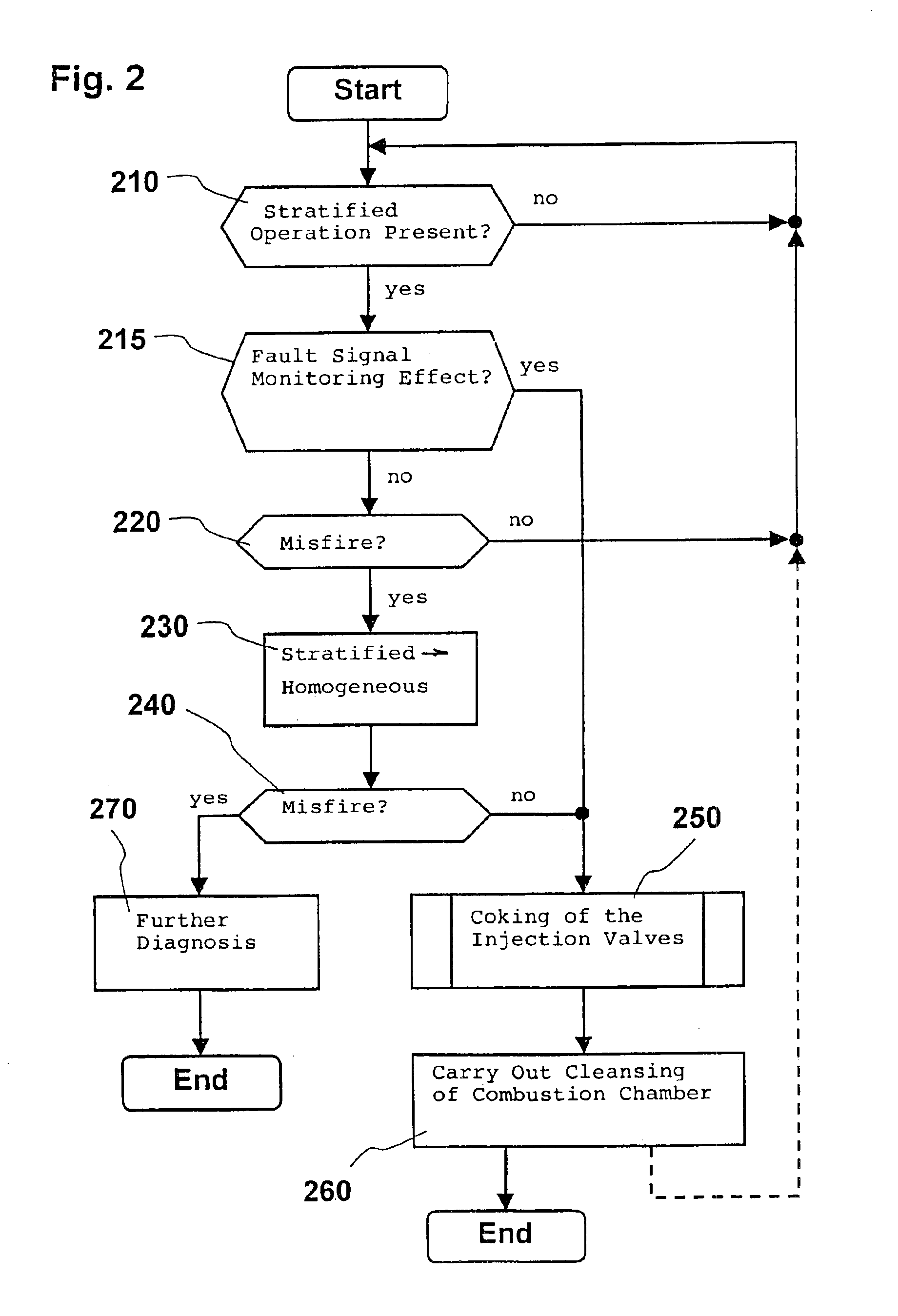
Method for operating an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6892691B1Simple meansPromote combustionAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlExternal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
The operation of an internal combustion engine under unfavorable operating conditions can lead to the formation of deposits in the combustion chamber (4). A method and an arrangement for operating an internal combustion engine (1), especially of a motor vehicle, is suggested, wherein fuel is conducted into a combustion chamber (4) and is there combusted. When deposits are detected in the combustion chamber (4), measures are initiated in a targeted manner for cleansing the combustion chamber (4). A knocking combustion is especially introduced and / or a cleansing liquid is added to the inducted combustion air.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
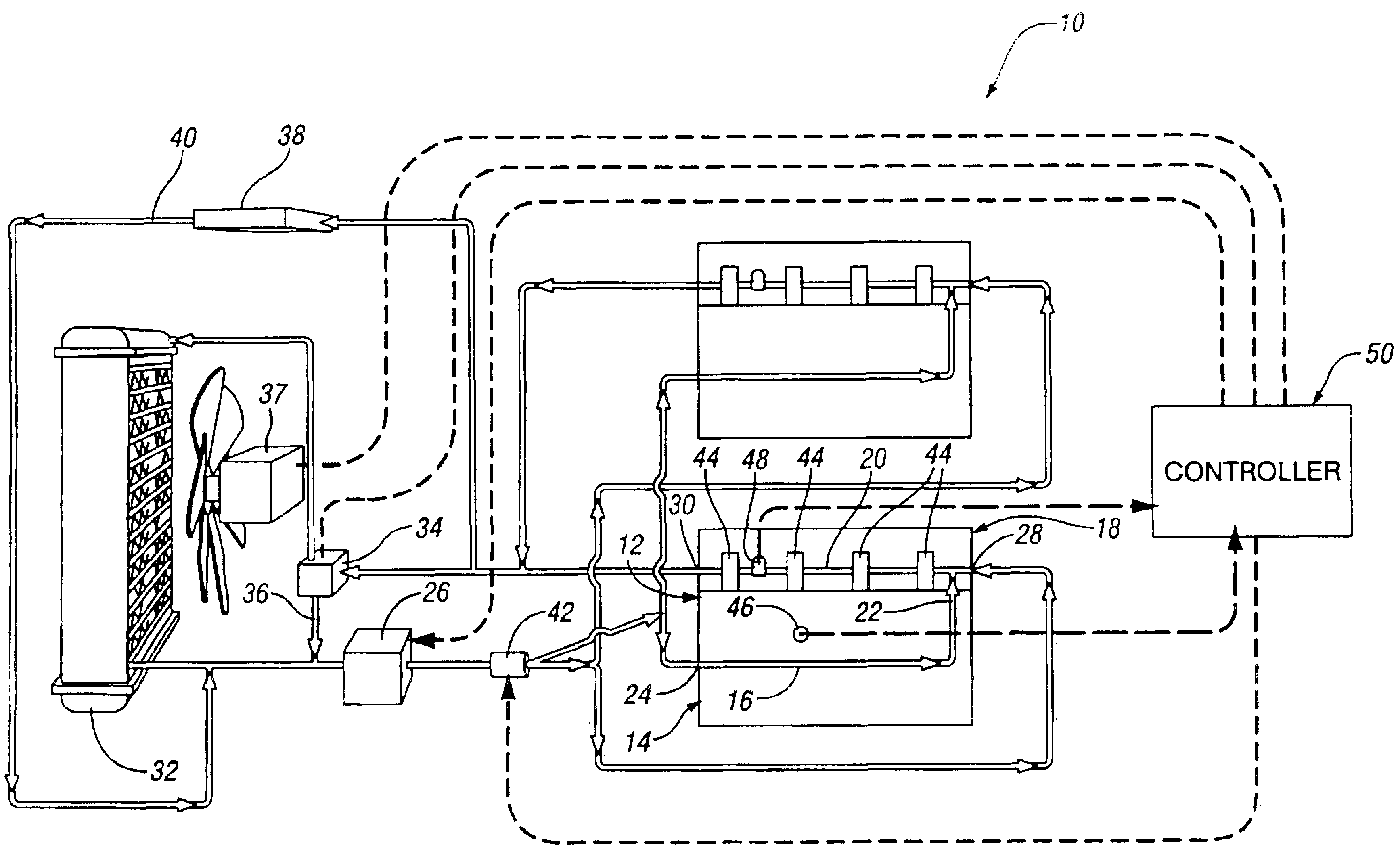
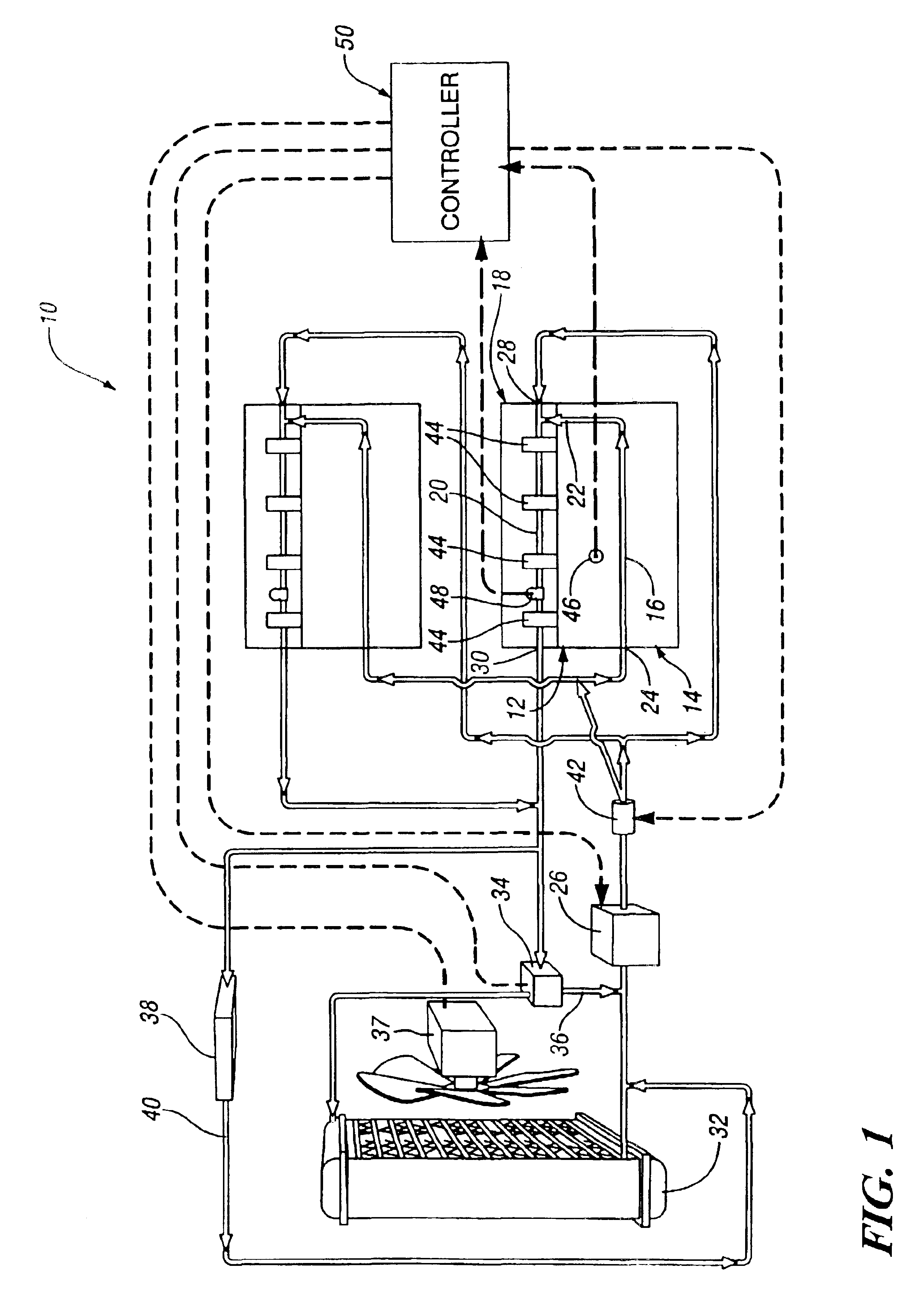
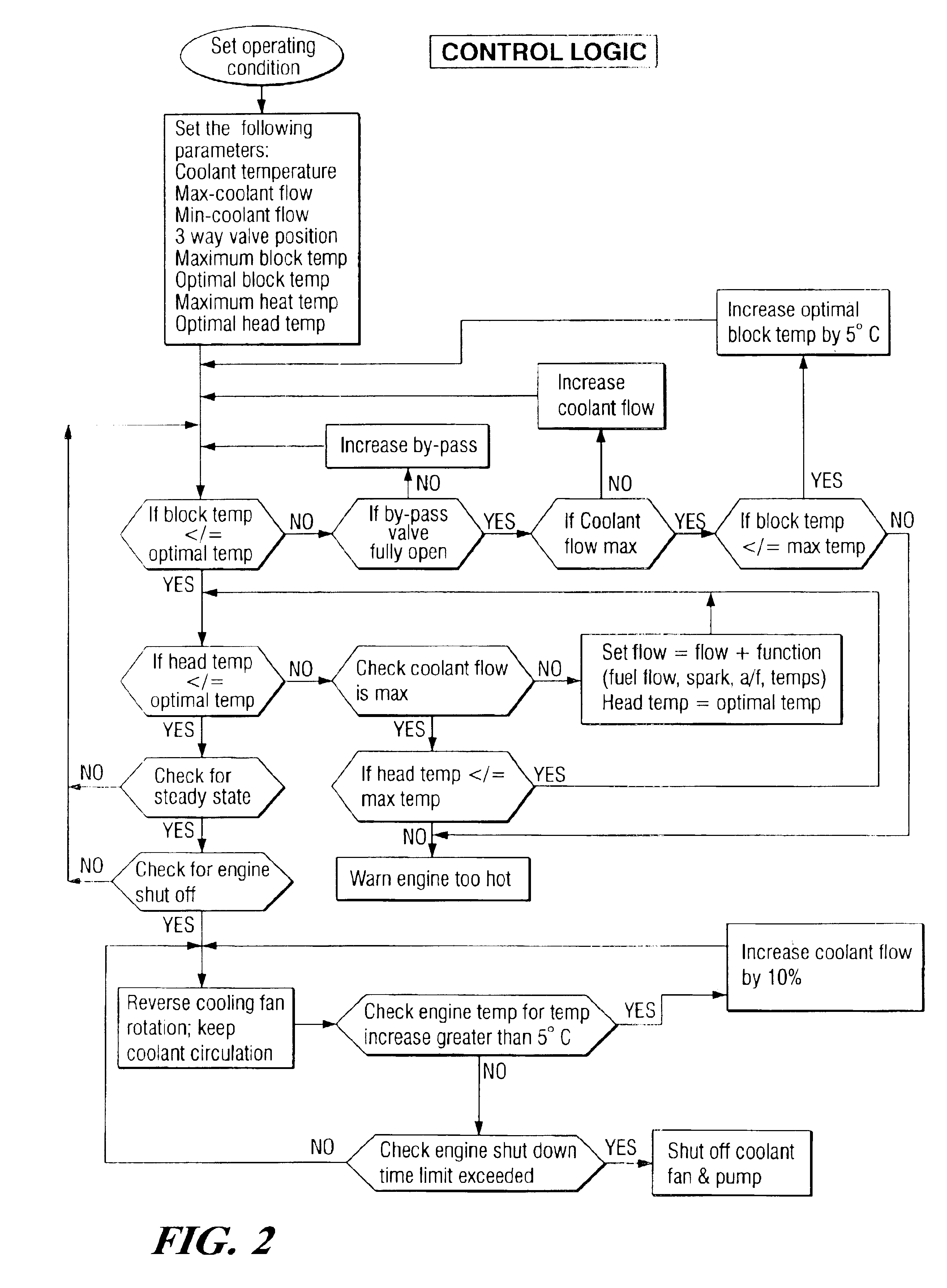
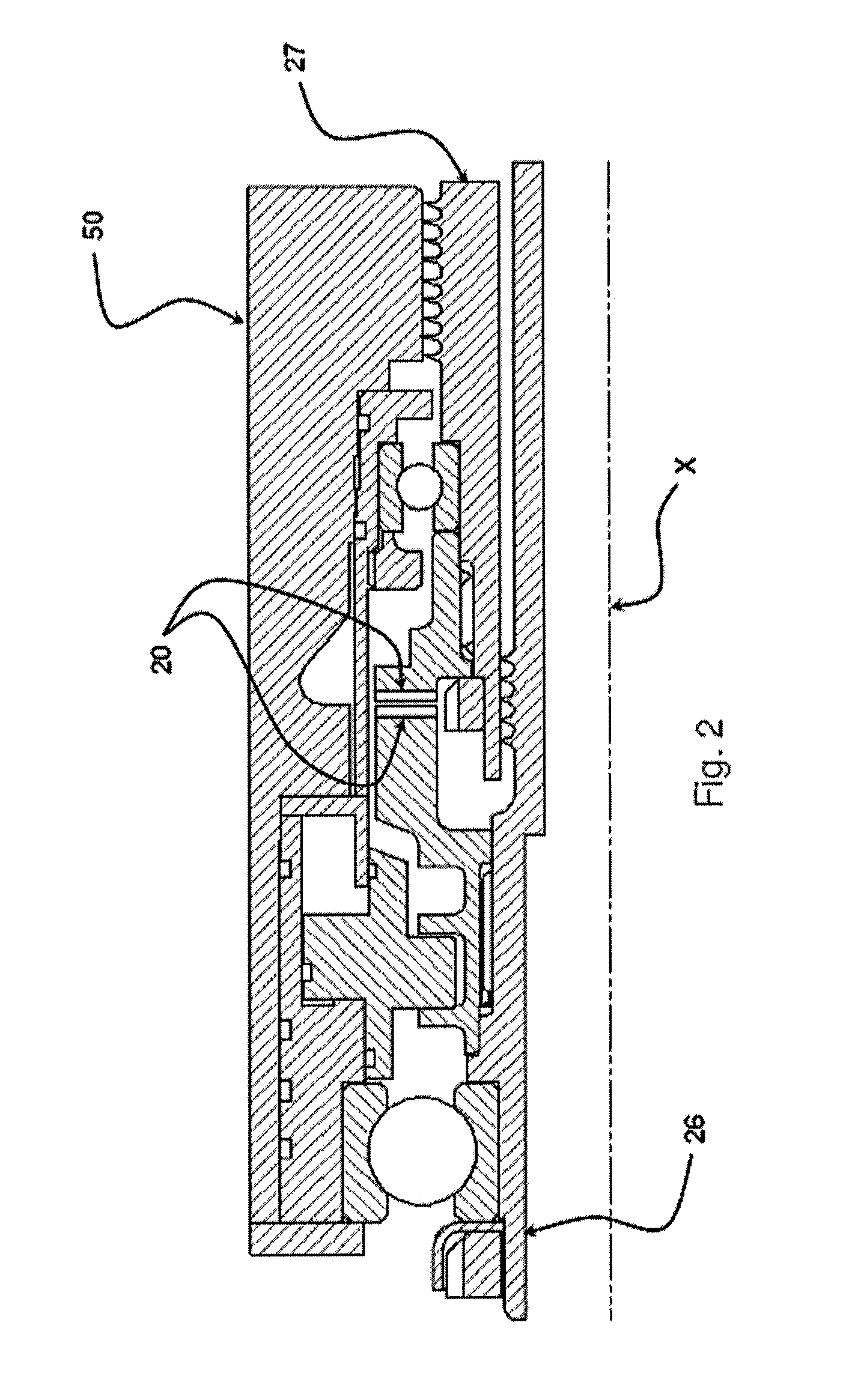
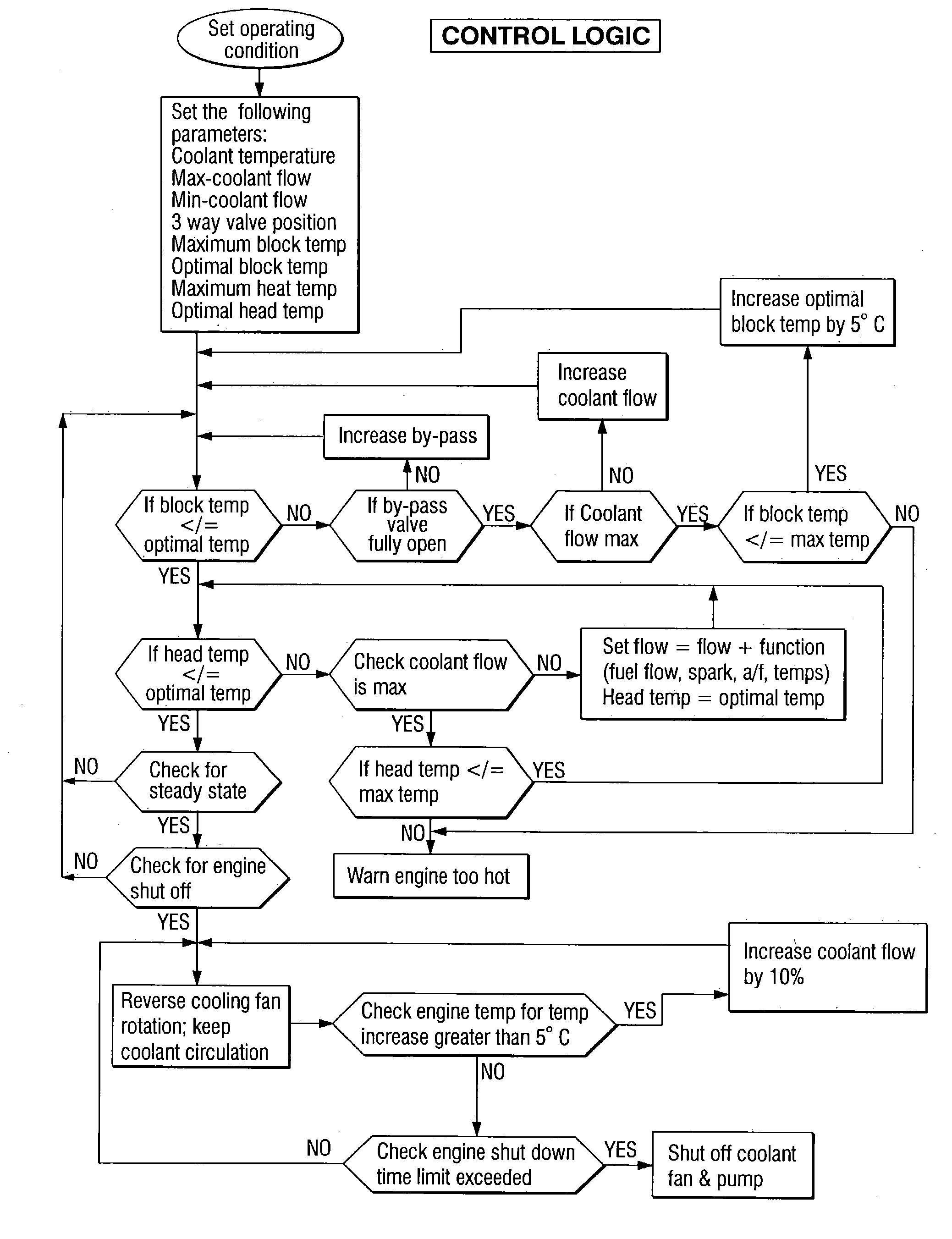
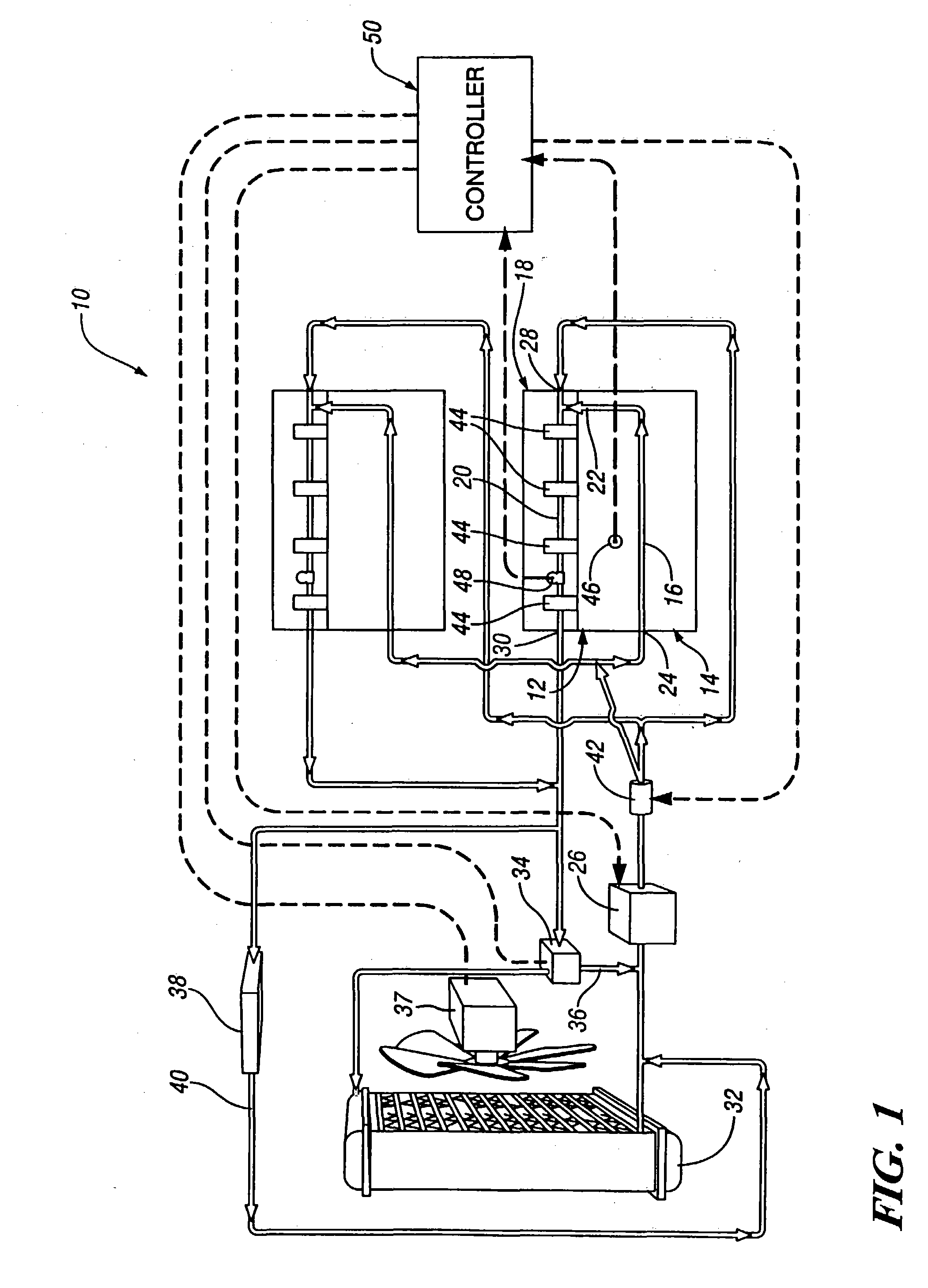
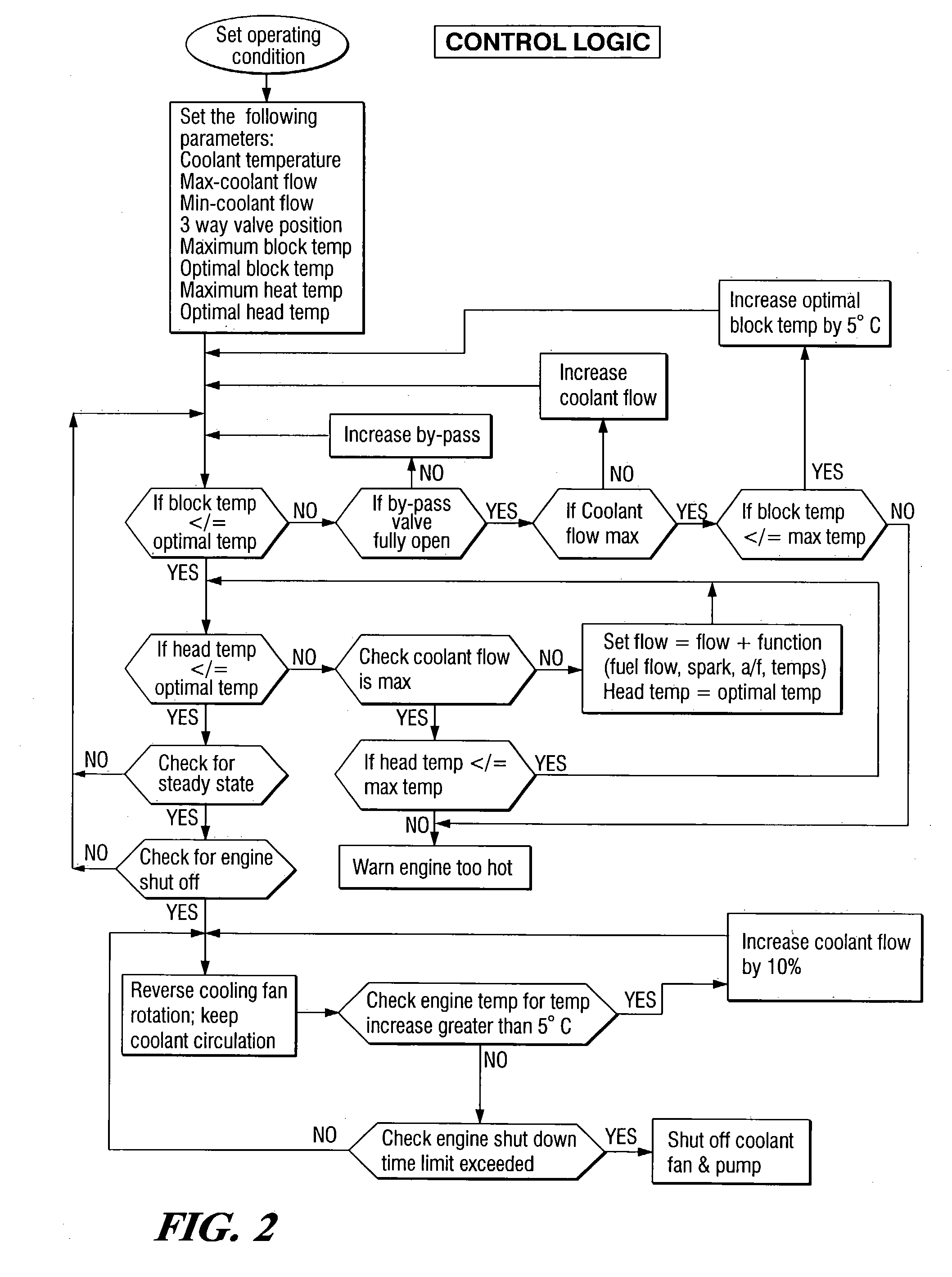
Engine cooling system
InactiveUS6955141B2Minimizes parasitic lossIncrease and decrease flow of coolantLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlCoolant flowCylinder head
A cooling system has a diverter valve to selectively control the flow of coolant through an internal combustion engine having a cylinder block with a cooling jacket and a cylinder head mounted on the block with a cooling jacket. A controller, responsive to the temperature of the block and the head, controls the diverter valve and a water pump to provide adequate coolant flow through the head and the block as needed to maintain optimal operating temperatures. After the engine is shut off, the controller continues to operate the water pump and a cooling fan to continue to cool the engine for a period of time.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
