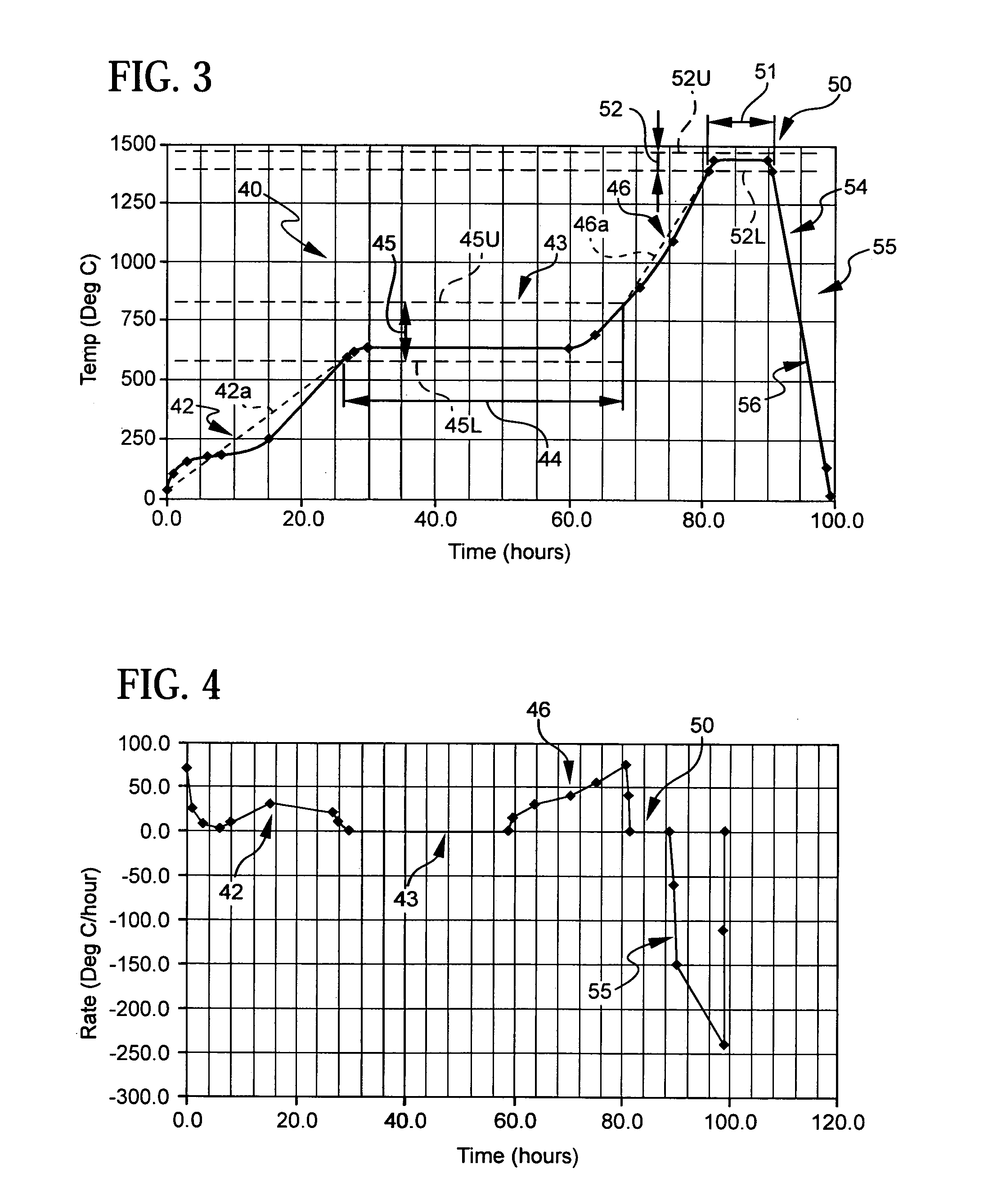
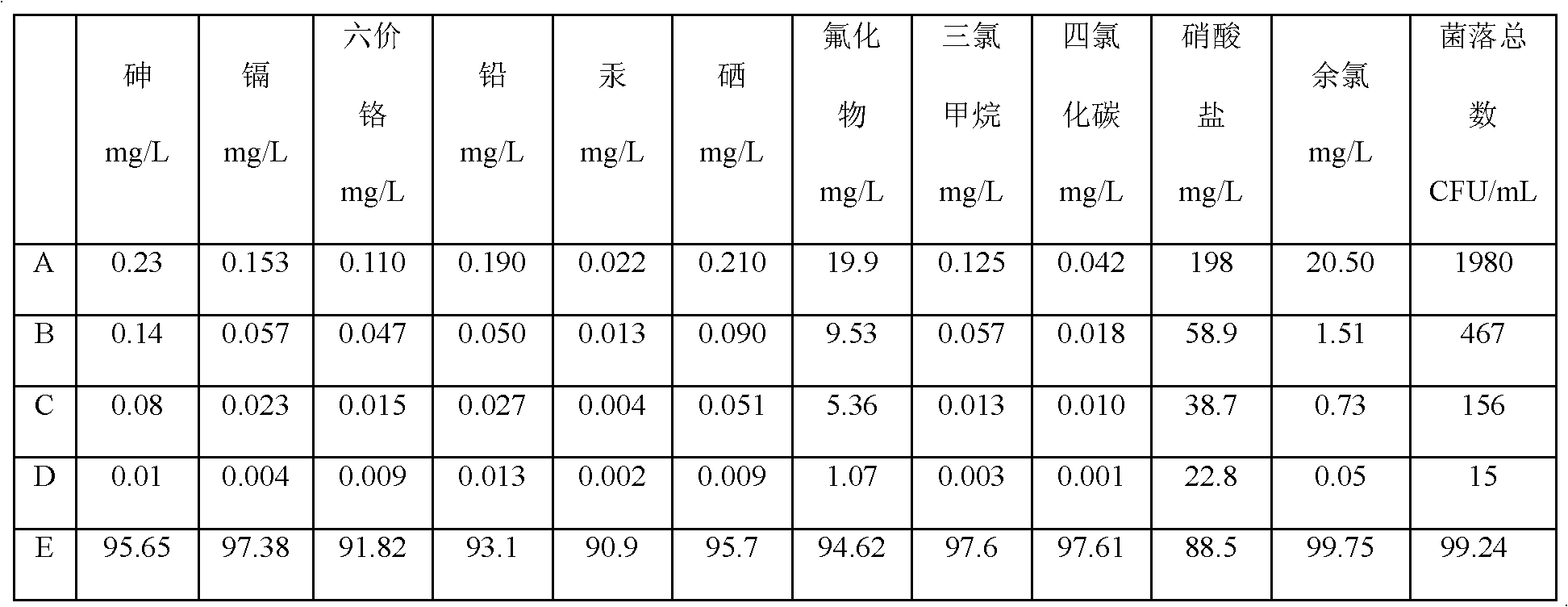
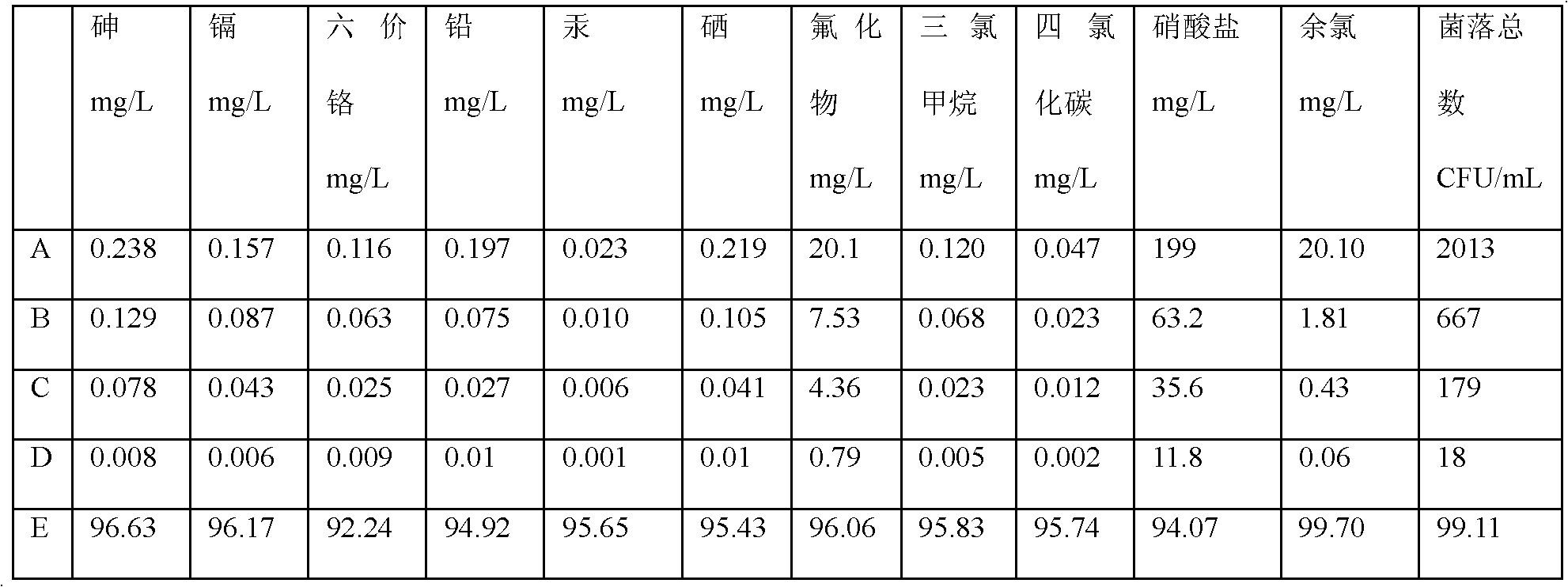
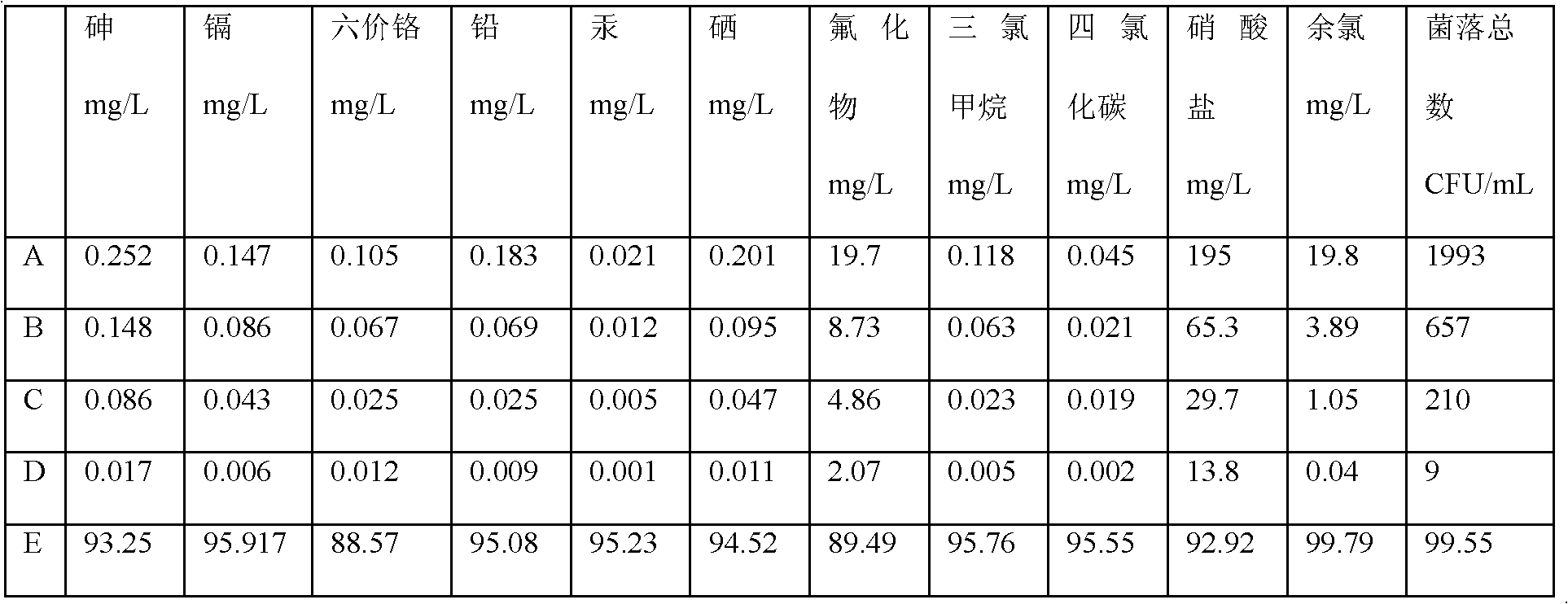
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
55594 results about "Titanium dioxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania, is the naturally occurring oxide of titanium, chemical formula TiO₂. When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or CI 77891. Generally, it is sourced from ilmenite, rutile and anatase. It has a wide range of applications, including paint, sunscreen and food coloring. When used as a food coloring, it has E number E171. World production in 2014 exceeded 9 million metric tons. It has been estimated that titanium dioxide is used in two-thirds of all pigments, and pigments based on the oxide have been valued at $13.2 billion.
Atomic layer deposition of high-k metal oxides
InactiveUS20060258078A1Improve thermal stabilityLess growthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectric layerTitanium oxide
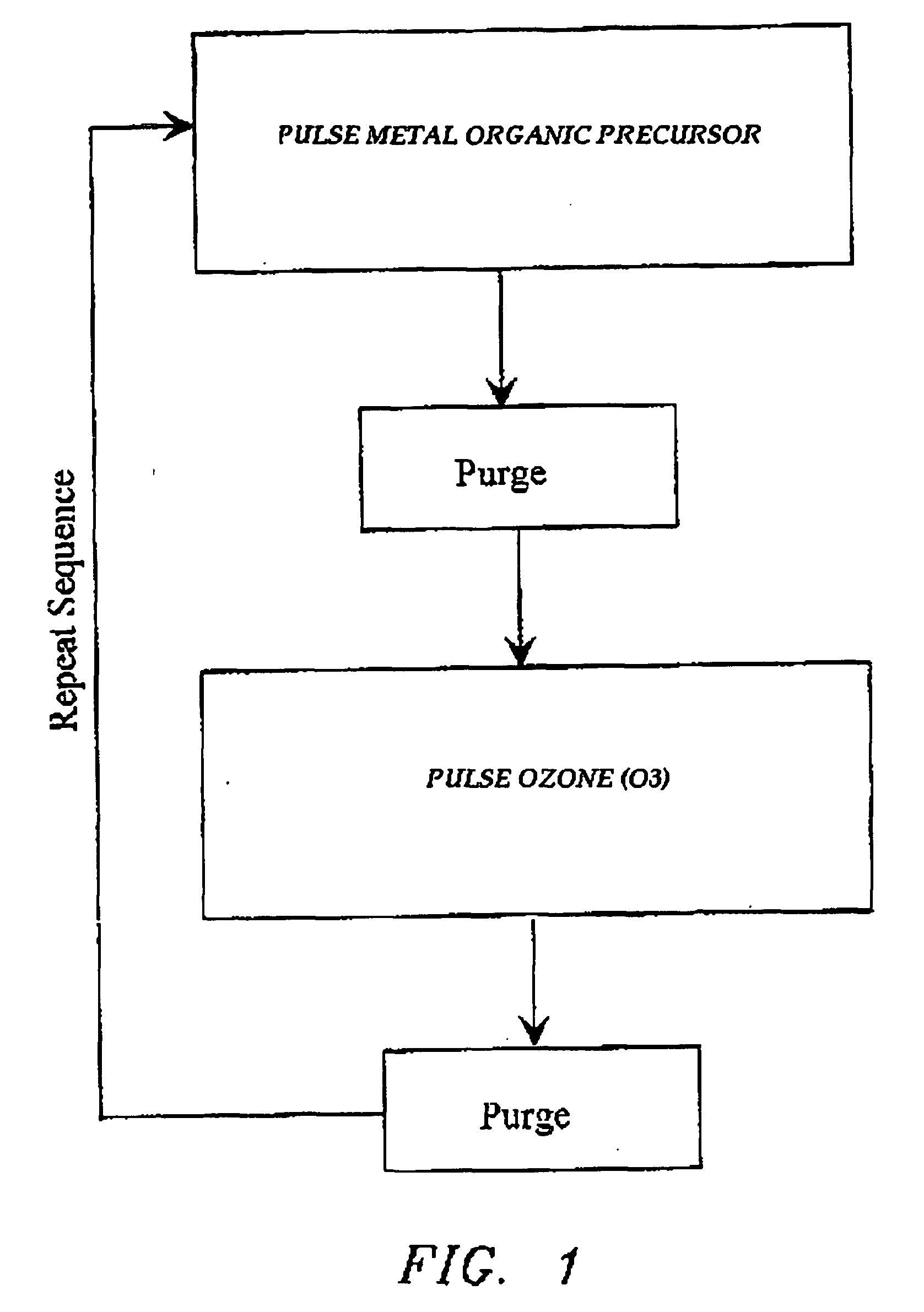
The present invention relates to the atomic layer deposition (“ALD”) of high k dielectric layers of metal oxides containing Group 4 metals, including hafnium oxide, zirconium oxide, and titanium oxide. More particularly, the present invention relates to the ALD formation of Group 4 metal oxide films using an metal alkyl amide as a metal organic precursor and ozone as a co-reactant.
Owner:AVIZA TECHNOLOGY INC +1
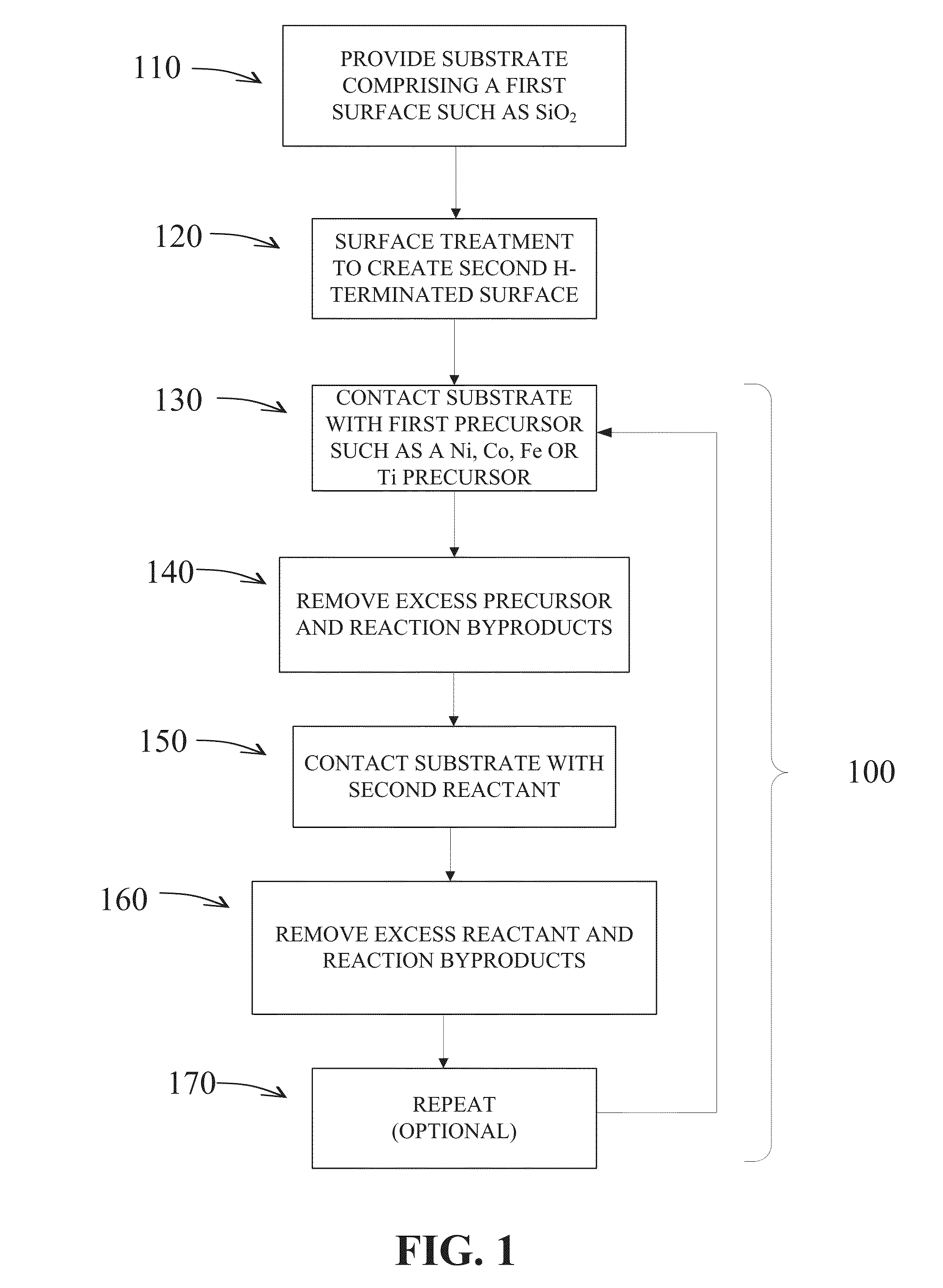
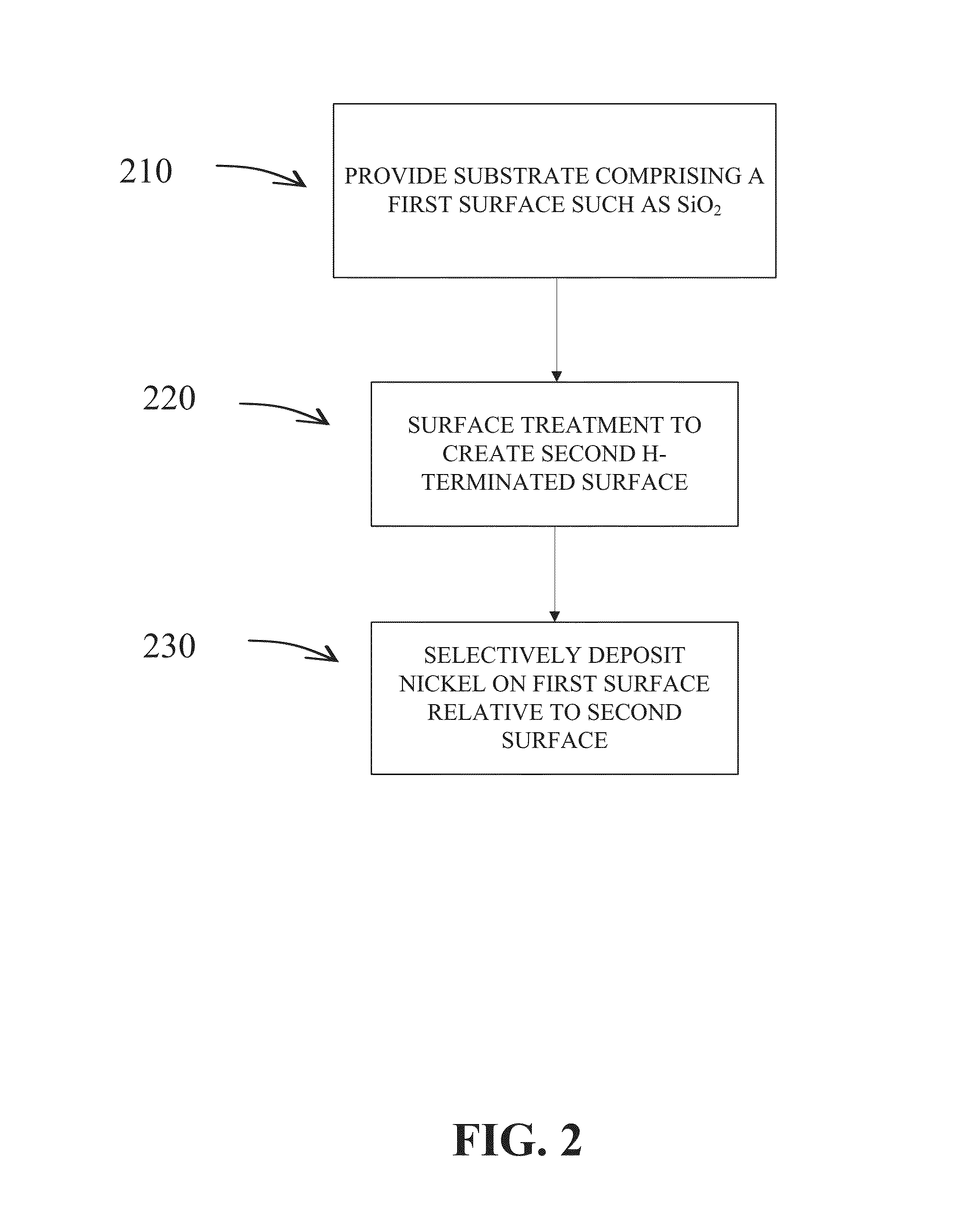
Selective deposition
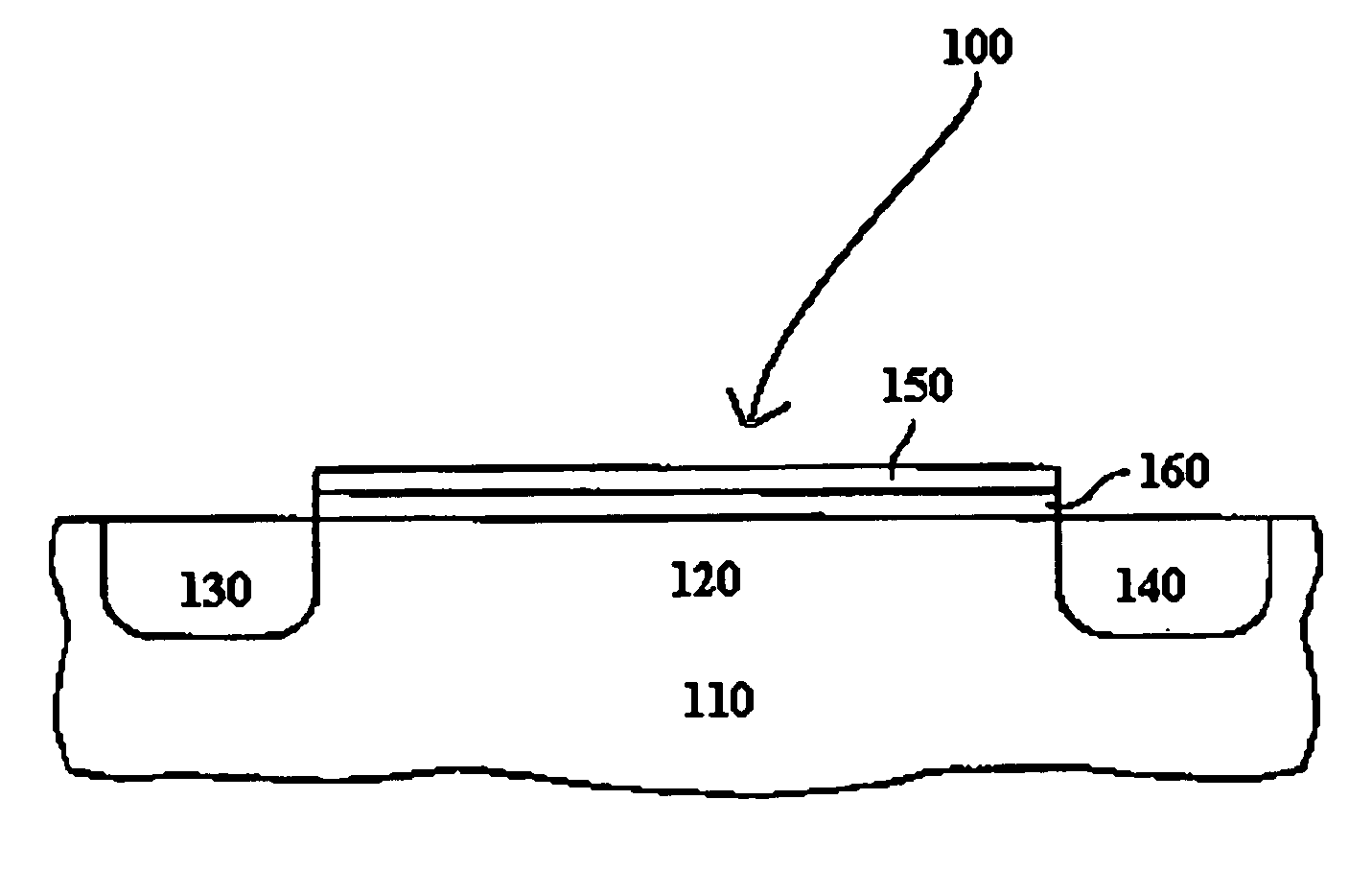
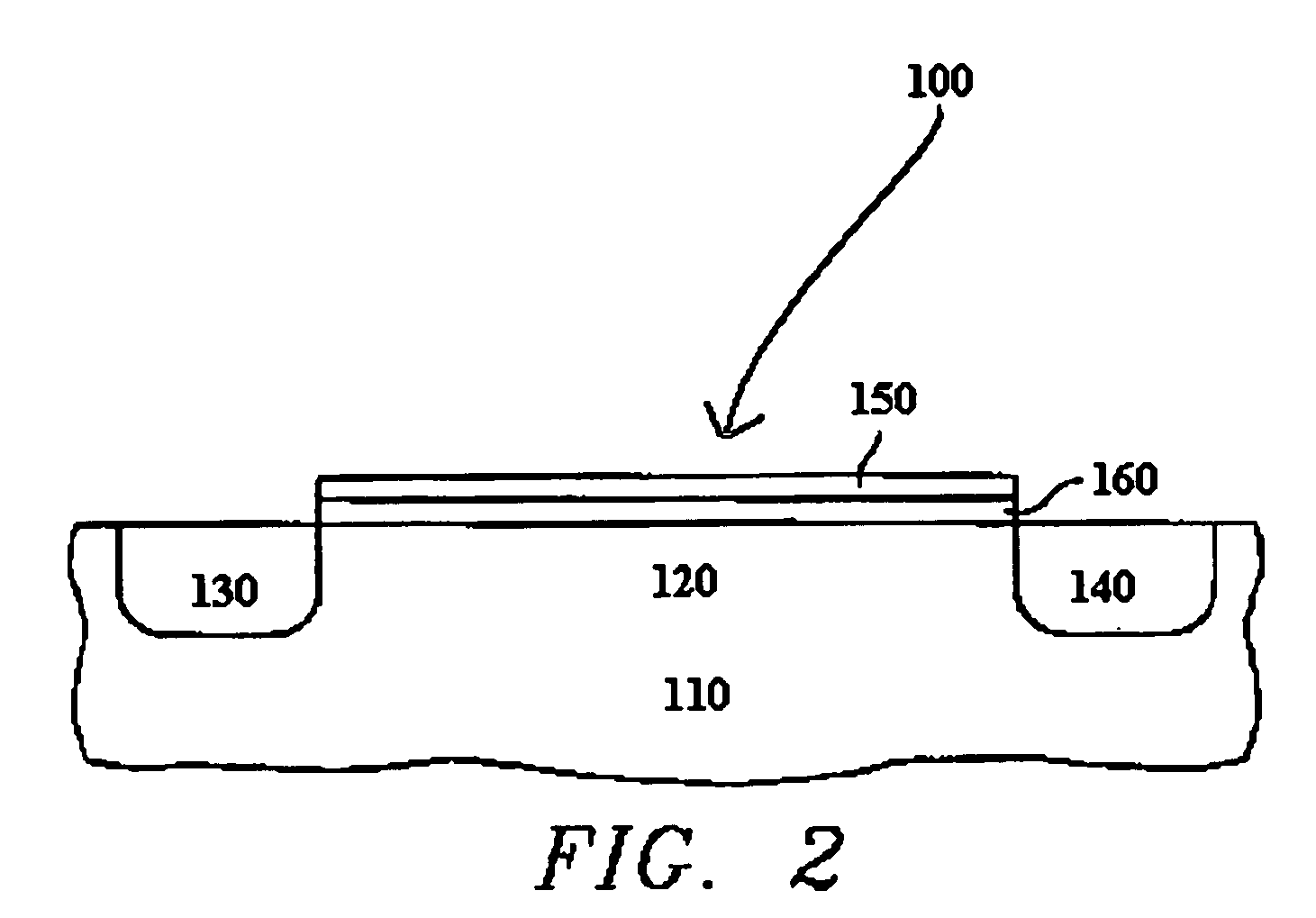
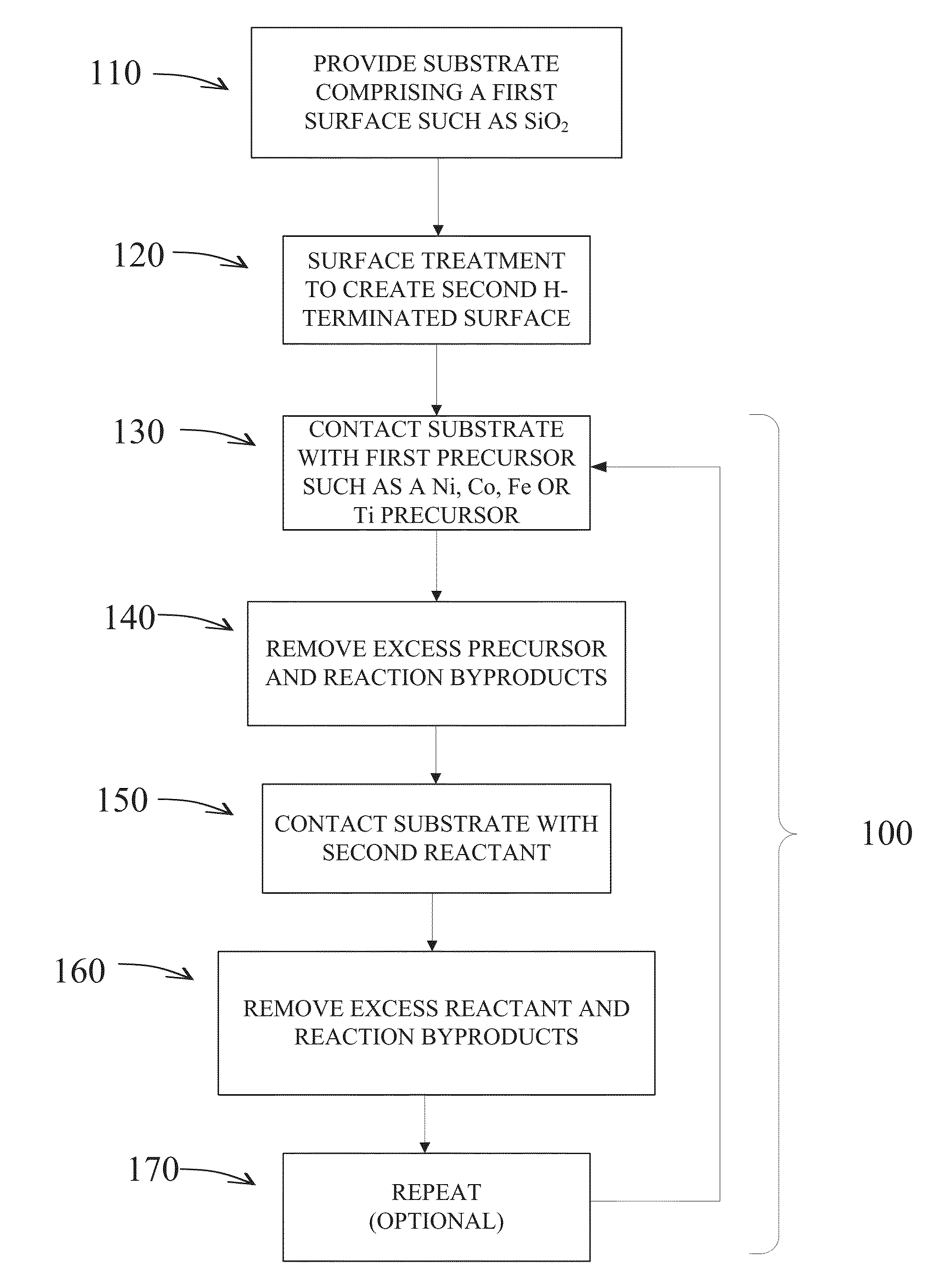
Methods are provided for selectively depositing a surface of a substrate relative to a second, different surface. An exemplary deposition method can include selectively depositing a material, such as a material comprising nickel, nickel nitride, cobalt, iron, and / or titanium oxide on a first surface, such as a SiO2 surface, relative to a second, different surface, such as a H-terminated surface, of the same substrate. Methods can include treating a surface of the substrate to provide H-terminations prior to deposition.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
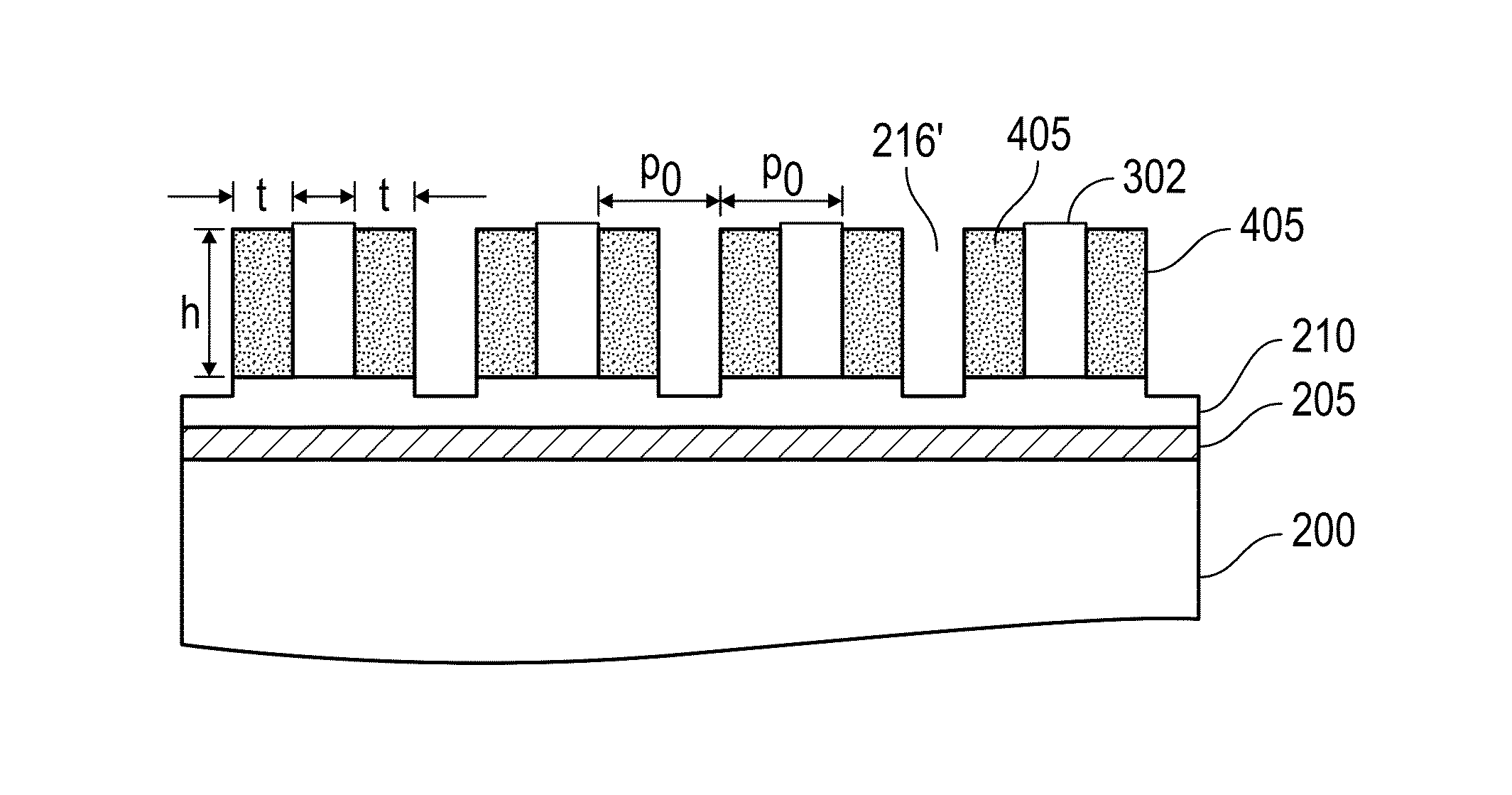
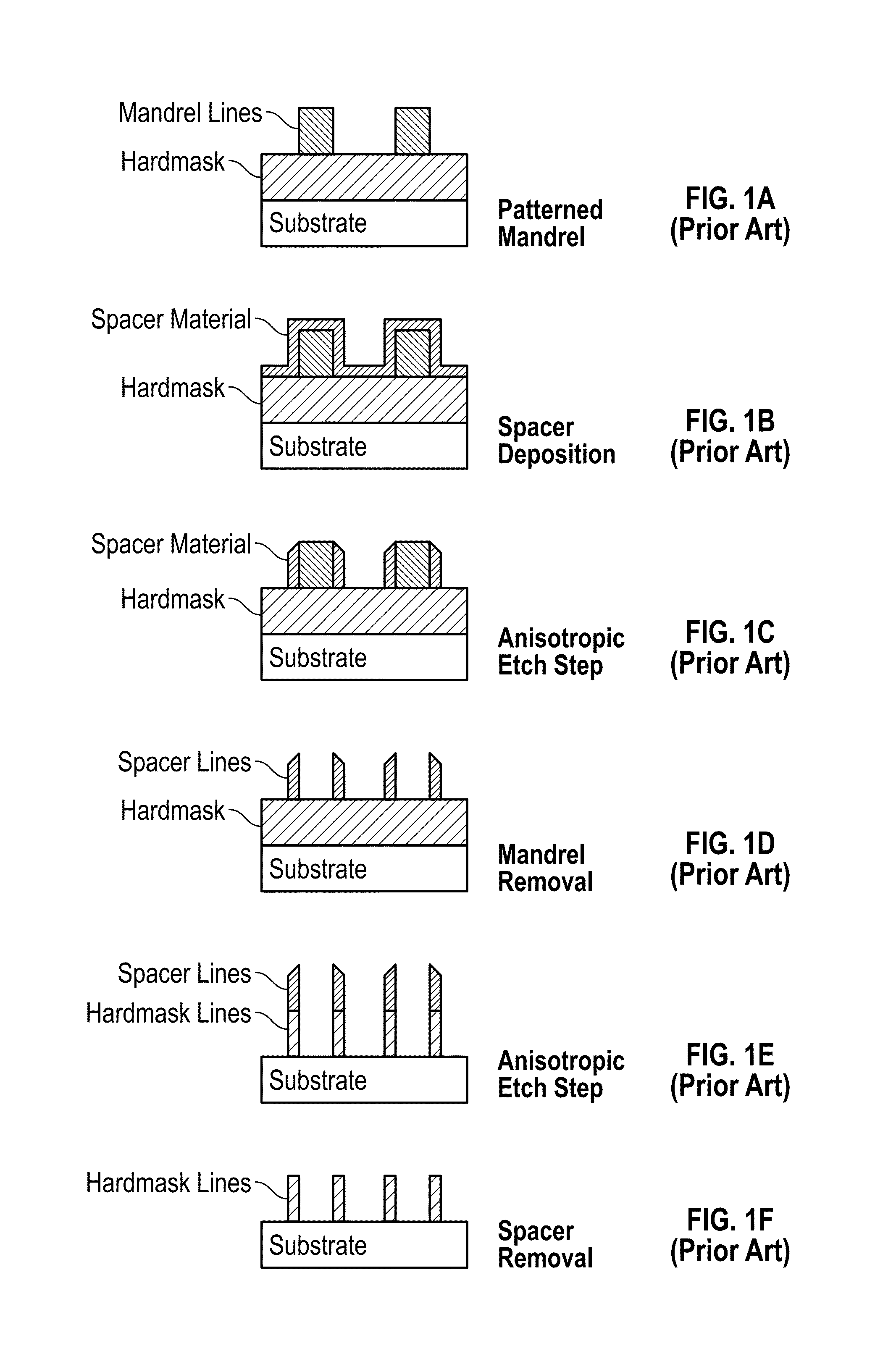
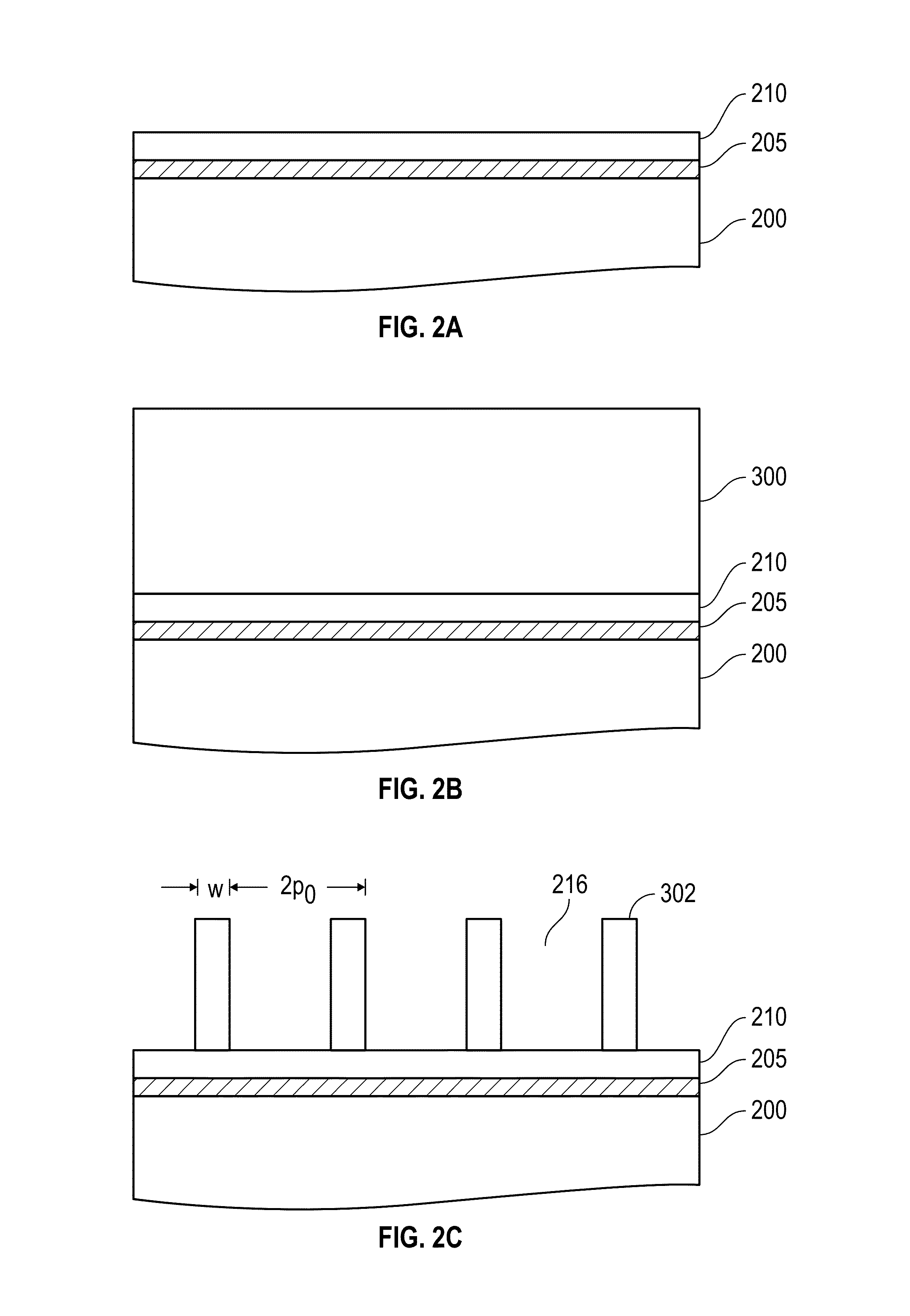
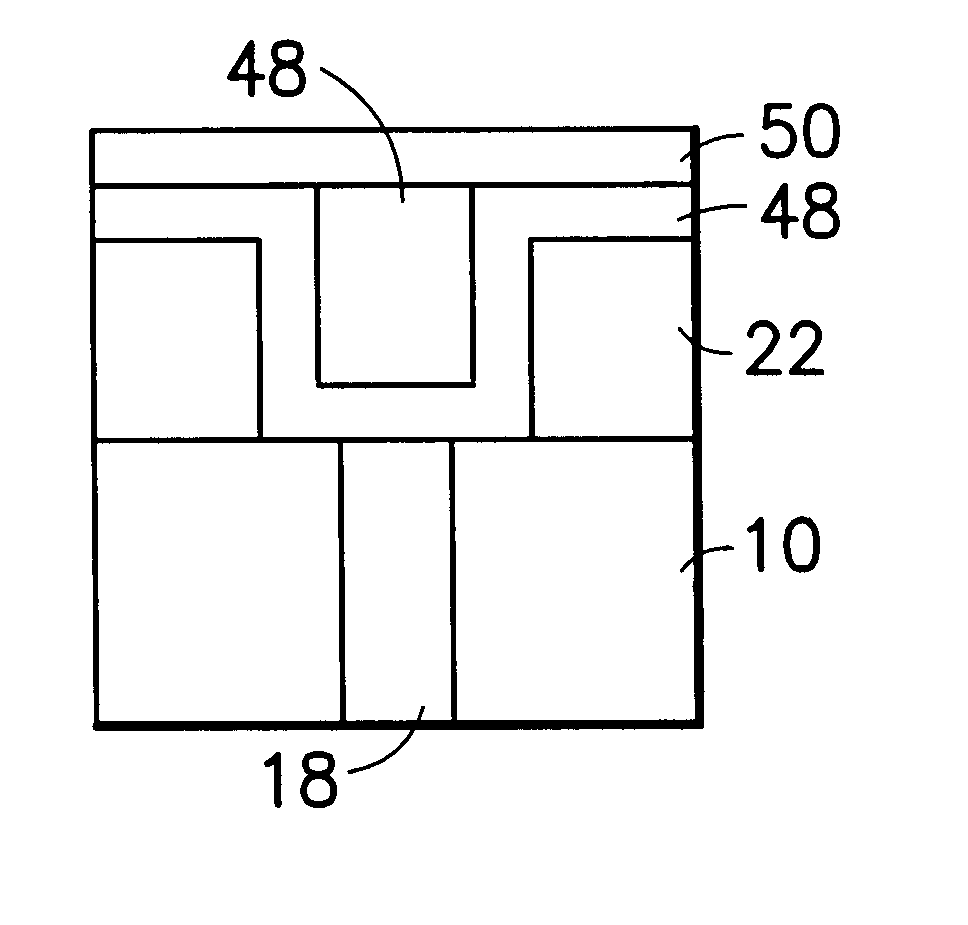
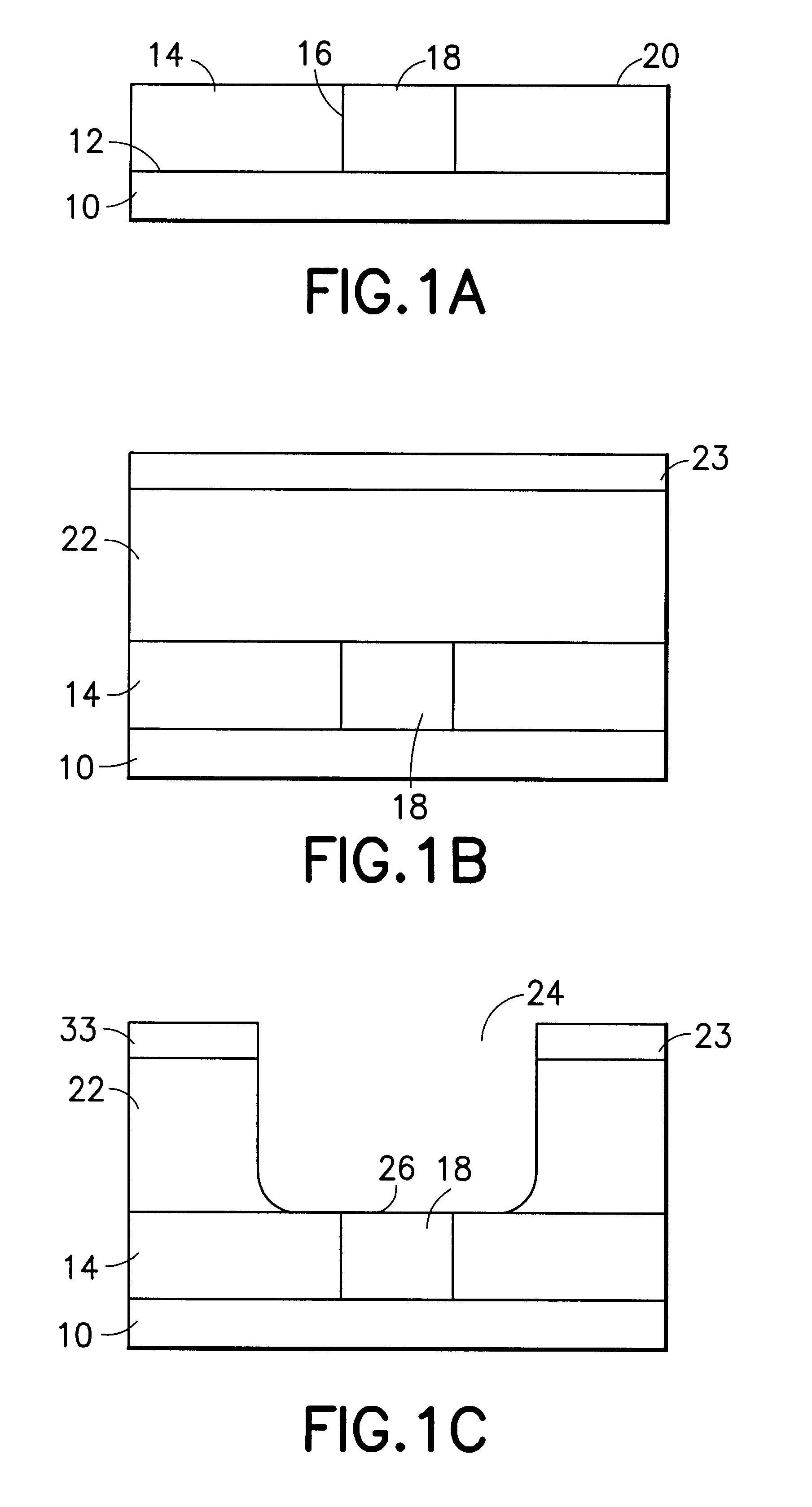
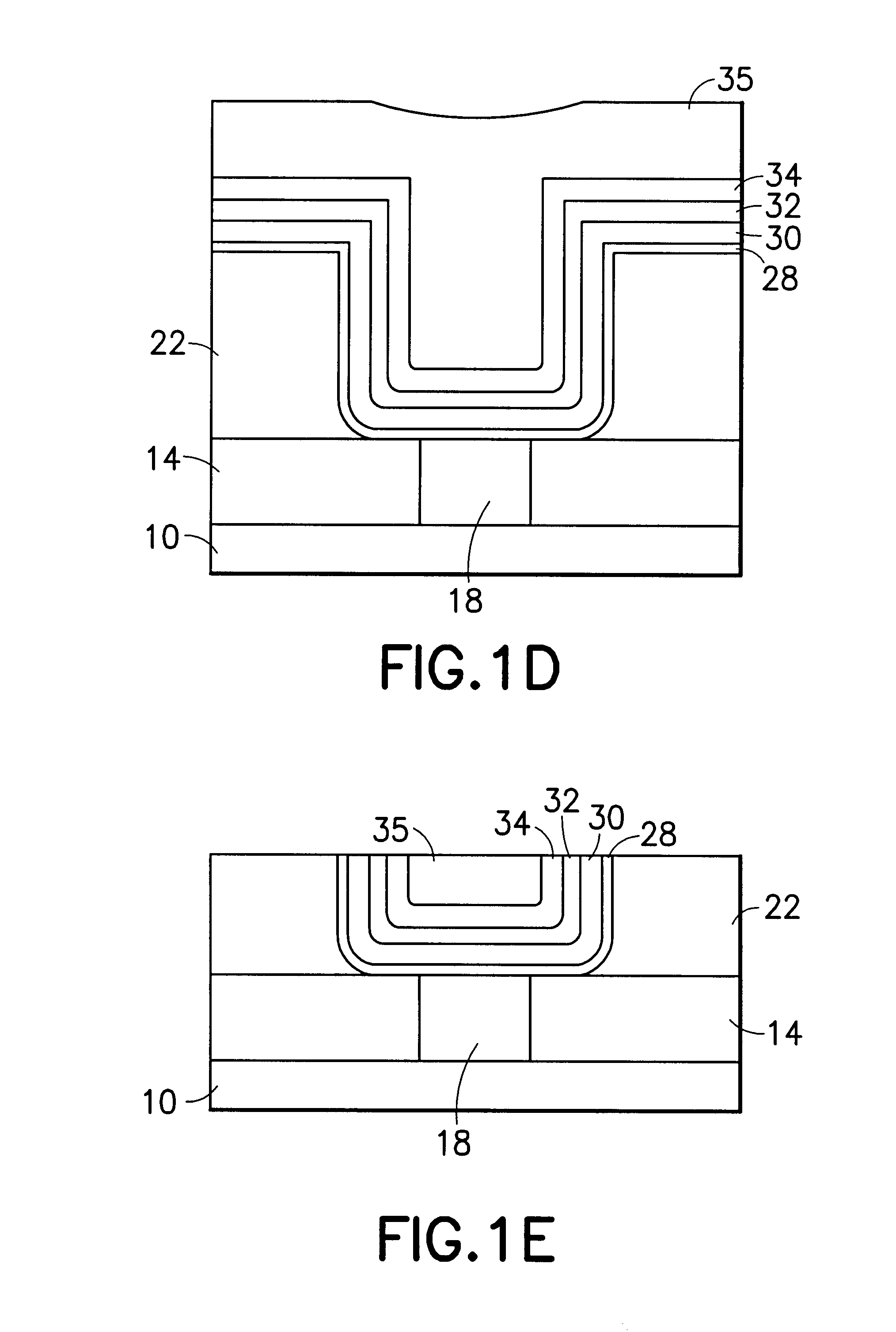
Method for sidewall spacer line doubling using atomic layer deposition of a titanium oxide
