Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
501 results about "Axial flux" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
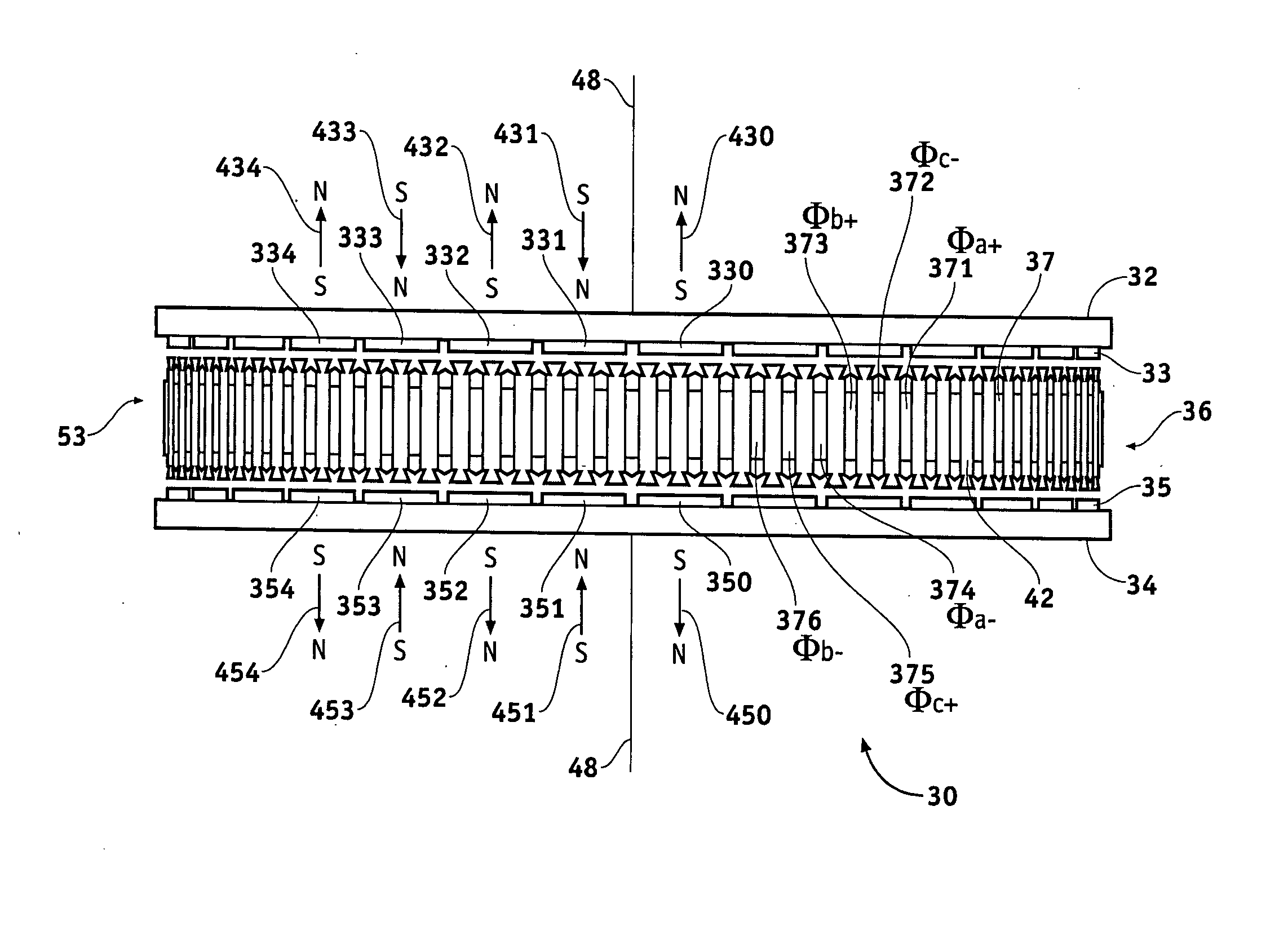
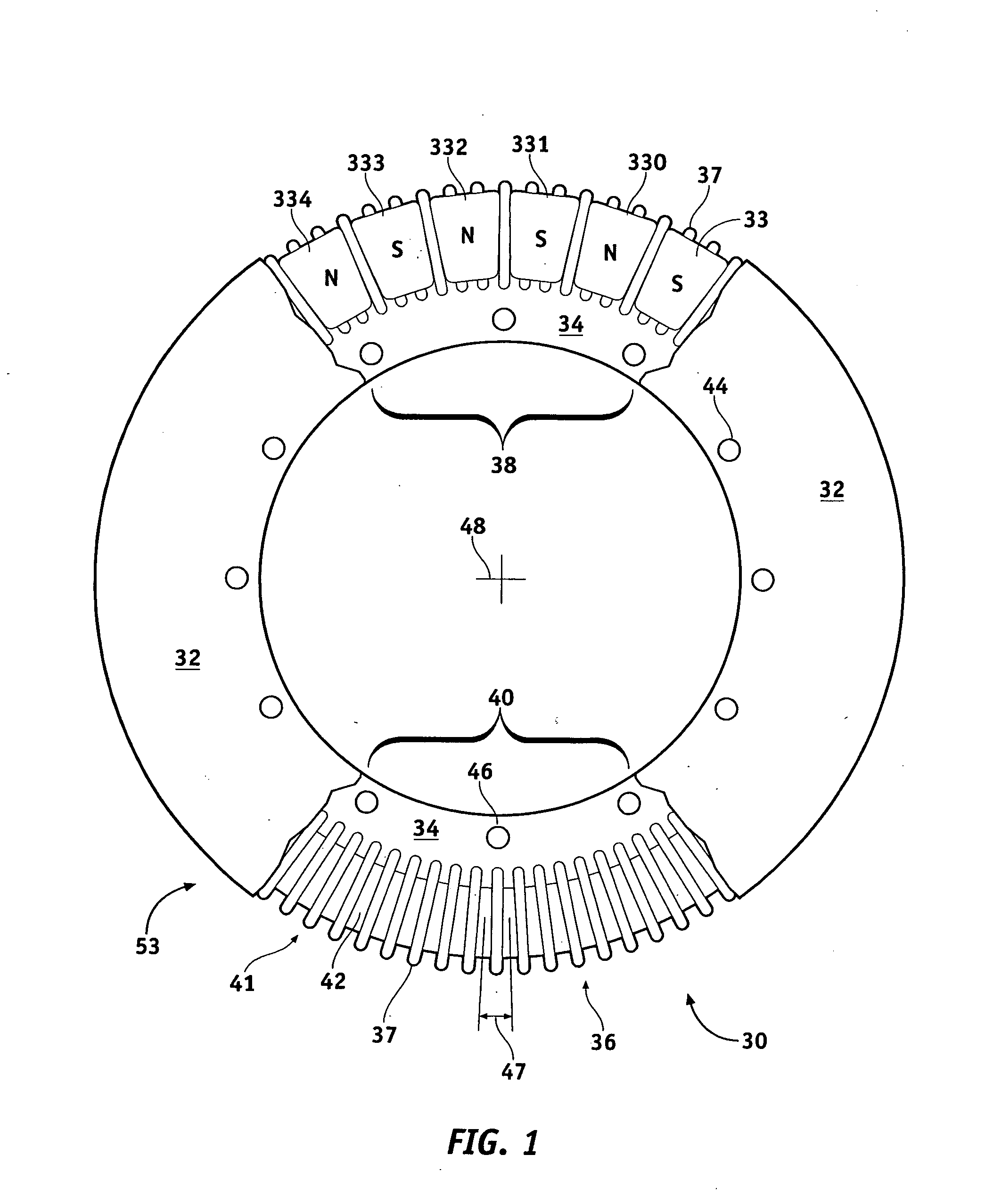
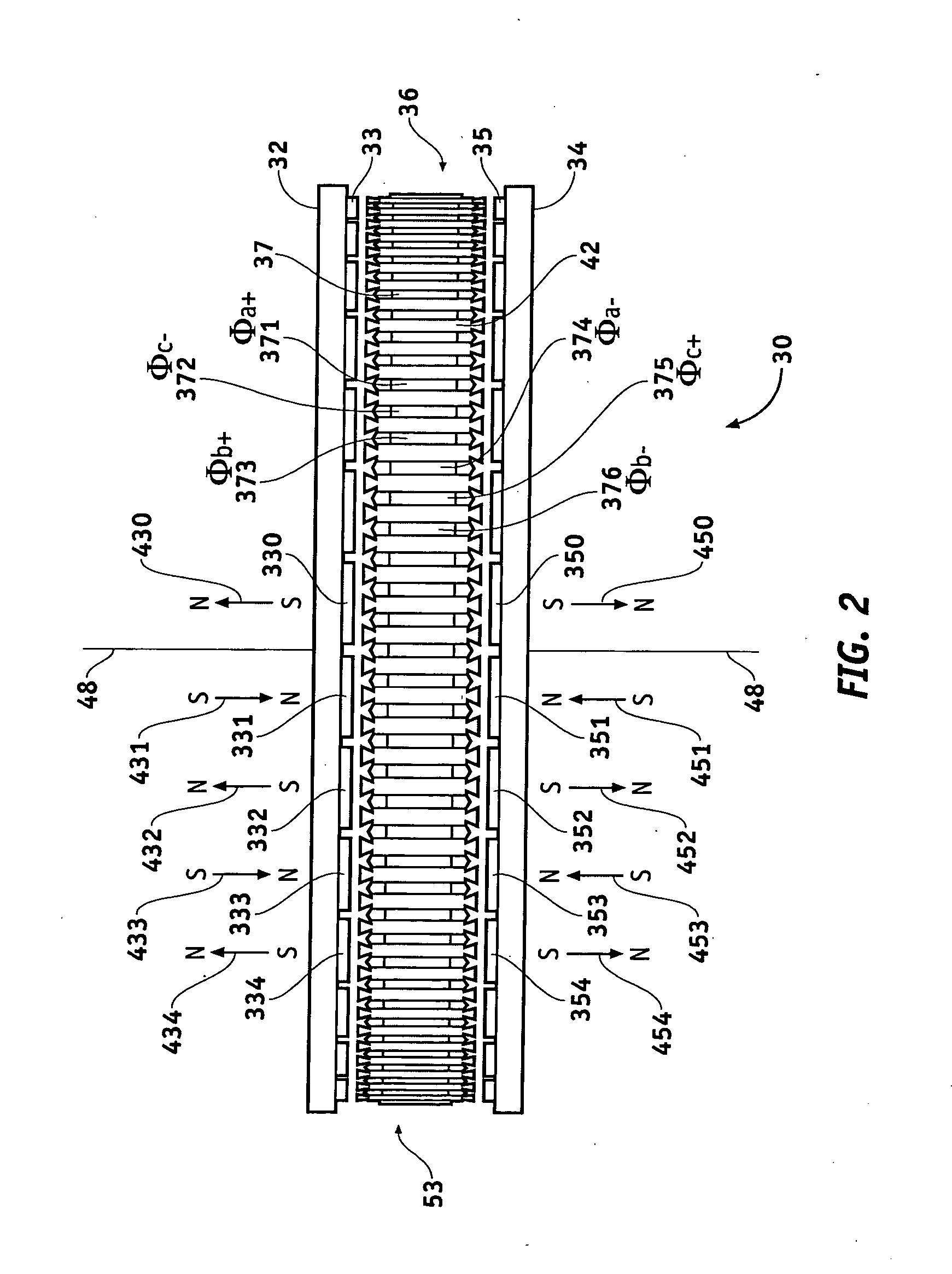
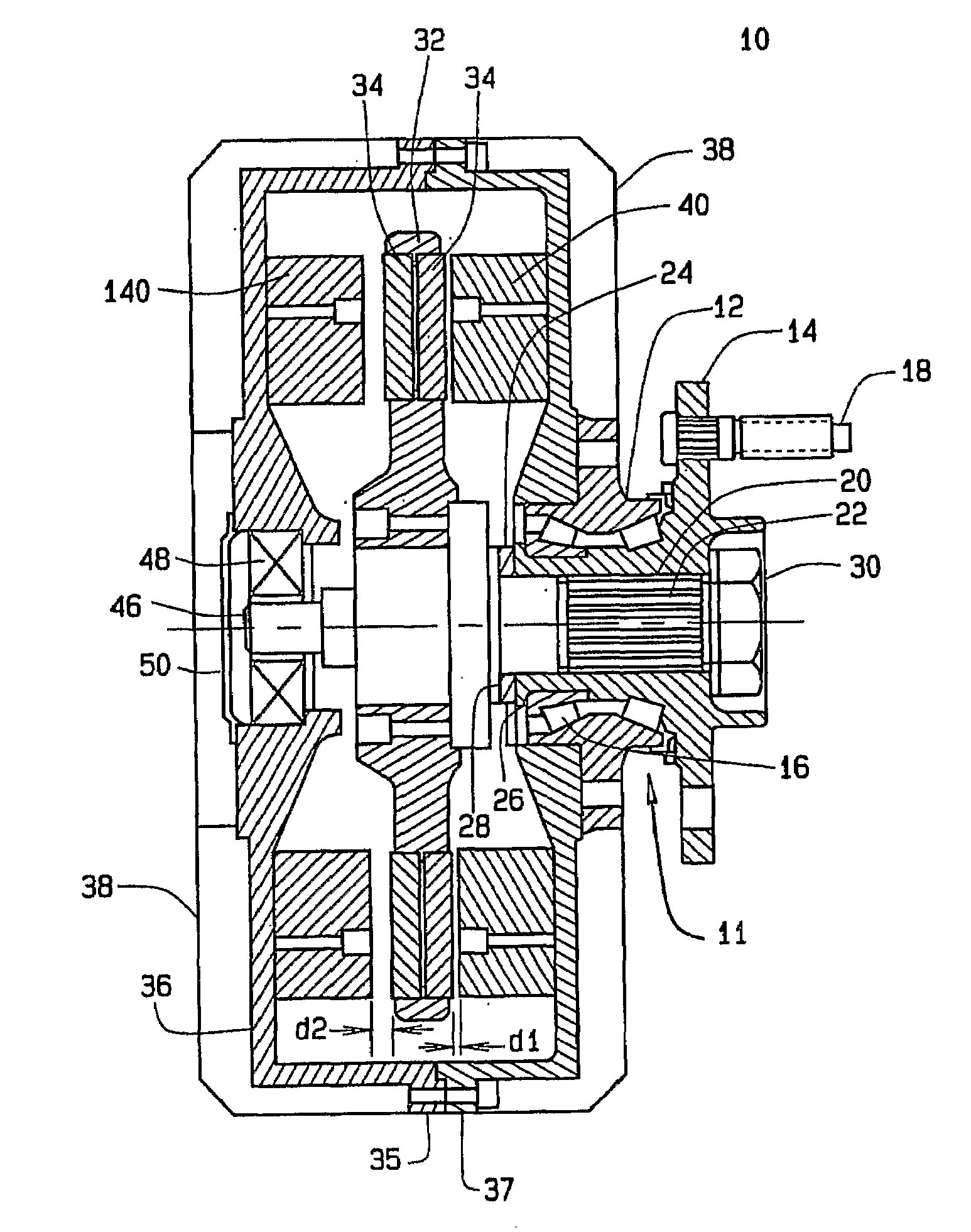
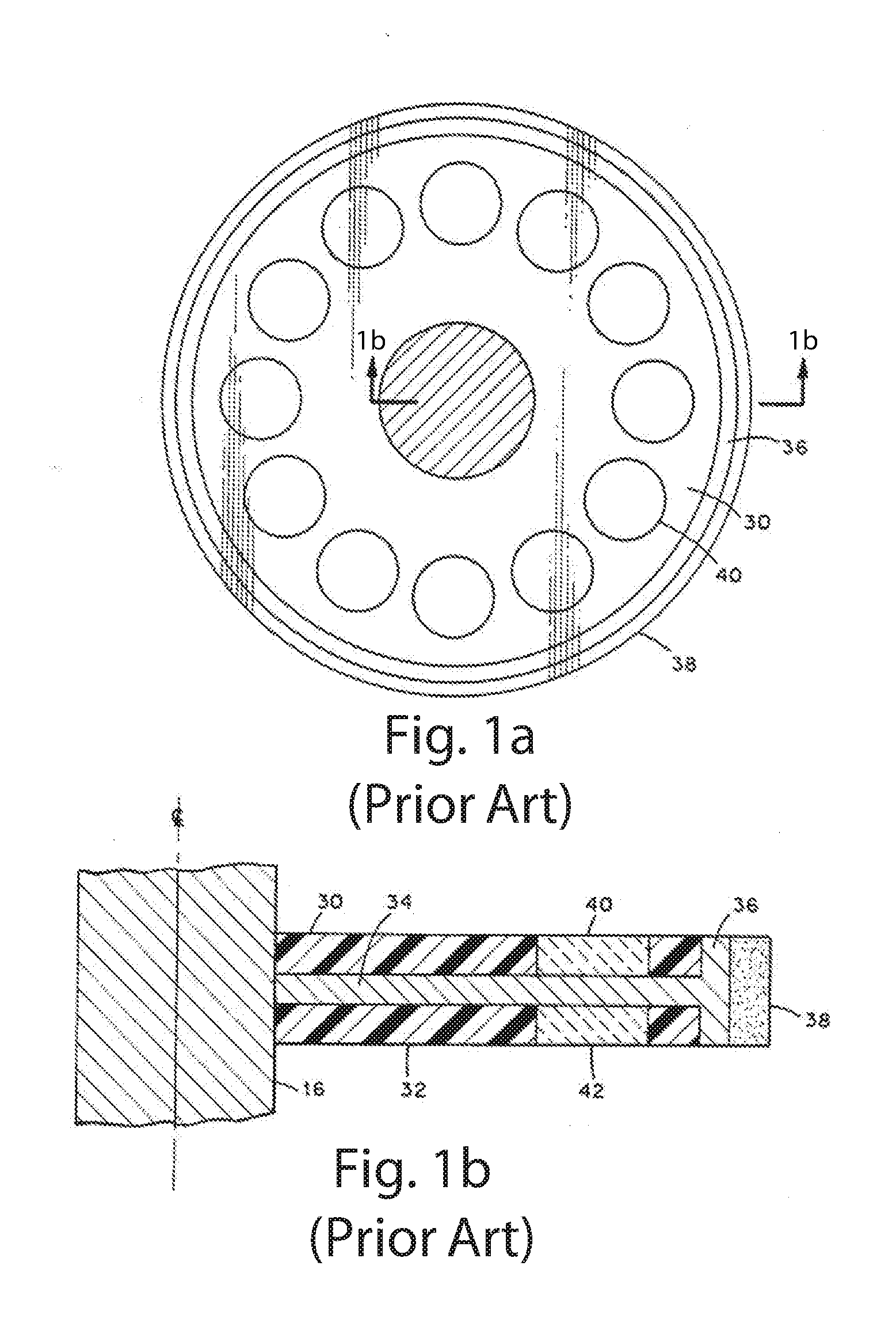
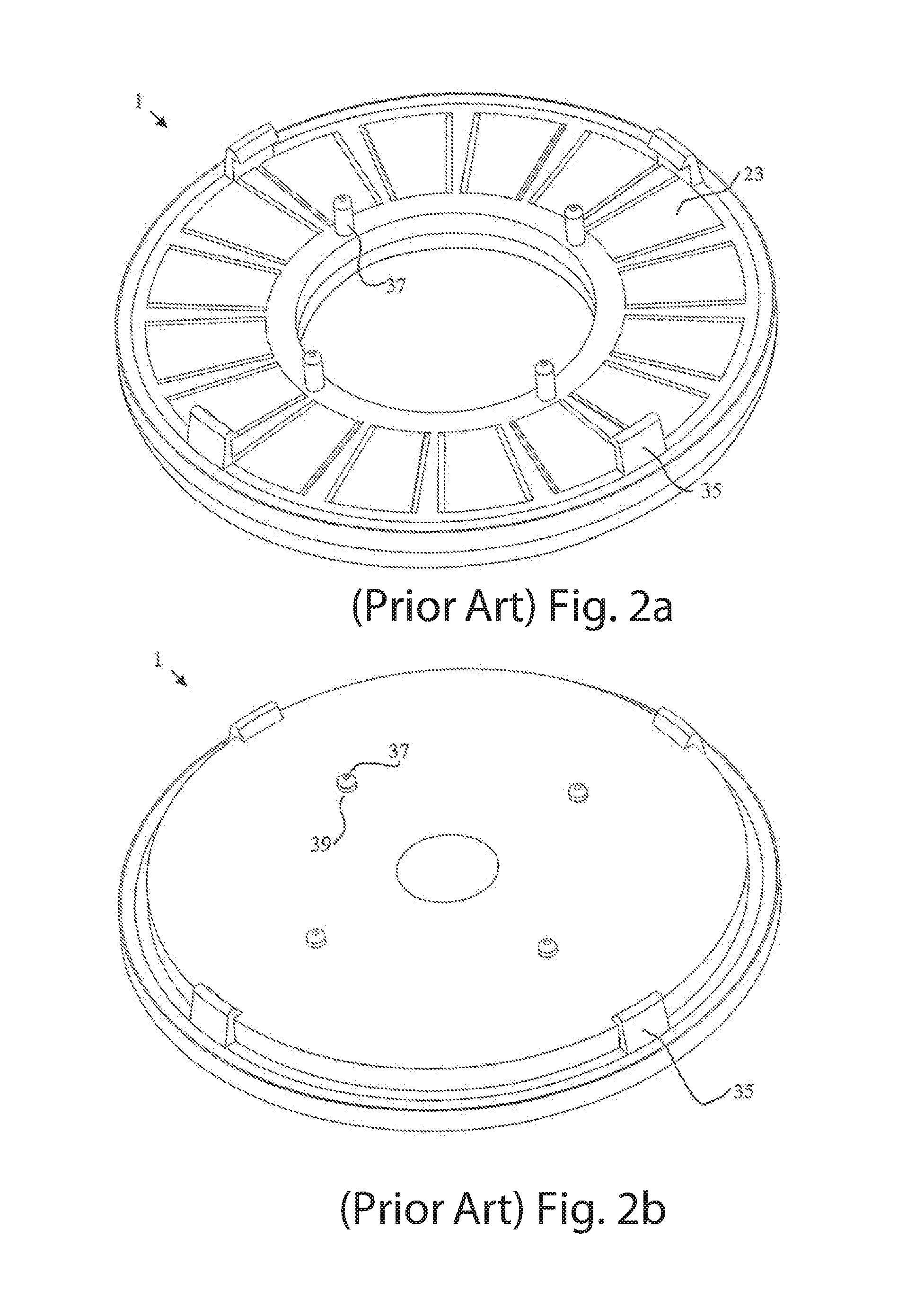
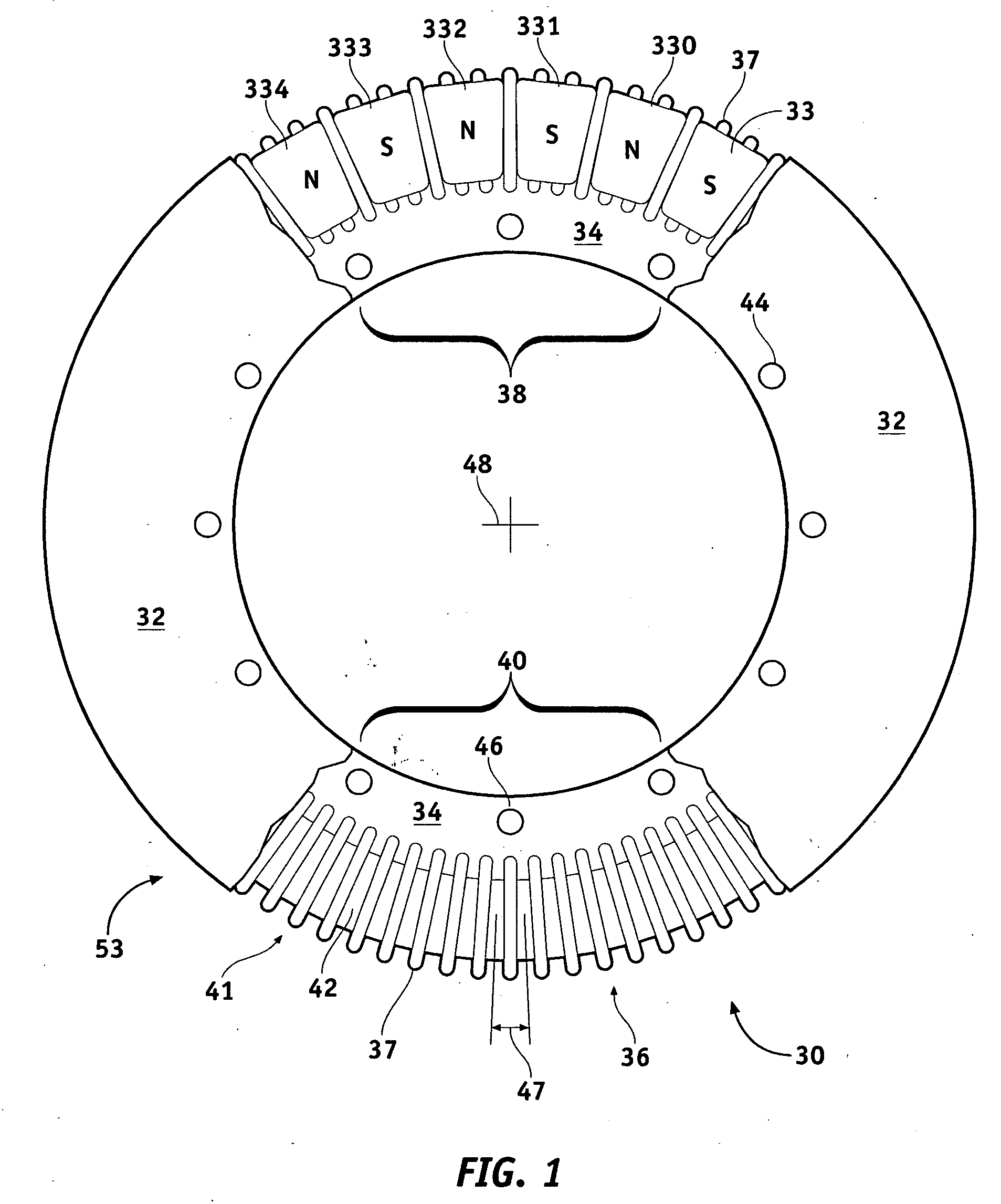
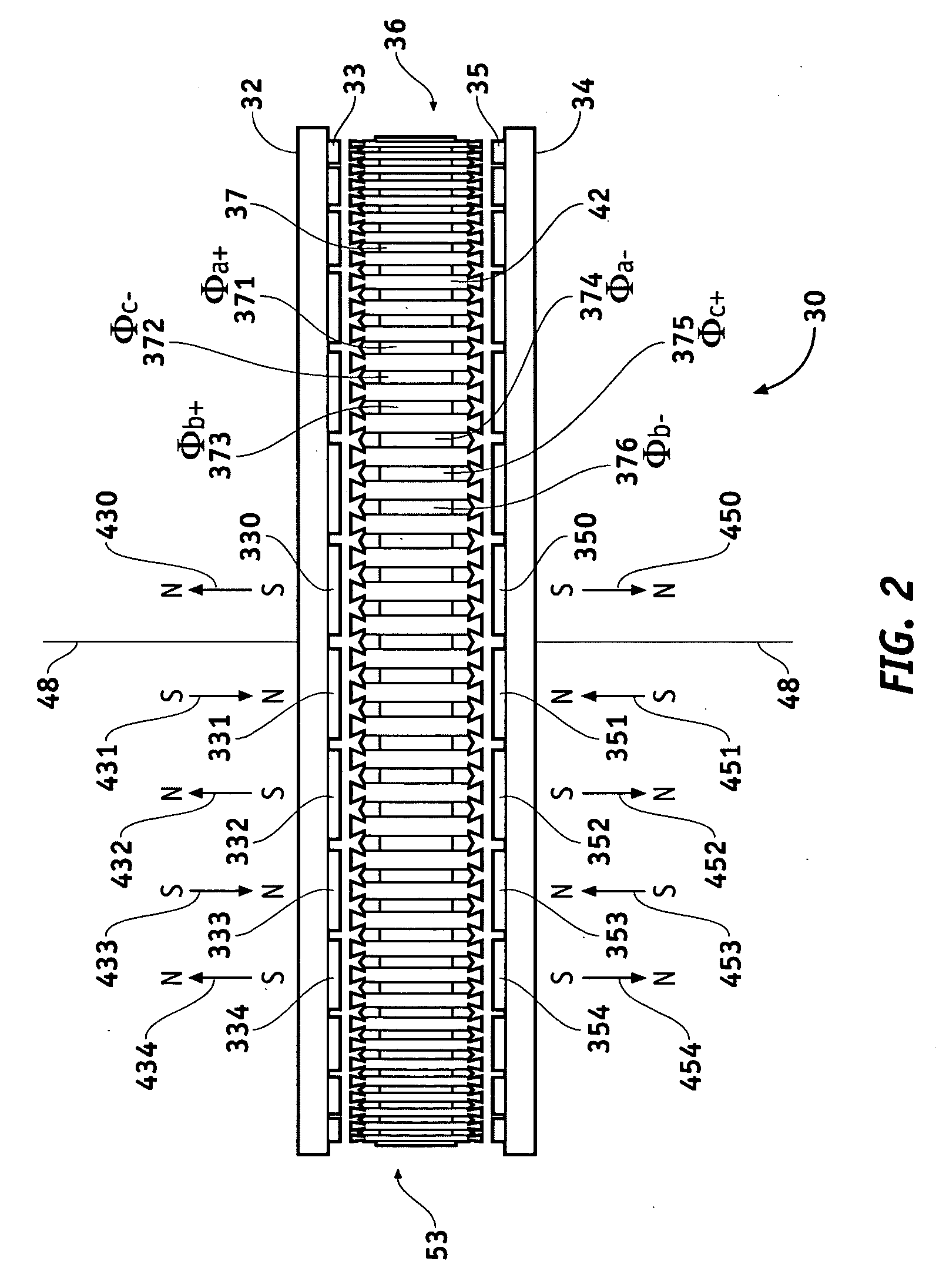
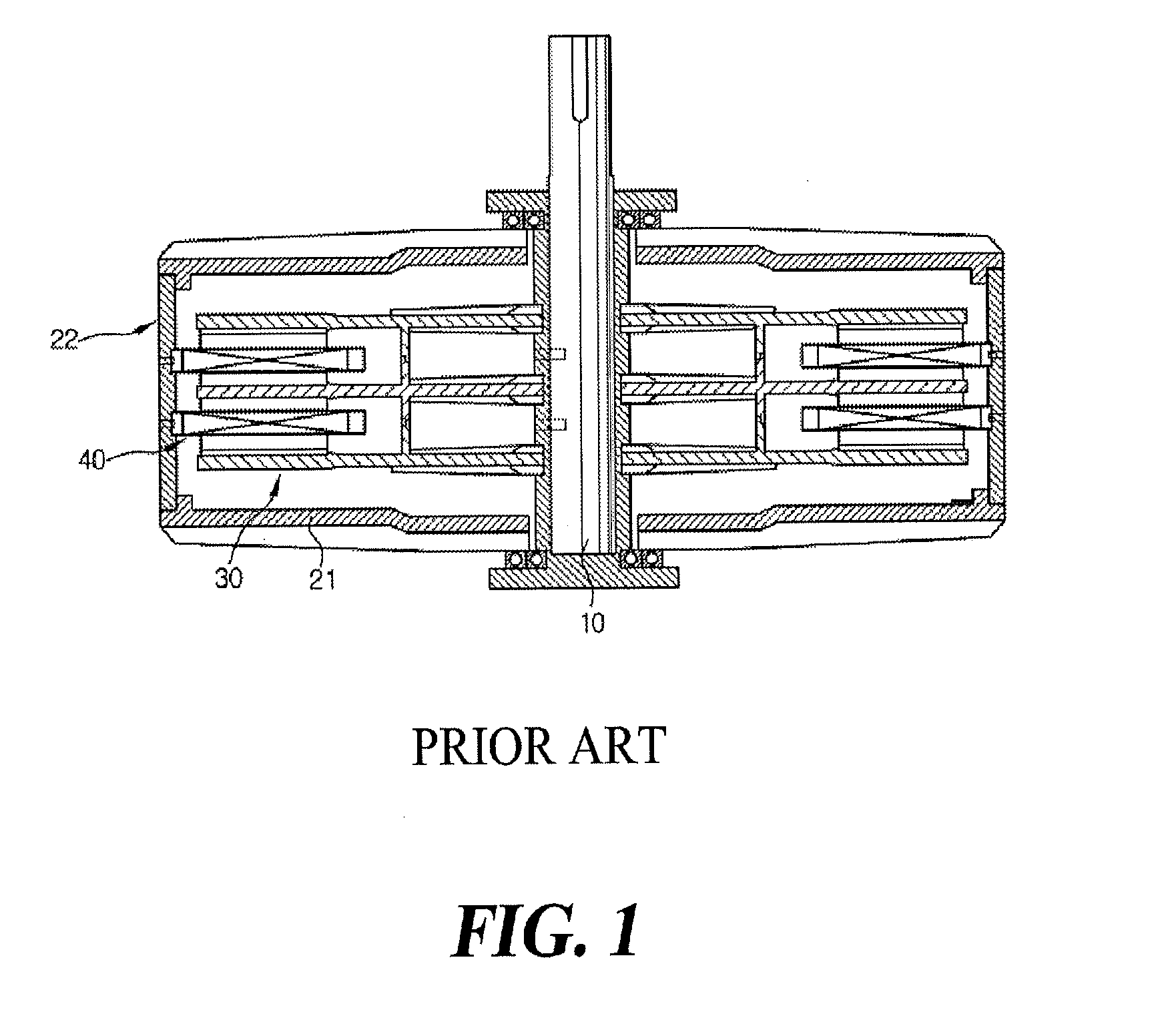
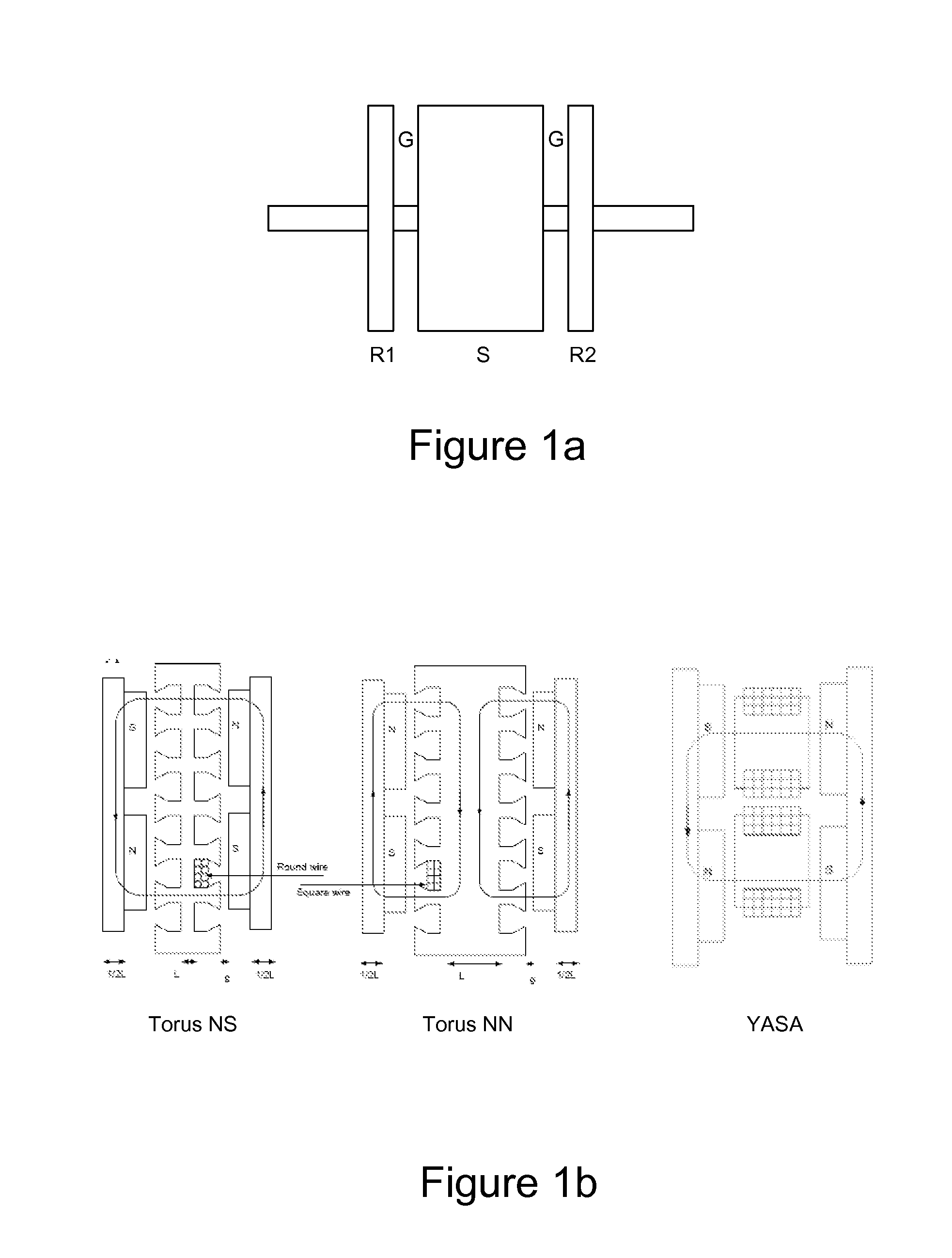
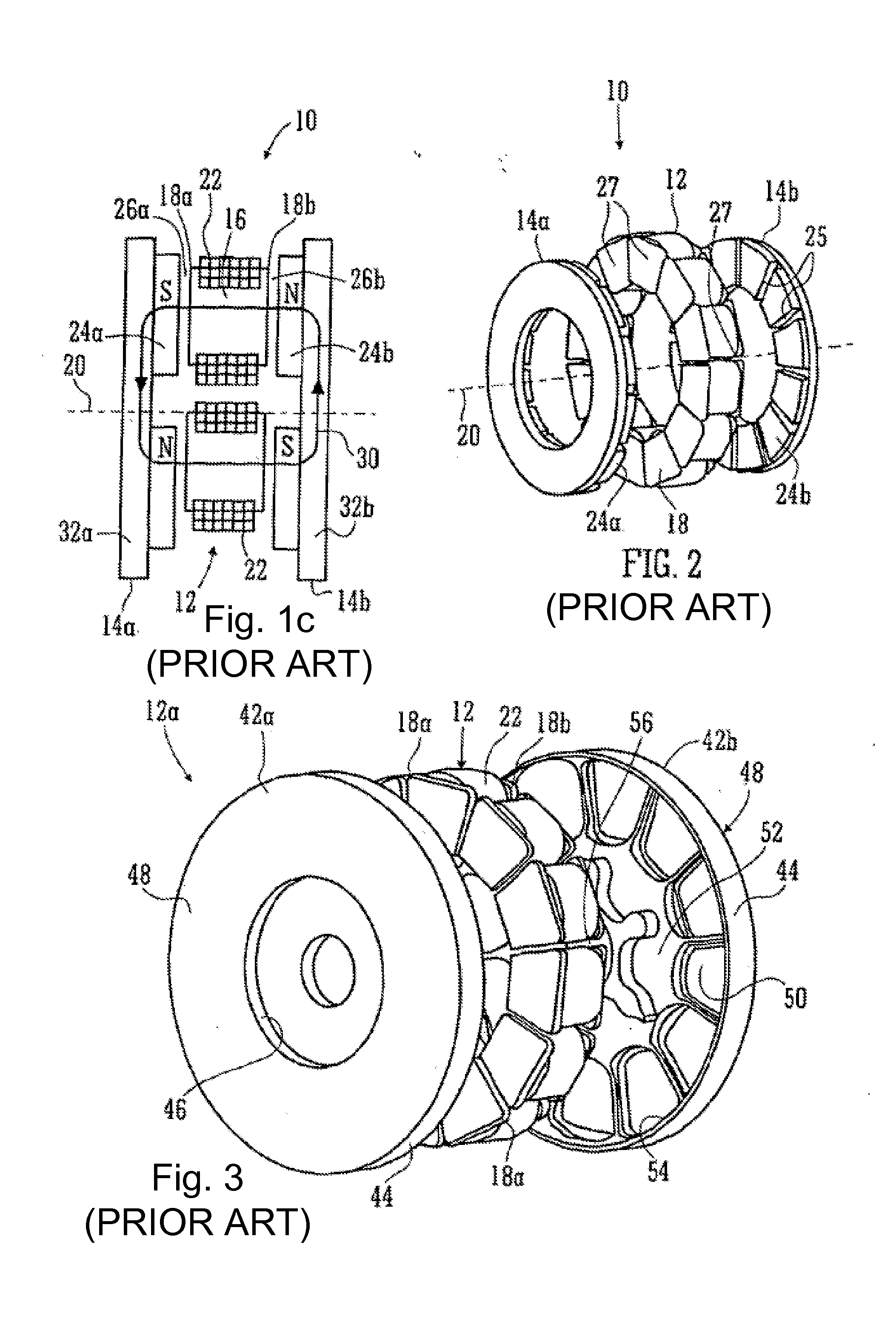
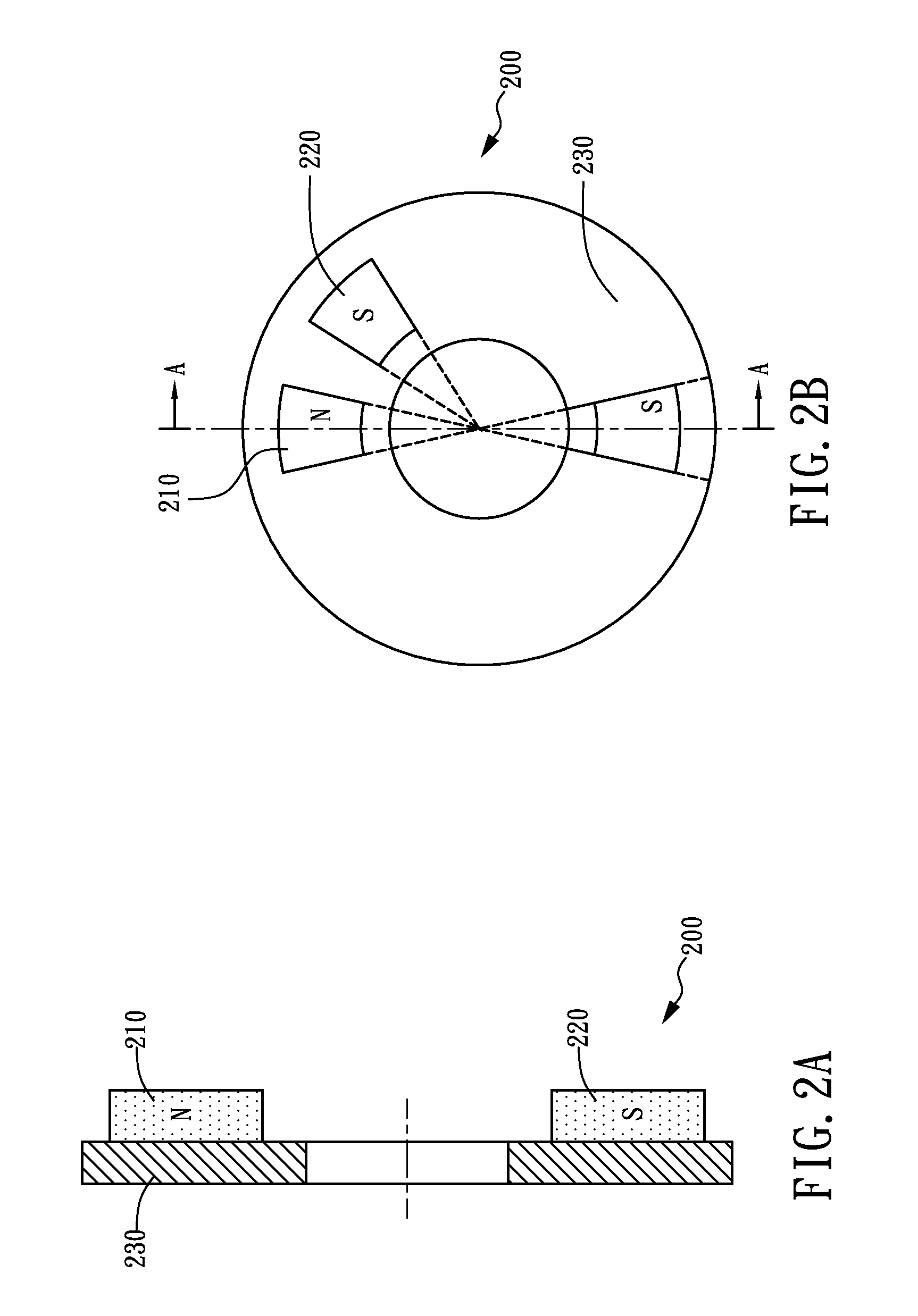
Axial Flux simply means the lines of magnetic flux that past through the coils of wire, travel along the "axis" of the turning motion. The other type of magnetic flux in an alternator is called RADIAL FLUX and it occurs when the flux occurs "around" the magnet.
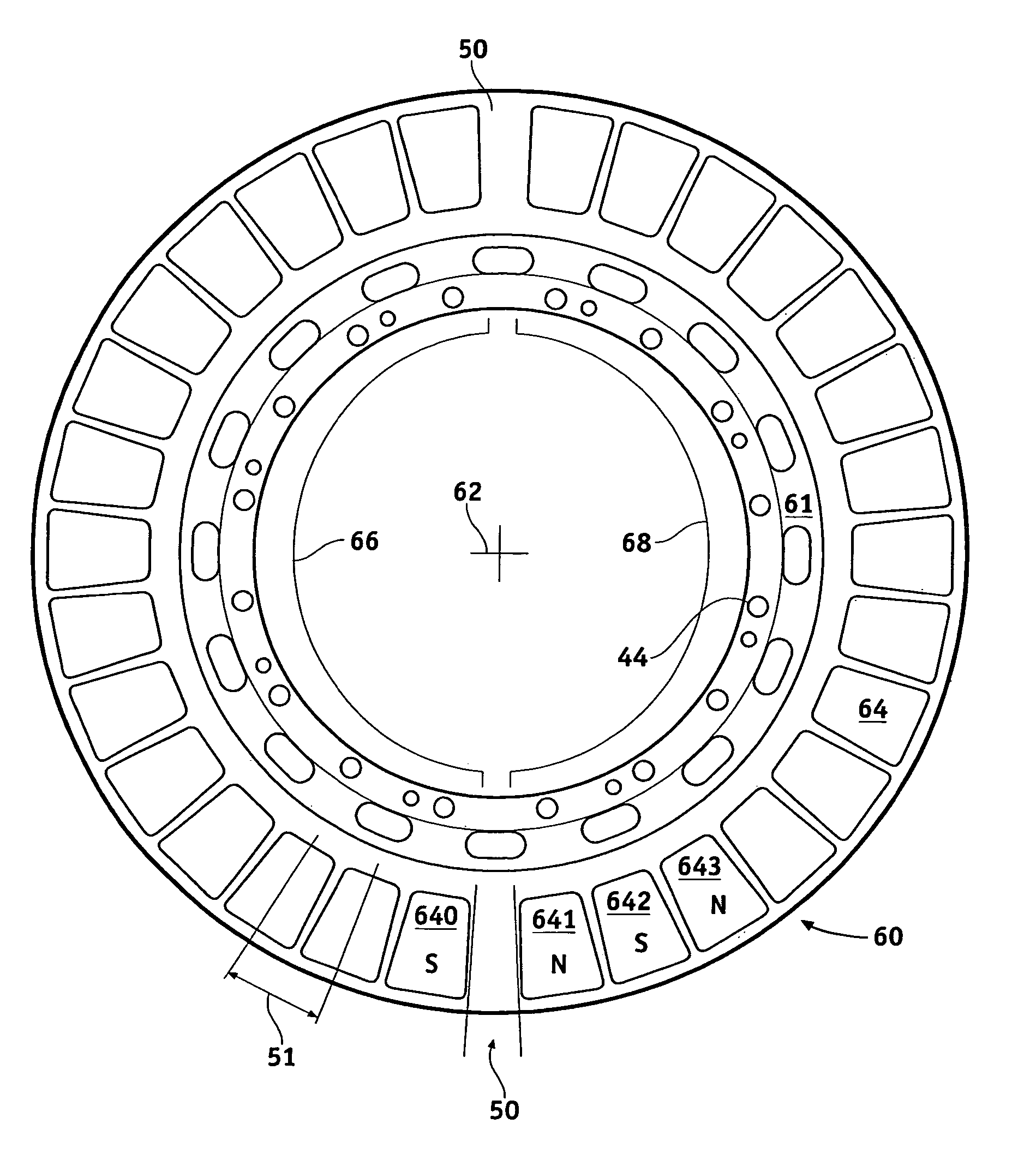
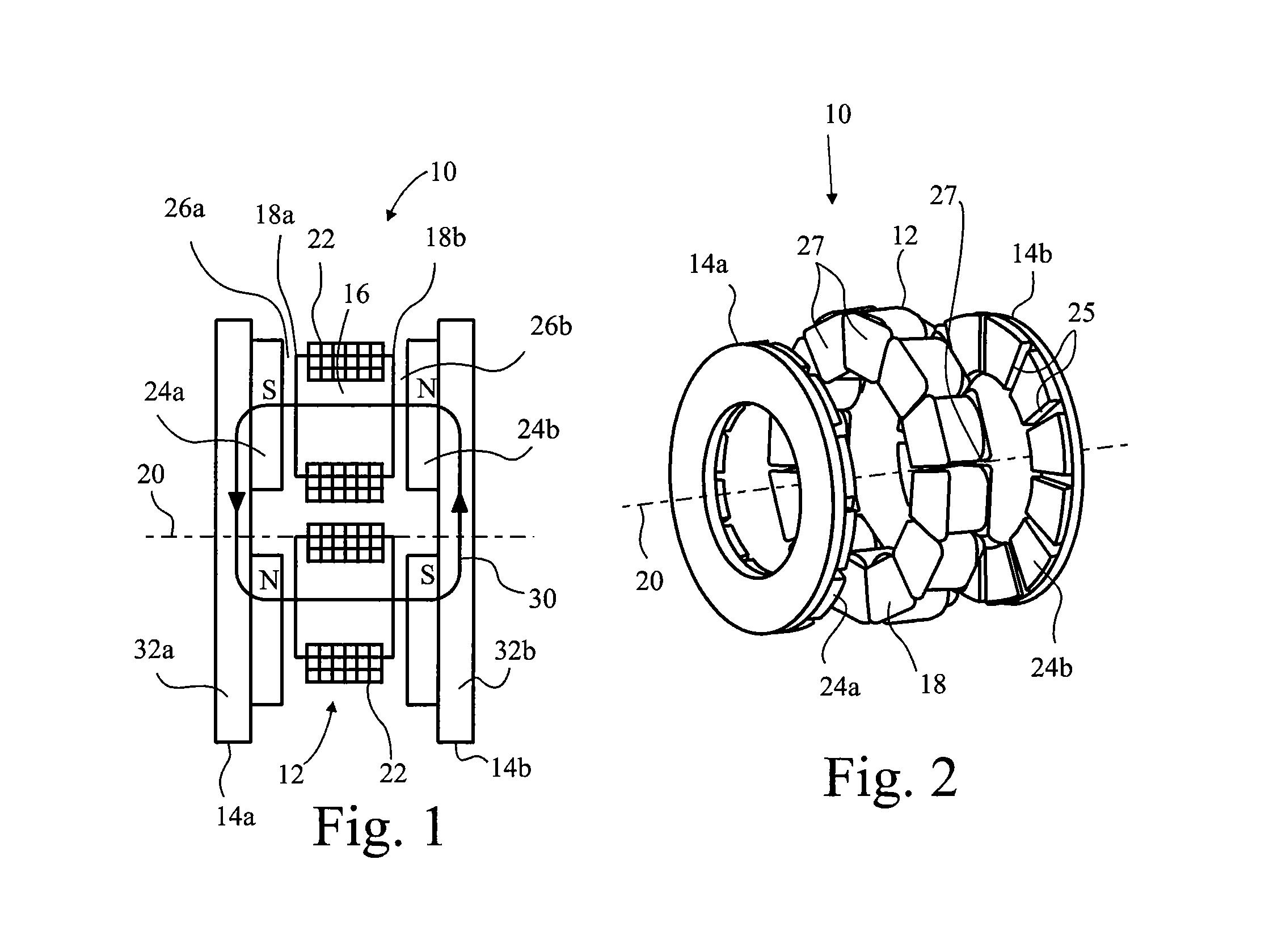
Field controlled axial flux permanent magnet electrical machine
ActiveUS20070046124A1Implementing controlLess expensiveMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsElectric machinePole piece
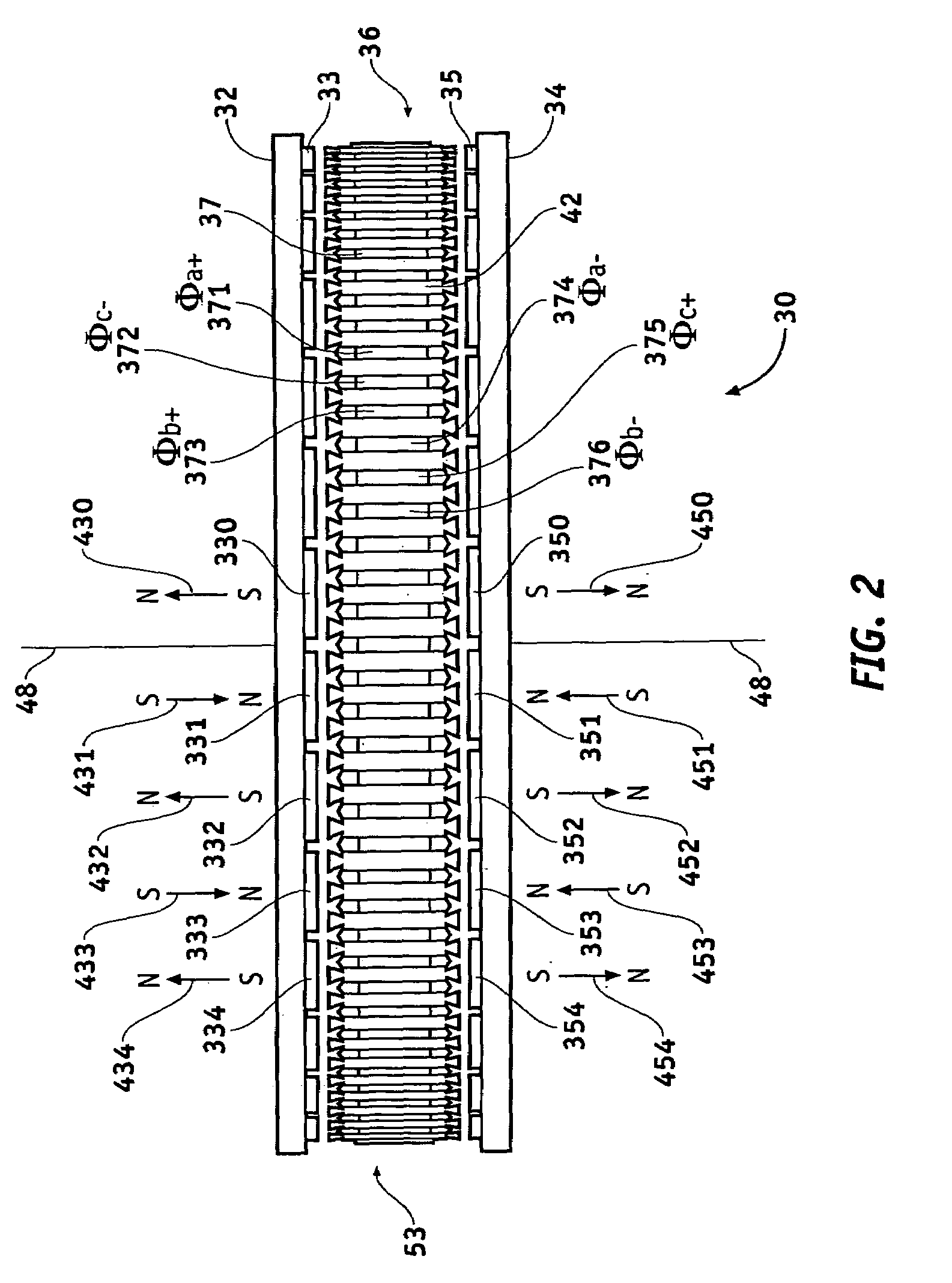
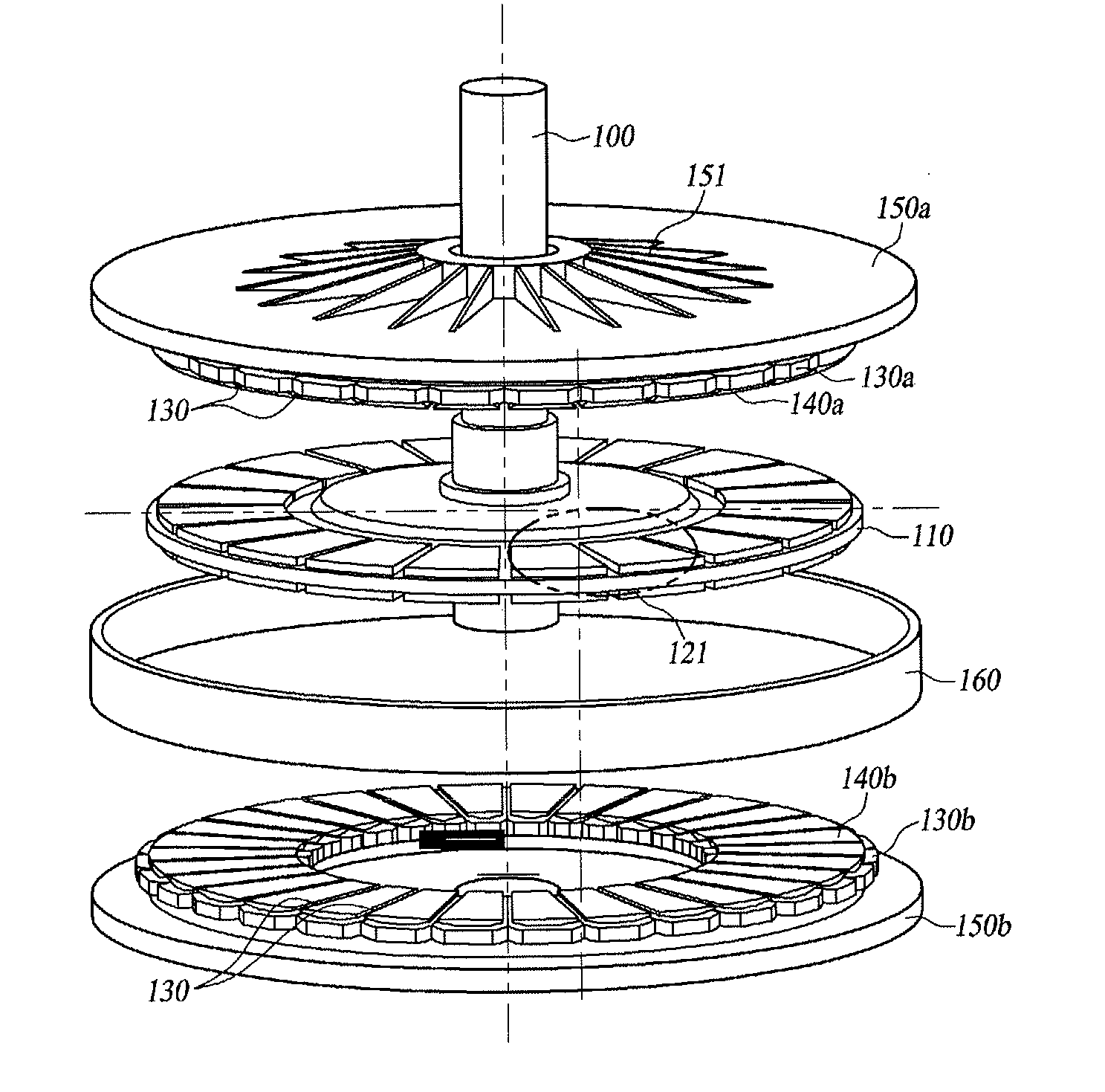
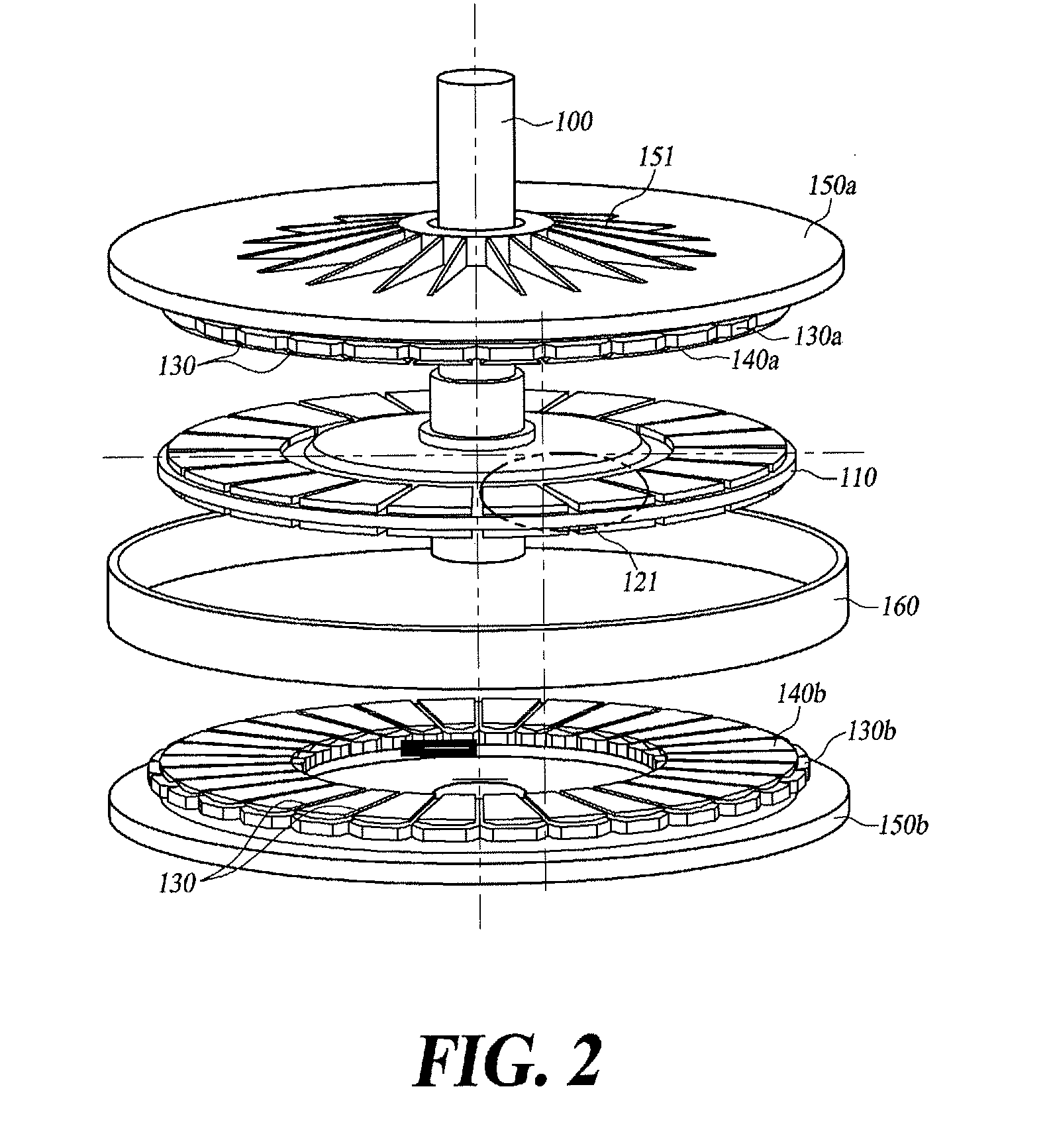
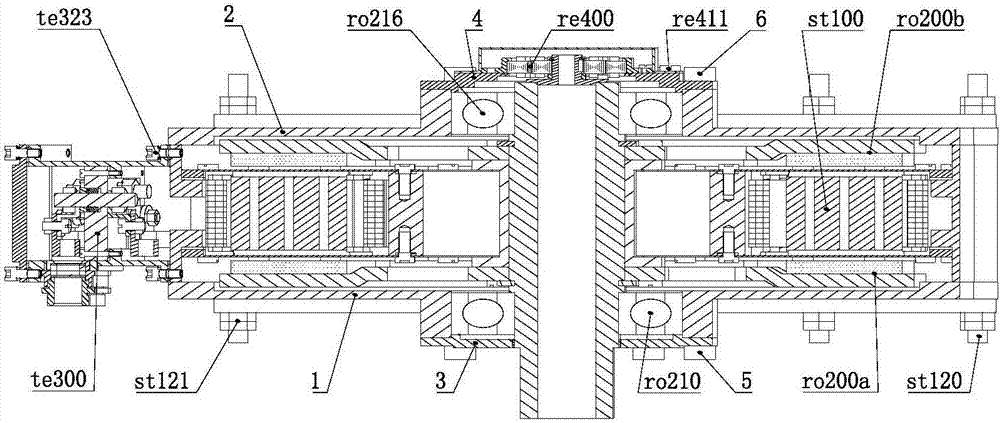
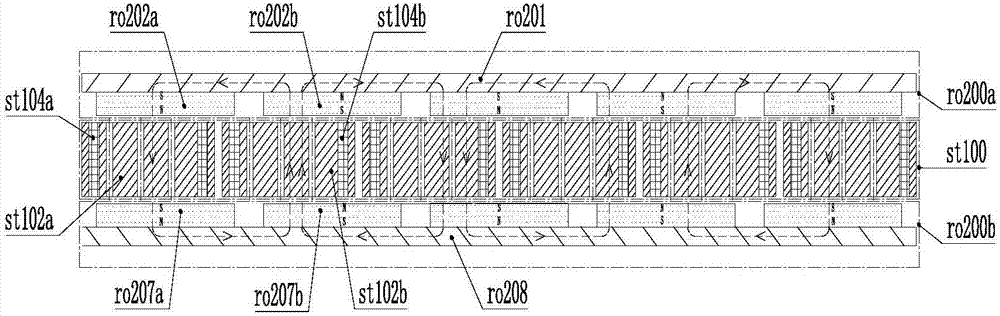
An electrical machine is provided. The machine includes at least one rotor mounted for rotation about a central axis and at least two stator sections mounted axially adjacent to and on opposite sides of the rotor. The rotor includes two circumferentially arrayed rows of alternating segments of permanent magnet and ferromagnetic pole pieces. One of the rows is spaced radially inwardly from the other row. The permanent magnet and ferromagnetic pole pieces are separated by a non-ferromagnetic material. The pole pieces are arranged so that the