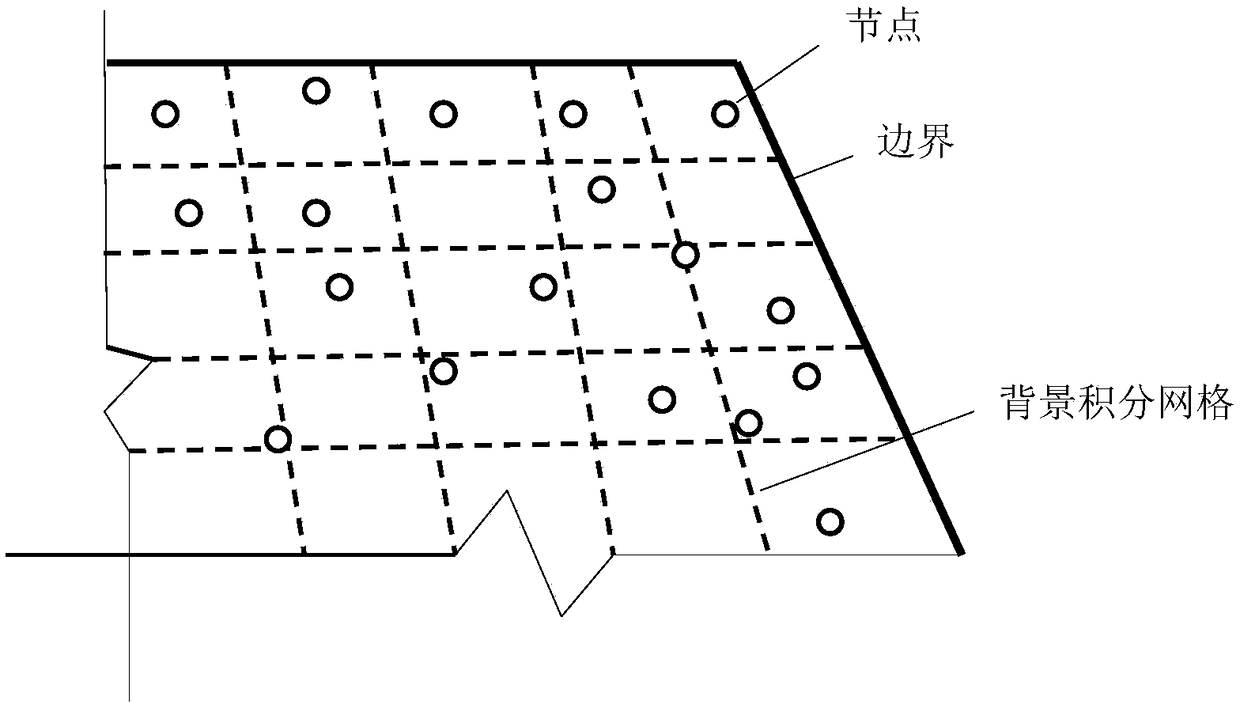
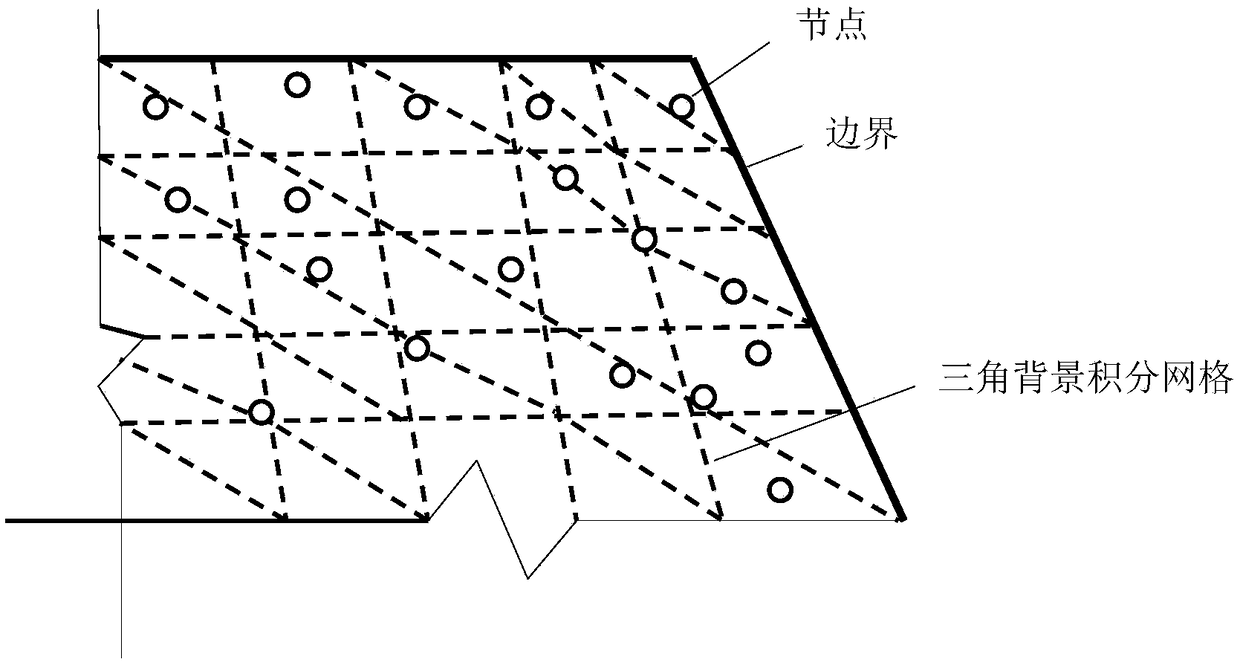
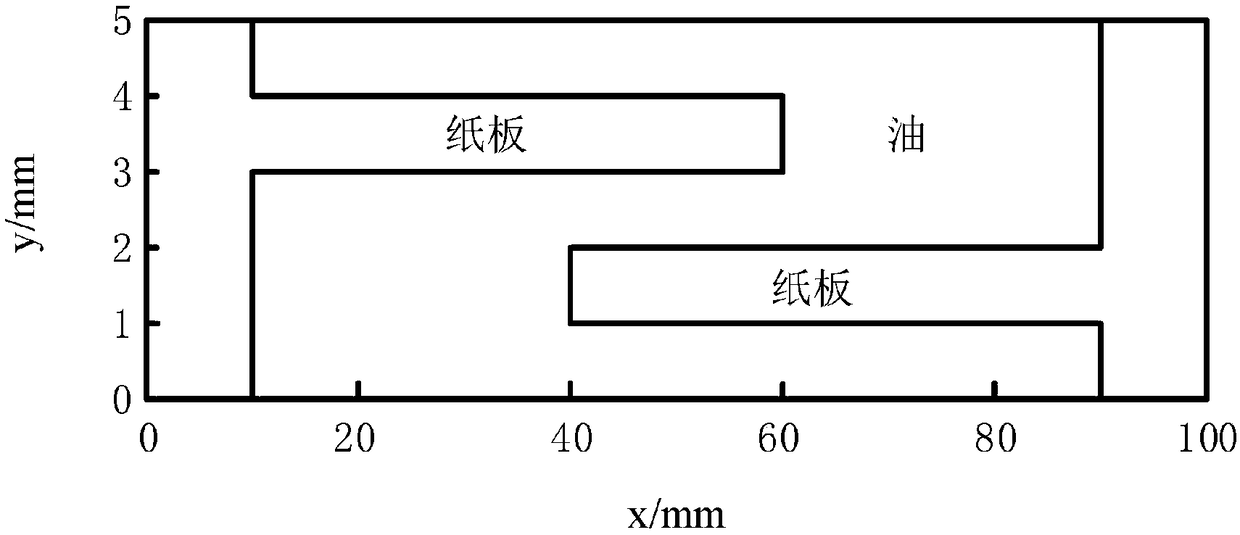
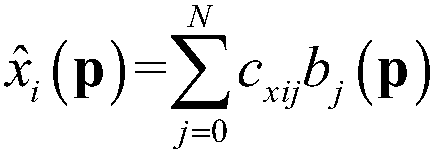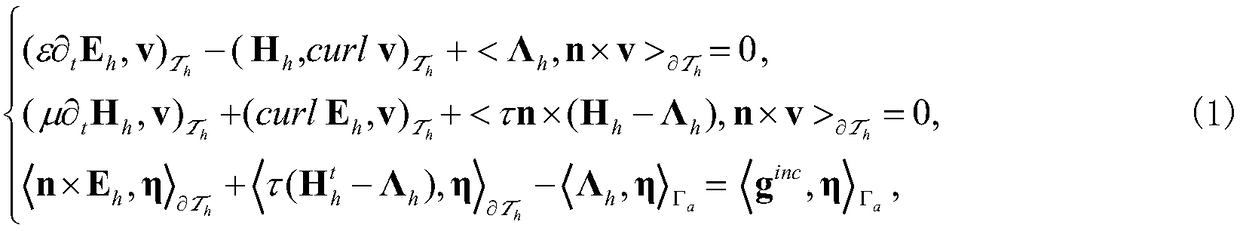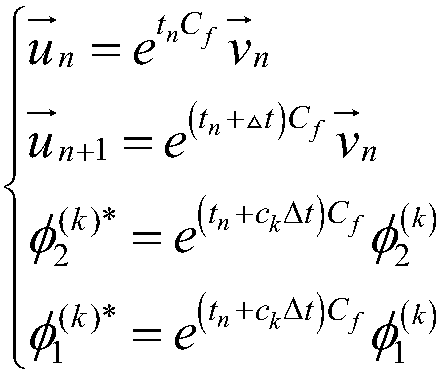Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
72 results about "Galerkin method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, in the area of numerical analysis, Galerkin methods are a class of methods for converting a continuous operator problem (such as a differential equation) to a discrete problem. In principle, it is the equivalent of applying the method of variation of parameters to a function space, by converting the equation to a weak formulation. Typically one then applies some constraints on the function space to characterize the space with a finite set of basis functions.