A method for sidewall spacer line doubling uses thermal atomic layer deposition (ALD) of a titanium oxide (TiOx) spacer layer. A hardmask layer is deposited on a suitable substrate. A mandrel layer of diamond-like carbon (DLC) is deposited on the hardmask layer and patterned into stripes with tops and sidewalls. A layer of TiOx is deposited, by thermal ALD without the assistance of plasma or ozone, on the tops and sidewalls of the mandrel stripes. Thermal ALD of the TiO2, without energy assistance by plasma or ozone, has been found to cause no damage to the DLC mandrel stripes. After removal of the TiOx from the tops of the mandrel stripes and removal of the mandrel stripes, stripes of TiO2 are left on the hardmask layer and may be used as an etch mask to transfer the pattern into the hardmask layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Temperature controlled chamber liner
InactiveUS6099651APrevent unwanted condensationPrevent decomposition and condensationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingEngineeringTitanium oxide
The invention relates to an apparatus and process for the vaporization of liquid precursors and deposition of a film on a suitable substrate. Particularly contemplated is an apparatus and process for the deposition of a metal-oxide film, such as a barium, strontium, titanium oxide (BST) film, on a silicon wafer to make integrated circuit capacitors useful in high capacity dynamic memory modules.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Compositions and structures for chemical mechanical polishing of FeRAM capacitors and method of fabricating FeRAM capacitors using same
InactiveUS6346741B1Easy to manufactureBig advantageOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLead zirconate titanateBarium strontium titanate
An integrated circuit structures formed by chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) process, which comprises a conductive pathway recessed in a dielectric substrate, wherein the conductive pathway comprises conductive transmission lines encapsulated in a transmission-enhancement material, and wherein the conductive pathway is filled sequentially by a first layer of the transmission-enhancement material followed by the conductive transmission line; a second layer of transmission-enhancement material encapsulating the conductive transmission line and contacting the first layer of the transmission-enhancement material, wherein the transmission-enhancement material is selected from the group consisting of high magnetic permeability material and high permittivity material. Such integrated circuit structure may comprise a device structure selected from the group consisting of capacitors, inductors, and resistors. Preferably, the transmission-enhancement material comprises MgMn ferrites, MgMnAl ferrites, barium strontium titanate, lead zirconium titanate, titanium oxide, tantalum oxide, etc.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
