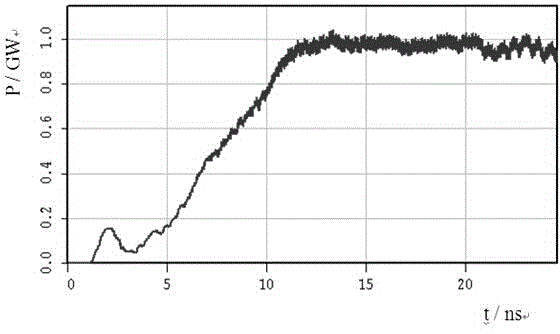
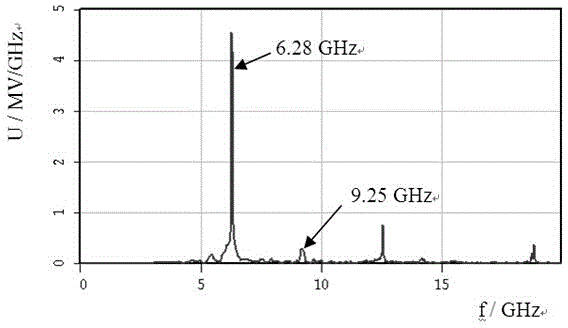
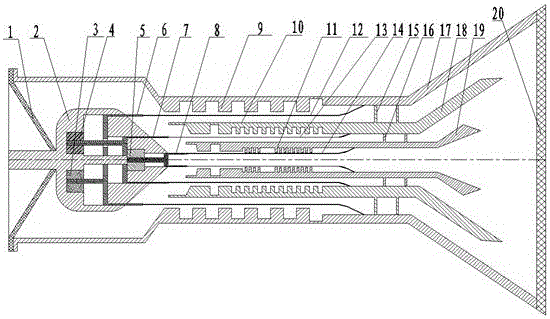
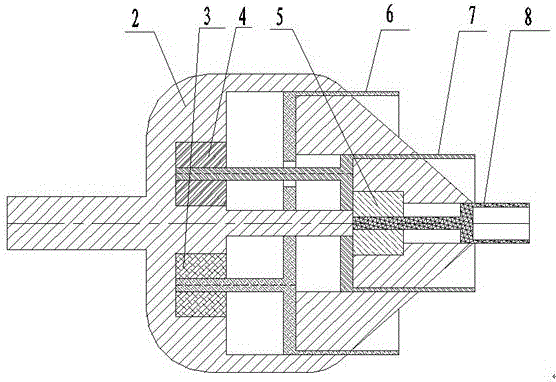
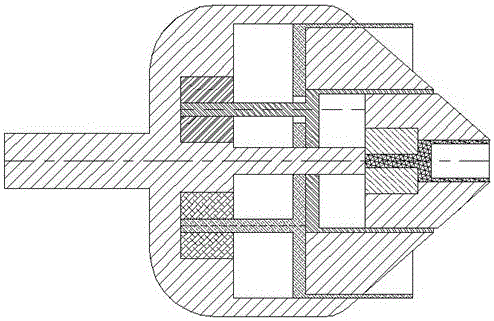
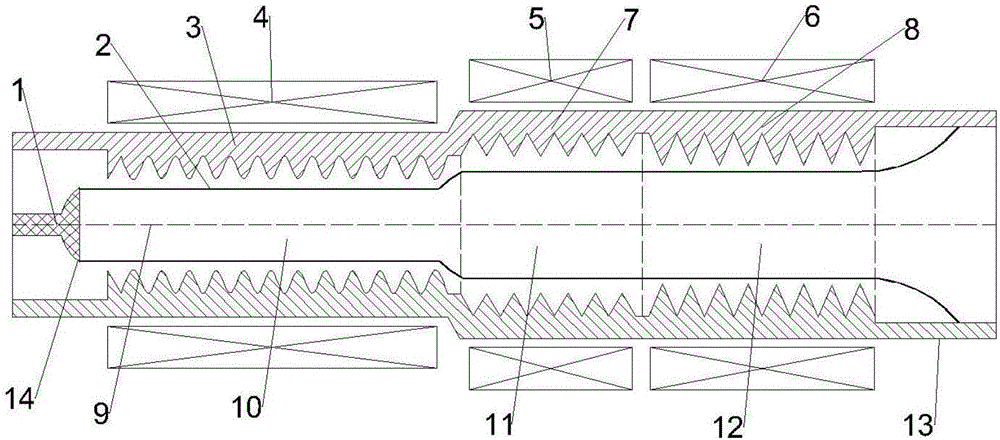
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
60 results about "Backward-wave oscillator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
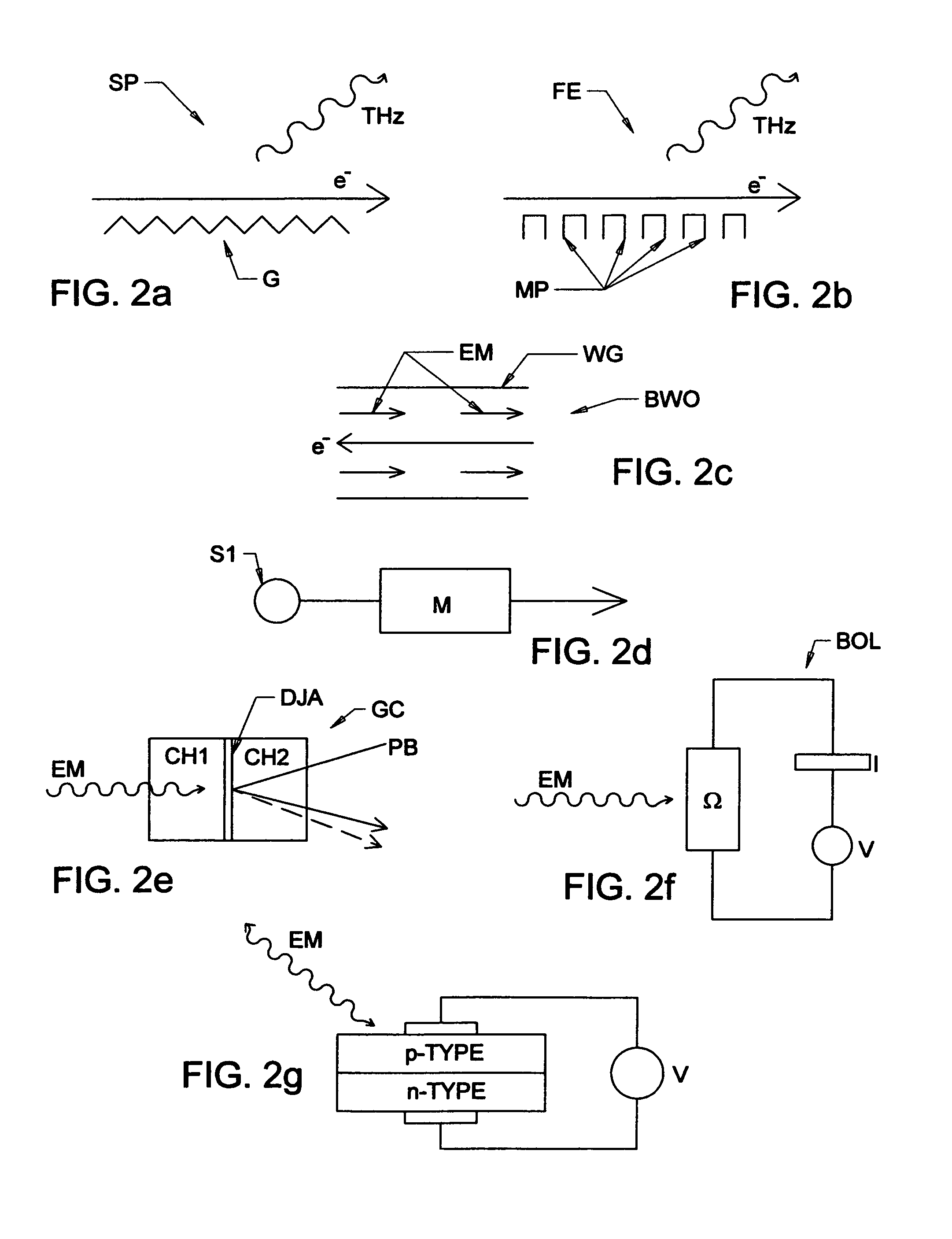
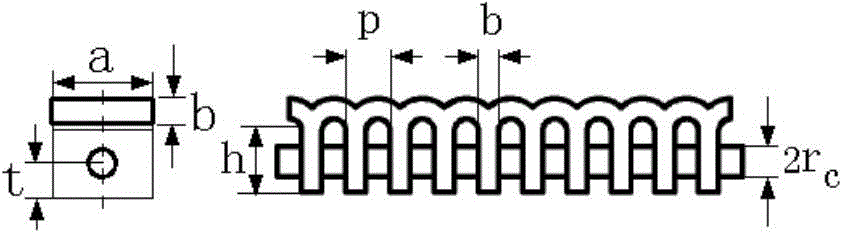
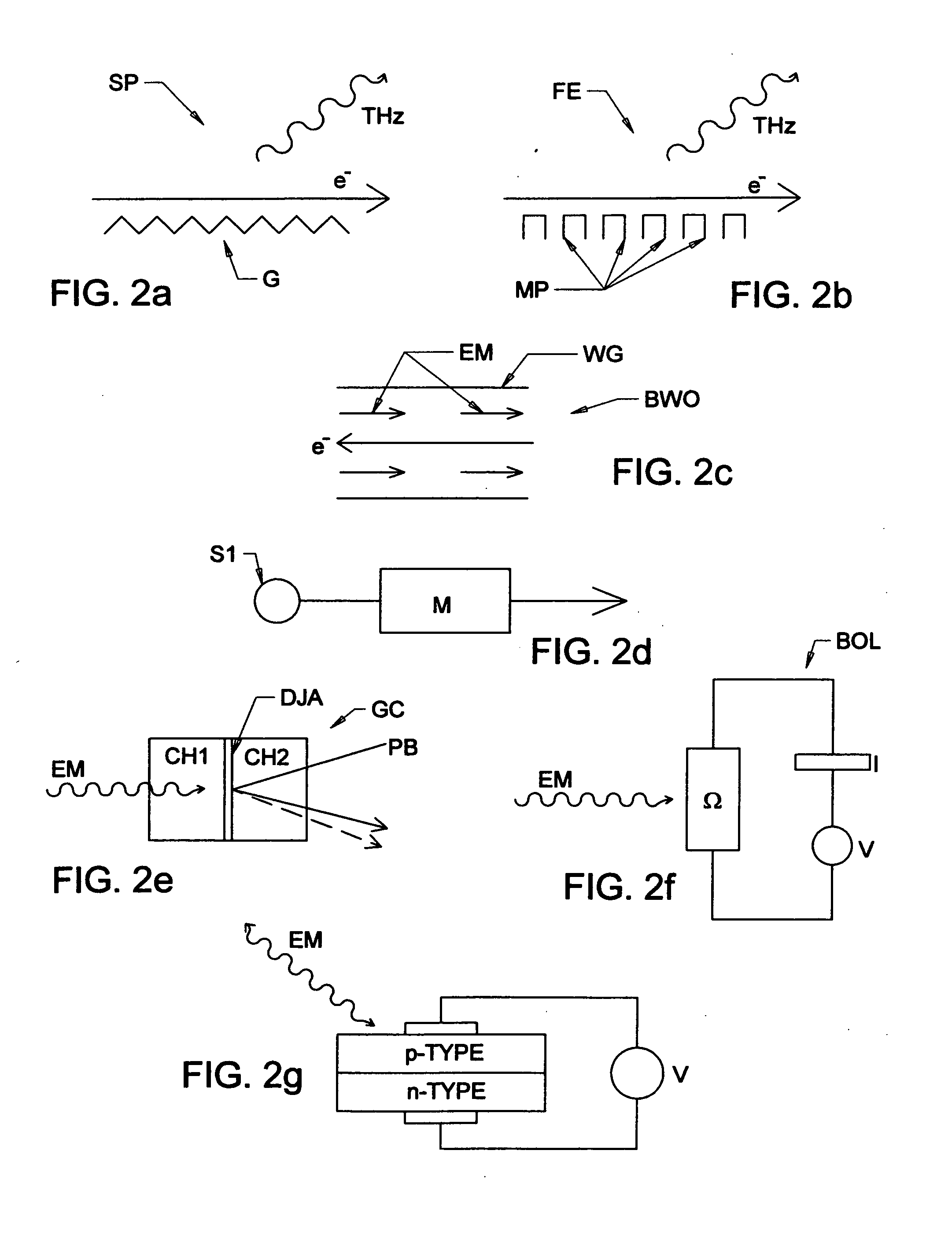
A backward wave oscillator (BWO), also called carcinotron (a trade name for tubes manufactured by CSF, now Thales) or backward wave tube, is a vacuum tube that is used to generate microwaves up to the terahertz range. Belonging to the traveling-wave tube family, it is an oscillator with a wide electronic tuning range.
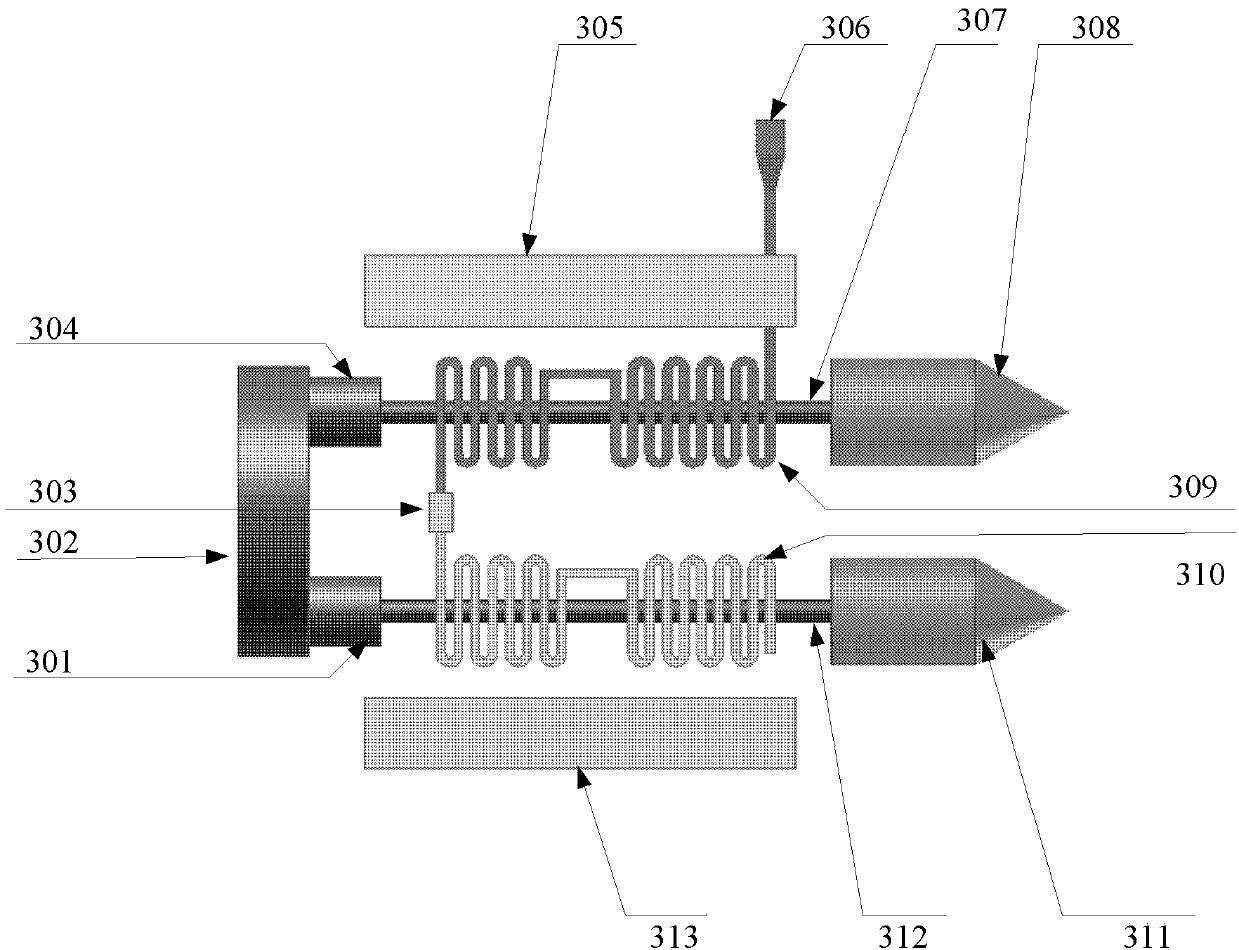
Compact relativity backward wave oscillator (RBWO) with adjustable low-frequency-range frequency
ActiveCN102208315AReduce radial sizeCan be smallTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube collectorsWave structureElectrical conductor
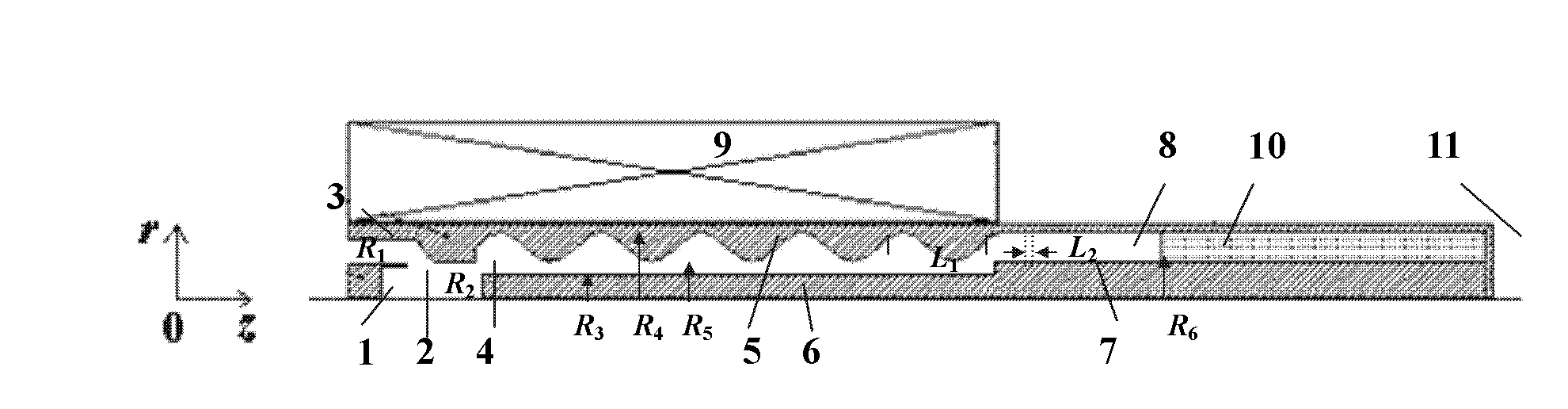
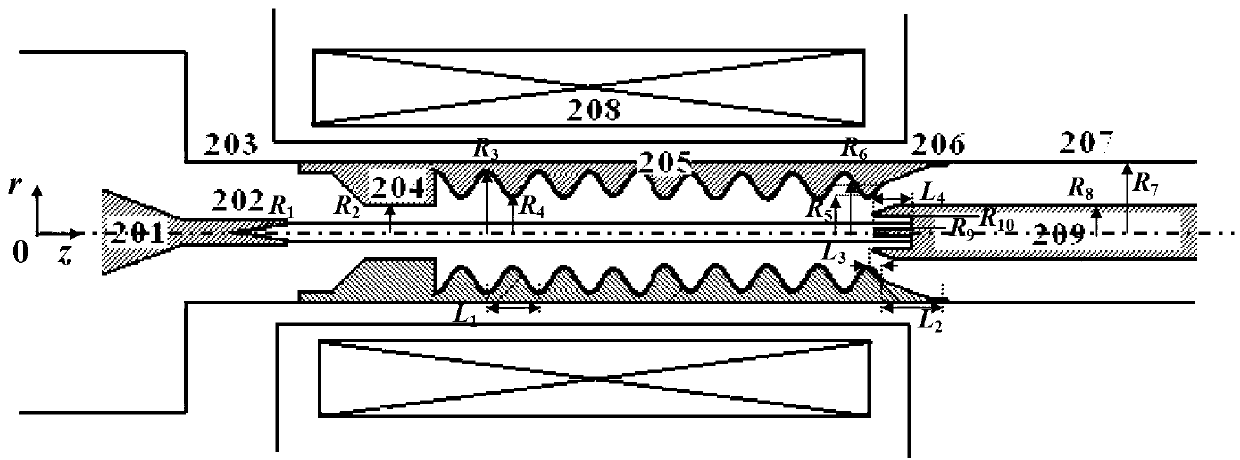
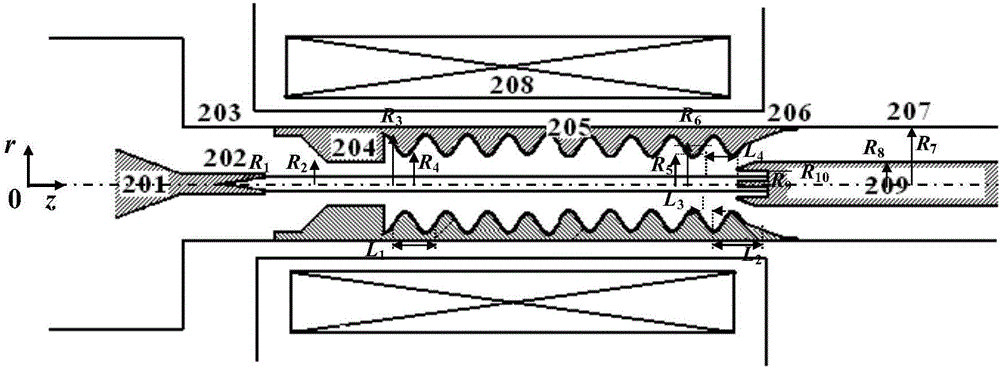
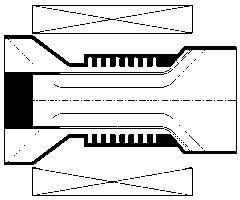
The invention discloses a compact relativity backward wave oscillator (RBWO) with an adjustable low-frequency-range frequency, and the oscillator provided by the invention is used for solving the problems that the RBWO size in a low frequency range is great, and the output microwave frequency is hard to adjust. The compact RBWO is in rotational symmetry with respect to a central axis, and composed of a cathode base, a cathode, an anode outer barrel, a stop neck, a slow wave structure, an inner conductor, a collector, a microwave output port, a solenoid field, two rows of supporting rods, a mode converter, a radiation port and a sealing plate; the slow wave structure is composed of five slow wave blades, the inner surface of each slow wave blade is in a trapezoid structure; the left end face of the collector is provided with an annular groove; the left end of the mode converter is cylindrical, and the right end of the mode converter is in a tapered structure; the radiation port is cylindrical, the left end of the radiation port is in a tapered structure and the right end of the radiation port is cylindrical; the sealing plate is pressed on the radiation port; and the frequency of the output microwave is adjusted by virtue of adjusting the semi-diameter R3 of the inner conductor. The compact RBWO has the advantages of compact structure and convenient and adjustable work frequency, thereby being beneficial to outputting a long pulse of the microwave.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Coaxial-extraction long-pulse relativistic backward-wave oscillator
