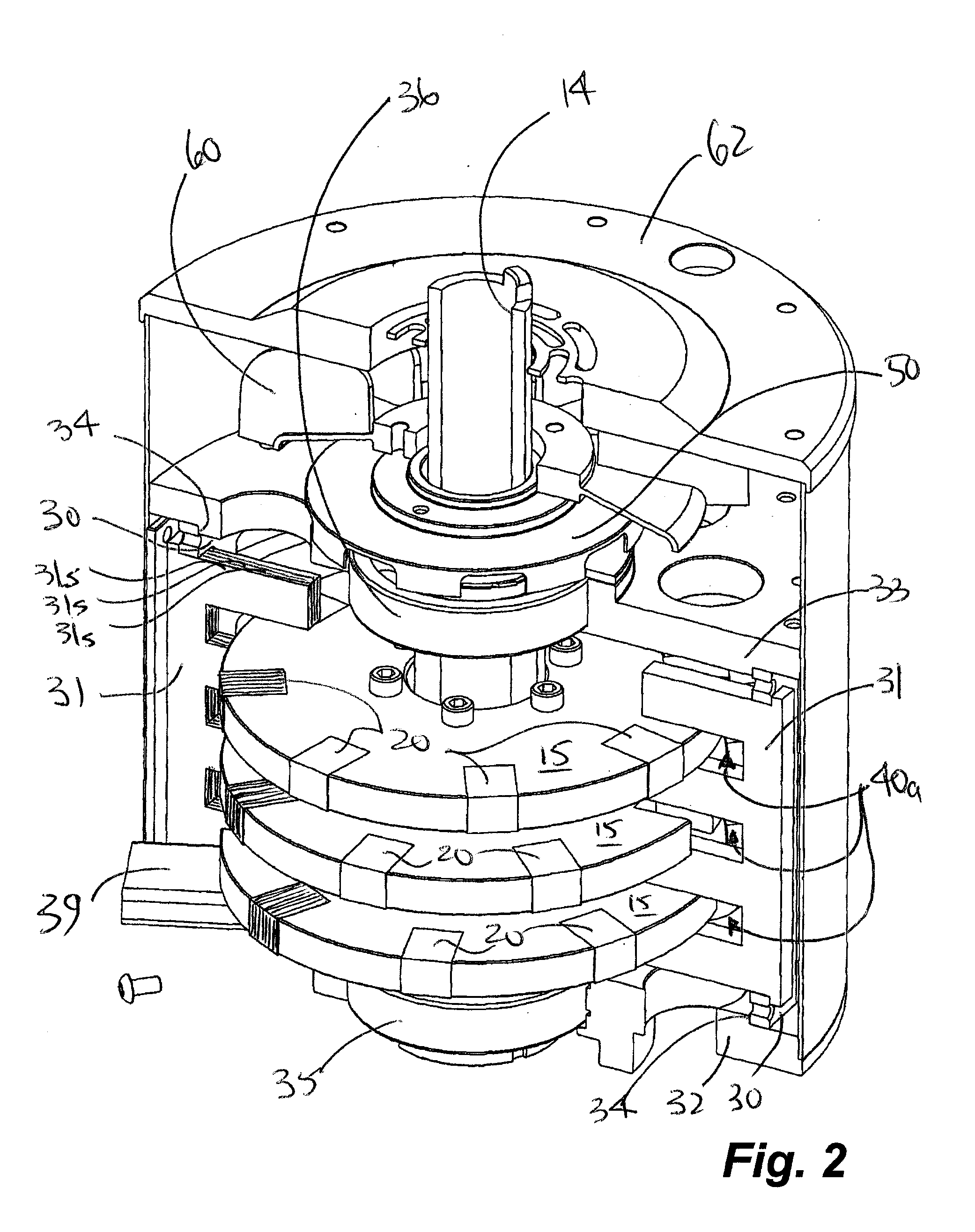
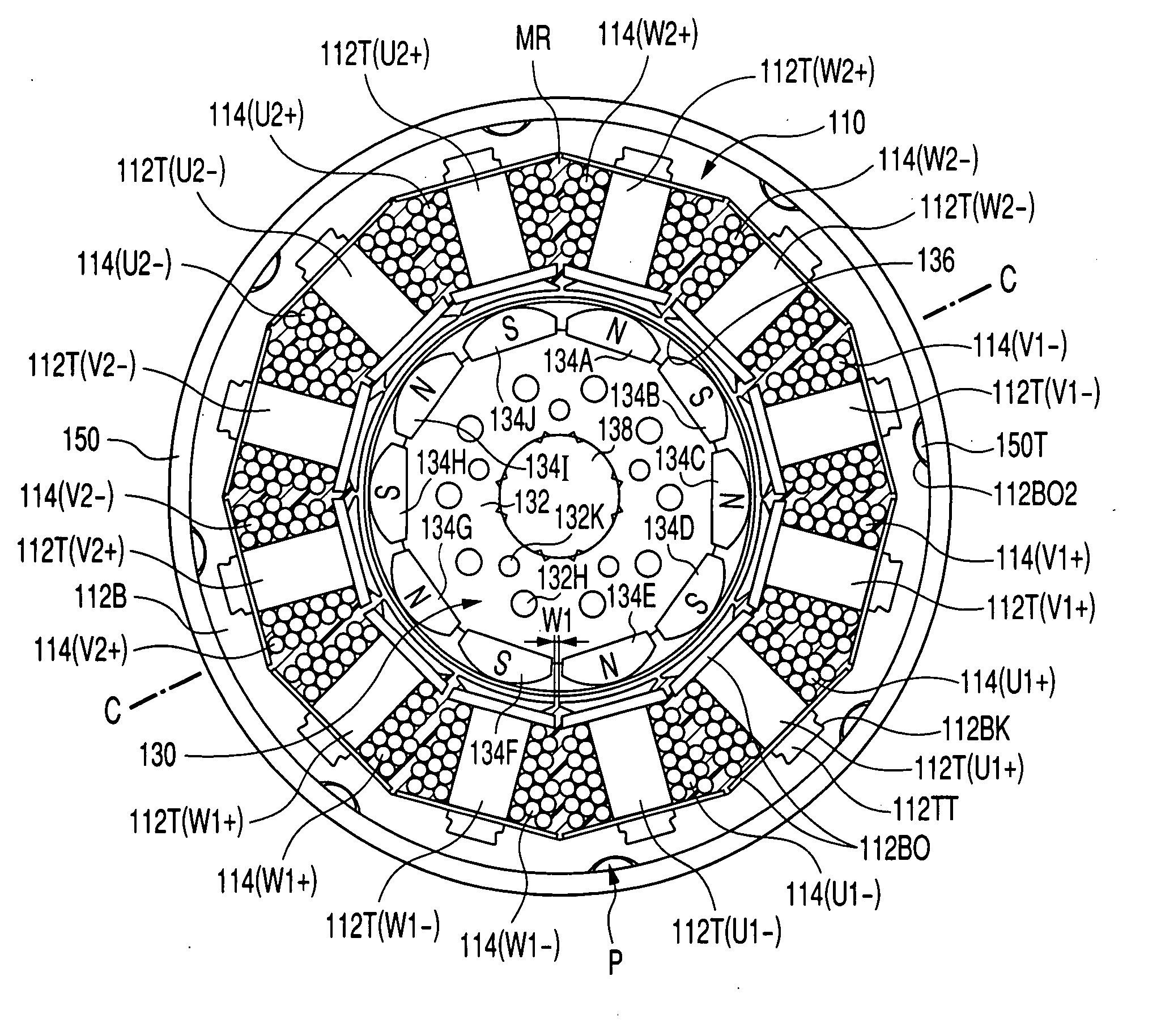
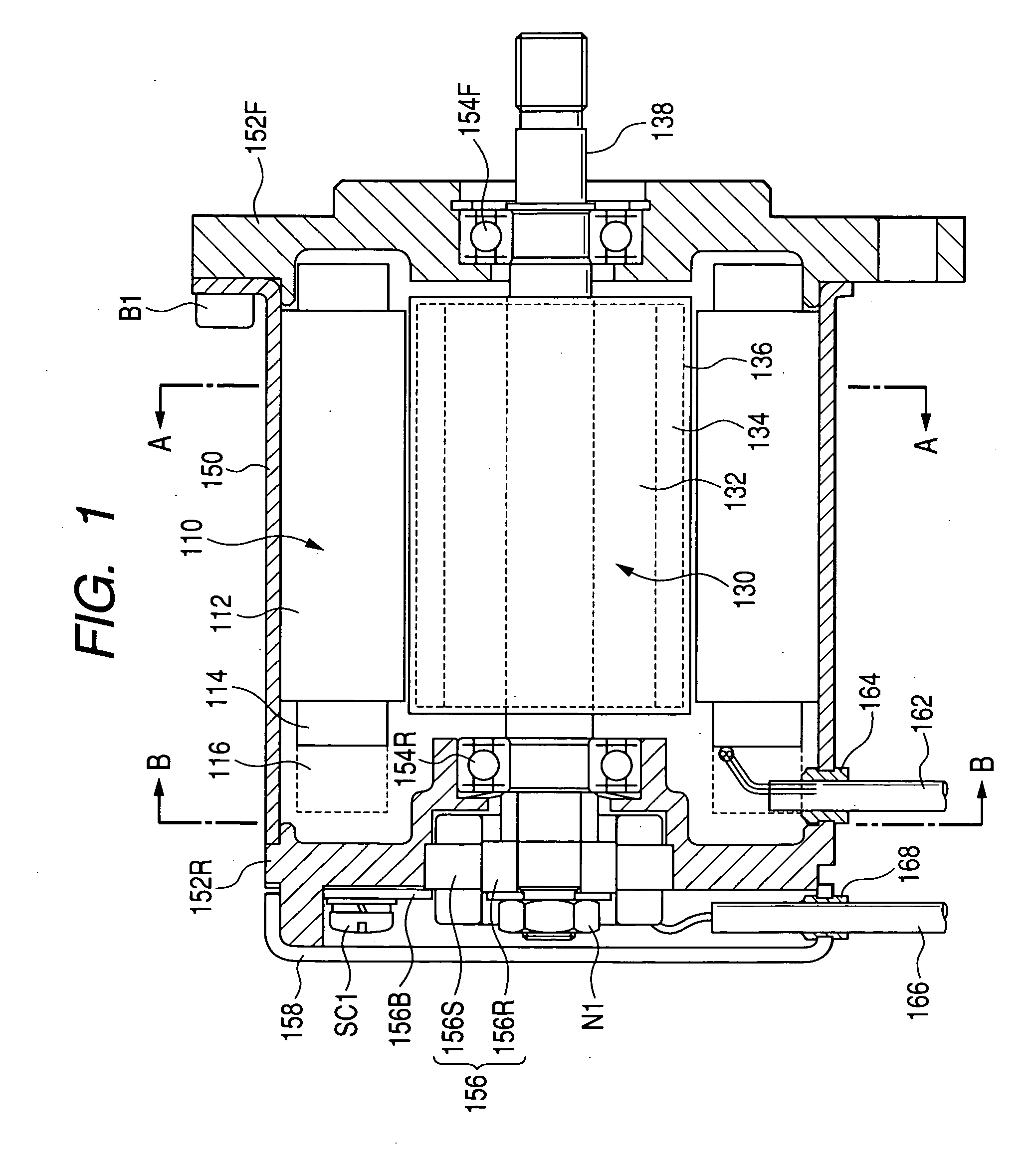
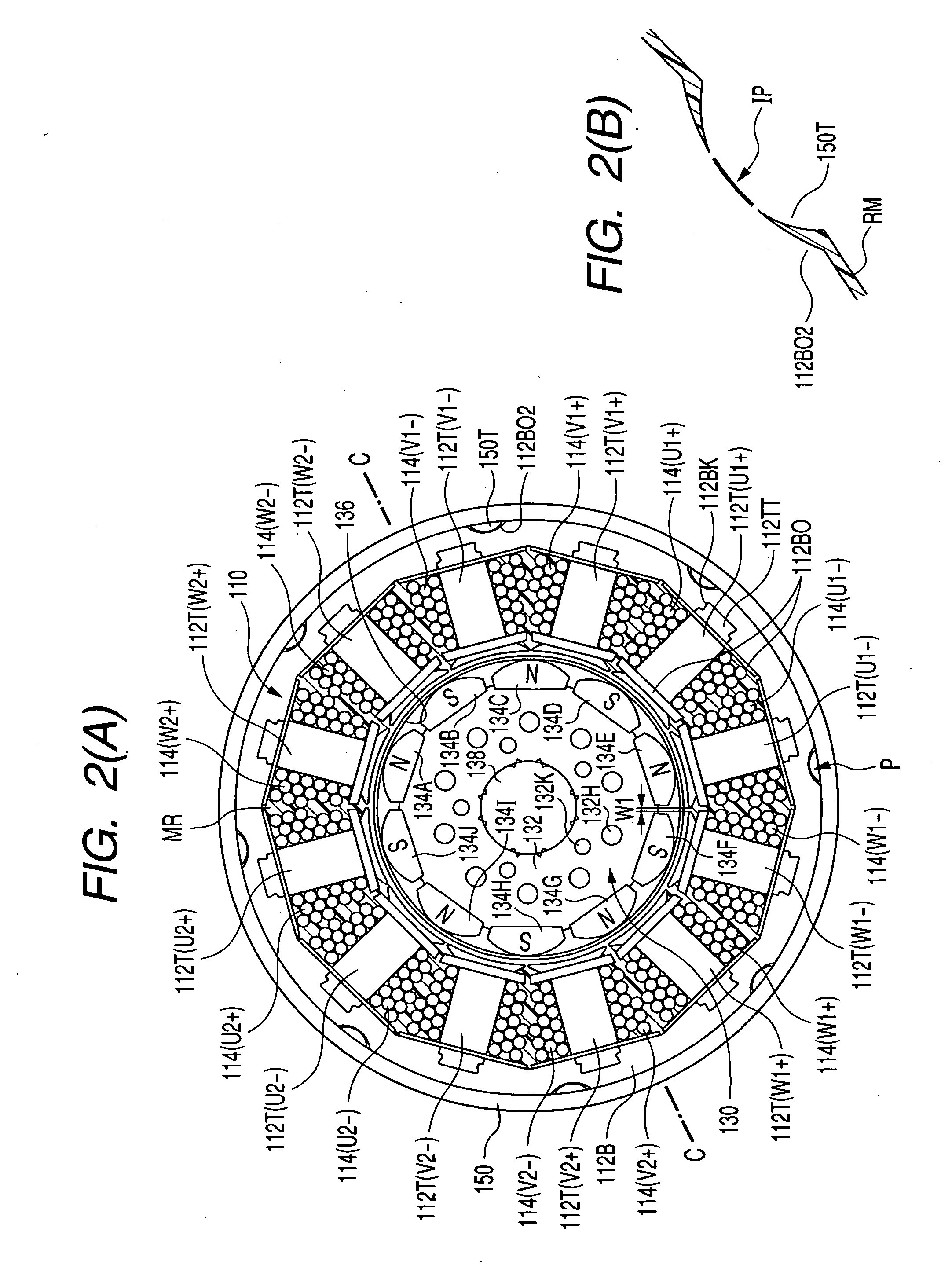
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3654 results about "Stator coil" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
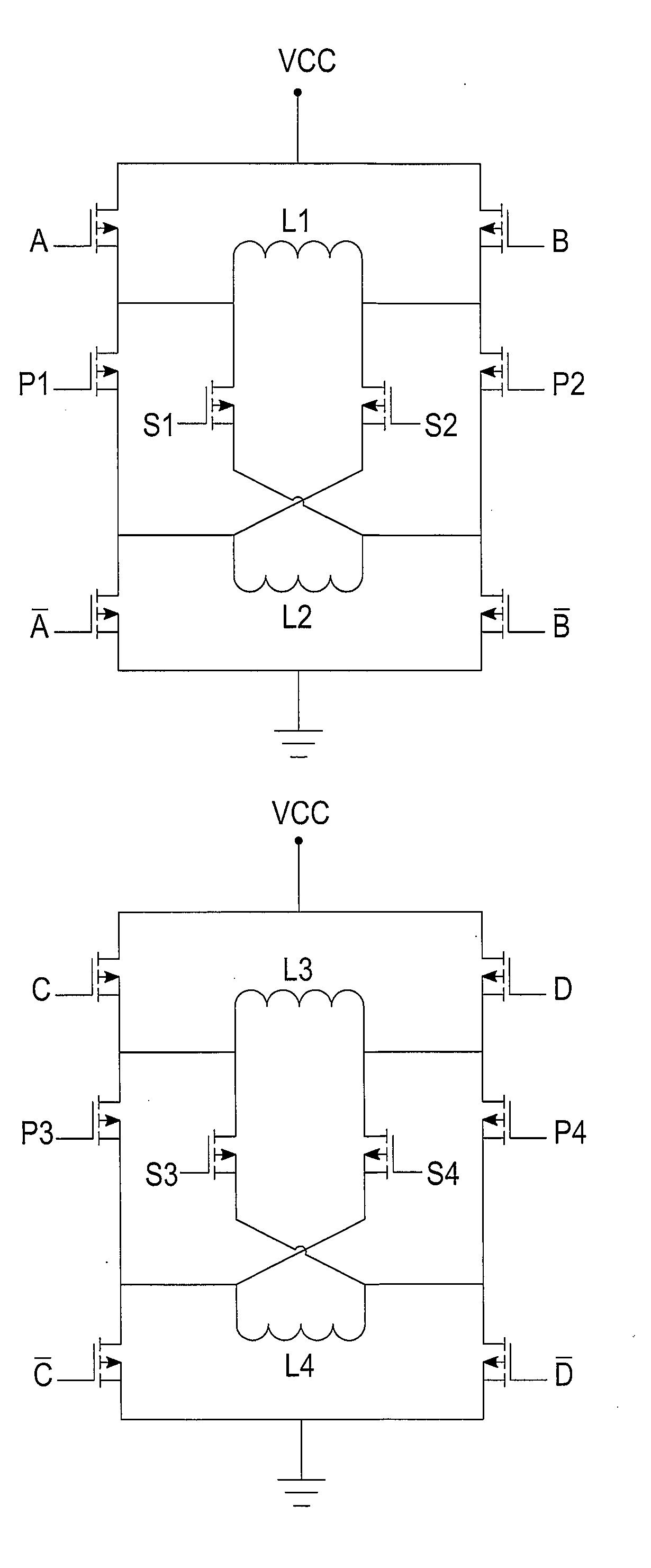
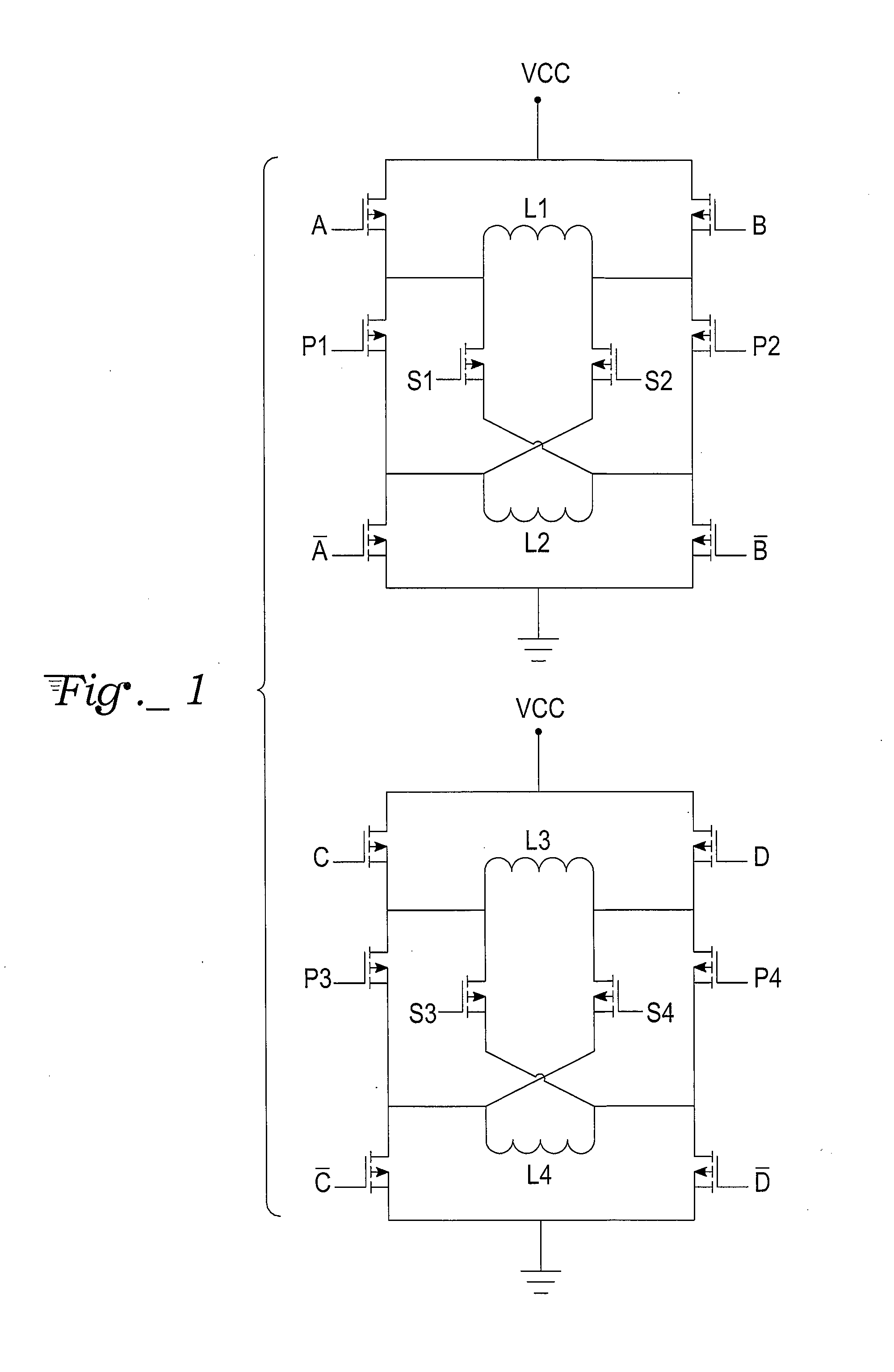
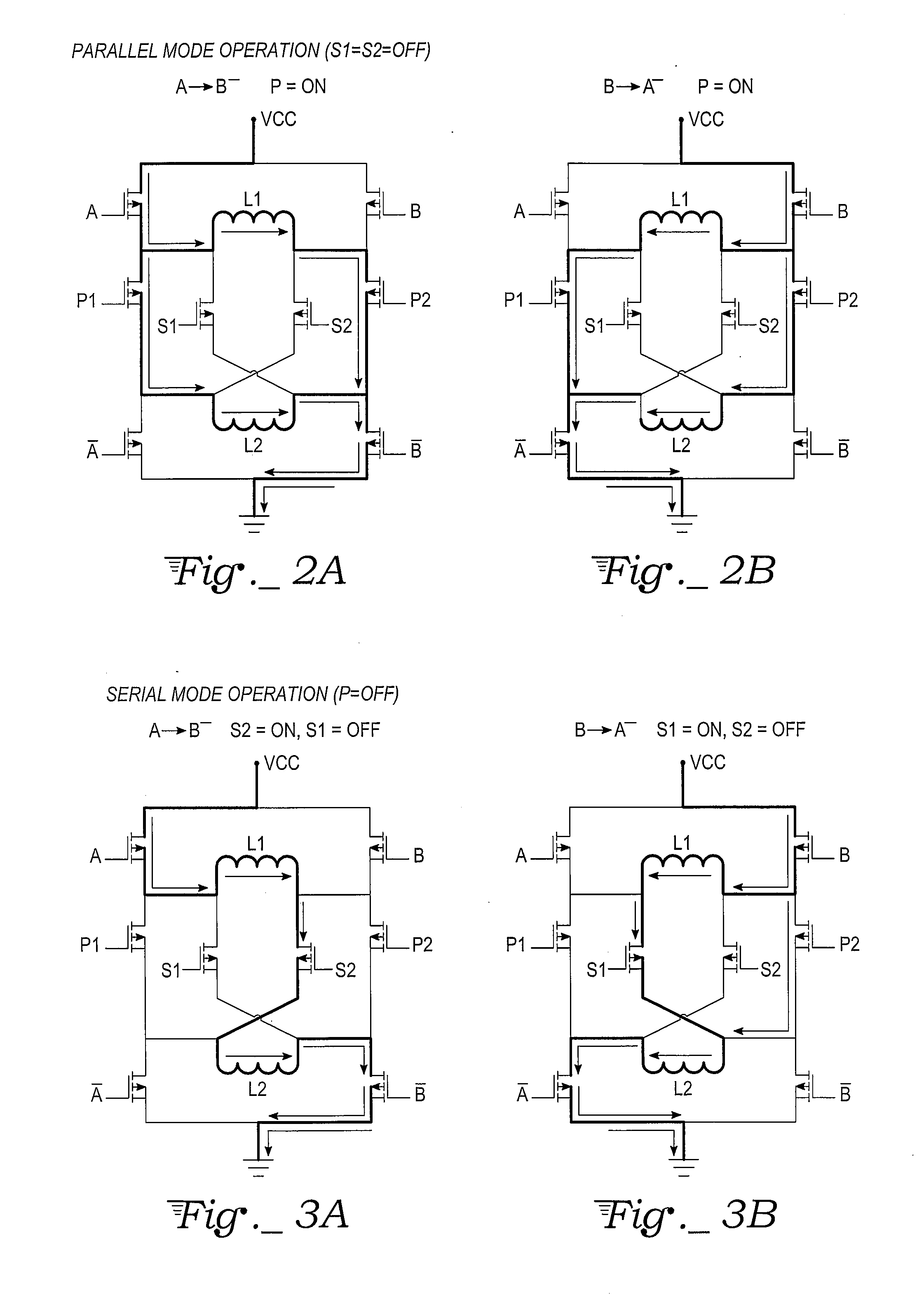
H-bridge drive circuit for step motor control
InactiveUS20110241597A1Improve stand-alone performanceEasy to implementDynamo-electric converter controlMotor speedDriving current
A drive circuit for step motors with bifilar windings is provided in which both parallel and series winding configurations for the stator coils are selectable by a motor controller based on the motor speed. For low speeds a series configuration is selected, while for higher speeds a parallel configuration is selected. Dynamic torque is optimized by the selection for more efficient motor operation with less drive current.
