Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
815results about "Dynamo-electric brakes/clutches" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
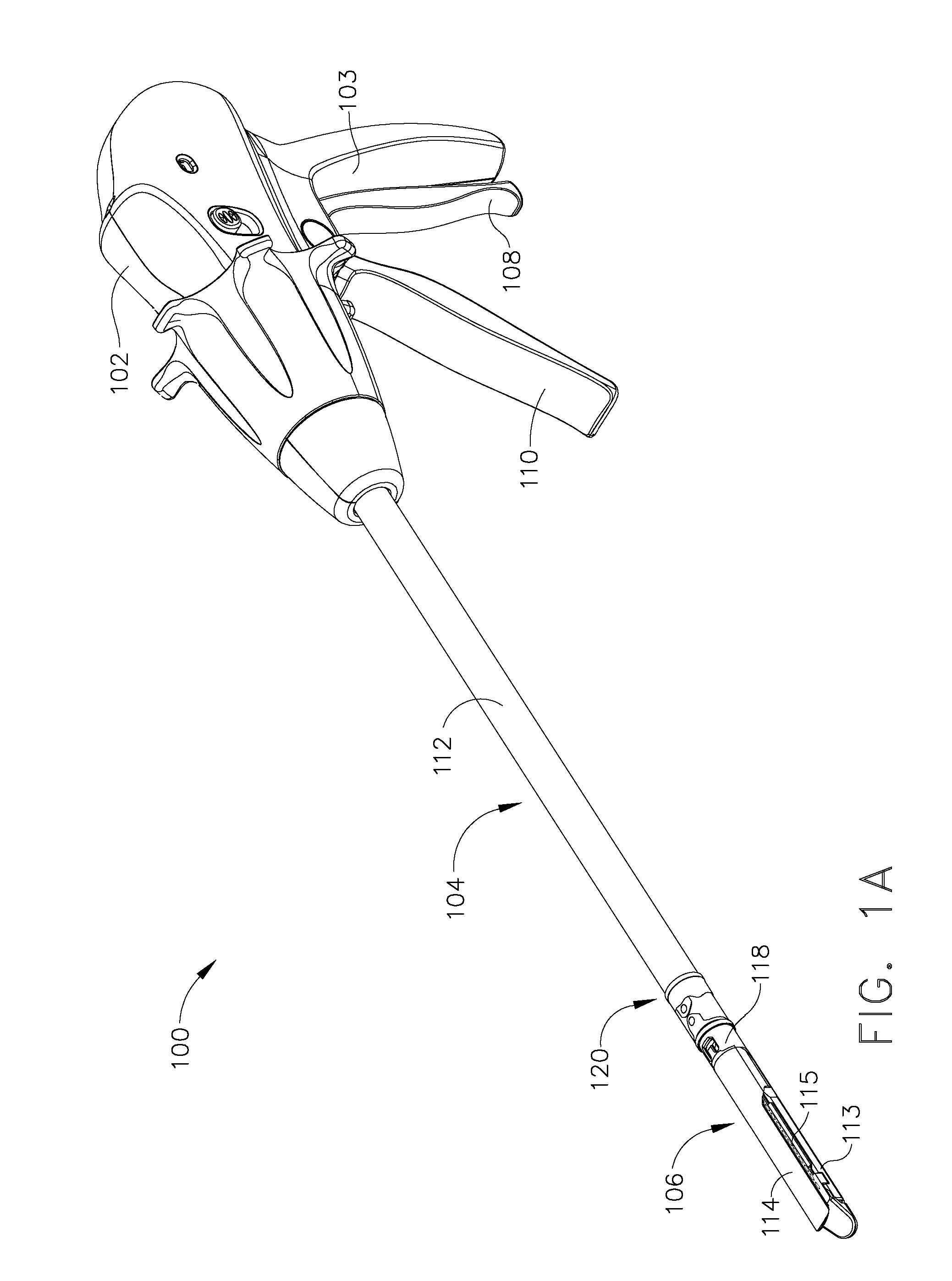
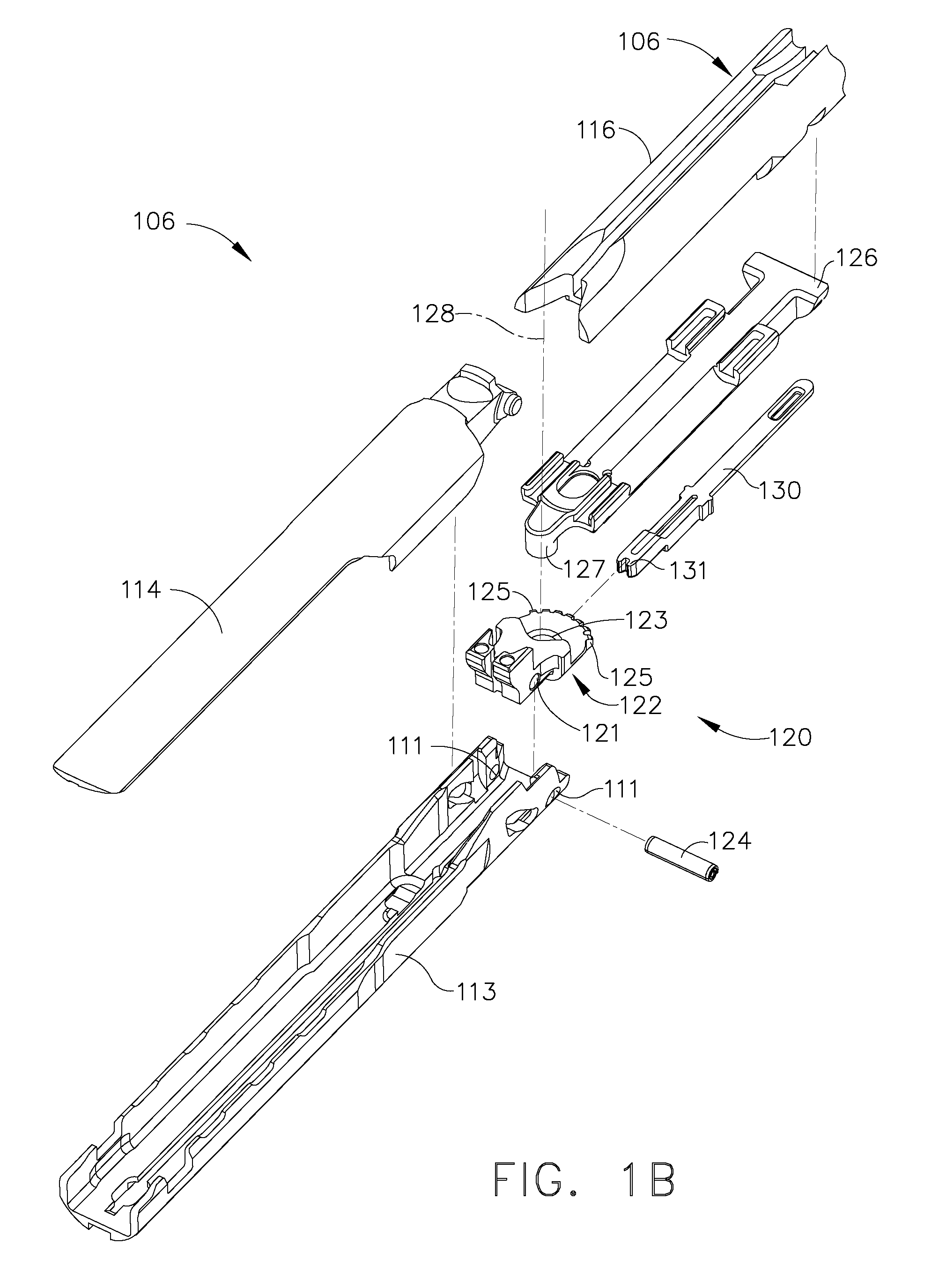
Surgical stapling instrument comprising a magnetic element driver
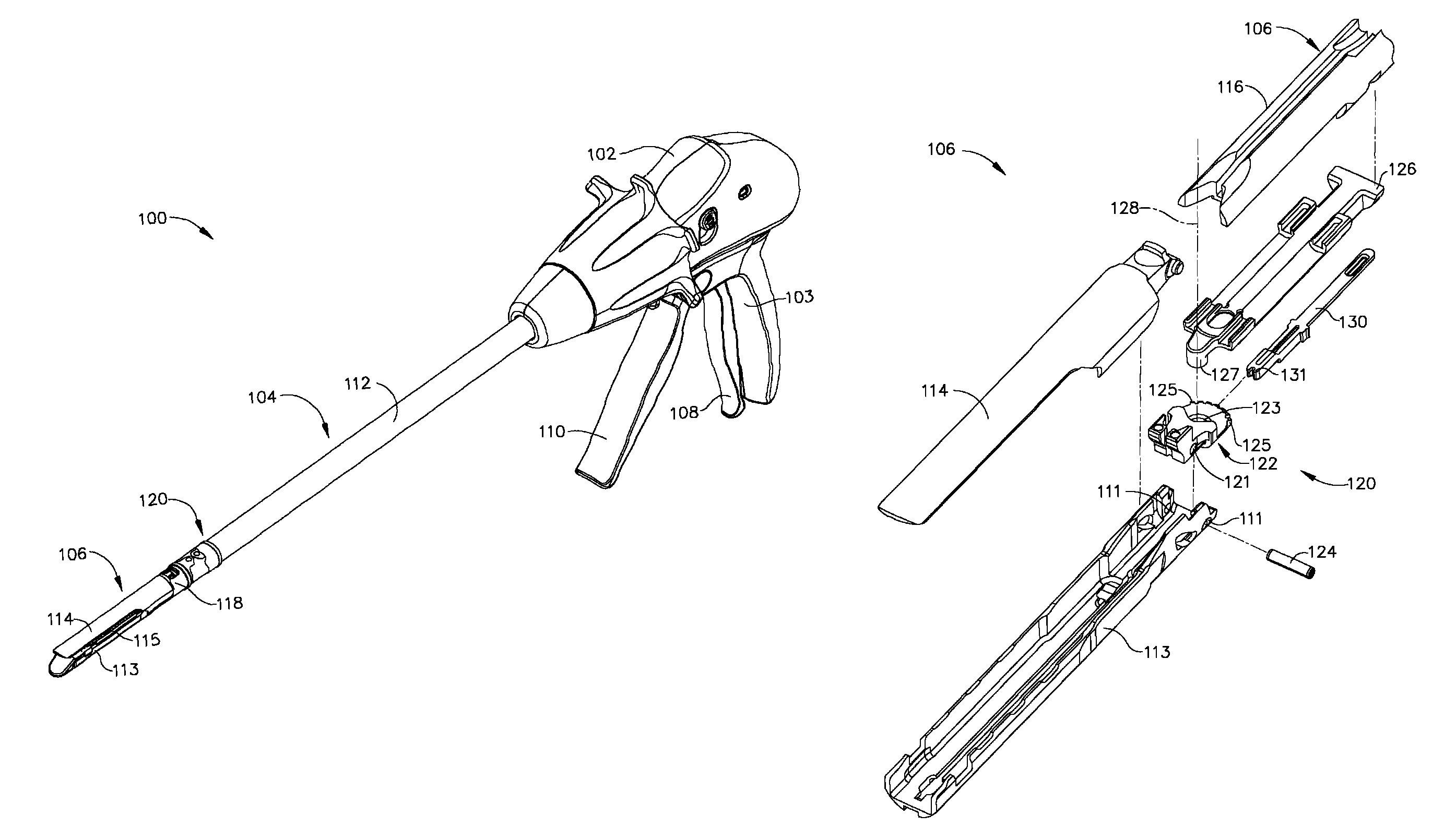
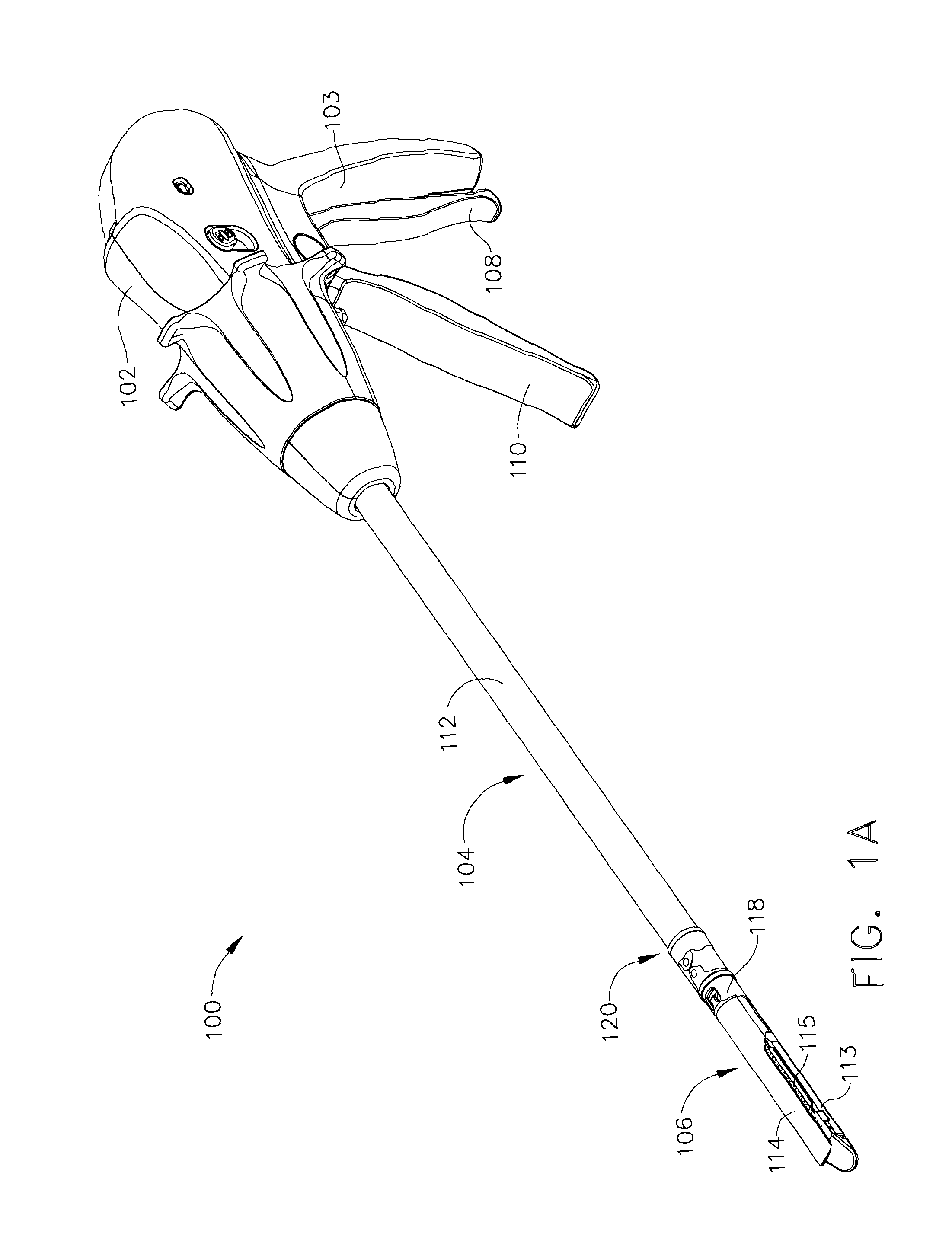
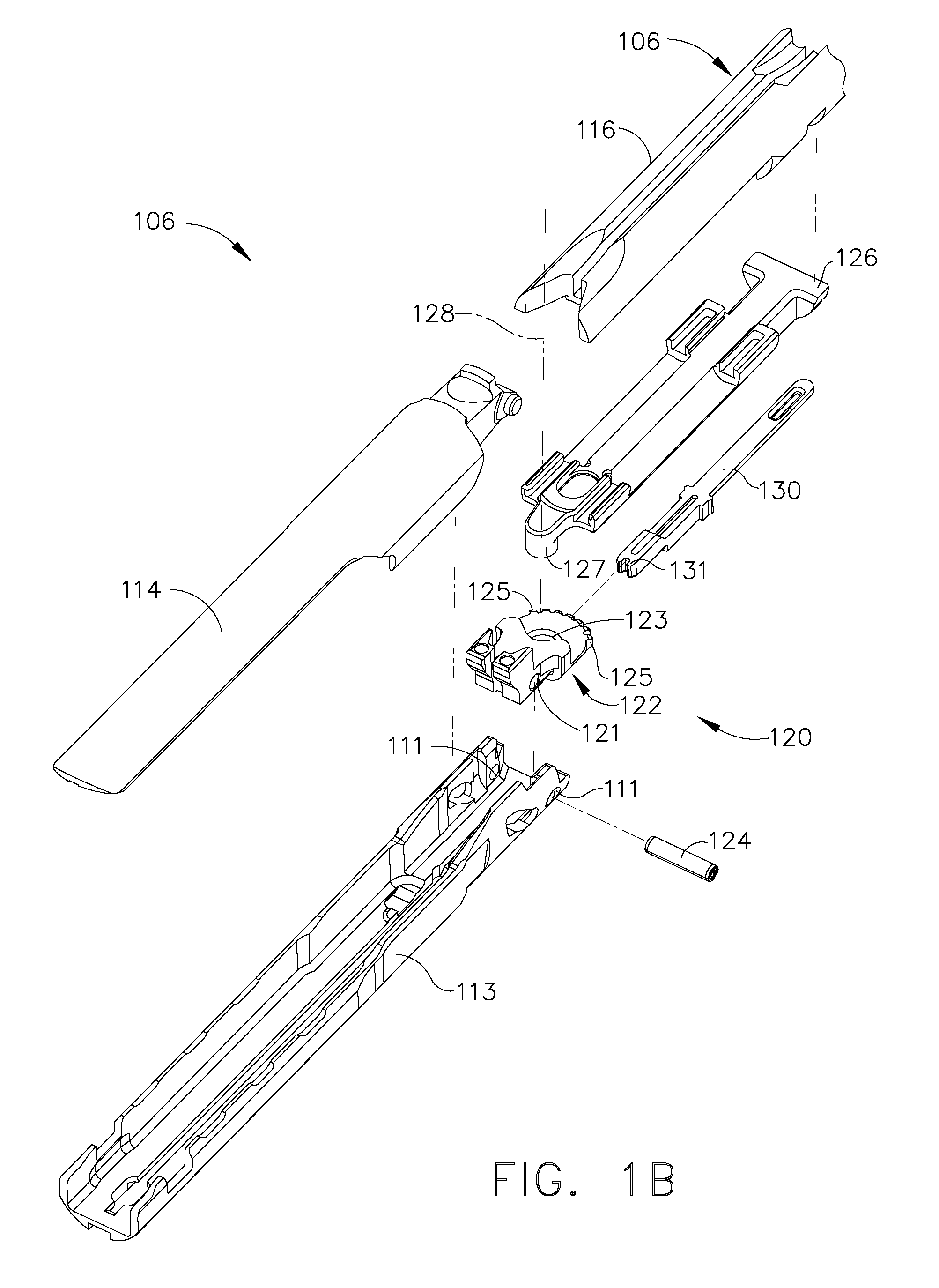
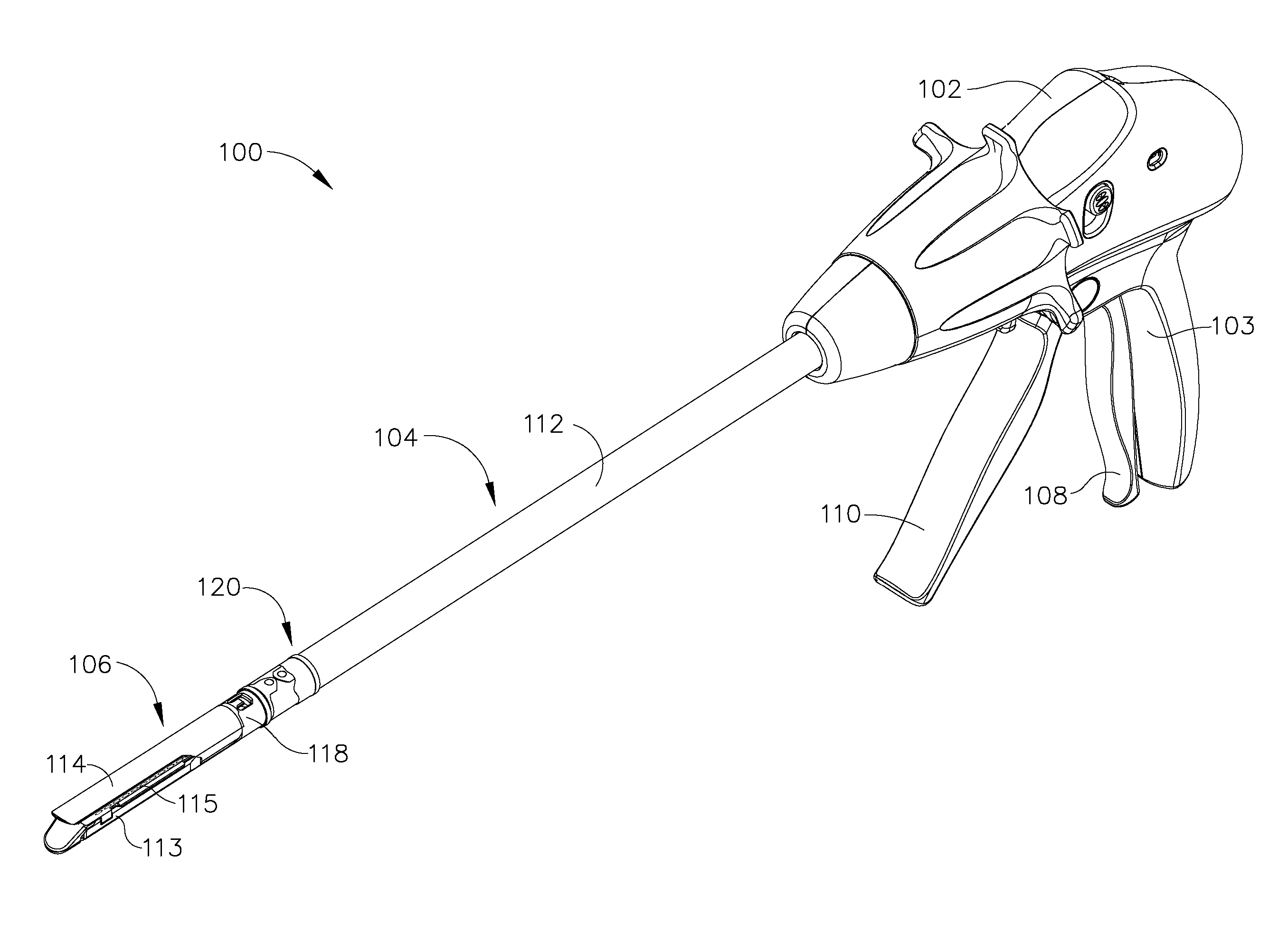
In various embodiments, a surgical stapling instrument can comprise a plurality of magnetic elements configured to articulate an end effector of the surgical instrument. The surgical instrument can comprise at least one electromagnet which can be selectively activated, or polarized, to generate a magnetic field sufficient to motivate a second magnetic element, such as a permanent magnet and / or an iron core, for example, mounted to the end effector. In certain embodiments, a surgical stapling instrument can comprise a plurality of magnetic elements configured to open and / or close an end effector of the surgical instrument. In at least one embodiment, a surgical stapling instrument can comprise a plurality of magnetic elements configured to advance and / or retract a firing bar, cutting member, and / or staple sled within the surgical instrument in order to incise and / or staple tissue positioned within an end effector of the surgical instrument.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Surgical stapling instrument comprising a magnetic element driver
In various embodiments, a surgical stapling instrument can comprise a plurality of magnetic elements configured to articulate an end effector of the surgical instrument. The surgical instrument can comprise at least one electromagnet which can be selectively activated, or polarized, to generate a magnetic field sufficient to motivate a second magnetic element, such as a permanent