Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1529 results about "Optical attenuator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An optical attenuator, or fiber optic attenuator, is a device used to reduce the power level of an optical signal, either in free space or in an optical fiber. The basic types of optical attenuators are fixed, step-wise variable, and continuously variable.
Optical attenuator
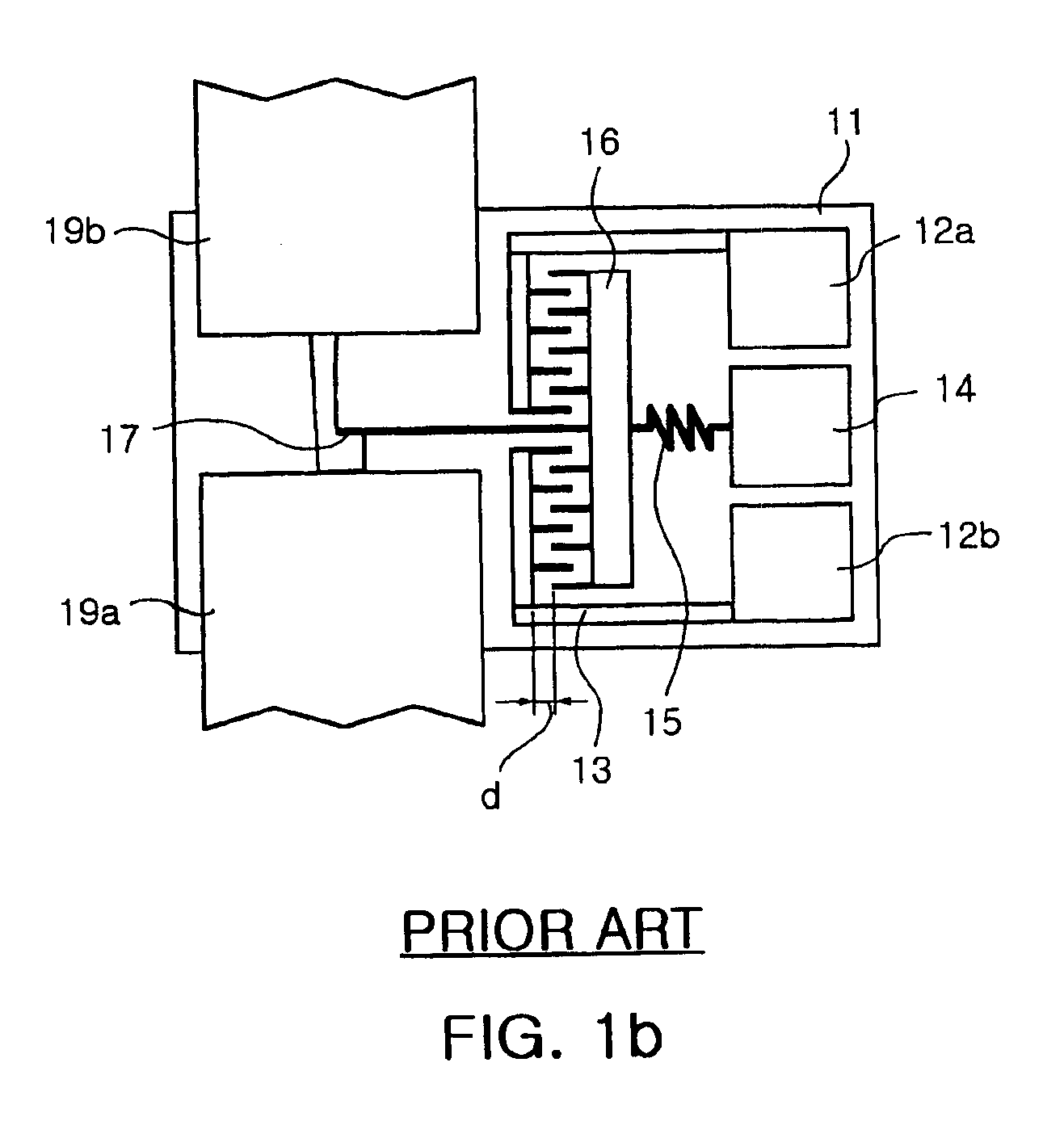
An optical attenuator having a structure in which a membrane covers a cavity formed on a substrate is disclosed. The membrane covering the cavity formed in the substrate is movable relative to the bottom surface of the cavity constituting a deformable mirror. Movement of the membrane relative to the bottom surface of the cavity attenuates optical signals impinging on the surface thereof. The movement of the membrane relative to the bottom surface of the cavity attenuates impinging optical signals by controlling the angle at which such impinging optical signals are reflected from the membrane surface.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Controller which controls a variable optical attenuator to control the power level of a wavelength-multiplexed optical signal when the number of channels are varied
InactiveUS6025947AReduce degradationWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical transmission with multiple stagesAudio power amplifierTransmittance
An optical amplifying apparatus which includes an optical amplifier, an optical attenuator and a controller. The optical amplifier amplifies a light signal having a variable number of channels. The optical attenuator passes the amplified light signal and has a variable light transmissivity. Prior to varying the number of channels in the light signal, the controller varies the light transmissivity of the optical attenuator so that a power level of the amplified light signal is maintained at an approximately constant level that depends on the number of channels in the light signal prior to the varying the number of channels. While the number of channels in the light signal is being varied, the controller maintains the light transmissivity of the optical attenuator to be constant. Subsequent to varying the number of channels in the light signal, the controller varies the light transmissivity of the optical attenuator so that a power level of the amplified light signal is maintained at an approximately constant level that depends on the number of channels in the light signal subsequent to the varying the number of channels.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical module calibration system
InactiveUS6590644B1Fluid pressure measurement using elastically-deformable gaugesMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical power meterEngineering
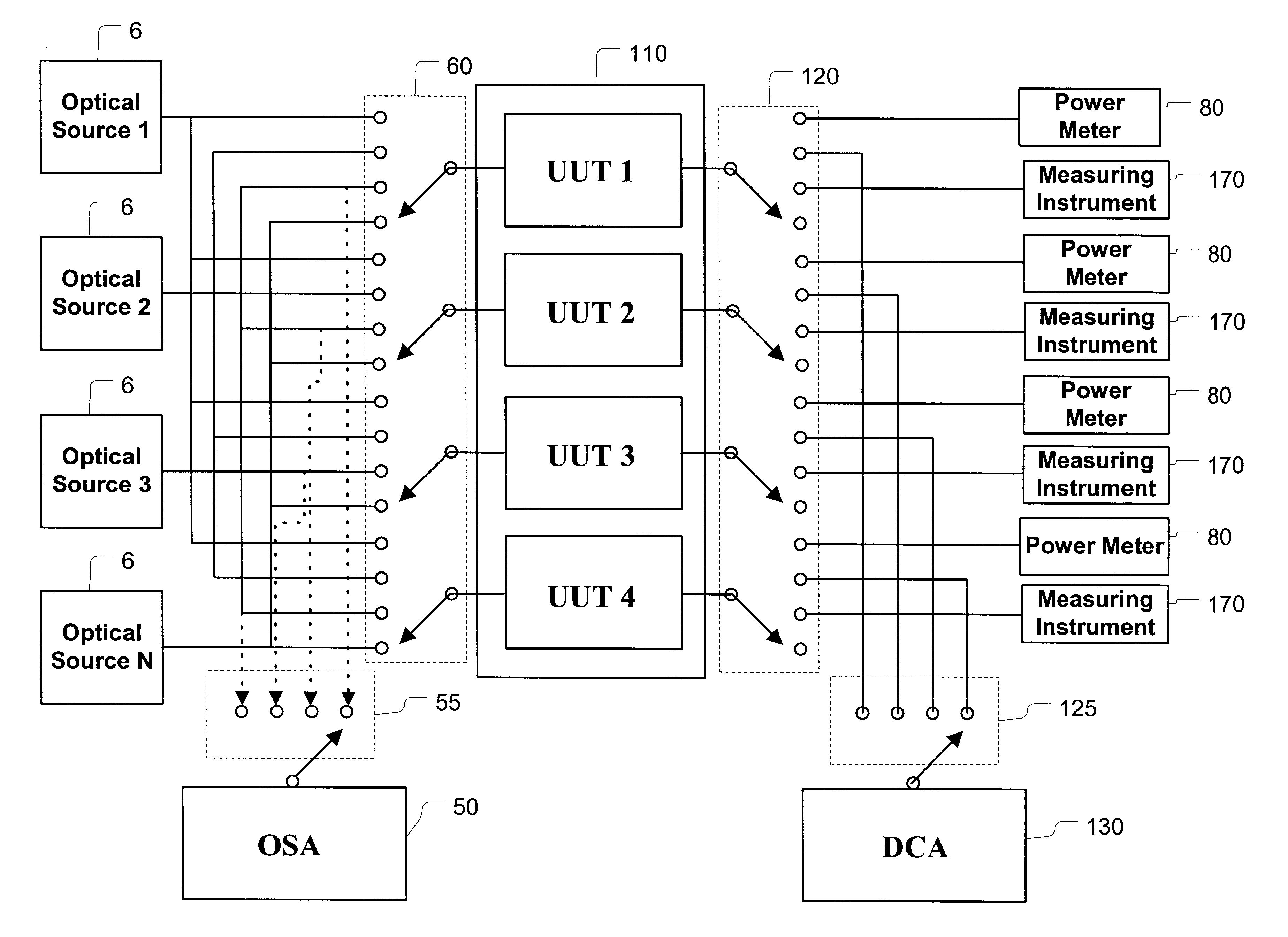
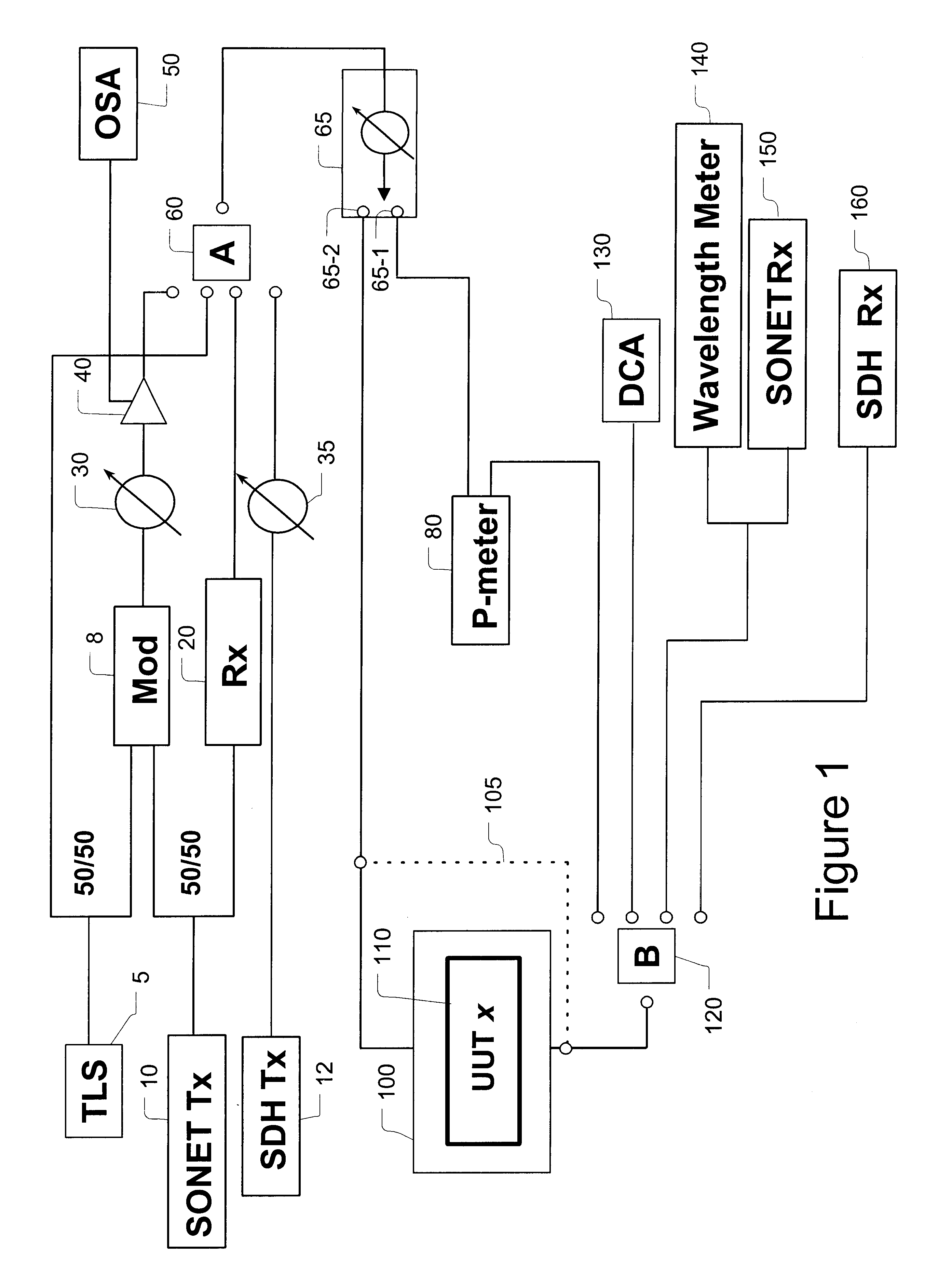
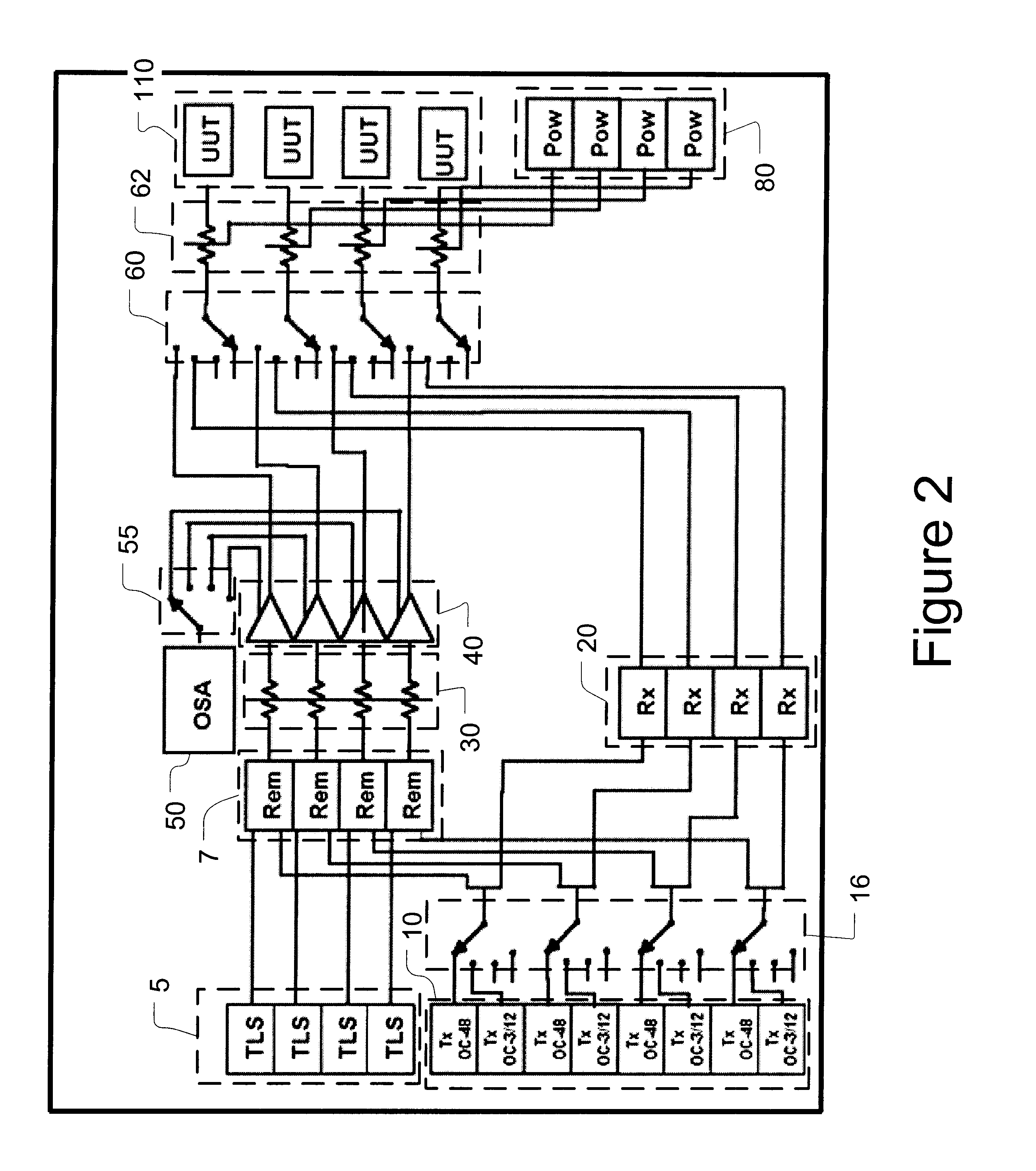
A system for calibrating a plurality of optical modules includes a plurality of optical signal sources and optical signal degradation elements optically communicating with input switches. The input switches supply optical test signals to optical modules (units under test) plugged into a common shelf. Calibration switches including variable optical attenuators may be used to adjust the input signal levels and alternately supply adjusted signals to an optical power meter and the units under test. A controller is used to control the adjustment and thereby provide defined, measured signal levels to the units under test. By reading data from the units under test and using these defined signal levels, the optical modules may be calibrated or diagnosed. Output optical switches are used in a similar fashion to calibrate or diagnose the outputs of the units under test. In addition to input / output power calibration, the invention may also perform wavelength calibrations.
