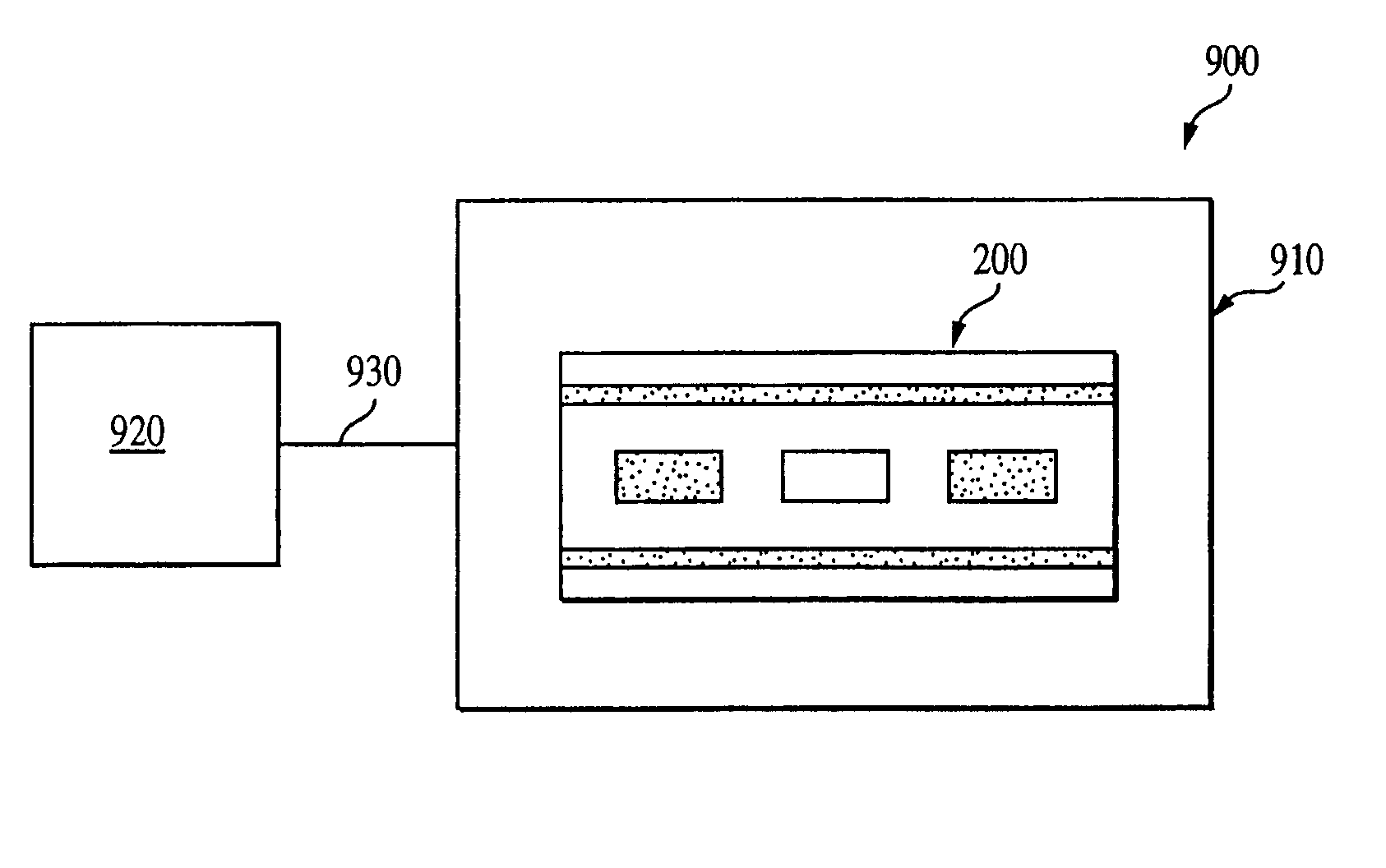
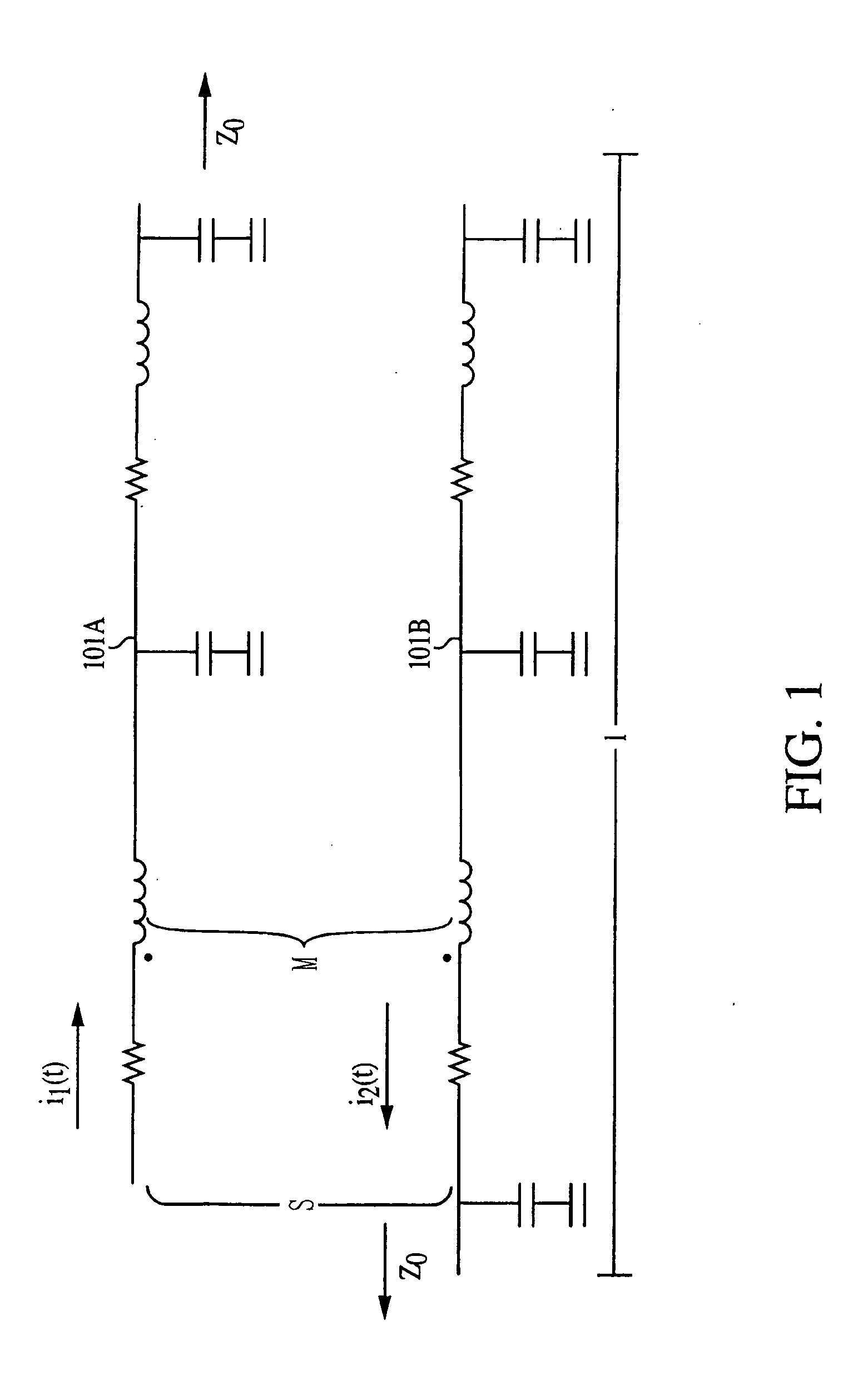
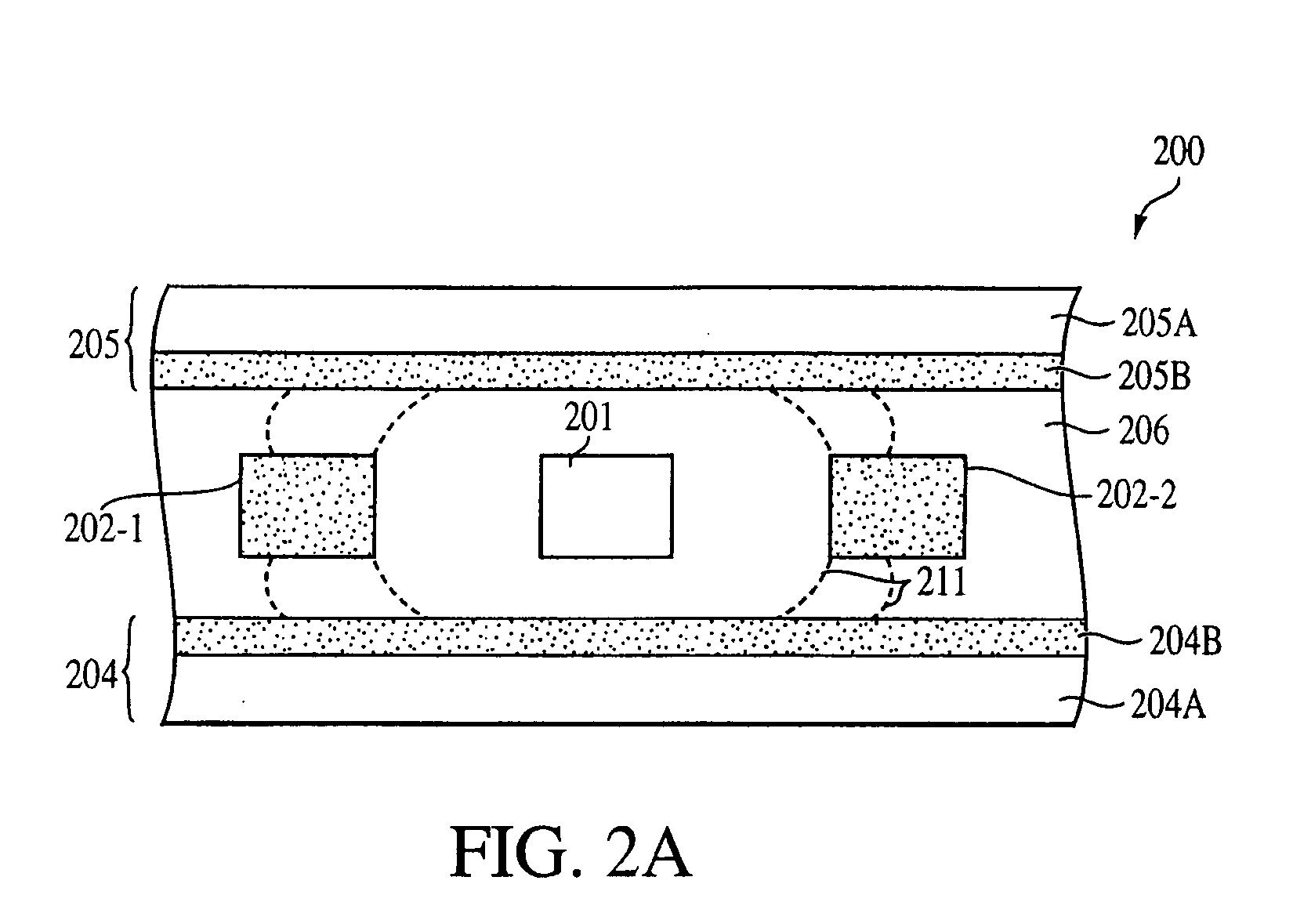
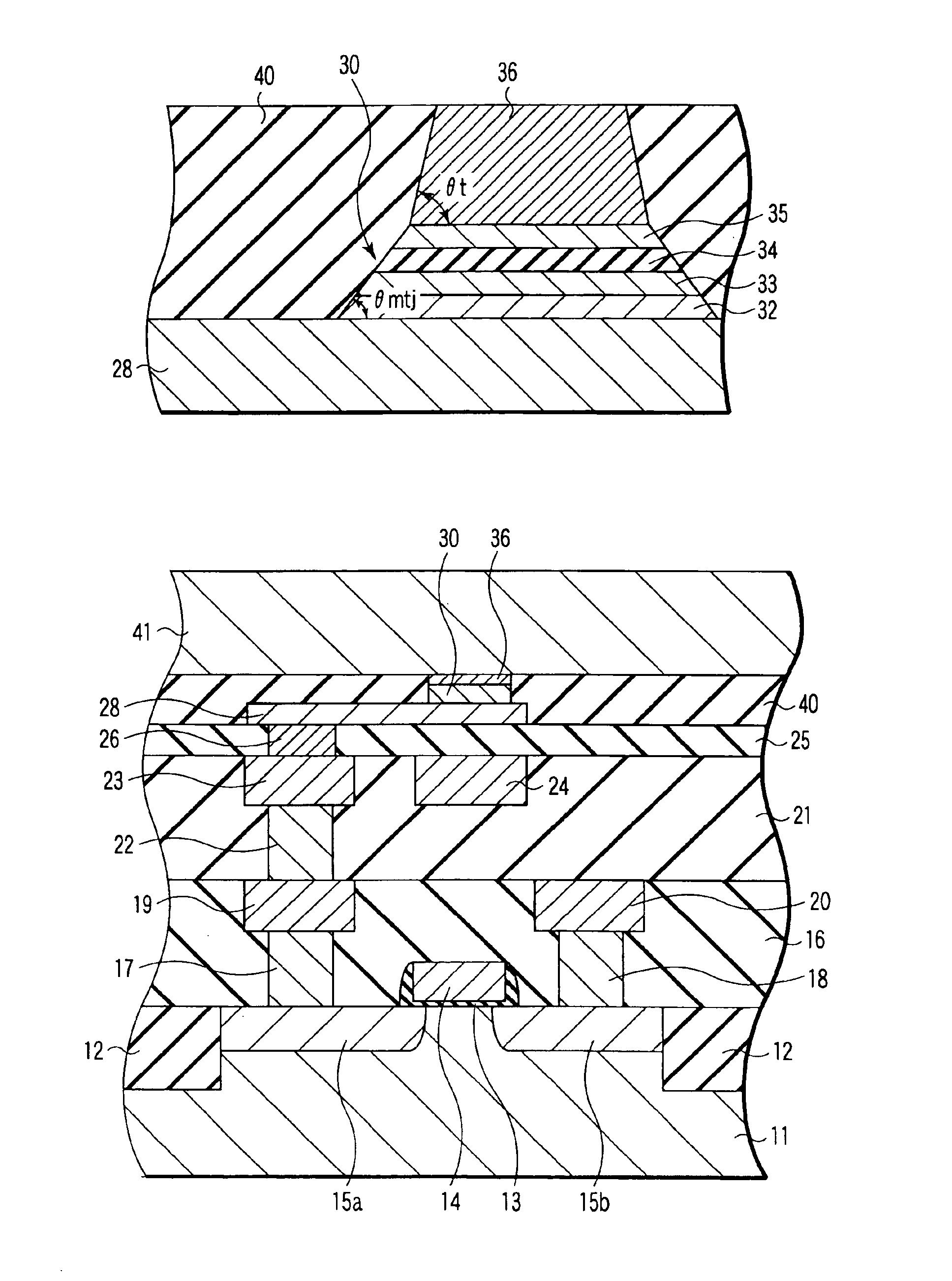
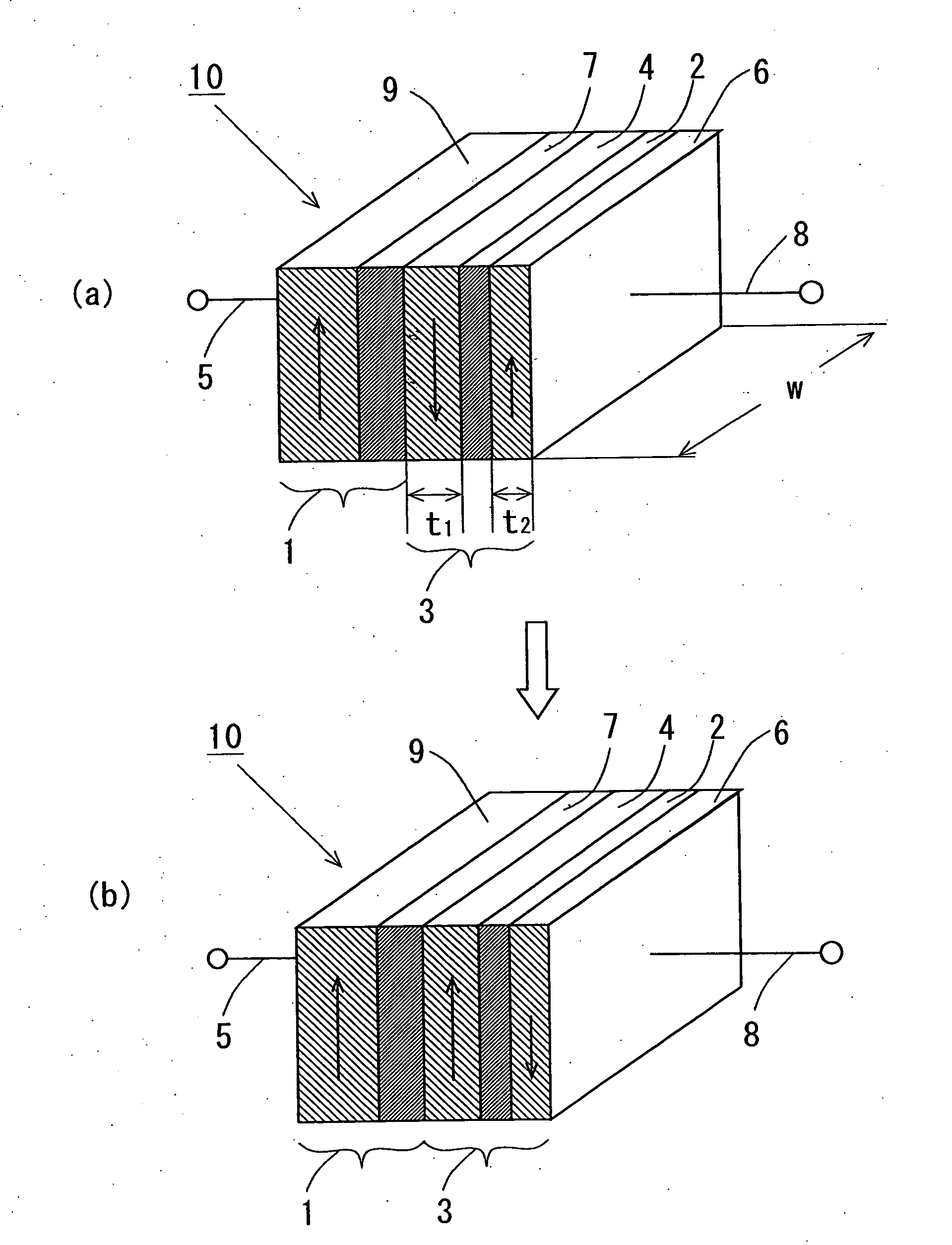
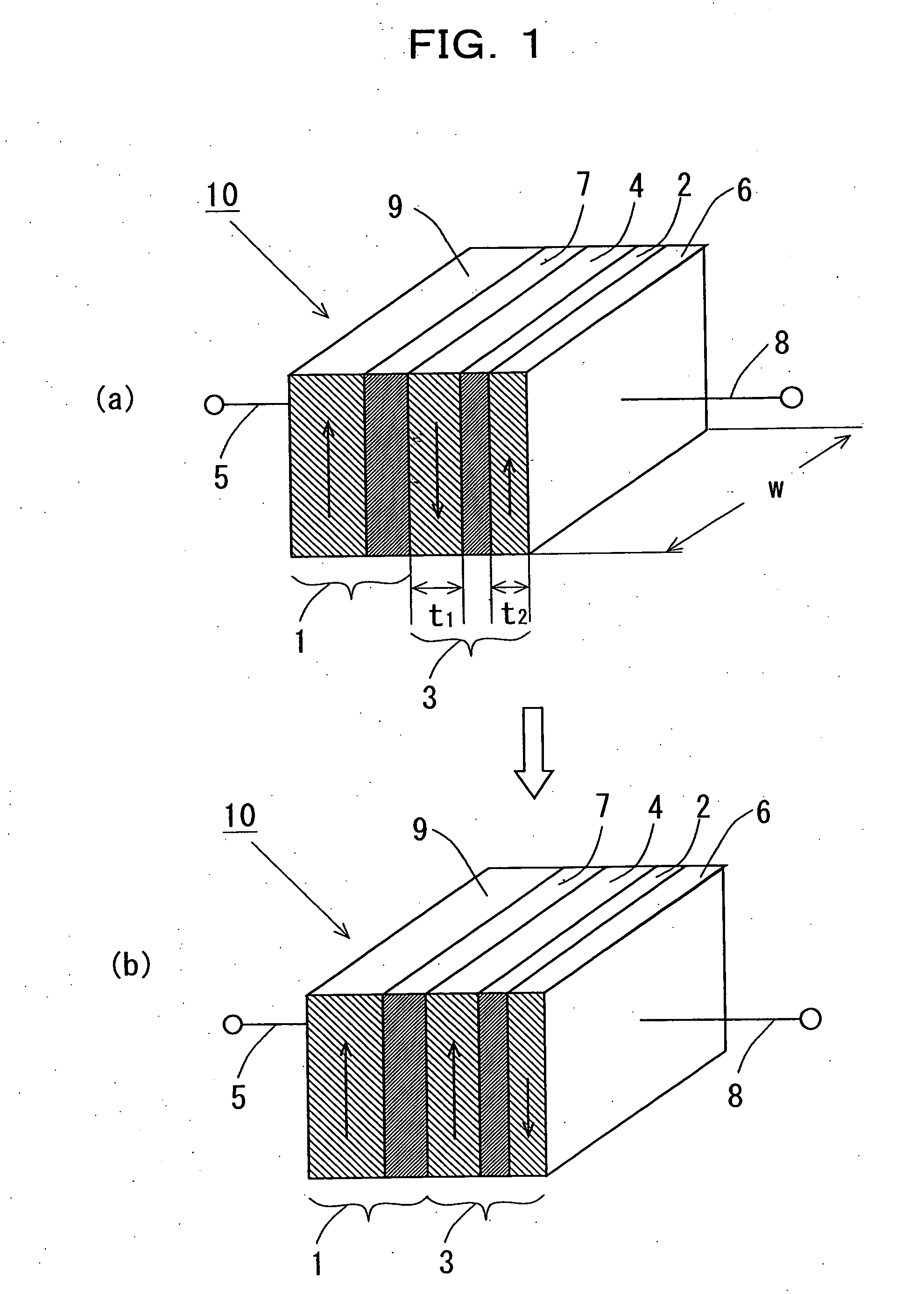
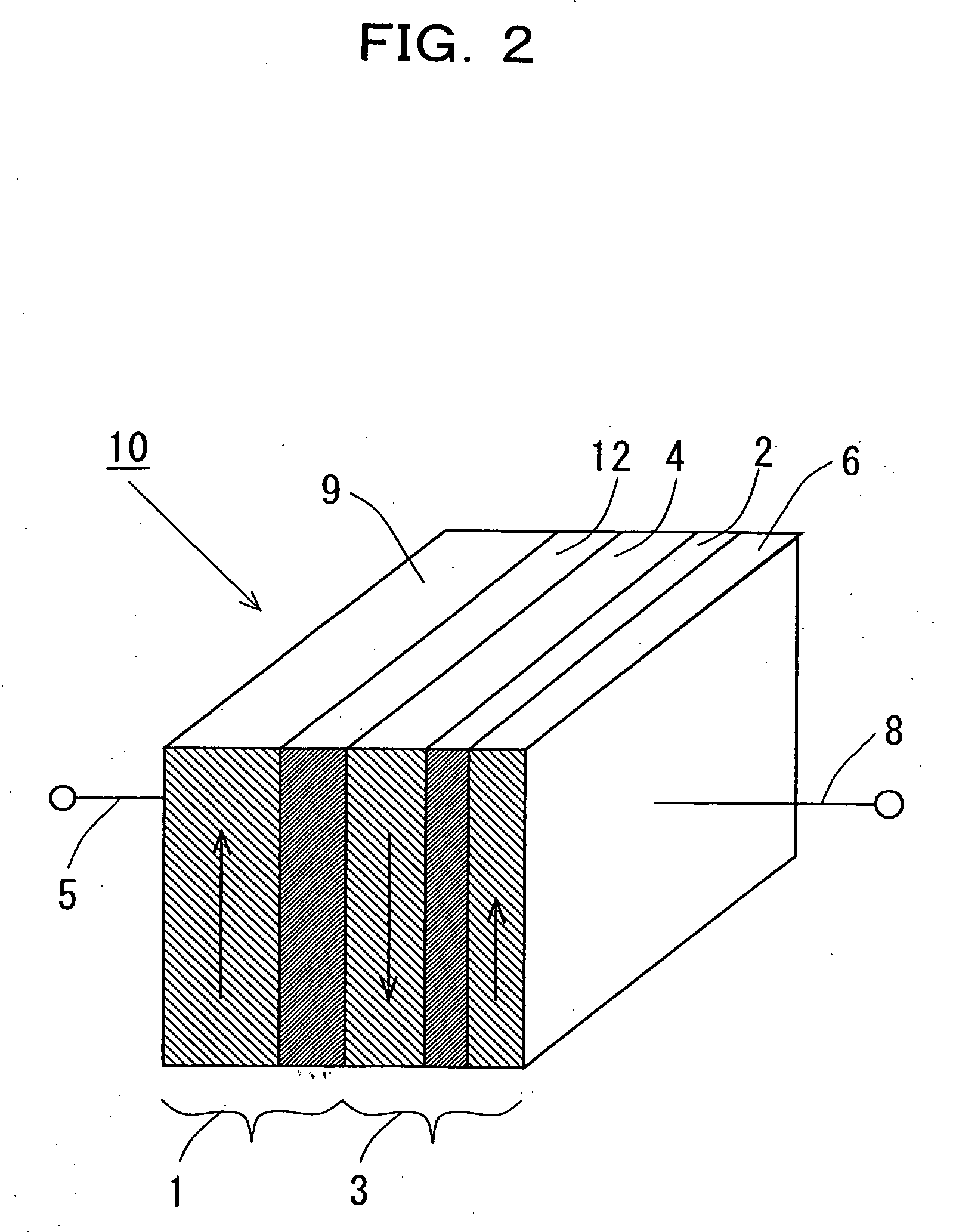
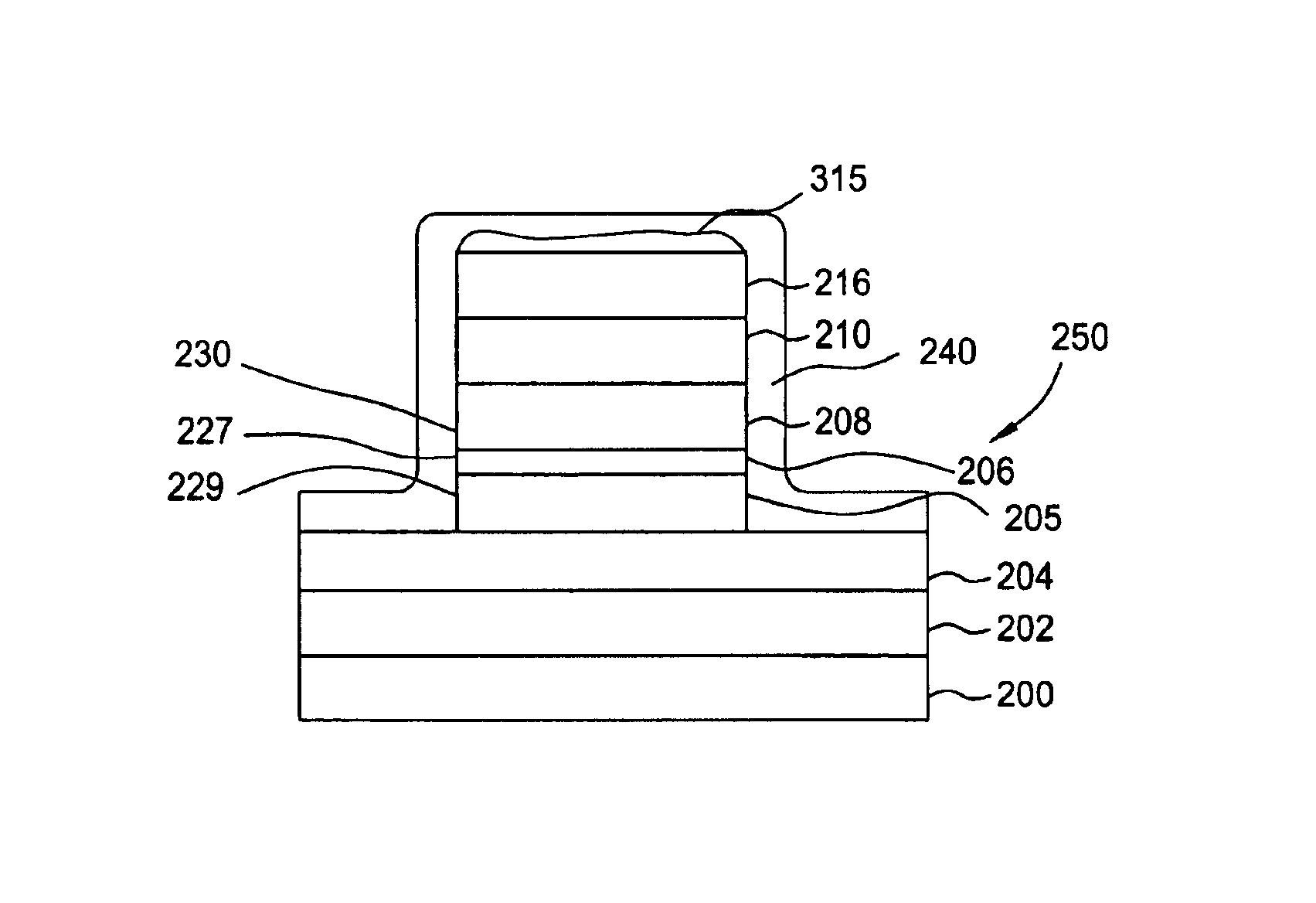
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
686 results about "Magnetic thin film" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
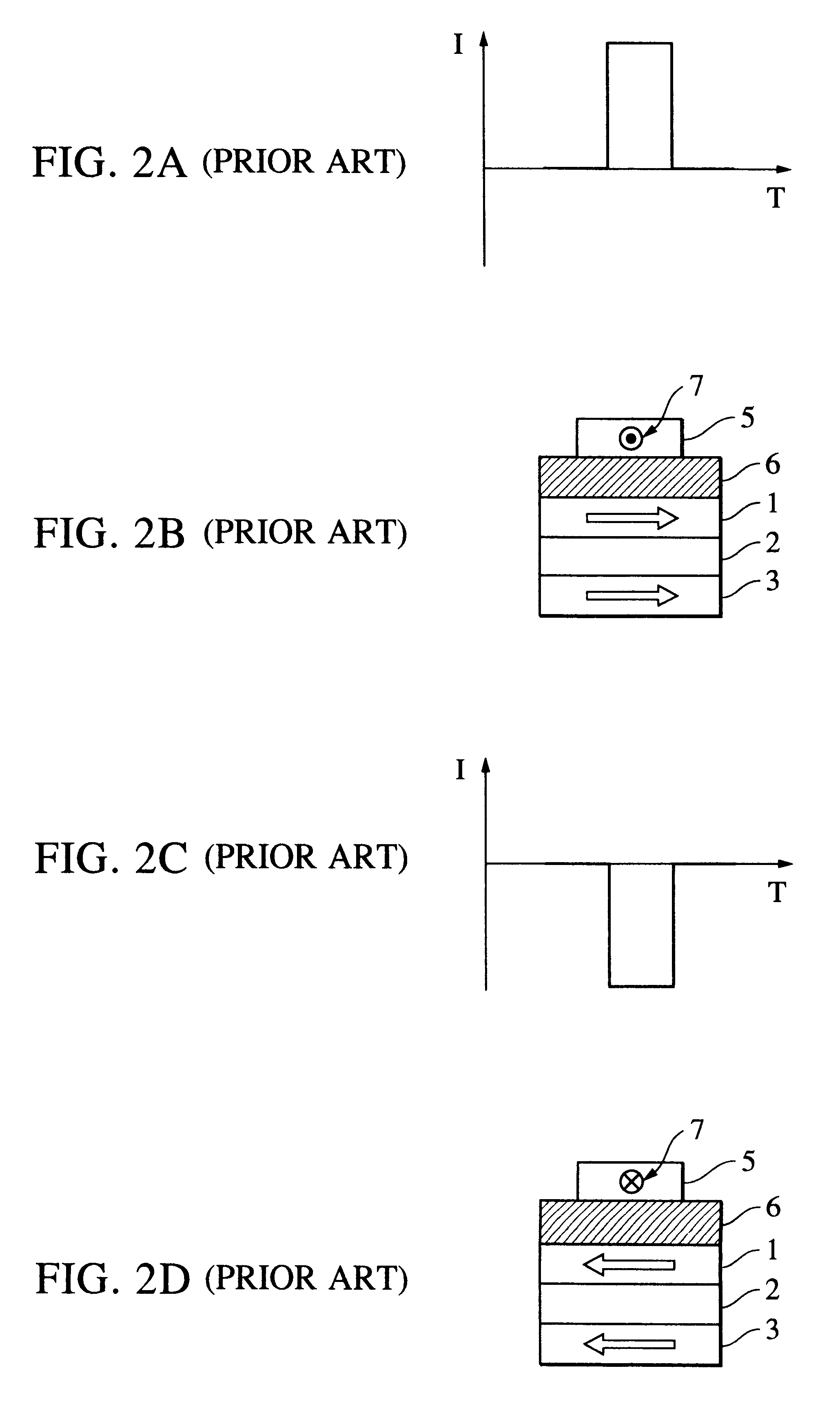
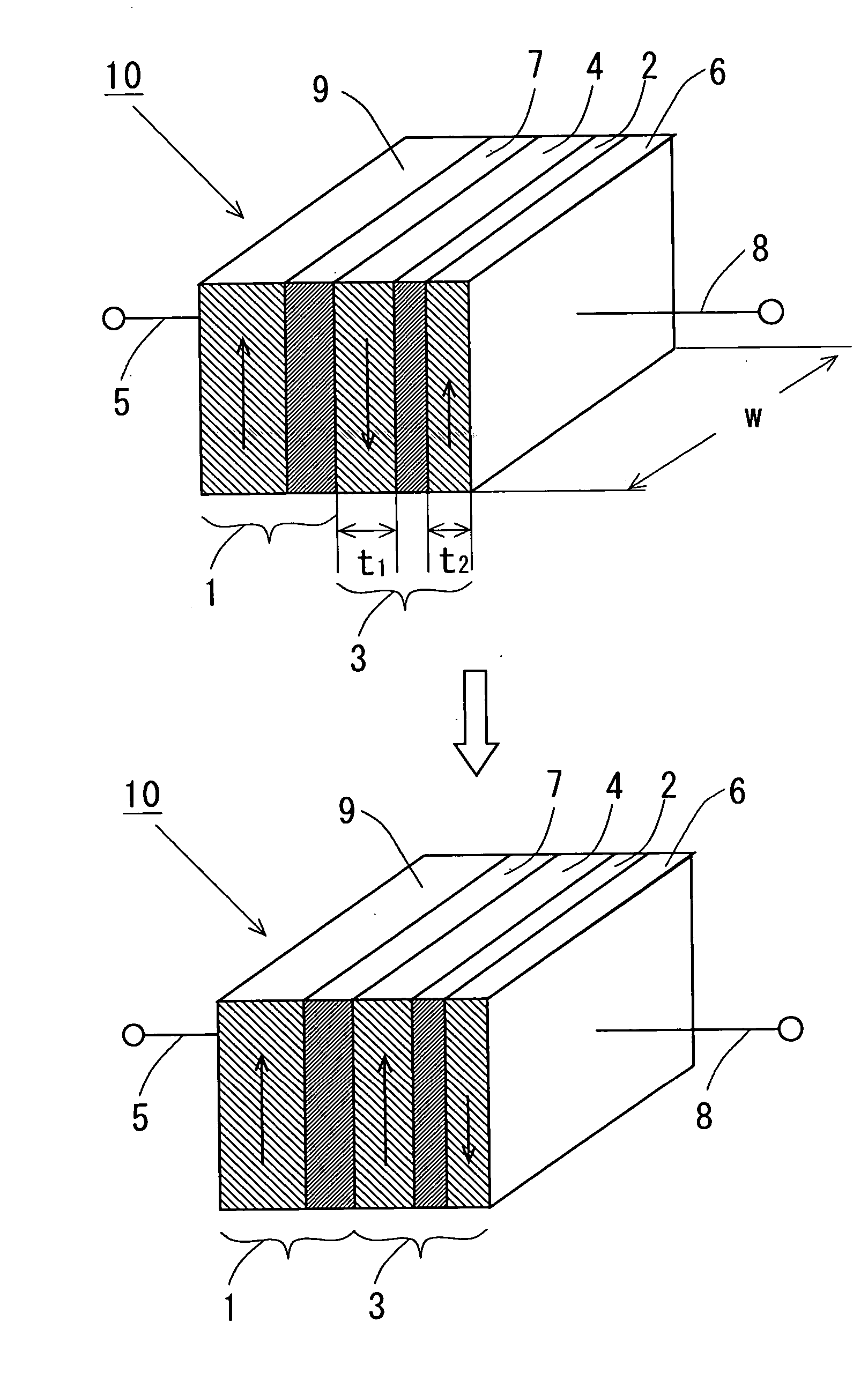
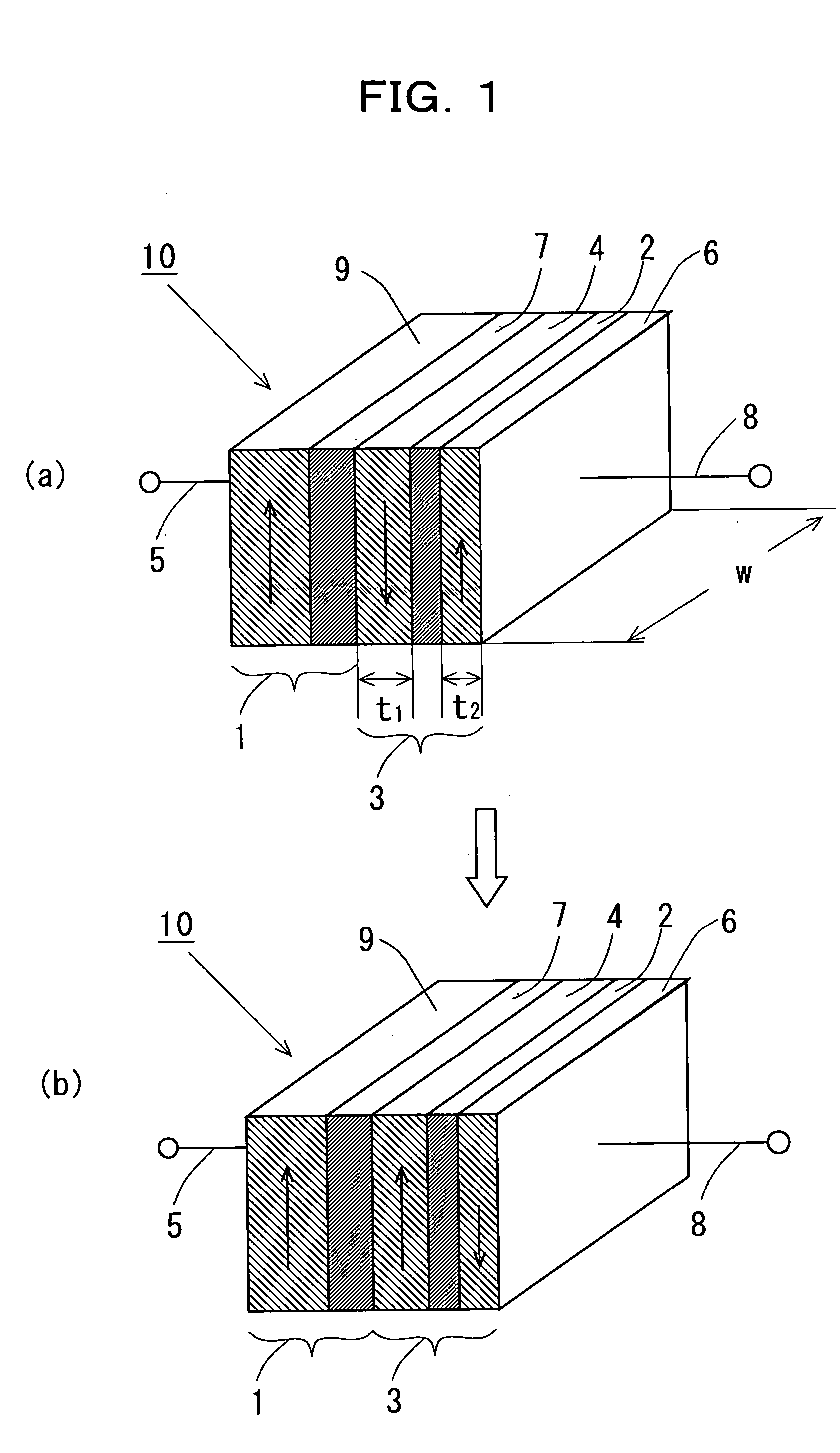
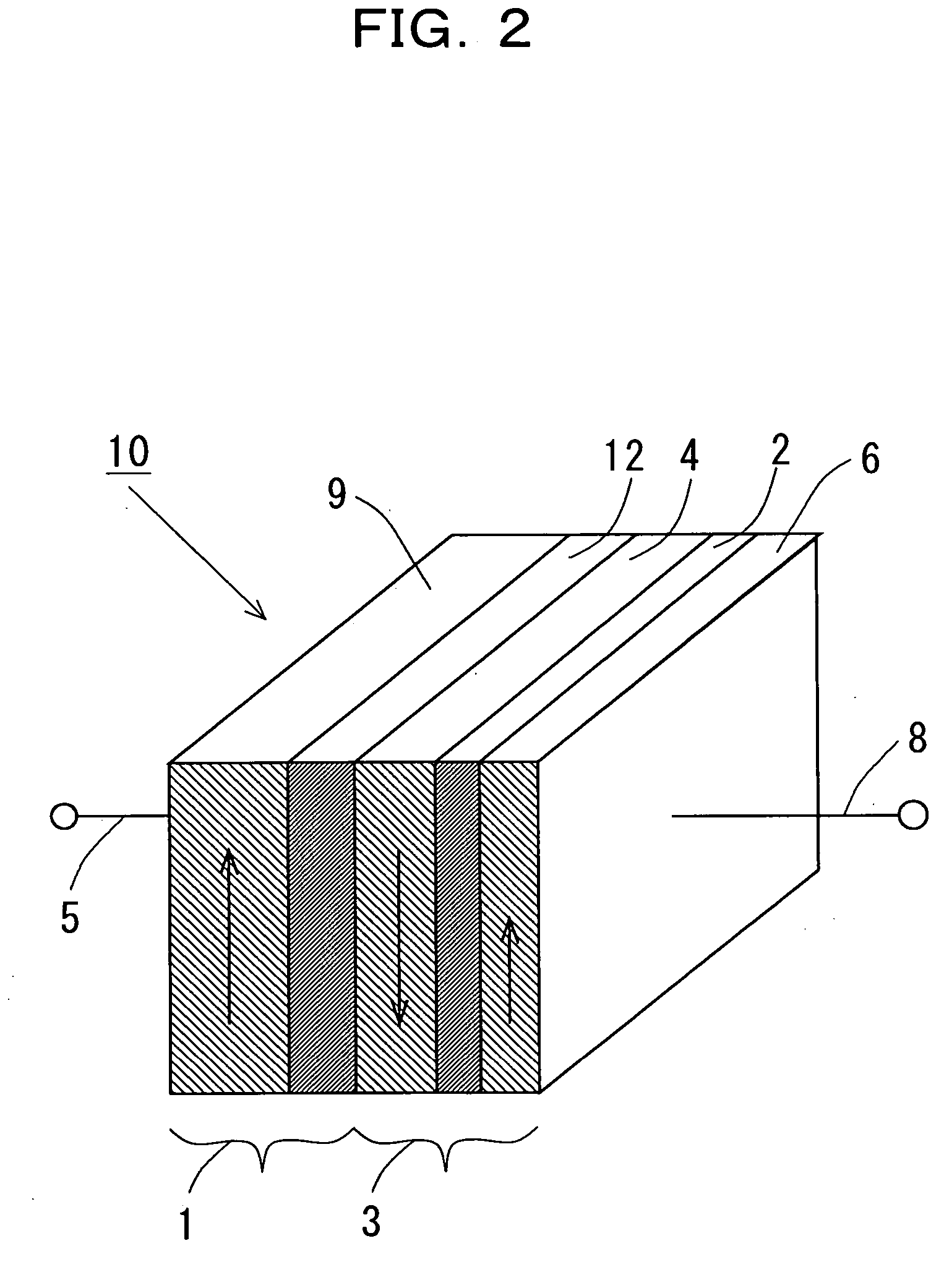
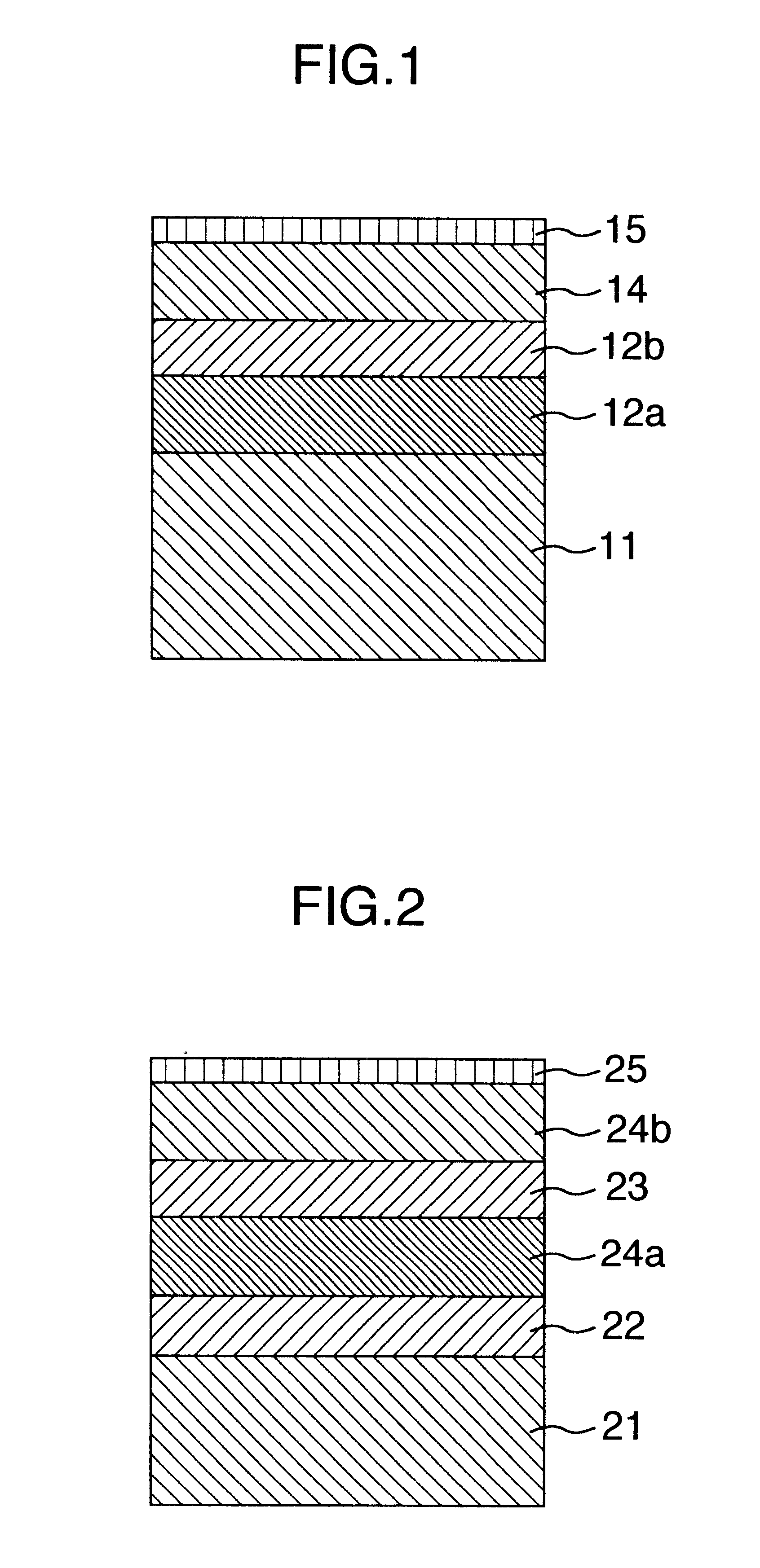
Magnetic thin film memory, method of writing information in it, and me
InactiveUS6226197B1NanoinformaticsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic reluctanceField-effect transistor
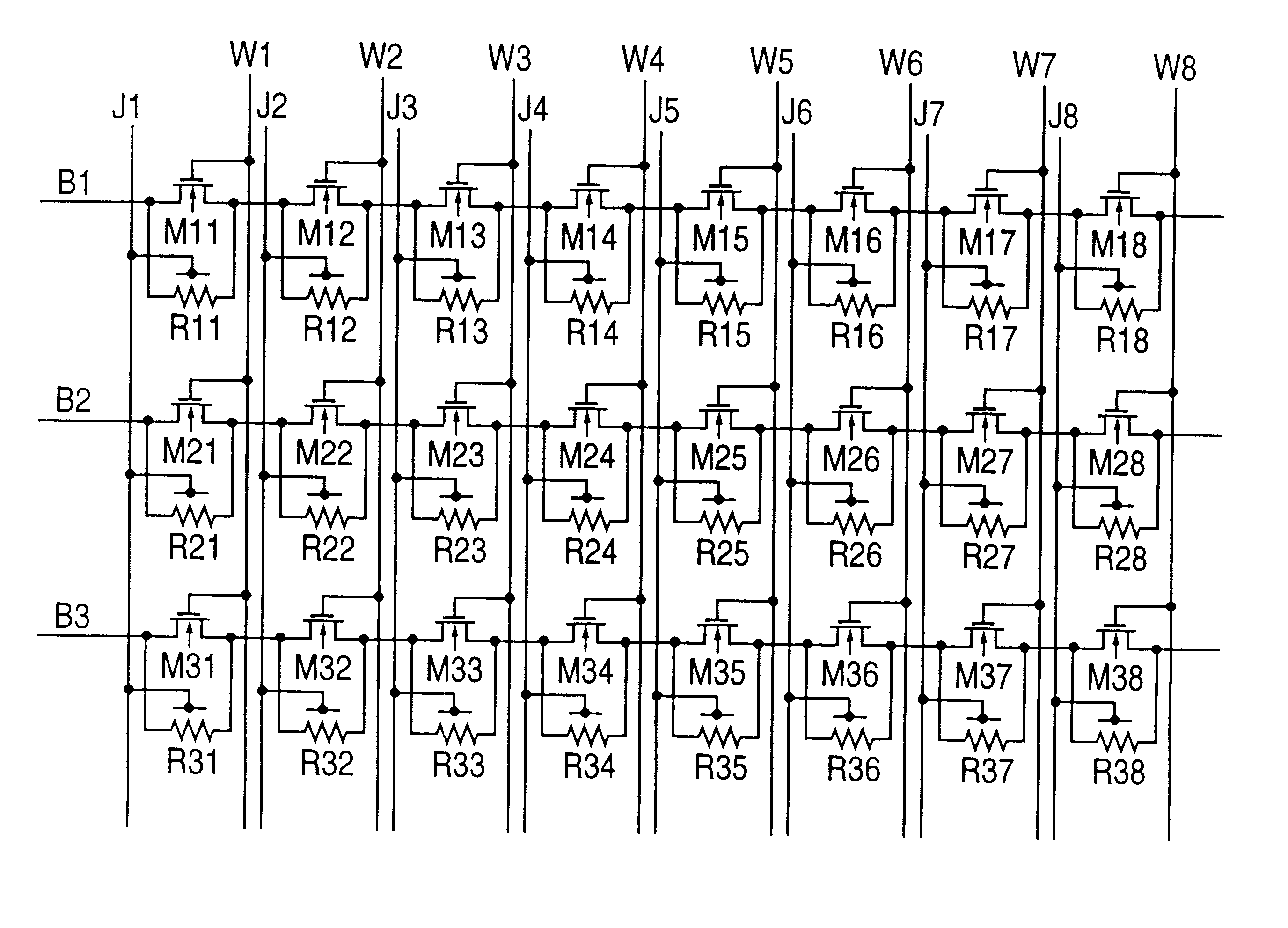
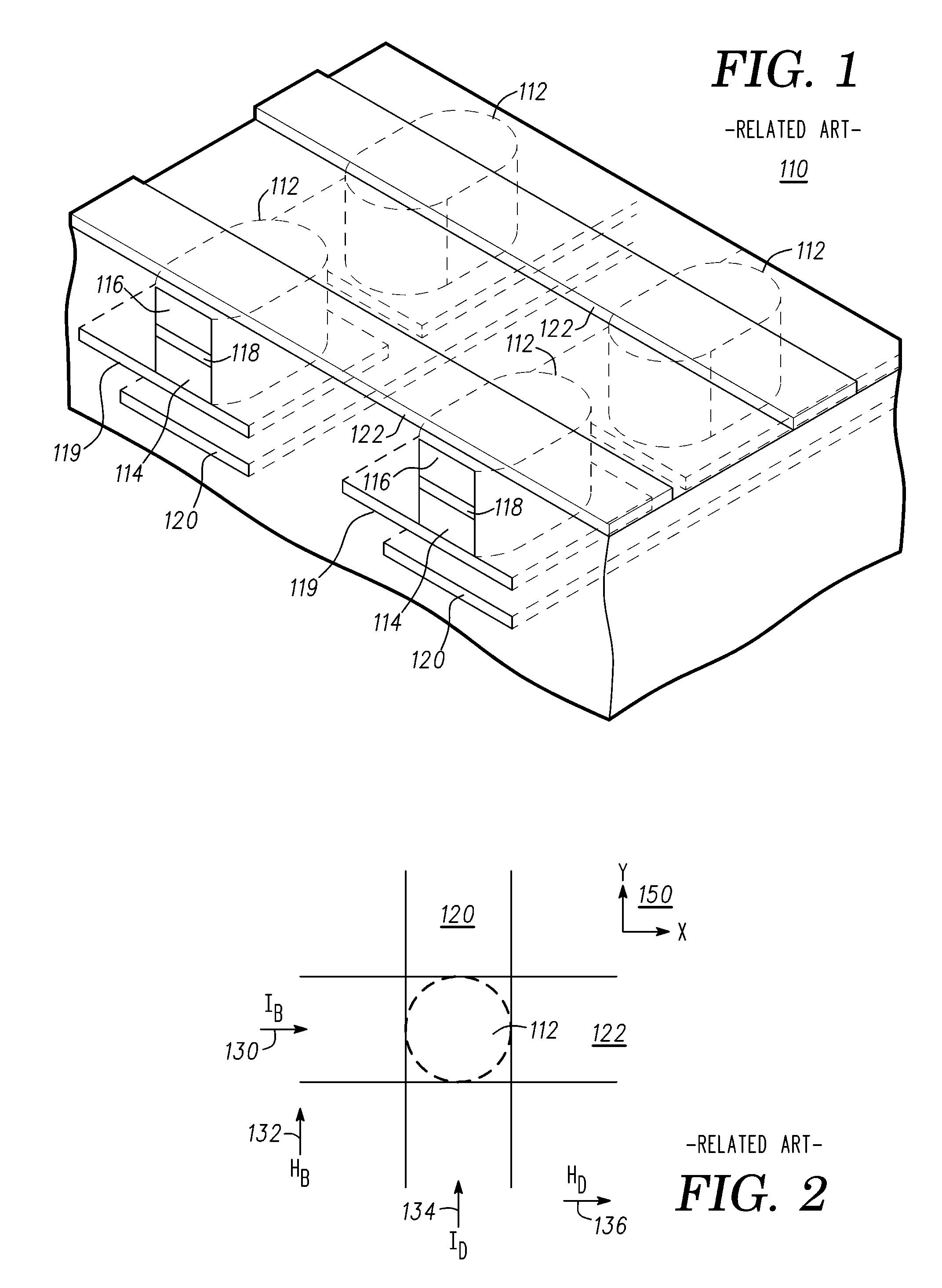
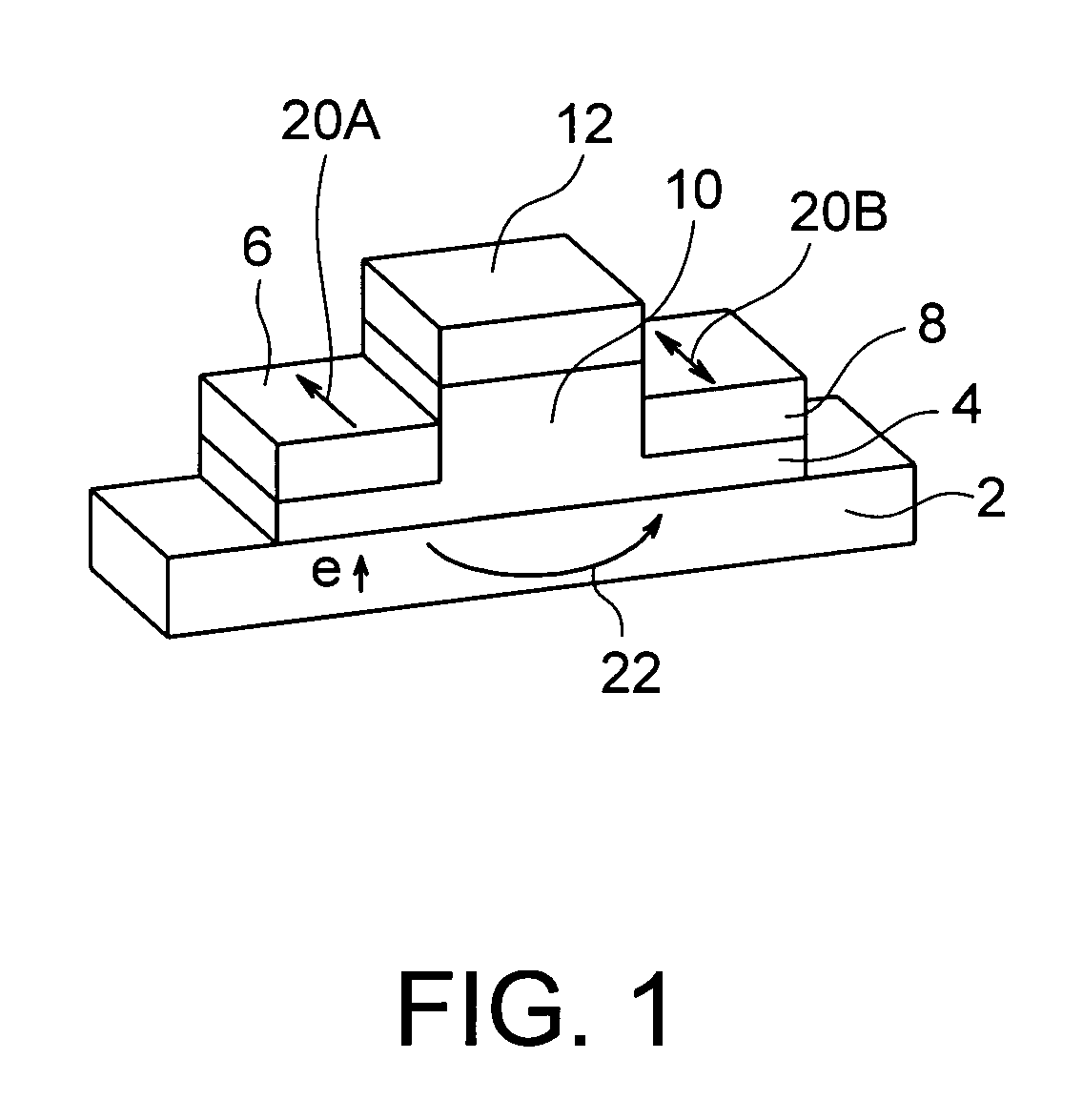
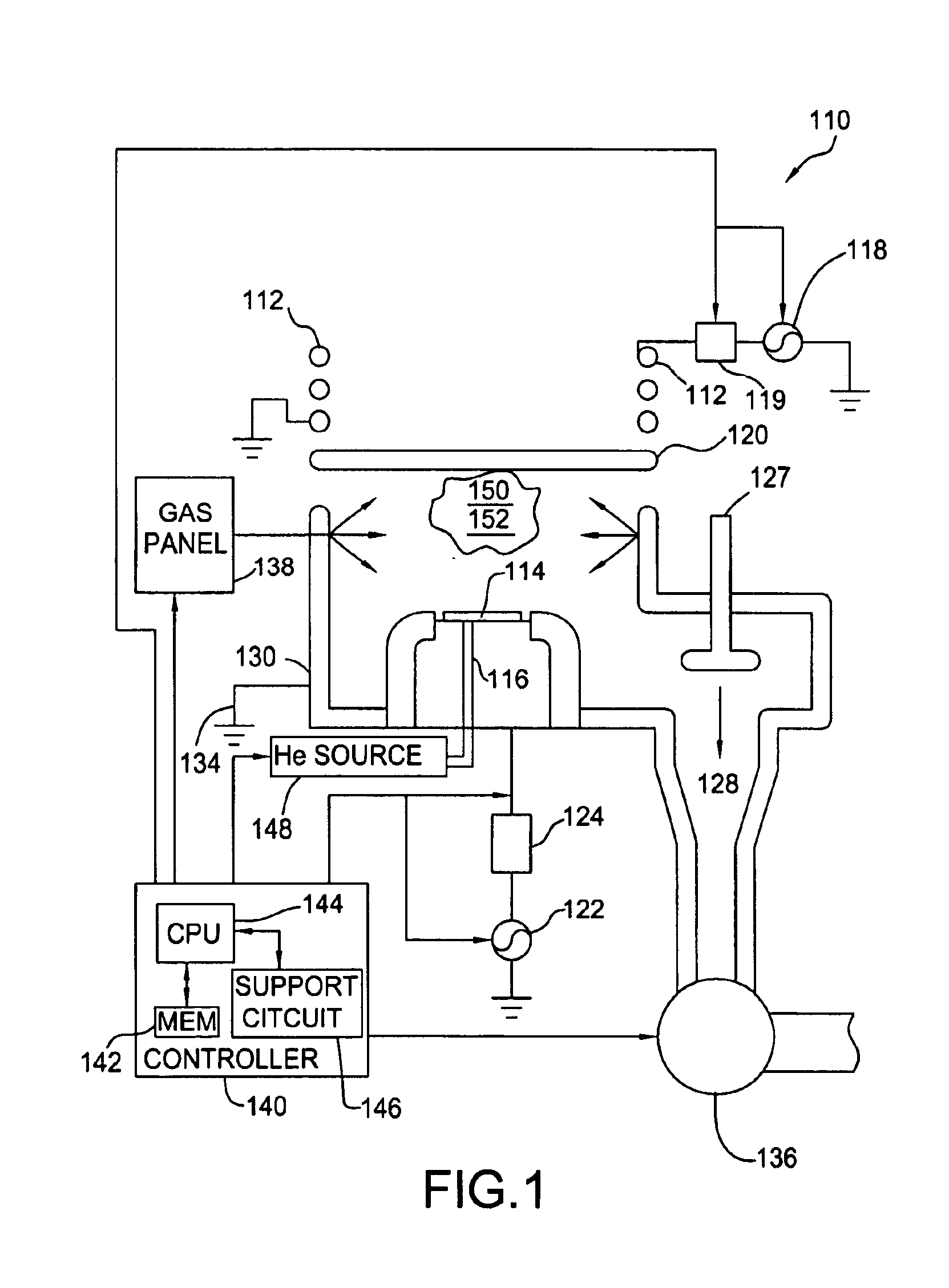
