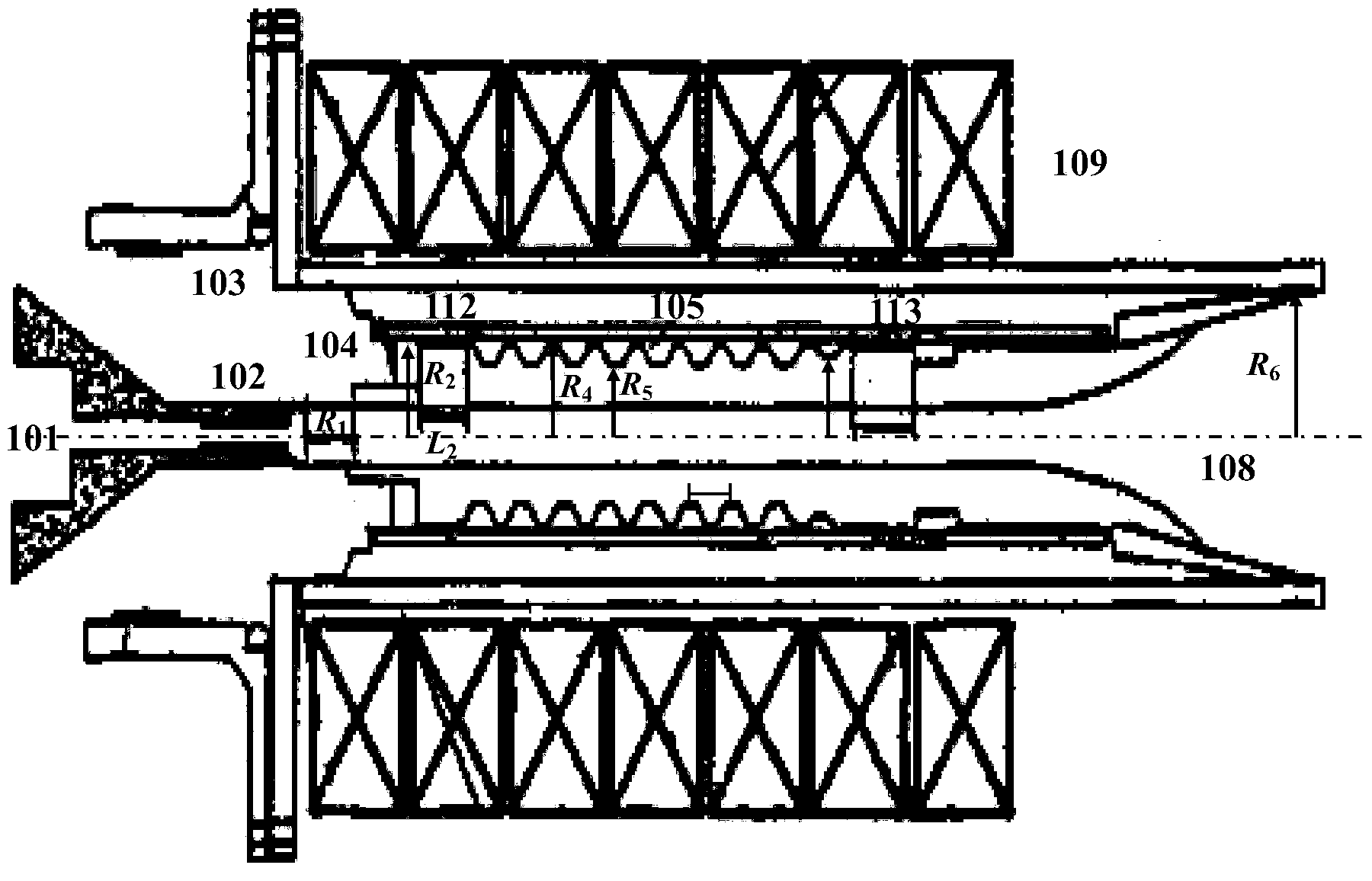
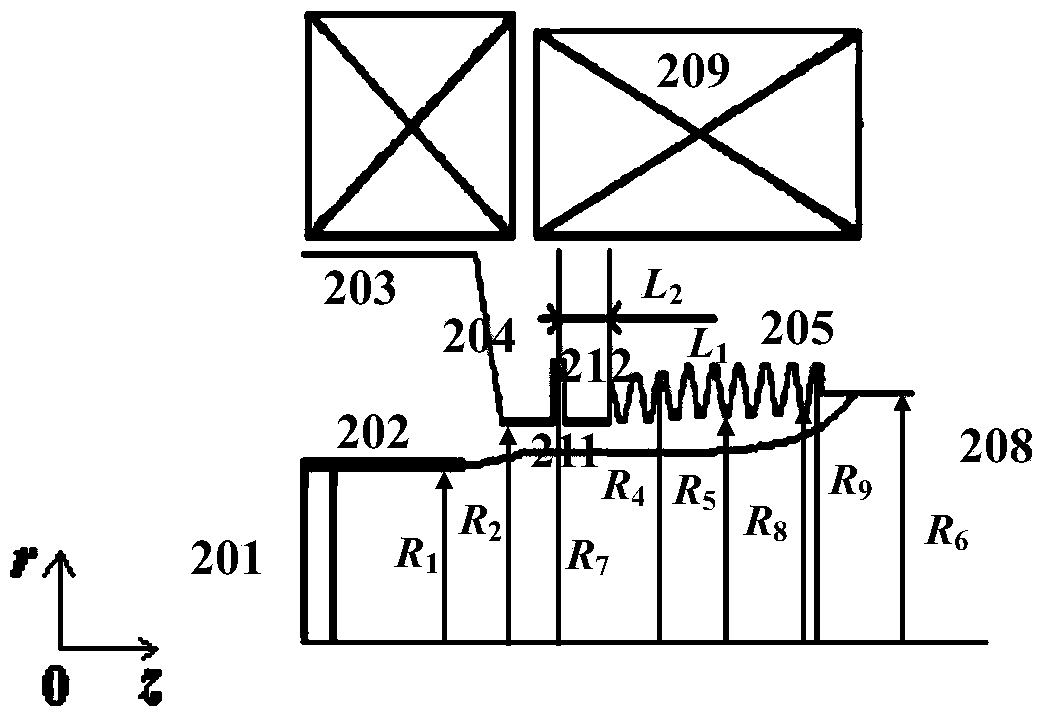
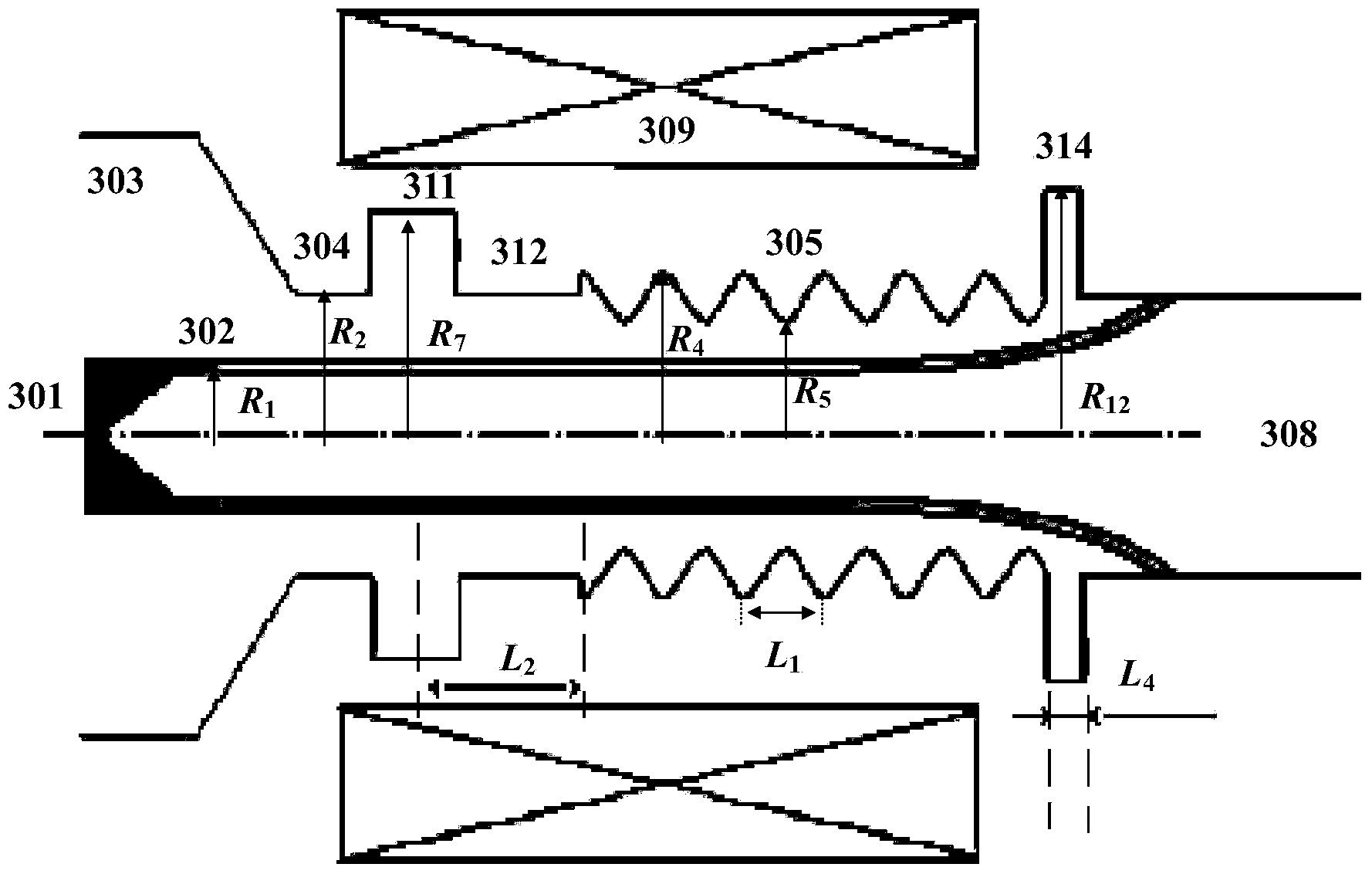
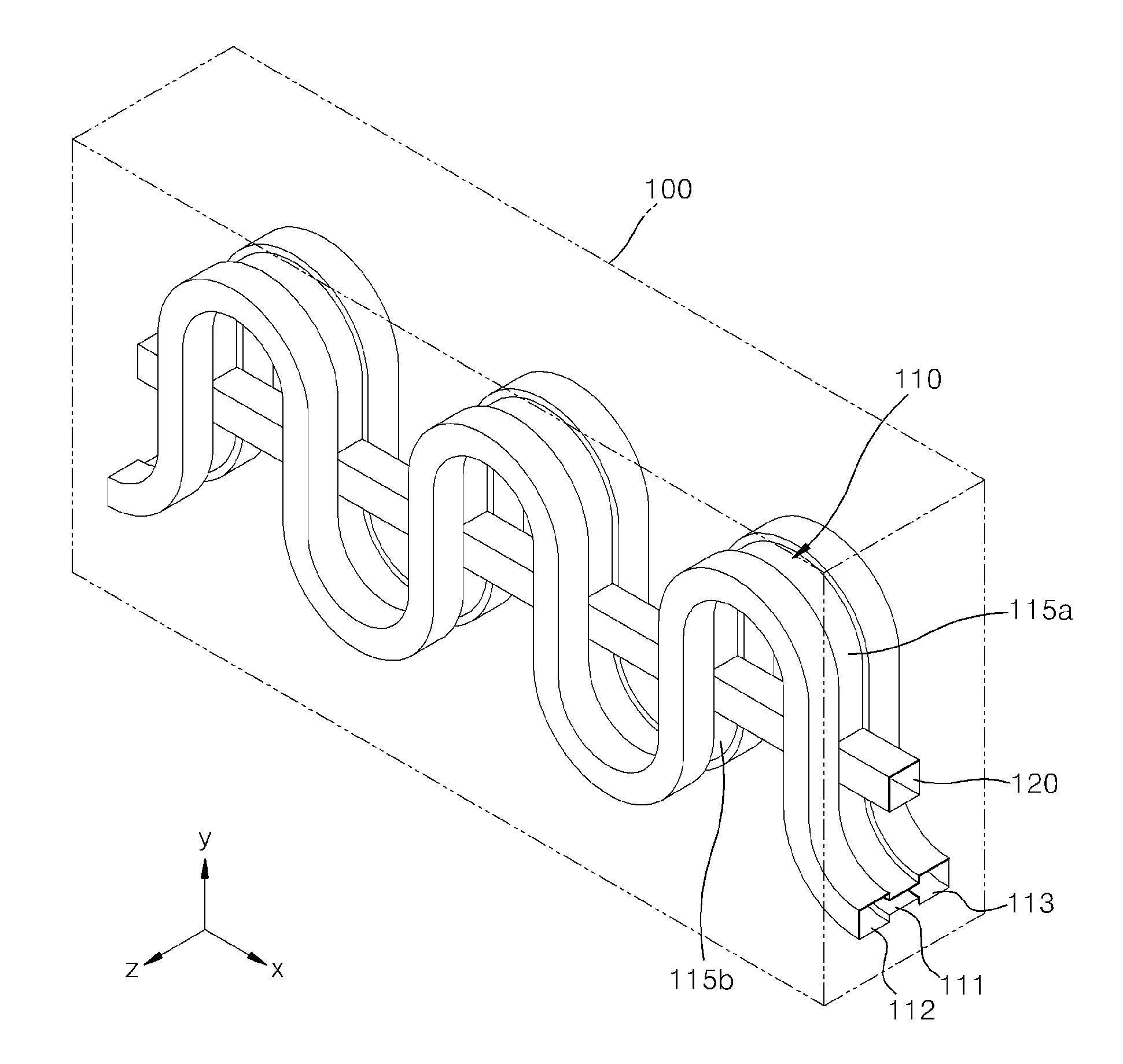
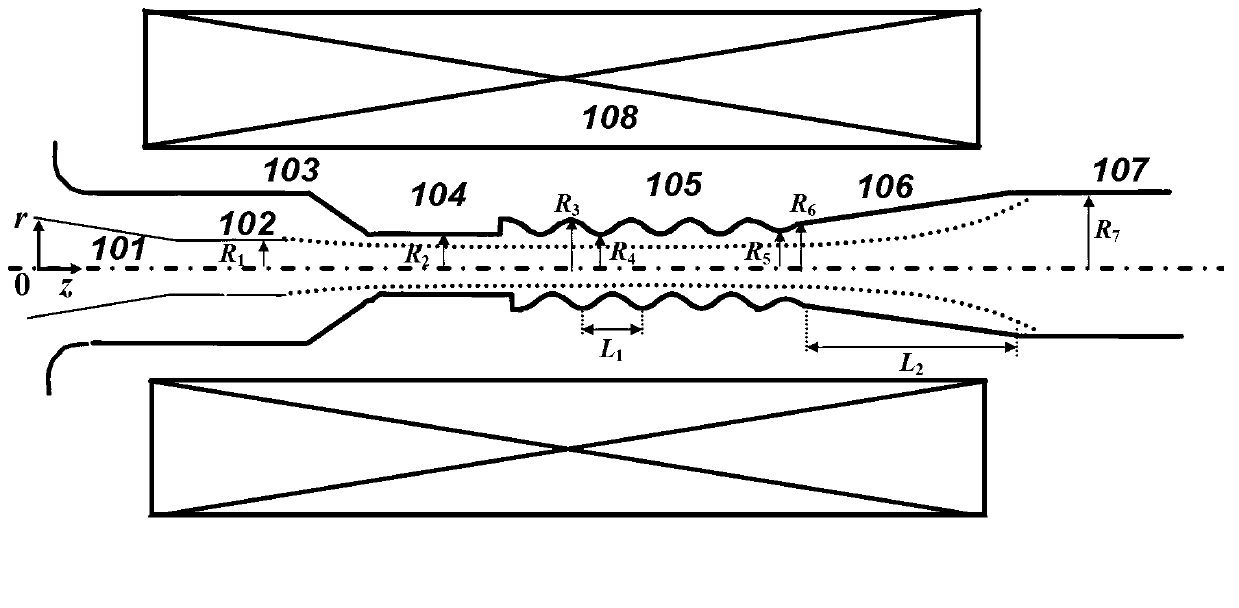
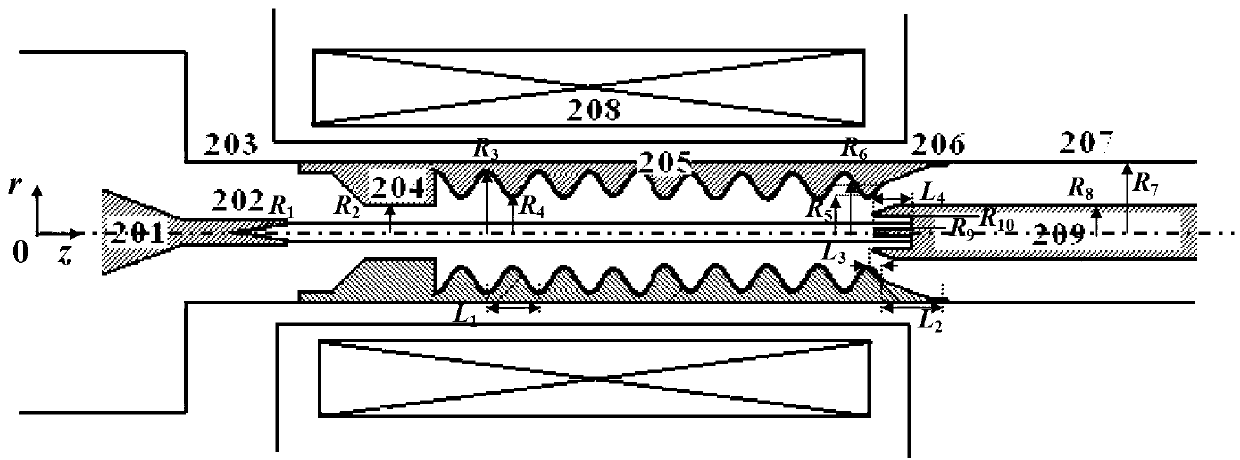
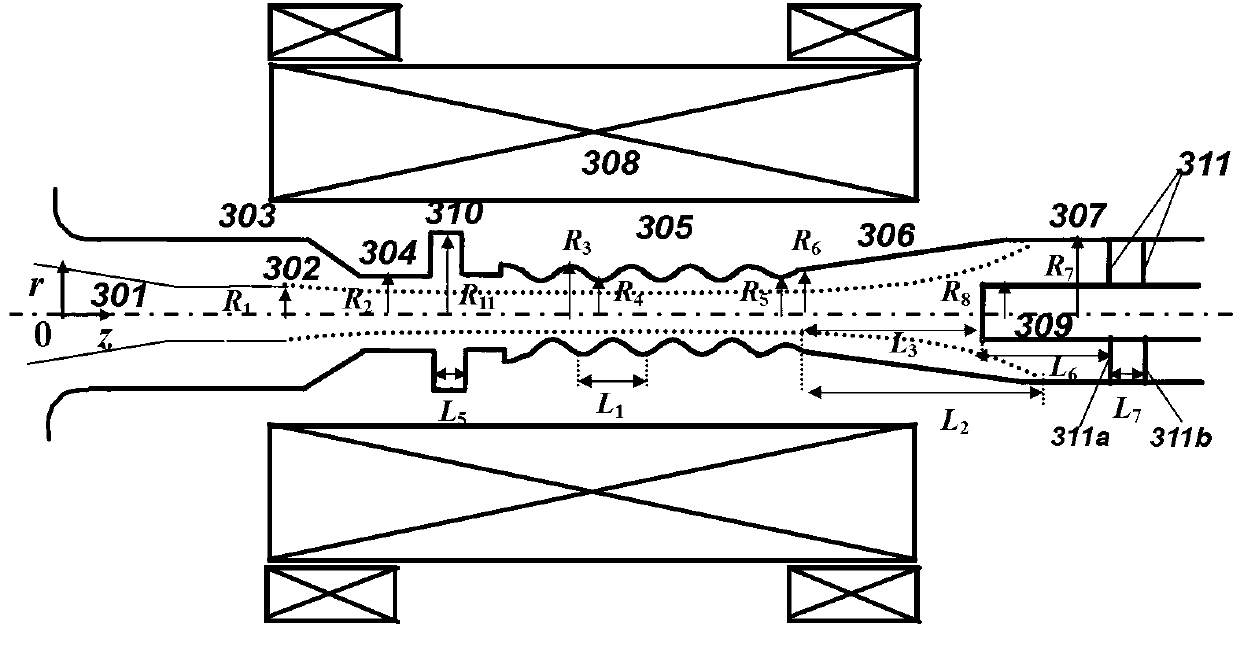
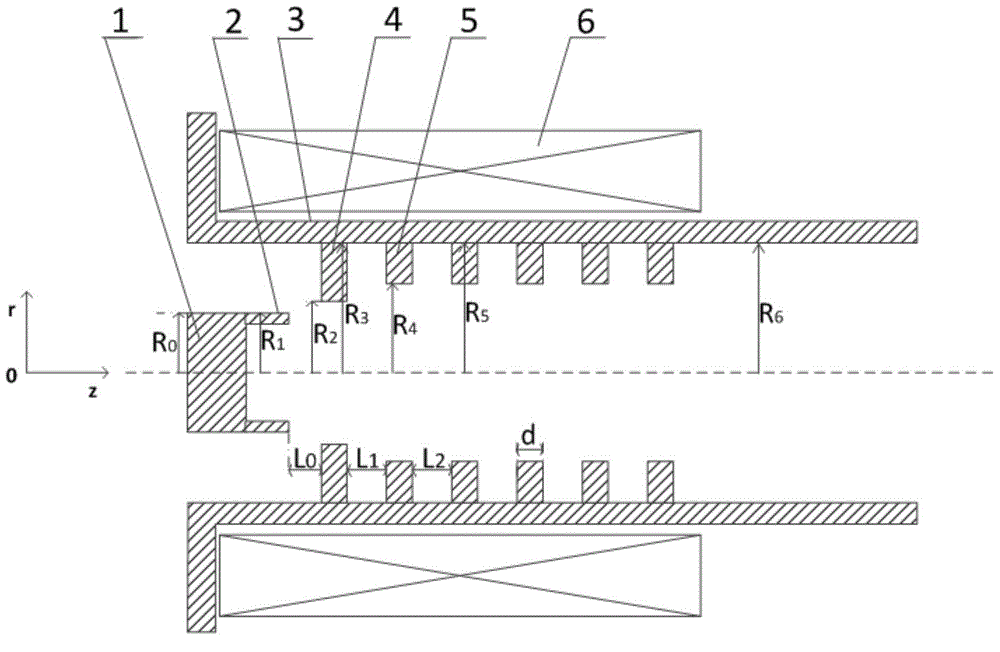
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
483results about "Travelling-wave tubes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
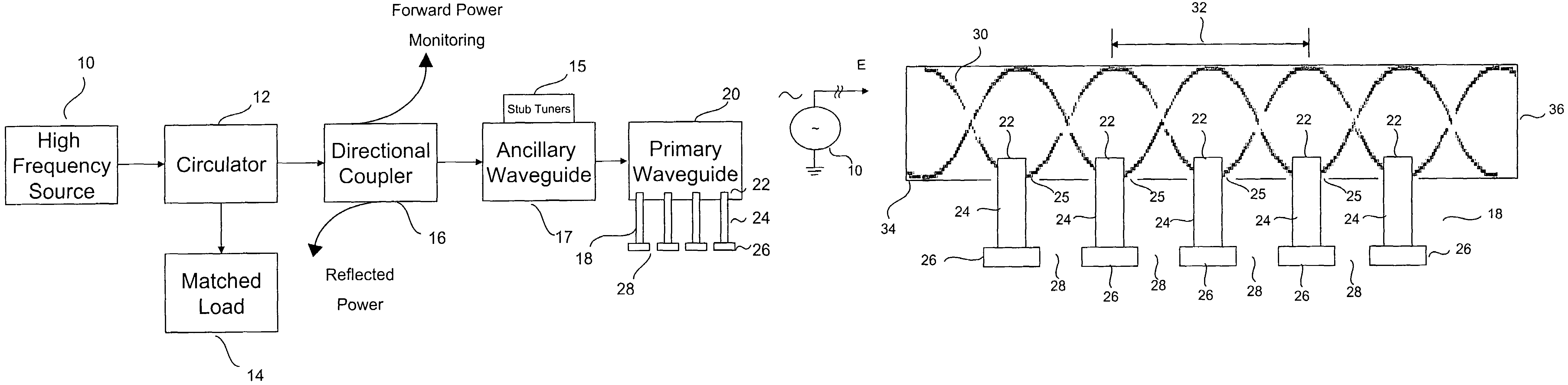
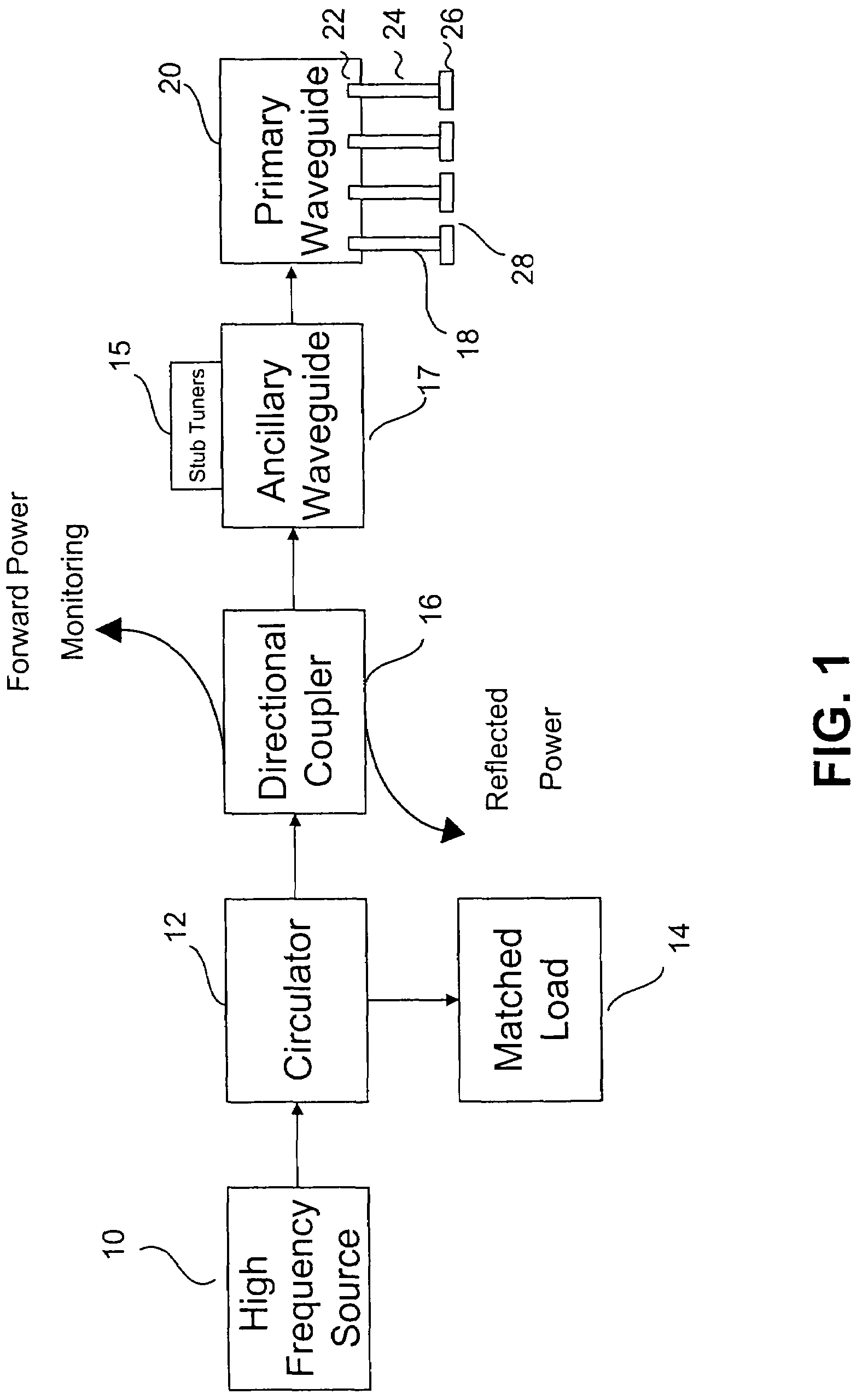
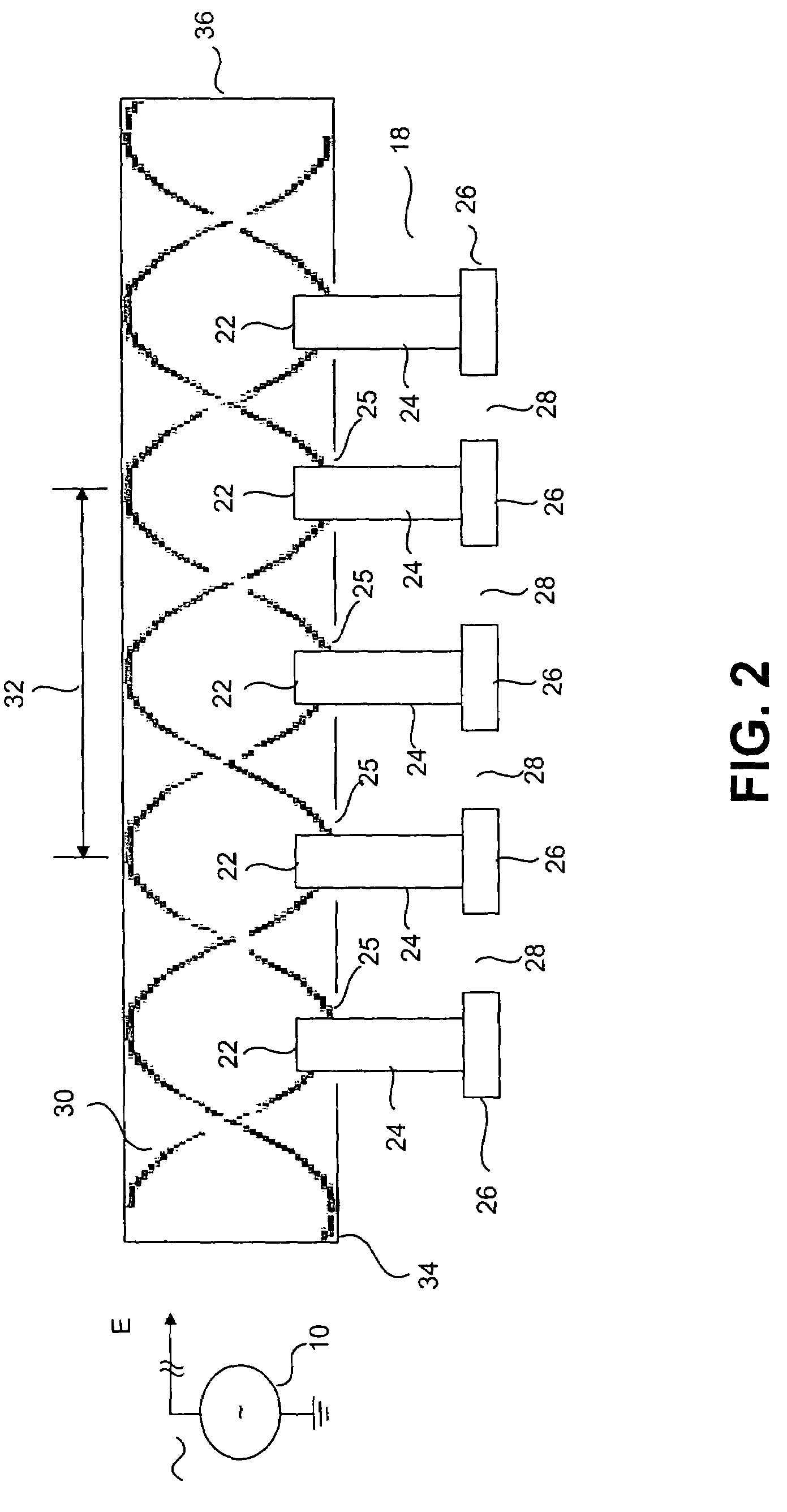
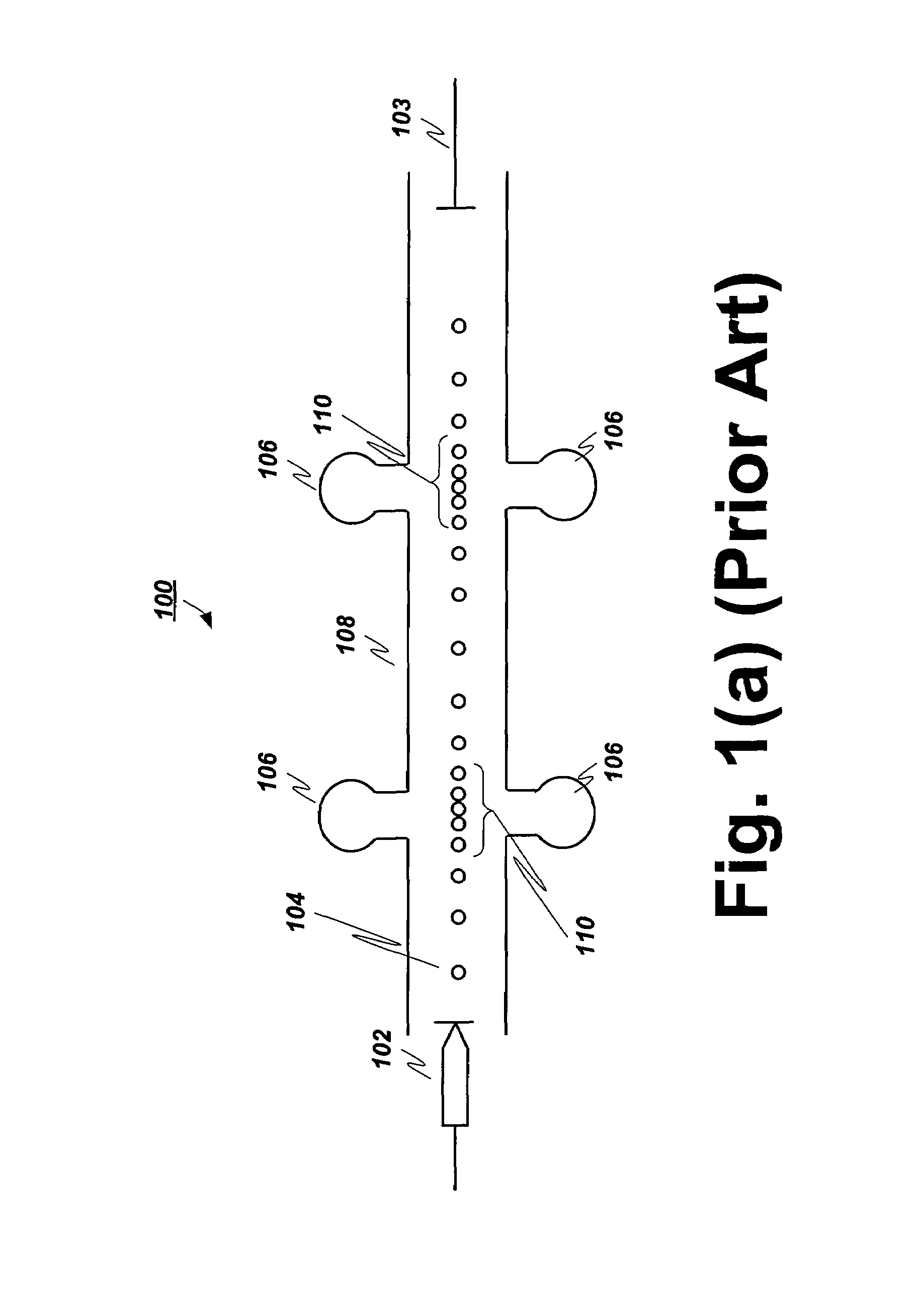
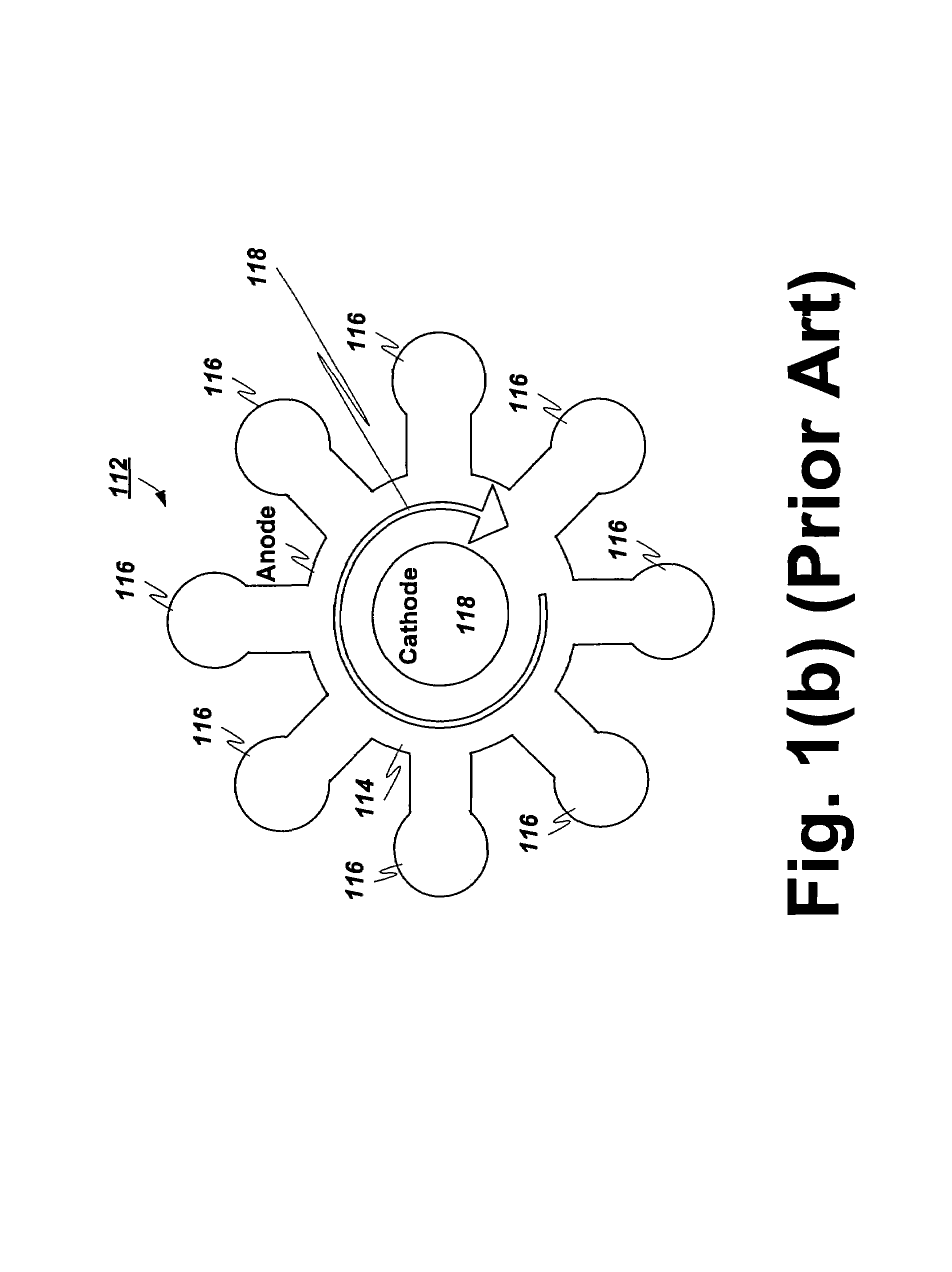
Method and apparatus for producing plasma
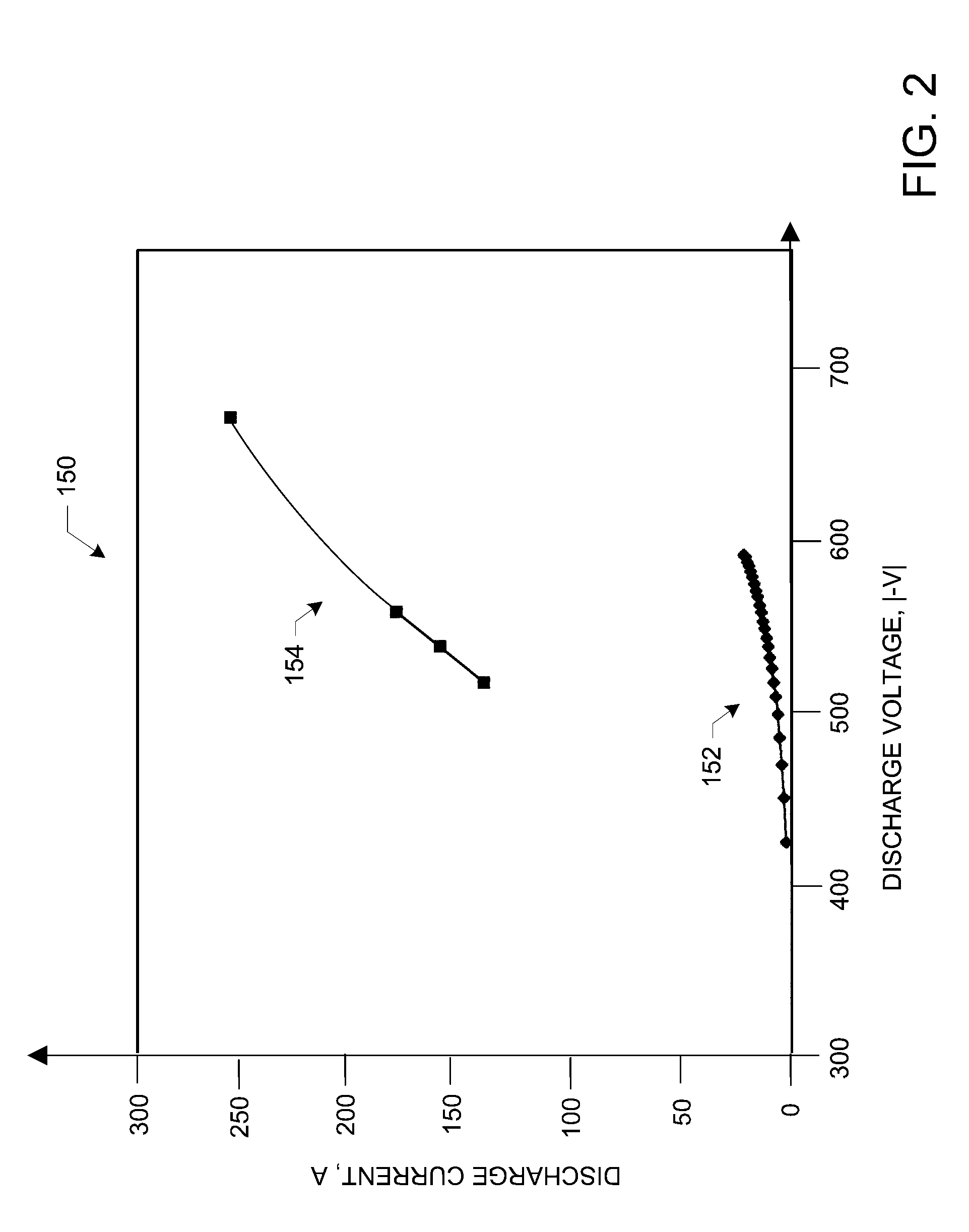
InactiveUS7589470B2Low costIncreases electric fieldMagnetronsTravelling-wave tubesHigh frequency powerLength wave
A method and apparatus for producing a distributed plasma at atmospheric pressure. A distributed plasma can be produced at atmospheric pressure by using an inexpensive high frequency power source in communication with a waveguide having a plurality particularly configured couplers disposed therein. The plurality of particularly arranged couplers can be configured in the waveguide to enhance the electromagnetic field strength therein. The plurality of couplers have internal portions disposed inside the waveguide and spaced apart by a distance of ½ wavelength of the high frequency power source and external portions disposed outside the waveguide and spaced apart by a predetermined distance which is calculated to cause the electromagnetic fields in the external portions of adjacent couplers to couple and thereby further enhance the strength of the electromagnetic field in the waveguide. Plasma can be formed in plasma areas defined by gaps between electrodes disposed on the external portions.
