Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
264 results about "Laser beam quality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
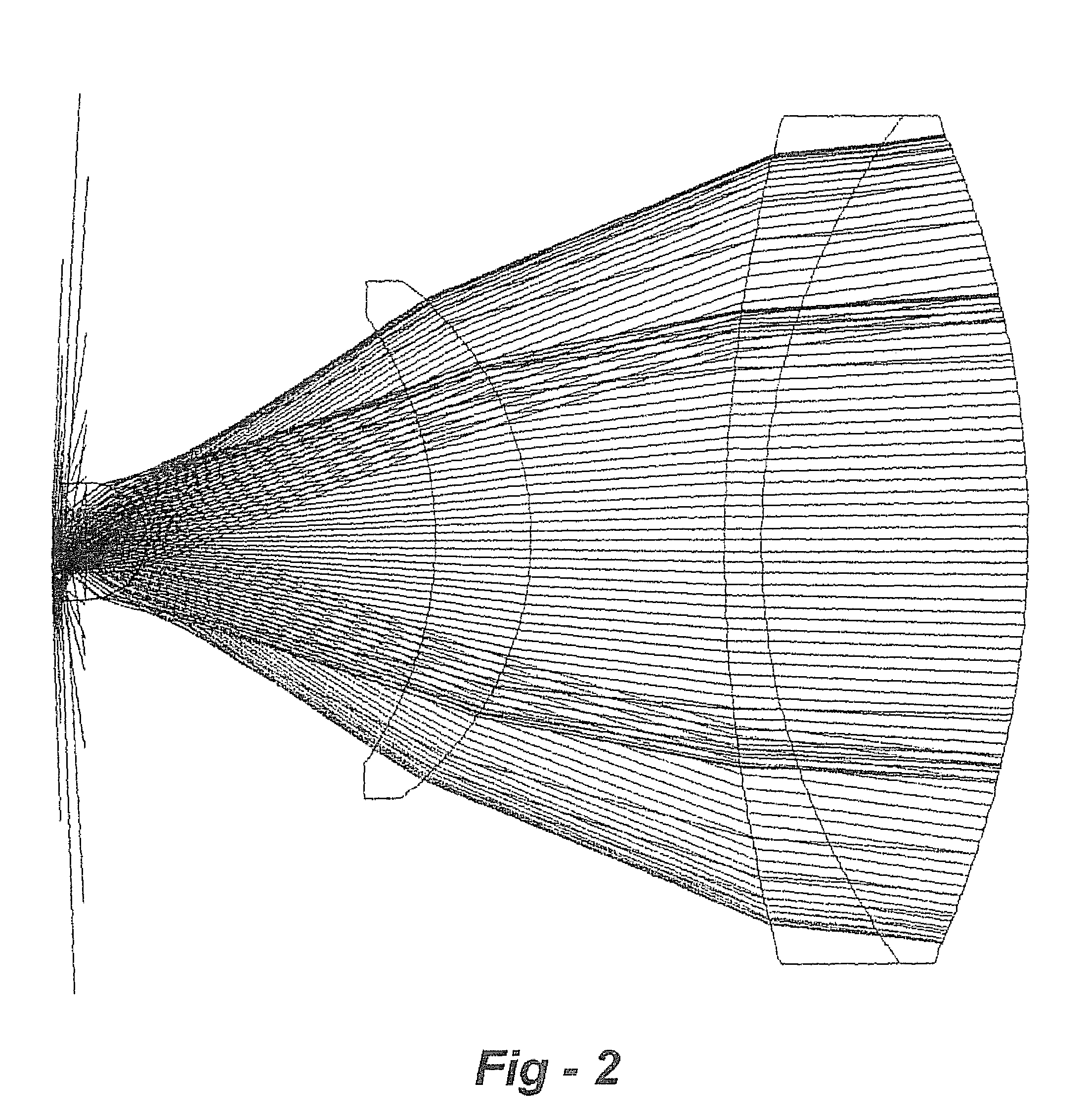
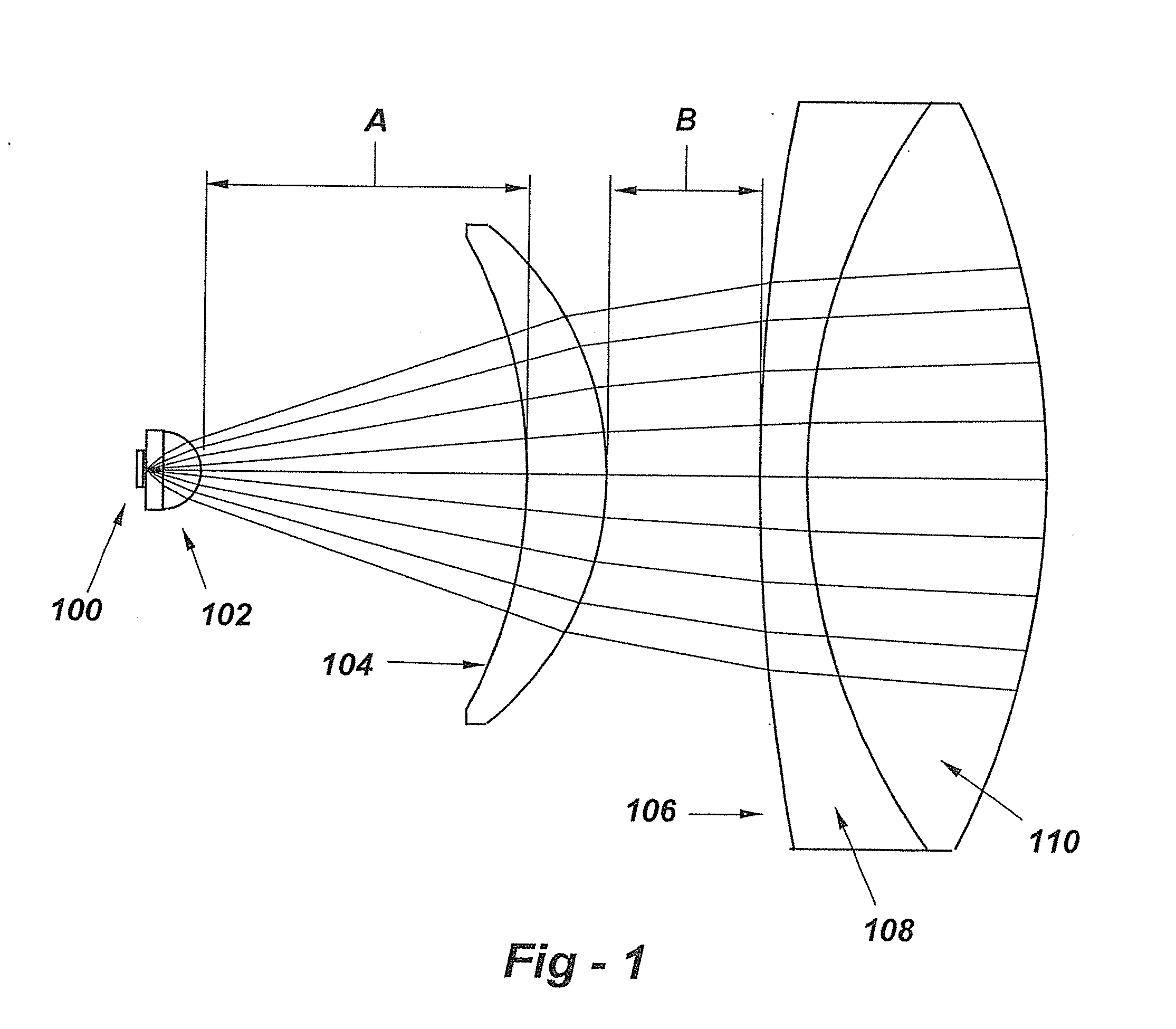
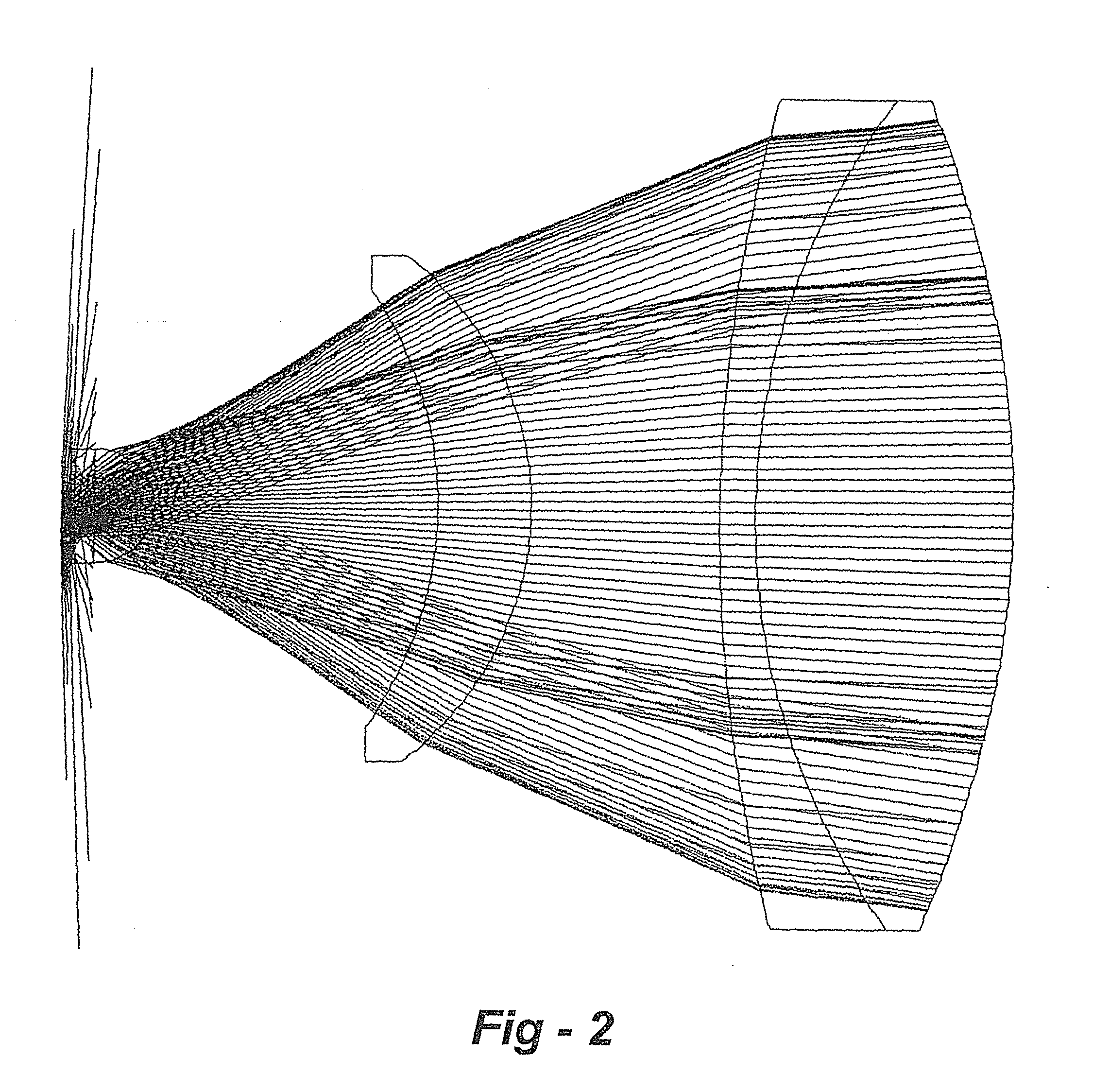
In laser science, laser beam quality defines aspects of the beam illumination pattern and the merits of a particular laser beam's propagation and transformation properties (space-bandwidth criterion). By observing and recording the beam pattern, for example, one can infer the spatial mode properties of the beam and whether or not the beam is being clipped by an obstruction; By focusing the laser beam with a lens and measuring the minimum spot size, the number of times diffraction limit or focusing quality can be computed.
