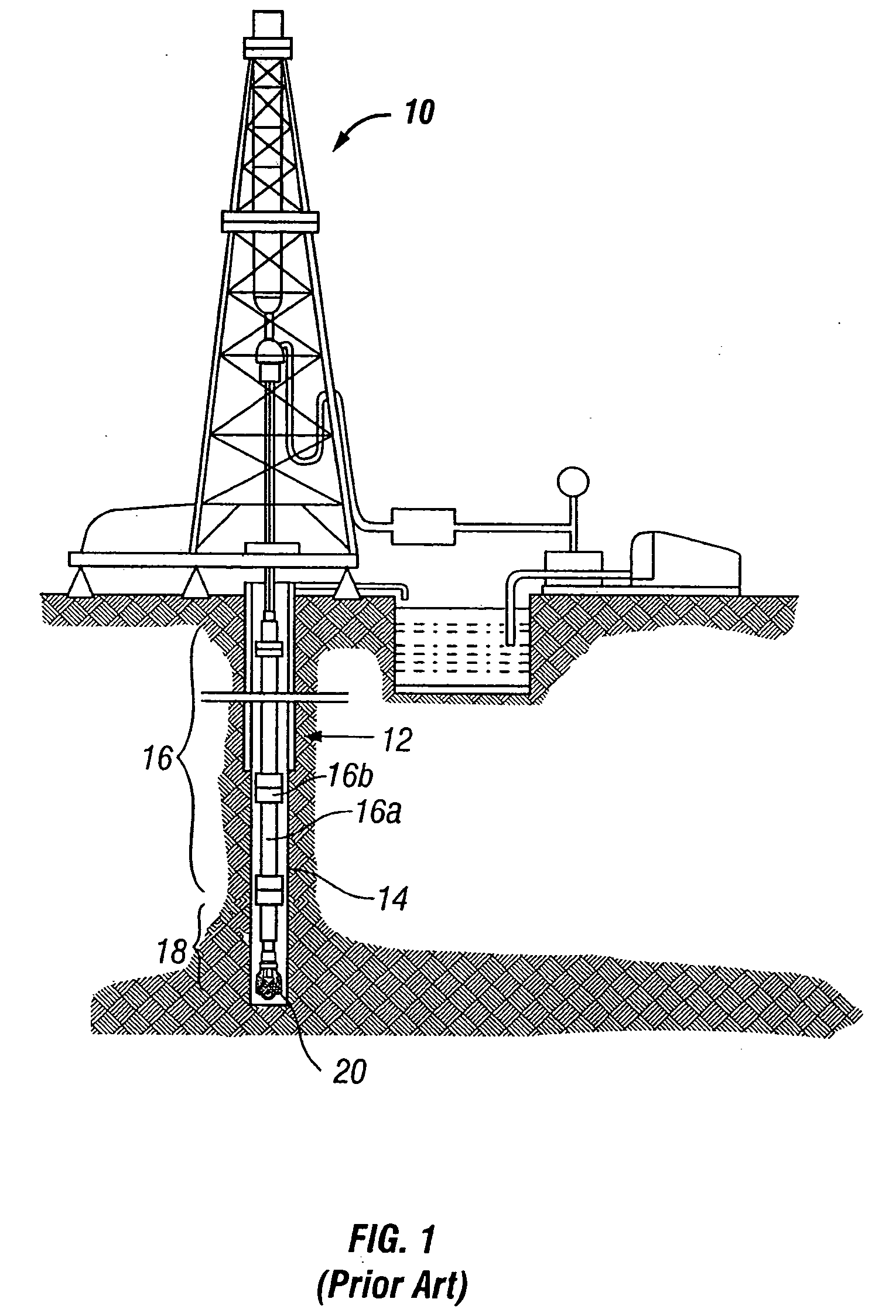
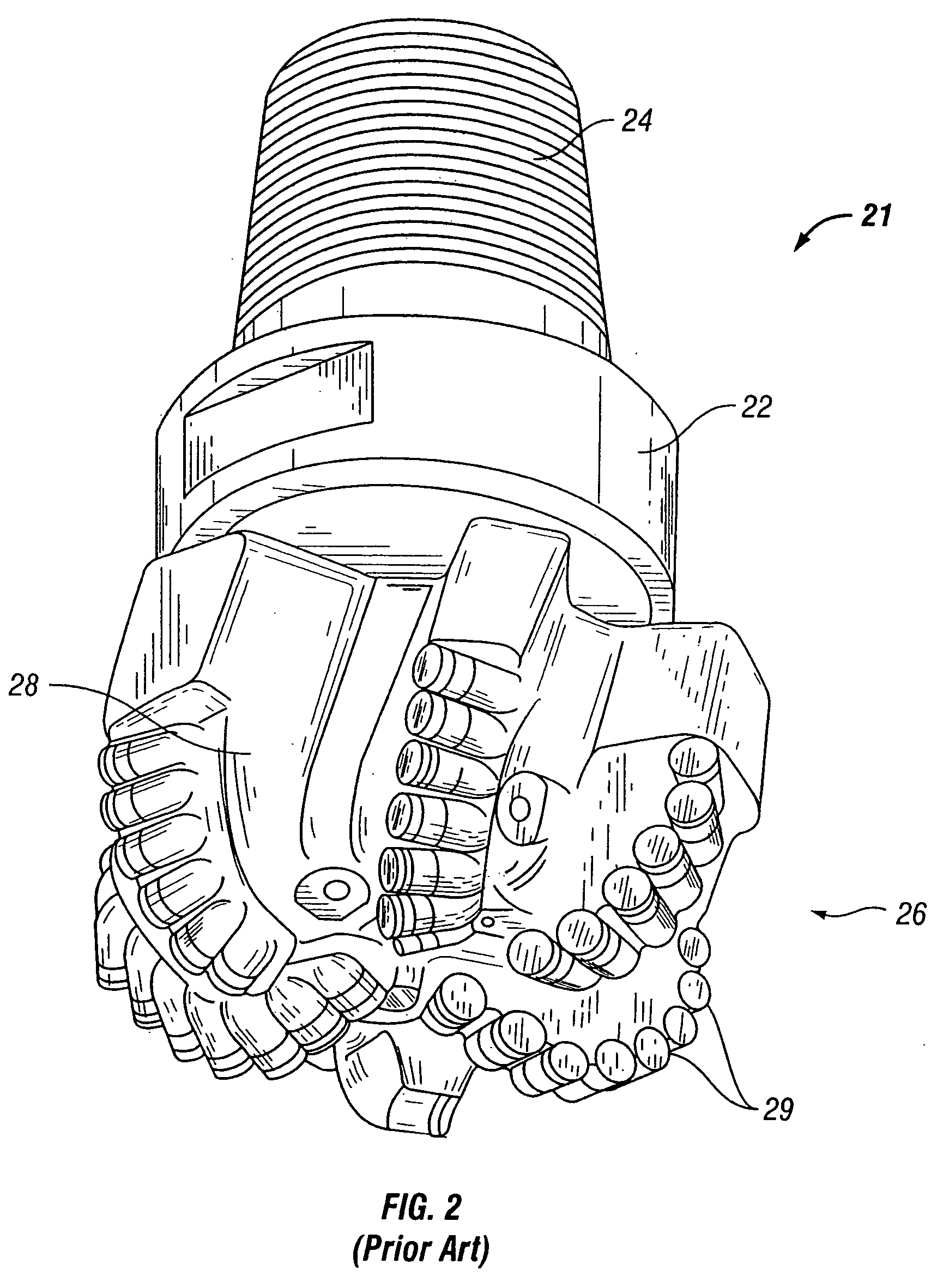
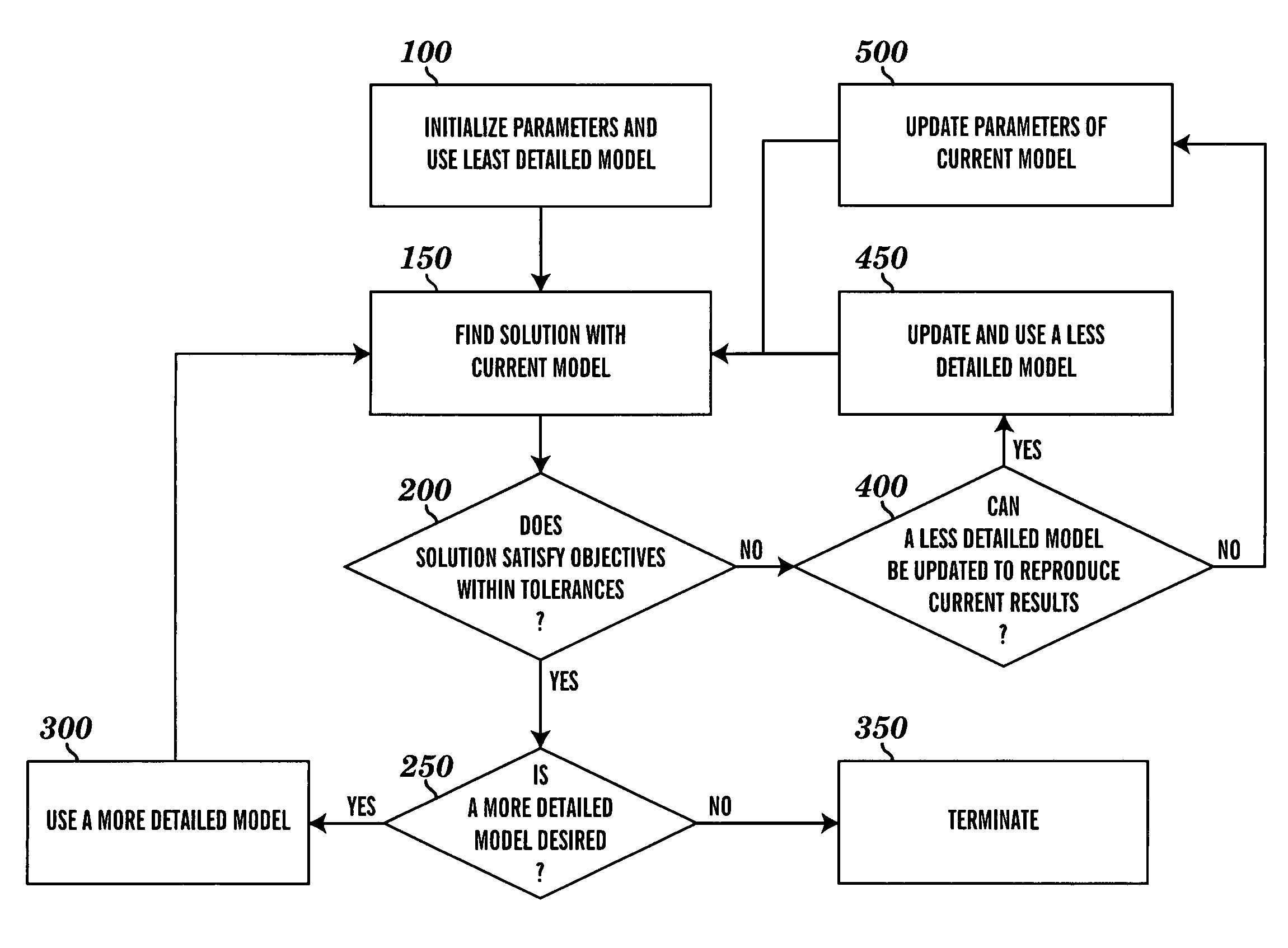
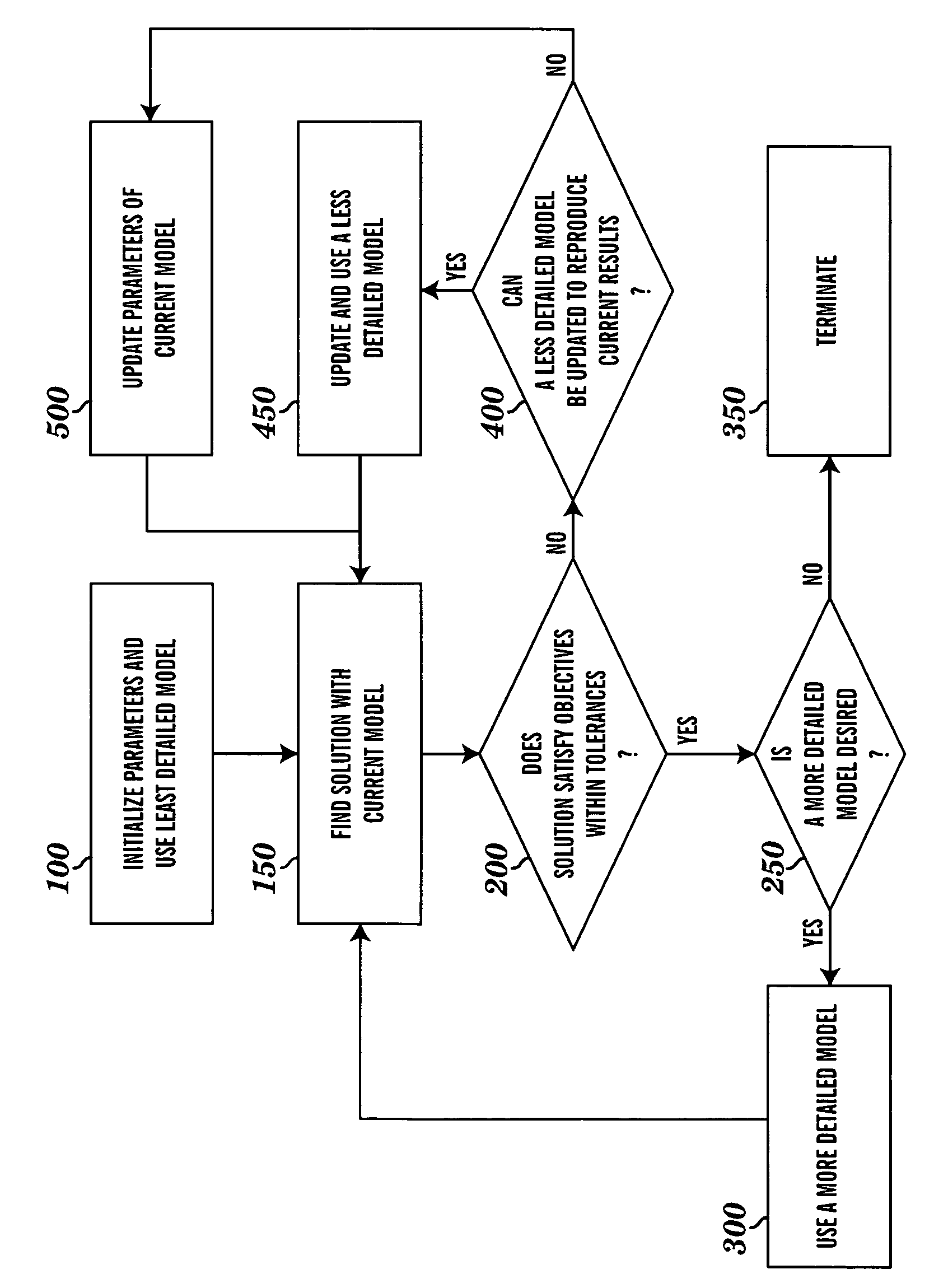
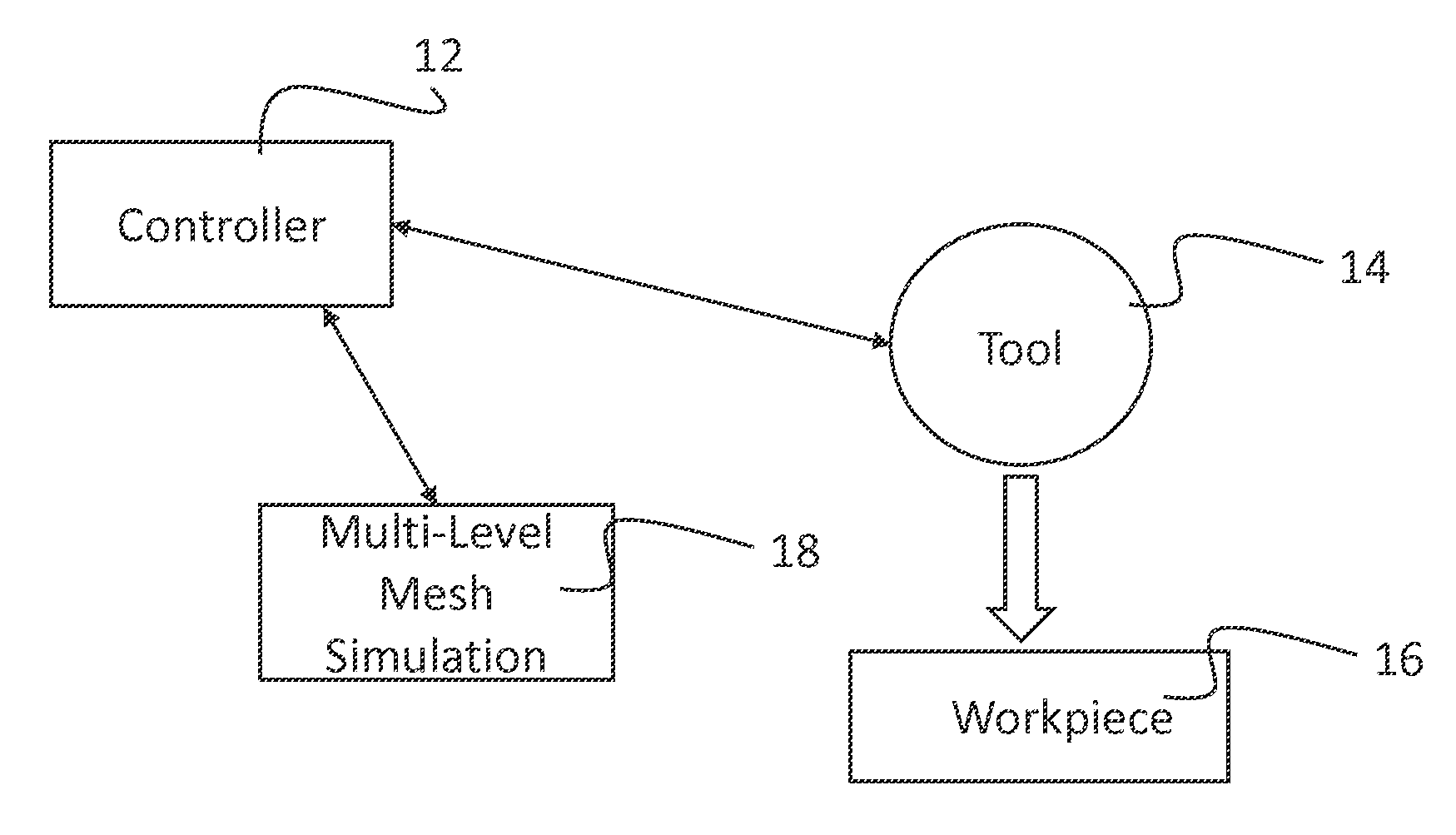
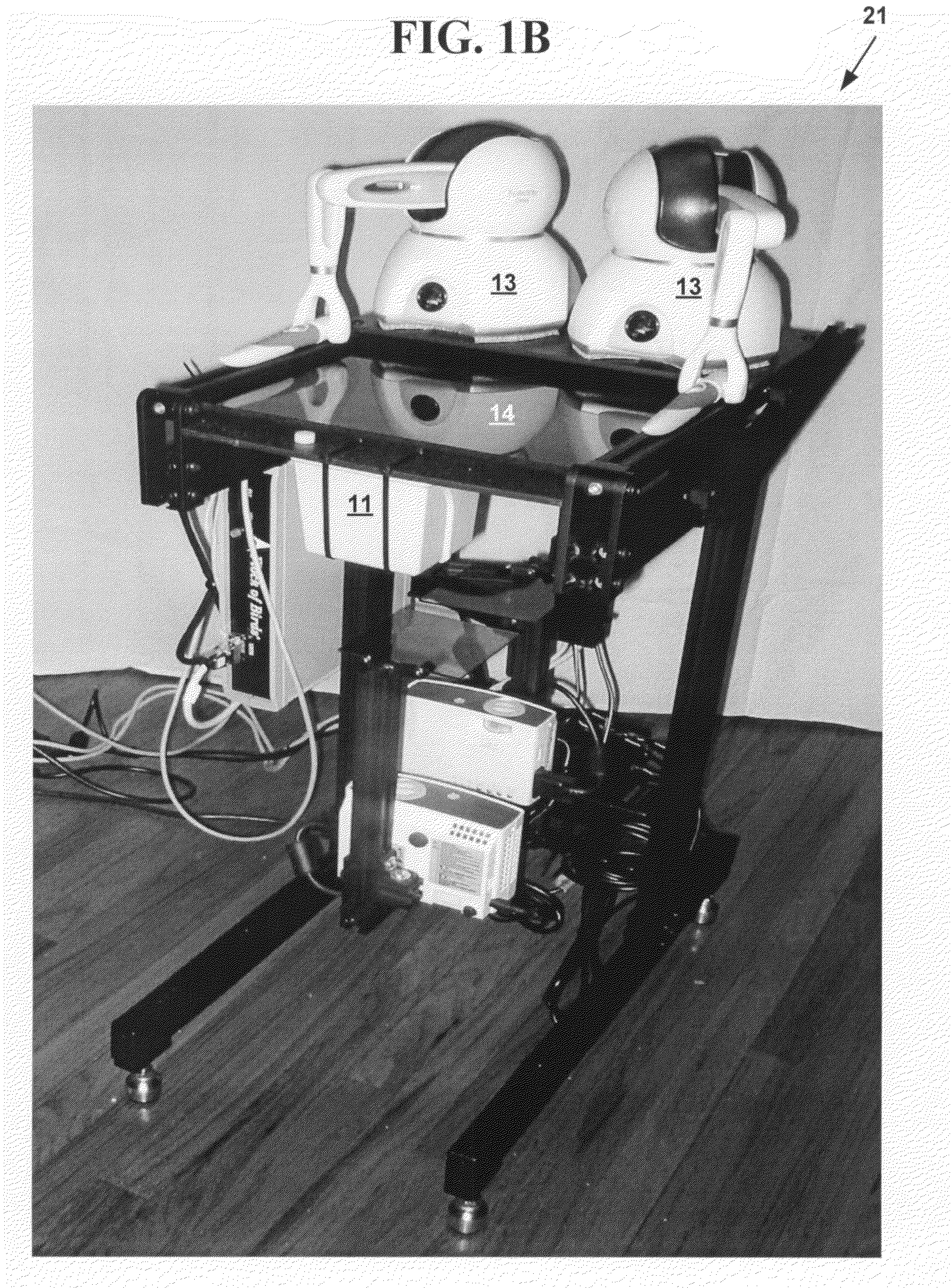Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
10284results about "CAD numerical modelling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
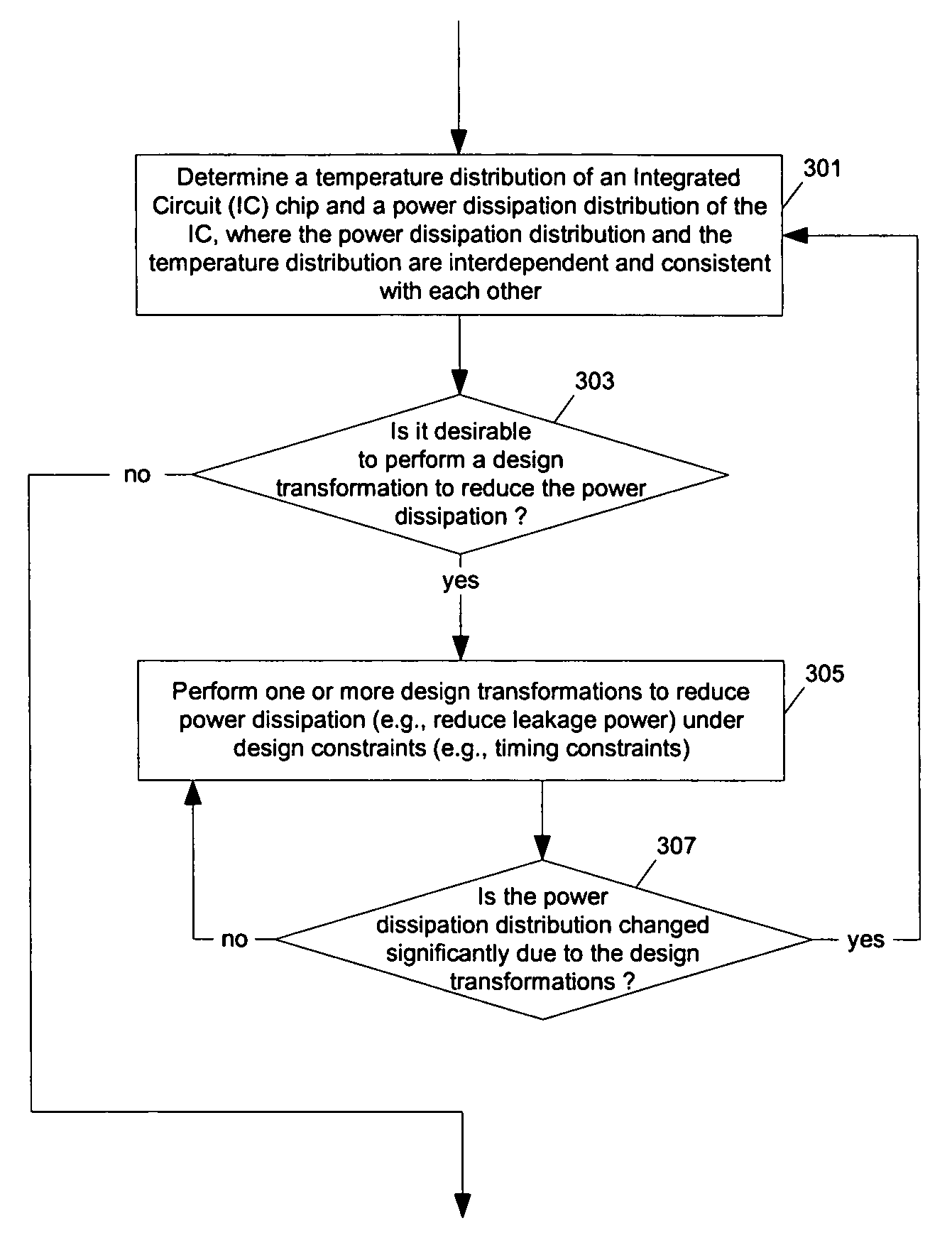
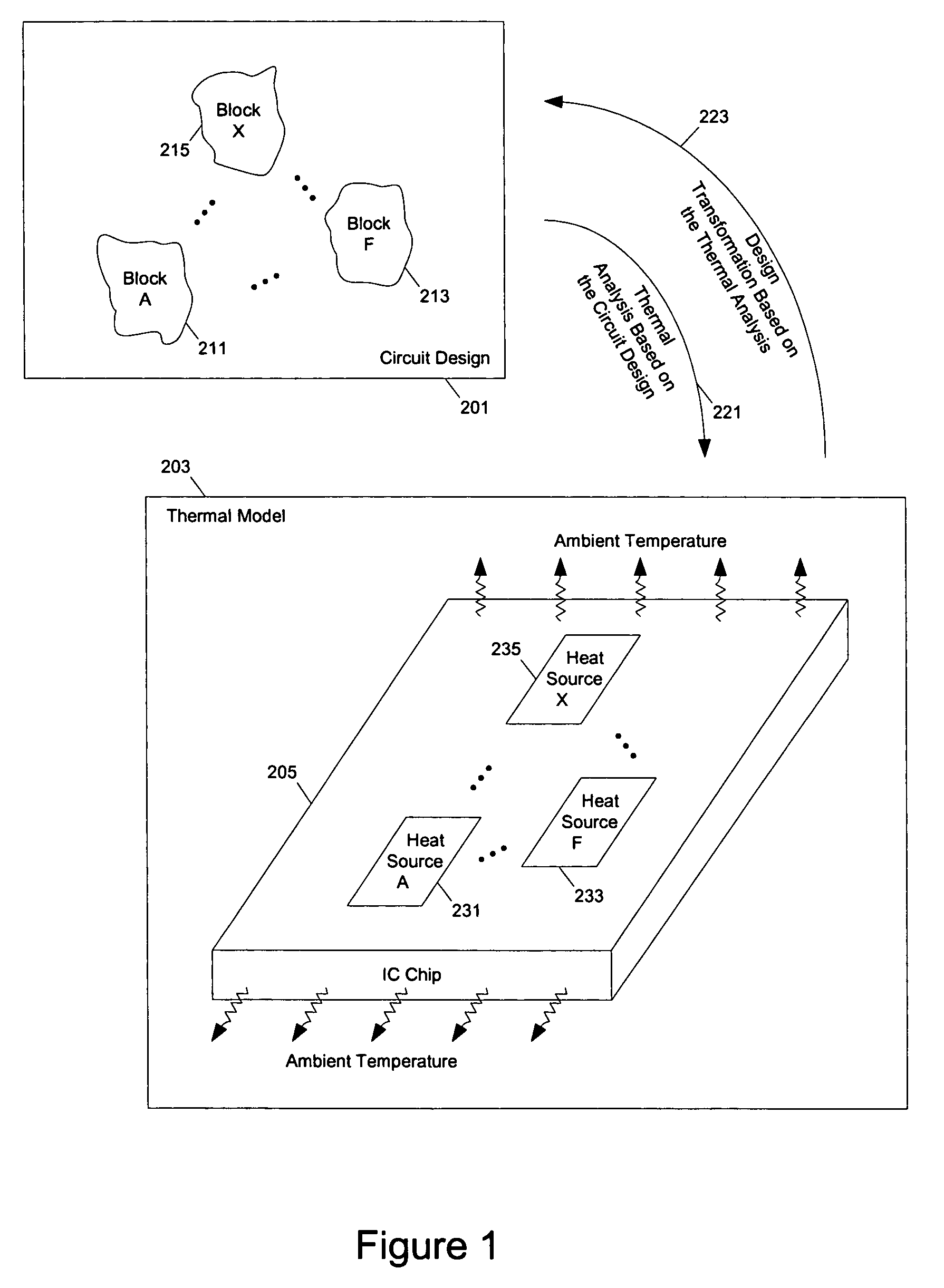
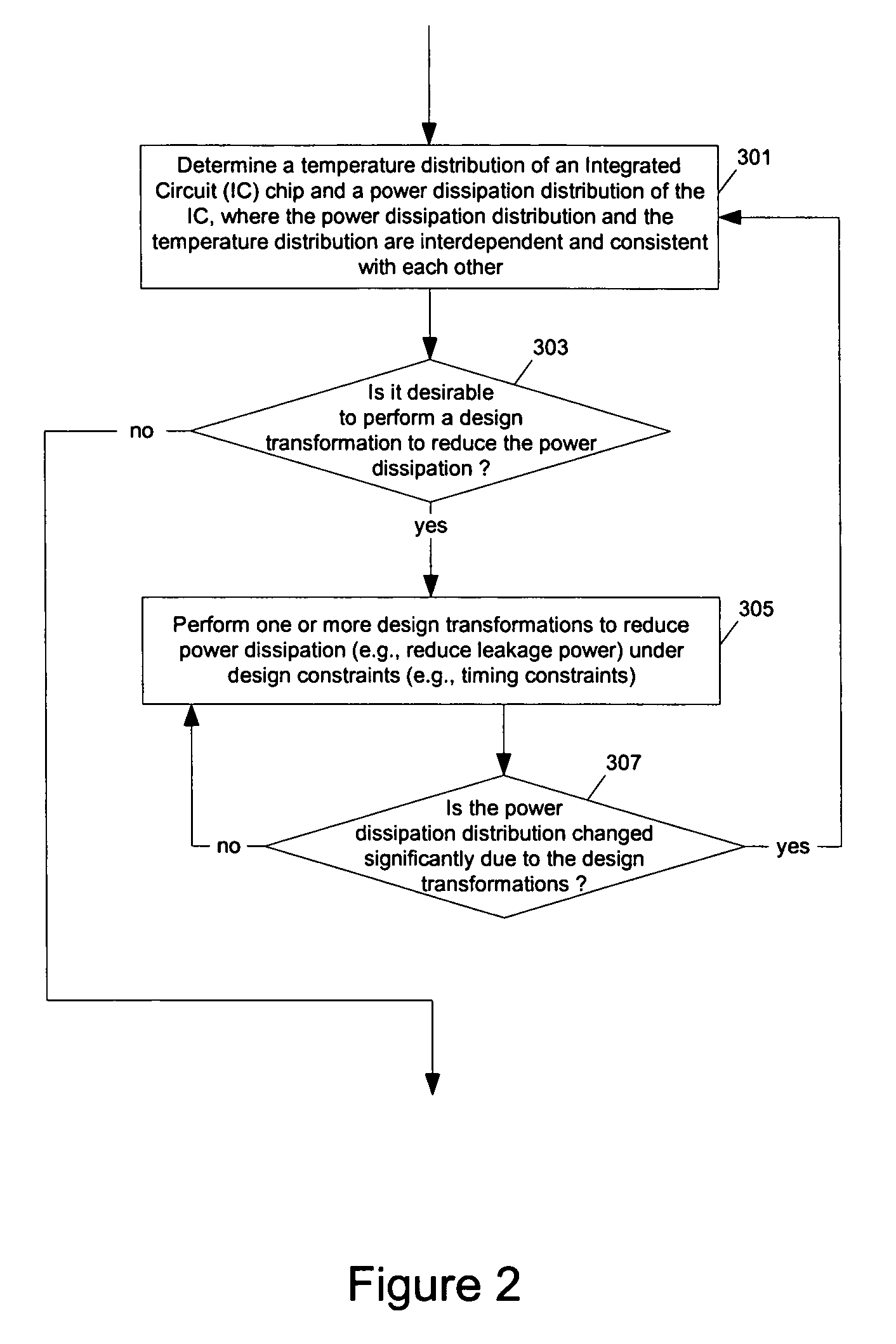
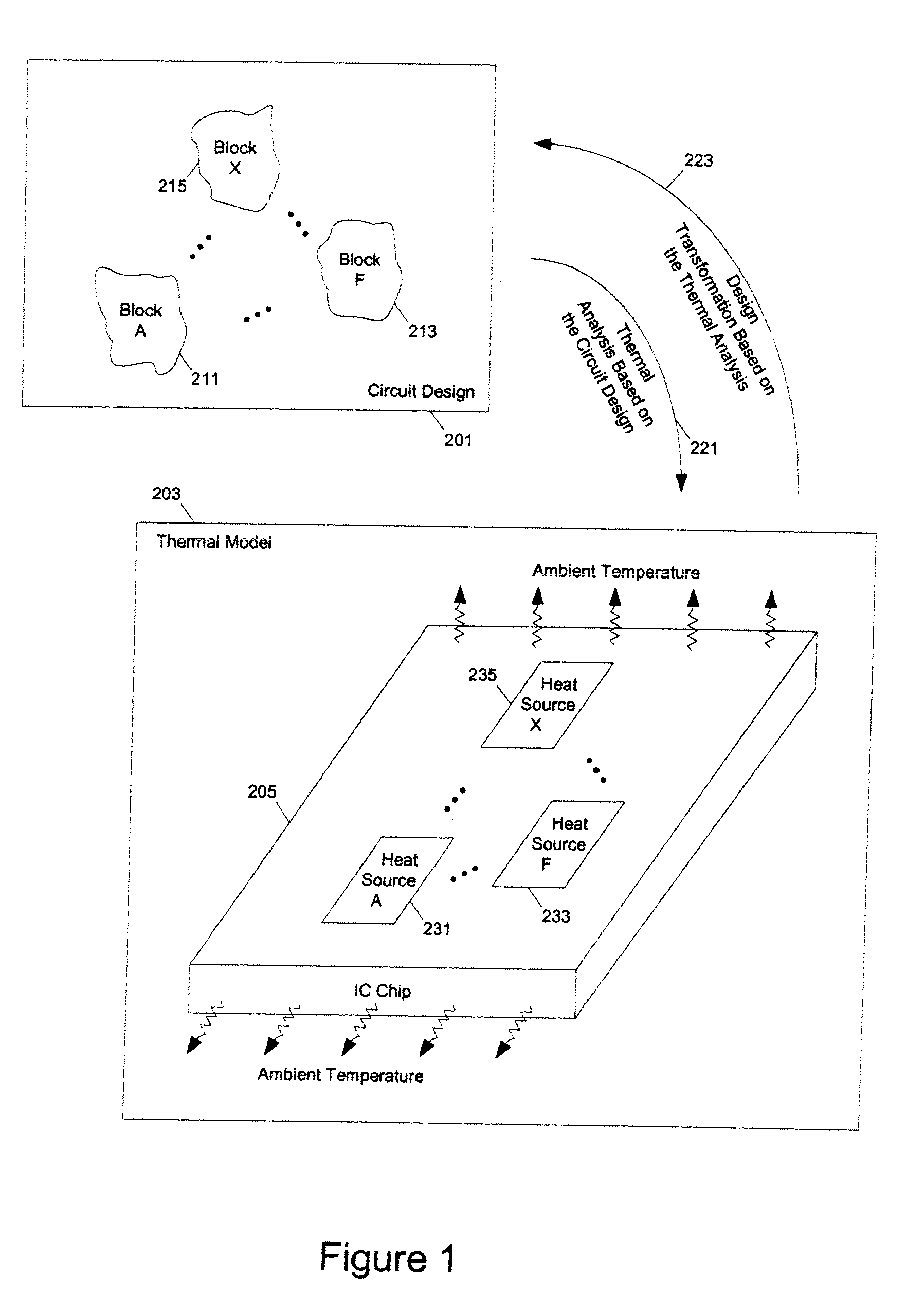
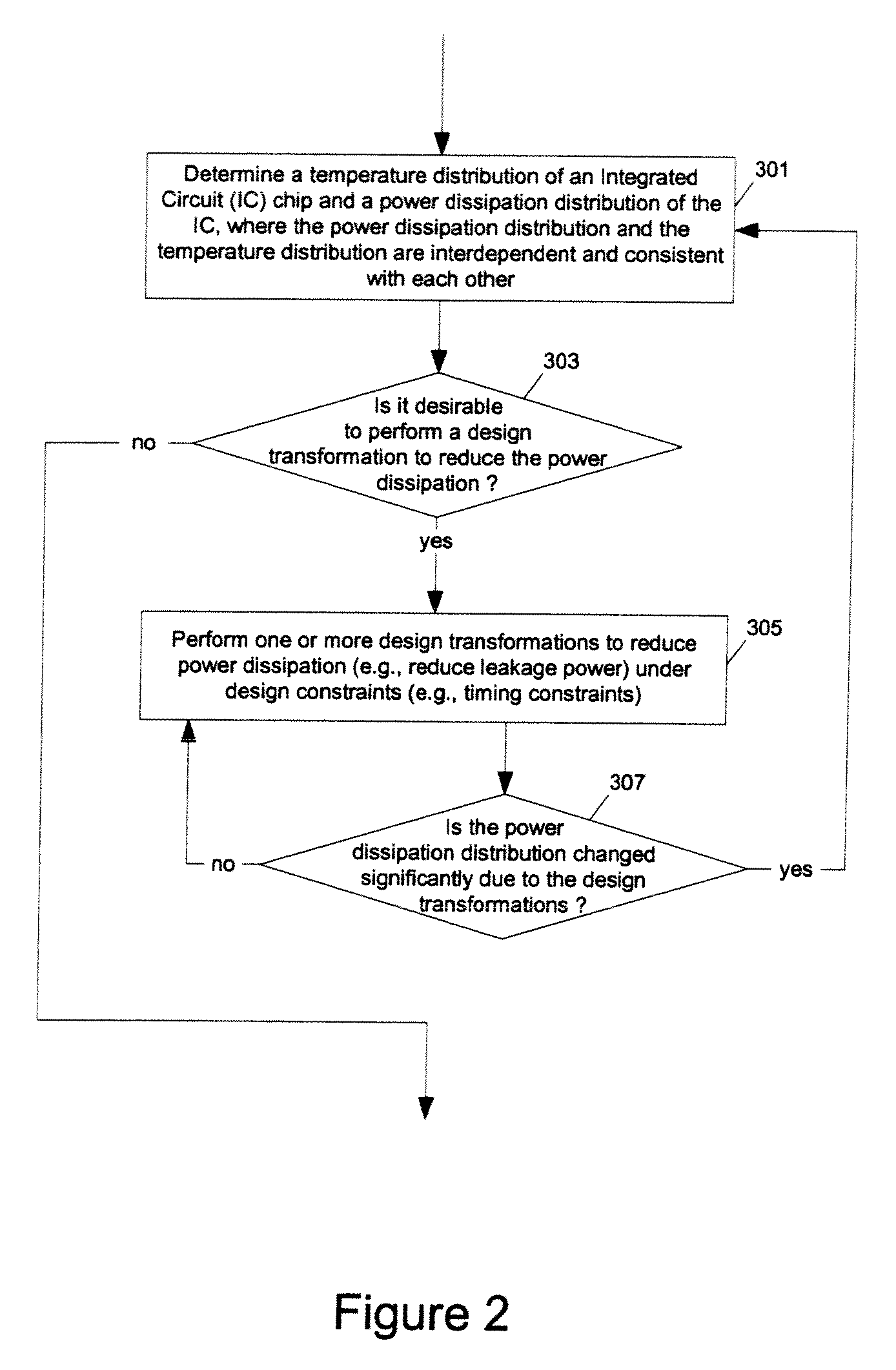
Methods and apparatuses for thermal analysis based circuit design
ActiveUS7366997B1Reduce power consumptionExtension of timeSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSpecial data processing applicationsPower usageTransition time
Methods and apparatuses for circuit design to reduce power usage, such as reducing temperature dependent power usage, and / or to improve timing, such as reducing temperature dependent delay or transition time. At least one embodiment of the present invention reduces the power dissipation and improves the timing of an integrated circuit to optimize the design. A thermal analysis is used to determine the temperature dependent power dissipation of a circuit and the temperature distribution of the circuit resulting from dissipating the heat created by the temperature dependent power dissipation. Then, the components of the design are selectively transformed to reduce the power dissipation and to improve timing based on the temperature solution. The transformation may include placement changes and netlist changes, such as the change of transistor threshold voltages for cells or for blocks of the circuit chip.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
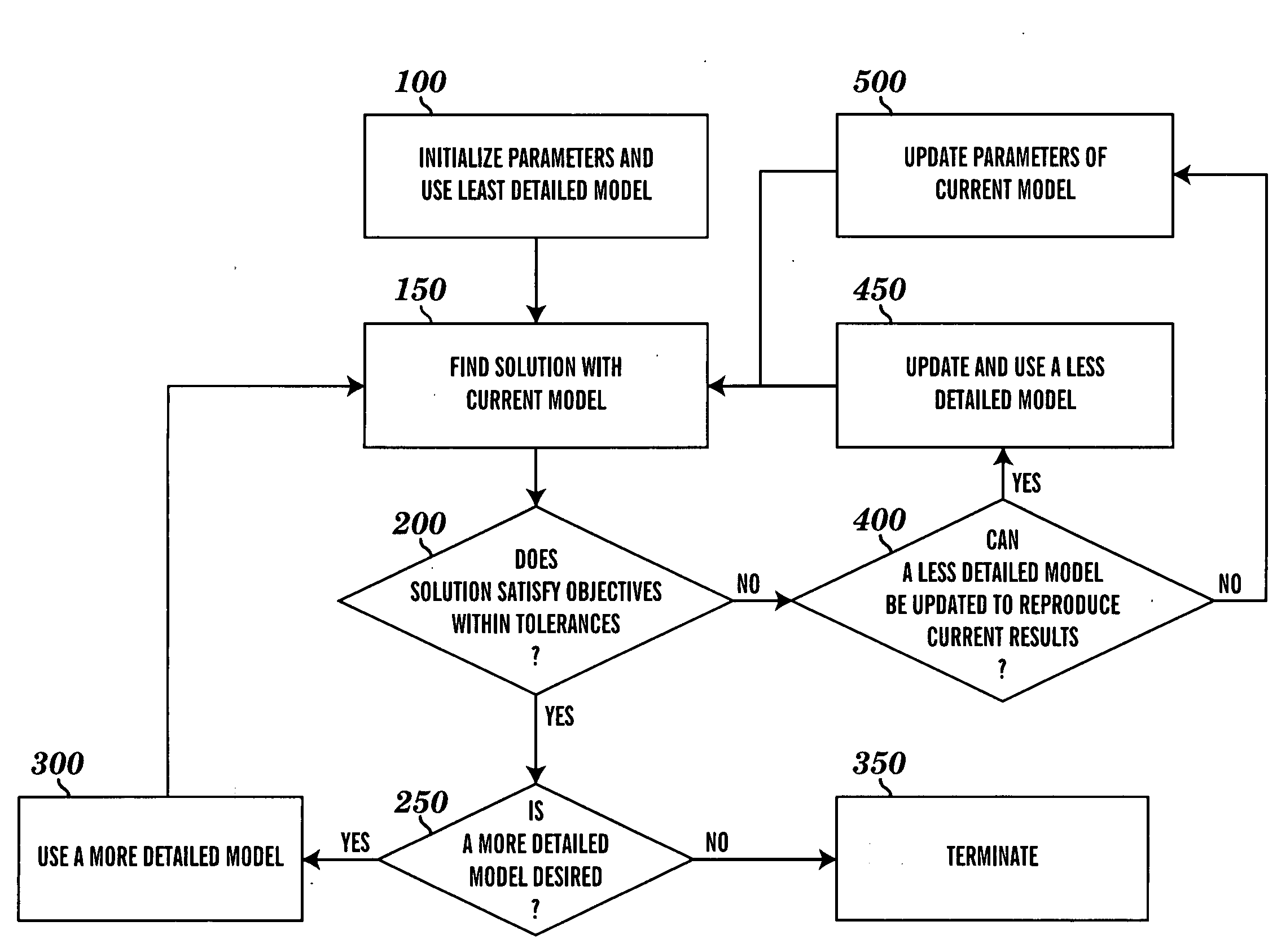
Method for tuning patient-specific cardiovascular simulations
ActiveUS20100017171A1Improve understandingImprove representationMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesReduced modelComputing Methodologies
Computational methods are used to create cardiovascular simulations having desired hemodynamic features. Cardiovascular modeling methods produce descriptions of blood flow and pressure in the heart and vascular networks. Numerical methods optimize and solve nonlinear equations to find parameter values that result in desired hemodynamic characteristics including related flow and pressure at various locations in the cardiovascular system, movements of soft tissues, and changes for different physiological states. The modeling methods employ simplified models to approximate the behavior of more complex models with the goal of to reducing computational expense. The user describes the desired features of the final cardiovascular simulation and provides minimal input, and the system automates the search for the final patient-specific cardiovascular model.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Hardware system design improvement using deep learning algorithms
Methods and apparatus for deep learning-based system design improvement are provided. An example system design engine apparatus includes a deep learning network (DLN) model associated with each component of a target system to be emulated, each DLN model to be trained using known input and known output, wherein the known input and known output simulate input and output of the associated component of the target system, and wherein each DLN model is connected as each associated component to be emulated is connected in the target system to form a digital model of the target system. The example apparatus also includes a model processor to simulate behavior of the target system and / or each component of the target system to be emulated using the digital model to generate a recommendation regarding a configuration of a component of the target system and / or a structure of the component of the target system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatuses for thermal analysis based circuit design
