Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Swing-piston engine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
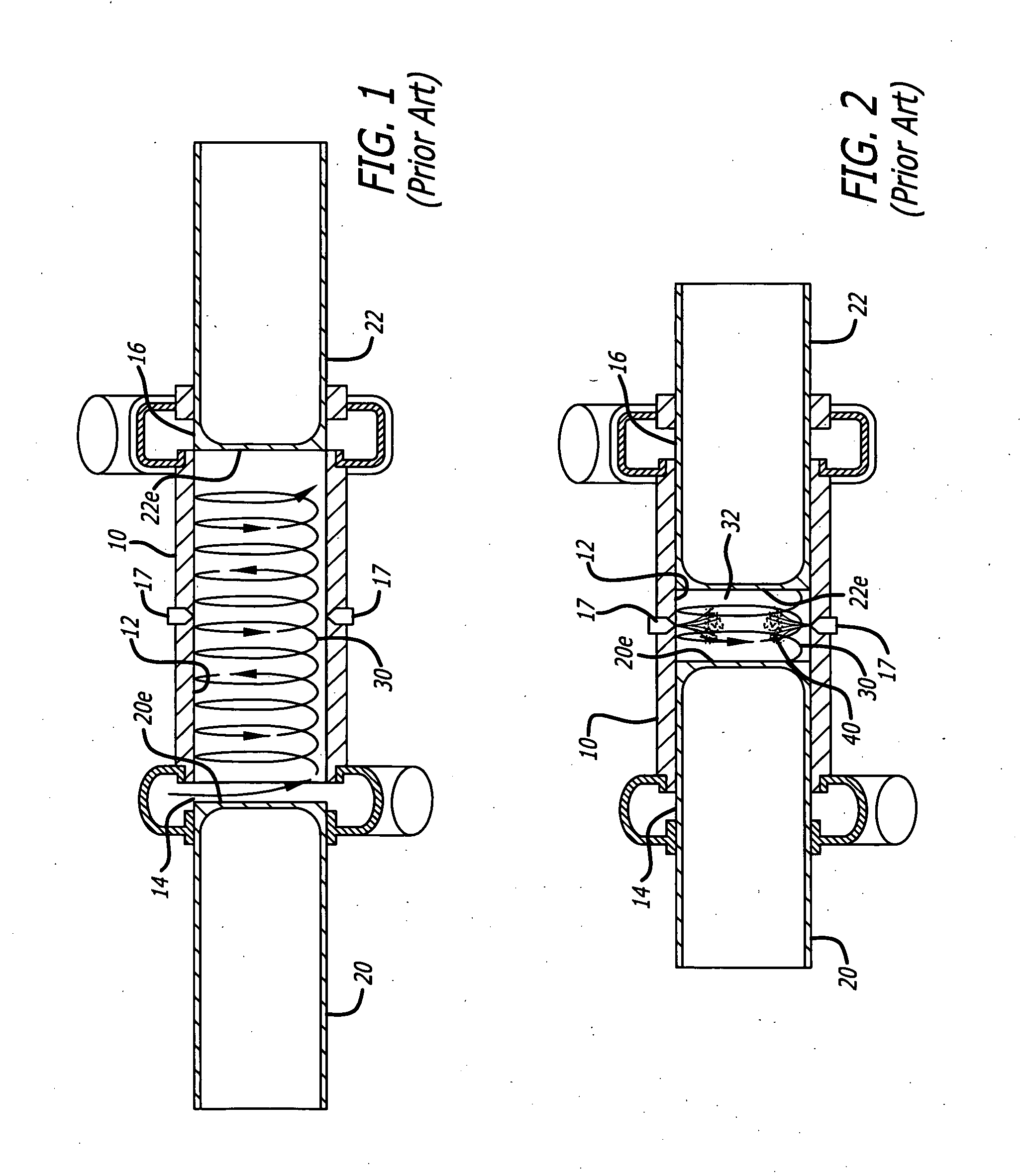
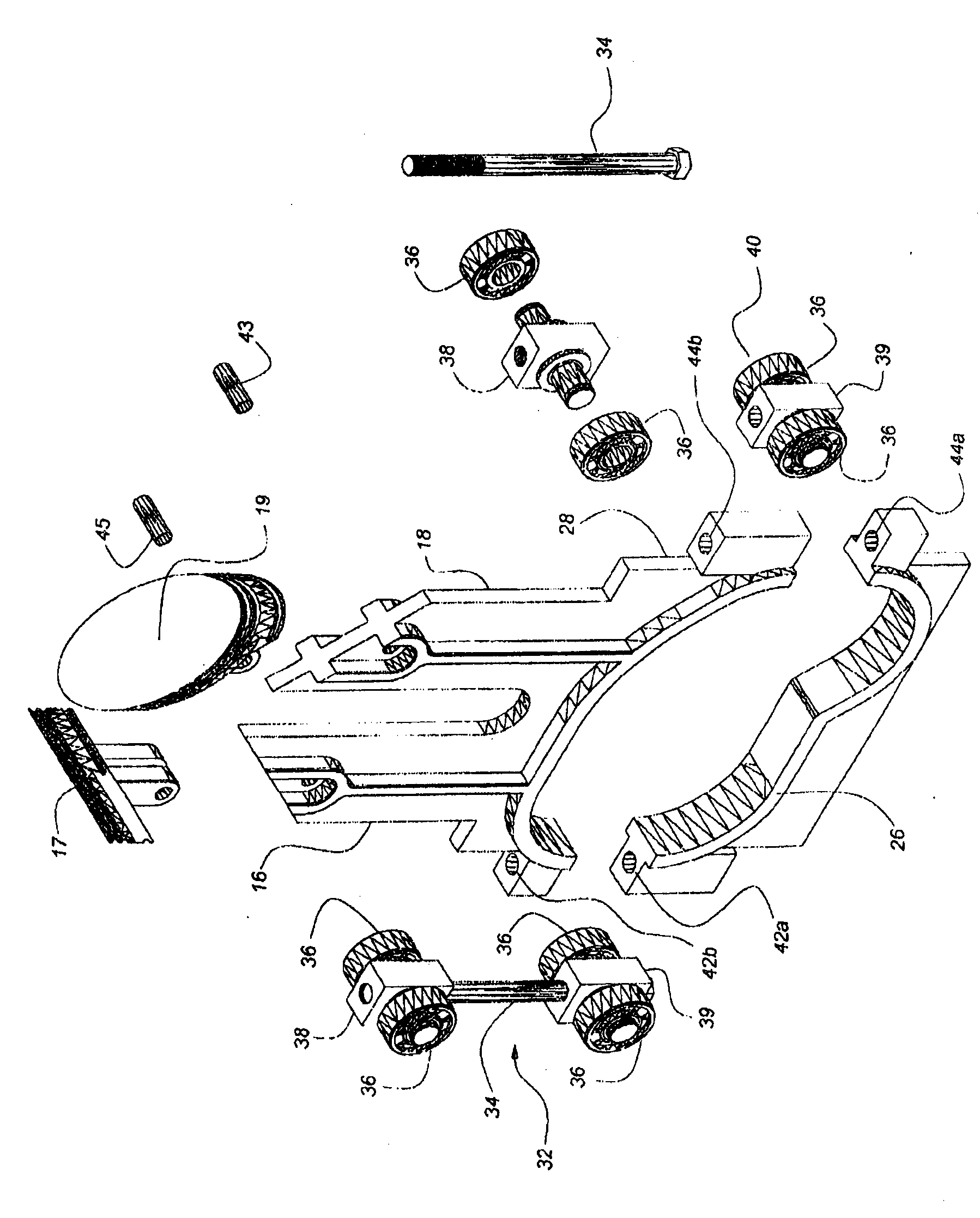
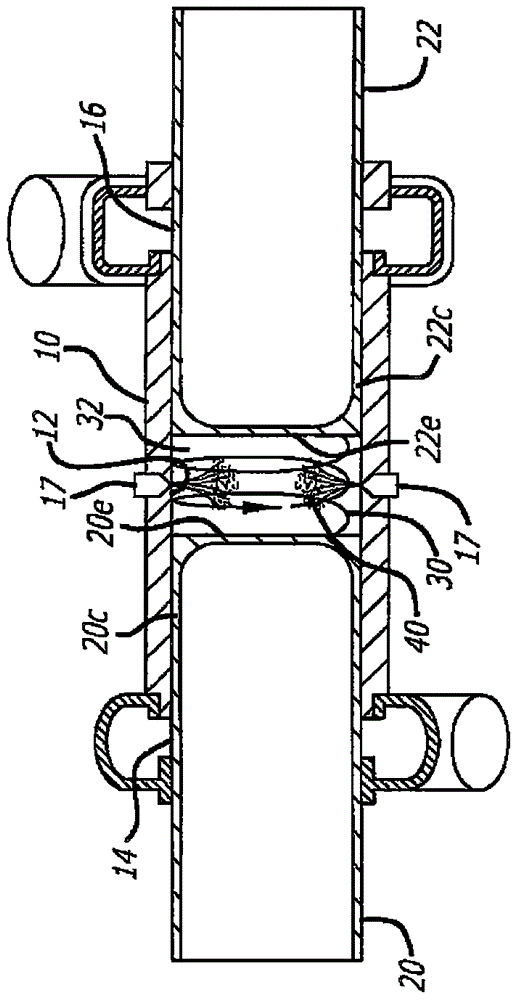
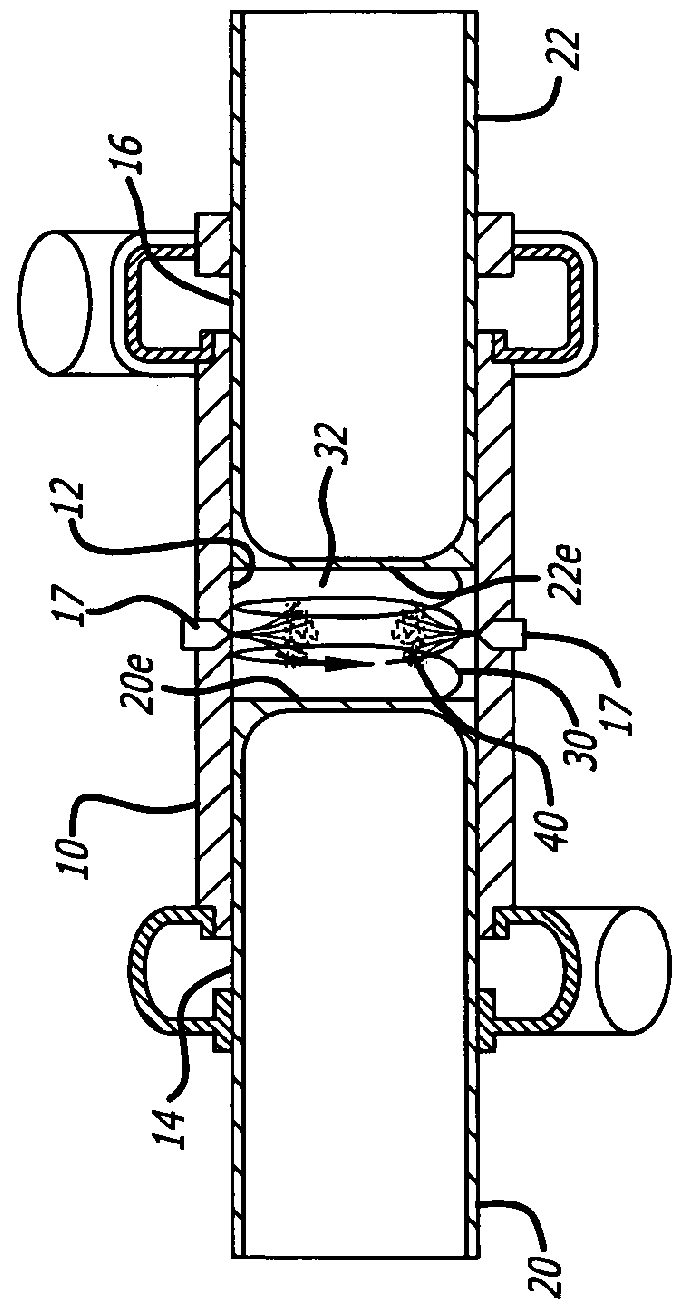
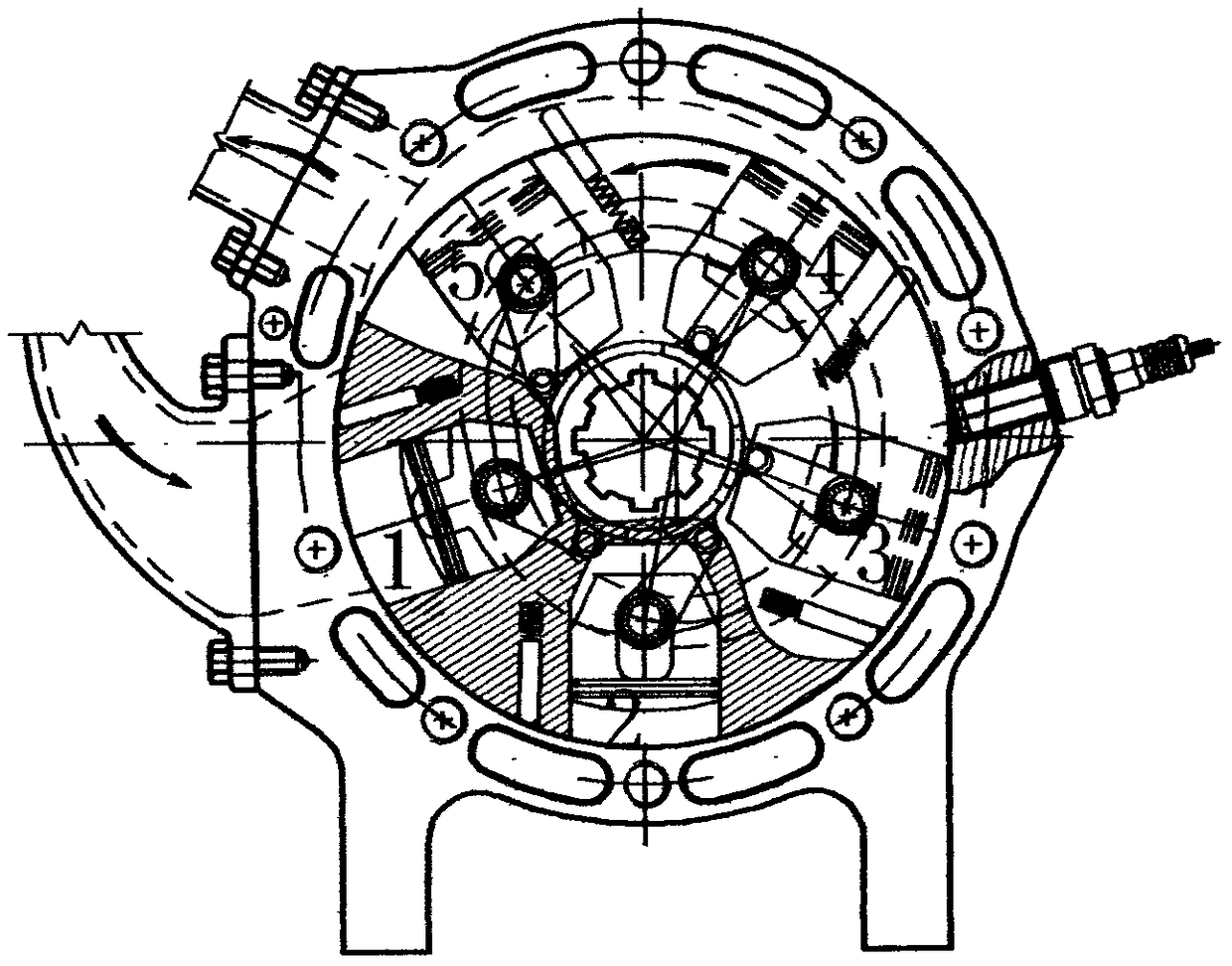
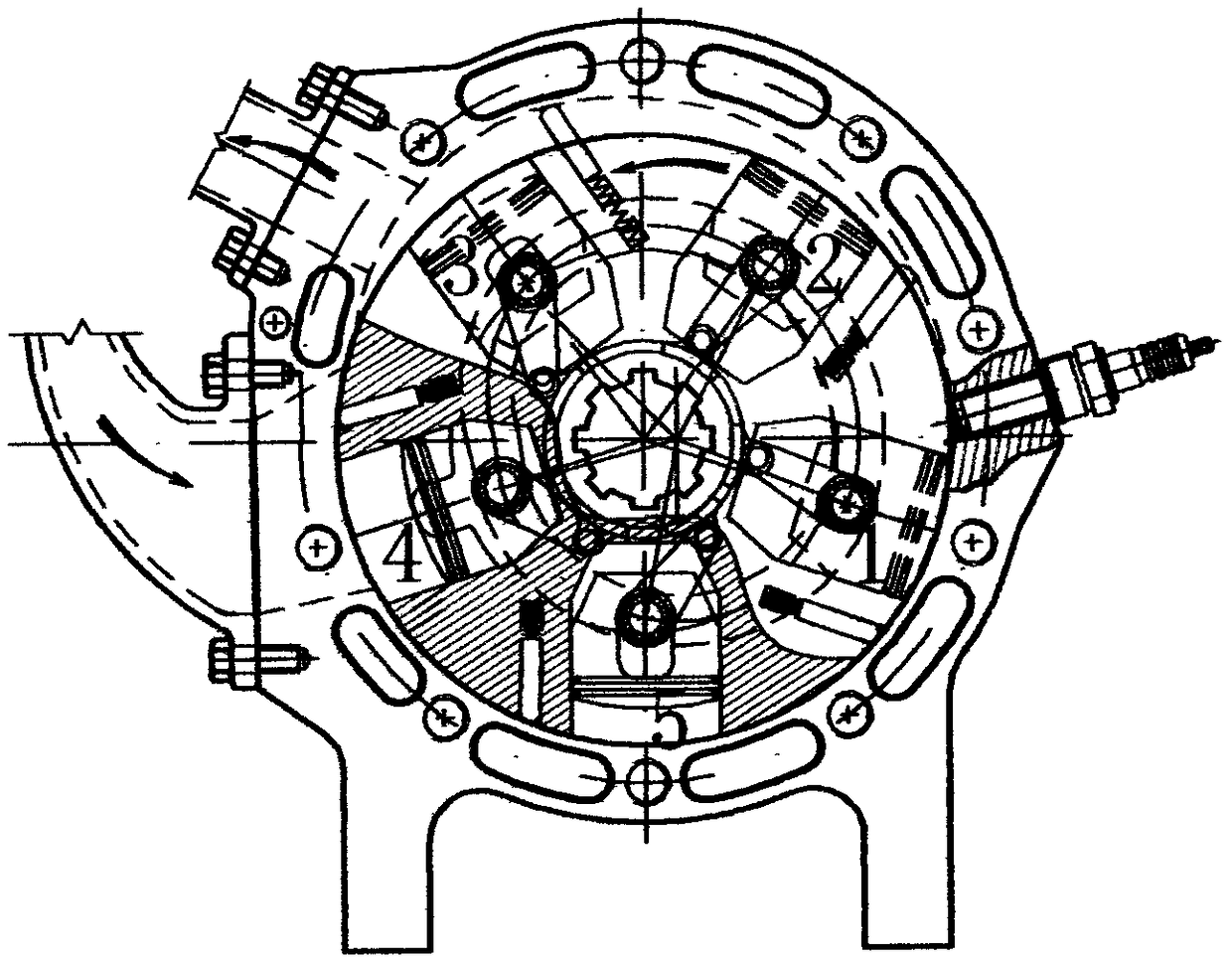
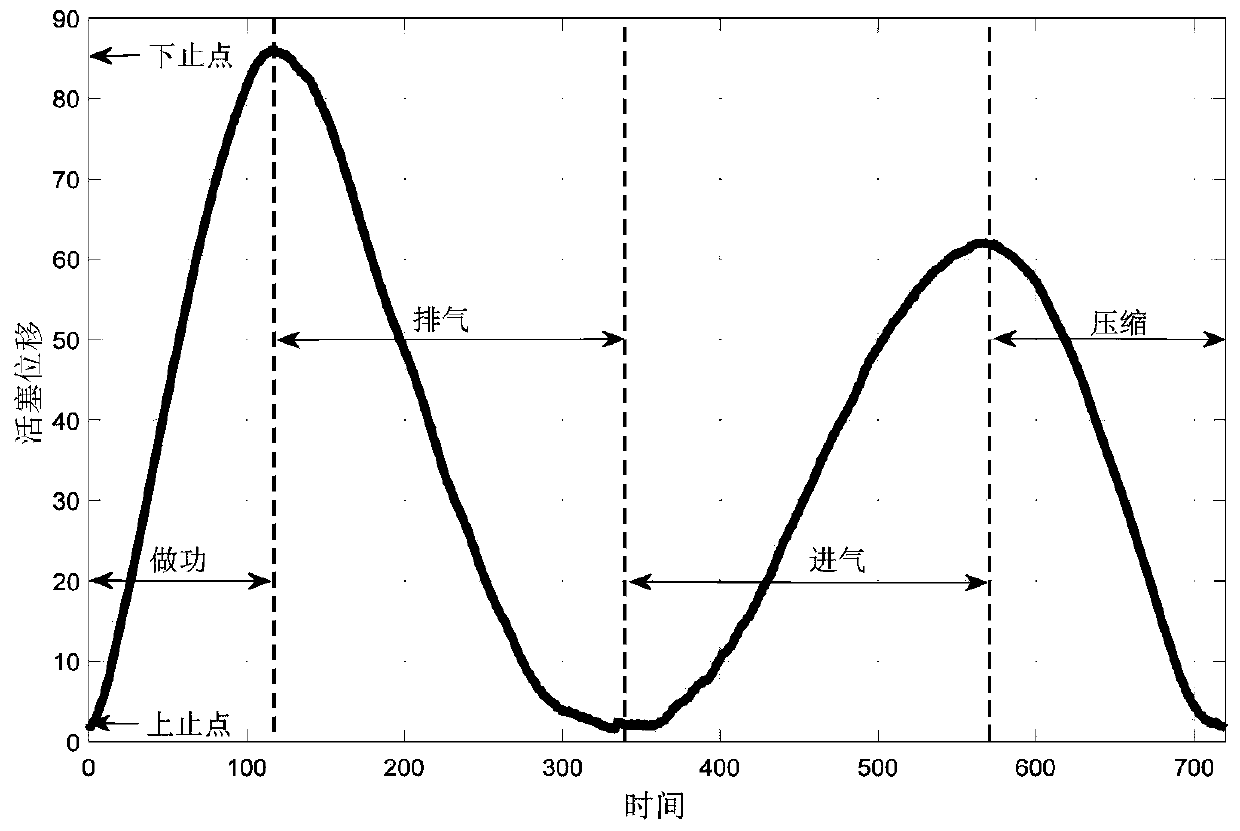
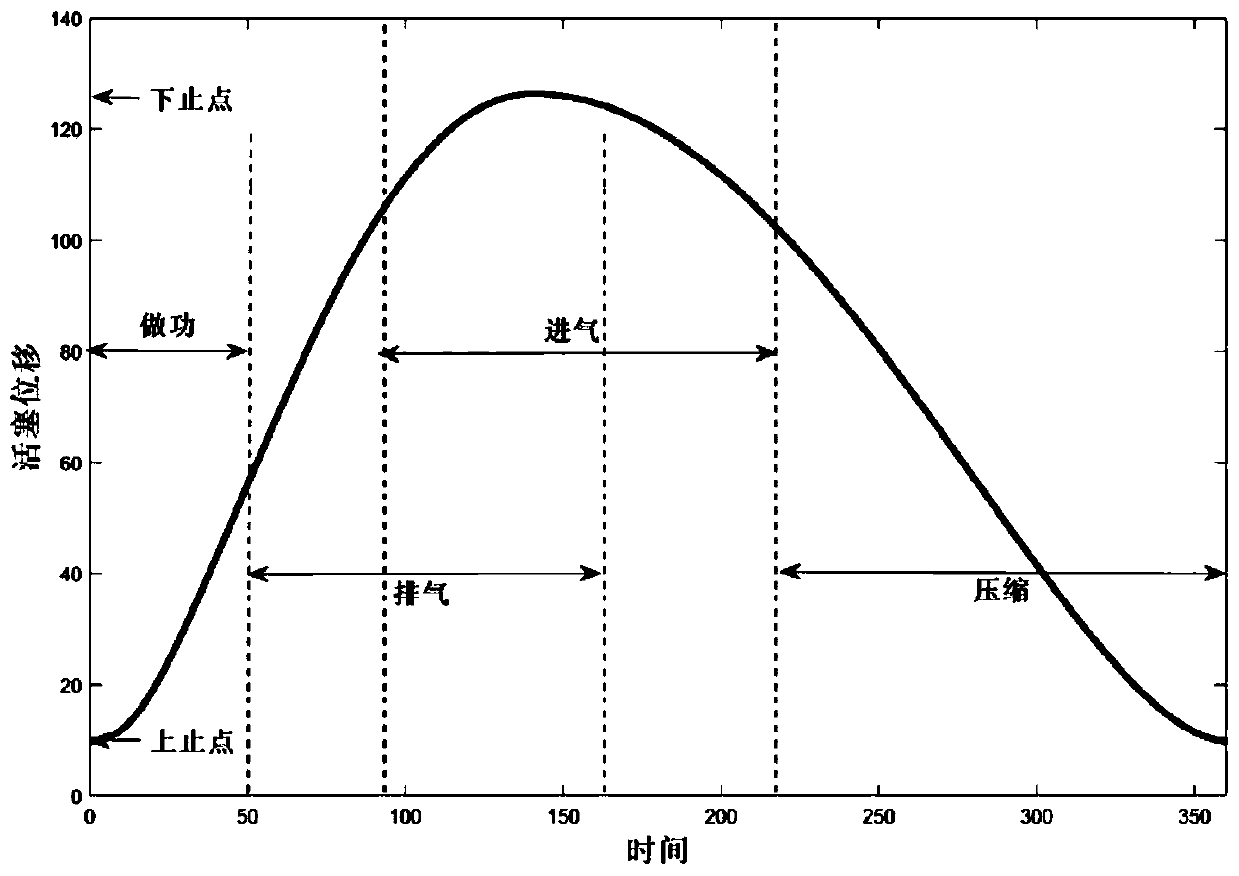
A swing-piston engine is a type of internal combustion engine in which the pistons move in a circular motion inside a ring-shaped "cylinder", moving closer and further from each other to provide compression and expansion. Generally two sets of pistons are used, geared to move in a fixed relationship as they rotate around the cylinder. In some versions the pistons oscillate around a fixed center, as opposed to rotating around the entire engine. The design has also been referred to as a oscillating piston engine, vibratory engine when the pistons oscillate instead of rotate, or toroidal engine based on the shape of the "cylinder".