permanent magnet segments in the first row are radially adjacent to ferromagnetic segments in the second row so that the N-S magnetic fields of the permanent magnet segments are aligned axially. Each stator section includes a ferromagnetic stator frame, at least a first AC winding wound in circumferential slots in the stator frame, and a DC field winding wound on the stator frame.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
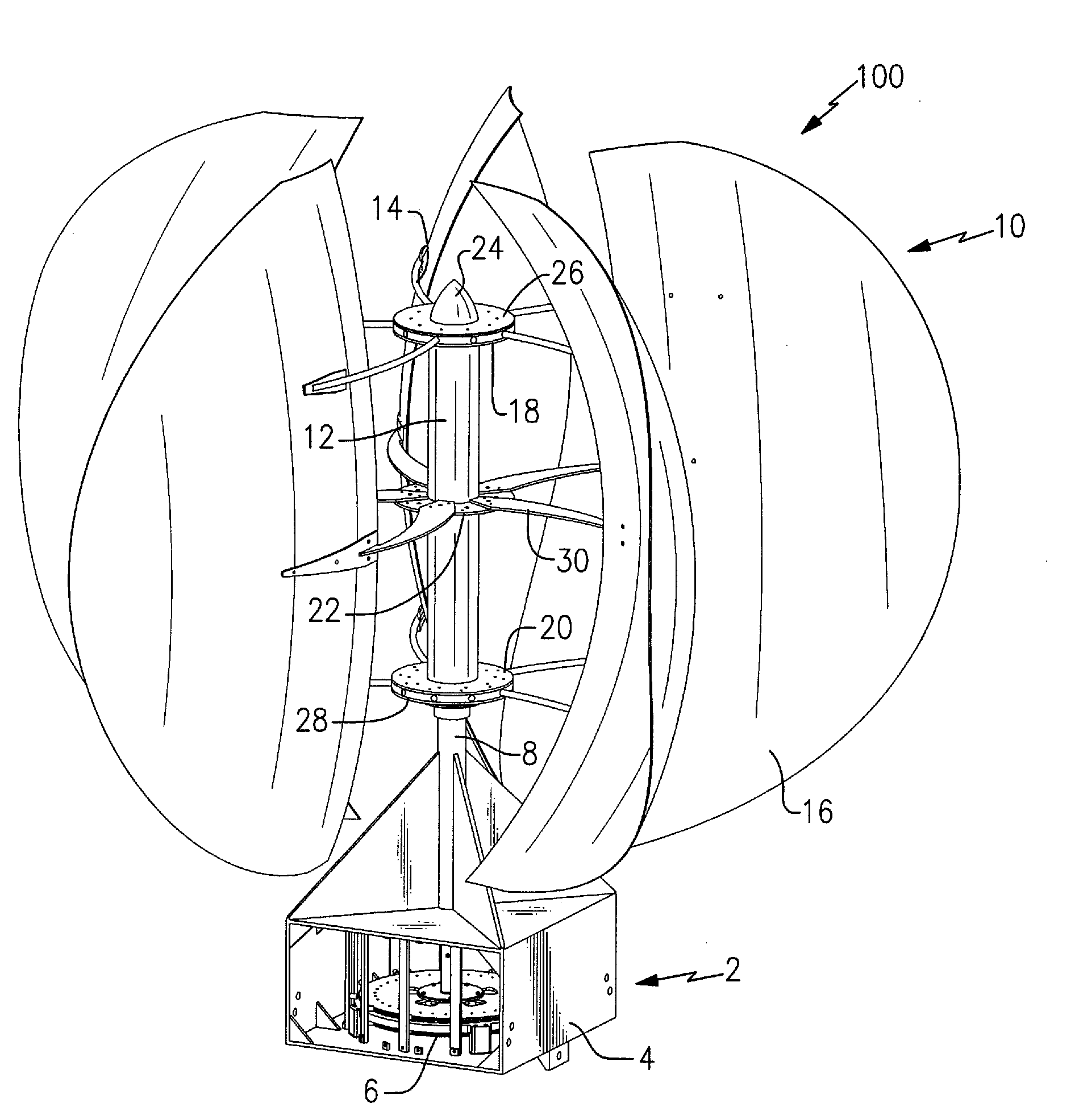
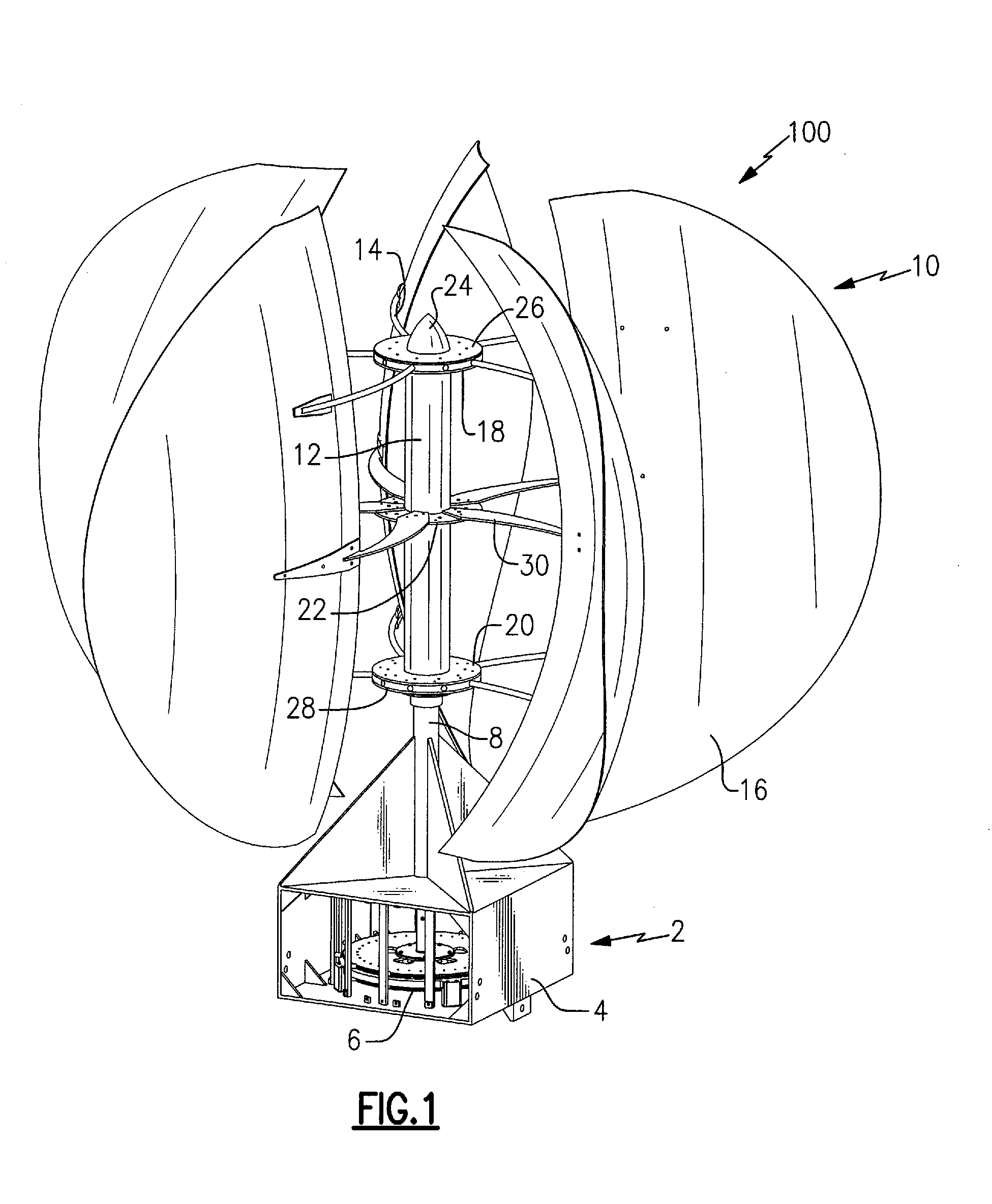
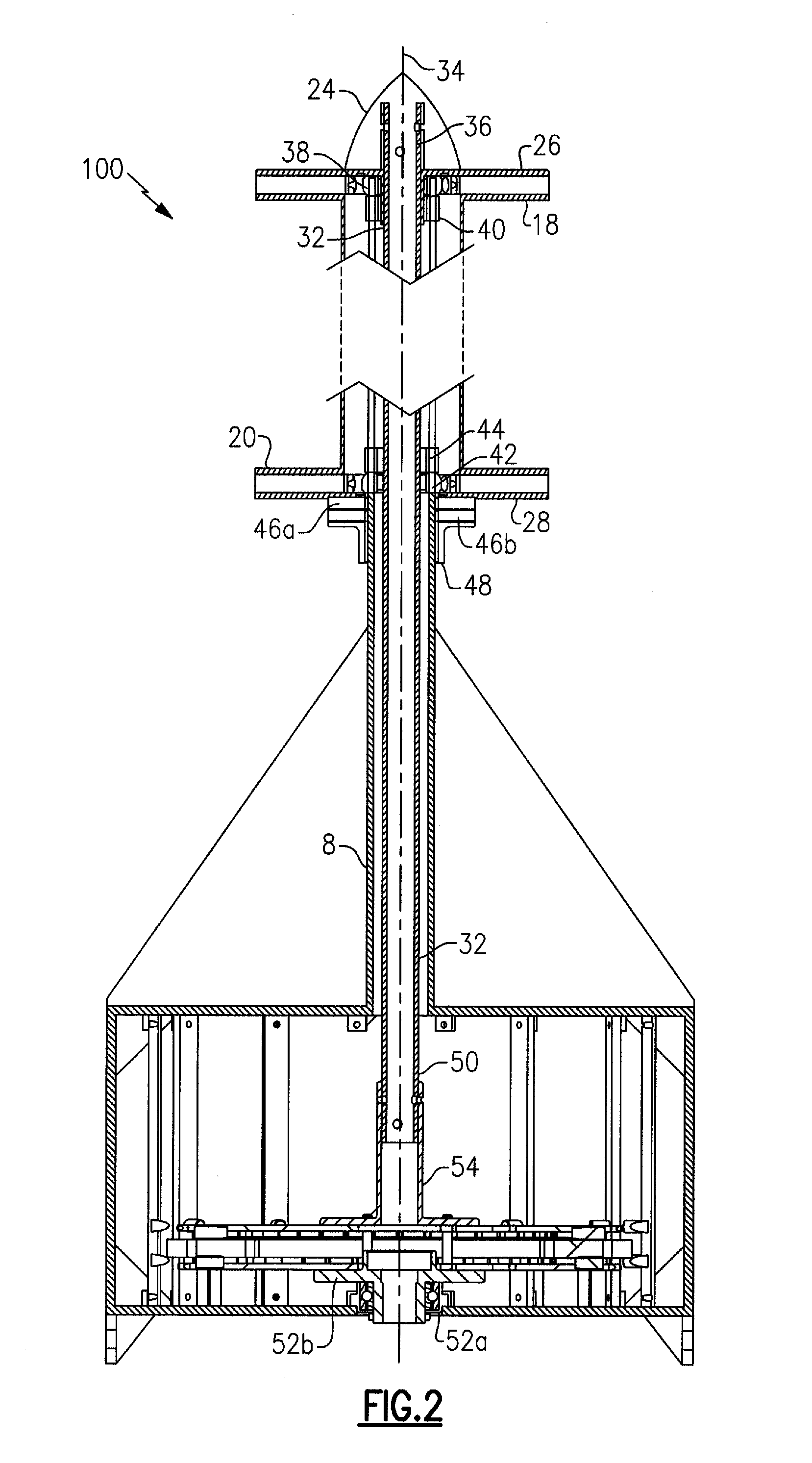
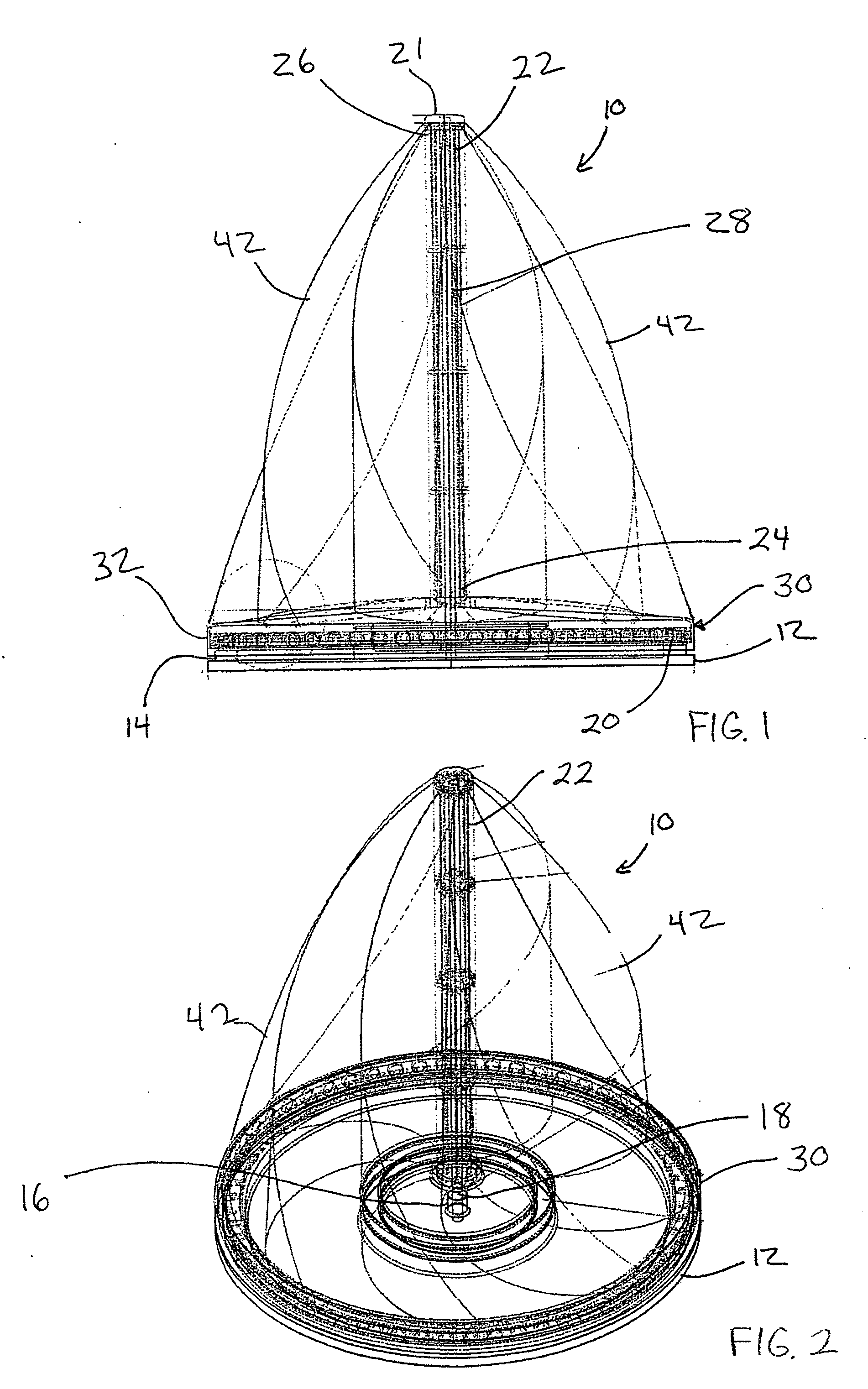
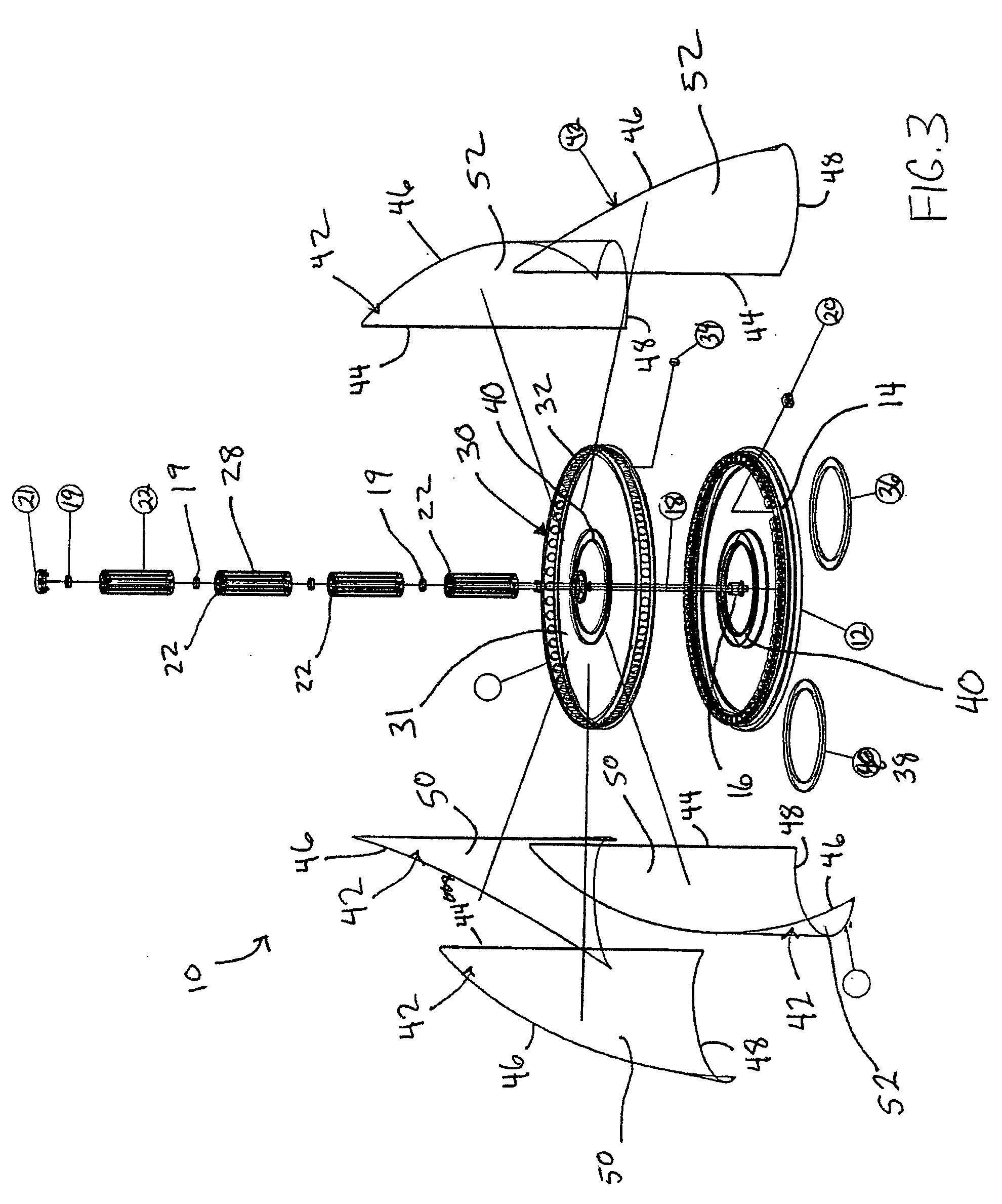
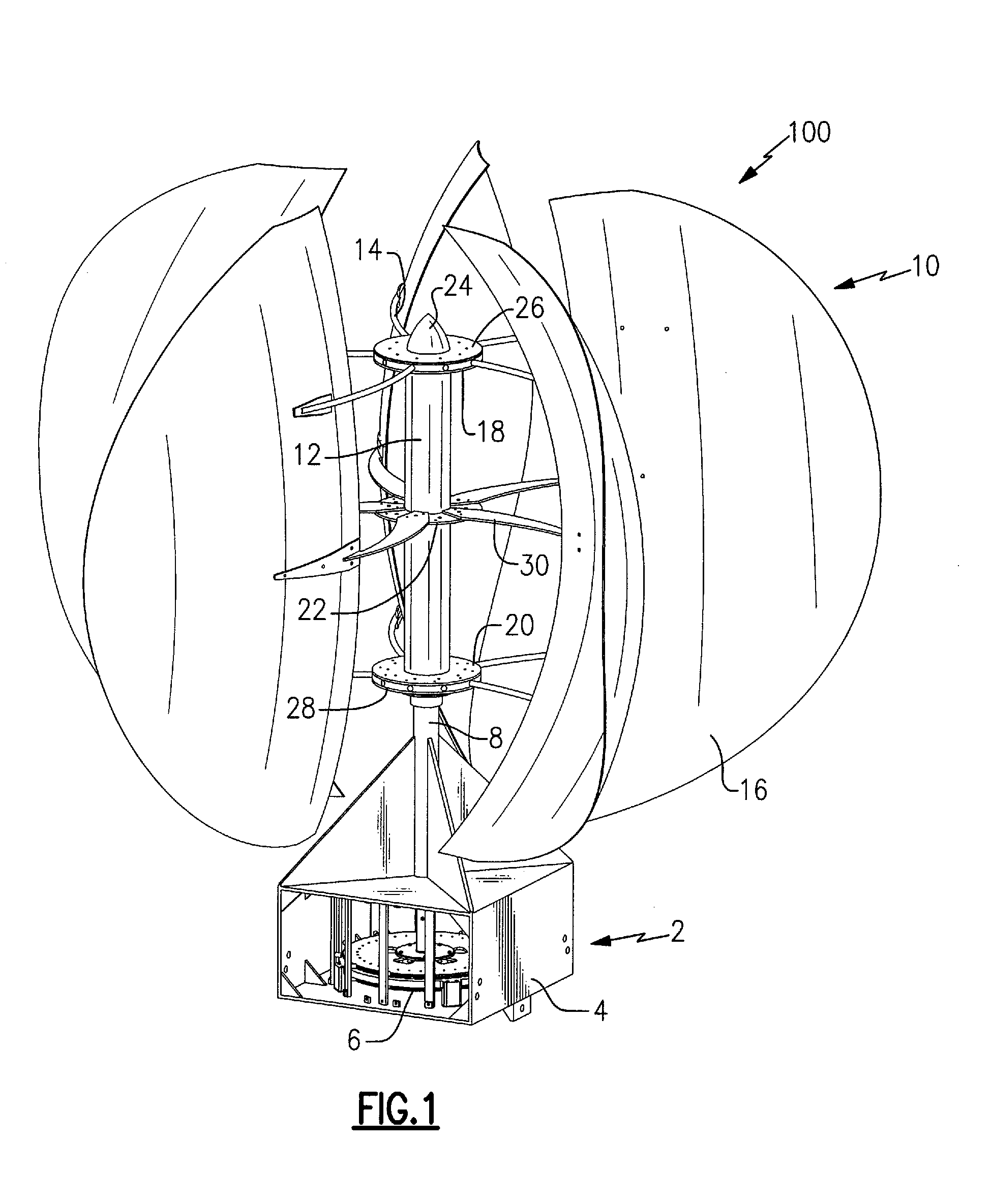
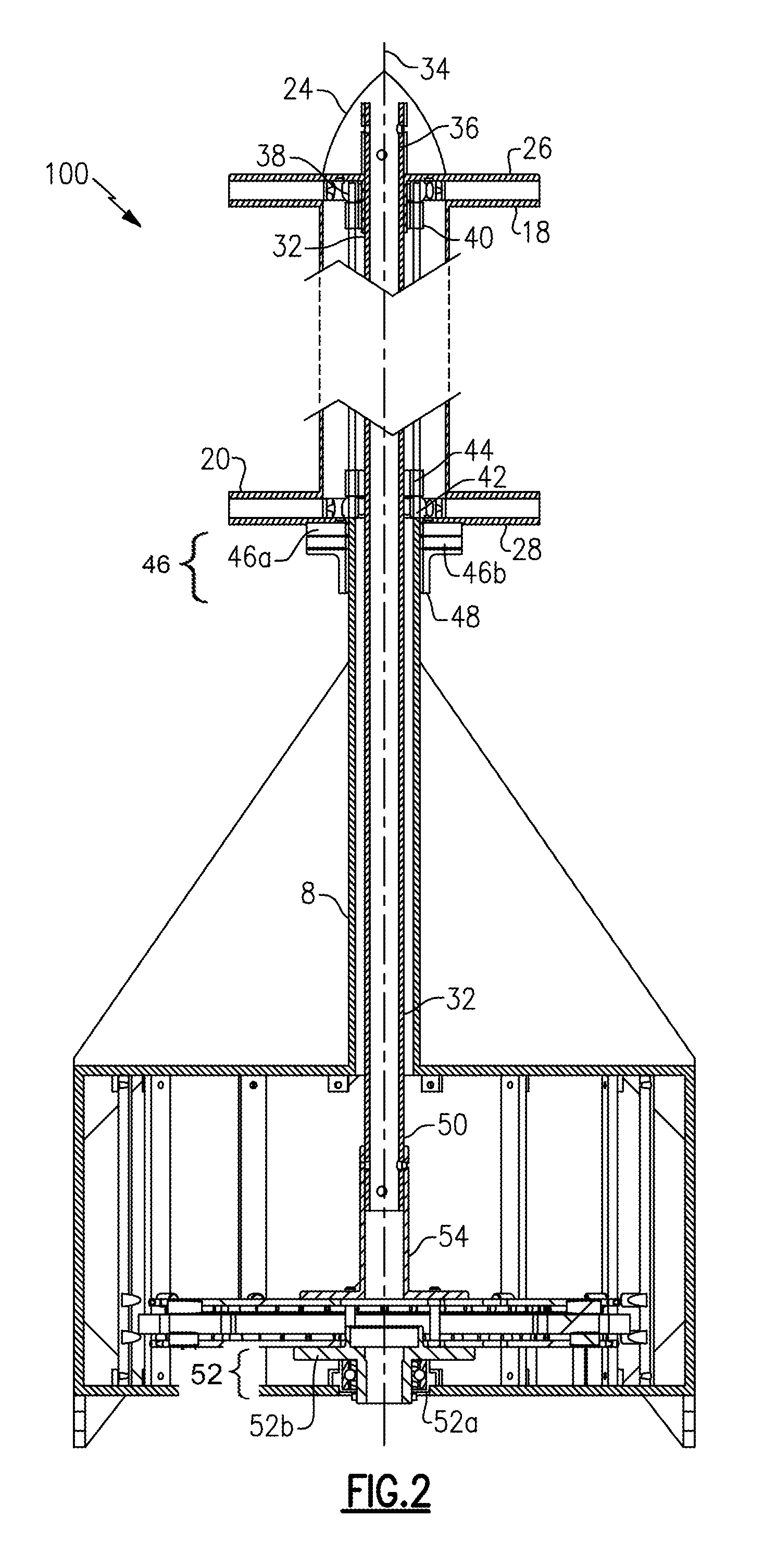
Vertical axis wind turbine and generator therefore
A vertical wind turbine is provided that includes a support base defined about an axis, a bearing assembly, a drive shaft having a proximal end and an opposing distal end, and a multistage axial flux generator. The bearing assembly includes a fixed ring and a rotating ring, wherein the fixed ring is coupled to the support base. The drive shaft is coupled to the rotating ring of the bearing assembly, and a plurality of sails are coupled to the drive shaft. The multistage axial flux generator includes a rotor assembly coupled to the drive shaft and a stator assembly coupled to the support base. The rotor assembly includes a plurality of permanent magnets, and the stator assembly includes a plurality of coils defining at least two voltage output stages. The permanent magnets on the rotor assembly are close-coupled to the coils on the stator assembly.
Owner:GRASSMAN DEREK
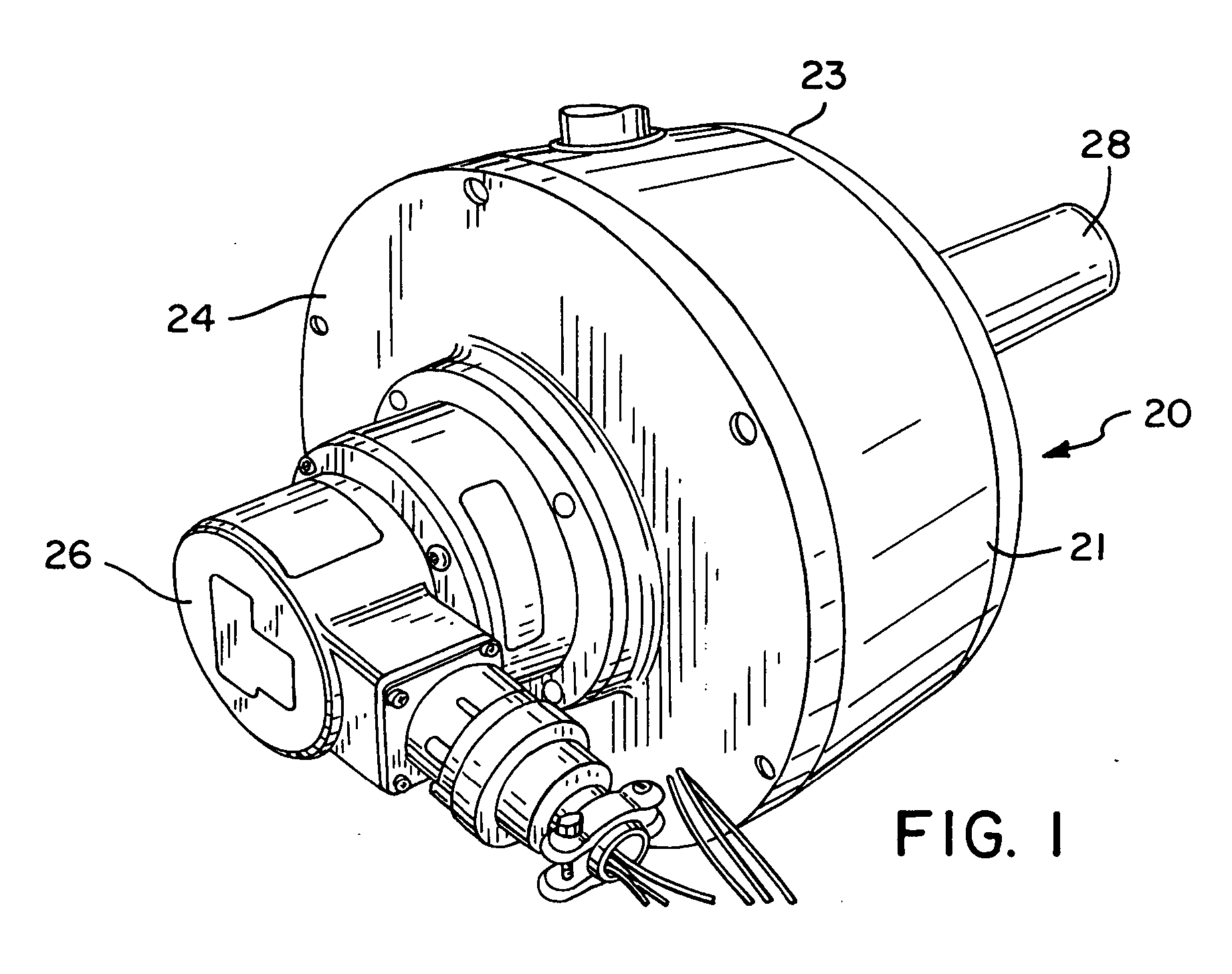
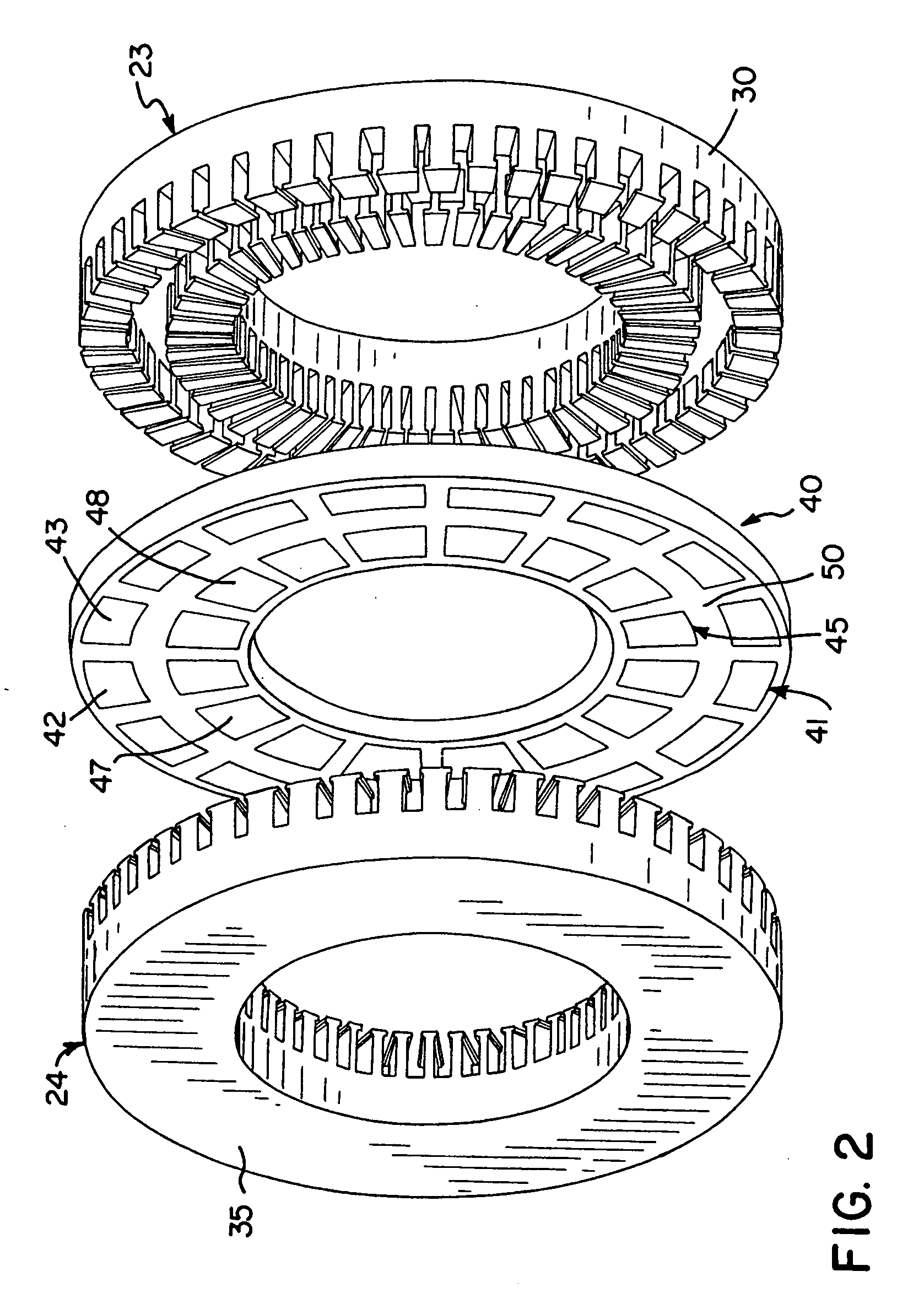
Gearless wheel motor drive system
