Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34results about How to "Reduced diffraction loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tuneable unipolar lasers
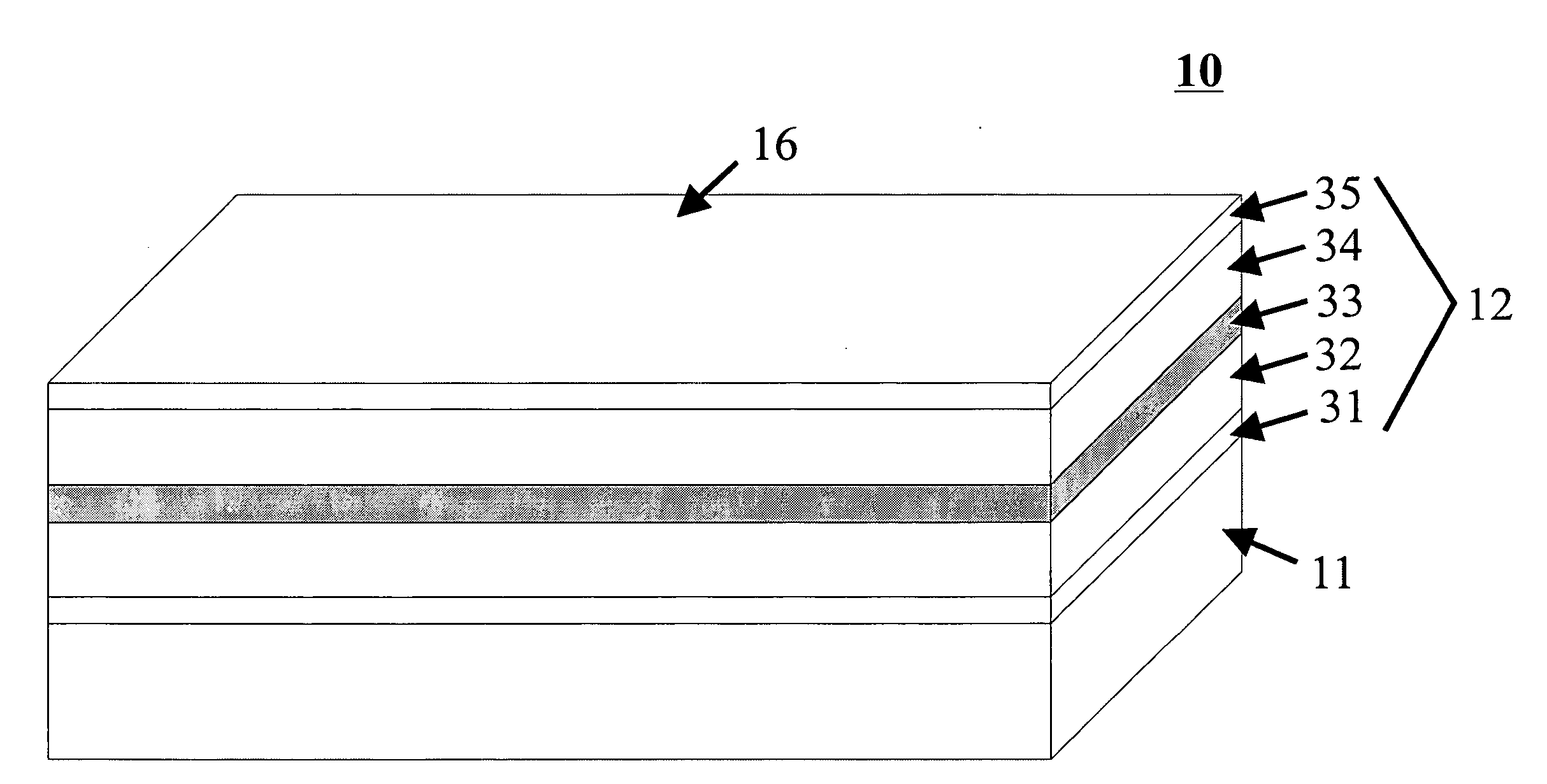
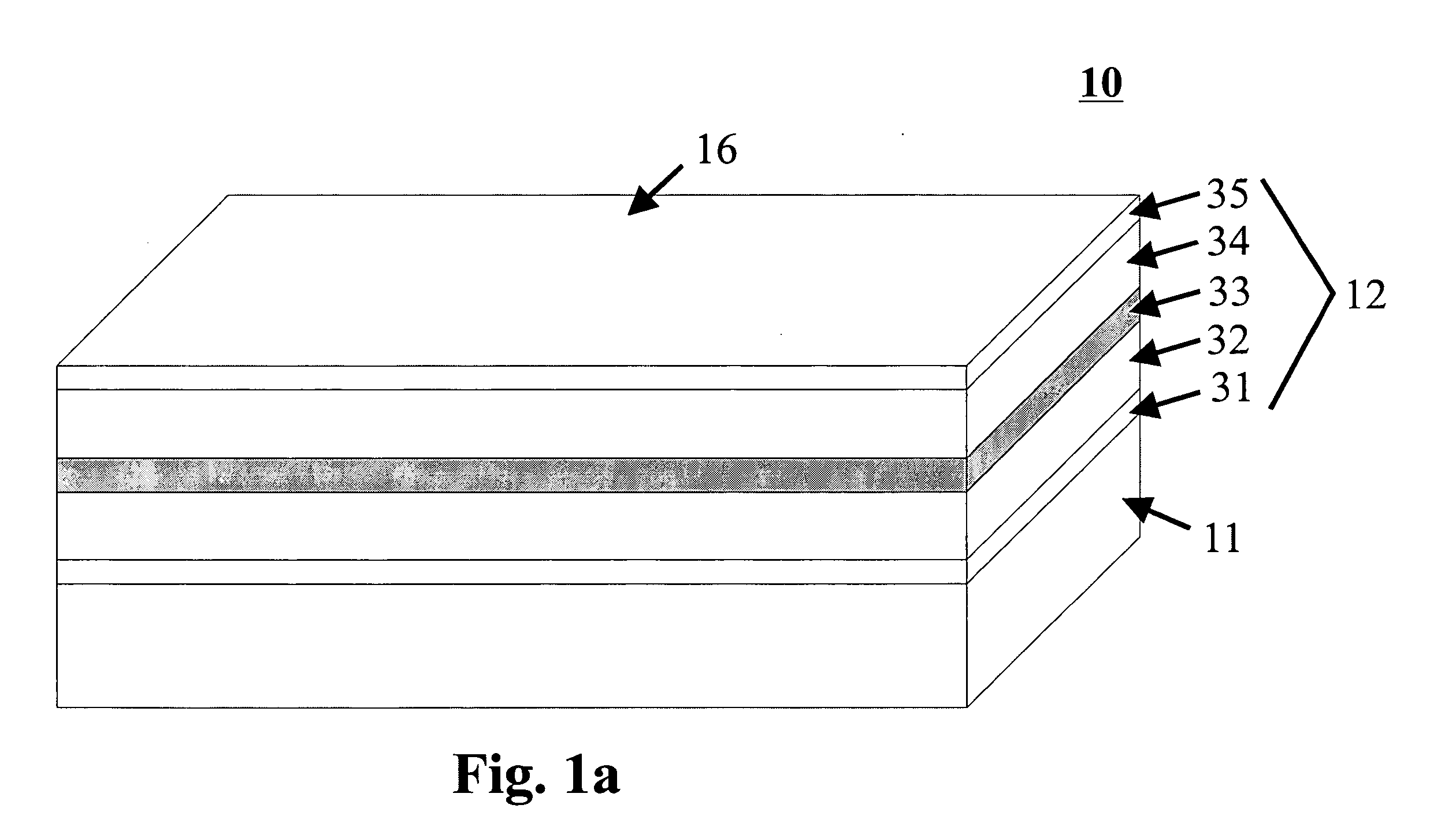
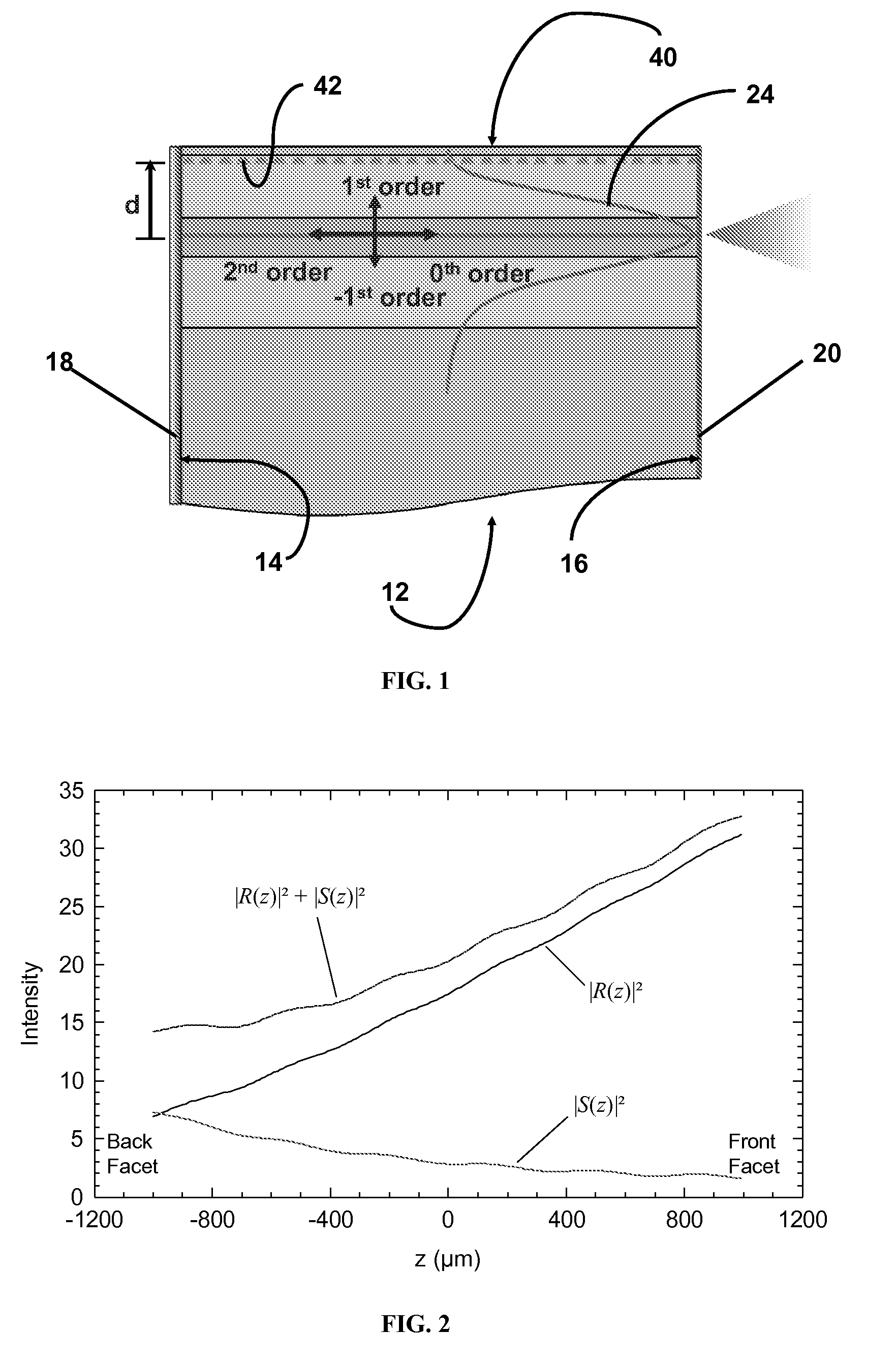
ActiveUS20050276298A1Improve back reflectivityDecreasing mirror lossLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionMetallic electrodeWaveguide
A unipolar semiconductor laser is provided in which an active region is sandwiched in a guiding structure between an upper and lower cladding layer, the lower cladding layer being situated on a semiconducting substrate. The unipolar semiconductor laser comprises a raised ridge section running from end to end between end mirrors defining the laser cavity. The ridge section aids in optical and electrical confinement. The ridge waveguide is divided in a plurality of cavity segments (at least two). Lattice structures can be arranged to these cavity segments. Each cavity segment is in contact with upper metallic electrodes. A metallic electrode coupled to the bottom surface of the semiconducting substrate facilitates current injection through the device.
