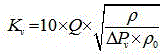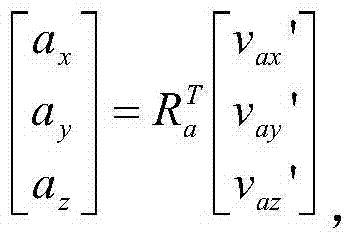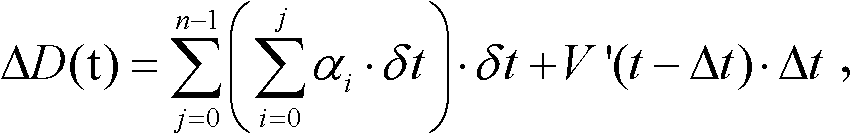Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
279 results about "Computing Methodologies" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Computer-assisted analysis and processing of problems in a particular area.
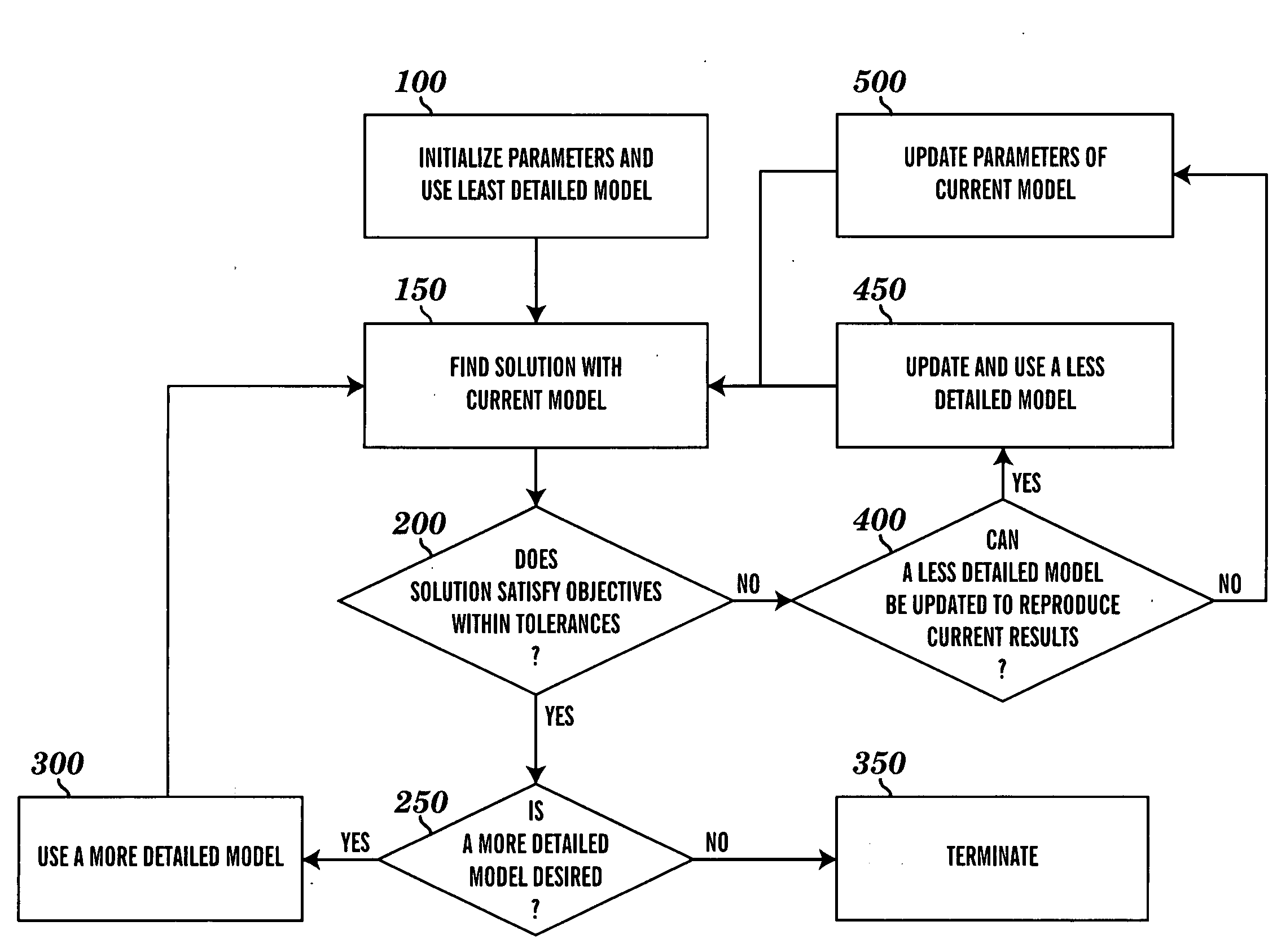
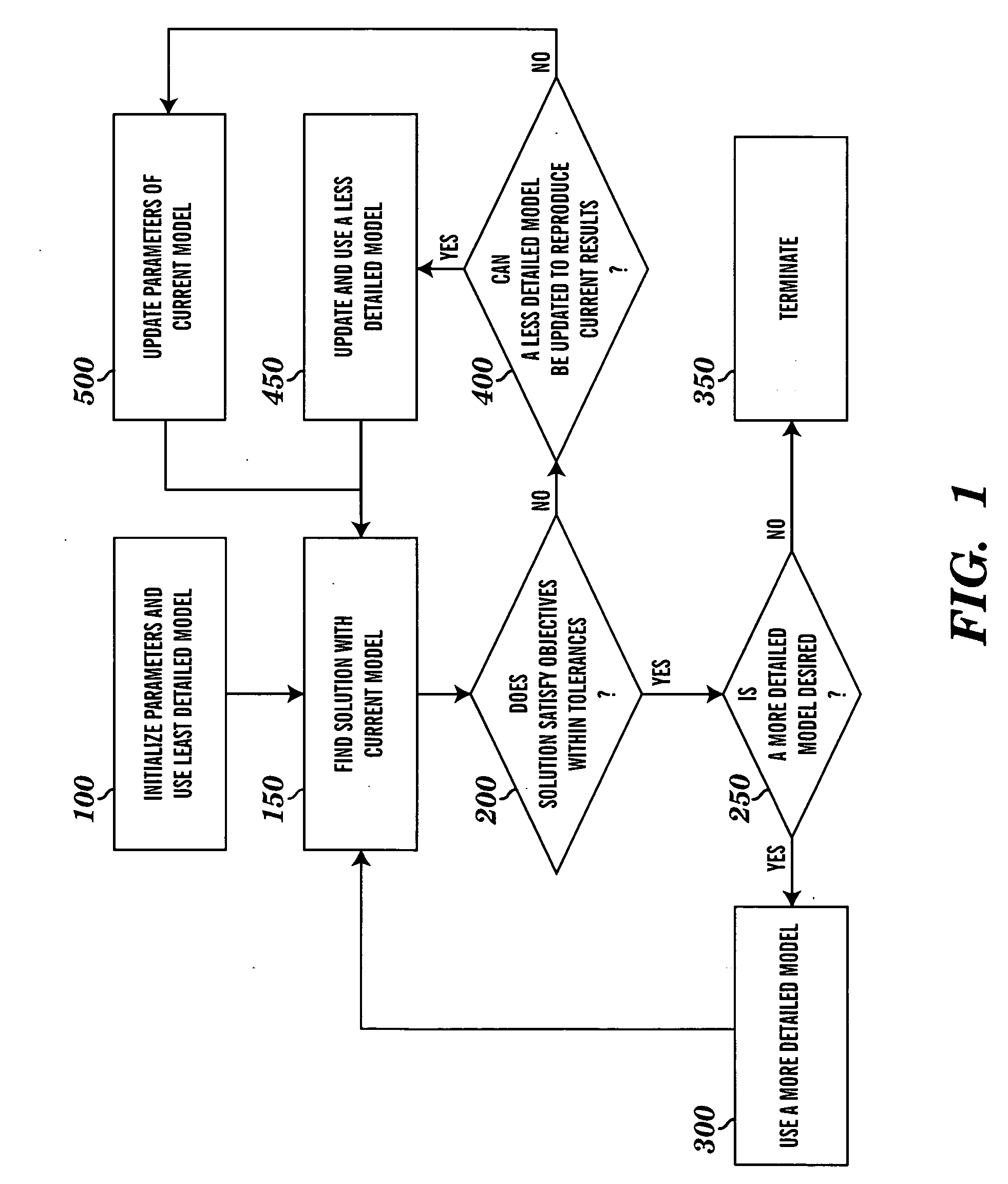
Method for tuning patient-specific cardiovascular simulations
ActiveUS20100017171A1Improve understandingImprove representationMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesReduced modelComputing Methodologies
Computational methods are used to create cardiovascular simulations having desired hemodynamic features. Cardiovascular modeling methods produce descriptions of blood flow and pressure in the heart and vascular networks. Numerical methods optimize and solve nonlinear equations to find parameter values that result in desired hemodynamic characteristics including related flow and pressure at various locations in the cardiovascular system, movements of soft tissues, and changes for different physiological states. The modeling methods employ simplified models to approximate the behavior of more complex models with the goal of to reducing computational expense. The user describes the desired features of the final cardiovascular simulation and provides minimal input, and the system automates the search for the final patient-specific cardiovascular model.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
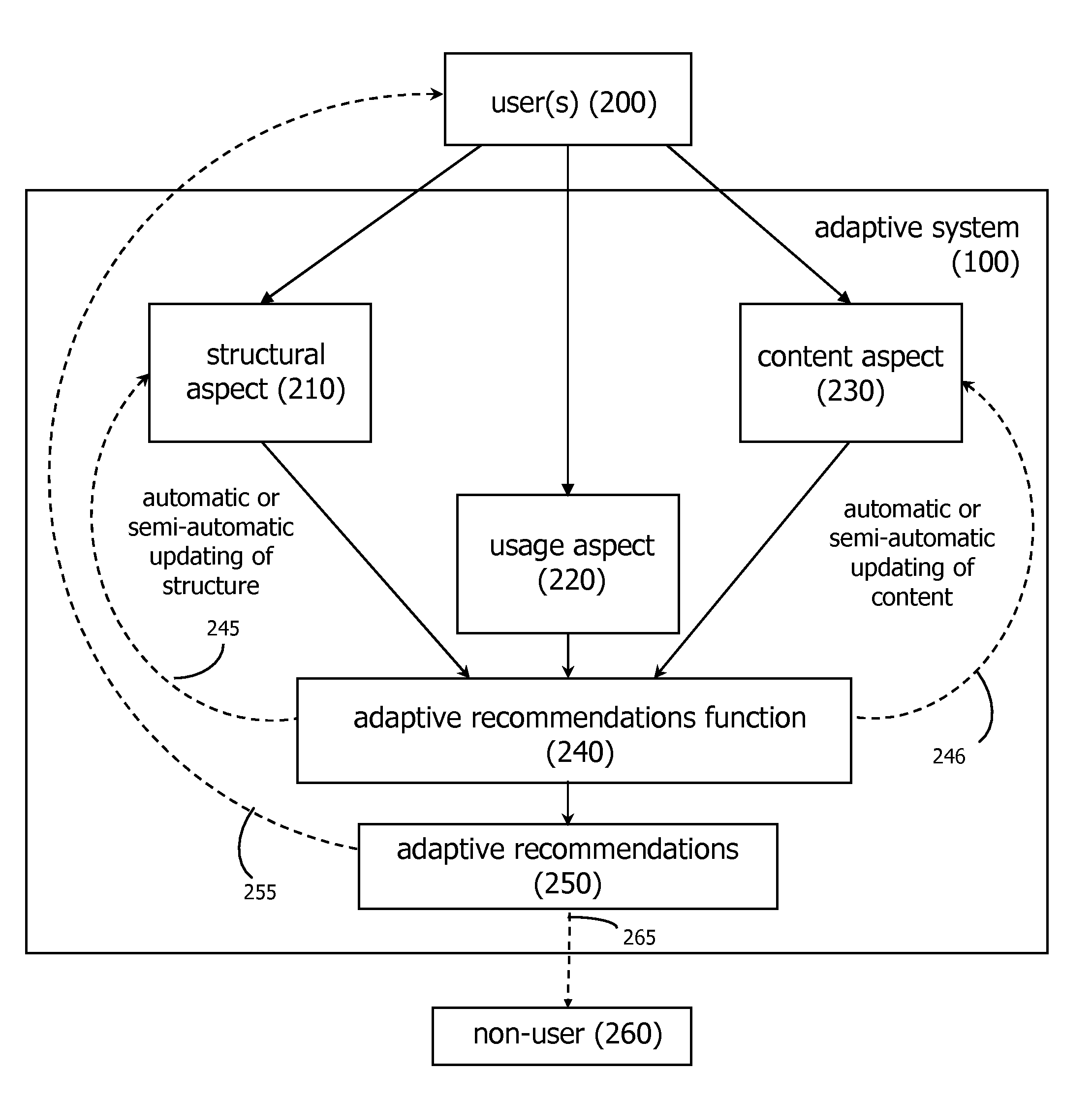
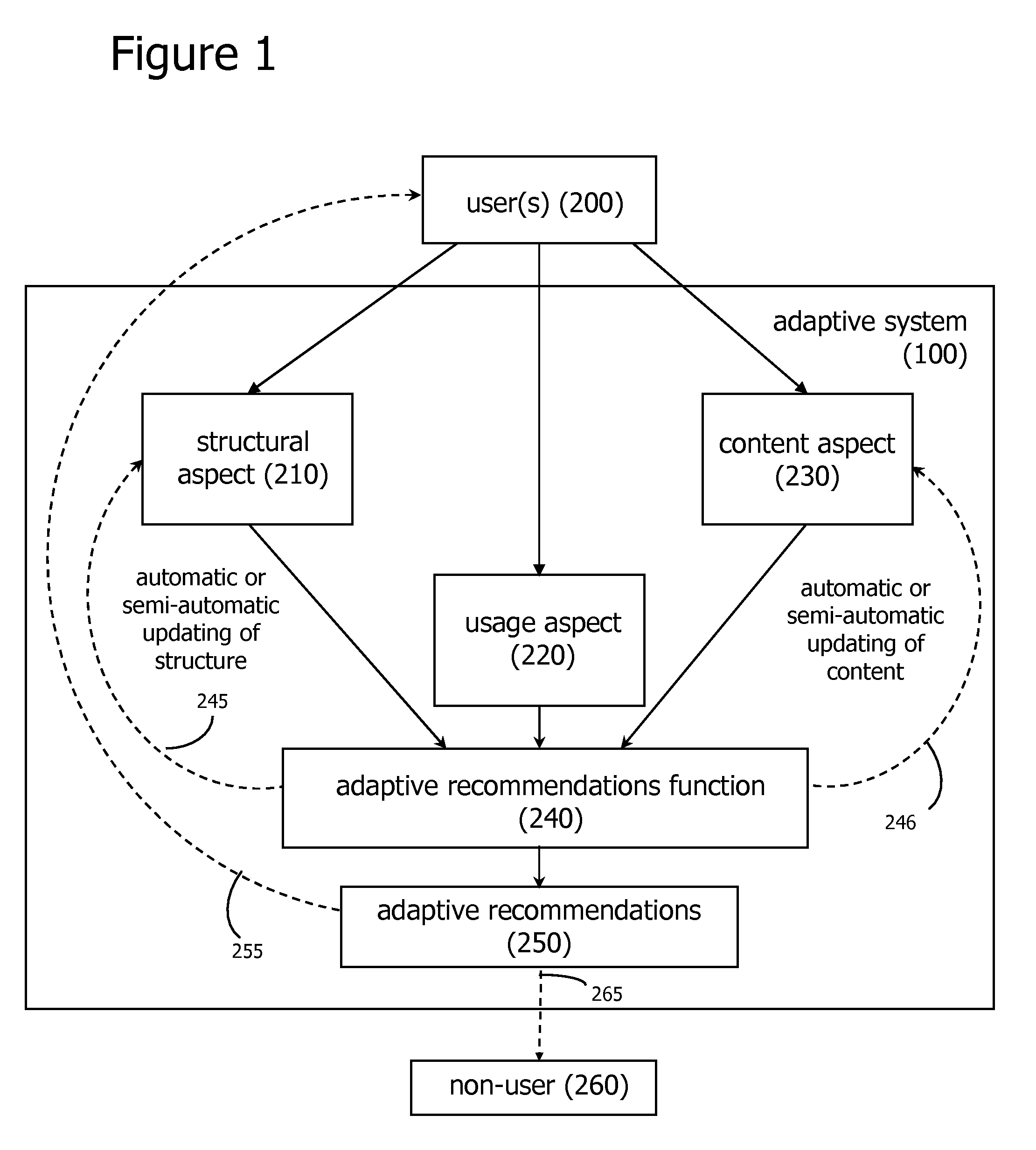
Adaptive social computing methods
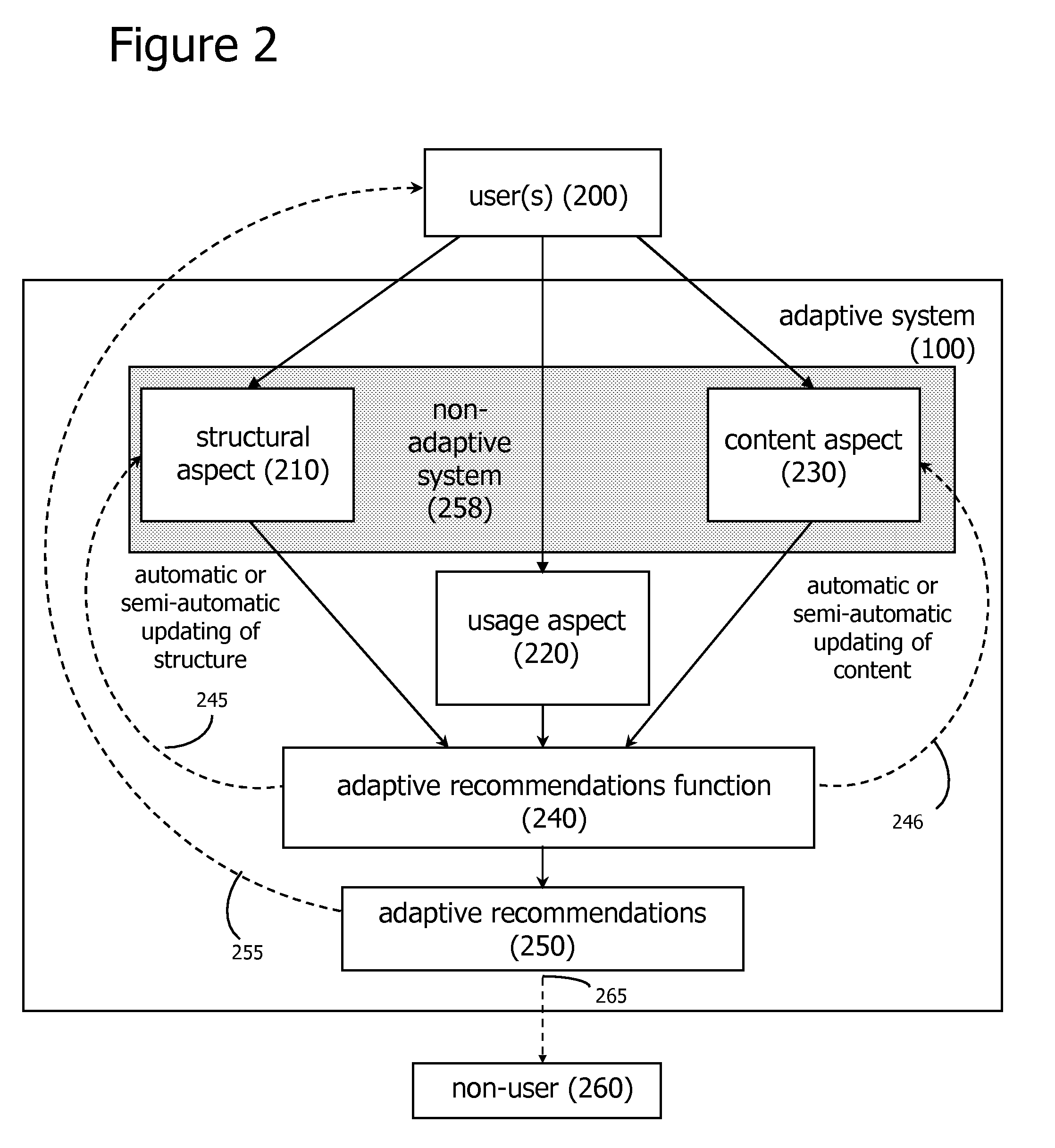
ActiveUS7606772B2Easy to adaptEfficiently navigateDigital computer detailsMachine learningComputing MethodologiesVision based
Methods of applying adaptive social computing systems are disclosed. The social computing systems include capabilities to generate adaptive recommendations and representations of social networks derived, at least in part, from inferences of the preferences and interests of system users based on a plurality of usage behaviors, spanning a plurality of usage behavior categories. The behavioral categories include system navigation behaviors, content referencing behaviors, collaborative behaviors, and the monitoring of physical location and changes in location. Privacy control functions and compensatory functions related to insincere usage behaviors can be applied. Adaptive recommendation delivery can take the form of visual-based or audio-based formats.
Owner:WORLD ASSETS CONSULTING AG
Method for tuning patient-specific cardiovascular simulations
ActiveUS8200466B2Improve understandingImprove representationMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesReduced modelComputing Methodologies
Computational methods are used to create cardiovascular simulations having desired hemodynamic features. Cardiovascular modeling methods produce descriptions of blood flow and pressure in the heart and vascular networks. Numerical methods optimize and solve nonlinear equations to find parameter values that result in desired hemodynamic characteristics including related flow and pressure at various locations in the cardiovascular system, movements of soft tissues, and changes for different physiological states. The modeling methods employ simplified models to approximate the behavior of more complex models with the goal of to reducing computational expense. The user describes the desired features of the final cardiovascular simulation and provides minimal input, and the system automates the search for the final patient-specific cardiovascular model.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
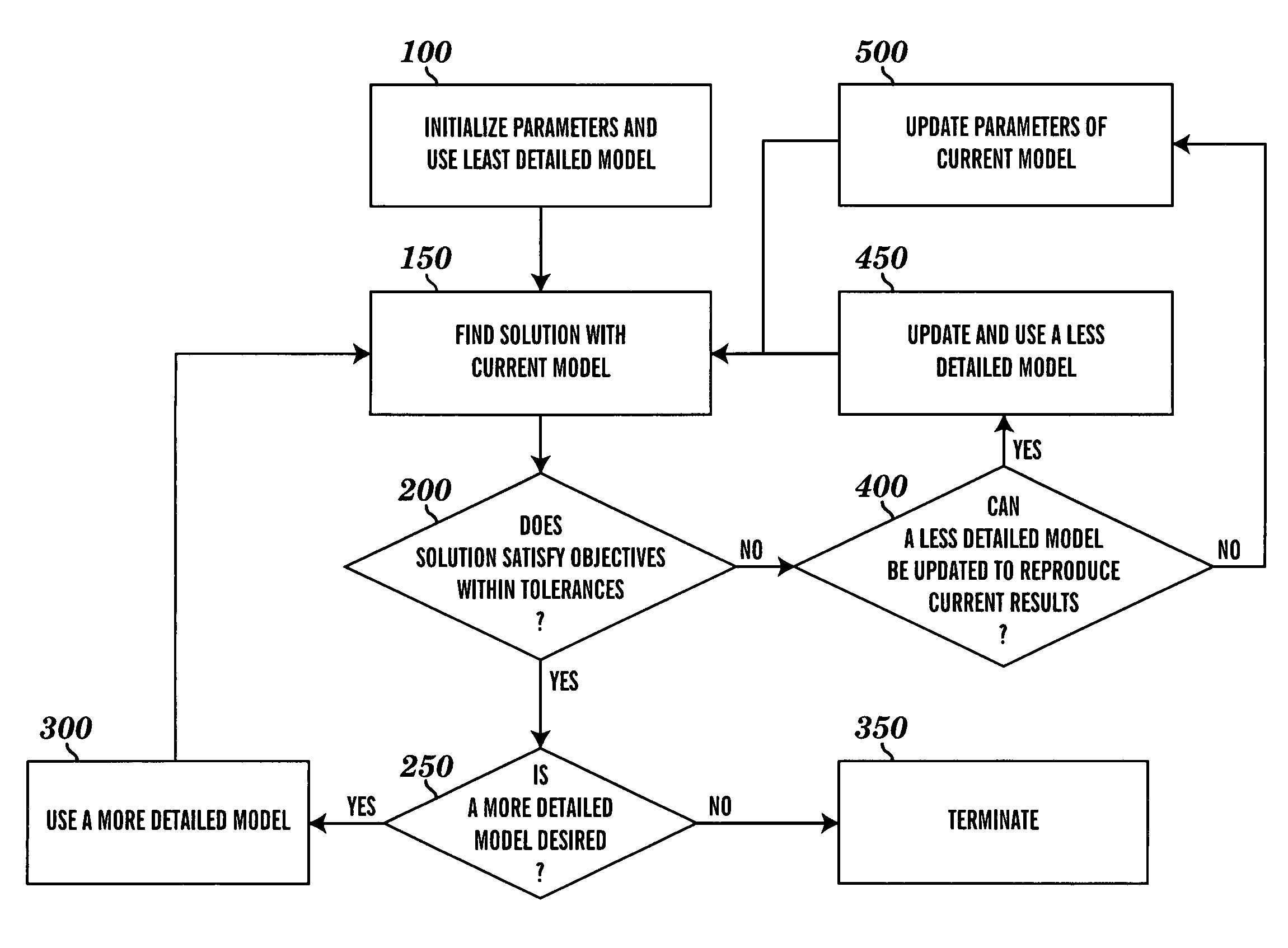
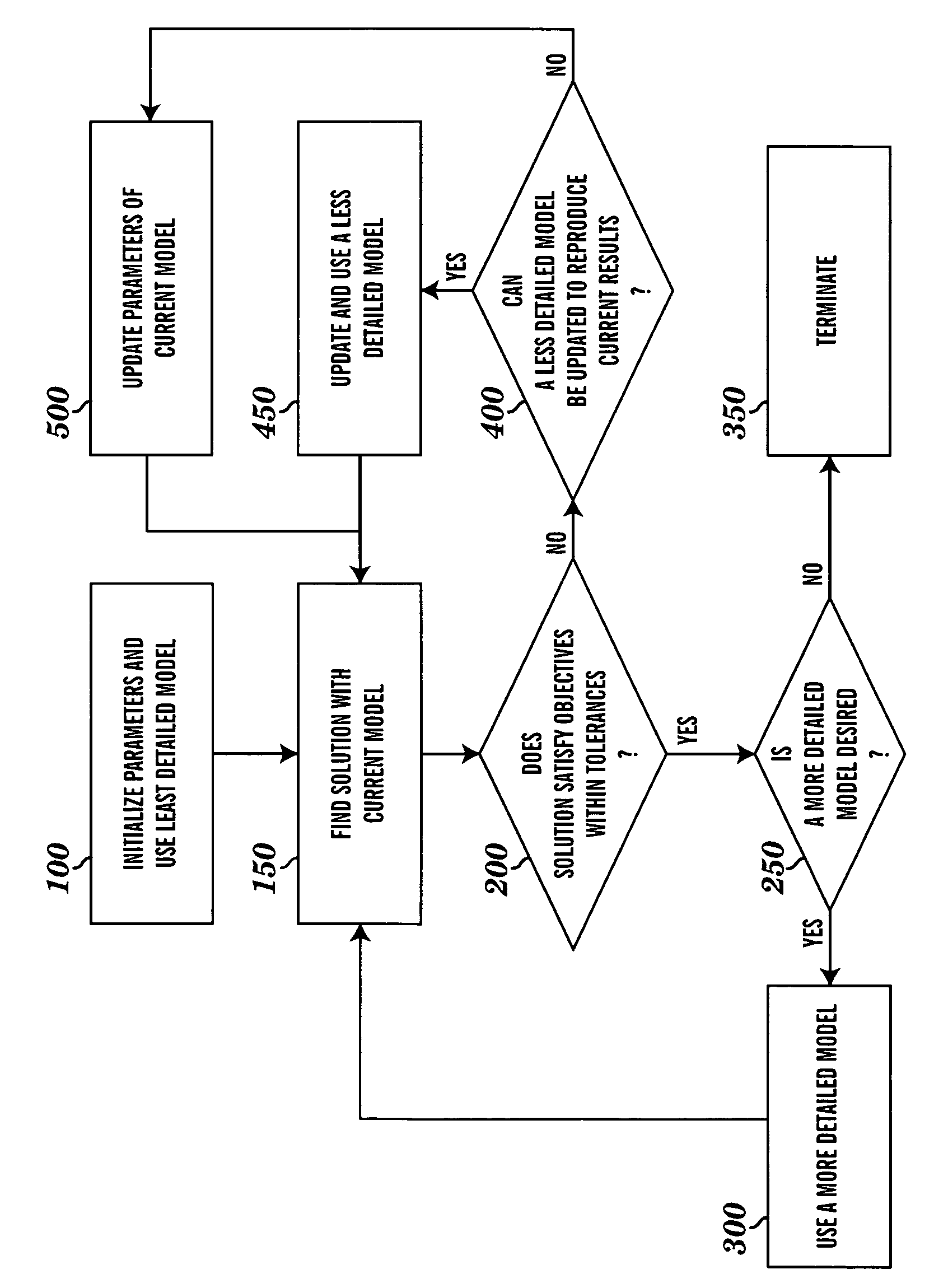
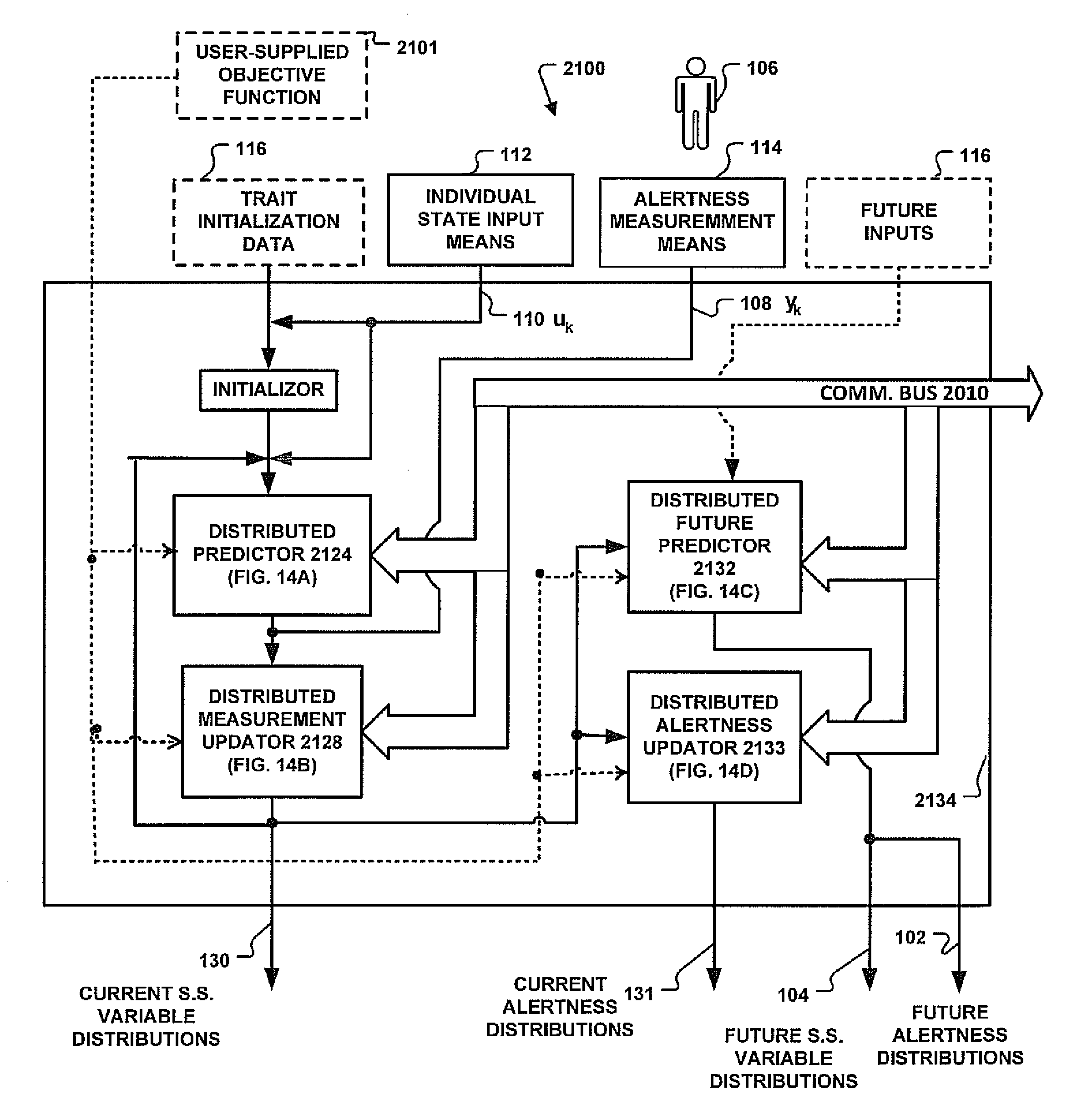
Systems and Methods for Distributed Calculation of Fatigue-Risk Prediction and Optimization