The present invention relates to a magnetic thin film memory having a hybrid element including a field effect transistor and a magnetoresistive thin film connected to the field effect transistor in parallel. In the magnetic thin film memory, the hybrid element is preferably arranged in plurality in a matrix state. The present invention also relates to a method of writing information in this magnetic thin film memory, and a method of reading the information written in this magnetic thin film memory.
Owner:CANON KK
Magnetic write head with high moment magnetic thin film formed over seed layer
A magnetic write head includes a seed layer and a magnetic layer on the seed layer. The seed layer includes seed-layer grains having either a face-centered cubic (fcc) crystalline structure with a surface plane substantially oriented in a [111] direction or a hexagonal-close-packed (hcp) crystalline structure with a surface plane substantially oriented in a [0001] direction. The magnetic layer includes magnetic-layer grains having a body-centered-cubic (bcc) crystalline structure with a surface plane substantially oriented in a [110] direction.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
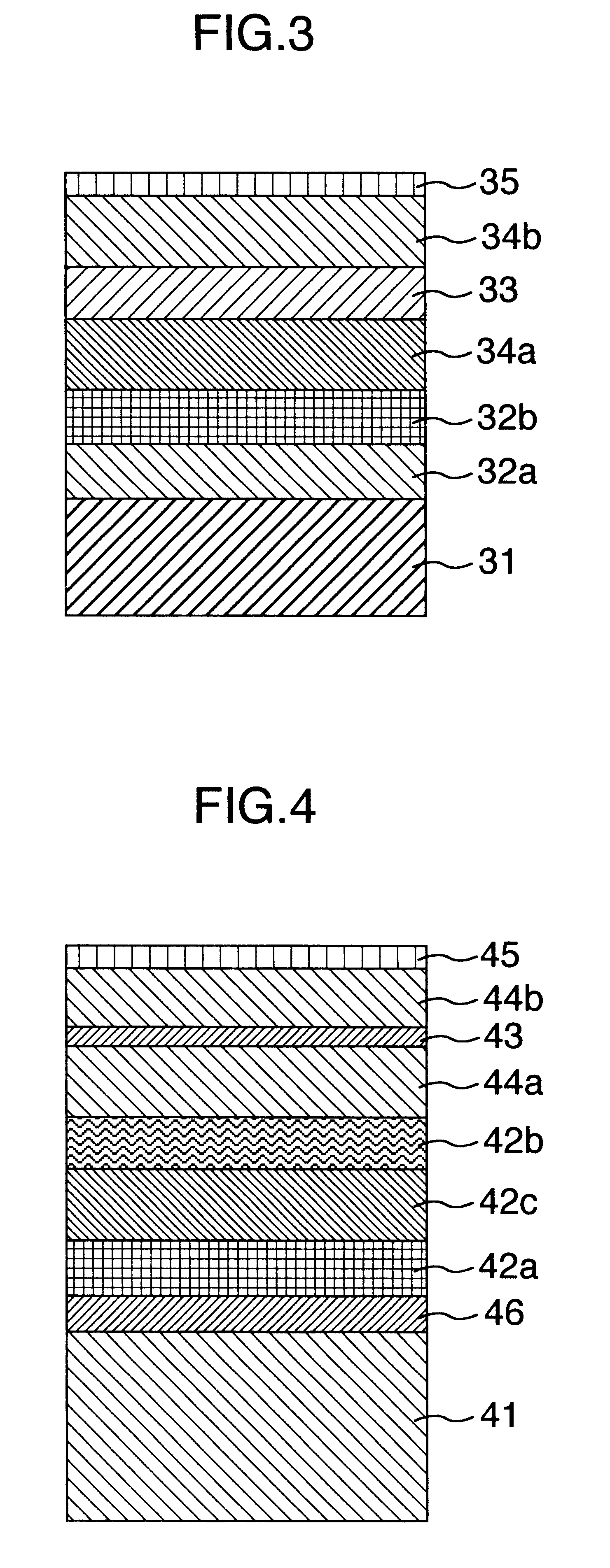
Magnetic thin film element, memory element using the same, and method for recording and reproducing using the memory element
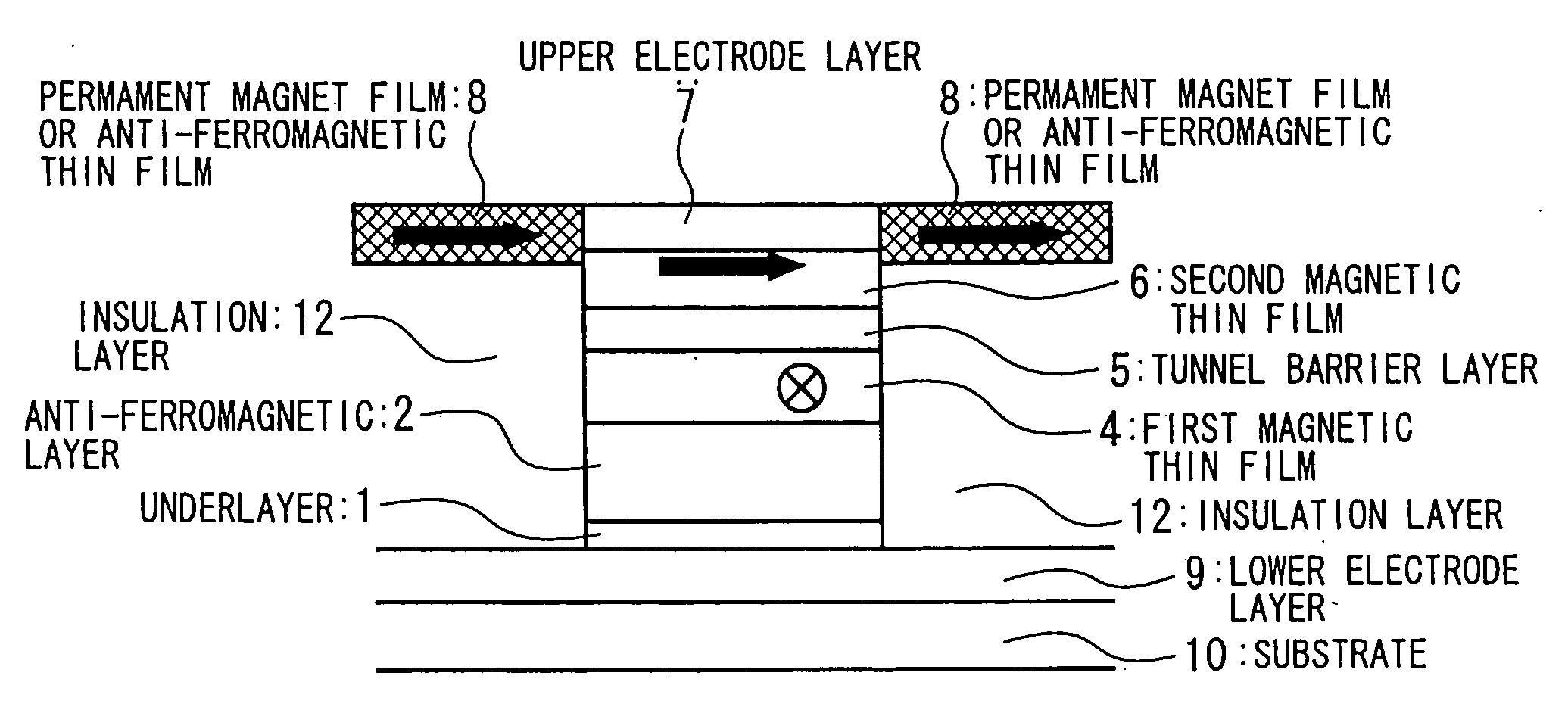
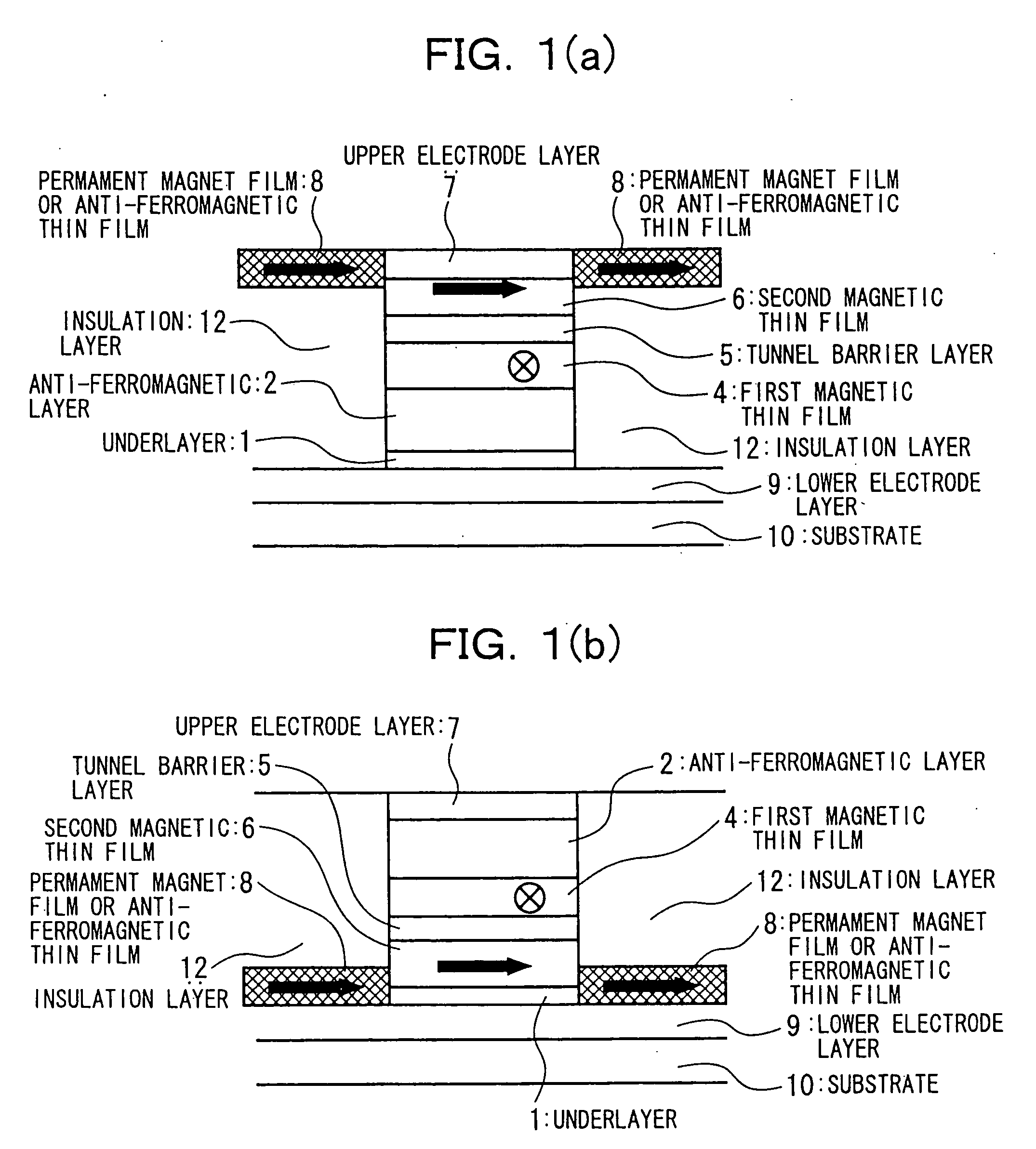
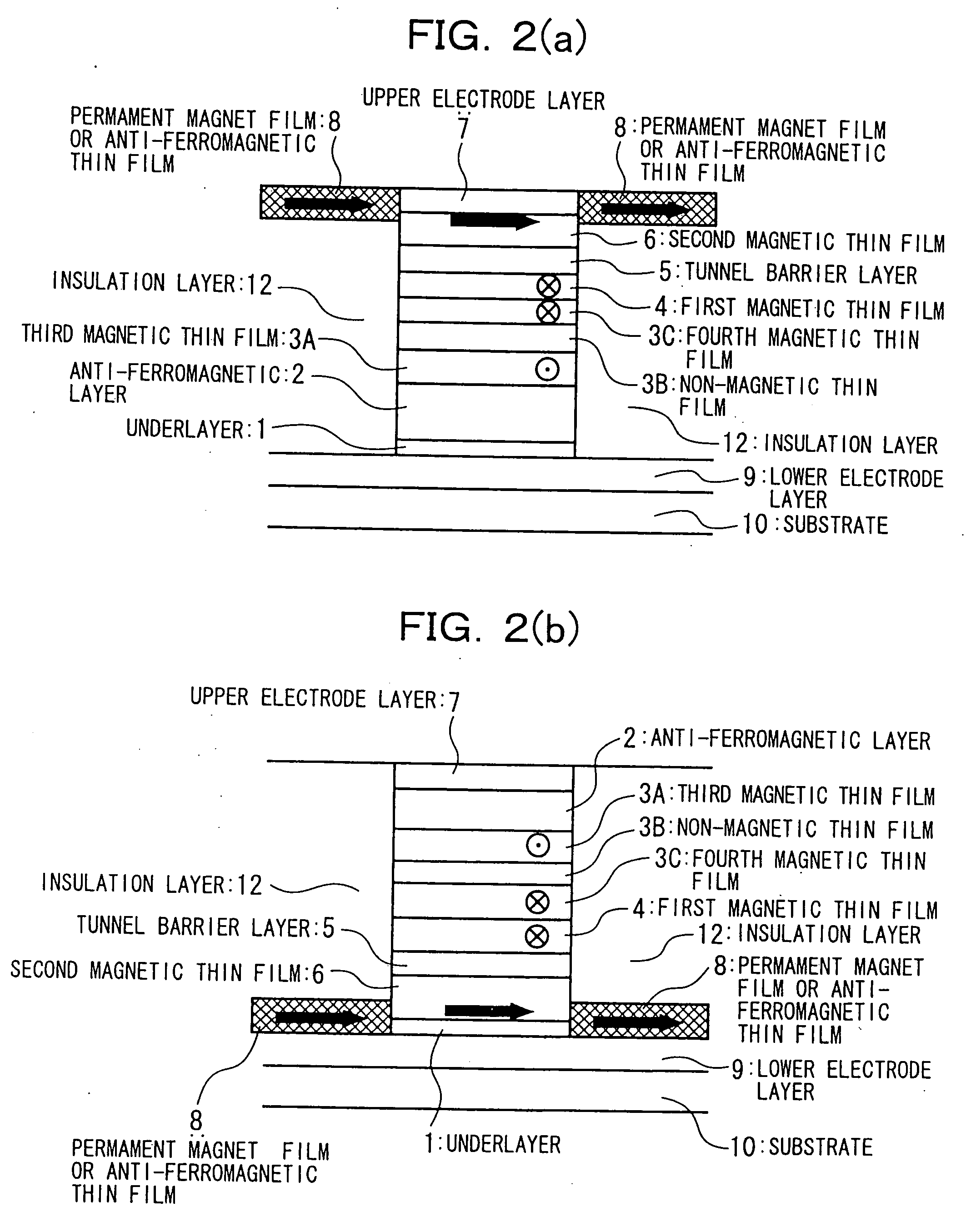
A magnetic thin film element is provided with a magnetoresistive film including a first magnetic layer composed of a perpendicular magnetization film, a second magnetic layer composed of a perpendicular magnetization film having a higher coercive force than that of the first magnetic layer, and a nonmagnetic layer interposed between the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer. The resistance of the magnetoresistive film varies depending on whether or not the magnetic spins of the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer are in the same direction.
