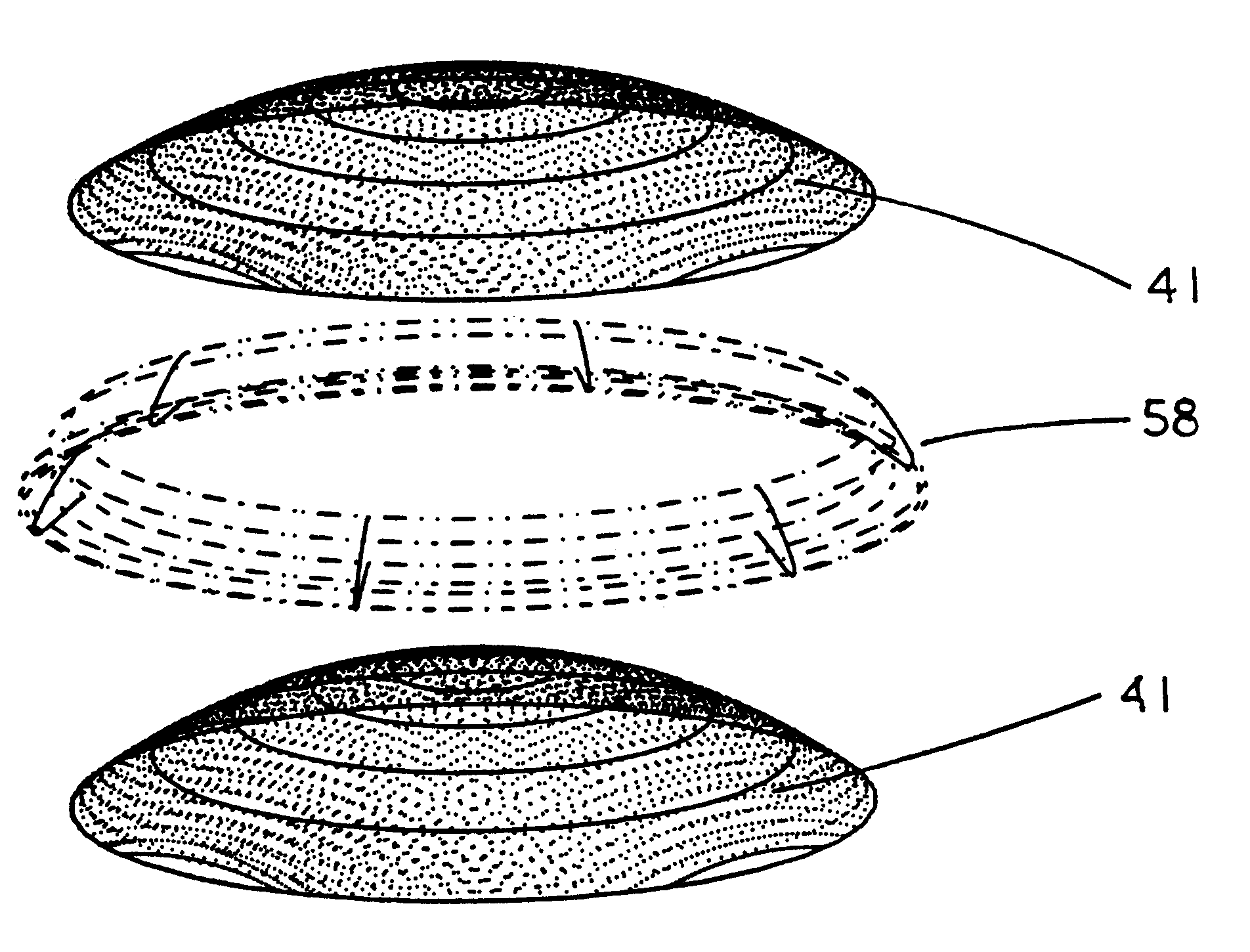
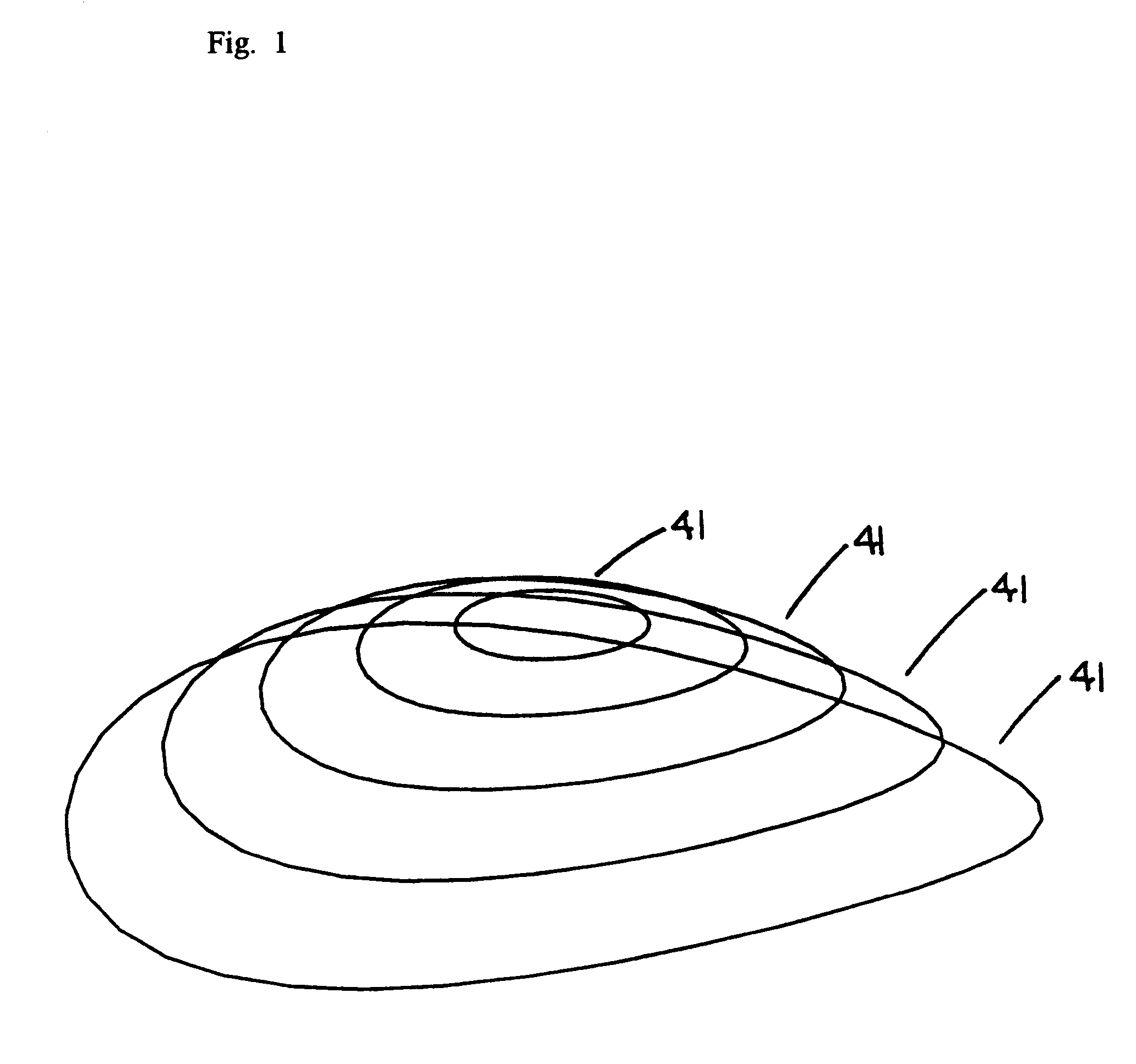
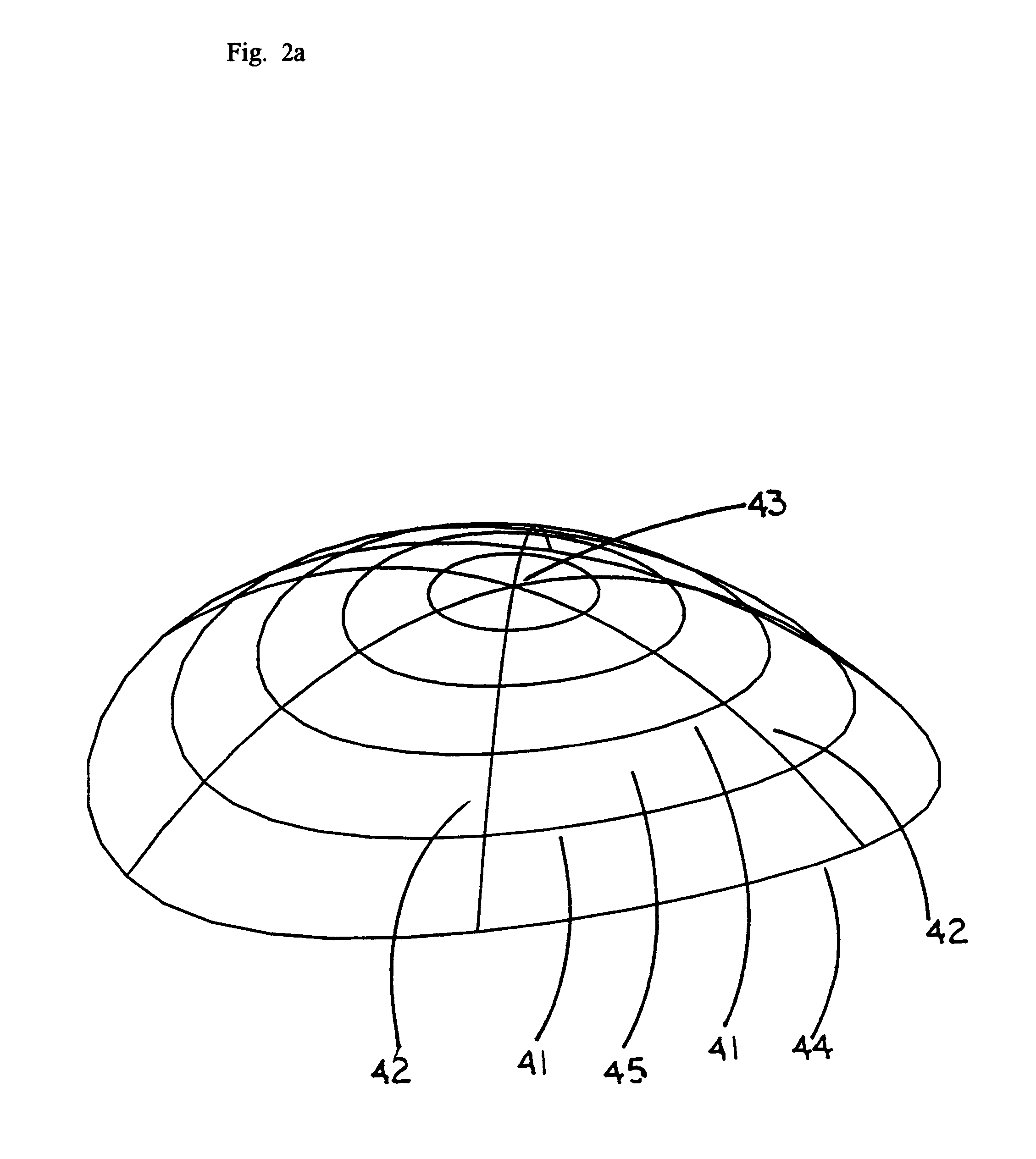
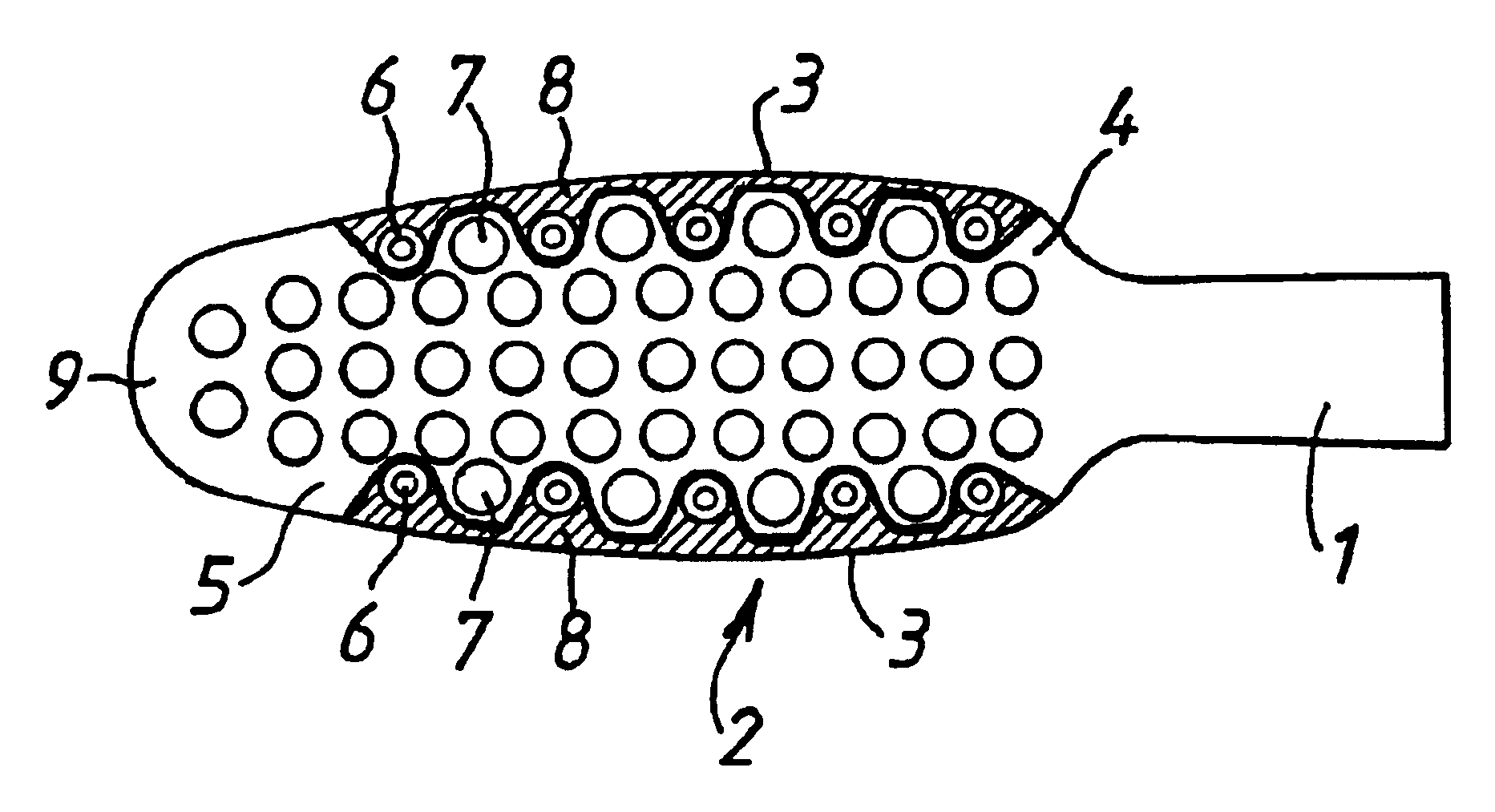
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
884 results about "Rotational symmetry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
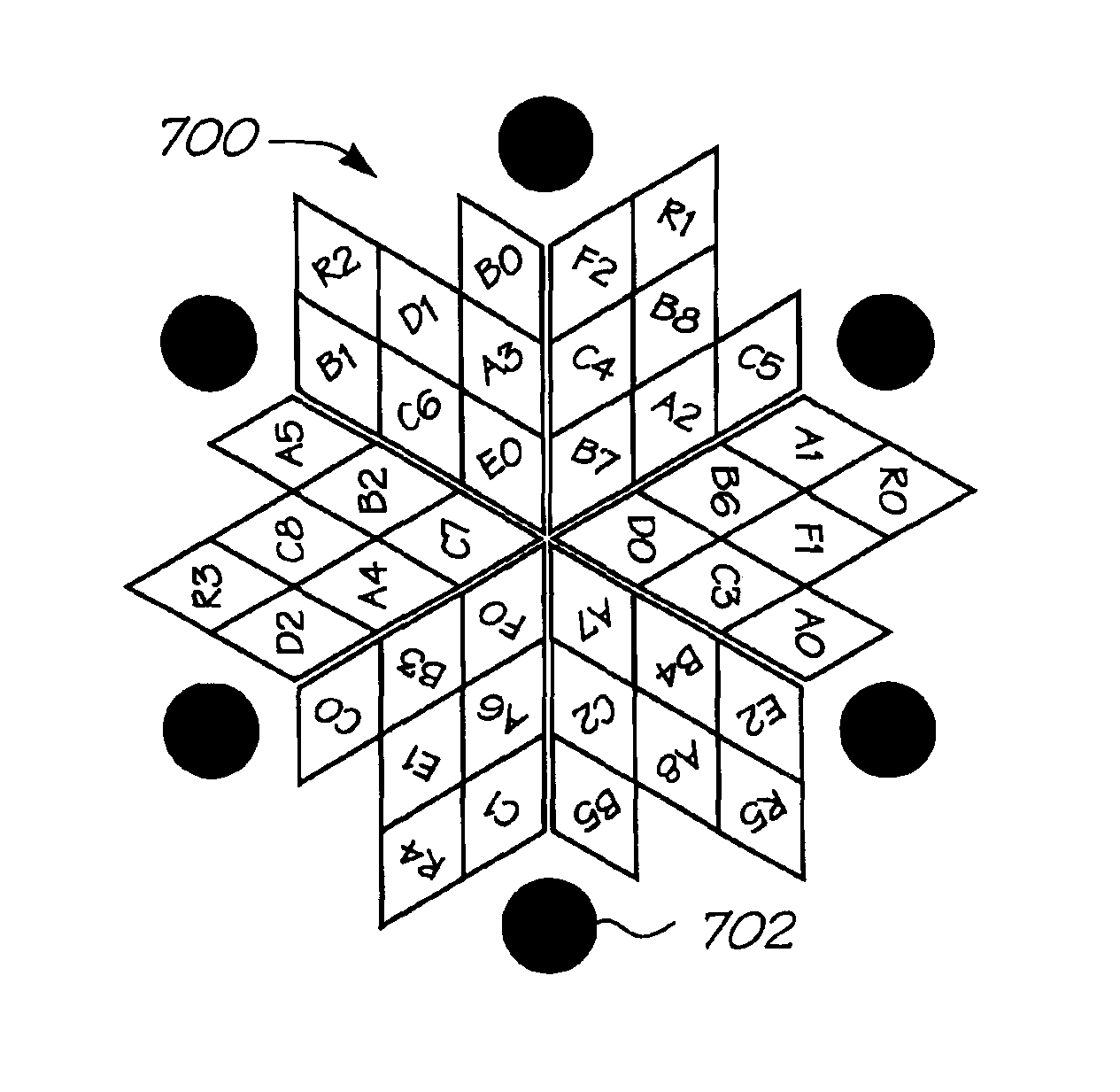
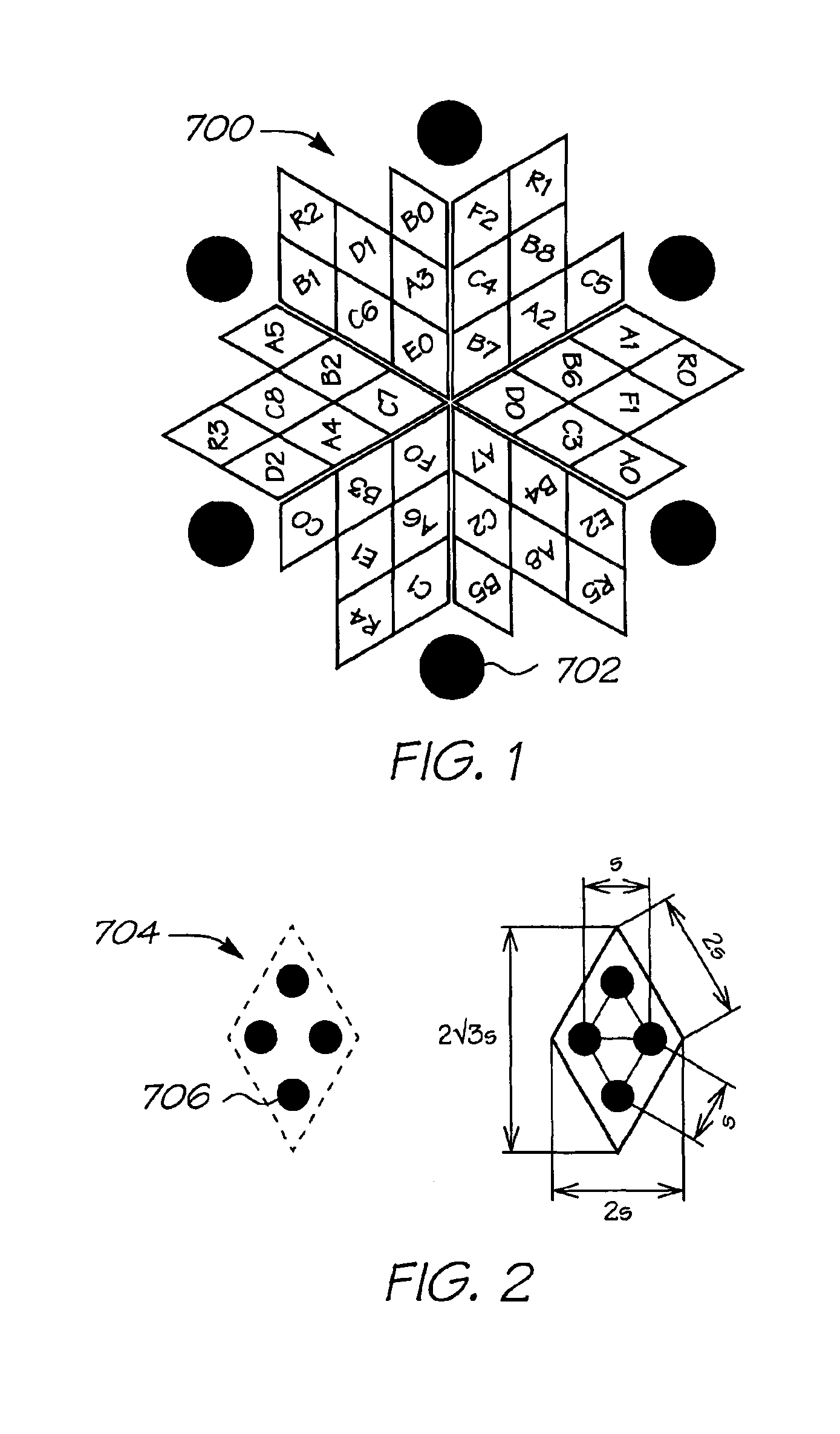
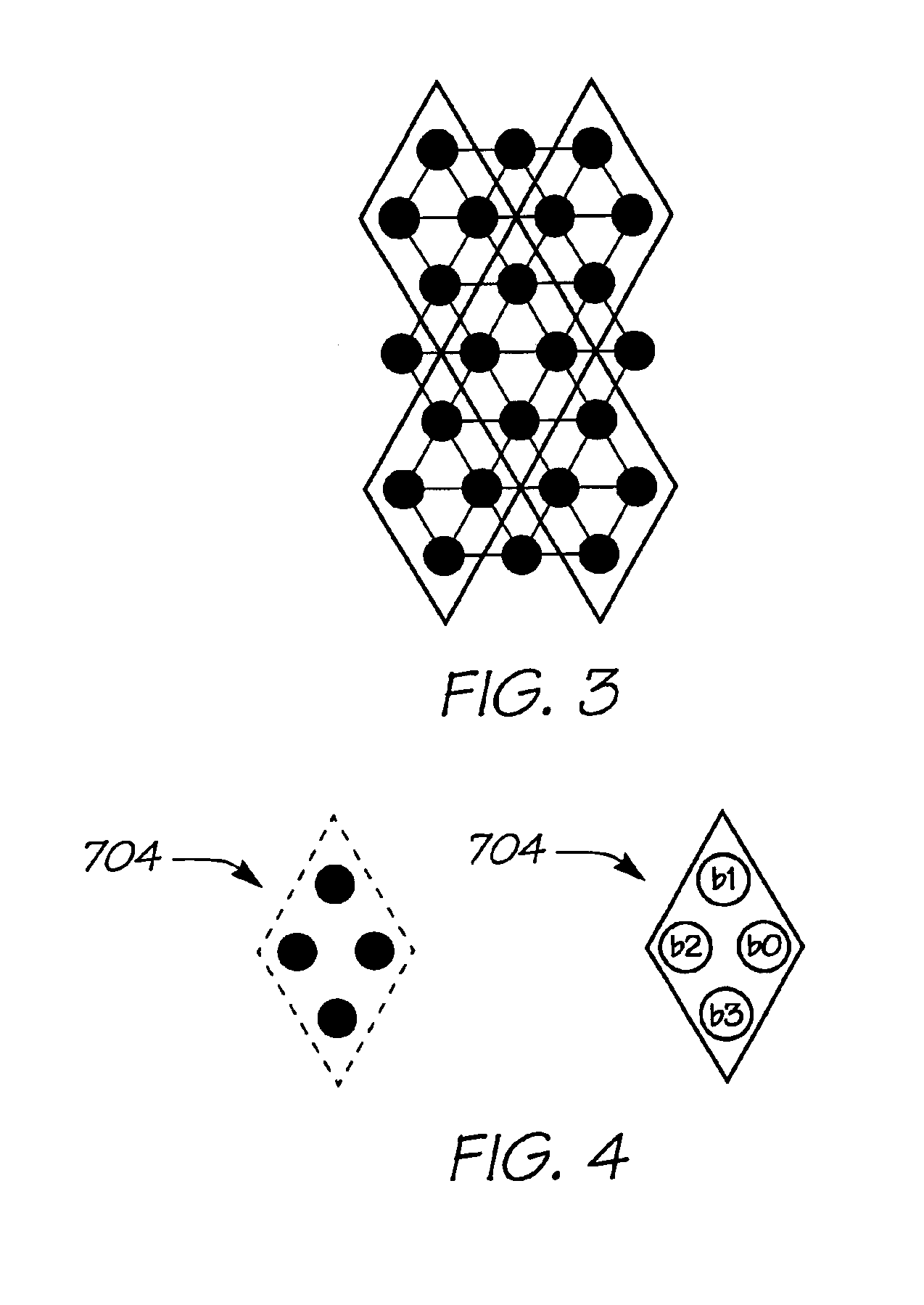
Rotational symmetry, also known as radial symmetry in biology, is the property a shape has when it looks the same after some rotation by a partial turn. An object's degree of rotational symmetry is the number of distinct orientations in which it looks exactly the same for each rotation.