ActiveUS20080168406A1Reduce power consumptionExtension of timeSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringPower usage
Methods and apparatuses for circuit design to reduce power usage, such as reducing temperature dependent power usage, and / or to improve timing, such as reducing temperature dependent delay or transition time. At least one embodiment of the present invention reduces the power dissipation and improves the timing of an integrated circuit to optimize the design. A thermal analysis is used to determine the temperature dependent power dissipation of a circuit and the temperature distribution of the circuit resulting from dissipating the heat created by the temperature dependent power dissipation. Then, the components of the design are selectively transformed to reduce the power dissipation and to improve timing based on the temperature solution. The transformation may include placement changes and netlist changes, such as the change of transistor threshold voltages for cells or for blocks of the circuit chip.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
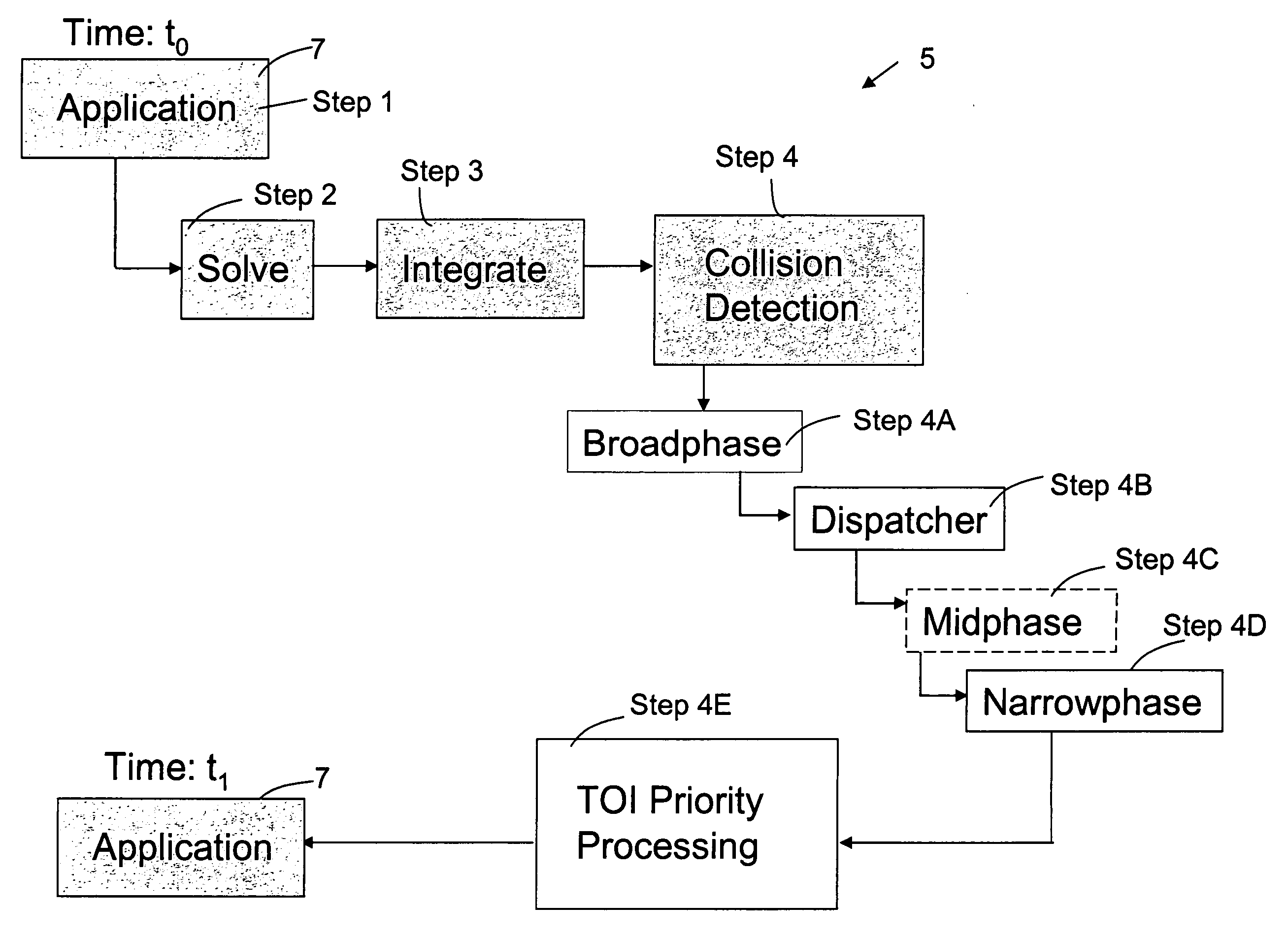
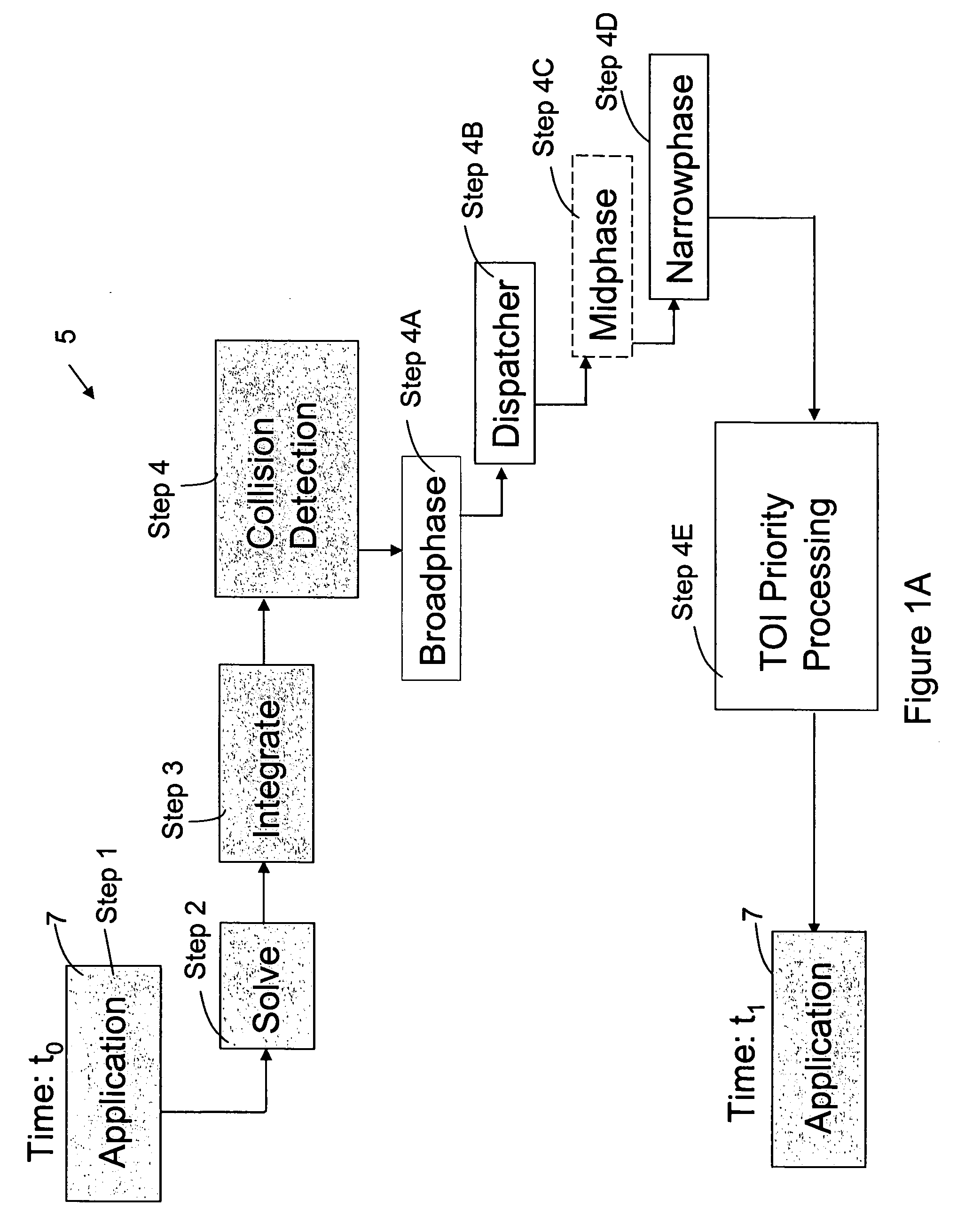
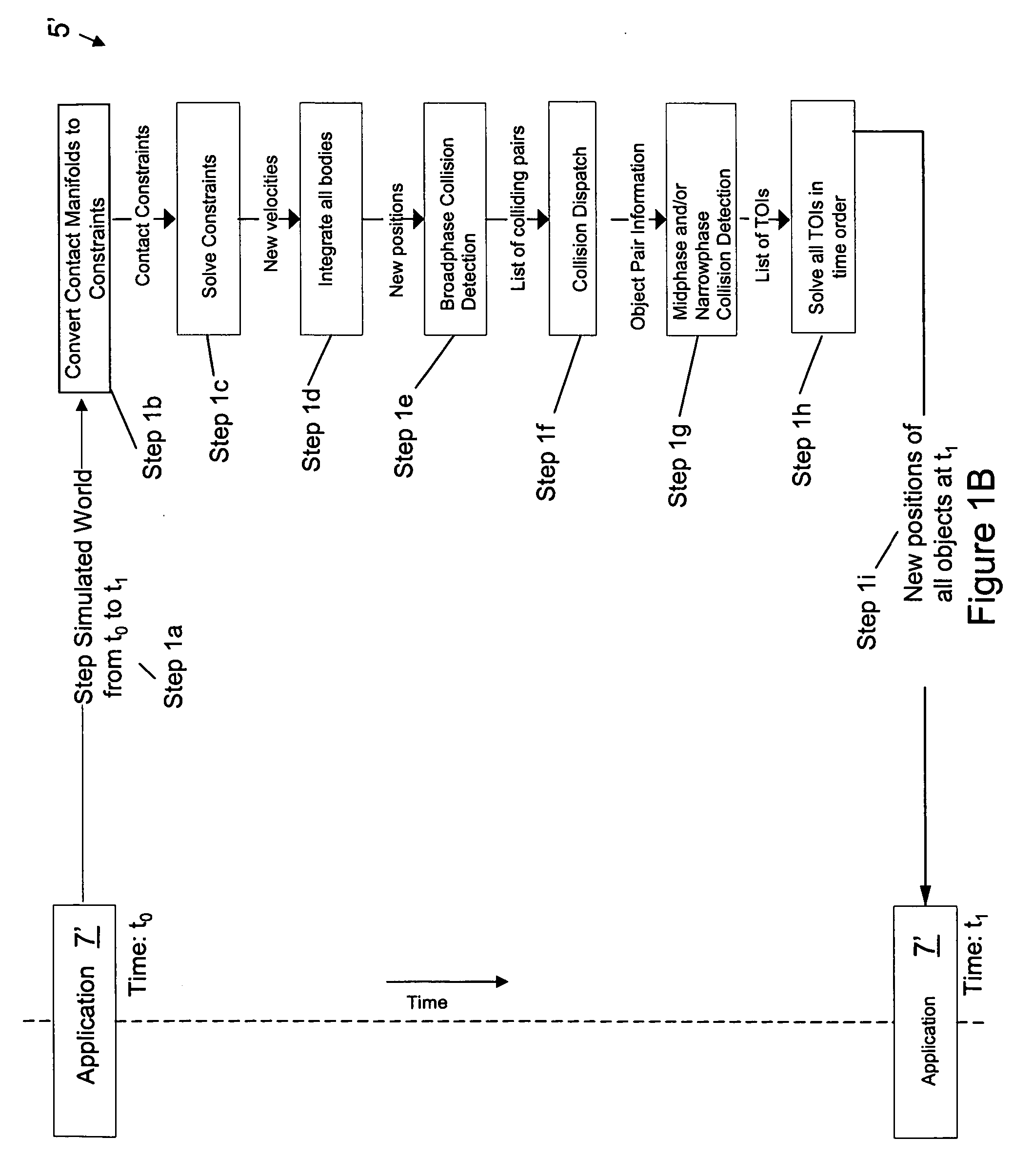
Physics simulation apparatus and method
InactiveUS20060149516A1Improve the level ofImprove stabilityGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationLevel of detailCollision response
A method and apparatus wherein complex physical interactions and collisions are modeled at a high level of detail while reducing the computational demands placed on the processing system. In one embodiment the method comprising the steps of defining a first object and a second object, each object adapted for colliding with the other object; assigning an interaction type for at least one of the first and second object in response to an object parameter; and selecting between a continuous simulation of a collision and a discrete simulation of the collision in response to the interaction type.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
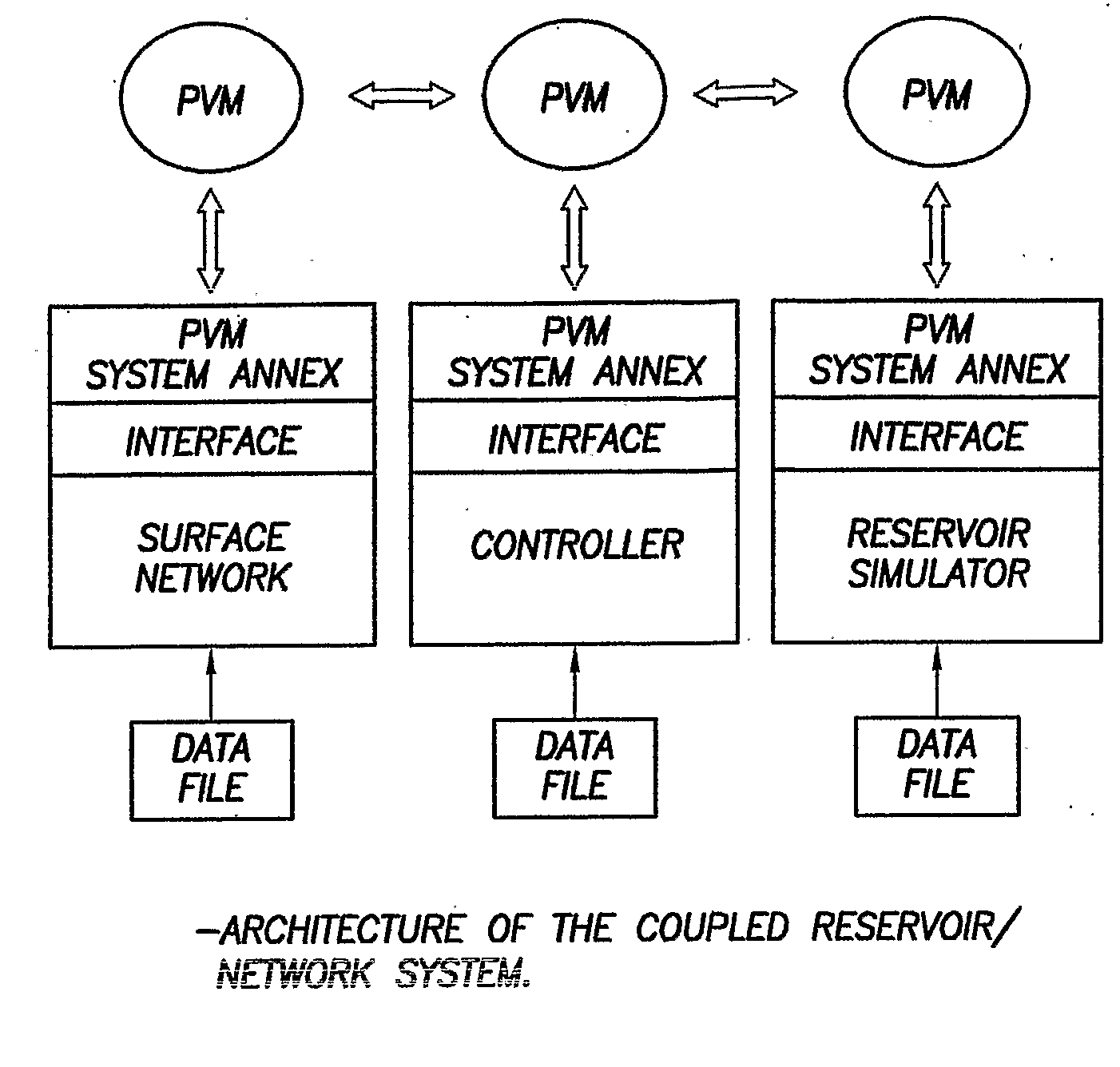
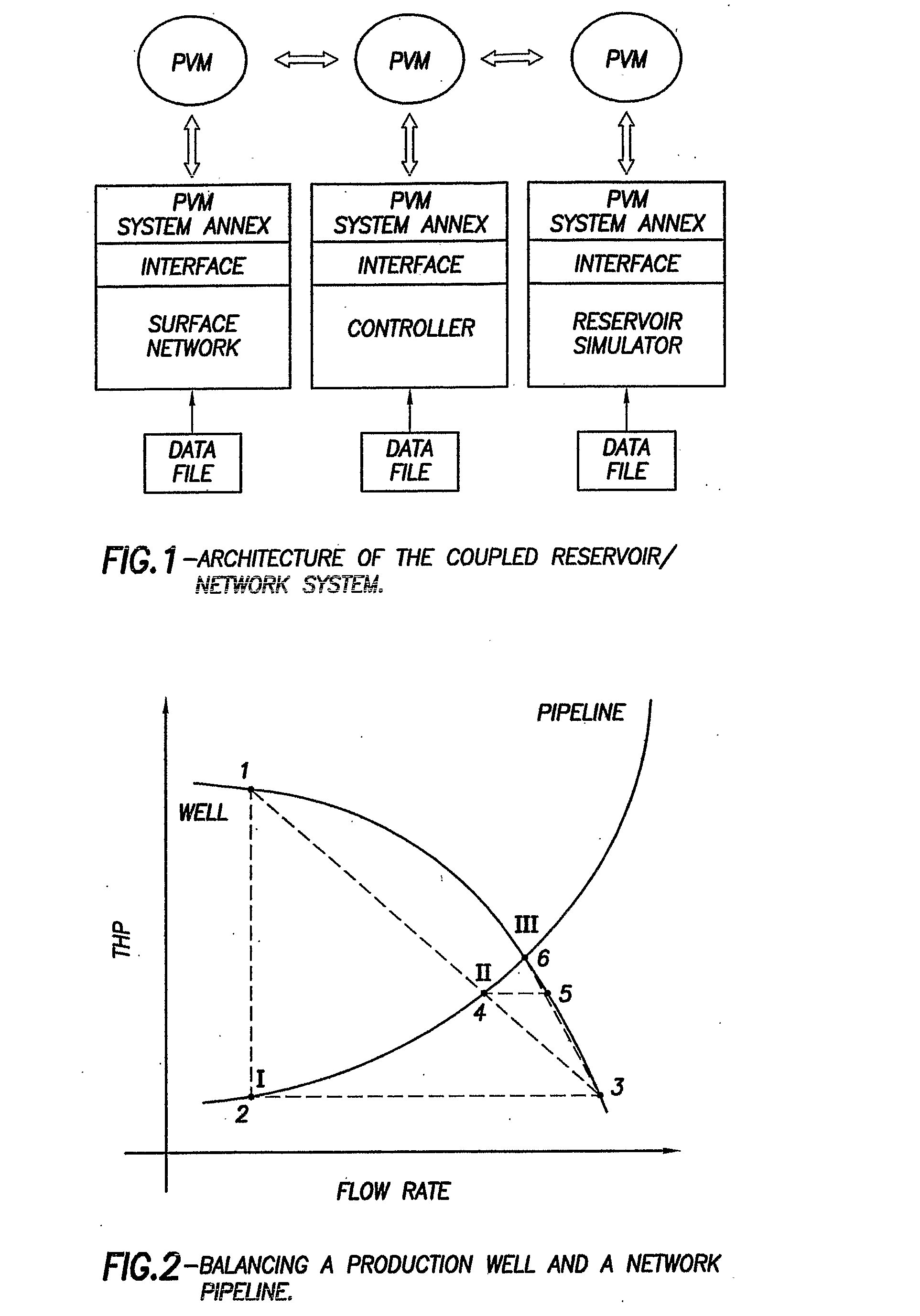
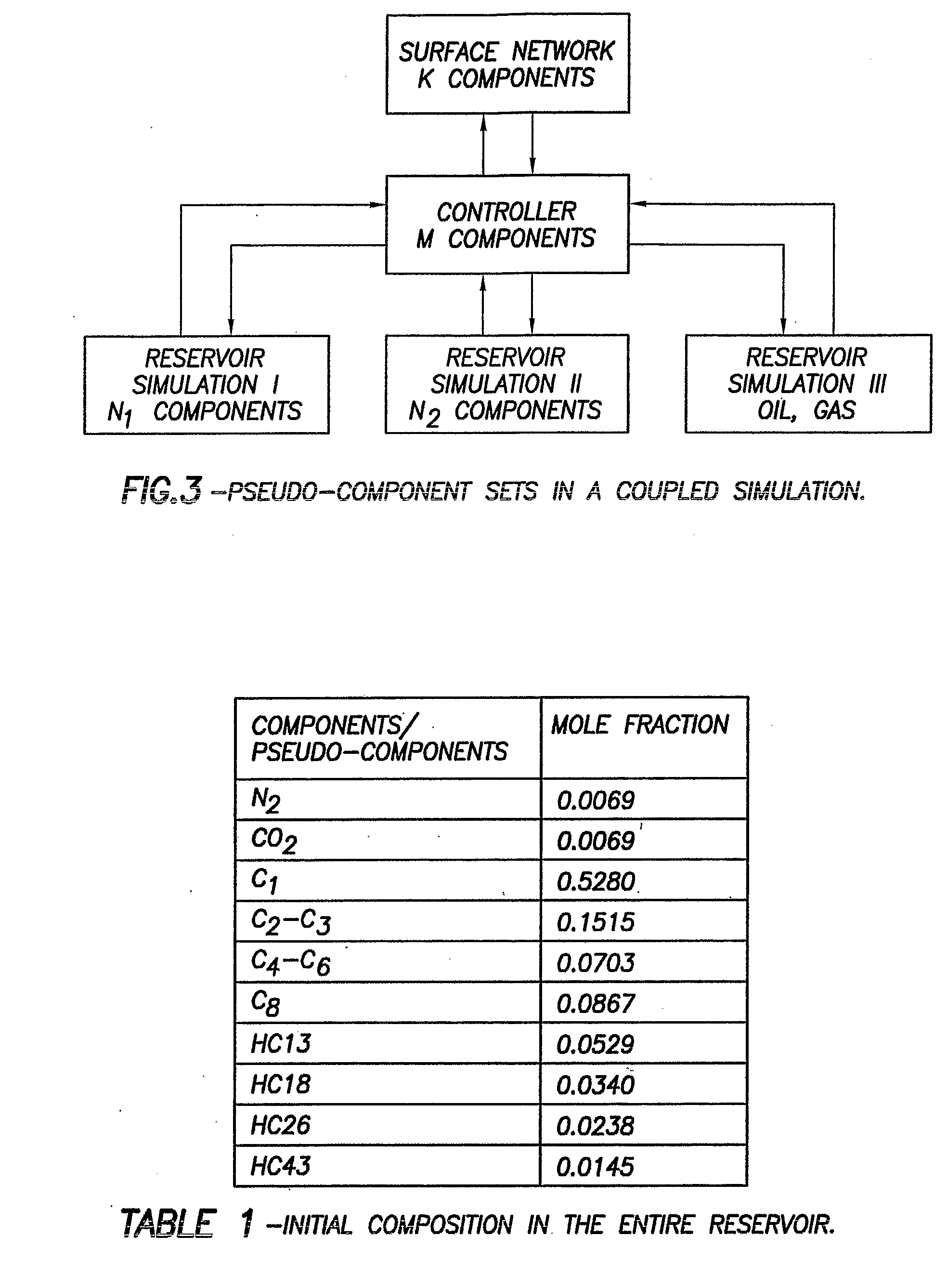
Method and system for integrated reservoir and surface facility networks simulations
InactiveUS20070112547A1Design optimisation/simulationConstraint-based CADMulti platformNetwork model
Integrated surface-subsurface modeling has been shown to have a critical impact on field development and optimization. Integrated models are often necessary to analyze properly the pressure interaction between a reservoir and a constrained surface facility network, or to predict the behavior of several fields, which may have different fluid compositions, sharing a common surface facility. The latter is gaining a tremendous significance in recent deepwater field development. These applications require an integrated solution with the following capabilities: * to balance a surface network model with a reservoir simulation model in a robust and efficient manner. * To couple multiple reservoir models, production and injection networks, synchronising their advancement through time. * To allow the reservoir and surface network models to use their own independent fluid descriptions (black oil or compositional descriptions with differing sets of pseudo-components). * To apply global production and