magnet and / or an iron core, for example, mounted to the end effector. In certain embodiments, a surgical stapling instrument can comprise a plurality of magnetic elements configured to open and / or close an end effector of the surgical instrument. In at least one embodiment, a surgical stapling instrument can comprise a plurality of magnetic elements configured to advance and / or retract a firing bar, cutting member, and / or staple sled within the surgical instrument in order to incise and / or staple tissue positioned within an end effector of the surgical instrument.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
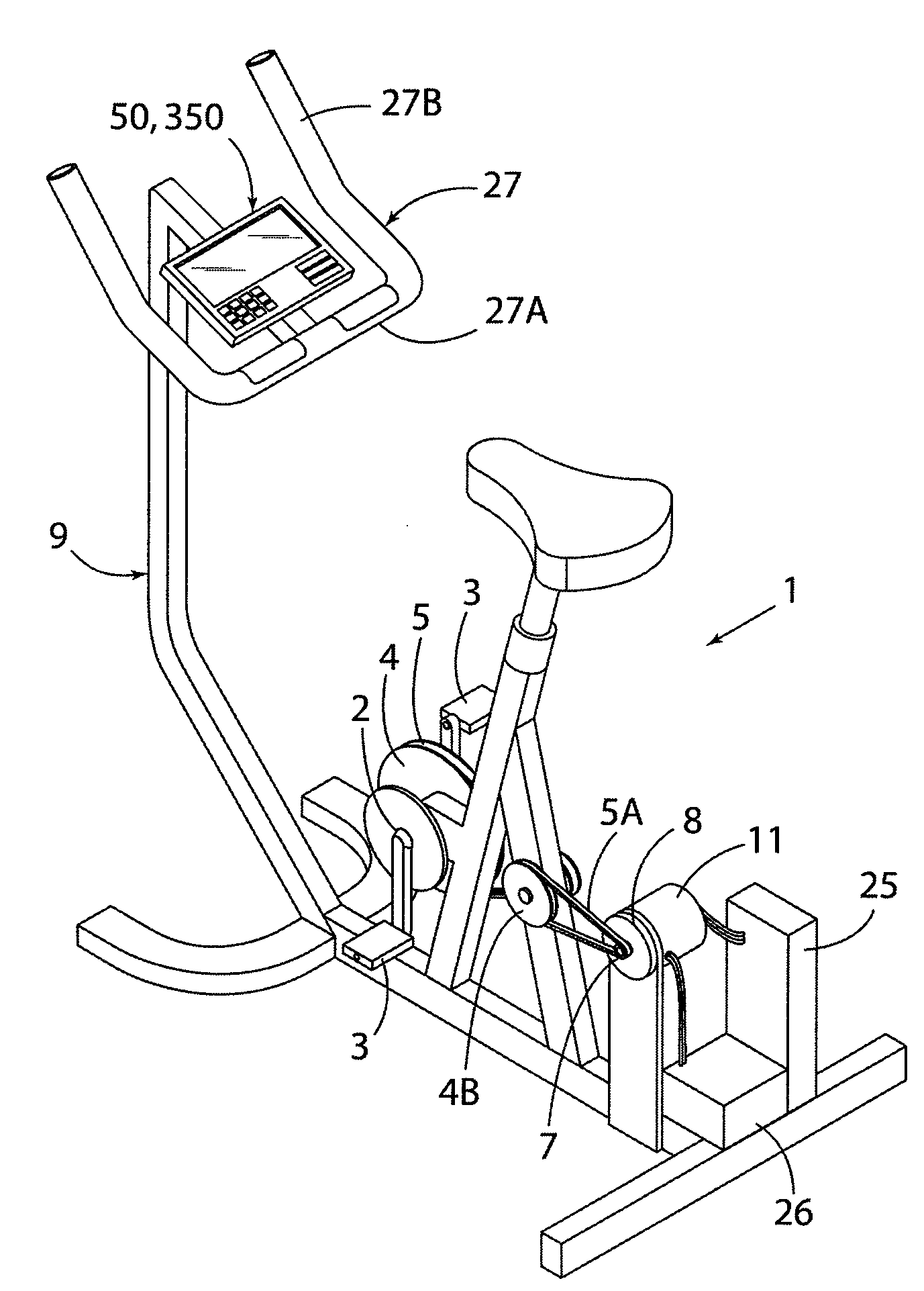
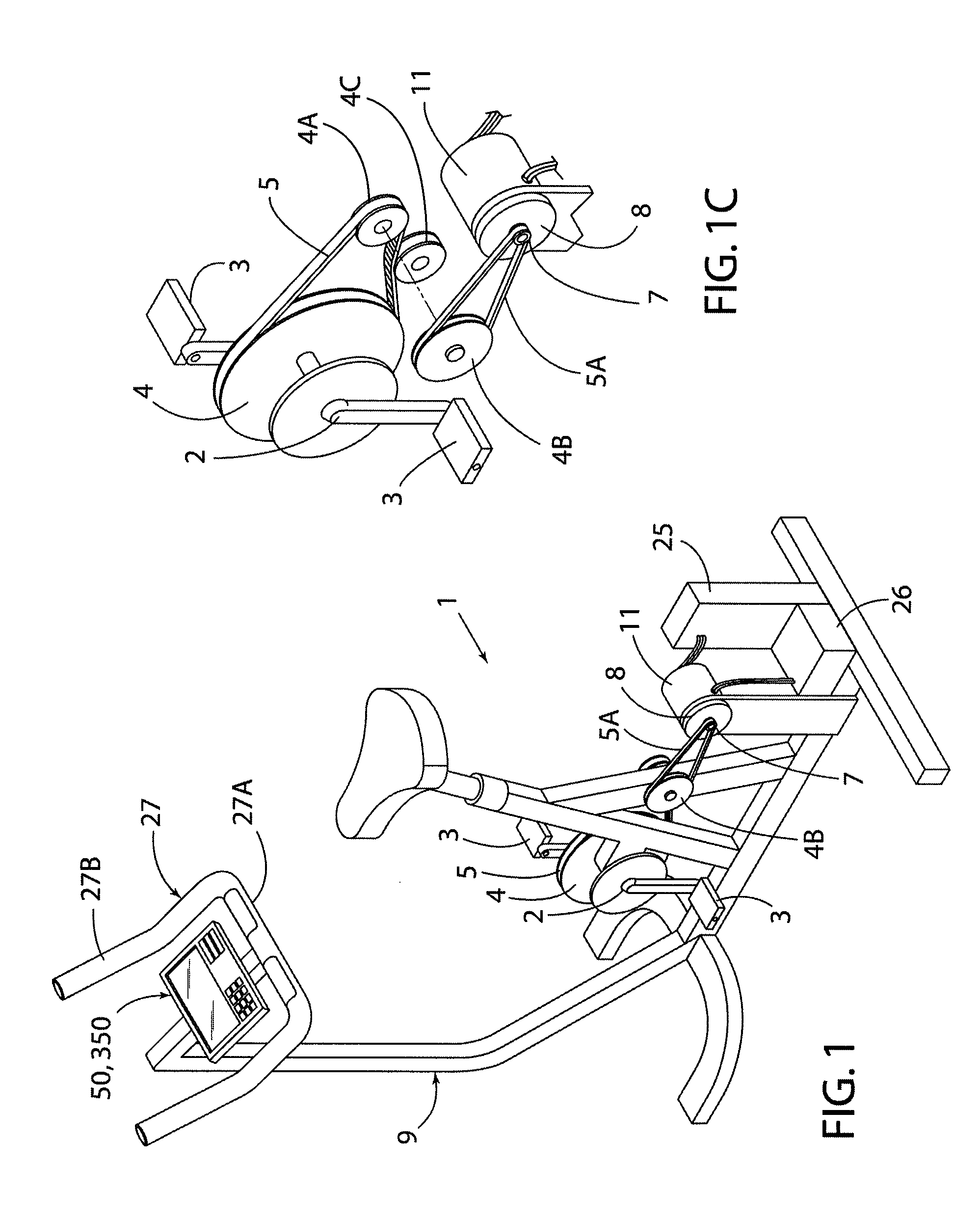
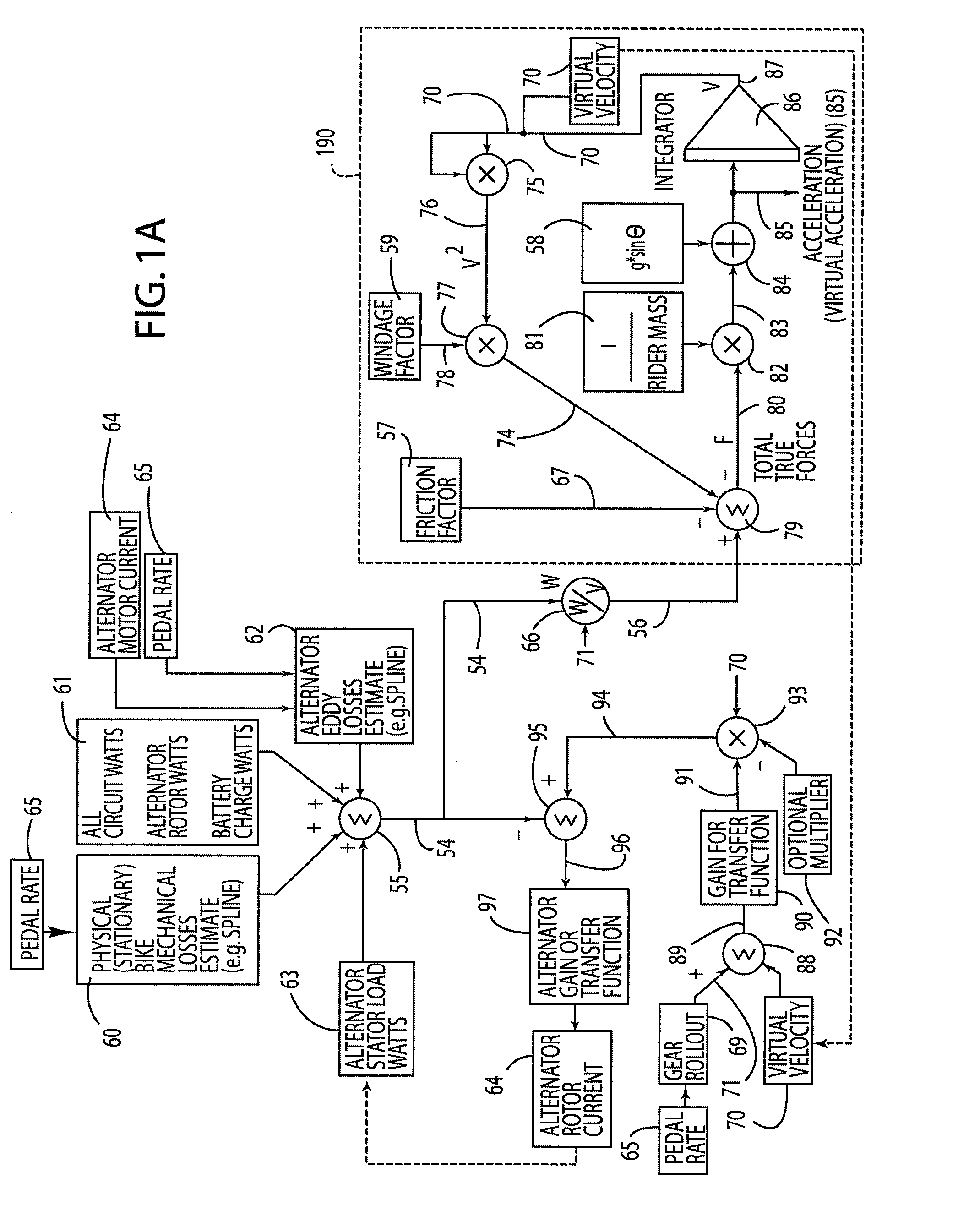
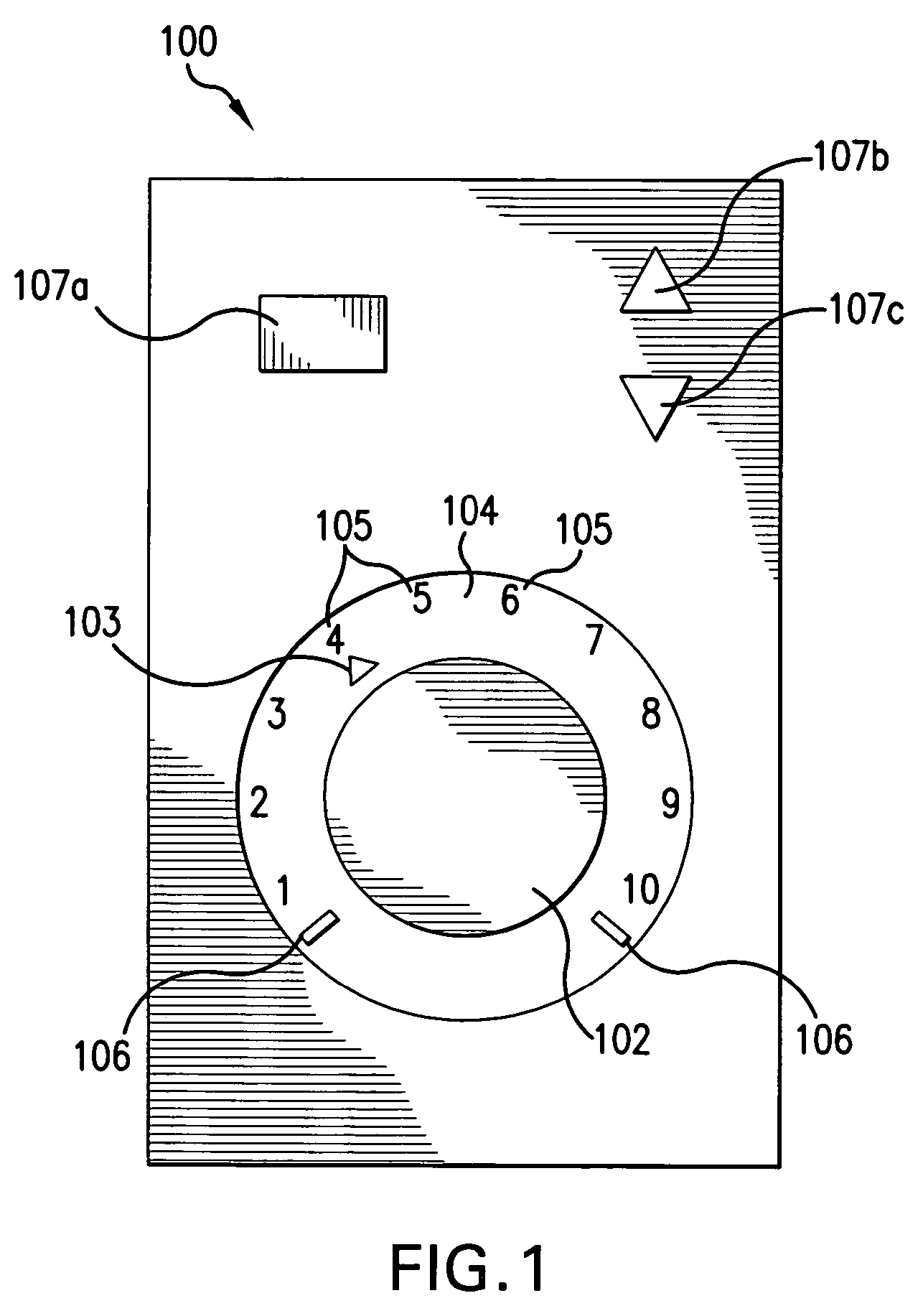
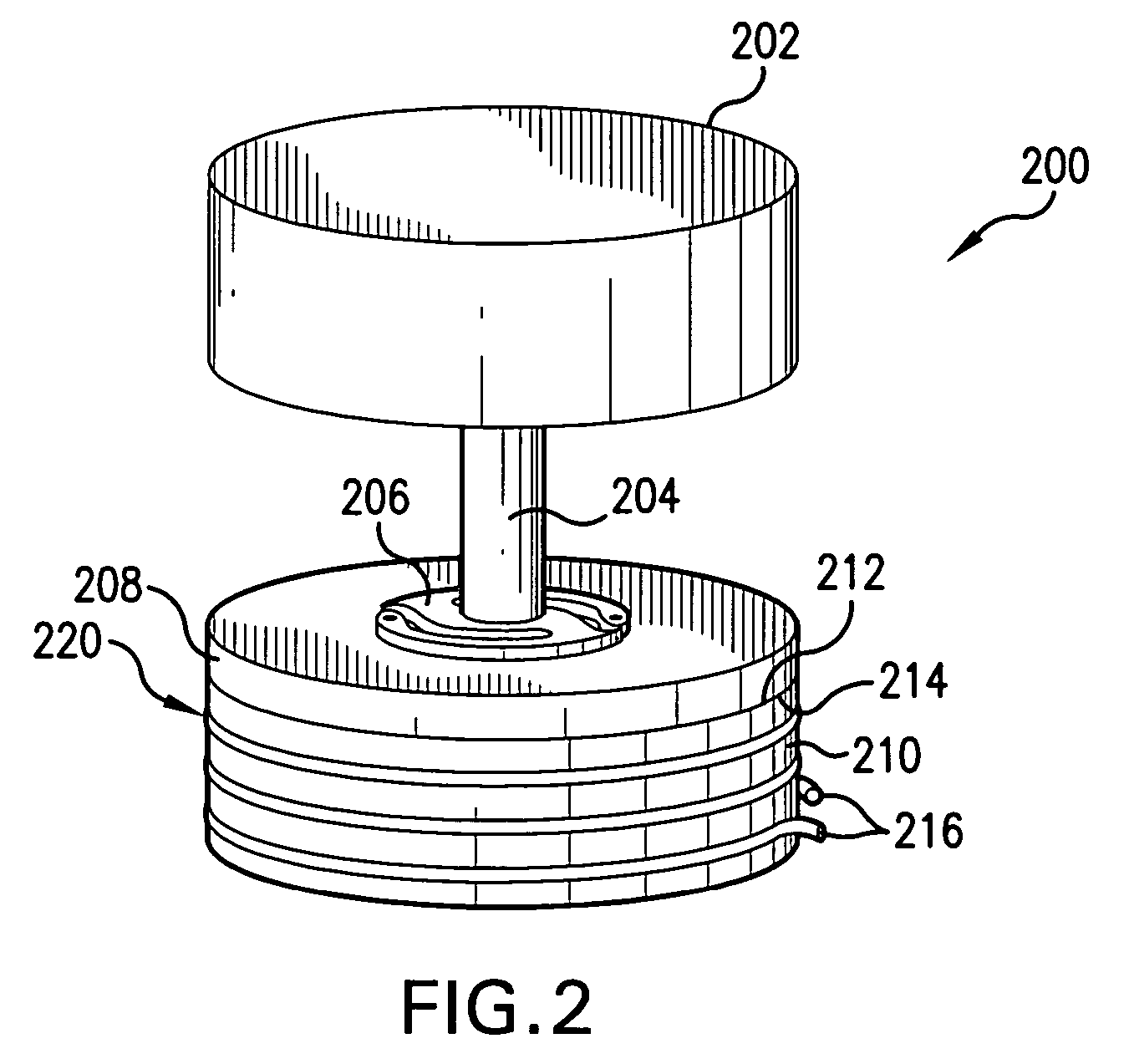
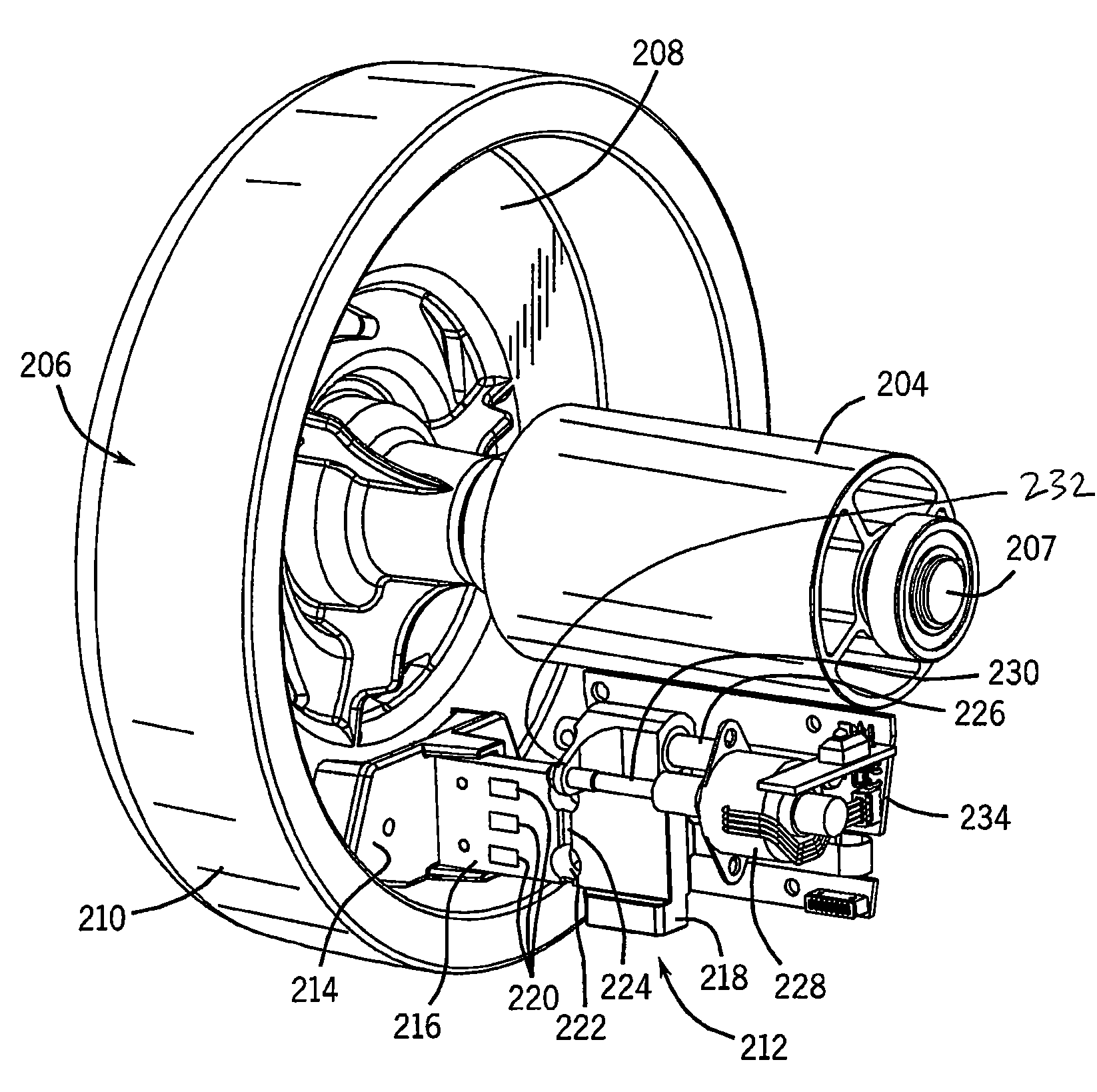
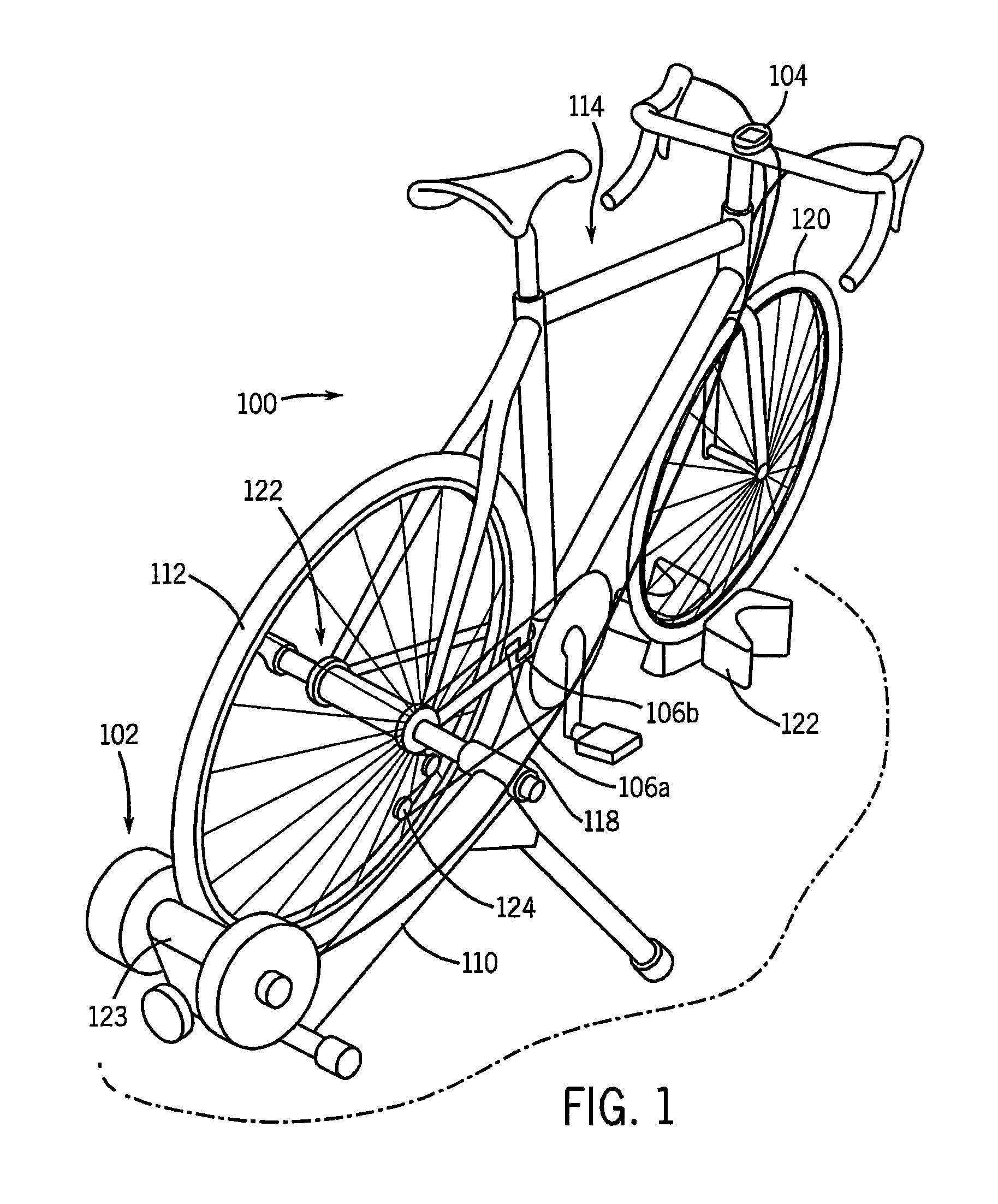
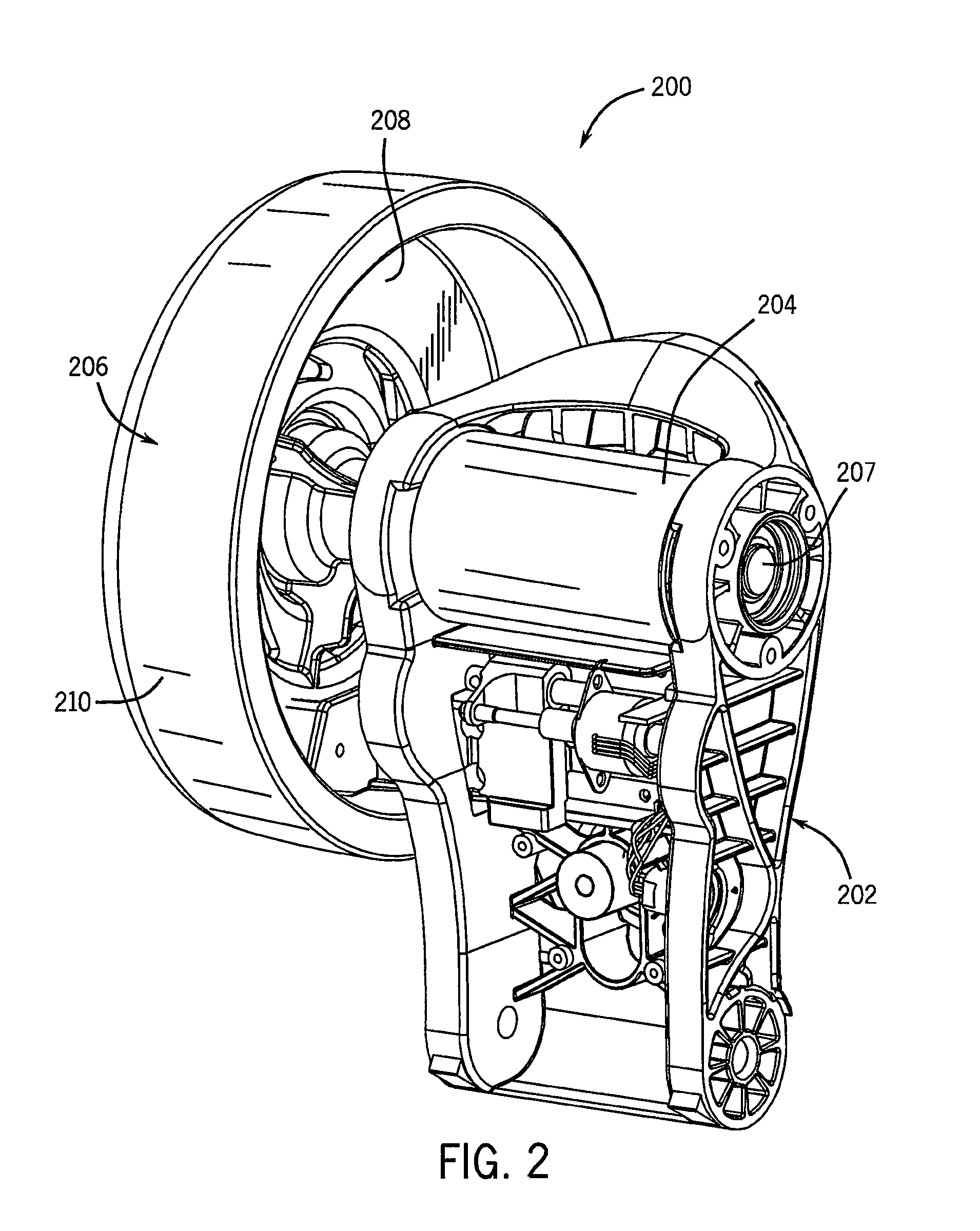
Stationary Exercise Equipment
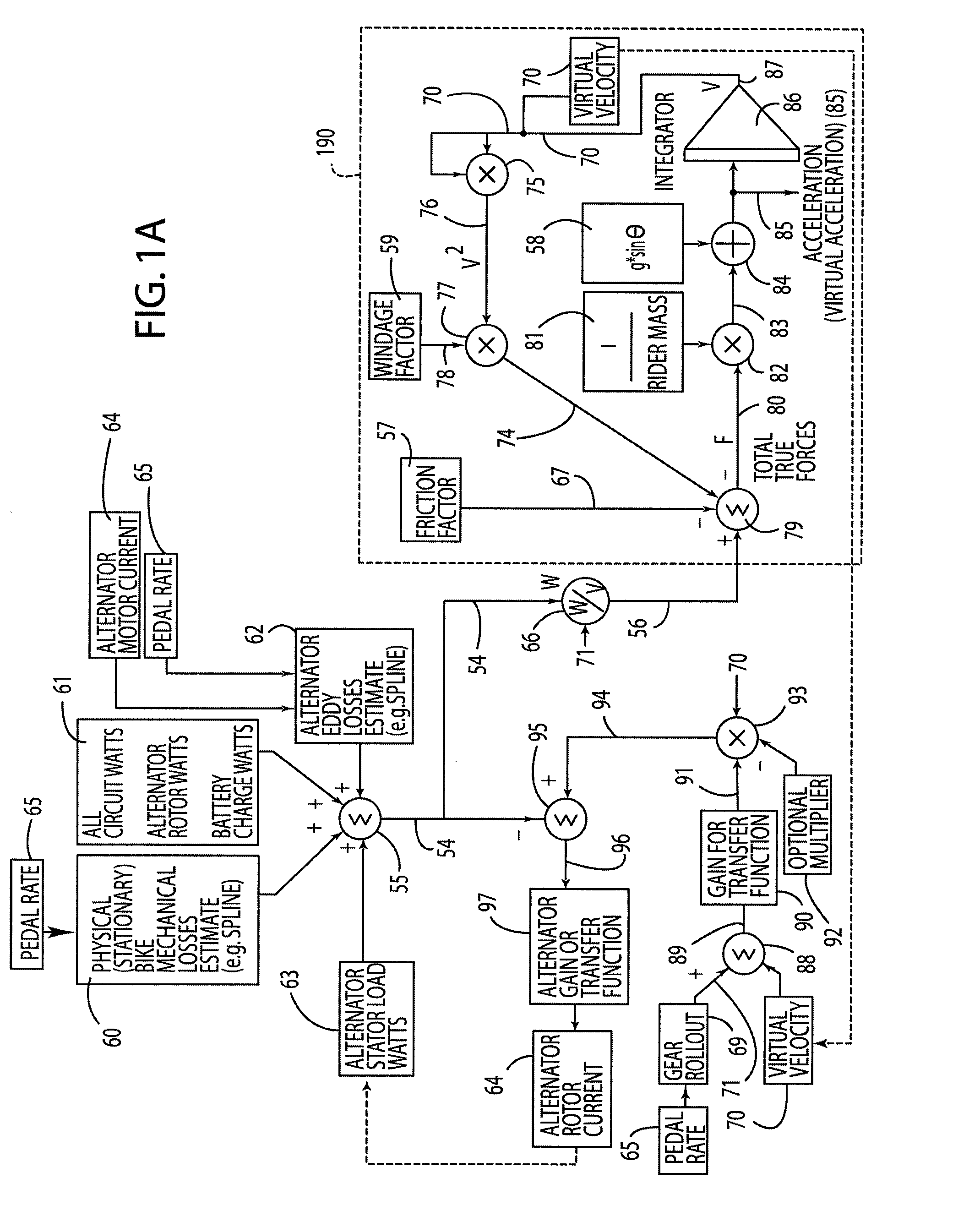
A control system and method for exercise equipment and the like provides a way to simulate a physical activity in a manner that takes into account the physics of the physical activity being simulated to provide an accurate simulation. According to one aspect of the present invention, the control system and method takes into account the physics of the corresponding physical activity to generate a virtual or predicted value of a variable such as velocity, acceleration, force, or the like. The difference between the virtual or expected physical variable and a measured variable is used as a control input to control resistance forces of the exercise equipment in a way that causes the user to experience forces that are the same or similar to the forces that would be encountered if the user were actually performing the physical activity being simulated rather than using the exercise equipment.
