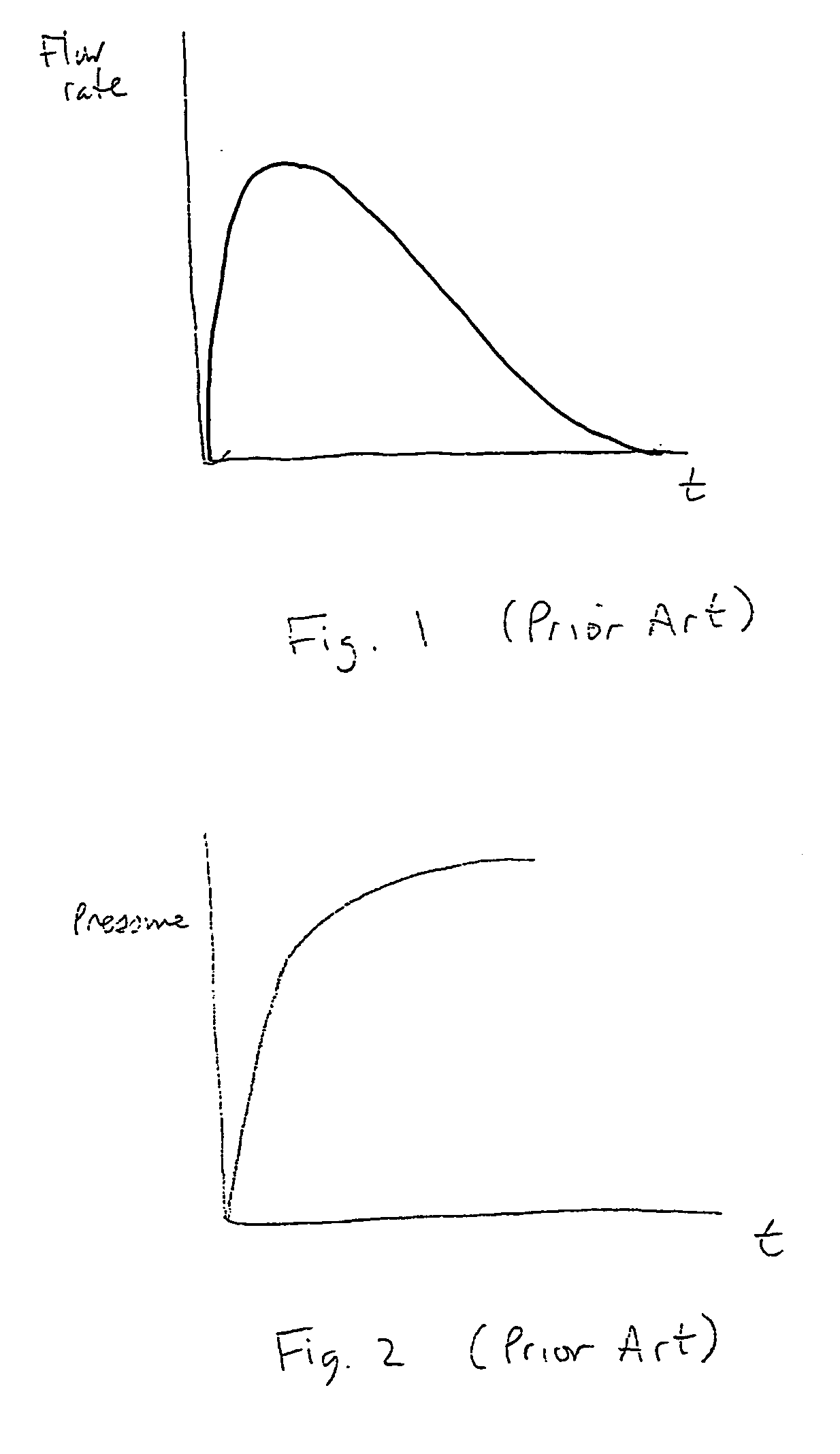Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
685results about "Engine of counter-engagement type" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
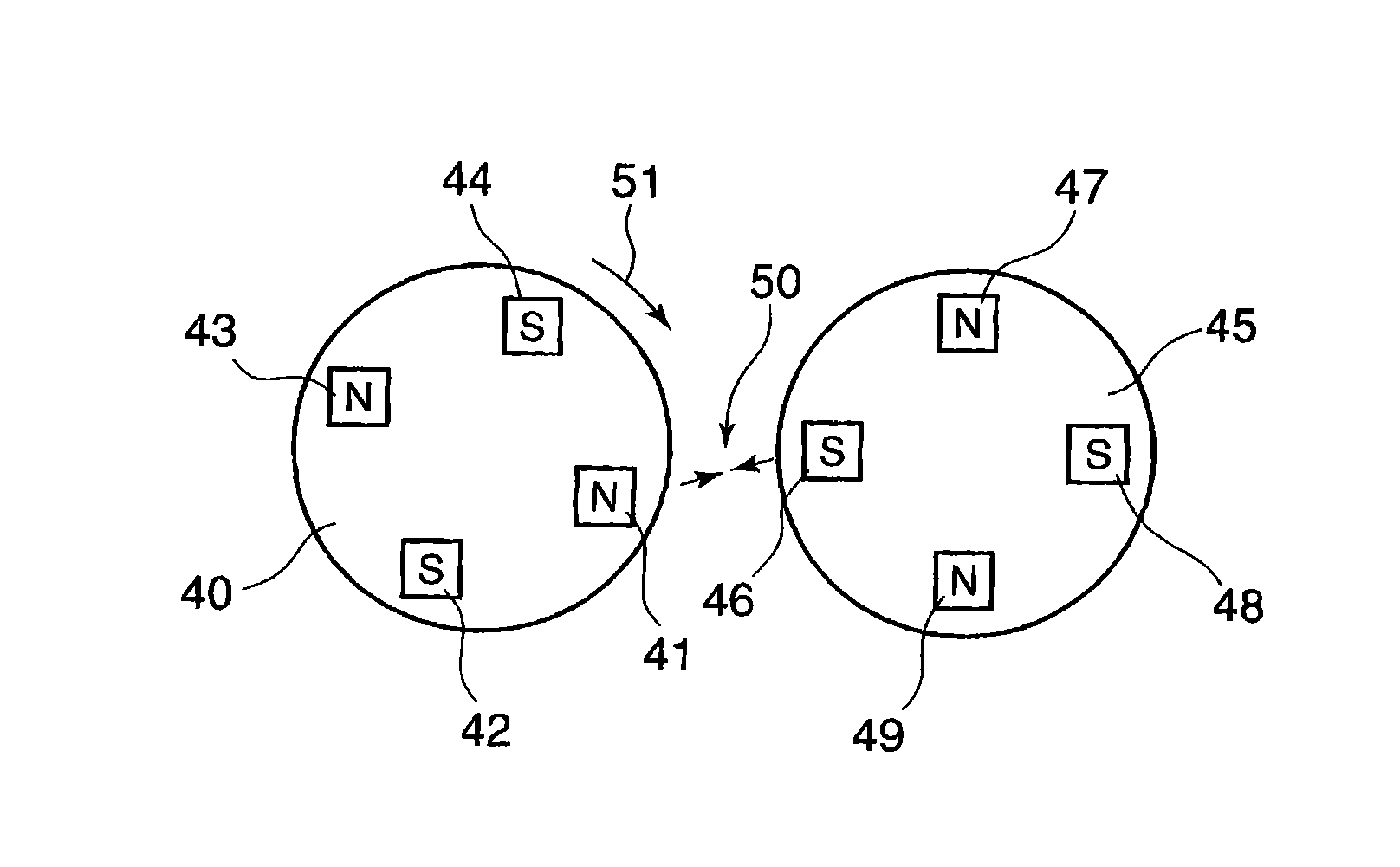
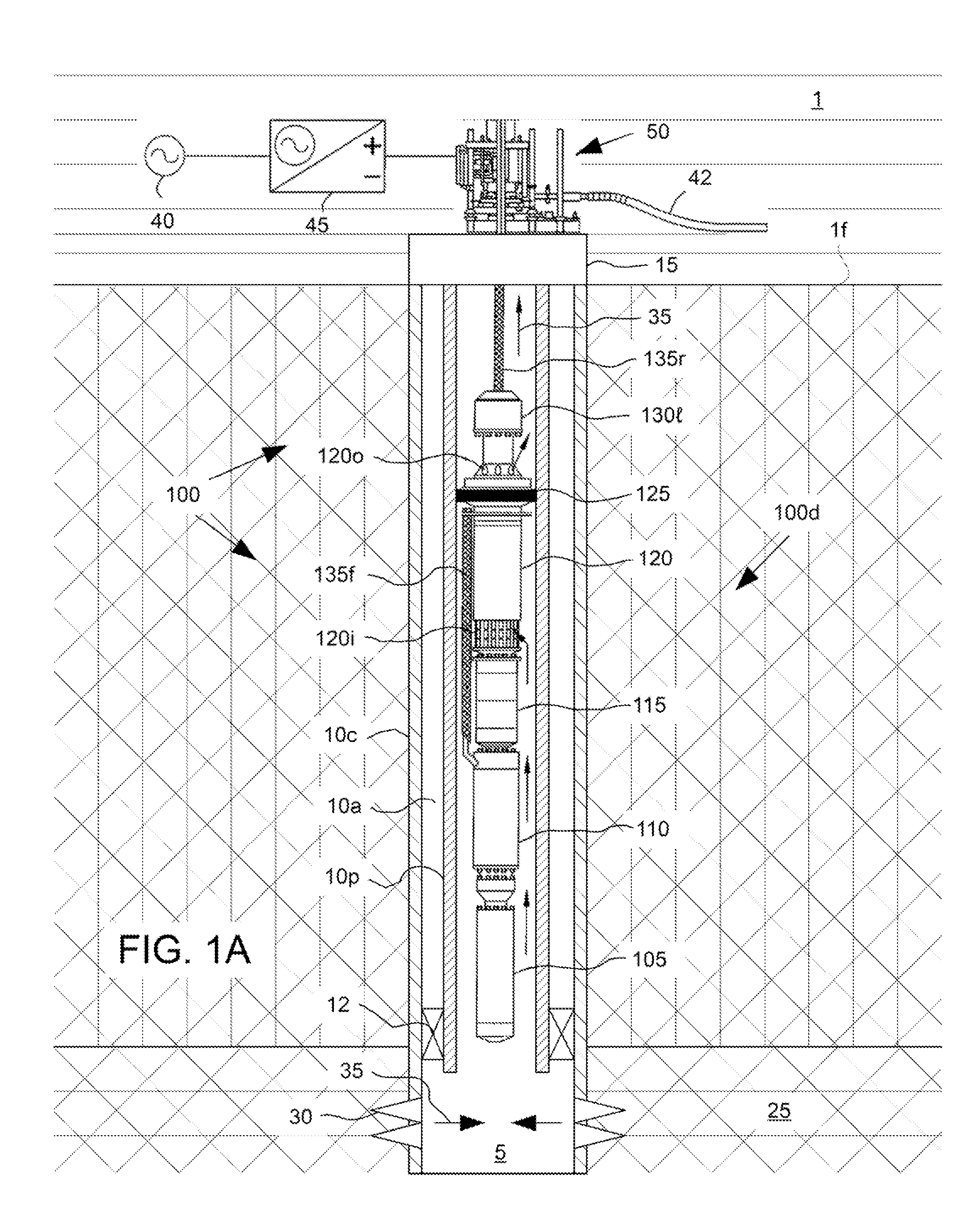
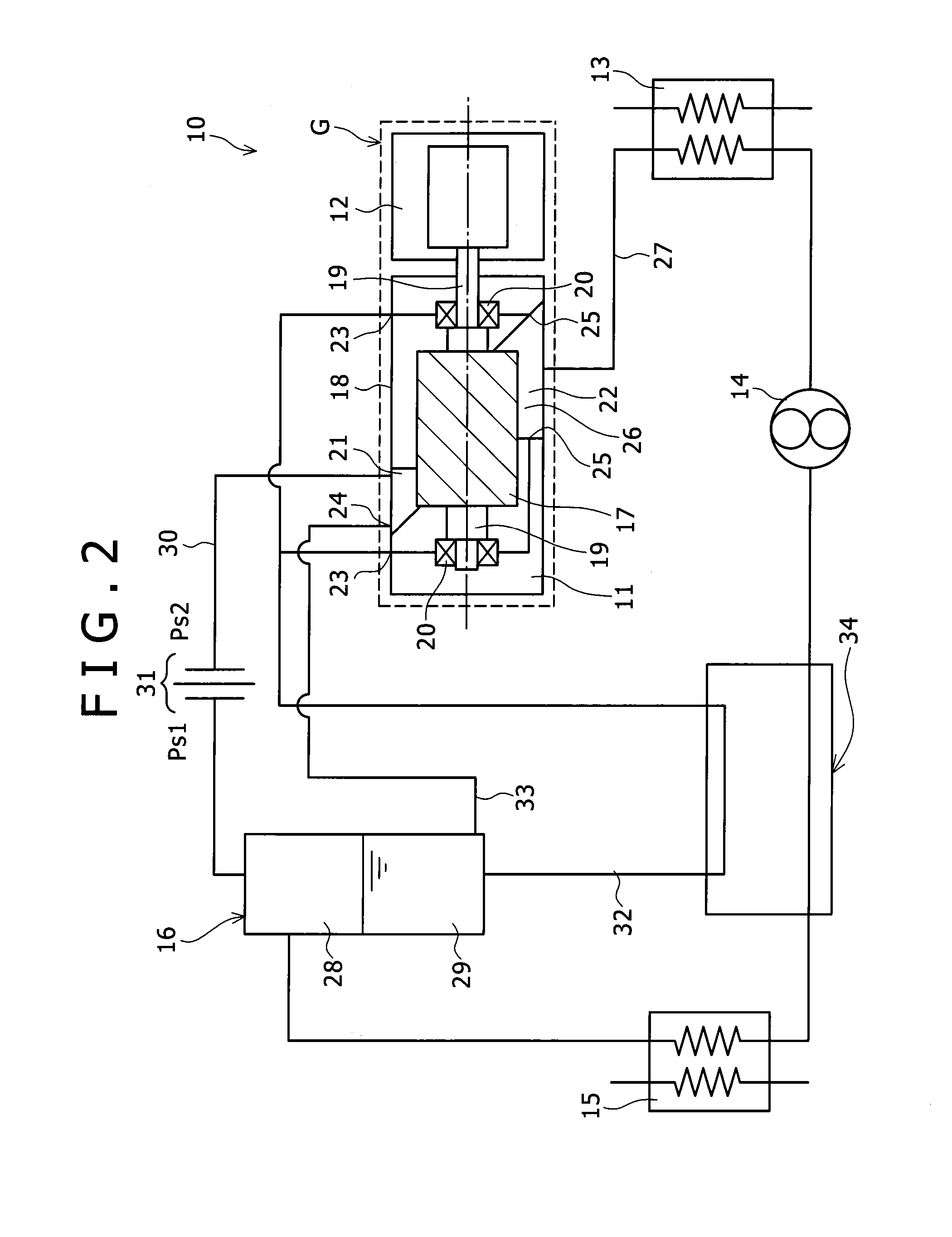
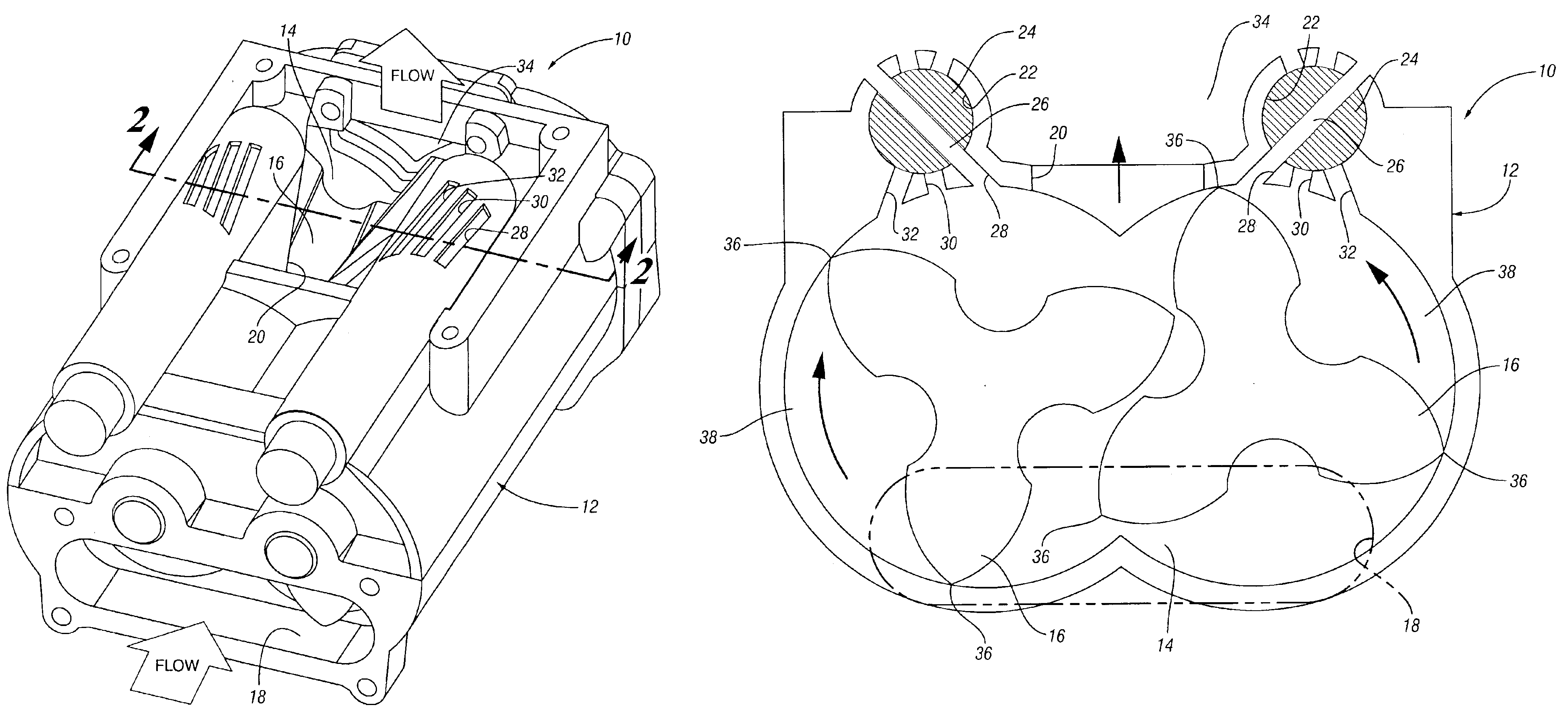
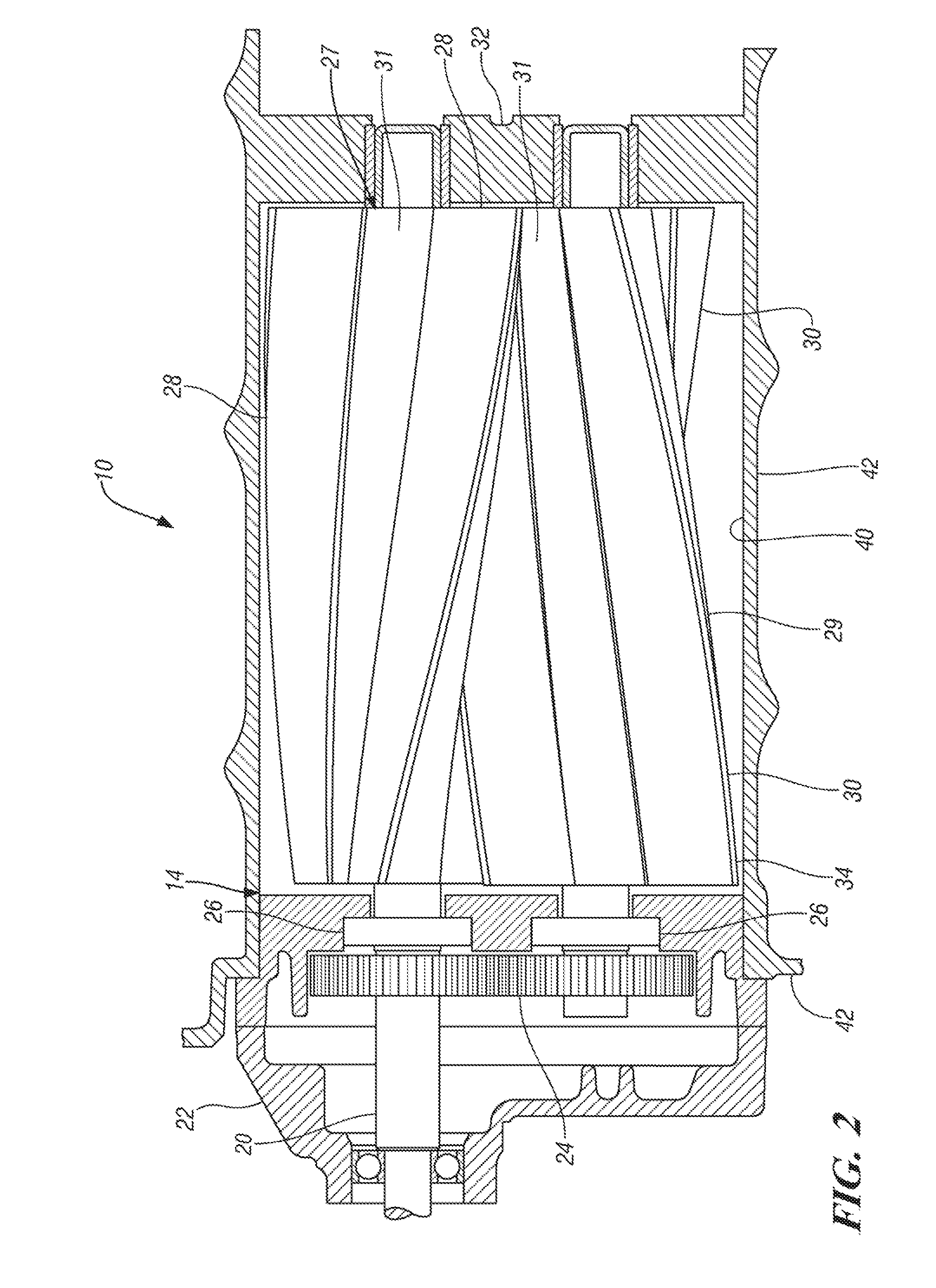
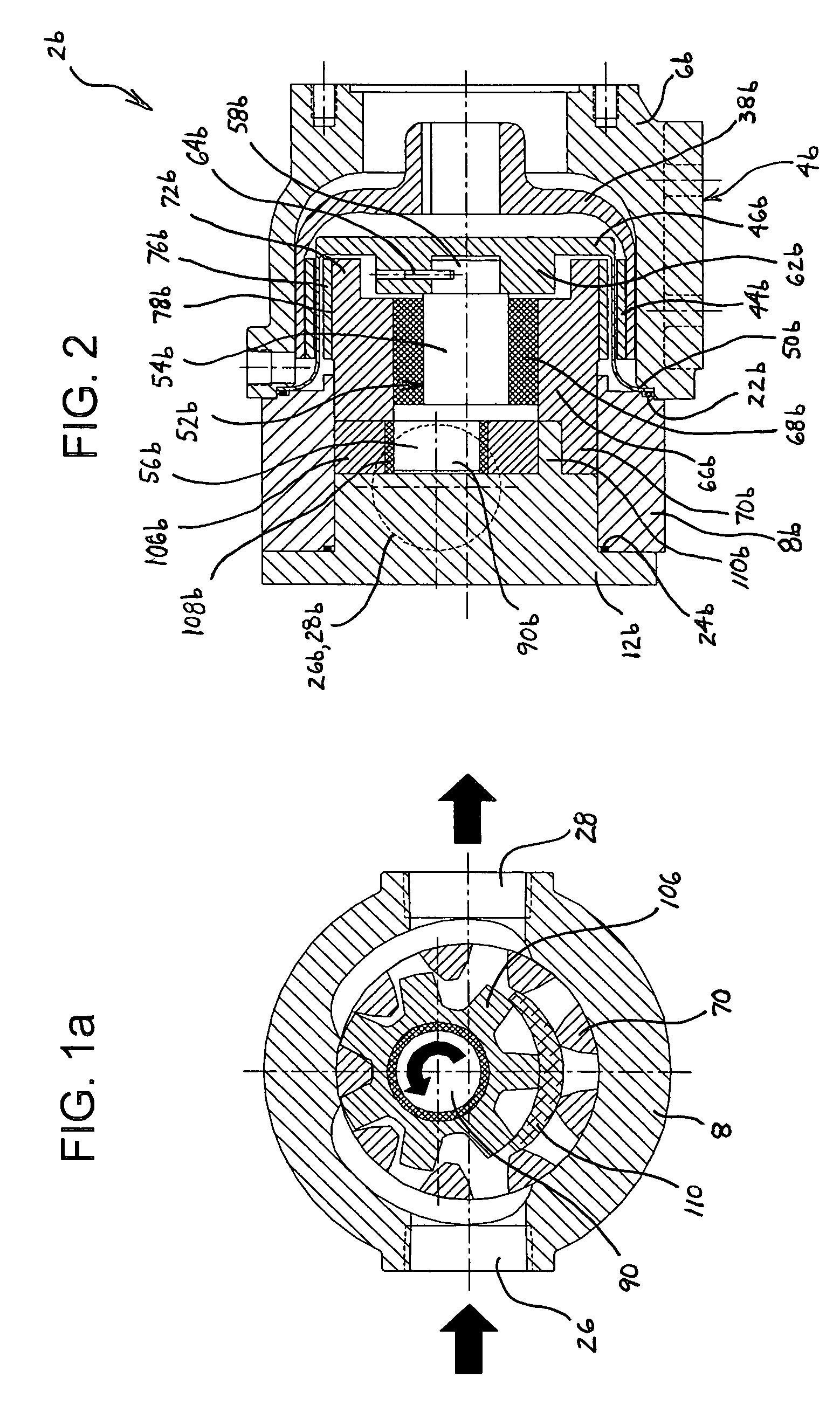
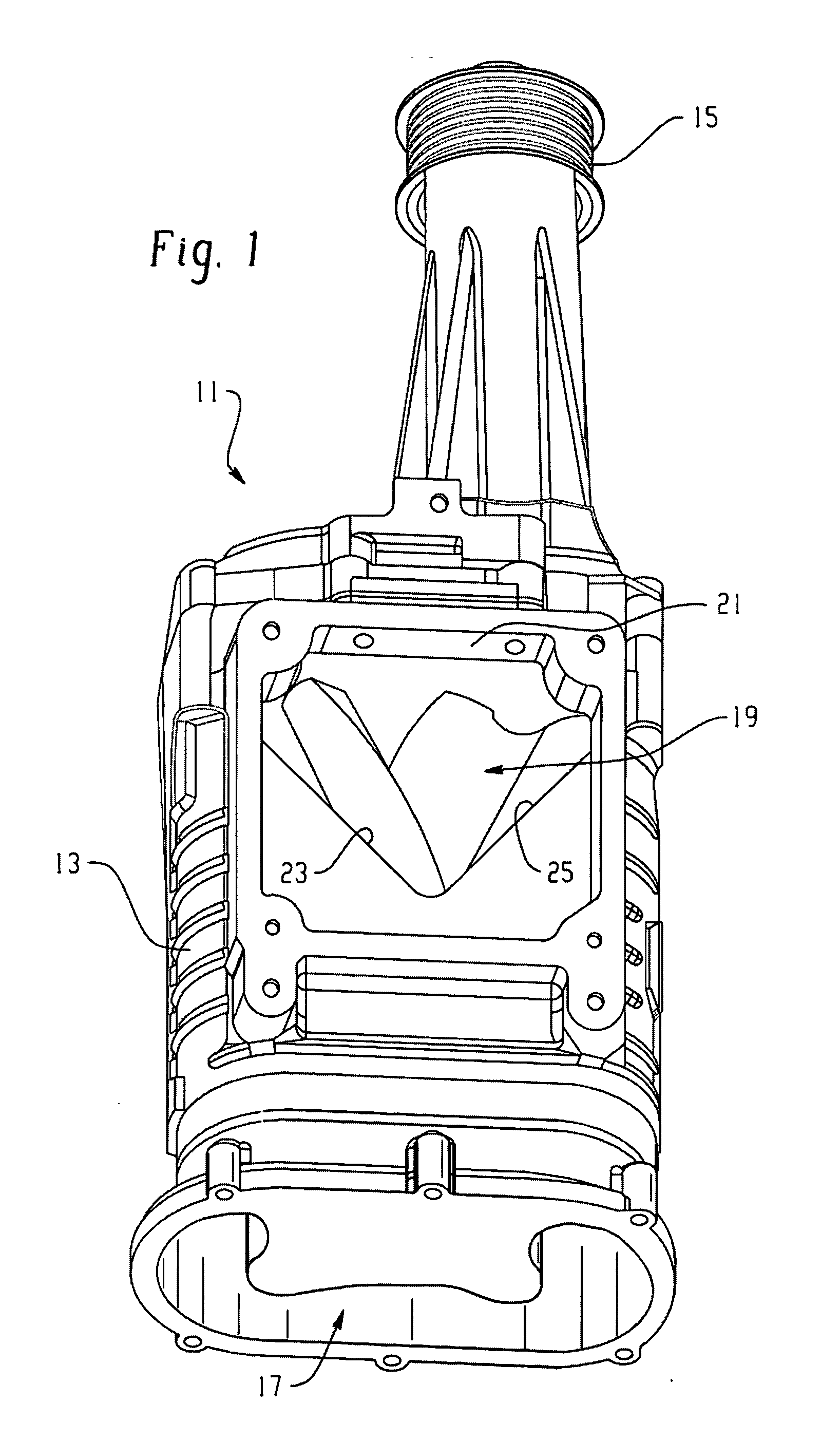
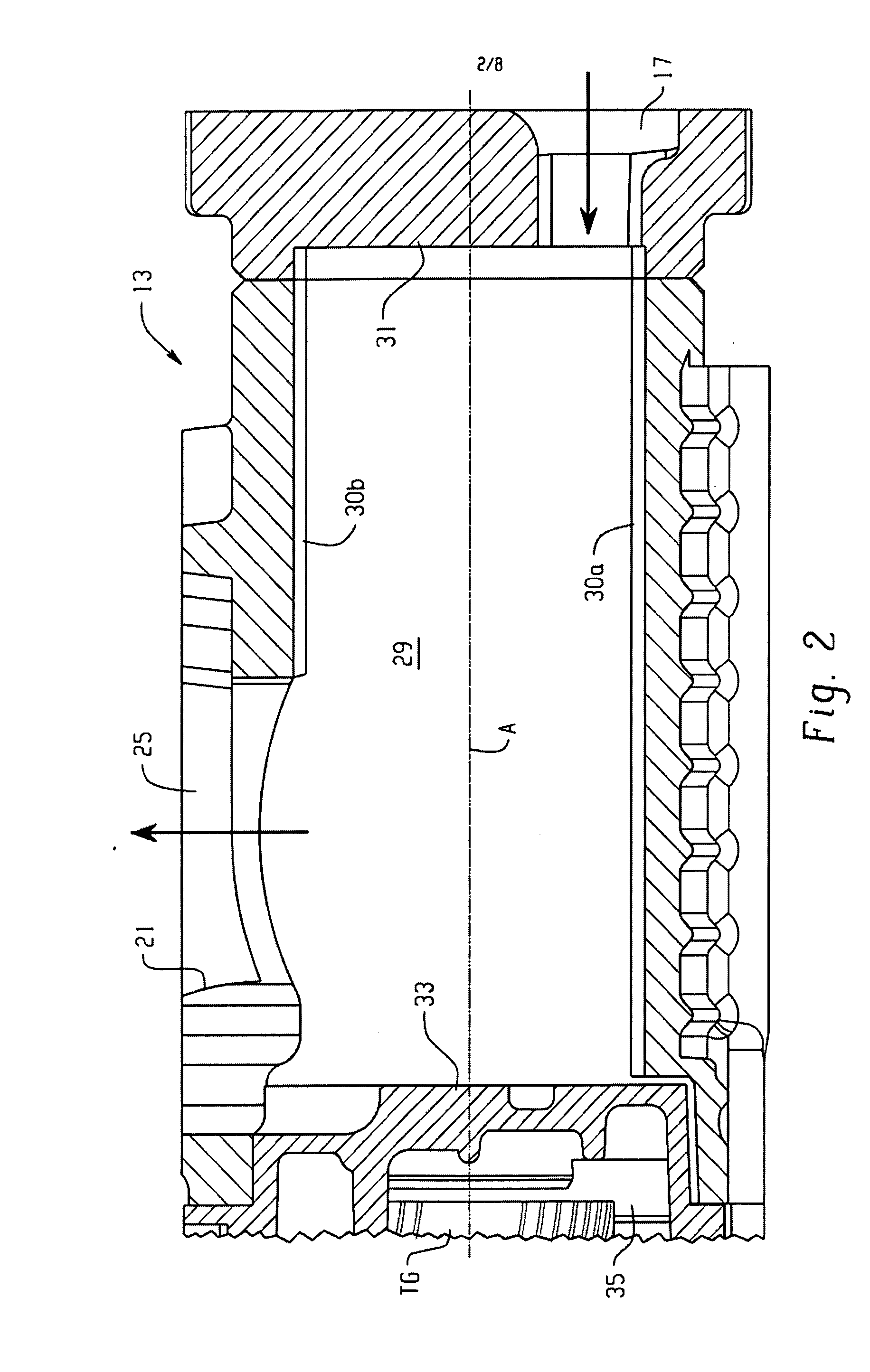
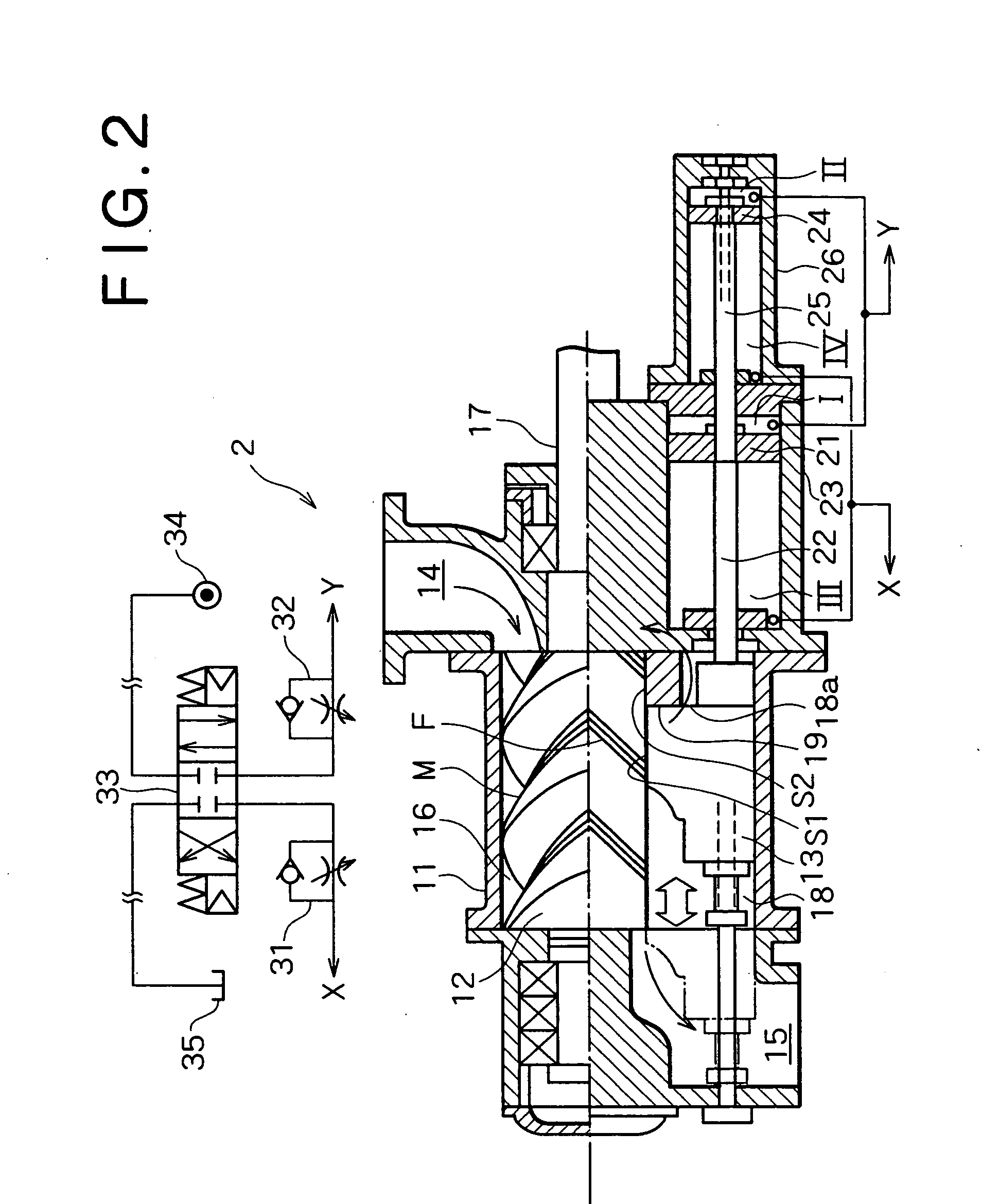
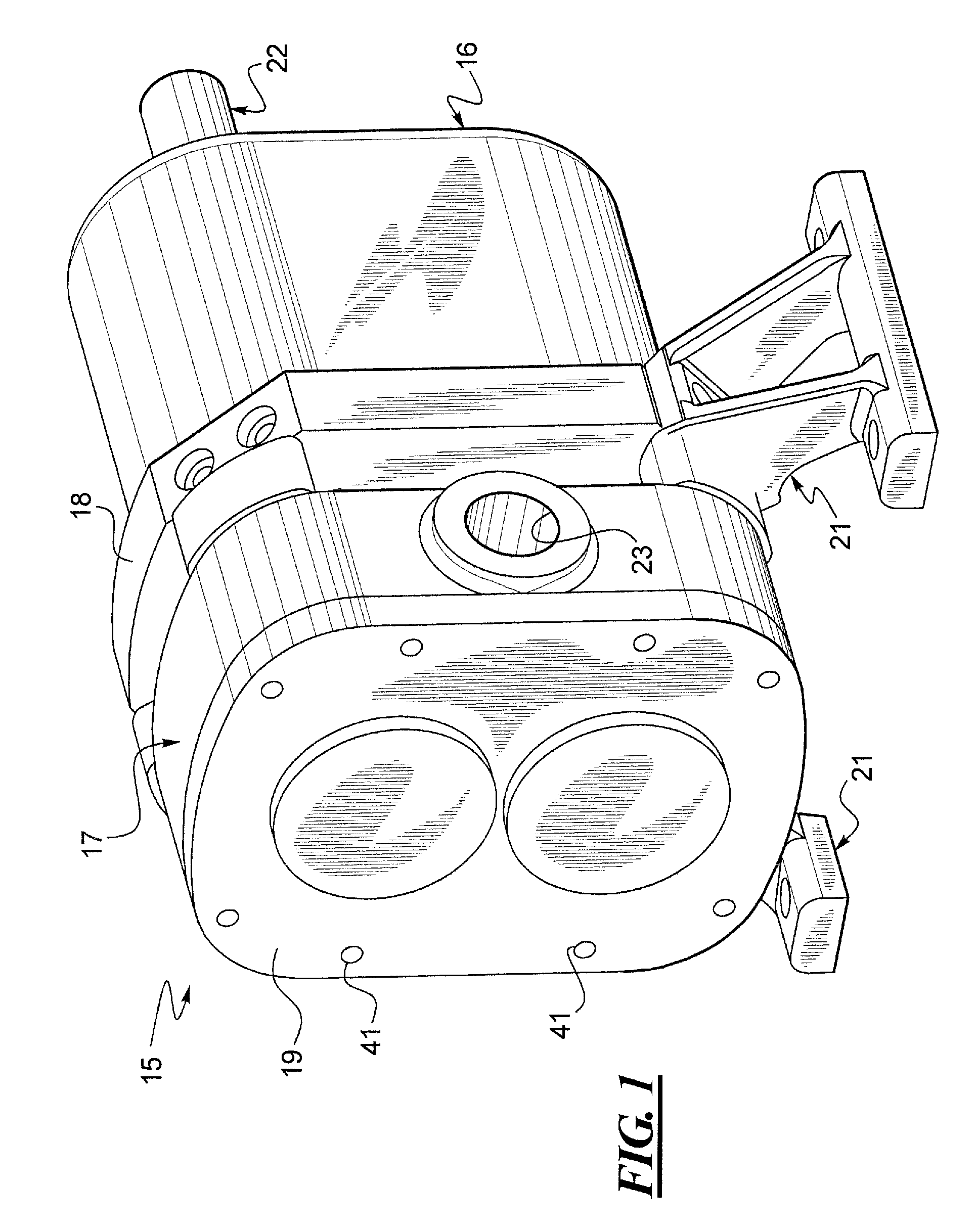
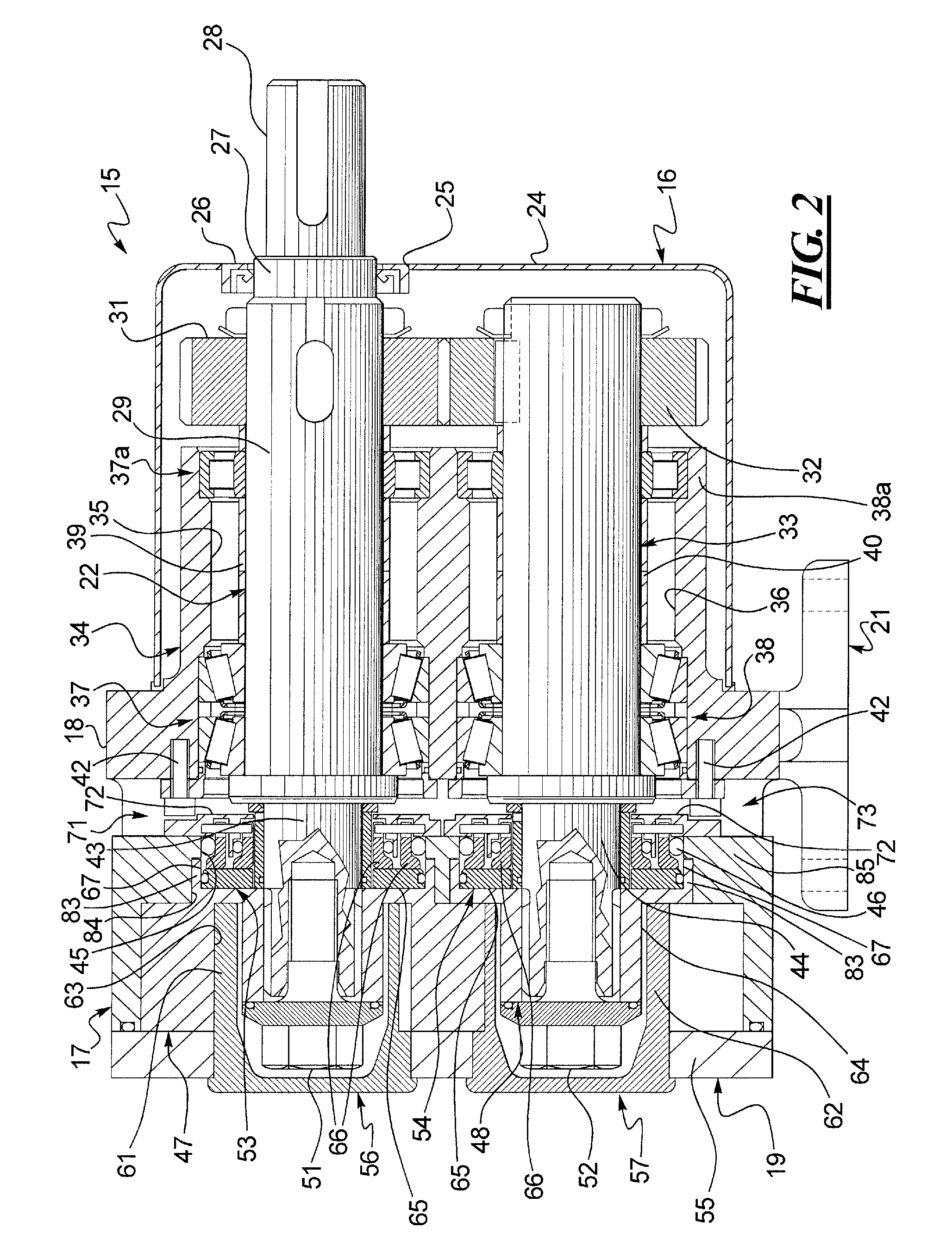
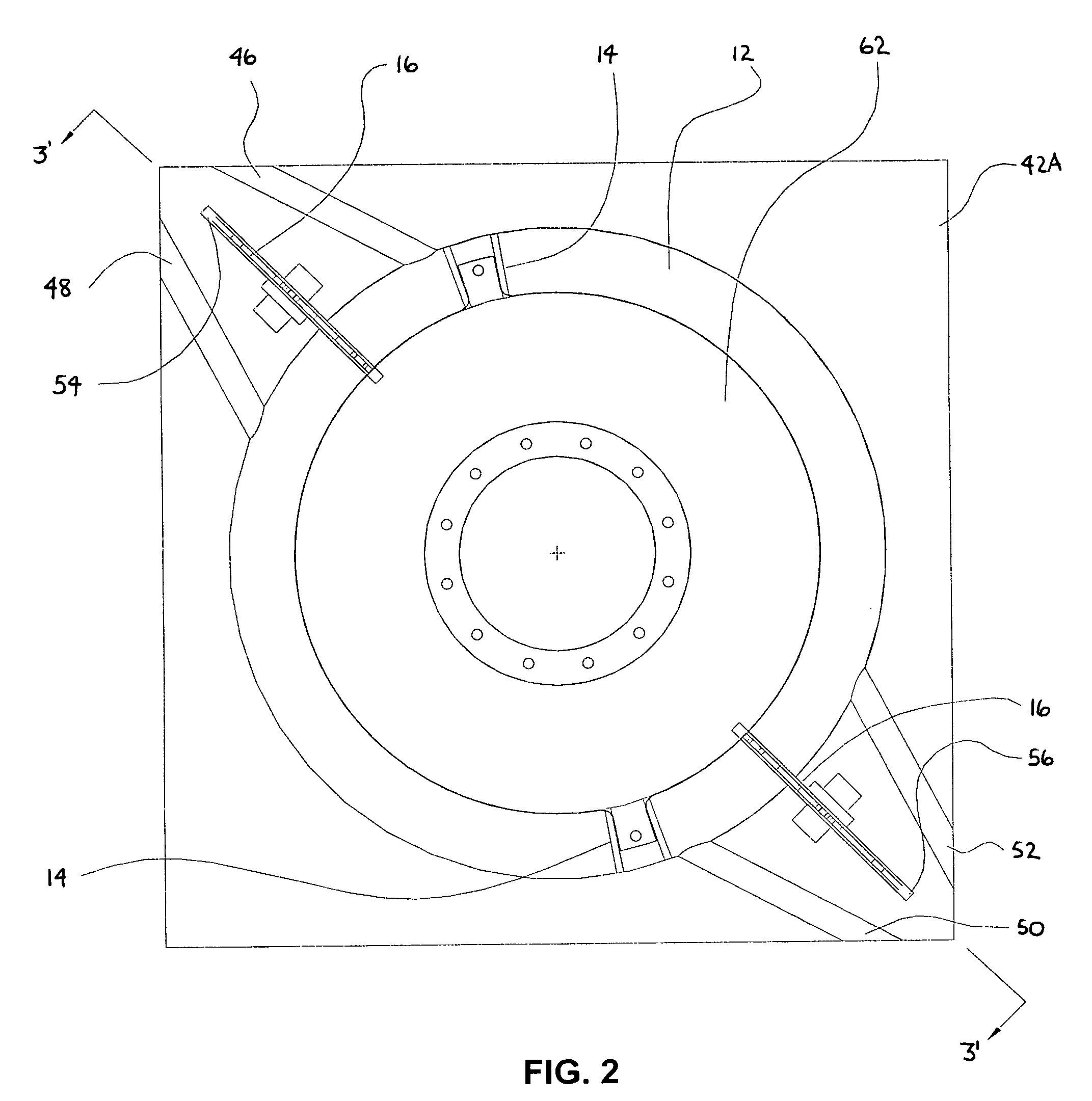
Drive transmission mechanism between two or more rotary shafts and oil-free fluid machine equipped with the mechanism
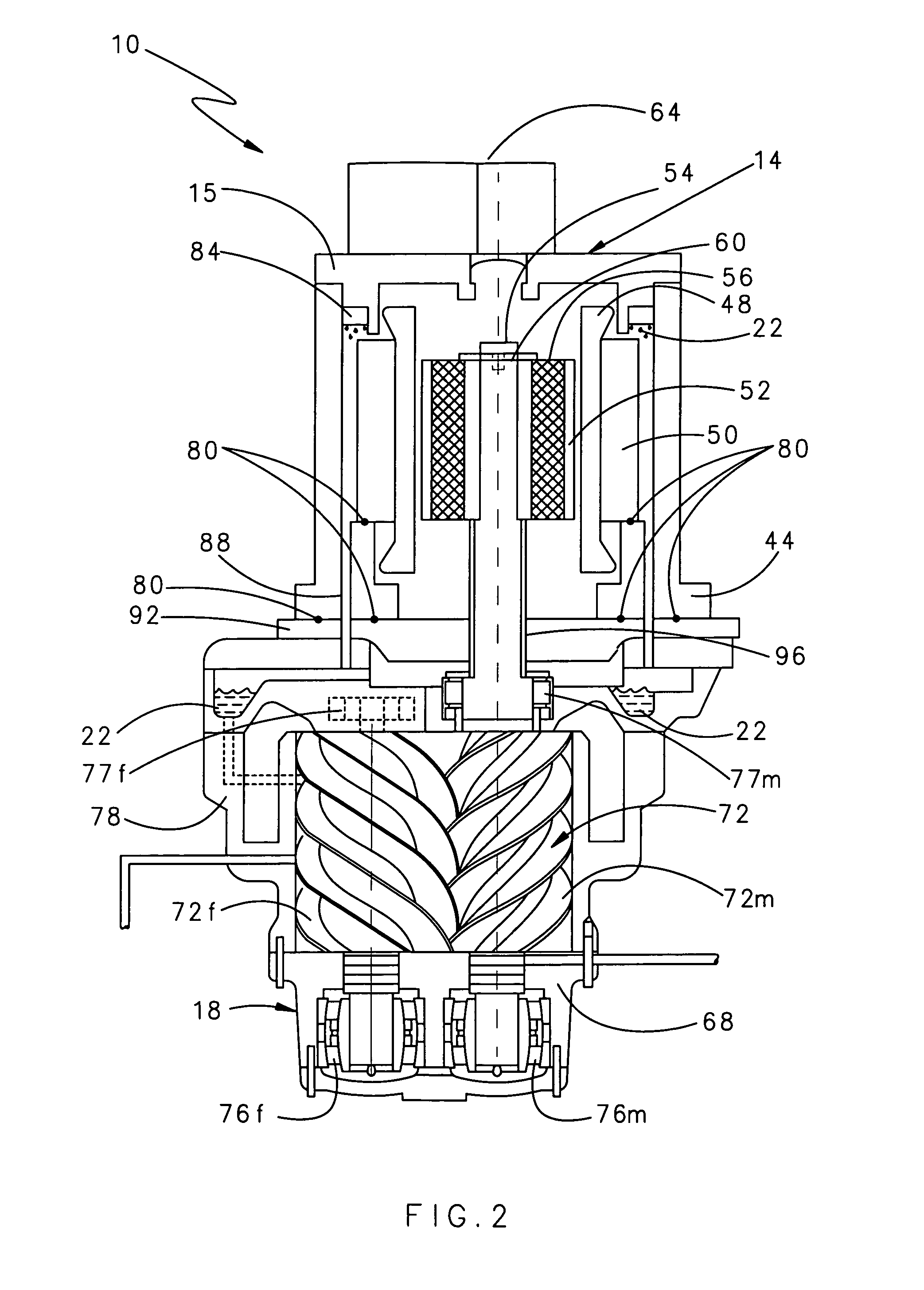
InactiveUS20080181804A1Reduced service lifeEliminate pollutionDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesEngine of counter-engagement typePlastic materialsOil free