InactiveUS20120316845A1Useful resultImprove accuracyEnergy efficient ICTResource allocationUser needsComputing Methodologies
Distributed computing methods and systems are disclosed, wherein intensive fatigue-risk calculations are partitioned according to available computing resources, parameters of the fatigue-risk calculation, time-sensitive user demands, and the like. Methods are disclosed wherein execution-cost functions are used to allocate accessible computing resources. Additional methods include partitioning calculation tasks by user-prioritized needs and by general mathematical features of the calculations themselves. Included herein are methods to calculate only prediction-maximum likelihoods instead of full probability distributions, to calculate prediction likelihoods using Bayesian prediction techniques (instead of full re-tabulation of all data), to collate interim results of fatigue-risk calculations where serial results can be appropriately collated (e.g., serial time-slice independence of the cumulative task involved), to use simplified (e.g., linear, first-order) approximations of richer models of fatigue prediction, to assign user-identified priorities to each computational task within a plurality of such requests, and the like.
Owner:PULSAR INFORMATICS
Power distribution network single-phase earth fault locating method based on transient state
InactiveCN102944814AIncrease success rateImprove efficiencyFault locationInformation technology support systemHigh pressureTransient current
The invention relates to a method for detecting faults in cables, transmission lines or networks, in particular to a power distribution network single-phase earth fault locating method based on a transient state. The method includes: first, determining fault section in a large range according to a flow direction of detecting point transient current, and then determining a final fault section according to the similarity of zero-module current waveforms between two adjacent detecting points. The current waveform similarity calculating processing adopts a general correlation coefficient calculating method and a maximum correlation coefficient calculating method respectively. The technical scheme is that the method is a passive route selection method which is high in locating success rate and efficiency and not subject to effects of unstable arc and intermittent arc, an additional high-voltage primary device or movement coordination of other primary devices is not required, and high safety is achieved. Outage is not required for installing and detecting, and required installing space is small.
Owner:STATE GRID FUJIAN ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD +2
Method for Opportunistic Computing
InactiveUS20080005332A1Overcome disadvantagesReduce conflictDigital computer detailsProgram controlComputing MethodologiesApplication software
In a method of dynamically changing a computation performed by an application executing on a digital computer, the application is characterized in terms of slack and workloads of underlying components of the application and of interactions therebetween. The application is enhanced dynamically based on predictive models generated from the characterizing action and on the dynamic availability of computational resources. Strictness of data consistency constraints is adjusted dynamically between threads in the application, thereby providing runtime control mechanisms for dynamically enhancing the application.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
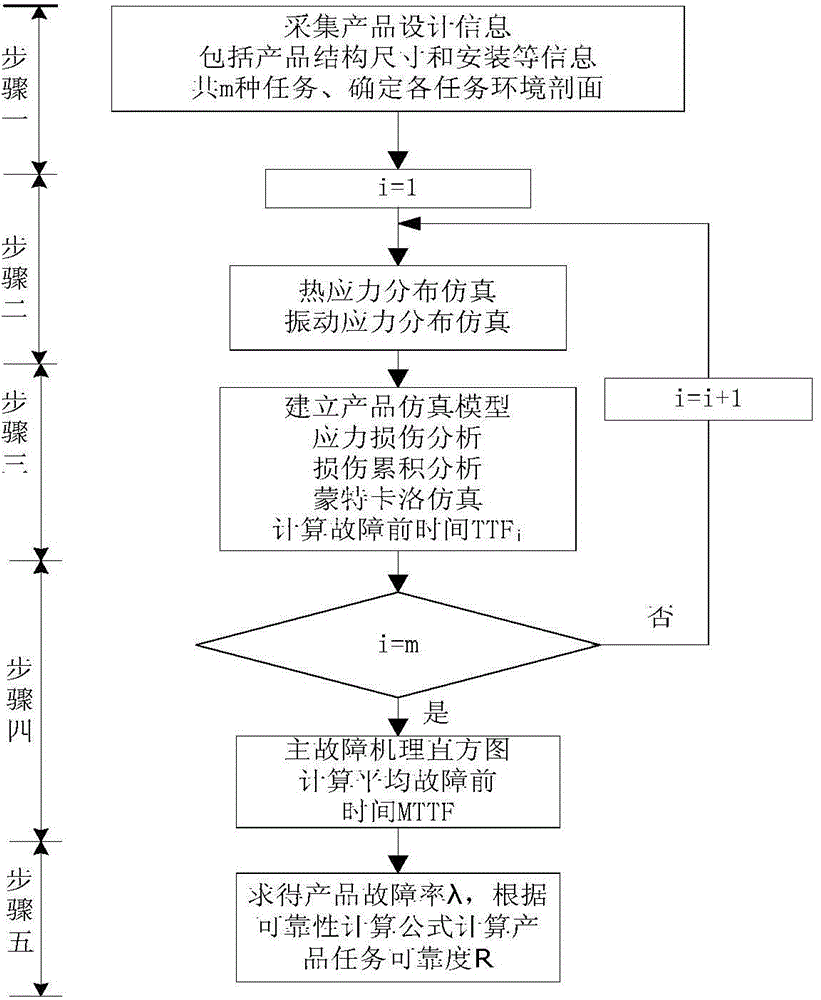
PoF (physics of failure) based method for calculating mission reliability of electronic product
ActiveCN103559418AIn line with the real situationReflect the stress situationSustainable transportationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputing MethodologiesDesign improvement