Selective titanium nitride removal
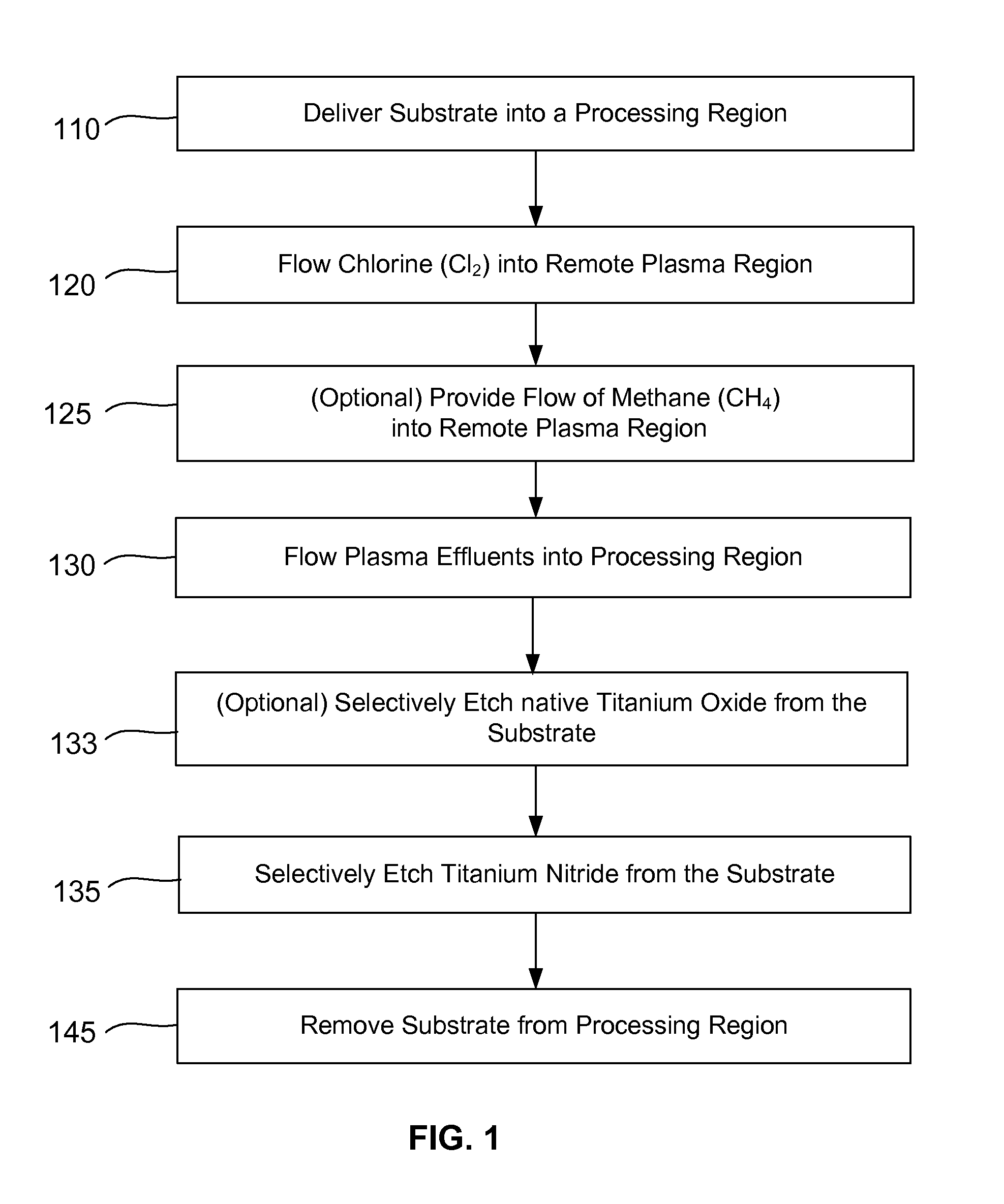
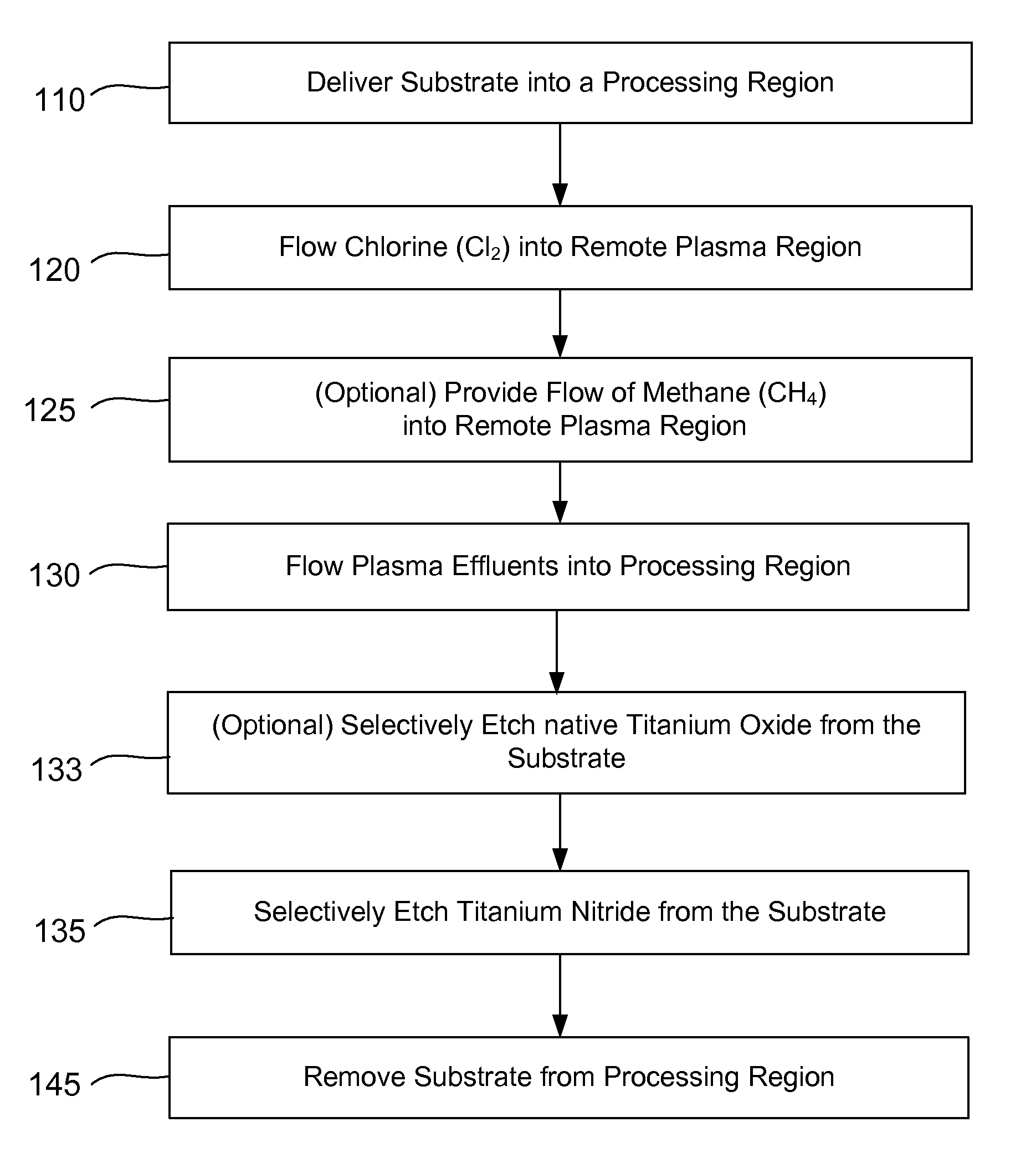
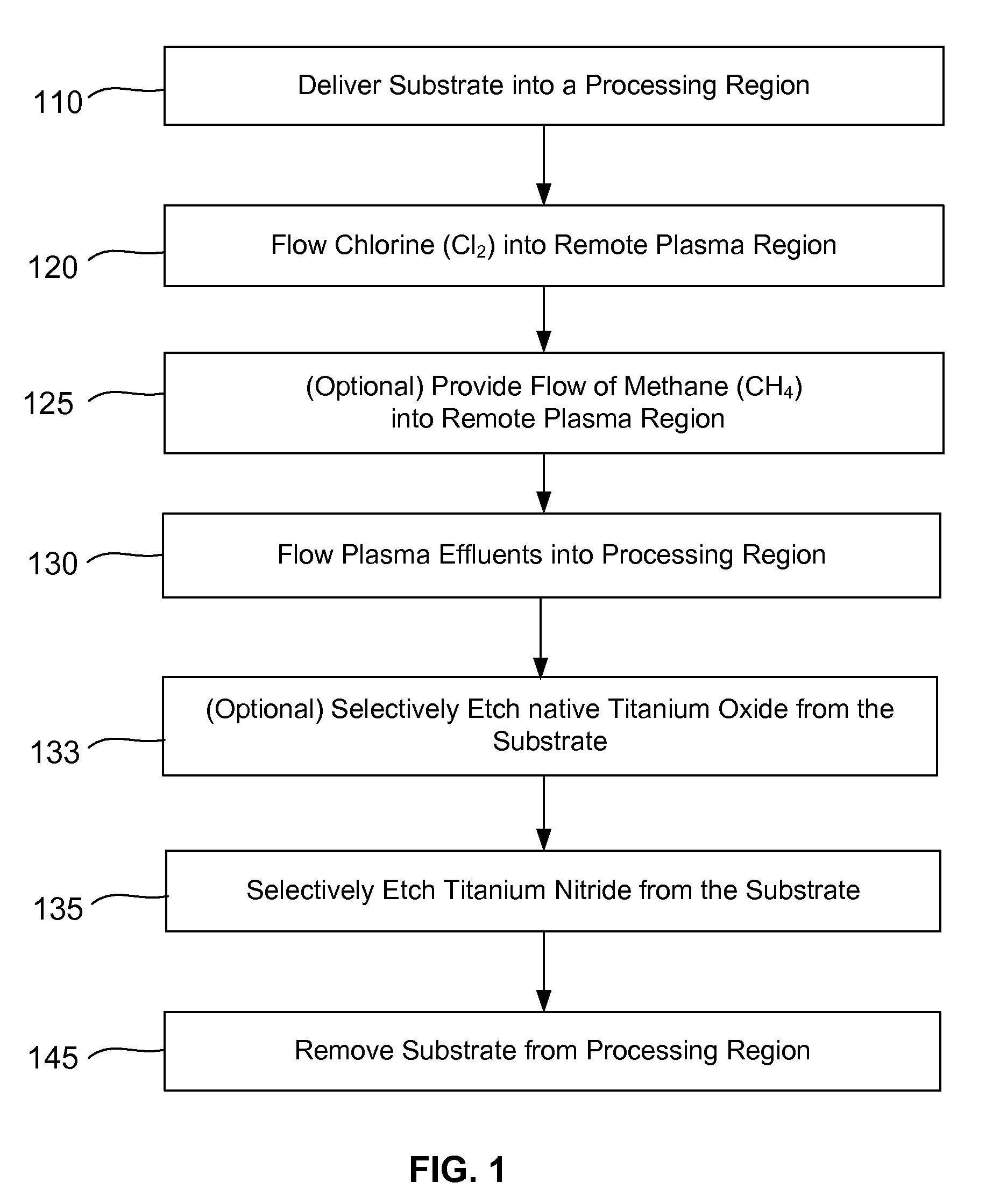
ActiveUS20140256131A1Convenient restHigh removal rateElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaTitanium nitride
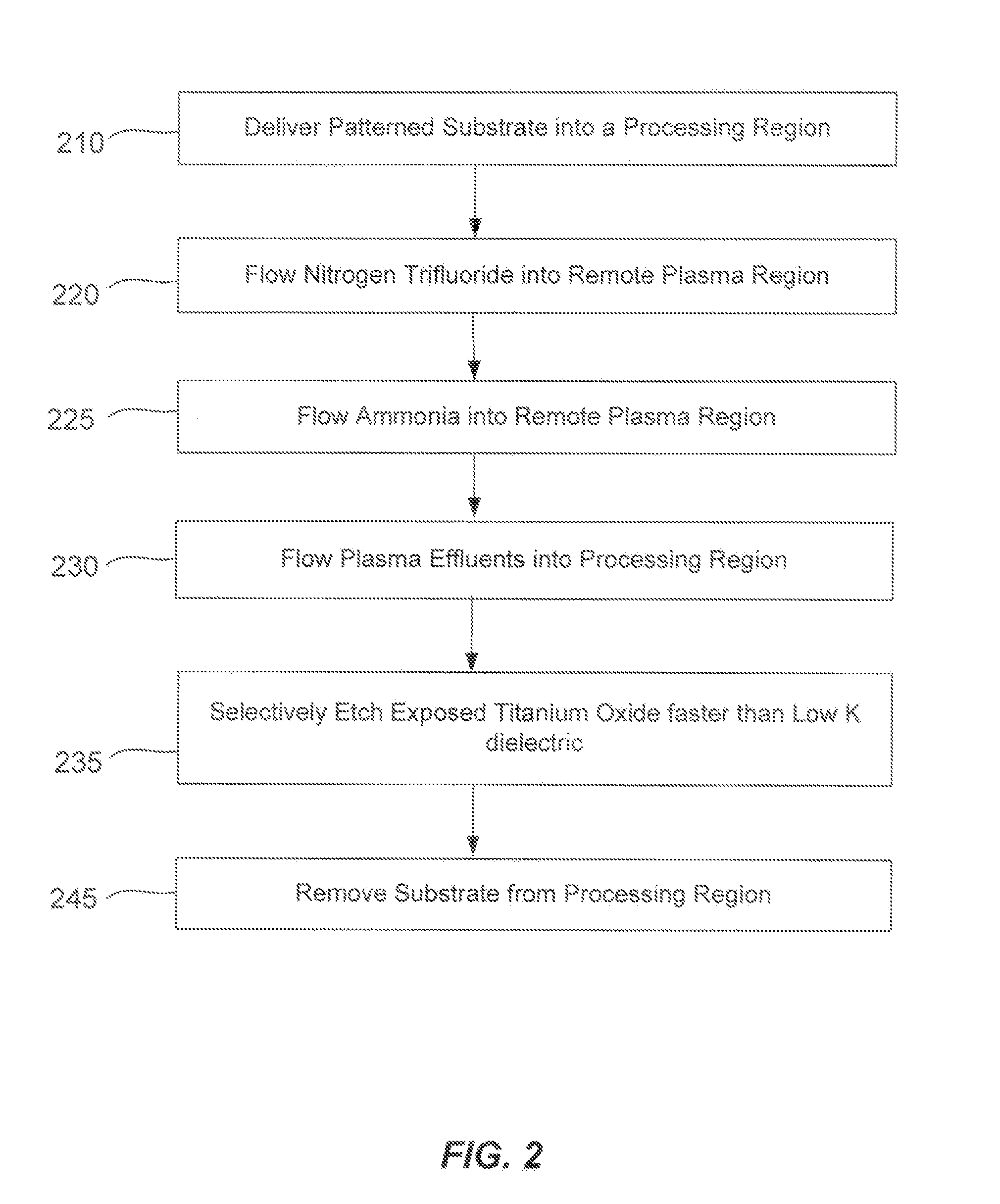
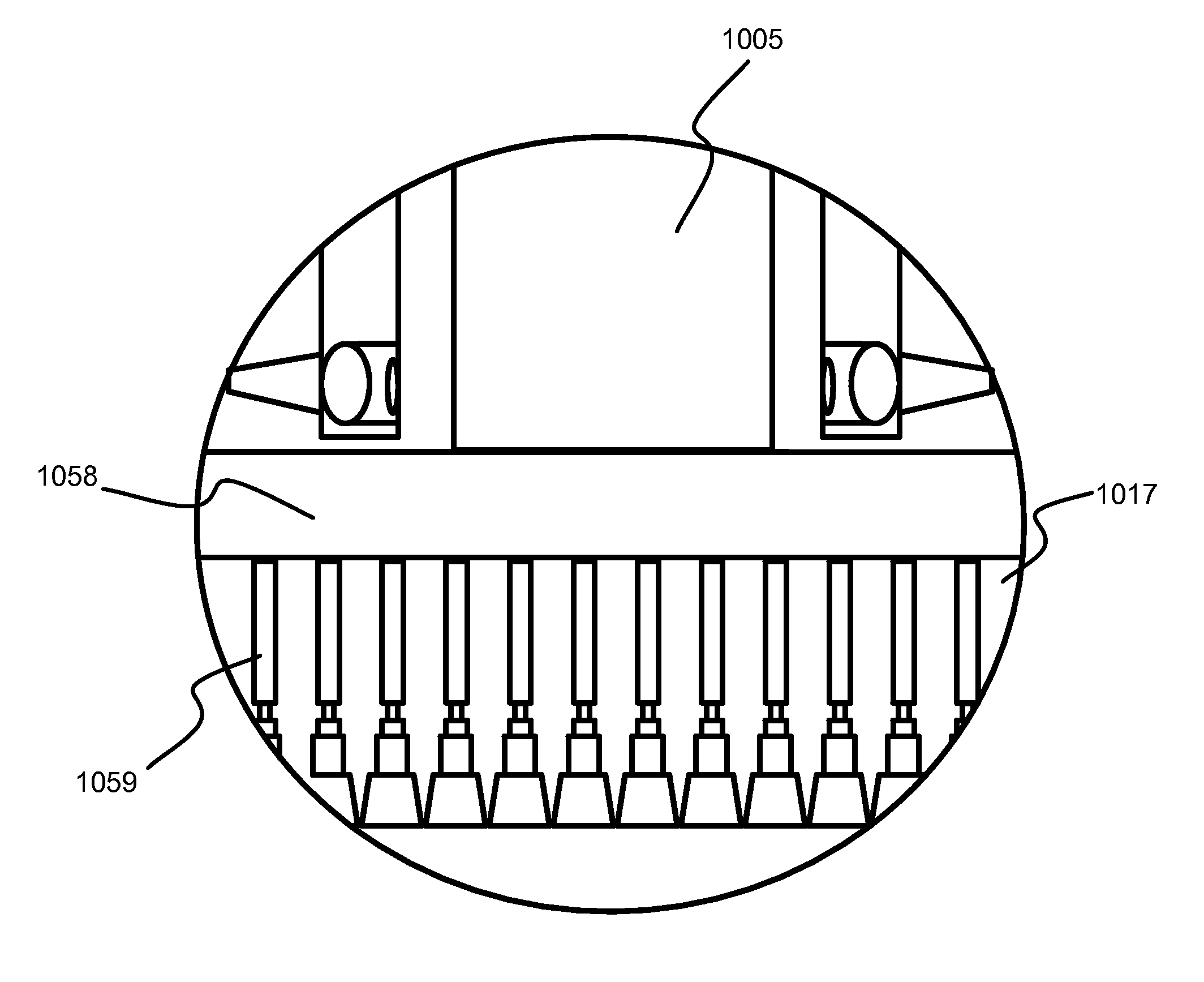
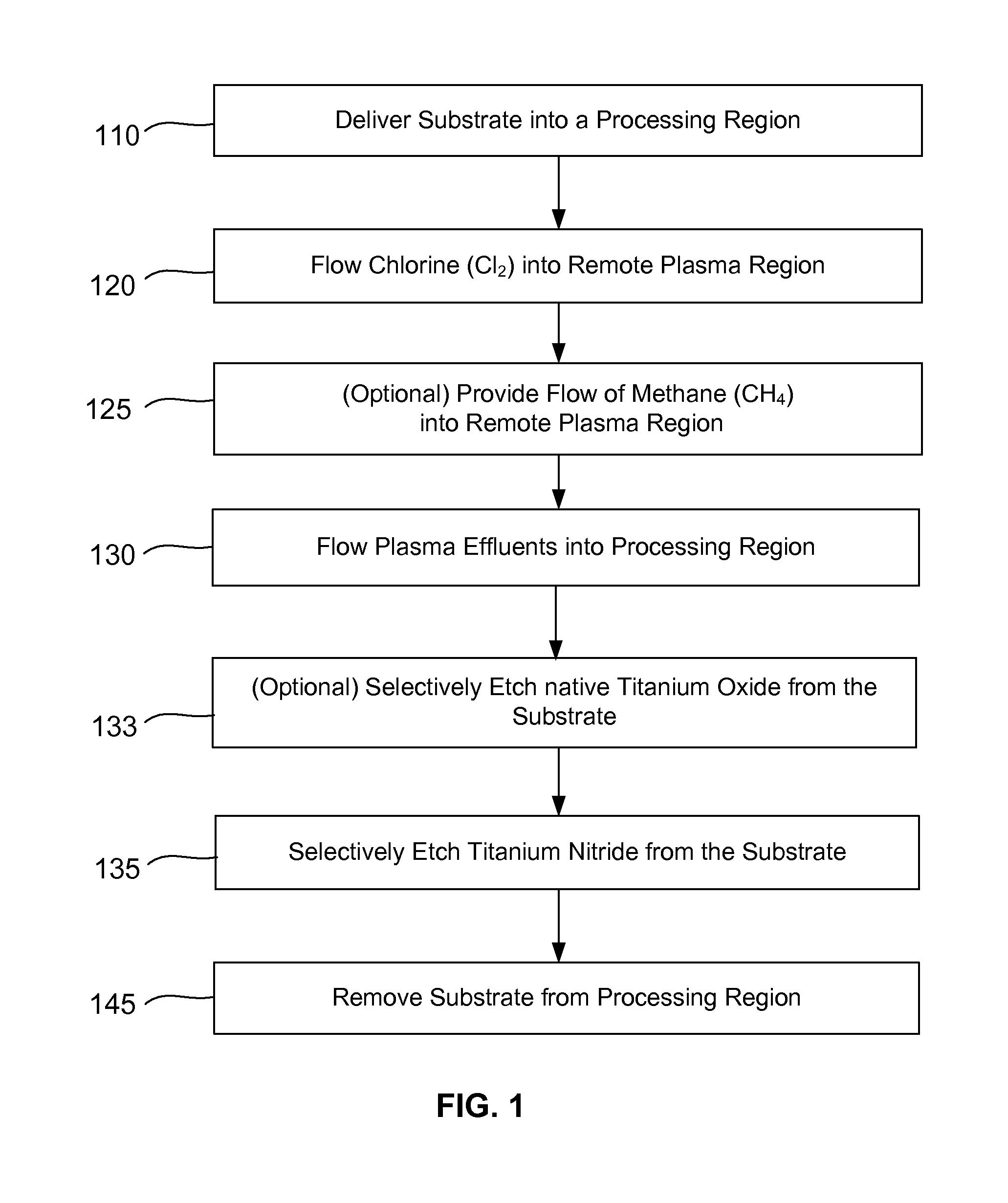
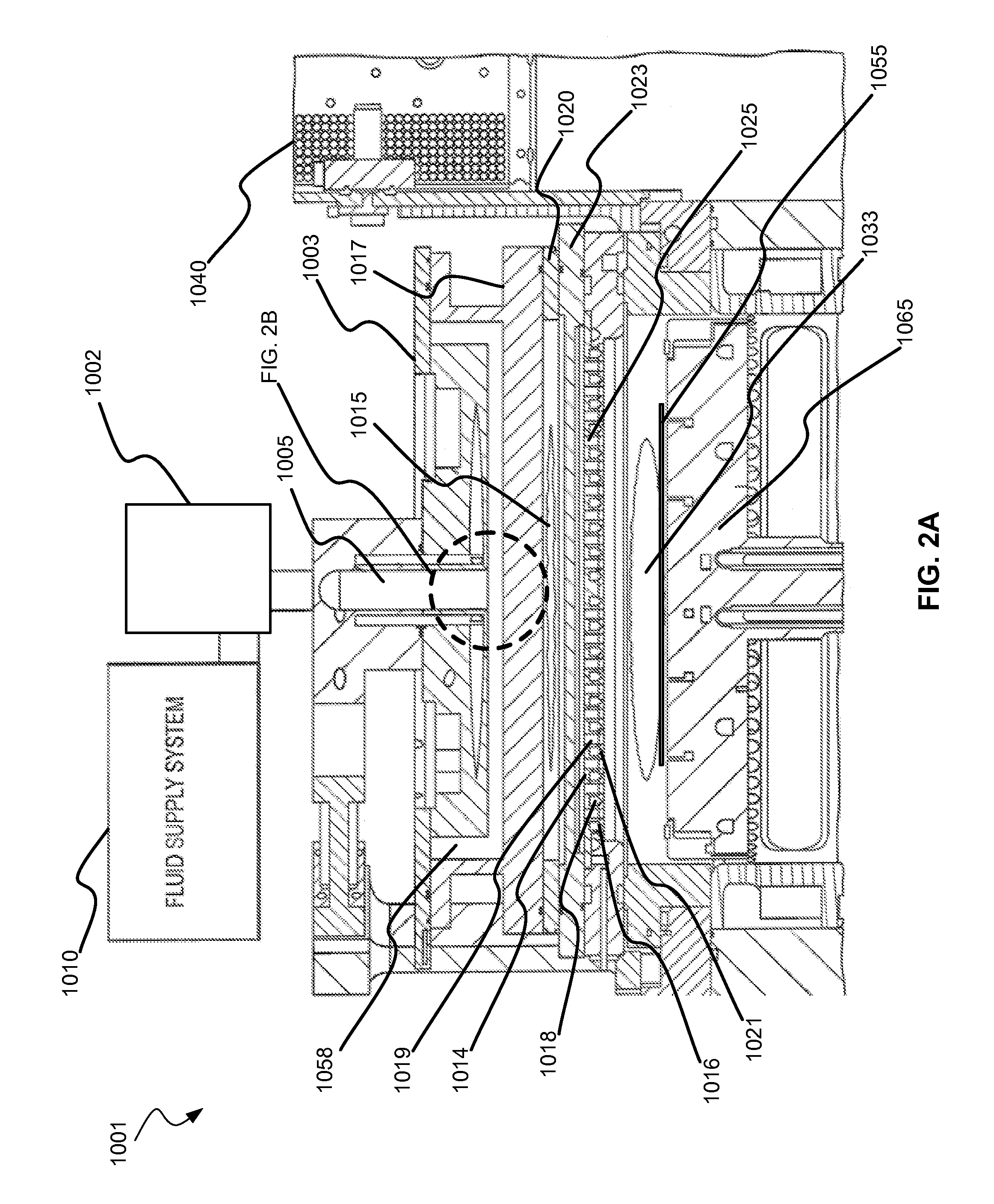
Methods are described herein for selectively etching titanium nitride relative to dielectric films, which may include, for example, alternative metals and metal oxides lacking in titanium and / or silicon-containing films (e.g. silicon oxide, silicon carbon nitride and low-K dielectric films). The methods include a remote plasma etch formed from a chlorine-containing precursor. Plasma effluents from the remote plasma are flowed into a substrate processing region where the plasma effluents react with the titanium nitride. The plasma effluents react with exposed surfaces and selectively remove titanium nitride while very slowly removing the other exposed materials. The substrate processing region may also contain a plasma to facilitate breaking through any titanium oxide layer present on the titanium nitride. The plasma in the substrate processing region may be gently biased relative to the substrate to enhance removal rate of the titanium oxide layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Selective titanium nitride removal
ActiveUS9040422B2Convenient restHigh removal rateElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaTitanium nitride
Methods are described herein for selectively etching titanium nitride relative to dielectric films, which may include, for example, alternative metals and metal oxides lacking in titanium and / or silicon-containing films (e.g. silicon oxide, silicon carbon nitride and low-K dielectric films). The methods include a remote plasma etch formed from a chlorine-containing precursor. Plasma effluents from the remote plasma are flowed into a substrate processing region where the plasma effluents react with the titanium nitride. The plasma effluents react with exposed surfaces and selectively remove titanium nitride while very slowly removing the other exposed materials. The substrate processing region may also contain a plasma to facilitate breaking through any titanium oxide layer present on the titanium nitride. The plasma in the substrate processing region may be gently biased relative to the substrate to enhance removal rate of the titanium oxide layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Non-local plasma oxide etch
