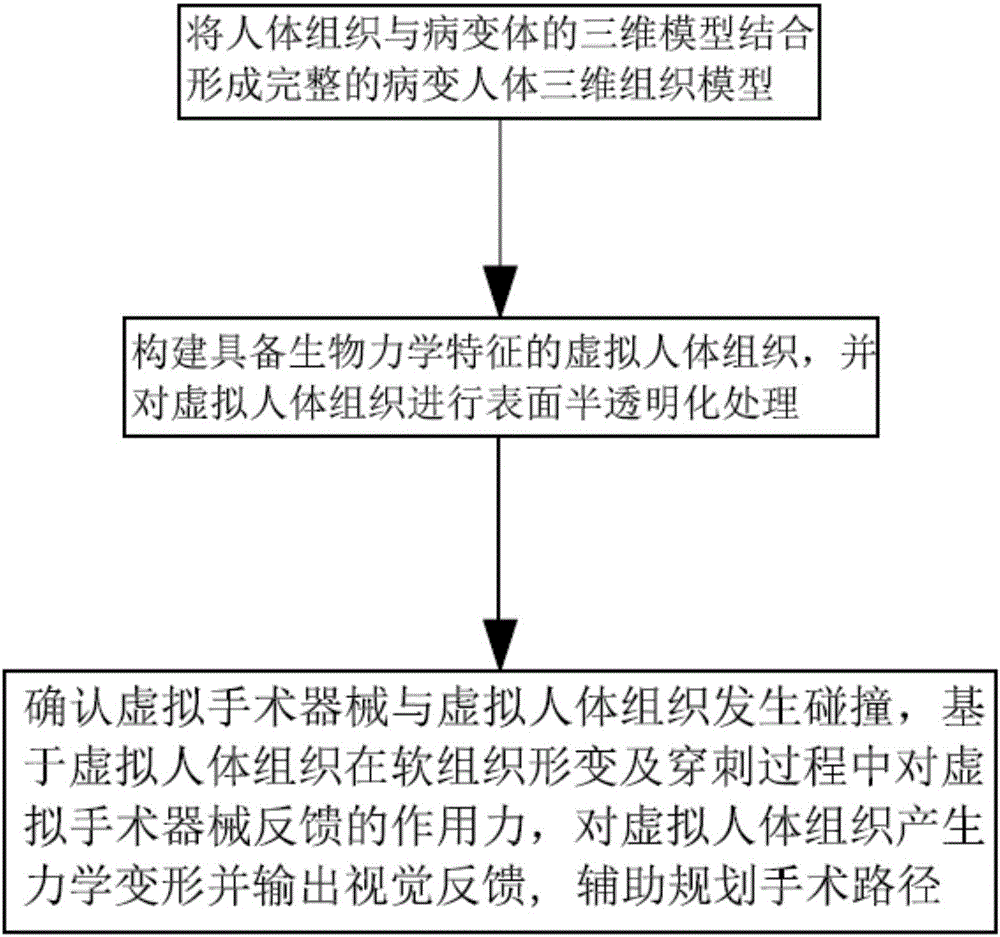
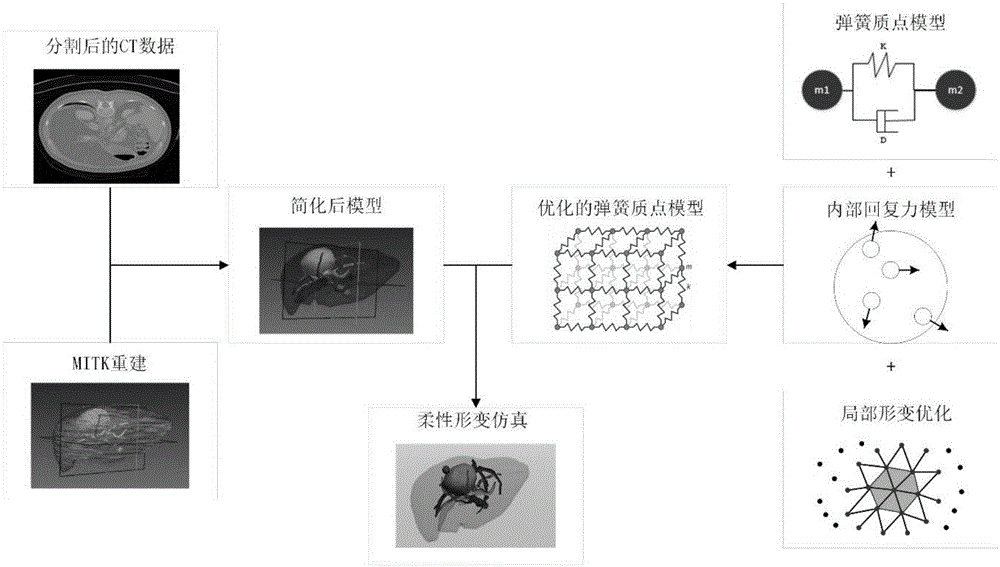
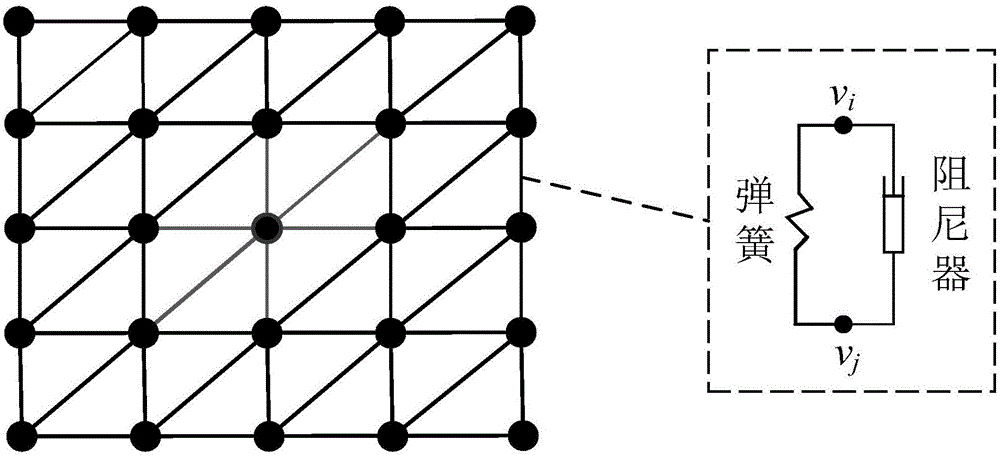
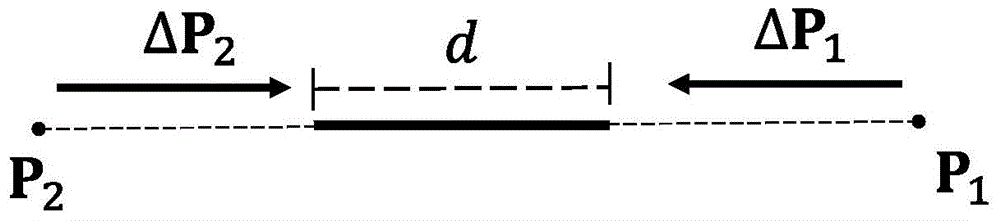Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
68 results about "Soft tissue deformation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
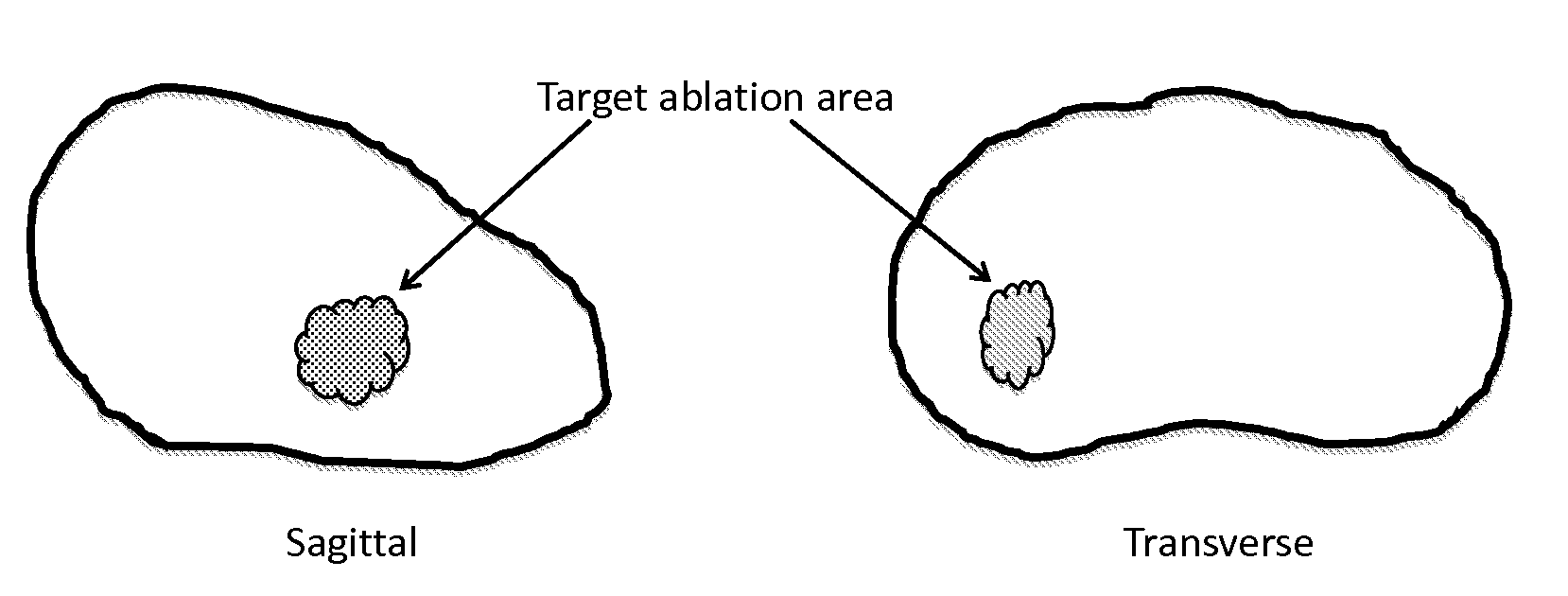
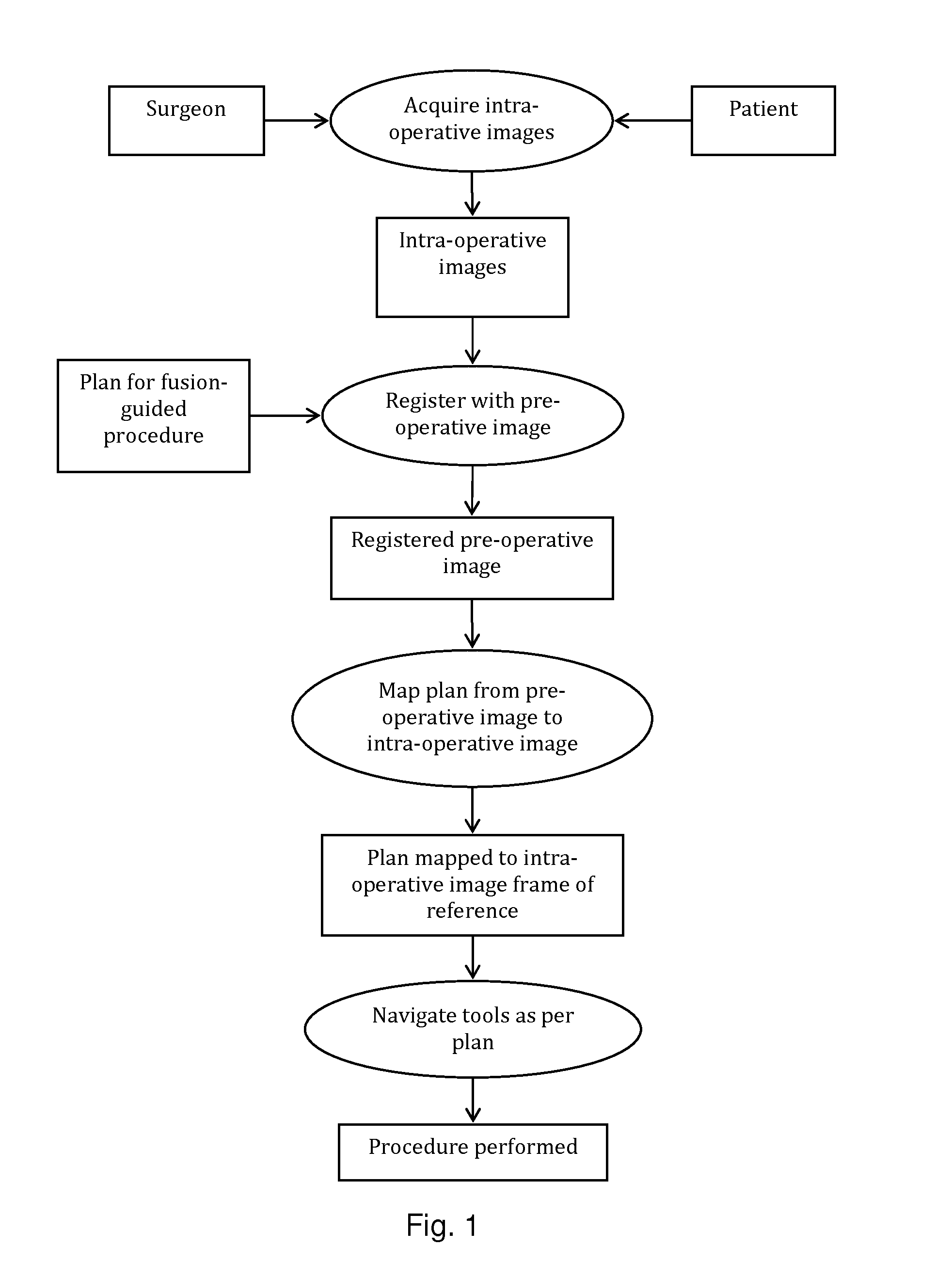
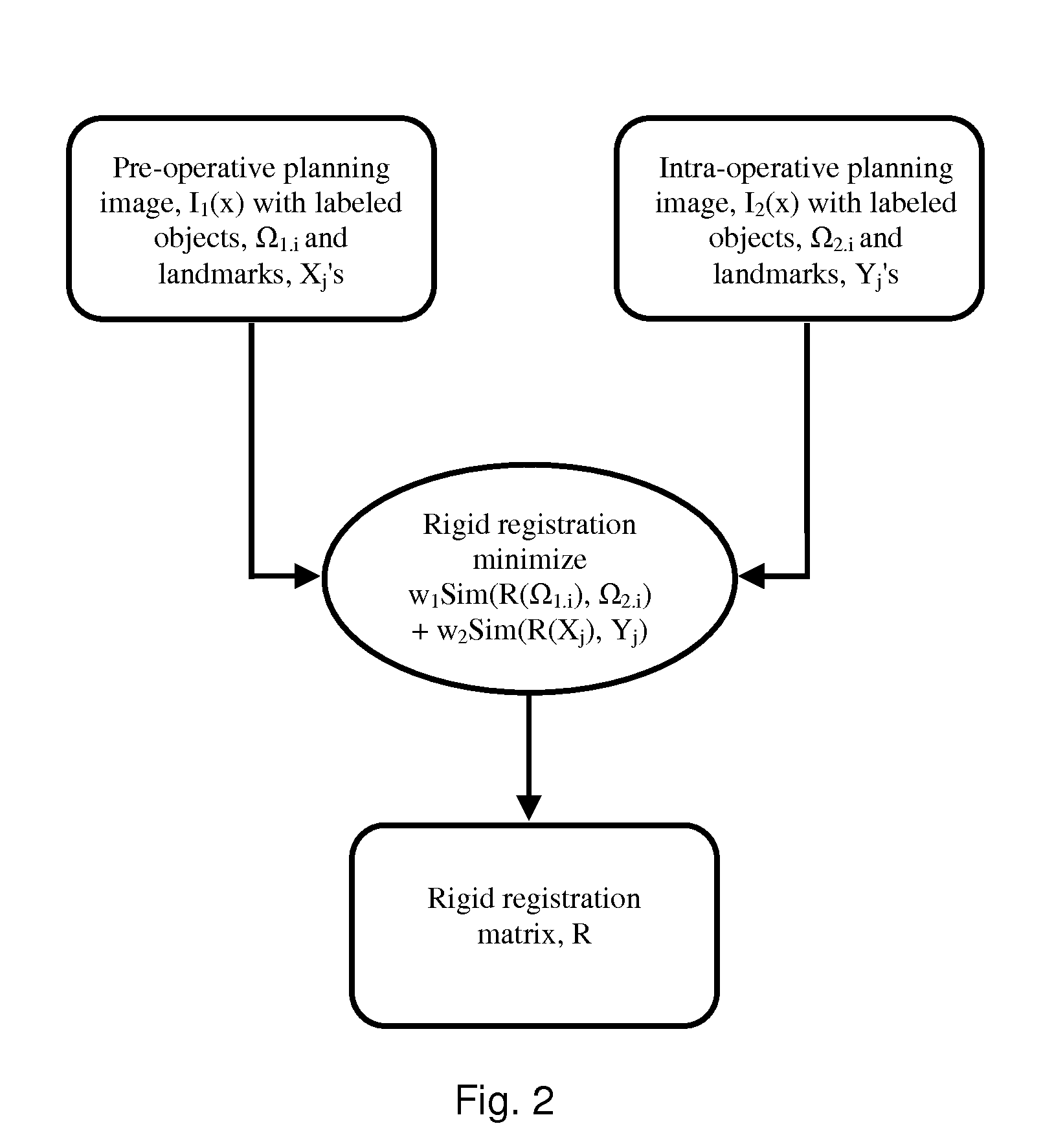
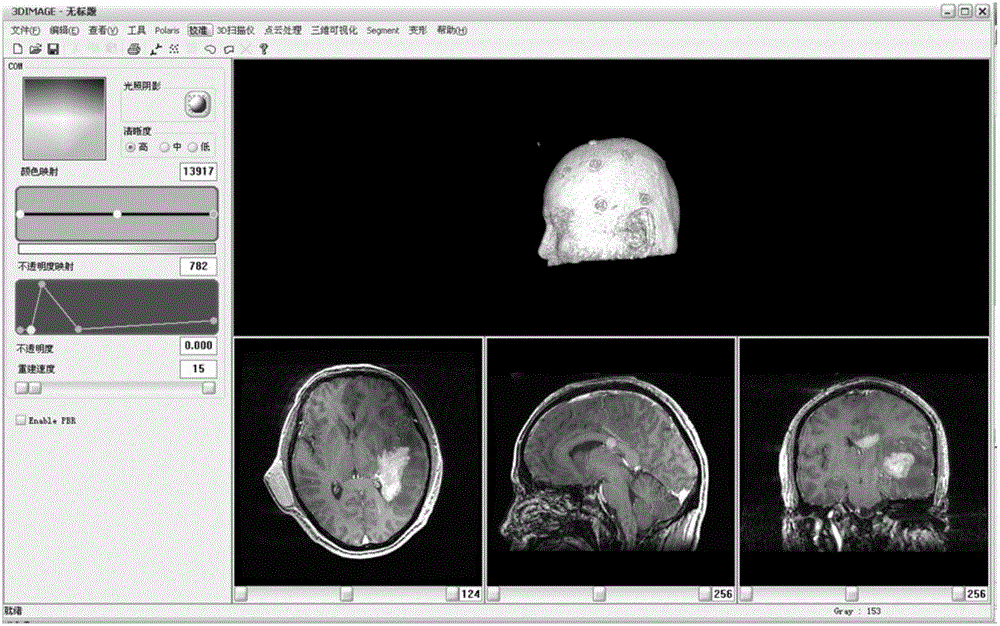
System and method for image guided medical procedures
InactiveUS20140073907A1Correction can be minimizedEasy to useUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesDiagnostic Radiology ModalitySoft tissue deformation
A system and method combines information from a plurality of medical imaging modalities, such as PET, CT, MRI, MRSI, Ultrasound, Echo Cardiograms, Photoacoustic Imaging and Elastography for a medical image guided procedure, such that a pre-procedure image using one of these imaging modalities, is fused with an intra-procedure imaging modality used for real time image guidance for a medical procedure for any soft tissue organ or gland such as prostate, skin, heart, lung, kidney, liver, bladder, ovaries, and thyroid, wherein the soft tissue deformation and changes between the two imaging instances are modeled and accounted for automatically.