Owner:RADOW SCOTT B
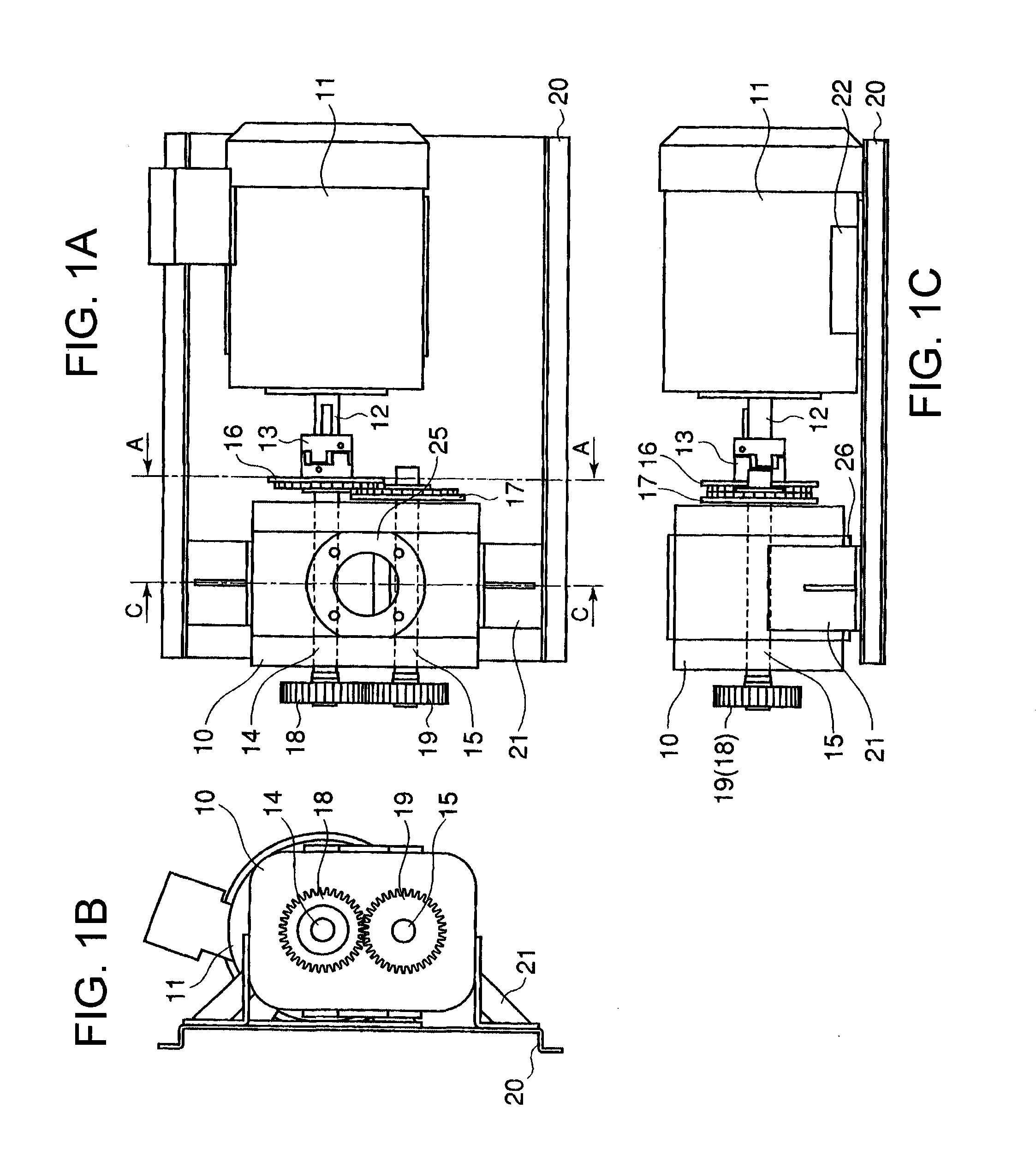
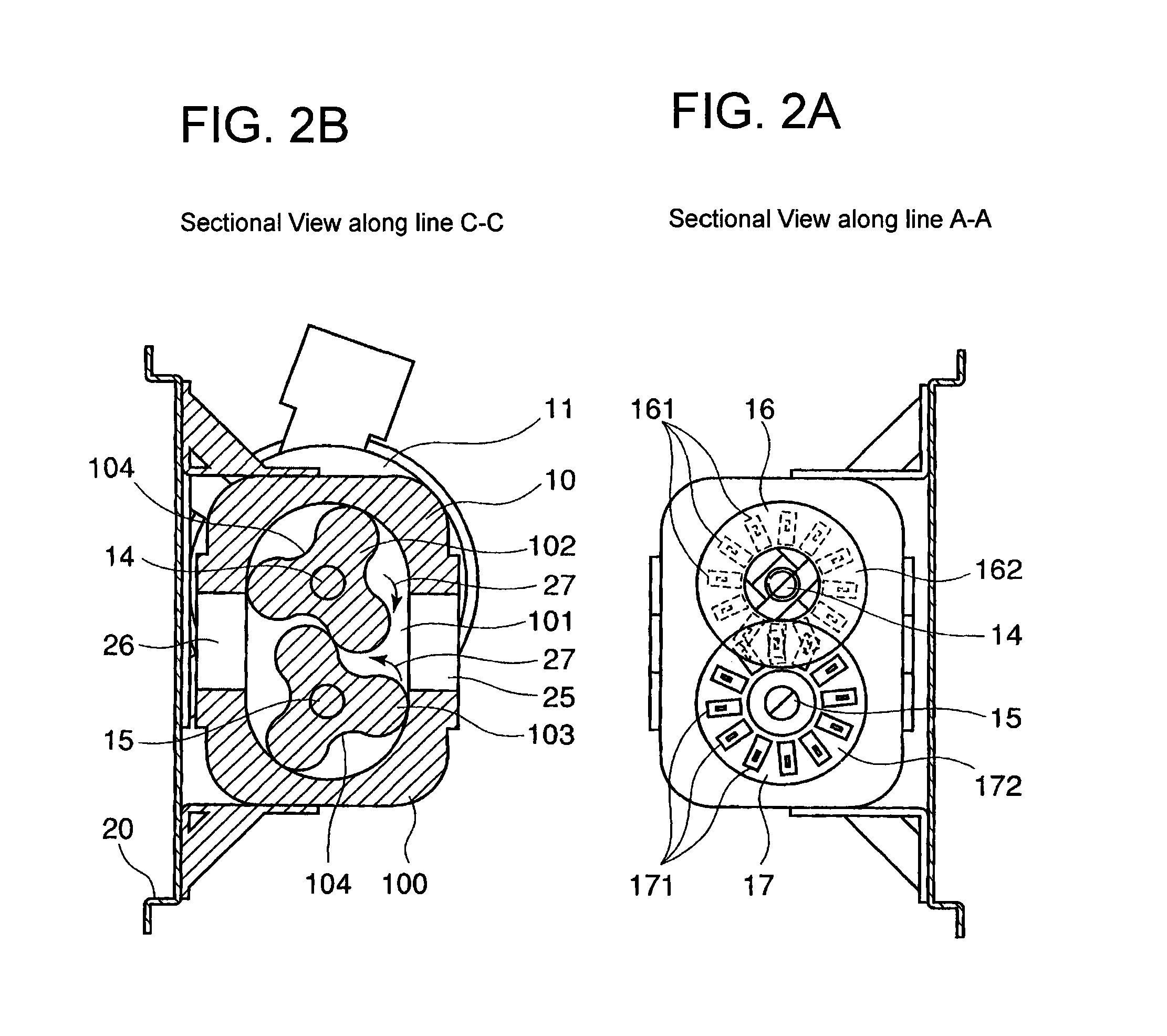
Drive transmission mechanism between two or more rotary shafts and oil-free fluid machine equipped with the mechanism
InactiveUS20080181804A1Reduced service lifeEliminate pollutionDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesEngine of counter-engagement typePlastic materialsOil free
A drive transmission mechanism for transmitting torque between two or more rotary shafts in synchronization with one another without need for lubrication thereby eliminating occurrence of oil contamination, and an oil-free fluid machine equipped with the mechanism, are provided. A magnetic drive disk 16 and a synchronization gear 18 are attached to a rotary shaft 14 connected to a drive motor 11, a magnetic drive disk 17 and a synchronization gear 19 is attached to a rotary shaft 15, torque transmission from the rotary shaft 14 to the rotary shaft 15 is carried out in two ways, via the magnetic drive disks 16, 17 and via the synchronization gears 18, 19, and at least one of the synchronization gears is made of plastic material. With the construction, torque transmit load between the rotary shafts via the synchronization gears is decreased, and a plastic gear or gears can be adopted for synchronization gears without reducing life of the gears without need for lubrication oil.
Owner:ANEST IWATA CORP
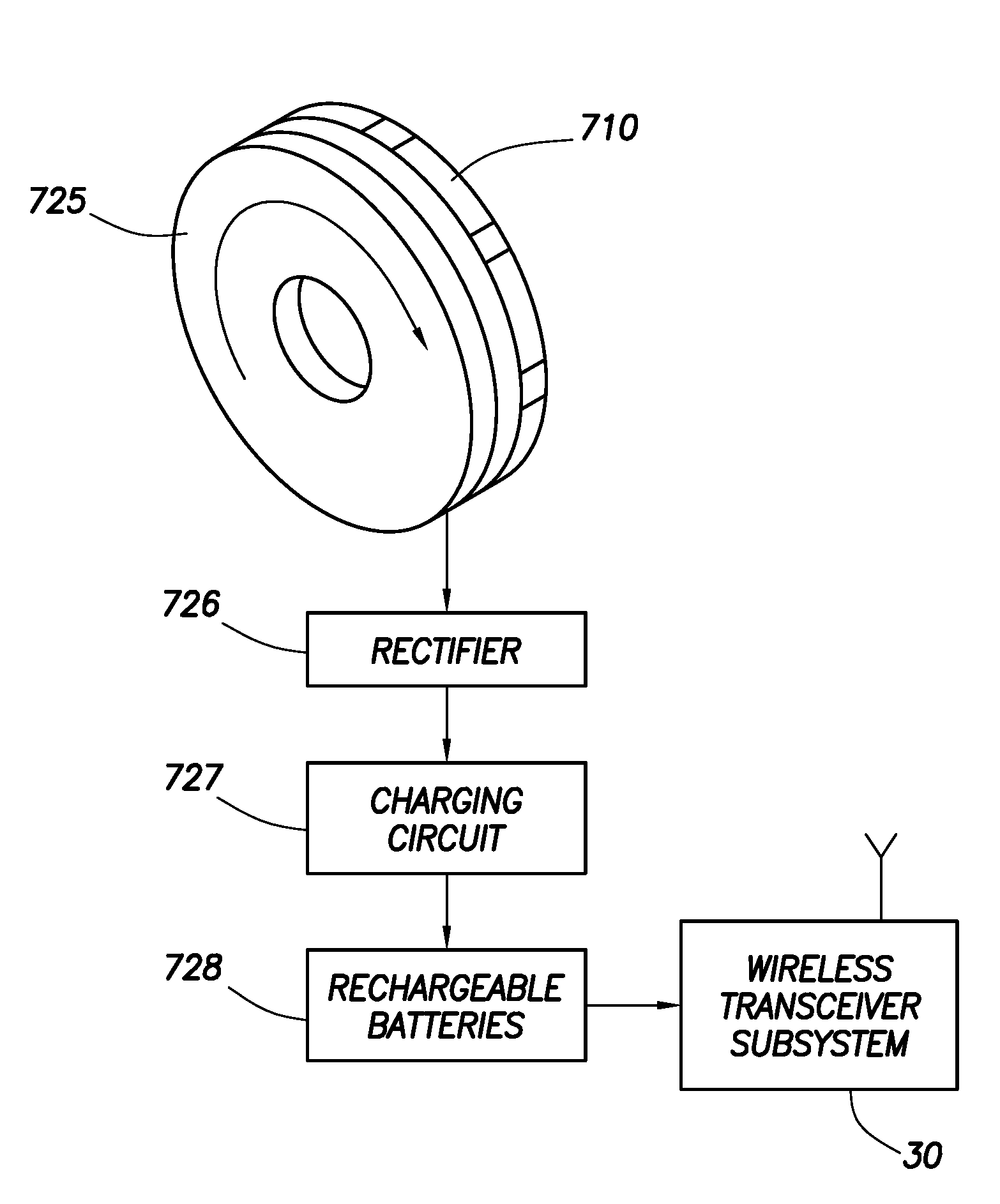
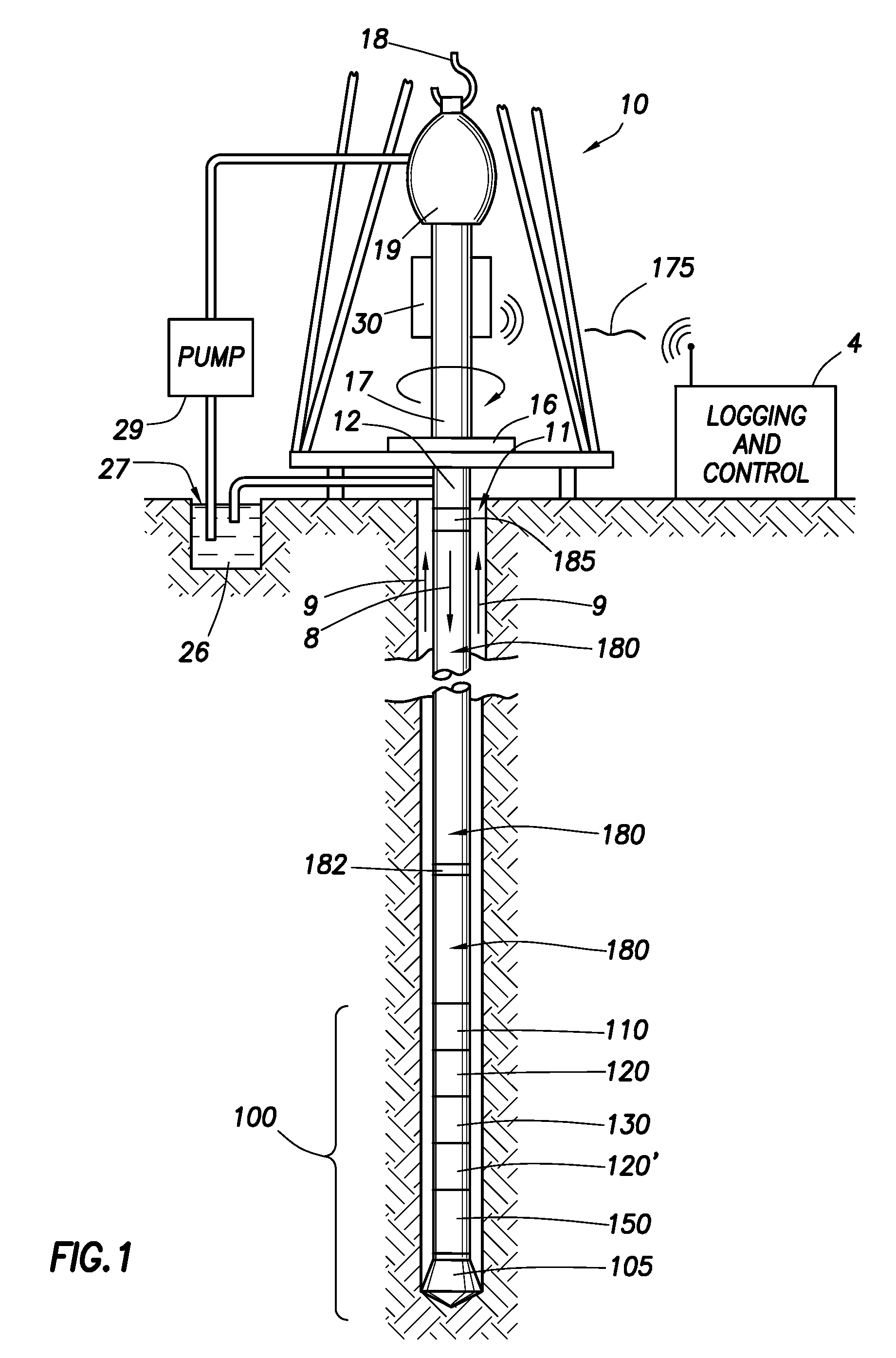
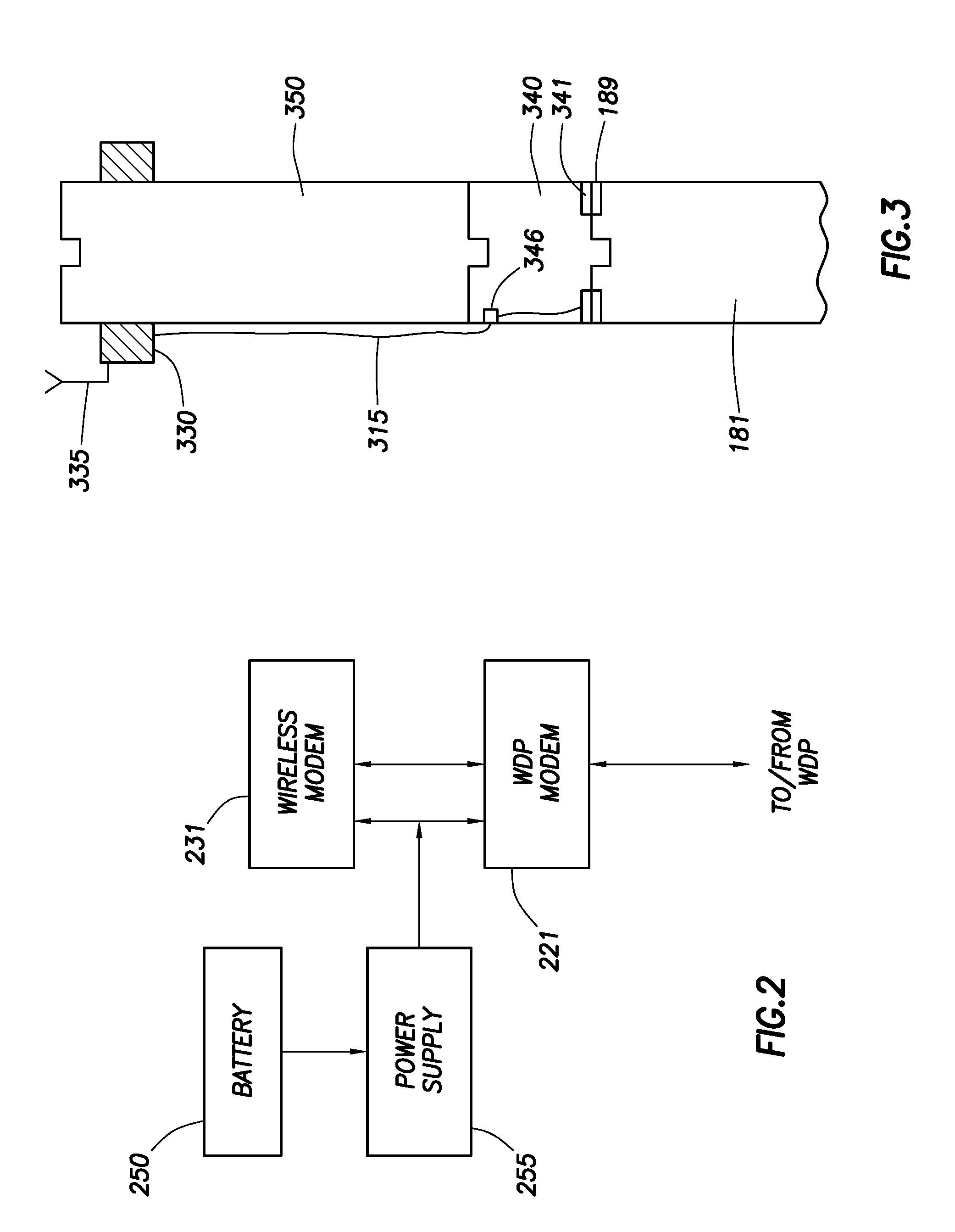
Surface communication apparatus and method for use with drill string telemetry
An operation of drilling an earth borehole uses a drilling rig, a drill string of drill pipes having its generally upper end mechanically coupleable with and suspendable from the drilling rig, a drive string portion of the drill string, mechanically coupleable with the topmost drill pipe of said drill string, and a drive mechanism mechanically coupleable with the drive string for rotating the drive string and the drill string. A system for generating electric power in the region of the drive string includes an electric generator, which includes a rotating generator component mounted on said drive string for rotation therewith and a stationary generator component mounted on a stationary portion of the drilling rig. The rotating generator component produces electric power in the region of the drive string.