Owner:CANON KK
Spin injection device, magnetic device using the same, magnetic thin film used in the same
InactiveUS20060044703A1Large TMRLarge capacityNanomagnetismBase layers for recording layersElectrical conductorMagnetic memory
A spin injection device capable of spin injection magnetization reversal at low current density, a magnetic apparatus using the same, and magnetic thin film using the same, whereby the spin injection device (14) including a spin injection part (1) comprising a spin polarization part (9) including a ferromagnetic fixed layer (26) and an injection junction part (7) of nonmagnetic layer, and a ferromagnetic free layer (27) provided in contact with the spin injection part (1) is such that in which the nonmagnetic layer (7) is made of either an insulator (12) or a conductor (25), a nonmagnetic layer (28) is provided on the surface of the ferromagnetic free layer (27), electric current is flown in the direction perpendicular to the film surface of the spin injection device (14), and the magnetization of the ferromagnetic free layer (27) is reversed. This is applicable to such various magnetic apparatuses and magnetic memory devices as super gigabit large capacity, high speed, non-volatile MRAM and the like.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
High permeability layered magnetic films to reduce noise in high speed interconnection
InactiveUS20050140462A1Mutual inductanceIncreased signal noiseMultiple-port networksCross-talk/noise/interference reductionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
A structure for magnetically shielded transmission lines for use with high speed integrated circuits having an improved signal to noise ratio, and a method for forming the same are disclosed. At least one magnetic shield structure contains electrically induced magnetic fields generated around a number of transmission lines. The shield material is made of alternating layers of magnetic material and insulating material.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Magnetic memory device and method of manufacturing the same
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Inspection Device and Inspection Method
ActiveUS20140225606A1High magnetic field sensitivityHigh sensitivityPolarisation-affecting propertiesMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesLight irradiationLength wave
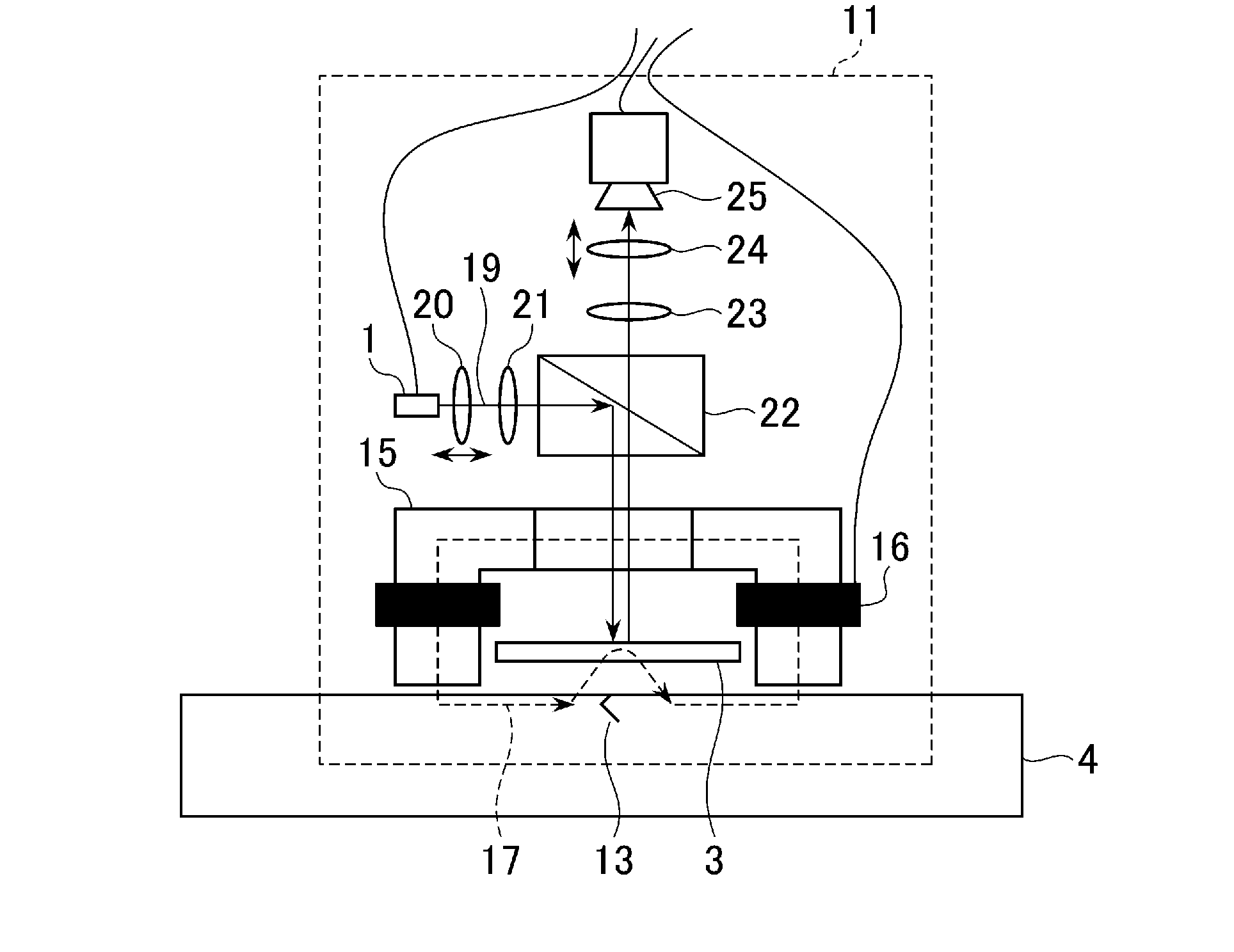
Provided are an inspection device and an inspection method capable of achieving improved magnetic field sensitivity by using a magnetic thin film of a small film thickness. A light-emitting unit 1 emits light of a first wavelength for acquiring magnetic field inspection information and a second wavelength for acquiring inspection object surface information. A selection unit 6 selects information from an inspection object 4 and information from a magnetophotonic crystal film 3 acquired by light irradiation performed by an irradiation unit 2. An image generation unit 9 generates image data based on the magnetic field inspection information acquired with the first wavelength and the inspection object surface information acquired with the second wavelength selected by the selection unit. Each of the generated image data is displayed on a display unit 10.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Structure and method for fabricating a magnetic thin film memory having a high field anisotropy
InactiveUS20120015099A1High magnetic materialLow critical currentNanomagnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureDiffusionHigh energy
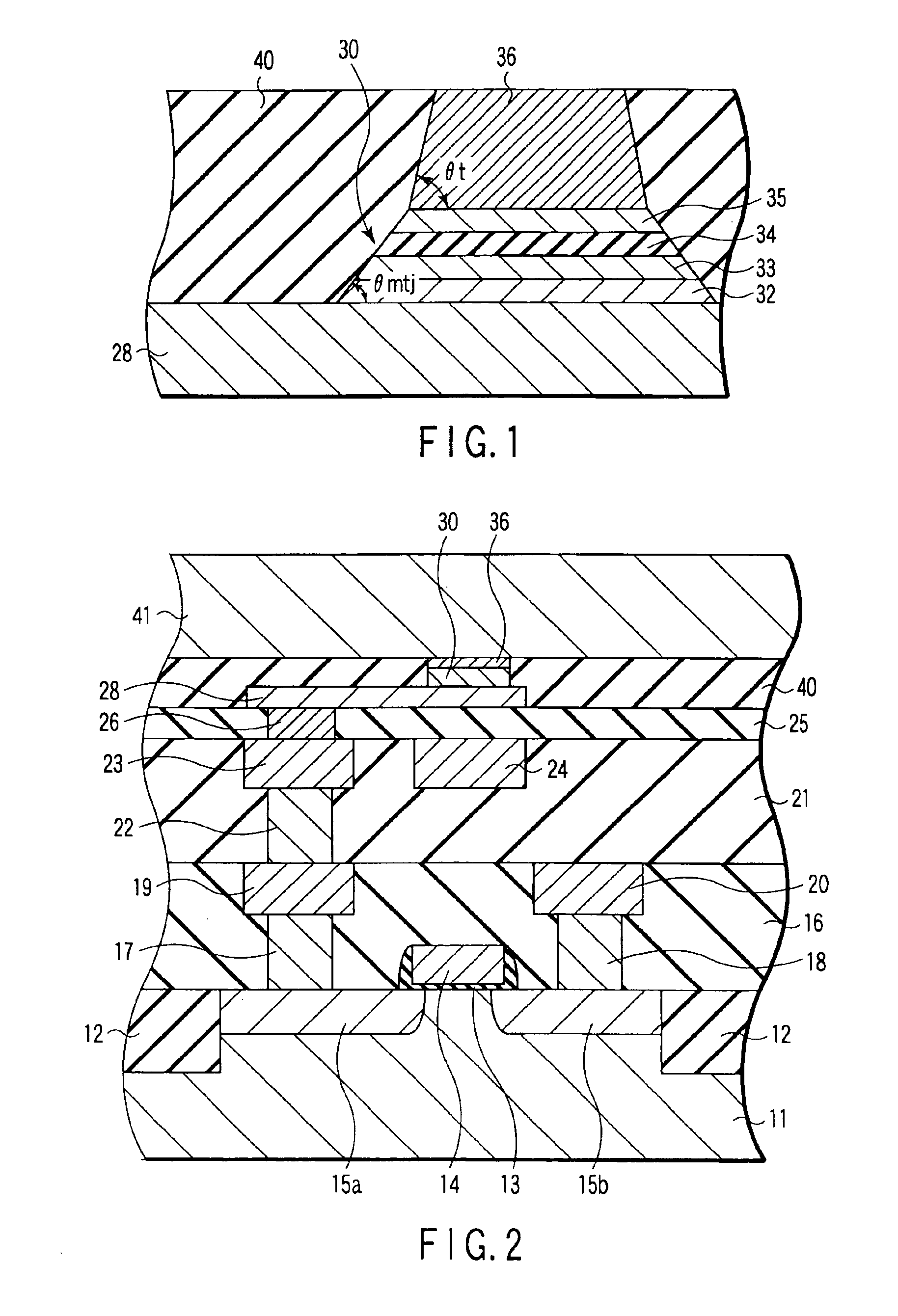
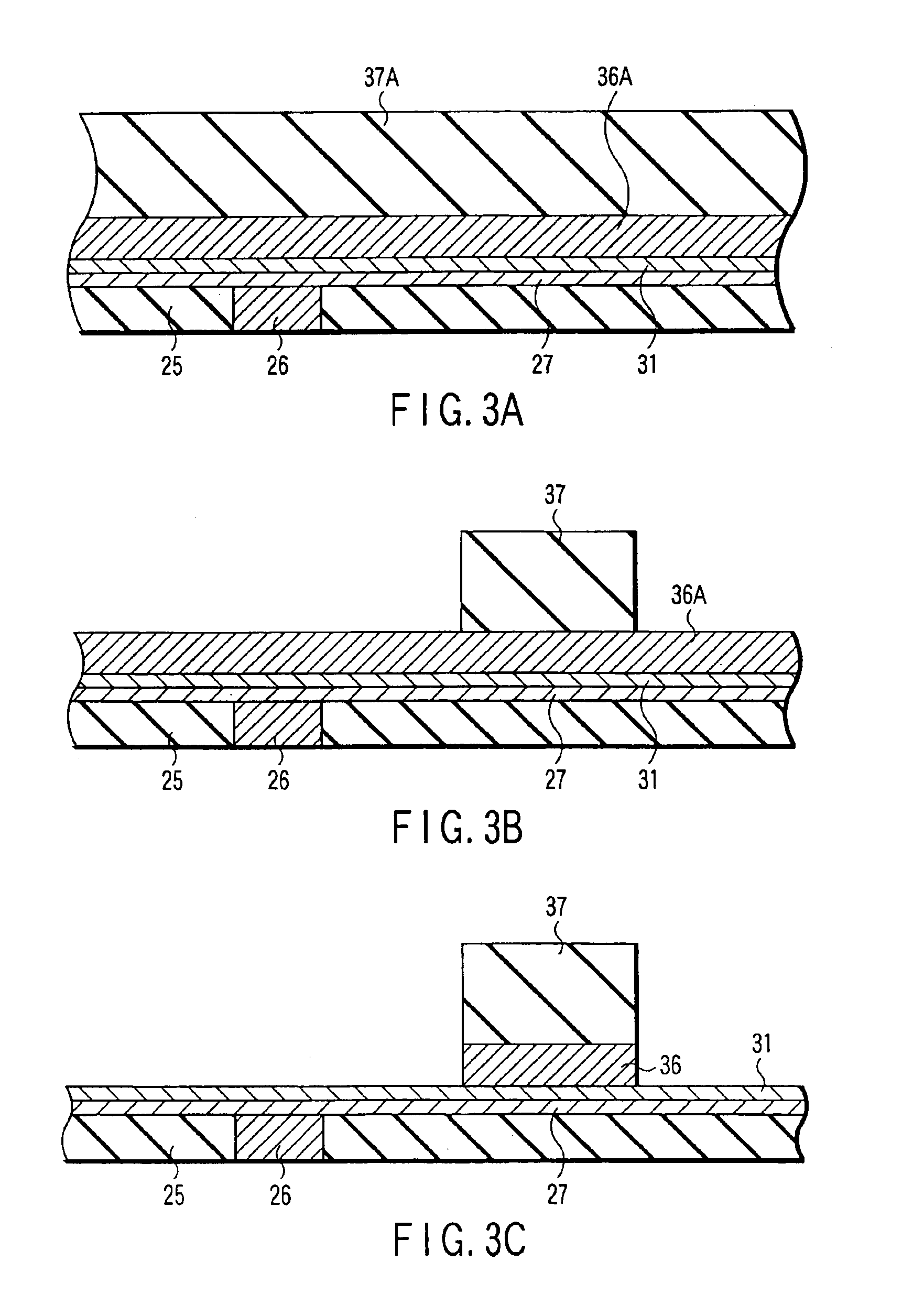
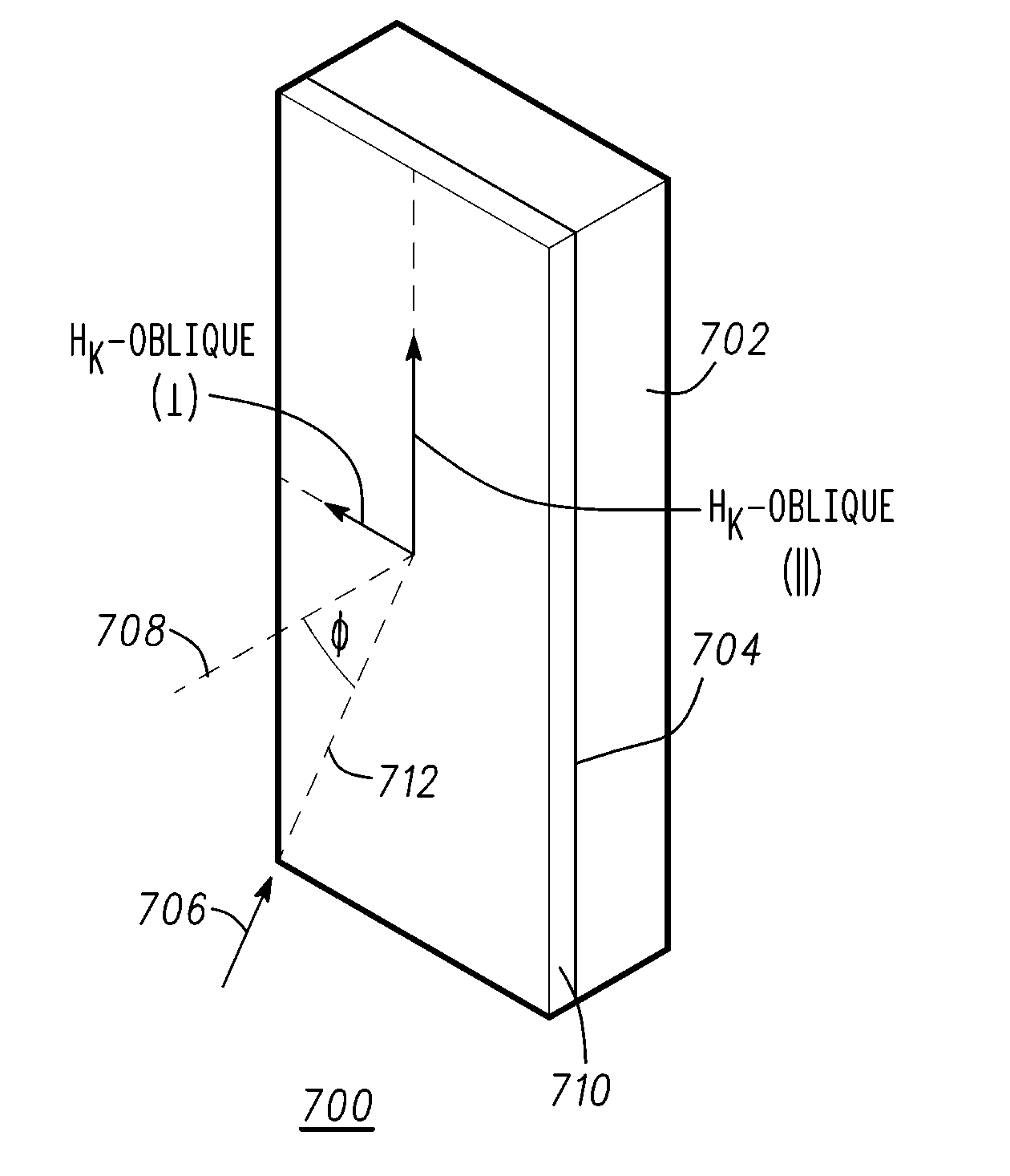
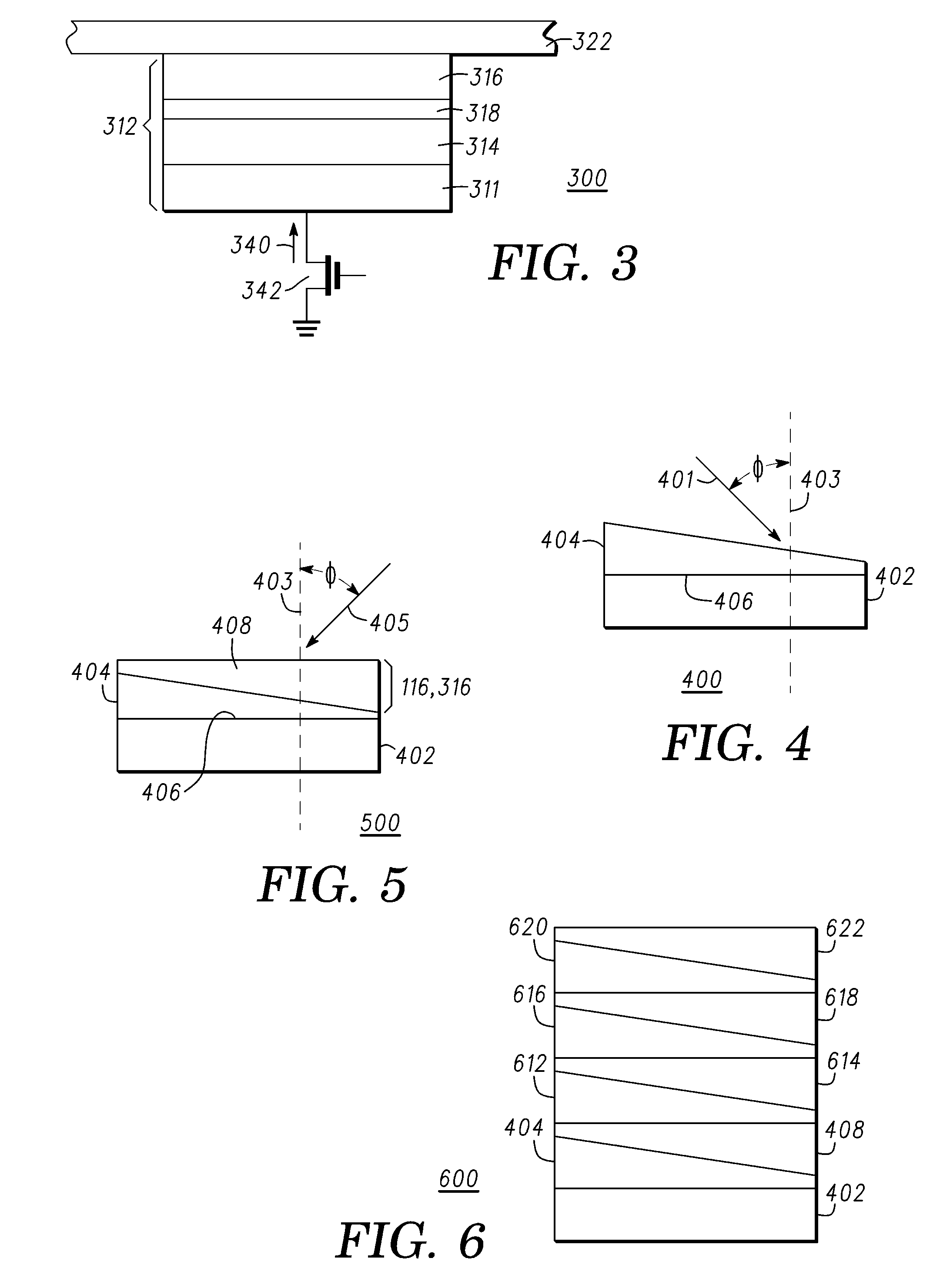
A method for depositing uniform and smooth ferromagnetic thin films with high deposition-induced microstructural anisotropy includes a magnetic material deposited in two or more static oblique deposition steps from opposed directions to form a free layer having a high kink Hk, a high energy barrier to thermal reversal, a low critical current in spin-torque switching embodiments, and improved resistance to diffusion of material from adjacent layers in the device. Nonmagnetic layers deposited by the static oblique deposition technique may be used as seed layers for a ferromagnetic free layer or to generate other types of anisotropy determined by the deposition-induced microstructural anisotropy. Additional magnetic or non-magnetic layers may be deposited by conventional methods adjacent to oblique layer to provide magnetic coupling control, reduction of surface roughness, and barriers to diffusion from additional adjacent layers in the device.
Owner:EVERSPIN TECHNOLOGIES
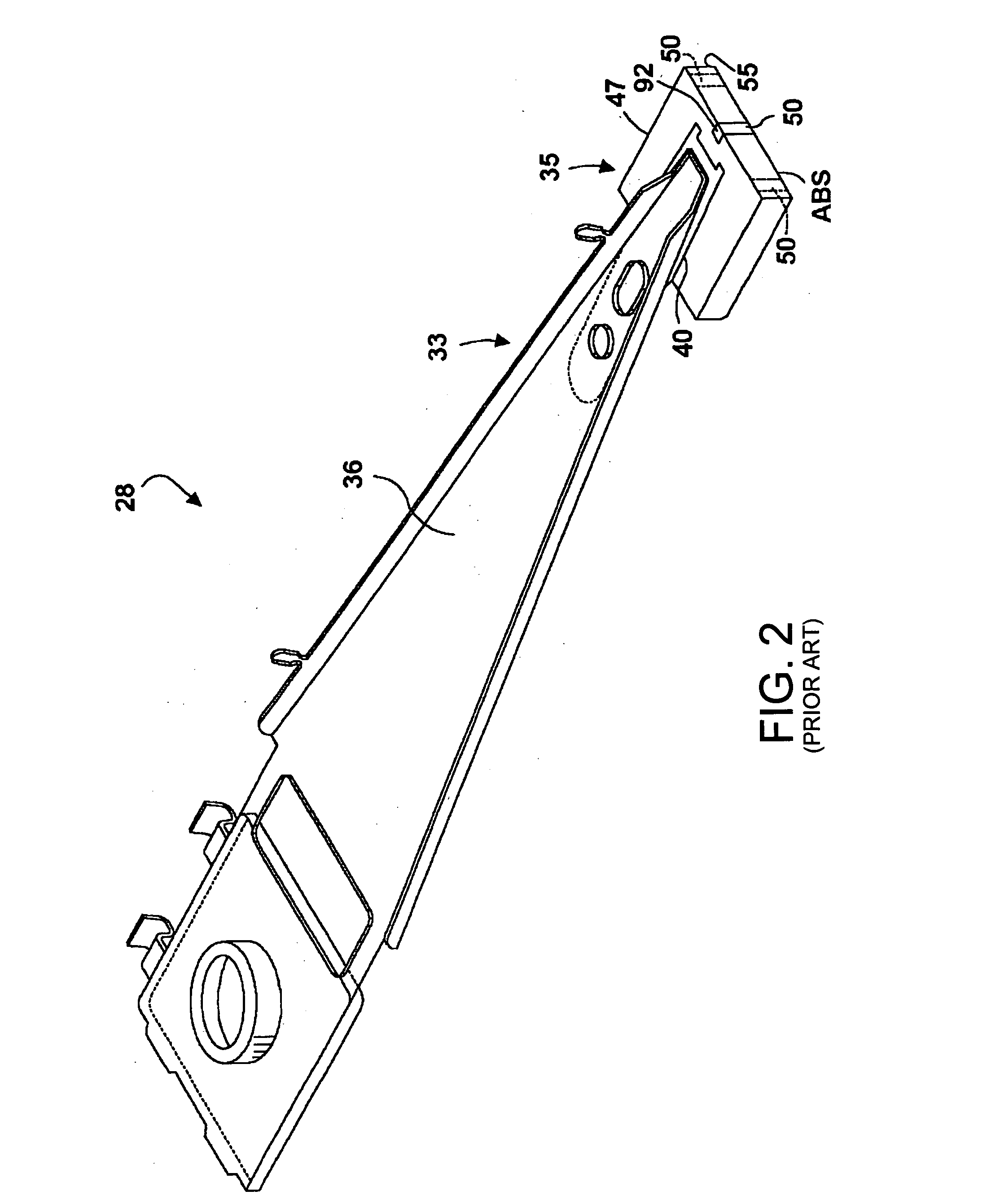
Magnetic thin film head with heat-assisted write section and hard disk drive incorporating same
InactiveUS20060143635A1High densityImproves servo writing processCombination recordingManufacturing heads with multiple gapsHard disc driveEngineering
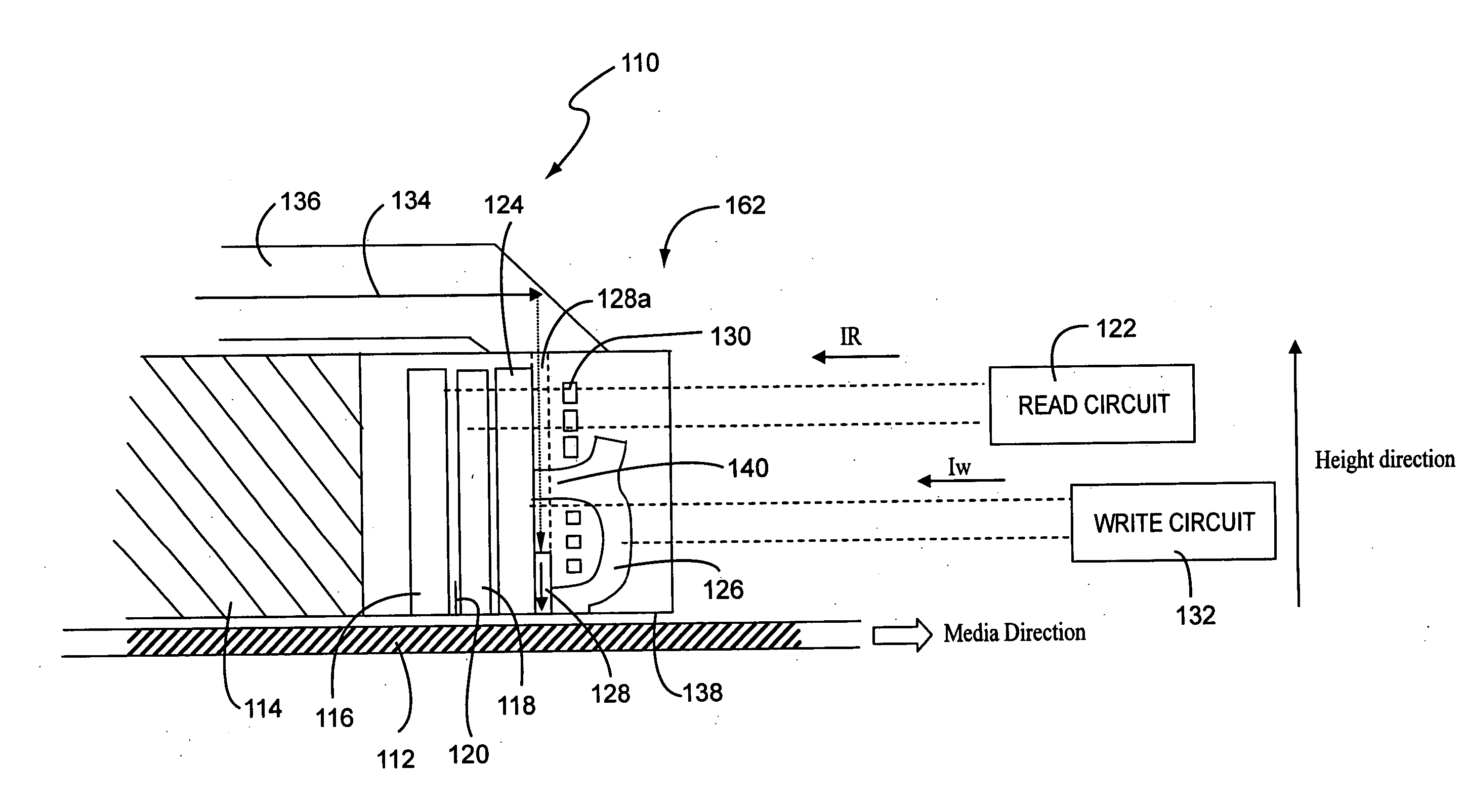
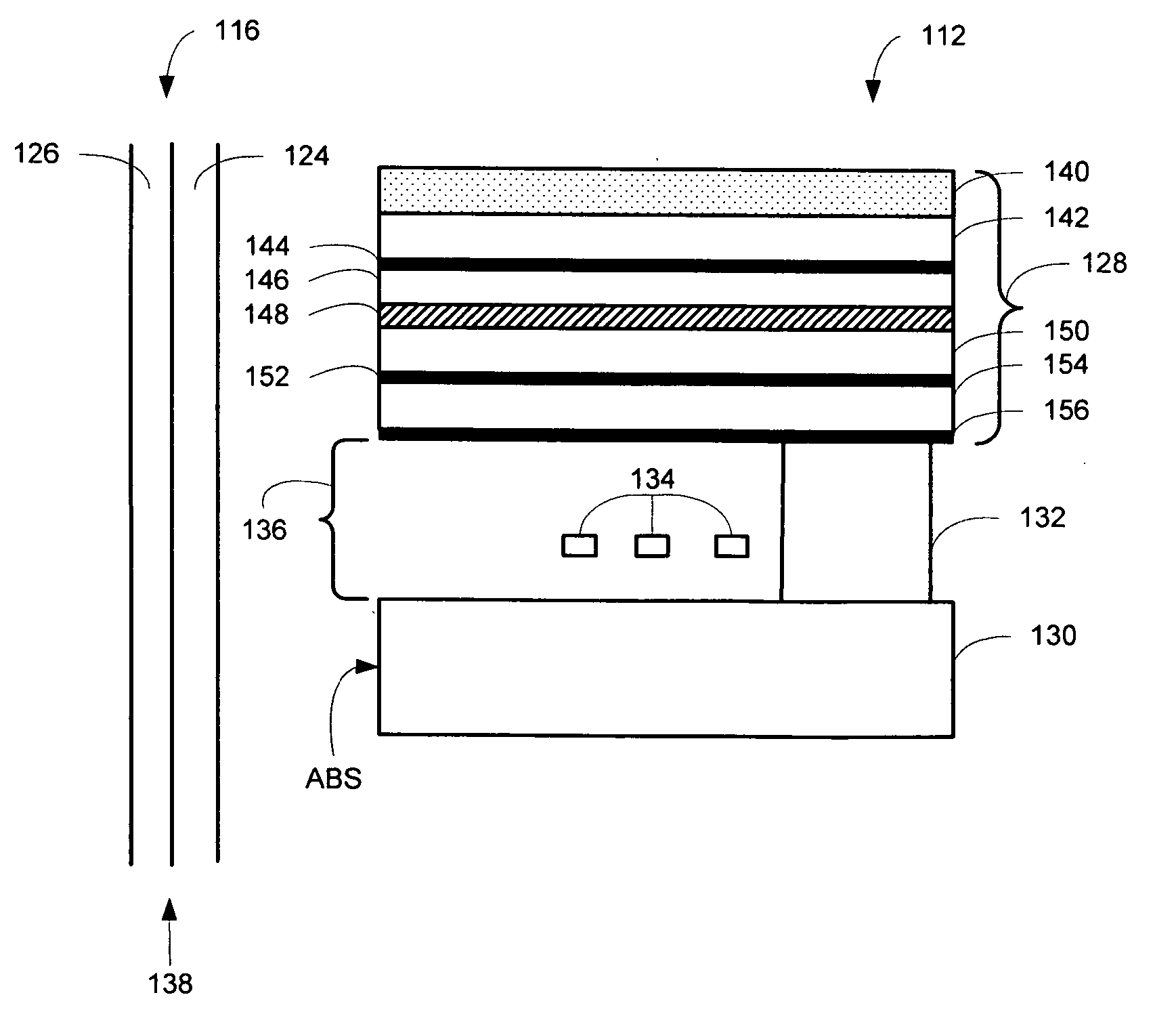
A thin film magnetic read / write head for use in magnetic data storage systems to enable writing of data to a magnetic data storage medium with the assistance of laser heating. The read / write head allows magnetic reading of data from the storage medium, and thermally assisted magnetic writing of data on the storage medium. A waveguide is provided in a write gap in the form of an optical circuit having a plurality of inputs and a single output at the air bearing surface (ABS) for concentrating laser light used for heating the storage medium during the write operation. The thermally assisted magnetic writing improves the thermal stability of the recorded data and usefulness thereof throughout a wide temperature range.
