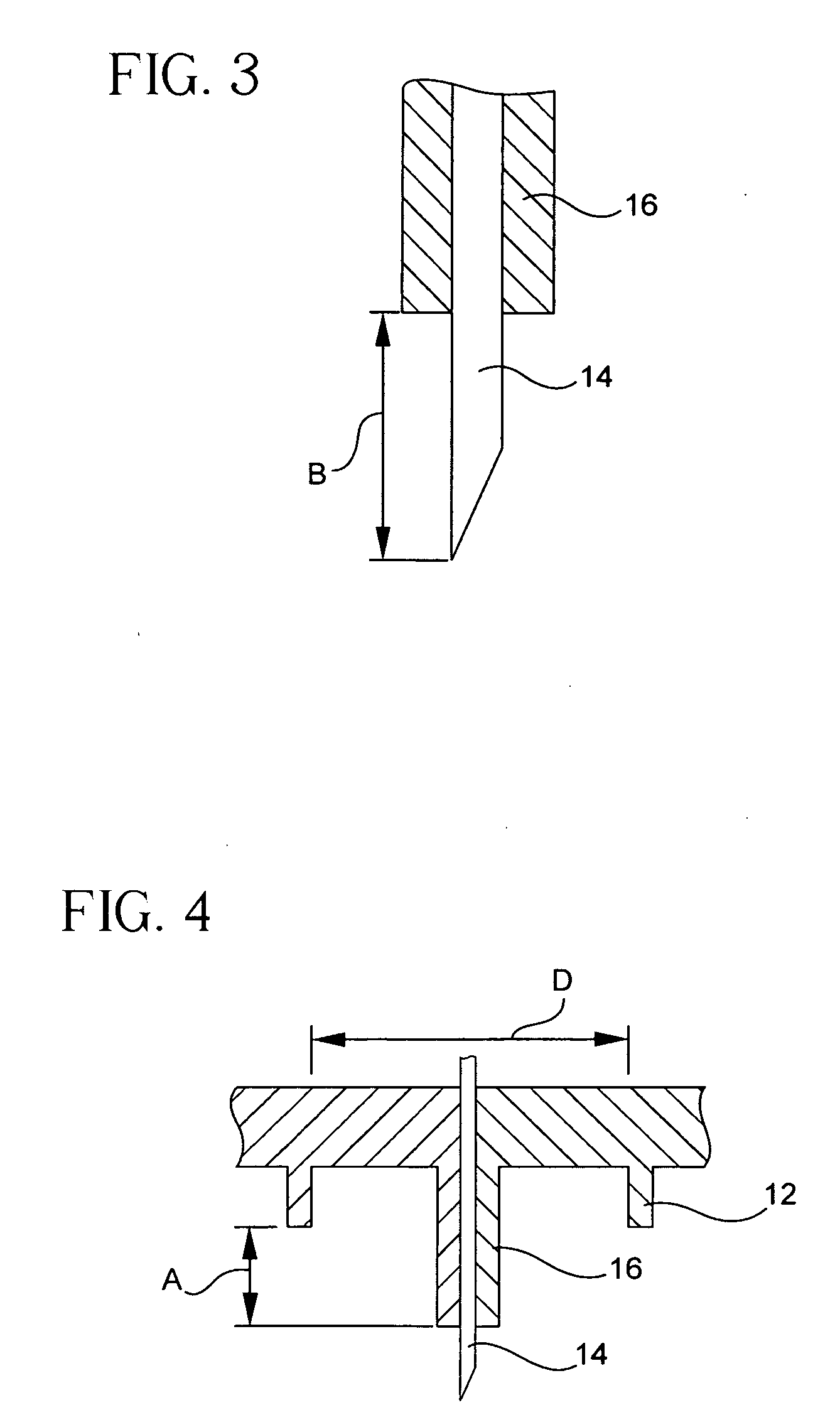
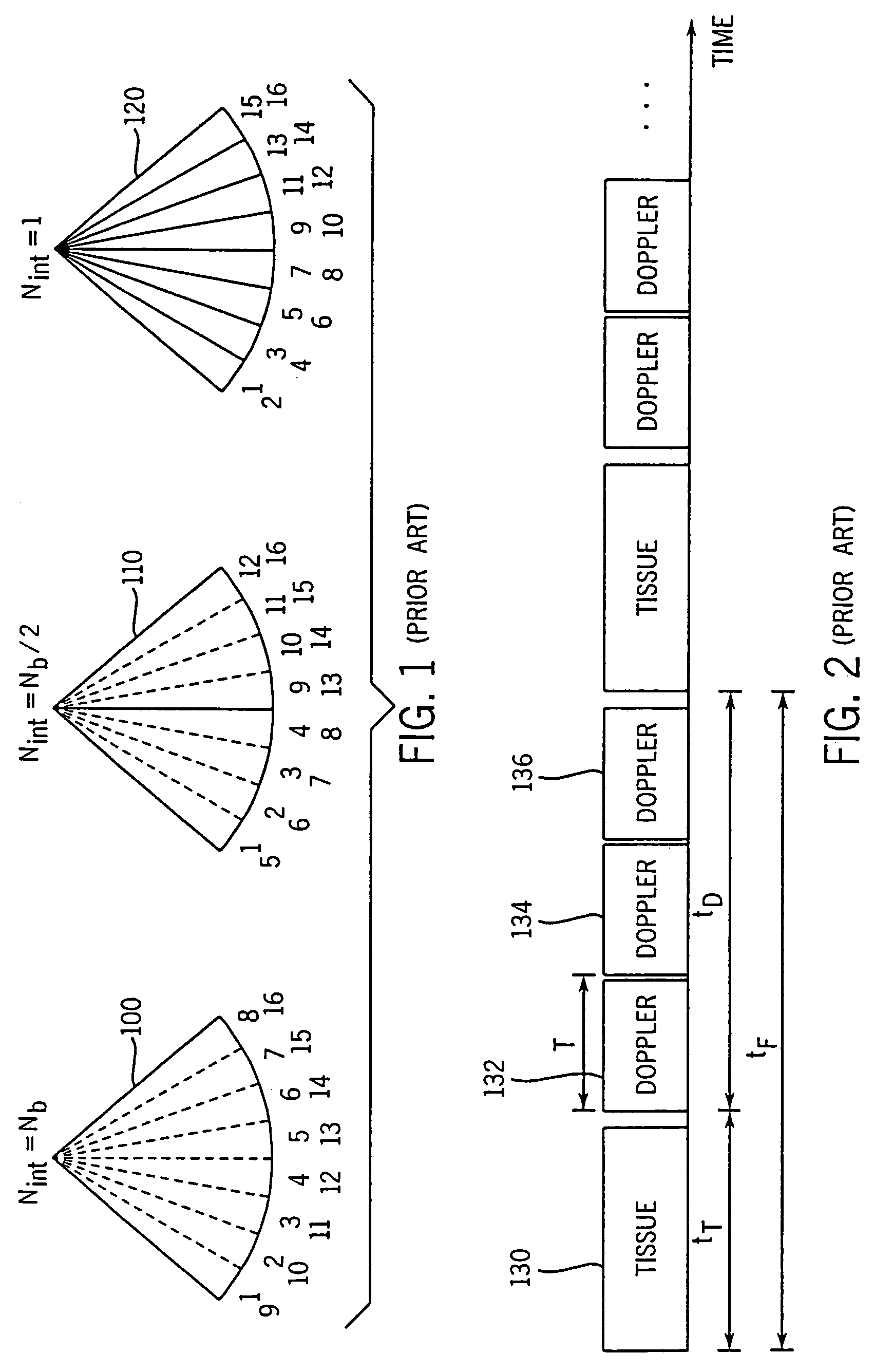
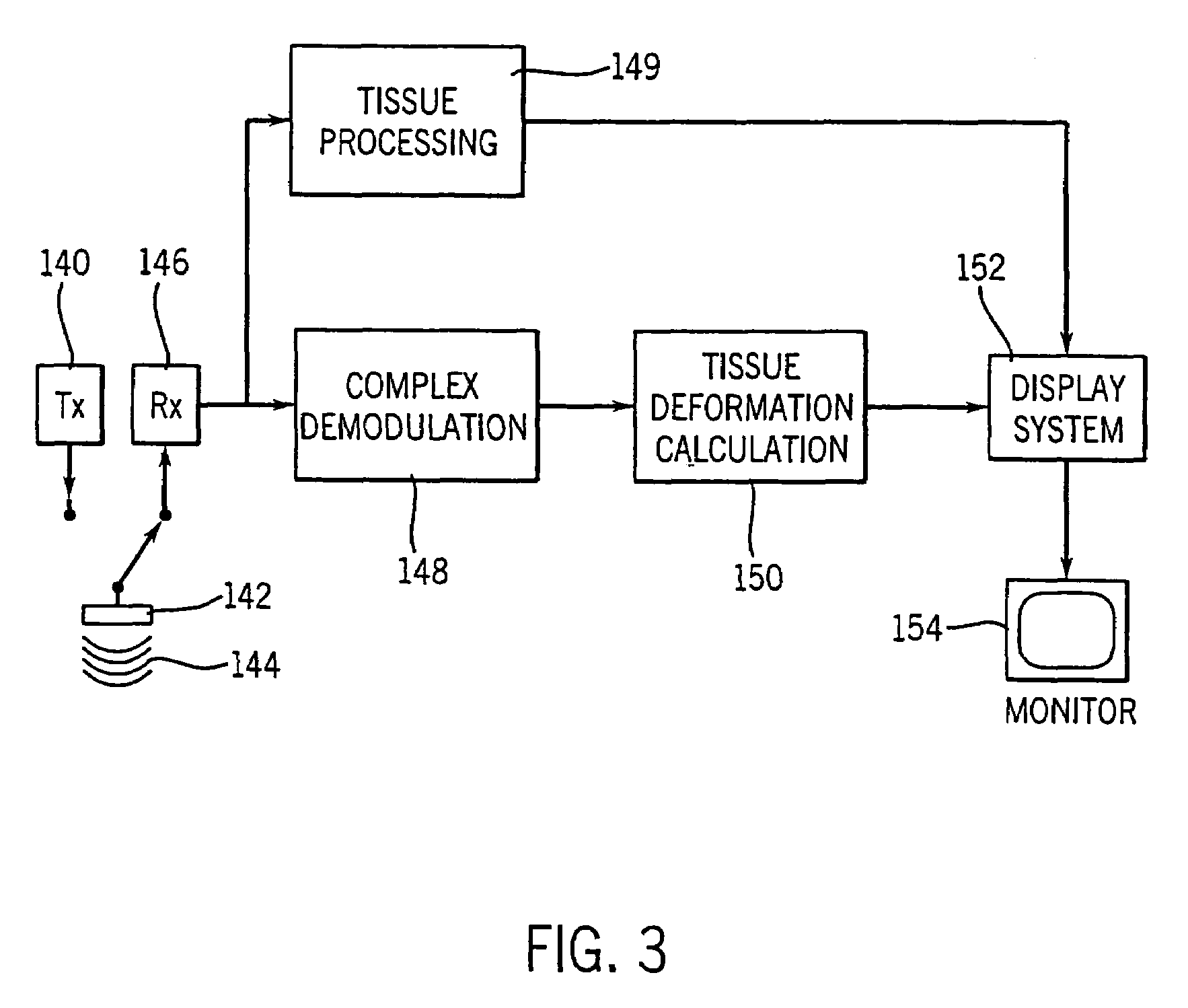
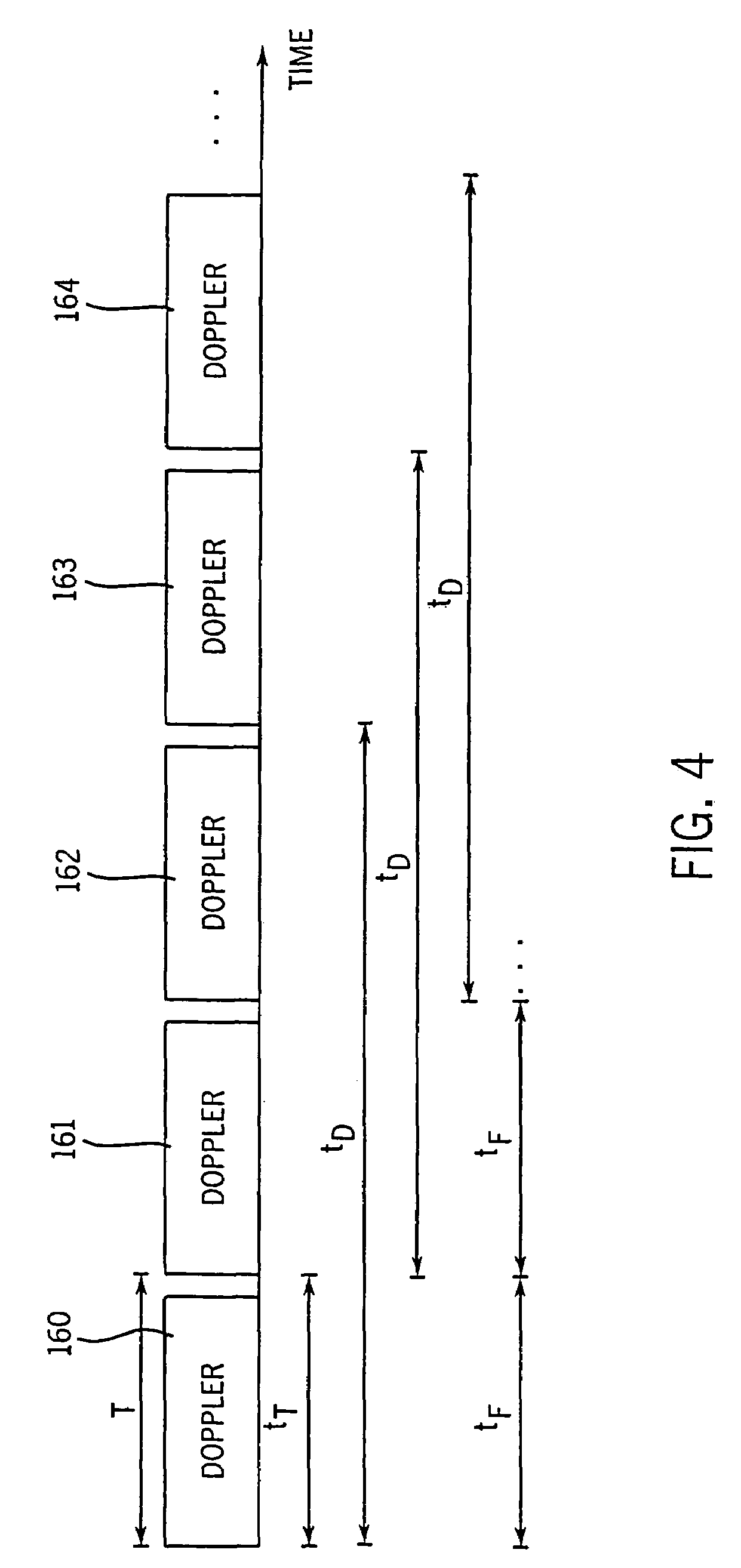
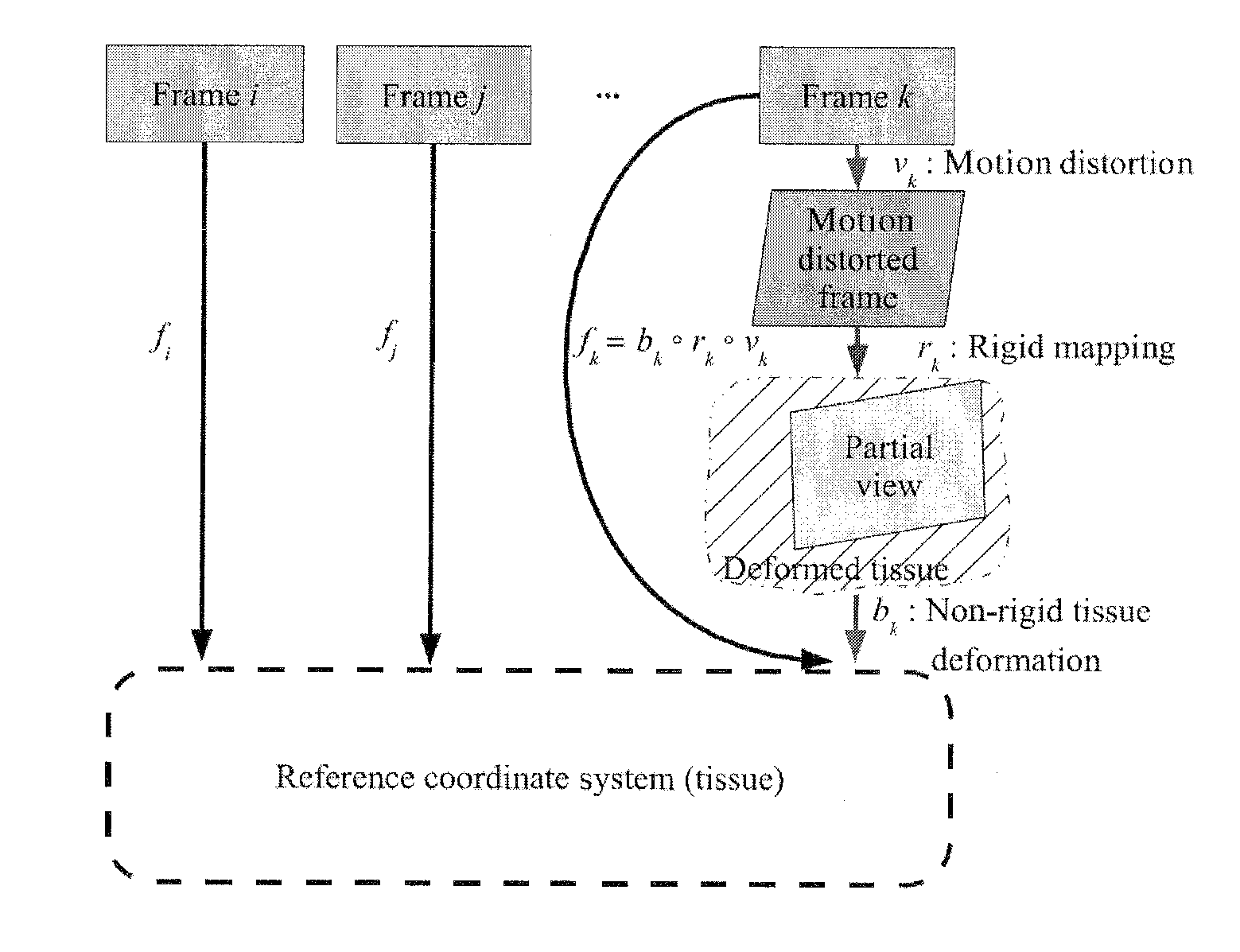
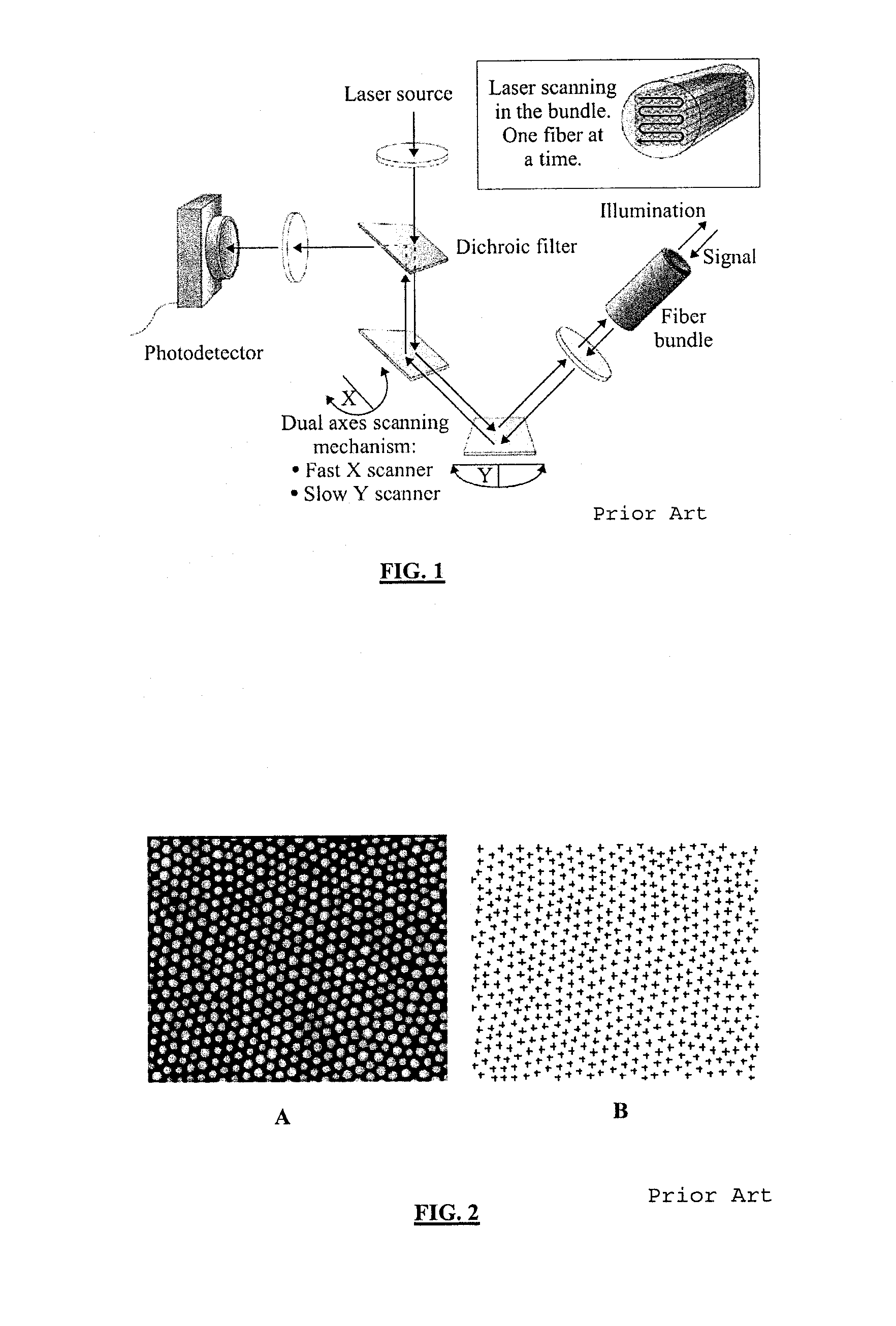
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
83 results about "Tissue deformation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
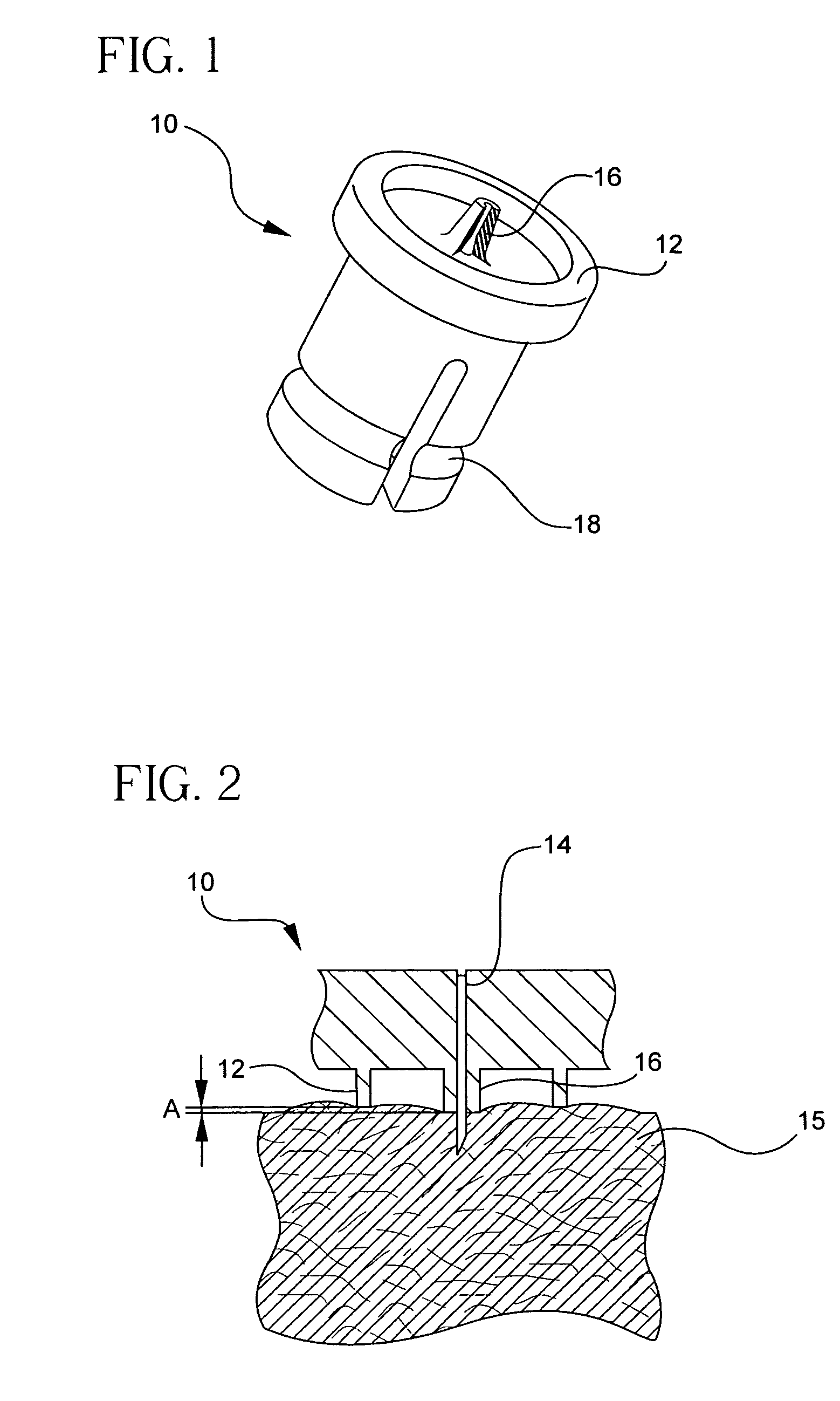
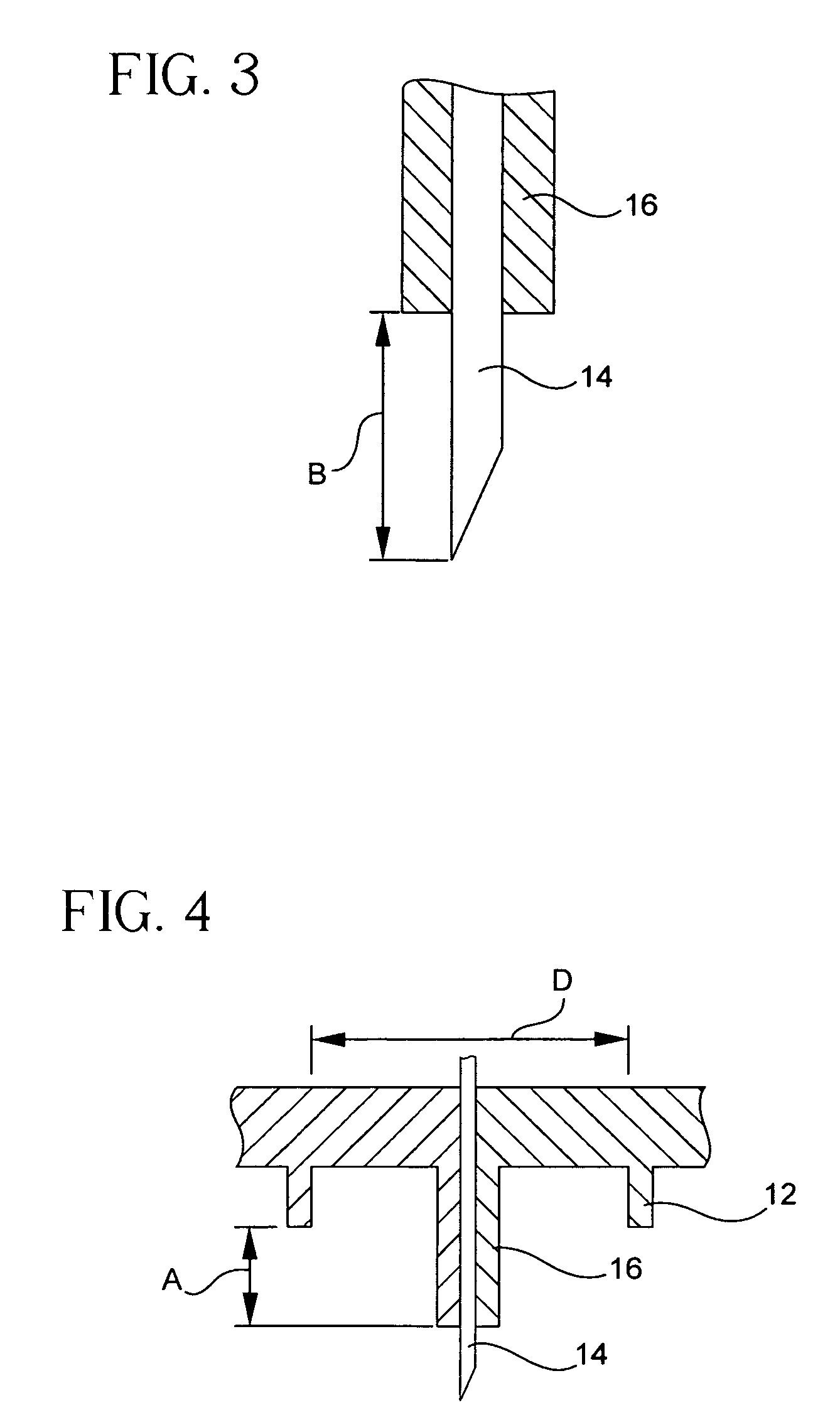
2. the process of adapting in shape or form. elastic deformation temporary elongation of tissue when a prolonged force has been applied. See also creep. plastic deformation permanent elongation of tissue when a prolonged nondisruptive mechanical force has been applied.
Surface treatments and modifications using nanostructure materials
InactiveUS20050113936A1Reduce surface tensionPromote and inhibit ingrowthSuture equipmentsHeart valvesGas phaseNanostructure
The invention is directed to nanostructure surface treatments, coatings or modifications formed from nanoscale building blocks. The nanostructure surface treatments, modifications or coatings have hydrophobic, hydrophilic and surface adherence properties. The nanoscale building blocks have orientation, geometry, packing density and composition that may be adjusted to control the unique surface characteristics of the desired treatment, coating or modification. Applications of this nanostructure technology include surgical clips, staples, retractors, sutures and manipulators where an improvement in traction, retention or occlusion is desired without excessive material or tissue deformation or where high compressive forces would be undesirable, dangerous or ineffective. In one aspect, a nanostructure surface treatment for a medical device having an external surface is disclosed, wherein the treatment is applied on the external surface to provide a hydrophobic or a hydrophilic surface. With this aspect, the treatment comprises titanium dioxide and provides nanoscopic structures having nearly vertical sidewalls. The treated surface of the device has contact angles greater than or equal to 150 degrees. The vertical sidewalls provide a negative capillary effect and have a width of about 200 nm. The vertical sidewalls attach to a wet surface by the negative capillary effect. The van der Waals forces of the vertical sidewalls enable the treated surface to attach to a dry surface. The treatment may be vapor deposited and cured on the device, or the treatment may be laser blasted on the device.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