Methods and apparatus are provided for an electric vehicle embodying an axial flux traction motor directly coupled to a wheel thereof. The fraction motor includes a stator having coils for producing a magnetic field, an annular rotor magnetically coupled to the stator and mechanically to an output shaft Permanent magnets of alternating polarity are mounted on the annular rotor. Magnetic shunts bridge a portion of the stator slots above the coils. The magnets are arranged in groups with group-to-group spacing exceeding magnet-to-magnet spacing. Adjacent edges of the magnets diverge. The method comprises, looking up d- and q-axis currents to provide the requested torque and motor speed for the available DC voltage, combining at least one of the d- and q-axis currents with a field weakening correction term, converting the result from synchronous to stationary frame and operating an inverter therewith to provide current to the coils of the motor.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Magnetic vertical axis wind turbine
InactiveUS7303369B2Reduce frictionMaximize operation of systemPropellersWind motor controlElectricityAlternator
A lift and drag-based vertical axis wind turbine in which the vertical axis and foils mounted thereon are magnetically levitated above the turbine's base, thereby reducing friction within the system. The foils or vanes are three-dimensionally shaped about the vertical axis so as to resemble the billowed sail of a sailing ship and capture wind through 360 degrees of rotation under any wind condition. The system has an axial flux alternator using variable resistance coils which can be individually and selectively turned on or off depending on wind conditions and electrical draw requirements. The coils can also be used to produce mechanical drag on the system as desired to brake the turbine in high wind conditions or for maintenance. The system may be programmed to assess whether electricity generated by the system can be or should be transmitted to a public grid or stored locally on a chargeable battery system.