ActiveCN103137399AHigh Q valueOvercome the impact on work efficiencyTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube collectorsWave structureMicrowave
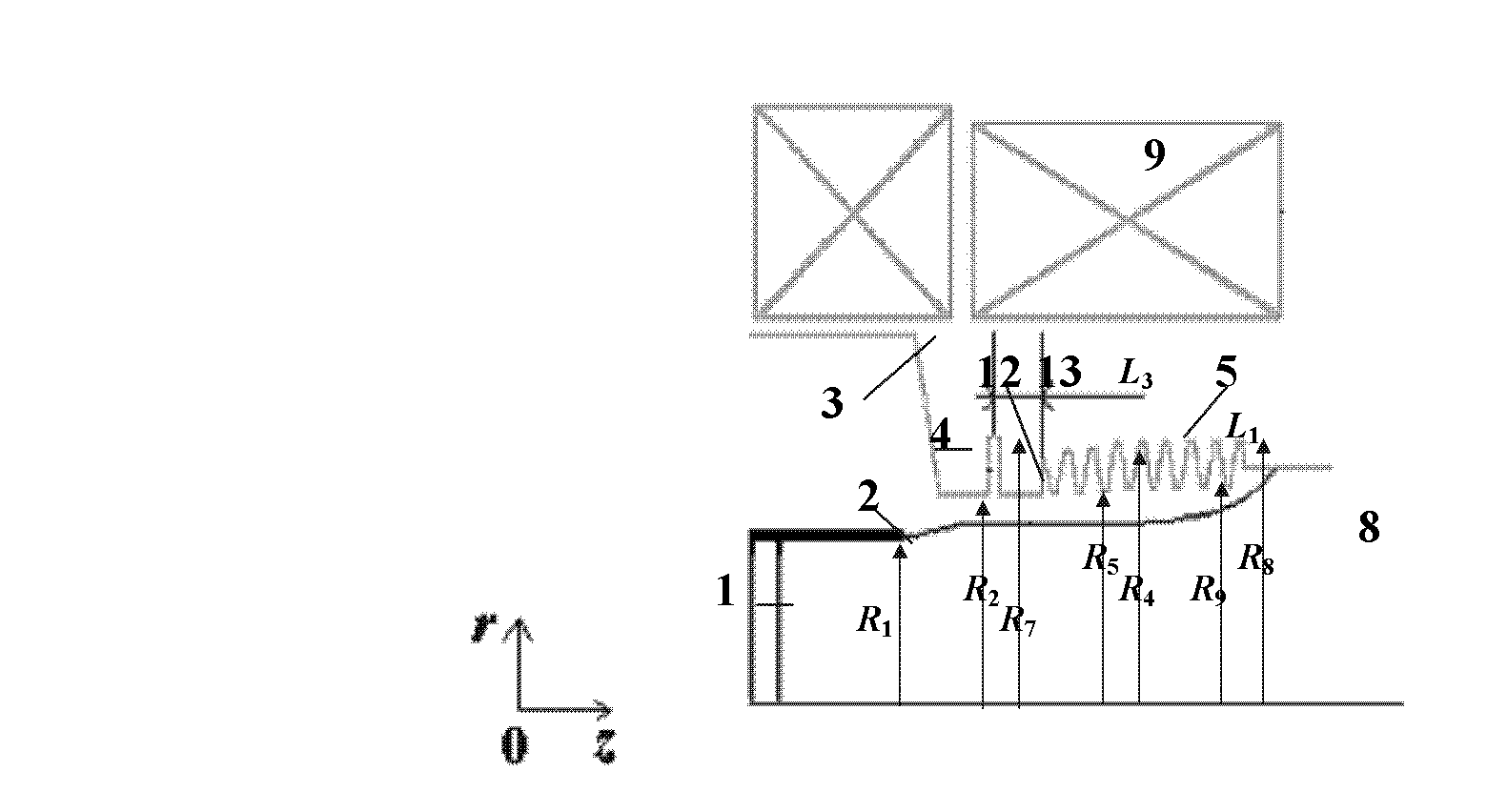
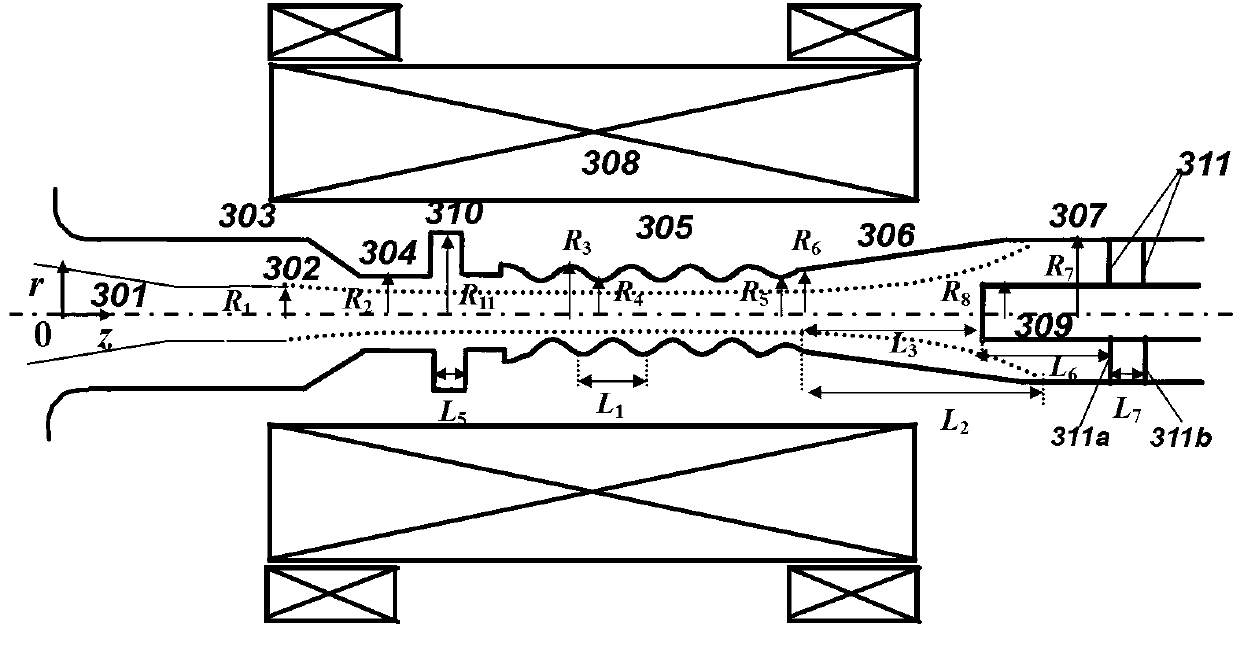
The invention relates to a microwave component in the technical field of high power microwave and provides a coaxial-extraction long-pulse relativistic backward-wave oscillator. The coaxial-extraction long-pulse relativistic backward-wave oscillator comprises a cathode base, a cathode, an anode outer cylinder, a cut-off neck, a slow wave structure, a tapered waveguide, an output waveguide, a solenoidal field, a coaxial-extraction structure and a front-arranged reflection cavity. The coaxial-extraction structure is a cylinder. The front-arranged reflection cavity is disposed between the cut-off neck and the slow wave structure. According to the coaxial-extraction long-pulse relativistic backward-wave oscillator, a cylinder is adopted as the coaxial-extraction structure, and therefore the defect that the coaxial-extraction structure with a groove generates plasma is overcome, and meanwhile in the electromagnetic wave mode, function transformation can be carried out and installation can be achieved conveniently. The front-arranged reflection cavity is utilized to replace the cut-off neck so that the resonance characteristic of the front-arranged reflection cavity can be utilized to achieve the effect of the cut-off neck, electron beam scraping or electron beam bombardment of the front-arranged reflection cavity can be avoided, and premodulation of electron beams emitted from the cathode also can be carried out. Therefore, the coaxial-extraction long-pulse relativistic backward-wave oscillator is beneficial for subsequent beam wave interaction and improves power conversion efficiency of the component.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Dielectric filled compact type relativistic backward wave oscillator
ActiveCN104362060AReduce microwave frequencyReduce radial sizeTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureDielectric
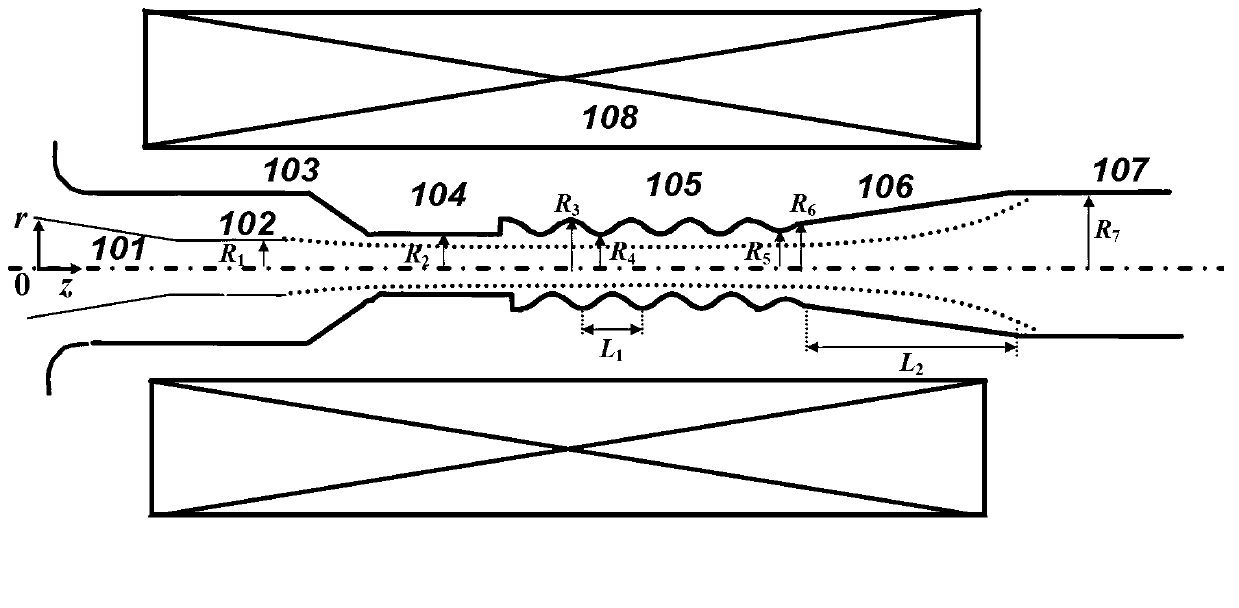
The invention discloses a dielectric filled compact type relativistic backward wave oscillator and belongs to the technical field of high-power microwave. The dielectric filled compact type relativistic backward wave oscillator is rotationally symmetrical relative to the central axis and consists of a cathode seat, a cathode, an anode outer barrel, a cut-off neck, a slow wave structure and a solenoidal field coil. The slow wave structure is a disk loaded waveguide