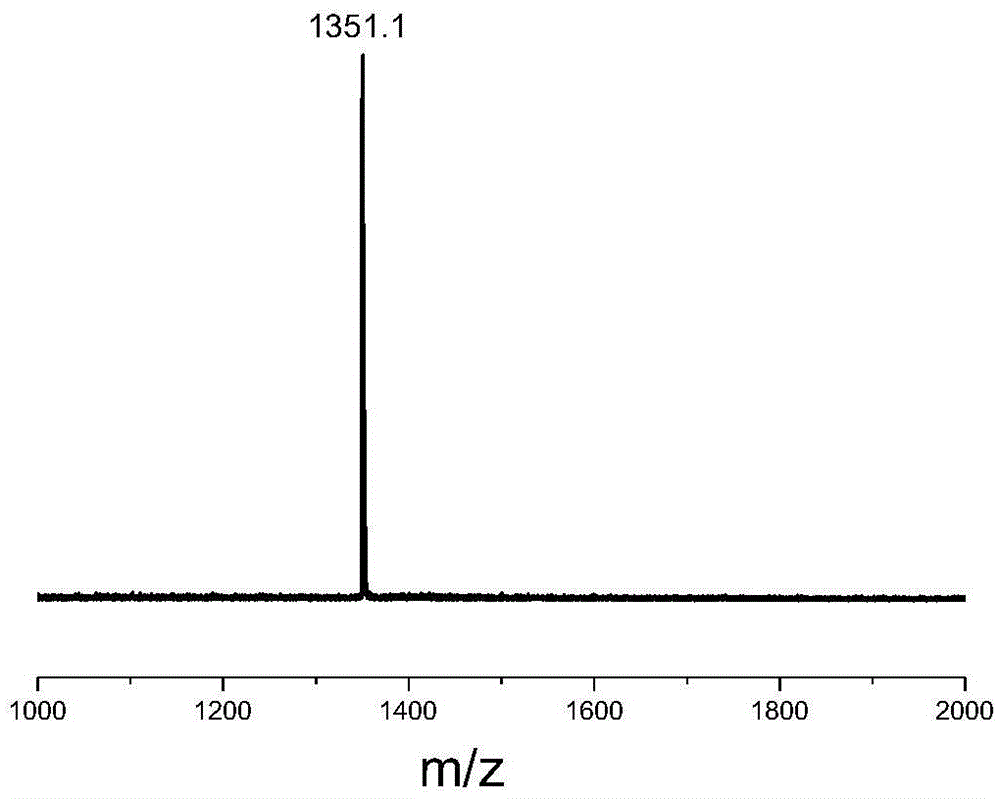
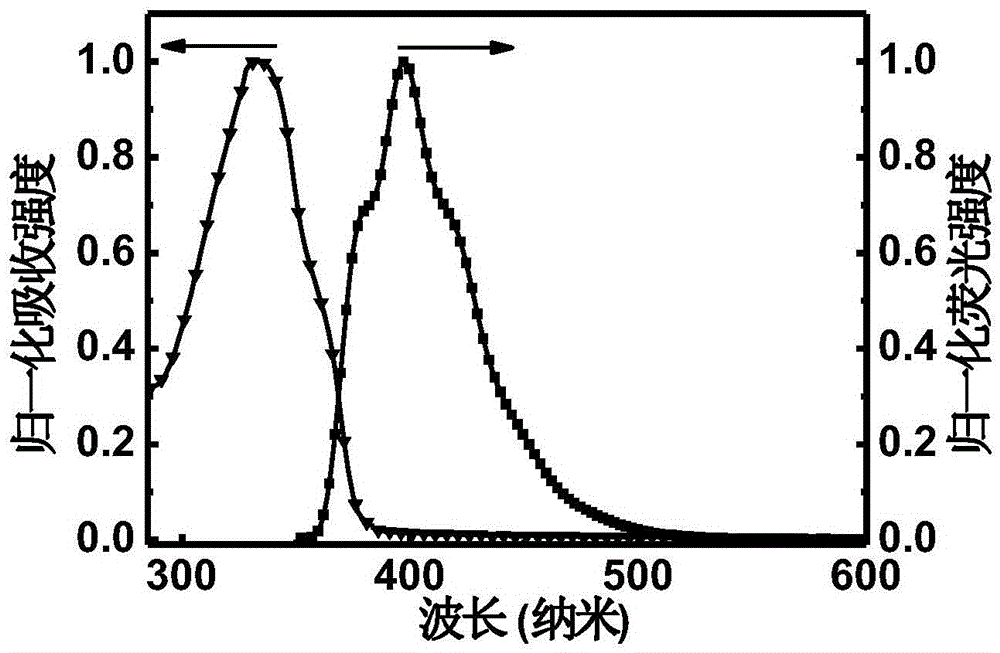
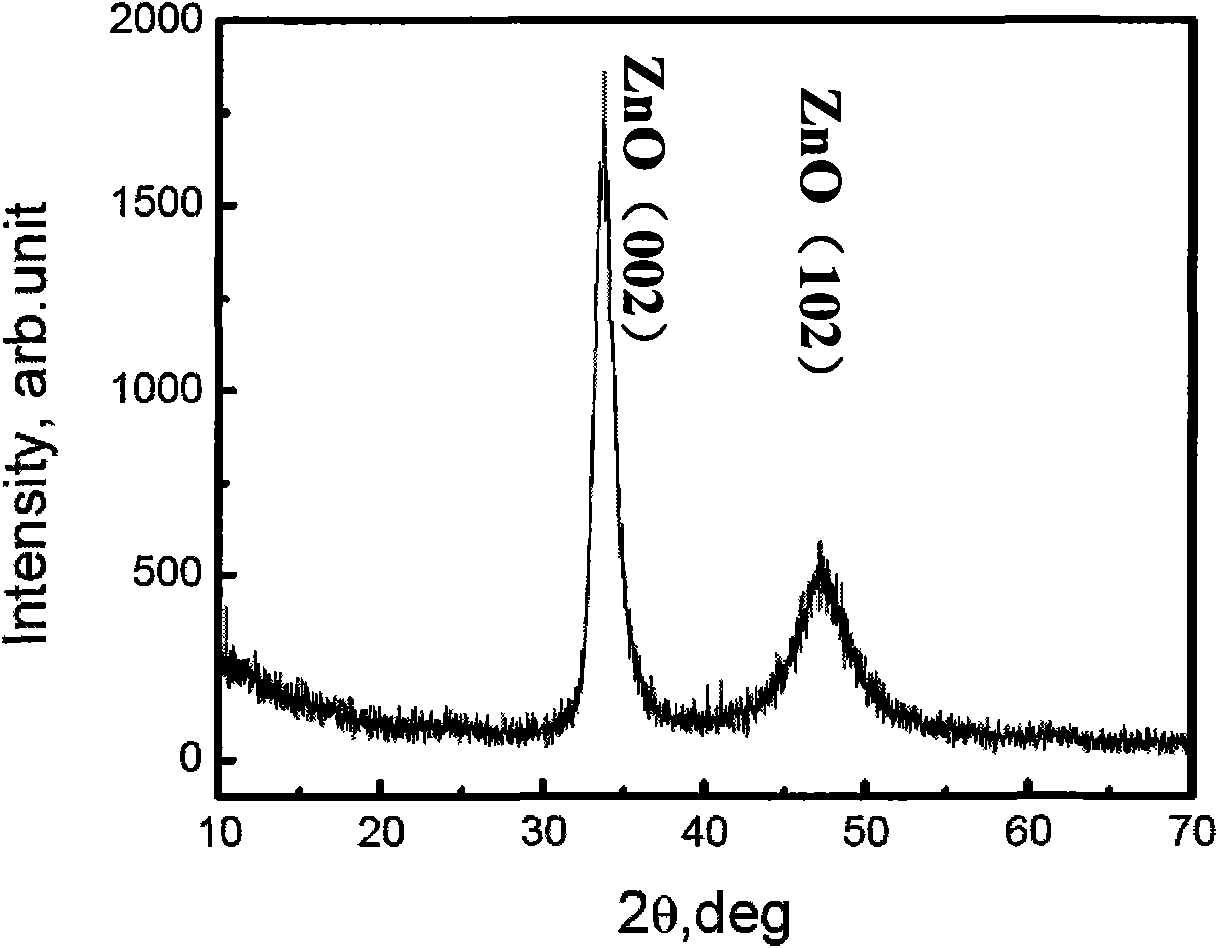
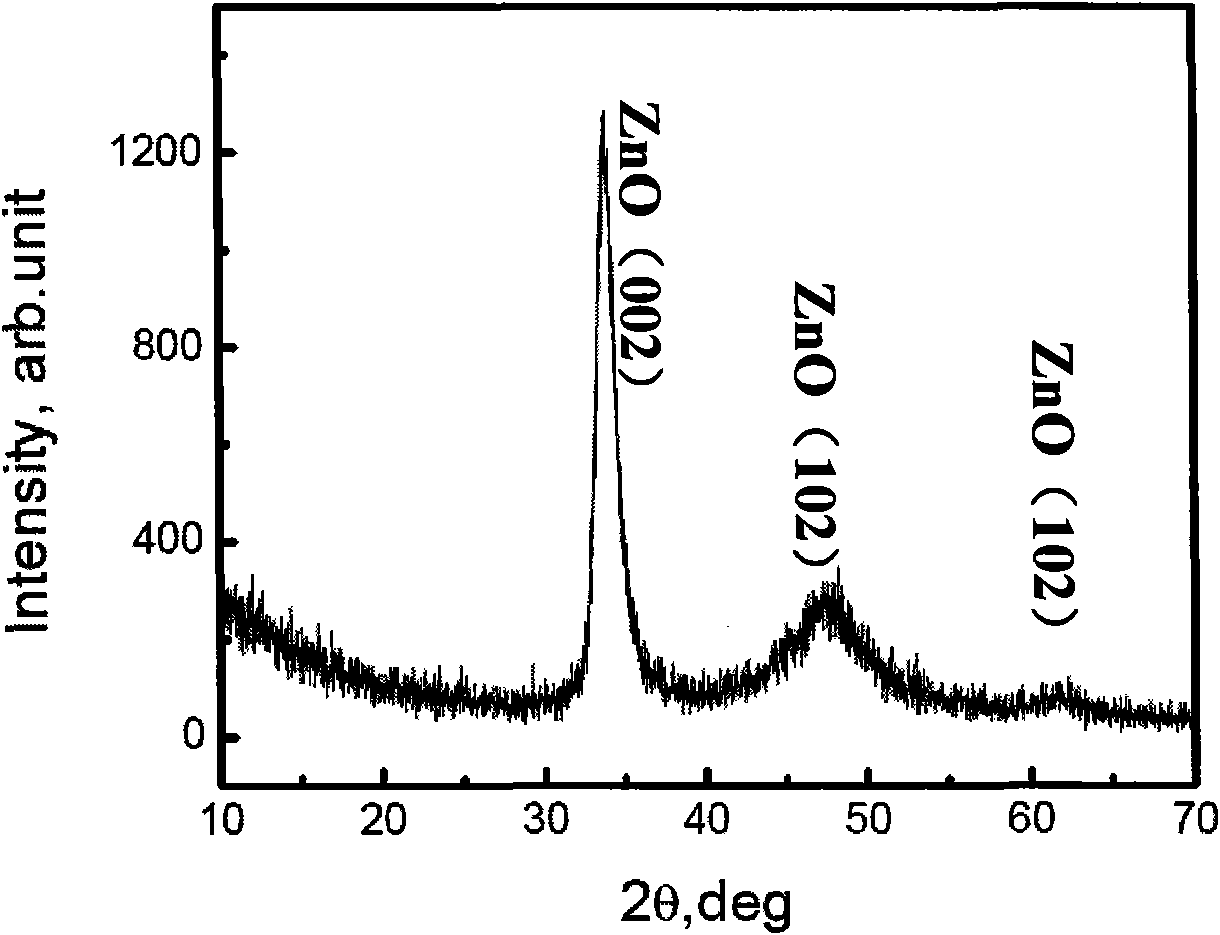
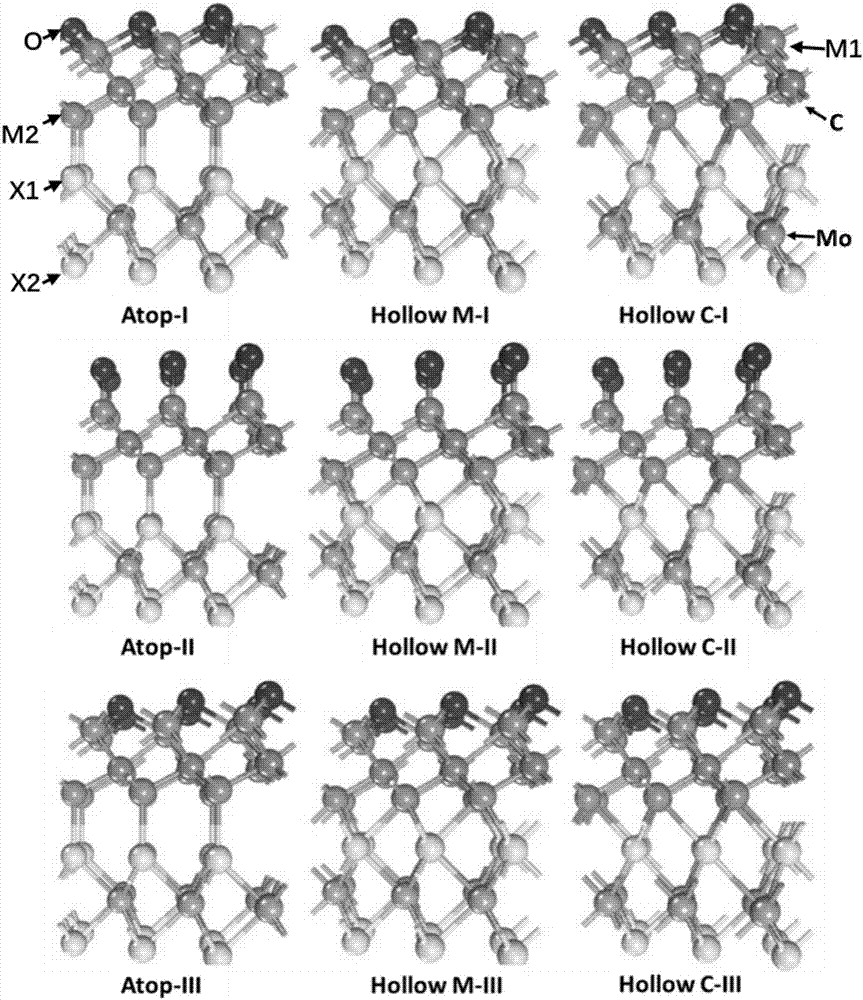
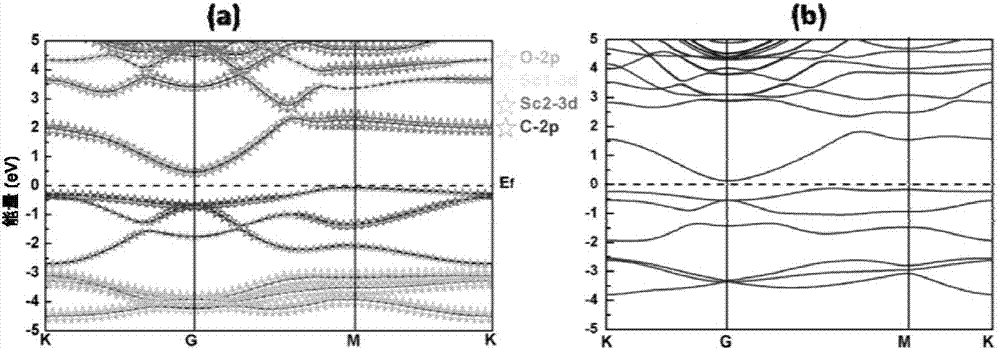
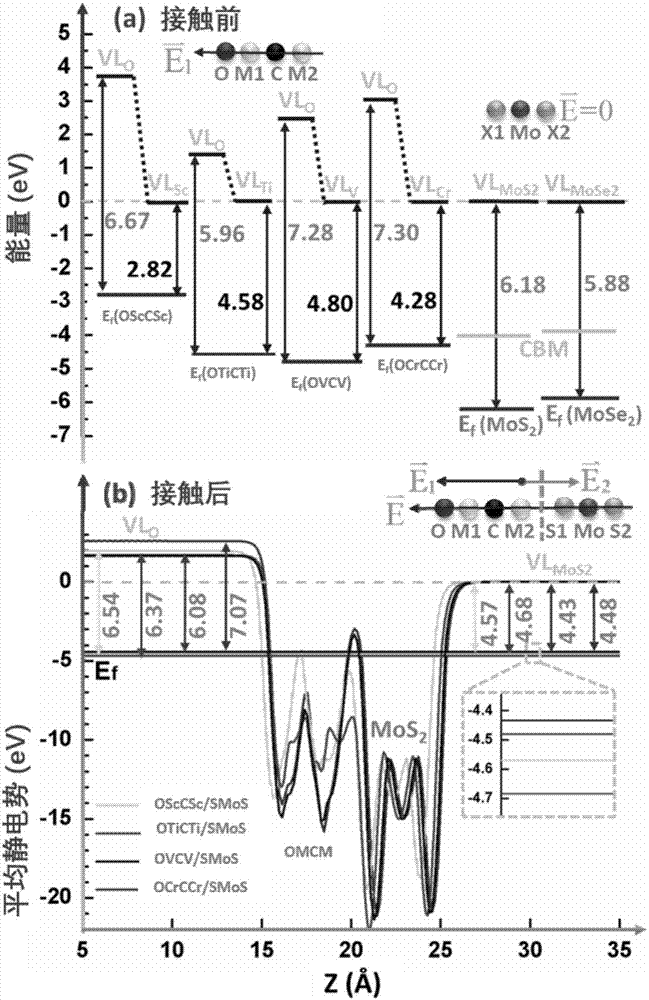
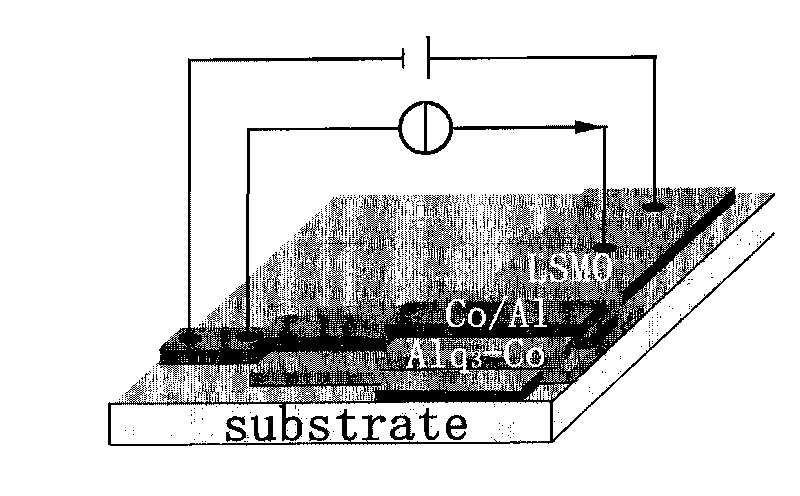
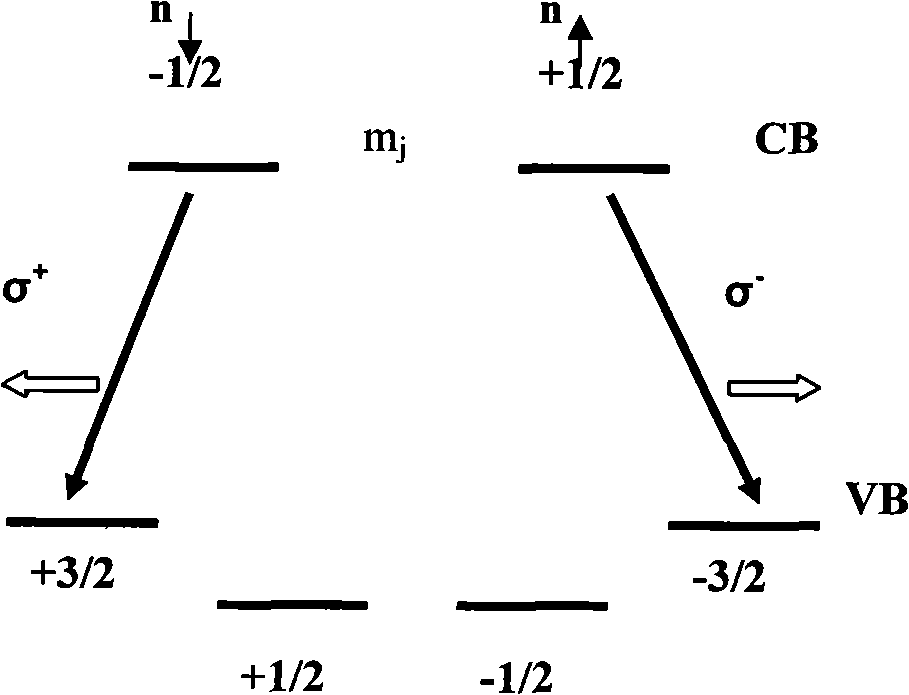Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
197 results about "Spintronics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spintronics (a portmanteau meaning spin transport electronics), also known as spin electronics, is the study of the intrinsic spin of the electron and its associated magnetic moment, in addition to its fundamental electronic charge, in solid-state devices. The field of spintronics concerns spin-charge coupling in metallic systems; the analogous effects in insulators fall into the field of multiferroics.