A drive transmission mechanism for transmitting torque between two or more rotary shafts in synchronization with one another without need for lubrication thereby eliminating occurrence of oil contamination, and an oil-free fluid machine equipped with the mechanism, are provided. A magnetic drive disk 16 and a synchronization gear 18 are attached to a rotary shaft 14 connected to a drive motor 11, a magnetic drive disk 17 and a synchronization gear 19 is attached to a rotary shaft 15, torque transmission from the rotary shaft 14 to the rotary shaft 15 is carried out in two ways, via the magnetic drive disks 16, 17 and via the synchronization gears 18, 19, and at least one of the synchronization gears is made of plastic material. With the construction, torque transmit load between the rotary shafts via the synchronization gears is decreased, and a plastic gear or gears can be adopted for synchronization gears without reducing life of the gears without need for lubrication oil.
Owner:ANEST IWATA CORP
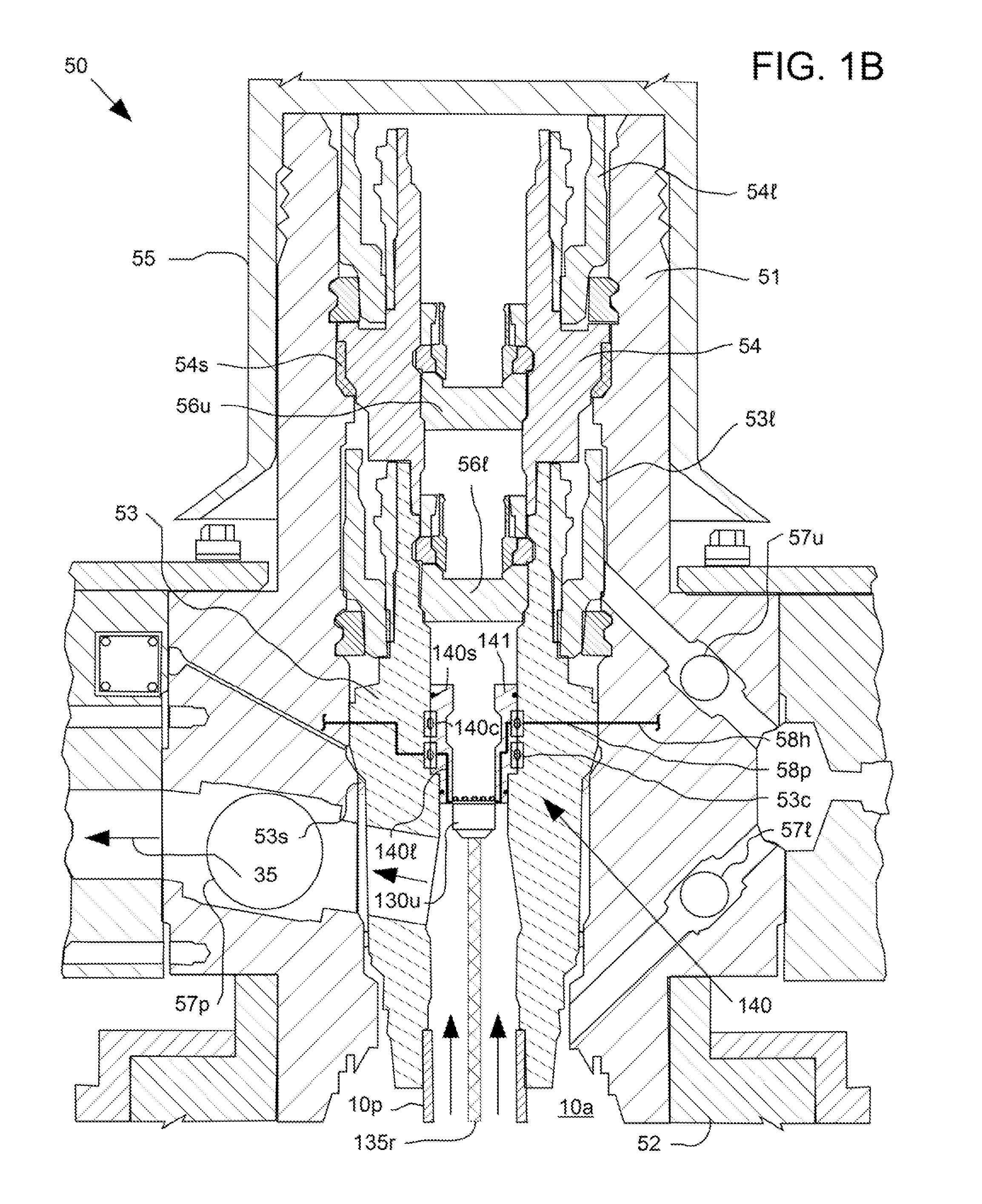
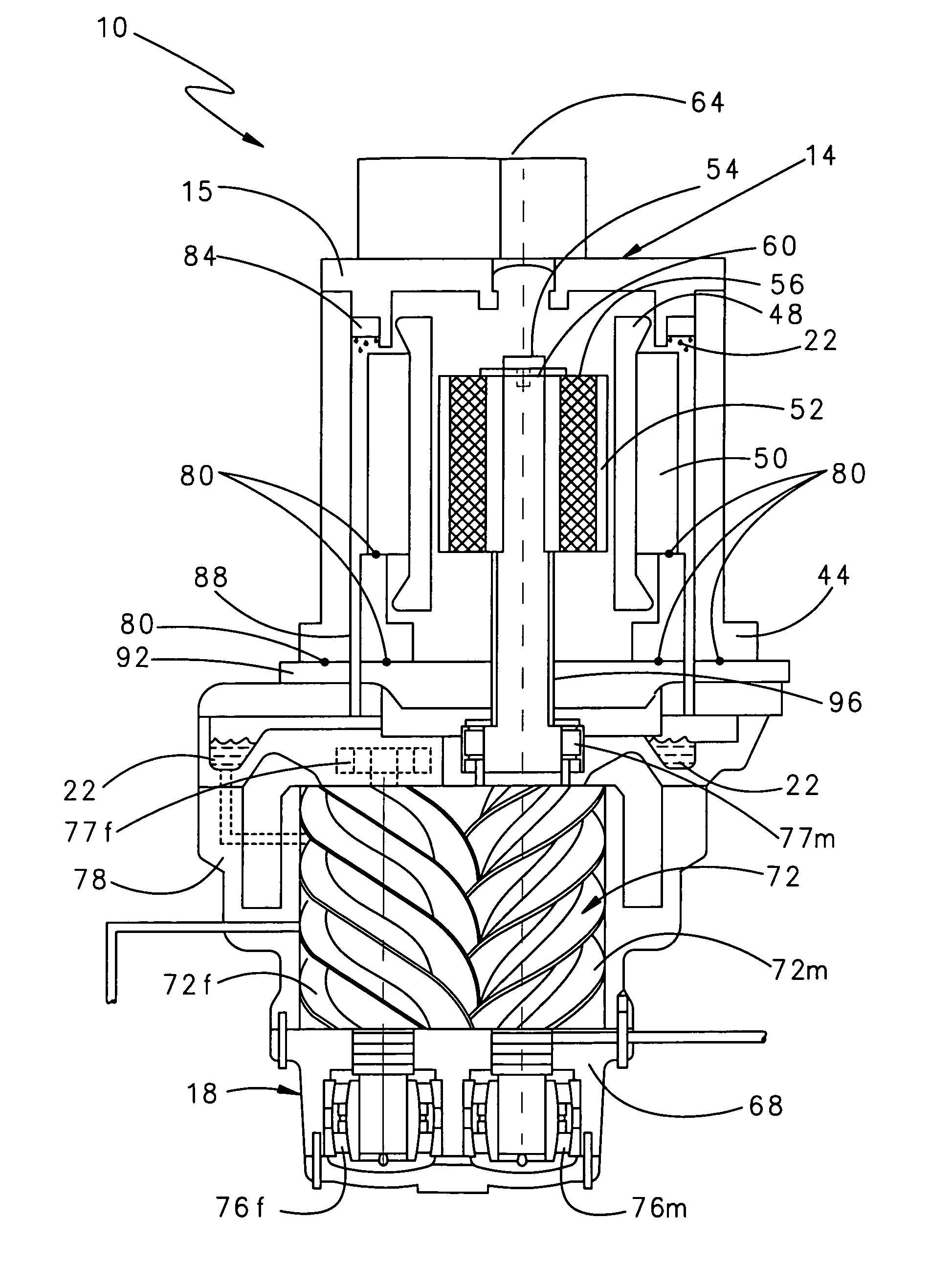
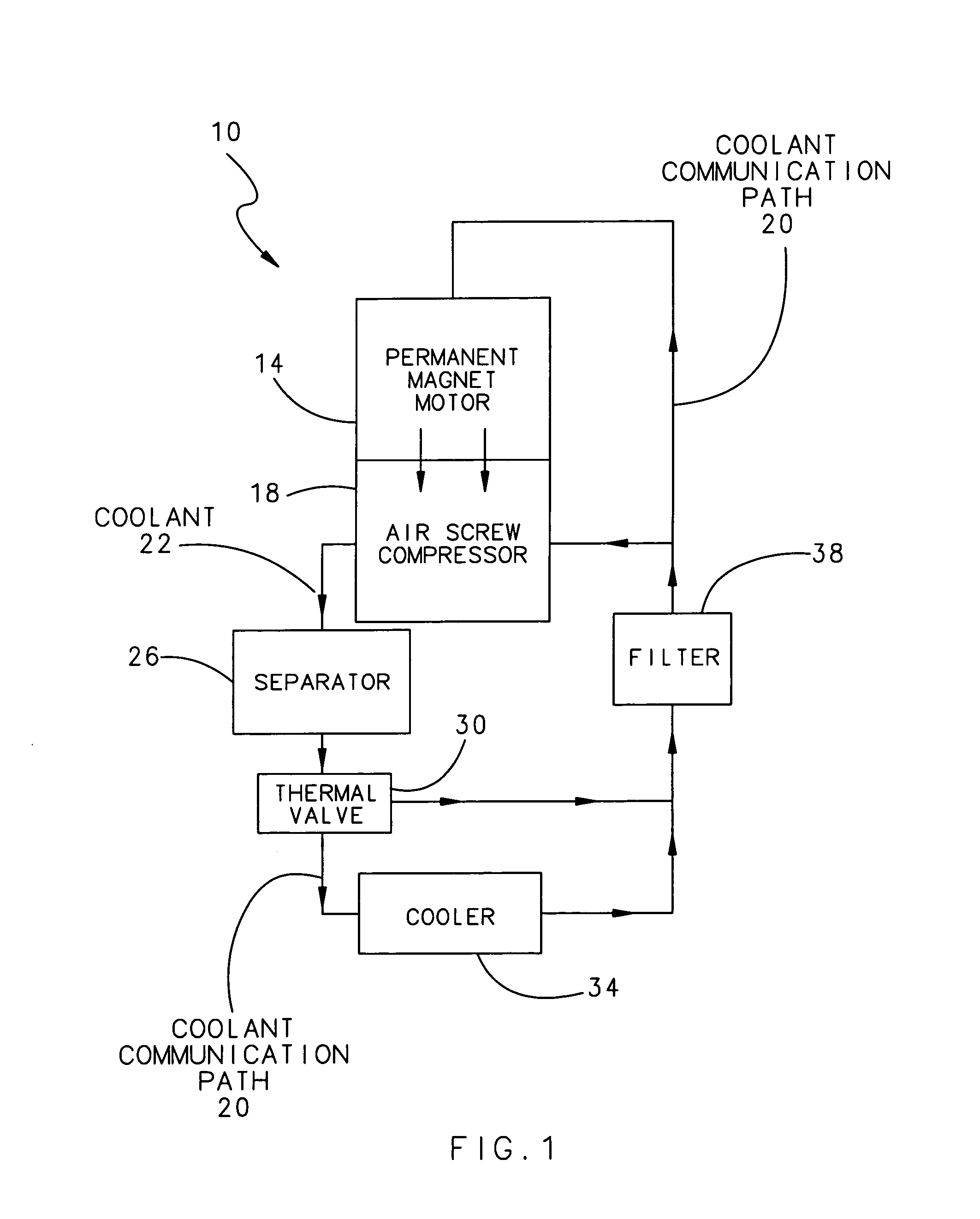
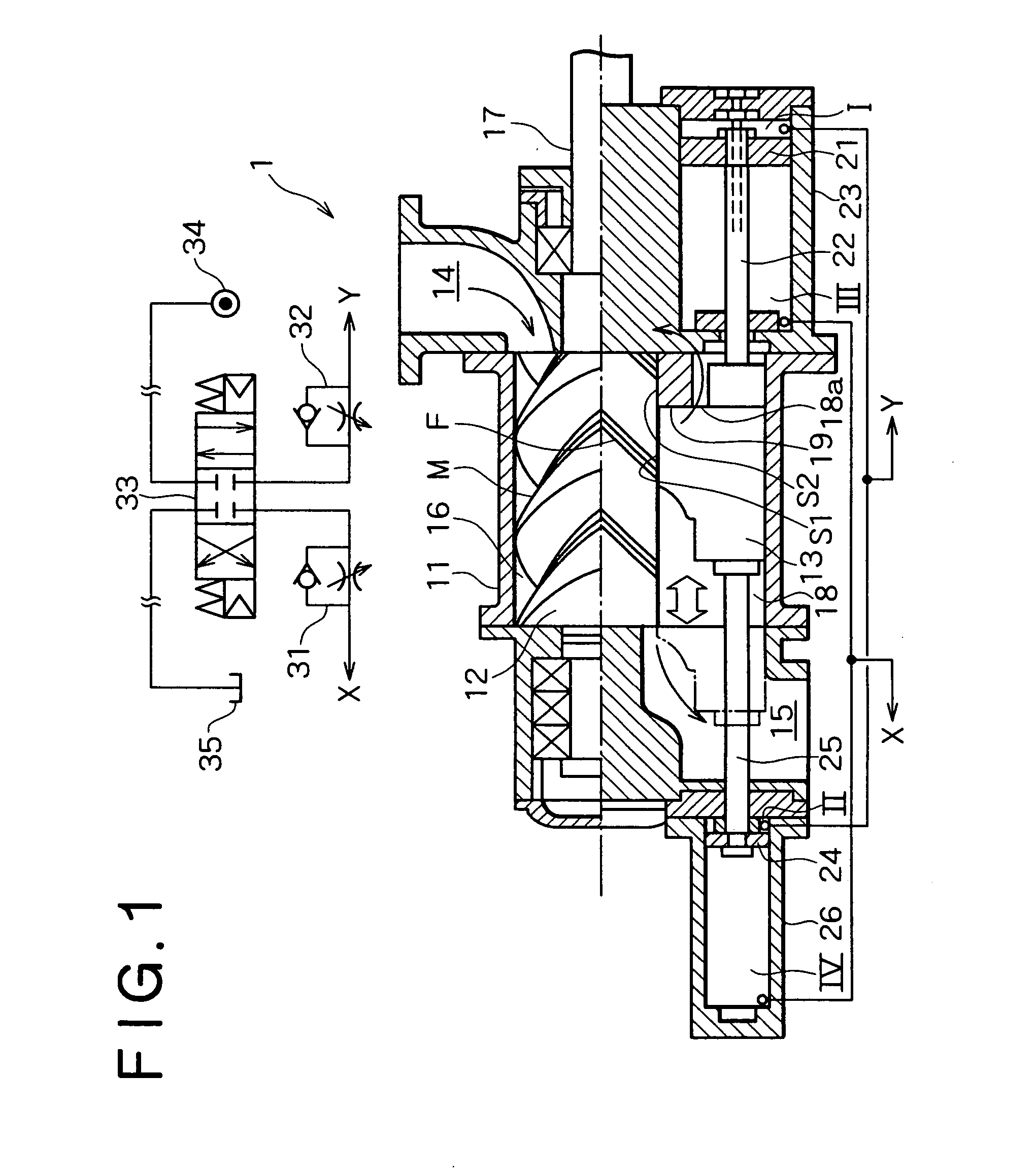
Lubricant cooled integrated motor/compressor design
InactiveUS20070241627A1Prevent overboard leakageThe process is compact and efficientRotary/oscillating piston combinations for elastic fluidsEngine of counter-engagement typePermanent magnet motorGear train
A compressor system according to the present invention utilizes direct rotational input from a permanent magnet motor to generate compressed air. The permanent magnet motor is mounted directly to an air screw compressor. The rotational input is provided by the permanent magnet motor to the air screw compressor without a gear train. The permanent magnet motor and associated variable speed drive controls the rotational speed of the permanent magnet motor and hence the screw compressor. Differing motors may selectively mount, and provide rotational input to, the air screw compressor.