Owner:LIN ENG INC
Underwater ducted turbine
InactiveUS7471009B2Minimize loss of efficiencyThe process is stable and efficientEngine fuctionsWorking fluid for enginesUnderwaterStator coil
An apparatus is disclosed for a turbine for generating electrical power from water or air flow comprising at least one rotor disk having a plurality of hydrofoil blades, a guide vanes, a cylindrical housing, and a generator means. A rim generator comprising a magnet race rotor rim and fixed stator coils in the housing is used. The apparatus is fitted with a screen to stop the ingress of debris and marine life, and a skirt augmenter device to reduce the Betz effect. The apparatus is preferably for sub-sea deployment and driven by tidal currents, but may be powered by river current or wave driven air or by wind. The apparatus may be deployed on at least one telescoping pole, tethered to the sea-bed and kept buoyant by buoyant concrete in the housing, inserted in a dam, under a barge or in a tidal power array.
Owner:CLEAN CURRENT PARTNERSHIP
Hydro turbine generator
InactiveUS20050285407A1Minimize downstream efficiency lossMinimizing swirl lossEngine fuctionsWorking fluid for enginesStator coilEngineering
An apparatus is disclosed for a turbine for generating electrical power from water or air flow comprising at least one rotor disk having a plurality of hydrofoil blades, a guide vanes, a cylindrical housing, and a generator means. A rim generator comprising a magnet race rotor rim and fixed stator coils in the housing is used. The apparatus is fitted with a screen to stop the ingress of debris and marine life, and a skirt augmenter device to reduce the Betz effect. The apparatus is preferably for sub-sea deployment and driven by tidal currents, but may be powered by river current or wave driven air or by wind. The apparatus may be deployed on at least one telescoping pole, tethered to the sea-bed and kept buoyant by buoyant concrete in the housing, inserted in a dam, under a barge or in a tidal power array.
Owner:CLEAN CURRENT PARTNERSHIP
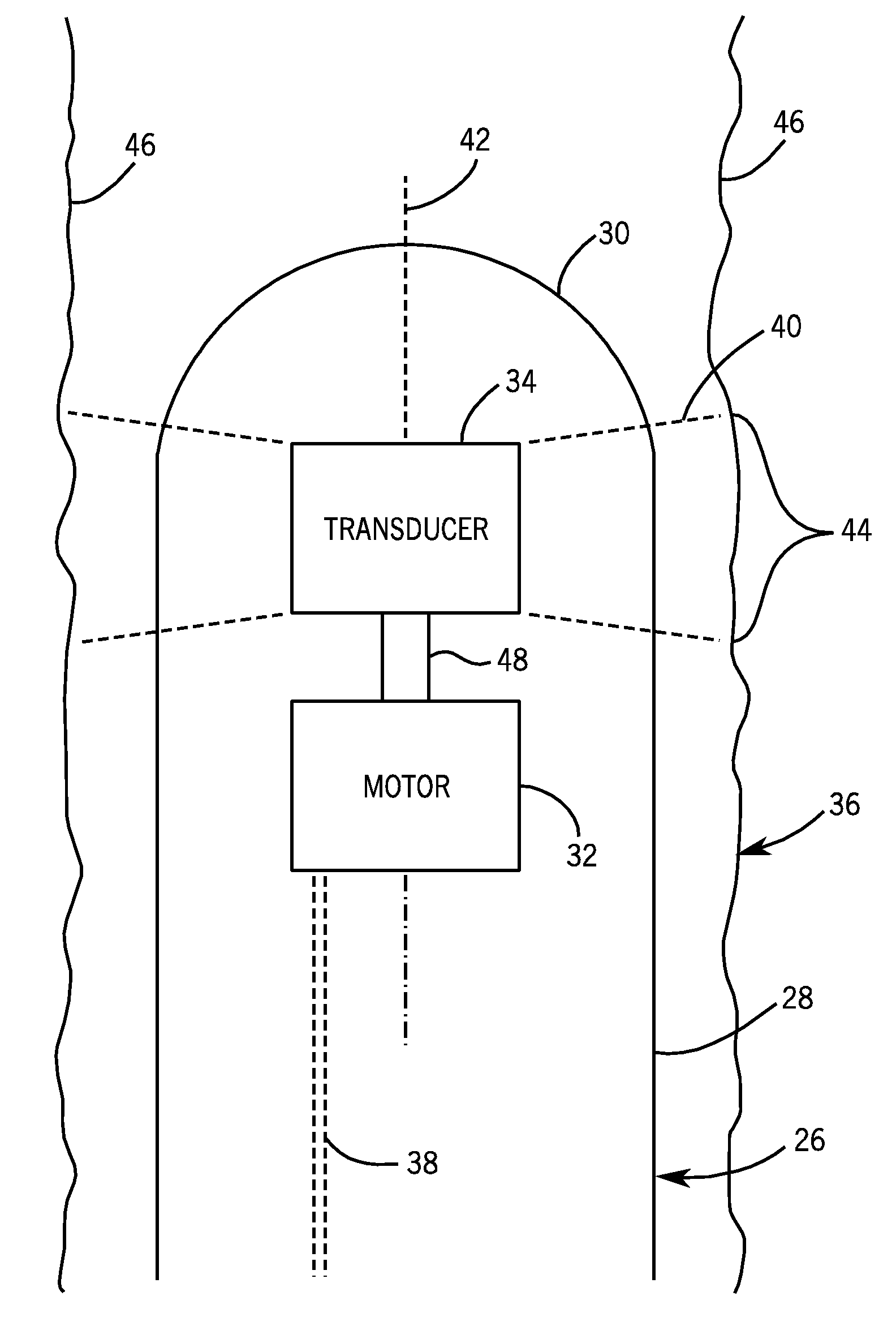
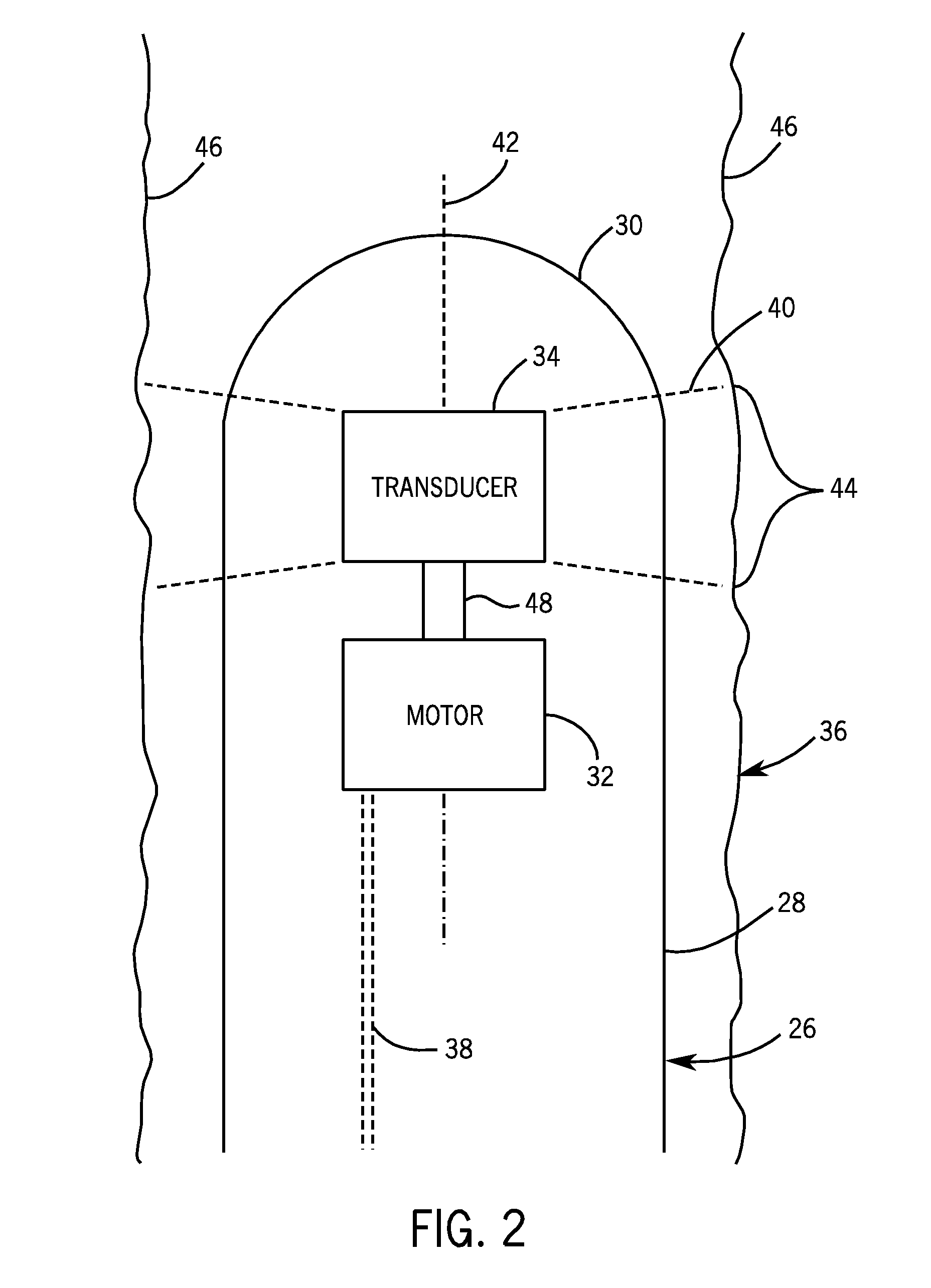
Electric Motor Tracking System and Method
InactiveUS20090069671A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic measurementsElectric machineStator coil
Provided is a tracking system, including a motor coupled to a medical instrument and configured to generate at least one magnetic field, and at least one receiver coil configured to sense the magnetic field. Also provided is a method of tracking, including rotating a rotor of a motor, wherein the rotor comprises a permanent magnet that generates a rotating magnetic field when the rotor is rotated, sensing the rotating magnetic field with at least one receiver, transmitting to a processor a signal indicative of the rotating magnetic field, and processing the signal to determine a position of the motor. Further provided is a method of tracking, comprising energizing a stator coil of a motor to generate at least one magnetic field, sensing the at least one magnetic field with at least one receiver, transmitting to a processor a signal indicative of the at least one magnetic field, and processing the signal to determine a position of the motor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
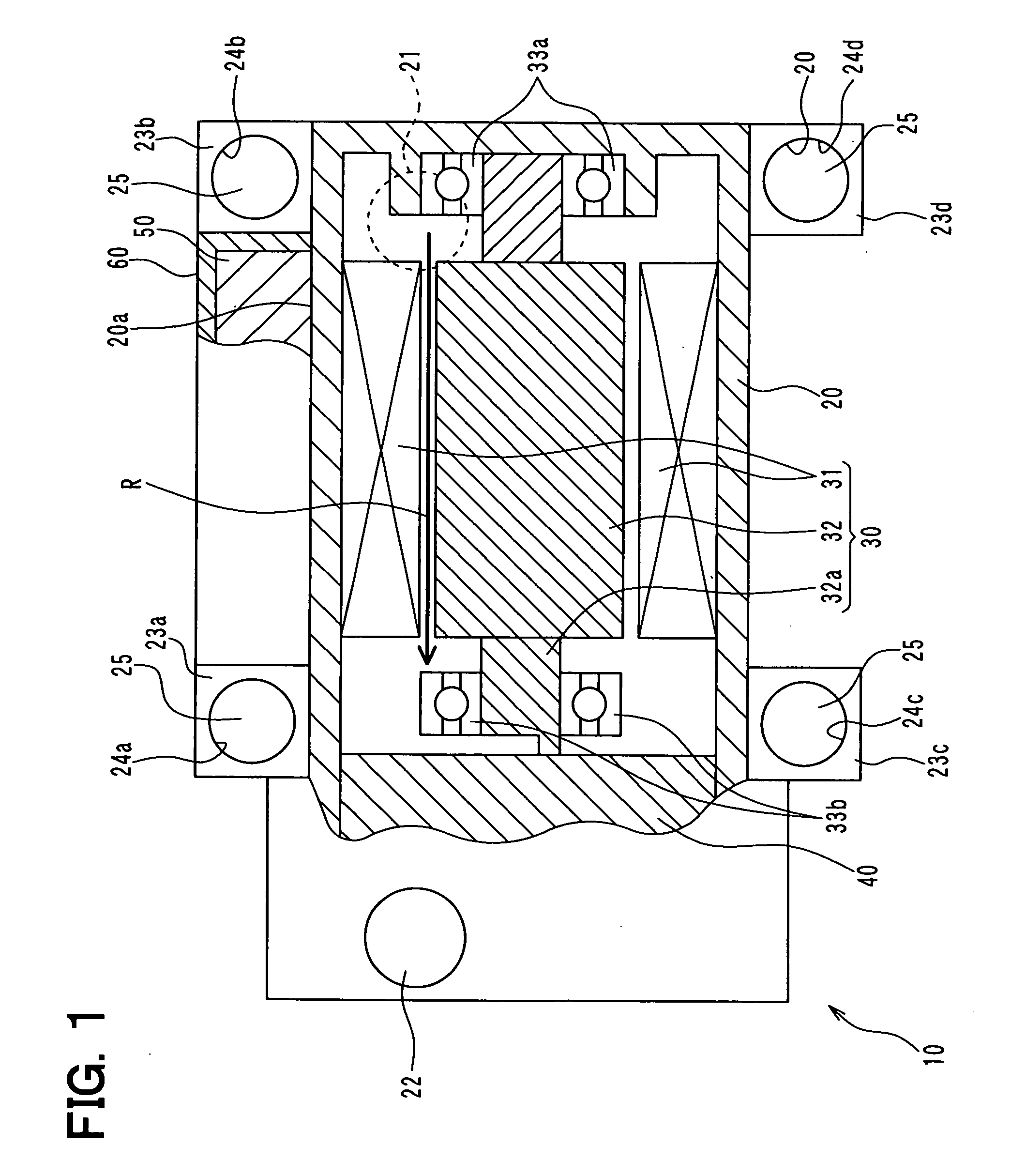
Motor for electric power steering and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060138883A1Firmly connectedEasy to implementMagnetic circuitStructural associationElectric power steeringElectricity
A small-sized motor for electric power steering, in which coil connection can be easily performed with space saving, and a method for manufacturing the motor. Multi-phase stator coils assembled in a stator coil are connected per phase by connecting rings at coil ends of the stator coils. A bus bar supplied with electric power from the exterior is stacked onto the connecting rings in the axial direction of the motor and is electrically connected to the connecting rings.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Fan with magnetic blades
InactiveUS6194798B1MiniaturizationReduce manufacturing costMagnetic circuit rotating partsPump componentsStator coilEngineering
A DC driven fan with blades made of magnetized material and permanently magnetized in the radial direction and cooperating with a plurality of electromagnetic stator coils mounted external to the outer fan edges. Adjacent blades have alternate N-S, S-N radial magnetic orientations. In one embodiment, the blades are mounted in a non-ferrous hub and in an alternate embodiment they are mounted in a ferrous hub so that adjacent blades function like a U or V-shaped magnet. Blades can be made of magnetized ferrous, ferromagnetic, or magnetized plastic depending upon the application and blade strength specifications.
Owner:AIR CONCEPTS
Hub motors
InactiveUS20060273686A1Raise countIncrease surface areaSingle-phase induction motor startersSynchronous motors startersDrive wheelStator coil
The present invention discloses small compact motor systems which may be located inside a vehicle drive wheel, and which allow a drive motor to provide the necessary torque with reasonable system mass. The motor systems of the invention utilize polyphase electric motors, and are preferably connected to appropriate drive systems via mesh connections, to provide variable V / Hz ratios. In one embodiment the stator coils are wound around the inside and outside of the stator. In a further embodiment, the machine contains a high number of phases, greater than three. In a further embodiment, the phases are connected in a mesh connection. In a further embodiment, each half-phase is independently driven to enable second harmonic drive for an impedance effect. Improvements are apparent in efficiency and packing density.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH LTD
Electric Rotating Tool
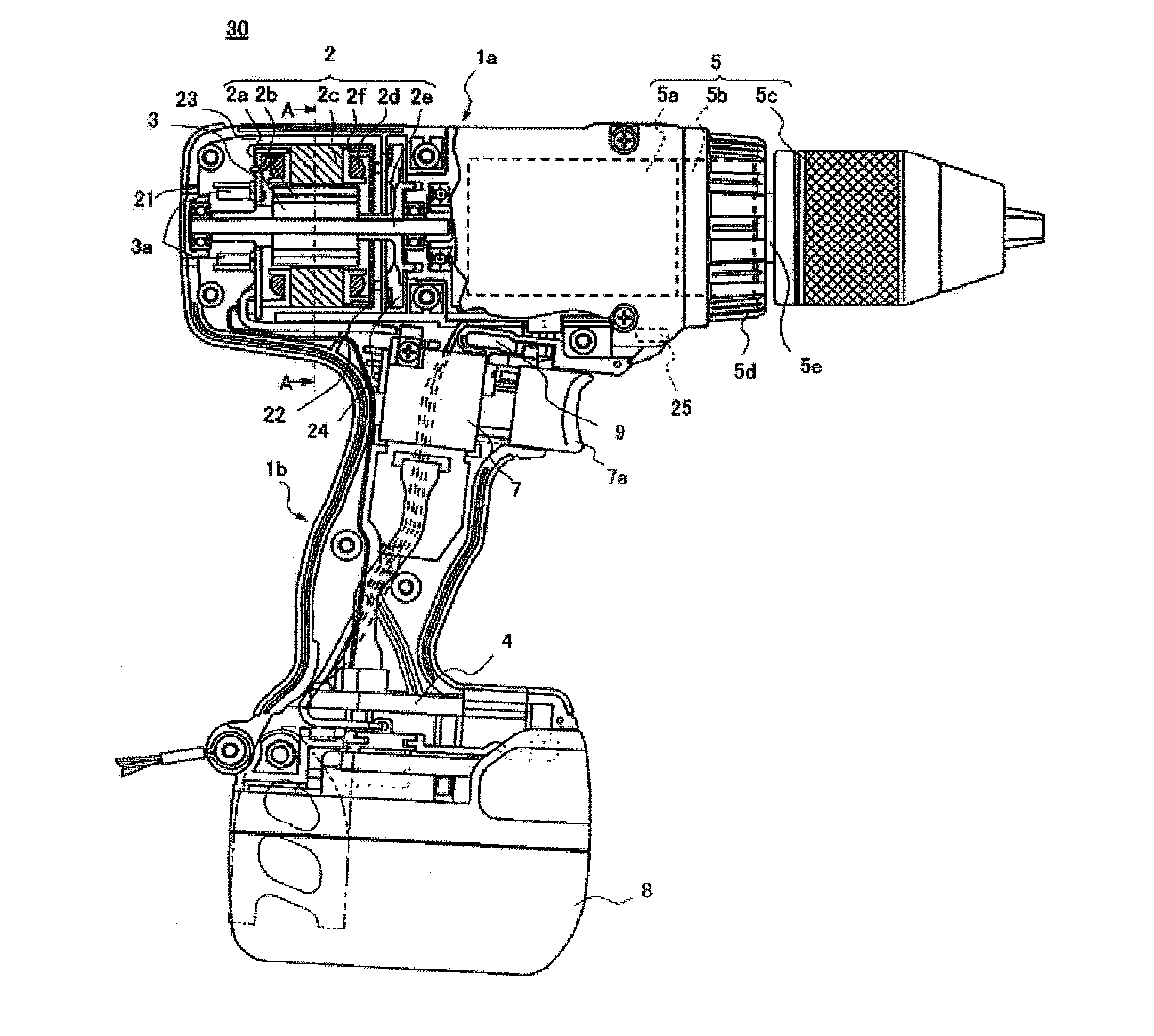
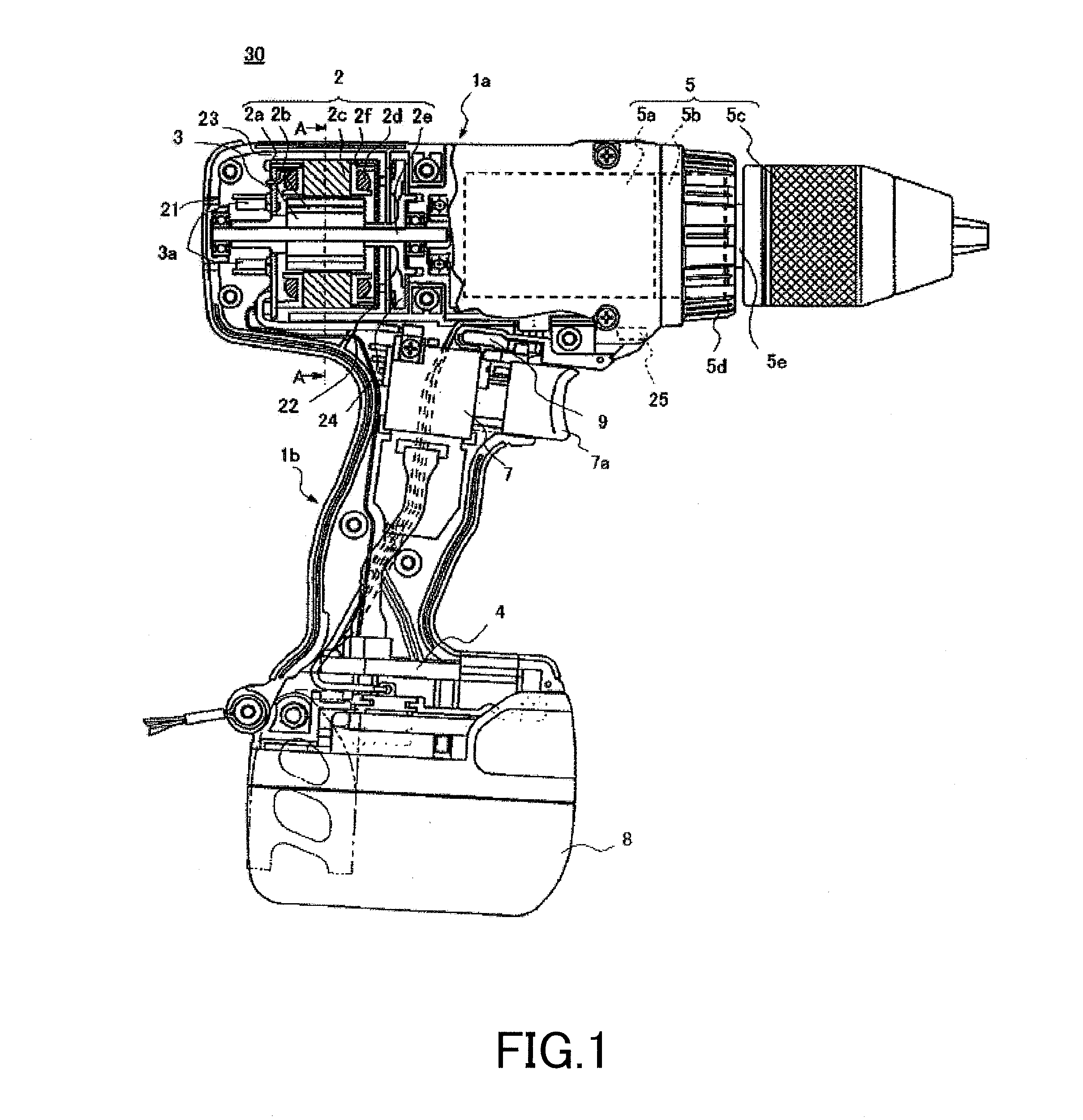
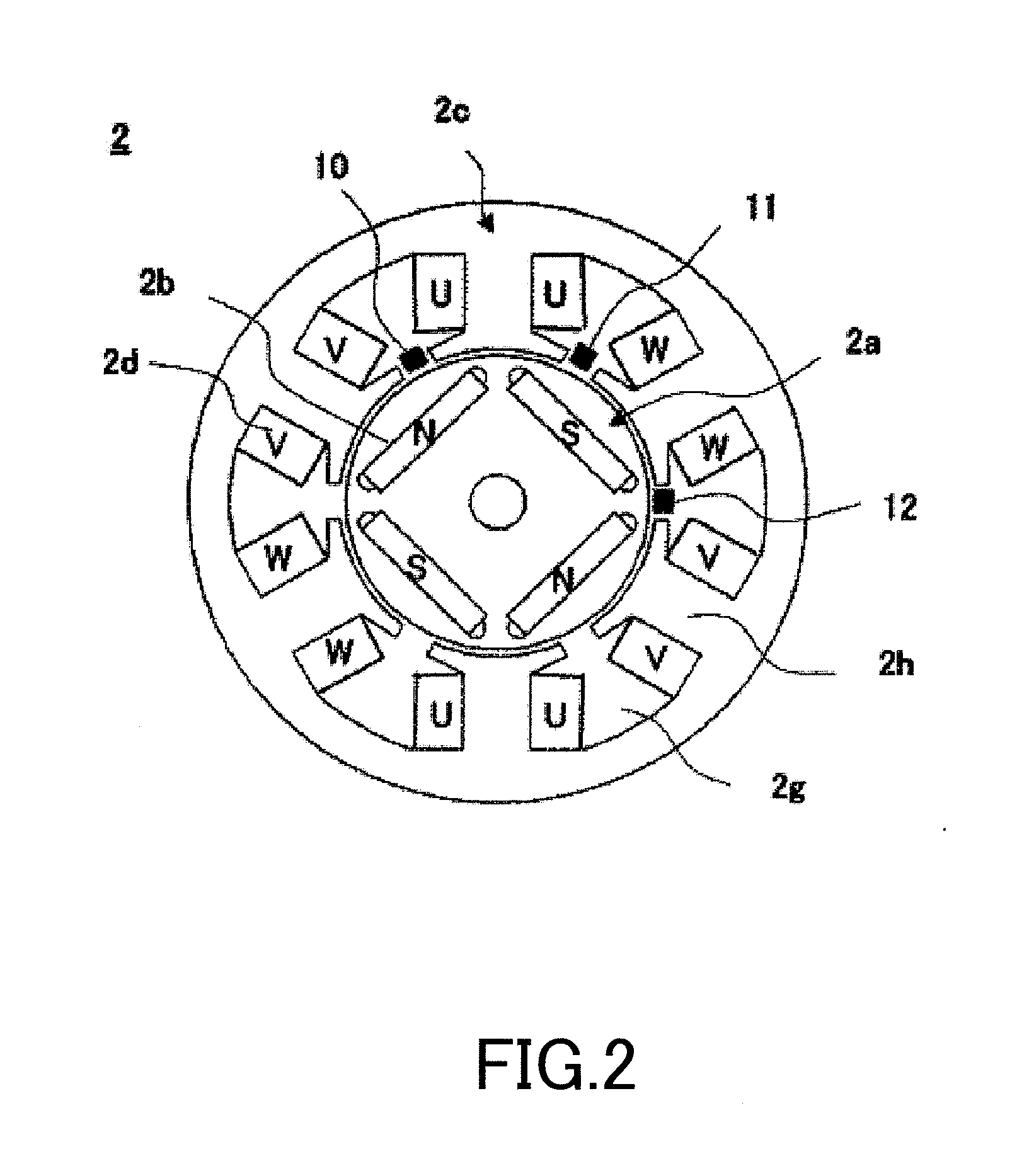
ActiveUS20100307782A1Accurately and appropriately detectedAvoid partialDrilling rodsConstructionsDriving currentStator coil
A current detection circuit (18) detects that a drive current of the stator coil (2d) is exceeding a threshold value Ir. A rotation number detection circuit (17) detects that the number of rotations of a rotor (2a) is lower than a threshold value Nr. A computing part (20) outputs a PWM signal which switches a semiconductor switching element (3a) of the inverter circuit part (3). The computing part (20) changes the threshold values Ir and Nr in accordance with the PWM duty of the PWM signal determined in accordance with a pressed distance of a switch trigger (7) and detects a locked state of the motor (2) on the conditions that the motor current I is exceeding the set threshold value Ir and that the number of rotations N thereof is lower than the threshold value Nr.