type slow wave structure and consists of five slow wave blades, wherein the inner surface of each slow wave blade is of a rectangular structure. During dielectric filling, an original structure of the RBWO is not needed to be changed, and only dielectric materials are needed to be filled among all blades of the slow wave structure. The problem that a low-frequency relativistic backward wave oscillator is too large in size and weight can be solved, and the dielectric filled compact type relativistic backward wave oscillator has wide application prospect and important scientific research value on research of small-sized compact type relativistic backward wave oscillators, promotion of engineering application process of high-power microwave systems and expansion of the RBWO application field.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Relativistic backward wave oscillator for generating linearly polarized TE11 mode directly
ActiveCN105280462AEnhanced interactionImprove beam conversion efficiencyTransit-tube cathodesTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureMaser
The invention, which belongs to the maser field, directly relates to a relativistic backward wave oscillator for generating a linearly polarized TE11 mode directly. The relativistic backward wave oscillator comprises an arc cathode, a reflector, an angular partition slow wave structure, an output waveguide and a magnetic field coil. The arc cathode is arranged at the front end of the relativistic backward wave oscillator; the reflector, the angular partition slow wave structure, and the output waveguide are arranged at the rear side of the arc cathode successively; and the magnetic field coil is installed at the periphery. According to the invention, with the nonaxisymmetrical arc cathode and the angular partition slow wave structure, the TE11 mode is excited directly. The reflector employs the dual-premodulation-cavity unit preferably and is used for carrying out premodulation on an arc relativistic electron beam and leaking the part of TE11 mode to enter the arc cathode zone, so that certain premodulation of the electron beam at the arc cathode zone is realized and thus the beam wave conversion efficiency is improved. Moreover, the oscillator has advantages of simple structure and high conversion efficiency; and the linearly polarized TE11 mode can be generated directly.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Relativistic backward-wave oscillator with collector shaped as Chinese character chang
ActiveCN106449337ALow densityReduce the impactTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureChinese characters
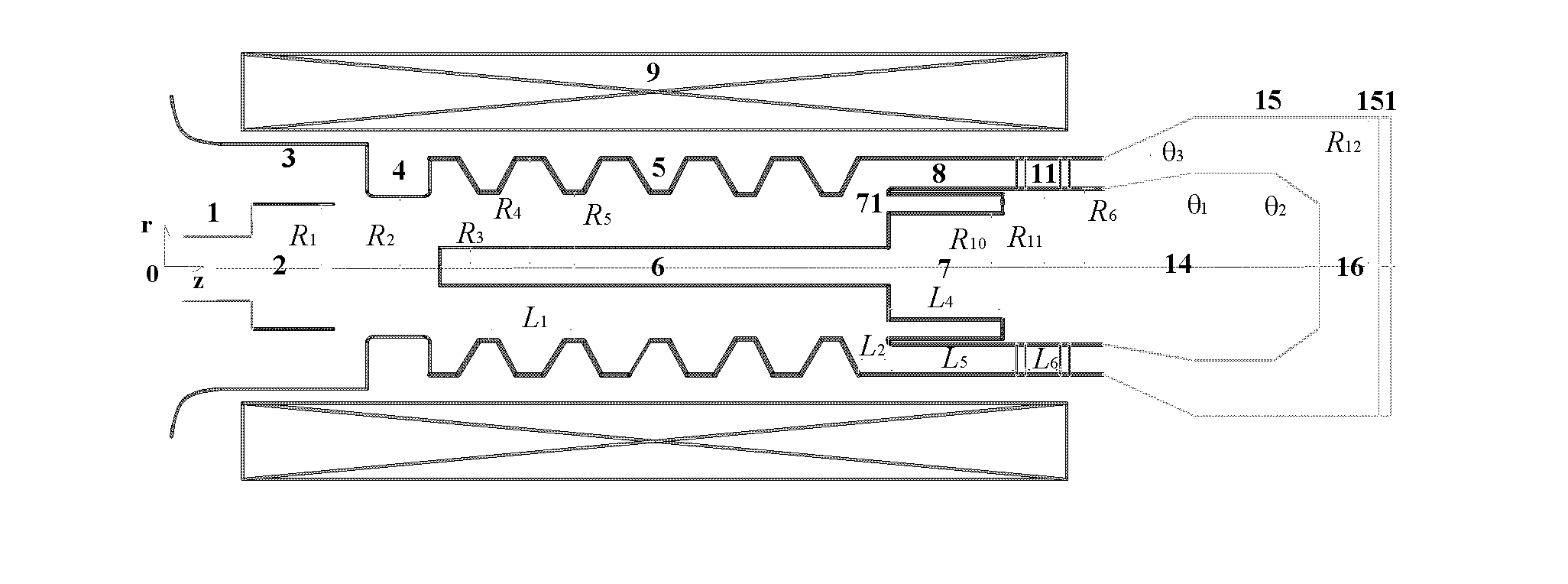
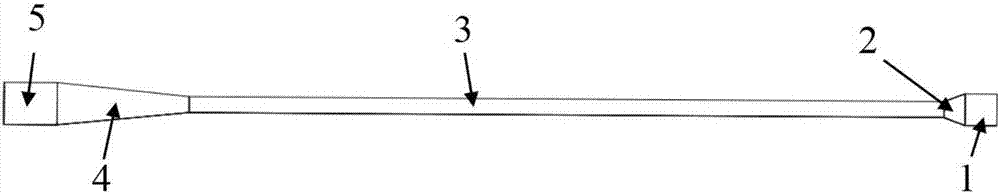