Owner:NANOPLUS GMBH
Vertical laser cavity with a non-planar top mirror
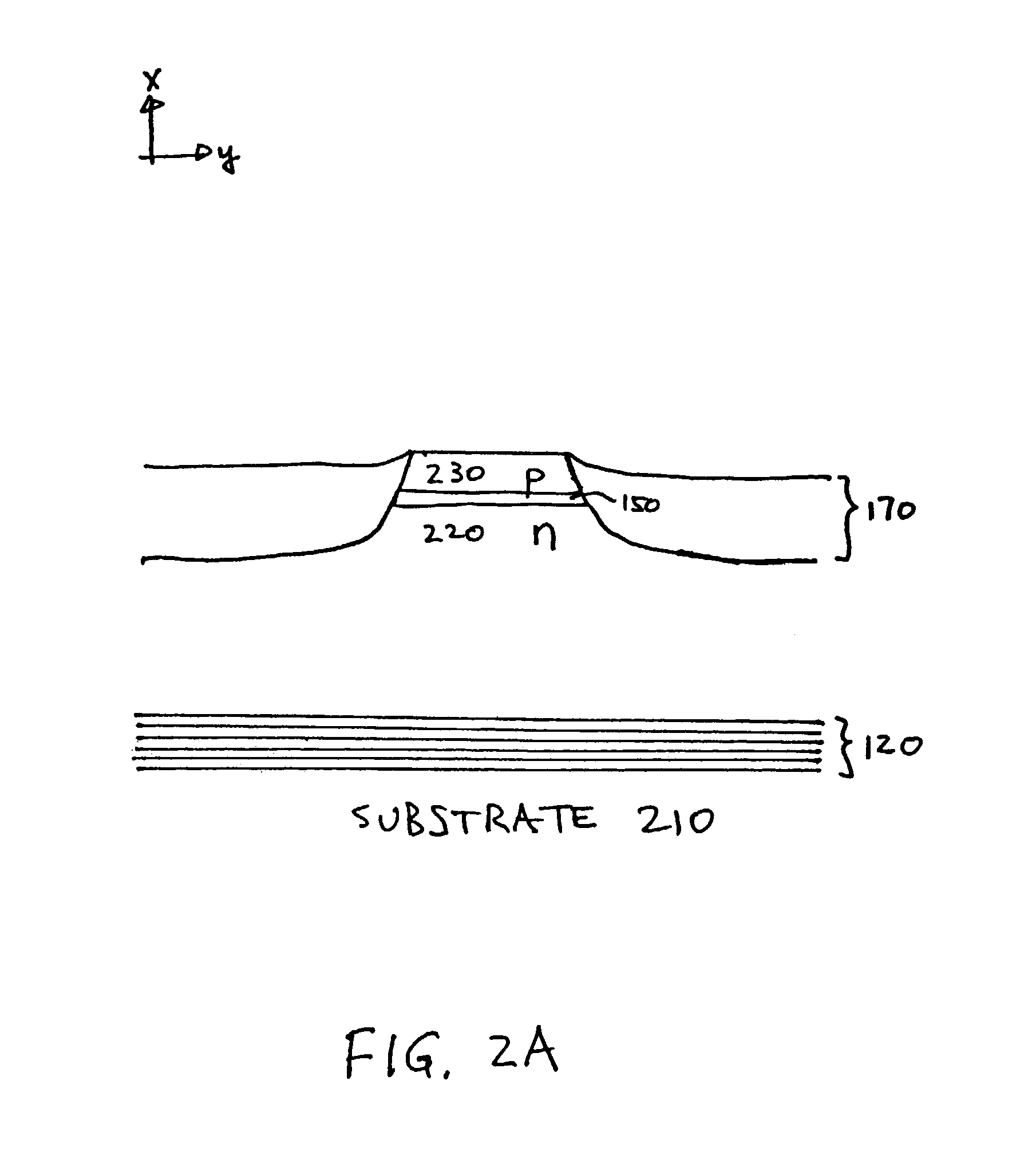
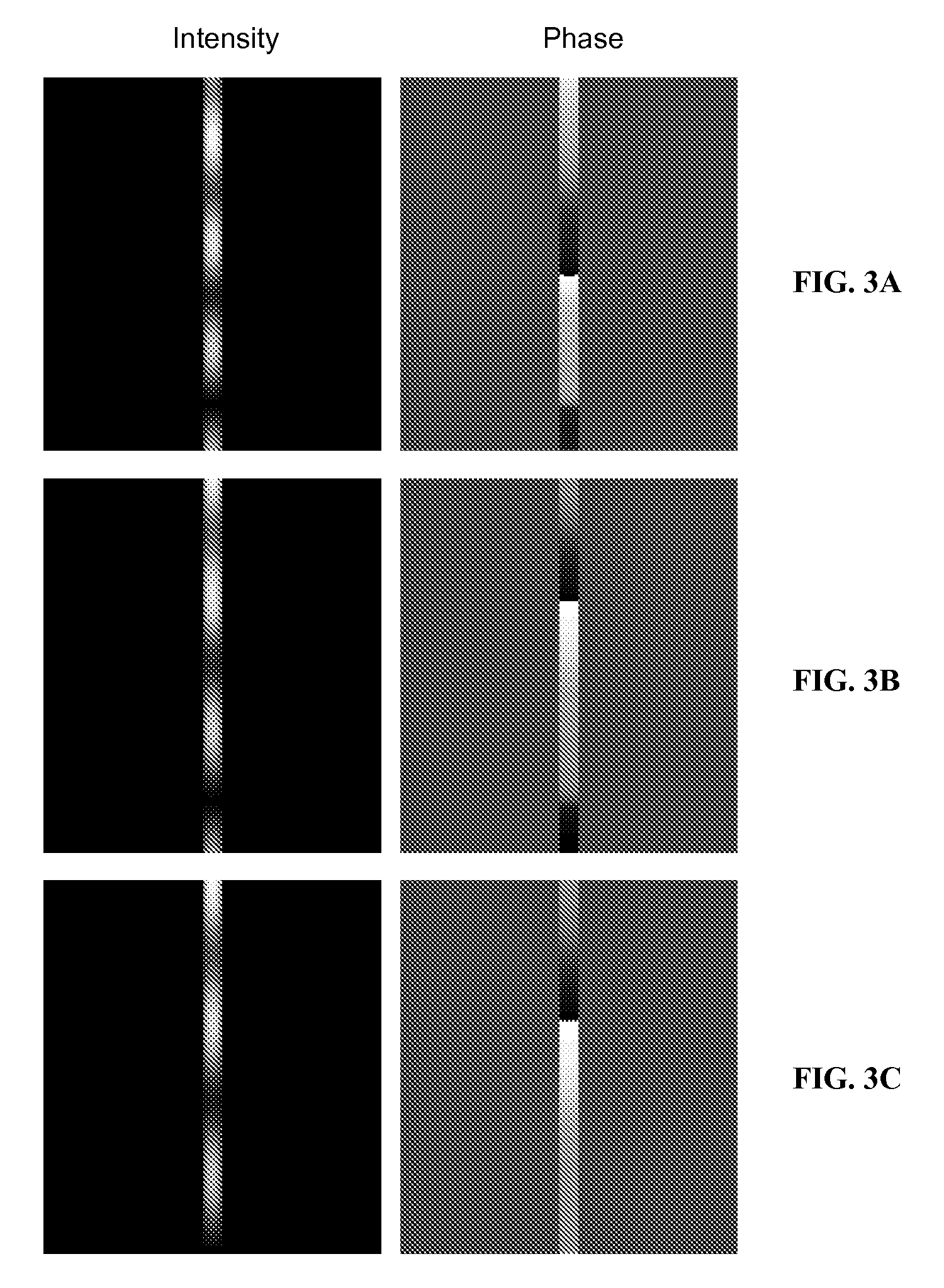
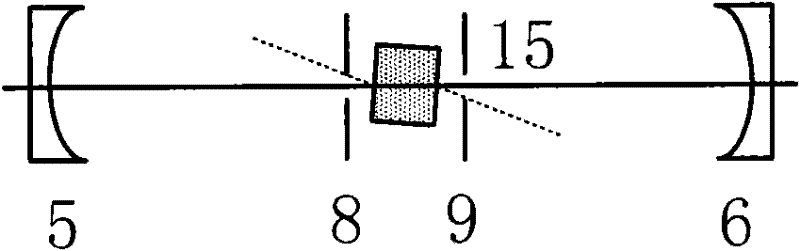
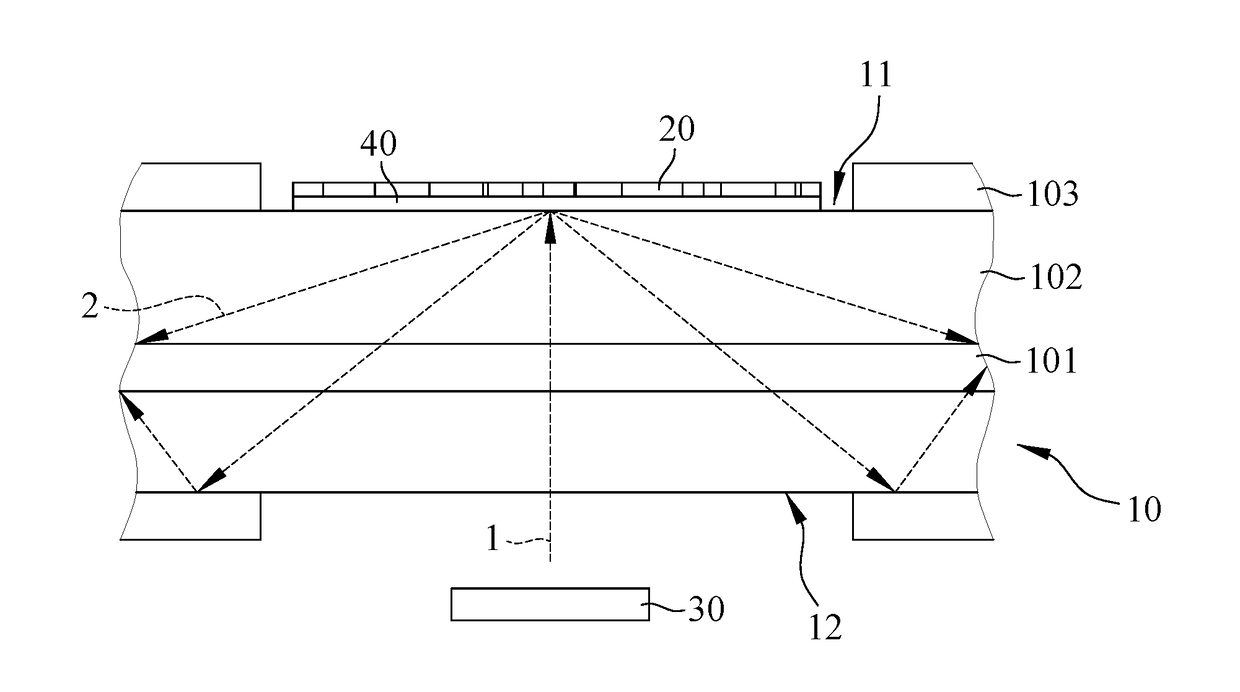
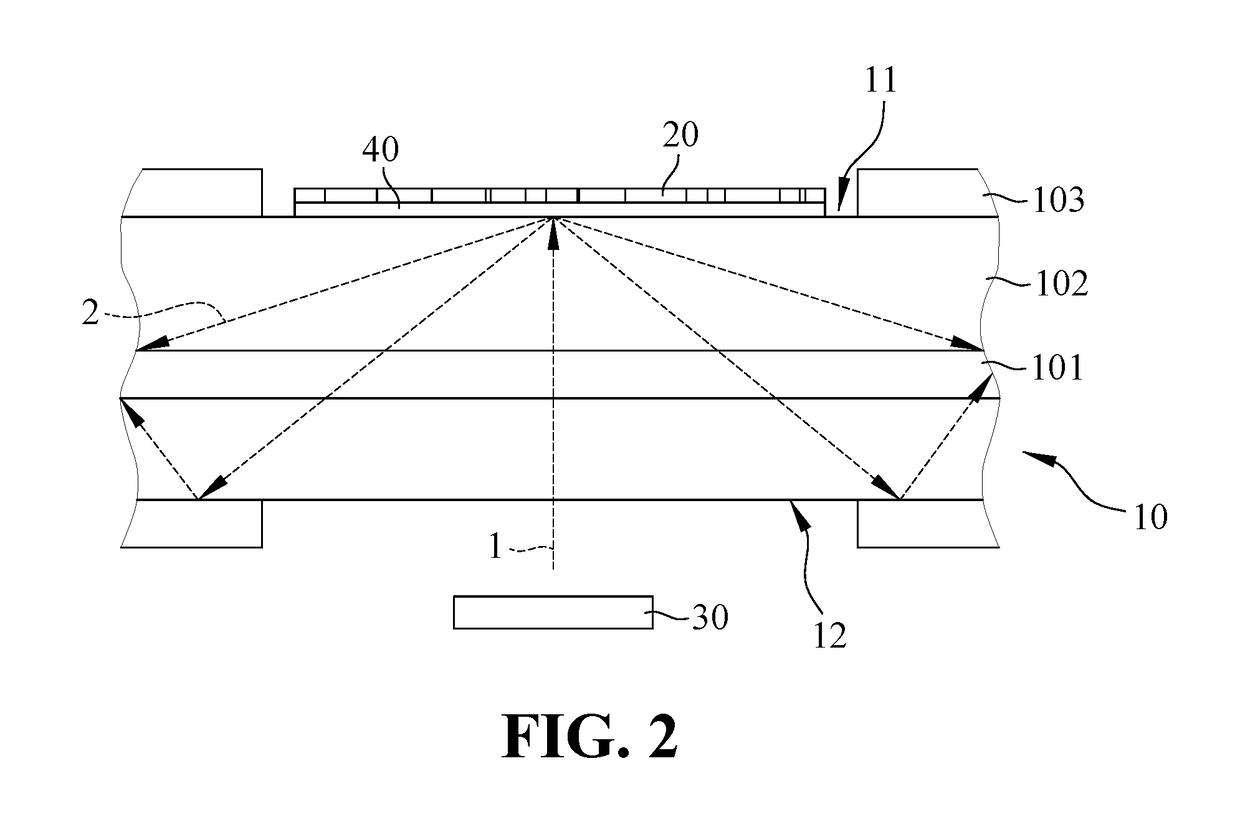
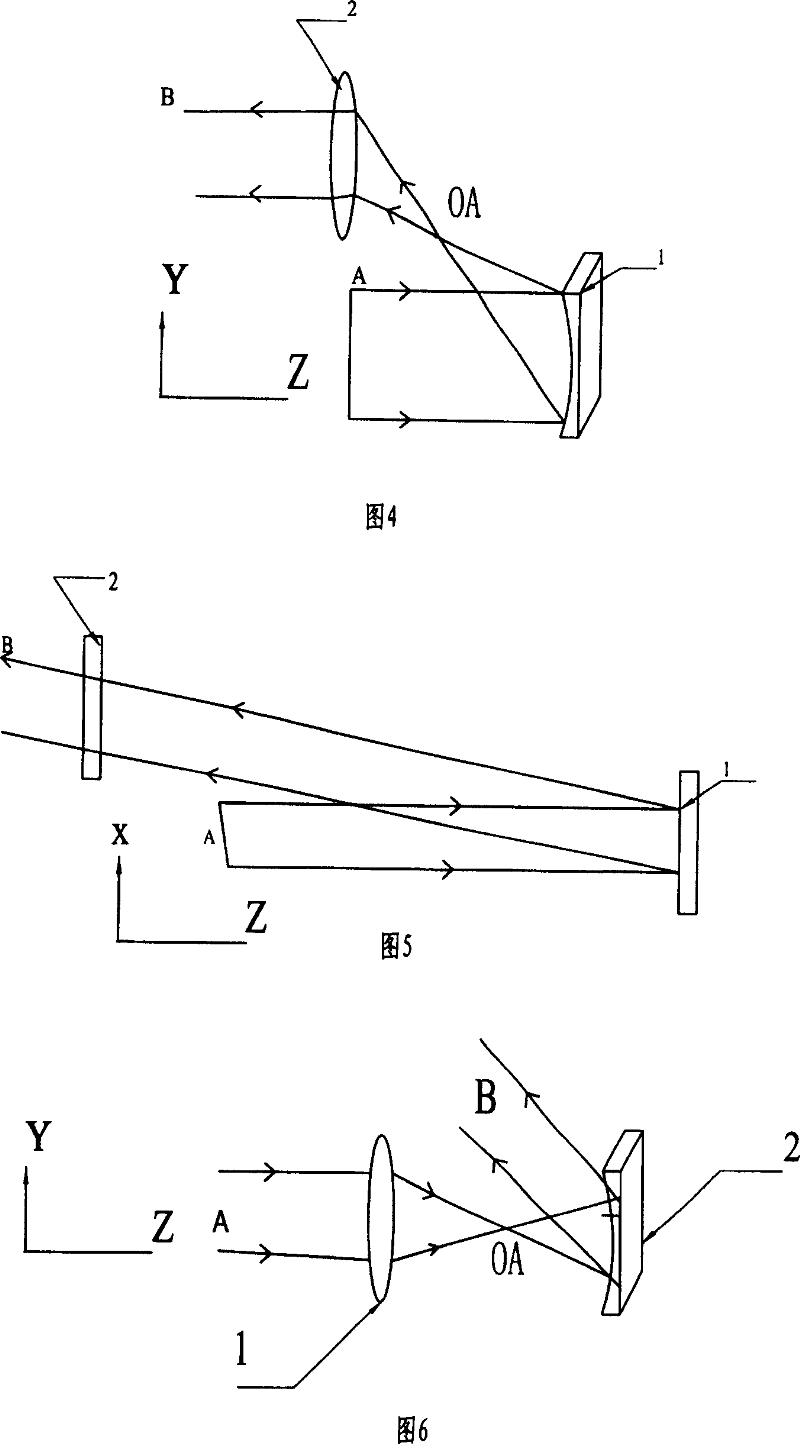
InactiveUS6980577B1Good optical performanceReduced diffraction lossOptical wave guidanceOptical resonator shape and constructionOptoelectronicsLaser
A vertical laser cavity includes a non-planar top mirror in order to improve the optical performance of the laser cavity. In one approach, the top mirror is curved to form a plano-concave geometry with the bottom mirror, as opposed to the typical plano—plano geometry. This can reduce diffraction losses and otherwise improve optical performance.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Photon crystal tunable filter and its manufacture method
InactiveCN101210979ASmall sizeReduce unevennessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical coating apparatusFilm resistanceLight spot
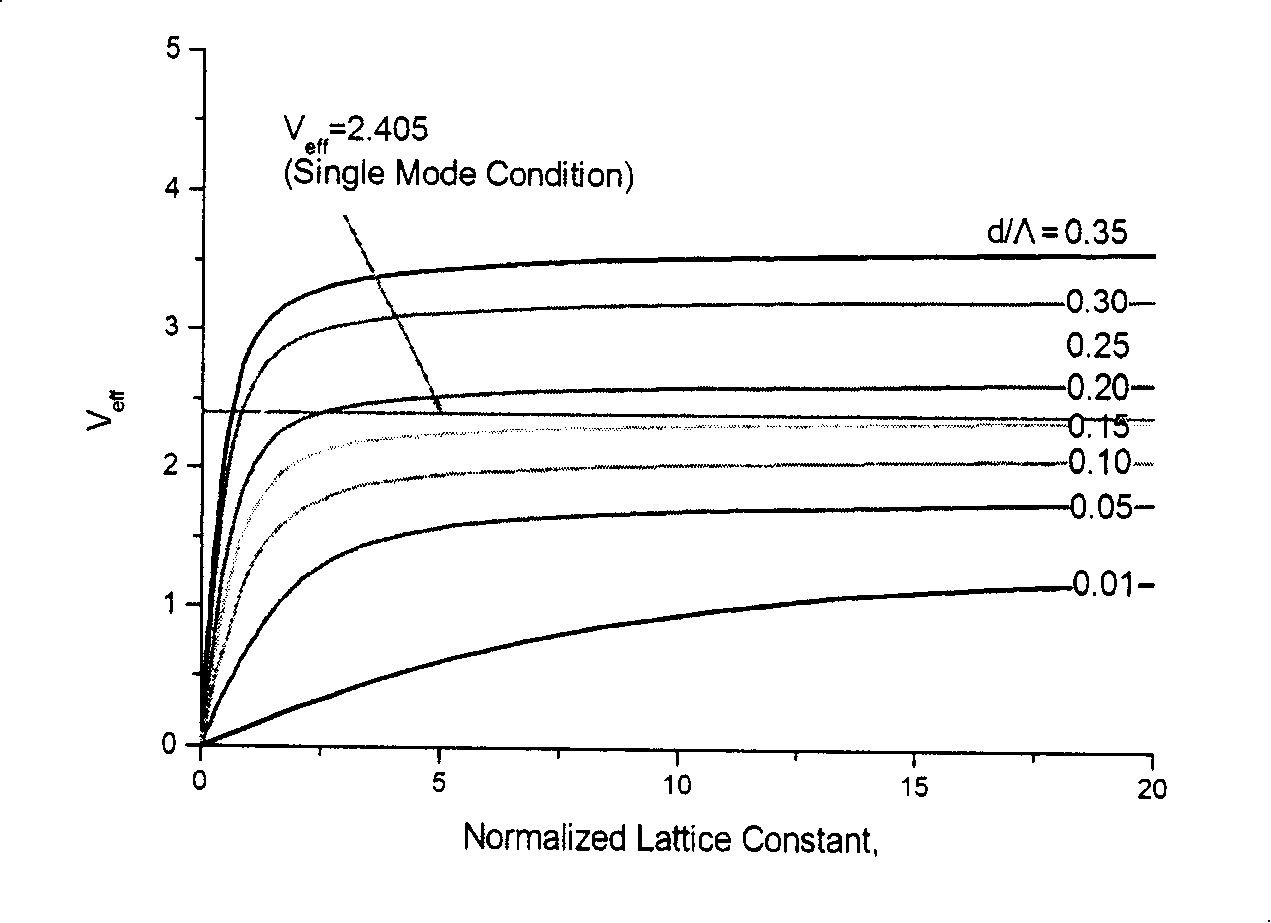
The invention relates to the technical field of thermo-optical tuned filter, and discloses a photon crystal tunable filter, comprising a lower reflector, a separation wall and an upper reflector on the silicon on an insulation layer (SOI) and air ports through the upper reflector, the separation wall, the lower reflector and the top silicon of SOI. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the photon crystal tunable filter. With the method, the invention can reduce the uneven film temperature from the traditional heating of film resistance, lift the limit of the minimum size of input light spot caused by the diffraction loss, lower the consumption and the power of the tunable filter and accelerate the tuning speed of the tunable filter.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Low-threshold-value femtosecond pulse fiber laser
InactiveCN103401134AReduced diffraction lossImprove stabilityLaser detailsMode-lockingFaraday rotator
The invention relates to a low-threshold-value femtosecond pulse fiber laser. The low-threshold-value femtosecond pulse fiber laser consists of an optical-fiber coupling semiconductor laser, a wavelength division multiplexer, a ytterbium-doped single-mode gain fiber, two optical-fiber collimators, two quarter slides, two half slides, a polarization beam splitter, a faraday rotator, two reflection