Owner:INTELLISERV LLC
Systems and methods for providing a haptic device
ActiveUS8002089B2Degree of rotationControlling membersDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesEngineeringActuator
Systems and methods for providing a haptic device are described. In one described system, a first brake surface of a first element contacts a second brake surface of a second element. At least one actuator is configured to exert a force on at least one of the first and second elements. A flexure is coupled to at least one of the first element, the second element, a housing, a manipulandum, and a shaft coupled to the manipulandum. The flexure provides a degree of rotational flexibility to the manipulandum when the at least one actuator exerts the force. The described system may include a processor in communication with the at least one actuator for providing the haptic effects.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
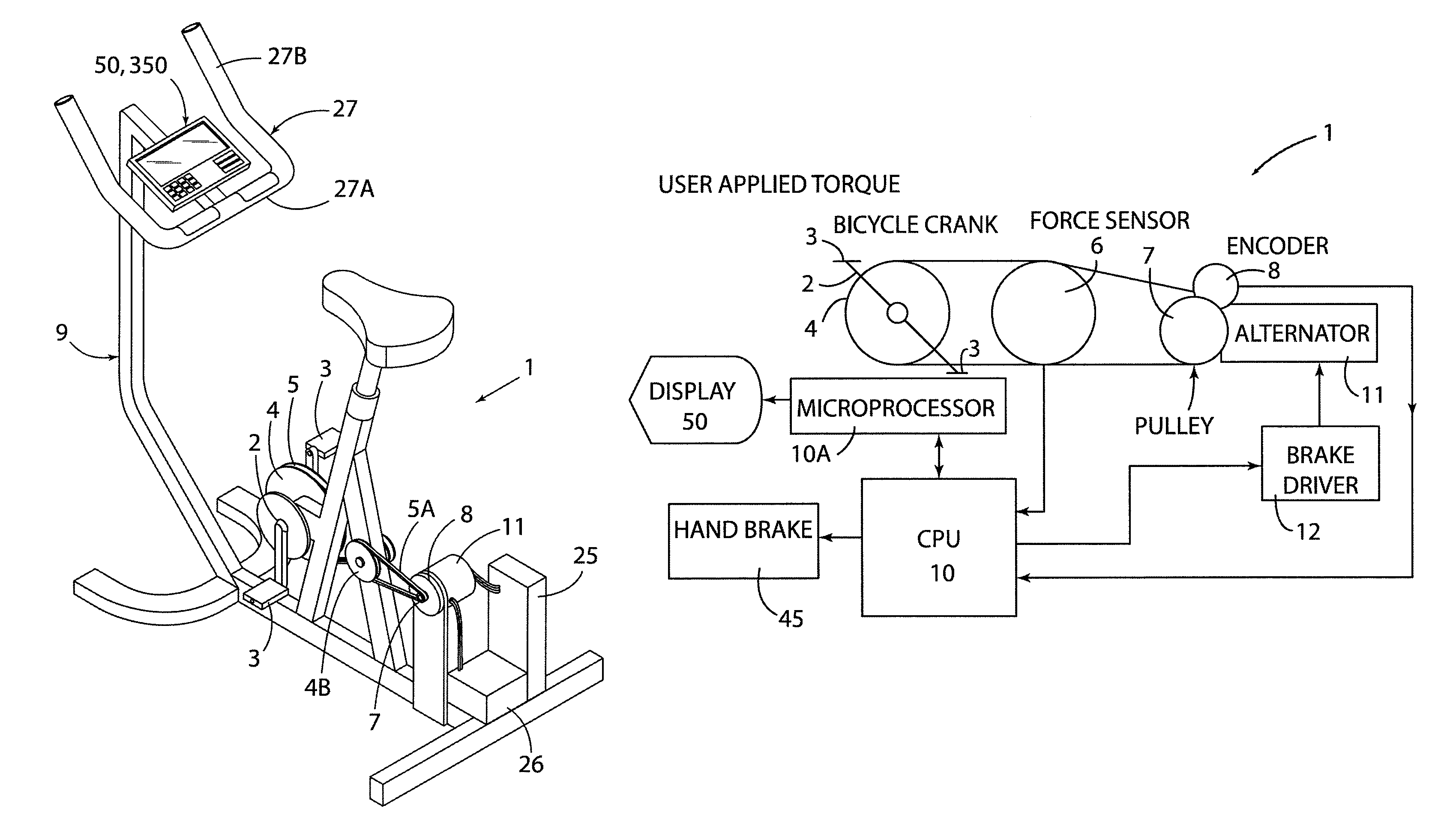
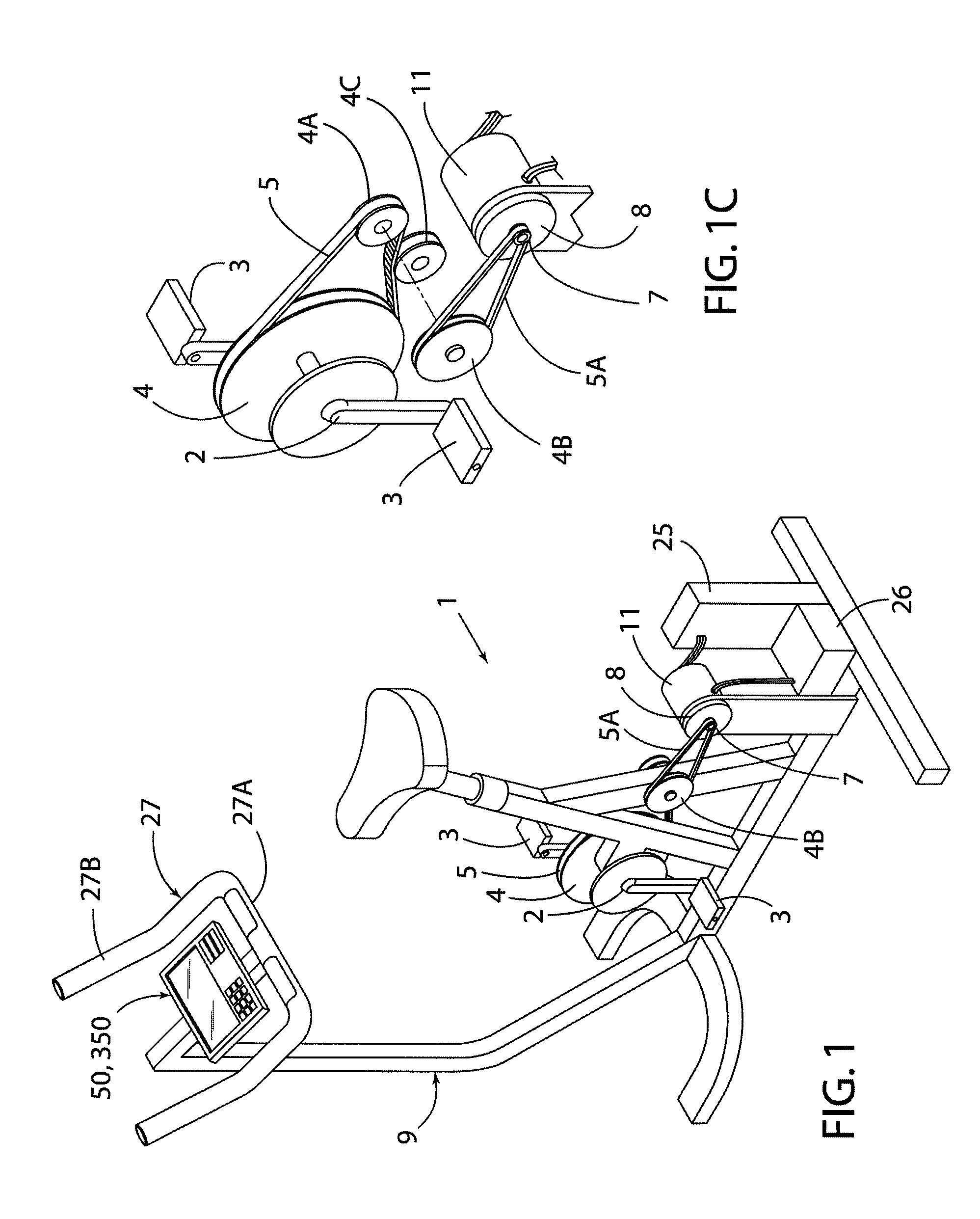
Stationary exercise equipment
A control system and method for exercise equipment and the like provides a way to simulate a physical activity in a manner that takes into account the physics of the physical activity being simulated to provide an accurate simulation. According to one aspect of the present invention, the control system and method takes into account the physics of the corresponding physical activity to generate a virtual or predicted value of a variable such as velocity, acceleration, force, or the like. The difference between the virtual or expected physical variable and a measured variable is used as a control input to control resistance forces of the exercise equipment in a way that causes the user to experience forces that are the same or similar to the forces that would be encountered if the user were actually performing the physical activity being simulated rather than using the exercise equipment.
Owner:RADOW SCOTT B
Fall protection safety device with a braking mechanism
ActiveUS20110147125A1Assisted movementSolve the lack of tensionDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesSafety beltsFall protectionElectromagnetic field
A fall protection safety device including a braking mechanism comprises a first component, a second component configured and arranged to move relative to the first component, and at least one magnet operatively connected to one of the components and another of the components being at least partially made of a non-ferromagnetic and electrically conductive material. The at least one magnet and the non-ferromagnetic and electrically conductive material creating an electromagnetic field force when the second component moves at a rate greater than a predetermined rate relative to the first component.
Owner:D B IND
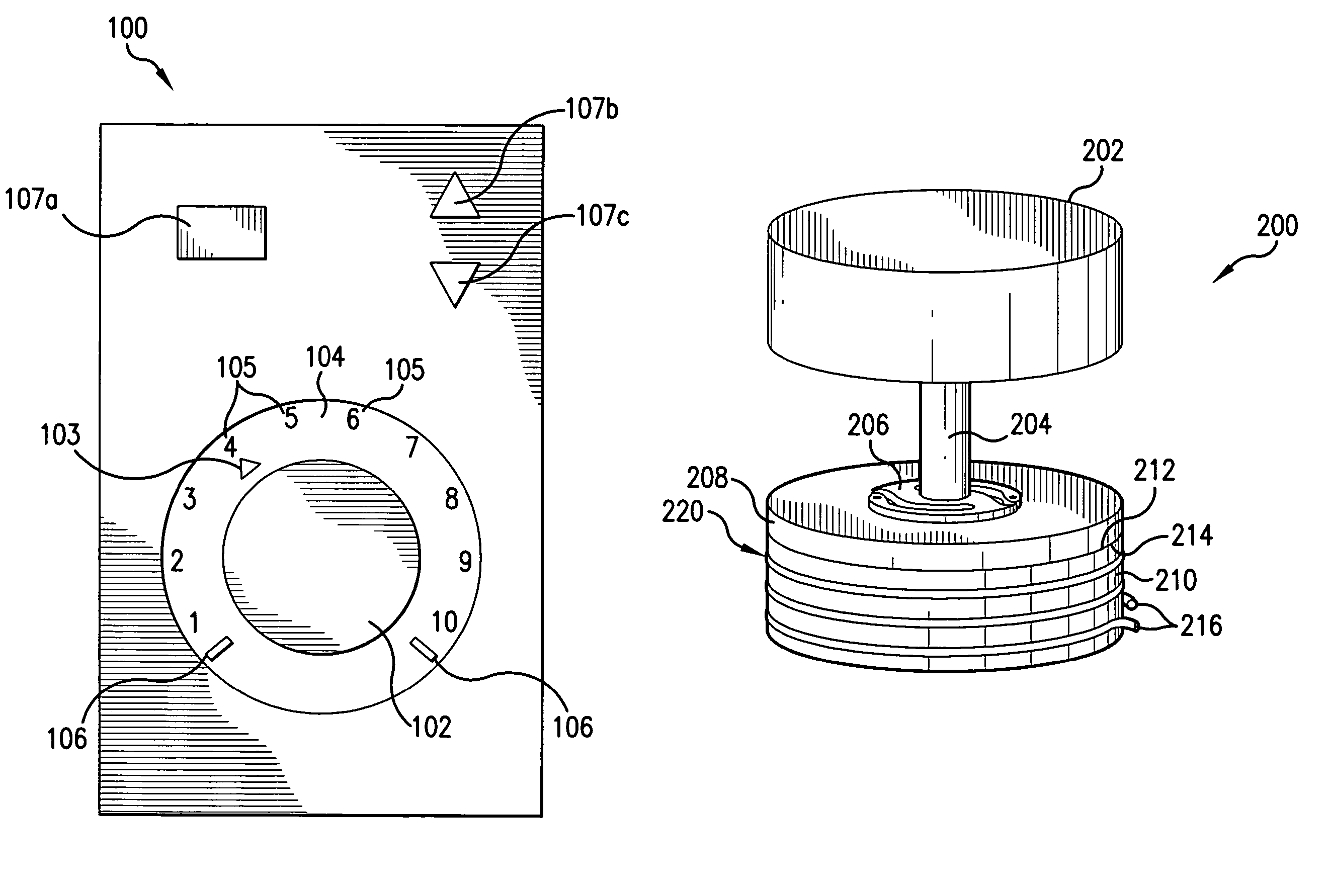
Speed changing magnetic pump
InactiveCN102434467ASo as not to damageAvoid electromagnetic interferenceDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesDynamo-electric gearsImpellerRotor magnets
The invention provides a speed changing magnetic pump, which comprises a pump body, a speed changing magnetic transmission device installed in a casing cavity and a driving motor. The speed changing magnetic transmission device comprises an inner magnetic rotor, an outer magnetic rotor, an isolation sleeve and a magnetic field adjusting ring. The inner magnetic rotor comprises an inner magnetic rotor magnet ring and an inner magnetic rotor magnet core, the outer magnetic rotor comprises an outer magnetic rotor magnet core and an outer magnetic rotor magnet ring which forms an annular cavity with the inner magnetic rotor magnet ring, and the isolation sleeve fixedly connected with a pump body is arranged in the annular cavity. The magnetic field adjusting ring fixedly installed on the isolation sleeve is an annular body formed by connecting a plurality of magnet core blocks and a plurality of epoxy blocks at intervals and used for adjusting magnetic fields of the inner magnetic rotor and the outer magnetic rotor to enable the rotating speed of an output rotating shaft connected to an impeller in a pump body to be different from the rotating speed of an input rotating shaft connected to the driving motor.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
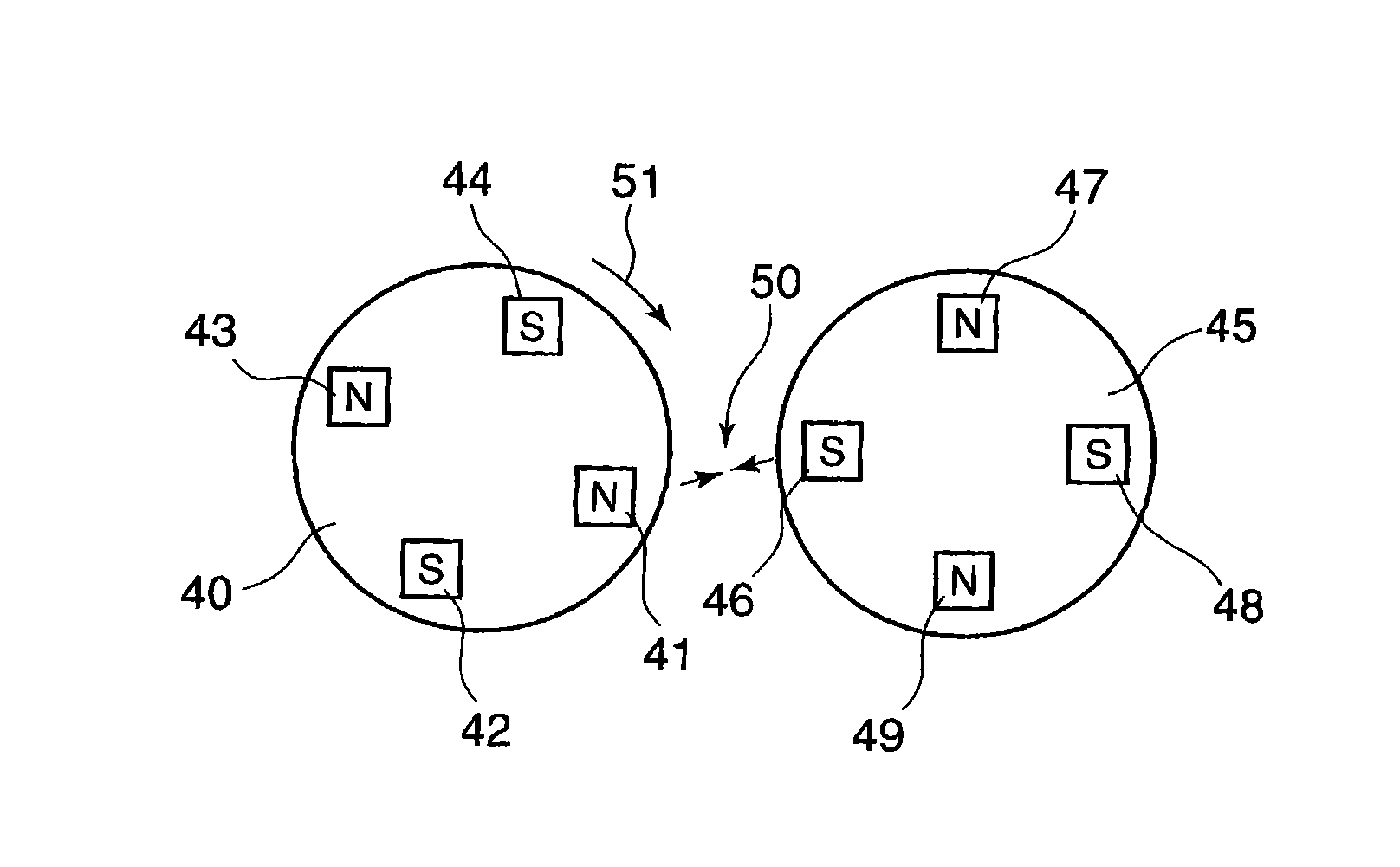
Magnetic transmission
Owner:NISSEN EDWARD WILLIAM
Magnetic controlled loading device in combination of a power generating set and an adjusting drive mechanism
InactiveUS7018324B1Lower the volumeAdjustment of loading resistanceDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesNon-rotating vibration suppressionMicro power generatorMagnetic flux
A magnetic controlled loading device in combination of a power generating set and an adjusting drive mechanism having a flywheel, a shaft, a transmission element, a magnetic controlled loading device, a micro power generating set and an adjusting drive mechanism integrated into one single unit. It can also be taken apart and used in various combinations. By fully utilizing the limited space without increasing the volume of the flywheel and internal components, a rotor and a stator are disposed in the center of the magnetic controlled loading device. This makes the rotor's permanent magnets to be set on top of the flywheel's inner ring, so that when the flywheel is in operation, it turns into a micro power generating set. By utilizing its self generating power supply, it can provide the power needed by a small motor and by manual adjustments it can also control the changes in magnetic flux density between the flywheel and device as well to achieve continuous adjustment of loading resistance.
Owner:LIN LILY
Power sensing eddy current resistance unit for an exercise device
InactiveUS7585258B2Accurately achieve desired power outputDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesElectrodynamic brake systemsElectrical resistance and conductanceUser input
Owner:SARIS CYCLING GROUP
Eddy current braking apparatus with adjustable braking force
InactiveUS20060278478A1Adjustable distanceGuaranteed uniform velocityDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesElectrodynamic brake systemsEngineeringLinearity
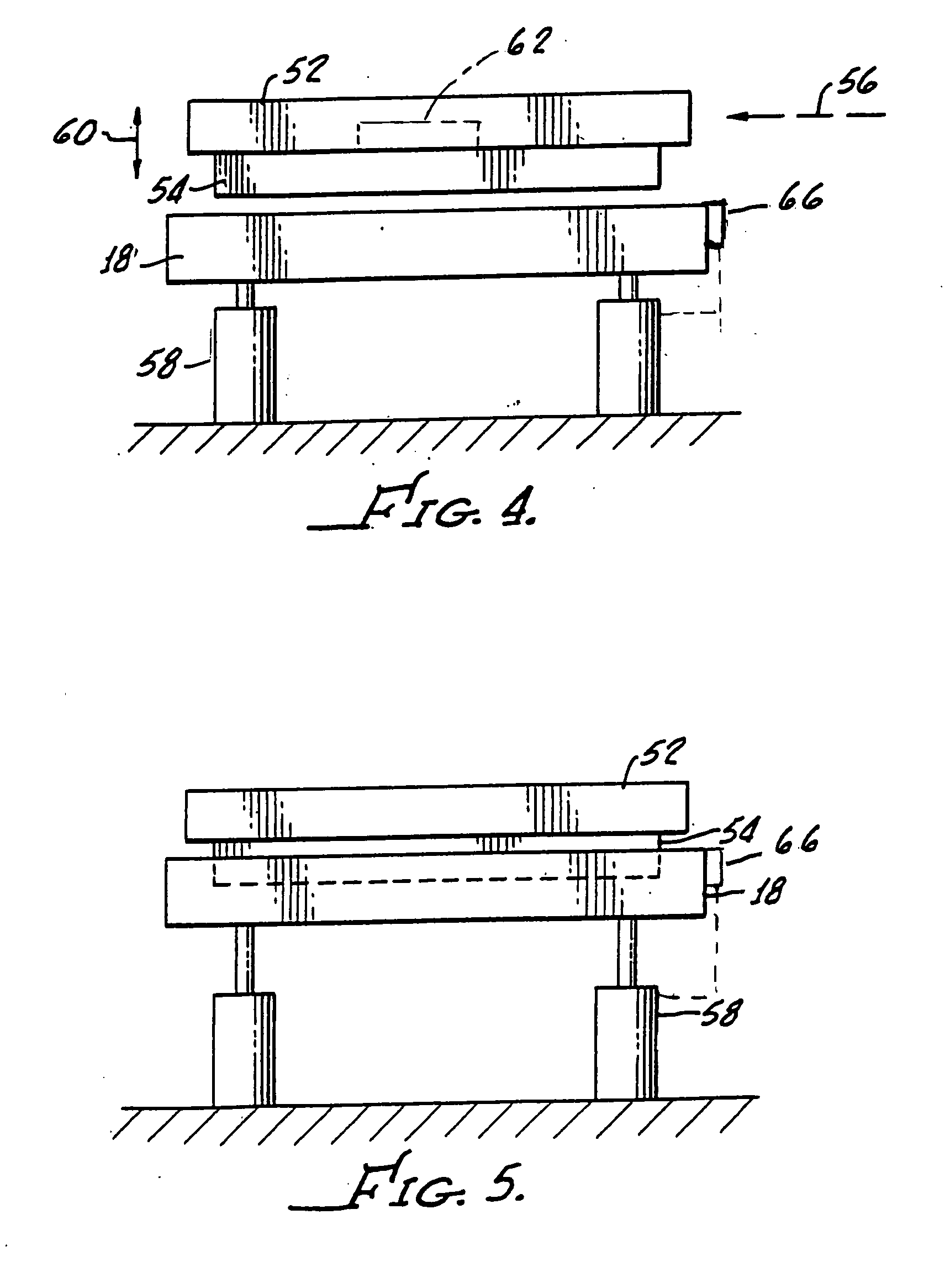
An eddy current brake includes a diamagnetic member, a first support wall and a second support wall with the first and second linear arrays of permanent magnets disposed on the walls facing one another. Apparatus is provided for moving at least one of the walls in order to control eddy current induced in the member in the passage of the member therepast to adjust the braking force between the magnets and the member. Apparatus is also provided for causing the velocity of the member to change the braking force between the magnets and the member.
Owner:MAGNETAR TECH
Apparatus, systems and methods for levitating and moving objects
InactiveUS6899036B2Rail devicesDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesElectrical polarityConductive materials
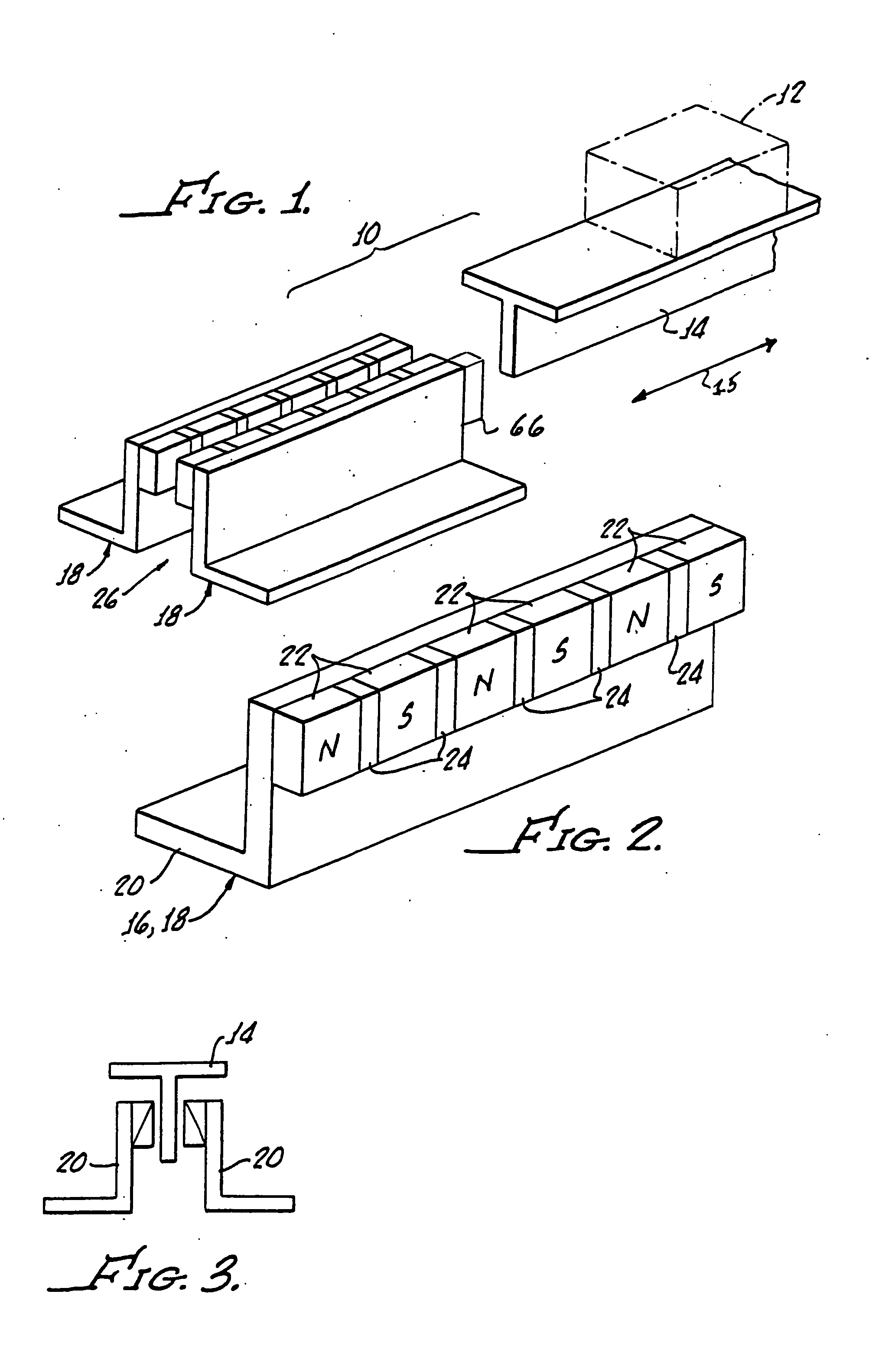
Apparatus, systems and methods for levitating and moving objects are shown and described herein. The embodiments incorporate a track with lower rails having permanent magnets abutted against each other and aligned such that the upper surface of each of the lower rails has a uniform polarity; and the object with upper rails having permanent magnets aligned with the lower rails and oriented to oppose the polarity of the lower permanent magnets. Ferrous backing plates behind the lower rails and / or the upper rails may be incorporated. Embodiments may also incorporate a third rail of an electroconductive material, and a driving disc positioned near the third rail. Permanent magnets in the driving disc may be rotated with the driving disc in the presence of the third rail to accelerate the upper rails with respects to the lower rails.