Four-cylinder, four-cycle, free piston, premixed charge compression ignition, internal combustion reciprocating piston engine with a variable piston stroke
ActiveUS7258086B2Increase the compression ratioImprove engine efficiencyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesFree-piston engineHomogeneous charge compression ignition
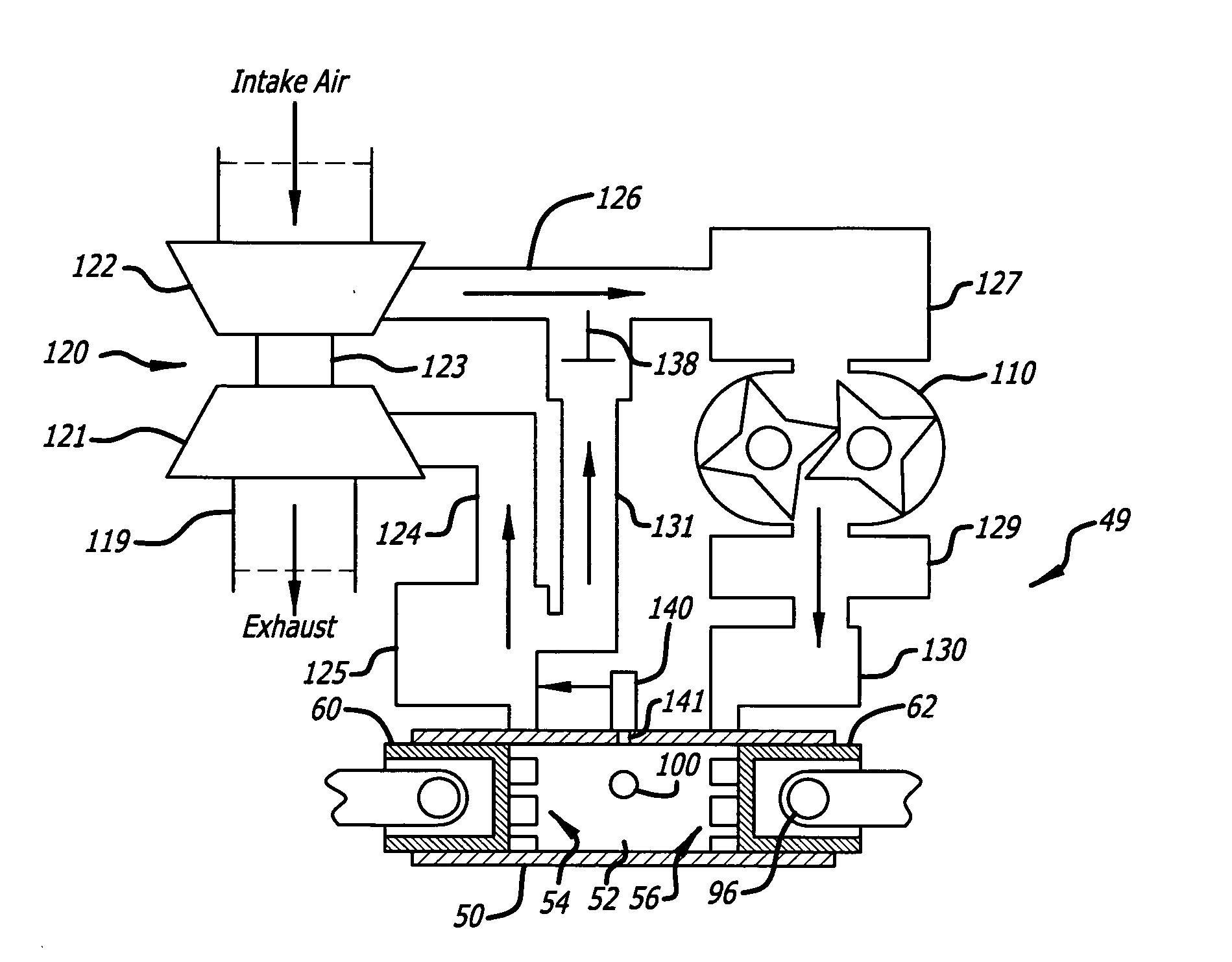
A four-cycle, four-cylinder, premixed charge compression ignition internal combustion reciprocating free piston engine with a variable piston stroke and a compression ratio that varies as needed to provide charge ignition, to offer the potential of higher efficiency, lower emissions, and multi-fuel operation. The engine does not have a crankshaft, and therefore does not provide direct rotary output. Instead its free pistons oscillate, in a manner similar to a two cycle free piston engine. For many applications, such as piston pumps and compressors, the engine provides an output directly driven by the oscillating pistons. In other applications, such as but not limited to use as a gas generator for a power turbine, the engine provides an indirect means of producing rotary power. When the engine is used with high-speed power turbines, the power turbine may be directly coupled to a high-speed alternator for electrical power output.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE ENERGY TECH DEV TRUST
Two stroke, opposed-piston engines with engine braking
ActiveUS20120210985A1Simple and inexpensiveHigh trafficInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelFree-piston engineSwing-piston engine
In a two-stroke opposed-piston engine, a ported cylinder with a pair of opposed pistons is equipped with an engine brake including an engine braking valve that can be opened to release air from the cylinder as the pistons cycle between BDC and TDC positions.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
Shaft type connecting rod transmission system and opposed piston engine
ActiveCN105114179AEfficient use ofSimple structureGearingMachines/enginesLinear motionReciprocating motion
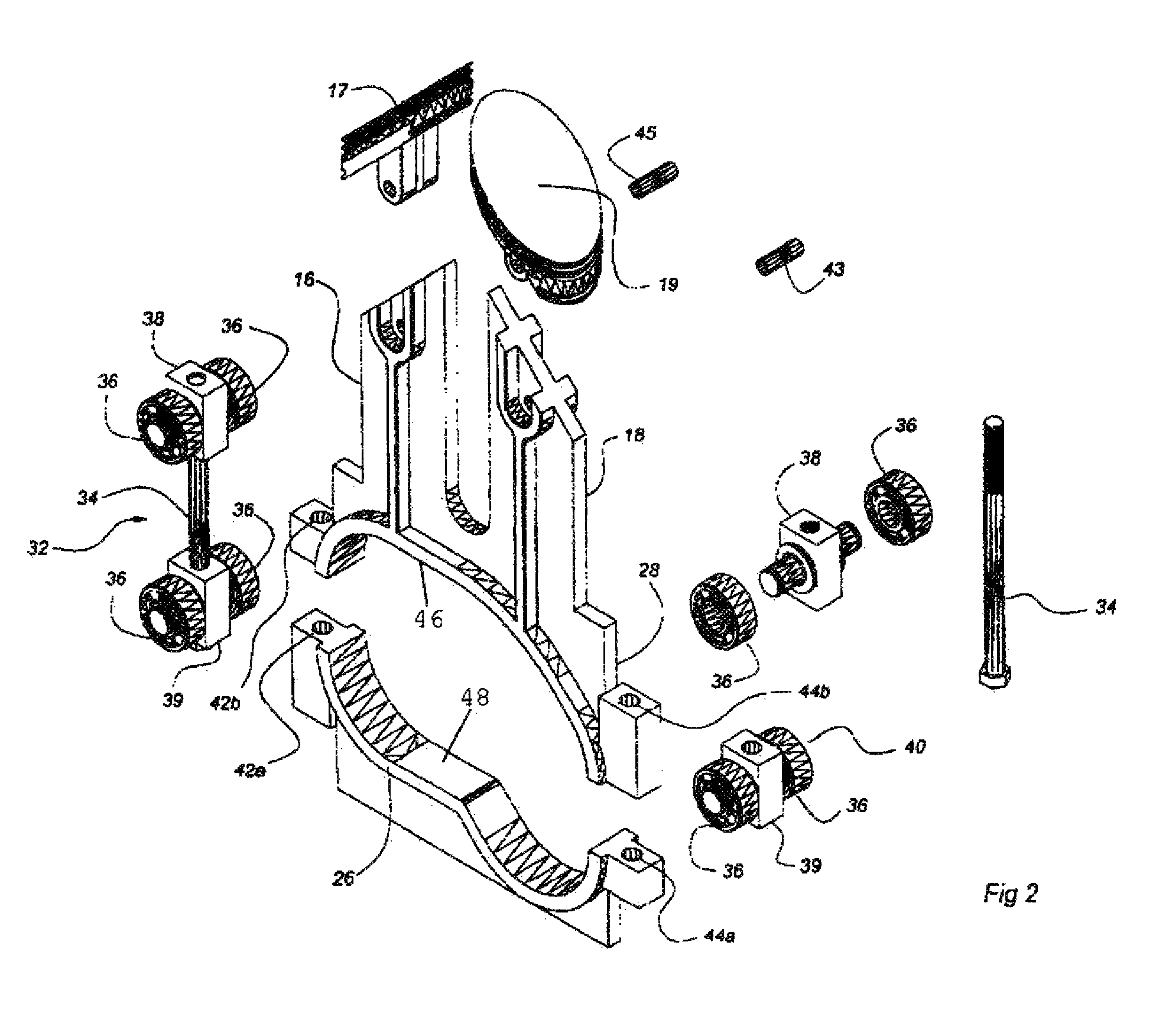
The invention discloses a shaft type connecting rod transmission system and an opposed piston engine; and a traditional reciprocating linear motion is converted to a rotating motion in the same direction, so that the reliability of the transmission system is effectively improved, the transmission system is simplified to become more compact, and effective utilization of a space between the back surface of a piston of an internal combustion engine and a cylinder becomes possible. The shaft type connecting rod transmission system comprises a main shaft and at least one linear reciprocating motion unit, wherein the linear reciprocating motion unit comprises at least one linear reciprocating motion body. The linear reciprocating motion bodies are fixedly connected with one ends of corresponding shaft type connecting rods; the other ends of the shaft type connecting rods are fixedly connected with one sides of corresponding push-pull frames; and the axles of the shaft type connecting rods and the main shaft are perpendicular to each other. Slip blocks are arranged in the push-pull frames; two transverse outer side walls of the slip blocks and two transverse inner side walls of the push-pull frames are formed to vertical slide fit; inner rings of the slip blocks have inner teeth with elliptic indexing circles; and the inner teeth are circularly engaged with gears correspondingly arranged on the main shaft. Reversing mechanisms are arranged between the main shaft and the slip blocks.
Owner:郑安庆
Opposed-piston engine having a single crankshaft coupled to the opposed pistons by linkages with pivoted rocker arms
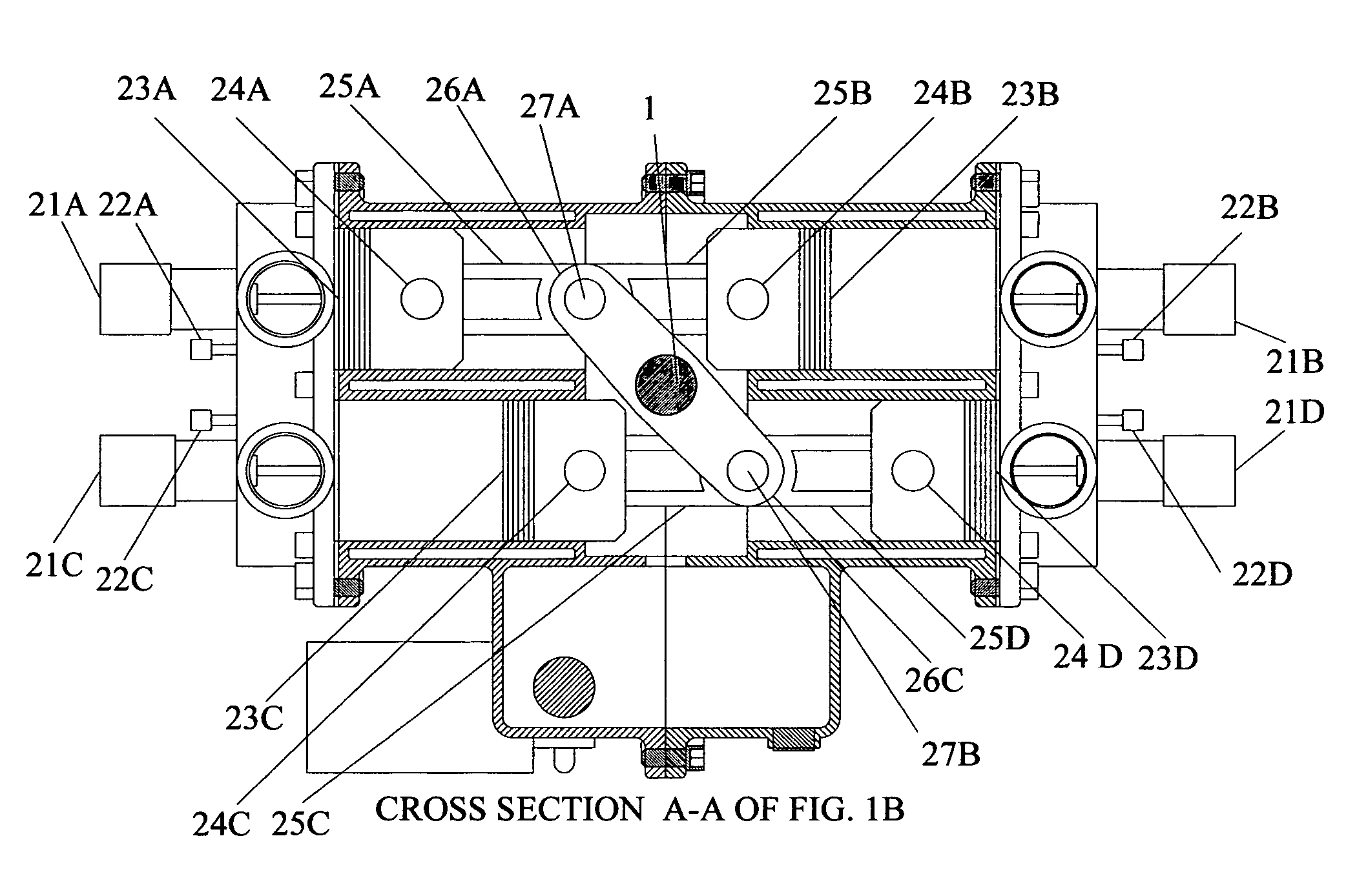
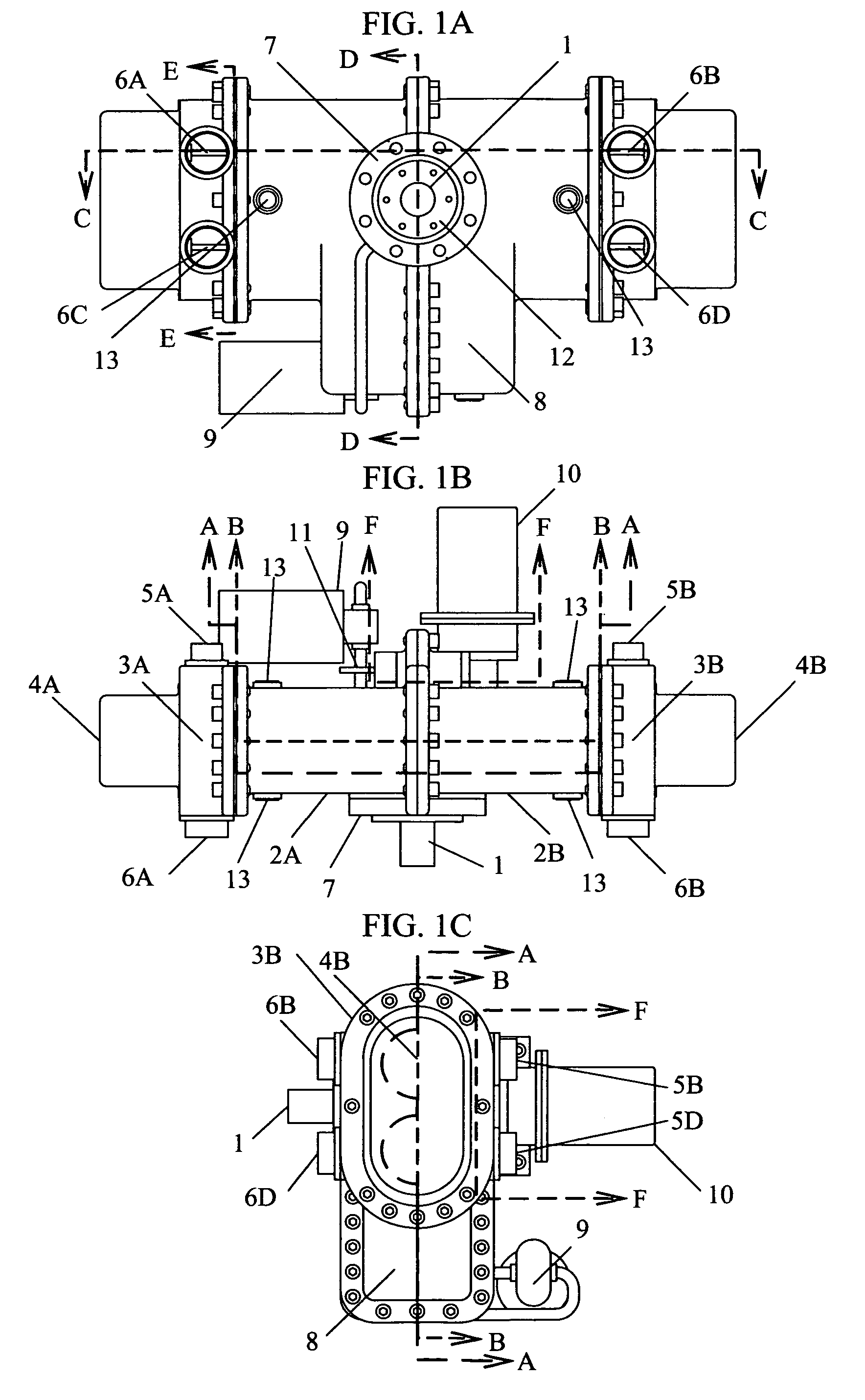
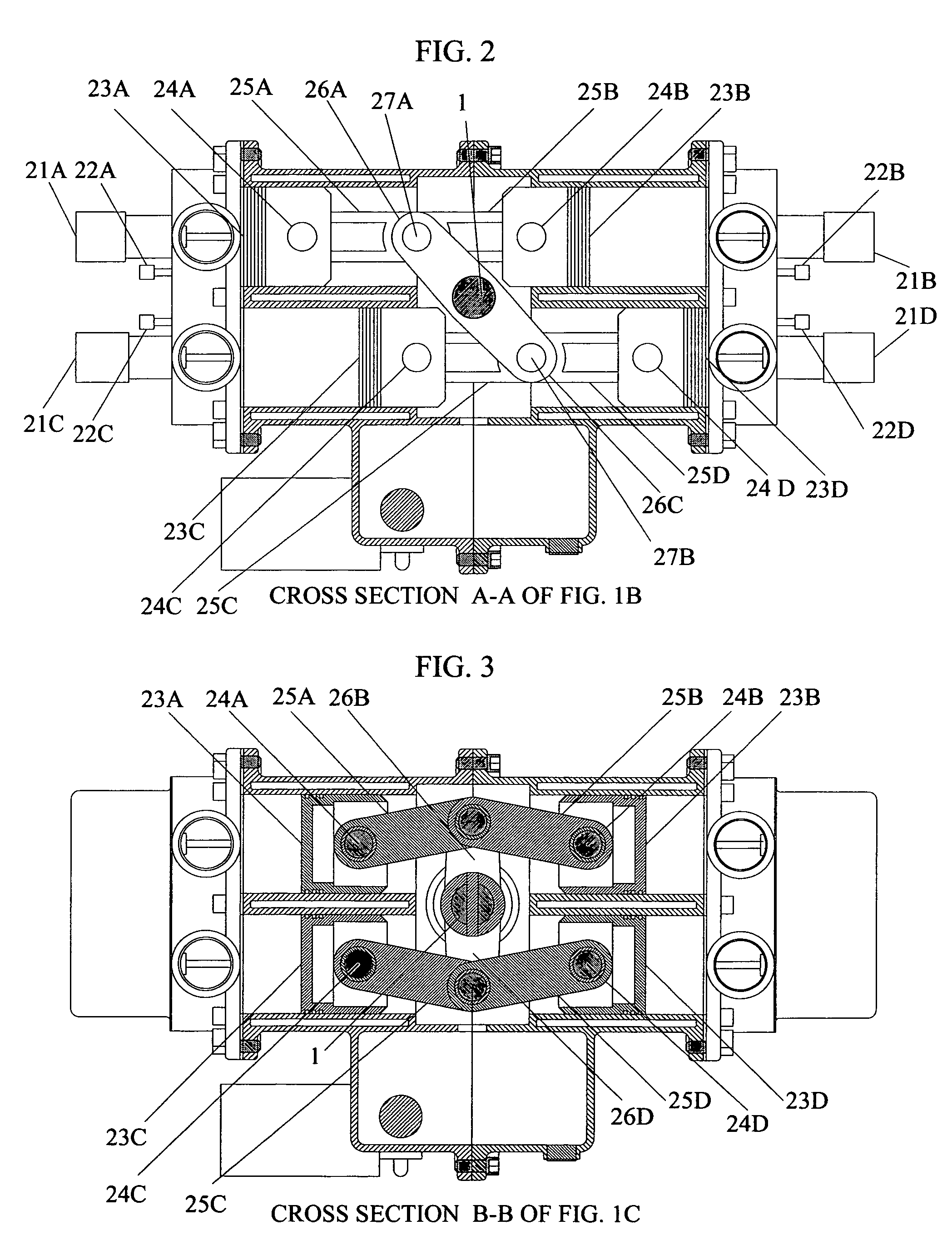
ActiveUS20120037130A1Alleviates lubricant-blocking effectImprove durability of bearingConnecting rod bearingsInternal combustion piston enginesTop dead centerSwing-piston engine
An opposed-piston engine with a single crankshaft has a rocker-type linkage coupling the crankshaft to the pistons that utilizes a rotatable pivot rocker arm with full-contact plain bearings. A rocker-type linkage utilizes a rotatable pivot bearing with an eccentric aspect to vary translation of piston linkage along the axial direction of a cylinder, which shifts the top dead center (TDC) and bottom dead center (BDC) locations of a piston so as to change the volume of charge air compressed during the power stroke.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
Opposed piston engine
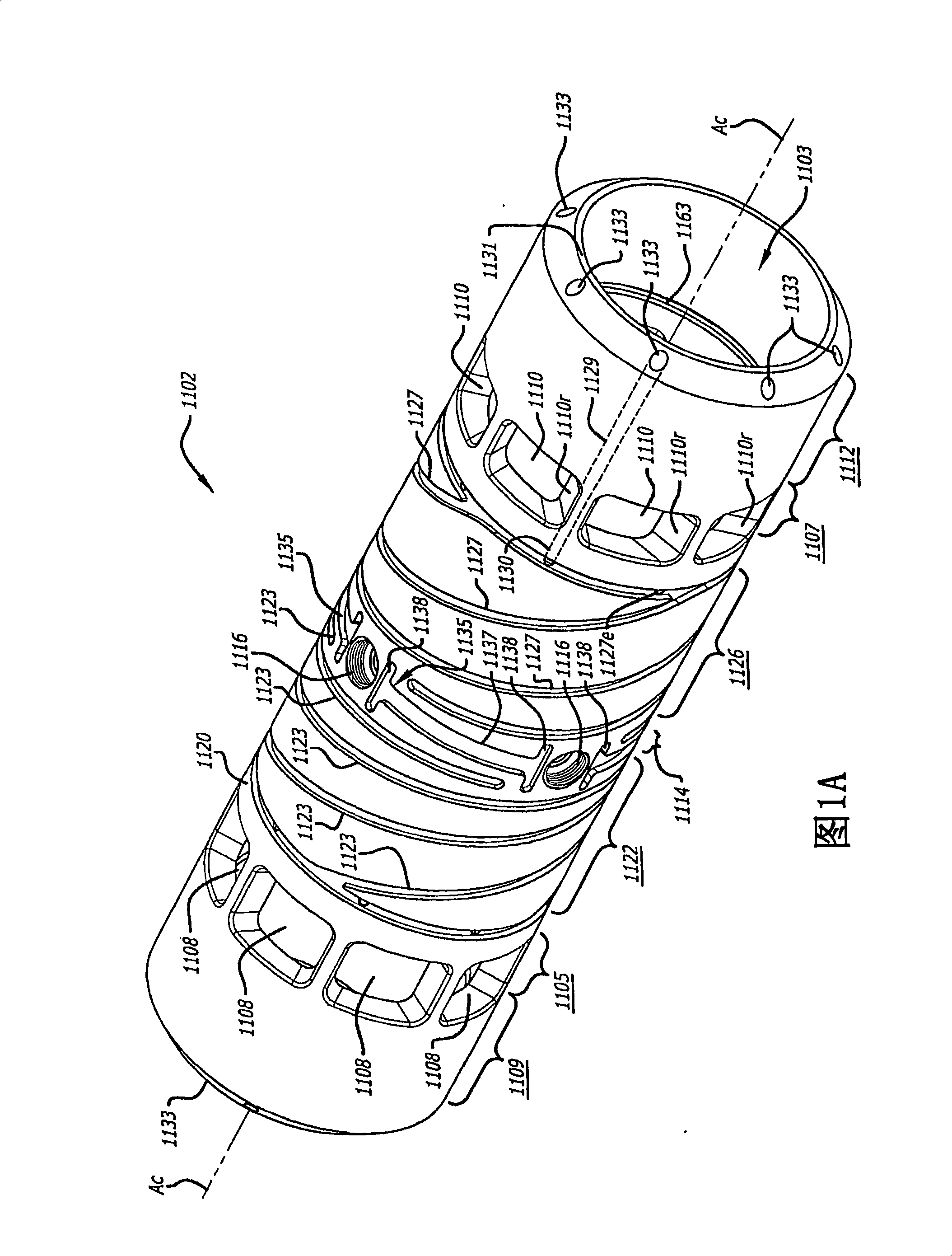
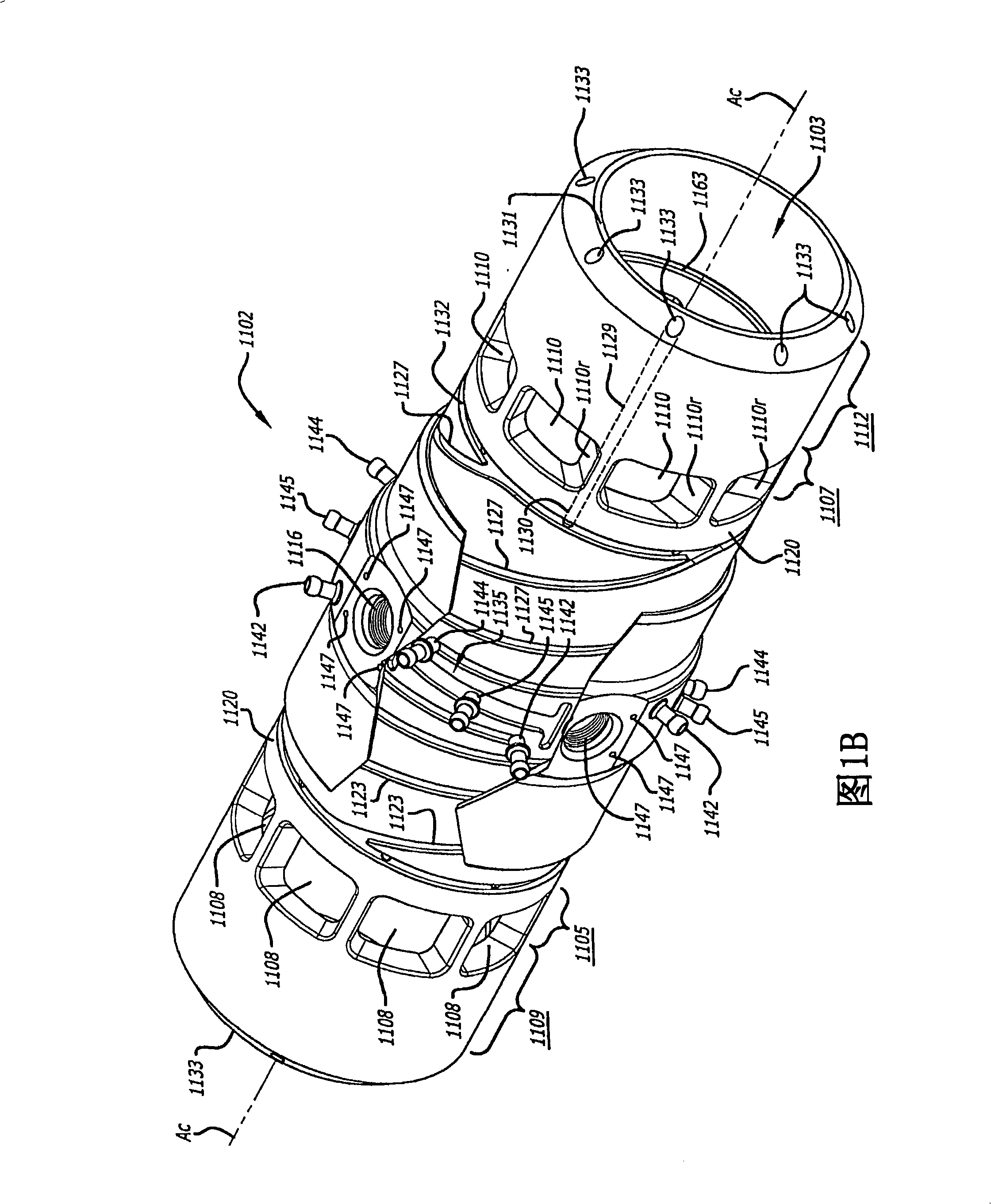
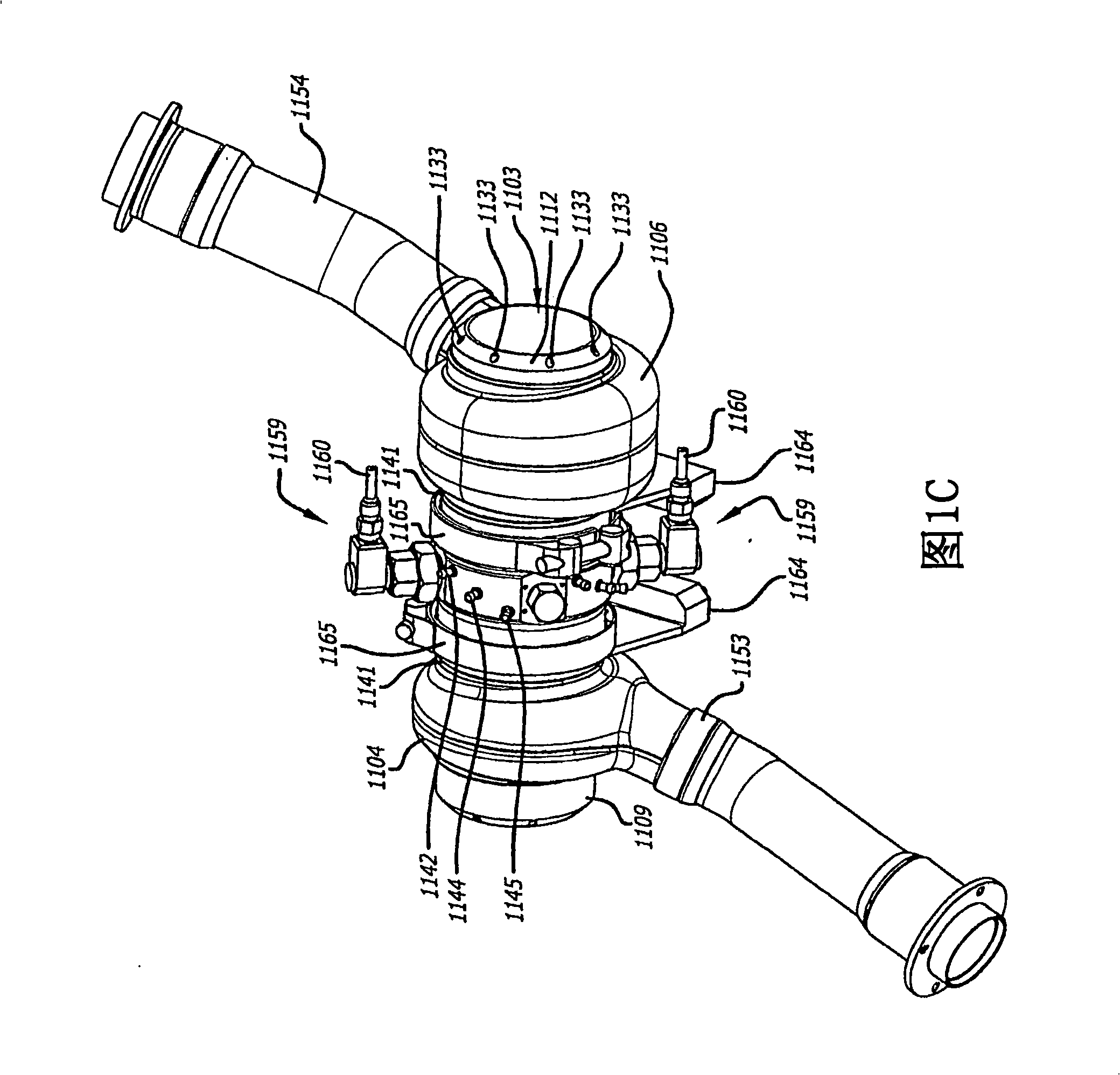
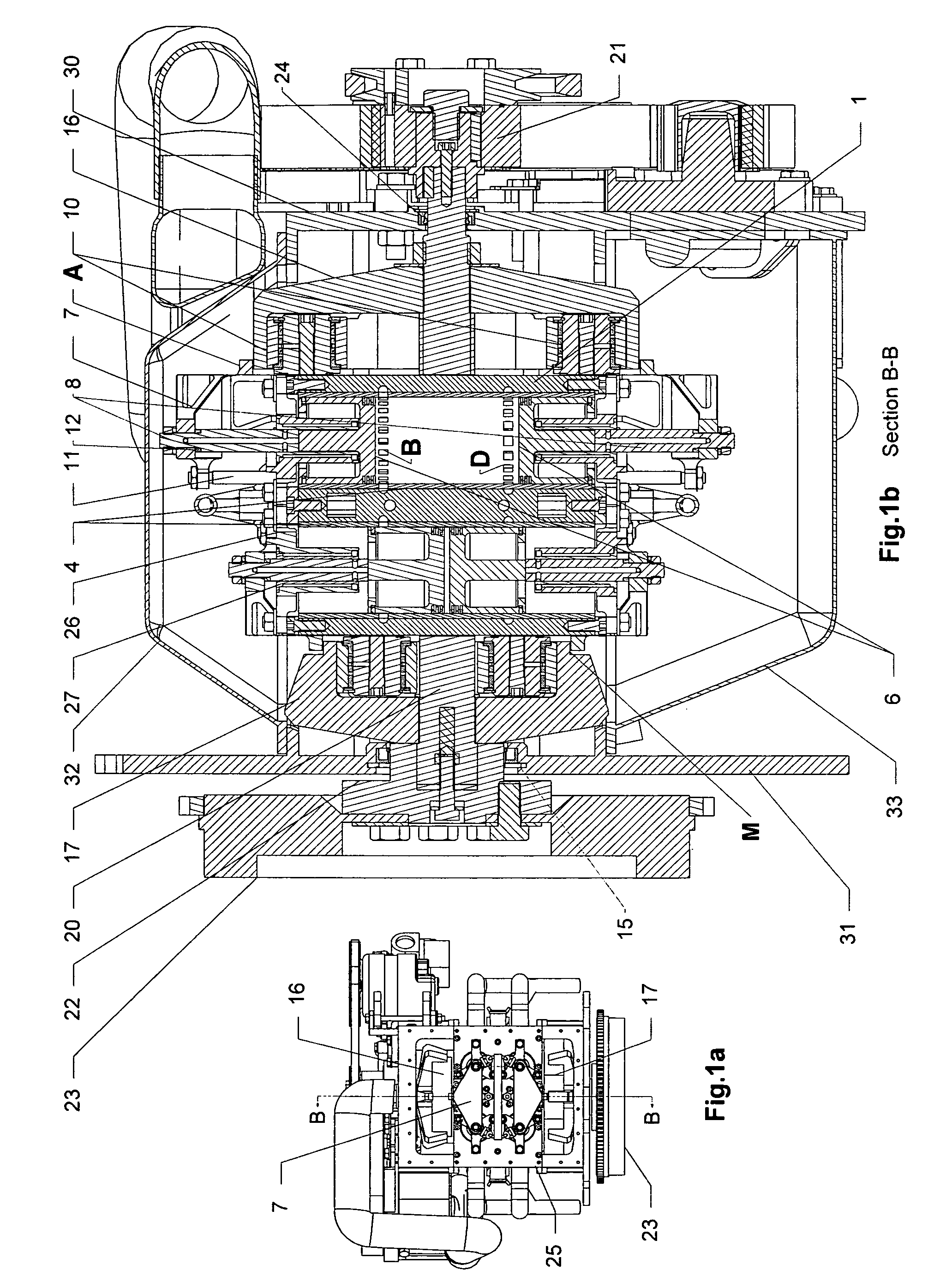
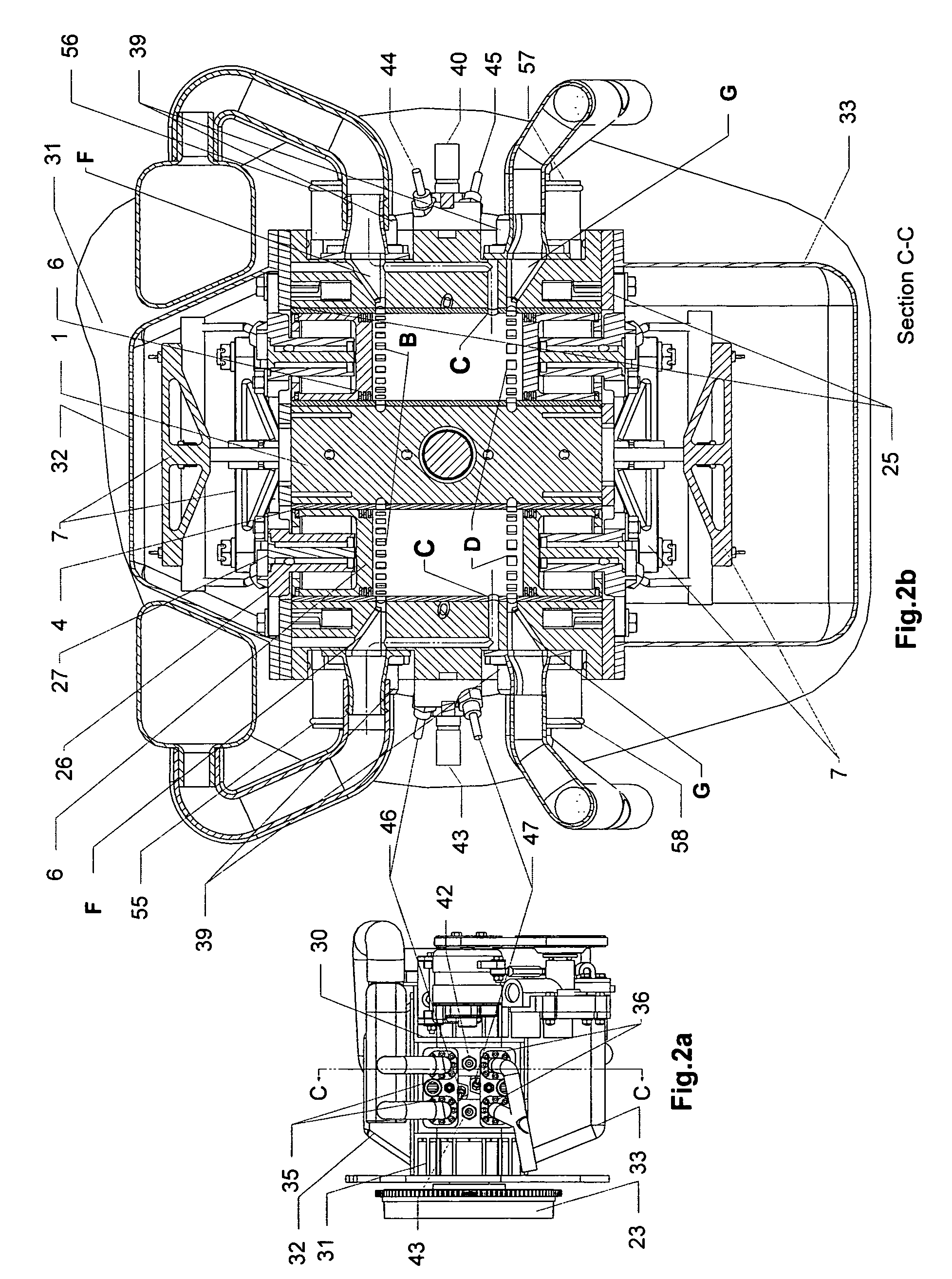
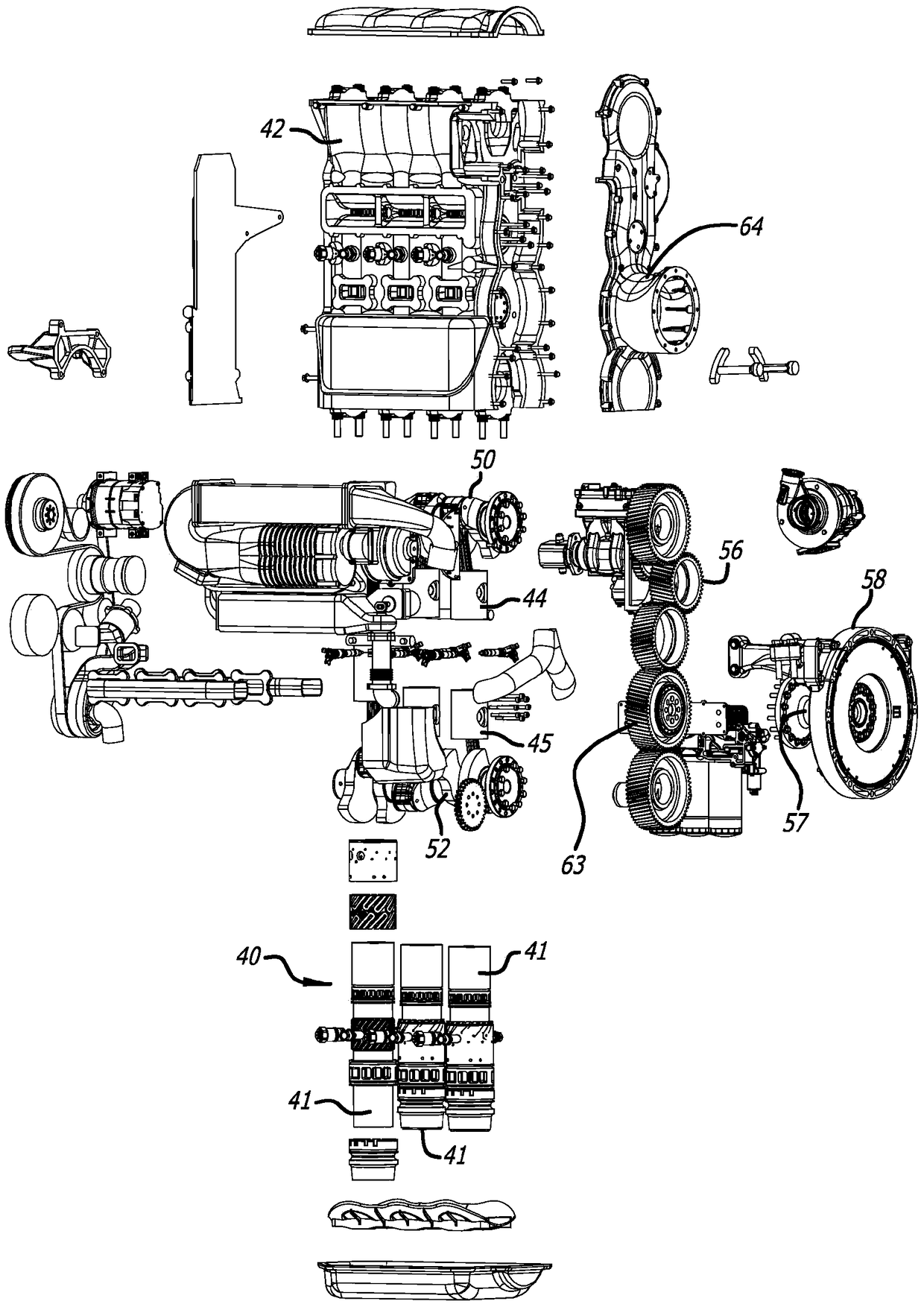
A two-cycle, opposed piston engine with side-mounted crankshafts and cylinders isolated from mechanical stresses of the engine includes tailored cooling of cylinders and symmetrical cooling of the interior surfaces of piston crowns. Each opposed piston includes a compliant member that permits movement of an axially-centered rod mounted in the piston in order to maintain axial alignment with the bore of a cylinder in which the piston is disposed during engine operation. A single wristpin is disposed externally of the piston to connect the piston with connecting rods that run between the piston and the crankshafts.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