Owner:CIENA
Variable optical attenuator systems
InactiveUS7333685B2Reduce lossPolarising elementsCoupling light guidesOptical attenuatorOptical polarization
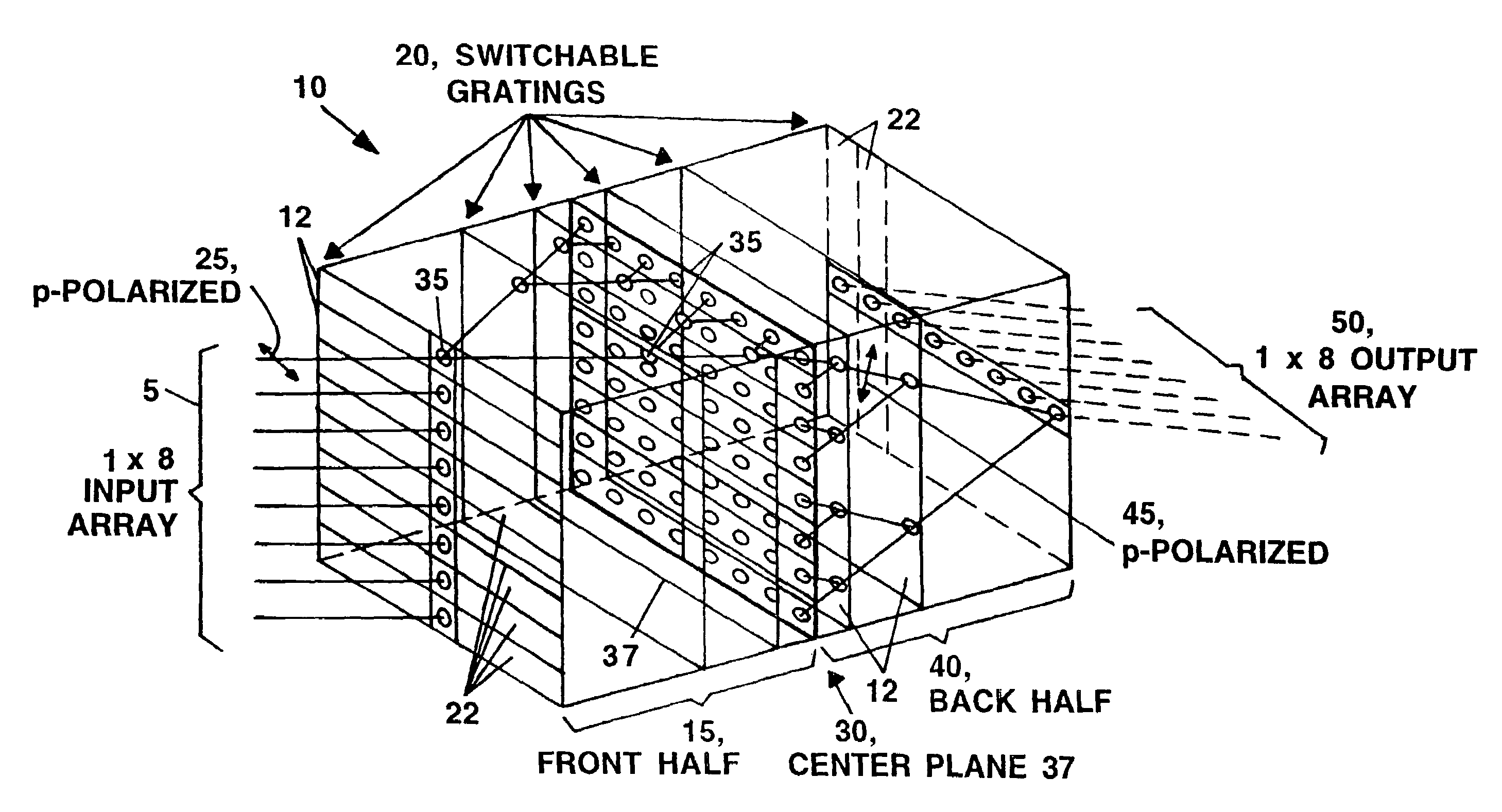
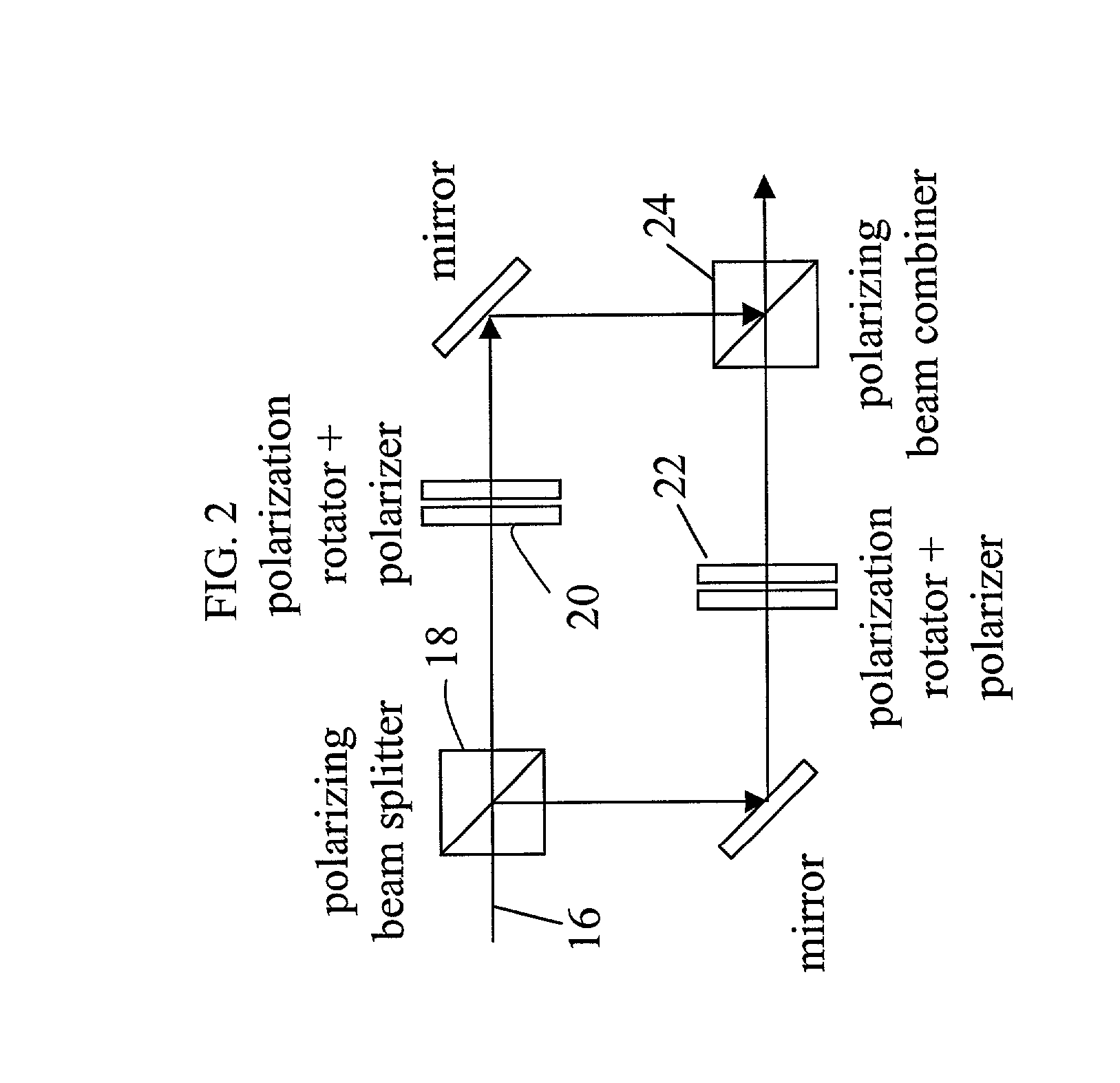
Low loss, reliable variable optical attenuators and 1×2 switches and polarization insensitive low loss, reliable variable optical attenuators and 1×2 optical switches are described. In one embodiment, a system of the present invention includes a polarization separating sub-system a polarization recombining sub-system and one or more switchable volume diffraction gratings to provide polarization insensitive low loss, reliable variable optical attenuators and 1×2 optical switches.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Micromachined voltage controlled optical attenuator
InactiveUS6343178B1Improve seismic performanceReduce the starting voltageMirrorsCoupling light guidesUltrasound attenuationSemiconductor structure
This invention provides a very sensitive optical attenuator, which can be used to couple and attenuate optical signals between optical fibers with a wide range of attenuation level. Such an optical attenuator includes a flexible conductive membrane to be moved by an external force, such as electrostatic force, to achieve deformation of the conductive membrane. The conductive membrane can be formed, for example, by a vacuum deposited silicon nitride film. A thin metallic, conductive layer is then deposited on the flexible membrane to form a reflective mirror to receive and reflect incident optical signals. The semiconductor structure includes one or more spacing posts, with which the first structural member is to be joined and bonded. Electrodes are placed on the semiconductor structure in close proximity to the flexible membrane. At various areas of the semiconductor structure, additional spacing posts are added to cause deformation of the conductive membrane when a voltage is applied between the membrane and the electrodes on the semiconductor structure.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Electrophoretic device having a transparent light state
ActiveUS20160026061A1Improved release flexibilityLow peel adhesionStatic indicating devicesCoatingsElectrophoresisEngineering
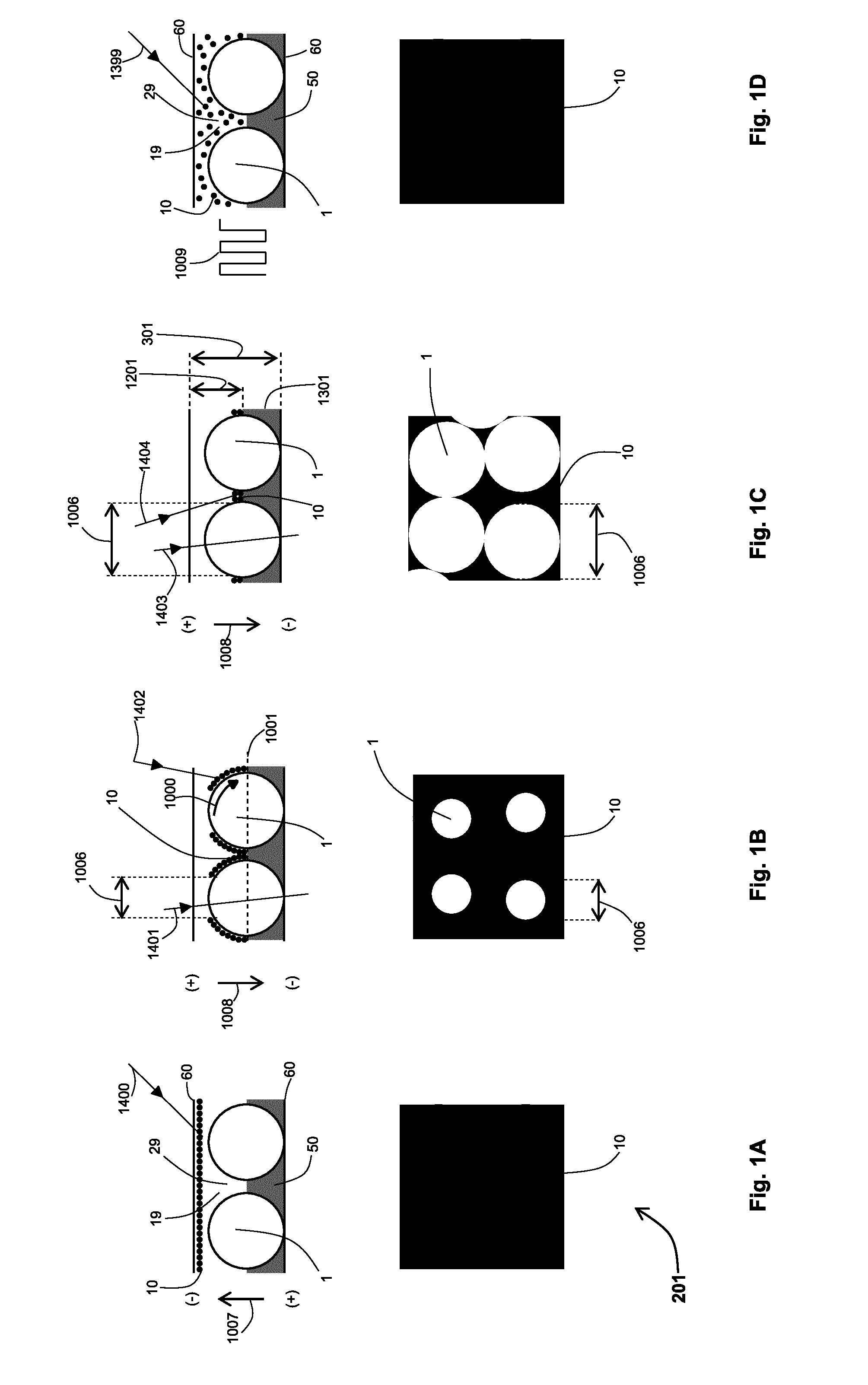
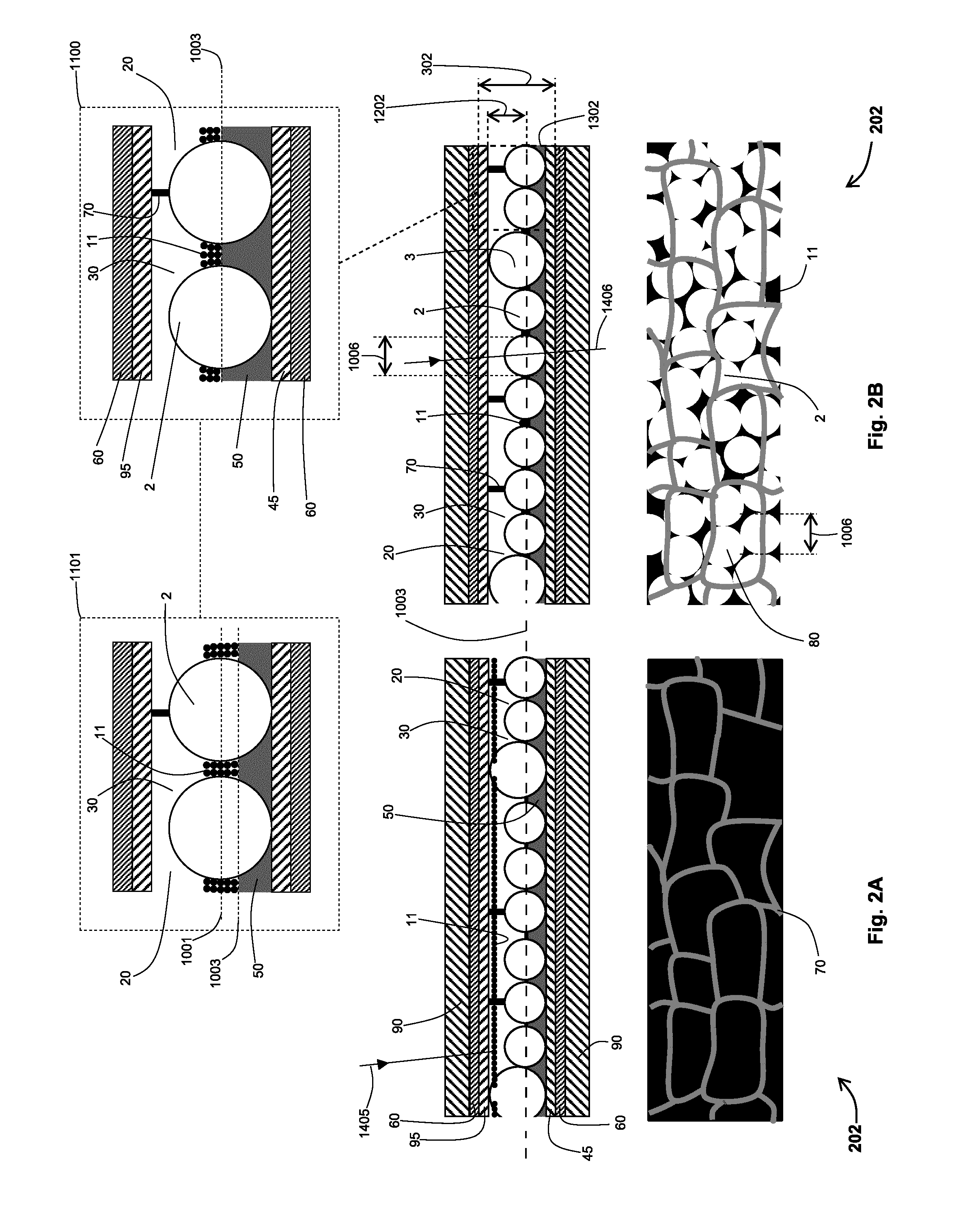
An electrophoretic light attenuator comprises a cell including a first substrate (90), a second substrate (90) spaced apart from the first substrate, a layer arranged between the substrates and containing an electrophoretic ink (30), and a monolayer of closely packed protrusions (2) projecting into the electrophoretic ink (30) and arranged adjacent a surface of the second substrate. The protrusions (2) have surfaces defining a plurality of depressions between adjacent protrusions. The ink (30) includes charged particles (11) of at least one type, the particles being responsive to an electric field applied to the cell to move between a first extreme light state, in which the particles (11) are maximally spread within the cell so as to lie in the path of light through the cell and thus strongly attenuate light transmitted from one substrate to the opposite substrate, and a second extreme light state, in which the particles (11) are maximally concentrated within the depressions so as to let light be transmitted.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Controller which controls a variable optical attenuator to control the power level of a wavelength-multiplexed optical signal when the number of channels are varied
InactiveUS6144485AReduce degradationWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical transmission with multiple stagesAudio power amplifierTransmittance
An optical amplifying apparatus which includes an optical amplifier, an optical attenuator and a controller. The optical amplifier amplifies a light signal having a variable number of channels. The optical attenuator passes the amplified light signal and has a variable light transmissivity. Prior to varying the number of channels in the light signal, the controller varies the light transmissivity of the optical attenuator so that a power level of the amplified light signal is maintained at an approximately constant level that depends on the number of channels in the light signal prior to the varying the number of channels. While the number of channels in the light signal is being varied, the controller maintains the light transmissivity of the optical attenuator to be constant. Subsequent to varying the number of channels in the light signal, the controller varies the light transmissivity of the optical attenuator so that a power level of the amplified light signal is maintained at an approximately constant level that depends on the number of channels in the light signal subsequent to the varying the number of channels.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
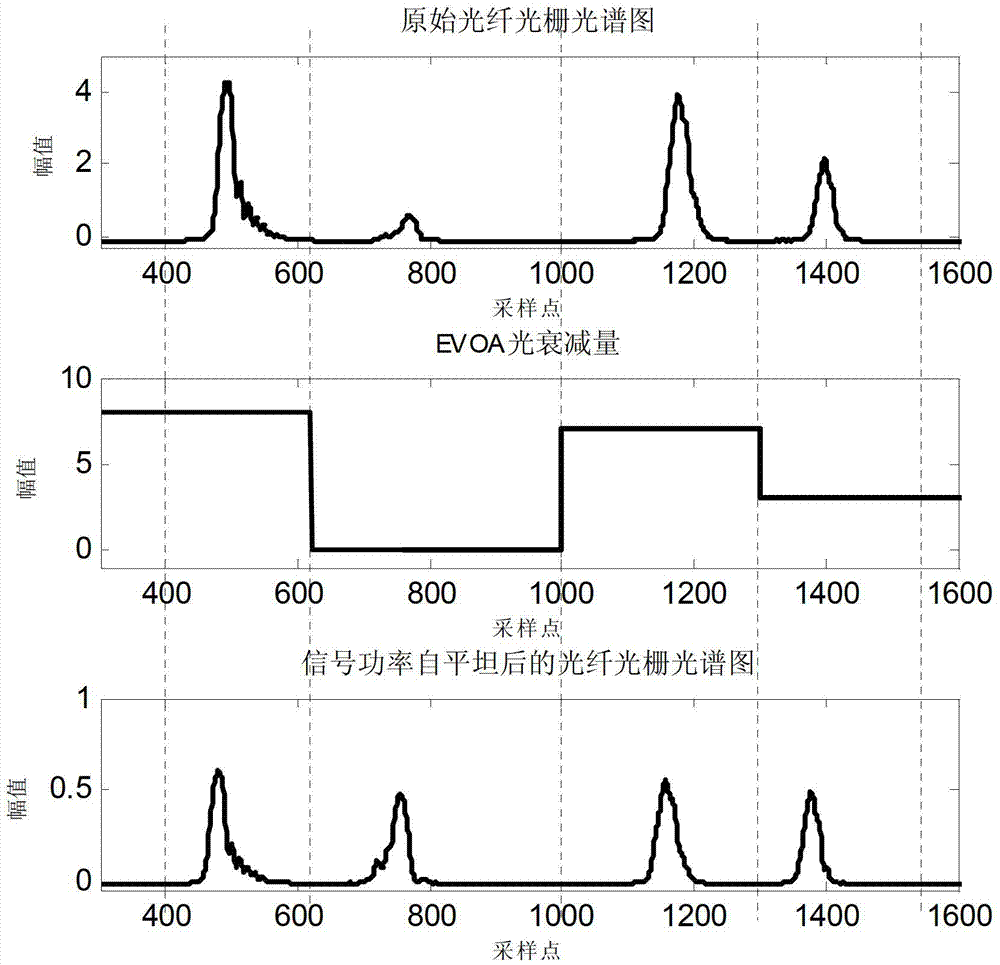
Demodulating device of multi-channel high-precision fiber grating sensing and demodulating method thereof