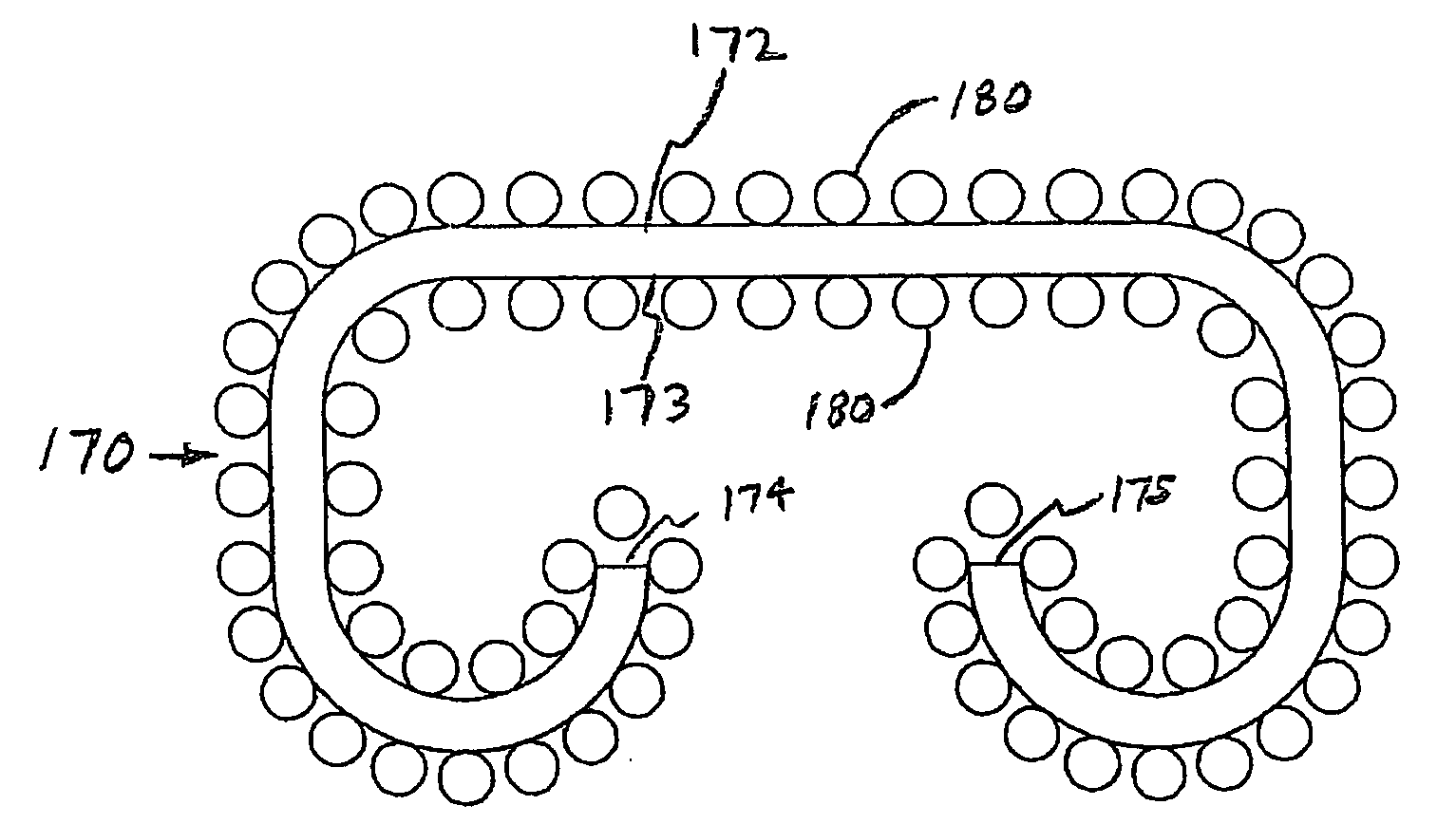
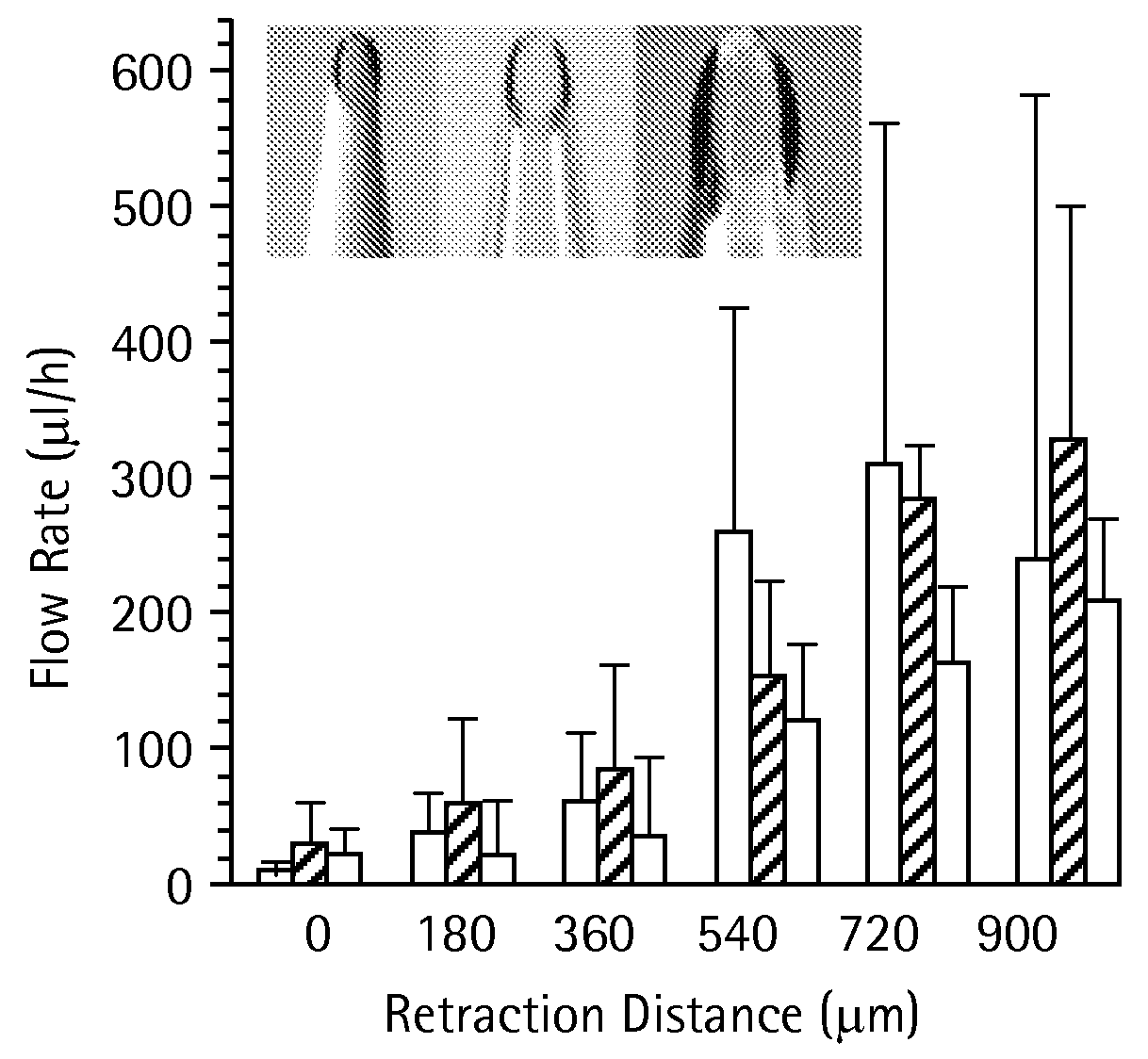
Microneedles and Methods for Microinfusion
Methods and devices are provided for delivering a drug to or withdrawing a fluid from a biological tissue, such the skin, sclera, cornea, and conjunctiva. One method includes the steps of inserting at least one microneedle into the biological tissue; partially retracting the at least one microneedle from the tissue; and then delivering at least one drug formulation into the biological tissue via the partially retracted at least one microneedle. The microneedle deforms and penetrates the biological tissue during the insertion step, and the retraction step at least partially relaxes the tissue deformation while maintaining at least part of the tissue penetration, facilitating drug delivery or fluid withdrawal.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Intradermal delivery device
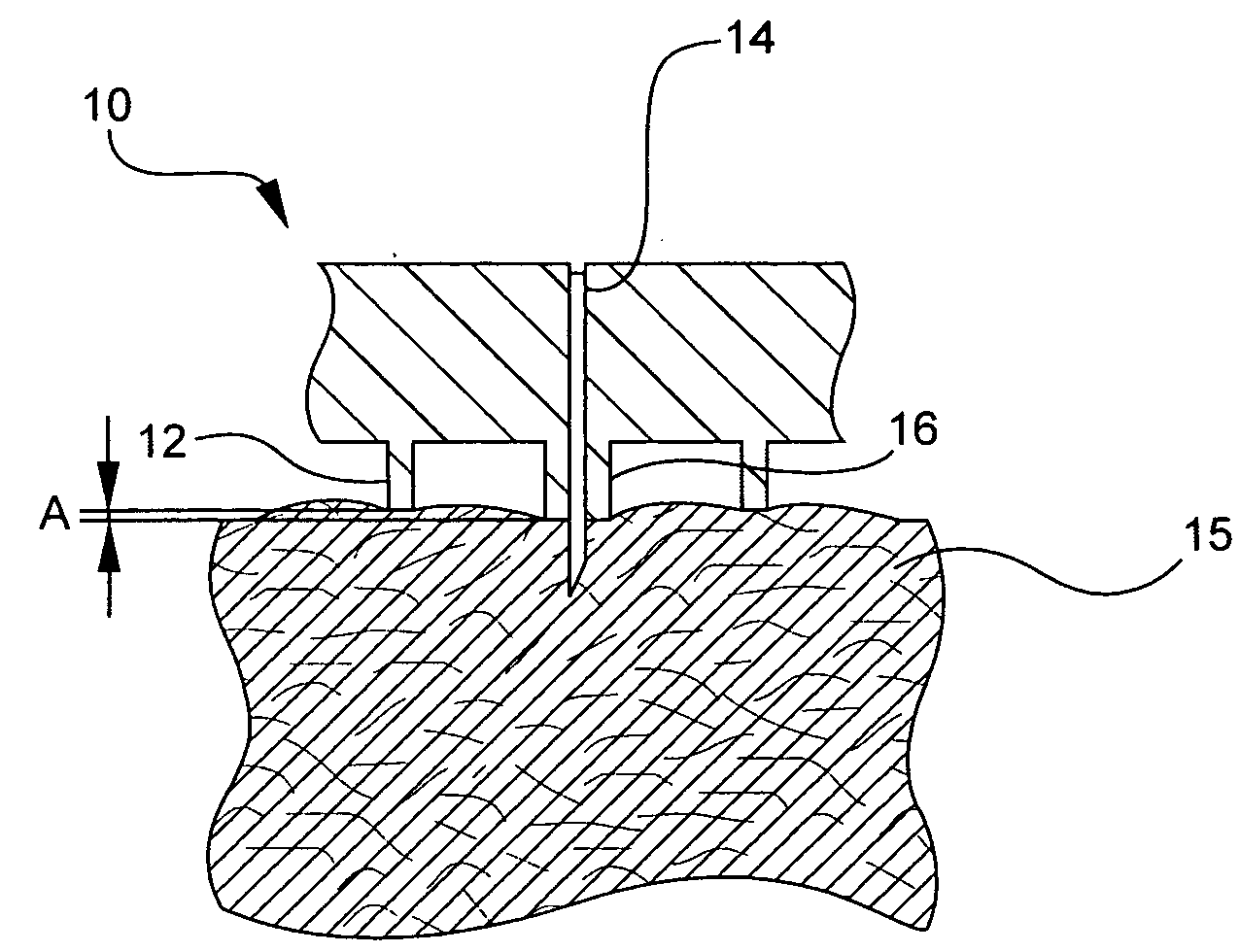
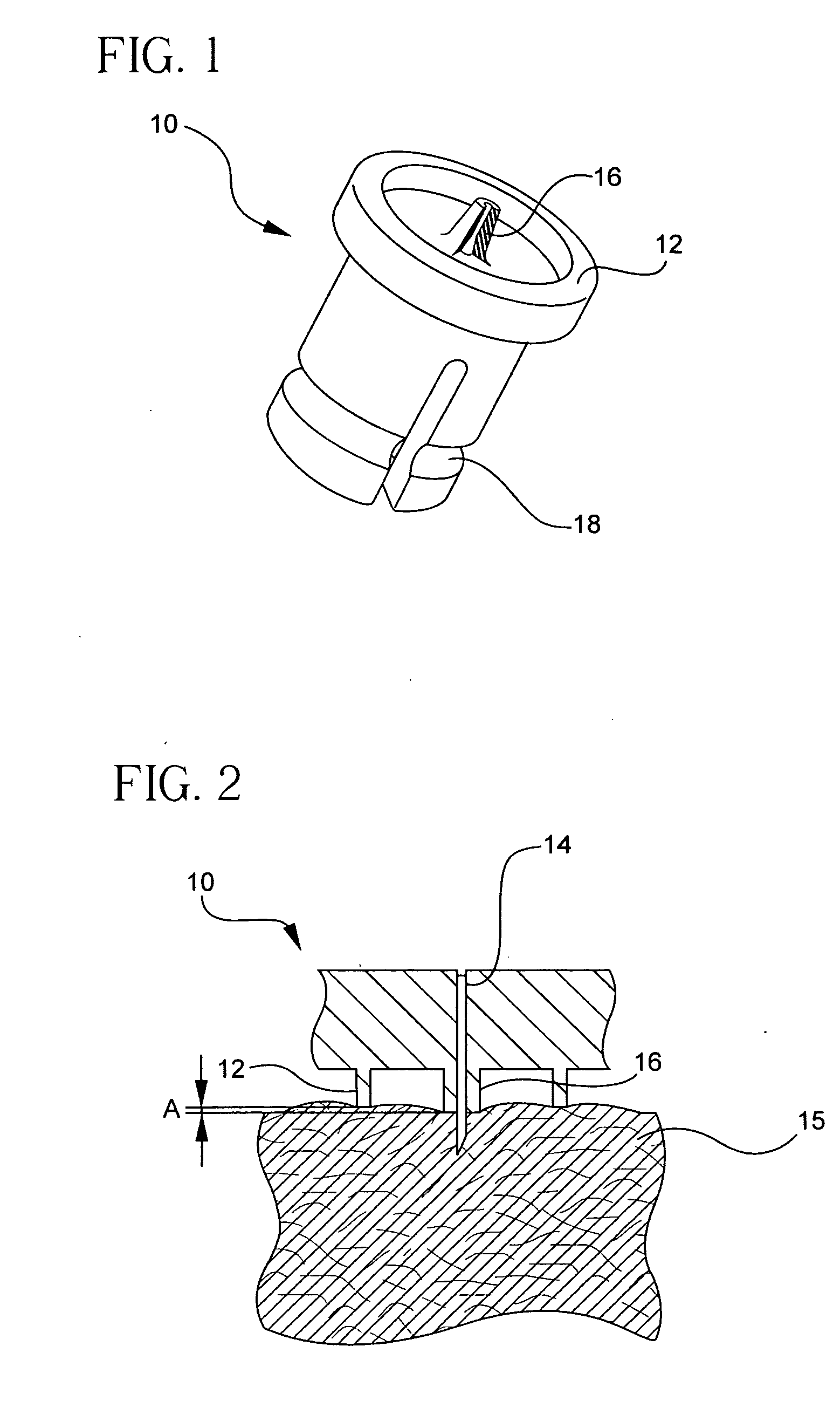
ActiveUS20070118077A1Minimal leakageReduce pressureCatheterInfusion needlesProportional controlInsertion depth
A system and method is provided for an injectable substance delivery device comprising a limiter, shoulder or post, that controls how deep the needle is inserted into the tissue. The limiter is sized in proportions that control the maximum insertion depth of the needle into the tissue without excessively restricting the complete insertion of the needle. The system and method further comprises an normalization or stabilizer ring that prevents distortion of the tissue in the vicinity of the infusion, so that the needle length is the major determining factor as to how deep the infusion is delivered.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Intraoperative tissue tracking method combined with preoperative image
InactiveCN101862205AReflect spatial relationshipUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryComputer visionEndoscope
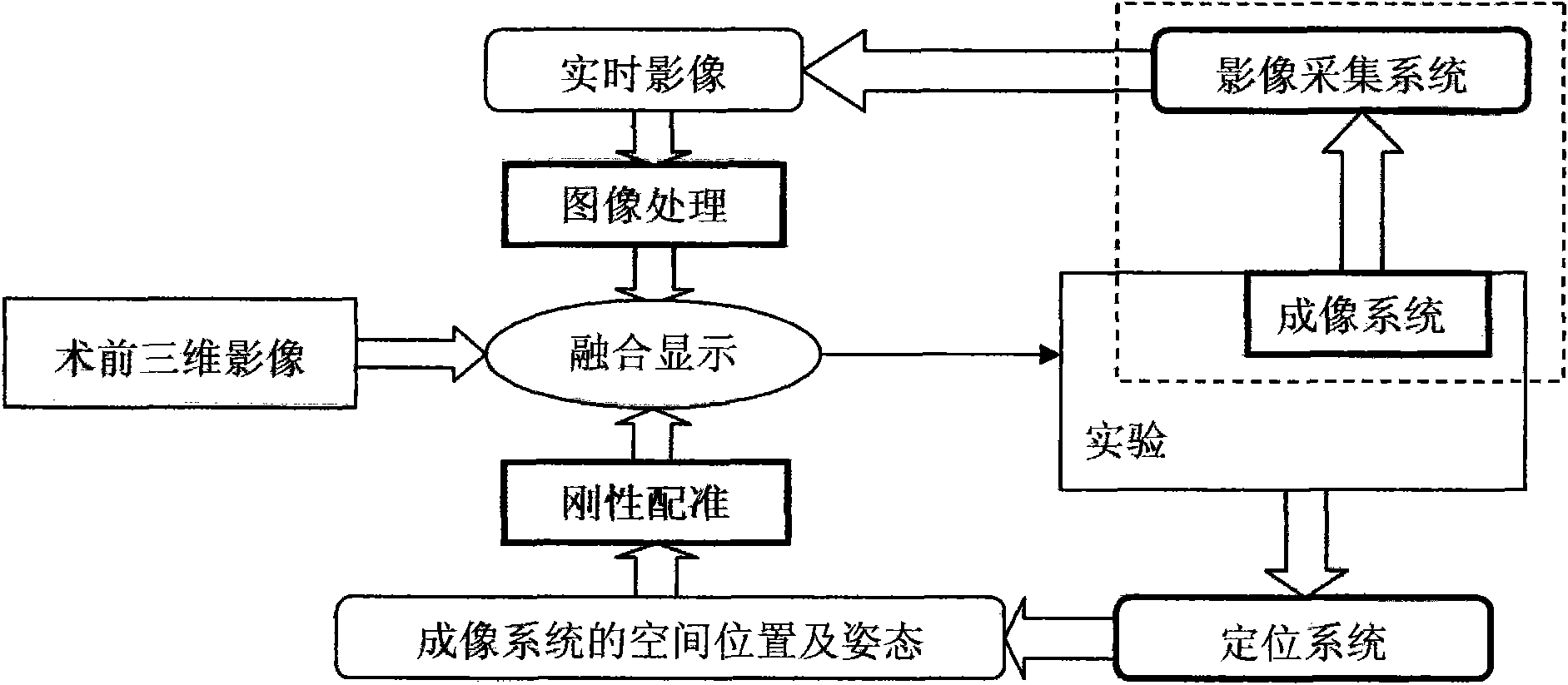
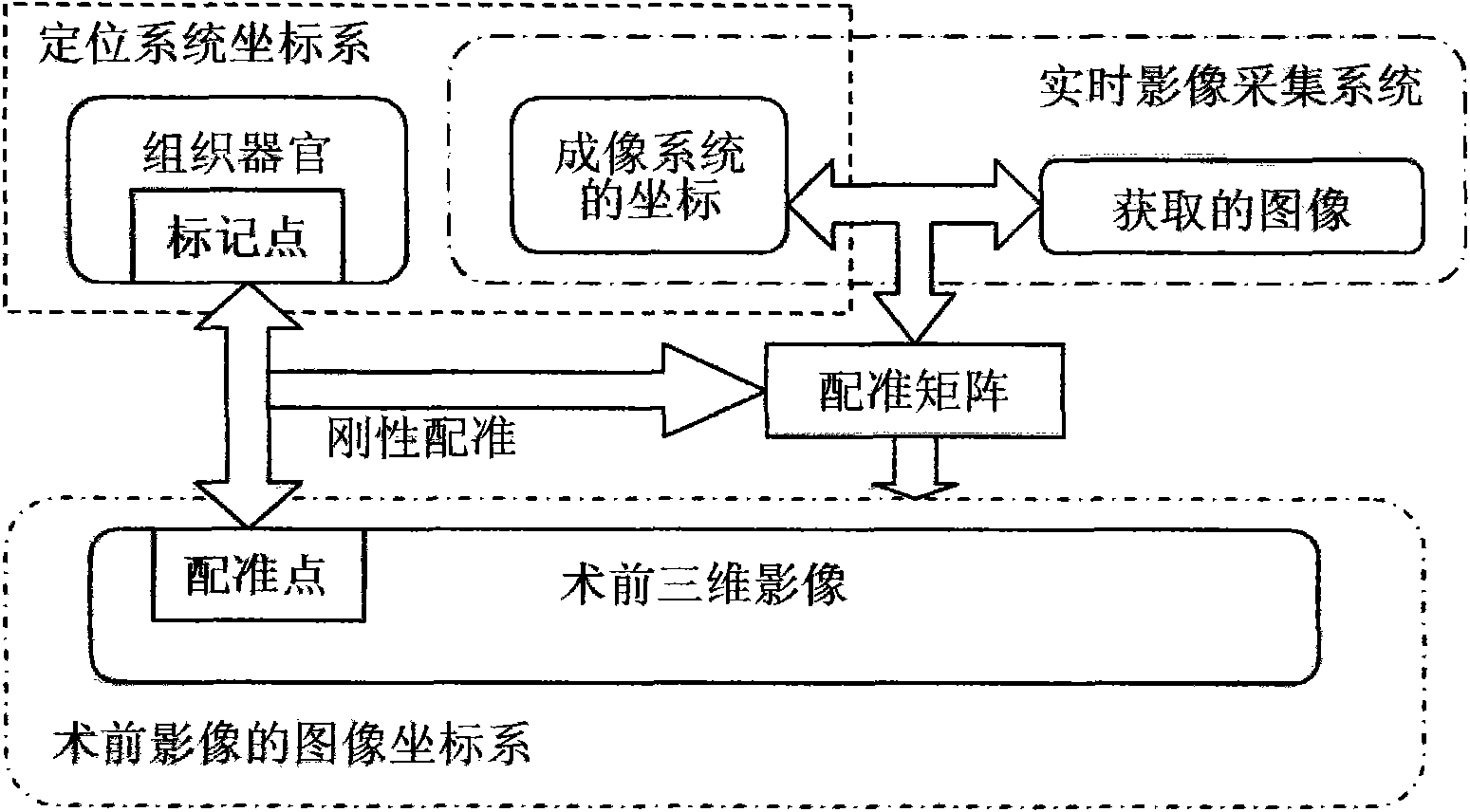
The invention provides an intraoperative tissue tracking method combined with a preoperative image, which comprises the following sequential steps: the first step: preoperative preparation, including the steps of acquiring a space position of a marking point in the preoperative image and calibration of equipment; and the second step: deformation tracking of an intraoperative tissue, including 