gratings, a reflection mirror and an optical isolator. The femtosecond laser adopts a semi-space semi-fiber annular cavity structure, the combined action of the faraday rotator and the half slides is adopted, and a group of grating pairs is adopted to carry out intra-cavity chromatic dispersion management on the laser, so that the polarization direction of the laser which passes through the faraday rotator twice is enabled to rotate for 90DEG and to be reflected from a vertical reflection port of the polarization beam splitter, a light path can be prevented from being lowered, and the introduction of an additional reflection mirror can be avoided; The polarization direction of the incident light which radiates on the first reflection grating is adjusted through the half slides, so that the highest diffraction efficiency can be achieved, the intra-cavity loss of the laser can be reduced, and an effect for reducing a mode locking threshold value can be realized.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
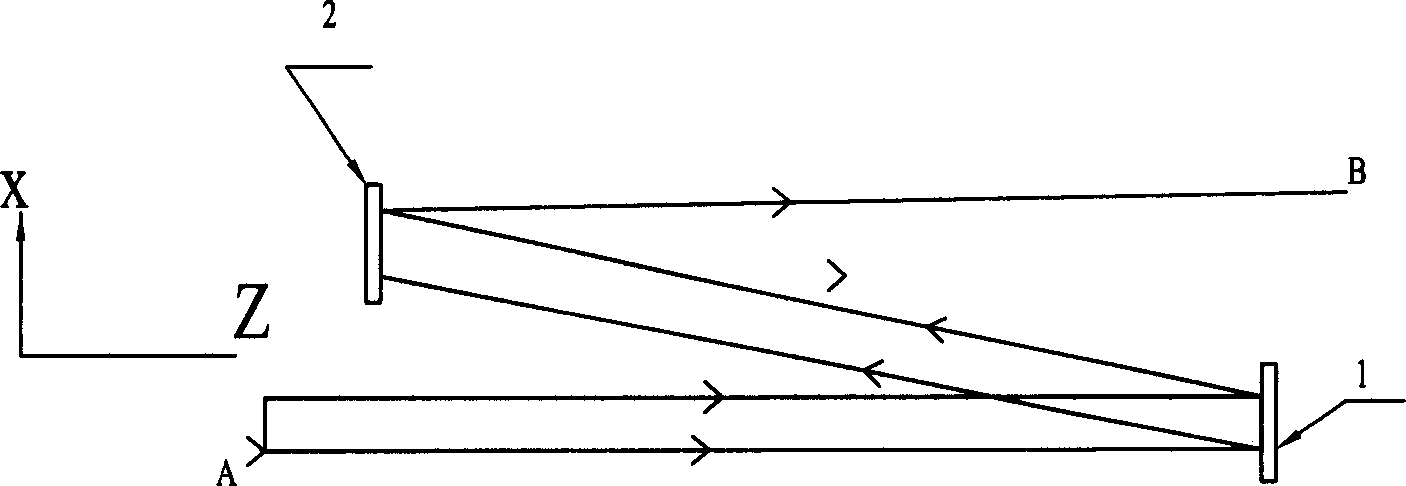
Optical fibre coherence coupling method for large power semiconductor laser array and optical fibre shaper
InactiveCN1738119AChanging the difference in cycle scaleReduce lossSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser arrangementsFiberLaser technology
The invention relates to a fiber coherence coupling method of high power semi-conductor laser array and the fiber-shaping device, belonging to the laser technique field. The characters of invention comprise: guiding the fiber into the space between the semiconductor laser array and the external-cavity glass; using microlens to compress the fast axis divergence angle of each luminous unit, to make N luminous units be coupling to N fibers one to one; utilizing the flexibility of fiber, rearranging the fiber on the another end of fiber into the fiber array with bidimensional periodic time. The designed fiber shaping device is arranged between the semi-conductor laser array (1) and the external-cavity glass (6), comprising aligning hub (3), fiber (4) and rearrangement hub (5); the compressed fiber, via the microlens, is one-to-one coupling to the fiber which is fixed in the aligning hub, while the rearrangement hub rearranges and fixes another end of with bidimensional fiber. The invention reaches the rearrangement of luminous light beam and improves the coherence coupling of high power semi-conductor laser array.