ActiveCN103196473AEasy to detectImprove detection accuracyConverting sensor output opticallyFiberGrating
The invention discloses a demodulating device of multi-channel high-precision fiber grating sensing and a demodulating method of the demodulating device of the multi-channel high-precision fiber grating sensing. According to the demodulating device of the multi-channel high-precision fiber Bragg grating sensing, a broadband light source, a turnable FP filter and a light amplifier are connected in series and form a turnable laser, and high-stability high-power turnable laser output is obtained. Reflected signal amplitude of a fiber bragging grating serves as dynamic feedback, and an electronic control variable optical attenuator is used for dynamically adjusting the optical power decrement corresponding to each fiber grating wavelength in real time. Therefore, a sending signal optical power with the high signal to noise ratio and the stable amplitude is obtained under the condition of each fiber grating wavelength. Unevenness of the light source and array arrangement of fiber grating sensors and unpredictable dynamic changes of the fiber grating sensors in the process of utilization are compensated compressively. Therefore, long-term detection ability and the detection precision of the fiber grating sensors are effectively improved. In addition, the demodulating device of the multi-channel high-precision fiber grating sensing and the demodulating method of the demodulating device of the multi-channel high-precision fiber grating sensing have a good application prospect in the aerospace field, in the aviation field, in the petrifaction field, in the construction field and in the power field.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
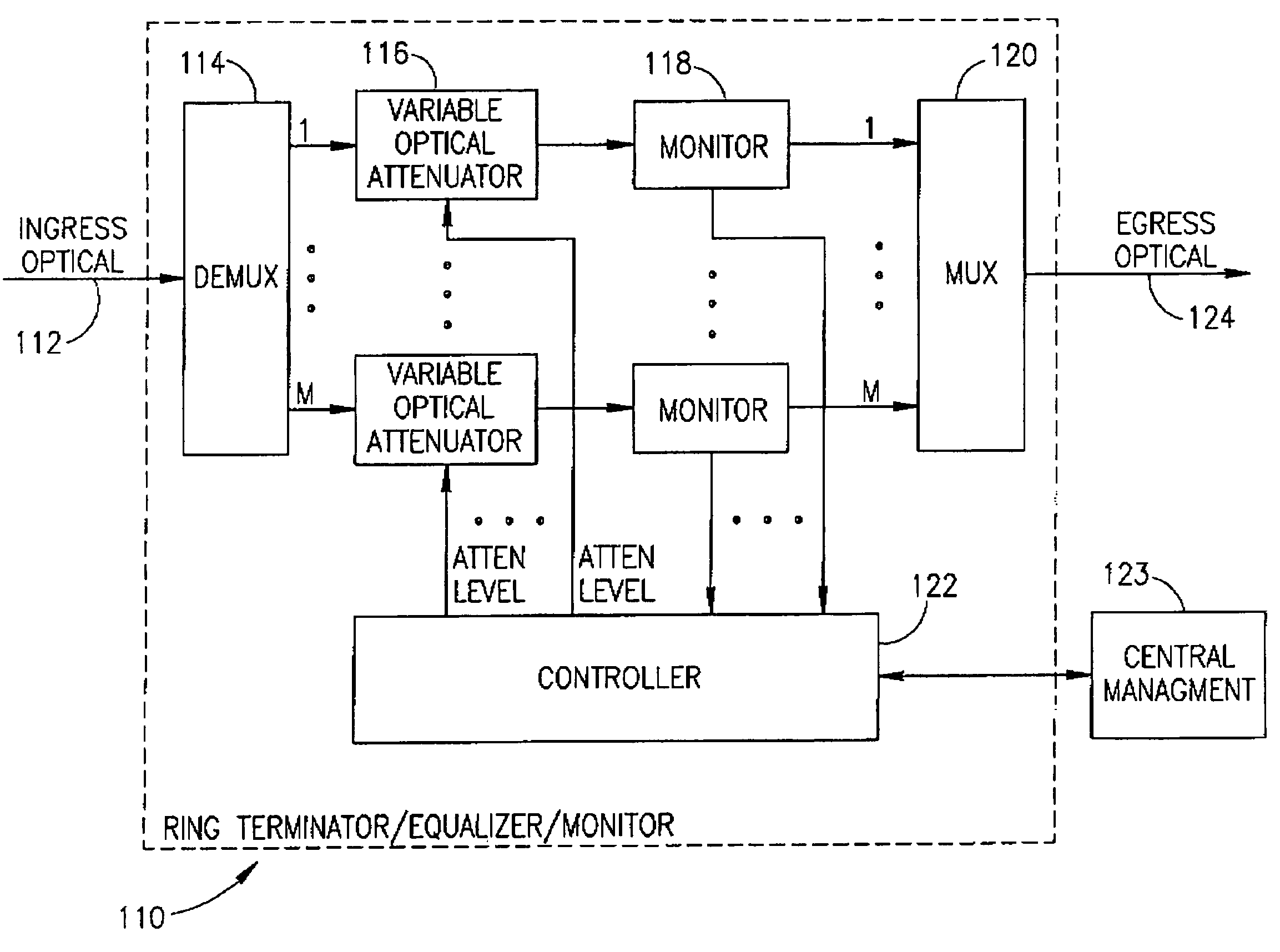
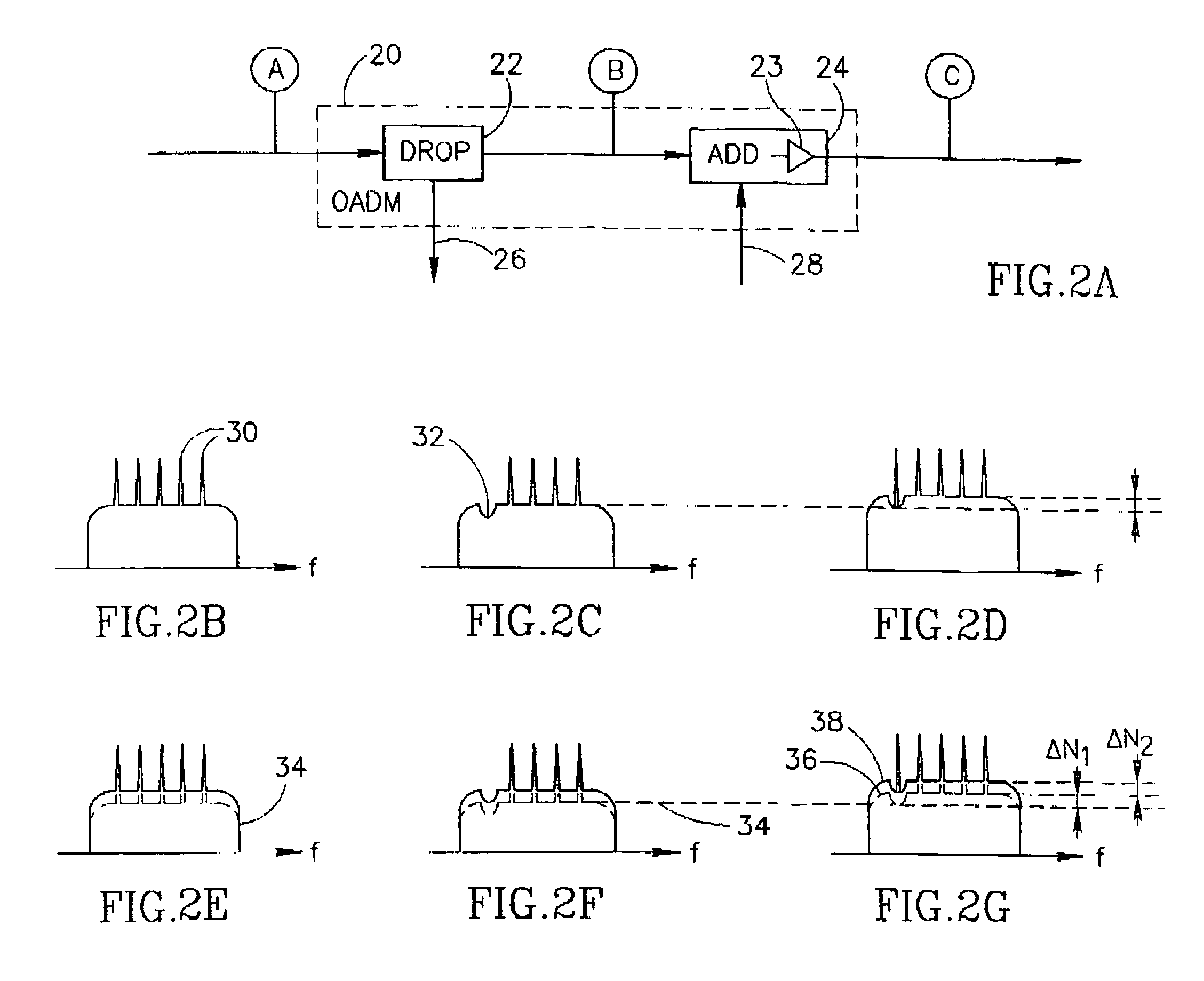
Optical network terminator
InactiveUS7106969B1Removing unwanted noiseEliminate the problemWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringAudio power amplifierFiber Bragg grating
An optical network terminator for terminating and reducing the accumulated noise in optical networks, particularly ring based networks. The terminator eliminates problems of noise accumulation from amplifier spontaneous emission (ASE), thermal noise, etc., while providing bi-directional communications in the optical network. The optical network may have any topology including ring, star, mesh, point-to-point, etc. In the case of an optical ring, the ring is broken and an optical terminator is placed in line therewith. The optical network terminator includes a filer such as an optical demultiplexer / multiplexer or Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) based filter. Each individual wavelength of light is filtered and a multi-wavelength optical output is generated whereby the noise accumulation is removed. Each channel is adapted to only pass a band-limited signal around the center frequency corresponding to the wavelengths supported by the particular optical ring network. Channel equalization uses variable optical attenuators and monitors in line with each channel. Channels currently not in use may be disconnected from the ring remotely by setting the corresponding optical attenuator to a low enough level.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING III
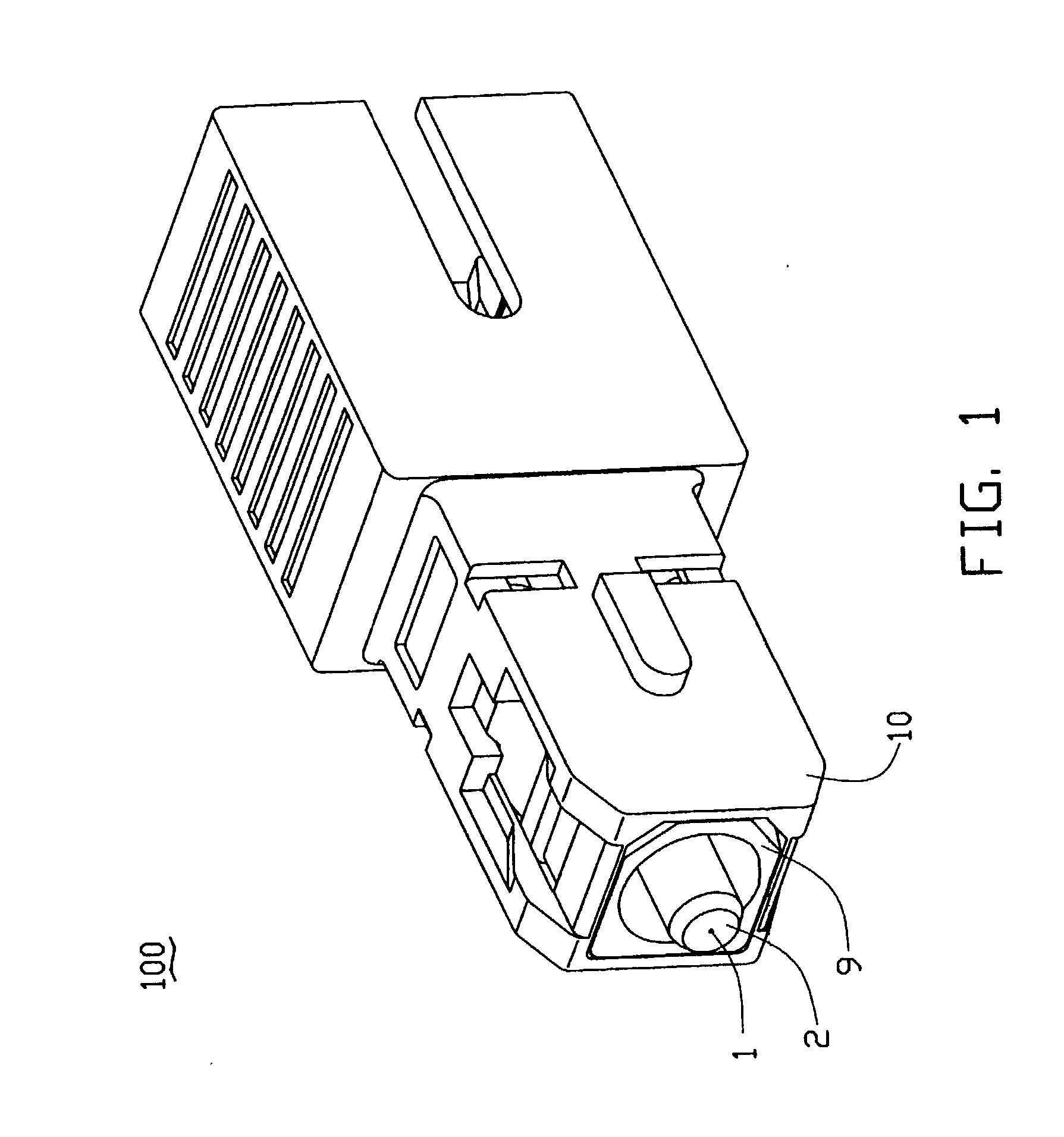
Optical attenuator
An optical attenuator (100) has an optical attenuation fiber (1) doped with cobalt. Two ferrules (2A), (2B) retain the optical attenuation fiber therein. Two butting ends of the ferrules are enclosed in a flange (6), which is received in a front end of an interconnection housing (7). An alignment sleeve (4) retains a rear end of the rear ferrule and is enclosed in a rear end of the interconnection housing. A latch (8) engages with the rear end of the interconnection housing. A plug housing (9) engages with the front end of the interconnection housing. A cover (10) then attaches over all the aforesaid components. A front end of the front ferrule is exposed outside the cover, for connecting with a complementary optical connector.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Terrestrial optical communication network of integrated fiber and free-space links which requires no electro-optical conversion between links
InactiveUS6868237B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsUltrasound attenuationLight beam
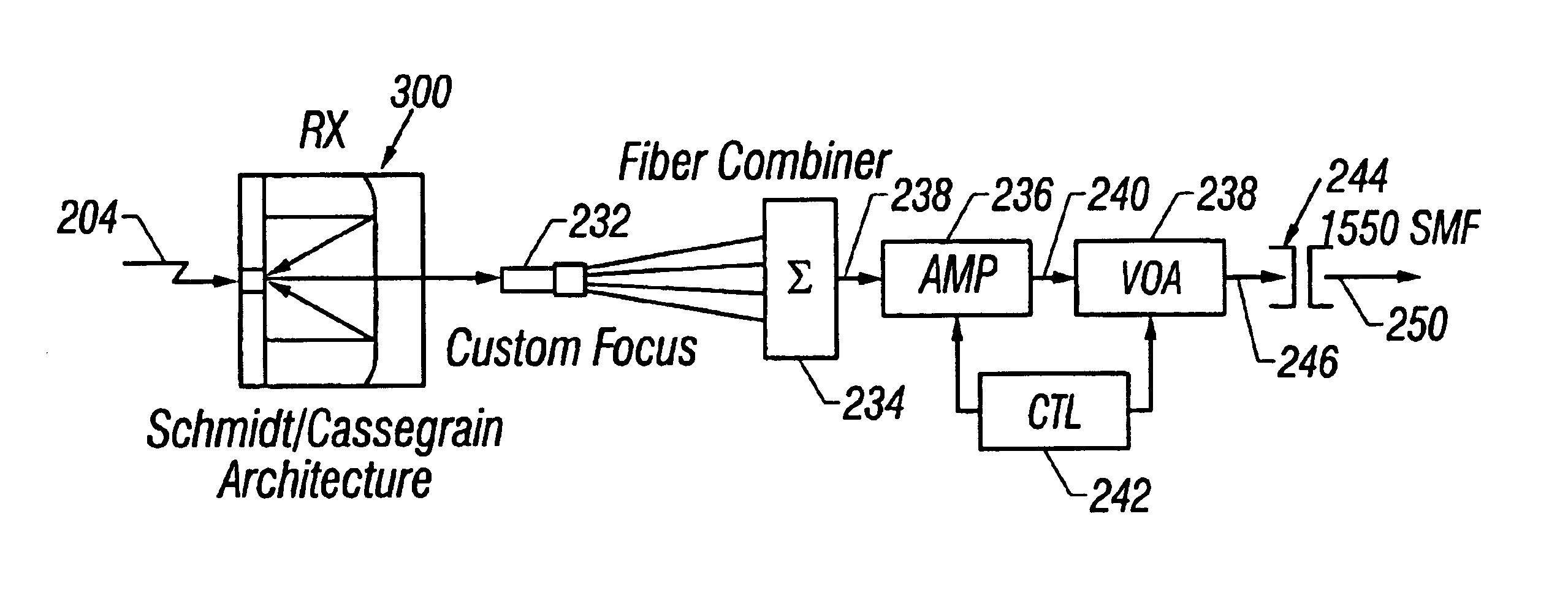
Optical signals are received from a free-space link by directing received light onto a plurality of microlenses and then directing light received through each of the microlenses into a respective single mode optical fiber (SMF). Light beams from the SMFs are combined into a single light beam in one SMF. The single light beam is amplified with a multi-wavelength fiber amplifier and attenuated with a variable optical attenuator. The power gain of the multi-wavelength fiber amplifier and the attenuation of the variable optical attenuator are controlled. The single light beam is directed into a fiber optic communication system that is optically coupled to the variable optical attenuator.