Owner:NIAGARA CENT RES
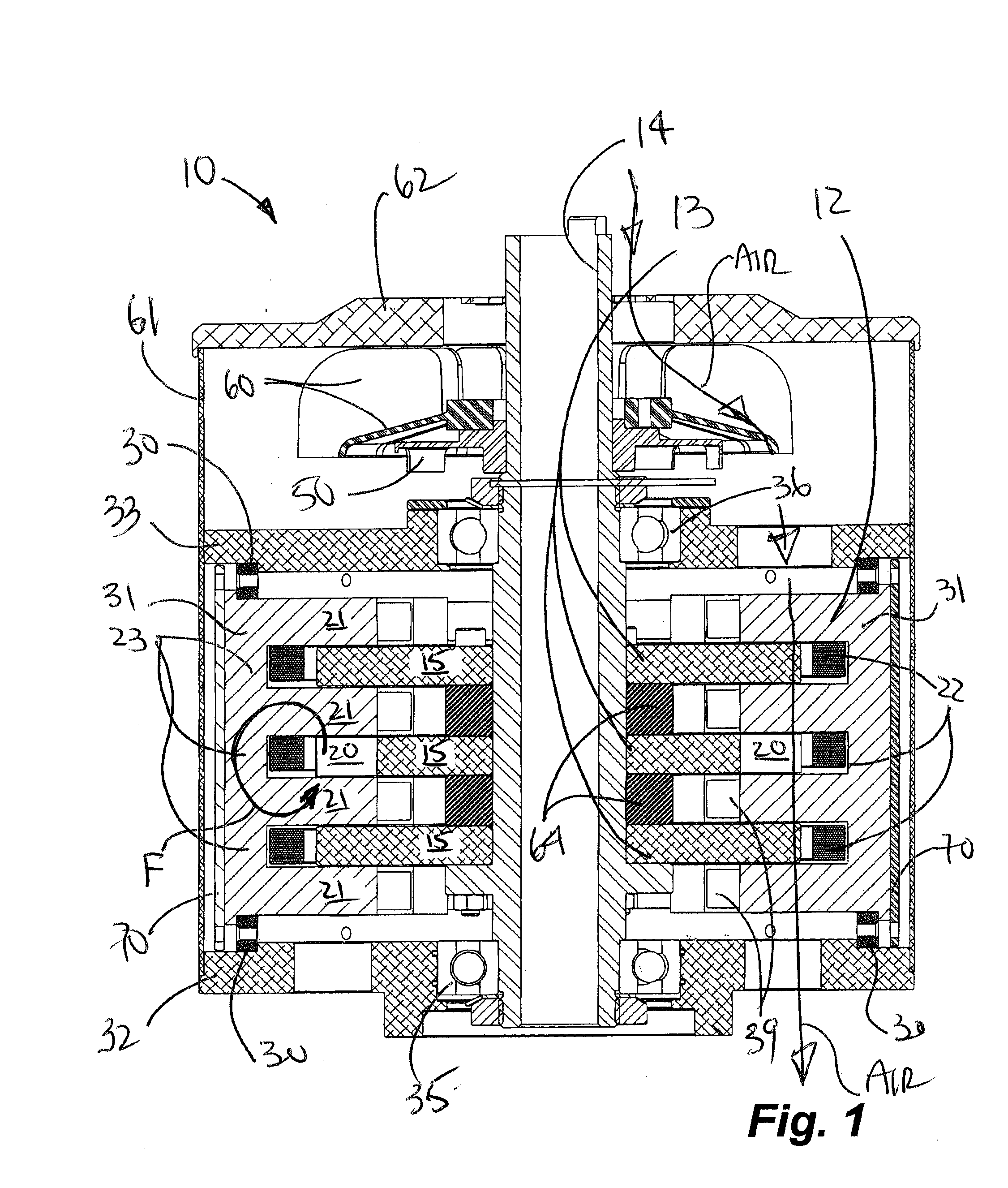
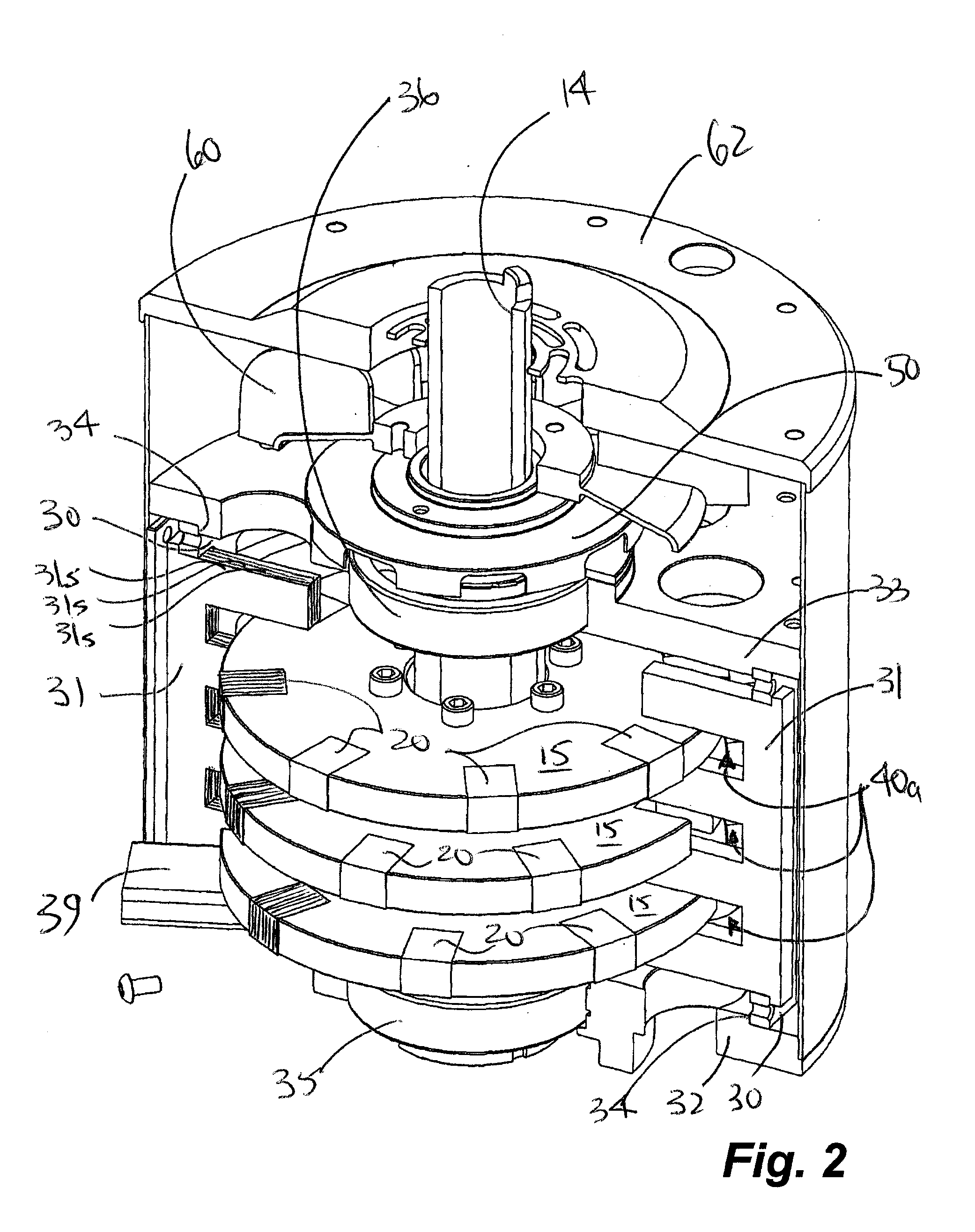
Cooling and handling of reaction torque for an axial flux motor
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
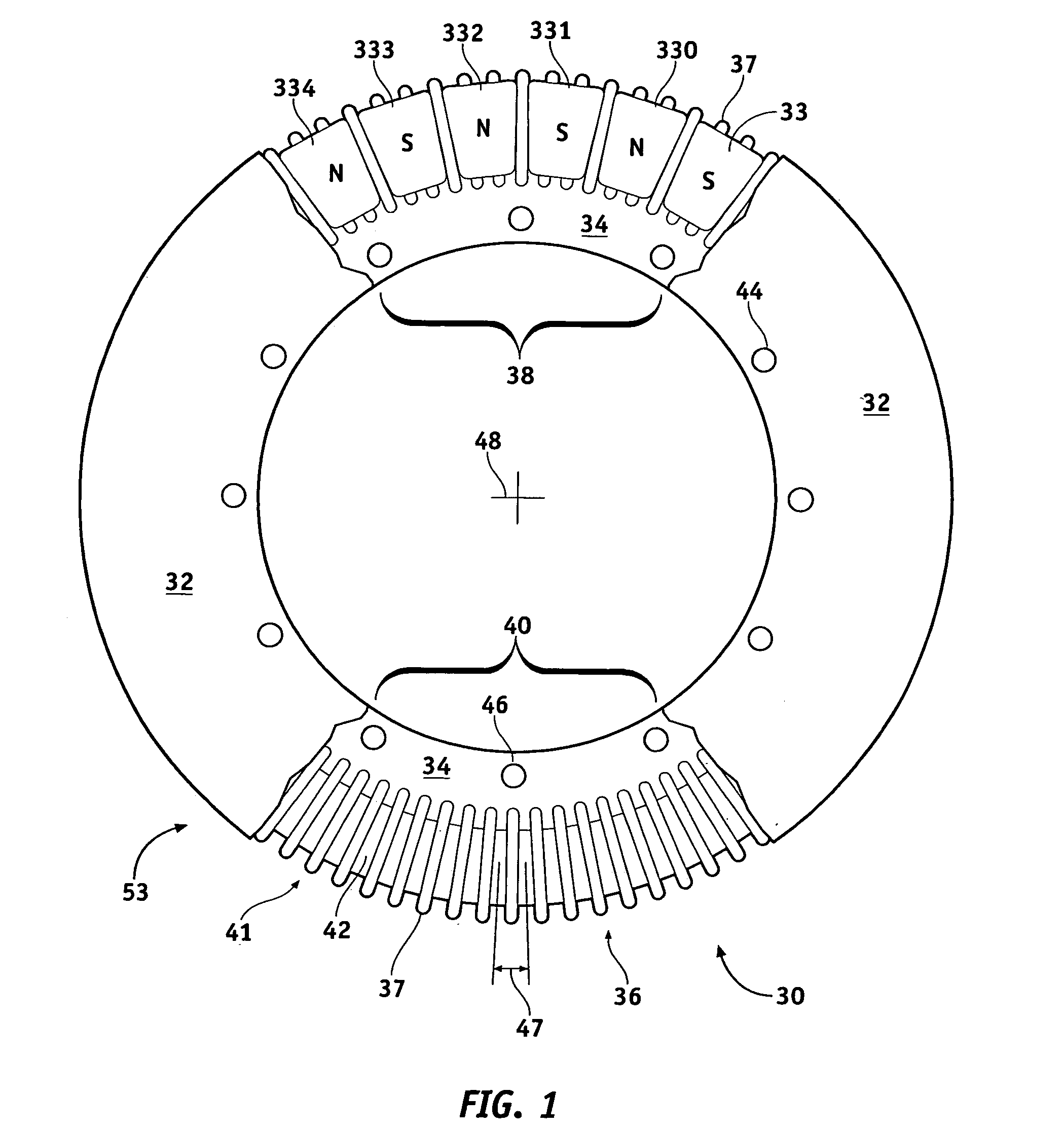
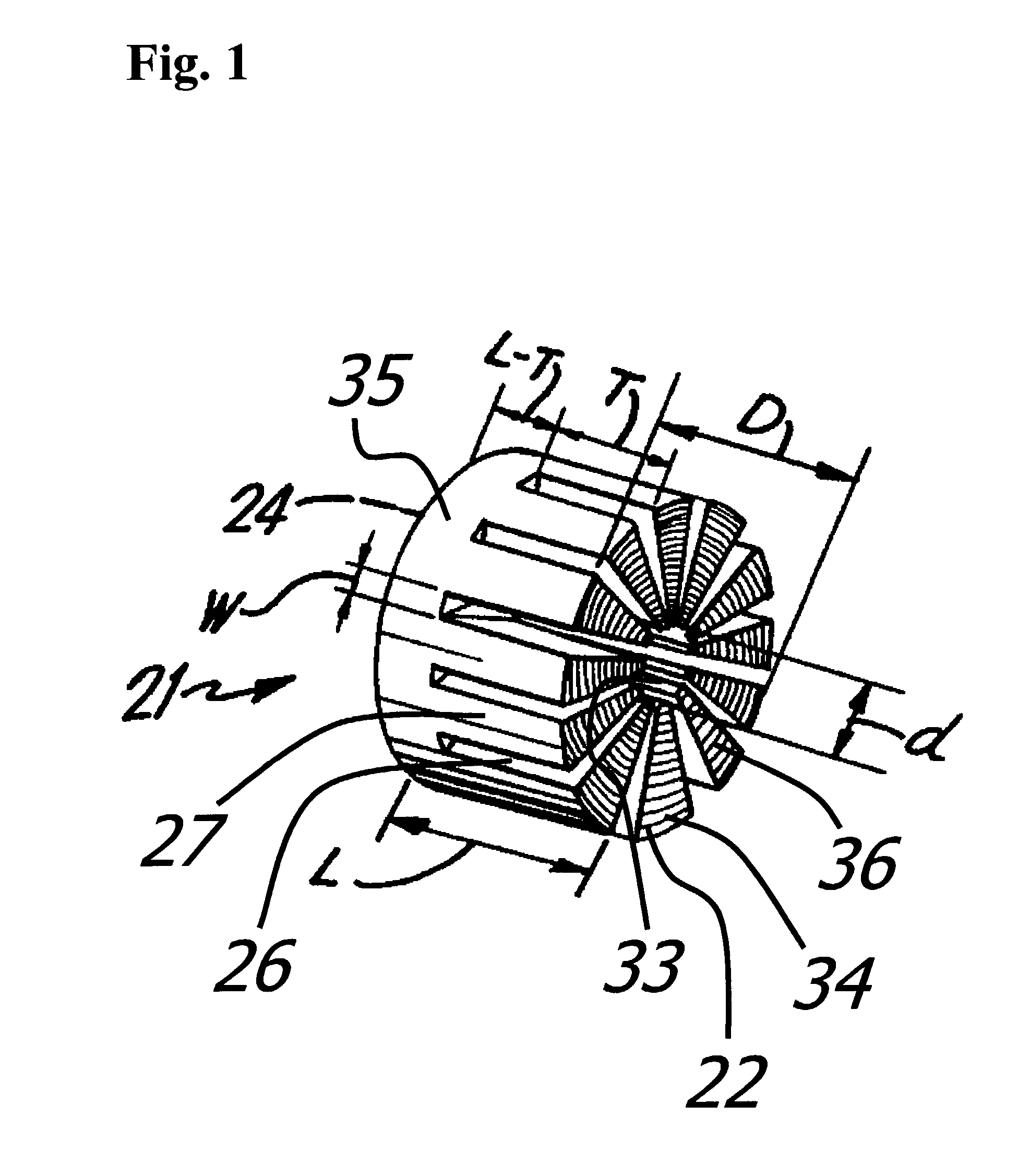
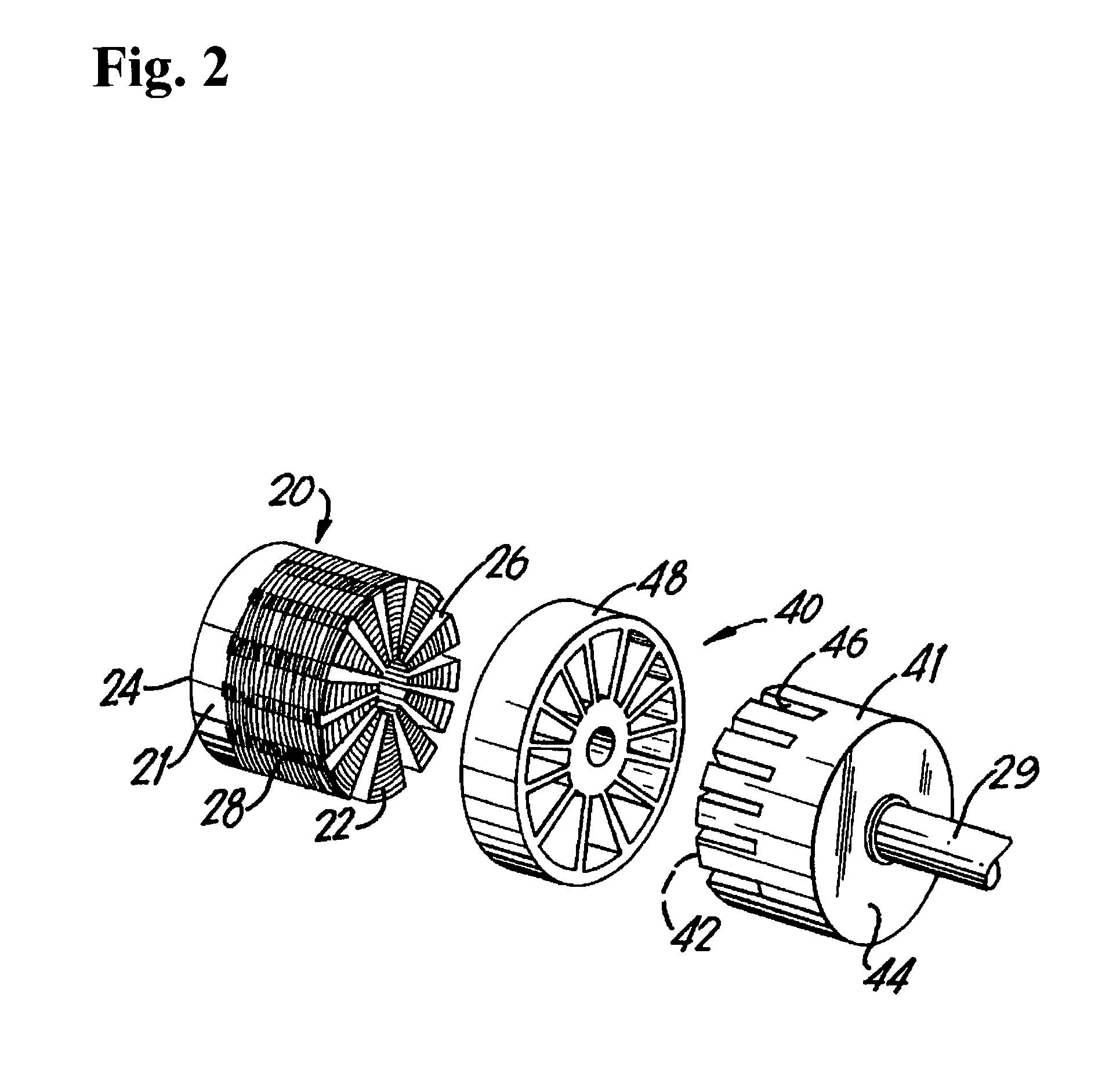
Axial flux switched reluctance motor and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20100295389A1Use minimizedIron and copper lossMagnetic circuitSynchronous motorsStator coilReluctance motor
An axial flux switched reluctance motor utilizes one or more rotor discs spaced along a rotor shaft, each rotor disc having a plurality of rotor poles spaced along the periphery thereof. Stator elements are distributed circumferentially about the rotor discs and form pairs of radially extending stator poles for axially straddling the rotor discs. Stator coils as switched on to energize pairs of stator poles for forming an axial and radially inward flux path for rotating the rotor poles for minimizing the flux path before switching off the stator coil. Two or more rotor discs can be rotationally indexed for providing two or more motor phases. In manufacture, rotor discs and circumferentially extending stator coils about the periphery of each rotor disc are fit to a stator housing. Each stator element is then fit radially through the stator housing and secured thereto for straddling the rotor discs.