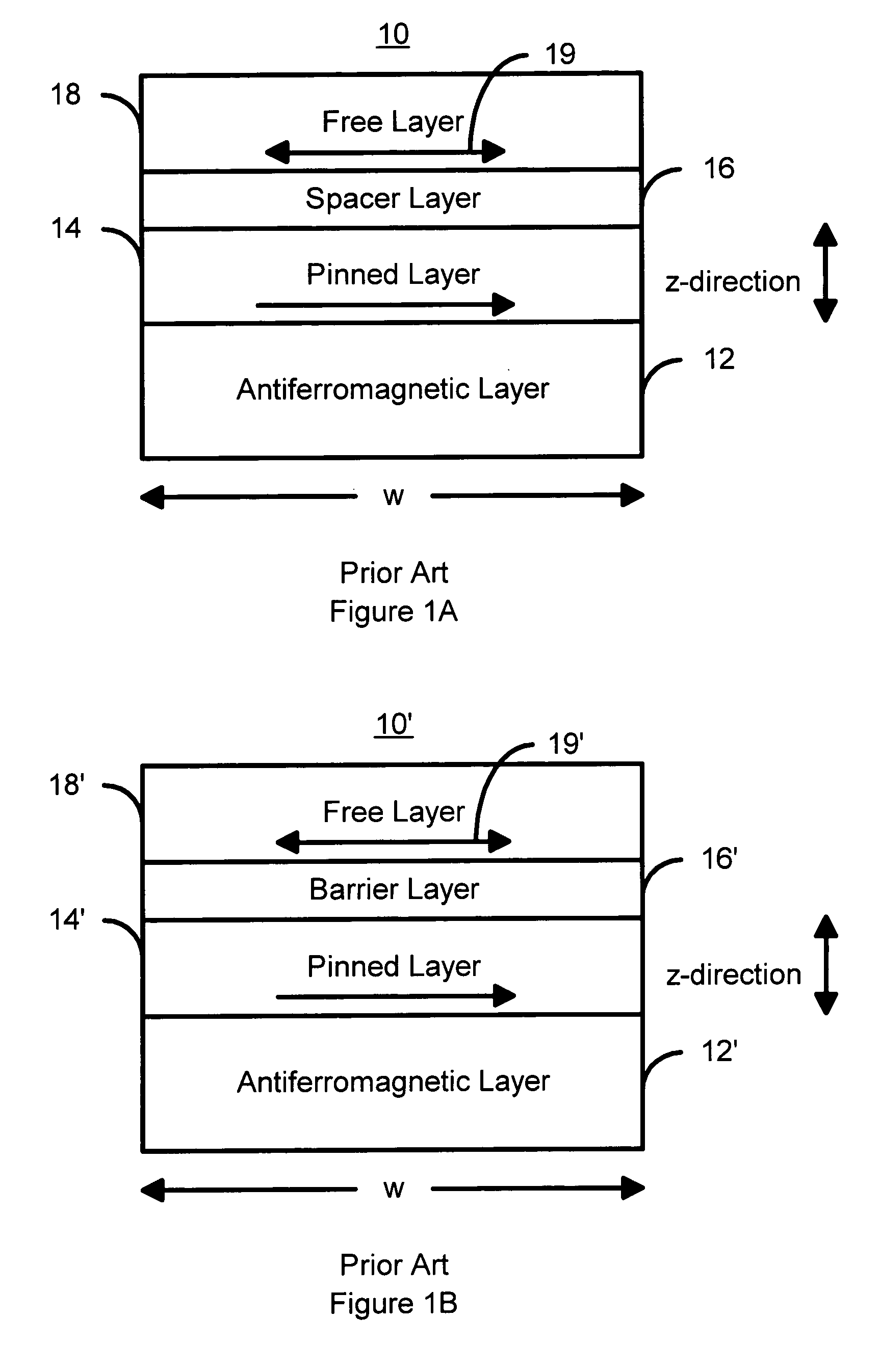
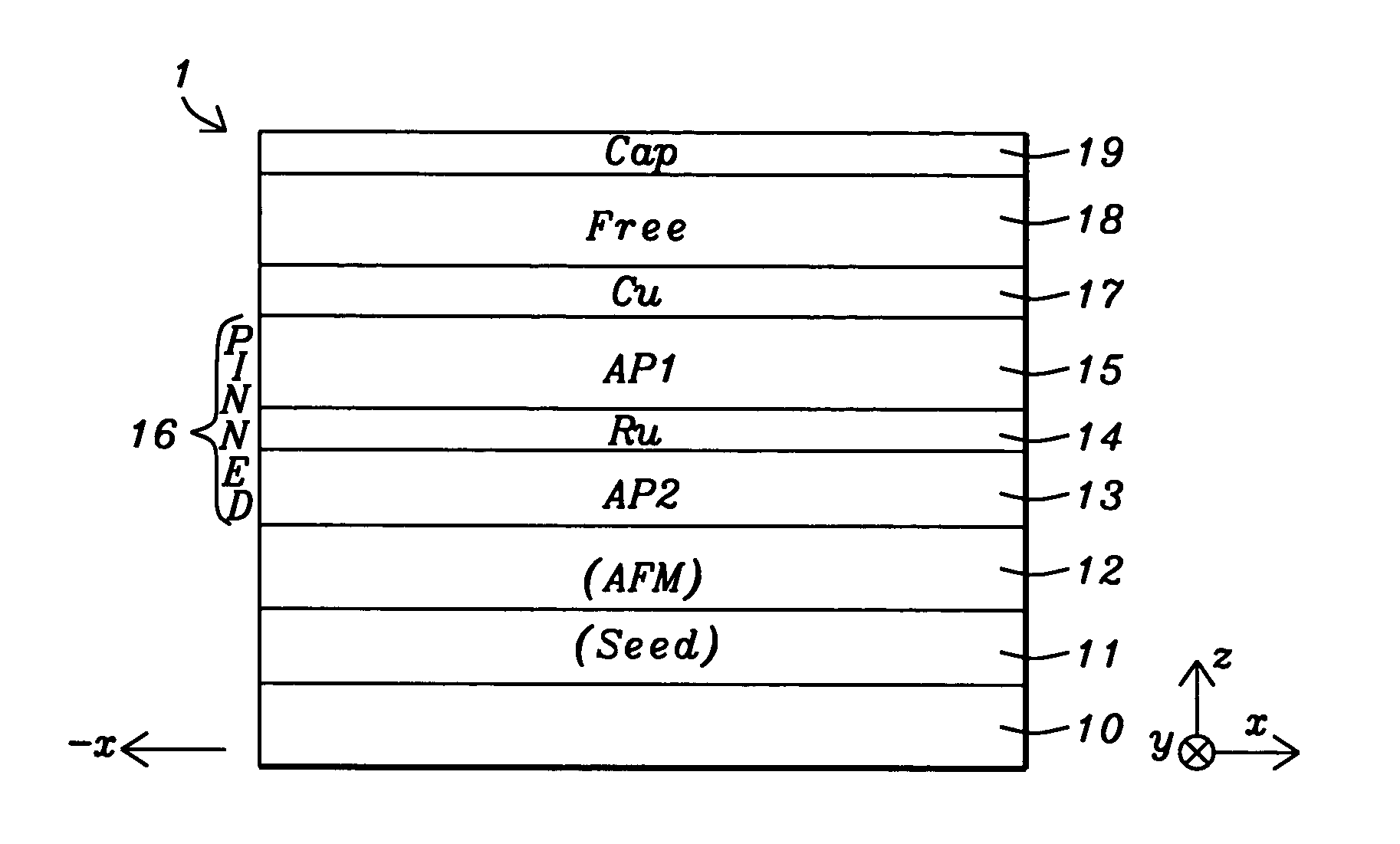
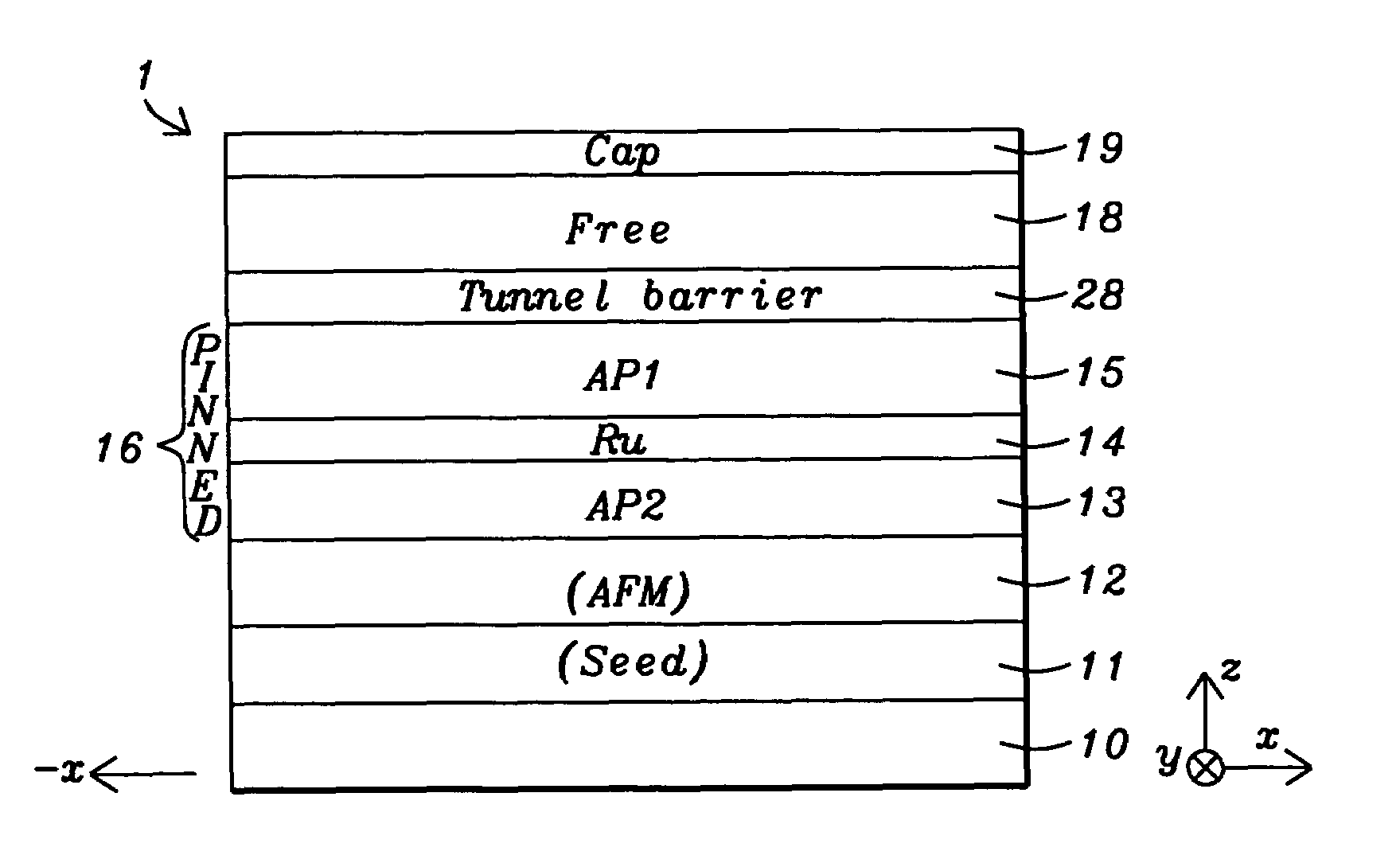
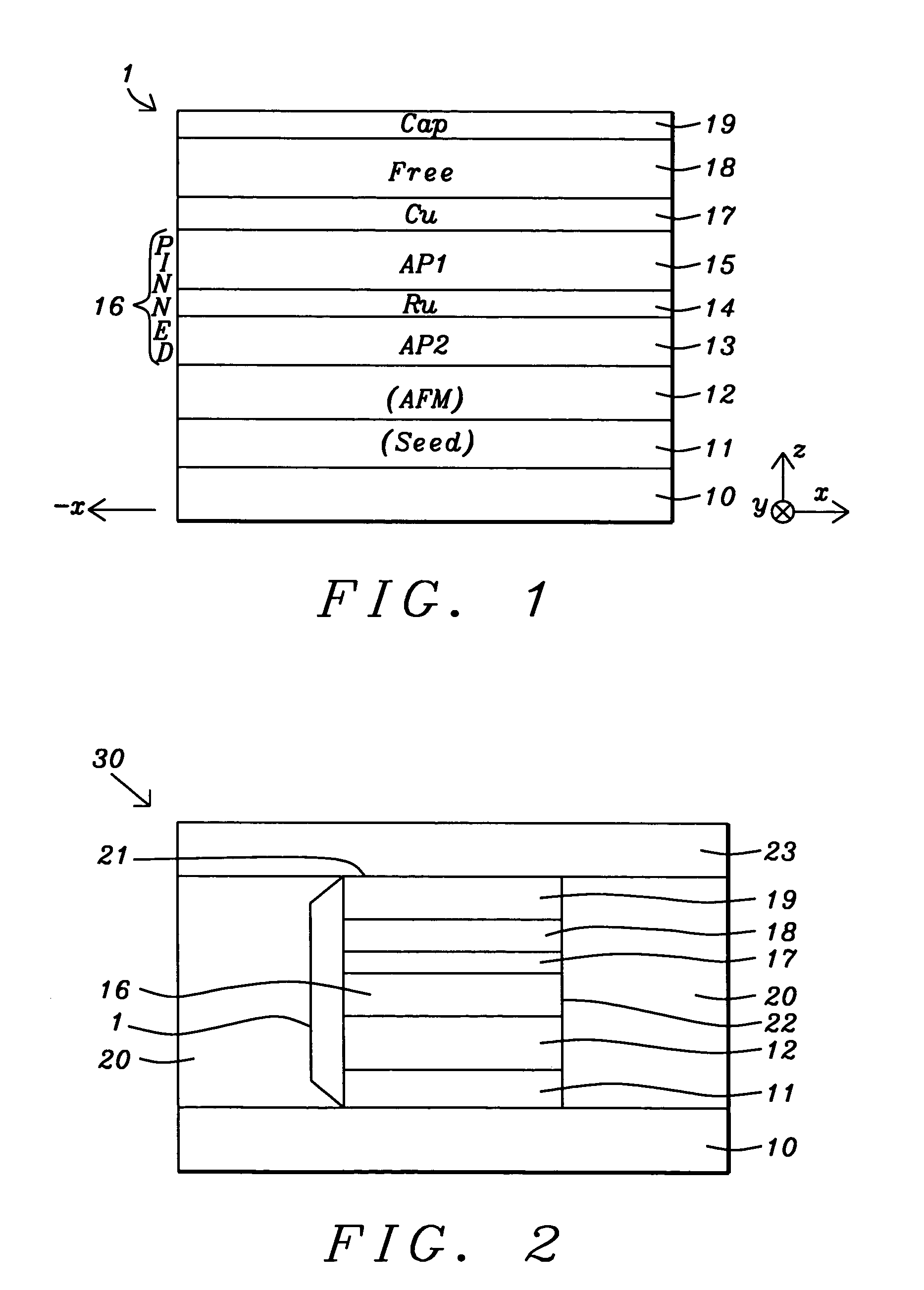
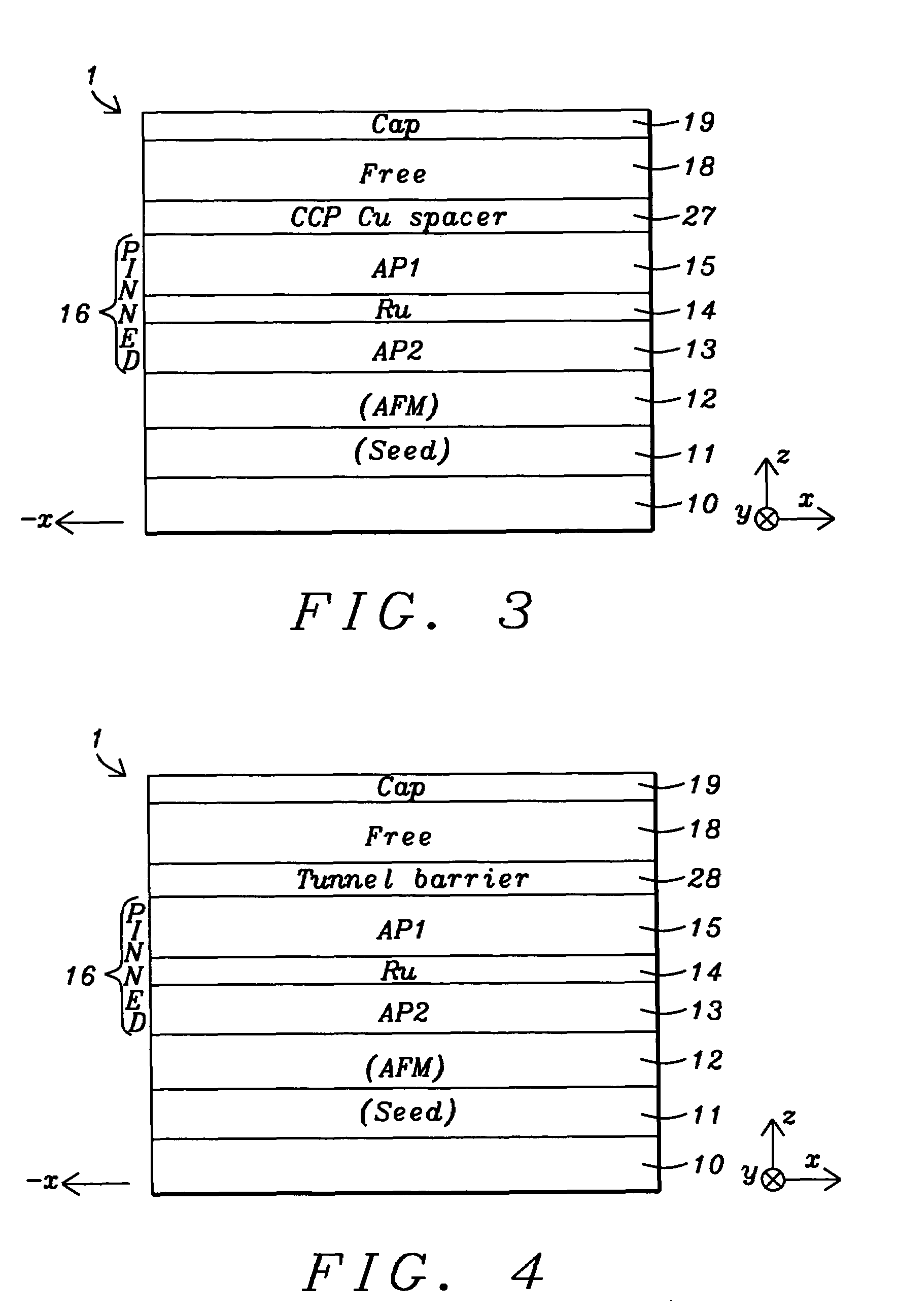
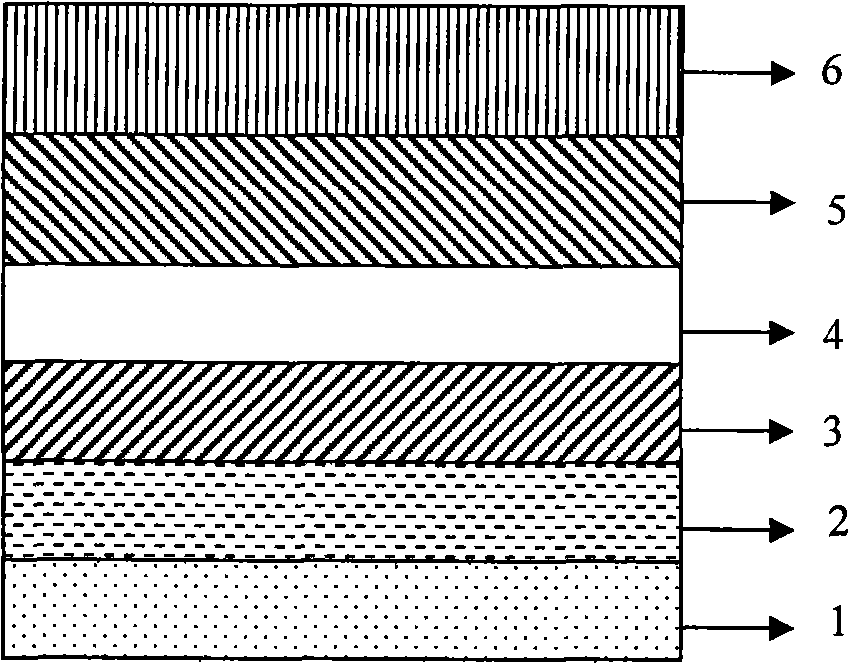
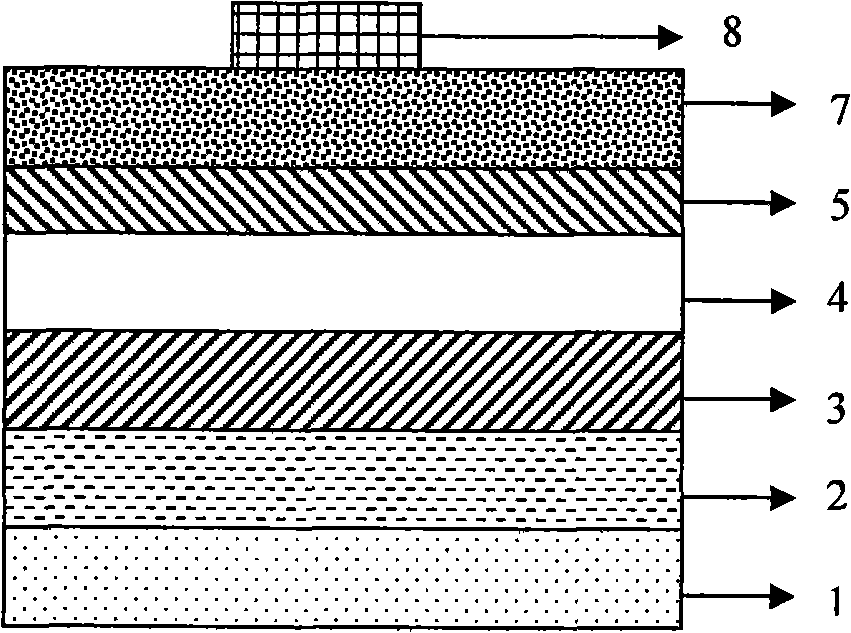
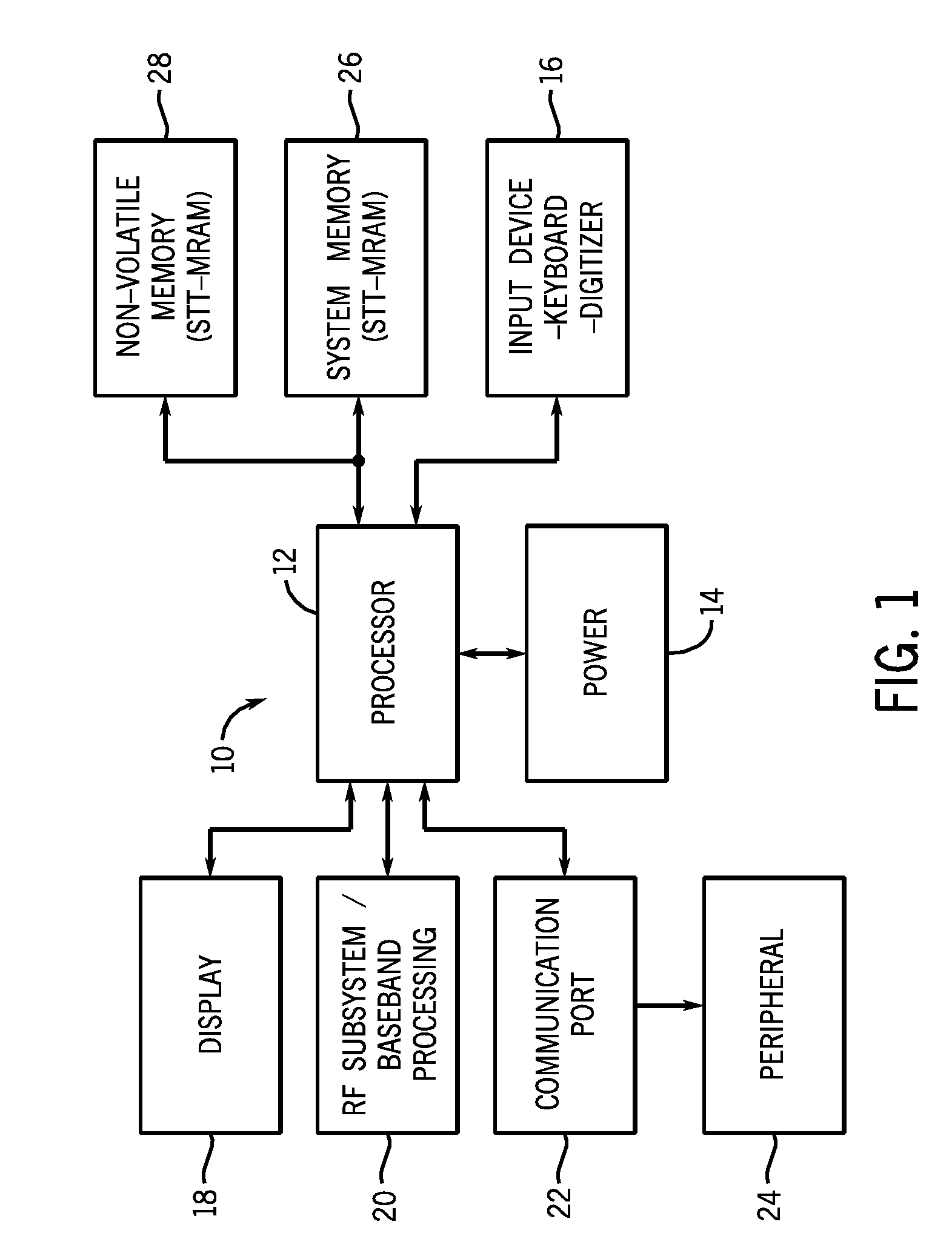
MTJ elements with high spin polarization layers configured for spin-transfer switching and spintronics devices using the magnetic elements
ActiveUS20060141640A1Write currentEnhanced signalNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpin transferSpin polarization
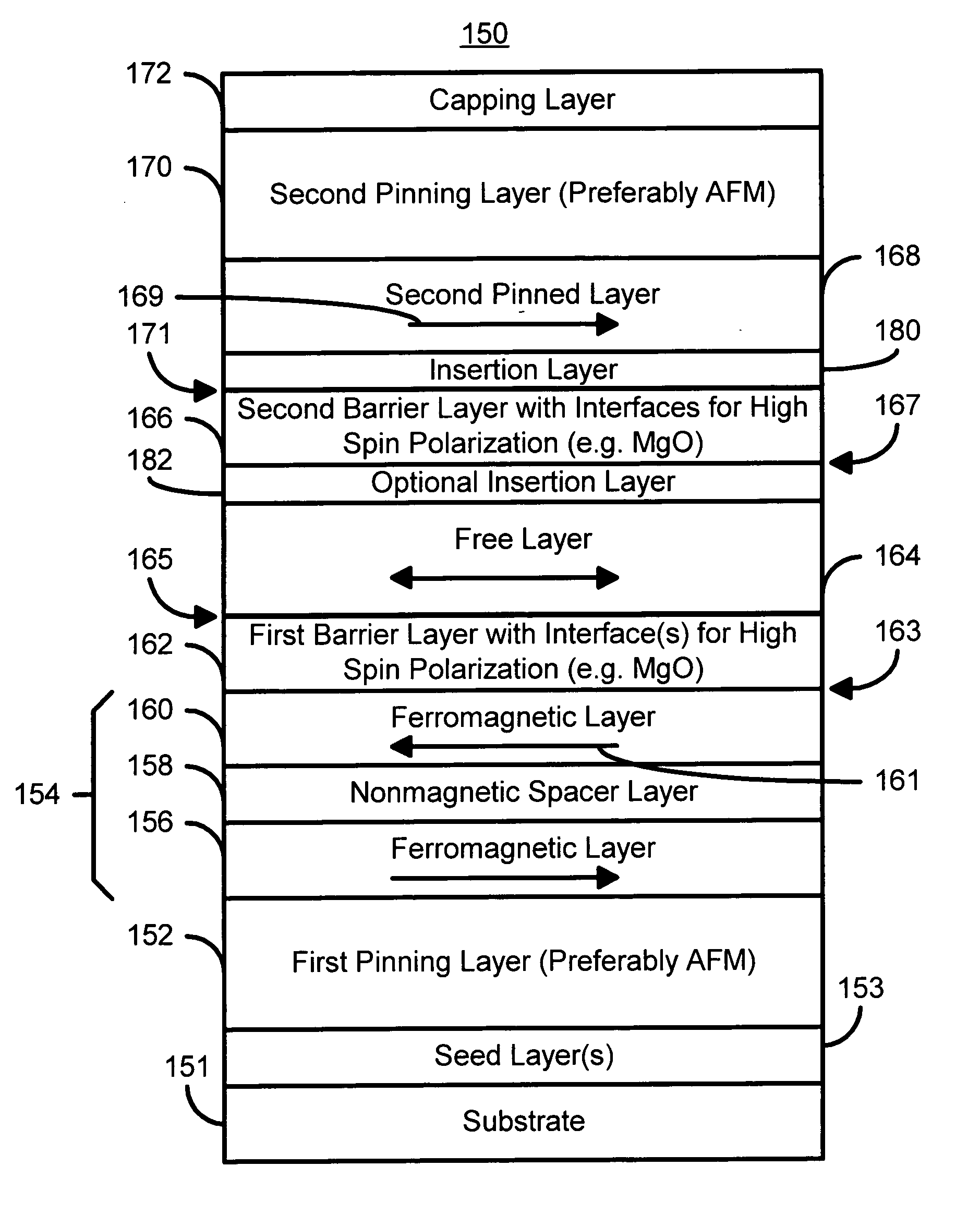
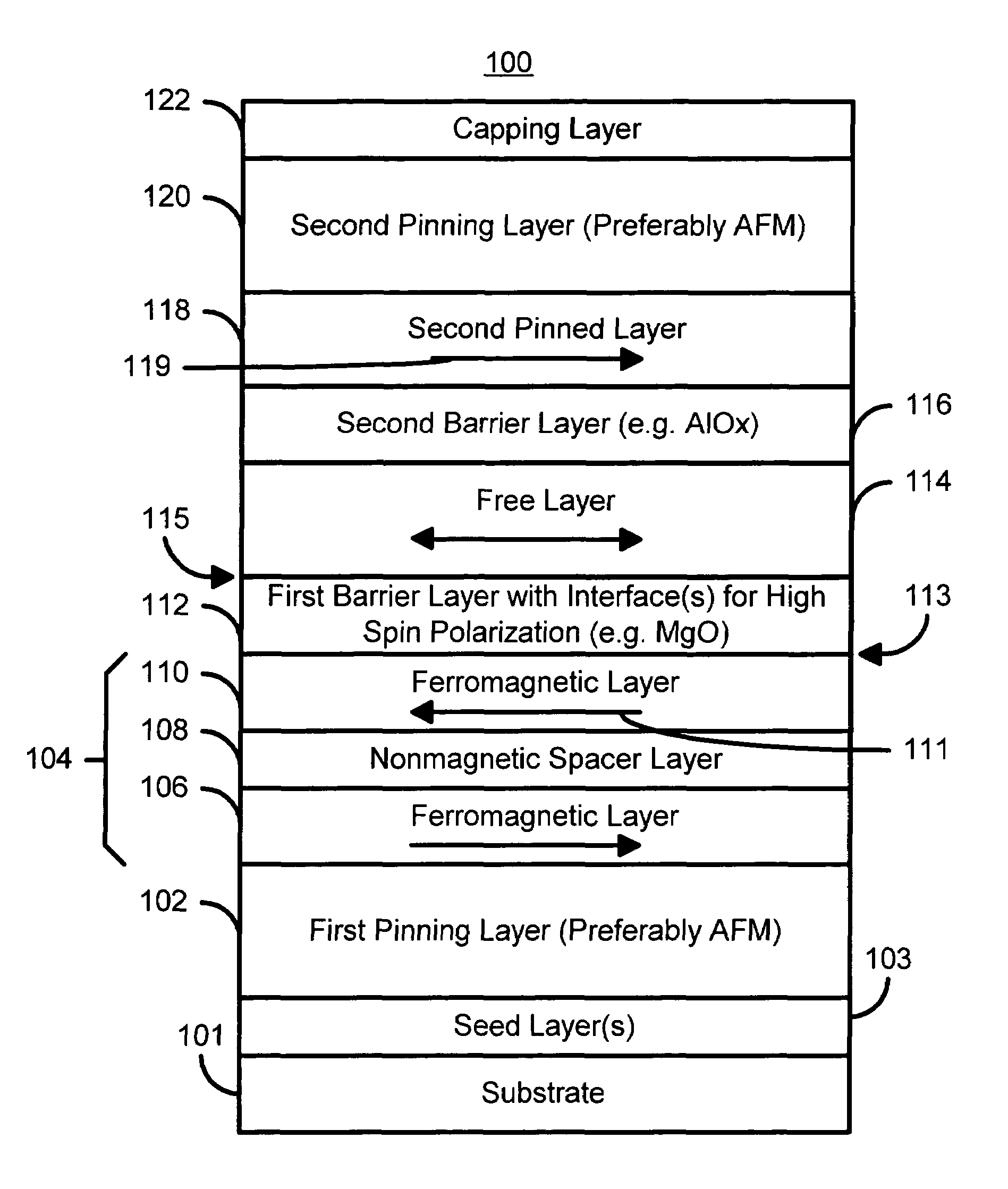
A method and system for providing a magnetic element are disclosed. The method and system include providing first and second pinned layers, a free layer, and first and second barrier layers between the first and second pinned layers, respectively, and the free layer. The first barrier layer is preferably crystalline MgO, which is insulating, and configured to allow tunneling through the first barrier layer. Furthermore, the first barrier layer has an interface with another layer, such as the free layer or the first pinned layer. The interface has a structure that provides a high spin polarization of at least fifty percent and preferably over eighty percent. The second barrier layer is insulating and configured to allow tunneling through the second barrier layer. The magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer to be switched due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
MTJ elements with high spin polarization layers configured for spin-transfer switching and spintronics devices using the magnetic elements
ActiveUS7241631B2Write currentEnhanced signalNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpin transferSpin polarization
A method and system for providing a magnetic element are disclosed. The method and system include providing first and second pinned layers, a free layer, and first and second barrier layers between the first and second pinned layers, respectively, and the free layer. The first barrier layer is preferably crystalline MgO, which is insulating, and configured to allow tunneling through the first barrier layer. Furthermore, the first barrier layer has an interface with another layer, such as the free layer or the first pinned layer. The interface has a structure that provides a high spin polarization of at least fifty percent and preferably over eighty percent. The second barrier layer is insulating and configured to allow tunneling through the second barrier layer. The magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer to be switched due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
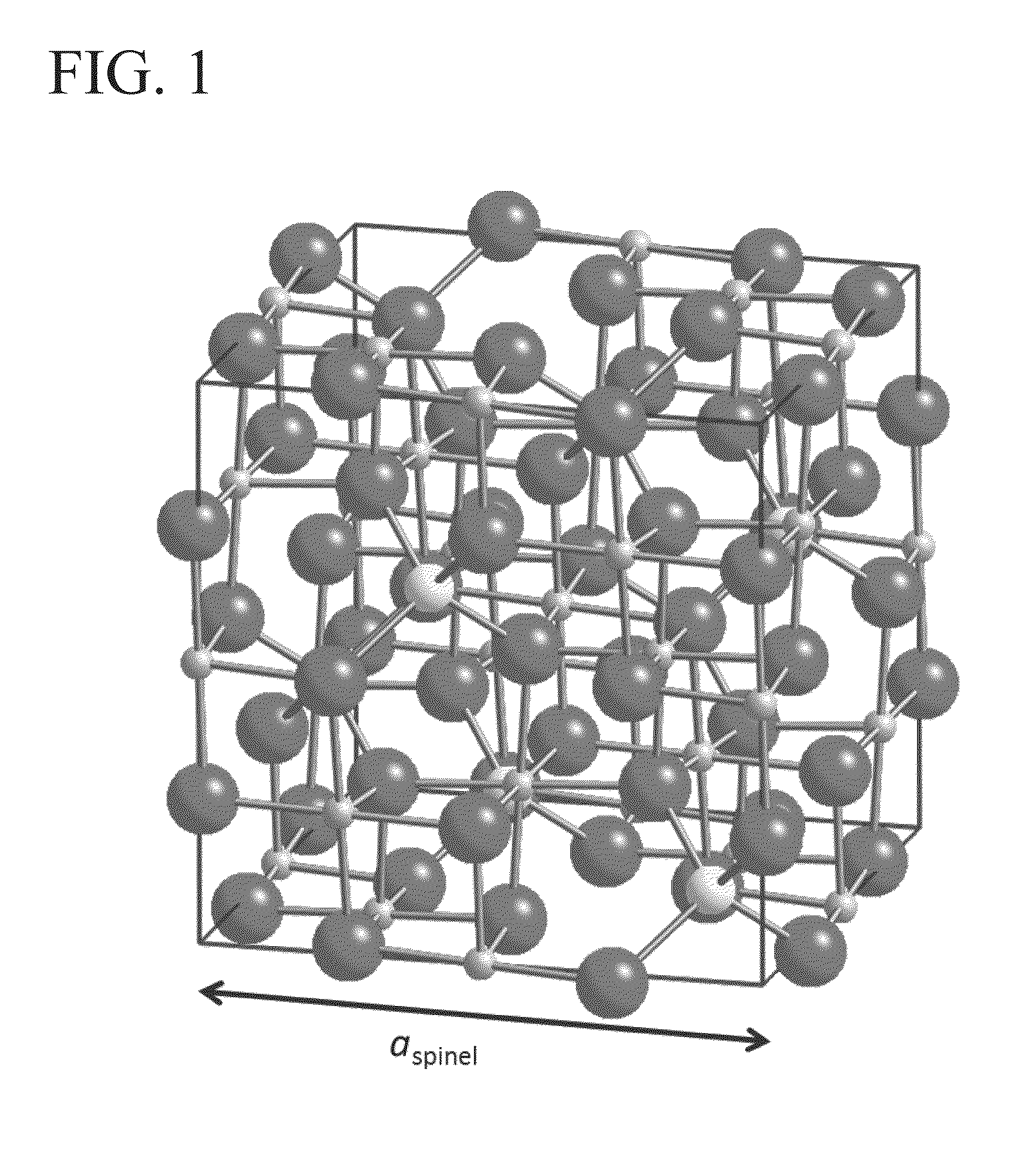
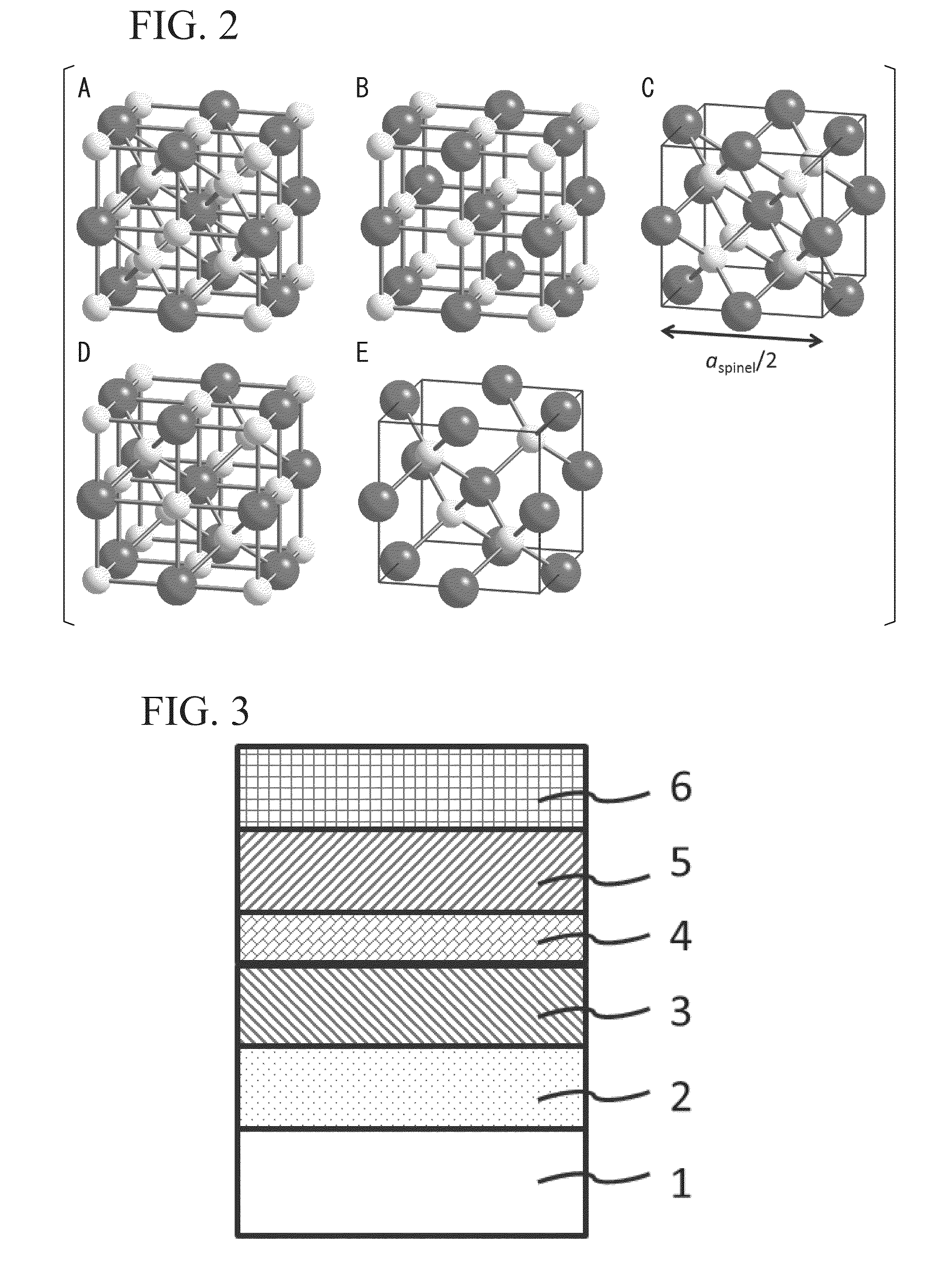
Ferromagnetic Tunnel Junction Structure and Magnetoresistive Effect Device and Spintronics Device Utilizing Same
ActiveUS20130221461A1High TMR valueQuality improvementMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesCrystalline oxideSpace group