A PoF based method for calculating mission reliability of an electronic product comprises steps as follows: step one, information of all mission profiles of the product is collected, and an environment profile of each mission is determined; step two, thermal simulation and vibration simulation of environmental stress of each mission are performed, and a local response of the product to an environmental load is obtained; step three, a product simulation model is established; step four, simulation calculation of the product in all the mission profiles is completed, and the mean time to failure and a main failure mechanism of the product are obtained; and step five, the mission reliability of the product is calculated according to the mean time to failure. According to the PoF based method for calculating the mission reliability of the electronic product, all missions of the product during lifetime use are considered, the environmental stress of each mission is simulated, and the mean time to failure and the mission reliability of the product are comprehensively calculated. By means of a PoF model, the direction relation between parameters of a product material, structure, process and the like and the reliability can be obtained, and a design improvement direction is clearly and directly provided for the product.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
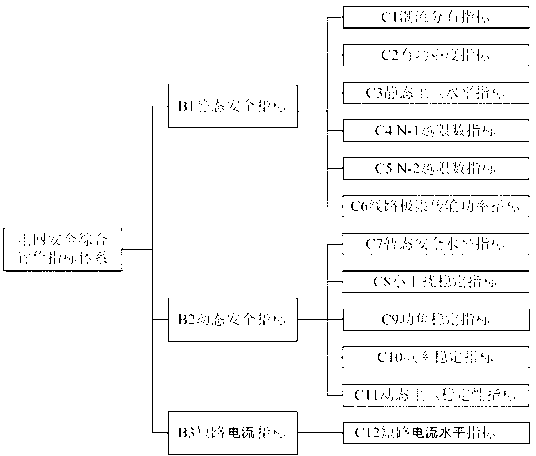
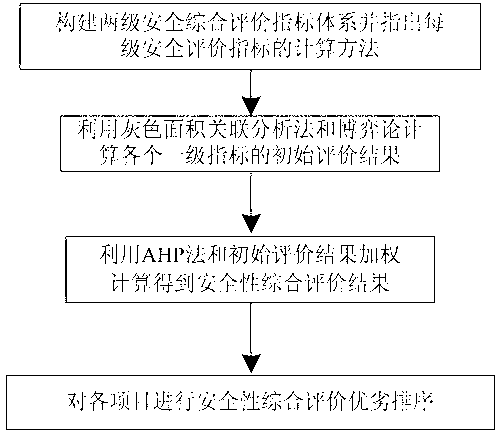
Grid security comprehensive evaluation method
InactiveCN103310390AAchieve sufficiencyAchieve comprehensivenessData processing applicationsInformation technology support systemComputing MethodologiesCorrelation coefficient
The invention provides a grid security comprehensive evaluation method which includes that a set of complete two-stage in-advance comprehensive evaluation index system and an each-stage security evaluation index calculating method are built aiming at the requirement of grid security operation evaluation, a grid security comprehensive evaluation model based on a gray area correlation analysis method and the game theory is further provided, initial evaluation is conducted on each one-stage index by the model, an obtained evaluation result is subjected to comprehensive evaluation, a correlation coefficient matrix of each one-stage index is determined by adopting the gray area correlation analysis method, weights are obtained by utilizing a game collection model pair analytic hierarchy process (AHP), an artificial neural network (ANN) and an entropy weight method and are objectively combined to obtain a combined weight, initial evaluation is conducted on each one-stage index, the AHP is adopted to determine a one-stage index weight, and the one-stage index weight and an initial evaluation result are subjected to weighing calculation to further obtain a grid security comprehensive evaluation result, namely the grid security quality ordering.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
System and method for dynamic path- and state-dependent stochastic control allocation
The invention includes a system and process that employs contractual bargaining with agent-based computational methods for the dynamic allocation, optimization, and pricing of contingent rights and obligations between multiple counterparties with overlapping interests. The processes employ a dynamic and endogenous hierarchy or tiering of binding incentive compatible contingent strategies, which may include optimal liquidation policies for matched assets and liabilities based upon stochastic volume / price schedule related to statistically non-stationary supply / demand elasticities and order-flow, as well as variations in market microstructure. The invention includes a dynamic open system with distributed stochastic control of strategic interactions among dynamic optimizing agents across random states, wherein the actions of any one affects the joint costs and benefits for all the agents.