Owner:MSI MACHINEERING SOLUTIONS
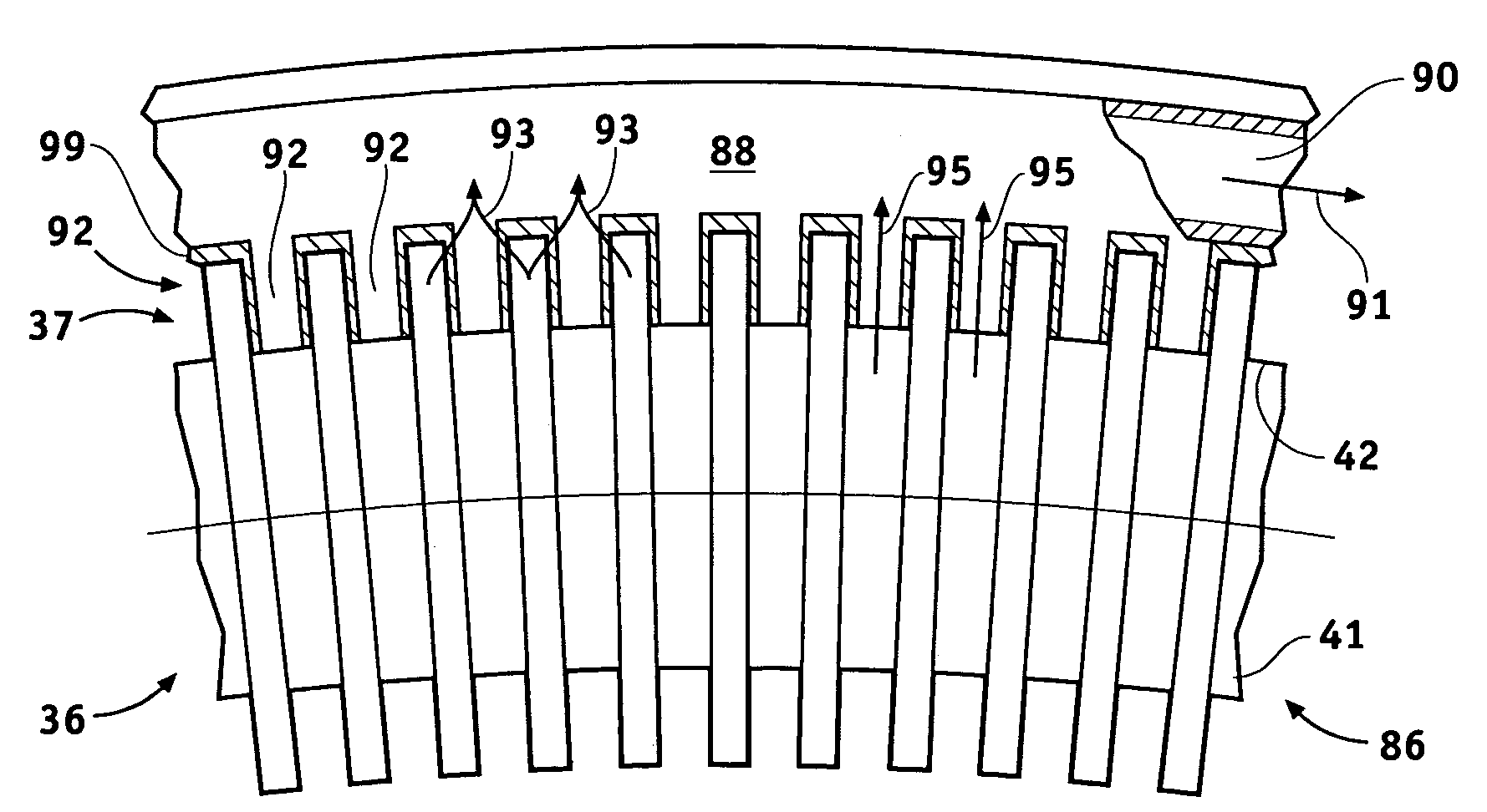
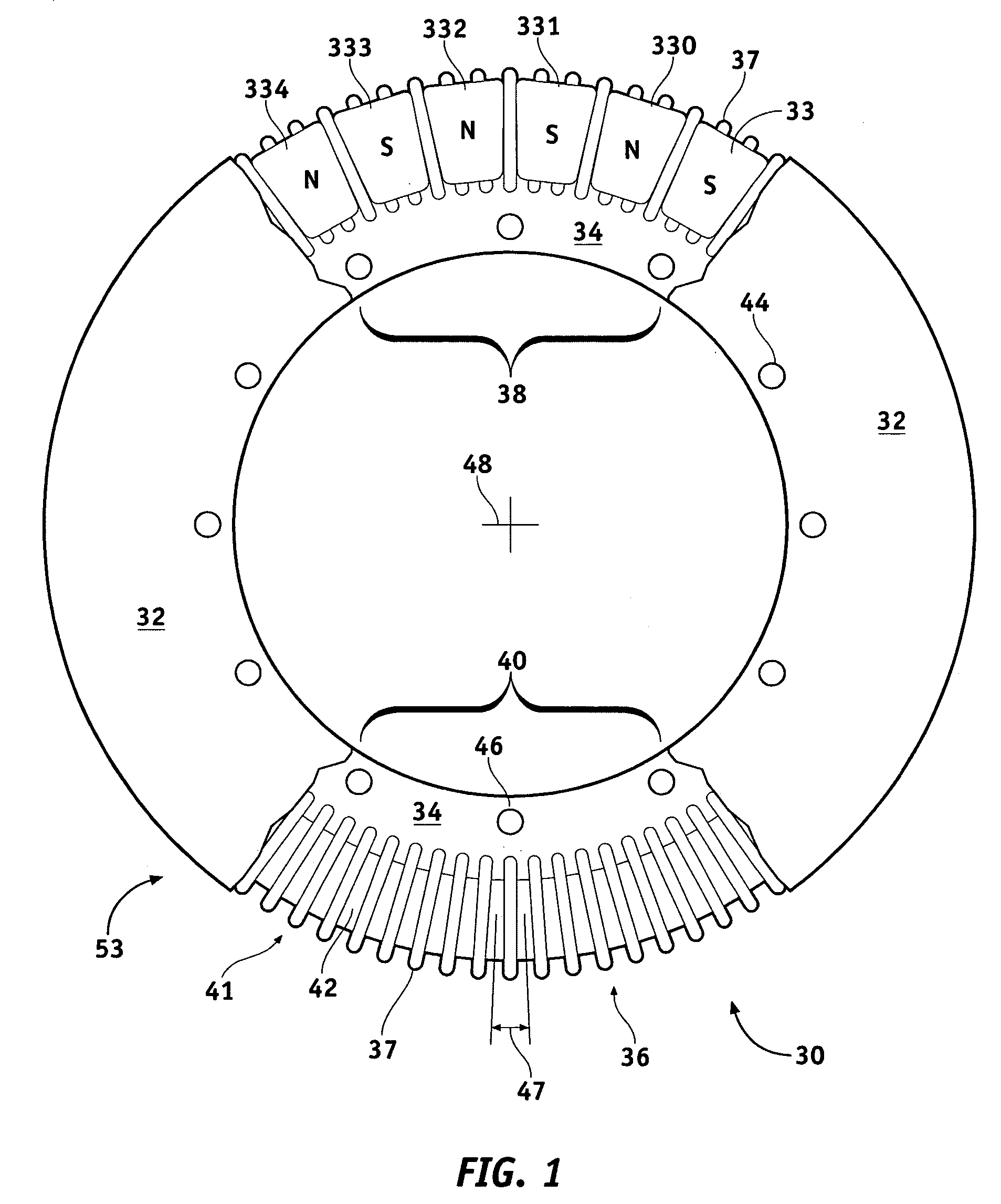
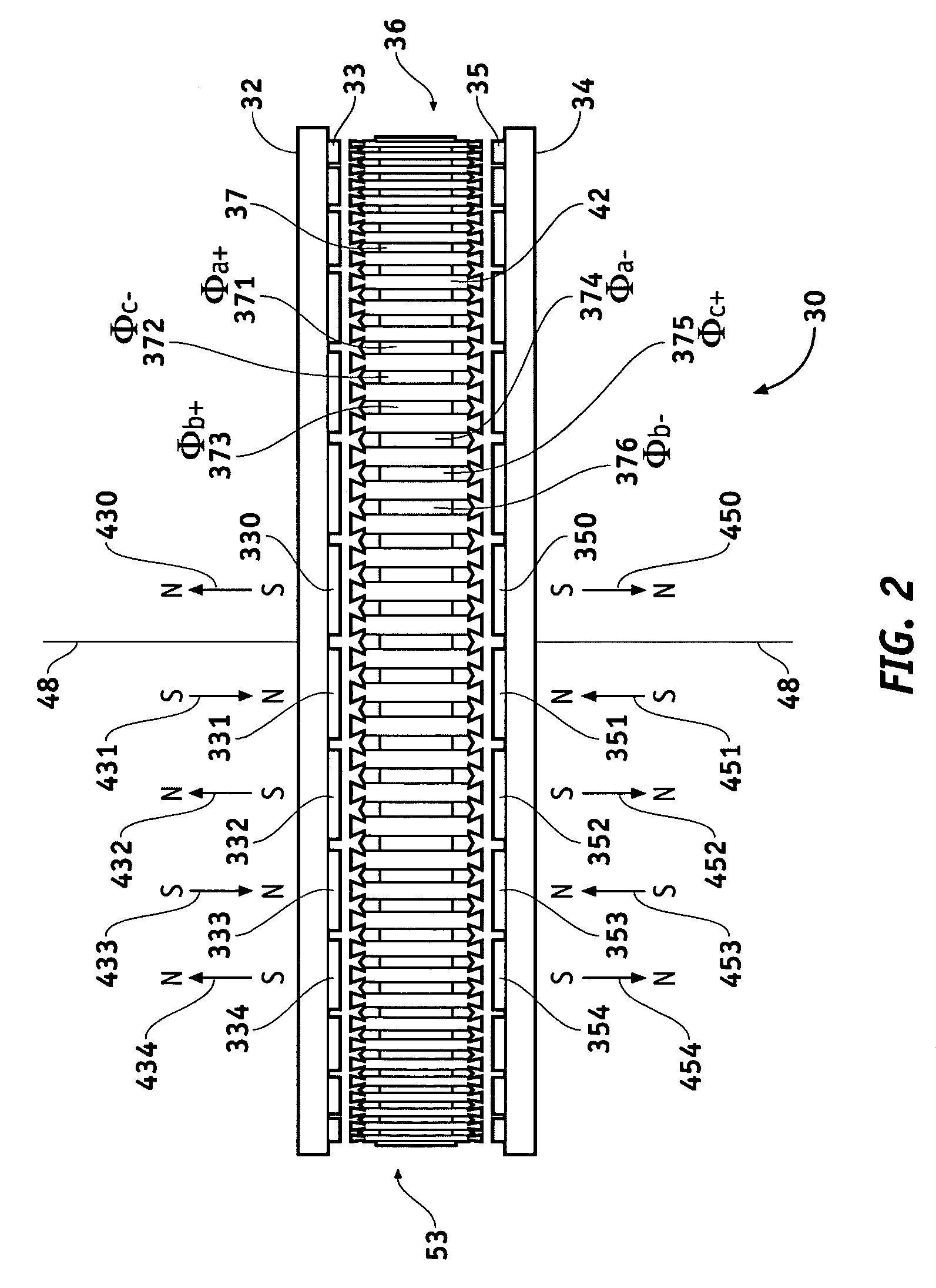
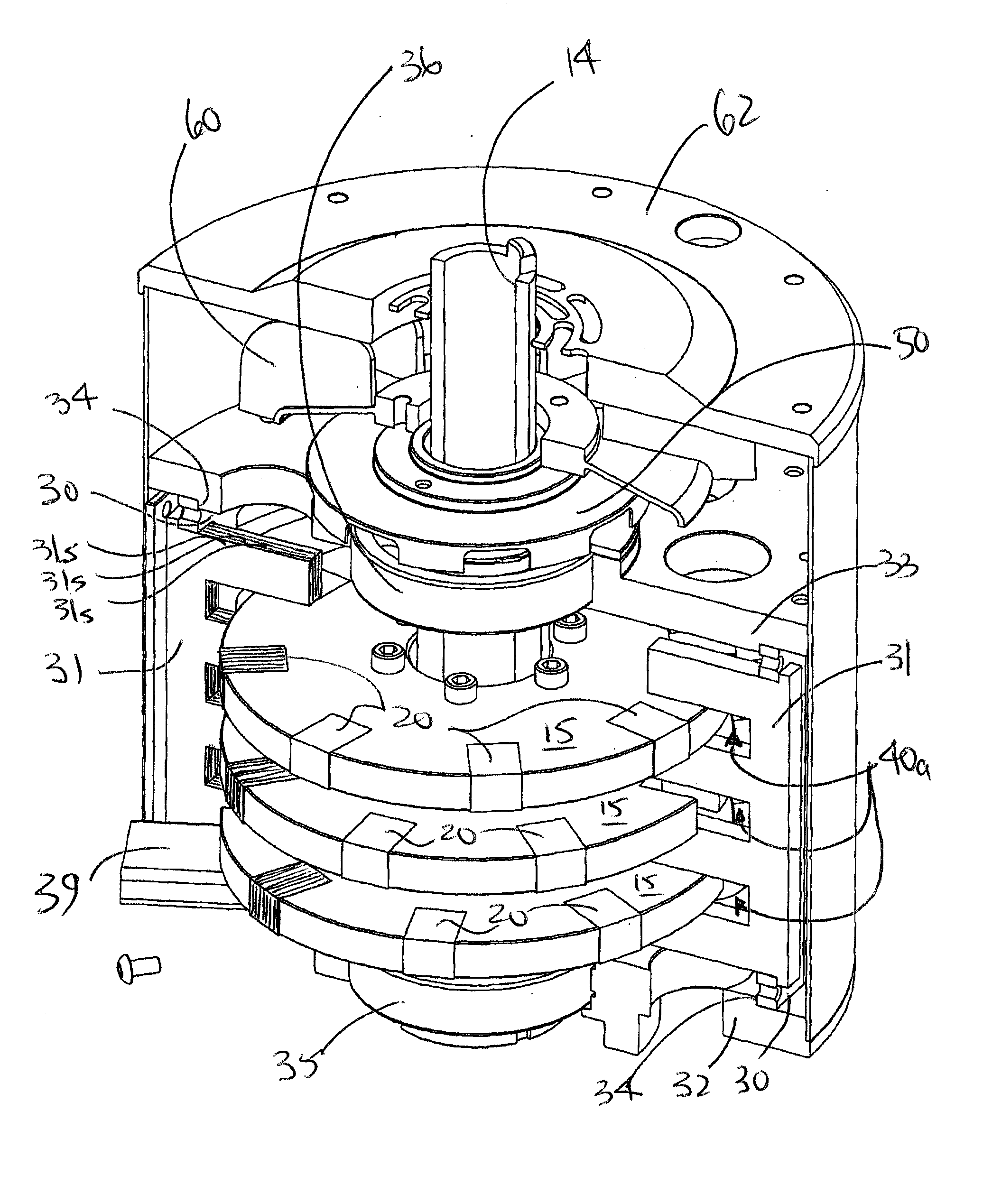
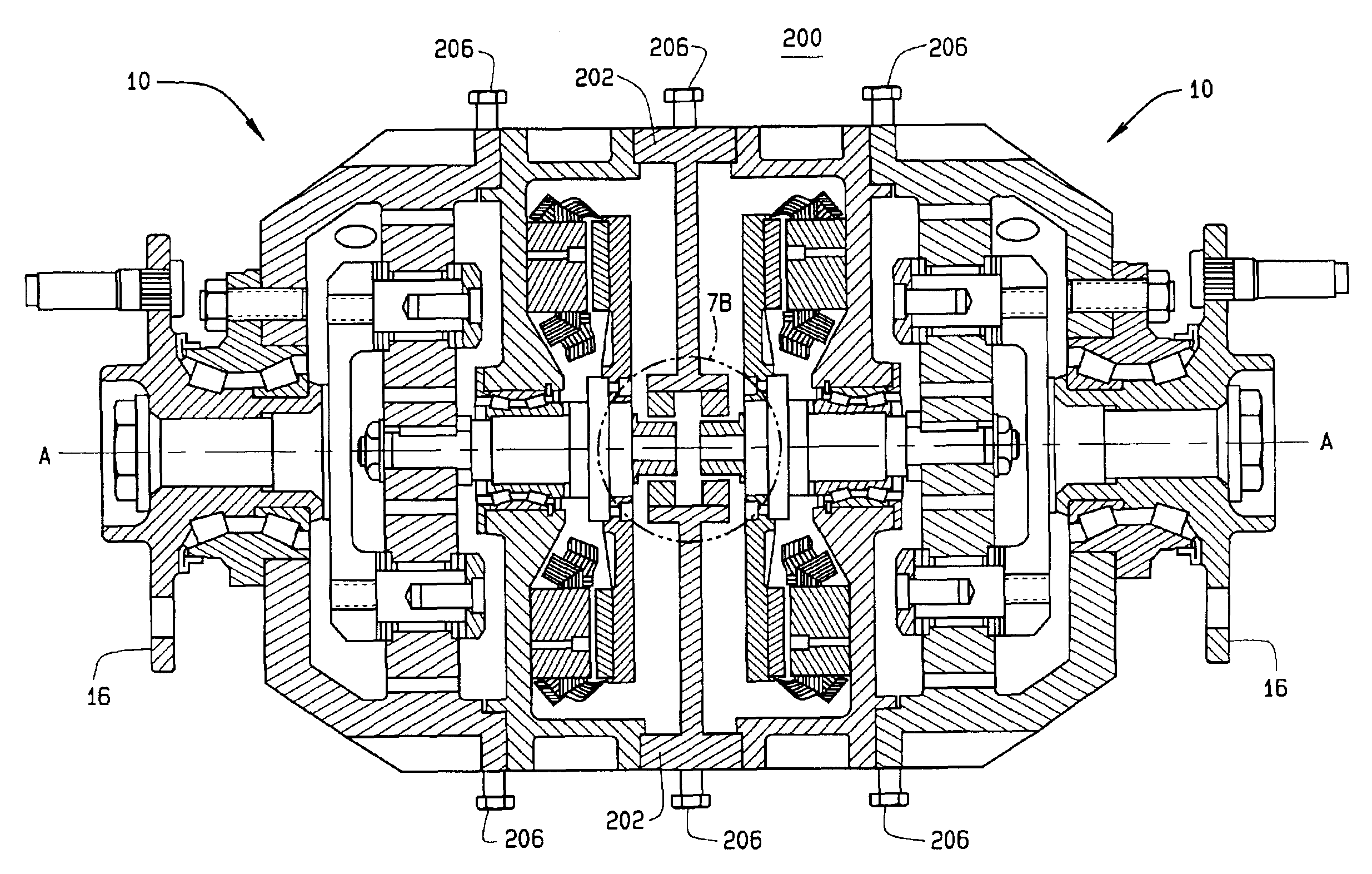
Axial flux motor assembly
A power unit assembly which has a pair of mirrored axial flux electric motors having a common axis of rotation, each axial flux motor including a rotor disposed on a rotor shaft and at least one stator disposed in operative relationship to said rotor. A common end plate is disposed between each of the pair of axial flux electric motors to provide a common mounting structure, while an output hub is operatively coupled to each rotor shaft of the pair of mirrored axial flux electric motors. Each of the pair of mirrored axial flux electric motors is operatively configured to provide independent speed and torque to each associated output hub.
Owner:THE TIMKEN CO
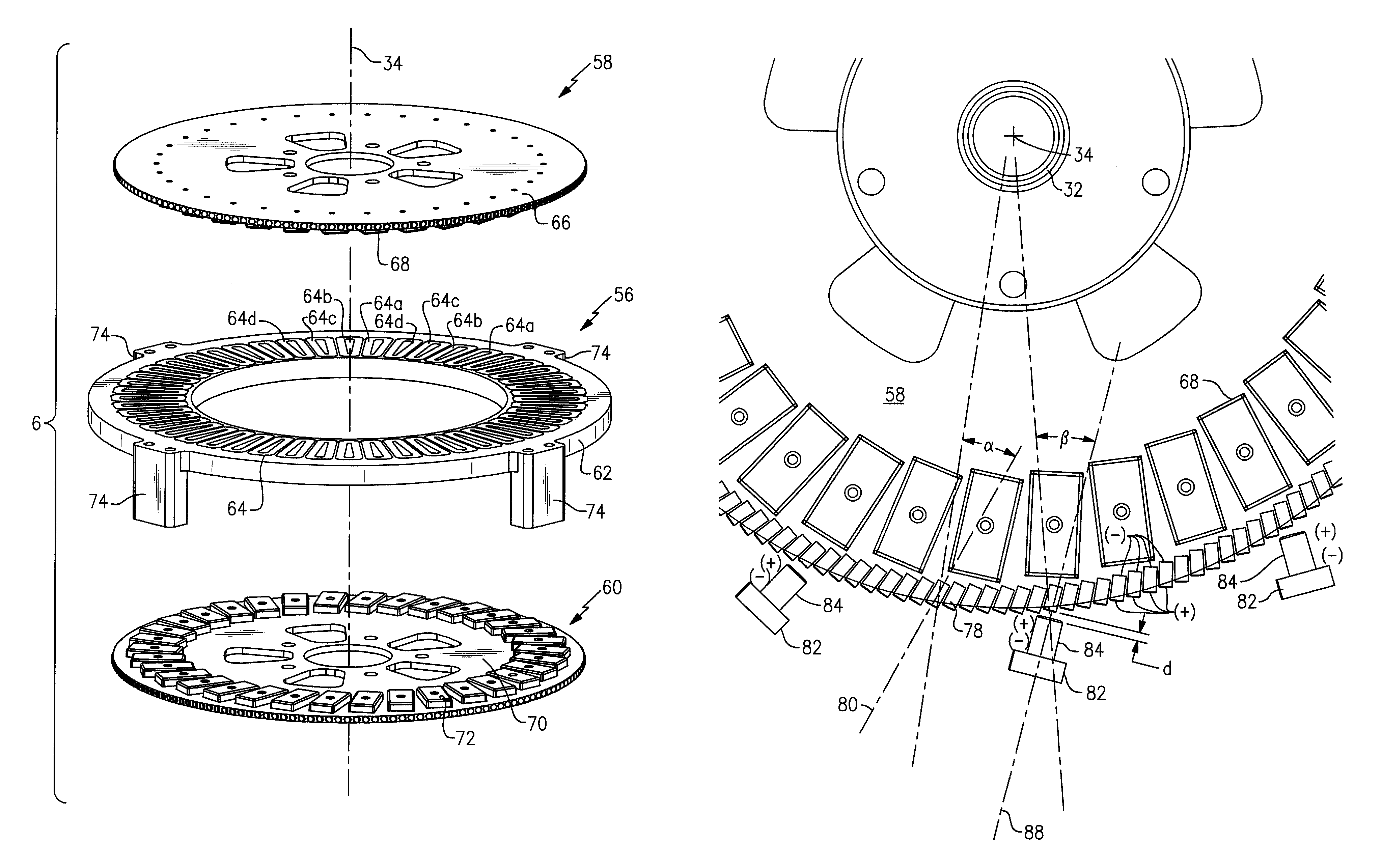
Systems and methods for improved direct drive generators
InactiveUS9154024B2Reducing weight and sizeEasy to assembleMagnetic circuit rotating partsWind energy generationEngineeringAxial flux
Systems and methods for improved generators are described. One embodiment includes an assembly for an axial flux generator, the assembly comprising an arc-shaped rotor section that includes a rotor support configured to rotate around an axis of a generator, and an at least one rotor element for power generation that is connected to the rotor support; an arc-shaped stator section comprising a stator support and an at least one stator element for power generation connected to the stator support; wherein the rotor section and the stator section are configured to provide an axial air gap between the at least one rotor element and the at least one stator element, and wherein the at least one rotor element and the at least one stator element are positioned to be at substantially the same radial distance from the axis of the generator.
Owner:BWP GRP
Permanent magnet generator
InactiveUS6087750AIncreased longevityIncreased durabilitySynchronous generatorsDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesEngineeringPermanent magnet synchronous generator
A permanent magnet generator is described. The generator includes a shaft which defines a longitudinal axis. A rotatable magnetic field assembly is mounted on the shaft and adapted for rotation about the shaft. The magnetic field assembly includes a plurality of axially magnetized magnets which are retained in a cavity about the shaft for generating an axial magnetic flux. A plurality of vanes are mounted on the magnetic field assembly housing for rotating the magnetic field assembly about the shaft when a fluid flows past the vanes. A stationary armature assembly is also located around the shaft in a position axially spaced from the magnetic field assembly. The armature assembly generates AC power when the magnetic field assembly is rotated. The stationary armature assembly includes an armature housing. An axial bore is formed through the armature housing for receiving the shaft. The armature housing defines a cavity about the axial bore in which a plurality of laminated bars are retained. A plurality of electrically conductive wires are wrapped around the laminated bars to form coils.
Owner:PACIFIC SCI ELECTRO KINETICS DIV
Magnetic vertical axis wind turbine
InactiveUS20070098563A1Reduce frictionMaximize operation of systemOther chemical processesPump componentsElectricityAlternator
A lift and drag-based vertical axis wind turbine in which the vertical axis and foils mounted thereon are magnetically levitated above the turbine's base, thereby reducing friction within the system. The foils or vanes are three-dimensionally shaped about the vertical axis so as to resemble the billowed sail of a sailing ship and capture wind through 360 degrees of rotation under any wind condition. The system has an axial flux alternator using variable resistance coils which can be individually and selectively turned on or off depending on wind conditions and electrical draw requirements. The coils can also be used to produce mechanical drag on the system as desired to brake the turbine in high wind conditions or for maintenance. The system may be programmed to assess whether electricity generated by the system can be or should be transmitted to a public grid or stored locally on a chargeable battery system.
Owner:NIAGARA CENT RES
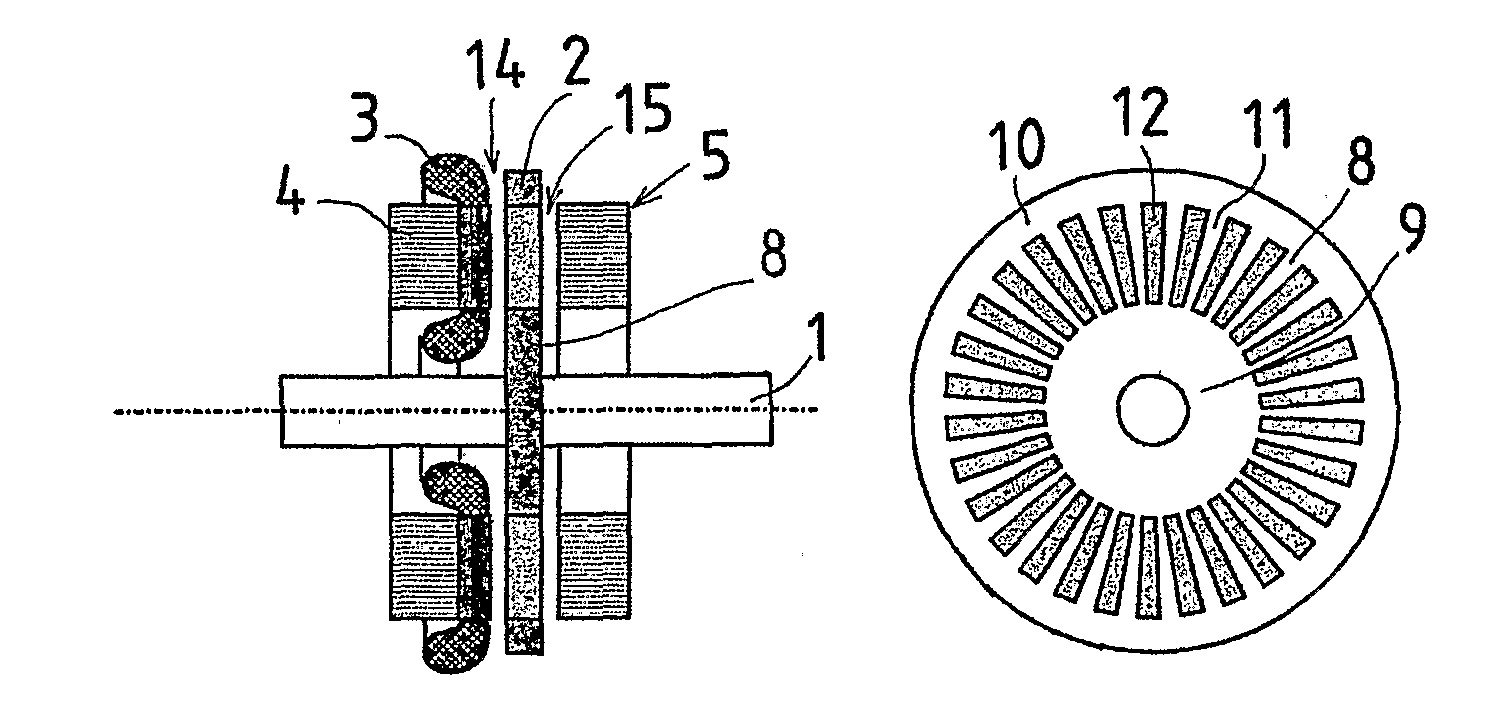
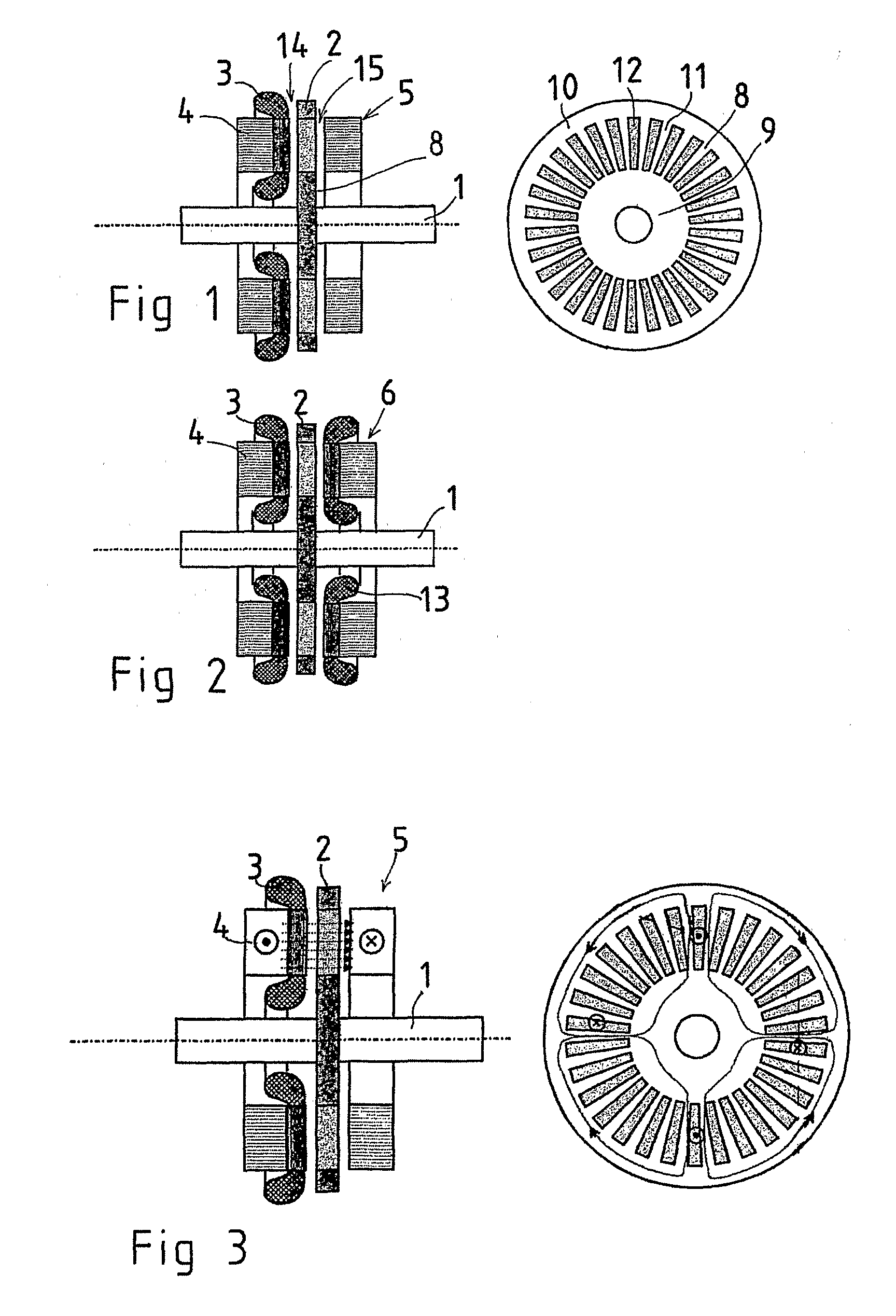
Axial Flux Induction Electric Machine
InactiveUS20080001488A1Easy to with power toolIncrease speedSynchronous generatorsWindingsAxial fluxWork hardening
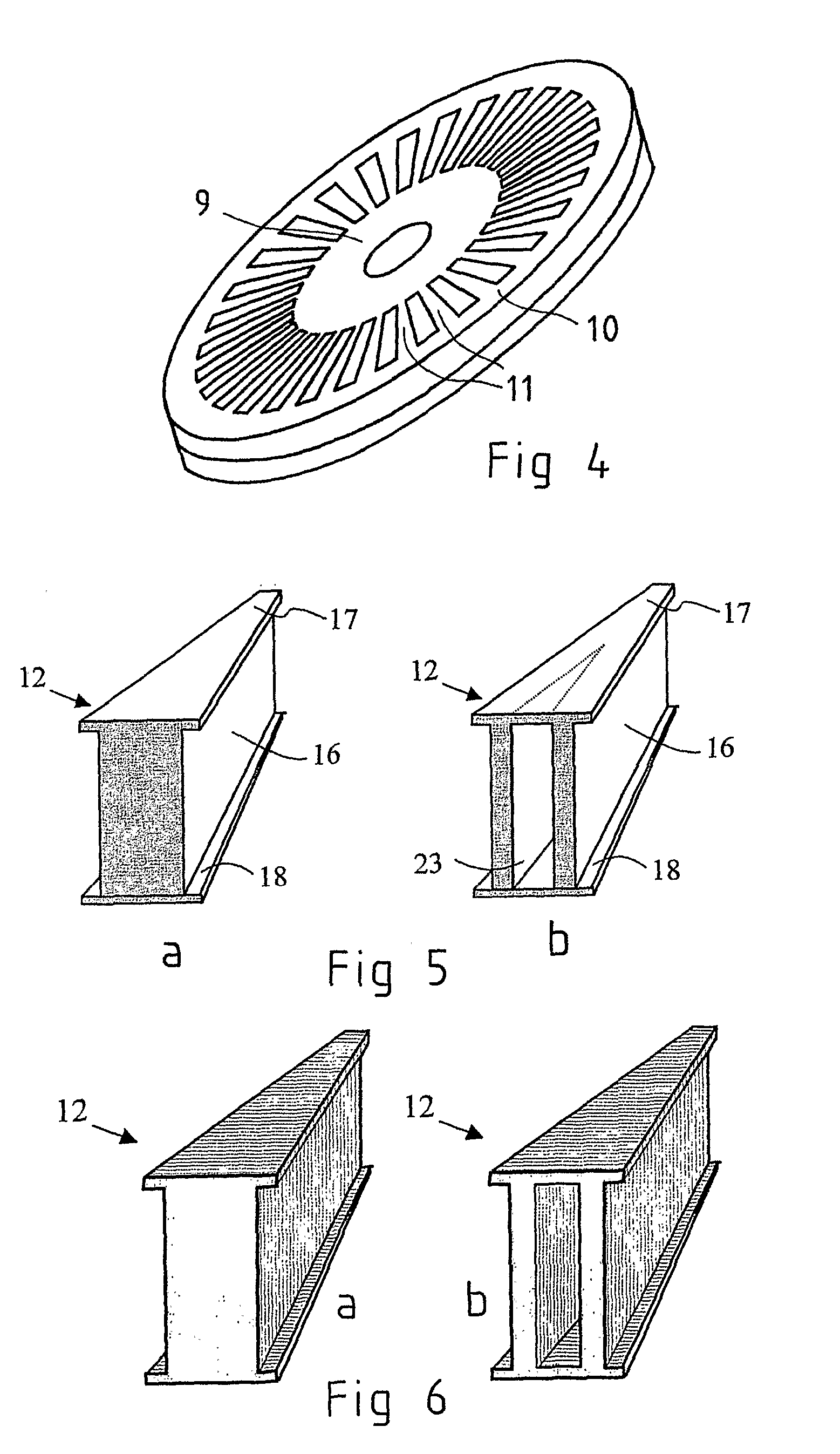
The invention relates to an axial flux induction electrical machine comprising a frame, a shaft (1) bearing-mounted to the frame, a disc-like rotor (2) supported to the shaft, a stator (4) comprising a stator winding (3) and supported by the frame on the first side of the rotor in axial direction. The disc-like rotor (2) comprises a non-ferromagnetic rotor frame (8) fabricated of a material with high electrical conductivity and comprising a uniform inner periphery (9) and an outer periphery (10) and conductor bars (11) fabricated of the same material and galvanically connecting the peripheries (11), the conductor bars together with the inner and outer peripheries forming in addition to the rotor frame also the cage winding of the rotor. In addition, between the inner periphery and the outer periphery there is a plurality of ferromagnetic pieces (12) extending through the frame plate and being spaced apart from each other at an appropriate distance so that the radial conductor bars are appropriately located between the pieces. According to the invention, the disc-like rotor frame (8) comprises at least one circular plate machined of work-hardened metal sheet.
Owner:AXCO MOTORS OY
Systems and methods for improved direct drive generators
ActiveUS20120217831A1Reduce weightSmall sizeMagnetic circuit rotating partsWind energy generationEngineeringMechanical engineering
Systems and methods for improved generators are described. One embodiment includes an assembly for an axial flux generator, the assembly comprising an arc-shaped rotor section that includes a rotor support configured to rotate around an axis of a generator, and an at least one rotor element for power generation that is connected to the rotor support; an arc-shaped stator section comprising a stator support and an at least one stator element for power generation connected to the stator support; wherein the rotor section and the stator section are configured to provide an axial air gap between the at least one rotor element and the at least one stator element, and wherein the at least one rotor element and the at least one stator element are positioned to be at substantially the same radial distance from the axis of the generator.