Computer aided contact lens design and fabrication using spline surfaces
A method of computer-aided contact lens design and fabrication uses spline-based mathematical surfaces without restrictions of rotational symmetry. The spline encompasses any piecewise function with any associated constraints of smoothness or continuity. The method comprises some or all of the following steps: data acquisition, three-dimensional mathematical surface model construction, posterior surface description, ray tracing for anterior surface, and peripheral edge system (PES) design. The result is a mathematical or algorithmic description of a contact lens. Based on the more powerful mathematical representation of splines, these contact lenses can have posterior surfaces that provide a good fit to corneas having complicated shapes. This enables the design and fabrication of lenses (including soft lenses) with good optics for irregularly shaped corneas.
Owner:BARSKY BRIAN A
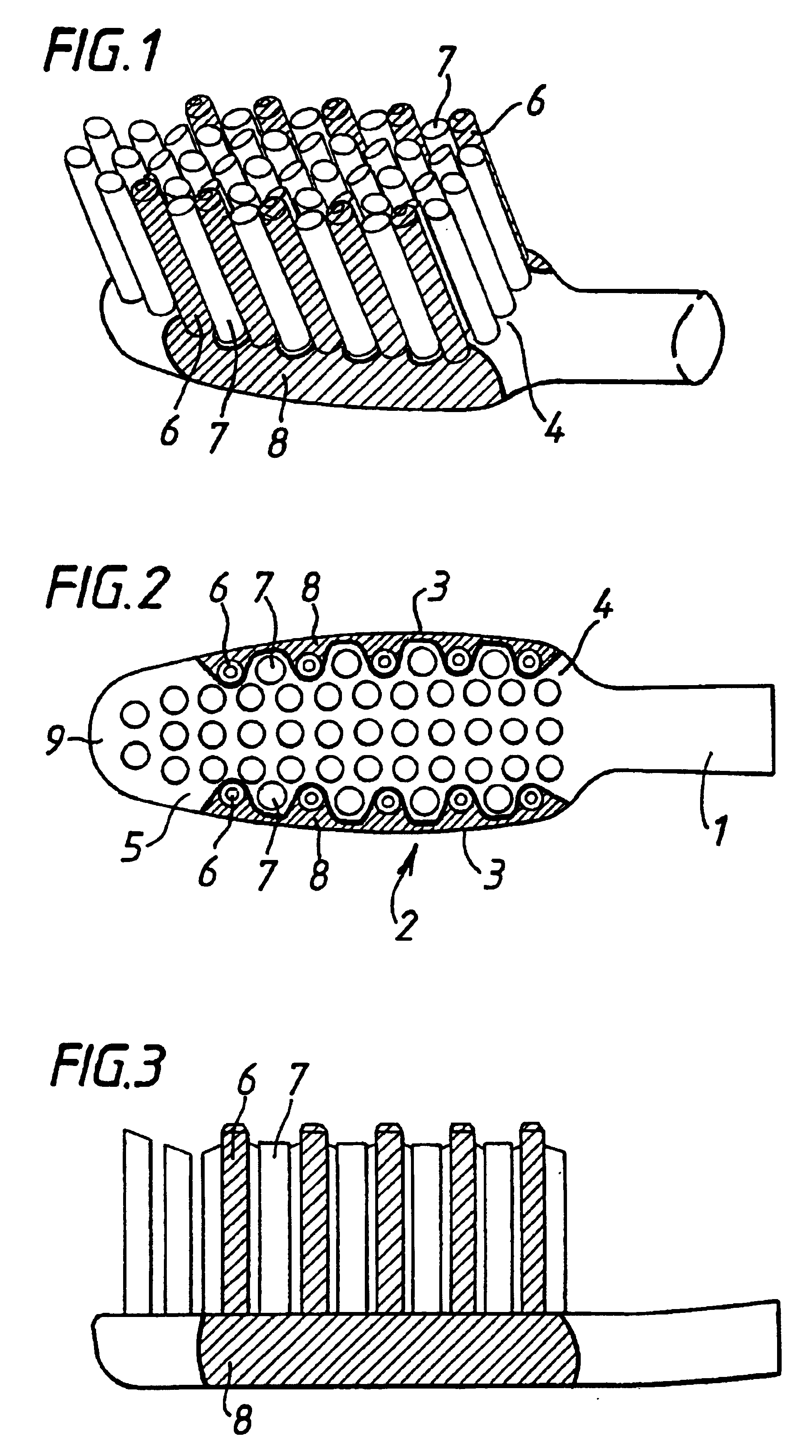
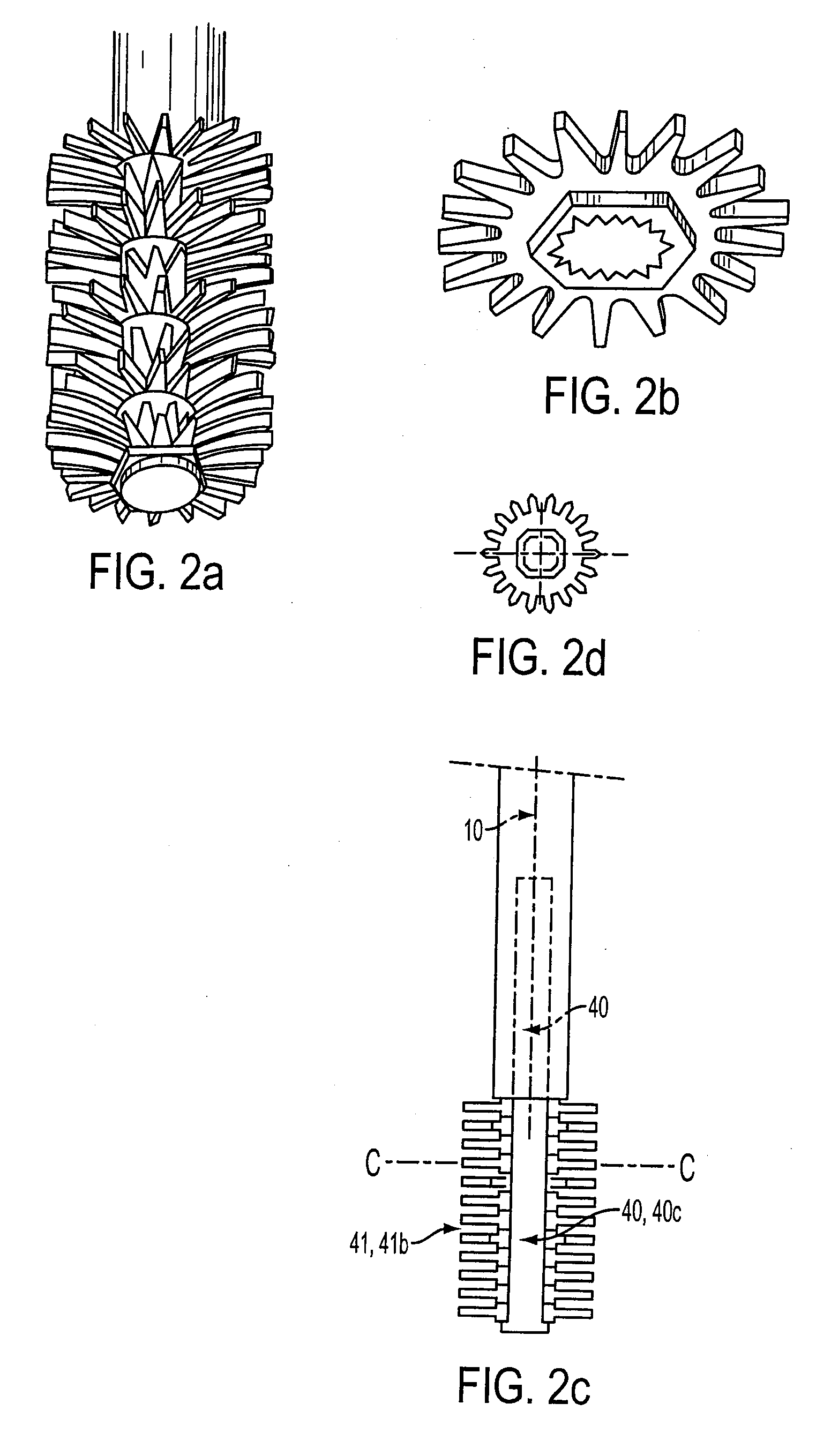
Toothbrush
InactiveUS6886207B1Use minimizedEqual bending momentsCarpet cleanersFloor cleanersBristleMechanical engineering
The toothbrush of the present invention comprises an elongated handle having a head attached to one end. The head has a bristle-bearing face having longitudinal perimeter portions adjacent longitudinal edges and at least two perimetric, elastomeric massaging elements alternately arranged with groups of bristle tufts along each of the longitudinal perimeter portions. The brush can comprise further massaging elements which are not located along the longitudinal perimeter portions though the use of such additional elements is preferably minimised. The perimetric massaging elements have rotational symmetry through an angle of 120° or less, preferably being circular. The cross-sectional area proportion of elastomeric massaging elements to bristles on the brush head is less than 25%. Alternately there are four or fewer elastomeric massaging elements which are not perimetric massaging elements. A brush with both bristles and gum massaging elements arranged as set out above provides both cleaning and gum massaging benefits without creating an undesirable aesthetic impression derived from the use of rubber-like materials in the part of the brush head traditionally comprising only bristles.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
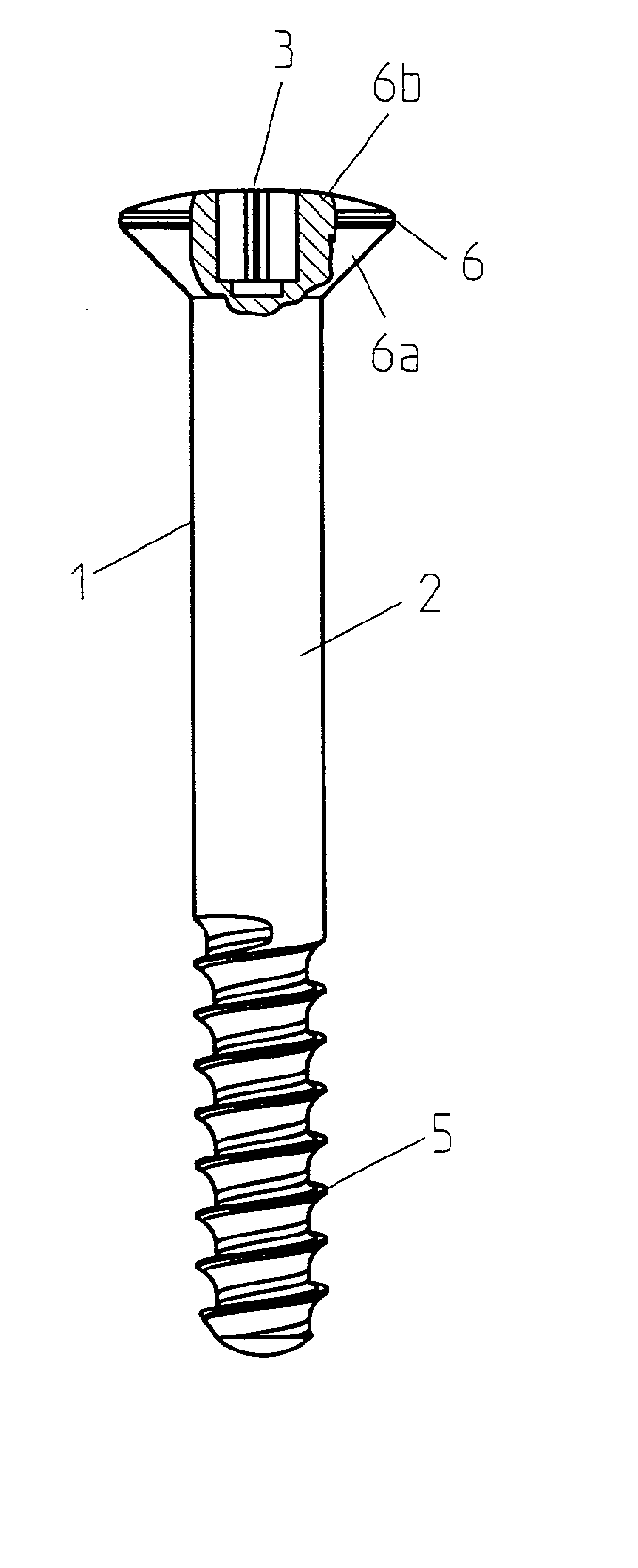
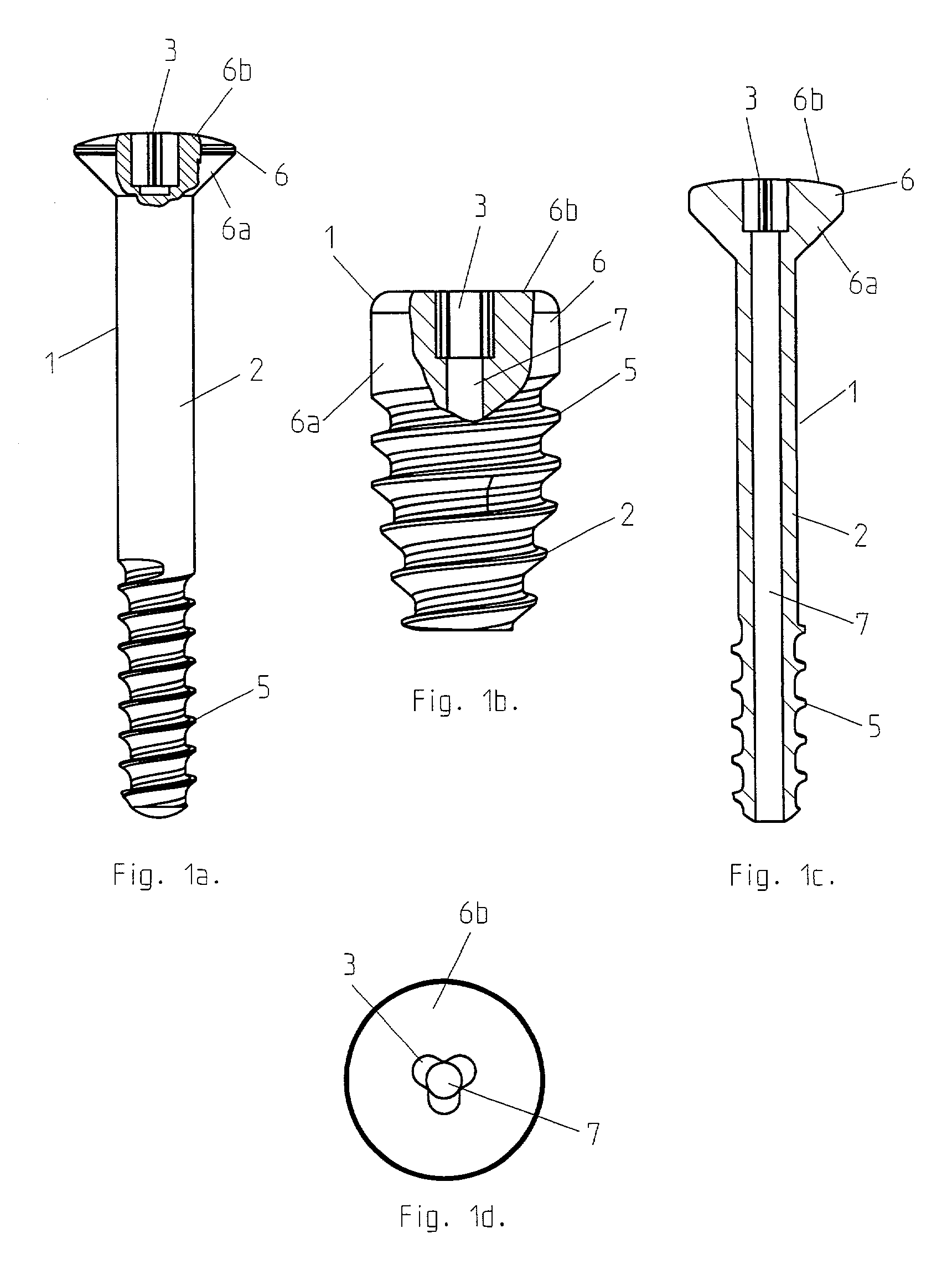
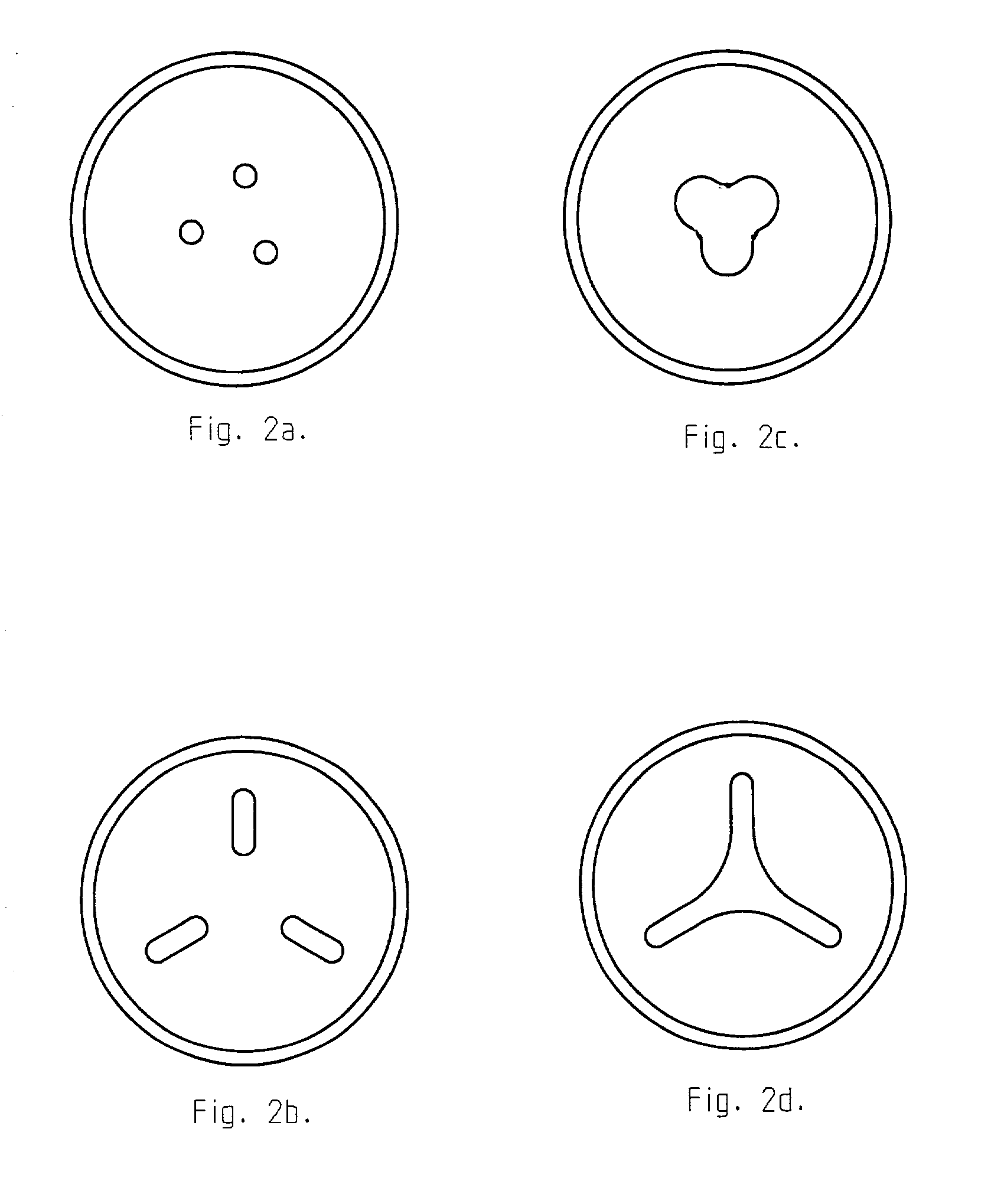
Surgical screw and tool for its insertion
InactiveUS20030158555A1Minimal concentration of torsional stressImprove the immunitySuture equipmentsLigamentsScrew systemEngineering
A surgical screw system using a surgical screw that is at least partially bioabsorbable in vivo, the screw having a recess (or optionally recesses) in its head for receiving an inserter instrument, wherein the recess has a rotational symmetry around the longitudinal axis of the screw. The recess comprises an odd number of rounded lobes extending away from the center of the head. The inserter for the screw comprises a distal end that matches the shape of the recess in the screw and can be slidably engaged with the recess.