Valve system for opposed piston engines
The valve system for opposed piston engines essentially comprises a single poppet valve opening into the common combustion chamber between the two opposed pistons of each piston and cylinder pair. The engine for which the mechanism is adapted includes a rotating internal cylinder surrounding each piston pair, with a stationary outer cylinder or case surrounding the rotating cylinder. The valve is pivotally attached at one side or end thereof to the edge of the valve port of the rotating cylinder, and is actuated by an arm or arms having guides (rollers, etc.) at the distal end(s) thereof, which are captured in corresponding cam track(s) or channel(s) formed in the fixed outer cylinder or case of the engine. The cam track has a variable radius, with the valve arm(s) and guide(s) alternately lifting and lowering as the guide(s) travel(s) in the variable radius cam track(s), thereby closing and opening the valve.
Owner:ENGINUITY POWER SYST INC
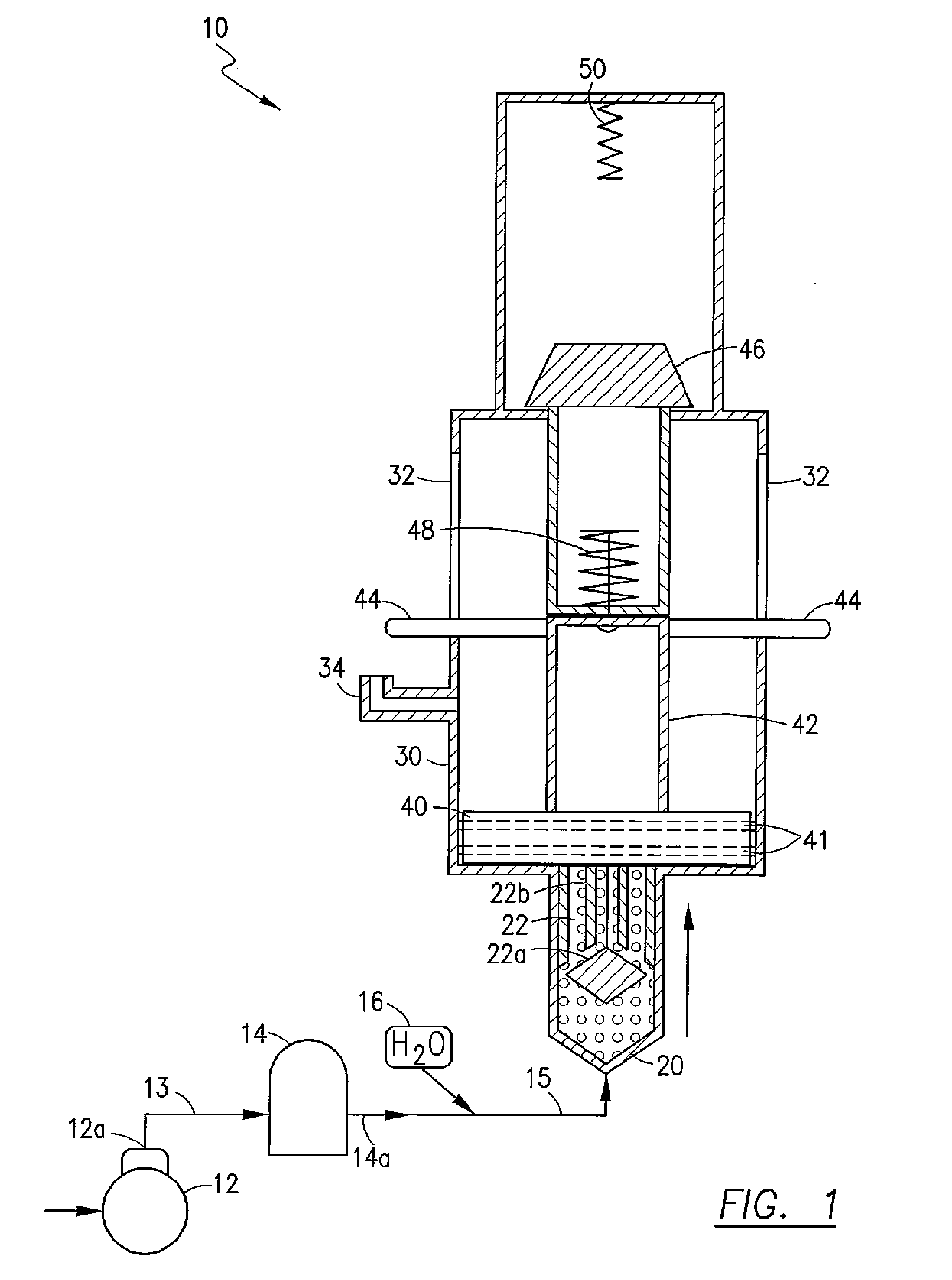
Reciprocating pneumatic piston gravity engine
A pneumatic reciprocating piston engine that uses a mixture of compressed air and water as the working fluid with a combination of gravity and spring force functioning to return the piston after completion of the power stroke is disclosed. A working fluid, preferably comprising a source of compressed air, is in fluid communication with the bottom portion of a generally vertically disposed cylinder via an inlet valve biased to a normally closed position. A piston is configured for reciprocating motion within the cylinder and traverses between bottommost and topmost positions. The piston is configured to engage the inlet valve when at the bottommost position thereby actuating the valve for a limited period of time to an open position so as to allow the introduction of compressed air and initiating of the power stroke to drive the piston upward. In a preferred embodiment, water is injected into the compressed air stream entering the cylinder to provide lubrication for the piston. The piston is drive upward by the working fluid until an uppermost stop is reached wherein the piston head has cleared an exhaust port formed in the cylinder thereby allowing the working fluid to escape. A mass is connected to the piston, in overhead relation, by a spring connection. When the piston reaches the uppermost stop, momentum causes the spring connected mass to continue upward thereby placing the spring in compression and maintaining the piston above the exhaust port so as to allow escape of the working fluid therethrough. Return of the mass downward, caused both by gravity and spring energy, causes the mass to engage the piston and return the piston to its bottommost position whereby another stroke is initiated. Power output may be transferred to any suitable system.
Owner:CHAVEZ JULIO
Hydraulic control type opposed piston engine
InactiveCN102425494AReduce volumeLower the altitudeInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion systemFree-piston engine
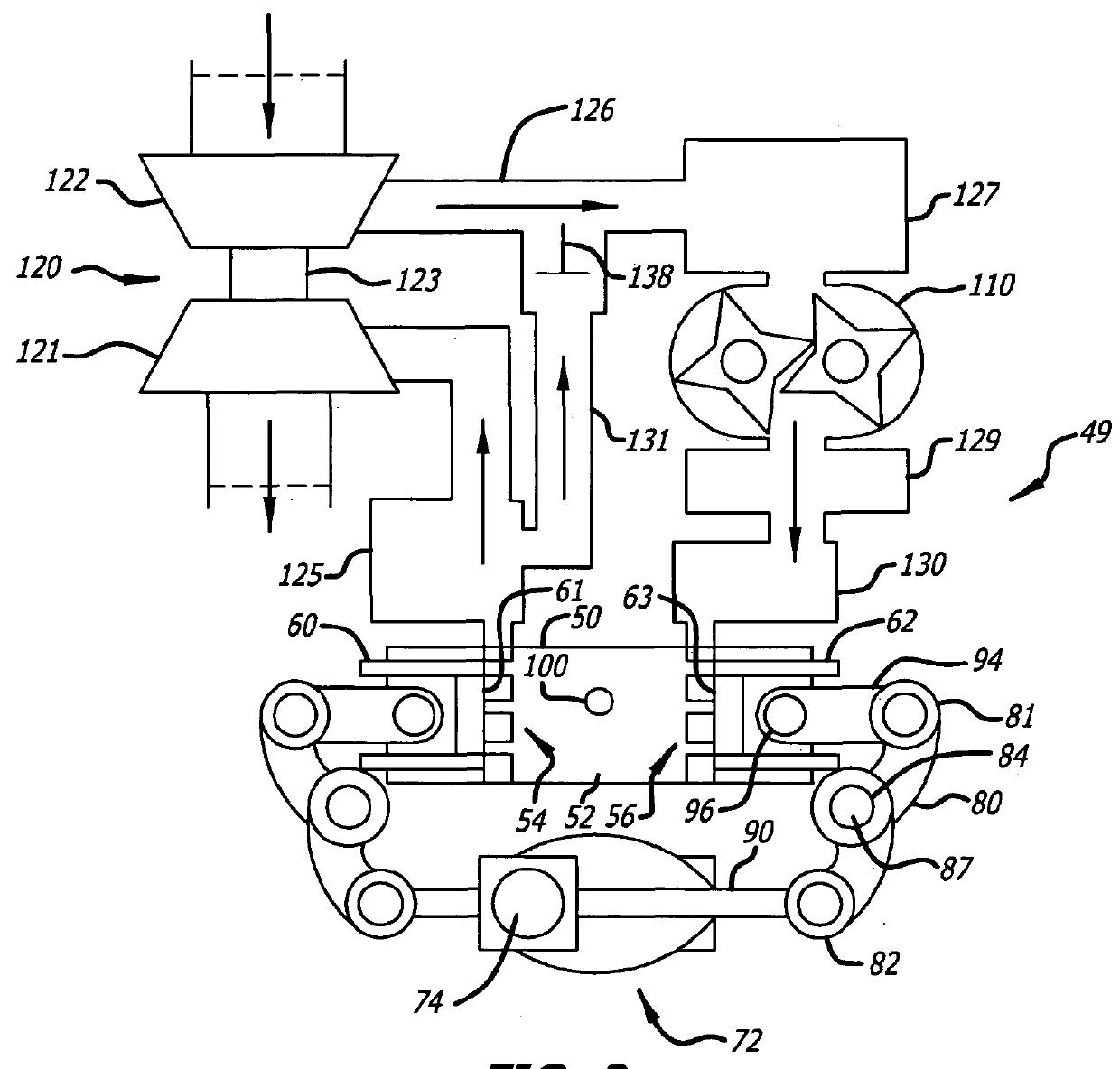
The invention discloses a hydraulic control type opposed piston engine. In the scheme, each unit opposed piston component is provided with a group of opposed movable pistons, and interfaces at oil receiving ends of the pistons respectively correspond to interfaces of two groups of reciprocating positive displacement pumps on a rotating crankshaft. Changes in the rotating crankshaft and the positive displacement pumps are directly coupled onto the pistons to accurately control the movement direction of the pistons and the positions of upper dead center and lower dead center so as to respectively complete the working stroke of air intake, compression, acting expansion and expansion work and also the power output. The pistons can be controlled in a simple way to achieve the advantages of a conventional engine and a hydraulic free piston engine and overcome the defects of the conventional engine and the hydraulic free piston engine. A startup system, an oil supply system, a combustion system, a cooling system, a sealing system and other systems all adopt the existing completely mature techniques to facilitate the implementation of projects. The engine is suitable for promotion in the engine industry.
Owner:欧益忠 +2
Revolving piston internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20110048370A1Reduce lossesEasier and improved sealing and cooling propertiesInternal combustion piston enginesEngine componentsFree-piston engineExternal combustion engine
A revolving piston engine incorporating dual revolving pistons for improving fuel efficiency, increasing power output, easy sealing, easy cooling and reduced vibration. One or more of revolving pistons, each consisting of one piston and one cylinder head, revolve within a ring cylinder, around a common axis in a same direction, but with different velocities. A revolving piston compressor is also disclosed, incorporating appropriately designed and relocated ports / valves for both of associated intake and outlet components.