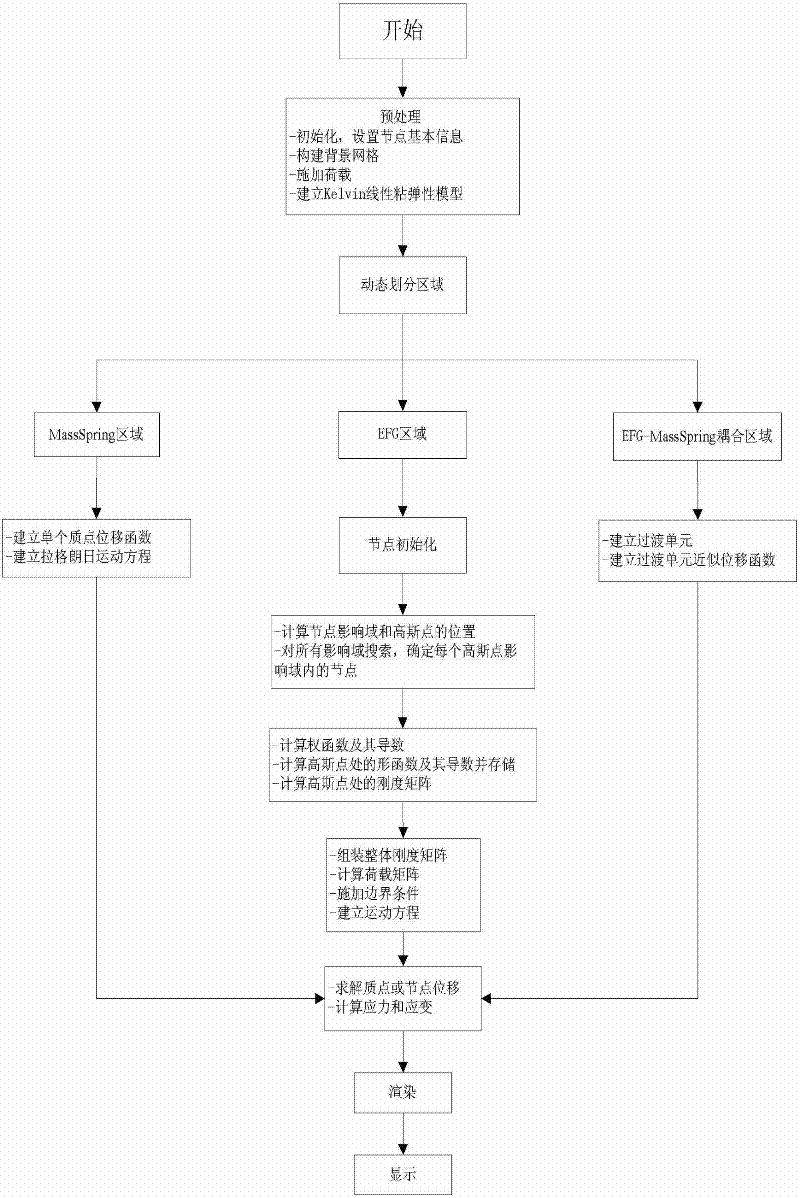
Simulation Method of Soft Tissue Deformation Based on Meshless Galerkin and Particle Spring Coupling
InactiveCN102262699AImprove continuityImprove stabilitySpecial data processing applicationsComputation complexitySoft tissue deformation
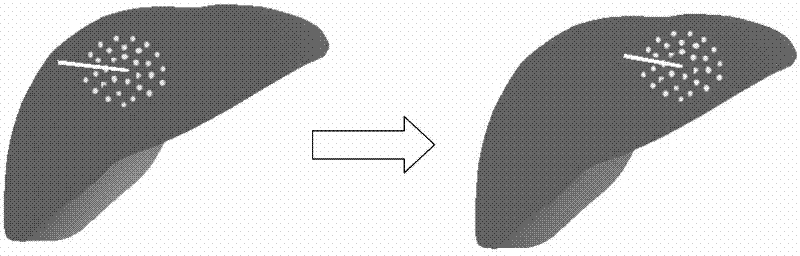
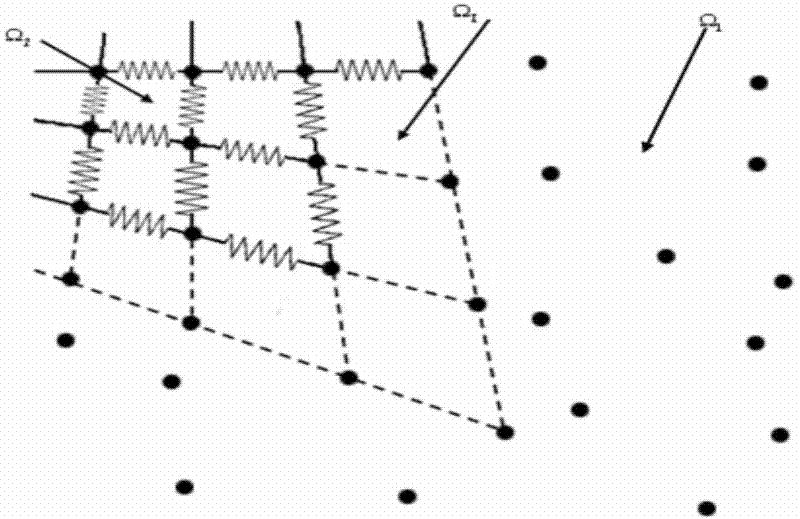
The invention relates to an object deformation real-time simulation graphic processing technique, particularly a soft tissue deformation simulation method based on coupling of mesh-free Galerkin and mass spring, which comprises the following steps: in the pretreatment process, establishing a linear viscoelasticity biomechanical model for soft tissues; in the deformation computation process, dynamically partitioning a mesh-free region and a mass spring region according to the load carried by the soft tissues, establishing a transitional unit of the connection region between the mesh-free region and mass spring region, and constructing a transitional unit approximation displacement function, thereby implementing self-adapting coupling of a mesh-free Galerkin method and a mass spring method;and in the after-treatment process, outputting the state of the mass or node of each time step in the deformation process onto a screen, carrying out illumination rendering, and finally displaying the real-time deformation process of the soft tissue organ under stressed conditions on the screen, thereby implementing visualization effect of dynamic deformation. By utilizing the advantage of high efficiency in the mass spring method and the advantages of high precision and no need of mesh reconstruction in the mesh-free Galerkin method, the invention overcomes the defect that the Galerkin method is not suitable for solving a large-scale problem, thereby effectively lowering the complexity of computation in the soft tissue deformation simulation and enhancing the operation efficiency.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIV OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
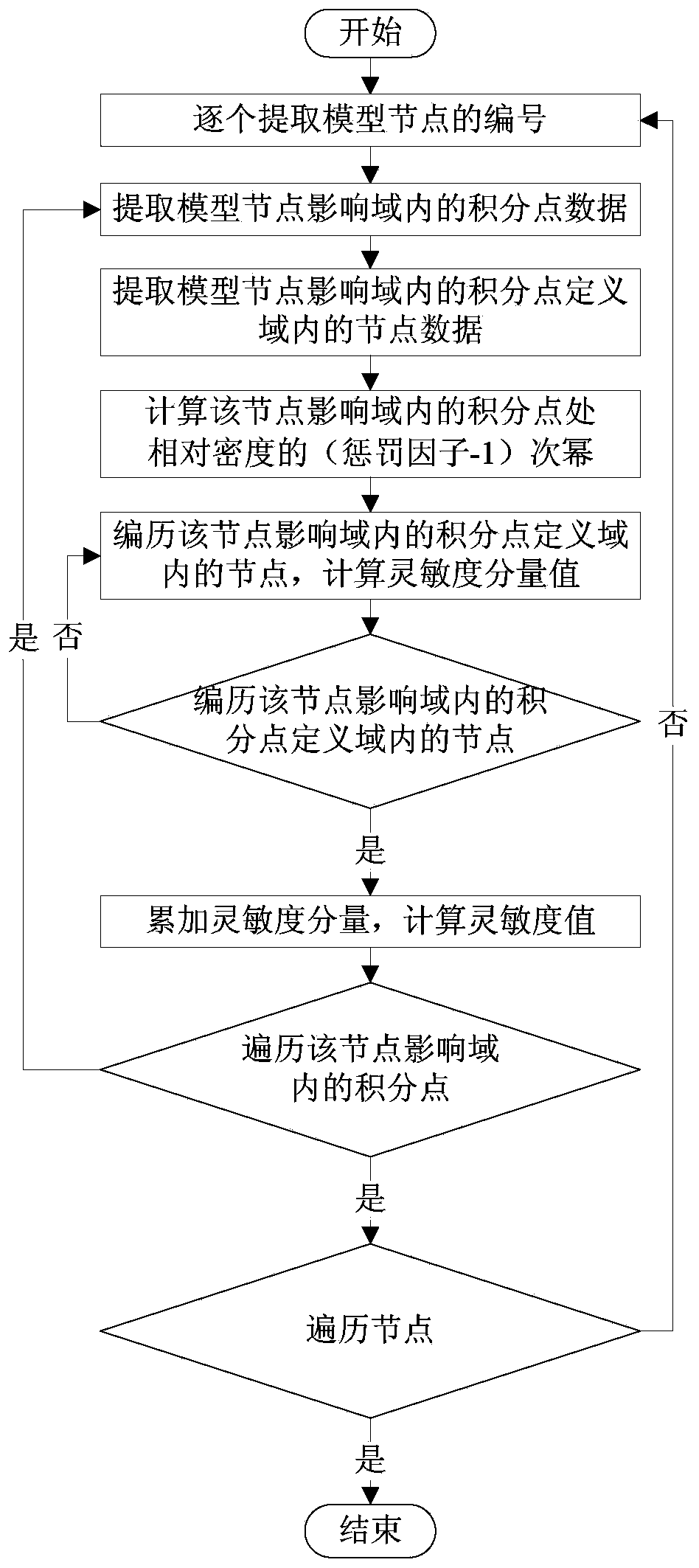
Grid-free Galerkin method structural topology optimization method based on GPU parallel acceleration
InactiveCN103970960AAdaptableAvoid globbingSpecial data processing applicationsTopology optimizationParallel computing
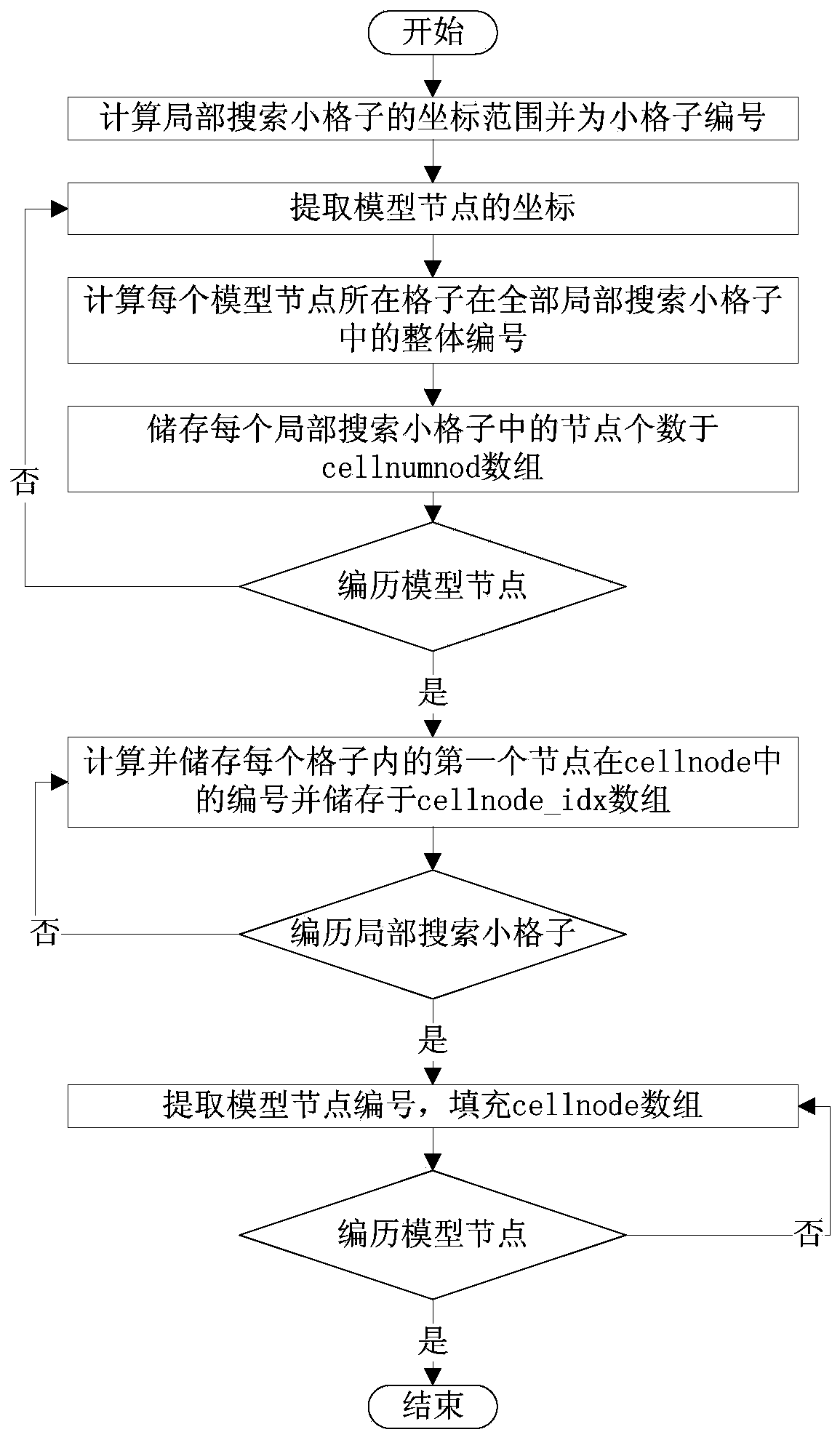
The invention discloses a grid-free Galerkin method structural topology optimization method based on GPU parallel acceleration. The grid-free Galerkin method structural topology optimization method mainly comprises the steps of 1 reading data into a host machine memory, arranging integral points through a CPU, establishing the relation of nodes, the integral points and local lattice searching, computing node influence domain radiuses and the integral point definition domain radiuses, confirming the relation of the nodes and the integral points and then copying the data into a GPU global memory; 2 setting different GPU thread blocks and the thread number according to different calculating data; 3 performing asynchronous assembly through the CPU and a GPU and solving a grid-free Galerkin method global discrete system equation to obtain a displacement approximate solution; 4 performing structural topology optimization calculation in the GPU and judging whether iteration is finished or not and a result is output or not according to residual errors of design variables. The grid-free Galerkin method structural topology optimization method is low in hardware cost and good in universality and can reduce a large amount of time consumption on the premise that the engineering accuracy requirement is met.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
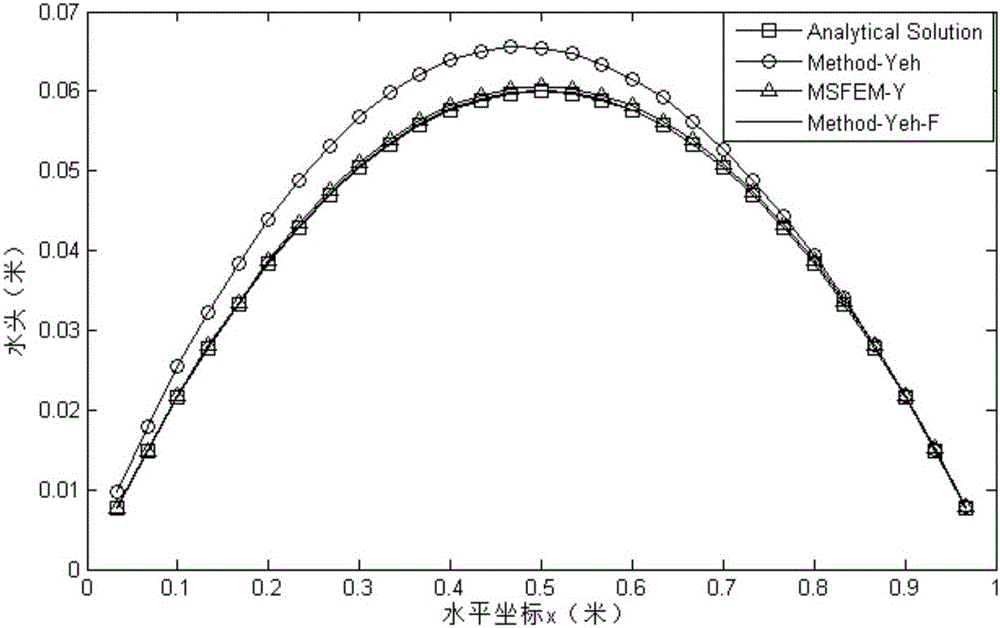
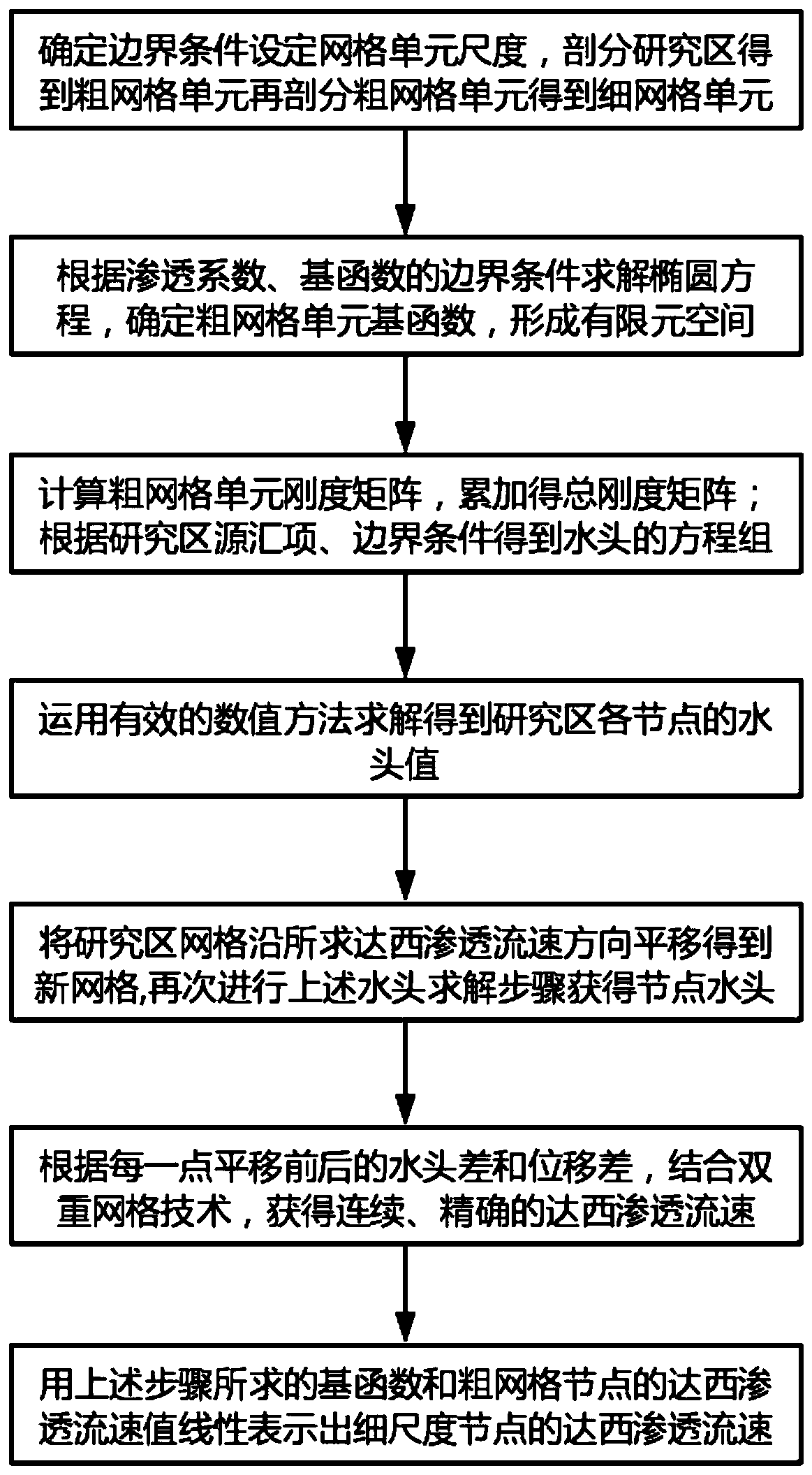
Yeh-multi-scale finite element method for simulating water flow Darcy velocity of porous medium
ActiveCN106202746AGuaranteed continuityEfficient solutionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALElement model
The invention discloses a Yeh-multi-scale finite element method for simulating water flow Darcy velocity of a porous medium, comprising the steps of: performing variation on the problem which needs resolution by a Galerkin method; subdividing a research area into coarse grid cells and subdividing all the coarse grid cells into fine grid units; resolving a degradation elliptic equation on each coarse grid cell to construct a basis function; resolving variational form by applying the basis function to obtain a total rigidity matrix; obtaining a right-hand term according to the source sink term and the boundary condition of the research area; performing simultaneous operation to obtain a waterhead equation set; resolving the equation set by an effective numerical method to obtain the node waterhead of the research area; and resolving a Darcy equation directly in the research area by combining a Galerkin finite element model of Yeh and applying the constructed basis function and the waterhead value of the research area to obtain continuous Darcy permeating velocity on the coarse-scale node, and linearly expressing the fine-scale Darcy permeating velocity by the basis function. Compared with the prior art, the method has similar precision and higher efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
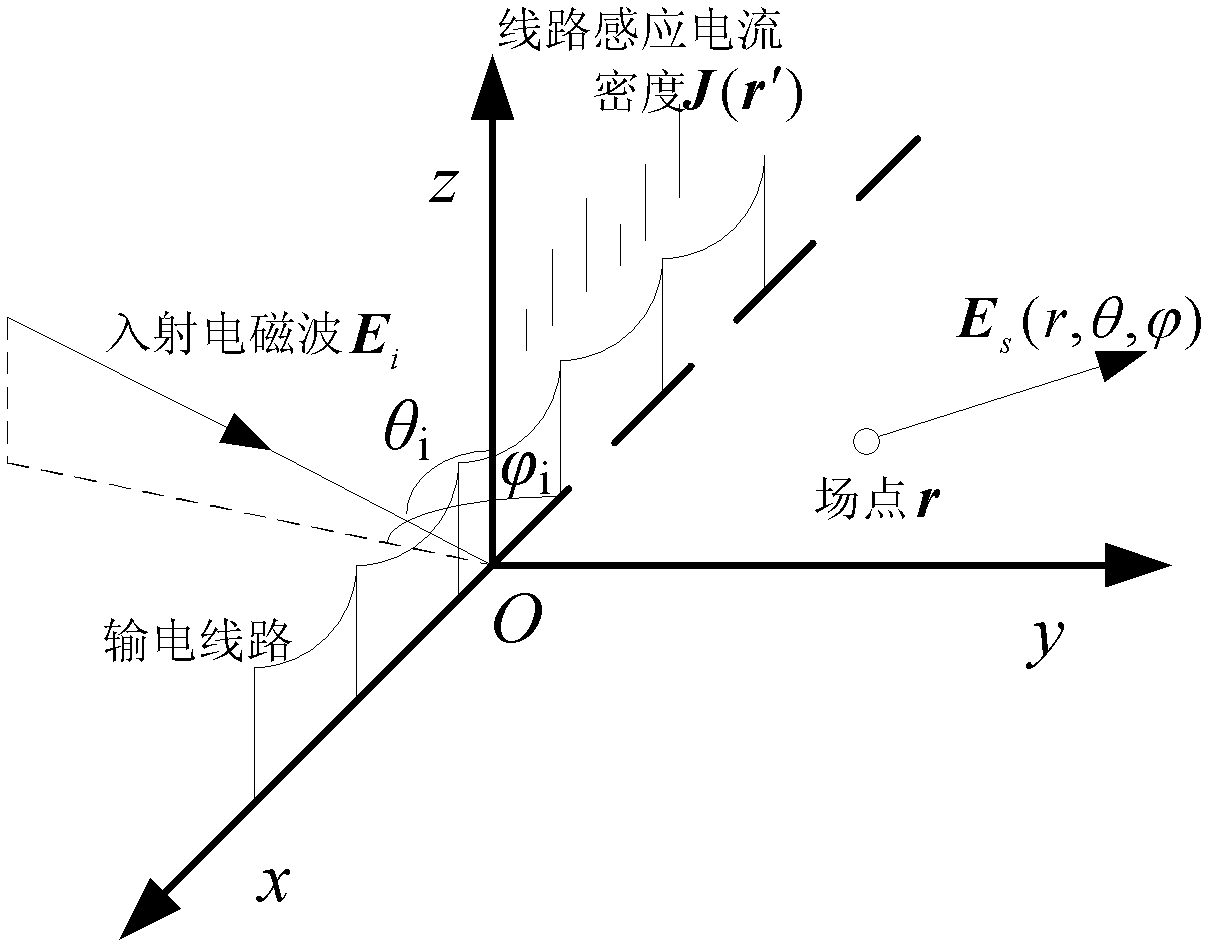
Method for determining protection space between ultra-high-voltage DC (direct current) transmission line and wireless station
The invention relates to a method for determining the protection space between an ultra-high-voltage DC (direct current) transmission line and a wireless station. The method comprises the methods of constructing a passive jamming line-surface model of an ultra-high-voltage DC transmission line and solving an electric field integral equation corresponding to the model. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, constructing a passive jamming simulation surface model of the line according to the real space truss structure of transmission towers of the line, and constructing the passive jamming line-surface model of the transmission line in combination with the line model of an overhead wire and ground wire; solving induced current of each part of the ultra-high-voltage DC transmission line by using a moment method checked by RWG (Rao-Wilton- Glisson) basis function and Galerkin method, and calculating secondary radiation intensity vector generated by the induced current; and superposing the vector with a source electromagnetic filed to obtain the jamming level of the ultra-high-voltage DC transmission line to the wireless station. Comparison of test data obtained through the test proves that the method provided by the invention has higher accuracy, and can be used for accurately determining the passive jamming protection space between high-voltage transmission line and adjacent wireless stations in the future.