Owner:CONVERGENT LIFE SCI
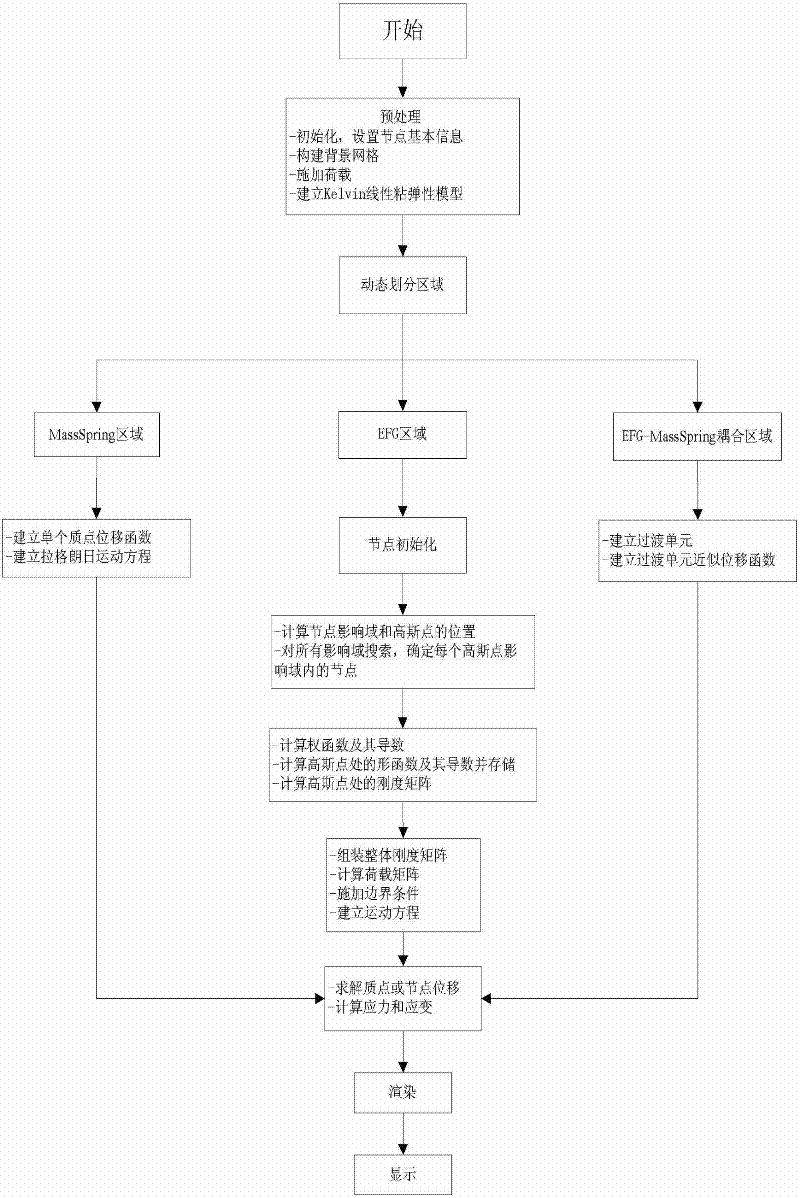
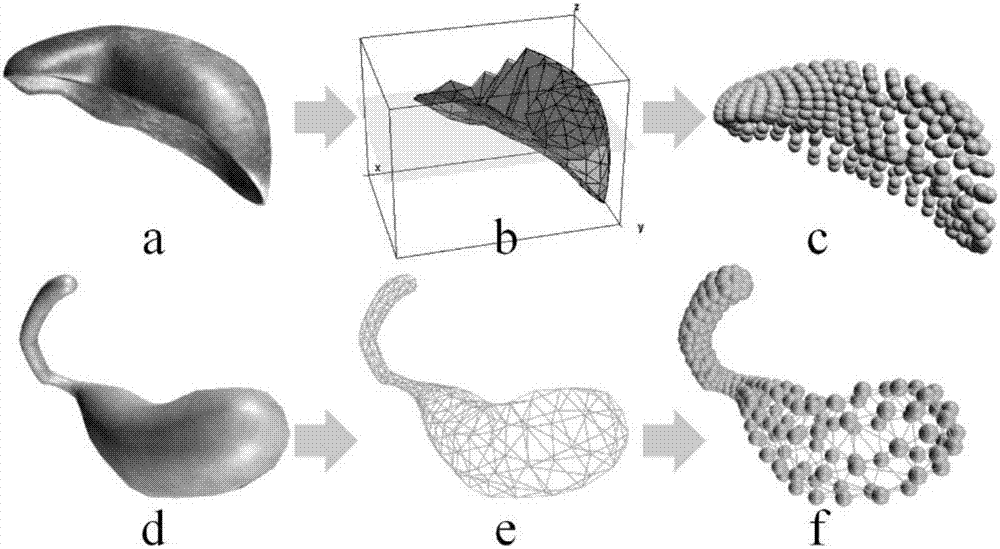
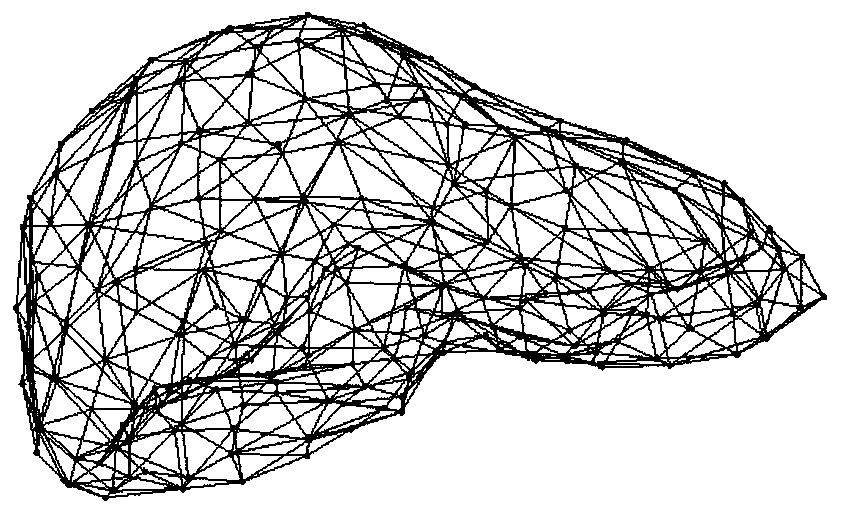
Simulation Method of Soft Tissue Deformation Based on Meshless Galerkin and Particle Spring Coupling
InactiveCN102262699AImprove continuityImprove stabilitySpecial data processing applicationsComputation complexitySoft tissue deformation
The invention relates to an object deformation real-time simulation graphic processing technique, particularly a soft tissue deformation simulation method based on coupling of mesh-free Galerkin and mass spring, which comprises the following steps: in the pretreatment process, establishing a linear viscoelasticity biomechanical model for soft tissues; in the deformation computation process, dynamically partitioning a mesh-free region and a mass spring region according to the load carried by the soft tissues, establishing a transitional unit of the connection region between the mesh-free region and mass spring region, and constructing a transitional unit approximation displacement function, thereby implementing self-adapting coupling of a mesh-free Galerkin method and a mass spring method;and in the after-treatment process, outputting the state of the mass or node of each time step in the deformation process onto a screen, carrying out illumination rendering, and finally displaying the real-time deformation process of the soft tissue organ under stressed conditions on the screen, thereby implementing visualization effect of dynamic deformation. By utilizing the advantage of high efficiency in the mass spring method and the advantages of high precision and no need of mesh reconstruction in the mesh-free Galerkin method, the invention overcomes the defect that the Galerkin method is not suitable for solving a large-scale problem, thereby effectively lowering the complexity of computation in the soft tissue deformation simulation and enhancing the operation efficiency.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIV OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
Soft tissue deformation simulation method
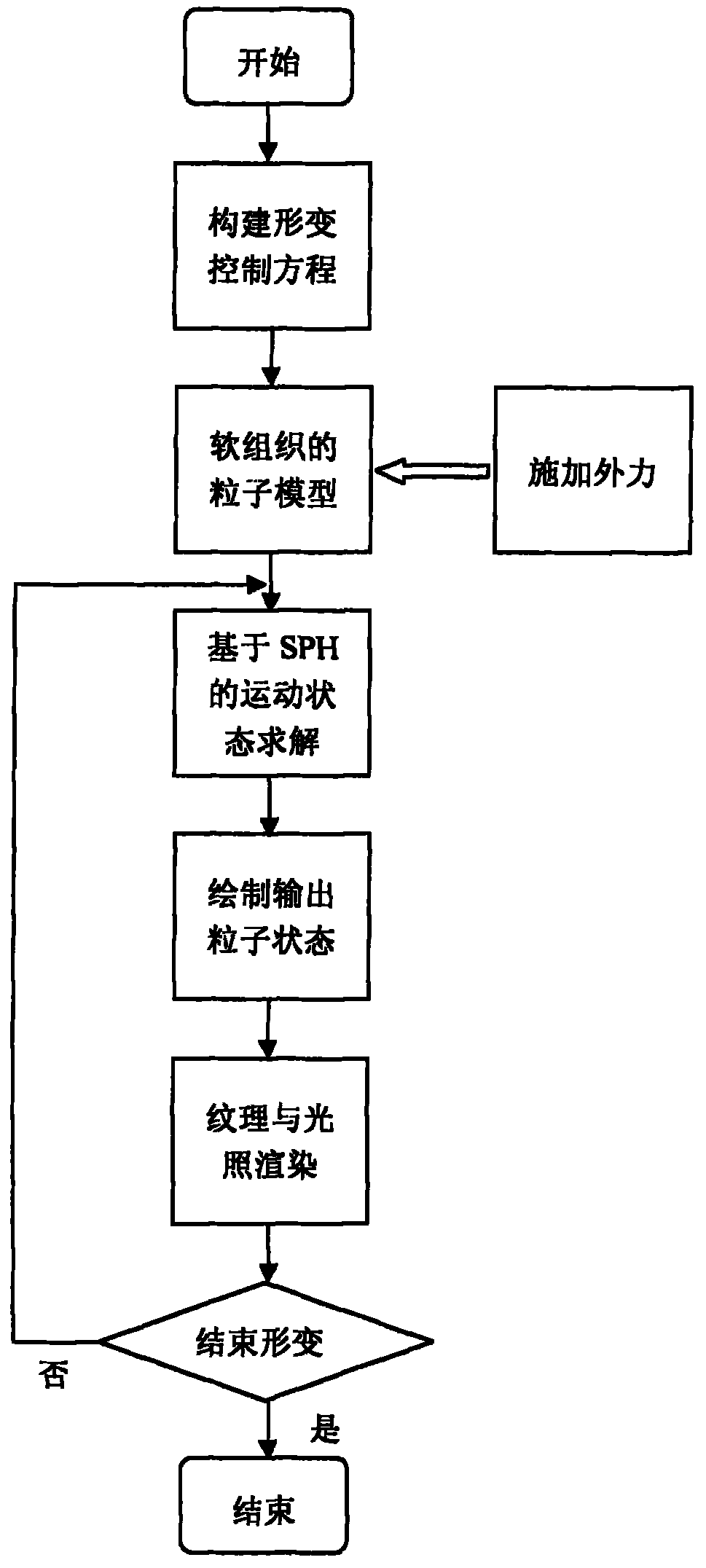
InactiveCN102044086AAvoid subsection calculationsSimplified representationSpecial data processing applications3D modellingSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsBiomechanics
The invention relates to a soft tissue deformation simulation method based on smooth particle hydrodynamics, belonging to the technical field of graphic processing. In the method, a smooth particle hydrodynamics method is selected, and a viscoelastic mechanics model is used for reflecting the biomechanical characteristics of soft tissue. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing a series of equations related to soft tissue deformation simulation according to the viscoelastic model; selecting a proper support domain search strategy and a smooth kernel function, approximately calculating each related item of the equation by adopting the particle approximation method, and calculating the variation values of the density, the position, the velocity and the like of each particle along with time through the display integration method; and dynamically outputting the status of each time step size of the particle model to a screen, rendering texture irradiation, and displaying the real-time deformation process of soft tissues and organs under stressing conditions. The method does not need troublesome grid computing, thereby increasing the accuracy and the real-time performance of soft tissue deformation simulation.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIV OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
Soft tissue deformation simulation method
InactiveCN103400023AHigh precisionImprove real-time performanceSpecial data processing applicationsSoft tissue deformationMedicine
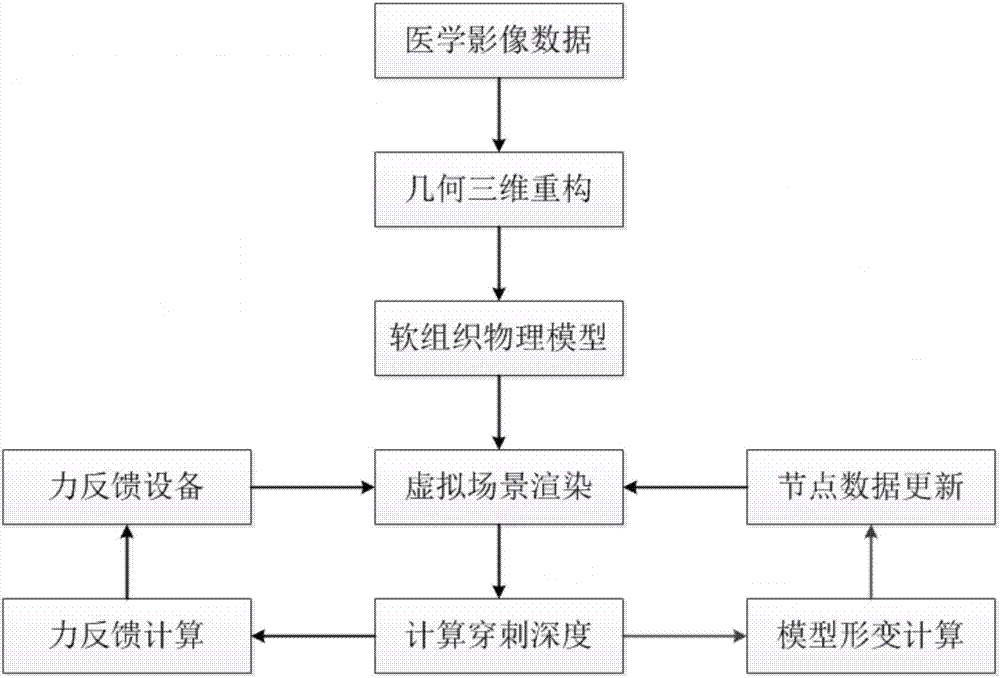
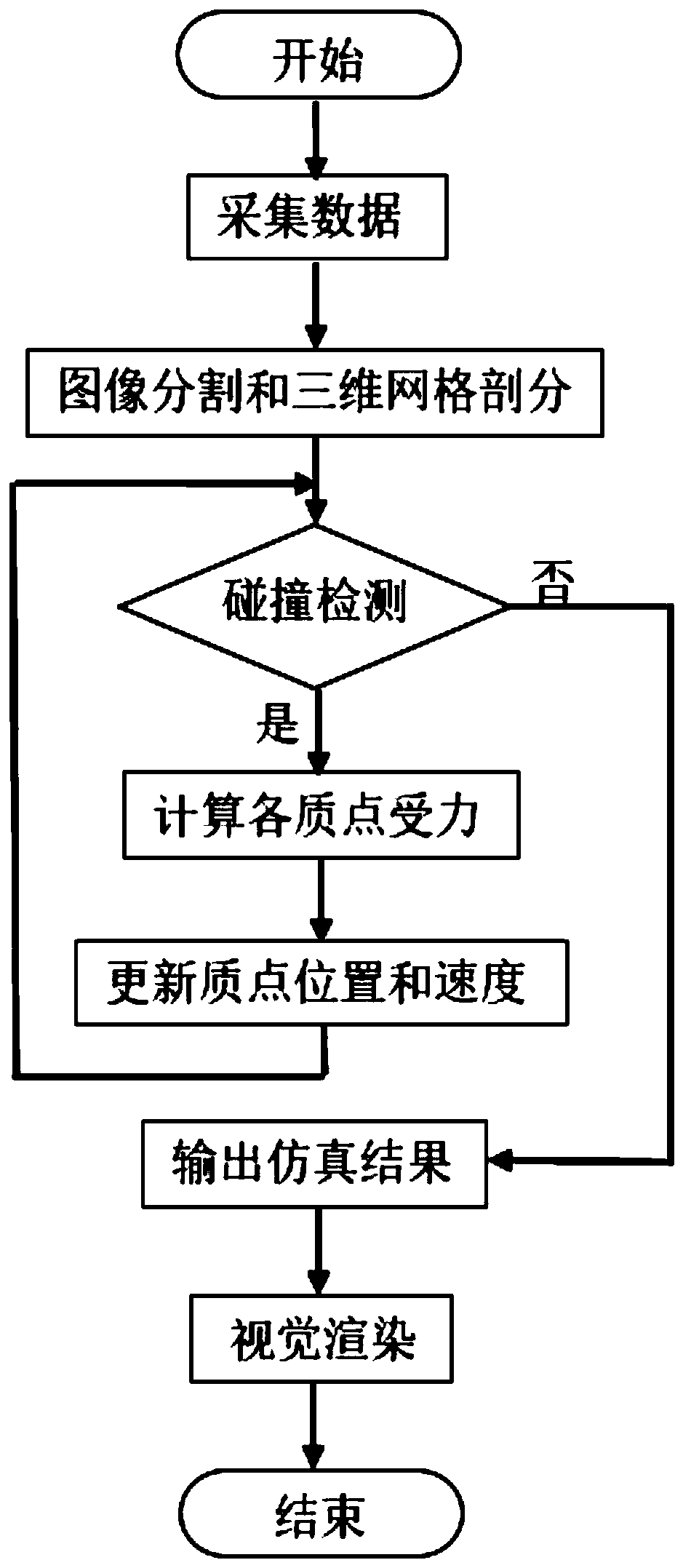
The method relates to a soft tissue deformation simulation method. The soft tissue deformation simulation method includes the following steps: a biomechanics model of soft tissue is built, and mass points in the biomechanics model are initialized; force feedback equipment exerts action force on the soft tissue to carry out collision detection; motion state information is calculated in an improved Euler algorithm; the state of each time step of the model is output to a display screen, and the deformation process of the soft tissue is displayed in a dynamic mode; feedback force is calculated, and touch feedback is output. By means of the steps, real-time performance, precision and smoothness of the feedback force in virtual operation simulation can be effectively achieved, precision and real-time performance of soft tissue deformation simulation are improved, and accordingly requirements of virtual operation simulation are met.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIV OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
Soft tissue deformation and cutting simulation method based on position dynamics
ActiveCN104318056AImprove real-time performanceDeformed realSpecial data processing applicationsTouch PerceptionDynamic models
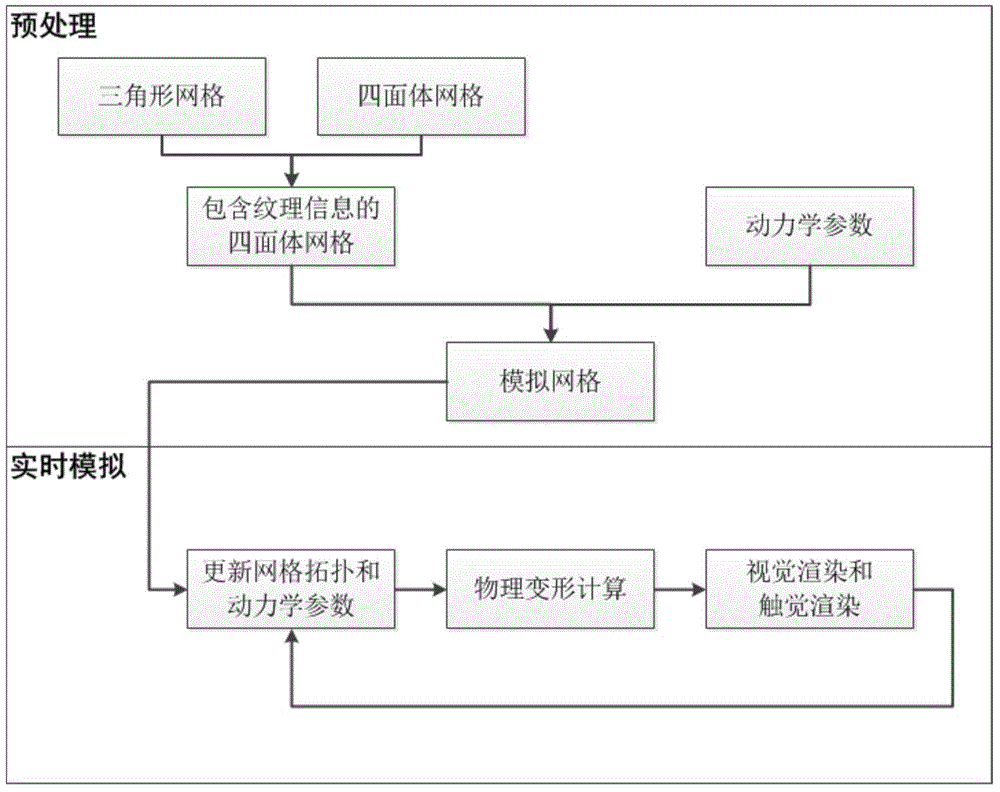
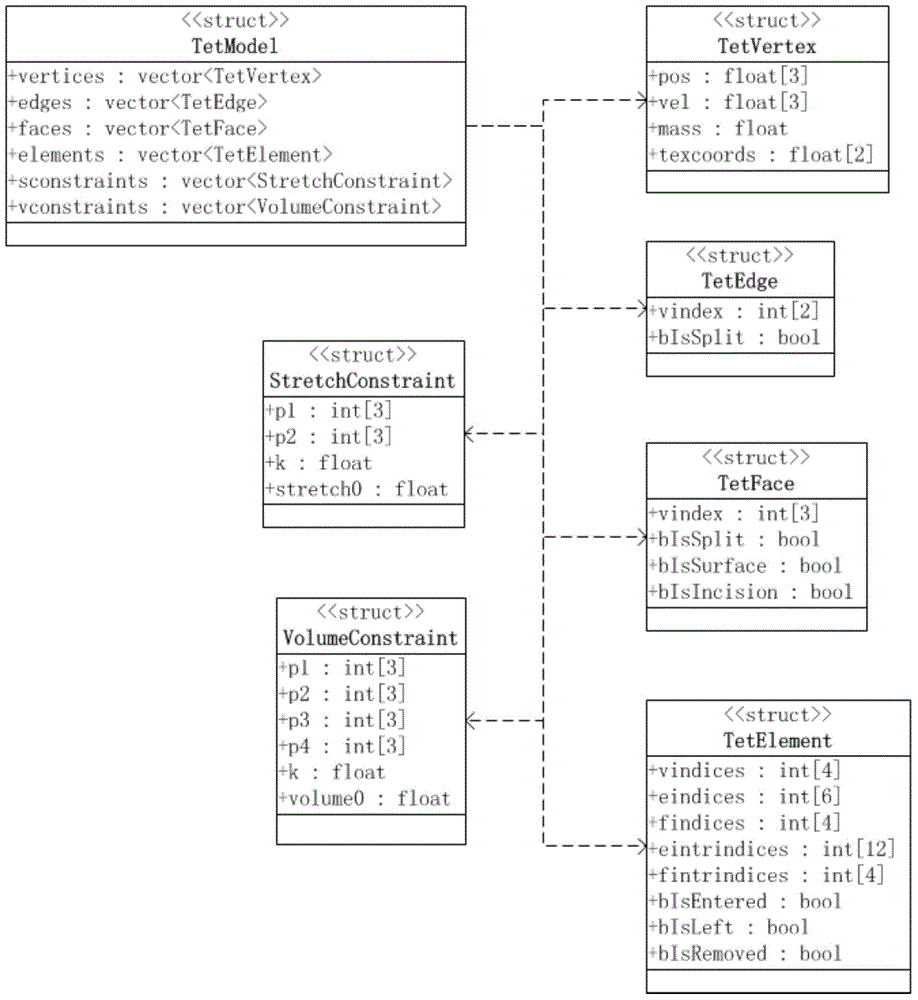