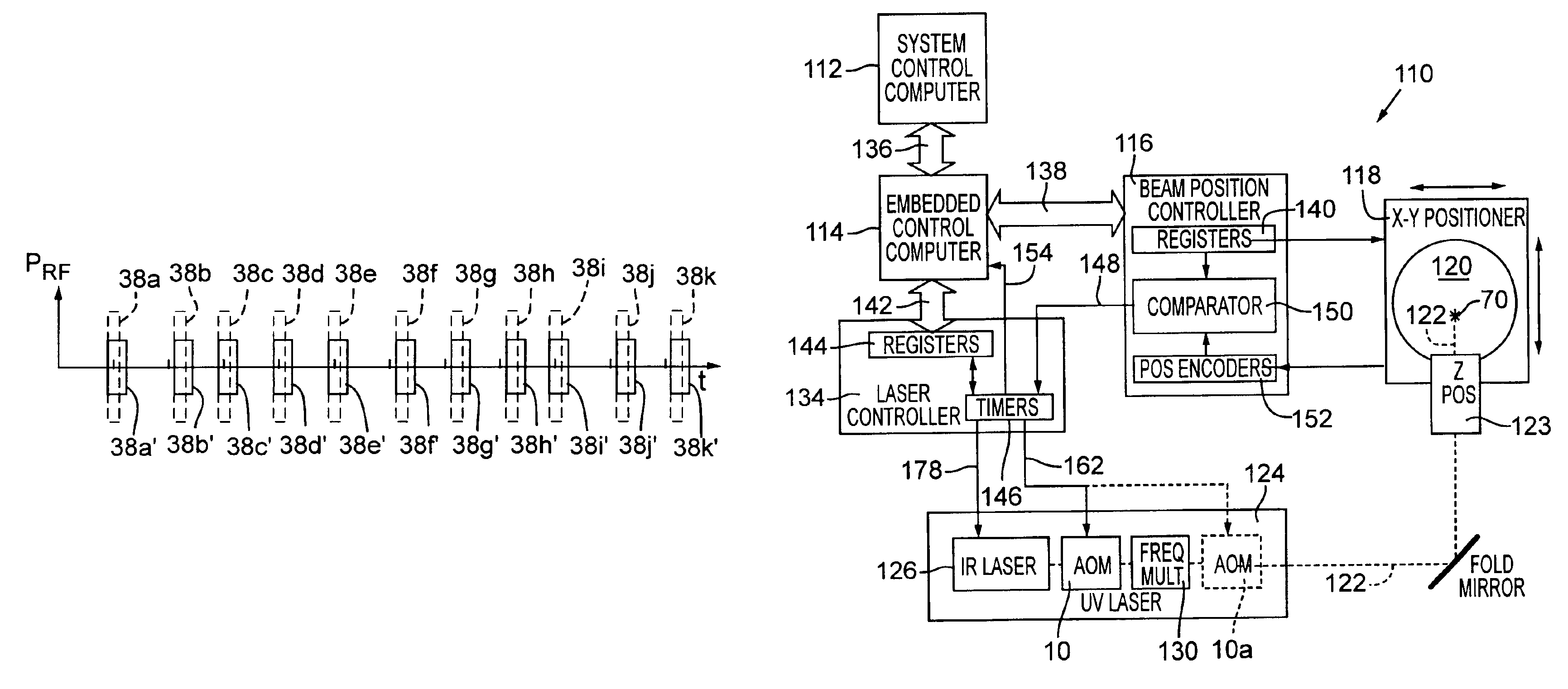
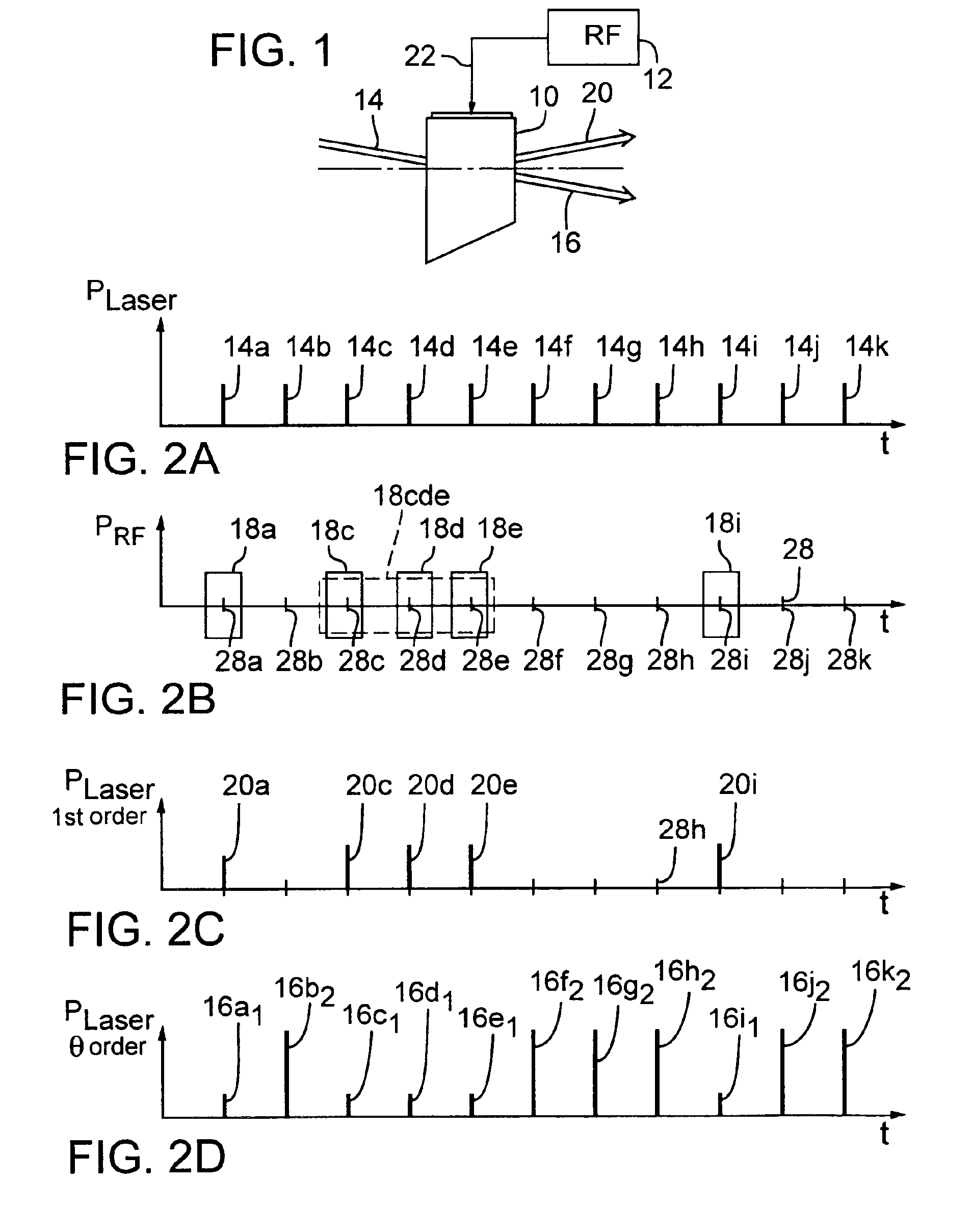
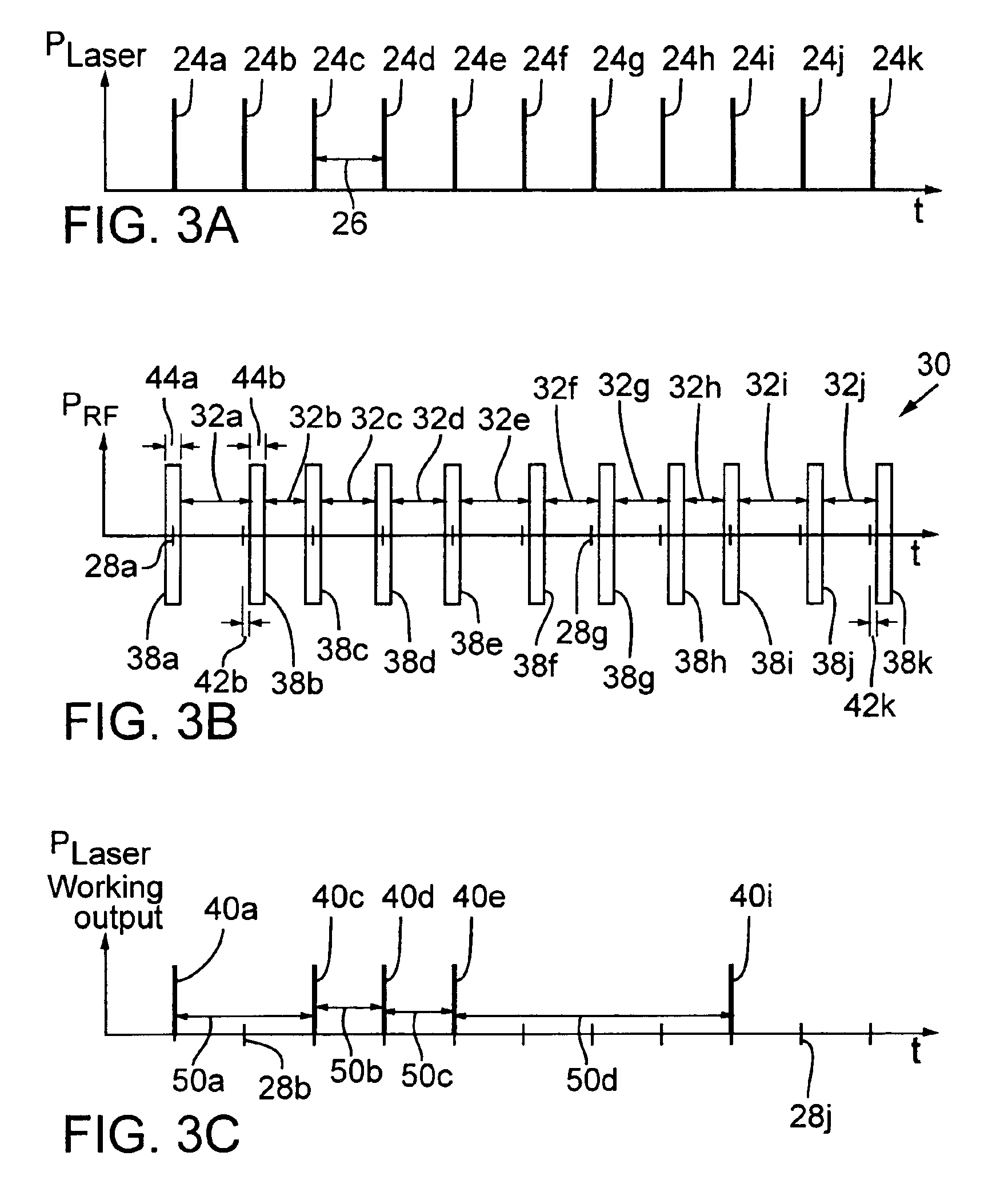
Laser pulse picking employing controlled AOM loading
ActiveUS6947454B2Constant RF powerConstant thermal loadingExcitation process/apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPulse energyOptoelectronics
A laser (126) and an AOM (10) are pulsed at substantially regular and substantially similar constant high repetition rates to provide working laser outputs (40) with variable nonimpingement intervals (50) without sacrificing laser pulse-to-pulse energy stability. When a working laser output (40) is demanded, an RF pulse (38) is applied to the AOM (10) in coincidence with the laser output (24) to transmit it to a target. When no working laser output (40) is demanded, an RF pulse (38) is applied to the AOM (10) in noncoincidence with the laser output (24) so it gets blocked. So the average thermal loading on the AOM (10) remains substantially constant regardless of how randomly the working laser outputs (40) are demanded. The AOM (10) can also be used to control the energy of the working laser output (40) by controlling the power of the RF pulse (38) applied. When the RF power is changed, the RF duration (44) of the RF pulse (38) is modified to maintain the constant average RF power. Consistent loading on the AOM (10) eliminates deterioration of laser beam quality and laser beam pointing accuracy associated with thermal loading variation on the AOM (10) and is advantageous for applications such as IC chip link processing where stable working laser outputs (40) with variable output intervals (50) are needed.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Laser beam machining method for wafer
ActiveUS20090004828A1Carry-out smoothly and easilyMachining efficiency can be moreSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFine working devicesSplit linesLaser beam machining
A laser beam machining method for a wafer, wherein an operation of irradiating the inside of a wafer with a laser beam L along each of planned dividing lines is repeated a plural number of times from a position proximate to a back-side surface of the wafer toward a face-side surface of the wafer so that a plurality of composite layers each including a denatured layer and a cracked layer extending from the denatured layer toward the face-side surface are formed stepwise at intervals (first laser beam irradiation step). Subsequently, each of some of non-cracked layers between the composite layers is irradiated with the laser beam L so as to extend the cracked layer of a given one of the composite layers and to cause the cracked layer to reach the denatured layer of the composite layer which is adjacent to the given one composite layer. The denatured layers and the cracked layers which are sufficient for enabling the wafer to be split are formed by a reduced number of laser beam irradiation operations.
Owner:DISCO CORP
LED illuminator with improved beam quality
Owner:GEN SCI
Semiconductor structure processing using multiple laterally spaced laser beam spots delivering multiple blows
InactiveUS20100089881A1Increase intimacySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser beam welding apparatusTime structureSemiconductor structure
Methods and systems process a semiconductor substrate having a plurality of structures to be selectively irradiated with multiple laser beams. The structures are arranged in a plurality of substantially parallel rows extending in a generally lengthwise direction. The method generates a first laser beam that propagates along a first laser beam axis that intersects a first target location on or within the semiconductor substrate. The method also generates a second laser beam that propagates along a second laser beam axis that intersects a second target location on or within the semiconductor substrate. The second target location is offset from the first target location in a direction perpendicular to the lengthwise direction of the rows by some amount such that, when the first target location is a structure on a first row of structures, the second target location is a structure or between two adjacent structures on a second row distinct from the first row. The method moves the semiconductor substrate relative to the first and second laser axes in a direction approximately parallel to the rows of structures, so as to pass the first target location along the first row to irradiate for a first time selected structures in the first row, and so as to simultaneously pass the second target location along the second row to irradiate for a second time structures previously irradiated by the first laser beam during a previous pass of the first target location along the second row.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Device for an atomic clock
ActiveUS20120212298A1Apparatus using atomic clocksPulse automatic controlPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A device for an atomic clock, including: a laser source (102) that generates a laser beam; a splitter (101) that makes it possible to divert and allow a portion of the laser beam to pass therethrough in accordance with a predefined percentage; a quarter-wave plate (105) that modifies the linear polarization of the laser beam into circular polarization and vice versa; a gas cell arranged on the circular polarization laser beam; a mirror (107) sending the laser beam back toward the gas cell (106); a first photodetector (108a), and a polarizer (103) arranged between the laser beam outlet and the splitter in order to protect the laser source from the retroreflections emitted by different optical elements constituting the device.
Owner:ROLEX SA
LED illuminator with improved beam quality
An improved illuminator with an adjustable beam pattern to be worn by medical and dental professionals includes a housing, a light-emitting diode (LED) disposed in the housing outputting light through a distal opening in the housing, an achromatic doublet lens mounted in the opening in the housing, and a singlet lens disposed between the LED and the achromatic lens. The distance between the singlet lens and the doublet lens may be adjustable, and / or distance between the LED and the singlet lens may be adjustable, through a threaded connections, for example.
Owner:GEN SCI
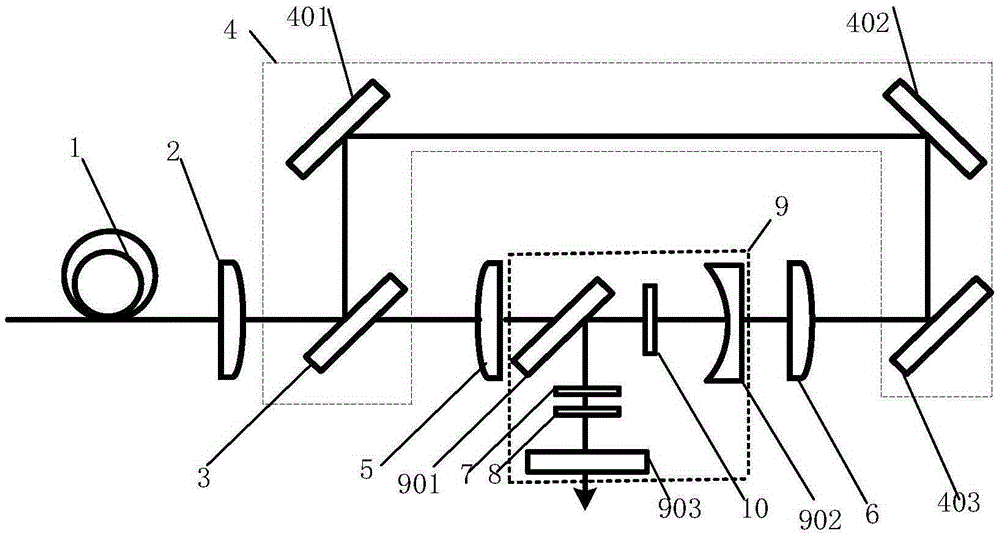
Apparatus for improving light beam quality of solid laser by using in-chamber adaptive optical technology
InactiveCN1804711AHigh beam qualityChange output modeLaser detailsNon-linear opticsBeam splitterWavefront sensor
The invention relates to a device for using intracavity self-adaptive optical technique to improve the solid laser beam quality which is formed by a He-Ne laser, a variable density fading disk, a beam-amplifying system, a distorting lens, a solid laser yield medium, a matching beam-amplifying concave mirror, a beam splitter, an output coupling mirror, a Hageman wave front sensor, a power meter, a high pressure amplifier, a high speed processor and a host computer, wherein the He-Ne laser sent light beacon is leaded into the solid laser yield medium by the concave mirror and is divided into two paths of signal by the beam splitter, one path uses the output coupling mirror to output the laser beam of the solid laser beam; the other path uses the Hageman wave front sensor to real-time probe the intracavity image differential information and uses the high speed processor to process it and obtains the corresponding voltage control signal; it adds the voltage to the deformation driver so that it can compensate the intracavity image difference of the solid laser.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High beam quality signal light fiber beam combiner and manufacture method thereof
The invention provides a high beam quality signal light fiber beam combiner and a manufacture method thereof. The beam combiner comprises at least one signal optical fiber which forms one group and output optical fibers. The signal optical fiber comprises an optical fiber cladding and a fiber core, the fiber core comprises a fiber core body and a fiber core through connection portion, one end of the fiber core through connection portion is connected with one end of the fiber core body, and the cross sectional area of the fiber core through connection portion gradually increases from one end to the other end to enable the fiber core through connection portion to approximately be conical, the refractive index of the fiber core through connection portion gradually reduces from one end to the other end, and a V parameter is invariant. One ends of the output optical fibers are connected with the other end of the fiber core through connection portion of the group of the signal optical fiber. The high beam quality signal light fiber beam combiner adopts the fiber core through connection portion to enable the duty ratio of signal light at a welding position of a plurality of optical fibers and the output optical fibers to achieve 1, enables combined output laser angle relative packing ratio (angles of 1) to be greatly reduced, and effectively promotes output laser beam quality.