Owner:STATE GRID ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Hybrid time-domain discontinuous-Galerkin-method-based numerical method of time-domain computational-electromagnetics
InactiveCN107944141AObtaining Electromagnetic Response CharacteristicsImprove parallelismDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsElectromagnetic environmentTime domain electromagnetics
The invention discloses a hybrid time-domain discontinuous-Galerkin-method-based numerical method of time-domain computational-electromagnetics. The method is applied to the numerical-solving field oftime-domain computational-electromagnetics. A hybrid term is introduced on interface units of adjacent body units, and is used to define numerical flux of electromagnetic fields, an implicit Crank-Nicolson time format is used to disperse three-dimensional time-domain Maxwell equations, after introducing the hybrid term, to obtain a global linear system related only to the hybrid term, and the electromagnetic fields of all the units are obtained through solving for the hybrid term. Therefore, the deficiency of calculation time, memory and precision of existing time-domain electromagnetic-fieldnumerical-methods in processing multi-scale equipment under complex electromagnetic environments can be effectively avoided.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Parametric elastic vibration analysis method of rotating annular periodic structure
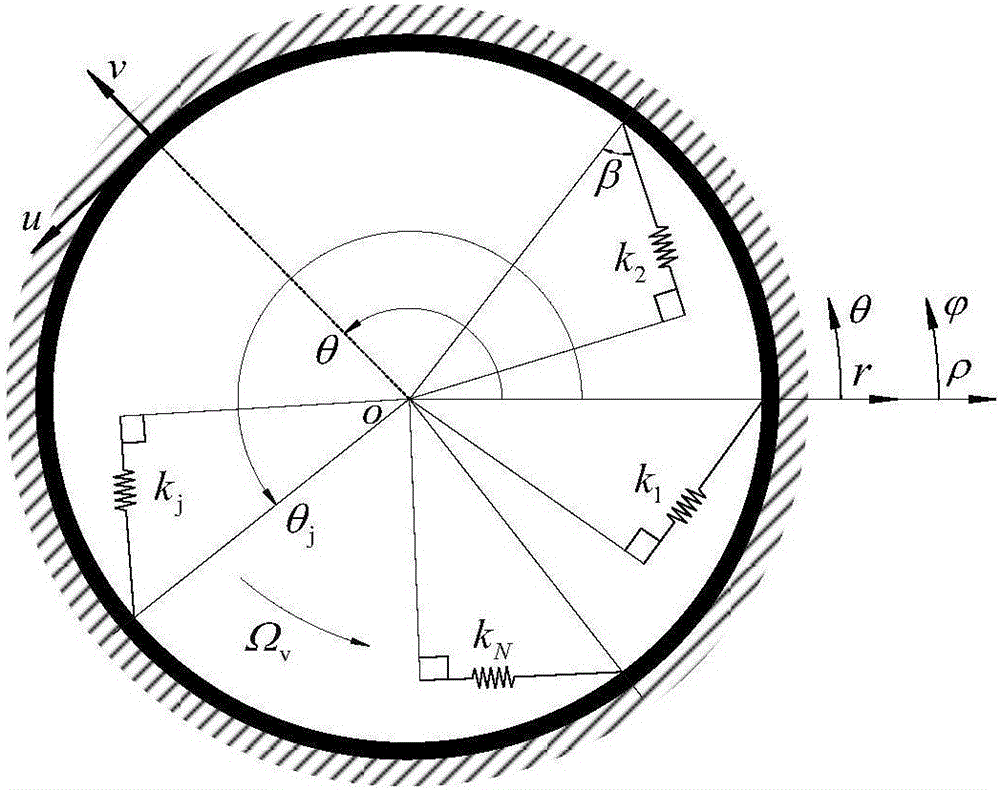
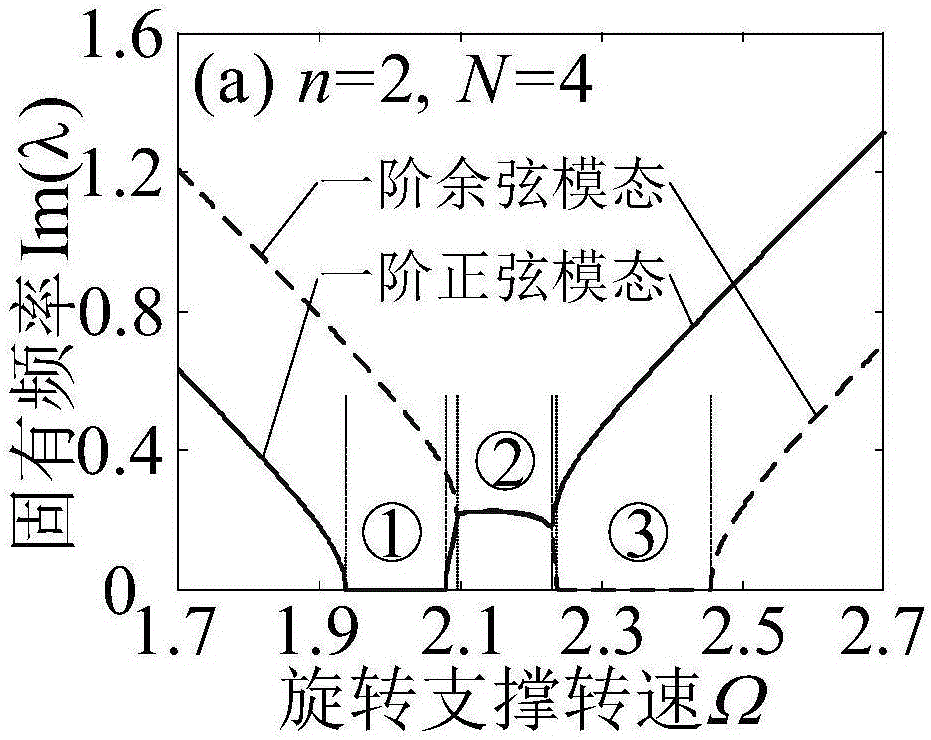
ActiveCN106547957AStable structural designOvercoming inefficienciesGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsDynamic modelsDynamic equation
A parametric elastic vibration analysis method of a rotating annular periodic structure comprises the steps of building a rigid-elastic coupling dynamic model of the rotating annular periodic structure according to a Hamilton principle under a global stationary coordinate system; introducing coordinate conversion, and converting the dynamic model to a support follow-up coordinate system so that a parametric item in an original equation is eliminated; performing discrete processing on a partial differential constant coefficient dynamic equation under the rotating support follow-up coordinate system by a Galerkin method to obtain an ordinary differential matrix equation; analyzing a characteristic value of the ordinary differential matrix equation by using a classical vibration theory; and respectively analyzing mode characteristic of the rotating annular periodic structure and a dynamic stability rule of parametric elastic vibration by employing an imaginary part and a real part of the characteristic value of the ordinary differential matrix equation. The parametric elastic vibration analysis method can be used for dynamic analysis of rotating machinery, calculation and solution of the mode characteristic of a system, and analysis on the dynamic stability and the dynamic response of the system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Numerical simulation method for obtaining aircraft flow fields
ActiveCN106682262AHigh precisionSolving Complex Flow PhenomenaGeometric CADSustainable transportationRegular gridFlight vehicle
The invention relates to a numerical simulation method for obtaining aircraft flow fields, wherein an interrupted Galerkin method based on non-structural right angle meshes is used to solve the flow field, and right angle meshes with a quadtree structure are used to disperse a to-be-solved flow field area into a set of meshes; each quadrilateral mesh is processed by dual-linear coordinate conversion, so each mesh under a current physical coordinate system can be mapped onto the next regular mesh in a computational coordinate system, so standard square meshes can be obtained; conservation variables in units under the computational coordinate system are obtained through numerical computation; a front face, a lower face, a left face and a right face of each mesh under the physical coordinate system are determined; according to differences between the left and right vibrations of unit interfaces, an interrupted detector is established; and the conservation variables in each mesh are processed by flow field display on the disperse meshes, so flow field distribution can be obtained. According to the invention, the interrupted Galerkin method based on the non-structural right angle meshes is introduced into flow field computation, so accuracy of the flow field computation is increased, and complicated flow phenomena can be solved.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
Efficient decomposition parallel method for time domain finite element regions
InactiveCN107688680AReduce simulation calculation timeScale upDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALTime domain
The invention discloses an efficient decomposition parallel method for time domain finite element regions. The method comprises the following steps of establishing a solution model, conducting discretization, and obtaining tetrahedral node information and unit information of the model; determining the total number of processes to make sub-regions correspond to process numbers in a one-to-one mode,distributing units into all the sub-regions, determining the thickness of a buffering area according to the time step length, and establishing numbering indexes of each sub-region and a global calculation region and communication indexes between every adjacent sub-regions; from a first-order Maxwell's curl equation with electric field intensity and magnetic flux as unknown quantities, adopting aGalerkin method to test the two sides of the equation, using a primary function for expansion, and obtaining a final iterative formula to fill a matrix of each solution sub-region; adopting an iterative formula of time domain finite elements in CN difference schemes to conduct time iteration, and obtaining the electric field value and the magnetic flux in the space. By means of the method, the calculation time is effectively saved, the capability of solving large-scale electromagnetic problems is improved, and the method has great significance in practical application.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Parameterization Thevenin equivalence-based alternating current direct current received end power grid commutation failure fault preventive method
ActiveCN107681683AImprove the ability to defend against commutation failure faultsImprove applicabilityElectric power transfer ac networkPower gridEngineering