Owner:LIGHTPOINTE COMM
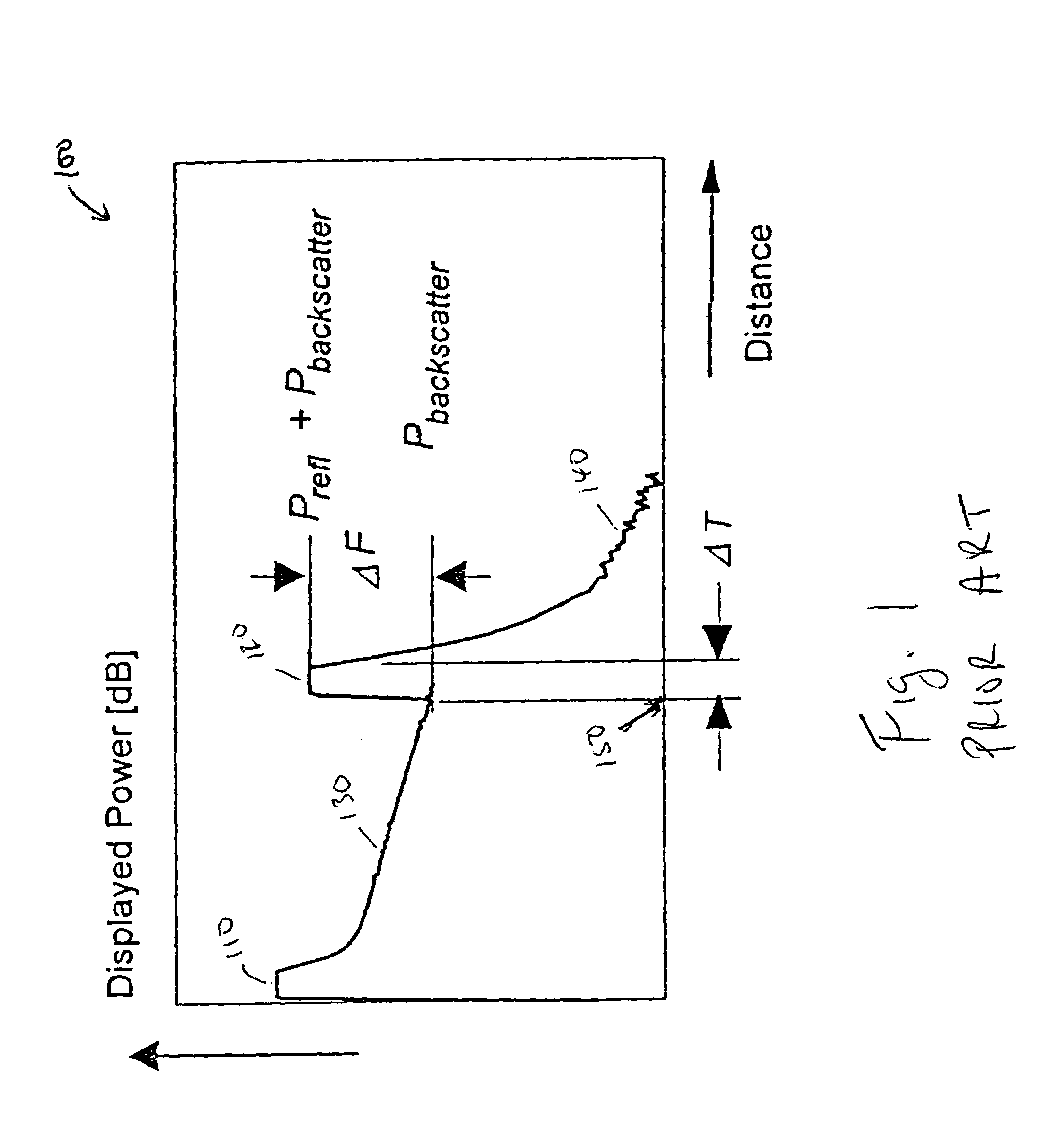
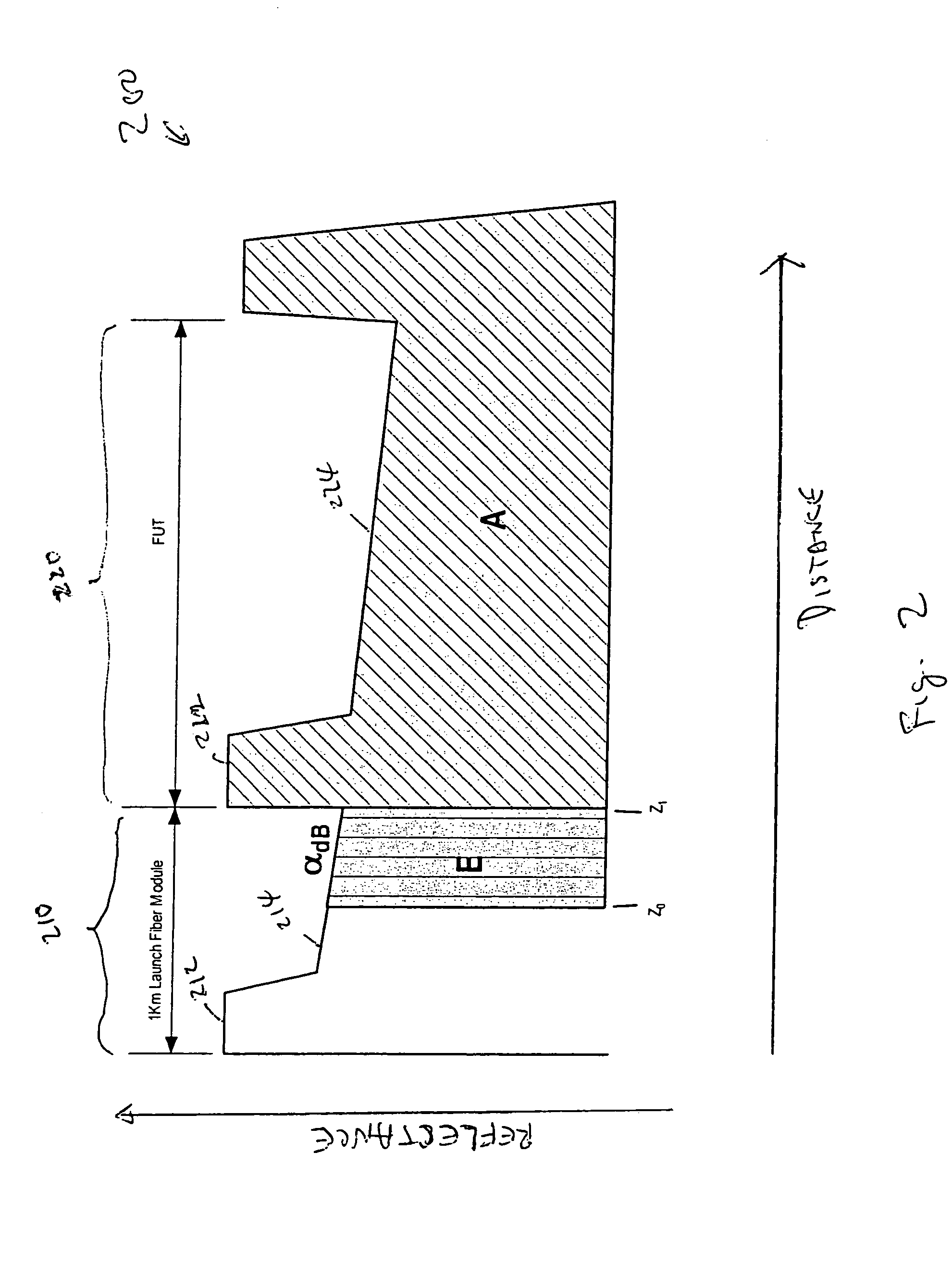
Accuracy automated optical time domain reflectometry optical return loss measurements using a "Smart" Test Fiber Module
InactiveUS7016024B2Eliminate conditionSuitable signal-to-noise ratioMaterial analysis by optical meansReflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domainFiberTime domain
The invention provides automated systems and methods for measuring ORL of fibers under test. A computer-based test instrument using OTDR tests fibers with the help of a STFM having predefined characteristics that are recorded in a machine-readable memory. The information recorded in the memory is accessible to the computer-based instrument and is used to calibrate a power level of an illumination source in real time using the reflectance response of the STFM. The calibrated illumination power allows the instrument to automatically determine the ORL of the fiber being tested with precision, and without requiring the intervention of an operator. The instrument also has the capability to automatically sense the presence of a test fiber, and to automatically attenuate the reflectance signal to remove a saturation condition by controlling at least one of the illumination, the detector gain, an amplifier gain, and an optional in-line optical attenuator.