Owner:HITACHI KOKI CO LTD
Stator for an electrical machine and method for production of a stator
InactiveUS6369473B1Simple and cost-effectiveReduce areaManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesStructural associationElectrical conductorStator coil
A stator for an electrical machine includes a stator yoke and a plurality of stator coils arranged on the stator yoke. An interconnection arrangement is arranged on one end face of the stator yoke. The interconnection arrangement has connecting conductors which are electrically insulated from one another. The connecting conductors are arranged concentrically with respect to one another and each have a different diameter. The connecting conductors have connections for the ends of the stator coils and for connection to the electrical machine. To minimize the space requirement of the stator and simultaneously allow the stator coils to be automatically interconnected in an automated manner, the interconnection arrangement is arranged inside an area bounded by the stator coils. Furthermore, the connections for the ends of the stator coils include connection projections designed such that they project outward at an angle to the respective connecting conductor to attach the stator coil ends. A number of cutouts are provided in the connection conductors and are arranged so that the connection projections are bendable into the cutouts once the coil ends have been connected.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
DC brushless motor for electrical power steering and the production method thereof
InactiveUS20050269895A1Torque pulsation can be reducedEffective reduction of torque pulsationAssociation with control/drive circuitsWindings insulation shape/form/constructionBrushless motorsElectric power steering
The stator core of a motor comprises an annular back core, and a plurality of tees created separately from the back core and secured onto the inner periphery of the back core. A stator coil is wound on each of the tees by a distributed or concentrated winding method. The stator core and stator coil are formed by molding.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
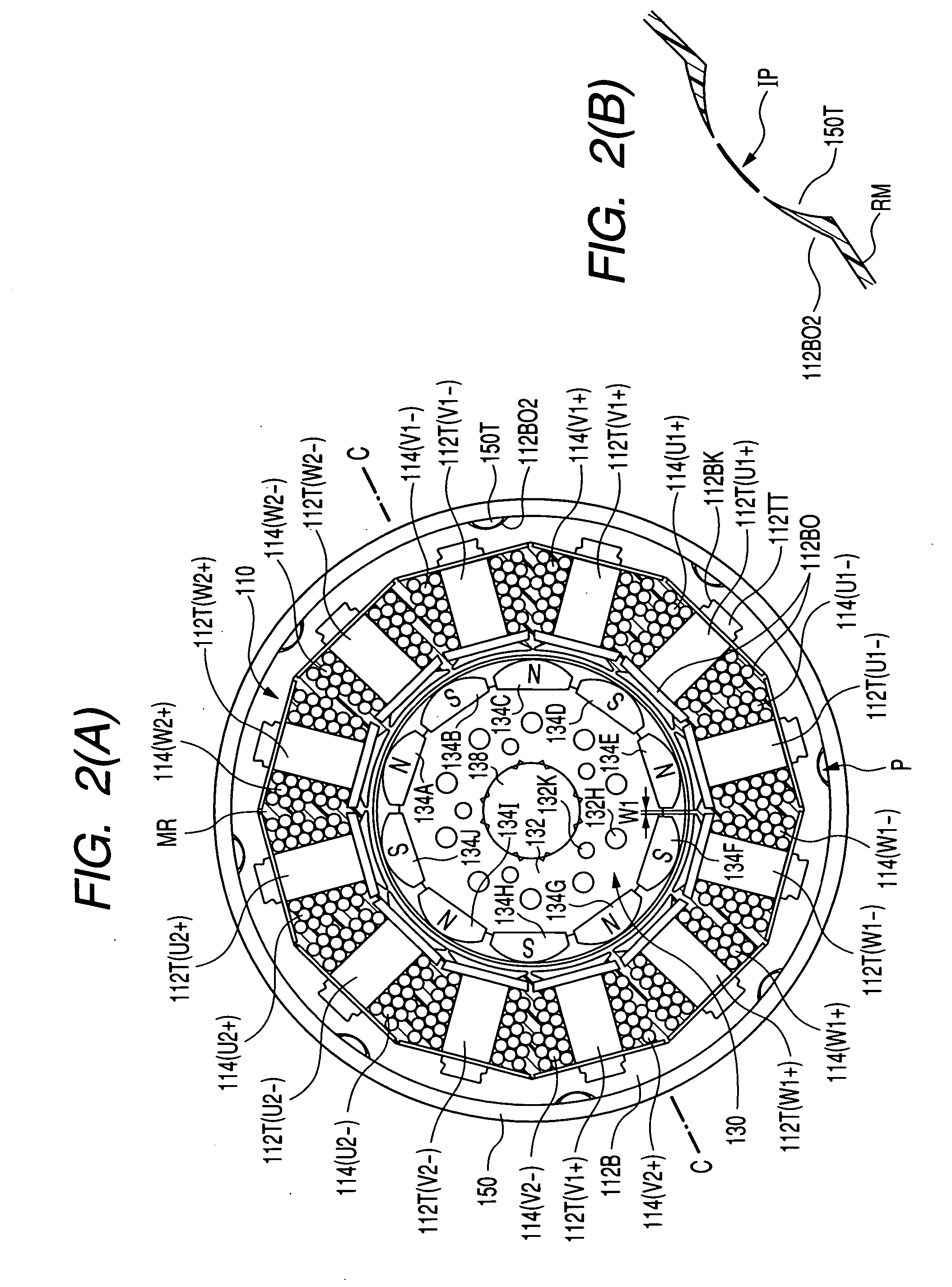
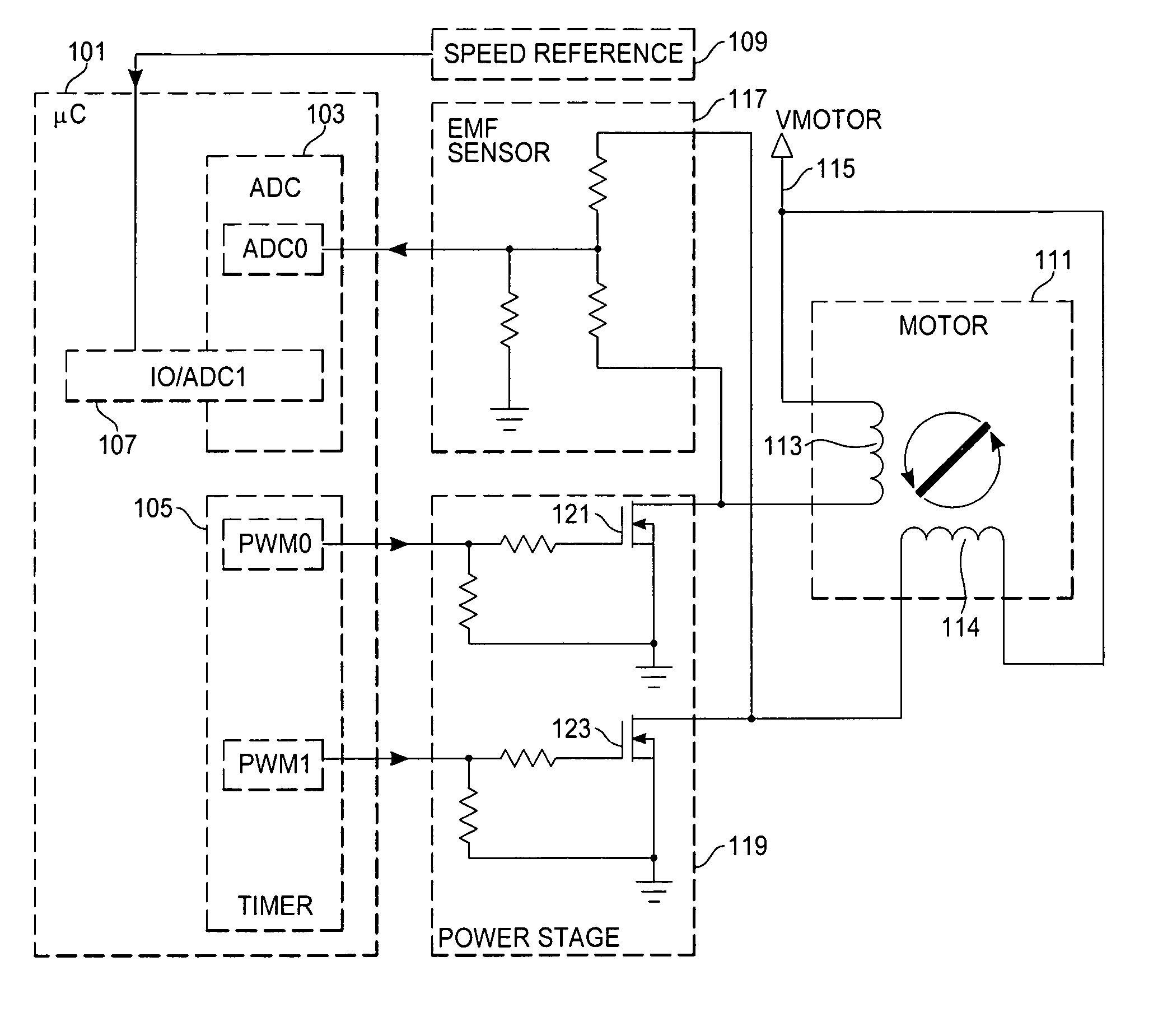
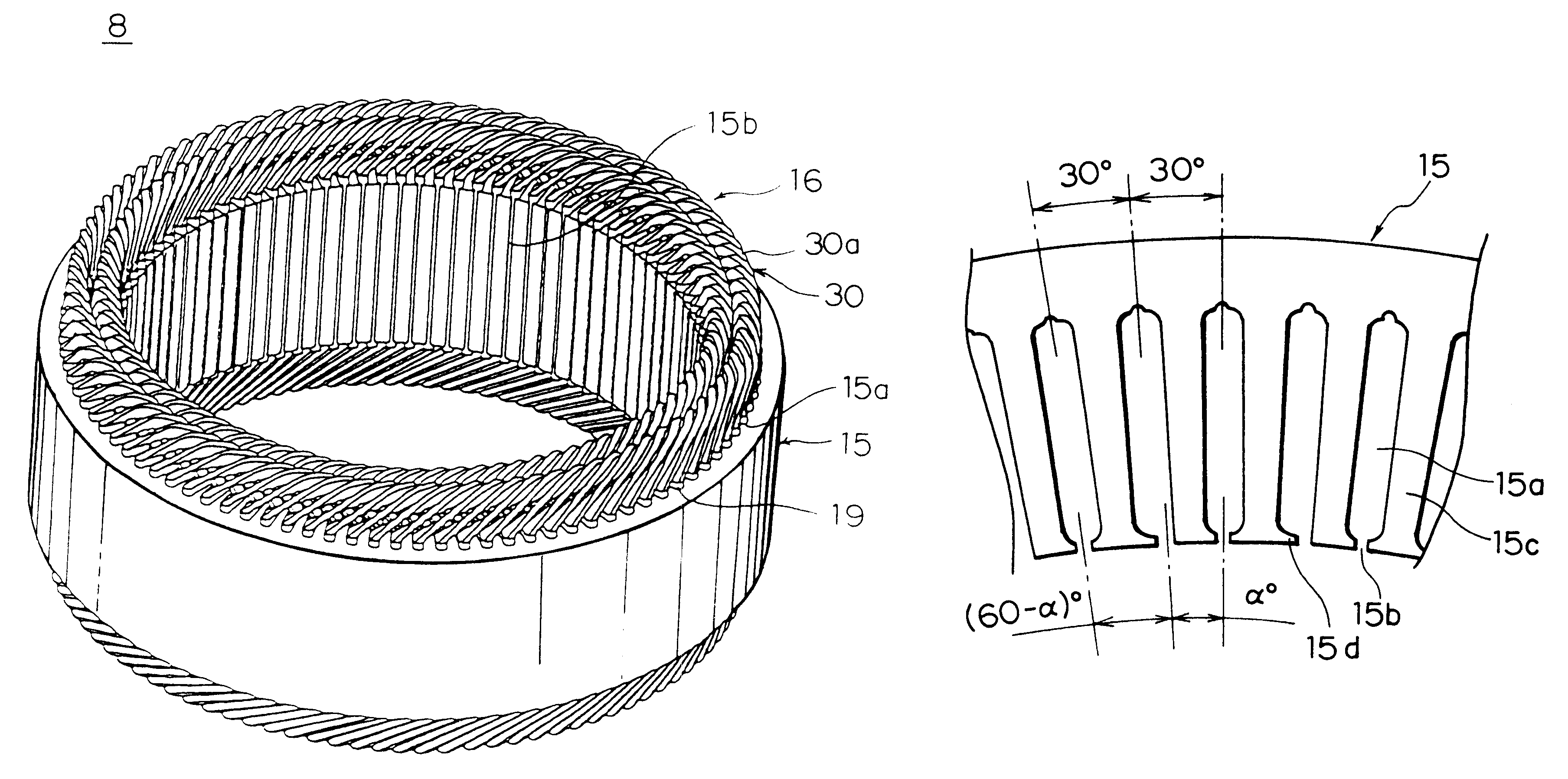
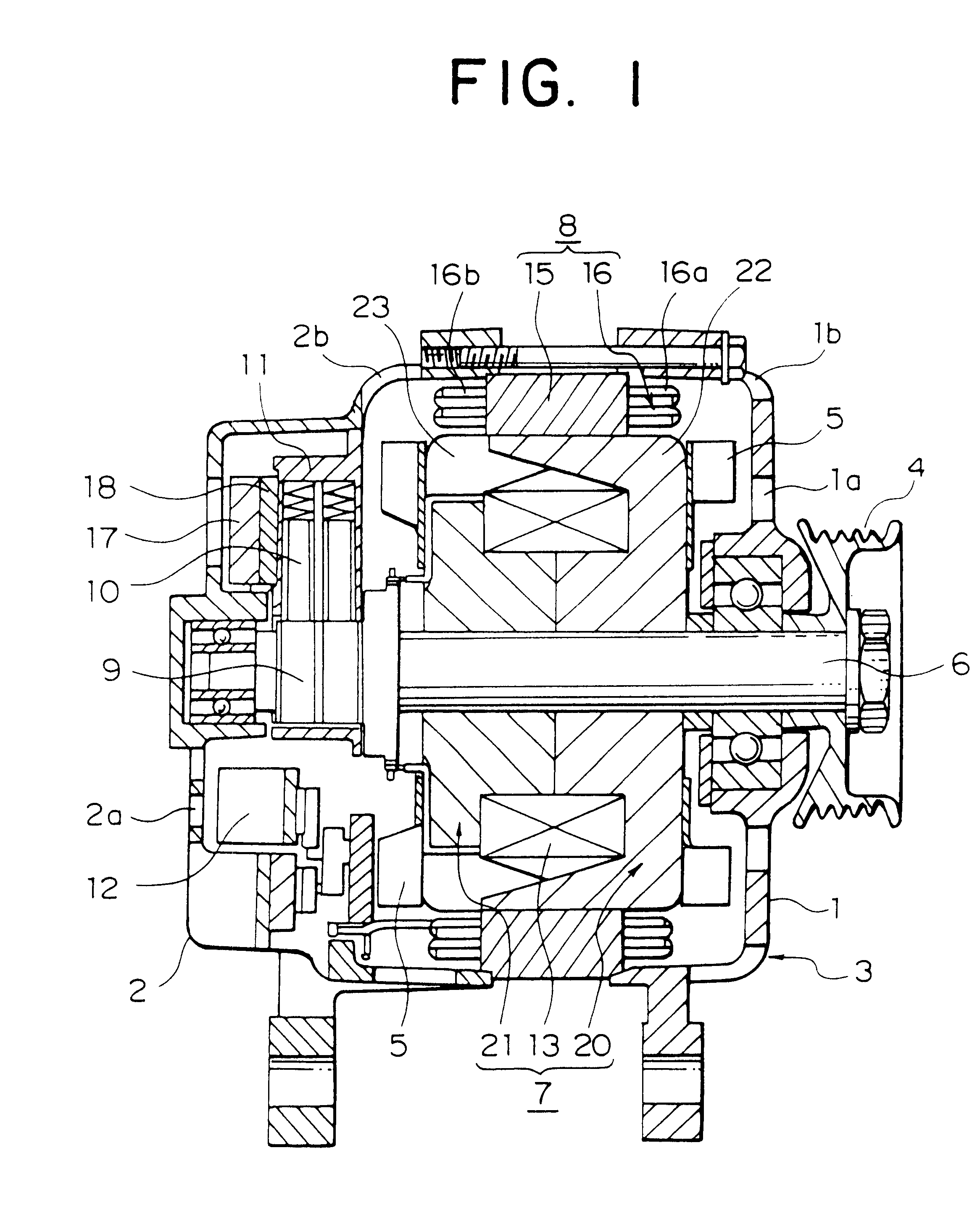
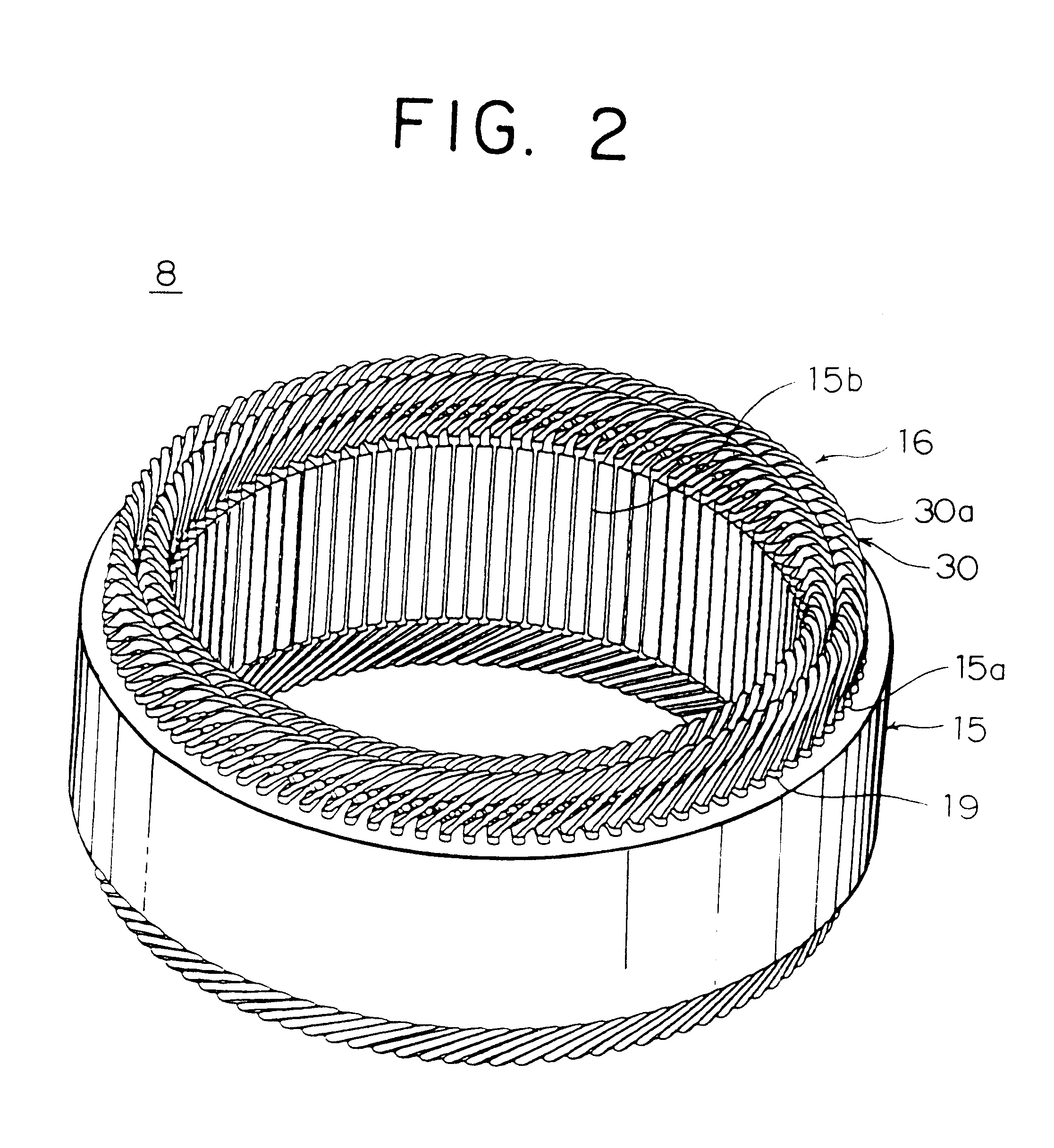
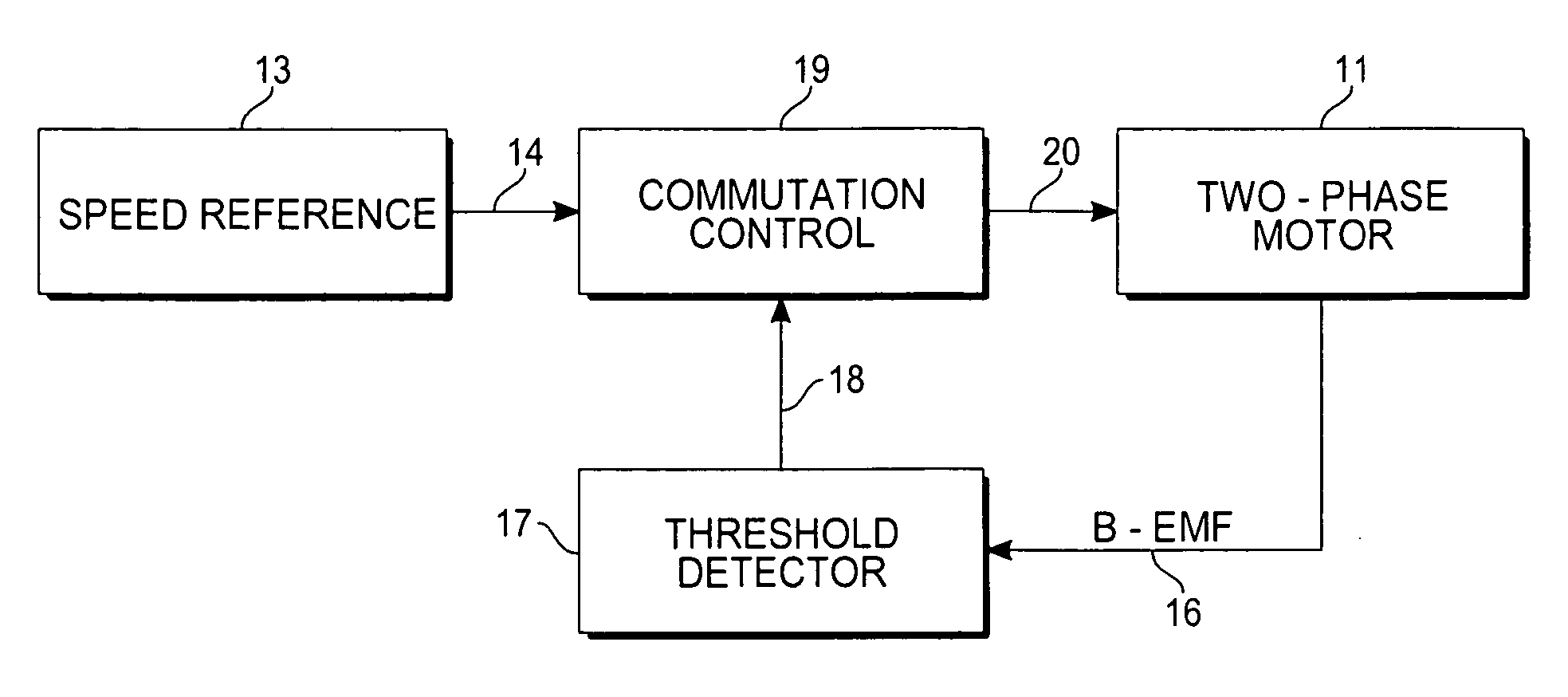
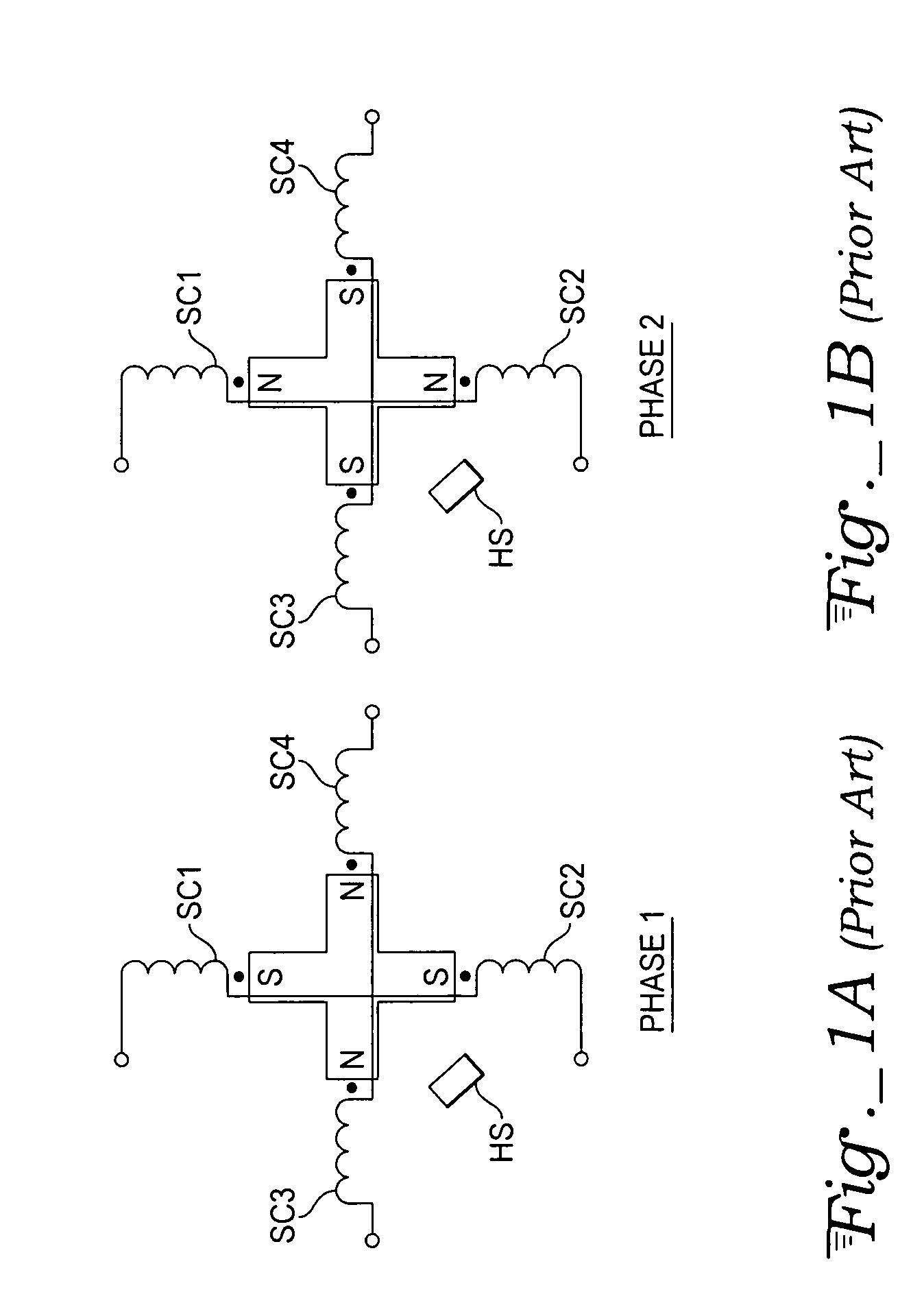
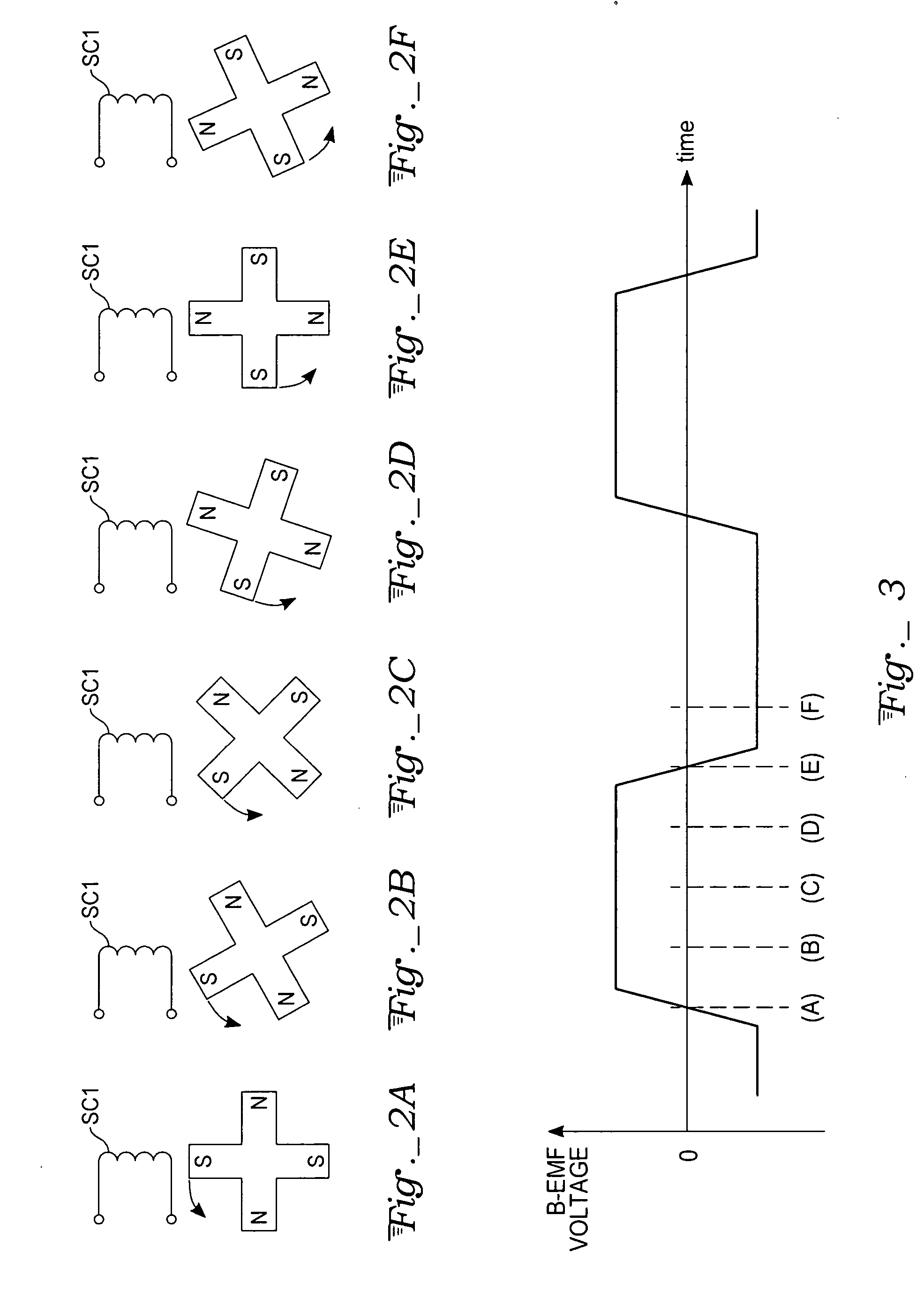
Sensorless control of two-phase brushless DC motor
A motor control system for a two-phase brushless DC motor uses measured EMF voltage from the passive set of stator coils to control commutation. A microcontroller receives the EMF voltage measurement and compares it to a threshold voltage value, which may be speed-dependent for advance commutation at high motor speeds. A match of the EMF voltage measurement with the threshold value triggers commutation of the drive to the opposite set of stator coils. The microcontroller also has an up-down counter timer whose count value is compared to an external speed reference. Each match of the count value triggers a transition in a pulse-width modulated (PWM) drive signal. The duty cycle of the PWM signal establishes an average drive voltage that controls motor speed.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Rotating electrical machine
InactiveUS20090001843A1Increase productivityImprove efficiencyMagnetic circuit stationary partsSupports/enclosures/casingsMagnetic polesStator coil