The invention provides a soft tissue deformation and cutting simulation method based on position dynamics. The method comprises the following four steps: grid preprocessing: according to an original triangular grid and a tetrahedron grid, and calculating a texture coordinate of each peak, calculating a set of edges in the grid, setting dynamics simulation parameters, and generating an improved tetrahedron grid; the deformation calculation of a soft tissue object: according to the current positions and the stressing situation of the peaks of the grids, calculating the positions of the peaks of the grids at a next moment according to the position dynamics; updating during grid topology change: according to an intersection situation of a cutting plane and grid intersection points, dividing an original tetrahedron, and updating the parameters of a geometric model and a position dynamics model; and visual rendering and touch rendering: displaying the soft tissue object and generating force feedback. The invention can truly simulate a process of cutting soft tissues in a virtual surgery, and exhibits high instantaneity.
Owner:BEIJING UNIDRAW VR TECH RES INST CO LTD
Method and system for simulating minimally invasive puncture surgery
InactiveCN106781941AIncrease the chance of successAccurately informedEducational modelsSoft tissue deformationData information
The invention provides a method and system for simulating minimally invasive puncture surgery. Data information of a surgical site can be accurately acquired by scanning image data, the accuracy of a surgery simulation operating environment is ensured, and a lesion body and human tissue are modeled independently. A surgery simulation scene and a real scene are combined by means of the augmented reality technique, so that sensory experience of users is improved, an operator can accurately observe the condition of surrounding important blood vessels of human tissue when looking for a puncture point during surgery simulation, the operator can be trained to find out the puncture point accurately, and therefore the success rate of surgery can be increased. Meanwhile, during collision detection, interaction between a virtual surgical instrument and virtual human tissue is divided into two phases, force feedback equations of a soft tissue deformation phase and a puncturing phase are established respectively, reception and output are conducted by means of force feedback equipment, as a result, the operator can sense current operation force accurately during simulated experiment operation, and experiment immersion sense is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Virtual operation artificial system based on force feedback
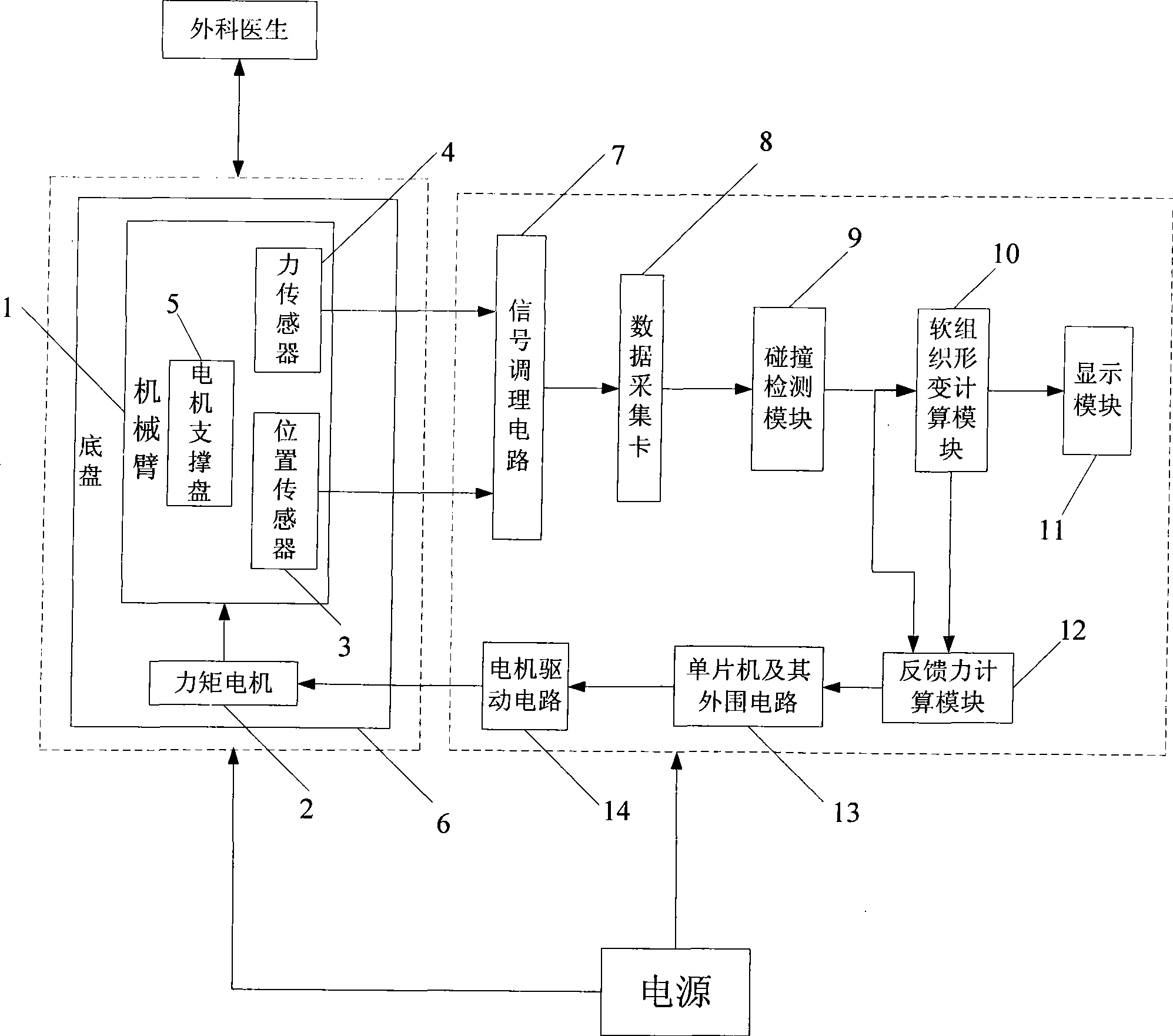
InactiveCN101441831AReal-time force senseImprove efficiencyEducational modelsMicrocontrollerHuman–machine interface
The invention discloses a virtual surgery simulation system based on force feedback and belongs to a virtual surgery simulation system. The virtual surgery simulation system based on force feedback comprises a single-degree-of-freedom manipulator, a control circuit and a power supply, wherein the single-degree-of-freedom manipulator comprises a manipulator, a moment motor, a position sensor, a force sensor, a motor supporting tray and a chassis; and the control circuit comprises a signal conditioning circuit, a data acquisition card, a collision detection module, a soft tissue deformation computing module, a display module, a feedback force computing module, a singlechip, a peripheral circuit of the singlechip and a motor drive circuit. The virtual surgery simulation system utilizes information feedback of various sensors to establish an environmental model which is interactive with operators and tasks through a human-computer interactive device, provides a direct-viewing and friendly human-computer interface, and has high operation precision and operation reliability, so that patients and the system are safe; and the operative process is displayed in real time, so that operation failure is reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Skinned multi-person linear model
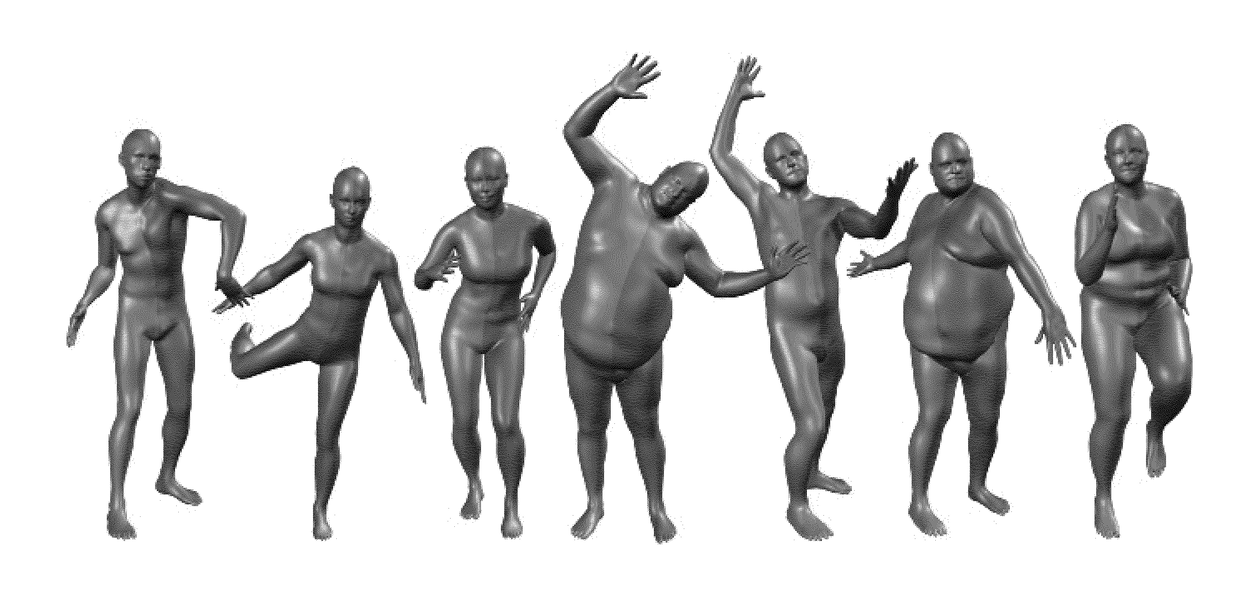
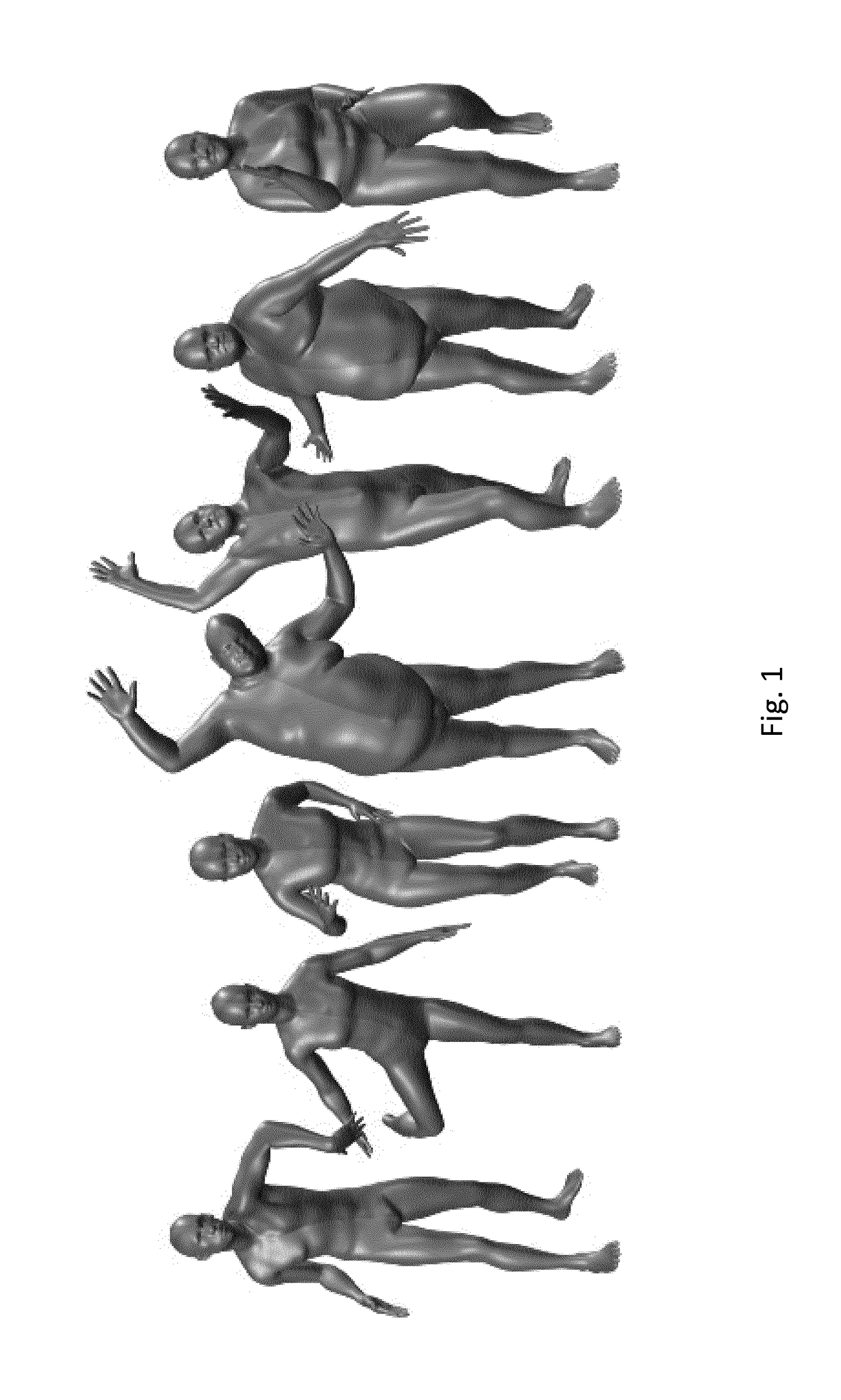
ActiveUS20180315230A1Error minimizationAccurate limitImage enhancementImage analysisBody shapePattern recognition
The invention comprises a learned model of human body shape and pose dependent shape variation that is more accurate than previous models and is compatible with existing graphics pipelines. Our Skinned Multi-Person Linear model (SMPL) is a skinned vertex based model that accurately represents a wide variety of body shapes in natural human poses. The parameters of the model are learned from data including the rest pose template, blend weights, pose-dependent blend shapes, identity-dependent blend shapes, and a regressor from vertices to joint locations. Unlike previous models, the pose-dependent blend shapes are a linear function of the elements of the pose rotation matrices. This simple formulation enables training the entire model from a relatively large number of aligned 3D meshes of different people in different poses. The invention quantitatively evaluates variants of SMPL using linear or dual-quaternion blend skinning and show that both are more accurate than a Blend SCAPE model trained on the same data. In a further embodiment, the invention realistically models dynamic soft-tissue deformations. Because it is based on blend skinning SMPL is compatible with existing rendering engines and we make it available for research purposes.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Device and method for puncturing soft tissues by ultrasonic vibration