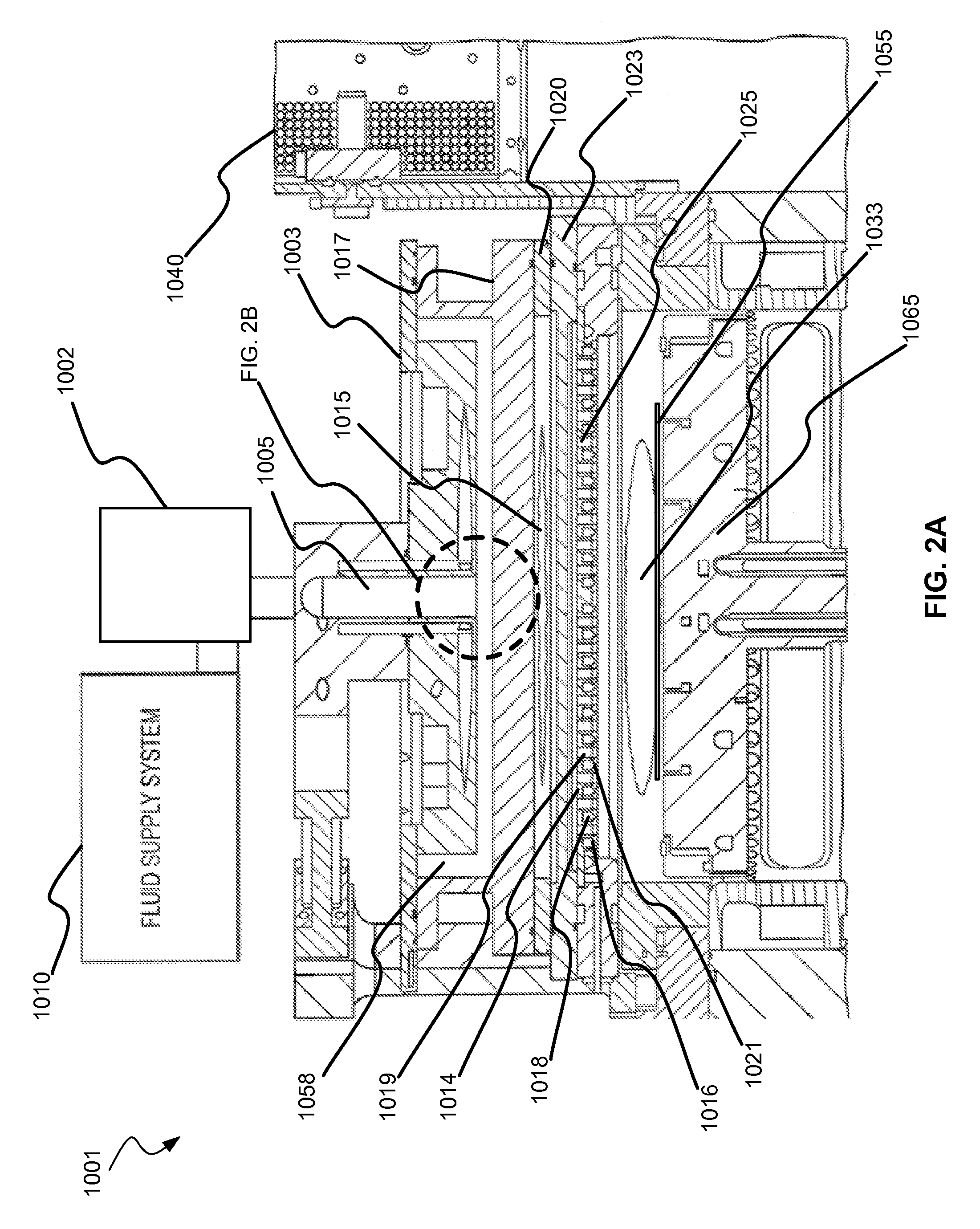
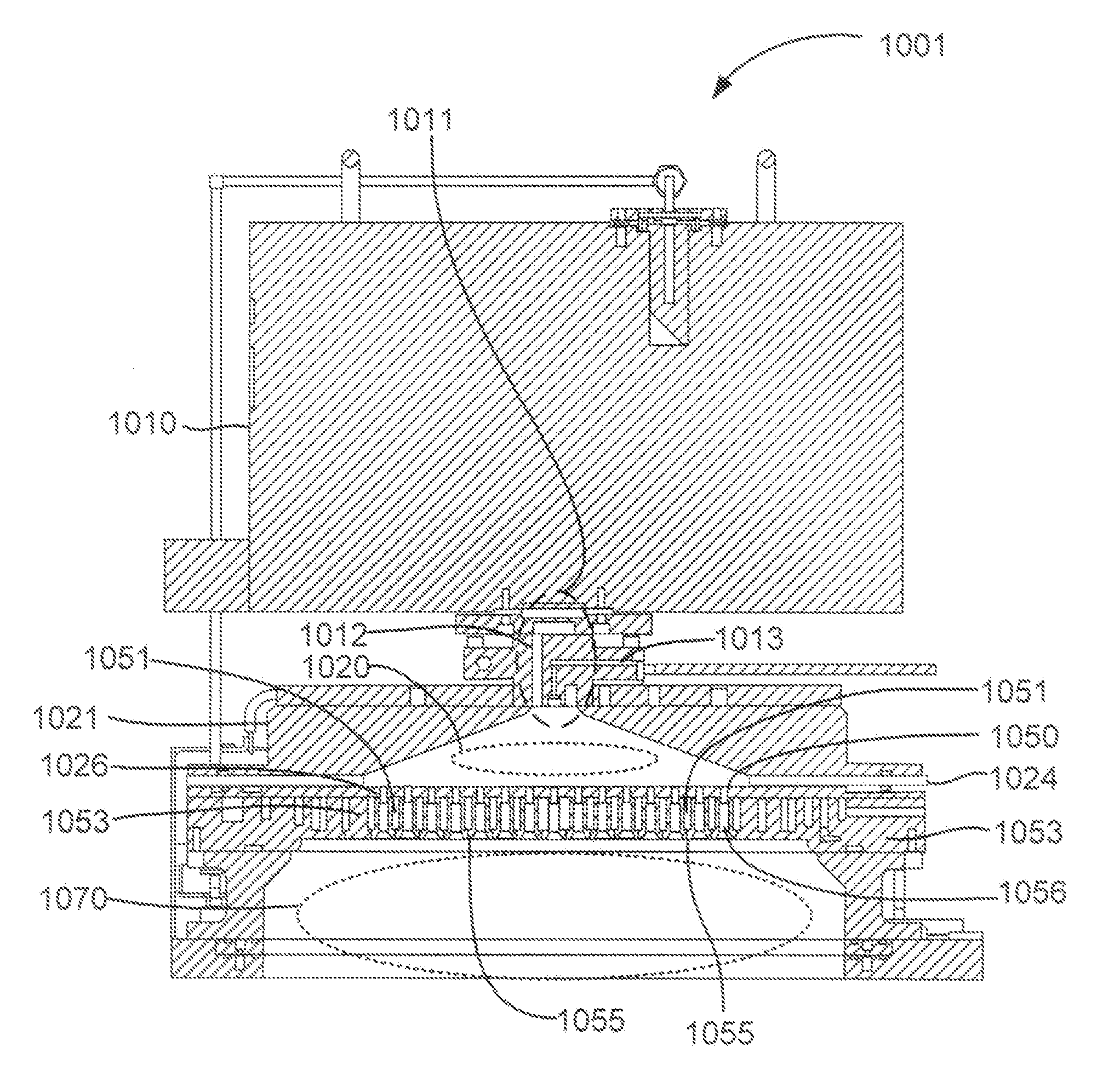
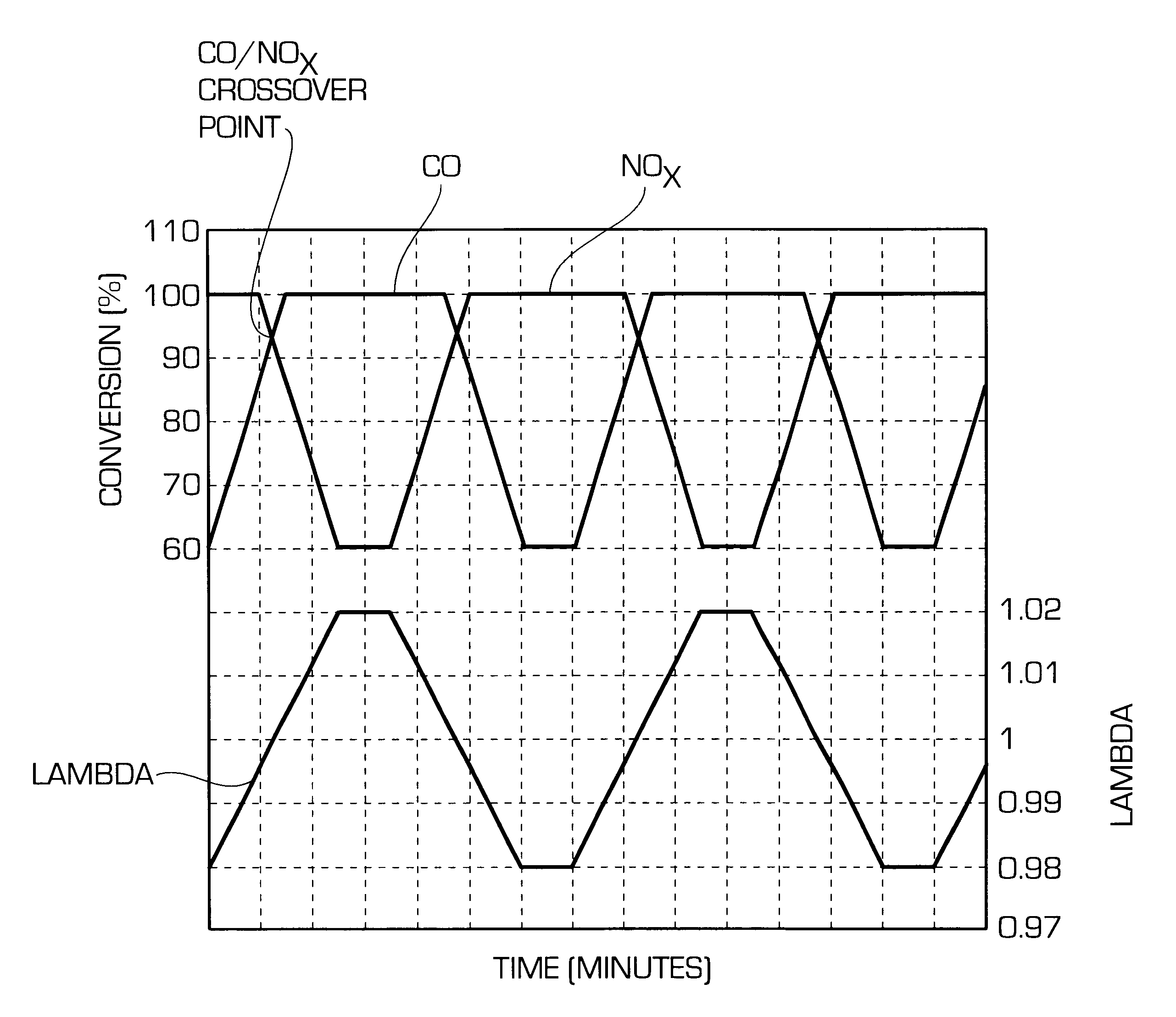
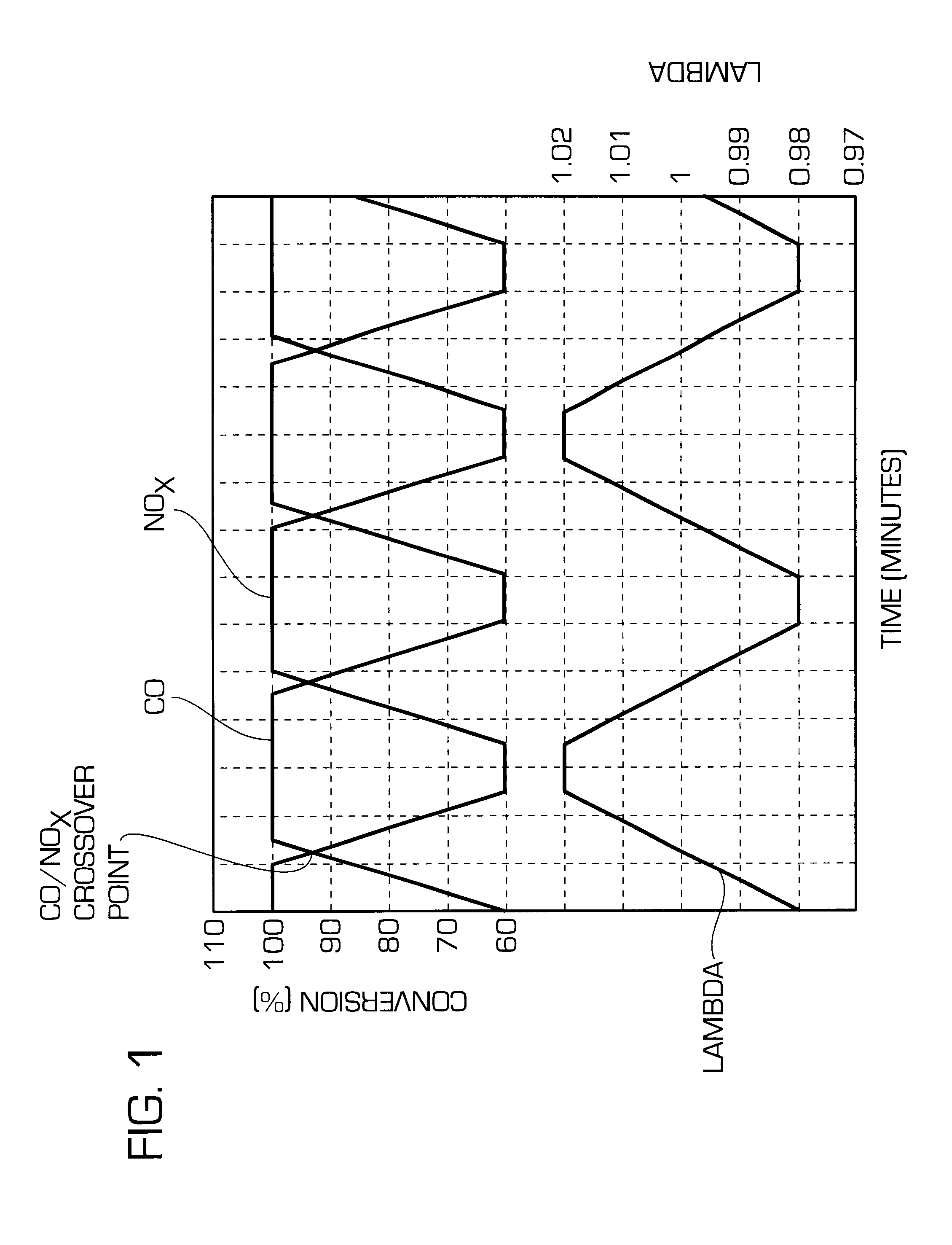
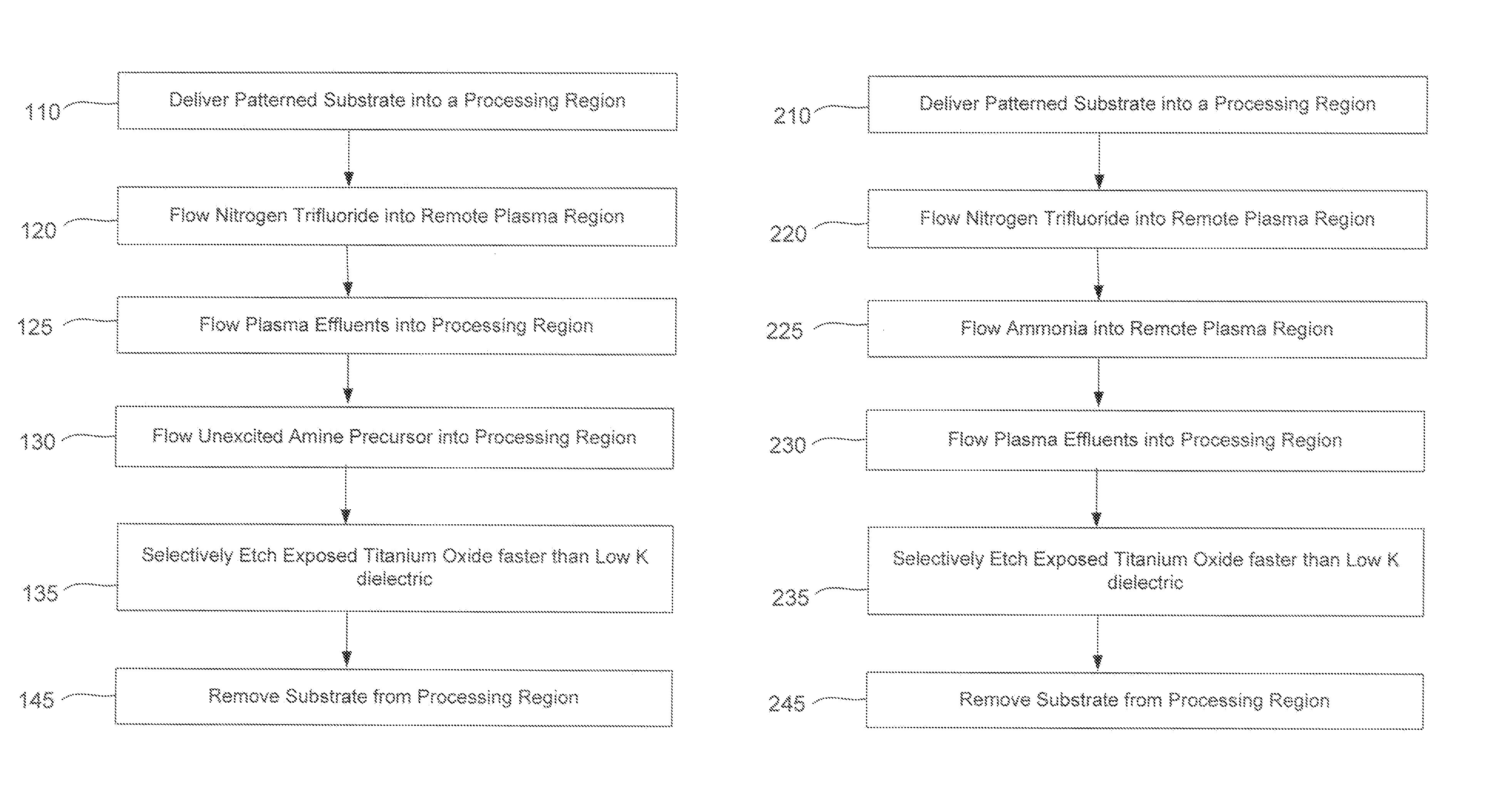
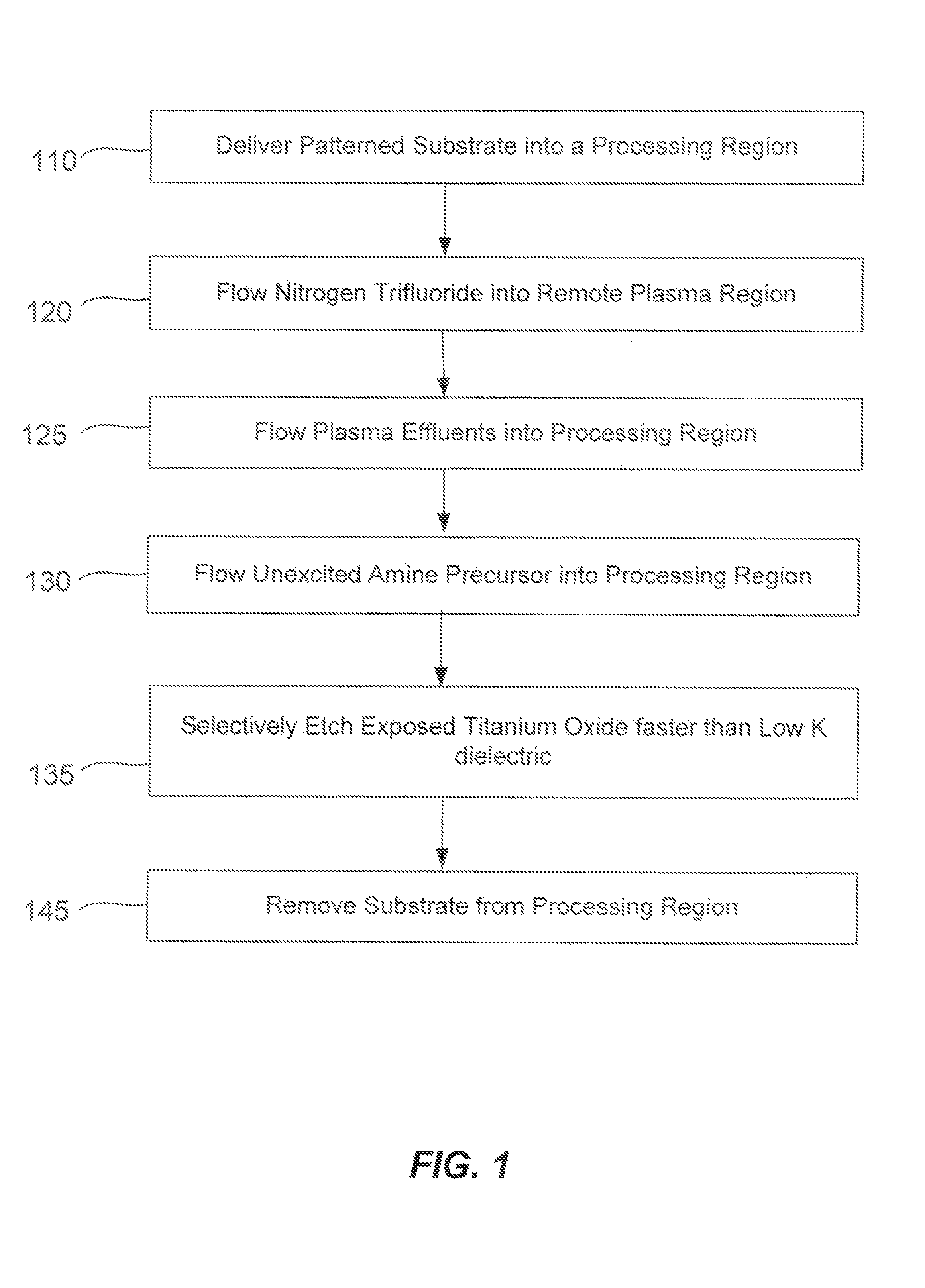
ActiveUS20140166617A1High titanium oxide selectivityElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsRemote plasmaHydrogen
A method of etching exposed titanium oxide on heterogeneous structures is described and includes a remote plasma etch formed from a fluorine-containing precursor. Plasma effluents from the remote plasma are flawed into a substrate processing region where the plasma effluents may combine with a nitrogen-containing precursor such as an amine (N:) containing precursor. Reactants thereby produced etch, the patterned heterogeneous structures with high titanium oxide selectivity while the substrate is at elevated temperature. Titanium oxide etch may alternatively involve supplying a fluorine-containing precursor and a source of nitrogen-and-hydrogen-containing precursor to the remote plasma. The methods may be used to remove titanium oxide while removing little or no low-K dielectric, polysilicon, silicon nitride or titanium nitride.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Layered noble metal-containing exhaust gas catalyst and its preparation
InactiveUS6294140B1Shorten recovery timeImprove conversion efficiencyOrganic chemistryNitrogen compoundsCerium(IV) oxideEngineering
A catalyst for treating exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine includes a carrier body coated with an inner layer and an outer layer. The inner layer includes platinum deposited on a first support material and on a first oxygen storage component, and the outer layer includes platinum and rhodium deposited on a second support material and on a second oxygen storage component. The first and second support materials may be the same or different, and may be selected from the group of: silica, alumina, titania, zirconia, mixed oxides or mixtures thereof, and zirconia-rich zirconia / ceria mixed oxide. The first and second oxygen storage components may include ceria-rich ceria / zirconia mixed oxide compounds, optionally including praseodymia, yttria, neodymia, lanthana or mixtures thereof.