injection constraints to the coupled system (including the transfer of re-injection fluids between reservoirs). In this paper we describe a general-purpose multi-platform reservoir and network coupling controller having all the above features. The controller communicates with a selection of reservoir simulators and surface network simulators via an open message-passing interface. It manages the balancing of the reservoirs and surface networks, and synchronizes their advancement through time. The controller also applies the global production and injection constraints, and converts the hydrocarbon fluid streams between the different sets of pseudo-components used in the simulation models. The controller's coupling and synchronization algorithms are described, and example applications are provided. The flexibility of the controller's open interface makes it possible to plug in further modules (to perform optimization, for example) and additional simulators.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
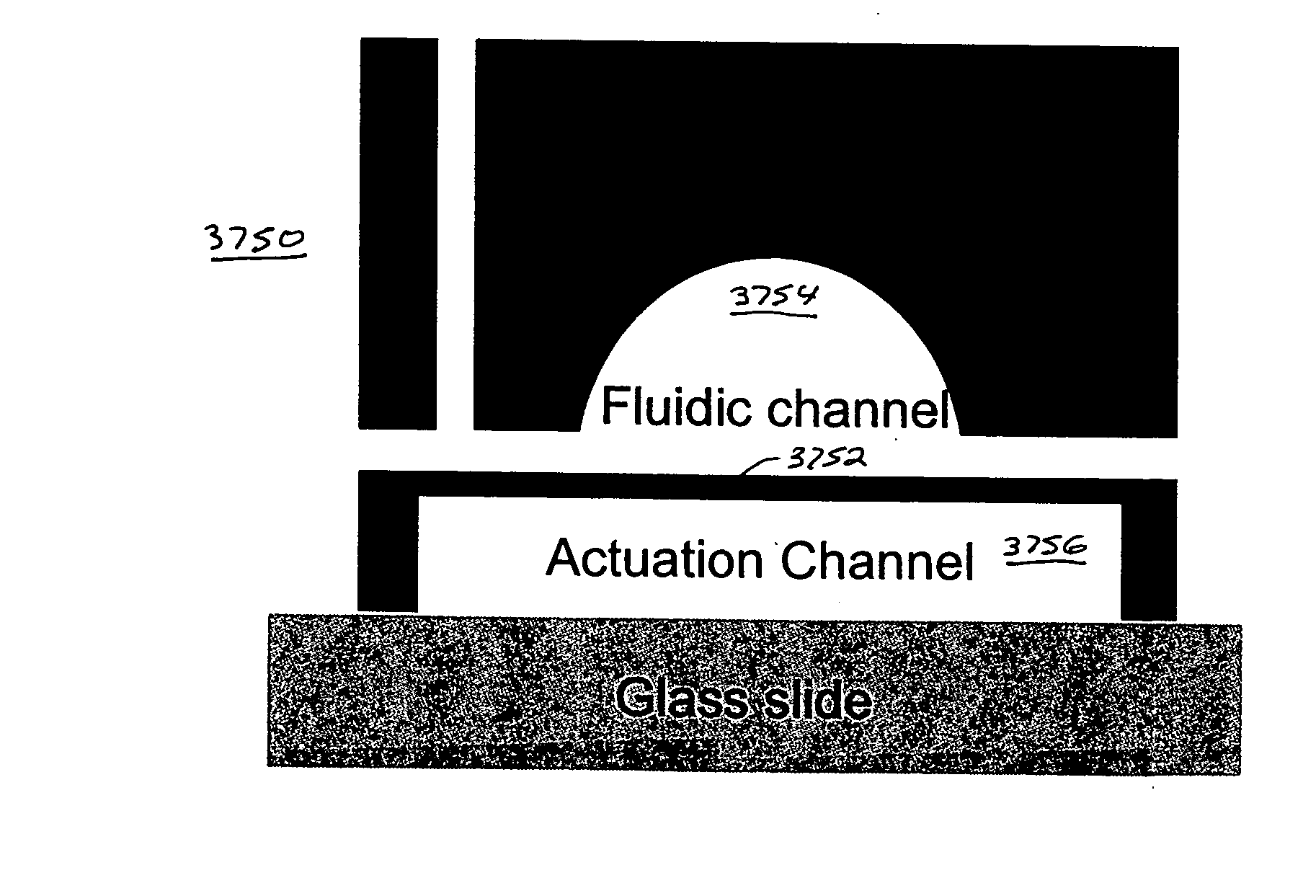
Microfluidic large scale integration
InactiveUS20050072946A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesCircuit elementsElastomerFlow resistivity
Using basic physical arguments, a design and method for the fabrication of microfluidic valves using multilayer soft lithography is presented. Embodiments of valves in accordance with the present invention feature elastomer membrane portions of substantially constant thickness, allowing the membranes to experience similar resistance to an applied pressure across their entire width. Such on-off valves fabricated with upwardly- or downwardly-deflectable membranes can have extremely low actuation pressures, and can be used to implement active functions such as pumps and mixers in integrated microfluidic chips. Valve performance was characterized by measuring both the actuation pressure and flow resistance over a wide range of design parameters, and comparing them to both finite element simulations and alternative valve geometries.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
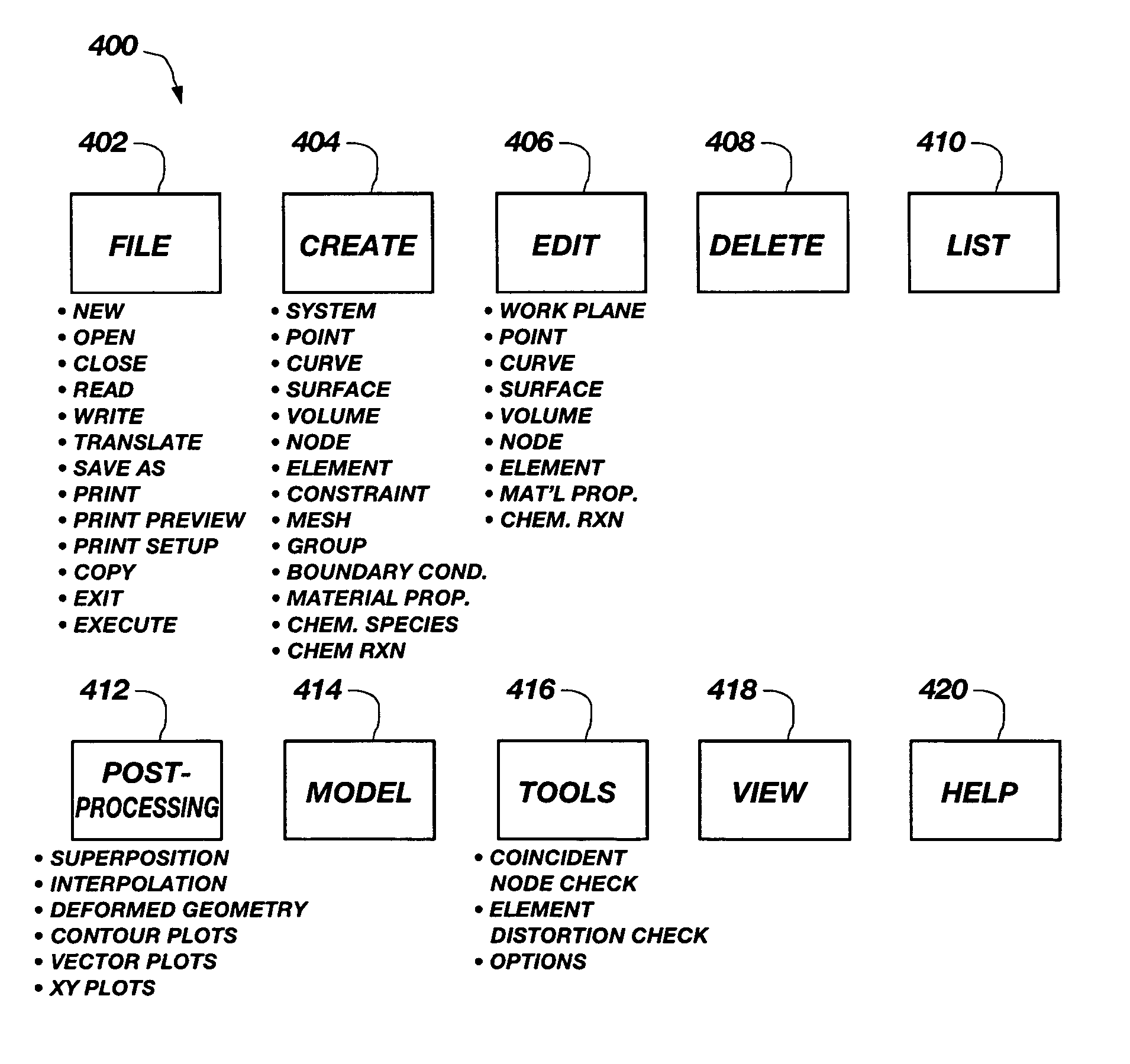
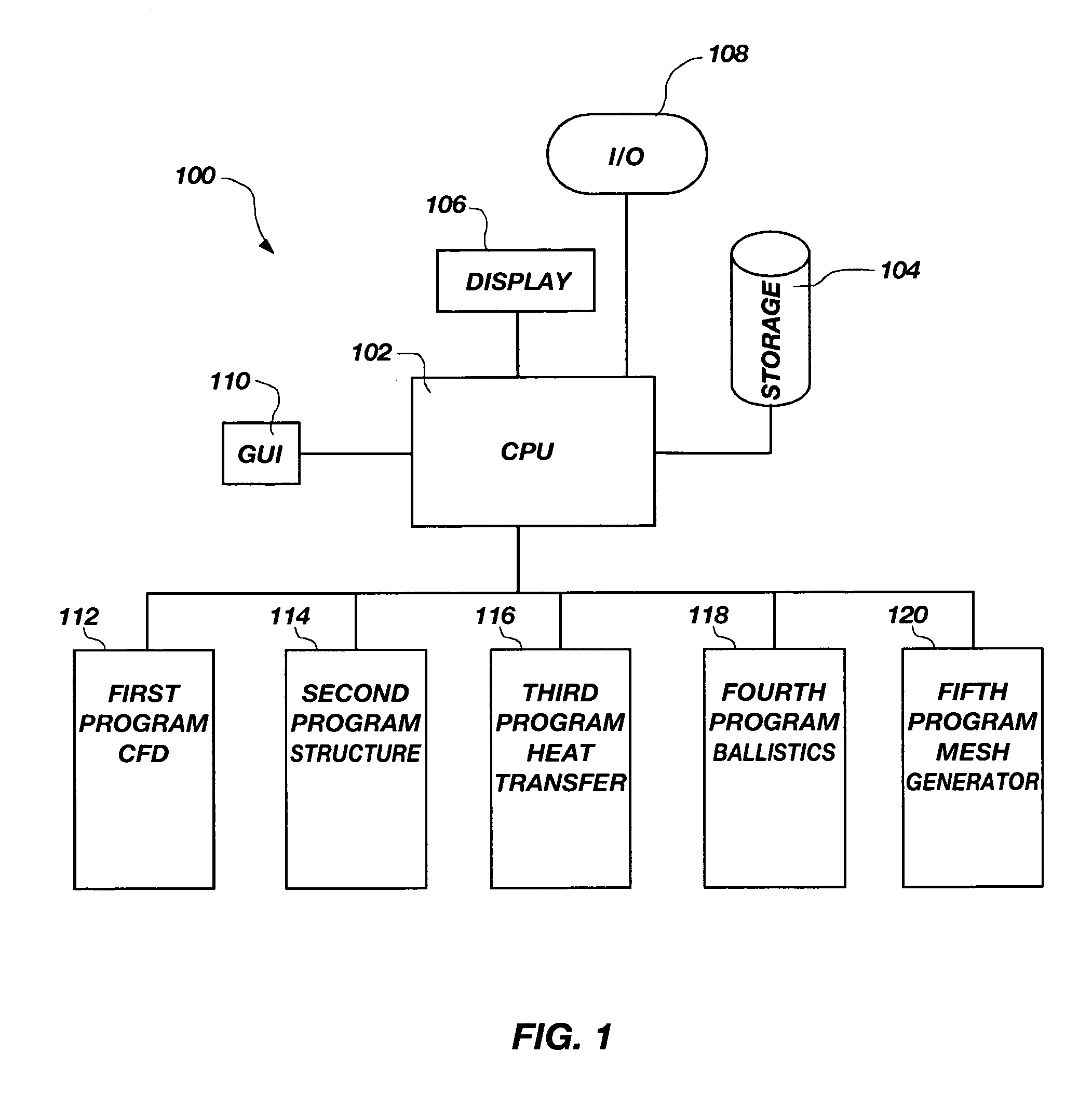
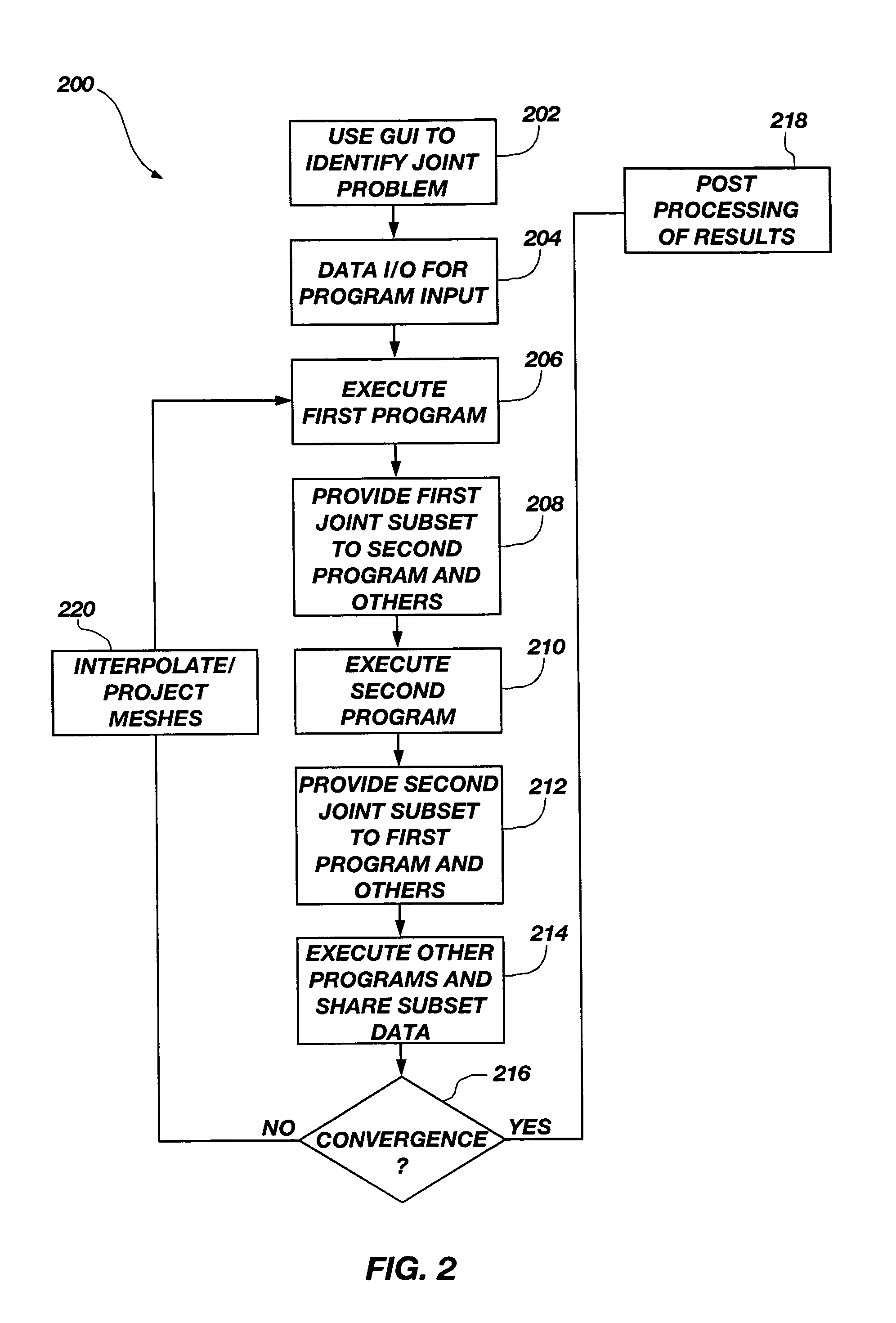
System for performing coupled finite analysis
ActiveUS7127380B1Stay flexibleAccelerated settlementComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationComputational scienceGraphics
A graphical user interface, together with a comparable scripting interface, couples a plurality of finite element, finite volume, or finite difference analytical programs and permits iterative convergence of multiple programs through one set of predefined commands. The user is permitted to select the joint problem for solution by choosing program selections. Data linkages that couple the program are predefined by an expert system administrator to permit less skilled modelers access to a comprehensive and multifaceted solution that would not be possible for the less skilled modelers to complete absent the graphical user interface.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
System and method for evaluation of object autonomy
A method, computer program product, and computer system for configuring a stochastic simulation scenario, wherein the stochastic simulation scenario may include one or more variables without a complete probability distribution. The stochastic simulation scenario may be executed to generate one or more results of the stochastic simulation scenario. At least a portion of the one or more variables without the probability distribution may be optimized using one or more optimization metrics on the one or more results of the stochastic simulation scenario.