Owner:MORDECAI DAVID K A
Power distribution system probability reliability assessing method based on analytical method
ActiveCN104376504AGuaranteed calculation accuracySimulation speedData processing applicationsFailure rateComputing Methodologies
The invention discloses a power distribution system probability reliability assessing method based on an analytical method. The method comprises the steps that a given power distribution network is partitioned into a fault area, an isolation area, a gapless island area and an influence-free area are classified, a fault mode impact analysis sheet base is established, and parameters are initialized; a stimulation clock is initialized, a random number is generated, the minimum non-failure operation time is obtained according to failure rate parameters of all element state models, the fault isolation time and the load band transferring time are worked out, and the stimulation clock is pushed; the fault mode impact analysis sheet base is inquired, classifications of all cells are determined, whether an island is formed or not is judged, and different methods are adopted for processing the island area and the non-island area; the state sample of an energy storage device is established according to the energy storage device electrical charge state probability distribution obtained through the probability reliability calculating method; distribution probabilities of single-time fault indexes of load points are overlapped, and the probability reliability indexes of the loads and the system are calculated. The simulation speed is increased while certain calculation precision is ensured, and the power grid situation is comprehensively reflected.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
Spatial complex flexible structure multi-body system dynamics modeling and calculating method
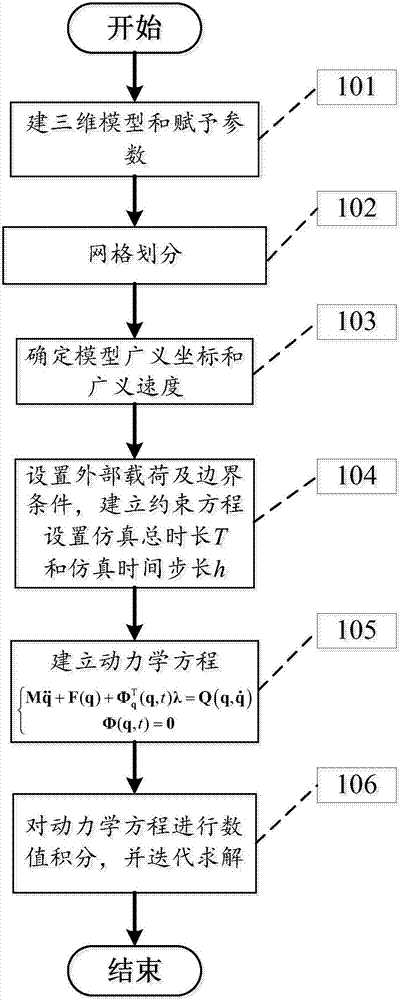
InactiveCN107220421AImproving computational efficiency in dynamics simulationsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationComputing MethodologiesSimulation
The invention provides a spatial complex flexible structure multi-body system dynamics modeling and calculating method. The method comprises the steps of 101, building a three-dimensional model and giving parameters; 102, performing mesh generation on the model; 103, calculating a mesh unit generalized coordinate vector q and a generalized velocity vector; 104, building a mesh model constraint equation; 105, according to the mesh unit type, the generalized coordinate vector, the generalized velocity vector and the constraint equation, building a multi-body system dynamics equation on the basis of a first-class lagrange equation; 106, calculating the built multi-body system dynamics equation, and completing modeling calculating of the spatial complex flexible structure multi-body system dynamics problem. The simple and effective dynamics modeling method is provided for the flexible structure multi-body system, and the calculating efficiency is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Calculating method and system for multi-dimensional division
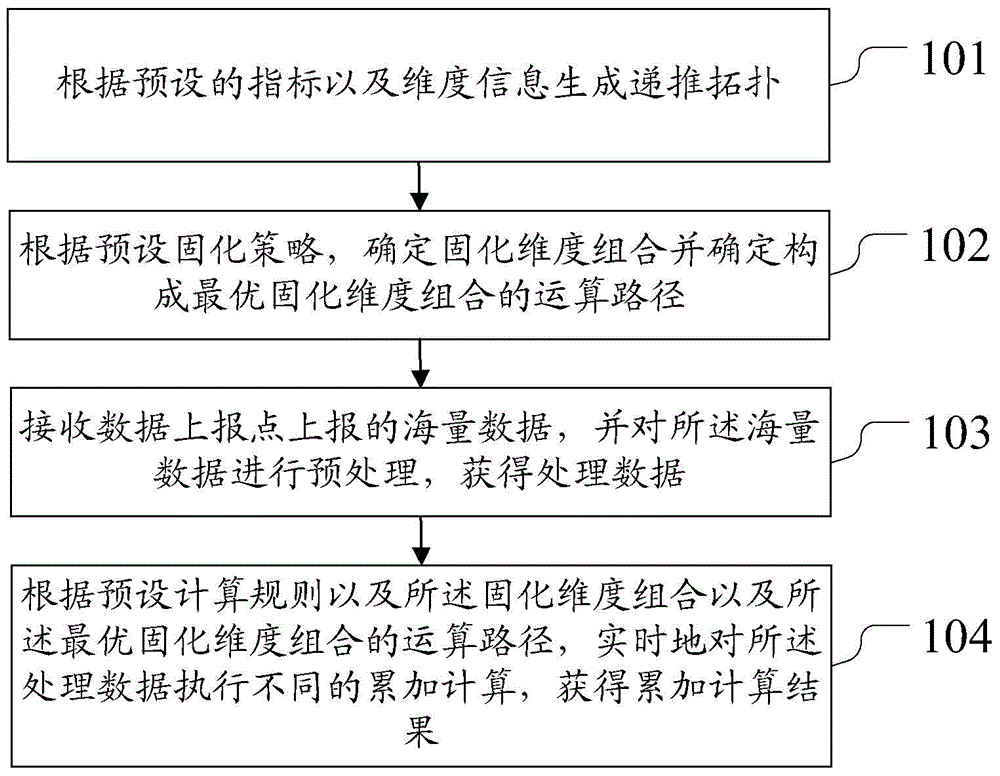
ActiveCN104424229AReduce computational complexitySpecial data processing applicationsComputing MethodologiesComputation complexity
The invention discloses calculating method and system for multi-dimensional division, relates to the technical field of multi-dimensional division, and aims at performing multi-dimensional division calculation for mass data on real time in order to lower down the complexity in calculating. The method comprises the steps of generating a recursive topology according to the default indicators and dimension information; determining the curing dimension combination and the operation path for generating the optimal curing dimension combination according to the preset curing strategy; receiving mass data reported by a data reporting point; preprocessing the mass data to obtain the processed data; performing different accumulation calculations for the processed data on real time according to the preset calculation rules, the curing dimension combination and the optimal curing dimension combination, so as to obtain the accumulation calculation result. The method and system are applied to multi-dimensional division.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Computing system and computing method for big data processing
ActiveCN103488775AOvercome limitationsSolve complexitySpecial data processing applicationsComputing MethodologiesDistributed File System
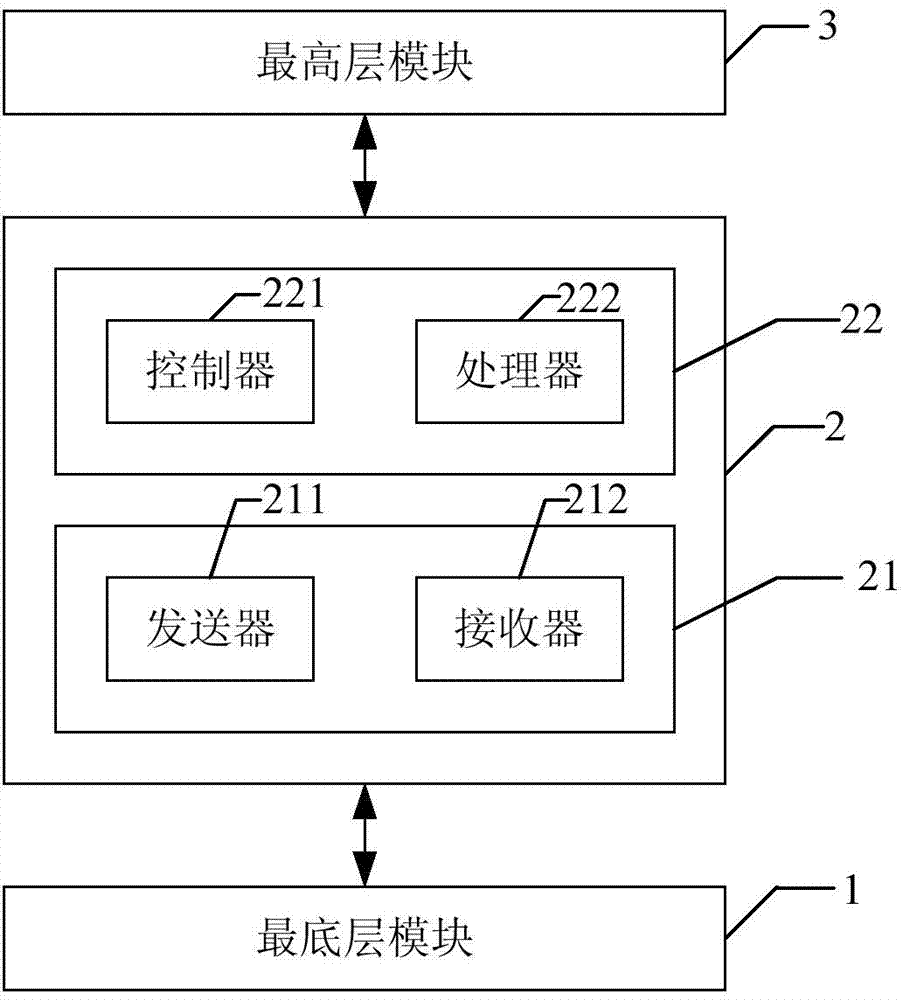
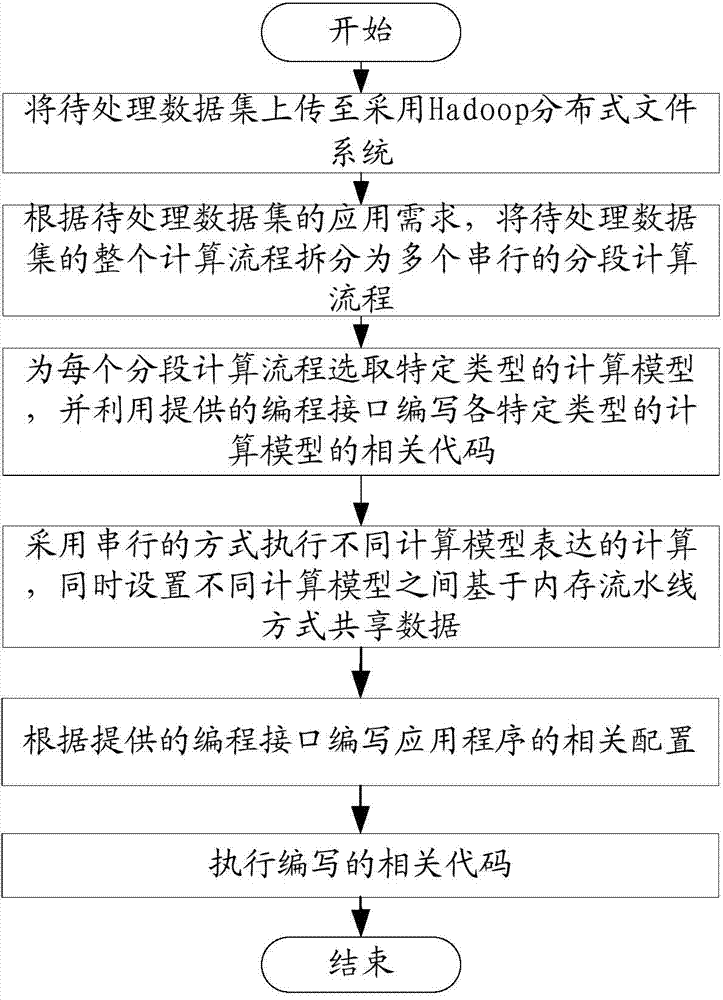
The invention relates to a computing system and computing method for big data processing. The computing system comprises a bottommost-layer module, a middle-layer module and a topmost-layer module sequentially from bottom to top. The middle-layer module comprises a message transmission module and computation model modules. A Hadoop distributed file system is adopted in the bottommost-layer module, and the bottommost-layer module is used for storing data. The message transmission module is used for transmitting messages between the computation model modules operating at different computing nodes. The computation model modules operating at the different computing nodes work cooperatively according to the messages transmitted by the message transmission module and establish specific types of computation models respectively to process the data. The topmost-layer module is used for providing programmatic interfaces for the computation models, combining computation expressed by the different computation models in a serial mode and enabling the different computation models to share the data based on an internal storage flow line mode through setting at the same time. According to the computing system and computing method for big data processing, application programs can be written in one system through the multiple computation models, and more complex problems can be solved.