1, coordinate system registration which is one of main parts of the invention; and 2. tissue deformation and fusion display which is also one of the main parts of the invention. By using intraoperative real-time two-dimensional ultrasound image and endoscope image and intraoperative electromagnetic or optical positioning system and using algorithm analysis and geometric registration calculation, a tissue structure of an intraoperative interest tissue can be reflected in the image.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
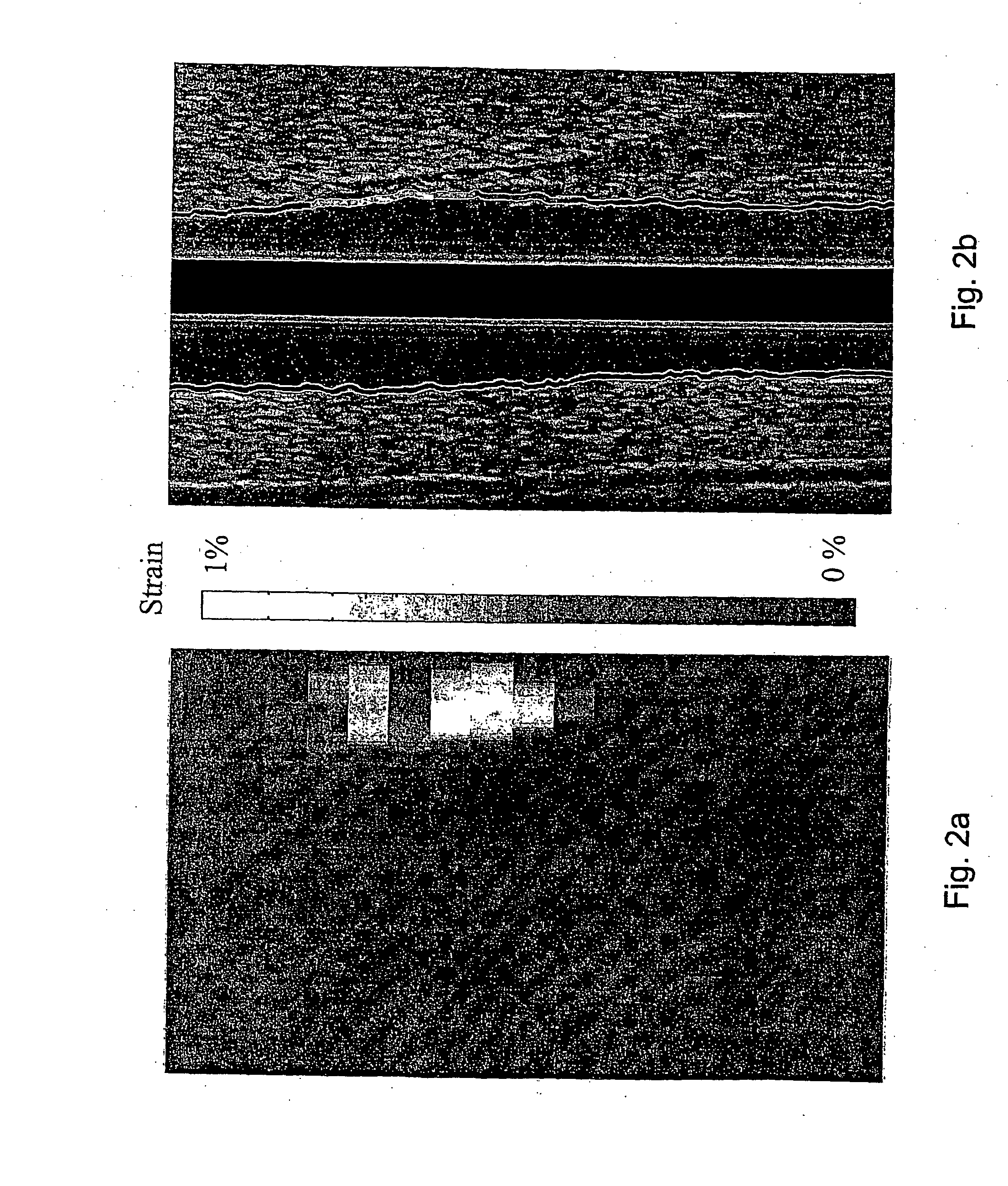
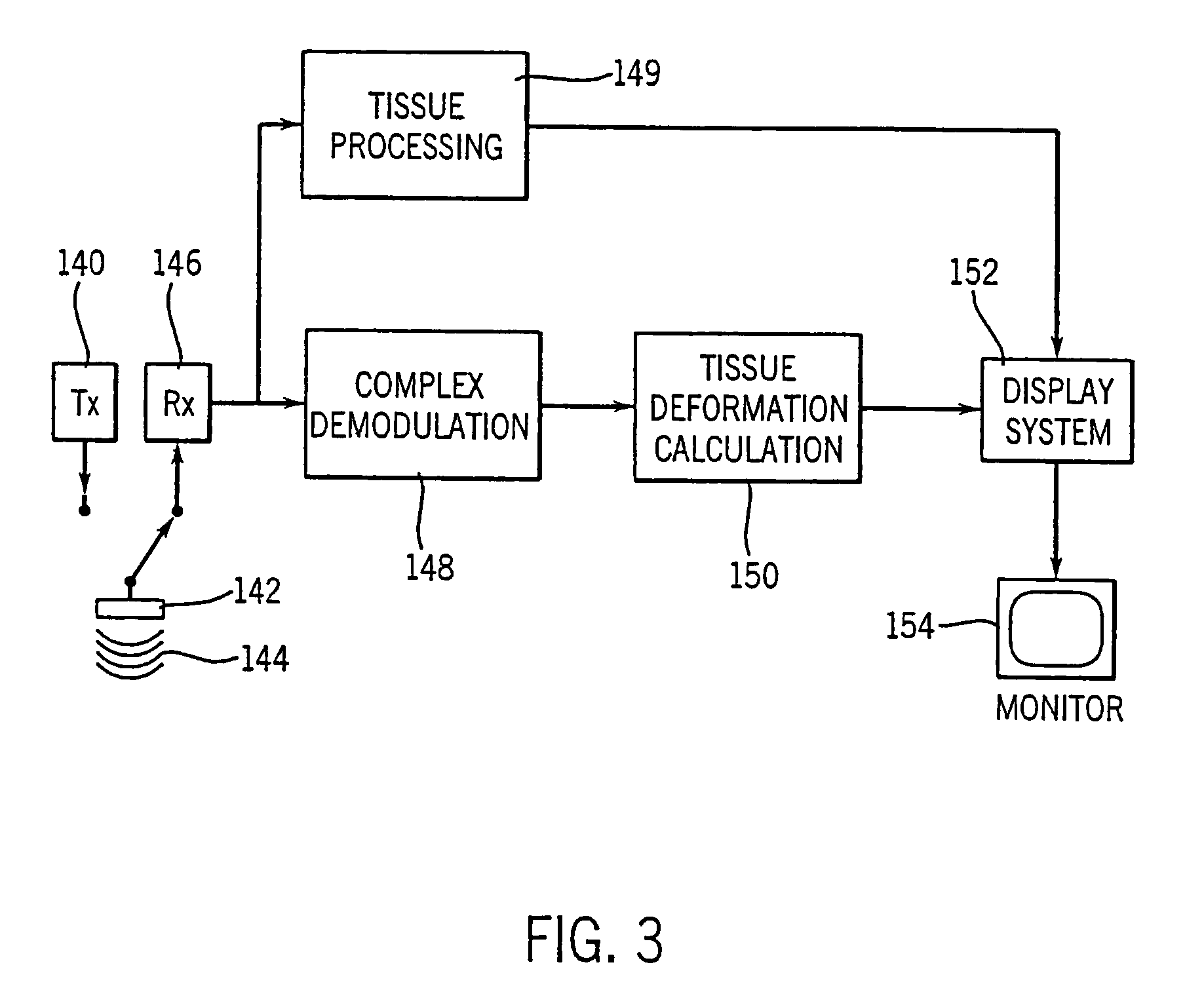
Method and apparatus for providing real-time calculation and display of tissue deformation in ultrasound imaging
InactiveUS7077807B2Reduce impactReduce aliasingElectrocardiographyOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasound imagingSonification
An ultrasound system and method for calculation and display of tissue deformation parameters are disclosed. A method to estimate a strain rate in any direction, not necessarily along the ultrasound beam, based on tissue velocity data from a small region of interest around a sample volume is disclosed. Quantitative tissue deformation parameters, such as tissue velocity, tissue velocity integrals, strain rate and / or strain, may be presented as functions of time and / or spatial position for applications such as stress echo. For example, strain rate or strain values for three different stress levels may be plotted together with respect to time over a cardiac cycle.
Owner:G E VINGMED ULTRASOUND
Three-dimensional tissue hardness imaging
InactiveUS20050033199A1Correlation between consecutive images is optimizedNegative effectOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryMedicineHardness
A method for generating hardness information of tissue subject to a varying pressure. The method comprises receiving signals from the tissue from a sensor for measuring the deformation of the tissue in a measuring plane defined by the sensor, which sensor, during a varying pressure exerted on the tissue, is moved along the tissue in a direction transverse to the measuring plane; identifying strain of the tissue from the resulting signals; and relating the strain to elasticity and / or hardness parameters of the tissue. The method may comprise the step of displaying elasticity and / or hardness parameters of a tissue surface or tissue volume part extending practically parallel to the direction of motion of the sensor.