Owner:UNIVERSAL ROBOTS USA INC
Additive fabrication support structures
ActiveUS20140300017A1Minimize contactProgramme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusManufacturing technologyEngineering
Some aspects provide a method of generating a support structure for an object, the support structure and the object to be fabricated via one or more additive fabrication techniques, comprising identifying one or more regions of the object as one or more regions to which mechanical support is to be provided, identifying one or more support points within at least a first region of the one or more regions, and generating the support structure for the object, the support structure comprising one or more support tips coupled to the object at the one or more support points, the support tips being generated based at least in part on a direction normal to the surface of the object at the respective support point.
Owner:FORMLABS INC
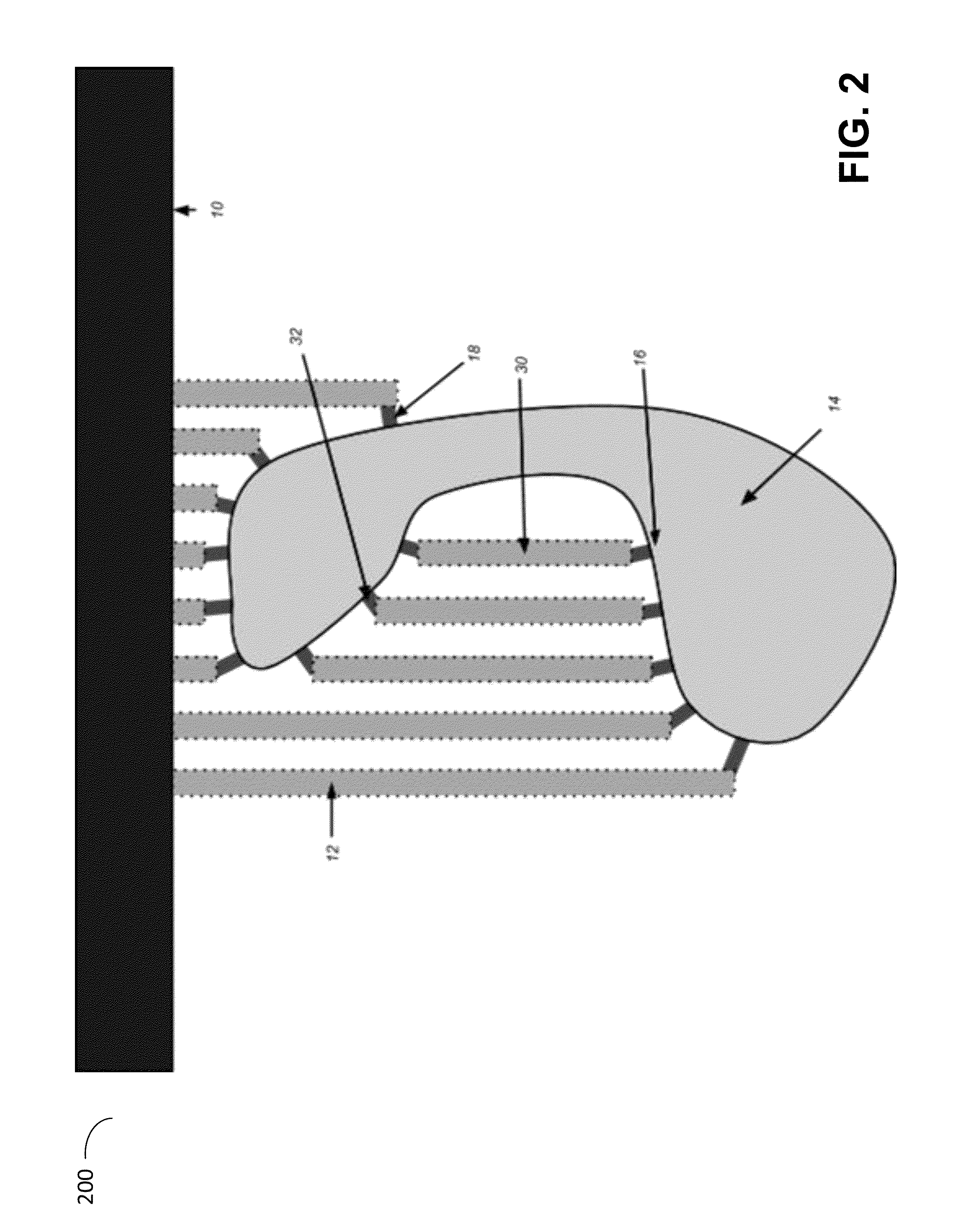
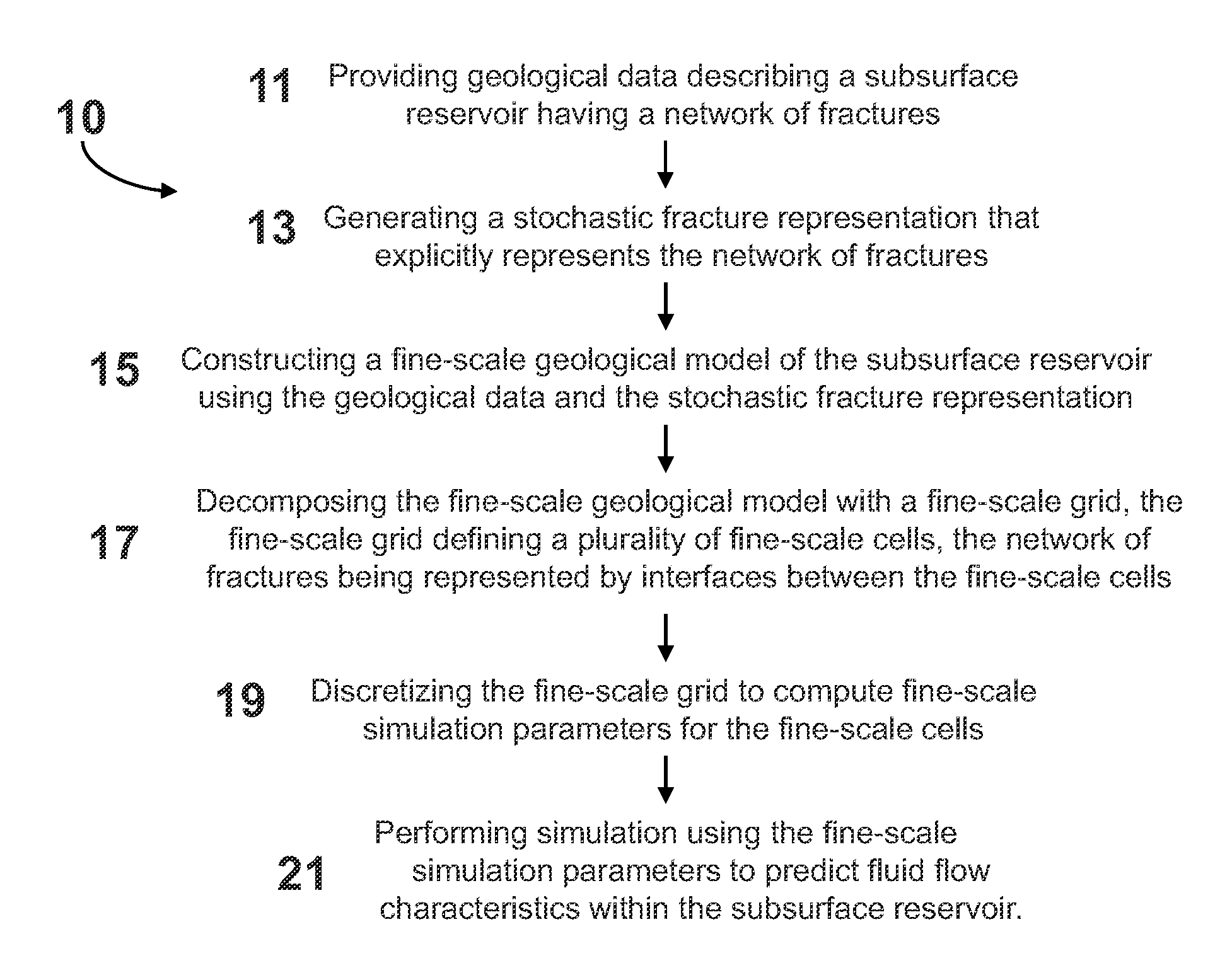
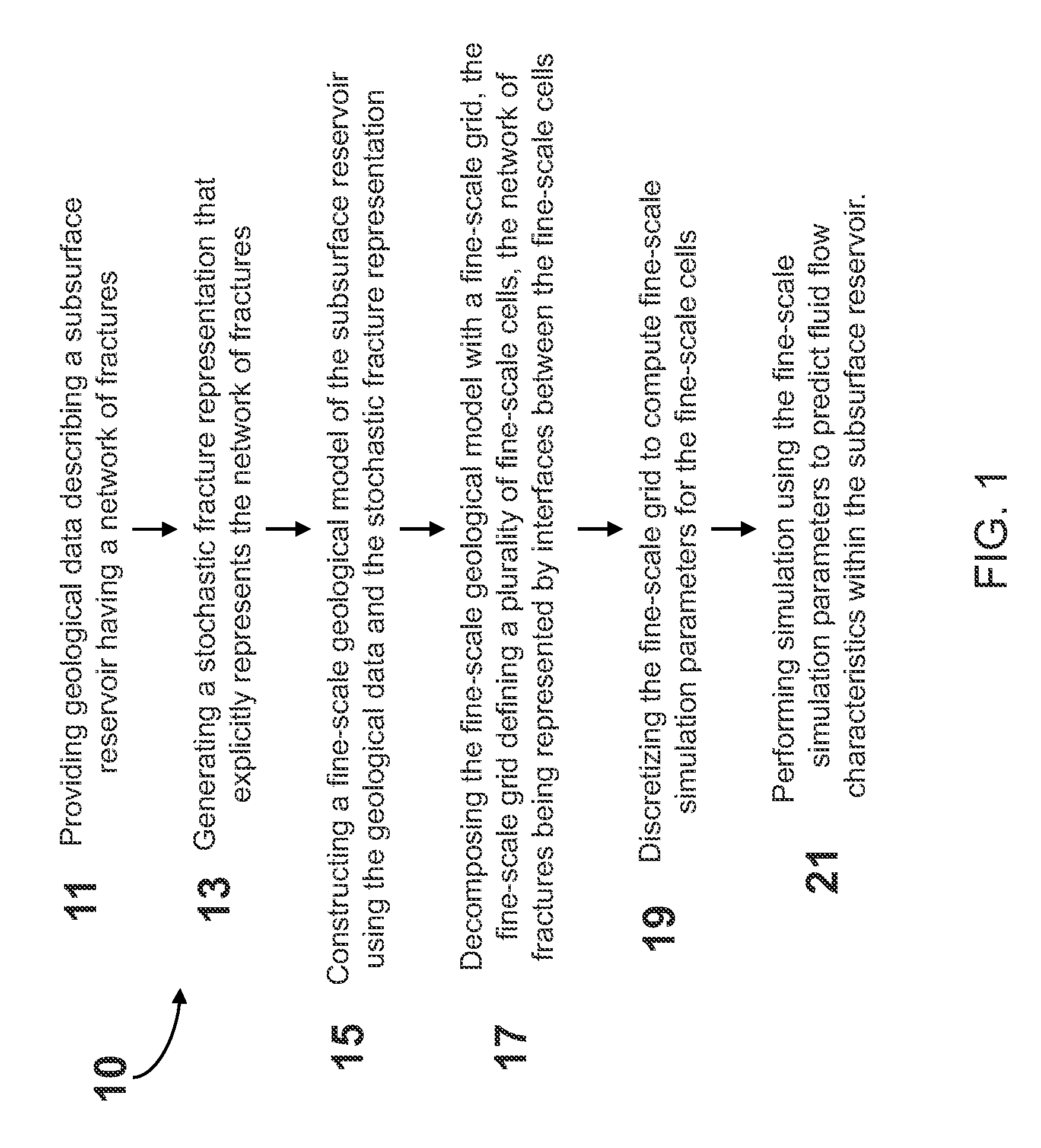
System and method for predicting fluid flow characteristics within fractured subsurface reservoirs
A system and method having application notably towards predicting fluid flow characteristics within fractured subsurface reservoirs. The system and method include steps of reservoir characterization, gridding, discretization, and simulation of geologically realistic models describing the fractured subsurface reservoirs. A stochastic fracture representation that explicitly represents a network of fractures within a subsurface reservoir is constructed and used to build a fine-scale geological model. The model is then gridded such that the network of fractures is represented by interfaces between the fine-scale cells. The model is the discretized and simulated. Simulation can be on a fine-scale or on an upscaled course-scale to produce efficient and reliable prediction of fluid flow characteristics within the subsurface reservoir.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
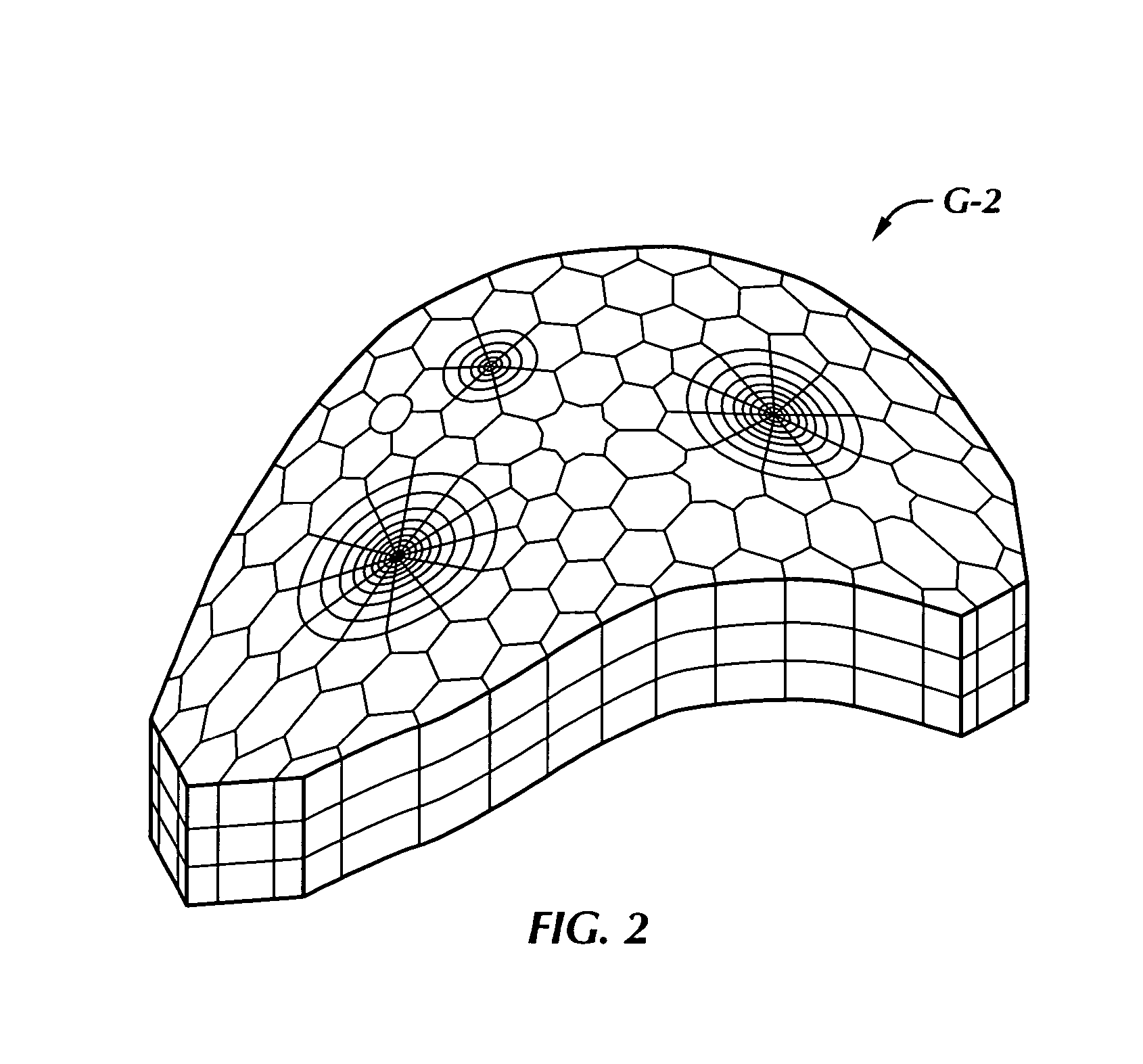
Solution method and apparatus for large-scale simulation of layered formations
ActiveUS20060235667A1Design optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSupercomputerAngular point
A targeted heterogeneous medium in the form of an underground layered formation is gridded into a layered structured grid or a layered semi-unstructured grid. The structured grid can be of the irregular corner-point-geometry grid type or the simple Cartesian grid type. The semi-unstructured grid is areally unstructured, formed by arbitrarily connected control-volumes derived from the dual grid of a suitable triangulation; but the connectivity pattern does not change from layer to layer. Problems with determining fluid movement and other state changes in the formation are solved by exploiting the layered structure of the medium. The techniques are particularly suited for large-scale simulation by parallel processing on a supercomputer with multiple central processing units (CPU's).