Owner:SULLAIR CORP
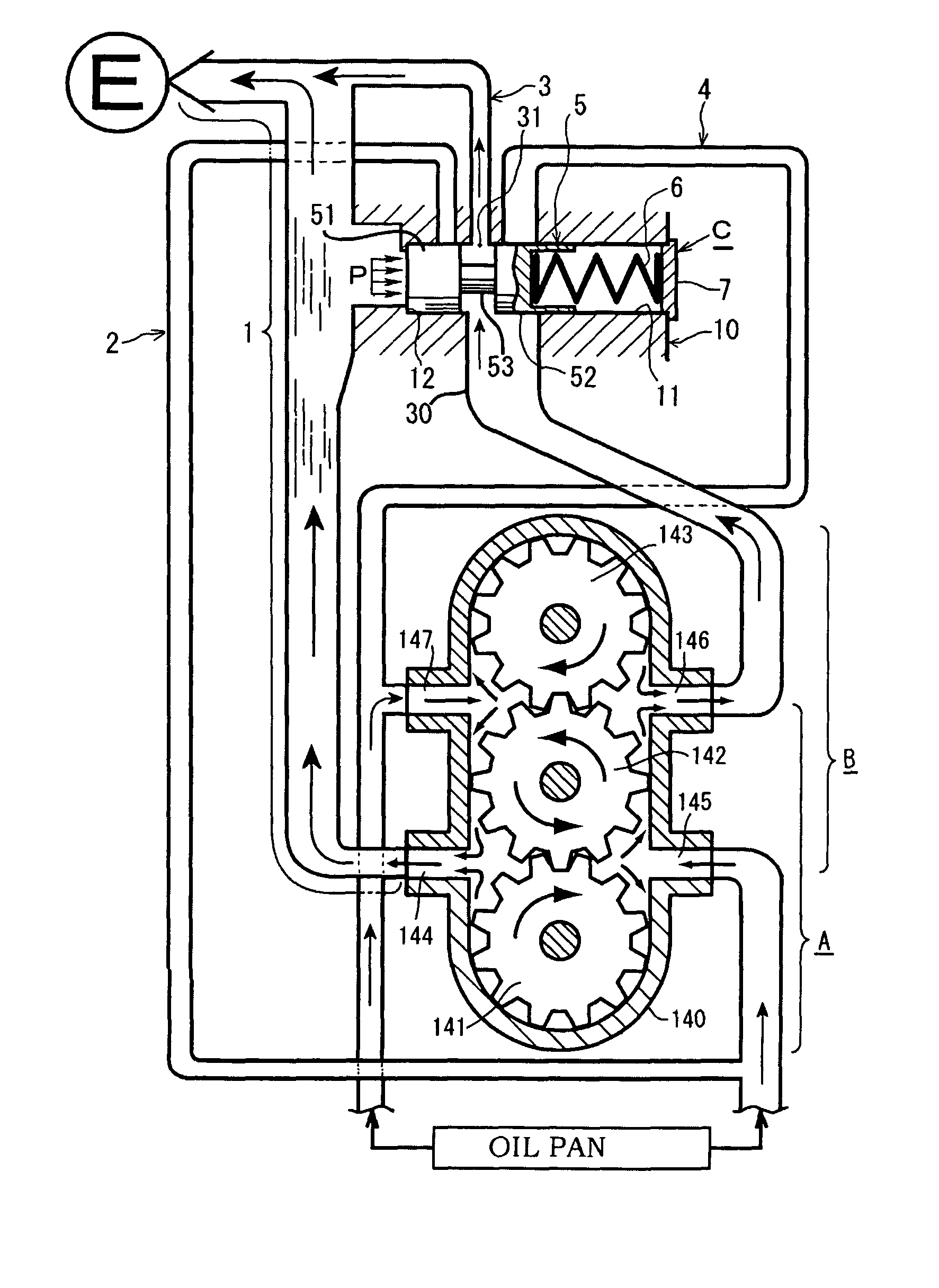
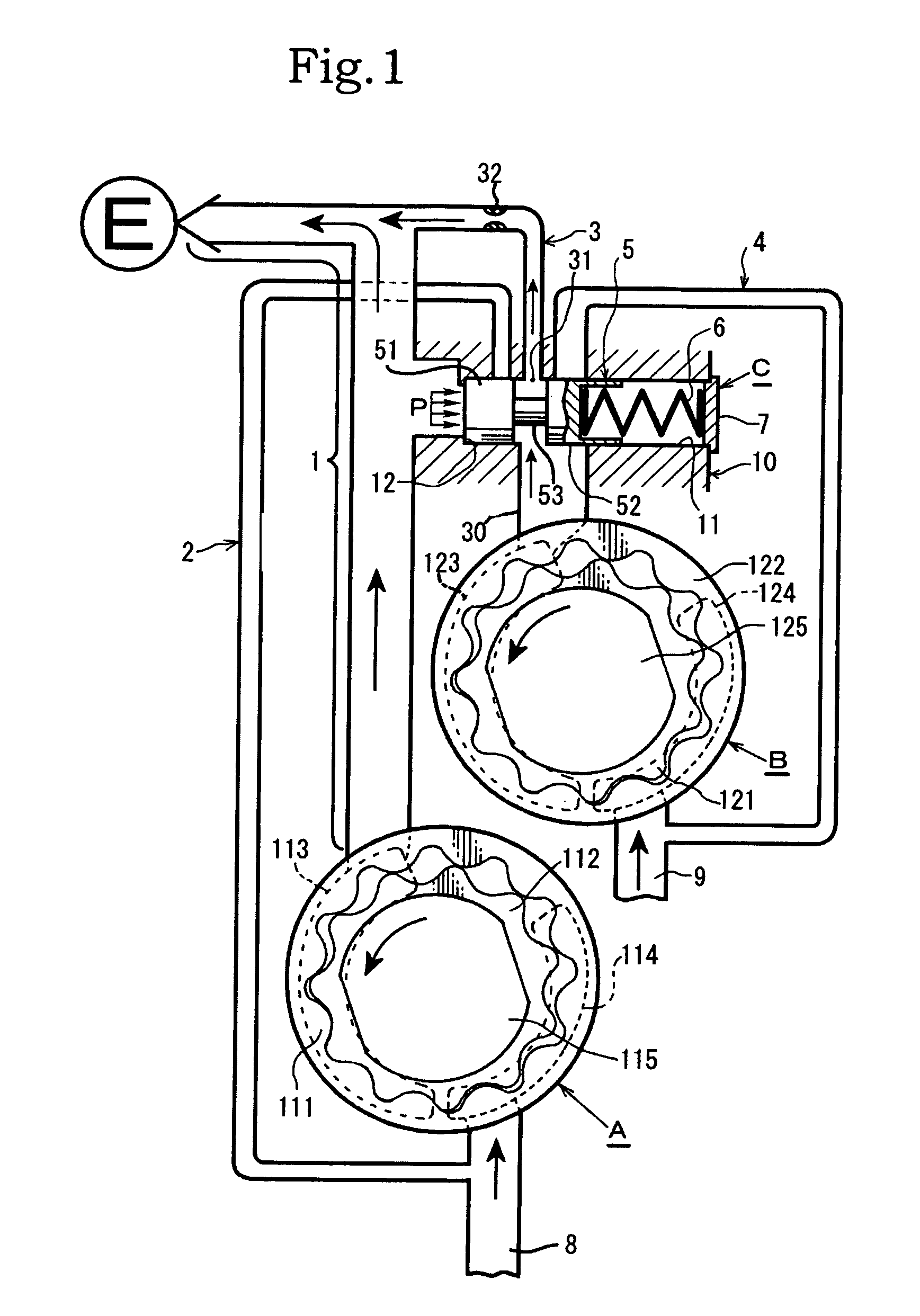
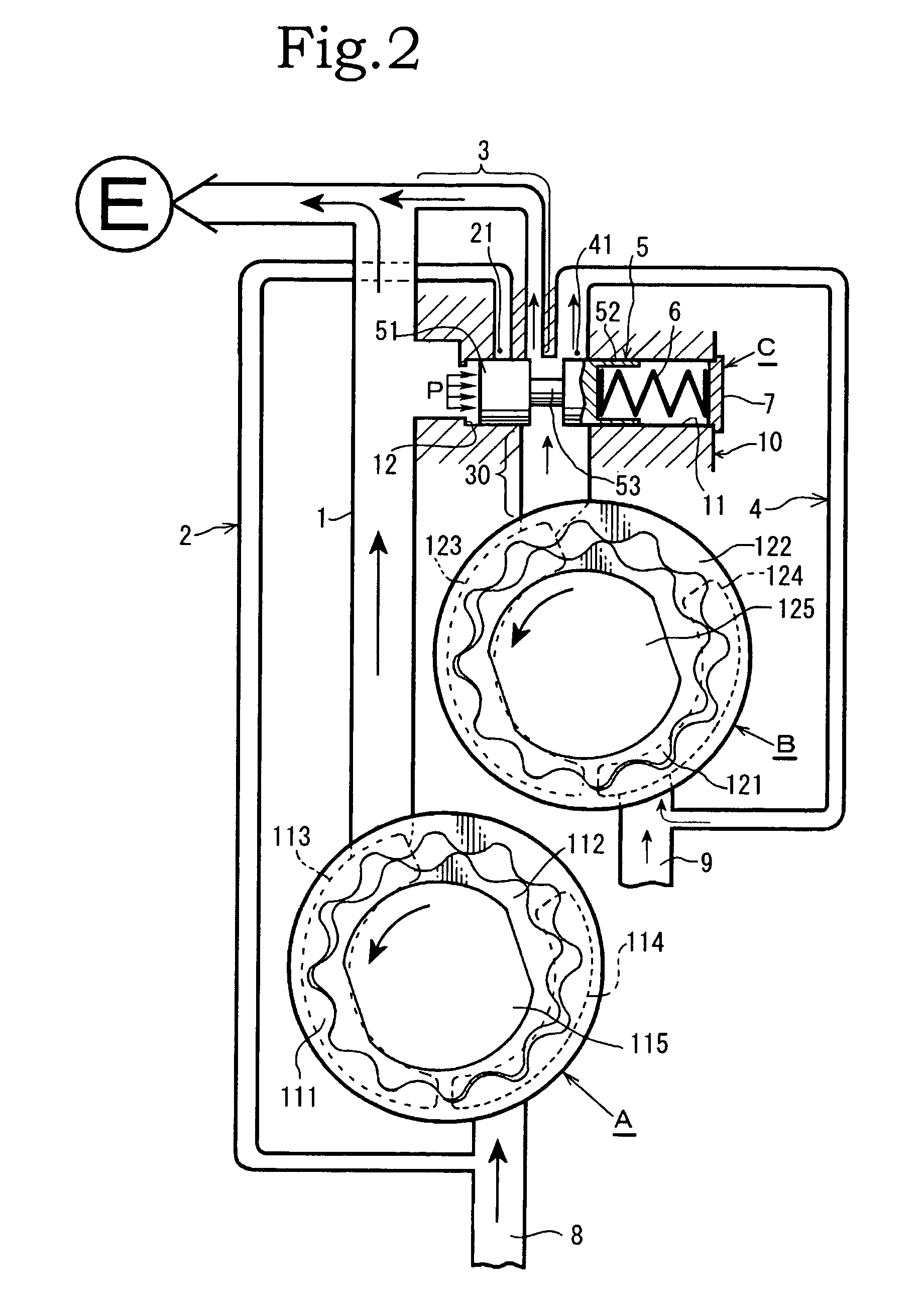
Oil pump pressure control device
InactiveUS8038416B2Drop in overall pump pressureWork moreOscillating piston enginesEngine of counter-engagement typeControl valvesReturn channel
A device including a first discharge passage from a first rotor assembly to an engine, a first return passage that returns to an intake side of the first rotor assembly, a second discharge passage from a second rotor assembly to the engine, a second return passage that returns to an intake side of the second rotor assembly, and a pressure control valve whose valve main body is provided between a discharge port from the second rotor assembly and the first discharge passage. The first discharge passage and the second discharge passage are coupled, and a flow passage control is executed in each of: a low revolution range; an intermediate revolution range; and a high revolution range.