Owner:MAGNA FORCE
Apparatus, systems and methods for levitating and moving objects
InactiveUS7204192B2Improve efficiencyForce generatedRail devicesDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesEngineeringConductive materials
Owner:MAGNA FORCE
Electric machine apparatus with integrated, high torque density magnetic gearing
InactiveUS20070186692A1Dynamo-electric brakes/clutchesMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machineHigh torque
An electrical machine apparatus having magnetic gearing embedded therein includes a moveable rotor having a first magnetic field associated therewith, a stator configured with a plurality of stationary stator windings therein, and a magnetic flux modulator interposed between the moveable rotor and the stator windings. The magnetic flux modulator is configured to transmit torque between the first magnetic field associated with said moveable rotor and a second magnetic field excited by the plurality of stationary stator windings.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Modular transverse flux motor with integrated brake
InactiveUS20060192453A1Increased torque densityImprove efficiencySynchronous generatorsDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesTransverse fluxMotor end plates
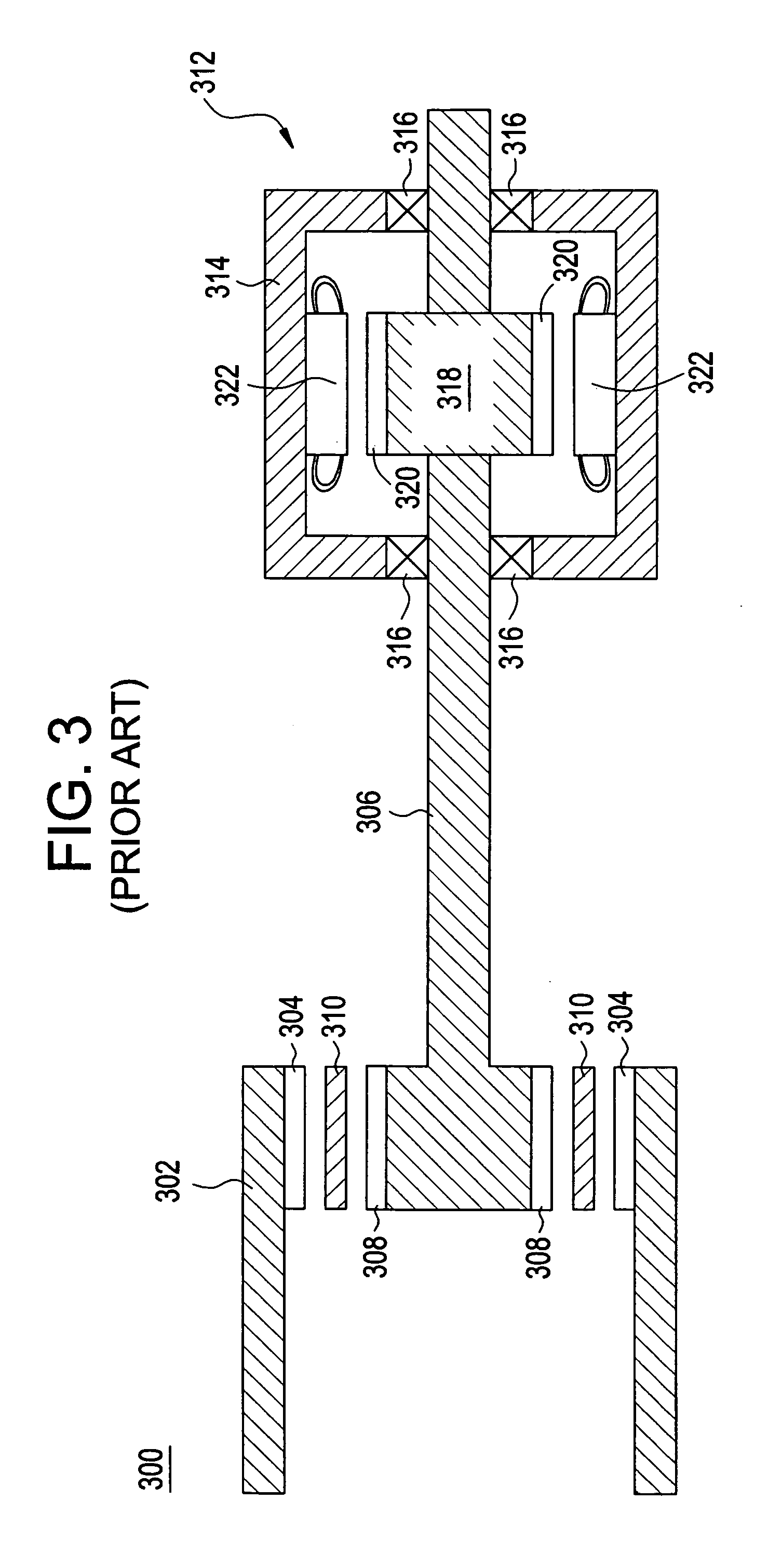
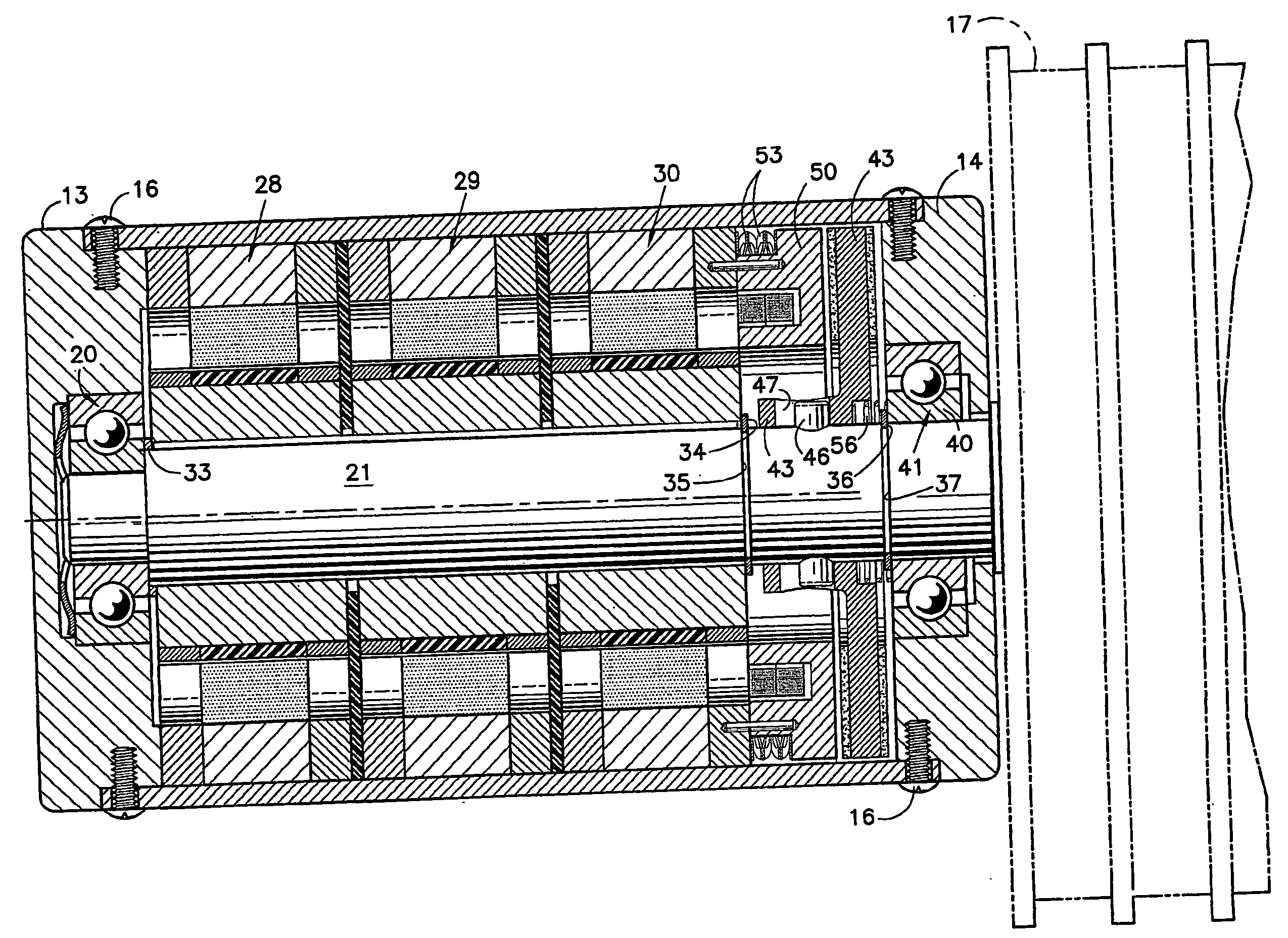
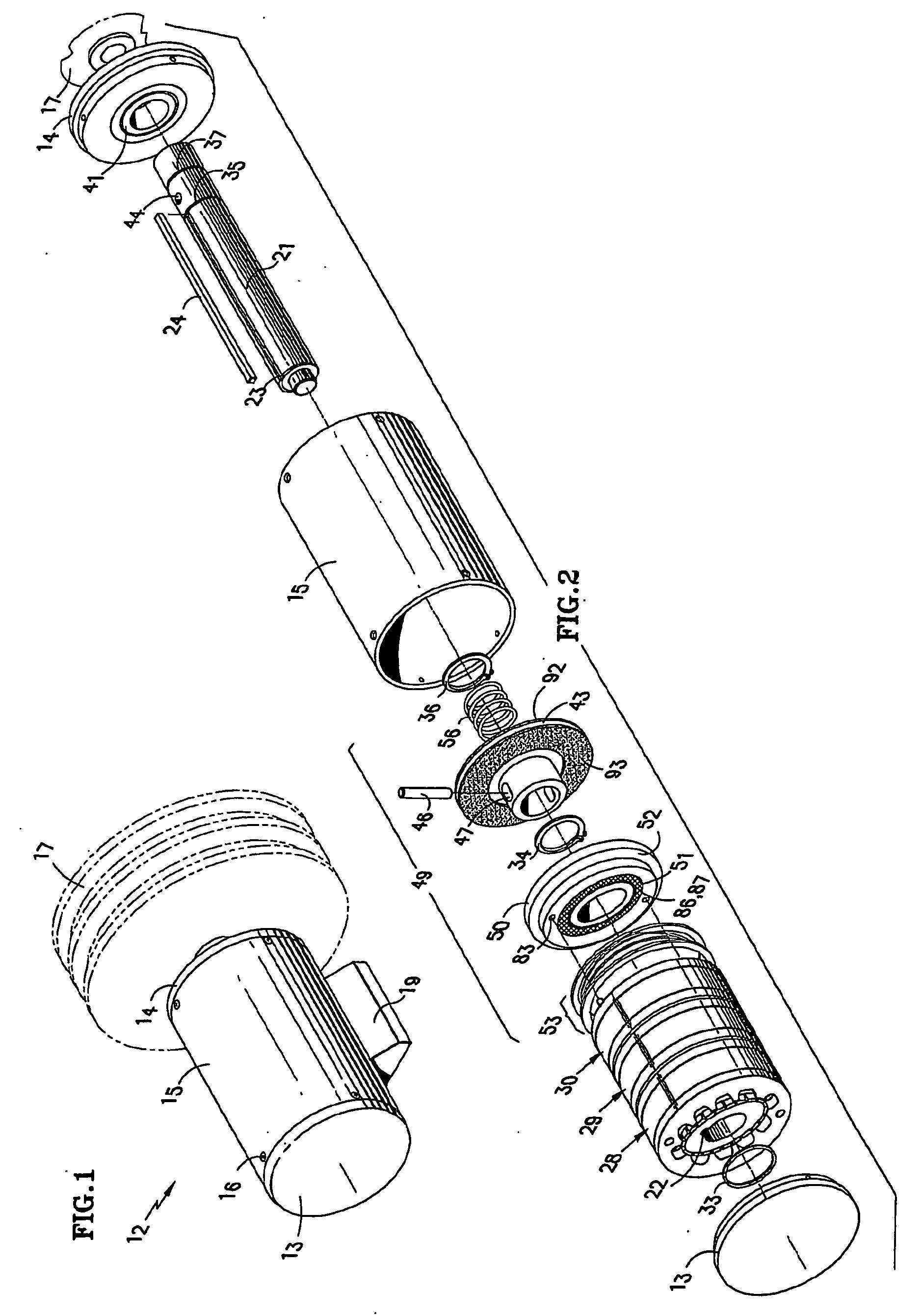
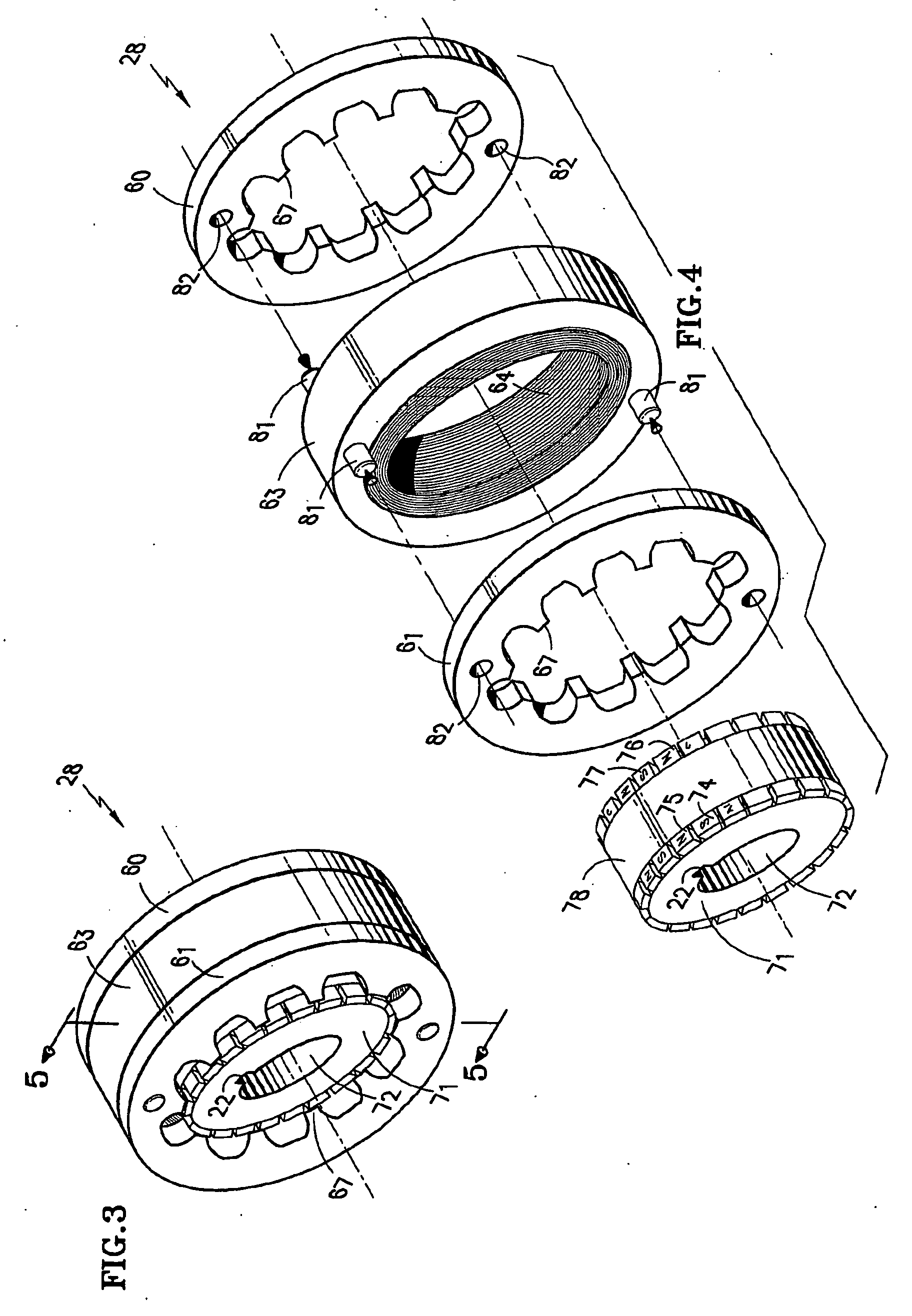
An elevator machine (12) has a plurality of identical transverse flux rotor / stator modules (28-30) of a generally cylindrical configuration arranged contiguously on a common shaft (21) to provide torque to the shaft equal to the torque capability of the modules times the number of modules. A disc brake (49) is integrated with the motor; a two-sided brake disc (49) has friction pads (92, 93) on both sides, braking force being applied to motor end plate (14) and through the brake disc to a stator (60) of one phase (30) of the motor. A process (113) forms variously-sized motors from identically sized modular components, in various configurations (12, 100, 110).
Owner:OTIS ELEVATOR CO
Variable magnetic coupling of rotating machinery
ActiveUS7791235B2Reduce vibration transmissionDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesMechanical actuated clutchesCouplingEngineering
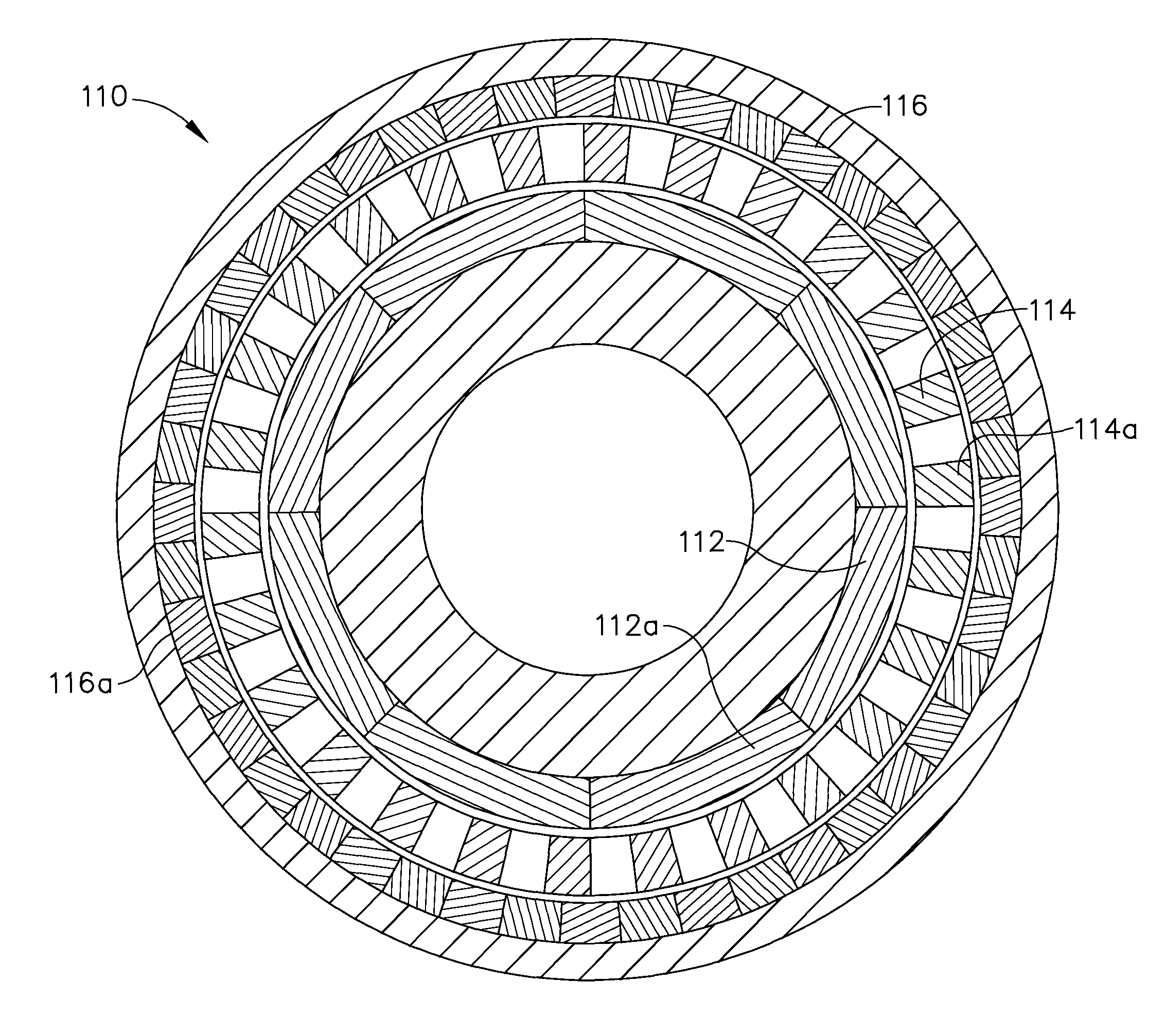
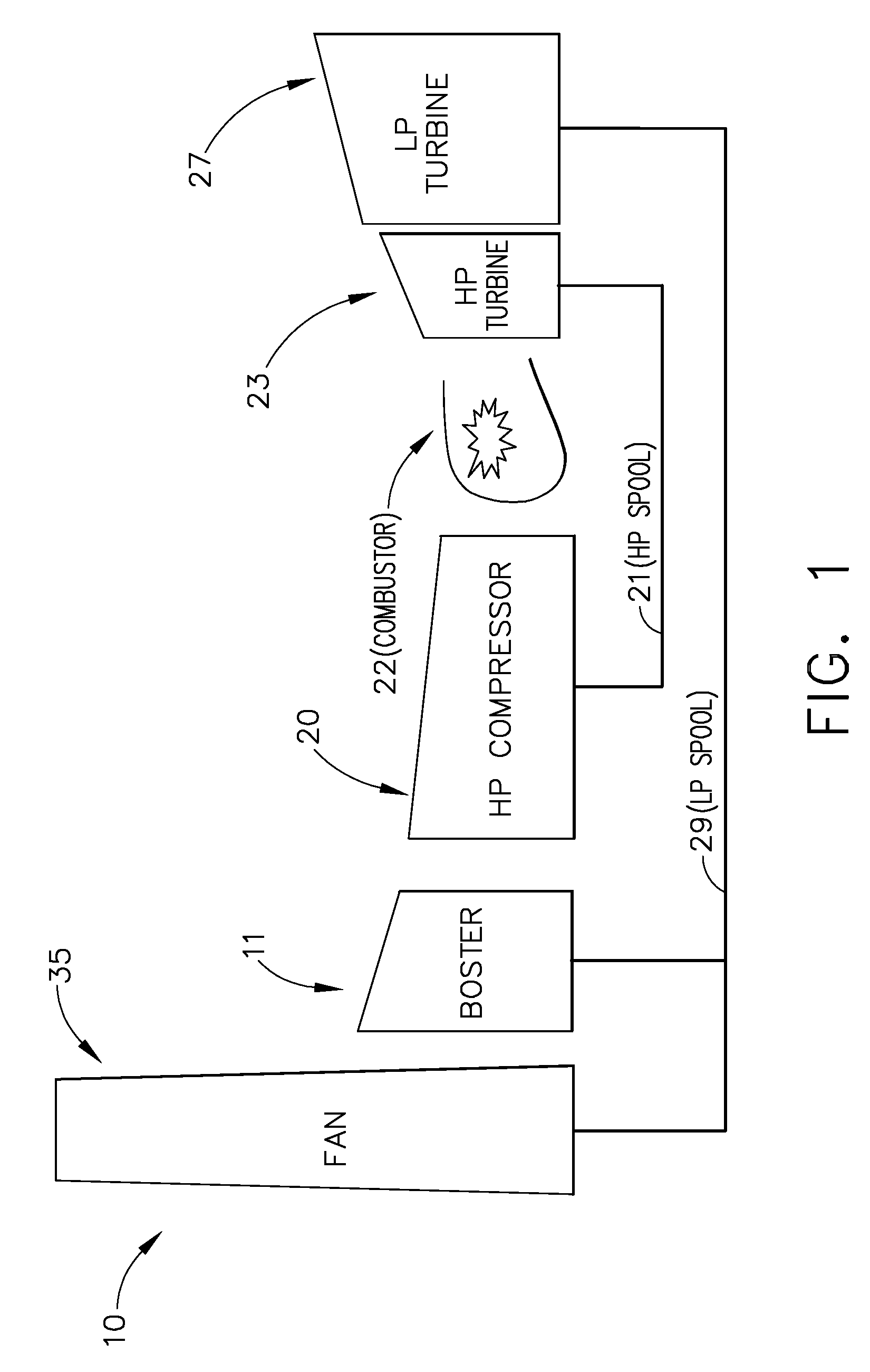
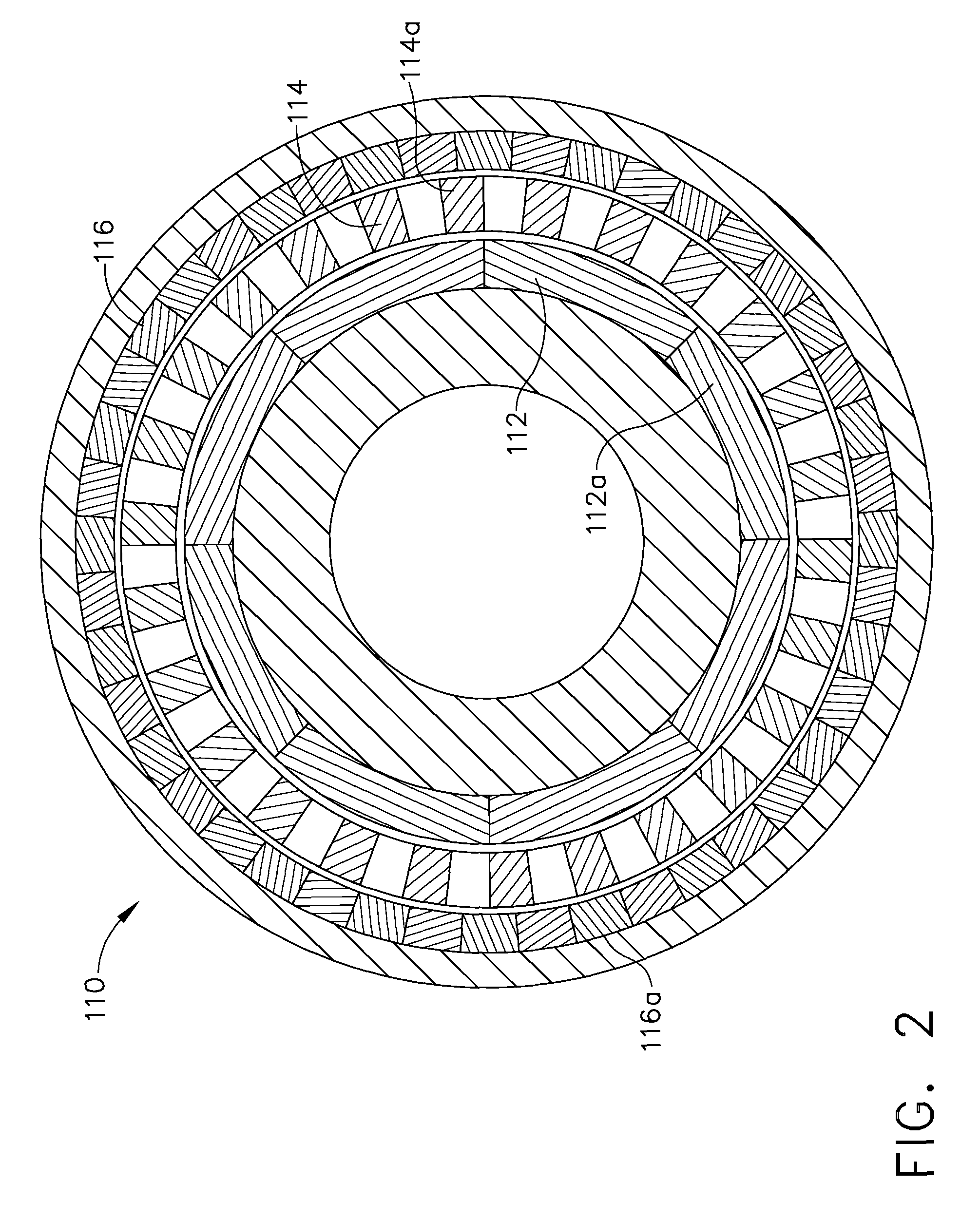
A system for transferring torque between a pair of independently, concurrently rotating shafts of a turbofan engine includes a magnetic gearbox. The magnetic gearbox has a first ring structure, a second ring structure and an intermediate ring structure. Each ring structure has an annular aperture therethrough and a plurality of permanent magnets embedded therein. The intermediate ring structure is disposed between the first and the second ring structures. Each ring structure is coaxially concentric with, and independently rotatable with respect to the remaining ring structures. The first and second ring structures are each coupled to separate ones of the rotating engine shafts, and the intermediate ring is operable to transfer torque between the pair of shafts. Preferably, the intermediate ring structure is coupled to a rotating machine. The rotating machine has a controller, and is operable for adjusting a ratio of torque transferred between the pair of shafts.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
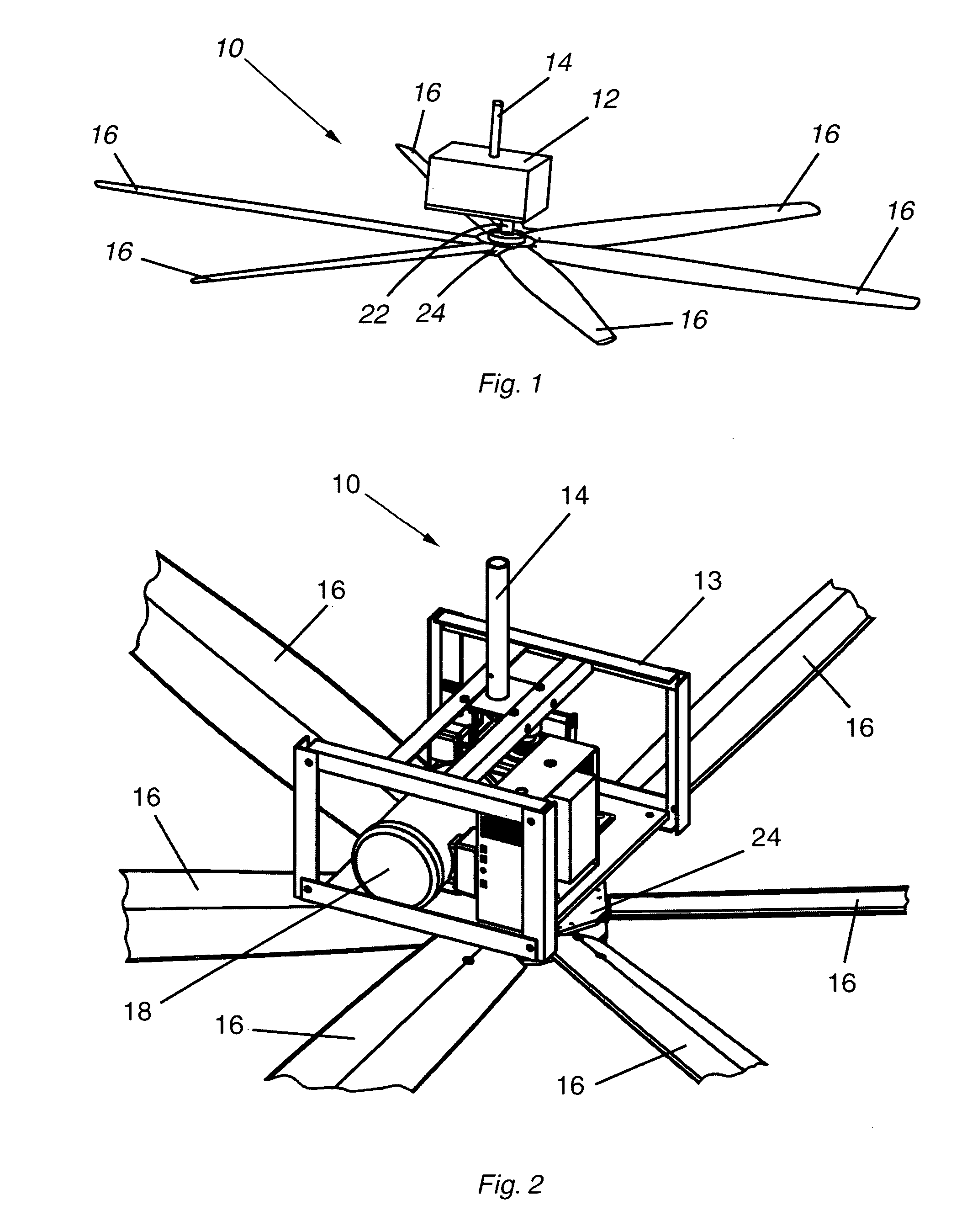
High volume low speed fan
ActiveUS8066480B2Promote circulationEasy to controlDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesPropellersAir cycleLow speed
A high volume low speed (HVLS) fan provides improved air circulation and thermal control in a building by incorporating composite fan blades pivotable to both positive and negative pitch angles. The blades are molded of polymer material over a metal tube core for strength and ease of attachment to the fan hub, and have a symmetrical airfoil shape to produce an efficient bi-directional conical airflow. The fan includes a control unit providing manual and automated intelligent control over blade angle and rotational speed, as well as startup with approximately zero blade angle for more economical power consumption and less motor wear. The fan structure and mounting system allows the fan to be installed at an optimal height inside a variety of buildings to provide increased efficiency of air destratification and air mixing. An array of multiple HVLS fans with alternating directions of airflow can further increase efficiency of air movement.