A rotating electrical machine includes: a claw pole stator constituted with a stator core that includes a plurality of claw poles and a stator coil wound inside the stator core; and a rotor rotatably disposed at a position facing opposite the claw poles. The stator core is constituted of split blocks each corresponding to at least one of magnetic pole pairs each made up with two claw poles assuming different magnetic polarities when an electric current is supplied to the stator coil.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
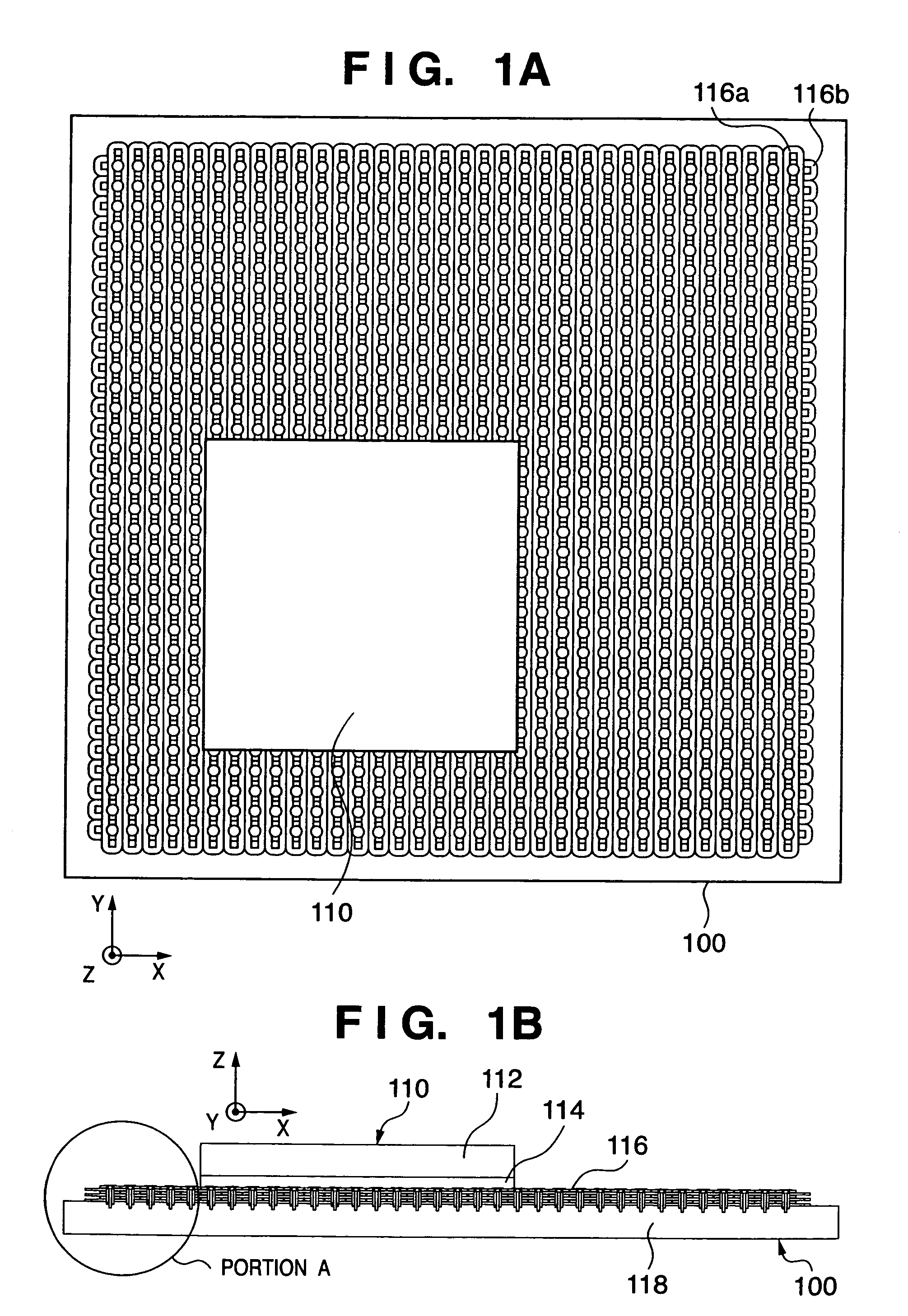
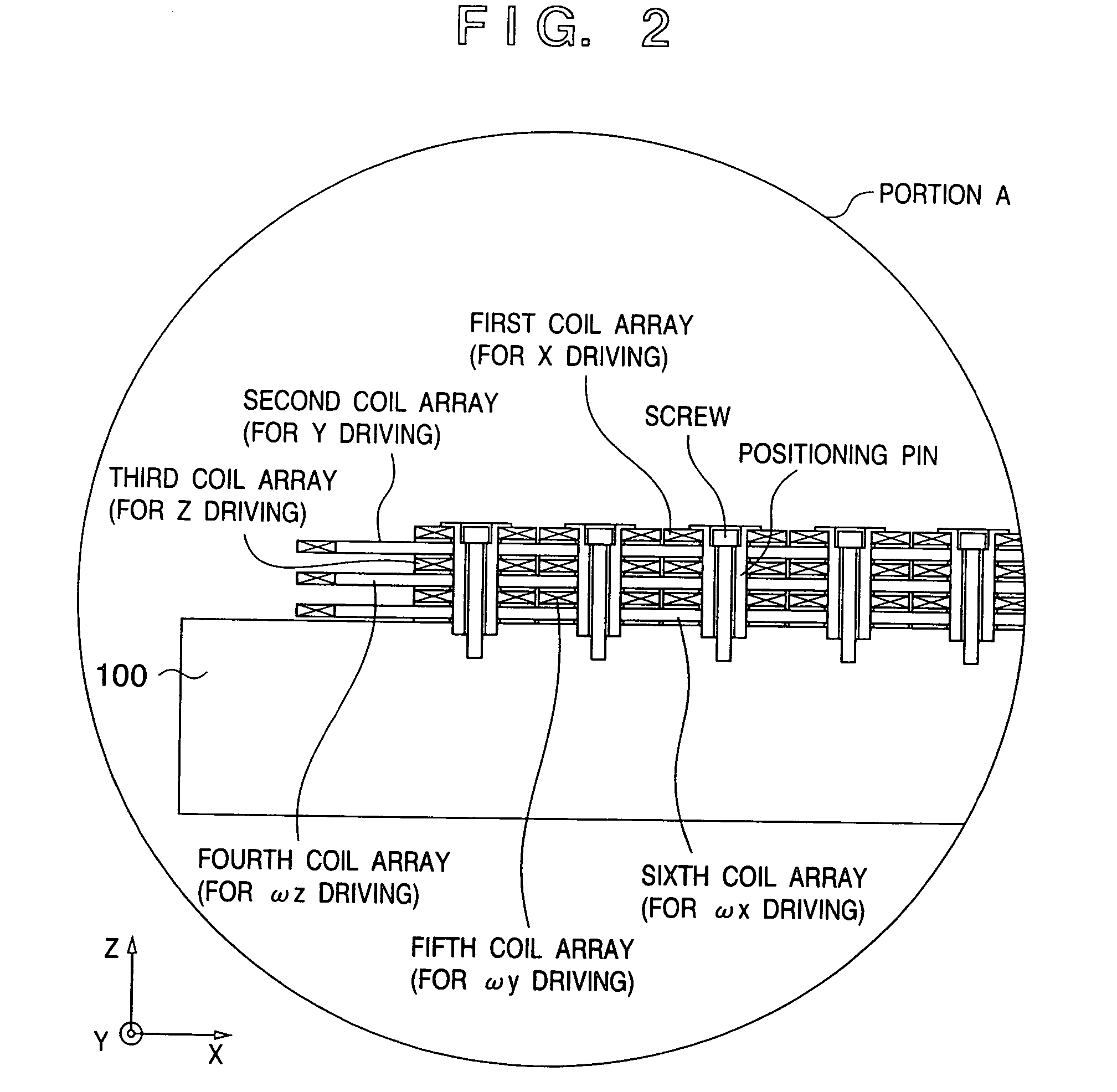
Alignment apparatus and exposure apparatus using the same
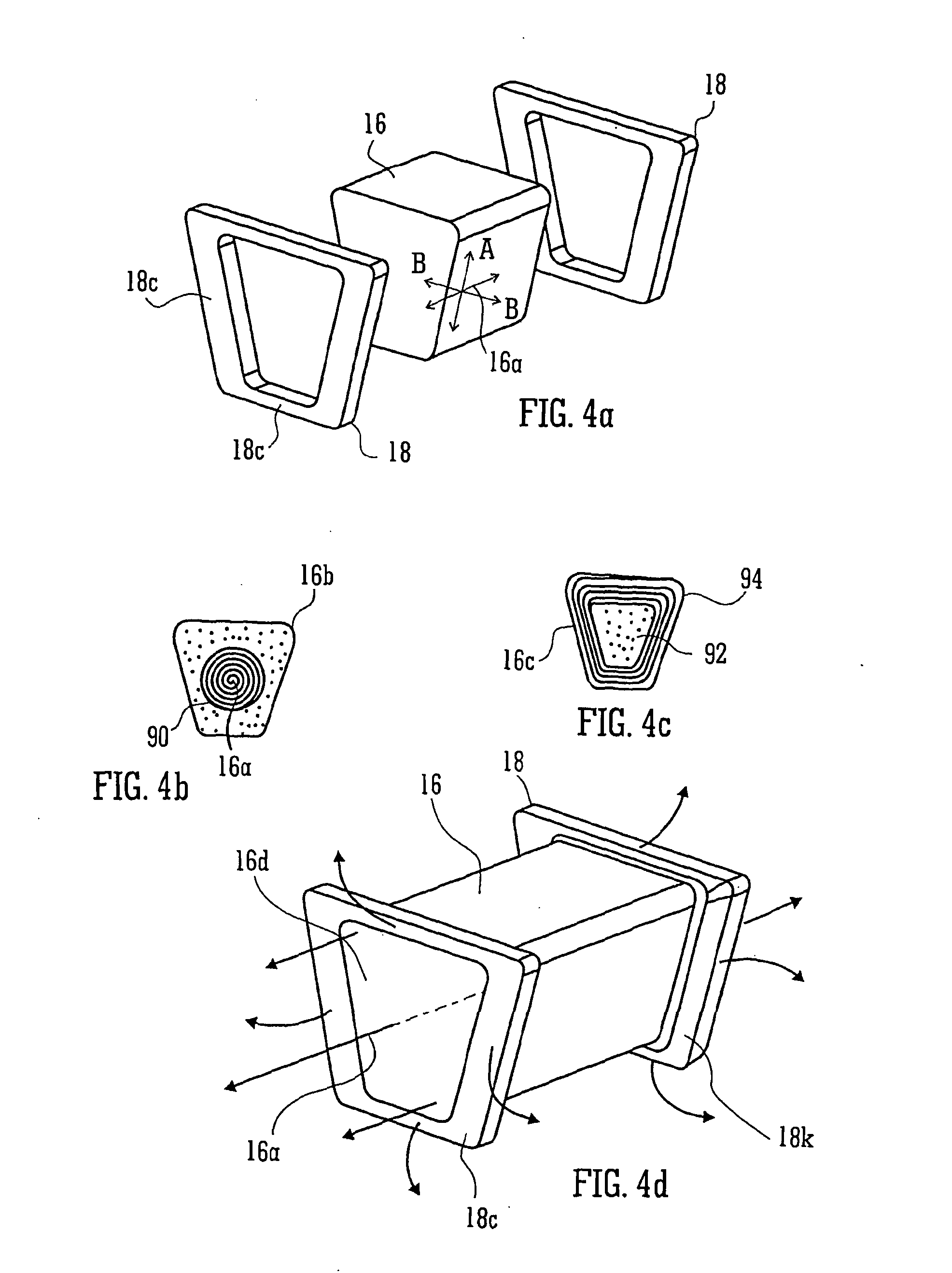
An alignment apparatus which generates a driving force between a plate-like movable element and a stator facing the movable element to control alignment of the movable element includes movable element magnets which are arrayed in a plate-like plane of the movable element in accordance with an array cycle and are magnetized in predetermined directions, stator coils which are arrayed at intervals corresponding to the array cycle, and a current controller which supplies control currents having phase differences to each pair of adjacent ones of the stator coils to generate a driving force for driving the movable element between the movable element magnets and the stator coils facing the movable element magnets. The stator coils, formed by stacking three pairs of the first and second layers, generate translational driving forces with three degrees of freedom and rotational driving forces with three degrees of freedom between the movable element magnets and the stator coils of each layer facing the movable element magnets on the basis of the control currents.
Owner:CANON KK
Rotating Electrical Machine
ActiveUS20090184591A1Windings insulation shape/form/constructionPower to auxillary motorsStator coilEngineering
A rotating electrical machine includes: a stator that including a stator core and a teeth section, with a stator coil wound at the teeth section; a rotor arranged via a clearance at an inner periphery side of the stator and supported in a freely rotating manner; and a distribution unit supported by a resin holder, and including a conductor connected to the stator coil. The rotating electrical machine is cooled by coolant. The stator coil includes a coil end section projecting from an end of the stator in an axial direction. A gap is formed between an end of the stator core and a lower surface of the distribution unit by mounting the distribution unit on an upper part of the coil end section. The gap constitutes a path for the coolant.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Linear position sensing system and coil switching methods for closed-loop control of large linear induction motor systems
ActiveUS6952086B1Reduce in quantityPotentially damaging lateral forces called by switch failure can be avoidedMotor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlFailure preventionTime delays
A control system for a linear motor adapted to accurately supply a moving window of power to the stator coils. A plurality of individually switched stator coils run the length of a linear motor to move a rotor down the long axis of the stator. Accurate inductive-based position sensors continuously provide position data for the moving rotor. A processing unit calculates a proper time delay from a source voltage peak in order to apply power to the next stator coil in the moving direction of the rotor such that no DC offshoot / undershoot occurs. The linear motor control system optionally includes a failure prevention switching scheme in which pairs of individual stator coils on opposite sides of a double-sided stator are switched together.