Owner:BWP GRP
Axial flux motor mass reduction with improved cooling
InactiveUS20050035678A1Low densityReduce weightWindingsVector control systemsEngineeringNon magnetic
Methods and apparatus are provided for an axial electric motor. The apparatus comprises, a stator having coils thereon for producing a magnetic field, a rotor rotated by the magnetic field, and an output shaft coupled to the rotor. The rotor includes a magnetic and non-magnetic component. The non-magnetic component has a lower density than the magnetic component. One or both of the rotor components have apertures therein for ventilation and weight reduction. Permanent magnets are desirably mounted on the magnetic component of the rotor facing the stator and portions of the rotor behind the permanent magnets are hollowed out to be thinner than portions of the rotor between the permanent magnets. This reduces rotor weight without significantly affecting magnetic flux density in the rotor or motor torque.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
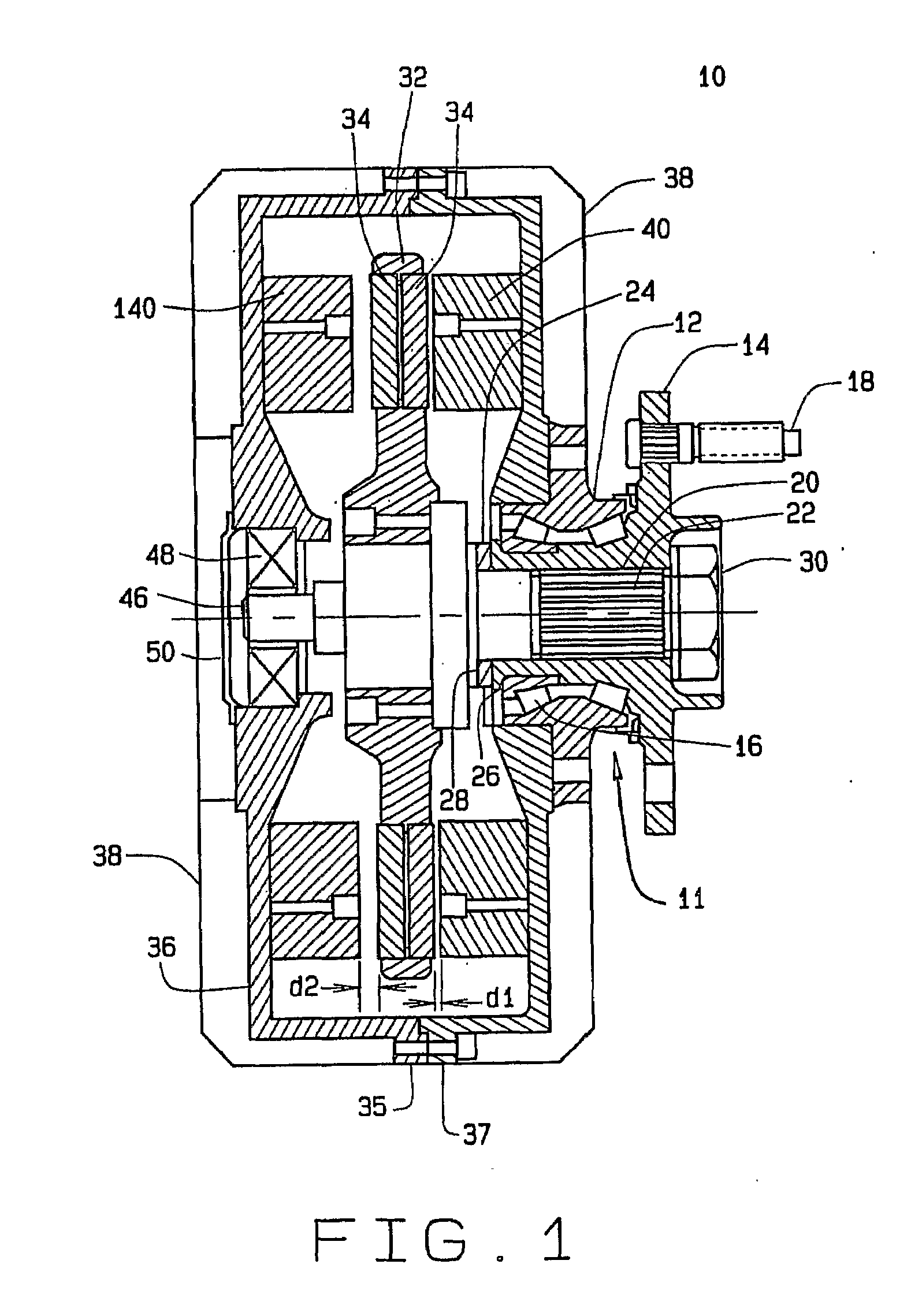
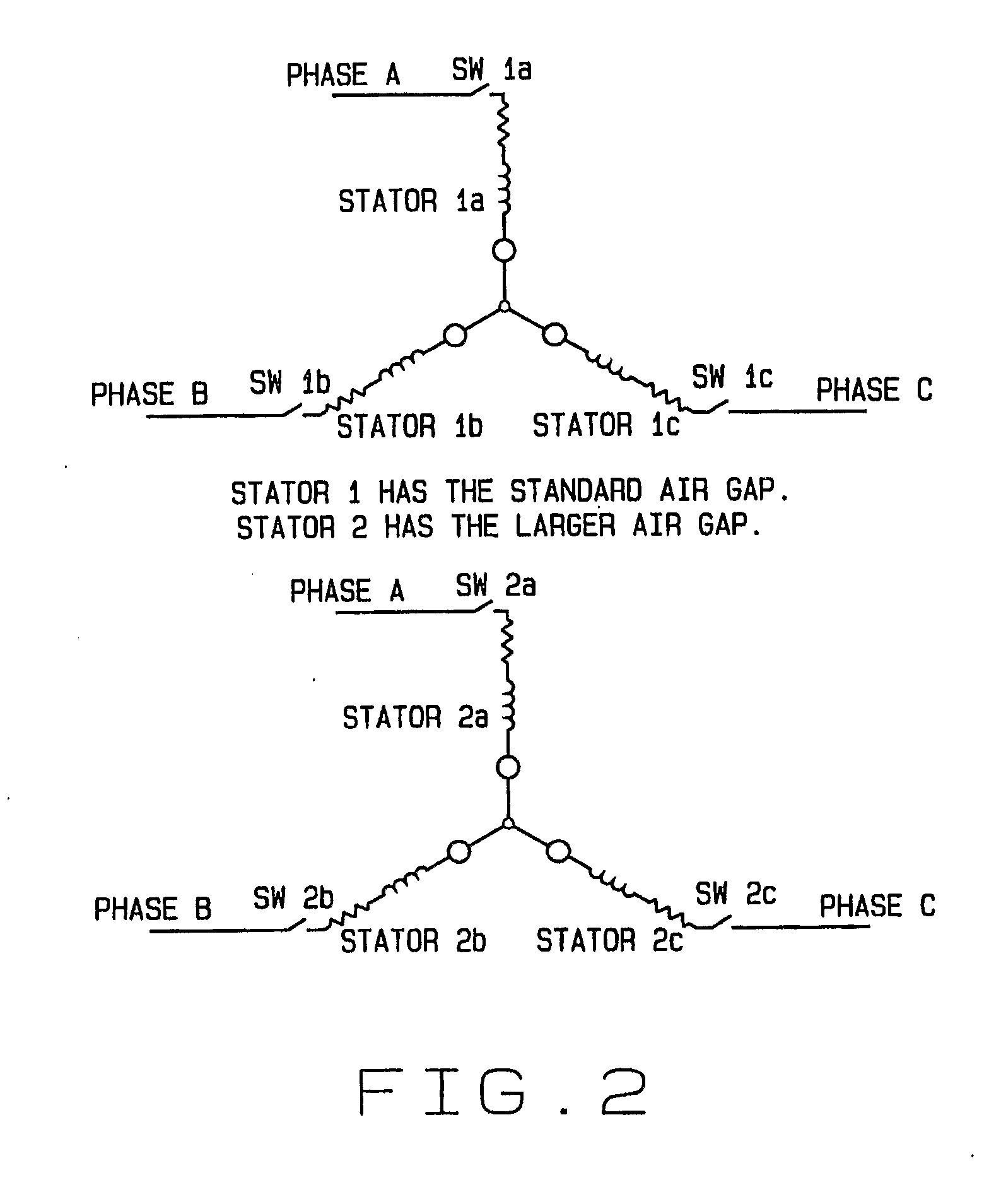
Virtual Moving Air Gap For An Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Motor With Dual Stators
InactiveUS20090160392A1Electronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPermanent magnet motorCounter-electromotive force
An axial flux electric motor comprising a rotor and a first and second stator. The first and second stators have a first and second air gap located between the first and second stators and the rotor, respectively, and the second air gap is greater than the first gap. In one embodiment, the coils of the first stator and the coils of the second stator are in parallel. The motor further comprises switches which alternatingly energize the coils of the first stator and of the second stator based upon required torque and required speed of the motor. In a second embodiment, the coils of the first stator and the coils of the second stator are in series and the motor further comprises switches which selectively bypass the coils of the second stator in order to reduce the back EMF of the motor and increase the maximum speed of the motor at a given input voltage.
Owner:THE TIMKEN CO
Axial flux brushless permanent magnet electrical machine rotor
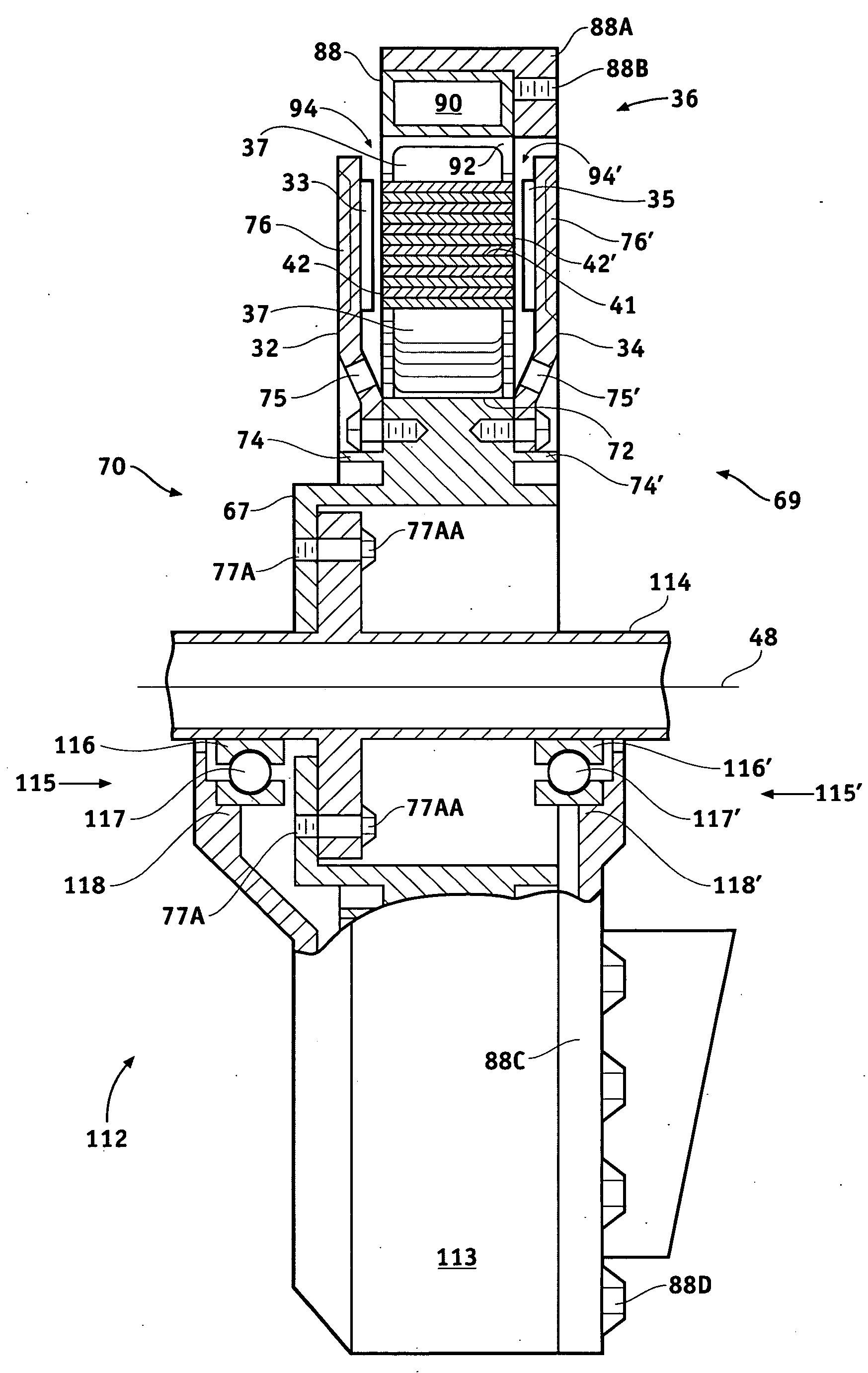
ActiveUS20160329795A1Maximize rotor strengthMinimizing structural massMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsRotor magnetsAxial flux
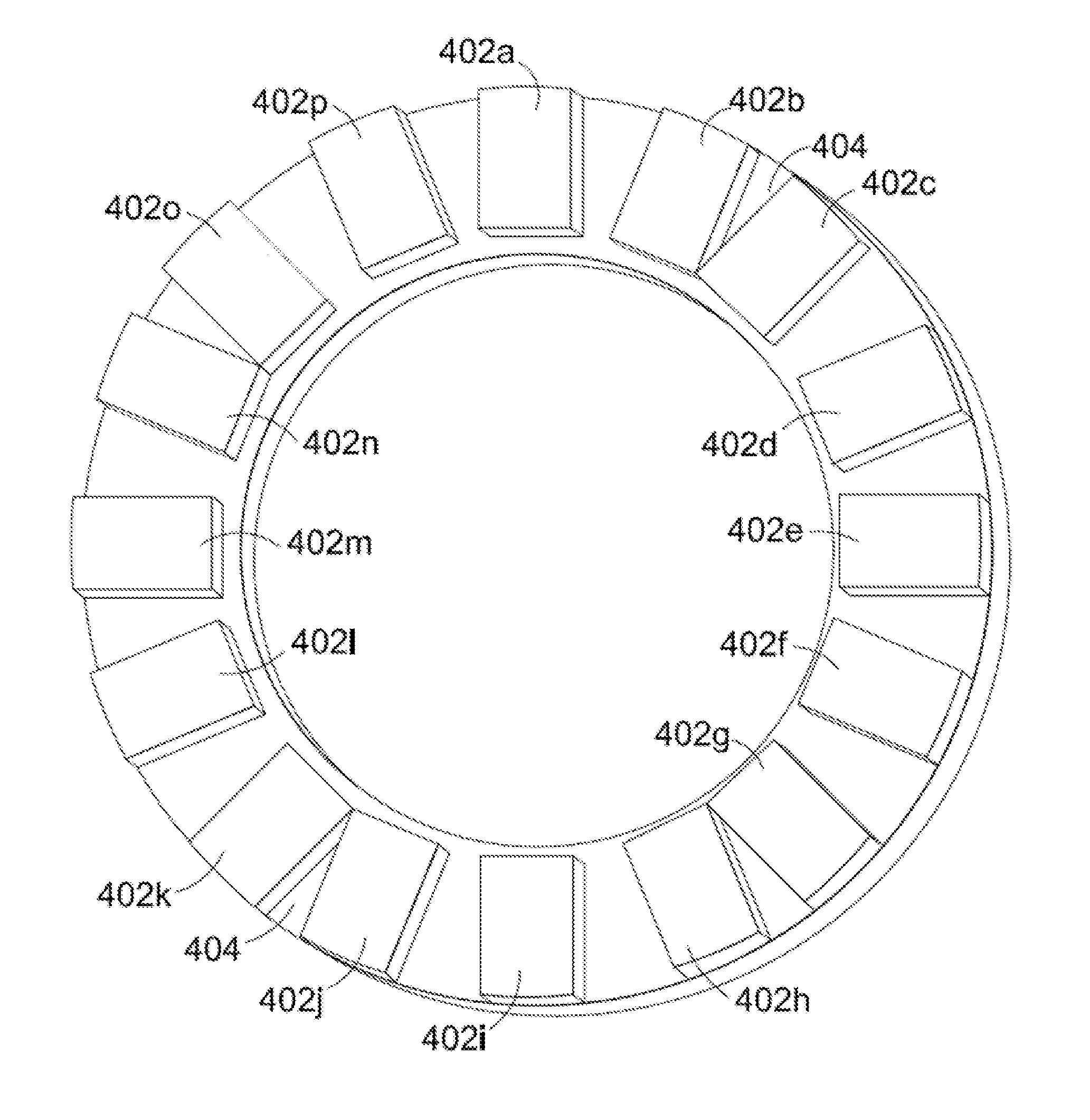
An axial flux brushless permanent magnet electrical machine having a stator and at least one rotor. The rotor includes a Halbach array of magnets with at least four magnets per magnetic cycle. The rotor magnets are contained within pockets in the rotor. The pockets are formed with magnet pocket walls being radial walls, active surface walls, and / or inactive surface walls where the walls retain the magnets within the pockets.
Owner:LAUNCHPOINT ELECTRIC PROPULSION SYST INC
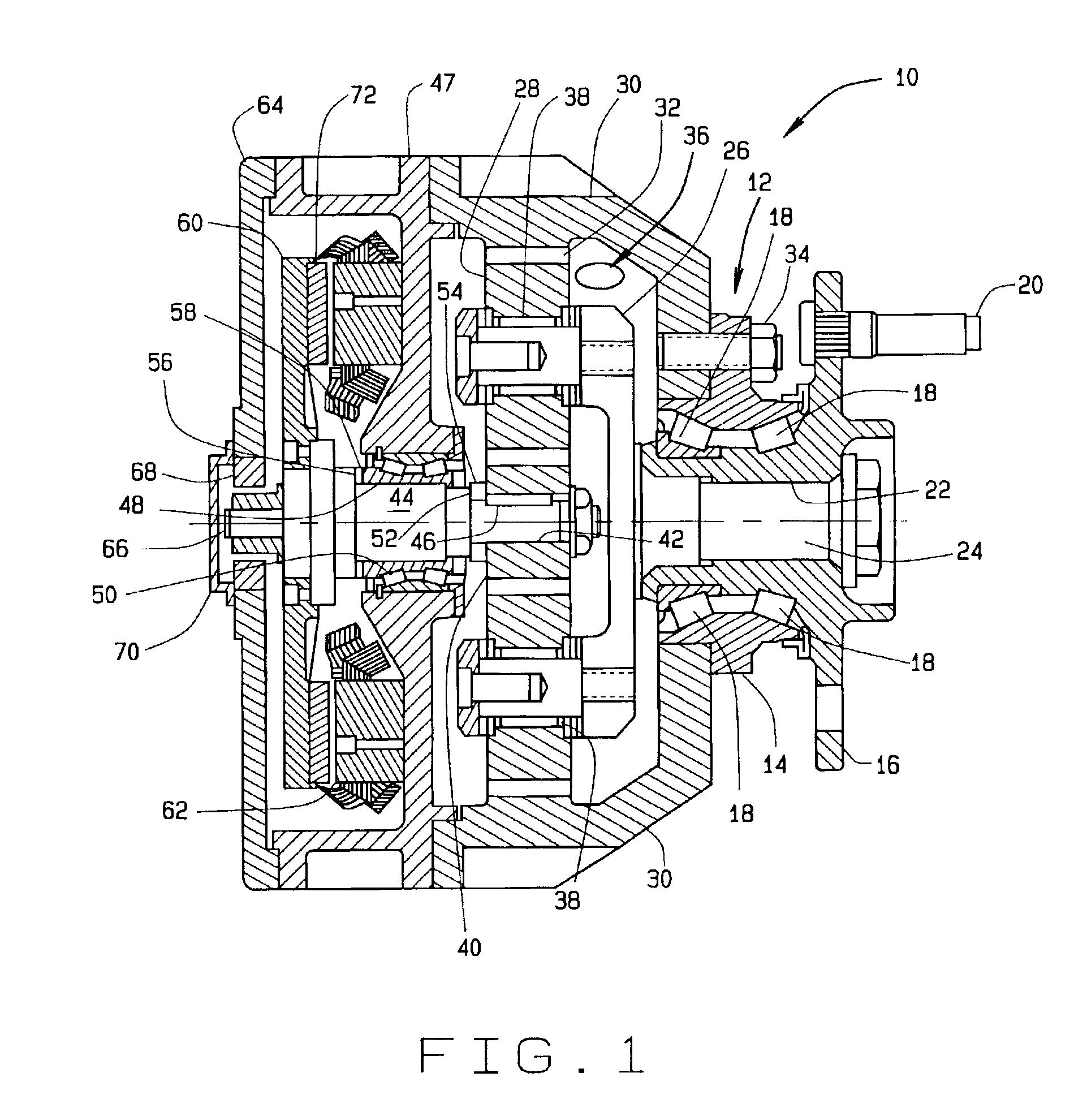
Cooling and handling of reaction torque for an axial flux motor
Methods and apparatus are provided for an axial electric motor. The apparatus comprises, a stator having coils thereon for producing a magnetic field, a rotor rotated by the magnetic field, an output shaft coupled to the rotor, and a ring incorporating a coolant channel circumferentially engaging the stator for absorbing heat and reaction torque from the stator. It is preferable that that the ring have inwardly extending teeth that mesh with the coils on the stator. The space between the teeth and the coils is preferably filled with a substantially solid thermally conductive material to transmit stator reaction torque to the teeth and cool the stator. The coils are preferably formed from a flat ribbon a portion of whose principal surface is perpendicular to the teeth. A supporting frame is desirably fixedly coupled to the ring and rotatably coupled to the output shaft.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Stator section for an axial flux electric machine with liquid cooling system
InactiveUS20110221287A1Improve cooling effectSimple processCooling/ventillation arrangementWindings conductor shape/form/constructionElectrical conductorElectric machine
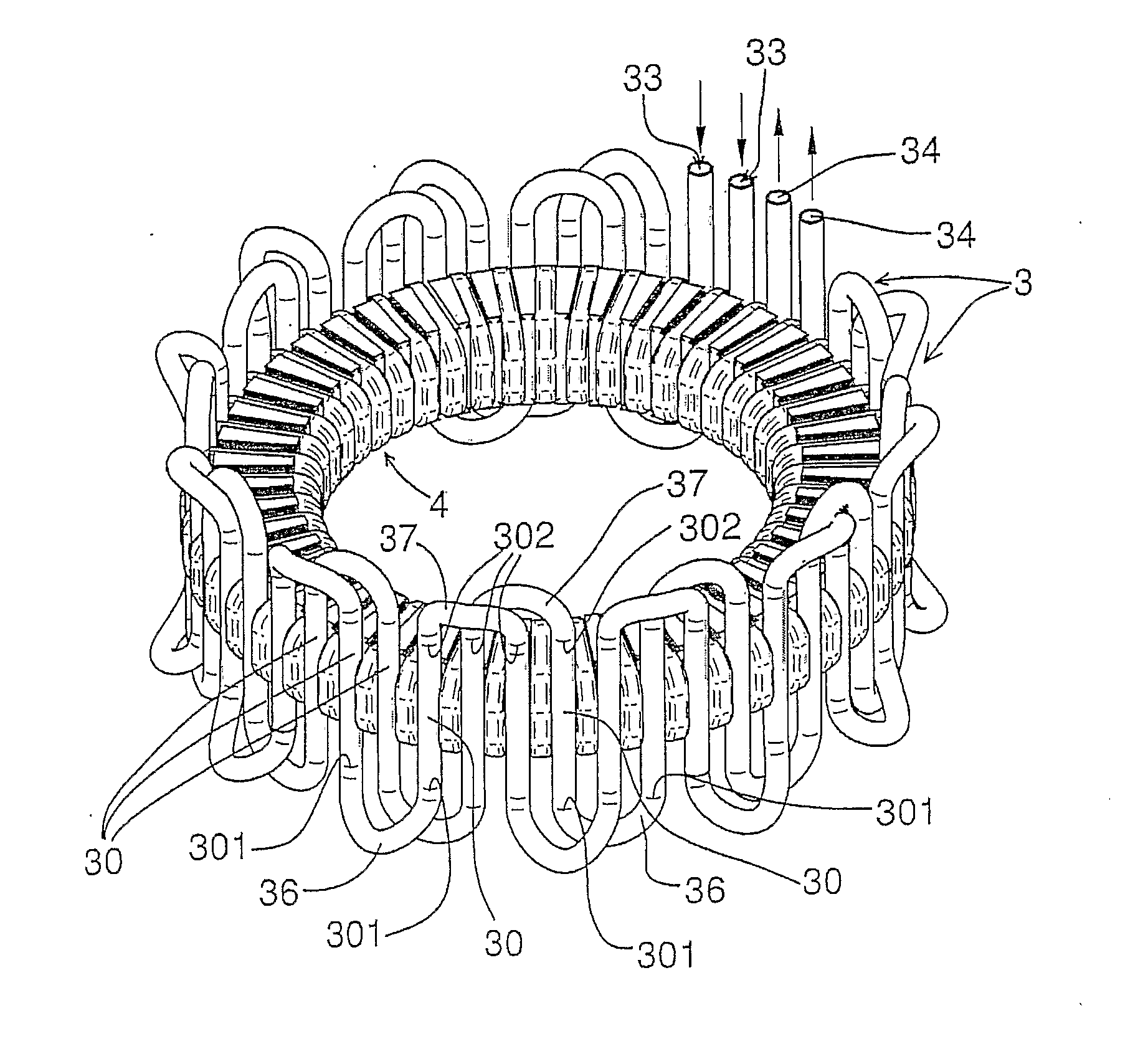
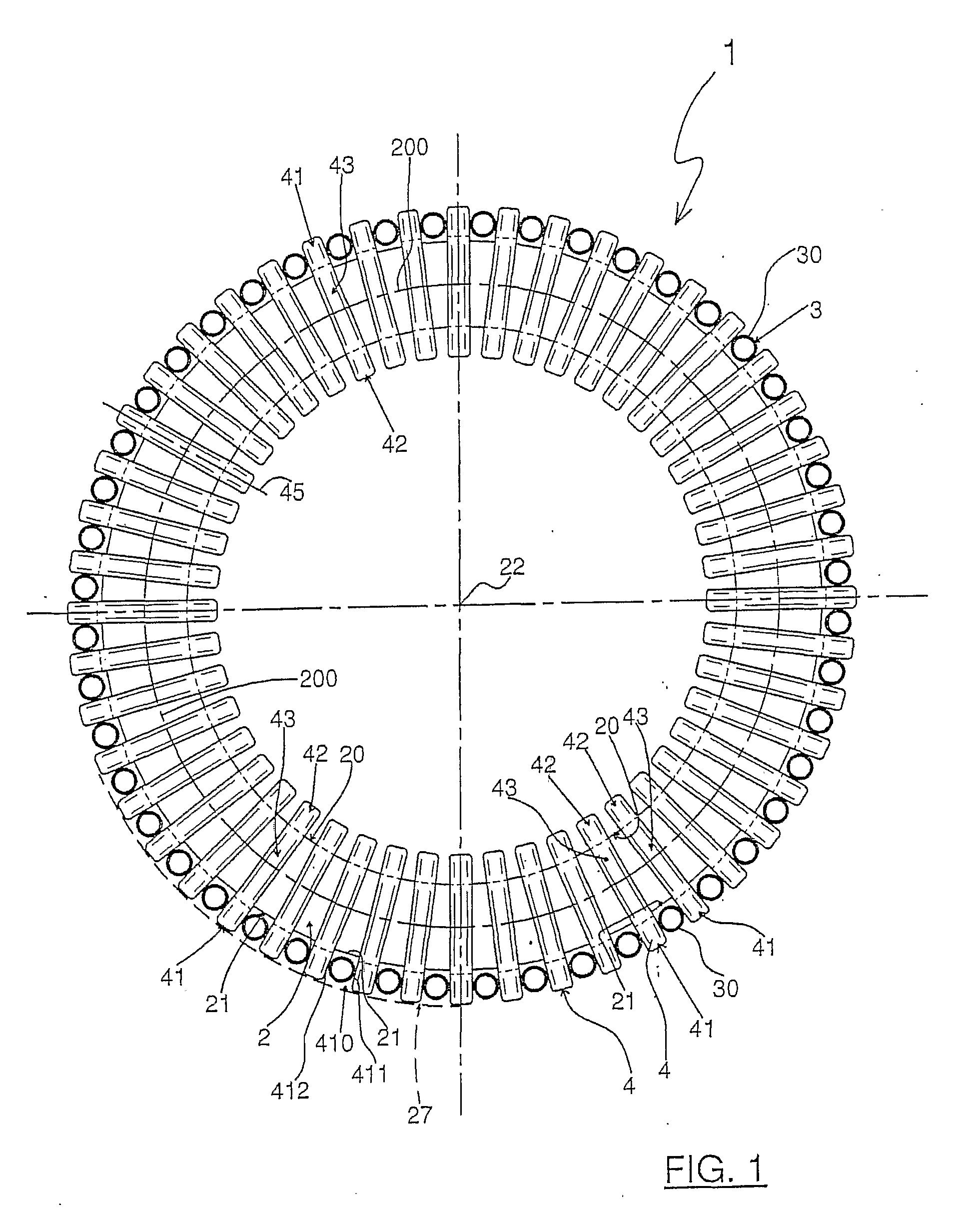
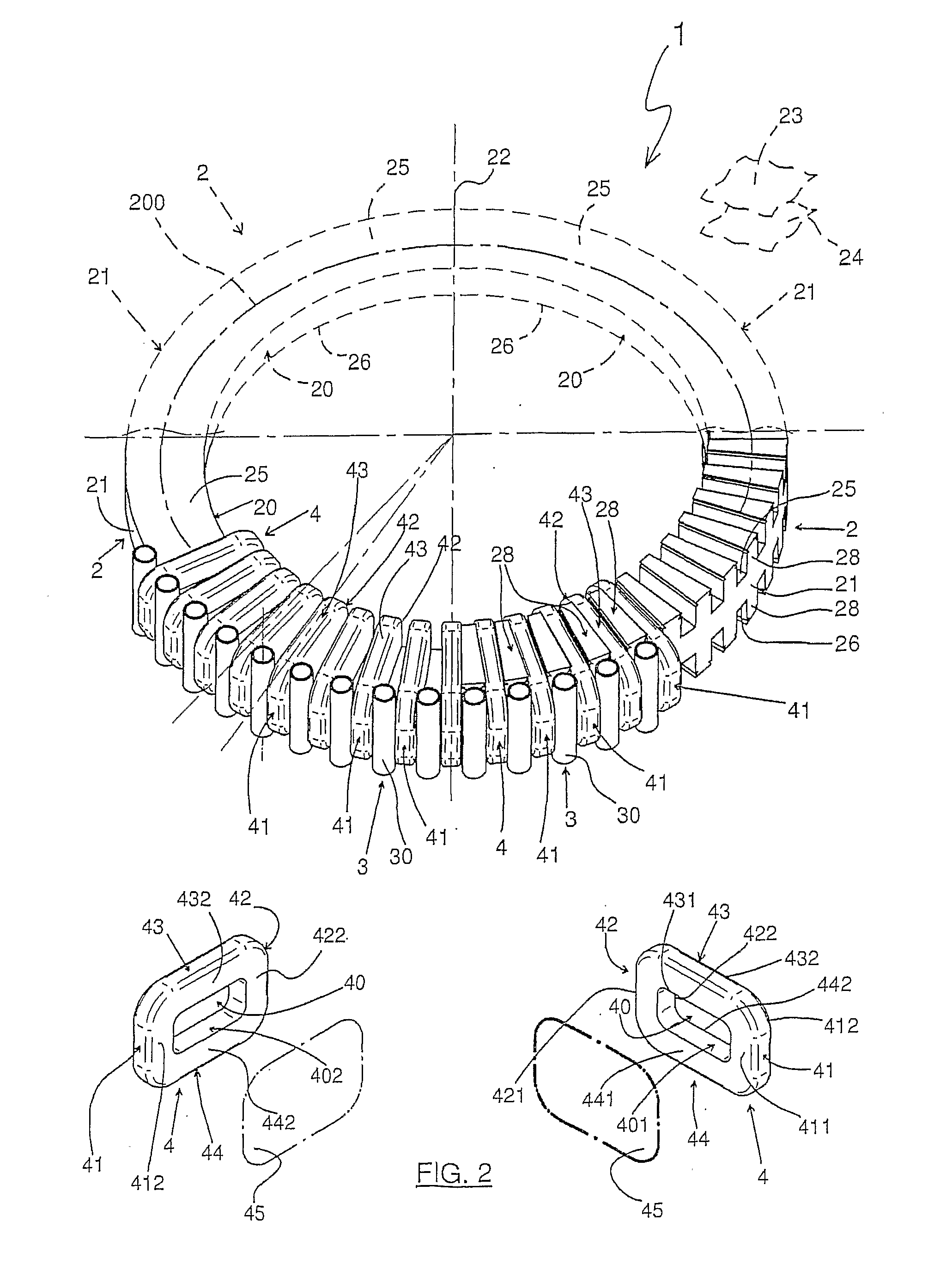
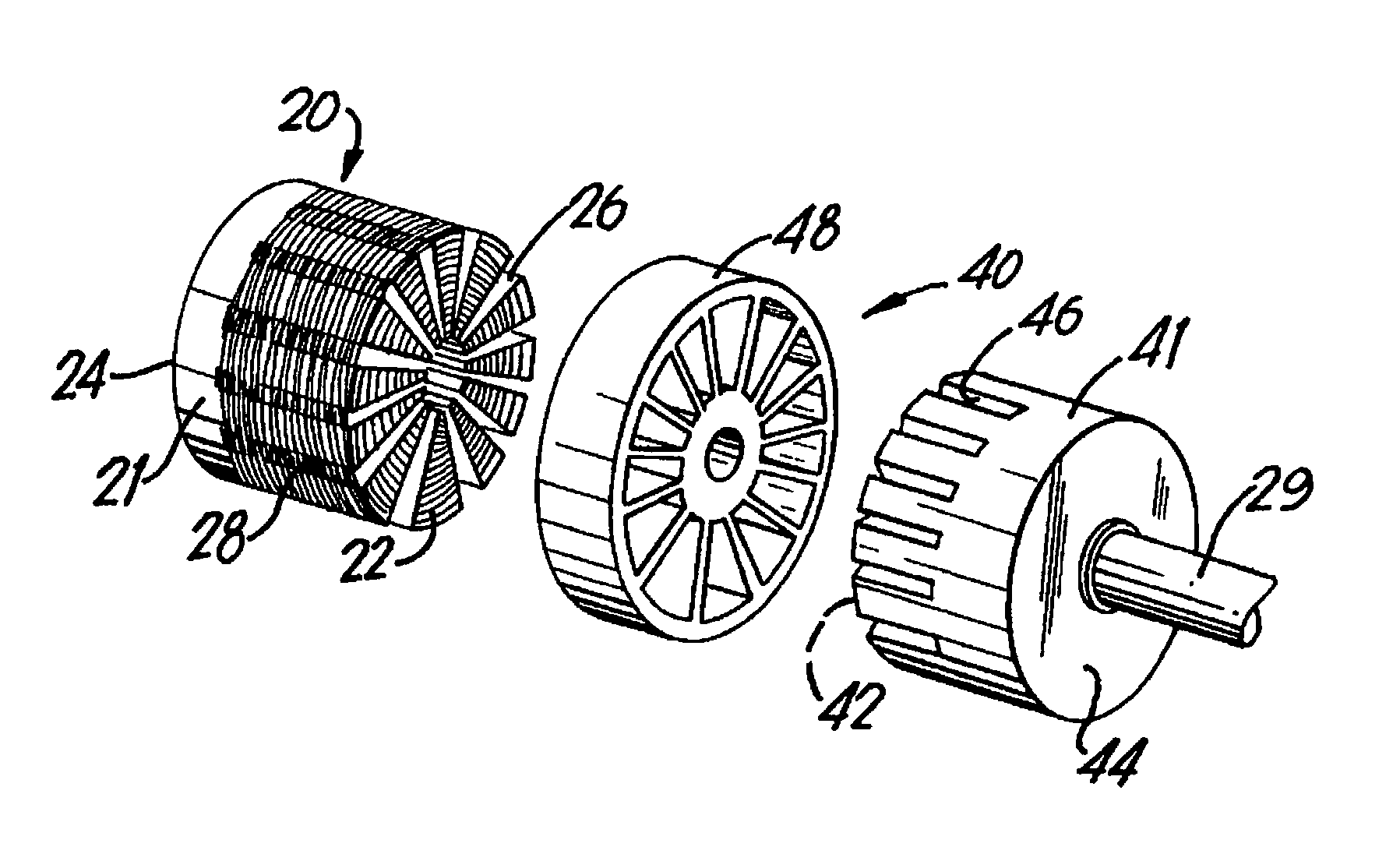
In a stator section (1) of an axial flux electric machine with liquid cooling system, a toroidal core (2) having an inside cylindrical surface (20) and an outside cylindrical surface (21) coaxial with each other along a reference axis (22), is provided along its annular centre line (200) with a plurality of electrical conductor coils (4) spaced from each other and each placed around the core (2) with a first face of it (41) lying on the outside cylindrical surface (21), a second face of it (42) lying on the inside cylindrical surface (20) and a third and fourth face of it (43, 44) lying transversally to the first and second faces (41, 42). Each cooling duct section (30) of a plurality of cooling duct sections (30) produces a movement of the liquid coolant from a first base surface (25) of the core (2) to a second base surface (26) of the core (2) and is located between the two first faces (41) of two consecutive coils (4) or between the two second faces (42) of two consecutive coils (4). At least the first or the second face (41, 42) of any one coil (4) of the plurality of coils (4) is adjacent to and in contact with at least one respective cooling duct section (30) of the plurality of cooling duct sections (30).