Owner:AMBARDEKAR VISHVAS
Method of determining cylinder health in reciprocating piston engine
Computer-implemented methods, computer program products, and computer systems are described for determining cylinder health characteristic in a reciprocating piston engine of the type including a piston-cylinder assembly and a crankshaft. The piston-cylinder assembly includes a cylinder and a piston configured to translate within the cylinder as the crankshaft rotates. In one embodiment, the computer-implemented method includes rotating the crankshaft in a first direction, while generating a first data set comprising a first plurality of piston position measurements and corresponding pressure indicator measurements. The crankshaft is further rotated in a second opposing direction, while a second data set is generated comprising a second plurality of piston position measurements and corresponding pressure indicator measurements. A symmetric aspect between the first and second data sets is then identified and utilized to determining a cylinder health characteristic for the piston-cylinder assembly.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Opposite radial rotary-piston engine of Choronski
InactiveUS7832368B2Enhancing efficiency and size and weightOvercomes drawbackInternal combustion piston enginesPlungersTransverse axisSwing-piston engine
Owner:CHORONSKI EVGENI +1
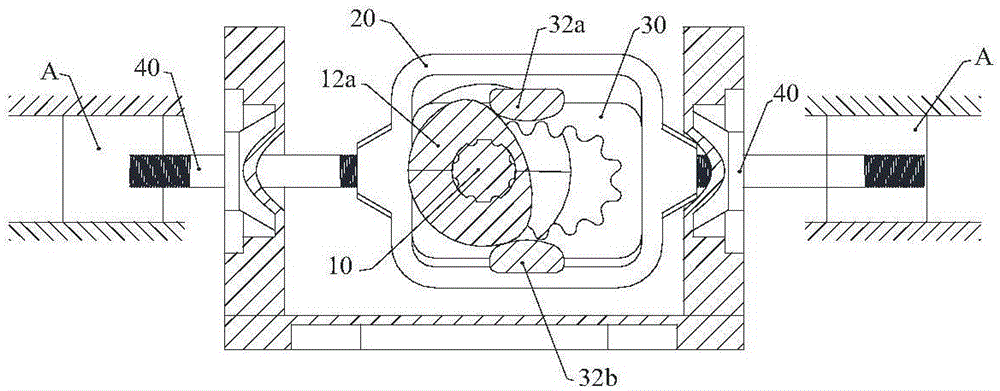
Oscillating piston engine
InactiveCN1908377ATake advantage ofIncrease volumeEngines with oscillating pistonsRotary piston enginesSwing-piston engineEngineering
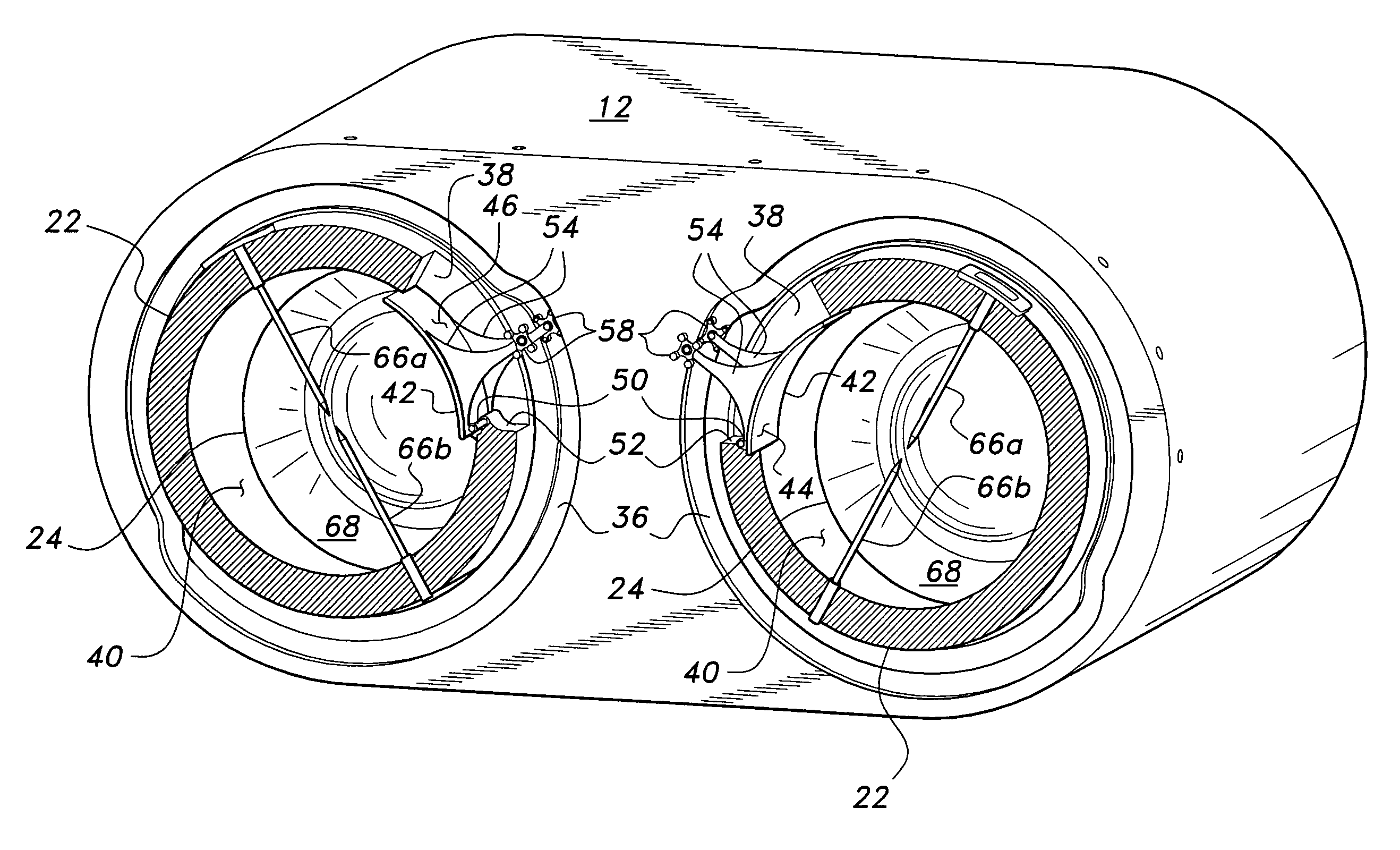
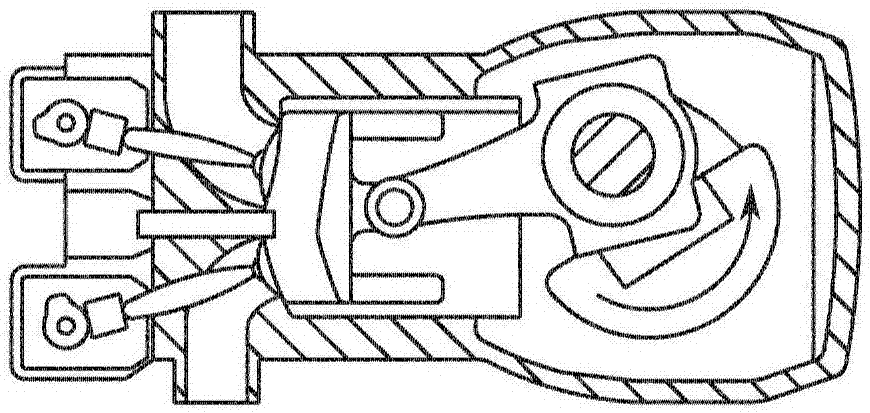