Owner:NETTEST NEW YORK
Optical transmission system with automatic signal level adjustment and startup functions
ActiveUS20050158057A1Easy maintenanceEasy to operateWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsEngineeringOperation mode
An optical transmission system with automatic startup functions to optimize the power level of optical signals entering each optical amplifier and operate those amplifiers in appropriate mode. In the process of starting up an optical transmission system, upstream and downstream optical transmission devices set up themselves under the coordination of their internal controllers. The downstream device controller adjusts its local variable optical attenuator by utilizing optical noise emission from a post-amplifier in the upstream optical transmission device, and it selects and sets a preamplifier unit to work in appropriate operating mode. The upstream device controller, on the other hand, selects and sets operating mode of its local post-amplifier unit. During this process, the upstream and downstream device controllers exchange messages over supervisory control channels to achieve the purpose.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
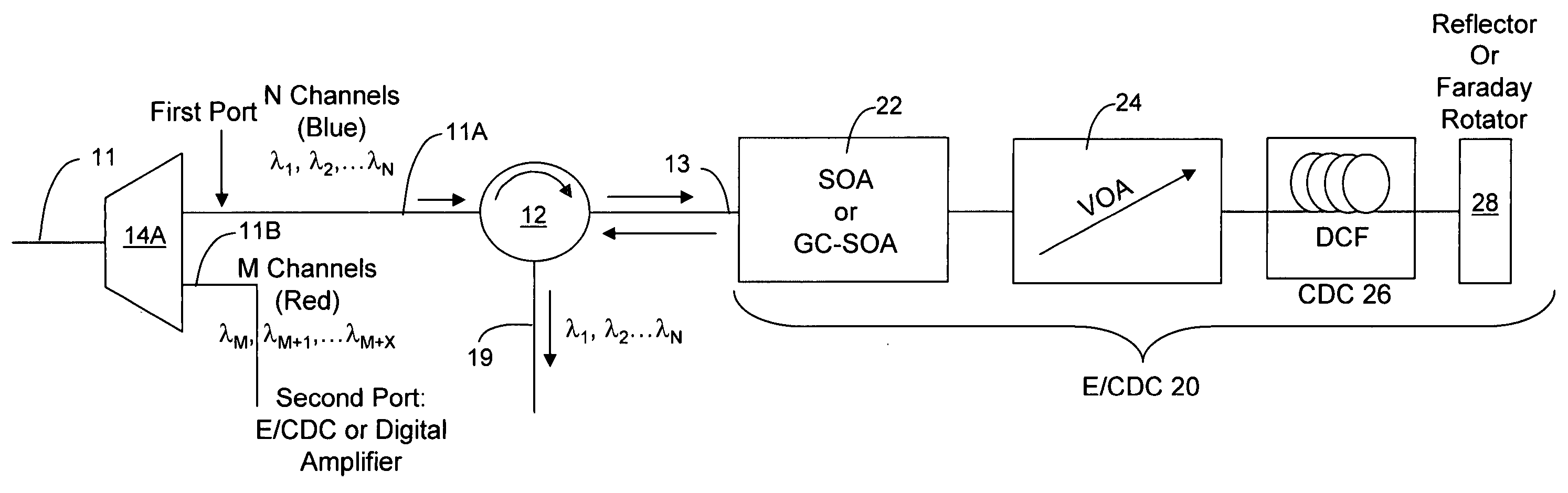
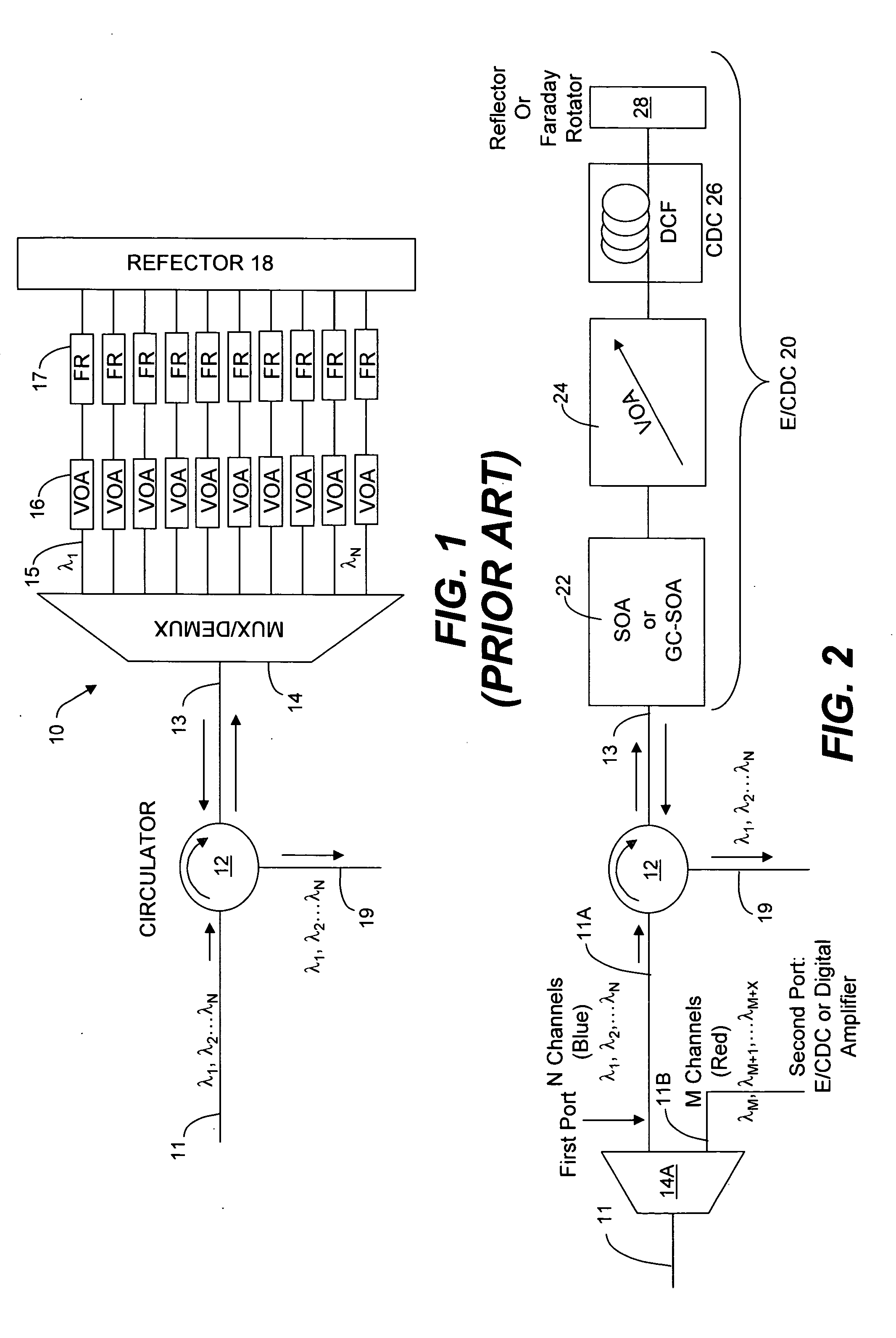
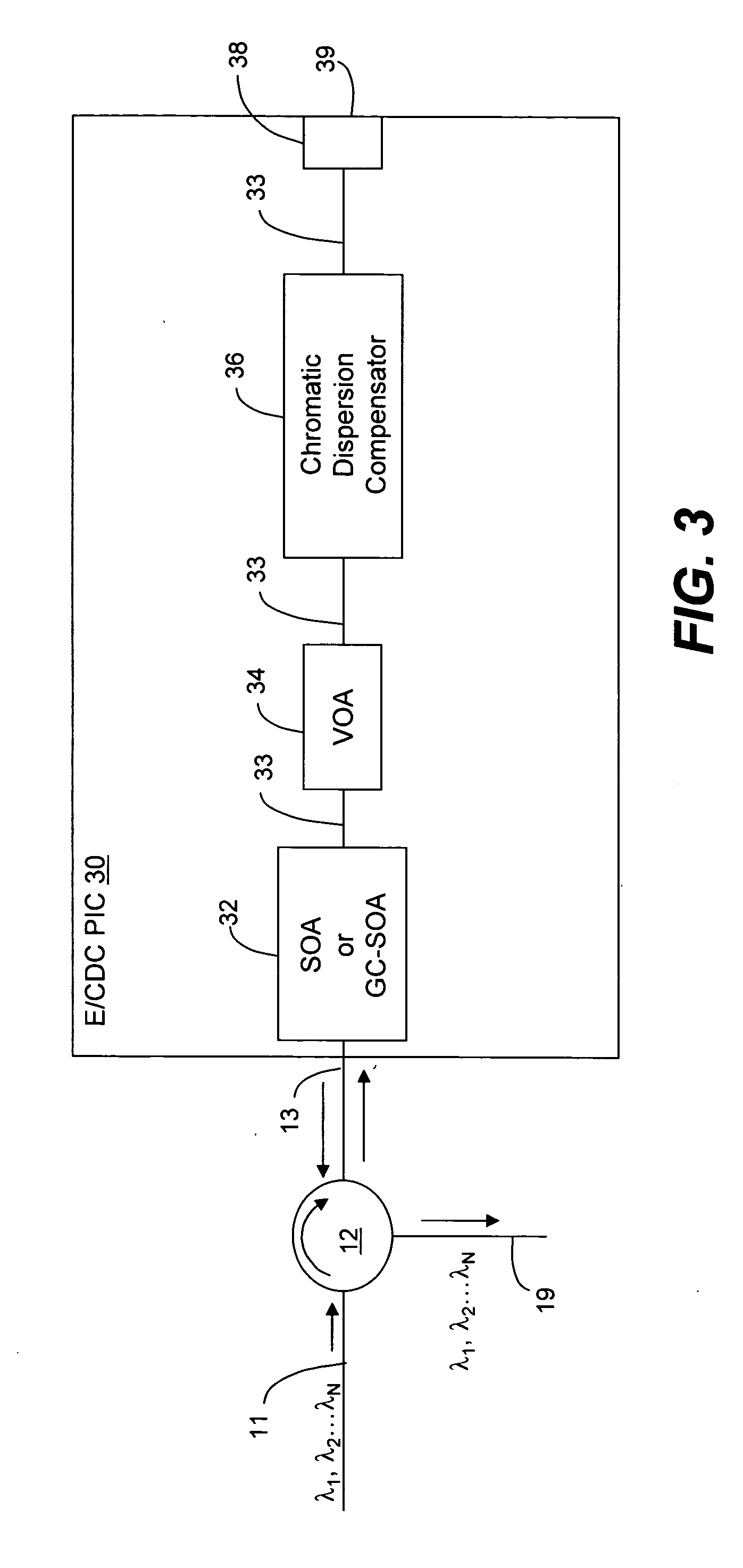
Chromatic dispersion compensator (CDC) in a photonic integrated circuit (PIC) chip and method of operation
InactiveUS20050111848A1Effective functionOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingWavelength-division multiplex systemsGratingMach–Zehnder interferometer
An optical equalizer / dispersion compensator (E / CDC) comprises an input / output for receiving a multiplexed channel signal comprising a plurality of channel signals of different wavelengths. An optical amplifier may be coupled to receive, as an input / output, the multiplexed channel signals which amplifier may be a semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA) or a gain clamped-semiconductor optical amplifier (GC-SOA). A variable optical attenuator (VOA) is coupled to the optical amplifier and a chromatic dispersion compensator (CDC) is coupled to the variable optical attenuator. A mirror or Faraday rotator mirror (FRM) is coupled to the chromatic dispersion compensator to reflect the multiplexed channel signal back through optical components comprising the chromatic dispersion compensator, the variable optical attenuator and the optical amplifier so that the multiplexed channel signal is corrected partially for equalization and chromatic dispersion compensation with respect to each pass through these optical components. The E / CDC components may be integrated in a photonic integrated circuit (PIC) chip. In several embodiments, a photonic integrated circuit (PIC) chip comprises an input into the chip that receives at least one channel signal having experienced chromatic dispersion, a chromatic dispersion compensator (CDC) that separates the at least one channel signal into separate wavelength components over a free spectral range (FSR) spanning only a signal channel width and subjects the wavelength components to a phase shift to change the wavelength group delay in the wavelength components and that recombines the wavelength components to reconstitute the at least one channel signal, and an output from the chip for the recombined at least one channel signal having reduced chromatic dispersion compared to the same channel signal received at the chip input. The CDC device may include a tuning section to vary the phase shift of wavelength components as they propagate through the device. Such a CDC device may include a Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZI) or a cascaded group of Mach-Zehnder interferometers, or at least one arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) or at least one Echelle grating.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
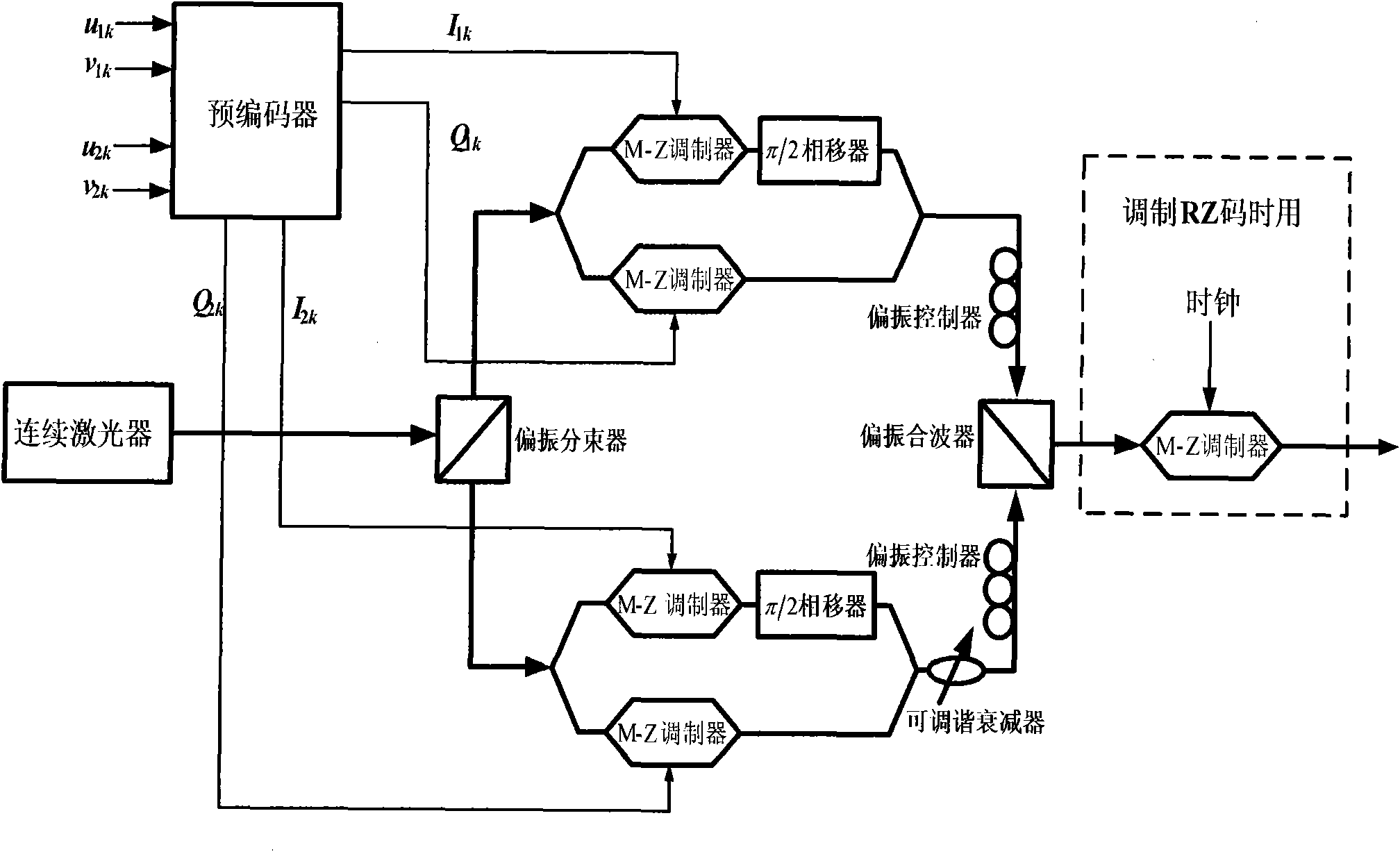
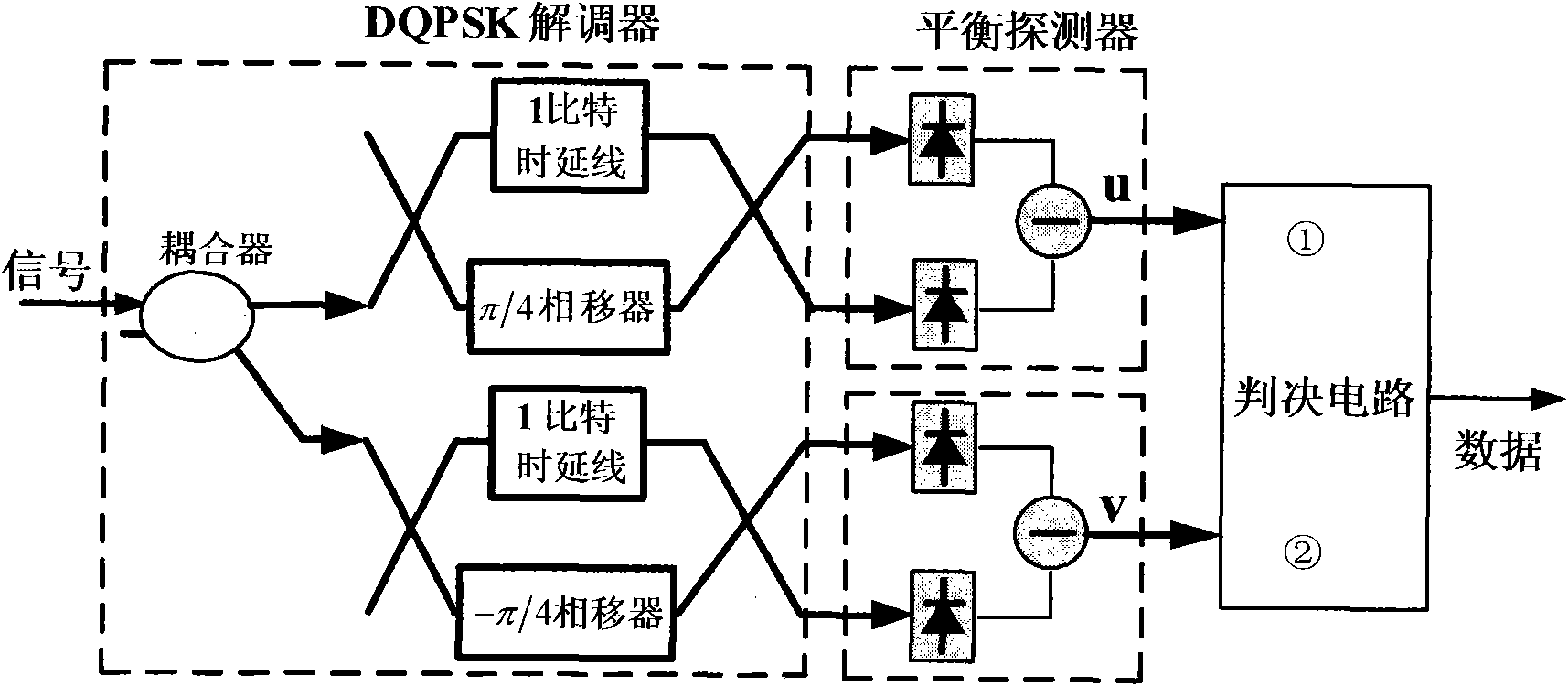
Method and system for transmitting and receiving by orthogonally dual-polarized differential quaternary phase shift keying
InactiveCN101895495AImprove stabilityReduce complexityPhase-modulated carrier systemsDecision circuitPolarization beam splitter