Owner:LUCCHI FABIO
Method of constructing a unitary amorphous metal component for an electric machine
ActiveUS7144468B2Easy to manufactureShorten production timeLamination ancillary operationsLaminationElectric machineEngineering
A unitary amorphous metal magnetic component for an axial flux electric machine such as a motor or generator is formed from a spirally wound annular cylinder of ferromagnetic amorphous metal strips. The cylinder is adhesively bonded and provided with a plurality of slots formed in one of the annular faces of the cylinder and extending from the inner diameter to the outer diameter of the cylinder. The component is preferably employed in constructing a high efficiency, axial flux electric motor. When operated at an excitation frequency “f” to a peak induction level Bmax the unitary amorphous metal magnetic component has a core-loss less than “L” wherein L is given by the formula L=0.0074f(Bmax)1.3+0.000282f1.5(Bmax)2.4, the core loss, excitation frequency and peak induction level being measured in watts per kilogram, hertz, and teslas, respectively.
Owner:METGLAS INC
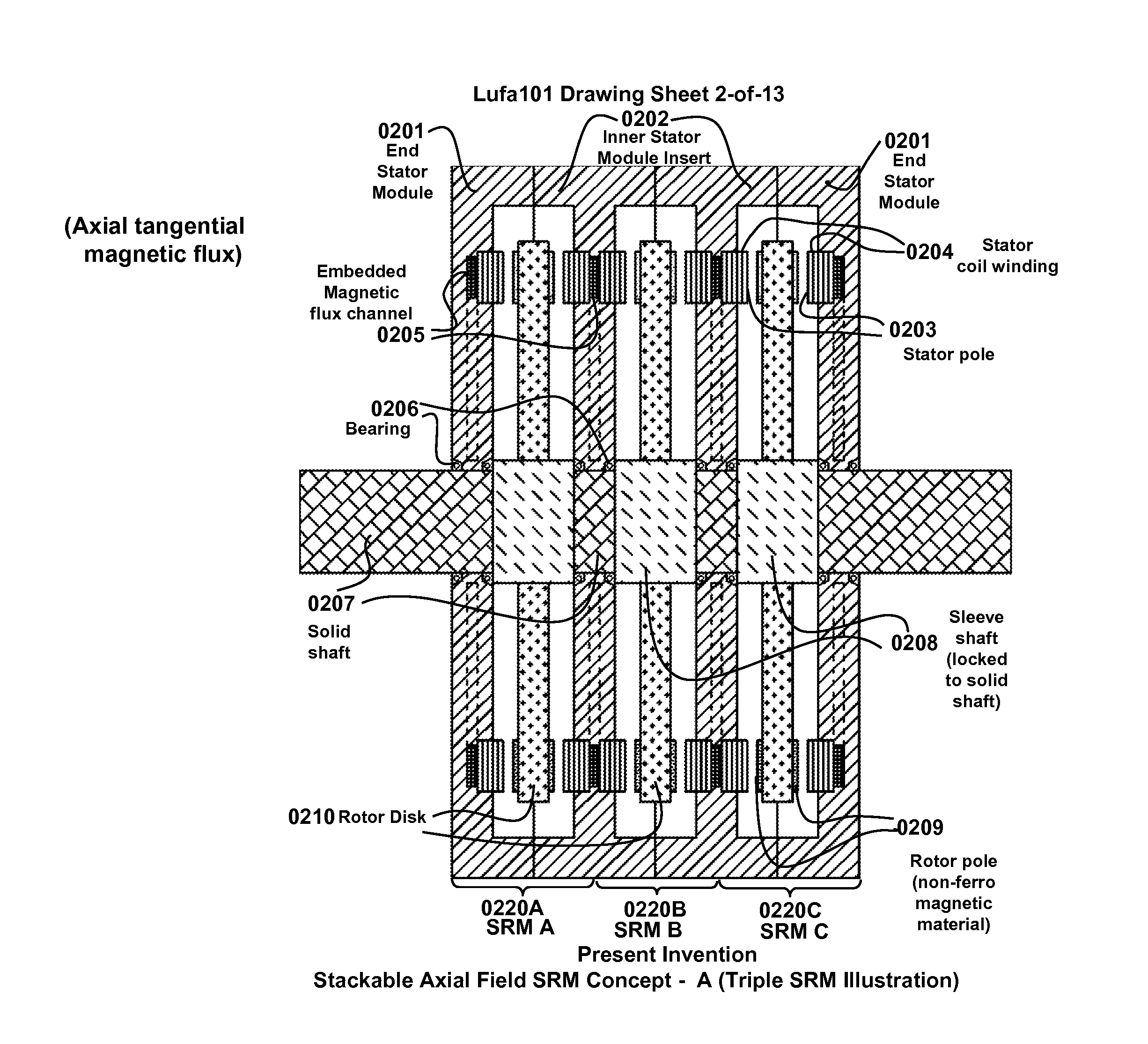
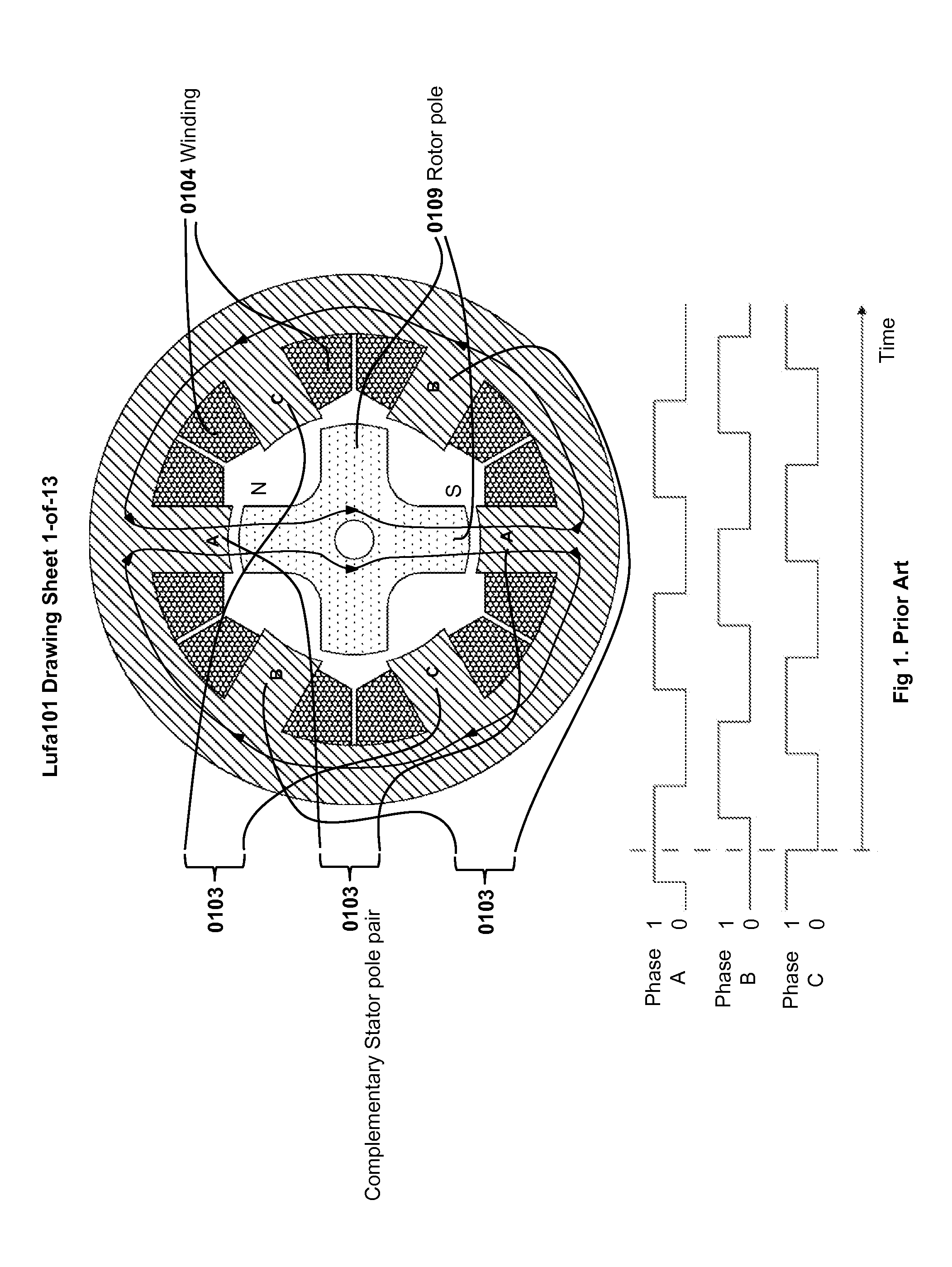
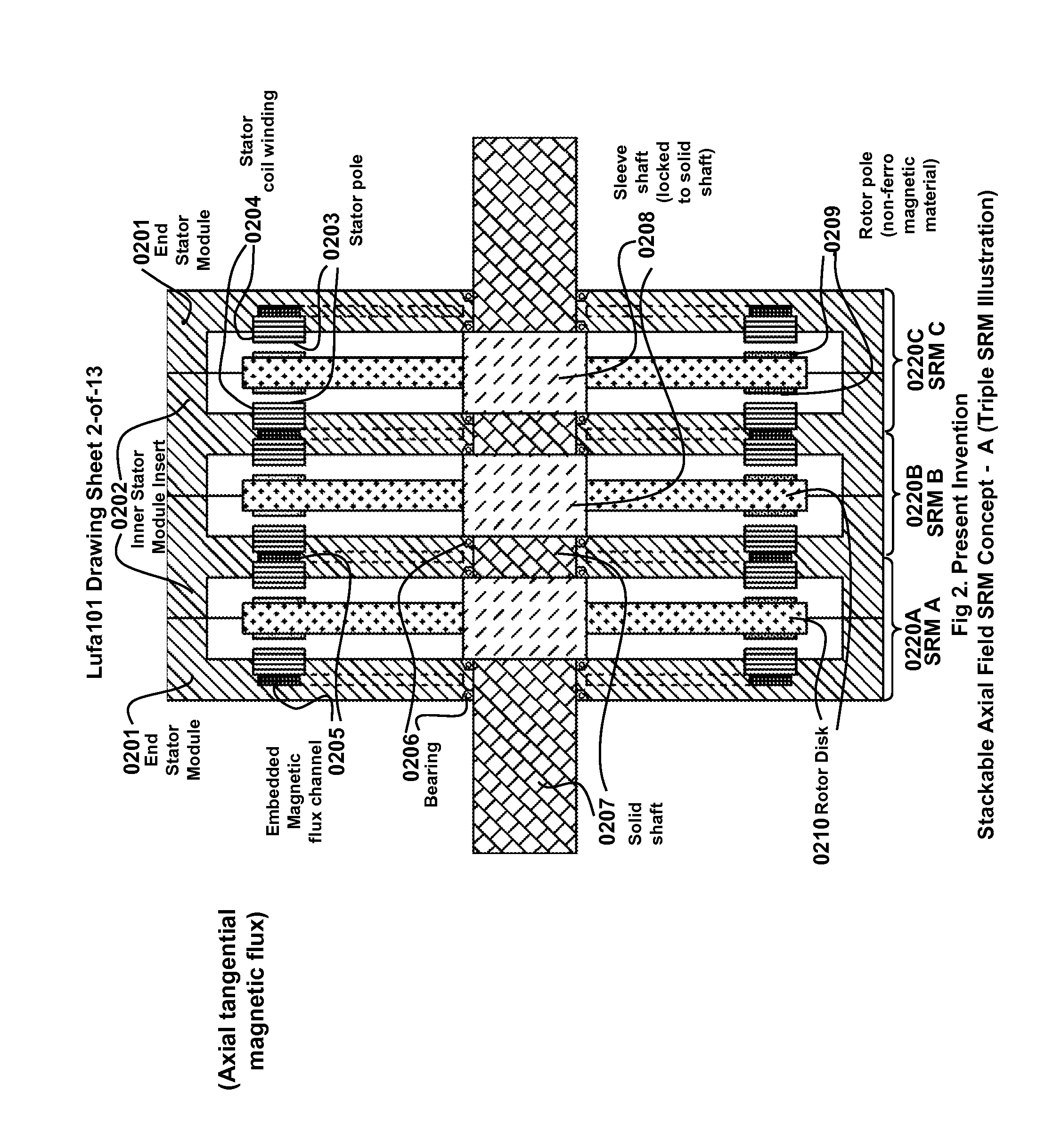
Multi-unit Modular Stackable Switched Reluctance Motor System with Parallely Excited Low Reluctance Circumferential Magnetic Flux loops for High Torque Density Generation
InactiveUS20120001502A1Increased torque densityLow costMagnetic circuitSynchronous machinesFlux loopTransformer
The present invention is a apparatus of multi-unit modular stackable switched reluctance motor system with parallely excited low reluctance circumferential magnetic flux loops for high torque density generation. For maximized benefits and advanced motor features, the present invention takes full combined advantages of both SRM architecture and “Axial Flux” architecture by applying “Axial Flux” architecture into SRM design without using any permanent magnet, by modularizing and stacking the “Axial Flux” SRM design for easy configuration and customization to satisfy various drive torque requirements and broad applications, and by incorporating an en energy recovery transformer for minimizing switching circuitry thus further lowering the cost and further increasing the reliability and robustness. Unlike prior arts, the present invention does not use any permanent magnet and this “Axial Flux” SRM system is modularized and stackable with many benefits.
Owner:LUSTONE TECH
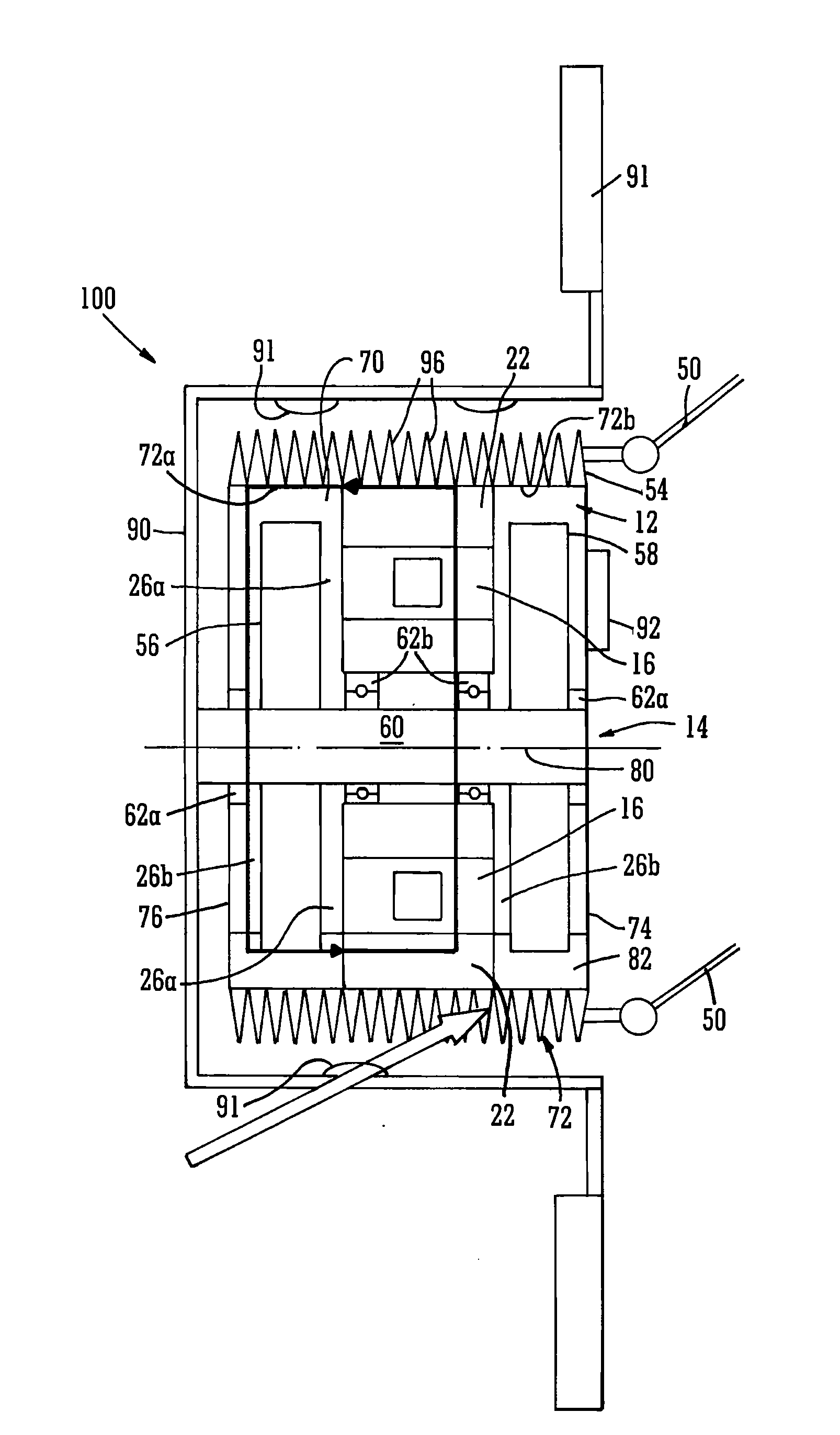
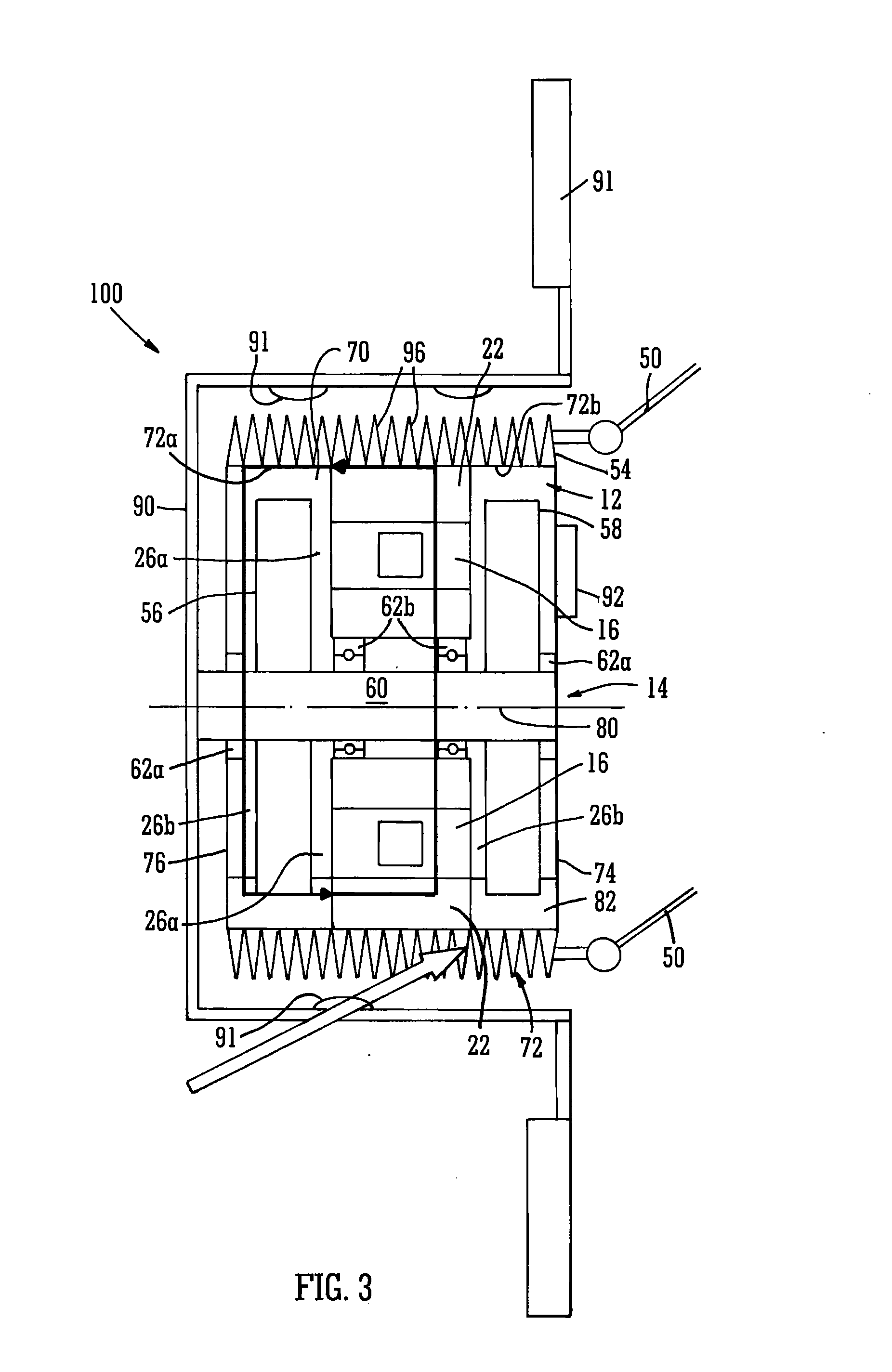
Wheel-hub motor cooling
InactiveUS20130187492A1Improve cooling effectMechanical energy handlingCooling/ventillation arrangementAir movementEngineering
A wheel-hub motor (100) comprises a rotor (14) having permanent magnets, although other field generation means are available, and a stator (12). The stator has coils (22) wound on stator bars (16) for interaction with the magnetic field of the rotor across an air gap (26a,b) defined between them. The stator (12) forms a housing of a chamber (70) containing refrigerant (82). The stator housing has heat dissipating fins (96) accessible by the open environment whereby air movement relative to the housing caused at least by rotation of the rotor absorbs heat from the fins. The motor may be an axial flux machine, the coils being wound on bars that are disposed circumferentially spaced around a rotation axis (80) of the rotor. The wheel of the vehicle is mounted directly on the rotor housing.
Owner:YASA MOTORS
Axial flux alternator with air gap maintaining arrangement
InactiveUS8178992B1Large magnetic attractionSmooth movementMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsAlternatorEngineering
Axial flux alternator for a wind turbine arrangement includes at least one magnetic disk including magnets and at least one coil disk including electromagnetic assemblies. One or both disks are mounted to wind turbines such that adjacent disks rotate in opposite directions, or such that the magnets of a magnetic disk move relative to the electromagnetic assemblies of an adjacent coil disk which may move or be stationary, or vice versa. Between adjacent disks, rolling elements on one disk roll, slide or move on or against the surface of the opposite disk in order to fix and maintain air gaps between the magnets on a magnetic disk and magnetic cores of the electromagnetic assemblies on the coil disk, and thus enable continued motion and use of the alternator.