A ferromagnetic tunnel junction structure comprising a first ferromagnetic layer, a second ferromagnetic layer, and a tunnel barrier layer that is interposed between the first ferromagnetic layer and the second ferromagnetic layer, wherein the tunnel barrier layer includes a crystalline non-magnetic material having constituent elements that are similar to those of an crystalline oxide that has spinel structure as a stable phase structure; the non-magnetic material has a cubic structure having a symmetry of space group Fm-3m or F-43m in which atomic arrangement in the spinel structure is disordered; and an effective lattice constant of the cubic structure is substantially half of the lattice constant of the oxide of the spinel structure.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
Ferromagnetic tunnel junction structure, and magneto-resistive element and spintronics device each using same
ActiveUS20120091548A1Quality improvementLarge TMRNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic reluctanceAlloy
Disclosed is a ferromagnetic tunnel junction structure which is characterized by having a tunnel barrier layer that comprises a non-magnetic material having a spinel structure. The ferromagnetic tunnel junction structure is also characterized in that the non-magnetic material is substantially MgAl2O4. The ferromagnetic tunnel junction is also characterized in that at least one of the ferromagnetic layers comprises a Co-based full Heusler alloy having an L21 or B2 structure. The ferromagnetic tunnel junction structure is also characterized in that the Co-based full Heusler alloy comprises a substance represented by the following formula: Co2FeAlxSi1-x (0≦x≦1). Also disclosed are a magnetoresistive element and a spintronics device, each of which utilizes the ferromagnetic tunnel junction structure and can achieve a high TMR value, that cannot be achieved by employing conventional tunnel barrier layers other than a MgO barrier.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
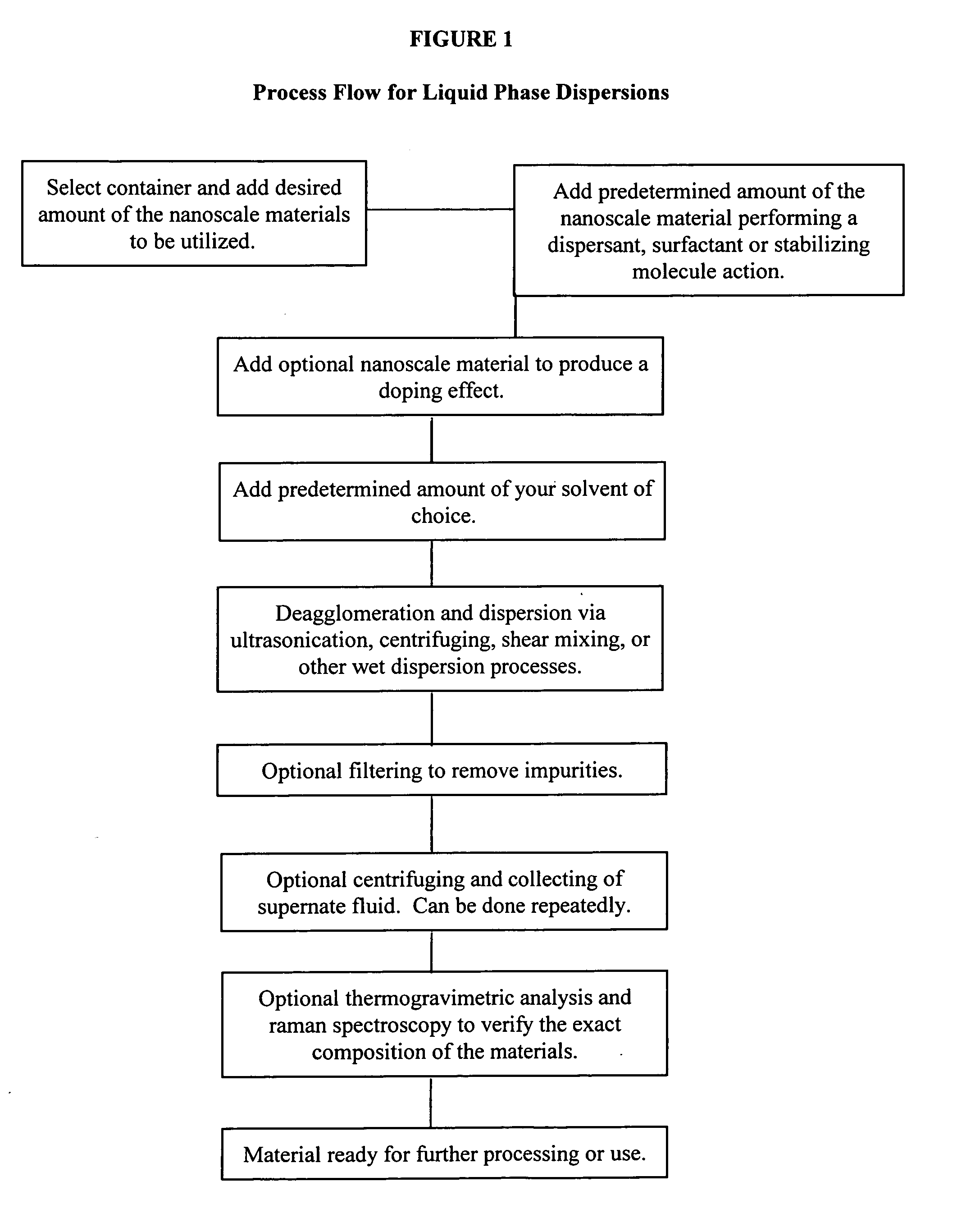
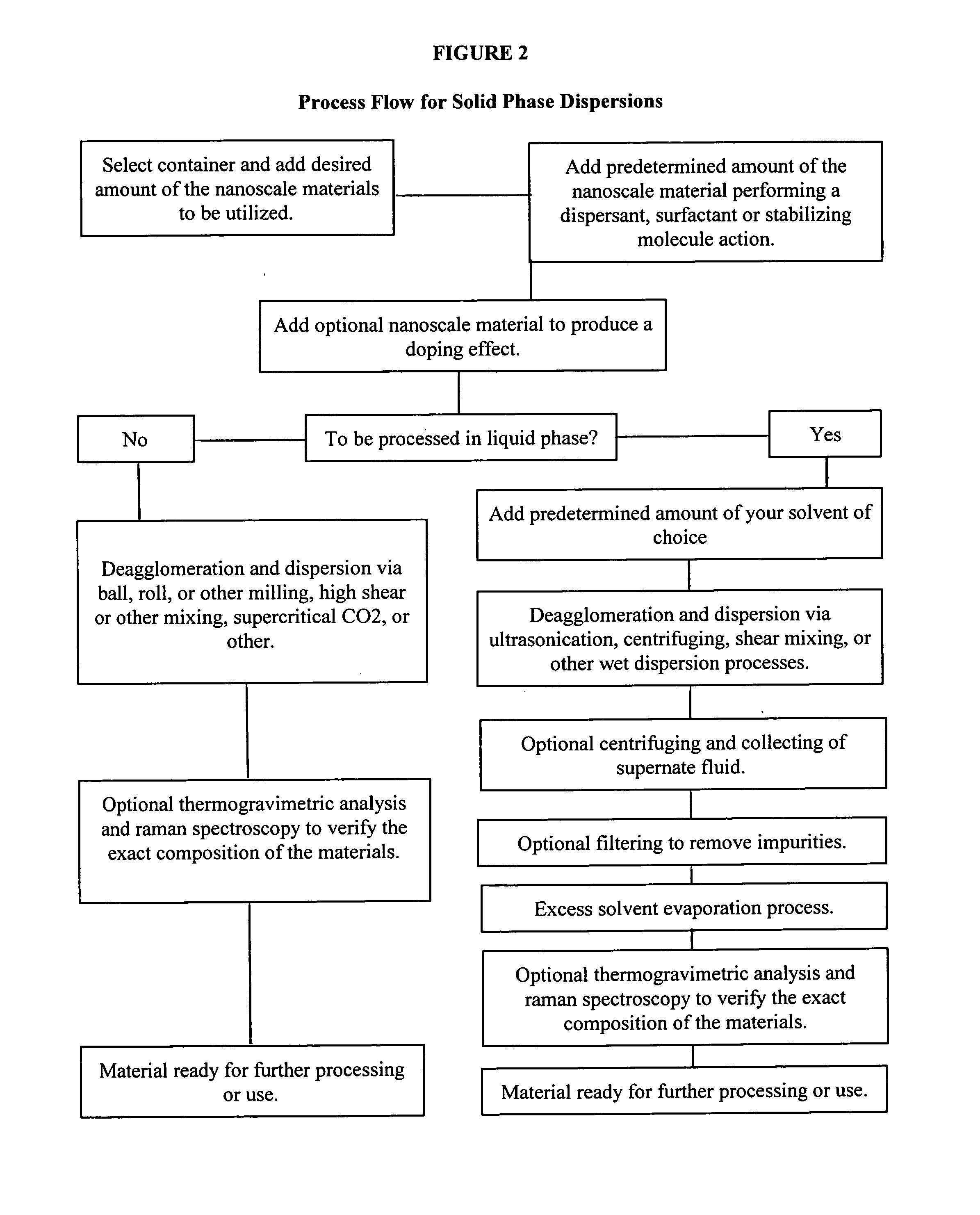
Utilizing nanoscale materials as dispersants, surfactants or stabilizing molecules, methods of making the same, and products produced therefrom
ActiveUS20110210282A1Good effectEasy to processMaterial nanotechnologyNanomagnetismDielectricCapacitance
Novel dispersions of nanoparticles such as carbon nanotubes, carbon nanofibers, boron nanotubes, clay nanotubes, other nanotube species, buckminster fullerenes, graphene, graphene nanoplatelets, elements, oxides, nanoparticles, nanoclusters, nanopowders, nanocrystals, nanoscale molecules, other nanoscale materials, as well as products produced therefrom are described. These dispersions can then be further processed into a wide variety of products including but not limited to composite materials, polymers, resins, epoxies, emulsions, cements, coatings, clays, films, membranes, paper, fibers, inks, paints, pastes, electronics, spintronics, optics, biotechnology materials, electrodes, field emission or other displays, plating, capacitance, ceramics, catalysts, clays, ballistic materials, drug delivery, doping, magnetics, dielectrics, barrier layers, selective ion flow membranes, batteries, fuel cells, solar and other applications. The invention can also be used to protect electronics from electromagnetic interference, radio frequency interference or radio frequency identification. Most applications that utilize nanoparticles can benefit from this invention.