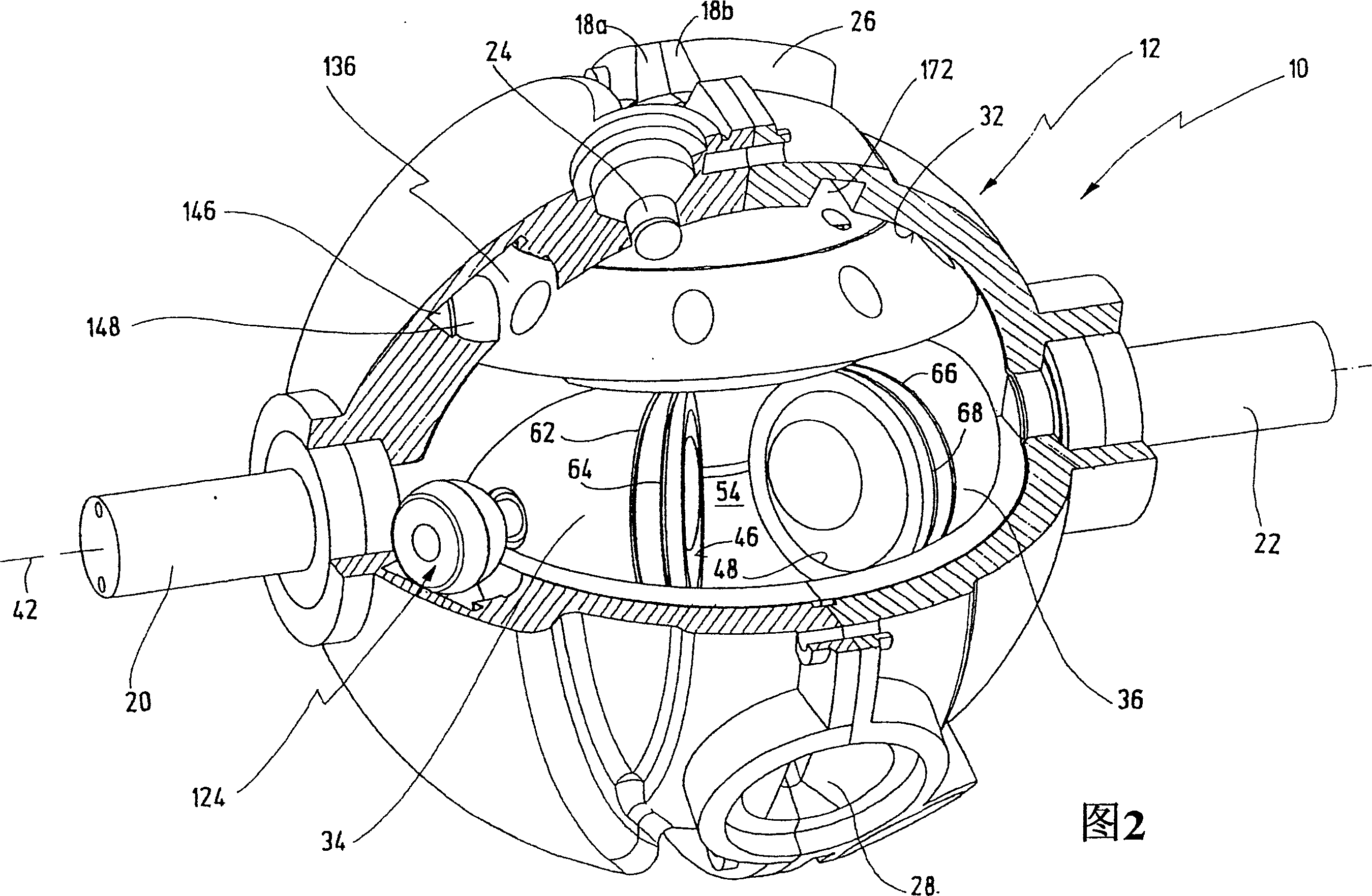
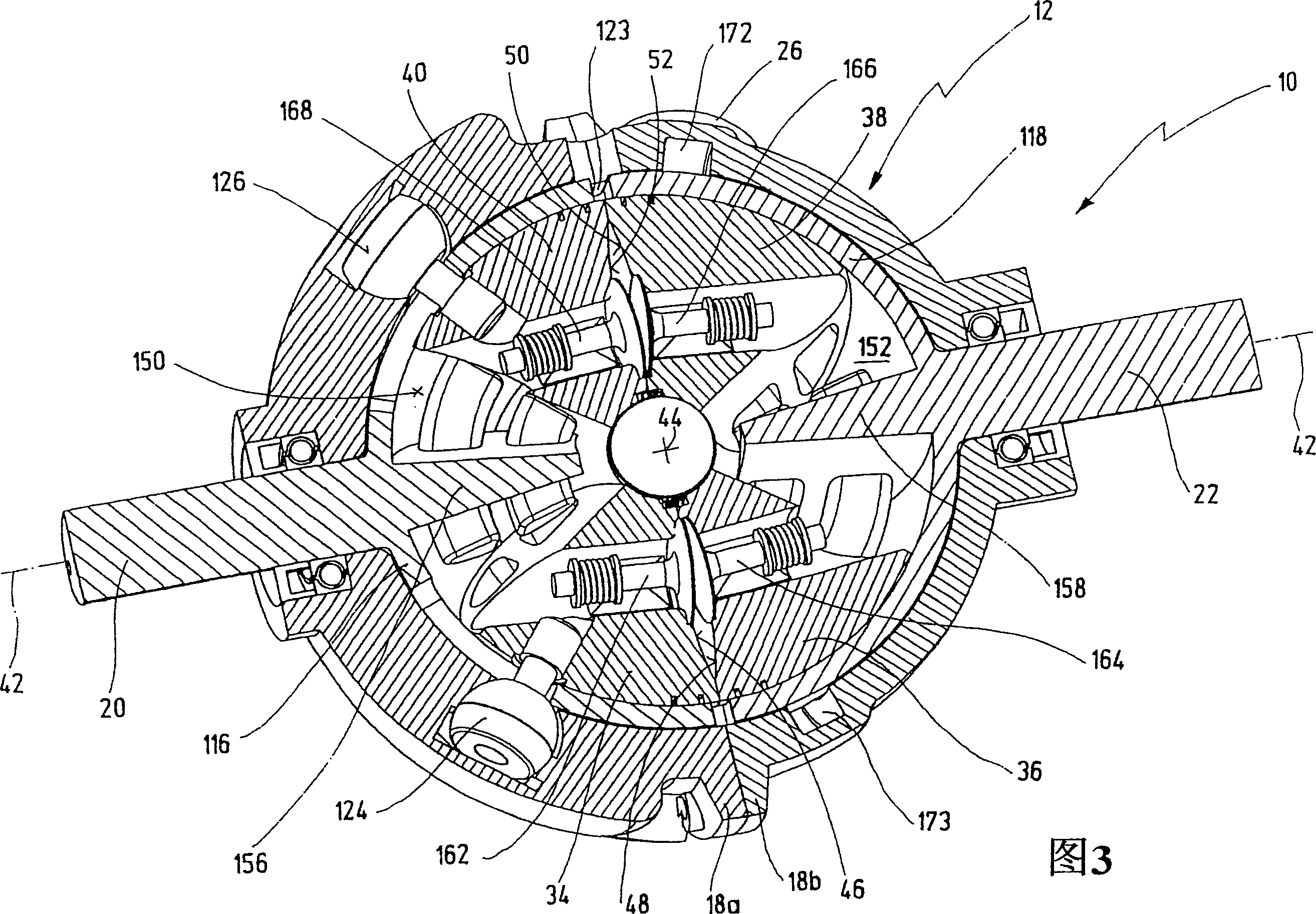
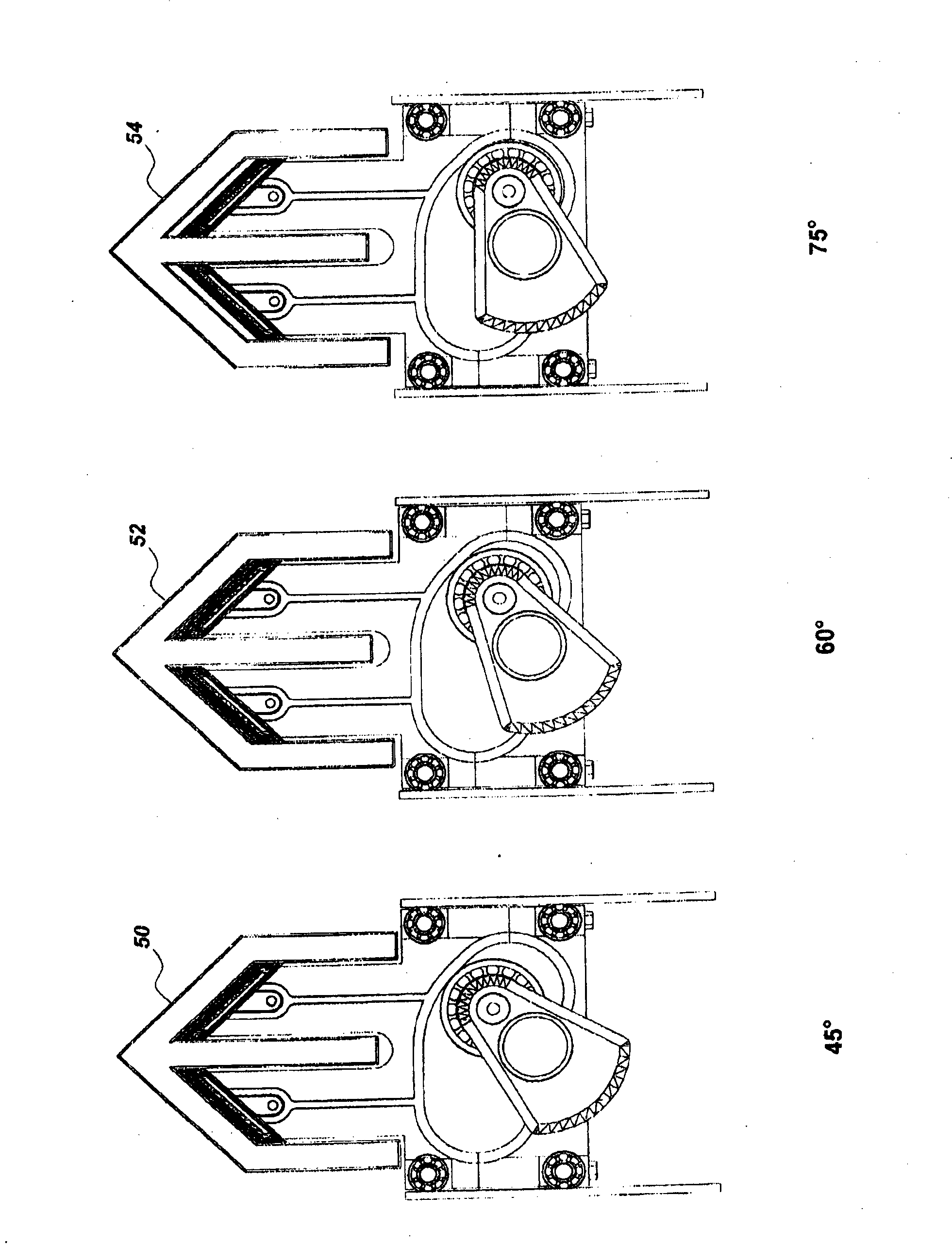
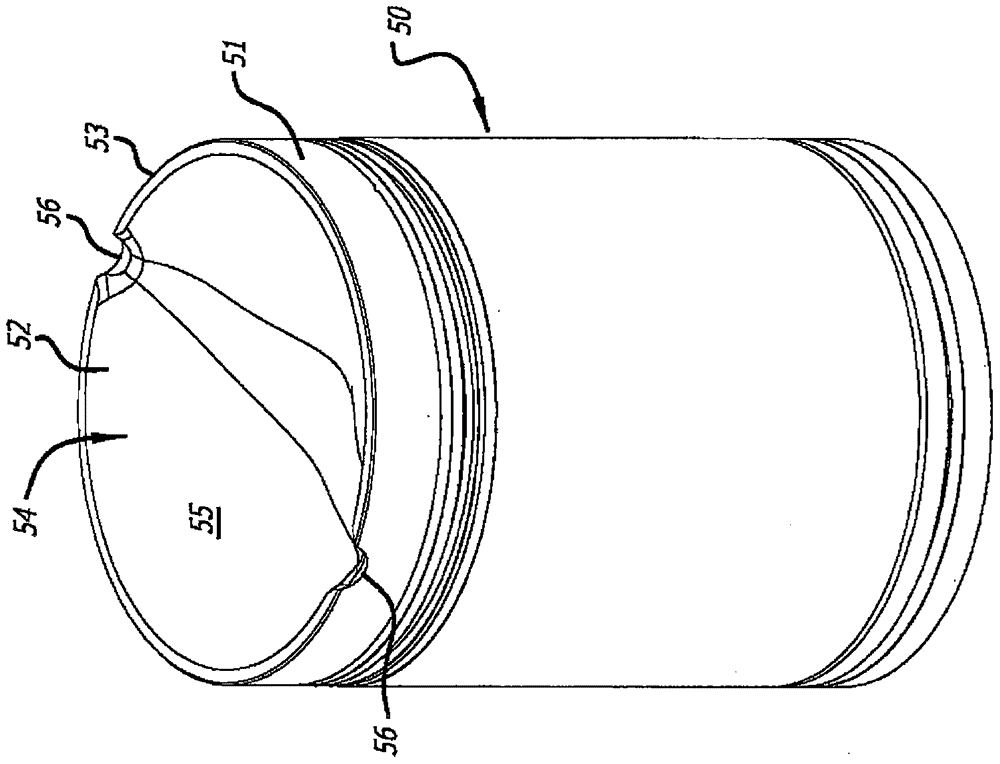
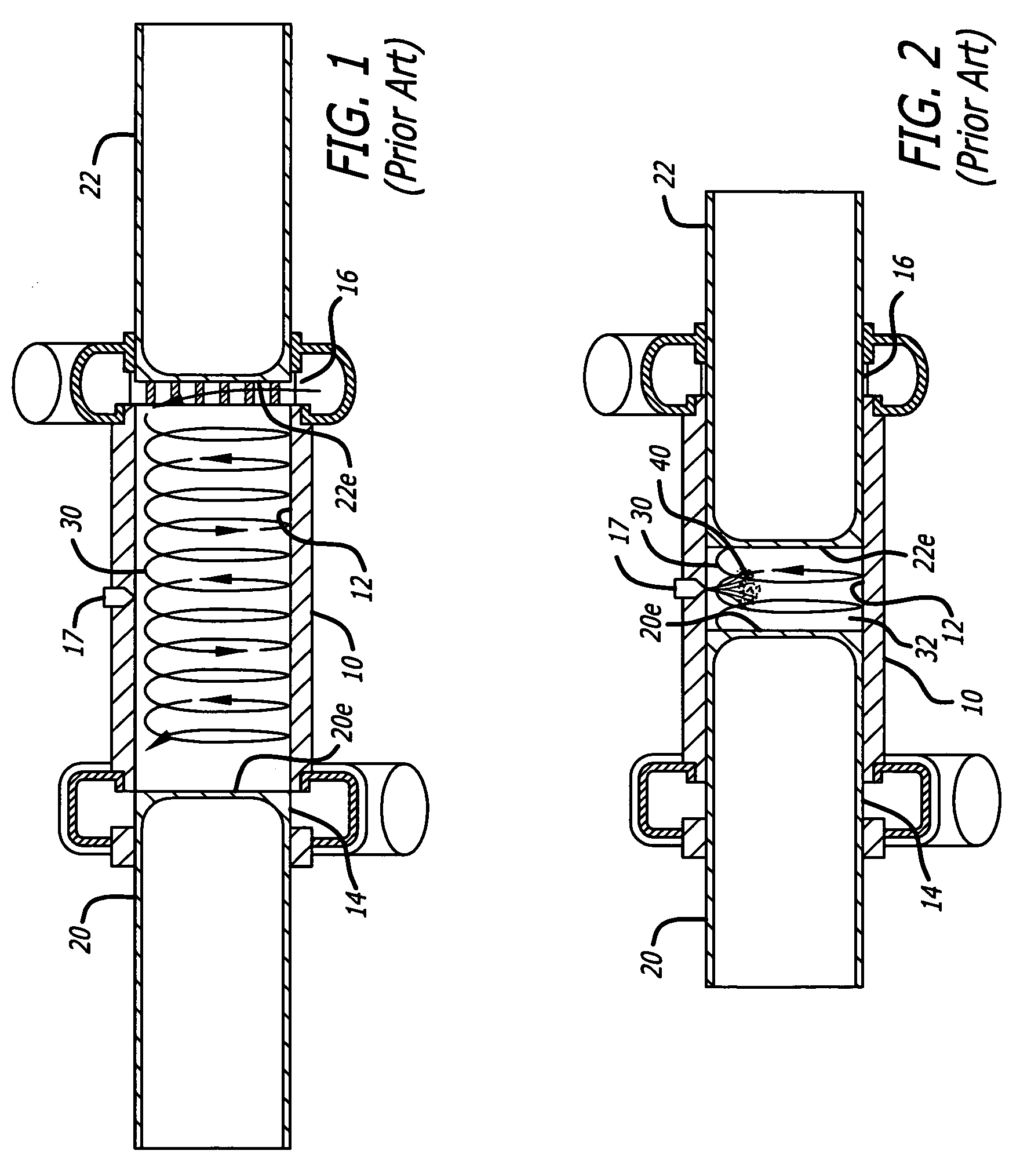
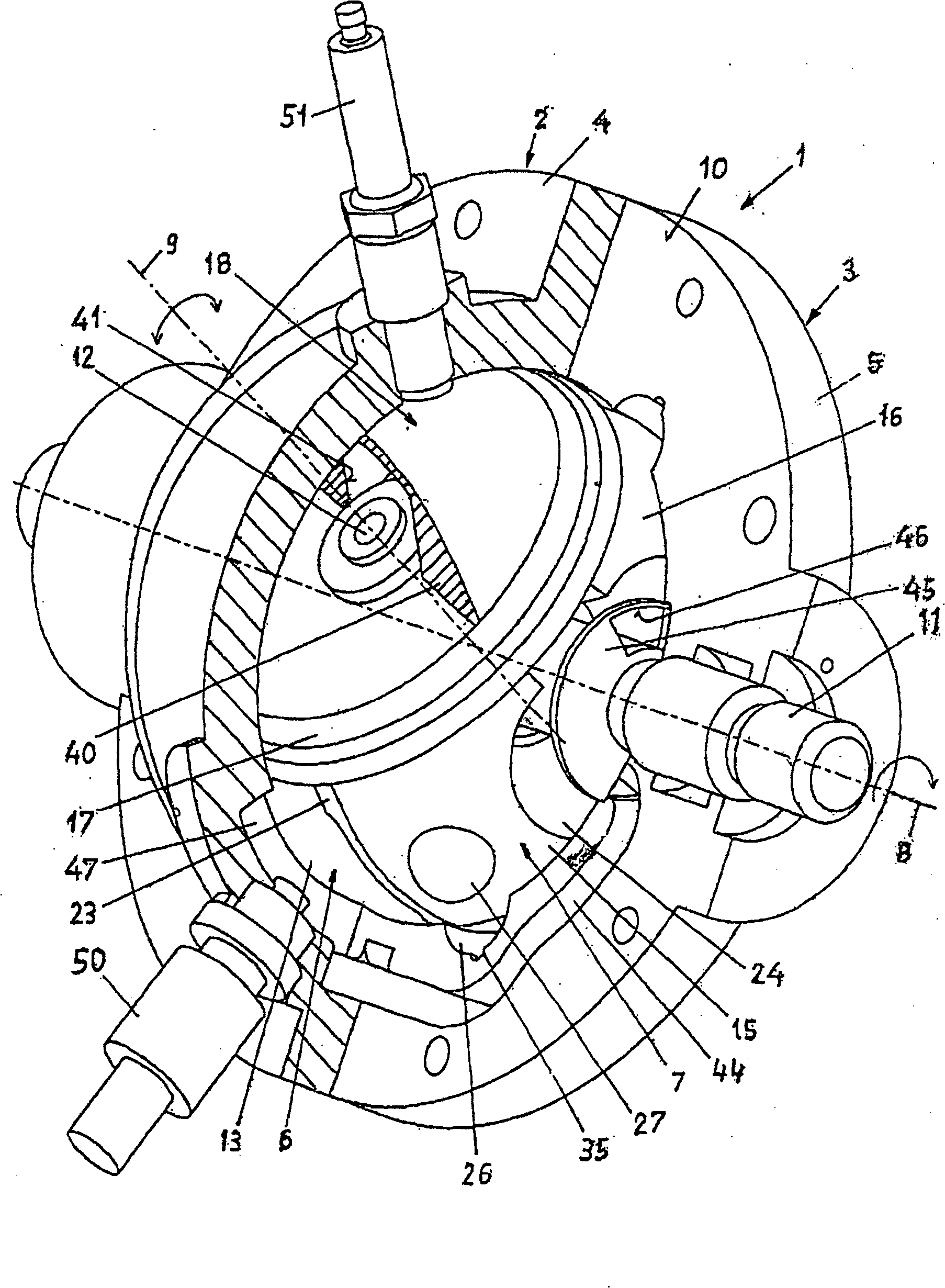
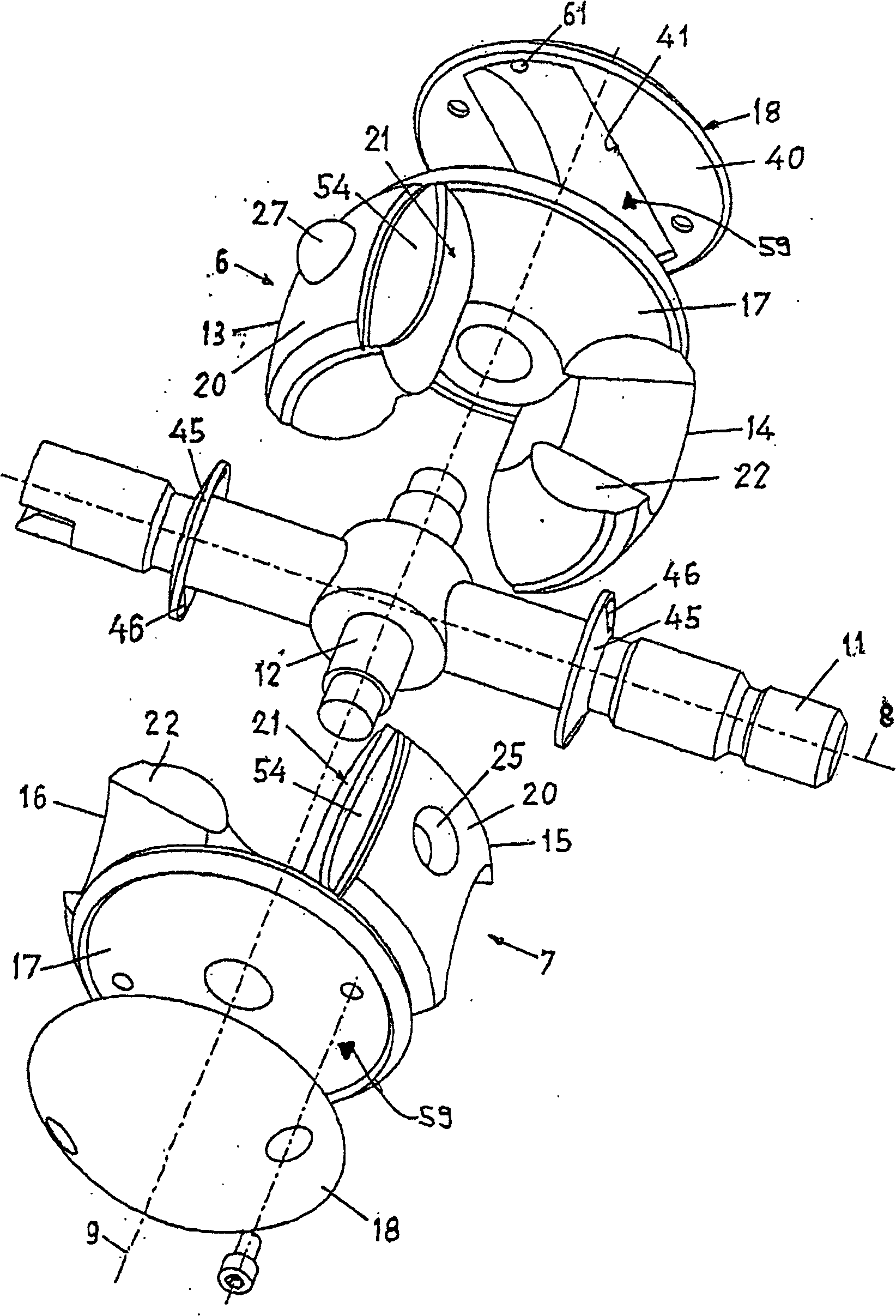
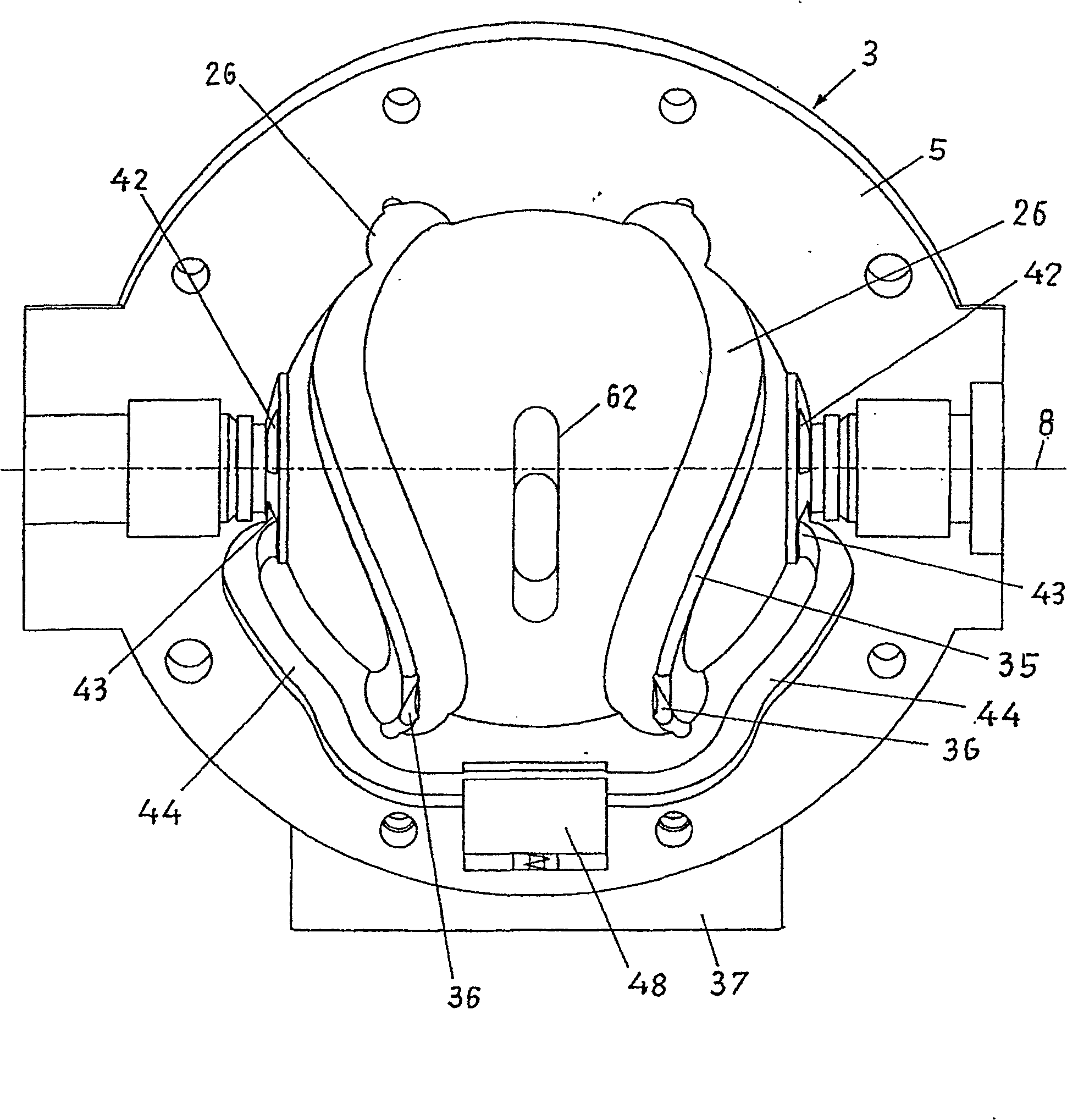
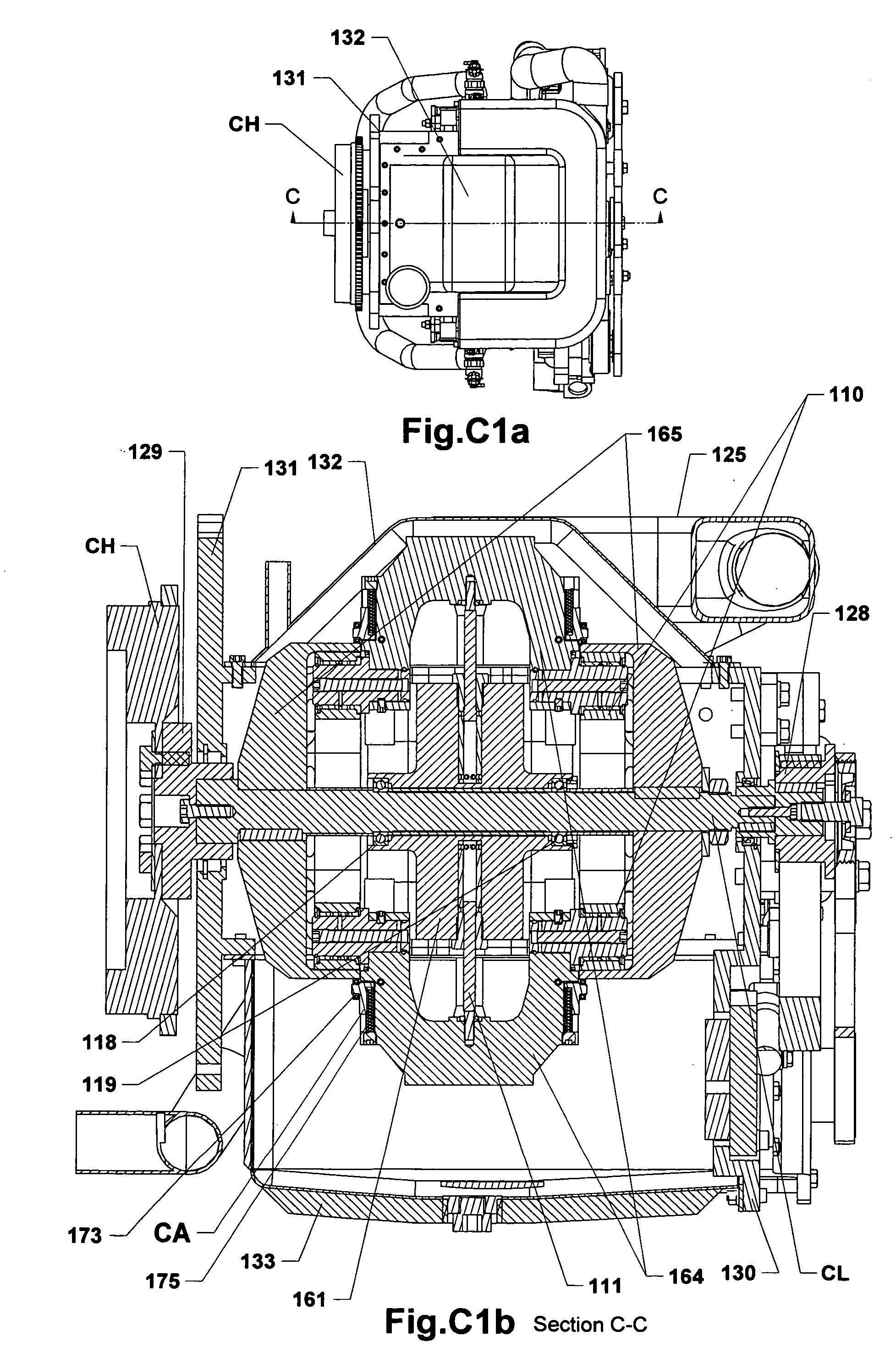
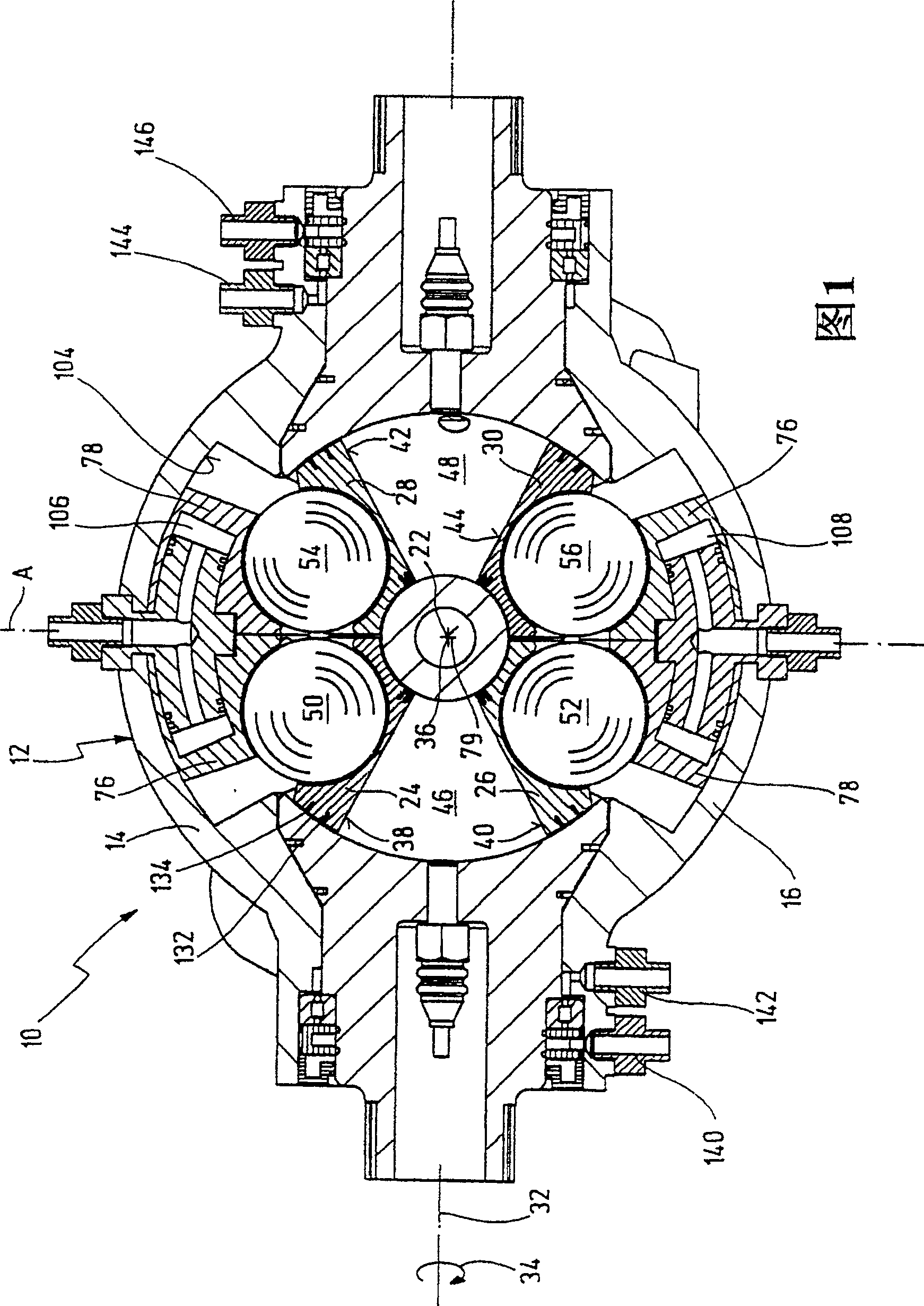
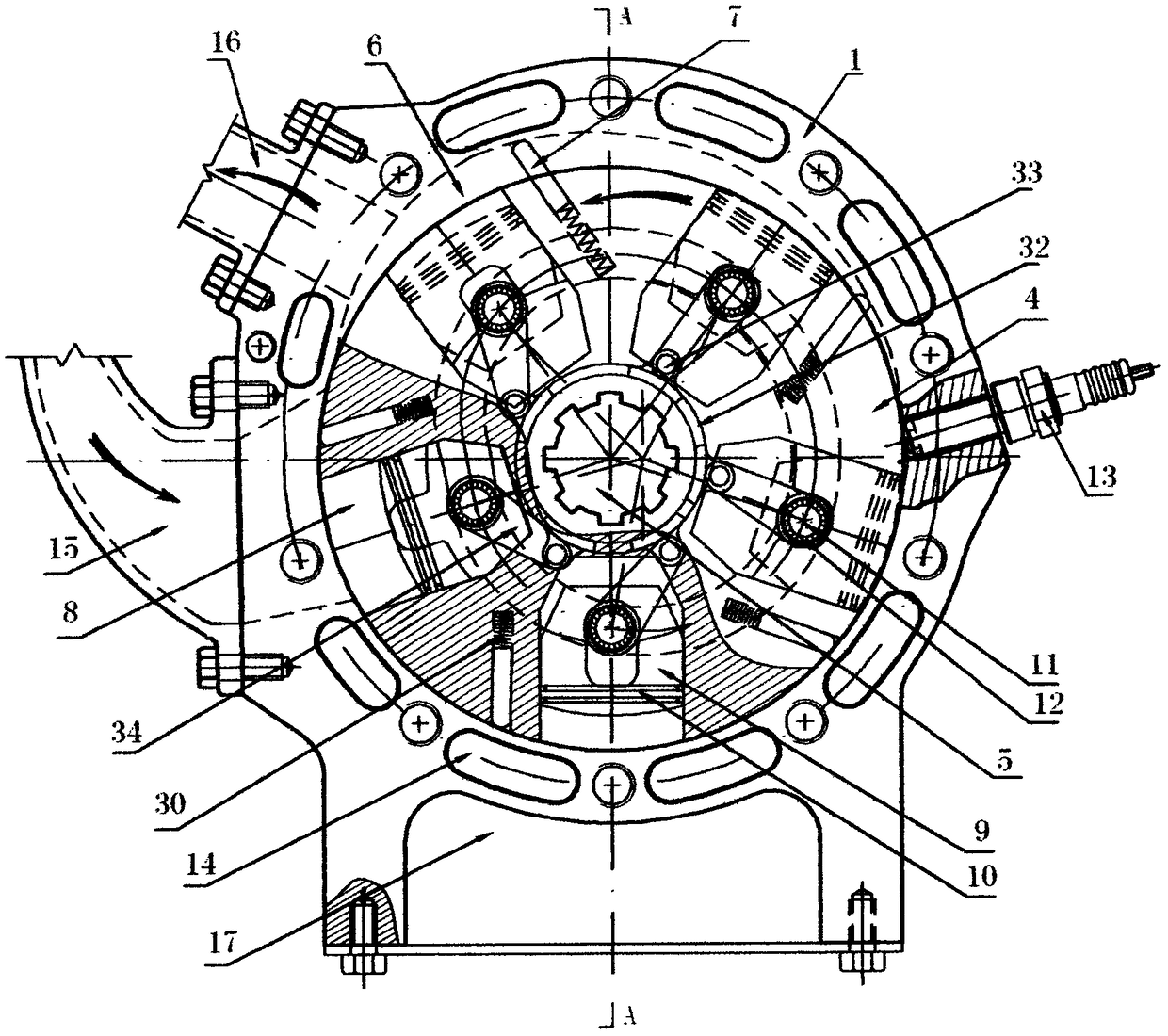
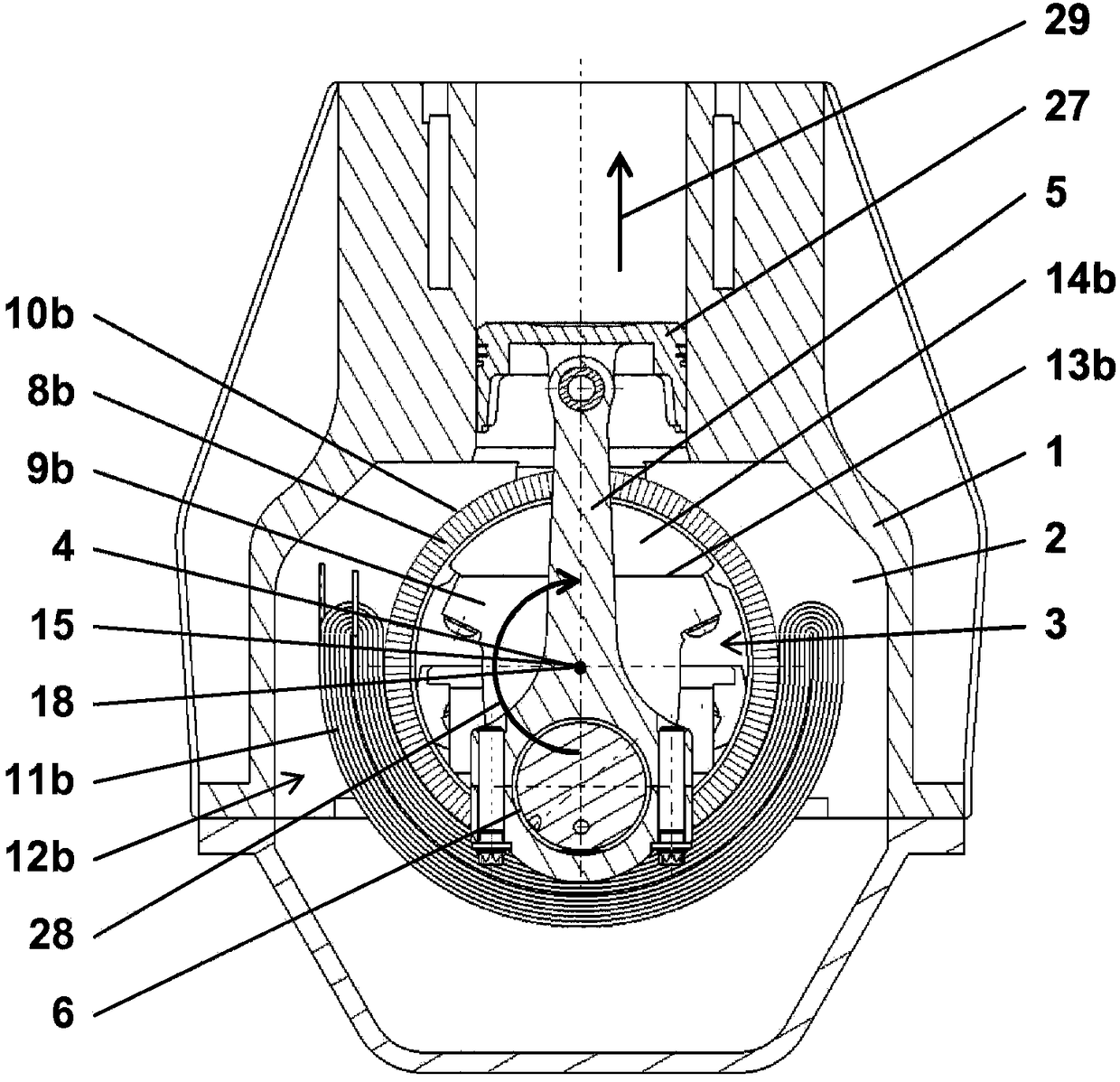
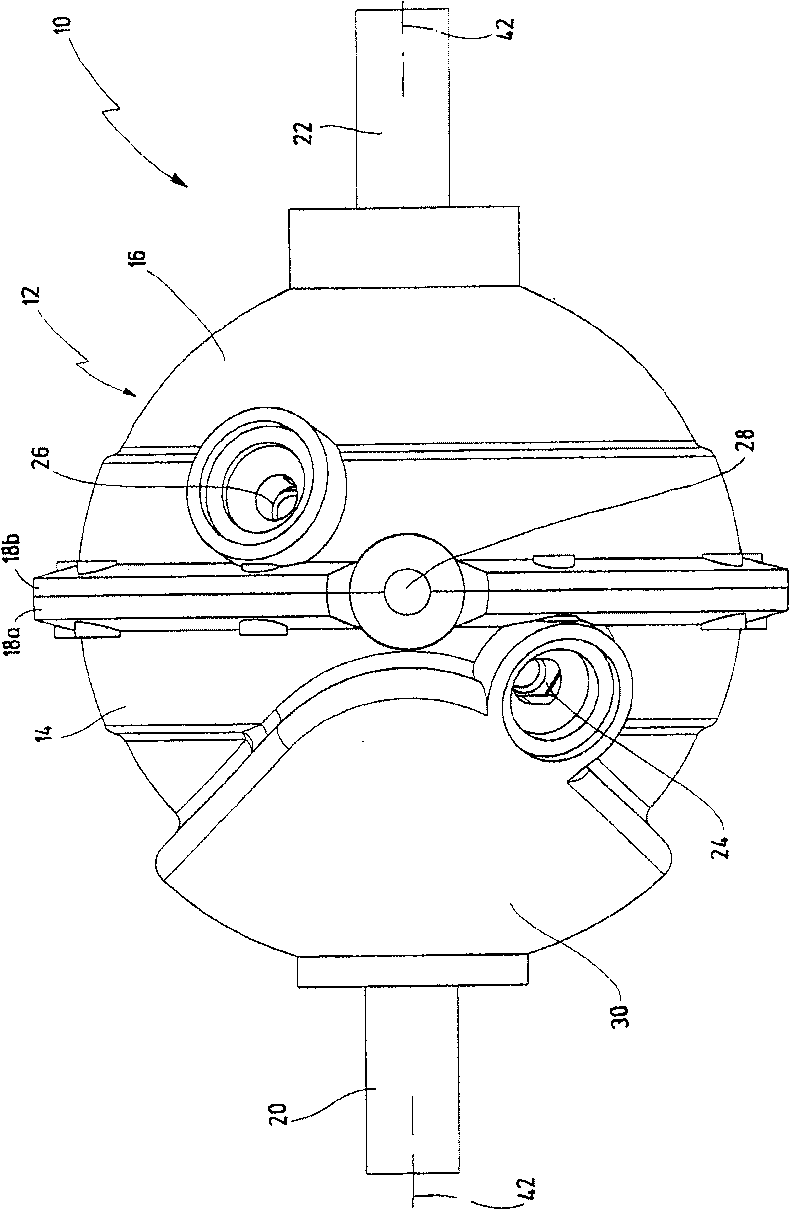
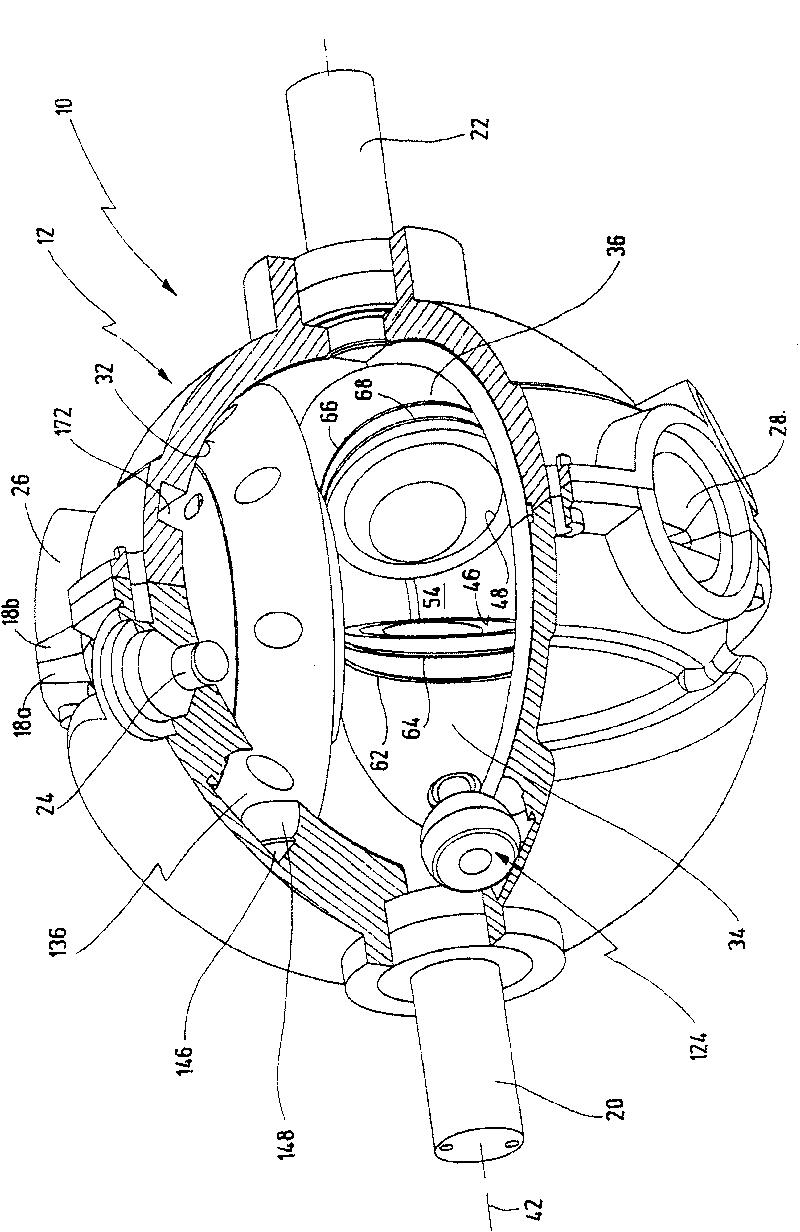
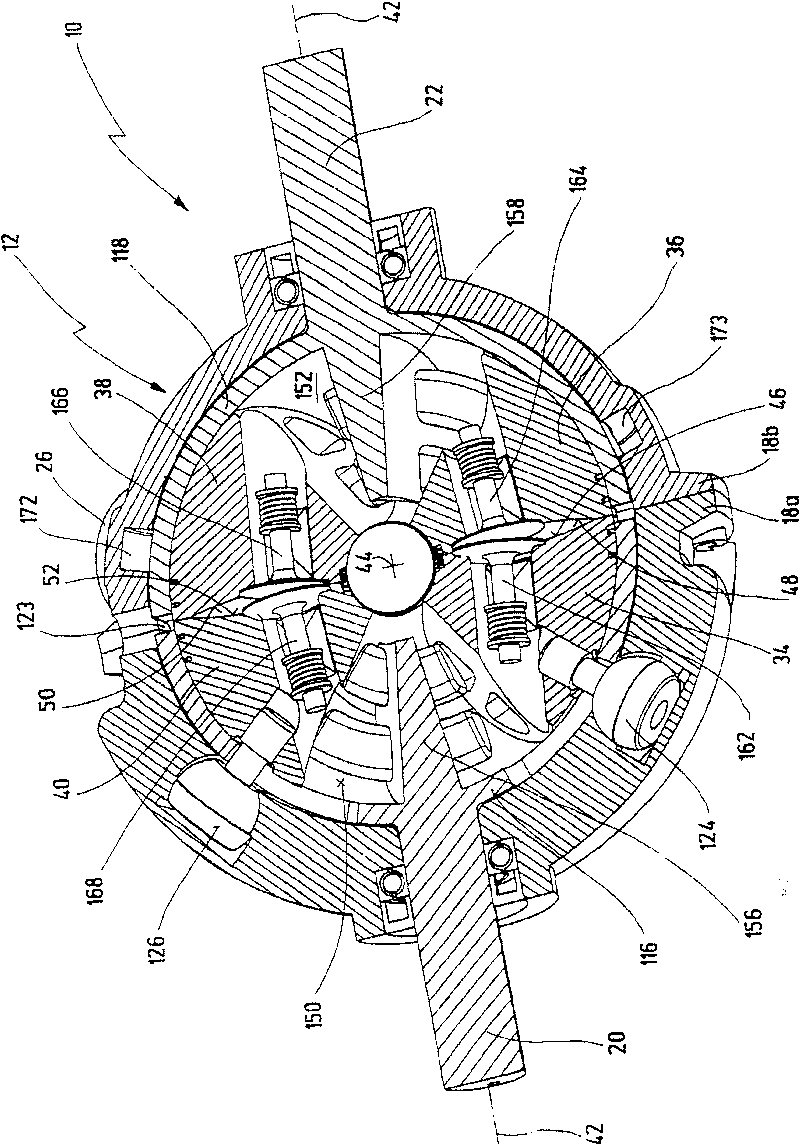
An oscillating piston engine is described, having a housing (12) which has an at least approximately spherical inner wall (32), and having at least two pistons (34, 36) which can jointly revolve in the housing (12) about a fixed rotation axis (42) and, when revolving about the rotation axis (42), perform back-and-forth swivelling movements about at least one swivel axis (44) perpendicular to the rotation axis (42), wherein the swivelling movements of the two pistons (34, 36) are in opposition to one another, and wherein the two pistons (34, 36) each have an end face (46, 48), said end faces (46, 48) facing one another and each defining a front end of a working chamber (54) which is arranged completely outside the rotation axis (42) and is defined at the circumference by a working chamber wall (58). The working chamber (54), formed by the two end faces (46, 48) of the two pistons (34, 36) and the working chamber wall (58), and the pistons (34, 36) have the shape of a toroid section at least in the region of their ends facing the working chamber (54).