Owner:MELLER MOSHE
Axial-flux electric machine
InactiveUS20120212085A1Mechanical energy handlingCooling/ventillation arrangementElectric machineConductor Coil
An axial-flux electric motor includes a stator having a plurality of stator windings and a plurality of stator pole-pairs, a first rotor configured to magnetically interact with the stator in an axial direction, the first rotor is positioned on one side of the stator, having a plurality of permanent magnets embedded thereon with a plurality of rotor pole-pairs, a second rotor configured to magnetically interact with the stator in the axial direction, the second rotor is position on another side of the stator, having a plurality of permanent magnets embedded thereon with a plurality of rotor pole-pairs, and a plurality of stationary ferromagnetic segments, positioned between the stator and the first rotor and between the stator and the second rotor, the ferromagnetic segments are adapted to modulate magnetic field of the permanent magnets in the axial direction.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Axial flux electrical machine
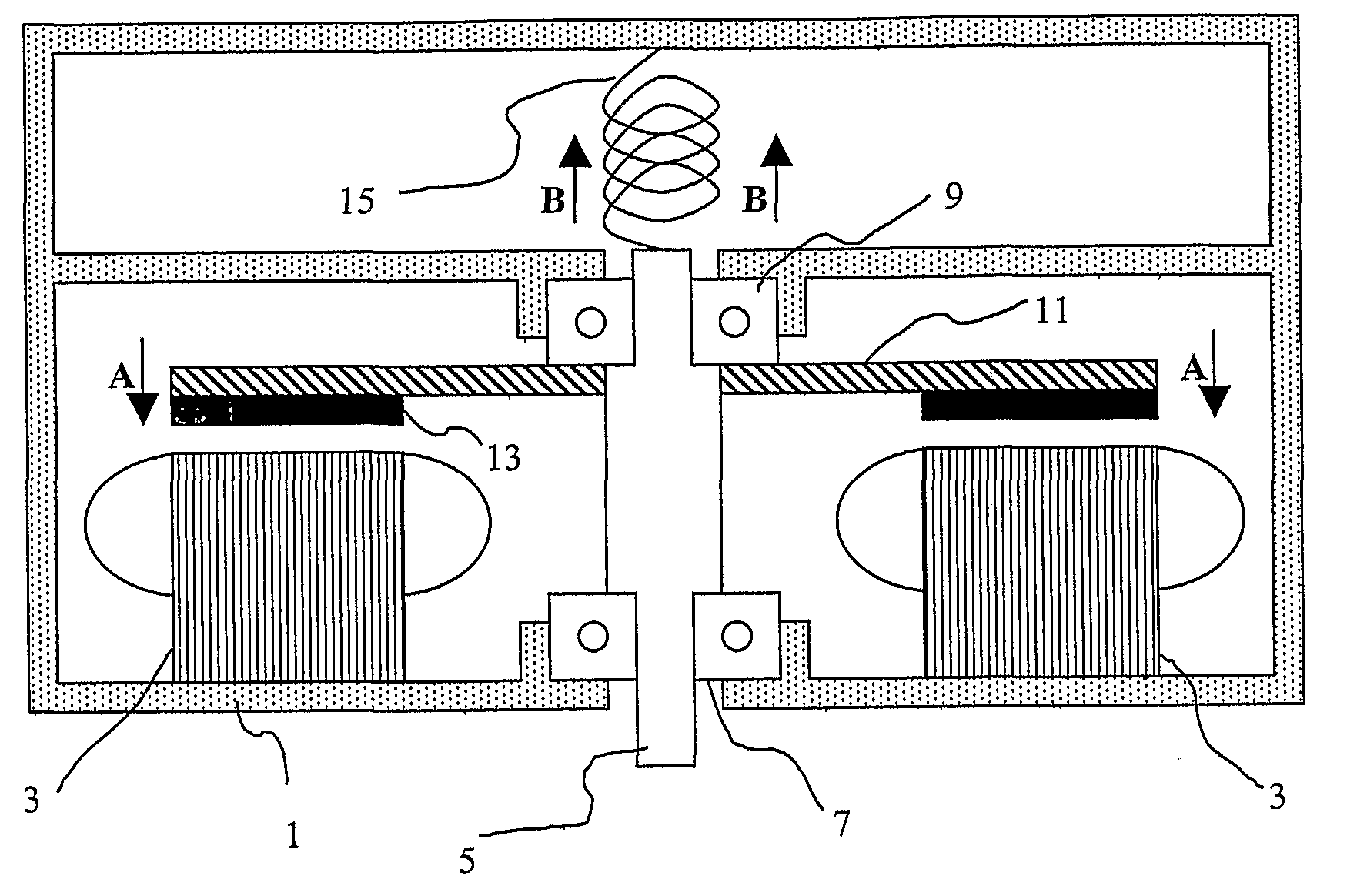
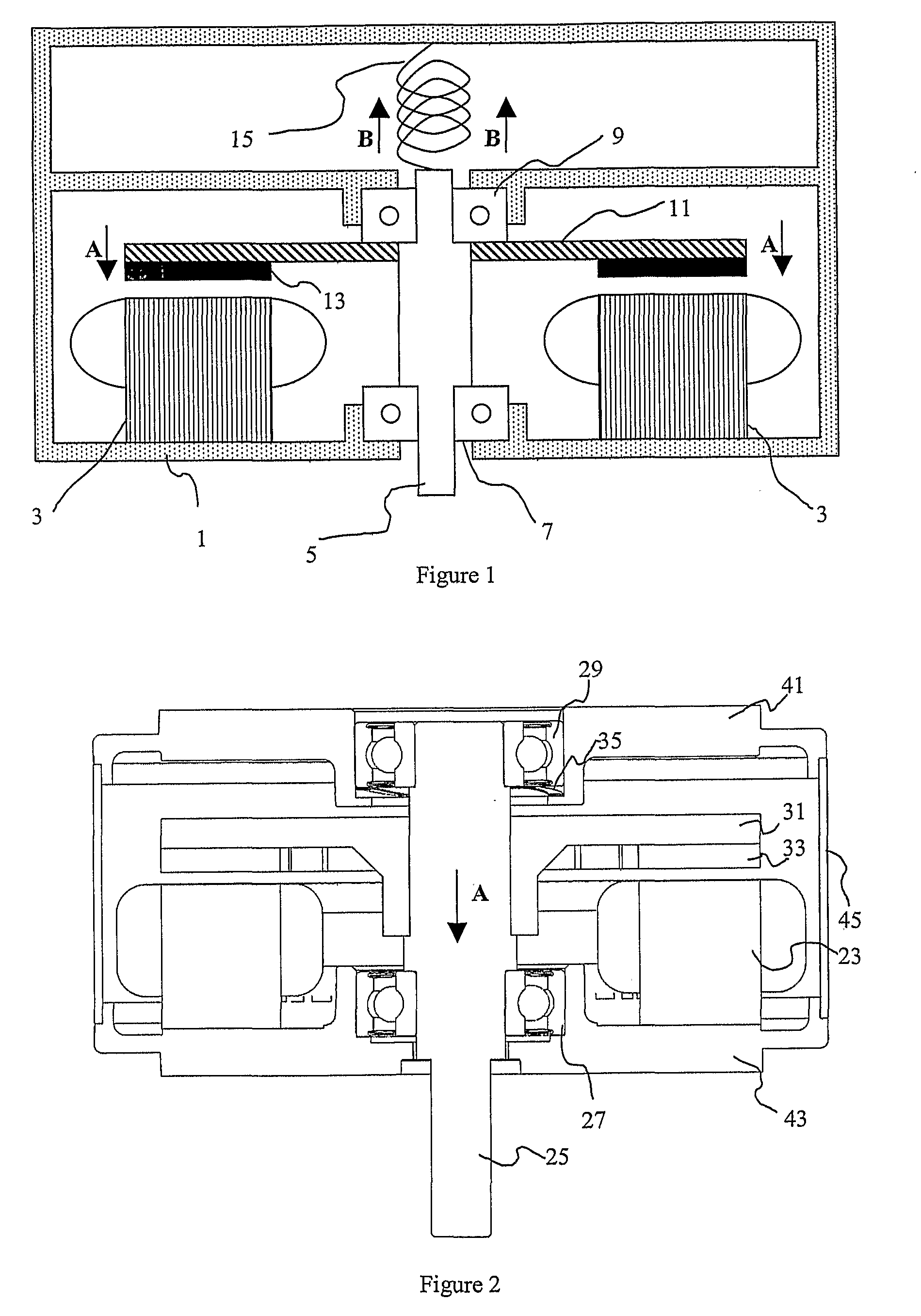
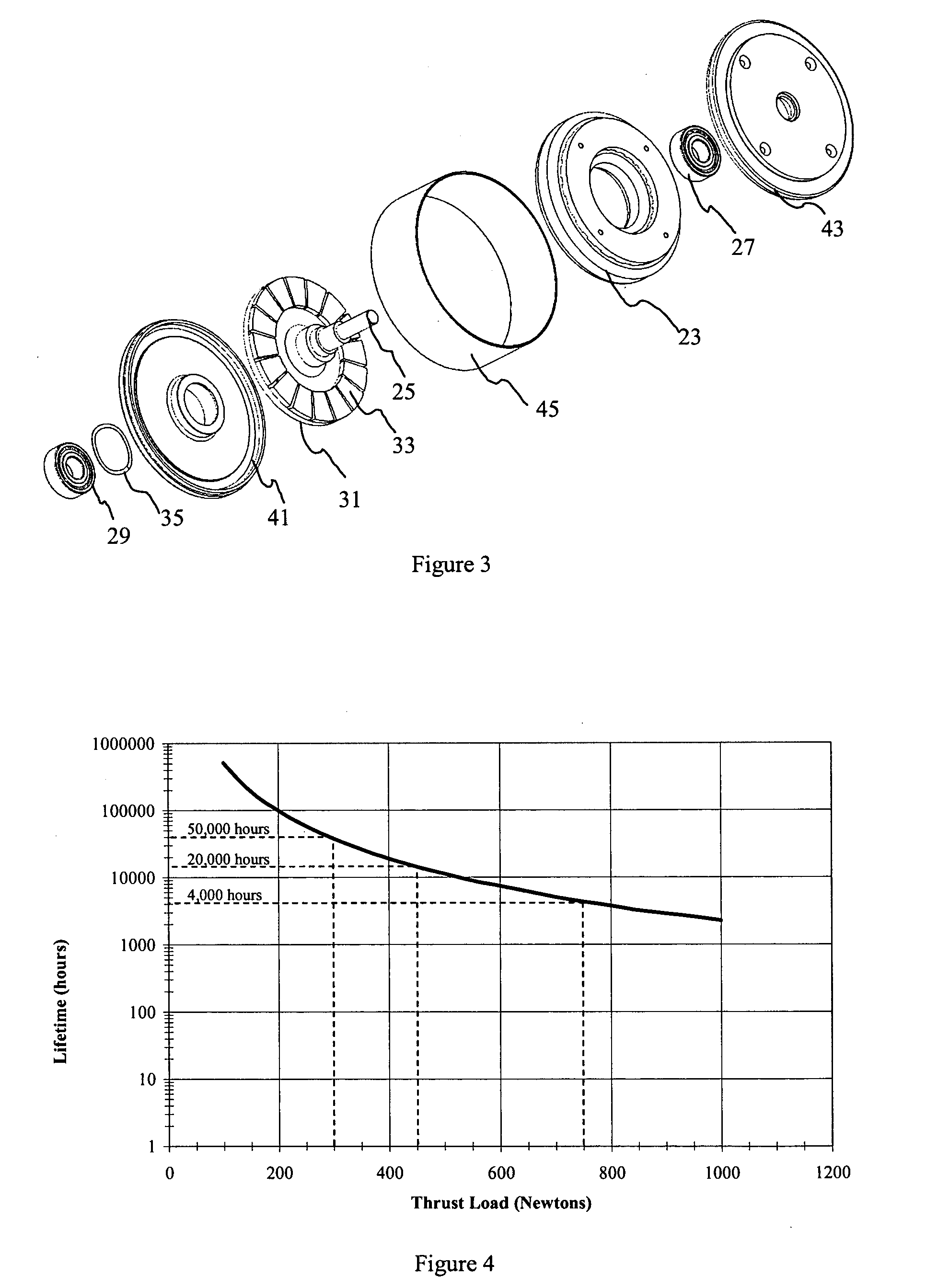
ActiveUS20100164313A1Reduce loadExtended service lifeRolling contact bearingsShaftsAxial thrustAxial flux
An axial flux electrical machine including a housing, a stator located within the housing, a rotatable shaft carried by the housing by means of at least a main bearing, and a rotor fixed to the shaft within the housing. Magnetic attractive forces between the rotor and the stator produce an axial thrust on the main bearing and a biasing means (preferably in the form of a spring) is arranged to urge the shaft in a direction opposite to the axial thrust so as to reduce the net load on the main bearing. This reduction in net load on the main bearing increases bearing life and improves motor efficiency.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AUSTRALIA PTY LTD
Axial flux permanent magnet synchronous generator and motor
InactiveUS20130049512A1Improve power generation efficiencyIncrease the output voltageMagnetic circuitSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsPermanent magnet synchronous generatorConductor Coil
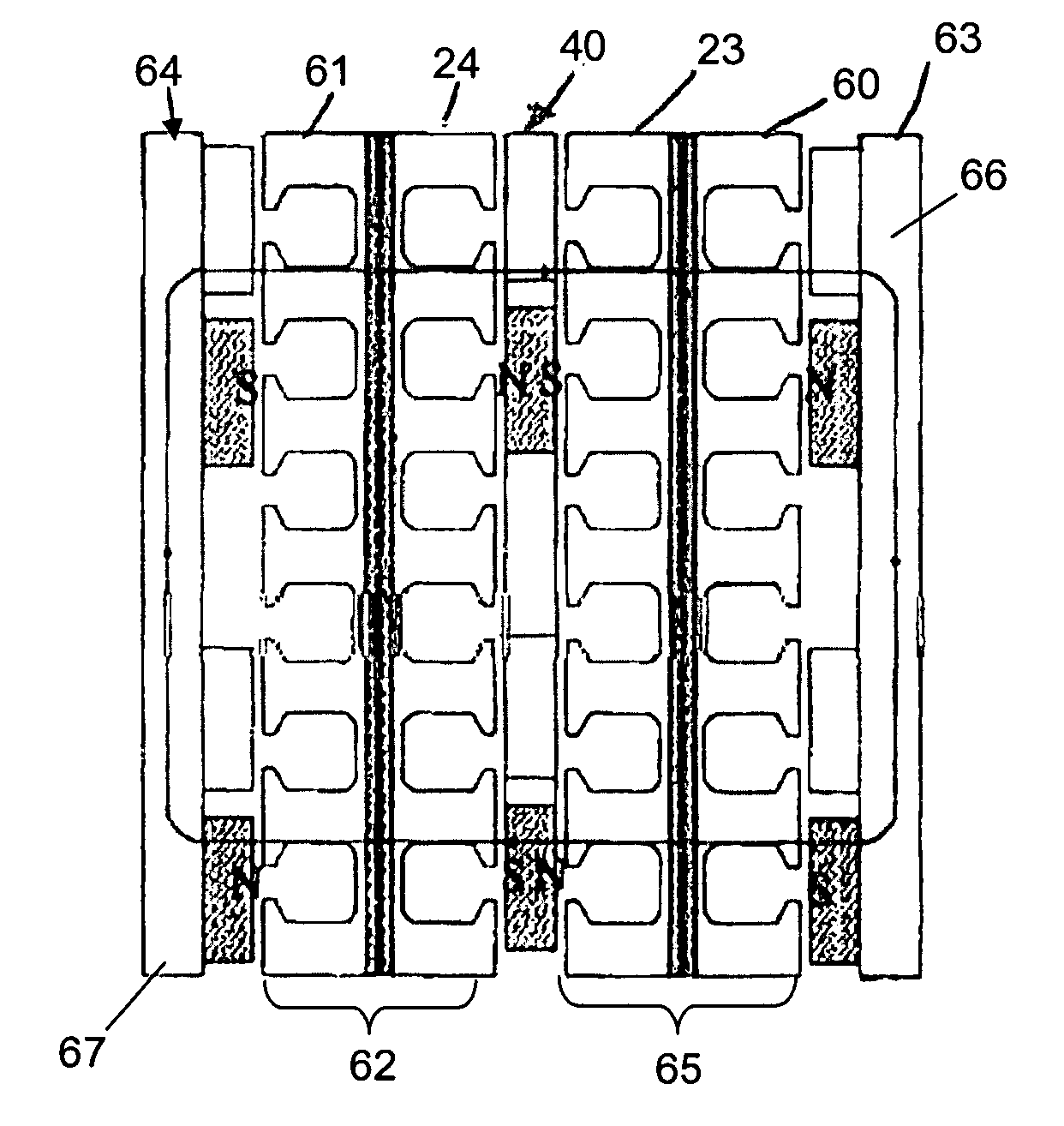
An axial flux synchronous generator for wind turbine generators is provided including a shaft coupled to receive power with a power generating apparatus for the wind turbine; a rotor coupled rotatably to the shaft and having upper and lower disk-like faces affixed with a plurality of skewed permanent magnets having north-south (N-S) pole pairs and distantly arranged; an upper stator and a lower stator both having a plurality of slots formed similar to the skewed permanent magnets for taking windings of a coil, the upper stator being displaced relative to the lower stator by an electric angle in the range of 25˜30°; an upper housing and a lower housing for housing the rotor, the upper stator and the lower stator together; and a hub housing for fastening the upper housing and the lower housing to maintain constant gaps between the rotor and the upper stator and the lower stator.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND OF KYUNGNAM UNIV
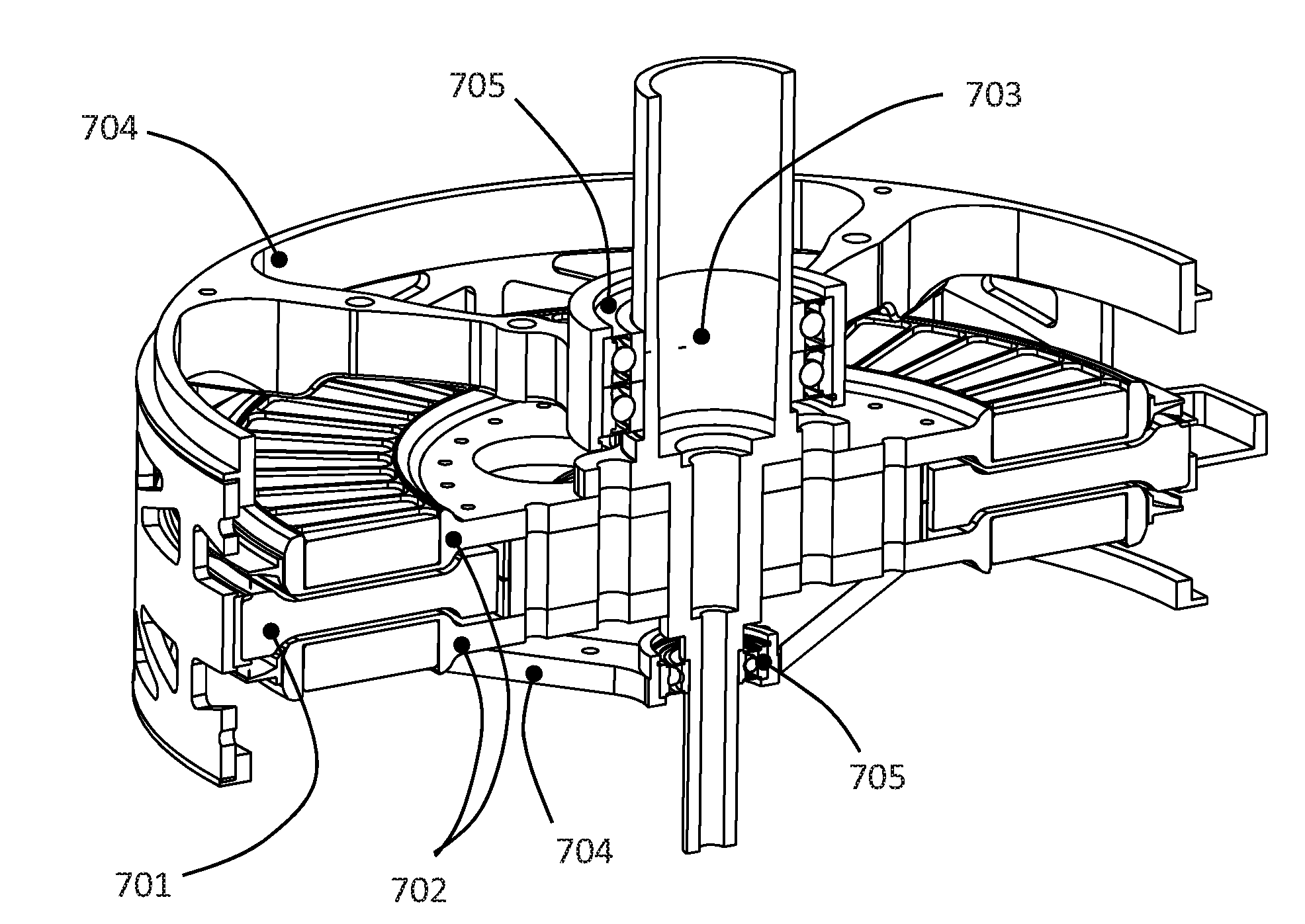
Disc type axial-flux motor with oil-immersed circularly cooled stator and segmented armatures
InactiveCN107196480AImprove power densityIncreased torque densityStructural associationCooling/ventillation arrangementSurface mountingTorque density
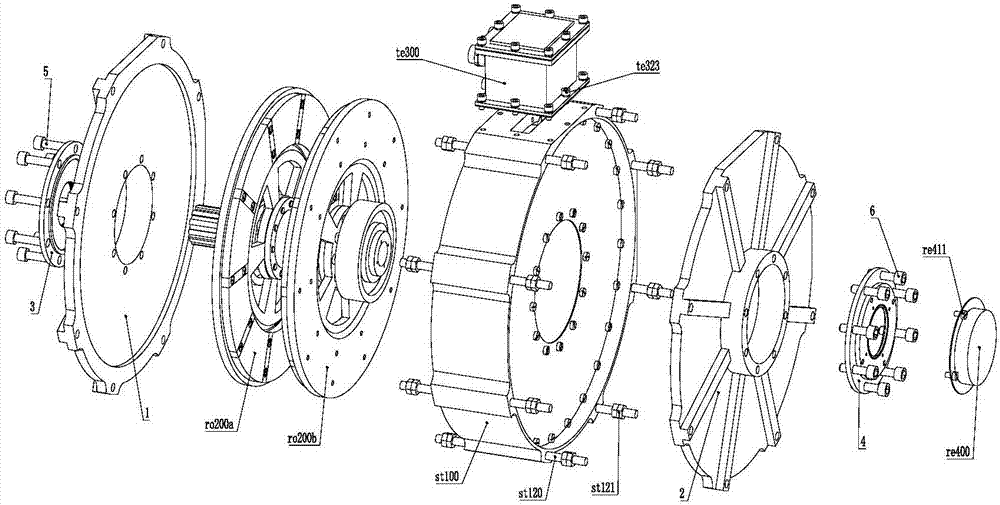
The invention discloses a disc type axial-flux motor with an oil-immersed circularly cooled stator and segmented armatures. A framework with double rotors and single stator is adopted; and a main shaft is designed. Each rotor adopts a magnetic steel surface-mounting type structure; and a whole stator oil-immersion circulation cooling and heat dissipation mode is adopted for temperature rise management. The disc type axial-flux motor with the oil-immersed circularly cooled stator and the segmented armatures comprises a stator assembly, a driving end rotor assembly, a non-driving end rotor assembly, a wire outlet box assembly and a rotary transformer assembly. An engine base is provided with an oil inlet joint and an oil outlet joint, both of which can carry out oil-immersion circulation cooling for the stator and have the advantages such as high convective heat transfer efficiency, big heat exchange area and fast heat transfer speed. The disc type motor adopting such a heat dissipation structure can achieve higher power density and higher torque density, is more compact in structure and is suitable for the occasions with strict requirements on the motor mounting space in future.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Asymmetric machines
ActiveUS20150244219A1Conveniently manufacturedImprove connectivityMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsPhysicsAxial flux
A rotor for an axial flux permanent magnet machine is described. The machine has a stator comprising a stator housing enclosing a set of coils wound on stator bars or teeth and disposed circumferentially at intervals about an axis on the machine, and a rotor bearing a set of permanent magnets and mounted for rotation about the said axis. The rotor and stator are spaced apart along said axis to define a gap therebetween in which magnet flux in the machine is generally in an axial direction. The magnets are disposed circumferentially around said rotor and define a plurality, n, of matching sets of magnets. Each set of magnets includes a plurality of magnets, wherein said n sets of magnets on said rotor have n-fold rotational symmetry. Within a said set, the magnets have different shapes and / or relative circumferential spacings of adjacent magnets within the set of magnets are irregular.
Owner:YASA LIMITED
Vertical axis wind turbine and generator therefore
A vertical wind turbine is provided that includes a support base defined about an axis, a bearing assembly, a drive shaft having a proximal end and an opposing distal end, and a multistage axial flux generator. The bearing assembly includes a fixed ring and a rotating ring, wherein the fixed ring is coupled to the support base. The drive shaft is coupled to the rotating ring of the bearing assembly, and a plurality of sails are coupled to the drive shaft. The multistage axial flux generator includes a rotor assembly coupled to the drive shaft and a stator assembly coupled to the support base. The rotor assembly includes a plurality of permanent magnets, and the stator assembly includes a plurality of coils defining at least two voltage output stages. The permanent magnets on the rotor assembly are close-coupled to the coils on the stator assembly.
Owner:GRASSMAN DEREK
Electrical machine
InactiveUS20170155291A1Reduce manufacturing costReduced Tolerance RequirementsWindingsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machineEngineering
An electrical machine, in particular an axial flux motor, with a rotor, mounted rotatably about a machine axis, and with a stator. The stator has a sintered support structure and an insert connected thereto, which forms at least partially a pole shoe, and which comprises a lamination stack.
Owner:BAUMULLER NURNBERG GMBH
Winding insulation arrangement for axial flux machines
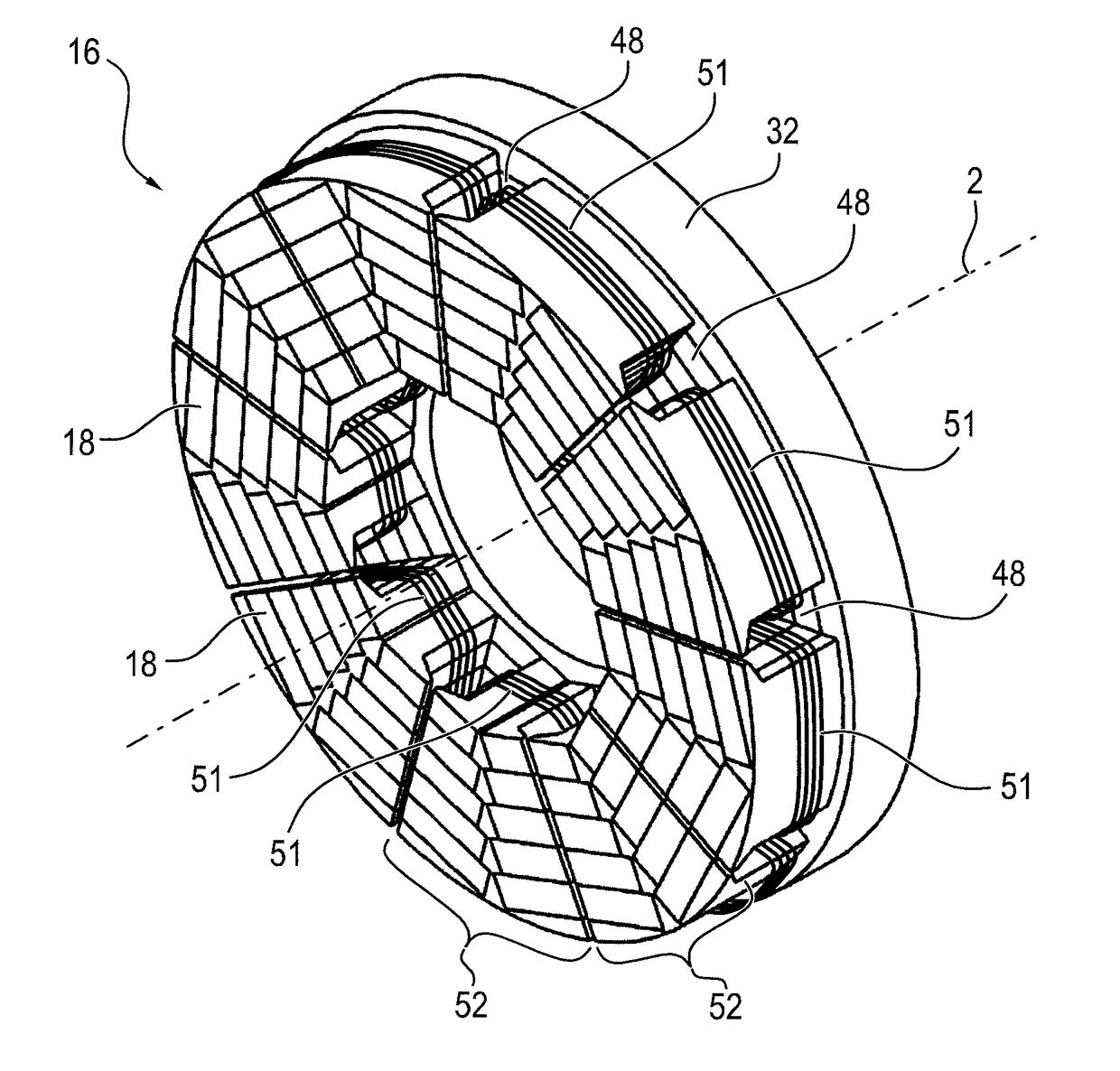
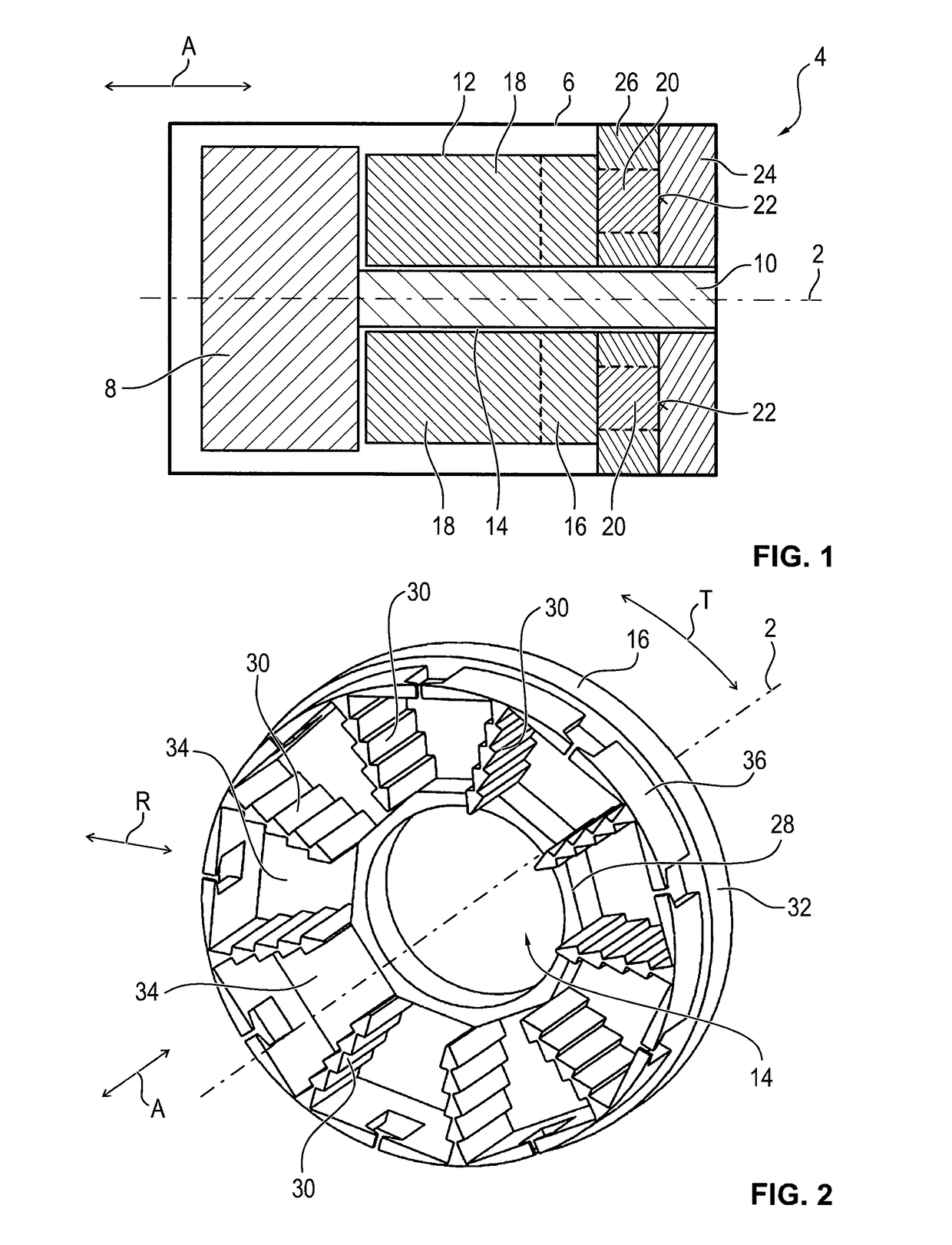
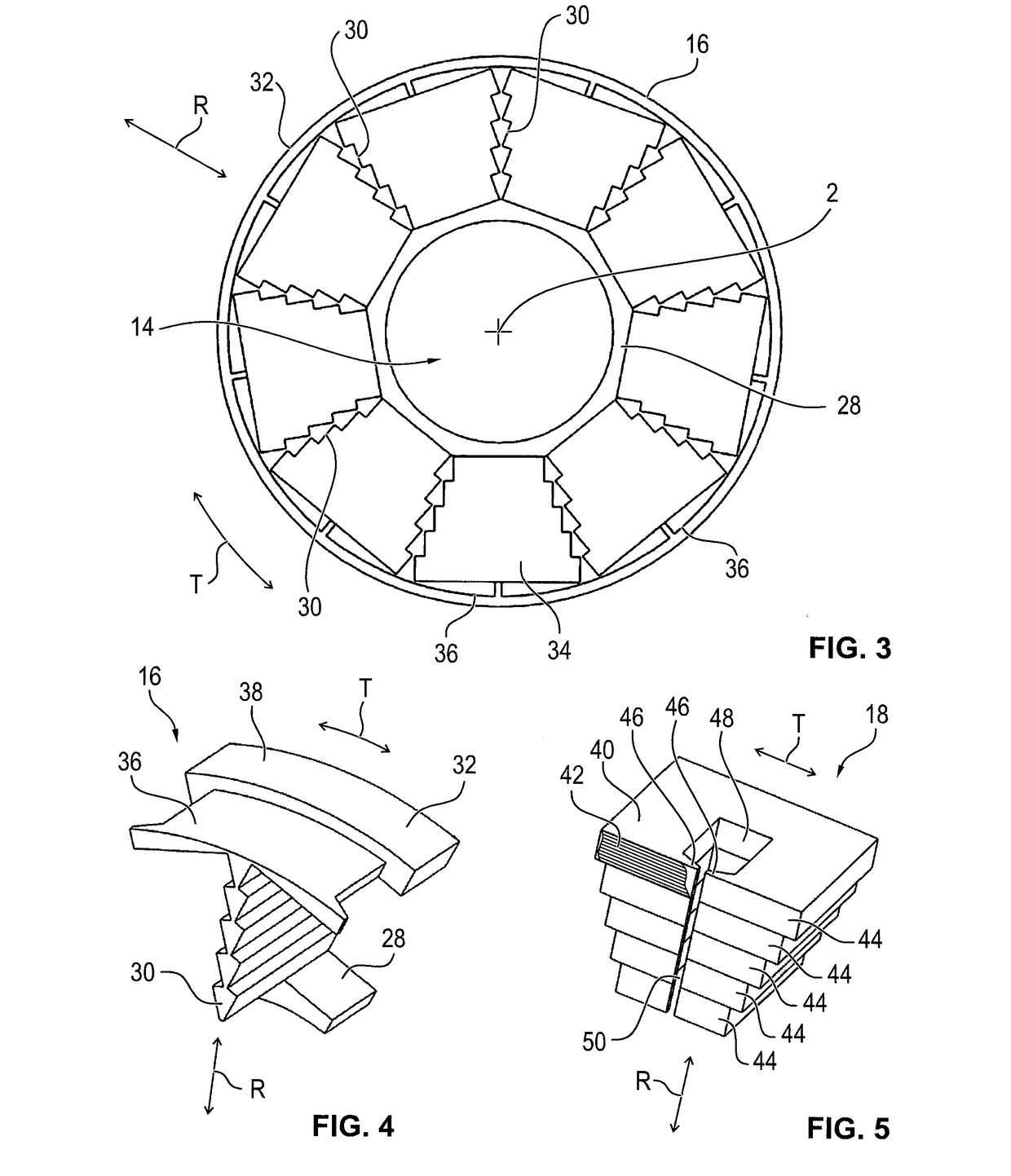
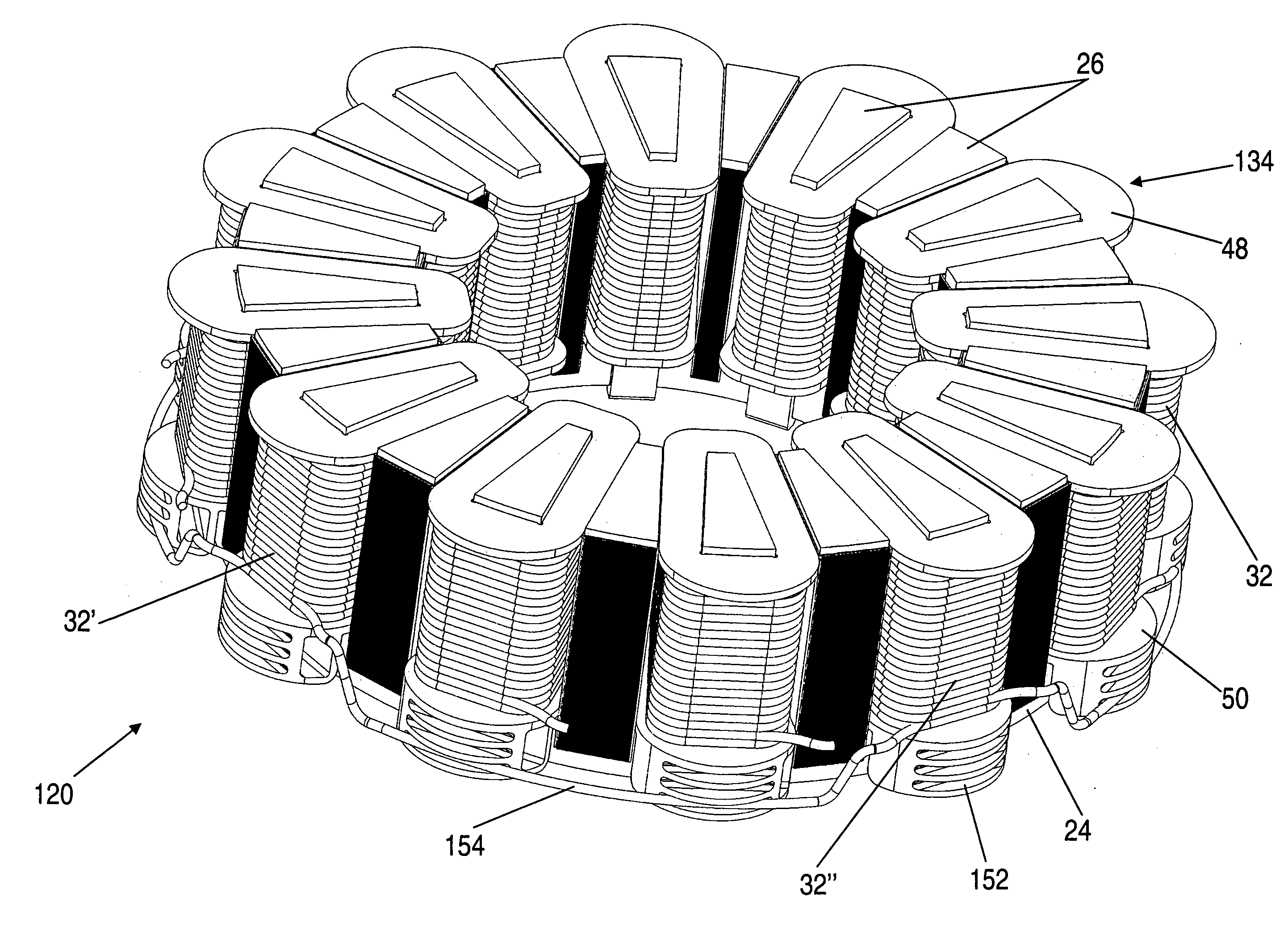
InactiveUS20110221297A1Reduce resistanceImprove machine efficiencyWindings insulation shape/form/constructionMagnetic circuitRotational axisAxial flux
A stator 20 for an axial flux machine such as a motor or generator. The stator includes a stator core 32 having a back plane 24 which in use is disposed perpendicularly about a rotational axis of the machine. A plurality of teeth 26 extend axially from the back plane so as to form winding receiving slots 28 between adjacent teeth. The stator also includes an electrical winding 30 including a plurality of coils 32, each coil being located about a tooth of the stator core and being electrically isolated from the stator tooth by means of an insulating former 34 having a shape which closely conforms to the shape of the stator tooth. The coils 32 are interconnected to form the winding 30. A method of constructing a stator is also disclosed.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AUSTRALIA PTY LTD
Axial-flux thin-plate motor
InactiveUS20120126653A1Low costImprove production efficiencyWindings insulation shape/form/constructionMagnetic circuitEngineeringConductor Coil
An axial-flux thin-plate motor is disclosed, which includes: a stator formed of an annular disk of silicon steel and comprising a plurality of teeth formed on one side of the annular disk, a plurality of insulation sleeves, each insulation sleeve having a shape which matches each tooth, and a plurality of coils, each coil formed around outside of each insulation sleeve, the coils connected and grouped to form n-phase windings in accordance with a phase number n of the motor; and a rotor formed of a ferromagnetic disk with a plurality of permanent magnets embedded on one side of the ferromagnetic disk.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com