Owner:CTI NANOTECH
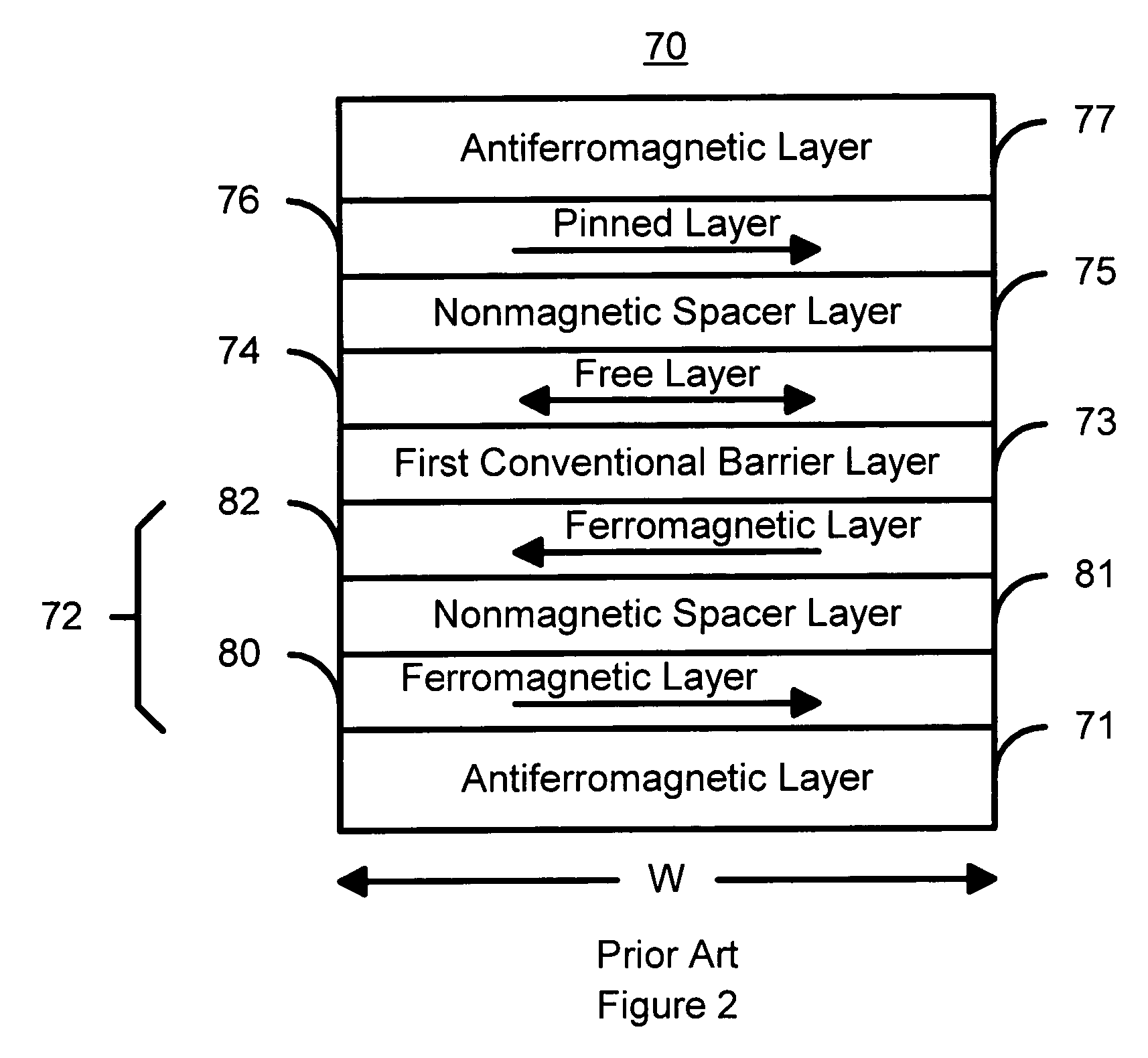
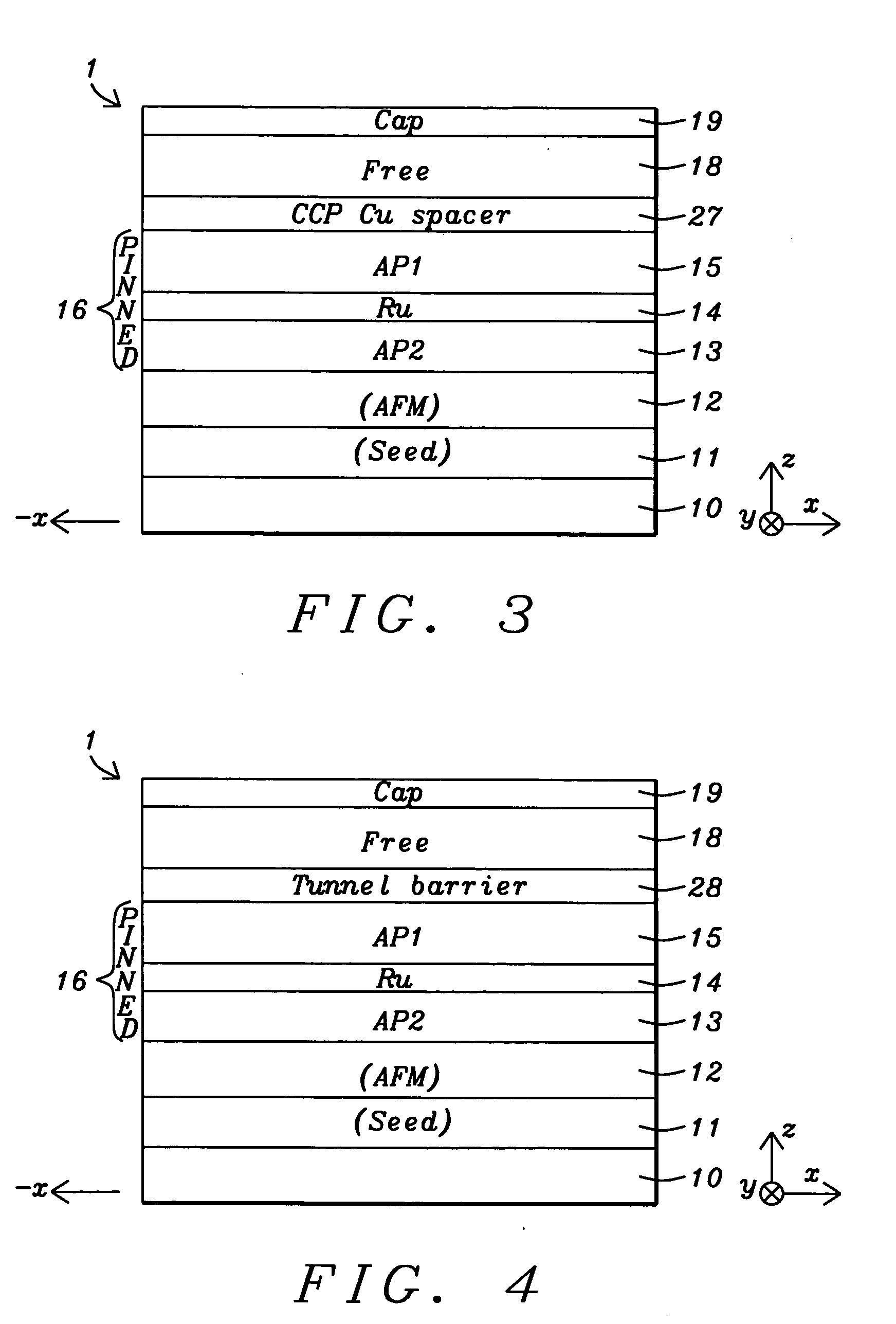
Novel way to reduce the ordering temperature for Co2MnSi-like Heusler alloys for CPP, TMR, MRAM, or other spintronics device applications
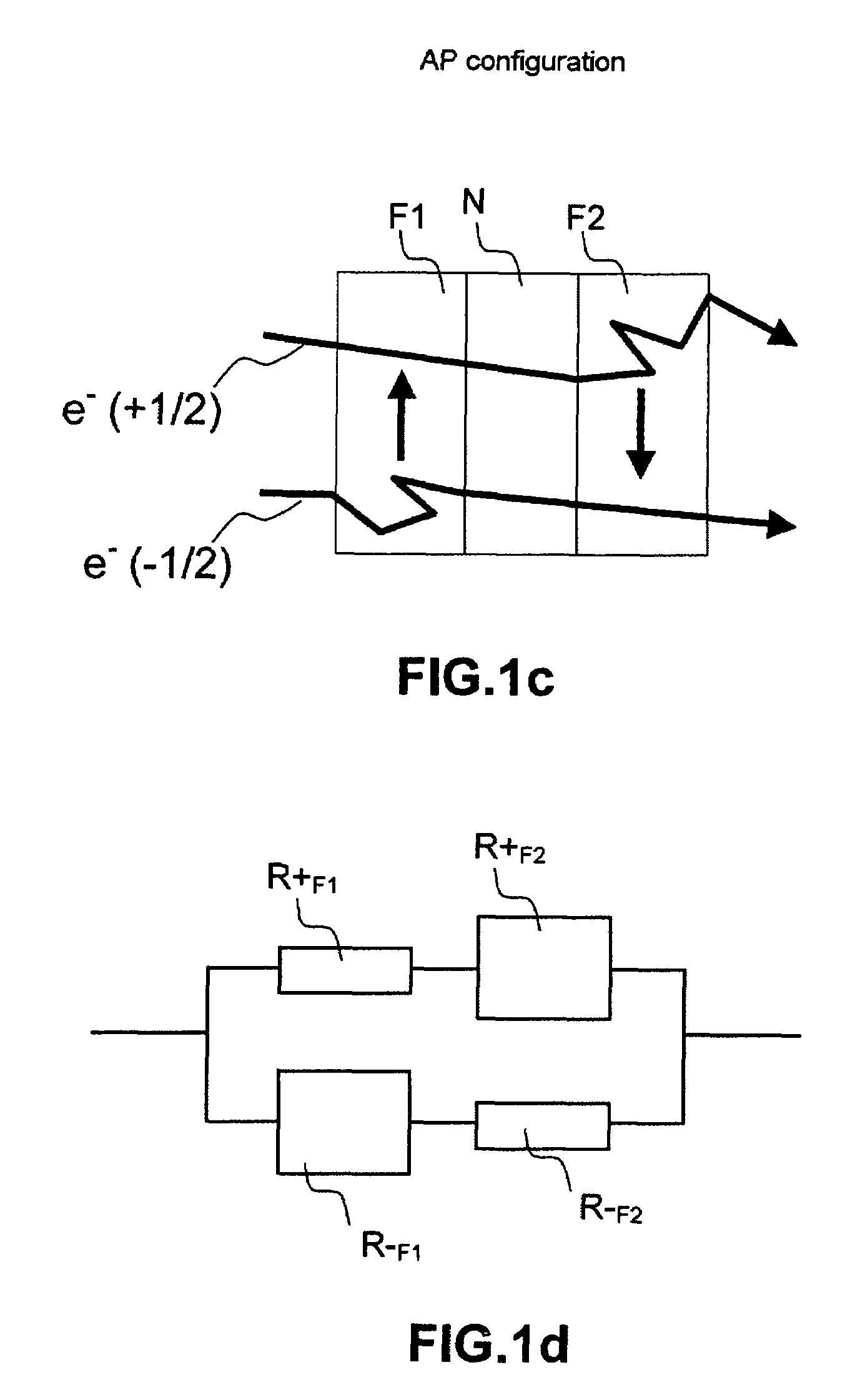
ActiveUS20070297103A1Decreased ordering temperatureReduce the temperatureNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsAlloySpin valve
A spin valve structure is disclosed in which an AP1 layer and / or free layer are made of a laminated Heusler alloy having Al or FeCo insertion layers. The ordering temperature of a Heusler alloy such as Co2MnSi is thereby lowered from about 350° C. to 280° C. which becomes practical for spintronics device applications. The insertion layer is 0.5 to 5 Angstroms thick and may also be Sn, Ge, Ga, Sb, or Cr. The AP1 layer or free layer can contain one or two additional FeCo layers to give a configuration represented by FeCo / [HA / IL]nHA, [HA / IL]nHA / FeCo, or FeCo / [HA / IL]nHA / FeCo where n is an integer≧1, HA is a Heusler alloy layer, and IL is an insertion layer. Optionally, a Heusler alloy insertion scheme is possible by doping Al or FeCo in the HA layer. For example, Co2MnSi may be co-sputtered with an Al or FeCo target or with a Co2MnAl or Co2FeSi target.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Magnetic shift register with shiftable magnetic domains between two regions, and method of using the same
InactiveUS20050094427A1Comparable in costIncrease memory capacityLiquid applicationDigital storageShift registerSpins
A magnetic shift register uses the inherent, natural properties of domain walls in magnetic materials to store data. The shift register uses spin electronics without changing the physical nature of its constituent materials. The shift register comprises a fine track or strip of magnetic materials. Information is stored as domain walls in the track. An electric current is applied to the track to move the magnetic moments along the track past a reading or writing device. In a magnetic material with domain walls, a current passed across the domain wall moves the domain wall in the direction of the current flow. As the current passes through a domain, it becomes “spin polarized”. When this spin polarized current passes through the next domain and across a domain wall, it develops a circle of spin torque. This spin torque moves the domain wall.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method for changing spin relaxation, method for detecting spin current and spintronics device using spin relaxation
InactiveUS20100097063A1Novel configurationShorten spin relaxation timeMagnetic measurementsNanoinformaticsSpin currentSpin relaxation time
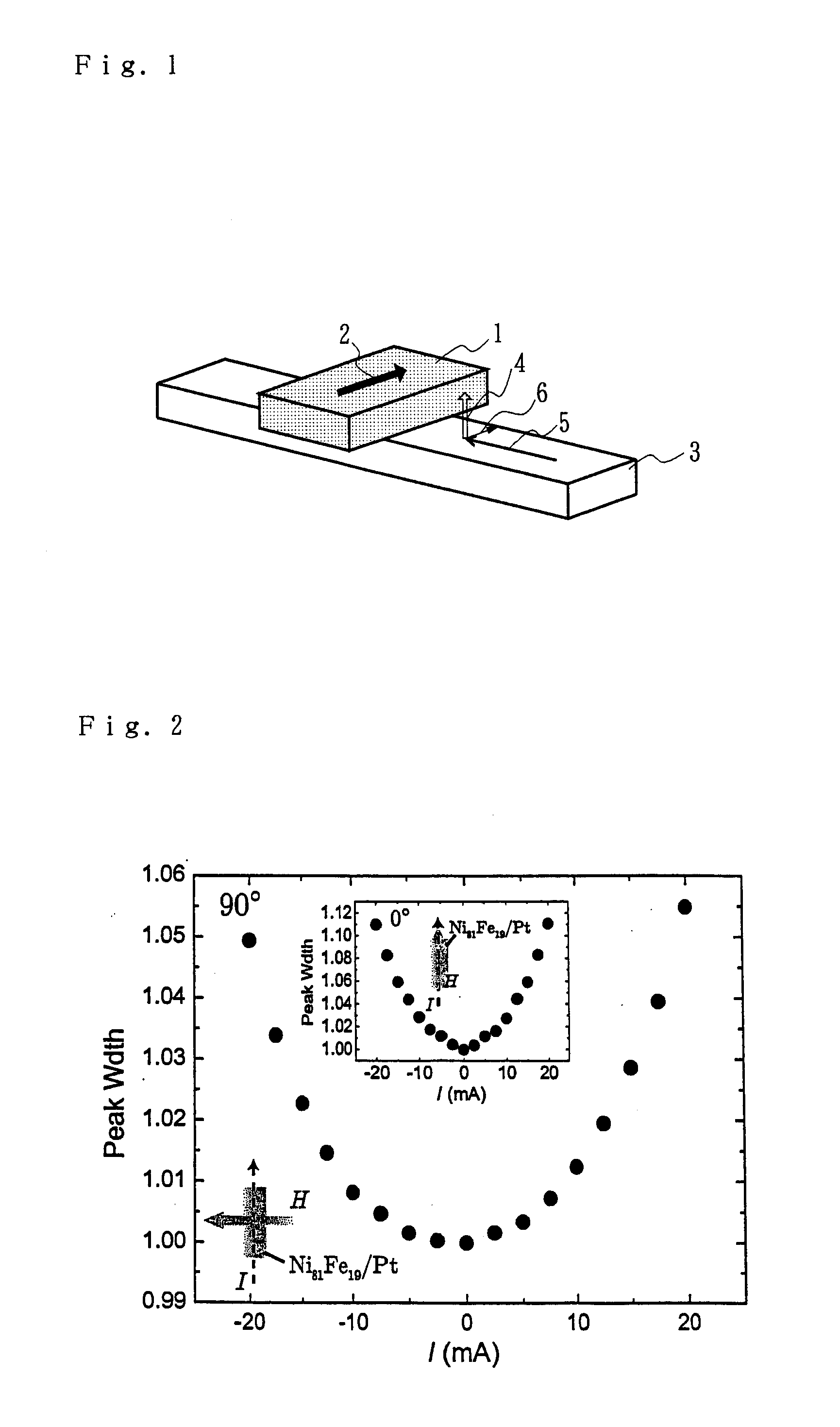
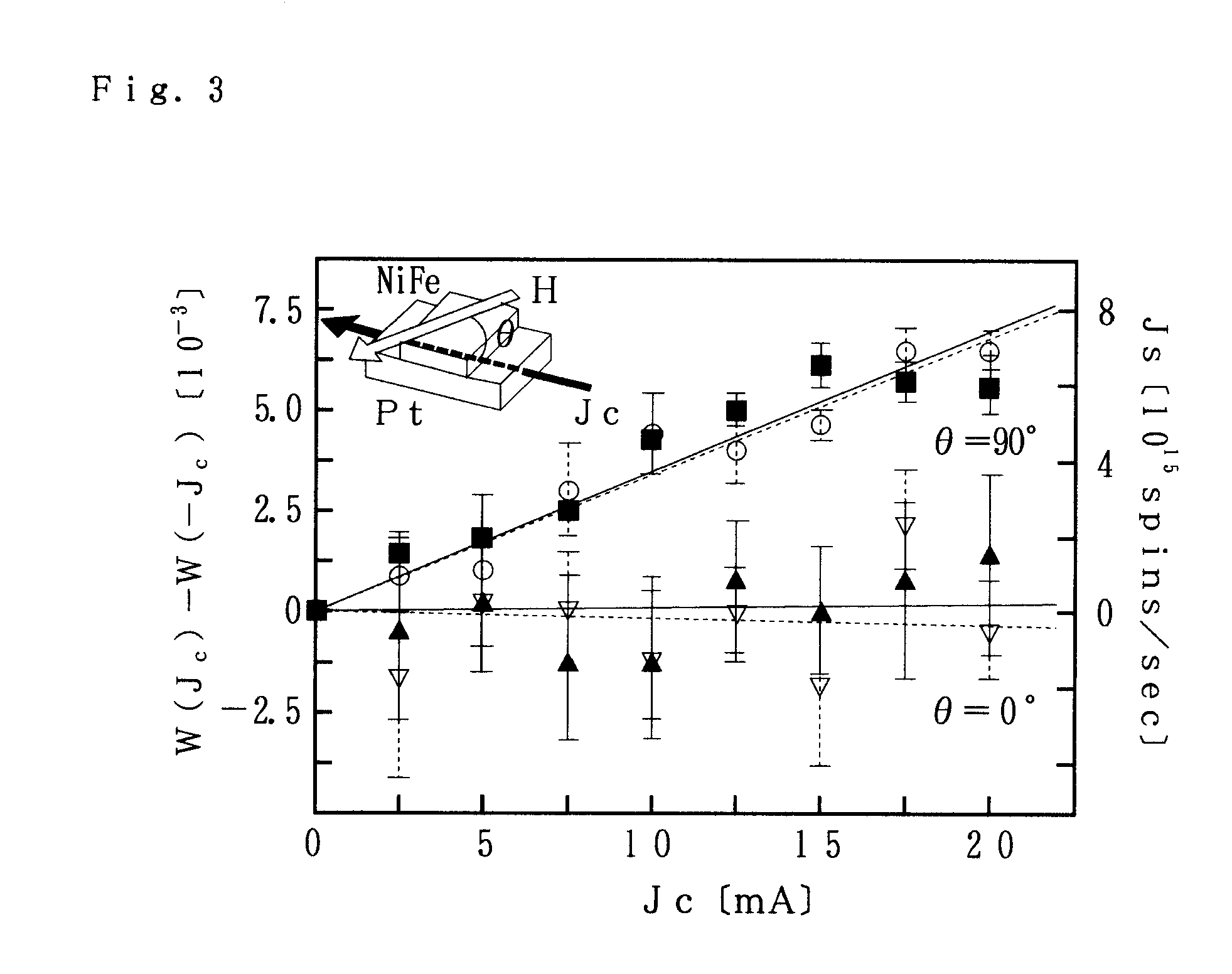
The invention relates to a method for changing spin relaxation, a method for detecting a spin current, and a spintronic device using spin relaxation, and spin relaxation is changed through injection of a spin current.A spin current 4 is injected into a material 1 in a certain spin state, so that the spin relaxation time can be controlled.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Nanodevices for Spintronics and Methods of Using Same
Graphene magnet multilayers (GMMs) are employed to facilitate development of spintronic devices. The GMMs can include a sheet of monolayer (ML) or few-layer (FL) graphene in contact with a magnetic material, such as a ferromagnetic (FM) or an antiferromagnetic material. Electrode terminals can be disposed on the GMMs to be in electrical contact with the graphene. A magnetic field effect is induced in the graphene sheet based on an exchange magnetic field resulting from a magnetization of the magnetic material which is in contact with graphene. Electrical characteristics of the graphene can be manipulated based on the magnetization of the magnetic material in the GMM.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Spin oscillator device
ActiveUS20170033742A1Detection is limitedPulse automatic controlMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpin-transfer torqueMagnetic memory
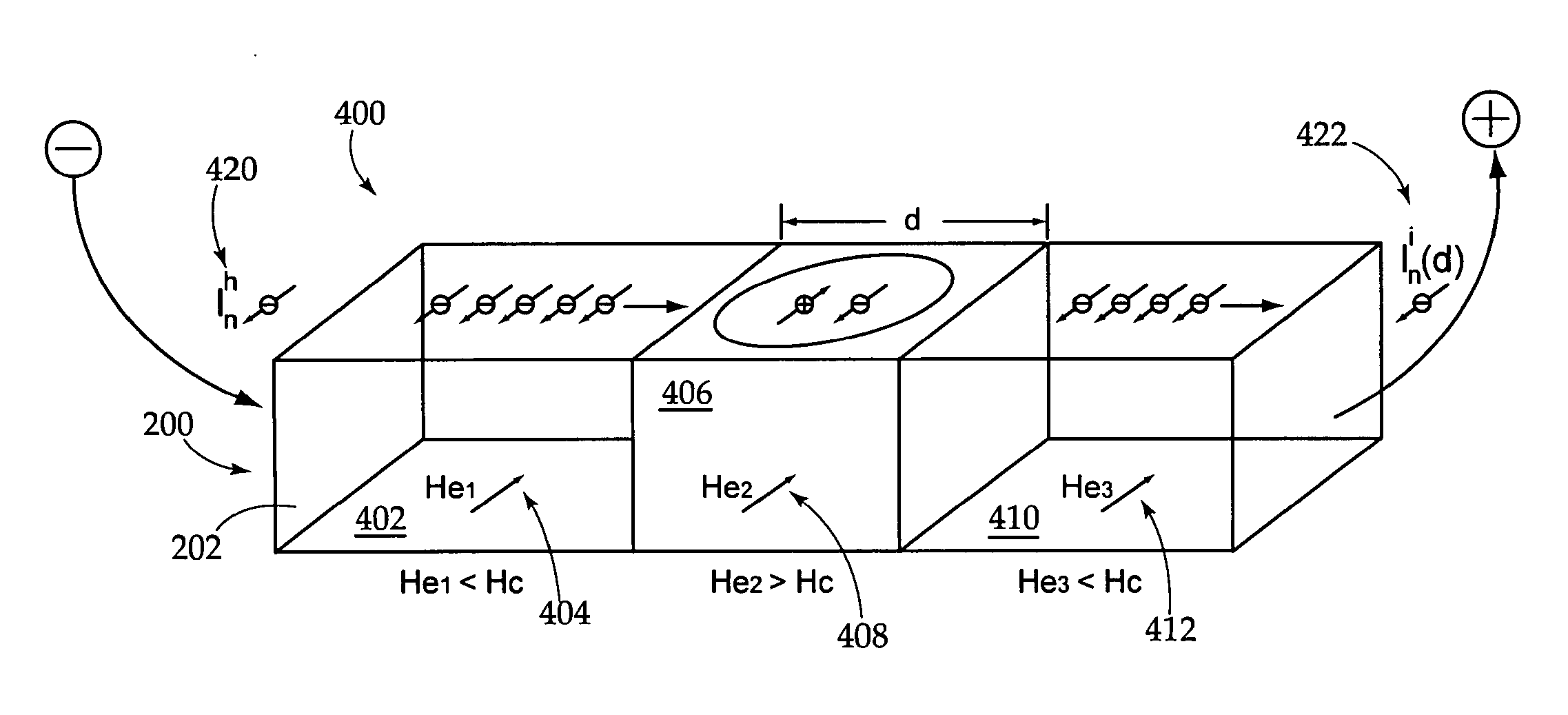
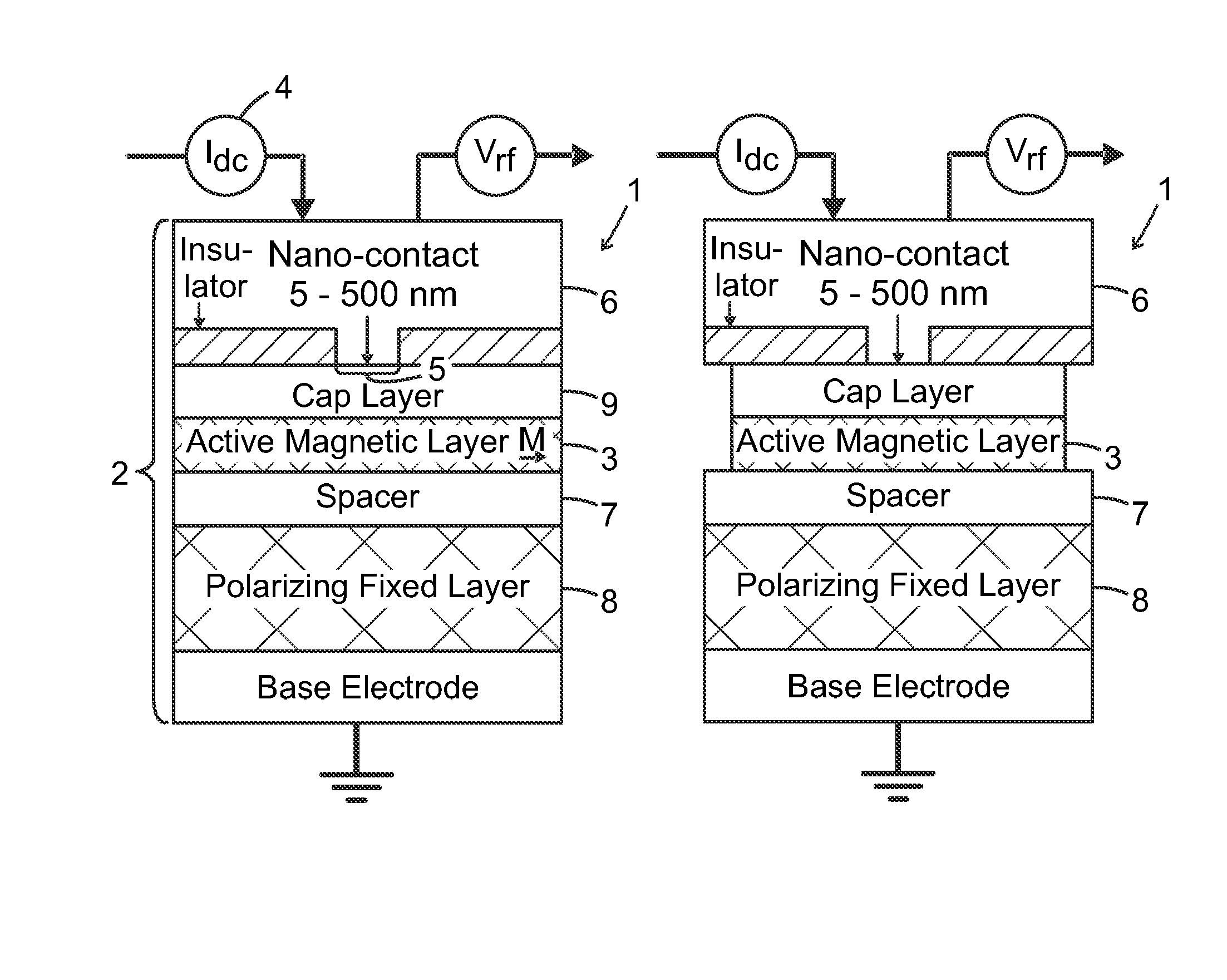
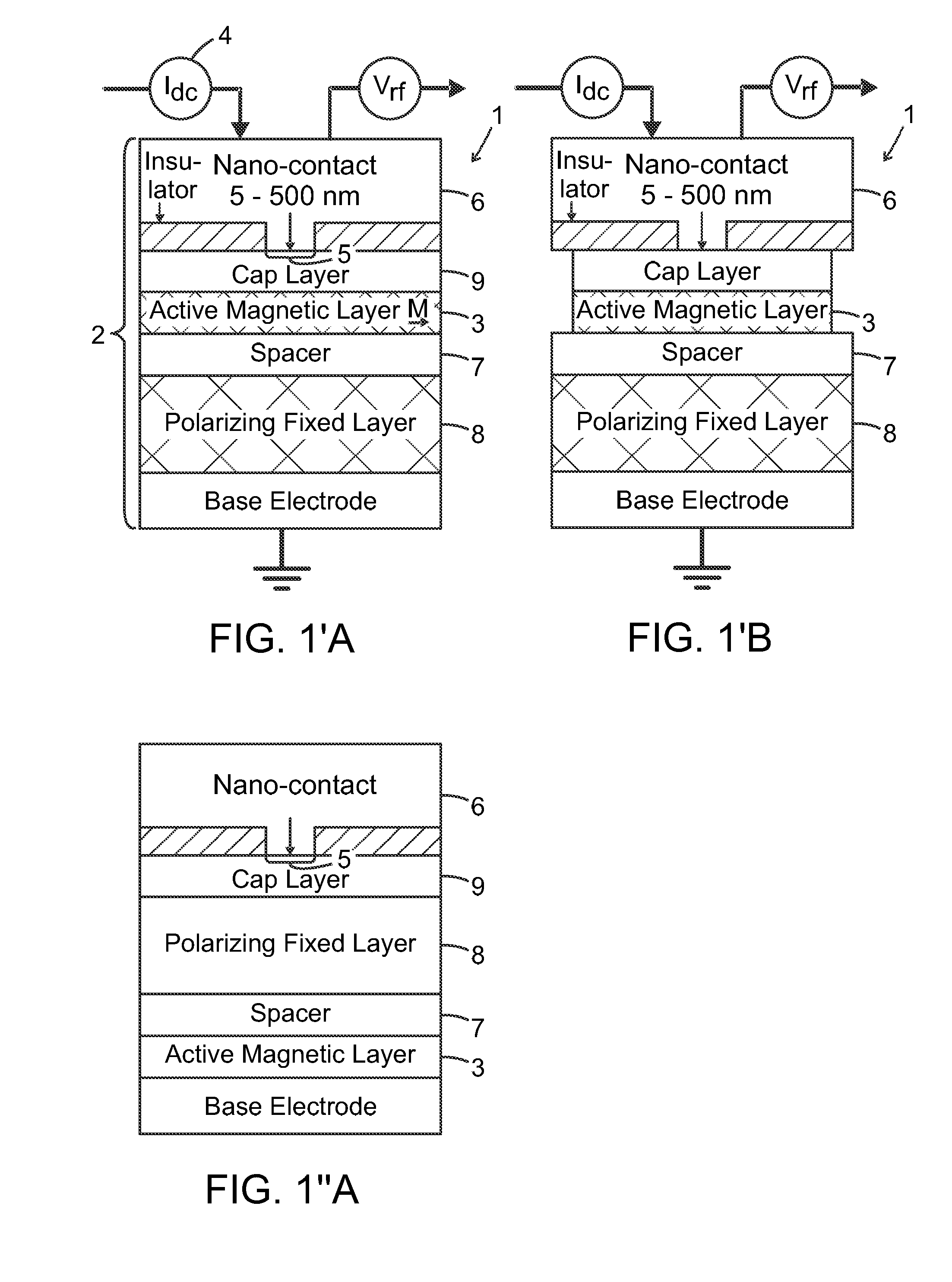
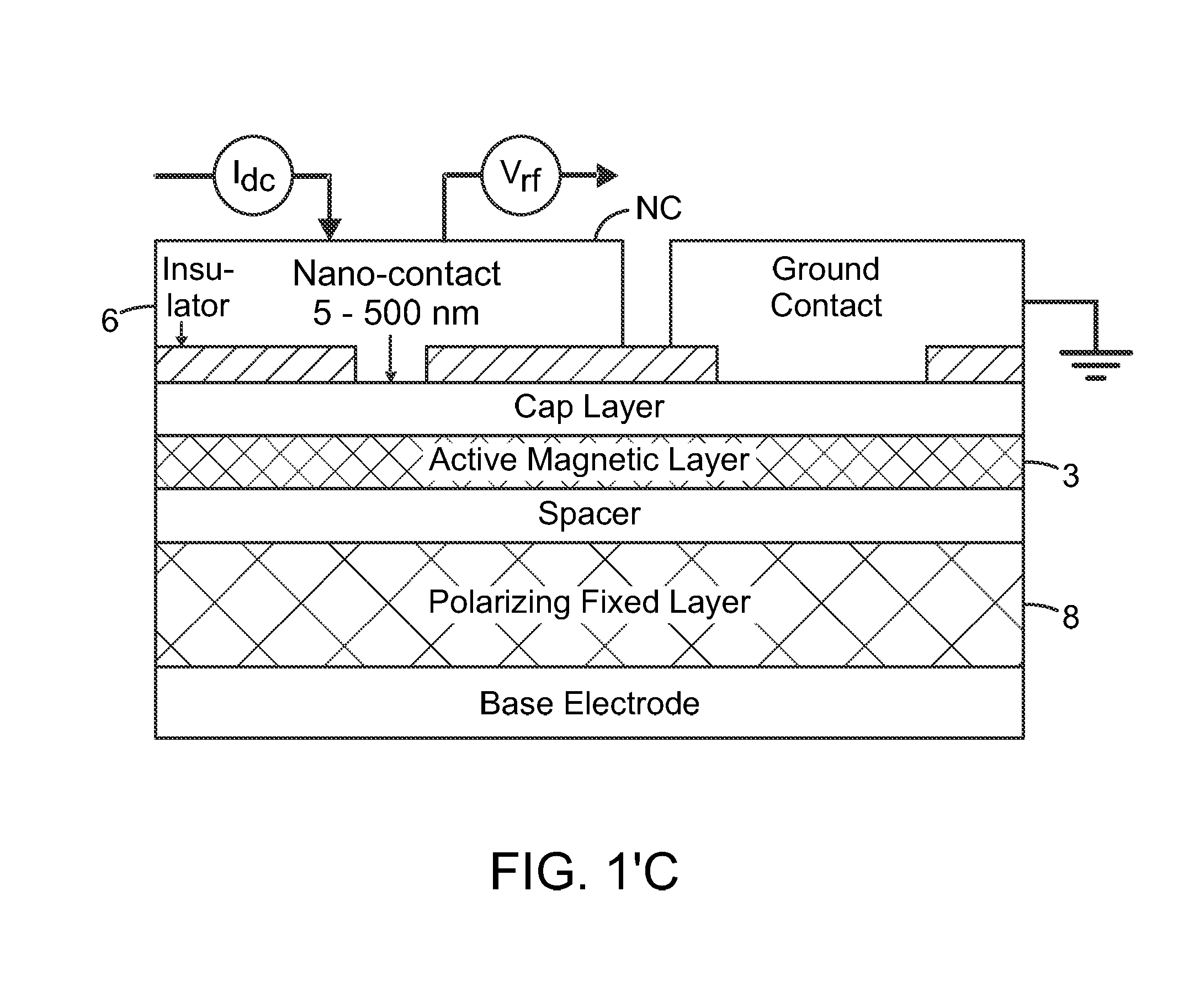
The present invention relates to using spin transfer torque underneath a nanocontact on a magnetic thin film with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA), provides generation of dissipative magnetic droplet solitons and magnetic droplet-skyrmions and report on their rich dynamical properties. Micromagnetic simulations identify the conditions necessary to nucleate and drive droplet-skyrmions over a wide range of currents and fields. Micromagnetic simulations also demonstrate how droplets and droplet-skyrmions can be used as skyrmion injectors and detectors in skyrmion-based magnetic memories. The droplet-skyrmion can be controlled using both current and magnetic fields, and is expected to have applications in spintronics, magnonics, skyrmionics, and PMA-based domain-wall devices.