Owner:赫伯特·许特林
Oscillating piston engine
InactiveCN101025090AOscillating piston pumpsInternal combustion piston enginesSwing-piston engineCam
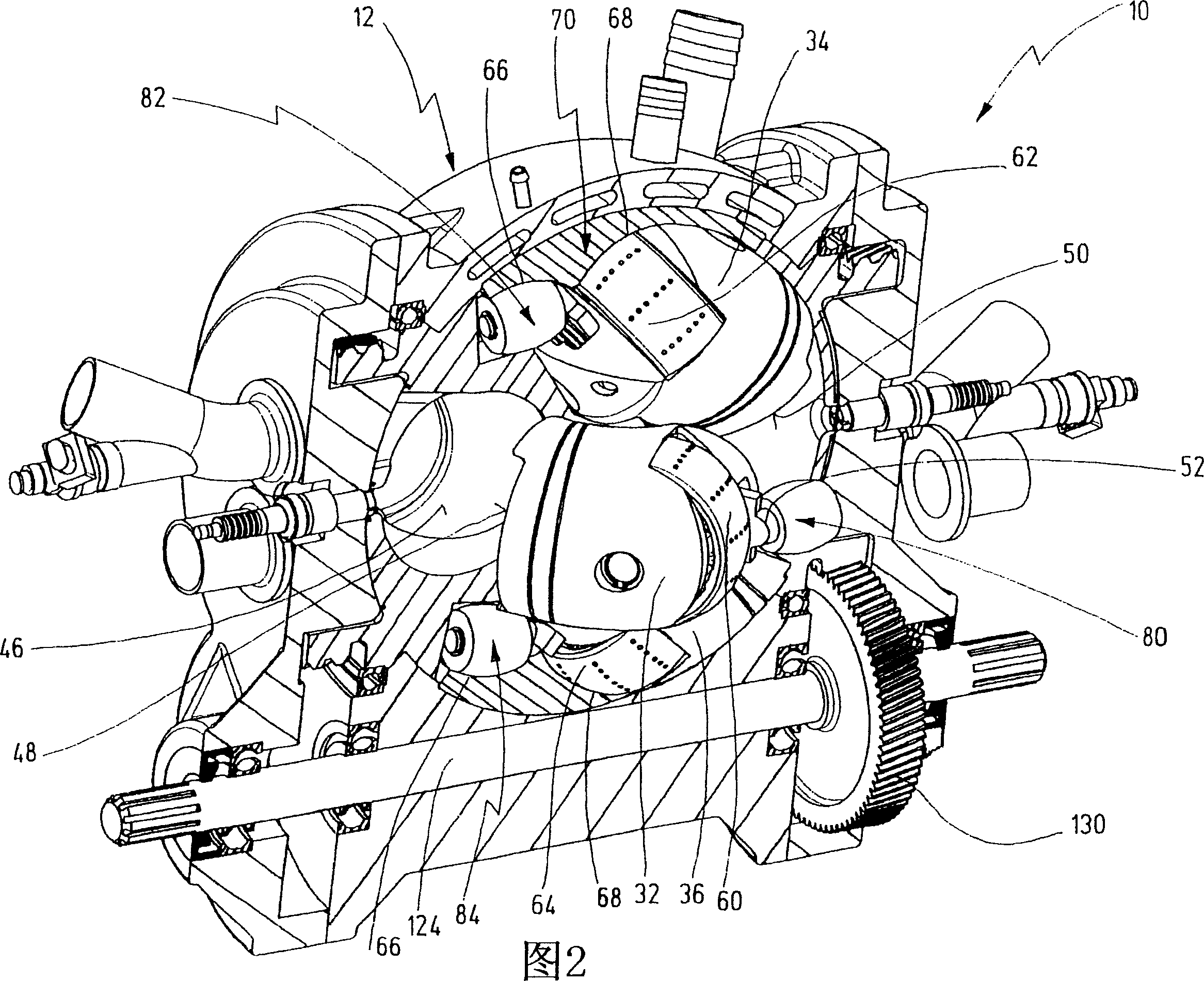
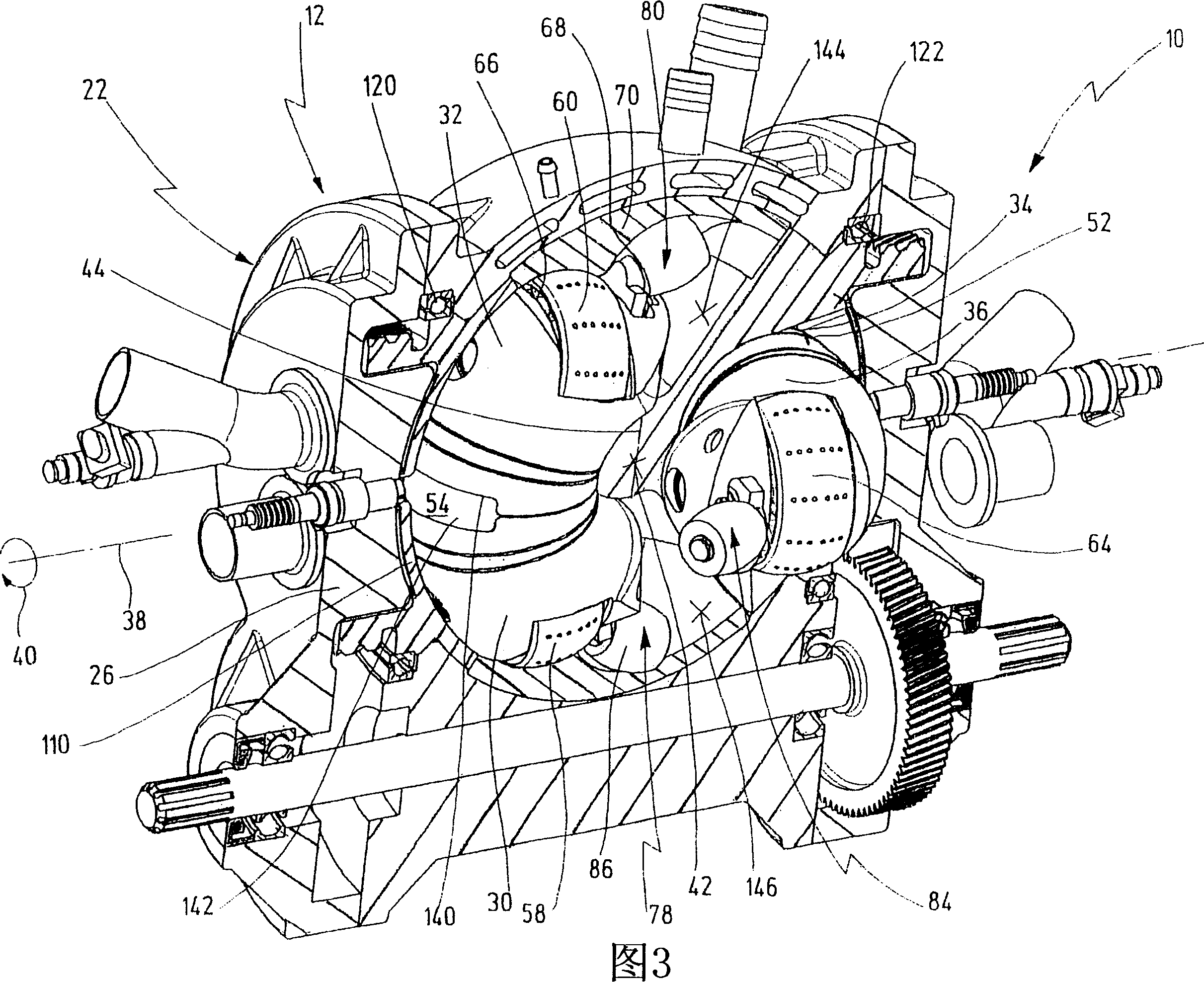
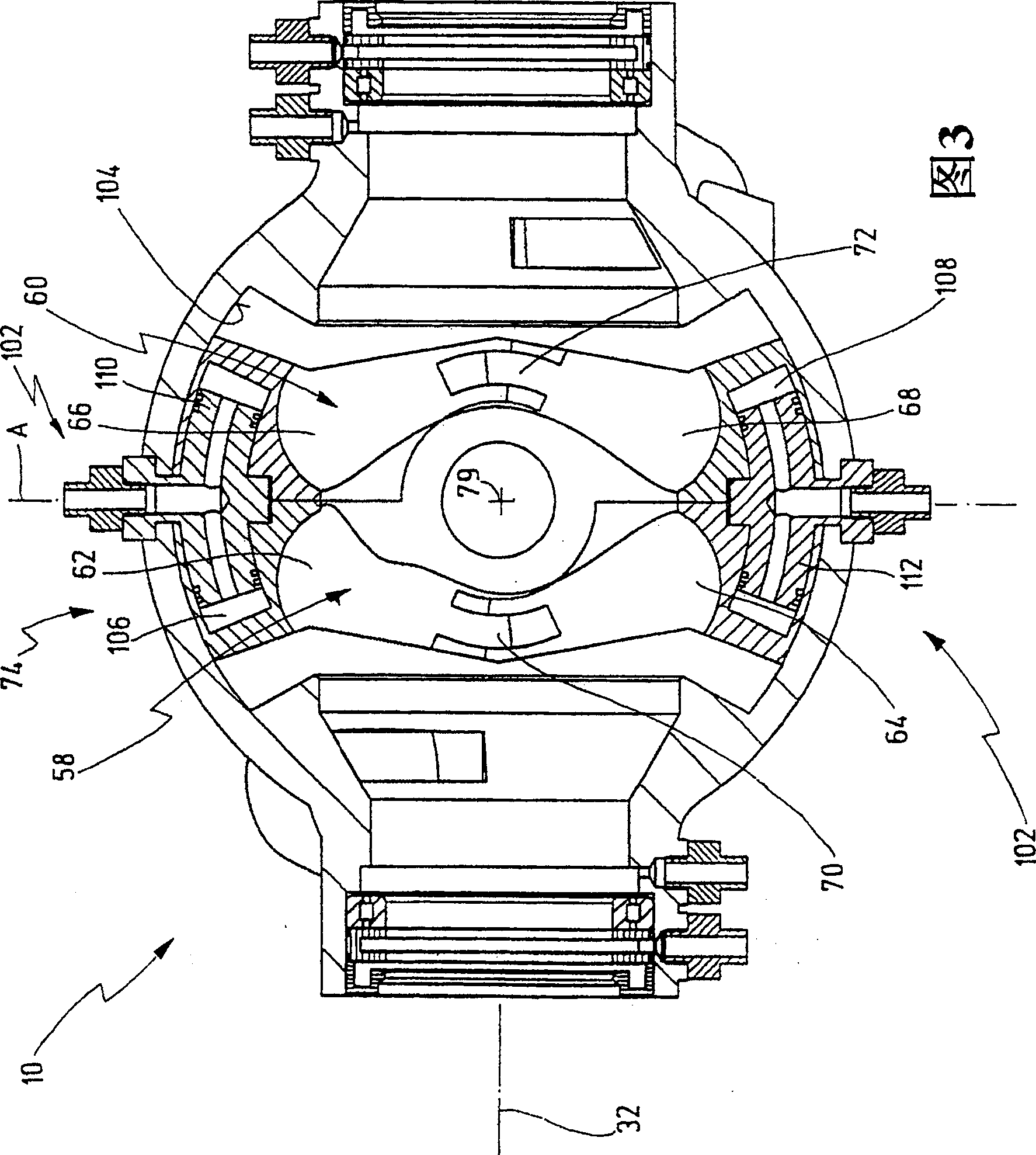
The invention relates to an oscillating piston engine comprising a housing (12) wherein at least one piston (30) is arranged. Said piston can revolve about a rotation axis (38) which is fixed in relation to the housing (12), and which, when revolving about the rotation axis (38), performs reciprocating oscillating movements about an oscillating axis (42) running perpendicular to the rotation axis (28), between a first end position (OT) and a second end position (UT). The at least one piston (30) comprises a first running element (58) which extends along at least one control cam (66) when revolving the piston (30) about the rotation axis (38). Said control cam is configured in such a manner that the pivoting movements of the at least one piston (30) are derived from the peripheral movement of the running element (58) along said control cam. Return means for supporting the return of the at least one piston (30) at least from the first end position (OT) into the second end position (UT) are associated with the piston in addition to the running element (58).
Owner:赫伯特·许特林
Ring turbo-piston engine and ring turbo-piston supercharger
InactiveUS20090028739A1Increase heightLow powerOscillating piston enginesEngine of counter-engagement typeCombustionSwing-piston engine
The inventive turbo-piston machine is embodied in the form of a turbo-piston expander and / or a turbo-piston supercharger and / or internal combustion engine comprising two mating working members i.e. a rotor and a valve. The rotor is provided with a piston embodied thereon and the valve is provided with a groove. The working members are arranged in the body of the turbo-piston machine, wherein the rotor is placed in at least one cylinder formed by the body walls and, for example, by the sidewalls. The operating process is carried out in at least two working chambers formed by the division of the cylinder space. A working medium is injected into one of the working chambers of the turbo-piston expander and is pumped into the other working chamber. The combination of the turbo-piston supercharger and the turbo-piston expander in one turbo-piston machine makes it possible to develop the internal combustion engines which can operate according to any known cycles, for example according to the Otto, Diesel, Trinkler, Atkinson, Miller, Brayton, Ericsson-Joule, Humphrey, Lenoir, Rankine and Stirling cycles.
Owner:VELITSKO VLADISLAV VLADIMIROVICH
Improved combustion engine
InactiveCN102985638AFunctional changeEfficient separationGearingReciprocating piston enginesCombustionCoupling
The present invention relates to internal combustion engines and more particularly reciprocating piston engines utilising Scotch yokes to translate rectilinear movement to rotary motion. In particular, the piston and / or pistons of the engine of the present invention can be placed in their topmost position for a period of time for the effective ignition and combustion of the air / fuel mixture for a given fuel charge, hence therefore providing an increased efficiency of the piston engine with a more efficient coupling between the piston and / or the power shaft driving the crank.
Owner:EXODUS R&D INT PTE
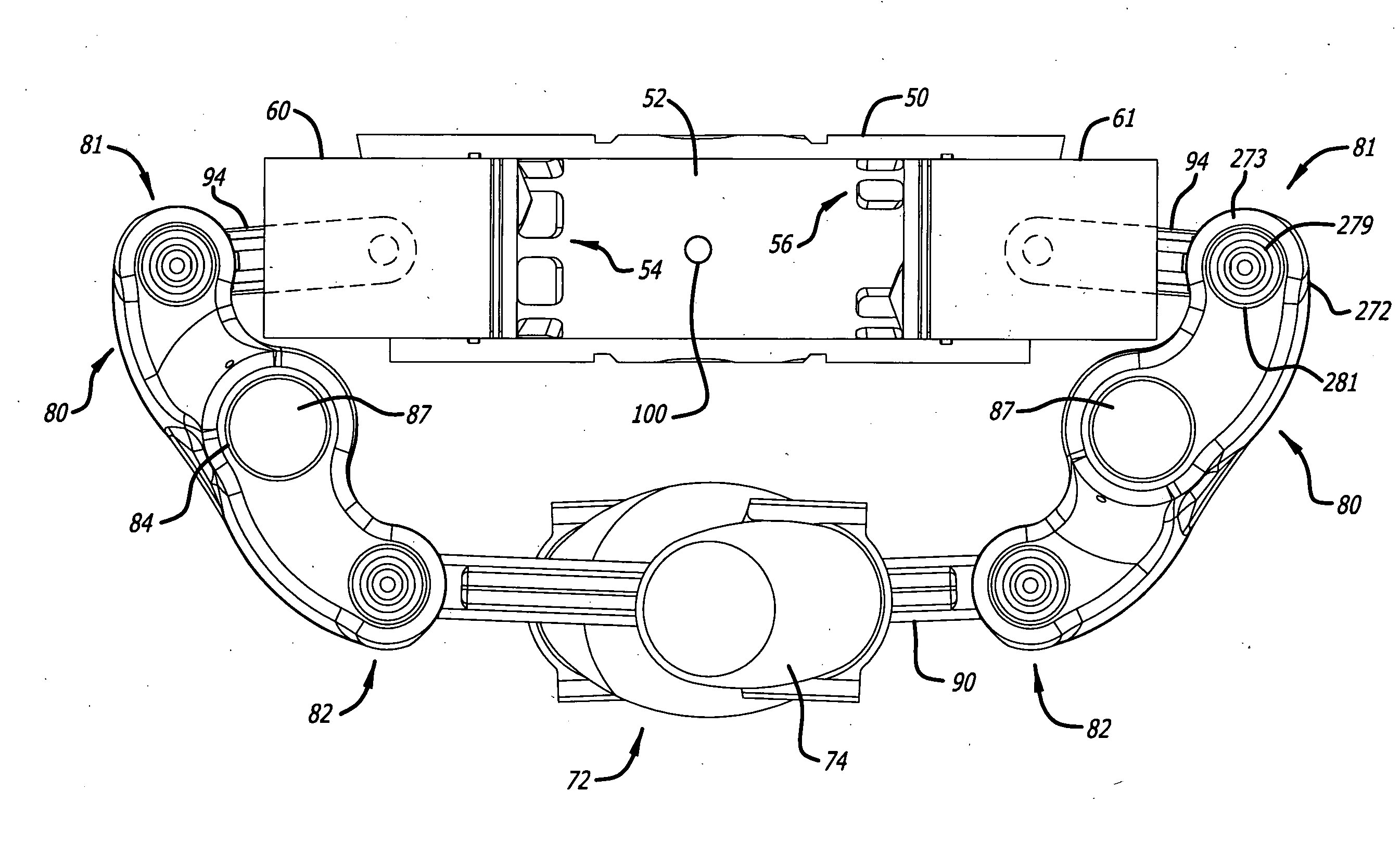
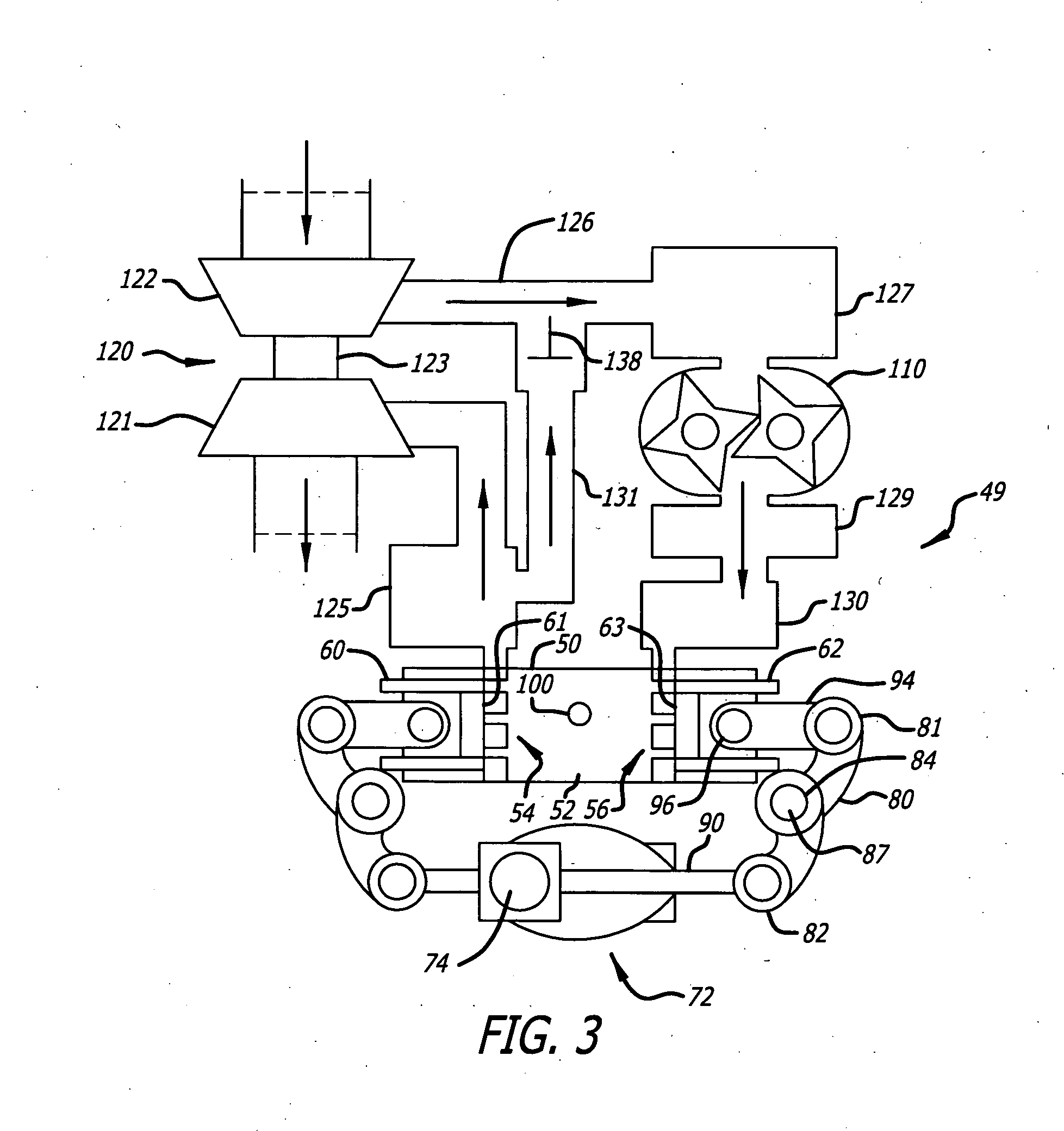
A swirl-conserving combustion chamber construction for opposed-piston engines
ActiveCN105829676AInternal combustion piston enginesReciprocating piston enginesInjection portCombustion chamber
A combustion chamber construction for opposed-piston engines includes an elongated, bilaterally symmetrical shape referenced to a major axis and a pair of injection ports located on the major axis when the pistons are near respective top center positions. The combustion chamber is defined between a bowl in the end surface of a first piston of a pair of pistons and mirrored ridges protruding from the end surface of a second piston of the pair. Each ridge includes a central portion that curves toward a periphery of the end surface of the second piston and which transitions to flanking portions that curve away from the periphery. The ridge configuration imparts a substantially spherical configuration to a central portion of the combustion chamber where swirling motion of charge air is conserved.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
Two stroke, opposed-piston engines with engine braking
ActiveUS8919304B2Simple and inexpensiveHigh trafficInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelFree-piston engineSwing-piston engine
In a two-stroke opposed-piston engine, a ported cylinder with a pair of opposed pistons is equipped with an engine brake including an engine braking valve that can be opened to release air from the cylinder as the pistons cycle between BDC and TDC positions.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
Rotary-piston engine and vehicle comprising an engine of this type
InactiveCN100540851CCompact structureReduce wearEngines with oscillating pistonsSafety/regulatory devicesRotational axisClassical mechanics
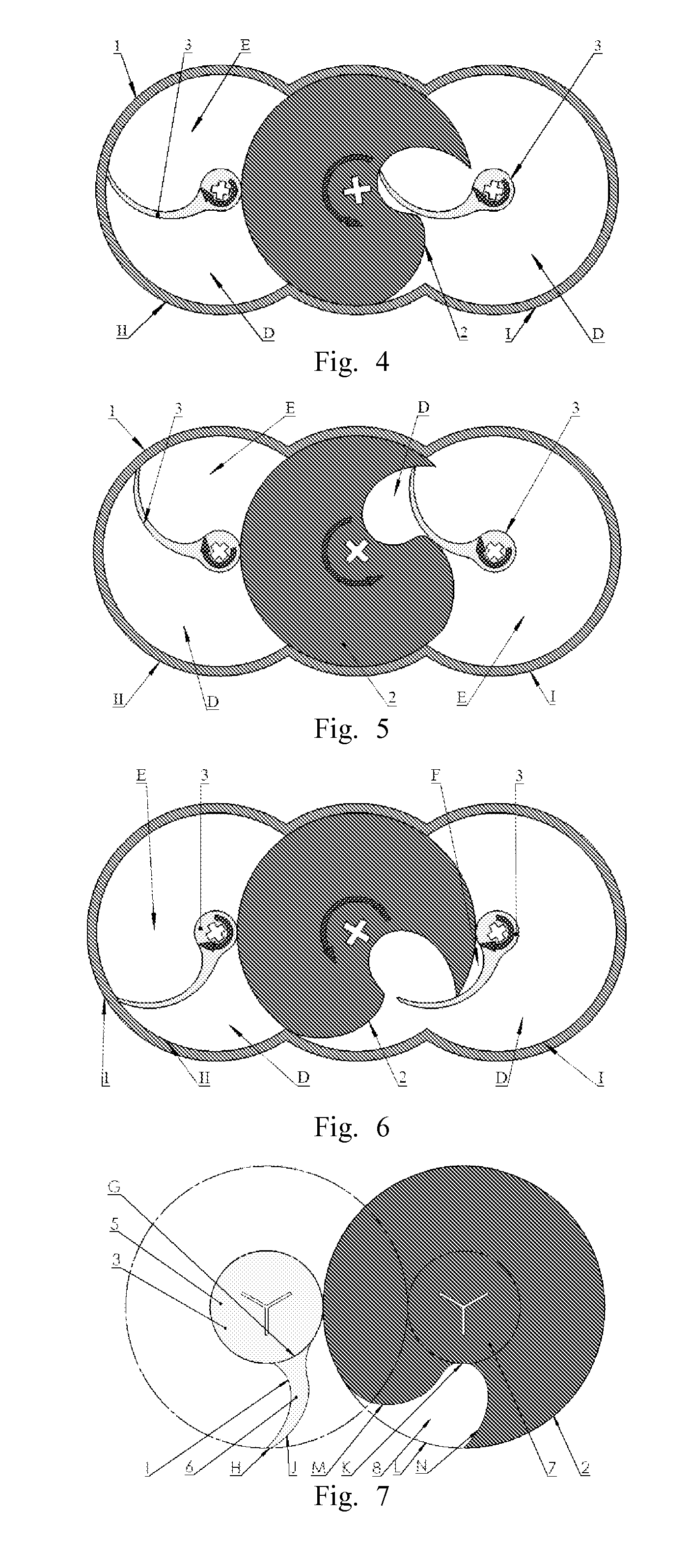
A rotary-piston engine includes at least two rotary pistons, which are located in an essentially spherical housing and which rotate in common about a rotational axis running through the center of the housing, each of the rotary pistons comprising two pistons that are interconnected in a fixed manner, lie diametrically opposite the center of the housing and execute pivoting displacements back and forth in opposite directions about a pivoting axis running perpendicular to the rotational axis, during their rotation. To control the pivoting displacements, the engine is provided with loose spherical or ellipsoidal rotational bodies, which are rotatably mounted in the sliding surfaces of the pistons in respective guide sockets that are hemispherical or ellipsoidal and which engage in at least one guide groove that is configured in the housing. The groove has an essentially hemispherical or ellipsoidal profile.