Owner:DMC2 DEGUSSA METALS +1
Non-local plasma oxide etch
InactiveUS9111877B2Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenRemote plasma
A method of etching exposed titanium oxide on heterogeneous structures is described and includes a remote plasma etch formed from a fluorine-containing precursor. Plasma effluents from the remote plasma are flawed into a substrate processing region where the plasma effluents may combine with a nitrogen-containing precursor such as an amine (N:) containing precursor. Reactants thereby produced etch, the patterned heterogeneous structures with high titanium oxide selectivity while the substrate is at elevated temperature. Titanium oxide etch may alternatively involve supplying a fluorine-containing precursor and a source of nitrogen-and-hydrogen-containing precursor to the remote plasma. The methods may be used to remove titanium oxide while removing little or no low-K dielectric, polysilicon, silicon nitride or titanium nitride.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Selective titanium nitride removal
ActiveUS20150357205A1Convenient restHigh removal rateElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTitanium nitrideSilicon oxide
Methods are described herein for selectively etching titanium nitride relative to dielectric films, which may include, for example, alternative metals and metal oxides lacking in titanium and / or silicon-containing films (e.g. silicon oxide, silicon carbon nitride and low-K dielectric films). The methods include a remote plasma etch formed from a chlorine-containing precursor. Plasma effluents from the remote plasma are flowed into a substrate processing region where the plasma effluents react with the titanium nitride. The plasma effluents react with exposed surfaces and selectively remove titanium nitride while very slowly removing the other exposed materials. The substrate processing region may also contain a plasma to facilitate breaking through any titanium oxide layer present on the titanium nitride. The plasma in the substrate processing region may be gently biased relative to the substrate to enhance removal rate of the titanium oxide layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for photocatalytically hydrophilifying surface and composite material with photocatalytically hydrophilifiable surface
InactiveUS6090489AImproved oil repellencyEasy to disassembleOther chemical processesPretreated surfacesAtmospheric airSolid acid
A method for hydrophilifying the surface of a substrate by taking advantage of photocatalytic action. The substrate has a photocatalytic titania coating (10). The surface of the photocatalytic coating (10) bears the solid acid that increases a hydrogen bond component ( gamma Sh) in the surface energy in the solid / gas interface of the coating. Photoexcitation of the photocatalyst enhances the hydrogen bond component ( gamma Sh) in the surface energy of the photocatalytic coating (10), accelerating the physical adsorption of molecules of water in the atmosphere through a hydrogen bond (16) onto hydrogen atoms in a terminal OH group (12), bonded to a titanium atom, and a bridge OH group (14) on the surface of the coating. This results in the formation of a high density, physically adsorbed water layer (18) on the surface of the photocatalytic coating (10), thus permitting the surface of the substrate to be easily hydrophilified. The method is applicable to antifogging, antifouling, selfcleaning and cleaning of articles.
Owner:TOTO LTD
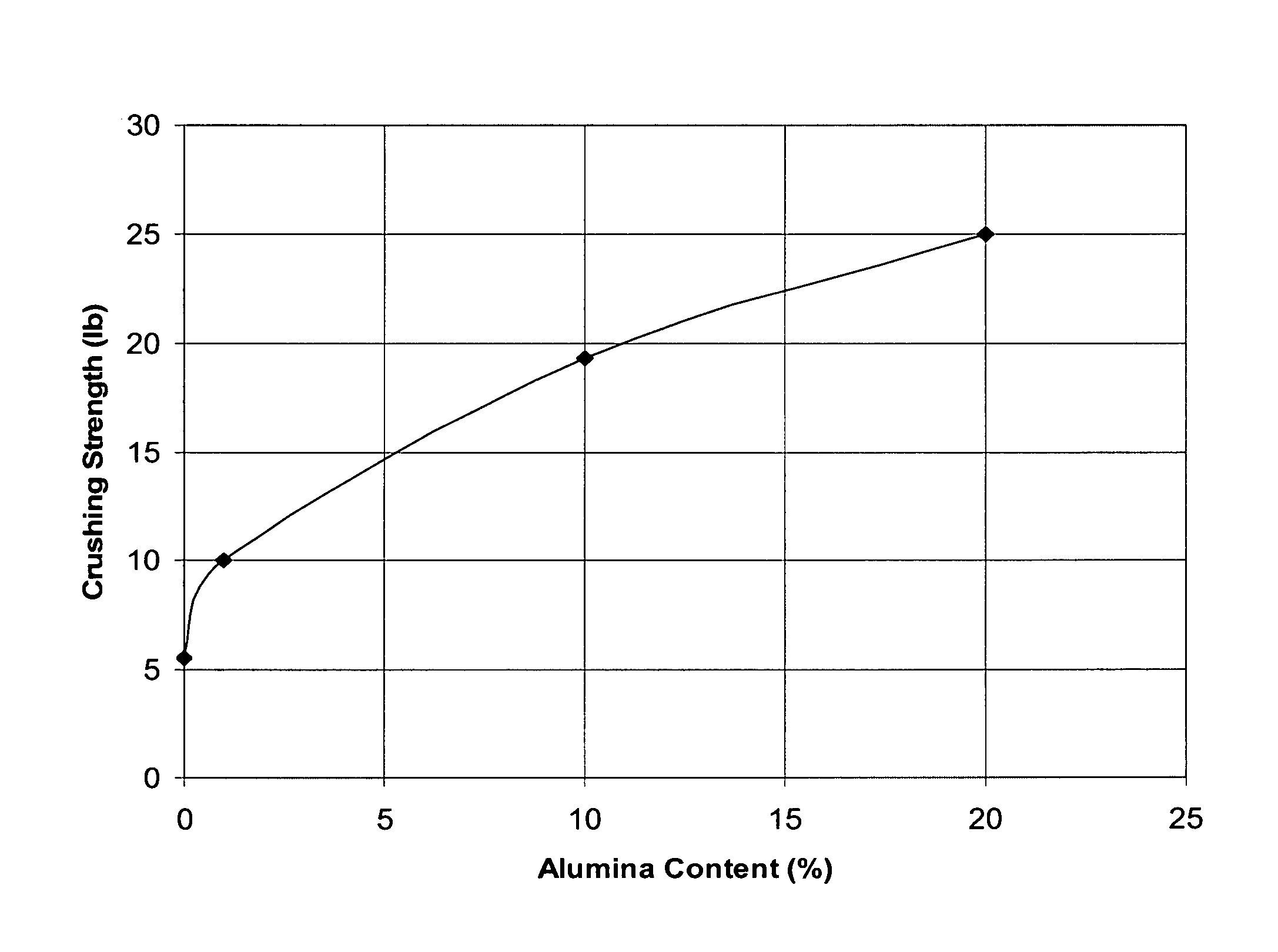
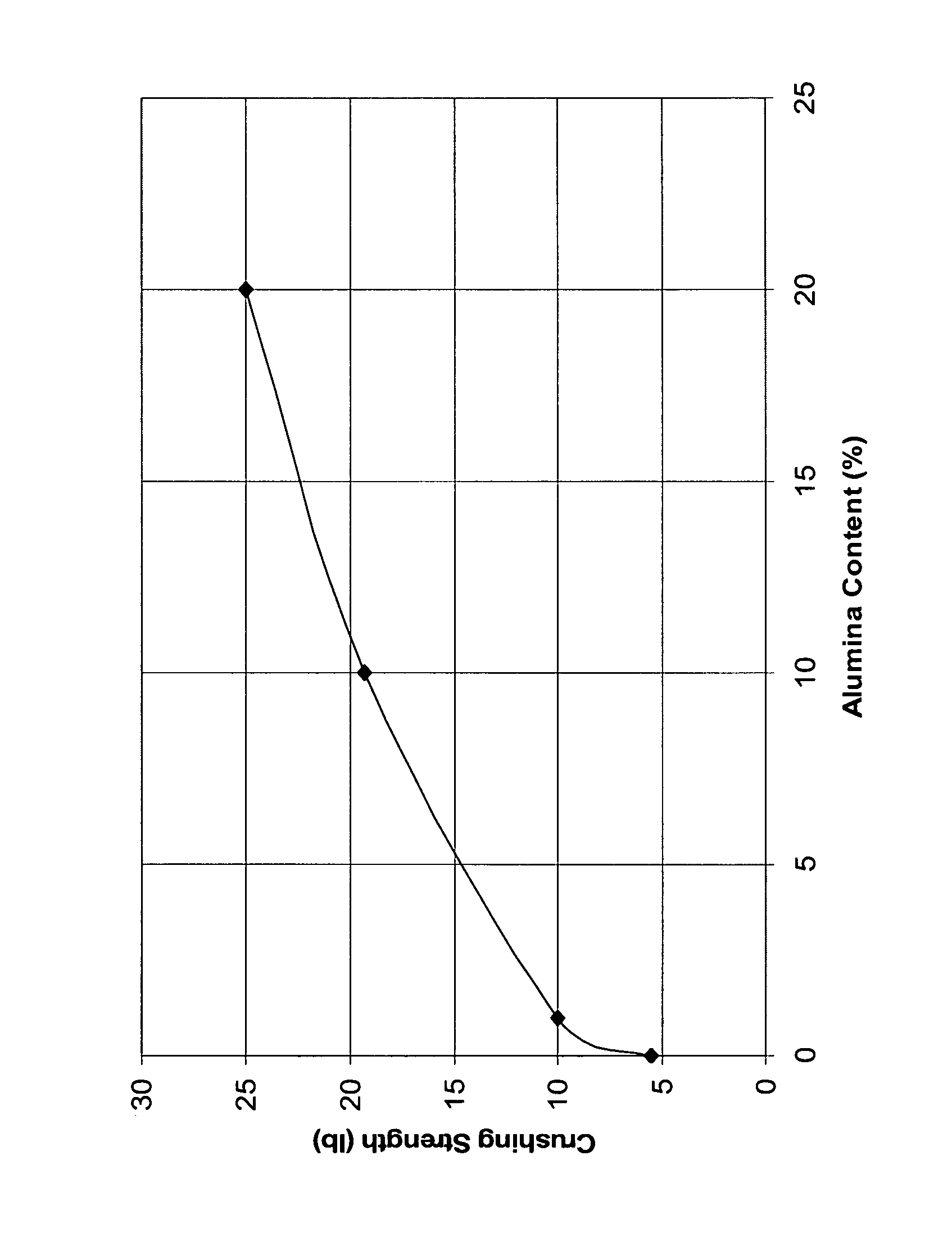
Titania-alumina supported palladium catalyst
InactiveUS8507720B2High activityHigh compressive strengthOther chemical processesOrganic compound preparationPalladium catalystOrganic chemistry
A catalyst comprising palladium supported on a titania-alumina extrudate is disclosed. The extrudate comprises at least 80 wt % titania and 0.1 to 15 wt % alumina. A palladium catalyst prepared from the titania-alumina extrudate has significantly higher crush strength. Its catalytic performance in vinyl acetate production is improved.
Owner:LYONDELLBASELL ACETYLS
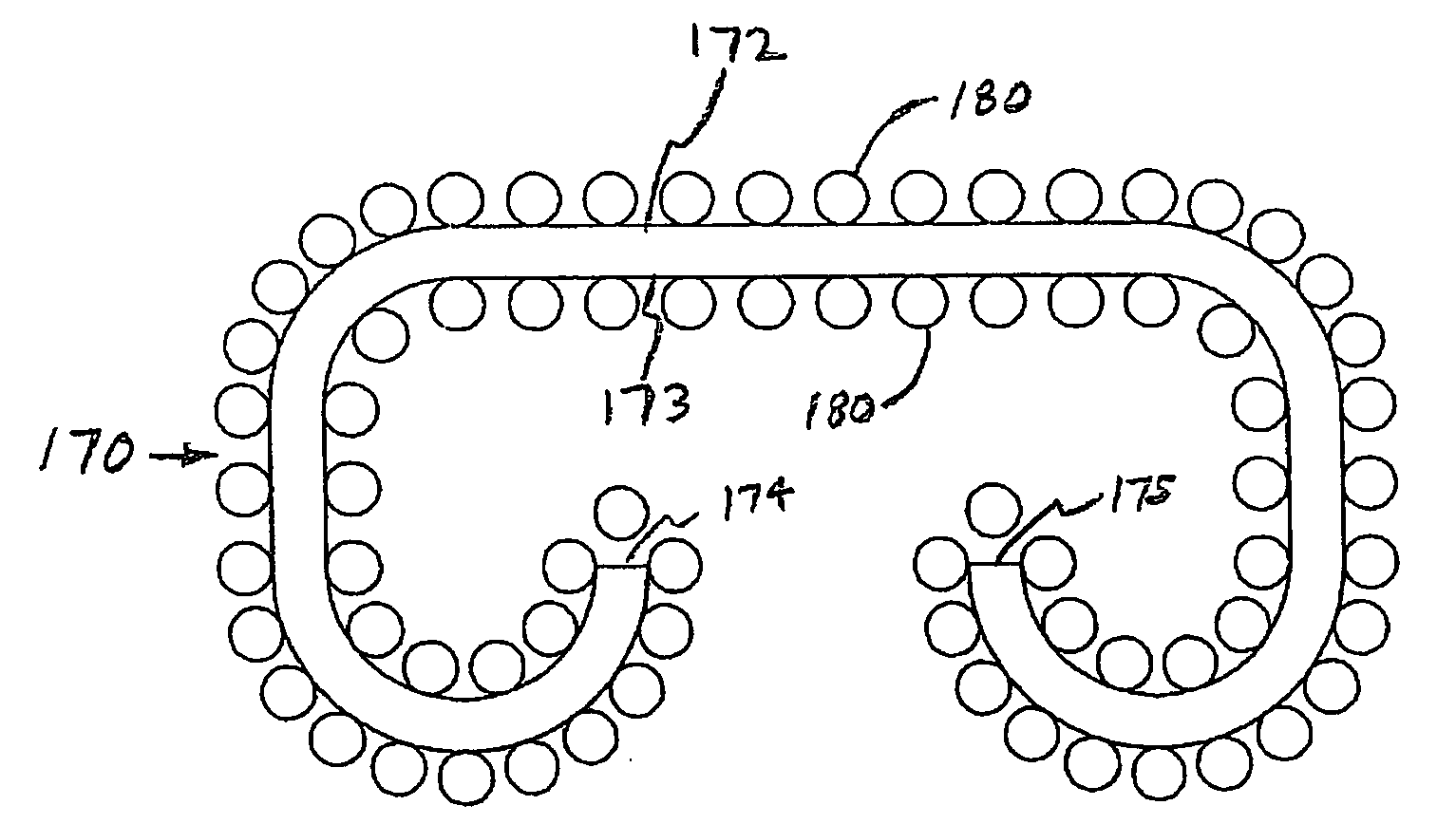
Surface treatments and modifications using nanostructure materials
InactiveUS20050113936A1Reduce surface tensionPromote and inhibit ingrowthSuture equipmentsHeart valvesGas phaseNanostructure
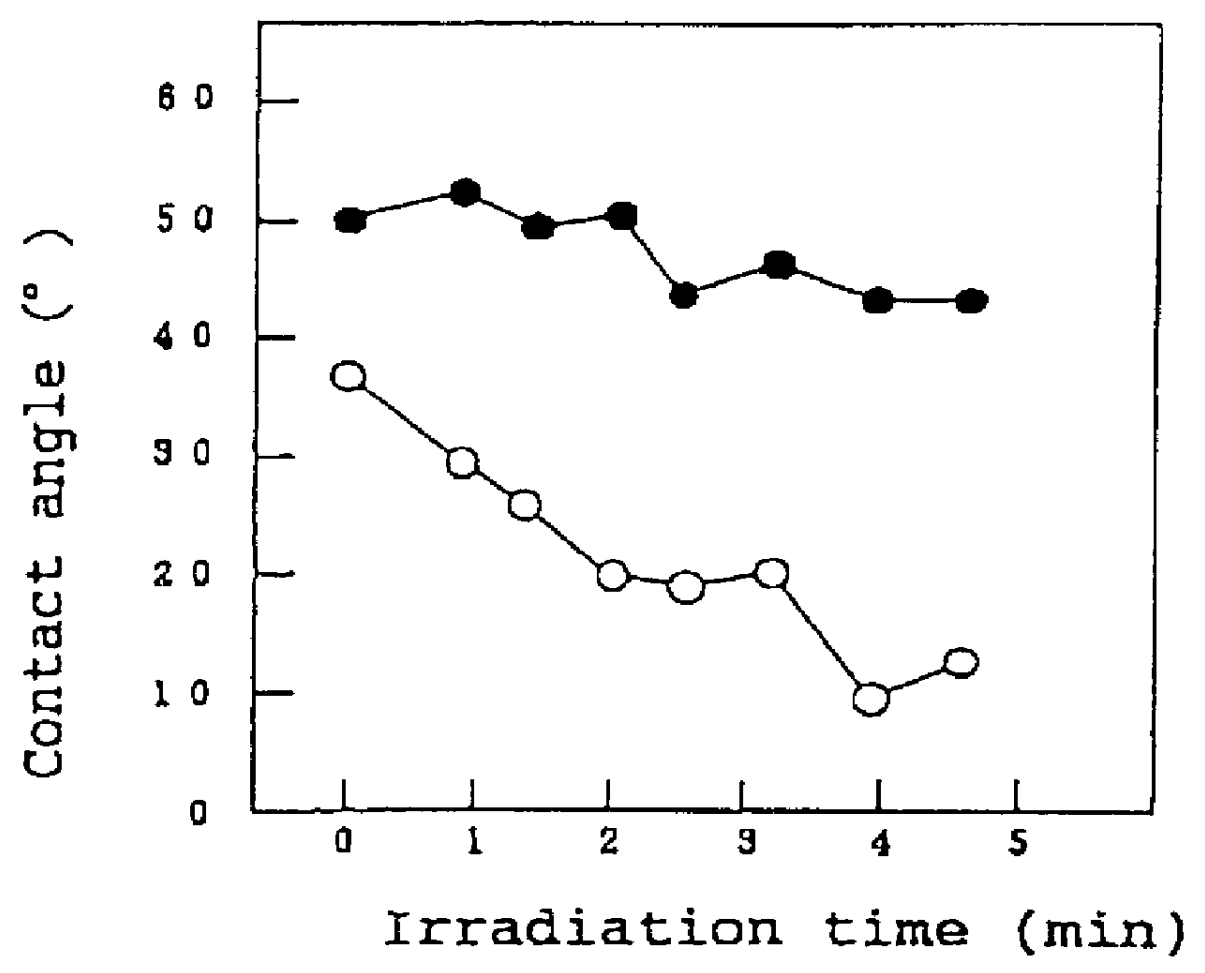
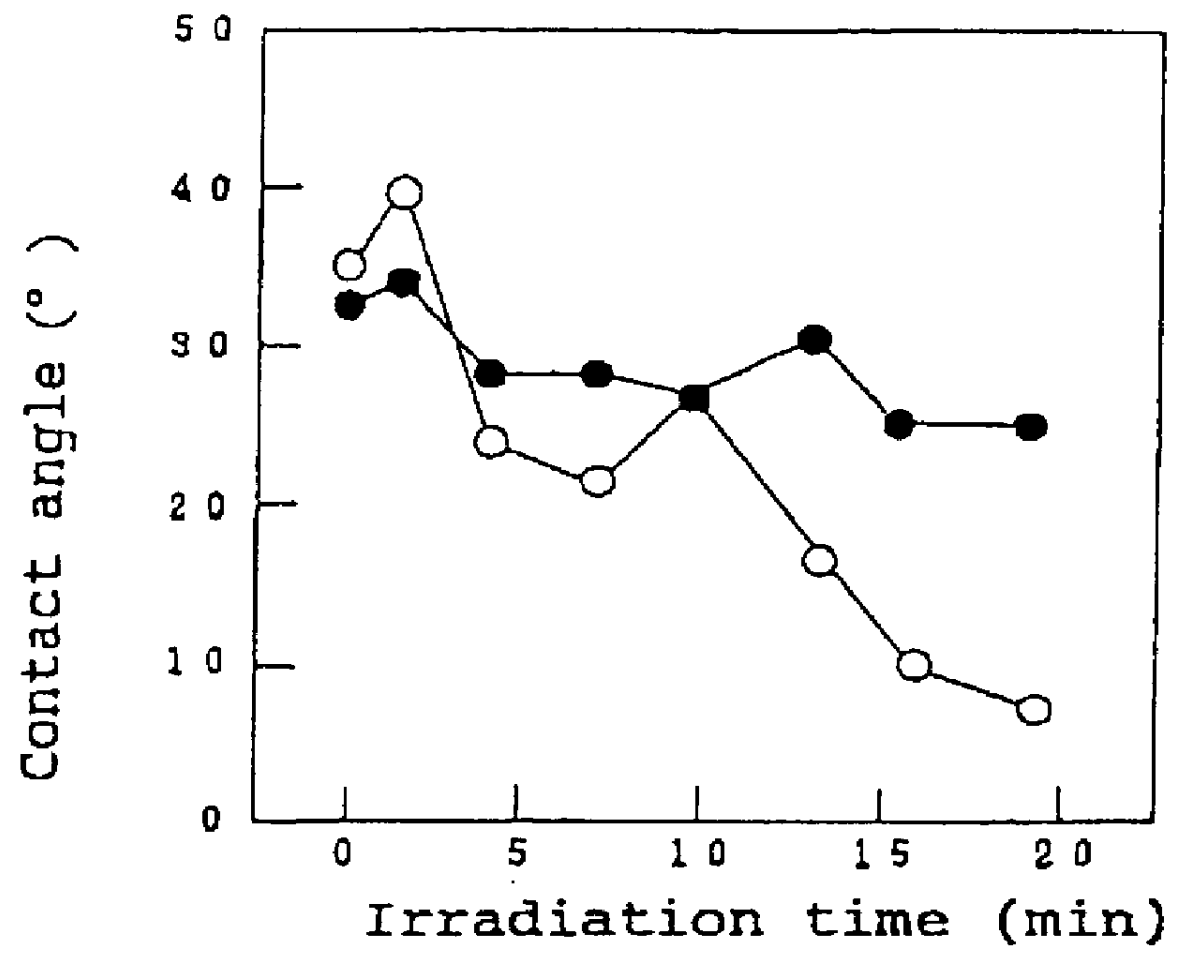
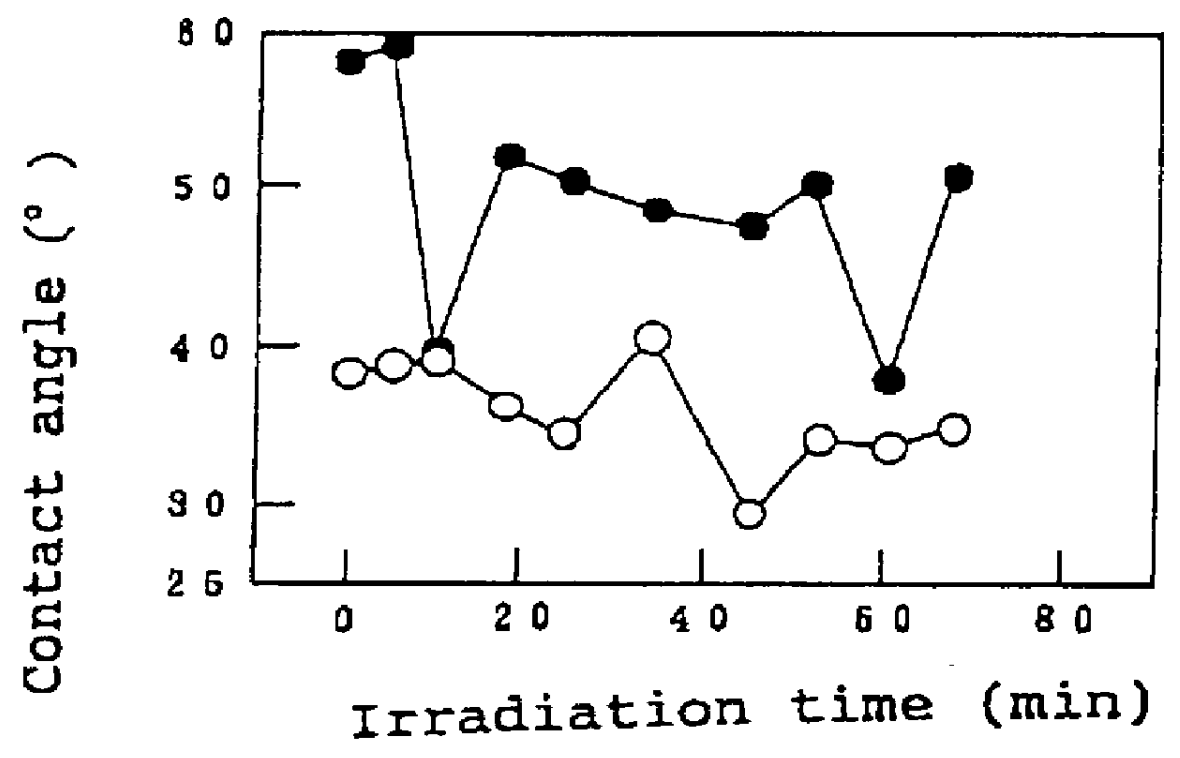
The invention is directed to nanostructure surface treatments, coatings or modifications formed from nanoscale building blocks. The nanostructure surface treatments, modifications or coatings have hydrophobic, hydrophilic and surface adherence properties. The nanoscale building blocks have orientation, geometry, packing density and composition that may be adjusted to control the unique surface characteristics of the desired treatment, coating or modification. Applications of this nanostructure technology include surgical clips, staples, retractors, sutures and manipulators where an improvement in traction, retention or occlusion is desired without excessive material or tissue deformation or where high compressive forces would be undesirable, dangerous or ineffective. In one aspect, a nanostructure surface treatment for a medical device having an external surface is disclosed, wherein the treatment is applied on the external surface to provide a hydrophobic or a hydrophilic surface. With this aspect, the treatment comprises titanium dioxide and provides nanoscopic structures having nearly vertical sidewalls. The treated surface of the device has contact angles greater than or equal to 150 degrees. The vertical sidewalls provide a negative capillary effect and have a width of about 200 nm. The vertical sidewalls attach to a wet surface by the negative capillary effect. The van der Waals forces of the vertical sidewalls enable the treated surface to attach to a dry surface. The treatment may be vapor deposited and cured on the device, or the treatment may be laser blasted on the device.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