Owner:YAMADA MANUFACTURING CO LTD
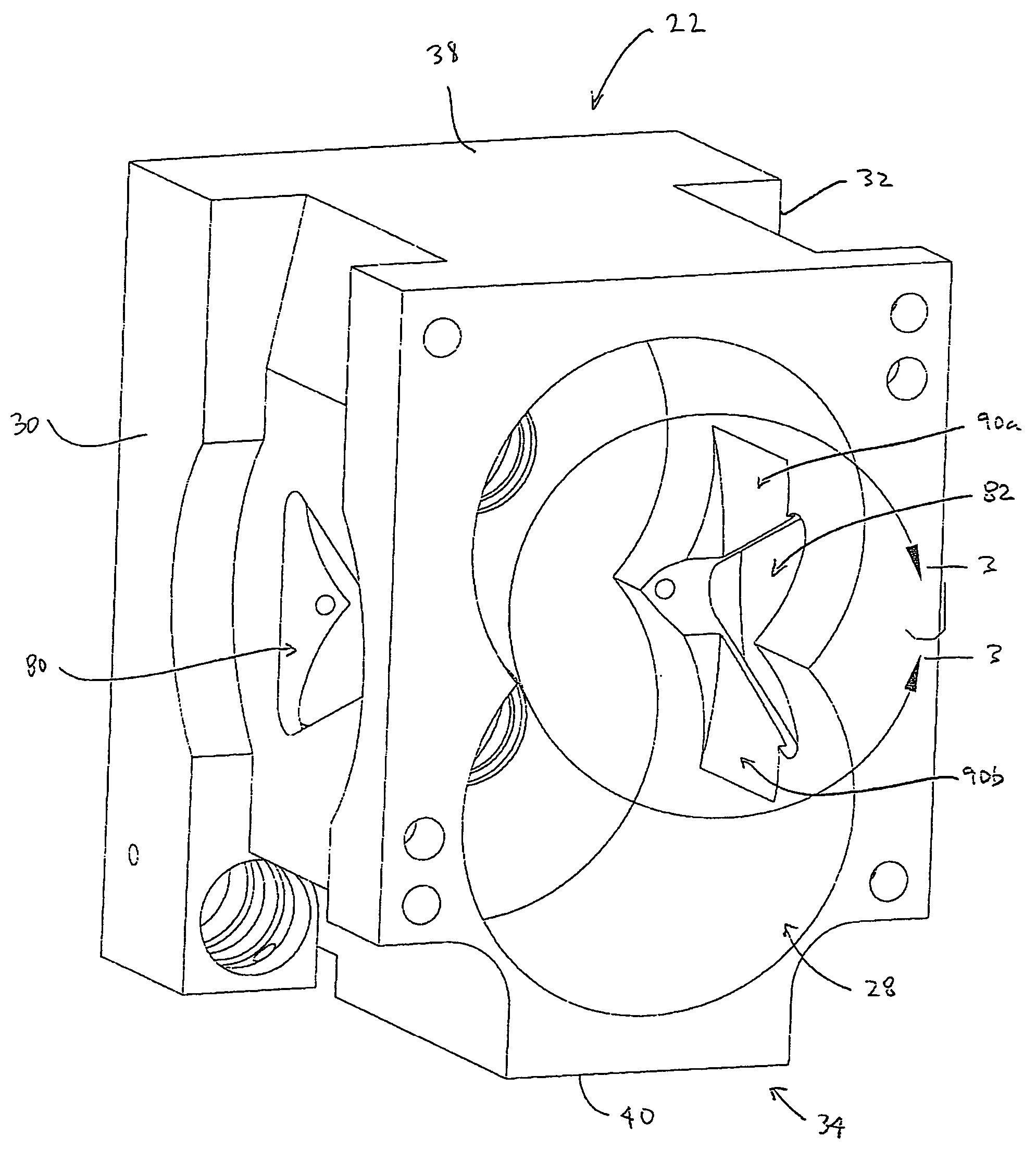
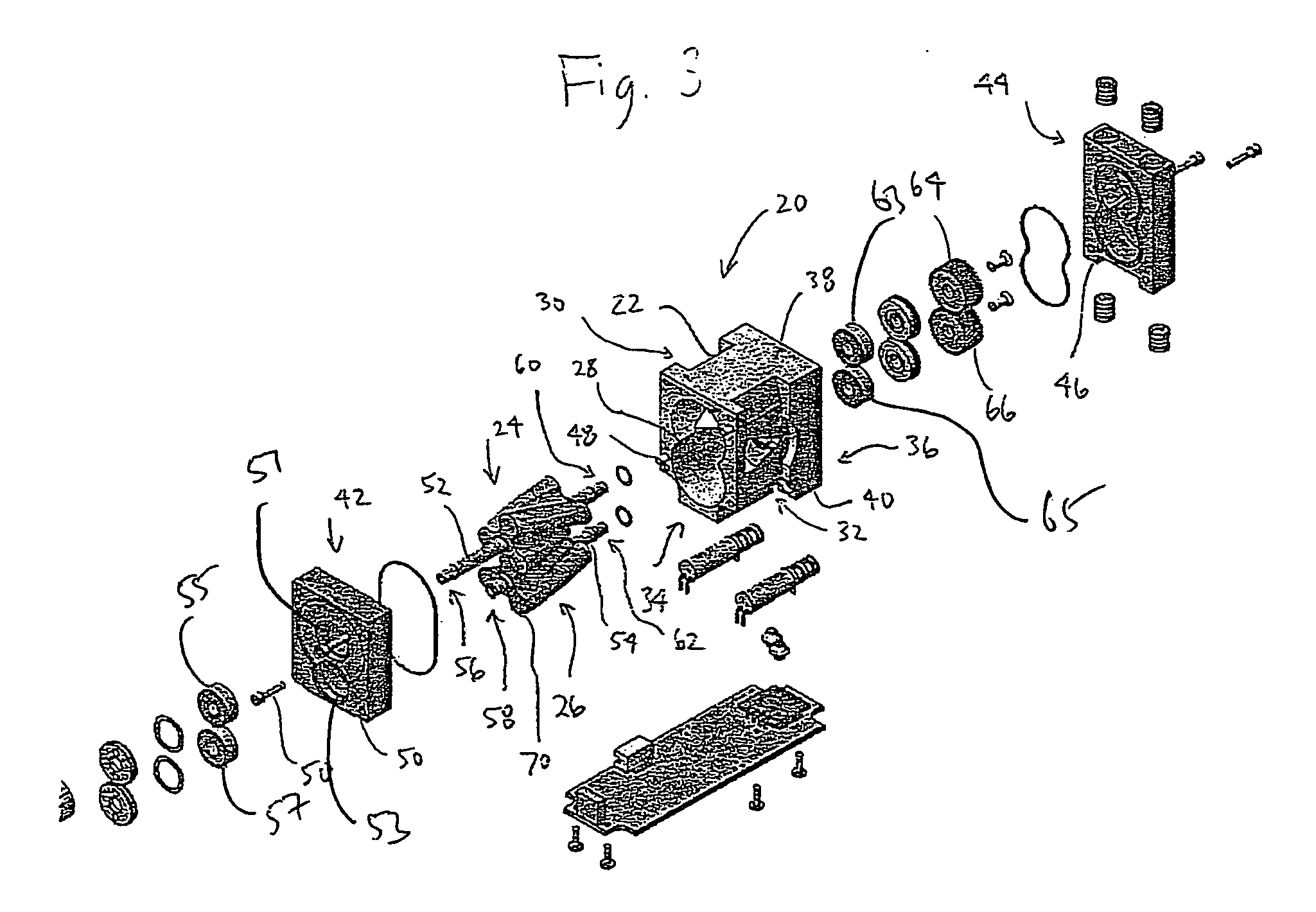
Method and apparatus for reducing noise in a roots-type blower
InactiveUS20050112013A1Reduce noisePhysical therapyEngine of counter-engagement typeNoise levelEngineering
A Roots-type blower comprises a housing defining a rotor chamber and an inlet and outlet to the rotor chamber. First and second rotors are mounted in the rotor chamber, each rotor defining a plurality of lobes, adjacent lobes and the housing cooperating to define gas transport chambers. The blower is configured so that a net flow rate of gas into a gas transport chamber is generally or approximately constant, whereby a change in gas pressure in the gas transport chamber is generally or approximately linear, as the gas transport chamber approaches the outlet. In one embodiment, this is accomplished by providing flow channels extending from the outlet towards the inlet, and from the inlet towards the outlet, corresponding to each rotor. The flow channels permit gas to flow from the high pressure outlet to a gas transport chamber and from the gas transport chamber to the low pressure inlet. The resulting amelioration of pressure spikes associated with flow back substantially reduces the operational noise level of the blower.
Owner:PULMONETIC SYST
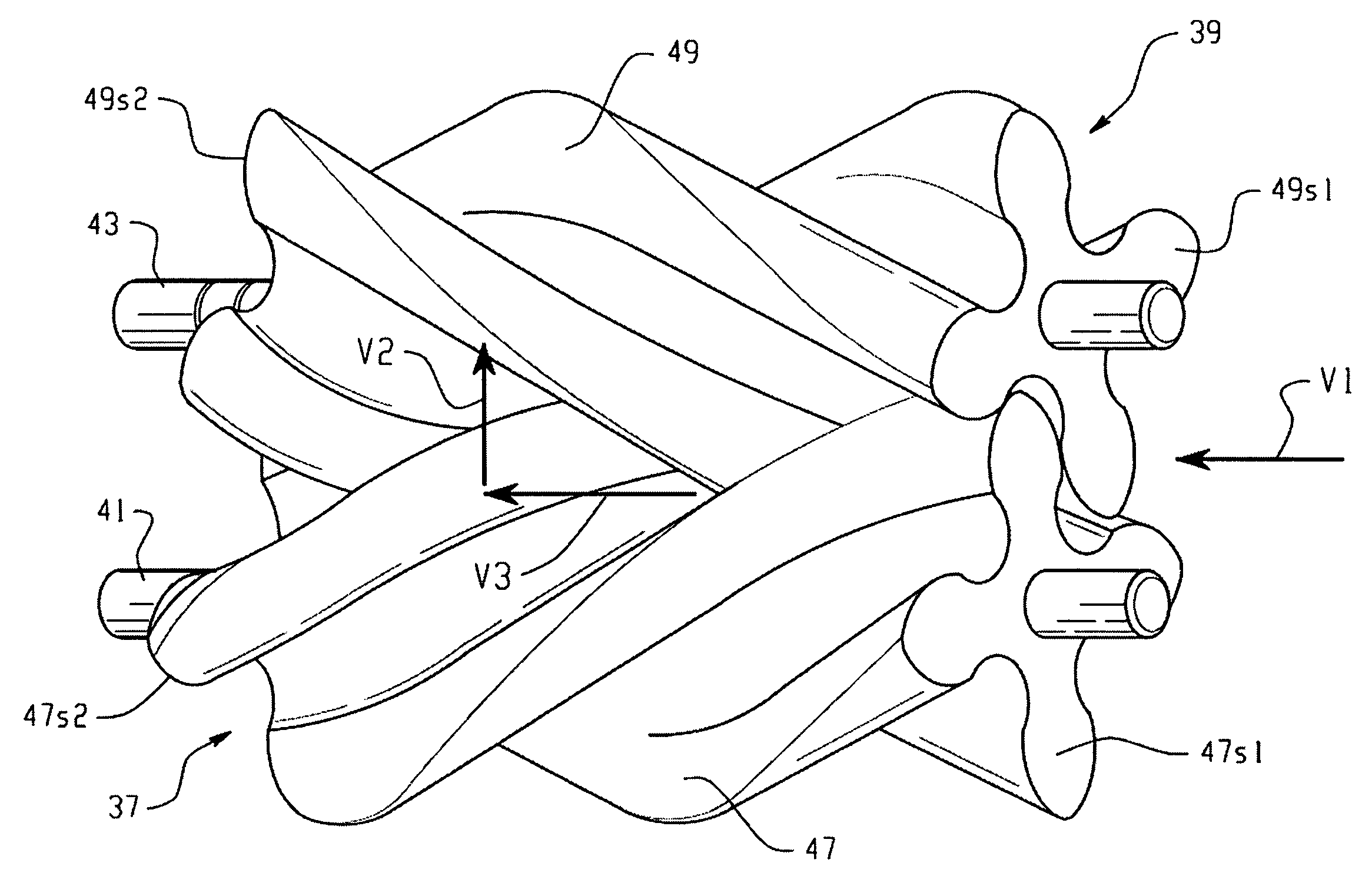
Optimized helix angle rotors for Roots-style supercharger
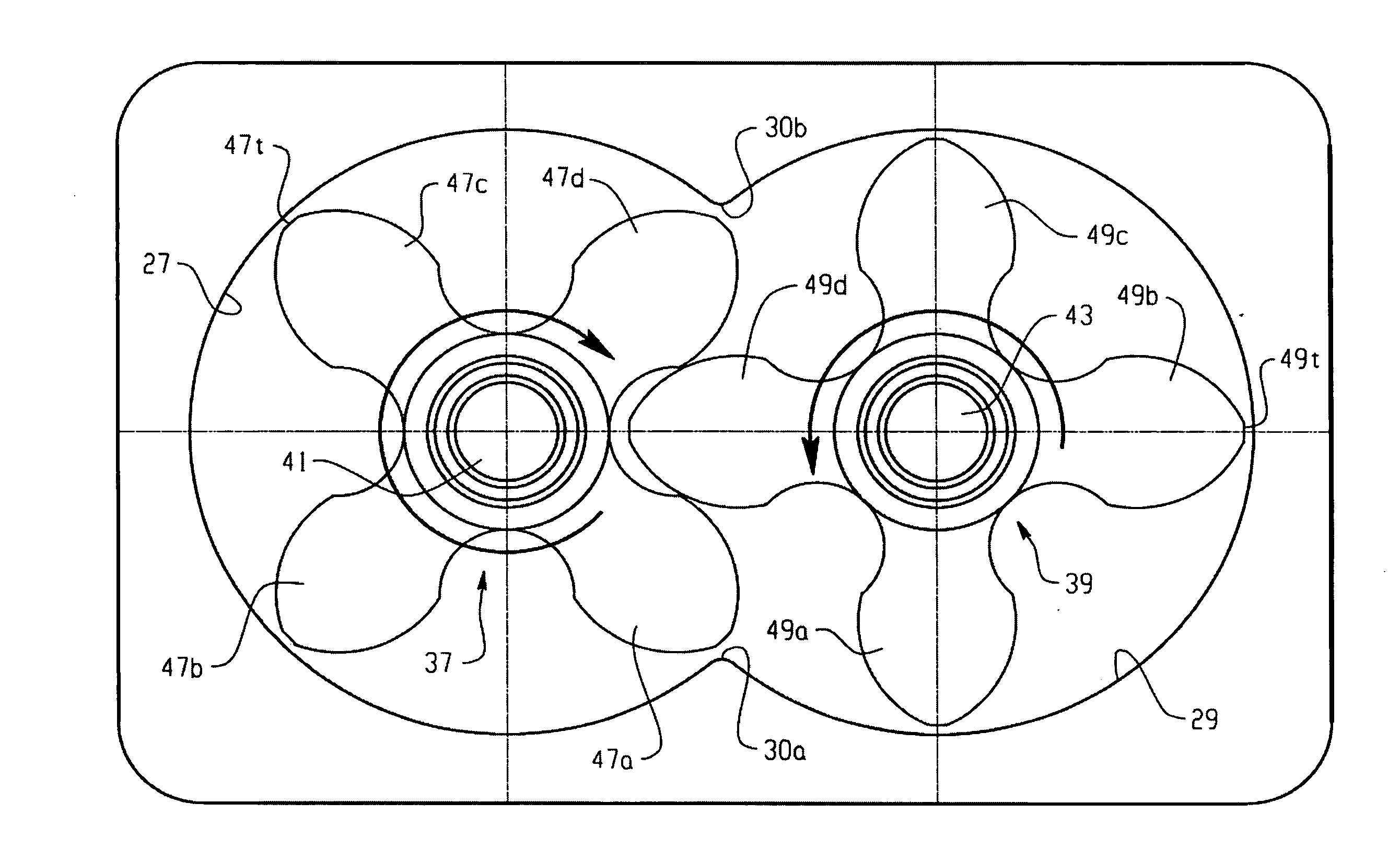
ActiveUS7488164B2Improve blower efficiencyImprove thermal efficiencyOscillating piston enginesEngine of counter-engagement typeEngineeringHelix angle
A method of designing rotors for a Roots blower comprising a housing having cylindrical chambers, the housing defining an outlet port (19). The blower includes meshed, lobed rotors (37,39) disposed in the chambers, each rotor including a plurality N of lobes (47,49), each lobe having first (47a,49a) and second (47b,49b) axially facing end surfaces. Each lobe has its axially facing surfaces defining a twist angle (TA), and each lobe defines a helix angle (HA). The method of designing the rotor comprises determining a maximum ideal twist angle (TAM) for the lobe as a function of the number N of lobes on the rotor, and then determining a helix angle (HA) for each lobe as a function of the maximum ideal twist angle (TAM) and an axial length (L) between the end surfaces of the lobe. A rotor designed in accordance with this method is also provided.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