Owner:JIAXING DAHE LASER EQUIP
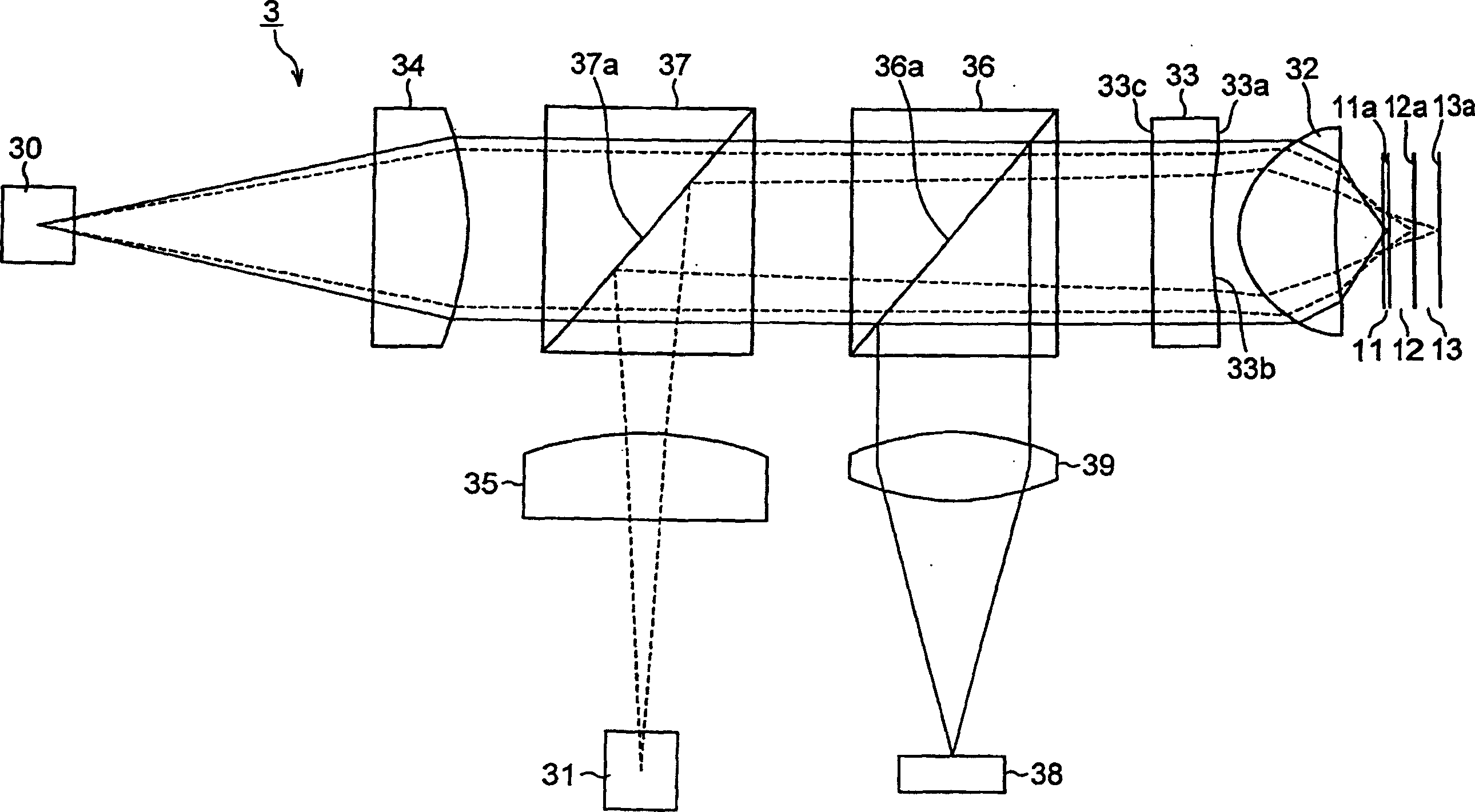
Converging optical apparatus, optical pickup and optical disc apparatus
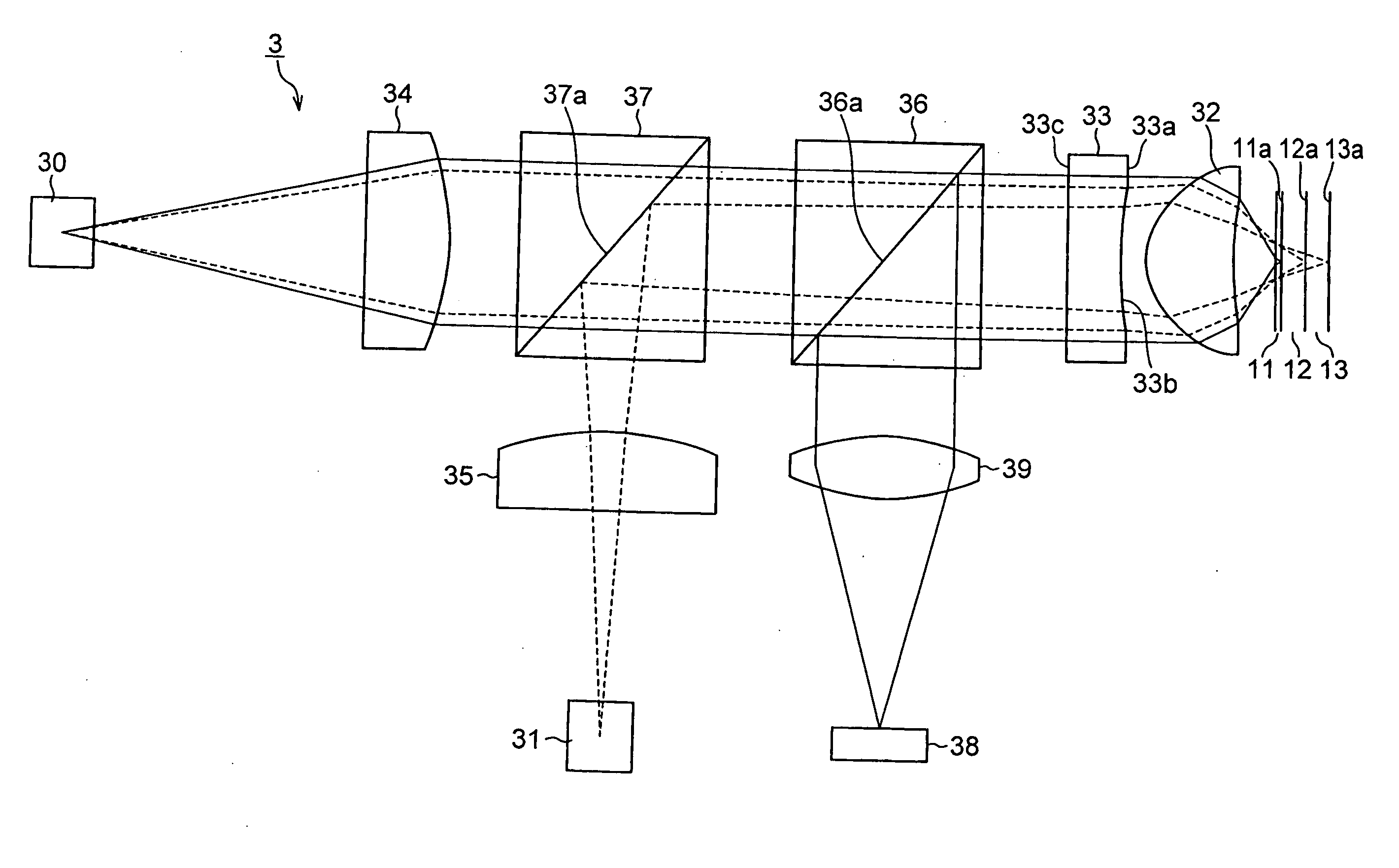
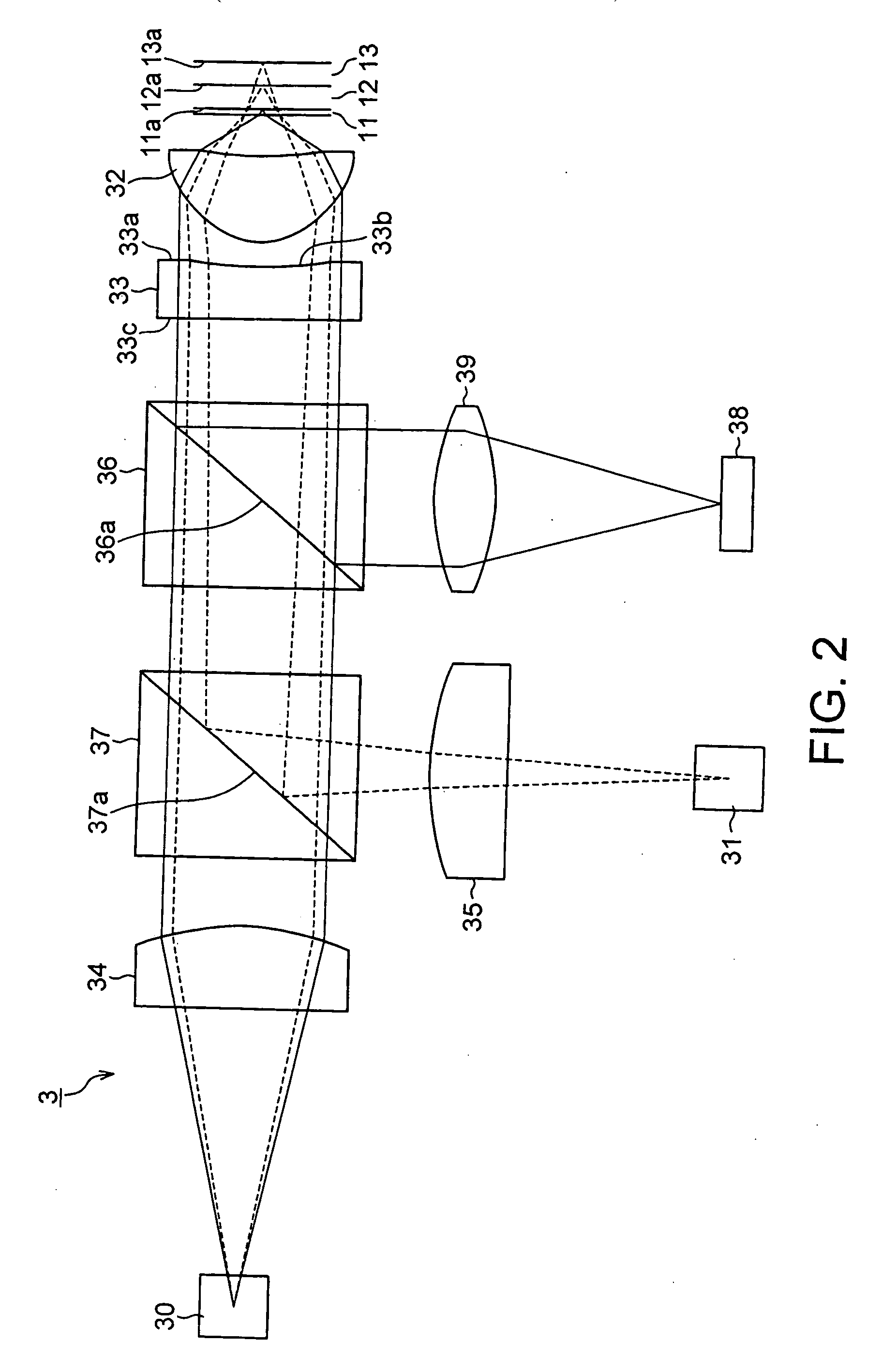
InactiveUS20060158990A1Reduce diffraction lossExcellent performanceRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansSignal onOptical pickup
A converging optical apparatus reduces the diffraction loss and realizes compatibility with three different wavelengths by means of a hologram element. The present invention provides an optical pickup for recording signals on and / or reproducing signals from a plurality of optical discs having respective protection substrates of different thicknesses for protecting the recording surfaces thereof by means of light beams of different wavelengths, the optical pickup including a first emission section that emits a light beam of a first wavelength, a second emission section that emits a light beam of a second wavelength, a third emission section that emits a light beam of a third wavelength, an objective lens for converging the light beams of the first through third wavelengths emitted respectively from the first through third emission sections on the signal recording surfaces of the optical discs, and a hologram element arranged between the first through third emission sections and the objective lens, the hologram element having two major surfaces, wherein the hologram element is provided with a reference curved surface on one of the major surfaces thereof, the reference curved surface being an aspherical shape, and a hologram section is formed on the reference curved surface.
Owner:SONY CORP
Distribution attenuating confocal waveguide gyrotron travelling wave tube high frequency system
ActiveCN107230607AControl echo oscillationReduced diffraction lossTransit-tube coupling devicesTotal efficiencyMicrowave
The invention discloses a distribution attenuating confocal waveguide gyrotron travelling wave tube high frequency system and belongs to the technical field of microwave, millimeter wave and terahertz devices. The structure is composed of confocal waveguides which are symmetrical up and down. Side faces of the confocal waveguides are opened. Mirror surface curvatures of the confocal waveguides are consistent. Each confocal waveguide comprises an input uniform section, an input transition section, an interaction section, an output transition section and an output uniform section. According to the structure, a backward wave oscillator circuit of a parasitic mode is cut off through adoption of the interaction sections of the confocal waveguides with very narrow mirror surface widths, and moreover, it is ensured that the interaction sections are long enough, thereby realizing relatively high linear gain. Diffraction losses of a high frequency field after amplification are reduced by increasing the mirror surface widths of the output uniform sections, so the output power and total efficiency of a working mode are improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Tuneable unipolar lasers
ActiveUS7301977B2Easy injectionGuaranteed current efficiencyLaser optical resonator constructionLaser active region structureMetallic electrodeWaveguide
A unipolar semiconductor laser is provided in which an active region is sandwiched in a guiding structure between an upper and lower cladding layer, the lower cladding layer being situated on a semiconducting substrate. The unipolar semiconductor laser comprises a raised ridge section running from end to end between end mirrors defining the laser cavity. The ridge section aids in optical and electrical confinement. The ridge waveguide is divided in a plurality of cavity segments (at least two). Lattice structures can be arranged on and / or adjacent to these cavity segments. Each cavity segment is in contact with upper metallic electrodes. A metallic electrode coupled to the bottom surface of the semiconducting substrate facilitates current injection through the device.