The invention relates to a parameterization Thevenin equivalence-based alternating current direct current received end power grid commutation failure fault preventive method. A parameterization received end power grid Thevenin equivalence model is obtained by adopting a generalized Galerkin method according to an alternating current direct current received end power grid short circuit current calculation model by considering a direct current commutation failure and multi-convertor-station concurrence failure caused by the alternating current system faults; and by taking the weight sum for improving the single convertor station commutation failure immune factor and the multi-convertor-station commutation failure immune factor as the optimization target, and by taking the parameterization Thevenin equivalence model as the constraint condition, an optimization model is established, so that the alternating current direct current received end power grid commutation failure fault defensive capability is improved. The method has relatively high applicability and high calculation speed, and can adapt to the alternating current direct current received end power grids in different operationmodes, and can better satisfy the actual demands.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +3
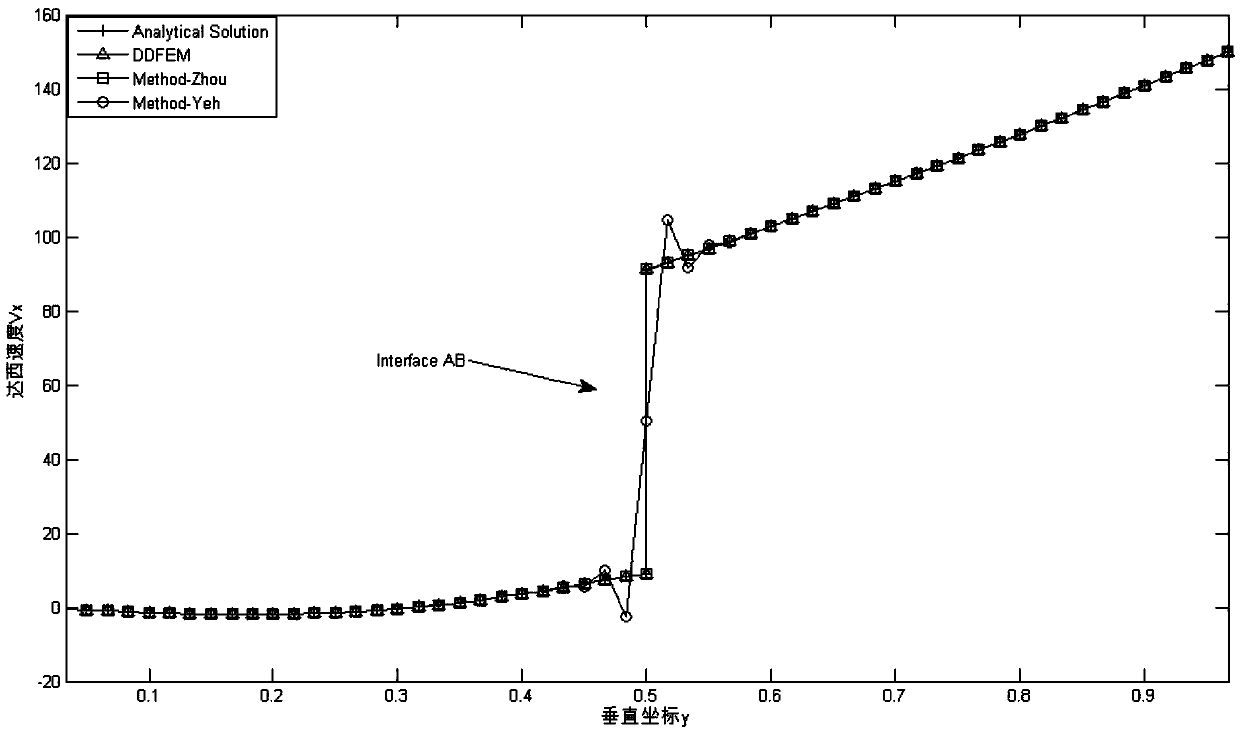
Domain decomposition finite element method for simulating Darcy speed at underground medium interface
ActiveCN107657075AImprove computing efficiencyGuaranteed accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDecompositionExtended finite element method
The invention discloses a domain decomposition finite element method for simulating Darcy speed at an underground medium interface. The method comprises the following steps: performing variation on anunderground flow problem by using a Galerkin method, sub-dividing a research domain, and acquiring waterhead by applying the finite element method; decomposing the research domain into a plurality ofsingle-medium sub-domains by applying interfaces of different mediums according to the medium composition of the research domain, and decomposing an underground Darcy speed solution problem on the research domain into sub-problems on the sub-domain by applying the domain decomposition method; selecting one sub-problem, performing variation by using the Galerkin method, and acquiring the Darcy speed by applying a Galerkin model of the Yeh, acquiring the Darcy speed at the other side of the interface of the sub-domain and other sub-domain by combining with the refraction law as the first classof boundary condition of the adjacent sub-problem; selecting the next sub-problem to solve, and repeating this process until all sub-problems are completely solved. By using the method disclosed by the invention, the computing consumption of the Darcy speed is reduced through the domain decomposition method, and the precision of the Darcy speed at the interface is guaranteed by using the refraction law.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
An extended smooth meshless Galerkin method
ActiveCN109165404AStrong topology adaptabilityDiscretization process is simple and easyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDiscretizationComputer science
The invention discloses an extended smooth meshless Galerkin method, which combines the extended finite element, meshless Galerkin and smooth integration technology, wherein the traditional meshless Galerkin method is modified, and a triangle with stronger topological adaptability is used as a background integration cell, so that the discretization process of a geometric body is more simple and easy to perform. The traditional Gaussian integration method is abandoned and the smooth integration technique is introduced to avoid the tedious derivation process of the shape function, which improvesthe calculation accuracy to some extent. The improved meshless method is applied to the simulation of crack propagation in concrete, and the simulation results are closer to the real situation than the traditional finite element method.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Metal target transient electromagnetic scattering analysis method based on delay laguerre polynomials
InactiveCN104915465ALittle unknownSave memorySpecial data processing applicationsTransient electromagneticsReference Document
The invention discloses a metal target transient electromagnetic scattering analysis method based on delay laguerre polynomials. A target is subdivided through curved surface triangle surface elements. Spatial dispersion and time dispersion are carried out on a time domain mixed field integral equation through a CRWG primary function and the delay laguerre polynomials. A test is carried out through a galerkin method. An order-stepped matrix equation is finally formed, and the transient electromagnetic scattering characteristic of the target can be obtained through resolution of the equation and post-processing. As a delay item related to the spatial position of the target is introduced into a time primary function, the time primary function contains the spatial phase information of the target is adopted, and the target can be subdivided with less curved surface triangle surface elements. The unknown calculation amount is greatly reduced, consumption of an inner storage is effectively reduced, the calculation time is shortened, and important reference documents are provided for accurate analysis of the transient electromagnetic scattering characteristic of an electric large-size metal target.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Complex frequency domain calculation method for a converter transformer alternating current and direct current composite electric field
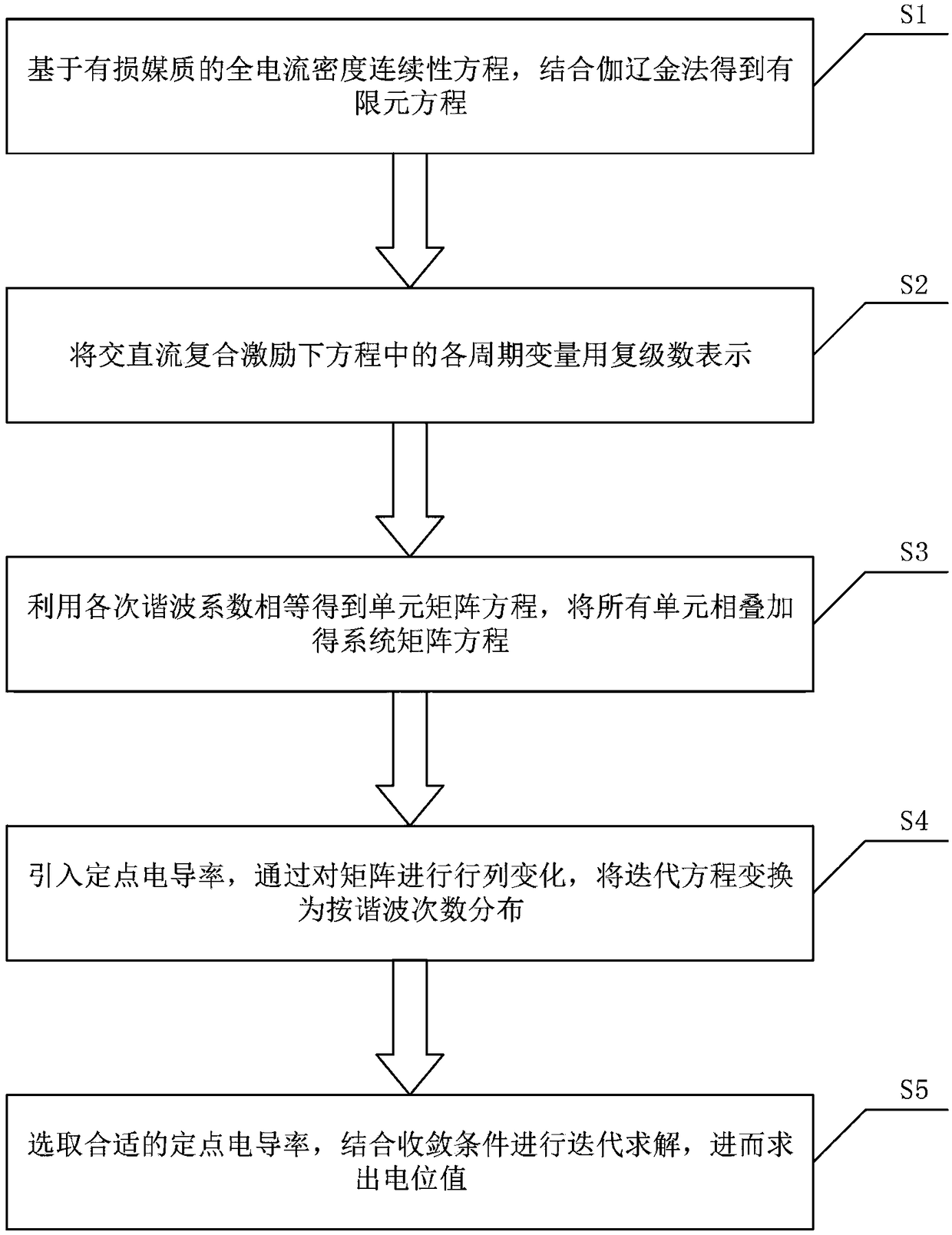
ActiveCN109492268AReduce repeat formationReduce storage memoryDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTransformerSystem matrix
The invention relates to a complex frequency domain calculation method for a converter transformer alternating current and direct current composite electric field, which comprises the following steps:obtaining a finite element equation by combining a Galerkin method based on a full current density continuity equation of a lossy medium; expressing each periodic variable in the equation under the AC / DC composite excitation by using a complex stage number; obtaining a unit matrix equation by using the equal harmonic coefficients, and superposing all the units to obtain a system matrix equation;introducing fixed-point conductivity, and converting an iterative equation into distribution according to harmonic frequency by performing row and column change on the matrix; and selecting fixed point conductivity, carrying out iterative solution according to a set convergence criterion, and carrying out convergence to obtain a potential value. According to the method, the finite element stiffness matrix of each iteration is decomposed according to the harmonic frequency by adopting a fixed-point method, so that the memory consumption of a harmonic balance algorithm is reduced, and the calculation cost for analyzing a nonlinear alternating-current and direct-current composite electric field can be effectively reduced.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