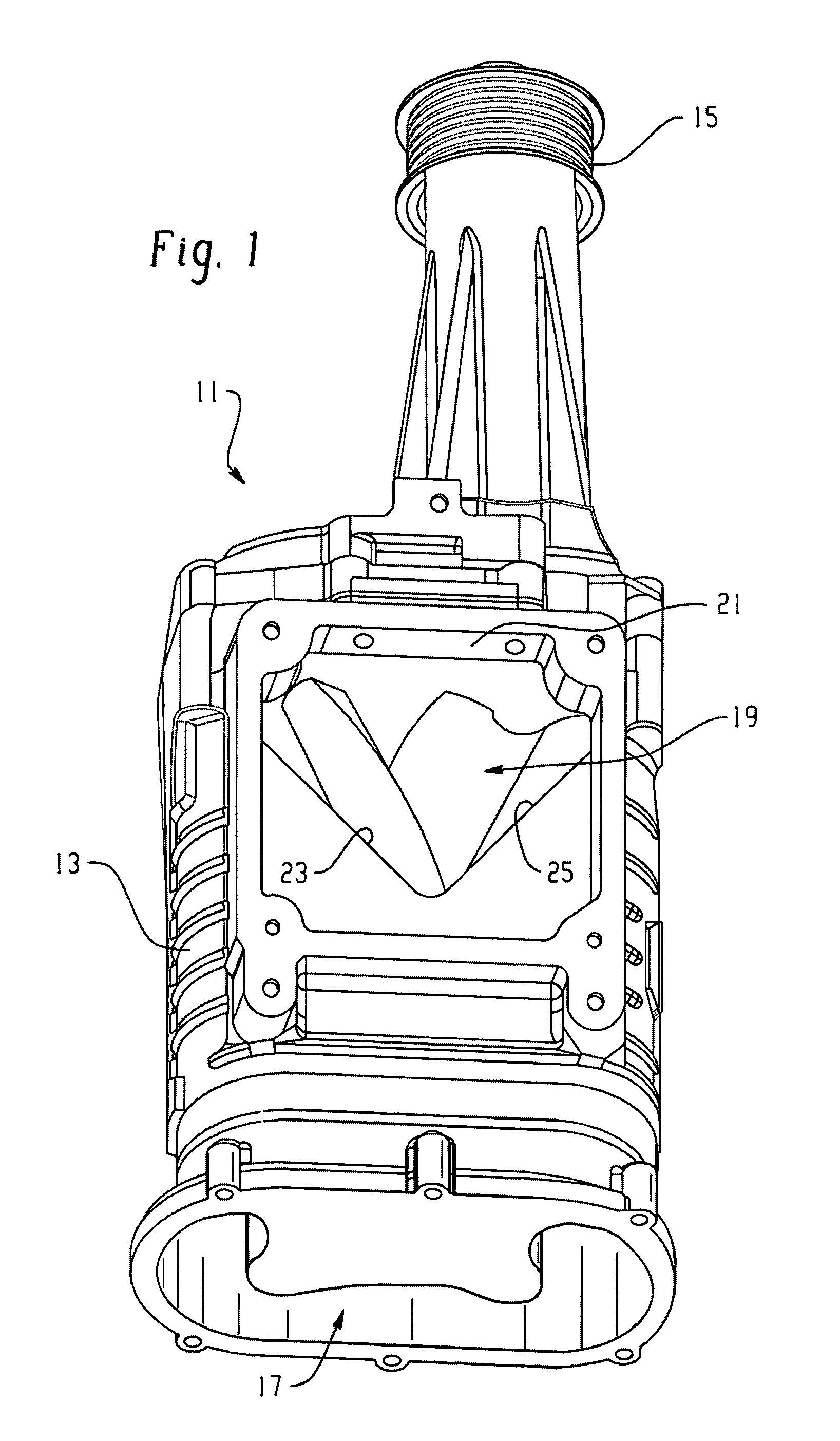
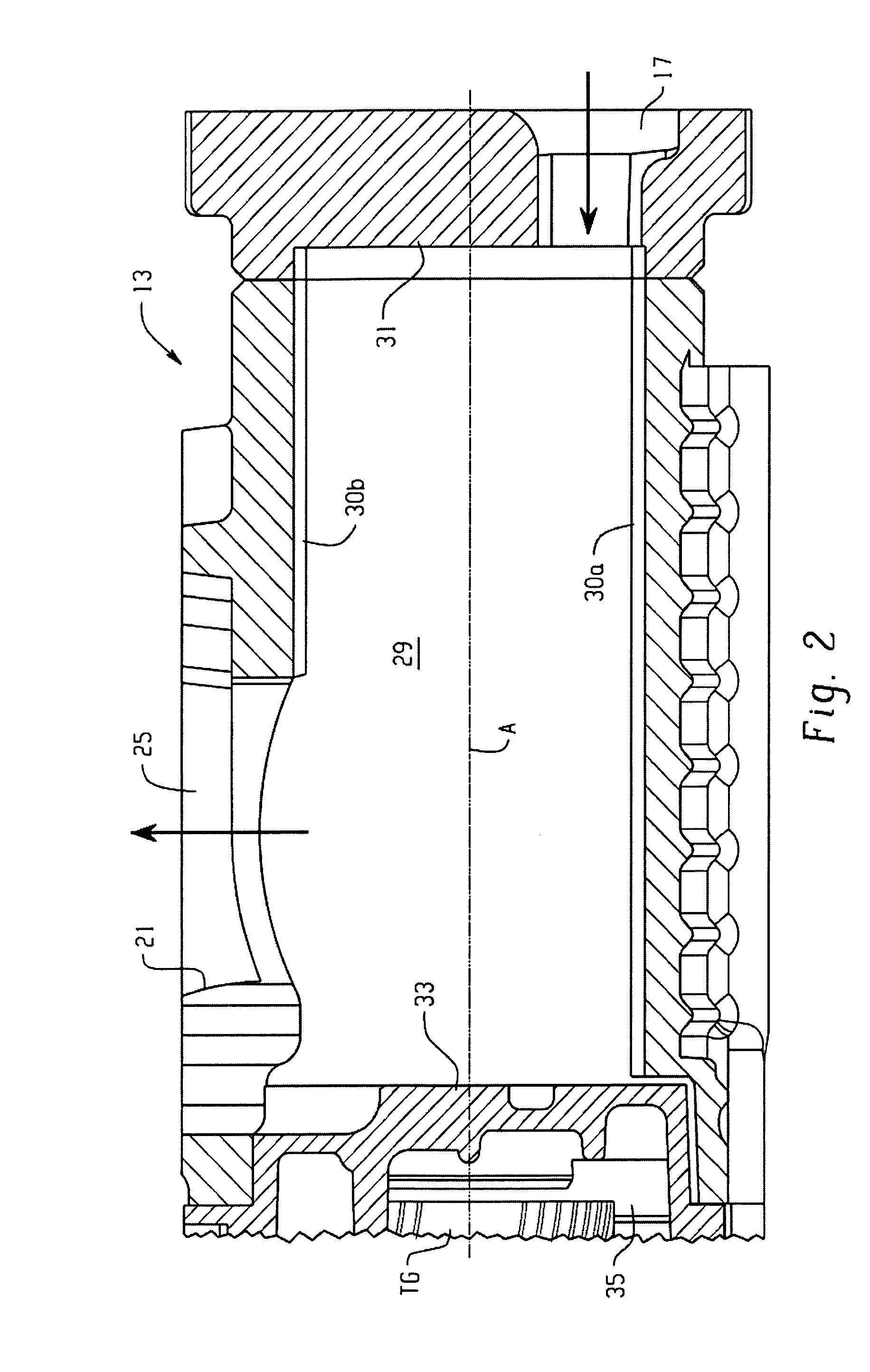
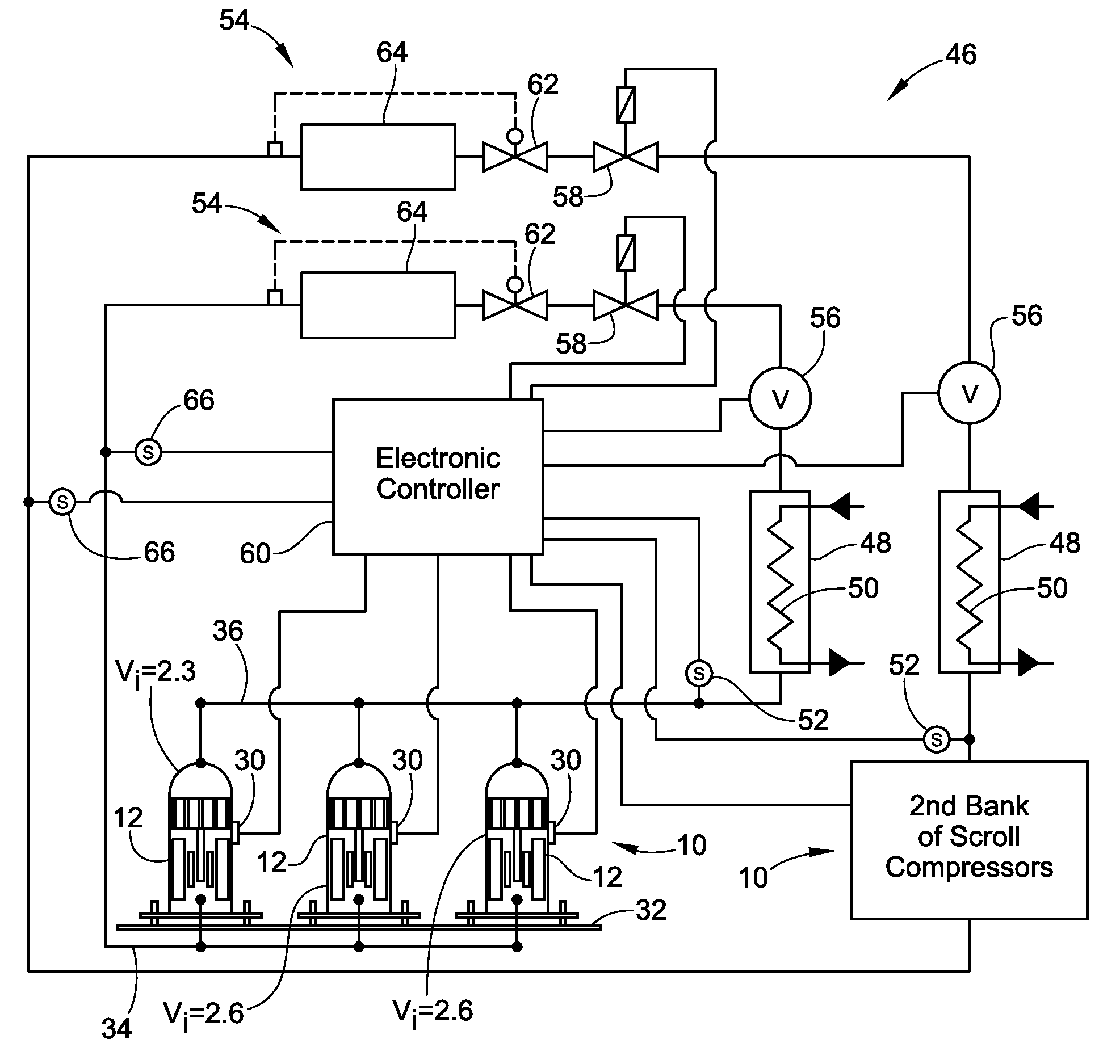
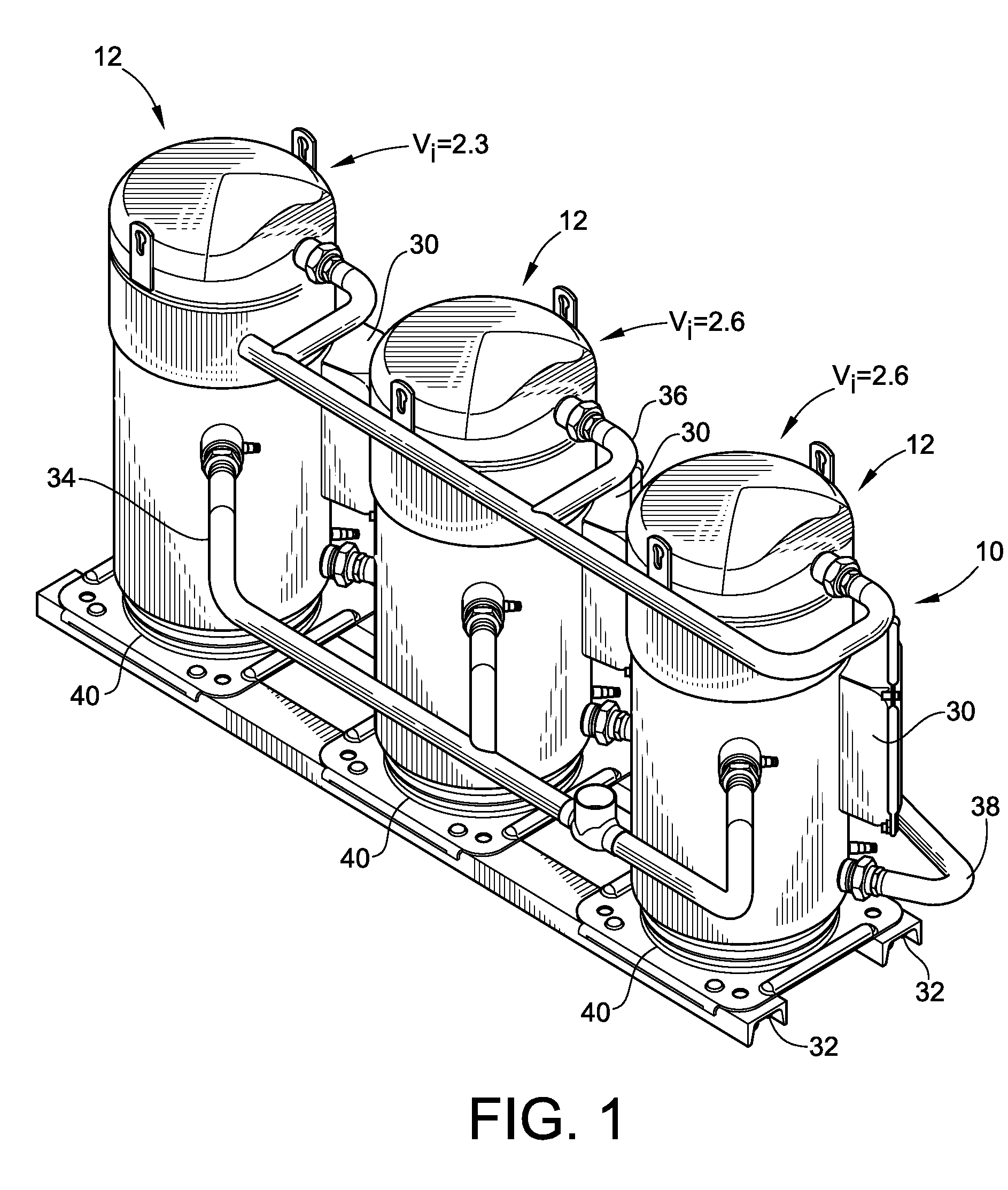
Scroll Compressors with Different Volume Indexes and Systems and Methods for Same
InactiveUS20100186433A1Improve efficiencyRotary/oscillating piston combinations for elastic fluidsCompressorEngineeringScroll compressor
Owner:BITZER KUEHLMASCHINENBAU GMBH
Method of controlling a gear pump as well as an application of the method
ActiveUS20100322805A1Reduce impactOscillating piston enginesEngine of counter-engagement typeGear pumpGear wheel
A method of controlling a gear pump comprising two meshing gear wheels (11, 12), wherein the two gear wheels (11, 12) are driven via respective shafts (2, 3) each by a drive unit (7, 8). A current position of the one gear wheel (11, 12) is determined with respect to the current position of the other gear wheel (12, 11), and the current position of the one gear wheel (11, 12) is continuously adjusted with respect to the current position of the other gear wheel (12, 11) according to specified predefined operating conditions.
Owner:MAAG PUMP SYST TEXTRON
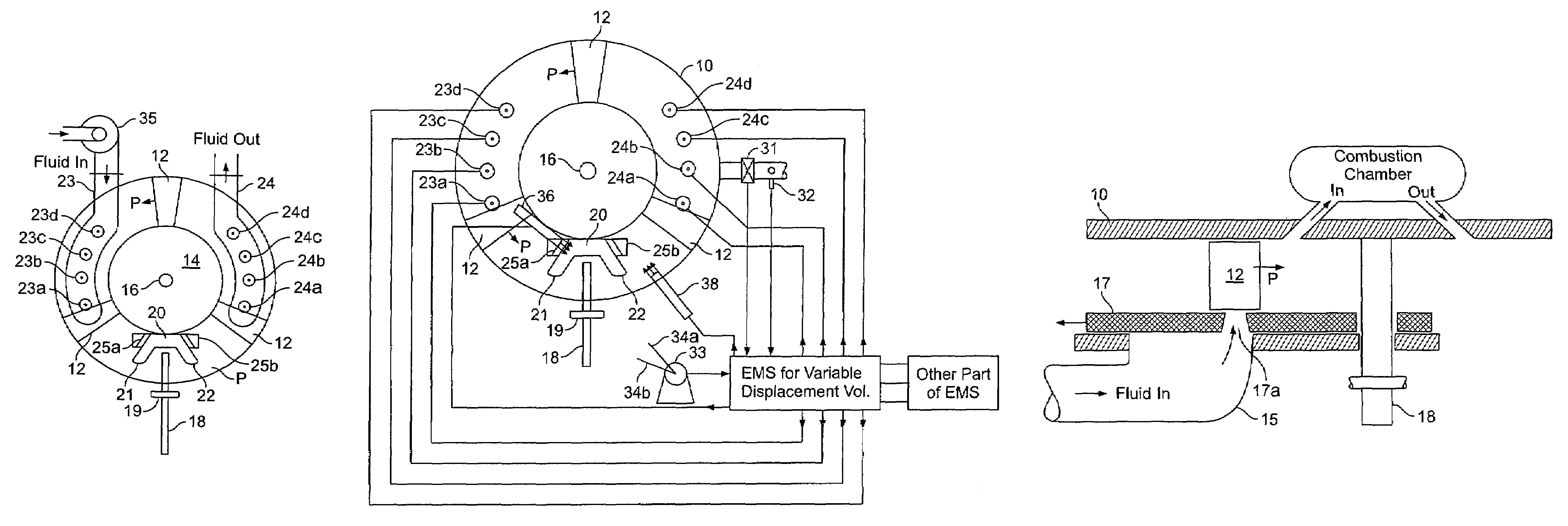
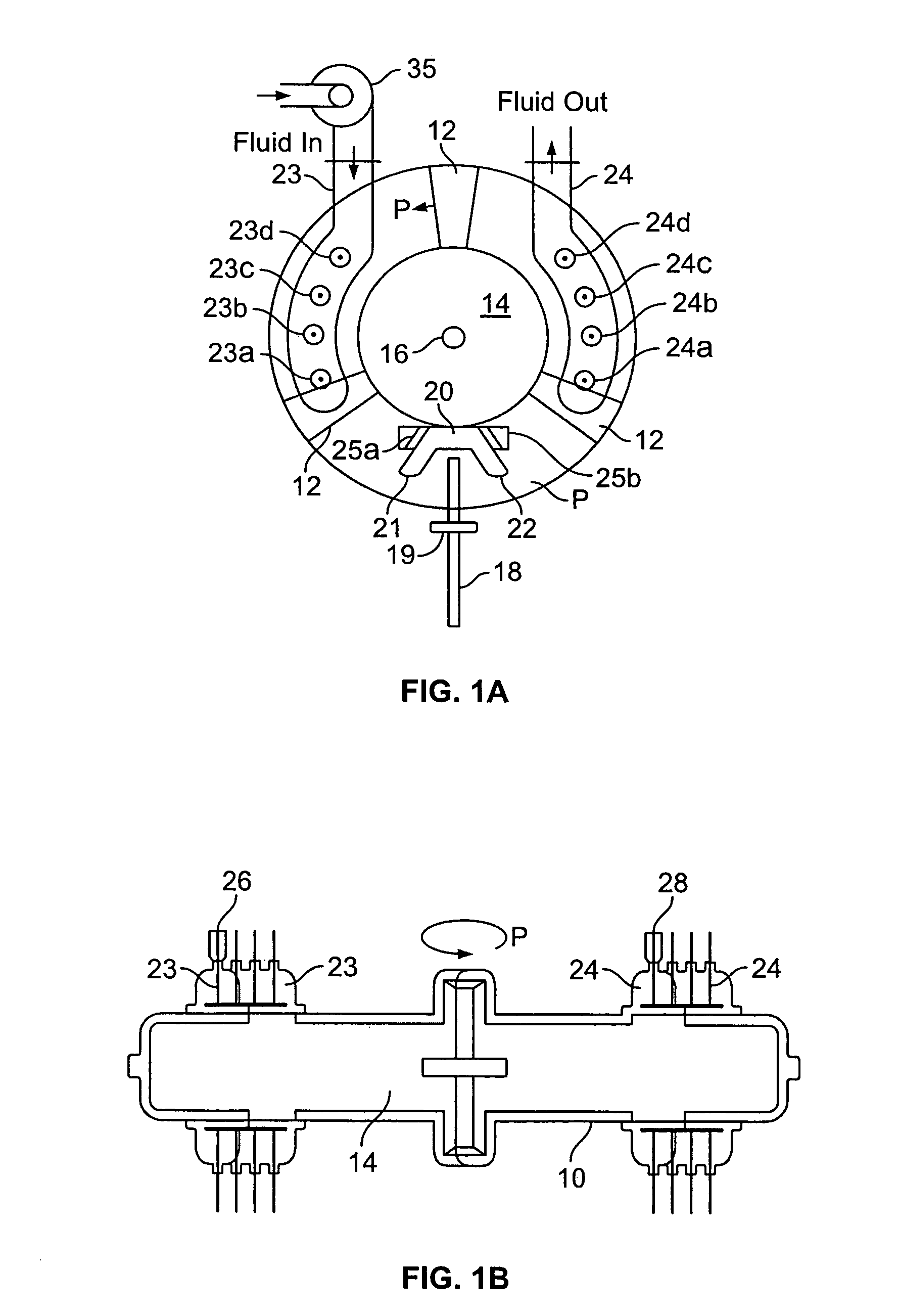
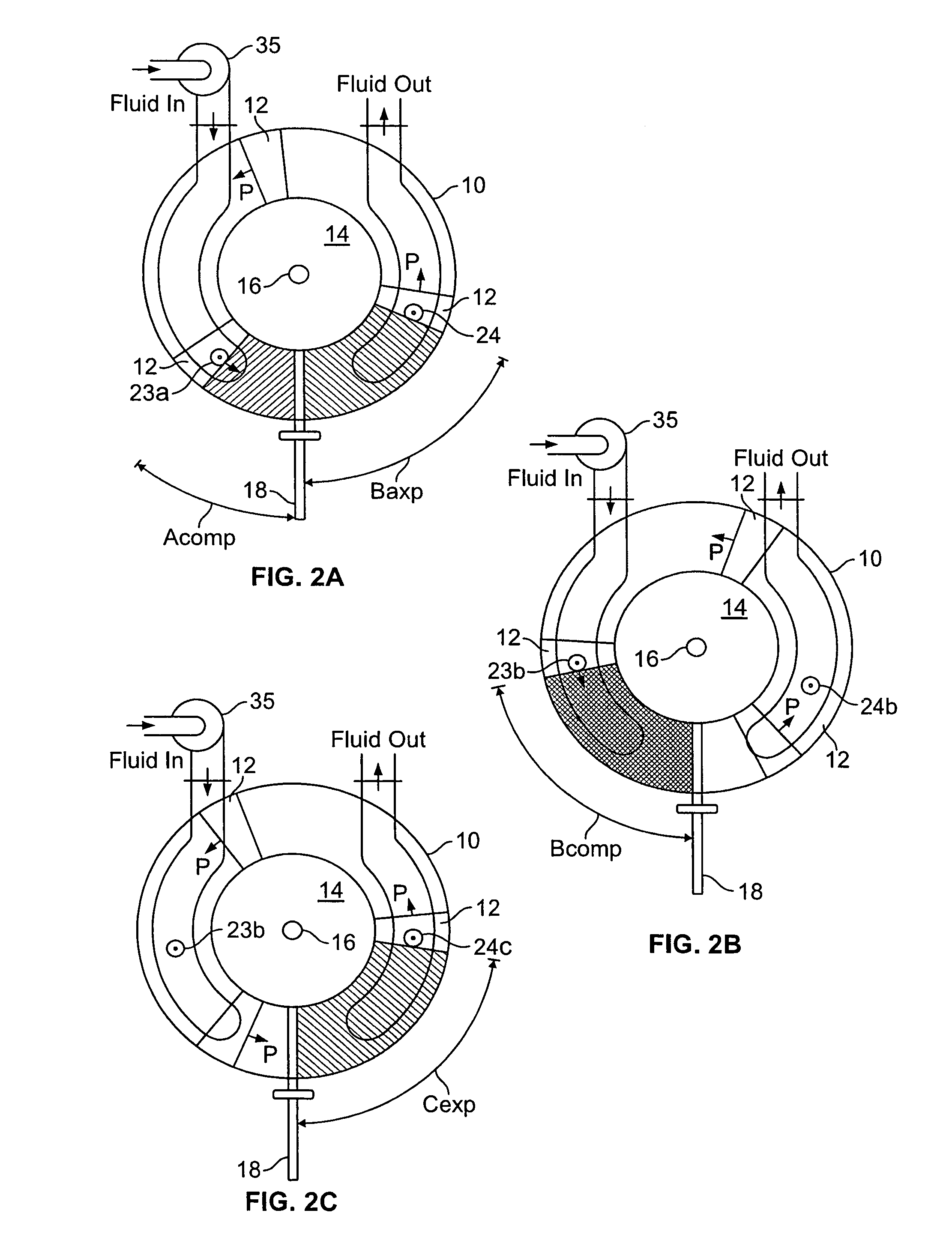
Toroidal engine with variable displacement volume
InactiveUS7341041B2Increase consumptionImprove efficiencyInternal combustion piston enginesOscillating piston enginesRotary engineEngine management
A novel rotary engine of the kind having a toroidal cylinder and a set of pistons on a rotating circular piston assembly provides instantaneous adjustment of the displacement volume of the engine by varying the intake and expansion stroke length on the circular path of the pistons through the opening and closing of valves into the engine cylinder under the control of an engine management system responsive to the speed / load conditions of the engine and the throttle position.