Owner:DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY
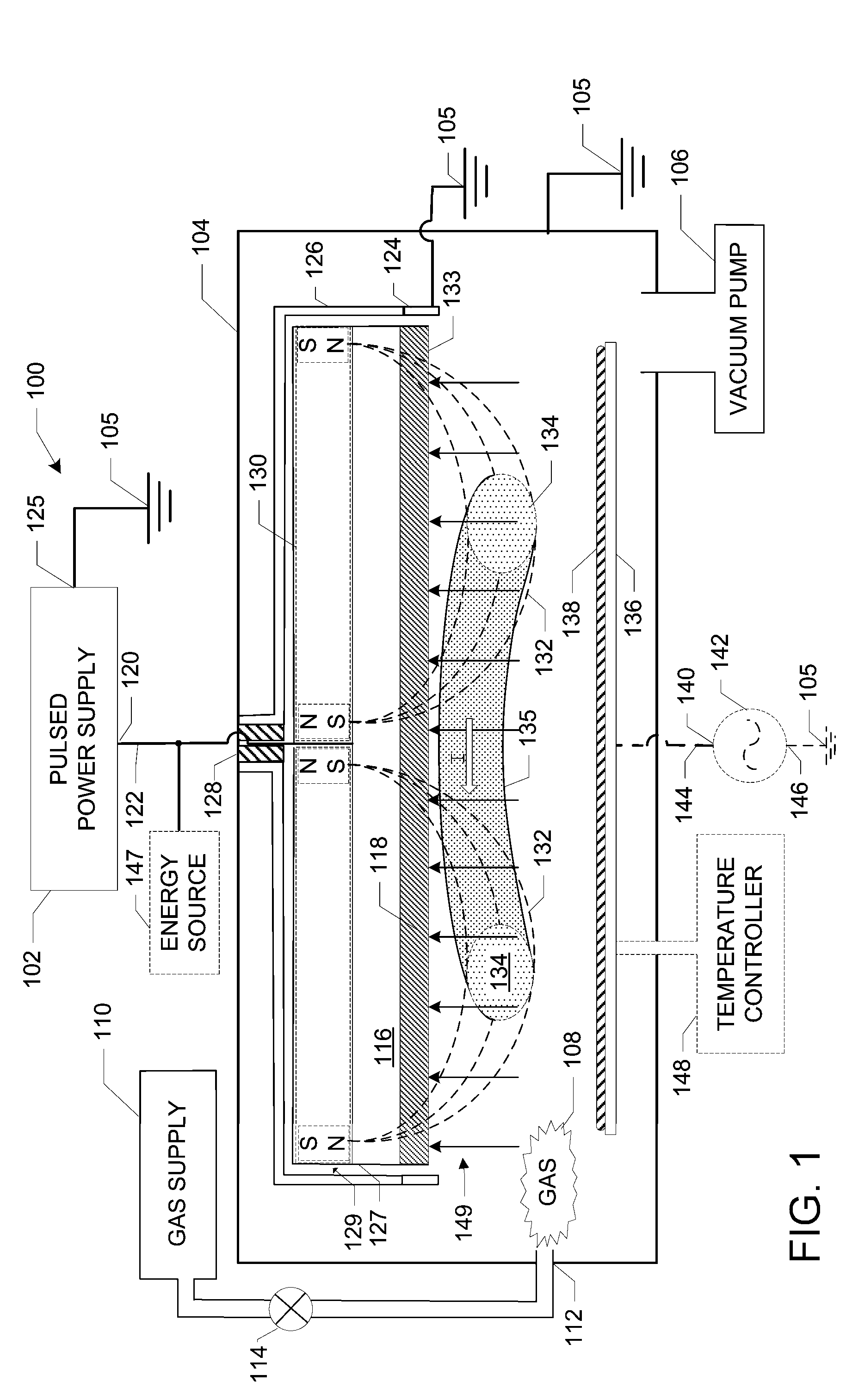
Methods and Apparatus for Generating Strongly-Ionized Plasmas with Ionizational Instabilities
Methods and apparatus for generating strongly-ionized plasmas are disclosed. A strongly-ionized plasma generator according to one embodiment includes a chamber for confining a feed gas. An anode and a cathode assembly are positioned inside the chamber. A pulsed power supply is electrically connected between the anode and the cathode assembly. The pulsed power supply generates a multi-stage voltage pulse that includes a low-power stage with a first peak voltage having a magnitude and a rise time that is sufficient to generate a weakly-ionized plasma from the feed gas. The multi-stage voltage pulse also includes a transient stage with a second peak voltage having a magnitude and a rise time that is sufficient to shift an electron energy distribution in the weakly-ionized plasma to higher energies that increase an ionization rate which results in a rapid increase in electron density and a formation of a strongly-ionized plasma.
Owner:ZOND
Compact relativity backward wave oscillator (RBWO) with adjustable low-frequency-range frequency
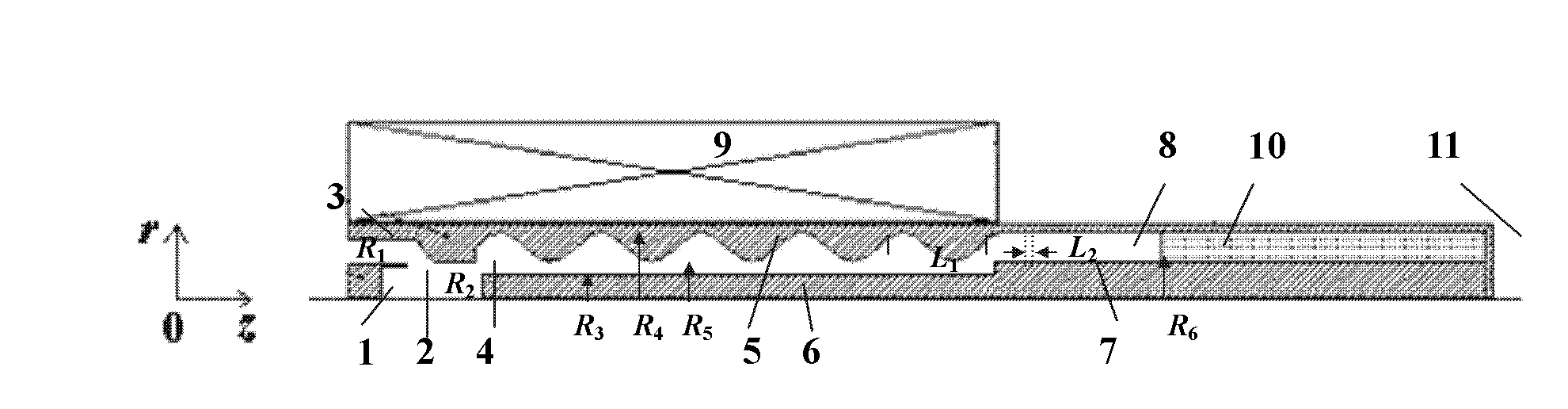
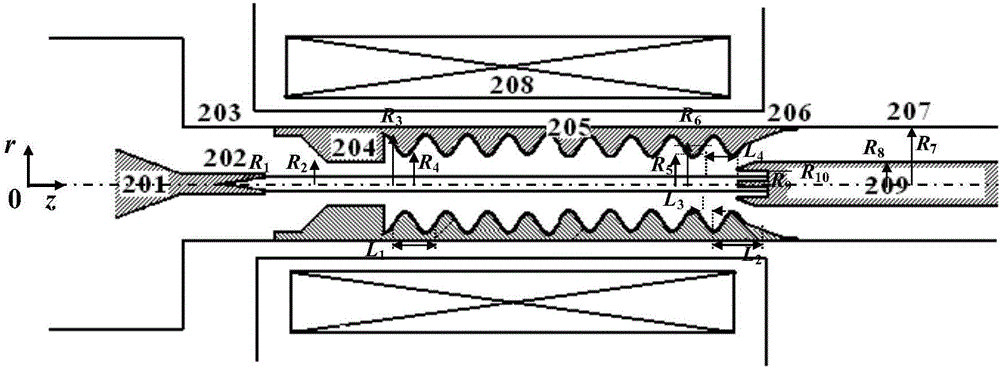
ActiveCN102208315AReduce radial sizeCan be smallTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube collectorsWave structureElectrical conductor
The invention discloses a compact relativity backward wave oscillator (RBWO) with an adjustable low-frequency-range frequency, and the oscillator provided by the invention is used for solving the problems that the RBWO size in a low frequency range is great, and the output microwave frequency is hard to adjust. The compact RBWO is in rotational symmetry with respect to a central axis, and composed of a cathode base, a cathode, an anode outer barrel, a stop neck, a slow wave structure, an inner conductor, a collector, a microwave output port, a solenoid field, two rows of supporting rods, a mode converter, a radiation port and a sealing plate; the slow wave structure is composed of five slow wave blades, the inner surface of each slow wave blade is in a trapezoid structure; the left end face of the collector is provided with an annular groove; the left end of the mode converter is cylindrical, and the right end of the mode converter is in a tapered structure; the radiation port is cylindrical, the left end of the radiation port is in a tapered structure and the right end of the radiation port is cylindrical; the sealing plate is pressed on the radiation port; and the frequency of the output microwave is adjusted by virtue of adjusting the semi-diameter R3 of the inner conductor. The compact RBWO has the advantages of compact structure and convenient and adjustable work frequency, thereby being beneficial to outputting a long pulse of the microwave.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Wave-band-cross mechanical frequency modulation relativity back wave oscillator
ActiveCN103456587AChange lengthEasy to adjustTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube collectorsWave structureElectrical conductor
The invention relates to microwave source devices in the technical field of high-power microwaves and provides a wave-band-cross mechanical frequency modulation relativity back wave oscillator. The wave-band-cross mechanical frequency modulation relativity back wave oscillator comprises a cathode seat, a cathode, an anode outer cylinder, a cut-off neck, a slow wave structure, an inner conductor, a collector, a microwave output and a solenoidal magnetic field. The inner conductor is a cylinder, by adjusting the length of the inner conductor, the frequency of outputting microwaves can be adjusted, and outputting of wave-band-cross microwaves is achieved. An annular groove is formed in the collector, and a supporting rod is fixed on the anode outer cylinder. The wave-band-cross mechanical frequency modulation relativity back wave oscillator has the advantages that by adjusting the length of the inner conductor, frequency can jump between L wavebands and S wavebands, the adjusting manner is simple, the frequency in the wavebands can be adjusted, the bandwidth in the L-waveband frequency is adjusted by 7% or so, and the bandwidth in the S-waveband frequency is adjusted by 2% or so. The outer radius of a slow-wave vane can have a low value, and miniaturization is achieved. A groove structure is reserved at the left end of the collector, reflection of the tail end of the device can be increased, and achieving long-pulse outputting of the wavebands is facilitated.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
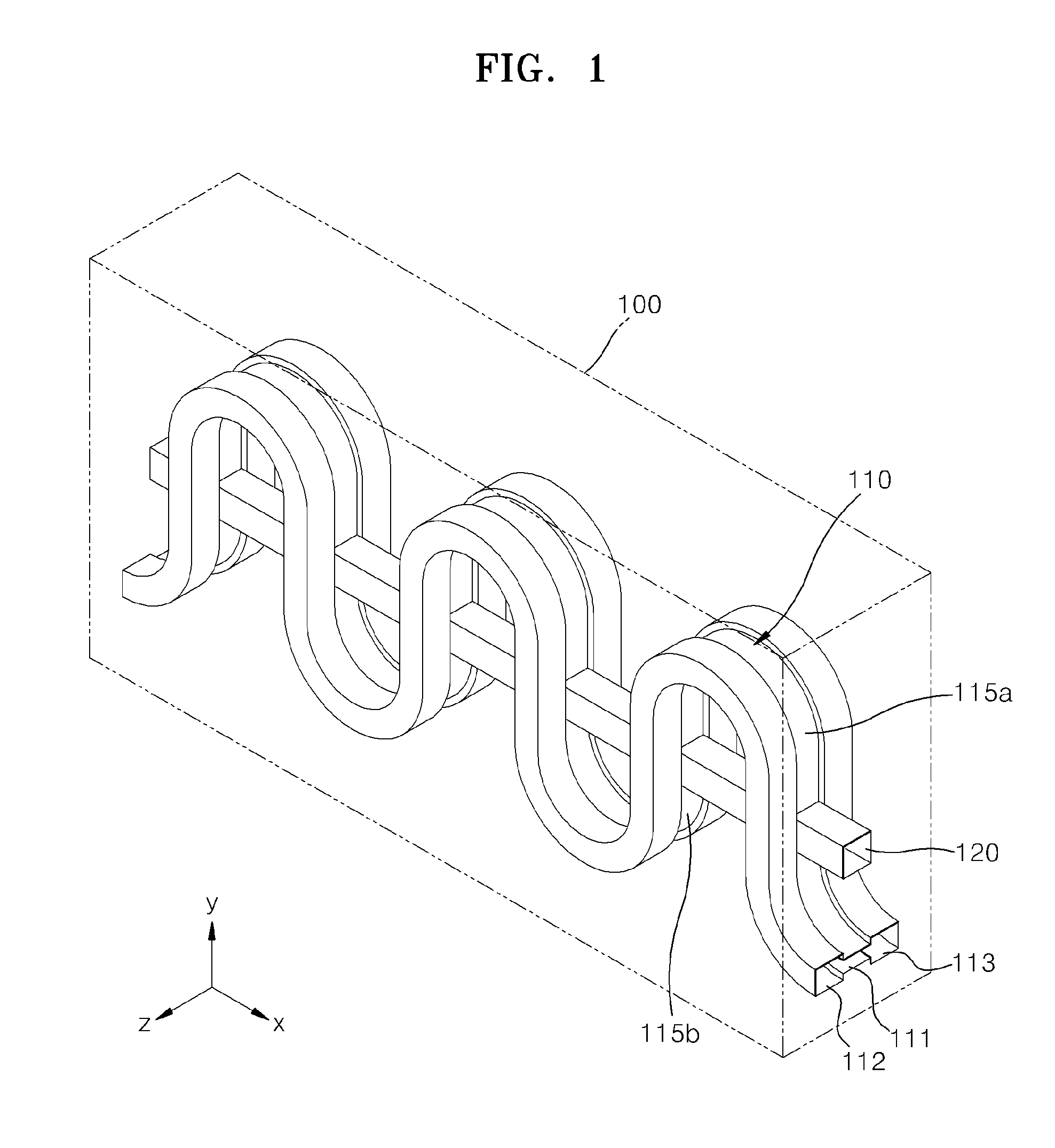
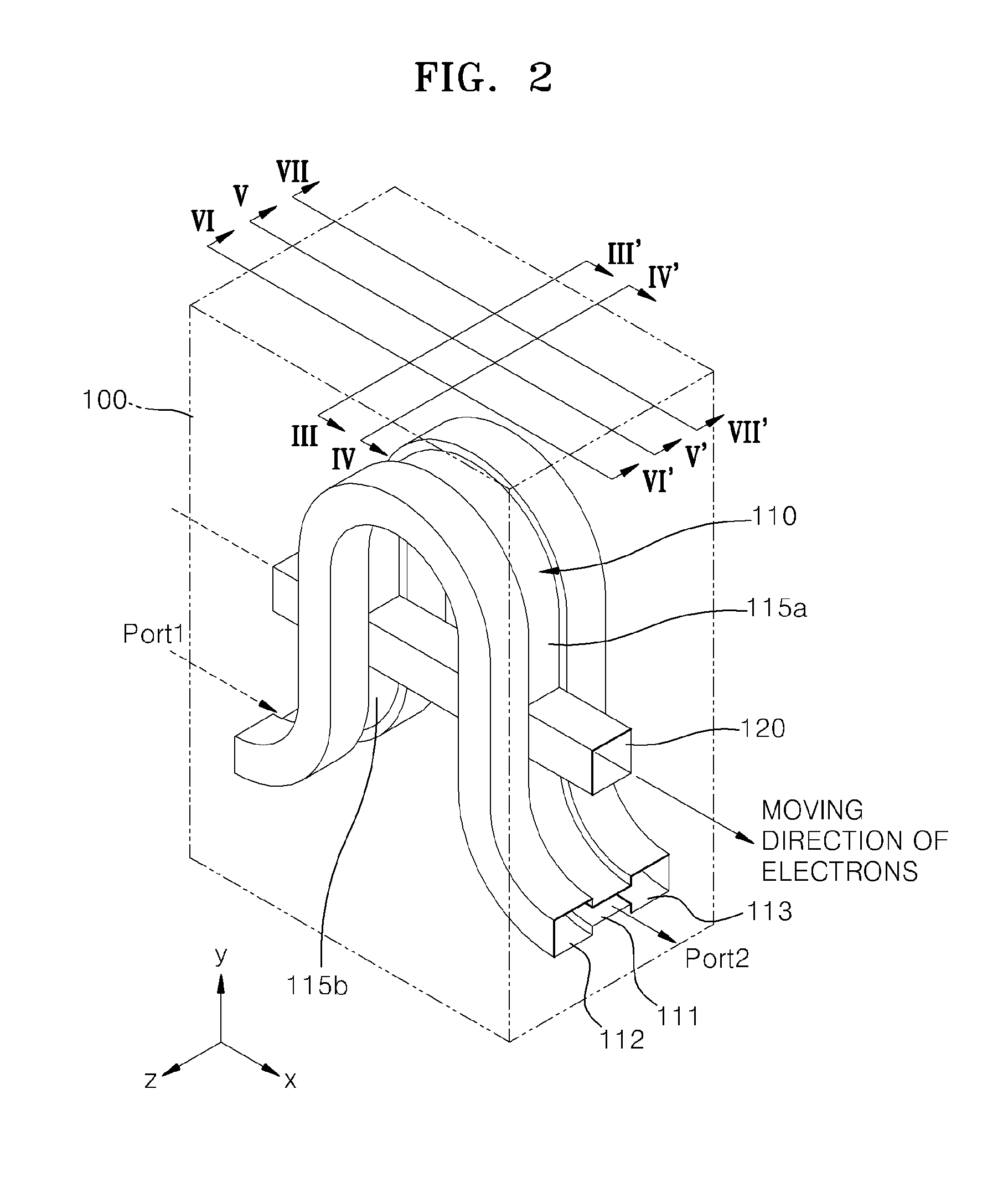
Terahertz interaction circuit having ridged structure
A terahertz interaction circuit is provided. The terahertz interaction circuit includes a waveguide and an electron beam tunnel. The waveguide has a folded shape and in which an electromagnetic wave propagates. The electron beam tunnel is formed to penetrate through the waveguide. An electron beam passes through the electron beam tunnel. The waveguide includes a ridge portion in which a portion of a surface of the waveguide protrudes into the waveguide.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Linear accelerator
InactiveUS6376990B1Good flexibilityGreat flexibility.TheTravelling-wave tubesElectric arc lampsElectrical resistance and conductanceRelative magnitude