Owner:WUXI RES INST OF APPLIED TECH TSINGHUA UNIV
High brightness dense wavelength multiplexing laser
ActiveUS20150104180A1Efficiency lossDegrades beam qualityLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsResonant cavityMultiplexing
The present disclosure describes systems and methods for beam wavelength stabilization and output beam combining in dense wavelength multiplexing (DWM) systems. Systems and methods are described for performing beam wavelength stabilization and output beam combining in DWM systems while achieving increased wall-plug efficiency and enhanced beam quality. Interferometric external resonator configurations can be used to greatly increase the brightness of DWM system output beams by stabilizing the wavelengths of the beams emitted by the emitters of the DWM laser source. The resonant cavities described by the present disclosure provide advantages over the prior art in the form of decreased cost, increased wall plug efficiency and increased output beam quality. Particular implementations of the disclosure achieve increased wall plug efficiency and increased output beam quality through a combination of innovative cavity designs and the utilization of reflection diffraction elements for beam combining.
Owner:TRUMPF LASER GMBH CO KG
Fiber laser beam quality measurement method base on photoelectric detector and CCD camera
ActiveCN105784334ASolve the defect that it is difficult to evaluate the quality of large-scale fiber laser beamsThe principle is simple and correctTesting optical propertiesBeam splitterMeasuring instrument
The invention relates to a fiber laser beam quality measurement method base on a photoelectric detector and a CCD camera. The method comprises: an optical axis of a measured light beam is adjusted to be in a horizontal state, and a beam splitter is arranged at an optical path and thus the measured light beam is divided into two parts that are used for measuring a near field and a far field of the light beam. On the basis of measurement of the near field and the far field of the measured light beam as well as a related data analysis, a near field width and a far field width of the light beam are calculated, so that light beam quality M <2> x and light beam quality M <2>y at a corresponding direction are obtained by calculation. An M<2> factor expression based on near field and far field light intensity distribution of a beam is deduced in theory, so that a defect that the existing M<2> factor measuring instrument can not evaluate the large-size fiber laser beam quality easily can be overcome. The provided fiber laser beam quality measurement method is suitable for fiber laser beam quality measurement including a few of high order modes and some cut fiber laser beam quality measurement.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Laser beam light balancing and shaping and speckle eliminating integrated device
InactiveCN102103270ACompact structureImprove light energy utilizationDiffraction gratingsLight energyLaser light
The invention provides a laser beam light balancing and shaping and speckle eliminating integrated device, which belongs to the field of laser displaying and illuminating and particularly relates to the fields of laser projection displaying and infrared laser night viewing. In the device, laser beam light balancing and shaping and speckle eliminating are considered uniformly, speckles are eliminated by adopting a rotary holographic scattering device, light balancing and shaping are realized by adopting a pure phase diffusion apparatus, and a holographic scattering apparatus, a micro direct current motor, the pure phase diffusion apparatus and a Fourier transform lens are connected and fixed into an entire body with a compact structure, so that the aims of balancing and shaping laser beam light and eliminating speckles are fulfilled simultaneously. The holographic scattering apparatus and the pure phase diffusion apparatus are thin-sheet diffusion optical apparatuses, have small sizes and are thin and light, so that optical-mechanical-electrical integration and miniaturization are easy to realize; moreover, the integrated device is made of a double refraction material, so that the integrated device has polarization maintaining performance, makes full use of the inherit linear polarization property of laser light and further increases the utilization ratio of light energy.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
LED illuminator with improved beam quality
ActiveUS20110122598A1Existing designLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceLight beamBeam pattern
Owner:GEN SCI
Laser marker
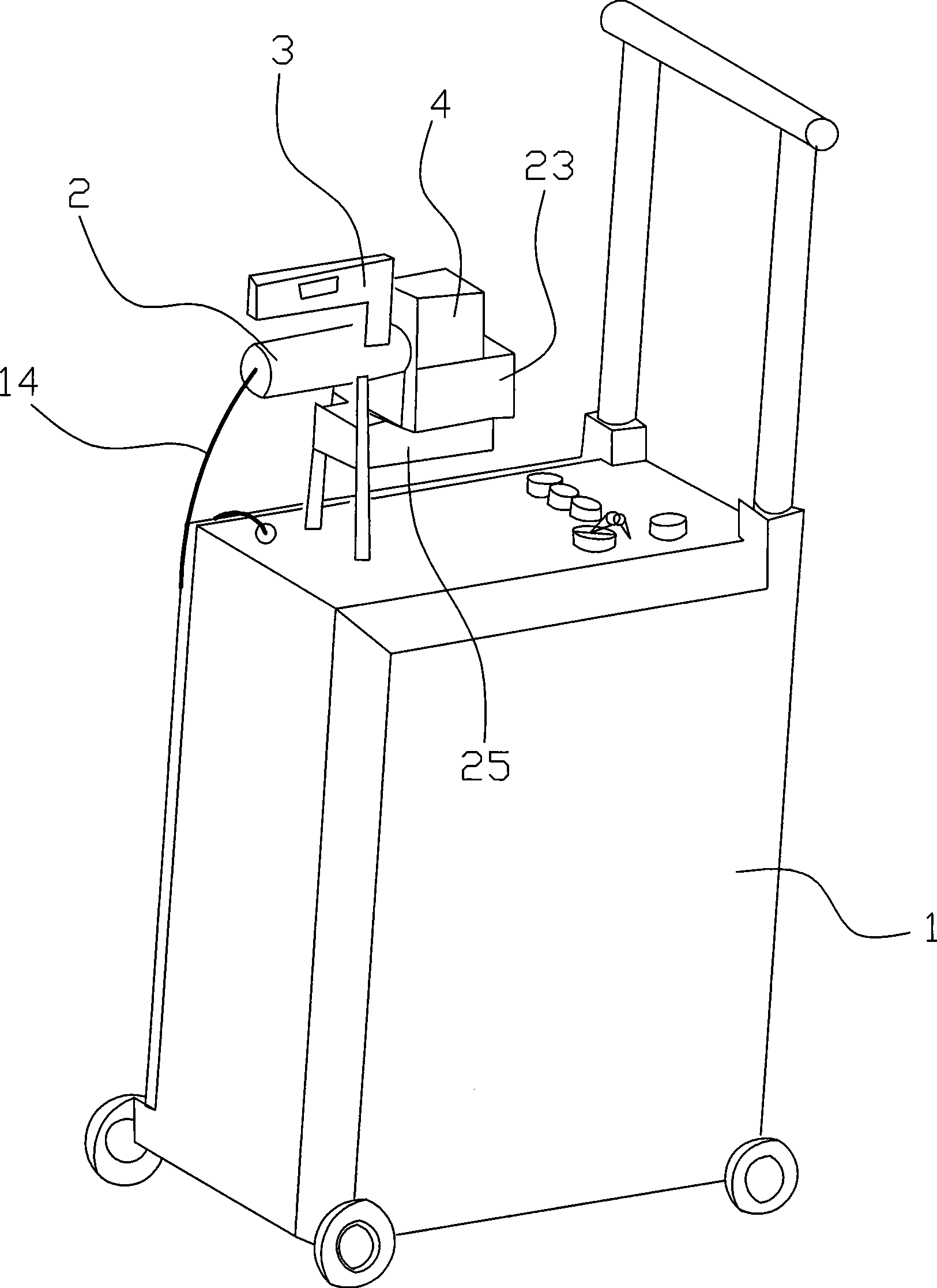
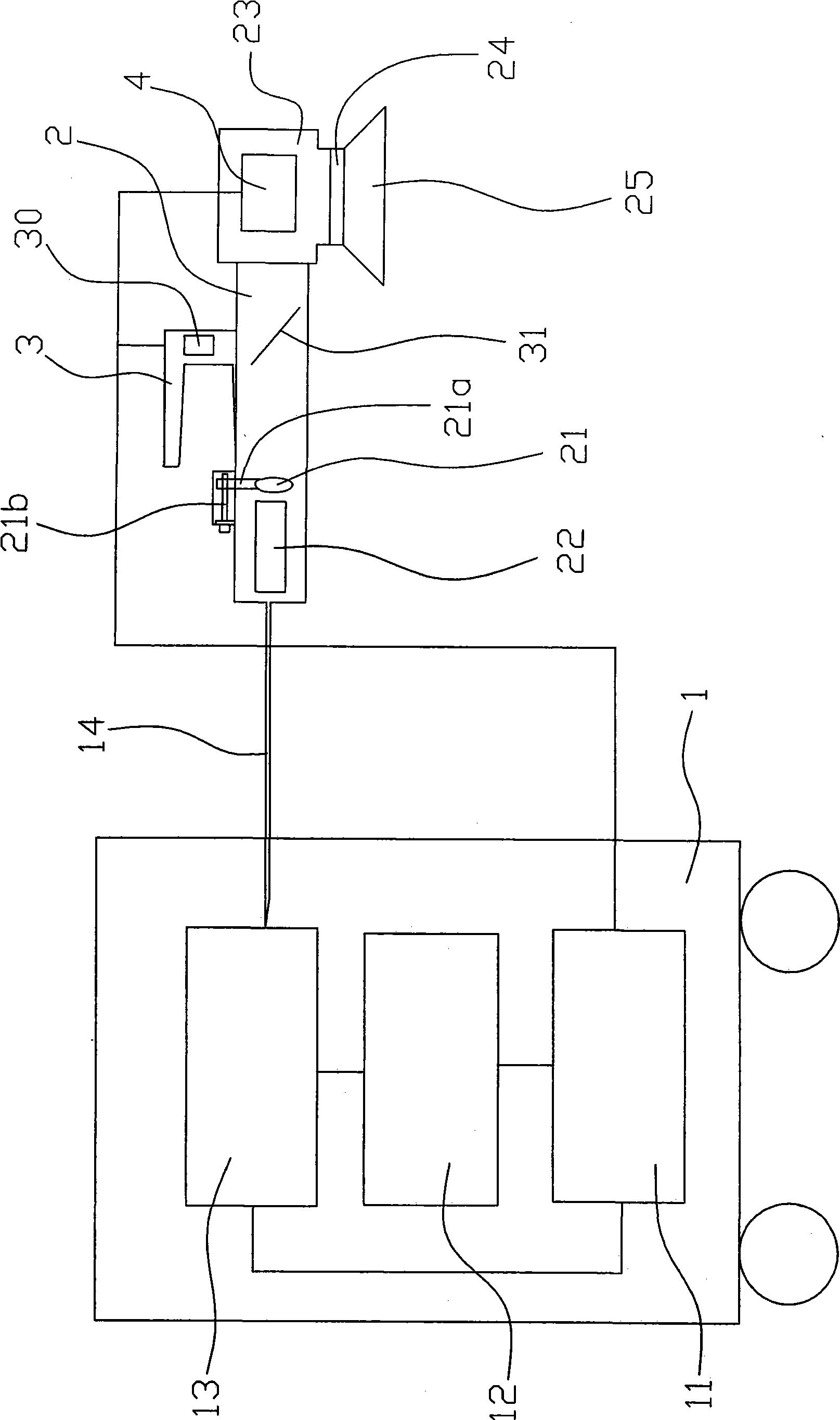
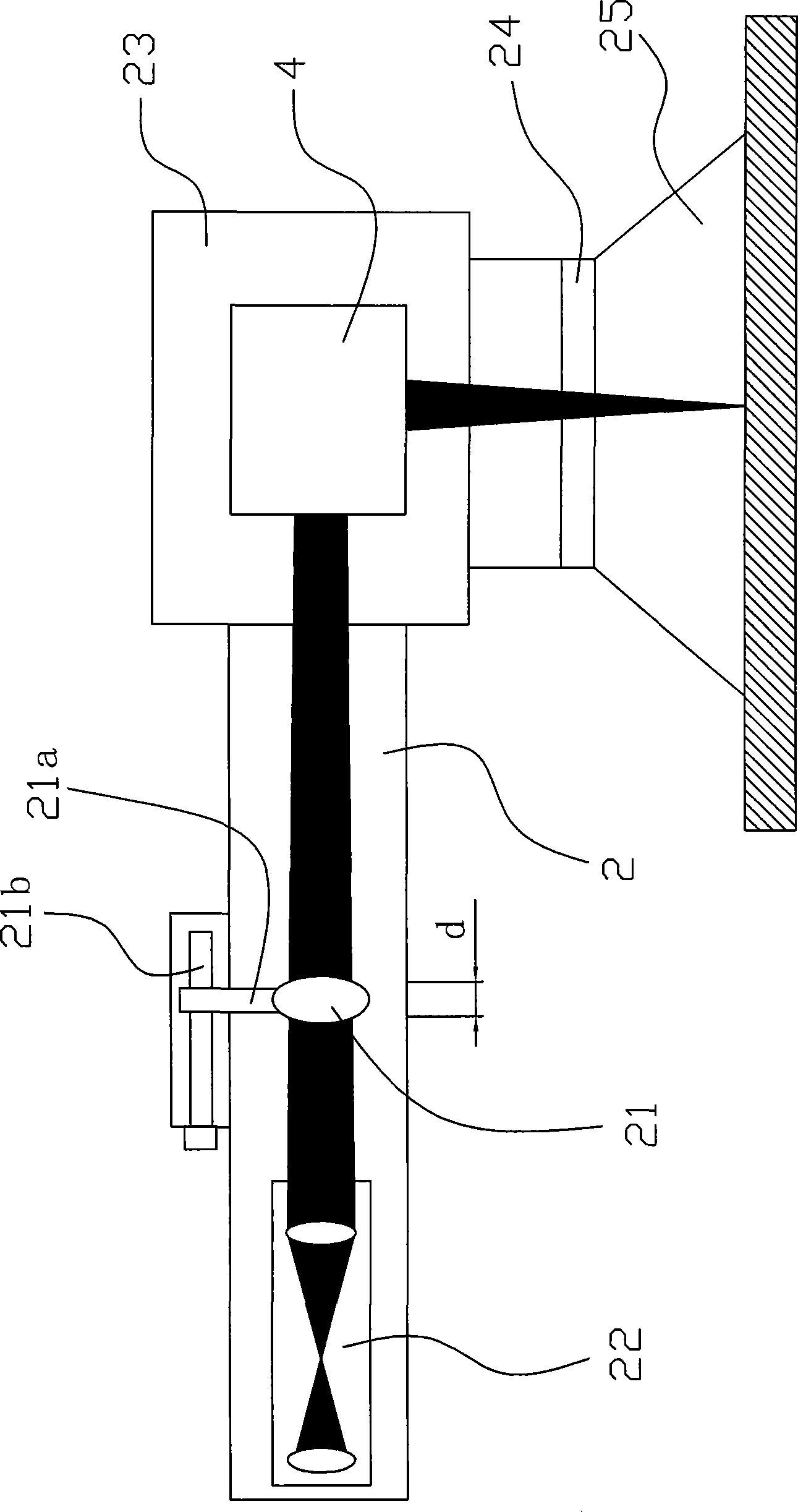
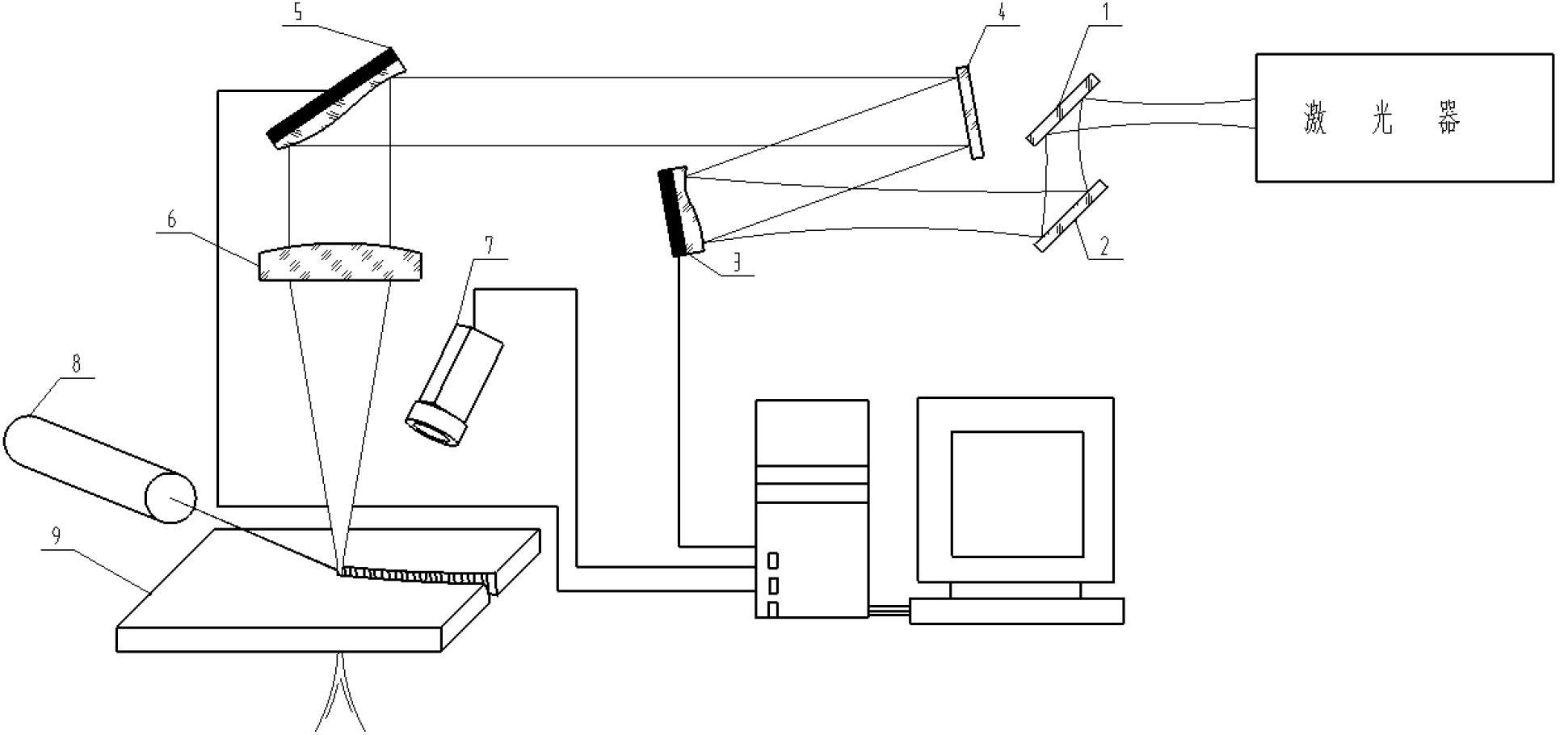
InactiveCN101486279AConvenient markingLight dragSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTypewritersEngineeringLaser beam quality
The invention relates to a laser marking machine, which comprises a laser (13), an embedded industrial control system (12) and a galvanometer system (4), wherein the embedded industrial control system (12) and the laser (13) form a loop with a power supply through conducting wires, and the galvanometer system (4) is arranged on a marking working head (23). The laser marking machine is characterized in that the laser (13) is an optical fiber laser, and the laser (13) and the embedded industrial control system (12) can be positioned in a movable moving box (1); the laser (13) is connected with a focusing device through an optical fiber (14); and the focusing device is adapted together with the galvanometer system (4). Adopting a semiconductor pump fiber laser as a light source, the laser marking machine has the advantages of simple structure, small volume, high conversion efficiency, good laser beam quality, long service life and no maintenance so that a bulky cooling device is not needed in the marking process for the convenience of movable marking. Besides, the movable optical fiber laser marking machine not only requires a simple environment without constant temperature, constant humidity and a water-cooling facility, but also is applicable to a severe environment, thereby having the advantages of least material consumption, international common software, easy learning and understanding, small volume, light weight, small occupied area, and long service life.