InactiveCN106137342AReduce distortionReduce the impactSurgical needlesTrocarSoft tissue deformationUltrasonic vibration
The invention relates to the field of medical appliances, belongs to the medicine, machinery and acoustics interdiscipline, and particularly relates to a device and a method for puncturing soft tissues by ultrasonic vibration. According to the device and method, a piezoelectric ultrasonic vibration mechanism is adopted to implement soft tissue high-frequency puncture and reduce the influence of noise on the medical environment; furthermore, a high-frequency vibration and rotary needle-insertion puncture method can be adopted to effectively reduce puncture force and reduce soft tissue deformation and needle deflection, so that the positioning accuracy of a puncture needle can be improved.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Real-time cutting simulation method of flexible object on the basis of finite element and time-variant modal analysis
ActiveCN105302974AQuick analysisBig errorSpecial data processing applicationsSoft tissue deformationSimulation
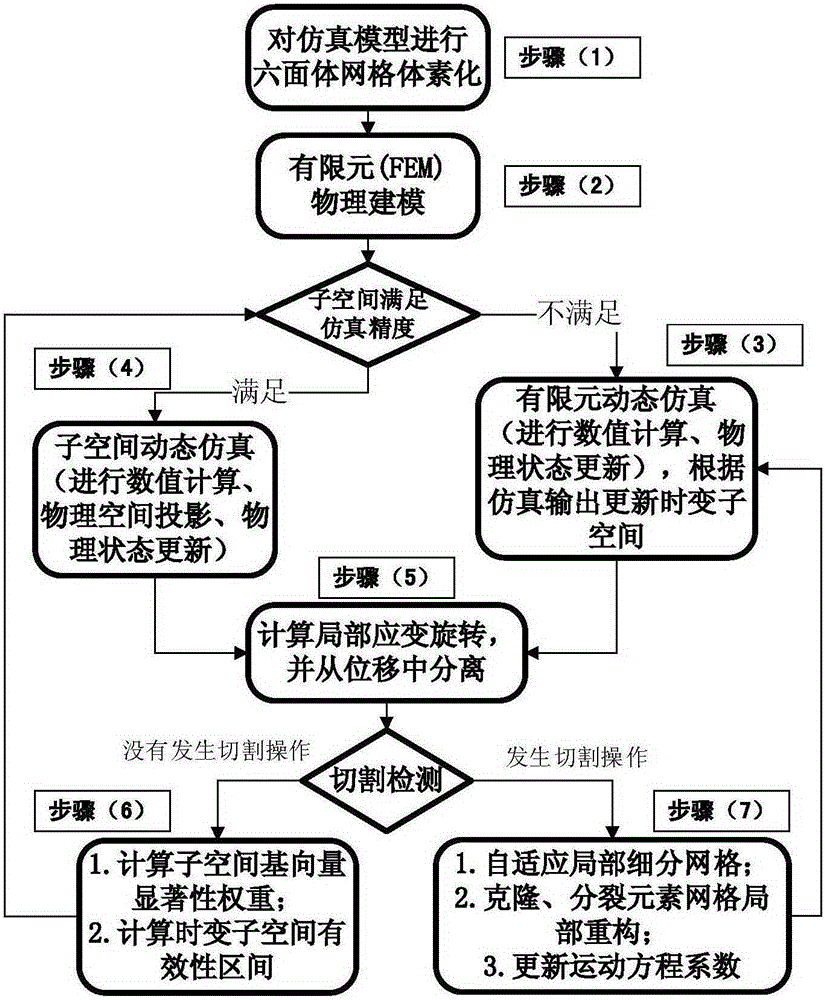
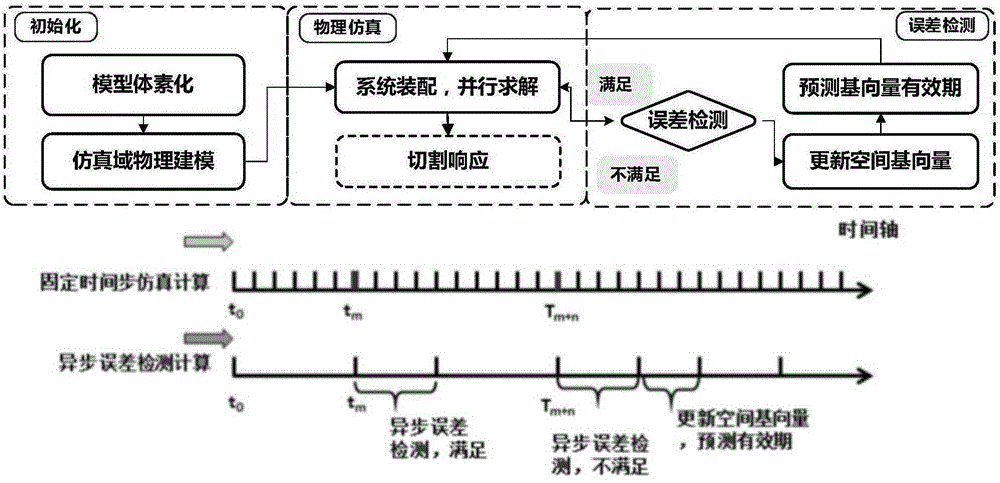
The invention relates to a real-time cutting simulation method of a flexible object on the basis of finite element and time-variant modal analysis. The real-time cutting simulation method carries out researches and is implemented mainly by aiming at a real-time interactive soft tissue deformation and cutting simulation algorithm of a virtual surgery. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out voxelization and finite element physical modeling on a simulation domain of a model, carrying out subspace construction on the basis of priori modal analysis, carrying out cutting operation response, carrying out significance analysis and screening on a subspace base vector, and carrying out subspace time-variant effectiveness estimation. The method carries out parallel design on the simulation algorithm and achieves real-time interactive efficiency by virtue of the powerful calculation capability of GPU (Graphics Processing Unit).
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Soft tissue deformation method based on mixing of gridding method and non-gridding method
ActiveCN105513130AMedical simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSoft tissue deformationEngineering
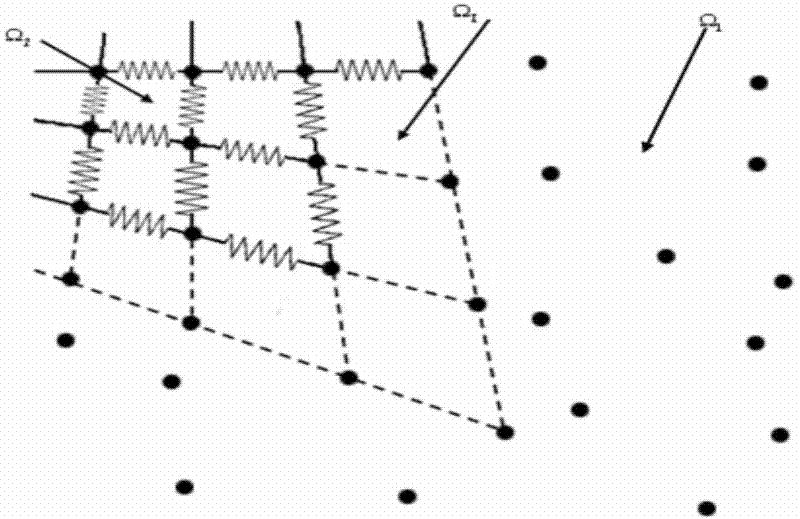
The invention relates to a soft tissue deformation method based on mixing of a gridding method and a non-gridding method. The non-gridding method is adopted in a large-deformation region of an operation, and the gridding method is adopted in a non-operation region. By means of the non-gridding method in the operation region, the gridding deformation problem during large deformation can be avoided, deformation is in smooth transition so that deformation-simulated real sense can be achieved easily, meanwhile, the region model joint number is small while the operation region is small, and the real-time requirement can be met when the non-gridding method is adopted for the operation region; a particle-spring-based gridding deformation method is adopted in the non-operation region so that the defect that non-gridding calculation efficiency is low can be avoided, the advantages of a particle spring on real-time performance are given play to, meanwhile, because the non-operation region deformation is small, gridding deformation will not occur even a particle-spring method is adopted, and a deformation simulating effect is good. By means of the soft tissue deformation method, advantages of the gridding method and the non-gridding method in deformation simulation are given play to, the real sense and the real-time performance compromise, and the soft tissue deformation method is applicable to virtual deformation operation simulation.
Owner:FUQING BRANCH OF FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
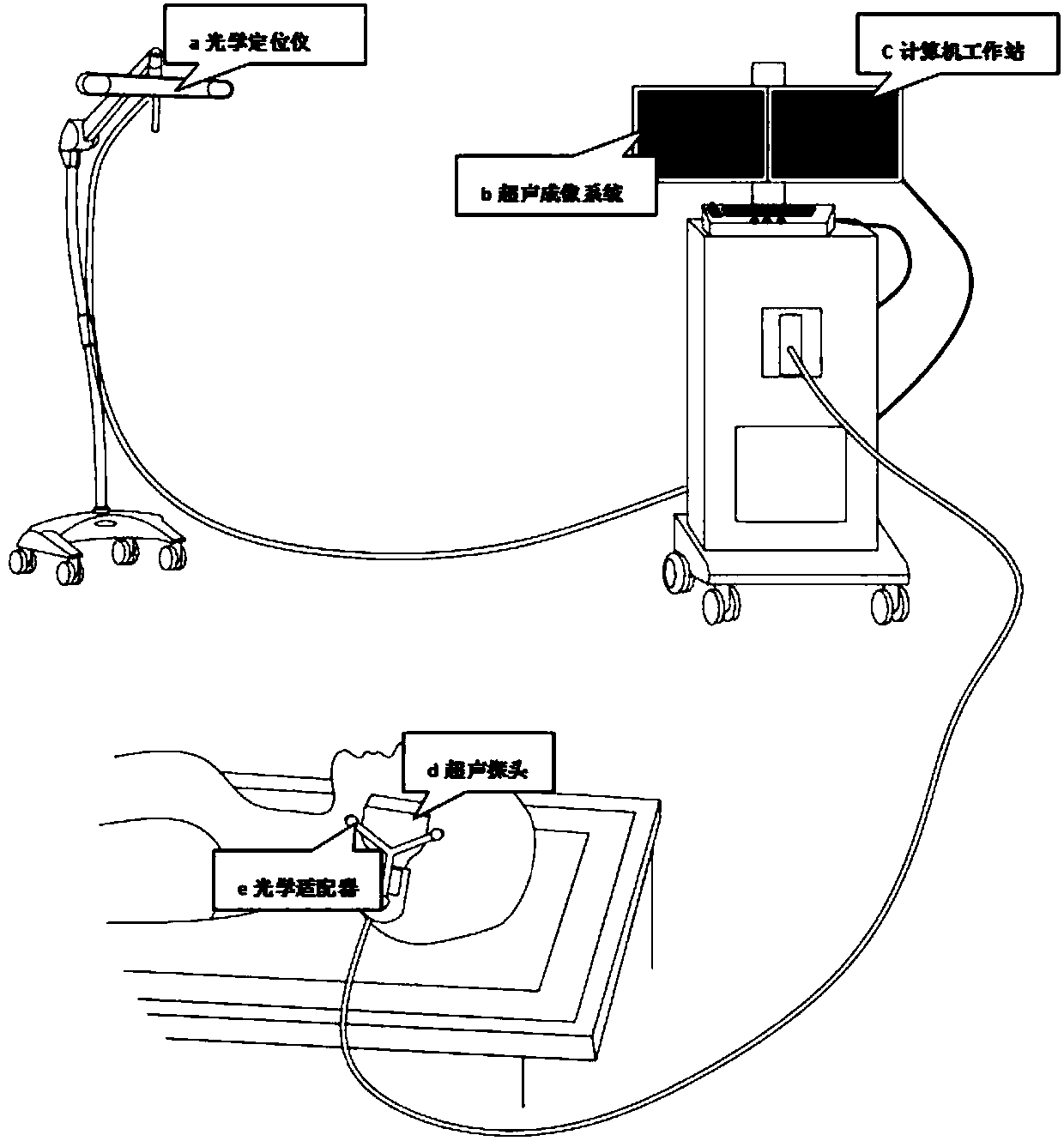
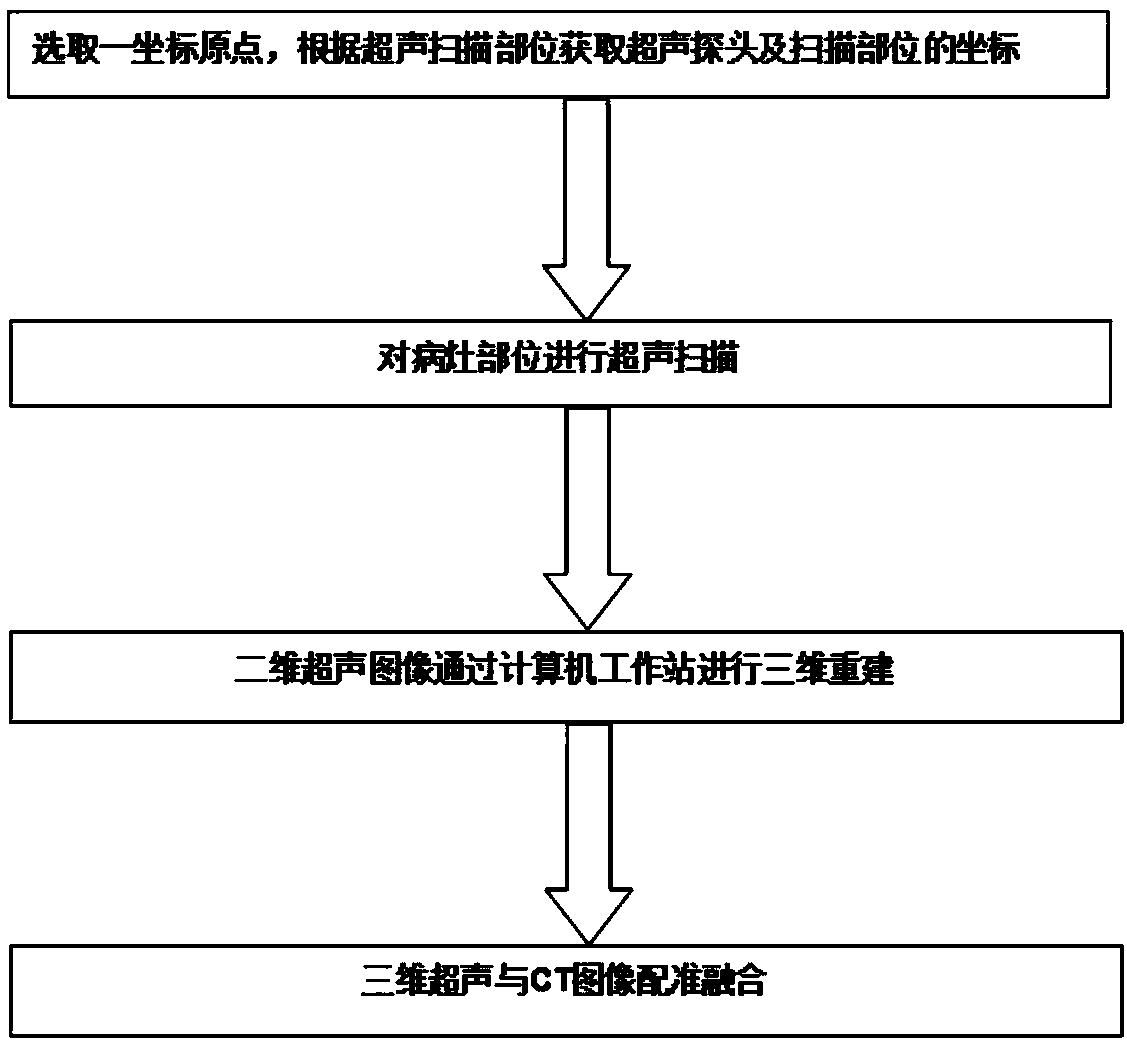
Ultrasonic and CT/MR image fusion surgical navigation system and method based on optical localization rectification
InactiveCN107854177APrecise positioningReal-time monitoring of deformationSurgical navigation systemsCranio maxillofacial surgeryUltrasound imaging
The invention provides an ultrasonic and CT / MR image fusion surgical navigation system and method based on optical localization rectification. The system comprises an ultrasonic imaging system, a tracking and locating system and a computer workstation. The ultrasonic imaging system comprises an ultrasonic probe and an image workstation. The tracking and locating system comprises an adapter fixed to the ultrasonic probe and a locater for obtaining the coordinates of the ultrasonic prone according to a marker. The computer workstation records the space position for three-dimensional reconstruction according to a real-time ultrasonic image obtained by the ultrasonic probe and displays a fused image. In combination with an optical localization system, the fusion of ultrasonic and CT / MR image is realized, the system can be applied for monitoring soft tissue deformation in real time in craniomaxillofacial surgery, precise surgery localization is realized, and surgery navigation errors are reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Patient-specific craniofacial implants