Owner:LINVATEC BIOMATERIALS
Symmetric target design in scatterometry overlay metrology
ActiveUS20150204664A1Photomechanical apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansMetrologyPhase shifted
Metrology methods, systems and targets are provided, which implement a side by side paradigm. Adjacent cells with periodic structures are used to extract the overlay error, e.g., by introducing controllable phase shifts or image shifts which enable algorithmic computation of the overlay. The periodic structures are designed to exhibit a rotational symmetry to support the computation and reduce errors.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
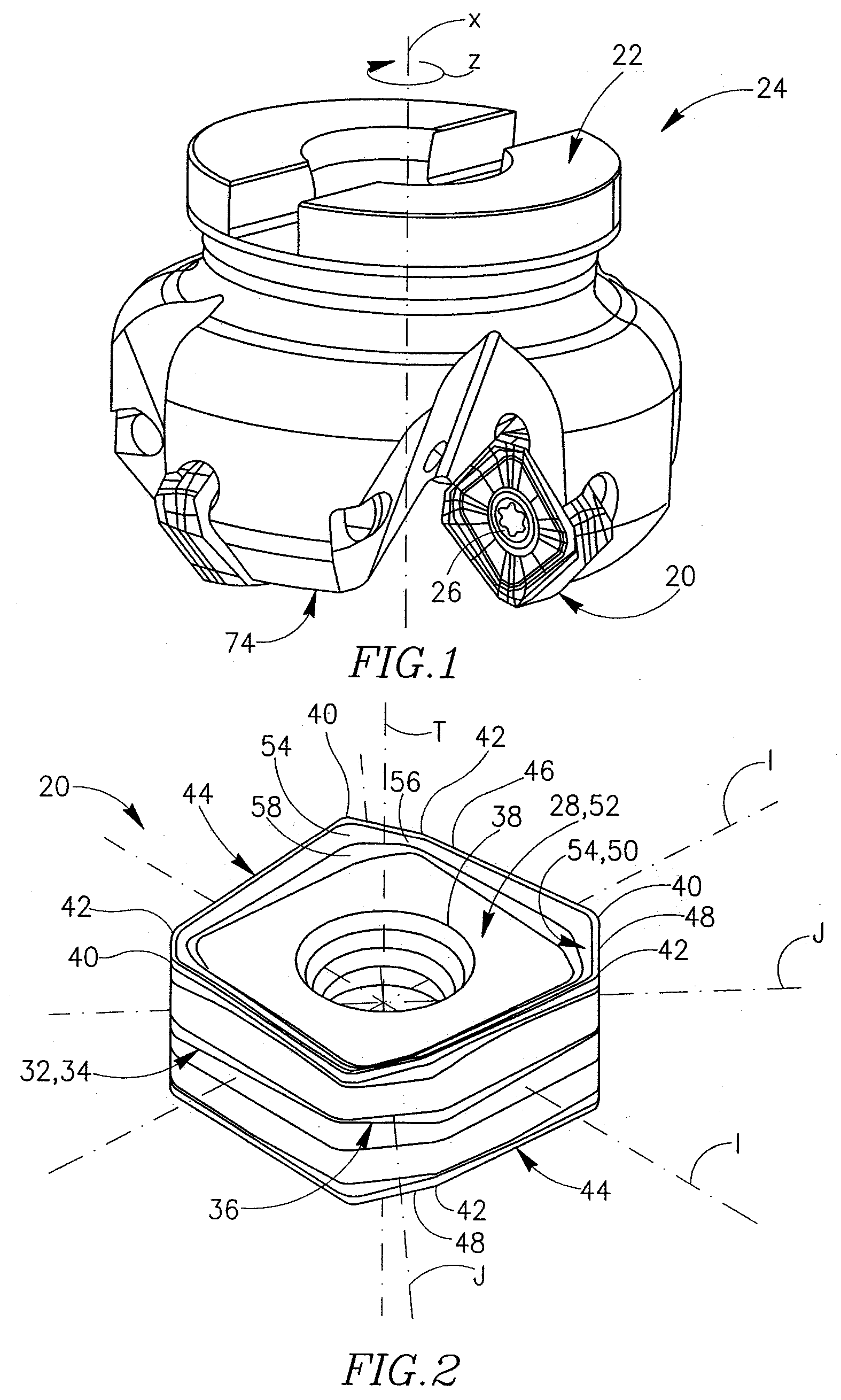
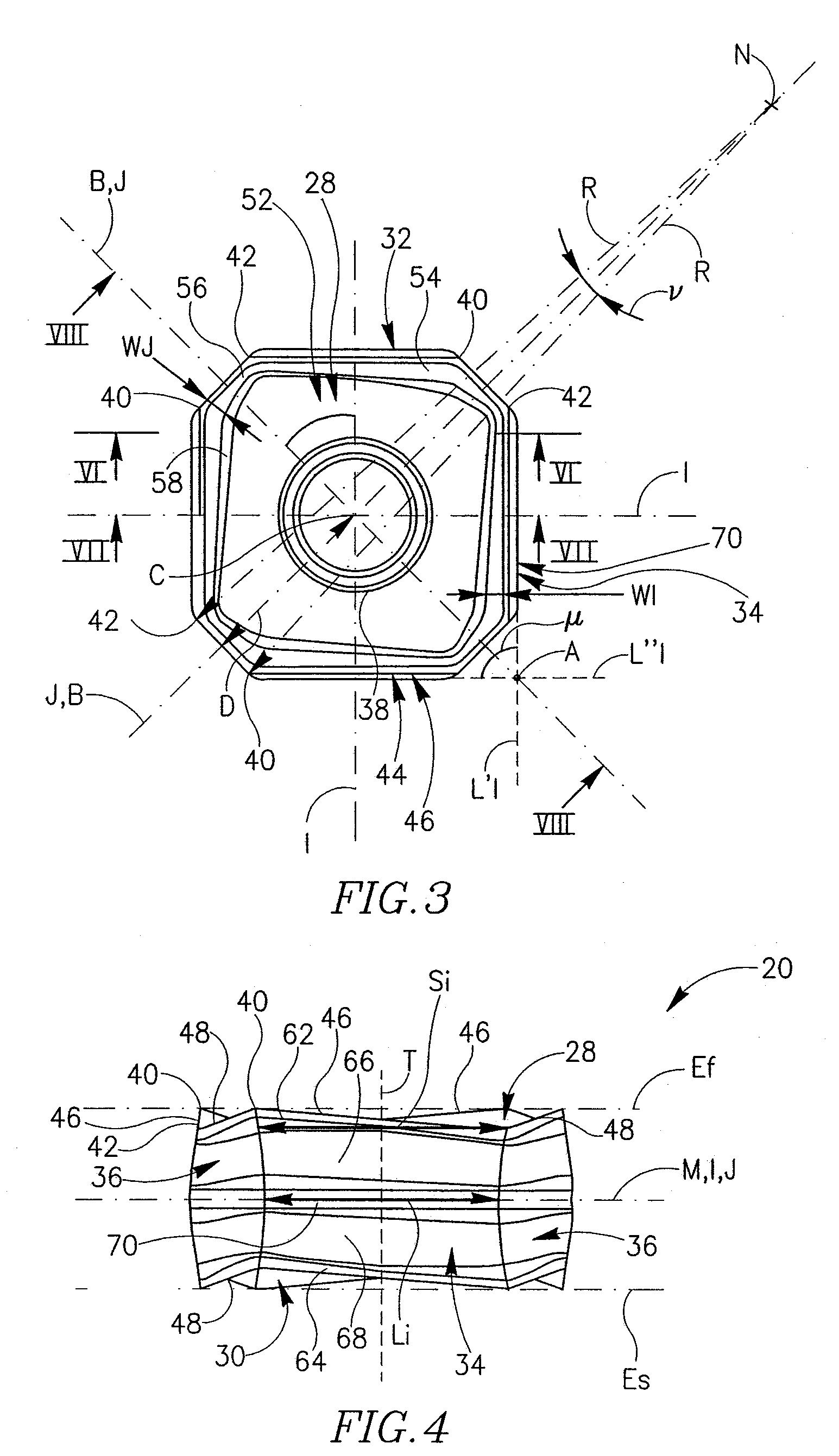
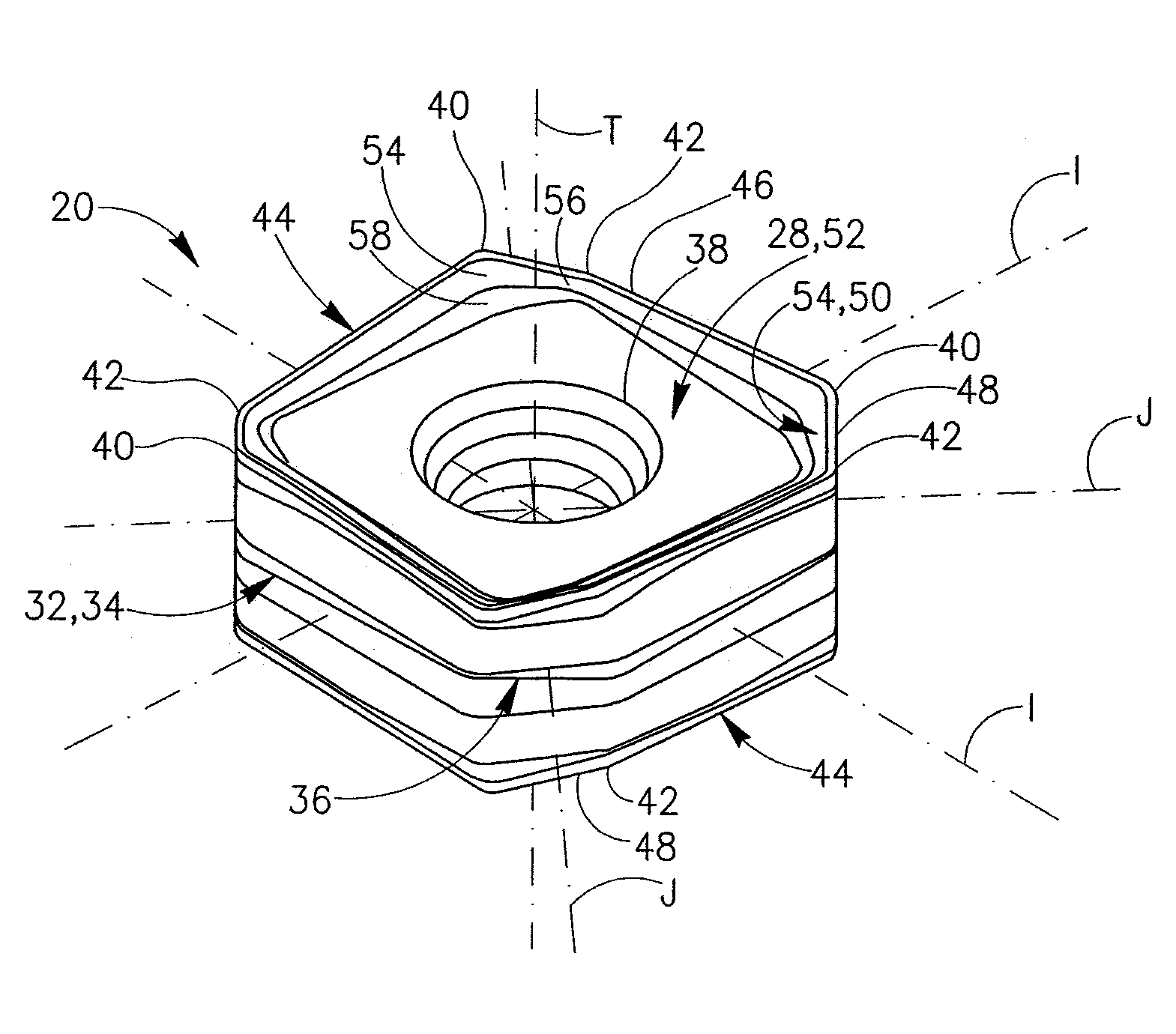
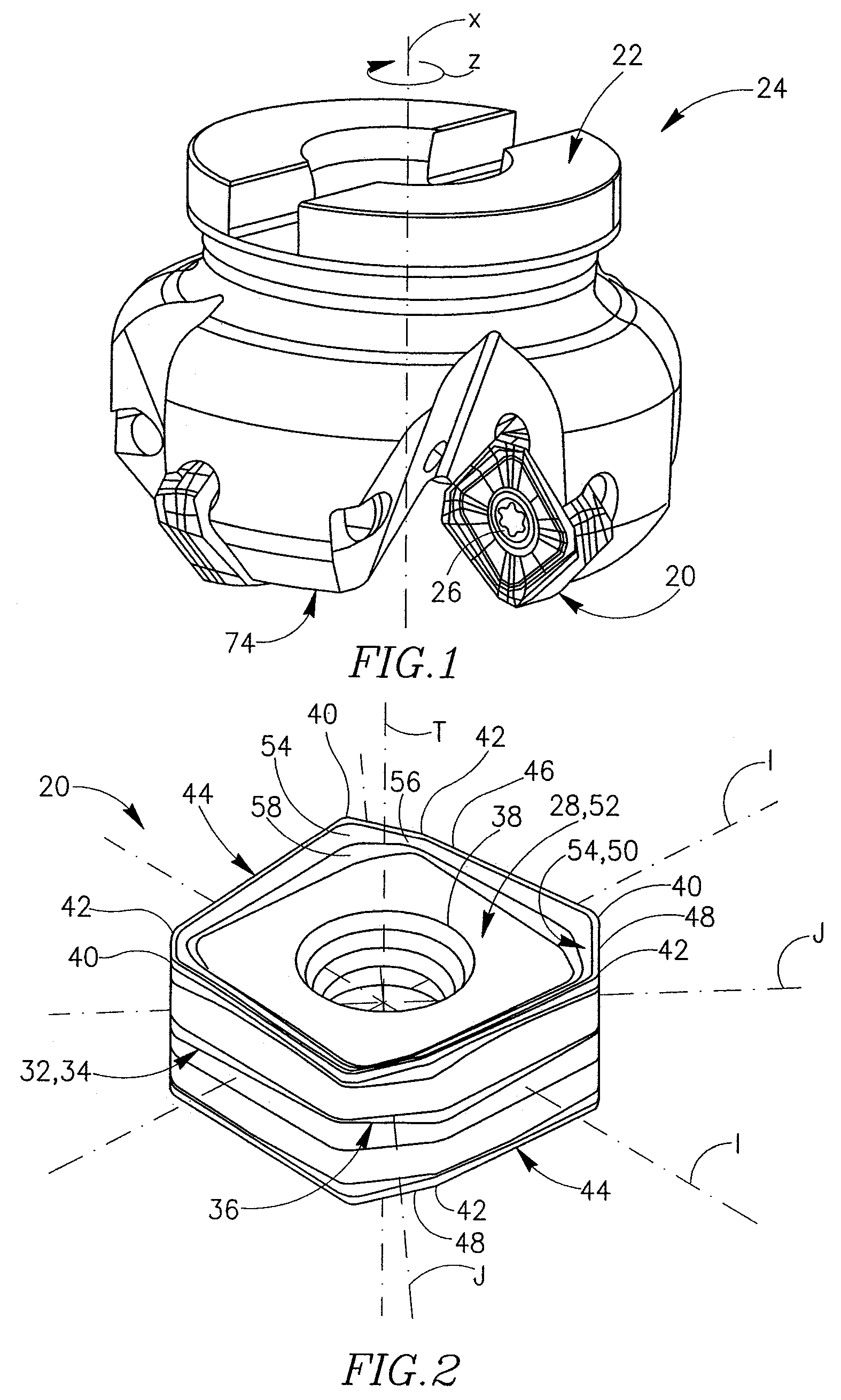
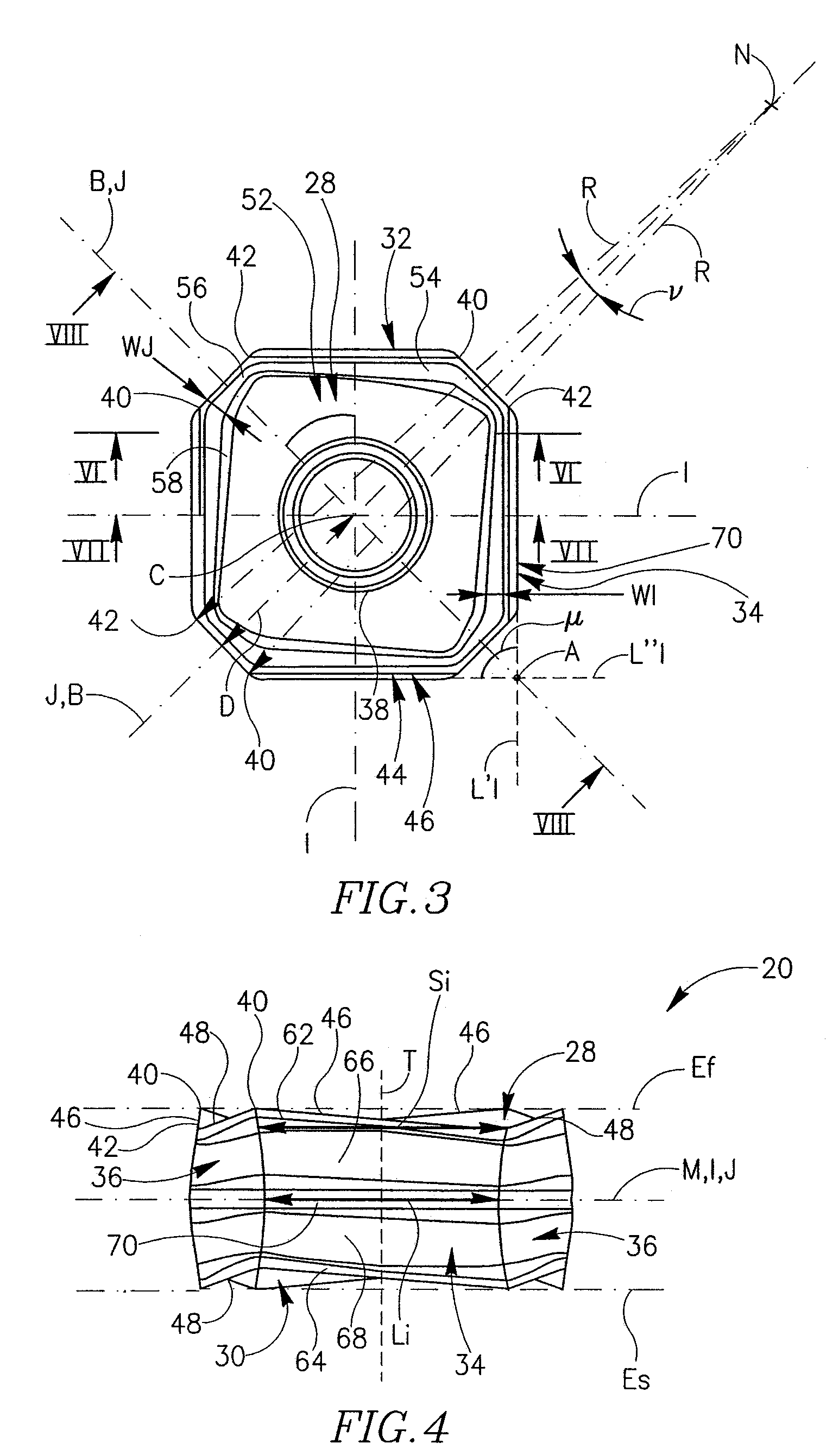
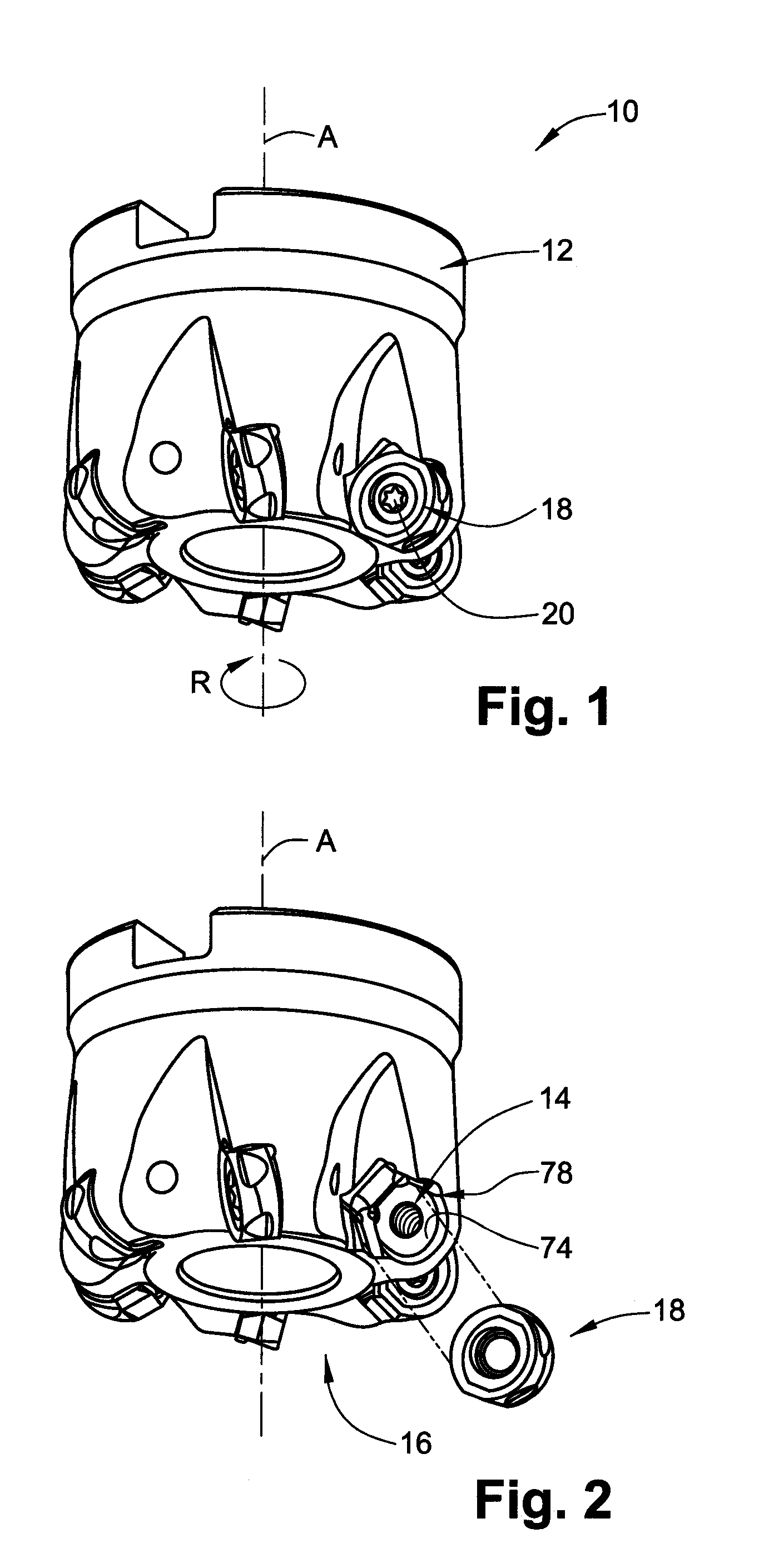
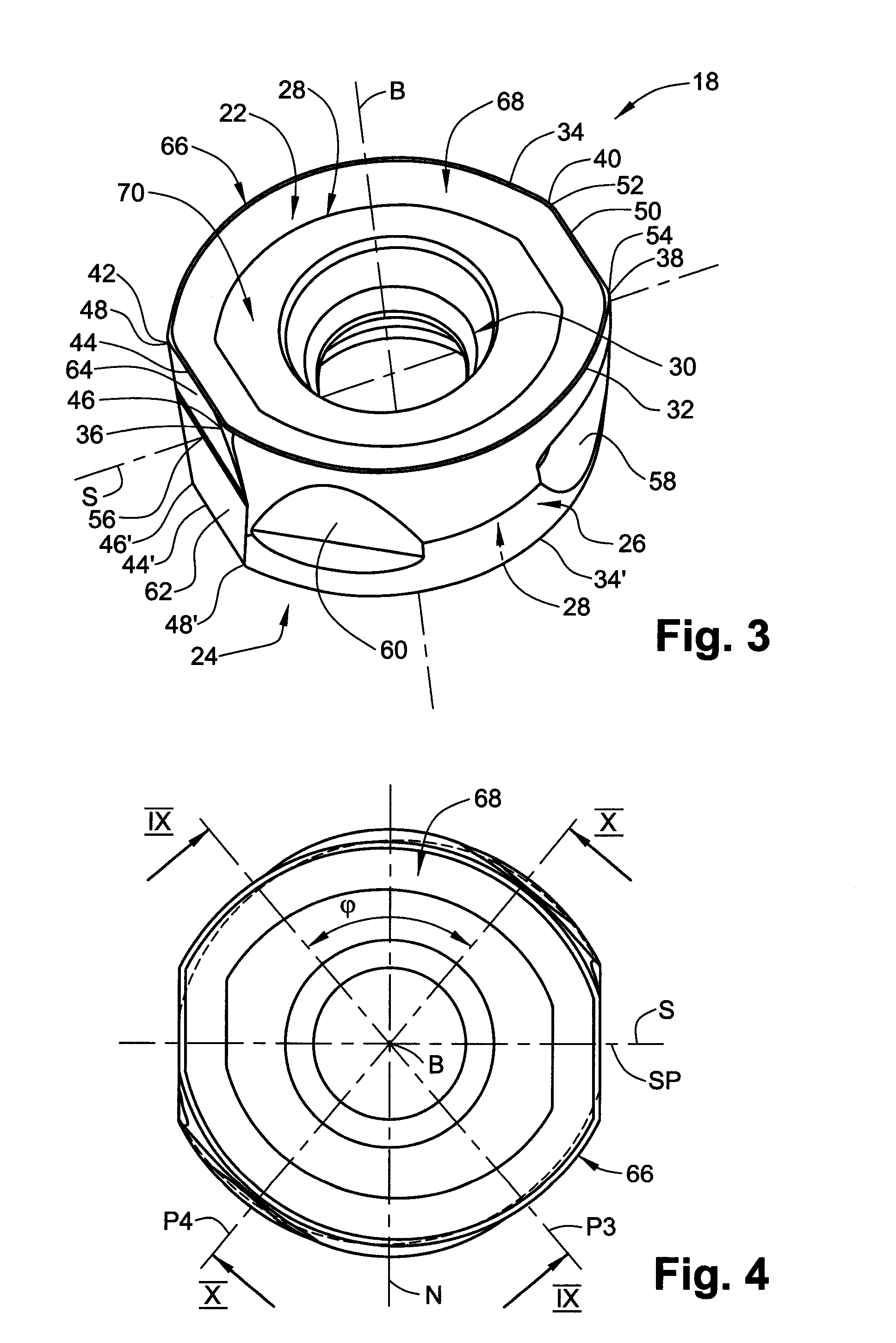
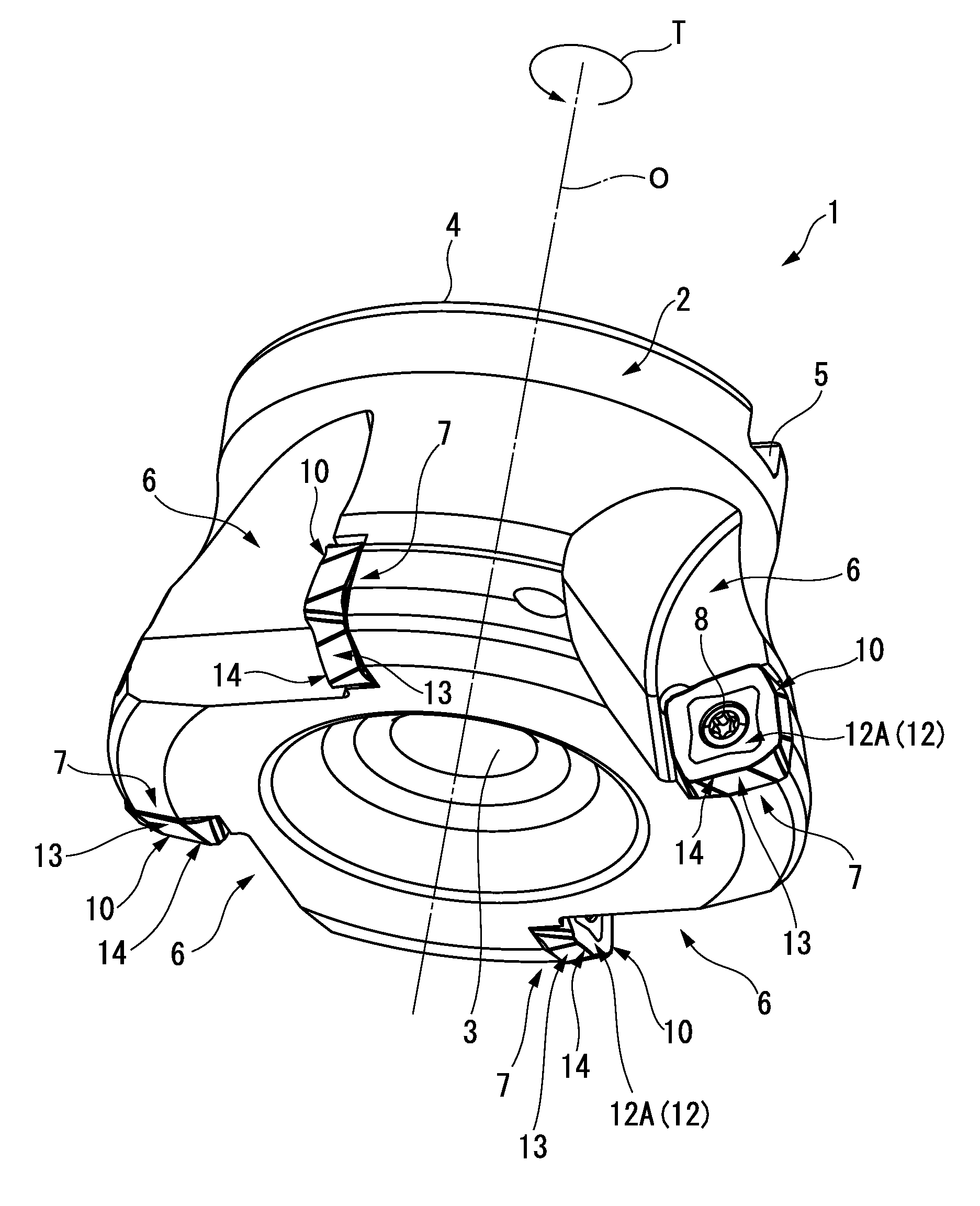
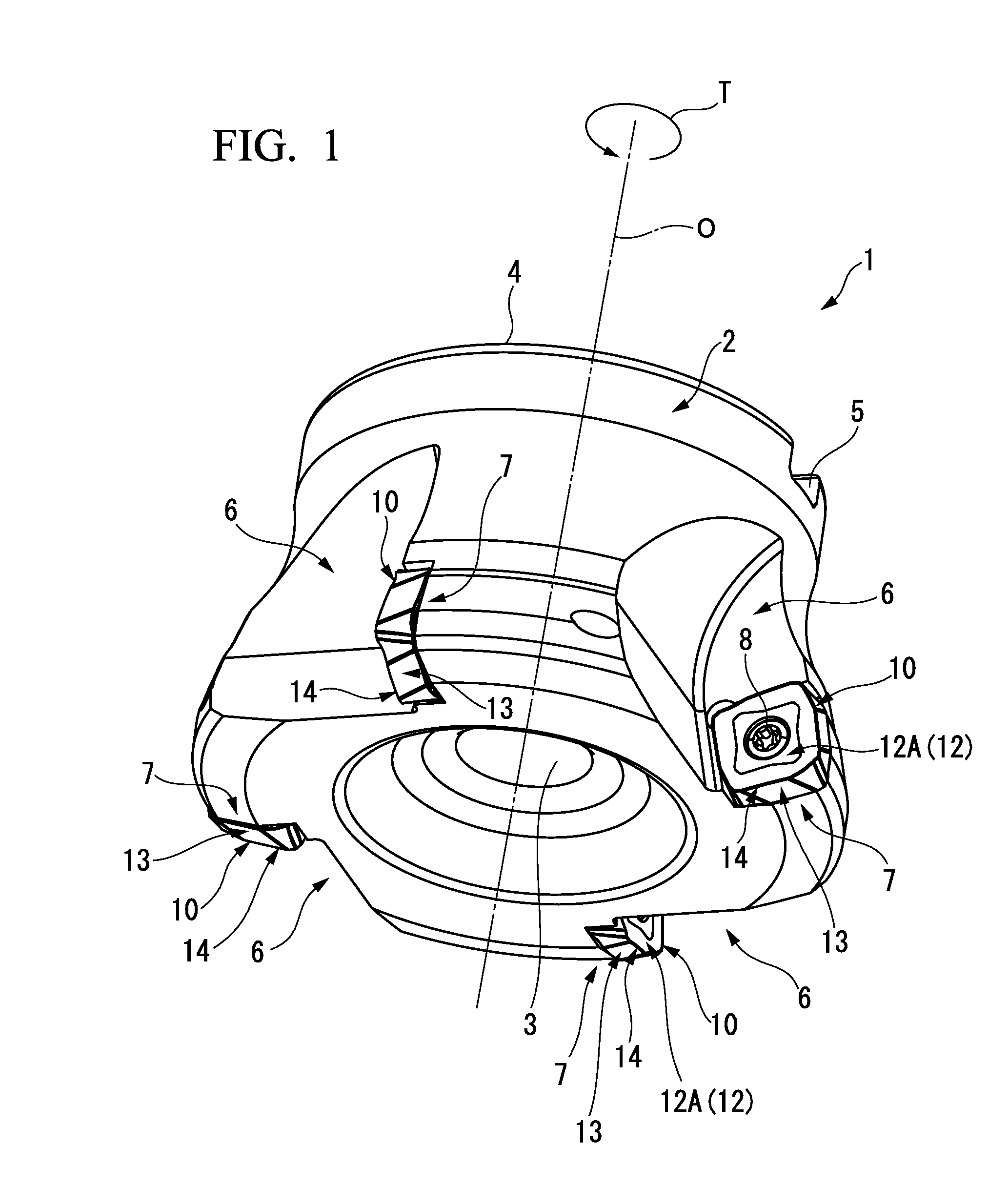
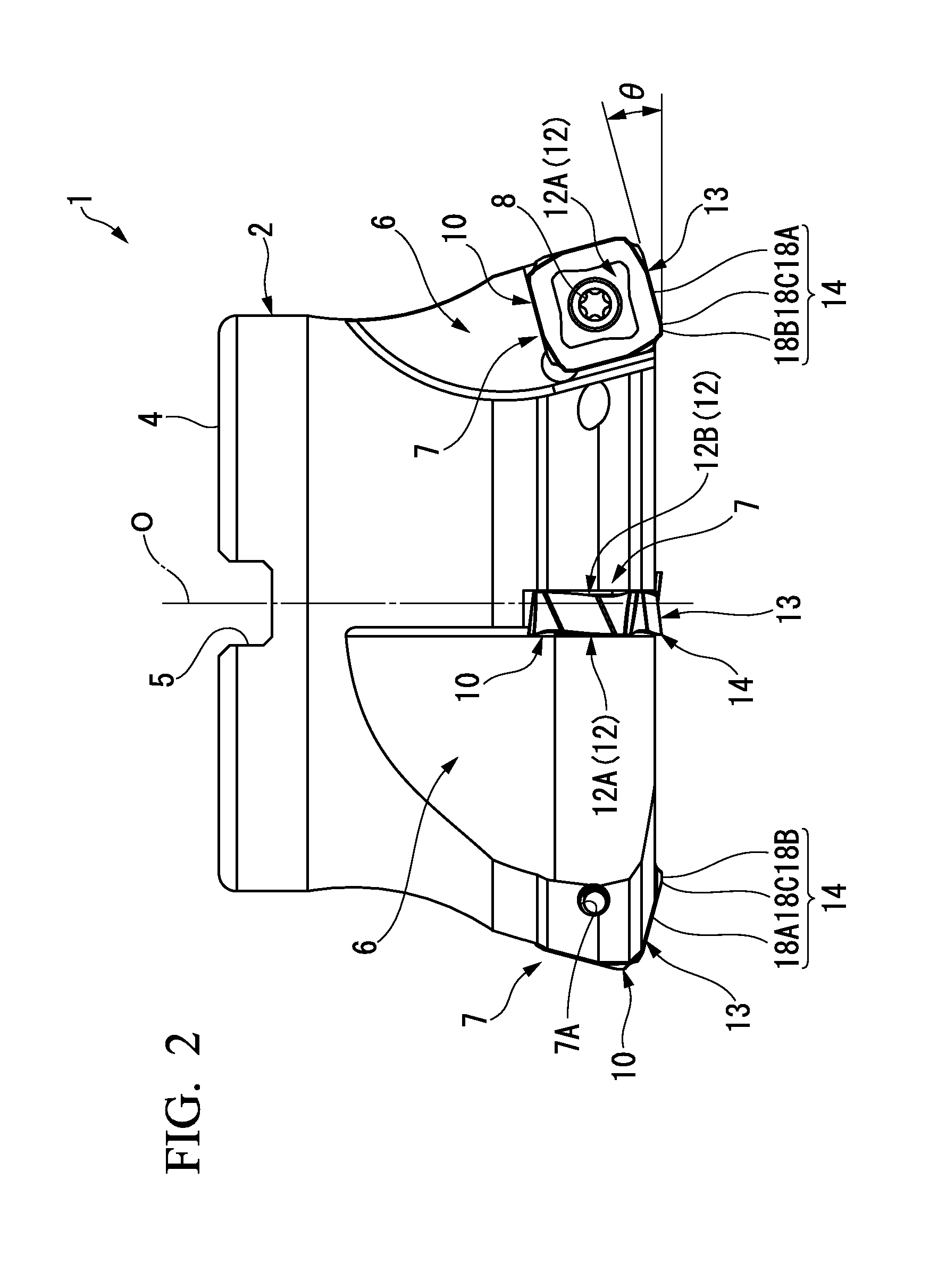
Cutting Insert Having Cylindrically Shaped Side Surface Portions
ActiveUS20070003384A1Reduced cutting performanceReduce the impactMilling cuttersCutting insertsRotational symmetryMedian plane
A double-sided reversible and indexable cutting insert has identical opposing first and second end faces and a peripheral side surface extending therebetween. A clamping through-bore extends between, and opens out to, the first and second end faces. The cutting insert has a median plane between the first and second end faces, and a through-bore axis extending perpendicularly through the median plane. The cutting insert also has a Y-fold rotational symmetry about the through-bore axis. The peripheral side surface has Y major side surfaces and Y minor side surfaces, each minor side surface interconnecting two adjacent major side surfaces. Each minor side surface is a section of a single cylindrical surface having a given radius, the given radius being greater than a minor side surface distance of each minor side surface from the through-bore axis.
Owner:ISCAR LTD
Atomic level ion source and method of manufacture and operation
ActiveUS20070051900A1Long-term performanceLong-term reliabilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by optical meansElectrical conductorScanning electron microscope
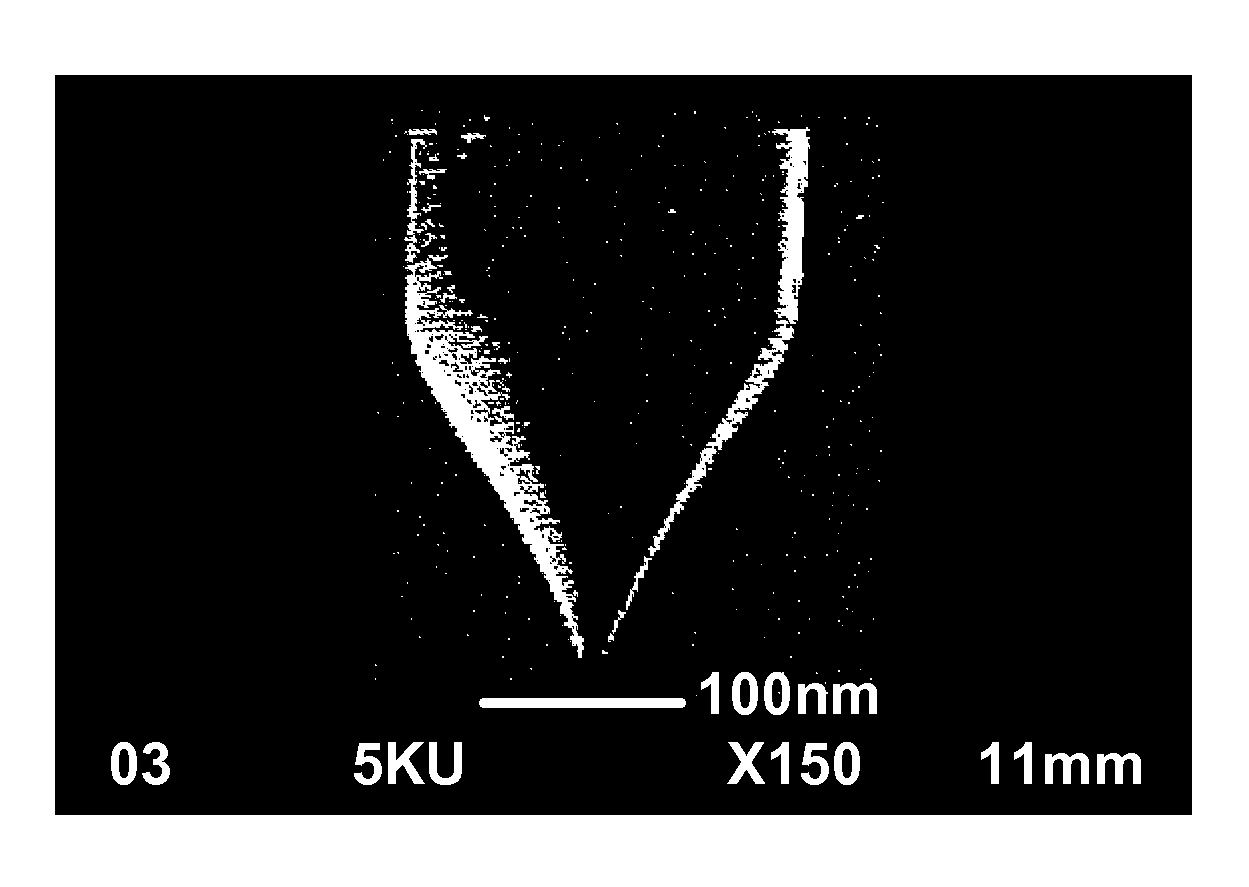
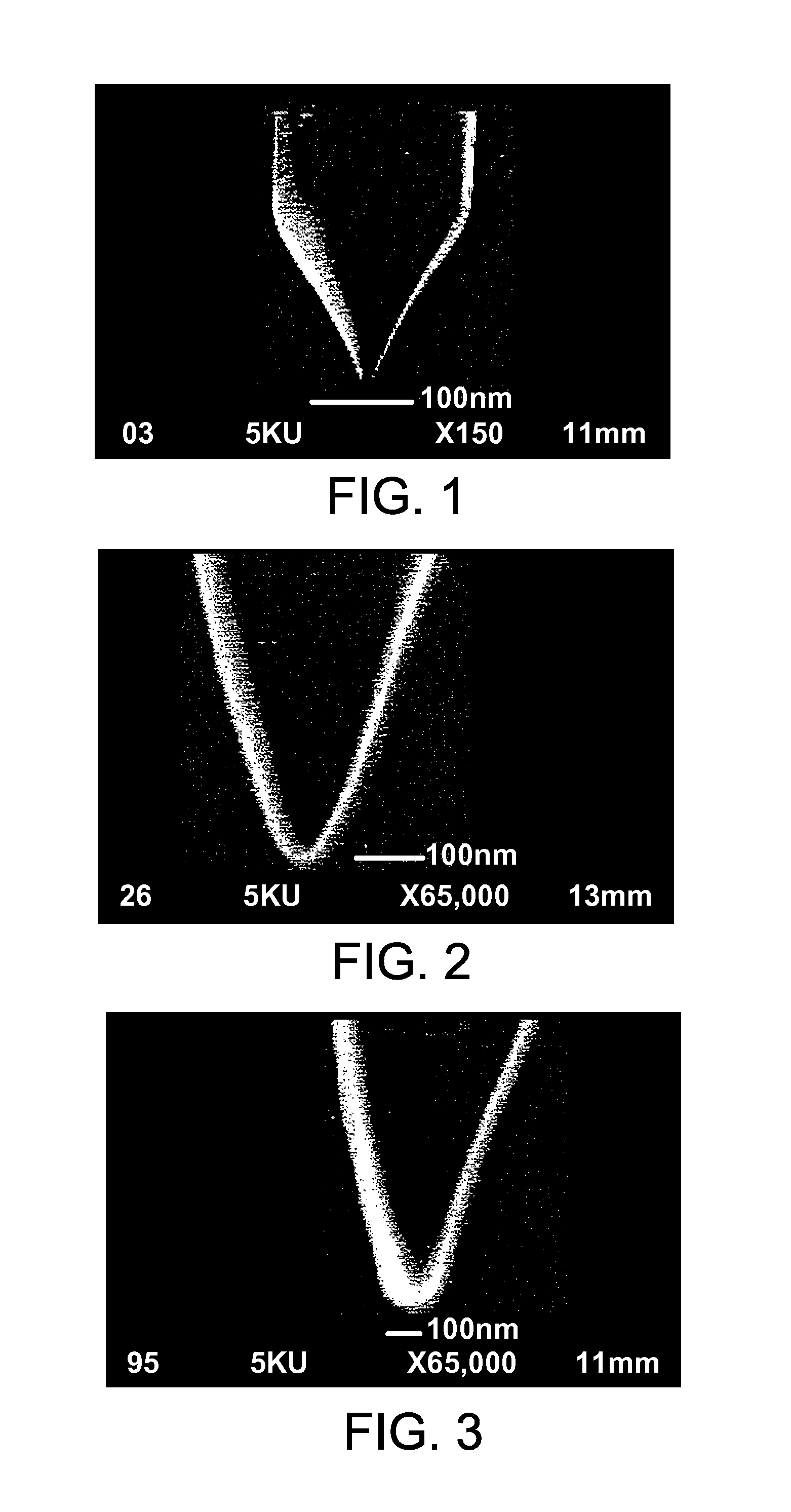
Ion source and method of making and sharpening. The ion source is a single crystal metal conductor having a substantially conical tip portion with substantial rotational symmetry. The tip portion terminates with a tip radius of curvature in the range of 50-100 nanometers. The ion source is made by electrochemical etching so that a conical tip of a selected geometry is formed. The ion source is then sharpened to provide a source of ions from a volume near the size of a single atom. Further, this ion source makes possible a stable and practical light ion microscope which will have higher resolution than existing scanning electron microscopes and scanning metal-ion microscopes.
Owner:ALIS CORP
Orientation-indicating machine readable coded data
InactiveUS6929186B2Accurate decodingCharacter and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesData encodingComputer science
Machine-readable coded data disposed on or in a substrate. The coded data includes a layout having order n rotational symmetry, formed from n identical sub-layouts rotated 1 / n revolutions apart about a center of rotation. The layout encodes a first codeword formed from a sequence of a multiple m of n first symbols, with each sub-layout defining respective positions for each of m first symbols, such that the m first symbols uniquely identify each sub-layout. Decoding the first symbols provided at one or more of the respective locations within each sub-layout is therefore indicative of the degree of rotation of the layout.
Owner:SILVERBROOK RES PTY LTD
Atomic level ion source and method of manufacture and operation