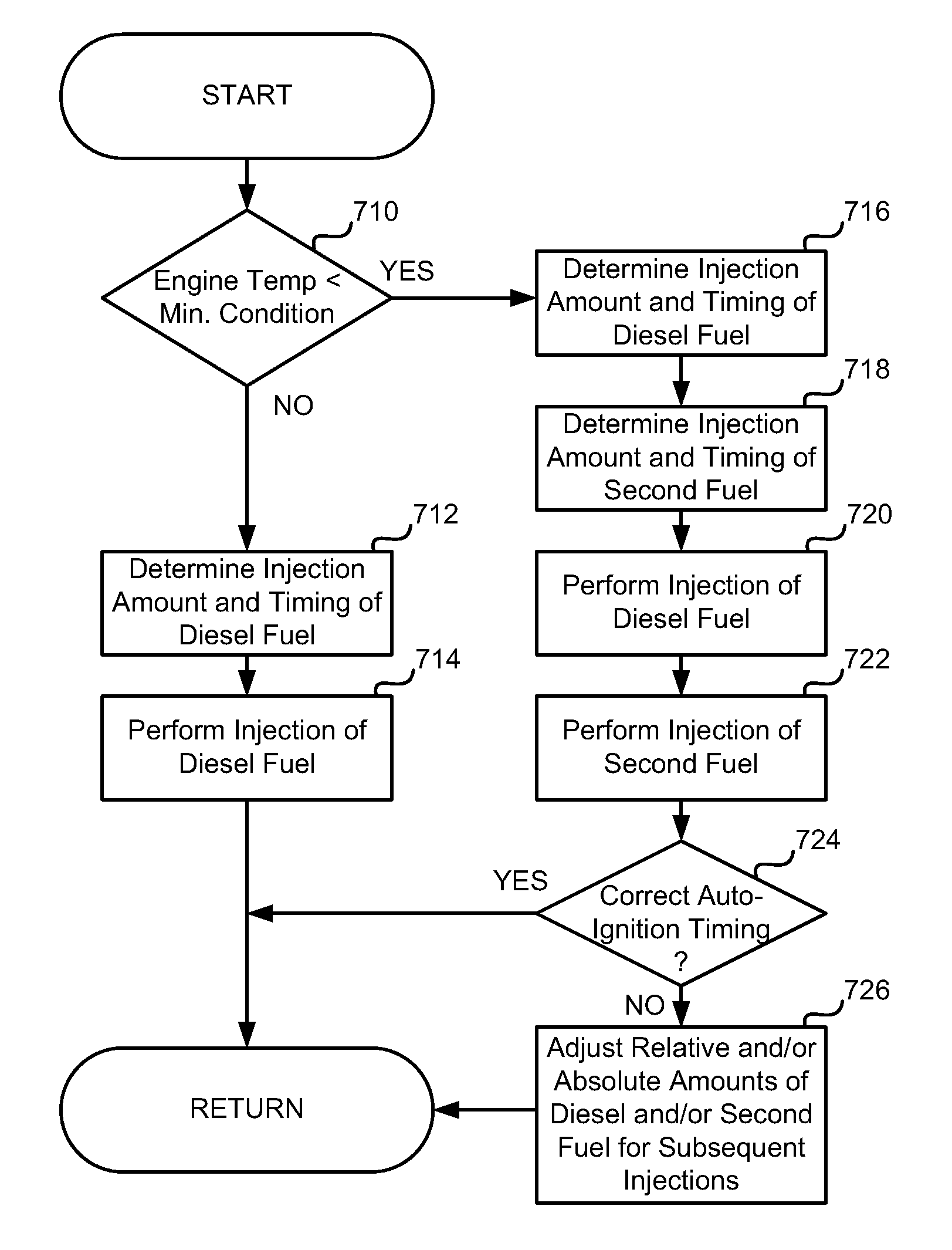
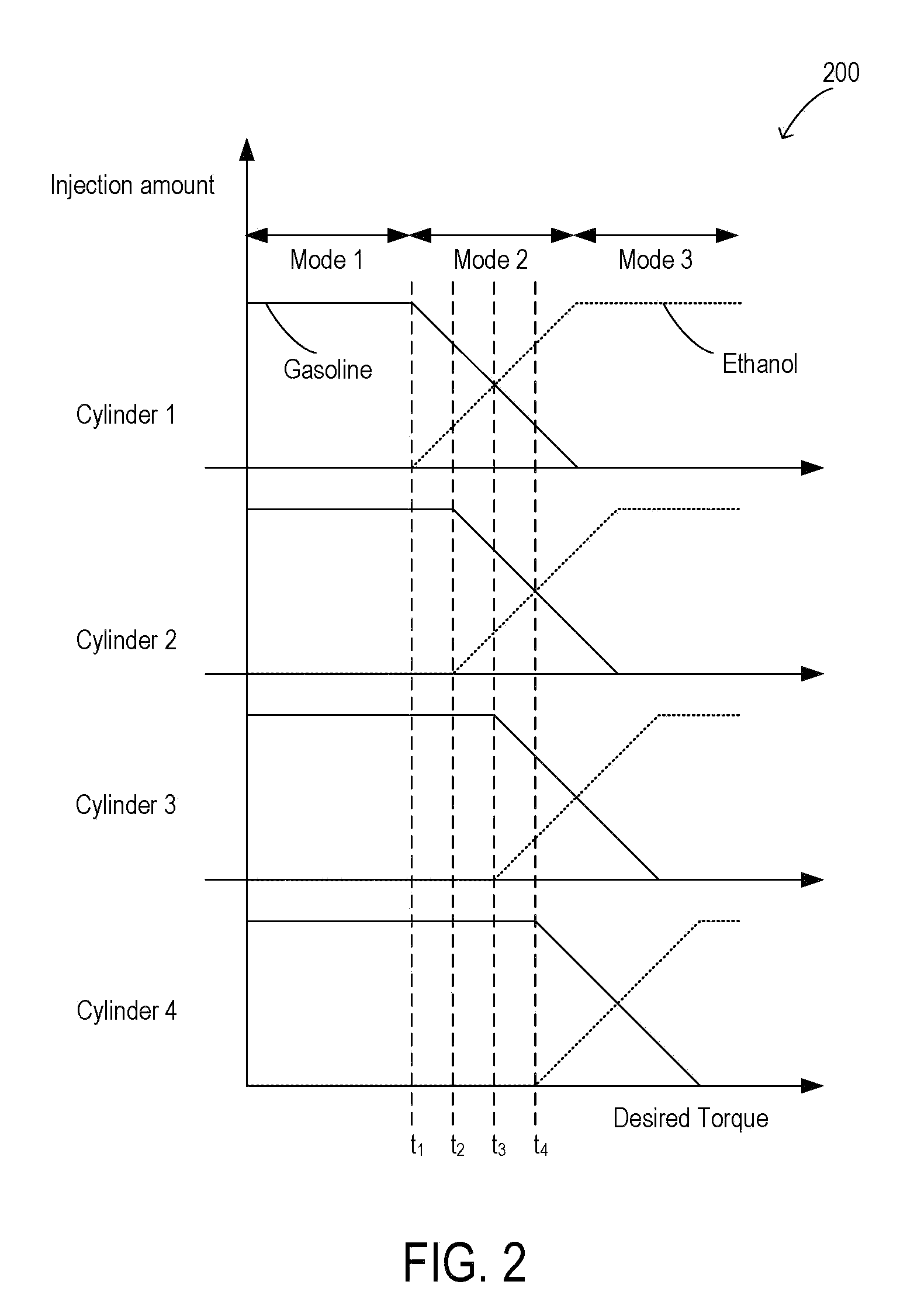
Controlling engine operation with a first and second fuel
InactiveUS7284506B1Less sootHigh production of sootElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberInternal combustion engine
A method of operating an internal combustion engine including at least a combustion chamber having a piston disposed therein, wherein the combustion chamber is configured to receive air, a first fuel and a second fuel to form a substantially homogeneous mixture, and wherein the piston is configured to compress said mixture so that auto-ignition of said mixture is achieved is disclosed. The method comprises varying the amount of at least one of the first fuel and the second fuel that is received by the combustion chamber to adjust the timing of auto-ignition, where the first fuel includes diesel fuel and the second fuel includes such low cetane fuels as: methanol and ethanol.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Hydrogen generator for uses in a vehicle fuel system
InactiveUS6866756B2Increase electrode surface areaSimple designCellsPhotography auxillary processesHydrogenElectrolysis
The present invention discloses an electrolyzer for electrolyzing water into a gaseous mixture comprising hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. The electrolyzer is adapted to deliver this gaseous mixture to the fuel system of an internal combustion engine. The electrolyzer of the present invention comprises one or more supplemental electrode at least partially immersed in an aqueous electrolyte solution interposed between two principle electrodes. The gaseous mixture is generated by applying an electrical potential between the two principal electrodes. The electrolyzer further includes a gas reservoir region for collecting the generated gaseous mixture. The present invention further discloses a method of utilizing the electrolyzer in conjunction with the fuel system of an internal combustion engine to improve the efficiency of said internal combustion engine.