Owner:VGT TECH
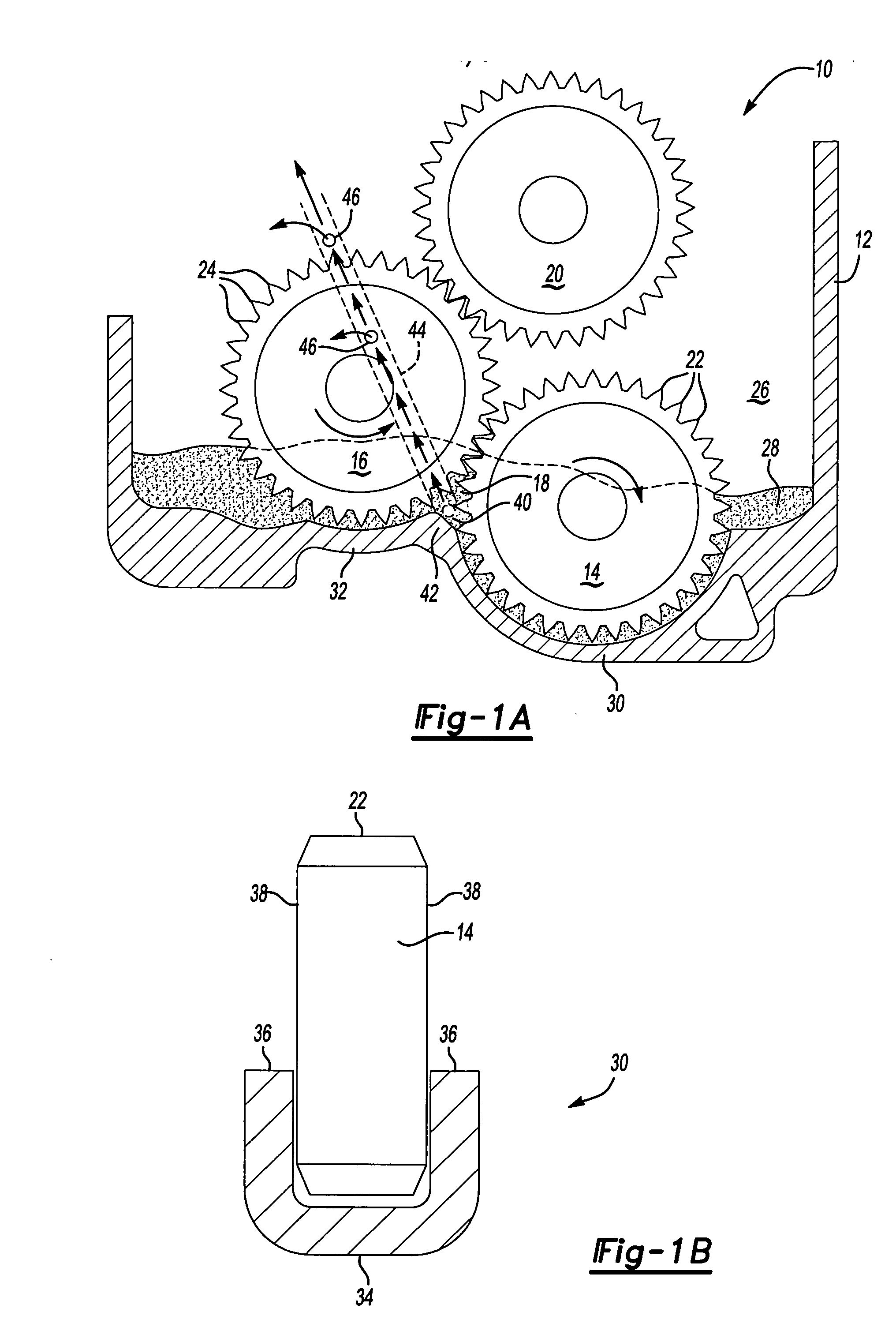
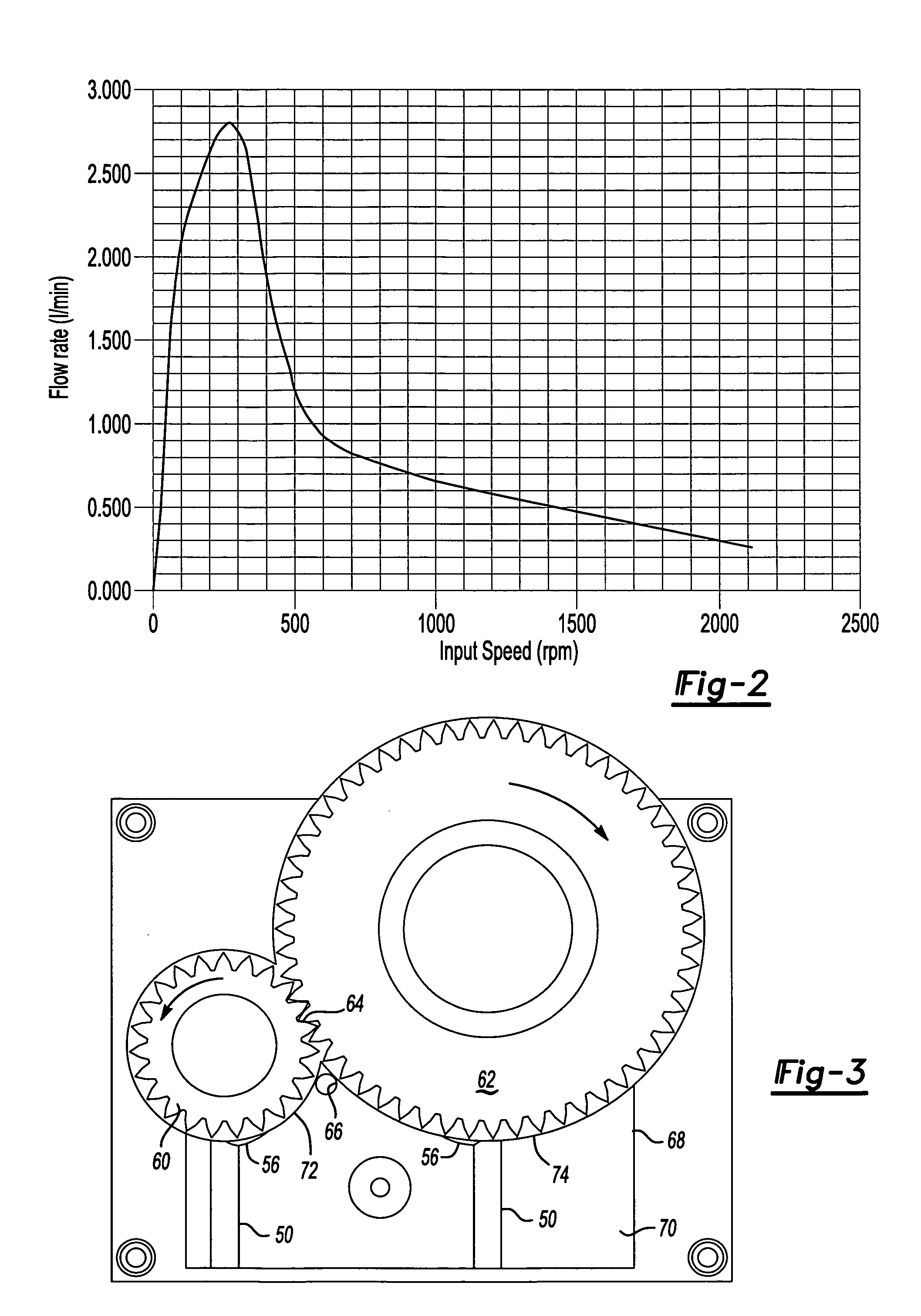
Fluid pump mechanism for use in existing helical gearsets
A fluid pump cowling for attachment to at least a pair of helical drivetrain gears having teeth and lands. The cowling has a pair of sidewalls adapted to extend at least partially over the lands of a first of the pair of drivetrain gears and a curved sump wall extending between the sidewalls that corresponds generally to the outermost circumference of the first gear. A sump channel is defined between the sidewalls on the sump wall adjacent a distal end of the sump wall. The sump channel has a generally frustoconical shape and leads to a fluid outlet opening defined in one of the sidewalls. The cowling is positioned such that the teeth of the pair of helical gears mesh in an area in fluid communication with the sump channel to create an area of high fluid pressure upon rotational movement of the gears with a fluid.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Screw expander system
InactiveUS20120237382A1Reduce device sizeLoss of mechanical powerOscillating piston enginesSealing arrangement for pumpsPetroleum engineeringEvaporator
A screw expander system includes a screw expander provided with an expansion space for expanding an operating medium, an operating medium inlet, an operating medium outlet, oil inlets, and oil outlets, a condenser which condenses a mixture, sent from the screw expander, of oil and the operating medium, a pump which pressure-feeds the mixture sent from the condenser, and an evaporator which evaporates the operating medium contained in the mixture. The screw expander system circulates and supplies the operating medium sent from the evaporator, to the operating medium inlet, and circulates and supplies the oil sent from the evaporator, to the oil inlets. An oil separating tank which separates the mixture into the operating medium and the oil is disposed between the evaporator and the screw expander, and an oil containing section of the oil separating tank and the oil inlets of the screw expander are connected.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Roots vacuum pump
ActiveUS7226280B1Reduce noiseReduce the temperatureOscillating piston enginesEngine of counter-engagement typeRotational axisVacuum pump
In a Roots vacuum pump, an inlet port is located at a position n spaced by a positive displacement angle of 120° in one direction from a center of each rotational axis relative to an imaginary line m connecting rotor axes. An outlet port is located at a position o opposite to the inlet port relative to the line. An air feed port is formed at a position t on a casing wall obtained by returning by 90° from the position o to the inlet port side so that two closed spaces are defined by adjacent rotor lobes and a casing inner wall at both port sides immediately after air suction respectively. The casing has discharge grooves in an area of the inner wall so as to communicate with the outlet port. The area ranges from the position o to a position u obtained by returning by 45° from the position o to the inlet port side. The discharge grooves have a total volume ranging from 2% to 5% of a volume of one of the closed spaces.
Owner:ANLET CO LTD
Multi-stage vacuum pump
InactiveUS20050089424A1Reduce overall outer diameterReduce volumeRotary/oscillating piston combinations for elastic fluidsEngine of counter-engagement typeElectrical and Electronics engineeringCompressed air
A multi-stage vacuum pump includes a plurality of casings connected in series and each casing defining a respective compression chamber, a plurality of partition plates each set in between each two casings. When compressed by rotors at shafts in one compression chamber, compressed air passes through the air path formed in the corresponding partition plate to the next compression chamber for further compression, and finally compressed air passes to the last compression chamber through the air path formed in the last partition plate. Because the invention is designed to let compressed air directly pass through the air path in each partition plate, the outer diameter and volume of the multi-stage vacuum pump can be minimized to reduce the weight and the manufacturing cost.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Supercharger with multiple backflow ports for noise control
InactiveUS6874486B2Reduce supercharger noiseEffective maintenanceInternal combustion piston enginesEngine of counter-engagement typeNoise controlEngineering
A supercharger includes multiple back flow ports which are controlled by valves. The valves regulate the timing and area for back flow of pressurized outlet air into the rotor chambers. The back flow air tends to equalize air pressure in the chambers prior to their exhausting into the outlet and thereby reduces flow back noise. The multiple ports are opened selectively or sequentially to provide noise control with improved efficiency at varying speeds.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Supercharger with housing internal noise attenuation
InactiveUS20080060622A1High efficiency and low costReduce noiseOscillating piston enginesEngine of counter-engagement typeUltrasound attenuationInternal noise
A positive displacement supercharger includes a housing defining a rotor cavity with a pair of positive displacement rotors operative to carry air axially from an inlet end to an outlet in the cavity wall near an outlet end of the cavity. The outlet communicates with an outlet plenum partially defined by the cavity wall. The cavity wall includes a stiff portion defining a plurality of lightening recesses, such as a waffle pattern, limiting distortion of the wall by pulsations in the plenum. The recesses may be time and cost efficiently converted to Helmholtz tuners by covering the recesses with a cover plate, which may be perforated to include at least one tuning opening (perforation) into each tuning chamber (recess) and forming tuning volumes of the tuning chambers and their associated tuning openings effective to attenuate selected frequencies of pulsations in the plenum and thereby reduce undesired noise emanating from the air system of the supercharger.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Magnetically driven gear pump
ActiveUS7137793B2Simple structureEngine of arcuate-engagement typeOscillating piston enginesGear driveGear pump
A magnetically driven gear pump having a housing, a rotatable annular magnetic drive assembly magnetically coupled to but spaced from an annular driven magnet and rotor gear assembly with an annular canister disposed therebetween, and wherein when the annular magnetic drive assembly is rotated, the annular driven magnet and rotor gear assembly rotate on a first shaft portion of an offset stationary shaft and the rotor gear drives an idler gear that rotates on a second shaft portion of the offset stationary shaft.