Owner:NANOPLUS GMBH
Broadband confocal waveguide HE0n mode excitation device
The invention discloses a broadband confocal waveguide HE0n mode excitation device, belonging to the technical field of vacuum electronics. The device comprises an output open confocal waveguide section, a closed confocal waveguide mode transition section, a cutoff transition section and an even open waveguide section. A Y-shaped 3dB power divider is arranged at the junction of the closed confocal waveguide mode transition section and the cutoff transition section. The two-channel output waveguide is bent inwardly by 90 degrees and perpendicular to the input waveguide; and the output port receives two microwave signals of equal amplitude in opposite directions. The device of the invention adopts a doubly-fed structure which is perpendicular to the confocal waveguide mirror surface, and hroguh the two pairs of reflection mirrors of the cutoff transition section, high-efficiency conversion of the confocal waveguide HE0n mode can be realized in the broadband range with the flatness in the band. In the millimeter wave and terahertz band, this can be realized by traditional processing methods; for the low sensitivity structural parameters, the device can be directly applied to the input coupling device of a millimeter wave and terahertz band confocal waveguide convolution amplifier and the cold tests for high frequency system characteristics of the convolution amplifier.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Waveguide mode-locked laser
InactiveCN102738693ASolve the increase of diffraction lossReduced diffraction lossLaser detailsMode-lockingWaveguide mode
The invention provides a waveguide mode-locked laser, comprising a semiconductor saturable absorption mirror, a waveguide grain medium, a waveguide grating and a pumping source. The semiconductor saturable absorption mirror and the waveguide grating are respectively arranged at the both ends of the waveguide grain medium; and the pumping source is arranged above the waveguide grating. According to the waveguide mode-locked laser provided by the invention, the semiconductor saturable absorption mirror is fixedly arranged at one end of the grain medium by using a special means as a cavity mirror in a laser cavity; and furthermore, the grating is written into a waveguide channel on a doped substrate in a point-to-point manner by using a femtosecond micromachining system, and the passive mode locking is realized by utilizing dispersion compensation of the grating and characteristics of the semiconductor saturable absorption mirror.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
HIGH EFFICIENCY PARTIAL DISTRIBUTED FEEDBACK (p-DFB) LASER
ActiveUS20080205476A1Improve efficiencyIncrease output powerLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingLine width
A second-order multi-mode partial distributed feedback (p-DFB) laser having increased electrical-to-optical power conversion efficiency, stabilized wavelength and narrowed emission linewidth. The laser includes an abbreviated grating housed in the laser cavity that is separated from both the front-end and the back-end of the laser facets.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
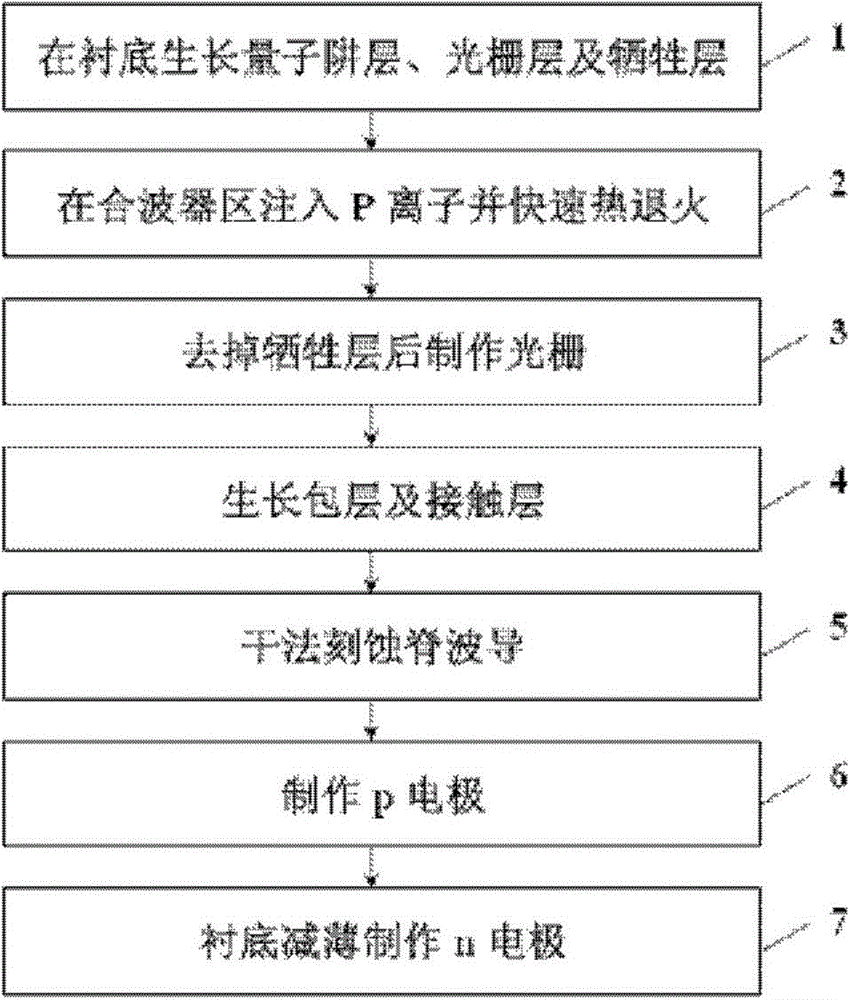
Method for manufacturing laser array and combiner monolithic integration chip
ActiveCN103545715AReduce light diffraction lossReduced Combiner SizeOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsIonQuantum well
A method for manufacturing a laser array and combiner monolithic integration chip comprises the steps that an n-type InP buffer layer, an n-type AlGaInAs covering layer, an AlGaInAs multi-quantum well layer, a p-type AlGaInAs covering layer, an InP interlayer, an InGaAsP grating layer and an InP sacrificial layer are grown on an n-type InP substrate in sequence to form a substrate, an active region is arranged on one side of the base chip, and a combiner region is arranged on the other side of the substrate; P ions are injected into the InP sacrificial layer of the combiner region, and fast thermal annealing is carried out; the InP sacrificial layer is removed, and gratings are manufactured in the InGaAsP grating layer of the active region; a p-type InP covering layer and a p-type InGaAs contact layer are grown on the InGaAsP grating layer of the active region and the InGaAsP grating layer of the combiner region; the p-type InGaAs contact layer, the p-type InP covering layer, the InGaAsP grating layer and the InP interlayer are removed through dry etching, ridge type waveguides of all laser units are formed in the active region, and combiner ridge type waveguides are formed in the combiner region; p electrodes are manufactured on the ridge type waveguides of the active region; the n-type InP substrate is thinned, an n electrode is manufactured on the back face of the n-type InP substrate, and manufacturing is completed.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
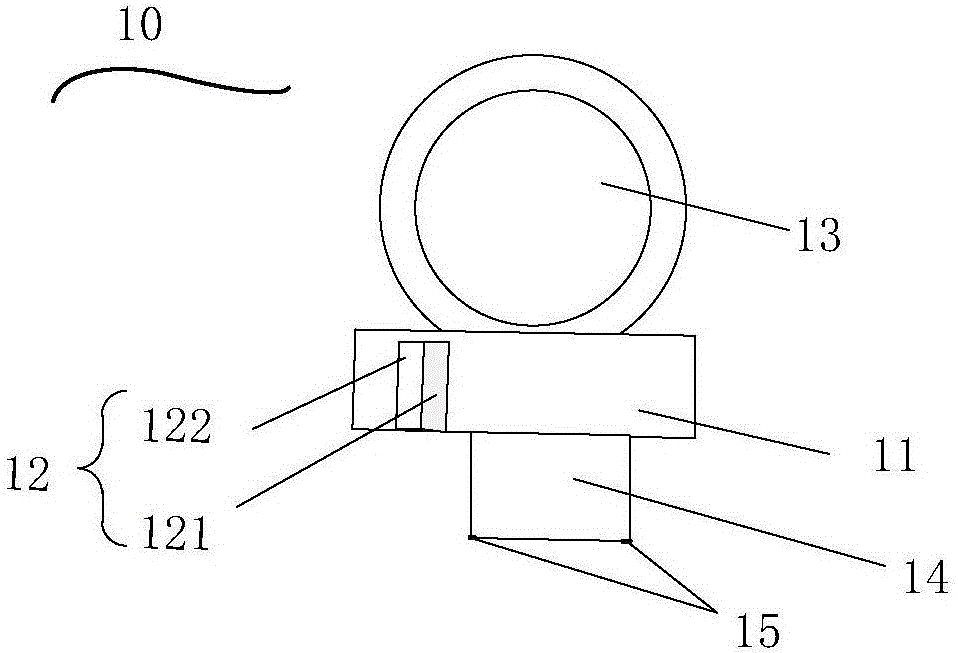
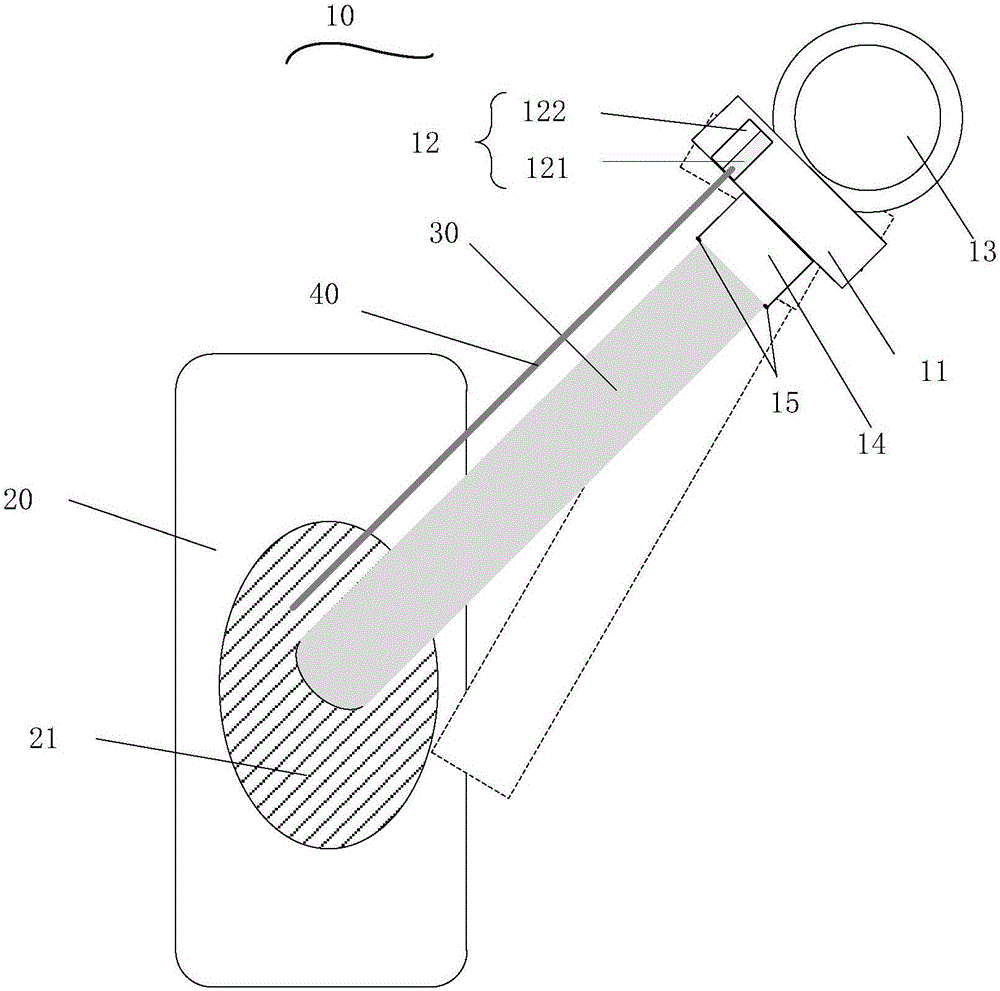
Millimeter wave wireless charging device and method
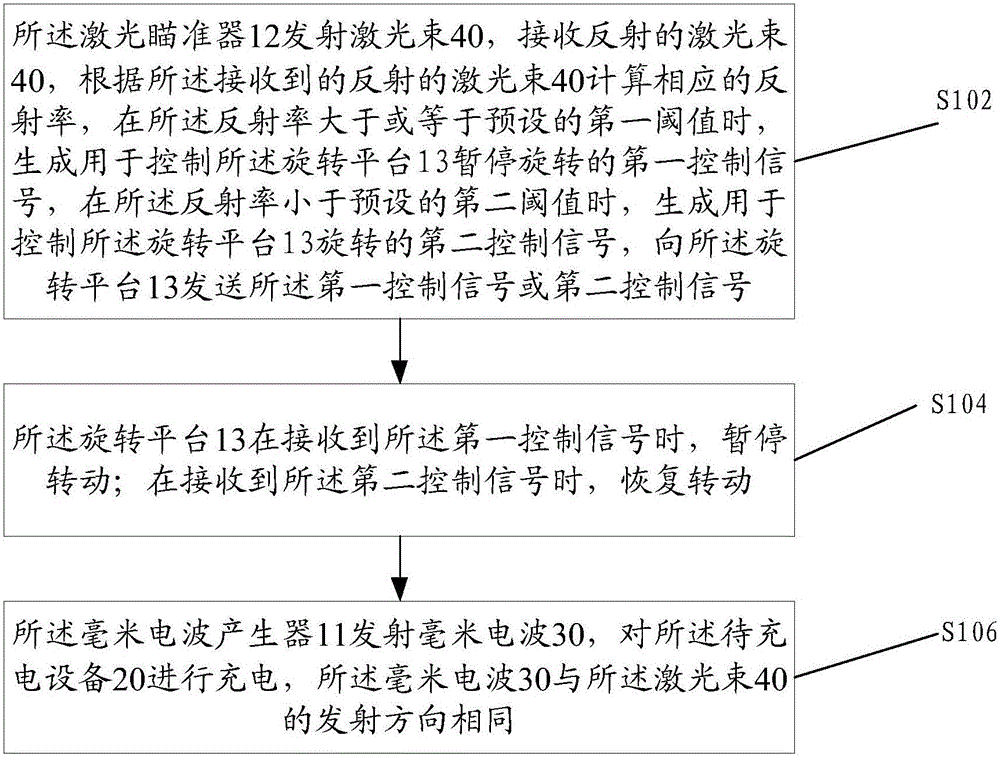
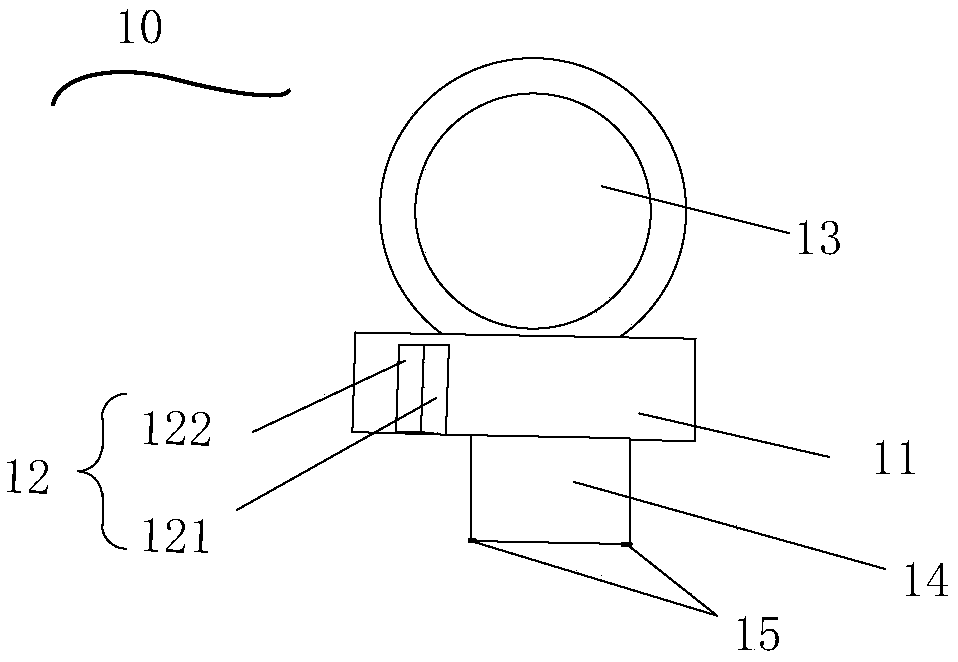
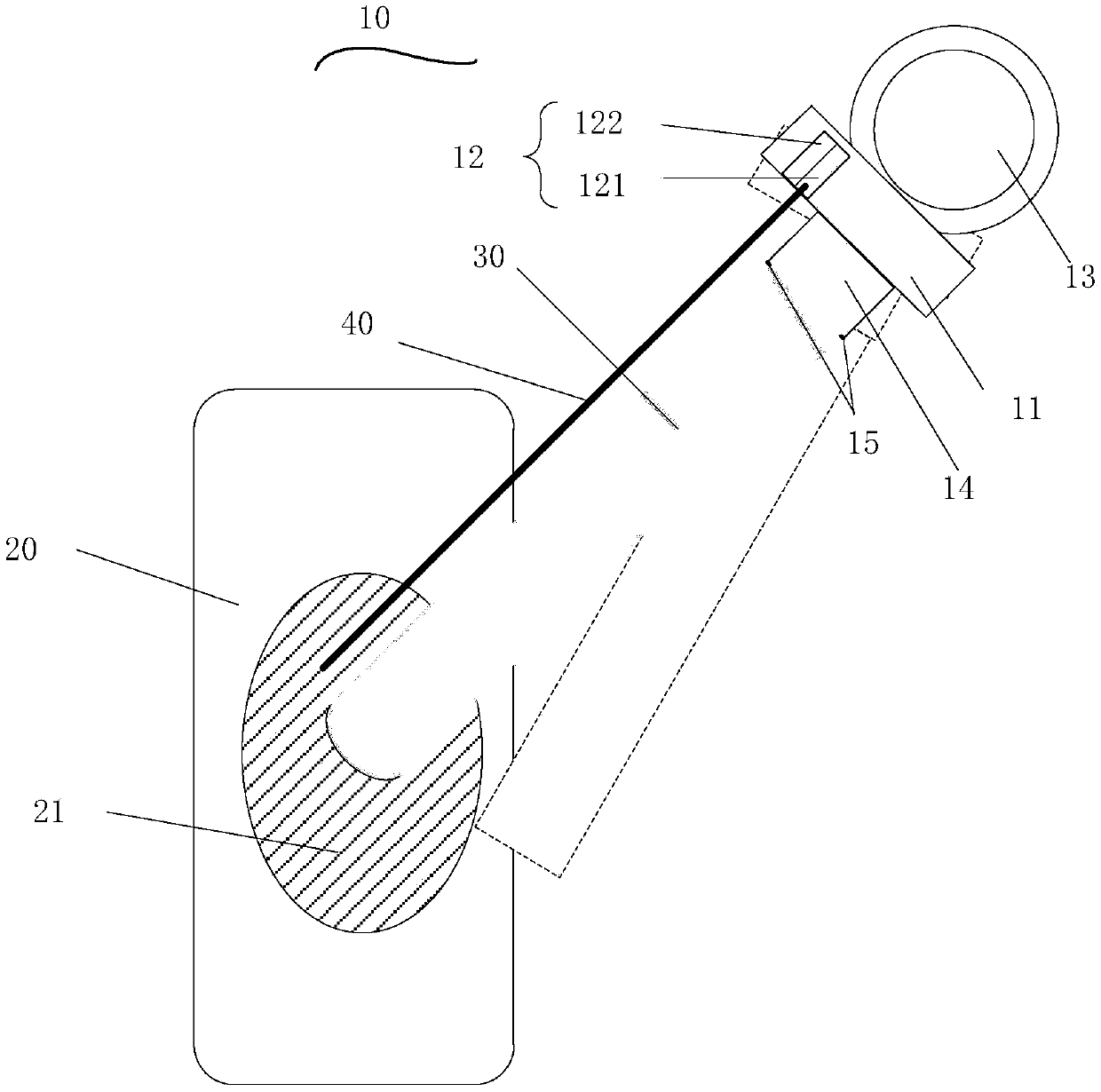
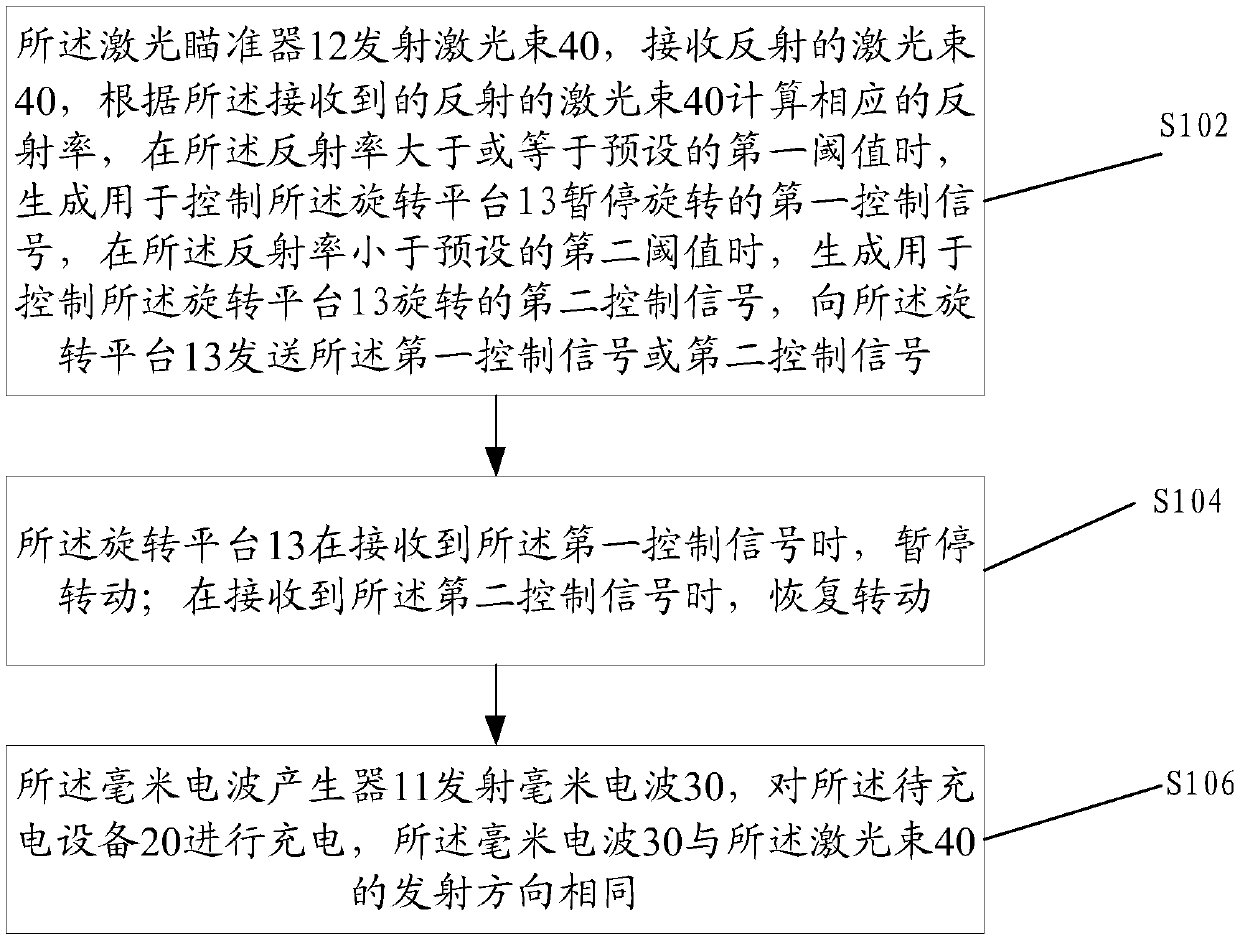
ActiveCN106451666AReduced diffraction lossReduce the impactBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerPhysicsReflectivity
The embodiment of the invention discloses a millimeter wave wireless charging device which comprises a millimeter wave generator used for generating and emitting millimeter waves, wherein the millimeter waves are used for charging to-be-charged equipment. The device further comprises a laser sight and a rotating platform, wherein the laser sight is fixedly mounted on the millimeter wave generator and used for emitting and receiving laser beams; the laser beams and the millimeter waves are the same in emission direction; the millimeter wave generator is fixedly connected to the outer surface of the rotating platform; the rotating platform is used for adjusting the direction of the millimeter waves emitted by the millimeter wave generator through rotation. The laser sight is further used for calculating the corresponding reflectivity of the received laser beams and generating a first control signal used for controlling the rotating platform to pause rotating and a second control signal used for controlling the rotating platform to rotate according to the reflectivity. After the adoption of the millimeter wave wireless charging device provided by the invention, the wireless charging efficiency can be improved.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Changing and shaping method for plate strip wave guide laser output laser beam
ActiveCN1822449AEasy to Synchronize ShapingImprove roundnessLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersLaser technologyWaveguide lasers
Present invention relates to a strip waveguide laser outgoing laser conversion reshape method. Present invention uses two cylindrical mirror or cylindrical lens constituting one dimension directional extend beam system, making extend beam to short arm direction of rectangular cross section light beam, to form foursquare cross section light beam then utilizing two spherical reflector or spherical lens to form two-dimensional directional extend beam system, to convert foursquare cross section light beam into required size, at the same time setting one round or variety shape spatial filter on intermediate focus accessory of two spherical reflector or spherical lens, to make output beam cross section becoming circular symmetry or variety shape. Reshaped light beam can be widely used to laser technology field.
Owner:BEIJING BDHLASER SCI & TECH
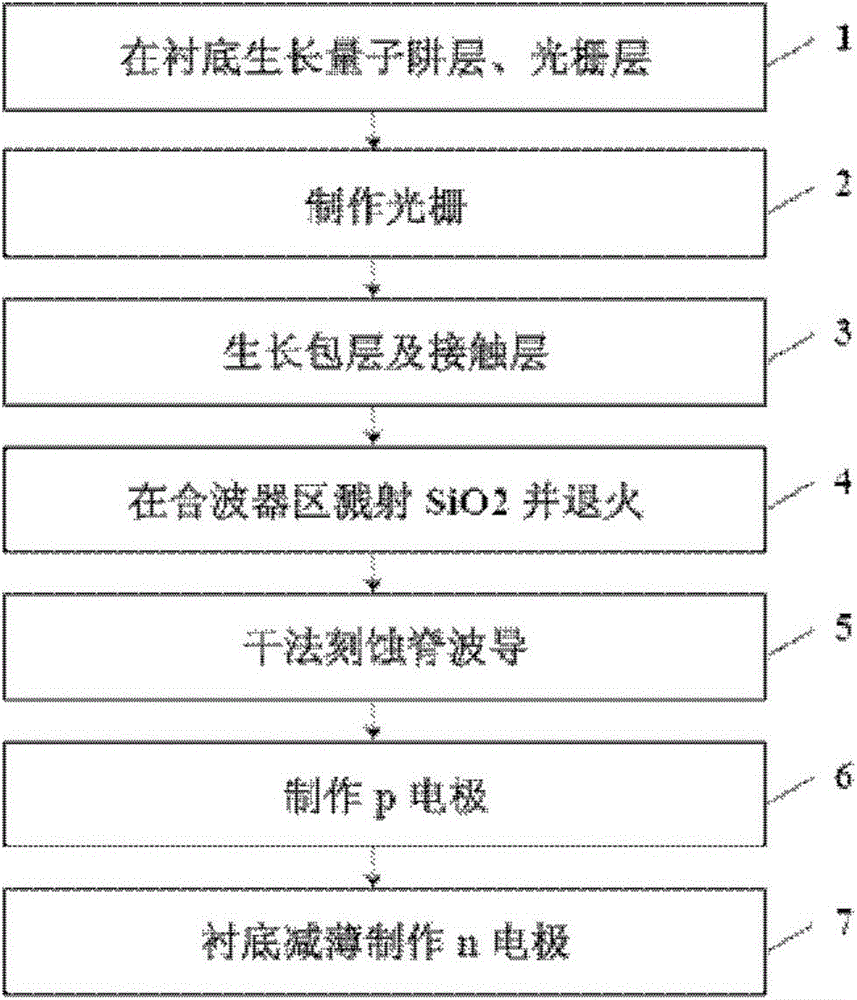
Fabrication method of monolithic integrated chip of laser array and combiner
ActiveCN103545715BSmall sizePerformance is not affectedOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsGratingLaser array
A method for manufacturing a laser array and combiner monolithic integration chip comprises the steps that an n-type InP buffer layer, an n-type AlGaInAs covering layer, an AlGaInAs multi-quantum well layer, a p-type AlGaInAs covering layer, an InP interlayer, an InGaAsP grating layer and an InP sacrificial layer are grown on an n-type InP substrate in sequence to form a substrate, an active region is arranged on one side of the base chip, and a combiner region is arranged on the other side of the substrate; P ions are injected into the InP sacrificial layer of the combiner region, and fast thermal annealing is carried out; the InP sacrificial layer is removed, and gratings are manufactured in the InGaAsP grating layer of the active region; a p-type InP covering layer and a p-type InGaAs contact layer are grown on the InGaAsP grating layer of the active region and the InGaAsP grating layer of the combiner region; the p-type InGaAs contact layer, the p-type InP covering layer, the InGaAsP grating layer and the InP interlayer are removed through dry etching, ridge type waveguides of all laser units are formed in the active region, and combiner ridge type waveguides are formed in the combiner region; p electrodes are manufactured on the ridge type waveguides of the active region; the n-type InP substrate is thinned, an n electrode is manufactured on the back face of the n-type InP substrate, and manufacturing is completed.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Converging optical apparatus, optical pickup and optical disc apparatus
InactiveCN1831976APrevent beam light from decreasingReduced diffraction lossRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansOptical pickupSignal on
A converging optical apparatus reduces the diffraction loss and realizes compatibility with three different wavelengths by means of a hologram element. The present invention provides an optical pickup for recording signals on and / or reproducing signals from a plurality of optical discs having respective protection substrates of different thicknesses for protecting the recording surfaces thereof by means of light beams of different wavelengths, the optical pickup including a first emission section that emits a light beam of a first wavelength, a second emission section that emits a light beam of a second wavelength, a third emission section that emits a light beam of a third wavelength, an objective lens for converging the light beams of the first through third wavelengths emitted respectively from the first through third emission sections on the signal recording surfaces of the optical discs, and a hologram element arranged between the first through third emission sections and the objective lens, the hologram element having two major surfaces, wherein the hologram element is provided with a reference curved surface on one of the major surfaces thereof, the reference curved surface being an aspherical shape, and a hologram section is formed on the reference curved surface.
Owner:SONY CORP
Laser resonant cavity of preventing mismatching
InactiveCN101090194AReduced diffraction lossEasy to debugOptical resonator shape and constructionResonatorResonant cavity
This invention discloses an anti-detuning laser resonator with high optical beam quality including an output mirror and a rear mirror set oppositely in co-axis, said rear mirror is in the shape of right angle taper of 90deg. This invention is helpful to realize output of laser of high beam quality having the advantages of anti-detuning, easy tuning, no hard edge difraction loss and high emission rate.