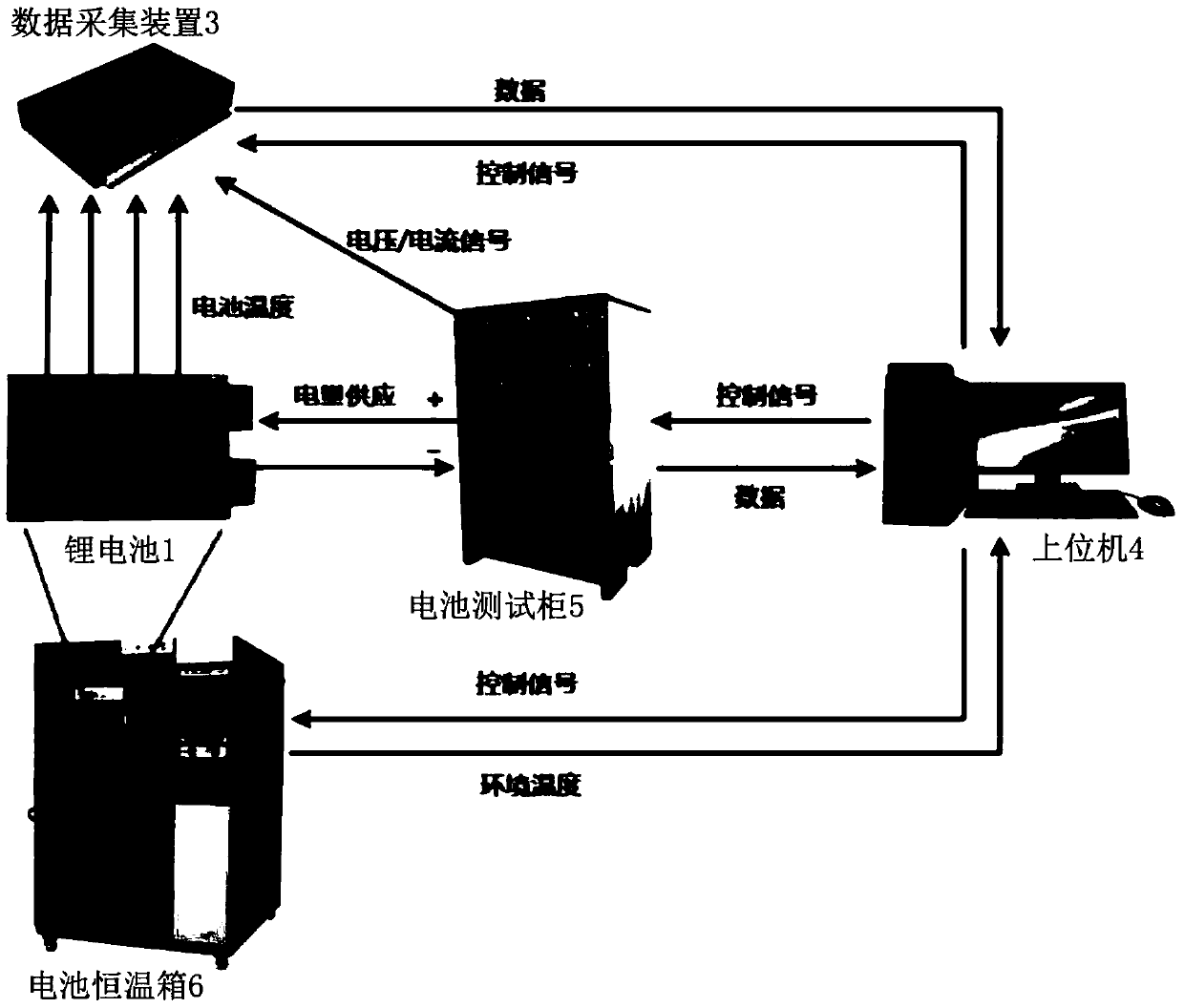
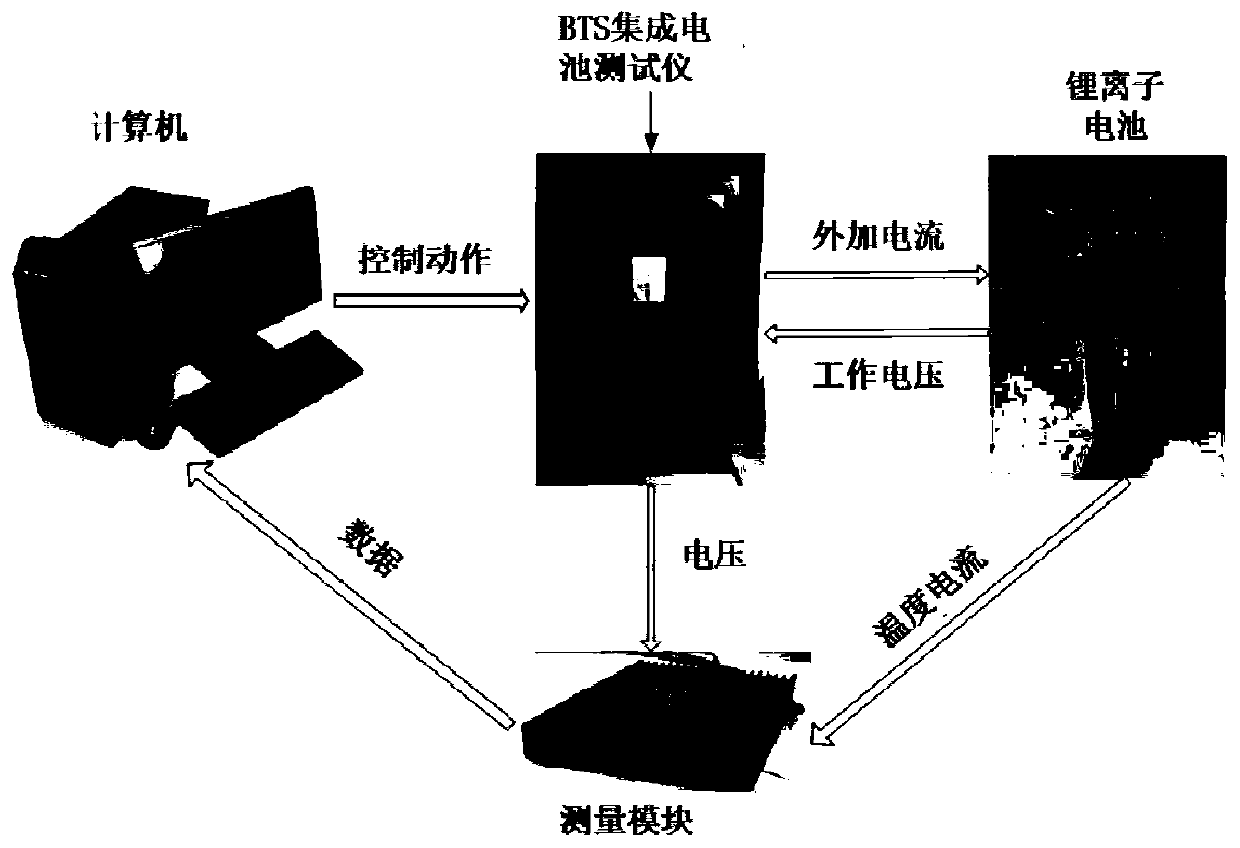
Lithium battery hot process space time modeling method based on dual-LS-SVM
InactiveCN108733943ACharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsDistributed parameter systemCoupling
The invention discloses a lithium battery hot process space time modeling method based on dual-LS-SVM. The method comprises the steps that S1, a lithium battery charge / discharge control platform is set up; S2, space time data of a lithium battery under a cyclic charge / discharge condition is obtained, wherein according to the space time data, temperature distribution changes along with time; S3, anupper computer learns a set of space primary functions representing space nonlinear characteristics, through utilization of a PCA algorithm (namely, a principal component analysis algorithm); S4, theupper computer decomposes an ordinary differential equation ai(t) into two nonlinear modules g(.) and h(.) through utilization of a Galerkin method; and S5, the upper computer carries out series connection on two least squares support vector machines (LS-SVMs) to form a dual-LS-SVM model, thereby approaching to the nonlinear modules g(.) and h(.). The method is used for online estimation of LIBs temperature distribution. The two least squares support vector machines (LS-SVMs) are connected in series to form the dual-LS-SVM model, thereby simulating a distributed parameter system comprising two inherent coupling nonlinearities. The method is relatively effective in the performance approximate aspect of the two inherent coupling nonlinearities. The model precision is high.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
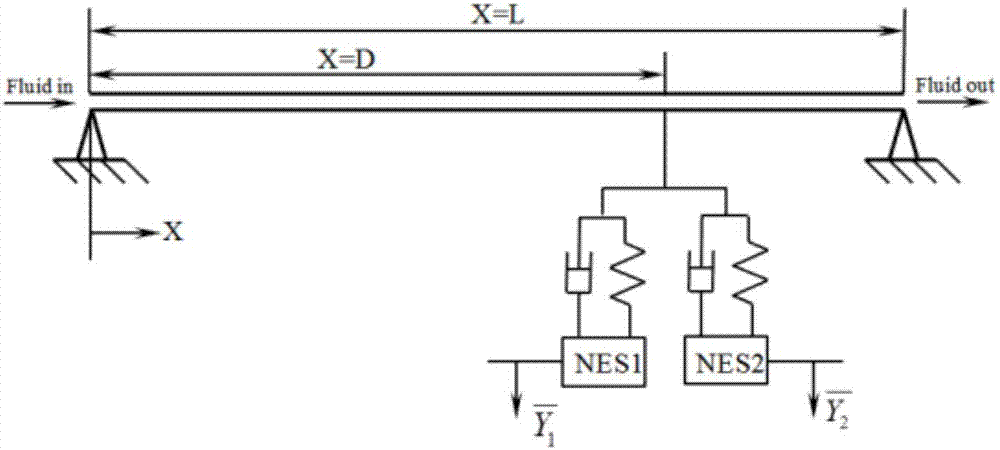
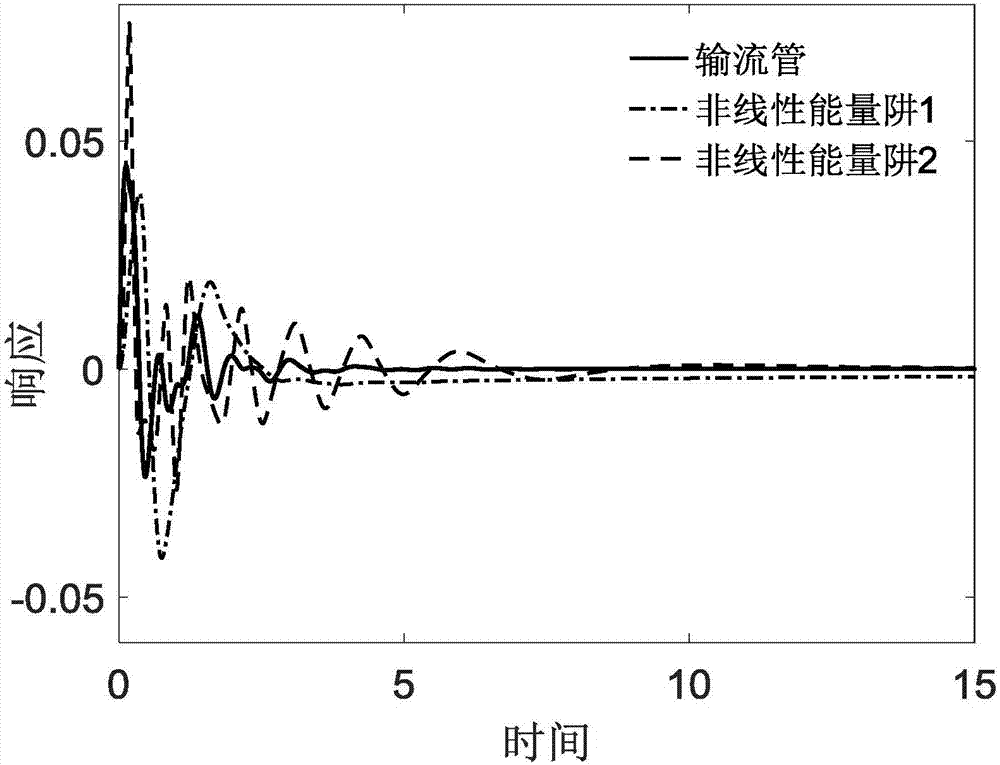
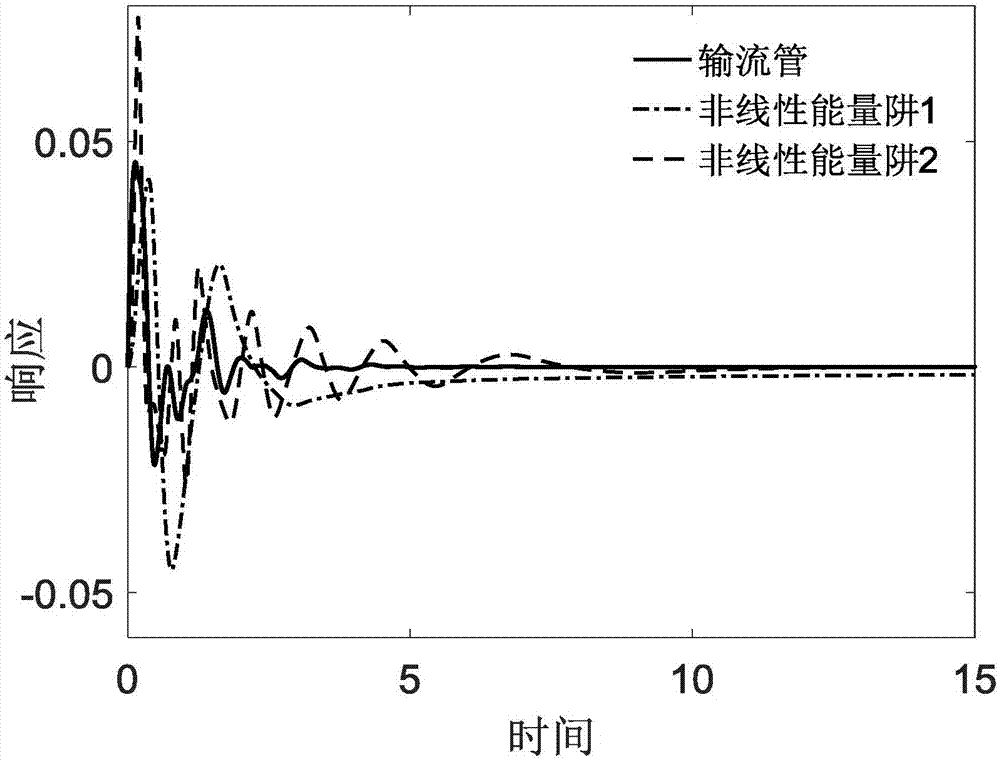
Method and device for designing and optimizing passive vibration controller for fluid conveying pipe vibration control
ActiveCN107169220ASimple structureLow reliabilityDesign optimisation/simulationMulti-objective optimisationEnergy transferVibration control
The invention discloses a method for designing and optimizing a passive vibration controller for fluid conveying pipe vibration control, and aims at solving the excessive vibration problem of fluid conveying pipes, providing the advantages of being free of external energy input and simple in installation operation, and breaking through the problem that the passive controller are relatively large in mass. The passive controller consists of parallel nonlinear energy traps; in order to verify the vibration control effect of the vibration controller, a mathematic model of a fluid conveying pipe-vibration controller system is established on the basis of a target energy transfer theory; and after dimension reduction and discretization are carried out on a dimensionless model through a standard Galerkin method, numerical simulation of the system is completed under a boundary condition of the system. Results indicate that the vibration controller is capable of rapidly and effectively dissipating the vibration energy of the fluid conveying pipes via a mass which is 5% of the mass of the whole system. Finally, the control is optimized through a ratio function of the energy dissipated by the controller and the total energy of the system; and the optimization result indicates that the precision requirement for mounting positions is not high in a certain range.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
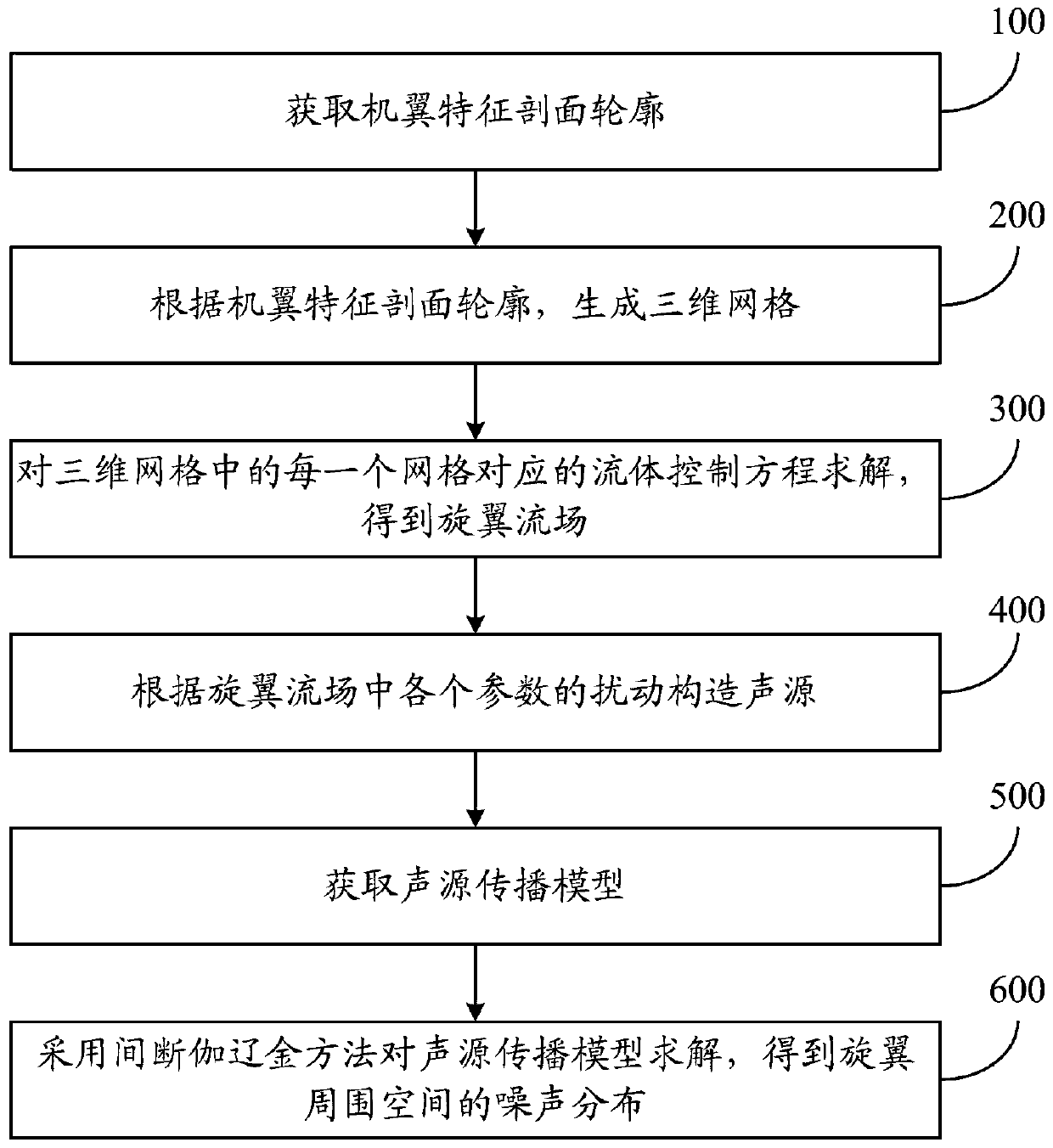
Rotor noise determination method and system
PendingCN111563299AImprove calculation accuracyGeometric CADSustainable transportationSound sourcesNoise
The invention relates to a rotor noise determination method and system. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a rotor characteristic profile contour; generating a three-dimensional gridaccording to the rotor characteristic profile contour, wherein the rotor three-dimensional grid comprises a rotor three-dimensional airfoil grid and a background grid; solving the fluid control equation corresponding to each grid in the three-dimensional grids to obtain a rotor flow field, wherein the rotor flow field comprises the pressure around the rotor, the fluid density, the speed of the fluid in the x direction, the speed of the fluid in the y direction and the speed of the fluid in the z direction, and the x direction, the y direction and the z direction are perpendicular to one another; constructing a sound source according to the disturbance of each parameter in the rotor flow field; acquiring a sound source propagation model, wherein the sound source propagation model is a linear Euler equation; and solving the sound source propagation model by adopting an intermittent Galerkin method to obtain the noise distribution of the space around the rotor. According to the invention,the calculation accuracy of the rotor noise can be improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Compressible gas and incompressible liquid multimedia interface tracking numerical method
ActiveCN105653860AExact Interface Boundary ConditionsHigh precisionInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsShock waveDiscretization
The present invention discloses a compressible gas and incompressible liquid multimedia interface tracking numerical method. Single gas and fluid medium regions both adopt discontinuity galerkin method for calculation, and due to non-uniformity variation of time step length of a multimedia flow field, the method disclosed by the present invention induces a time discretization format based non-uniformity time step length when solving an incompressible Navier-Stokers equation by adopting the discontinuity galerkin method. A multimedia interface boundary condition is defined by adopting a modified virtual fluid method. A new compressible and incompressible riemann problem is constructed in a normal direction in a stuff interface to predict an interface state, and the predicted interface state is not only used for pushing a multimedia interface, but also can directly update a density on one side of compressible gas near the interface and obtain a corresponding virtual fluid state by extrapolation. By verification of multiple classic numerical calculation examples, it is found that the method is capable of obtaining a more accurate numerical simulation result for a multimedia problem of shock-waves appearing in gas.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Improved exponential time integral constructing method in complicated dispersive medium