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
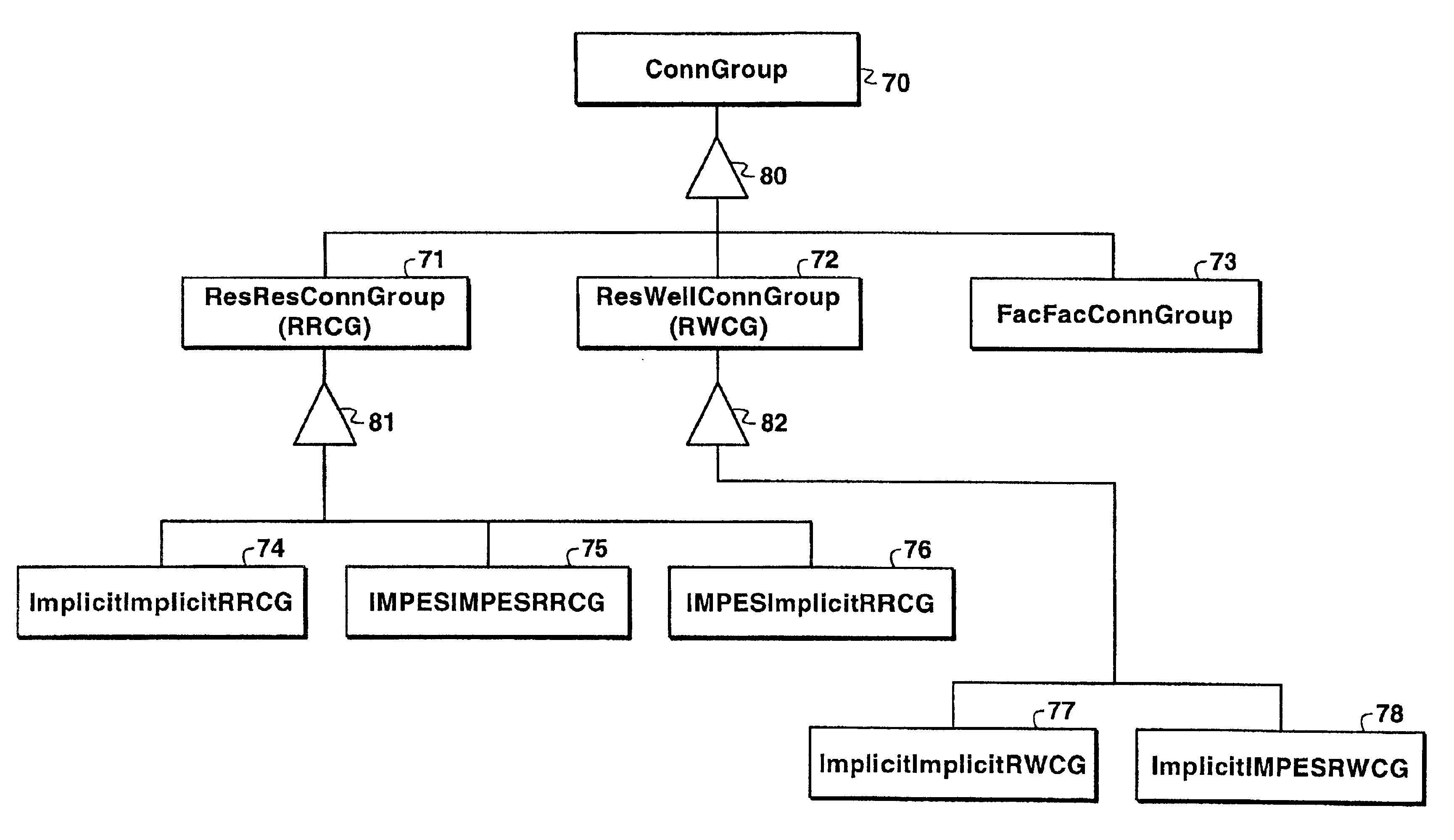
Method and program for simulating a physical system using object-oriented programming
InactiveUS6928399B1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingFluid removalPhysical systemComputer science
The invention relates to an object-oriented method for simulating a property of at least one fluid in a fluid-containing physical system in which the physical system is represented by a multiplicity of volumetric cells and a multiplicity of connections between cells. The method uses cell-group objects and connection-group objects in the simulation. The invention can optionally comprise additional objects such as an object containing the entire model of the simulation and another object containing a portion of the entire model.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
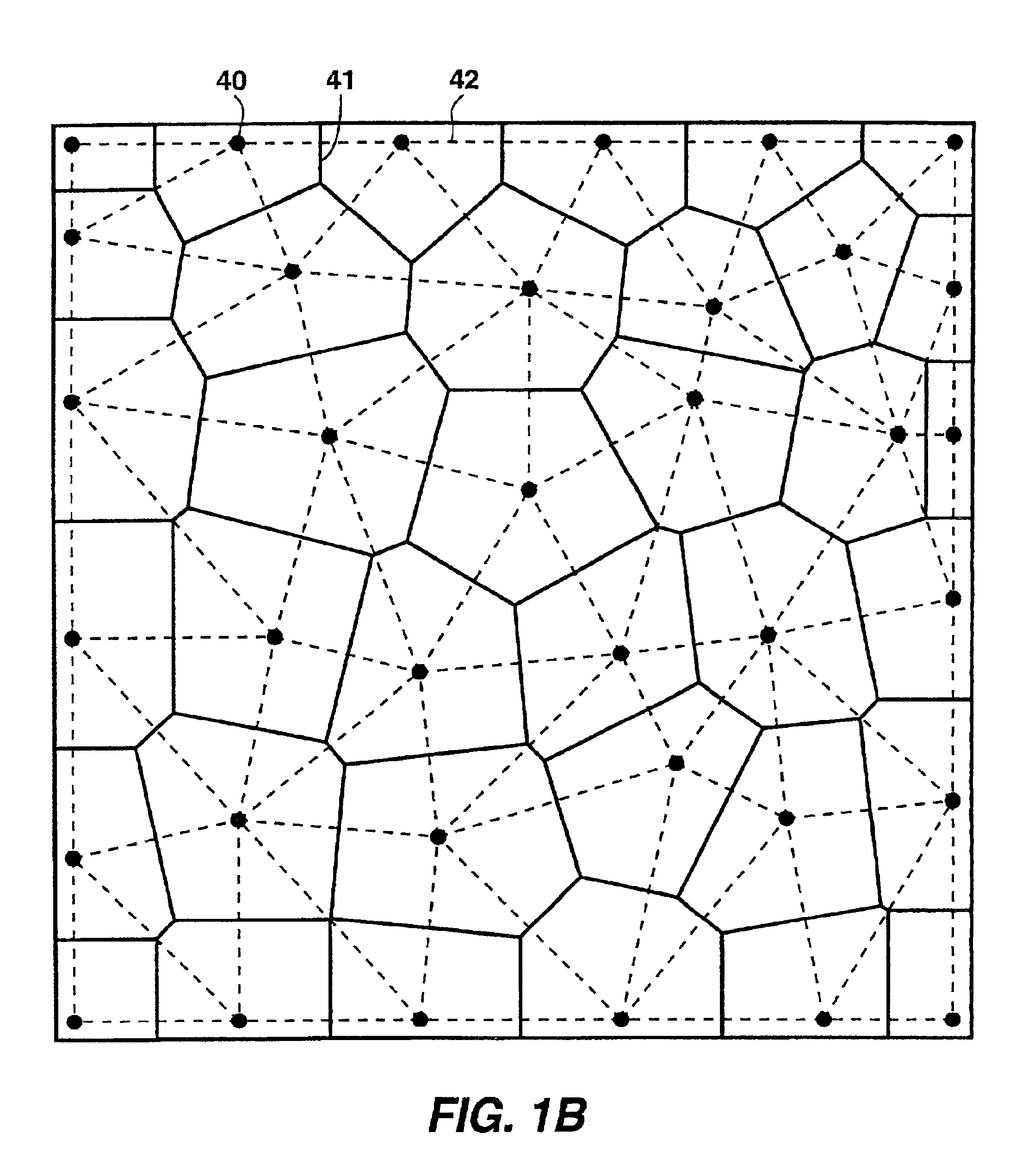
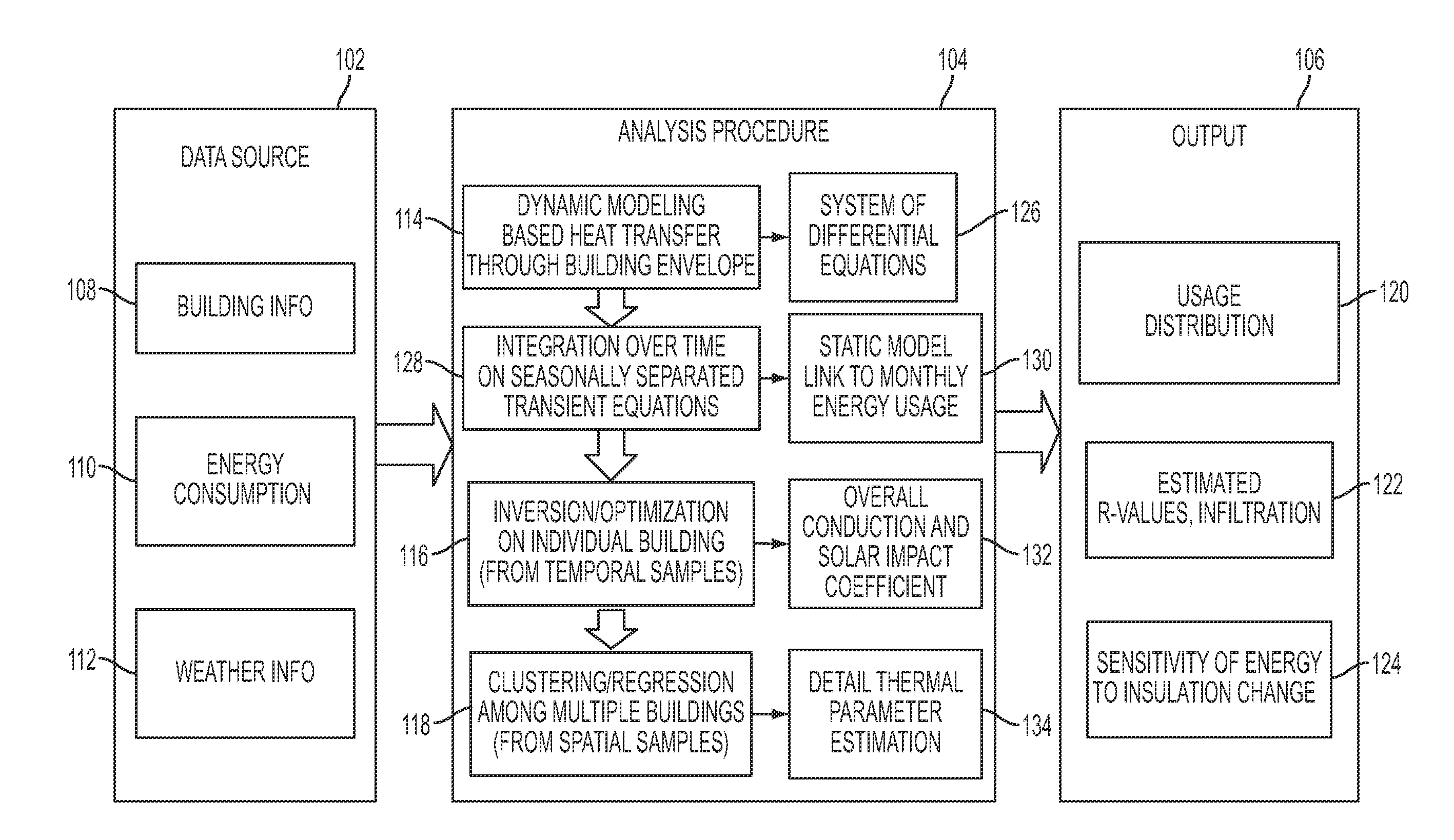
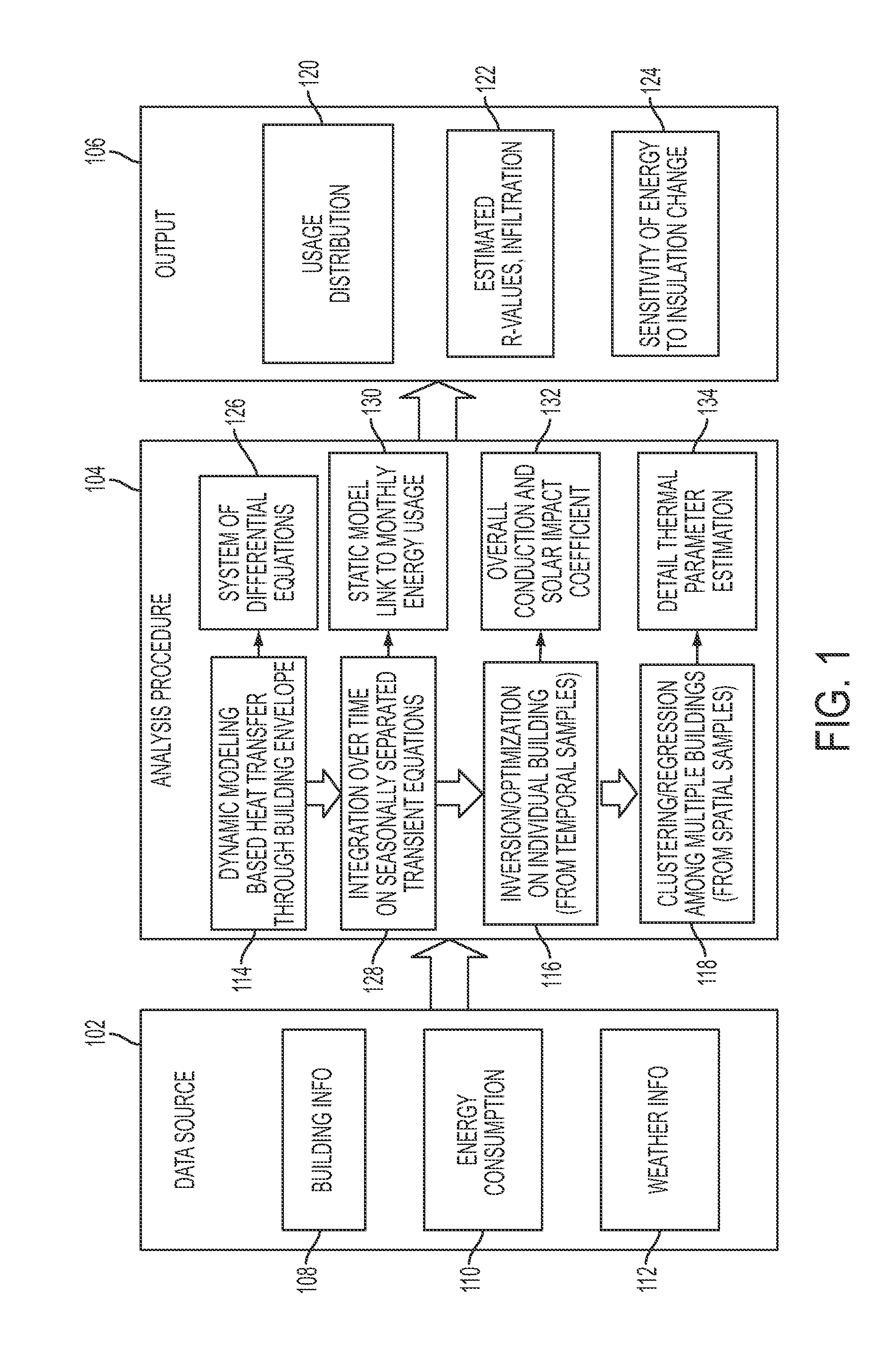
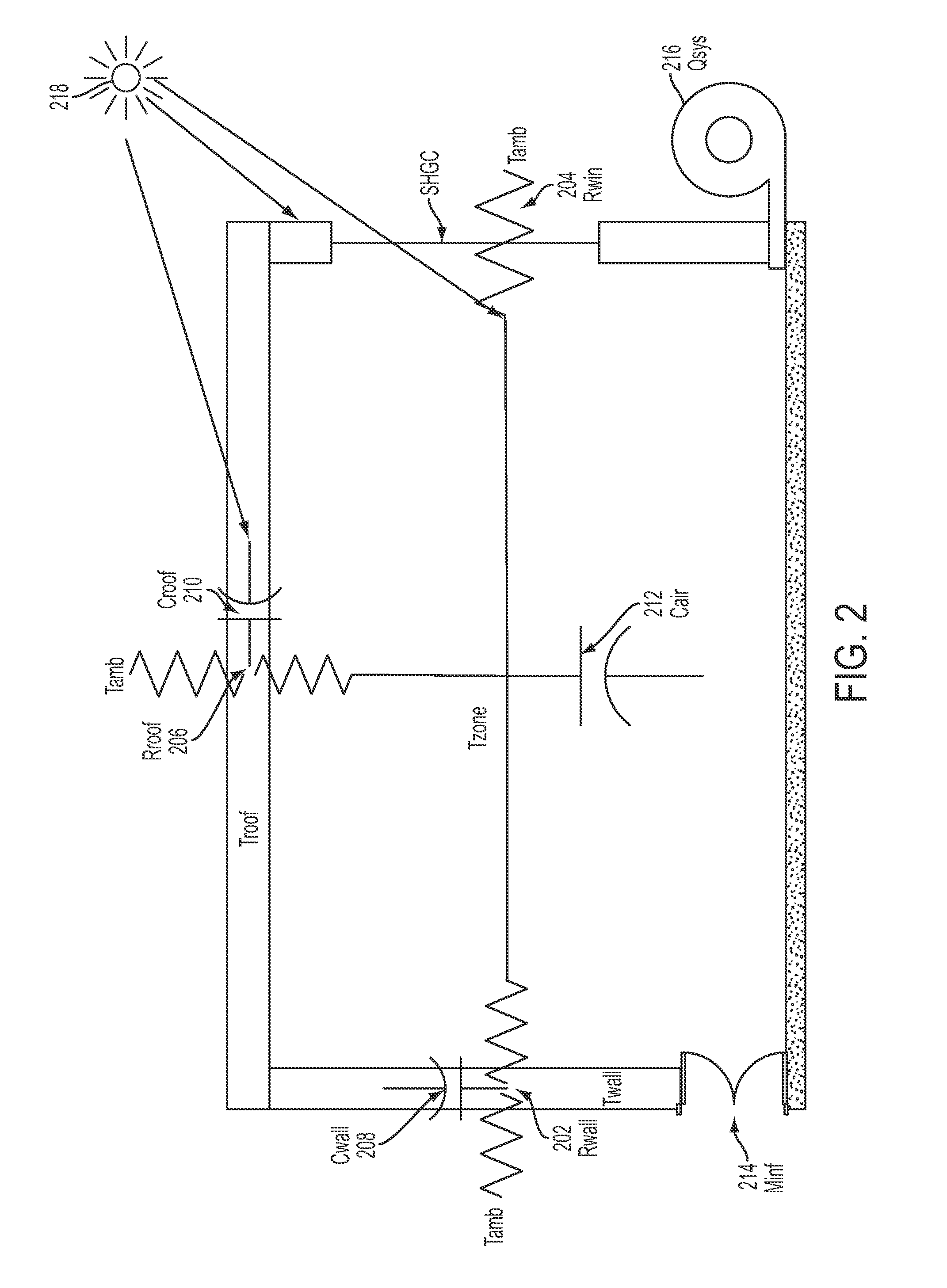
Estimating building thermal properties by integrating heat transfer inversion model with clustering and regression techniques for a portfolio of existing buildings
A static heat transfer model is derived from a system of dynamic equations by integrating the dynamic equations over different time periods. That static heat transfer model links periodic (e.g., monthly) energy usage with cooling and heating degree hours, humidifying and dehumidifying hours. Its coefficients of measuring correlations correspond to the thermal parameters of buildings. Temporal data from a building may be used to estimate the overall heat transfer parameters. A clustering scheme may be developed to decompose all the buildings into different clusters based on one or more similarity criteria. The overall heat transfer parameters are separated into values for the wall, roof and window using multiple buildings' data in the same cluster or group.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
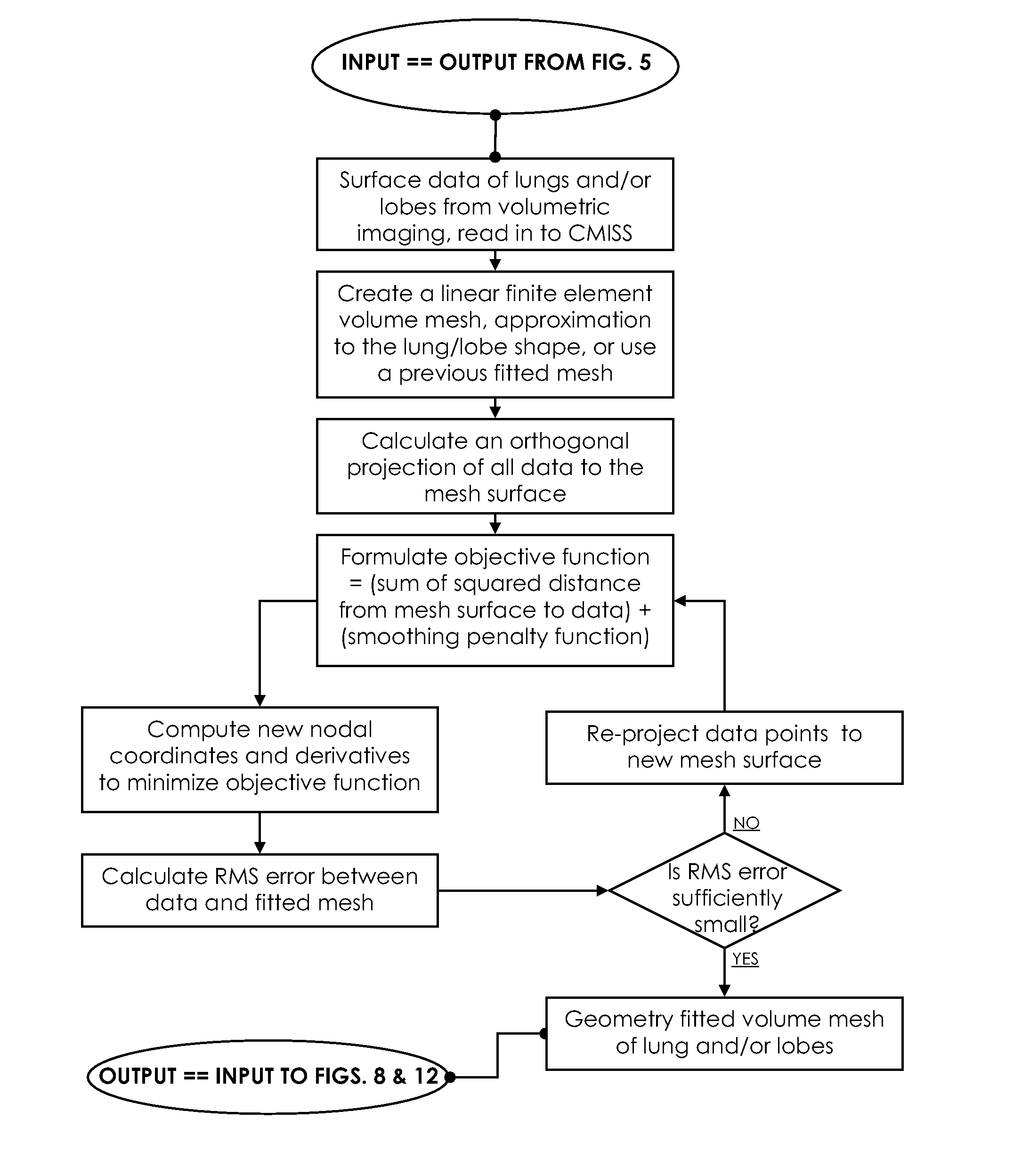
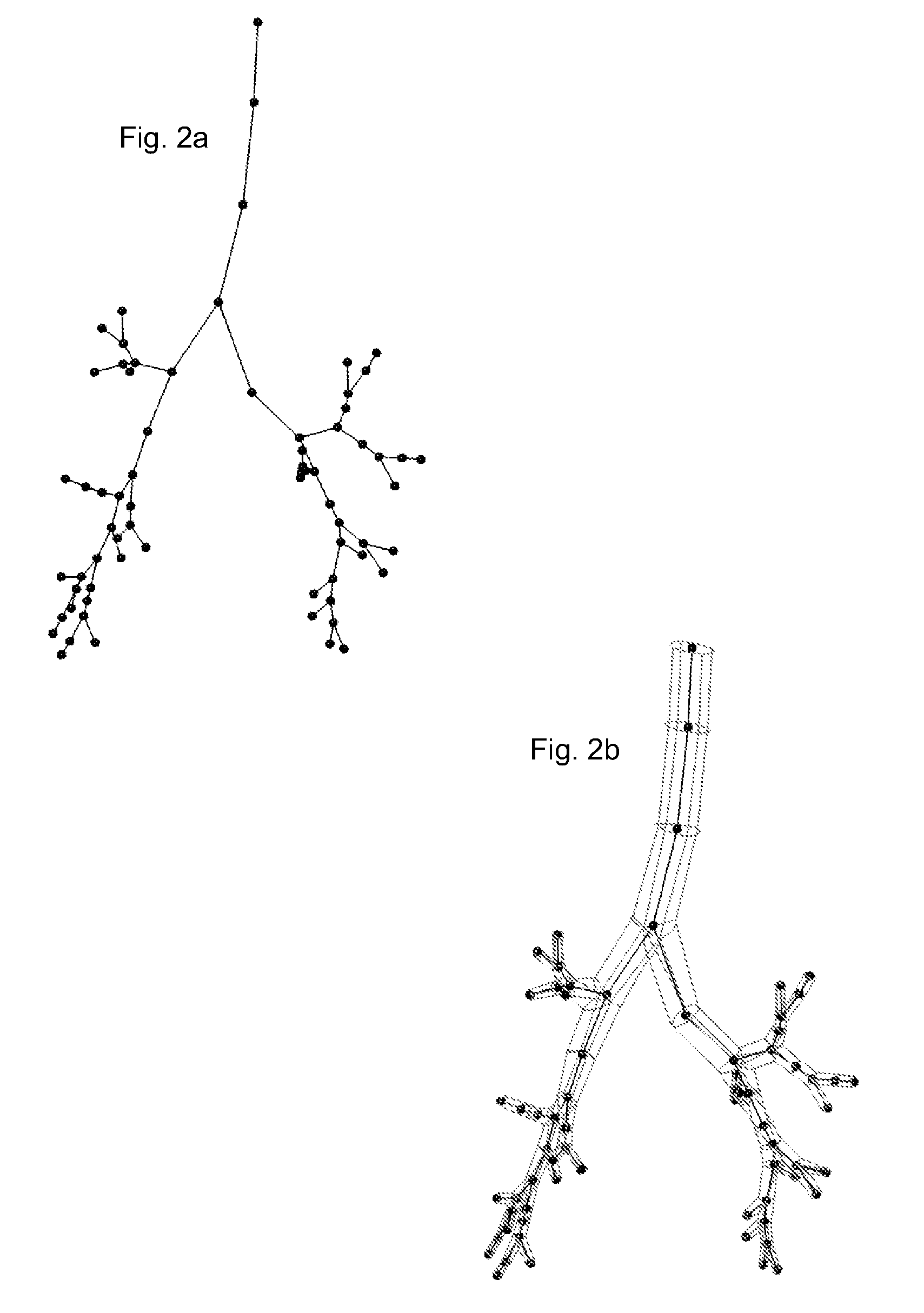
Method for multi-scale meshing of branching biological structures
InactiveUS20110093243A1Good specificationIncrease computing speedMedical simulationImage enhancementLocal pressureGrid partition
A structural and functional model for a lung or similar organ is virtually defined by encoding aspects of branching passageways. Larger passageways that are visible in medical images are surface mesh fitted to the anatomical surface geometry. Smaller distal passageways, beyond a given number of branch generations, are modeled by inference as linear passages with nominal diameters and branching characteristics, virtually filling the space within the outer envelope