Owner:STICHTING VOOR DE TECH WETENSCHAPPEN
Intradermal delivery device
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging
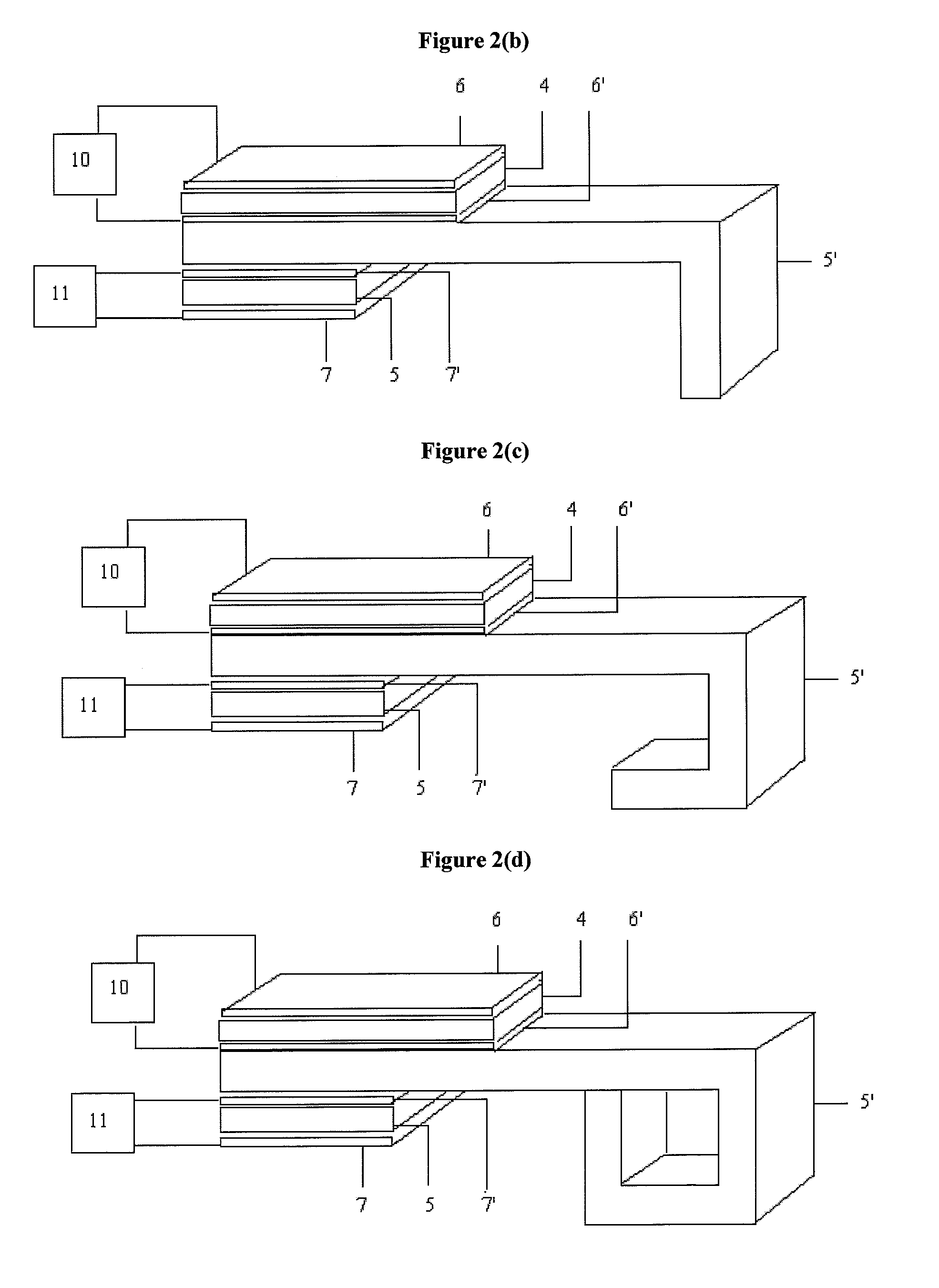
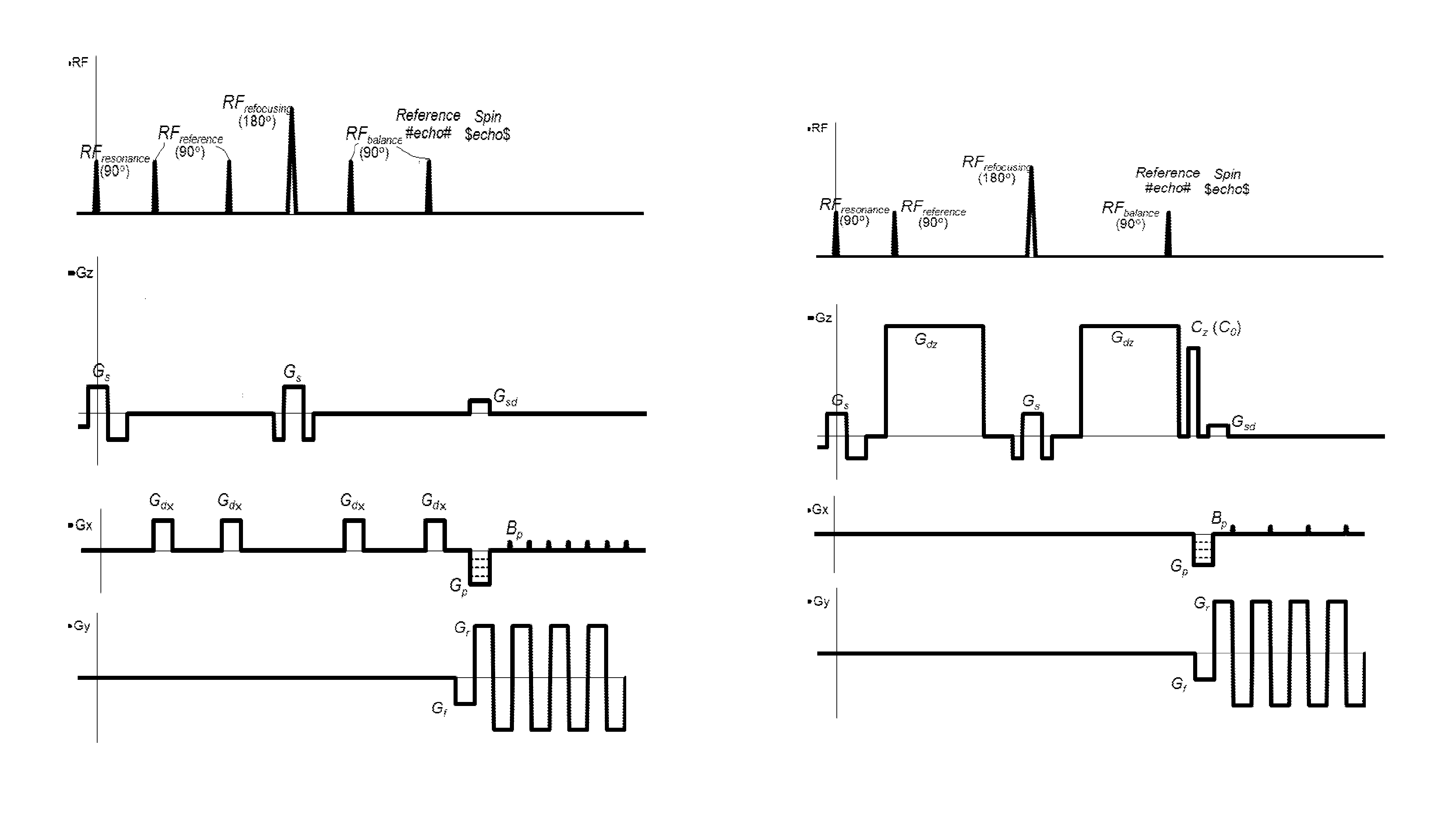
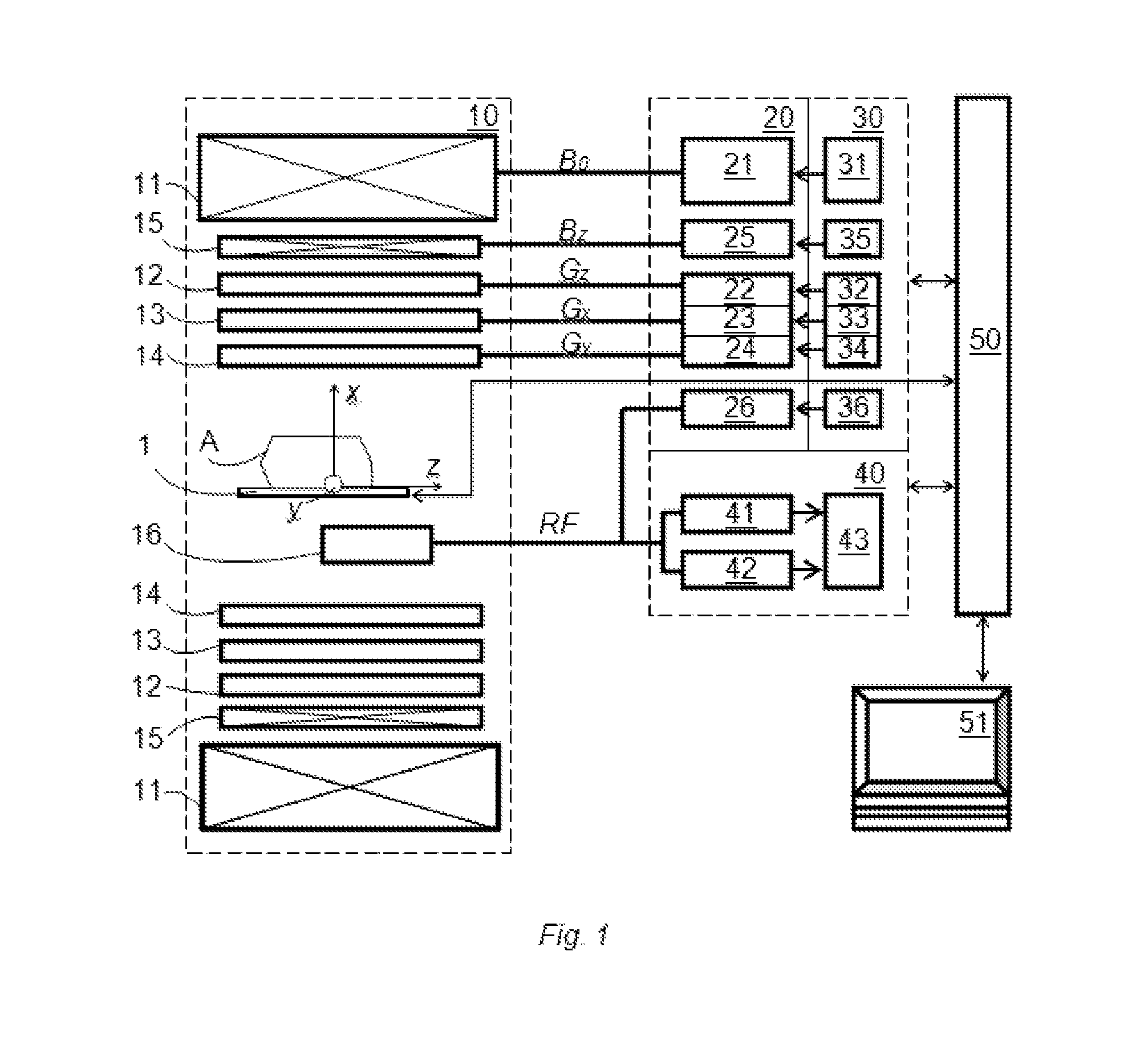
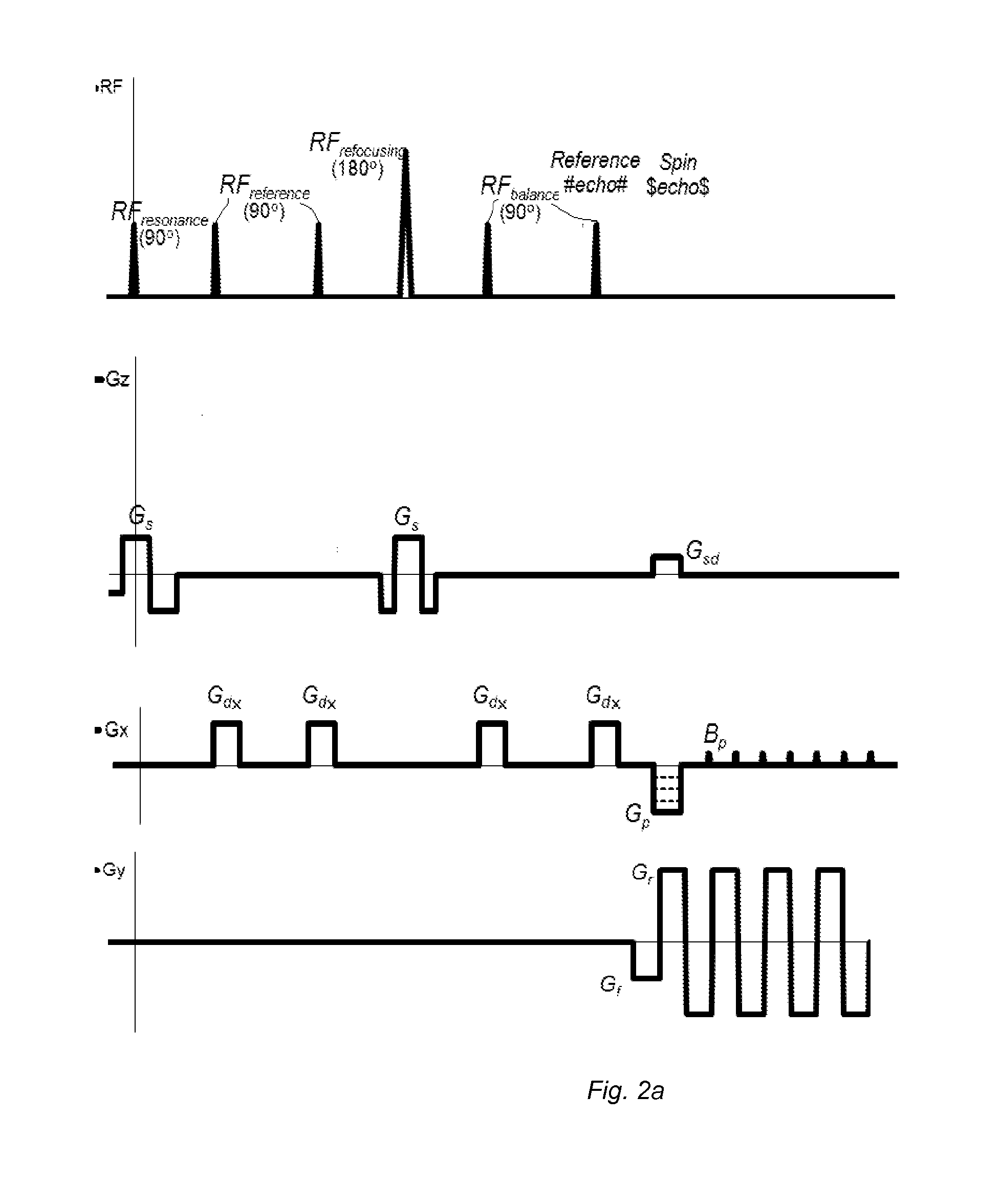
ActiveUS20140266195A1Reduce sensitivityReduce scan timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionPhase shiftedResonance
The method and system for correcting motion-induced phase errors in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) use a phase shift of the non-phase encoded reference echo-signal accumulated during the diffusion-weighting in order to characterize bulk motion and tissue deformation and to compensate their effect for correcting the diffusion / perfusion-weighted image. The sequences unbalanced with respect to the first motion derivative are used for distinguishing the perfusion component. The MRI apparatus provides additional excitation resonance-frequency ranges for forming the reference echo signals.
Owner:VAPOSUN
Method and apparatus for providing real-time calculation and display of tissue deformation in ultrasound imaging
InactiveUS7261694B2Reduce impactReduce aliasingElectrocardiographyOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasound imagingSonification
An ultrasound system and method for calculation and display of tissue deformation parameters are disclosed. The tissue deformation parameter strain is determined by an accumulation of strain rate estimates for consecutive frames over an interval. The interval may be a triggered interval generated by, for example, an R-wave in an ECG trace. Three quantitative tissue deformation parameters, such as tissue velocity, tissue velocity integrals, strain rate and / or strain, may be presented as functions of time and / or spatial position for applications such as stress echo. For example, strain rate or strain values for three different stress levels may be plotted together with respect to time over a cardiac cycle. Parameters which are derived from strain rate or strain velocity, such as peak systolic wall thickening percentage, may be plotted with respect to various stress levels.
Owner:G E VINGMED ULTRASOUND
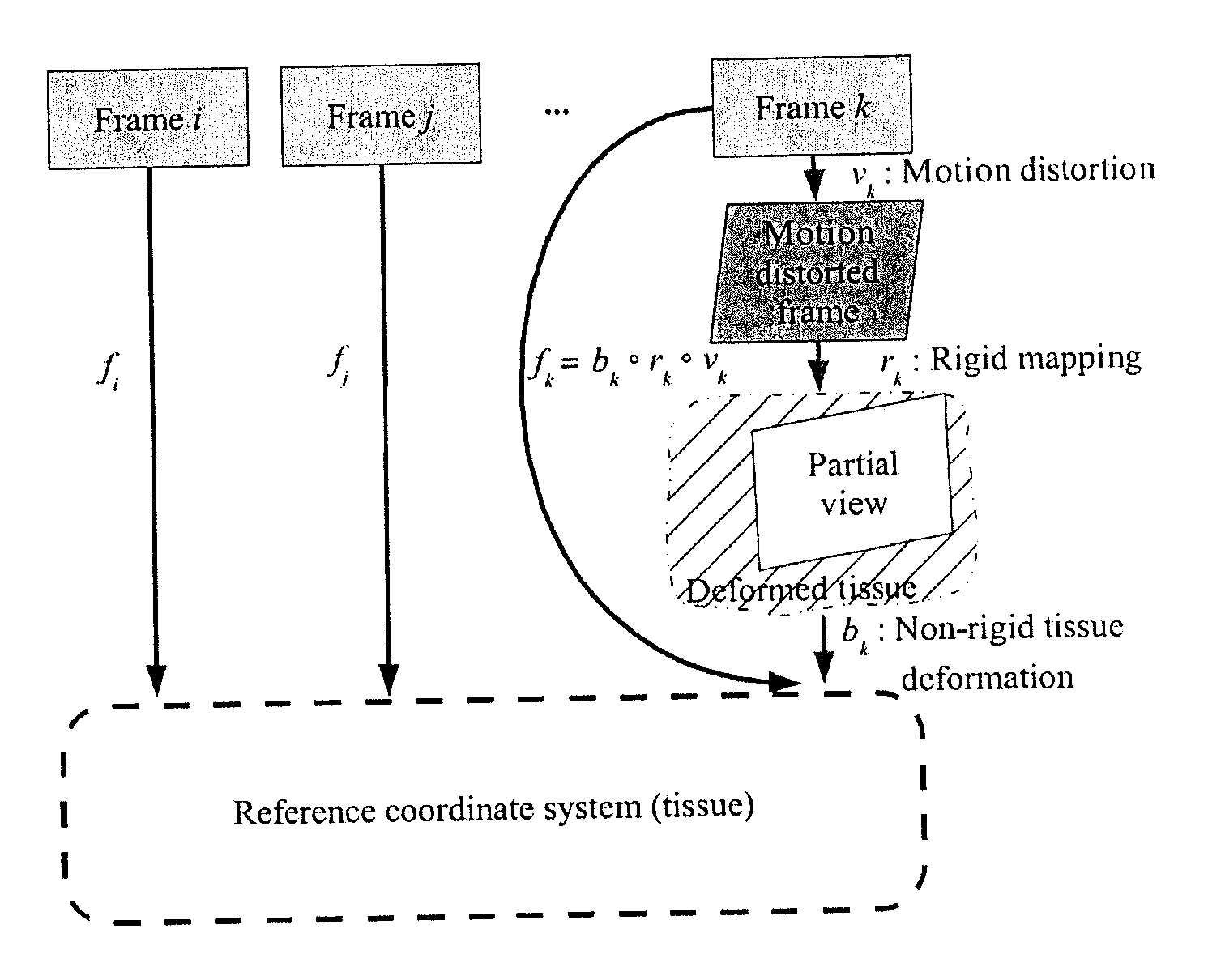
Robust mosaicing method. notably with correction of motion distortions and tissue deformations for a vivo fibered microscopy
The present invention concerns a mosaicing method taking into account motion distortions, irregularly sampled frames and non-rigid deformations of the imaged tissue. The invention relates to a method for mosaicing frames from a video sequence acquired from a scanning device such as a scanning microscope, the method comprising the steps of:a) compensating for motion and motion distortion due to the scanning microscope,b) applying a global optimisation of inter-frame registration to align consistently the framesc) applying a construction algorithm on the registered frames to construct a mosaic, andd) applying a fine frame-to-mosaic non rigid registration.The method is based on a hierarchical framework that is able to recover a globally consistent alignment of the input frames, to compensate for the motion distortions and to capture the non-rigid deformations.