Owner:CURTISS WRIGHT ELECTRO MECHANICAL
Alternator
InactiveUS6504283B1Reduce noise levelComponent with highSynchronous generatorsAsynchronous induction motorsAlternatorStator coil
An alternator includes a stator having an annular stator core provided with a number of slots extending axially disposed in lines circumferentially so as to open on an inner circumferential side and a stator coil wound into the stator core so as to be installed in the slots, a rotor having a number of claw-shaped magnetic poles for alternately forming north-seeking (N) and south-seeking (S) poles about a rotational circumference, the rotor being rotatably disposed on the inner circumferential side of the stator core, a bracket supporting the rotor and the stator, and a rectifier disposed at a first axial end of the stator and connected to end portions of the stator coil, the rectifier converting alternating current from the stator coil into direct current, wherein a number of slots is two per phase per pole, and the stator coil comprises a number of winding sub-portions in each of which a long strand of wire is wound so as to alternately occupy an inner layer and an outer layer in a slot depth direction within the slots at intervals of a predetermined number of slots by folding back the strand of wire outside the slots at axial end surfaces of the stator core.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Sensorless control of two-phase brushless DC motor
ActiveUS20060186846A1Improve speed performanceMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersMotor speedMicrocontroller
A motor control system for a two-phase brushless DC motor uses measured EMF voltage from the passive set of stator coils to control commutation. A microcontroller receives the EMF voltage measurement and compares it to a threshold voltage value, which may be speed-dependent for advance commutation at high motor speeds. A match of the EMF voltage measurement with the threshold value triggers commutation of the drive to the opposite set of stator coils. The microcontroller also has an up-down counter timer whose count value is compared to an external speed reference. Each match of the count value triggers a transition in a pulse-width modulated (PWM) drive signal. The duty cycle of the PWM signal establishes an average drive voltage that controls motor speed.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
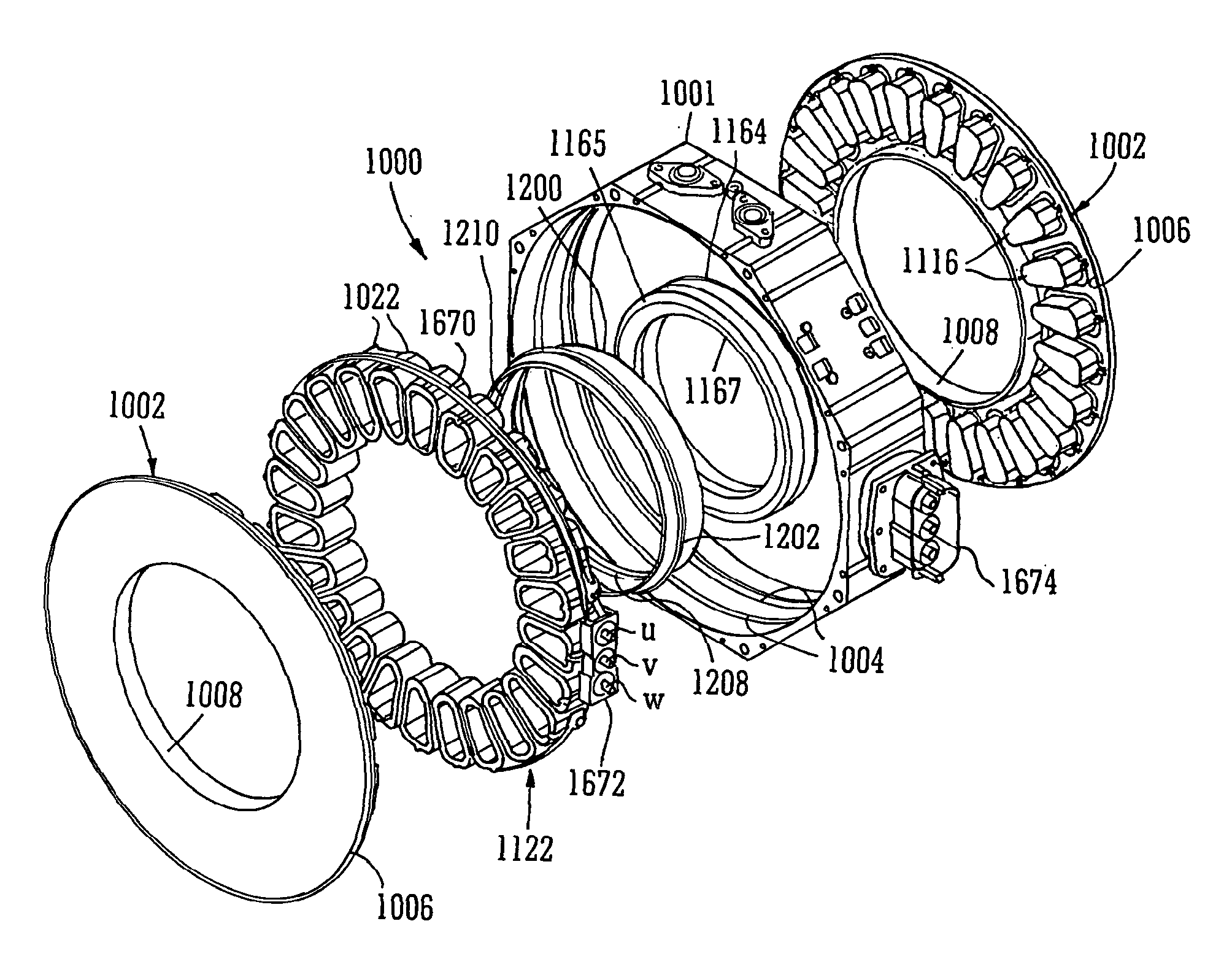
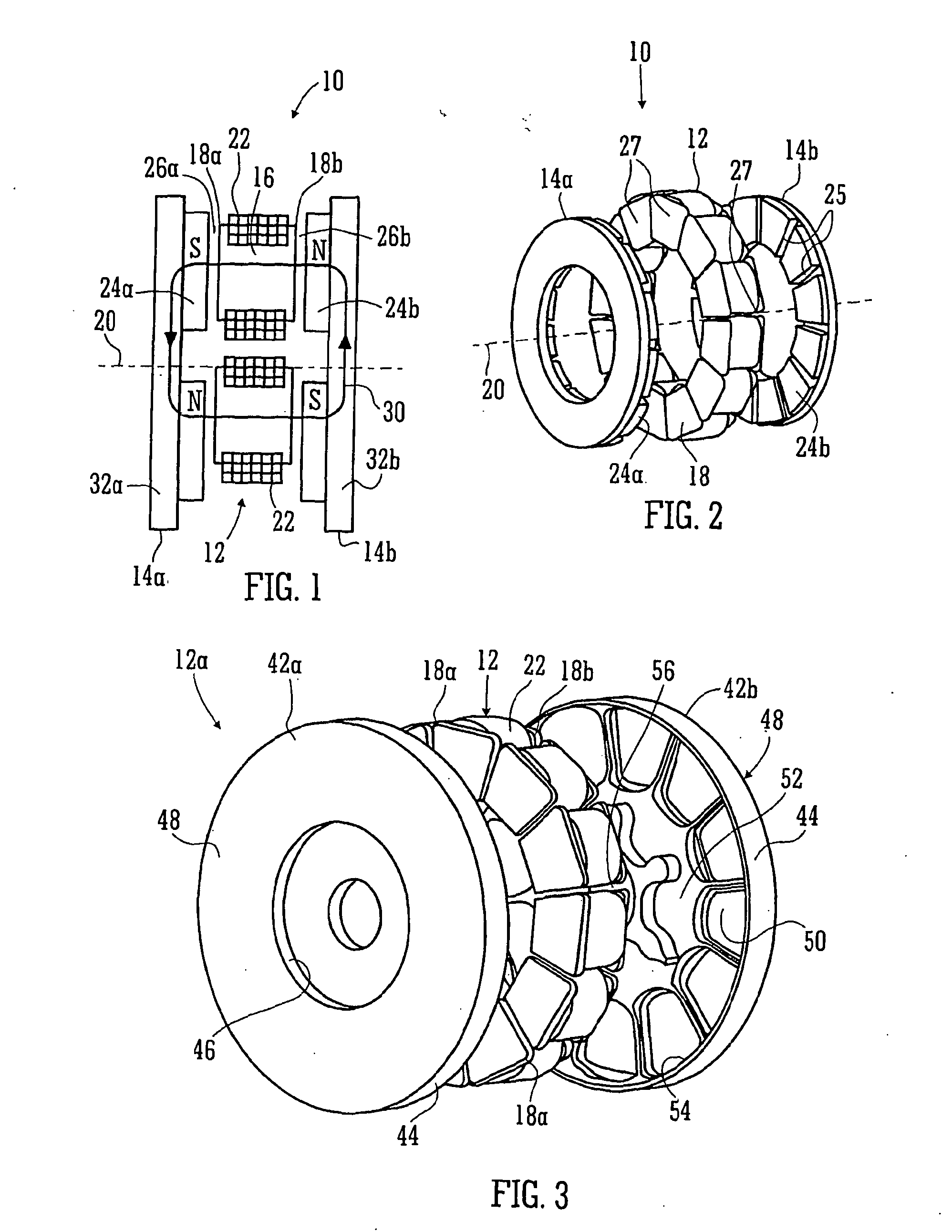
Electric machine - over-moulding construction
ActiveUS20130147291A1Gap minimizationImprove machine efficiencyMagnetic circuit stationary partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesElectric machineStator coil
An electric machine (10) comprises a rotor (14a, b) having permanent magnets (24a, b) and a stator (12) having coils (22) wound on stator bars (16) for interaction with the magnets across an air gap (26a, b) defined between them. The bars (16) and coils (22) are enclosed by an annular stator housing (42a, b) that extends between the air gap. A chamber (52, 54, 56) is defined that incorporates cooling medium to cool the coils. The stator housing comprises two mating clamshells (42a, b) that mount the stator bars and coils in the machine. Each clamshell is moulded from reinforced plastics and interconnected (optionally through one or more intermediate components). At least one clamshell has over-moulded therein stator bar shoes that form part of said radial wall, and optionally one or more of the following components: cylindrical boss supports extending along the cylindrical outer wall part; connection studs that communicate electrically the chamber externally; stator coils; coolant inlet and outlet ports; and an outer race of a rotor bearing.
Owner:YASA LIMITED
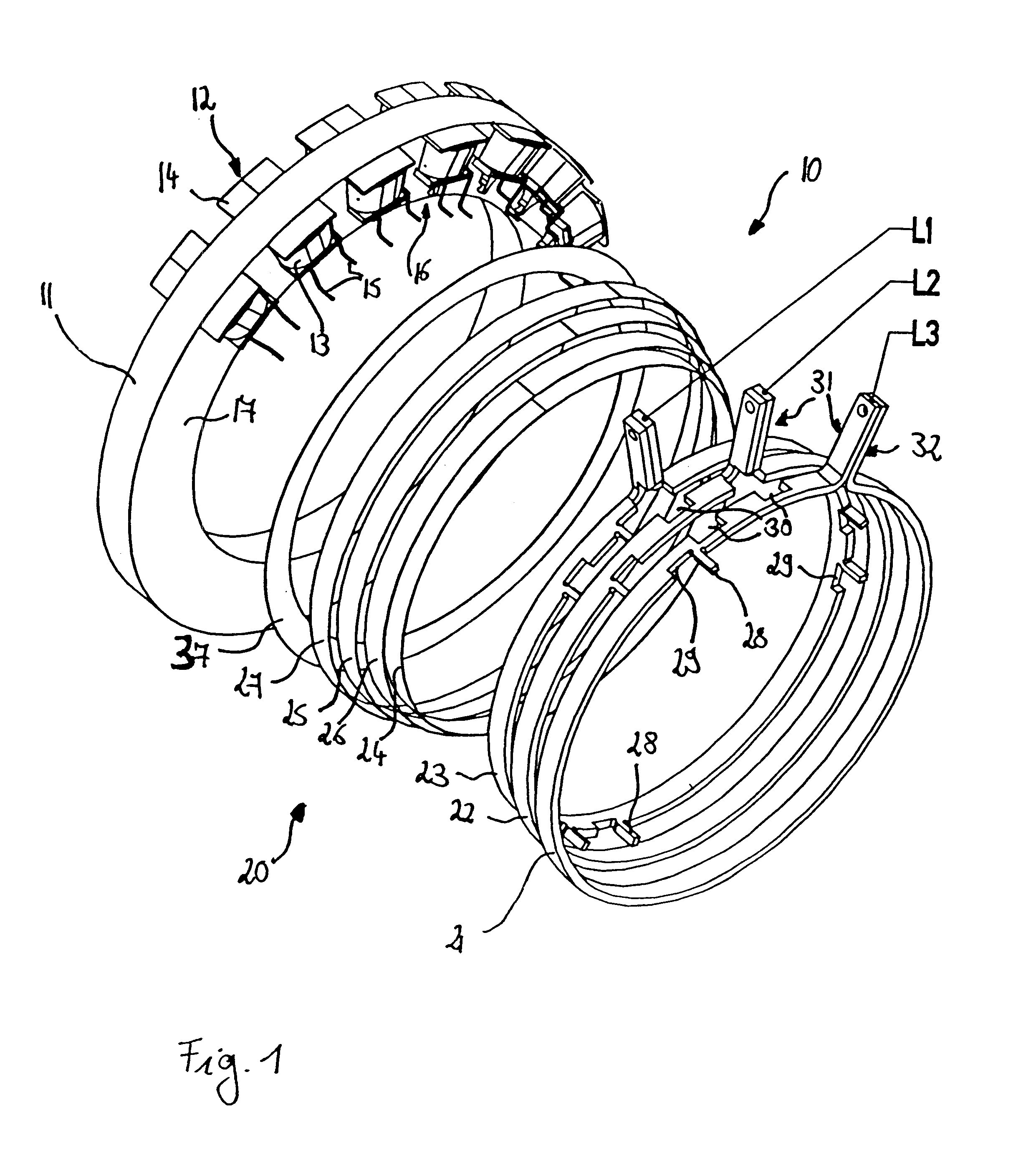
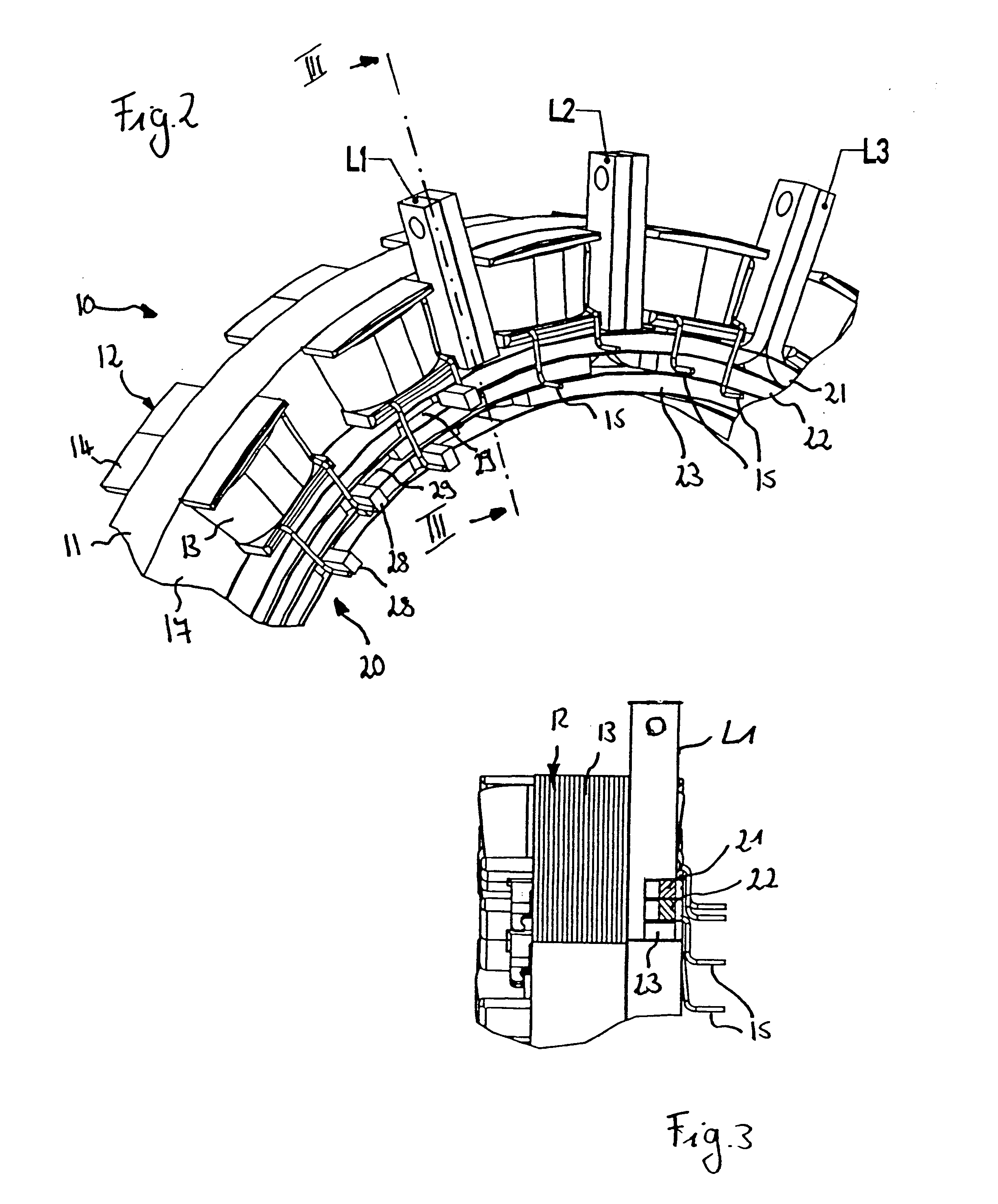
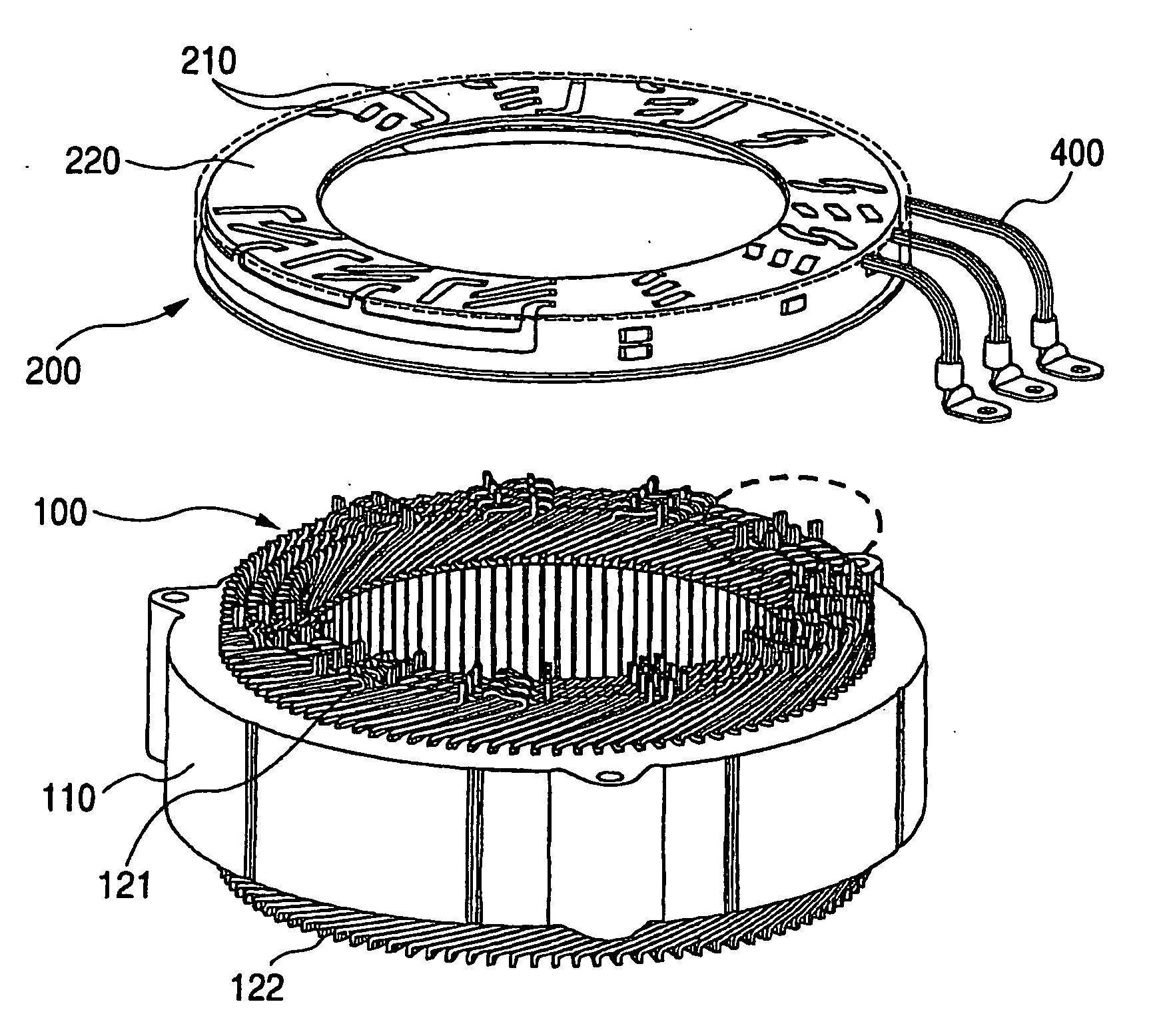
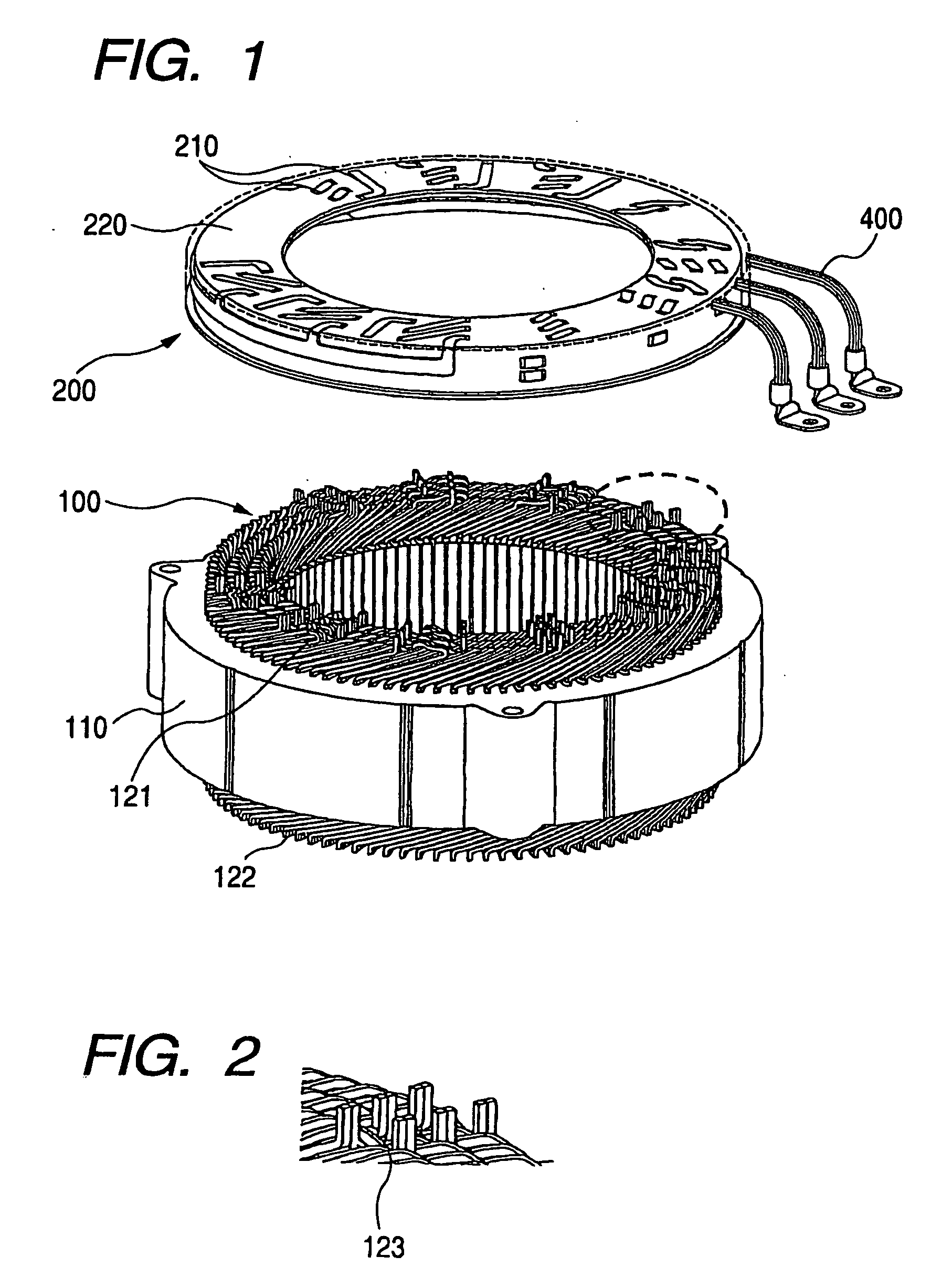
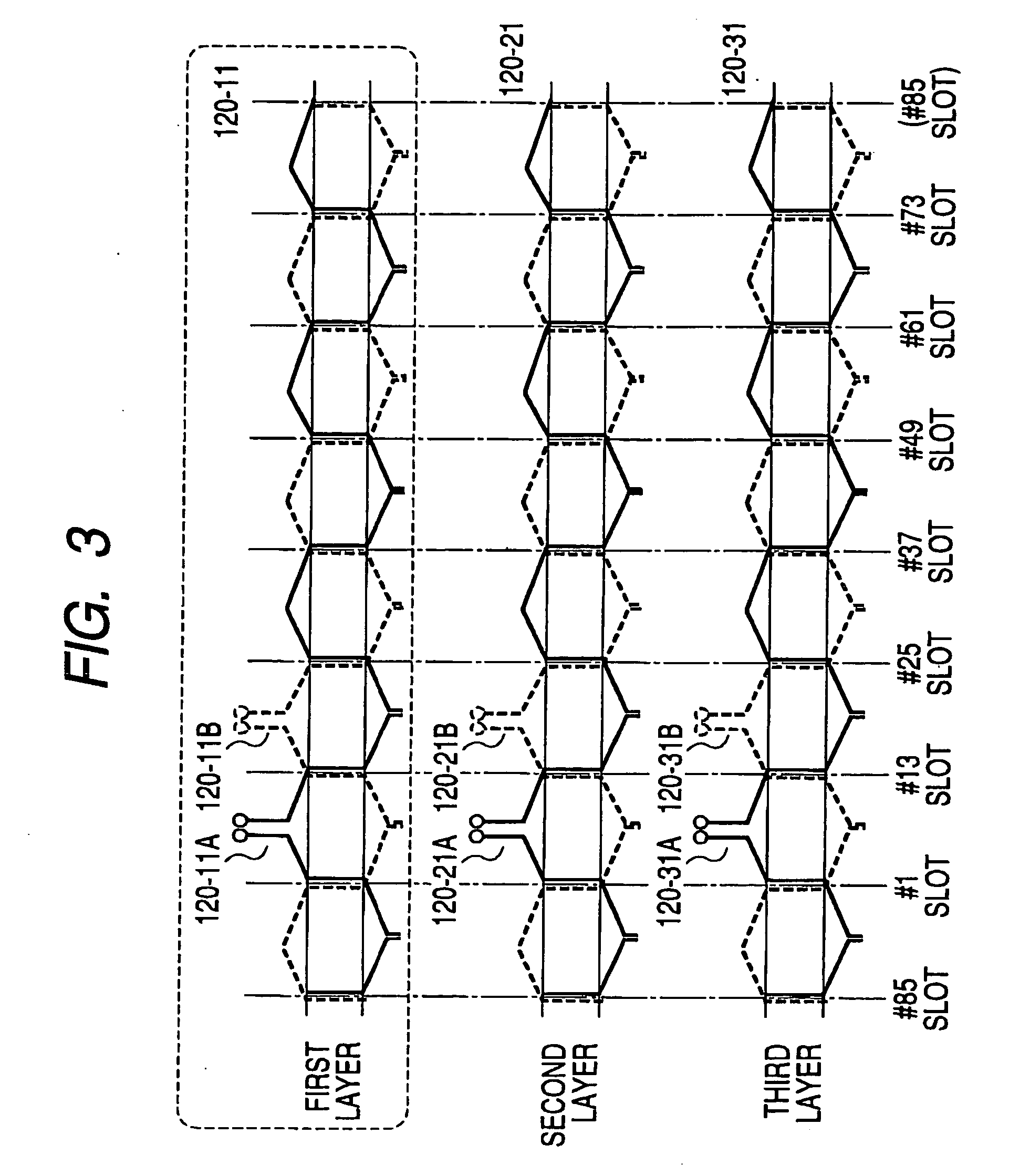
Stator coil including sequentially connected segment conductors preferably applicable to an electric rotary machine
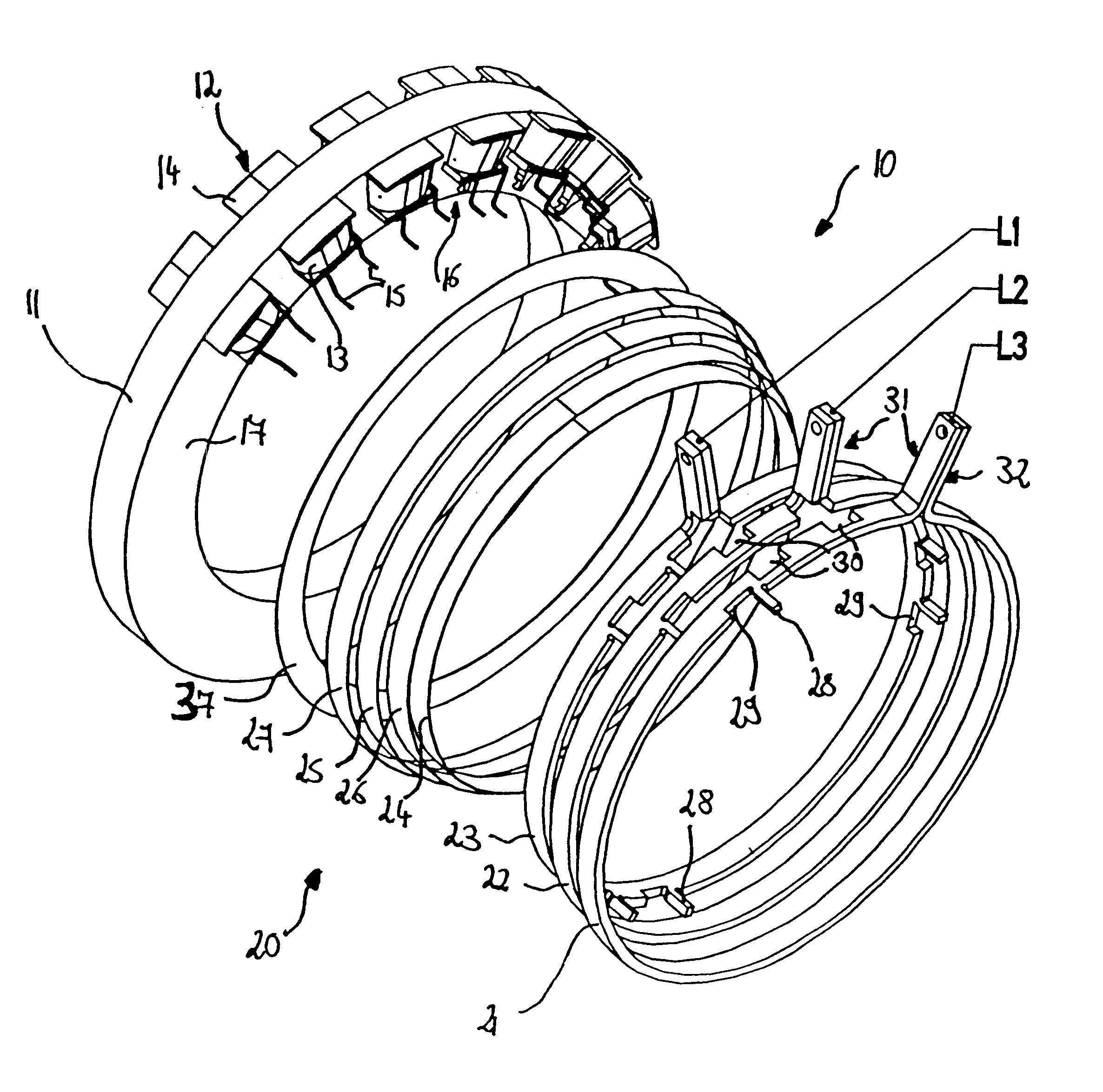
ActiveUS20050253466A1Easy to changeSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuitElectrical conductorStator coil
A stator coil includes a coil portion wound around a stator core and a terminal board serving as a bus bar array board. The coil portion is arranged by sequentially connected segment conductors. The terminal board is a molded ring plate member disposed adjacently to a head coil end of the coil portion in the axial direction and elongated in the radial direction. The turn number of the stator coil is easily adjustable by selecting an optimum one of a plurality of terminal boards.