The invention relates to a method and a system for transmitting and receiving by orthogonally dual-polarized differential quaternary phase shift keying. The system comprises a transmitting device and a receiving device, wherein the transmitting device comprises a continuous laser; the continuous laser is connected with a polarization beam splitter which is connected with a DQPSK modulator; the DQPSK modulator is connected with a precoder of which the output end is connected with a tunable optical attenuator or a polarization controller; and the polarization controller is connected with a polarization beam combiner; and the receiving device comprises a DQPSK demodulator, and the DQPSK demodulator is connected with a balanced detector which is connected with a decision circuit. In the method, four paths of electrical signals can be multiplexed, and only one demodulator and two balanced detectors are used at a receiving end to demodulate two orthogonally polarized DQPSK signals at the same time; therefore, compared with D8PSK and x-QAM systems, the system has the advantages of greatly reducing the complexity and remarkably enhancing the stability of components.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Integrated variable optical attenuator and related components
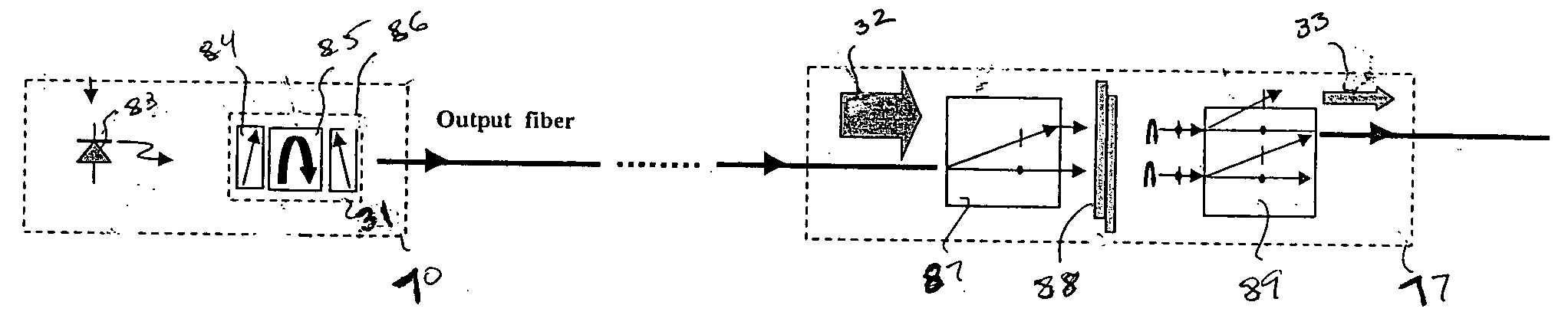
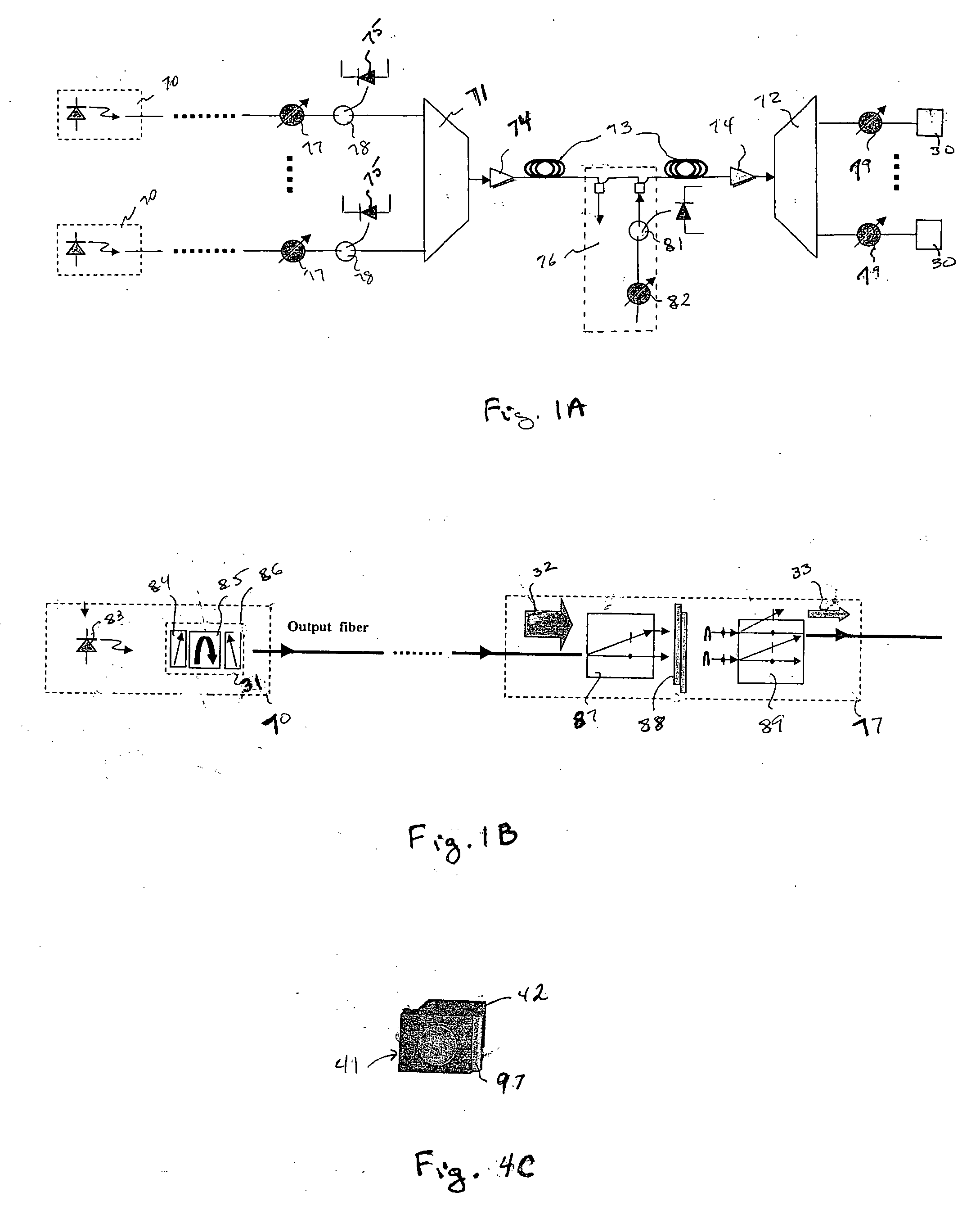
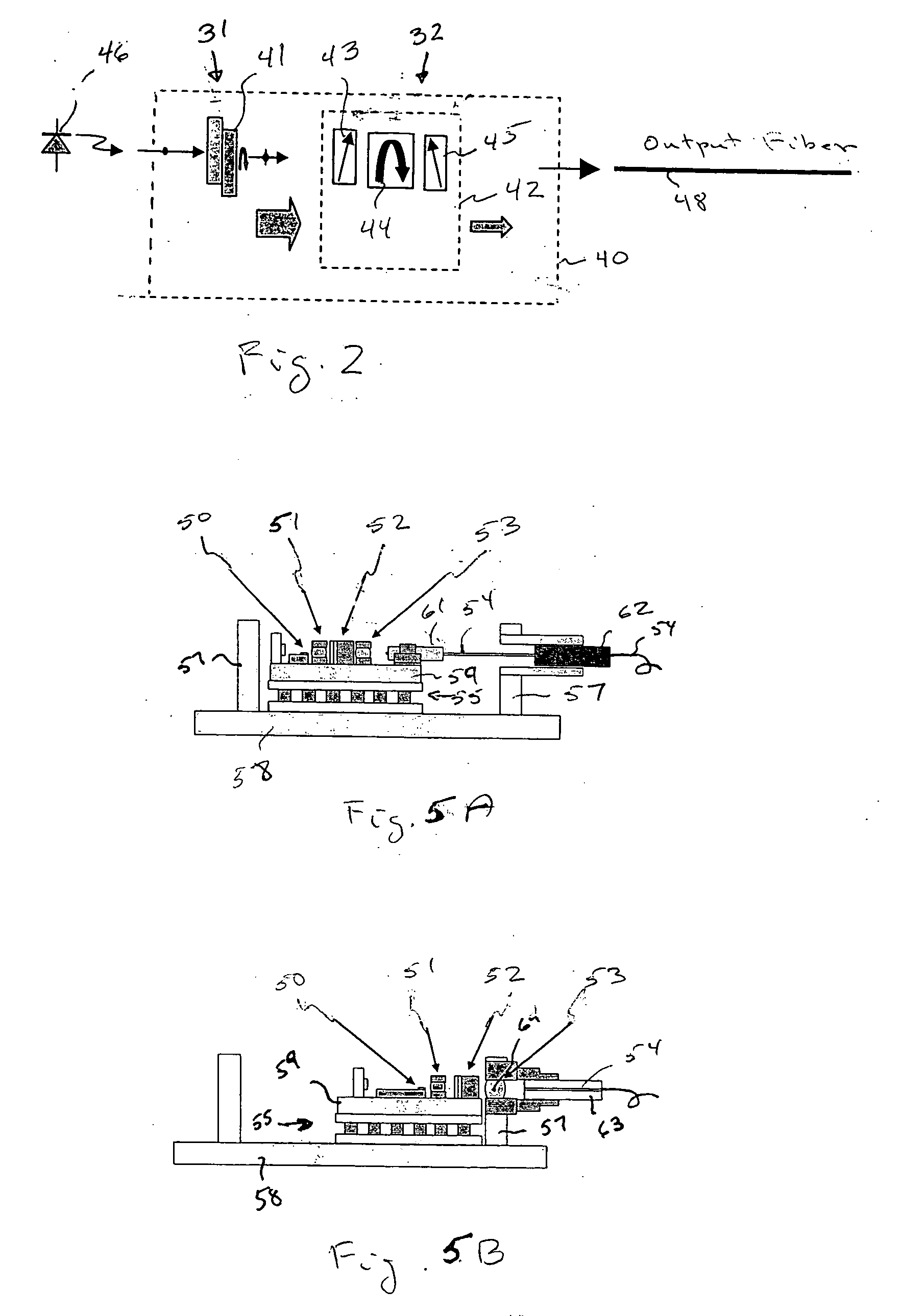
A polarization element and a polarization-sensitive optical isolator are integrated to form an integrated VOA. A preferred embodiment uses a liquid crystal cell as the polarization element to which is attached an optical isolator core of a first polarizer, Faraday rotator, and second polarizer. Voltage on the liquid crystal cell electrodes controls the amount of polarized light from the liquid crystal cell passing through the first polarizer and light in the opposite direction is blocked. The integrated VOA can be mounted within a laser device package so that the power of the source laser diode on the output fiber can be controlled and yet the laser diode is protected from light undesirably entering laser device package through the output fiber.
Owner:LIGHTWAVES 2020
Semiconductor monolithic integrated optical transmitter
InactiveUS20050006654A1Minimizing distortion of lightIncrease powerLaser detailsSolid-state devicesGratingElectro-absorption modulator
A semiconductor monolithic integrated optical transmitter including a plurality of active layers formed on a semiconductor substrate is disclosed, which comprises: a distributed feedback laser diode including a grating for reflecting light with a predetermined wavelength and a first active layer for oscillating received light from the grating; an electro-absorption modulator including a second active layer for receiving light from the first active layer, wherein the received light intensity is modulated through a change of absorbency in accordance with an applied voltage; an optical amplifier including a third active layer for amplifying received light from the second active layer; a first optical attenuator between the first active layer and the second active layer; and a second optical attenuator between the second active layer and the third active layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical fiber having enhanced separation of higher-order modes
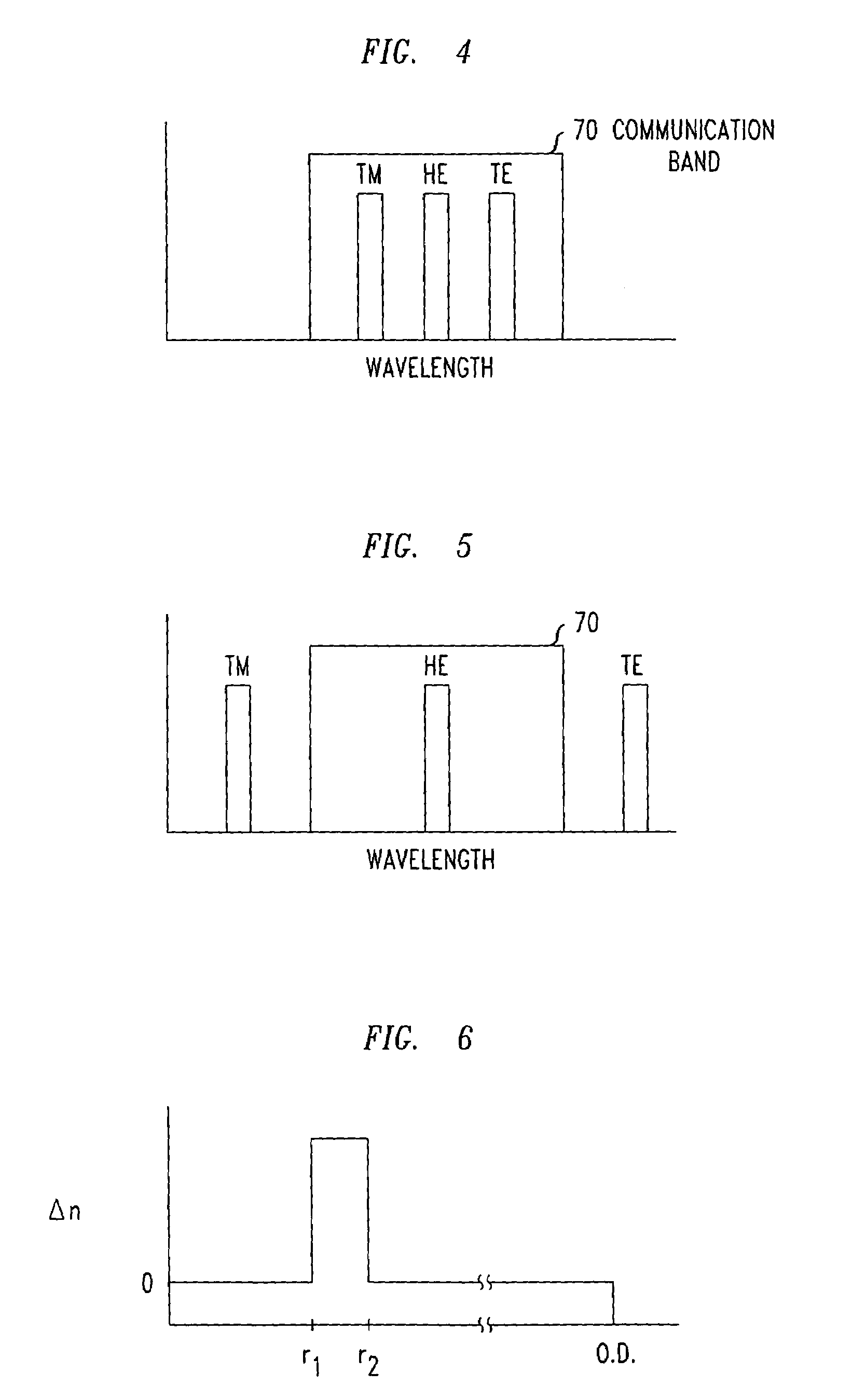
A new annular-core optical fiber is useful, inter alia, for stabilizing the behavior of an optical attenuator based on a Long Period Grating (LPG) against fluctuations in the polarization of the fundamental optical signal. The fiber dimensions and Δn are selected such that when a LPG of some period is used to couple fundamental-mode radiation in the fiber into higher-order modes, the wavelength of peak coupling into an HE mode is removed by at least 30 nm from the wavelength of peak coupling into the nearer of a TE mode or a TM mode.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
High-speed autocompensation scheme of quantum key distribution
ActiveUS20180191496A1Key distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationBeam splitterQuantum channel
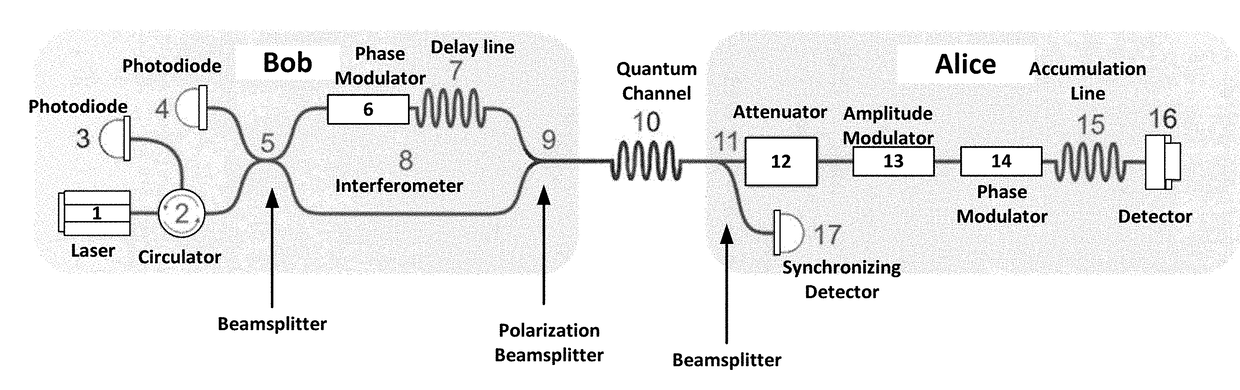
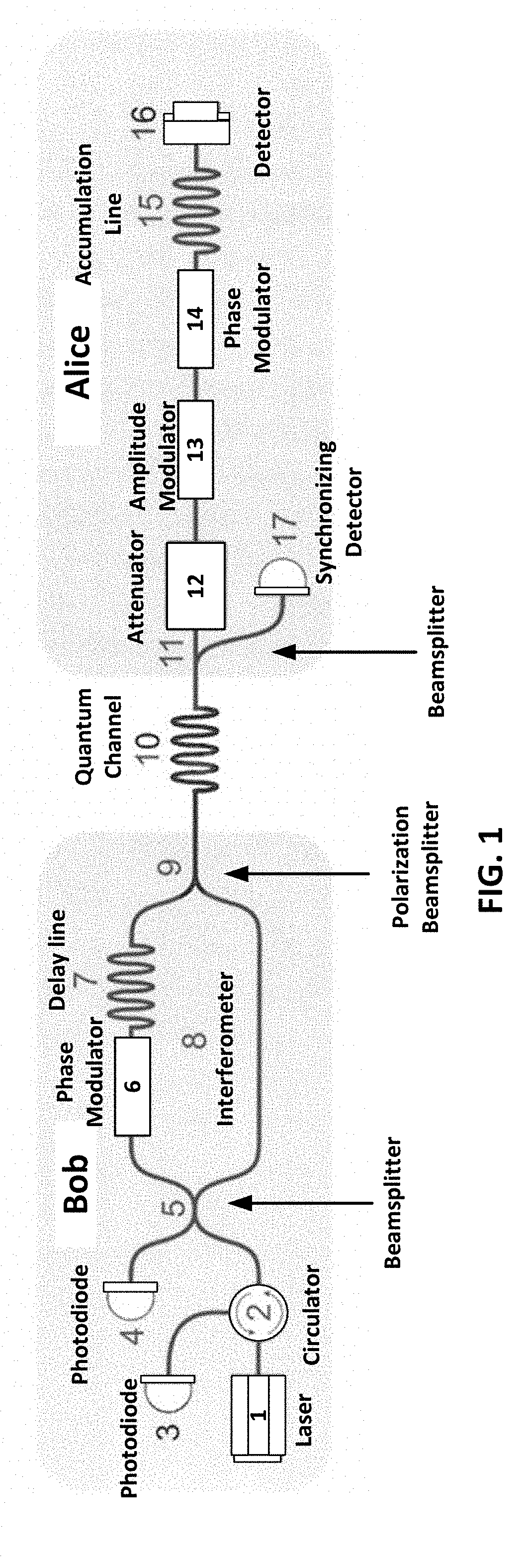
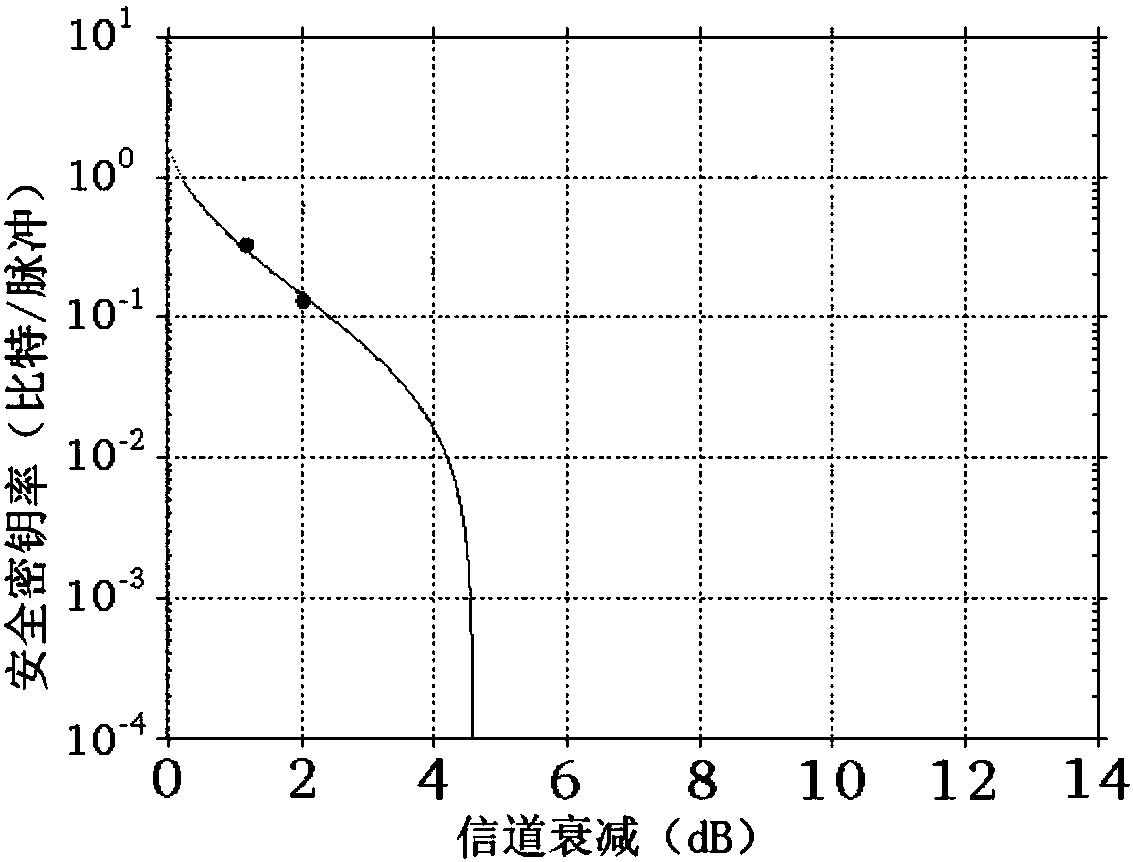
The invention relates to quantum cryptography, and includes a communication system for transmitting a cryptographic key between the ends of a channel, including a transmitting node (Alice) comprising a beam splitter, an electro-optical attenuator, an amplitude modulator, a phase modulator, a storage line, a Faraday mirror, a synchronization detector; a receiving node (Bob) that includes avalanche photodiodes, a beam splitter, a circulator, a delay line, a phase modulator, a polarizing beam splitter, a Mach-Zehnder interferometer, and also a quantum channel for connecting these nodes. In this case, for the storage line is placed between the electro-optical phase modulator of the sender and the Faraday mirror. The limiting frequency of the laser pulse repetition at a fixed value of their width is increased, which makes it possible to use an autocompensation circuit at a frequency corresponding to the width of the laser pulse, which is the maximum possible result.