ActiveUS20150045897A1Restore appearanceAugmenting temporal areaCosmetic implantsTomographyTemporal resolutionSoft tissue deformation
Disclosed herein are patient-specific craniofacial implants structured for filling bone voids in the cranium as well as for simultaneously providing soft tissue reconstruction and / or augmentation for improved aesthetic symmetry and appearance. Pterional voids or defects generally result from a chromic skull deformity along with a compromised temporalis muscle or soft tissue distortion from previous surgery. When muscle atrophy occurs in the pterion, temporal hollowing generally results where there would be soft tissue but for the atrophy. The patient-specific temporal implants herein are configured to have an augmented region adjacent the temporal region of the cranium in order to account for and correct any such temporal hollowing.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
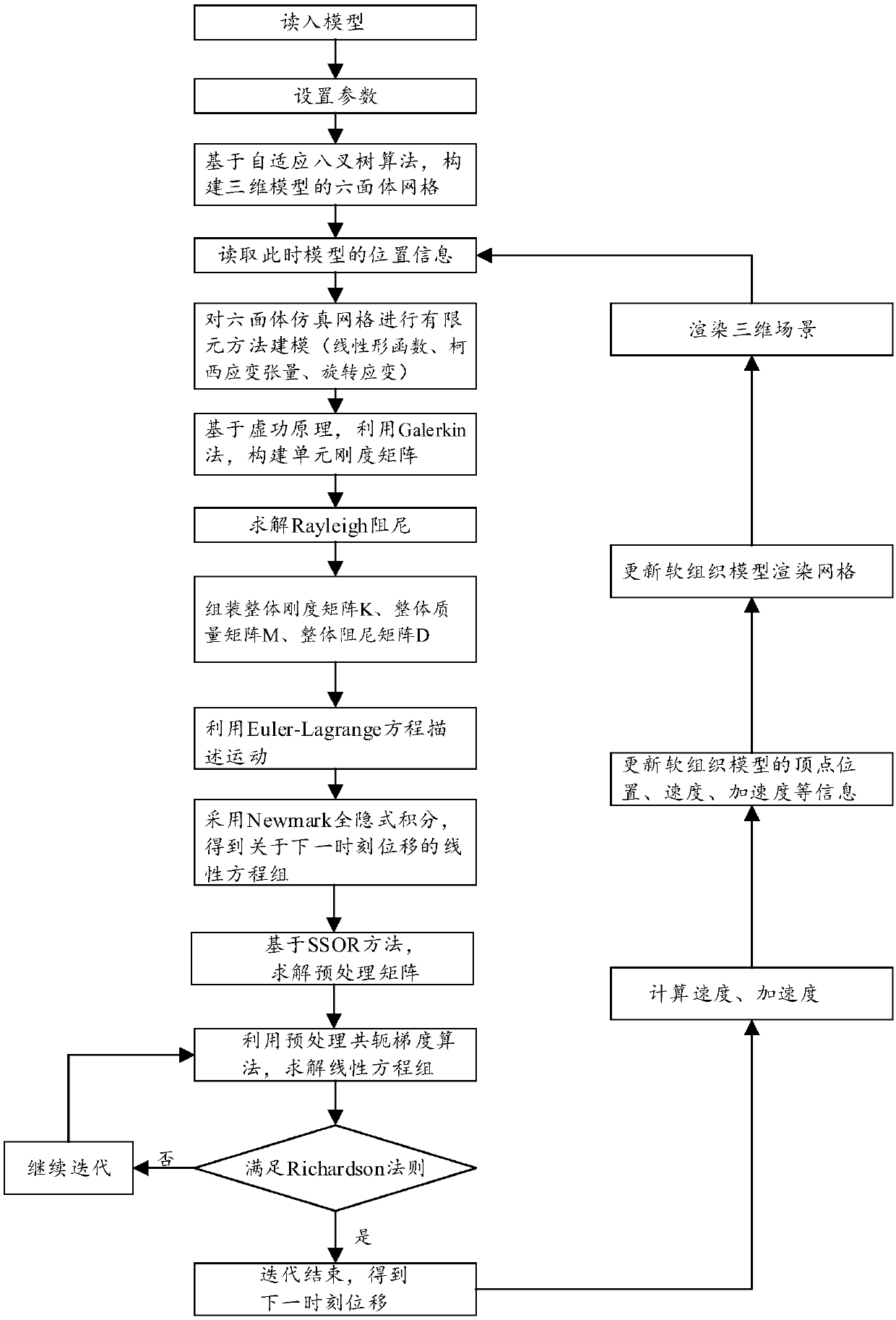
Soft tissue deformation method based on finite element model of octree mesh
InactiveCN108694290AImprove real-time performanceSmall amount of calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALElement model
The invention provides a soft tissue deformation method based on a finite element model of an octree mesh. The method comprises: drawing a three-dimensional model of soft tissue, constructing a plurality of uniform hexahedral meshes based on the AABB method, and generating an octree mesh based on the mesh generation algorithm of an octree based on the hexahedral mesh, modeling the hexahedron meshby the finite element method, solving the deformation process of the soft tissue, assembling the element stiffness matrixes on adjacent element nodes into the total stiffness matrix of the discrete domain, solving the dynamic equilibrium differential equation for each matrix by time integral under dynamic equilibrium, to obtain the displacement of the nodes with time, and displaying the stress deformation of the soft tissue by the rendering of the displacement of the nodes. The method realistically simulates the process of tension deformation of the soft tissue epidermis of any shape in virtual surgery, has high real-time performance, reduces the calculation amount, and solves the problem that the number of finite element meshes is complicated and the soft tissue deformation process cannotbe simulated in real time.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
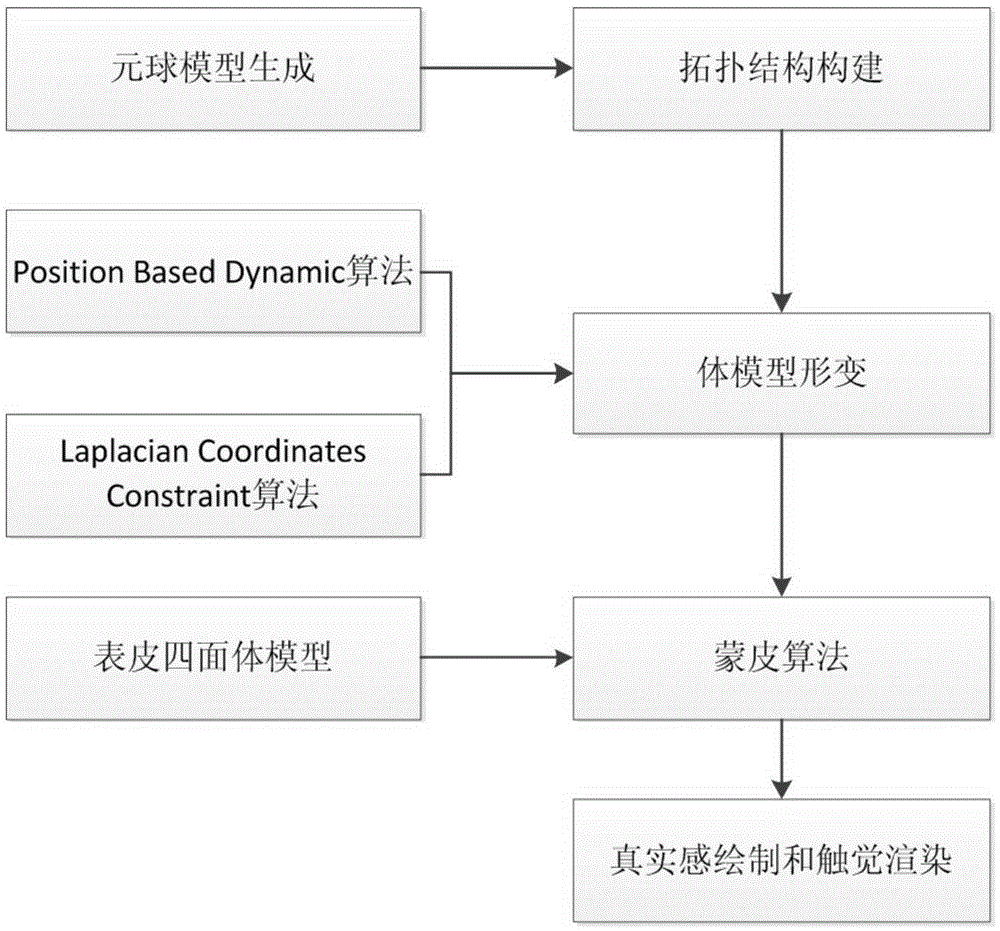
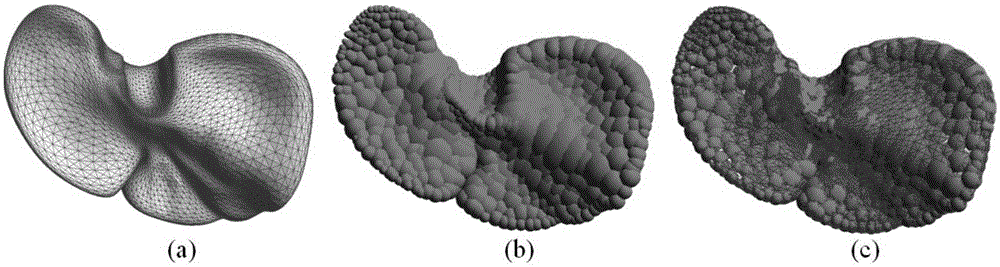
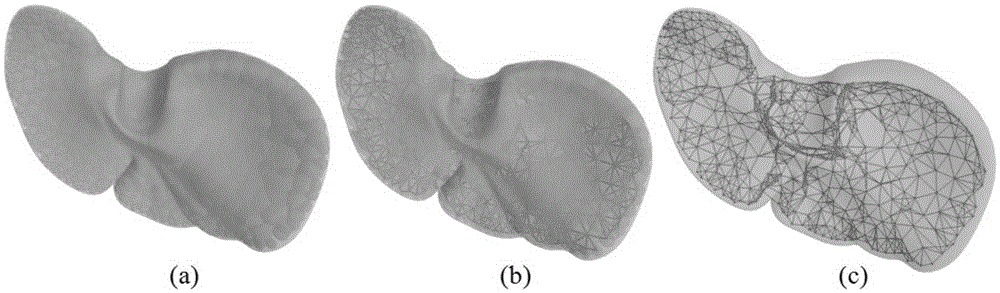
Metaball model based soft tissue deformation method
InactiveCN105302972AOvercome limitationsPhysical authenticity no lessSpecial data processing applications3D-image renderingField functionLaplacian coordinates
The invention provides a metaball model based soft tissue deformation method. The method comprises the four steps of: a stage of constructing a topological structure of a metaball model, wherein a Voronoi diagram is generated according to an original grid model by using a Bradshow Gareth ball tree generation algorithm, the metaball model is generated, and the topological structure of the metaball model is constructed with a threshold setting method; a stage of calculating deformation of the metaball model, wherein a deformation process of a soft tissue model is simulated in combination with Laplacian coordinate restriction by using a Position Based Dynamic (PBD) algorithm; a stage of realizing a skin process of the soft tissue model, wherein distance field functions are established for metaballs in a body model respectively, and a mapping relationship between the body model and a skin grid model is established, so that the skin process is realized; and a stage of realistic rendering and real-time haptic rendering, wherein the realistic rendering is performed according to the physical deformation of soft tissues, and the real-time haptic rendering is performed based on a Geomagic Touch force feedback device. The method can truly simulate the deformation process of the soft tissues in operation and has the characteristics of strong physical realism and good timeliness.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
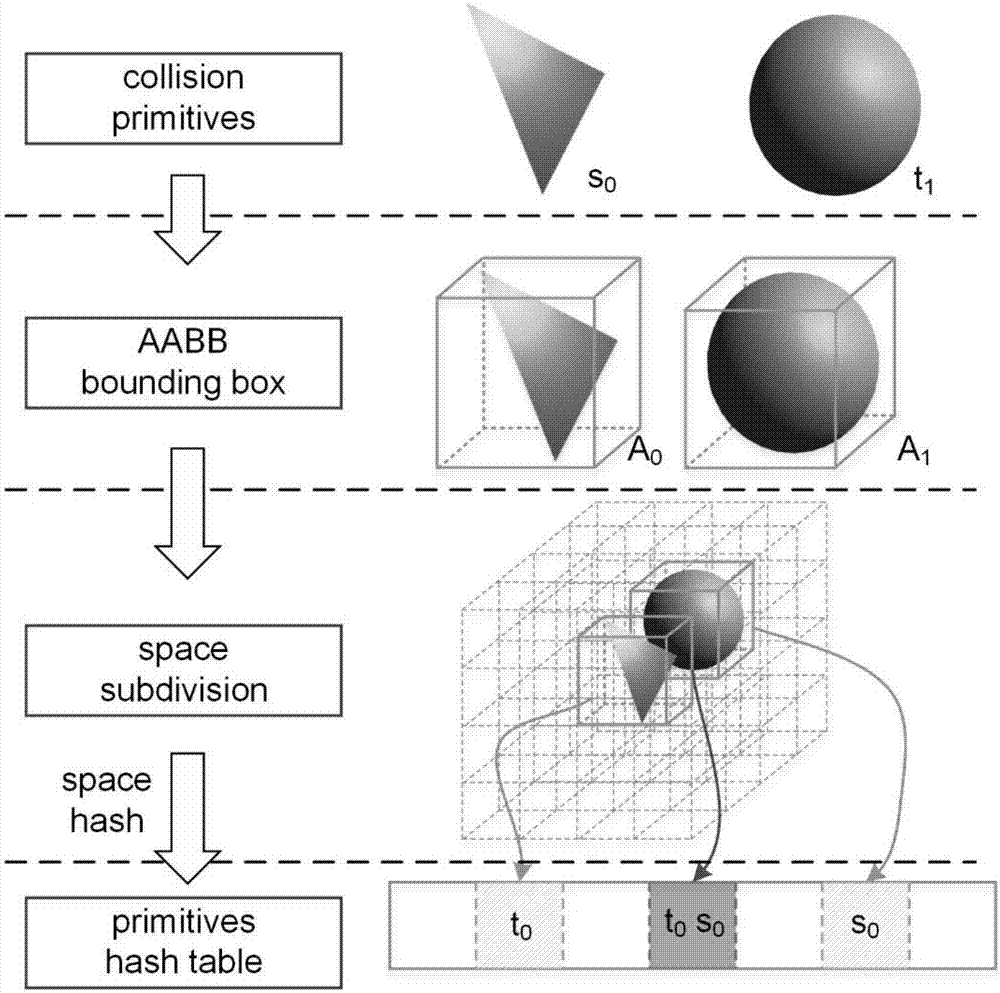
Real-time soft tissue deformation method and system for simulating biomechanical properties
ActiveCN107330972ASolve for stabilityHigh speedSpecial data processing applications3D modellingSoft tissue deformationCollision detection
A real-time soft tissue deformation method for simulating biomechanical properties is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of S1, generating soft tissue physical model data based on soft tissue organ three-dimensional visualization data; S2, generating collision detection model data based on the soft tissue physical model data; S3, loading the physical model data and the collision detection model data by a game engine for collision detection; and S4, calculating the state after soft tissue deformation through a constrained optimization method.