Owner:DENSO CORP
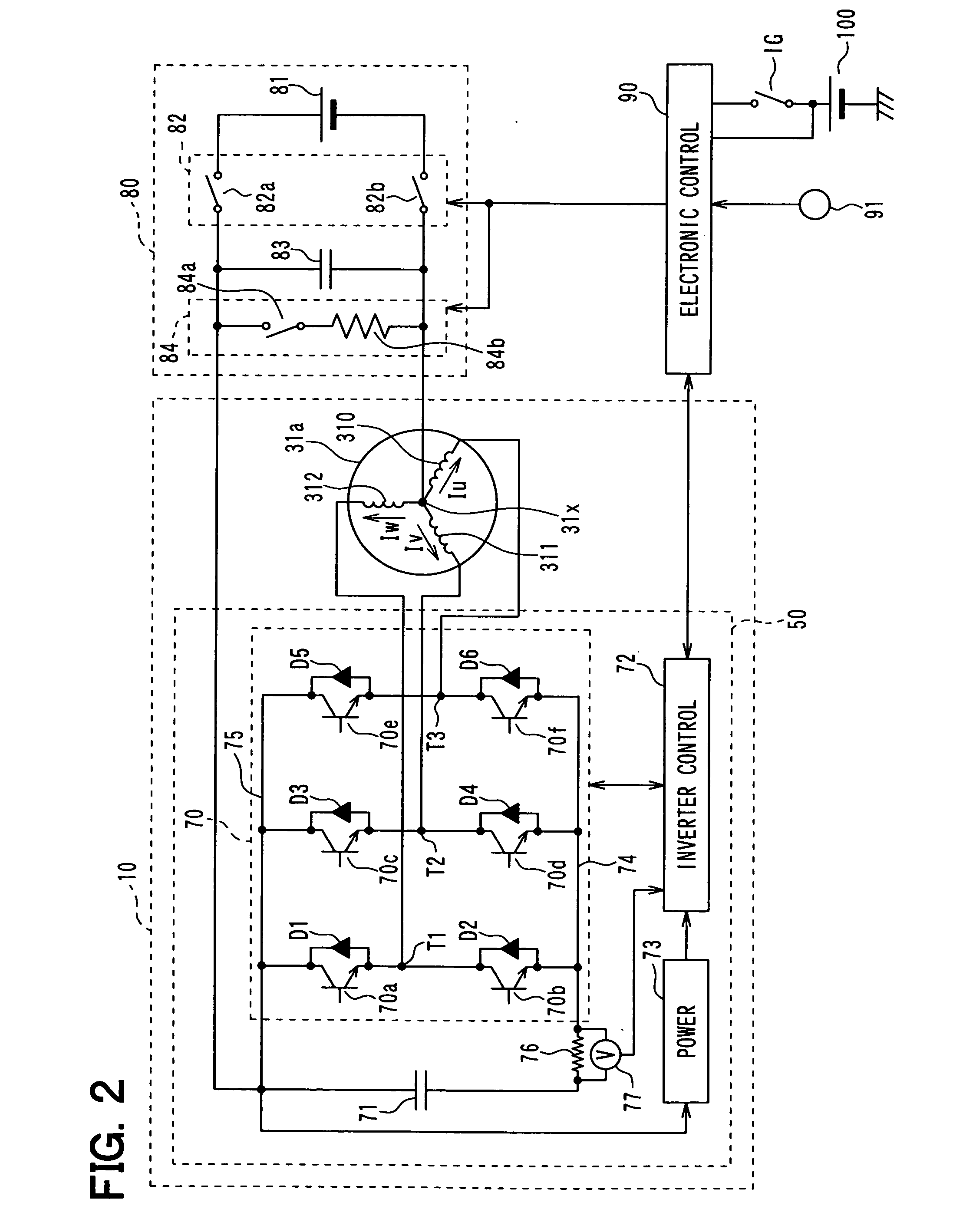
AC rotating machine with improved drive for its stator coil
InactiveUS20090302792A1Improve reliabilityIncrease torqueSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlFull bridgeStator coil
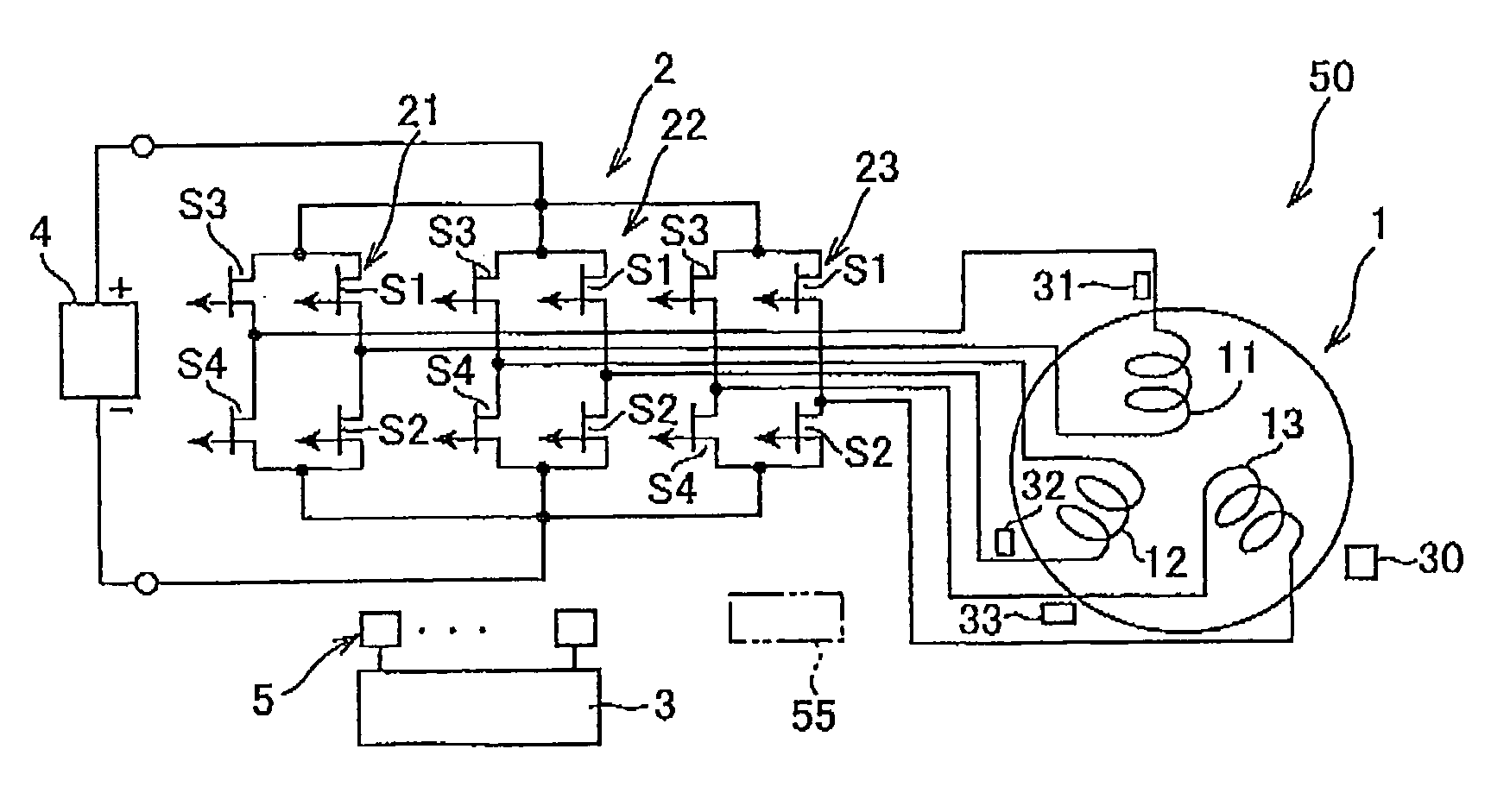
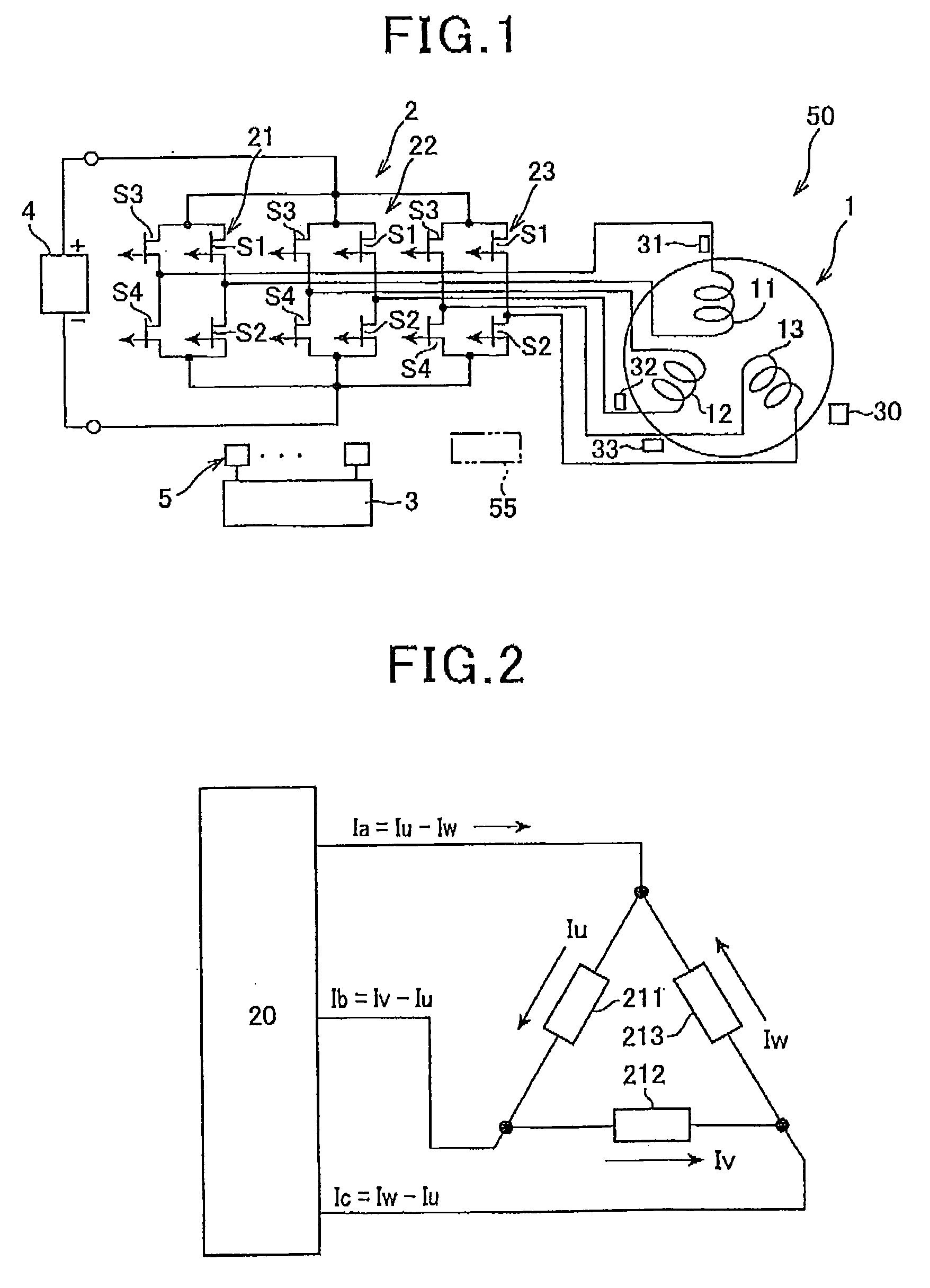
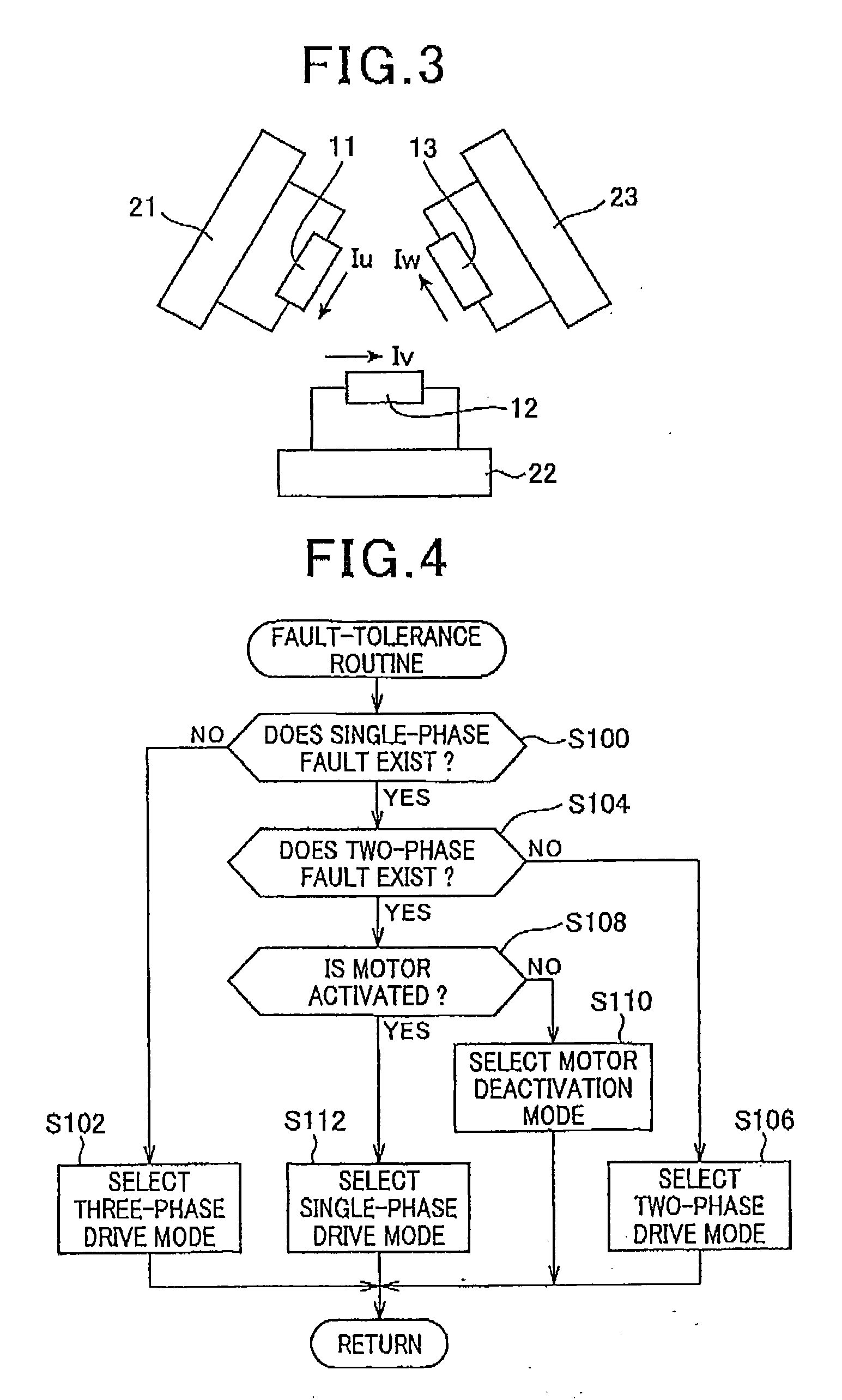
In an AC rotating machine, a stator is provided with N-phase stator windings and located relative to the rotor. The N is an integer equal to or greater than 3, and the N-phase stator windings are arranged to be electrically isolated from each other. An inverter circuit is provided with first to N-th full-bridge inverters. Each of the first to N-th full-bridge inverters includes a first pair of series-connected switching elements and a second pair of series-connected switching elements. The first pair of series-connected switching elements and the second pair of series-connected switching elements are connected in parallel to each other. Each of the first to N-th full-bridge inverters is configured to individually apply a single-phase AC voltage to a corresponding one of the N-phase stator windings to thereby create a torque that rotates the rotor.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Driving apparatus for a vehicle-mounted electric motor
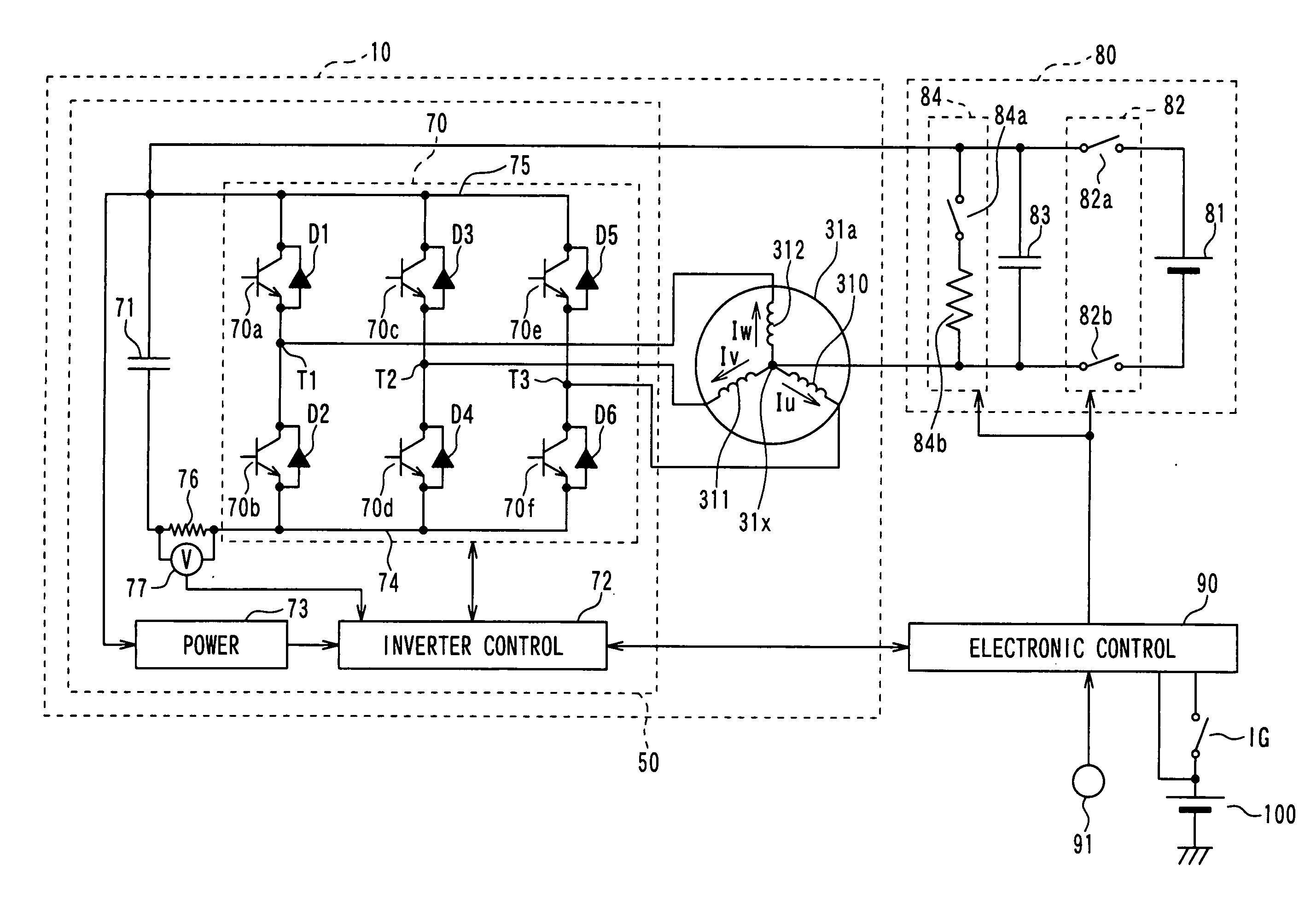
An inverter circuit for a motor outputs three-phase AC currents, which are outputted from common connection points to stator coils, based on output voltage of a DC power source and a power supply capacitor by a switching operation of transistors. An inverter control circuit determines that a system main relay is turned off, upon receiving a main relay-off signal from an electronic control unit. The inverter control circuit turns on the low-side transistors, while turning off the high-side transistors. A discharge current flows from the positive electrode to the negative electrode of the power supply capacitor through the stator coil and the low-side transistors, so that electric charge stored in the power supply capacitor is discharged.