Owner:INRIA NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR RESEARCH IN COMPUTER SCIENCE AND CONTROL +1
Navigation system and method of minimally invasive surgery
ActiveCN106890025AReduce surgical riskSurgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modellingEntry pointNavigation system
The invention discloses a navigation system and method of a minimally invasive surgery. The navigation system comprises a composite endoscope body, a spatial positioning device and a surgery navigation server. The method comprises the steps that preoperative diagnostic images are subjected to three-dimensional model reconstruction and preoperative planning before navigation is performed; during the navigation, three-dimensional optical image signals and two-dimensional ultrasonic image signals of intraoperative organs and tissue are simultaneously acquired and three-dimensional reconstruction is performed, a three-dimensional model of the preoperative diagnostic images with preoperative planning information is subjected to organ and tissue deformation correction, and a three-dimensional optical model and a dynamic preoperative registration model are subjected to registration and fusion, so that the functions of optical navigation and ultrasonic navigation are simultaneously achieved, the intraoperative optical navigation can be switched to the intraoperative ultrasonic navigation continuously in real time, and a key position point, an optimum surgical entry point and an internal travel path of the intraoperative organs and tissue are continuously achieved in all dimensions from surfaces of organs and tissue to inner structure of organs and tissue. The navigation system and method of the minimally invasive surgery overcomes the defect of relatively single and discontinuous functions existing in the prior art, and is capable of lowering surgical risks.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
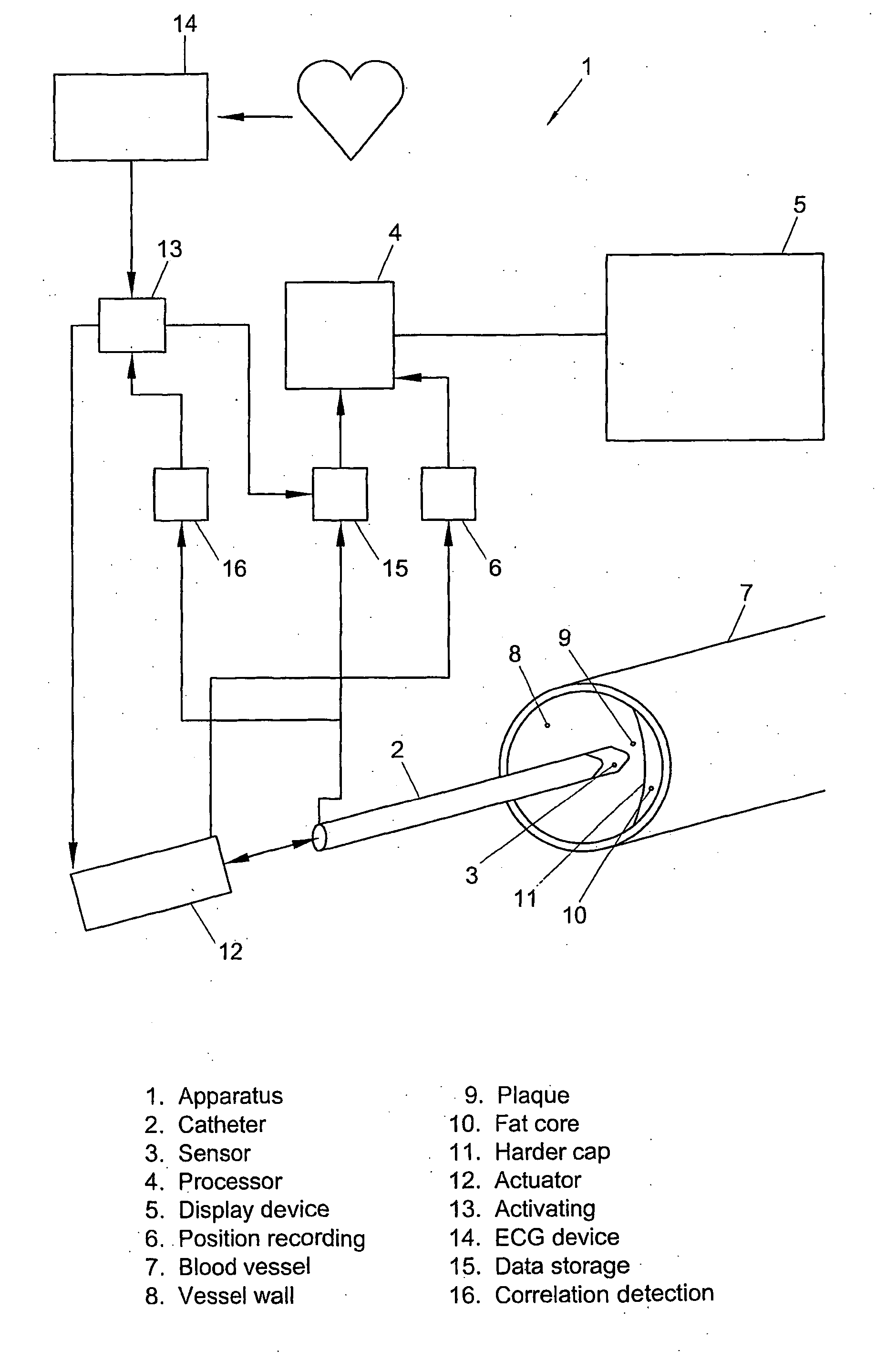
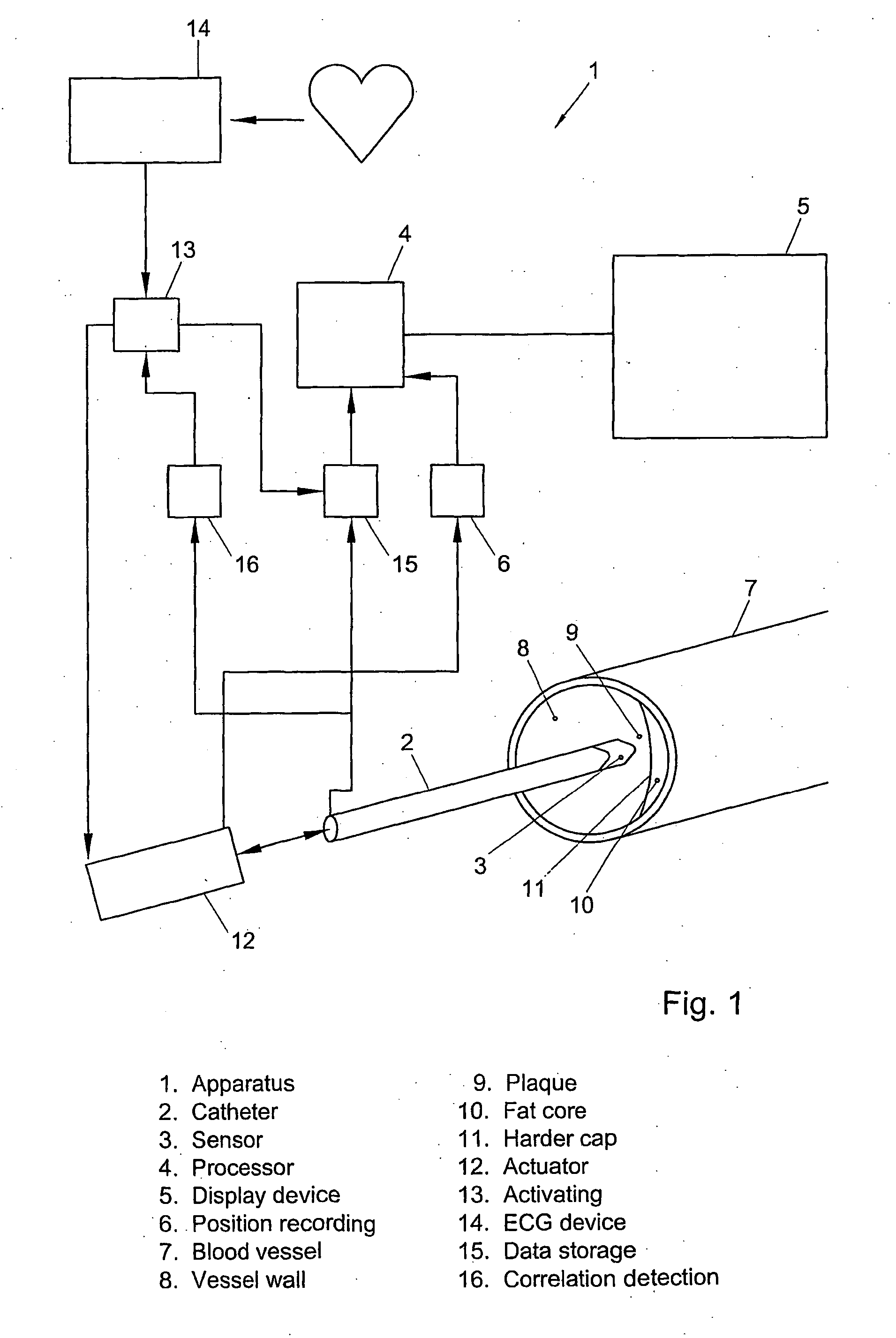
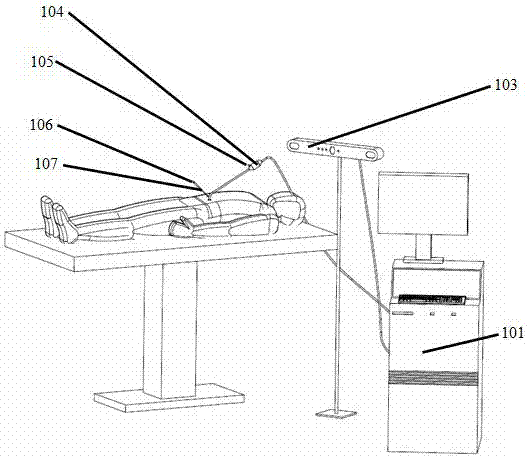
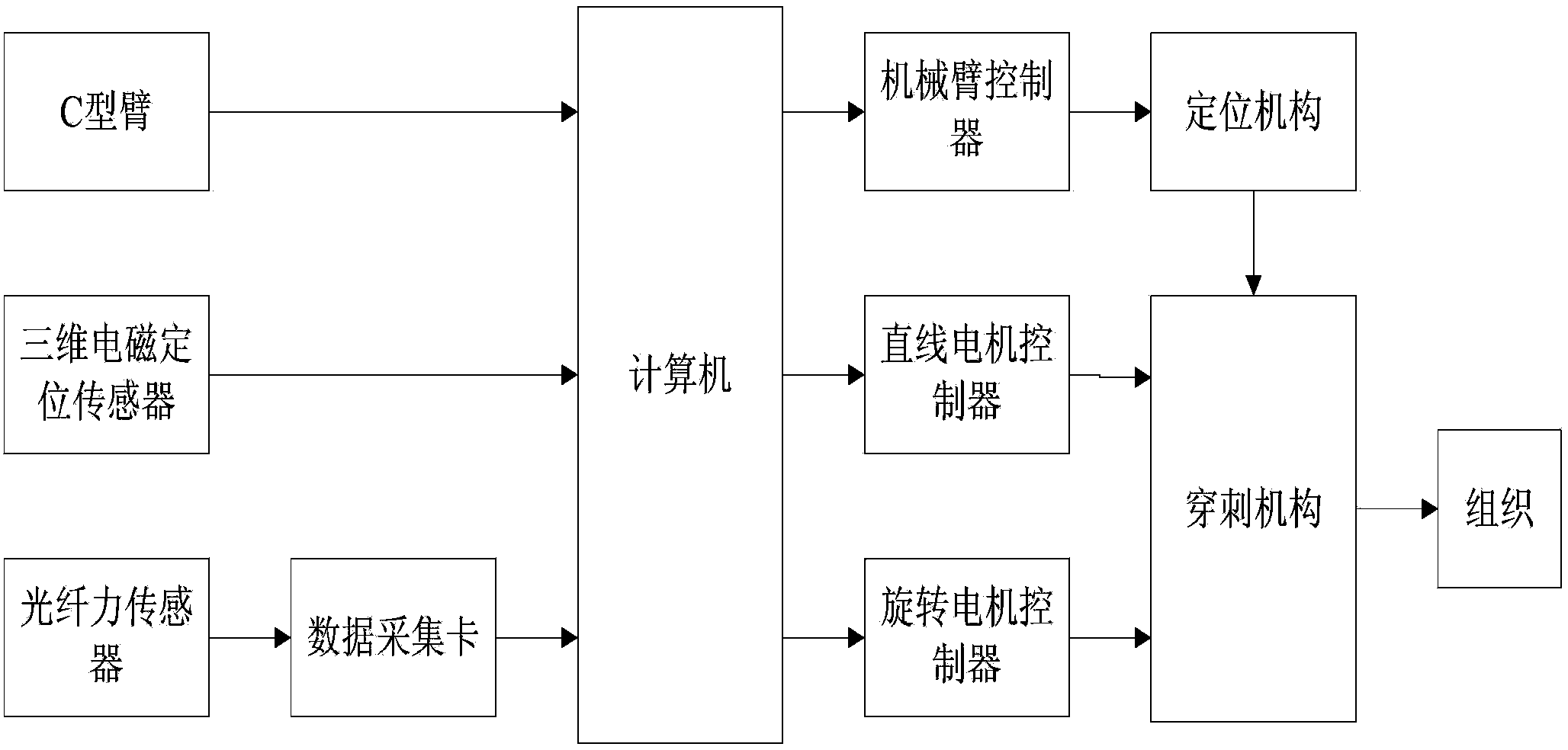
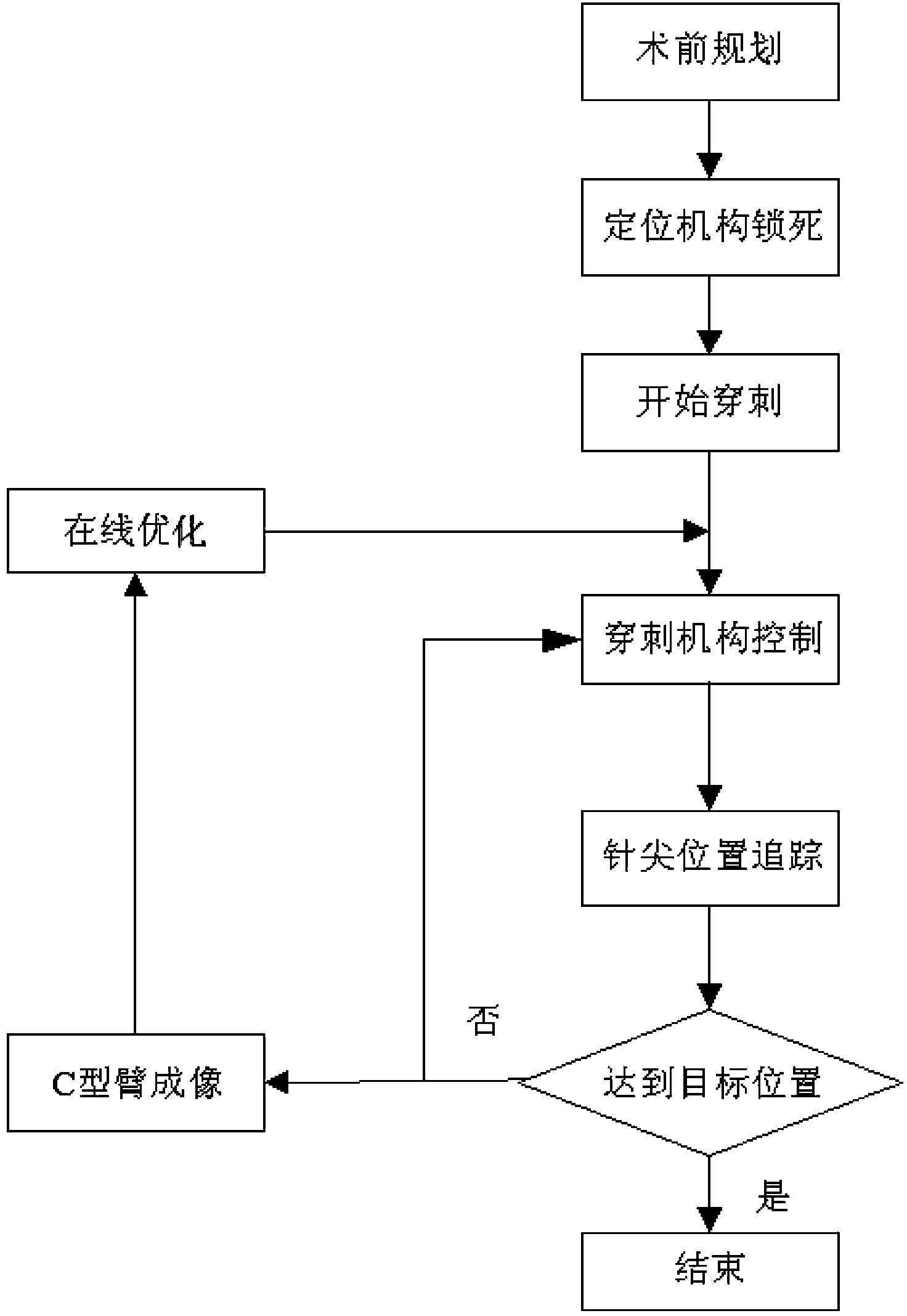
Robot-assisted oblique-tip flexible needle puncture system and method
ActiveCN104248471AReduce biasTimely assessment of disease severityDiagnosticsSurgical needlesTip positionNeedle puncture
The invention relates to a robot-assisted oblique-tip flexible needle puncture system and method. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining the position of a puncture platform and a puncture path through preoperative planning; moving a positioning mechanism to a specified position and locking the positioning mechanism, and controlling a puncture mechanism to enable a flexible needle to reach a penetration point of puncture; puncturing according to the planned puncture path; optimizing, by a path planning module, the puncture path of the flexible needle on line in real time according to flexible needle tip position information, attitude information and a puncture region tissue image fed back by a three-dimensional electromagnetic positioning sensor and a C-shaped arm in the puncture process; correcting the flexible needle by a controller according to a real-time on-line optimization strategy of the path planning module; ending the puncture process after the puncture needle reaches a target position. According to the method and the device, the position of the needle tip can be obtained in real time, the stress of the needle tip is obtained in real time, the puncture strategy is corrected on line according to tissue deformation to guarantee that the oblique-tip flexible needle can bypass an unpuncturable region to accurately reach a focus, and the puncture process is put under the monitoring of a doctor to guarantee the safety of the puncture surgery.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