ActiveCN107992696AImprove Simulation EfficiencyReduce computational efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingEuclidean vectorTime integral
The invention discloses an improved exponential time integral constructing method in a complicated dispersive medium, and is applied to the field of three-dimensional electromagnetic analysis numerical values. The improved exponential time integral constructing method in the complicated dispersive medium comprises the following steps: carrying out three-dimensional molding on a to-be-analyzed multi-scale target which comprises the complicated dispersive medium, and establishing a corresponding geometry structure model; splitting the established geometry structure model by using a tetrahedral mesh; separately integrating all local field components into respective corresponding global unknown quantities to construct a global semi-discrete format at first; and then integrating electric fieldand magnetic field components into an unknown quantity to obtain an ordinary differential equation, namely an electric field and magnetic field updating equation. Therefore, updating of electric fields and magnetic fields only needs vector manipulation, the circumstance that matrix exponentials are introduced to implement updating by a traditional exponential time integral method is avoided, to-be-solved matrix exponent dimensionality is reduced remarkably, the matrix exponent calculating efficiency is reduced effectively, and therefore, the simulating efficiency based on a time domain discontinuous Galerkin method of the exponential time integral method is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Length proportion design method of soft and hard pipe spliced pipeline
ActiveCN107688703AReduce parametric resonanceReduce or even avoid parametric resonance phenomenonGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationResonanceDynamic models
The invention provides a length proportion design method of soft and hard pipe spliced pipeline, and relates to the technical field of dynamics stability analysis. The design method includes the steps: building a dynamics differential equation of a soft pipe and a dynamics differential equation of a hard pipe based on a dynamics model of the soft and hard pipe spliced pipeline; performing space discretization on the dynamics differential equations by an improved Galerkin method to obtain corresponding matrix equations, and assembling the matrix equations into a target equation of a unified time and space coordinate system; converting the target equation into a periodic coefficient linear ordinary differential state equation, and introducing monodromy matrixes into the periodic coefficientlinear ordinary differential state equation to obtain characteristic values of a plurality of monodromy matrixes; taking the characteristic values of the monodromy matrixes as Floquet characteristic multipliers, and determining the length proportion of the soft pipe to the hard pipe when any Floquet characteristic multiplier reaches a critical threshold value. The method can reduce and avoid parameter resonance of the soft and hard pipe spliced pipeline.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
A three-dimensional hybrid time-domain discontinuous Galerkin numerical method for time-domain electromagnetism
ActiveCN109190169ASpeed up the solutionImprove computing powerDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsLinear matrixTime domain electromagnetics
The invention belongs to the technical field of three-dimensional time-domain electromagnetics numerical solution, and relates to a three-dimensional time-domain electromagnetics hybrid time-domain discontinuous Galerkin numerical method based on a high-order stack basis function. The method introduces the hybrid discontinuous Galerkin method in the frequency domain into the time domain and formsa fully discrete form in a simpler way to improve the computational performance. High-order interpolation stack basis functions are constructed to obtain high-precision numerical simulation results, and then p-type multigrid preprocessing is constructed to accelerate the solution of global linear matrix, so as to improve the computational performance. When the invention solves the unstructured local refinement mesh, the computational performance is improved on the premise of ensuring the high-order precision.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
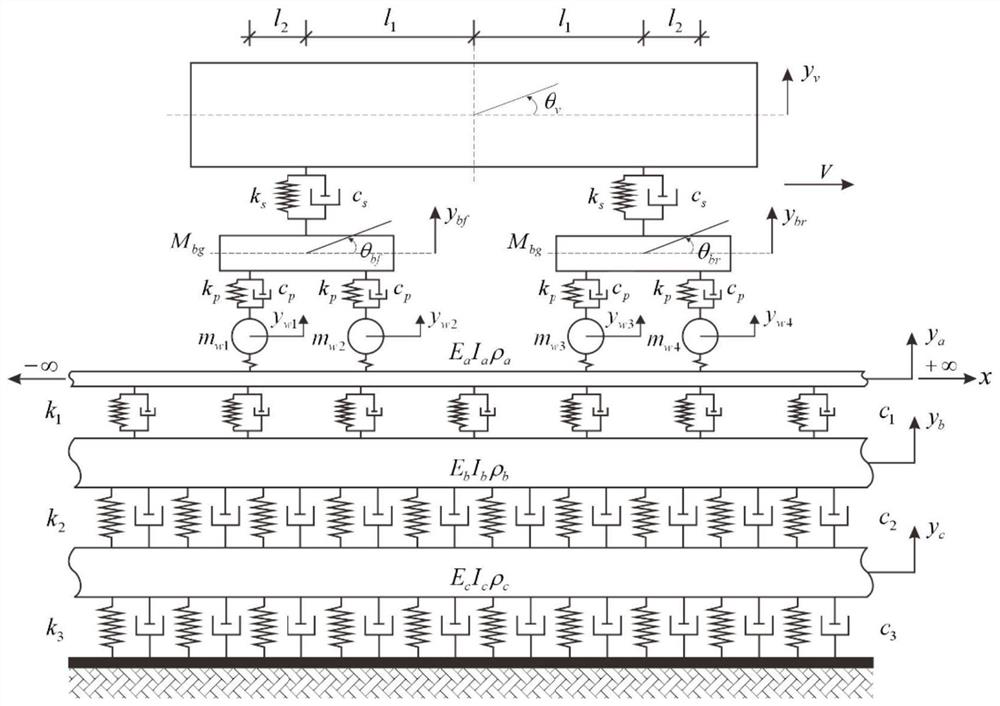
Novel moving unit method for analyzing coupling vibration of ballastless track of high-speed railway
ActiveCN111695200AExtended service lifeImprove operational safetyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationNonlinear modelEngineering
The invention discloses a novel moving unit method for analyzing coupling vibration of a ballastless track of a high-speed railway. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a three-layerTimoshenko beam vibration equation considering discrete track cushion blocks, transforming a control equation by introducing moving coordinates moving along with a vehicle, and establishing a mass, rigidity and damping matrix of a track by adopting a Galerkin method; adopting a nonlinear Hertz model to couple an orbit MEM unit and a 10-degree-of-freedom vehicle multi-body dynamic model, and finally, adopting a Newton-Raphson iteration method and a Newmark integral method to solve. By calculating the dynamic response of the track under the moving load, the actual use conditions or damage conditions of the track under different use environments are obtained, and relative design or renovation is performed, so that the service life is prolonged, the operation safety is improved, and the use cost is reduced. Compared with other analysis methods, the method can greatly improve the calculation efficiency, is more realistic, and is accurate and effective.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Method for obtaining electromagnetic property of any chromatic dispersion material based on generalized coordinate system
InactiveCN108021533ASolve dispersionHigh precisionComplex mathematical operationsMaxwell's equationsElectromagnetic field