Owner:DENSO CORP
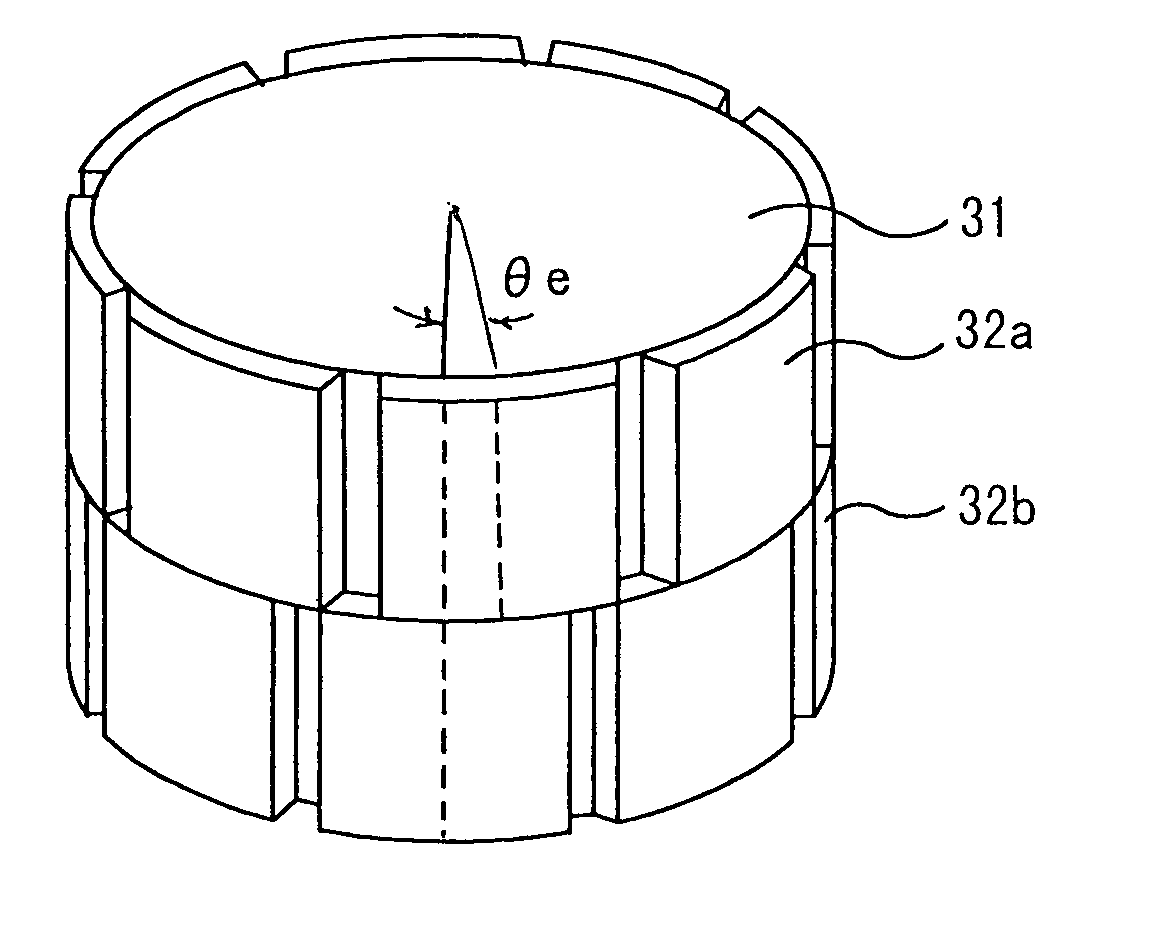
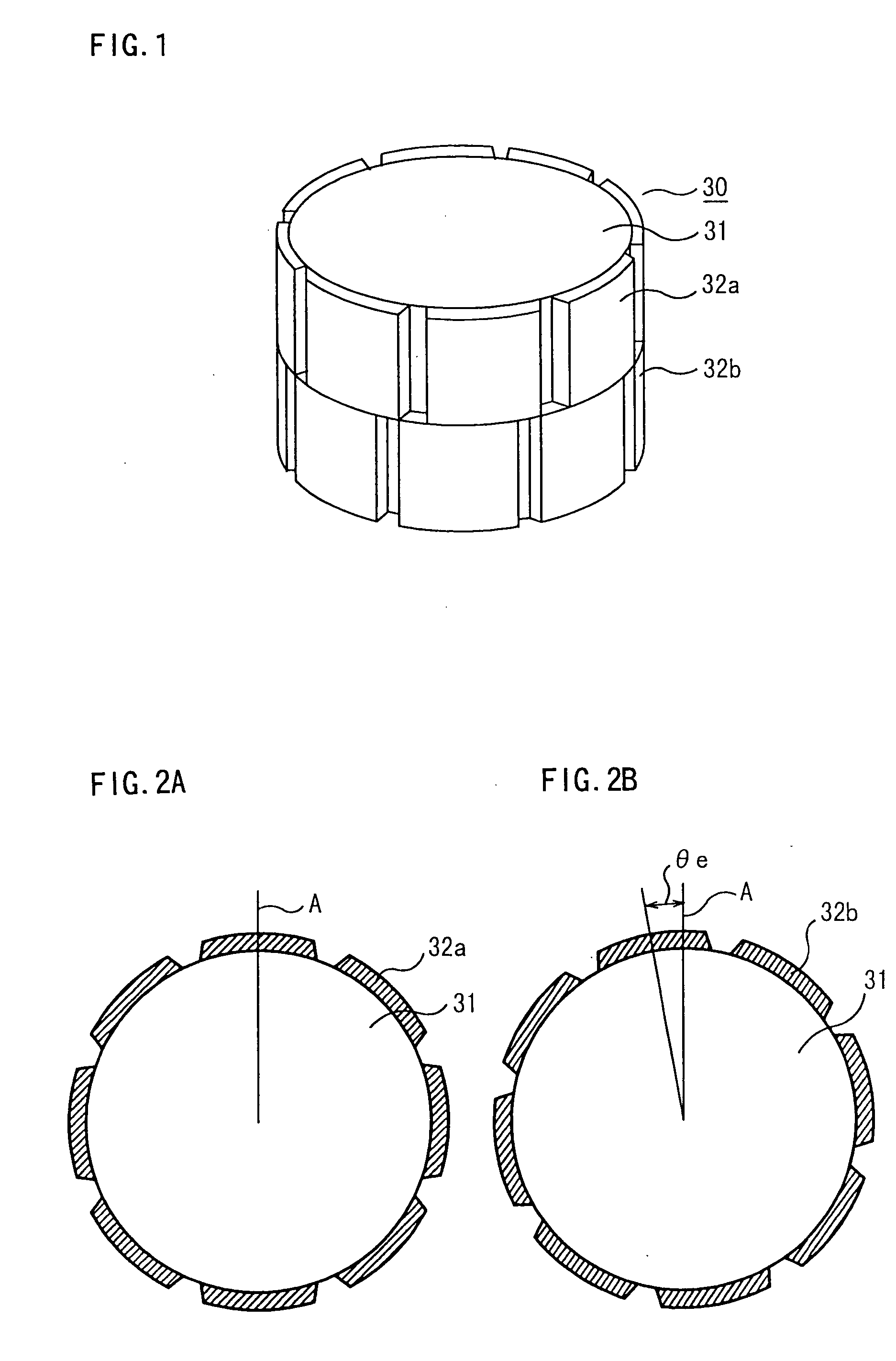
Permanent-magnet rotating machine
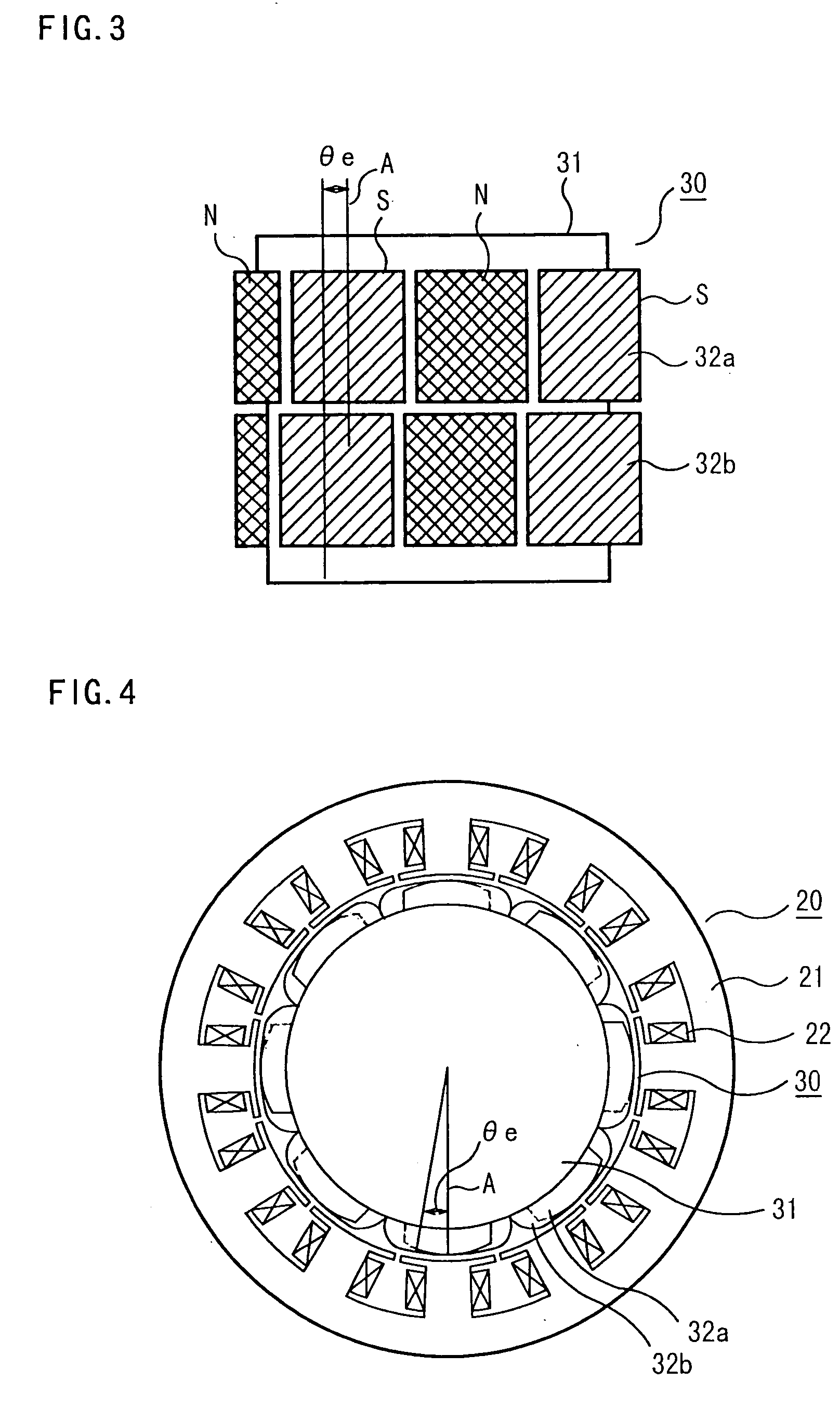
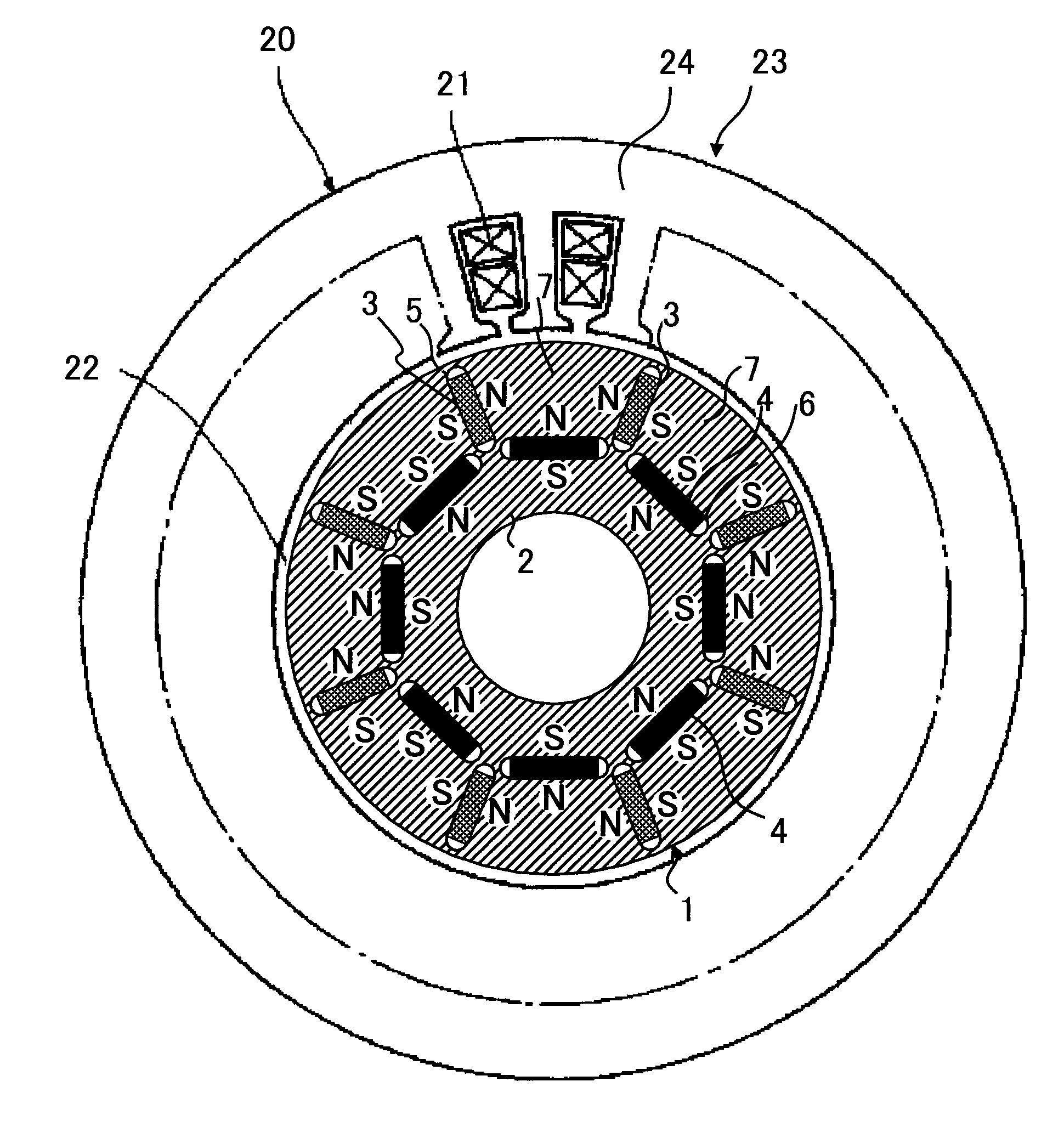
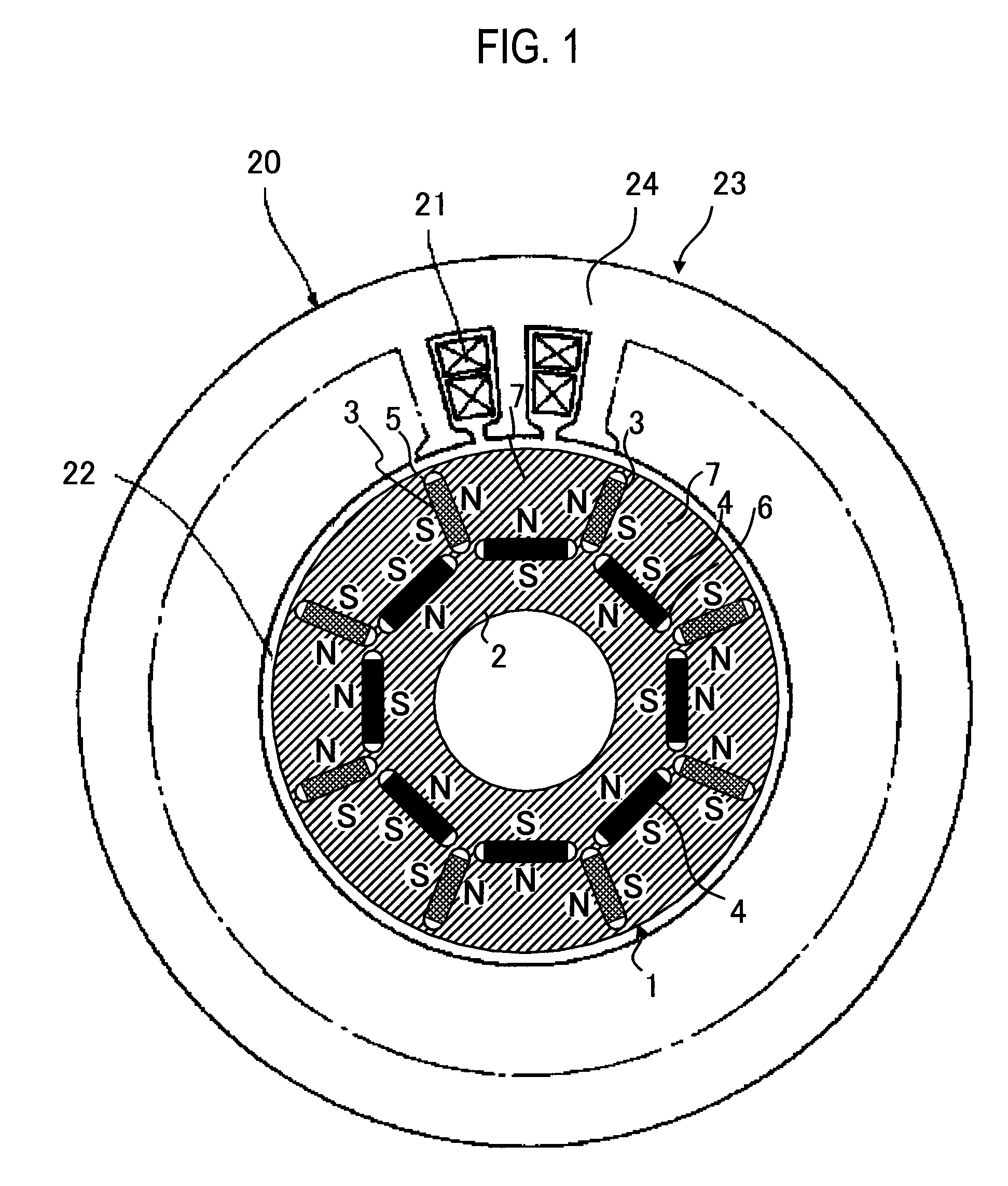
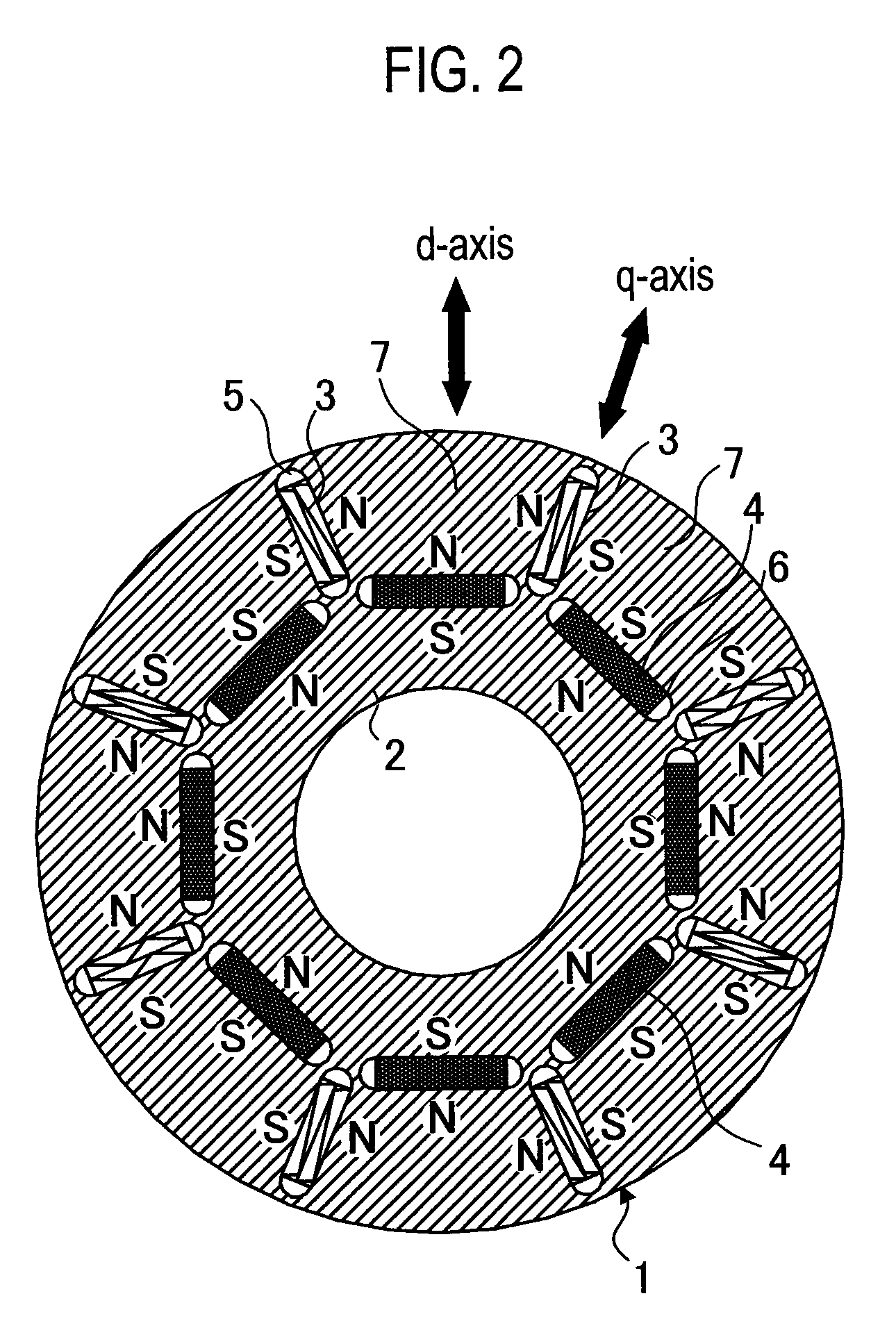
ActiveUS20040124728A1Efficiently reduce cogging torque and torque ripplesMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsLower limitSkew angle
A permanent-magnet rotating machine includes a rotor having a rotor core carrying on its curved outer surface multiple permanent magnets arranged in two rows along an axial direction in such a manner that the permanent magnets in one row are skewed from those in the other row in a circumferential direction by a row-to-row skew angle (electrical angle) thetae, and a stator having a cylindrical stator core in which the rotor is disposed, the stator core being provided with stator coils for producing a rotating magnetic field for rotating the rotor. A lower limit of the row-to-row skew angle thetae is set at a value larger than 30 degrees (electrical angle). A cogging torque ratio, or the ratio of a cogging torque occurring in the absence of skew to a cogging torque occurring when the permanent magnets are skewed, at a row-to-row skew angle of 30 degrees is calculated based on the relationship between the cogging torque ratio and the row-to-row skew angle thetae and B-H curve properties of the stator core, and an upper limit of the row-to-row skew angle thetae is set at a value not larger than its maximum value at which the cogging torque ratio does not exceed the calculated cogging torque ratio at 30 degrees.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Permanent-magnet-type rotating electrical machine
ActiveUS20090236923A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityMagnetic circuitSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsLow speedElectric machine
An object of the present invention is to provide a permanent-magnet-type rotating electrical machine capable of realizing a variable-speed operation at high output in a wide range from low speed to high speed and improving efficiency and reliability. The permanent-magnet-type rotating electrical machine of the present invention includes a stator provided with a coil and a rotor in which there are arranged a low-coercive-force permanent magnet whose coercive force is of such a level that a magnetic field created by a current of the stator coil may irreversibly change the flux density of the magnet and a high-coercive-force permanent magnet whose coercive force is equal to or larger than twice that of the low-coercive-force permanent magnet. At the time of high-speed rotation with a voltage of the permanent-magnet-type rotating electrical machine being around or over a power source maximum voltage, the low-coercive-force permanent magnet is magnetized with a magnetic field created by a current in such a way as to decrease total linkage flux of the low- and high-coercive-force permanent magnets, thereby adjusting a total linkage flux amount.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
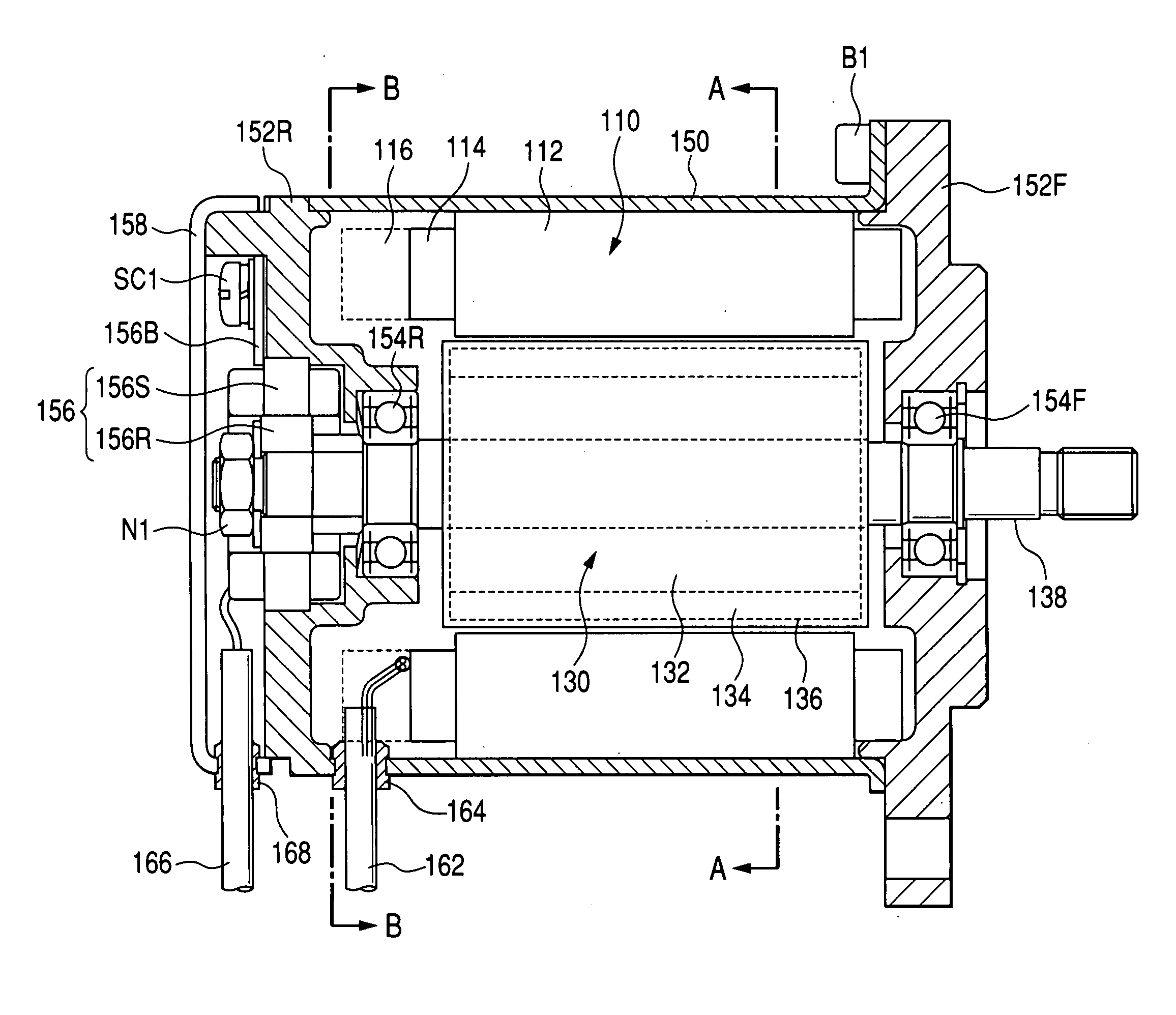
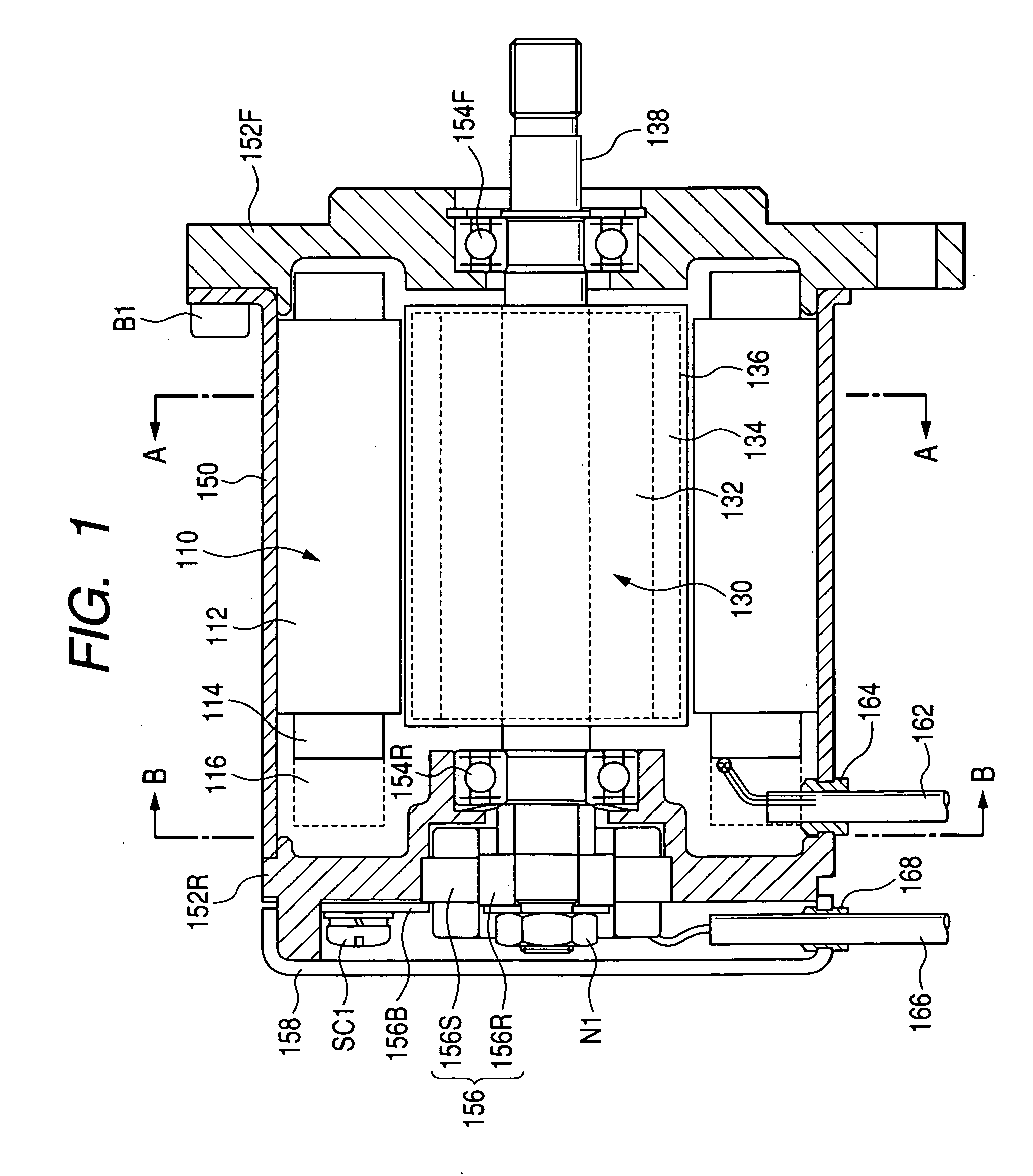
A.C. motor-inverter integrated drive unit
ActiveUS20040090130A1Association with control/drive circuitsCooling/ventillation arrangementStator coilEngineering
An a.c. motor-inverter integrated drive unit comprises an a.c. motor powered by an alternating current. The motor includes a rotor rotatable about a rotation axis, a plurality of stator cores arranged about the rotation axis at evenly spaced intervals to constitute a cylindrical stator structure, a plurality of stator coils disposed on the stator cores respectively and a plurality of cooling passages formed in the stator cores respectively. An inverter is combined with the motor. The inverter converts a direct current to an alternating current and includes a plurality of power drivers which are arranged on the stator cores respectively. Wire members are used for connecting the power drivers and the stator coils respectively.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
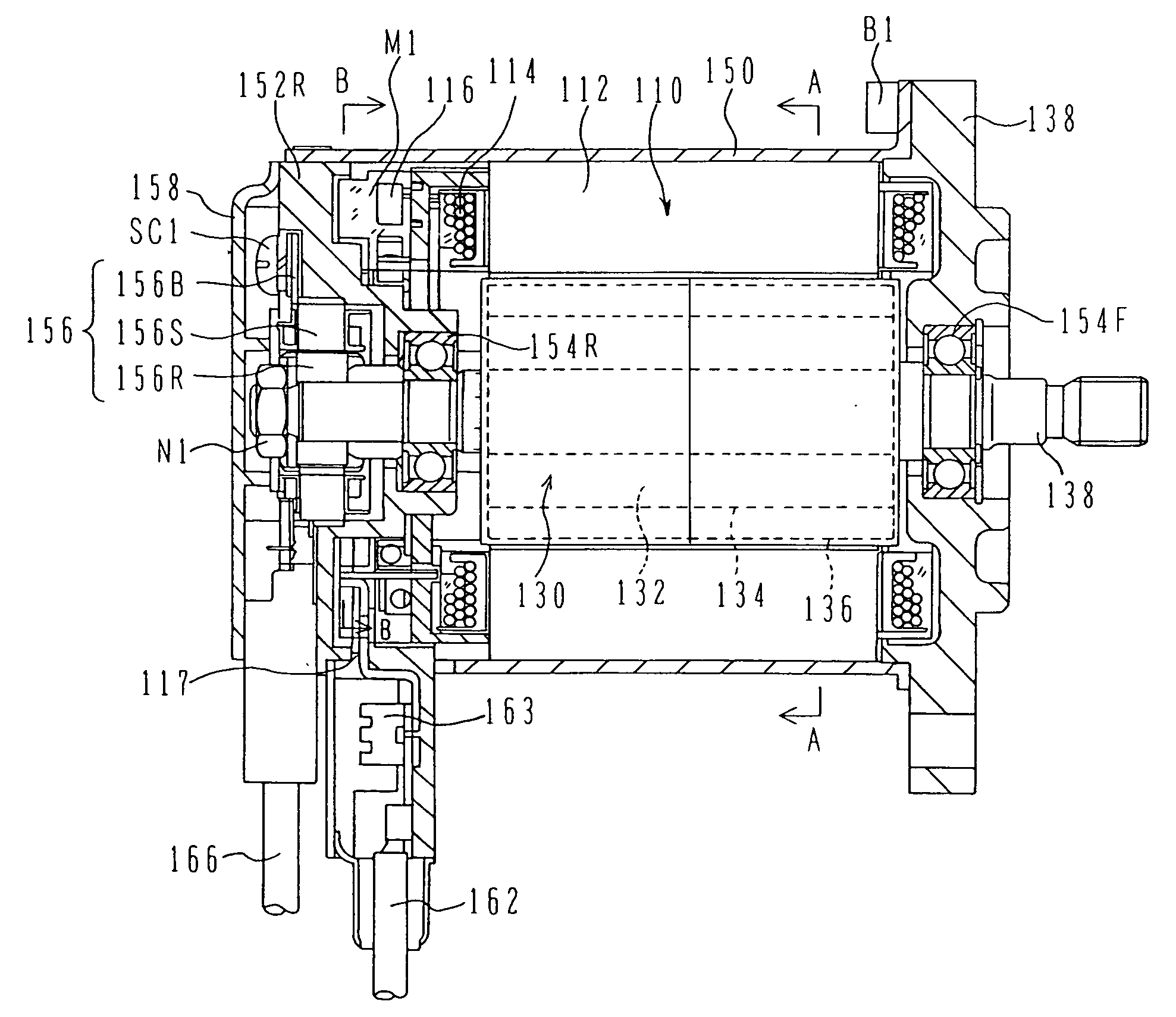
Stator for electric rotating machine
InactiveUS20120019081A1Avoid displacementImprove insulation performanceWindings insulation materialManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesElectric machineStator coil
A stator includes an annular stator core and a stator coil. The stator coil is formed of a plurality of electric wires mounted on the stator core. The stator coil has a coil end part that protrudes from an axial end face of the stator core so as to be located outside slots of the stator core. The electric wires forming the stator coil are grouped into a plurality of electric wire sets. Each of the electric wire sets consists of a predetermined number of the electric wires which are electrically connected to one another. The stator coil further includes a plurality of bridging wires. Each of the bridging wires extends, on an axially outer periphery of the coil end part of the stator coil, to electrically connect a corresponding pair of the electric wire sets. Further, at least two of the bridging wires are fixed to one another.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Axial flux switched reluctance motor and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20100295389A1Use minimizedIron and copper lossMagnetic circuitSynchronous motorsStator coilReluctance motor