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
Magnetic thin film interference device or pigment and method of making it, printing ink or coating composition containing said magnetic thin fim interference device
InactiveCN1459034ARich varietyExact matchOther printing matterMagnetic paintsPrinting inkMagnetic thin film
The invention discloses magnetic OVP, said pigment consisting of thin-layer flakes having a basic metal-dielectric-metal structure to result in a viewing-angle dependent color appearance, and having, in addition to said viewing-angle dependent color appearance, incorporated magnetic properties, to make them distinguishable from OVP of similar appearance but not having said magnetic properties. The invention discloses as well methods for obtaining such pigments and the use of such pigments as security elements in inks, coatings and articles.
Owner:SICPA HLDG SA
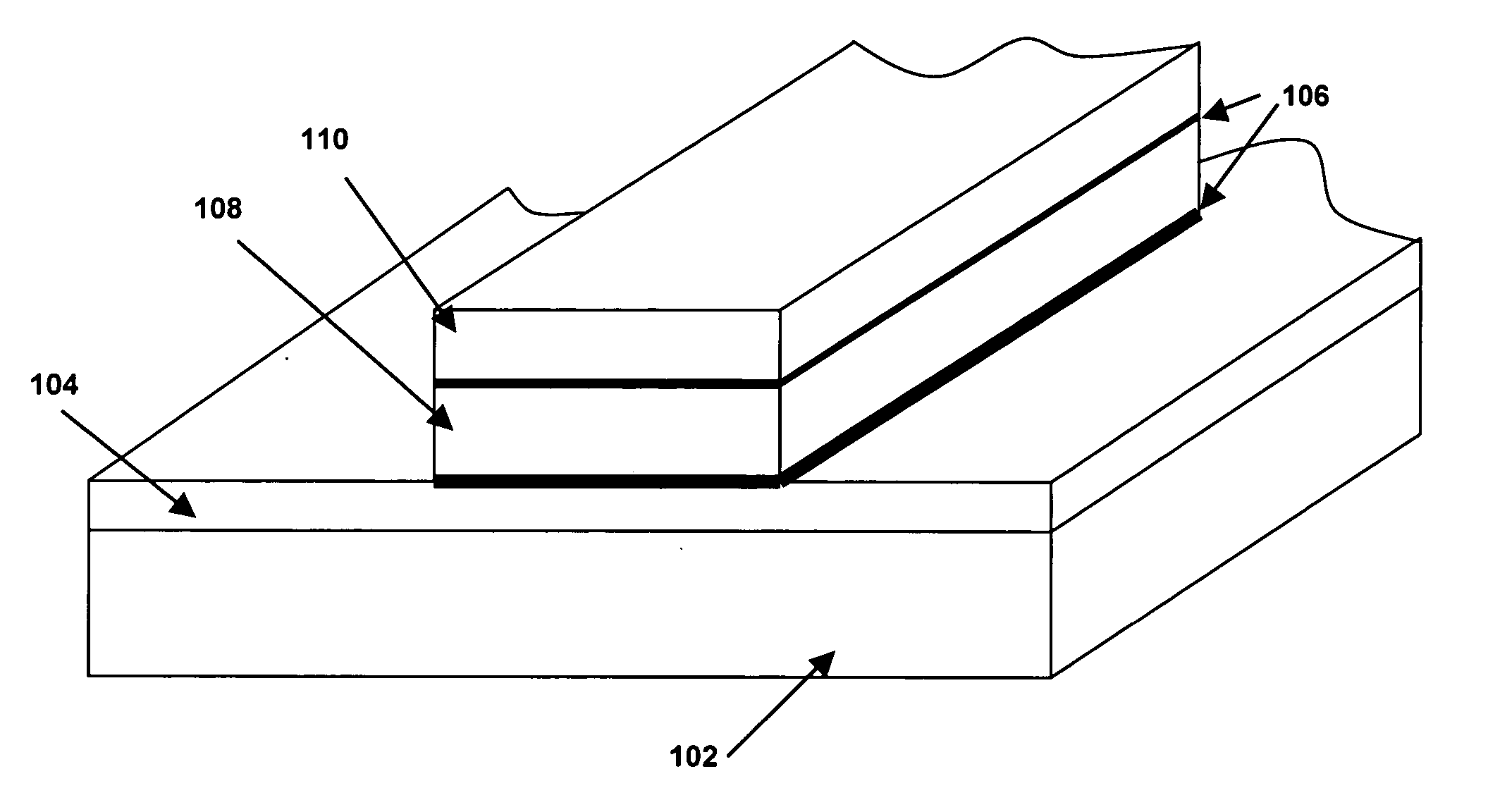
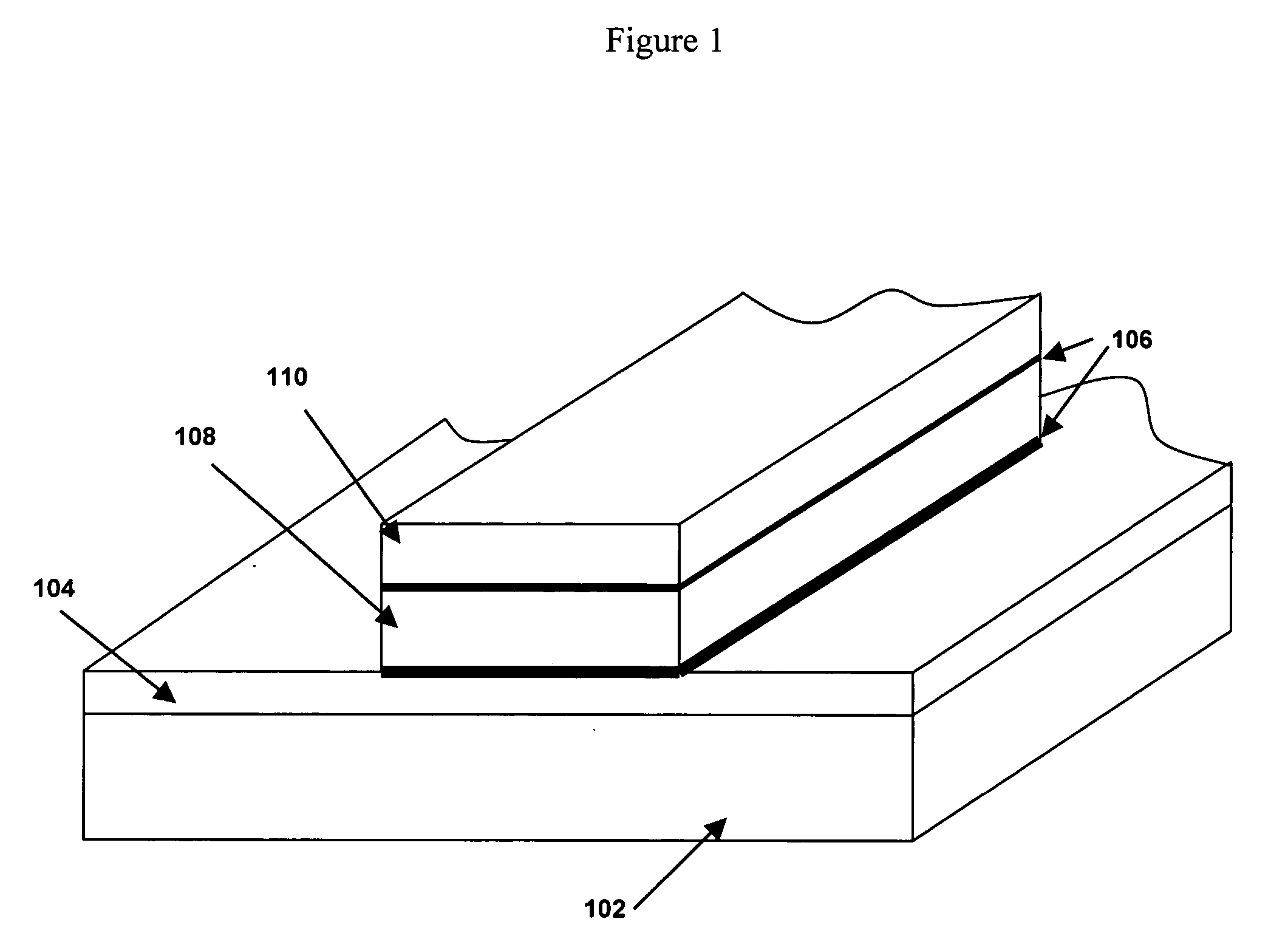
Semiconductor storage device and production method therefor
InactiveUS20050174876A1Increase capacityReduce power consumptionNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismBit lineSemiconductor storage devices
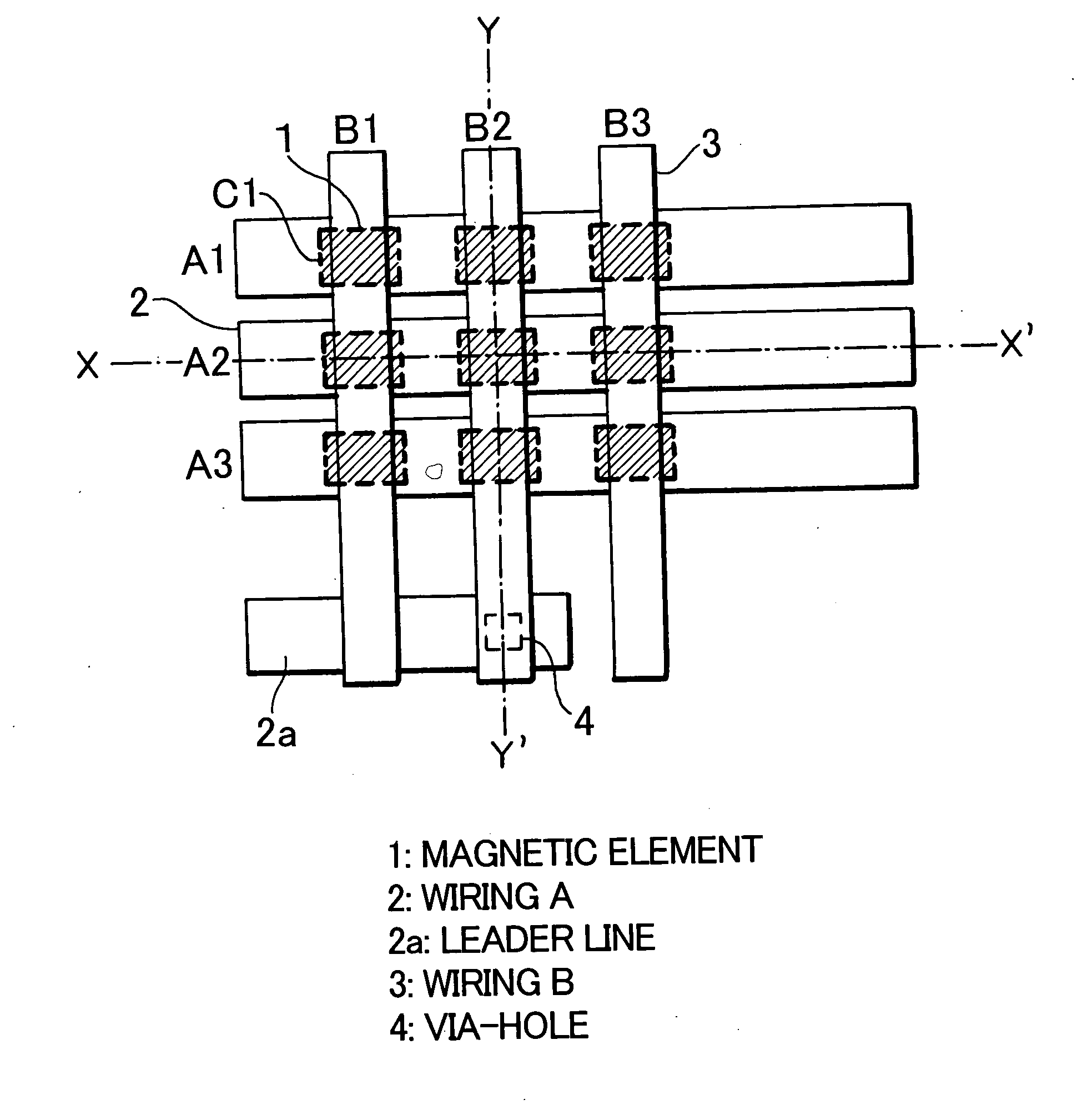
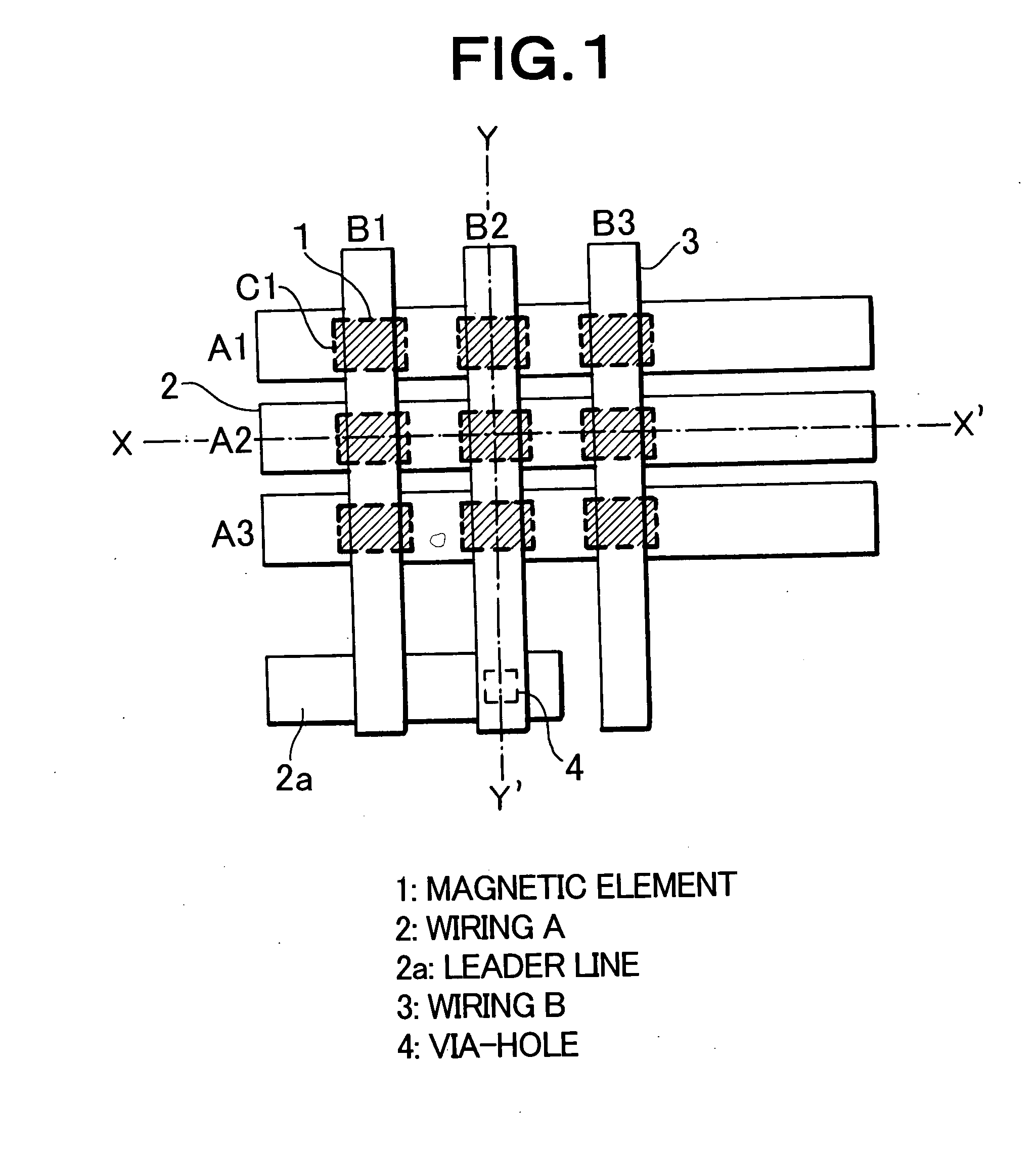
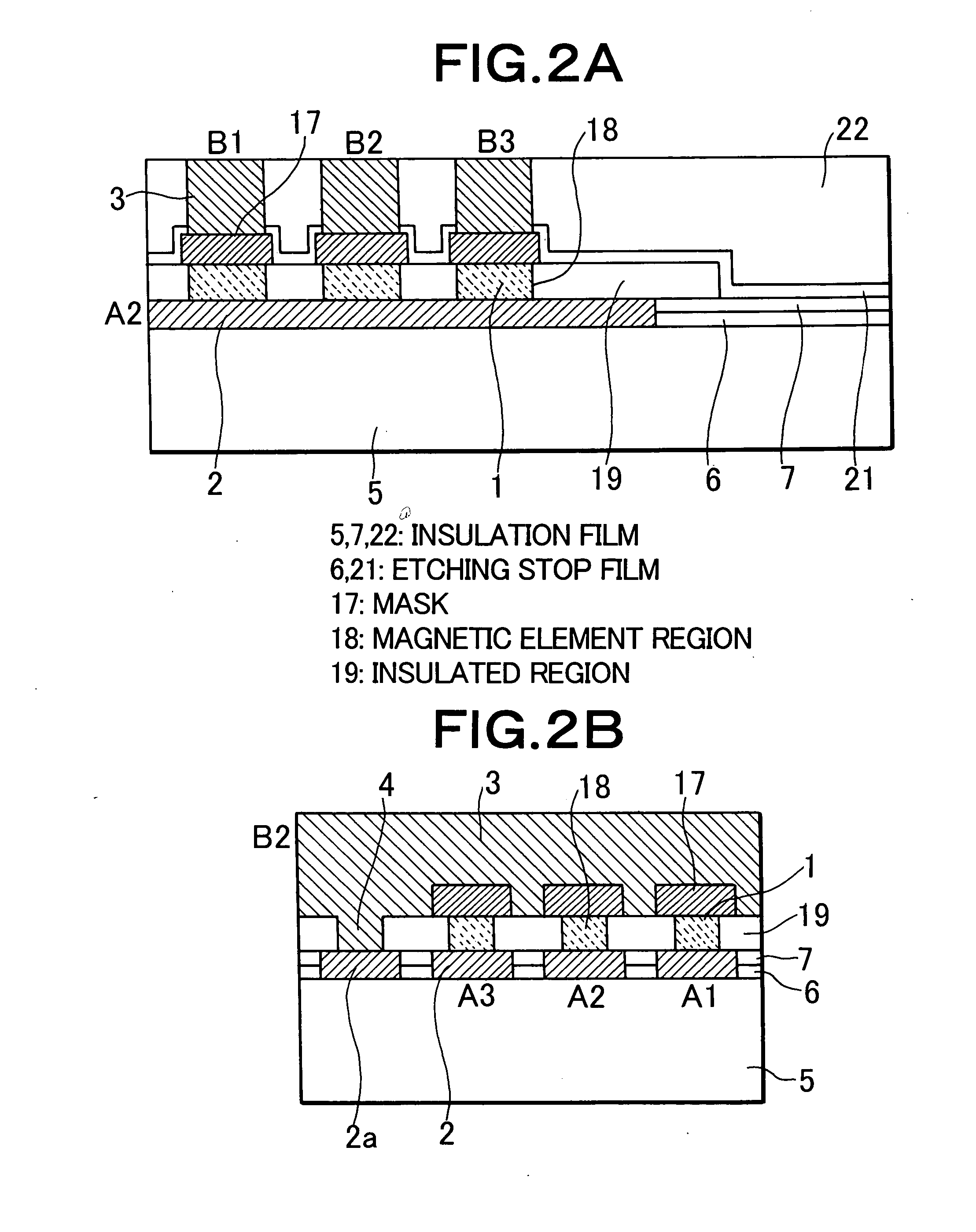
Portions excluding magnetic elements of a laminate film of magnetic films or the like constituting magnetic elements (1) are oxidized / nitrided or oxynitrided to be insulated by a plasma processing using a conductive mask (17), whereby a plurality of magnetic elements are separated. This laminate film comprises a magnetic element region (18) formed with magnetic elements (1) and an insulated region (19) consisting of oxides / nitrides or oxynitrides. Upper wiring such as a bit line (3) is formed later. Since the conductive mask used in forming the insulated region is made part of the upper wiring, the magnetic elements and the upper wiring can be disposed in contact with each other.