The invention discloses a method for obtaining the electromagnetic property of any chromatic dispersion material based on a generalized coordinate system. The method is applied in the field of three-dimensional electromagnetic field numerical value obtaining. By establishing the link between a generalized chromatic dispersion model and a traditional chromatic dispersion model, a corresponding coefficient is selected according to the material property of a target device, a specific chromatic dispersion model is obtained, and therefore a Maxwell equation set satisfied by the chromatic dispersionmaterial is deduced; spatial discretization is conducted on a Maxwell equation weak form through an intermittent galerkin method to form a semi-discrete form, and time discretization is conducted through a leapfrog time format to obtain a full-discrete format; due to the high dependency of units in the method, the same target device can be divided through different grids, it is ensured that parallel computing can be applied, and the chromatic dispersion problem of a multi-dimensional device can be solved at high precision, high speed and low computing cost, and the universality of the methodis increased by deducing the full-discrete format under the generalized coordinate system.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
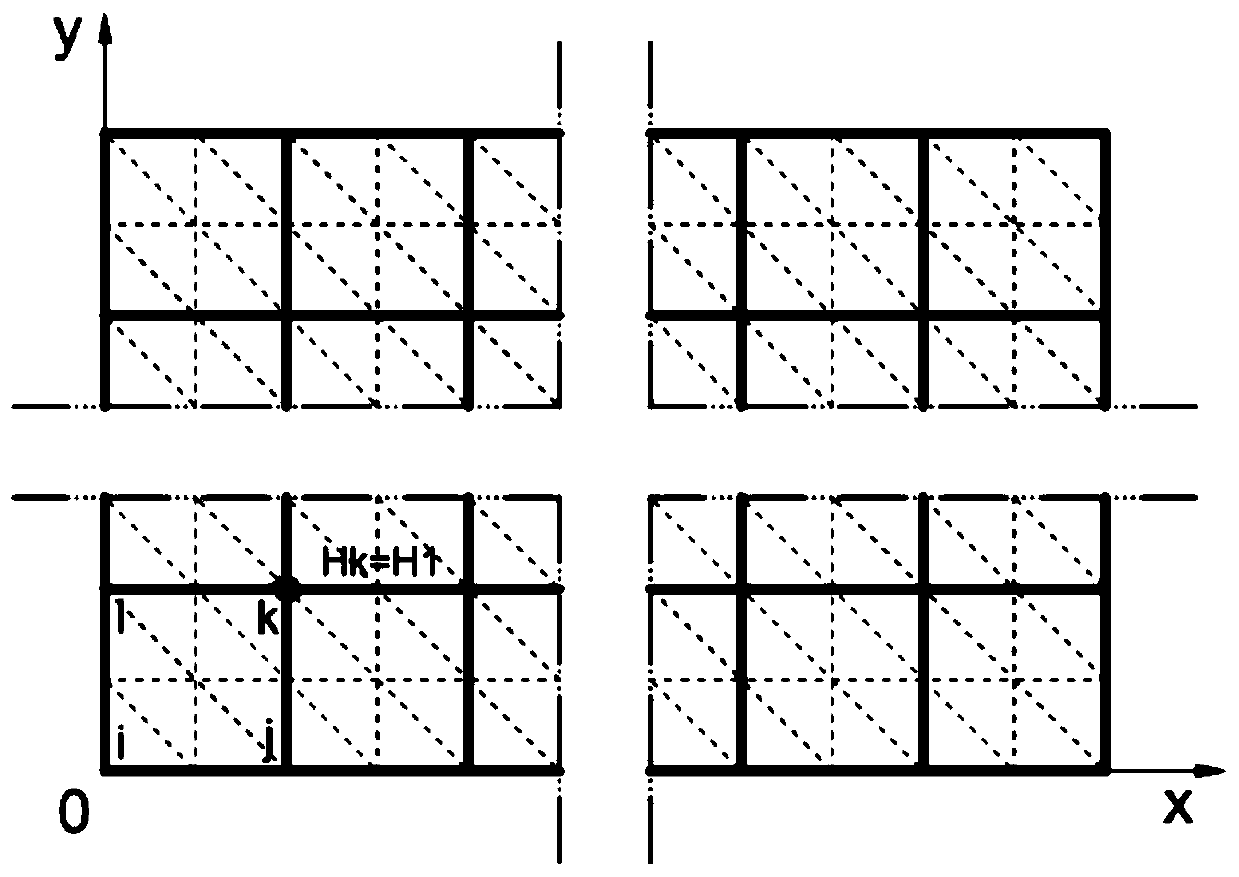
Double-grid multi-scale finite element method for simulating node Darcy permeation flow velocity
PendingCN111507026AGuaranteed continuityImprove computing efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationCoarse meshEngineering
The invention discloses a double-grid multi-scale finite element method for simulating node Darcy seepage velocity, which comprises the following steps of: dividing a research area into coarse grid units, and dividing the coarse grid units into fine grid units; obtaining a variation form of the solved problem by using a Galerkin method; constructing a primary function on each coarse mesh unit; solving a variational form by using a primary function to obtain a total stiffness matrix; obtaining an equation set of the water head according to the source confluence item and the boundary condition of the research area; solving by using an effective numerical method to obtain a water head value of each node in the research area; translating the grid of the research area for a very small distancealong the direction or the reverse direction of the obtained Darcy permeation flow velocity to obtain a translated grid; carrying out the water head solving step on the horizontally-moved grid again,and obtaininga water head; obtaining a continuous water head first-order derivative according to the water head difference and the displacement difference of each point before and after translation, and obtaining a continuous and accurate Darcy permeation flow velocity; and directly obtainingthe Darcy permeation flow velocity of a fine-scale node by applying interpolation.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV +1
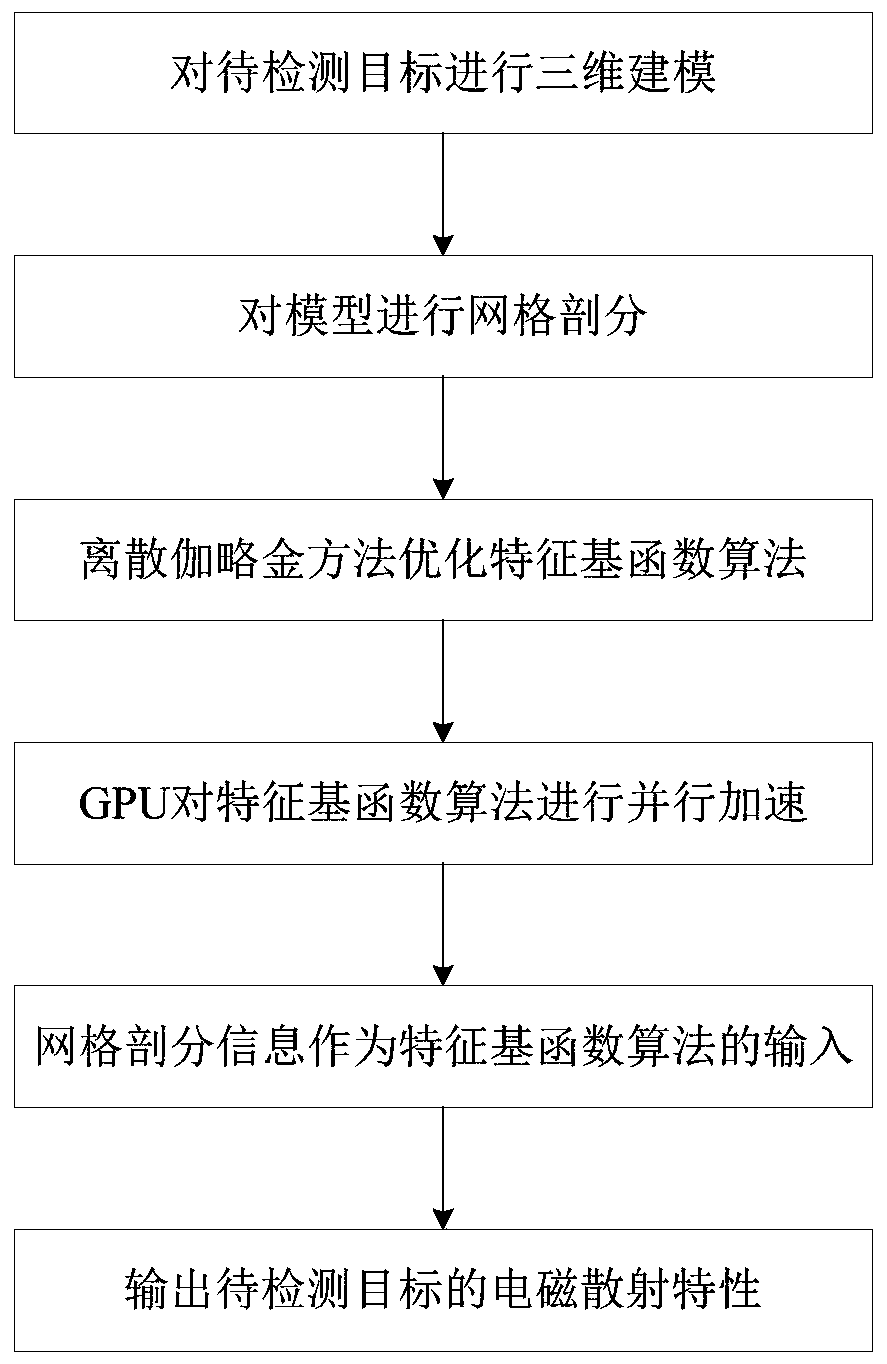
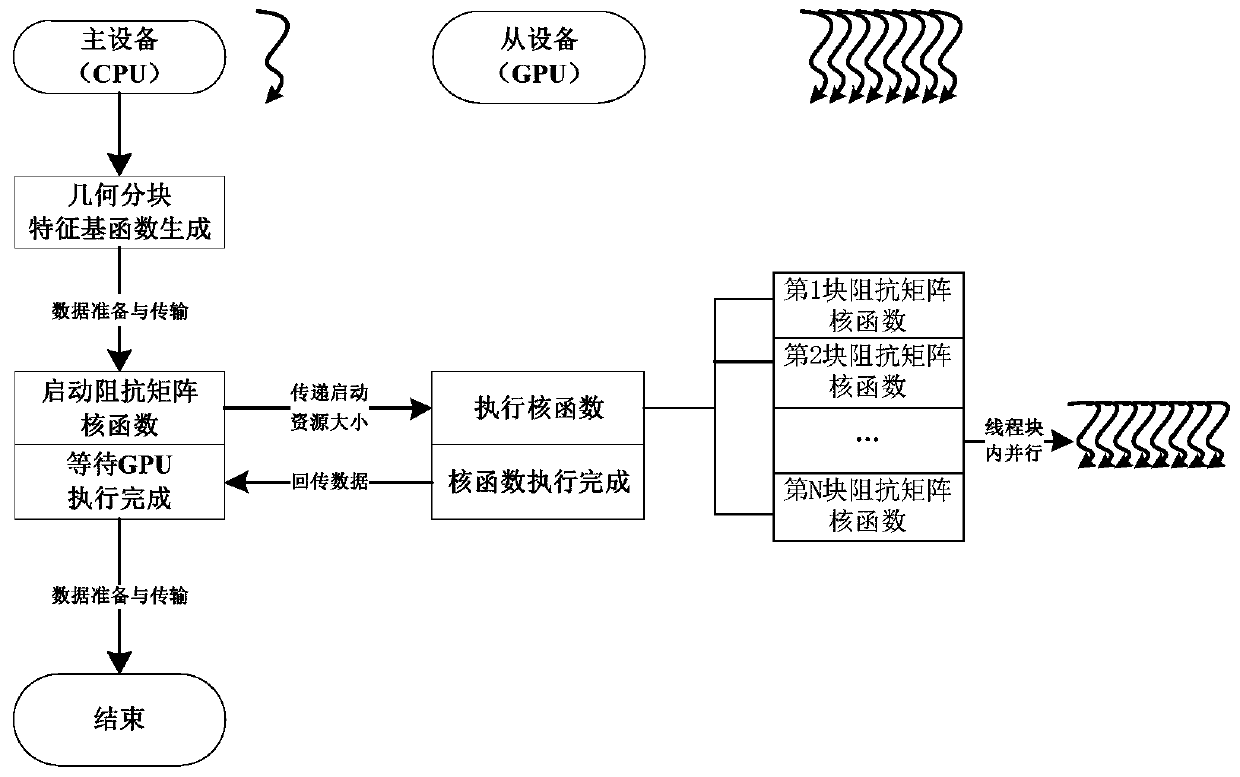
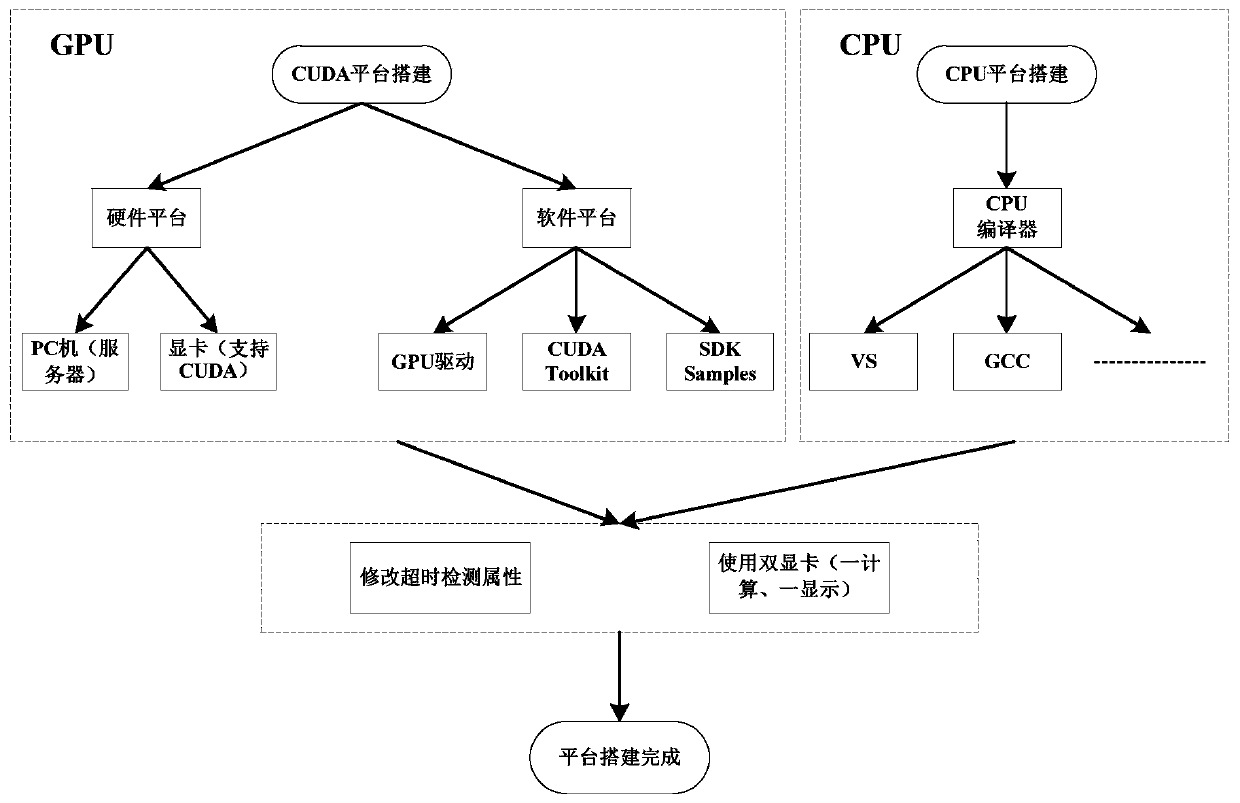
Electromagnetic scattering characteristic analysis method for parallel acceleration of characteristic basis function algorithm based on GPU
InactiveCN111046603AGood eigenbasis functionImprove accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationAlgorithmGrid based
The invention discloses an electromagnetic scattering characteristic analysis method for parallel acceleration of a characteristic basis function algorithm based on a GPU. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out three-dimensional modeling on a to-be-detected target; carrying out mesh generation on the model of the to-be-detected target based on an RWG basis function; optimizing thecharacteristic basis function algorithm by using a discrete Galerkin method based on the mesh generation information; carrying out parallel acceleration on the characteristic basis function algorithmby utilizing the GPU; and taking the mesh generation information as the input of the characteristic basis function algorithm after parallel acceleration, and outputting electromagnetic scattering characteristics of the to-be-detected target. According to the method, the discrete Galerkin method is used for optimizing the characteristic basis function algorithm, and the GPU is used for carrying outparallel acceleration on the characteristic basis function algorithm, so that the electromagnetic scattering problem in the separation process of the electrically large-size target and the complex target can be solved, and calculation has high accuracy and high efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for decoupling matrix index time of index time integral method in complicated dispersive medium
ActiveCN107908903AAvoid calculationReduce the number of calculationsDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsTime domainTime integral
The invention discloses a method for decoupling matrix index time of an index time integral method in a complicated dispersive medium. The method comprises the following steps of: deducing a local semi-discrete format by adoption of a time domain discontinuous Galerkin method, and constructing an index time integral format; carrying out time discretion on the index time integral format by adoptionof a high-order low-storage Runge-Kutta time format so as to obtain a hybrid Runge-Kutta-index time format; constructing an index form vector and combining a matrix index item to process the hybrid Runge-Kutta-index time format; and constructing a decoupling vector to decouple the hybrid Runge-Kutta-index time format so as to obtain a matrix time-based decoupled hybrid Runge-Kutta-index time format. According to the method, the matrix index item and the time are decoupled, so that the condition of calculating the same matrix index in iteration at each time can be avoided, the calculation frequency of the matrix index can be greatly decreased, and the simulative analysis time of multi-scale complicated dispersive medium problems can be remarkably shortened.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Dynamic p adaptive DG-FETD method based on laminated vector basis function
ActiveCN110580365ARealize dynamic adaptationImprove computing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsTime domainDiscretization