Owner:AIRMOTION SCI
Hybrid-vehicle drive unit
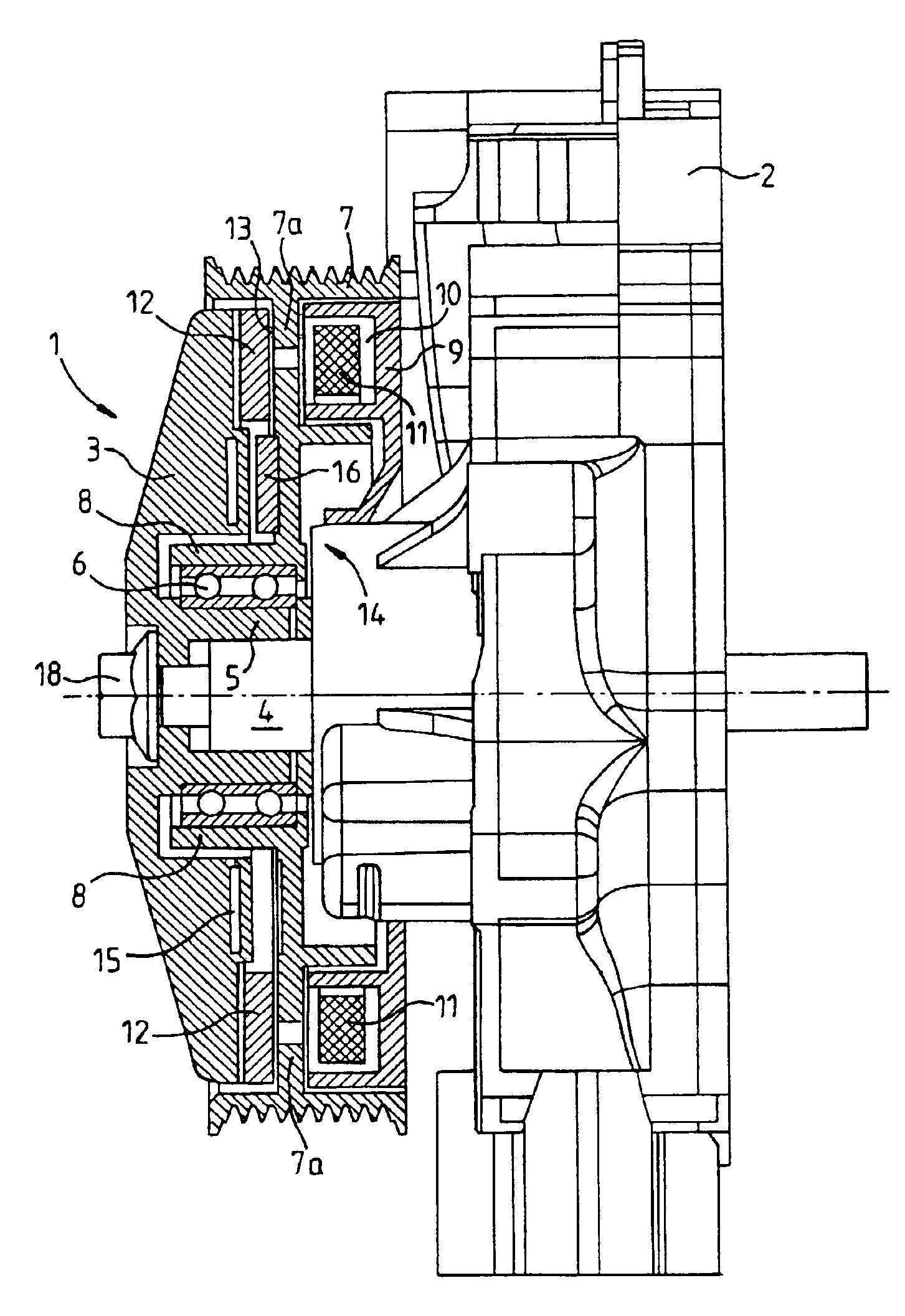
InactiveUS6777837B2Improve accuracyImprove motor efficiencyReciprocating combination enginesDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesInternal combustion engineHybrid vehicle
A hybrid-vehicle drive unit supports a motor-generator with high precision, improving the efficiency of the motor-generator, and reducing the size of the motor-generator, independent of any influence of centering precision of the crank shaft and of deformation of the torque converter. According to the invention, a motor housing is disposed between a converter housing and an internal combustion engine, and a bearing is fitted to a lateral wall provided in a front portion of the motor housing. Rotor supporting members are independently supported by the bearing. Eccentric rotation of the crank shaft resulting from explosive vibrations of the engine is counteracted by two flex plates. Owing to a predetermined clearance, one of the rotor supporting members as a separate component is free from the influence of deformation of the torque converter.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD +1
Permanent magnet machine
A permanent magnet machine and a rotor assembly for the permanent magnet machine. The permanent magnet machine includes a stator assembly including a stator core configured to generate a magnetic field and extending along a longitudinal axis with an inner surface defining a cavity and a rotor assembly including a rotor core and a rotor shaft. The rotor core is disposed inside the stator cavity and configured to rotate about the longitudinal axis. The rotor assembly further including a plurality of permanent magnets for generating a magnetic field which interacts with the stator magnetic field to produce torque. The permanent magnets are disposed within one or more cavities formed in a sleeve component. The sleeve component configured to include a plurality of cavities or voids therein and thus provide minimal weight to the permanent magnet machine. The permanent magnet machine providing increased centrifugal load capacity, increased power density and improved electrical performance.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Magnetic rotation transmitting device, hermetic stirring unit, and electric furnace
InactiveUS20050206260A1Dynamo-electric brakes/clutchesRotary stirring mixersElectric arc furnaceMagnetic rotation
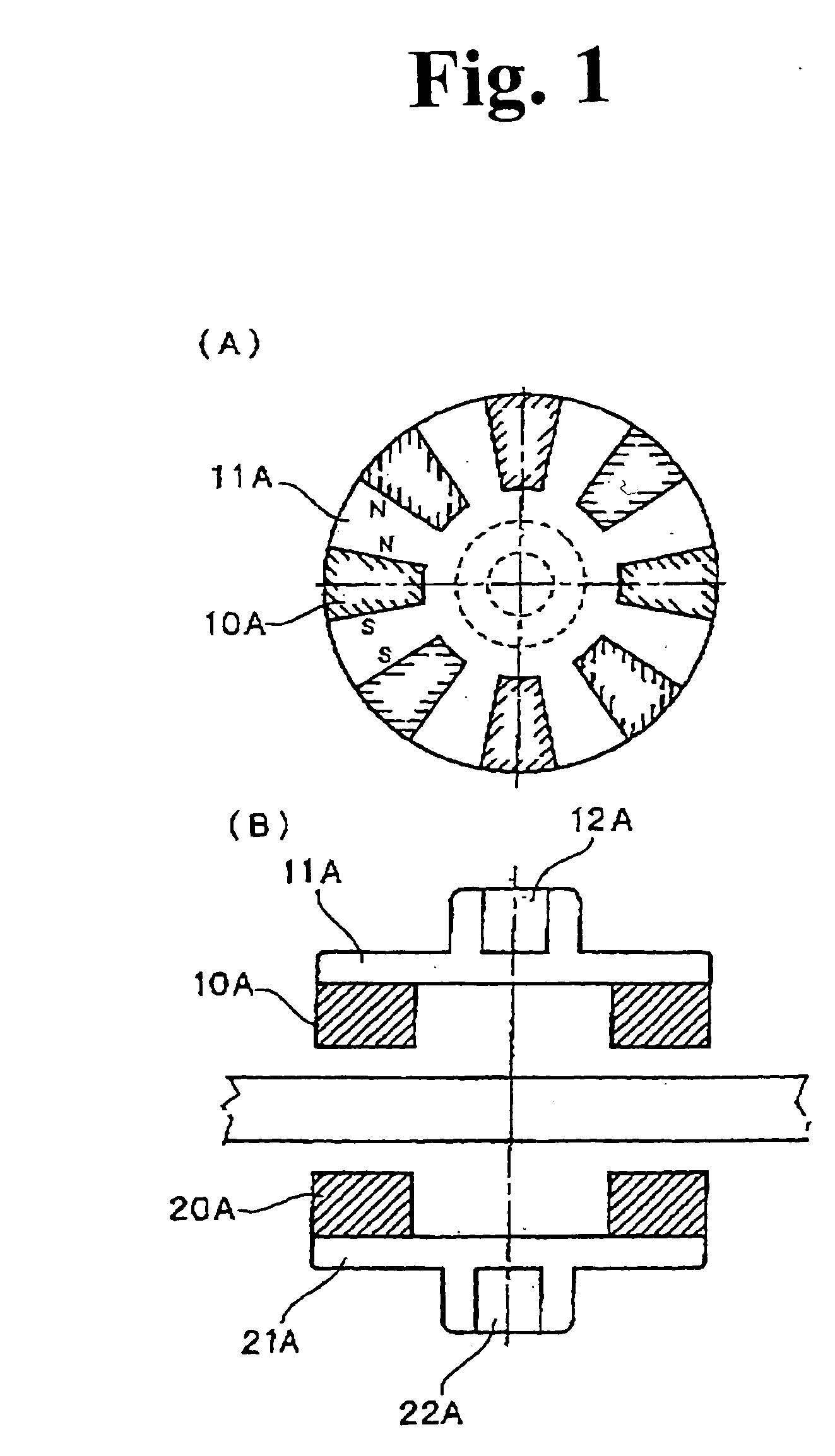
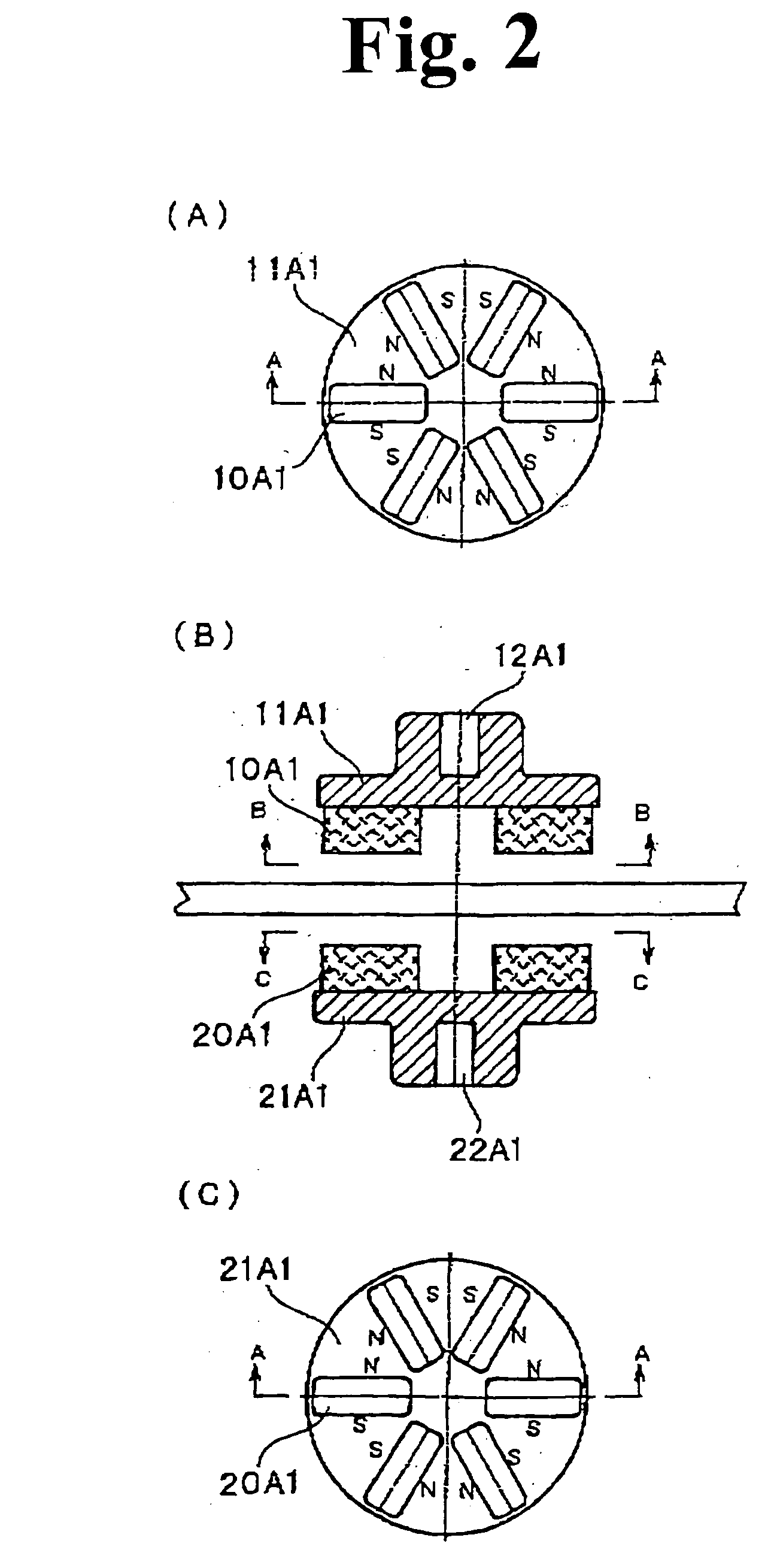
In order to provide a magnetic rotation transmitting device capable of obtaining a large transmitting torque without using a large-sized permanent magnet, in an axial-type magnetic rotation transmitting device, which includes a driving rotation body having one or plural magnetic line(s) in which plural first magnets (10A) are disposed in a circumferential direction on a first disk (11A) at almost equal intervals, a drive source rotationally driving a drive shaft of the driving rotation body, and a driven rotation body having one or plural magnet line(s) in which second magnets (20A) of the same number as the first magnets (10A) are disposed in the circumferential direction on a second disk (21A) at almost equal intervals, symmetrically disposed to, and magnetically coupled with the driving rotation body with a magnetic coupling gap and, which utilizes a magnetic operation and which allows the driven rotation body to rotate by rotationally driving the drive shaft by means of the drive source, the first magnet (10A) has a N-magnetic pole portion and a S-magnetic pole portion, and an extended surface of a boundary surface between the N-magnetic pole portion and the S-magnetic pole portion approximately overlaps with a driving center line as being a rotation center line of the driving rotation body, the second magnet (20A) has the N-magnetic pole portion and the S-magnetic pole portion, and the extended surface of the boundary surface between the N-magnetic pole portion and the S-magnetic pole portion approximately overlaps with a driven center line as being the rotation center line of the driven rotation body, adjacent and facing surfaces of the first magnets (10A) adjacent to each other on the first disk (11A) are disposed so that magnetic pole faces having the same polarity make pairs, and adjacent and facing surfaces of the second magnets (20A) adjacent to each other on the second disk (21A) are disposed so that the magnetic pole faces having the same polarity make pairs.