of the organ. The model encodes finite volumetric elements for elasticity and compliance in passageway walls, and for local pressure and flow conditions in passageway lumens during respiration. The modeling can assess organ performance, help to plan surgery or therapy, determine likely particle deposition, assess respiratory pharmaceutical dosing, and otherwise represent structural and functional organ parameters.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND +1
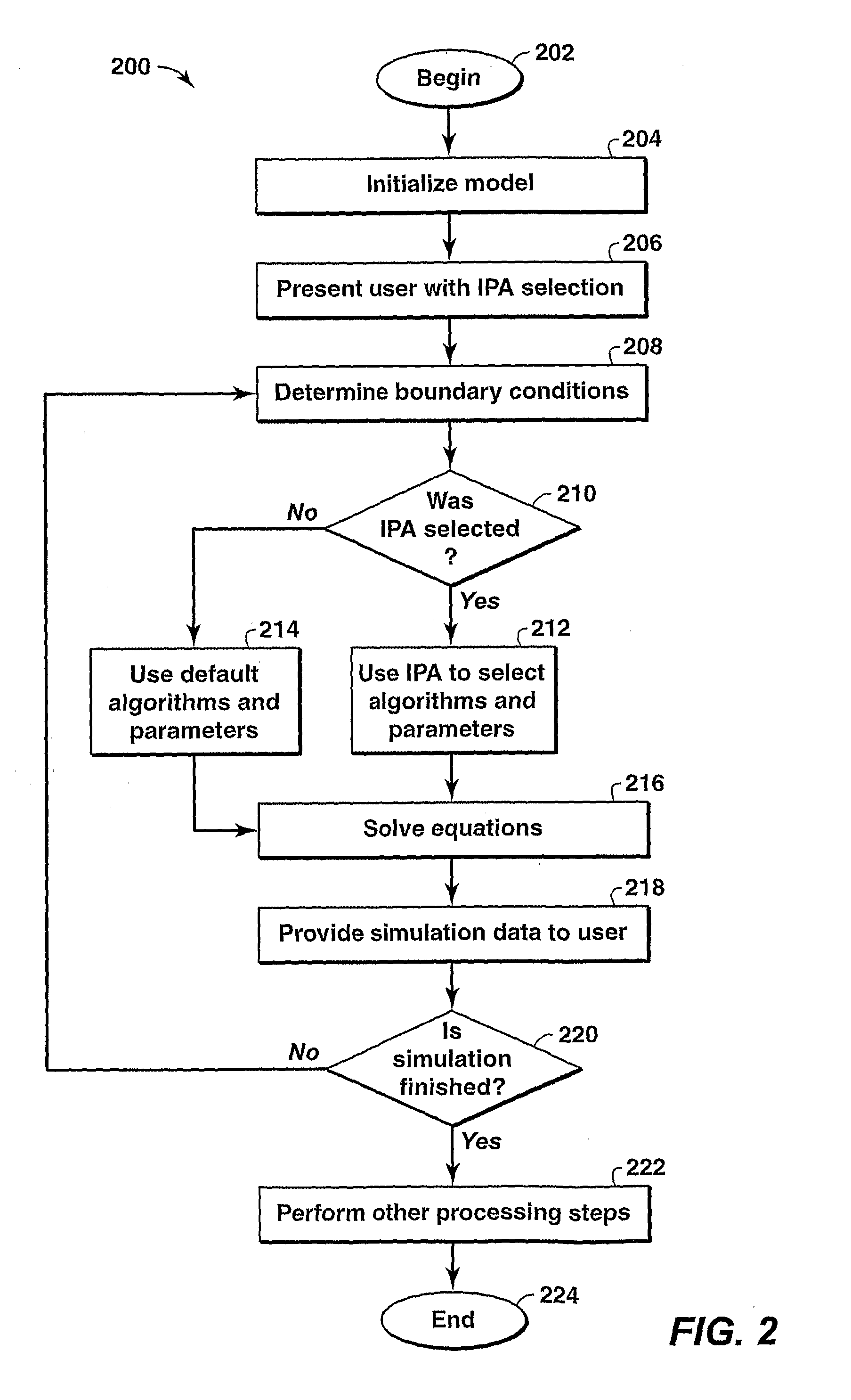
Simulation System and Method
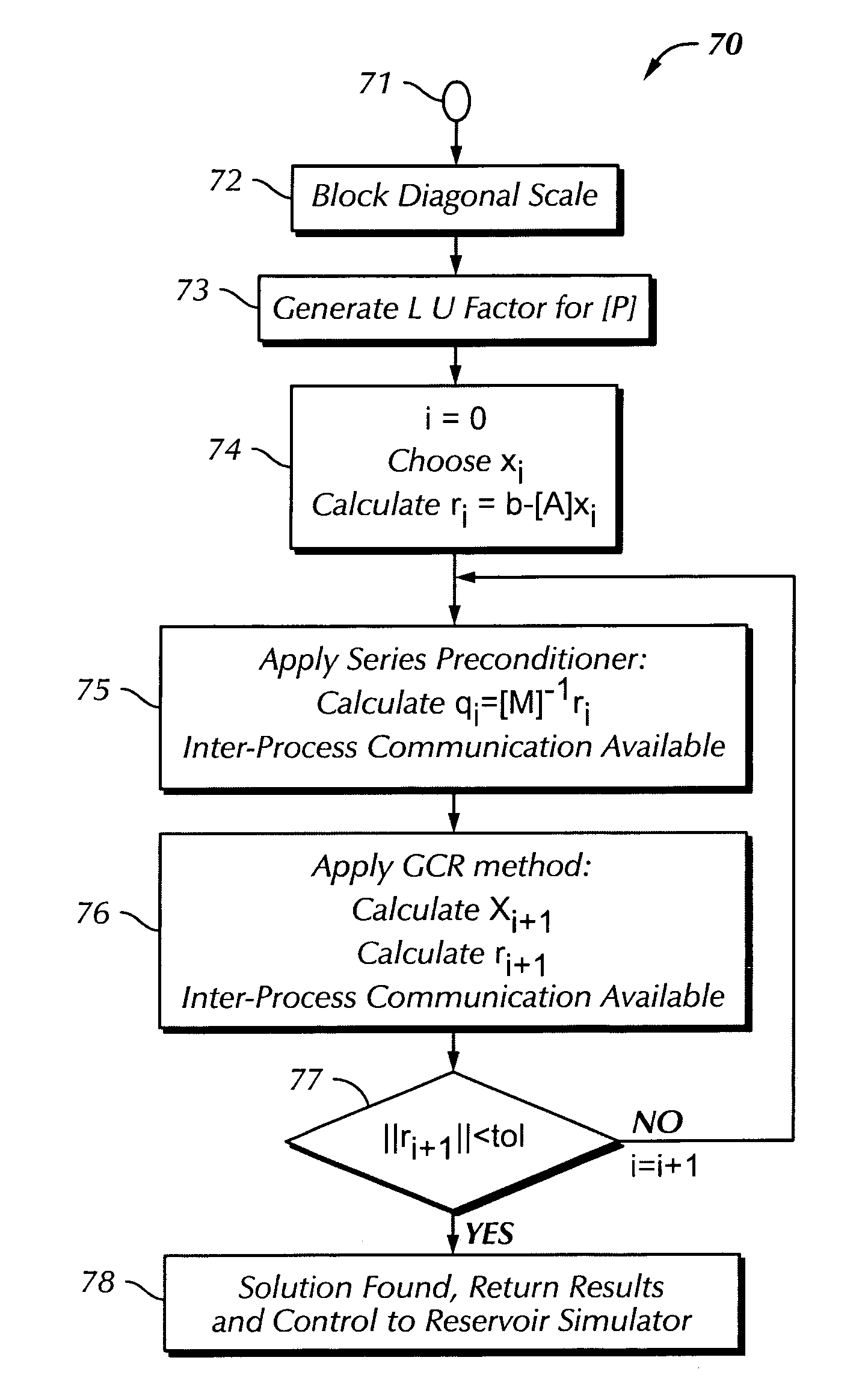
InactiveUS20100082142A1Enhance run-time performanceImprove running stabilityComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationPorous mediumComputational simulation
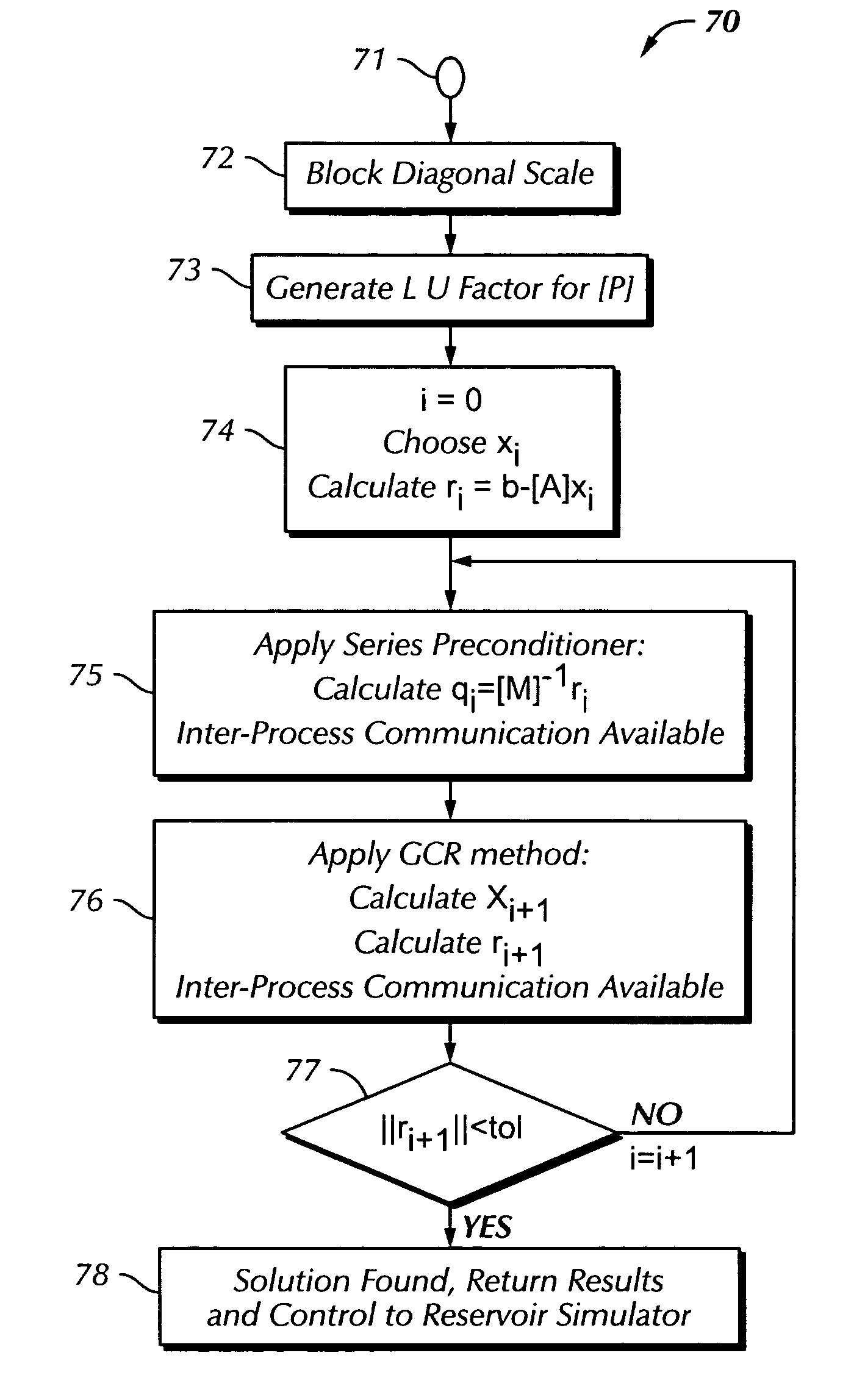
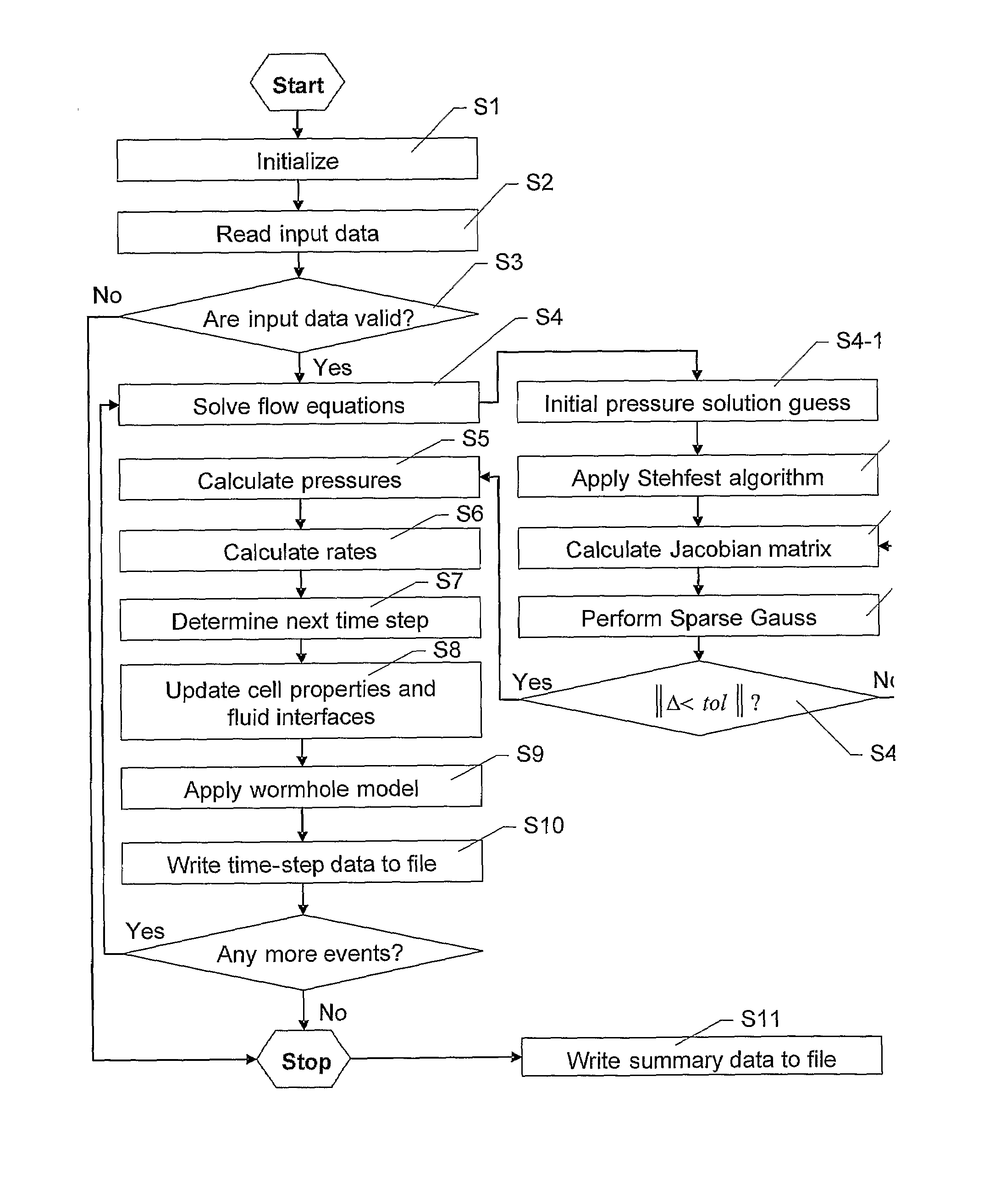
A method and system are described that enhance the computational simulation, such as a fluid flowing through a porous media, under the present techniques. In particular, a computer implemented simulation method is described that includes initializing a simulator and utilizing an intelligent performance assistant to select a set of parameters and algorithms for the simulator. Then, equations are solved with the set of parameters and algorithms and the solution to the equations is then obtained.
Owner:USADI ADAM K +6
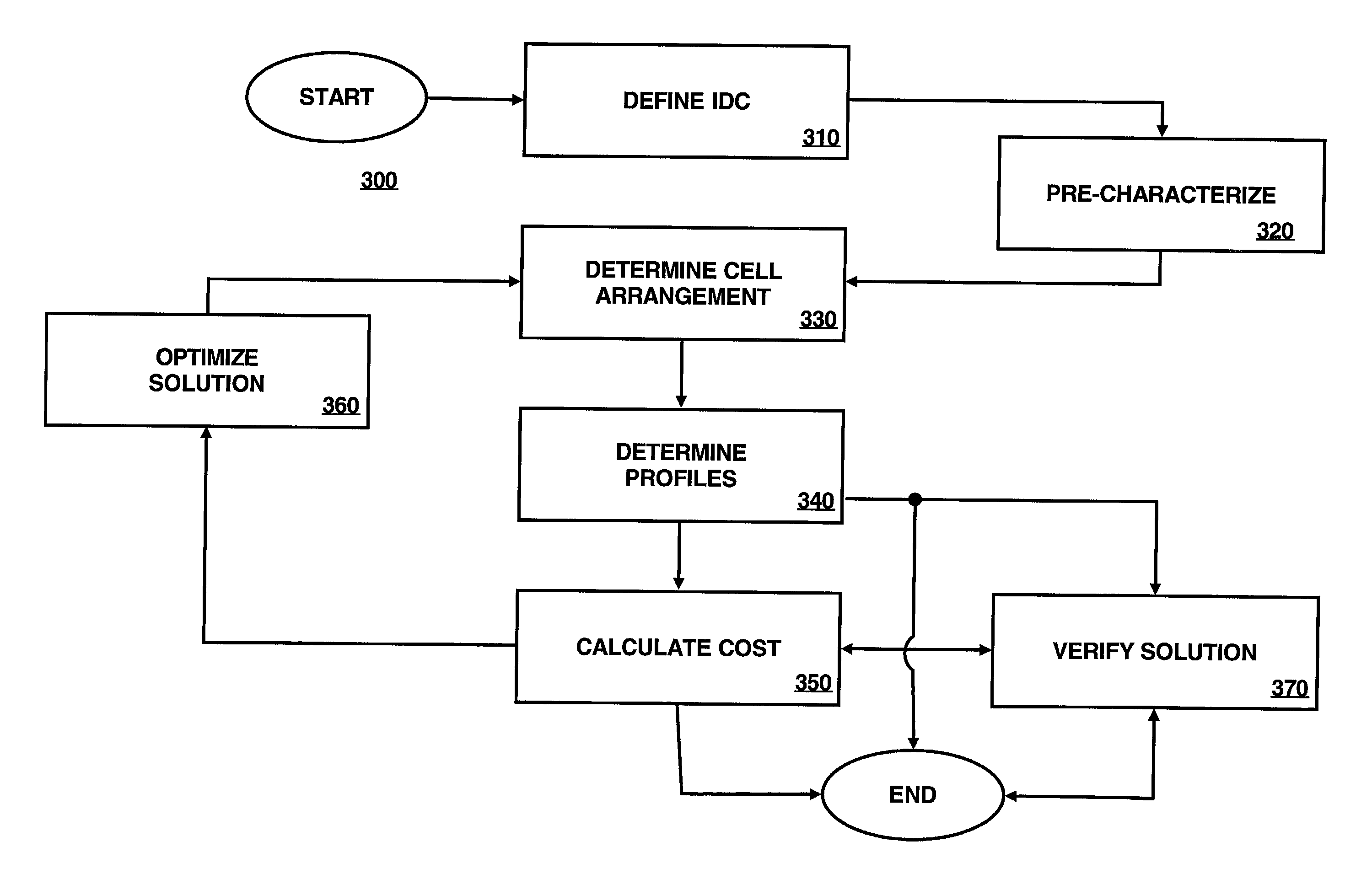
Designing layout for internet datacenter cooling
ActiveUS7313503B2Lighting and heating apparatusDomestic refrigeratorsEngineeringInternet data center
A system and method to model and design a layout of an Internet Datacenter (IDC) for cooling. The IDC is defined as a collection of cells, the cells of the IDC are pre-characterized, an arrangement of the cells within the IDC is determined, and a profile for one or more parameters of interest for each cell are determined.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Flow simulation in a well or pipe
ActiveUS20090294122A1Accurate and efficient numerical solutionImprove modeling accuracySurveyFluid removalFluid transportEngineering
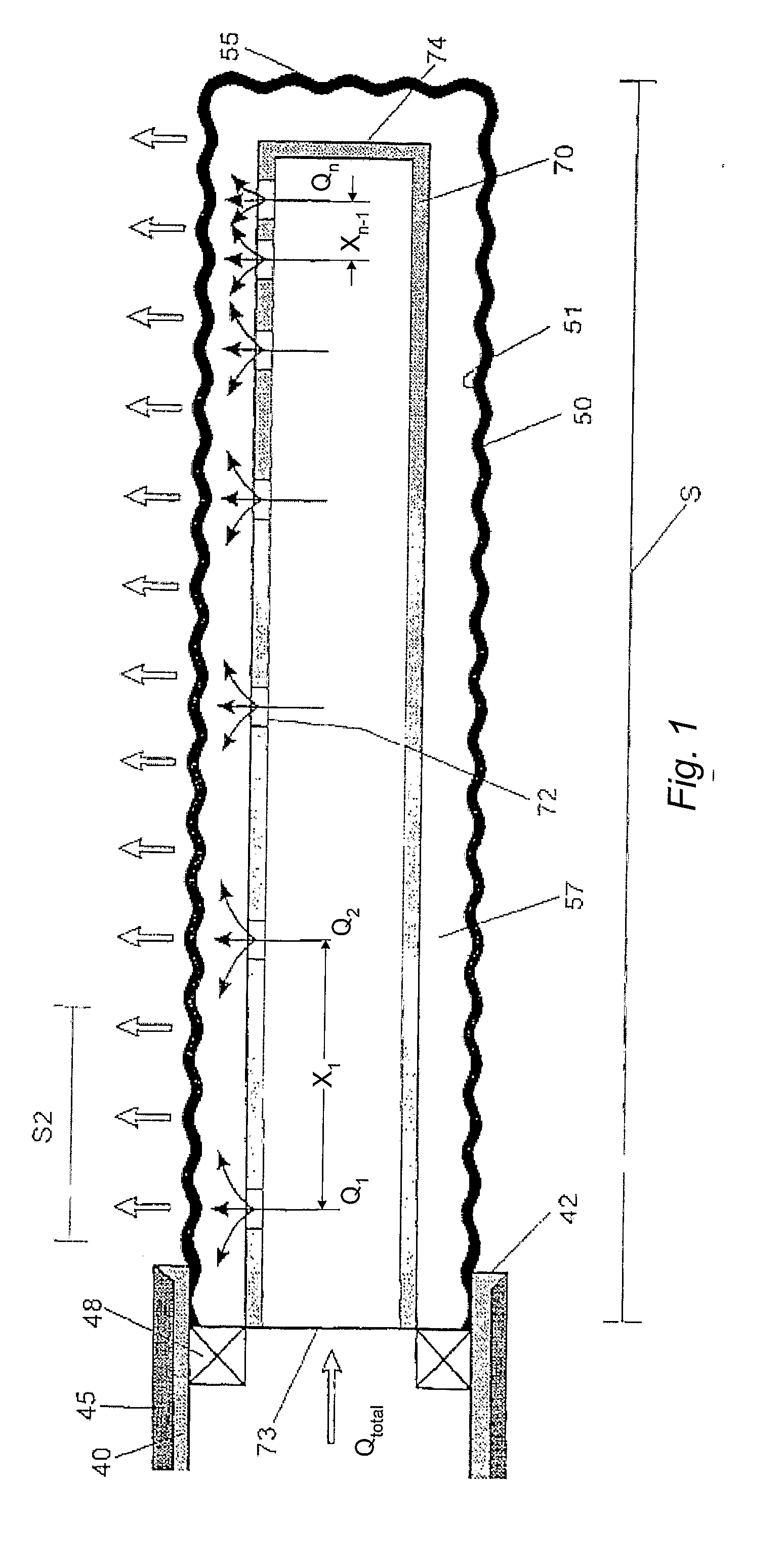
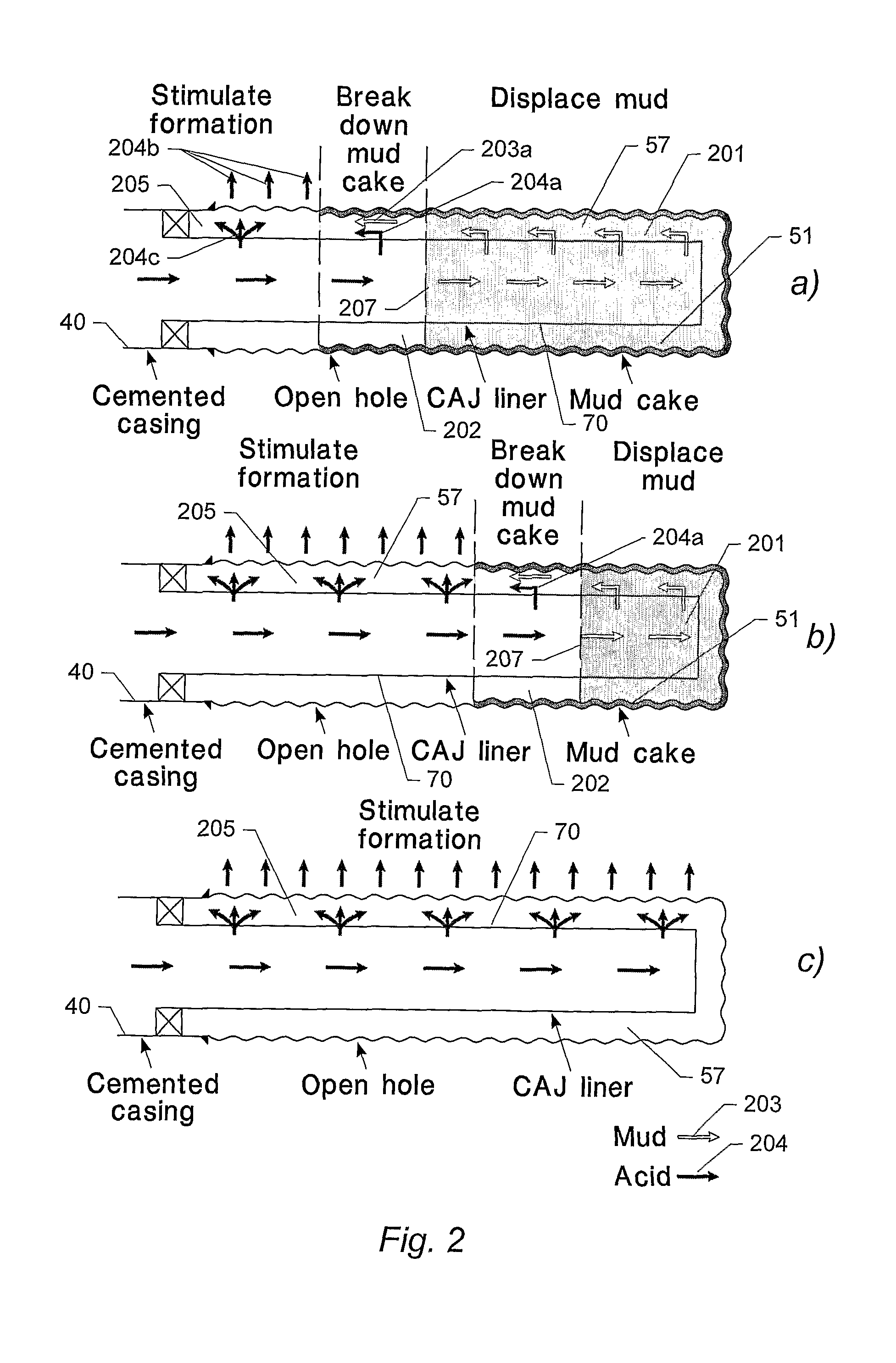
A method of simulating fluid transport in a system for stimulating a well in a material formation of a resource reservoir, the system comprising a conduit element arranged in said well, the conduit element comprising a conduit wall including one or more openings for discharging a fluid into the material formation surrounding the conduit element; the method comprising establishing and numerically processing a transport model of fluid transport inside the conduit element. The transport model further includes a model of fluid transport in a predetermined space around said conduit element.