Owner:NINGBO WELL LASER TECH
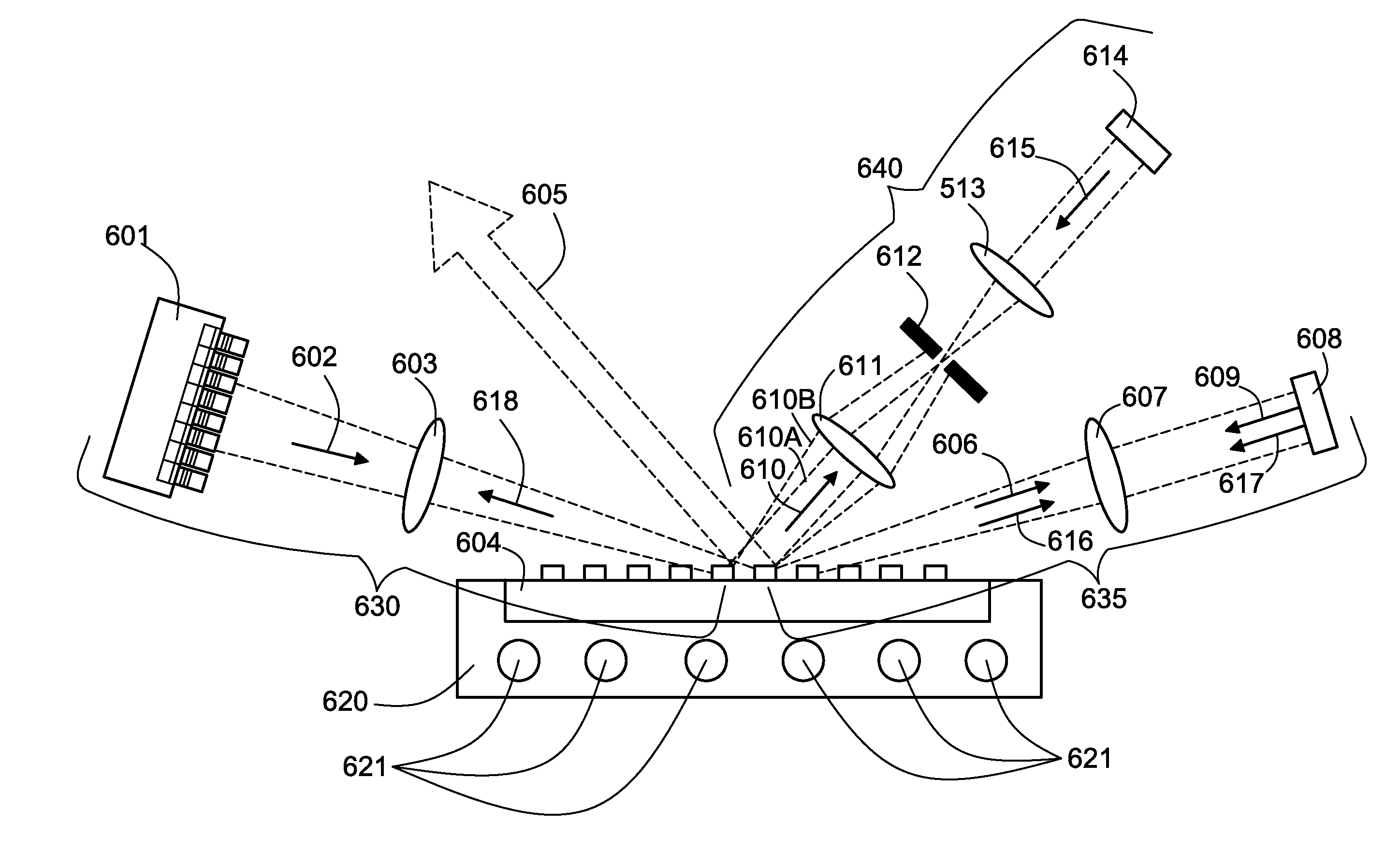
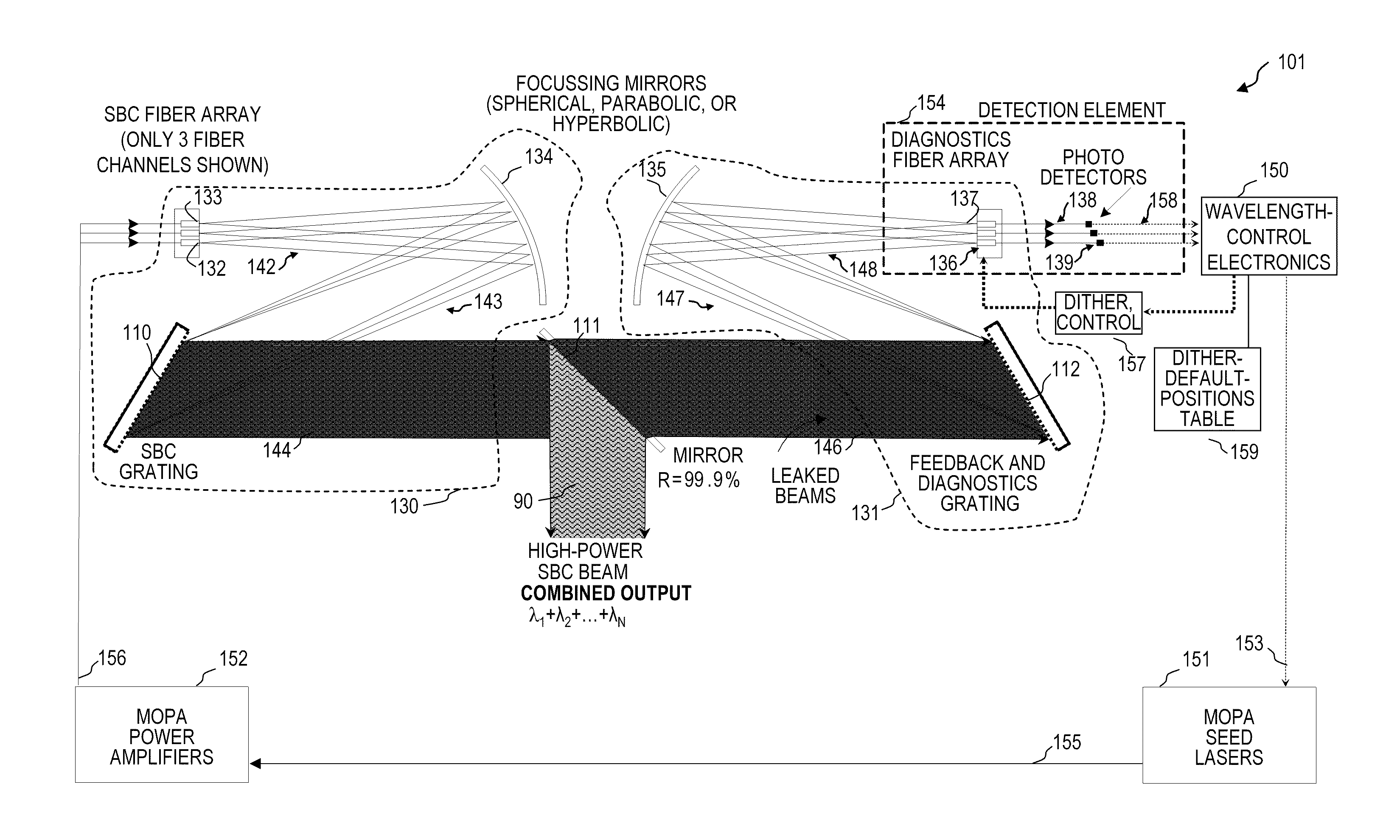
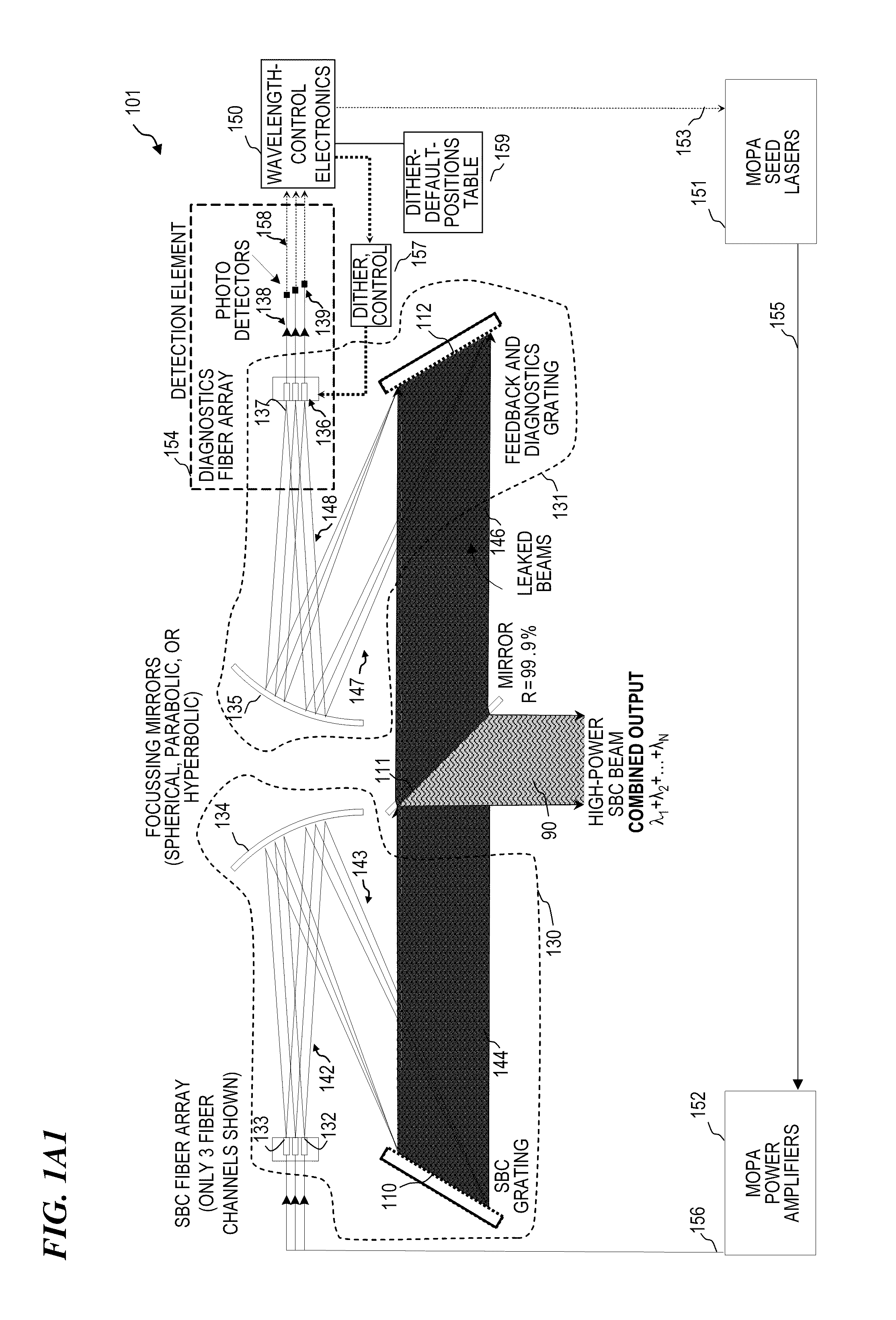
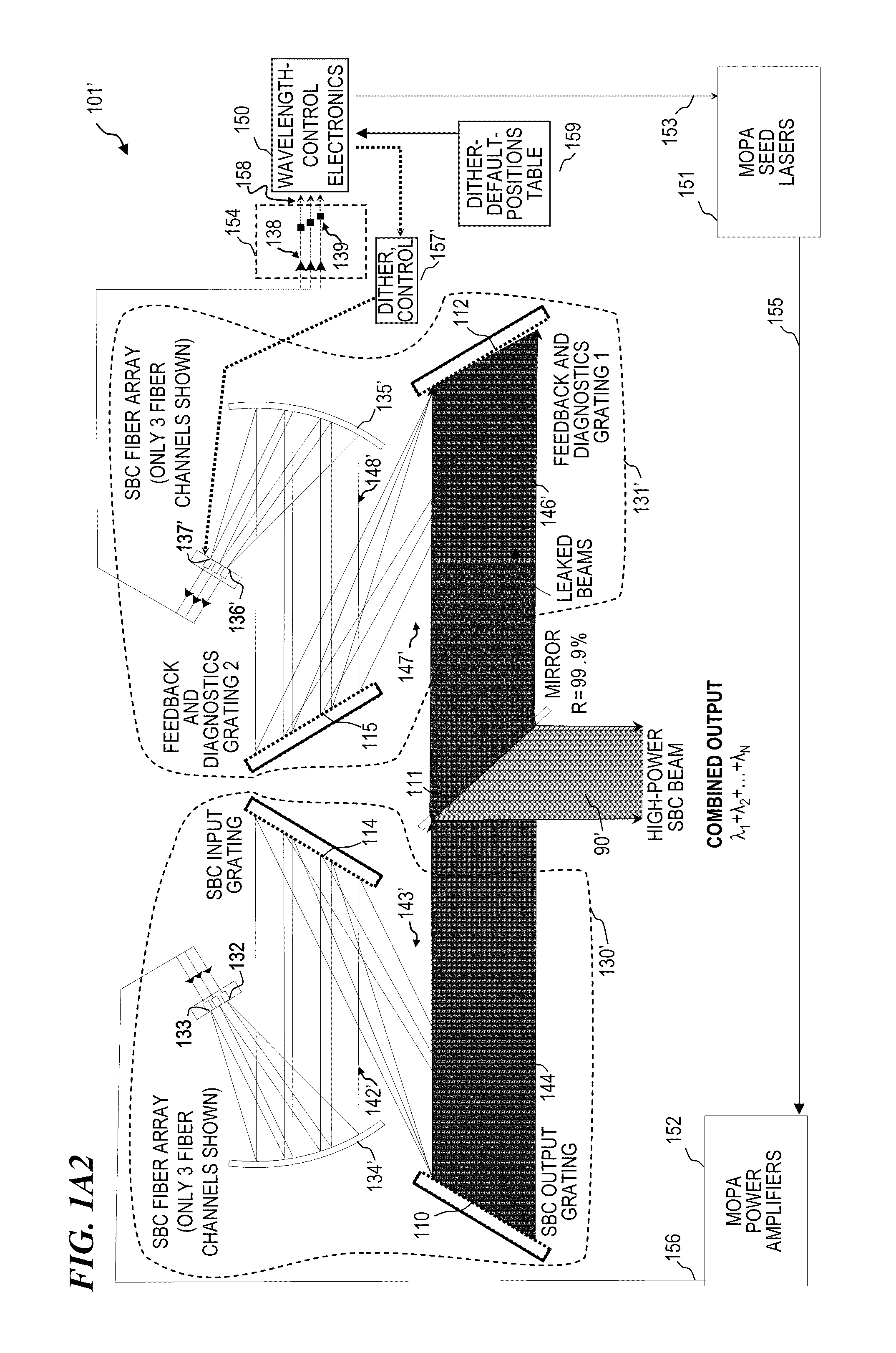
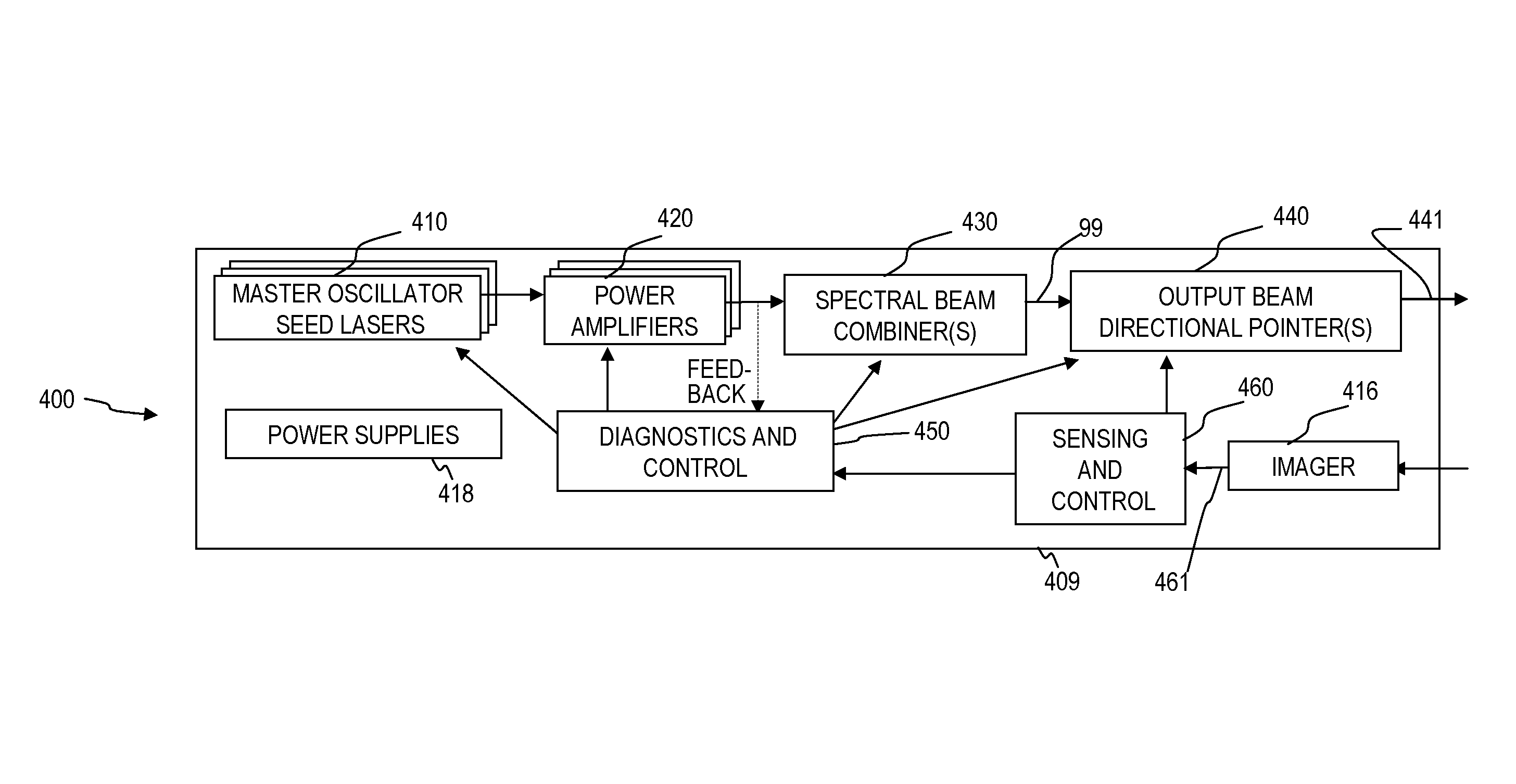
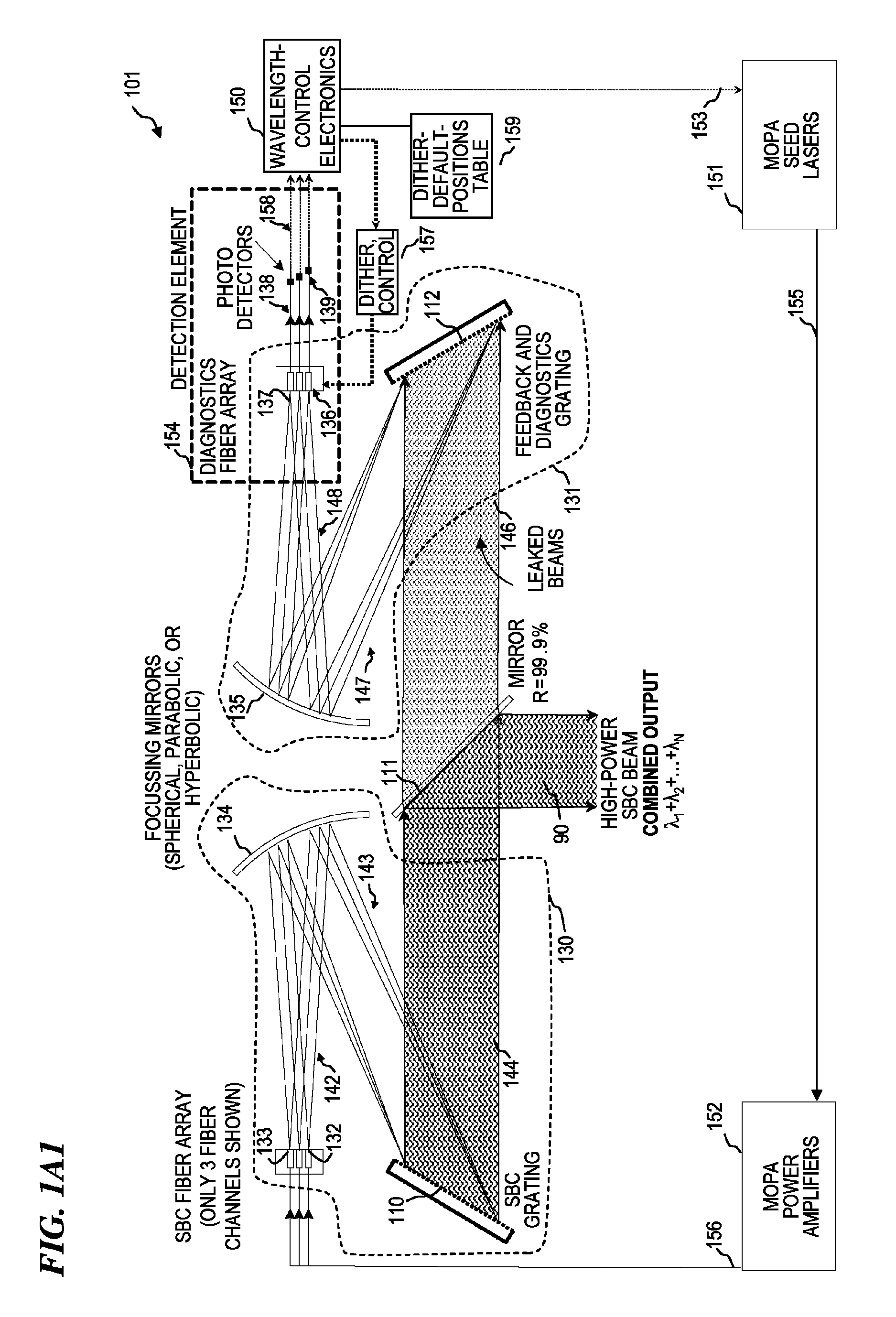
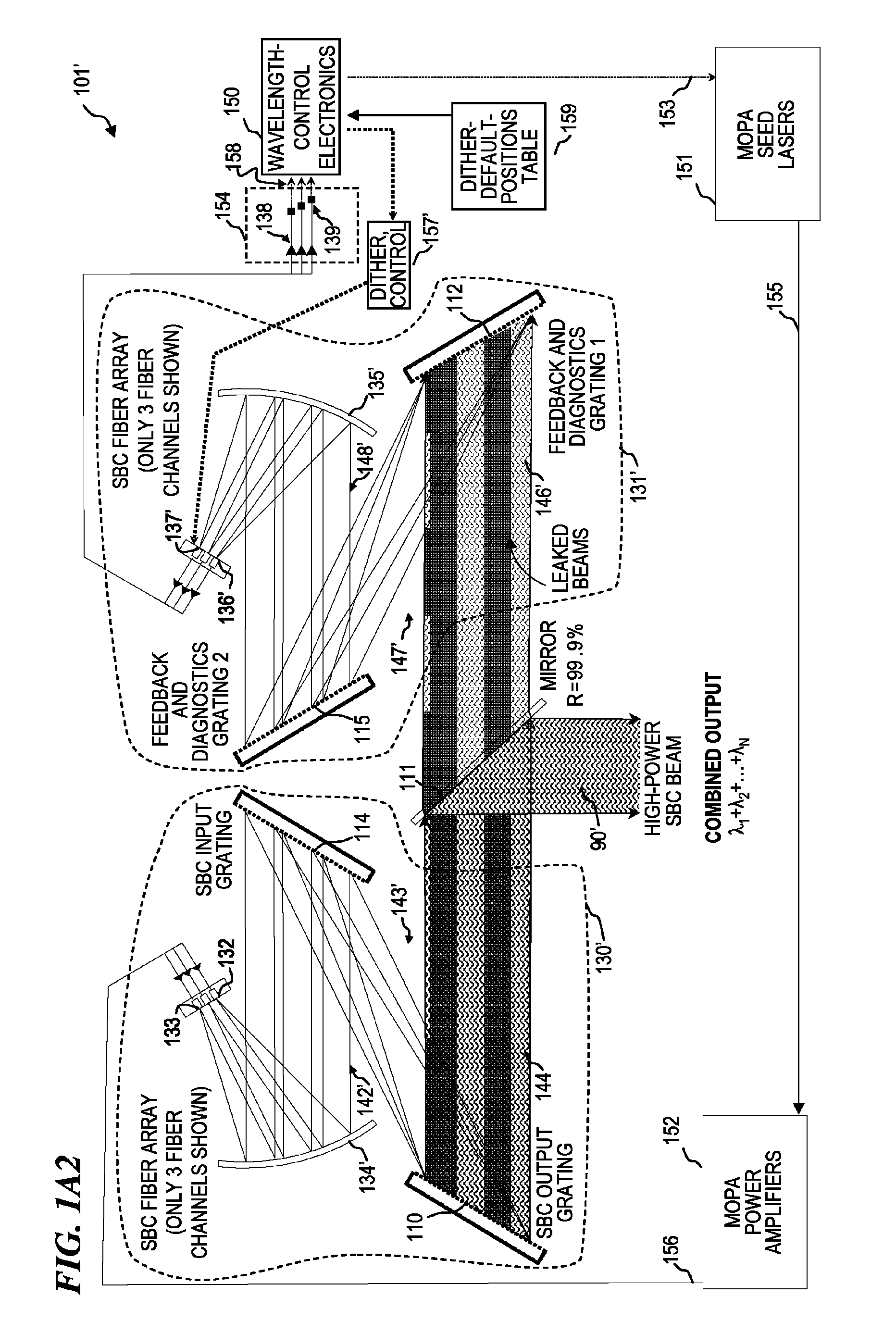
Beam diagnostics and feedback system and method for spectrally beam-combined lasers
Apparatus and method for control of lasers (which use an array of optical gain fibers) in order to improve spectrally beam-combined (SBC) laser beam quality along the plane of the SBC fiber array via spectral-to-spatial mapping of a portion of the spectrally beam-combined laser beams, detection of optical power in each of the spatially dispersed beams and feedback control of the lasers for wavelength-drift correction. The apparatus includes a diffractive element; a source of a plurality of substantially monochromatic light beams directed from different angles to a single location on the diffractive element, wherein the diffractive element spectrally combines the plurality of light beams into a single beam. A controller adjusts characteristics of the light beams if one of the light beams has become misadjusted. In some embodiments, the controller adjusts the wavelength tuning of the respective fiber laser.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
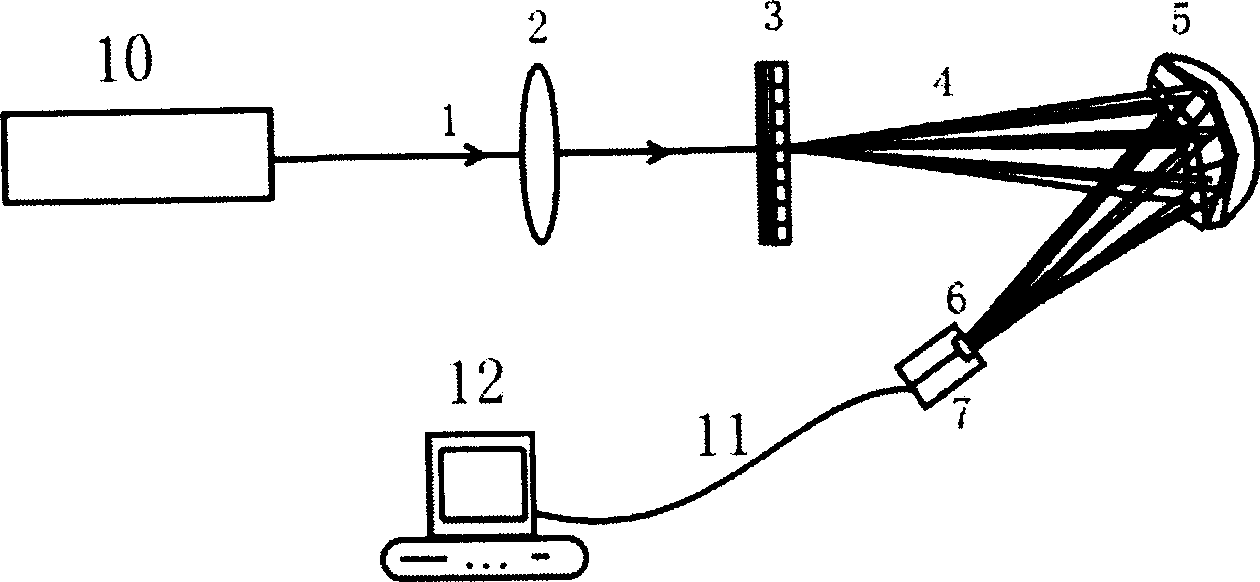
Real-time detector for laser beam quality factor M2
The invention relates to a laser beam quality M2 factor real time tester, which is formed by a focusing lens, a grid group, a light path adjuster and a CCD, wherein the output end of the CCD is connected with the computer by signal wire; the focus of the focusing lens is f; the dilemma is D; the grid group is a grid light-dividing system which is formed by two oppressed blocks of grid; the grid light-dividing system can divide a beam laser into 3í‡3 strips light beam groups with isocandela; the light path adjuster includes a lens array which is formed by nine reflecting lenses with the corresponding micro-adjusting screw; the distance from the grid group, the light path adjuster to the receiving side of the CCD of the zero-grade diffracted beam of the focusing lens equals to the focus of the focusing lens.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tapered optical fiber based high-power optical fiber end cap
ActiveCN106959489AImprove securityImprove stabilityCoupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresEngineeringLaser beam quality