Owner:HYDROGEN TECH APPL
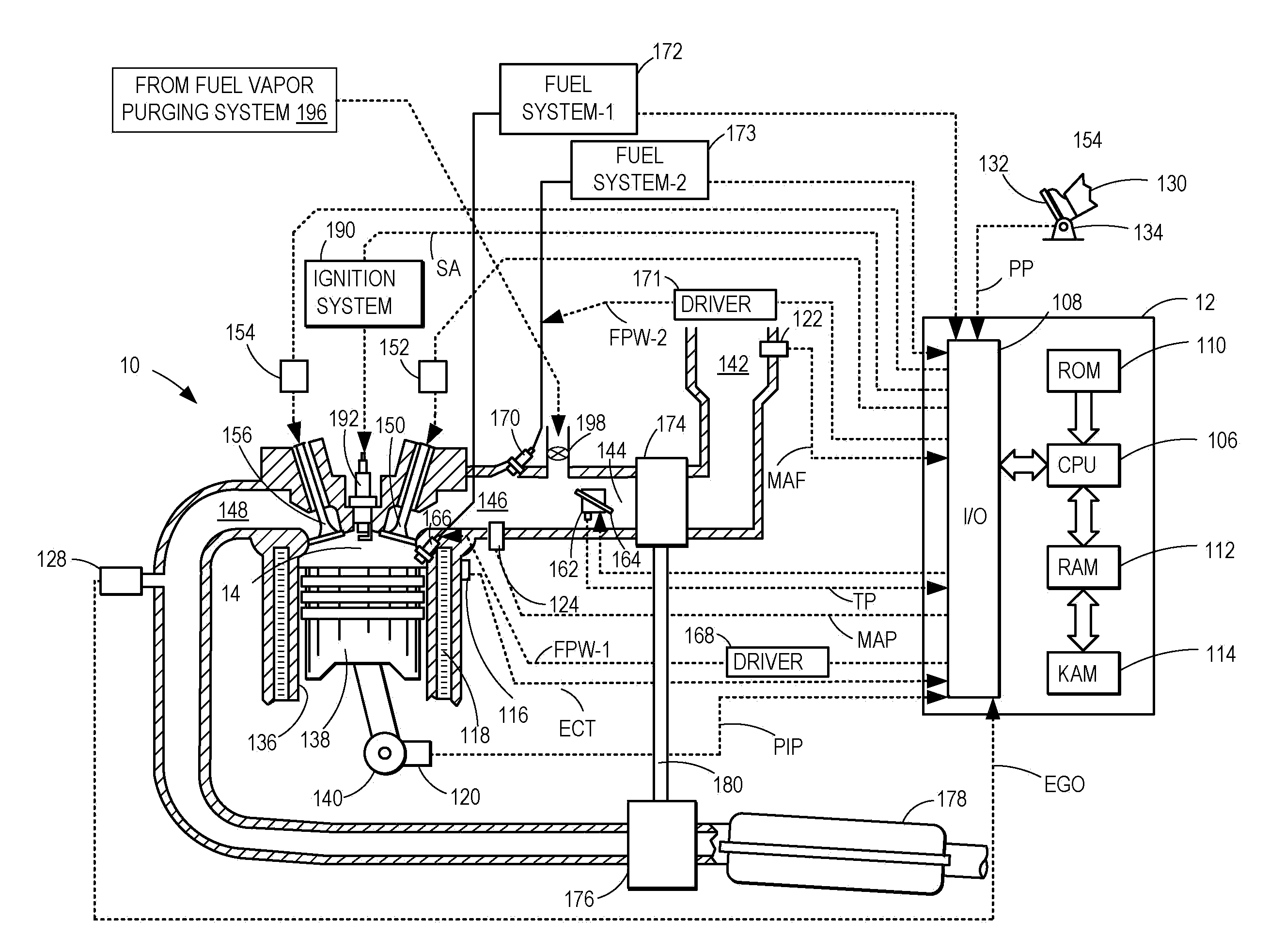
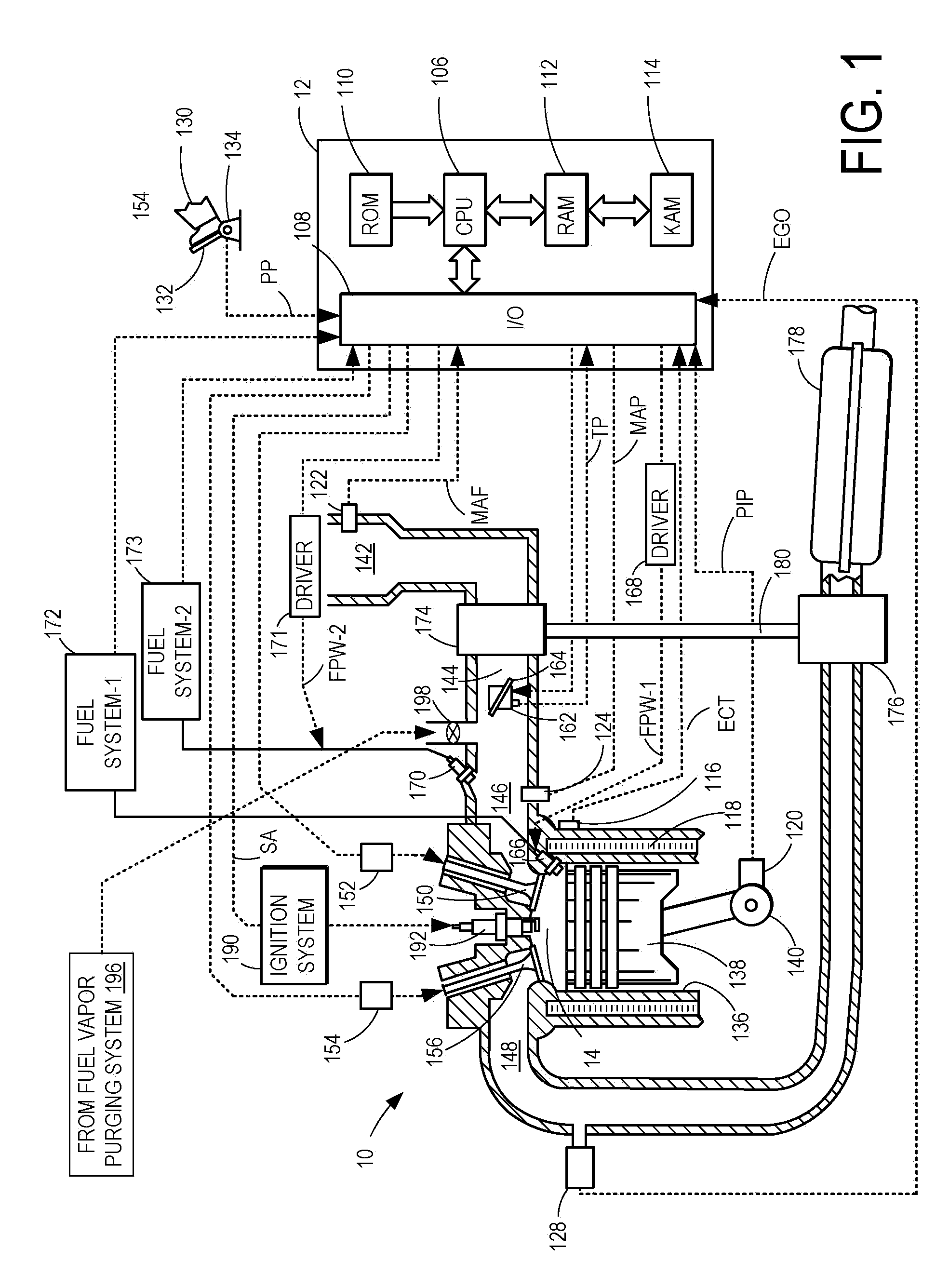
Engine control device
InactiveUS6959241B2Short timeImprove responsivenessAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlEngine efficiencyResponsivity
An engine control device capable of improving engine efficiency by operating the engine in an area where fuel consumption is small (good) while allowing high responsivity of the engine to be maintained. The object can be achieved by operating to match at a point on a target torque line of a torque diagram and operating an electric motor when a matching point moves on the target torque line in a direction in which a load applied to the engine output shaft becomes large.
Owner:KOMATSU LTD
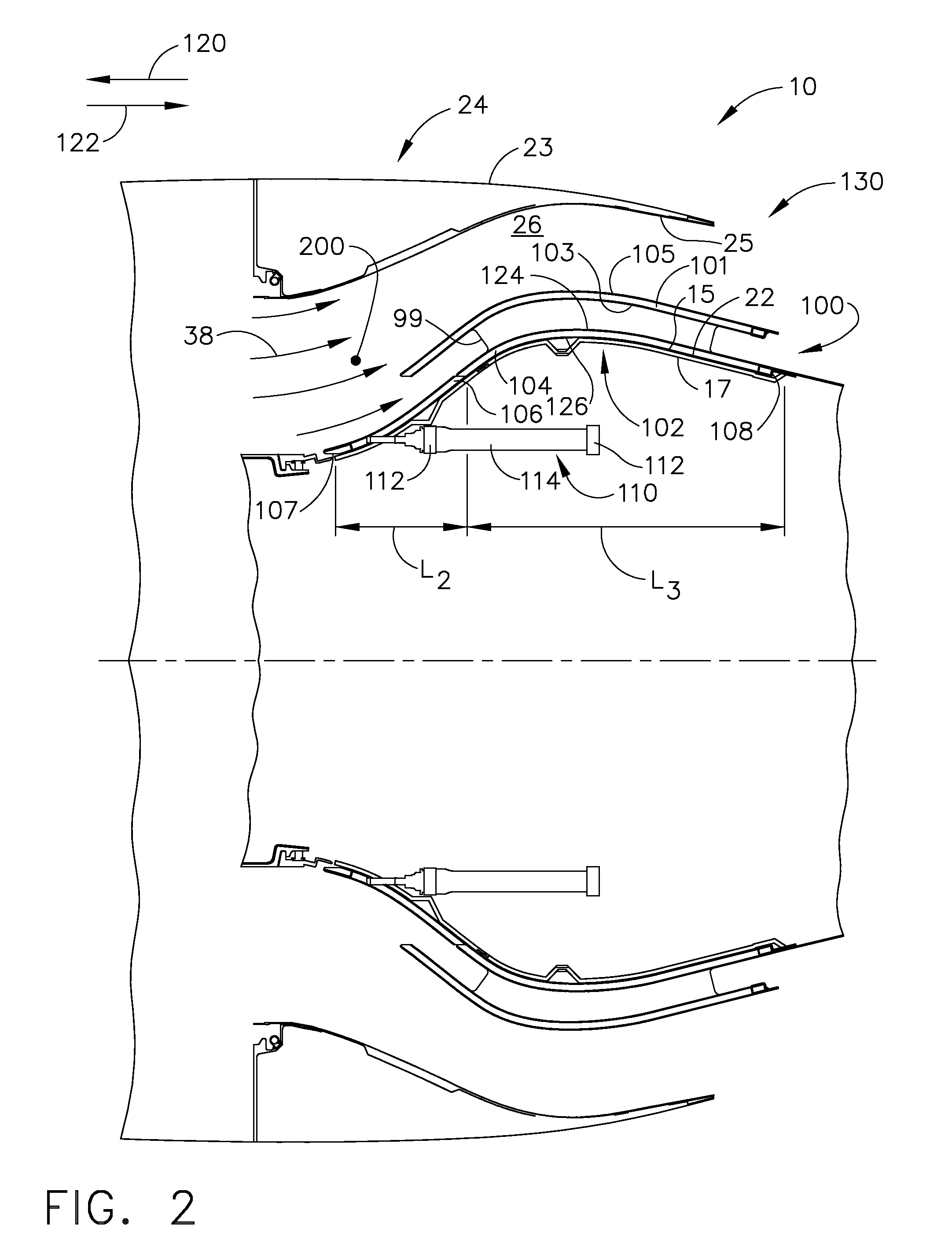
Turbofan engine cowl assembly and method of operating the same
A turbofan engine assembly is provided. The turbofan engine assembly includes a core gas turbine engine, a core cowl which circumscribes the core gas turbine engine, a nacelle positioned radially outward from the core cowl, a fan nozzle duct defined between the core cowl and the nacelle, and an inner core cowl baffle assembly positioned within the fan nozzle duct. The inner core cowl baffle assembly includes a first core cowl baffle coupled to a portion of the core cowl within the fan nozzle duct, a second core cowl baffle coupled to a portion of the core cowl and positioned a distance radially inward from the first core cowl baffle, and an actuator assembly configured to vary the throat area of the fan nozzle duct by selectively repositioning the second core cowl baffle with respect to the first core cowl baffle. A method for operating the turbofan engine assembly is also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Fuel based cylinder knock control
ActiveUS20090308367A1Improve engine performanceReduce knockingElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesInjectorAutomotive engineering
Various systems and methods are described for controlling engine operation of an engine having a plurality of cylinders, each cylinder including a first and second injector for delivering fuel to the cylinder. One example method comprises operating a first cylinder to combust fuel delivered from both the first and second fuel injector of the first cylinder, and operating a second cylinder to combust fuel delivered from only one of the first and second fuel injectors of the second cylinder. One example system comprises both a port injector and a direct injector coupled to both of a first and second cylinder of the engine with a first fuel reservoir coupled to the port injectors and a second fuel reservoir coupled to the direct injectors. The system further includes a controller configured to vary delivery of the fuels from the injectors to the cylinders during differing operating modes.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
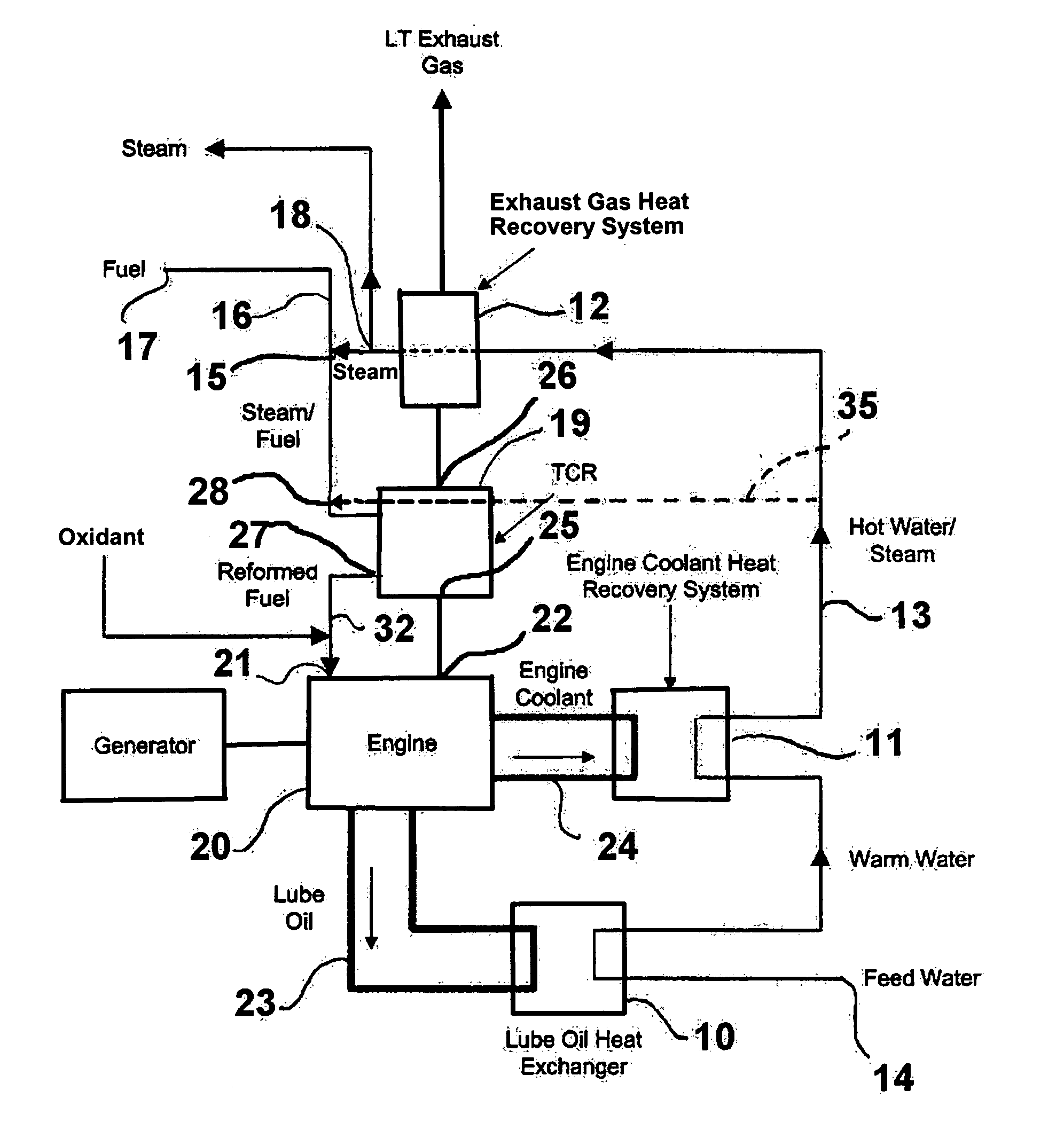
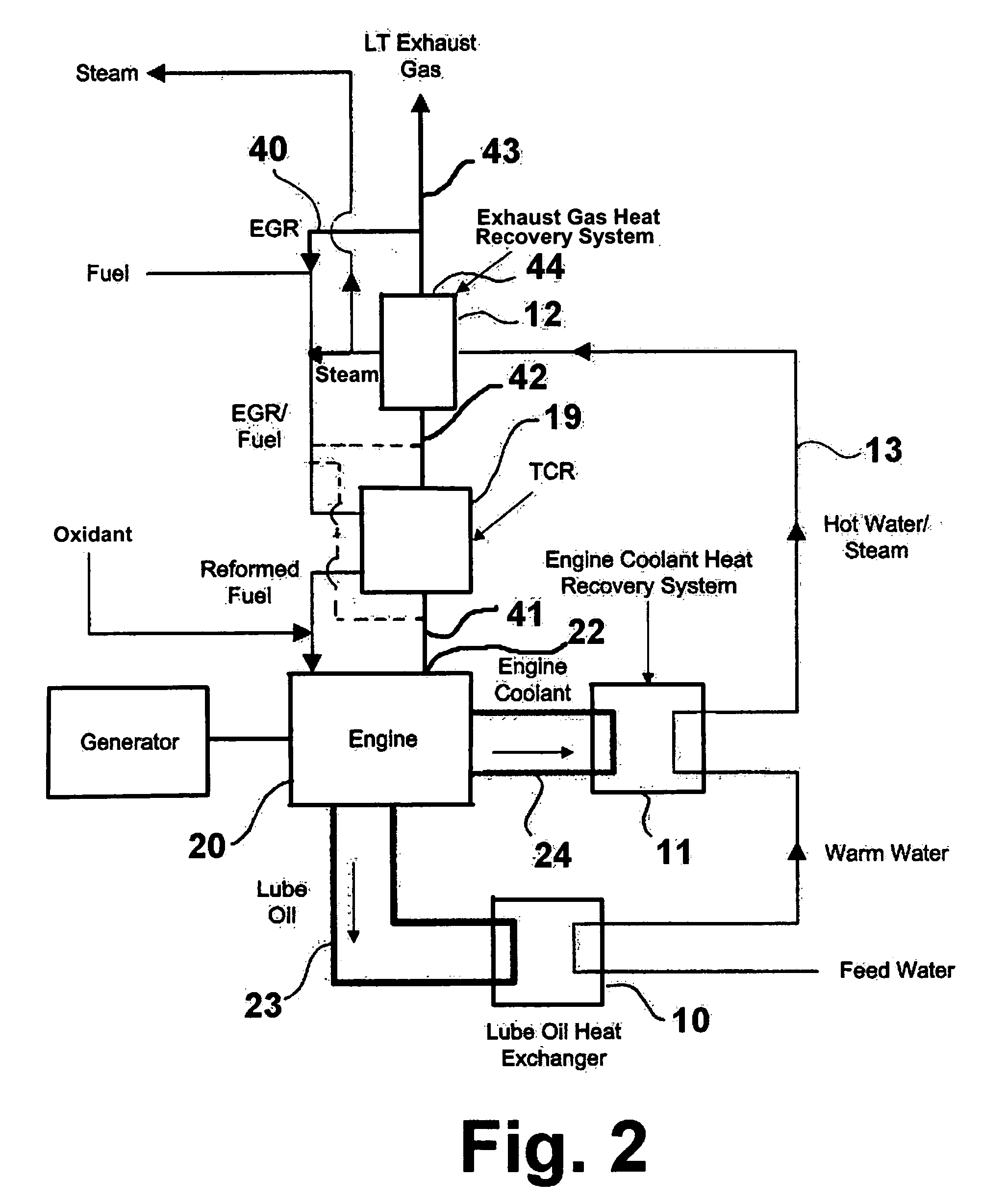
Advanced high efficiency, ultra-low emission, thermochemically recuperated reciprocating internal combustion engine
ActiveUS7210467B2Emission reductionImprove efficiencyInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusExternal combustion engineEngineering
An apparatus including a reciprocating internal combustion engine and a thermochemical recuperator in which a fuel is reformed. The thermochemical recuperator is heated by exhaust gases from the reciprocating internal combustion engine and steam for the reforming process is produced by passing feed water through an engine lubricating oil heat exchanger, an engine cooling system heat recovery system and an exhaust gas heat recovery system arranged in series.