ActiveUS7368727B2Good symmetryLong-term performance and reliabilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by optical meansElectrical conductorScanning electron microscope
Ion source and method of making and sharpening. The ion source is a single crystal metal conductor having a substantially conical tip portion with substantial rotational symmetry. The tip portion terminates with a tip radius of curvature in the range of 50–100 nanometers. The ion source is made by electrochemical etching so that a conical tip of a selected geometry is formed. The ion source is then sharpened to provide a source of ions from a volume near the size of a single atom. Further, this ion source makes possible a stable and practical light ion microscope which will have higher resolution than existing scanning electron microscopes and scanning metal-ion microscopes.
Owner:ALIS CORP
Tangential cutting insert and insert holder
A tangential indexable cutting insert can be used for metal cutting processes in general and for radial and axial turning of a stepped square shoulder in particular. The cutting insert exhibits 180° rotational symmetry about three mutually perpendicular axes. The cutting insert has generally “S”-shaped cutting edges extending between raised and lowered corners. The cutting edges and side surfaces are concave in an end view of the cutting insert. The cutting insert enables radial and axial turning operations of a square shoulder with unlimited depth of cut.
Owner:ISCAR LTD
Phase correction element and optical head device
InactiveUS20050226122A1Polarising elementsRecord information storagePhase differenceNumerical aperture
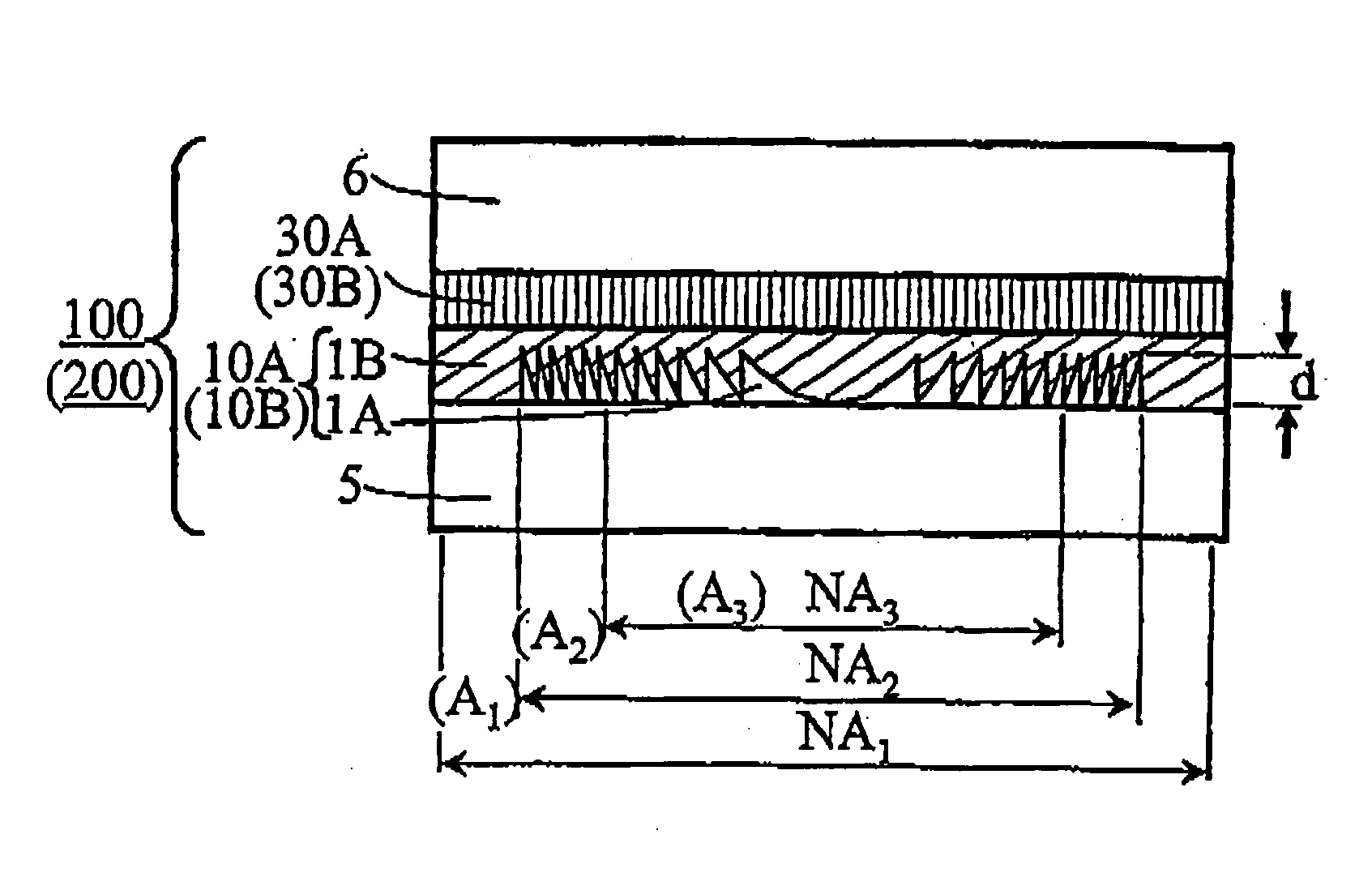
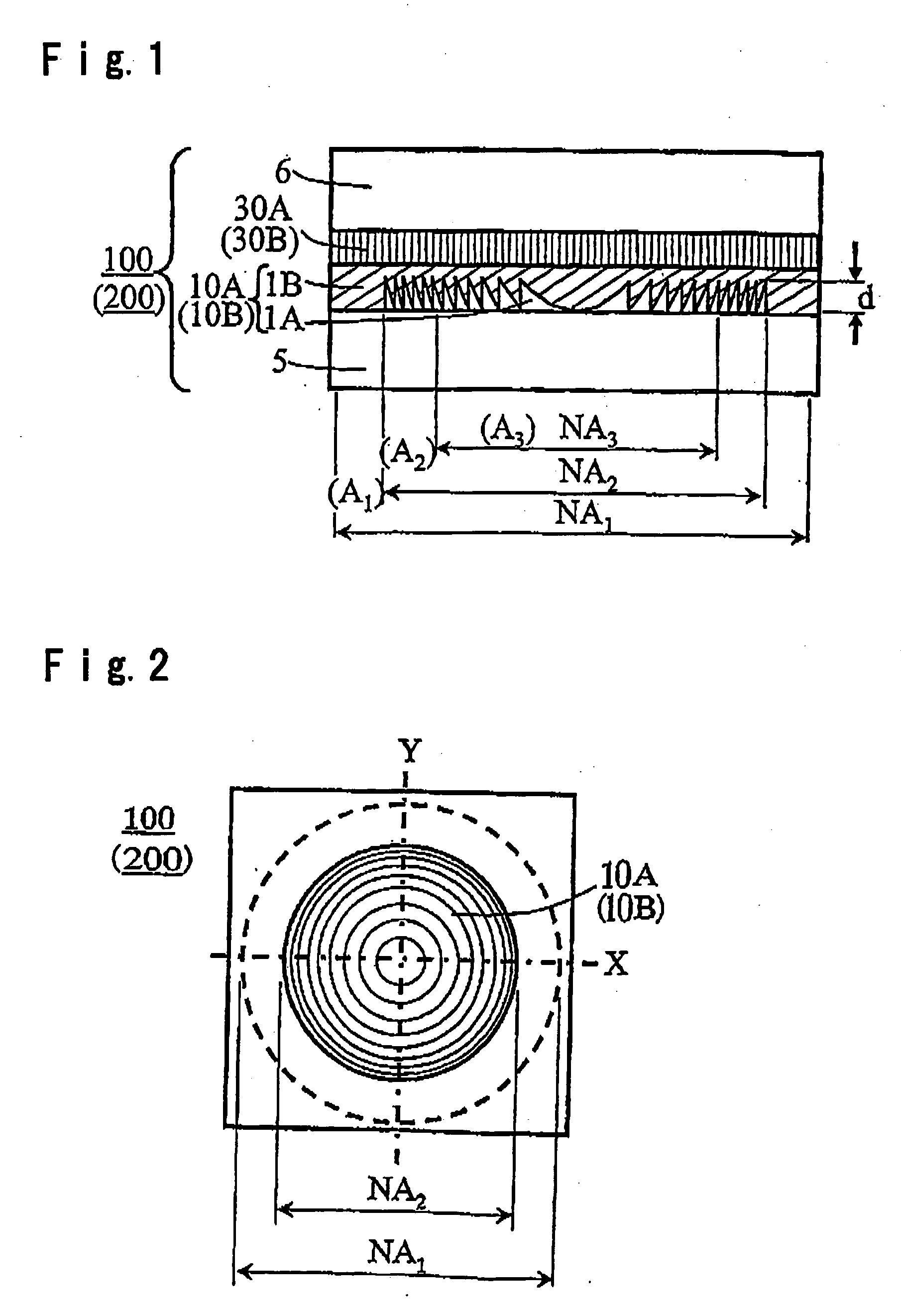
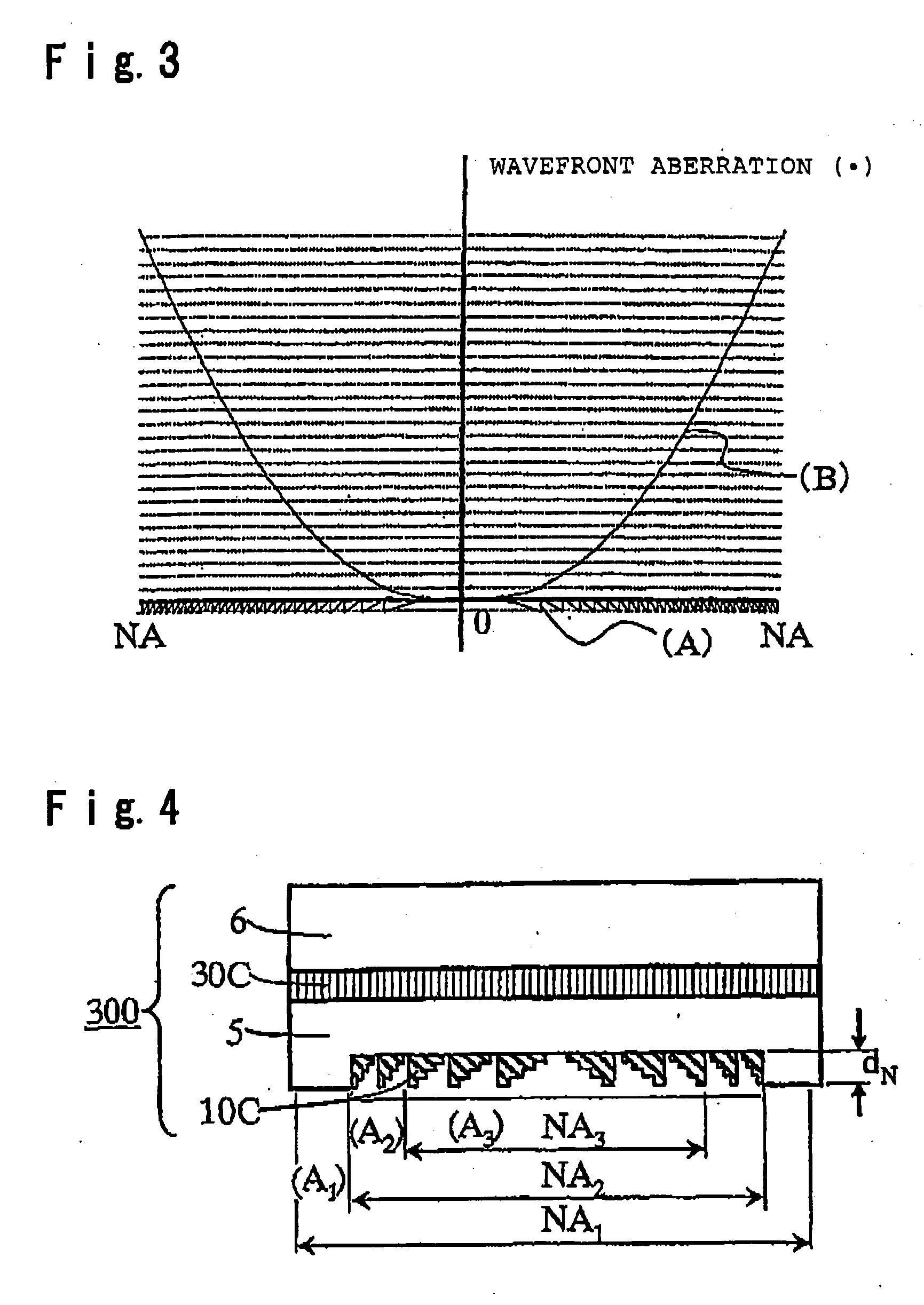
The present invention provides a phase correction element which can be used for recording and / or reproducing an information of three types of optical disks for HD, DVD and CD by employing a single objective lens for HD, and an optical head device. The phase correction element 100 of present invention comprises a first phase correction layer 10A formed in a region of numerical aperture NA2, and a first phase plate 30A integrally formed; the first phase correction layer 10A comprising a concavo-convex portion having a rotational symmetry with respect to the optical axis of incident light and having a cross-sectional shape of a saw-tooth-form or a saw-tooth-form whose convex portions are each approximated by a step form; the first phase plate 30A generating a birefringent phase difference of about an odd number times of π / 2 for linearly polarized light having a wavelength of λ1; and the phase correction element 100 having a function of not changing a transmitted wavefront of the wavelength of λ1 and changing a transmitted wavefront of the wavelength of λ2 or transmitted wavefront of both wavelengths of λ2 and λ3 when three types of incident light in a λ1=410 nm wavelength band, a λ2=650 nm wavelength band and a λ3=780 nm wavelength band respectively, are incident.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Cutting insert having cylindrically shaped side surface portions
ActiveUS7232279B2Reduced cutting performanceWithout of to qualityMilling cuttersCutting insertsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A double-sided reversible and indexable cutting insert has identical opposing first and second end faces and a peripheral side surface extending therebetween. A clamping through-bore extends between, and opens out to, the first and second end faces. The cutting insert has a median plane between the first and second end faces, and a through-bore axis extending perpendicularly through the median plane. The cutting insert also has a Y-fold rotational symmetry about the through-bore axis. The peripheral side surface has Y major side surfaces and Y minor side surfaces, each minor side surface interconnecting two adjacent major side surfaces. Each minor side surface is a section of a single cylindrical surface having a given radius, the given radius being greater than a minor side surface distance of each minor side surface from the through-bore axis.