Owner:EZHOU INST OF IND TECH HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
A soft tissue deformation simulation method based on nonlinear anisotropic mass spring model
PendingCN109492250AHigh precisionThere is no increase in the calculation amount of the solutionGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationMuscle tissueDynamic equation
The invention discloses a soft tissue deformation simulation method based on a roll nonlinear anisotropic mass spring model, which comprises the following steps: 1) constructing a mass spring model, and determining initial elastic parameters of that mass spring model by a finite element method; 2) setting spring parameters in the deformation process according to the stress and strain relationshipof the muscle tissue; 3) parameterize describing that anisotropic characteristic of the soft tissue by constructing a mechanical equation of the spring; 4) constructing that dynamic equation of the mass spring model and solving it. The invention has the beneficial effect that the setting of the spring parameter in the mass spring model is solved, the anisotropy is parameterized, and an improved Euler algorithm is adopted in solving the dynamic equation of the mass spring model.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Patient-specific craniofacial implants
ActiveUS9216084B2Augmenting temporal areaIncrease the areaCosmetic implantsJoint implantsCranium boneSoft tissue deformation
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Soft tissue surface deformation tracking method based on sub-blocks
ActiveCN105310776AGood tracking effectCorrection of deformationImage analysisDiagnosticsSoft tissue deformationLaser scanning
The invention belongs to the field of medical image treatment and application, and relates to a soft tissue surface deformation tracking method. The method comprises a soft tissue division algorithm and comprises the following steps: carrying out grid processing on an extracted target tissue to obtain an initial soft tissue surface point set; acquiring a deformed soft tissue surface point set by a three-dimensional laser scanning instrument or intraoperative three-dimensional imaging equipment; carrying out crude registration on a deformed soft tissue surface and an initial soft tissue surface by a rigid registration method; and finally acquiring a point-to-point mapping relation of the two point sets on the basis of a sub-block type energy function minimum non-rigid registration algorithm. The method is easy to implement and reliable in precision, and can be integrated in an existing navigation system, intraoperative soft tissue deformation correction is implemented, so that the precision of the navigation system is improved greatly, and clinical application is facilitated.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Real-time and accurate soft tissue deformation prediction
For soft tissue deformation prediction, a biomechanical or other tissue-related physics model is used to find an instantaneous state of the soft tissue. A machine-learned artificial neural network isapplied to predict the position of volumetric elements (e.g., mesh node) from the instantaneous state. Since the machine-learned artificial neural network may predict quickly (e.g., in a second or less), the soft tissue position at different times or a further time given the instantaneous state is provided in real-time without the minutes of physics model computation. For example, a real-time, biomechanical solver is provided, allowing interaction with the soft tissue model, while still getting accurate results. The accuracy allows for generating images of a soft tissue with greater accuracy and / or the benefit of user interaction in real-time.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Laparoscopic surgery simulation training system based on computer aided medical display
InactiveCN108492693AIncrease success rateEasy to operateEducational modelsJoystickSoft tissue deformation
The invention discloses a laparoscopic surgery simulation training system based on computer aided medical display. A CT data preprocessing module, a CT organ segmentation module and a three-dimensional volume rendering module can use artificial intelligence and a 3D volume rendering integrated rendering technology to construct a three-dimensional abdominal cavity model in real time according to customized CT scan data of a patient. A volume data mechanics loading module, a joystick control module and a joystick mechanics feedback module are used to establish an accurate force feedback model and a tissue deformation model. Simulated actual laparoscopic surgical instruments are used and the joystick mechanics feedback module is combined to truly simulate the operation position and operationmode of surgical instruments. The real-time stress state of organs and tissues can be accurately fed back. Soft tissue deformation or a cutting effect can be truly reproduced. The system can accumulate real operation experience for a laparoscopic operator, can improve the operation skills of the laparoscopic operator, and can help the laparoscopic operator to be proficient in the relative depth ofa surgical instrument and a lesion organ.
Owner:盛玉涛
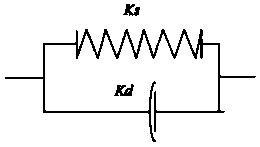
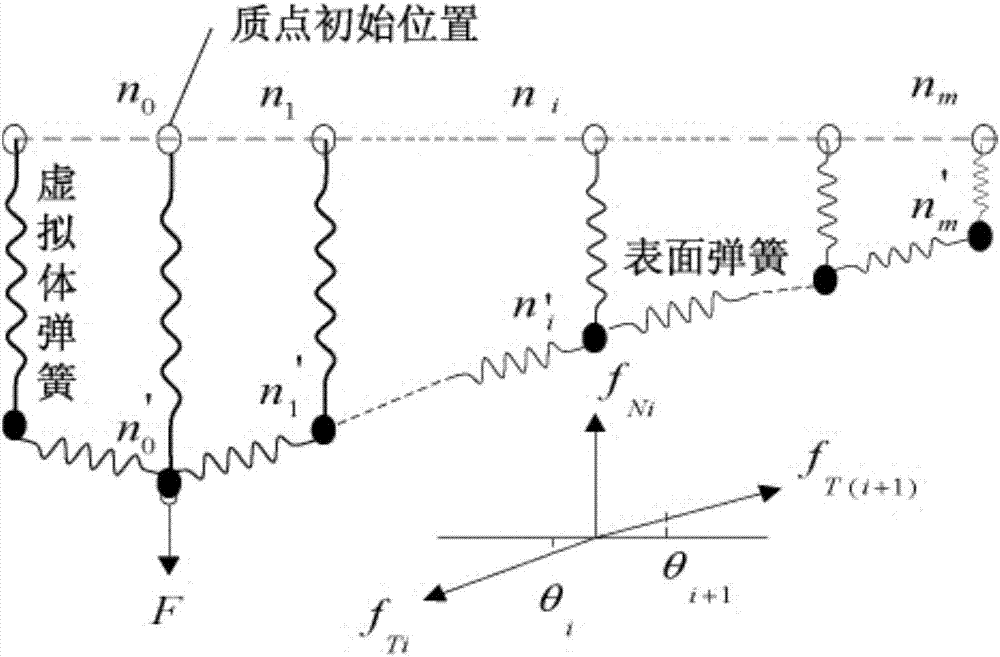
Soft tissue deformation modeling method based on virtual springs
InactiveCN107992672AReal-time feedbackGuaranteed high refresh rate requirementsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDeformation effectNet force
The invention discloses a soft tissue deformation modeling method based on virtual springs. The soft tissue deformation modeling method based on virtual springs is based on the spring-particle model to establish an improved real-time deformation model of soft tissue, virtual body springs are added by the topological structure soft tissue surface model combining the square and the isosceles right triangle, so that a more real deformation effect is achieved; at the position of each particle in the system, the superposition of surface springs variable is equivalent to the surface deformation of an object, the resultant force of the elastic forces of the virtual springs is equivalent to the contact force on the surface of the object; the model inherits the advantages of the classical spring particle model that the principle is simple, the model is easy to establish, the calculation speed is quick, at the same time, the model has an ability to control the deformation area.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
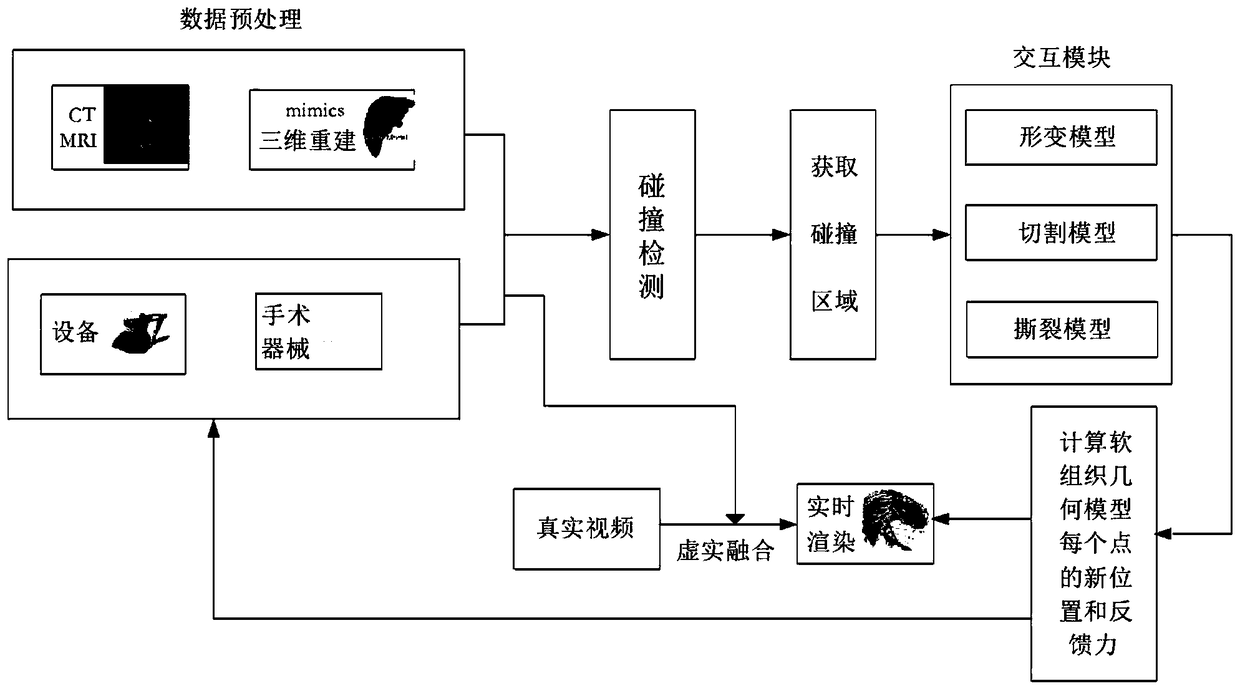
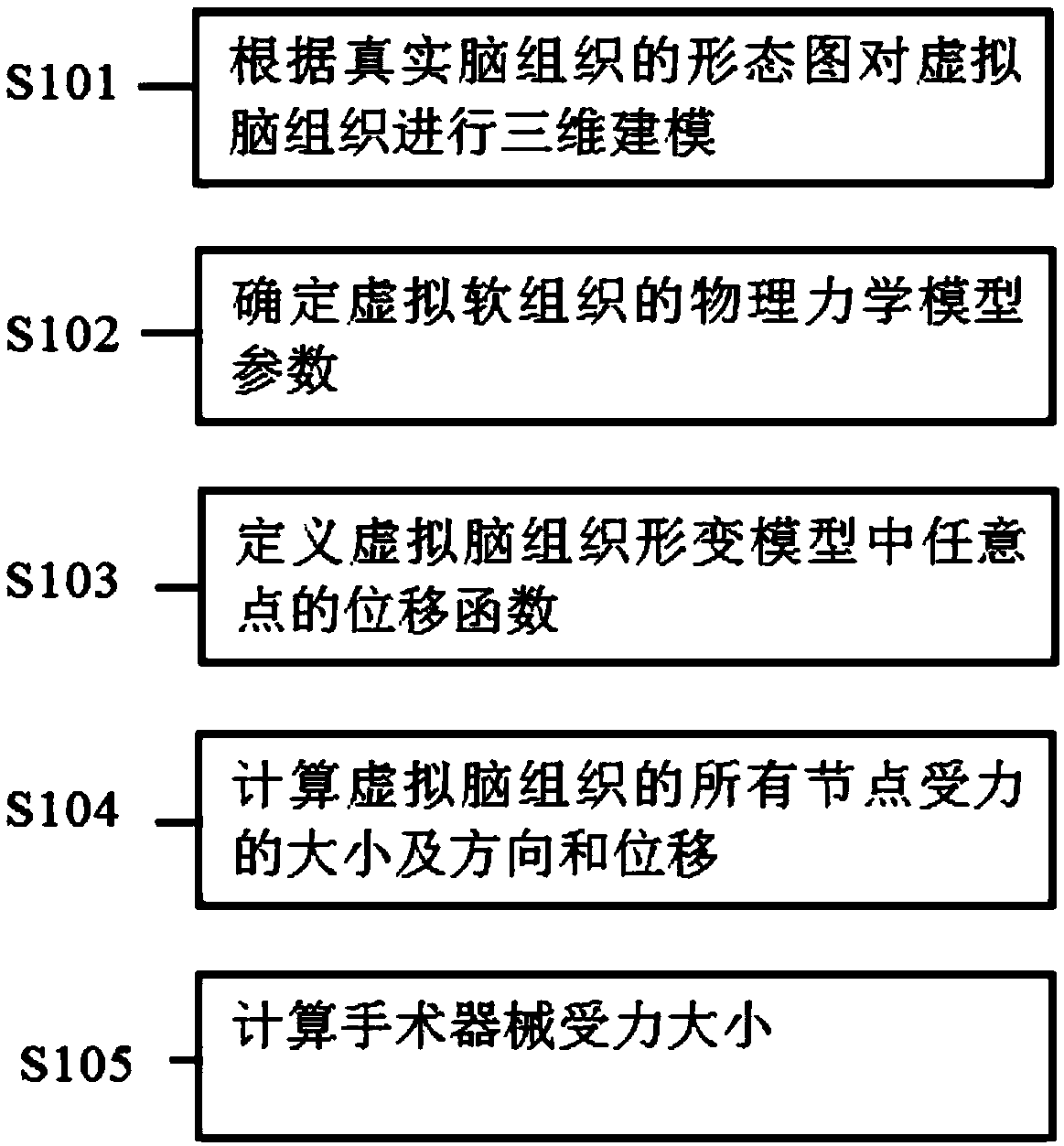
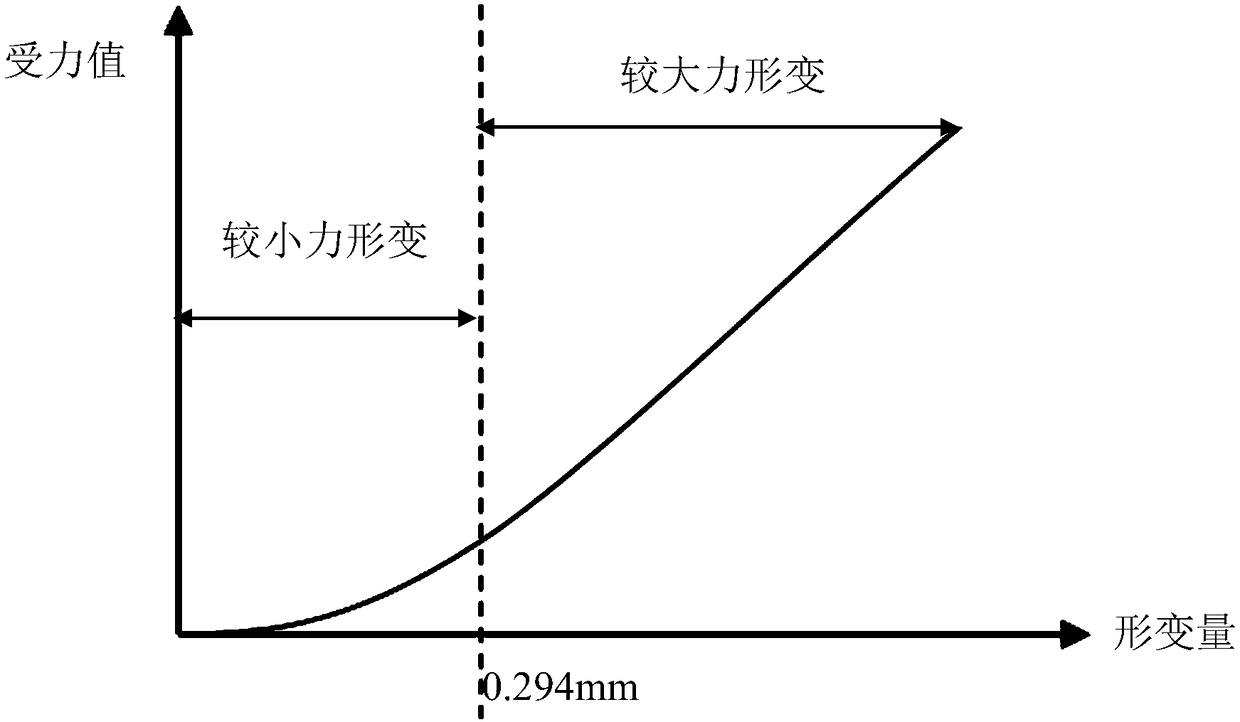
Virtual brain surgery simulation method based on high-fusion-degree augmented reality
ActiveCN108766579AAccurate deformation calculation resultsImprove synchronicityMedical simulationCosmonautic condition simulationsHuman bodyMechanical models
The invention discloses a virtual brain surgery simulation method based on high-fusion-degree augmented reality. The method includes steps: fully considering the mechanical property of in-vivo soft tissues, integrating viscoelasticity into a human body soft tissue deformation model, conducting a biomechanical test on the real soft tissues, determining soft tissue physical mechanical model parameters, and obtaining an accurate deformation calculation result. Dynamic texture mapping and rendering is performed on a high-simulation brain tissue area background, and real-time dynamic scene information with high reality sense is established; mirror surface environment texture mapping is performed on a virtual brain tumor model, and reality sense textures homogenous to a brain tissue environmentare obtained; registration and fusion output of the real-time dynamic scene information and the textures is performed, a synchronization effect of reality and virtuality on the textures is realized, athree-dimensional stereoscopic scene is presented through a binocular visual system, and the reality sense and the immersion of the system are enhanced.