Owner:PERAVES
Opposite radial rotary-piston engine of choronski-modification
ActiveUS20090314251A1Eliminate lateral forceExtend your lifeInternal combustion piston enginesReciprocating piston enginesSwing-piston engineEngineering
A two-stroke opposite radial rotary-piston engine is proposed, comprising a block including sleeves, pairs of pistons disposed within the sleeves and oppositely movable, a power takeoff shaft, two parallel positioned rotors mounted thereon having an inner surface formed by a closed curved line. The rotors have concaved surface portions. Cross-like traverses are mounted, pair-wise spanning the pistons. The traverses are associated with engagement means, cooperating with the concaved portions. The engine comprises support bearings, coupled to the traverses. Support bearings include an external bushing, rolling over the rotor's inner surface, thereby impelling the rotor. The engagement means are mounted in the region of contact of the support bearings and rotors, thereby eliminating lateral force moment, extending the lifespan of the engine. Other elements, module engine embodiments with different angular positions of the rotors, and power installation embodiments are disclosed, enhancing the efficiency, size, weight, and power variety of the engine.
Owner:EVGENI CHORONSKI +1
Rotary-piston engine
InactiveCN1865664AVariable displacementAdjustability does not conflictOscillating piston pumpsOscillating piston enginesSwing-piston engineEngineering
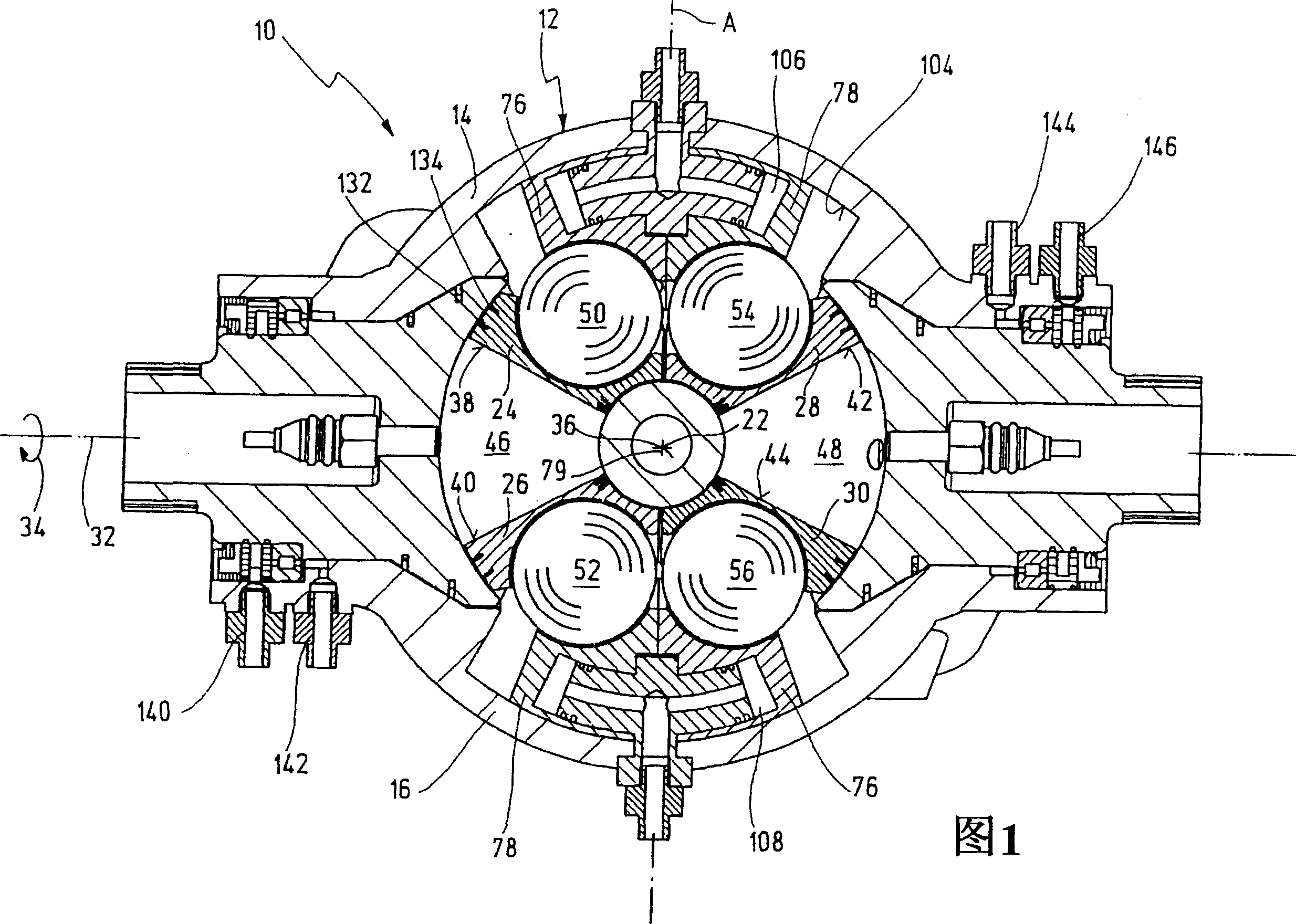
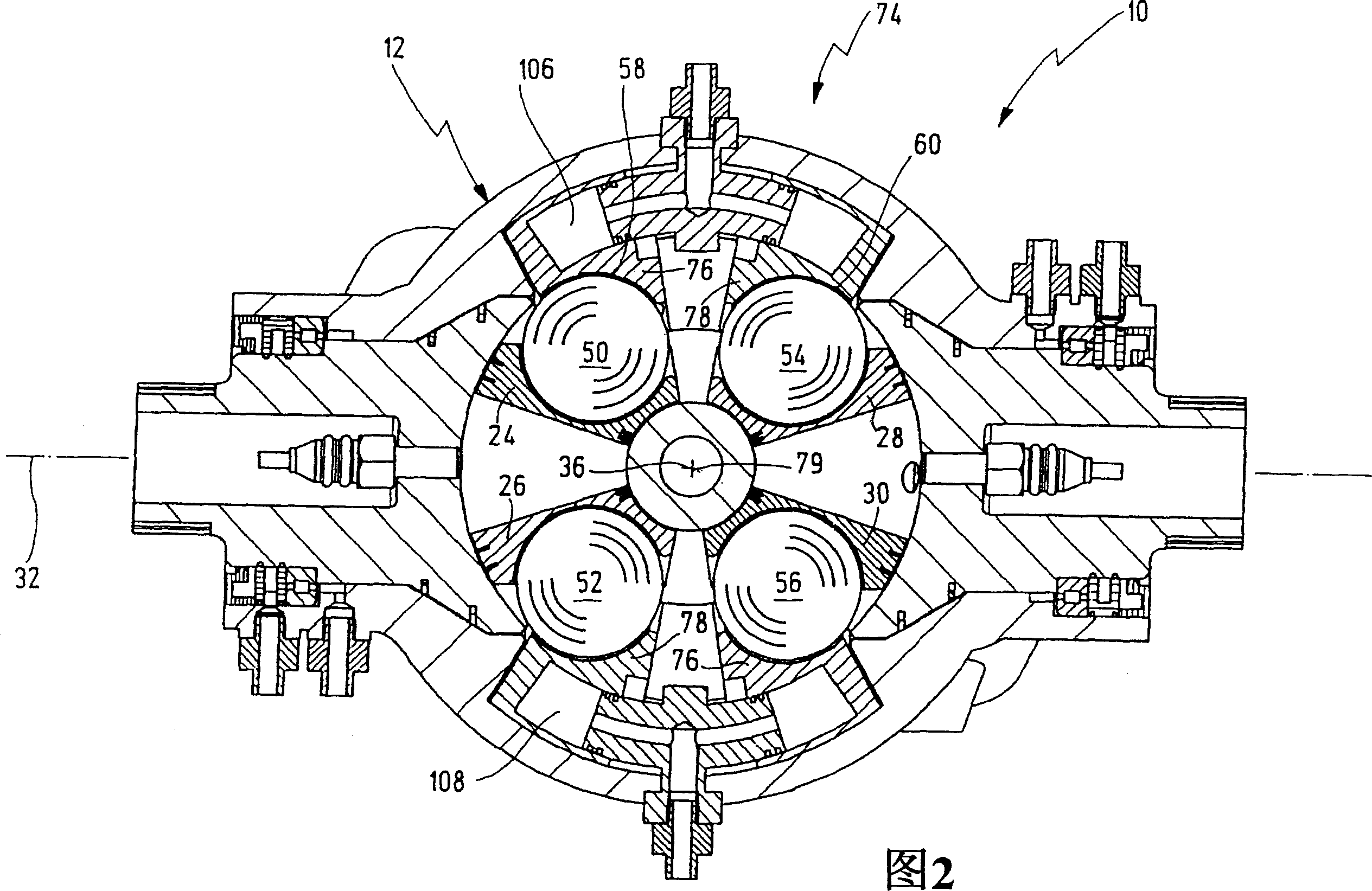
A rotary piston engine having a casing (12) in which are arranged a first and at least one second piston (24, 26), which are capable of encircling a casing-fixed axis of rotation (32) within the casing (12) Rotation, and when they rotate around the axis of rotation (32), around the axis of rotation (36) fixed to the piston perpendicular to the axis of rotation and distributed through the center of the housing, between the first end position and the second end position in opposite directions to each other back and forth rotary motion, wherein the first and at least second piston (24, 26) define a working chamber (48), wherein the first piston (24) and / or the at least second piston (26) have at least one operating mechanism (50, 52), the mechanism is guided along at least one control cam (58) as the first and / or second piston (24, 26) rotates to produce the first and / or at least second piston (24, 26) rotary motion. The control cam (58) is positionally adjustable by means of an adjusting mechanism (74) to adjust at least one of the first and second end positions of at least one of the first and second pistons (24, 26).
Owner:赫伯特·许特林
Opposed-piston engine having a single crankshaft coupled to the opposed pistons by linkages with pivoted rocker arms
ActiveUS9359896B2Alleviates lubricant-blocking effectIncreased durabilityConnecting rod bearingsInternal combustion piston enginesTop dead centerSwing-piston engine
An opposed-piston engine with a single crankshaft has a rocker-type linkage coupling the crankshaft to the pistons that utilizes a rotatable pivot rocker arm with full-contact plain bearings. A rocker-type linkage utilizes a rotatable pivot bearing with an eccentric aspect to vary translation of piston linkage along the axial direction of a cylinder, which shifts the top dead center (TDC) and bottom dead center (BDC) locations of a piston so as to change the volume of charge air compressed during the power stroke.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
Opposed Piston Engine Layout in Heavy Trucks
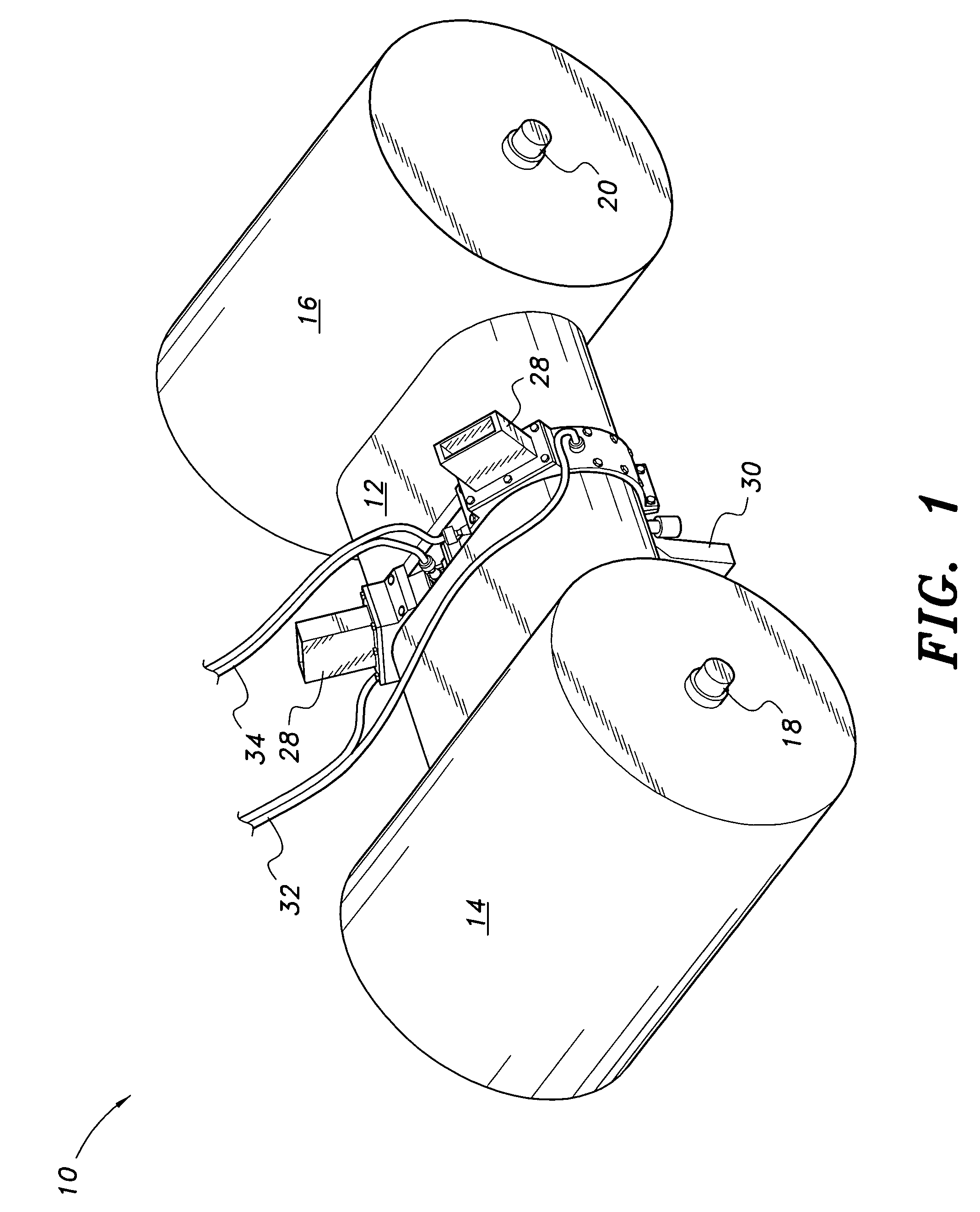
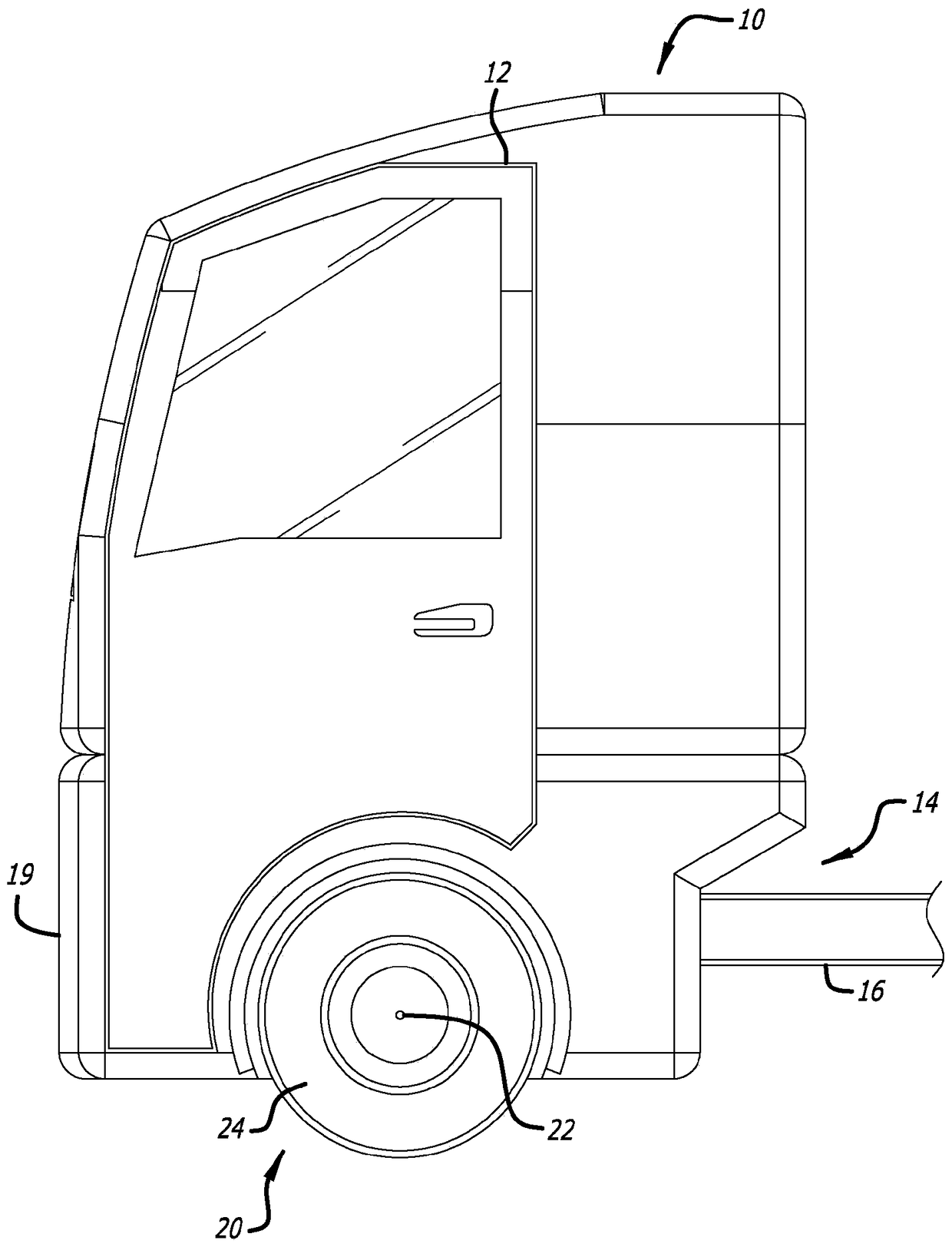
An engine placement configuration for a heavy-duty truck includes a chassis having two spaced-apart frame rails running in a longitudinal direction of the chassis, between front and rear ends, and a front wheel assembly with an axle attached to the frame rails. An opposed-piston engine is supported on the frame rails and positioned between the front end and the axle. The opposed-piston engine includes a cylinder assembly with a longitudinal axis disposed between the frame rails and oriented vertically with respect to the longitudinal direction. Alternatively, the opposed-piston engine includes a row of cylinders disposed between the rails and running in the longitudinal direction.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
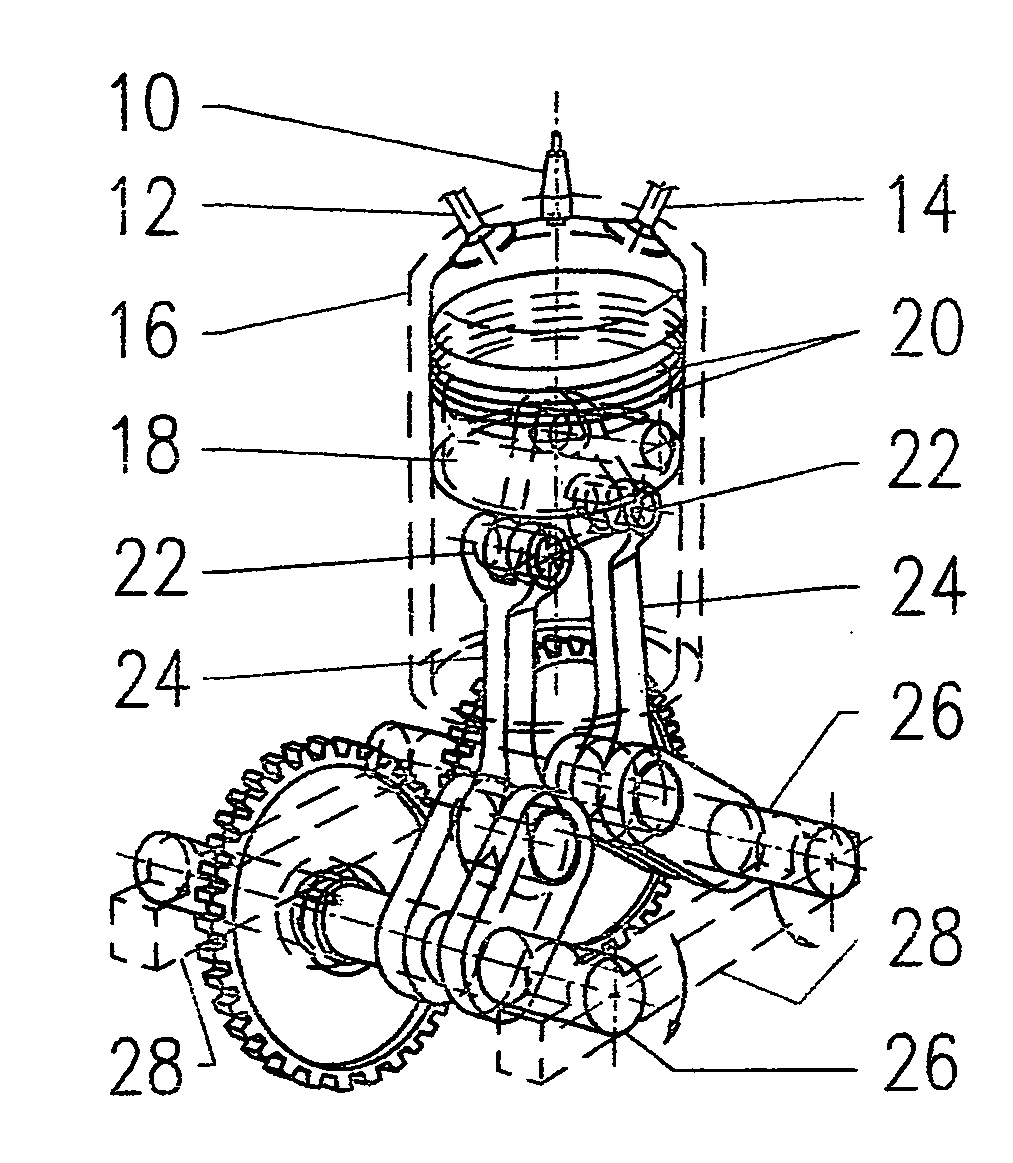
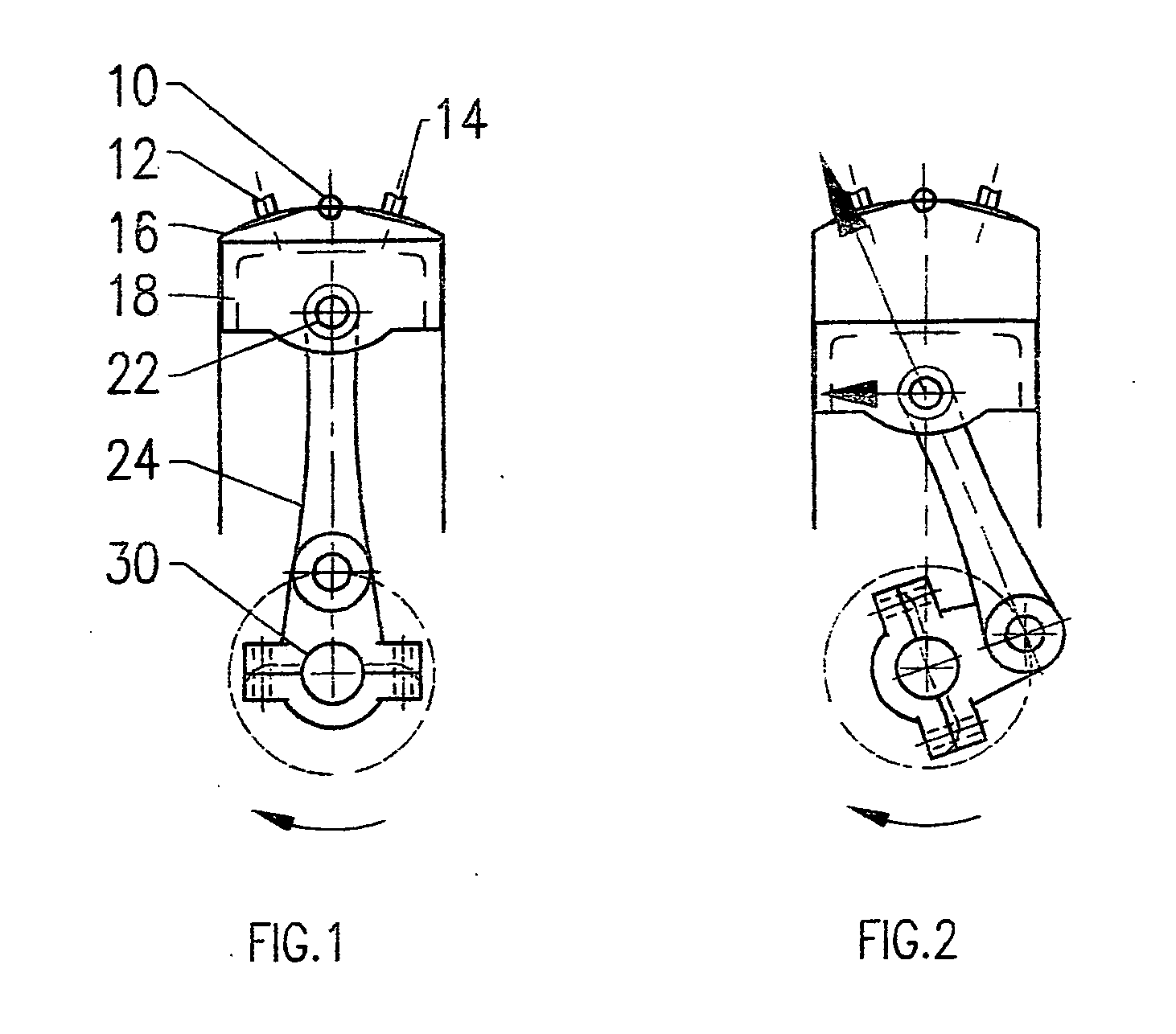
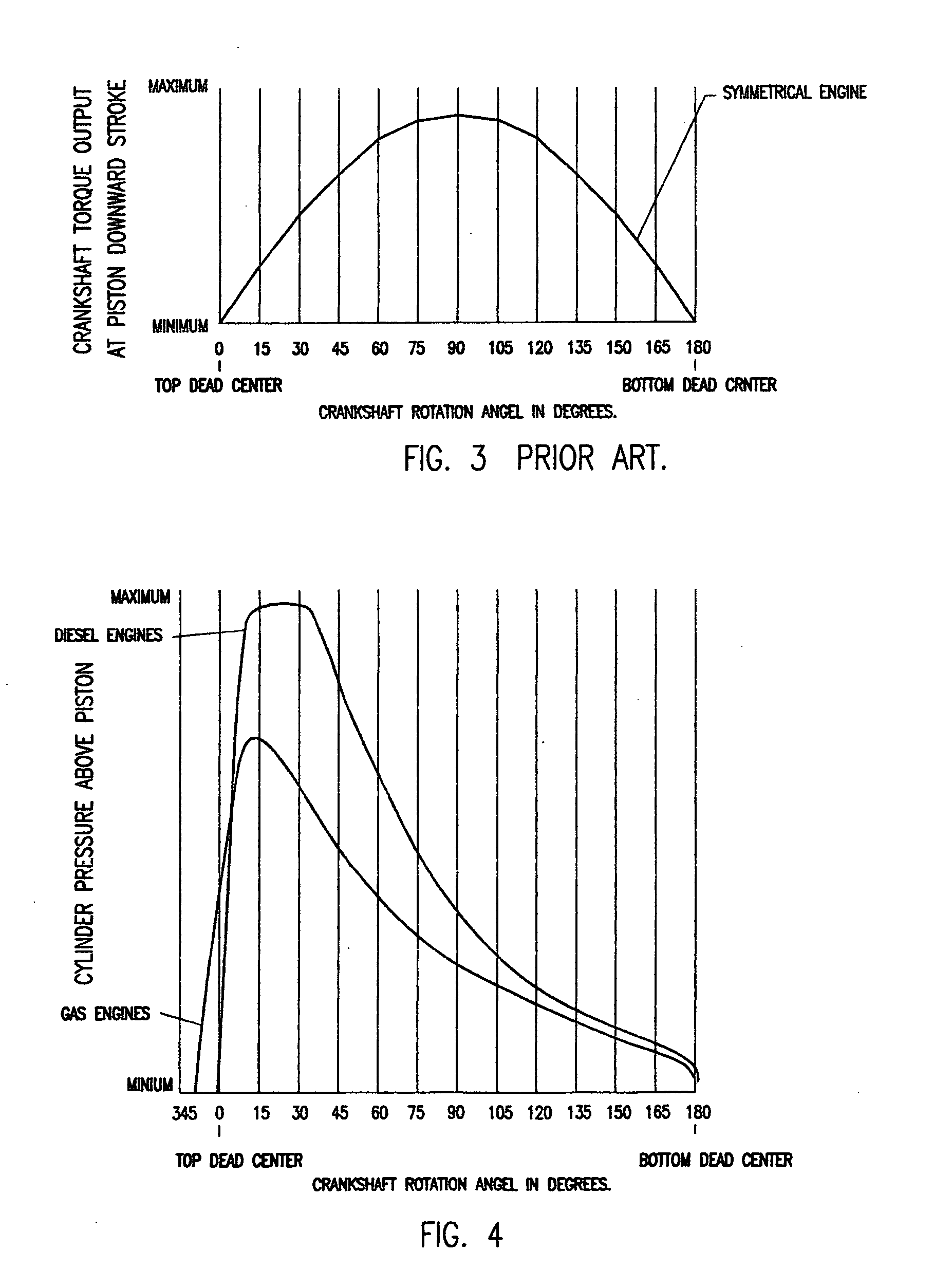
Increase torque output from reciprocating piston engine
Reciprocating powered driven engine having a piston with multiplier connecting rods, driving multiplier crankshafts. Maximum crankshaft torque output positioned closer to the detonation timing and piston “top dead center” when cylinder above piston volume is at a lower value. Reduced engine friction losses by canceling piston side forces with the use of multiplier crankshafts positioned in offset and mirror image from piston and cylinder center line.