Owner:TOTAL E&P DANMARK AS
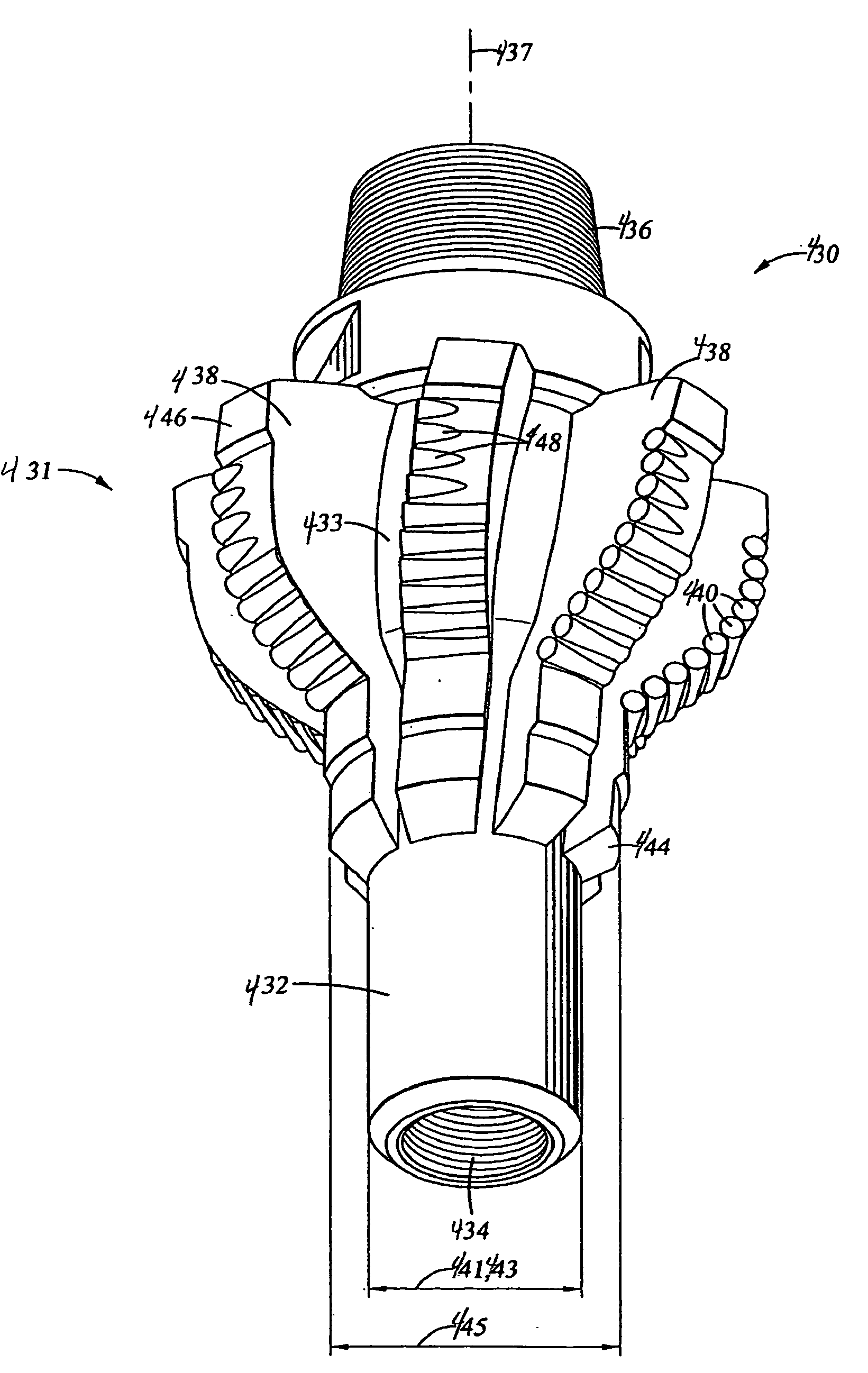
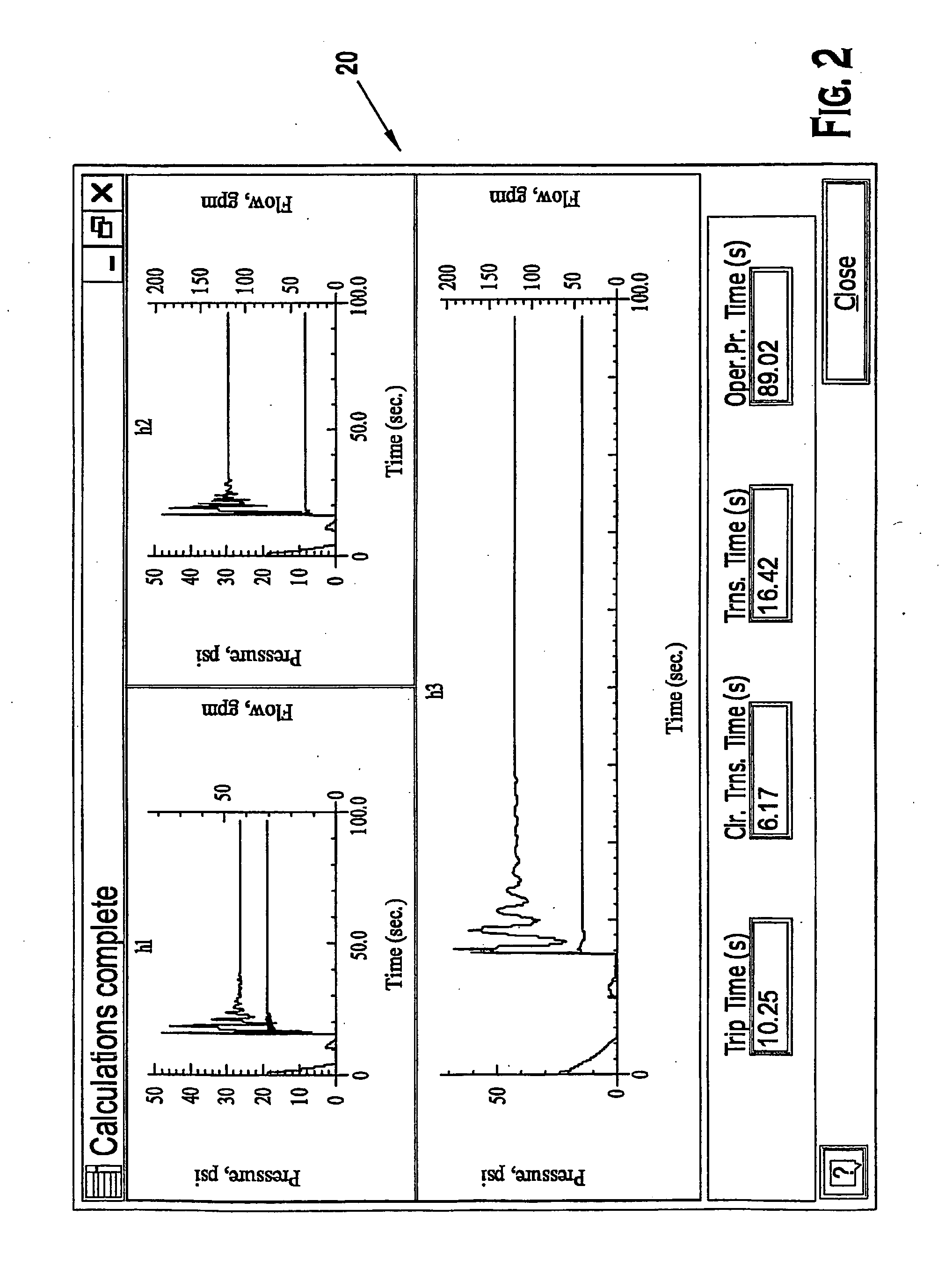
Dynamically balanced cutting tool system
A method of dynamically balancing a hole enlargement system is disclosed. The method includes modeling the hole enlargement system based on input parameters, simulating the hole enlargement system, adjusting one or more of the input parameters, and repeating the modeling, simulating, and adjusting until a balanced condition is met.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
Method for tuning patient-specific cardiovascular simulations
ActiveUS8200466B2Improve understandingImprove representationMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesReduced modelComputing Methodologies
Computational methods are used to create cardiovascular simulations having desired hemodynamic features. Cardiovascular modeling methods produce descriptions of blood flow and pressure in the heart and vascular networks. Numerical methods optimize and solve nonlinear equations to find parameter values that result in desired hemodynamic characteristics including related flow and pressure at various locations in the cardiovascular system, movements of soft tissues, and changes for different physiological states. The modeling methods employ simplified models to approximate the behavior of more complex models with the goal of to reducing computational expense. The user describes the desired features of the final cardiovascular simulation and provides minimal input, and the system automates the search for the final patient-specific cardiovascular model.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
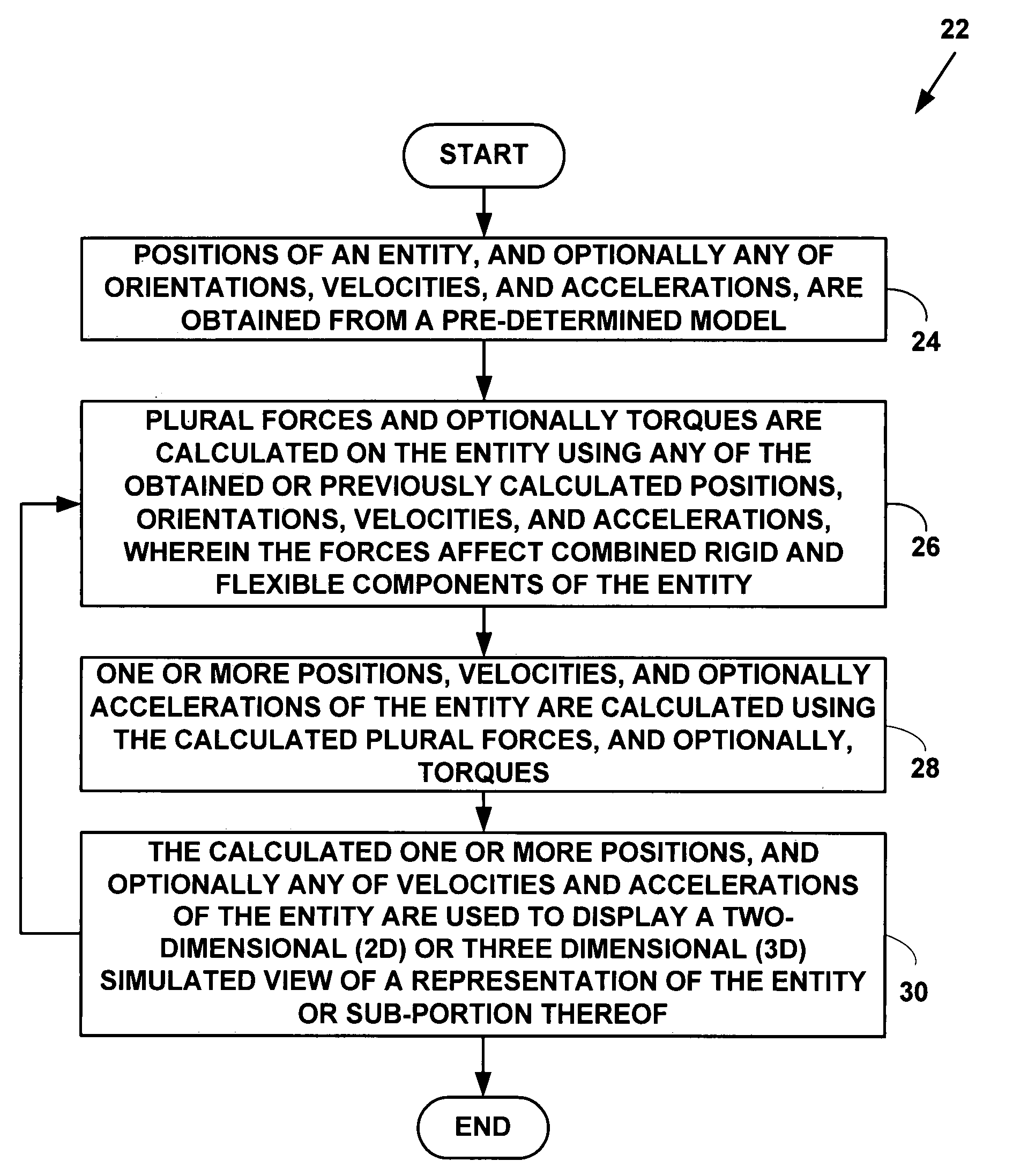
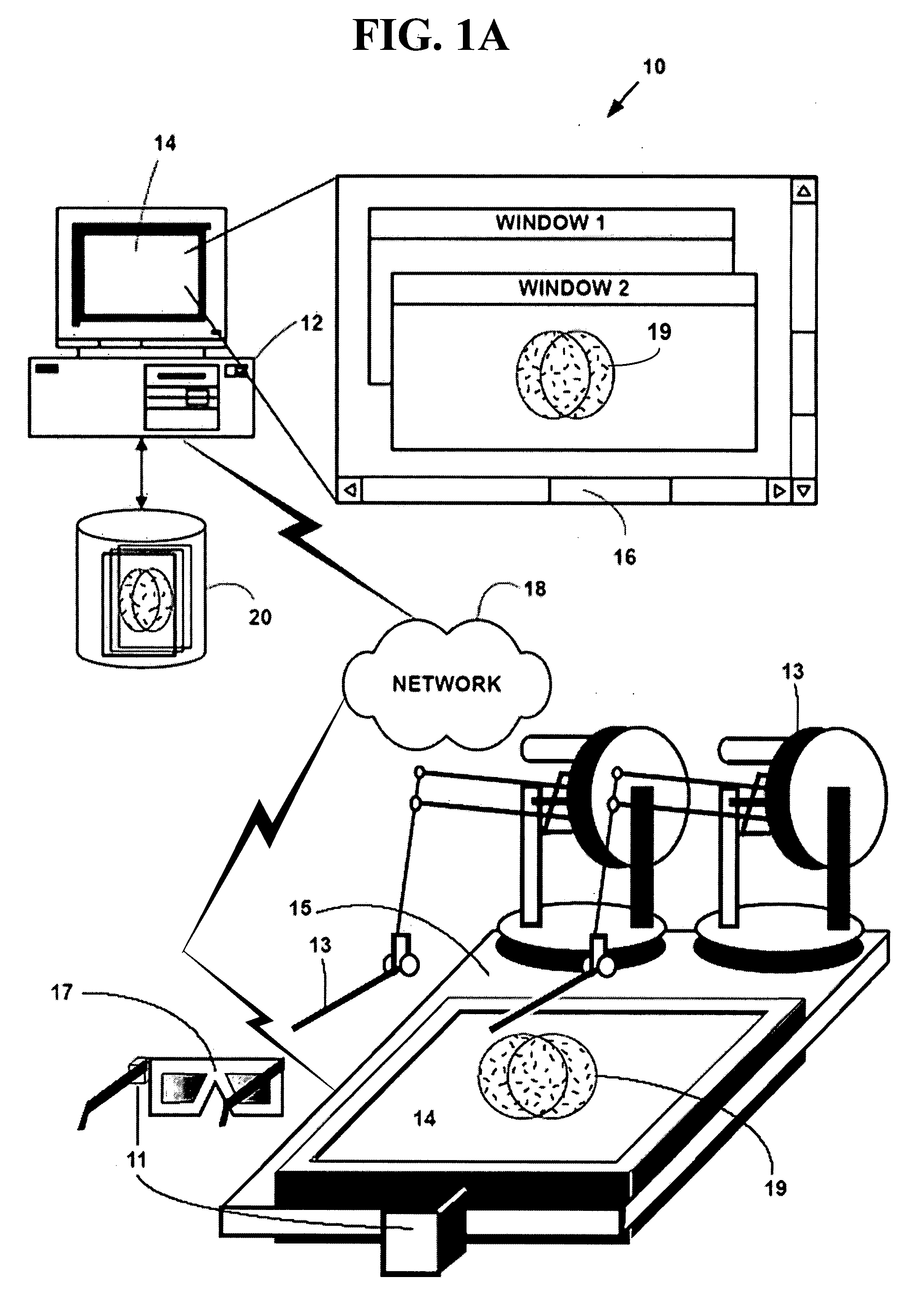
Method and system for interactive simulation of materials
ActiveUS20070239409A1Flexible simulationComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationCollision detectionComputer science
A method and system for interactive simulation of materials. The method and system provide flexible simulation, the ability to combine rigid and flexible simulation, a collision-detection method for simulating objects and other entities, and a system for displaying and interacting with simulated objects which includes a harness for registering the hardware components of the simulation with respect to each other.
Owner:MILLMAN ALAN
System and method for evaluation of fluid flow in a piping system
A method to model a complex system of pipes. The model takes into account the physical processes in a tree-type piping system and provides for an accurate modeling of a real world tree-type piping system. In a preferred embodiment, a computer program is provided for analyzing models of dry pipe systems. The computer program includes a user interface and a computational engine. The user interface allows a model of a dry pipe system to be defined and the computational engine determines a liquid flow time through the model of the dry pipe system. The computational engine provides a verification of the liquid flow time in a model of a referential dry pipe system within 20% of an actual liquid flow time in the referential dry pipe system.
Owner:TYCO FIRE PRODS LP
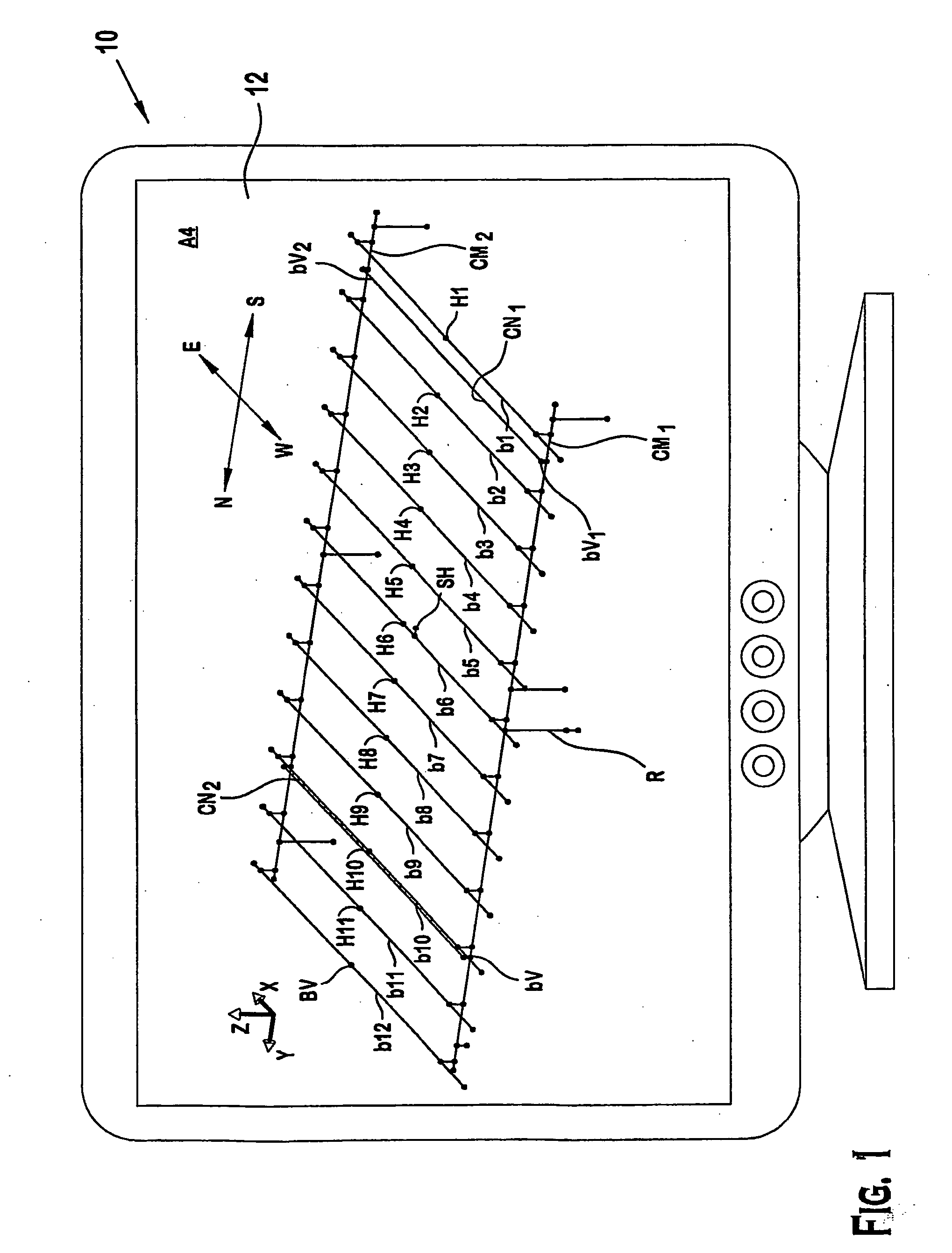
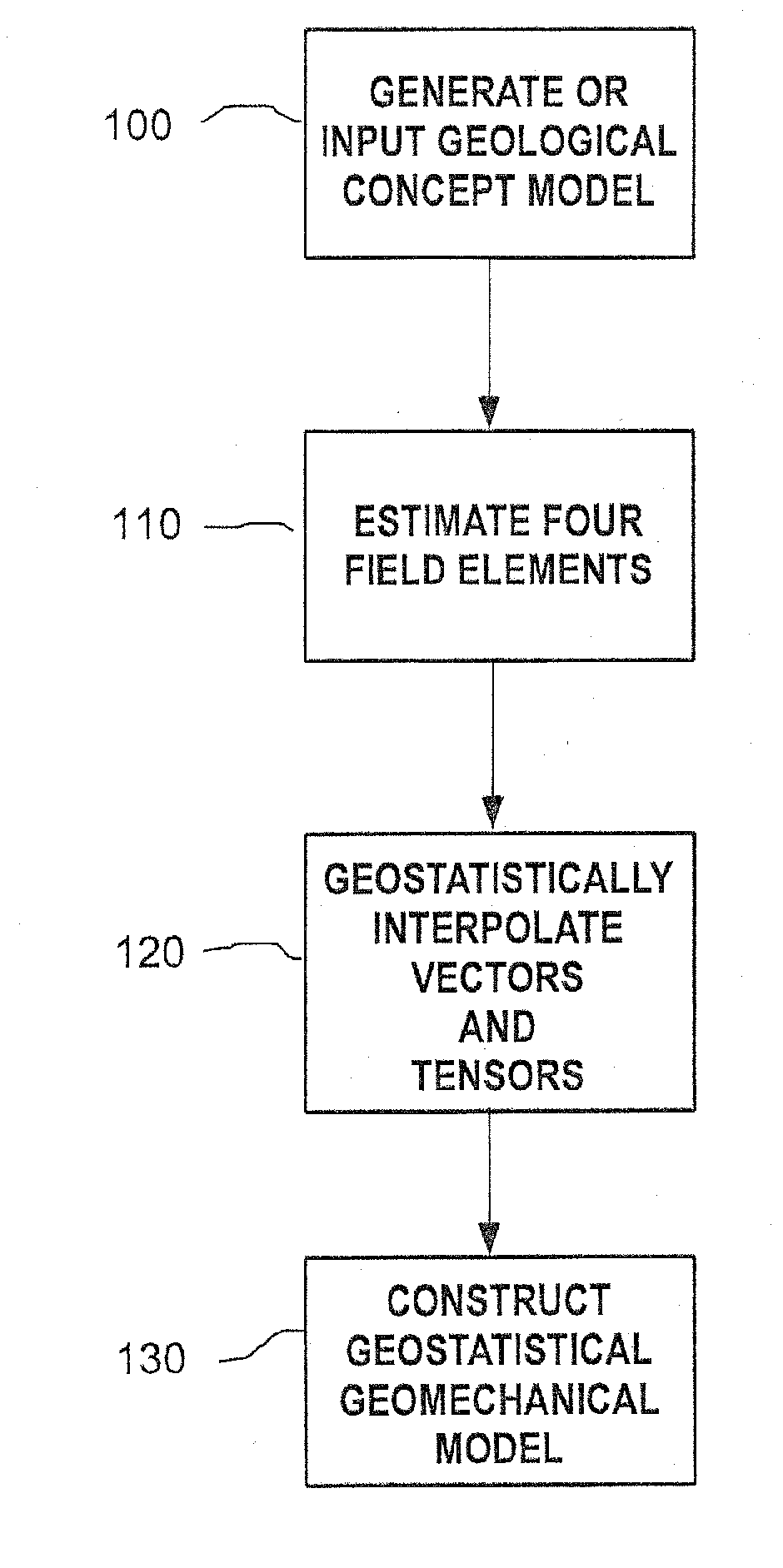
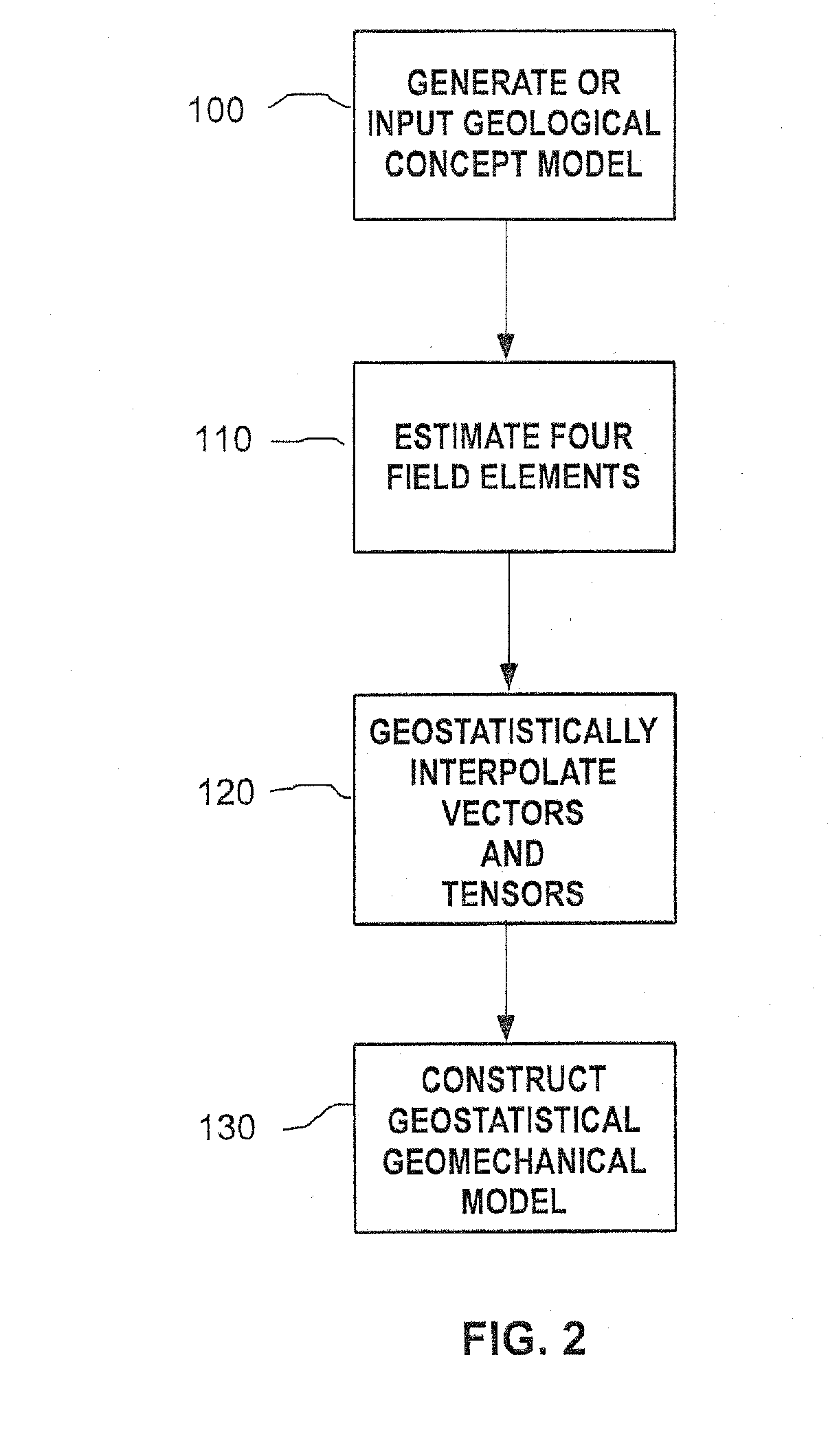
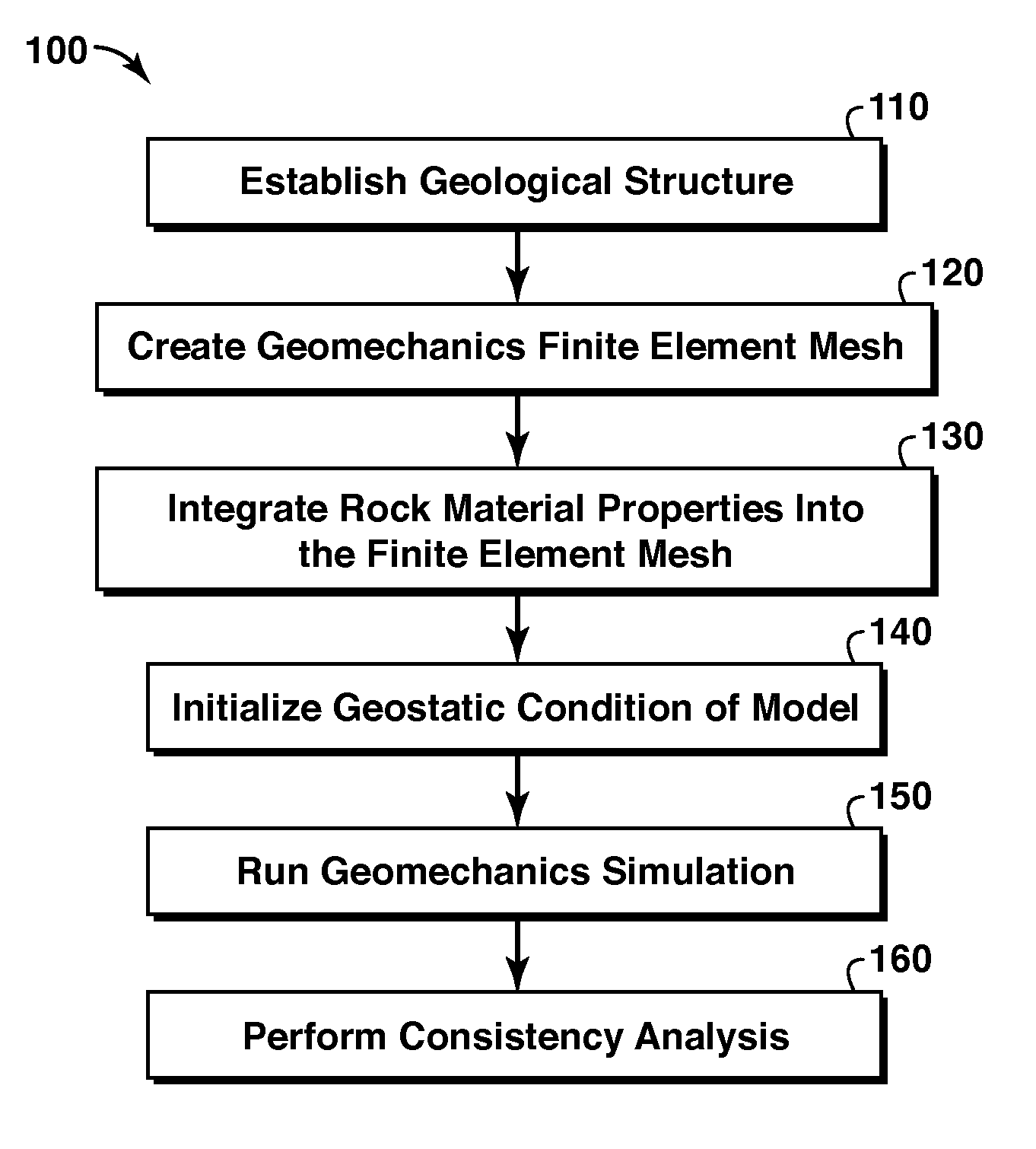
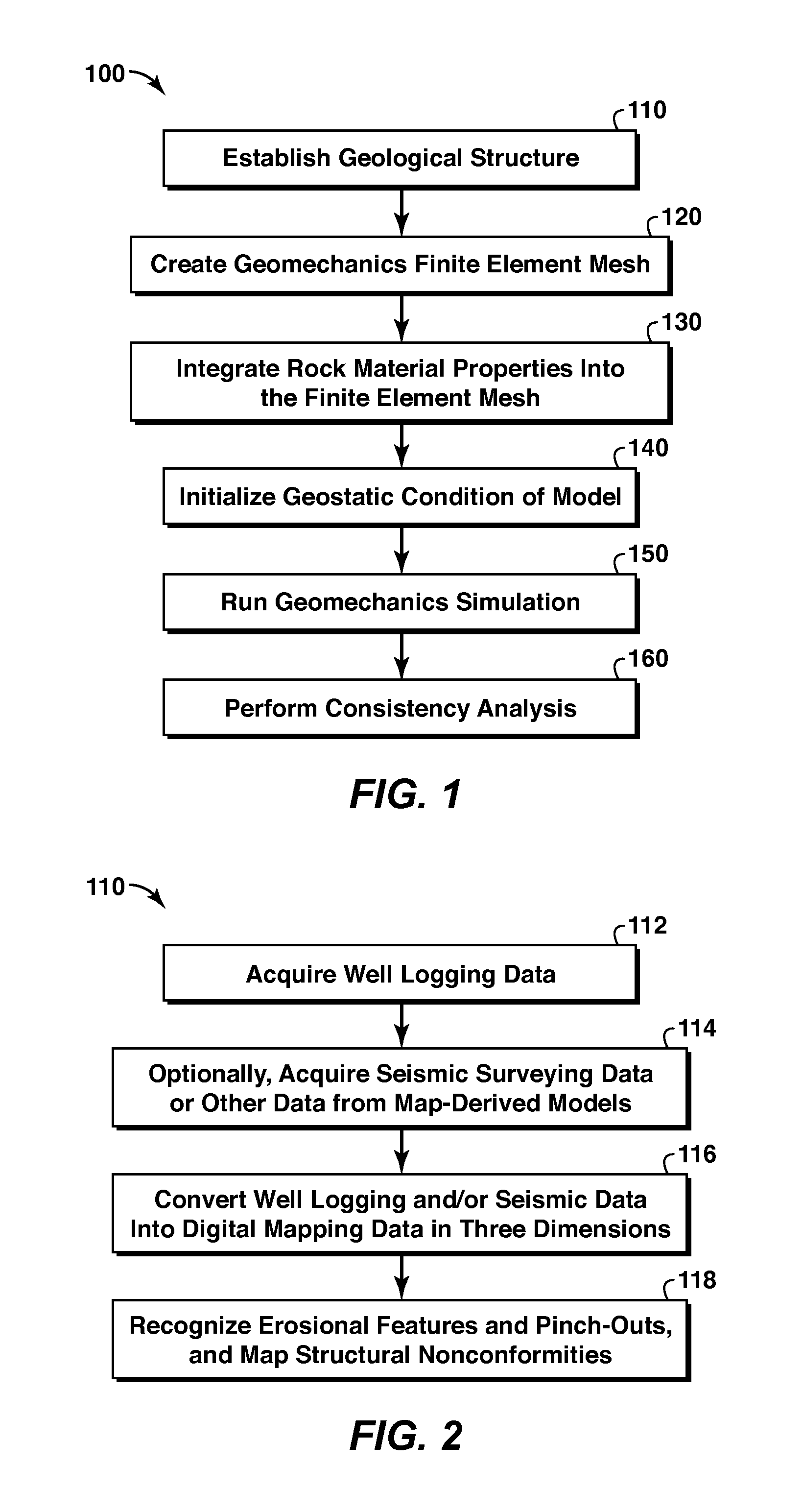
Methods and systems for constructing and using a subterranean geomechanics model spanning local to zonal scale in complex geological environments
ActiveUS20100121623A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingGeomodellingSoil scienceSubsurface geology
In an exemplary embodiment, a method and system is disclosed for developing a subterranean geomechanics model of a complex geological environment. The method can include estimating a pore pressure field, a stress field, a geomechanics property field, and a geological structure field from a geological concept model; geostatistically interpolating vectors and tensors from the estimated fields; and combining the results from the estimated fields and the geostatistically interpolated vectors and tensors to derive a geostatistical geomechanical model of the geological environment.