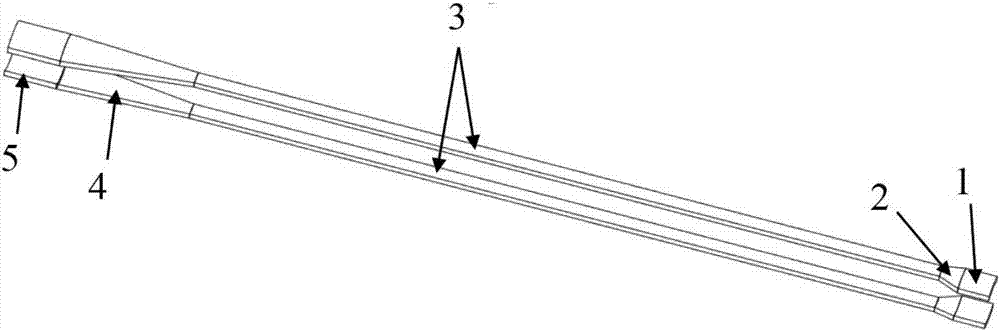
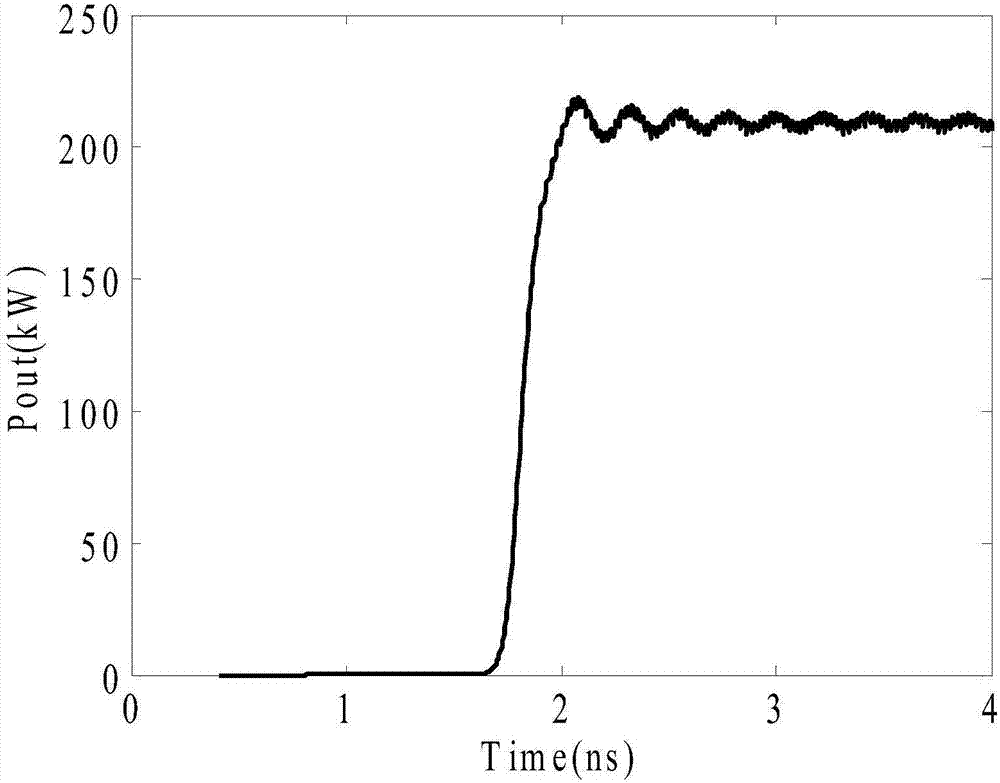
The present invention relates to a microwave source of the high-power microwave technology field, and provides a relativistic backward-wave oscillator with a collector shaped as a Chinese character chang. The relativistic backward-wave oscillator comprises a cathode base, a cathode, an anode outer cylinder, a cut-off neck, a slow wave structure, a tapered waveguide, a reflector, an output waveguide and a solenoidal magnetic field. The collector shaped as the Chinese character chang is arranged behind the tapered waveguide, a stepped reflection cavity is arranged between the cut-off neck and the slow wave structure, and double extraction cavities are also arranged between the tail end of the slow wave structure and the tapered waveguide. The relativistic backward-wave oscillator of the present invention overcomes the disadvantage that the conventional relativistic backward-wave oscillator is difficult to consider the long output microwave pulse width and the high power conversion efficiency simultaneously, solves the problem that a coaxial extraction structure is easy to generate the plasmas to thereby influence the working efficiency, and realizes the microwave output that the pulse width is greater than 100 ns, the efficiency is greater than 40%, and the power is 6 GW, on the condition of using less slow wave blades. Moreover, a high-power microwave source is compact in structure, and is easy for the repeated frequency operation.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
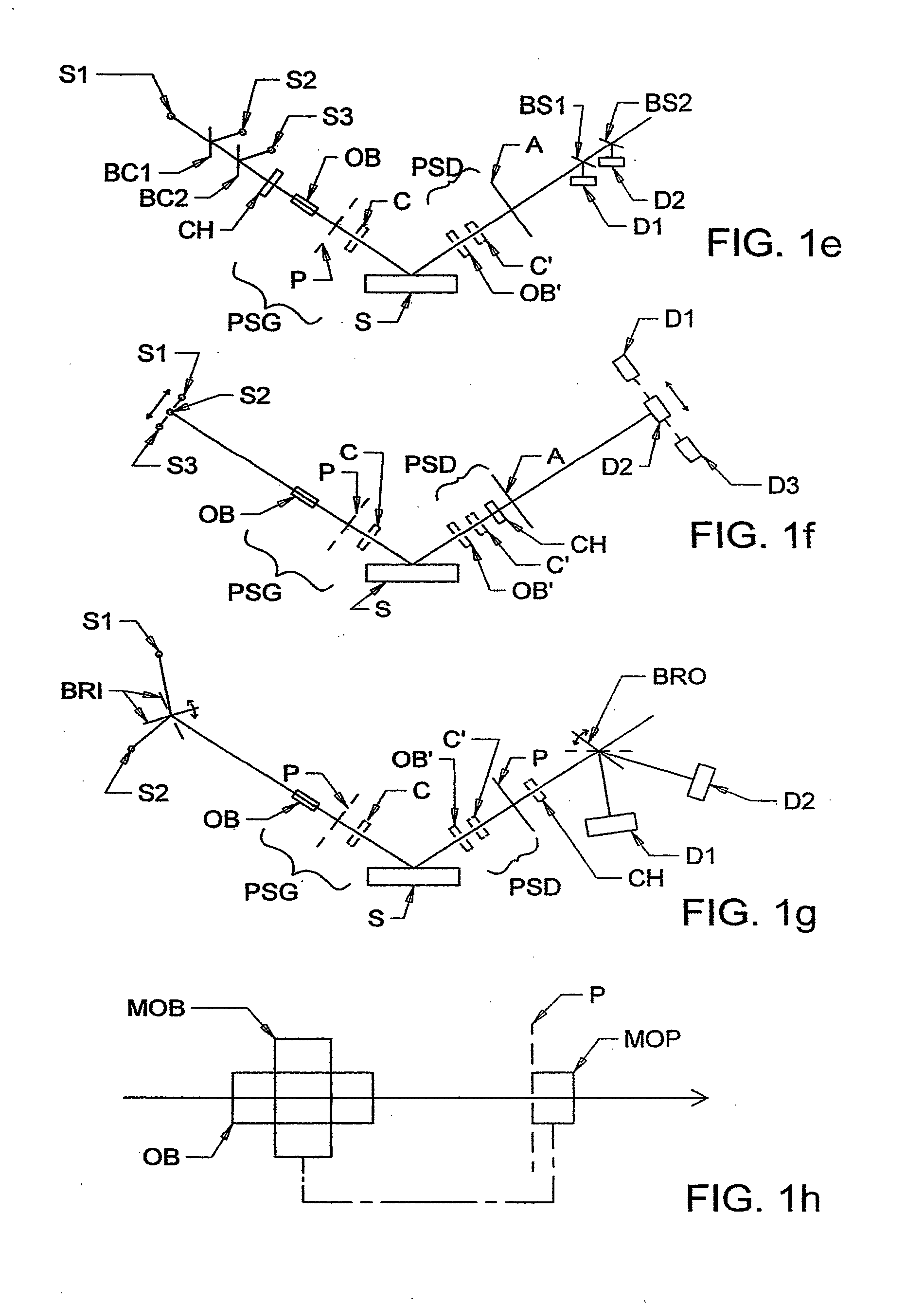
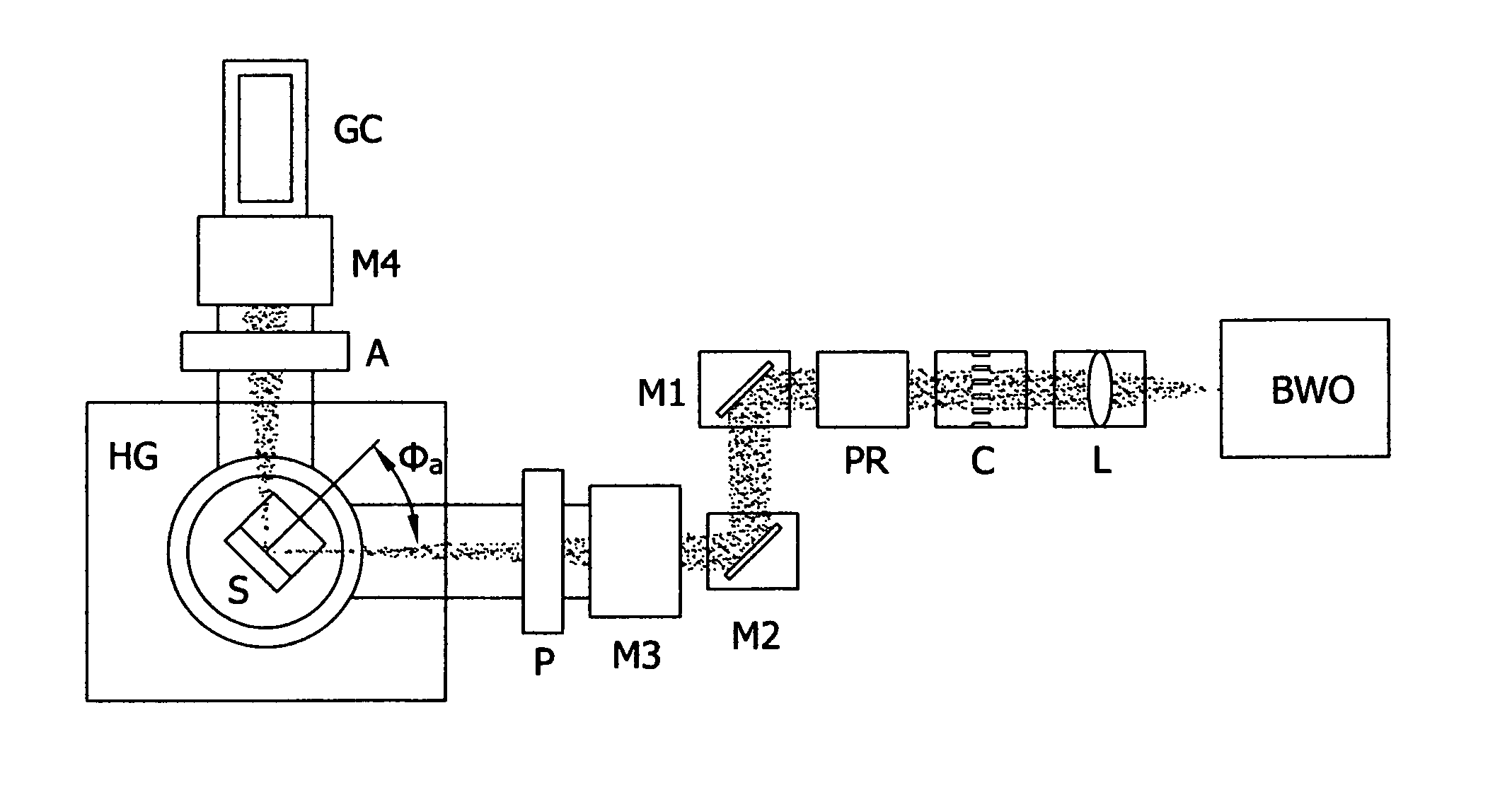
Terahertz ellipsometer system, and method of use
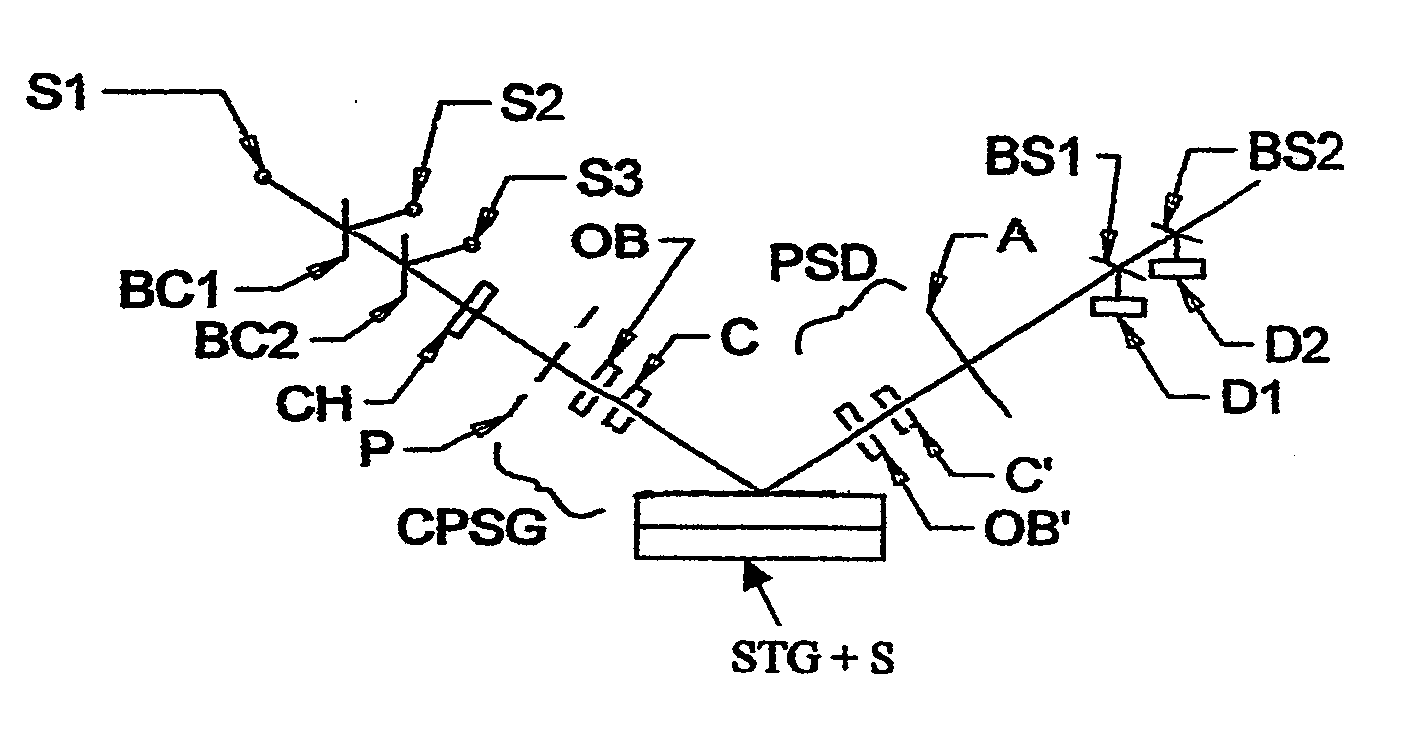
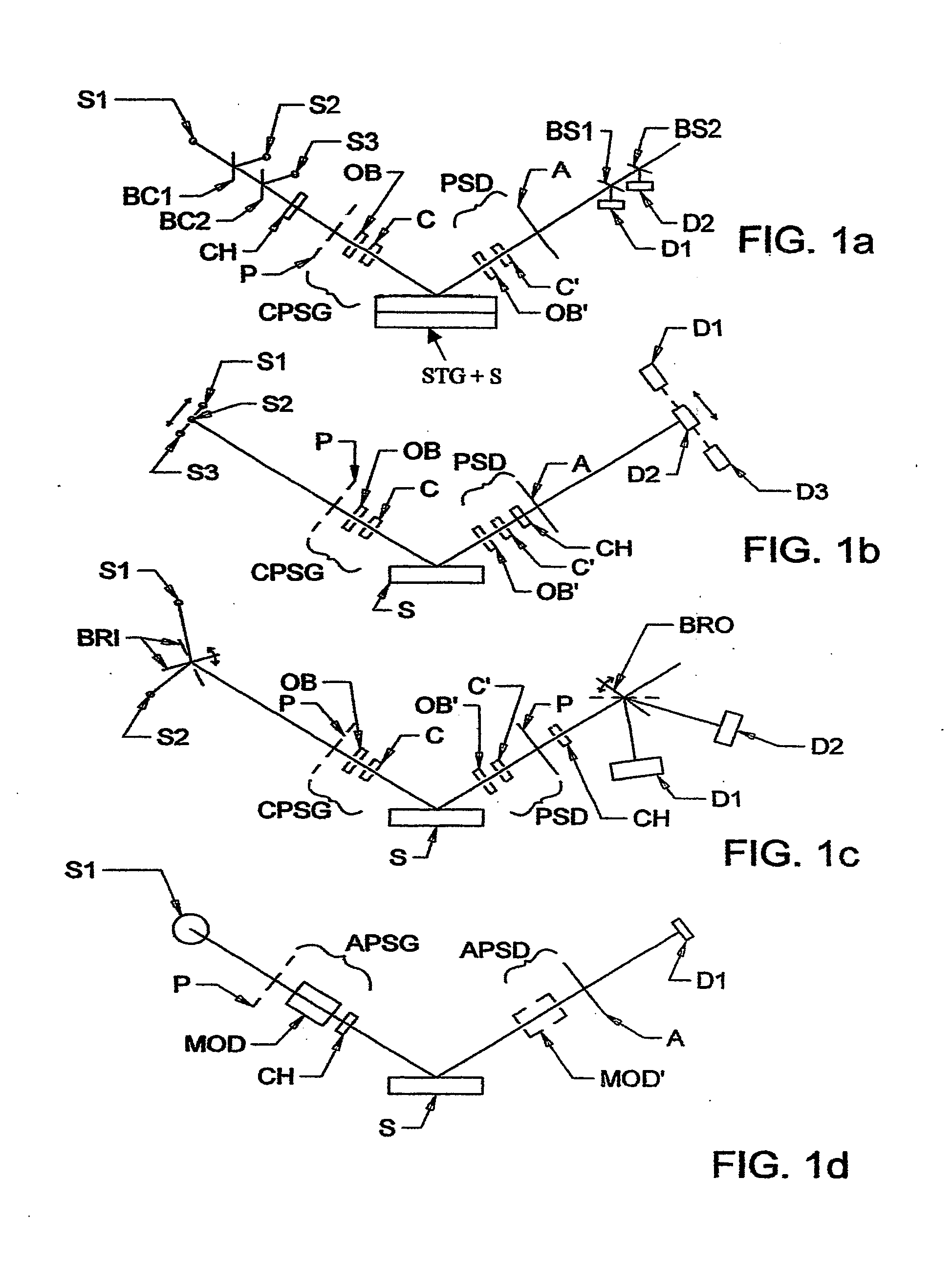
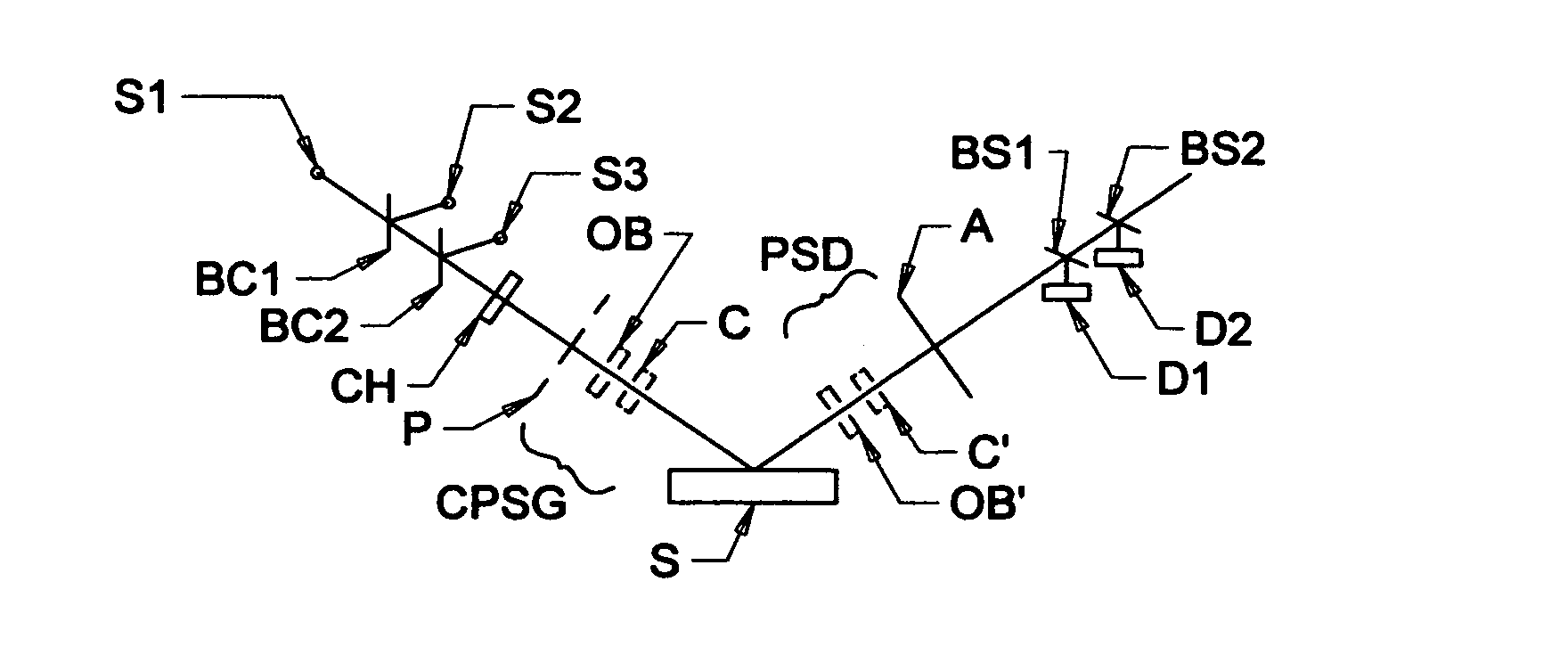
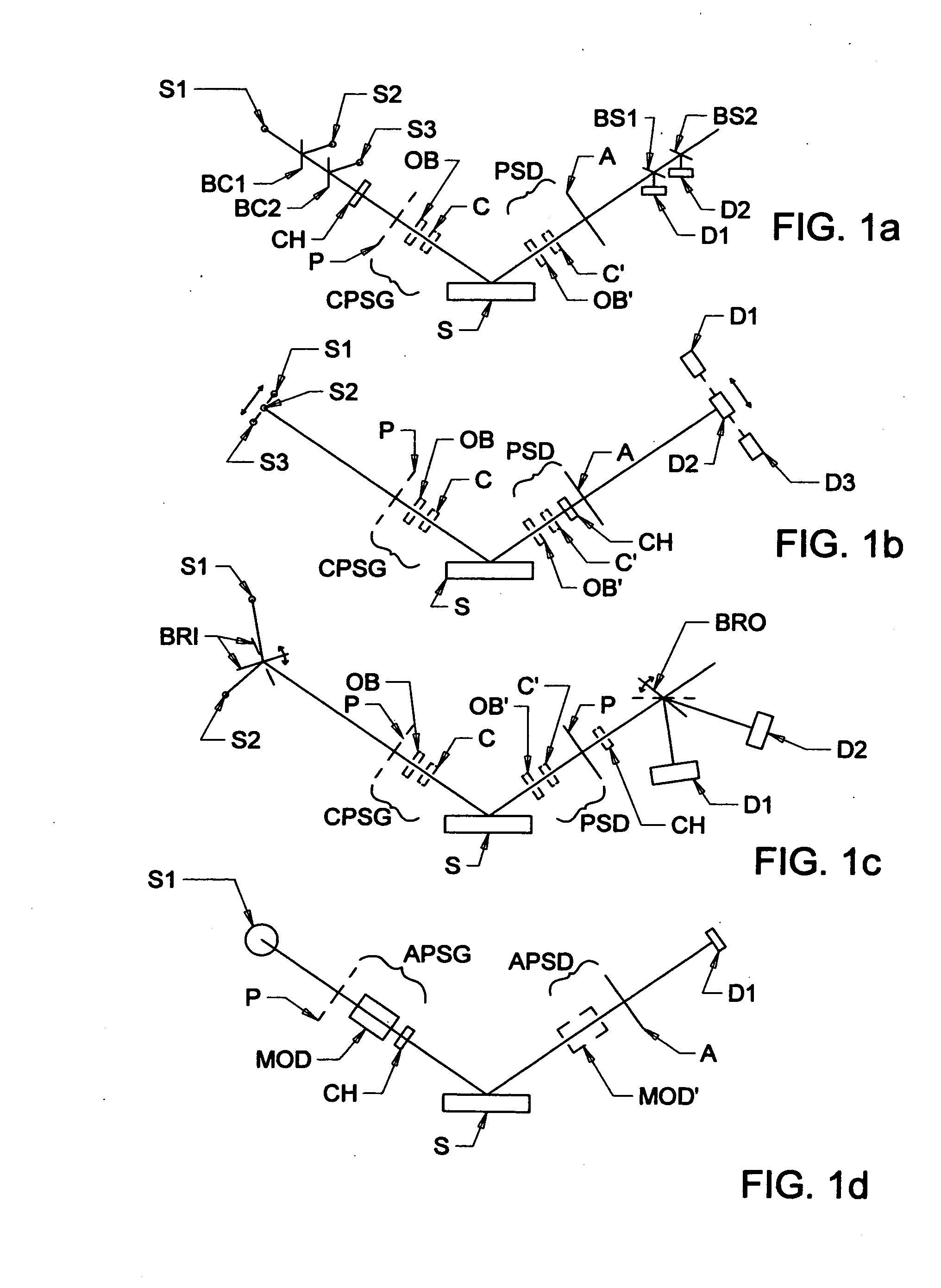
ActiveUS20130026368A1Less aberration effectEliminate needMaterial analysis by optical meansLight polarisation measurementWire gridComputational physics
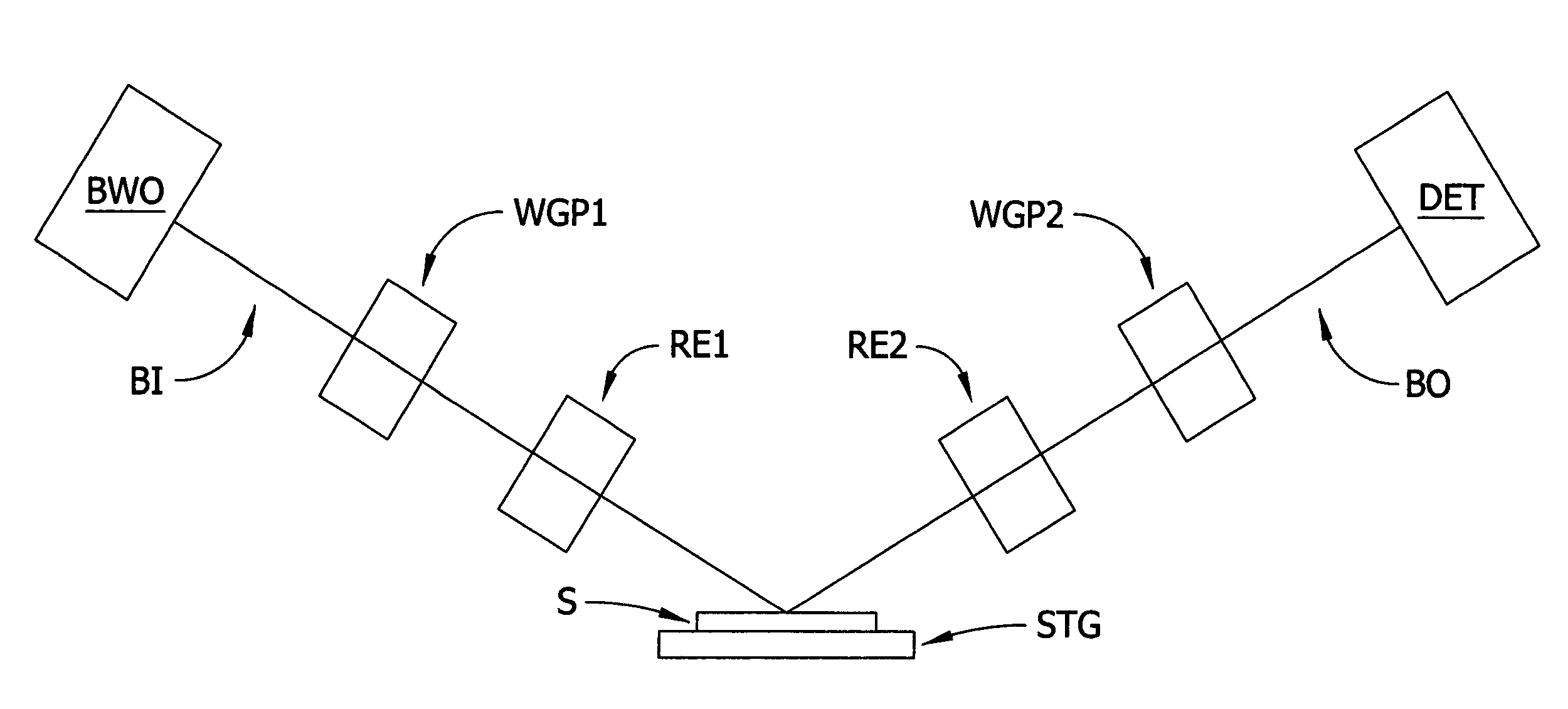
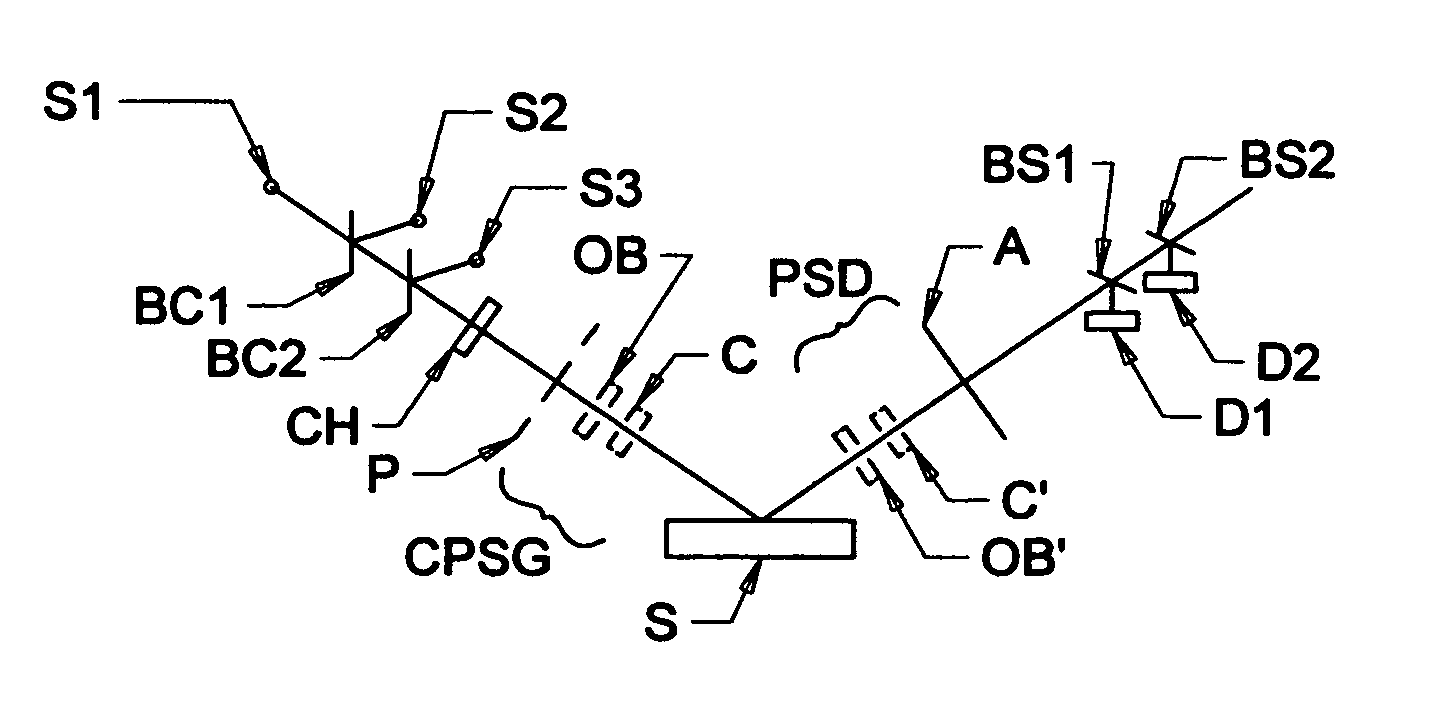
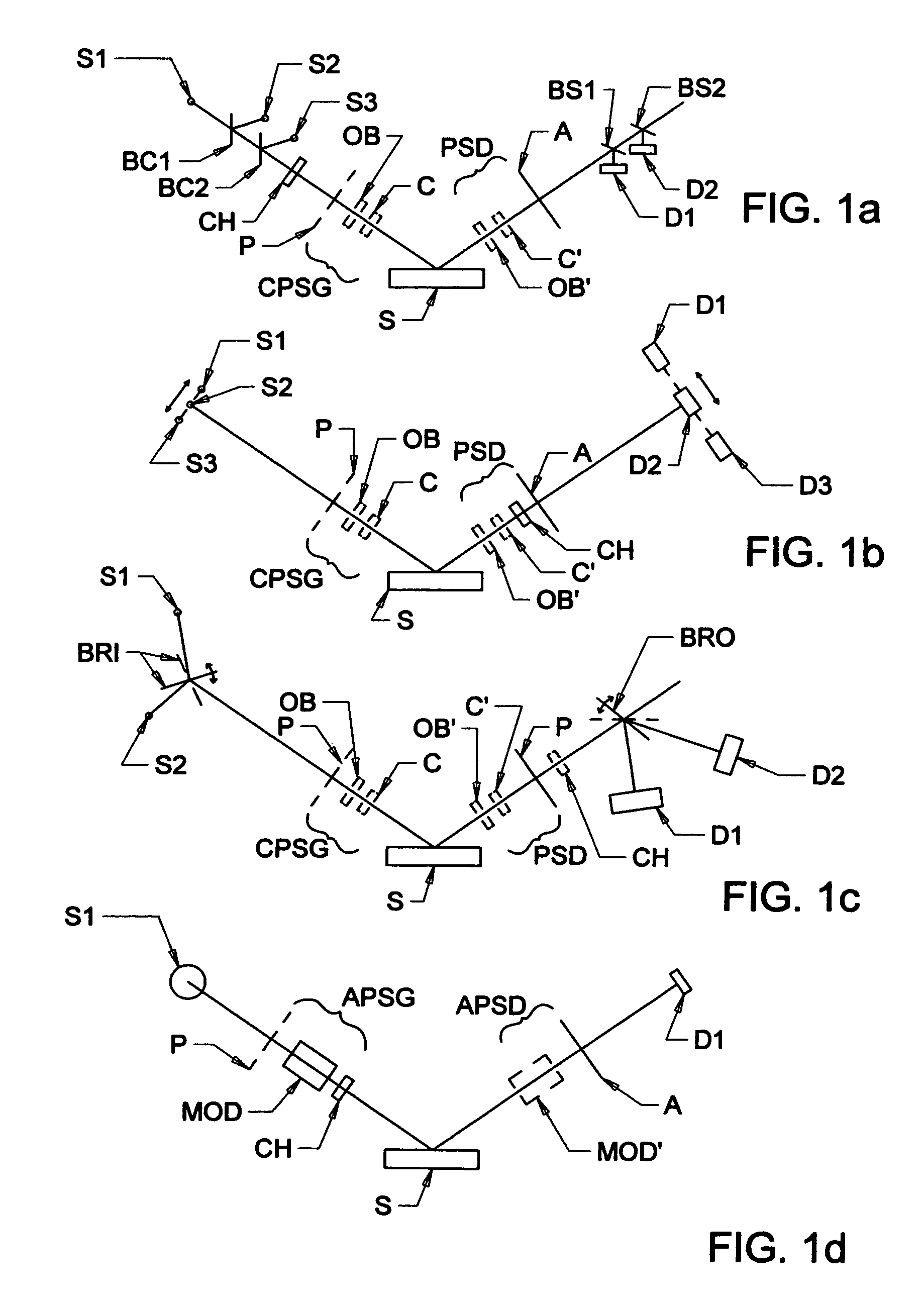
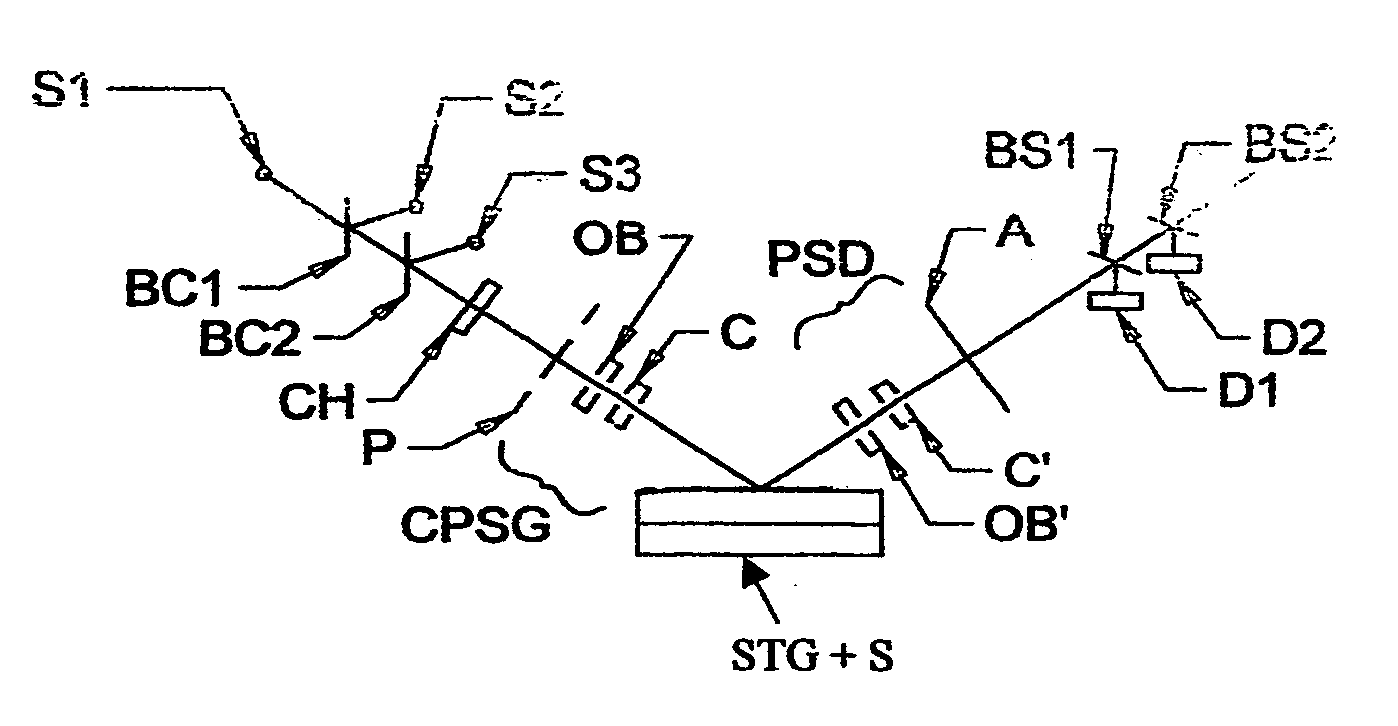
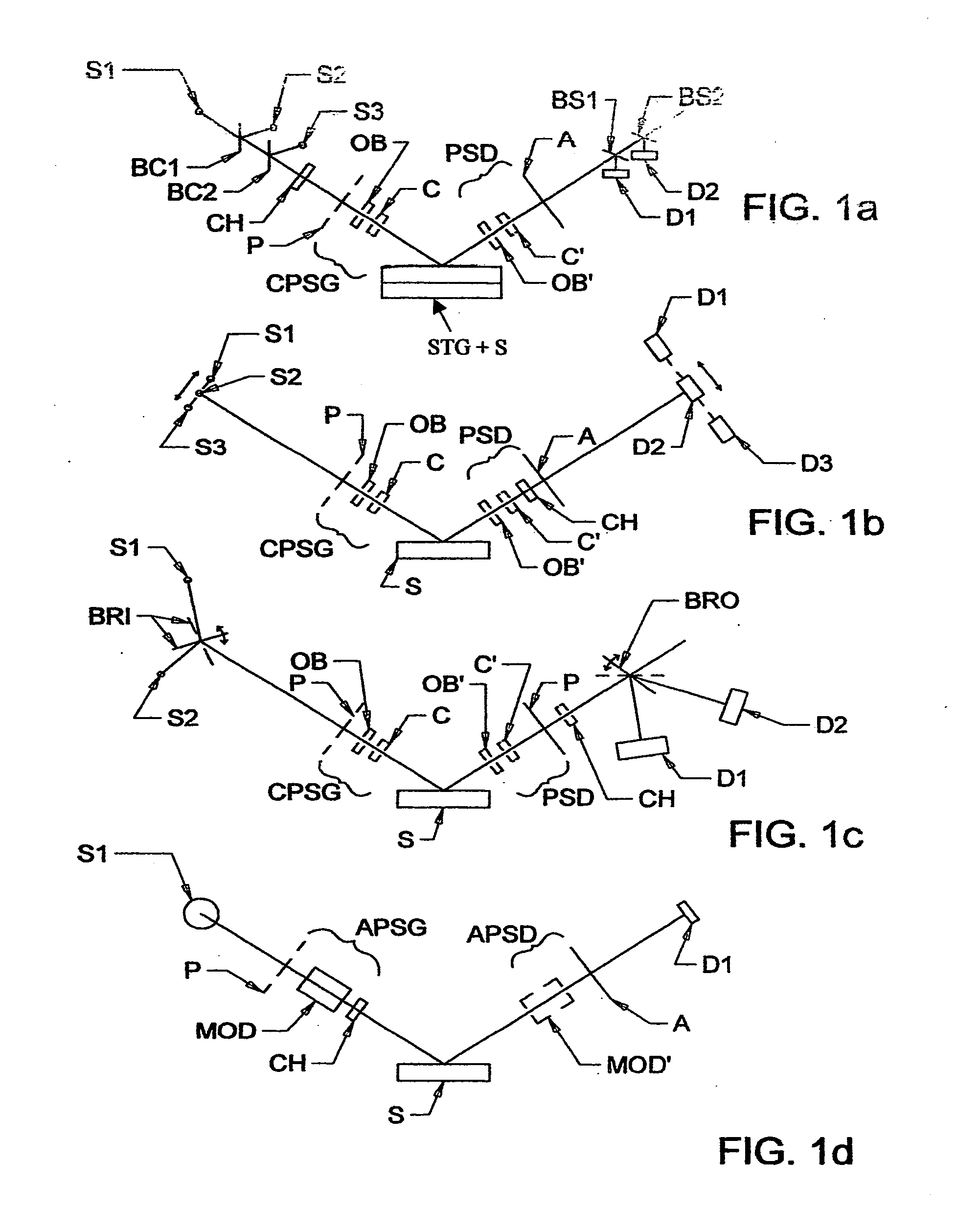
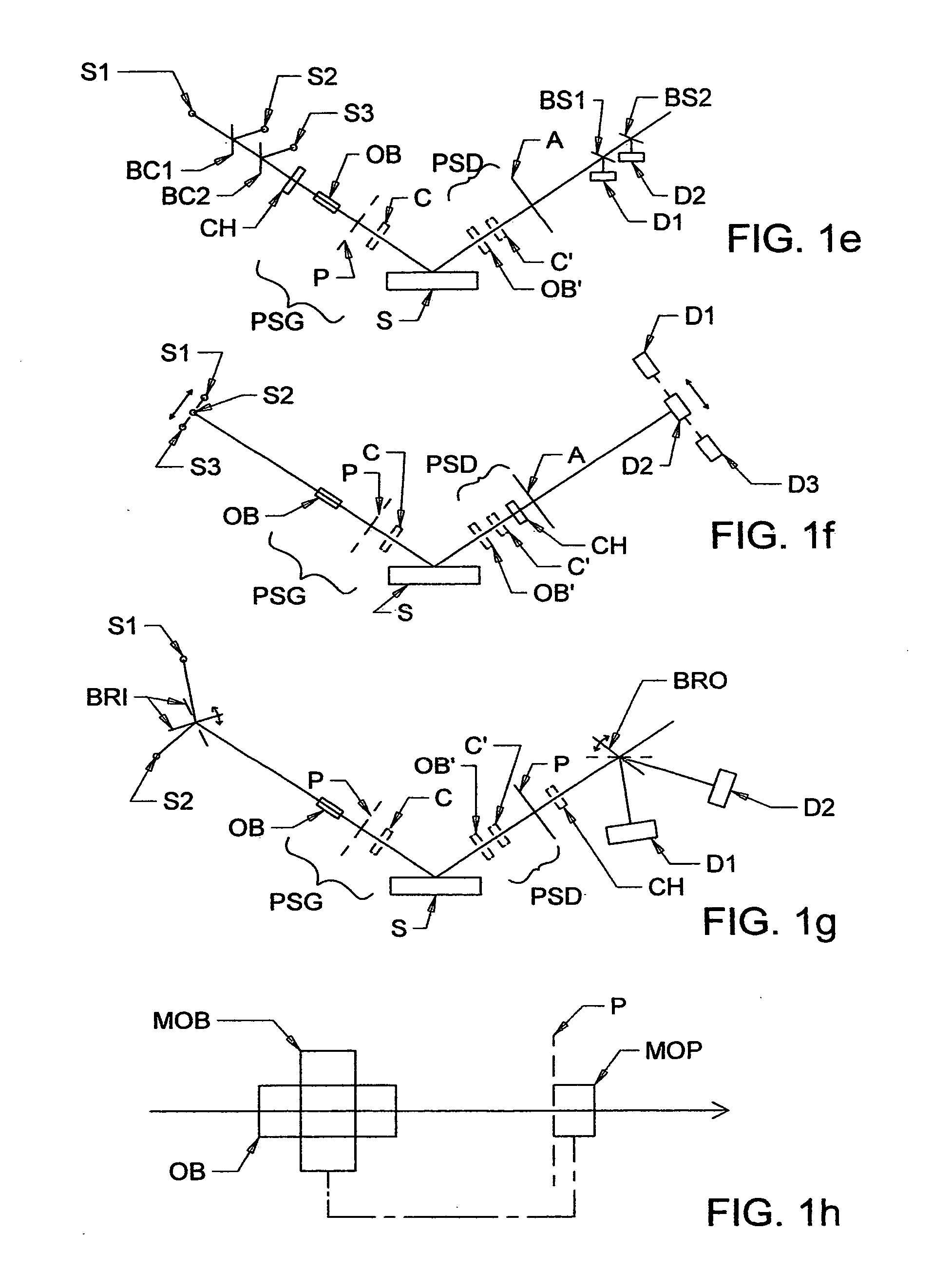
A terahertz ellipsometer, the basic preferred embodiment being a sequential system having a backward wave oscillator (BWO); a first rotatable polarizer that includes a wire grid (WGP1); a rotating polarizer that includes a wire grid (RWGP); a stage (STG) for supporting a sample (S); a rotating retarder (RRET) comprising first (RP), second (RM1), third (RM2) and fourth (RM3) elements; a second rotatable polarizer that includes a wire grid (WGP2); and a Golay cell detector (DET).