an air purifier
InactiveCN103861421BLarger than surface and uniformGood adsorption and decomposition effectOther chemical processesDispersed particle separationActivated carbonHazardous substance
Owner:QINGDAO CHUANSHAN NEW MATERIALS
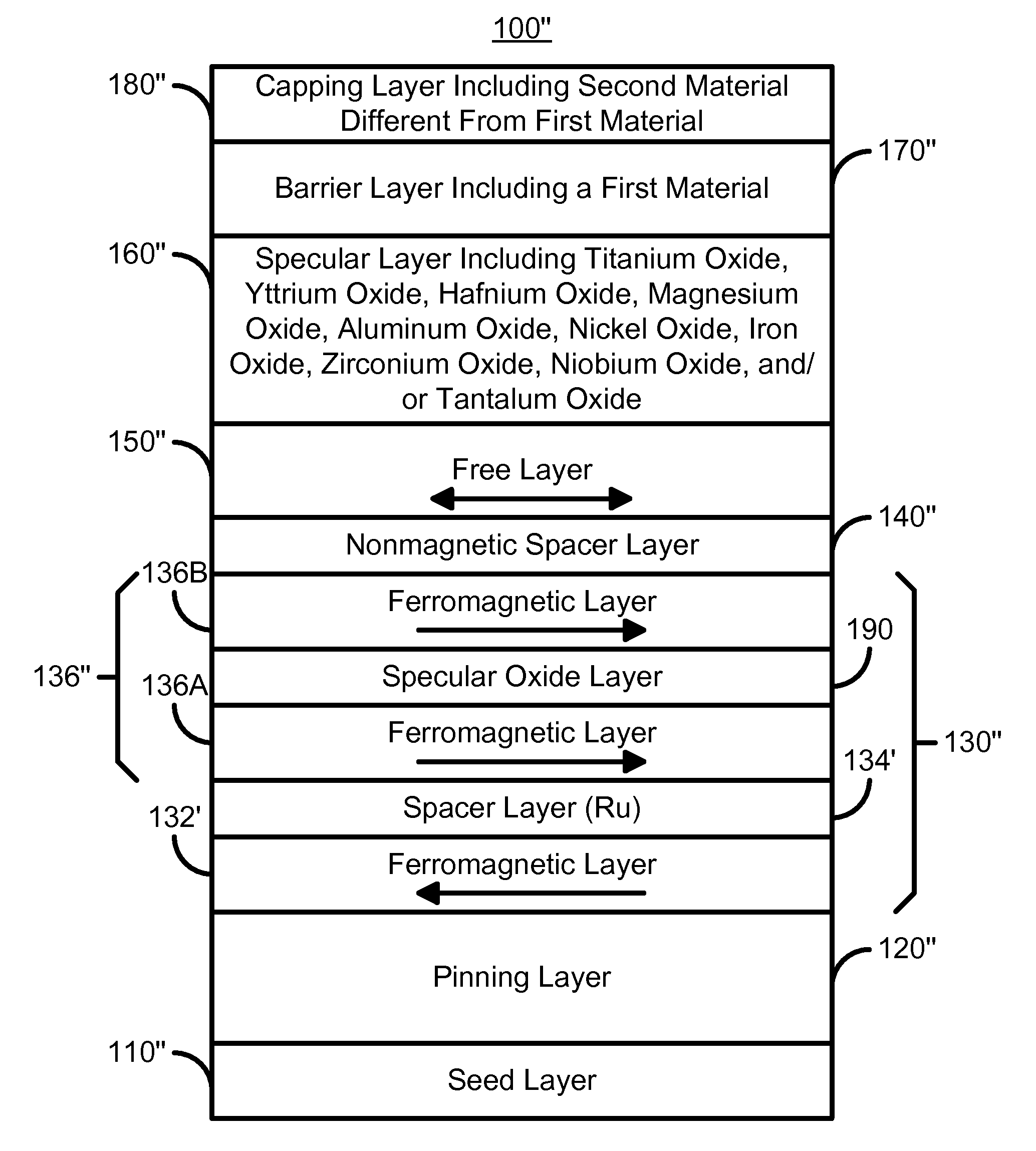
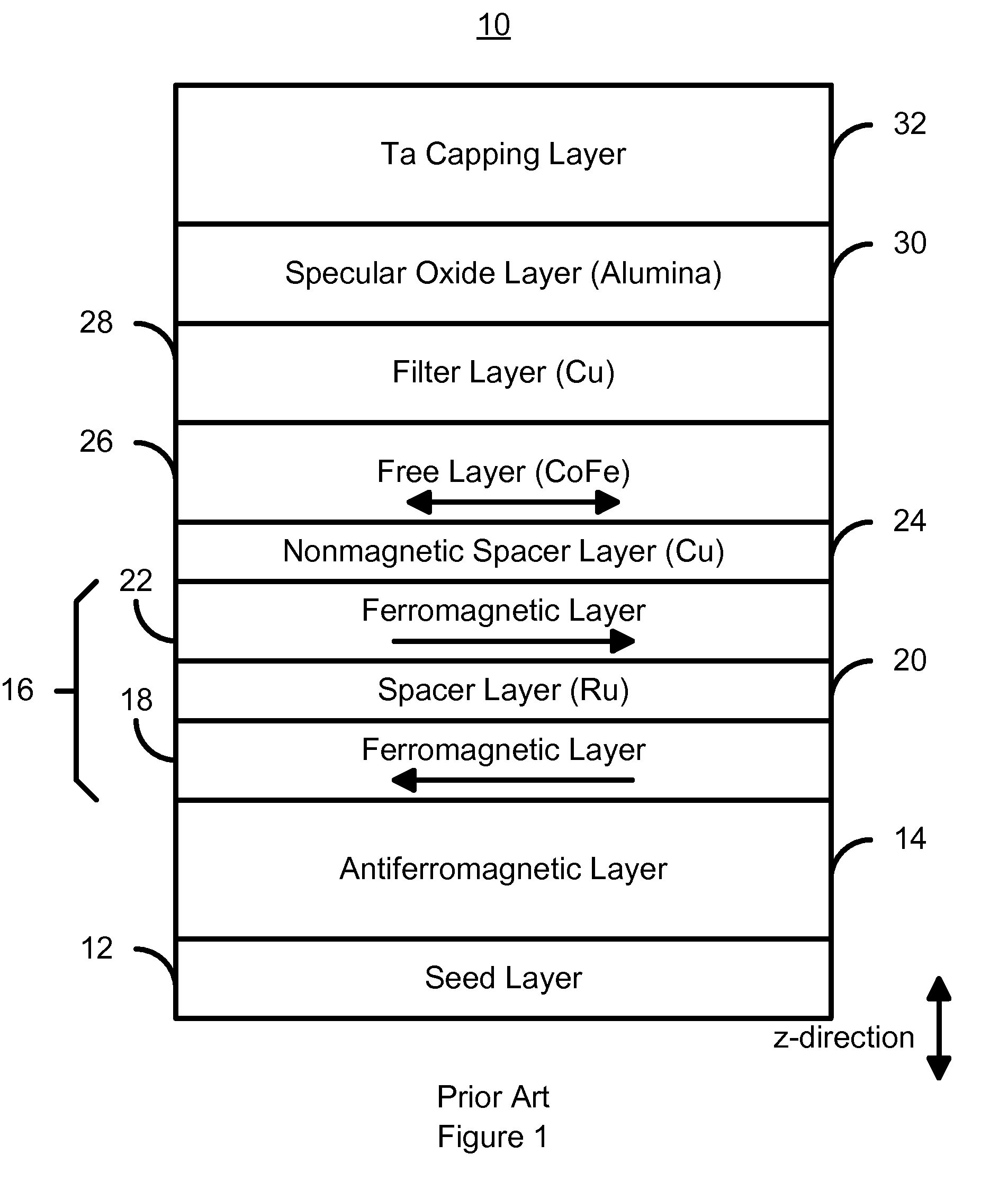
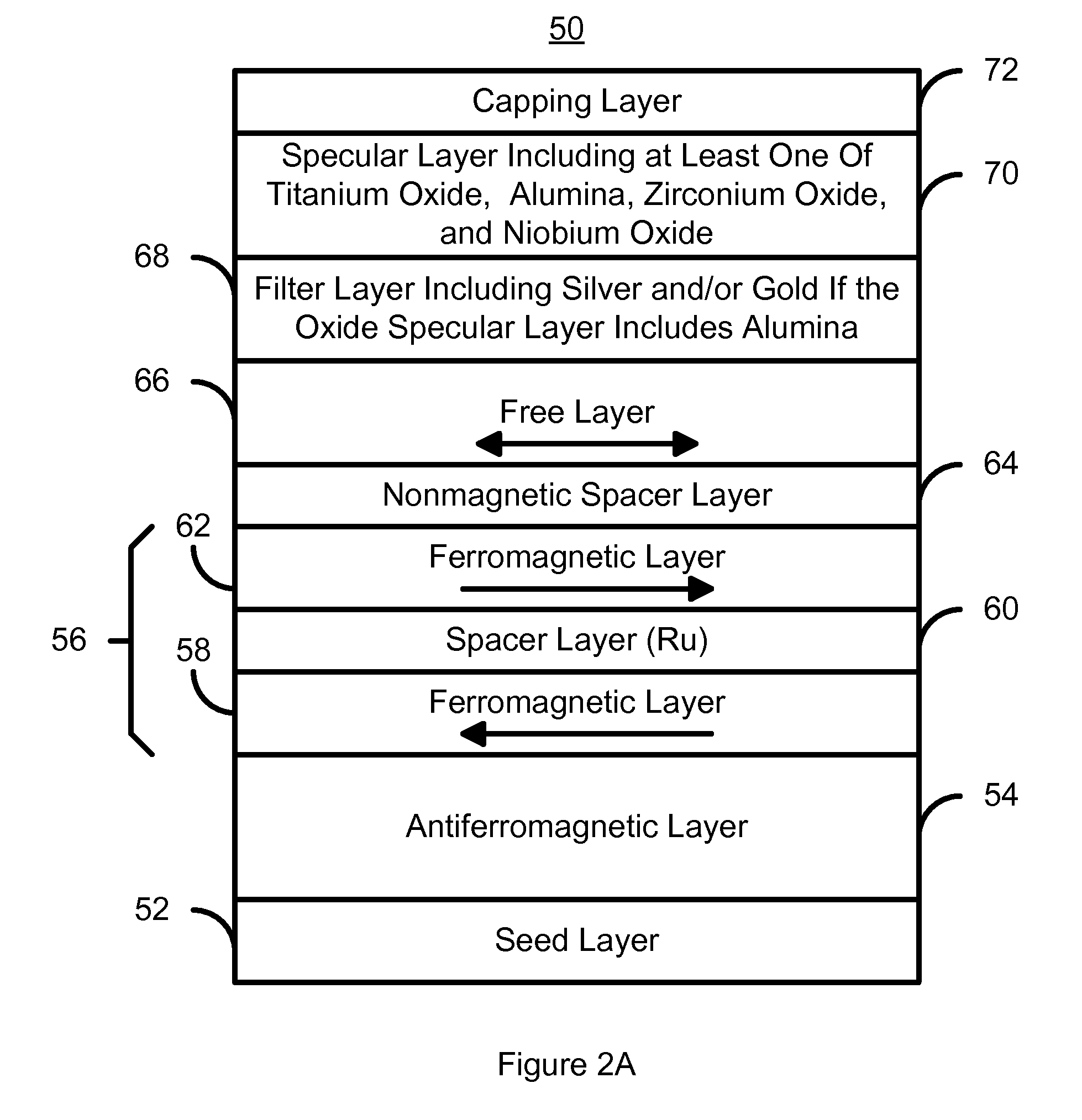
Magnetoresistive structure having a novel specular and barrier layer combination
InactiveUS7684160B1Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsConductive/insulating/magnetic material on magnetic film applicationYttriumTitanium oxide
A method and system for providing a magnetoresistive structure is disclosed. The magnetoresistive structure includes a pinned layer, a nonmagnetic spacer layer, a free layer, a specular layer, a barrier layer, and a capping layer. The spacer layer resides between the pinned layer and the free layer. The free layer is electrically conductive and resides between the specular layer and the nonmagnetic spacer layer. The specular layer is adjacent to the free layer and includes at least one of titanium oxide, yttrium oxide, hafnium oxide, magnesium oxide, aluminum oxide, nickel oxide, iron oxide, zirconium oxide, niobium oxide, and tantalum oxide. The barrier layer resides between the specular layer and the capping layer. The barrier layer is nonmagnetic and includes a first material. The capping layer includes a second material different from the first material.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Tubular titanium oxide particles, method for preparing the same, and use of the same
InactiveUS20040265587A1Large specific surface areaImprove detection accuracyMaterial nanotechnologyLight-sensitive devicesReduction treatmentSorbent
The process for preparing tubular titanium oxide particles comprises subjecting a water dispersion sol, which is obtained by dispersing (i) titanium oxide particles and / or (ii) titanium oxide type composite oxide particles comprising titanium oxide and an oxide other than titanium oxide in water, said particles having an average particle diameter of 2 to 100 nm, to hydrothermal treatment in the presence of an alkali metal hydroxide. After the hydrothermal treatment, reduction treatment (including nitriding treatment) may be carried out. The tubular titanium oxide particles obtained in this process are useful as catalysts, catalyst carriers, adsorbents, photocatalysts, decorative materials, optical materials and photoelectric conversion materials. Especially when the particles are used for semiconductor films for photovoltaic cells or photocatalysts, prominently excellent effects are exhibited.
Owner:JGC CATALYSTS & CHEM LTD
RFID device and method of forming
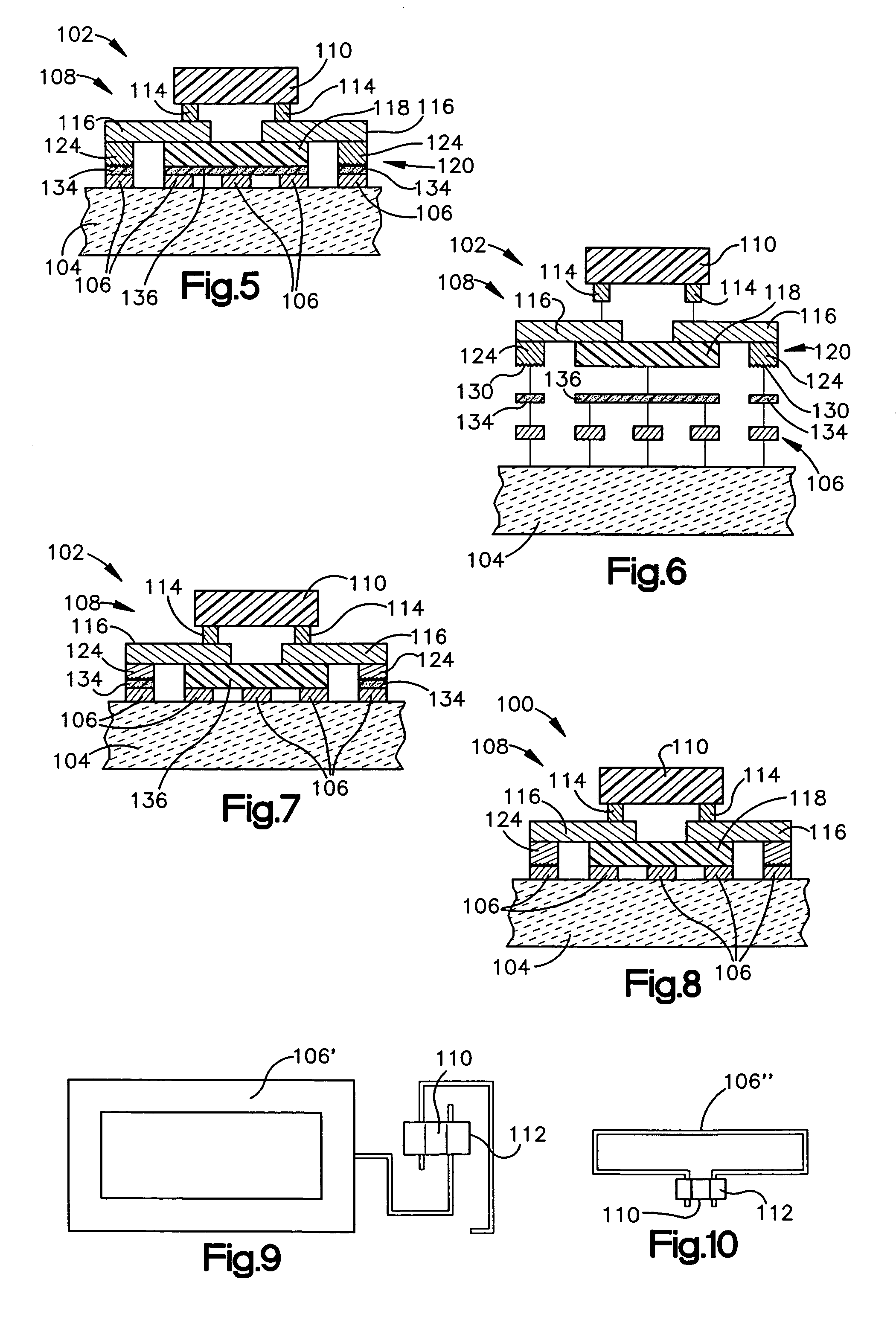
A radio frequency identification (RFID) inlay includes an electrical connection between a chip and an antenna. The electrical connection includes conductive interposer leads and a capacitive connection. The capacitive connection may involve putting the antenna and the interposer leads into close proximity, with dielectric pads therebetween, to allow capacitive coupling between the antenna and the interposer leads. The dielectric pads may include a non-conductive adhesive and a high dielectric material, such as a titanium oxide. The connections provide a convenient, fast, and effective way to operatively couple antennas and interposers. The RFID inlay may be part of an RFID lable or RFID tag.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
Catalyst for complete oxidation of formaldehyde at room temperature
ActiveCN101380574AEasy to makeEasy to operateDeodrantsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPorous carbonPt element
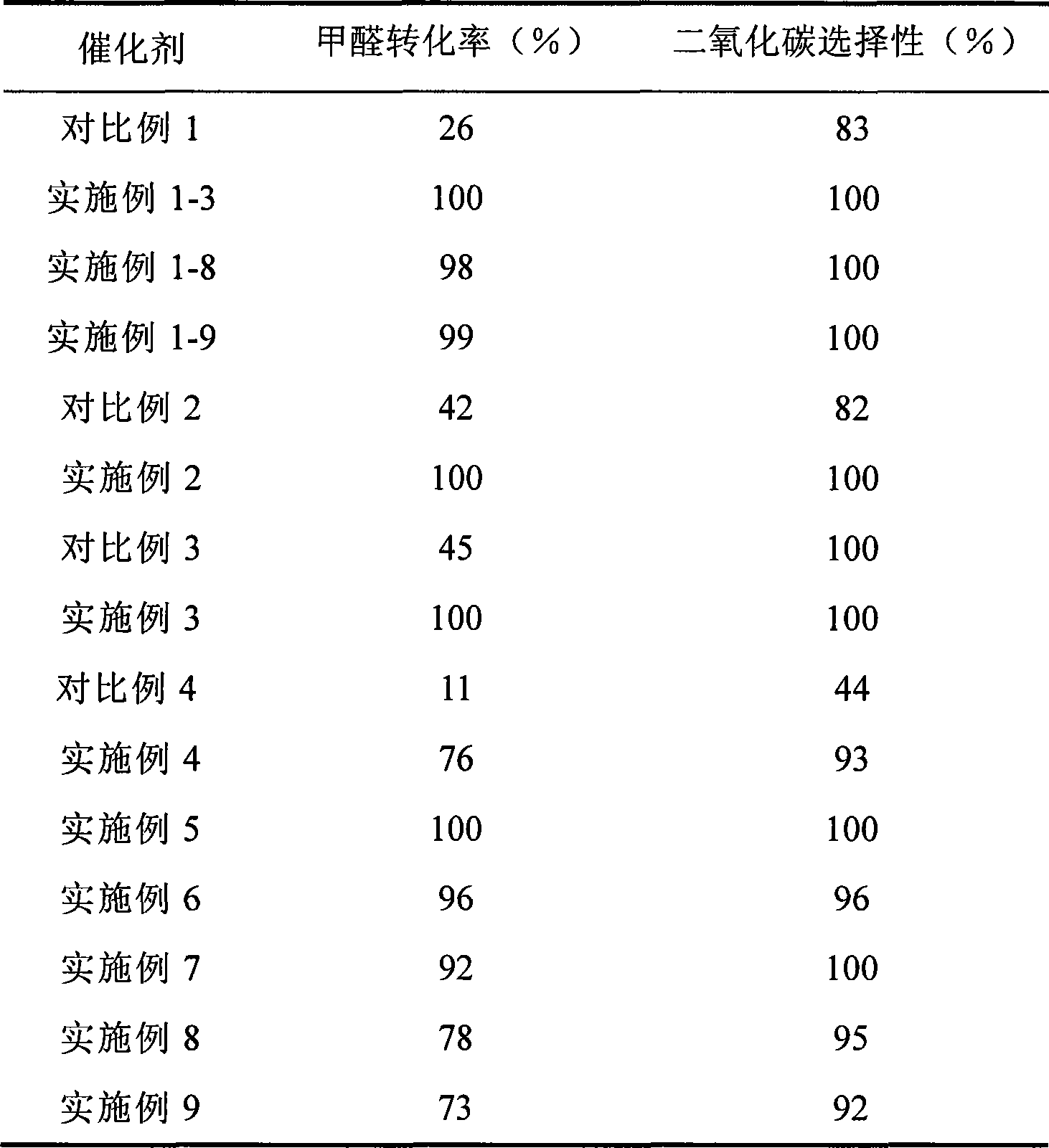
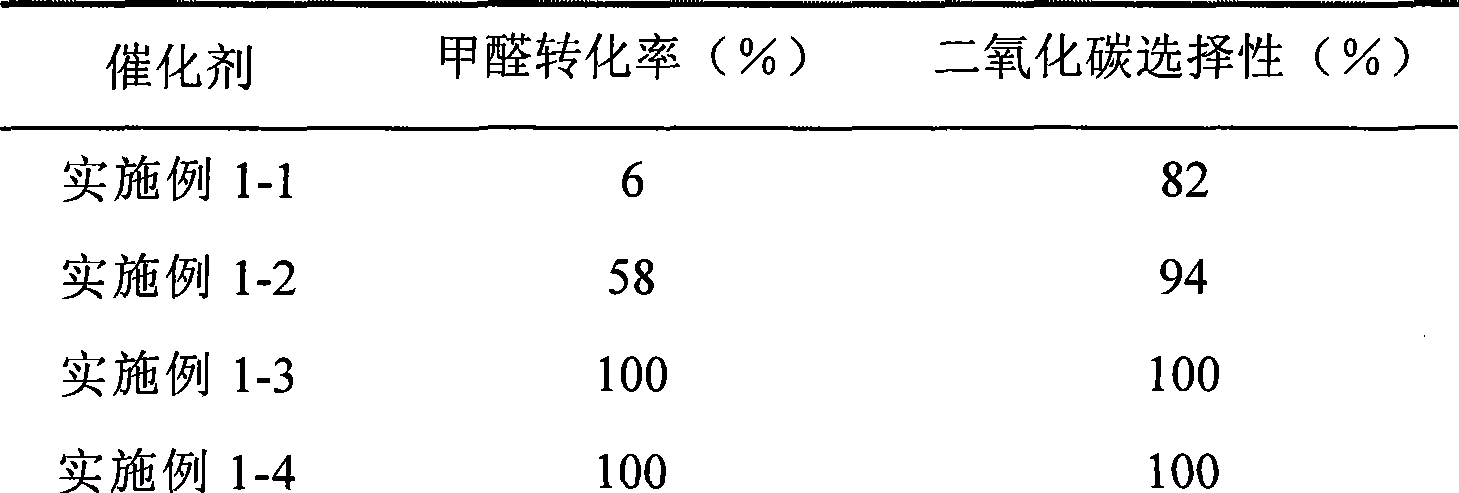
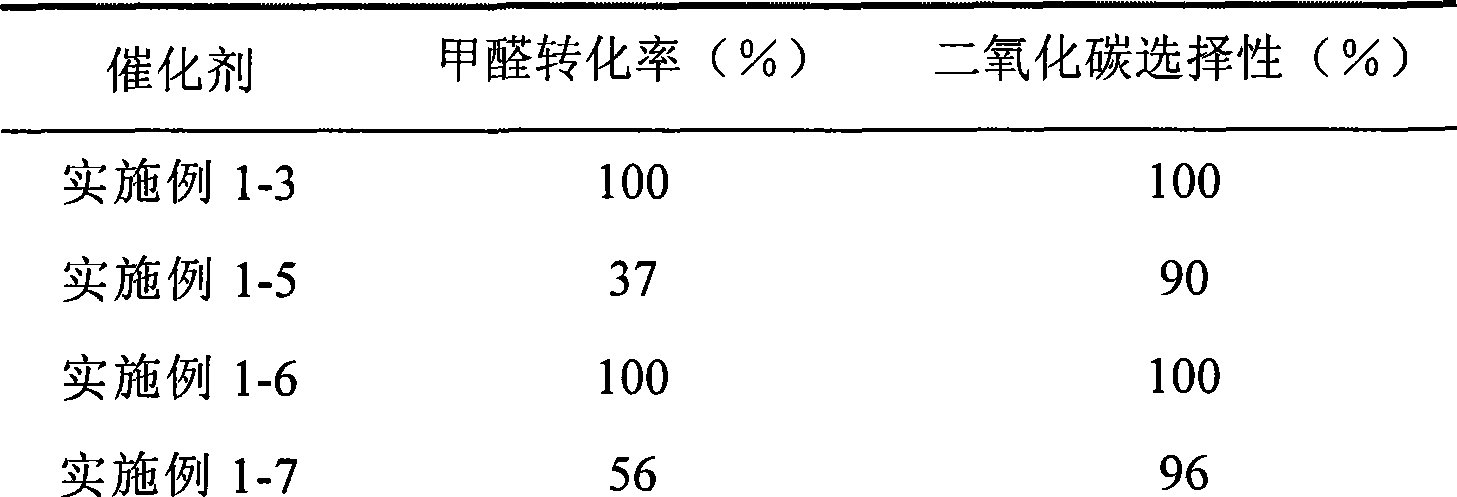
The invention provides a high selectivity catalyst used for catalyzing and completely oxidizing formaldehyde with low concentration at room temperature. The catalyst can catalyze formaldehyde completely so as to lead the formaldehyde to be converted into carbon dioxide and water at room temperature. In addition, the conversion rate of formaldehyde remains 100% within a long period of time, without complex auxiliary facilities such as light source, a heating oven and the like, and external conditions. The catalyst comprises three parts which are inorganic oxide carrier, noble metal component and auxiliary ingredient. Porous inorganic oxide carrier is one of cerium dioxide, zirconium dioxide, titanium dioxide, aluminium sesquioxide, tin dioxide, silicon dioxide, lanthanum sesquioxide, magnesium oxide and zinc oxide or the mixture thereof or composite oxide thereof, zeolite, sepiolite and porous carbon materials. The noble metal component of the catalyst is at least one of platinum, rhodium, palladium, gold and silver. The auxiliary ingredient is at least one of the alkali metals of lithium, sodium, kalium, rubidium and cesium. The loading of the noble metal component used in the catalyst of the invention is 0.1 to 10% according to weight converter of metal elements and the selective preference is 0.3 to 2%. The loading of the auxiliary ingredient is 0.2 to 30% according to weight converter of metal elements and the selective preference is 1 to 10%. When the loading of the auxiliary ingredient is lower than 0.2% or higher than 30%, the activity of the catalyst for catalyzing and oxidizing formaldehyde at room temperature is decreased remarkably.