Owner:GAS TECH INST
Thermionic generator
InactiveUS6229083B1Reduce manufacturing costAvoid small quantitiesElectric discharge tubesThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermionic converterEngineering
A method for building a thermionic converter comprises providing an electrode and creating a central depression of substantially uniform depth on a face of the electrode. A surface of the central depression is coated with a layer comprising a thermionic material. A second electrode comprising a face is also provided, wherein the face of the second electrode comprises a central depression of substantially uniform depth, wherein the central depression is coated with a layer comprising a thermionic material.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH LTD
Method and system for turbocharging an engine
ActiveUS8069663B2Improve engine efficiencyReduce displacementValve arrangementsElectrical controlEngine efficiencyEngineering
A method for improving operation of a turbocharged engine is presented. In one embodiment, the method may reduce engine emissions and improve engine efficiency during an engine start.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
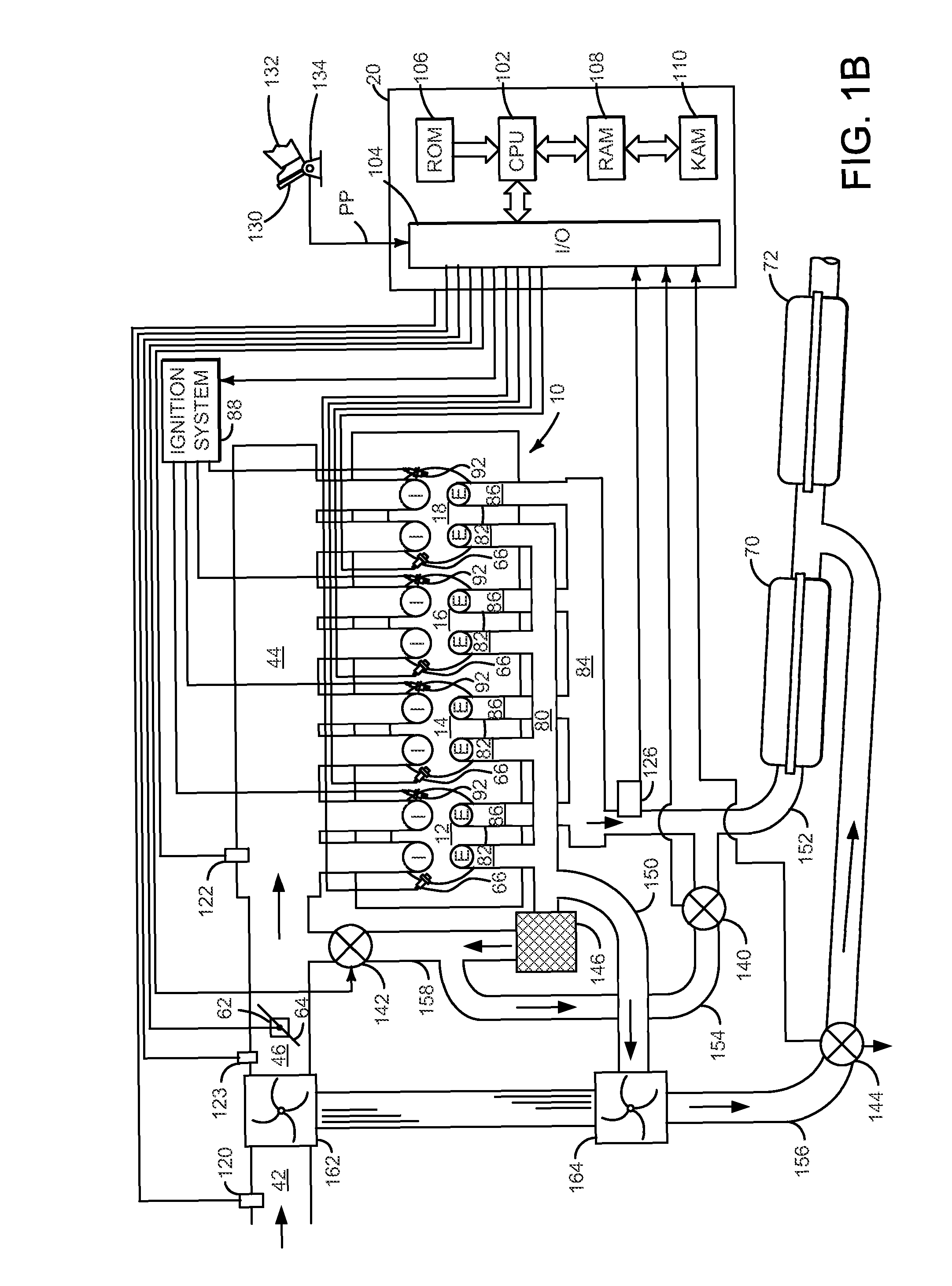
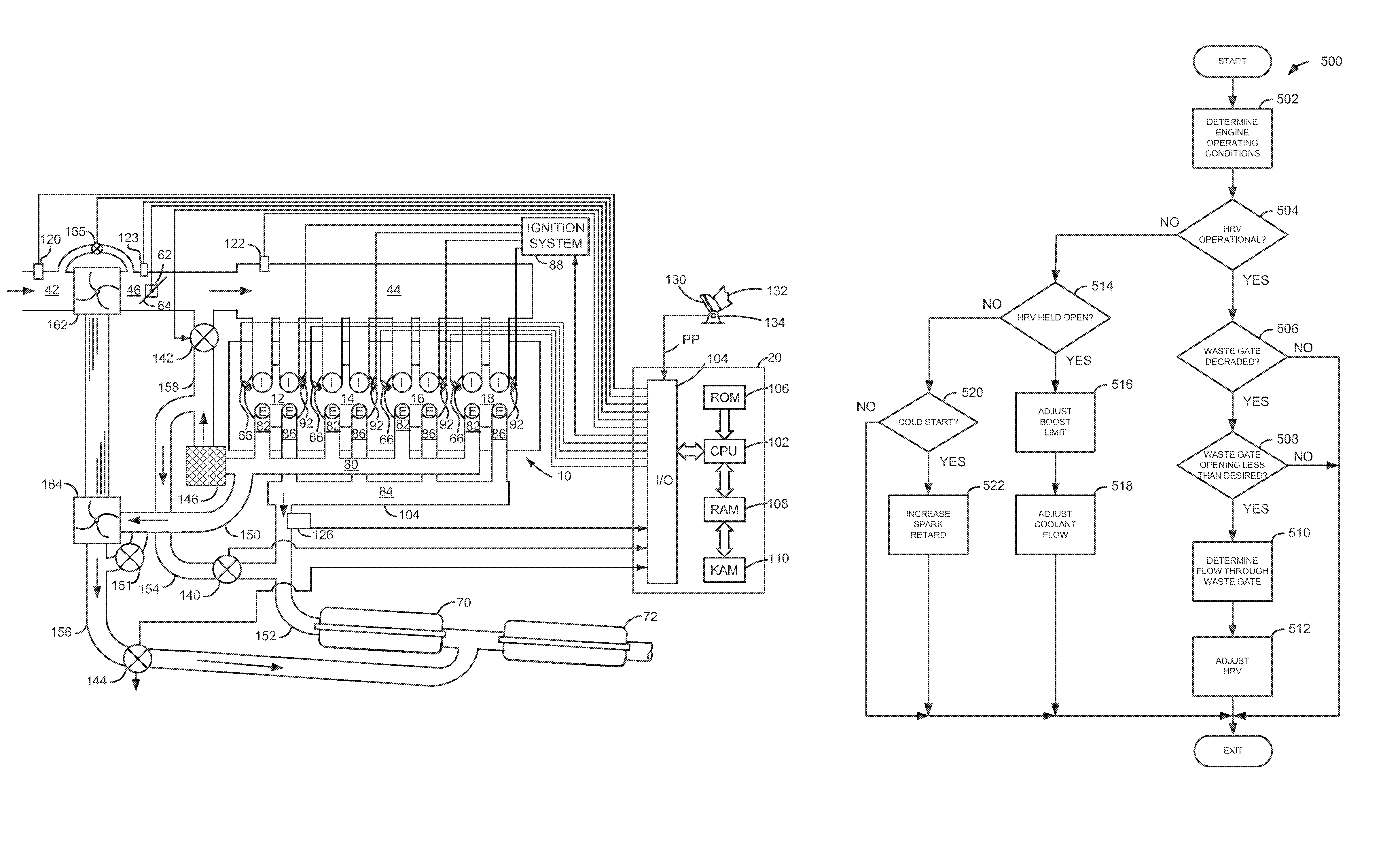
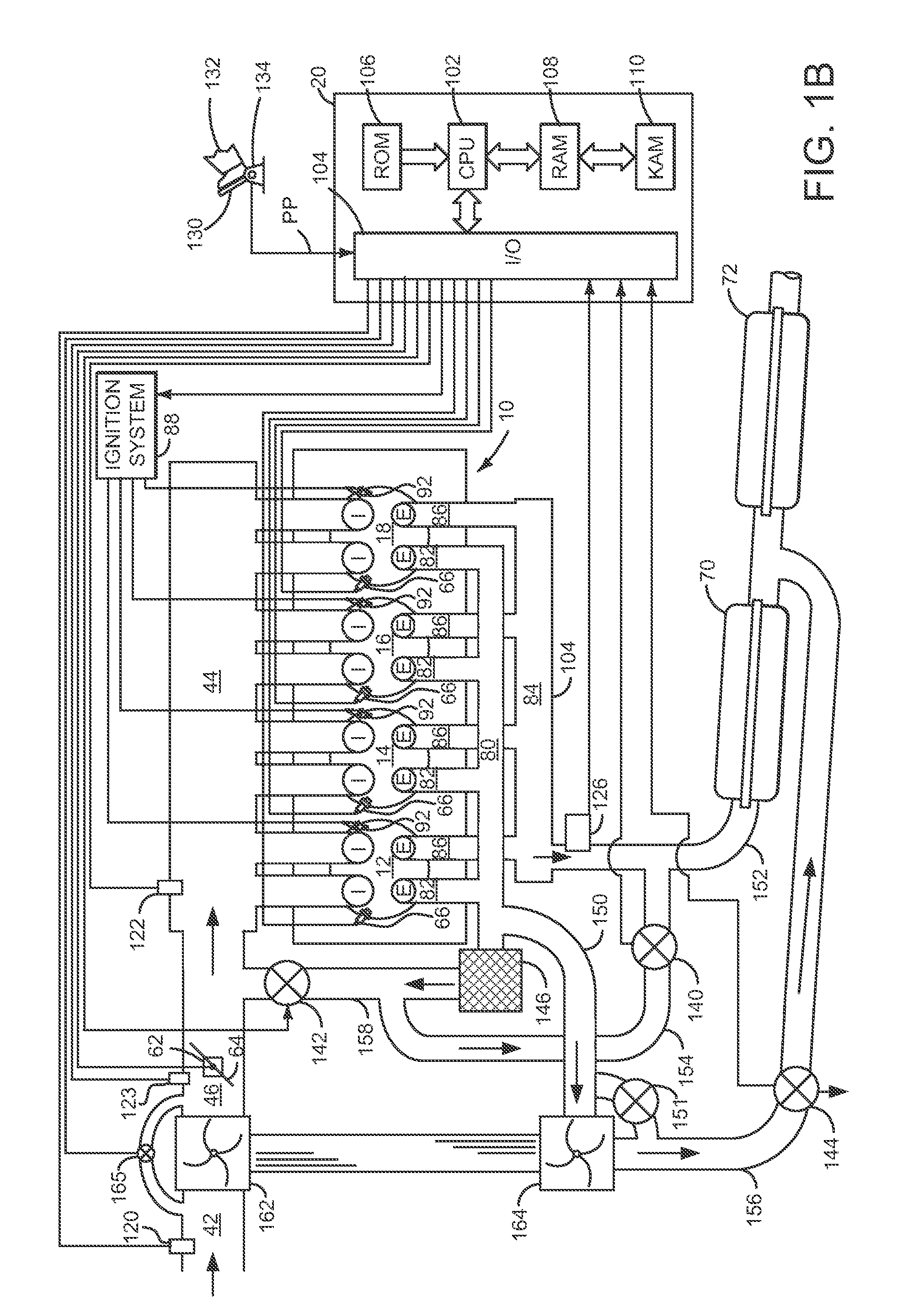
Method and system adjusting an exhaust heat recovery valve
ActiveUS8601811B2Improve engine efficiencyReduce displacementElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesTurbochargerProcess engineering
A method for adjusting an exhaust heat recovery valve is presented. In one embodiment, the method may control an amount of boost provided by a turbocharger to an engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
System and method for model based boost control of turbo-charged engines
ActiveUS20090090106A1Increase engine efficiencyAccurate boost controlInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelAcoustic waveVariable geometry turbine
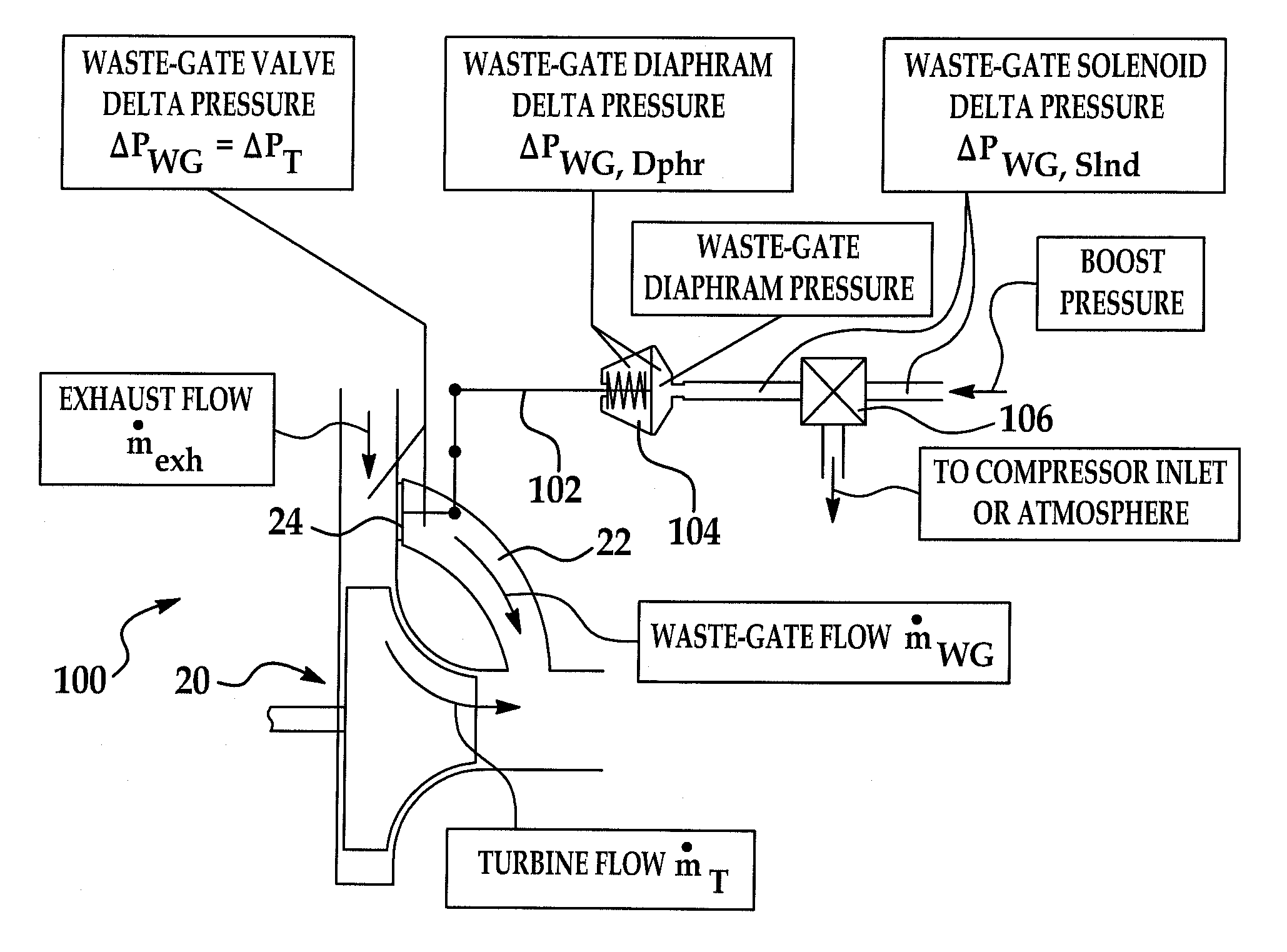
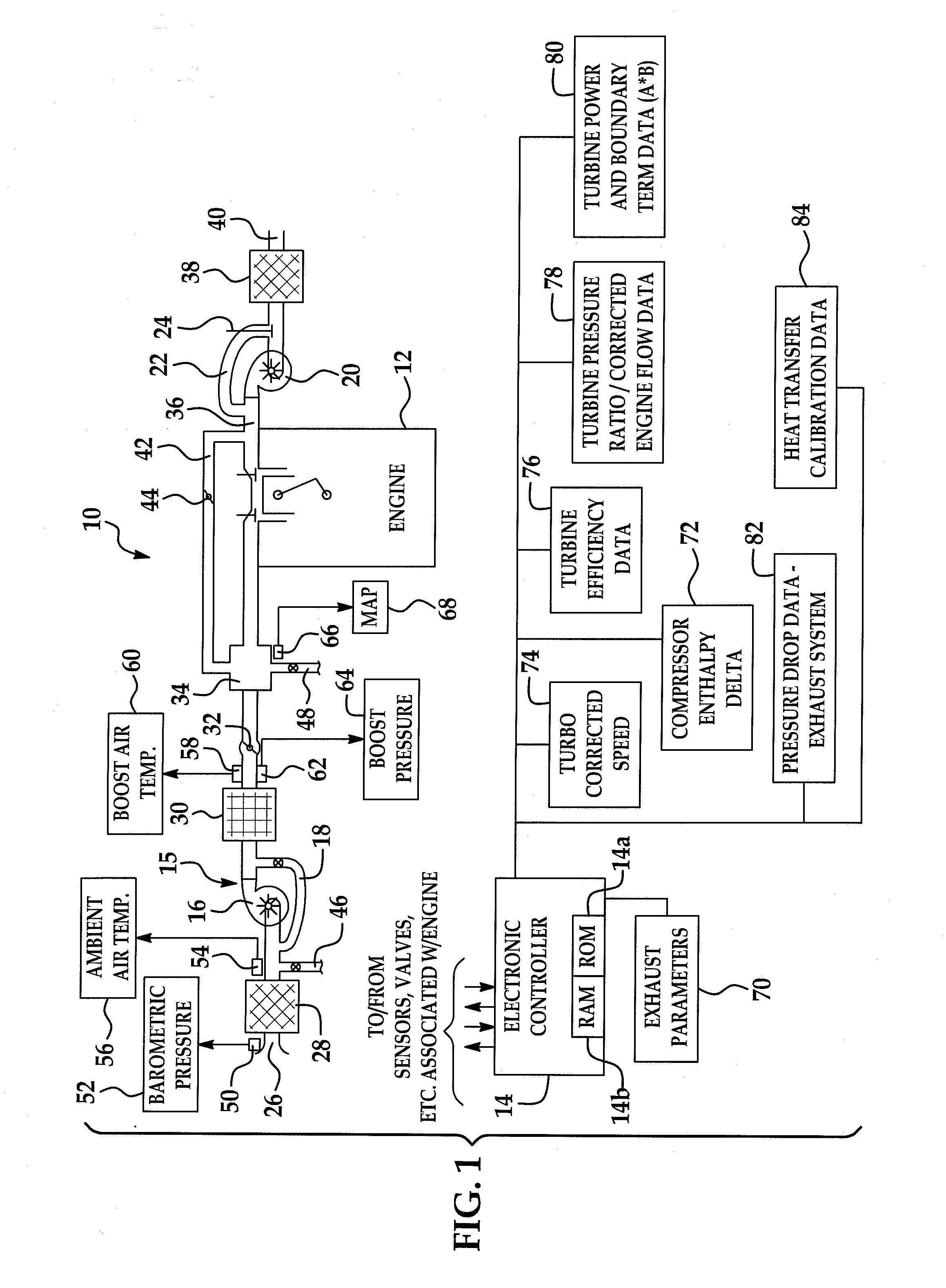
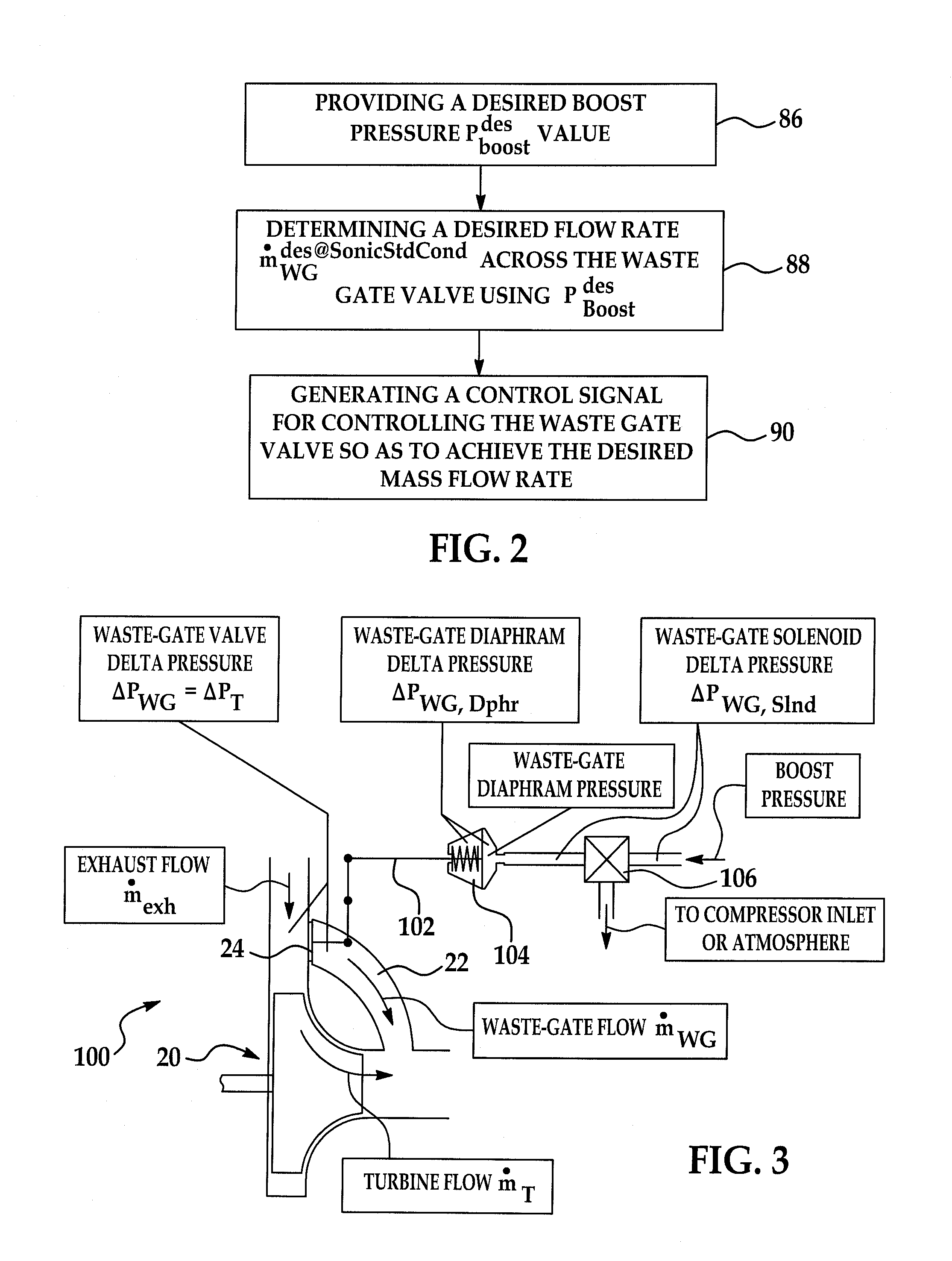
A system and method for controlling boost pressure in various turbo-charged engine configurations as well as variable geometry turbine (VGT) arrangements includes an electronic controller programmed to receive a predetermined desired boost pressure PBoostdes. A desired pressure delta ΔPWGdes across a waste-gate valve is determined using the desired boost pressure PBoostdes. A control signal is generated for controlling the waste-gate valve so as to achieve the desired pressure delta ΔPWGdes. In boost pressure and vacuum pneumatically-actuated waste-gate valve arrangements, the respective solenoid duty cycles are obtained through use of various data structures. Where a waste-gate valve position is controlled by an electrical motor, the valve position is determined using a data structure as a function of desired waste-gate valve flow at sonic standard conditions.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Four-cylinder, four-cycle, free piston, premixed charge compression ignition, internal combustion reciprocating piston engine with a variable piston stroke
ActiveUS20060185631A1Low fuel consumptionImprove efficiencyValve arrangementsElectrical controlSwing-piston engineElectric generator