Owner:NANOSC AB
Titanium dioxide nano thread, belt and tube block array and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101037225AEasy to controlGood process repeatabilityIndividual molecule manipulationTitanium dioxideSolar cellPt element
The present invention provides a titanium dioxide nanometer thread, strip and tube block array, and a preparation method of the same, which relates to a nanometer material and a preparation method of the same. A high purity titanium foil serves as a substrate; a mixture solution of ethylene glycol and fluorination ammonification with a content of 0.1~0.5 wt%; a titanium dioxide nanometer thread, strip and pipe block array, which has a nanometer thread, strip blended fasciculation substance of 1~20 micron at the upper end and a regular nanometer tube array at the lower part, is formed vertically at the substrate by constant pressure anodisation. The preparation method comprises the steps of that: the substrate serves as the anode, the platinum serves as the cathode, the distance between the anode and the cathode is 10~50 mm, the voltage is 10~60 V, the reaction time is 30~3000 min; the obtained product is roasted for 1~3 hours at 240~600 DEG C, and is cooled in the furnace, thereby the titanium dioxide nanometer thread, strip and tube block array is obtained. The method has a simple equipment, an excellent repetitiveness for technology, a steady quality of product, and can be used for the fields of photocatalysis, photolysis water, solar cell and spinning electron.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Heusler alloy with insertion layer to reduce the ordering temperature for CPP, TMR, MRAM, and other spintronics applications
A spin valve structure is disclosed in which an AP1 layer and / or free layer are made of a laminated Heusler alloy having Al or FeCo insertion layers. The ordering temperature of a Heusler alloy such as Co2MnSi is thereby lowered from about 350° C. to 280° C. which becomes practical for spintronics device applications. The insertion layer is 0.5 to 5 Angstroms thick and may also be Sn, Ge, Ga, Sb, or Cr. The AP1 layer or free layer can contain one or two additional FeCo layers to give a configuration represented by FeCo / [HA / IL]nHA, [HA / IL]nHA / FeCo, or FeCo / [HA / IL]nHA / FeCo where n is an integer ≧1, HA is a Heusler alloy layer, and IL is an insertion layer. Optionally, a Heusler alloy insertion scheme is possible by doping Al or FeCo in the HA layer. For example, Co2MnSi may be co-sputtered with an Al or FeCo target or with a Co2MnAl or Co2FeSi target.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
GaN base spinning LED and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101350385ASimple manufacturing methodSpin injection efficiency probeSemiconductor devicesOhmic contactSpins
The invention provides a GaN group spin luminescent diode (Spin-LED), which is formed form orderly arranging the following structures on a conducting substrate: a P type ohmic contact electrode, a P type GaN layer, an InGaN / GaN multiple quantum well active layer, a N type GaN layer, an ITO magnetic layer which is doped with transient metallic elements, and a N type ohmic contact electrode, wherein the GaN group Spin-LED is prepared through taking the ITO group magnetic layer as a spin injection source and combining the original and the existing GaN group LED lighting techniques, compared with the complex preparing process which combines a plurality of producing techniques of a GaMnN group Spin-LED which is provided at present, the method is characterized by arranging the magnetic layer on a transparent electrode part instead, the preparation method is simple and easy to carry out, and various novel spin luminescent diodes can be flexibly and rapidly obtained, and the detecting of the spin injection efficiency can be effectively carried out, simultaneously, the Spin-LED further can be used for researching and designing other various spin electronic devices.
Owner:DONGGUAN INST OF OPTO ELECTRONICS PEKING UNIV
Preparation method of ultrathin graphite phase carbon nitride
ActiveCN106477539AUniform thicknessGood dispersionNitrogen and non-metal compoundsOrganic solventCarbon nitride