Owner:QRATE LLC
Single-chip magnetic sensor, and laser heating-assisted annealing apparatus thereof and laser heating-assisted annealing method thereof
ActiveCN102208530AHigh sensitivityGood magnetoresistance matchingMagnetic measurementsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsOptoelectronicsOptical attenuator
The invention discloses a single-chip magnetic sensor, and a laser heating-assisted annealing apparatus thereof and a laser heating-assisted annealing method thereof. The laser heating-assisted annealing method comprises the following steps: (a), annealing is carried out on a magnetic thin film in a strong magnetic field, so that magnetic moments on a pinning layer of the magnetic thin film are towards a same direction; (b), the magnetic thin film is fixedly disposed on a clamp of a movable platform; (c), a laser source is opened to emit a laser beam, which is attenuated through an optical attenuator; the direction of the attenuated laser beam is changed through a reflective mirror; and the laser beam with the changed direction is focused into a light spot by a focusing objective lens; (d), the movable platform is moved, in order that the focused light spot of the laser beam is aimed at the magnetic thin film so as to enable the magnetic thin film to be heated by the laser beam; (e), a magnetic field intensity of an electromagnet arranged on the movable platform is adjusted, so that a magnetic domain of the heating area of the magnetic thin film can be overturned; and (f), the magnetic thin film is cut into slices, and the slices of the cut magnetic thin film are bound into one.
Owner:MULTIDIMENSION TECH CO LTD
Switch and variable optical attenuator for single or arrayed optical channels
An assembly that could be used either as a switch or an attenuator includes two or more optical channels defined by lithography within a substrate. The two or more optical channels are positioned so that the ends of the optical channels are at or near an edge of the substrate. A moveable MEMS mirror is positioned near the edge of the substrate and the openings, with the face of the mirror positioned to receive an optical signal from one of the optical channels. The mirror can direct an optical signal from one of the optical channels into another of the optical channels. Mirror position can be changed to alter the path of the optical signal and to change the coupling between the optical channels. In this way, the assembly of optical channels within the substrate and the MEMS mirror can act as a switch or as an attenuator.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD CO +1
Microwave frequency measuring method based on optical power detection and device thereof
InactiveCN101567723AReduce complexityLow costTransmission monitoringElectromagnetic transmissionContinuous lightCarrier signal
The invention discloses a microwave frequency measuring method based on optical power detection and a device thereof, which conducts real-time measurement on microwave frequency by adopting a system consisting of an electro-optical modulating module and a frequency demodulating module. A continuous microwave signal is loaded on a continuous light source in the modulating module in the modulating manner of carrier suppressed small signals, and only generates two plus or minus 1 stage optical margin strips; the modulated optical signal is divided into two paths, wherein one path is injected into a comb-like filter with sine-function transmission spectrum while the other path is injected into a tunable optical attenuator; the output optical power of the two paths are detected and compared with each other and the microwave frequency is obtained from the demodulation of power ratio. The invention lowers the complexity and cost of the system, eliminates the influence of fluctuation of output power of the light source on the measurement of the frequency and enlarges the measuring frequency band of frequency linear demodulation.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Accuracy automated optical time domain reflectometry optical return loss measurements using a "Smart" Test Fiber Module
InactiveUS20050259242A1Eliminate conditionSuitable signal-to-noise ratioMaterial analysis by optical meansReflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domainFiberTime domain
The invention provides automated systems and methods for measuring ORL of fibers under test. A computer-based test instrument using OTDR tests fibers with the help of a STFM having predefined characteristics that are recorded in a machine-readable memory. The information recorded in the memory is accessible to the computer-based instrument and is used to calibrate a power level of an illumination source in real time using the reflectance response of the STFM. The calibrated illumination power allows the instrument to automatically determine the ORL of the fiber being tested with precision, and without requiring the intervention of an operator. The instrument also has the capability to automatically sense the presence of a test fiber, and to automatically attenuate the reflectance signal to remove a saturation condition by controlling at least one of the illumination, the detector gain, an amplifier gain, and an optional in-line optical attenuator.
Owner:NETTEST NEW YORK
Methodology for a MEMS variable optical attenuator
InactiveUS6980727B1Improve service delivery timeEasy networkingCoupling light guidesUltrasound attenuationGrating
An improved cantilever beam optical switch methodology which provides the function of a variable optical attenuator (VOA). A small degree of intentional misalignment of the waveguide will create different levels of optical attenuation. By finely controlling the misalignment of a selected switched position, a single device may be realized that will provide the functions of both switching and attenuating or just attenuation alone. The optical MEMS device utilizes a latching mechanism in association with a thermal drive actuator for aligning a cantilever beam platform. The integration of the switching function and the VOA function reduce the optical loss which is otherwise unavoidable when the inevitable alterative of a separate switch and a separate VOA must necessarily be employed. The resultant improved device can also be applied for correcting the difference in optical intensity created by the manufacturing tolerances inherent in the fabrication of array waveguide gratings.
Owner:XEROX CORP
In-guide control of optical propagation
InactiveUS6859567B2Improve efficiencyCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsOptical propagationRefractive index
We propose a dynamically tunable electro-optic cladding using our proprietary electro-optic material, applied to various circular and planar wave-guides along with specific electrode configuration and excitation electric field format appropriate to that material. Based on the evanescent field coupling phenomena, the proposed device may be used in variable optical attenuators, tunable filters and couplers, etc. Different design of applied electrodes and optical properties of controllable refractive index materials allow polarization dependent or independent, as well as direct or inverse operation regimes of proposed devices.
Owner:PHOTINTECH
Nozzle arc temperature non-contact measurement system based on optical fiber transmission
InactiveCN103884449ARealize dynamic measurementEnhanced ability to avoid tight spacesThermometers using physical/chemical changesData acquisitionLight spectrum