Owner:ISCAR LTD
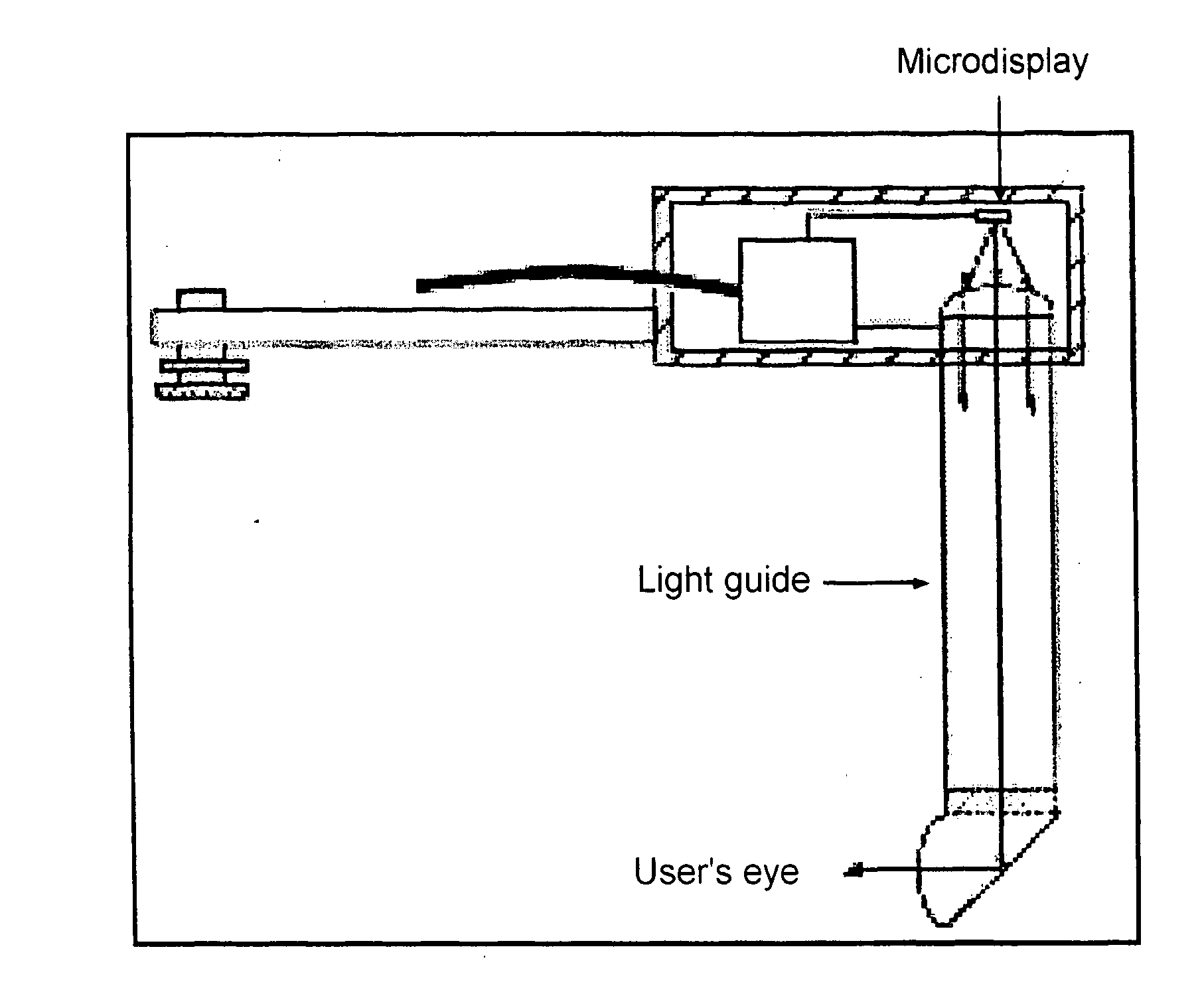
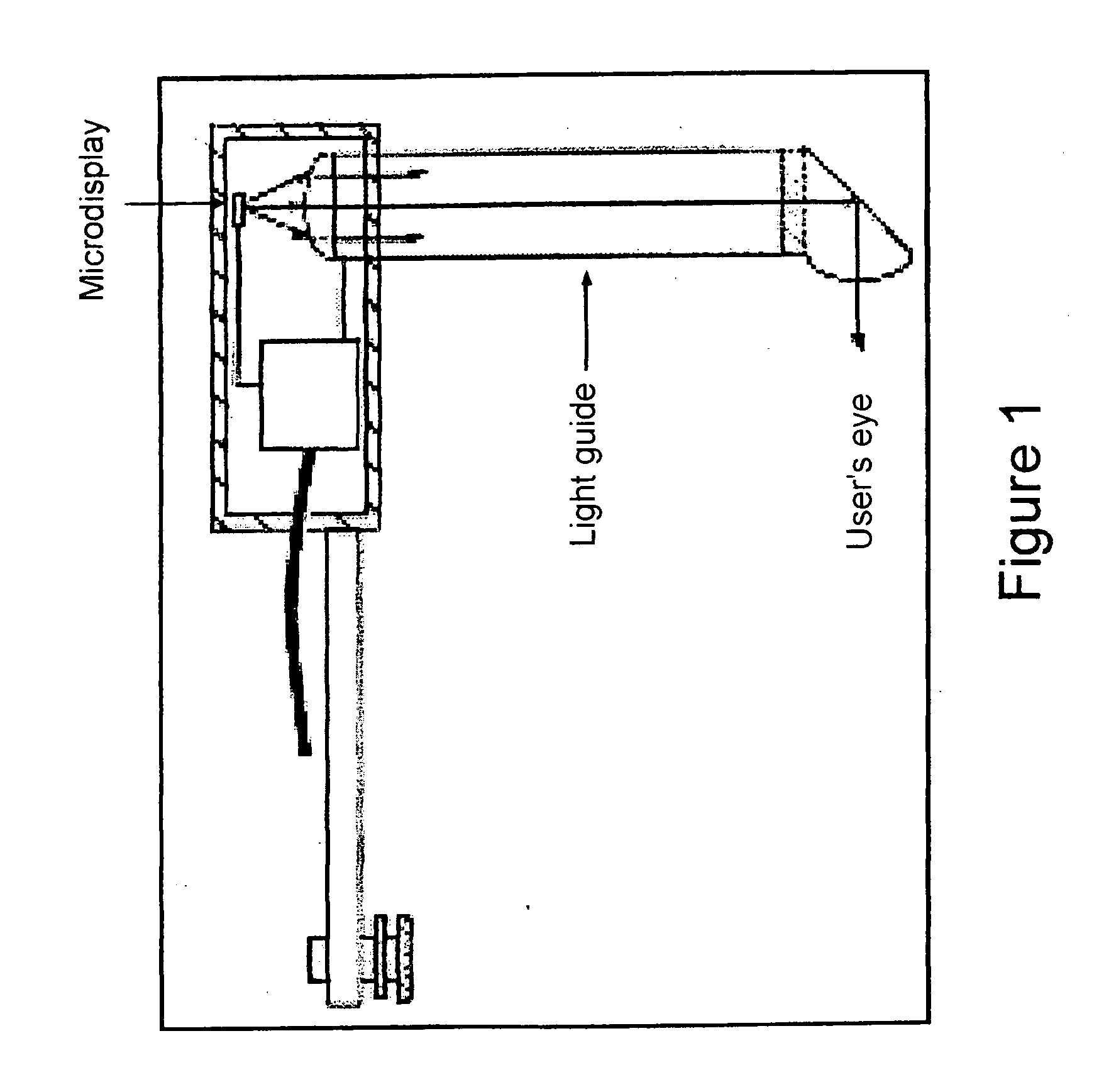
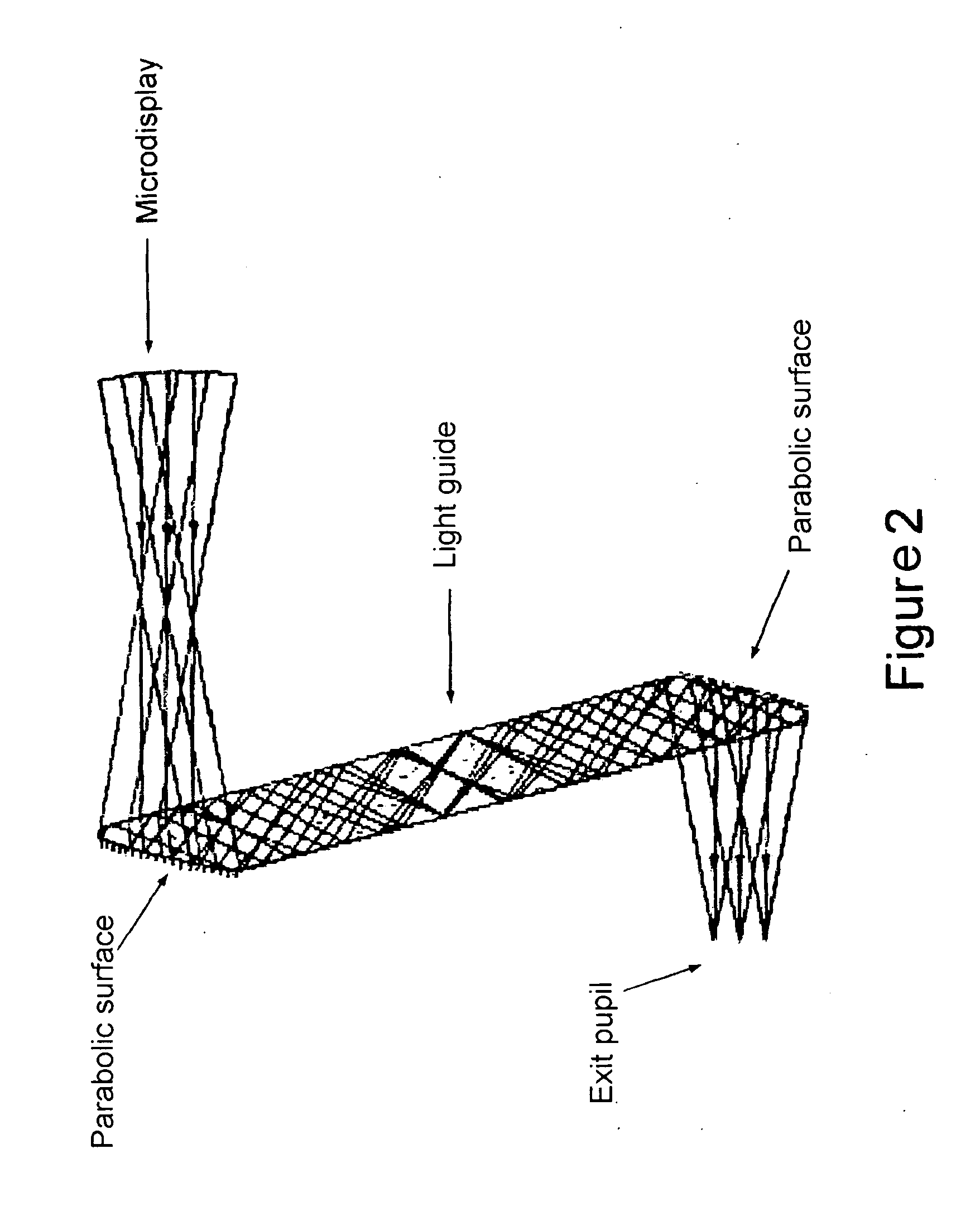
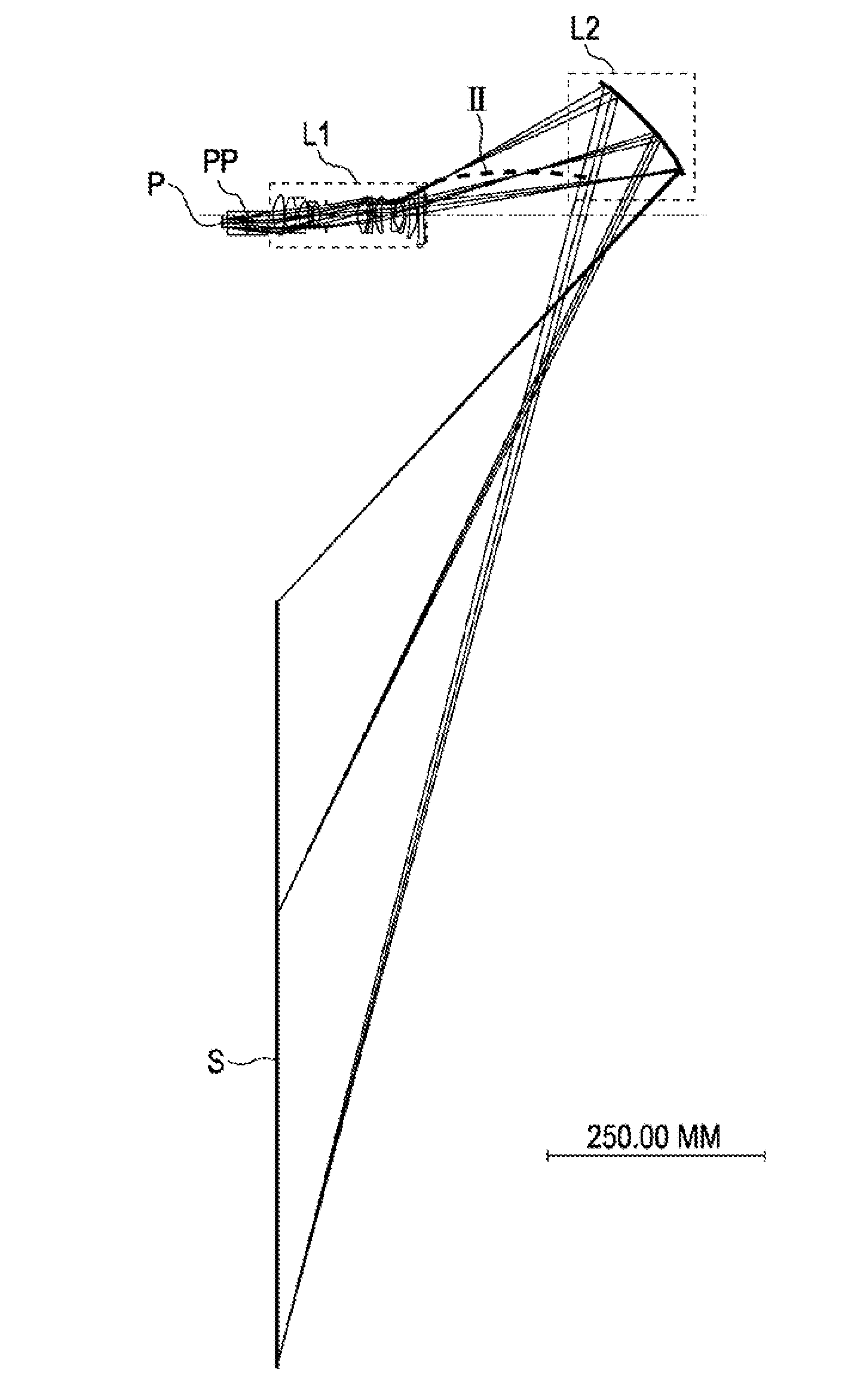
Optical system for image transmission, particularly for projection devices of the head-mounted type
An optical system for image projection, particularly for projection devices of the “head-mounted” type, includes a display, an optical system for focusing an image formed by the display, and a light guide having an extended body, with two opposite, longitudinal, plane and parallel faces, and opposite ends which define first reflecting surface for coupling into the light guide and second reflecting surface for extracting the image from the light guide. Each light ray which propagates through the light guide undergoes at least three internal total reflections on the parallel plane faces of the light guide. At least a surface of the focusing optical system is a portion of a surface free of rotational symmetry axes. Moreover, the two reflecting surfaces of the light guide are portions of surfaces free of rotational symmetry axes. Finally, the inlet pupil of the light guide coincides with the outlet pupil of the focusing system.