Owner:J A WOOLLAM CO
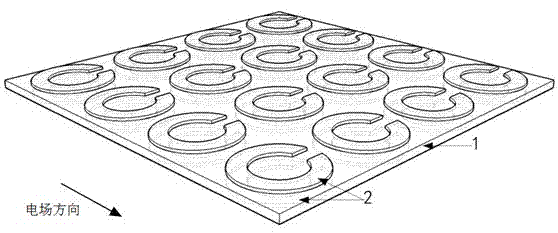
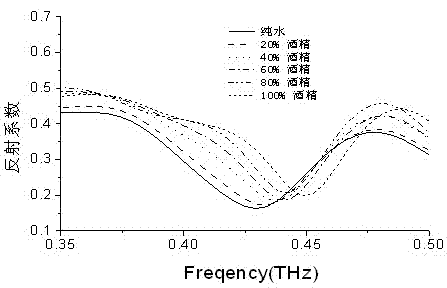
Alcohol concentration measuring device by using terahertz anisotropic medium resonance effect and method thereof
InactiveCN102830069AAccurately Measure Alcohol ContentMaterial analysis by optical meansFrequency spectrumParticle physics
The invention discloses an alcohol concentration measuring device by using terahertz anisotropic medium resonance effect and a method thereof. The terahertz anisotropic medium in the invention is formed by arranging two layers of metal resonance ring arrays on upper and lower surfaces of a polyimide substrate. An alcohol solution to be measured is disposed on the metal resonance ring array at one side of the anisotropic medium; terahertz waves sent by a backward wave oscillator vertically enter the metal resonance ring array at the other side; when the terahertz waves scan and change within a certain frequency range, a double-layer metal resonance ring array reflection coefficient curve is obtained by detection by two schottky diode detectors. The resonance effect of the metal resonance rings allows the resonance peaks on the reflection coefficient curve to move with the change of the alcohol concentration. The frequency spectrum resolution of the backward wave oscillator is less than 5 MHz, and the resonance peak movement in the reflection coefficient curve is more than 25 GHz when the solution to be measured changes from pure water to pure alcohol, so the precision of the measuring device for measuring alcohol concentration is up to more than 0.02%.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Power-adjustable backward wave oscillator
InactiveCN106992106AEnhanced interactionAdjustable powerTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube circuit elementsMulti bandBand shape
The invention discloses a power-adjustable backward wave oscillator. The power-adjustable backward wave oscillator is characterized in that: by inserting upper and lower two rows of periodically complementary split-ring resonator structure into the middle part of a cavity of rectangular waveguide vertically, the complementary split-ring resonator structure has a relatively higher electric field resonant response at the slit of the opening, that is, between the horizontal branches of the two half parts, and shows the meta-material electromagnetic characteristic with a negative dielectric constant epsilon and a negative magnetic permeability Mu; longitudinal resonant field intensity is formed at the upper surface and lower surface of the periodically complementary split-ring resonator structure, thus being conductive to interaction between charged particles of band-shaped electron beams and electromagnetic waves; and at the same time, three electron beam channels are formed. Therefore, compared with a traditional relativism backward wave oscillator, the power-adjustable backward wave oscillator has higher coupling impedance and can obtain very high power output and electron efficiency. Besides, the structure enables one electron beam to work individually, or enables two electron beams or three electron beams to work, so that three kinds of adjustable power output of single beam, double beam and three-beam can be formed and then multi-band-shaped power can be adjustable.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Terahertz ellipsometer system, and method of use
ActiveUS8736838B2Less aberration effectEliminate needMaterial analysis by optical meansLight polarisation measurementWire gridMechanical engineering
Owner:J A WOOLLAM CO
Frequency-agility relativistic backward wave oscillator
The invention discloses a frequency-agility relativistic backward wave oscillator. The frequency-agility relativistic backward wave oscillator comprises a solenoid coil, a cathode, an outer cylinder, an anode, a drifting section and a matching section, wherein the anode and the drifting section are arranged on the inner wall of the outer cylinder, the cathode is arranged at the position of the central axis of the interior of the outer cylinder, the outer cylinder is sleeved with the solenoid coil, a slow wave structure is arranged between a drifting tube and the matching section and is located on the inner wall of the outer cylinder, and a resonant reflecting cavity is formed between the anode and the drifting section. According to the frequency-agility relativistic backward wave oscillator, the intensity of a magnetic field can be adjusted and guided simply by changing the current in the solenoid coil, so that frequency agility at the microwave frequency is achieved, and the defect that according to a conventional relativistic backward wave oscillator, the microwave output frequency is stable, and frequency agility can not be achieved easily is overcome.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Comb line slow wave structure working on high-order pass band
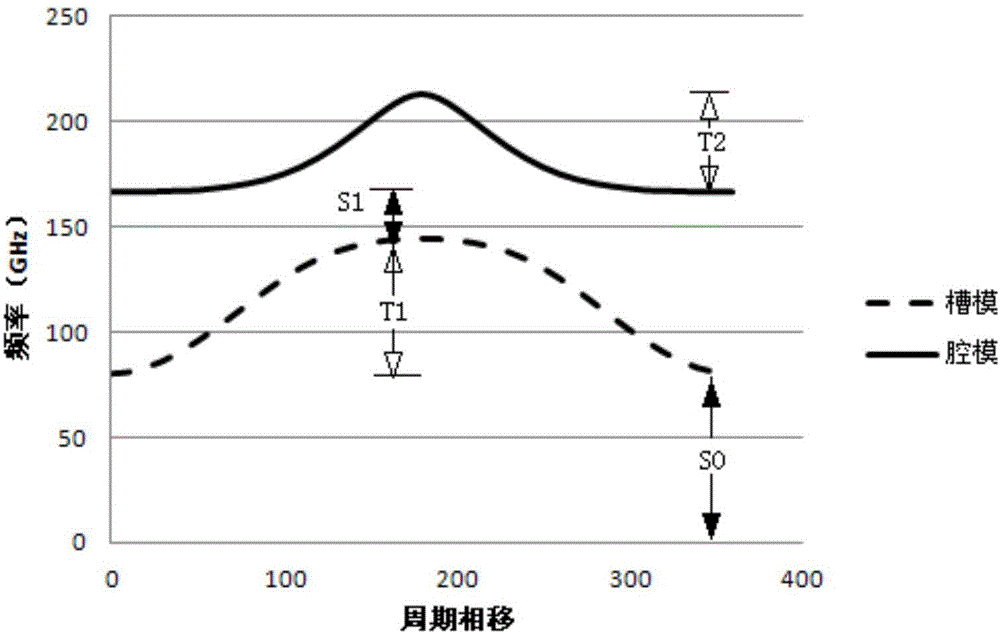
ActiveCN104538271AImprove power performanceTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube circuit elementsResonant cavityWave structure
The invention discloses a comb line slow wave structure working on a high-order pass band. The comb line slow wave structure comprises a cavity mode area, and a rectangular resonant cavity array is composed of a series of straight waveguides; electron beam channels penetrate through the rectangular resonant cavity array composed of the straight waveguides and used for transmitting electron beams; and the mutual action of the beams and waves occurs in the cavity mode area. The slow wave structure has the advantages of being suitable for the working of the high-order pass band, and free of the influence of low pass band mode competition, and the power performance of a terahertz backward wave oscillator can be improved.
Owner:NO 12 RES INST OF CETC
Relativistic backward wave oscillator of direct circular polarization TE11 mode
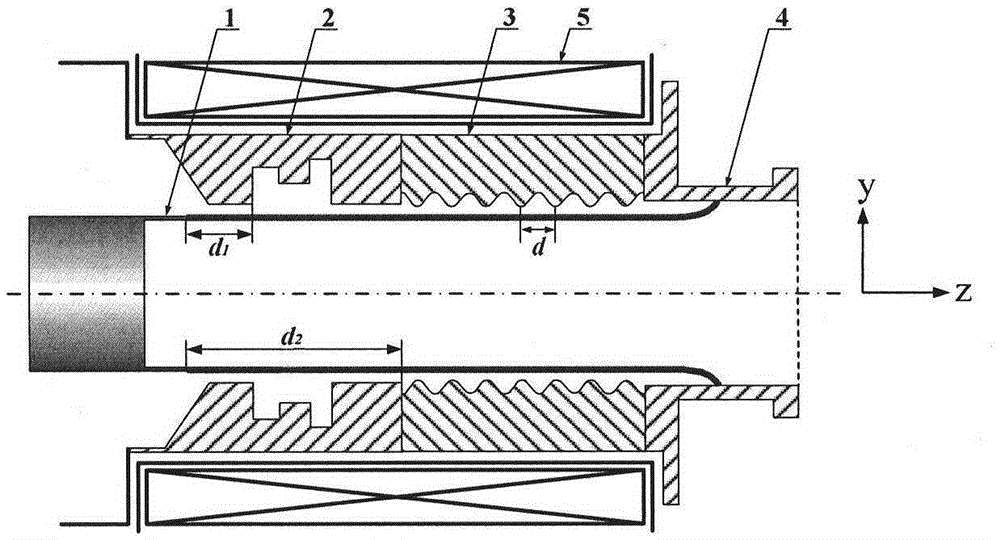
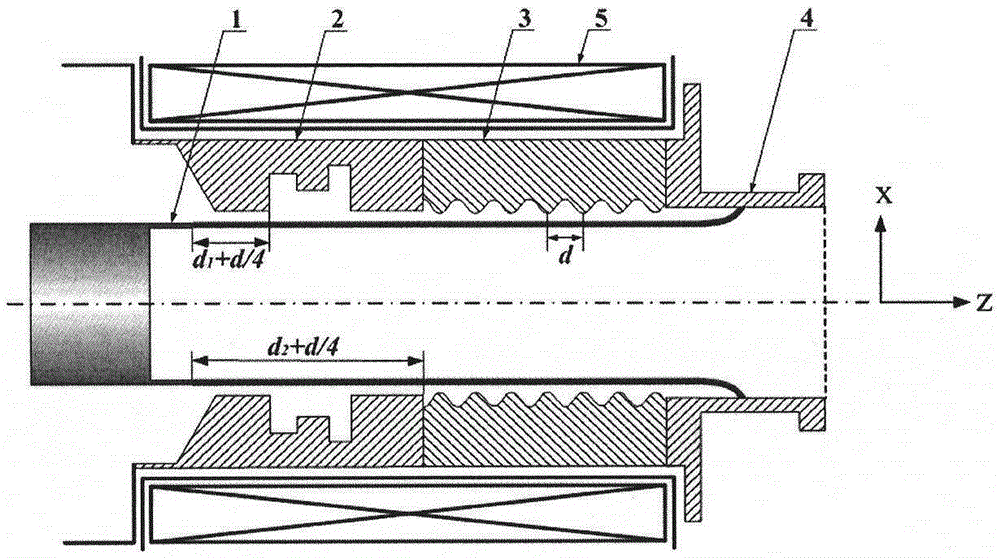
The invention belongs to the field of masers and relates to a relativistic backward wave oscillator of a direct circular polarization TE11 mode. The relativistic backward wave oscillator comprises an annular cathode, angular partition double-pre-modulation chambers, angular partition slow wave structures, an output waveguide and a magnetic field coil. The annular cathode is at the most front end of the structure and emits an annular relativistic electron beam under the effect of high voltage pulse. The angular partition double-pre-modulation chambers, the angular partition slow wave structures, and the output waveguide are orderly arranged behind the annular cathode. The magnetic field coil is at the periphery of the annular cathode, the angular partition double-pre-modulation chambers, and the angular partition slow wave structures. The angular partition double-pre-modulation chambers and the slow wave structures are employed by the invention, two linearly polarized TE11 modes with the same frequency, similar amplitude and orthogonal polarization can be generated in two groups of structure. Through the offset of d / 4 of two groups of the double-pre-modulation chambers and the slow wave structures in an axial position, thus a 90-degree phase difference is introduced between the linearly polarized TE11 modes with orthogonal polarization, and the circular polarization TE11 mode is obtained in an output waveguide.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
K-waveband coaxial relativistic backward wave oscillator
ActiveCN105489460AHigh Q valueImplement mode selectionTravelling-wave tubesWave structureElectrical conductor