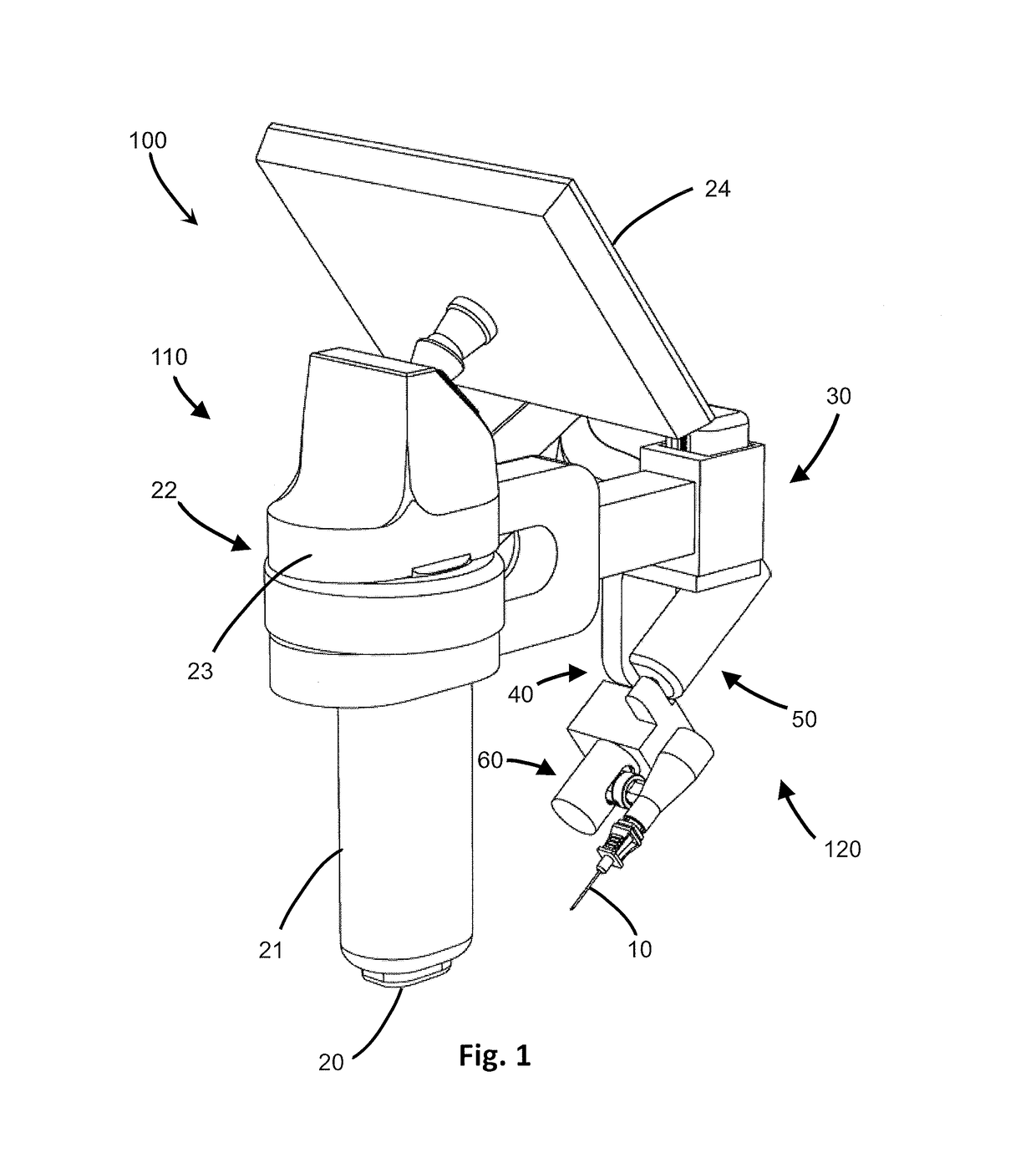
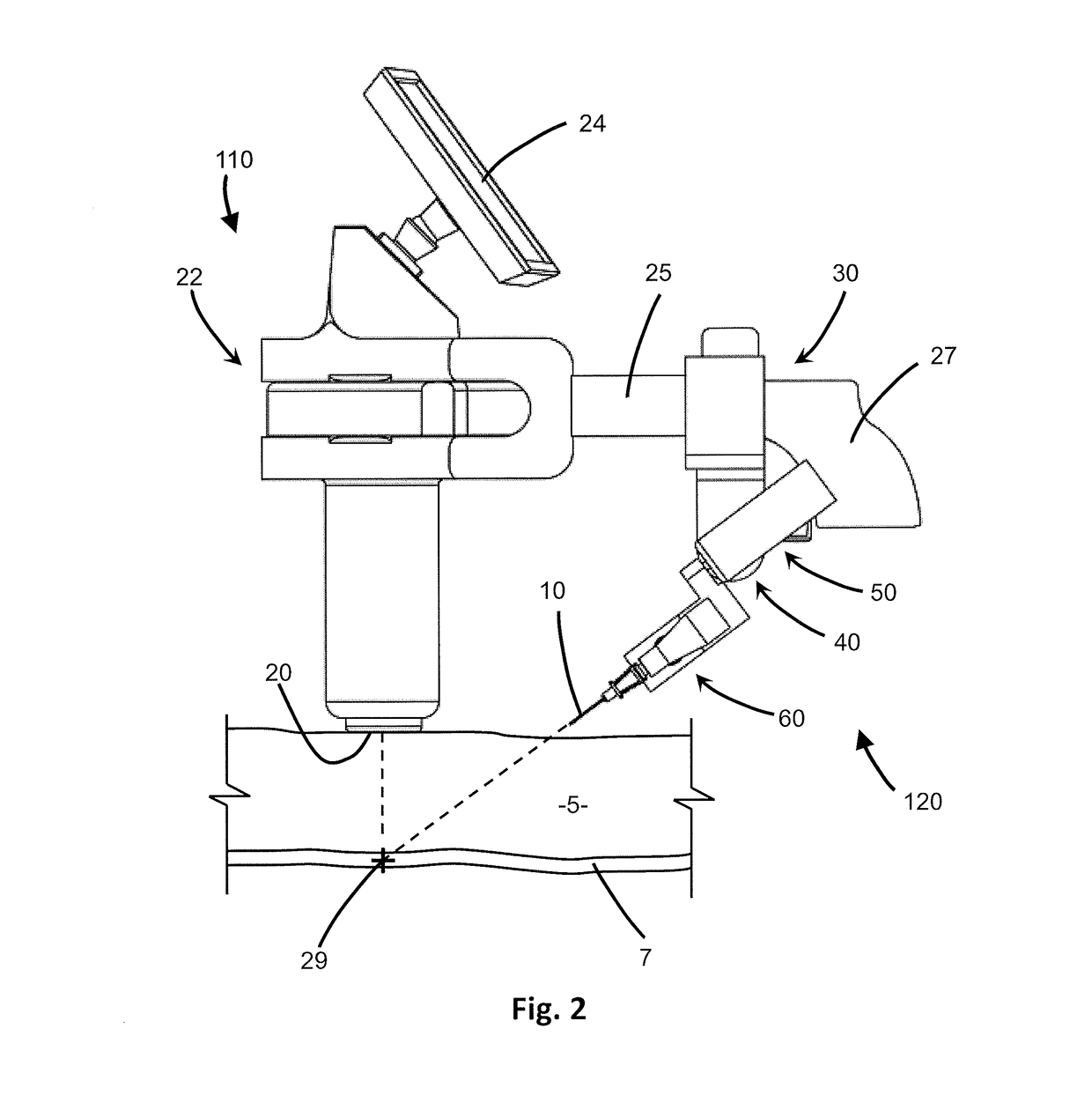
Device and System for Insertion of Penetrating Member
A system, device and method for insertion of a penetrating member into tissue is disclosed, which may be handheld and automated. A detector obtains data regarding subdermal locations of tissue structures, including cavities such as blood vessels. A processor calculates the distance between a preselected target point below the tissue surface, such as within a blood vessel, and the tissue surface, and adjustment data for vertical, angular and extension adjustment of the penetrating member. Vertical, angular and extension actuators carry out the adjustments in real-time as calculated and directed by the processor. Changes in the location of the target point result in automatic recalculation and adjustment by the processor and various actuators. A vibrational actuator induces vibration to the penetrating member during insertion, overcome tissue deformation and vein rolling. A guidewire may be inserted through or by the device, for dilator and catheter insertion once the penetrating member is removed.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE +1
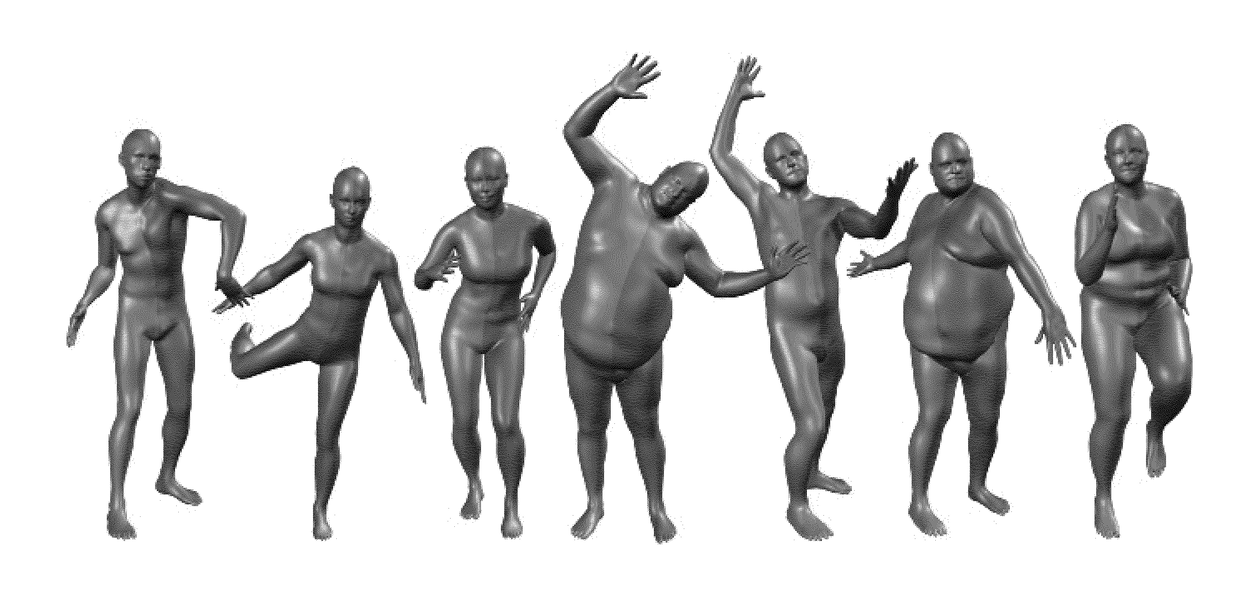
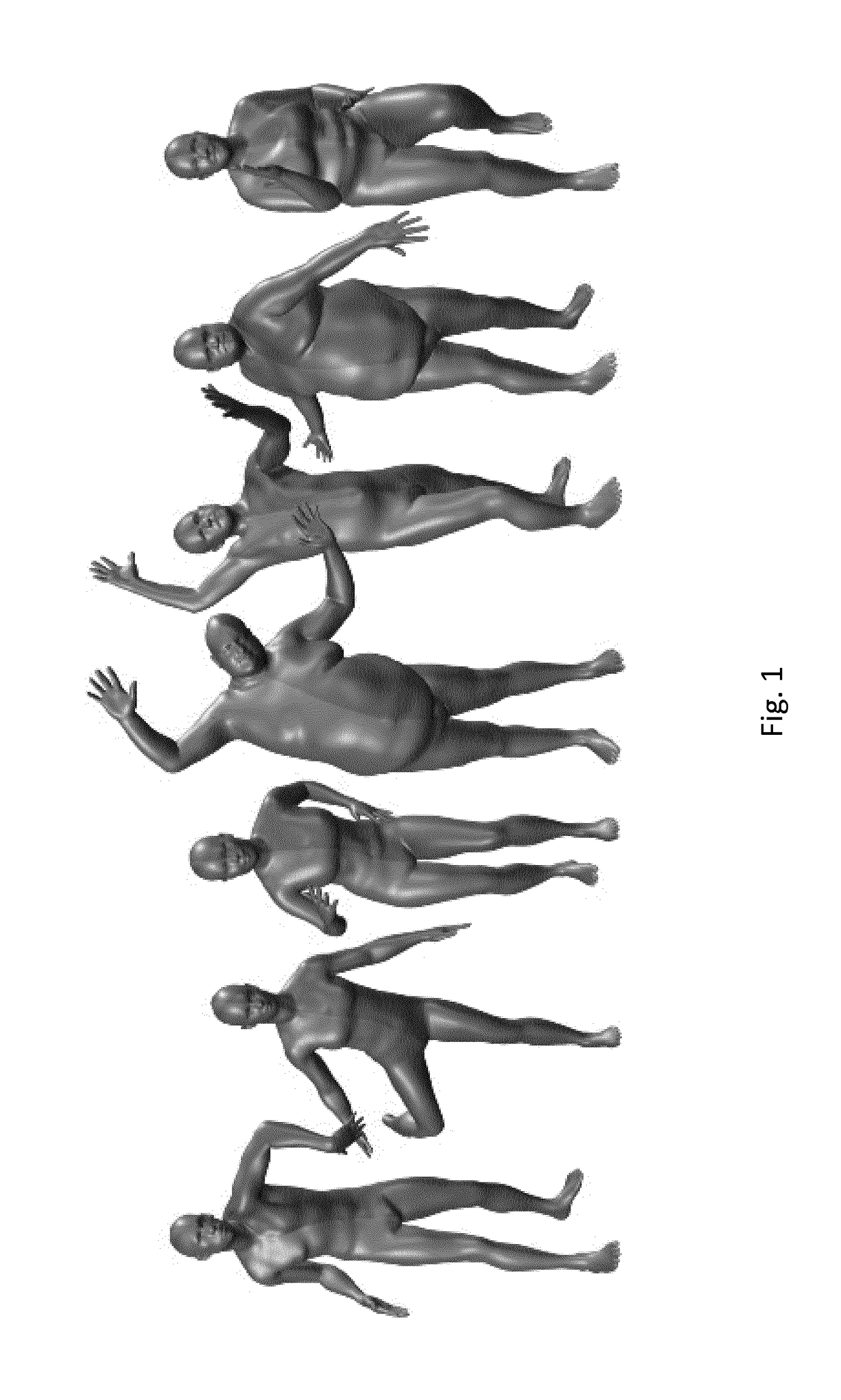
Skinned multi-person linear model
ActiveUS20180315230A1Error minimizationAccurate limitImage enhancementImage analysisBody shapePattern recognition
The invention comprises a learned model of human body shape and pose dependent shape variation that is more accurate than previous models and is compatible with existing graphics pipelines. Our Skinned Multi-Person Linear model (SMPL) is a skinned vertex based model that accurately represents a wide variety of body shapes in natural human poses. The parameters of the model are learned from data including the rest pose template, blend weights, pose-dependent blend shapes, identity-dependent blend shapes, and a regressor from vertices to joint locations. Unlike previous models, the pose-dependent blend shapes are a linear function of the elements of the pose rotation matrices. This simple formulation enables training the entire model from a relatively large number of aligned 3D meshes of different people in different poses. The invention quantitatively evaluates variants of SMPL using linear or dual-quaternion blend skinning and show that both are more accurate than a Blend SCAPE model trained on the same data. In a further embodiment, the invention realistically models dynamic soft-tissue deformations. Because it is based on blend skinning SMPL is compatible with existing rendering engines and we make it available for research purposes.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
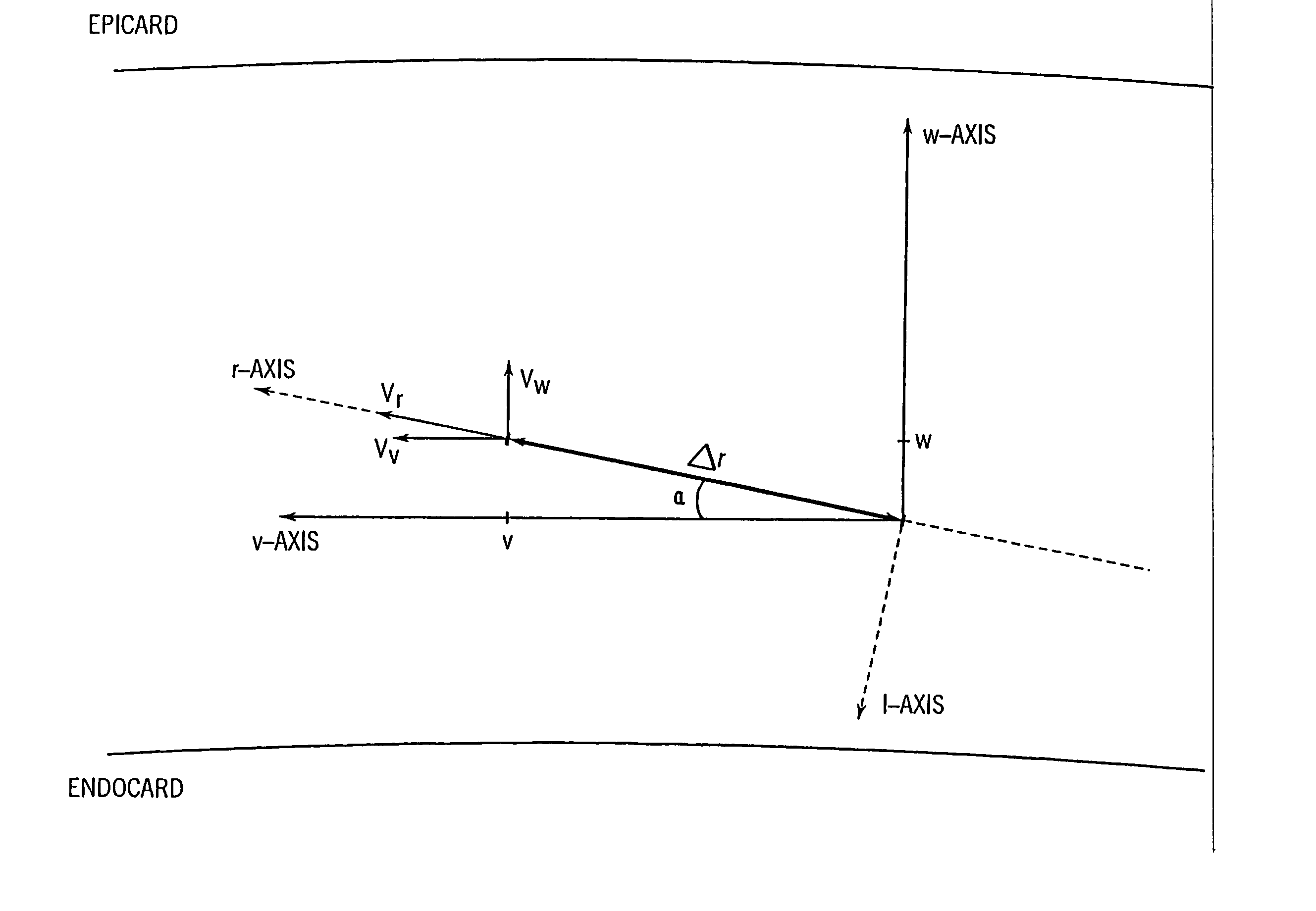
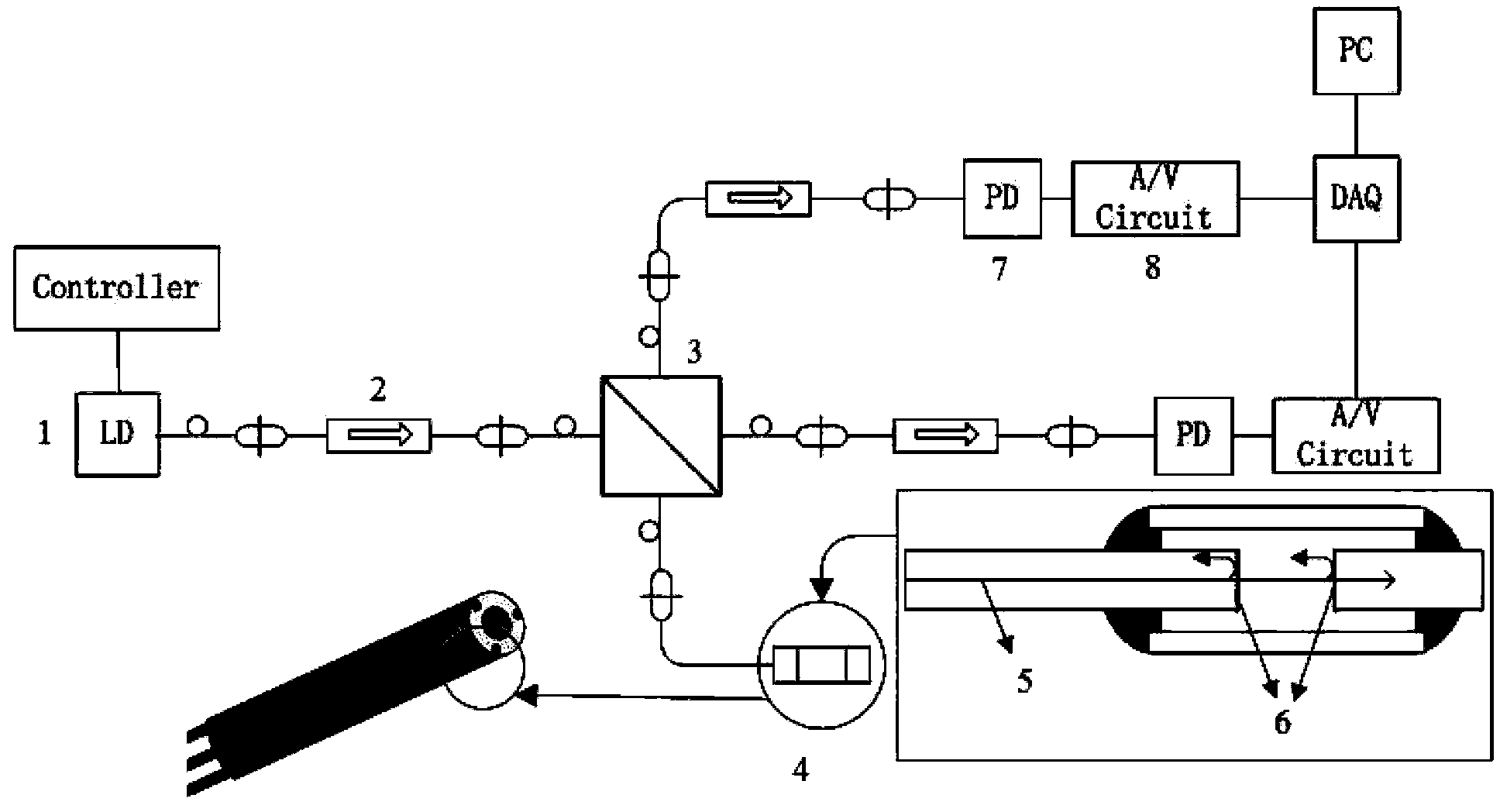
Method for estimating tissue velocity vectors and tissue deformation from ultrasonic diagnostic imaging data
A method is disclosed for estimating tissue velocity vectors and oriented strain from ultrasonic diagnostic imaging data. Reference points are defined from evaluation of image data derived from reflected ultrasonic beams in order to determine the direction of motion and the velocity vector of the reference points. The velocity of motion for corresponding reference points between two successive image frames is determined by applying a particle image velocimetry technique. Components of the tissue strain is then obtained from time integration of the strain-rate that is determined from the gradient of velocity estimated from the velocity data in two or more reference points.