A tapered optical fiber based high-power optical fiber end cap comprises a tapered optical fiber, a quartz block and an end cap housing, wherein a big end of the tapered optical fiber passes through one end of the end cap housing into the end cap housing and then is fixed to the end cap housing; a chamber in which the quartz block extends is formed in the other end of the end cap housing; the end, extending into the end cap housing, of the quartz block is a tapered table shaped end head; the end, extending out of the end cap housing, of the quartz block is cylindrical; an anti-reflection film coats the surface of the cylindrical end, extending out of the end cap housing, of the quartz block; the tapered table shaped end head of the quartz block is fused with the big end of the tapered optical fiber; an output end cap protecting window is arranged on the end cap housing section at the end, extending out of the end cap housing, of the quartz block; the cylindrical end, extending out of the end cap housing, of the quartz block is closed through the output end cap protecting window. The tapered optical fiber based high-power optical fiber end cap is simple in structure, and capable of improving the laser power bearing capacity of the optical fibers, and remains high laser beam quality while effectively inhibiting nonlinear effect.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Wavelength tunable coherent laser combined beam system based on double gratings
InactiveCN103197422AFlexibleHigh beam combining efficiencySemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser arrangementsGratingHigh power lasers
The utility model discloses a wavelength tunable coherent laser beam system based on double gratings and belongs to the field of laser combined beams. The system comprises a semiconductor laser array, a first lens, a dammam grating, a second lens, a diaphragm, a third lens, a blazed grating and a grating rotary device. The second lens, the diaphragm and the third lens form a space filter. The blazed grating is fixed on the grating rotary device. A group of parallel laser beams emitted by the semiconductor laser array converge to reach the dammam grating, and the dammam grating combines the laser beams. The space filter filters zero order light in the combined laser beams, and the filtered zero order light is used as first grade incident light to form a Littrow structure with the blazed grating. First grade direction reflection light is fed back to the dammam grating along an original light path. The beams are divided after reaching the damman grating, are injected into various light-emitting units of the semiconductor laser array and jointly lock the wavelength and phase positions so as to realize coherent combined beams. The wavelength tunable coherent laser beam system combines a plurality of laser beams into a beam of high-power laser, and has the advantages of being high in reliability and good in laser beam quality, working in a single wavelength mode, and the like.