A four-cycle, four-cylinder, premixed charge compression ignition internal combustion reciprocating free piston engine with a variable piston stroke and a compression ratio that varies as needed to provide charge ignition, to offer the potential of higher efficiency, lower emissions, and multi-fuel operation. The engine does not have a crankshaft, and therefore does not provide direct rotary output. Instead its free pistons oscillate, in a manner similar to a two cycle free piston engine. For many applications, such as piston pumps and compressors, the engine provides an output directly driven by the oscillating pistons. In other applications, such as but not limited to use as a gas generator for a power turbine, the engine provides an indirect means of producing rotary power. When the engine is used with high-speed power turbines, the power turbine may be directly coupled to a high-speed alternator for electrical power output.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE ENERGY TECH DEV TRUST
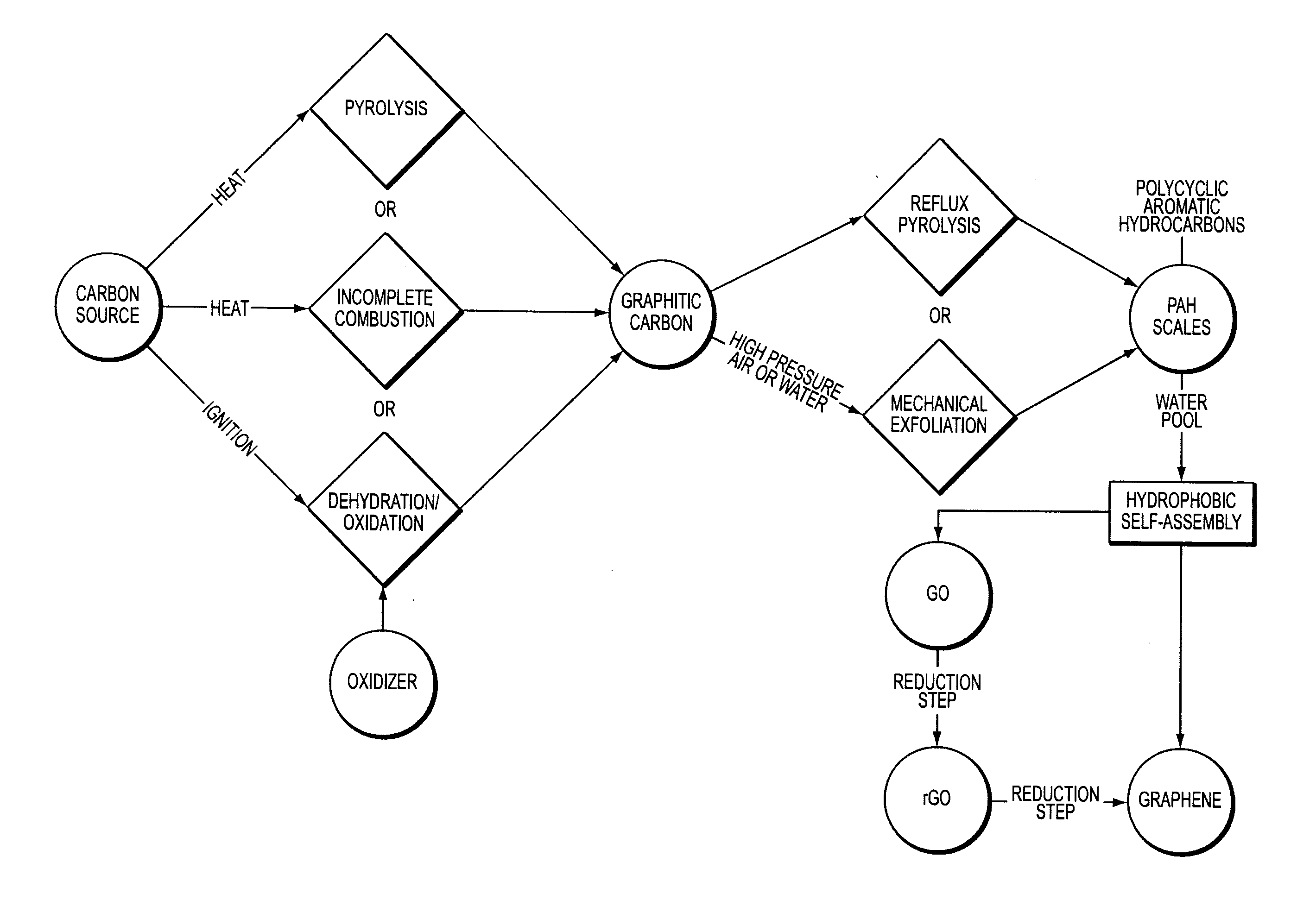
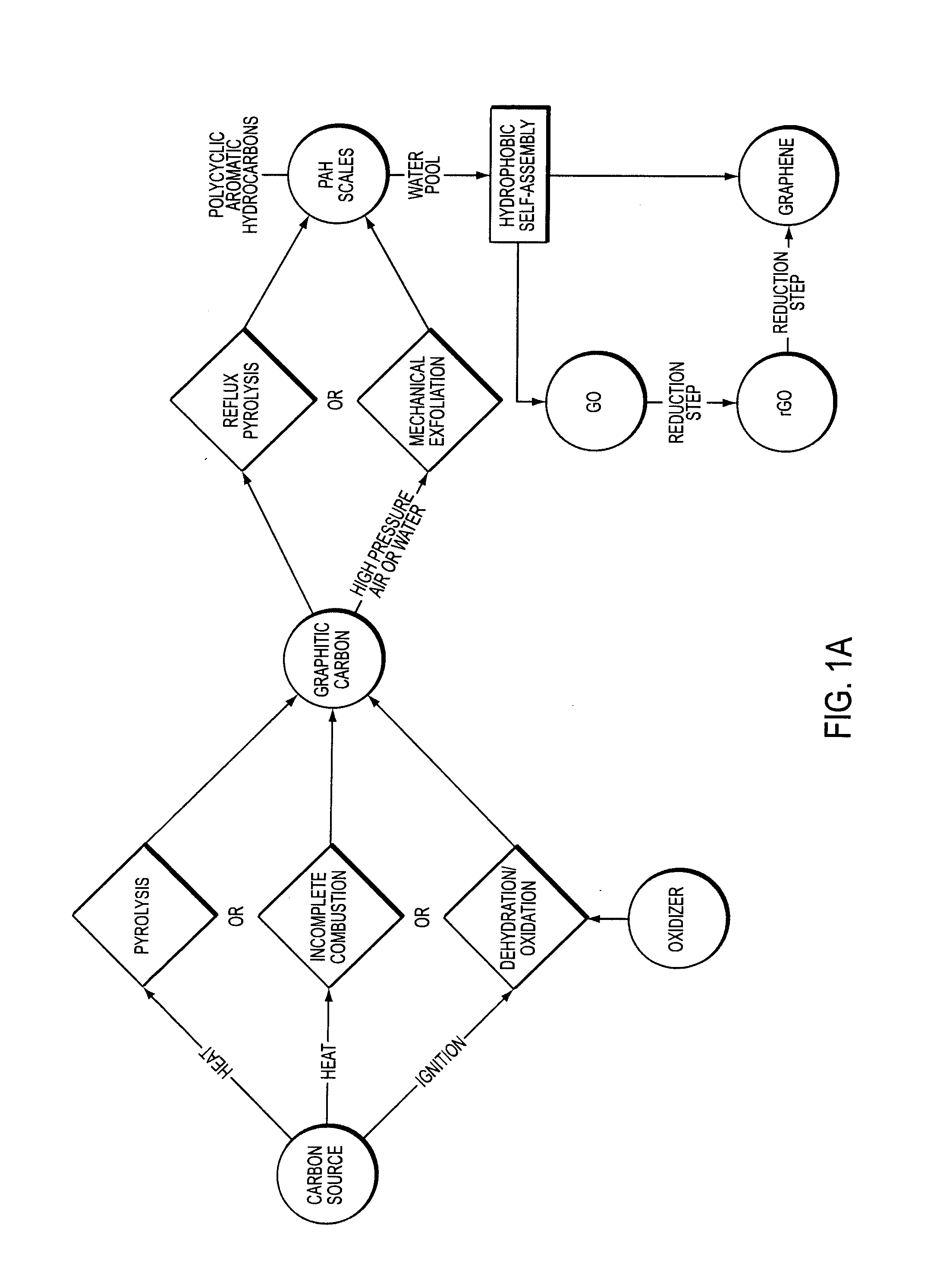
Facile synthesis of graphene, graphene derivatives and abrasive nanoparticles and their various uses, including as tribologically-beneficial lubricant additives
ActiveUS20140134092A1Reduce frictionImprove smoothnessMaterial nanotechnologyCosmetic preparationsNanoparticleGraphene derivatives
Owner:PEERLESS WORLDWIDE
System for sealing an inner retainer segment and support ring in a gas turbine and methods therefor
InactiveUS7094026B2Improve engine efficiencyReduce leakagePump componentsStatorsLeakage flowGas turbines
Arcuate seal layers conforming with one another are disposed between inner retainer segments and inner rails of nozzle segments of a gas turbine. The layers are secured to the aft axial face of the segments and project radially outwardly to seal against the forward axial faces of the rails. The rear axial faces of the rails have chordal seals for sealing against the forward axial faces of the support rings. The seal layers have radial cuts misaligned with one another in an axial direction to preclude leakage flows through gaps formed by the cuts. Arcuate spacers are staggered circumferentially with the arcuate retainer segments whereby an intermediate pressure plenum is formed between the finger seals and chordal seals.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and a system for control of a device for compression
InactiveUS20070151528A1Work lessImprove efficiencyNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesSteam pressureCombustion chamber
A method of compressing a medium in the combustion chamber of a combustion engine, wherein a liquid spray is introduced into the compression chamber during a compression stroke, the liquid is pressurized and heated before introduction into the compression chamber to such a degree that at least a part of the droplets of the spray explode spontaneously upon entrance in the compression chamber. The pressurized liquid has a steam pressure that is above the pressure in the compression chamber, and the liquid has a temperature that exceeds the boiling point of the liquid for the temperature and the pressure that, at the moment of introduction, exists in the compression chamber, and the heat being water. The liquid is heated to such an extent that, at the moment of introduction, it has a temperature that is below the temperature of the medium at the moment of introduction of the liquid.