Owner:CENT RICERCHE FIAT SCPA
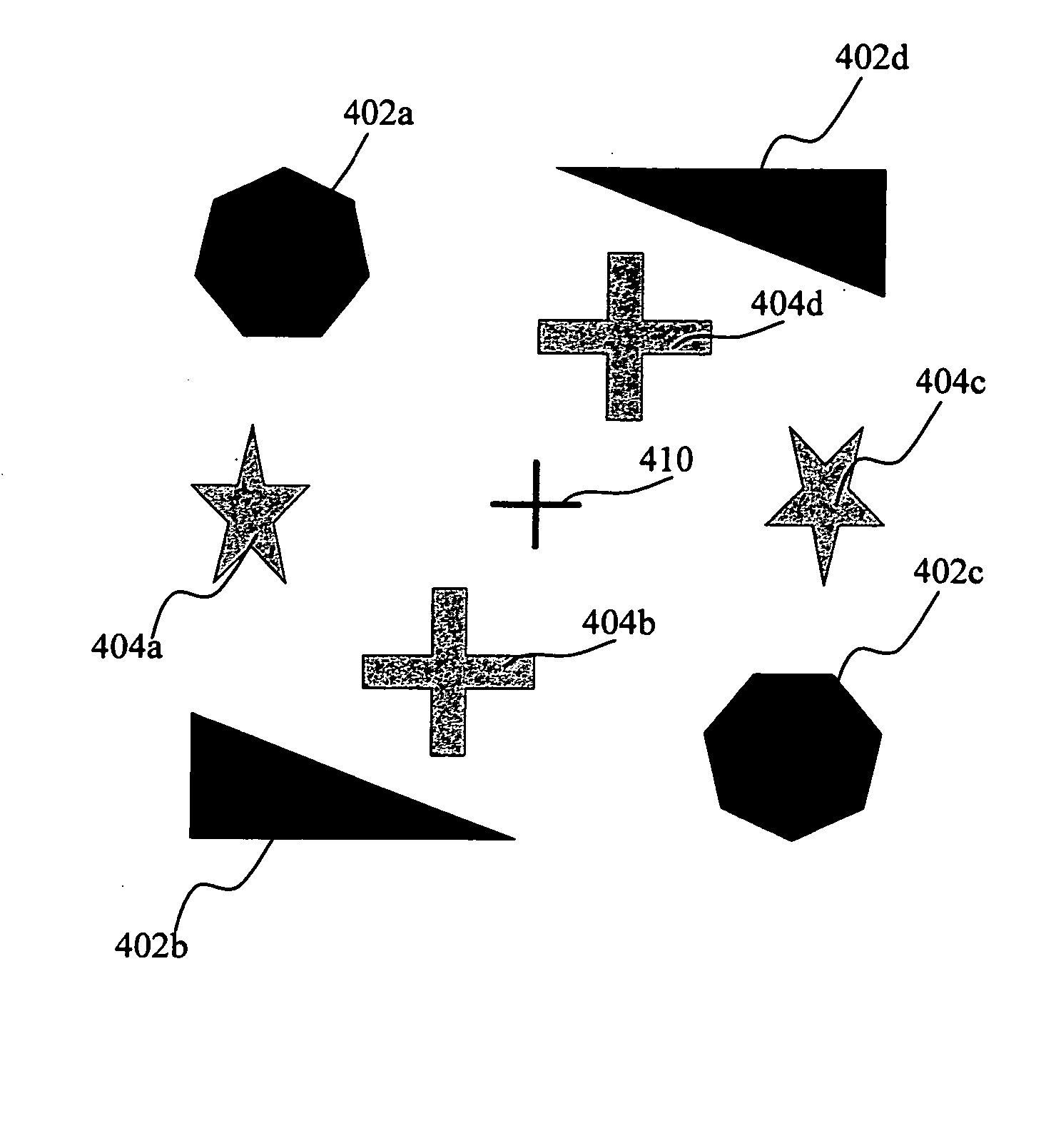
Apparatus and methods for determining overlay of structures having rotational or mirror symmetry
InactiveUS20070008533A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMetrologyPhysics
Disclosed are overlay targets having flexible symmetry characteristics and metrology techniques for measuring the overlay error between two or more successive layers of such targets. In one embodiment, a target includes structures for measuring overlay error (or a shift) in both the x and y direction, wherein the x structures have a different center of symmetry (COS) than the y structures. In another embodiment, one of the x and y structures is invariant with a 180° rotation and the other one of the x and y structures has a mirror symmetry. In one aspect, the x and y structures together are variant with a 180° rotation. In yet another example, a target for measuring overlay in the x and / or y direction includes structures on a first layer having a 180 symmetry and structures on a second layer having mirror symmetry. In another embodiment, a target for determining overlay in the x and / or y direction includes structures on a first layer and structures on a second layer, wherein the structures on the first layer have a COS that is offset by a known amount from the COS of the structures on the second layer. In a specific implementation, any of the disclosed target embodiments may take the form of device structures. In a use case, device structures that have an inherent 180° rotational symmetry or a mirror symmetry in each of the first and second layers are used to measure overlay in a first layer and a second layer. Techniques for imaging targets with flexible symmetry characteristics and analyzing the acquired images to determine overlay or alignment error are disclosed.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Picture element structure for panel display device
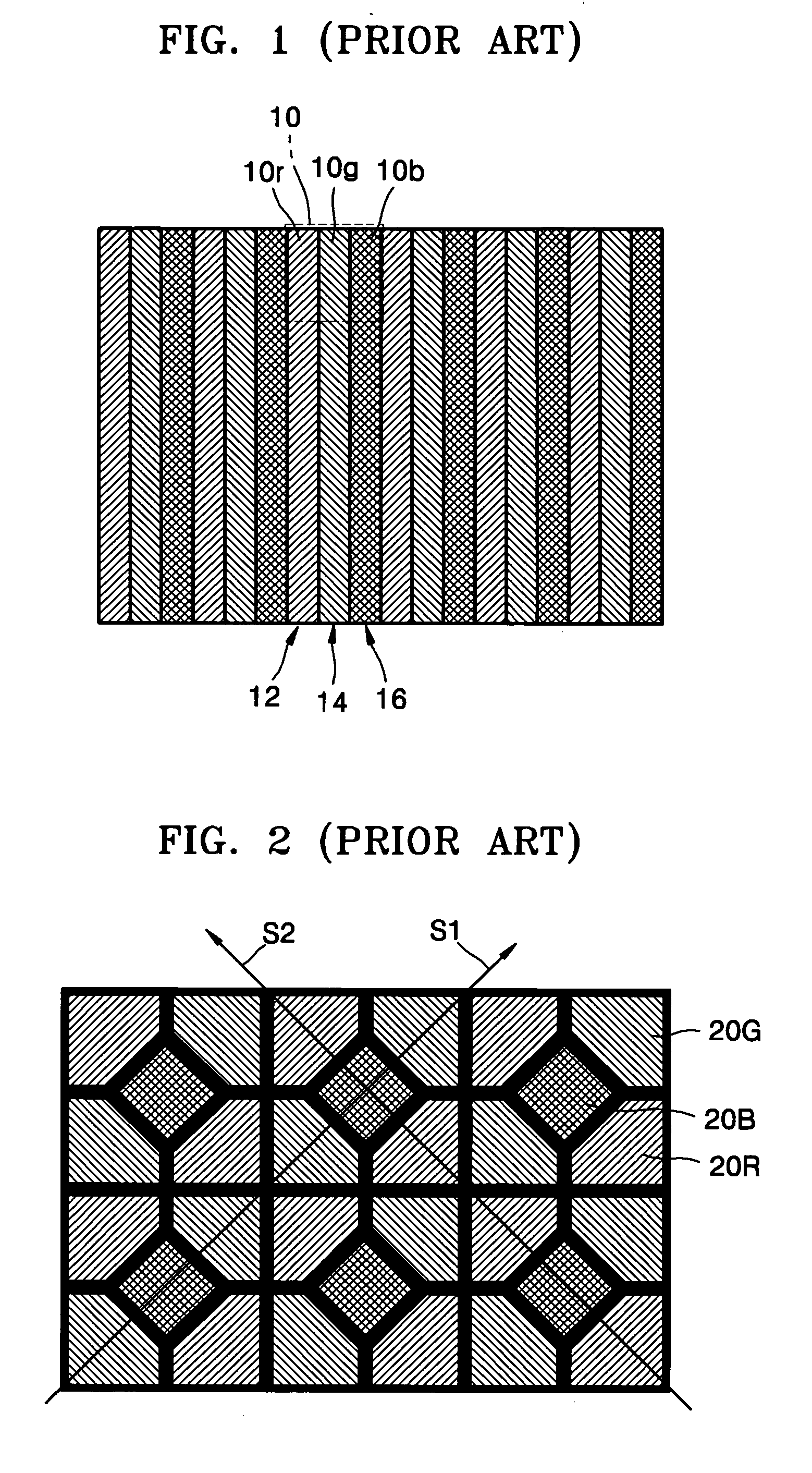
The present invention provides a pixel structure for a flat panel display apparatus displaying images using a plurality of pixels, each of the pixels including six or more sub-pixels. The flat panel display apparatus including the pixel structure is free from a color fringe error, and the pixel can include three or more primary colors. Thus, a color representation range of the flat panel display apparatus can be widened. In addition, since the sub-pixels of the pixel can be controlled by sub-pixel rendering, a resolution of the apparatus can be improved. Moreover, high resolution can be obtained in every direction on the display due to superior rotational symmetry of the pixels.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
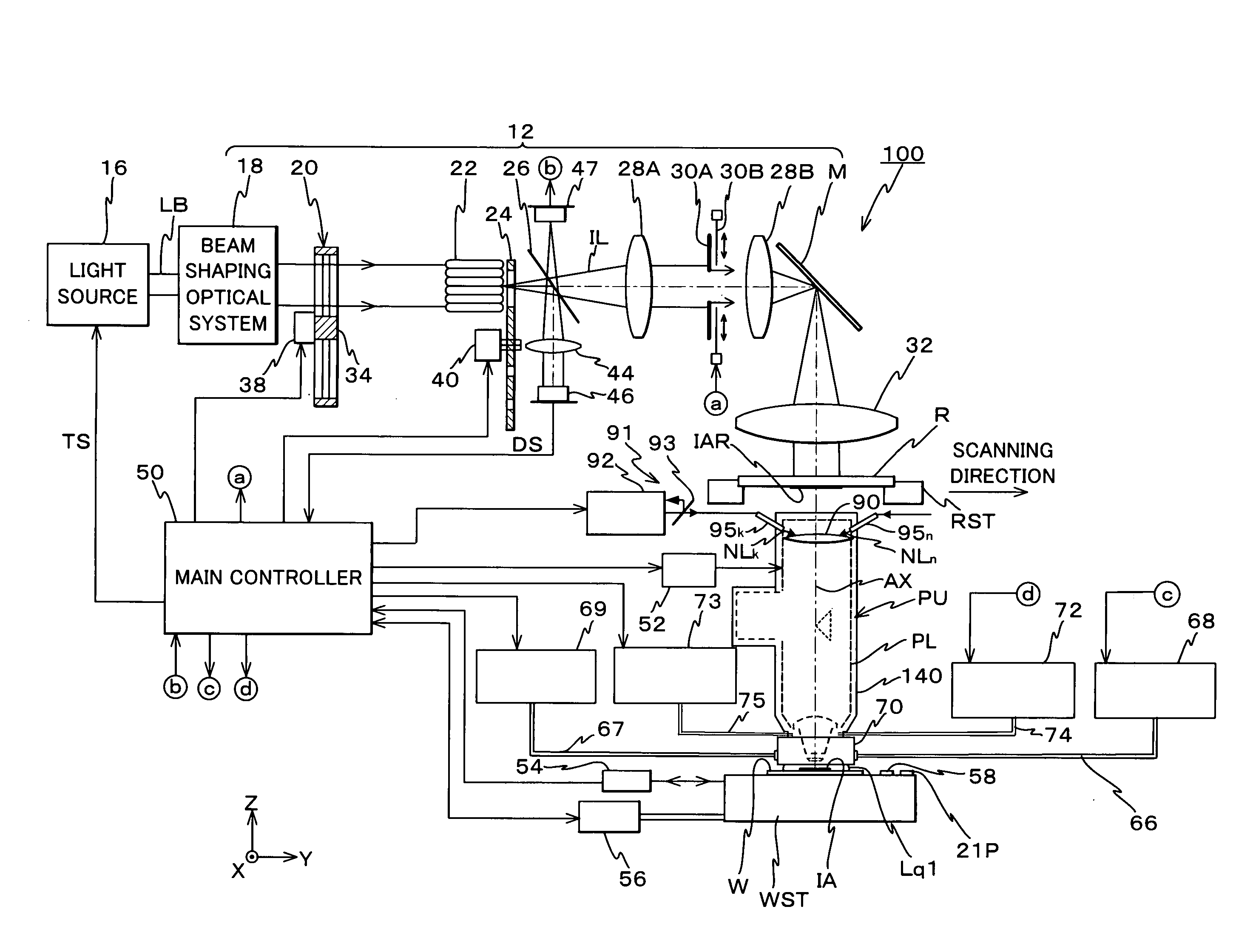
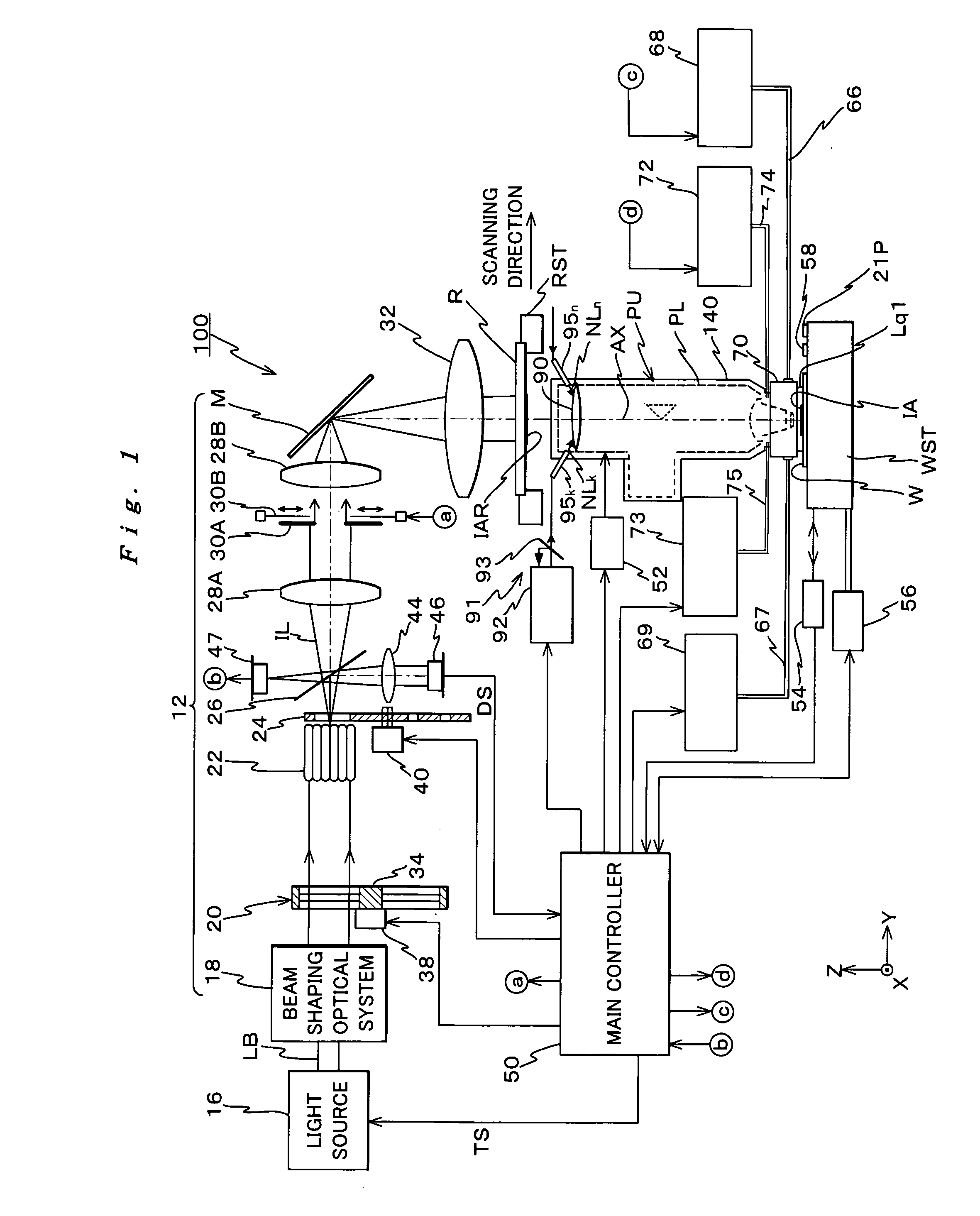
Exposure method and exposure apparatus, and device manufacturing method
InactiveUS20080204682A1Good precisionImprove accuracyPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingRotational symmetryOptical axis
By the combination of adjusting optical properties of an optical system by an irradiation unit irradiating non-exposure light on an optical element, which is movable, and adjusting the optical properties of the optical system with an optical properties adjustment unit by moving the optical element, for example, the change in the optical properties of the optical system caused by the temperature distribution of the optical elements whose center is at a position eccentric from the optical axis is corrected. Further, under a dipole illumination condition, in order to make optical properties of an optical system caused by non-rotational symmetry temperature distribution of optical elements in the vicinity of pupils into optical properties that can be corrected more easily by an optical properties adjustment unit, an irradiation unit irradiates non-exposure light on an optical element, which makes the optical element have a rotational symmetry temperature distribution. Accordingly, optical properties change in the optical system due to illumination light absorption can be effectively corrected.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Projection optical system and projection image display apparatus
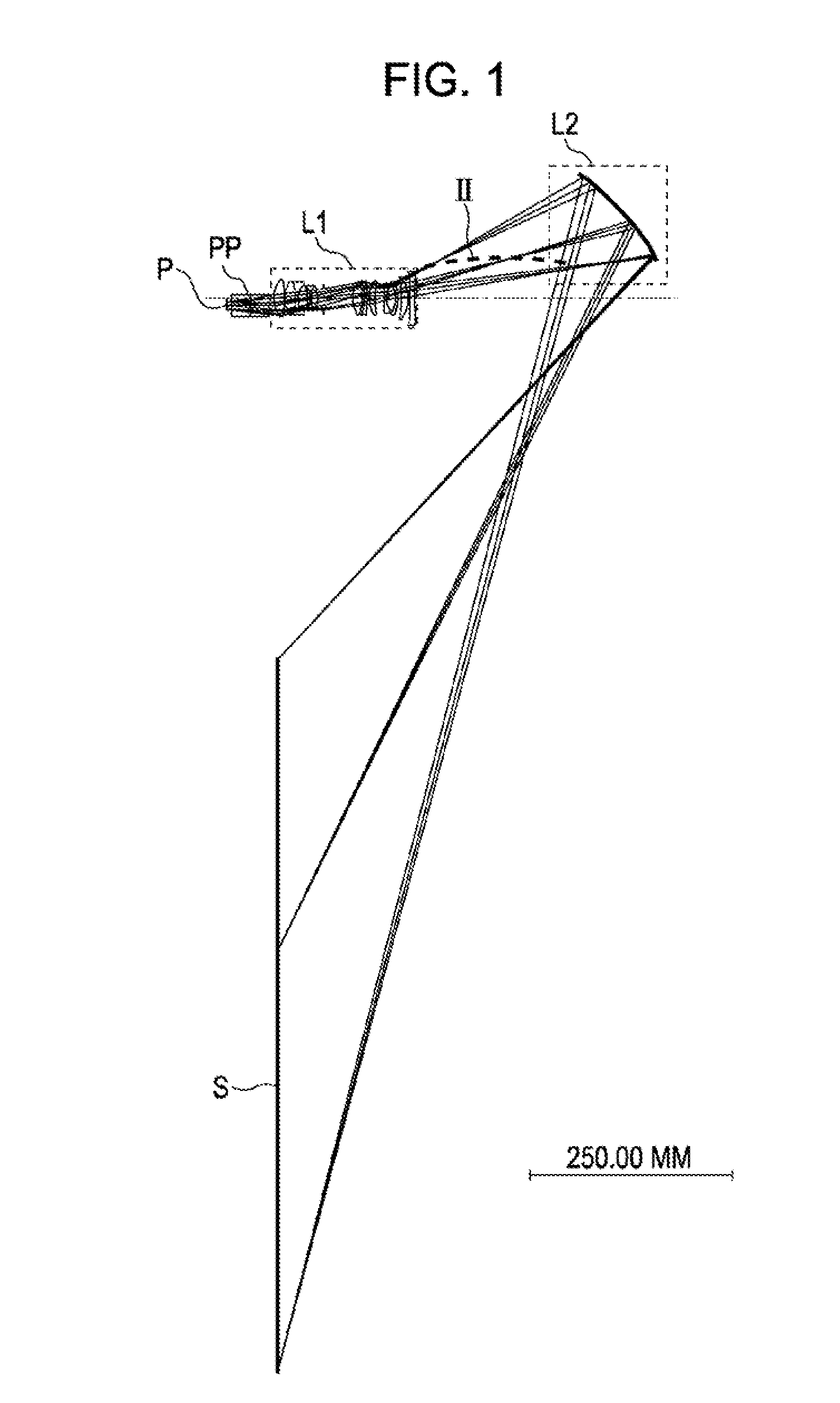
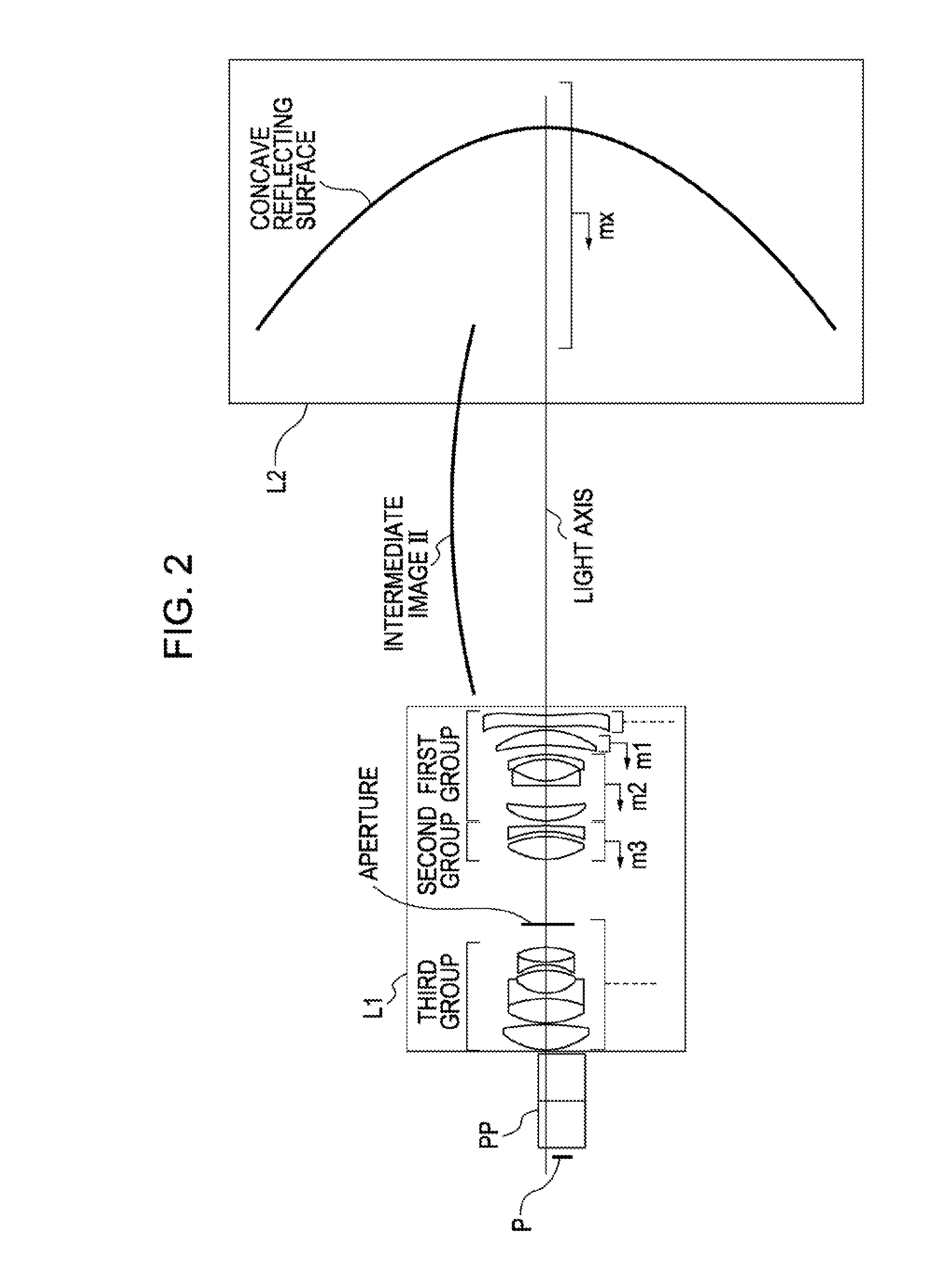
InactiveUS20080158439A1Wide viewing angleEasy to disassembleTelevision system detailsProjectorsIntermediate imageProjection image
A projection optical system for magnifying an image on a primary imaging plane onto a secondary imaging plane includes a first optical system for forming an intermediate image and a second optical system including a concave reflecting surface disposed between the intermediate image and the secondary plane. The first optical system includes first and second groups respectively having negative and positive power, an aperture, and a third group having positive power from the intermediate image. The surfaces of the first and second optical systems have rotational symmetry about a light axis. A ray traveling from the center of the primary plane to the center of the secondary plane intersects the light axis, is reflected off the reflecting surface, intersects the light axis again, and reaches the secondary plane. The following conditions are satisfied: 0.5<φ1 / φ2<3, 1<AST / ASS<5, |AST| / L12<1, and −3<K_rel.