Owner:广东顺德中科鸿图环境材料有限公司
Aqueous inkjet ink
InactiveUS20070060670A1Useful in printingEnhance the imageInksDyeing processTitanium dioxideChemistry
The present invention pertains to an aqueous inkjet ink, preferably white in color, comprising a polymerically dispersed titanium dioxide and a crosslinked polyurethane binder. The invention also pertains to an ink set with an aqueous white ink as one of its inks. The invention also pertains to a method of inkjet printing with the ink and ink set. The use of the dispersed titanium dioxide and crosslinked polyurethane binder described herein results in inkjet inks having adequate stability, and having a particular utility in printing on textiles.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Anti-infectious, biocompatible titanium coating for implants, and method for the production thereof
The present invention relates to a method for the preparation of a biocompatible metal ion-containing titanium oxide coating on an implant wherein the metal ions can be eluted under physiological conditions and are homogeneously dispersed within the coating, as well as to an implant which can be prepared according to the method of the present invention.
Owner:BIOCER ENTWICKLUNGS
Supported palladium-gold catalysts and preparation of vinyl acetate therewith
InactiveUS20100121100A1High activity selectivityImproves oxygen selectivityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationTungsten trioxidePalladium
Disclosed is a catalyst. The catalyst comprises palladium, gold, and a support comprising titanium dioxide and tungsten trioxide. The support preferably comprises from 75 wt % to 99 wt % of titanium dioxide and from 1 wt % to 25 wt % of tungsten trioxide. A method for preparing the catalyst is also disclosed. The method comprises impregnating the support with a palladium compound and a gold compound, calcining the impregnated support, and then reducing the calcined support. Further disclosed is a method for preparing vinyl acetate with the catalyst. The catalyst exhibits improved catalytic activity and selectivity.
Owner:LYONDELLBASELL ACETYLS
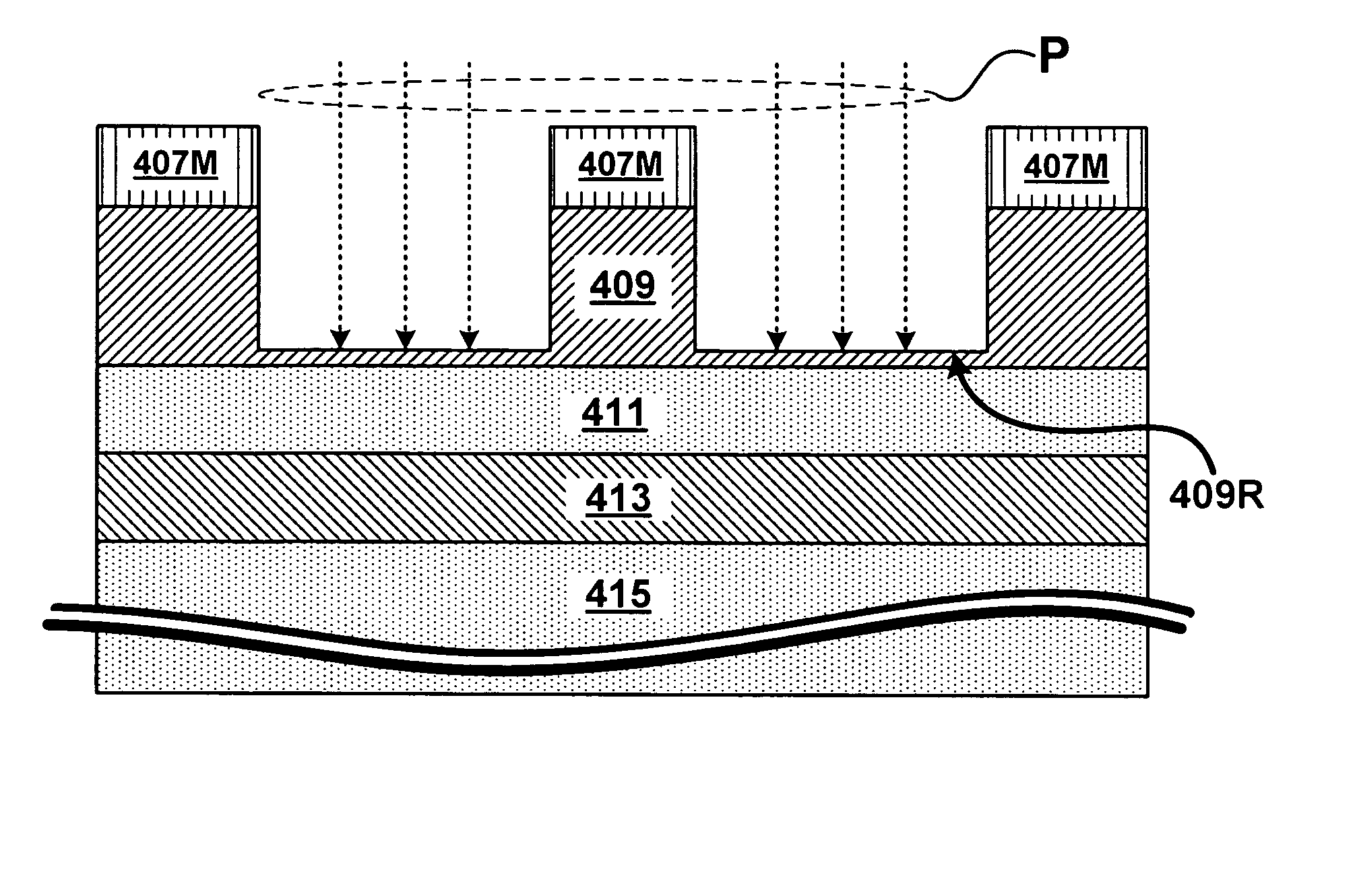
Structures, methods, and systems for ferroelectric memory transistors
InactiveUS20050030825A1Reliability can be promotedReduce layeringSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerPermittivity
Integrated memory circuits, key components in thousands of electronic and computer products, have recently been made using ferroelectric memory transistors, which offer faster write cycles and lower power requirements than over conventional floating-gate transistors. One problem that hinders the continued down-scaling of conventional ferroelectric memory transistors is the vulnerability of their gate insulations to failure at thinner dimensions. Accordingly, the inventors devised unique ferroelectric gate structures, one of which includes a high-integrity silicon-oxide insulative layer, a doped titanium-oxide layer, a weak-ferroelectric layer, and a control gate. The doped titanium-oxide layer replaces a metal layer in the conventional ferroelectric gate structure, and the weak-ferroelectric layer replaces a conventional ferroelectric layer. These replacements reduce the permittivity mismatch found in conventional gate structures, and thus reduce stress on gate insulation layers, thereby improving reliability of ferroelectric memory transistors, particularly those with thinner gate insulation.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
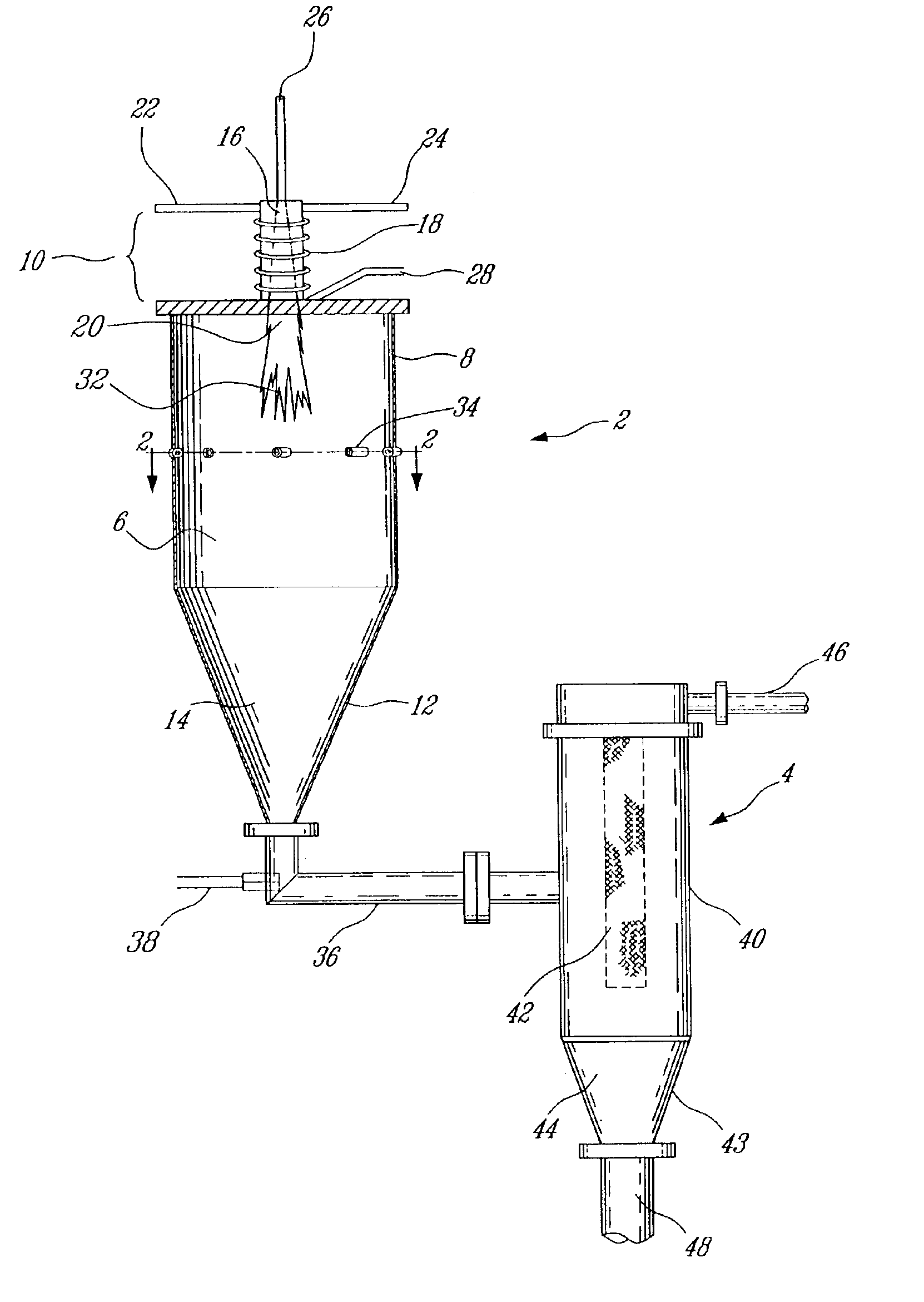
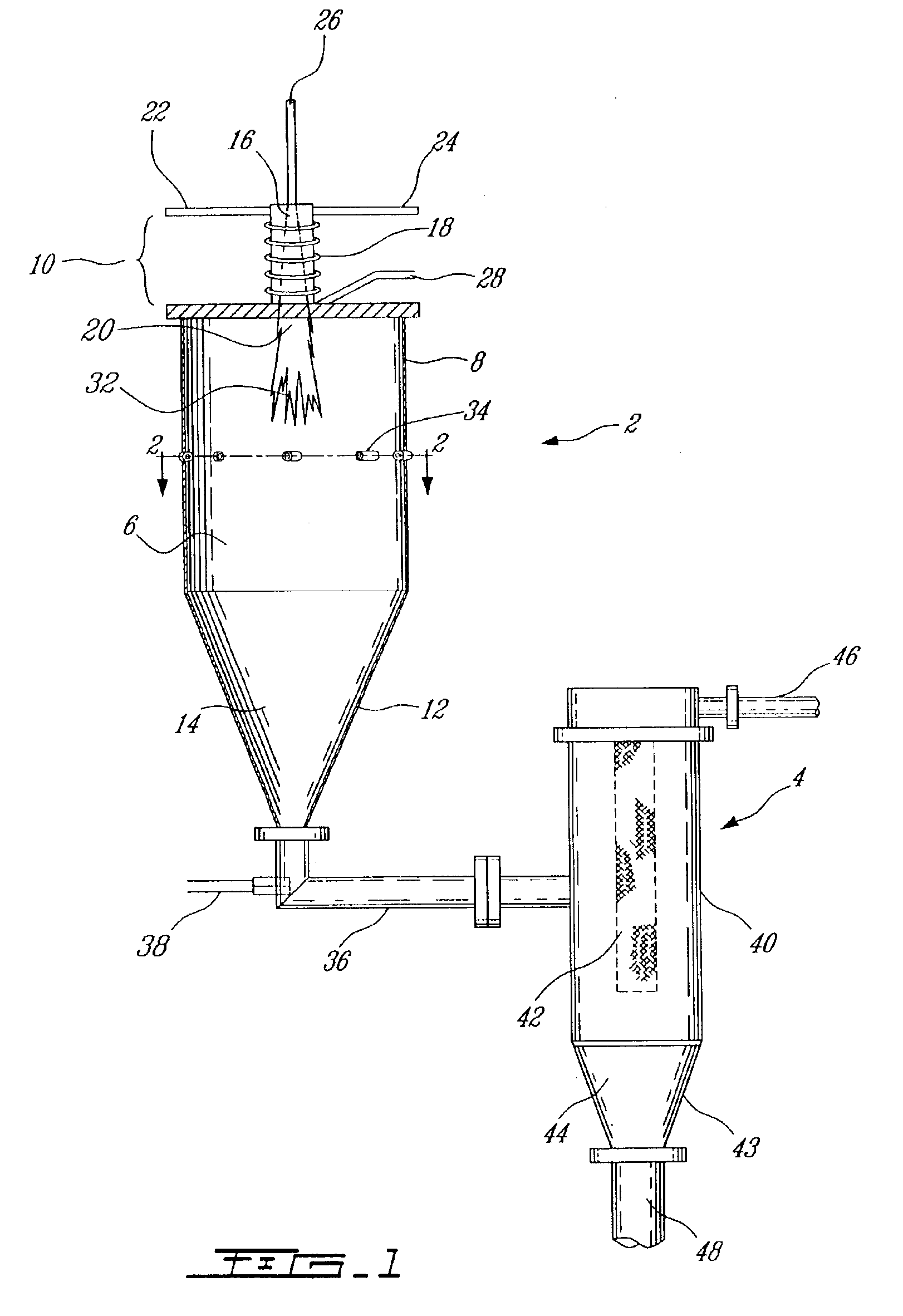
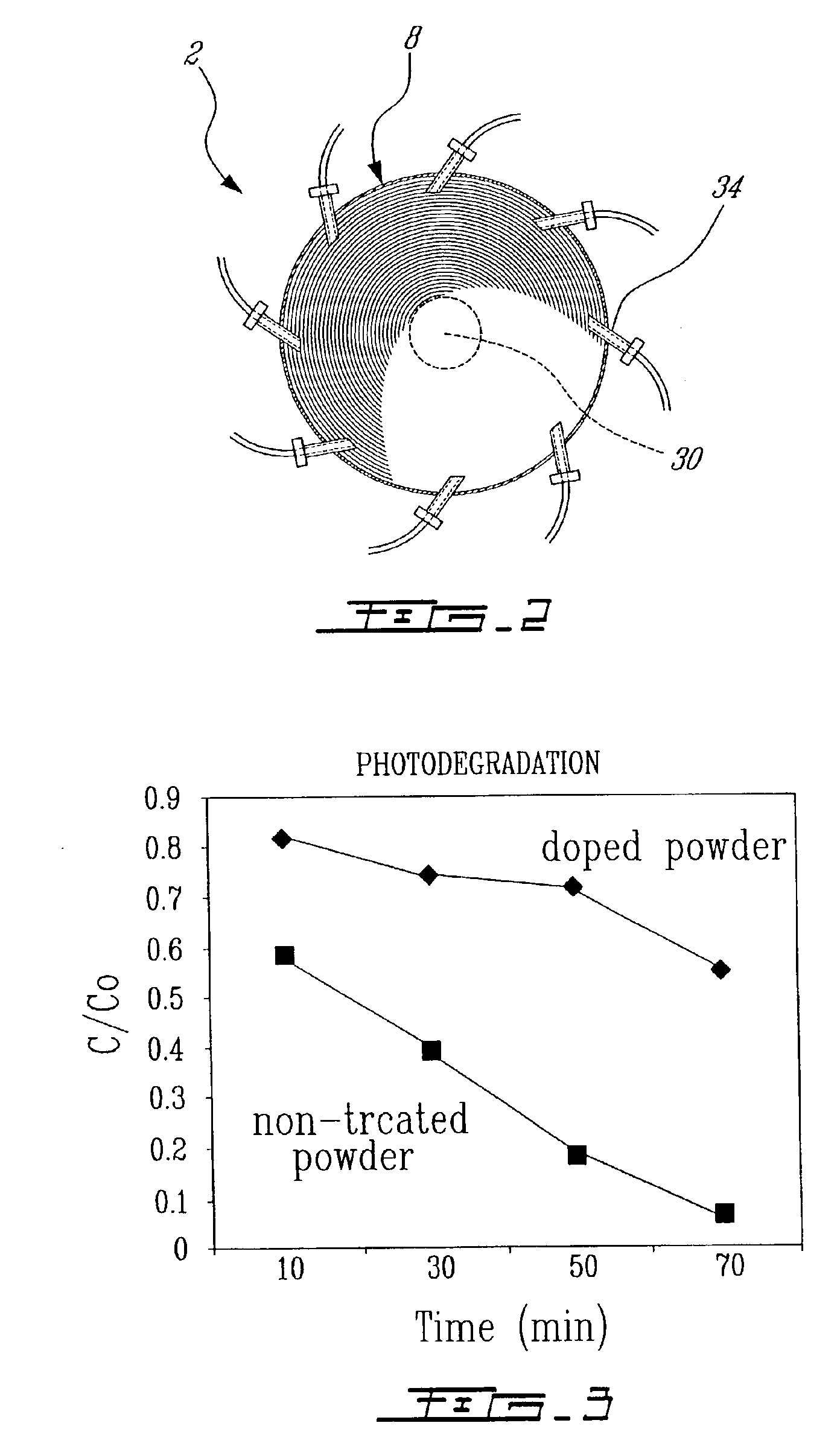
Plasma synthesis of metal oxide nanopowder and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS6994837B2Large dischargeKeep for a long timePigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyDopantPhysical chemistry
A process and apparatus for the synthesis of metal oxide nanopowder from a metal compound vapour is presented. In particular a process and apparatus for the synthesis of TiO2 nanopowder from TiCl4 is disclosed. The metal compound vapour is reacted with an oxidizing gas in electrically induced RF frequency plasma thus forming a metal oxide vapour. The metal oxide vapour is rapidly cooled using a highly turbulent gas quench zone which quickly halts the particle growth process, yielding a substantial reduction in the size of metal oxide particles formed compared with known processes. The metal compound vapour can also react with a doping agent to create a doped metal oxide nanopowder. Additionally, a process and apparatus for the inline synthesis of a coated metal oxide is disclosed wherein the metal oxide particles are coated with a surface agent after being cooled in a highly turbulent gas quench zone.
Owner:TEKNA PLASMA SYST INC
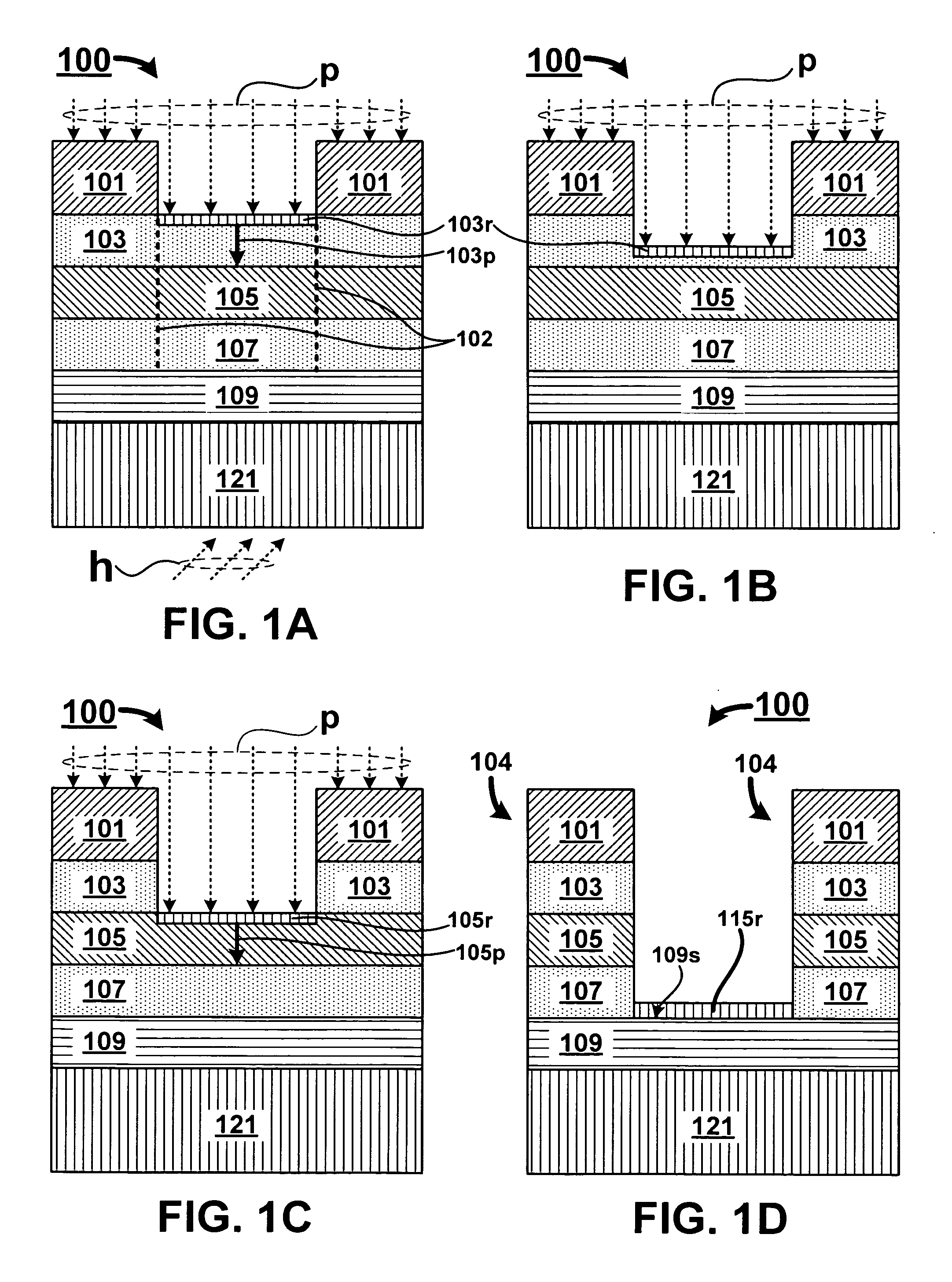
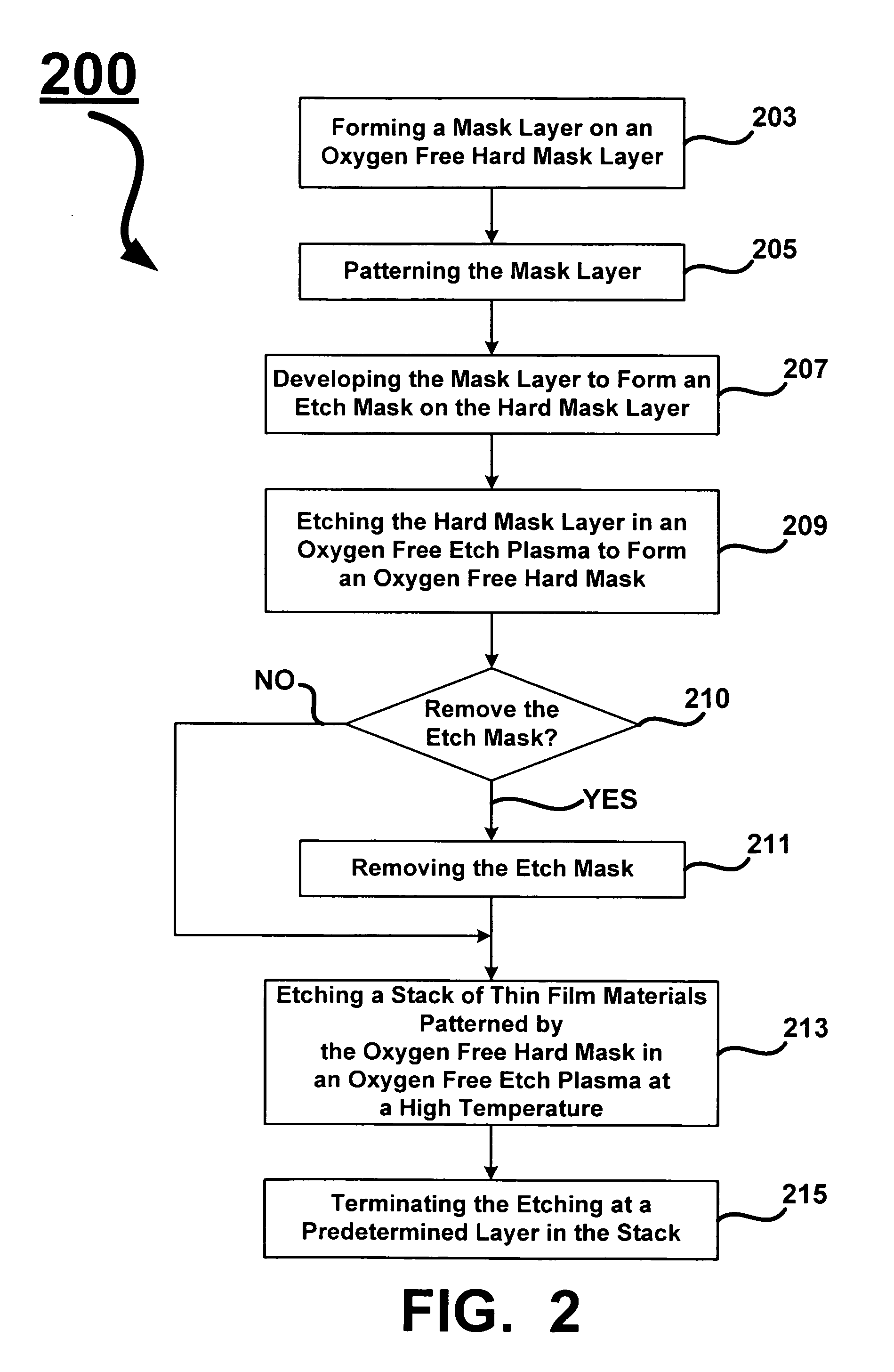
Oxygen depleted etching process
A method for oxygen depleted plasma etching and mixed mode plasma etching are disclosed. The method includes using an oxygen free etch plasma or a substantially oxygen free etch plasma at a high temperature to etch a stack including a plurality of layers of thin film materials. The oxygen depleted etching prevents or substantially reduces by-product re-deposition of titanium oxides generated by etching of titanium thin films in the stack. The titanium oxides can serve as a secondary mask layer that can cause defects in devices formed from the stack. Mixed mode plasma etching can include etching the stack with an oxygen free plasma, a substantially oxygen free plasma, and an oxygen containing plasma at different stages of a process.