Owner:CARGINE ENG AB
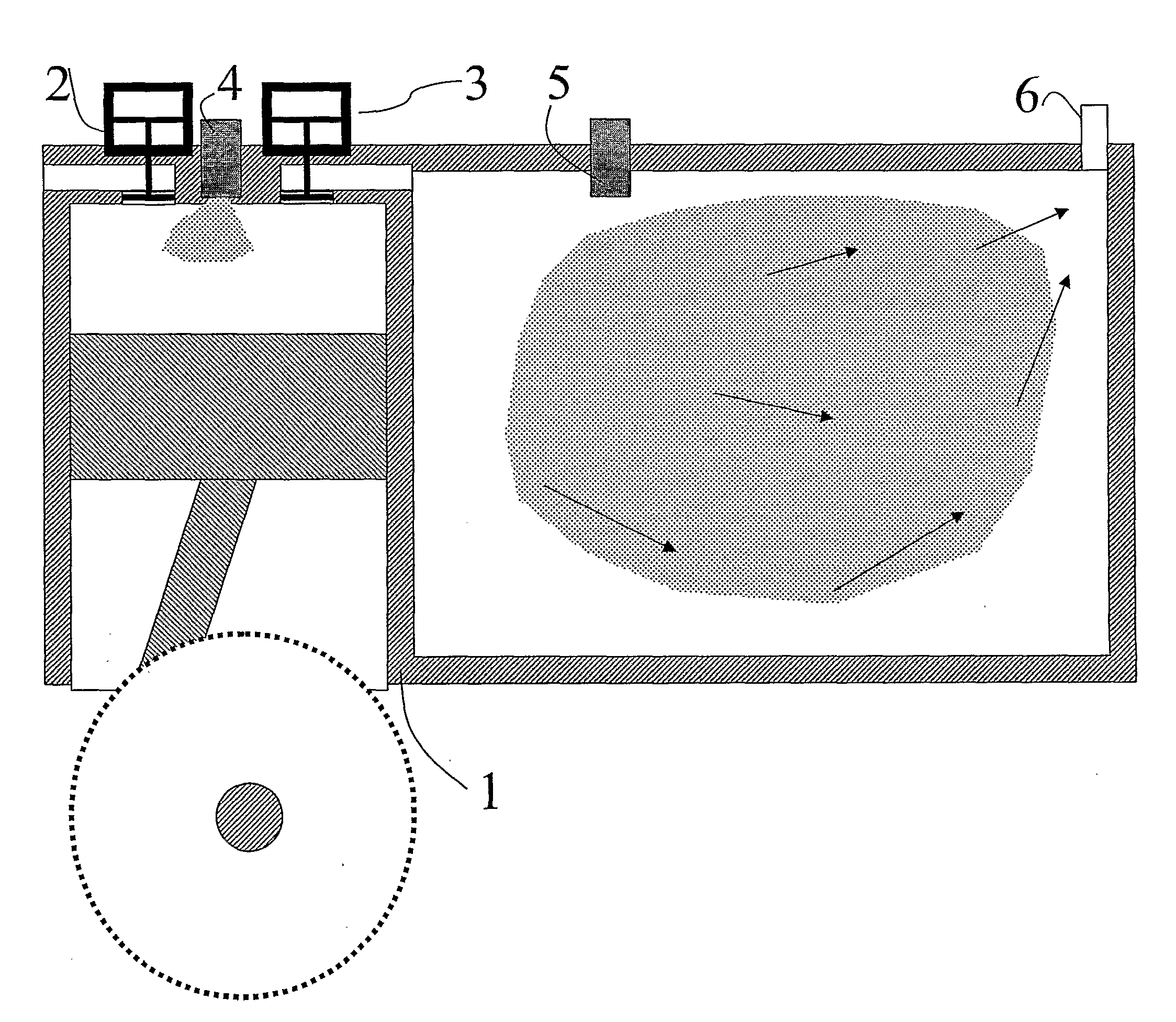
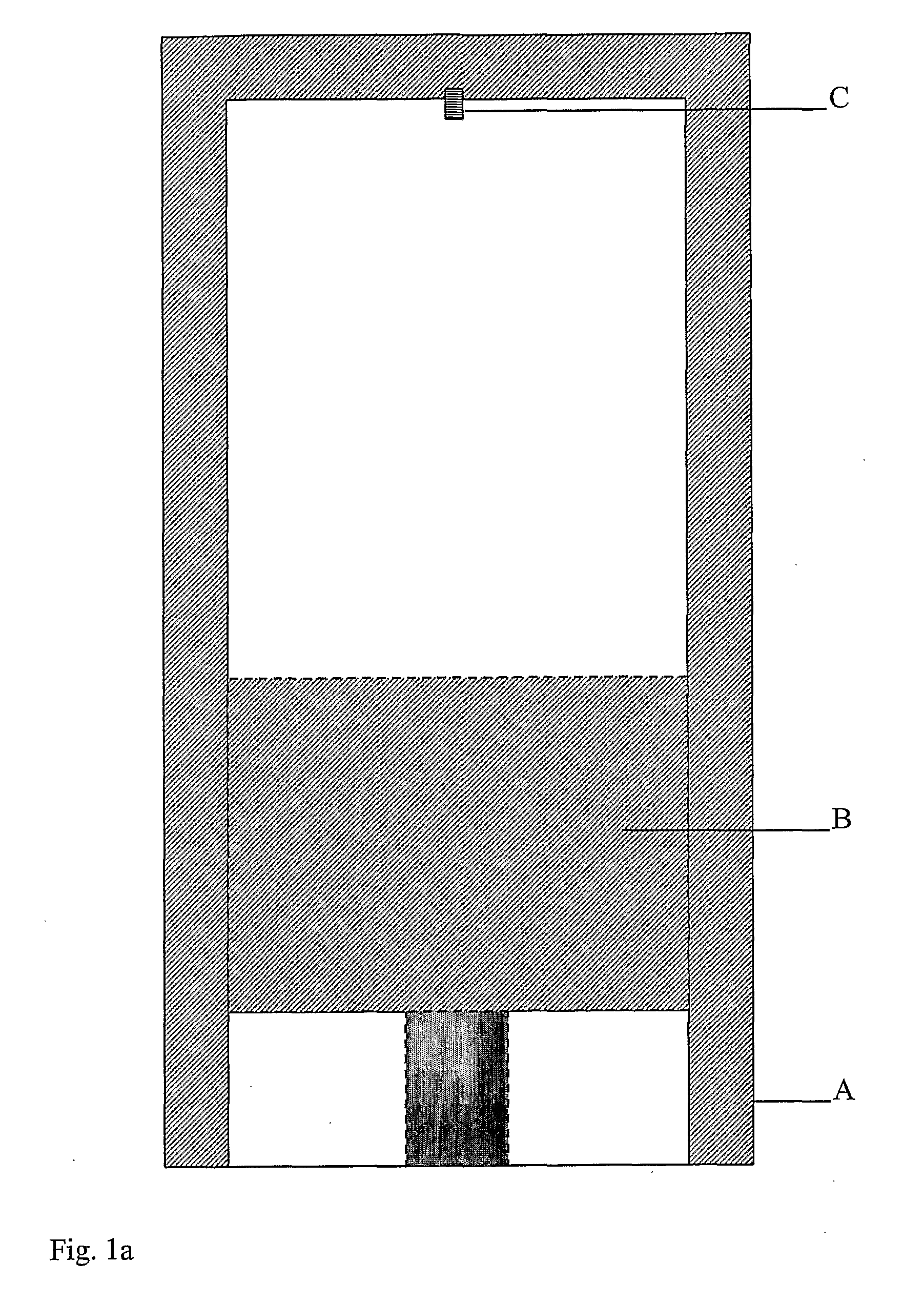
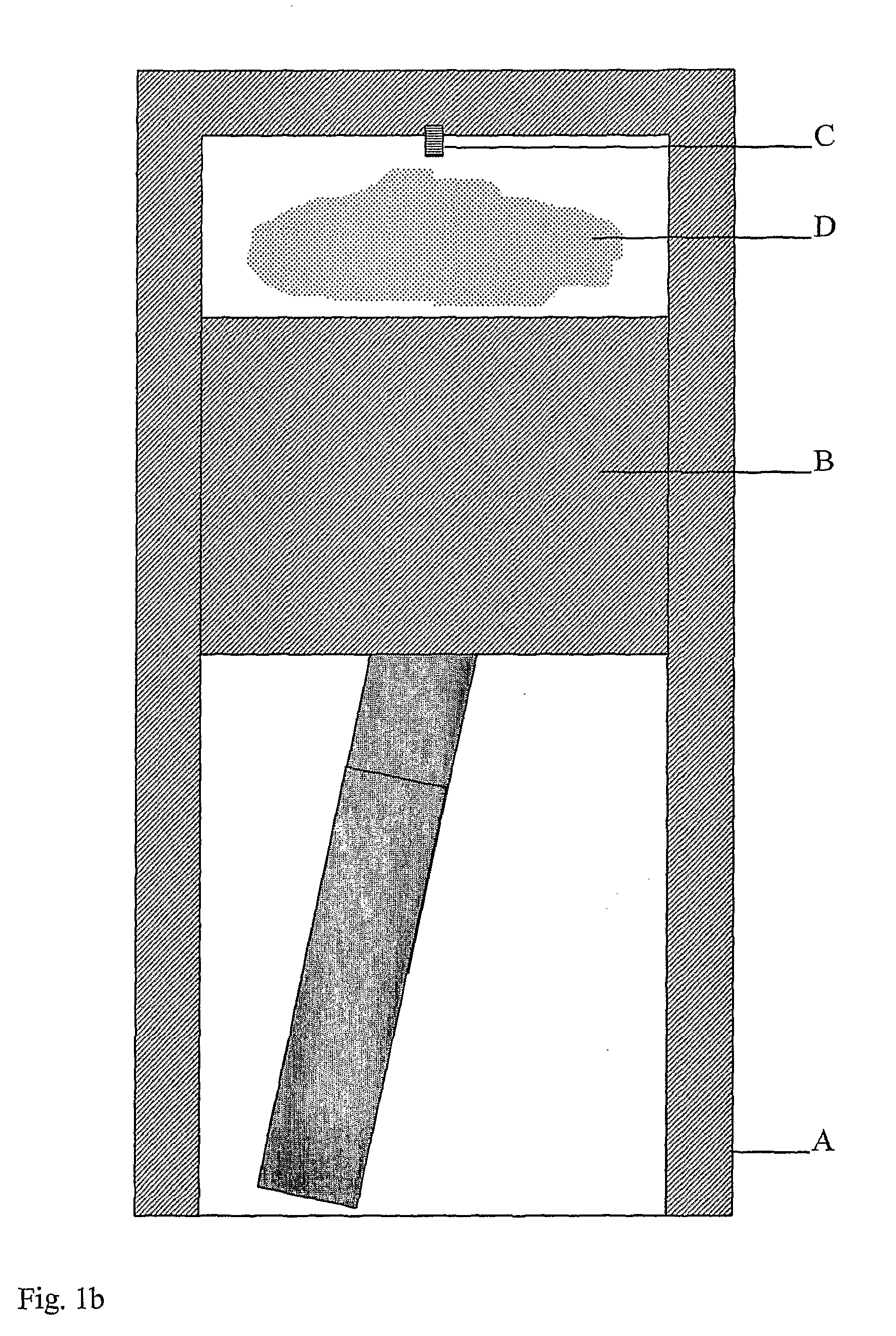
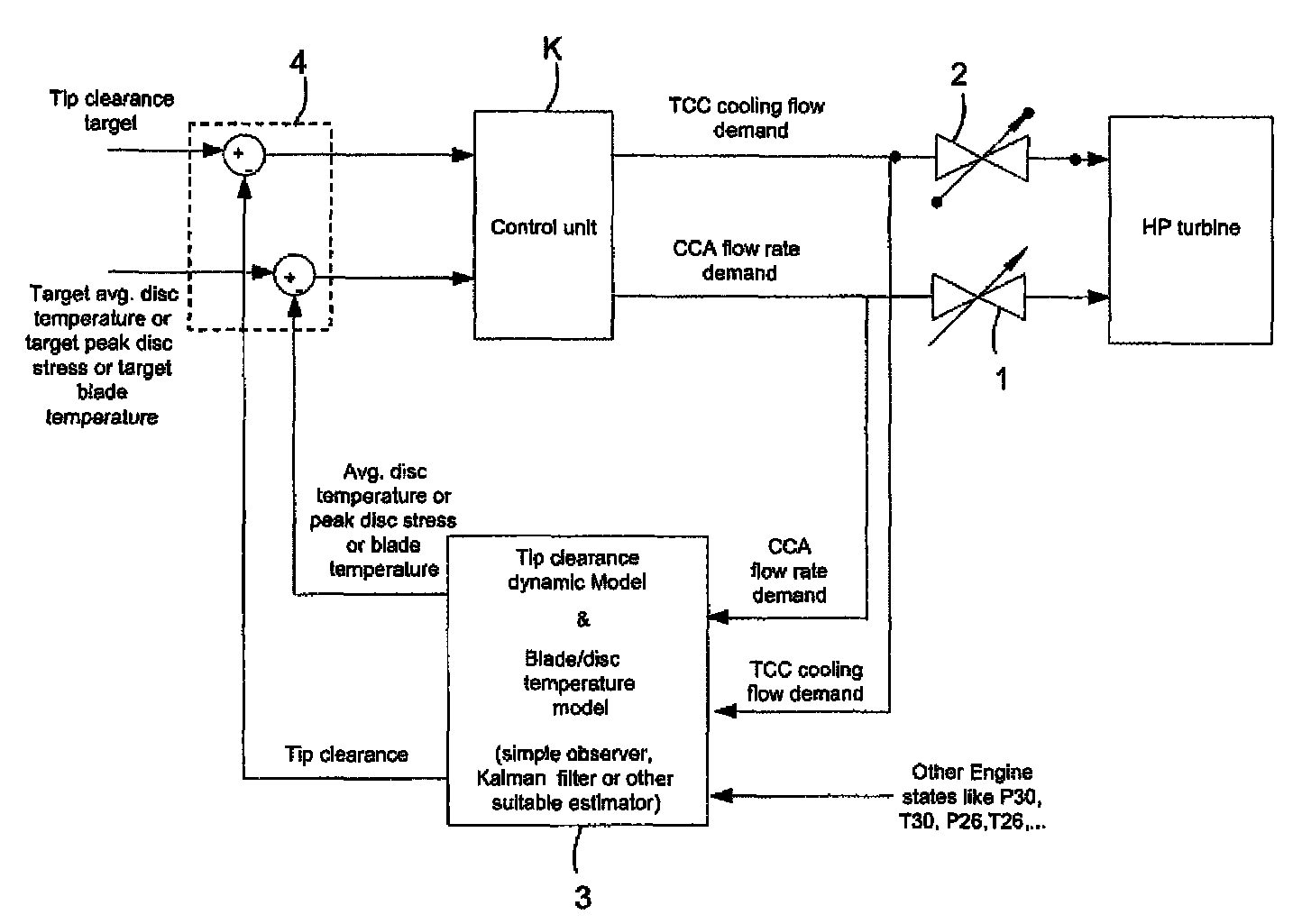
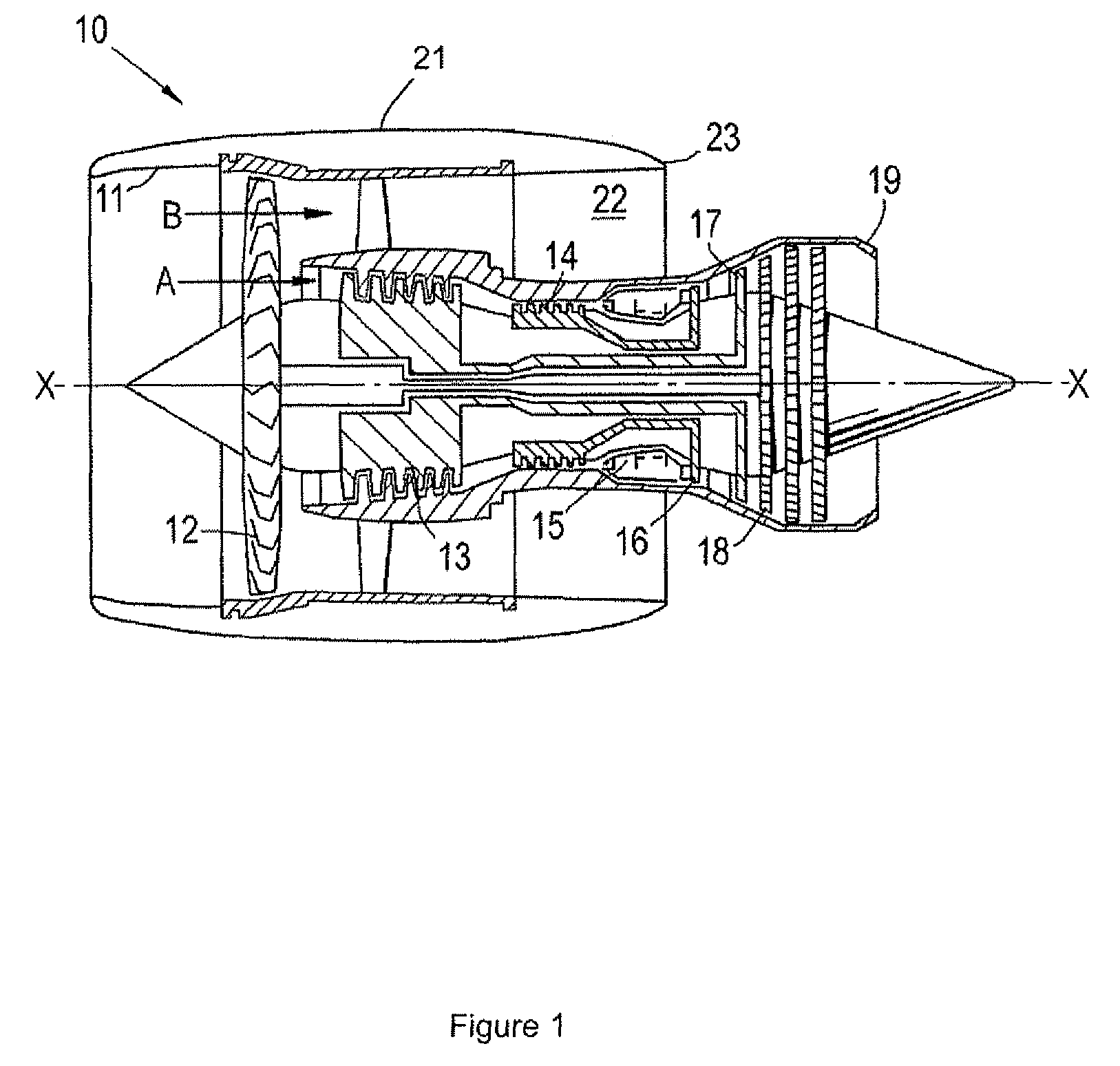
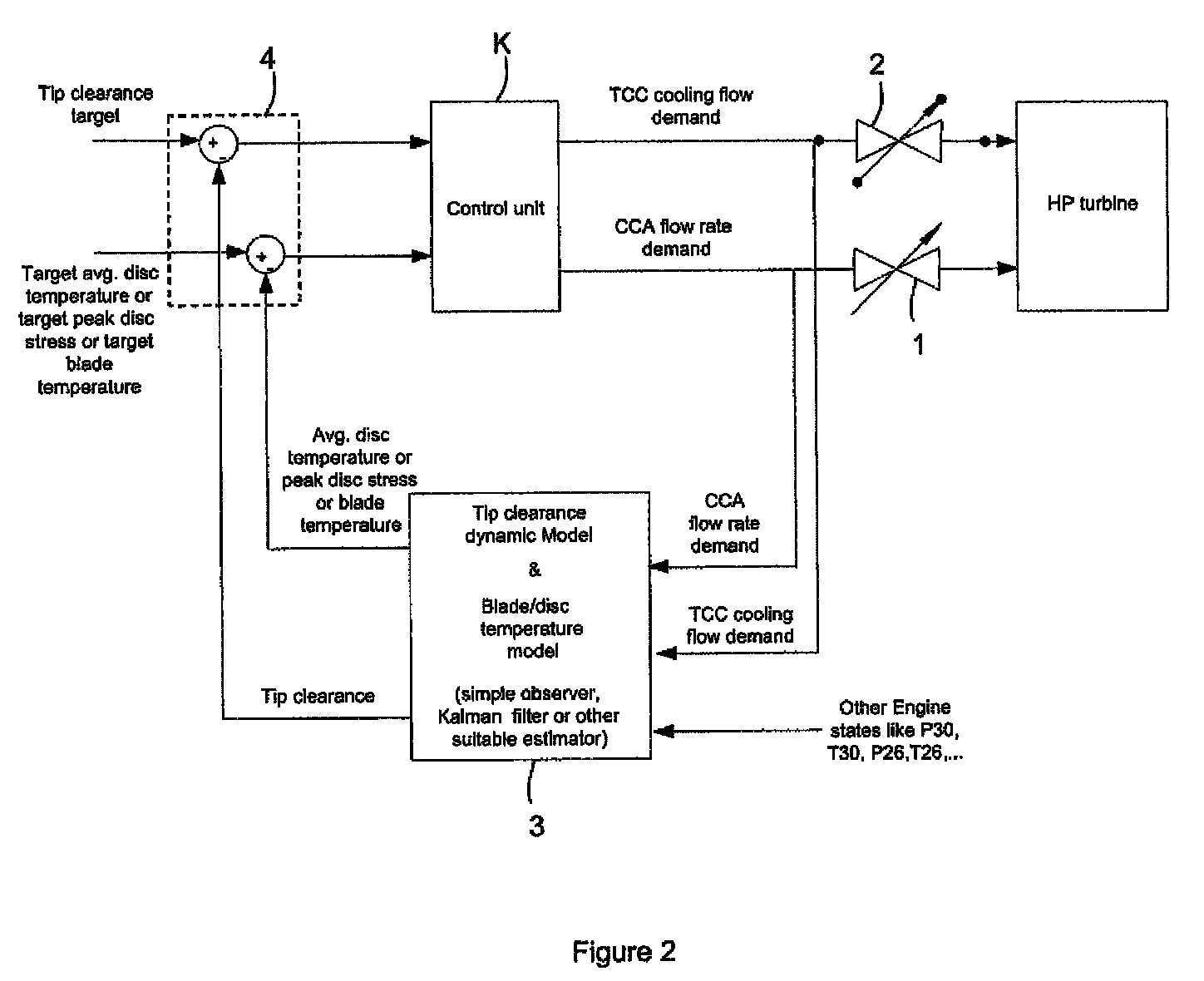
Gas turbine engine having a multi-variable closed loop controller for regulating tip clearance
ActiveUS9255492B2Improve engine efficiencyImprove efficiencyEngine fuctionsTurbine/propulsion engine coolingCombustorTurbine blade
A gas turbine engine has, in flow series, a compressor section, a combustor, and a turbine section. The gas turbine engine further has a system (i) for cooling the turbine section and (ii) for providing tip clearance control between turbine blades of the turbine section and a plurality of circumferentially distributed segments which form an annular shroud surrounding the outer tips of the turbine blades. The system includes a turbine section cooling sub-system which diverts a first cooling air flow received from the compressor section to a heat exchanger and then to the turbine section to cool components thereof. The first cooling air flow by-passes the combustor and is cooled in the heat exchanger. The turbine section cooling subsystem has a first valve arrangement which regulates the first cooling air flow. The system further includes a tip clearance control sub-system which supplies a second cooling air flow to an engine case to which the segments are mounted. The second cooling air flow regulates thermal expansion of the case and thereby controls the clearance between the segments and the outer tips. The tip clearance control sub-system has a second valve arrangement which regulates the second cooling air flow. The system further includes a closed-loop controller which issues first and second demand signals to respectively the first and the second valve arrangements. Each of the first and second demand signals are determined on the basis of: (i) a value of the first demand signal at a previous time step, and a measurement or estimate of turbine section component temperature, and (ii) a value of the second demand signal at a previous time step, and a measurement or estimate of tip clearance.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
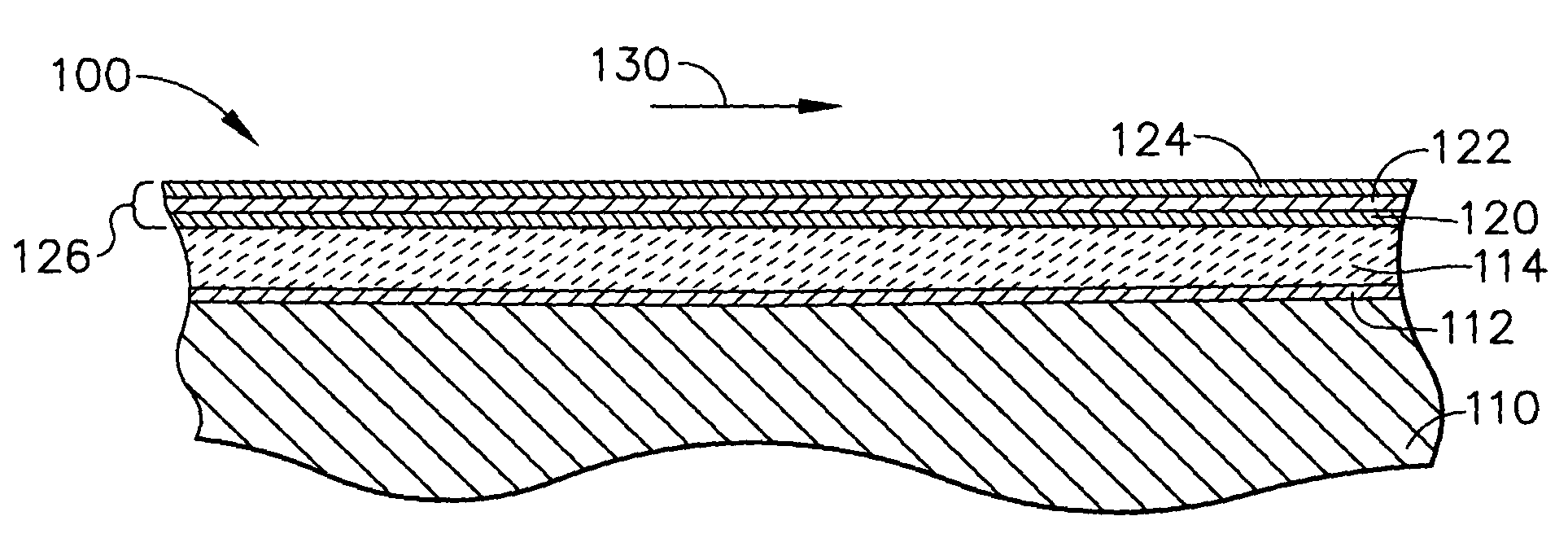
Optical reflector for reducing radiation heat transfer to hot engine parts
InactiveUS7208230B2Prolong lifeLess mean timePropellersMagnetic materialsOptical reflectionCoating system