Owner:北京交通大学长三角研究院
Skinned multi-person linear model
ActiveUS20190392626A1Error minimizationAccurate limitImage enhancementImage analysisBody shapePattern recognition
The invention comprises a learned model of human body shape and pose dependent shape variation that is more accurate than previous models and is compatible with existing graphics pipelines. Our Skinned Multi-Person Linear model (SMPL) is a skinned vertex based model that accurately represents a wide variety of body shapes in natural human poses. The parameters of the model are learned from data including the rest pose template, blend weights, pose-dependent blend shapes, identity-dependent blend shapes, and a regressor from vertices to joint locations. Unlike previous models, the pose-dependent blend shapes are a linear function of the elements of the pose rotation matrices. This simple formulation enables training the entire model from a relatively large number of aligned 3D meshes of different people in different poses. The invention quantitatively evaluates variants of SMPL using linear or dual quaternion blend skinning and show that both are more accurate than a BlendSCAPE model trained on the same data. In a further embodiment, the invention realistically models dynamic soft-tissue deformations. Because it is based on blend skinning, SMPL is compatible with existing rendering engines and we make it available for research purposes.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
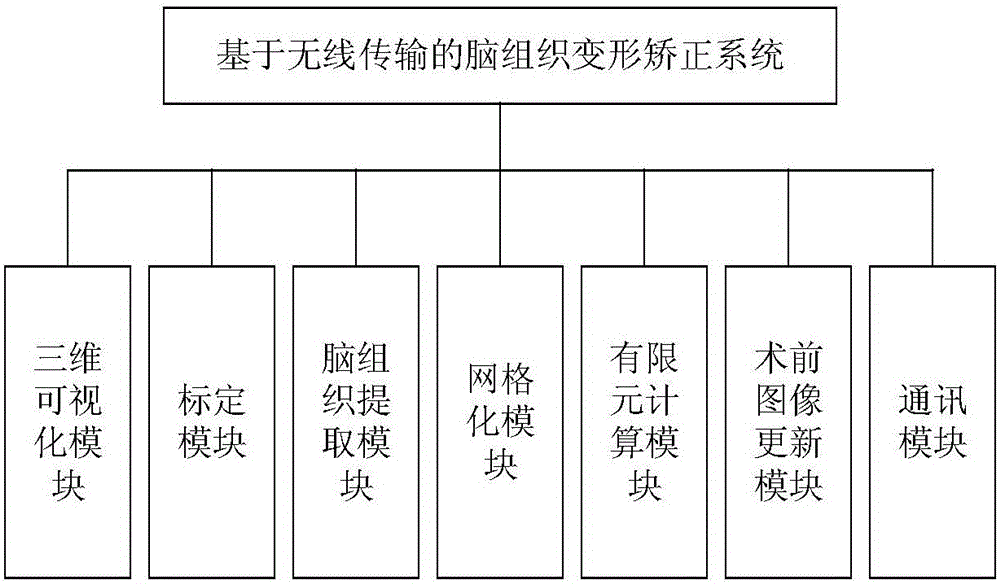
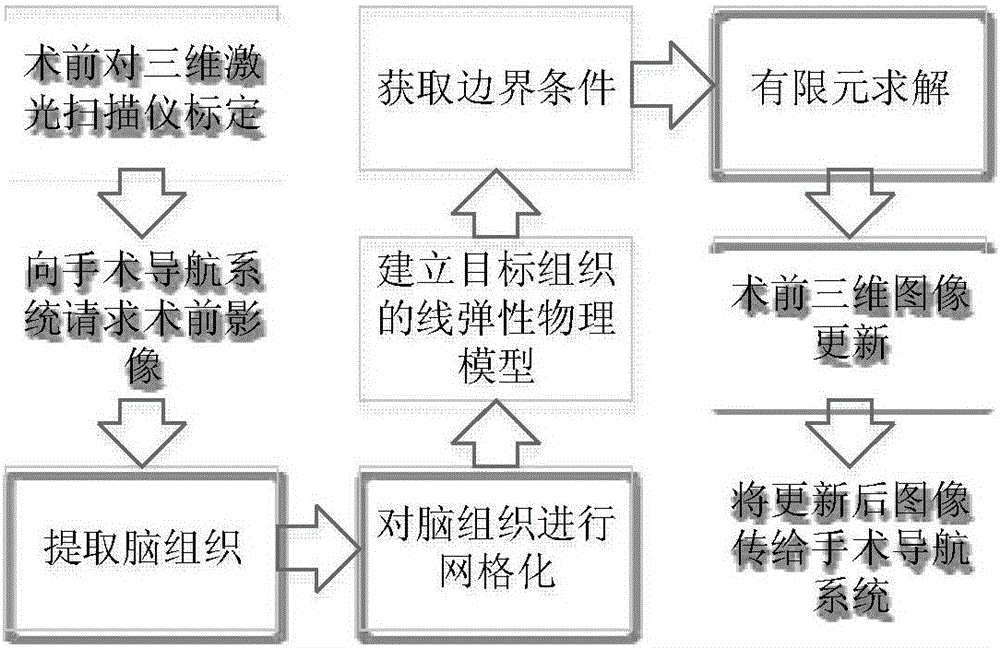
Brain tissue deformation correction system based on wireless transmission
InactiveCN106420055AAccurate and reliableHigh precisionSurgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modellingWireless transmissionImaging processing
The invention belongs to the fields of medical image processing and application, and relates to a brain tissue deformation correction system based on wireless transmission, in particular to an intraoperative brain tissue deformation correction system applied to neurosurgical department. The system comprises a brain tissue deformation workbench and a three-dimensional laser scanner workbench. A brain tissue deformation correction software system is loaded in the brain tissue deformation correction system workbench, and the brain tissue deformation correction software system can communicate with a neurosurgical operation navigation system by virtue of a wireless local area network. The brain tissue deformation correction software system comprises a three-dimensional visual module, a calibration module, a brain tissue extracting module, a grid module, a boundary condition acquisition module, a finite element calculating module, a preoperative image updating module and a communication module. The system is reliable in precision; the system can be integrated in the existing neurosurgical operation navigation system, and the system is conducive to the implementation of intraoperative soft tissue deformation correction, so that the precision of the navigation system is greatly improved, and the system is beneficial for clinical application.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
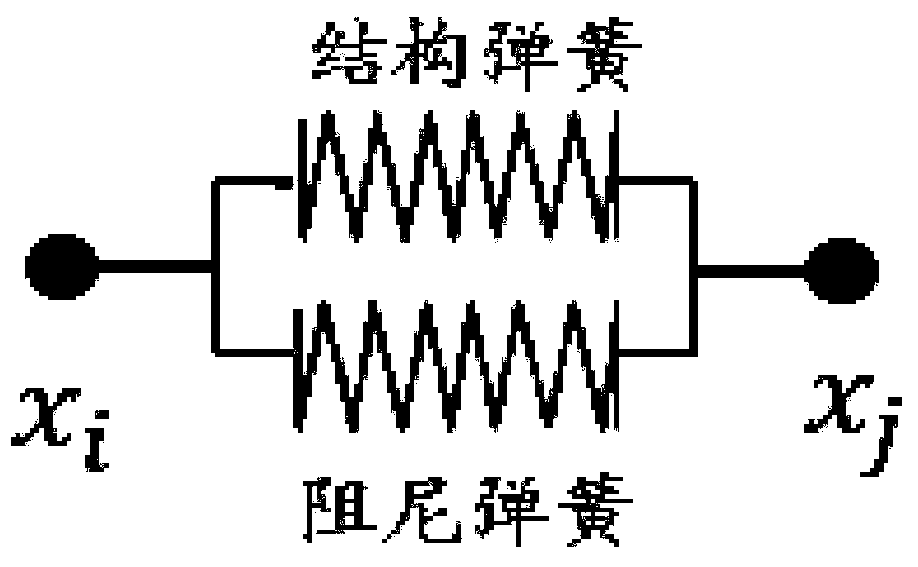
Non-linear particle spring soft tissue deformation simulation method
ActiveCN111488670AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed Computational ComplexityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMedical imaging dataSoft tissue deformation
The invention discloses a non-linear particle spring soft tissue deformation simulation method, which comprises the following steps of: acquiring medical image data of soft tissues, segmenting an organ image, and obtaining three-dimensional surface grid data by utilizing Delaunay triangular patch grid subdivision; based on three-dimensional mesh generation, taking grid nodes as mass points, enabling the edge connected between the nodes to be a spring assembly formed by connecting a structural spring and a damping spring in parallel; forming a mass point spring soft tissue model; judging whether collision occurs between the surgical instrument and the mass point spring soft tissue model or not; if collision occurs, calculating stress of each mass point, updating the mass point position andthe mass point speed, and calculating the deformation value of the mass point on the surface of the mass point spring soft tissue model until no collision occurs between the surgical instrument and the mass point spring soft tissue model; and outputting a simulation result and performing visual rendering to finish the whole process. According to the invention, deformation of soft tissues can be simulated more accurately in real time.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
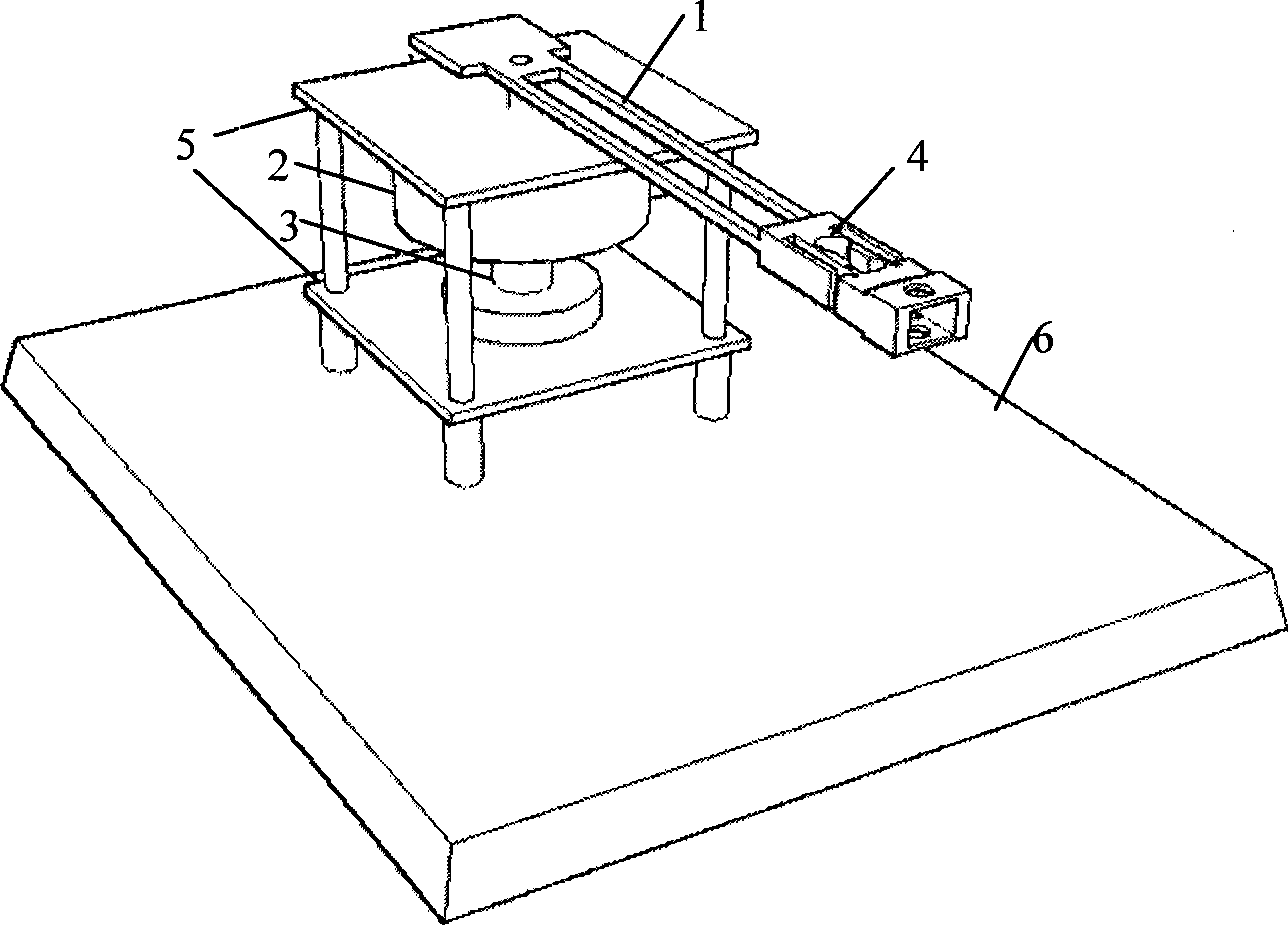
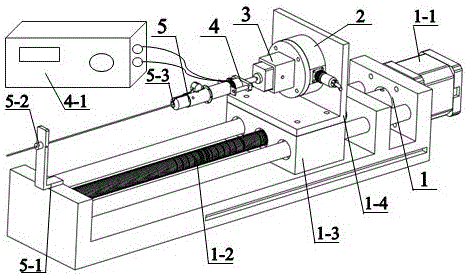
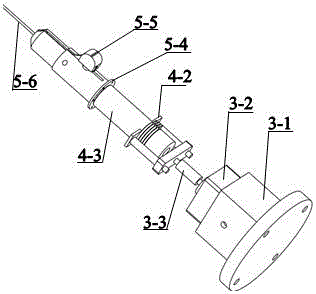
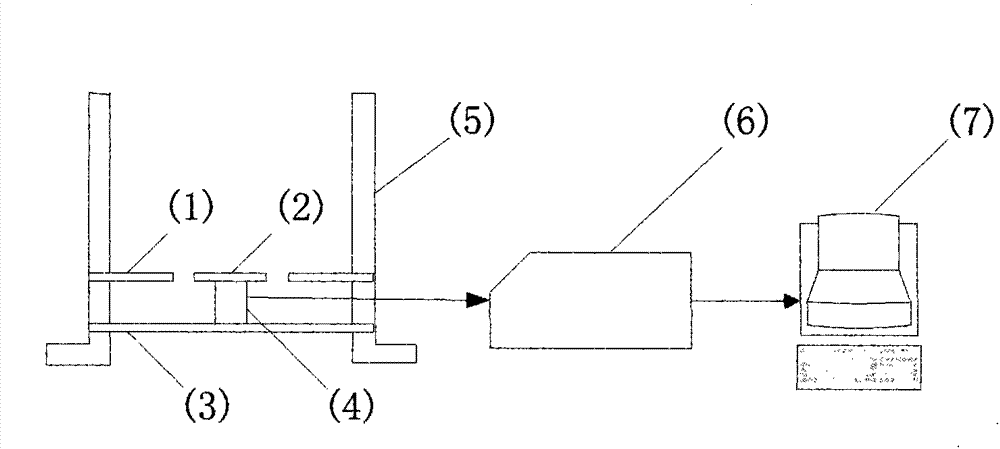
Real-time soft tissue deformation amount measurement method in robot-assisted flexible needle penetration experiments on soft tissues
Disclosed is a real-time soft tissue deformation amount measurement method which is applied to robot-assisted flexible needle penetration experiments on soft tissues. According to the method belonging to the technical field of medical instruments for minimally invasive surgery, a real-time soft tissue deformation amount measurement device and a real-time soft tissue deformation amount measurement algorithm are adopted. A six-axis force / torque sensor serves as a core component of the device. The device further comprises a rectangular tissue support plate, a round tissue tray, a rectangular bottom plate, a data collection card and a computer. The round tissue tray is connected with the top end of the sensor, and the rectangular bottom plate used for fixing the sensor is connected with the bottom surface of the sensor. The computer is provided with signal processing software. The measuring device is fixed at the bottom of a tissue container. The signal processing software includes a tissue squeezing force calculation algorithm and a tissue deformation amount calculation algorithm. By the two calculation algorithms, real-time reading and calling of tissue squeezing force and real-time recording and displaying of tissue deformation amount are achieved, and accordingly, real-time display of the tissue deformation amount in the needle penetration experiments on the soft tissues is achieved.