A nozzle arc temperature non-contact measurement system based on optical fiber transmission comprises an optical acquisition and processing system, a photoelectric converting system and a data processing unit. According to the nozzle arc temperature non-contact measurement system based on the optical fiber transmission, the optical fiber sensing technology is combined with optical signal processing device modulation and detection of optical wave characteristic parameters in the optical fiber transmission to achieve dynamic measurement on temperature physical quantity, and the system has the advantages of being good in beam quality, strong in anti-interference capacity, compact and compositive in structure, high in measurement precision, free of disturbance on arc fields, safe, reliable, fast in dynamic response speed and the like, and the problem that optical signals in a nozzle are difficult to sample is solved. Real-time control over dynamic saturation of optical signals and adjustment of dynamic gain balance can be achieved by using a variable optical attenuator. Monochromatic light beams of different characteristic wavelengths are separated through a wavelength division multiplexer, and an integration level is high. An infrared radiation thermometry and a visible spectrum thermometry are combined, the arc temperature is obtained by adopting a digital processing unit through operation of a relative spectral line intensity method, a dynamic measurement range is enlarged, and the dynamic response speed of measurement is improved.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
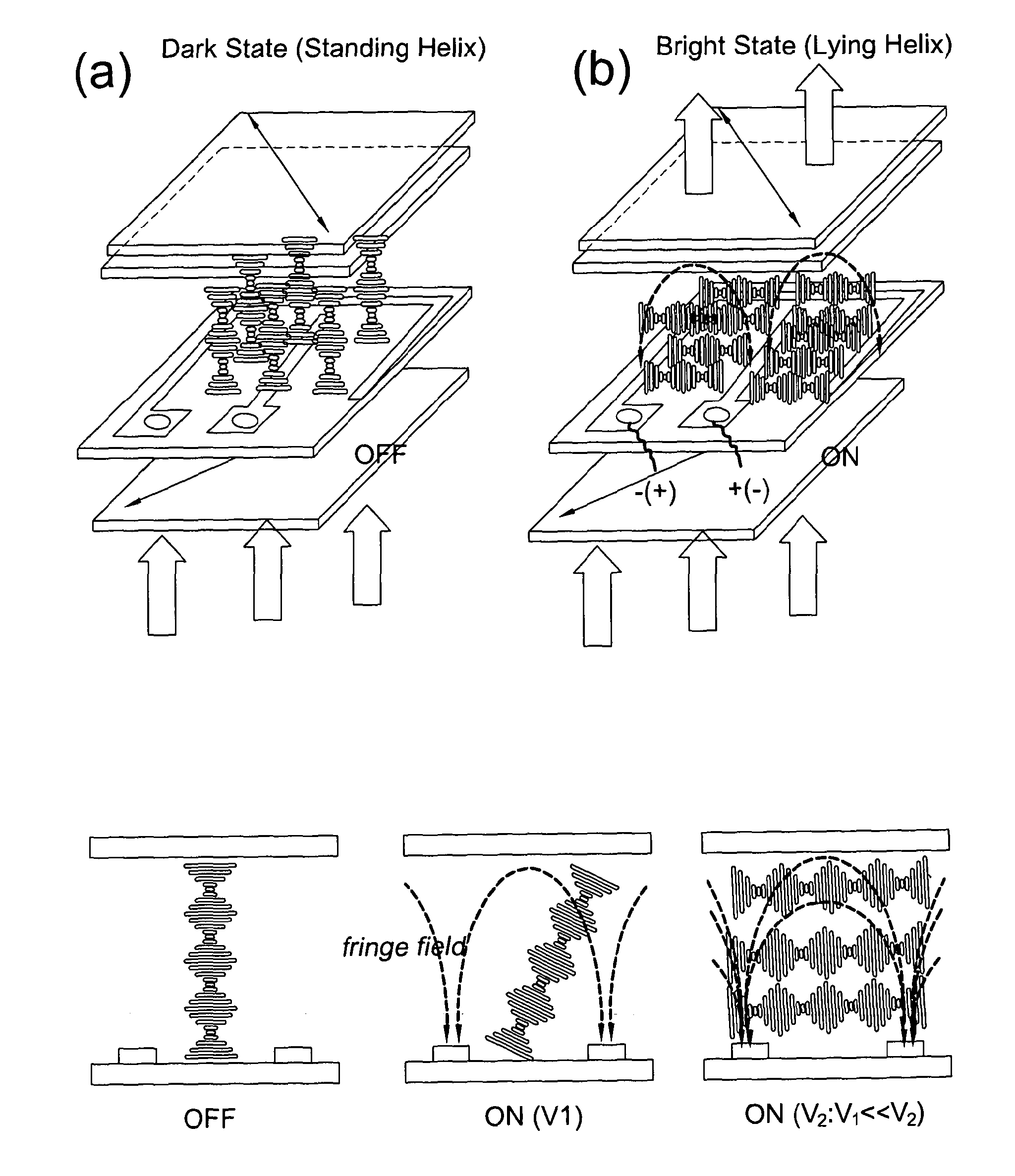
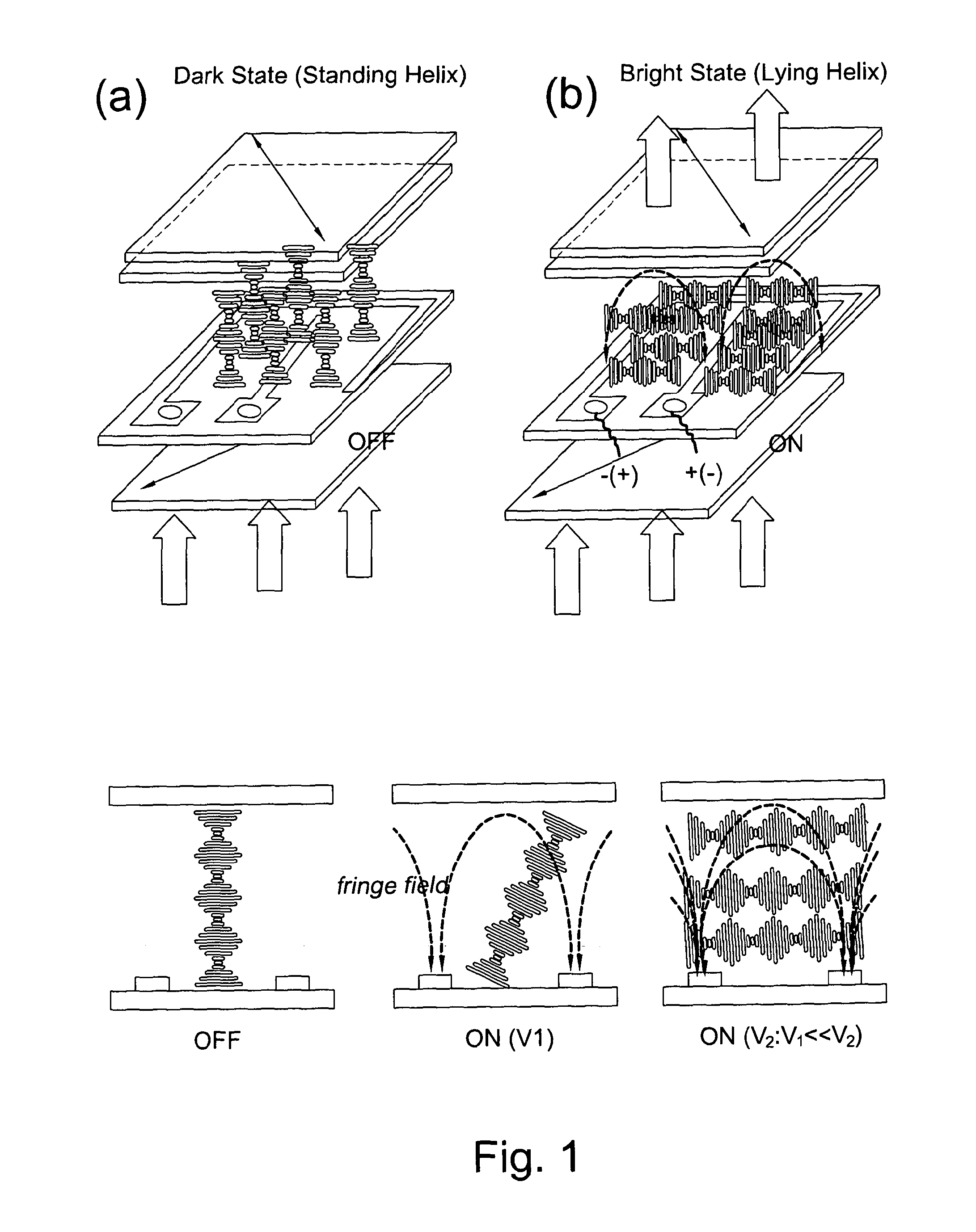
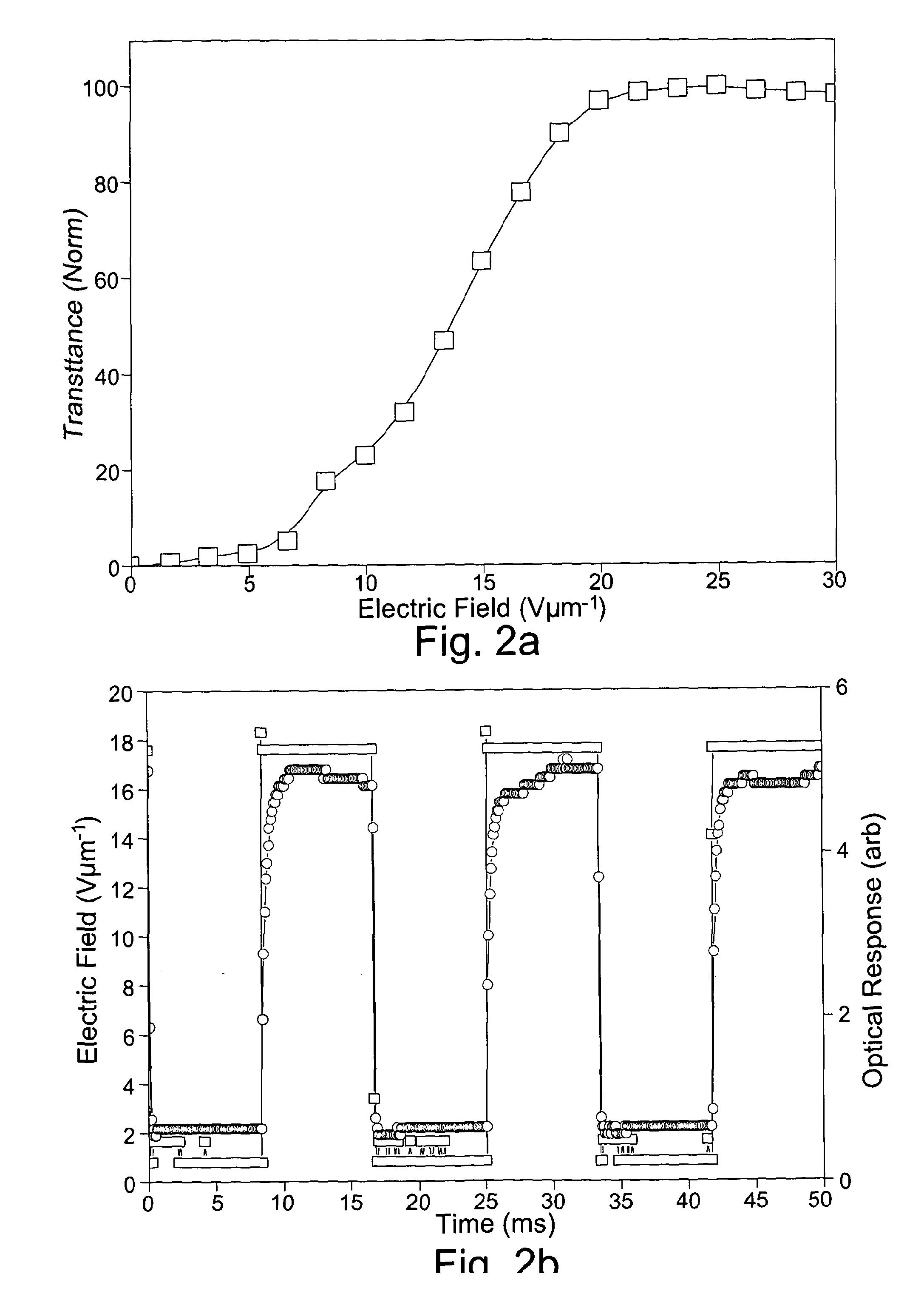
Liquid crystal device comprising chiral nematic liquid crystal material in a helical arrangement
InactiveUS20120140133A1Range of viewing angleEnhance the imageStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsDielectric anisotropyDisplay device
This invention generally relates to a liquid crystal device, and more particularly to such a device in the form of a liquid crystal cell such as for a display device, and further relates to a display device having the liquid crystal device, an optical waveguide device comprising the liquid crystal device, a Variable Optical Attenuator comprising the liquid crystal device, an optical switch comprising the liquid crystal device, a method of controlling transmission of polarised light, and to a further liquid crystal device. A liquid crystal device for controlling transmission of polarised light, comprising: chiral nematic liquid crystal having a helical arrangement of liquid crystal molecules in the absence of an electric field; and at least two electrodes for applying an electric field having a component normal to the helical axis of the chiral nematic liquid crystal, wherein the chiral nematic liquid crystal has negative dielectric anisotropy.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
One-dimensional modulation continuous variable quantum key distribution system based on heterodyne detection, and implementation method thereof
InactiveCN107612686ASimple structureReduce manufacturing costKey distribution for secure communicationManufacturing cost reductionBeam splitter
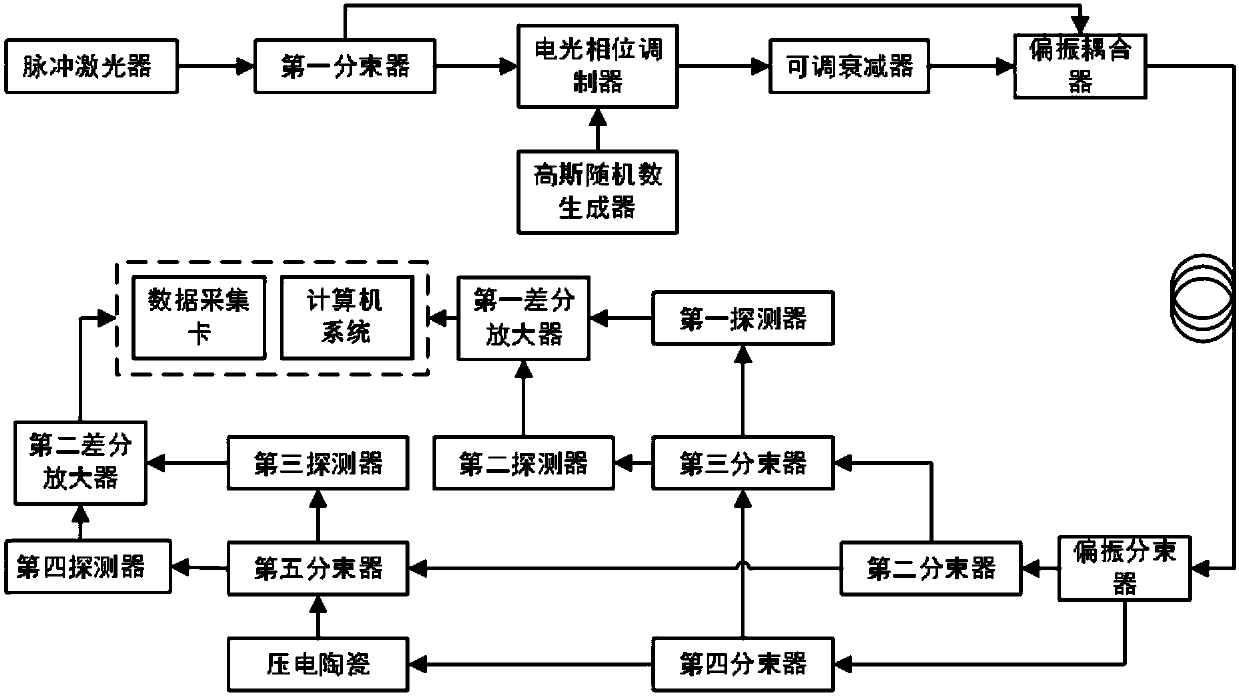
The invention discloses a one-dimensional modulation continuous variable quantum key distribution system based on heterodyne detection, and an implementation method thereof. Pulse laser is divided bya first beam splitter into signal light and local oscillator light at a sending end, an electro-optic phase modulator modulates the signal light, and the modulated signal light is attenuated to a quantum level by an adjustable light attenuator; the signal light at the quantum level is merged with the local oscillator light by a polarization coupler and is transmitted to a receiving end by a quantum channel; signal detection is performed on the receiving end by the heterodyne detection technology, the output information of a first differential amplifier and a second differential amplifier are sent to a data collection card and a computer system for collection and analysis processing, and a group of safe quantum keys is obtained on the sending end and the receiving end separately. Accordingto the one-dimensional modulation continuous variable quantum key distribution system, the modulation process in the continuous variable quantum key distribution system can be achieved just by one electro-optic phase modulator, thereby effectively simplifying the system structure, reducing the volume of the device, reducing the data processing volume and reducing the manufacturing cost.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
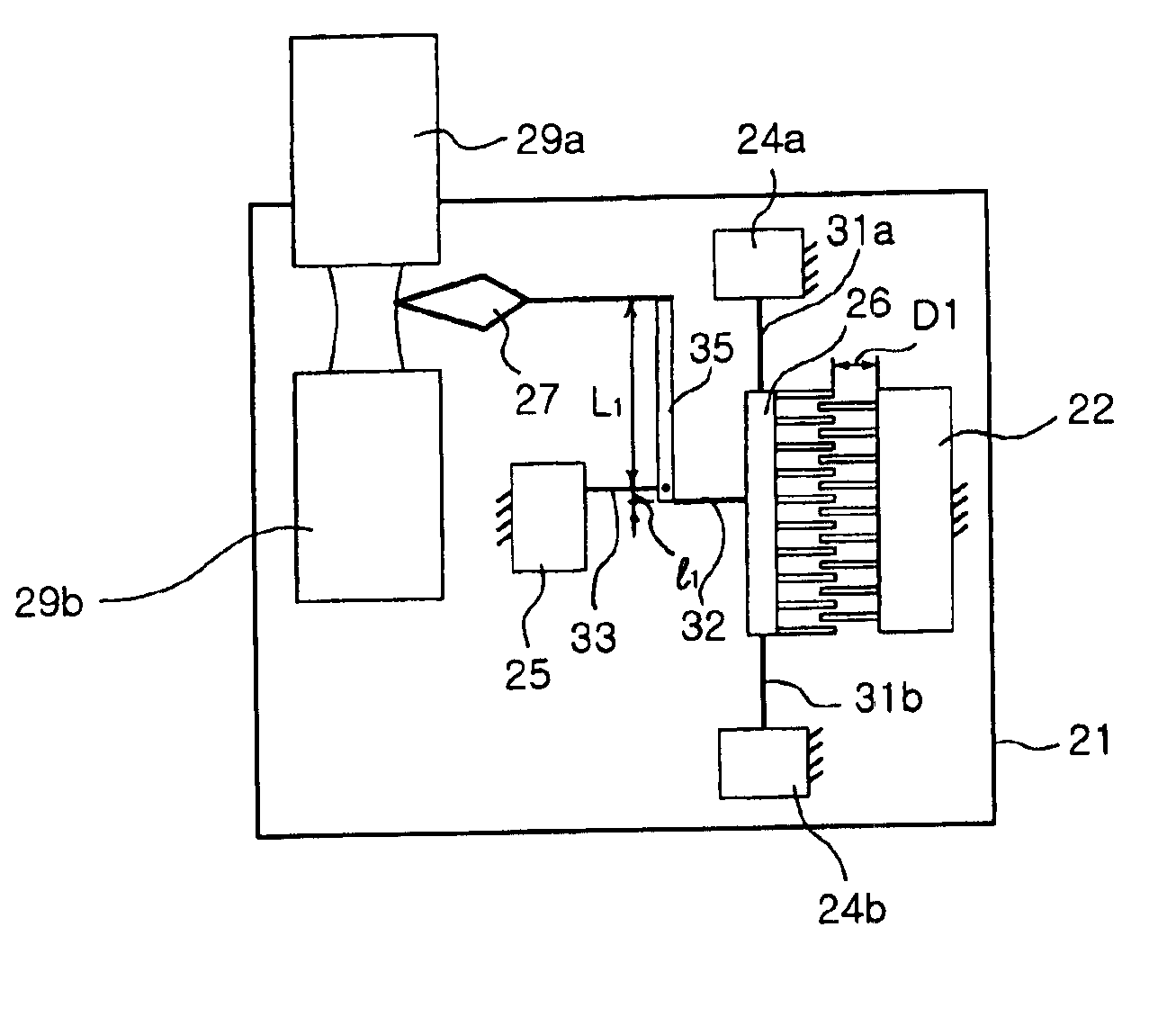
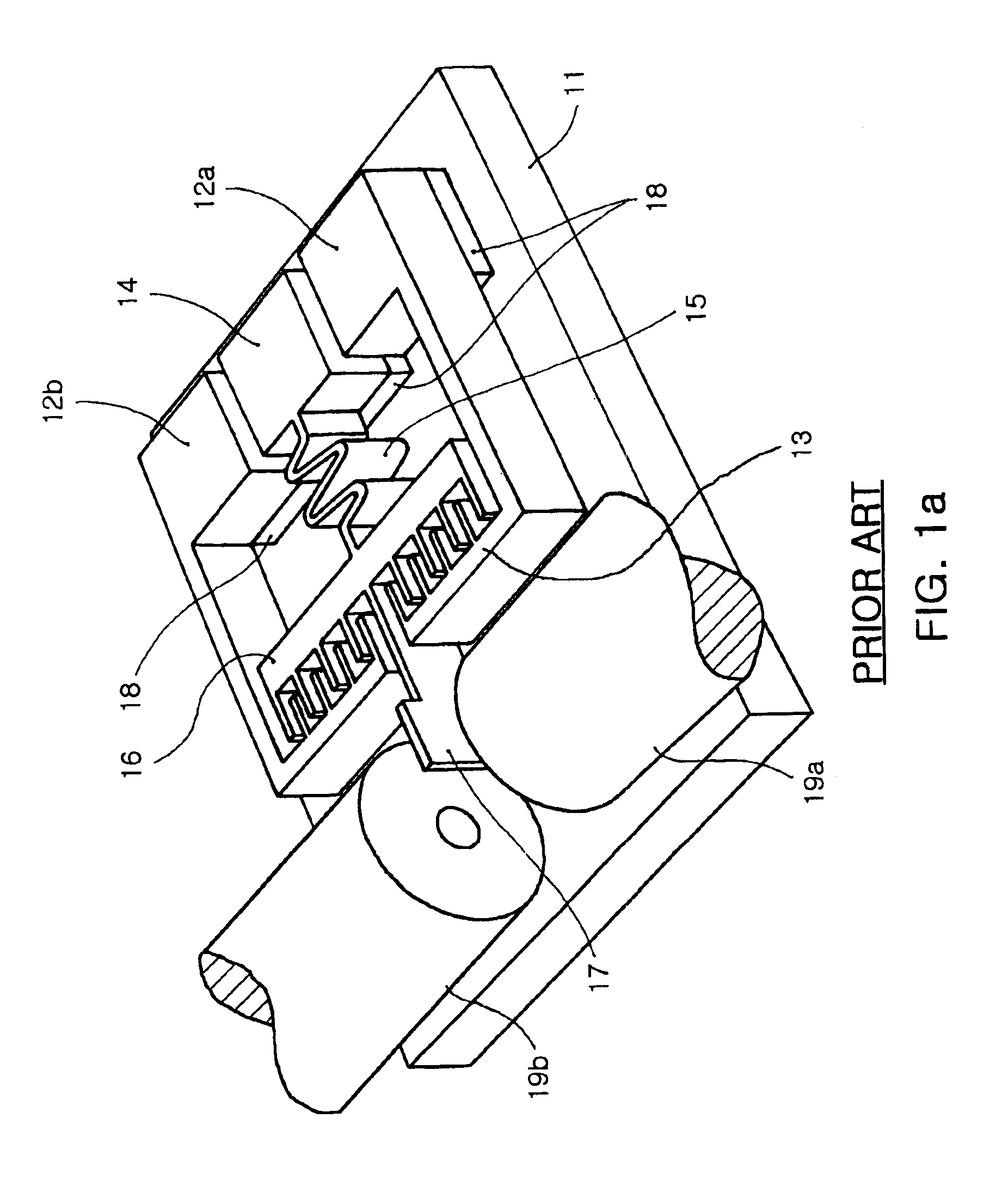
Microelectromechanical system (MEMS) variable optical attenuator
InactiveUS6901204B2Large displacement distanceBig distanceElectrostatic generators/motorsCoupling light guidesUltrasound attenuationOptical axis
Disclosed is an MEMS variable optical attenuator comprising a substrate having a planar surface, optical fibers having an optical signal transmitting end and an optical signal receiving end, respectively, coaxially arranged on the substrate, a micro-electric actuator arranged on the substrate for providing a driving stroke along a direction perpendicular to an optical axis of the optical beam, at least one lever structure arranged on the substrate for receiving the driving stroke of the micro-electric actuator at a first end thereof and transferring an amplified displacement distance to an optical shutter through a second end thereof, an optical shutter arranged on the substrate and connected to the second end of the lever structure so as to be moved by the amplified displacement distance, thereby being displaced to an attenuation position of the optical beam.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Method and system for quantum communication security
InactiveCN101820343AHighlight substantiveSignificant progressKey distribution for secure communicationCommunications securityPhoton emission
The invention relates to a method and a system for quantum communication security. An Alice terminal comprises a watchdog detector, an optical attenuator, a phase modulator, a reflector, a controller and a photon emitter; and a Bob terminal comprises a laser, a time division multiplex / demultiplex system, a phase modulator, a single photon detector, a controller, an optical switch and a reflector. The method and the system have the advantages that: (1) the two-way, stable and safe distribution of quantum keys is realized, the polarization and phase change of a single photon can be automatically compensated, and the aim of stable long-distance transmission is achieved; (2) the Alice terminal adopts the watchdog detector, on one hand, Trojan attack and intermediary attack can be detected by measuring the number of weak pulses reaching or leaving the Alice terminal, so that the communication security is improved greatly, and on the other hand, the communication speed and communication distance of the system are improved greatly; and (3) the Alice terminal and the Bob terminal can be adjusted and corrected respectively, can select mu independently without transmitting photons by means of unsafe optical fiber lines so as to ensure the system security.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com