This device allows the variation of the coupling between two points in an RF circuit in a very simple way while maintaining the RF phase relationship and varying the relative magnitude of the RF fields. The device is characterized by a simple mechanical control of coupling value, that has negligible effect on the phase shift across the device. This is achieved by the simple rotation of the polarisation of a TE111 mode inside a cylindrical cavity. Such a device does not contain resistive elements, and the sliding mechanical surfaces are free from high RF currents. This device finds an application in standing wave linear accelerators, where it is desirable to vary the relative RF field in one set of cavities with respect to another, in order that the accelerator can operate successfully over a wide range of energies.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
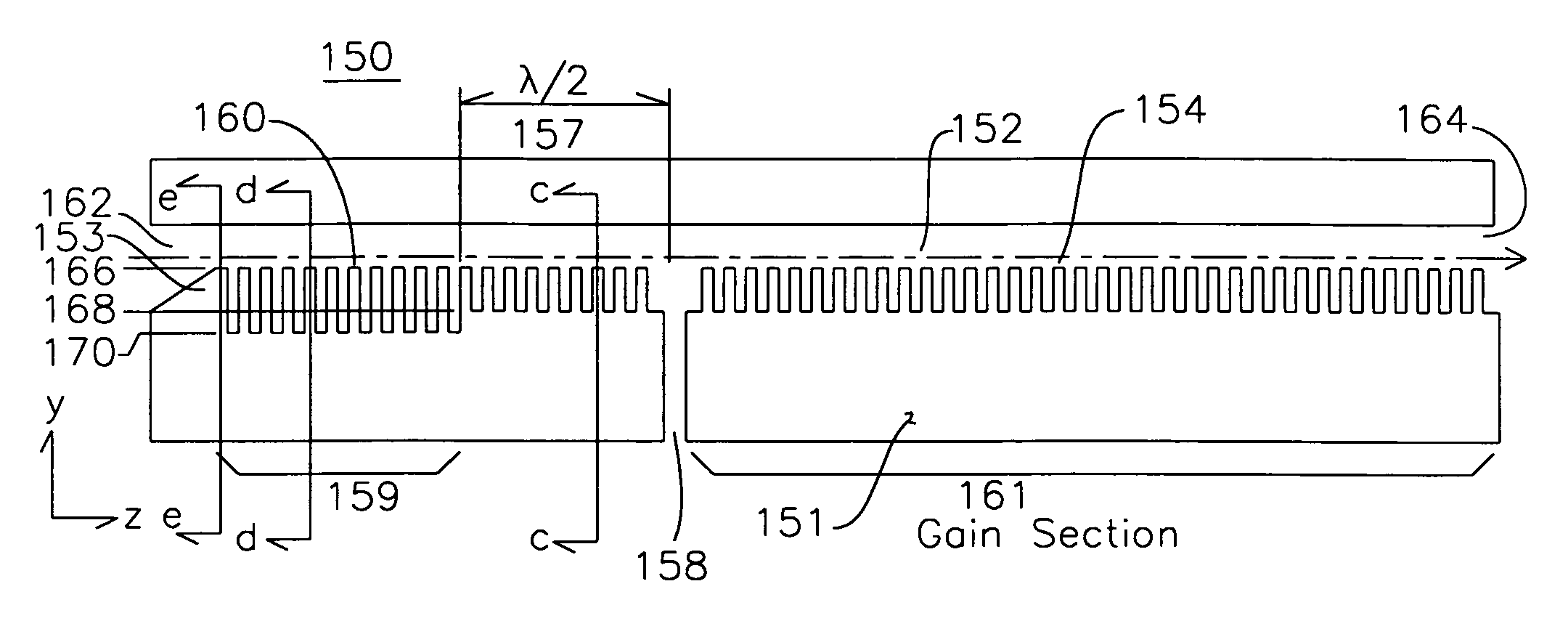
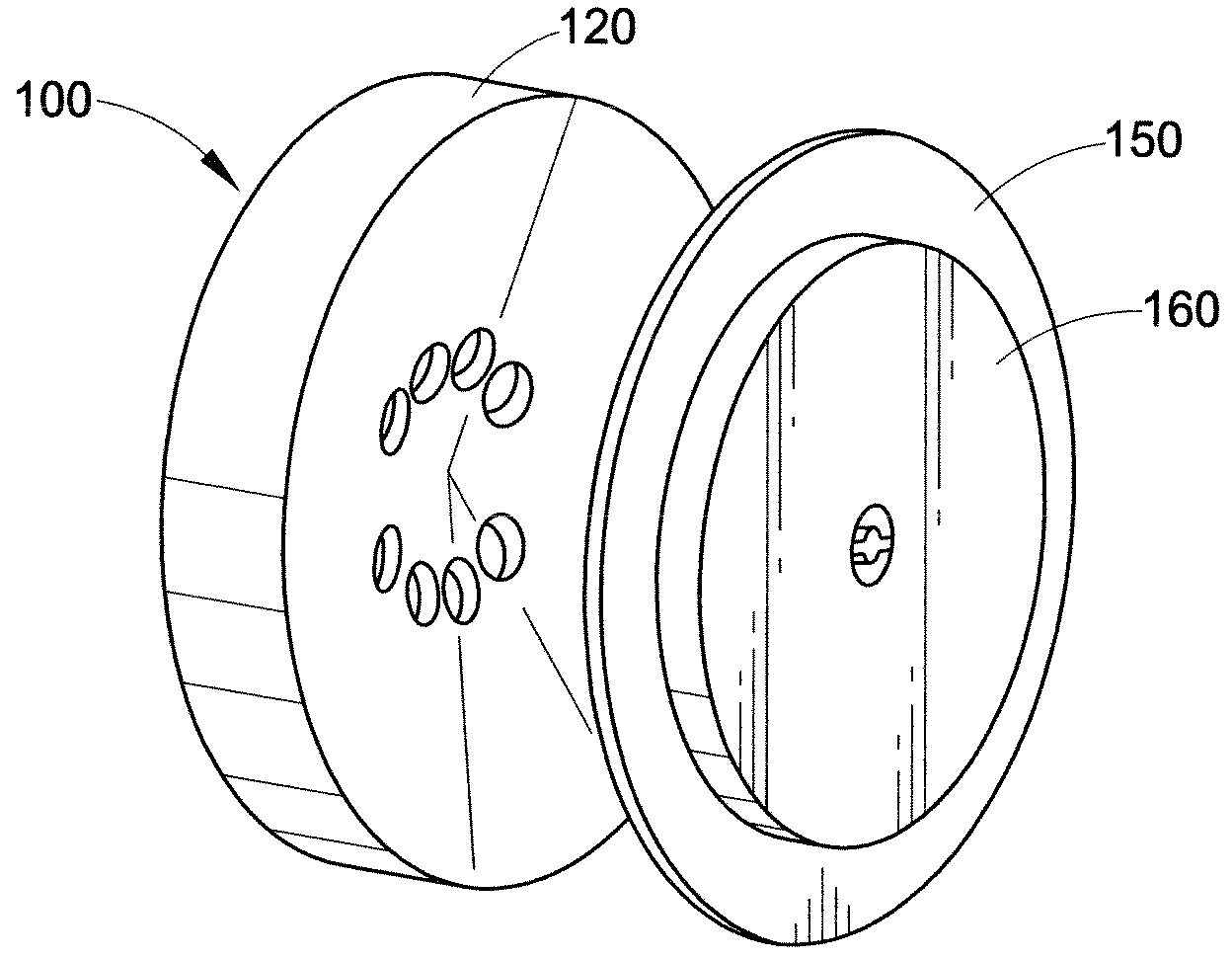
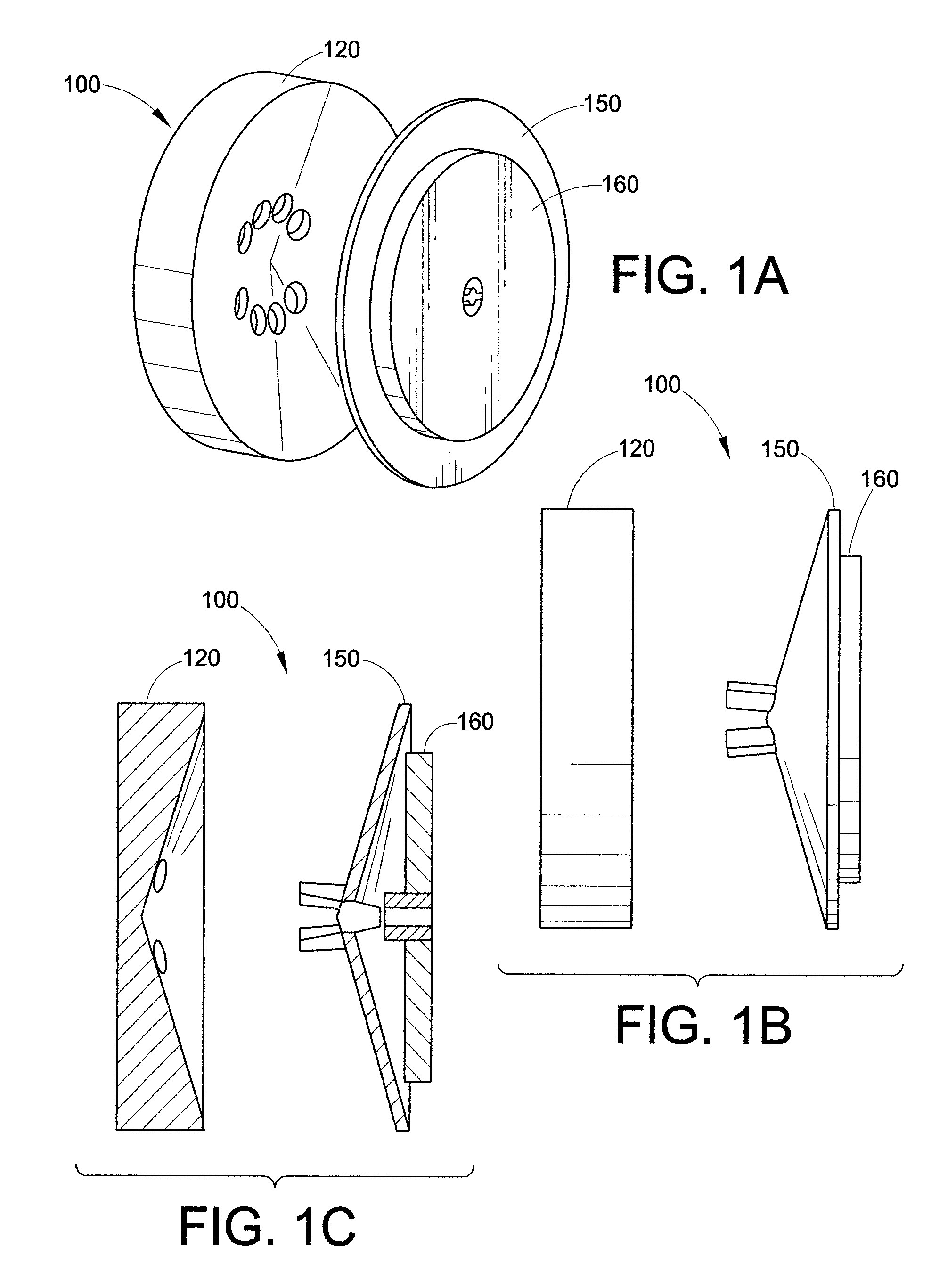
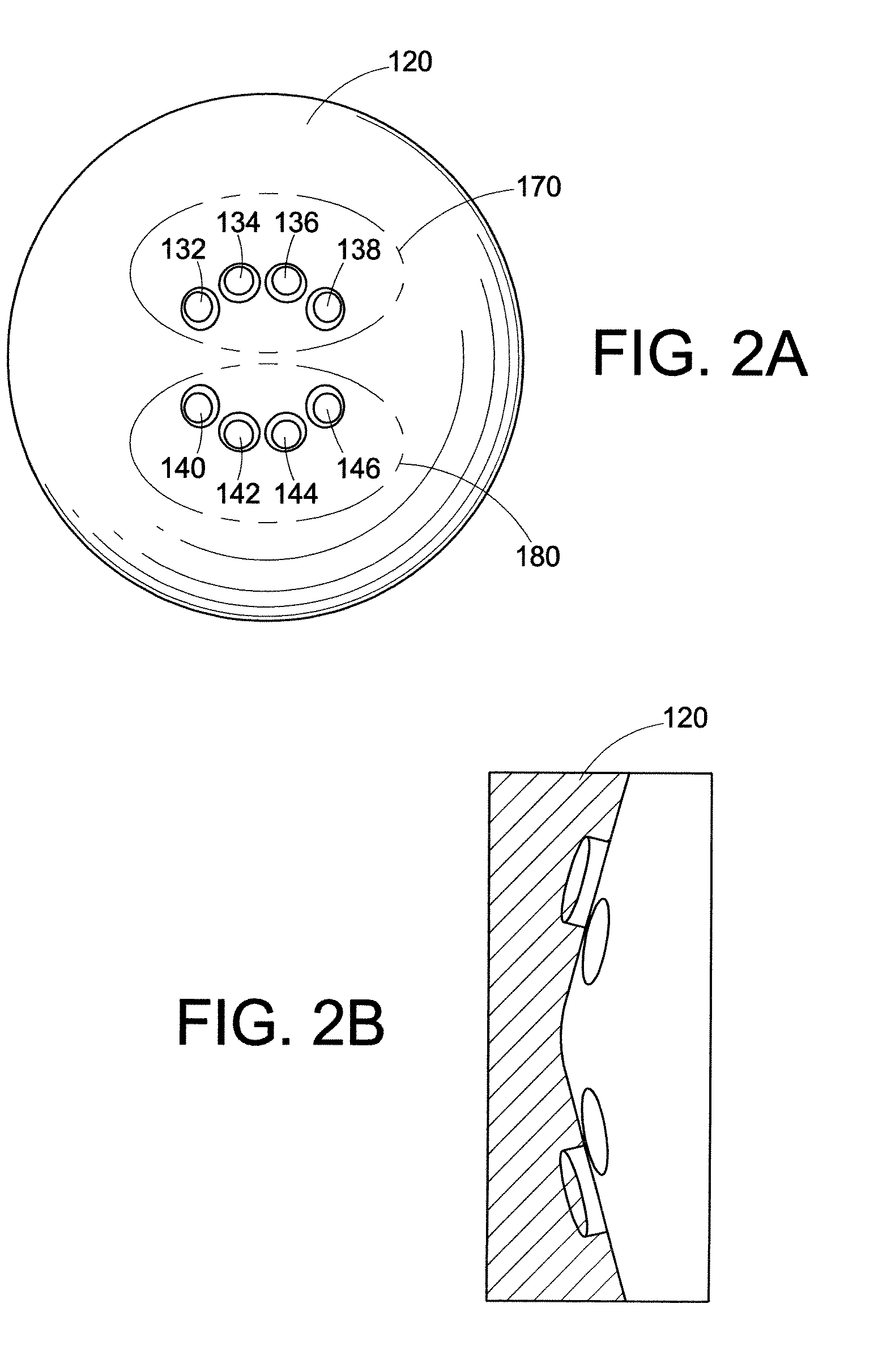
Traveling-Wave Tube 2D Slow Wave Circuit
InactiveUS20090096378A1Wider instantaneous bandwidth capabilityEnhanced interactionTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube circuit elementsAudio power amplifierSolid body
A two-dimensional circuit for a traveling-wave tube for millimeter and sub-millimeter electromagnetic waves synchronously interacts with an electron beam in a vacuum electronic microwave amplifier or oscillator. The circuit is a solid body having a length along the tube axis. The solid body has an electrically conductive top section and an electrically conductive bottom section. The top section is configured with a plurality of vertical vanes having a width and height and configured parallel to each other. The bottom section is similarly configured such that when the circuit is viewed in cross section along the length, the vanes on the bottom section are staggered with respect to the vanes on the top section. The top section and the bottom section are separated from each other to define a tunnel through the solid body along the length.
Owner:BARNETT LARRY R +1
Coaxial-extraction long-pulse relativistic backward-wave oscillator
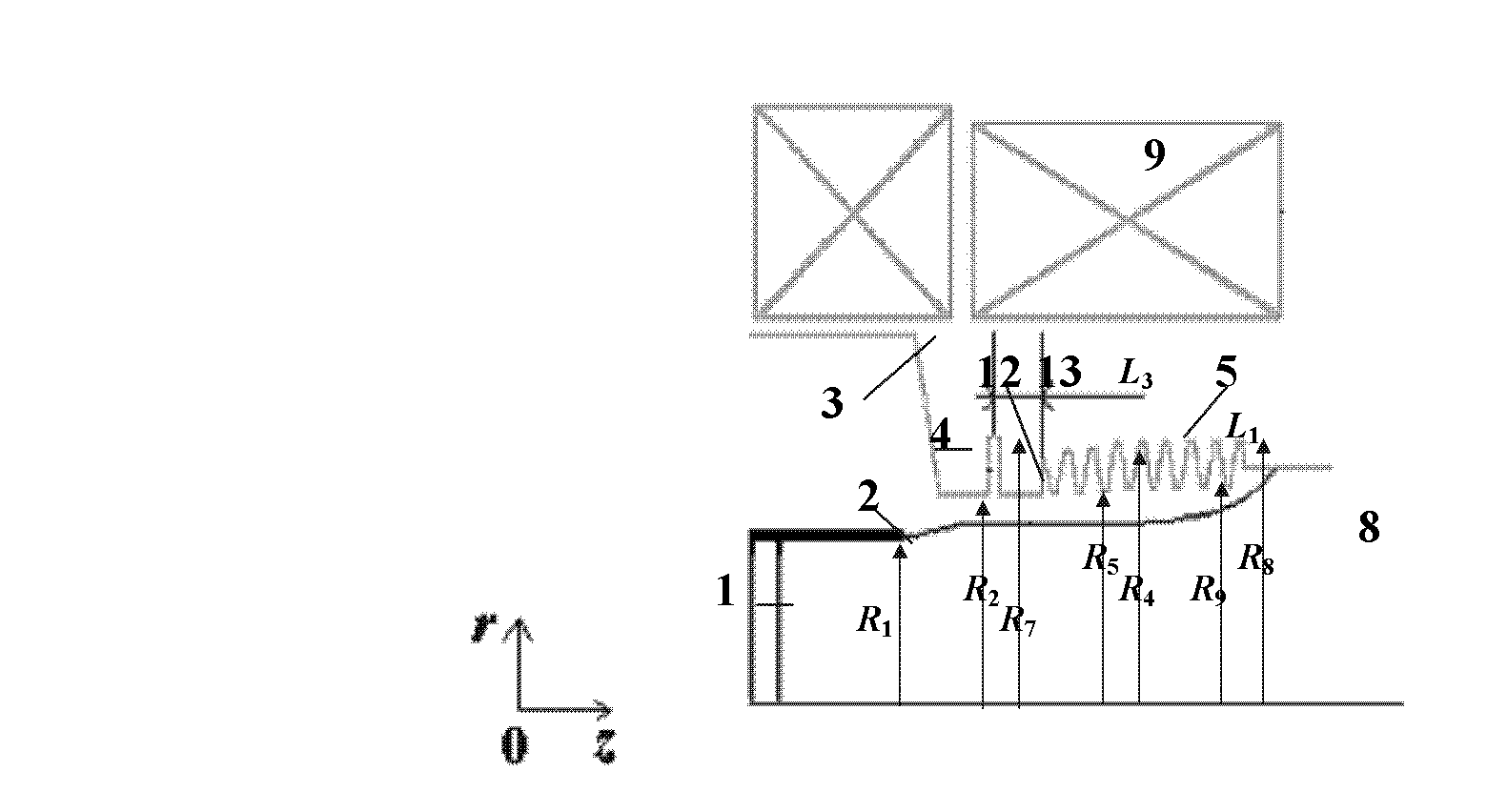
ActiveCN103137399AHigh Q valueOvercome the impact on work efficiencyTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube collectorsWave structureMicrowave
The invention relates to a microwave component in the technical field of high power microwave and provides a coaxial-extraction long-pulse relativistic backward-wave oscillator. The coaxial-extraction long-pulse relativistic backward-wave oscillator comprises a cathode base, a cathode, an anode outer cylinder, a cut-off neck, a slow wave structure, a tapered waveguide, an output waveguide, a solenoidal field, a coaxial-extraction structure and a front-arranged reflection cavity. The coaxial-extraction structure is a cylinder. The front-arranged reflection cavity is disposed between the cut-off neck and the slow wave structure. According to the coaxial-extraction long-pulse relativistic backward-wave oscillator, a cylinder is adopted as the coaxial-extraction structure, and therefore the defect that the coaxial-extraction structure with a groove generates plasma is overcome, and meanwhile in the electromagnetic wave mode, function transformation can be carried out and installation can be achieved conveniently. The front-arranged reflection cavity is utilized to replace the cut-off neck so that the resonance characteristic of the front-arranged reflection cavity can be utilized to achieve the effect of the cut-off neck, electron beam scraping or electron beam bombardment of the front-arranged reflection cavity can be avoided, and premodulation of electron beams emitted from the cathode also can be carried out. Therefore, the coaxial-extraction long-pulse relativistic backward-wave oscillator is beneficial for subsequent beam wave interaction and improves power conversion efficiency of the component.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Dielectric filled compact type relativistic backward wave oscillator
ActiveCN104362060AReduce microwave frequencyReduce radial sizeTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureDielectric
The invention discloses a dielectric filled compact type relativistic backward wave oscillator and belongs to the technical field of high-power microwave. The dielectric filled compact type relativistic backward wave oscillator is rotationally symmetrical relative to the central axis and consists of a cathode seat, a cathode, an anode outer barrel, a cut-off neck, a slow wave structure and a solenoidal field coil. The slow wave structure is a disk loaded waveguide type slow wave structure and consists of five slow wave blades, wherein the inner surface of each slow wave blade is of a rectangular structure. During dielectric filling, an original structure of the RBWO is not needed to be changed, and only dielectric materials are needed to be filled among all blades of the slow wave structure. The problem that a low-frequency relativistic backward wave oscillator is too large in size and weight can be solved, and the dielectric filled compact type relativistic backward wave oscillator has wide application prospect and important scientific research value on research of small-sized compact type relativistic backward wave oscillators, promotion of engineering application process of high-power microwave systems and expansion of the RBWO application field.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
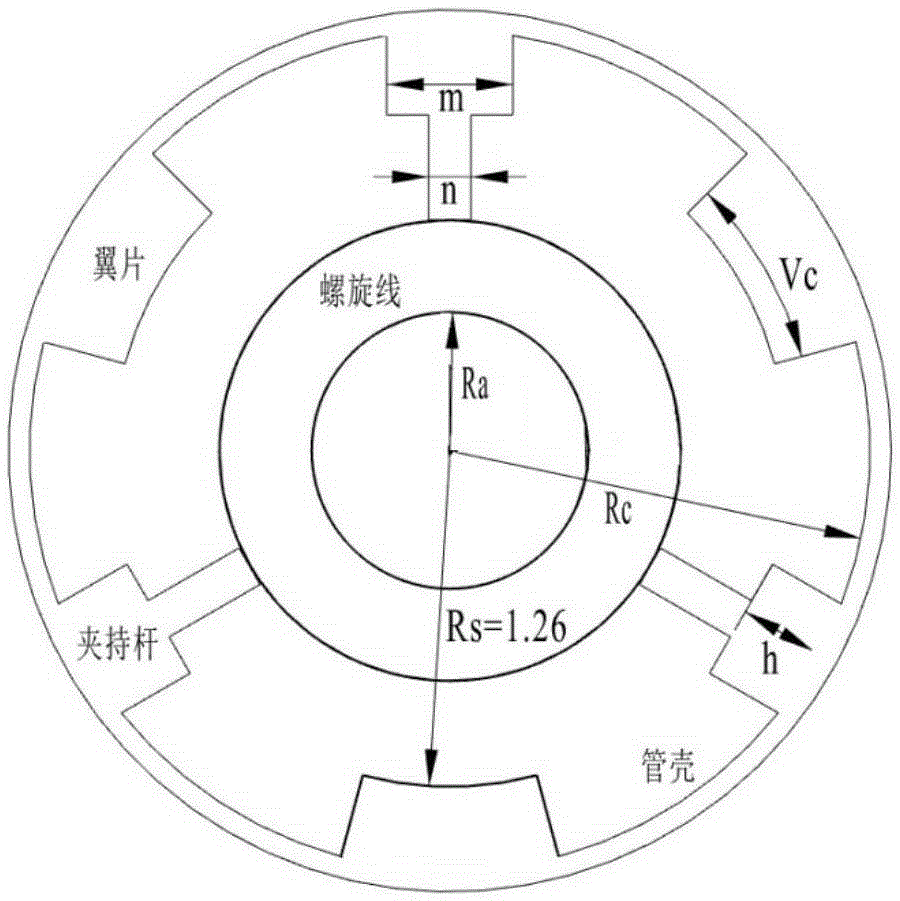
Secondary harmonic inhibition method for broadband helix travelling wave tube
ActiveCN105304438AImprove overall tube performanceGood harmonic suppressionTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube circuit elementsHarmonic mitigationHarmonic
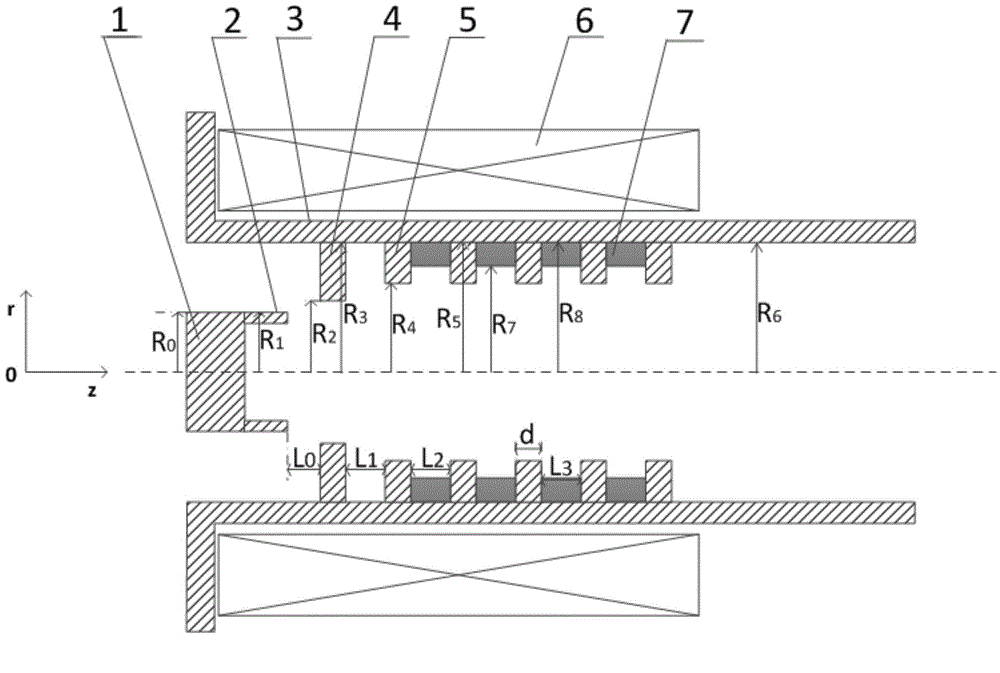
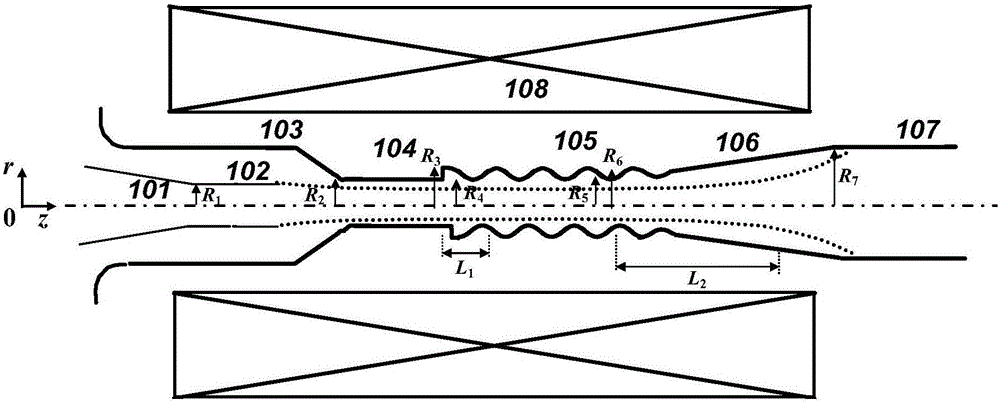