A high temperature gas turbine component for use in the gas flow path that comprises a specular optical reflector coating system. A thin specular optical reflector coating system is applied to the gas flow path of the component, that is, the surface of the component that forms a boundary for hot combustion gases. The component typically includes a thermal barrier coating overlying the high temperature metallic component that permits the component to operate at elevated temperatures. The thermal barrier coating must be polished in order to provide a surface that can suitably reflect the radiation into the gas flow path. The thin reflector coating system comprises a thin high temperature and corrosion resistant refractory stabilizing layer, which is applied over a thin reflective metal layer, which is applied over a thin high temperature and corrosion resistant refractory sealing layer. The coating system is applied over the polished thermal barrier coating by a process that can adequately adhere the reflector to the polished surface without increasing the roughness of the surface. The coating system reflects radiation back into the hot gas flow path or into the atmosphere. The reflected radiation is not focused onto any other hardware component. The design of the component is such that the radiation is returned to the gas flow path or sent to the atmosphere rather than absorbed into a component that only serves to increase the temperature of such a component.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
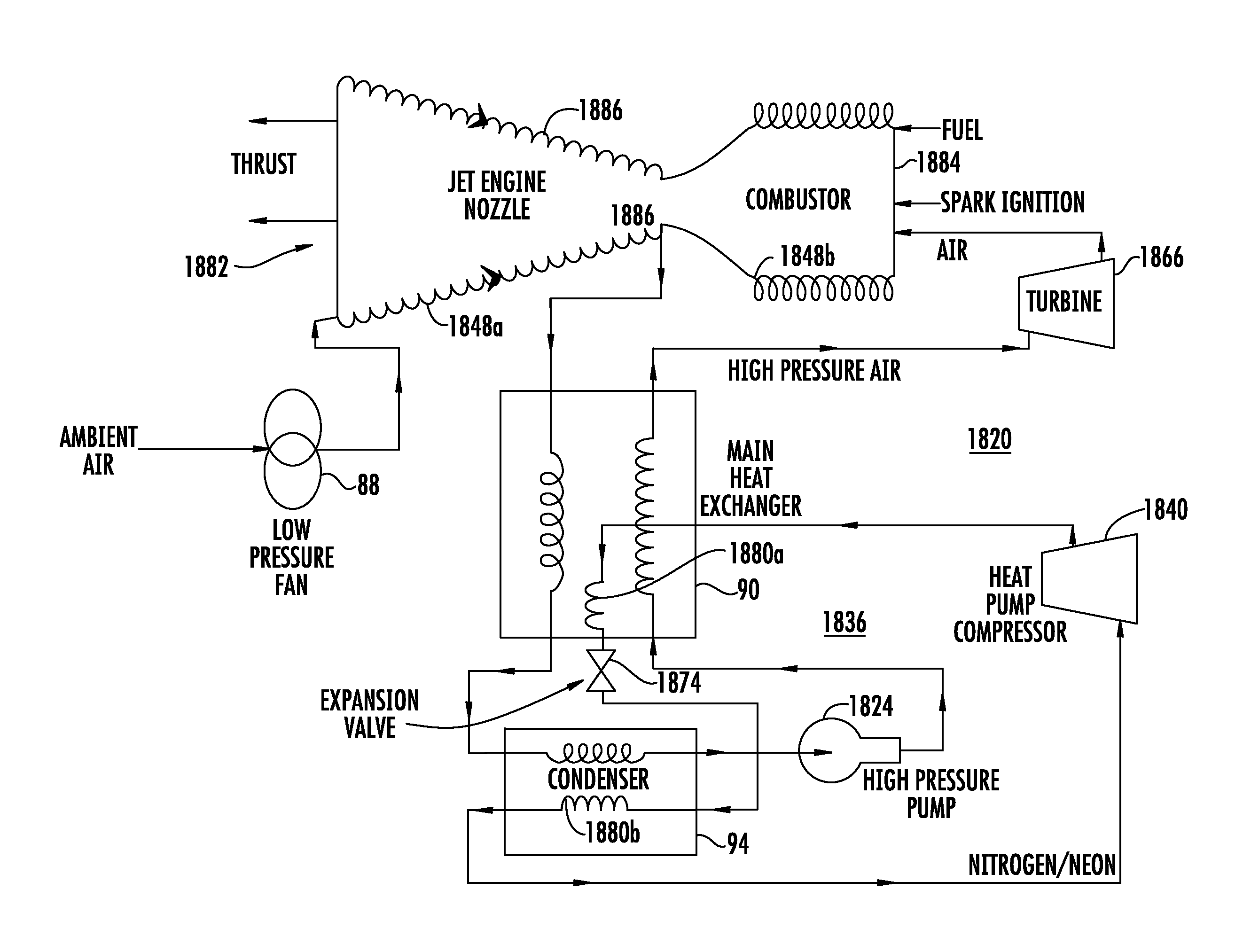
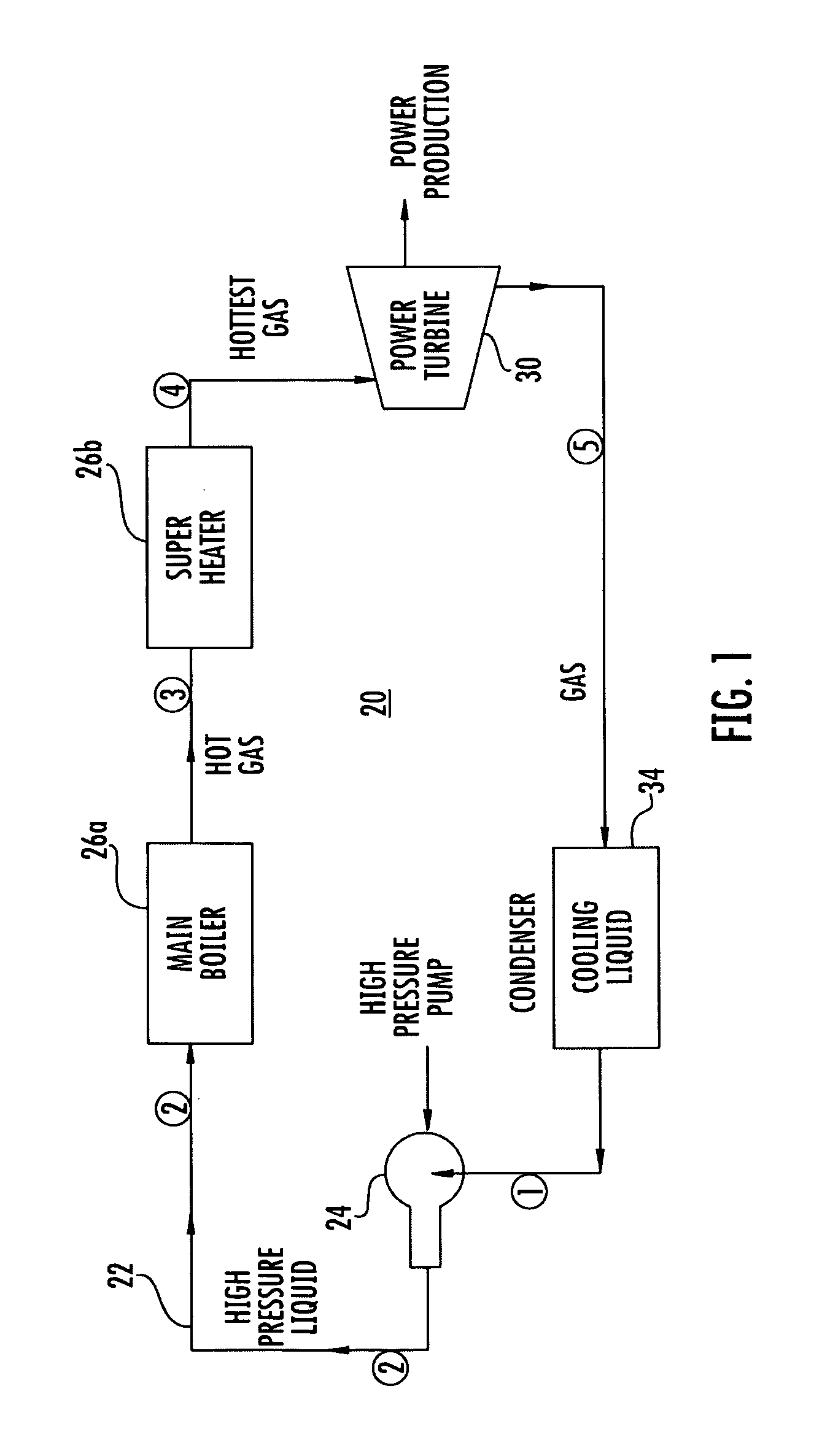
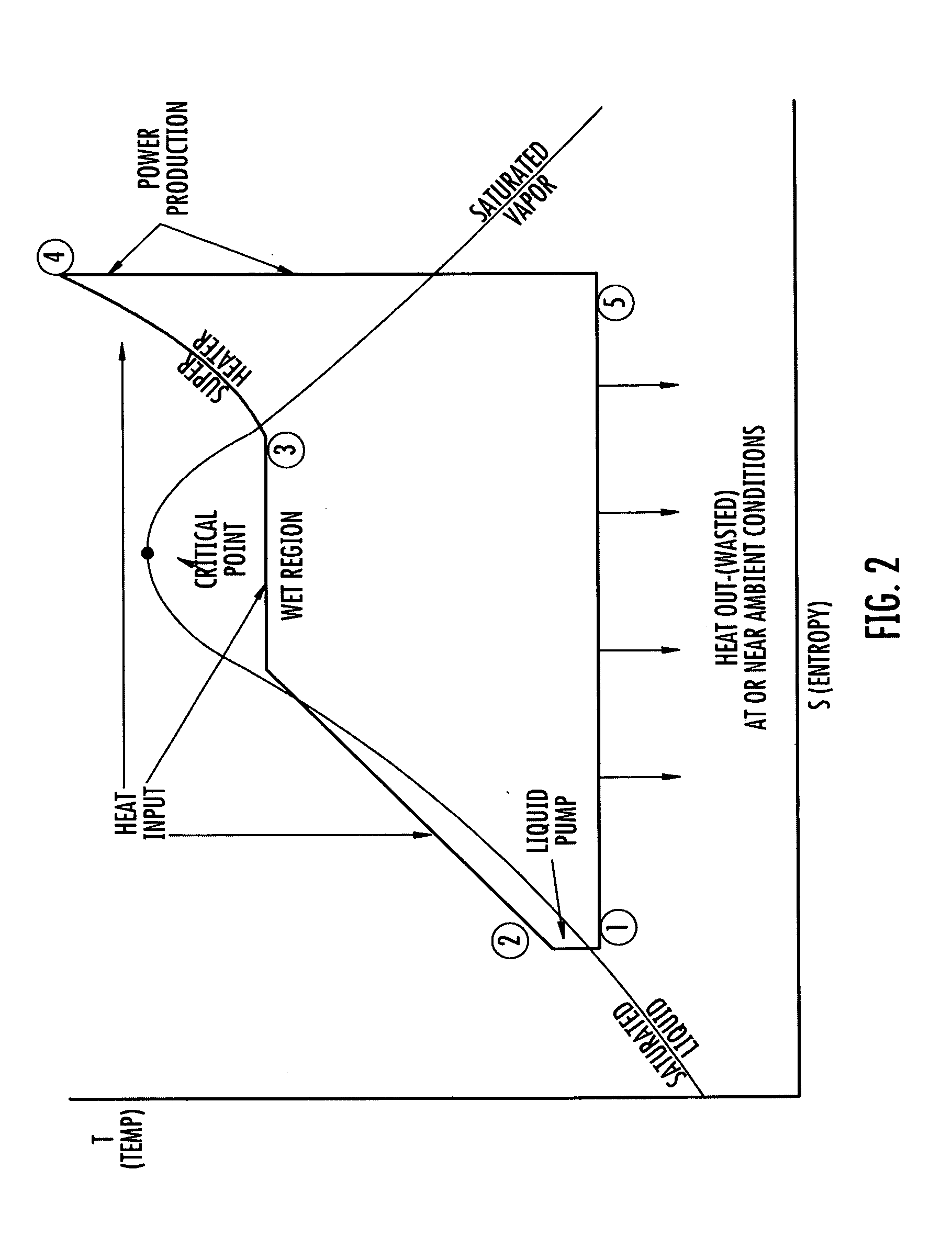
Ultra-high-efficiency engines and corresponding thermodynamic system
ActiveUS20110252796A1Improving the thermodynamic efficiency of a number of enginesImprove engine efficiencyGas turbine plantsEfficient propulsion technologiesWorking fluidEngineering
A thermodynamic system and method of producing useful work includes providing a working fluid and a fluid pump, or compressor, for pumping the working fluid in a cycle. A thermal input is provided for supplying heat to the working fluid. An expansion device downstream of the thermal input converts motion of the working fluid to useful work. A heat pump is provided. A number of different means of implementing the heat pump are presented, including direct transfer of working fluid mass flow. The heat pump pumps heat from one portion of the working fluid to another portion of the working fluid. For some applications, a regenerator, or recuperator, may be used to transfer heat from a high temperature portion of the working fluid to a lower temperature portion.