The invention provides a preparation method of ultrathin graphite phase carbon nitride. The preparation method comprises steps as follows: melamine is calcined firstly, and blocky g-C3N4 is obtained; blocky g-C3N4 is uniformly dispersed in deionized water and subjected to ultrasonication; a product obtained after ultrasonication is subjected to centrifugal separation, and solids are collected and dried; finally, a dried product is calcined again, and a target product is obtained. According to the preparation method of ultrathin graphite phase carbon nitride, mass preparation and thickness regulation of ultrathin g-C3N4 with the thickness of 0.8-1.2 nm equal to the thickness of 3-4 atom layers are realized, no organic solvent or toxic chemical reagent participates in a reaction process, so that the problems of structure defects and environmental pollution which are caused by introduction of impurities can be effectively solved, and on the basis of the non-toxic characteristic of prepared g-C3N4, the preparation method can be widely applied to photocatalysis, electro-catalysis, biosensing, bioimaging and spintronics. The whole preparation process is simple to operate, high in controllability, good in repeatability, green, environment-friendly and suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Synthesis of TiO2 nanometer particles and bars
Synthesis of TiO2 nanometer granules and rod is characterized by taking organic titanate ester or long-chain organic hydroxy acid or NH4HCO3 as raw materials under the existence of heat solvent, taking organic amine as mineralizer, taking low-boiling point organic matter as solvent, reacting at 100~200 degrees C in closed reactor, synthesizing TiO2 nanometer granules and rod with high crystallinity, homogeneous size and re-dispersion organic solvent, doping other metal ions into reactive system and forming TiO2 nanometer granules or rod doped with metal. It is simple and cheap, has better process reproducibility and quality. It can be used for battery electrode, catalyst, light catalyst and solar battery.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
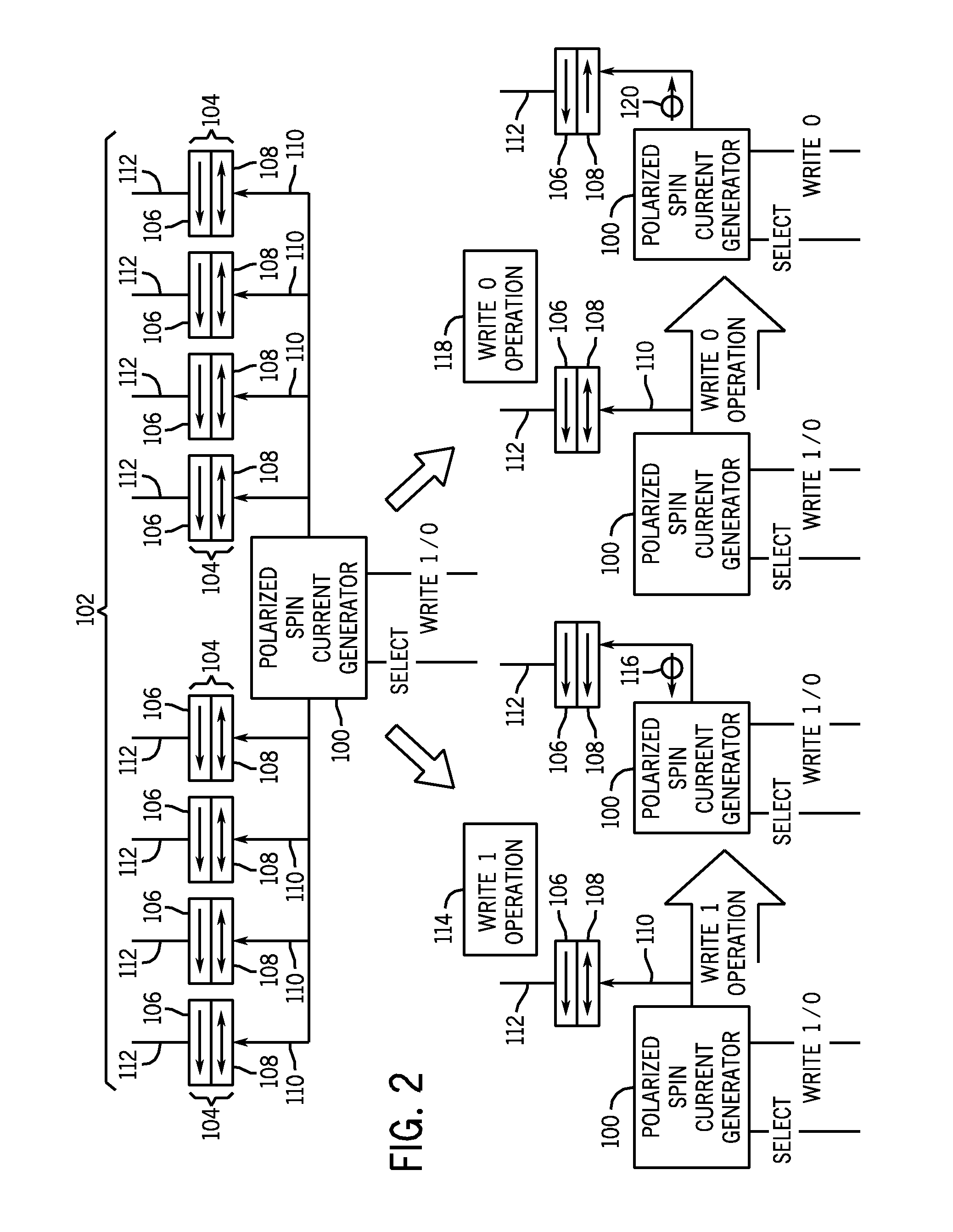
Spin current generator for stt-mram or other spintronics applications
Spin current generators and systems and methods for employing spin current generators. A spin current generator may be configured to generate a spin current polarized in one direction, or a spin current selectively polarized in two directions. The spin current generator may by employed in spintronics applications, wherein a spin current is desired.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
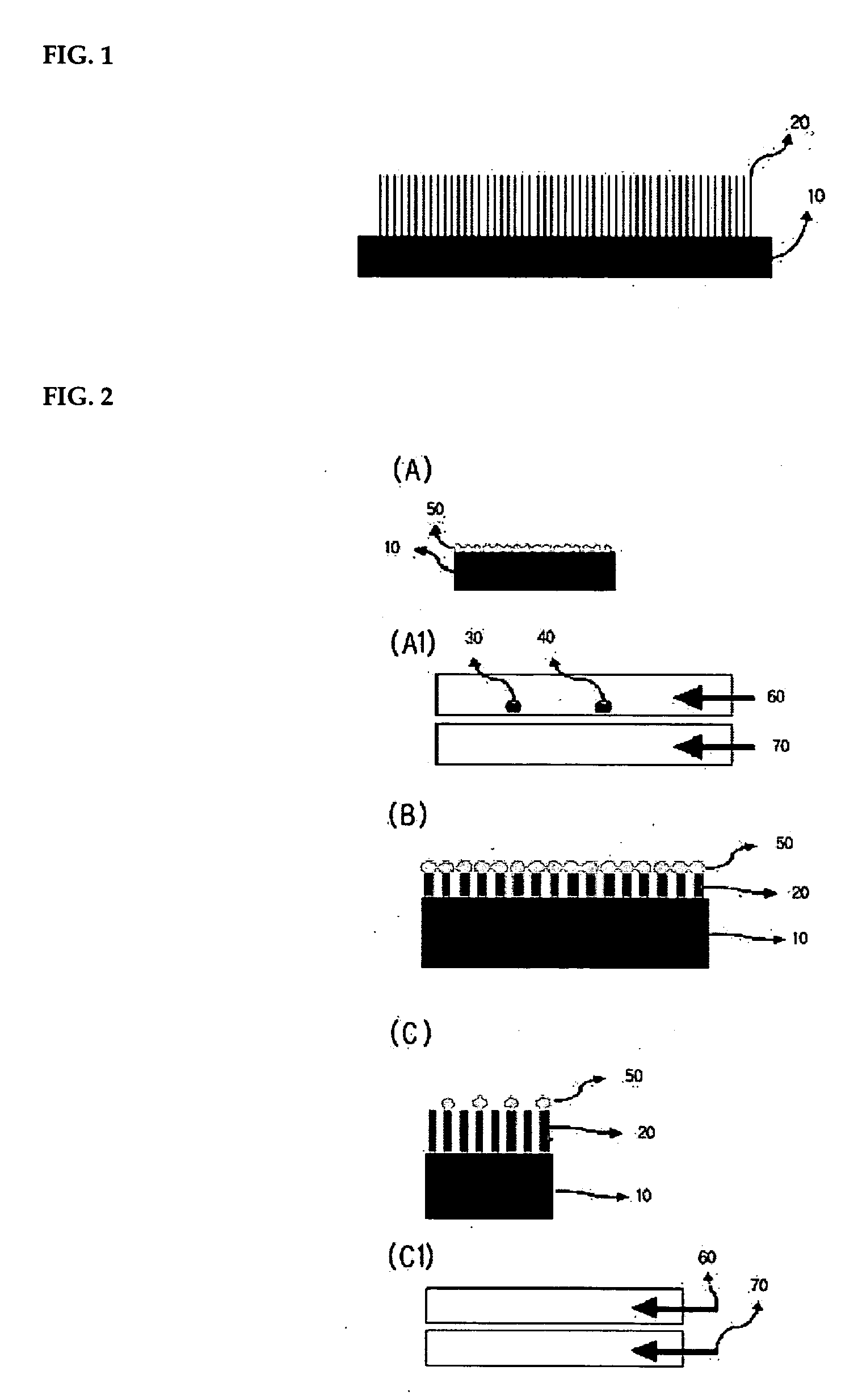
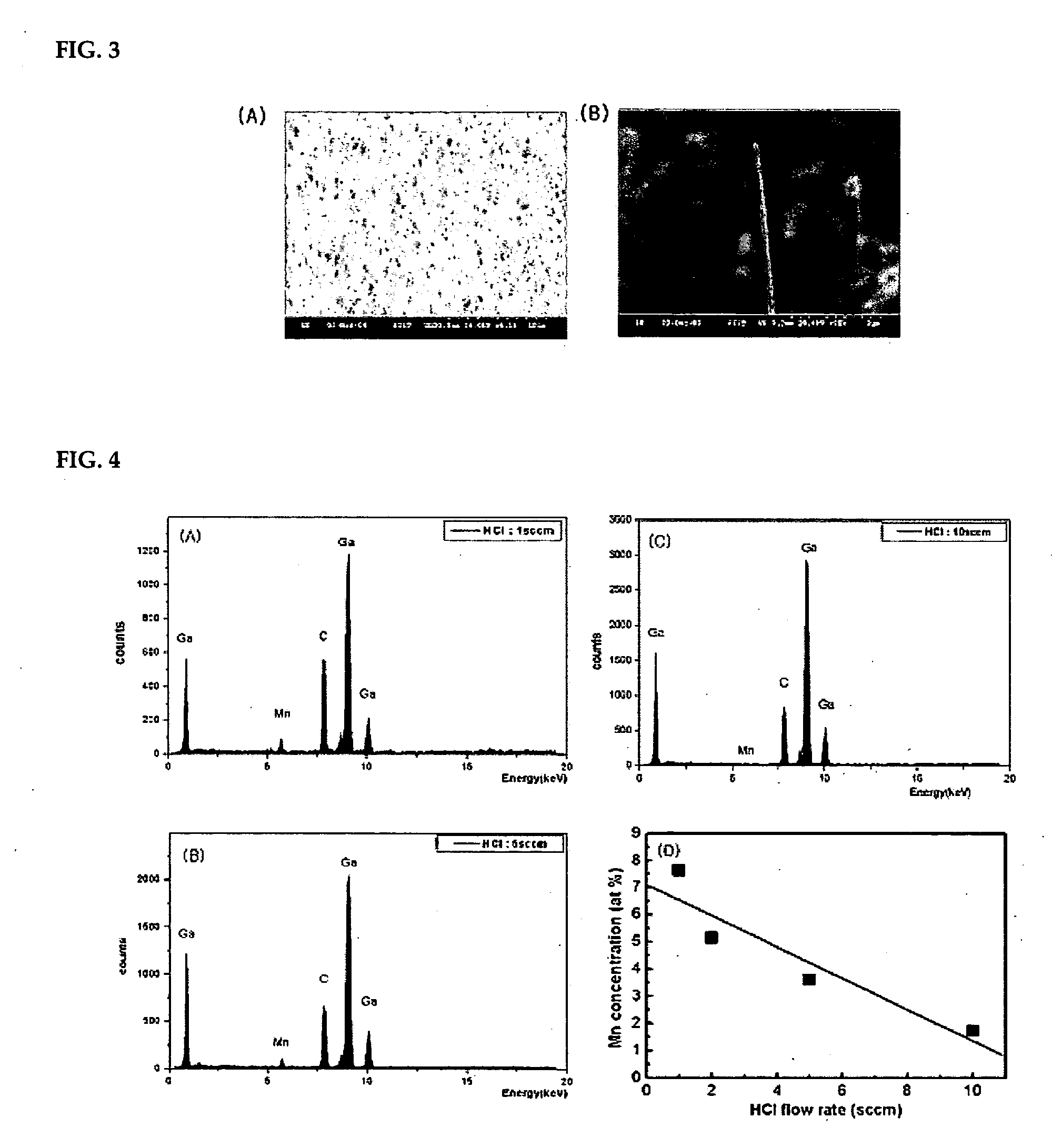
Fabrication method of gallium manganese nitride single crystal nanowire
InactiveUS20060292055A1Material nanotechnologyNitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsNanowireManganese
The present invention relates to a fabrication method of gallium manganese nitride (GaMnN) single crystal nanowire, more particularly to a fabrication method of GaMnN single crystal nanowire substrate by halide vapor phase epitaxy (HVPE) in which such metal components as gallium (Ga) and manganese (Mn) react with such gas components as nitrogen (N2), hydrogen chloride (HCl) and ammonia (NH3), wherein the amount of the gas components are adjusted to control the Mn doping concentration in order to obtain nanowire having a perfect, one-dimensional, single crystal structure without internal defect, concentration of holes, or carriers, and magnetization value of which being determined by the doping concentration and showing ferromagnetism at room temperature, thus being a useful spin transporter in the field of the next-generation spintronics, such as spin-polarized LED, spin-polarized FET, etc.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
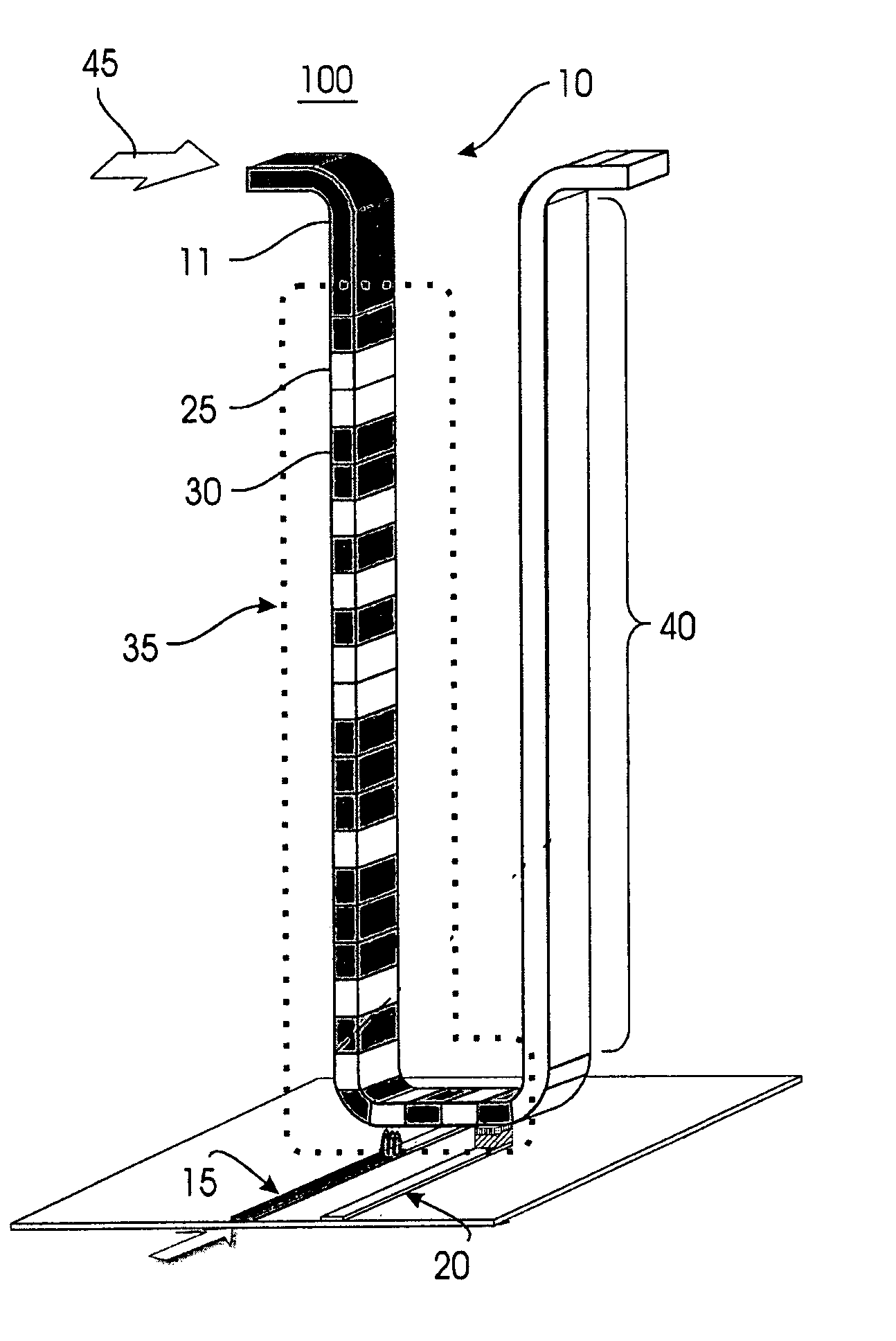
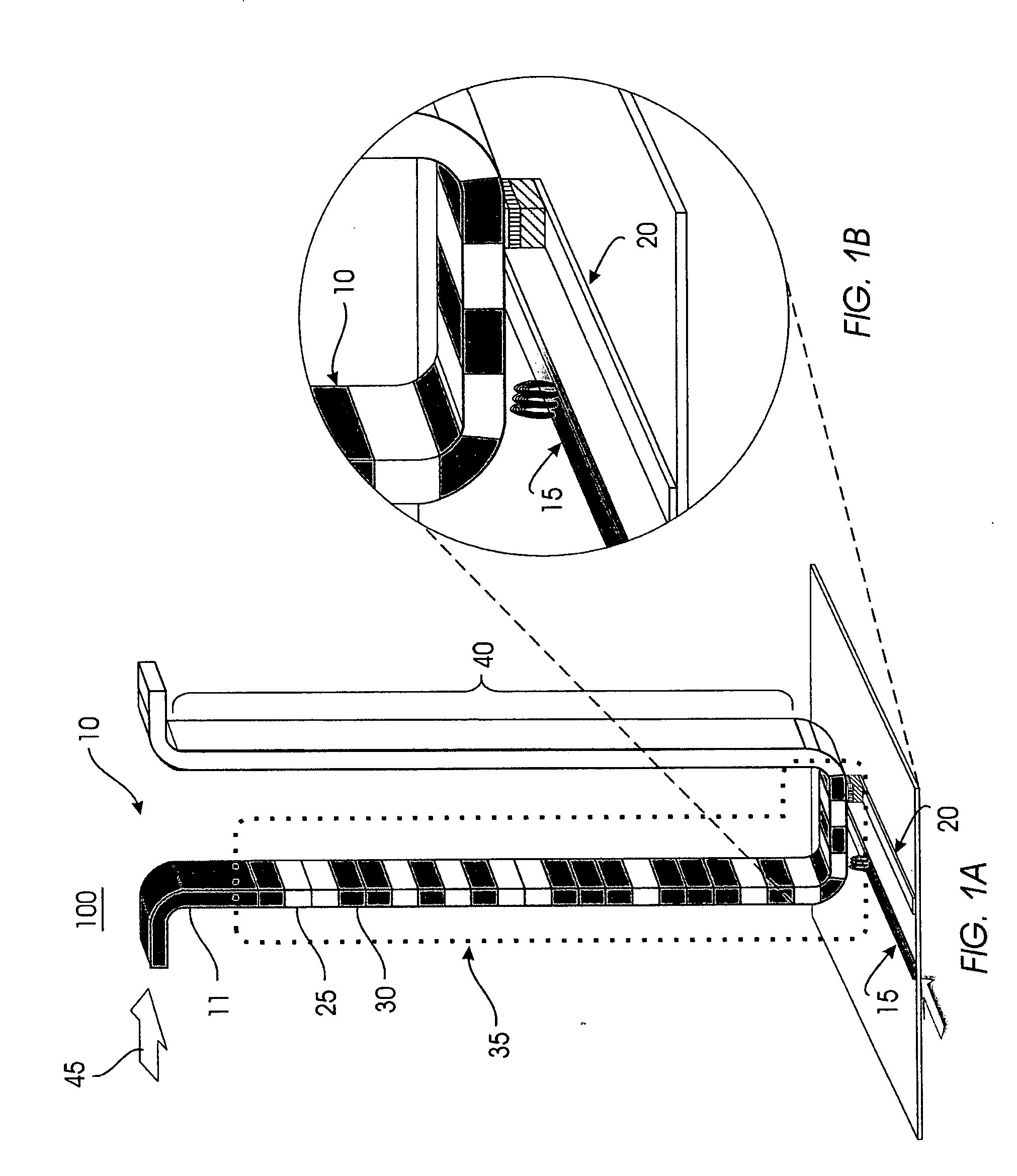
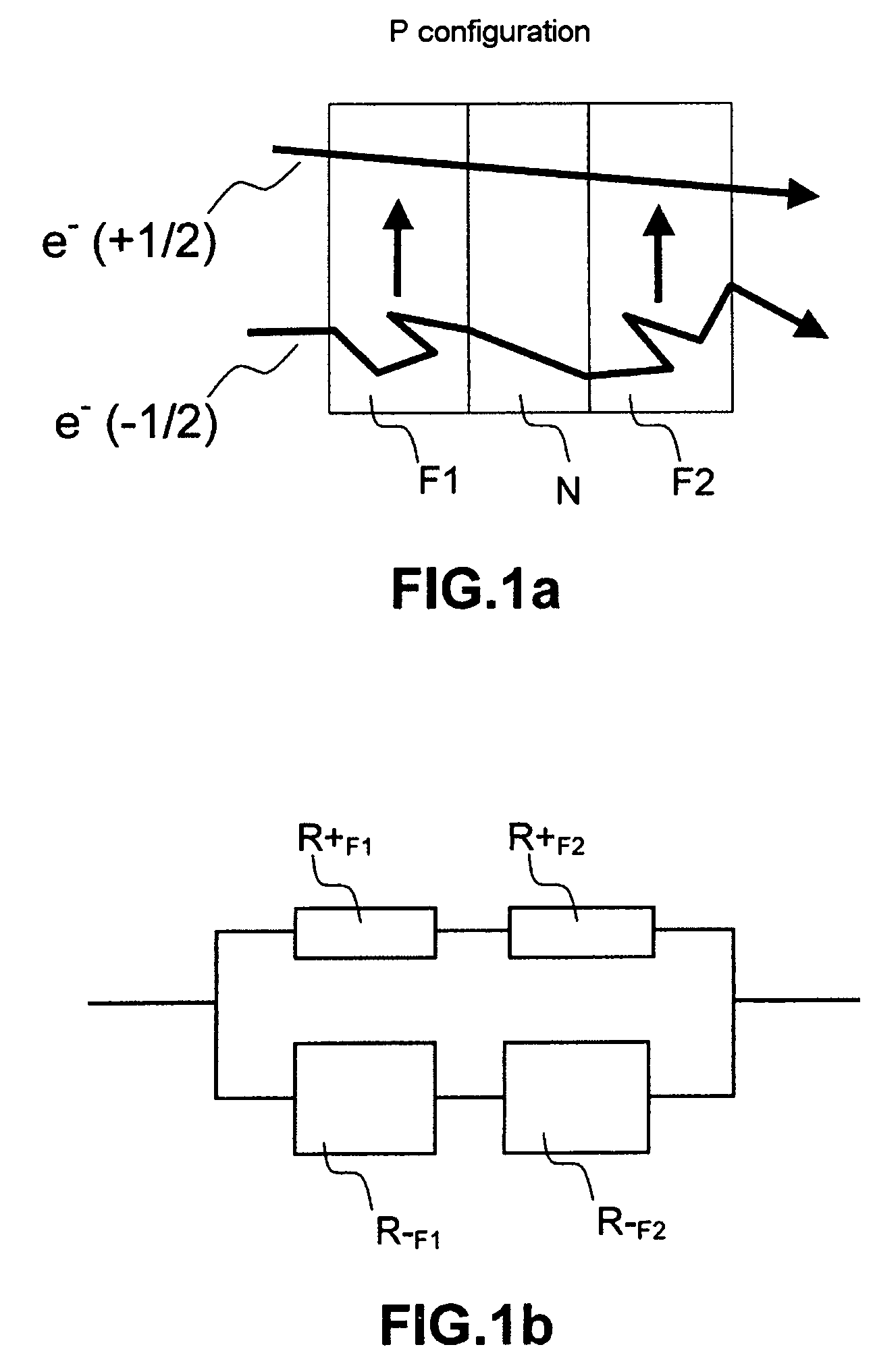
Spintronic magnetic nanoparticle sensors with an active area located on a magnetic domain wall
InactiveUS20110037463A1Improve predictabilityAffect valueMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsMaterial analysisMagnetic reluctanceSpins
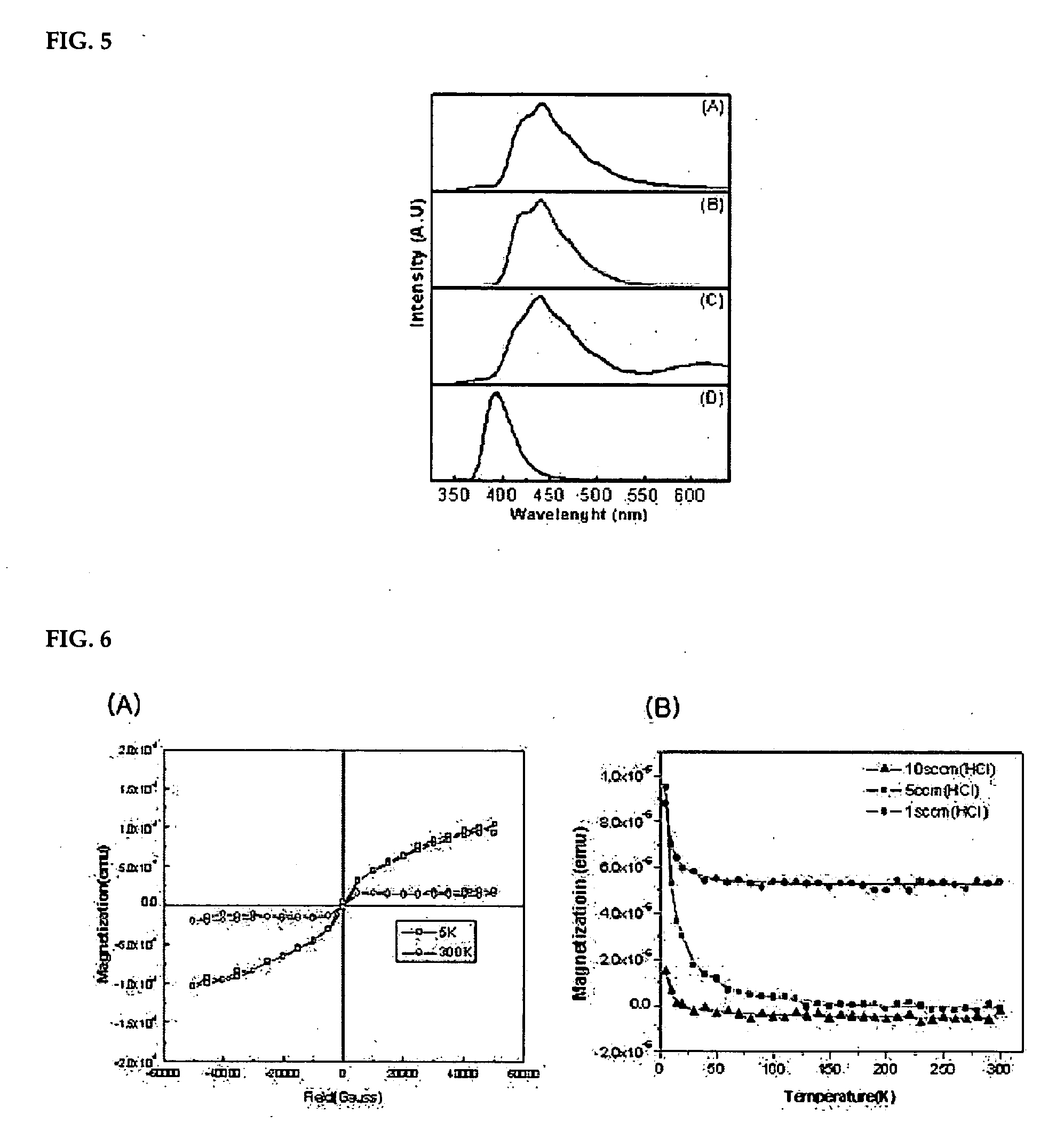
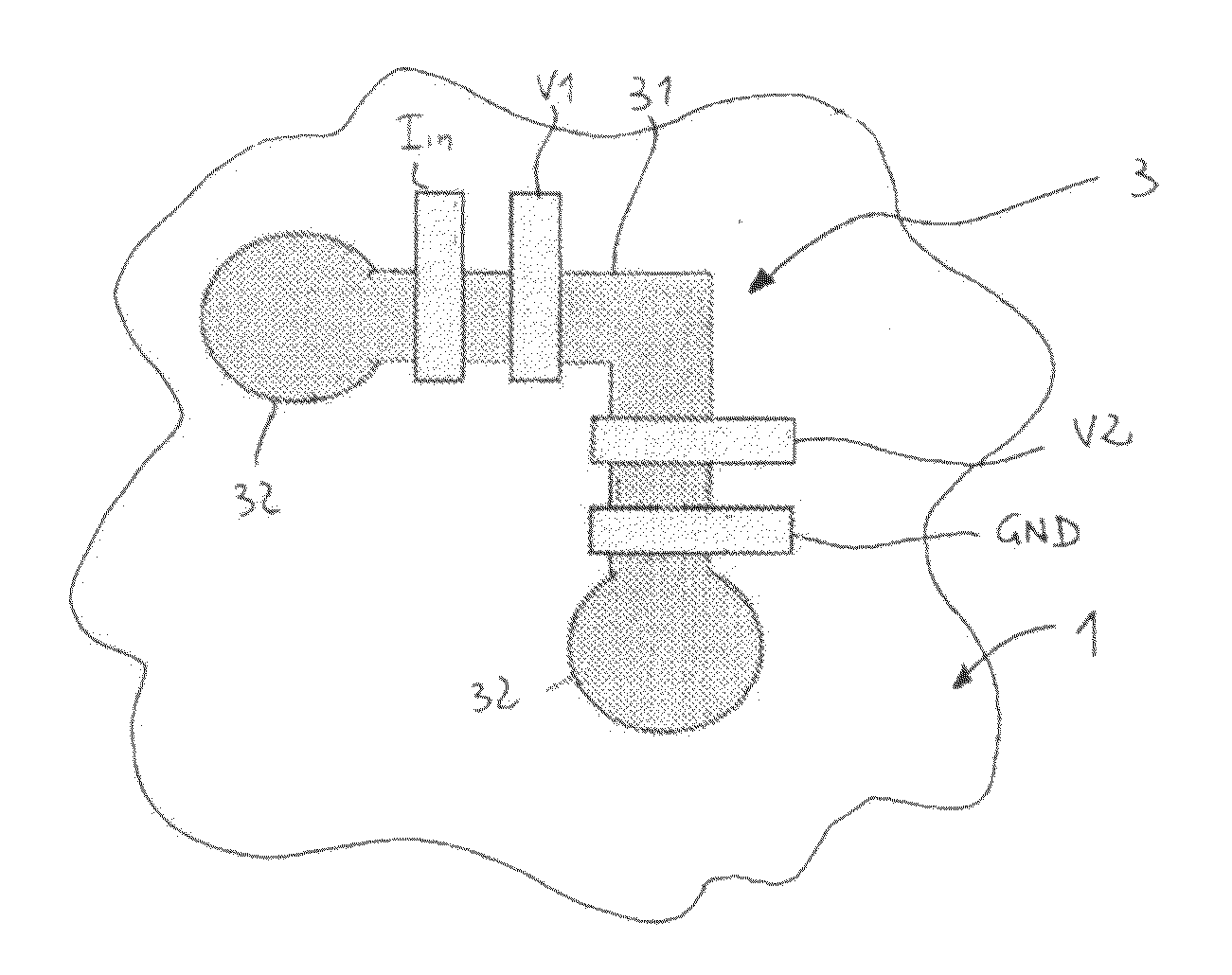
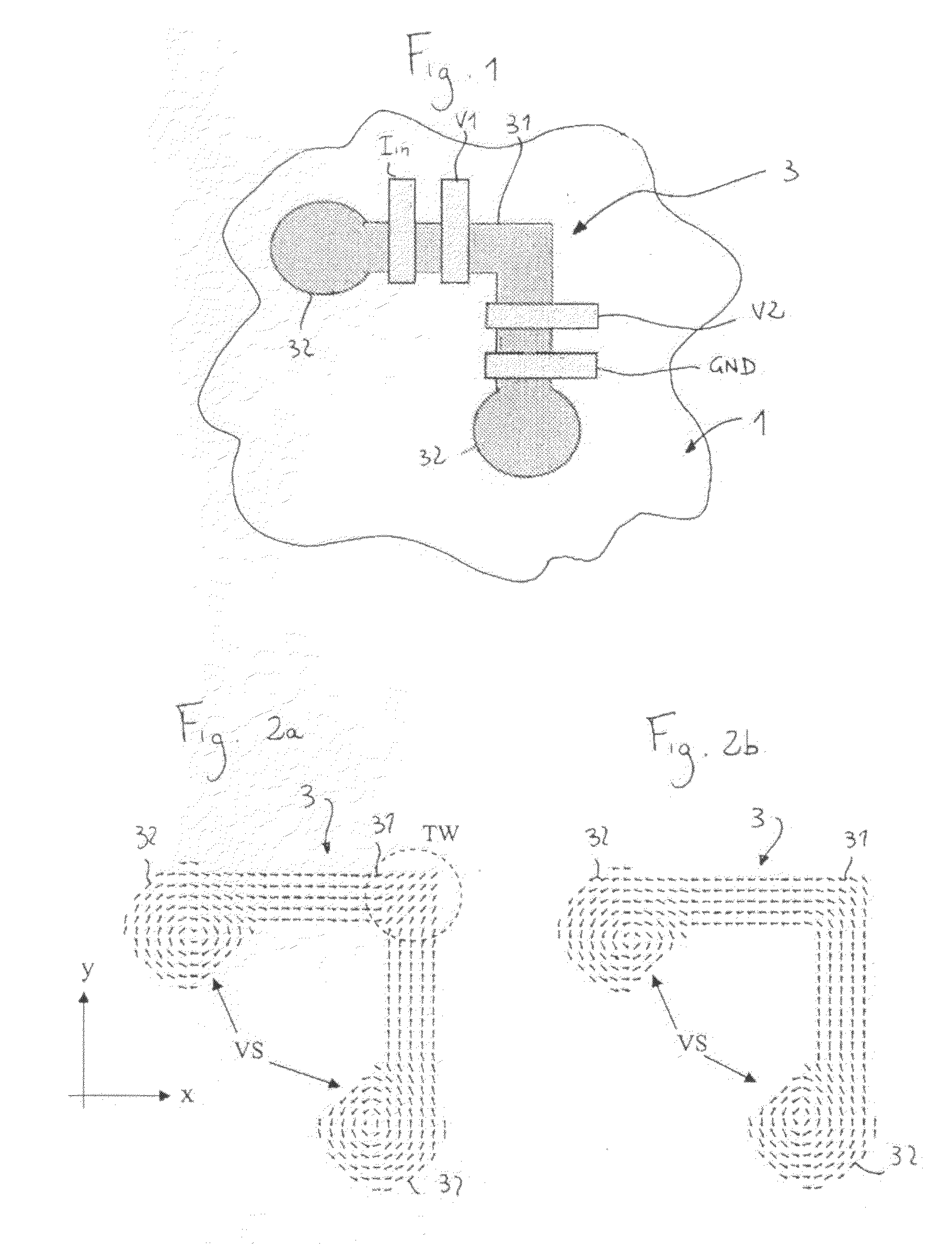
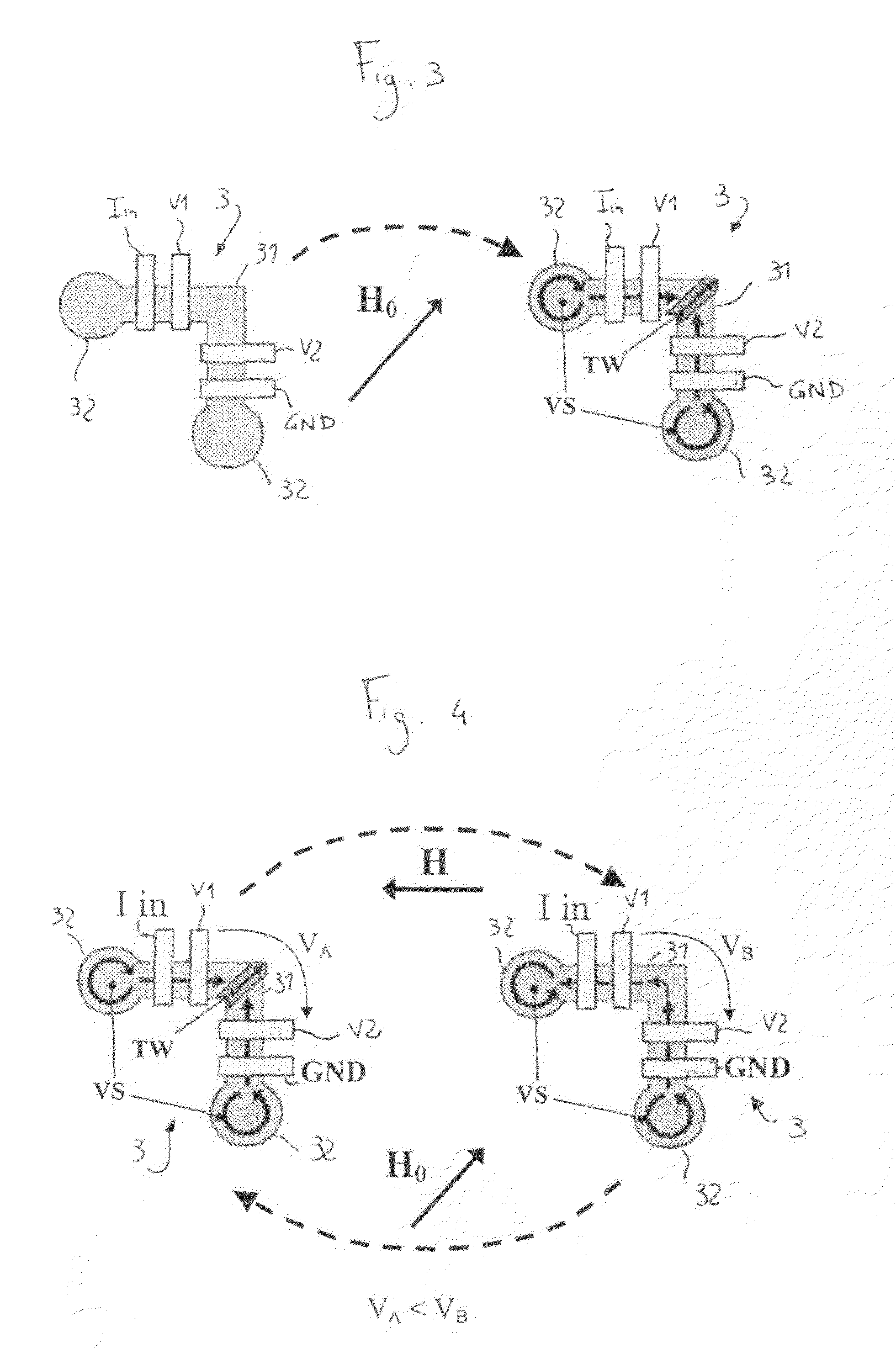
A sensor is described for detecting the presence of a magnetic nanoparticle (N). The sensor is arranged on a support (1), on which a plurality of non-magnetic contacts (Iin, GND, V1, V2) electrically conductively connected to the sensor is disposed. The contacts are adapted to be connected to means for measuring magnetoresistance. The sensor includes a planar ferromagnetic nanostructure (3), comprising a detection area (31) shaped as a strip bent to form a corner. The detection area is adapted to selectively assume, as a response to an applied magnetic field, a first spin configuration comprising a transverse “head-to-head” domain wall (TW), and a second spin configuration, wherein such domain wall (TW) is absent. The transition from the first configuration to the second configuration is affected by the proximity of a magnetic nanoparticle (N) to the detection area.