Improved direct laser drilling processing method
InactiveCN103596368AEliminate inconsistent ablation statusStable productionPrinted circuit manufactureInfraredWindow opening
The invention discloses an improved direct laser drilling processing method. The improved direct laser drilling processing method is characterized by including the steps of laminating and direct laser drilling. The laminating includes the steps of opening a window in a copper foil on a skylight layer in a milled mode to form a window opening target region, conducting laminating processing by using a folded plate table infrared ray generator to generate infrared rays to form four intersected ray pots to locate window opening target regions when folded plates are laminated, and conducting melanism processing. The direct laser drilling includes the steps of conducting ablation on prepregs exposed out of the four window opening target regions of the copper foil on the skylight layer through a preset procedure, enabling a sub-outer-layer receiving disc and an aligning target hole to be exposed out, and conducting direct laser drilling with the aligning target hole serving as a location standard. According to the improved direct laser drilling processing method, the mode that the window is directly opened at the position of a location target in the copper foil on the skylight layer is adopted, the problem that the ablation state of the location target is inconsistent due to uneven preprocessing is thoroughly solved, the production process is stable, the production efficiency is obviously improved, the infrared ray intersected ray pots are used for locating, the location accuracy is improved, and the laser ablation quality of the aligning target hole is sufficiently guaranteed.
Owner:DALIAN PACIFIC ELECTRONICS
Fast-slow axis beam quality homogenizing device of semiconductor laser
ActiveCN104836114AEasy to processSimple structureLaser output parameters controlCoupling light guidesLight beamPrism
The invention provides a technical scheme of a fast-slow axis beam quality homogenizing device of a semiconductor laser. Based on the beam total reflection principle, the scheme comprises the following steps: using a rectangular prism spatial combination as a beam rotating component, using a cylindrical lens assembly as Y-direction collimation, and using two-pieces type cylindrical beam-shrinking mirror as an X-direction beam-shrinking component so as to shape the fast-slow axis light beam quality of the semiconductor laser in a homogenizing manner. Through the adoption of the device provided by the invention, the beam rotation is aberration-free, the beam forward direction cannot be changed, and a shaping system is simple in adjustment and easy to operate. A semiconductor laser high-brightness optical fiber coupling output light source researched based on the device can be applied to various fields such as pumping optical fiber lasers, medical treatment and industry processing.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Beam diagnostics and feedback system and method for spectrally beam-combined lasers
Apparatus and method for control of lasers (which use an array of optical gain fibers) in order to improve spectrally beam-combined (SBC) laser beam quality along the plane of the SBC fiber array via spectral-to-spatial mapping of a portion of the spectrally beam-combined laser beams, detection of optical power in each of the spatially dispersed beams and feedback control of the lasers for wavelength-drift correction. The apparatus includes a diffractive element; a source of a plurality of substantially monochromatic light beams directed from different angles to a single location on the diffractive element, wherein the diffractive element spectrally combines the plurality of light beams into a single beam. A controller adjusts characteristics of the light beams if one of the light beams has become misadjusted. In some embodiments, the controller adjusts the wavelength tuning of the respective fiber laser.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Device capable of automatically diagnosing and correcting divergence angle and beam quality of laser beam
ActiveCN102658431AGood and stable working conditionEasy to processLaser beam welding apparatusDivergence angleLight beam
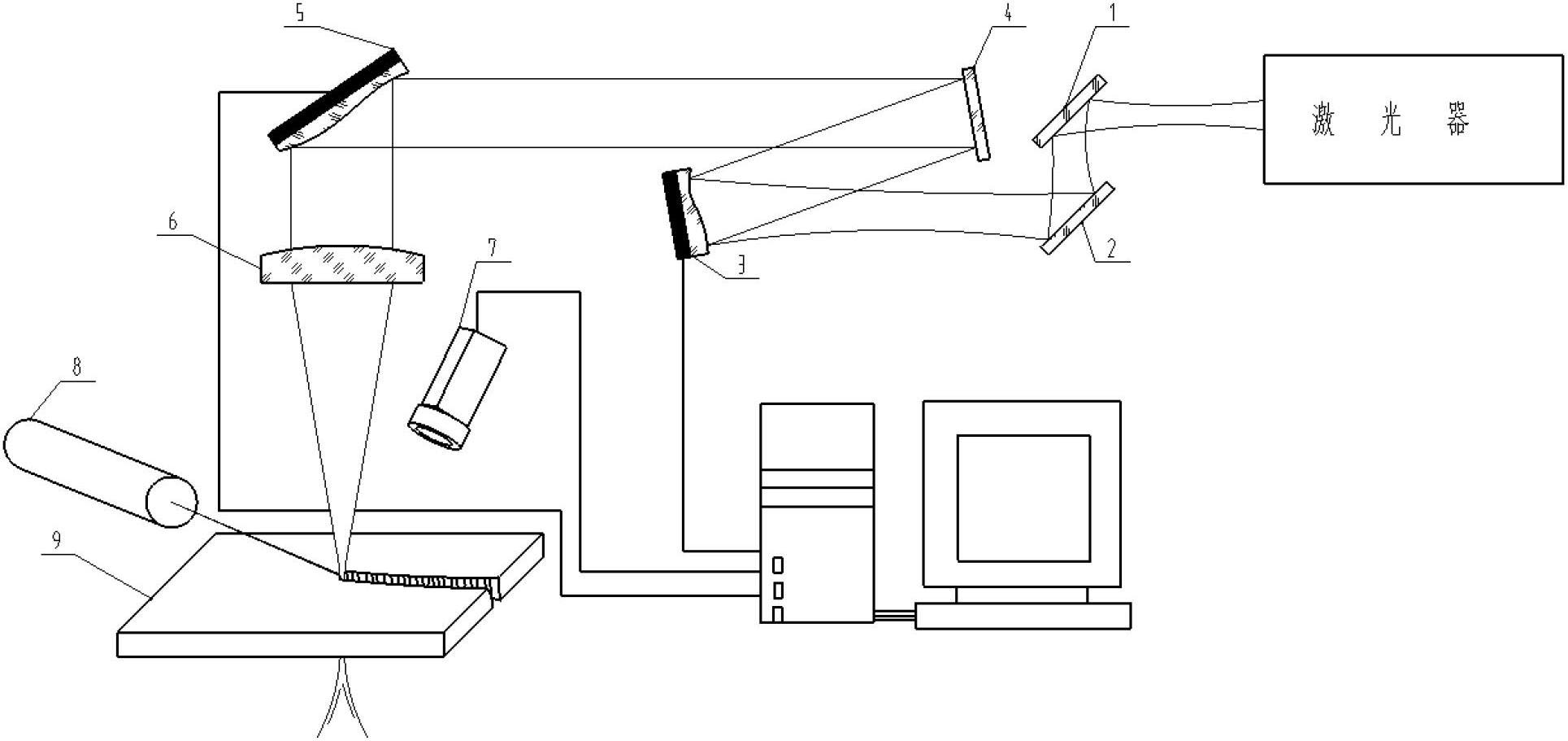
The invention relates to a device capable of automatically diagnosing and correcting divergence angle and beam quality of a laser beam. The device is used for extracting an erosion image formed by a laser beam to a refractory material or a processing mark image formed by the laser on a processed material, automatically diagnosing the divergence angle and the beam quality of the laser beam, in particular a laser beam for processing, and correcting the divergence angle and the beam quality of the laser beam by utilizing an optical deformation device, such as a deformable mirror, so that the laser equipment can be assisted to keep the excellent and stable working state, and the processing capacity and efficiency can be furthest improved.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mechanical-electrical compound dimming system for laser beam quality analyzer
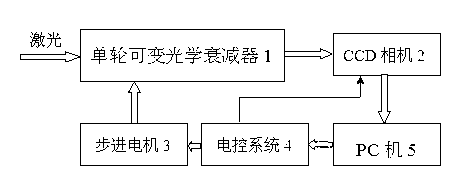
InactiveCN103309031AAttenuation module is smallEasy to useMeasurement apparatus componentsOptical elementsCcd cameraLaser beam quality
The invention provides a mechanical-electrical compound dimming system for a laser beam quality analyzer. The mechanical-electrical compound dimming system comprises a single-wheel variable optical attenuator, a CCD (charge coupled device) camera, a stepping motor, an electrical control system and a PC (personal computer). For an acquired image, an incident laser beam passes the single-wheel variable optical attenuator and is attenuated after shutter time is preset by the CCD camera, a new acquired spot image is processed by the PC, the electronic shutter time slot of the CCD camera is adjusted by the electrical control system according to a gray value, incident laser intensity is continuously attenuated by the aid of the single-wheel variable optical attenuator, linearity is fine, the dynamic range is wide, and a laser beam quality analyzer attenuation module is small in size and convenient to use. The dimming range of traditional optical wedge continuous attenuation of light intensity in the laser beam quality analyzer is narrow and is about 20-300 times, and the dimming system obtains the wide dynamic dimming range of 5000 times.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fast laser scanning imaging simulation method based on light beam and triangular patch intersection