Owner:INST OF INFORMATION ENG CAS
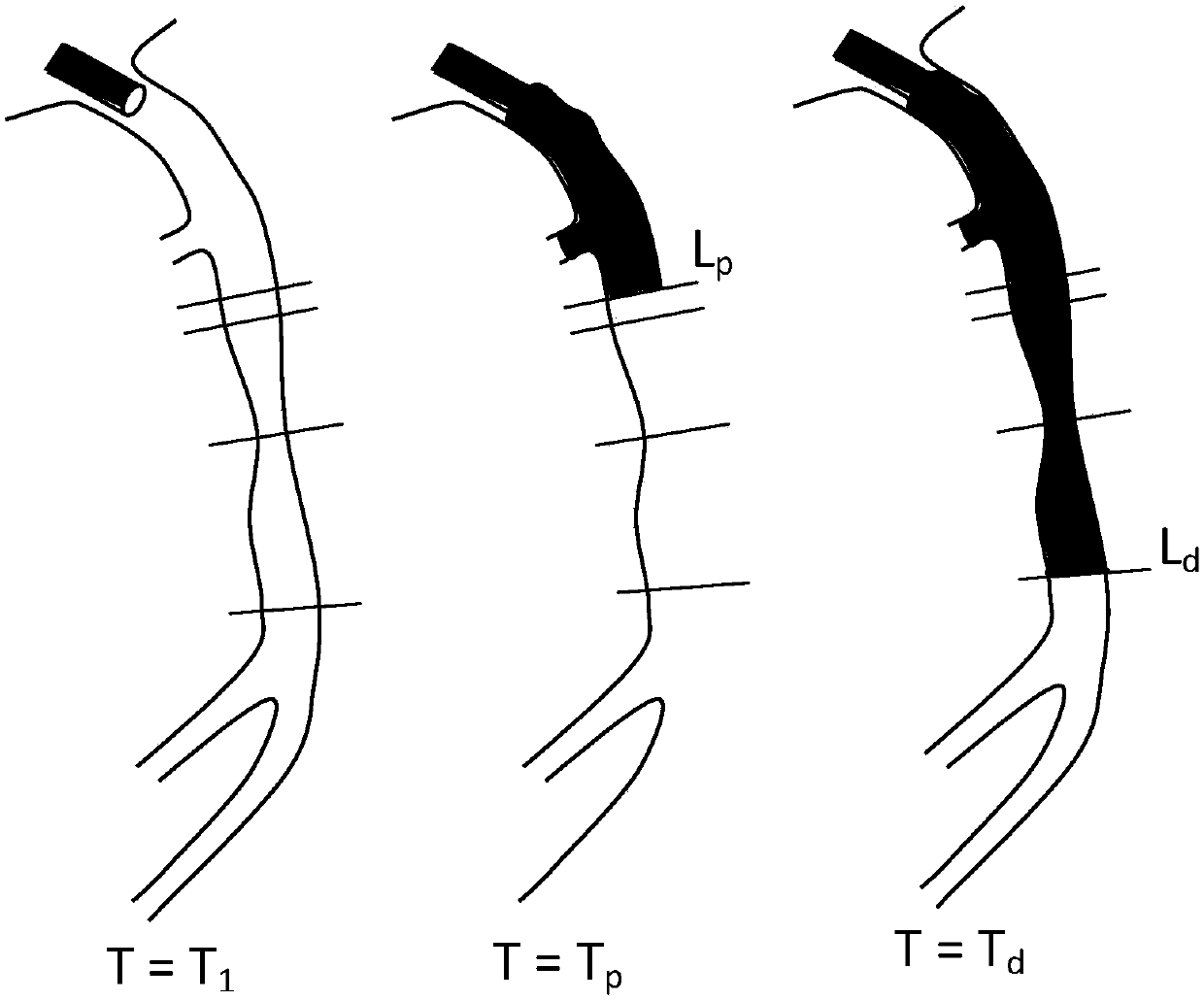
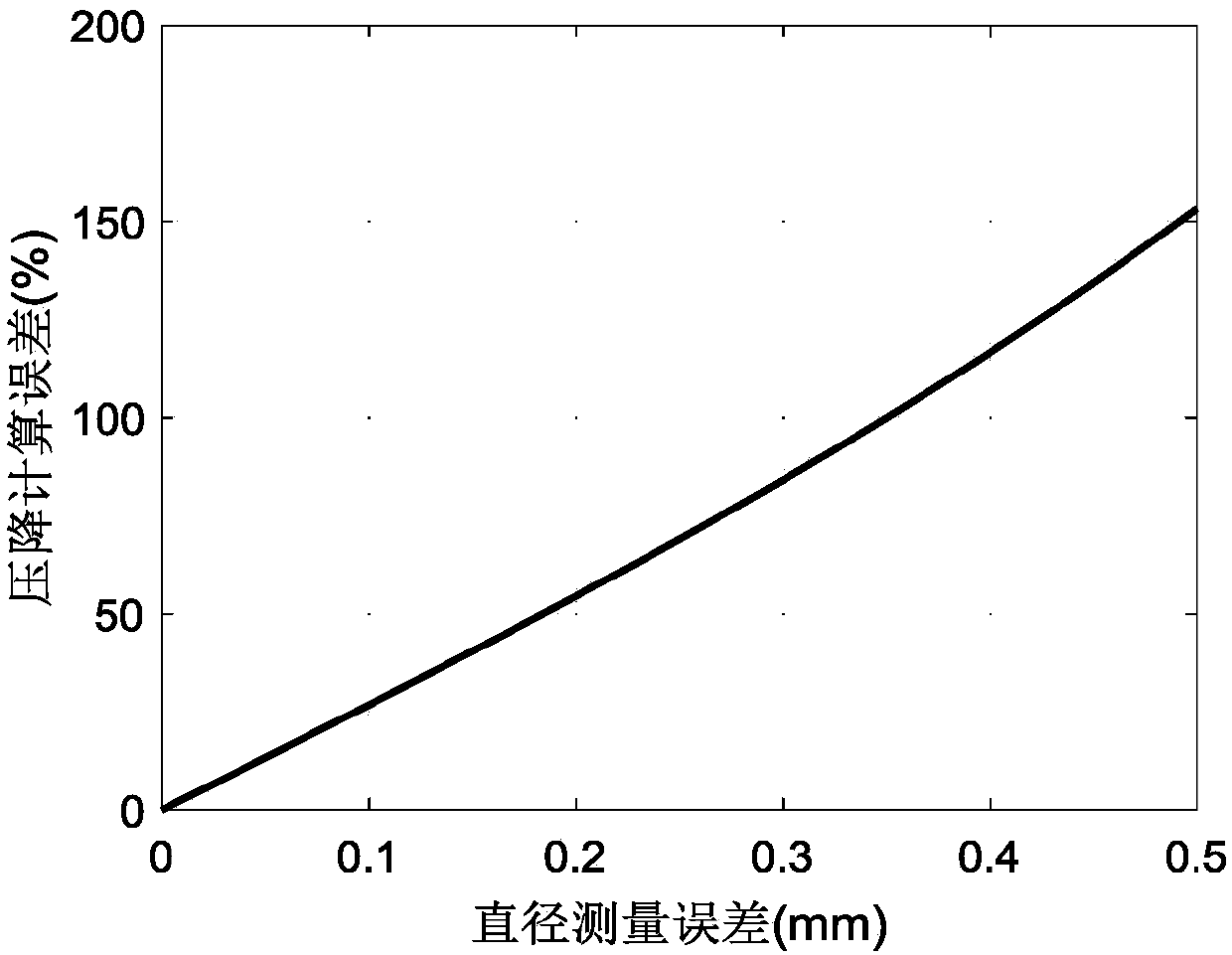
High-precision matching model-based method for calculating coronary artery parameters
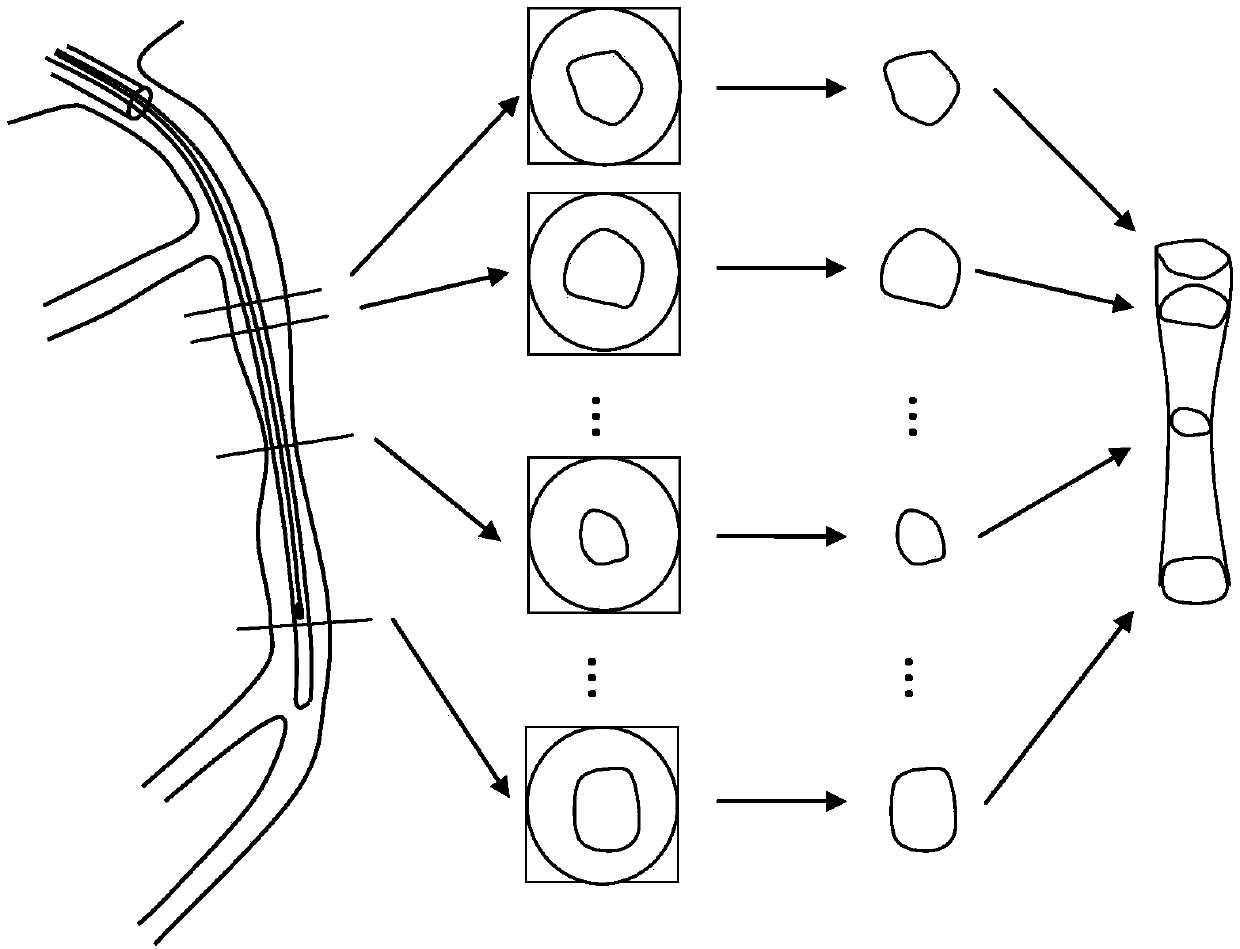
ActiveCN107730540AImprove practicalityThe calculation result is accurateImage enhancementImage analysisCoronary arteriesComputing Methodologies
The invention discloses a high-precision matching model-based method for calculating coronary artery parameters. According to the method, firstly, the angiography imaging means and the intravascular imaging means of a coronary vessel part are acquired. After that, an angiography image and an intravascular image are matched to form a high-precision matching model. The blood flow amount, the blood fractional Flow Reserve (FFR) and the microcirculation resistance index of microcirculatory resistance (IMR) of coronary vessels are calculated on the basis of the high-precision matching model. According to the method for calculating the coronary parameter blood flow, the blood flow reserve score and the microcirculation resistance index, the high-precision matching model of images is acquired through two ways, namely the angiography imaging means and the intravascular imaging means. The calculation result of the method is more accurate than the image of either the angiography imaging means orthe intravascular imaging means alone, so that the method is high in practicability.
Owner:QUANJING HENGSHENG BEIJING SCI & TECH CO LTD
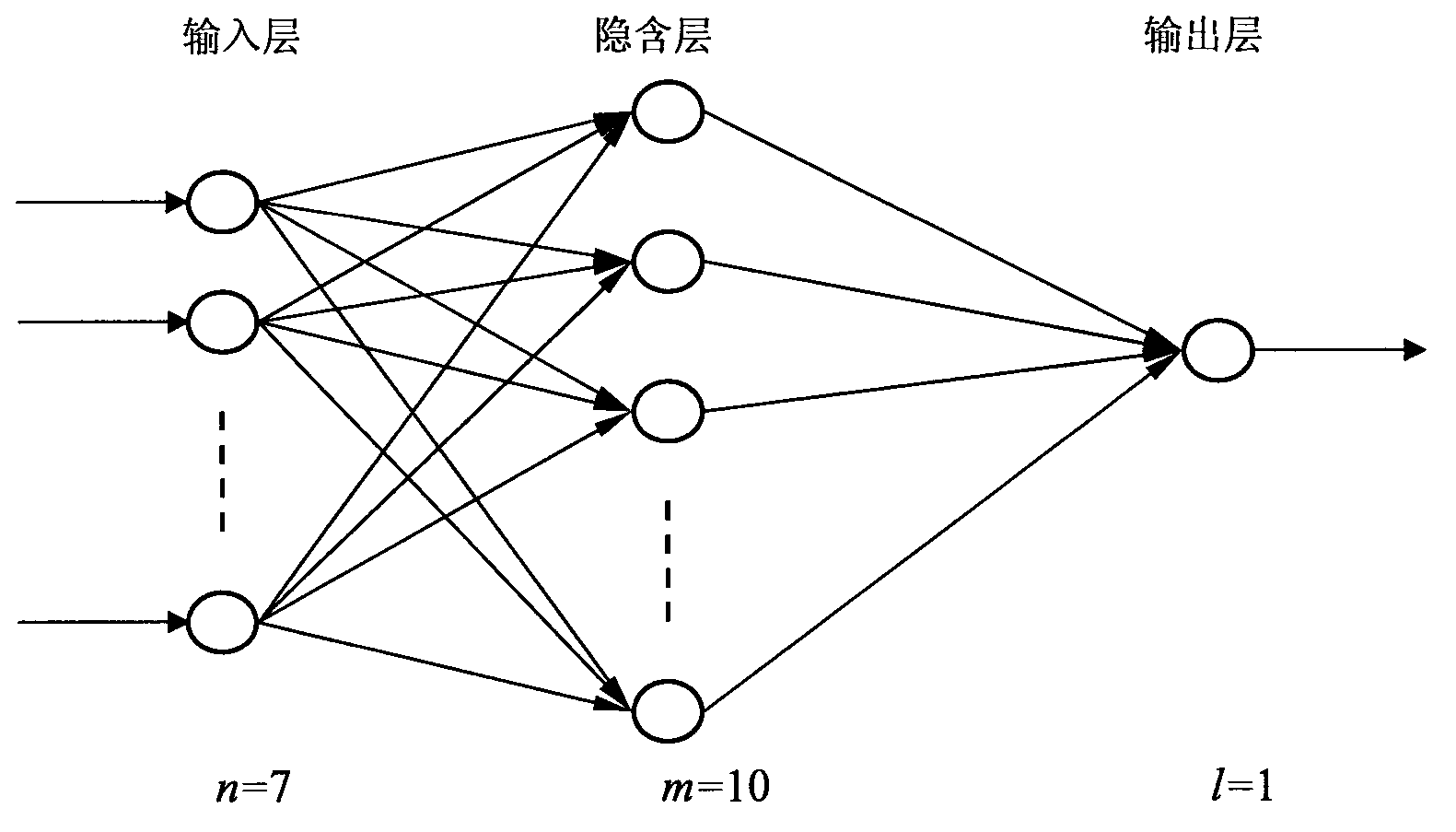
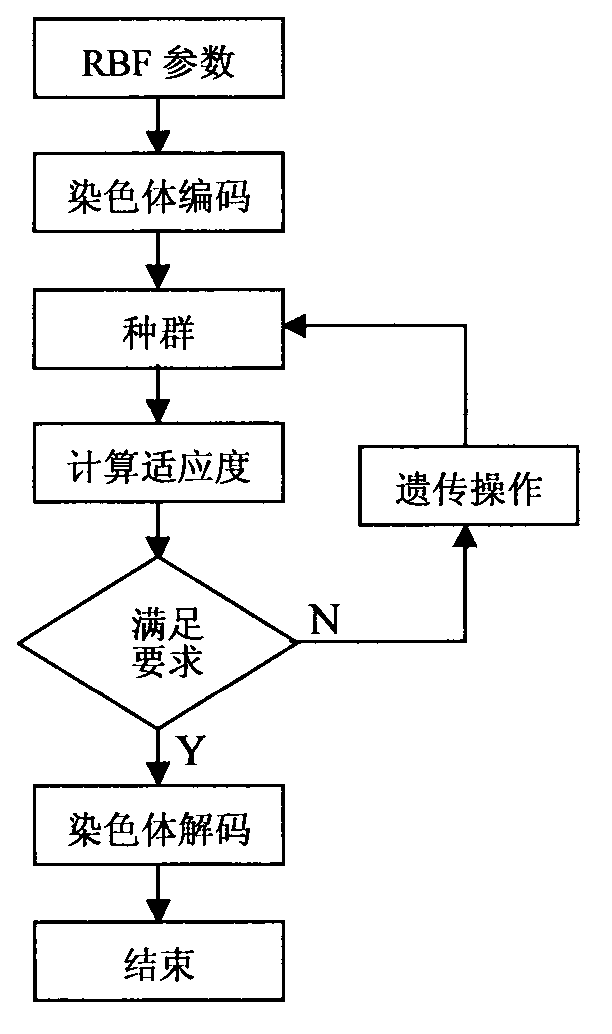
Real-time computing method for theoretical line loss of low-voltage distribution room
InactiveCN103577679AEasy to implementImprove calculation accuracySpecial data processing applicationsDynamic modelsLow voltage
The invention discloses a real-time computing method for the theoretical line loss of a low-voltage distribution room with dynamic change of the number of users and the power consumption. The real-time computing method comprises the following steps of (1) selecting the type of a model, utilizing the unique optimal approximation character of an RBF (Radial Basis Function) neural network, i.e., any continuous function can be approximated by any precision, adopting the RBF neural network with an online learning function to establish a dynamic model for a power supply and distribution system in the low-voltage distribution room; (2) determining the structure of the model, and determining the structure of the neural network model (neuron) according to the number of the users and the power consumption characteristic in the low-voltage distribution room; (3) identifying parameters of the model; (4) carrying out computation on the theoretical line loss by utilizing the model. The real-time computing method has the advantages that the implementation method is simple, and the neuron network is adopted for constructing the system model, so that the influence of external factors on results is reduced, and further the computing precision is high.