Owner:SWIENINK HENDRIKUS JOHAN
Rotary-piston engine
InactiveCN100480489COscillating piston pumpsOscillating piston enginesSwing-piston engineEngineering
The invention relates to a rotary-piston engine comprising a housing (12) provided with first and at least one second pistons (24, 26) which are placed and jointly rotatable therein about an axis of rotation (32) connected to the housing and can carry out pivoting back and forth movements in opposite direction when rotating about the axis (32) and a pivoting axis (36) which is perpendicular to the axis of rotation and passes through the housing center between first and second end positions, wherein the first and at least second pistons (24, 26) define a working chamber (48), the first piston (24) and / or at least one second piston (26) comprises at least one running member (50, 52) which is guided along at least one control cam (58) during the rotation of the first and / or second piston (24, 26) in such a way that a pivoting movement of the first and at least second pistons (24, 26) is produced. Said control cam (58) is positionally adjustable by means of an adjusting mechanism (74) in such a way that it makes it possible to displace at least one position of the first and at least second pistons (24, 26) between the first and second end positions.
Owner:赫伯特·许特林
rotary piston engine
ActiveCN105781727BHigh torqueAchieve the task of inventionInternal combustion piston enginesFree-piston engineLow noise
The invention relates to a rotating piston engine. The rotating piston engine comprises a shell consisting of a cylinder 1 and front and back end covers 2 and 3; a rotor 4 is mounted on a main shaft 5; the main shaft is mounted in main bearings of the front and back end covers; N cylinder chambers 8 are uniformly distributed on the rotor 4; N pistons 9 are embedded; two ends of piston pins 11 extend into piston pin moving rails 18 arranged on the front and back end covers to perform a same-speed misaligned rotating motion along with the rotor; the outer diameter of the rotor 4 and the inner diameter of the cylinder 1 are cylinders with the same diameter, and are in clearance sliding contact; a reciprocating crankshaft type internal combustion engine piston air sealing structure is adopted to solve the problem of difficult air sealing of a rotor engine; meanwhile, the principles of front-grade continuous air compression of a gas turbine and continuous acting of high-pressure gas in a combustion chamber are acted in the rotating piston engine; the rotating piston engine overcomes multiple defects in a traditional internal combustion engine technology; and the rotating piston engine has the excellent effects of simple structure, high mechanical efficiency, stable operation, no vibration and low noise.
Owner:贺坤山
Systems with reciprocating piston engines
ActiveCN106030072BReduce adverse effectsReduce long-term demagnetizationHybrid vehiclesCrankshaftsPistonSwing-piston engine
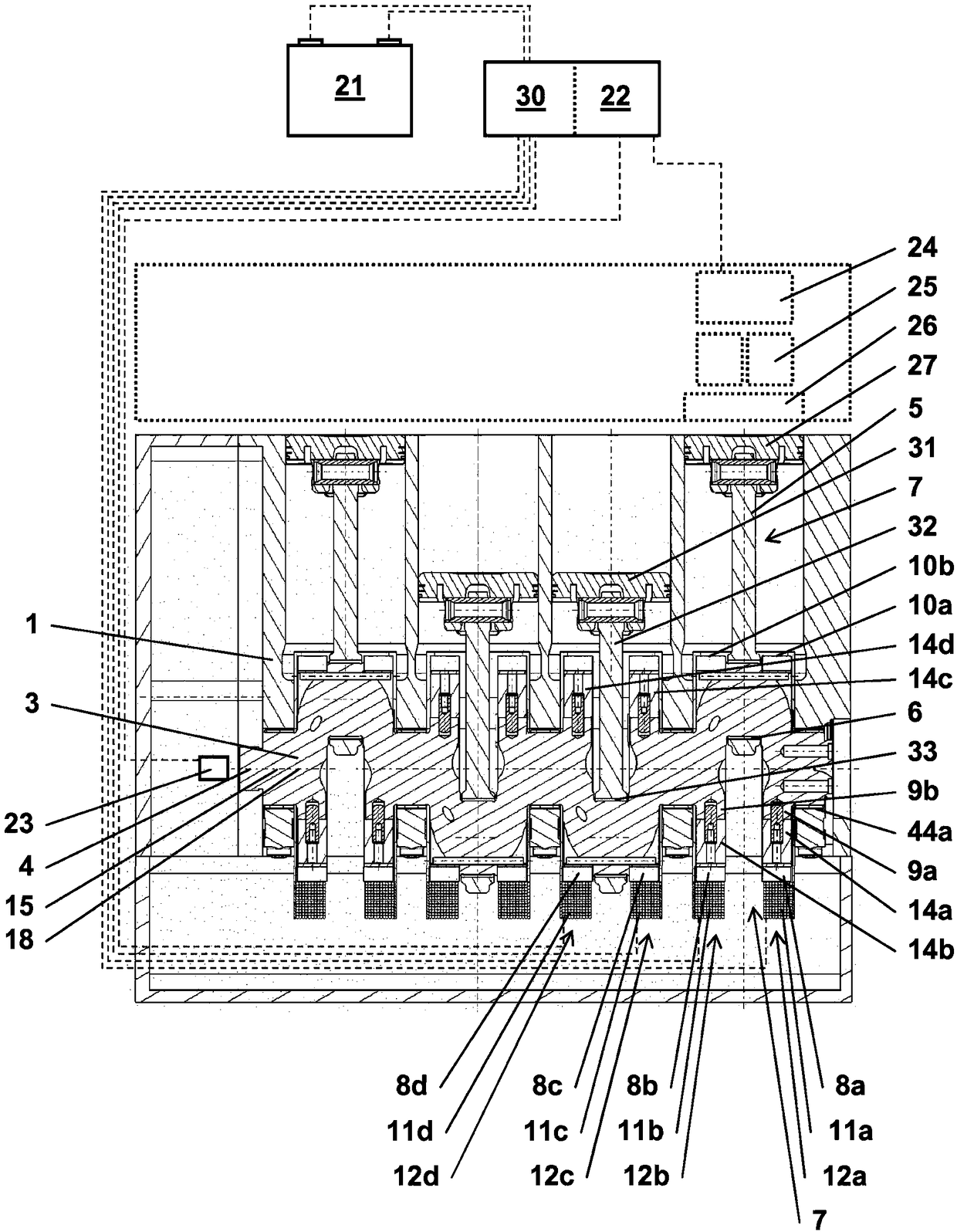
A reciprocating piston engine is disclosed having a first inner magnetic field unit, arranged on a first crank web of a crankshaft, and a stationary first outer magnetic field unit, wherein the first inner magnetic field unit and the first outer magnetic field unit together form a first electromagnetic converter, in particular an electric motor or an electric generator. The first crank web has a first compensating weight on a side that is opposite a first connecting rod bearing and that faces radially outwards in relation to a crankshaft axis, wherein the first compensating weight is made of a non-magnetizable material. The first inner magnetic field unit is arranged on a side of the first compensating weight that faces outwards in relation to the crankshaft axis. The invention also relates to a system comprising the reciprocating piston engine, an energy store, an electric control unit and a crankshaft sensor.
Owner:HVD
Oscillating piston engine
InactiveCN1908377BEngines with oscillating pistonsRotary piston enginesSwing-piston engineEngineering
An oscillating piston engine is described, having a housing (12) which has an at least approximately spherical inner wall (32), and having at least two pistons (34, 36) which can jointly revolve in the housing (12) about a fixed rotation axis (42) and, when revolving about the rotation axis (42), perform back-and-forth swivelling movements about at least one swivel axis (44) perpendicular to the rotation axis (42), wherein the swivelling movements of the two pistons (34, 36) are in opposition to one another, and wherein the two pistons (34, 36) each have an end face (46, 48), said end faces (46, 48) facing one another and each defining a front end of a working chamber (54) which is arranged completely outside the rotation axis (42) and is defined at the circumference by a working chamber wall (58). The working chamber (54), formed by the two end faces (46, 48) of the two pistons (34, 36) and the working chamber wall (58), and the pistons (34, 36) have the shape of a toroid section at least in the region of their ends facing the working chamber (54).
Owner:赫伯特·许特林
Lubrication arrangements for maintaining piston pin oil pressure in two-stroke cycle, opposed-piston engines
The present disclosure provides a lubrication arrangement for a piston pin of a piston in a two-stroke cycle opposed piston engine. A two-stroke cycle, opposed-piston engine for the piston-piston-pin lubrication arrangement minimizes oil pressure loss at the piston pin and reduces the required oil supply pressure to the engine as the piston approaches bottom dead center. The piston pin is configured to absorb and store oil pressure energy when the oil pressure at the piston pin is high, and to release this stored energy to pressurize the oil at the piston pin when the connecting rod oil pressure is low.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
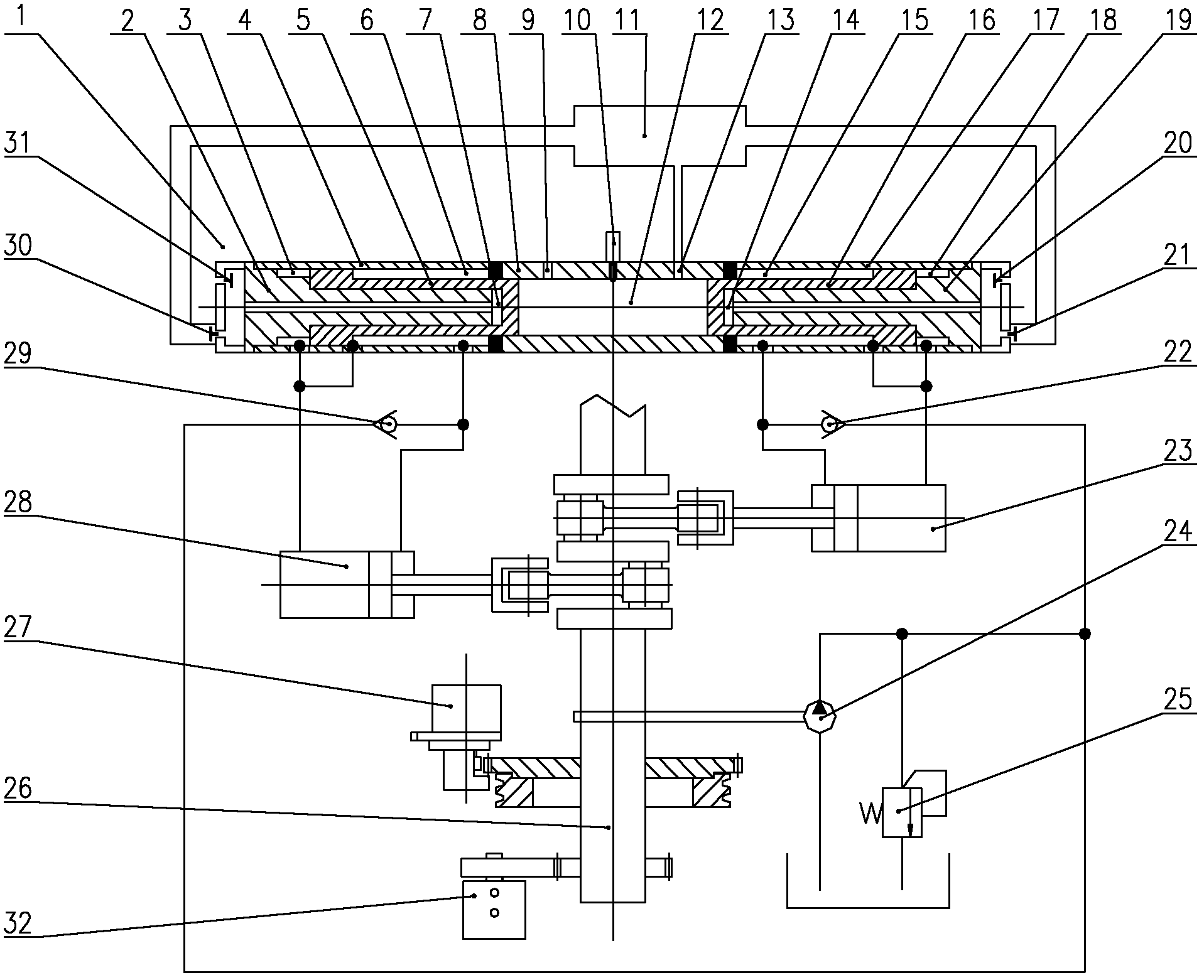
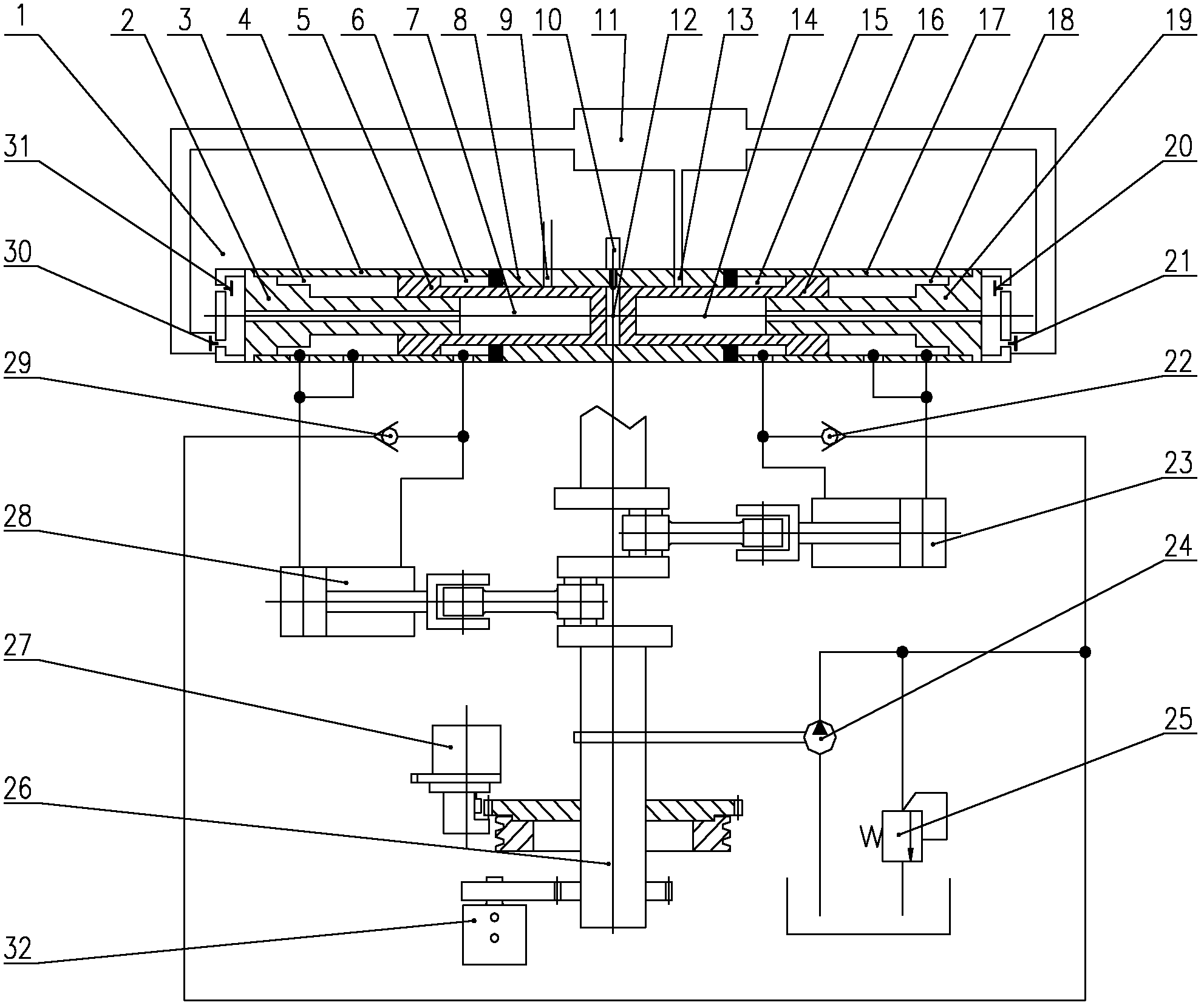
A variable stroke free piston engine
ActiveCN107701305BRealize fully flexible controlSimple structureInternal combustion piston enginesFree piston enginesFree-piston engineCombustion chamber
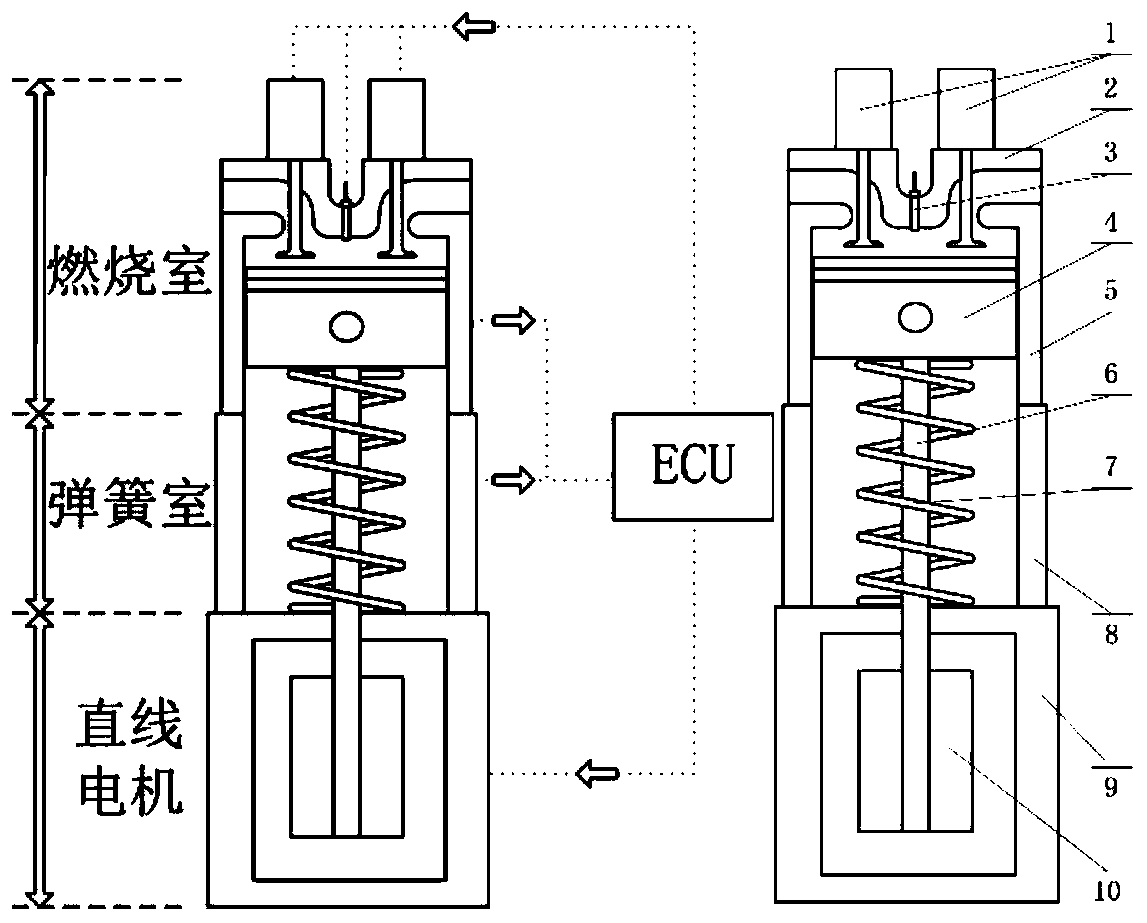
The invention discloses a stroke-variable free piston engine. The engine comprises a combustion chamber part, a spring chamber part, a permanent magnet linear motor part and an electronic control unitpart. A cam-free variable valve timing manner is adopted, and fully-flexible control over an inlet valve and an exhaust valve is achieved by electromagnetically driving a valve timing mechanism; an electronic control unit controls displacement of a piston by adjusting the powering-on current magnitude and direction of a permanent magnet linear motor coil, and the upper stop point, the lower stoppoint and the compression ratio of the piston are variable; and real-time control over the valve starting moment, the valve lift curve and the valve timing duration time is achieved by changing a control signal of the cam-free variable valve timing mechanism. The stroke-variable free piston engine is simple in structure and high in efficiency, fully-flexible control over various execution mechanisms of the engine is achieved, and the energy saving and environment protection performance of the engine is improved.
Owner:江苏铱莱德驱动系统有限公司
Combustion engine
The present invention relates to internal combustion engines and more particularly reciprocating piston engines utilizing Scotch yokes to translate rectilinear movement to rotary motion. In particular, the piston and / or pistons of the engine of the present invention can be placed in their topmost position for a period of time for the effective ignition and combustion of the air / fuel mixture for a given fuel charge, hence therefore providing an increased efficiency of the piston engine with a more efficient coupling between the piston and / or the power shaft driving the crank.
Owner:EXODUS R&D INT PTE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com