An axial flux switched reluctance motor utilizes one or more rotor discs spaced along a rotor shaft, each rotor disc having a plurality of rotor poles spaced along the periphery thereof. Stator elements are distributed circumferentially about the rotor discs and form pairs of radially extending stator poles for axially straddling the rotor discs. Stator coils as switched on to energize pairs of stator poles for forming an axial and radially inward flux path for rotating the rotor poles for minimizing the flux path before switching off the stator coil. Two or more rotor discs can be rotationally indexed for providing two or more motor phases. In manufacture, rotor discs and circumferentially extending stator coils about the periphery of each rotor disc are fit to a stator housing. Each stator element is then fit radially through the stator housing and secured thereto for straddling the rotor discs.
Owner:MSI MACHINEERING SOLUTIONS
Controller for electric power steering and electric power steering system
ActiveUS20060006749A1Minimize torque pulsationIncreased operating comfortAssociation with control/drive circuitsPrinted circuit board receptaclesElectric power steeringElectrical conductor
An electric power steering drive system provided with a motor with its torque pulsation reduced, and a controller characterized by excellent manufacturability. The stator core of a motor is composed of an annular back core and a plurality of teeth created separately from the back core and secured on the inner periphery of the back core. An 8-pole / 9-slot, 10-pole / 9-slot or 10-pole / 12-slot relationship is found between the number of the magnets of a rotor (number of poles) and the number of slots. The diameter of the stator coil is 1.0 mm or more. A motor controller comprises a power module, a conductor module and a control module. The terminal of the power module and the bus bar of the conductor module are connected by welding, whereas the terminal of the power module and terminal of the control module are connected by soldering.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Nested stator coils for permanent magnet machines
An arrangement of coils of different configurations for use in the stator of a slotless radial gap electromotive machine is described. The coils include coils of a first configuration and a second configuration. Each coil includes longitudinal sections and circumferential sections that form a substantially rectangular opening in the coil. The coils are nested together along the inside of a stator core so that the longitudinal sections of each coil of the first configuration are disposed in the rectangular openings of neighboring coils of the second configuration, and the longitudinal sections of the coils of the second configuration are disposed in the rectangular openings of neighboring coils of the first configuration. Other configurations of coils can be nested together inside the stator core to provide one or more additional layers of stator coils.
Owner:MOOG INC
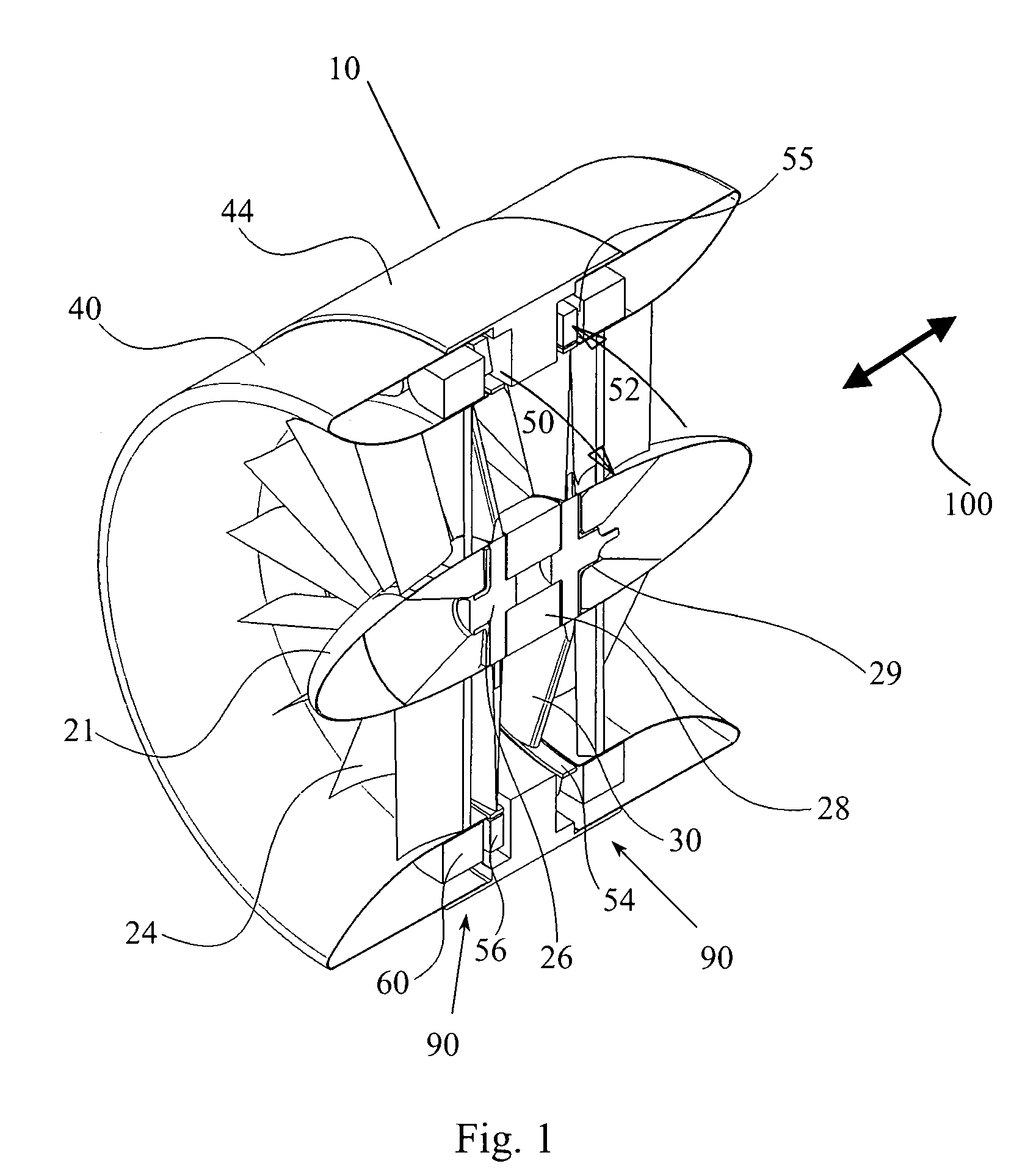
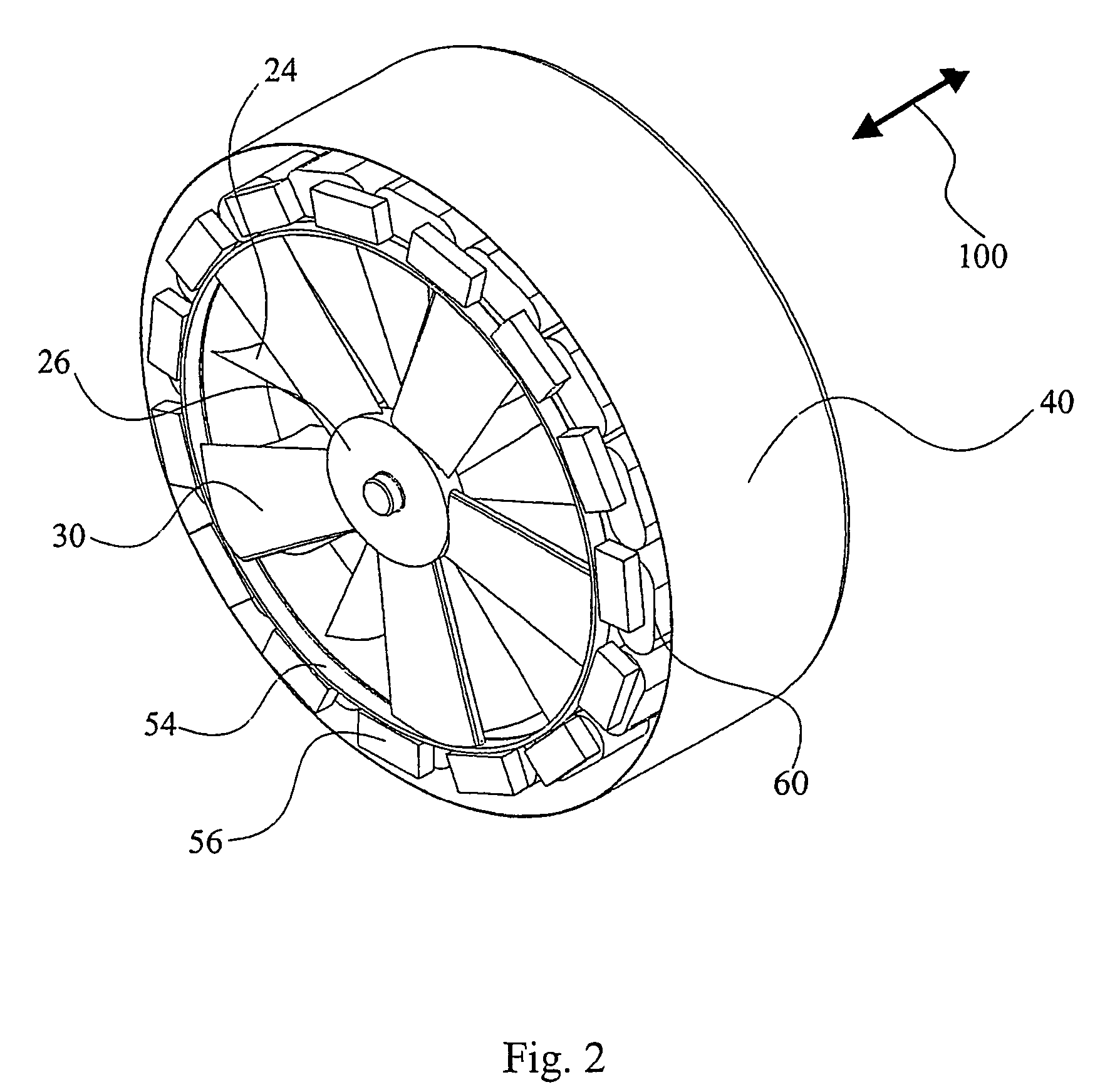
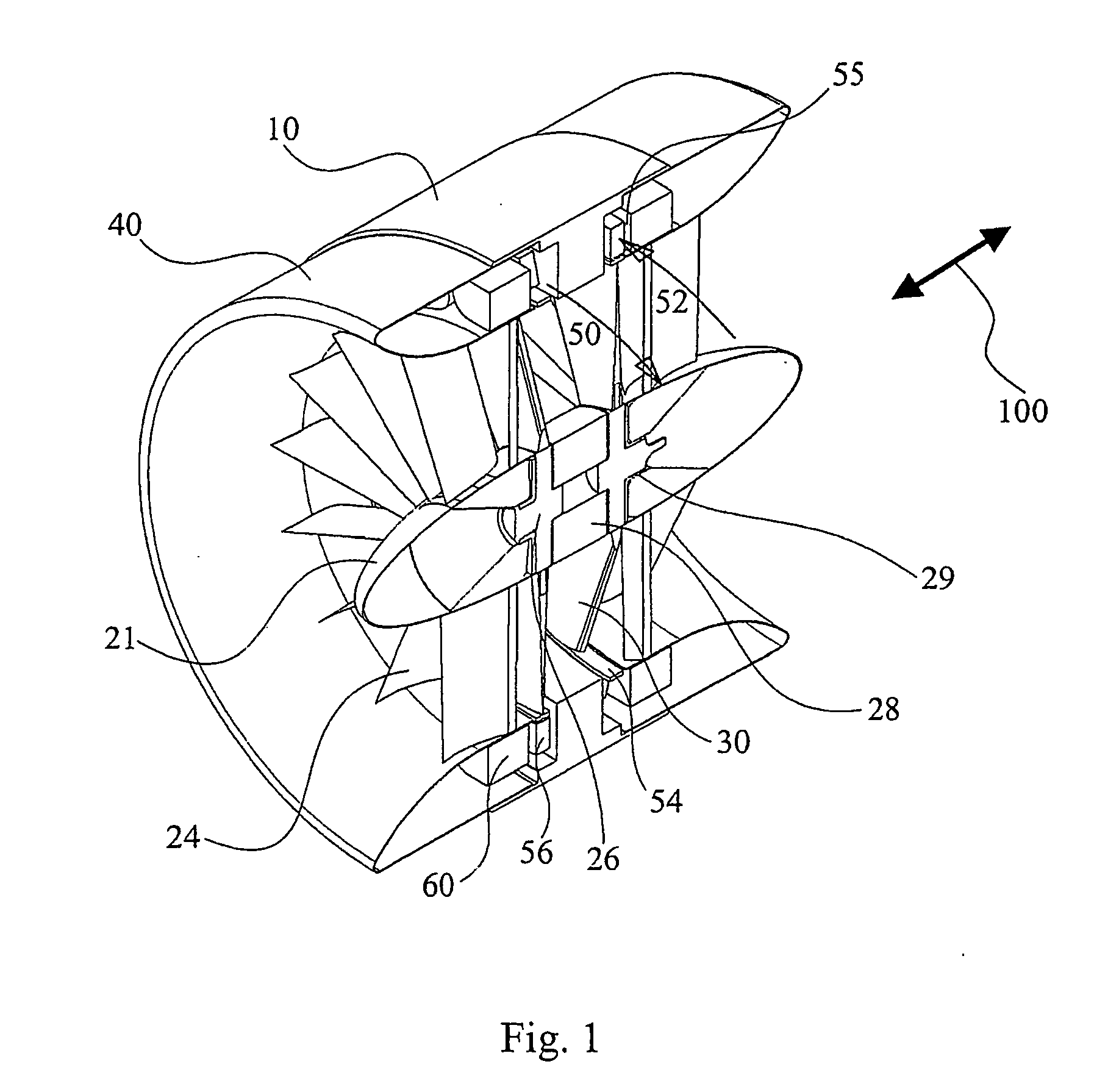
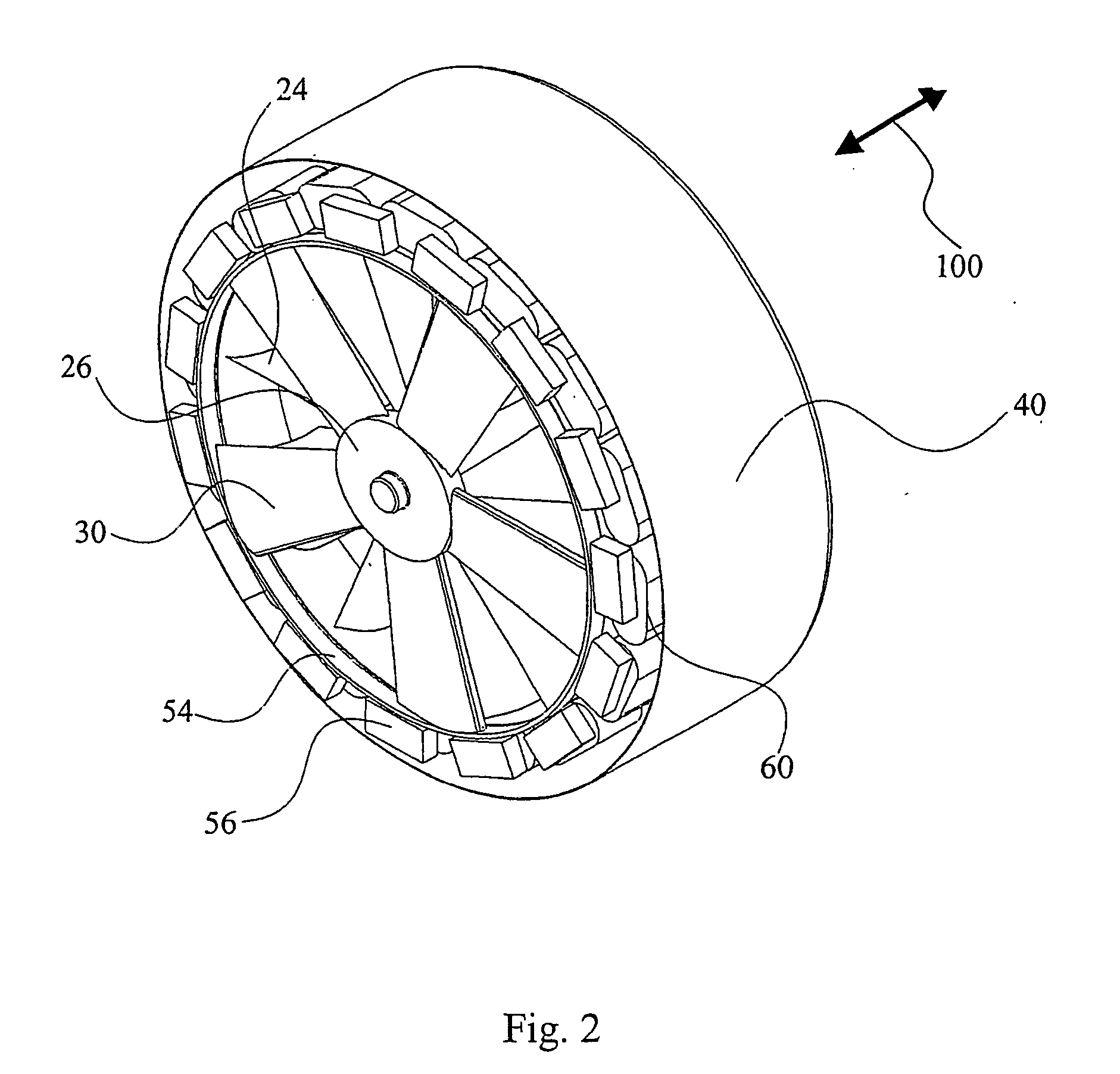
Airflow generator
Converting an air flow into a source of electricity by an airflow generator includes disposing the airflow generator in an air flow path of a machine for receiving the air flow to rotate a turbine bladed portion of the airflow generator that causes a plurality of permanent magnets disposed along the circumference of the bladed portion to cyclically move in close proximity to a plurality of fixed position stator coils thereby generating electrical currents in the coils that can be harvested.
Owner:US GREEN ENERGY SOLUTIONS
Disk drive employing a spindle motor comprising a locking spring arm disengaged through stator coil flux
InactiveUS6867946B1Dynamo-electric brakes/clutchesRecord information storageEngineeringMagnetic flux
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk, a head actuated radially over the disk, and a spindle motor for rotating the disk. The spindle motor comprises a stator having at least one stator coil wrapped around a stator tooth. The spindle motor further comprises a hub rotated by the stator when current is applied to the stator coil, and a locking spring arm having a fixed base. The locking spring arm engages the hub when no current is applied to the stator coil, and the locking spring arm disengages from the hub when current applied to the stator coil generates a magnetic flux which pulls the locking spring arm away from the hub.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com