Owner:MAGUNEO
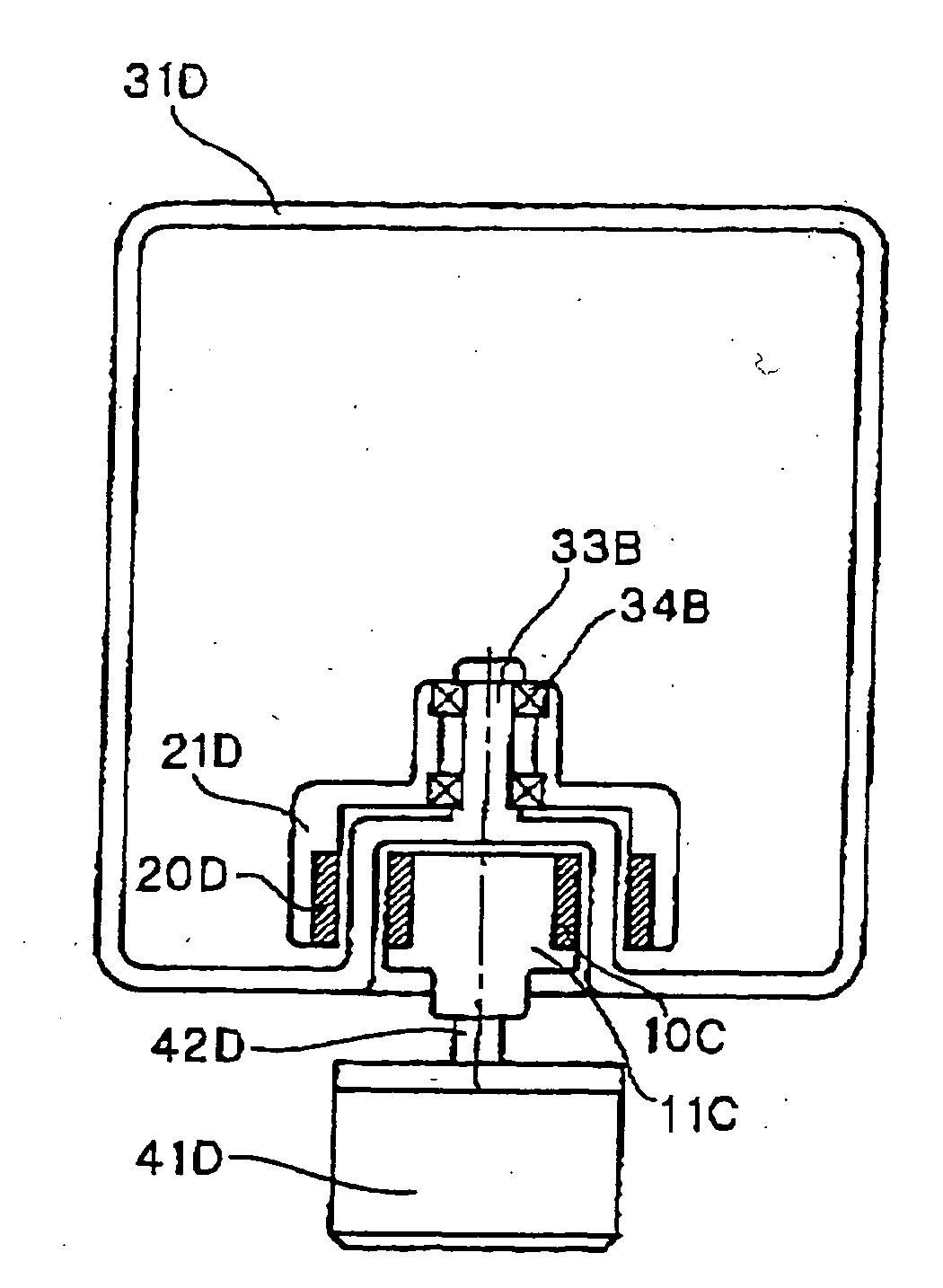
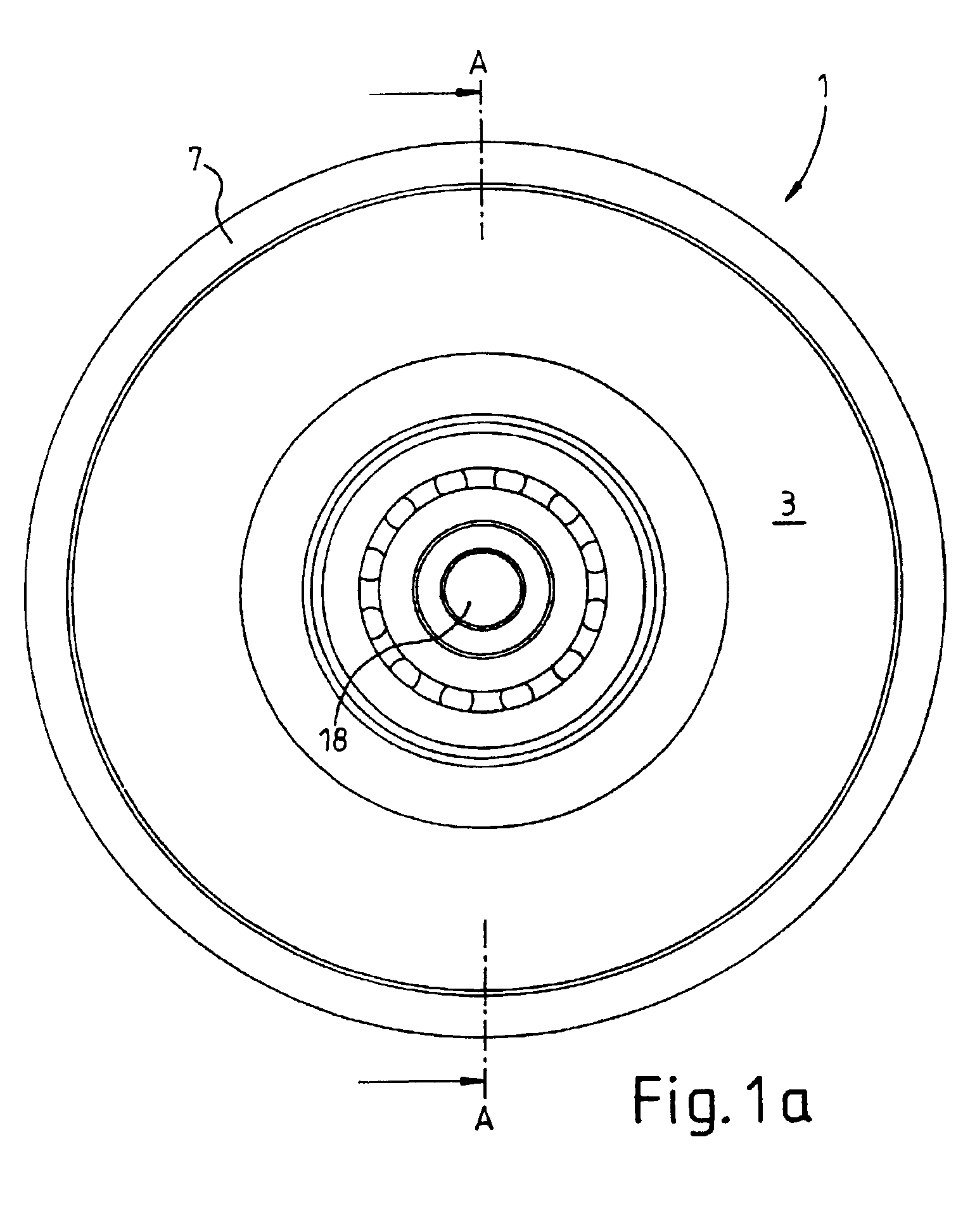
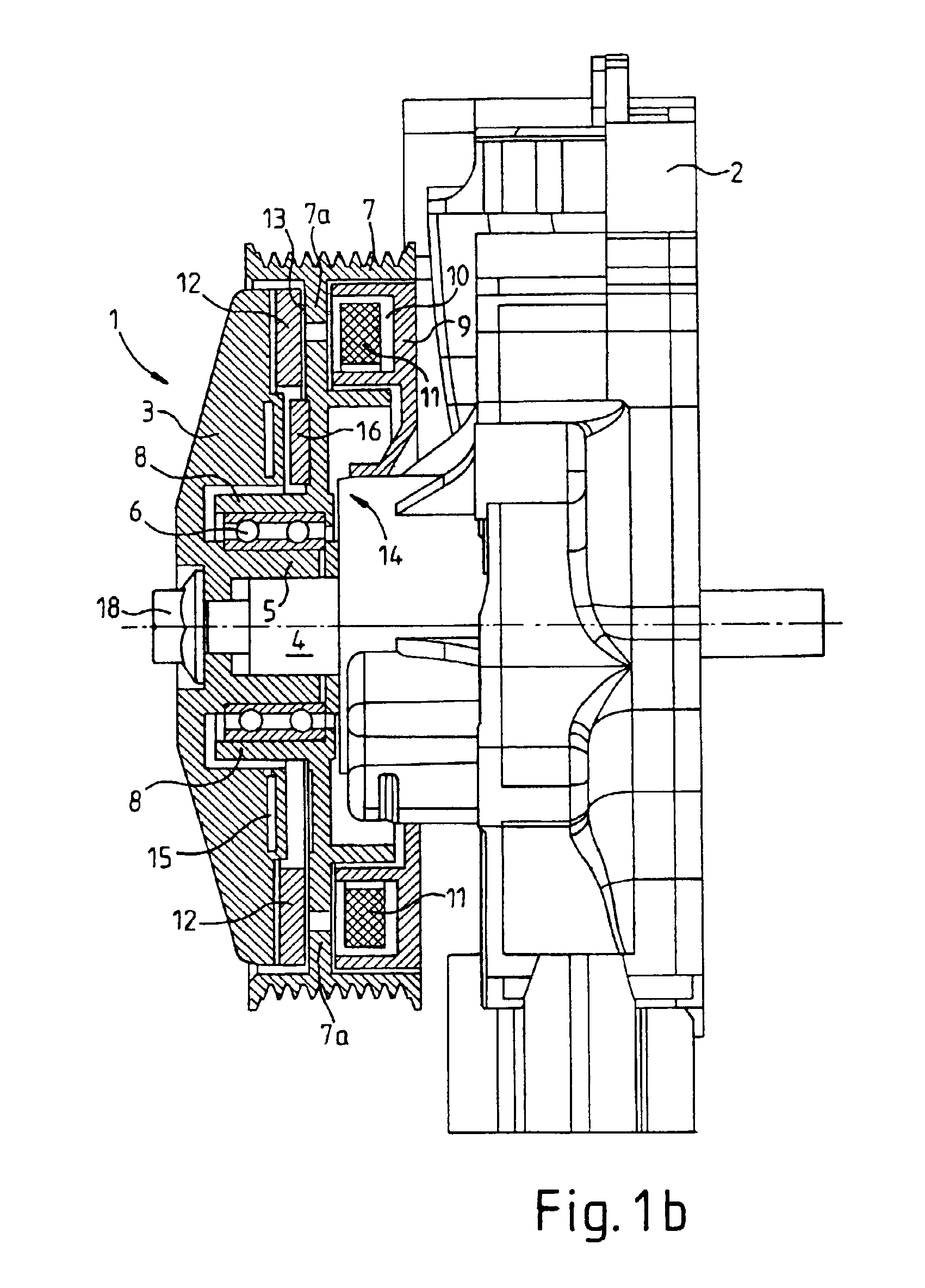
Drive member for a water pump of the cooling-water circuit of an internal combustion engine and frictional shift clutch
A drive member (1) for a water pump of the cooling-water circuit of an internal combustion engine, with a drive wheel (7) and a shaft (4) which is coupled to the water pump, is proposed. According to the invention, for the transmission of torque between the drive wheel (7) and the shaft (4), an electromagnetically actuable friction-disk clutch (9, 10, 11, 12) and a second clutch device in the form of an eddy-current clutch (14) are provided, the latter taking up the shaft (4) when the friction-disk clutch is out of engagement. Moreover, a frictional shift clutch for a drive member of this type is proposed.
Owner:LICOS TRUCKTEC
Permanent magnet generator
InactiveUS6087750AIncreased longevityIncreased durabilitySynchronous generatorsDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesEngineeringPermanent magnet synchronous generator
A permanent magnet generator is described. The generator includes a shaft which defines a longitudinal axis. A rotatable magnetic field assembly is mounted on the shaft and adapted for rotation about the shaft. The magnetic field assembly includes a plurality of axially magnetized magnets which are retained in a cavity about the shaft for generating an axial magnetic flux. A plurality of vanes are mounted on the magnetic field assembly housing for rotating the magnetic field assembly about the shaft when a fluid flows past the vanes. A stationary armature assembly is also located around the shaft in a position axially spaced from the magnetic field assembly. The armature assembly generates AC power when the magnetic field assembly is rotated. The stationary armature assembly includes an armature housing. An axial bore is formed through the armature housing for receiving the shaft. The armature housing defines a cavity about the axial bore in which a plurality of laminated bars are retained. A plurality of electrically conductive wires are wrapped around the laminated bars to form coils.
Owner:PACIFIC SCI ELECTRO KINETICS DIV
Centrifugal magnetic clutch
A centrifugal magnetic clutch device includes, an input shaft and, a plurality of input magnets that are rotatable about an axis of the input shaft, and are radially movable relative to the input shaft axis, and are rotationally fixed to the input shaft. The device further includes, a plurality of output magnets rotatable about the input shaft axis and in axial alignment with the plurality of input magnets, and an output shaft rotationally fixed to the plurality of output magnets. The device further includes, a housing for fluidically sealing the plurality of output magnets and the output shaft relative to the plurality of input magnets and the input shaft.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Axial rotary eddy current brake with adjustable braking force
InactiveUS20070000741A1Dynamo-electric brakes/clutchesNon-rotating vibration suppressionCentre of rotationEngineering
The present invention relates to an axial adjustable, rotary brake device using eddy current resistance, having an annular rotating conductive reaction member fastened on a central axle, having a frame, and fitted with permanent magnets disposed on either one side or both sides of said member, wherein the magnets produce a magnetic field between the magnet arrays, and through the member. Relative motion of the member and magnets produces eddy current resistance opposing the movement of the member. The magnets are mounted such that their respective positions relative to each other and thus to the intermediate conductive member can be changed by an adjusting Structure to increase or decrease the space between magnets and member, (air gap), distance from the rotational center or their relationship to each other. Various other configurations for changing the spatial relationship of magnets and members are presented which can be employed to produce many embodiments and variations of the present invention.
Owner:MAGNETAR TECH
Disk drive employing a spindle motor comprising a locking spring arm disengaged through stator coil flux
InactiveUS6867946B1Dynamo-electric brakes/clutchesRecord information storageEngineeringMagnetic flux
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk, a head actuated radially over the disk, and a spindle motor for rotating the disk. The spindle motor comprises a stator having at least one stator coil wrapped around a stator tooth. The spindle motor further comprises a hub rotated by the stator when current is applied to the stator coil, and a locking spring arm having a fixed base. The locking spring arm engages the hub when no current is applied to the stator coil, and the locking spring arm disengages from the hub when current applied to the stator coil generates a magnetic flux which pulls the locking spring arm away from the hub.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
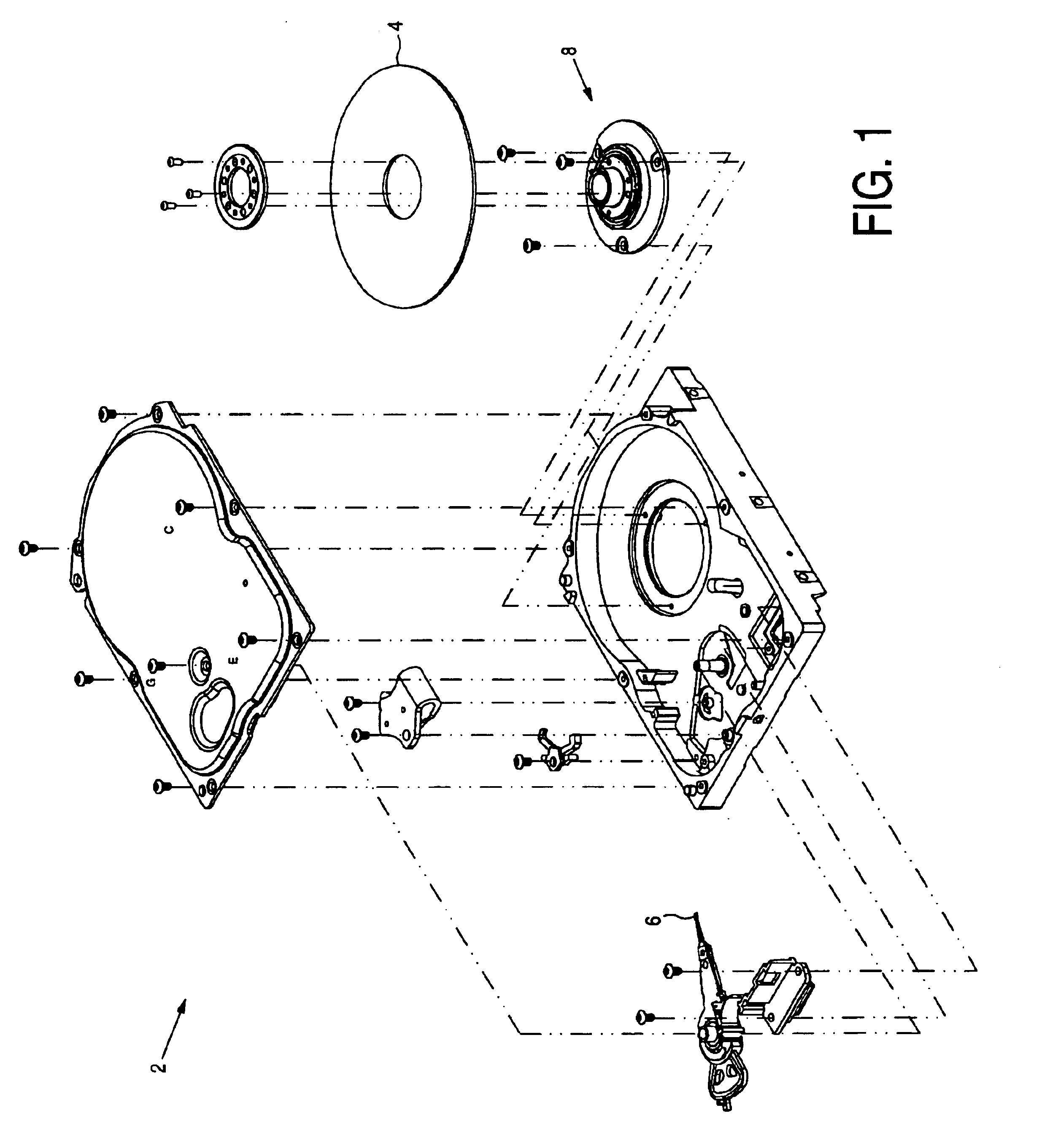
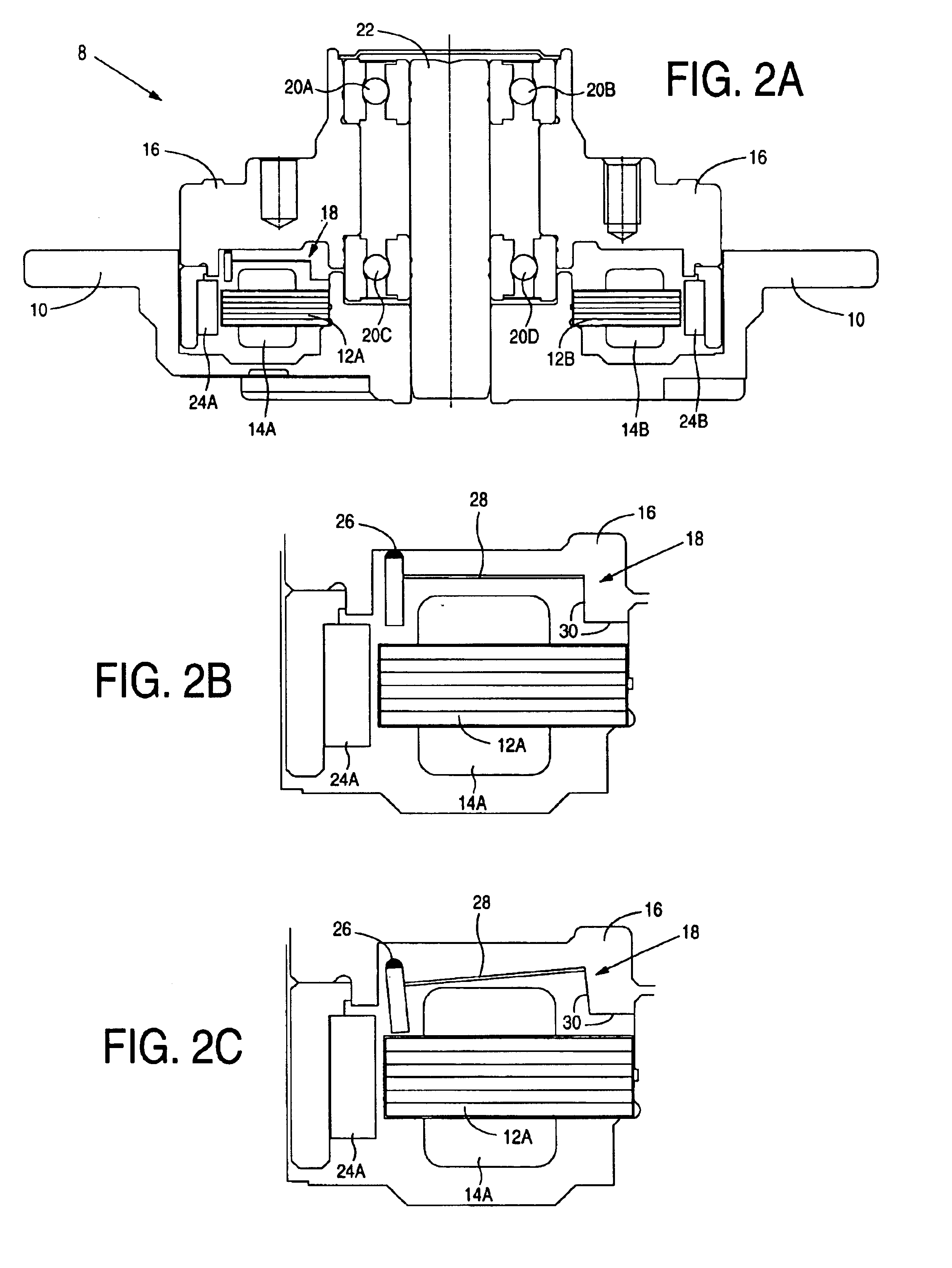
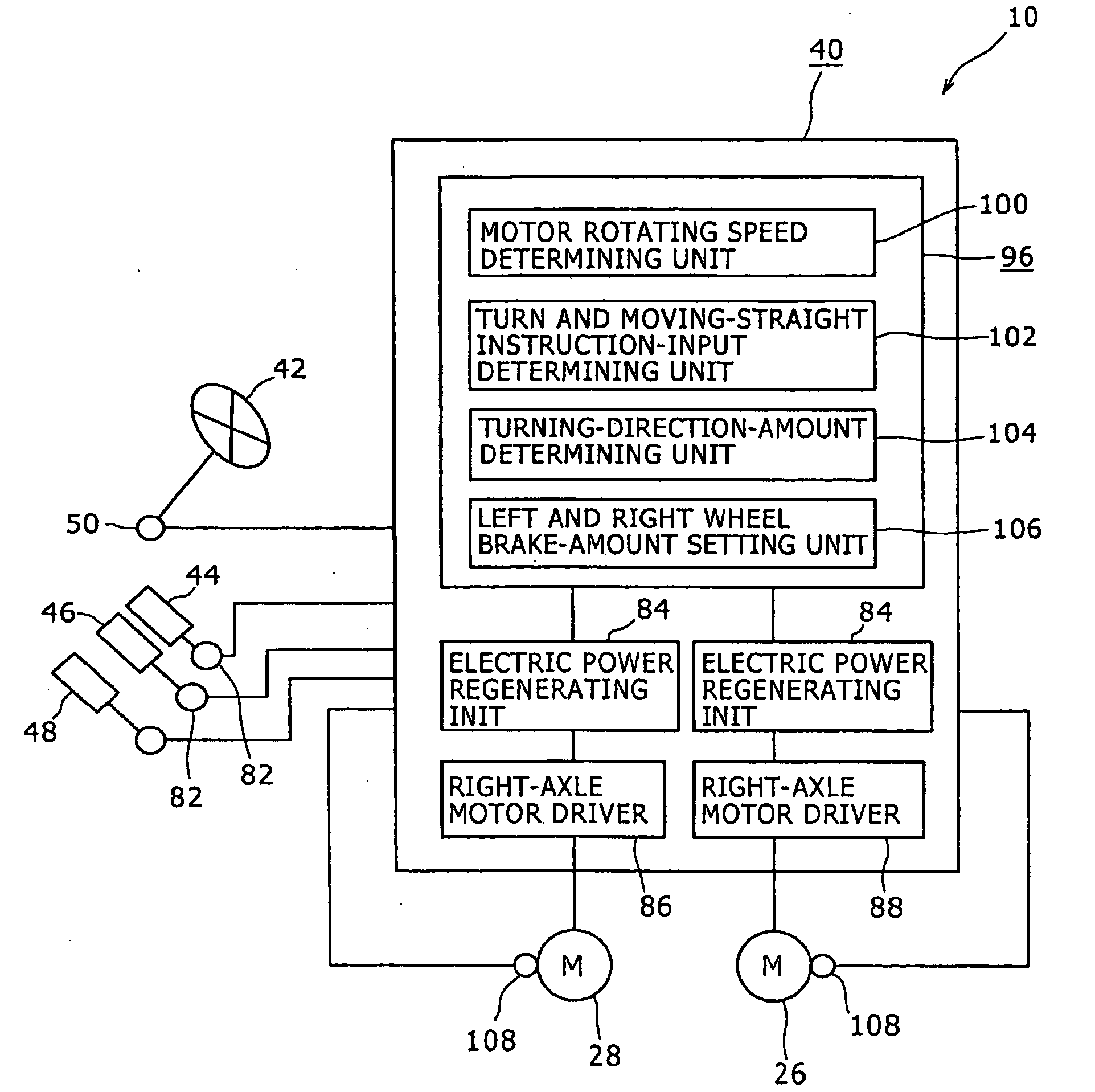
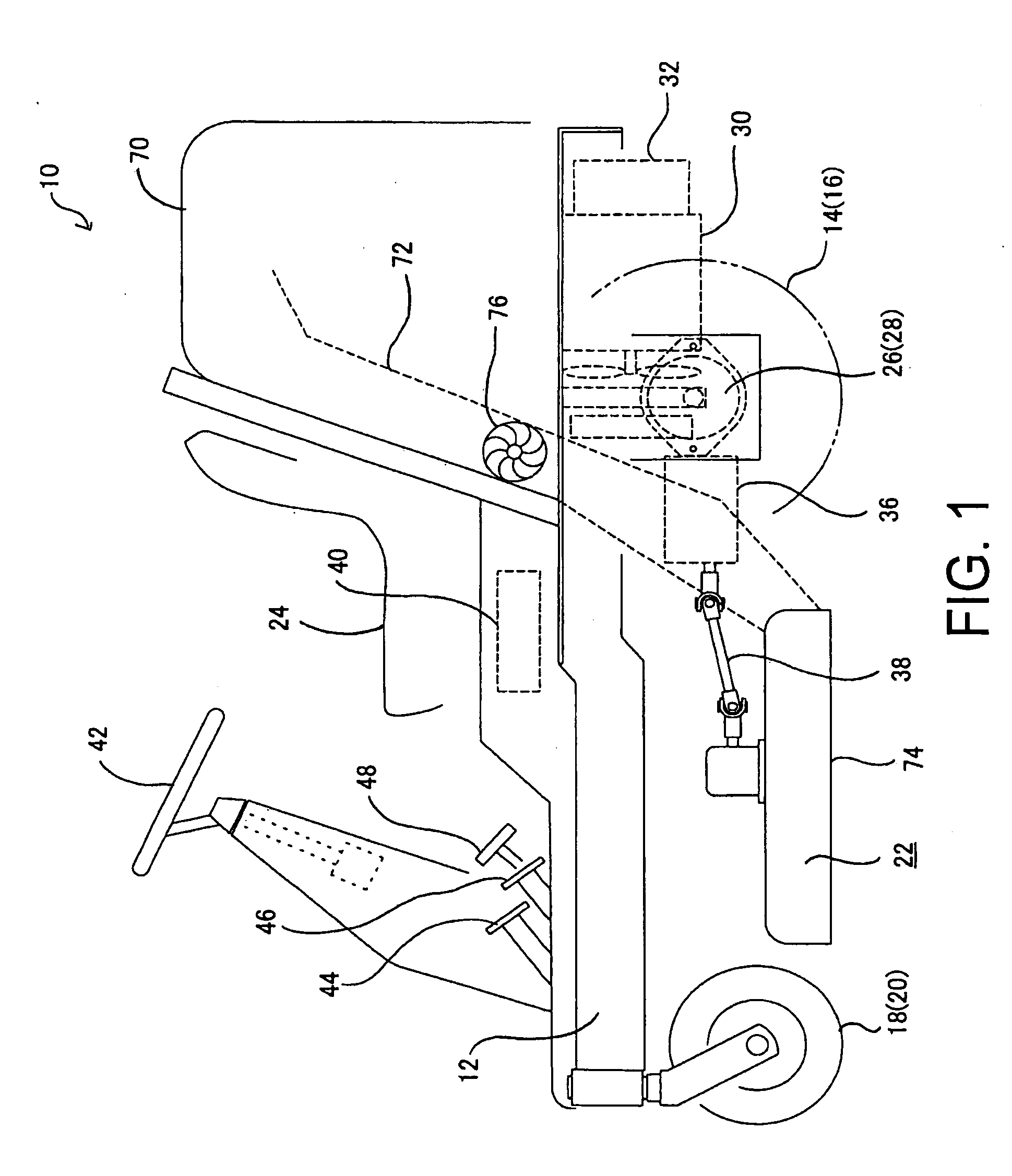
Electric ground working vehicle
ActiveUS20090260901A1Efficient executionReduce speedDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesDigital data processing detailsRegenerative brakeElectric power
There is provided an electric ground working vehicle including a left wheel and a right wheel, at least one caster, a working apparatus, an acceleration operating element for performing acceleration instructions, a turn operating element for performing turn instructions, and a control unit. The left wheel and the right wheel are independently driven by left and right electric motors respectively. The control unit controls a regenerative brake driving unit so that electric power is regenerated from the left and right electric motors to an electric power source unit when the acceleration operating element is not operated during traveling to regeneratively brake the left and right wheels. The control unit controls the brake force of the wheels so that the brake force of the wheel at the inside of a turn, among the left wheel and the right wheel, can be made greater than the brake force of the wheel at the outside of a turn when the acceleration operating element is not operated during traveling and turn instructions are inputted from the turn operating element.