The invention discloses a K-waveband coaxial relativistic backward wave oscillator. The oscillator comprises positive electrode, a negative electrode, an electron beam guide grid mesh and a coaxial inner conductor, wherein the positive electrode is a cylindrical waveguide cavity containing a slow-wave structure; the negative electrode is arranged in the cylindrical waveguide cavity and connected with one end plane of the positive electrode through an insulator; the electron beam guide grid mesh is arranged in the cylindrical waveguide cavity and positioned in the downstream of the electron transmitting end of the negative electrode; the coaxial inner conductor adopts a cylindrical structure; one end of the coaxial inner conductor is arranged in the cylindrical waveguide cavity while the other end of the coaxial inner conductor is connected with the other end plane of the positive electrode through a metal bracket; and a coaxial structure is formed by the coaxial inner conductor, the negative electrode and the cylindrical waveguide cavity. According to the K-waveband coaxial relativistic backward wave oscillator, the electron beam guide grid mesh with the electron beam transmittance of greater than 90% is adopted for guiding electron beams to enter a beam interaction region, so that the required external magnetic field intensity is lowered, the guide magnetic field required by a device is reduced to 0.5T, the huge size of the guide magnetic field system on the exterior of the device is reduced, and requirement on the energy source supply is reduced.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS +1
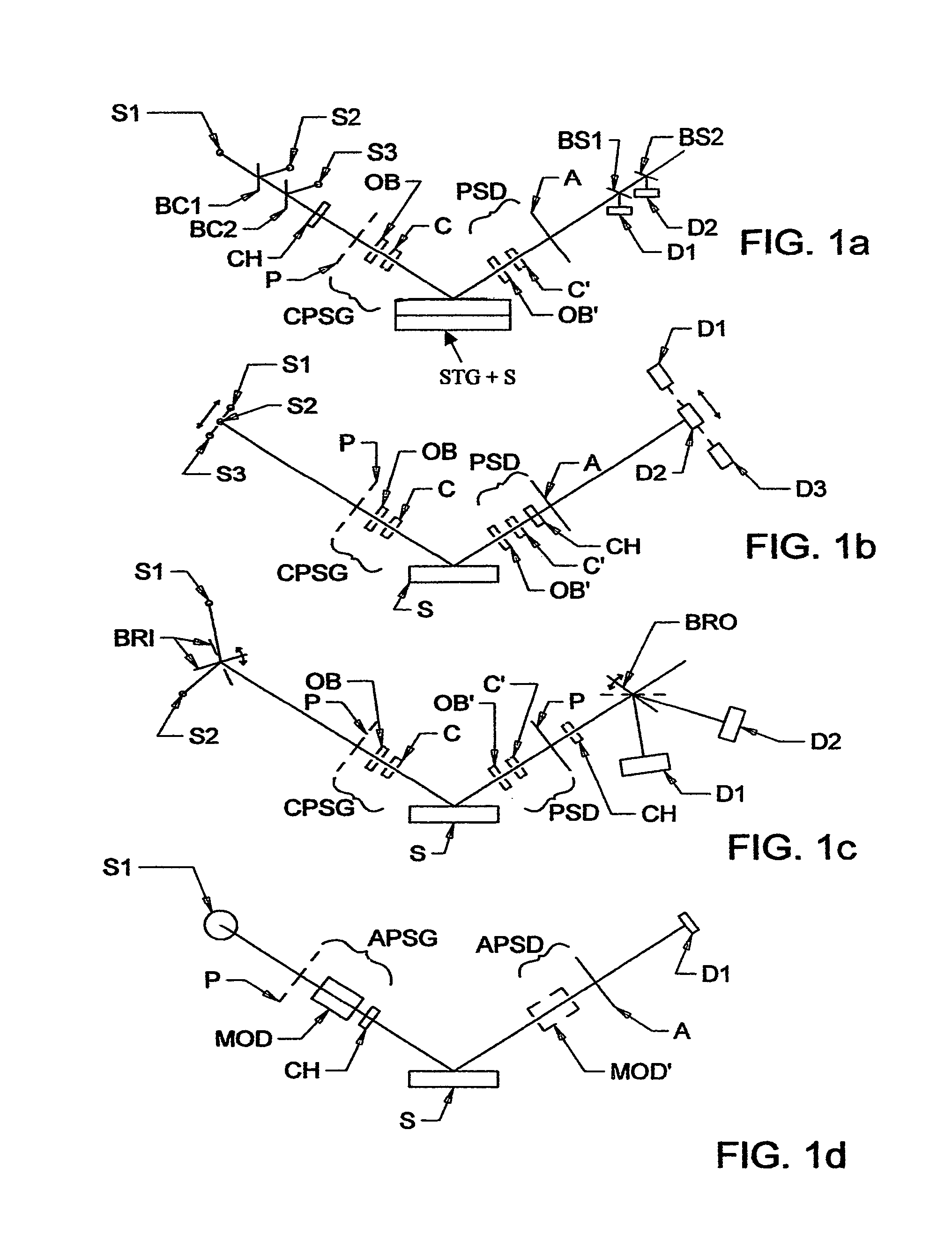
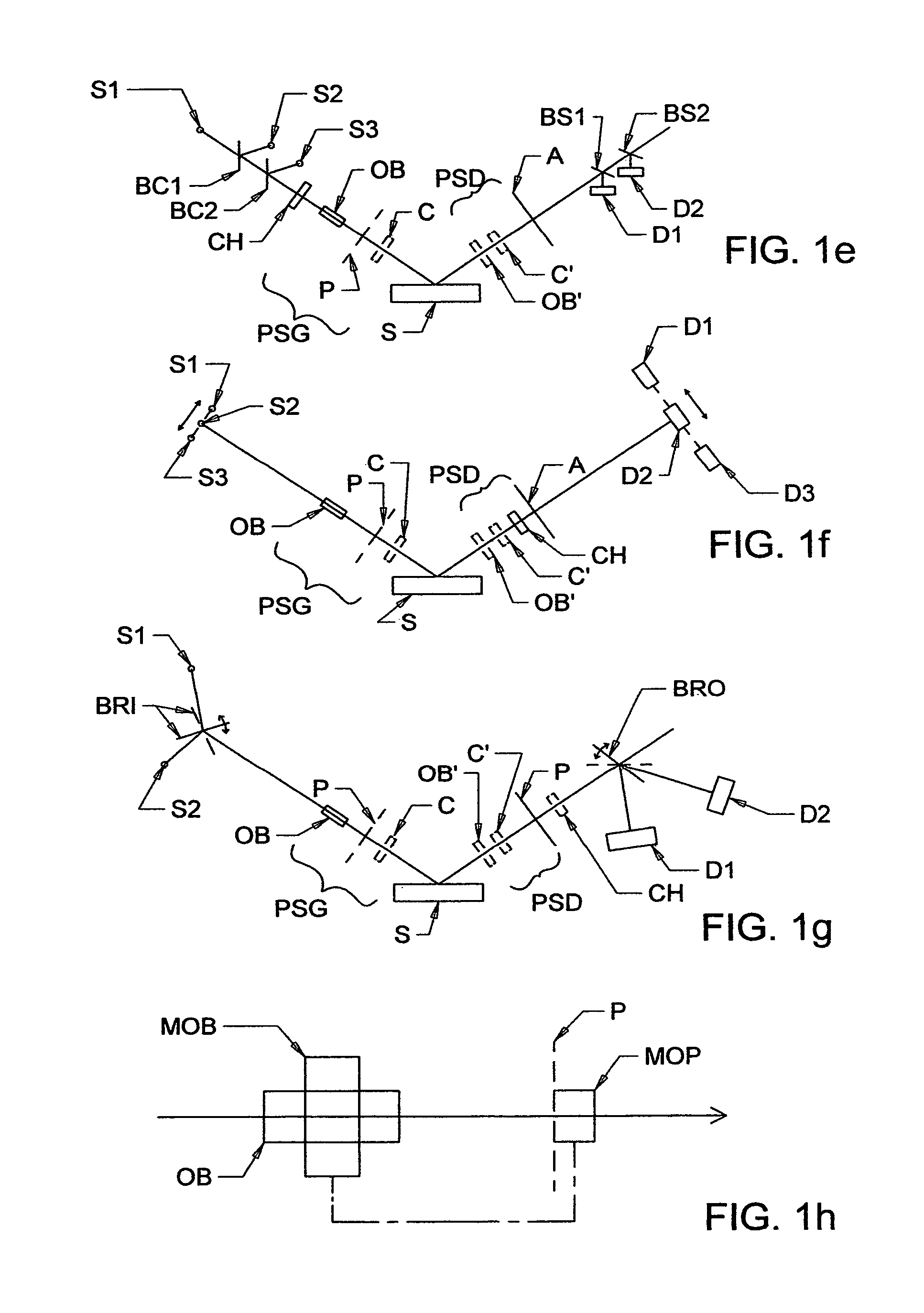
Terahertz-infrared ellipsometer system, and method of use
ActiveUS8169611B2Less aberration effectEliminate needMaterial analysis by optical meansLight polarisation measurementPolarimeterPolarizer
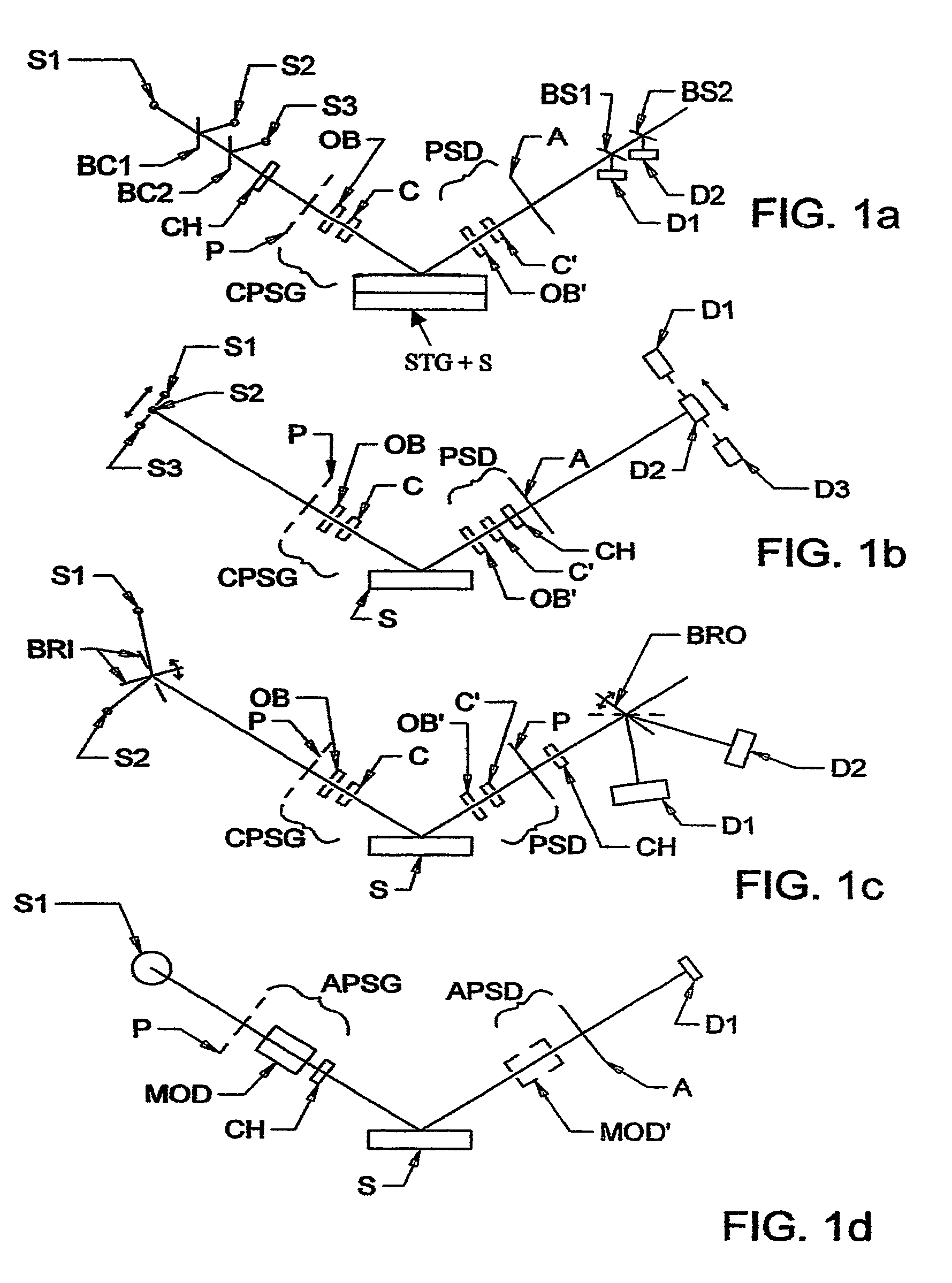
The present invention relates to ellipsometer and polarimeter systems, and more particularly is an ellipsometer or polarimeter or the like system which operates in a frequency range between 300 GHz or lower and extending to higher than at least 1 Tera-hertz (THz), and preferably through the Infra-red (IR) range up to, and higher than 100 THz, including:a source such as a backward wave oscillator; a Smith-Purcell cell; a free electron laser, or an FTIR source and a solid state device; anda detector such as a Golay cell; a bolometer or a solid state detector;and preferably including at least one odd-bounce polarization state image rotating system, and optionally including a polarizer, at least one compensator and / or modulator, in addition to an analyzer.
Owner:J A WOOLLAM CO +1
One-side folded waveguide slow wave structure for backward wave oscillator
ActiveCN104576266AAppropriate working voltageHigh coupling impedanceTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureMiddle line
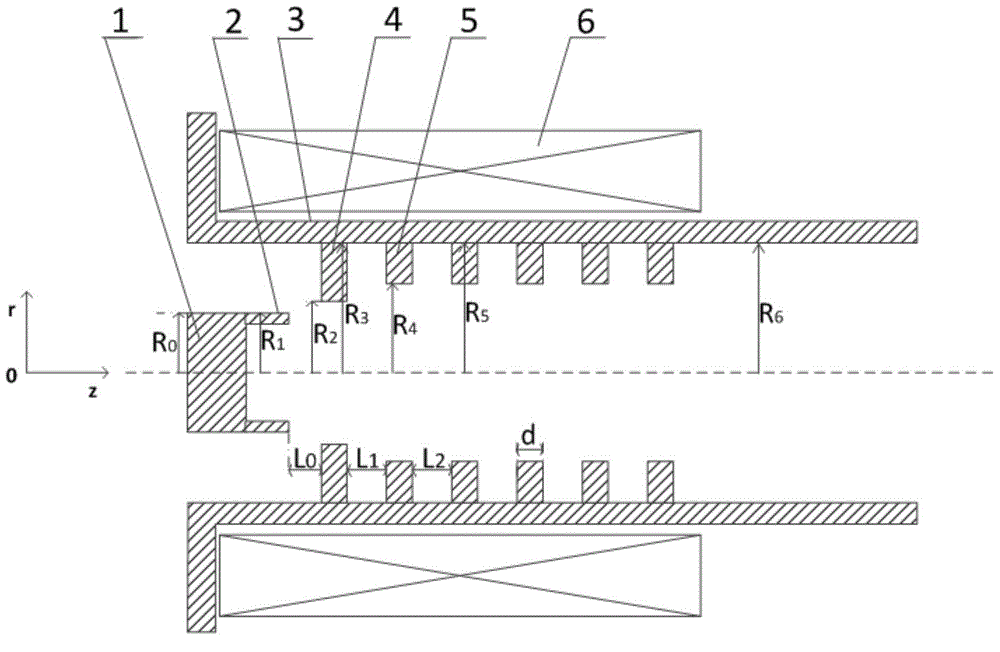
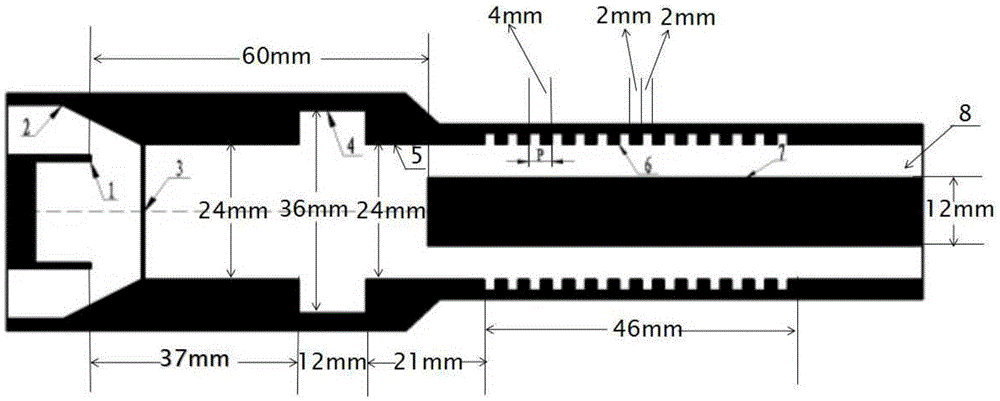
The invention discloses a one-side folded waveguide slow wave structure for a backward wave oscillator. Curved waveguides on one side of a folded waveguide are arranged in symmetrical positions along a midline. The one-side folded waveguide slow wave structure particularly structurally comprises a straight waveguide array consisting of a plurality of straight waveguides and a plurality of curved waveguides, wherein every two adjacent straight waveguides are connected via one curved waveguide to form a periodic structure; and an electron beam channel penetrates through the straight waveguide array. According to the one-side folded waveguide slow wave structure, the curved waveguides on one side are transferred to the symmetric positions along the midline, so that fundamental waves of the slow wave structure are forward waves; and the backward wave oscillator can achieve appropriate working voltage and higher coupling impedance simultaneously by using the one-side folded waveguide slow wave structure.
Owner:NO 12 RES INST OF CETC
Terahertz-infrared ellipsometer system, and method of use
ActiveUS20120206724A1High purityLess aberration effectMaterial analysis by optical meansLight polarisation measurementSolid state detectorPolarimeter
The present invention relates to ellipsometer and polarimeter systems, and more particularly is an ellipsometer or polarimeter or the like system which operates in a frequency range between 300 GHz or lower and extending to higher than at least 1 Tera-hertz (THz), and preferably through the Infra-red (IR) range up to, and higher than 100 THz, including:a source such as a backward wave oscillator; a Smith-Purcell cell; a free electron laser, or an FTIR source and a solid state device; anda detector such as a Golay cell; a bolometer or a solid state detector;and preferably including at least one odd-bounce polarization state image rotating system, and optionally including a polarizer, at least one compensator and / or modulator, in addition to an analyzer.
Owner:J A WOOLLAM CO +1
Terahertz-infrared ellipsometer system, and method of use
ActiveUS20100220313A1Less aberration effectEliminate needMaterial analysis by optical meansLight polarisation measurementPolarimeterPolarizer
The present invention relates to ellipsometer and polarimeter systems, and more particularly is an ellipsometer or polarimeter or the like system which operates in a frequency range between 300 GHz or lower and extending to higher than at least 1 Tera-hertz (THz), and preferably through the Infra-red (IR) range up to, and higher than 100 THz, including:a source such as a backward wave oscillator; a Smith-Purcell cell; a free electron laser, or an FTIR source and a solid state device; anda detector such as a Golay cell; a bolometer or a solid state detector;and preferably including at least one odd-bounce polarization state image rotating system, and optionally including a polarizer, at least one compensator and / or modulator, in addition to an analyzer.
Owner:J A WOOLLAM CO +1
Cross-band multifrequency controllable relativism backward-wave oscillator
ActiveCN106971929AImprove reliabilitySimple structureTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureElectrical conductor
The invention discloses a cross-band multifrequency controllable relativism backward-wave oscillator. The cross-band multifrequency controllable relativism backward-wave oscillator comprises an emission cathode, a reflection chamber, a drift chamber and a leading magnetic field. An internal portion of the relativism backward-wave oscillator is provided with a coaxial inner conductor and two slow wave structures, the two slow wave structures are mutually independent and are adjustable in periods, the slow wave structures with period change and a relativism electron beam penetrating through the slow wave structures and being same as the slow wave structures in diameter realize interaction, and the slow wave structures generate multifrequency controllable L-Ku wave band high-power microwaves. Through the two slow wave period structures, the property that the coaxial structure has no cut-off frequency is utilized, and thereby the single relativism backward-wave device generates the L-Ku wave band high-power microwaves.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Double electron beam Terahertz wave radiation source of cascade high-frequency structure
ActiveCN103632909AEasy to detectGood for long-distance detectionTransit-tube electron/ion gunsTravelling-wave tubesHigh resolution imagingElectron
The invention provides a double electron beam THz wave radiation source of a cascade high-frequency structure. The double electron beam THz wave radiation source uses a backward wave oscillator to generate THz signals as drive signals of a travelling wave amplifier. In a same THz wave radiation source, high-power THz waves are generated and at the same time the power amplification and band spread of the THz waves are realized, thereby being beneficial for applying the THz wave radiation source in anti-interference, harmful substance detection, ultra wide band radar long-range detection and high resolution imaging radar aspects, etc.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Terahertz-infrared ellipsometer system, and method of use
ActiveUS8416408B1High purityLess aberration effectMaterial analysis by optical meansLight polarisation measurementSolid state detectorPolarimeter
The present invention relates to ellipsometer and polarimeter systems, and more particularly is an ellipsometer or polarimeter or the like system which operates in a frequency range between 300 GHz or lower and extending to higher than at least 1 Tera-hertz (THz), and preferably through the Infra-red (IR) range up to, and higher than 100 THz, including:a source such as a backward wave oscillator; a Smith-Purcell cell; a free electron laser, or an FTIR source and a solid state device; anda detector such as a Golay cell; a bolometer or a solid state detector;and preferably including a polarization state generator comprising:an odd bounce image rotating system and a polarizer, or two polarizers;and optionally including least one compensator and / or modulator, in addition to an analyzer.