Owner:QINGHAI UNIVERSITY
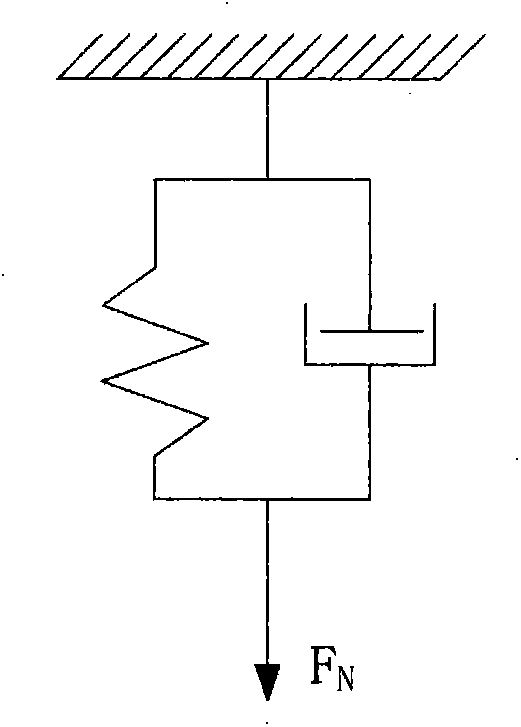
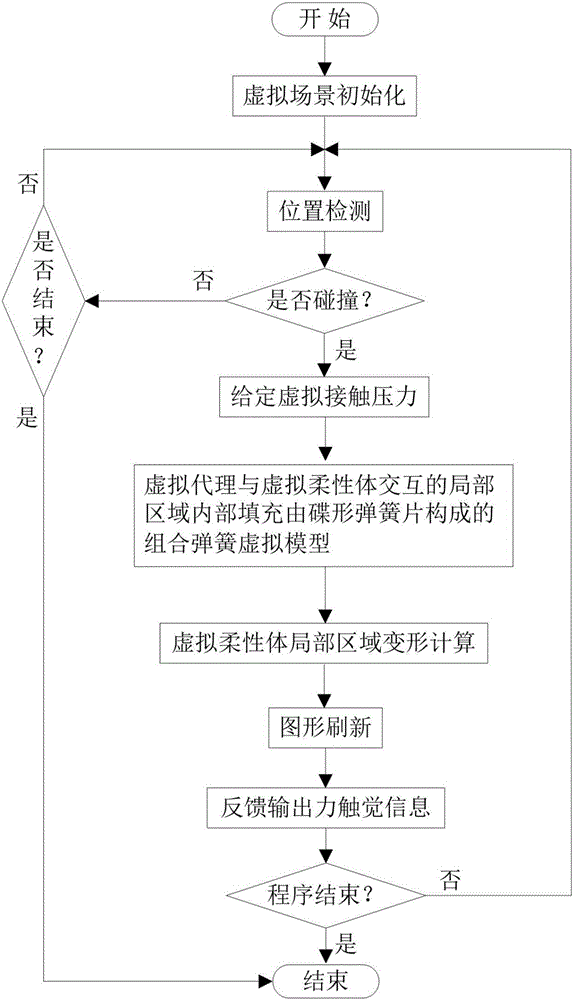
Modeling method based on combined spring virtual model composed of disc springs
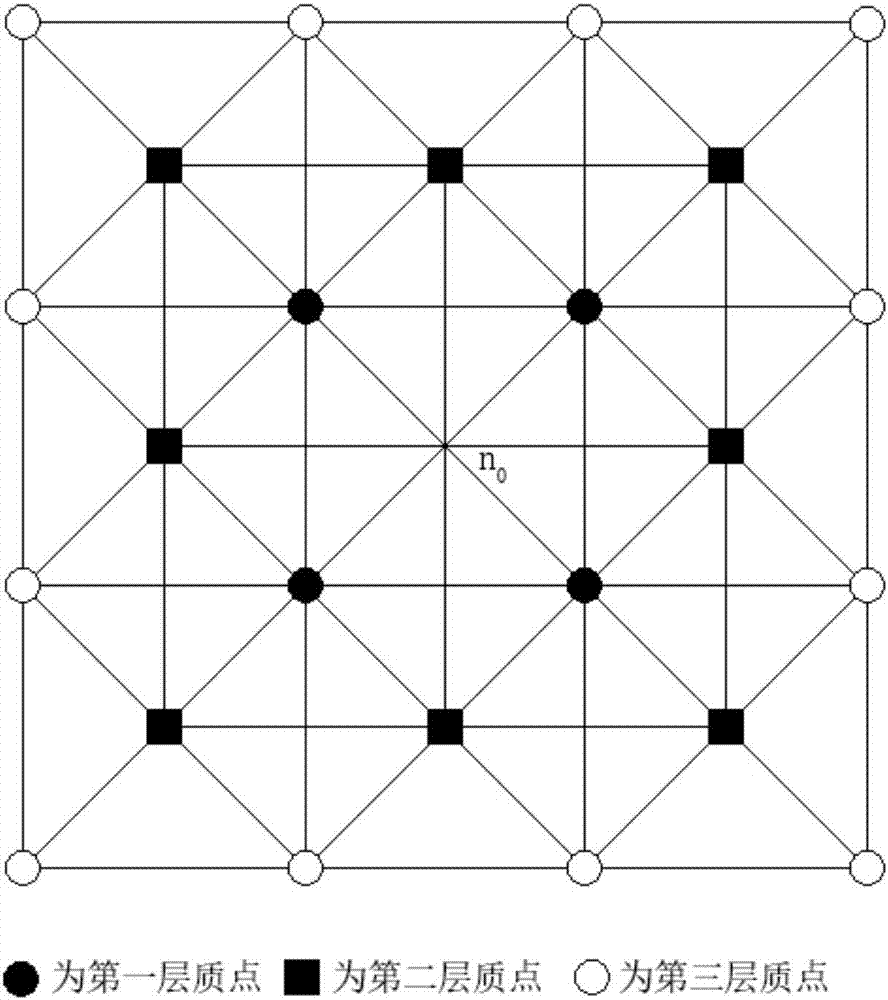
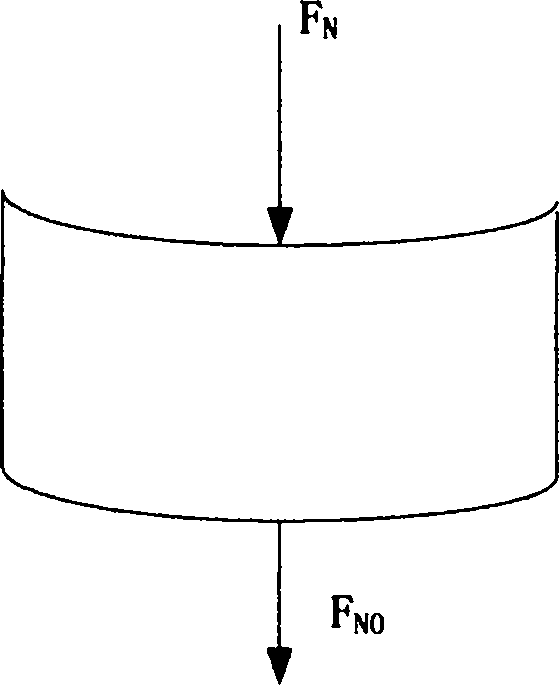
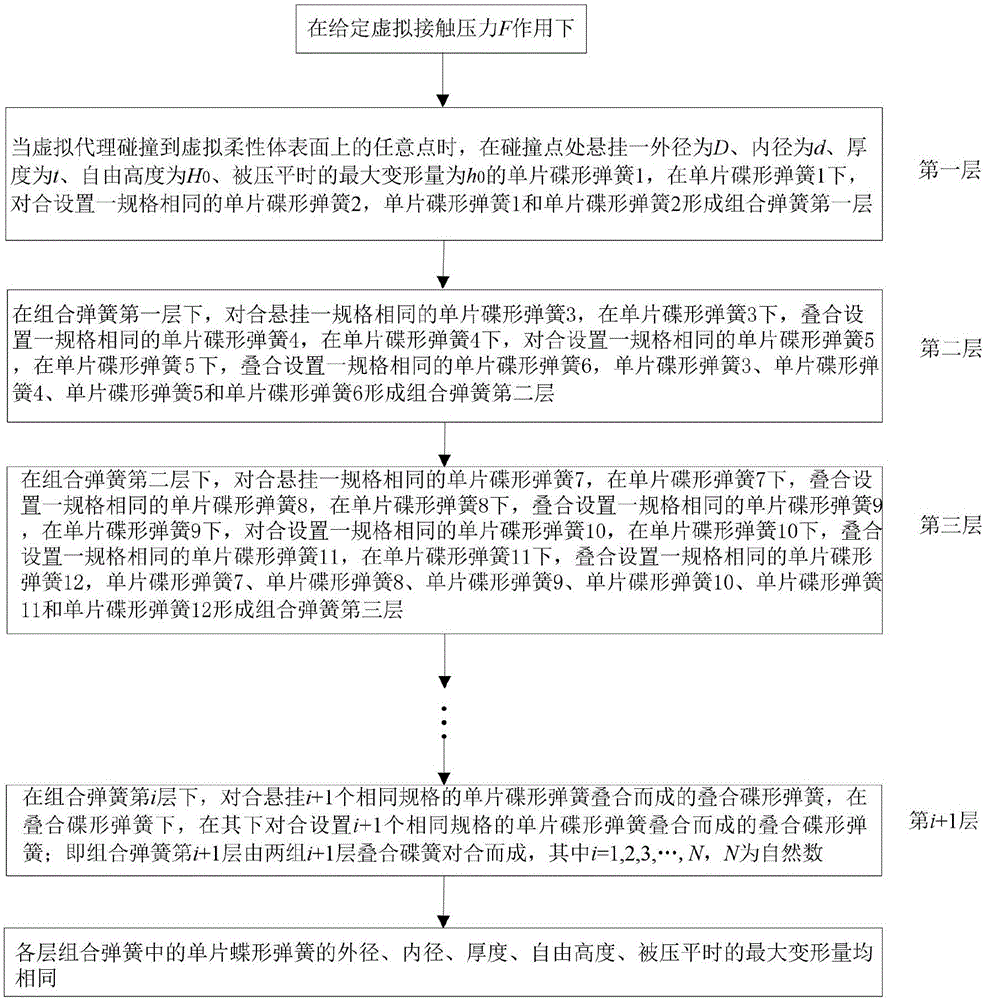
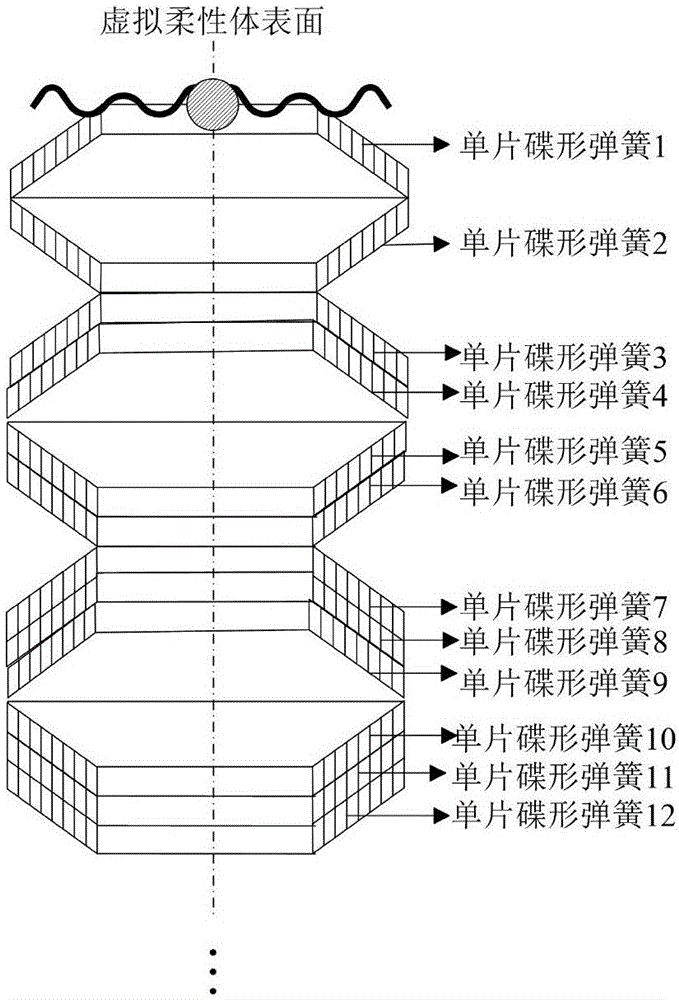
InactiveCN106528993ASimple calculationSpeed up deformation calculationsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsStress conditionsModel method
The invention discloses a modeling method based on a combined spring virtual model composed of disc springs. The method comprises the steps of S1, initializing a virtual scene; S2, establishing a combined spring which is formed by gradually increasing the number of the disc springs; and S3, calculating partial area deformation of a virtual flexible body. According to the modeling method provided by the invention, the [i+1]th layer of any combined spring is formed by folding two groups of [i+1] layers of superimposed disc springs; through application of relations of pressures consumed in each layer and among the layers of the combined spring, the condition of the pressure consumed by the single disc spring in each layer is solved, the deformation of the single disc spring in each layer is solved according to a computing relation between the stress and the deformation of the single disc spring; the total deformation of the model is obtained; under the effect of the same given virtual contact pressure, the computing volume of the combined spring is reduced; the method can be used for virtual operation simulation for body soft tissue deformation and is consistent with layer structures and stress condition of body soft tissues.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Real-time interaction mesh-free soft tissue deformation simulation method
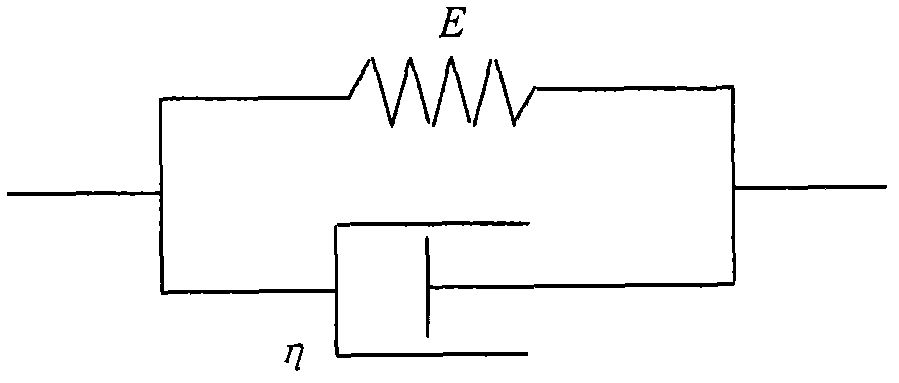
InactiveCN108710735AViscoelastic performanceImprove real-time performanceDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsHuman bodySoft tissue deformation
The invention discloses a real-time interaction mesh-free soft tissue deformation simulation method, which comprises the following steps that: (1) transforming the CT (Computed Tomography) image of asoft tissue into an OBJ file to conveniently obtain vertex information; (2) using MLS (Moving Least Squares) to construct a mesh-free function; (3) bringing Kelvin viscoelasticity into a tissue model;(4) according to the displacement of all nodes corresponding to given stress calculated in S(3), using a Marquardt algorithm to pre-fit a mathematical relationship between force on the soft tissue and the displacement of each node; and (5) importing an enrichment function to simulate tissue surface discontinuity cracks caused by operations including segmentation. By use of the method, the Kelvinviscoelasticity model is brought into the human body tissue model, the viscoelasticity of the soft tissue can be more favorably presented, simulation validity is improved, the Marquardt algorithm is used for pre-fitting the mathematical relationship between force on the soft tissue and the displacement of each node, simulation instantaneity is improved, and meanwhile, weight function enrichment isimported to realize the interactive simulation of soft tissues.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Simulation method for soft tissue pressing and deformation recovery
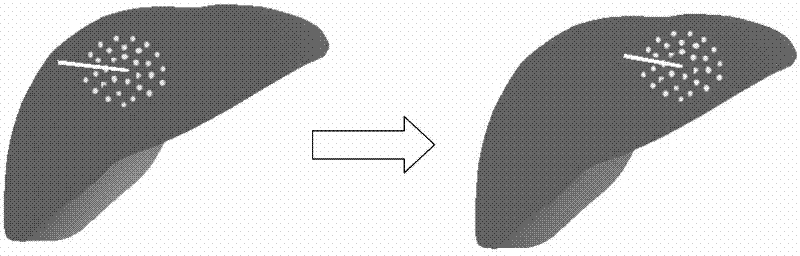
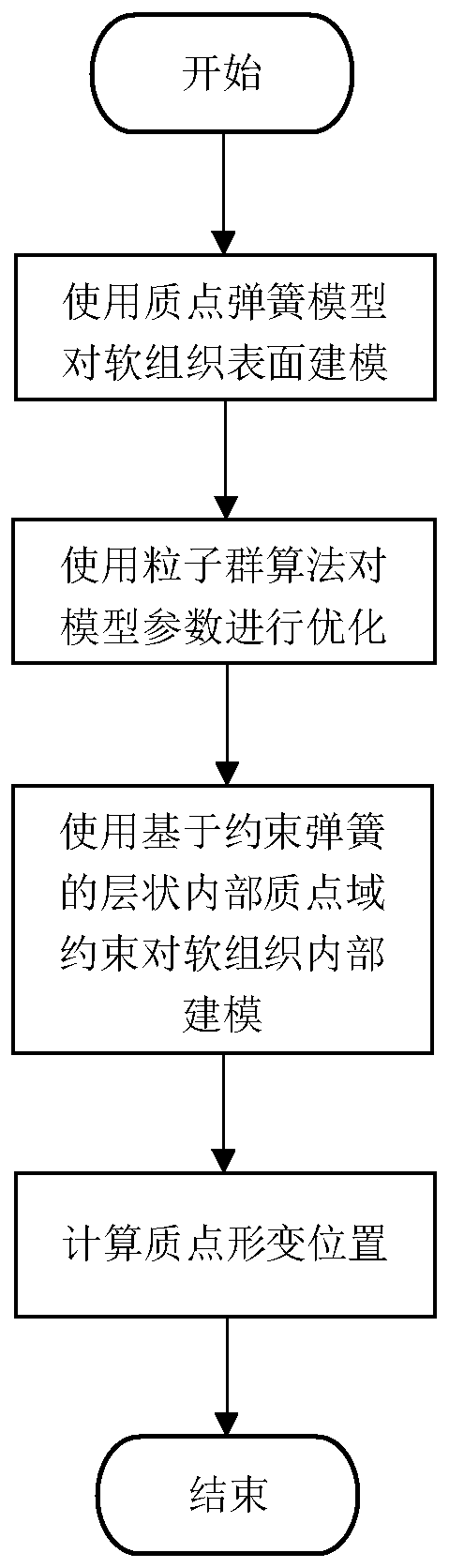
ActiveCN110289104AHigh precisionImprove deformation recovery abilityMedical simulationSoft tissue deformationModel parameters
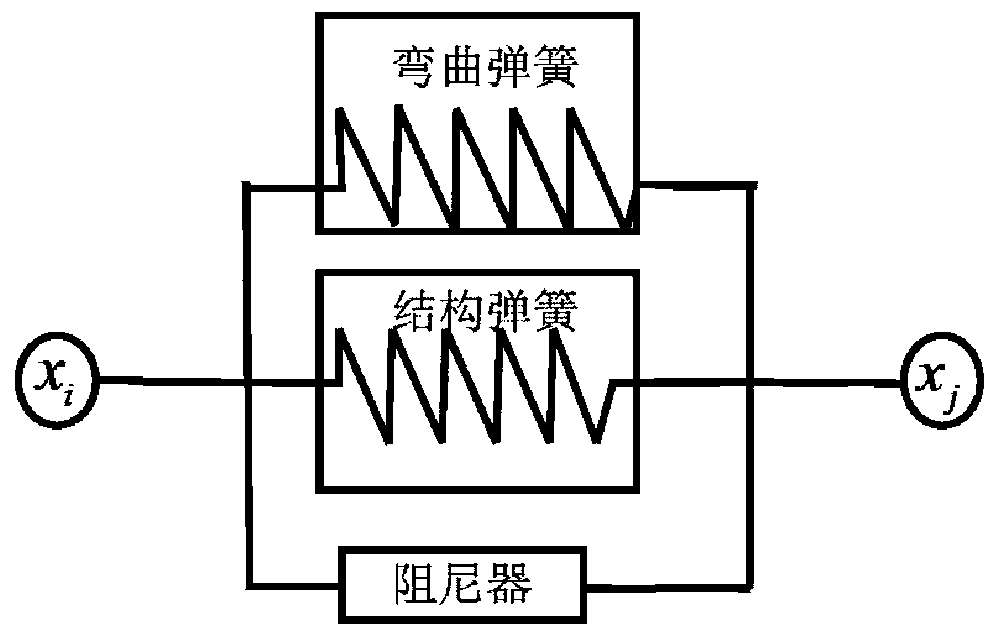
The invention discloses a simulation method for soft tissue pressing and deformation recovery. The method is used for simulating a pressing troubleshooting process of a liver in a virtual operation. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a surface model of a liver surface by using a mass point spring model with a bending spring, optimizing model parameters by using a particle swarm algorithm, then constructing a liver internal construct model by using internal mass point domain constraints based on stratification, and connecting stratification mass point domains by using constraint spring elements. According to the method, the deformation recovery capability and calculation efficiency of the mass point spring model during large deformation are improved, the deformation accuracy and authenticity of the mass point spring model are enhanced, the difficulty that a traditional mass point spring model cannot simulate the internal volume force is solved, and the viscoelastic characteristic of the soft tissue deformation process is simulated.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com