The invention discloses and especially relates to a secondary harmonic inhibition method for a broadband helix travelling wave tube, and belongs to the technical field of broadband helix travelling wave tubes. Within a certain range, a travelling wave tube harmonic inhibition situation becomes greater if a distance between a fin to a center is reduced, however, the reduced distance will make the fin closer to a helix and might cause engineering machining troubles and many other potential troubles. Therefore, two different fin structures are adopted by an input segment and an output segment respectively, and the distance from a fin on the input segment to the center is made to be greater. Through the even and symmetric fin structure, a better harmonic inhibition effect is exhibited, and other factors in terms of the design of a travelling wave tube can be better weighed.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Multibeam electronic tube with magnetic field for correcting beam trajectory
InactiveUS6486605B1Degrading gainDegrading efficiency characteristicTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube focussing arrangementsKlystronBeam trajectory
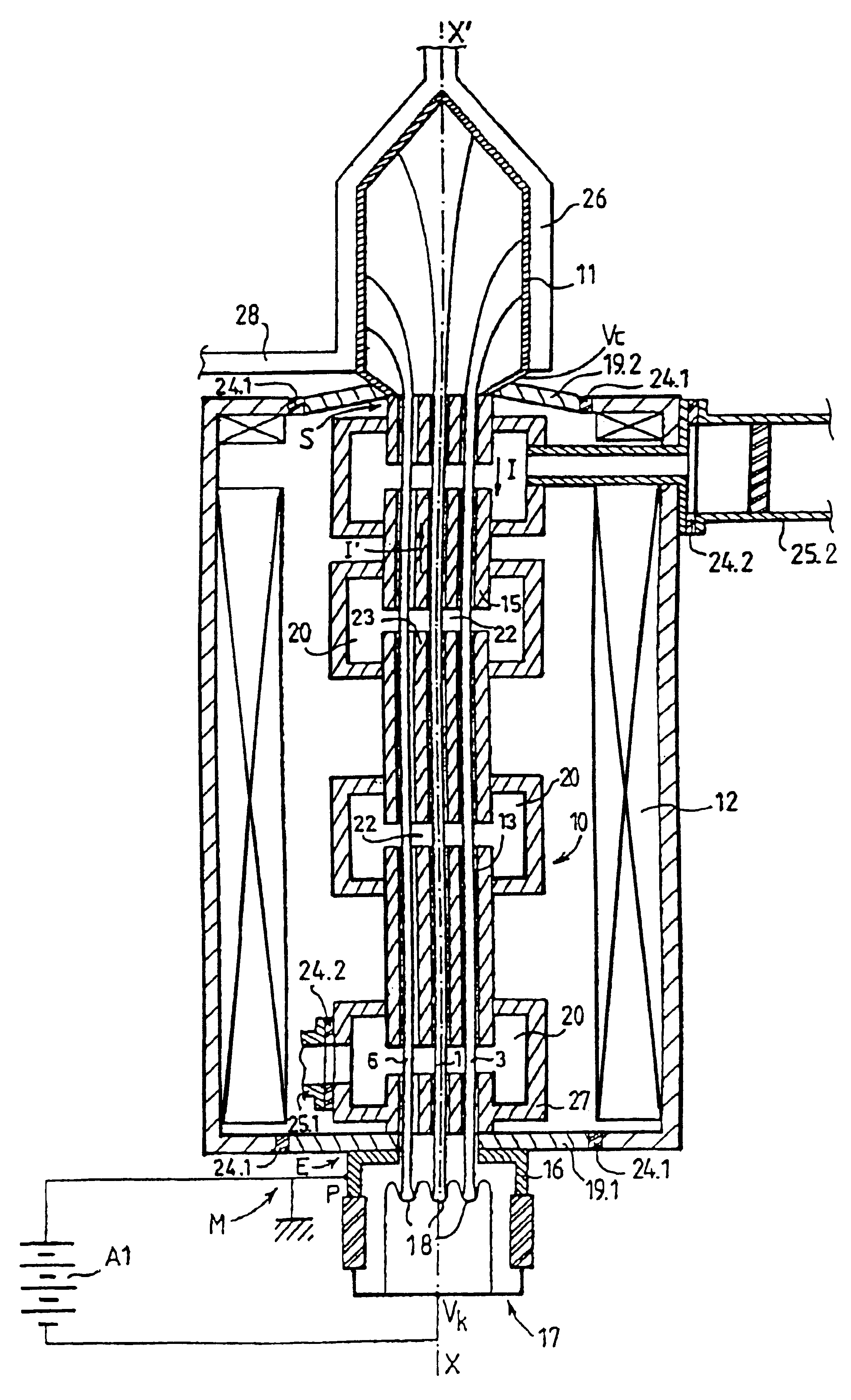
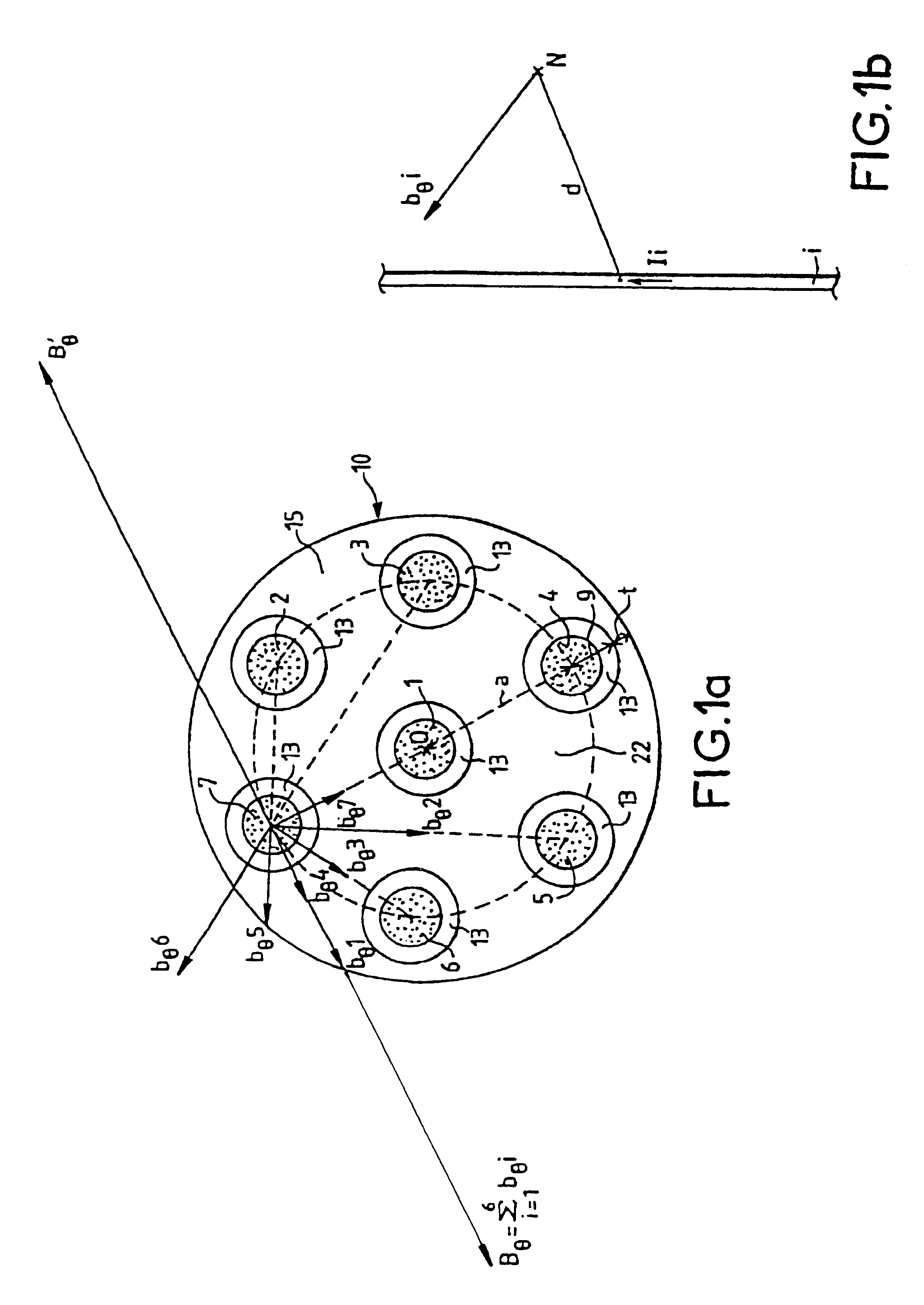
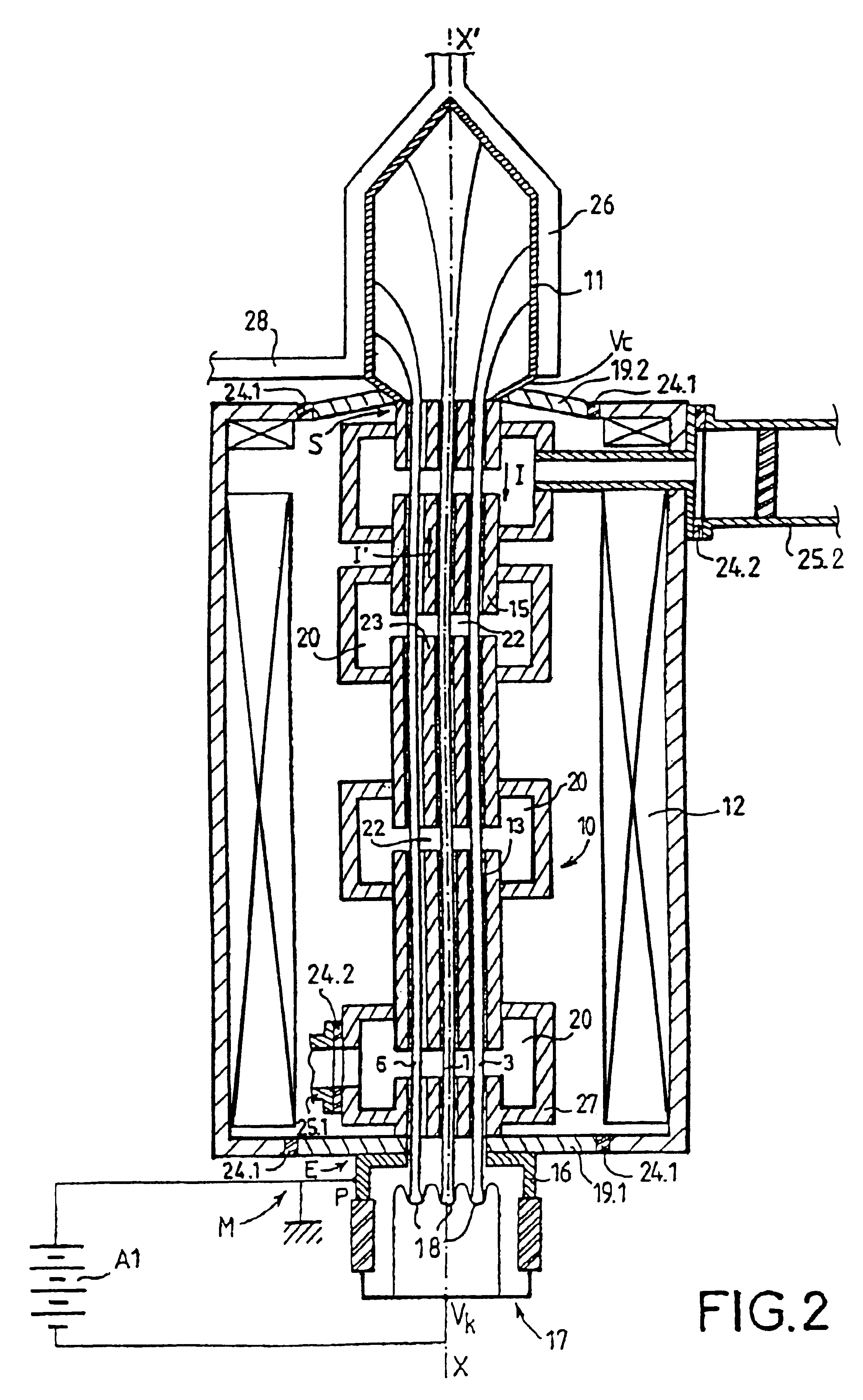
A multibeam electron tube with several approximately parallel electron beams passing through a body. Among the beams, at least some define an interbeam volume, each beam defining the interbeam volume being subjected to a perturbing azimuthal magnetic field induced by all the other beams. The tube includes an element allowing, in at least one conducting element located in the interbeam volume, flow of a reverse current in the opposite direction to that of the current of the beams, this reverse current generating, in the beams defining the interbeam space, a magnetic correction field whose purpose is to oppose the perturbing magnetic field. Exemplary embodiments of the present invention especially apply to the multibeam klystrons or traveling wave tubes.
Owner:THOMSON TUBES ELECTRONIQUES
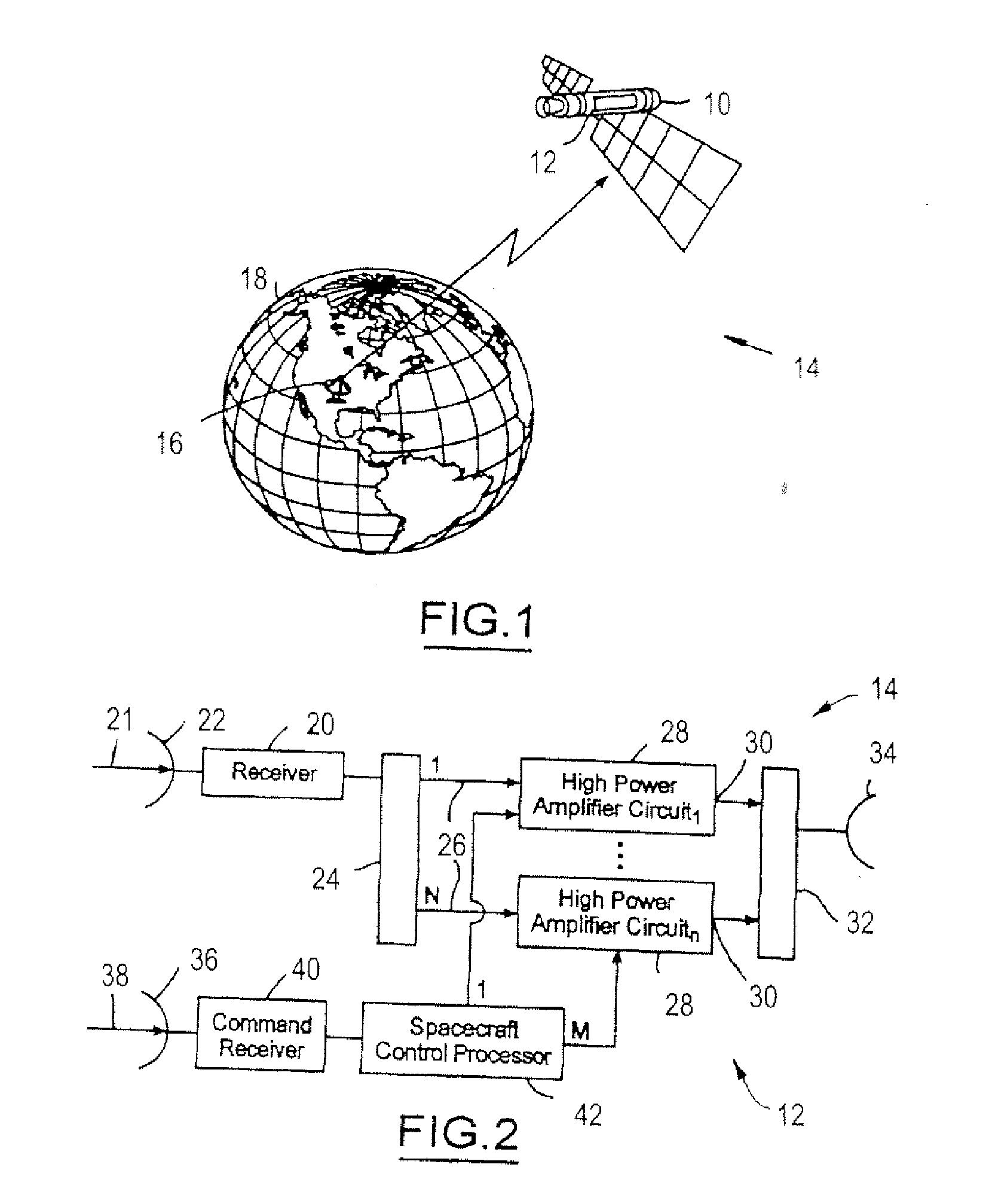
High-power microwave system employing a phase-locked array of inexpensive commercial magnetrons
InactiveUS20060208672A1Facilitates coherent combinationEfficient and inexpensiveTravelling-wave tubesRF amplifierMicrowave applicationsAs Directed
A high-power microwave generator employing a plurality of inexpensive commercial magnetron tubes cross-coupled by means of a secondary coupling path between each magnetron output pair, whereby a portion of the output energy from a first magnetron tube is injected into a second magnetron tube and a portion of the output energy from the second magnetron tube is similarly injected into the first magnetron tube. The resulting cross-injection of microwave energies brings the respective magnetron tube pair into a phase-lock sufficiently stable to permit coherent combination of their outputs for many high-power microwave applications, such as directed energy weapon systems. The magnetron phase-locking system requires no external components other than the secondary coupling paths of this invention.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
Relativistic backward-wave oscillator with collector shaped as Chinese character chang
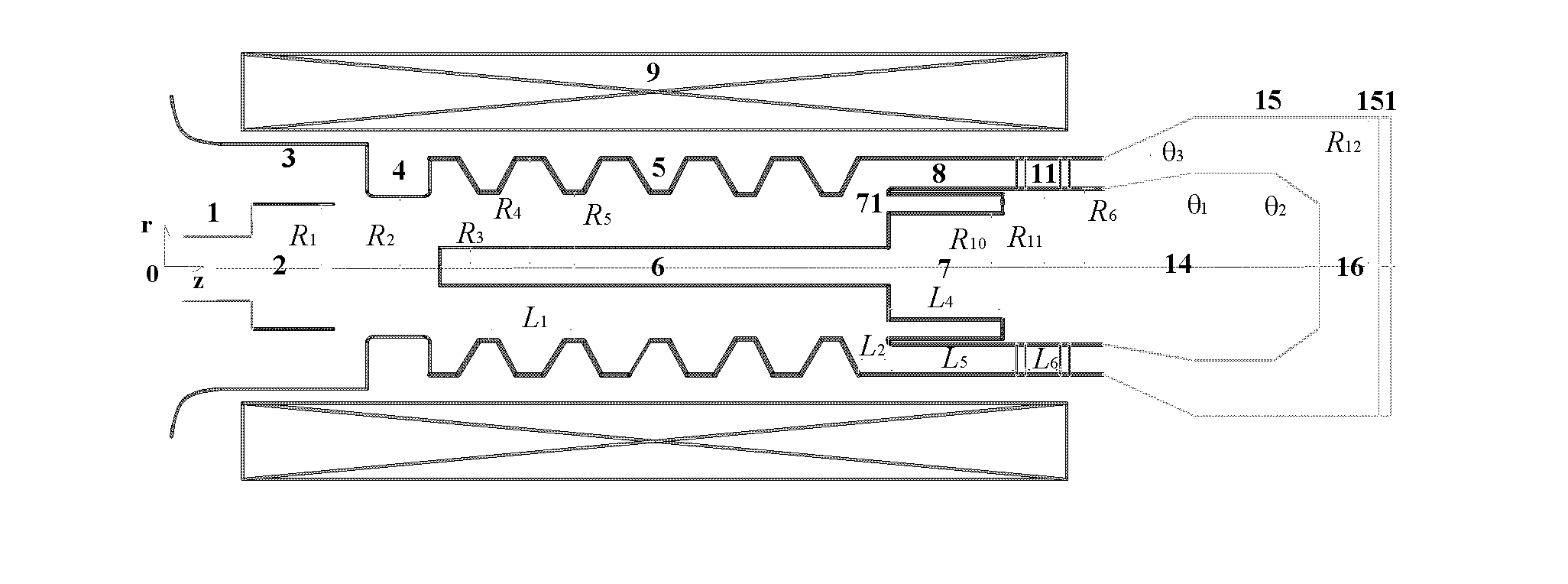
ActiveCN106449337ALow densityReduce the impactTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureChinese characters
The present invention relates to a microwave source of the high-power microwave technology field, and provides a relativistic backward-wave oscillator with a collector shaped as a Chinese character chang. The relativistic backward-wave oscillator comprises a cathode base, a cathode, an anode outer cylinder, a cut-off neck, a slow wave structure, a tapered waveguide, a reflector, an output waveguide and a solenoidal magnetic field. The collector shaped as the Chinese character chang is arranged behind the tapered waveguide, a stepped reflection cavity is arranged between the cut-off neck and the slow wave structure, and double extraction cavities are also arranged between the tail end of the slow wave structure and the tapered waveguide. The relativistic backward-wave oscillator of the present invention overcomes the disadvantage that the conventional relativistic backward-wave oscillator is difficult to consider the long output microwave pulse width and the high power conversion efficiency simultaneously, solves the problem that a coaxial extraction structure is easy to generate the plasmas to thereby influence the working efficiency, and realizes the microwave output that the pulse width is greater than 100 ns, the efficiency is greater than 40%, and the power is 6 GW, on the condition of using less slow wave blades. Moreover, a high-power microwave source is compact in structure, and is easy for the repeated frequency operation.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method and system for energy conversion using a screened-free-electron source
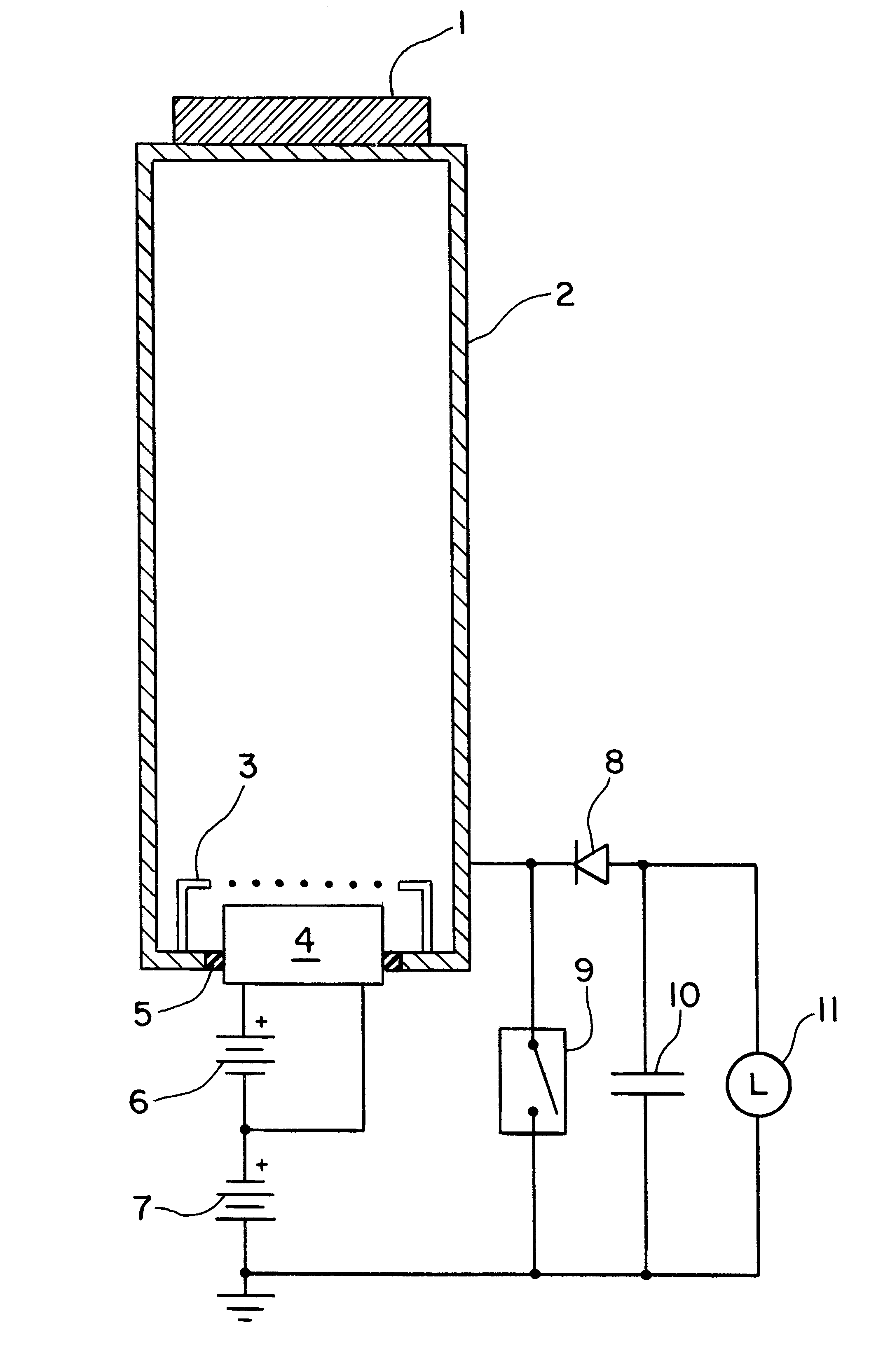
InactiveUS6465965B2Avoid chargingOther heat production devicesExcitation process/apparatusCapacitanceElectron source
A method and device for providing power to a load are disclosed. A beam of free electrons is directed from a free-electron source, such as an electron gun, into an enclosing conductive surface. The free-electron source includes a cathode, which is maintained at a negative voltage with respect to the enclosing conductive surface. A region around the free-electron source is maintained in a vacuum. The system is configured to switch over a time period between two configurations. In the first configuration, the enclosing conductive surface is isolated from a ground. In the second configuration, the enclosing conductive surface is in electrical communication with the ground. Capacitive energy is discharged from the enclosing conductive surface when in the second configuration with an electrical circuit arrangement and provided to the load.