Owner:KANZAKI KOKYUKOKI MFG
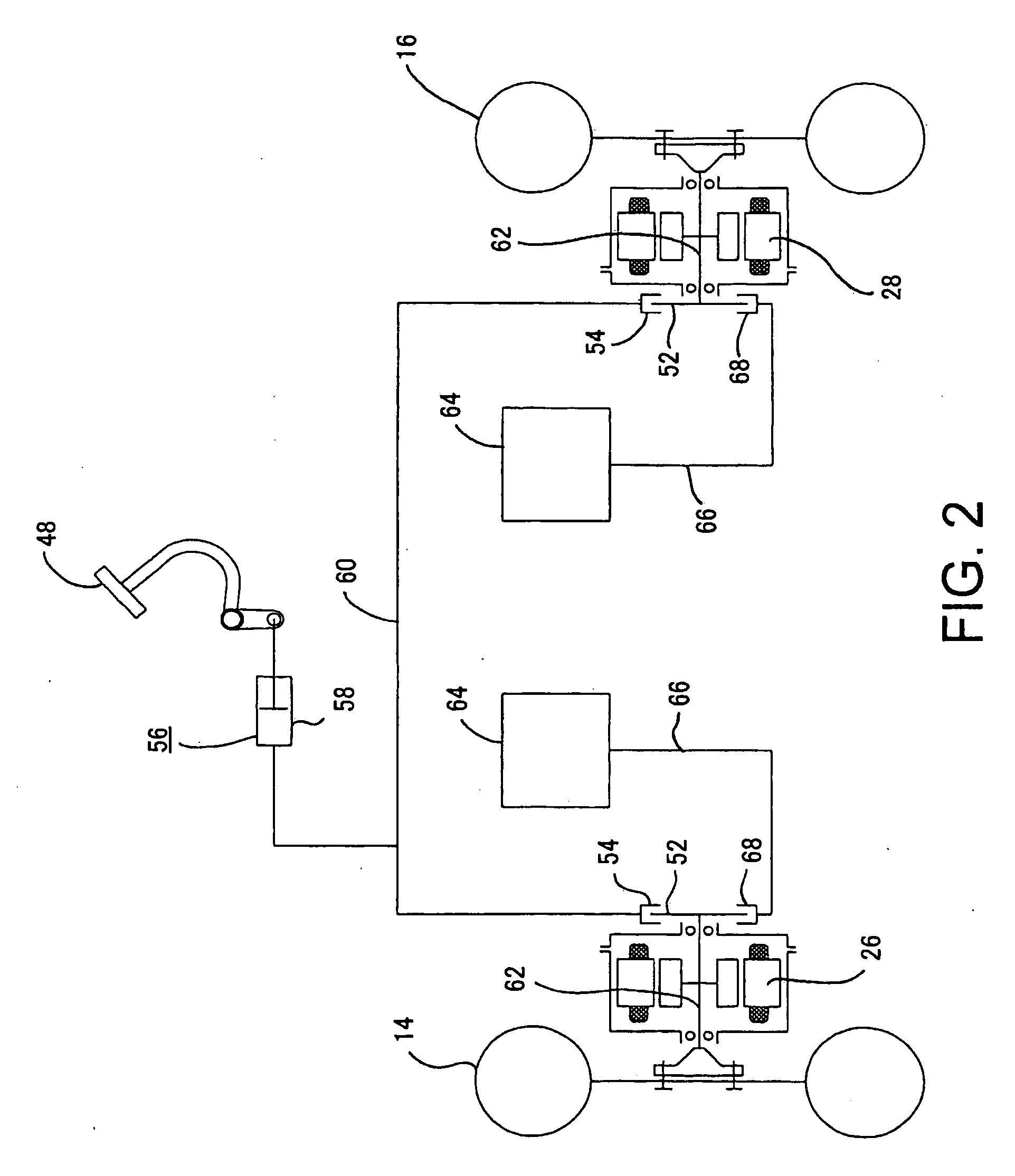
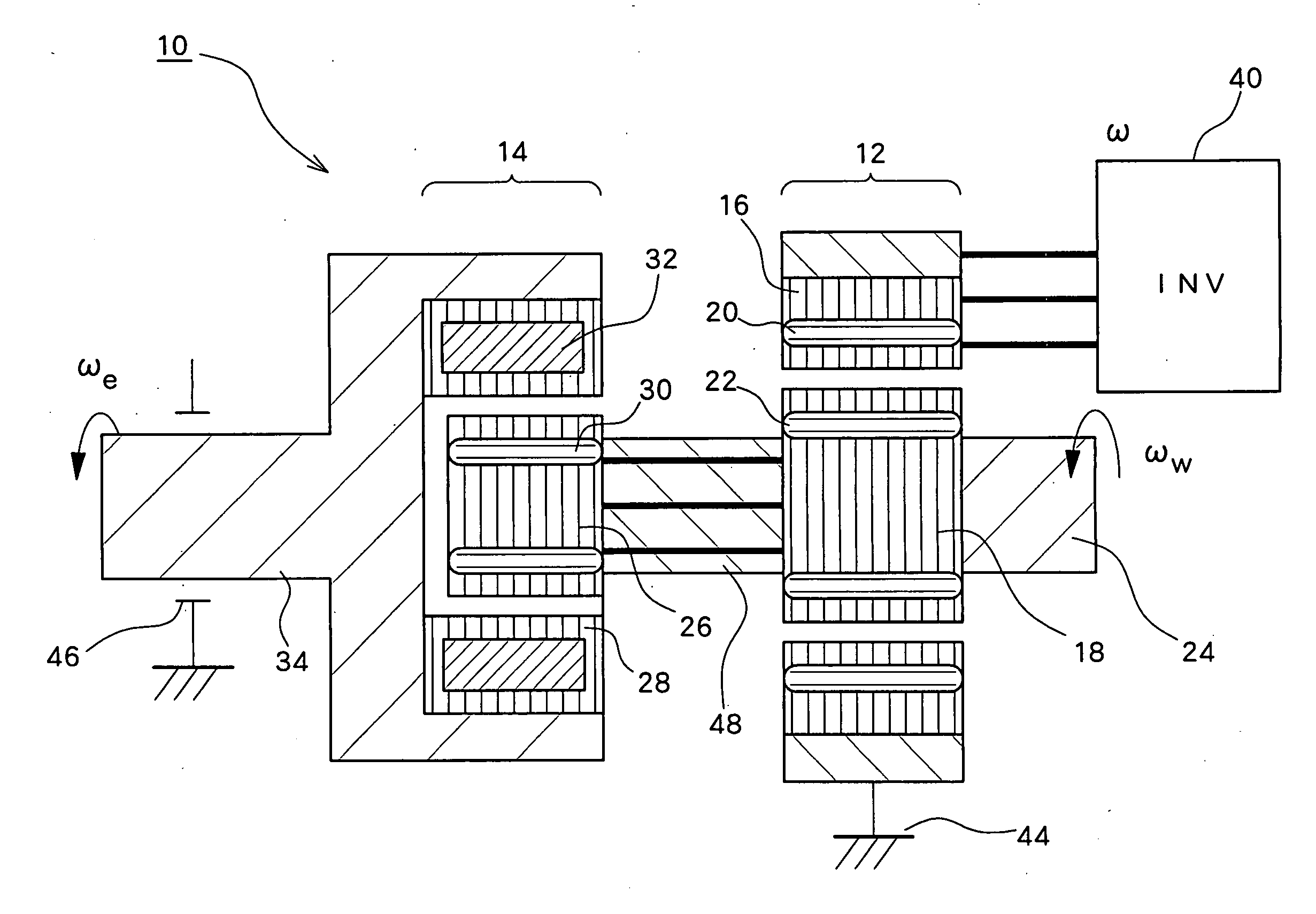
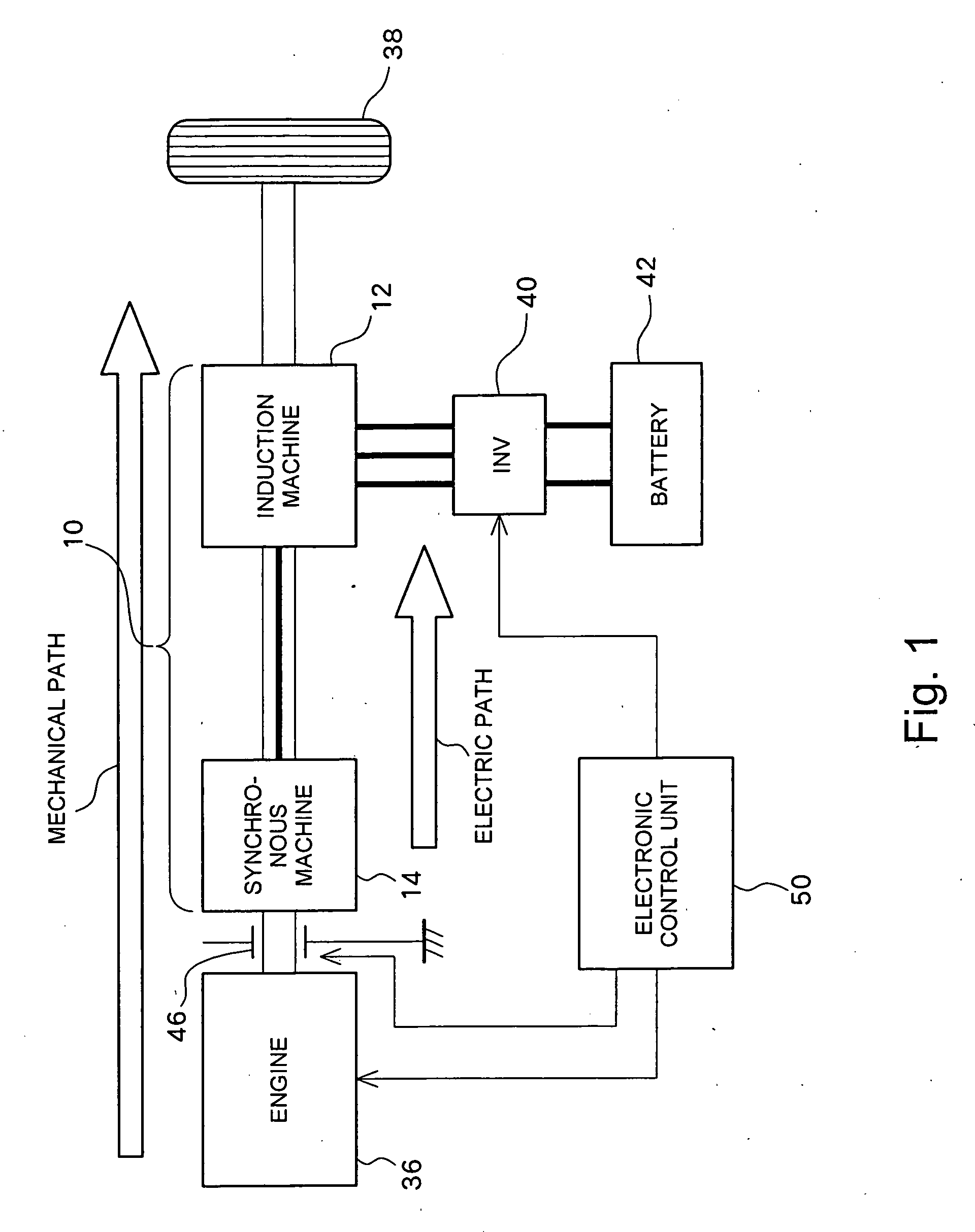
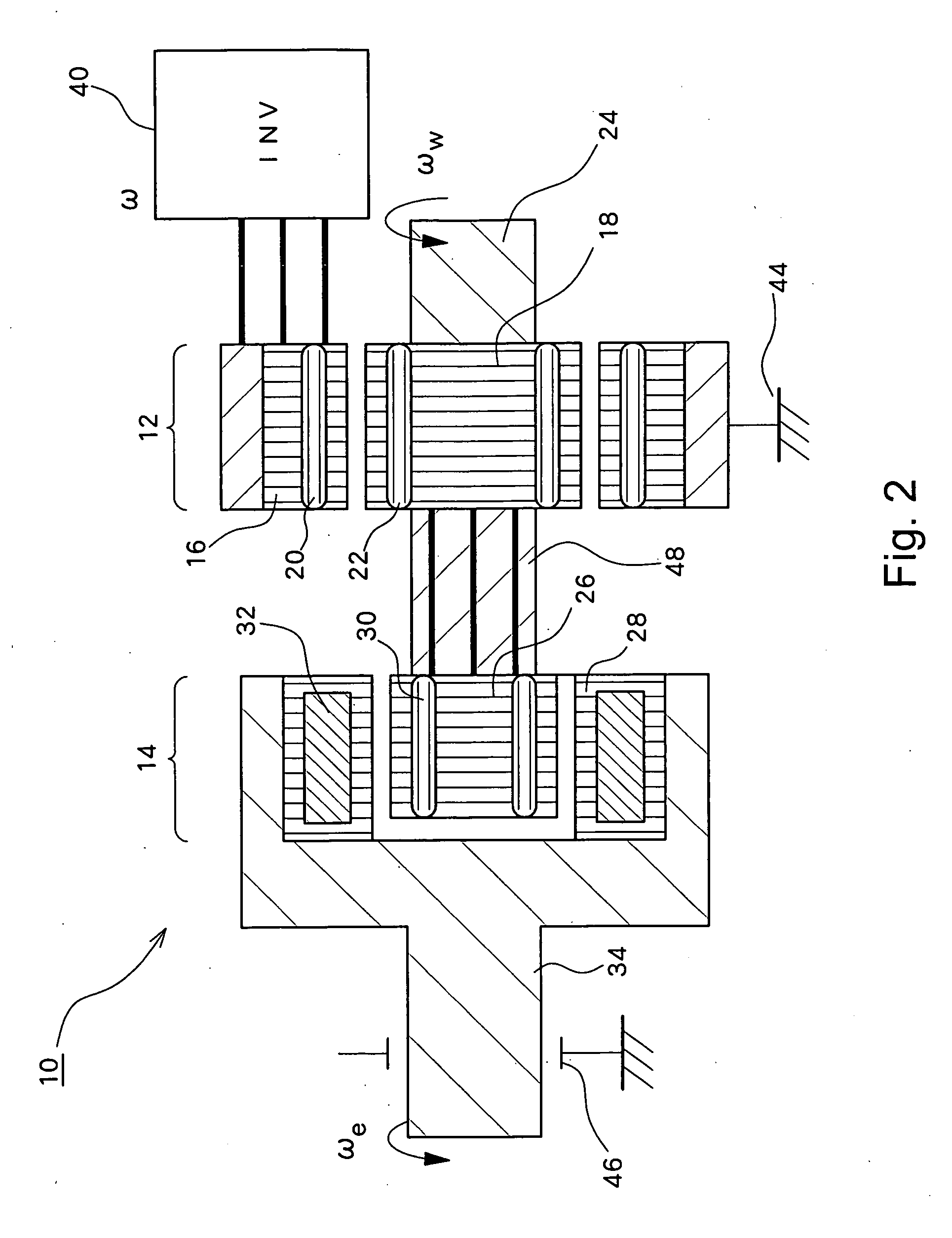
Rotating electrical machine and hybrid drive unit provided with the same
InactiveUS20070090707A1Loss can be reducedReduce lossesDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesAsynchronous induction motorsConductor CoilMagnet
An induction machine includes a stator provided with stator windings and a first rotor provided with first rotor windings, and generates an induction current in one of the stator windings and the first rotor windings by a rotating magnetic field generated in the other of the stator windings and the first rotor windings. A synchronous machine includes a second rotor which is provided with second rotor windings connected to the first rotor windings and coupled to the first rotor, and a third rotor which is provided with permanent magnets and rotatable independent of the second rotor, and a torque acts between the second rotor and the third rotor due to the interaction between the rotating magnetic field generated in the second rotor windings and the field flux generated in the permanent magnets.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
Wellbore motor having magnetic gear drive
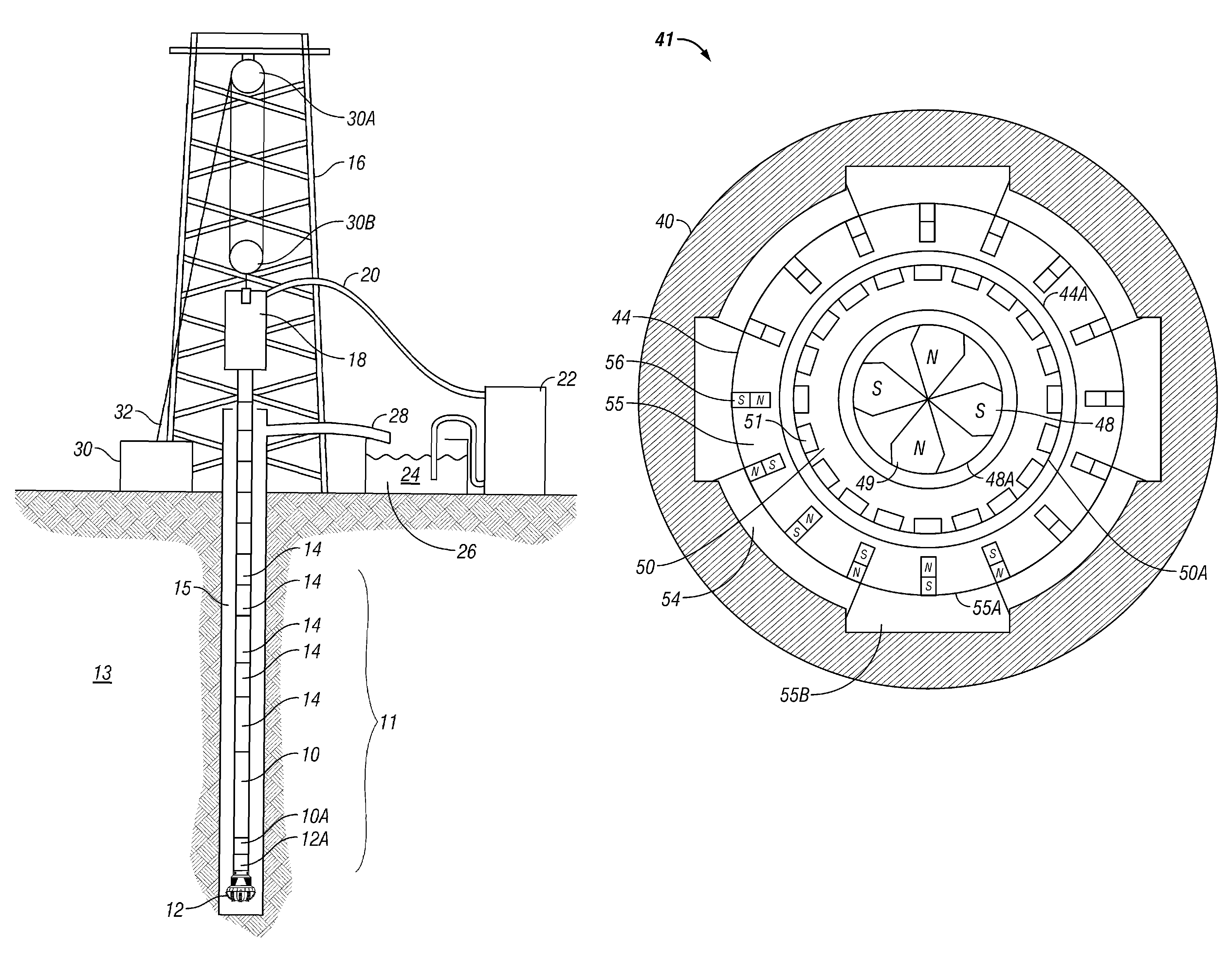
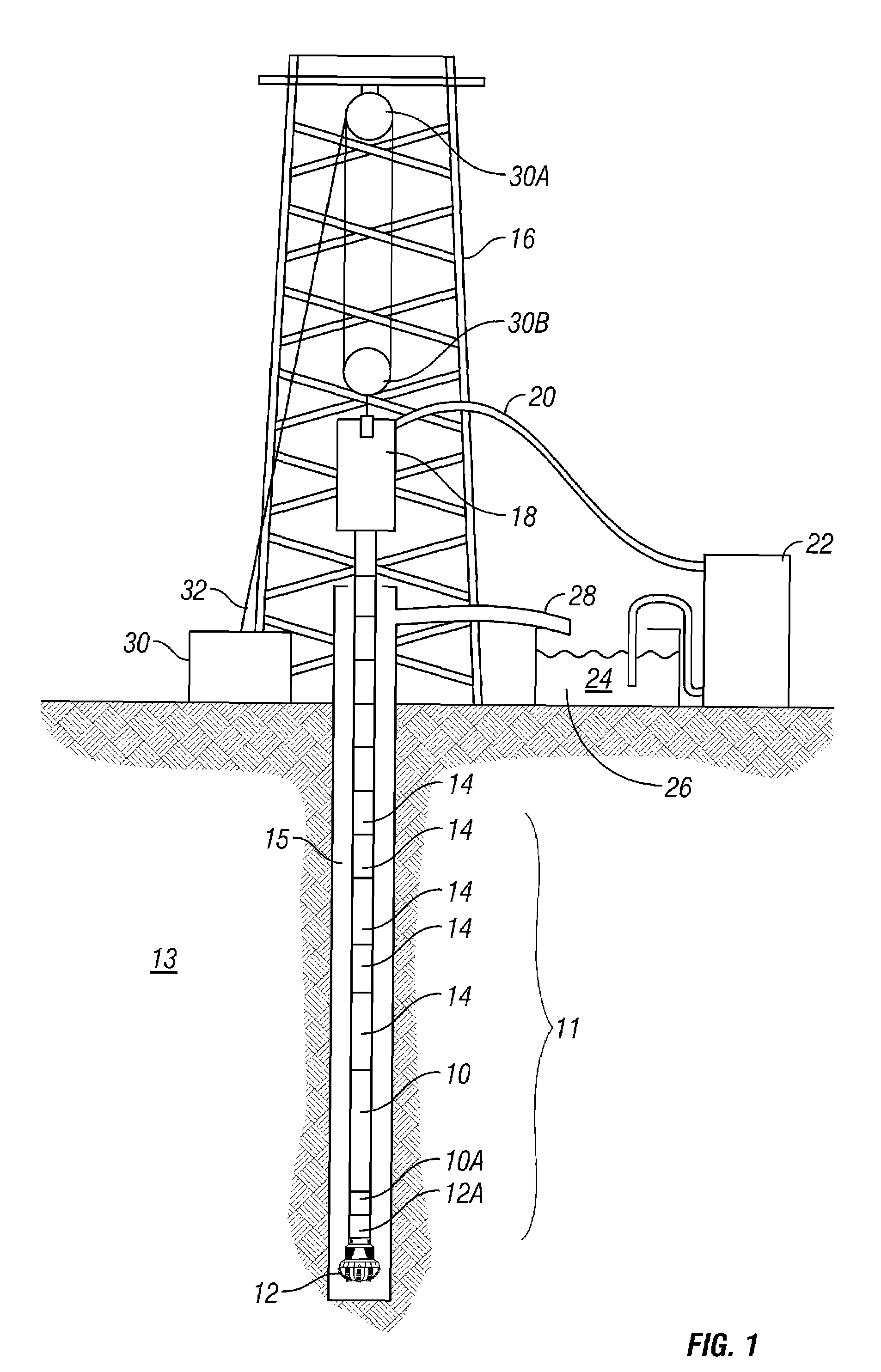
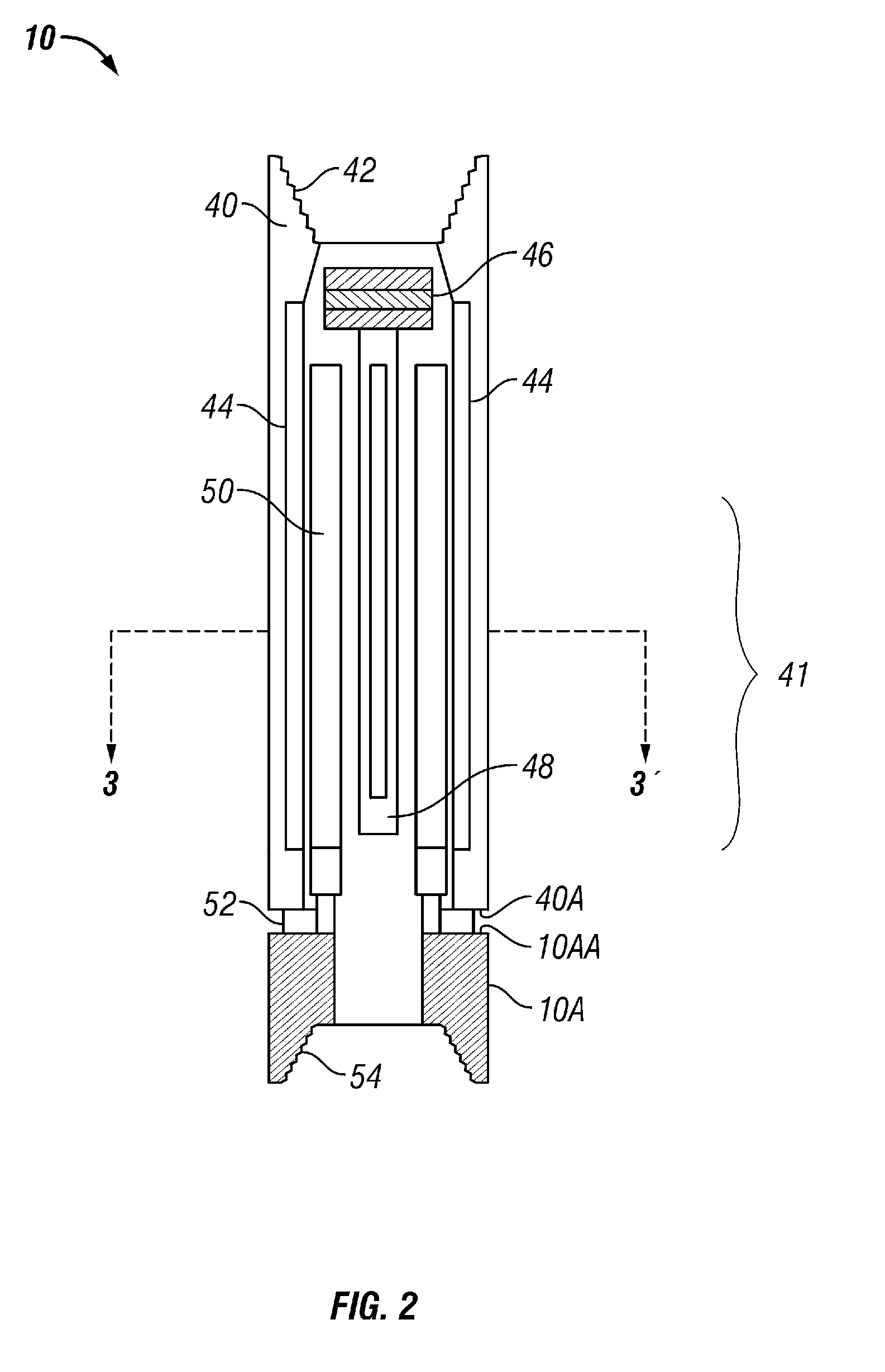
A wellbore motor includes a source of rotational motive power disposed in a wellbore, a magnetic gear member operatively coupled at an input thereof to the source; and a magnetic gear member output coupled rotationally to a rotary wellbore tool.
Owner:MAGNOMATICS LTD
Popular searches
DC motor speed/torque control Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machines Joint implants Staples Electric motor speed/torque regulation Dynamo-electric brake control Electric/dynamo-electric converter starters Surgical staples Synchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnets Fasteners
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com