Owner:NEC CORP
Spin mosfet
InactiveUS20080061332A1Large outputLow densityNanomagnetismSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETSpins
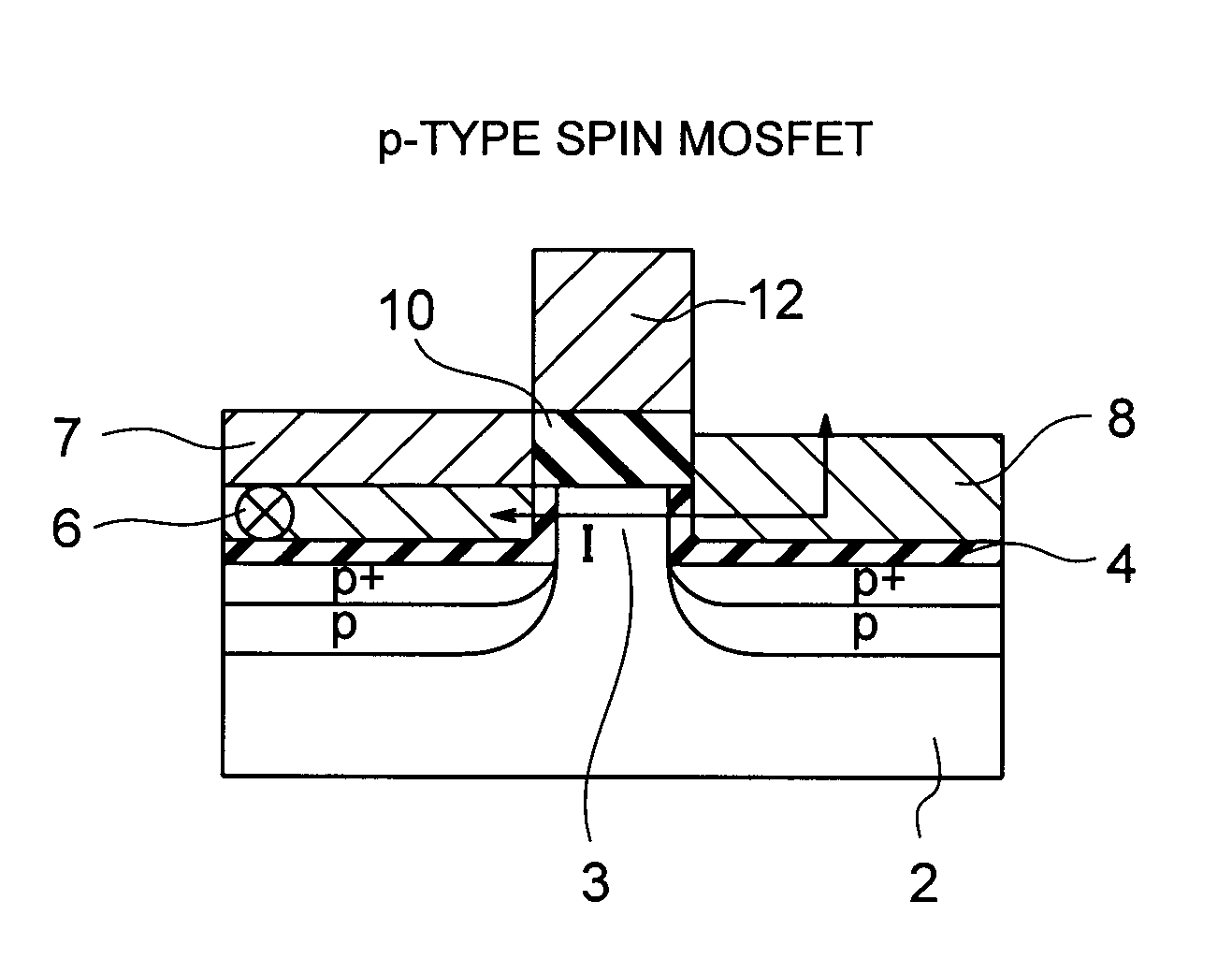
A spin MOSFET includes: a semiconductor substrate; a first magnetic film formed on the semiconductor substrate and including a first ferromagnetic layer, a magnetization direction of the first ferromagnetic layer being pinned; a second magnetic film formed on the semiconductor substrate to separate from the first magnetic film and including a magnetization free layer, a first nonmagnetic layer being a tunnel insulator and provided on the magnetization free layer, and a magnetization pinned layer provided on the first nonmagnetic layer, a magnetization direction of the magnetization free layer being changeable and a magnetization direction of the magnetization pinned layer being fixed; a gate insulating film provided at least on the semiconductor substrate between the first magnetic film and the second magnetic film; and a gate electrode formed on the gate insulating film.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Laminated high moment magnetic films with antiferromagnetic coupling as write pole of perpendicular magnetic recording head
InactiveUS20060044680A1Manufacture head surfaceRecord information storageAntiferromagnetic couplingEngineering
A perpendicular write head includes a main pole comprising high moment magnetic layers laminated with both soft magnetic layers and non-magnetic layers for antiferromagnetic coupling (AFC) between the high moment material layers.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Spin oscillator device
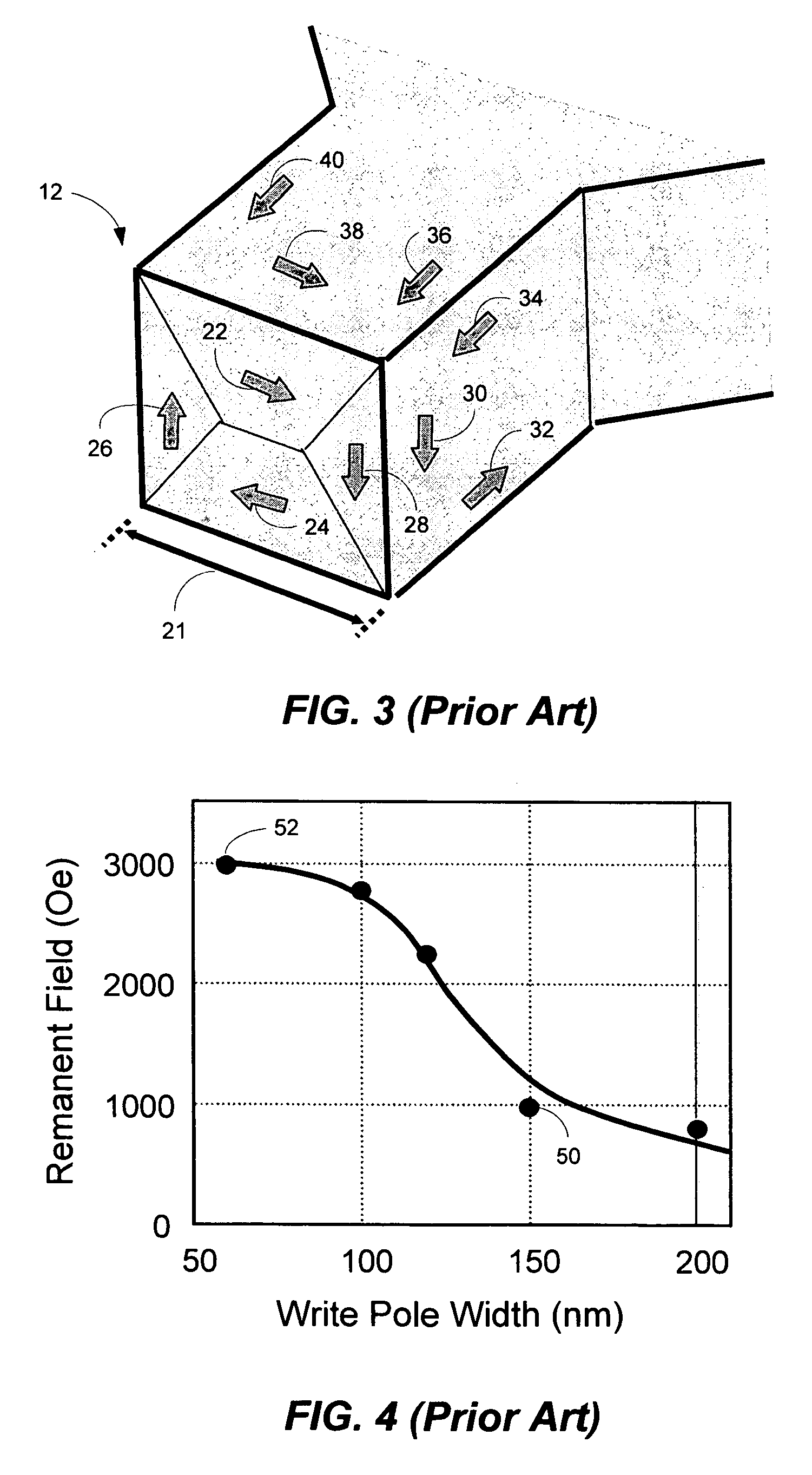
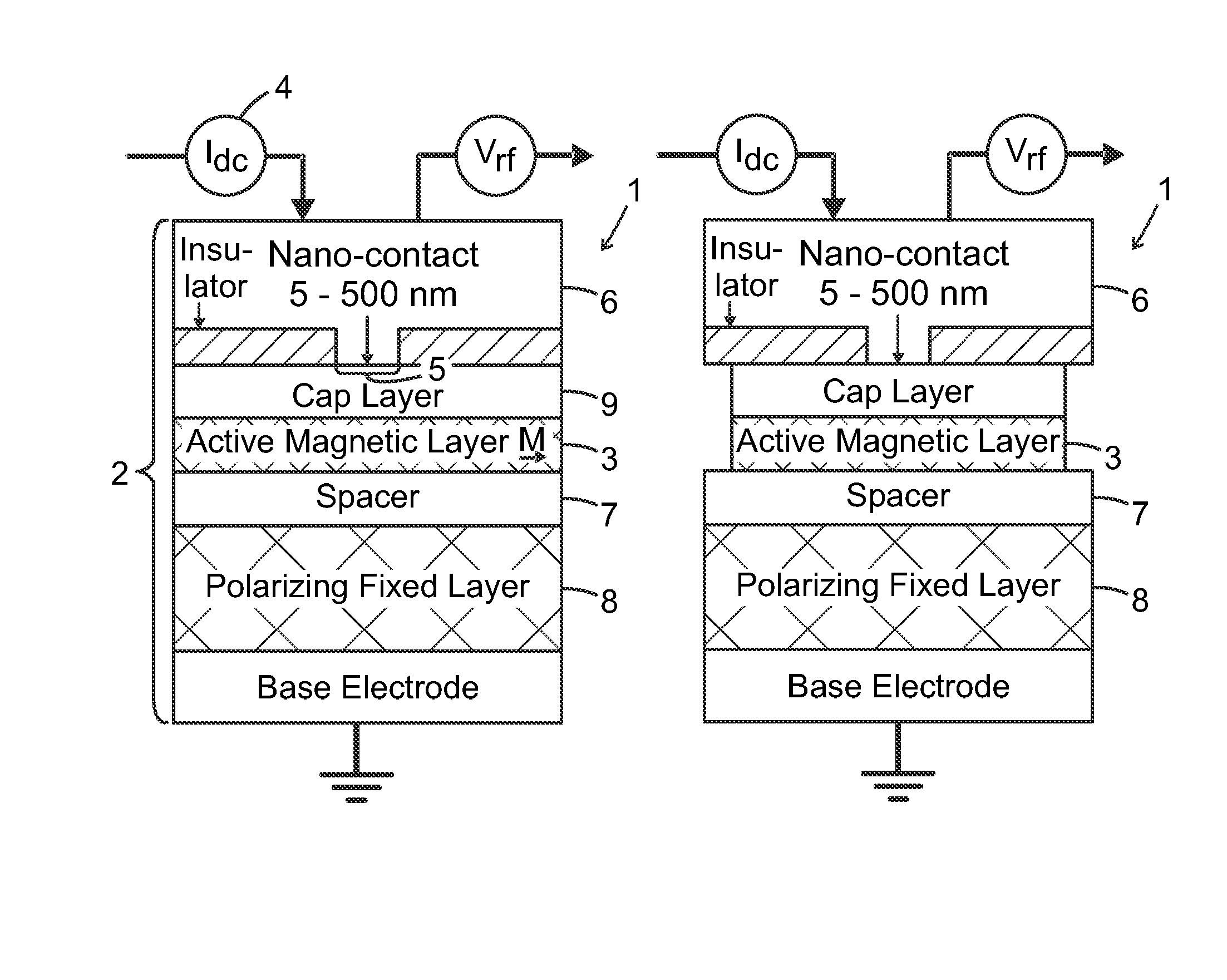
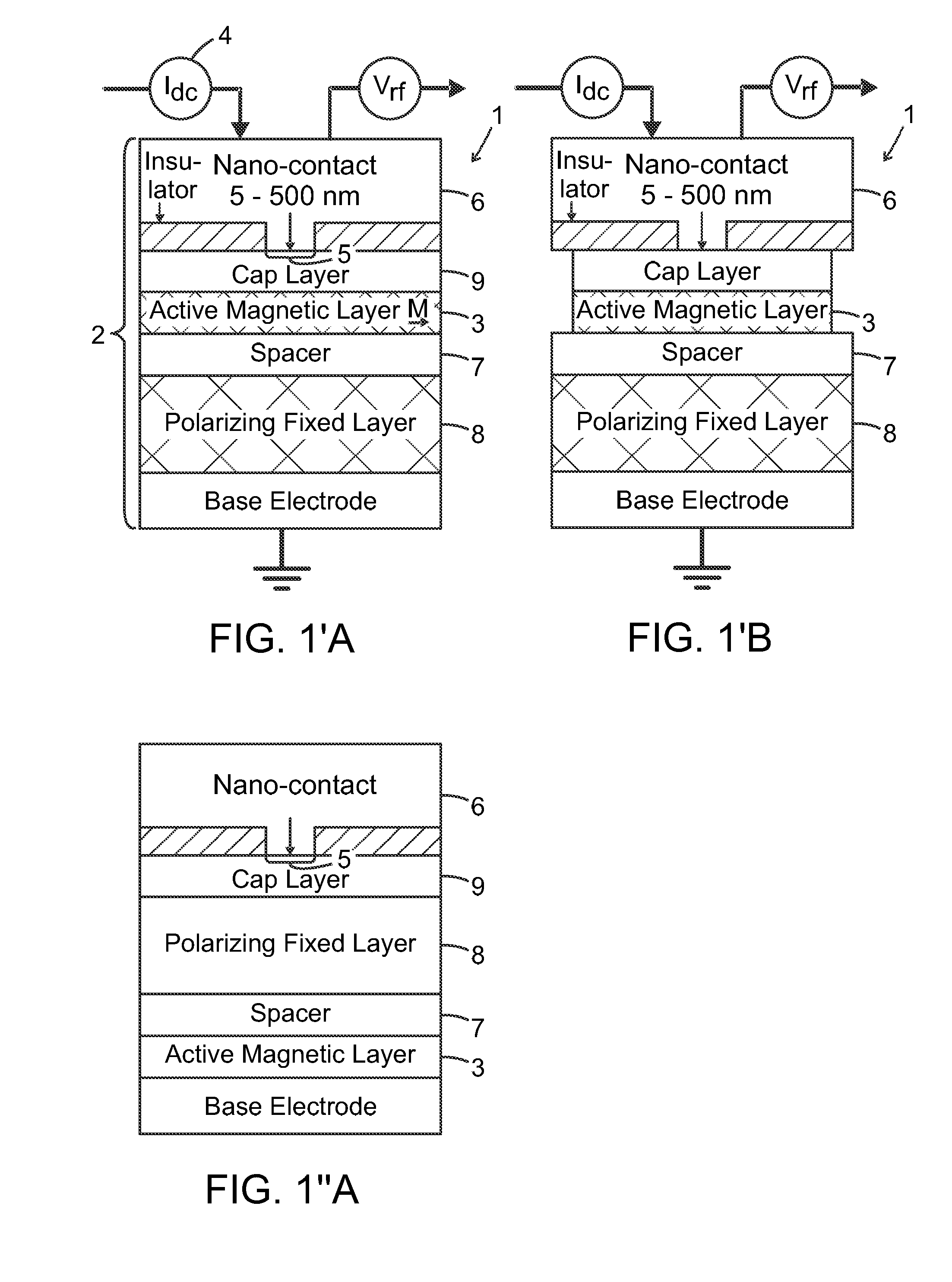
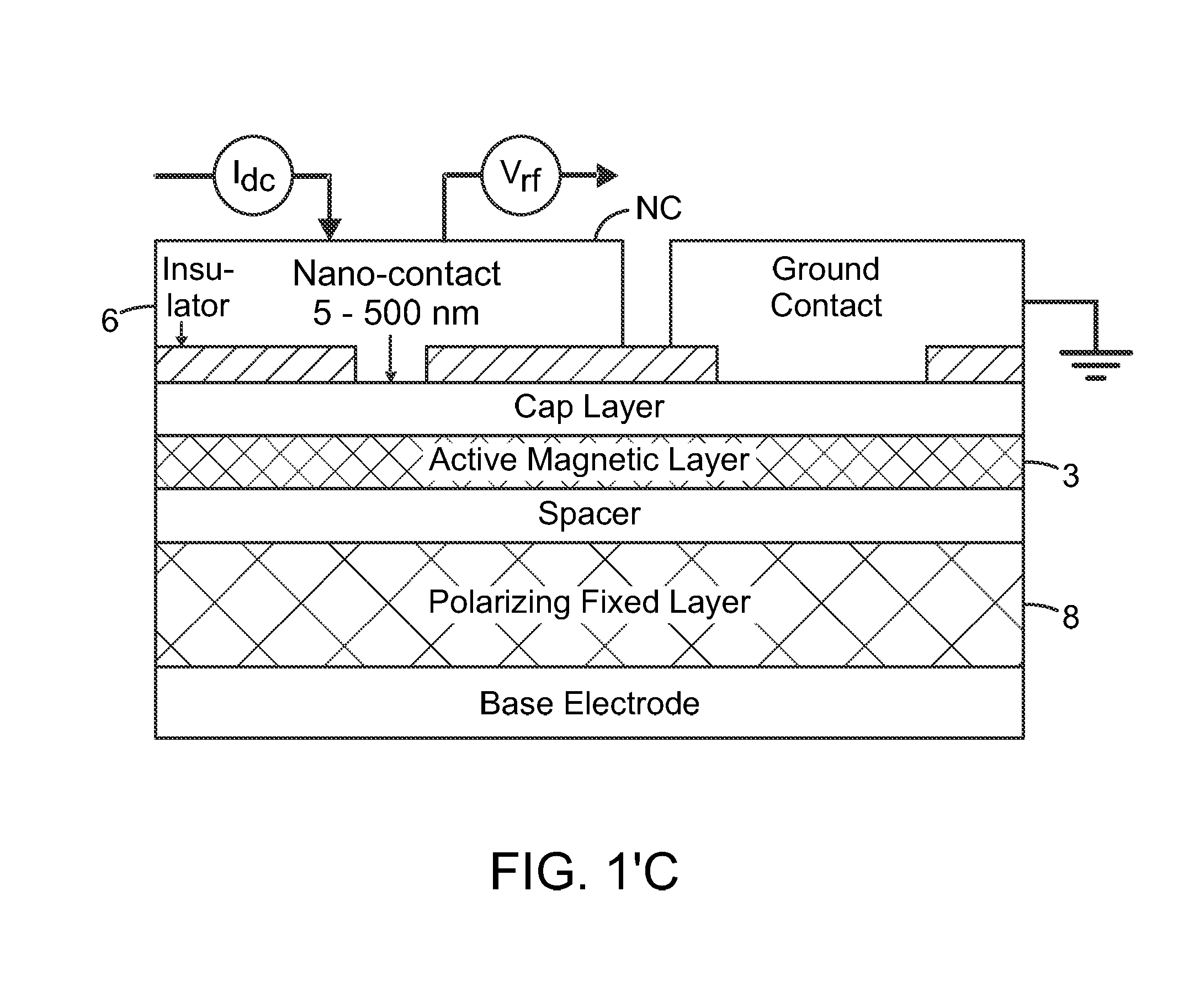
ActiveUS20170033742A1Detection is limitedPulse automatic controlMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpin-transfer torqueMagnetic memory
The present invention relates to using spin transfer torque underneath a nanocontact on a magnetic thin film with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA), provides generation of dissipative magnetic droplet solitons and magnetic droplet-skyrmions and report on their rich dynamical properties. Micromagnetic simulations identify the conditions necessary to nucleate and drive droplet-skyrmions over a wide range of currents and fields. Micromagnetic simulations also demonstrate how droplets and droplet-skyrmions can be used as skyrmion injectors and detectors in skyrmion-based magnetic memories. The droplet-skyrmion can be controlled using both current and magnetic fields, and is expected to have applications in spintronics, magnonics, skyrmionics, and PMA-based domain-wall devices.
Owner:NANOSC AB
Method of using spin injection device
InactiveUS20090180308A1Current densityNanomagnetismBase layers for recording layersElectrical conductorMagnetic memory
A spin injection device capable of spin injection magnetization reversal at low current density, a magnetic apparatus using the same, and magnetic thin film using the same, whereby the spin injection device (14) including a spin injection part (1) comprising a spin polarization part (9) including a ferromagnetic fixed layer (26) and an injection junction part (7) of nonmagnetic layer, and a ferromagnetic free layer (27) provided in contact with the spin injection part (1) is such that in which the nonmagnetic layer (7) is made of either an insulator (12) or a conductor (25), a nonmagnetic layer (28) is provided on the surface of the ferromagnetic free layer (27), electric current is flown in the direction perpendicular to the film surface of the spin injection device (14), and the magnetization of the ferromagnetic free layer (27) is reversed. This is applicable to such various magnetic apparatuses and magnetic memory devices as super gigabit large capacity, high speed, non-volatile MRAM and the like.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
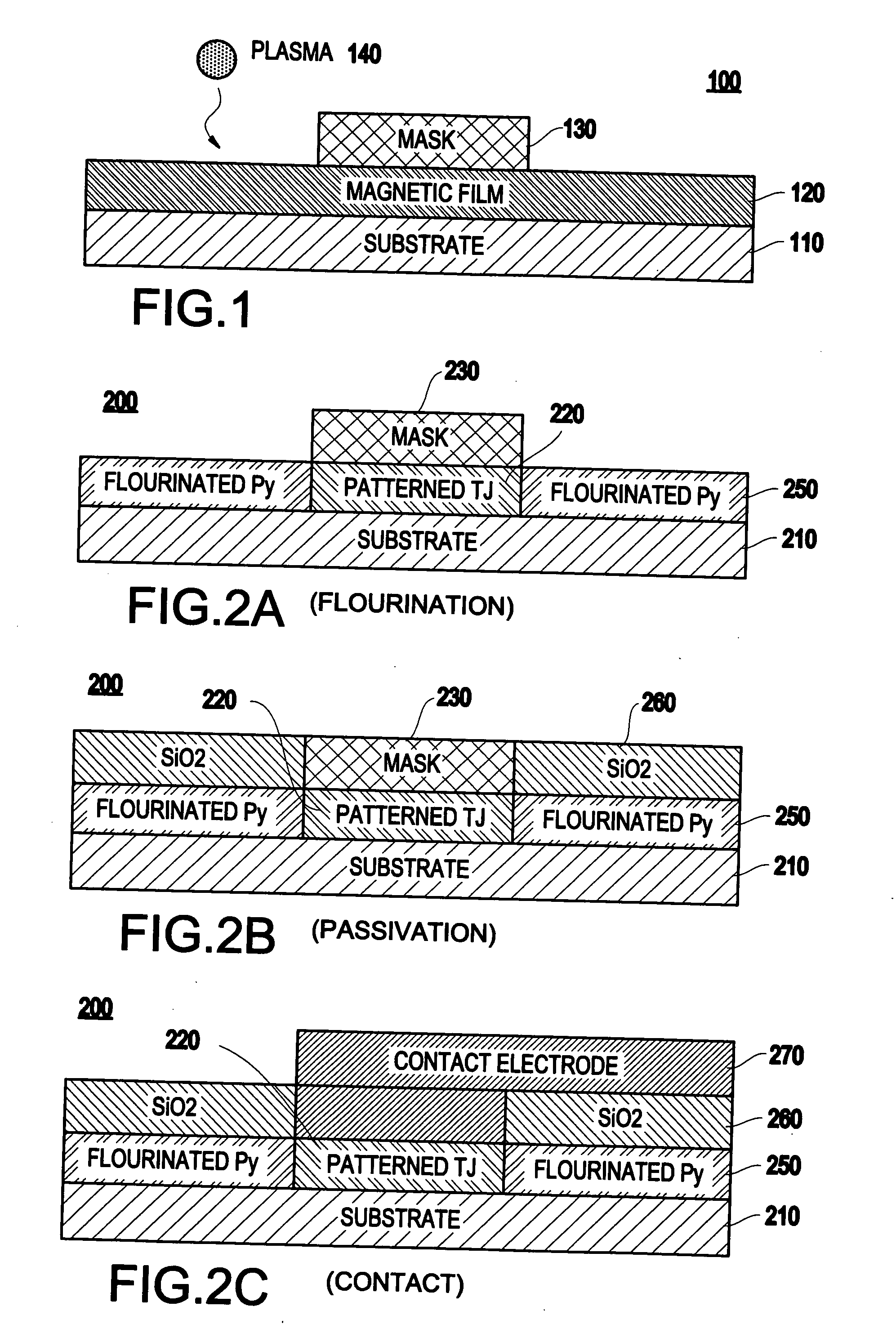
Method of preventing short circuits in magnetic film stacks
InactiveUS6893893B2Overcome disadvantagesAvoid contactSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRandom access memoryMagnetic reluctance
A method for preventing electrical short circuits in a multi-layer magnetic film stack comprises providing a film stack that includes a layer of magnetic material having an exposed surface. A protective layer is deposited on the exposed surface of the magnetic layer. The protective layer may comprise, for example, a fluorocarbon or a hydrofluorocarbon. The film stack is etched and the protective layer protects the exposed surface from a conductive residue produced while etching the film stack. The method may be used in film stacks to form a magneto-resistive random access memory (MRAM) device.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Single-chip magnetic sensor, and laser heating-assisted annealing apparatus thereof and laser heating-assisted annealing method thereof
ActiveCN102208530AHigh sensitivityGood magnetoresistance matchingMagnetic measurementsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsOptoelectronicsOptical attenuator
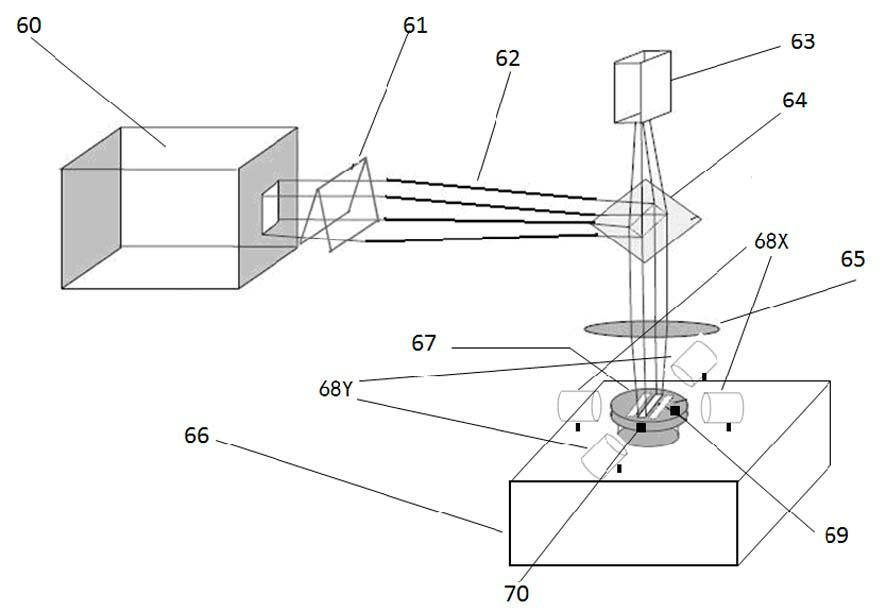
The invention discloses a single-chip magnetic sensor, and a laser heating-assisted annealing apparatus thereof and a laser heating-assisted annealing method thereof. The laser heating-assisted annealing method comprises the following steps: (a), annealing is carried out on a magnetic thin film in a strong magnetic field, so that magnetic moments on a pinning layer of the magnetic thin film are towards a same direction; (b), the magnetic thin film is fixedly disposed on a clamp of a movable platform; (c), a laser source is opened to emit a laser beam, which is attenuated through an optical attenuator; the direction of the attenuated laser beam is changed through a reflective mirror; and the laser beam with the changed direction is focused into a light spot by a focusing objective lens; (d), the movable platform is moved, in order that the focused light spot of the laser beam is aimed at the magnetic thin film so as to enable the magnetic thin film to be heated by the laser beam; (e), a magnetic field intensity of an electromagnet arranged on the movable platform is adjusted, so that a magnetic domain of the heating area of the magnetic thin film can be overturned; and (f), the magnetic thin film is cut into slices, and the slices of the cut magnetic thin film are bound into one.