Owner:深圳龙电华鑫控股集团股份有限公司 +1
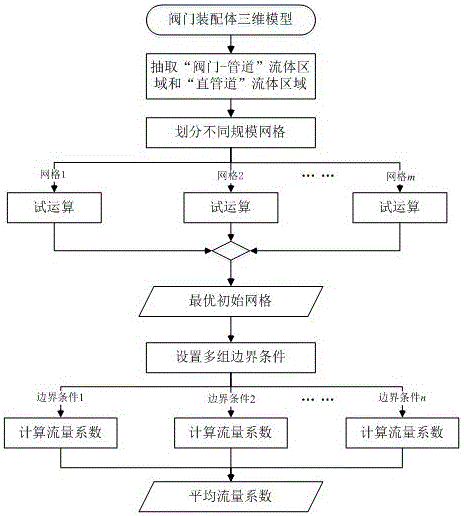
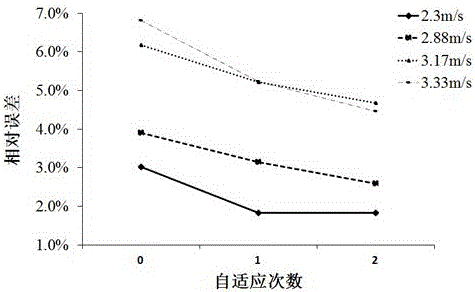
CFD simulation and grid self-adaption based valve flow coefficient calculating method
ActiveCN105677964AAccurately predict circulation capacityEnrich flow field detailsSpecial data processing applicationsComputing MethodologiesQuality by Design
The invention discloses a CFD simulation and grid self-adaption based valve flow coefficient calculating method. The CFD simulation and grid self-adaption based valve flow coefficient calculating method comprises the main steps that a 'valve-pipe' flow field model and a 'straight pipeline' flow field model are extracted based on a valve assembly body three-dimensional model; initial grids are divided for the flow field models, wherein multiple groups of initial grids different in scale are divided for the 'valve-pipe' flow field model; trial operation is performed by applying the groups of initial grids respectively, the change tends with grid scales of the obtained pressure differences are compared to select optimal initial grids; the optimal initial grids are applied to set different boundary conditions, and simulating calculation of corresponding flow coefficients is performed by combining a grid self-adaption technology; finally, the arithmetic average of the obtained flow coefficients is obtained to serve as a valve flow coefficient prediction result. The CFD simulation and grid self-adaption based valve flow coefficient calculating method can more rapidly and flexibly predict the flow capacity of a valve under various conditions, shorten a development period and improve the design quality and can effectively improve the calculation accuracy and reduce the dependence on specialization level of operators.
Owner:JIANGSU SHENTONG VALVE +1
Calculating method of attitude matrix and positioning navigation method based on attitude matrix
ActiveCN104748751AReal-time measurementUnderstand the mutual positional relationshipNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by terrestrial meansPattern recognitionImage correction
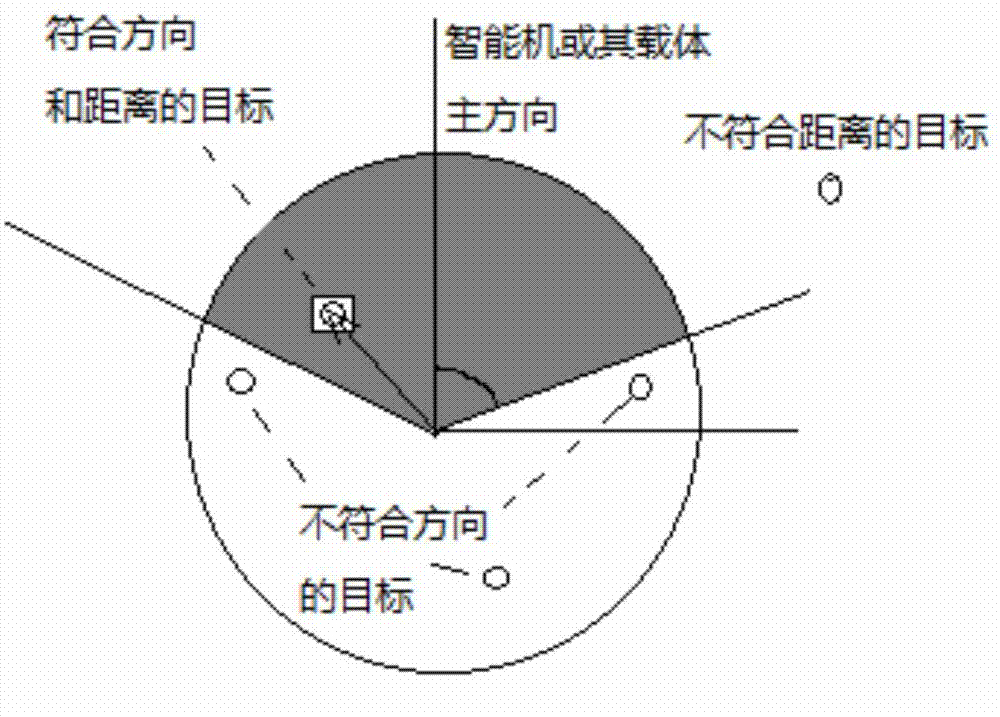
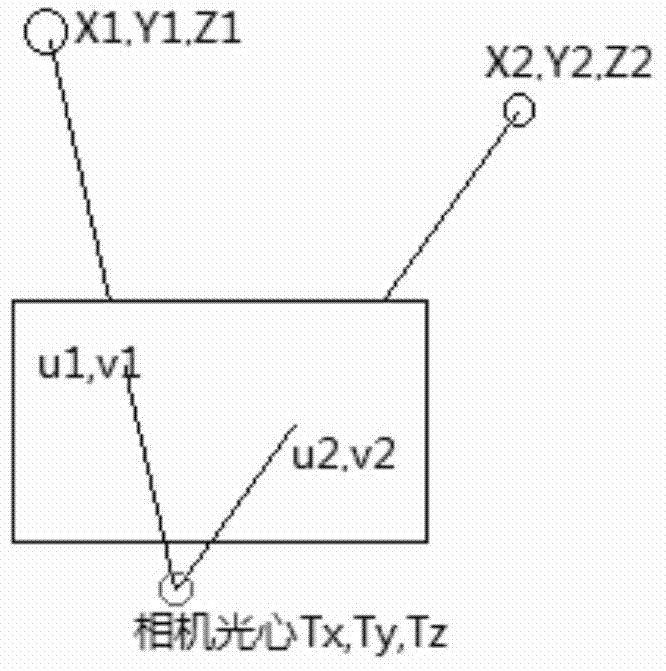
Disclosed are attitude determination, panoramic image generation and target recognition methods for an intelligent machine. The attitude determination method for the intelligent machine comprises the following steps: defining a local coordinate system; and determining an intelligent machine attitude matrix Rg, wherein Rg is a 3x3 unit orthogonal matrix relative to the local coordinate system and can be obtained through multiple methods according to different sensors inside the intelligent machine. By means of attitude determination of the intelligent machine, multiple applications can be achieved, comprising a virtual reality roaming method for the intelligent machine, multi-vision localization of the intelligent machine, monocular single-point localization of the intelligent machine, panoramic image generation of the intelligent machine, target direction selection in the intelligent machine, real-time video image correction, single-image localization of the intelligent machine, and relative localization among multiple cameras.
Owner:武汉雄楚高晶科技有限公司
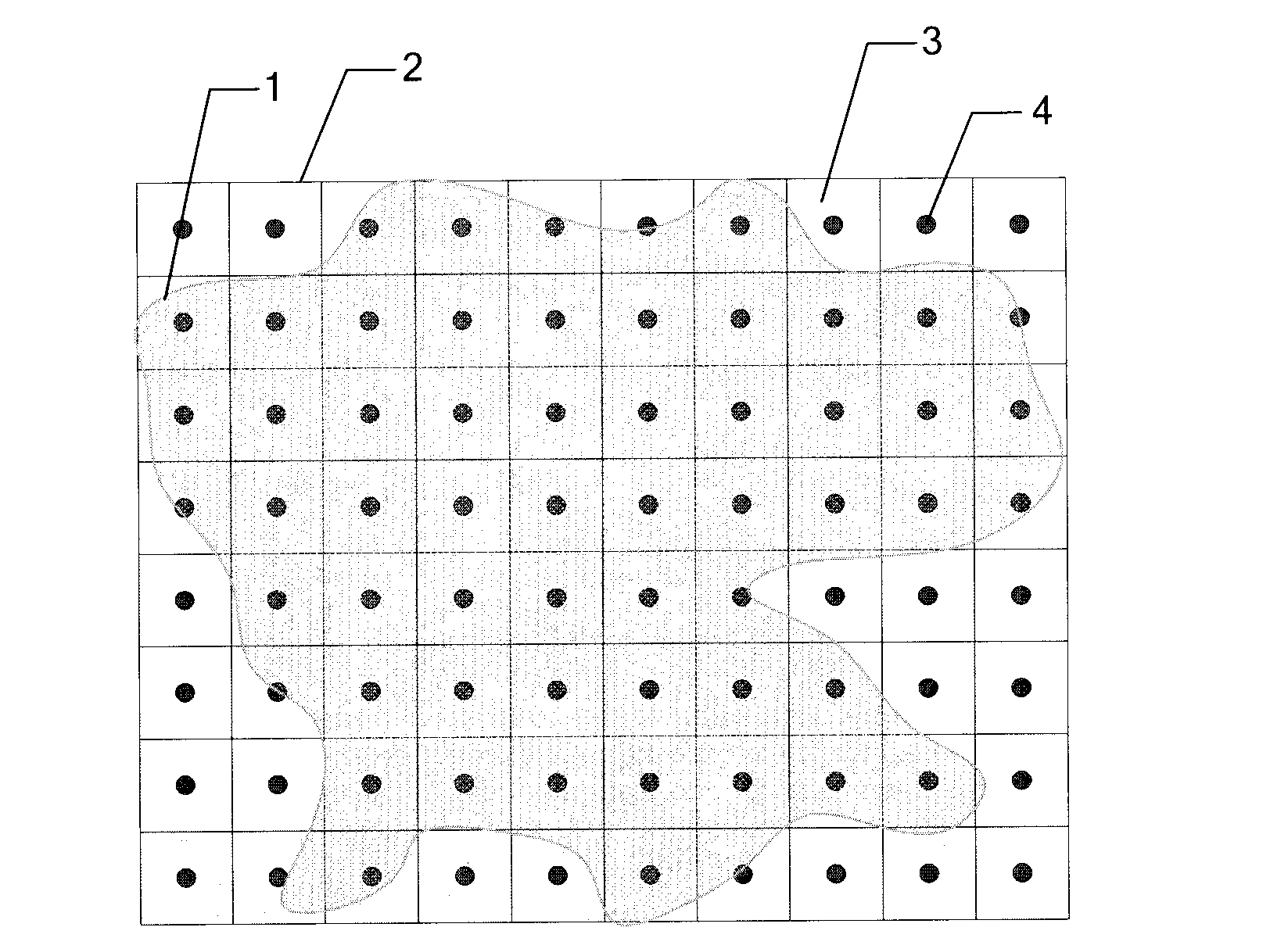
Area coverage rate calculating method based on mesh division
ActiveCN103136393AAvoid complex intersectionAvoid union geometrySpecial data processing applicationsComputing MethodologiesTerrain
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
Method and system for simulating calculation of transport capacity of urban rail transit network