Owner:YOWAREN ELAN
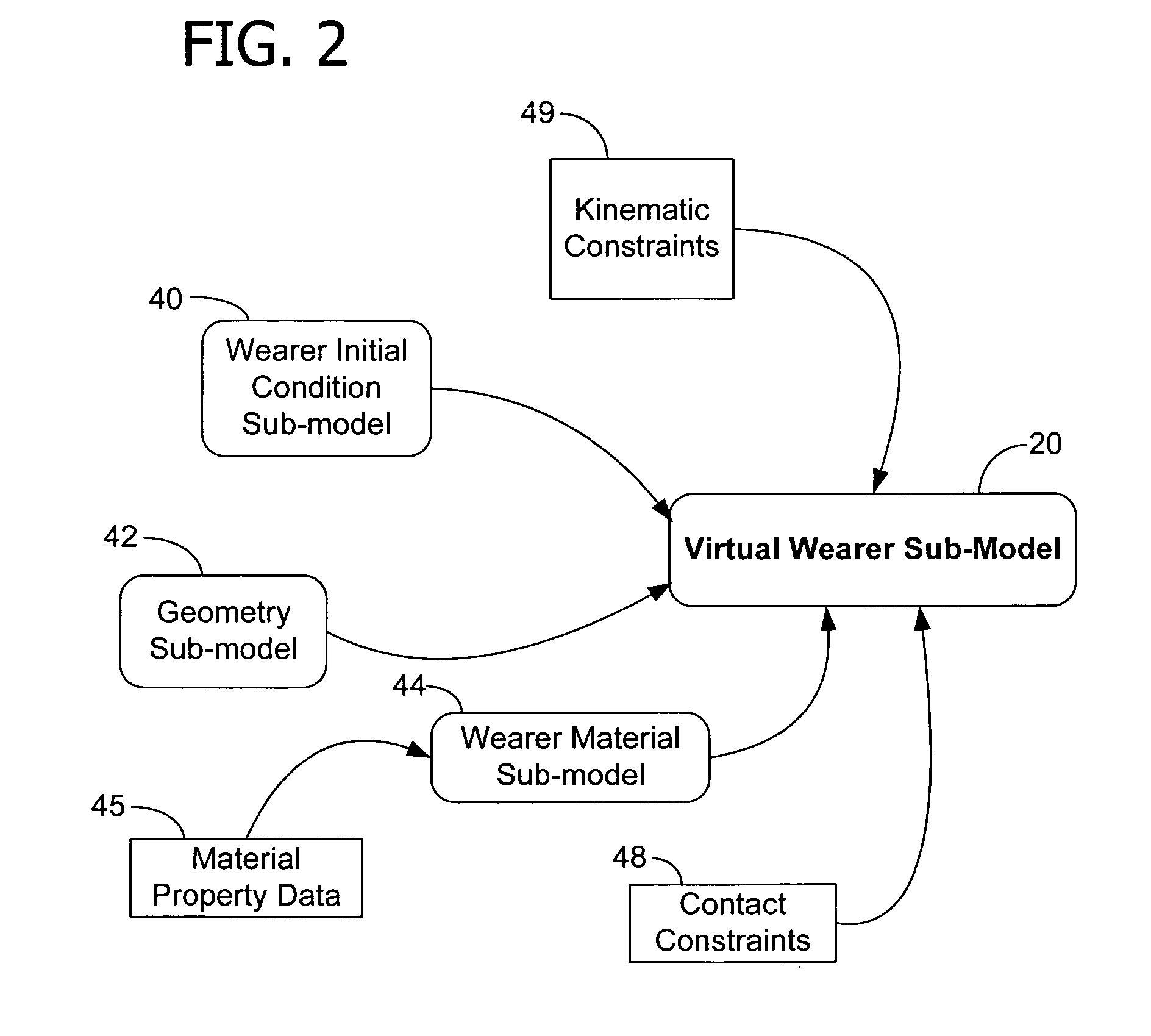
Method of evaluating the performance of a product using a virtual environment
InactiveUS20050256686A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsComputation using non-denominational number representationFluid loadingProduct characteristics
In a method of evaluating a product worn on a body, a computer based body sub-model of at least a portion of the body is created. A computer based product sub-model of the product is created, at least one parameter of which is variable as a function of fluid loading of the product. A computer based interaction model is also created to define instructions as to how the body sub-model and the product sub-model interact and to further define instructions corresponding to a fluid loading of the product. The body sub-model, the product sub-model and the interaction model are combined in a use model to simulate interaction between the body sub-model and the product sub-model in response to fluid loading of the product. The use model is evaluated to determine the performance of at least one product feature of the product in response to fluid loading of the product.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Solution method and apparatus for large-scale simulation of layered formations
ActiveUS7596480B2Design optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSupercomputerTypes of mesh
A targeted heterogeneous medium in the form of an underground layered formation is gridded into a layered structured grid or a layered semi-unstructured grid. The structured grid can be of the irregular corner-point-geometry grid type or the simple Cartesian grid type. The semi-unstructured grid is really unstructured, formed by arbitrarily connected control-volumes derived from the dual grid of a suitable triangulation; but the connectivity pattern does not change from layer to layer. Problems with determining fluid movement and other state changes in the formation are solved by exploiting the layered structure of the medium. The techniques are particularly suited for large-scale simulation by parallel processing on a supercomputer with multiple central processing units (CPU's).
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Multi-scale mesh modeling software products and controllers
ActiveUS20160321384A1Accurately predict thermalAccurately stress/strain fieldProgramme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusCoarse meshModeling software
Simulation systems, manufacturing systems, software products and controllers are provided with multi-scale modeling in which a coarse mesh and a fme mesh that models a stimulus are decoupled. The fine mesh can be moved within the coarse mesh with a cut and paste operation. The coarse mesh is updated by sparsely propagated effects through the coarse mesh. Simulations of the invention can be conducted in real-time, and be used as controllers in manufacturing systems, such as additive manufacturing systems. A number of efficient methods are provided for solving meshing determinations that arise from movement of a stimulus modeled within a fine mesh.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
Method For Modeling Deformation In Subsurface Strata
ActiveUS20110166843A1Minimize prospectElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyElement analysisMechanical property
A method for modeling deformation in subsurface strata, including defining physical boundaries for a geomechanical system. The method also includes acquiring one or more mechanical properties of the subsurface strata within the physical boundaries, and acquiring one or more thermal properties of the subsurface strata within the physical boundaries. The method also includes creating a computer-implemented finite element analysis program representing the geomechanical system and defining a plurality of nodes representing points in space, with each node being populated with at least one of each of the mechanical properties and the thermal properties. The program solves for in situ stress at selected nodes within the mesh.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Microfabricated fluidic circuit elements and applications
InactiveUS6953058B2Macroscopic control lines exiting the chip are minimized or eliminatedGeometric CADOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFluidicsNOR gate
The present invention provides microfabricated fluidic systems and methods. Microfabricated fluidic devices of the present invention include switches that can be opened and closed to allow or block the flow of fluid through a channel in response to the pressure level in a gate of the switch. The microfabricated fluidic switches may be coupled together to perform logic functions and Boolean algebra, such as inverters, AND gates, NAND, gates, NOR gates, and OR gates. The logic gates may be coupled together to form flip-flops that latch signals. The present invention also includes microfabricated fluidic pressure multipliers that increase the pressure in a second chamber relative to a first chamber. Microfabricated fluidic devices of the present invention also include pressure sources. A pressure source of the present includes a pump coupled to a reservoir through unidirectional valves. The pressure source may be high pressure source or a low pressure source. Microfabricated fluidic devices of the present invention may also include devices that perform analog functions such as switching regulator.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
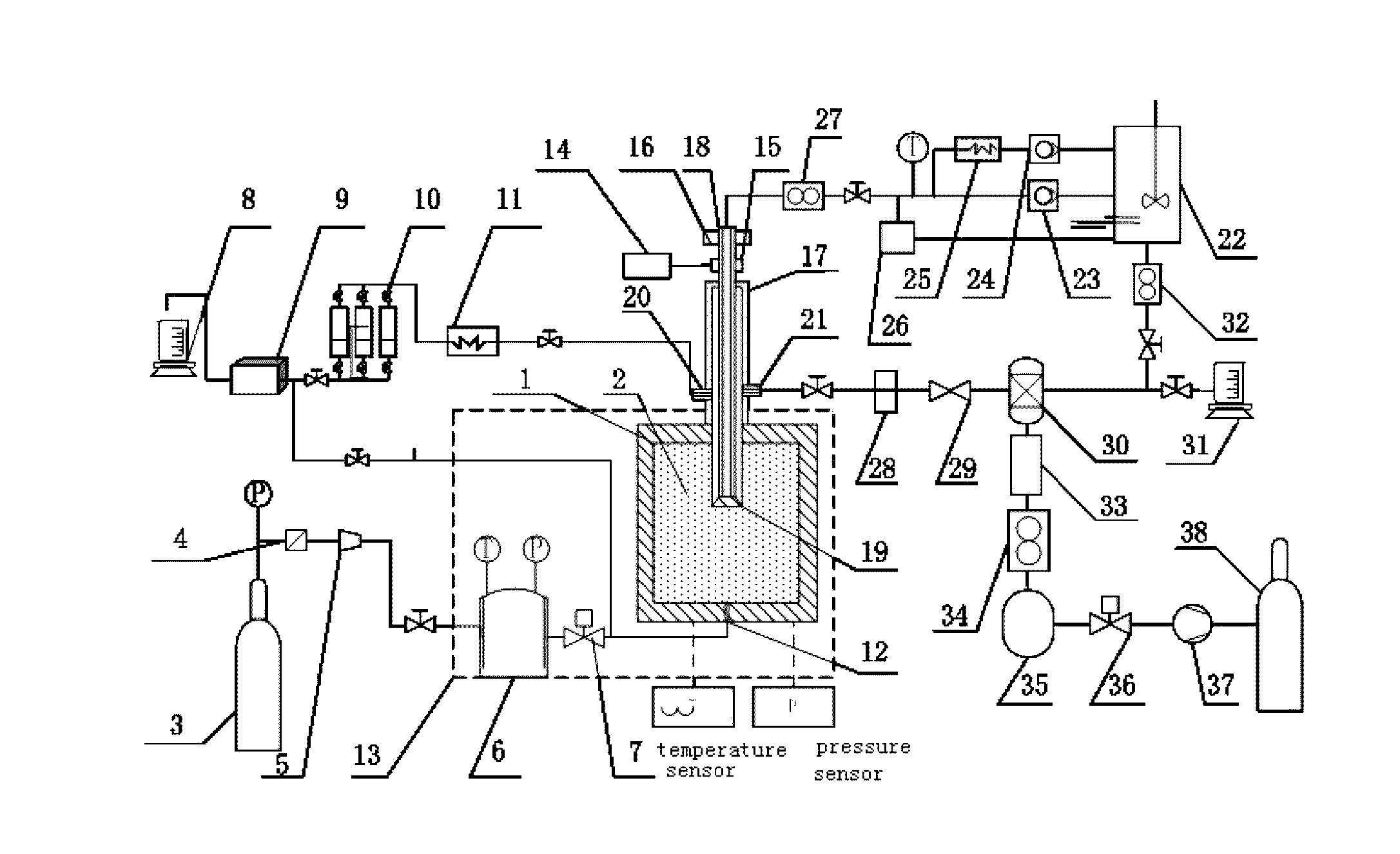
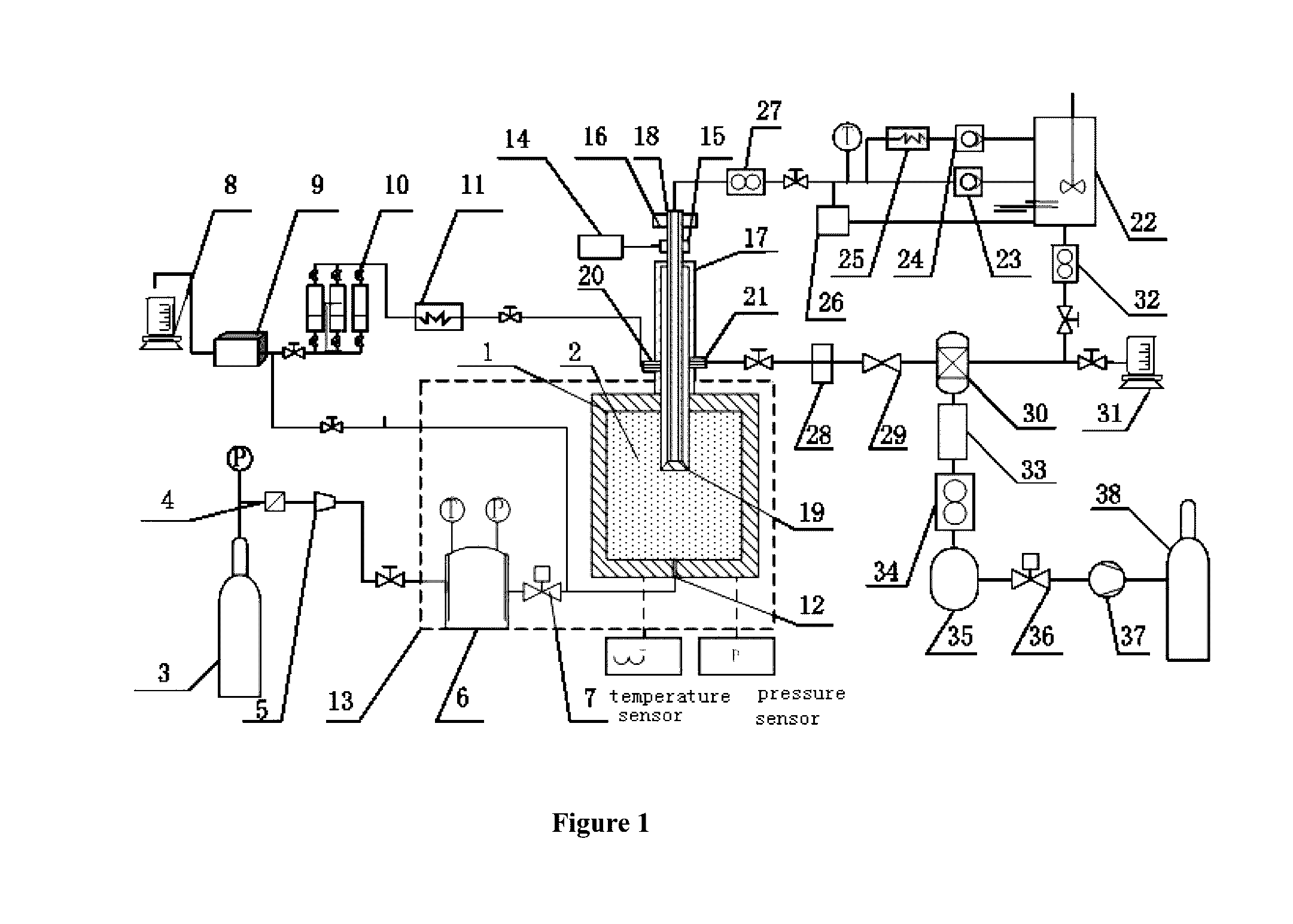
Simulation experiment system and simulation method of entire natural gas hydrate exploitation process
ActiveUS20160357888A1Easy to operateStrong practical valueSurveyConstructionsProduct gasHydrate decomposition
A simulation device of an entire natural gas hydrate exploitation process includes a high pressure reaction kettle, a gas-liquid separation device, a hydrate accumulation simulation subsystem simulating a hydrate accumulation process, a hydrate formation drilling simulation subsystem simulating a hydrate formation drilling process, a hydrate exploitation simulation subsystem simulating a hydrate decomposition and gas production process, and a produced gas collecting and processing simulation subsystem simulating a produced gas collecting and processing process. A method for simulating an entire natural gas hydrate exploitation process includes a hydrate accumulation process, a hydrate formation drilling process, a hydrate exploitation process and a produced gas collecting and processing process. With this simulation device and method, the external environment can be truly simulated, so that the authenticity and accuracy are better, and the entire natural gas hydrate exploitation process is continuously simulated and comprehensively evaluated to provide guidance for natural gas hydrate exploitation.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
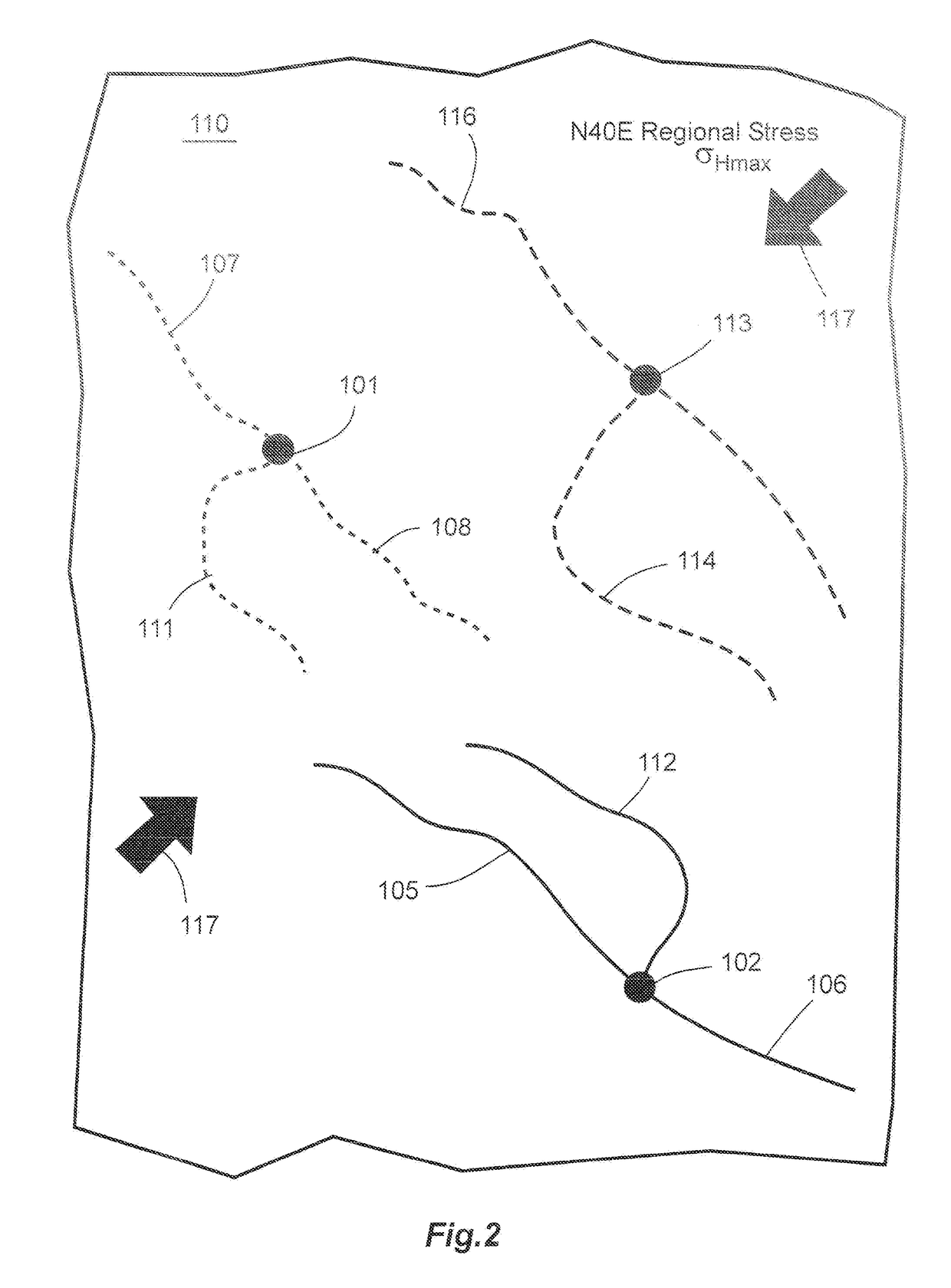
Method For Modeling Stimulated Reservoir Properties Resulting From Hydraulic Fracturing In Naturally Fractured Reservoirs
InactiveUS20170145793A1Increase productionLow costFluid removalDesign optimisation/simulationPrincipal stressHydraulic fracturing
A method for optimizing hydraulic fracturing simulates the geomechanical interaction between regional stress and natural fractures in a reservoir. An equivalent fracture model is created from data on the natural fracture density, regional stress and geomechanical properties of the reservoir, so that points in the reservoir are assigned a fracture length and fracture orientation. The horizontal differential stress and maximum principal stress direction at points in the reservoir are then estimated by meshless particle-based geomechanical simulation using the equivalent fracture model as an input. The meshless particle-based geomechanical simulator uses the derived initial geomechanical condition to simulate the sequence of hydraulic fracturing and derive the resulting strain and J integral that can be used to estimate the asymmetric half fracture lengths and initial propped permeability needed by hydraulic fracturing design and reservoir simulation software to optimize wellbore and completion stage positions.
Owner:FRACGEO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com