Owner:NELSON LAWRENCE
Distributed amplification gyro traveling wave tube amplifier
InactiveCN102044398AImprove stabilityImprove toleranceTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube circuit elementsHigh energyLinear amplification
The invention discloses a distributed amplification gyro traveling wave tube amplifier, which consists of two sections, namely a linear amplification section with a structure alternatively loading by using a smooth circular waveguide and a loss medium waveguide and a nonlinear amplification section of the smooth circular waveguide, wherein the smooth circular waveguide in the linear section is synchronous to electron beams so as to generate electronic cyclotron maser interaction; a mode in the loss medium waveguide is asynchronous to the electron beams, so that net energy exchange does not exist and a high-frequency field is absorbed by a lossy material; and the electron beams interact in the smooth waveguide and drift in the loss waveguide. Therefore, the linear section is a pre-bunchingsection with high stability. Cyclotron electron beams are fully modulated by driven power in the linear section, well-bunched electron beams intensely act with a working mode in the nonlinear sectionand transverse kinetic energy is converted into microwave energy, so that high-energy microwave output is obtained. The loss medium waveguide of the linear section can effectively absorb a competition mode so as to ensure the stability of a device. The nonlinear section works by using pre-bunched electron beams, so that high power, high stability and high efficiency are achieved.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
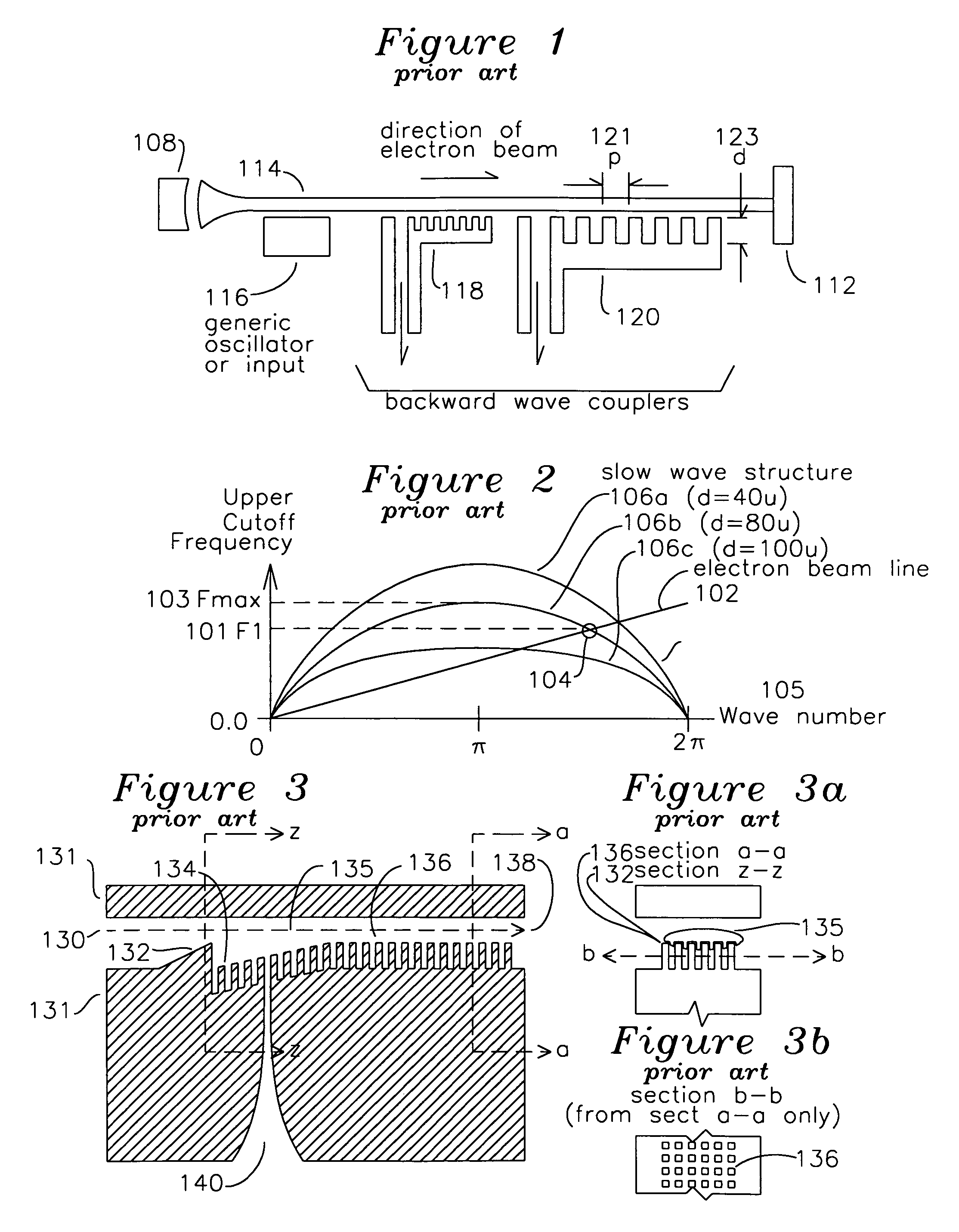
Backward wave coupler for sub-millimeter waves in a traveling wave tube
A slow wave structure for coupling RF energy with an electron beam comprises a co-propagating RF section including a plurality of pins having a uniform separation from the plane of an electron beam axis. An output aperture is positioned a half wavelength from a reflection section comprising a change in depth of the pintles, such that RF energy reflected by the change in pintle depth is added to the RF energy traveling with the electron beam. One or more rows of pintles are removed in the region of the output aperture to enhance coupling to the output aperture. The device may include a beam shaper for shaping the electron beam to surround the pintles, and the beam shaper and pintles may share common channels which are longitudinal to the electron beam axis. The slow wave structure may operate in forward and backward wave modes, and may be used in conjunction with other structures to form amplifiers and oscillators.
Owner:CALABAZAS CREEK RES
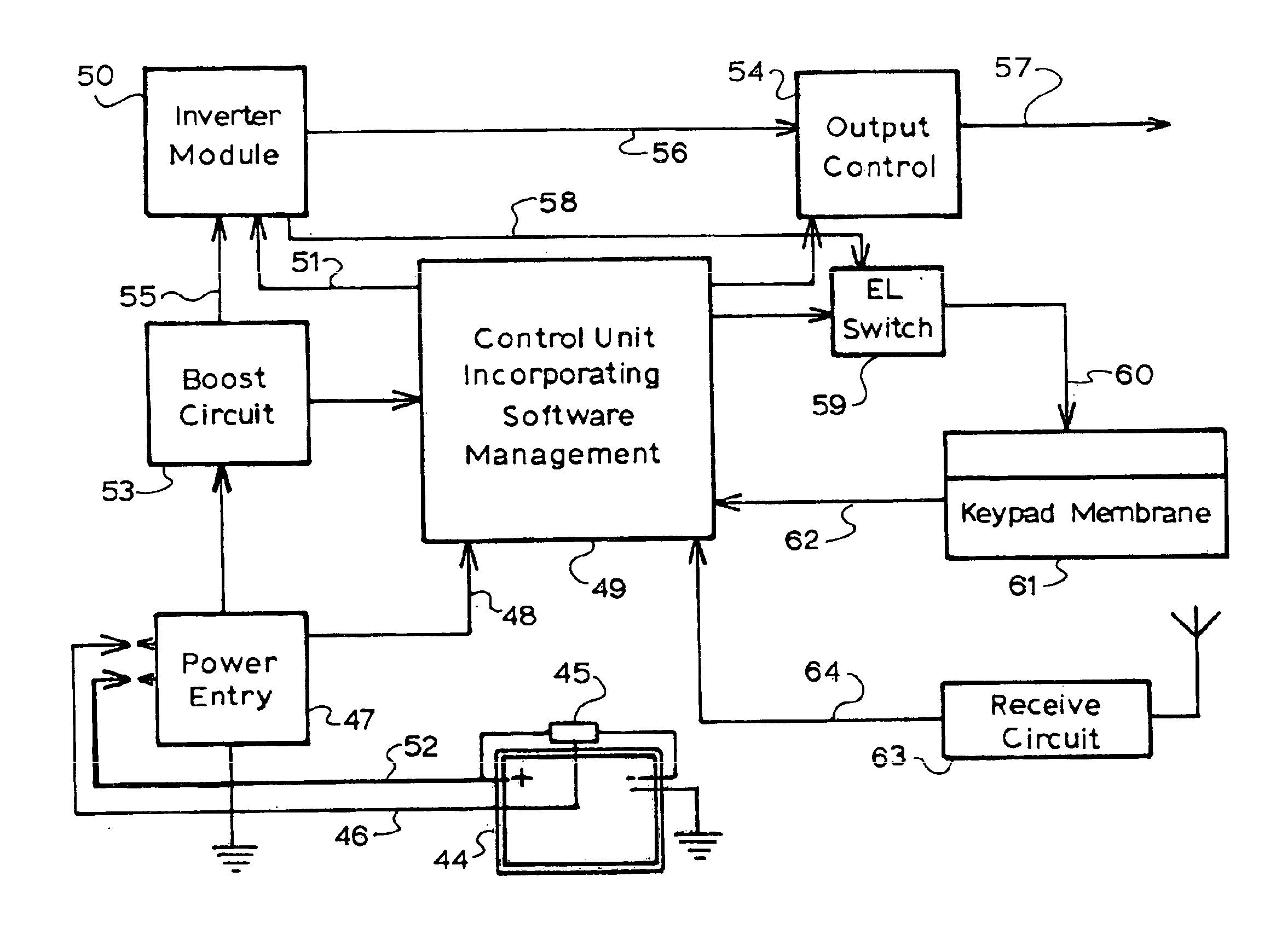
Portable power converter pack
InactiveUS6894439B2Sufficient operationBatteries circuit arrangementsMagnetronsElectricityVoltage converter
A portable power converter comprising input means to receive low voltage DC input, voltage converter means for converting the low voltage DC input into high DC voltage output, the voltage converter means in electrical communication with the input means, output means for operably supplying the high DC voltage to an appliance. The output means is in electrical communication with the converter includes a housing adapted to receive at least one of the input means, the voltage converter means and the output means. Preferably, the portable power converter also includes processing means for controlling some of the functions of the device such as shutting it down when power falls below preselected threshold. The device may also include a remote control which may be manually activated or in an alternative embodiment activated by external environment stimuli.
