Laser oscillator capable of generating light spots in any shape
A laser oscillator, a technology of arbitrary shape, applied in the field of lasers, can solve the problems of laser beam quality degradation, affecting laser efficiency, wavefront distortion, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing diffraction loss, high laser power, and releasing thermal stress
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
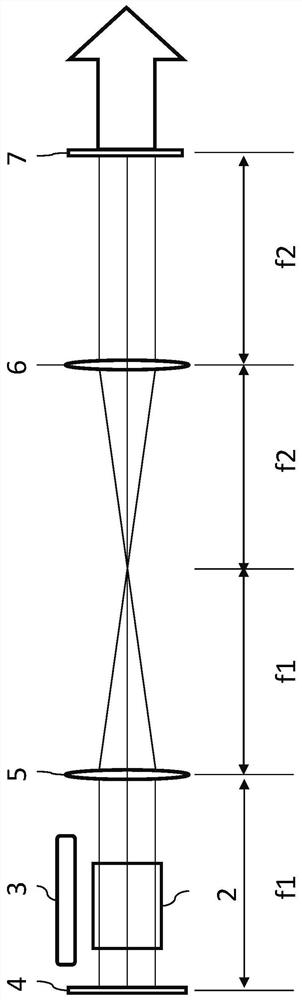
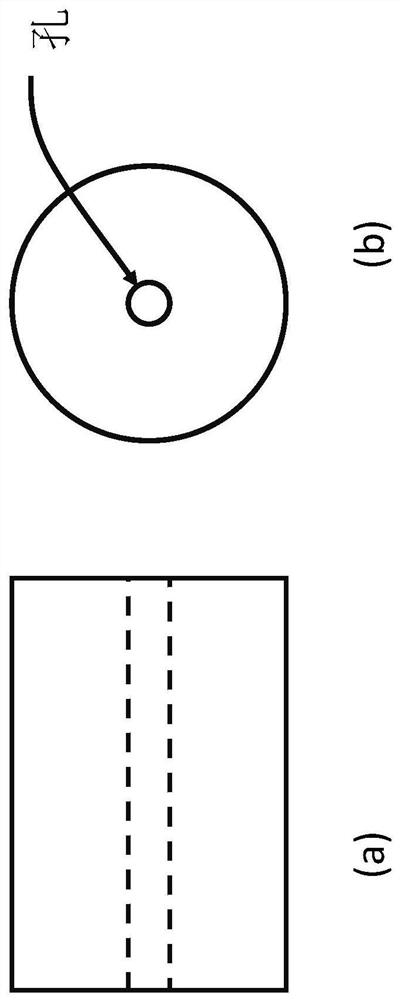
[0036] This embodiment is a laser oscillator of a 4F imaging resonator, such as figure 2 shown. The resonant cavity 1 of the imaging structure is composed of a total reflection mirror, an output mirror and a lens, wherein the object plane is a total reflection mirror, the image plane is an output mirror, and two lenses are used as frequency domain conversion elements. image 3 It is the anisotropic gain medium selected in this embodiment, with holes in the middle area. Although the center (or other places) of the shaped gain medium is empty, in the 4F imaging resonator, the gain medium is located between the lens and the object plane, so the shape of the gain medium can be imaged in the imaging plane, so the shape of the gain medium can be Determines the shape of the output spot. The higher the cutoff frequency of the 4F imaging system, the more high-order modes it can accommodate. The loss of high-order modes and low-order modes is determined by the structure of the imagin...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Figure 10 It is a schematic diagram of an embodiment in which a binary optical element 1 ( 8 ) and a binary optical element 2 ( 9 ) are used to replace ordinary lenses. The binary optical lens has the same Fourier transformation effect as the traditional lens, and can completely replace the traditional lens, and perform frequency conversion to form a frequency domain surface. If there are others that can replace the lens to generate the frequency domain surface, it is also included in the scope of the patent claims.
Embodiment 3
[0044] Such as Figure 11 As shown, on the basis of Embodiment 1, a filter hole is added on the frequency spectrum for mode limiting, and the shape of the filter hole is circular. The laser spot produced is as Figure 12 As shown, it can be seen that the laser spot has no burrs on the edge of the spot compared to the laser spot without pinholes, indicating that the high-frequency information (the edge of the object) has been filtered by the filter pinhole.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com