Owner:BURKHART TECH
Convergent/divergent nozzle with modulated cooling
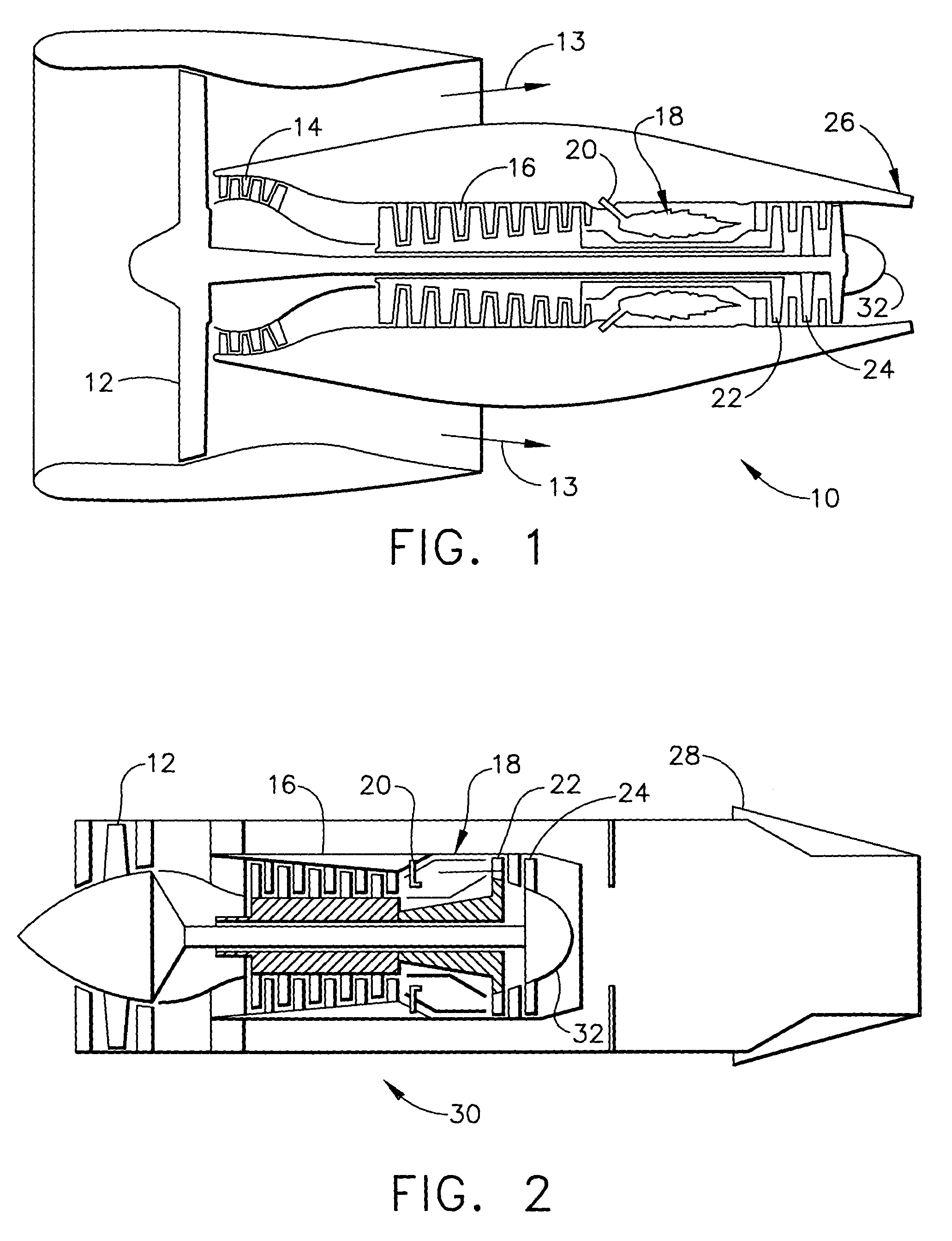
ActiveUS7032835B2Improve engine efficiencyReduce momentumAircraft navigation controlLiquid surface applicatorsCooling channelAirflow
A nozzle system includes a multiple of circumferentially distributed convergent flaps, divergent flaps and inter-flap seals which circumscribe an engine centerline and define the radial outer boundary of a gas path. Each divergent flap includes a multiple of cooling channels with respective intakes and outlets. As the nozzle transitions between positions, the divergent flap seals move relative a divergent flap longitudinal axis to modulate the cooling airflow which enters the separate intakes.
Owner:RTX CORP
Control strategy for multi-stroke engine system
ActiveUS20090277434A1Improve engine efficiencyHigh outputElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesFour-stroke enginePoppet valve
An engine system and a method of operation are described. As one example, the method may include: during a first operating condition, operating a cylinder of the engine in a two stroke cycle to combust a first mixture of air and fuel, and adjusting an opening overlap between an intake poppet valve and an exhaust poppet valve of the cylinder to vary a composition of exhaust gases exhausted by the cylinder via the exhaust poppet valve; and during a second operating condition, operating a cylinder of the engine in a four stroke cycle to combust a second mixture of air and fuel, and adjusting a relative amount of fuel contained in the second mixture of air and fuel to vary the composition of exhaust gases exhausted by the cylinder via the exhaust poppet valve.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
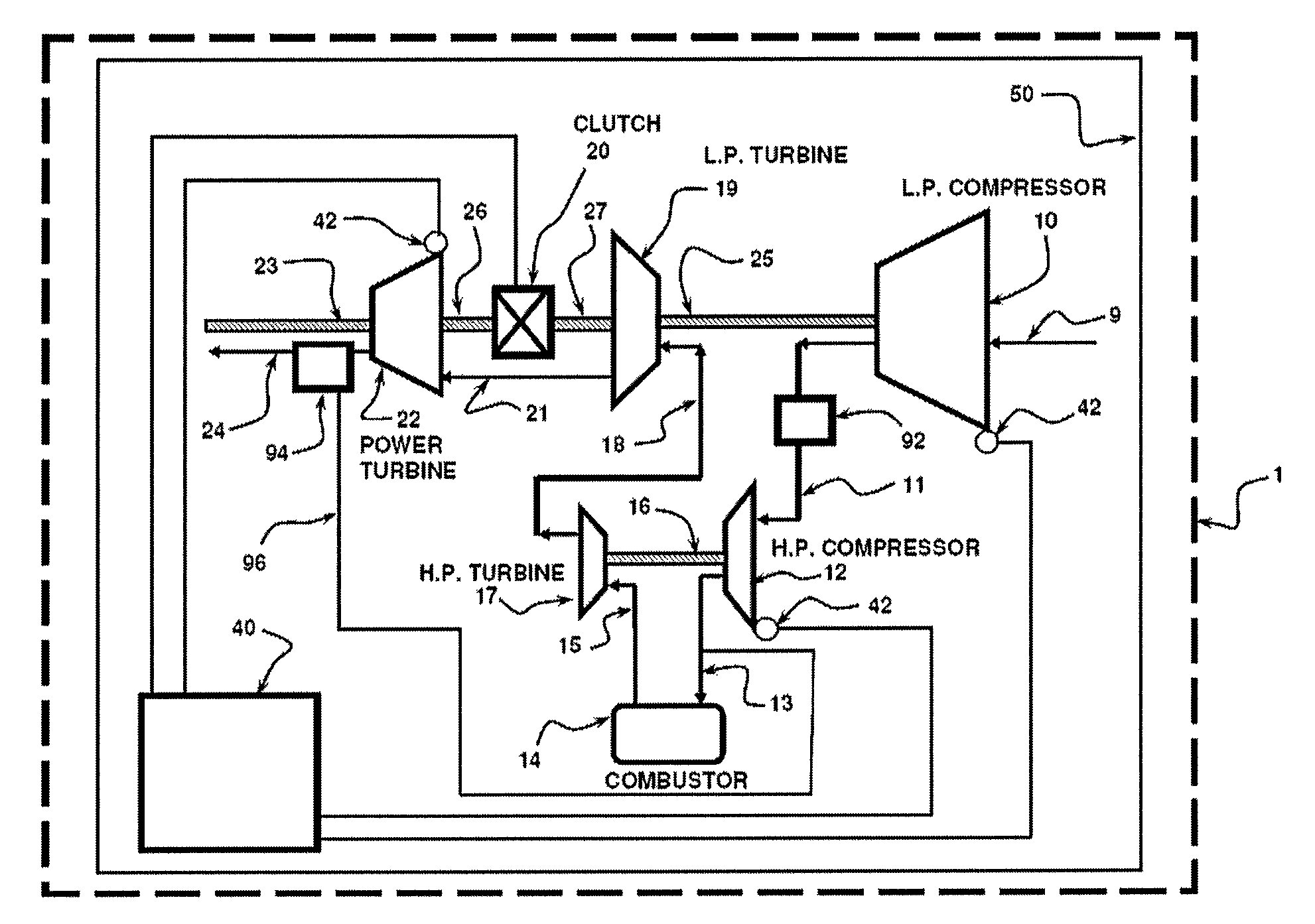
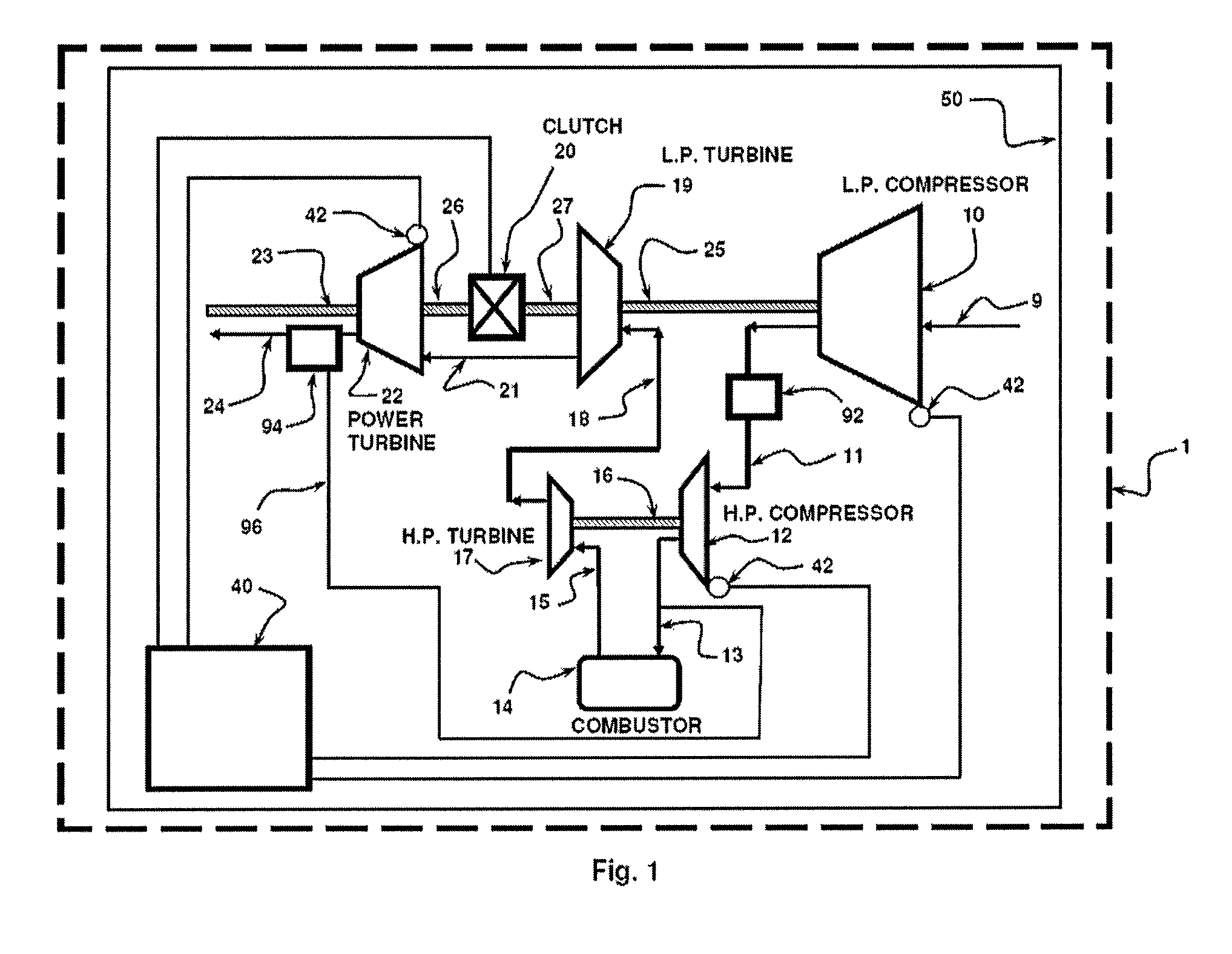
Multi spool gas turbine system
InactiveUS8220245B1Improve engine efficiencyEngine fuctionsFluid actuated clutchesCombustorDrive shaft
A gas turbine engine is provided, including an air inlet in fluid communication with a compressor, a combustor, a compressor turbine, and a power turbine. The compressor and compressor turbine may be mounted on a first drive shaft, and the power turbine may be mounted on a second shaft. The engine further includes an engagement mechanism adapted to selectively engage the first drive shaft to the second drive shaft, wherein the first drive shaft and second drive shaft rotate at substantially the same speed when the engagement mechanism is engaged. The disclosed multi-spool gas turbine engine provides improved part power fuel consumption at reduced output shaft speeds. The proposed invention can relate to turbines with two or more gas generator spools.
Owner:CANDENT TECH
Engine cooling system
ActiveUS20050028756A1Minimizes parasitic lossIncrease and decrease flow of coolantLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlTemperature controlCylinder head
A cooling system has a diverter valve to selectively control the flow of coolant through an internal combustion engine having a cylinder block with a cooling jacket and a cylinder head mounted on the block with a cooling jacket. A controller, responsive to the temperature of the block and the head, controls the diverter valve and a water pump to provide adequate coolant flow through the head and the block as needed to maintain optimal operating temperatures. After the engine is shut off, the controller continues to operate the water pump and a cooling fan to continue to cool the engine for a period of time.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Optimized Fuel Management System for Direct Injection Ethanol Enhancement of Gasoline Engines
InactiveUS20100006050A1Save gasImprove engine efficiencyElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelVaporizationProcess engineering
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and system for turbocharging an engine
ActiveUS20110167815A1Improve engine efficiencyIncrease engine efficiencyValve arrangementsElectrical controlAutomotive engineeringEngine efficiency
A method for improving operation of a turbocharged engine is presented. In one embodiment, the method may reduce engine emissions and improve engine efficiency during an engine start.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com