Owner:THE AUSSIE LIGHT
Power-adjustable backward wave oscillator
InactiveCN106992106AEnhanced interactionAdjustable powerTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube circuit elementsMulti bandBand shape
The invention discloses a power-adjustable backward wave oscillator. The power-adjustable backward wave oscillator is characterized in that: by inserting upper and lower two rows of periodically complementary split-ring resonator structure into the middle part of a cavity of rectangular waveguide vertically, the complementary split-ring resonator structure has a relatively higher electric field resonant response at the slit of the opening, that is, between the horizontal branches of the two half parts, and shows the meta-material electromagnetic characteristic with a negative dielectric constant epsilon and a negative magnetic permeability Mu; longitudinal resonant field intensity is formed at the upper surface and lower surface of the periodically complementary split-ring resonator structure, thus being conductive to interaction between charged particles of band-shaped electron beams and electromagnetic waves; and at the same time, three electron beam channels are formed. Therefore, compared with a traditional relativism backward wave oscillator, the power-adjustable backward wave oscillator has higher coupling impedance and can obtain very high power output and electron efficiency. Besides, the structure enables one electron beam to work individually, or enables two electron beams or three electron beams to work, so that three kinds of adjustable power output of single beam, double beam and three-beam can be formed and then multi-band-shaped power can be adjustable.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Pre-bunching high-power gyro traveling wave tube amplifier
InactiveCN102005354ALower requirementAvoid the disadvantage of high microwave energy lossTravelling-wave tubesMicrowaveHigh energy
The invention discloses a pre-bunching high-power gyro traveling wave tube amplifier and relates to a microwave source device technology, comprising three sections: a linear amplifying section which adopts loss loading metal waveguide; an inertial drifting section which adopts heavy loss loading over-mode waveguide to provide an inertial bunching space approximating zero field for a bunching electron beam; and a nonlinear amplifying section which adopts smooth metal waveguide, wherein the gyro electron beam is fully modulated by driving power in the linear section; the modulated electron beam obtains good bunching characteristic according to inertia in the inertial drifting section; and the electron beam with good bunching vehemently reacts with an operating mode in the nonlinear amplifying section and transforms transverse kinetic energy to microwave energy to obtain high-energy microwave output. Both the linear amplifying section and the inertial drifting section are loss loops to guarantee the stability of the device; and the nonlinear amplifying section adopts the pre-bunching electron beam to work, and has the advantages of high power, high stability, and high efficiency.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
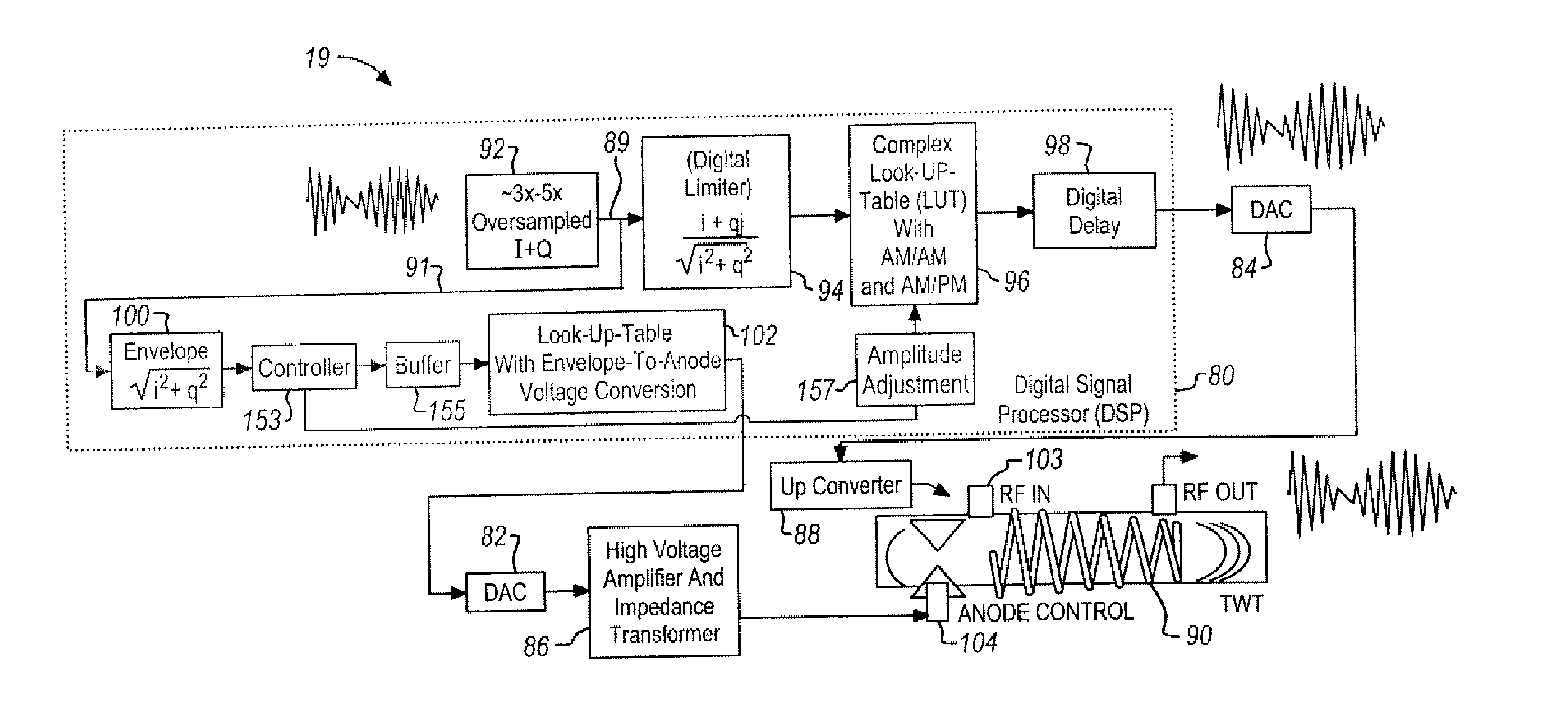
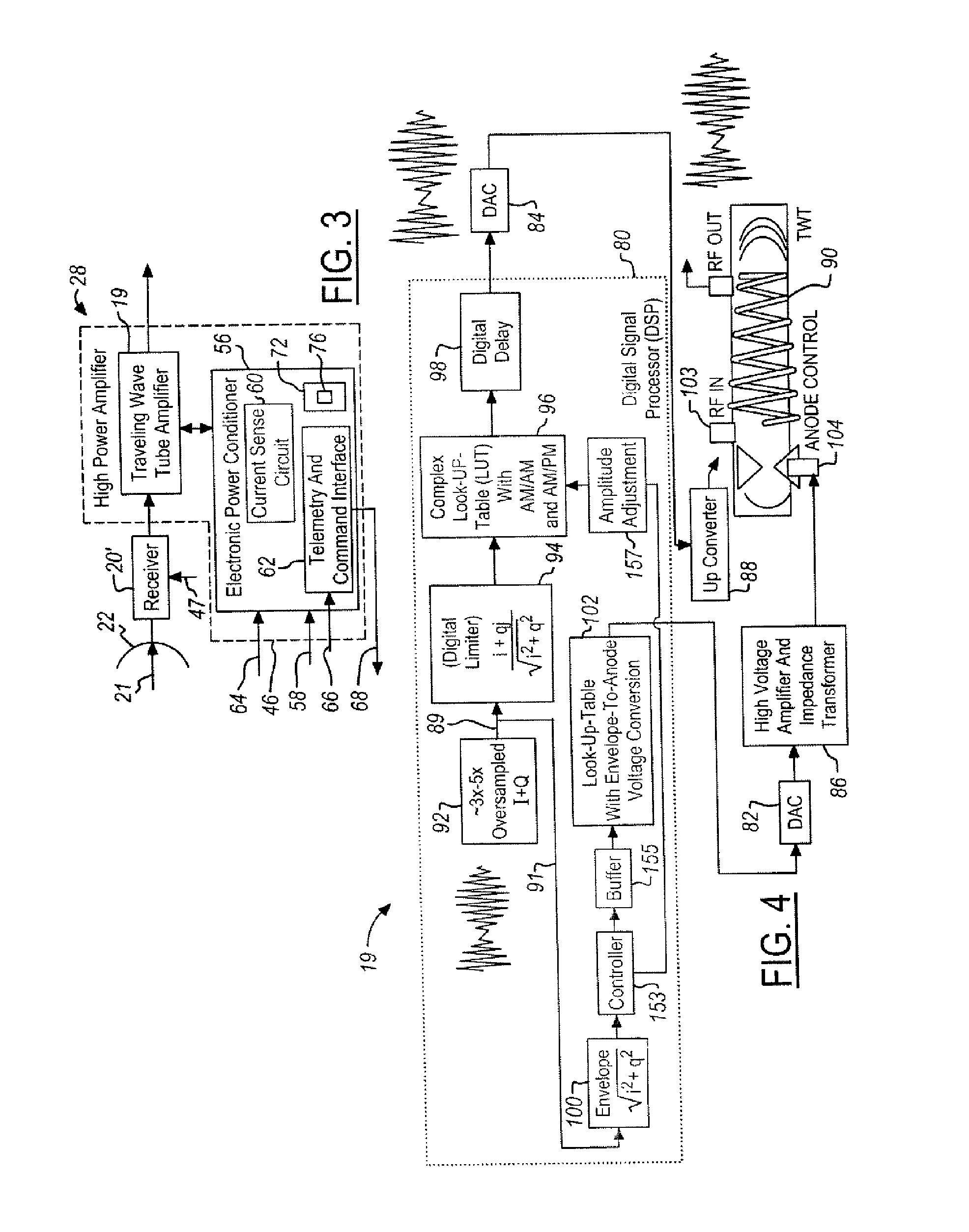
System and Method for Envelope Modulation
ActiveUS20060103460A1Maintain gainMaintain efficiencyTravelling-wave tubesAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyPower control systemWave shape
A power control system for a satellite receiving radio-frequency signals includes a digital processor and a traveling wave tube amplifier system and corresponding traveling wave tube. An anode voltage of the traveling wave tube amplifier system is used to modulate or saturate the current of the electron beam of the traveling wave tube so that the output power of the traveling wave tube amplifier system, from the saturated electron beam, is proportional to a waveform envelope of the radio-frequency signals. The digital processor controls anode and RF input signal amplitudes to the traveling wave tube and predicts necessary corrections.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Dual-electron-beam terahertz wave radiation source in overmode cascading high frequency structure
ActiveCN105355528AReduced emission density requirementsExtended service lifeTransit-tube electron/ion gunsTravelling-wave tubesWave structureHigh resolution imaging
The invention provides a dual-electron-beam terahertz wave radiation source. The terahertz wave radiation source adopts an overmode cascading folded waveguide traveling-wave amplified high frequency structure, so that the length of a single-section folded waveguide slow-wave structure can be dramatically shortened, and the demand on the magnetic field is reduced. The terahertz wave radiation source adopts the dual-electron beam excitation mode, so that the output power can be improved, and the demand on the negative electrode current emitting density is reduced as well; the input signal adopts a higher mode TE20 mode, so that the dimension of the slow-wave structure can be enlarged, and the processing of the slow-wave structure can be performed conveniently; within the same terahertz wave radiation source, the high power terahertz wave output is realized, and the design and the processing of the terahertz wave radiation source are facilitated; and therefore, the applications of the terahertz wave radiation source in the anti-interference, harmful substance detection, ultra wide band radar long-distance detection and high-resolution imaging radar and the like are promoted.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Four-stage depressed collector for space traveling-wave tube
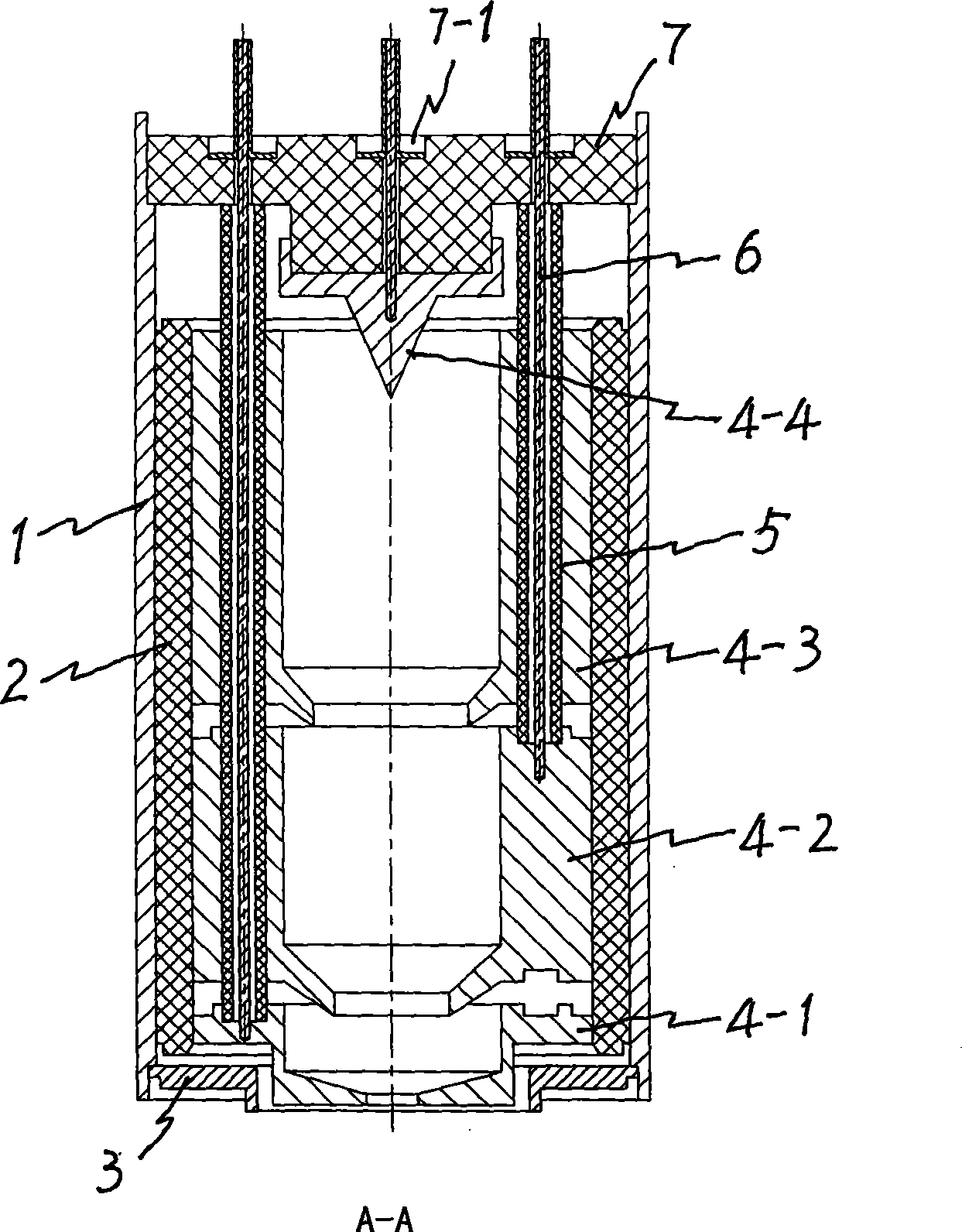
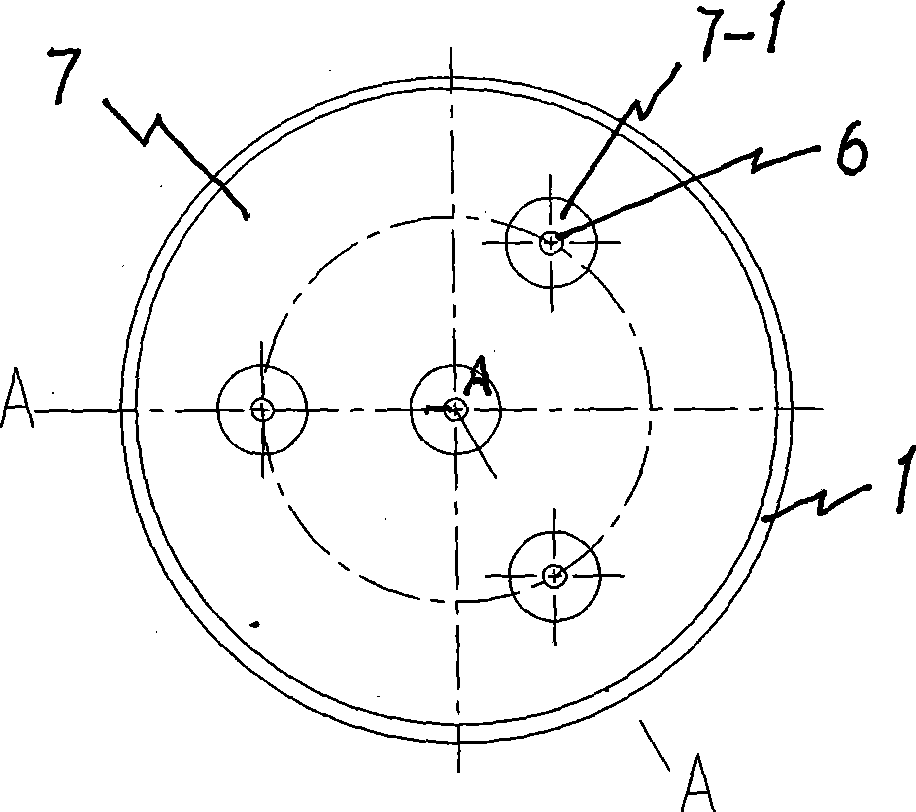
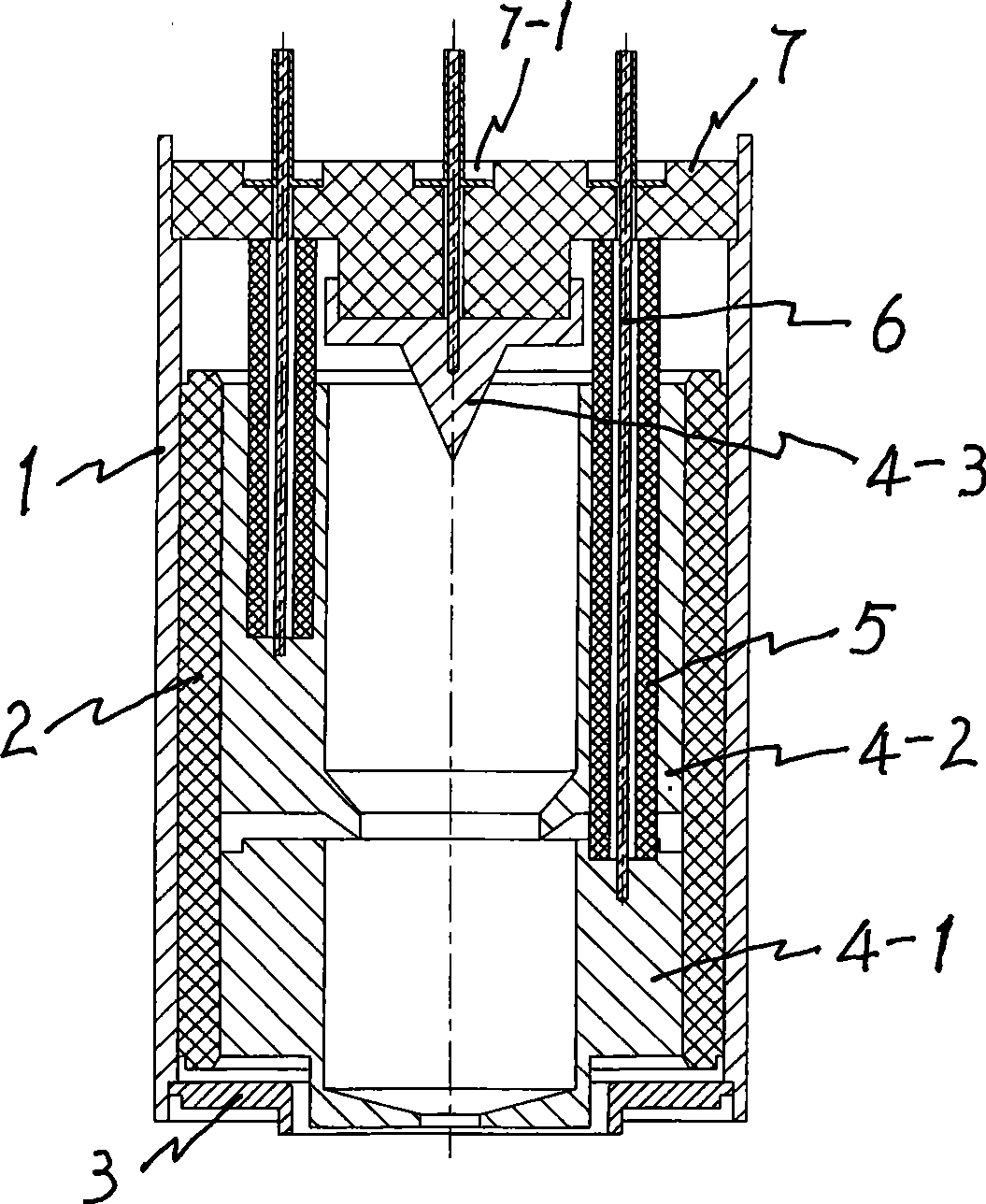
InactiveCN102110564AImprove recycling efficiencyImprove cooling effectTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube collectorsCeramicElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention relates to a four-stage depressed collector for a space traveling-wave tube. A first collector component, a second collector component, a third collector component and a fourth collector component are parallelly arranged inside a circular pipe-shaped collector outer cylinder in sequence in the axial direction, a certain insulating gap is formed between every two collector components, and the electrode lead of each collector passes through an insulating ceramic hole; each collector component comprises a collector electrode, electrode insulating ceramic and an electrode lead; the collector electrode is welded together with the collector outer cylinder through the insulating ceramic; the collector electrode is welded on the inner wall of the electrode insulating ceramic, the outer wall of the electrode insulating ceramic is welded together with the collector outer cylinder, and the electrode lead is directly welded together with the collector electrode and is insulated with other electrode through the insulating ceramic; and the collector outer cylinder is welded and fixed with a collector end cover to form the four-stage depressed collector.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Structures and methods for coupling energy from an electromagnetic wave
InactiveUS7557365B2Stability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis by optical meansElectromagnetic electron waveAngle modulation
A device couples energy from an electromagnetic wave to charged particles in a beam. The device includes a micro-resonant structure and a cathode for providing electrons along a path. The micro-resonant structure, on receiving the electromagnetic wave, generates a varying field in a space including a portion of the path. Electrons are deflected or angularly modulated to a second path.
Owner:ADVANCED PLASMONICS
Structure of coaxial-to-waveguide transition and traveling wave tube
ActiveUS20080246553A1Easy to adjustAvoid arcingMultiple-port networksTravelling-wave tubesElectrical conductorCoaxial waveguides
The present invention includes a waveguide for outputting radio frequency wave, a vacuum envelope provided with a slow-wave circuit, a coaxial connection part connecting the waveguide and the vacuum envelope, an insulating window member which is provided in the coaxial connection part and which hermetically seals a said of vacuum envelope and a said of waveguide, a coaxial center conductor of exterior portion with one end supported by the waveguide, and a coaxial center conductor of an interior portion with one end abutting on the slow-wave circuit and the other end connected to the coaxial center conductor of the exterior portion. The waveguide is provided with a screw part supporting the coaxial center conductor of the exterior portion movably in an axial direction of the coaxial center conductor of the exterior portion. An end portion of the coaxial center conductor of the exterior portion is connected to the end portion of the coaxial center conductor of the interior portion movably in the axial direction of the coaxial center conductor of the exterior portion.