Owner:POLITECNICO DI MILANO
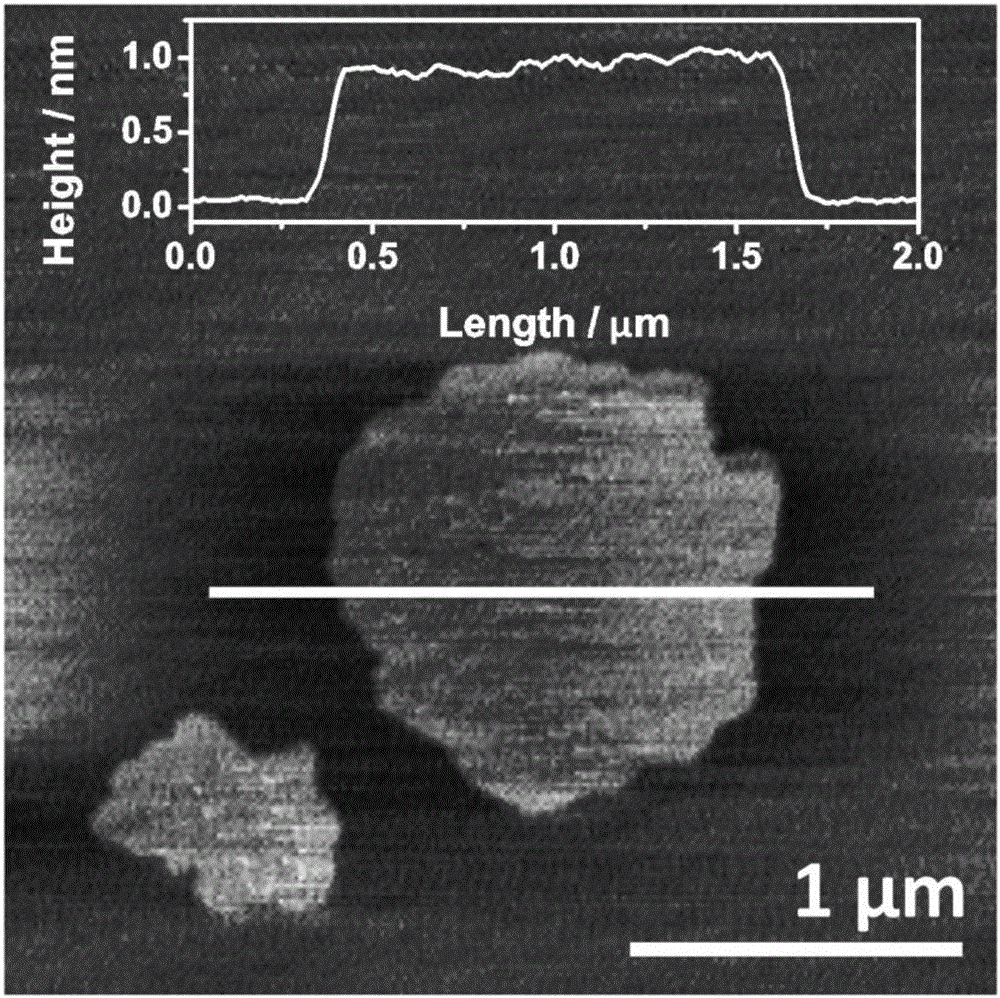
Method for preparing oriented graphene nanoribbon (GNR) array
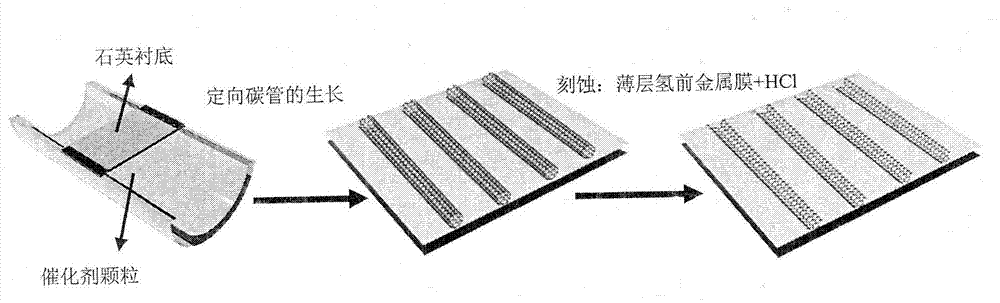
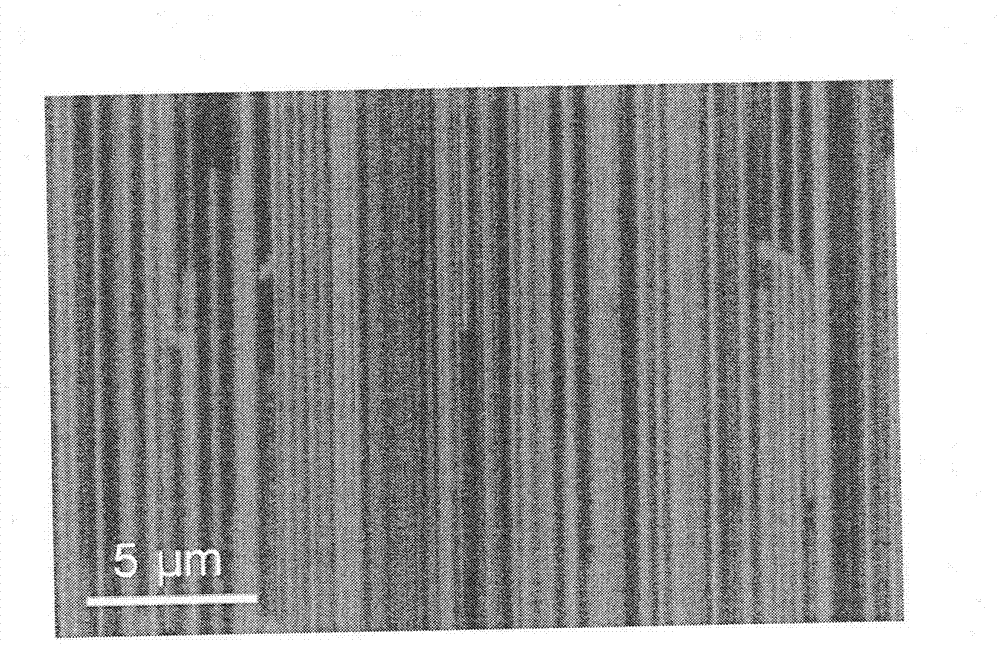
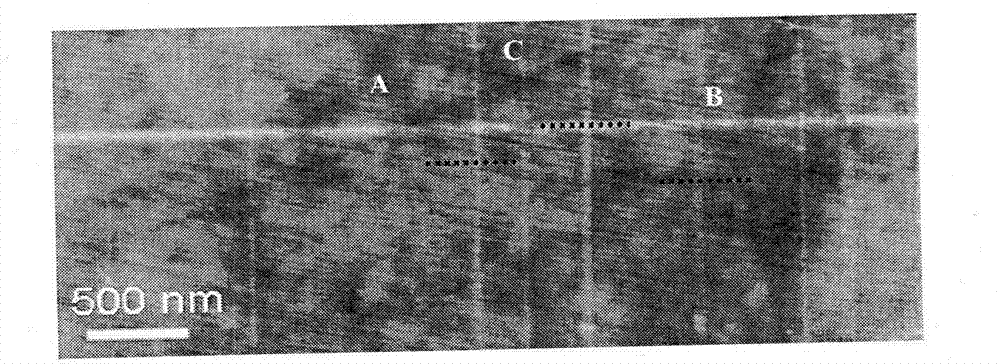
InactiveCN102757043AGood orientationHigh densityMaterial nanotechnologyGrapheneIn planeCarbon nanotube
The invention discloses a method for preparing an oriented graphene nanoribbon array. As one of optimized schemes, the method includes the following steps of (1) depositing nano-metal catalyst particles on a substrate surface which is subjected to a polishing process; (2) growing a directionally distributed carbon nanotube on the substrate surface; (3) depositing a thin layer hydrogen front metal film on the substrate surface; and (4) processing the substrate surface with an acid solution and dissecting the carbon nanotube along the axial direction to form the graphene nanoribbon array. The method for preparing the oriented graphene nanoribbon array has the advantages that the process is simple, the method is easy to implement, the prepared GNR has a high directionality, a high density, low in-plane defect density and edge disorder and a high electron mobility, the density and the like of the GNR array can be controlled through a growth technology and an etching process of a directional carbon tube, simultaneously a device based on the GNR array has a good electrical conduction performance, and the method has a significant application prospect in fields of spintronics, sensors, transistors and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Fluorenyl windmill grid material and preparation and application method thereof
ActiveCN105646529ATest thermal stabilityMild conditionsOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesSolubilityPolymer science
The invention relates to a fluorenyl windmill grid material and a preparation and application method thereof, and belongs to the field of organic molecular materials and high and new photoelectric technologies. The fluorenyl windmill grid material is cyclic oligomer with fluorenyl micromolecules as monomers, and the specific general structural formula is shown in the description. The material has the advantages that the fluorenyl windmill grid material has both porous characteristics and semiconductor photoelectric characteristics; raw materials are cheap and easy to obtain, reaction conditions are mild, and operation is easy; the fluorenyl windmill grid material has good mechanical properties of a nanomaterial; the fluorenyl windmill grid material has good solubility, and nanofilm processing or fibration processing is facilitated; with a rigid framework, the fluorenyl windmill grid material is high in glass transition temperature, high in thermal stability, electrochemical stability and spectrum stability and the like. Thus, the fluorenyl windmill grid material is expected to become a new-generation practical organic micromolecular photoelectric material and has good application prospects in the fields of organic electronics, spintronics, optoelectronics, mechatronics, nanobiology and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
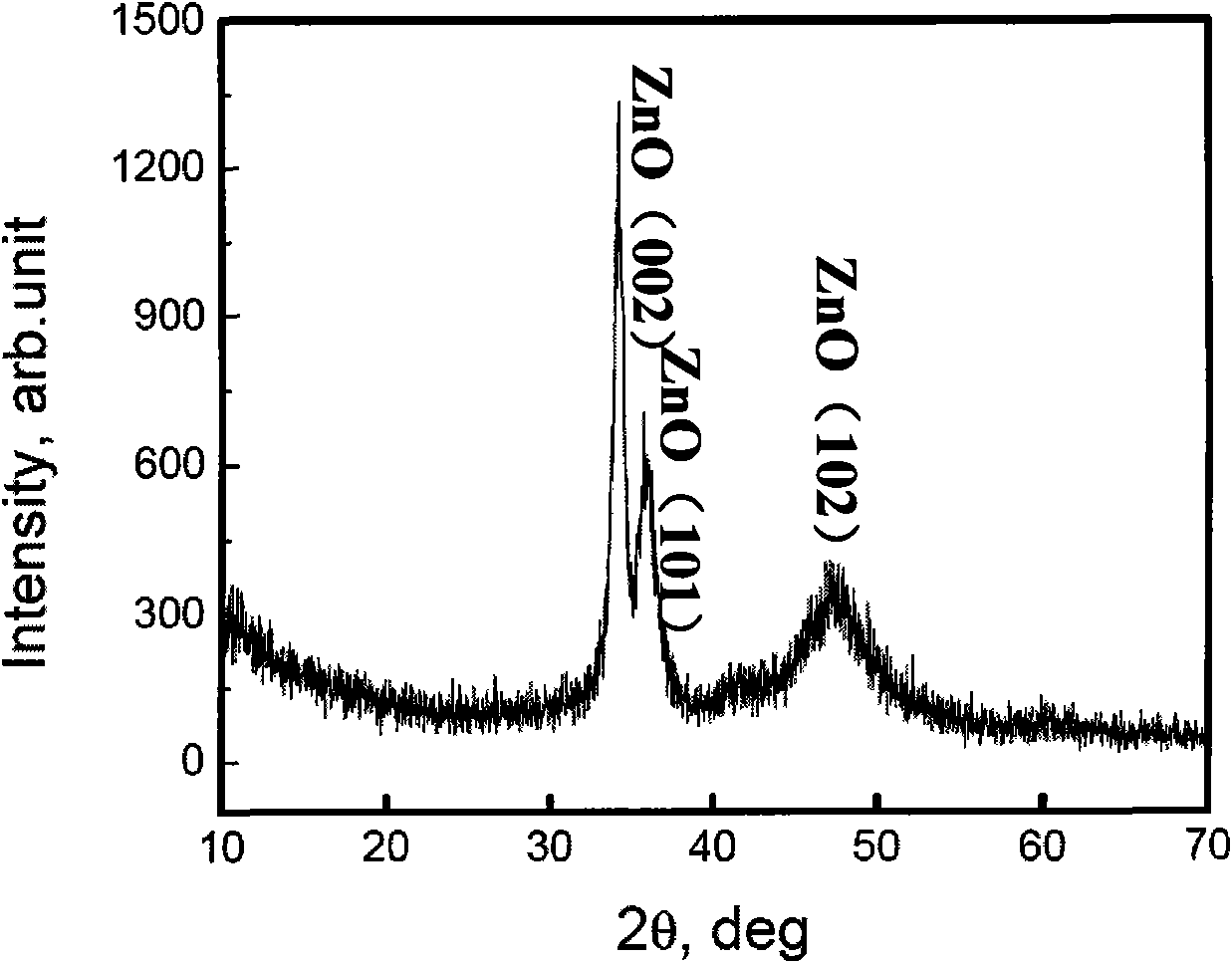
Method for preparing Cr doped ZnO-based diluted magnetic semiconductor film material
InactiveCN101615467ASimple preparation processIncrease deposition rateVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDevice materialCurie temperature
The invention relates to a method for preparing a Cr doped ZnO-based diluted magnetic semiconductor film material, belonging to the preparation field of novel semiconductor spintronics device materials. The method adopts double targets cosputtering of chromium and zinc oxide, wherein the background vacuum degree of the system is 10<-5>Pa-10<-3>Pa; high-purity argon is used as working gas in the sputtering process; the flow rate of the high-purity argon is 5-15 cm<3> / min; the working gas pressure is 10<-2>-10<-1>Pa in the sputtering process; and the distance between a target material and a basal body is 35-70 mm. Ultrasonic cleaning is carried out on the basal body, oxide and other impurities of the surface of the basal body are removed, and the ZnO-based diluted magnetic semiconductor film materials with different doping concentrations are obtained through changing different target powers. The method has simple preparation process and high deposition rate and can obtain the diluted magnetic semiconductor film material with room-temperature ferromagnetism, high Curie temperature and controllable performance, thereby having important research value and wide application prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
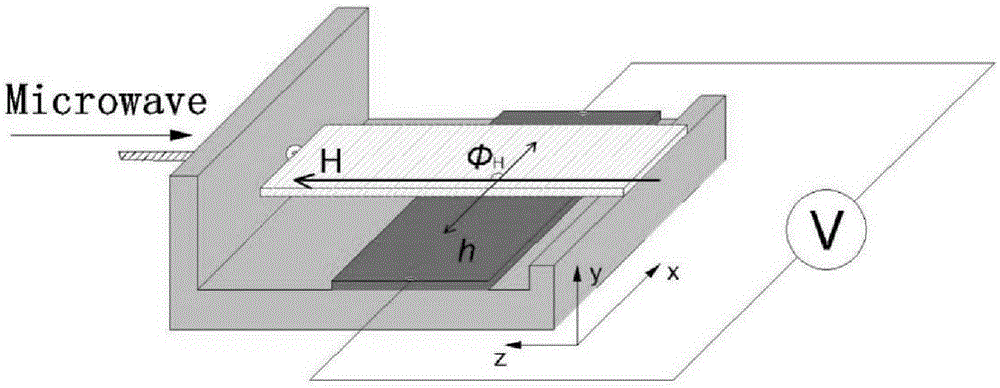
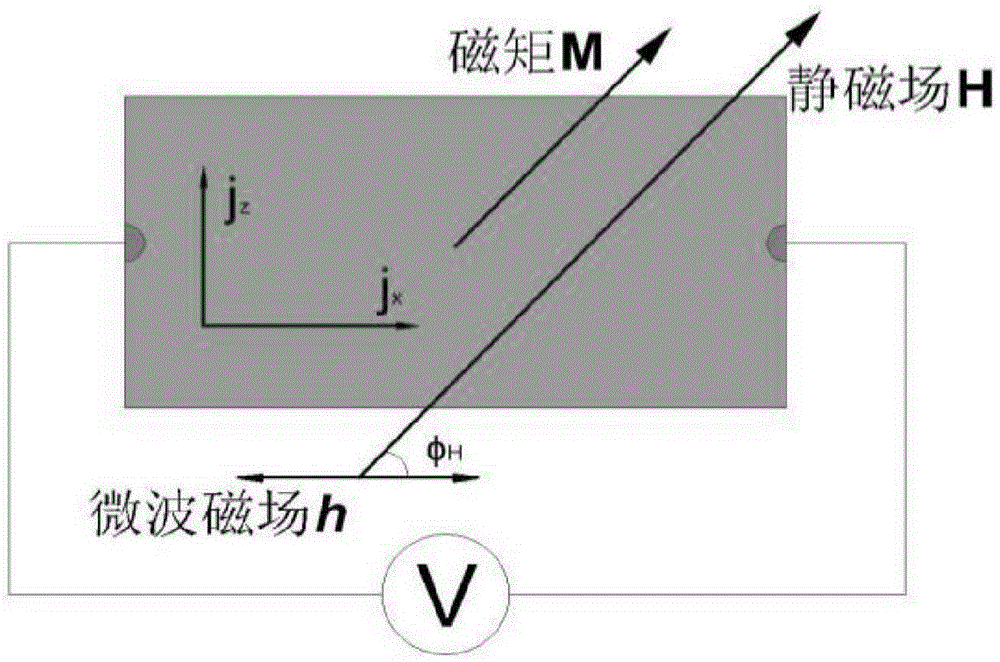
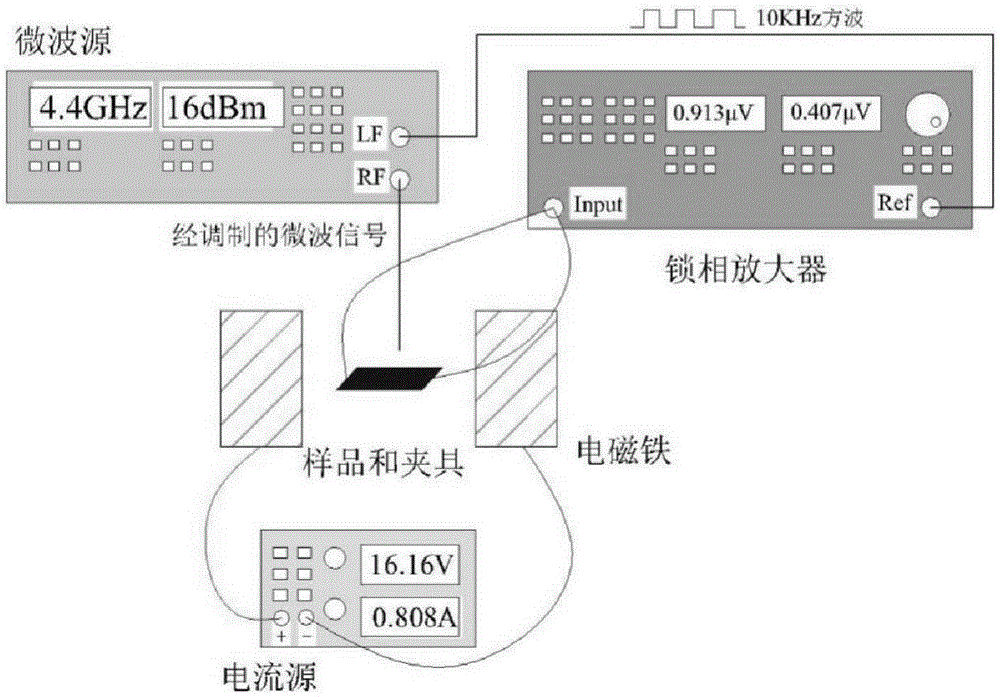
FM/NM thin-film structure inverse spin hall voltage value measurement method
InactiveCN105242094AOvercoming cumbersome stepsOvercome the bias caused by formula fittingCurrent/voltage measurementMaterial analysis by using resonanceSpinsSpin injection
The invention discloses an FM / NM thin-film structure inverse spin hall voltage value measurement method, and belongs to the field of spintronics research and manufacturing of the related spin devices. Voltage of the two ends of a sample is measured at configuration that the film surface is upward and then the film surface is downward by adopting a mode that the sample is vertically overturned in a microstrip line jig based on a method that spin pump-inverse spin hall effect voltage of the FM / NM thin-film structure sample is tested by utilizing a terminal short-circuit suspended microstrip transmission line jig. A spin rectification component and an inverse spin hall effect voltage component in measurement voltage can be accurately obtained by simple calculation according to difference of opposite direction of spin injection in the configuration of the sample so that reference is provided for accurate calculation of a spin hall angle.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Layered-structure asymmetric MXene and derived heterojunction thereof
The invention discloses a layered-structure asymmetric MXene (abbreviated as aMXene) and a derived heterojunction thereof. After one of top or bottom passivating functional group layers of a layered-structure symmetric MXene is removed, an aMXen with a high dipole moment is obtained. Proper single-layer transition metal disulfide (mTMDC) is selected to carry out passivation on one exposed side ofthe aMXen, so that an aMXen / mTMDC heterojunction is derived from the aMXen. According to the aMXen / mTMDC heterojunction, different layers have the high potential difference, so that charges between two-dimensional structures are allocated again conveniently and thus the energy band structure, relative positions of band edges, and generation and changing of carriers are controlled. Therefore, the aMXene / TMDC heterojunction has the great competitiveness in the electronics and chemical application fields and has broad application prospects in fields of spintronics, electronics / photoelectron, andcatalyzation / photocatalysis.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Nano-composite organic spin valve
InactiveCN101710528ALarge magnetoresistance characteristicsAchieve transformationMagnetic film to substrate applicationSubstrate/intermediate layersEvaporationOptoelectronics
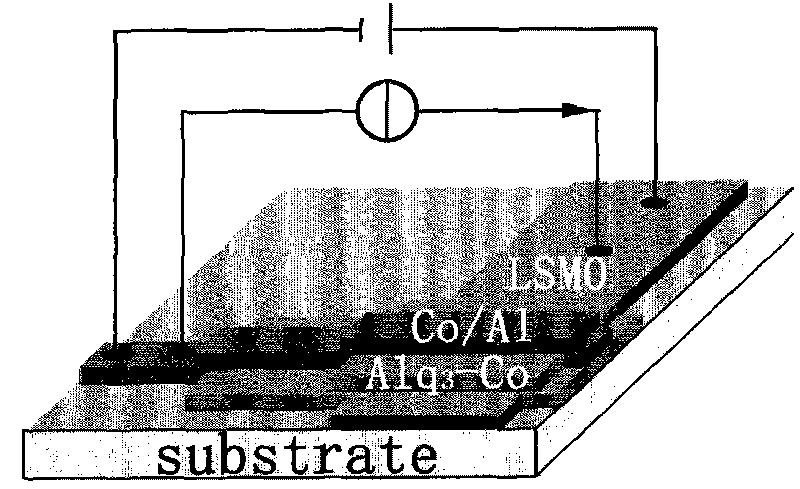
The invention discloses a nano-composite organic spin valve, belonging to technical field of spintronics. The spin valve comprises a sandwich structure; a top electrode is a transitional metallic cobalt thin film which is provided with an aluminum thin film as a protective layer; a bottom electrode is a La-Sr-Mn-O thin film; a middle transport layer is a nano-composite of the transitional metallic cobalt and organic micro-molecular 8-hydroxyquinoline aluminum. The preparation method of the spin valve comprises the following steps of: preparing a La-Sr-Mn-O thin film bottom electrode of the spin valve on a strontium titanate substrate by using a laser pulse deposition method; preparing the middle transport layer of the transitional metallic cobalt and 8-hydroxyquinoline aluminum by thermal evaporation; preparing the transitional metallic cobalt thin film as the top electrode on the middle transport layer of the nano-composite; and heating for evaporating the aluminum thin film as the protective layer on the top electrode of the transitional metallic cobalt thin film.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Regulation and control method based on energy valley polarization characteristic of two-dimensional transition metal chalcogenide