ActiveCN103279669ASmall amount of calculationEasy to operateRoad vehicles traffic controlSpecial data processing applicationsComputing MethodologiesComputer module
The invention discloses a method and a system for simulating calculation of transport capacity of an urban rail transit network. The method includes the following steps: setting a simulation scene which includes network features, passenger flow features and a running chart; loading initial passenger flow generation quantity into a network; starting to simulate; calculating and outputting service levels of all lines and all stations; judging whether the service levels meet conditions for calculation stopping or not, if yes, displaying current total passenger flow quantity; and if not, adding added passenger flow into the network, then repeatedly executing simulation starting. The system comprises a scene setting module, an initializing module, a service level calculating module, a stopping condition judging module, a pressure adding module, a displaying module and a simulating module. By adopting the idea of pressure testing, using computer simulation as a means and taking the network service level into consideration, calculation quantity is reduced, and reliability of calculation results is improved.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
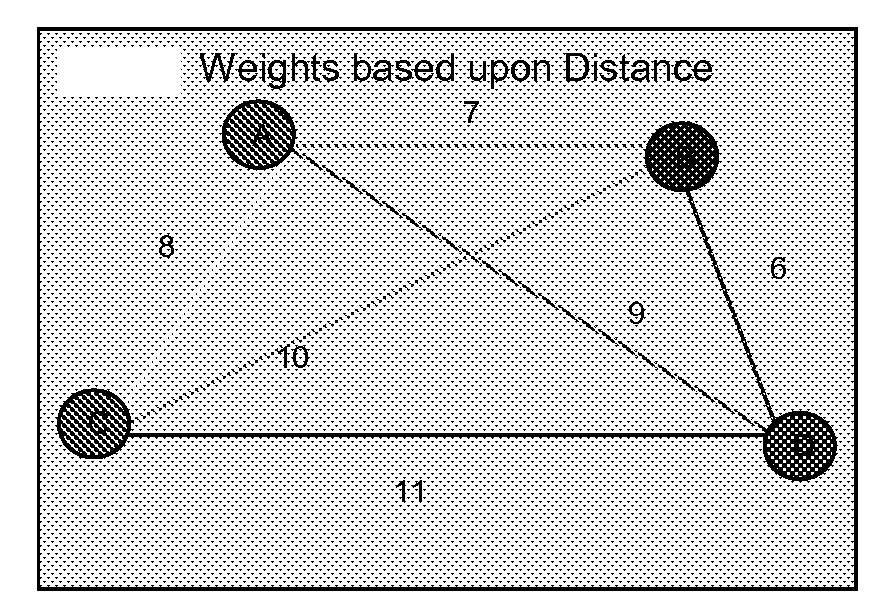
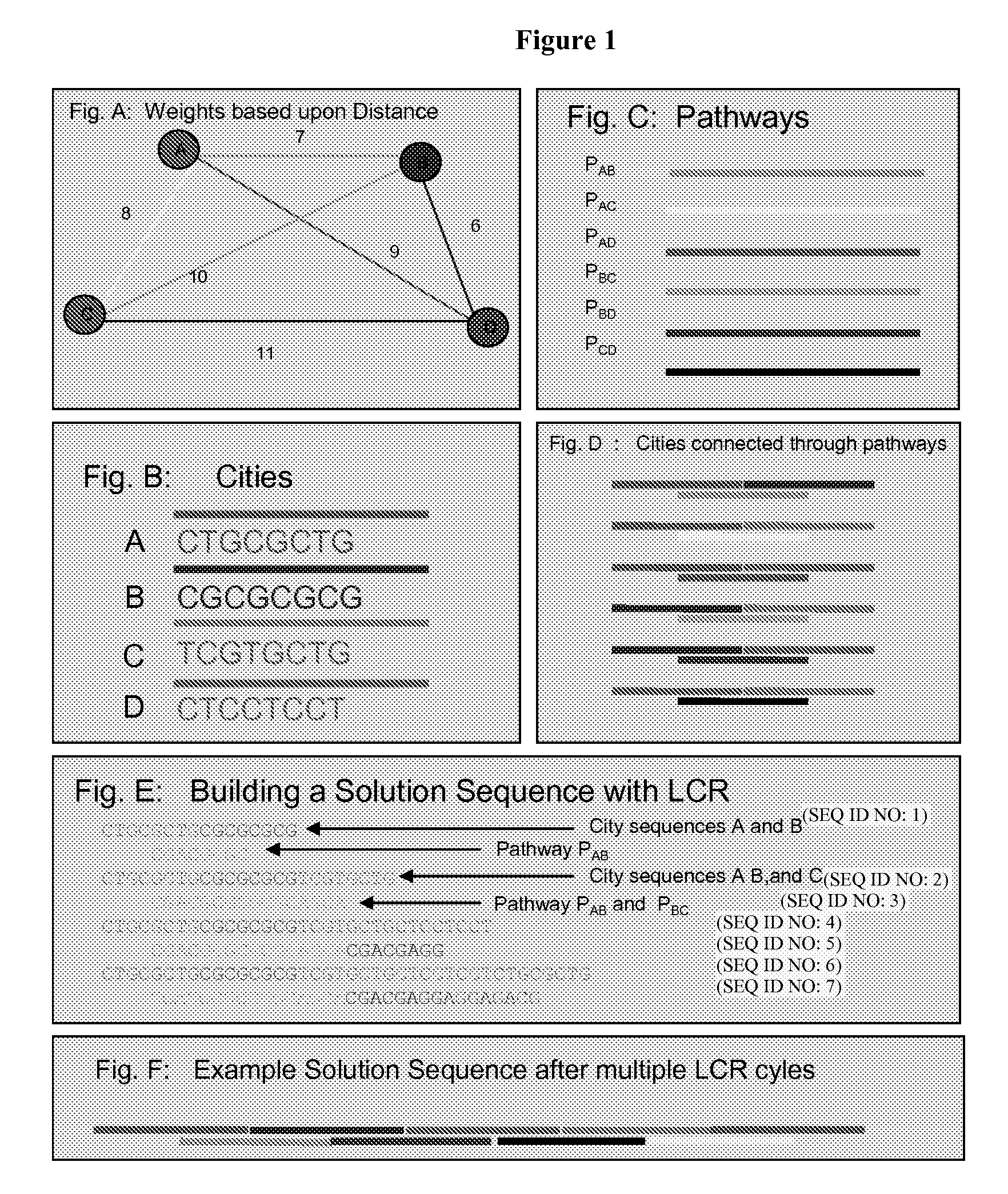
Methods for generating a distribution of optimal solutions to nondeterministic polynomial optimization problems
ActiveUS20090047677A1Reduce distanceEasy to set upMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsComputing MethodologiesOptimization problem
The present invention overcomes problems in prior art DNA-based computing methods for solving non-deterministic polynomial optimization problems, by providing methods that derive the most probable answers in a statistically significant manner that makes the methods scalable with increases in the number of data inputs, and thus makes the methods practical.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
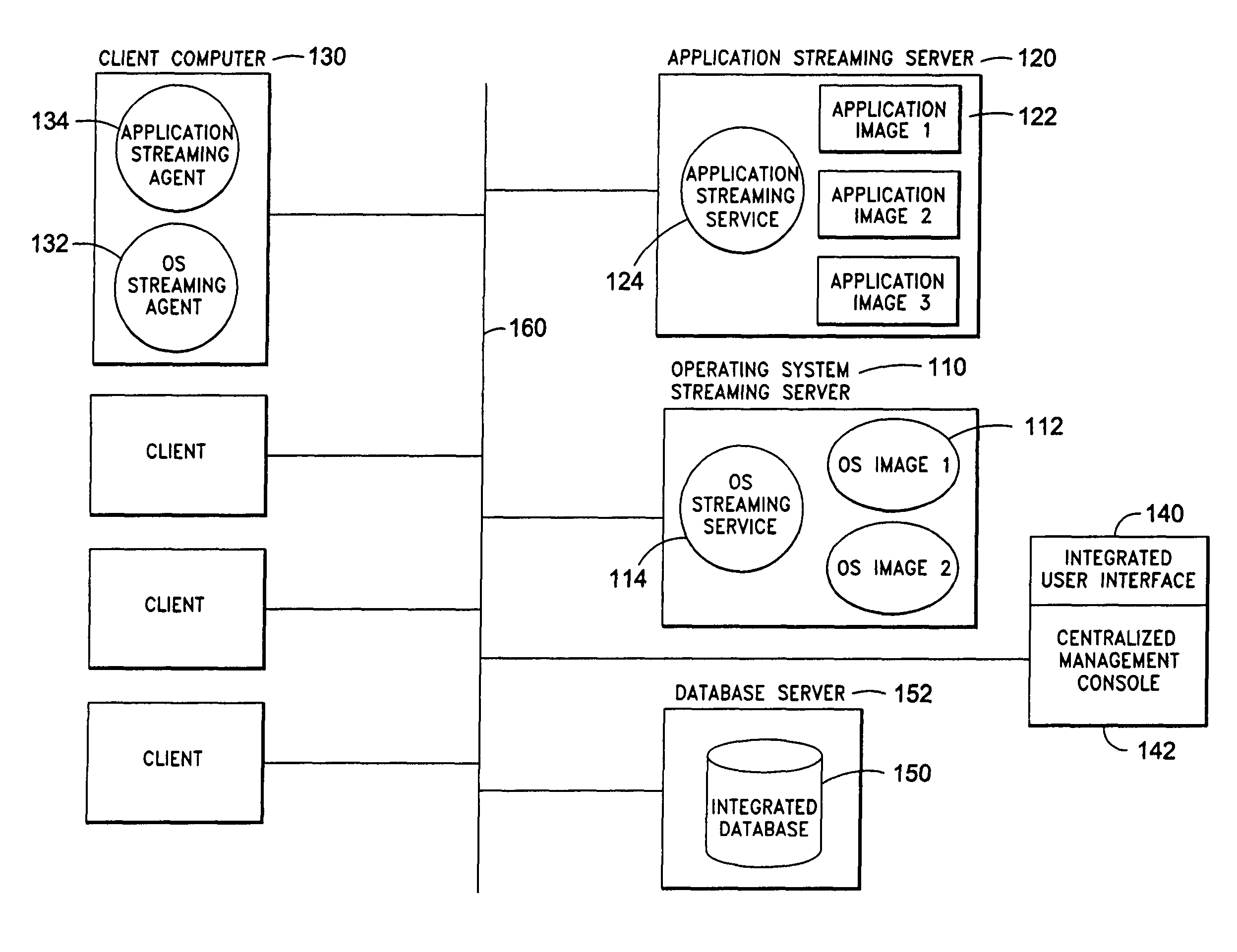
System and method for integrated on-demand delivery of operating system and applications
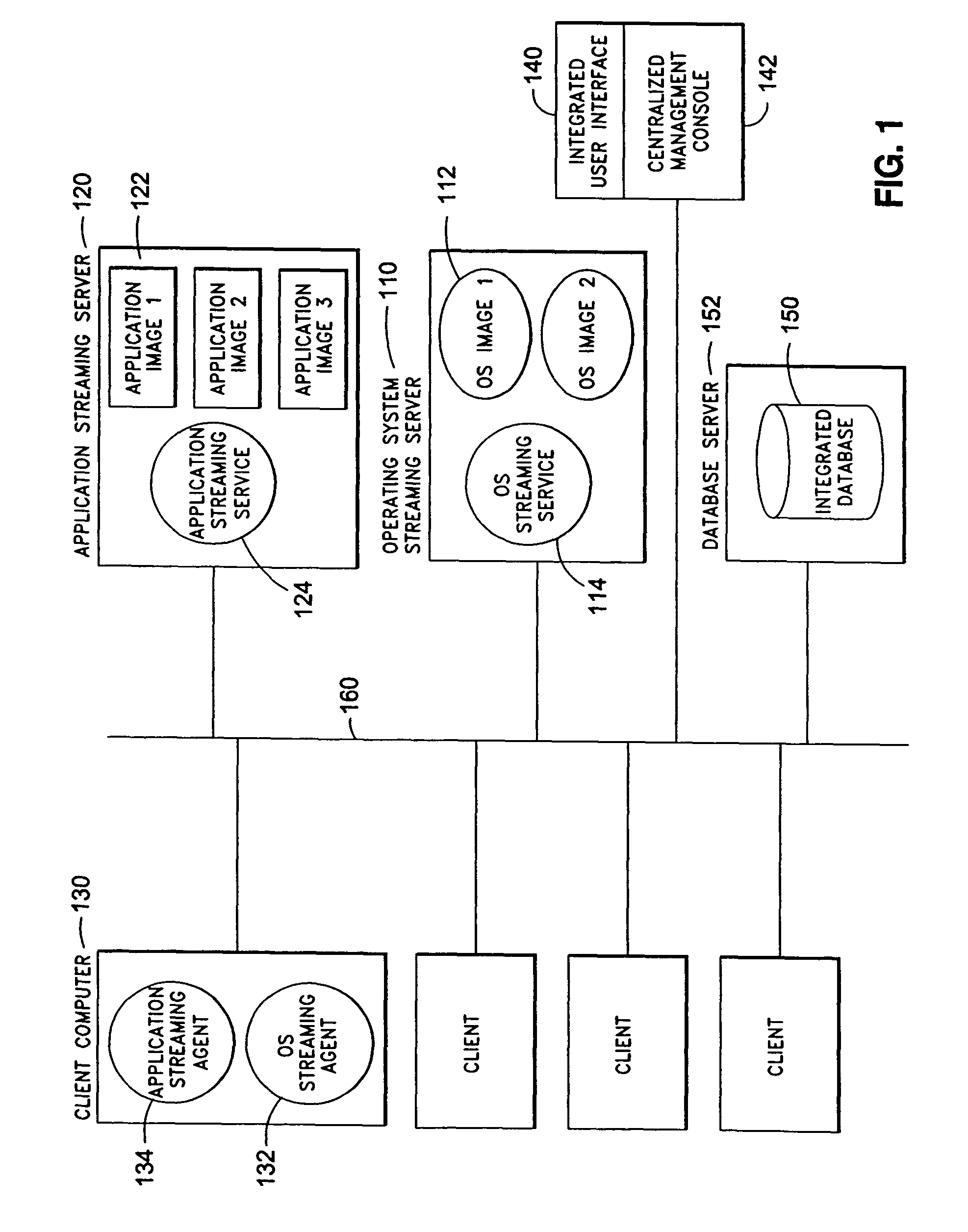
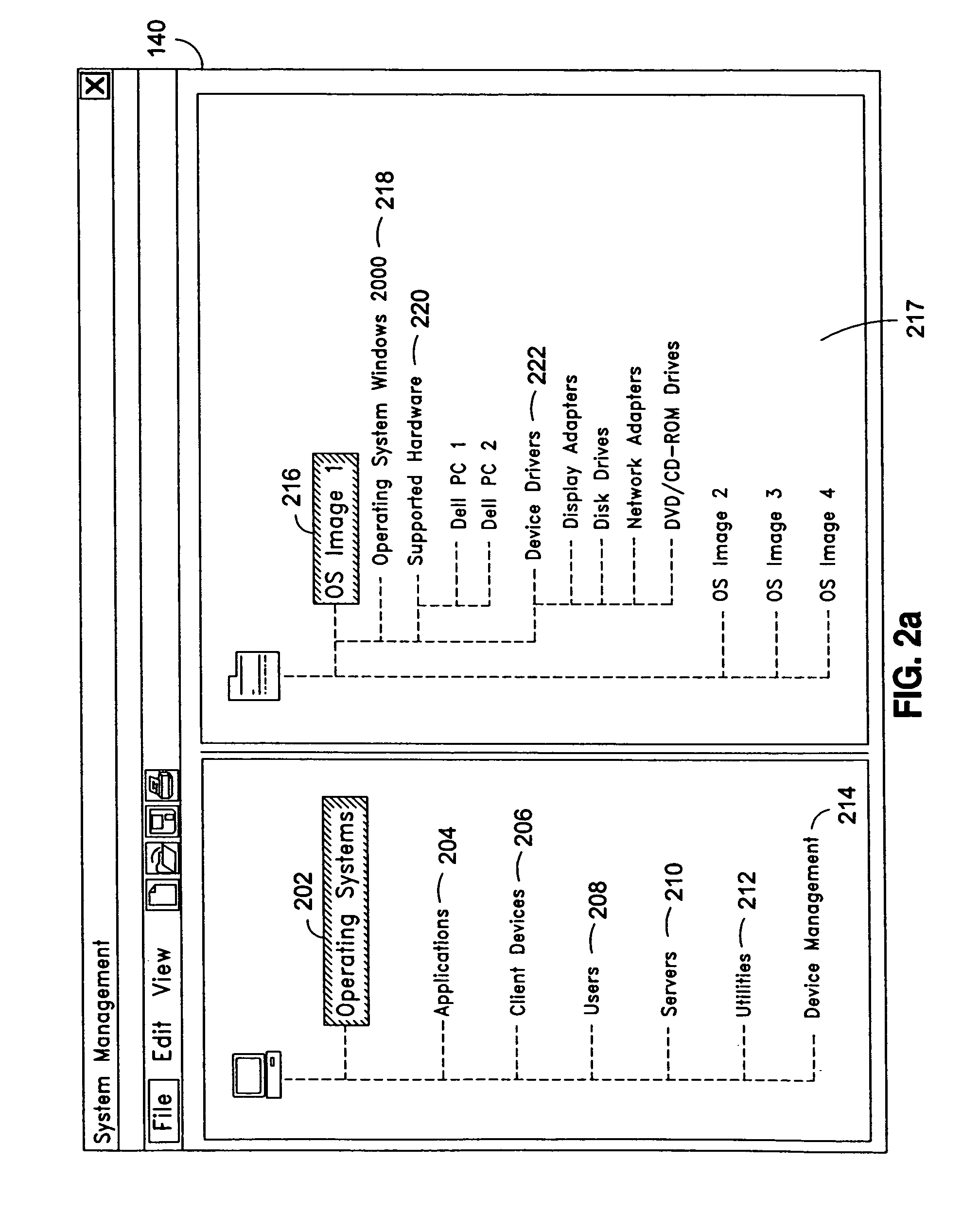
ActiveUS8230095B2Accurate scaleMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlOperational systemSystems management
The present invention discloses a system and a method for integrated on-demand delivery of operating system and applications, where operating system images are separate and distinct from application images. Integration of operating system streaming and application streaming services makes streaming delivery possible to a wide range of client devices, including those without any local disk space such as thin-clients and diskless workstations. In addition, by integrating the centralized management of operating system delivery and application delivery, the present invention provides a complete solution to server-centric application management, thereby further reducing the total cost of ownership of network-based computing approach. Implementing the operating management functions at the client machine level of specificity and application management functions at the user level of specificity combined with providing separate and distinct operating system images and application images provides an inherently canonical architecture that allows proper scaling and affords appropriate security management functions. The result is a complete, scalable, robust, and reliable server-centric application and operating system management system with a lower total cost of ownership than existing products.