Owner:ESAOTE
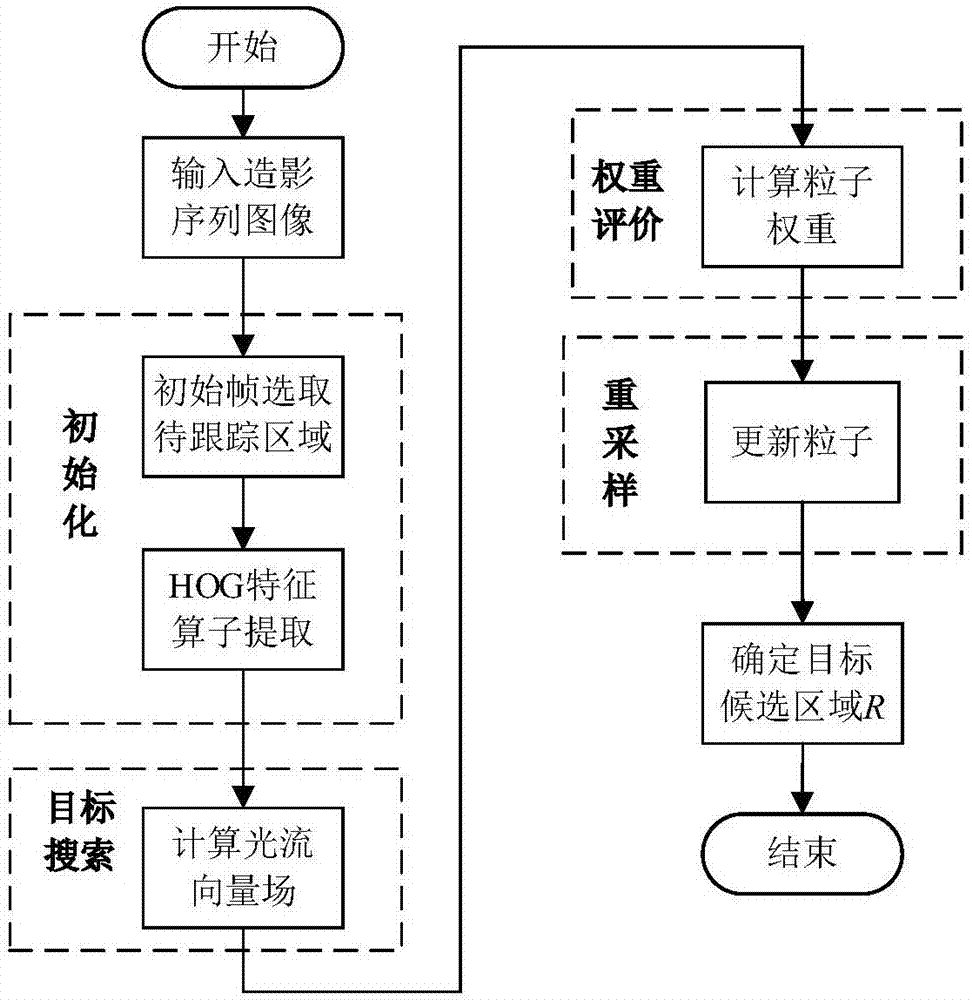
Real-time tracking and quantitative analysis method based on liver ultrasound contrast image
ActiveCN107169998AObjective and accurate reference valueGood real-time trackingImage enhancementImage analysisSonificationOptical flow
The invention belongs to the technical field of computer vision and digital image processing, and specifically relates to a real-time tracking and quantitative analysis method based on a liver ultrasound contrast image. The method mainly comprises the following steps: 1) selecting a region of interest from an initial frame of a liver sequence image, and determining a candidate region through combination of an optical flow method and a particle filtering method; 2) extracting features of a candidate sample by utilizing a deep neural network, and obtaining a tracking result; 3) judging accuracy of the current tracking result through similarity match; and 4) quantifying radiography parameters of an observation point area, eliminating fluctuation interference in the image, and fitting a time intensity curve through a cubic spline interpolation method to allow doctor's vision and differential diagnosis to be more visual. Compared with the prior art, the method, by utilizing the feature that tissue deformation has period, and through a global and local area combination method, has dominant advantages in tracking effect and speed.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
High-strength aluminum alloy isothermal direction-change open die forging method and device
ActiveCN101941039AConstant and uniform temperatureEasy to organizeForge furnacesFurnace temperatureStructure property
The invention relates to a high-strength aluminum alloy isothermal direction-change open die forging method which comprises the following steps: heating preprocessed high-strength aluminum alloy blank in a direction-change isothermal forging heating holding furnace at the temperature of 350-450 DEG C, and keeping the furnace temperature unchanged; and according to the structure property indices required by the blank, repeatedly upsetting and drawing the blank in the direction-change isothermal forging heating holding furnace until the blank reaches the design size of the forge piece. The isothermal direction-change open die forging device comprises a heating furnace and a forging press, wherein the furnace body is installed on the forging platform of the forging press; the forging rammer of the forging press is installed in a through hole in the furnace bottom plate; and the forging head of the forging press is installed in a through hole in the furnace top plate. The invention has the advantages of simple technique, convenient operation, and low tendency to recrystallization, enables the high-strength aluminum alloy to be under isothermal conditions all through the direction-change open die forging process, does not need to heat the blank again in the forging process, improves the quality of the forge piece and enhances the forging efficiency; and the forge piece has the advantages of sufficient structure deformation, uniform deformation at each part, and low tendency of cracking. The forge piece has favorable structure properties, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
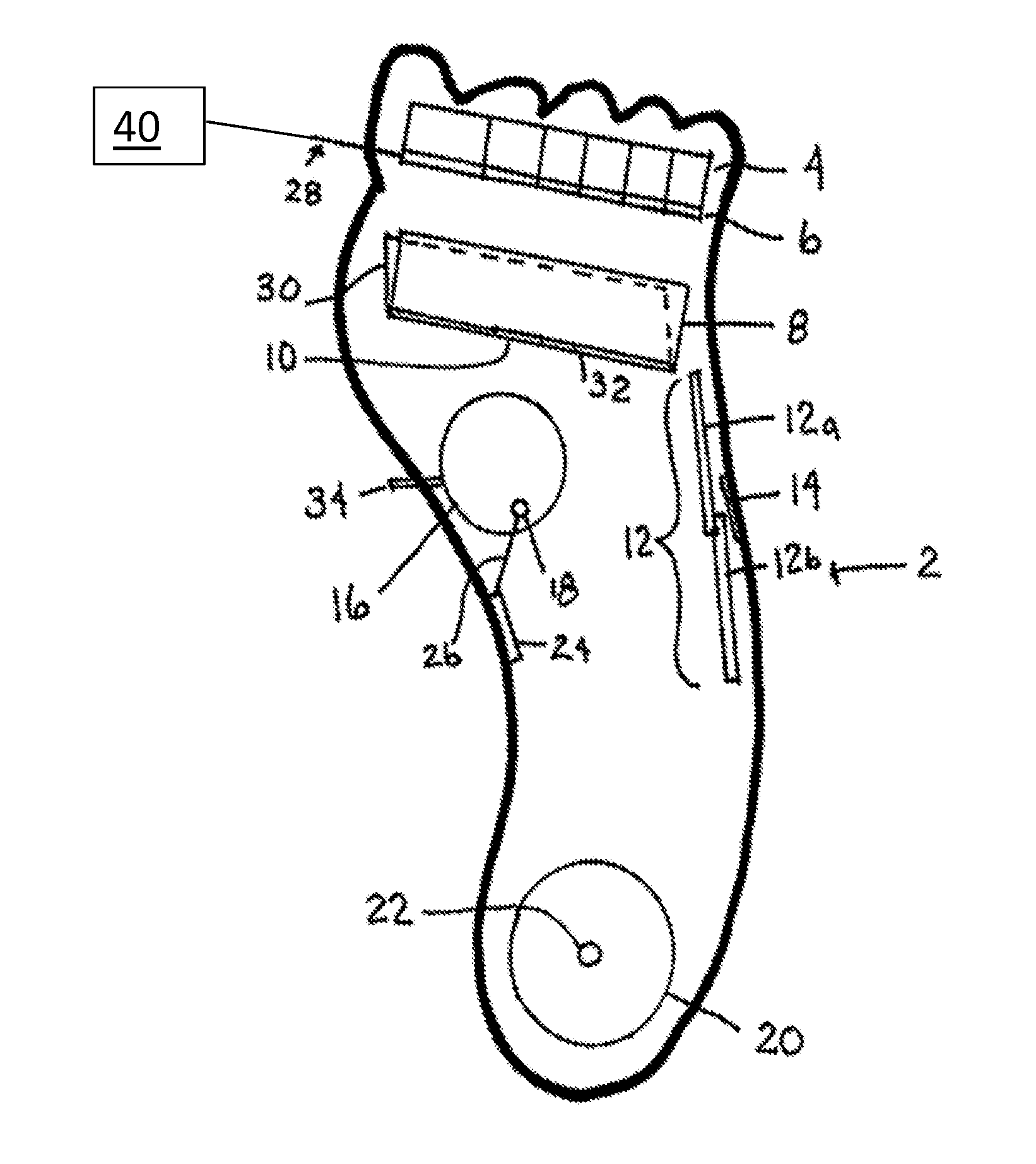
Actuated foot orthotic with sensors
Systems and methods of developing a tissue deformation profile for a foot of a patient. The tissue deformation profile can be used to identify a desired configuration for an orthotic device. A method uses a sensing orthotic device to assist in the treatment of foot issues. The orthotic device can have at least two sensors and at least one actuator for adjusting physical parameters of the orthotic device.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT NEVADA SYST OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF NEVADA RENO
Robust mosaicing method, notably with correction of motion distortions and tissue deformations for in vivo fibered microscopy
A mosaicing method taking into account motion distortions, irregularly sampled frames and non-rigid deformations of the imaged tissue. The method for mosaicing frames from a video sequence acquired from a scanning device such as a scanning microscope, includes the steps of: a) compensating for motion and motion distortion due to the scanning microscope, b) applying a global optimization of inter-frame registration to align consistently the frames c) applying a construction algorithm on the registered frames to construct a mosaic, and d) applying a fine frame-to-mosaic non rigid registration. The method is based on a hierarchical framework that is able to recover a globally consistent alignment of the input frames, to compensate for the motion distortions and to capture the non-rigid deformations.
Owner:INRIA NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR RESEARCH IN COMPUTER SCIENCE AND CONTROL +1
System and method for evaluating tissue
ActiveUS8562546B2Less readMinimization requirementsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAbnormal growthsShear modulus
The present invention provides a sensor system for measuring an elastic modulus and a shear modulus and a method for using the sensor system to evaluate a tissue by determining the presence of and / or characterizing abnormal growths. The method involves applying a set of forces of different magnitudes to one or more locations of tissue, detecting the corresponding displacements due to said applied forces, determining the forces acting on those locations of tissue which are a combination of forces from the applied voltages and the countering forces from tissue deformation, obtaining the elastic modulus and / or shear modulus for a plurality of locations, and determining abnormal growth invasiveness, malignancy or the presence of a tumor from said elastic and / or shear moduli.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
System and method for non-invasive determination of tissue wall viscoelasticity using ultrasound vibrometry
ActiveUS20140296709A1Non-invasively determinesNo painHealth-index calculationOrgan movement/changes detectionRadiologyNon invasive
System and method for determining viscoelasticity of curved tissue walls using ultrasound bladder vibrometry (UBV). The UBV is a non-invasive technique utilizing, in a specific case, a focused ultrasound radiation force to excite Lamb waves in a curved bladder wall and pulse-echo techniques to track the tissue deformation propagating through such curved wall. Cross-spectral analysis is used to calculate the wave velocity, which is directly related to the elastic properties of the bladder wall.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS9513358B2Reduce sensitivityReduce scan timeAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPerfusionMR - Magnetic resonance
The method and system for correcting motion-induced phase errors in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) use a phase shift of the non-phase encoded reference echo-signal accumulated during the diffusion-weighting in order to characterize bulk motion and tissue deformation and to compensate their effect for correcting the diffusion / perfusion-weighted image. The sequences unbalanced with respect to the first motion derivative are used for distinguishing the perfusion component. The MRI apparatus provides additional excitation resonance-frequency ranges for forming the reference echo signals.
Owner:VAPOSUN
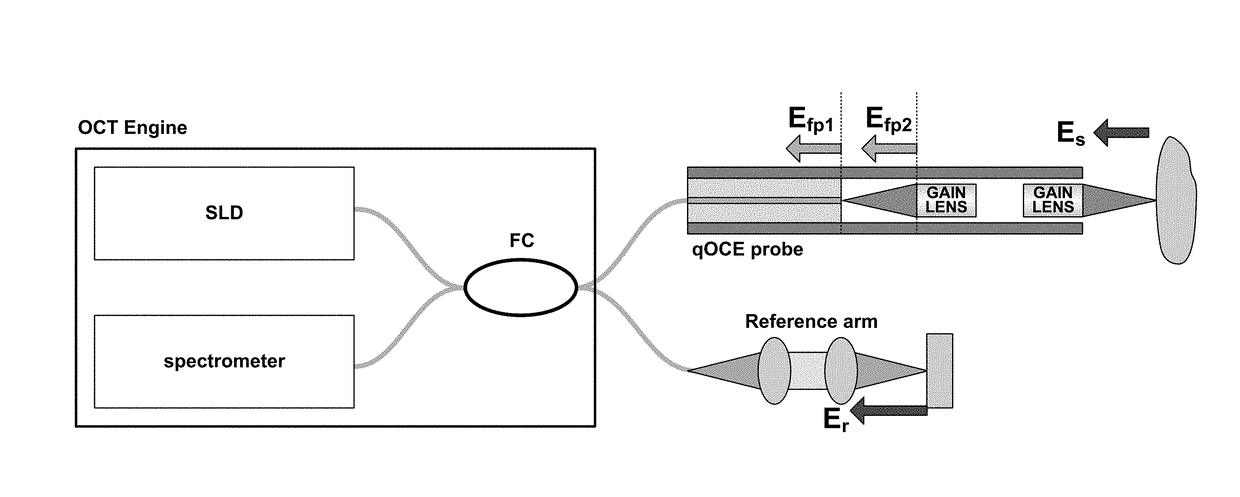
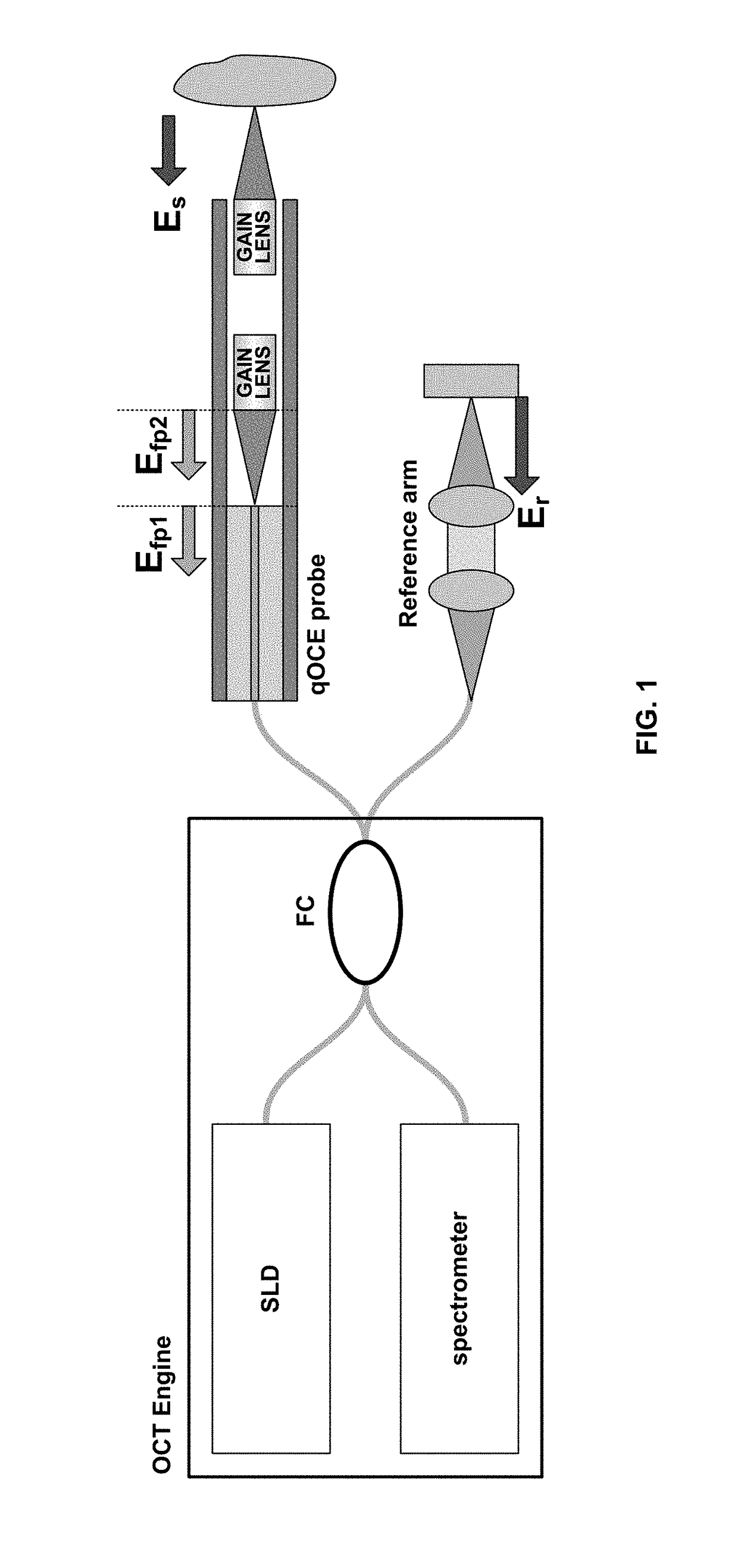
Optical coherence elastography
A miniature quantitative optical coherence elastography system with an integrated Fabry-Perot force sensor for in situ elasticity measurement of biological tissue is provided. The technique has great potential for biomechanics modeling and clinical diagnosis. The qOCE system contains a fiber-optic probe that exerts a compressive force to deform tissue at the tip of the probe. Using the space-division multiplexed optical coherence tomography signal detected by a spectral domain optical coherence tomography engine, probe deformation in proportion to the force applied is quantified, as well as the tissue deformation corresponding to the external stimulus. Simultaneous measurement of force and displacement allows for calculation of Young's modulus from the biological tissue. The provided system has had its effectiveness validated on tissue mimicking phantoms, as well as biological tissues, with the advantages of being minimal invasive and also not requiring the use of external agents or substantial pre-measuring preparation.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Laparoscopic surgery simulation training system based on computer aided medical display
InactiveCN108492693AIncrease success rateEasy to operateEducational modelsJoystickSoft tissue deformation
The invention discloses a laparoscopic surgery simulation training system based on computer aided medical display. A CT data preprocessing module, a CT organ segmentation module and a three-dimensional volume rendering module can use artificial intelligence and a 3D volume rendering integrated rendering technology to construct a three-dimensional abdominal cavity model in real time according to customized CT scan data of a patient. A volume data mechanics loading module, a joystick control module and a joystick mechanics feedback module are used to establish an accurate force feedback model and a tissue deformation model. Simulated actual laparoscopic surgical instruments are used and the joystick mechanics feedback module is combined to truly simulate the operation position and operationmode of surgical instruments. The real-time stress state of organs and tissues can be accurately fed back. Soft tissue deformation or a cutting effect can be truly reproduced. The system can accumulate real operation experience for a laparoscopic operator, can improve the operation skills of the laparoscopic operator, and can help the laparoscopic operator to be proficient in the relative depth ofa surgical instrument and a lesion organ.
Owner:盛玉涛
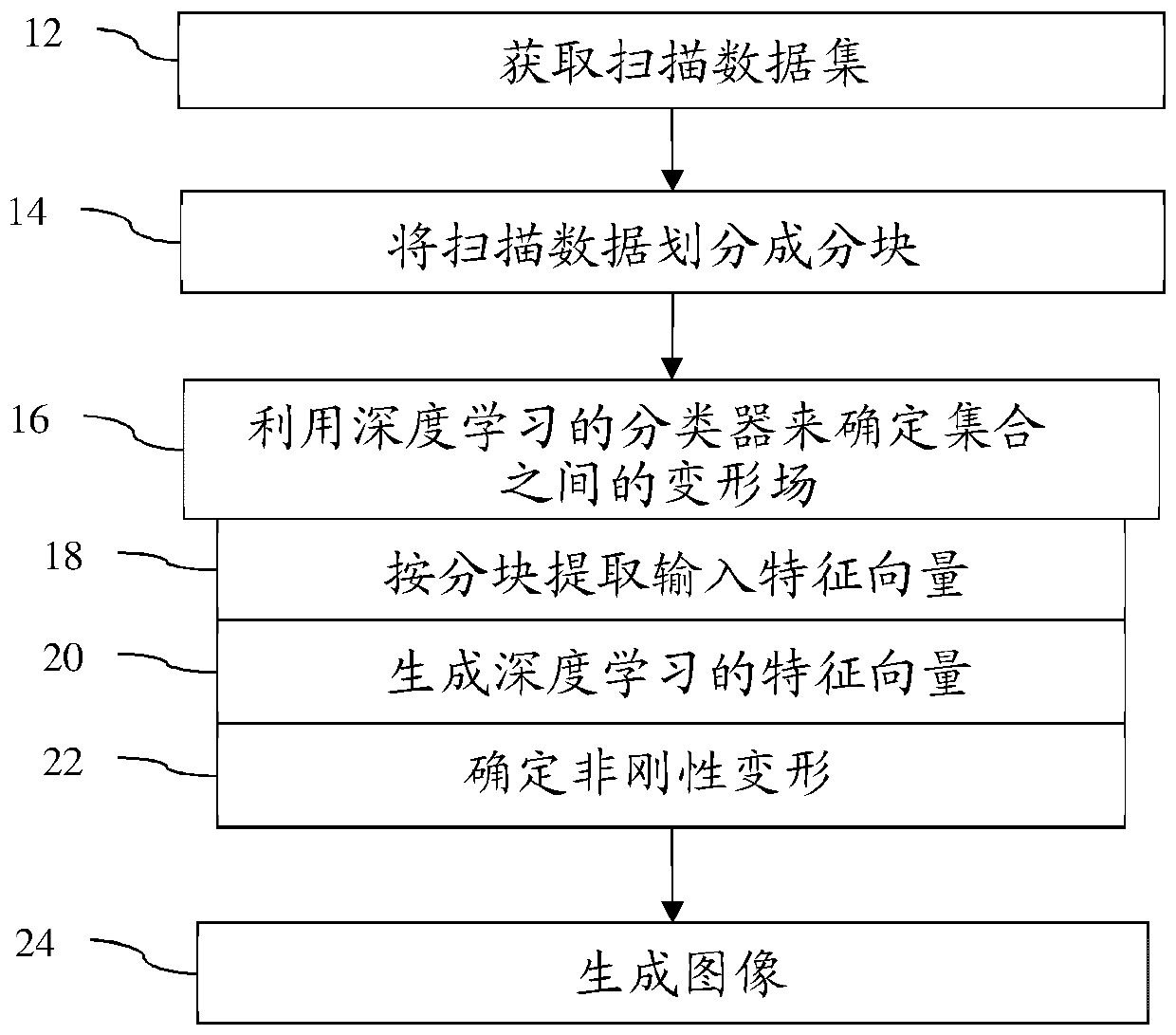
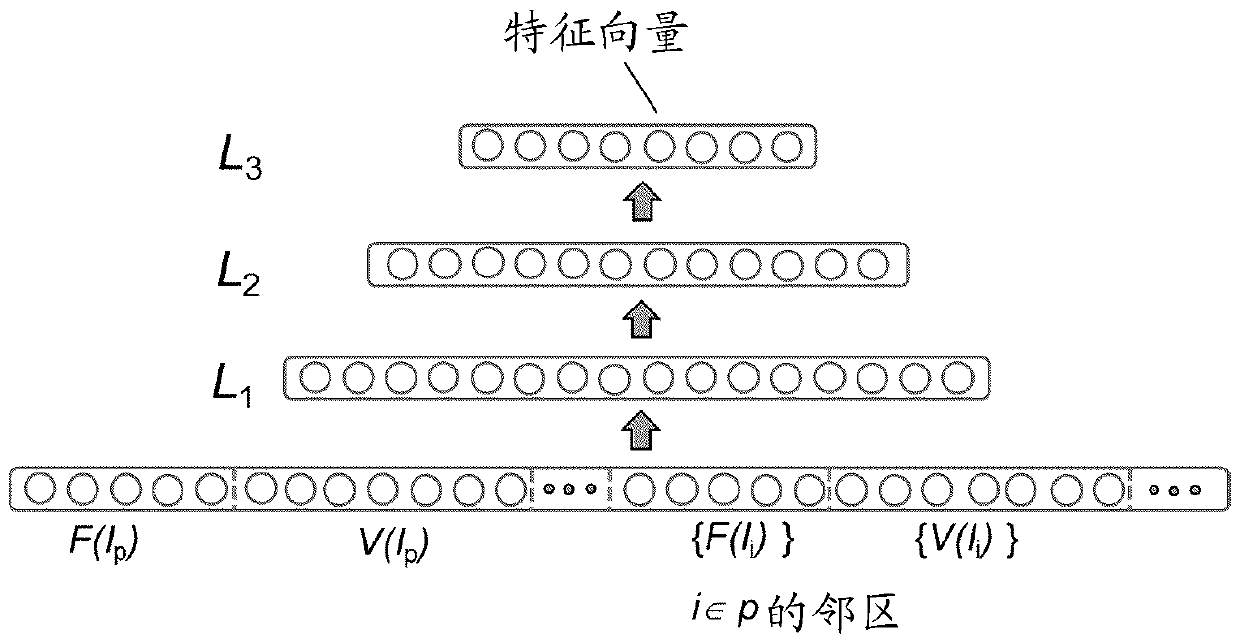
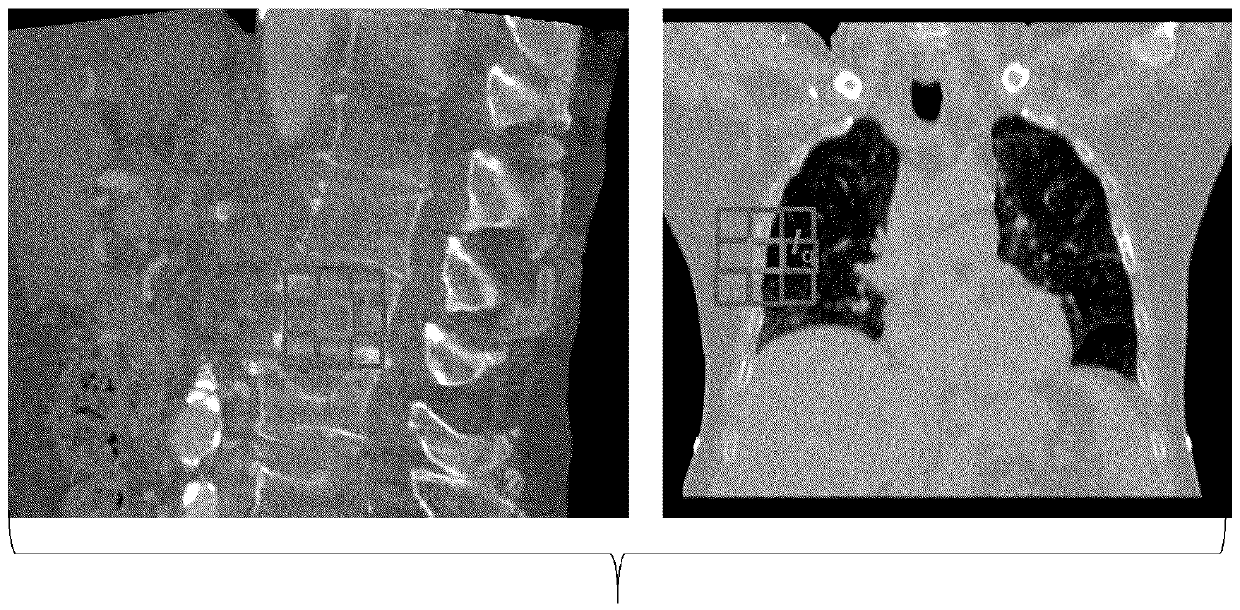
Deep-learnt tissue deformation for medical imaging
A deep machine-learning approach is used for medical image fusion (24) by a medical imaging system (48). This one approach may be used for different applications. For a given application, the same deep learning is used but with different application-specific training data. The resulting deep-learnt classifier provides a reduced feature vector in response to input of intensities of one image and displacement vectors for patches of the one image relative to another image. The output feature vector is used to determine (16) the deformation for medical image fusion (24).