ActiveCN110335819AGive full play to flexibilityAvoid the problem of destroying the characteristics of the two-dimensional material itselfVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical compoundChalcoides
The invention relates to a regulation and control method based on the energy valley polarization characteristic of a two-dimensional single-layer transition metal chalcogenide. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) growing a two-dimensional single-layer transition metal chalcogenide on a substrate by adopting a chemical vapor deposition method; (2) preparing two-dimensional ferromagnetic metal by adopting a mechanical stripping method; and (3) transferring the two-dimensional ferromagnetic metal to the two-dimensional single-layer transition metal chalcogenide in an aligning mannerthrough an aligning transfer platform to form a two-dimensional single-layer transition metal chalcogenide-two-dimensional ferromagnetic metal heterostructure. The heterostructure is formed by the two-dimensional ferromagnetic metal material and the two-dimensional single-layer transition metal chalcogenide, so that the characteristics of flexibility and atomic-level thinness of the two-dimensional material can be fully exerted, the problem that the characteristics of the two-dimensional material are damaged due to the three-dimensional-two-dimensional heterostructure formed by the traditionalferromagnetic metal material and the two-dimensional material is effectively solved, and the regulation and control method based on the energy valley polarization characteristic of a two-dimensionalsingle-layer transition metal chalcogenide can be applied to development and research of ultrathin microminiaturization, flexible spintronics, energy valley electronic devices and the like.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Method for controlling spin wave transmission
ActiveCN106206935AAvoid energy consumptionAvoid low efficacy problemsGalvano-magnetic device manufacture/treatmentSpin waveWaveguide
The invention discloses a method for controlling spin wave transmission and belongs to the field of spintronics. According to the method, through applying an electric field on a spin wave guide structure, the strength of exchange interaction in a magnetic waveguide material can be effectively changed. An exchange constant is controlled through the electric field, so that the spin wave dispersion relation can be regulated to realize a purpose of controlling the spin wave transmission. The exchange interaction is controlled through the electric field, so that the local precise control of the spin wave transmission can be realized at ultra-low power consumption to provide the possibility for actual application of an ultra-low-power magnonics device compatible with a CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Transistor) technological process.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Controllable graphene nanolayer preparation method
The invention relates to a controllable graphene nanolayer preparation method. The method comprises the steps that graphite powder is put into a reaction container, a solvent is injected into the reaction container, ultrasonic vibration is conducted, and a stirrer is started, so that the raw material-graphite powder is fully and uniformly distributed in the solvent; a laser path is adjusted, so that laser beams sequentially pass through a total reflective mirror and a focus lens and then are focused at the position 3 mm below the liquid level; a pulse laser is started, different kinds of laser energy are adjusted to enable laser light to irradiate graphite particles in a liquid environment, after the reaction process lasts 1 h to 2 h, the laser is stopped, and finally graphene with the different layer numbers can be obtained. The method is easy to operate, controllable in layer number and free of toxins and pollution and has potential application in the fields of nanometer equipment and spintronics.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for improving spin-orbit coupling strength of Co/Pt thin film material
InactiveCN104674161AIncreased spin-orbit coupling strengthImprove efficiencyVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingAlloy substrateShape-memory alloy
The invention discloses a method for improving spin-orbit coupling strength of a Co / Pt thin film material, and belongs to the field of magnetic materials. The method comprises the following steps: performing prestretching treatment, surface polishing and surface argon ion bombardment on a titanium-nickel TiNi memory alloy substrate; depositing [Cobalt Co / Platinum Pt] n multilayer films on the TiNi memory alloy substrate; after deposition, performing two-step thermal treatment on the substrate in a vacuum environment, namely low temperature treatment and high temperature treatment, triggering the shape memory effect of the substrate, and meanwhile inducing the crystallized Co / Pt multilayer films to epitaxially grow on the TiNi substrate; at last, cooling the substrate to the room temperature. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the cheap shape memory alloy is used as the substrate, then uniform and controllable high elastic stress is generated on the spintronic thin-film material, and then the spin-orbit coupling strength of the whole thin film can be effectively enhanced; the method is free of high-cost rare metals or an expensive additional device, has the advantages of being high in efficiency, low in cost, simple to prepare and the like, and can be applied to the spintronic technology in the future.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
High performance spin-valve transistor
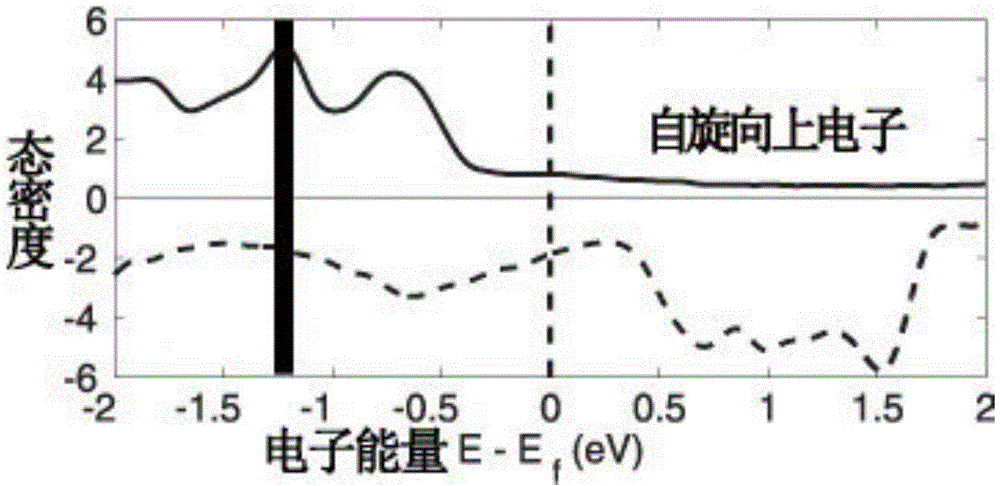
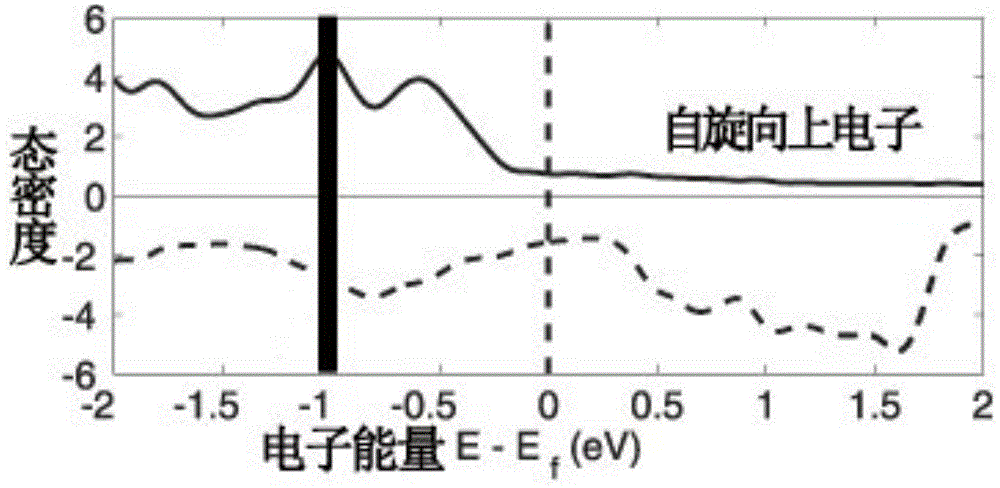
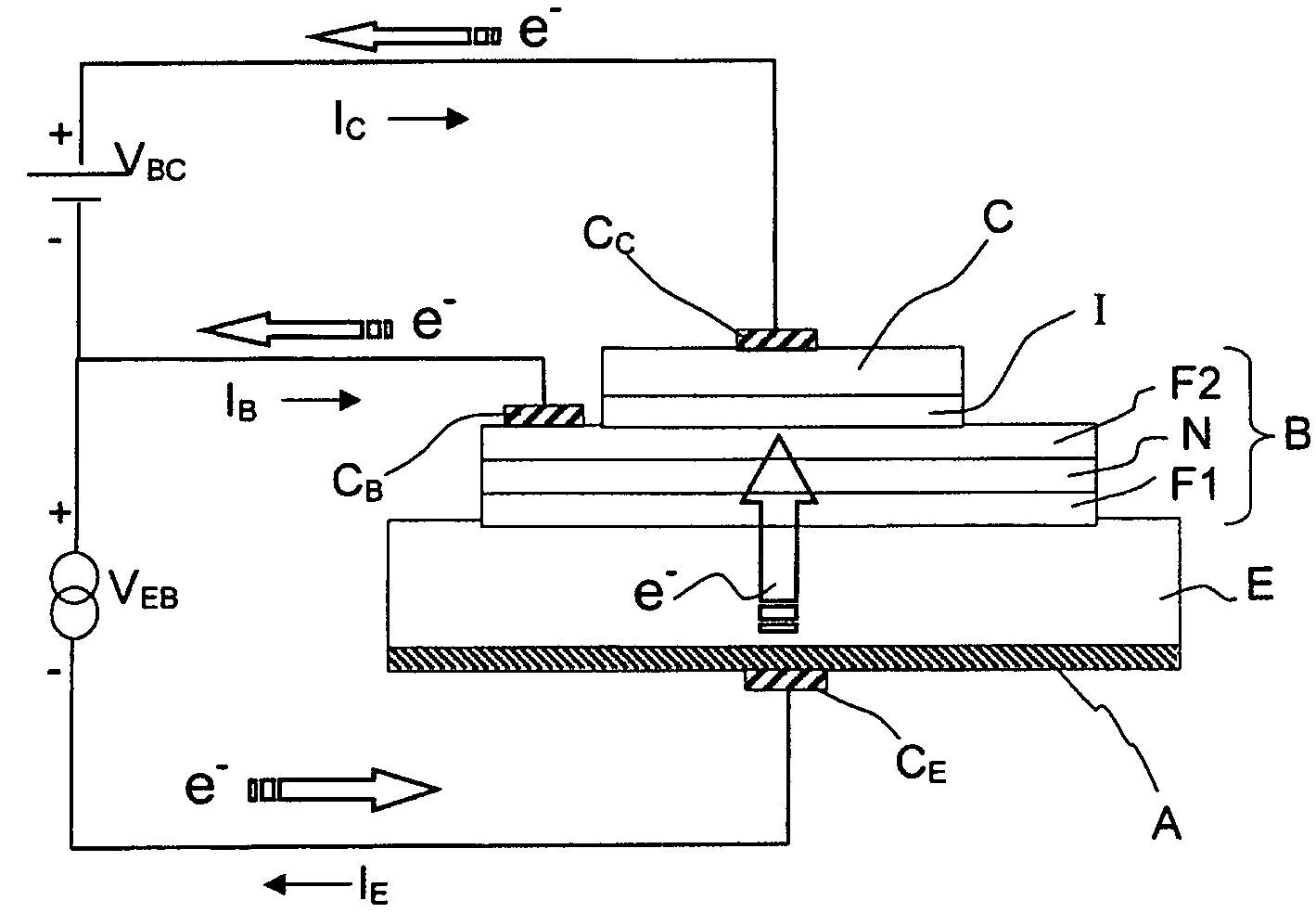
The invention generally relates to the field of spintronics, a branch of electronics using the magnetic spin properties of electrons. More particularly, the invention relates to the field of spin-valve transistors which can be used in numerous fields of electronics. The invention aims to propose an original arrangement for producing high-level and high-contrast collector currents simultaneously. The inventive spintronics transistor comprises a semiconductor emitter, a base fanning a spin valve and a metallic collector separated from the base by an insulating deposit. The emitter / base interface constitutes a Schottky barrier and the base / collector interface constitutes a tunnel-effect barrier.
Owner:THALES SA
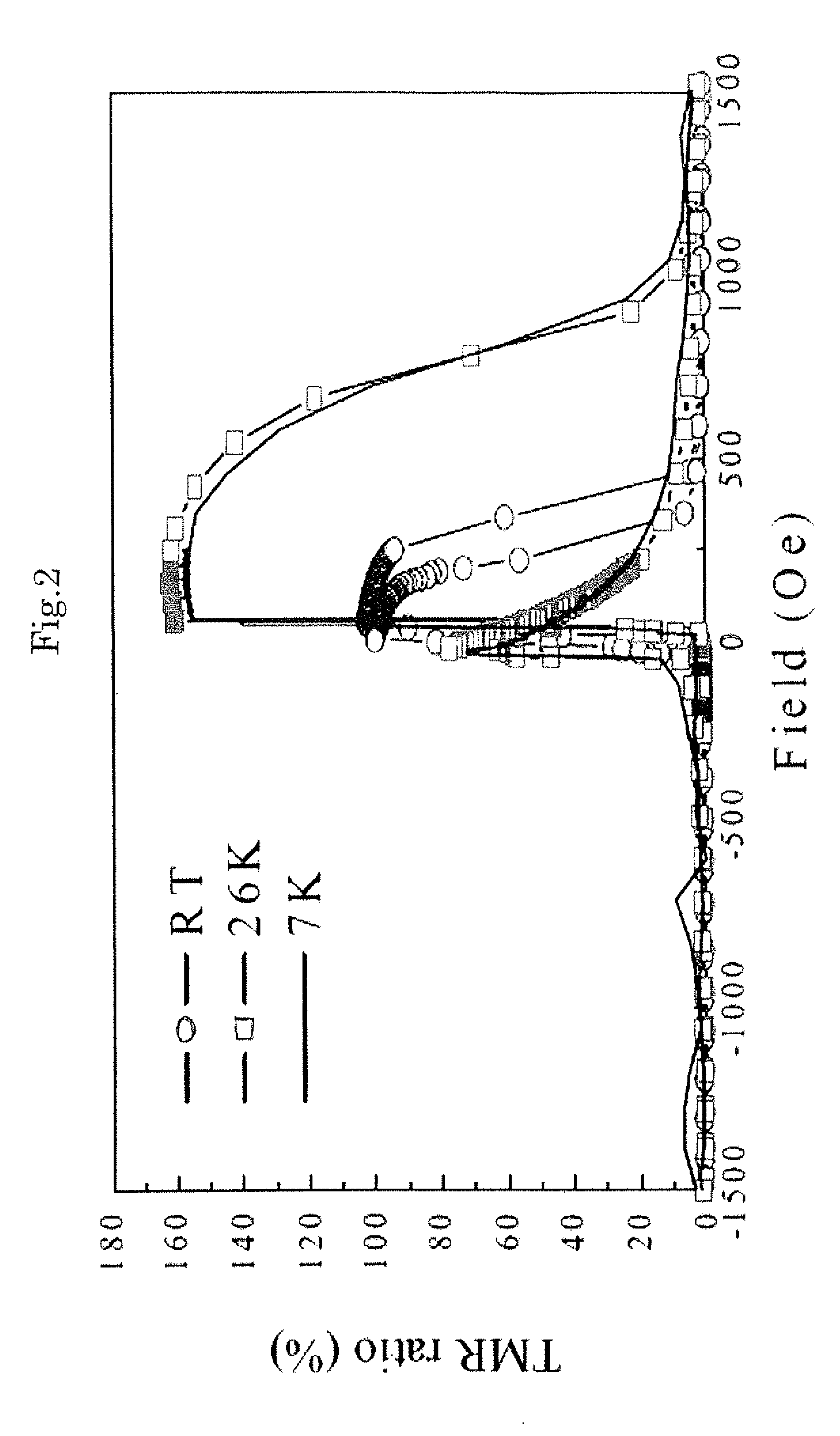
Co2fe-based heusler alloy and spintronics devices using the same
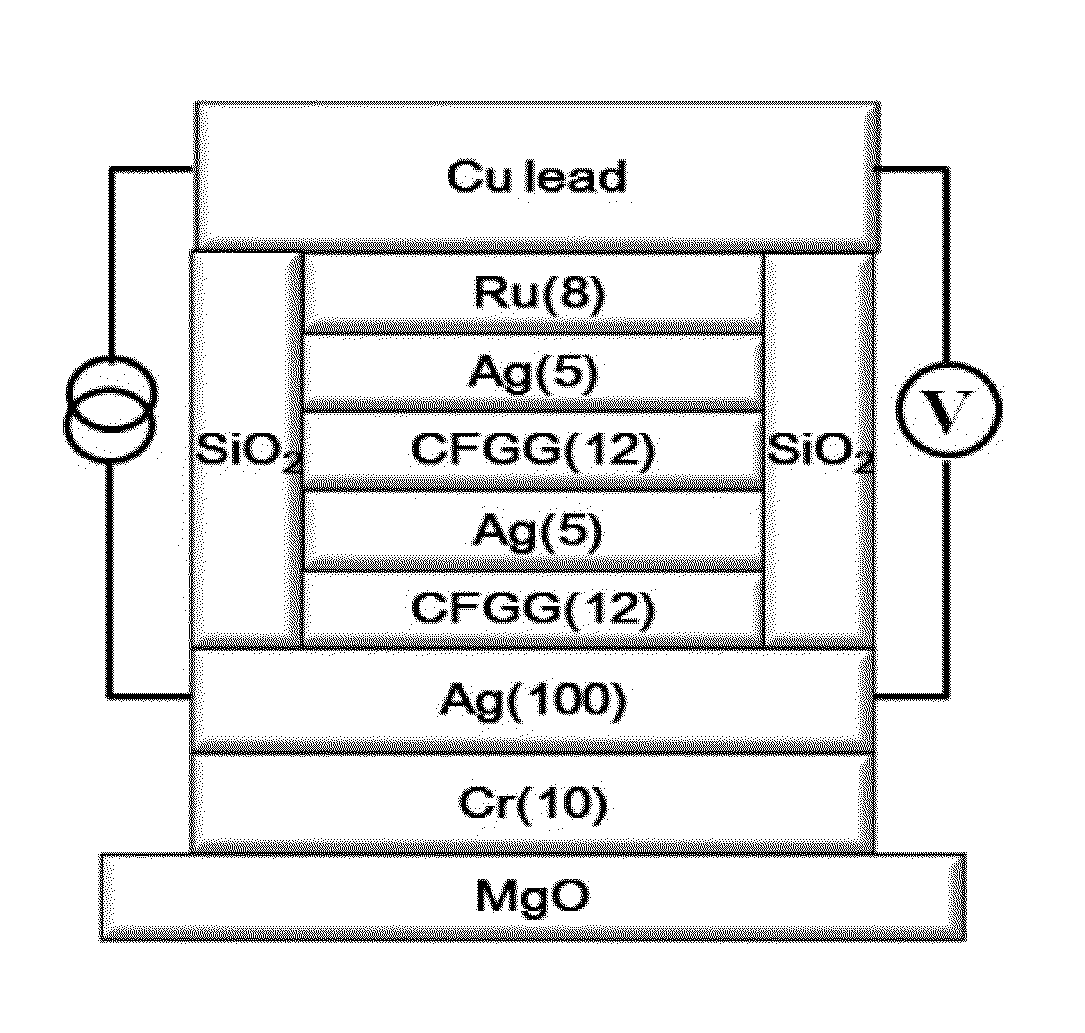
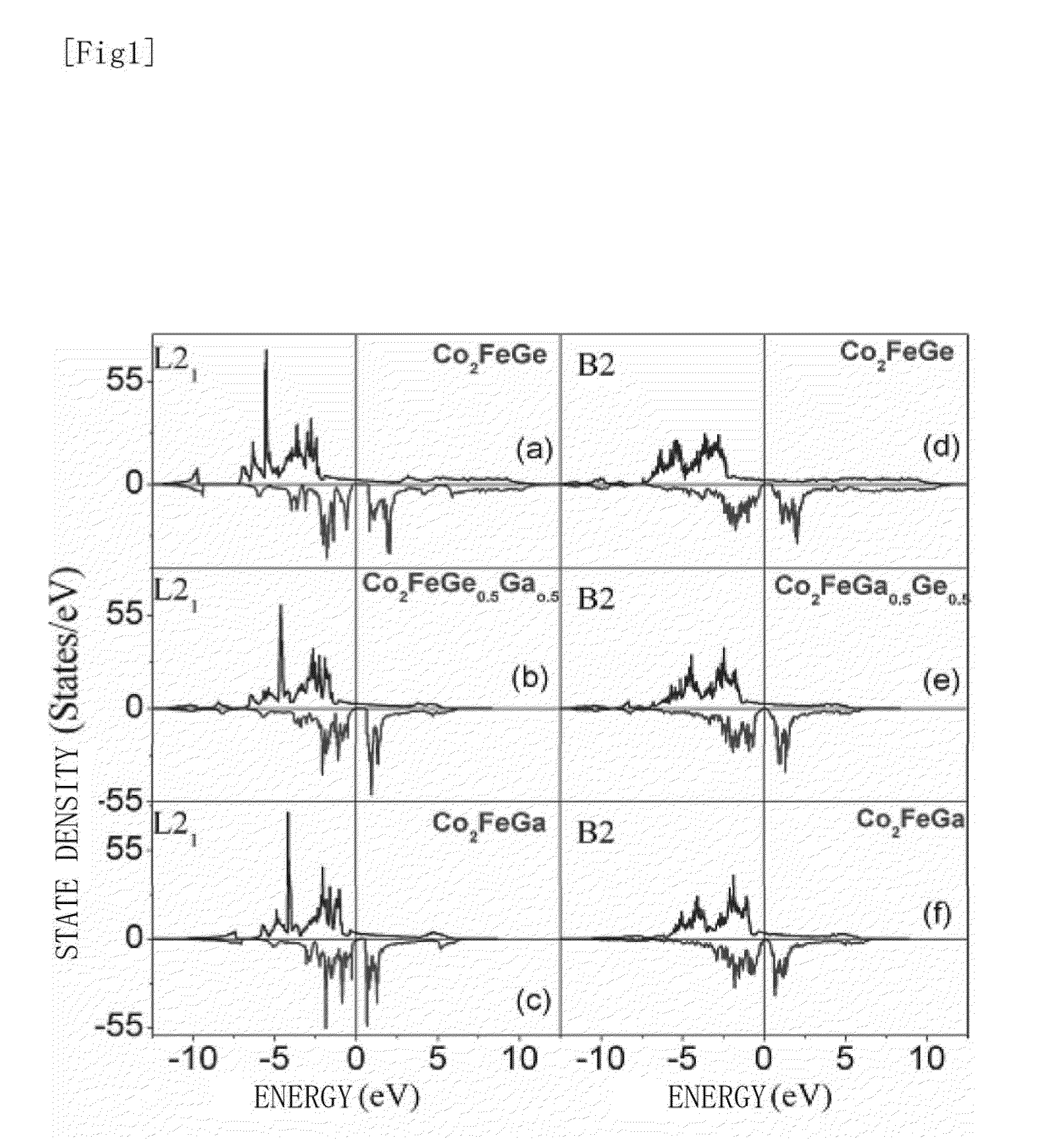
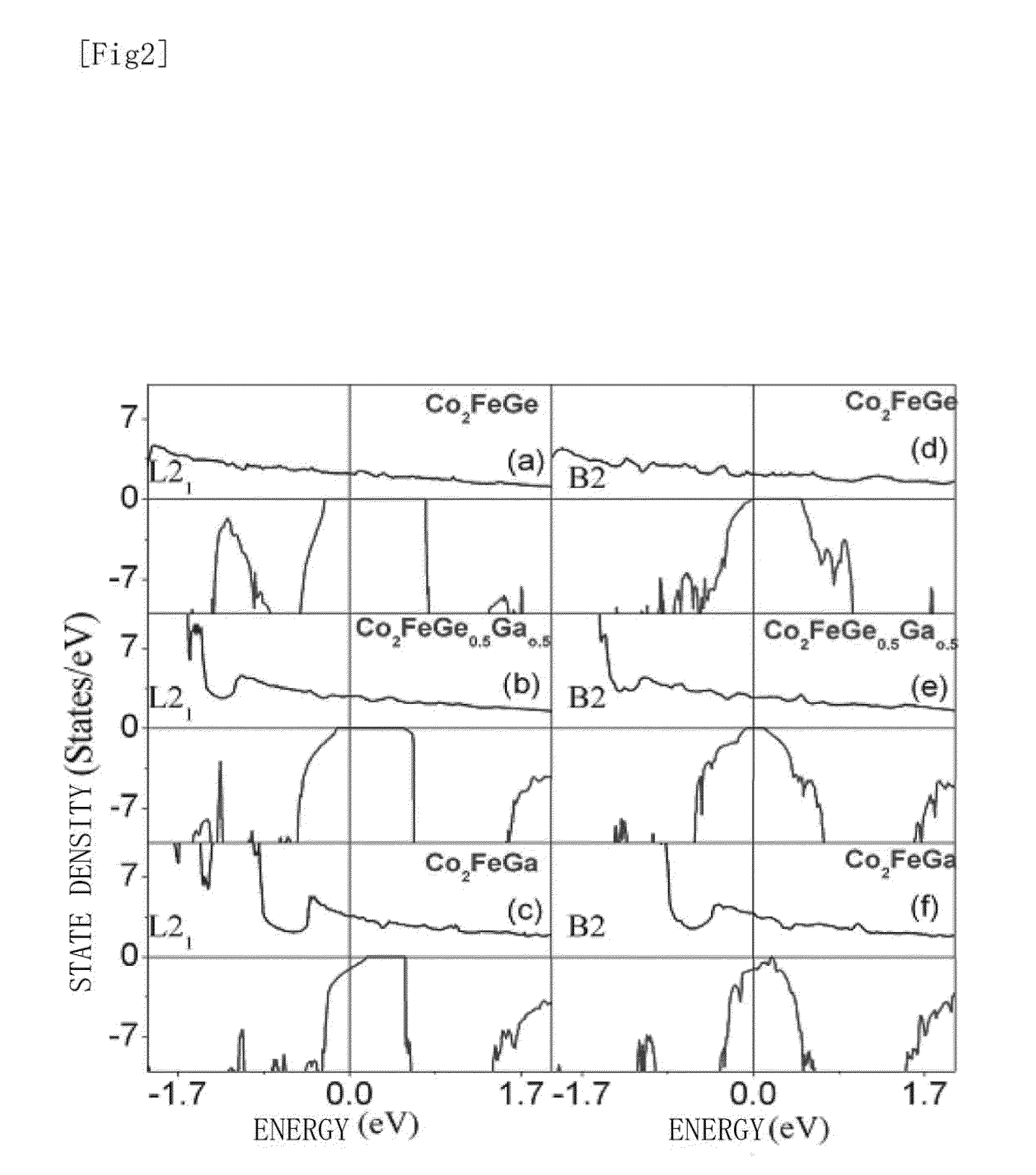
InactiveUS20130302649A1Raise the ratioIncrease productionNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsSpinsCurie temperature
[Problem to be Solved]To realize a spintronics device with high performance, it is an object of the present invention to provide a Co2Fe-based Heusler alloy having a spin polarization larger than 0.65, and a high performance spintronics devices using the same.[Solution]A Co2Fe(GaxGe1-x) Heusler alloy shows a spin polarization higher than 0.65 by a PCAR method in a region of 0.25<x<0.60 and it has a Curie temperature as high as 1288K. A CPP-GMR device that uses the Co2Fe(GaxGe1-x) Heusler alloy as an electrode exhibits the world's highest MR ratio, an STO device exhibits high output, and an NLSV device exhibits a high spin signal.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com