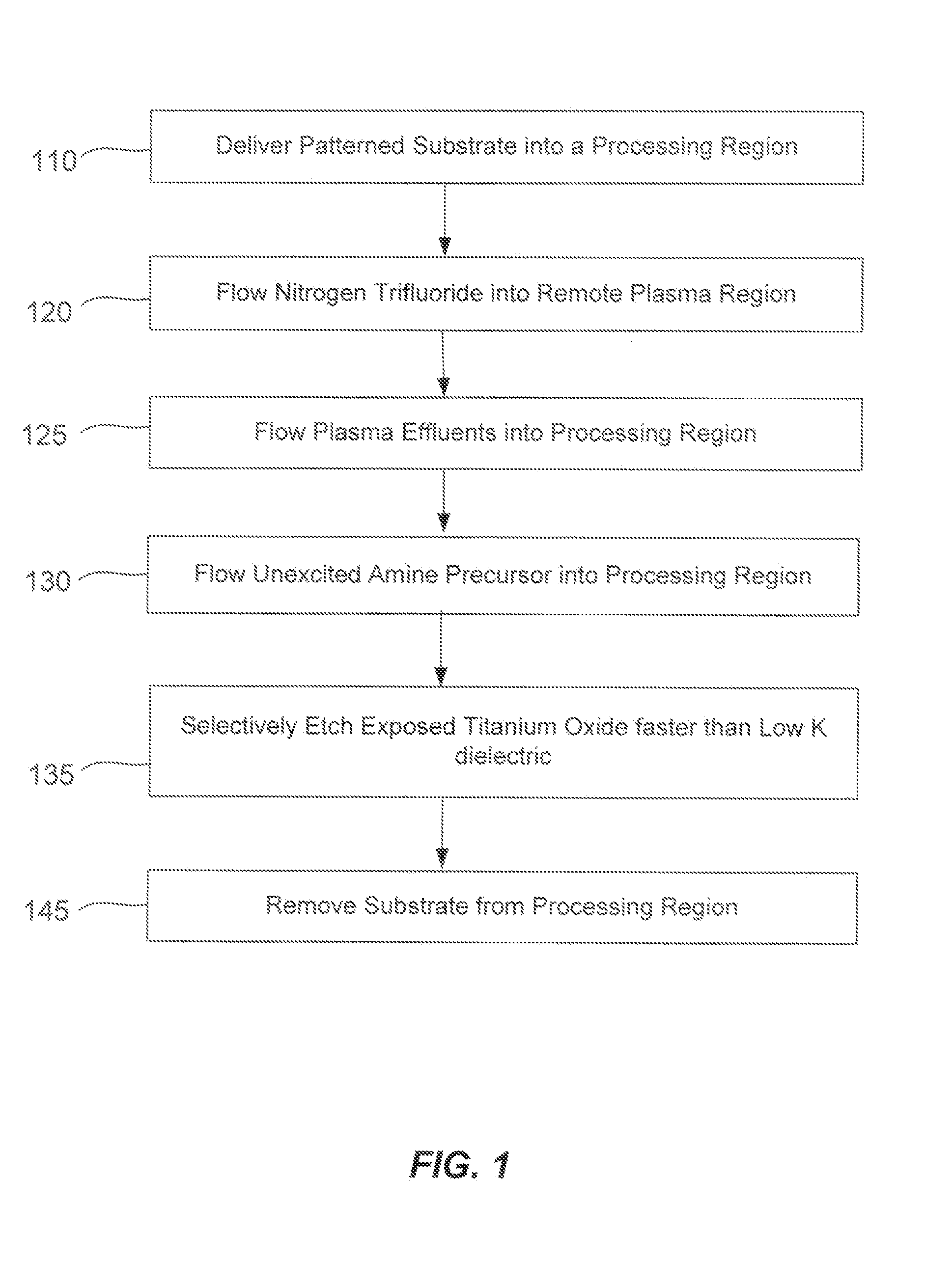
Owner:UNITY SEMICON
Aluminum titanate ceramic forming batch mixtures and green bodies including pore former combinations and methods of manufacturing and firing same
InactiveUS20070006561A1Low exothermic reaction and exothermic reactionReduction tendencyDispersed particle filtrationTransportation and packagingCeramic moldingSolvent
A ceramic forming batch mixture including inorganic batch materials, such as sources of alumina, titania, and silica, a pore former combination including first and second pore formers with different compositions; an organic binder; and a solvent. Also disclosed is a method for producing a ceramic article involving mixing the inorganic batch materials with the pore former combination having first and second pore formers of different composition, adding an organic binder and a solvent, forming a green body; and firing the green body. A green body having a combination of first and second pore formers with different compositions is disclosed, as are several methods for firing to produce ceramic articles such as aluminum titanate.
Owner:CORNING INC
Multifunctional composite absorbing material for purifying water and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102350298AReduce wasteEfficient removalOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisAcrylic resinCerium
The invention provides a multifunctional composite absorbing material for purifying water and a preparation method thereof, relating to an absorbing material. The invention provides the multifunctional composite absorbing material for purifying water, which can be used for effectively removing a plurality of harmful substances in the water and has higher removal efficiency and lower production cost, and the preparation method thereof. The absorbing material is selected from at least one of absorbing materials A, B and C; the absorbing material A takes a mesoporous adsorption ceramic material as a carrier to load nano metals including nano silver, nano zinc, nano iron and nano cerium; the absorbing material B takes the mesoporous adsorption ceramic material as the carrier to load nano metal oxides including nano titanium dioxide, nano zinc oxide, nano ferric oxide and nano cerium dioxide; and the absorbing material C is prepared from the following raw materials according to the mass ratio: 100-200 parts of active carbon powder, 20-30 parts of polyethylene powder, 10-30 parts of calcium sulfite powder, 10-30 parts of natural zeolite powder, 20-40 parts of macroporous acrylic resin and 10-20 parts of attapulgite powder.
Owner:XIAMEN BAILIN WATER PURIFICATION TECH CO LTD
Process for making durable rutile titanium dioxide pigment by vapor phase deposition of surface treatment
The present invention relates to a process for making durable titanium dioxide pigment by vapor phase deposition of surface treatments on the titanium dioxide particle surface by reacting titanium tetrachloride vapor, an oxygen containing gas and aluminum chloride in a plug flow reactor to form a product stream containing titanium dioxide particles; and introducing silicon tetrachloride into the reactor at a point down stream of the point where the titanium tetrachloride and oxygen were contacted and where at least 97% of the titanium tetrachloride has been converted to titanium dioxide or where the reaction temperature is no greater than about 1200° C., and preferably not more than about 1100° C.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
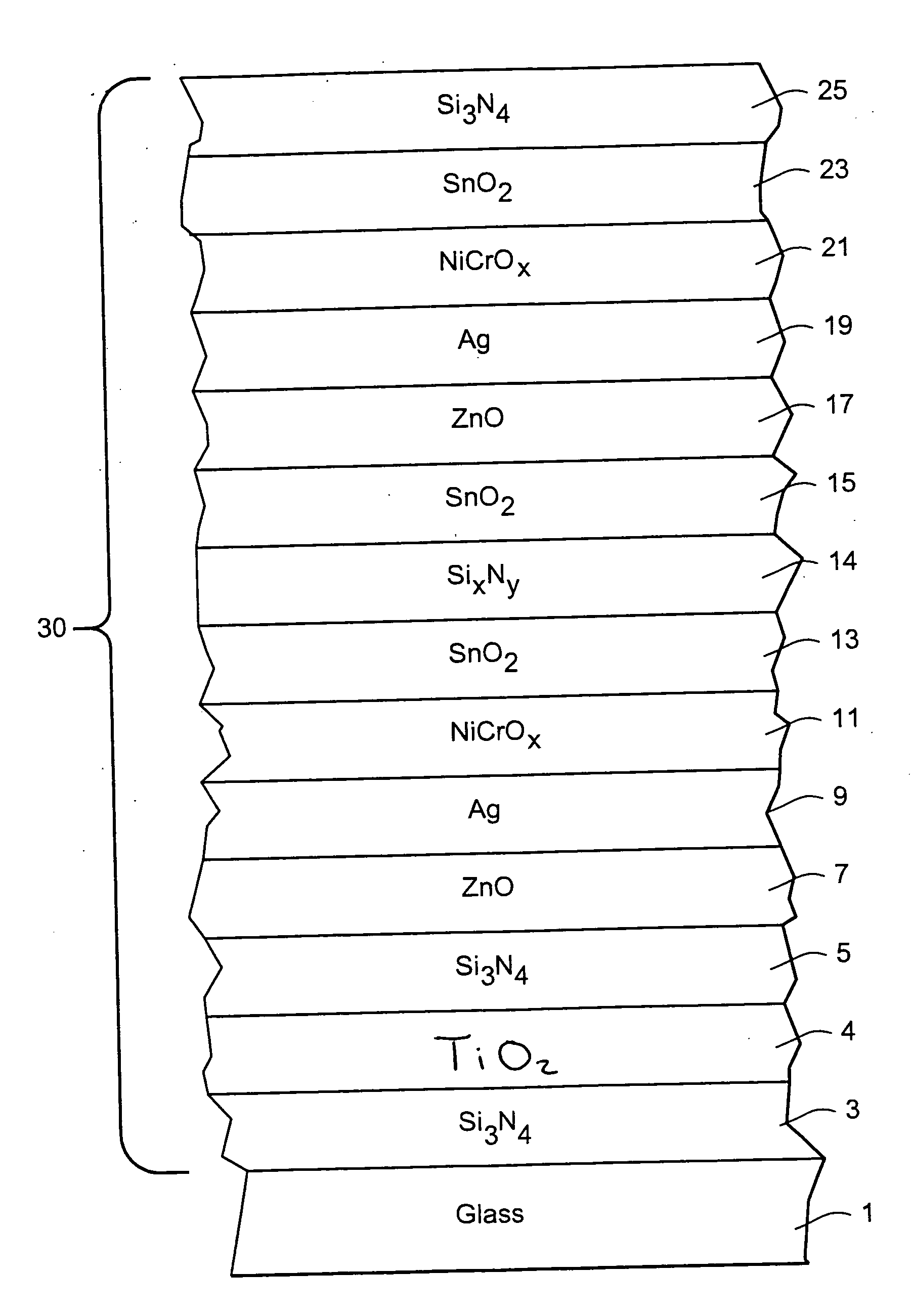
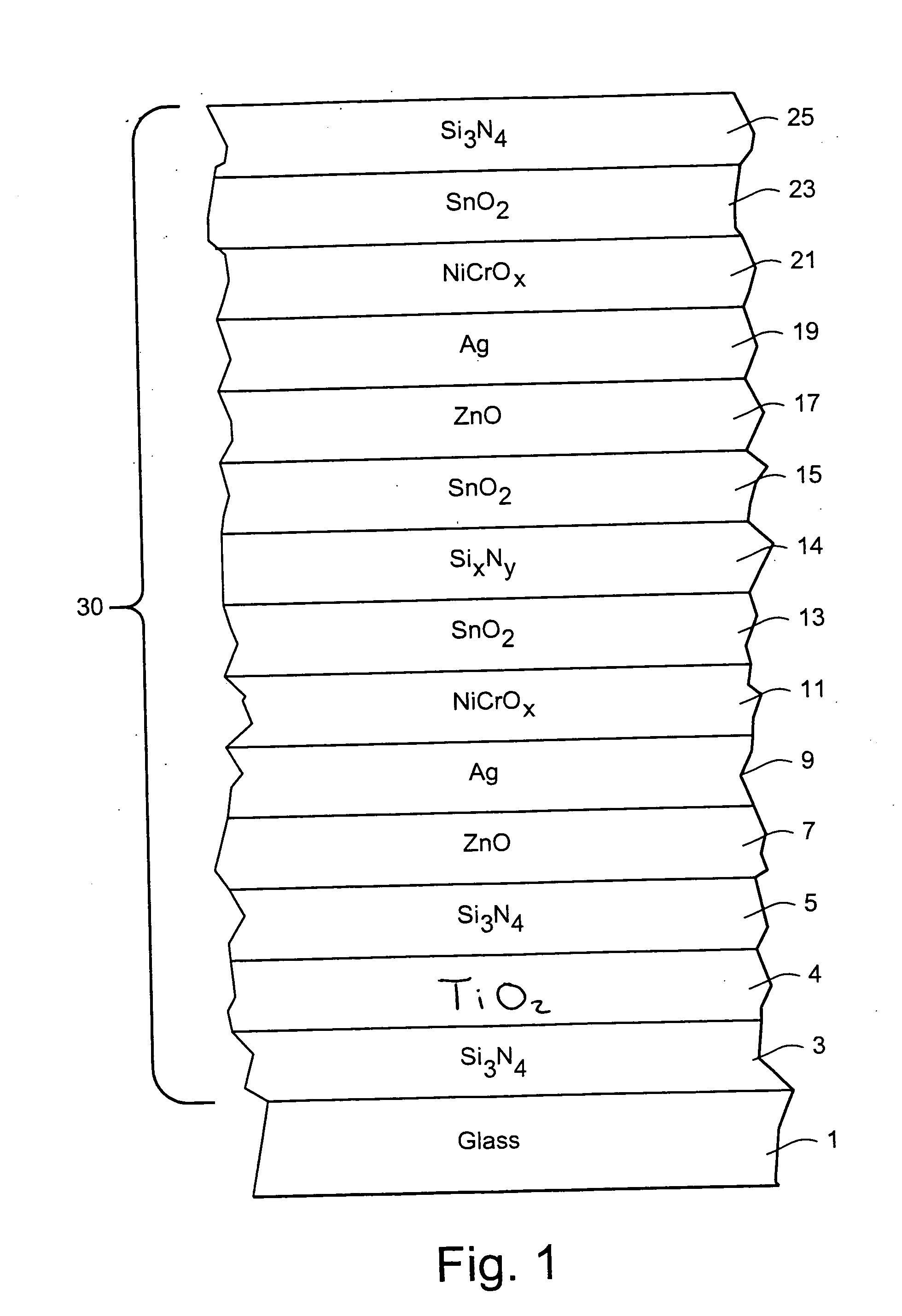
Coated article with low-E coating having titanium oxide layer and/or nicr based layer(s) to improve color values and/or transmission, and method of making same
InactiveUS20100279144A1Lower transmissive b * valueHigher visible transmissionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingInsulated glazingTransmittance
Certain example embodiments of this invention relate to a coated article including a low-E coating. In certain example embodiments, a titanium oxide inclusive bottom layer stack and / or a NiCr-based layer(s) are designed to improve b* coloration values and / or transmission of the coated article. These layer stack portions also are advantageous in that they permit a double-silver coated article to achieve (i) an LSG value (Tvis / SHGC) of at least 2.0, (ii) an SHGC value of no greater than 35%, more preferably no greater than 33, 32 or 30%, and (iii) a U-value (BTU h−1 ft−2° F.−1) (e.g., x=12 mm) of no greater than 0.30, more preferably no greater than 0.28 or 0.25. In certain example embodiments, the titanium oxide based layer may be an interlayer provided in a bottom portion of the layer stack between first and second layers comprising silicon nitride. Coated articles according to certain example embodiments of this invention may be used in the context of insulating glass (IG) window units, other types of windows, or in any other suitable application.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
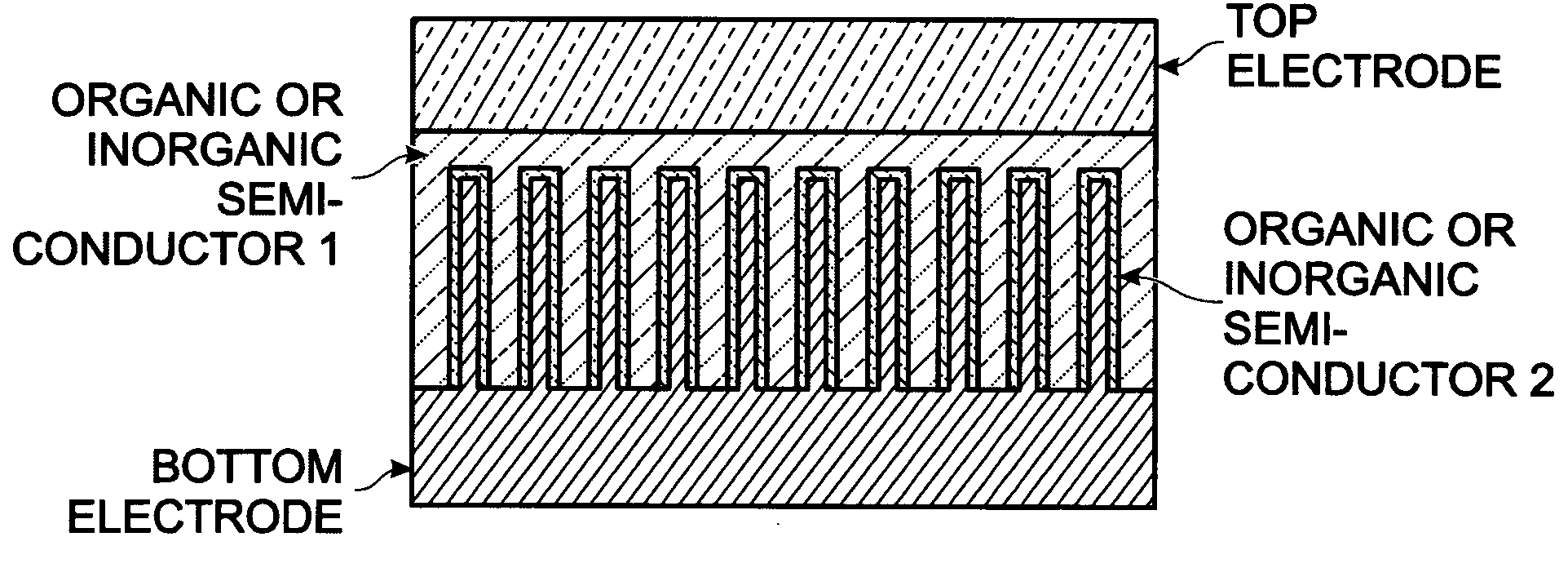
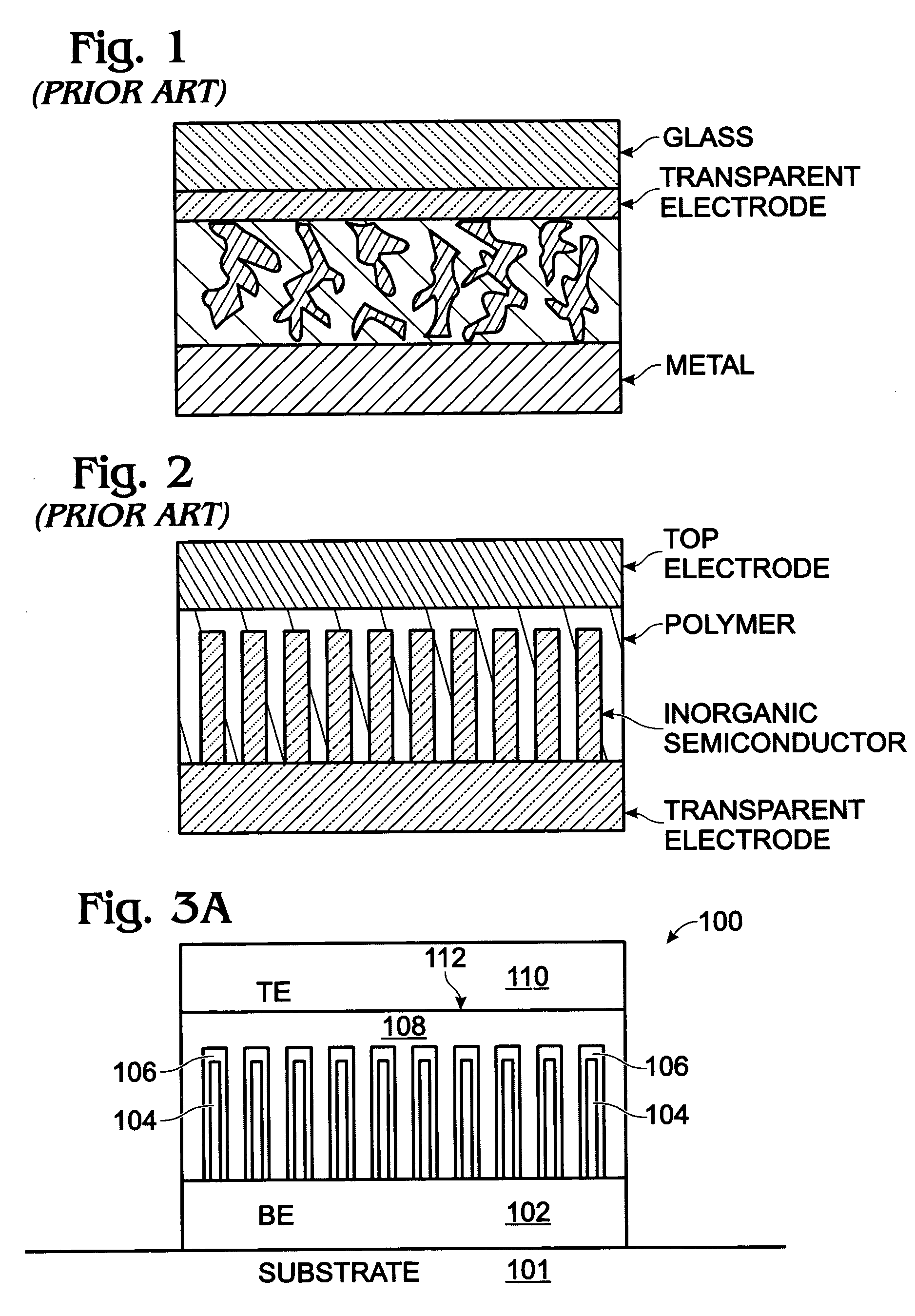
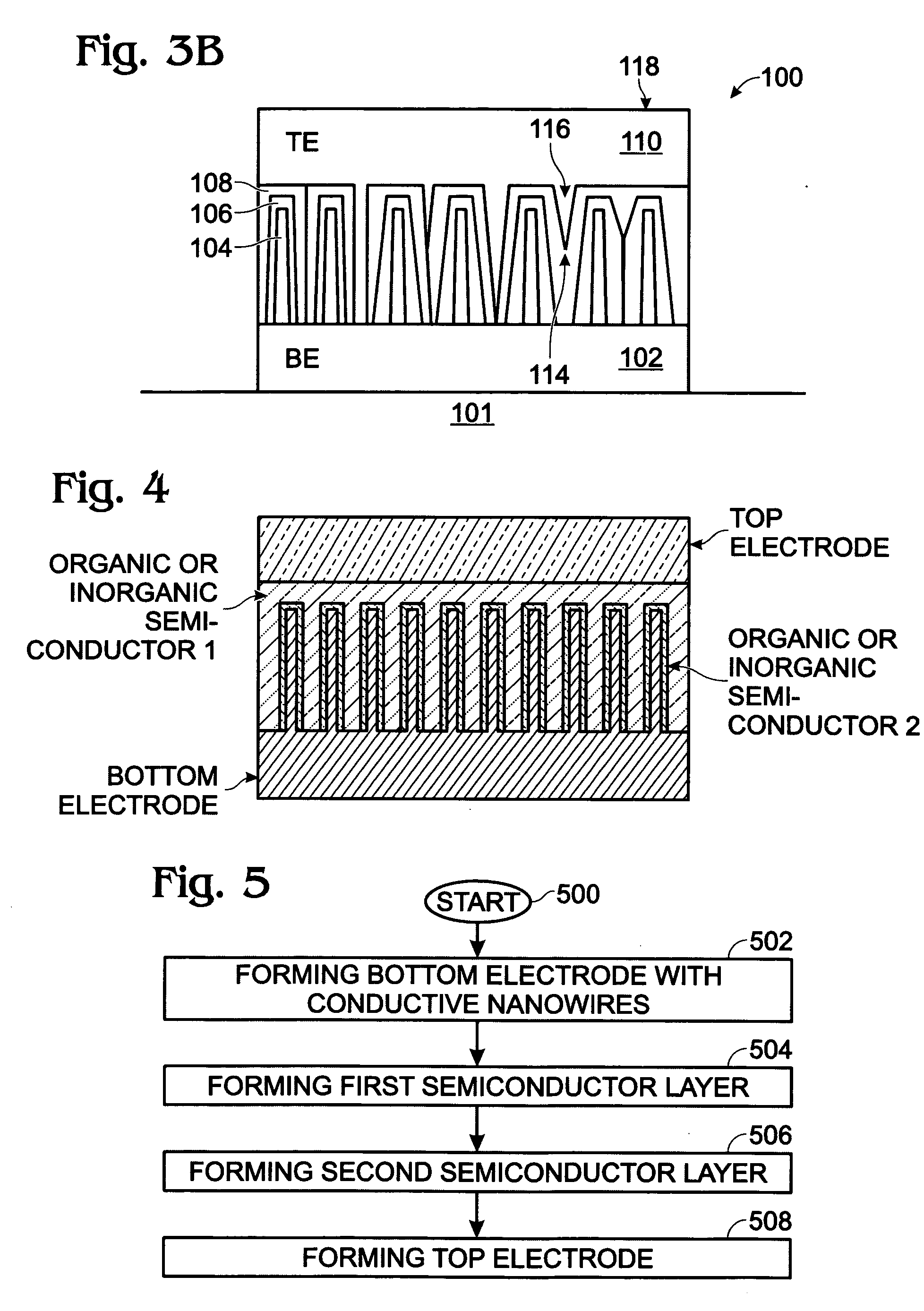
Photovoltaic structure with a conductive nanowire array electrode
A photovoltaic (PV) structure is provided, along with a method for forming a PV structure with a conductive nanowire array electrode. The method comprises: forming a bottom electrode with conductive nanowires; forming a first semiconductor layer of a first dopant type (i.e., n-type) overlying the nanowires; forming a second semiconductor layer of a second dopant type, opposite of the first dopant type (i.e., p-type), overlying the first semiconductor layer; and, forming a top electrode overlying the second semiconductor layer. The first and second semiconductor layers can be a material such as a conductive polymer, a conjugated polymer with a fullerene derivative, and inorganic materials such as CdSe, CdS, Titania, or ZnO. The conductive nanowires can be a material such as IrO2, In2O3, SnO2, or indium tin oxide (ITO).
Owner:SHARP KK
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com