Owner:BEIJING GK LASER TECH
High-order asymmetric body mode cyclotron oscillation tube quasi-optical mode transformer
InactiveCN105356013AReduced diffraction lossHigh purityWaveguide type devicesAsymmetry bodyEdge surface
The invention discloses a high-order asymmetric body mode cyclotron oscillation tube quasi-optical mode transformer. The high-order asymmetric body mode cyclotron oscillation tube quasi-optical mode transformer comprises a reflection mirror system and further comprises a pre-bunching type opening radiator, wherein the pre-bunching type opening radiator comprises a metal waveguide tube, an inner wall of the metal waveguide tube employs a perturbation structure, and the tail end of the metal waveguide tube is a spiral notch structure. According to the high-order asymmetric body mode cyclotron oscillation tube quasi-optical mode transformer, the pre-bunching type opening radiator is employed, the radiator comprises one segment of an irregular disturbance corrugated waveguide and spiral notch, through the specific perturbation structure, a work mode in the waveguide tube is converted into superposition of a series of modes which satisfy specific amplitudes and phase relationships, Gauss distribution is further formed, and outward radiation is realized through the spiral notch, as a notch position is at a position on a Gaussian beam speckle edge surface having weakest current distribution, diffraction loss is greatly reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Long-distance resonance light wireless energy supply device based on telescope optical modulator
InactiveCN110994814AChanging the longitudinal light field distributionRealize long-distance high-power energy outputCircuit arrangementsOptical elementsResonant cavityEngineering
The invention relates to a long-distance resonance light wireless energy supply device based on a telescope optical modulator. The device comprises a transmitter and a receiver, a first retro-reflector and a gain module are arranged in the transmitter. A second retro-reflector and a photoelectric conversion module are sequentially arranged in the receiver; a resonant light resonant cavity is formed between the first retro-reflector and the second retro-reflector; a telescope optical modulator is arranged in the transmitter; and the first retro-reflector, the gain module and the telescope optical modulator are sequentially arranged along an optical path. Compared with the prior art, the long-distance resonance light wireless energy supply device has the advantages that resonance light is compressed and stabilized, diffraction loss is reduced, high-power long-distance stable energy output is achieved, and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
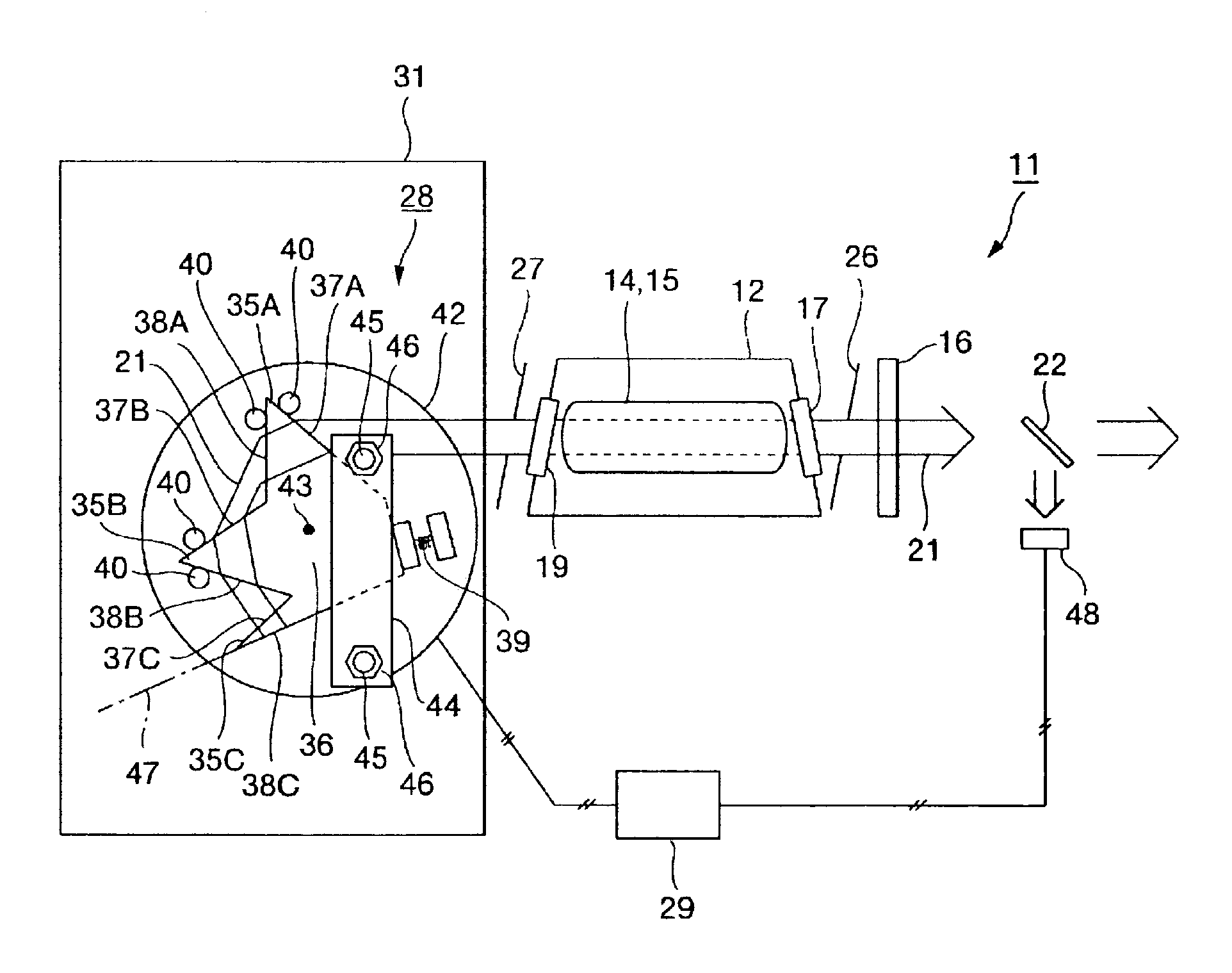
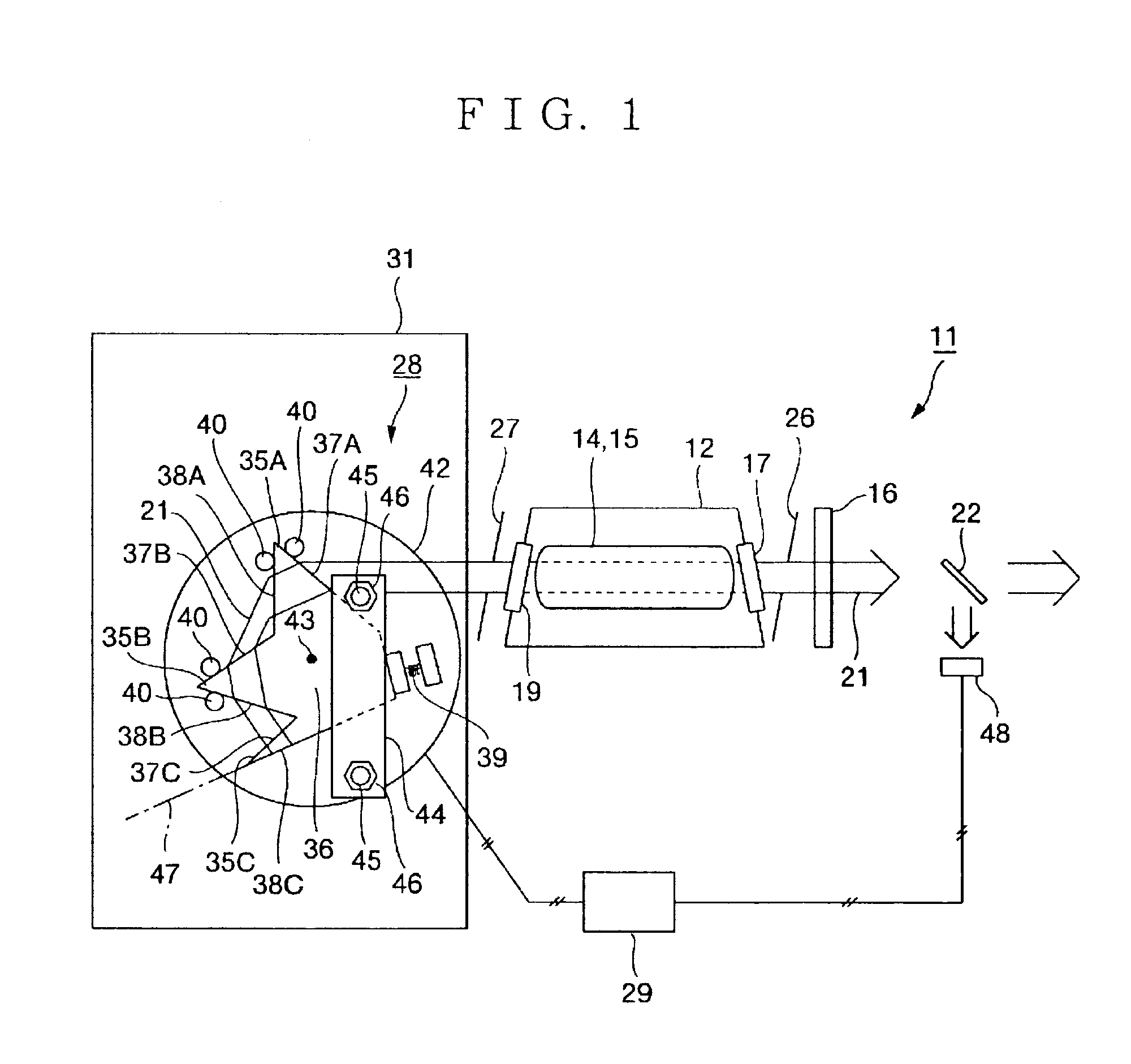
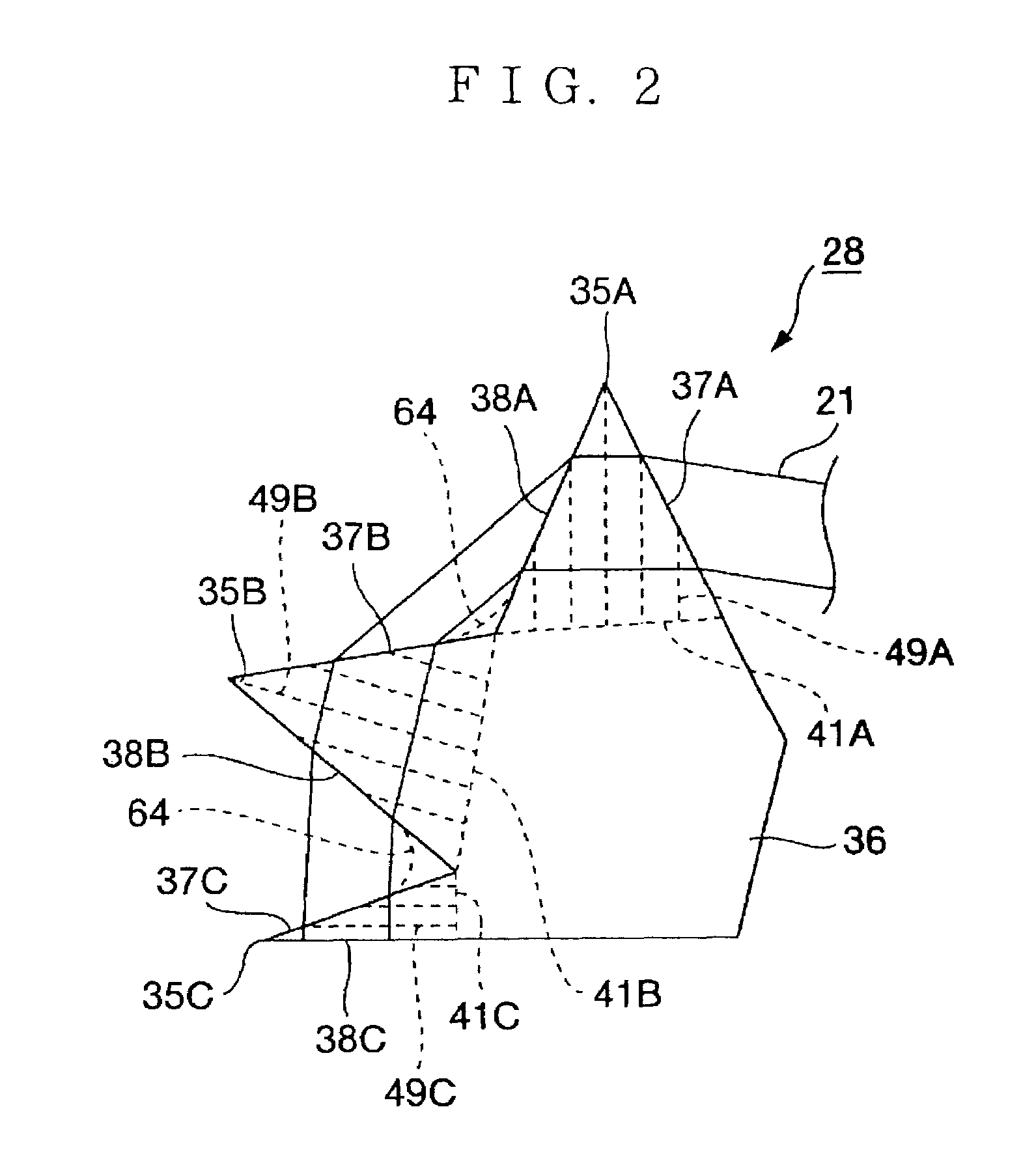
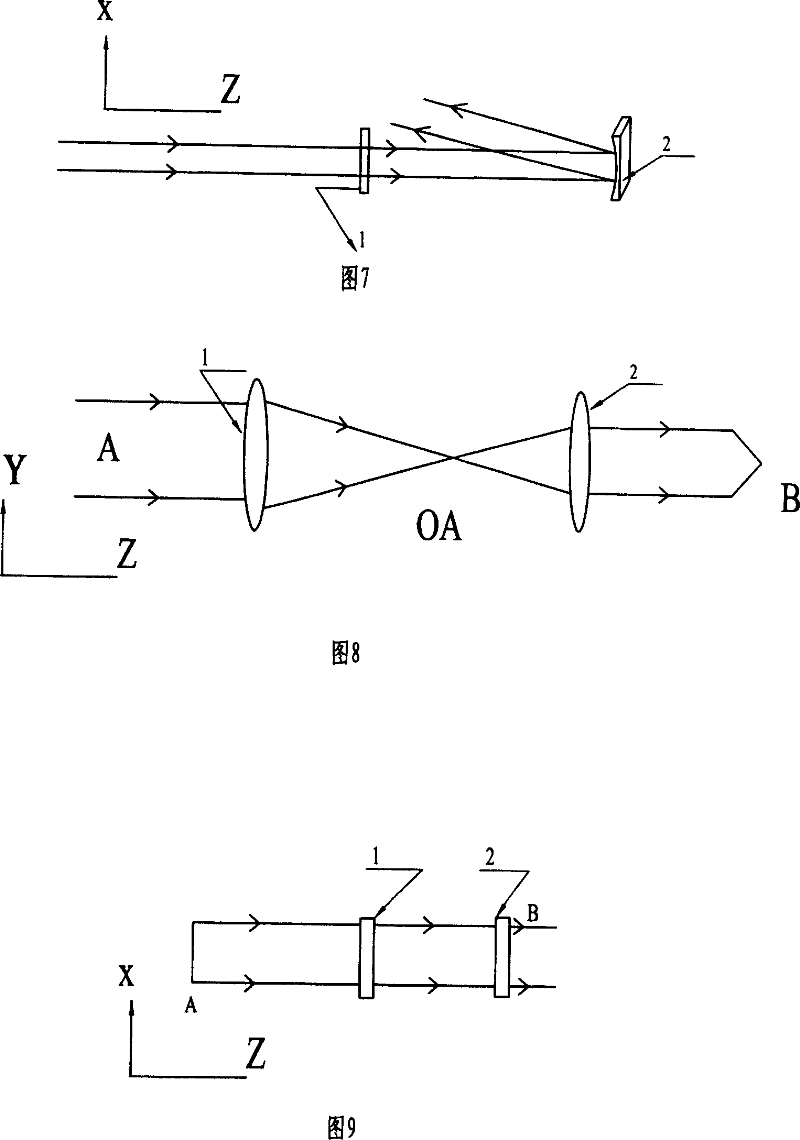
Prism unit and laser device
InactiveUS7006309B2Resonator length of becomes smallReduced diffraction lossPrismsOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser lightPrism
A prism unit, which is capable of firmly fixing a plurality of prism parts in a small space, and a laser device, which is capable of enhancing output power of laser light with use of the prism unit, are provided. For this purpose, a prism unit (28) includes a plurality of prism parts (35), which refract incident light (21), and a fixed part (36) which is fixed to or formed integrally with at least two of the plurality of prism parts. Further, a laser device includes the prism unit (28), and only a wavelength in a desired range out of a plurality of oscillation wavelengths is selectively oscillated by the prism unit.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
High-efficiency hydrogen fluoride laser grating unstable resonator
The invention relates to a high-efficiency hydrogen fluoride laser grating unstable resonator. The resonator is an annular chamber and comprises a convex-surface reflecting mirror, a concave-surface reflecting mirror, a film polaroid, a quarter wave plate, a half wave plate, plane total reflecting mirrors, a blazed grating, and a scraper mirror etc. Through change of the polarization characteristic of the oscillation light in the resonator, spherical waves in the resonator are changed into plane waves and reflected to the blazed grating, the aberration of the grating caused by diverging spherical waves of the conventional unstable resonator is reduced, the efficiency of the first-order diffracted light of the blazed grating is improved, and high-efficiency output of hydrogen fluoride single-spectral-line laser is realized.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Photon crystal tunable filter and its manufacture method
InactiveCN101210979BSmall sizeReduce unevennessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical coating apparatusFilm resistanceLight spot
The invention relates to the technical field of thermo-optical tuned filter, and discloses a photon crystal tunable filter, comprising a lower reflector, a separation wall and an upper reflector on the silicon on an insulation layer (SOI) and air ports through the upper reflector, the separation wall, the lower reflector and the top silicon of SOI. The invention also discloses a preparation methodfor the photon crystal tunable filter. With the method, the invention can reduce the uneven film temperature from the traditional heating of film resistance, lift the limit of the minimum size of input light spot caused by the diffraction loss, lower the consumption and the power of the tunable filter and accelerate the tuning speed of the tunable filter.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Solid laser resonance cavity system with automated optimization laser mode
ActiveCN101079530BQuality improvementIncrease brightnessOptical resonator shape and constructionBeam splitterHigh pressure
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Laser oscillator capable of generating light spots in any shape
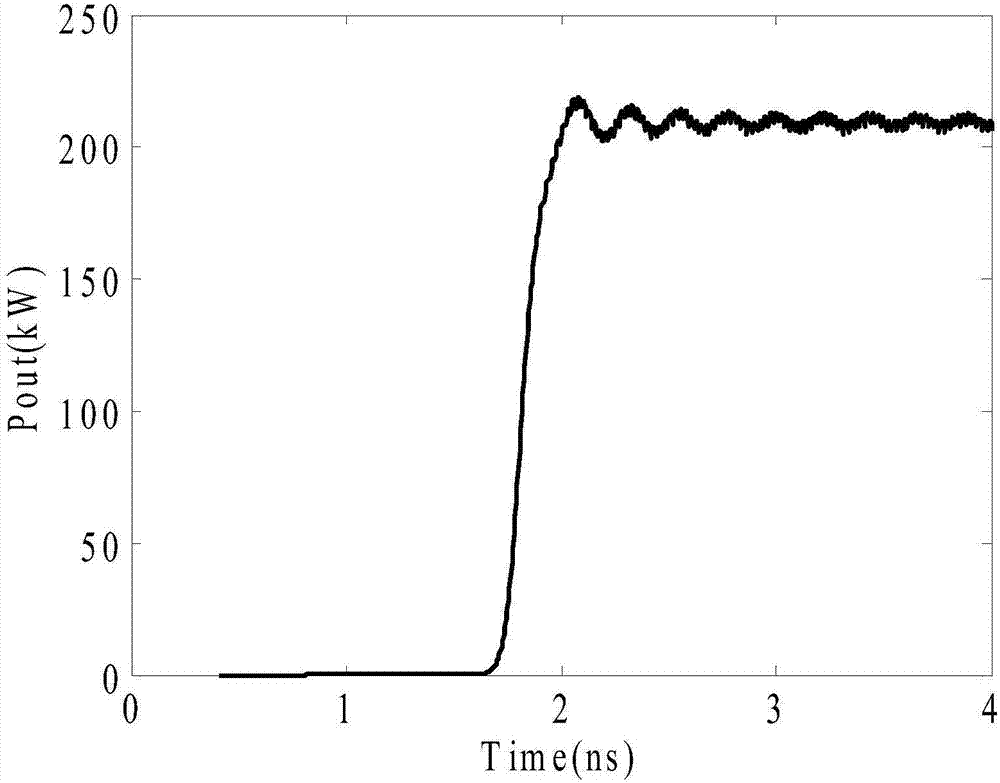
ActiveCN112928587AReduce lossDoes not affect laser efficiencyOptical resonator shape and constructionLight spotEngineering
The invention provides a laser oscillator, which adopts an imaging system as a resonant cavity, is combined with a special-shaped gain medium to generate laser spots with any shape similar to that of the laser gain medium, and has the effects of releasing thermal stress, improving laser wavefront, avoiding ghost images and the like. A resonant cavity of an imaging system can reduce the diffraction loss (high-frequency space information loss) of a high-order mode, so that the high-order mode and a low-order mode can form oscillation in the cavity without difference, which is totally different from the mode that only a low-order transverse mode of a traditional laser can oscillate, and therefore, any laser spot similar to the gain medium in shape can be generated according to the shape of the gain medium. The laser with any light spot shape can be used in the field of special laser processing or laser medical treatment and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Device and method for millimeter wave wireless charging
ActiveCN106451666BSmall divergenceIncrease profitBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerControl signalMillimeter