Owner:J A WOOLLAM CO +1
Three-frequency controllable high power microwave device
InactiveCN106298407AFlexible structureRealize three-frequency controllable high-power microwaveTravelling-wave tubesElectrical conductorMicrowave
The present invention discloses a three-frequency controllable high power microwave device, which utilizes structure features of a coaxial relativistic backward wave oscillator to make the coaxial inner conductor in a low frequency device a high frequency band device and makes use of coaxial controllable three-diameter electron beams to make the relativistic backward wave oscillator generate single-frequency high-power microwaves in sequence of low-frequency, medium-frequency and high-frequency according to the needs. The controllable three-diameter cathode consists of a coaxial inner annular cathode, a middle annular cathode and an outer annular cathode, and is fixedly connected to the stepping motors which controls the axial positions of the cathodes. For the controllable adjustment to the three stepping motors, it is possible to realize the control over the three-diameter cathodes to generate electron beams with varied diameters. In the invention, the frequencies of the microwave device can be designed for actual requirement. Simple and flexible in structure, it is possible to generate three-frequency controllable high power micro waves in a high power microwave device.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Double-frequency relativistic backward-wave oscillator capable of directly outputting TE11-mode electromagnetic waves
ActiveCN107527781ADirect output implementationTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureMicrowave
The invention relates to the technical field of high-power microwave devices, and discloses a double-frequency relativistic backward-wave oscillator capable of directly outputting TE11-mode electromagnetic waves. The oscillator comprises a Bragg reflector, a first slow wave structure and a second slow wave structure, wherein the Bragg reflector, the first slow wave structure and the second slow wave structure are sequentially set in a coaxial manner. The interior of the Bragg reflector is sequentially provided with an electron beam emission gun and a reflection work cavity. The first slow wave structure comprises a slow wave structure employing a periodic ripple design, and the interior of the slow wave structure is provided with a slow wave structure beam-wave interaction cavity. The second slow wave structure comprises a slow wave structure employing a periodic ripple design, and the interior of the slow wave structure is provided with a slow wave structure beam-wave interaction cavity. According to the invention, an electron beam sequentially passes through two coaxial slow wave structures, and performs the beam-wave interaction with the slow wave structures to generate a double-frequency TE11-mode electromagnetic wave traveling in an opposite direction. The double-frequency TE11-mode electromagnetic wave traveling in the opposite direction is converted into a TE11-mode electromagnetic wave propagating forwards through the Bragg reflector, and the electromagnetic wave with the beat effect is outputted at a radiation end.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Slow wave structure suitable for dual-sheet backward wave oscillator
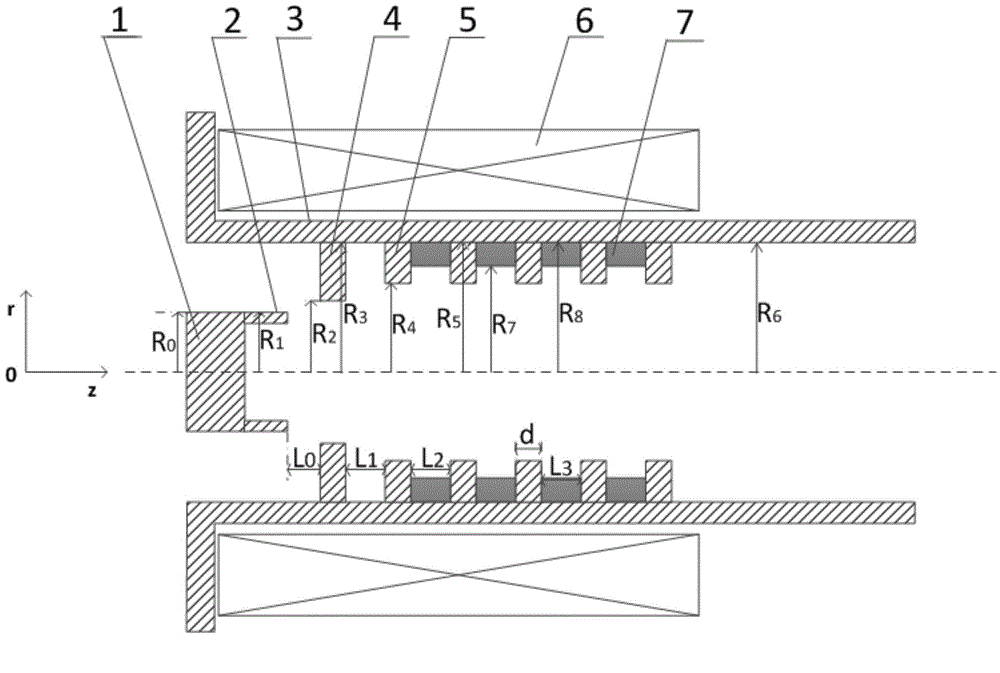
ActiveCN109119310AIncrease output powerImprove output efficiencyTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureMetal strips
The present invention discloses a slow wave structure suitable for a dual-sheet backward wave oscillator. The structure comprises a rectangular waveguide and a plurality of vertical metal panel pair structures, each vertical metal panel pair structure comprises a pair of vertical rectangular metal panels, one rectangular metal frame and a pair of metal strips, the upper and lower half portions ofthe vertical rectangular metal panels are respectively provided with rectangular holes, the two vertical rectangular metal panels are arranged at the internal portions of the rectangular metal framesin parallel, and the two metal strips are configured to respectively connect with vertical rectangular metal panels and the rectangular metal frames; and the rectangular metal frames in the vertical metal panel pair structures are connected in order to take as an integration inserted into the rectangular waveguide to form a slow wave structure. The slow wave structure suitable for a dual-sheet backward wave oscillator is high in output power and electron efficiency.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Terahertz gyrotron gallery mold backward wave interaction circuit and control method thereof
ActiveCN109887819AIncrease inhomogeneityImprove job stabilityTubes with velocity/density modulated electron streamTransit-tube circuit elementsMicrowaveComputer science
The invention discloses a terahertz gyrotron gallery mold backward wave interaction circuit and a control method thereof. According to the circuit and the control method, two gradation structures areled into a main cavity body, so that the nonuniformity of the circuit is improved; the cut-off frequency of a main high angular index competition mode is higher than that of an operating mode, so thata start oscillation characteristic of the circuit is that the circuit is particularly sensitive to a nonuniform circuit in a single-cavity oscillation state; a start oscillation current curve is greatly improved and effectively inhibited; and single-mode stable high-efficiency output of a high-order gallery operating mode is achieved. The circuit can specifically inhibit mode competition nearby the high-order gallery mode in a terahertz gyrotron backward wave oscillator; the operating stability and the operating efficiency of the gyrotron backward wave oscillator can be improved; and the significance from microwave and millimeter wave bands to a terahertz wave band is important for the gyrotron backward wave oscillator.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Ultra-wideband quasi-open slow-wave structure
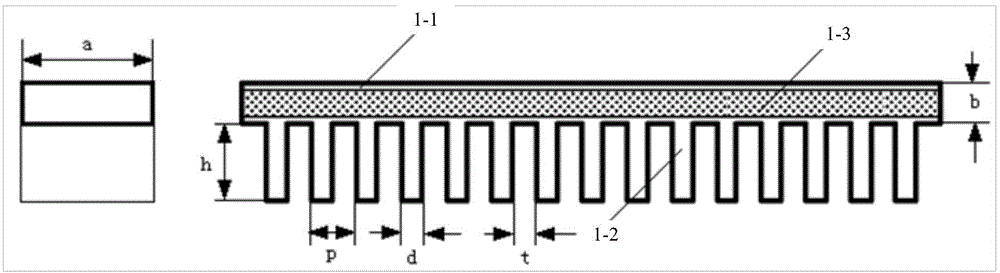
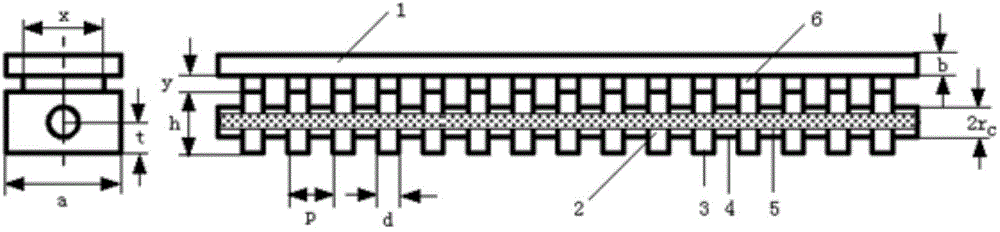
InactiveCN105513926AReduce processing difficultyGood for vibrationTransit-tube circuit elementsUltra-widebandWave structure
The invention discloses an ultra-wideband quasi-open slow-wave structure comprising two identical metal plates and supporting metal walls or mediums on the two sides. The center positions on the broad edges of the lower side of the upper metal plate and the upper side of the lower metal plate are each loaded with a striped metal ridge with periodic ups and downs along the longitudinal direction, wherein the width is Rw, the height is Rh, and the cycle length of the ups and downs is p. Thus, a striped electron beam channel is formed in the space between the striped metal ridges, and the height hb is the difference between the difference b of the metal plates and two times of ridge height Rh. The slow-wave structure has a natural electron beam channel, requires no additional processing, is of low processing difficulty and large coupling impedance, and is very beneficial to oscillation starting of a backward wave oscillator. The slow-wave structure is of low low-end cut-off frequency, and has the characteristics of ultra wideband and small high-frequency transmission reflection.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Distribution attenuating confocal waveguide gyrotron travelling wave tube high frequency system
ActiveCN107230607AControl echo oscillationReduced diffraction lossTransit-tube coupling devicesTotal efficiencyMicrowave
The invention discloses a distribution attenuating confocal waveguide gyrotron travelling wave tube high frequency system and belongs to the technical field of microwave, millimeter wave and terahertz devices. The structure is composed of confocal waveguides which are symmetrical up and down. Side faces of the confocal waveguides are opened. Mirror surface curvatures of the confocal waveguides are consistent. Each confocal waveguide comprises an input uniform section, an input transition section, an interaction section, an output transition section and an output uniform section. According to the structure, a backward wave oscillator circuit of a parasitic mode is cut off through adoption of the interaction sections of the confocal waveguides with very narrow mirror surface widths, and moreover, it is ensured that the interaction sections are long enough, thereby realizing relatively high linear gain. Diffraction losses of a high frequency field after amplification are reduced by increasing the mirror surface widths of the output uniform sections, so the output power and total efficiency of a working mode are improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Relativistic backward-wave oscillator employing magnet wake field
ActiveCN108615665ACompact structurePromote the development of miniaturizationTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureMicrowave
The invention discloses a relativistic backward-wave oscillator employing a magnet wake field. By the relativistic backward-wave oscillator, the problems that a traditional magnet system is excessively large in size and excessively heavy in weight and is not beneficial for miniaturization are solved. The relativistic backward-wave oscillator comprises a negative electrode and a slow wave structure, wherein the negative electrode and the slow wave structure are arranged in an outer cylinder of a device, the negative electrode is coaxial to the outer cylinder, the relativistic backward-wave oscillator is characterized in that the slow wave structure comprises a fundamental mode structure and an overmode structure which are sequentially arranged along an axial direction of a sleeve, and the overmode structure is used for amplifying a high-power microwave generated by the fundamental mode structure by utilizing a tail end guidance magnetic field of a magnet. By the relativistic backward-wave oscillator employing the structure, the generation of the high-power microwave can be achieved by fully utilizing a wake field of the guidance magnetic field, the integral structure of the device system is more compact, and the miniature development of the device system is facilitated.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
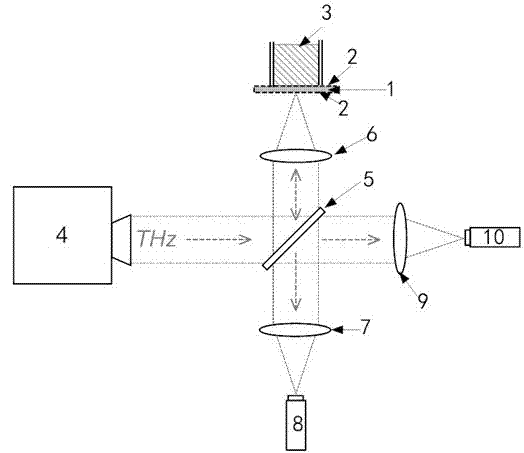
Electro-optical heterodyne detection type THz wave rapid two-dimension imaging apparatus
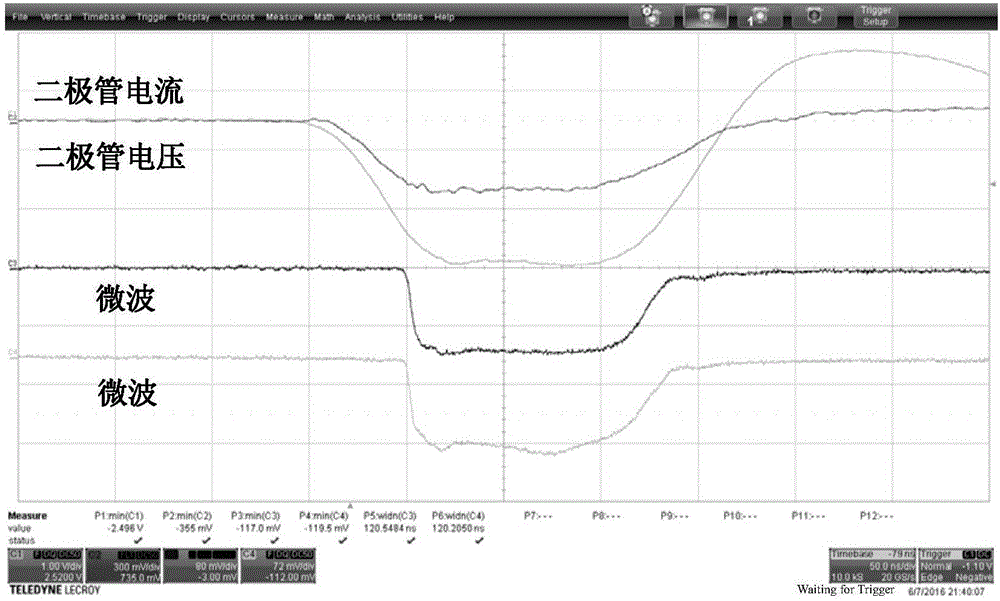
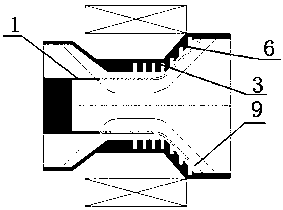
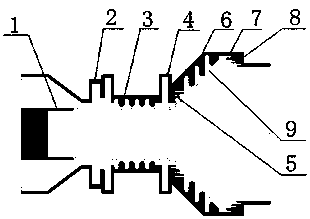
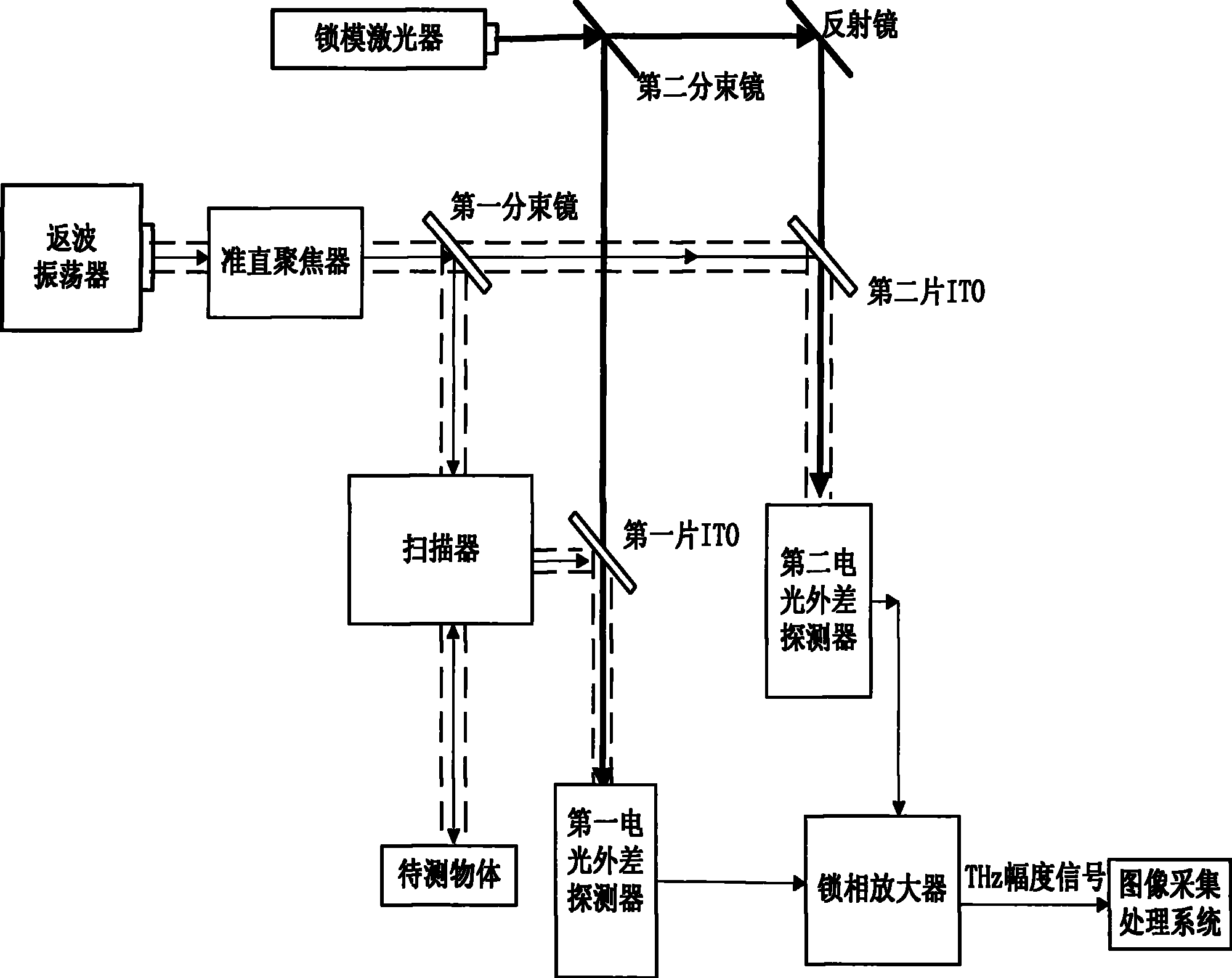
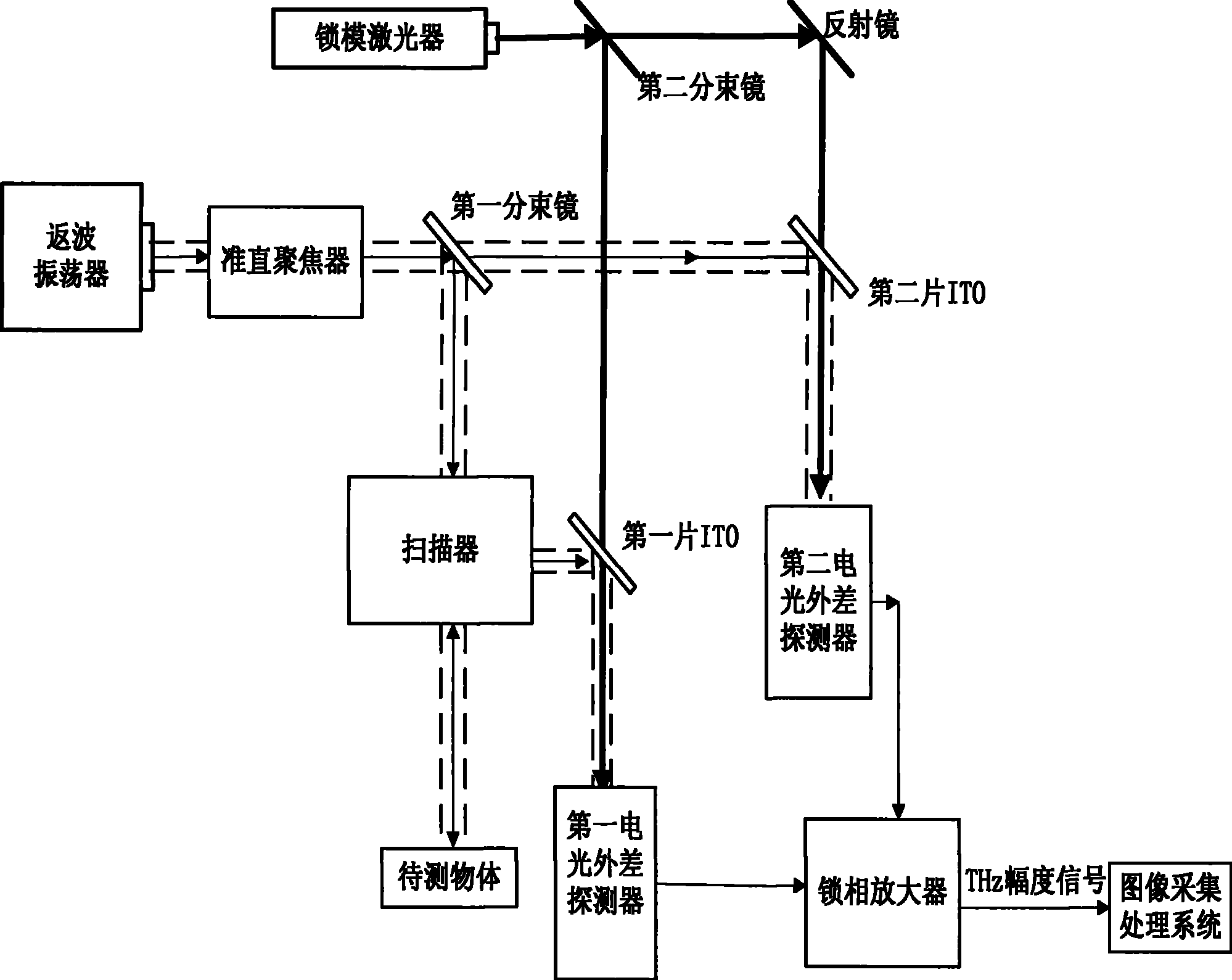
InactiveCN101354358BEasy accessAvoid measurement effectsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationTwo dimensional imagingBackward-wave oscillator
The invention discloses an electrooptic heterodyne detection typed quick two-dimensional terahertz wave imaging device. The whole imaging device mainly comprises a high-power backward-wave oscillator (BWO), a ZnTe electrooptic crystal, a mode-locked laser, a photosensitive diode array and a high-speed phase locking amplifier. The BWO with high output power is taken as a continuous terahertz radiation source and combined with the femtosecond mode-locked laser so as to realize the electrooptic heterodyne detection of THz intensity signals; a polyhedral tilting mirror is adopted for realizing line scanning and combined with pendulum mirror frame scanning so as to realize high-speed image scanning; a terahertz scanning system with separated optical shaft and receiving optical shaft is adoptedand combined with a technique with synchronous scanning view field and receiving view field so as to realize image obtaining with the high speed of 1 frame in 2 seconds and the high signal-to-noise ratio of over 40 dB. The system has the advantages that the system can overcome the system measurement influence that is caused by unstable output of the terahertz radiation source, and has quick imaging speed, high working stability and large dynamic range.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
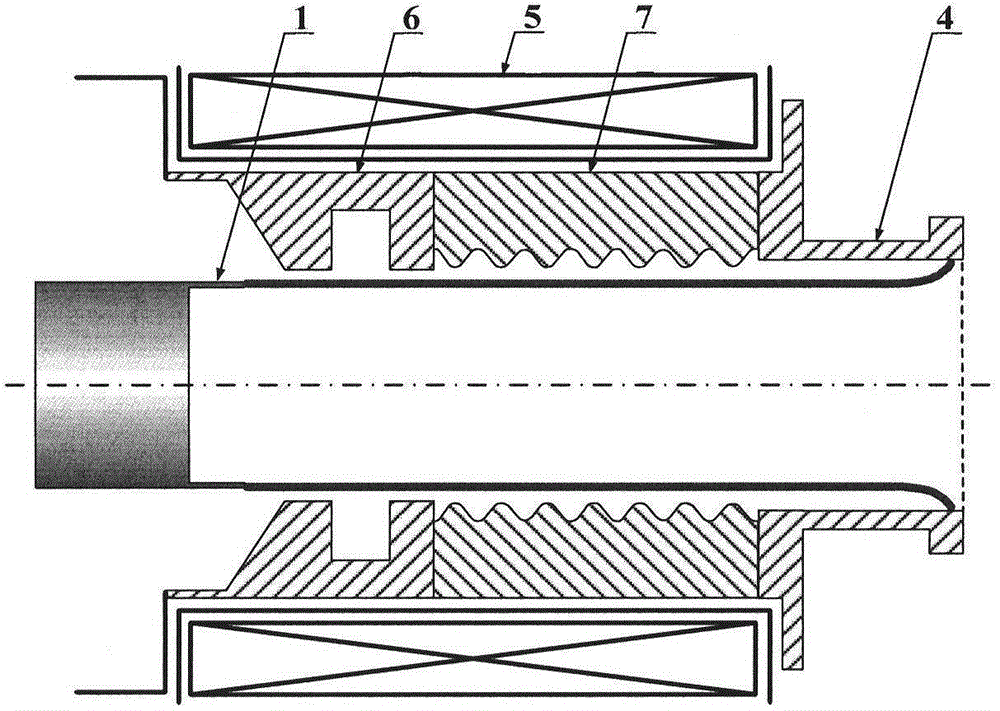
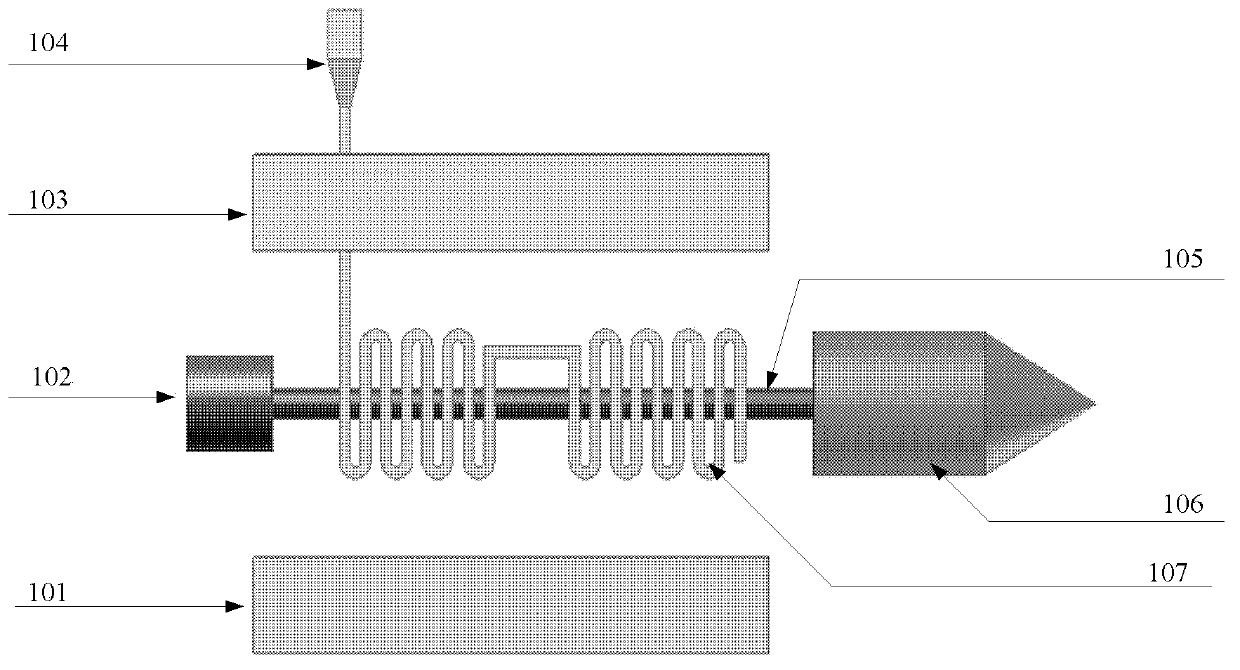
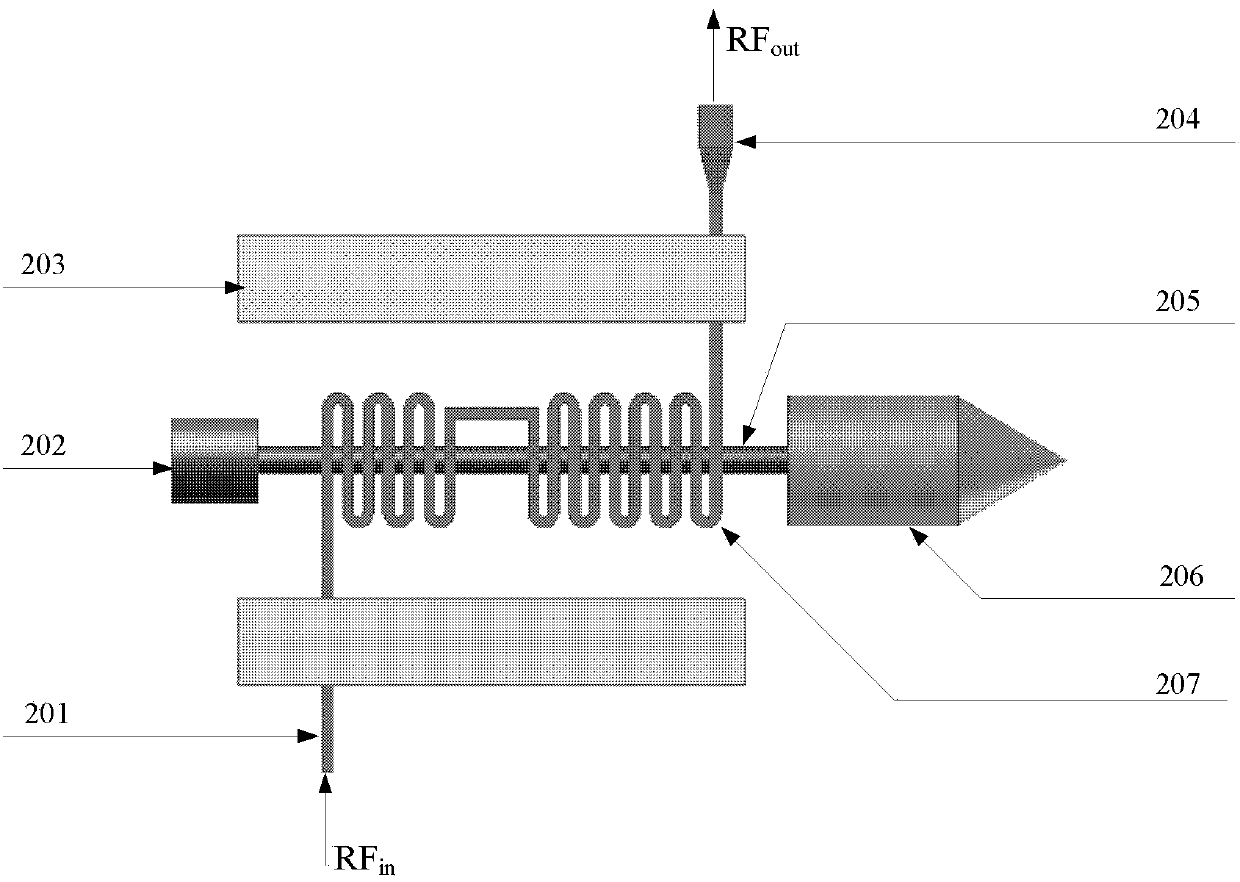
Backward wave oscillator (BWO)
InactiveCN111883406AIncrease output powerImprove interaction efficiencyTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube circuit elementsParticle physicsAtomic physics
The invention discloses a backward wave oscillator (BWO). Compared with a conventional backward-wave oscillator, the BWO has the advantages that a backward-wave amplification structure is added on thebasis of a backward-wave high-frequency structure, the interaction efficiency of electrons and electromagnetic waves is improved under the condition that voltage and current are not increased, and the final output power of the BWO is improved.