The invention discloses a dynamic p-adaptive DG-FETD method based on a laminated vector basis function, and the method comprises the steps: building a solving model, carrying out the discretization ofthe model through a tetrahedral mesh, and obtaining the structural information of the model; simulation parameters are set, and reading structure information of the model; testing two sides of the first-order Maxwell rotation equation equation by adopting a Galerkin method, and expanding by using a primary function to obtain a final iterative formula; performing time iteration through an iterative formula of a leapfrog differential format time domain finite element, calculating a space field value fluctuation parameter when each time step iteration begins, and adjusting a primary function order; and obtaining an electric field value and a magnetic field value in the space after iteration of all time steps is finished. According to the method, mixing of high-order and low-order primary functions in the discontinuous Galerkin time domain finite element method is achieved, the function that the primary functions in different discrete regions select proper orders by themselves is achieved, the simulation calculation time of the time domain finite element method is effectively saved under the condition that the precision is guaranteed, and the method has very high practical engineeringapplication value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Photo-thermal effect simulation method for a surface plasmon waveguide
ActiveCN109492341AImprove simulation accuracyImprove Simulation EfficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsWave equationField analysis
The invention discloses a photo-thermal effect simulation method for a surface plasmon waveguide. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, determining an edge value problem of a light fieldpart based on an electric field vector wave equation and an electromagnetic boundary condition, discretizing a light field analysis area by adopting tetrahedral vector edge elements, establishing a light field finite element matrix equation according to a Galerkin method, and solving to obtain electric field distribution of a three-dimensional surface plasmon waveguide; then, heat generated by anelectric field is used as a heat source; determining an edge value problem of a thermal field part based on a transient heat conduction equation and a thermal boundary condition; a tetrahedral scalarnode element is adopted to discretize a thermal field analysis area, an unconditionally stable backward difference format is adopted to discretize a time domain, a thermal field finite element matrixequation of each time step is established according to a Galerkin method, and transient temperature distribution of the three-dimensional surface plasmon waveguide is obtained through solving. The method has the advantages of being high in simulation precision, wide in application range and high in solving efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Novel multi-scale finite element method for simultaneously simulating underground water flow and Darcy speed
ActiveCN112347678ASolve accurately and efficientlyGuaranteed continuityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCoarse meshMatrix solution
The invention discloses a novel multi-scale finite element method for simultaneously simulating underground water flow and Darcy speed, which comprises the following steps of: setting scales of coarseand fine grid units, dividing a research area into the coarse grid units, and dividing the coarse grid units into the fine grid units to obtain a multi-scale grid; solving a degraded elliptic equation on the coarse mesh unit, and constructing a primary function; solving a Darcy equation and a speed matrix on the coarse mesh unit; obtaining a variation form of the problem by using a Galerkin method and a Green formula, and dispersing the variation form to the coarse mesh; substituting the Darcy law into variational components on each coarse mesh, converting a water head partial derivative terminto a speed term, linearly expressing the Darcy speed term by applying a coarse-scale solution of a water head by applying a speed matrix to obtain a unit stiffness matrix of the coarse mesh, and adding to obtain a total equation of the water head; and solving a total equation by using an effective matrix solution, and meanwhile, obtaining a Darcy speed value through a speed matrix. Compared with various classic methods, the novel multi-scale finite element method has higher efficiency.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
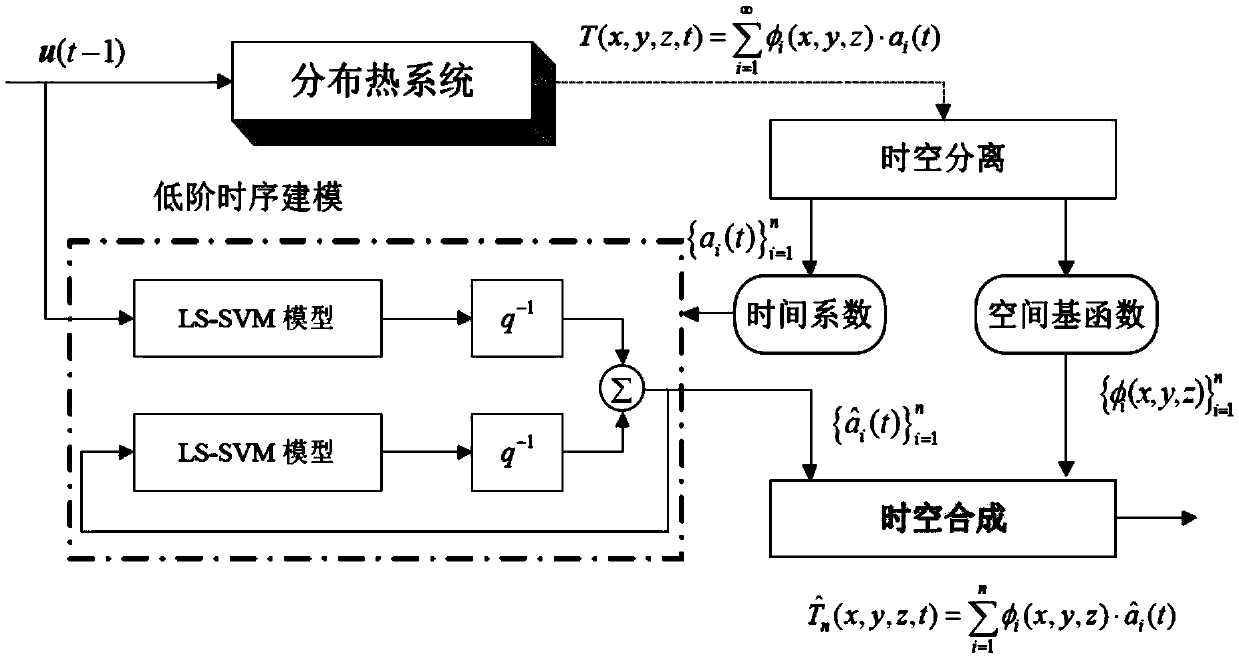
Lithium ion battery thermal process space-time modeling method based on dual-scale manifold learning
The invention provides a lithium ion battery thermal process space-time modeling method based on dual-scale manifold learning, which comprises the following steps: constructing a group of nonlinear space basis functions for time / space separation according to a manifold learning method; truncating the nonlinear space basis function by adopting a Galerkin method to obtain a time model based on physics; carrying out evaluation learning on unknown model structures and parameters existing in the time model by utilizing an extreme learning machine; and reconstructing an LIBs space-time model by using a space-time synthesis method based on the nonlinear space basis function and the time model. According to the lithium ion battery thermal process space-time modeling method based on dual-scale manifold learning provided by the invention, local and global nonlinear manifold structure information is considered at the same time through a BFs learning method, so that the method is superior to a modeling method based on local linear embedding (LLE) and isometric mapping (ISOMAP); and the method is suitable for space-time dynamic modeling of a distributed parameter system DPS.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
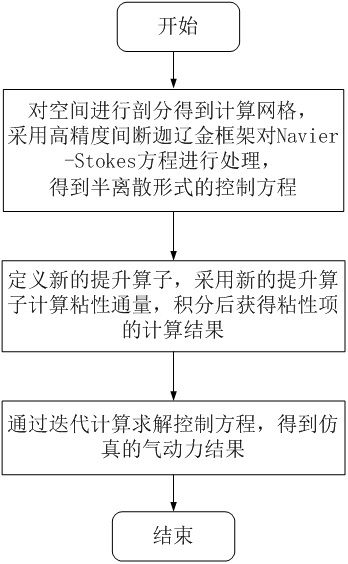
Viscous item processing method applied to high-precision discontinuous Galerkin fluid simulation
ActiveCN113591417AReduce calculationSimple calculationSustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a viscous item processing method applied to high-precision discontinuous Galerkin fluid simulation, which is used for solving the problem that the calculation precision is lower than the theoretical precision when a Navier-Stokes equation is calculated by a Galerkin method, so as to accurately capture information such as lift force, resistance, speed, density, pressure and the like for engineering application in a flow field. The method comprises the following steps: subdividing a space to obtain a computational grid, and processing a Navier-Stokes equation by adopting a high-precision discontinuous Galerkin framework to obtain a control equation in a semi-discrete form; defining a new lifting operator, calculating the viscosity flux by the new lifting operator to acquire a calculation result of the viscosity item after integration; and solving and calculating the equation by adopting an iteration mode to obtain a simulation result. Calculation precision of a high-order format is effectively kept while the calculation amount is saved, and the calculation precision is higher than the theoretical precision.
Owner:CALCULATION AERODYNAMICS INST CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com