Owner:SONY CORP
Diffractive optical device, refractive optical device, illumination optical system, exposure apparatus and exposure method
InactiveUS7095560B2Small sizeReduce in quantityDiffraction gratingsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOptical axisLight beam
An illumination optical system having a more simplified structure forms various quadrupole-shaped secondary light sources with two-time rotational symmetry with respect to an optical axis. The apparatus can provide illumination conditions that differ in two perpendicular directions on a radiation-receiving plane. In order to form a secondary light source with a quadrupole-shaped light intensity distribution on an illumination pupil plane, a diffractive optical device is provided in which an entrance light beam is converted into four light beams, and a light beam having a shape of four points centered about the optical axis is formed in a far field. The diffractive optical device is provided with a first diffractive optical member that is rotatable about a first axis parallel to the optical axis, and a second diffractive optical member that is rotatable about a second axis parallel to the optical axis, and that is arranged adjacent to the first diffractive optical member. A refractive optical device having first and second refractive optical members accomplishes similar results.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Compact relativity backward wave oscillator (RBWO) with adjustable low-frequency-range frequency
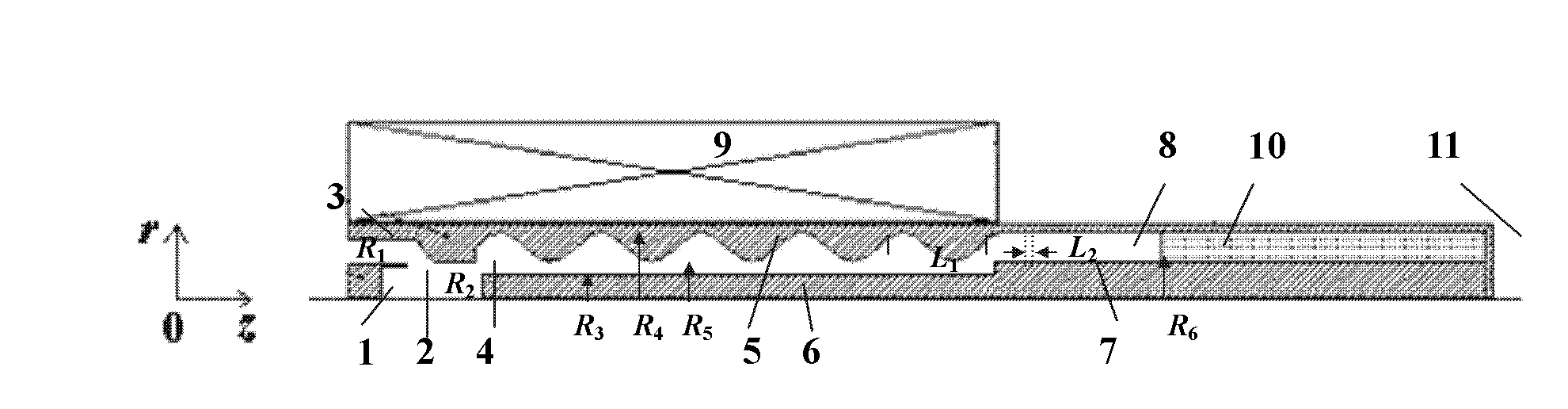
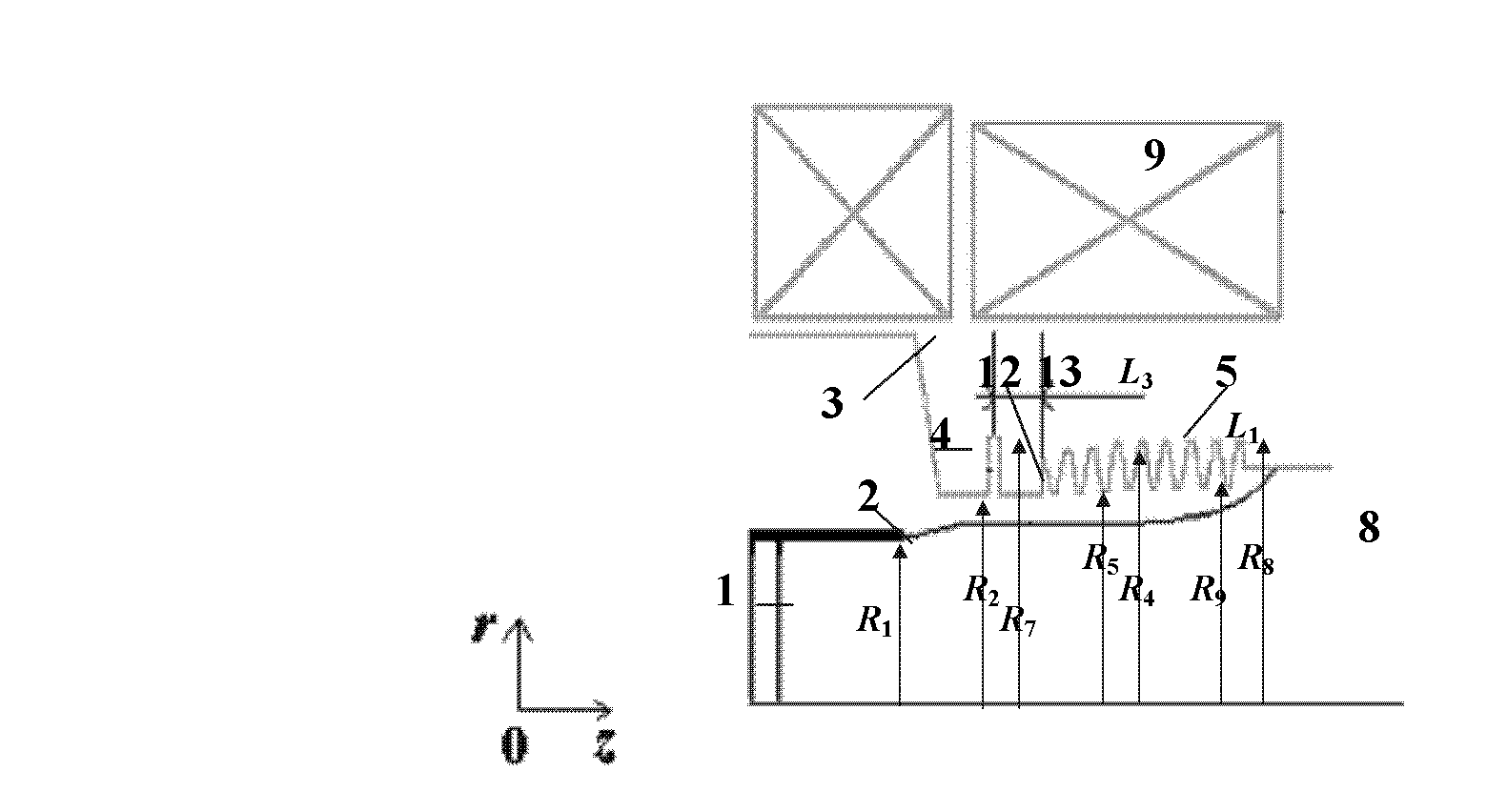
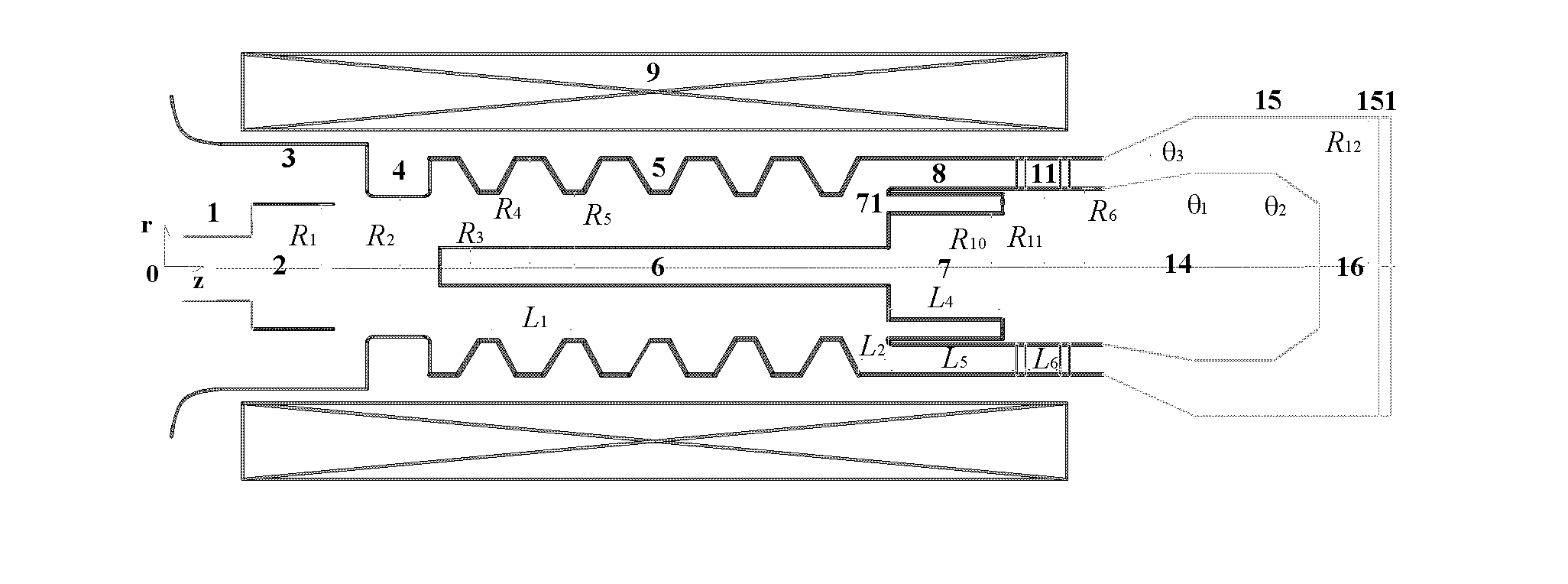
ActiveCN102208315AReduce radial sizeCan be smallTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube collectorsWave structureElectrical conductor
The invention discloses a compact relativity backward wave oscillator (RBWO) with an adjustable low-frequency-range frequency, and the oscillator provided by the invention is used for solving the problems that the RBWO size in a low frequency range is great, and the output microwave frequency is hard to adjust. The compact RBWO is in rotational symmetry with respect to a central axis, and composed of a cathode base, a cathode, an anode outer barrel, a stop neck, a slow wave structure, an inner conductor, a collector, a microwave output port, a solenoid field, two rows of supporting rods, a mode converter, a radiation port and a sealing plate; the slow wave structure is composed of five slow wave blades, the inner surface of each slow wave blade is in a trapezoid structure; the left end face of the collector is provided with an annular groove; the left end of the mode converter is cylindrical, and the right end of the mode converter is in a tapered structure; the radiation port is cylindrical, the left end of the radiation port is in a tapered structure and the right end of the radiation port is cylindrical; the sealing plate is pressed on the radiation port; and the frequency of the output microwave is adjusted by virtue of adjusting the semi-diameter R3 of the inner conductor. The compact RBWO has the advantages of compact structure and convenient and adjustable work frequency, thereby being beneficial to outputting a long pulse of the microwave.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
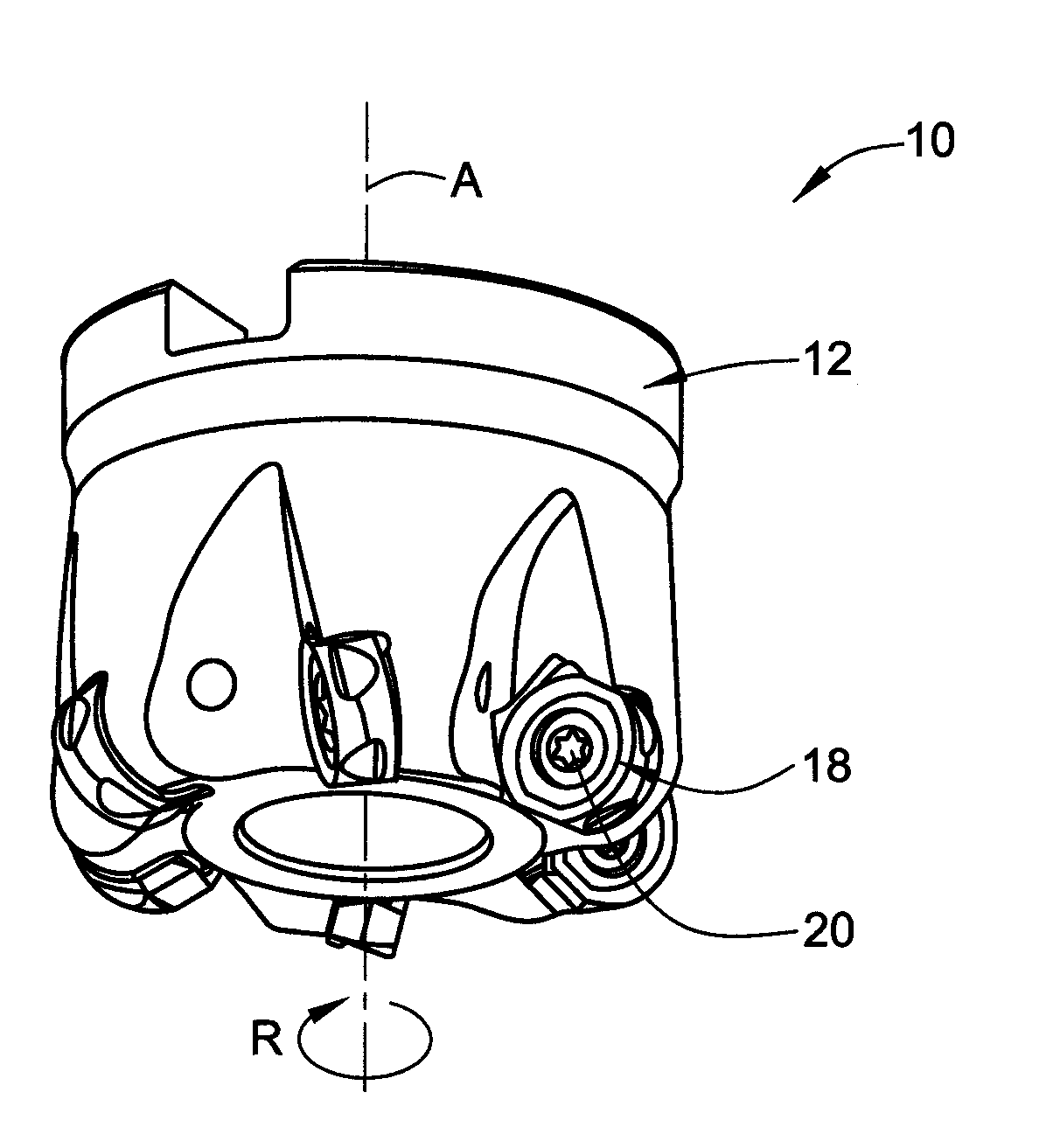
Cutting Tool and Round Double Sided Cutting Insert Therefor
A cutting insert for retention in a rotating cutting tool having an axis of rotation has two opposing end surfaces and a peripheral surface extending therebetween, each end surface having a mutual first axis of symmetry passing through the end surfaces about which each end surface has N-fold rotational symmetry for some value of N where N is chosen from the group consisting of 2, 3 and 4. A peripheral cutting edge is formed at the junction between each end surface and the peripheral surface, the peripheral cutting edge having N curved cutting edges merging with N straight cutting edges which extend between the curved cutting edges at extremities thereof. The curved cutting edges of the two end surfaces are not aligned in an end view of the cutting insert along the first axis of symmetry.
Owner:ISCAR LTD
Microphone array system and method for sound acquisition
ActiveUS8923529B2Reduce processing timeEffective regulationSignal processingMicrophones signal combinationSound source locationSound sources
A microphone array system (16) for sound acquisition from multiple sound sources in a reception space surrounding a microphone array (18) that is interfaced with a beamformer module (28) is disclosed. The microphone array (18) includes microphone transducers (22) that are arranged relative to each other in N-fold rotationally symmetry, and the beamformer includes beamformer weights that are associated with one of a plurality of spatial reception sectors corresponding to the N-fold rotational symmetry of the microphone array (18). Microphone indexes of the microphone transducers (18) are arithmetically displaceable angularly about the vertical axis during a process cycle, so that a same set of beamformer weights is used selectively for calculating a beamformer output signal associated with any one of the spatial reception sectors. A sound source location module (30) is also disclosed that includes a modified steered power response sound source location method. A post filter module (32) for a microphone array system is also disclosed.
Owner:BIAMP SYST LLC
Multiple image camera and lens system
A system for simultaneously producing multiple images substantially identical images on multiple separate detector planes is disclosed. A reflective spatially beam-splitting element preferably comprising multiple reflective areas is preferably placed at a location substantially coincident with the pupil or aperture of the system. In non-diffraction limited systems, each area preferably comprises an actual cross section that is circular or has the rotational symmetry (or a multiple thereof) of the number of images to be formed. In diffraction limited systems, all of the areas preferably comprise actual cross sections that have the same shape, size and orientation with respect to the incoming optical beam. Each individual actual cross section may be due to the shape of each area, optionally in combination with a mask. Appropriate selection of filters enables real-time multi-spectral scientific imaging, imaging polarimetry, or high dynamic range imaging (HDRI) for photography and cinematography, even with a moving camera and / or moving subjects.
Owner:CONTRAST INC
Cosmetic Product applicator With Multiple Typically Oriented Elements
Owner:ALBEA SERVICES SAS
Device and method for preparing a recess in a bone
InactiveUS20080269649A1Avoid necessityAvoid interferences from occurringChiropractic devicesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsPunchingEngineering
A punching device for preparing a recess in a bone has a punching tool usable for such a punching device. An implant usable with the punching tool is provided and a method for preparing a recess in a bone are disclosed. The punching device comprises an ultrasonic sonotrode and a punching tool which is fixable to the sonotrode at its proximal extremity. At its distal extremity, the punching tool has a thin-walled portion having a non-rotational symmetric cross-section. By ultrasonic vibration of the punching tool, the thin-walled portion can be forced into a bone thereby preparing a recess of which is not rotationally symmetric. Subsequently, an implant can be held in such recess. Due to its lack of rotational symmetry, the implant may absorb rotational forces around its longitudinal axis.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC +1
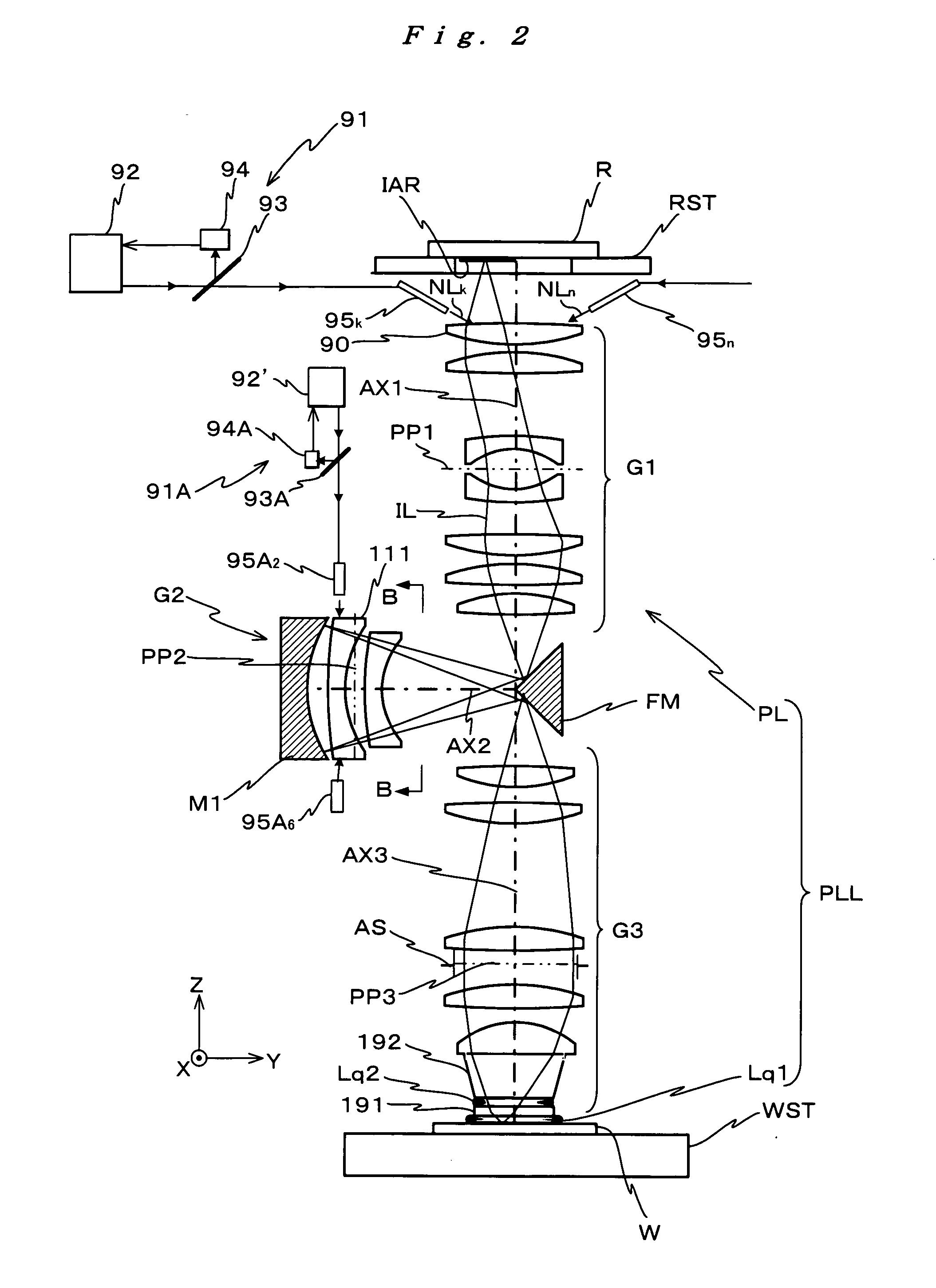
Microlithography reduction objective and projection exposure apparatus
InactiveUS6902283B2Efficiently maskedThe implementation process is simpleMirrorsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusImage planePhysics
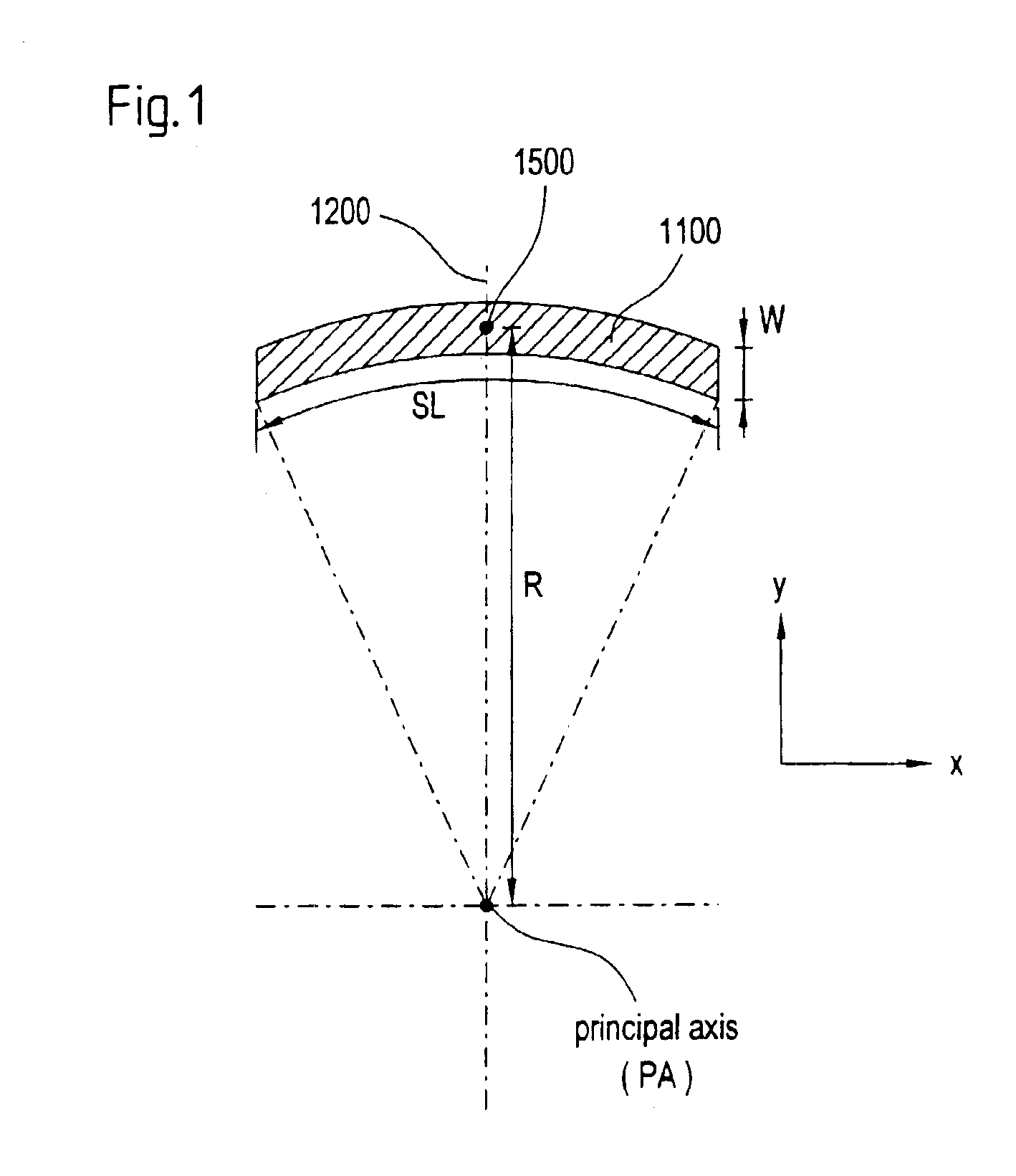
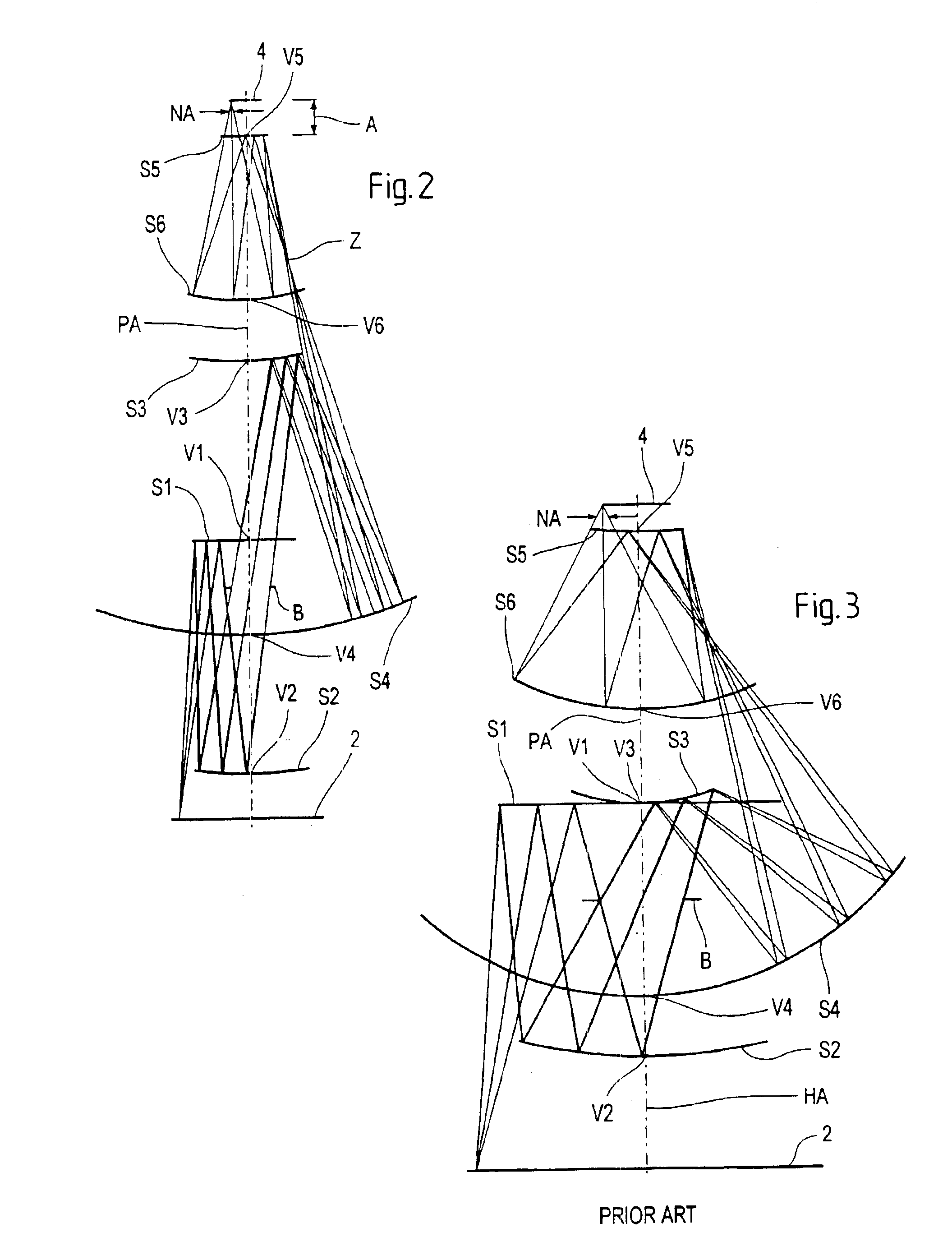
A projection objective formed from six mirrors arranged in a light path between an object plane and an image plane is provided. The projection objective, in some examples, is characterized by having a physical distance between the vertexes of adjacent mirrors that is large enough to allow for the six mirrors to have sufficient thickness and stability properties to prevent surface deformations due to high layer tensions. In some embodiments, mirror thickness are such that surface deformations are prevented with mirrors having layer tensions lower than 350 MPa. Mirror surfaces may comprise multilayer systems of Mo / Be or Mo / Si layer pairs. In some examples, the physical distance between a vertex of the third mirror and a vertex of the sixth mirror (S3S6) satisfies the following relationship: 0.3×(a used diameter of the third mirror S3+a used diameter of the sixth mirror S6)<S3S6. In some examples, a ratio of a physical distance between a vertex of the first mirror and a vertex of the third mirror (S1S3) to a physical distance between the vertex of the first mirror and a vertex of the second mirror (S1S2) is within the range of: 0.5<S1S3 / S1S2<2. In some examples, the physical mirror surfaces of the mirrors have a rotational symmetry with respect to a principal axis (PA). In some examples, all physical mirror surfaces are aspherical. In some examples, at most five physical mirror surfaces are aspherical. Other examples are provided, along with microlithography projection exposure apparatuses and processes for producing a microelectronic device.