Owner:MULTIDIMENSION TECH CO LTD
Single-chip three-shaft magnetic field sensor and production method
ActiveCN103105592AEasy to packWith miniaturizationManufacture of electrical instrumentsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsCapacitanceSingle chip
The invention provides a single-chip three-shaft magnetic field sensor and a production method. The single-chip three-shaft magnetic field sensor at least comprises a first substrate, at least two first electrodes, at least four second electrodes, a second substrate, a single-shaft rotation structure, a double-shaft rotation structure, a first magnetic film structure and a second magnetic film structure, wherein the first electrodes and the second electrodes are formed on the surface of the first substrate, the second substrate and the first substrate bond together through keys, the second substrate is provided with the single-shaft rotation structure and the double-shaft rotation structure, the single-shaft rotation structure and each of the two first electrodes form a capacitor structure, and the double-shaft rotation structure and each of the four second electrodes form a capacitor structure. The first magnetic film structure is formed on the surface of the single-shaft rotation structure and can generate corresponding torque under the action of a magnetic field in a first direction, and the second magnetic film structure is formed on the surface of the double-shaft rotation structure and can generate corresponding torque under the action of a magnetic field in a second direction and a magnetic field in a third direction. The single-chip three-shaft magnetic field sensor has the advantages of being high in sensitivity, small in size, low in power consumption and cost, easy to package and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Magnetic memory device and method of manufacturing the same
A method of manufacturing a magnetic memory device includes forming an insulation layer on a substrate, forming a lower electrode on the insulation layer, forming a magneto-resistive film on an upper surface of the lower electrode, the magneto-resistive film including an insulation barrier layer and a plurality of magnetic films stacked on both sides of the insulation barrier layer, stacking a mask layer on the magneto-resistive film, performing ion etching on the magneto-resistive film, using the mask layer as a mask, thereby forming a magneto-resistive element, forming an insulation film on upper surfaces of the mask, the magneto-resistive element and the lower electrode, and etching the insulation film with an ion beam such that a side surface of the magneto-resistive element is exposed.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
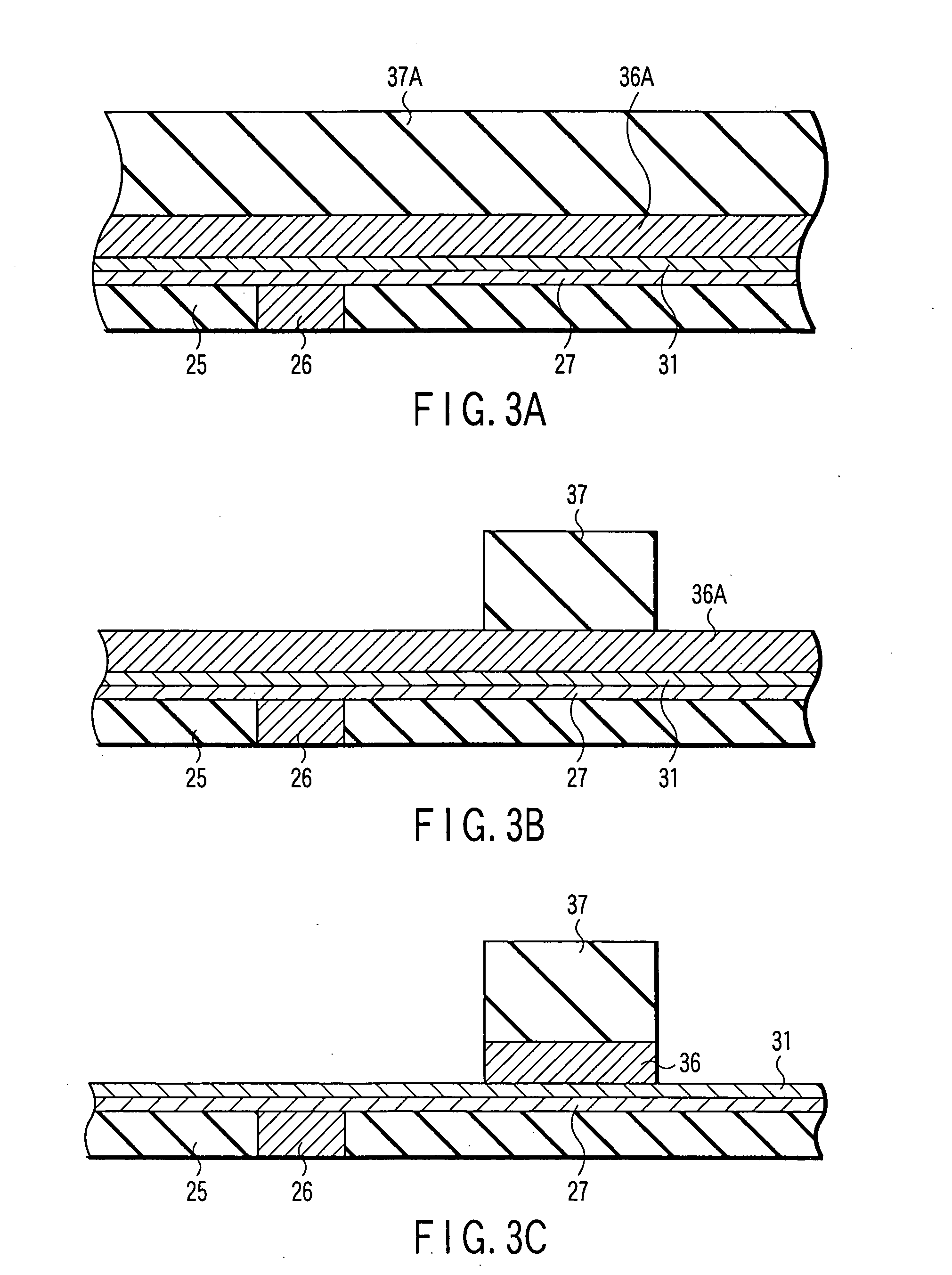
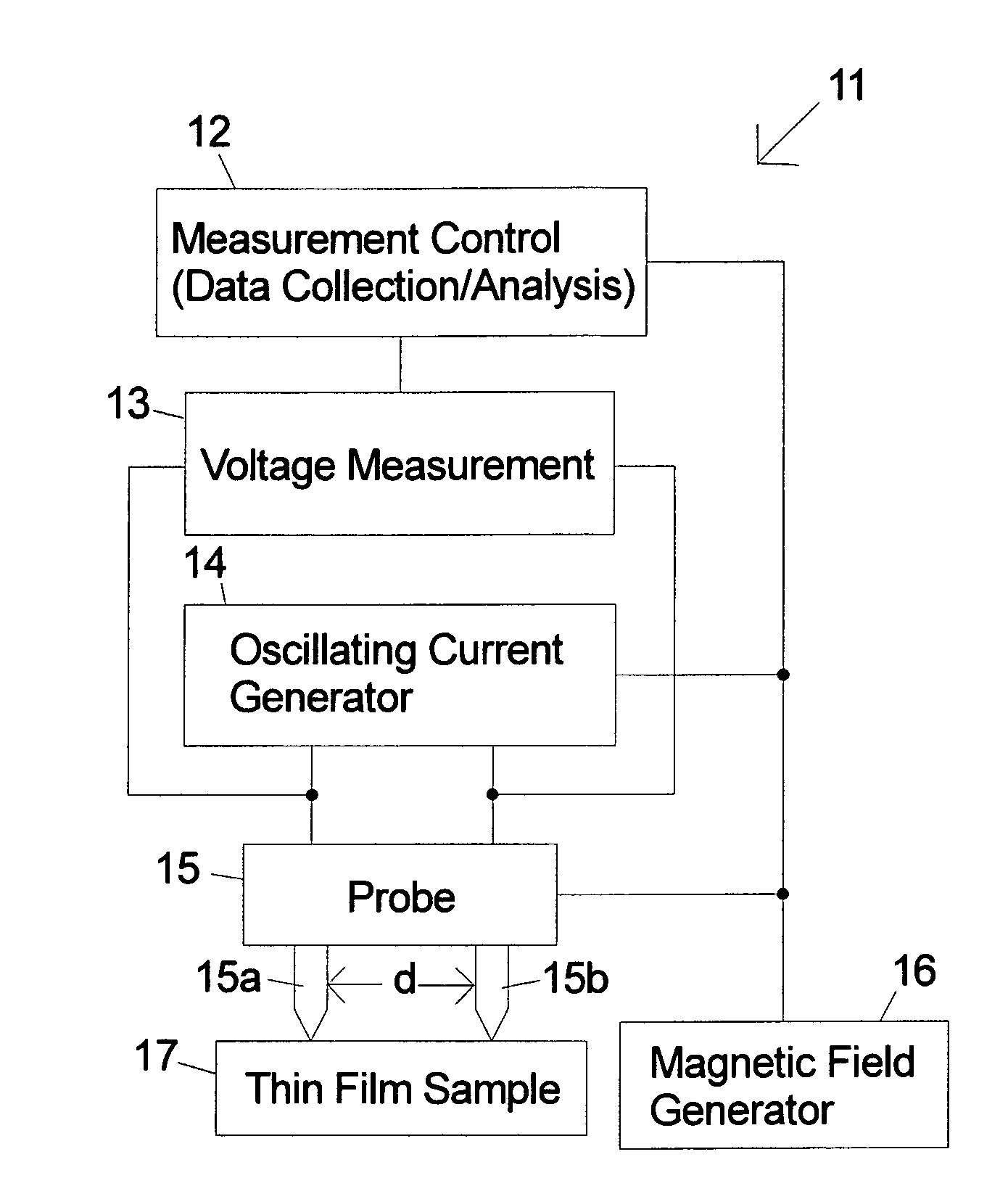
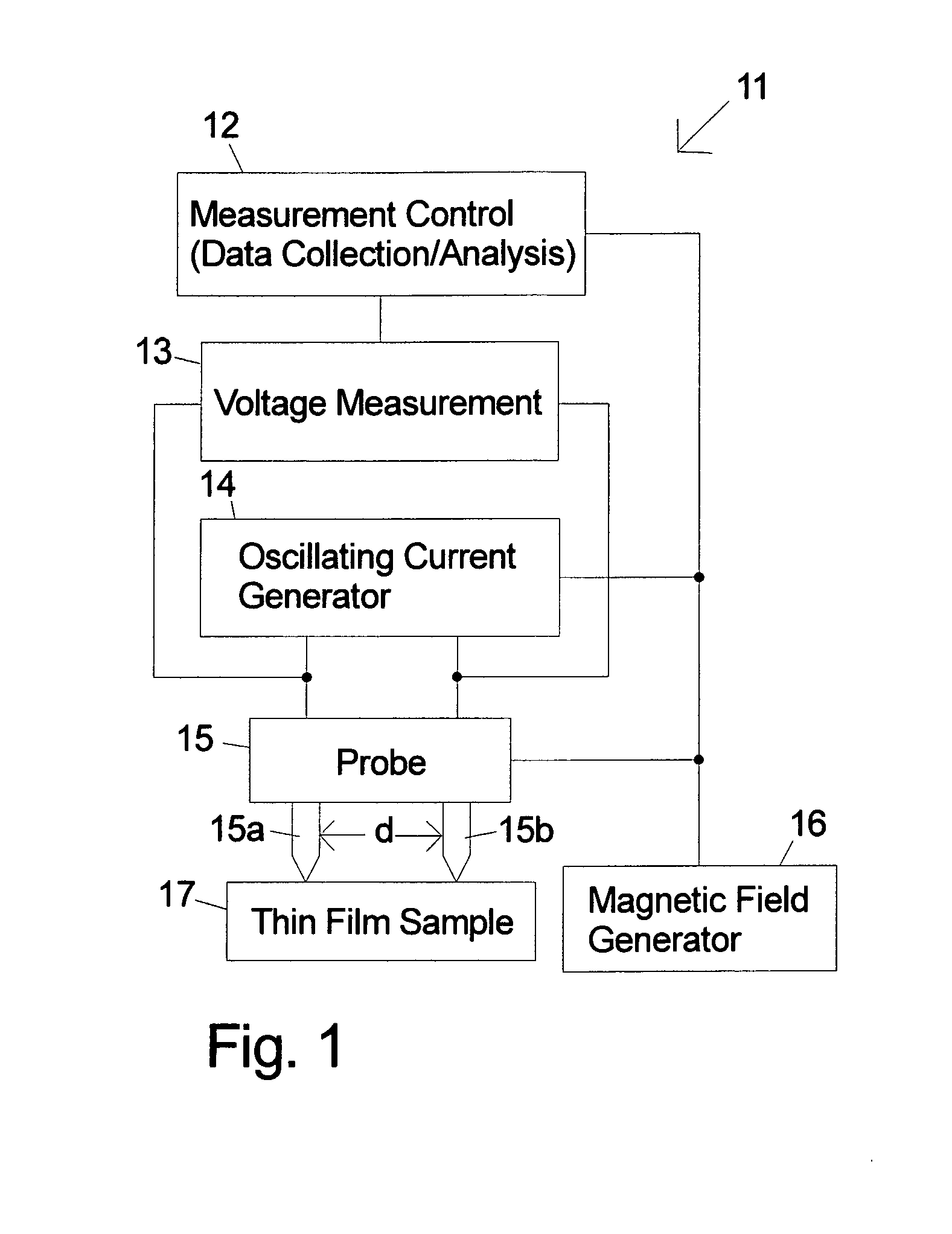
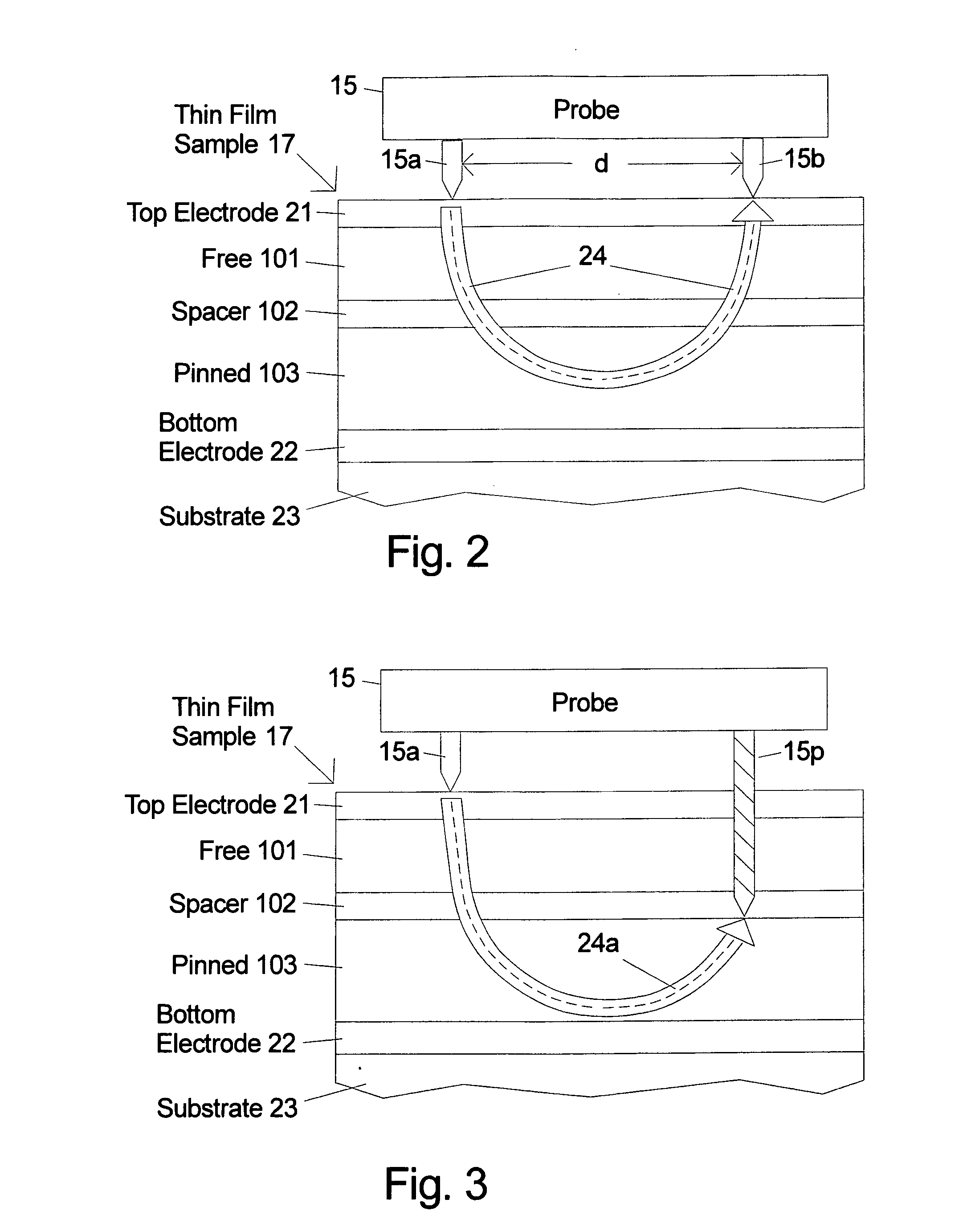
Method and apparatus for measuring magnetic parameters of magnetic thin film structures
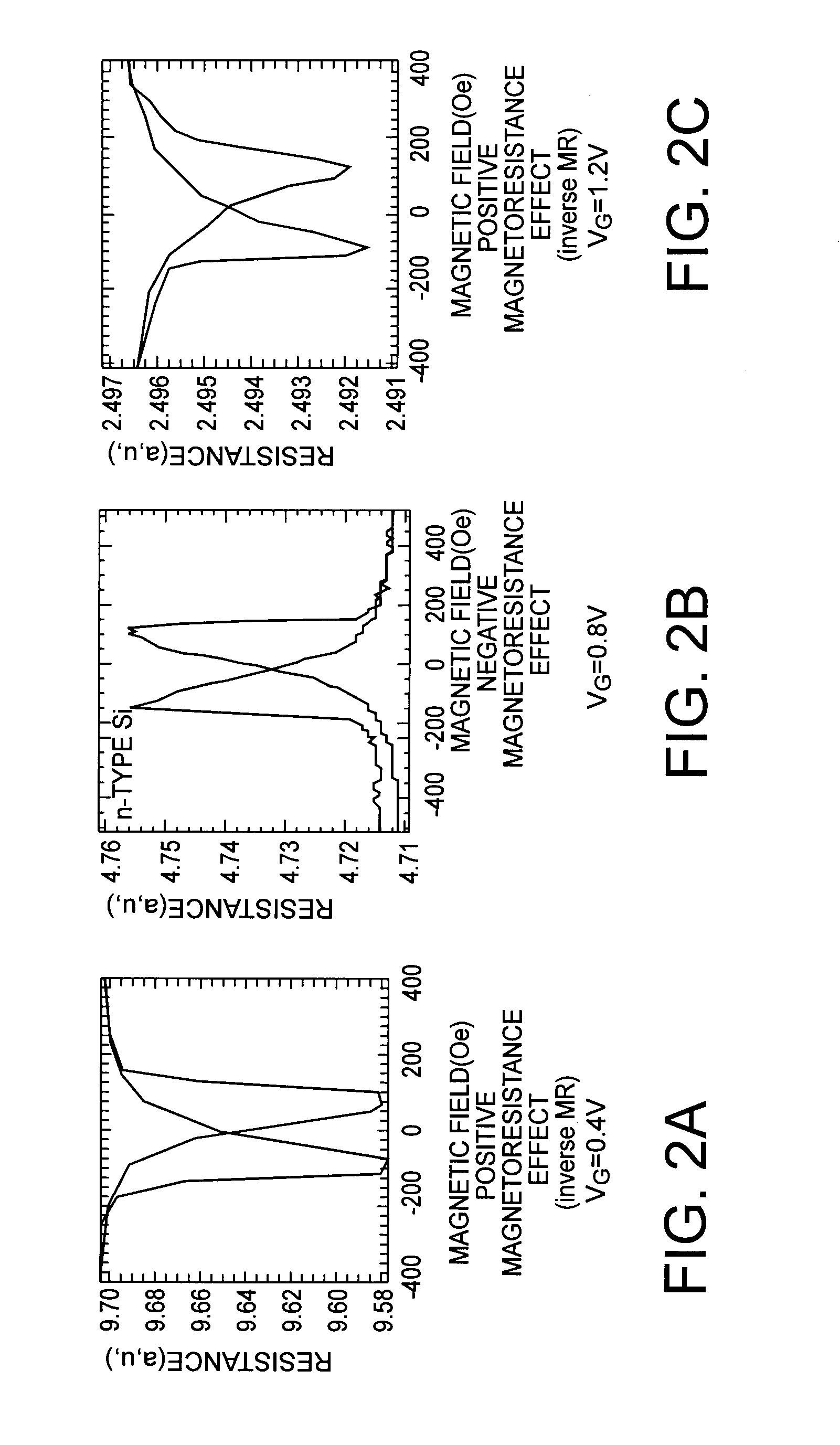
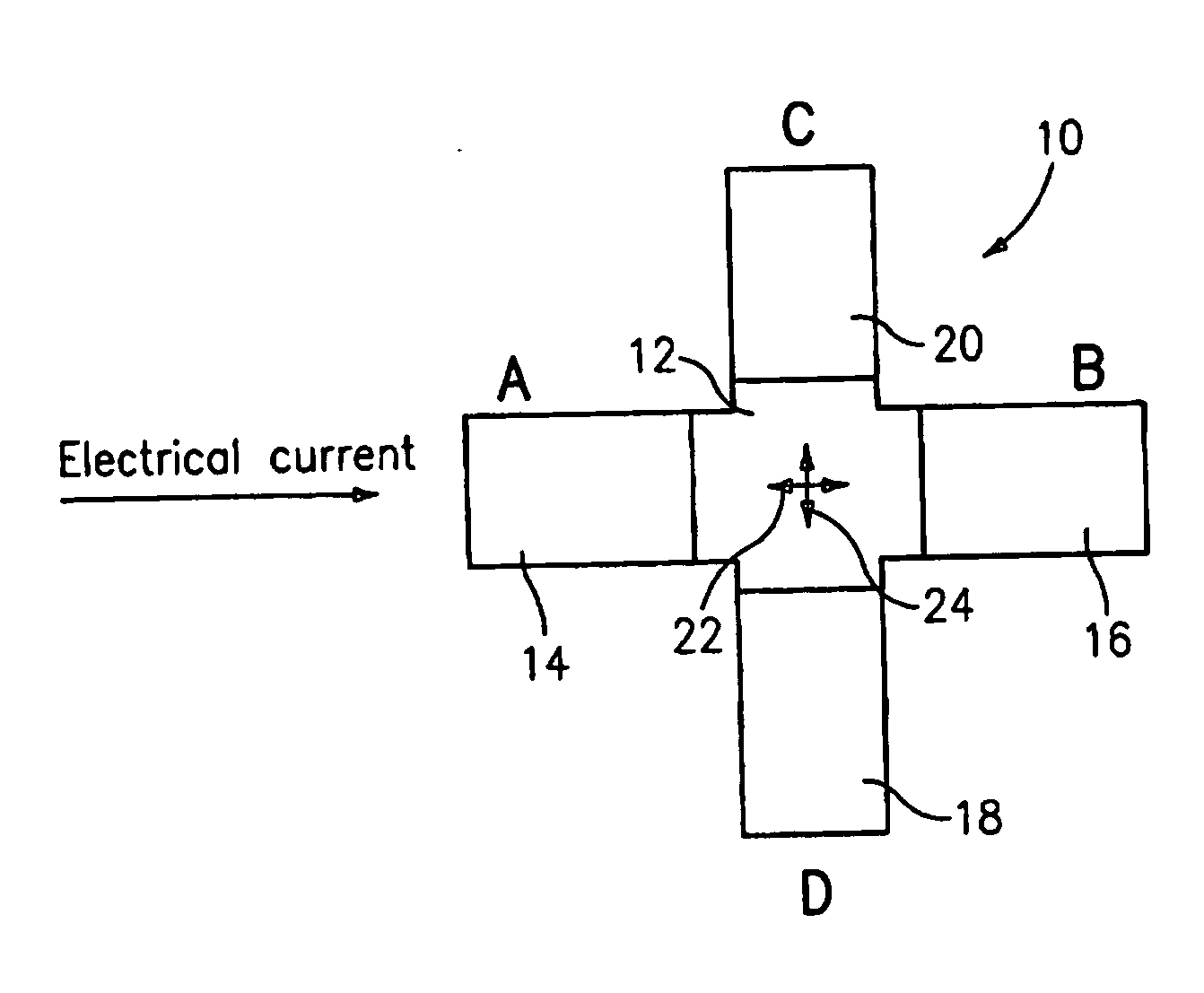
High-frequency resonance method is used to measure magnetic parameters of magnetic thin film stacks that show magnetoresistance including MTJs and giant magnetoresistance spin valves. The thin film sample can be unpatterned. Probe tips are electrically connected to the surface of the film (or alternatively one probe tip can be punched into the thin film stack) and voltage measurements are taken while injecting high frequency oscillating current between them to cause a change in electrical resistance when one of the layers in the magnetic film stack changes direction. A measured resonance curve can be determined from voltages at different current frequencies. The damping, related to the width of the resonance curve peak, is determined through curve fitting. In embodiments of the invention a variable magnetic field is also applied to vary the resonance frequency and extract the magnetic anisotropy and / or magnetic saturation of the magnetic layers.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
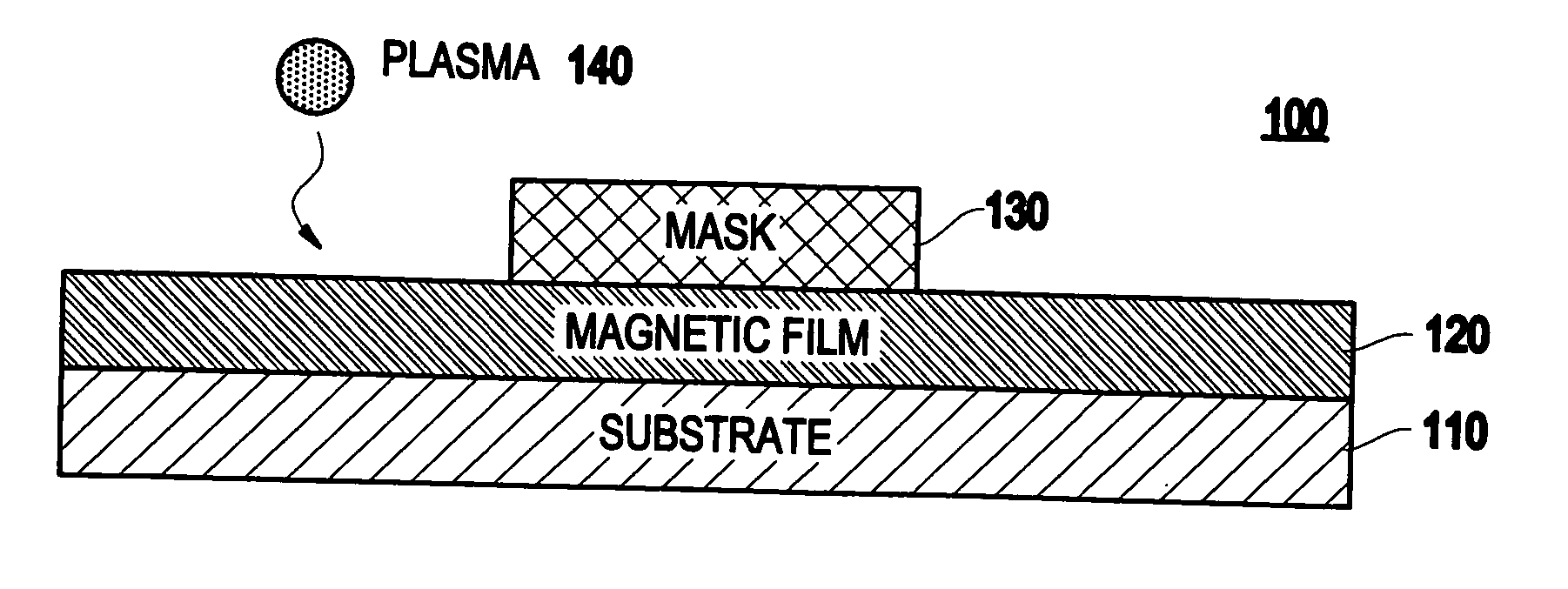
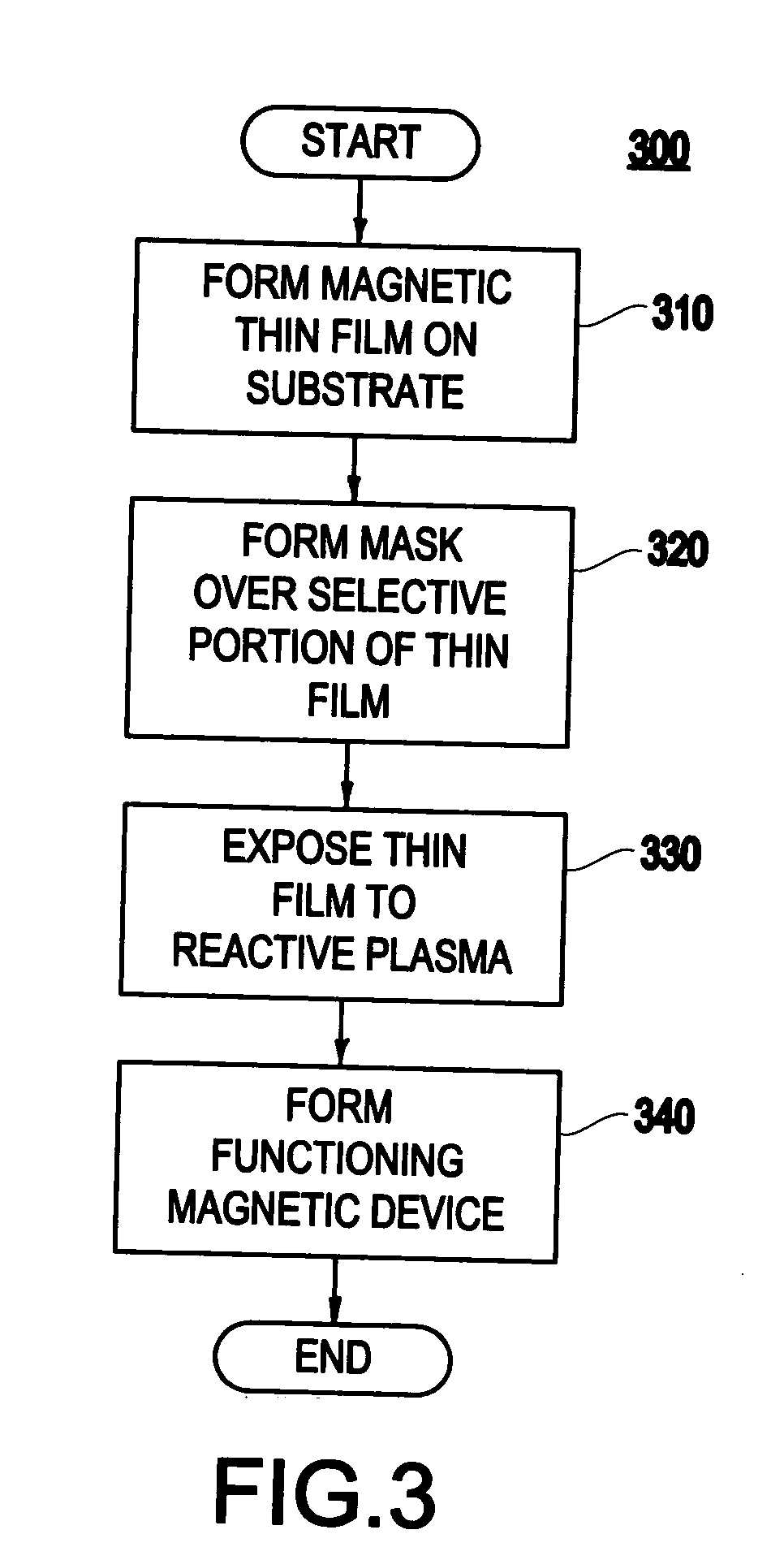
Method and system for patterning of magnetic thin films using gaseous transformation
A method (and resulting structure) of patterning a magnetic thin film, includes using a chemical transformation of a portion of the magnetic thin film to transform the portion to be non-magnetic and electrically insulating.