Owner:PSG CALIFORNIA LLC
Gear pump and liquid injection apparatus
InactiveUS20050238505A1Close openingAvoid positioningOscillating piston enginesEngine of counter-engagement typeGear pumpDrive shaft
A high-performance gear pump that does not require highly accurate machining is disclosed. The gear pump includes a housing having an accommodation chamber. A drive gear and a driven gear are positioned in contact with an inner surface of the accommodation chamber. The drive shaft is loosely received by the shaft hole of the drive gear, and the driven shaft is loosely received by the shaft support formed in the housing and the cover.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Optimized helix angle rotors for Roots-style supercharger
ActiveUS20060263230A1Improve blower efficiencyReduce input powerOscillating piston enginesEngine of counter-engagement typeEngineeringHelix angle
A method of designing rotors for a Roots blower comprising a housing having cylindrical chambers, the housing defining an outlet port (19). The blower includes meshed, lobed rotors (37,39) disposed in the chambers, each rotor including a plurality N of lobes (47,49), each lobe having first (47a,49a) and second (47b,49b) axially facing end surfaces. Each lobe has its axially facing surfaces defining a twist angle (TA), and each lobe defines a helix angle (HA). The method of designing the rotor comprises determining a maximum ideal twist angle (TAM) for the lobe as a function of the number N of lobes on the rotor, and then determining a helix angle (HA) for each lobe as a function of the maximum ideal twist angle (TAM) and an axial length (L) between the end surfaces of the lobe.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
Screw compressor
ActiveUS20060008375A1Easy to operateImprove responseOscillating piston enginesEngine of counter-engagement typeHydraulic cylinderSpool valve
A screw compressor according to the present invention includes a slide valve adapted to move forward and backward in parallel with the axis of a pair of screw rotors and also includes a plurality of hydraulic cylinders for moving the slide valve forward and backward, the plural hydraulic cylinders imparting, in synchronization with each other, a driving force to the slide valve in the same direction. With this configuration, it is possible to quicken an operation of the slide valve and improve the responsivity in volume control without increasing the diameters of pistons of the hydraulic cylinders for actuating the slide valve and without complicating equipment.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
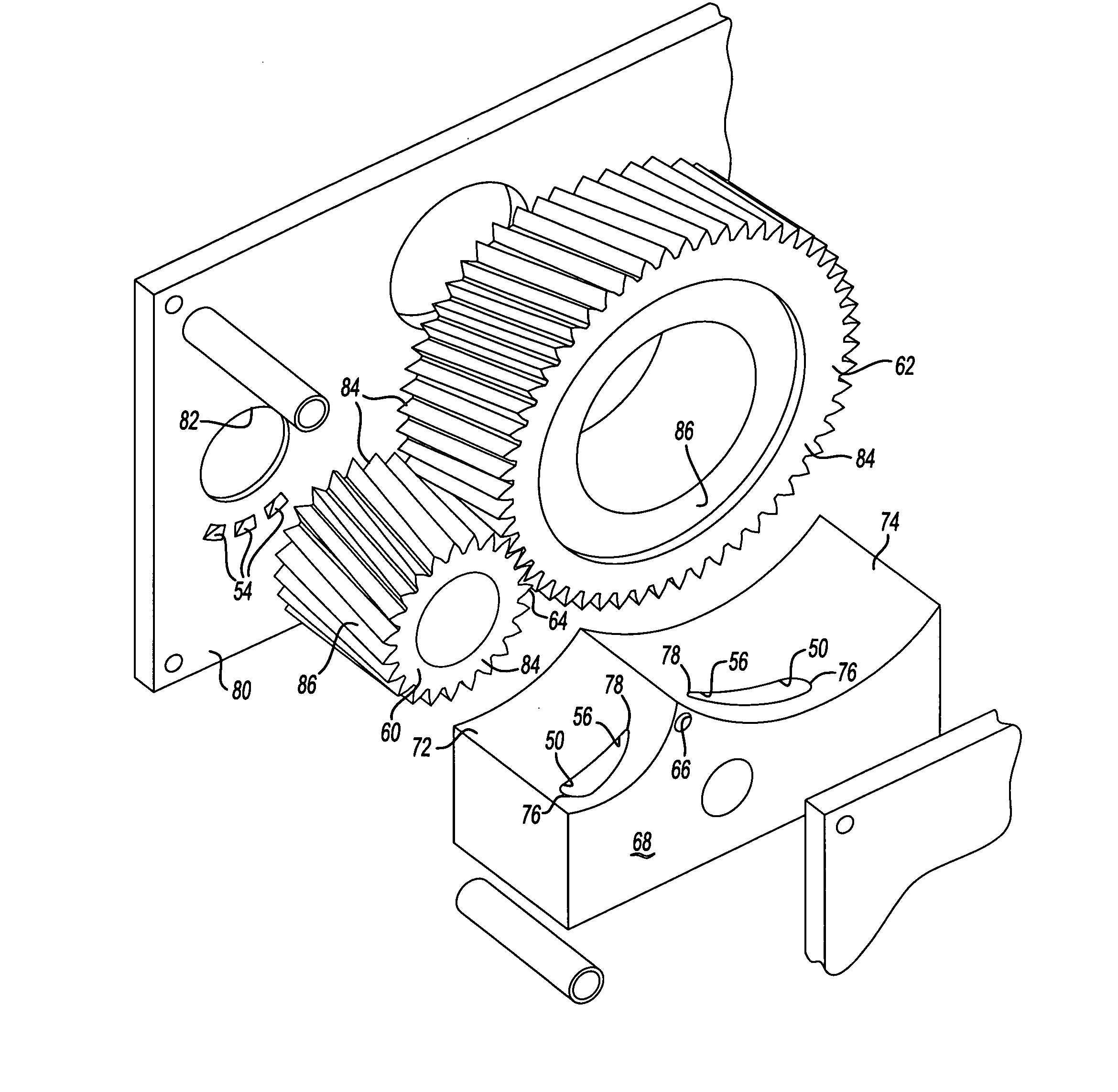
Ancillary oil pumping for gear box assembly
ActiveUS20070251348A1Effective lubricationSimple pumpingGearboxesOscillating piston enginesTransfer caseGear drive
A gear box assembly as used in an inverted portal axle or transfer case includes a drive gear and at least one driven gear in meshing engagement with the drive gear at a contact point. A gear housing closely surrounds portions of an outer circumference of the drive and driven gears to form a baffle area. The gear housing includes an discharge orifice that is located near the contact point and a fluid gallery that extends from the discharge orifice to other locations within the gear housing. As the drive gear drives the driven gear, fluid is pumped into the discharge orifice and through the fluid gallery to fluid outlets positioned at desired locations to lubricate other gear box components. Radial inlets with elongated chamfers and stator vanes can be formed within the gear housing to draw air ingested during pumping away from the discharge orifice. Additionally, a bypass loop can be used to scavenge unwanted air ingested into meshing gear teeth.
Owner:ARVINMERITOR TECH
Supercharger with heat insulated gear case
InactiveUS20080175739A1Low costTemperature controlOscillating piston enginesSealing arrangement for pumpsHeat flowOil temperature
A positive displacement supercharger includes a housing having a rotor cavity. A pair of positive displacement rotors are oppositely rotatable in the rotor cavity and have interleaved helical lobes forming rotor chambers operative to carry air axially from an inlet end to an outlet end of the cavity. A gear case adjacent the rotor cavity is drivably connected with and supports the rotors, the gear case including a bearing housing having an end surface facing the rotor cavity and the outlet ends of the rotors. A heat insulating material is applied to the end surface of the bearing housing and is effective to reduce heat flow between the rotor cavity and the end surface of the bearing housing to effectively reduce lubricating oil temperatures in the gear case. The insulating material may be a ceramic plate fixed to the bearing housing end surface.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Positive displacement pump apparatus and method
ActiveUS20080069707A1Promote sportsOscillating piston enginesSealing arrangement for pumpsRotary pumpDrive shaft
An improved positive displacement rotary pump apparatus and method is provided including a front cover, a rotor body forming a chamber with the front cover, a gear case supporting a pair of hollow drive shafts, and a pair of rotors disposed in the chambers and each detachably mounted to one end of a respective hollow drive shaft via a stud that extends from the rotor through the hollow shaft to a fastener. The pump can also have at least one respective face seal between each rotor and the body with at least one first rotating seal ring disposed at the backward facing face of each rotor, and at least one respective second stationary rotating seal ring disposed on a forward facing face of the pump body. The pump further has a pair of bearings that rotatably support the shaft in the gear case, with each bearing being located relative to the gear case by a respective locating ring that is axially movable relative to the gear case, so that each bearing is axially adjustable relative to the gear case. The pump also has a contoured inner relief region located adjacent one of the inlet port and the outlet port, and located next to the front of the rotor swept area to facilitate movement of material through the pumped rotor area
Owner:SPX FLOW INC
PD Pumps with a Common Gearbox Module and Varying Capacities and Easy Access to Mechanical Seals
ActiveUS20090304540A1Ease in which the seals can be serviced or replacedOscillating piston enginesSealing arrangement for pumpsDrive shaftEngineering
Rotary lobe pump and circumferential piston pump designs are disclosed where the drive and driven shafts are detachably connected to their respective rotors. The rotors are disposed in a pump or rotor casing, which is sandwiched between a head cover and a gearbox. The drive and driven shafts pass through mechanical seal assemblies, which are sandwiched between the first and second rotors and the gear box respectively. The seal assemblies can be serviced or replaced by simply removing the head cover and removing the rotors from the drive and driven shafts. The pump casing does not need to be removed to replace or service the seal assemblies. Further, the capacities of the disclosed rotary lobe and circumferential piston pumps can be modified without changing the gearboxes or shaft length. To modify a pump capacity, all that needs to be changed are the rotors, the pump or rotor casing and, in some designs, the head cover or cover plate. In some designs, the cover plate is universal to the gearbox so that only the rotors and pump casing need to be changed to modify the pump capacity.
Owner:VIKING PUMP HYGIENIC LTD
Orbital engine
InactiveUS7059294B2Easy to operateIncrease powerRotary/oscillating piston combinations for elastic fluidsInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringMechanical engineering
An engine is disclosed including at least one piston which is positioned within a toroidal piston chamber. A method of operating an engine is disclosed wherein a piston is advanced in a toroidal piston chamber past a first valve and the first valve is closed to form a first ignition chamber area located within the piston chamber between the first valve and the rear side of the piston. A second valve is closed ahead of the piston to form a first exhaust removal chamber area located within the piston chamber between the second valve and the front side of the piston, the exhaust removal chamber including exhaust gases from a preceding ignition which occurred in the first ignition chamber area. A fuel mixture is introduced into the first ignition chamber area and ignited thereby advancing the piston further along the toroidal piston chamber.
Owner:WRIGHT INNOVATIONS
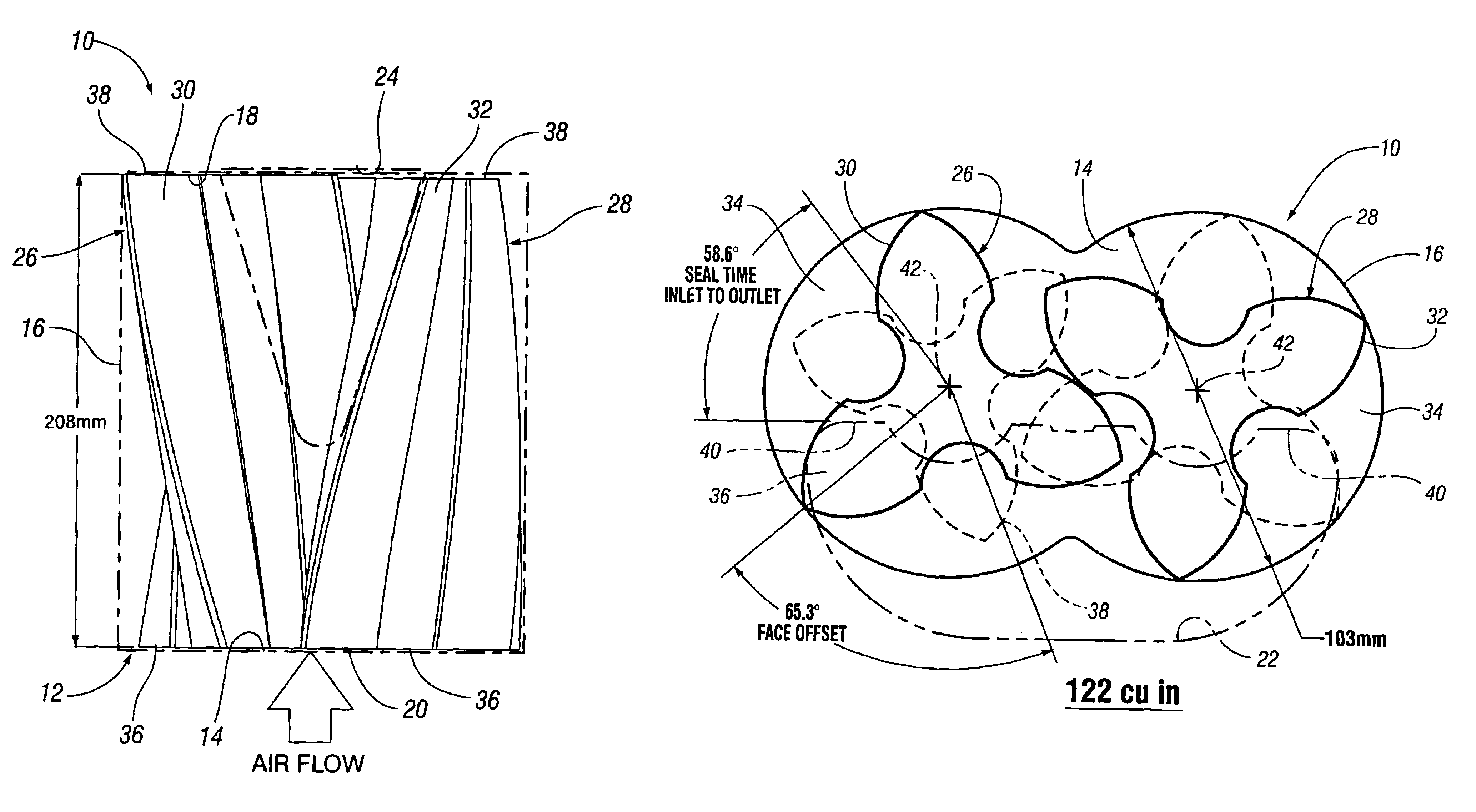
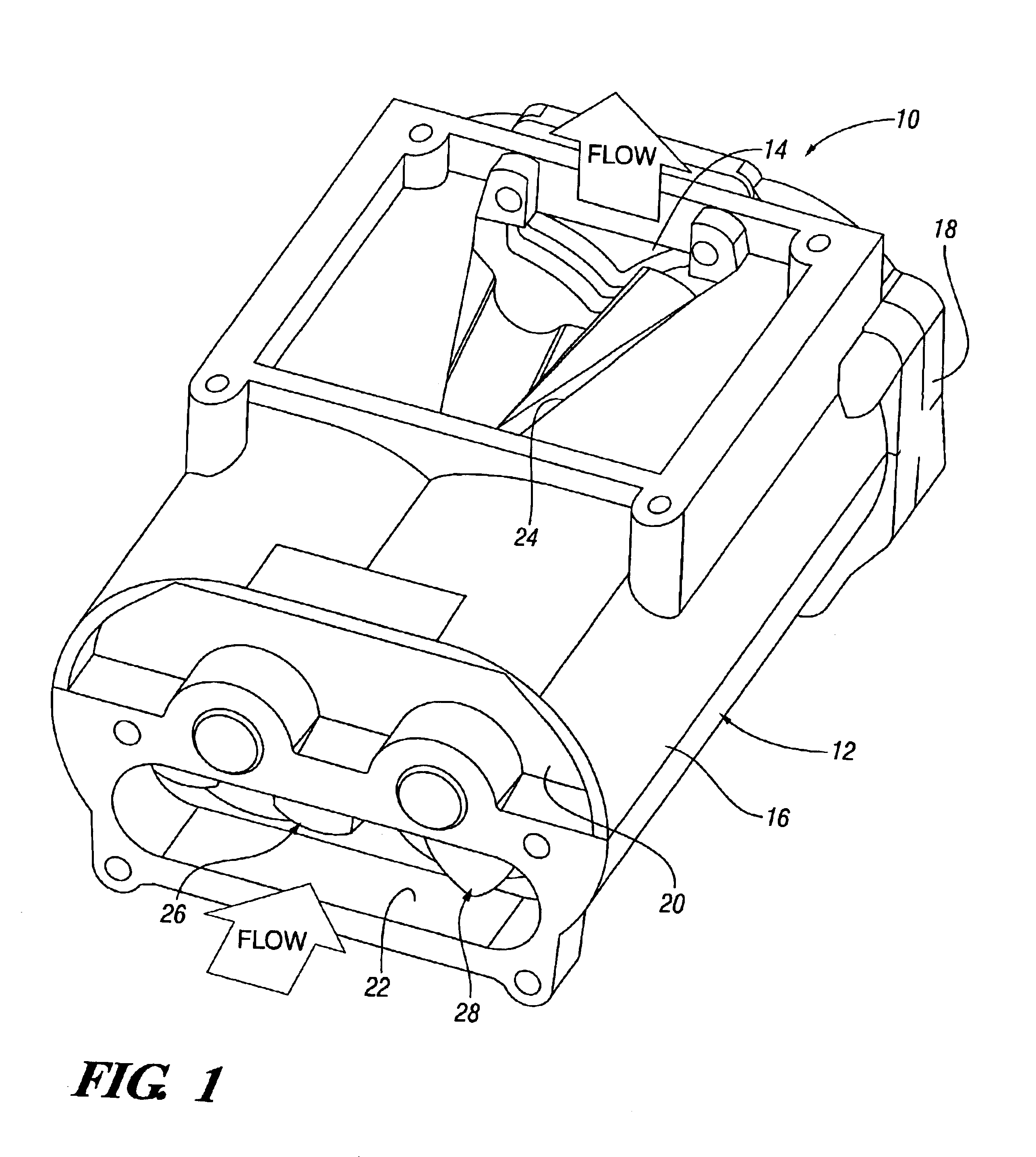
Roots supercharger with extended length helical rotors
InactiveUS6884050B2Improve efficiencyLow temperature changeOscillating piston enginesEngine of counter-engagement typeEngineeringHelix angle
A Roots supercharger has an extended cavity with 103 mm diameter rotors having chambers defined by interleaved helical lobes with equal angular face offsets exceeding 60 degrees from inlet to outlet end faces angled in directions opposite to directions of rotor rotation. The chambers have angular seal times of less than 67 degrees of rotation. A preferred embodiment has a displacement of 122 cu mm / revolution, rotor length of 208 mm, face offsets of 65.3 degrees and seal time of 58.6 degrees. The rotor lobe helix angle is essentially 0.314 deg / mm, equal to the helix angle of a prior art supercharger with rotors of common diameter, displacement of 112 cubic inch / revolution, rotor length of 191 mm, previously considered maximum, 60 degree face offset, previously considered optimum, and seal time of 67 degrees. Both flow volumes and efficiency of the new configuration are improved from the prior art wherein the 60 degree face offset was considered optimum.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Positive-displacement rotary pump
InactiveUS6887055B2Minimal dimensionPrecise positioningOscillating piston enginesSealing arrangement for pumpsRotary pumpEngineering
A positive-displacement rotary pump comprising a pair of meshing gears (13, 14) or rotors, consisting of a driving gear and a driven gear, contained in a shell (10) having an output opening and an intake opening for a fluid. The gears (13, 14) include shafts (23, 24) which are supported by bushings (15a, 15b) having two faces (17a, 17b) which are subjected, in use, to pressures which bring about an axial load on the bushing itself, wherein the resultant of the axial loads (S′, S″) on the two bushings has a predetermined direction so as to move the bushings (15a, 15b) and the gears (13, 14) as a whole into close abutment with a predetermined reference plane (VI—VI).
Owner:MORSELLI MARIO ANTONIO
Vane pump
ActiveUS20130280118A1Large lead timeOscillating piston enginesEngine of counter-engagement typeWorking fluidPump chamber
A vane pump including a cam ring, a rotor, slits formed in the rotor, vanes inserted slidably into the slits, pump chambers defined by the vanes, back pressure chambers defined between respective base end portions of the vanes and the slits, back pressure grooves capable of communicating with the back pressure chambers as the rotor rotates, and connecting grooves connecting back pressure grooves that are adjacent in a circumferential direction of the rotor to each other, wherein a connecting groove that communicates with a back pressure groove positioned in a suction region formed above a rotary center of the rotor so as to suction a working fluid into the pump chambers is formed to have a larger passage sectional area than a connecting groove that communicates with another back pressure groove positioned in another suction region formed below the rotary center of the rotor.
Owner:KYB CORP
Electric pump
InactiveUS20090175751A1Engine of counter-engagement typeEngine of intermeshing engagement typePositive pressureEngineering
According to an aspect of the present invention, an electric pump includes: a housing; an outer rotor; an inner rotor; a base member facing one side surface of the outer rotor and one side surface of the inner rotor; a side plate member, having a facing surface facing the other side surface of the outer rotor and the other side surface of the inner rotor and a non-facing surface opposed to the facing surface; a shaft; a suction port; a discharge port; a negative pressure applied region; a positive pressure applied region; and a relief valve, discharging the fluid from the positive pressure applied region to a non-facing surface side of the side plate member when a pressure applied at the positive pressure applied region exceeds a predetermined value.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
Screw compressor
ActiveUS20050226758A1Avoid noiseReduced cross sectionOscillating piston enginesSealing arrangement for pumpsInjection portEngineering
Disclosed is a screw compactor comprising two screw rotors which are disposed in screw rotor bores inside a compressor housing and compress a coolant that enters at a coolant inlet and discharge said coolant at a coolant outlet, and a coolant inlet that is arranged within the compressor housing, said coolant being supplied by a coolant-injecting device via a conduit system in order to additionally cool the screw compressor. The inlet is disposed so as to extend into compression spaces that are enclosed by the screw rotors and the screw rotor bores. The aim of the invention is to create a screw compactor in which the compressive oscillations occurring at the inlet do not travel at all or only in an attenuated manner into the conduit system for the coolant-injecting device. Said aim is achieved by mounting a first inlet duct section which runs inside the compressor housing upstream of the inlet, an injection port for the coolant that is supplied by the coolant-injecting device extending into said first inlet duct section, while making a cross-sectional area of the injection port more than about four times smaller than a cross-sectional area of the first inlet duct section.
Owner:BITZER KUEHLMASCHINENBAU GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com