Owner:NEC NETWORK & SENSOR SYST
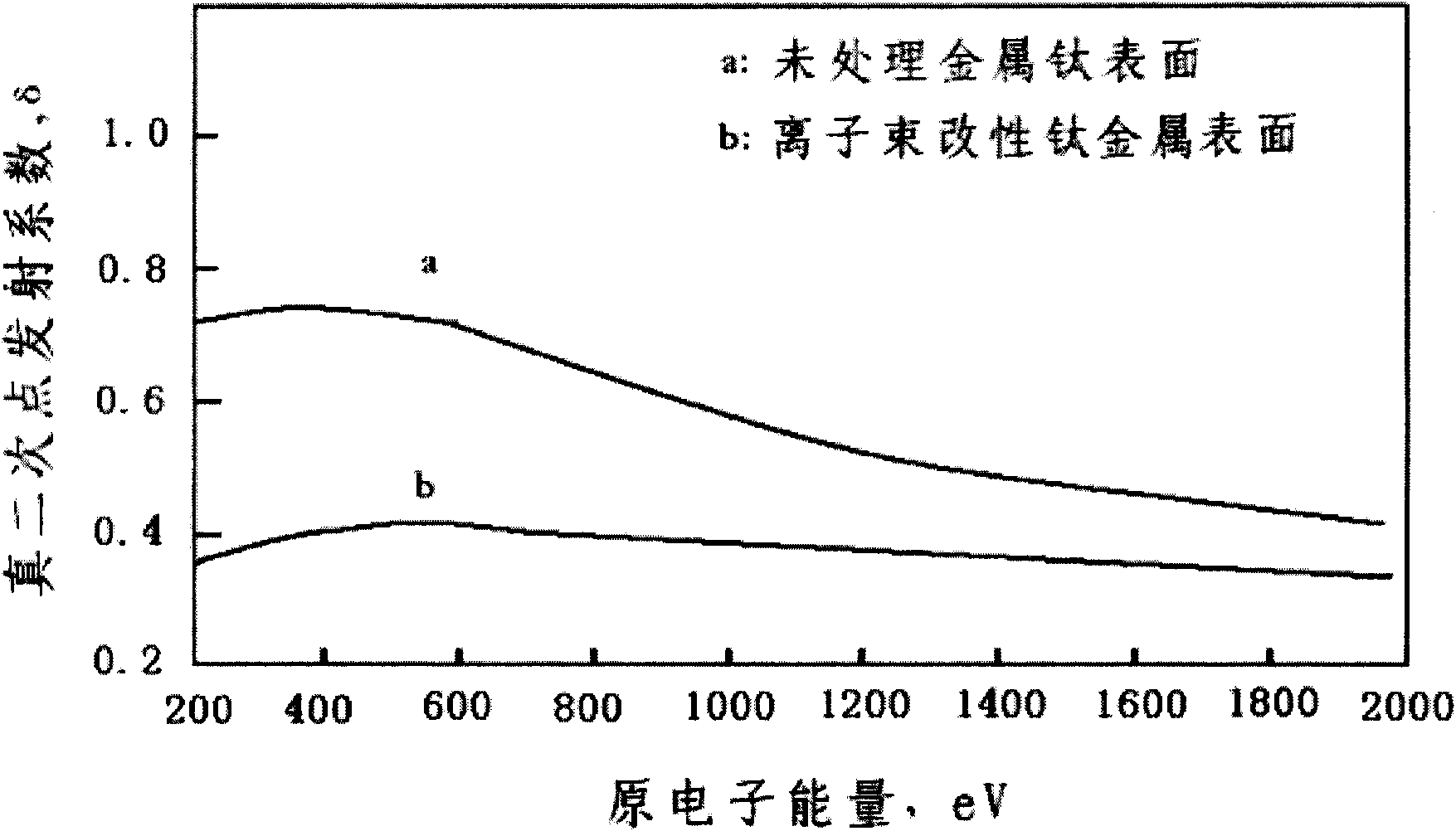
Multi-stage depressed collector material and preparation and surface treatment method thereof
InactiveCN101964290AImprove efficiencyTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube collectorsIon beamSecondary electrons
The invention discloses a multi-stage depressed collector material and preparation and a surface treatment method thereof, which relates to a vacuum electronic technology and is a novel microporous electrode material which can be used for a multi-stage depressed collector of a satellite traveling-wave tube and a treatment process thereof. The electrode material has a micron / submicron-level microporous structure and is beneficial to inhibiting secondary electron emission and improving the recovery efficiency of the multi-stage depressed collector, thereby improving the overall efficiency of the traveling-wave tube. The method has the advantages of simple and controllable process and low cost. Compared with the surface modified by ion beams, the electrode surface of the prepared multi-stage depressed collector has the same effect on inhibiting secondary electron emission.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi-level depressurization collector for traveling wave tube
InactiveCN101447384AAdaptableReduce volumeTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube collectorsEngineeringGuide tube
This invention belongs to a multi-level depressurization collector matched with traveling wave tube, comprising a cylindrical shell, each electrode and power source leading wire thereof mounted in the shell, an insulator mounted between each electrode and shell, an insulator rear cover provided with a power source leading hole, a front end cover. Because the original spare-parts type shell and the insulator thereof are designed to the integral cylindrical body with simple structure, the last level electrode is mounted at the central position of the inner wall of the rear cover, and the other each rear end electrodes are provided with the power source leading hole provided with an insulated sleeve for the front end electrode power source leading hole, this invention is featured with simple and compact structure, simple processing and assembling, strong suitability to the insulated material, small size, light weight and wider application range and so on, such that the defaults of complicated shapes the original spare-parts type shell and the insulator thereof has, need of mounting power source leading hole in the insulated layer, bad processing technology, difficult of assembling and bad suitability to the insulated material which are existed in the background technology are conquered.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
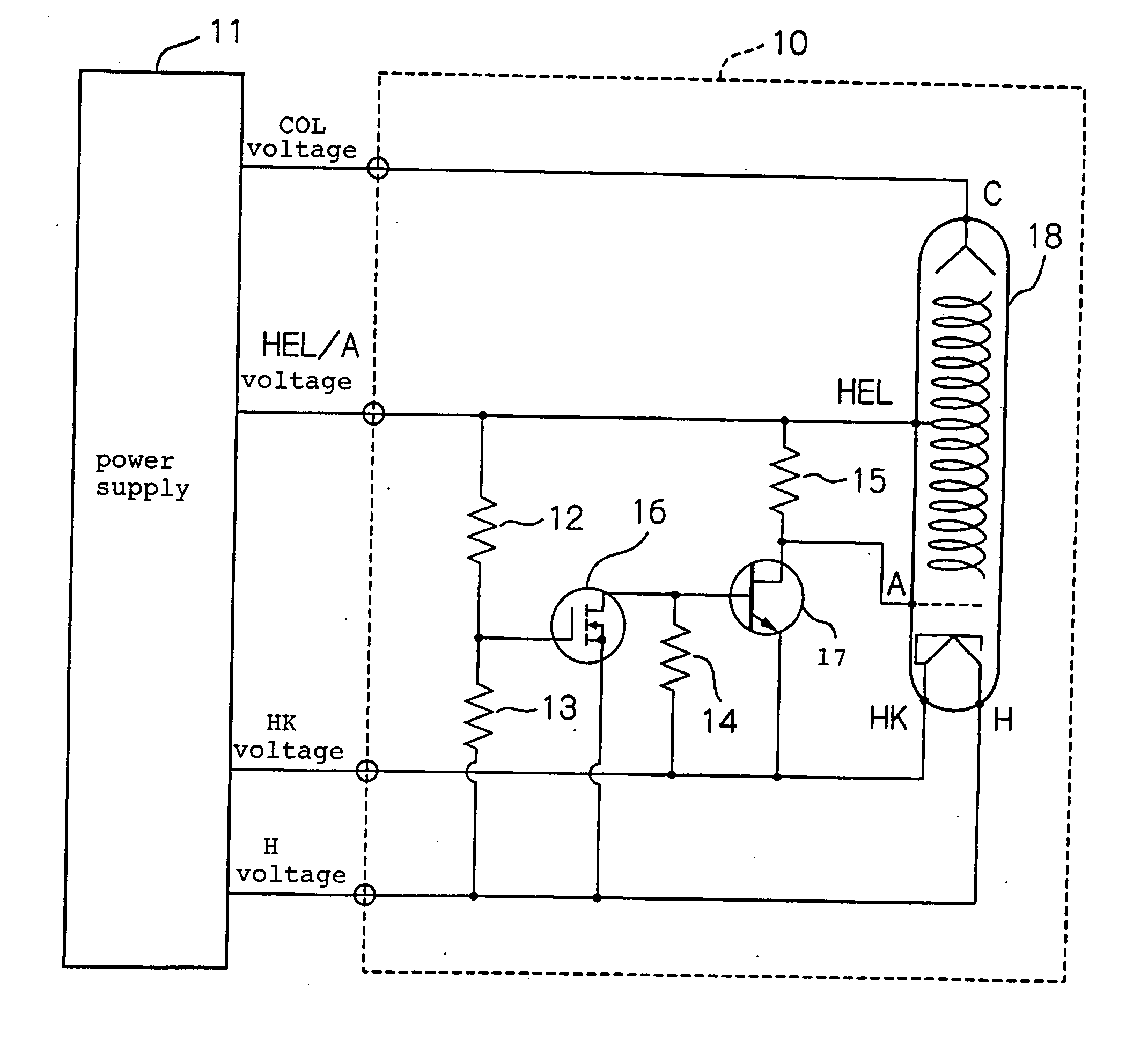
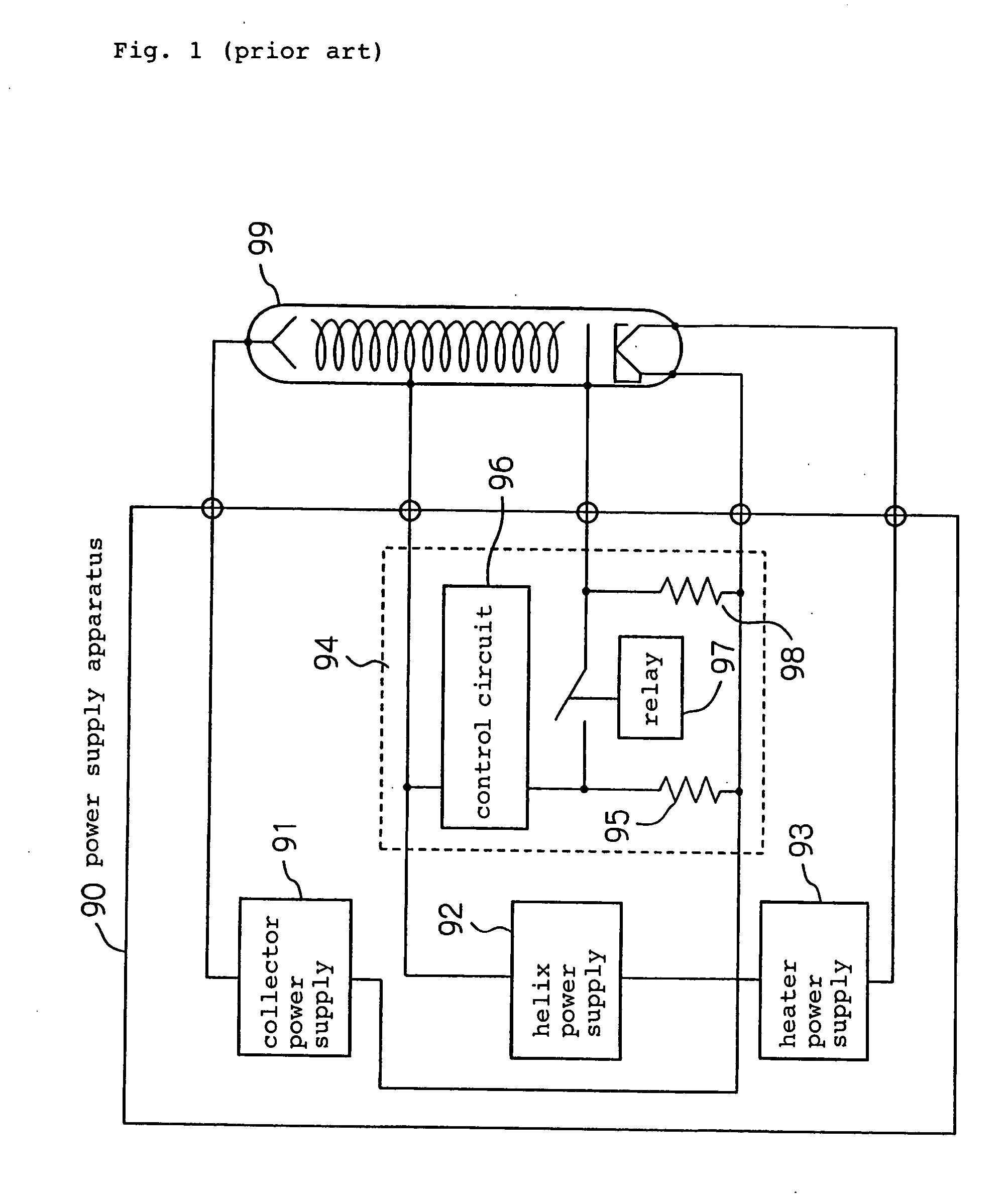
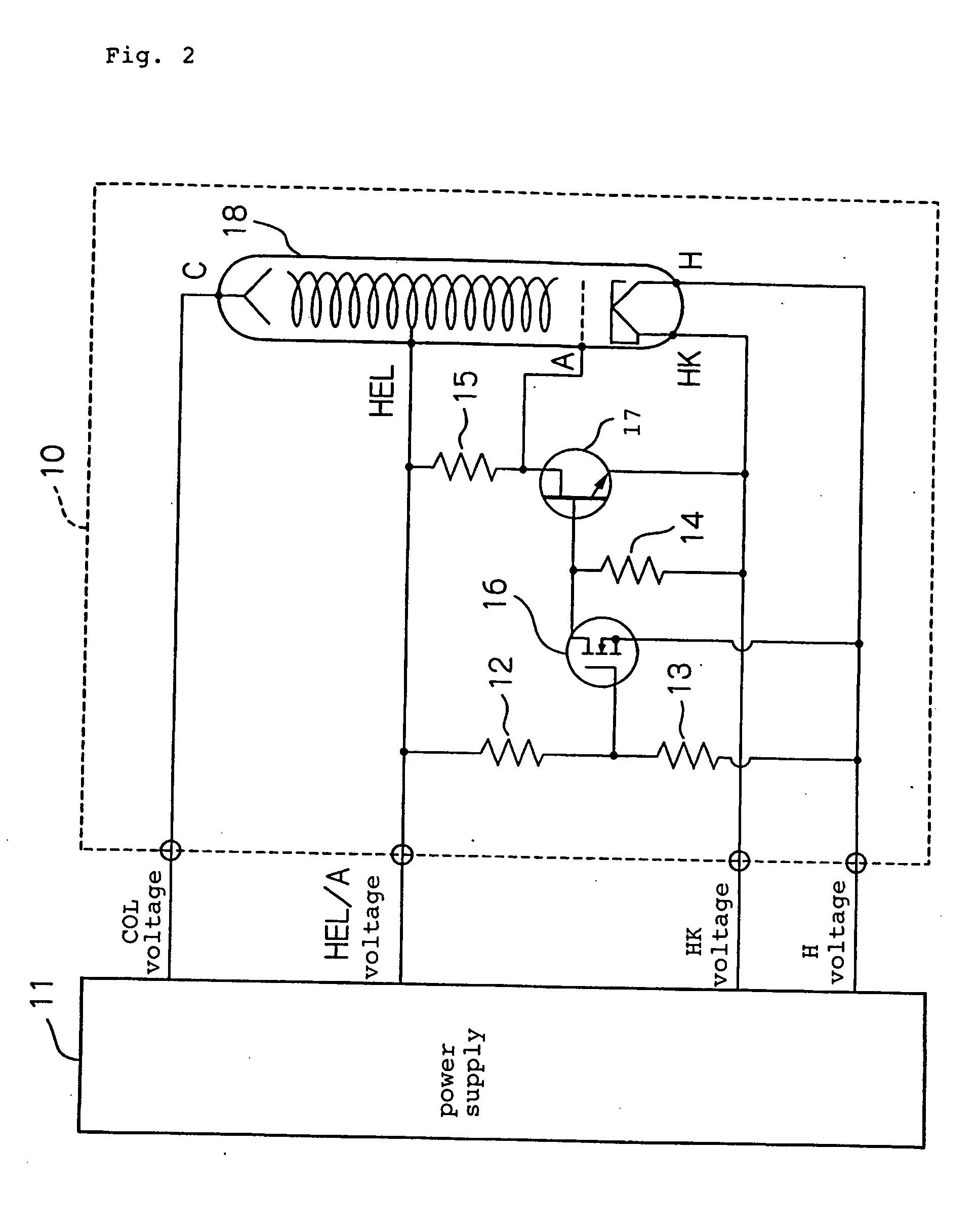
Power supply circuit for traveling-wave tube which eliminates large relay and relay driving power supply
ActiveUS20050057159A1Travelling-wave tubesSolid cathode detailsElectrical resistance and conductancePotential difference
A power supply circuit for a traveling-wave tube disclosed herein eliminates a large relay and a relay driving power supply to reduce the size and cost and to make itself tolerable to vibrations and impacts. A first control device turns on, when a potential on a helix electrode rises to a predetermined threshold determined by the ratio of the resistance of a first resistor to the resistance of a second resistor with respect to a potential on a positive heater electrode or a negative heater electrode, to conduct from a first terminal to a second terminal of the first control device. A second control device turns on when the first control device is off to maintain an anode electrode and a cathode electrode at the same potential. The second control device turns off when the first control device turns on to generate a potential difference between the anode electrode and cathode electrode, thereby applying a voltage to the anode electrode.
Owner:NEC NETWORK & SENSOR SYST
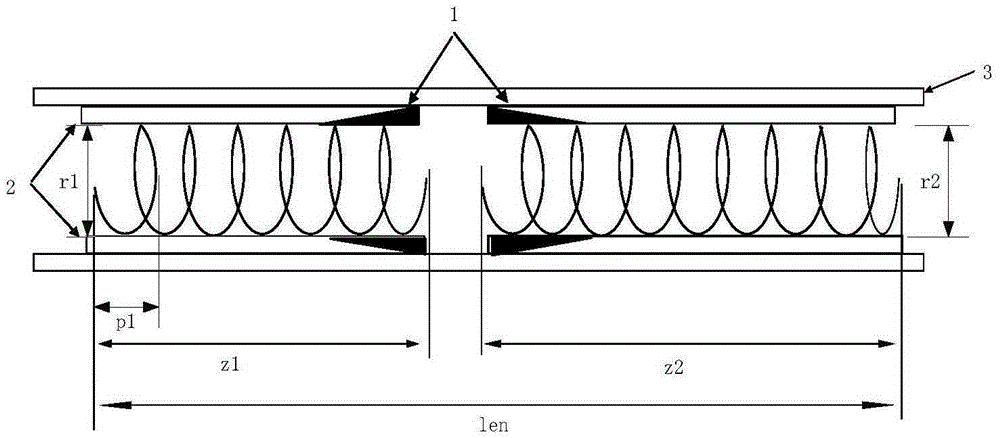
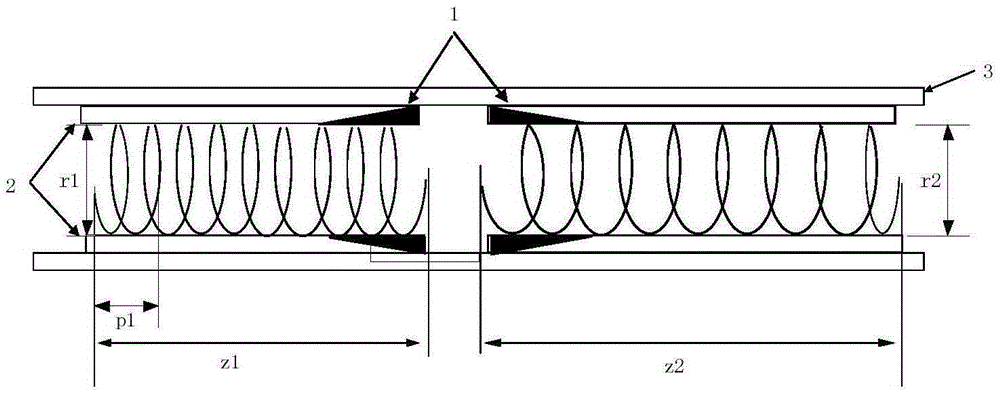
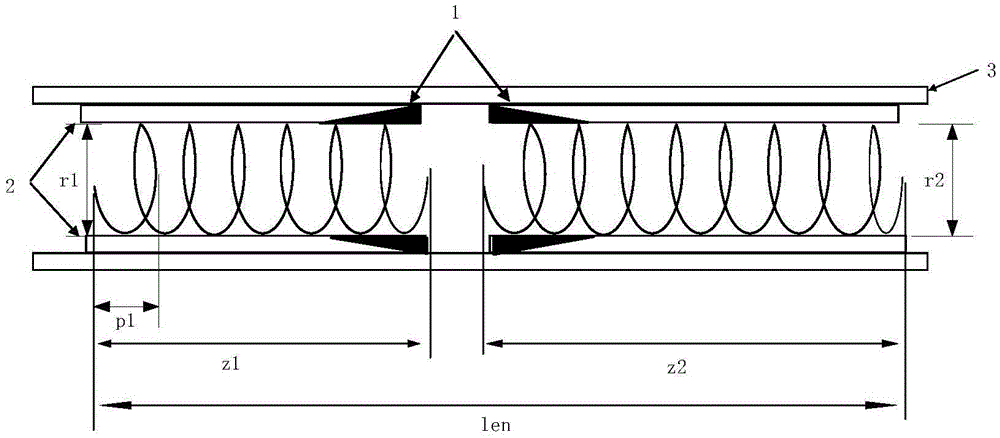
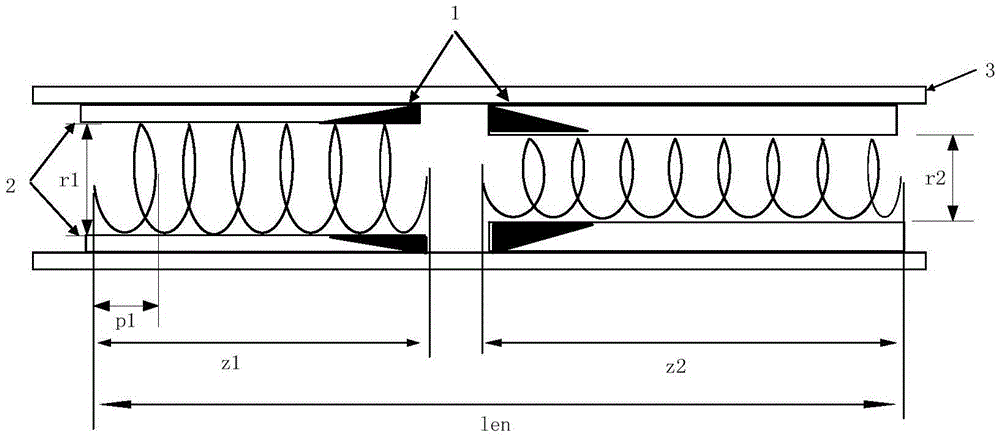
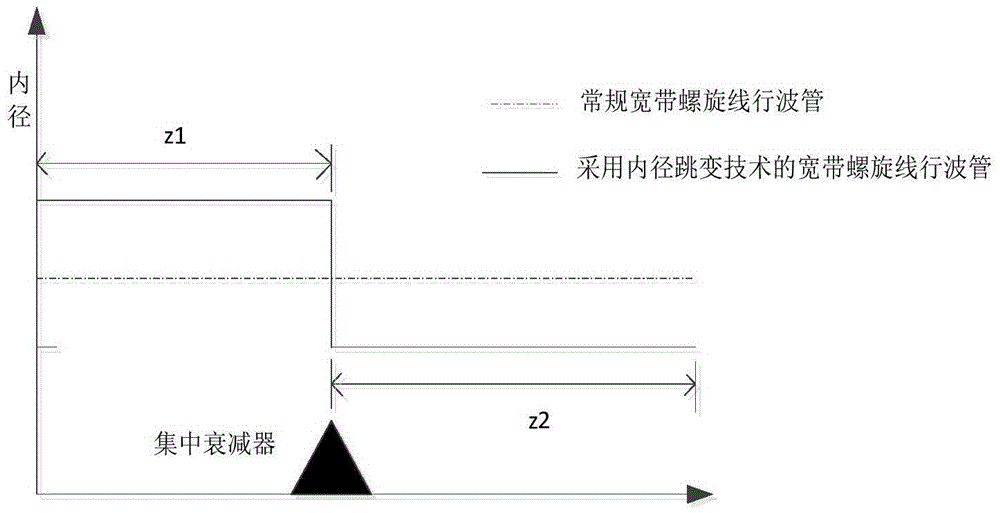
Efficient broadband helix traveling wave tube
ActiveCN105070623AIncrease output powerSolve satietyTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube circuit elementsEngineeringWide band
The invention belongs to the technical field of broadband helix traveling wave tubes, and provides an efficient broadband helix traveling wave tube with inner diameter hopping for the shortcoming of low output power of the existing broadband helix traveling wave tube. The efficient broadband helix traveling wave tube comprises an input helix, an output helix, a clamping rod, a tube casing and a centralized attenuator. The input helix and the output helix are fixed in the tube casing through the clamping rod. The input helix and the output helix are separated through cutting. Both sides are cut, and the centralized attenuator is arranged. The efficient broadband helix traveling wave tube is characterized in that the inner diameter of the output helix is hopping compared with the inner diameter of the input helix, so that the helix traveling wave tube realizes saturation output power point gathering in a work band. According to the broadband helix traveling wave tube provided by the invention, an inner diameter hopping technology is used to effectively solve the problem of saturation output power synchronization in bandwidth; the output power of the broadband helix traveling wave tube is effectively improved; and the output power is high under an equal excitation input condition.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Multibeam doubly convergent electron gun
InactiveUS20100045160A1Reduced radiusTransit-tube electron/ion gunsTravelling-wave tubesLight beamElectron
This disclosure describes a multibeam doubly convergent electron gun. Two or more beamlets can be run parallel to the axis at a prescribed radius to produce sufficient current to drive the VED. In order to obtain sufficient cathode surface area to provide the required current, the beamlets are launched from a cathode radius greater than the radius required in a slow wave circuit. In one embodiment, an electron gun includes a focus electrode that surrounds two or more cathodes, wherein each cathode emits a beamlet comprised of a plurality of electrons directed to a predetermined location. A first anode receives each beamlet at the predetermined location, accelerates each beamlet and changes the radius of each beamlet. A second anode receives each beamlet from the first anode, directs each beamlet along a predetermined axis, further accelerates, and can further compress each beamlet.
Owner:MANHATTAN TECH LTD
Traveling-wave valve arrangement
InactiveUS6486604B1Reduce heatLong signal pathTravelling-wave tubesDischarge tube main electrodesActive coolingMechanical engineering
For a traveling-wave valve arrangement with a traveling-wave valve and a linearizing circuit arrangement, it is proposed to design the linearizing circuit arrangement and the traveling-wave valve as one constructional unit and, for the thermal protection of the linearizing circuit arrangement in the simultaneous presence of a high permissible temperature of the valve housing, to maintain the circuit arrangement by means of an active cooling element at a nondamaging temperature lower than the one of the wall of the valve or of a common wall. The cooling element is preferably a Peltier element.
Owner:THALES ELECTRON DEVICES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com