The embodiment of the invention discloses a millimeter wave wireless charging device which comprises a millimeter wave generator used for generating and emitting millimeter waves, wherein the millimeter waves are used for charging to-be-charged equipment. The device further comprises a laser sight and a rotating platform, wherein the laser sight is fixedly mounted on the millimeter wave generator and used for emitting and receiving laser beams; the laser beams and the millimeter waves are the same in emission direction; the millimeter wave generator is fixedly connected to the outer surface of the rotating platform; the rotating platform is used for adjusting the direction of the millimeter waves emitted by the millimeter wave generator through rotation. The laser sight is further used for calculating the corresponding reflectivity of the received laser beams and generating a first control signal used for controlling the rotating platform to pause rotating and a second control signal used for controlling the rotating platform to rotate according to the reflectivity. After the adoption of the millimeter wave wireless charging device provided by the invention, the wireless charging efficiency can be improved.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Method for measuring transmission loss of optical element
ActiveCN101995328BSolve the measurement problem of weak absorption lossIncrease amplitudeTransmissivity measurementsTesting optical propertiesResonant cavityOptical axis
The invention relates to a method for measuring transmission loss of an optical element. The method comprises the following steps that: continuous laser is reshaped through a mode matching lens, and then enters an optical resonant cavity along an optical axis; two iris diaphragms of which the standoff distance is slightly larger than the thickness of the optical element to be measured are placed into the optical resonant cavity, wherein the clear aperture is less than the aperture of the optical element to be measured; after a shutoff laser beam is triggered, an output signal of the optical resonant cavity is recorded to fit fading time tau 0; the optical element to be measured is placed between the two iris diaphragms in the optical resonant cavity; the optical element to be measured is adjusted to make the surface of the optical element vertical to the optical axis; the output signal of the optical resonant cavity is recorded to fit fading time tau 1; the angle of the optical element to be measured is adjusted to make directly reflected light on the surface escape from the optical resonant cavity; the output signal of the optical resonant cavity is recorded to fit fading time tau 2; the absorption loss A of the optical element to be measured can be acquired by using the tau 0 and the tau 1; and the surface antireflective film residual reflectance R of the optical element to be measured is acquired by using the tau 1 and the tau 2. The method has the advantages of simple structure, high measurement precision, low system cost and the like.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
An optical resonant cavity composed of non-parallel mirrors and a method for generating optical resonance
ActiveCN107508142BReduce line widthHigh Q valueLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersResonant cavityLine width
The invention provides an optical resonant cavity formed by non-parallel reflecting mirrors and a method for generating optical resonance. The optical resonant cavity comprises a top reflecting mirror and a bottom reflecting mirror, and is characterized in that a cavity is formed between the top reflecting mirror and the bottom reflecting mirror, and the cavity is filled with a medium; the top reflecting mirror comprises two oppositely arranged plane reflecting mirrors, and the two plane reflecting mirrors have the same inclination angle relative to the bottom reflecting mirror; and the bottom reflecting mirror is a plane reflecting mirror. According to the invention, the resonant cavity is provided with the inclined top reflecting mirror, so that an incident beam perpendicular to the bottom reflecting mirror is enabled to be increased in optical path during reproduction in the process of advancing in the resonant cavity. The optical resonant cavity provided by the invention has different resonance conditions from a parallel plane resonant cavity, and can acquire small linewidth and a greater Q-value. In addition, the optical field energy can be effectively controlled within a certain area, and the diffraction loss is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Side grating based light coupling system
InactiveUS20170146731A1Reduce secondary diffraction loss lossReduce loss scattering lossLaser detailsCladded optical fibreTotal internal reflectionLaser array
A side grating based light coupling system comprises an optical fiber, a side grating disposed on one side of the lateral wall of the optical fiber, and a laser array disposed adjacent to the other side of the lateral wall of the optical fiber. The side grating comprises a plurality of grating elements arranged in a non-uniform arrangement. The laser array for generating a laser beam towards and passes through the optical fiber, and the laser beam is converted into at least one laser beam through the plurality grating elements. The diffraction efficiencies of the converted laser beams are different. The converted laser beams propagate inside the optical fiber based on total internal reflection. The plurality of grating elements of the side grating are heterogeneous arrangement without loading the optical collimating lens, and can reduce scattering loss by controlling the asymmetric diffraction efficiency, to improve optical coupling efficiency.
Owner:NAT TAIPEI UNIV OF TECH
Changing and shaping method for plate strip wave guide laser output laser beam
ActiveCN100356637CEasy to Synchronize ShapingImprove roundnessLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersLaser technologyWaveguide lasers
Present invention relates to a strip waveguide laser outgoing laser conversion reshape method. Present invention uses two cylindrical mirror or cylindrical lens constituting one dimension directional extend beam system, making extend beam to short arm direction of rectangular cross section light beam, to form foursquare cross section light beam then utilizing two spherical reflector or spherical lens to form two-dimensional directional extend beam system, to convert foursquare cross section light beam into required size, at the same time setting one round or variety shape spatial filter on intermediate focus accessory of two spherical reflector or spherical lens, to make output beam cross section becoming circular symmetry or variety shape. Reshaped light beam can be widely used to laser technology field.
Owner:BEIJING BDHLASER SCI & TECH
Laser gain structure and laser
PendingCN109378693AEfficient thermal managementImprove energy storage performanceLaser cooling arrangementsHigh energyCooling effect
The invention discloses a laser gain structure and a laser. The laser gain structure includes gain tubes for increasing light beam energy under the action of a pump source. A first fluid passage is formed in each gain tube. The outside of each gain tube is wrapped in a sealing tube. A gap exists between each sealing tube and the corresponding gain tube. A second fluid passage is formed in each gap. The first fluid passages and the second fluid passages are used for passing a cooling medium so as to make the temperature of the outside of the gain tubes and the inside of the gain tubes tend to coincide. The outside of each gain tube is also wrapped in a reflective surface for total reflection of light beams. When the laser gain structure of the embodiments is used for increasing the laser energy, diffraction loss of the laser beams in a propagation process can be reduced. The gain tubes are better in cooling effect and higher in energy storage so as to achieve output with higher energy.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com