Owner:IBM CORP
Magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS6383667B1High energyBase layers for recording layersRecord information storageAlloyThermal stability
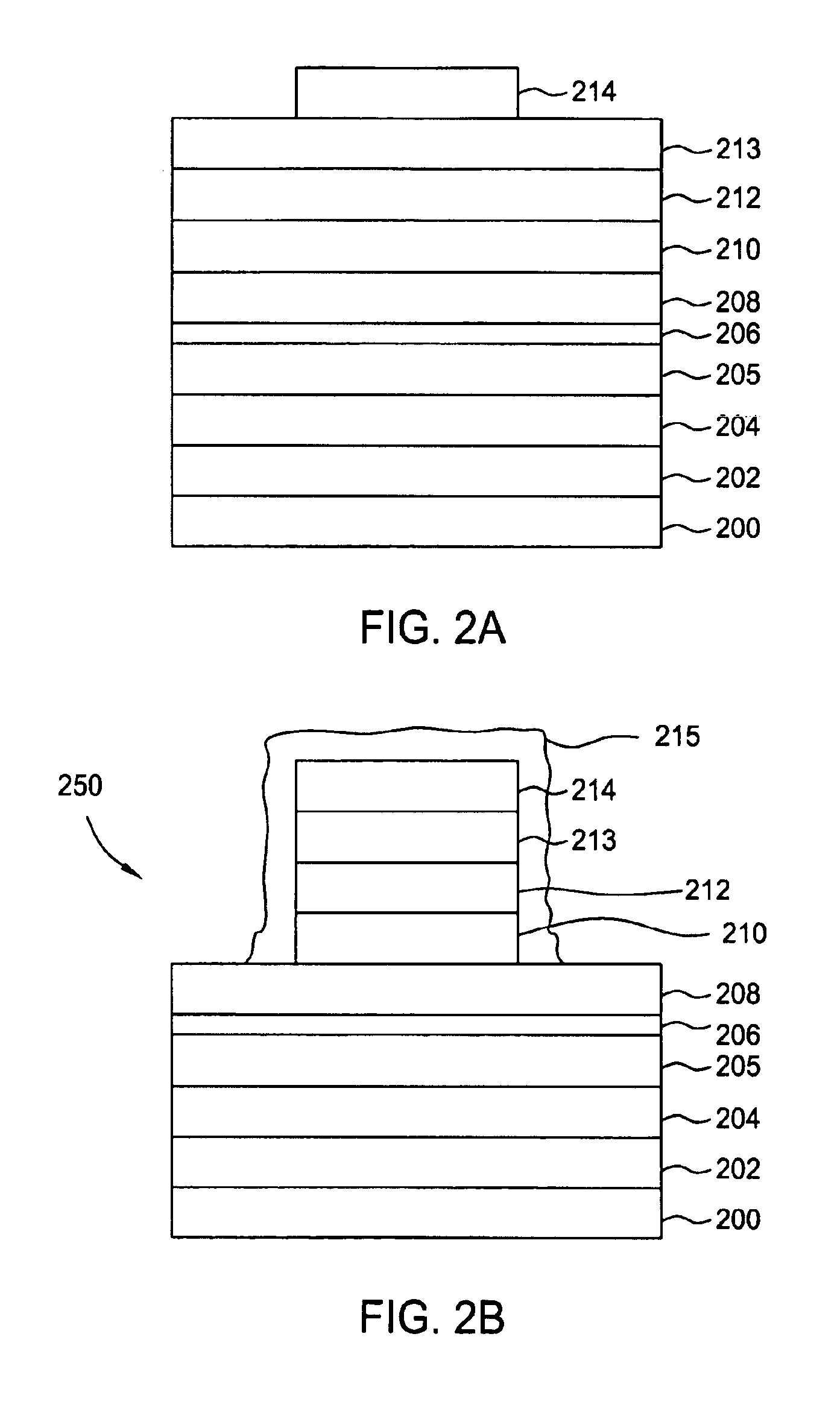
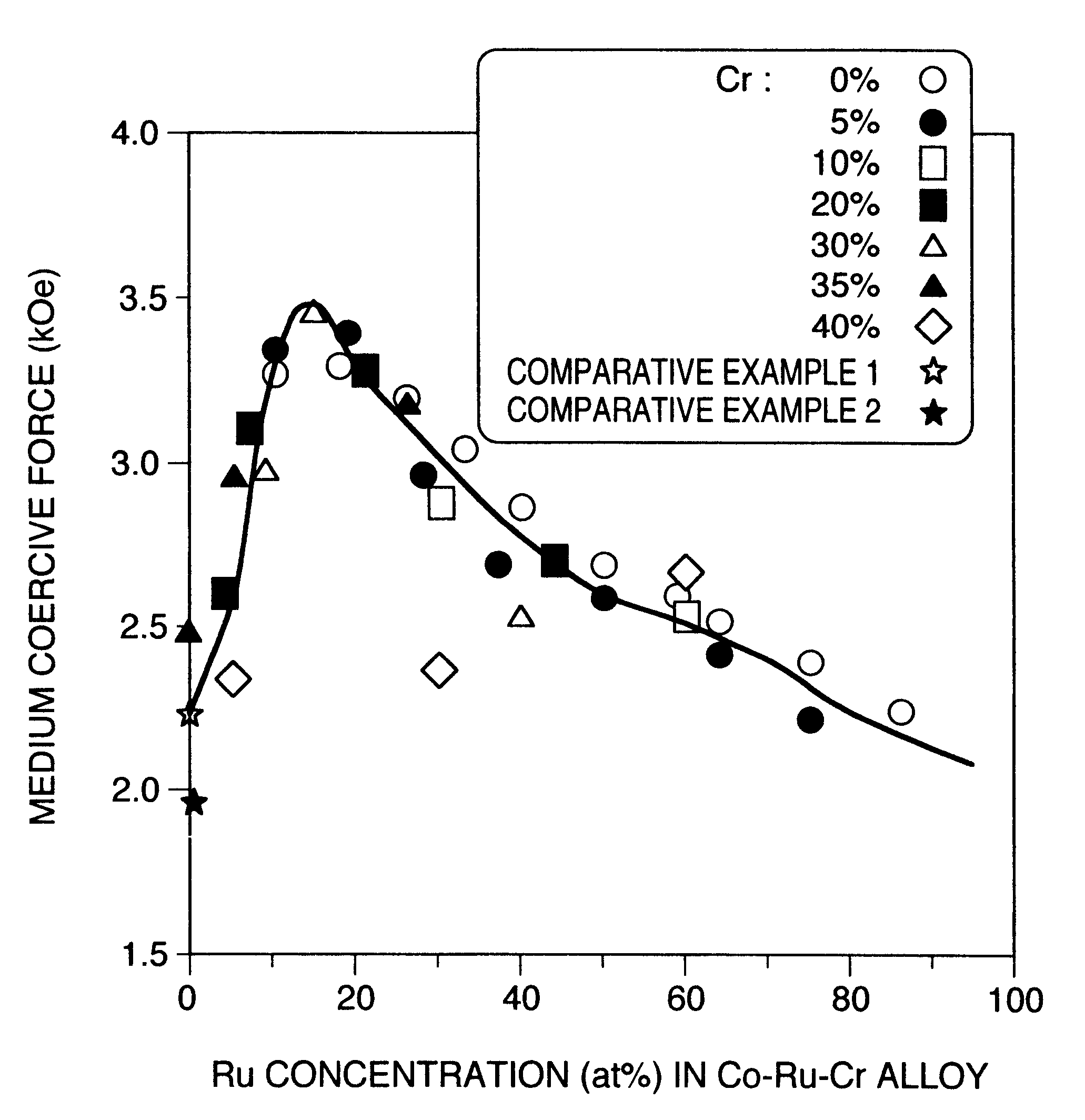
A magnetic recording medium includes a substrate, an underlayer provided on the substrate, a Co alloy magnetic film formed through the underlayer, and a protective film for protecting the magnetic film, wherein the underlayer has a two-layer structure of an lower underlayer contacted with the substrate and an upper underlayer contacted with the Co alloy magnetic film, the upper underlayer is a Co-Crx-My alloy film having a hexagonal close-packed structure, where 25 atomic %<=x+y<=50 atomic %, 0.5 atomic %<=y, nonmagnetic element M is one selected from the group of elements B, Si, Ge, C, Al, P, Ti, V, Nb, Zr, Hf, Mn, Rh, Os, Ir, Re, Pd, Pt, Mo, Ta, W, Ag and Au. Thereby the medium can be increased in its coercive force and can be improved in its thermal stability characteristics.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD
High frequency magnetic thin film filter
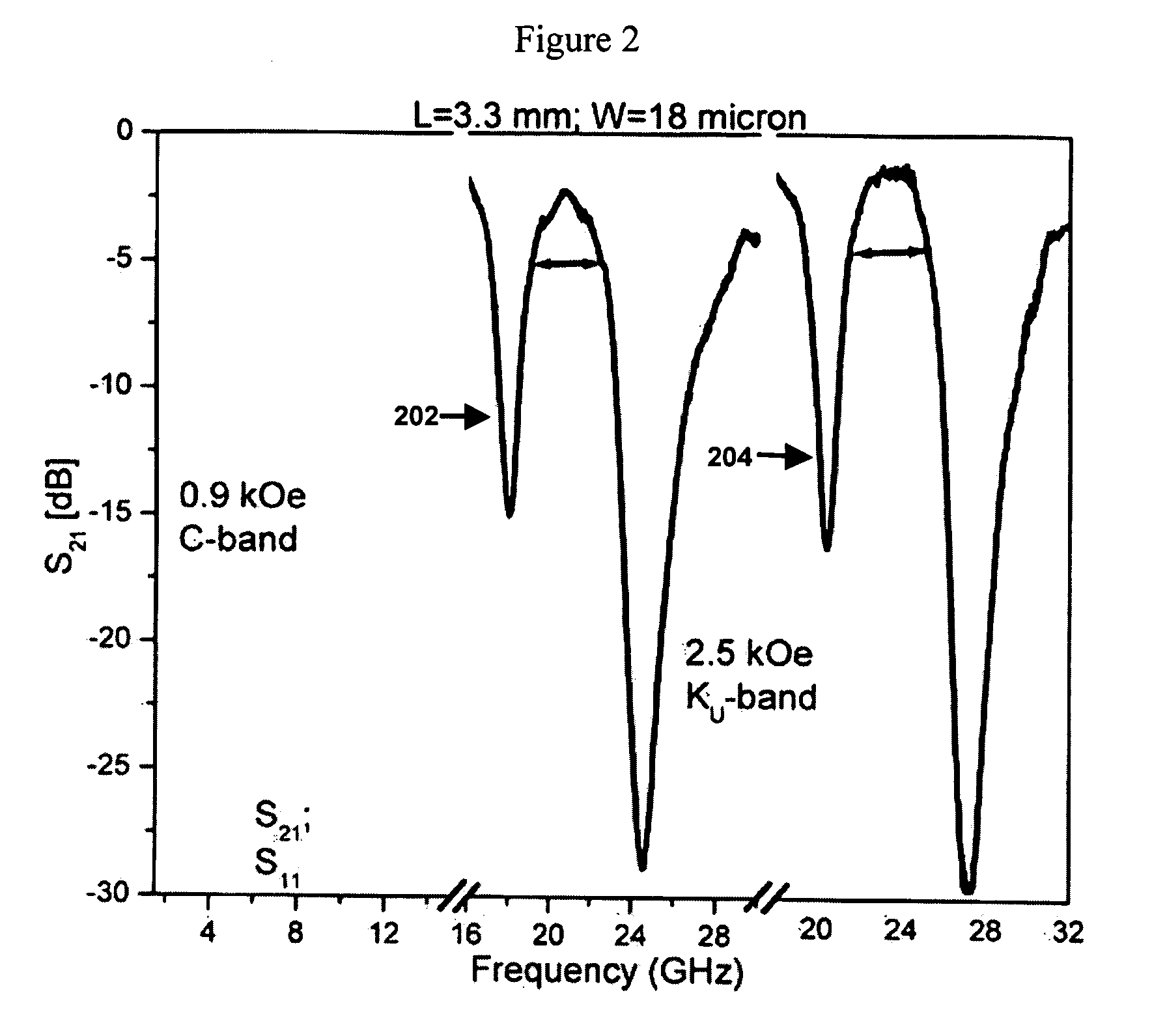
InactiveUS20050212625A1Wide range of functionsSatisfies needColor television signals processingResonatorsResonanceElectron
A layered microstrip device is described, in which at least two layers of different high internal field / high resonance frequency materials serve as the active elements of the device. The device is designed to filter ranges of high frequency electromagnetic waves, and is on a small scale to enable integration with high frequency electronics. The ranges of frequencies to be filtered depend on the active elements and device geometry selected for the device. The tradeoffs regarding active material and device geometry choices are explored in detail. The ranges of frequencies to be filtered can be modified in real time with the application of an external magnetic field. A variety of the devices were fabricated, and a number of experimental and theoretical studies were carried out.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Magnetic thin film, magnetic component that uses this magnetic thin film, manufacturing methods for the same, and a power conversion device
InactiveUS20050094302A1Soft qualityEasy to manufactureNanomagnetismSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectric forceElectrical conductor
On top of a silicon substrate, a polyimide film with a thickness of 10 μm is formed. On top of this, a magnetic thin film that is a polyimide film containing Fe fine particles and that has a thickness of 20 μm is formed. On top of this magnetic thin film, a patterned Ti / Au film and a Ti / Au connection conductor are formed. On top of this, a polyimide film with a thickness of 10 μm, and a Cu coil with a height 35 μm, width 90 μm, space 25 μm, and a polyimide layer that fills the spaces in the Cu coil are formed. On top of this, via a polyimide film with a thickness of 10 μm, a magnetic thin film that is a polyimide film containing Fe particles and that has a thickness of 20 μm is formed. This thin film inductor has a small alternating current resistance. The present invention provides a magnetic thin film that is well suited for mass production, can be manufactured easily, can be made into a thick film, has soft magnetic qualities, and is inexpensive. The present invention also provides a magnetic component that uses this magnetic thin film, manufacturing methods for these, and a power conversion device.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC DEVICE TECH CO
Spin tunnel magnetoresistive effect film and element, magnetoresistive sensor using same, magnetic apparatus, and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20050019610A1Reduced effectivenessPrevent oxidationNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsNon magneticOxygen
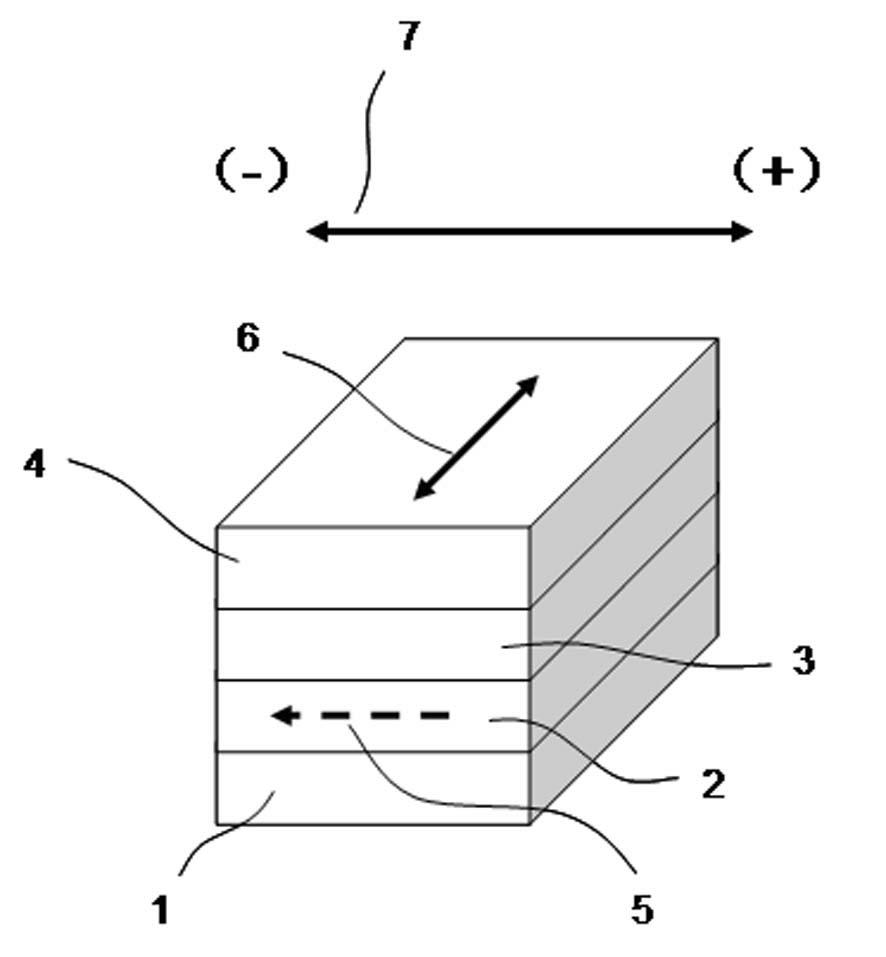
In a spin tunnel magnetoresistive effect film in which a magnetic thin film to which an exchange bias is applied by exchange coupling via an anti-ferromagnetic thin film and a magnetic thin film that detects a magnetic field are laminated, a magnetic thin film or an anti-ferromagnetic thin film (PtMn, PdMn, NiMn) is laminated onto an underlayer (Ta, Zr, Hf), the surface roughness thereof being in the range from 0.1 to 5 Angstroms. A means used to control the surface roughness introduces into the film growing chamber oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, or a gas mixture thereof into a vacuum of 10−6 Torr to 10−9 Torr, reduces the substrate temperature to 0° C. or lower during film growth, or oxidizes an underlayer. The lower electrode layer material used is a film laminate of a high-permeability amorphous magnetic material and a non-magnetic metallic layer.
Owner:NEC CORP
Magnetoelectronic devices based on colossal magnetoresistive thin films
ActiveUS20070096228A1Reduce complexityNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsPerovskite manganitesAlkaline earth metal
The present invention is directed to the use of perovskite manganite thin films and other magnetic films that exhibit both planar Hall effect and biaxial magnetic anisotropy to form the active area in magnetic sensor devices and in magnetic bit cells used in magnetoresistive random access memory (MRAM) devices. The manganite thin films of the invention are ferromagnetic manganites of the formula R1-xAxMnO3, wherein R is a rare-earth metal, A is an alkaline earth metal, and x is generally between about 0.15 and about 0.5.
Owner:BAR ILAN UNIV +1
Co alloy target and its production method, soft magnetic film for perpendicular magnetic recording and perpendicular magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20050223848A1Reduce unevennessReduce particlesBase layers for recording layersTransportation and packagingAlloyImpurity
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Mn alloy materials for magnetic materials, Mn alloy sputtering targets, and magnetic thin films
InactiveUS6270593B1High purityLower Level RequirementsVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingThin membraneManganese
Mn alloy materials for magnetic materials contain 500 ppm or less, preferably 100 ppm or less, oxygen, 100 ppm or less, probably 20 ppm or less, sulfur, and preferably a total of 1000 ppm or less, more preferably 500 ppm or less, impurities (elements other than Mn and the alloying component). The alloying component that forms an alloy with Mn is one or two or more elements selected from the group consisting of Fe, Ir, Pt, pd, Rh, Ru, Ni, Cr and Co. Sputtering targets formed from the Mn alloy materials for use in depositing magnetic thin film, and the thin films so produced.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Ferromagnetic Material Sputtering Target
InactiveUS20130134038A1Smooth dischargeIncreasing pass-through fluxCellsTransportation and packagingSputteringMetallurgy
A ferromagnetic material sputtering target which is a sintered compact sputtering target made of a metal having Co as its main component, and nonmetallic inorganic material particles, wherein a plurality of metal phases having different saturated magnetization exist, and the nonmetallic inorganic material particles are dispersed in the respective metal phases. By increasing the pass-through flux of the sputtering target, it is possible to obtain a stable discharge. Moreover, it is also possible to obtain a ferromagnetic material sputtering target capable of obtaining a stable discharge in a magnetron sputtering device and which has a low generation of particles during sputtering. Thus, this invention aims to provide a ferromagnetic material sputtering target for use in the deposition of a magnetic thin film of a magnetic recording medium, and particularly of a magnetic recording layer of a hard disk adopting the perpendicular magnetic recording system.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CO LTD
Magnetic thin film head with heat-assisted write section and hard disk drive incorporating same
InactiveUS7310206B2Thickness minimizationHigh densityCombination recordingRecord information storageHard disc driveLaser light
A thin film magnetic read / write head for use in magnetic data storage systems to enable writing of data to a magnetic data storage medium with the assistance of laser heating. The read / write head allows magnetic reading of data from the storage medium, and thermally assisted magnetic writing of data on the storage medium. A waveguide is provided in a write gap in the form of an optical circuit having a plurality of inputs and a single output at the air bearing surface (ABS) for concentrating laser light used for heating the storage medium during the write operation. The thermally assisted magnetic writing improves the thermal stability of the recorded data and usefulness thereof throughout a wide temperature range.
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com