Owner:HUADONG PHOTOELECTRIC TECHN INST OF ANHUI PROVINCE
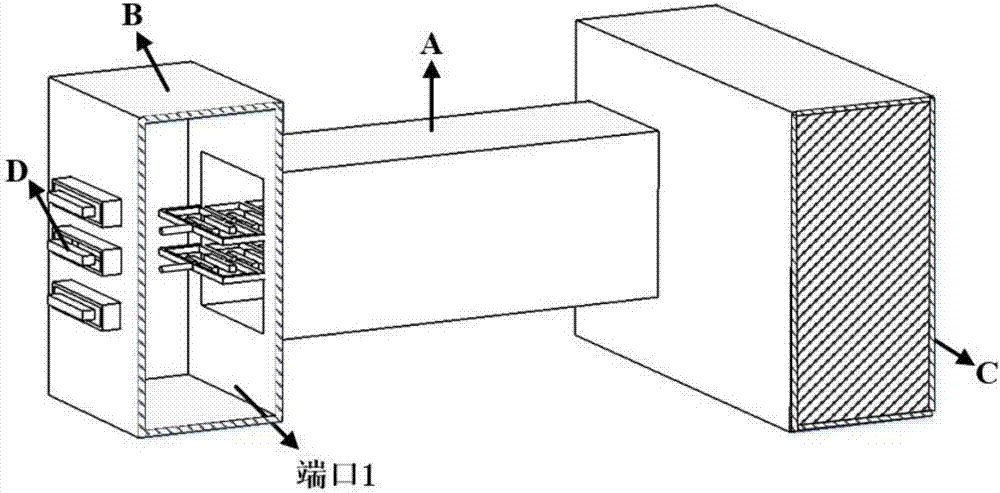
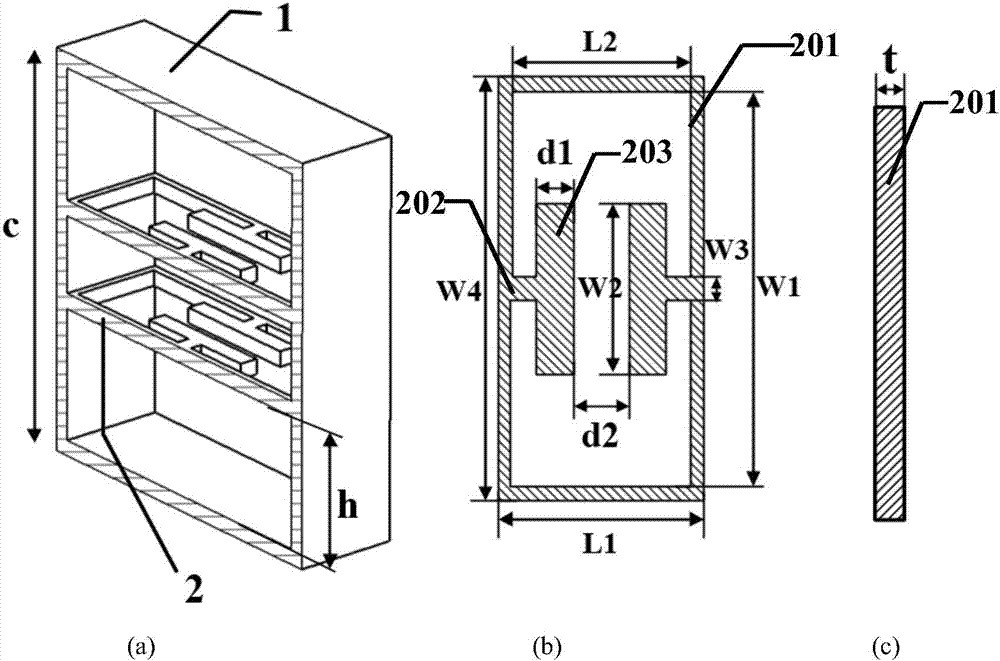
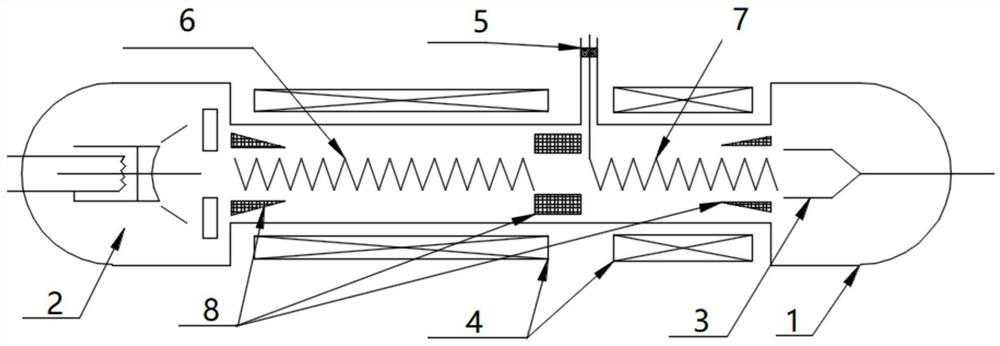
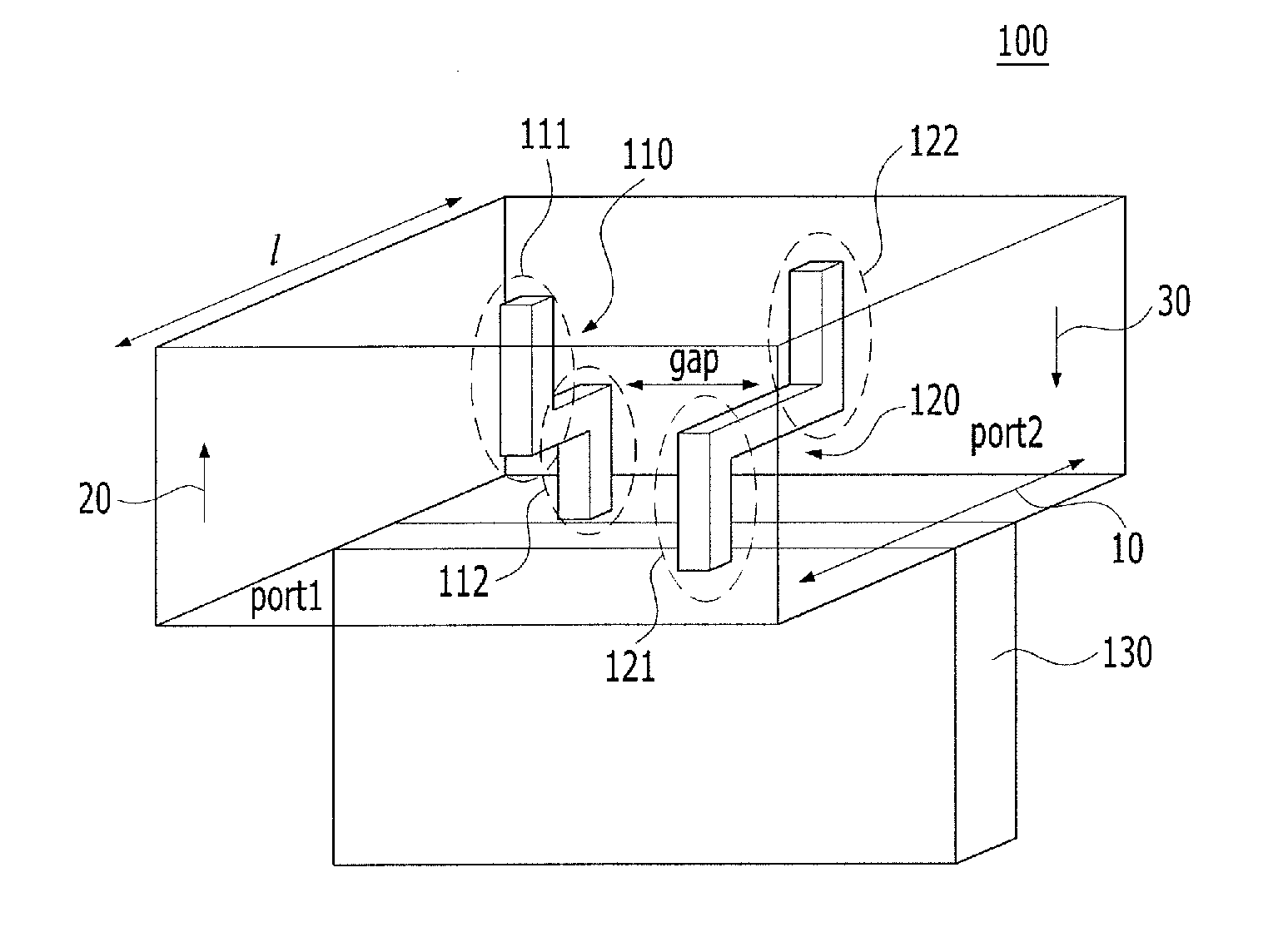
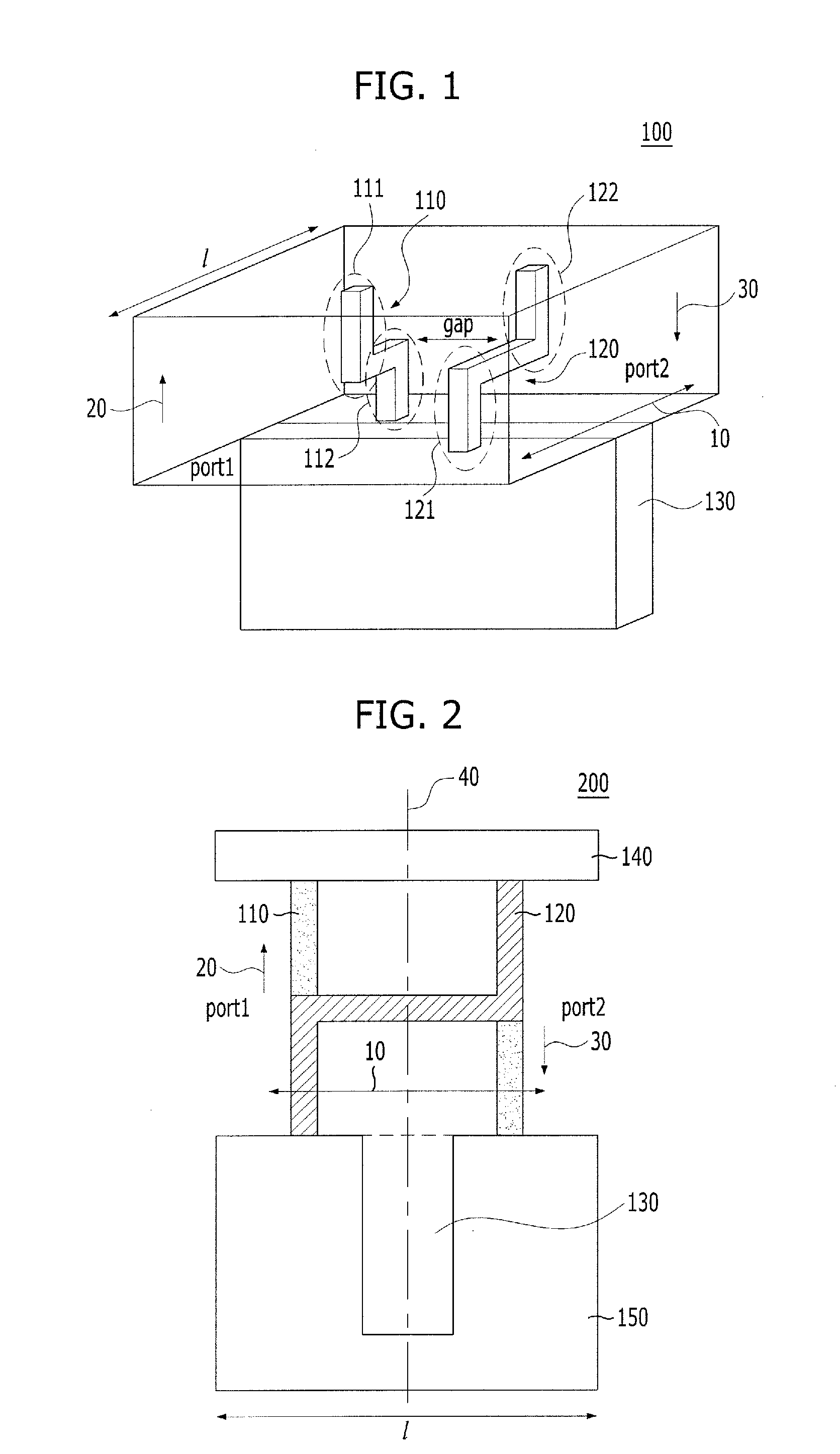
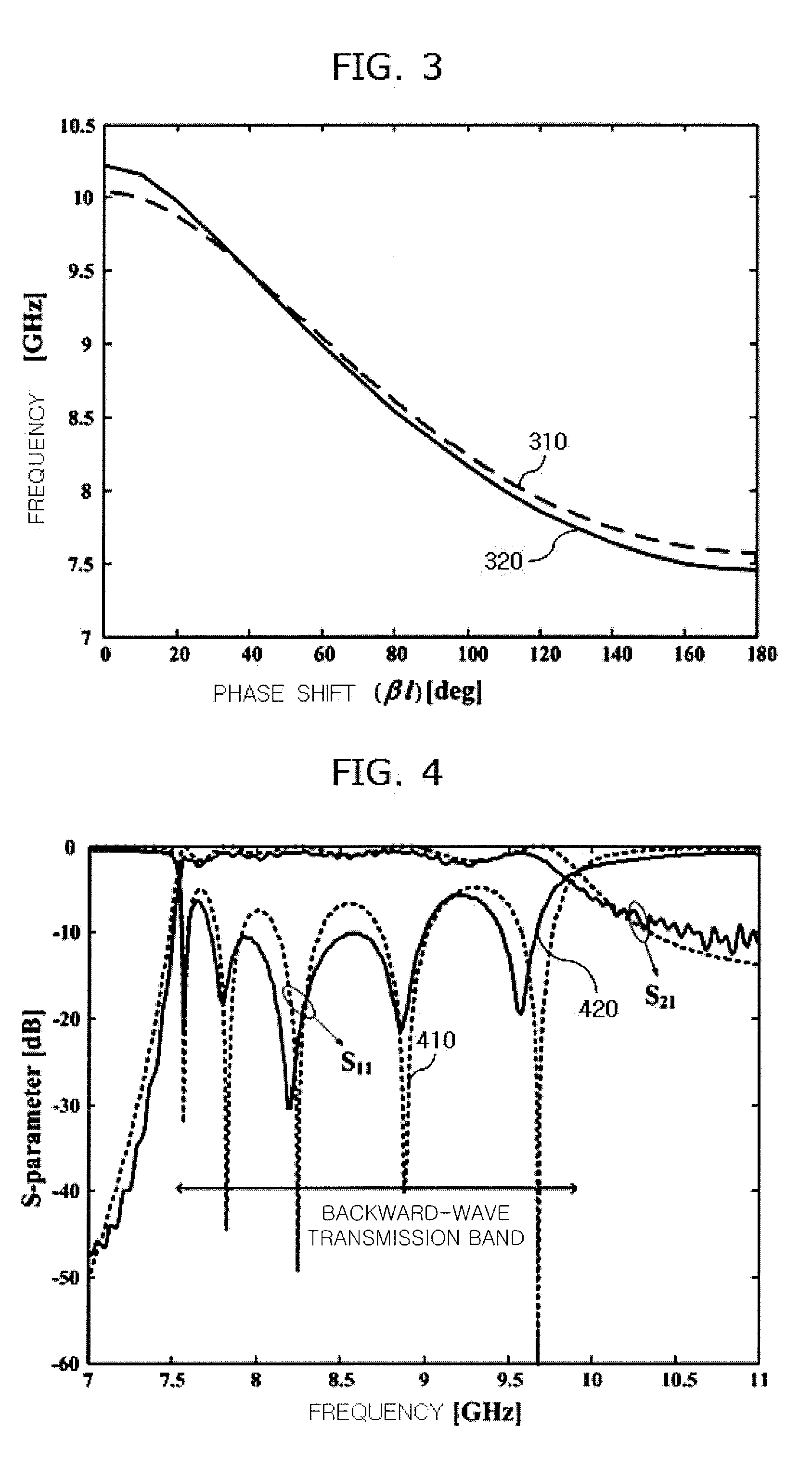
Backward-wave oscillator in communication system
Provided is a backward-wave oscillator in a communication system, including a waveguide formed of a metamaterial. A unit structure of the waveguide may include: a top plate; a short-circuited stub; a bottom plate separated at a predetermined gap from the top plate, and having the short-circuited stub formed in the center thereof; a first metal pillar connecting the top plate at a first port positioned on one surface based on the short-circuited stub to the bottom plate at a second port positioned on the opposite surface of the first port based on the short-circuited stub; and a second metal pillar separated from the first metal pillar, and connecting the top plate at the second port to the bottom plate at the first port.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com