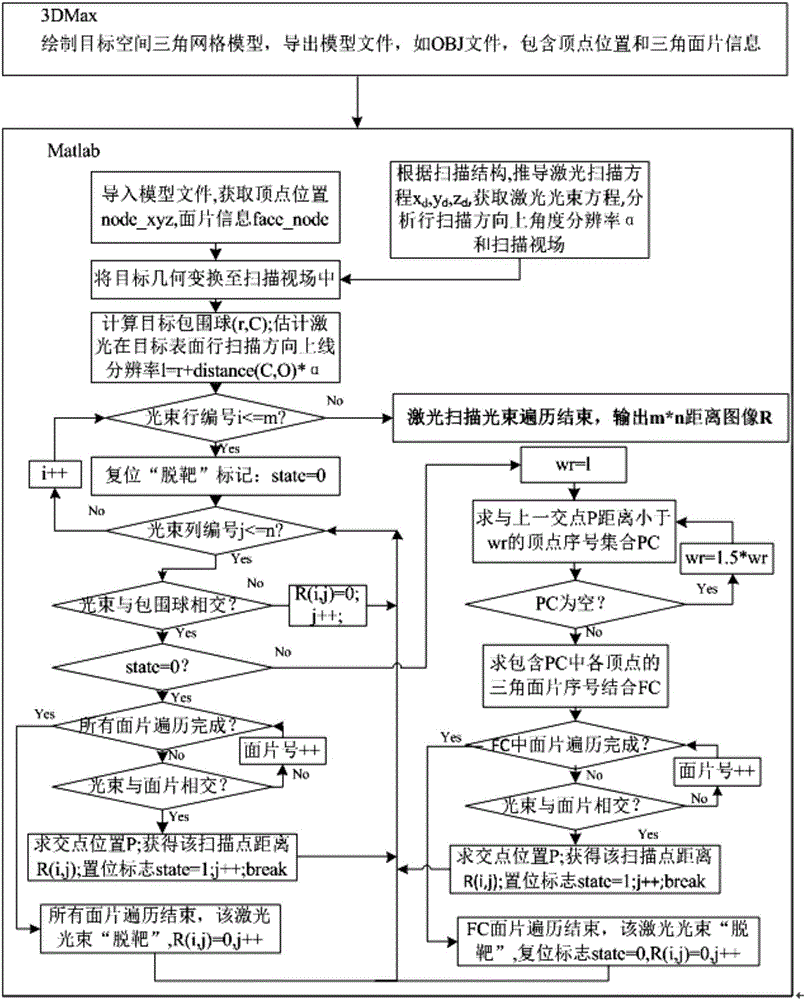
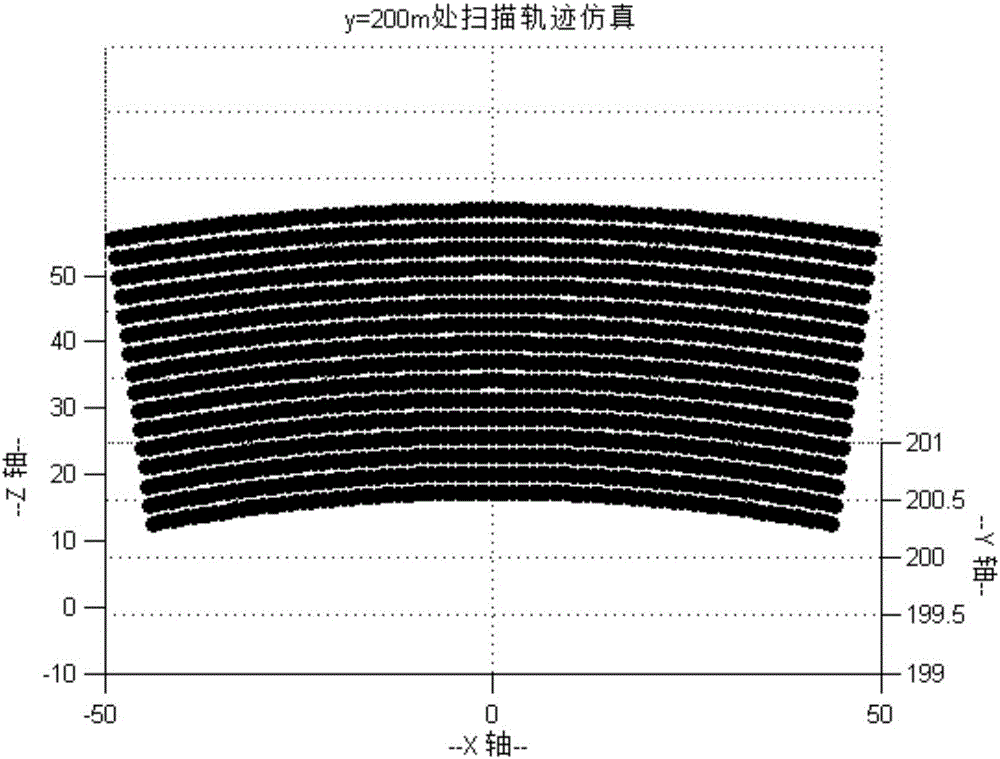
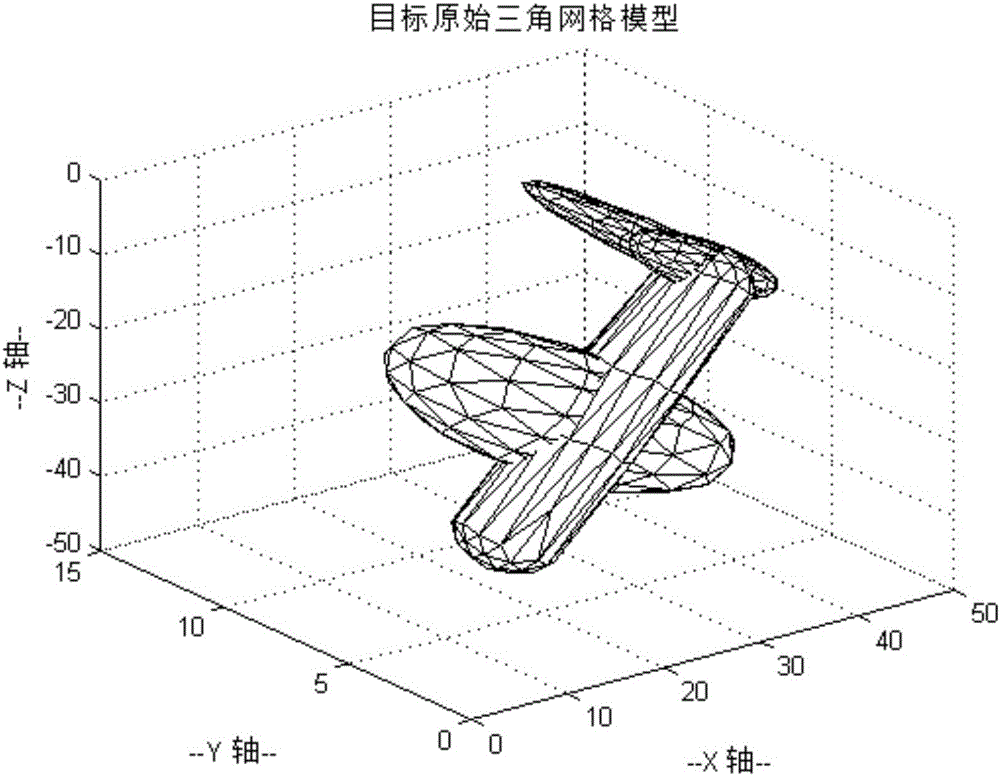
InactiveCN105844057AShorten the development cycleFast simulationGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsImage resolutionIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
The invention discloses a fast laser scanning imaging simulation method based on light beam and triangular patch interaction. The method comprises steps as follows: a target space triangular mesh model is drawn firstly; a laser beam equation, angle resolution and a view field are deduced according to a laser scanning structure; a target model is imported, and target geometry is transformed in the view field range of an imaging system; finally, on the basis of a light beam and triangular patch interaction algorithm, a local search technology is introduced, a traverse range is reduced, the solving process of intersection conditions of laser beams and the target space triangular mesh model is accelerated, the distance between each intersection point and a laser emergent point is solved, and a target distance image is simulated rapidly. The simulation method is simple and high in speed and can be applied to design verification of a laser scanning imaging prototype and algorithm testing such as three-dimensional imaging, recognition, tracing and the like of a target, and the system development cycle is shortened.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Evaluation method of laser beam quality of low-numerical aperture large-mode field area fiber
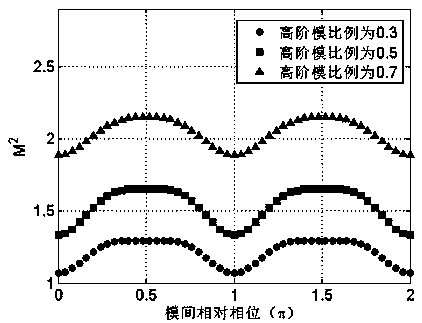
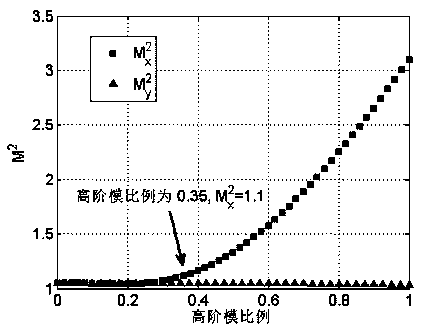
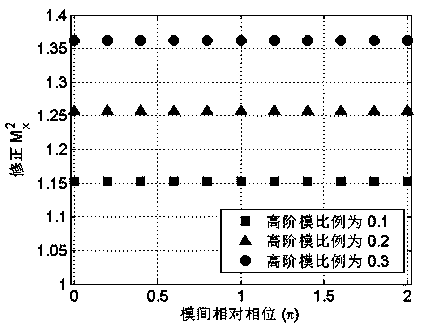
ActiveCN105571826AEliminate beam quality factor effectsEliminate the effects ofTesting optical propertiesFiberRelative phase
The invention relates to an evaluation method of laser beam quality of a low-numerical aperture large-mode field area fiber. According to the invention, effects on an M2 factor imposed by inter-mode relative phases can be eliminated, so the M2 factor which is only related to inter-mode power proportion but not related to the inter-mode relative phases can be obtained. The M2 factor modified with the method can precisely reflect mode components and laser beam quality of the low-numerical aperture large-mode field area fiber. The closer to 1 the numerical value of the M2 factor is, the better the laser beam quality is. In this way, effects on laser beam quality imposed by the inter-mode relative phases are eliminated, and a disadvantage is overcome that it is hard to evaluate the laser beam quality of the low-numerical aperture large-mode field area fiber via an M2 factor.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
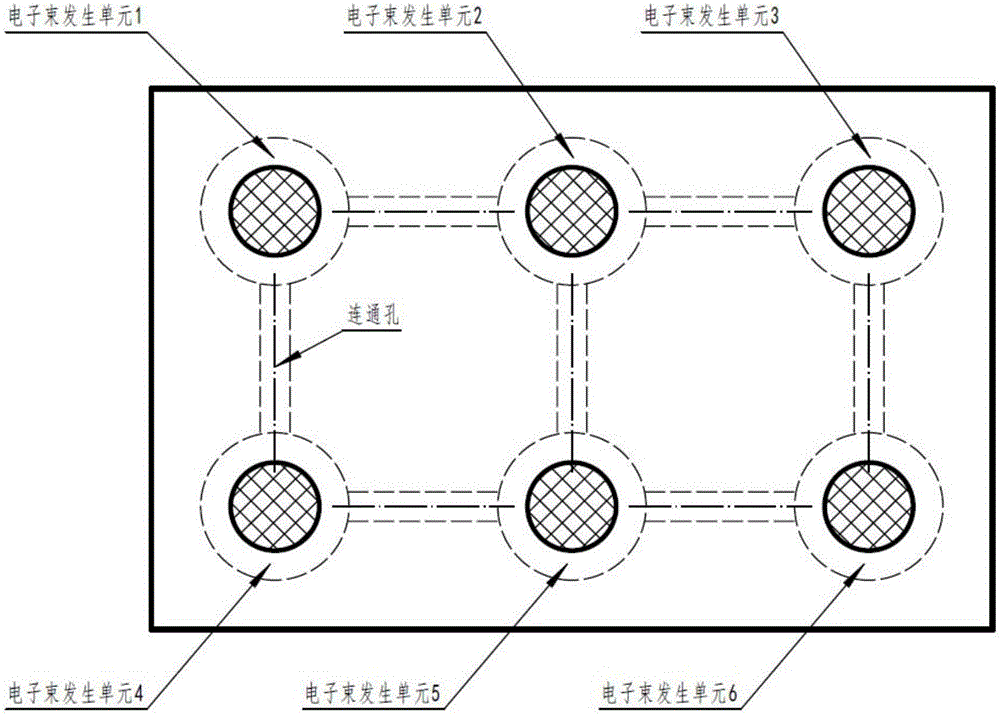
Integrated array electron gun and electron beam selective melting rapid formation system
ActiveCN106504966AGuaranteed forming accuracyGuaranteed forming qualityTubes with more than two output electrodesElectrode and associated part arrangementsLaser beam qualityLarge size
The invention relates to the technical field of additive manufacturing and processing equipment and especially relates to an integrated array electron gun and an electron beam selective melting rapid formation system. A plurality of electron beam emission units are arranged orderly in an array manner, and each electron beam emission unit is responsible for one region; the electron beam emission units in different array positions are controlled to carry out accurate scanning and forming on different positions of a powder bed, and thus electron beam quality of each electron beam emission unit is ensured; and through effective connection of the regions, under the condition of ensuring part forming precision and quality, the problem that an existing powder bed electron beam selective melting rapid formation device cannot produce large parts due to overlarge electron beam deflection angle is solved, and powder bed electron beam selective melting rapid manufacturing of the large-size parts is realized.
Owner:XIAN ZHIRONG METAL PRINTING SYST CO LTD
High-repeat frequency photonic crystal fiber ultraviolet ultrashort-pulse laser machine
InactiveCN101327548AIncrease powerImprove the ability to resist environmental interferenceLaser detailsCladded optical fibreUltravioletLaser beam quality
The present invention discloses a high pulse repetition frequency photonic crystal fiber ultraviolet ultrashort pulse laser processor, which belongs to the laser technology field. The processor is composed of a photonic crystal fiber or solid femtosecond laser oscillator stage, a high-power, large-mode-field photonic crystal fiber laser amplifier, a laser frequency multiplier, a collimating and focusing system, a precision three-dimensional micro-moving platform with the nanometer-level precision and a computerized control system. The processor has the advantages of high pulse repetition frequency, simple structure, good stability, low operation cost, high laser beam quality, small pulse width and high power.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
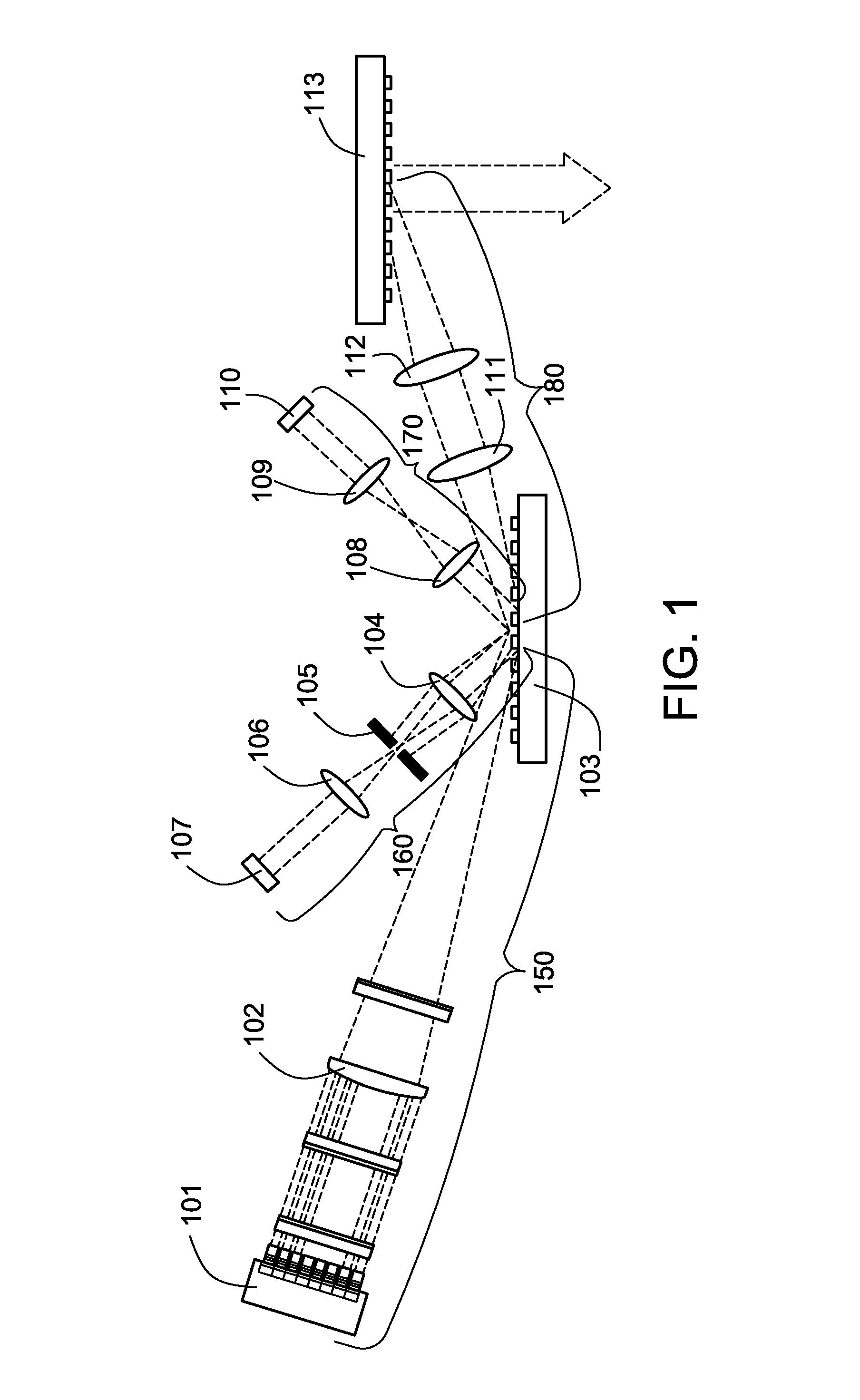
Laser resonator comprising an internal beam splitter
InactiveUS20080165821A1Increase output powerHigh beam qualityLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionGratingAngle of incidence
A simple and compact laser resonator is proposed which makes it possible to symmetrically operate a gain medium, preferably a semiconductor, which possesses more than one channel of emission. As a result higher output powers and / or better beam qualities and / or better spectral characteristics can be achieved. The resonator is very compact and ideally comprises only three optical elements: a laseractive gain medium (1), a cylindrical collimation lens (5), and a prism (6) which is adapted to the angle between the two emissions (4) and which carries a beam splitter (7) and a feedback mirror (9) on its faces. Preferably the gain medium (1) possesses a feedback element (2) and an antireflective coating (3) on its faces. If no antireflective coating (11) is desired the same effect can be achieved by arranging the angle of incidence to fulfill the Brewster-condition. In a preferred embodiment the gain medium (1) is a high-power diode laser chip with an internal stripe-array and / or the laser resonator is unstable along the direction parallel to the epitaxial layers. In alternative embodiments the feedback element (9) is wavelength selective like a grating, a dielectric filter, a holographic element or a volume Bragg grating.