Owner:CARL ZEISS STIFTUNG
Electronic component, module, module assembling method, module identification method and module environment setting method
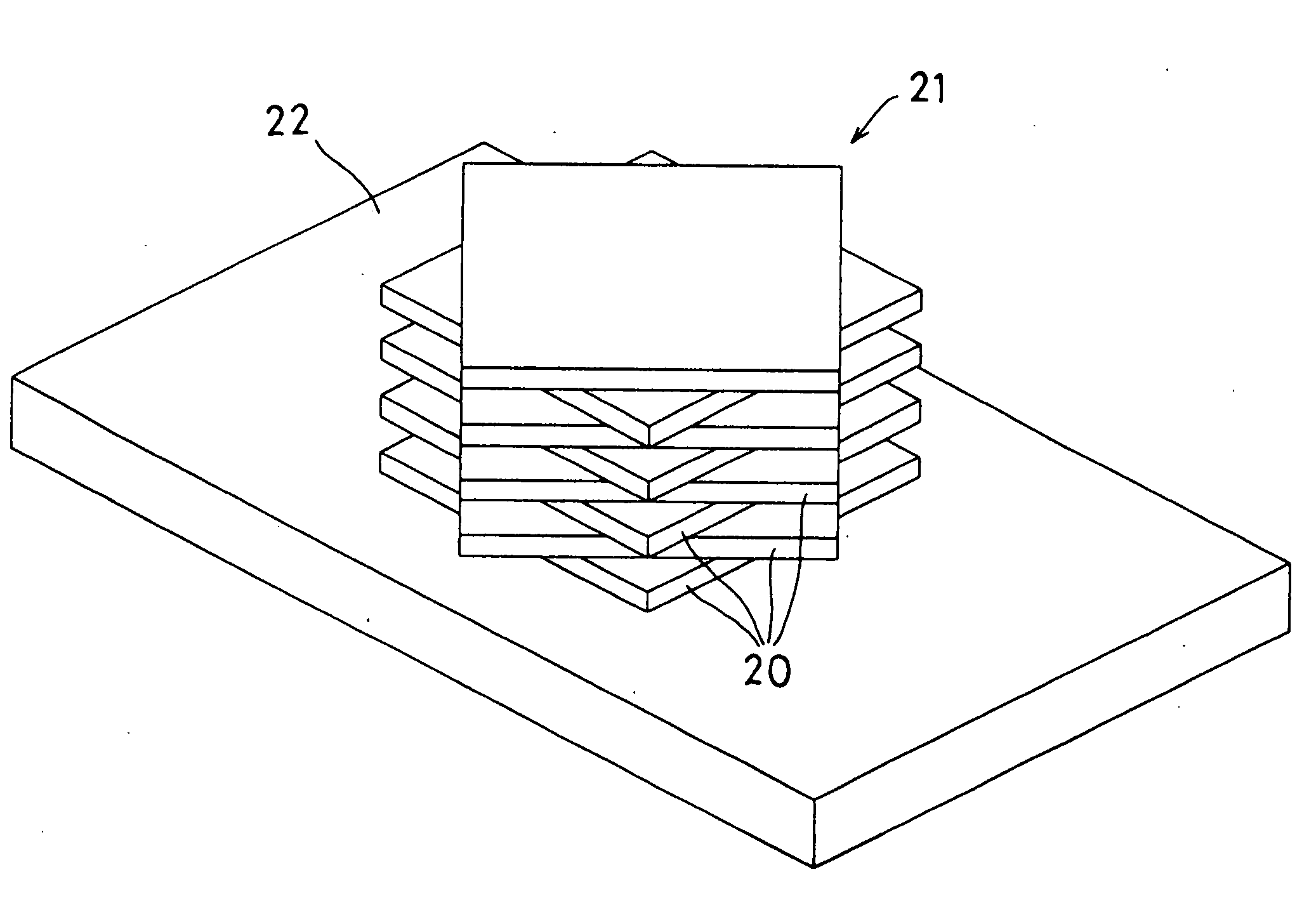
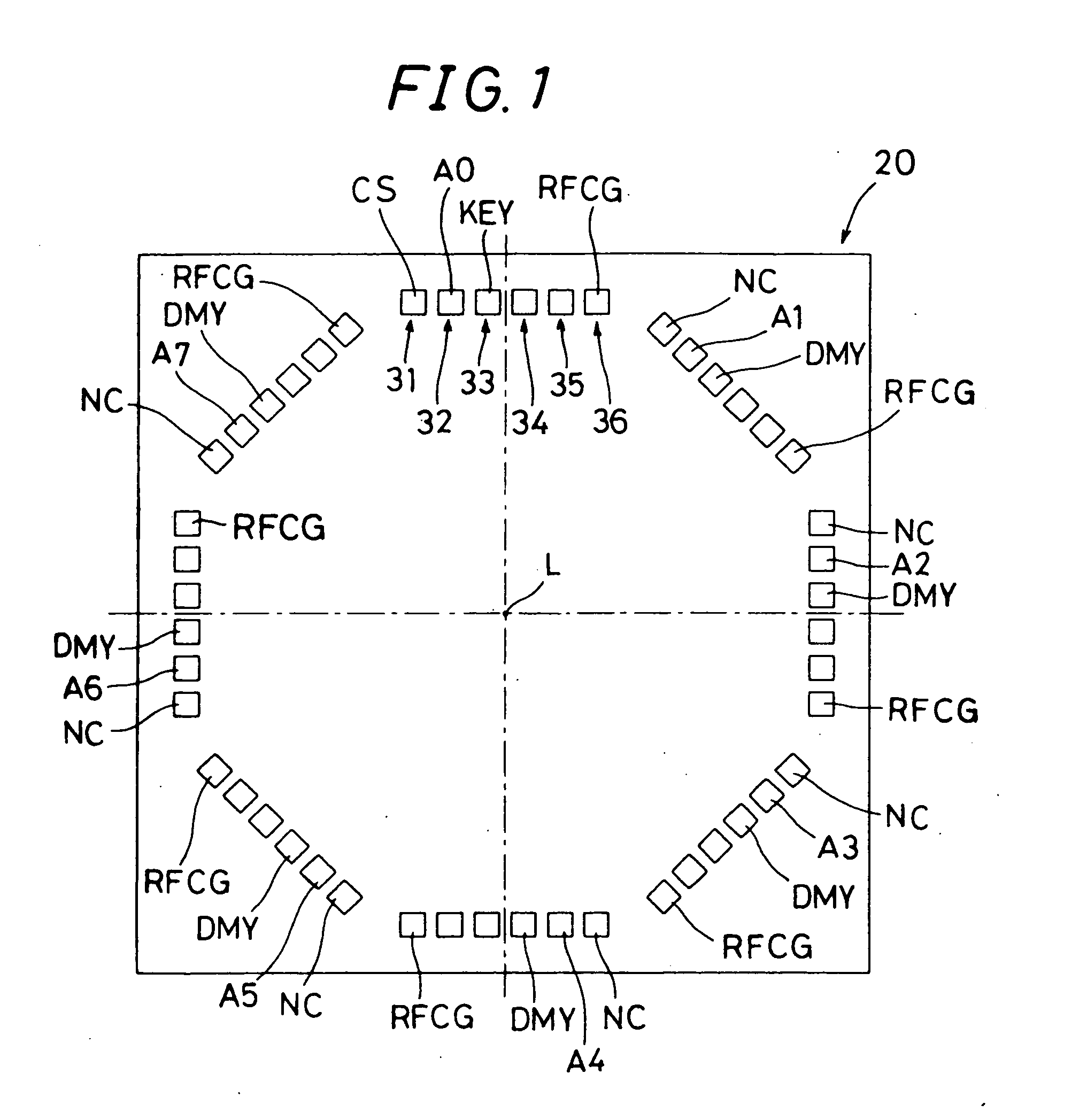
InactiveUS20070096332A1FavorableShorten the timeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectronic component
An electronic component capable of being assembled into a module in the form of a stack of a plurality of layers is provided. Terminals of terminal groups (31 to 36) are formed so as to have rotational symmetry of a predetermined fold-number or have rotational symmetry and symmetry with respect to the plane containing a symmetric axis line. The terminals (A0 to A7, RFCG) of common connection terminal groups (32, 36) have connecting portions formed on the both surfaces in a stacking direction. Among the terminals of individual connection terminal groups (31, 33), a specific terminal CS; KEY has a connection portion formed at least on one of the both surfaces in the stacking direction while the remaining associated terminals NC; DMY have connection portions formed on the both surfaces in the stacking direction. When such electronic components (20) are stacked so as to be shifted from each other by the angle obtained by dividing 360 degrees by the predetermined fold-number or in addition in the inverted state, it is possible to assemble a module using the electronic components (20) having the same configuration.
Owner:SHARP KK +2
Symmetric target design in scatterometry overlay metrology
ActiveUS20160216197A1Photomechanical apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansPhase shiftedMetrology
Metrology methods, systems and targets are provided, which implement a side by side paradigm. Adjacent cells with periodic structures are used to extract the overlay error, e.g., by introducing controllable phase shifts or image shifts which enable algorithmic computation of the overlay. The periodic structures are designed to exhibit a rotational symmetry to support the computation and reduce errors.
Owner:KLA CORP
Cutting insert and replaceable insert-type rotating tool
InactiveUS20120275868A1Extended service lifeLow production costMilling cuttersShaping cuttersCurve shapeEngineering
A rake face (12) is formed on the both sides of an insert main body facing outside in the thickness direction thereof to make a pair, a cutting edge (14) is arranged on each side which constitutes an outer periphery of the rake face (12), the cutting edge (14) is provided with a major cutting edge (18A) and a minor cutting edge (18B) A connection part (20) formed in a concave curved shape is formed on the insert main body over the entire thickness direction of the insert main body. Of the pair of rake faces (12), each cutting edge (14) on the outer periphery of the first rake face (12A) and each cutting edge (14) on the outer periphery of the second rake face (12B) have rotation symmetry with each other.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Pixel structure for flat panel display apparatus
A pixel structure for a flat panel display apparatus displaying images using a plurality of pixels, each of the pixels including six or more sub-pixels. The flat panel display apparatus including the pixel structure is free from a color fringe error, and the pixel can include three or more primary colors. Thus, a color representation range of the flat panel display apparatus can be widened. In addition, since the sub-pixels of the pixel can be controlled by sub-pixel rendering, a resolution of the apparatus can be improved. Moreover, high resolution can be obtained in every direction on the display due to superior rotational symmetry of the pixels.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Lane setting at road intersection and corresponding traffic light control method
ActiveCN102277804AImprove traffic capacityFlexible useControlling traffic signalsRoadwaysHorizontal axisEngineering
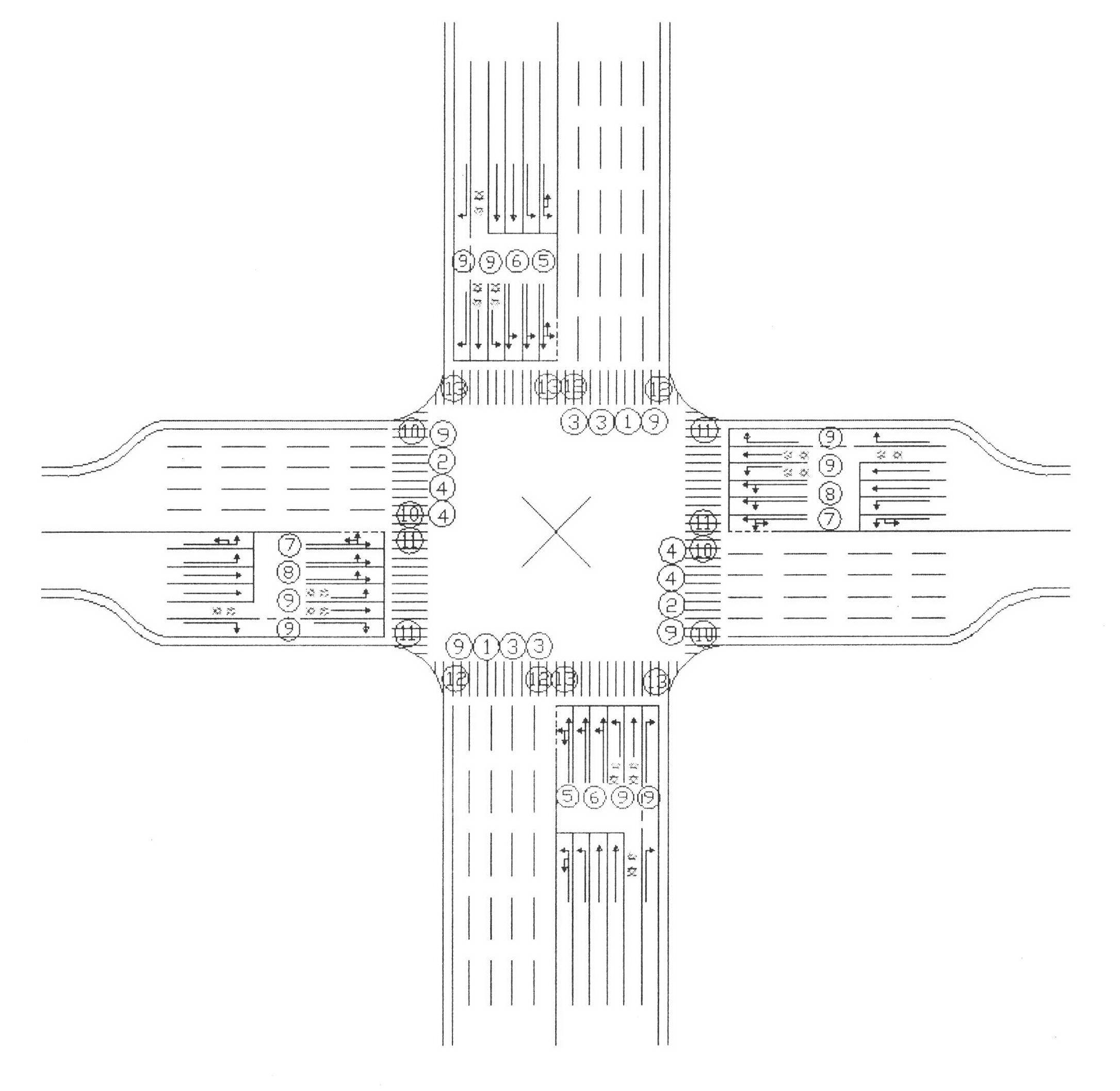
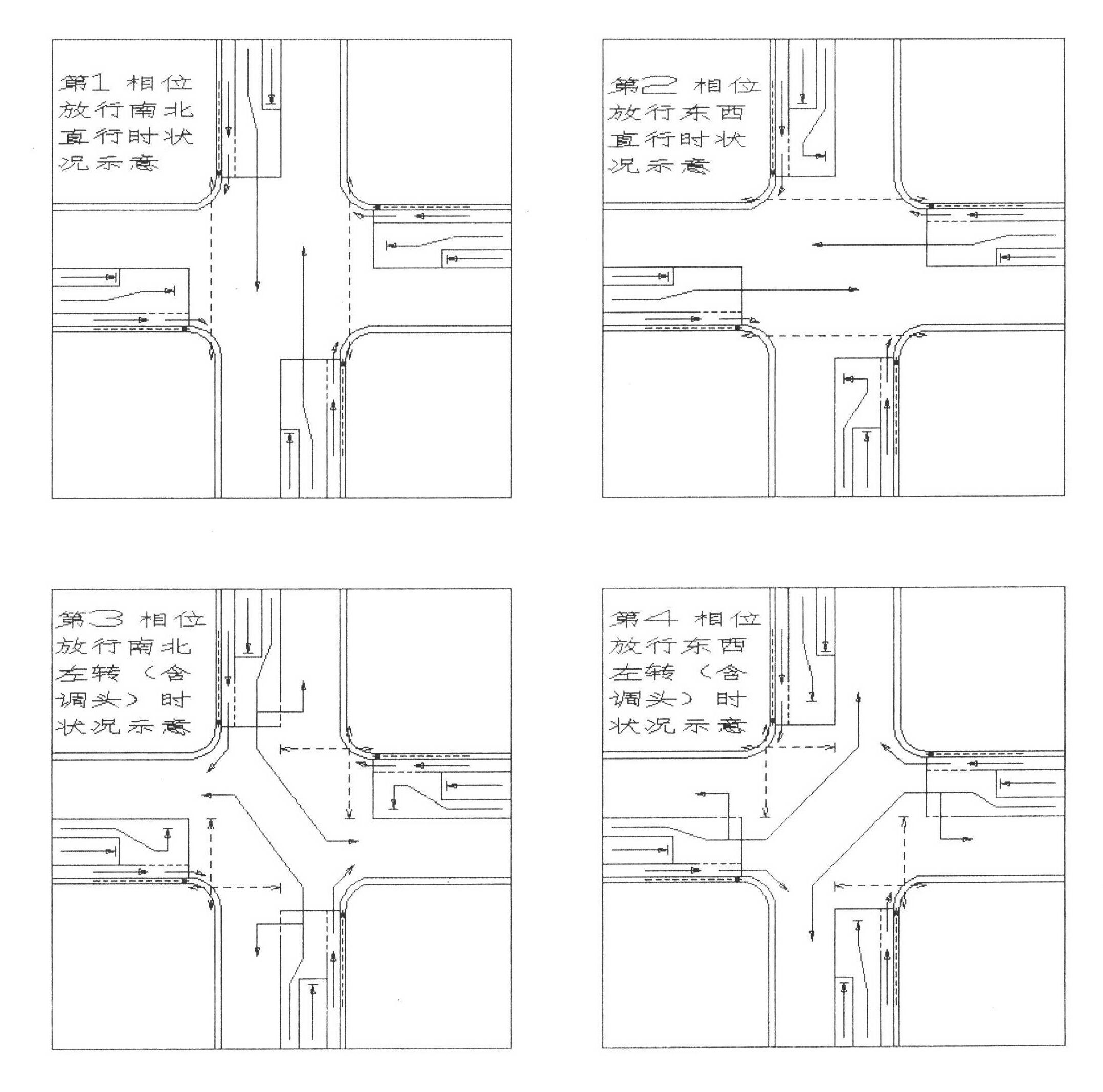
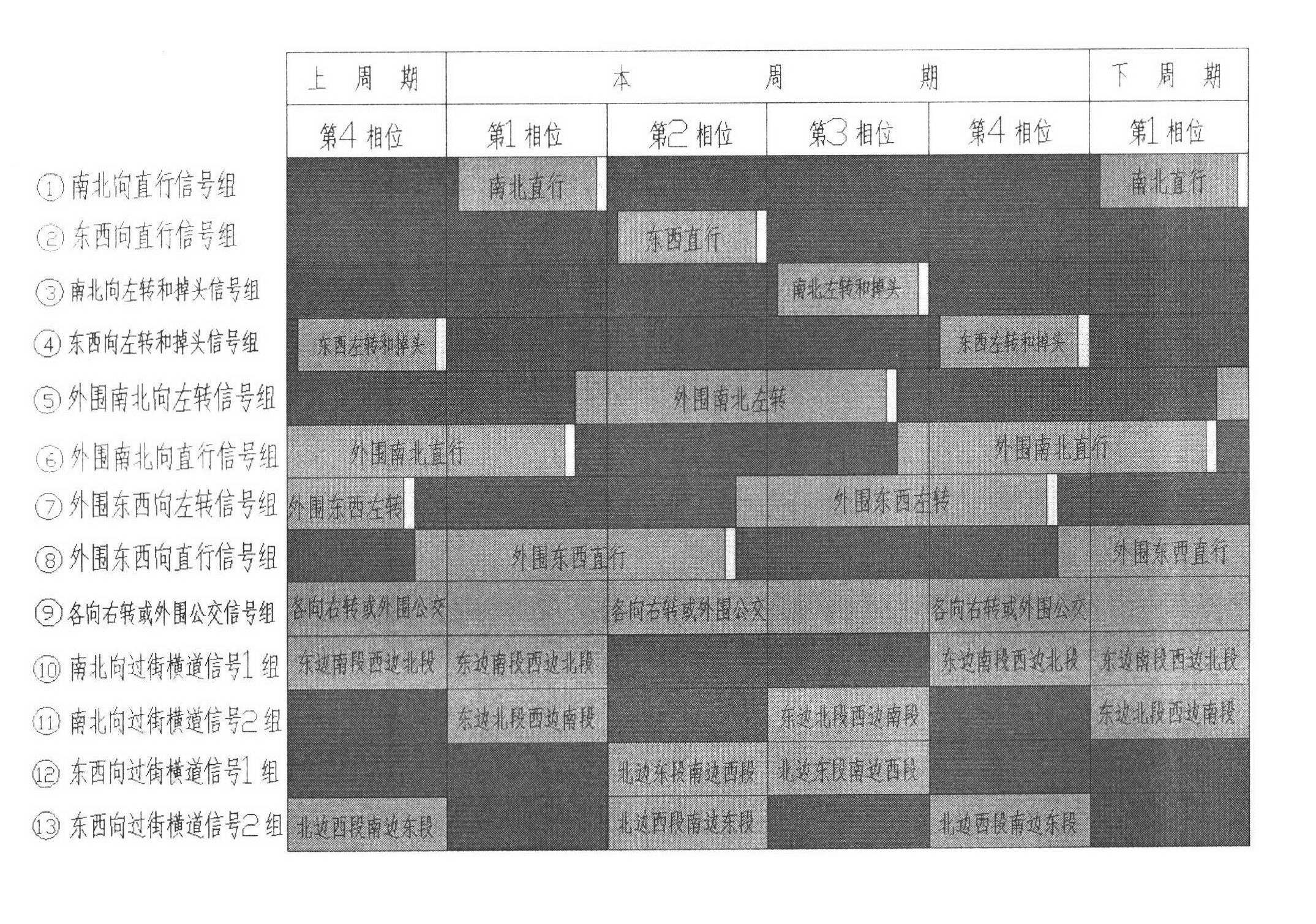
A lane setting at a road intersection and a corresponding traffic light control method. It does not distinguish between primary and secondary roads, so that the number of entrance and exit lanes of each main phase is kept equal; the entrance lanes are divided into three parts: "entrance guide lane", "peripheral guide lane" and "bus and right-turn lane"; according to the direction of travel Arrange the lanes, light groups, signal groups and phases symmetrically on the horizontal axis of the horizontal axis; at the intersection, run the main phase of A going straight——B going straight——A turning left (including U-turn)——B turning left (including U-turn); The "peripheral traffic lights" alternately operate the two phases of straight-going vehicles moving forward and left-turning (including U-turn) vehicles moving forward, and an evergreen phase and "electronic police" for directing right-turning vehicles and buses to pass; according to the number of left-turning vehicles Decide whether to control the clearance of pedestrian crossings in units of full or half-way. This method can make the number of lanes passing by each phase of the intersection reach the maximum on the basis of equilibrium, and is conducive to the priority of public transportation and the convenience of pedestrians.
Owner:胡又宏 +2
Particle-optic electrostatic lens
ActiveUS7199373B2Facilitate the magnetic shielding of an electrostatic lens systemReduce spacingStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsOptical axisParticle beam
In a charged-particle beam exposure device, an electrostatic lens (ML) comprises several (at least three) electrodes with rotational symmetry (EFR, EM, EFN) surrounding a particle beam path; the electrodes are arranged coaxially on a common optical axis representing the center of said particle beam path and are fed different electrostatic potentials through electric supplies. At least a subset of the electrodes (EM) form an electrode column realized as a series of electrodes of substantially equal shape arranged in consecutive order along the optical axis, wherein outer portions of said electrodes (EM) of the electrode column have outer portions (OR) of corresponding opposing surfaces (f1, f2) facing toward the next and previous electrodes, respectively. Preferably, the length of the electrode column is at least 4.1 times (3 times) the inner radius (ri1) of said surfaces (f1, f2).
Owner:IMS NANOFABTION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com