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Robust mosaicing method, notably with correction of motion distortions and tissue deformations for a vivo fibered microscopy
The present invention concerns a mosaicing method taking into account motion distortions, irregularly sampled frames and non-rigid deformations of the imaged tissue. The invention relates to a method for mosaicing frames from a video sequence acquired from a scanning device such as a scanning microscope, the method comprising the steps of:a) compensating for motion and motion distortion due to the scanning microscope,b) applying a global optimisation of inter-frame registration to align consistently the framesc) applying a construction algorithm on the registered frames to construct a mosaic, andd) applying a fine frame-to-mosaic non rigid registration.The method is based on a hierarchical framework that is able to recover a globally consistent alignment of the input frames, to compensate for the motion distortions and to capture the non-rigid deformations.
Owner:INRIA NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR RESEARCH IN COMPUTER SCIENCE AND CONTROL
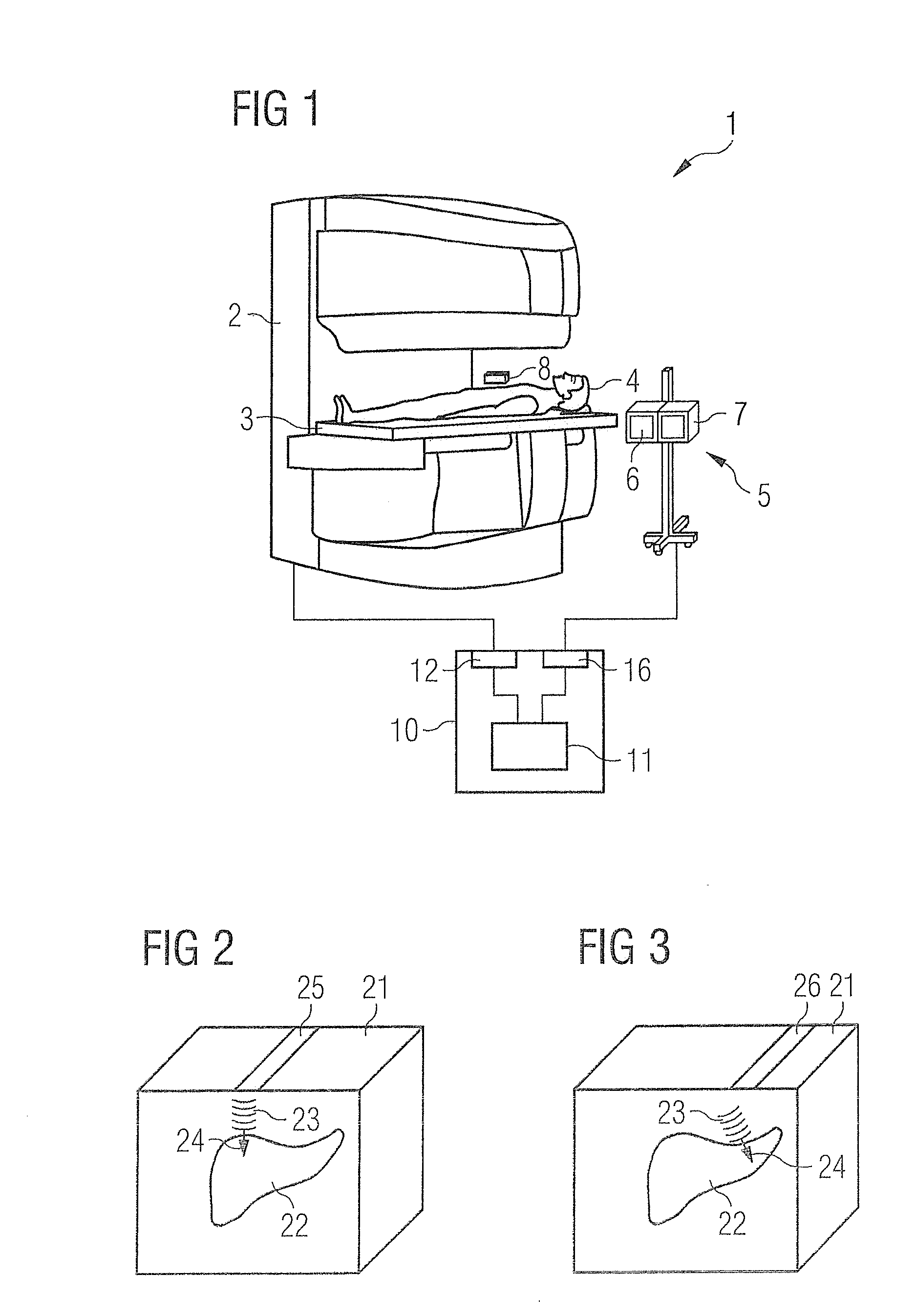
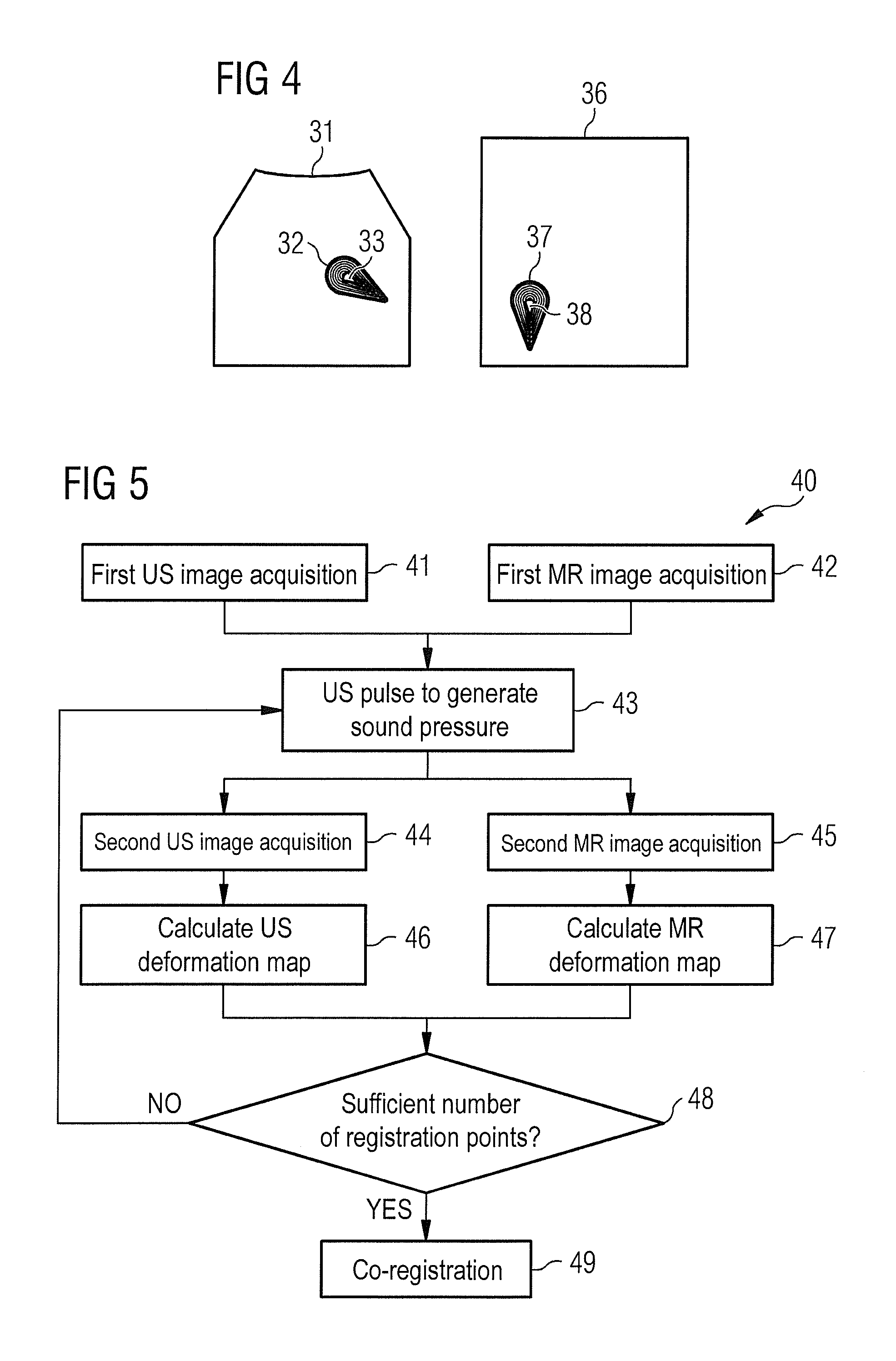
Medical imaging method and system
InactiveUS20130116542A1Reliable registration of imageReliable registrationOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsImage resolutionMedical imaging
In an imaging procedure, sound pressure is generated by applying ultrasound to the region to be imaged in order to cause a deformation of tissue therein from at least one acquired ultrasound image data set, first data are determined that represent, with spatial resolution, the deformation of the tissue as a reaction to the sound pressure. At least one magnetic resonance image data set is acquired, from which second data are determined that represent, with spatial resolution, the deformation of the tissue as a reaction to the sound pressure. The at least one ultrasound image data set and the at least one magnetic resonance image data set are brought into registration with each other by a comparison of the first data and the second data.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
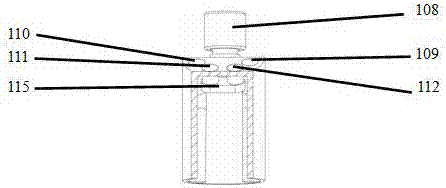
Loader and retriever for transcatheter heart valve, and methods of crimping transcatheter heart valve
ActiveUS20170049567A1Easy crimpingReduce shrinkage and other deformation and damageStentsBalloon catheterCatheterTissue deformation
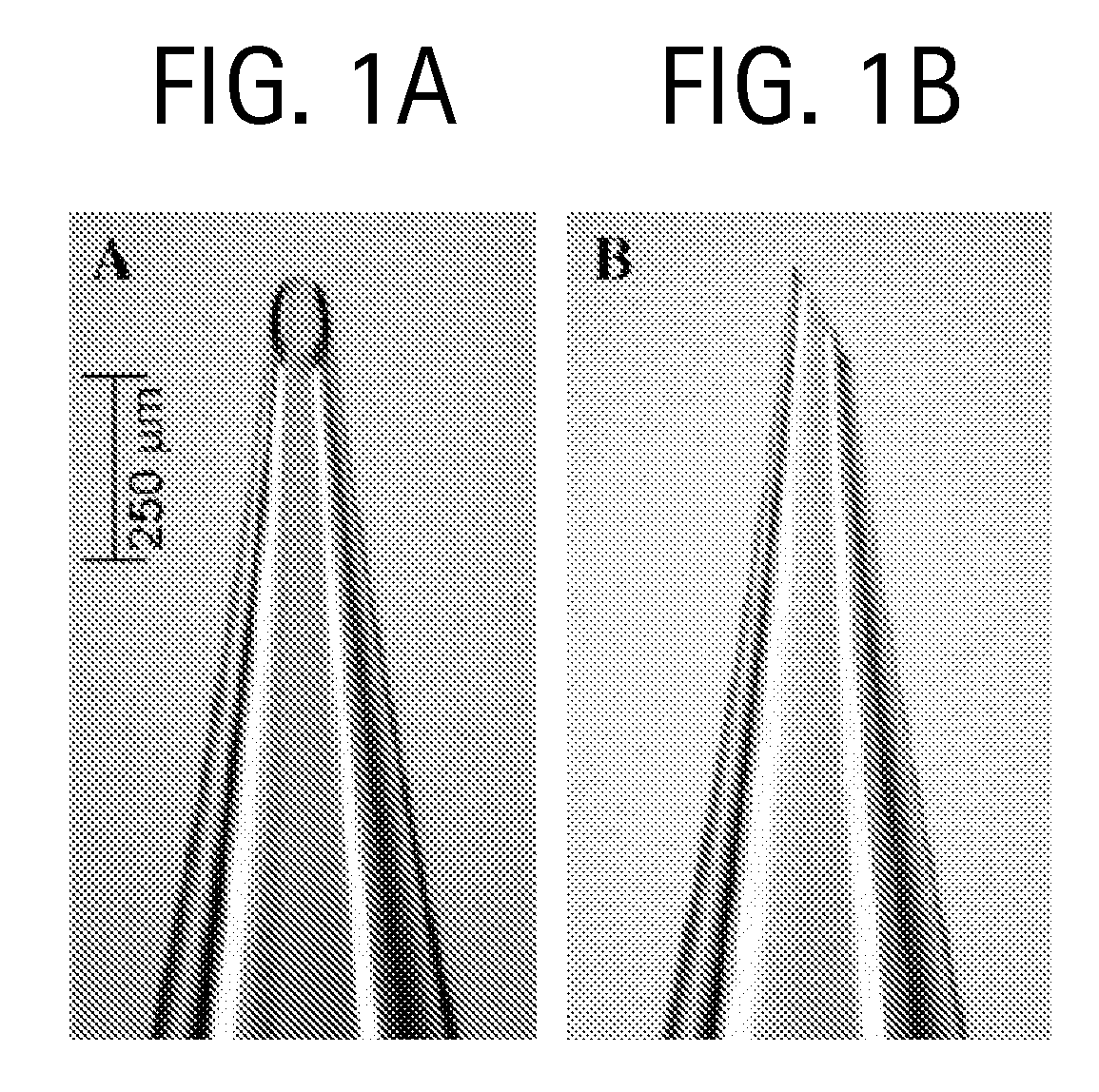
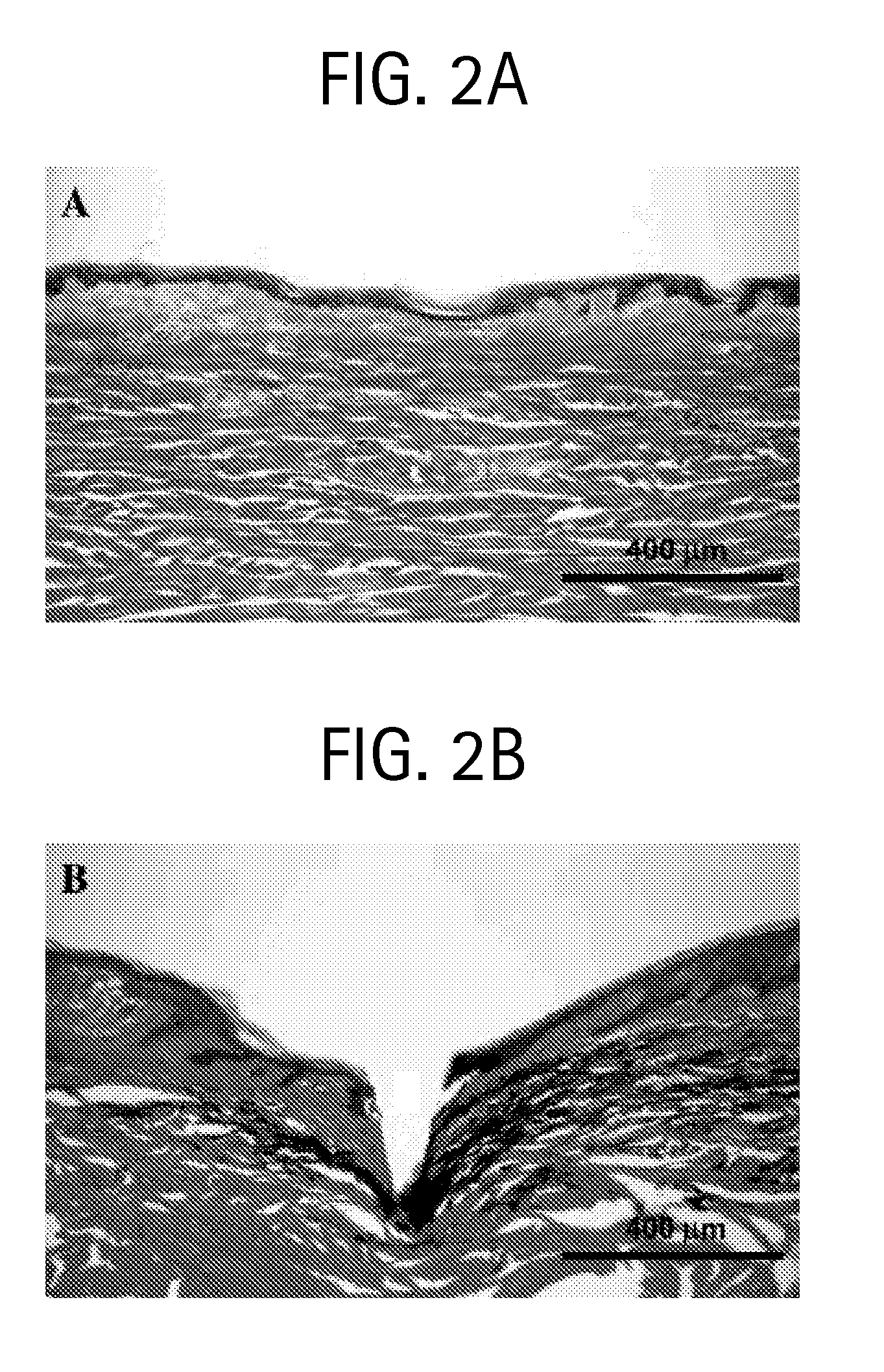
A loader and method for loading a transcatheter heart valve into a delivery sheath or catheter is described that is also configured to facilitate retrieval of the heart valve back through the delivery sheath while protecting the delivery sheath from damage. Another loader provides for easier crimping and loading of a THV into a delivery sheath or catheter from a storage jar or container. A method for crimping a THV facilitates easier end user preparation of the valve for implantation and reduces the likelihood of tissue deformation in the valve during storage. These devices and methods for deploying THVs simplify the valve replacement procedure.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Methods and systems for functional imaging of cardiac tissue
ActiveUS8666138B2Organ movement/changes detectionCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic Radiology ModalityCardiac muscle
One embodiment of these teachings includes an imaging modality that is based on the ability of imaging technologies to detect wave-induced tissue deformation at depth, that allows viewing the propagation of action potentials deep within myocardial tissue, thereby helping to clarify clinical and physiological dynamical issues.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Jellyfish paraffin section making method
ActiveCN104034570ACreate a manufacturing methodReduce distortionPreparing sample for investigationMaterials processingWater content
The invention discloses a jellyfish paraffin section making method. The method comprises the steps of raw materials processing and fixing, dehydration, transparency realization, waxing, embedding, sectioning and dyeing. The method is suitable for the fixing, dehydration, transparency realization, waxing, embedding, sectioning and dyeing of different raw jellyfishes. A secondary fixing method combining a neutral buffering formaldehyde fixing liquid with an alcohol-acetic acid-formaldehyde mixed liquid, and the formula of a routine alcohol-acetic acid-formaldehyde mixed fixing liquid is adjusted, so the dehydration time is shortened, and the section production efficiency is improved; and the waxing time and temperature control conditions suitable for the jellyfish are established. The tissue deformation problem in the jellyfish paraffin section making process is overcome in the invention, and ideal paraffin tissue blocks and dyeing effect are realized. The making is suitable for making jellyfish paraffin sections with high content and rich in collagens, and the method provides a histomorphologic support for the monitoring of the quality of jellyfish in the processing process.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com