Owner:RAAB VOLKER
High-efficiency LED illuminator with improved beam quality
ActiveUS20140247582A1Light collection efficiency is improvedAdjustable distanceMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceBeam patternLight beam
An improved illuminator with an adjustable beam pattern to be worn by medical and dental professionals includes a housing, a light-emitting diode (LED) disposed in the housing outputting light through a distal opening in the housing, an achromatic doublet lens mounted in the opening in the housing, and a singlet lens disposed between the LED and the achromatic lens. The distance between the singlet lens and the doublet lens may be adjustable, and / or distance between the LED and the singlet lens may be adjustable, through a threaded connections, for example. In the preferred embodiment, the achromatic doublet lens, the singlet lens, or both the singlet and the doublet lens have a planar surface. A conical mirror may be disposed between the LED and the singlet lens to increase the light collection efficiency of the LED.
Owner:GEN SCI
Solid-state laser generating green continuous laser and method thereof
A solid-state laser generating a green continuous laser and a method thereof are disclosed. The laser comprises a pumping source used for generating 798-801nm pumping light, a light splitting unit, an optical path conversion unit, an Er3+:YAlO3 crystal, a resonant cavity and two Fabry-Perot etalons. The light splitting unit is used for splitting the pumping light into a first light beam and a second light beam. The first light beam is entered into a first end surface of a laser crystal. The second light beam is entered into a second end surface of the laser crystal through the optical path conversion unit. The laser crystal is used for generating up-conversion fluorescence under excitation of the first light beam and the second light beam. The resonant cavity is used for outputting a laser of a green light wave band. The two Fabry-Perot etalons are located in the resonant cavity and are used for compressing a line width of an output laser. The structure of the laser is simple, cost is low and green-light continuous output of a narrow line width is realized. The invention also provides a method of generating the green-light continuous laser. Advantages that output laser beam quality is good; the line width is narrow; optical to optical conversion efficiency is high and so on are possessed.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG INST OF TECH
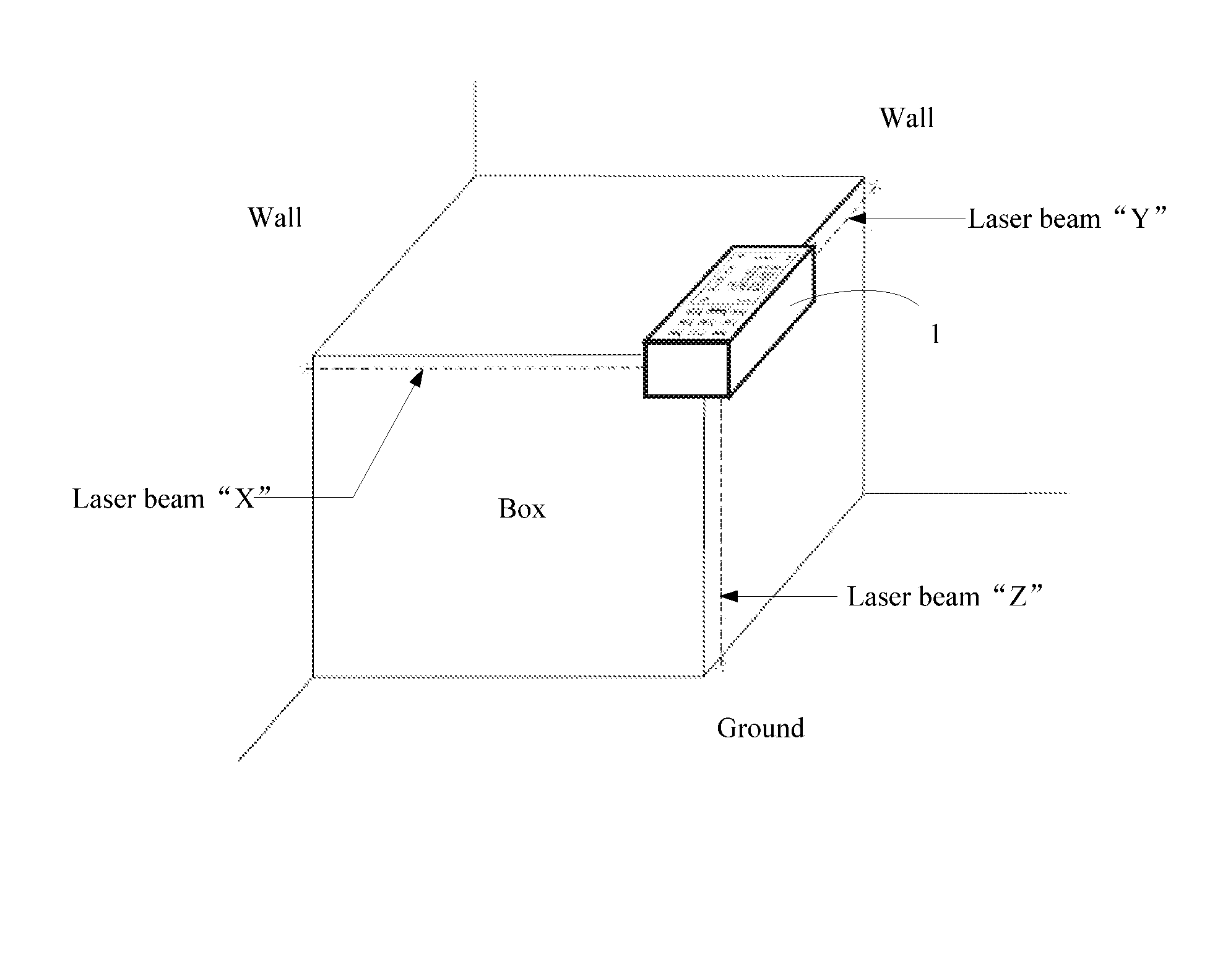
3D laser measuring device
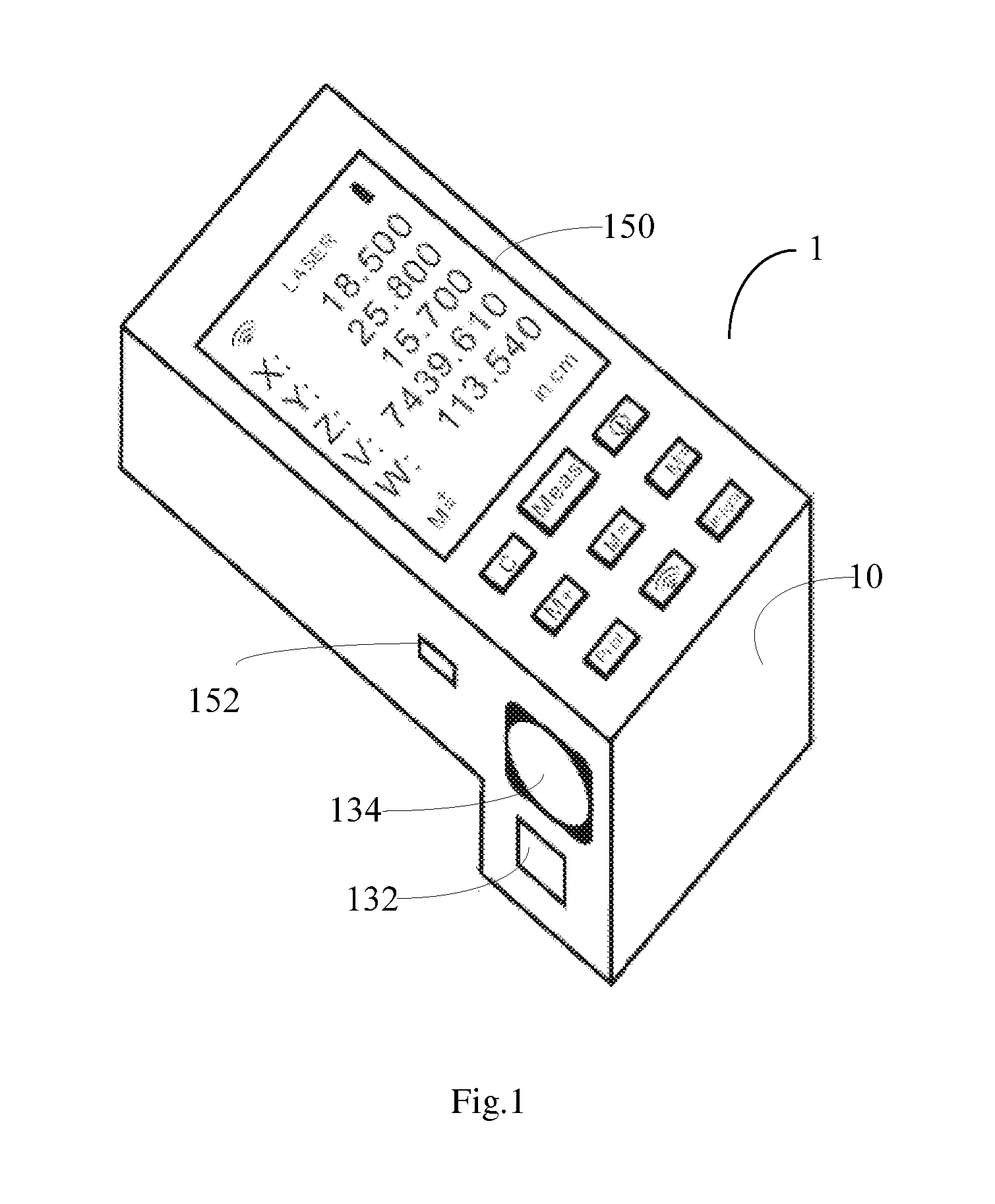
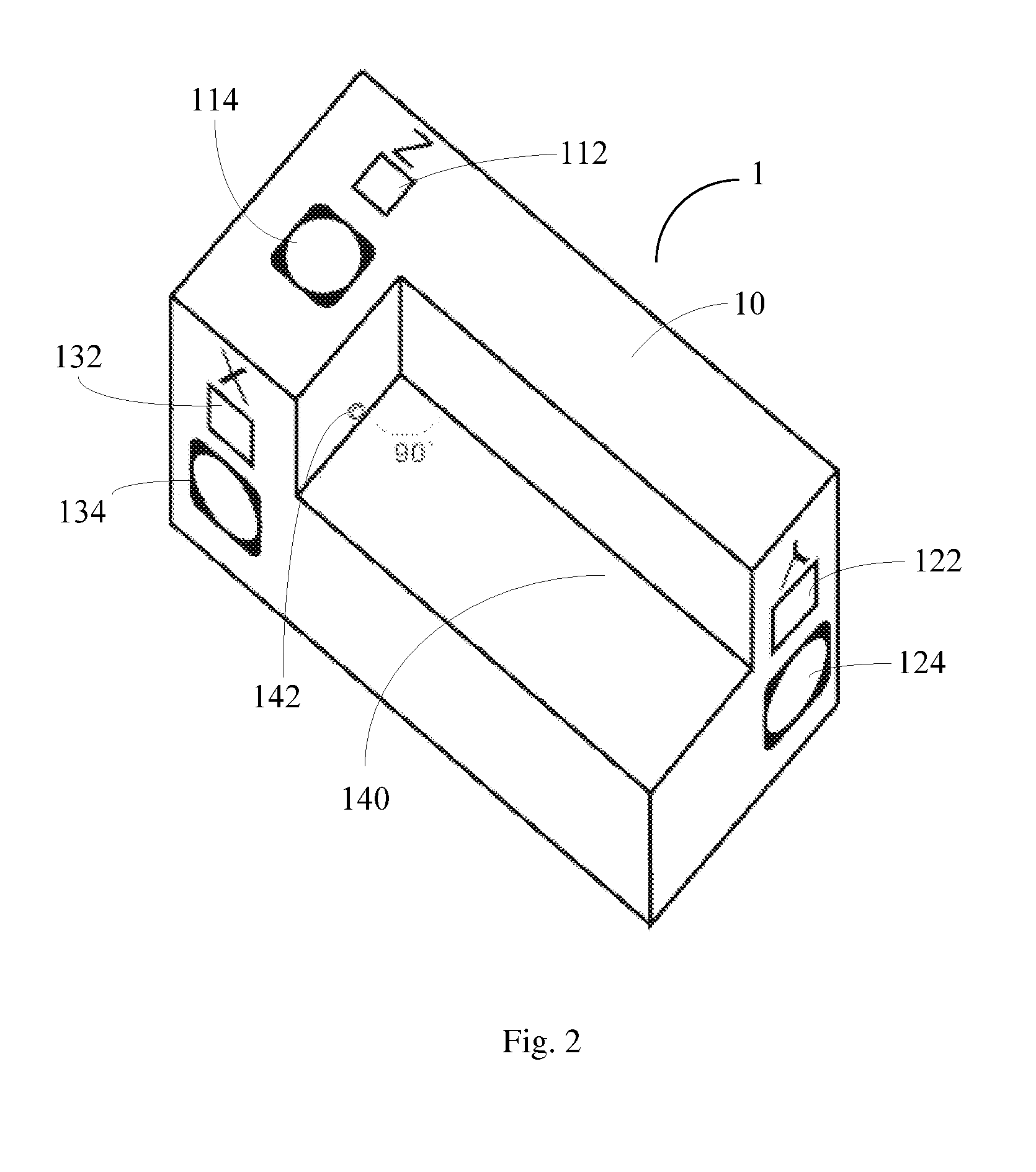
InactiveUS9239227B1Easy to operateEasy and efficientActive open surveying meansReflex reflectorsMeasurement deviceLight beam
The invention discloses a portable and movable 3D laser measuring device, comprising: a measurement body; an X-axial laser beam outlet and an X-axial reception lens arranged on a side wall of the measurement body, and a Y-axial laser beam outlet and a Y-axial reception lens arranged on another side wall; a Z-axial laser beam outlet and a Z-axial reception lens arranged on the bottom of the measurement body, and a groove formed in the bottom and being open at the side wall with the X-axial laser beam outlet and at the side wall with the Y-axial laser beam outlet; a control device placed inside the measurement body and configured to control the emitting of the laser beams from the laser beam outlets when receiving a measurement instruction through a measurement button on the measurement body. By using the 3D laser measuring device, the three dimensions of a shipping box can be easily measured.
Owner:LIN ZHONG JIAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com