Owner:DELL MARKETING CORP
Accurate detection and assessment of radiation induced lung injury based on a computational model and computed tomography imaging
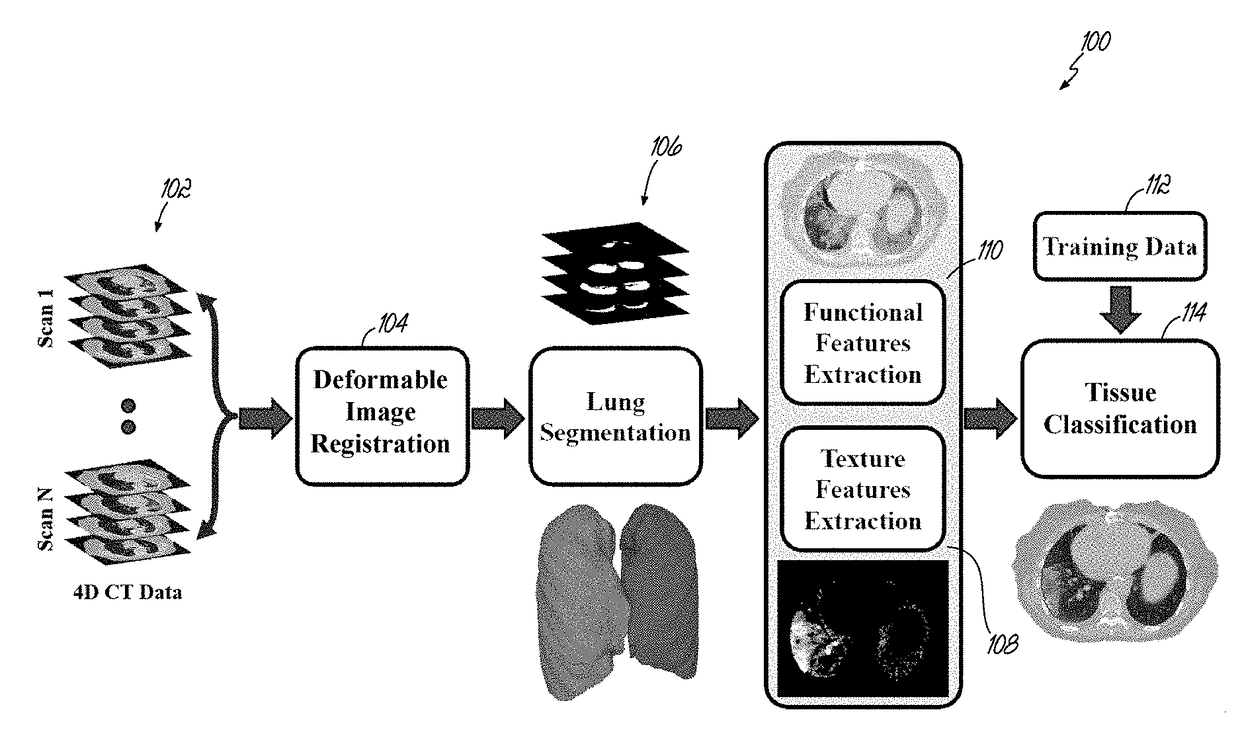
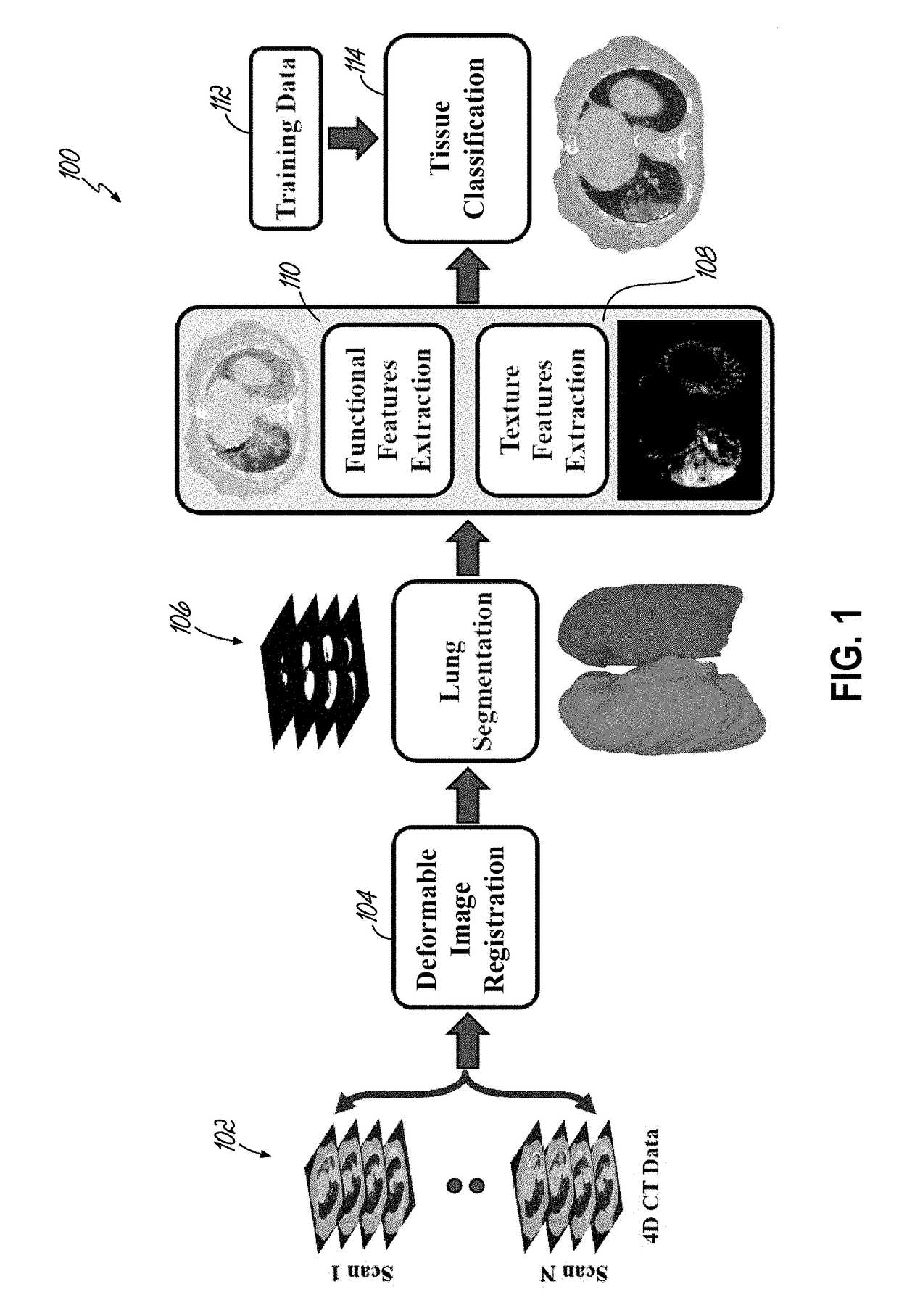
ActiveUS20180070905A1Overcome problemsImage enhancementMedical imagingComputational modelLung tissue
A system and computation method is disclosed that identifies radiation-induced lung injury after radiation therapy using 4D computed tomography (CT) scans. After deformable image registration, the method segments lung fields, extracts functional and textural features, and classifies lung tissues. The deformable registration locally aligns consecutive phases of the respiratory cycle using gradient descent minimization of the conventional dissimilarity metric. Then an adaptive shape prior, a first-order intensity model, and a second-order lung tissues homogeneity descriptor are integrated to segment the lung fields. In addition to common lung functionality features, such as ventilation and elasticity, specific regional textural features are estimated by modeling the segmented images as samples of a novel 7th-order contrast-offset-invariant Markov-Gibbs random field (MGRF). Finally, a tissue classifier is applied to distinguish between the injured and normal lung tissues.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
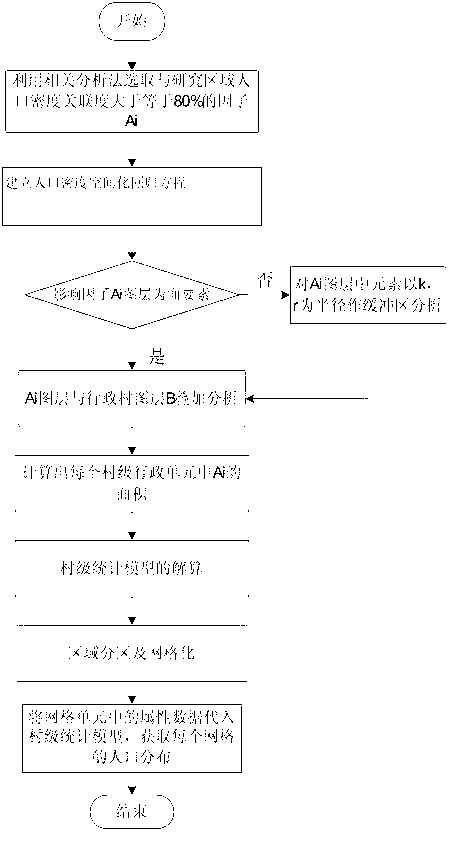
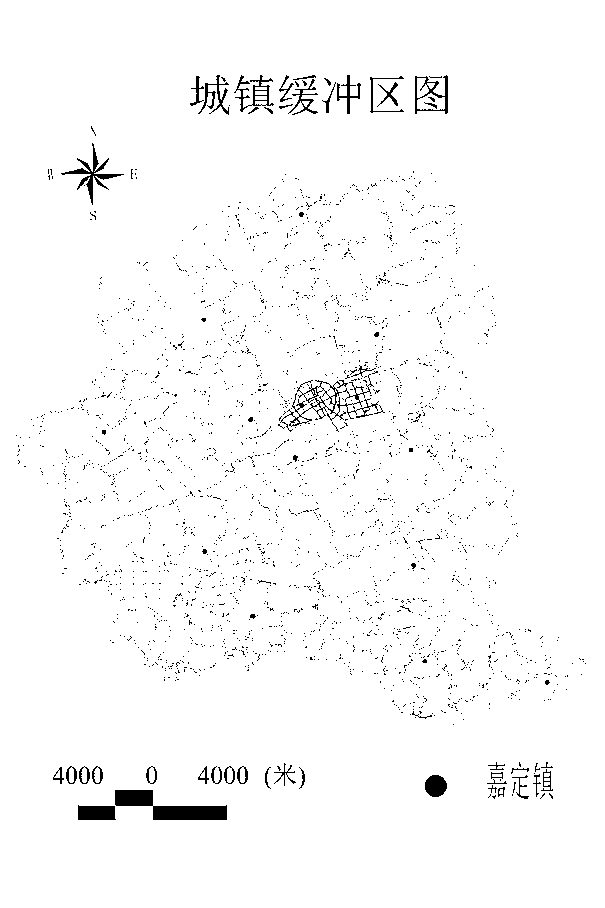
GIS (Geographic Information System)-based region-meshed spatial population density computing method
ActiveCN103218517AOvercome limitationsEasy to getSpecial data processing applicationsComputing MethodologiesDistribution characteristic
The invention discloses a GIS (Geographic Information System)-based region-meshed spatial population density computing method. According to the method, regional distribution characteristics of natural and socio-economic factors affecting population density are taken into full consideration, a statistical model is established in a manner that a village, namely a smallest regional administrative unit, serves as a unit, a research region is subjected to 100m*100m meshing, and the village-level statistical model is inverted to all meshes so as to describe population distribution by using the mesh units. The GIS-based region-meshed spatial population density computing method disclosed by the invention has the advantage that the spatial population analysis accuracy can be better improved.
Owner:苏州星宇测绘科技有限公司
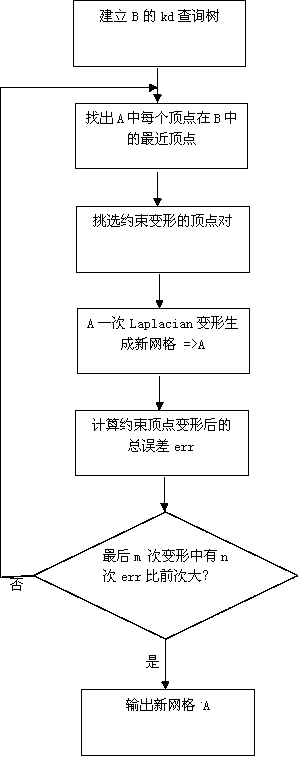
Compatibility mesh segmentation based skeleton parameter computation method
InactiveCN103632371AQuick Compatibility SplitAccuracy or efficiency improvementImage analysisComputing MethodologiesFeature based
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
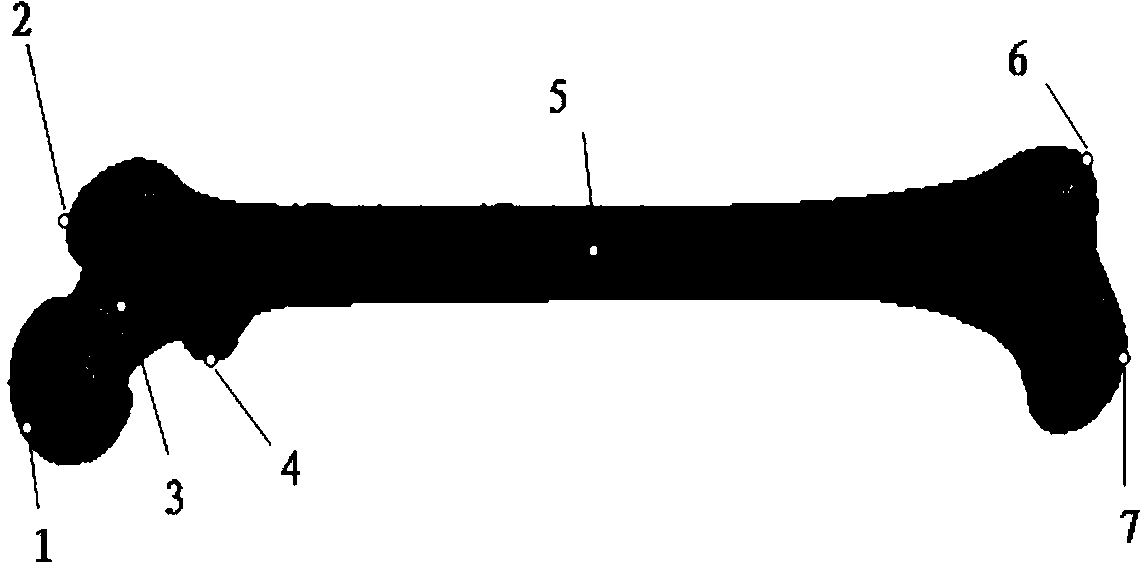
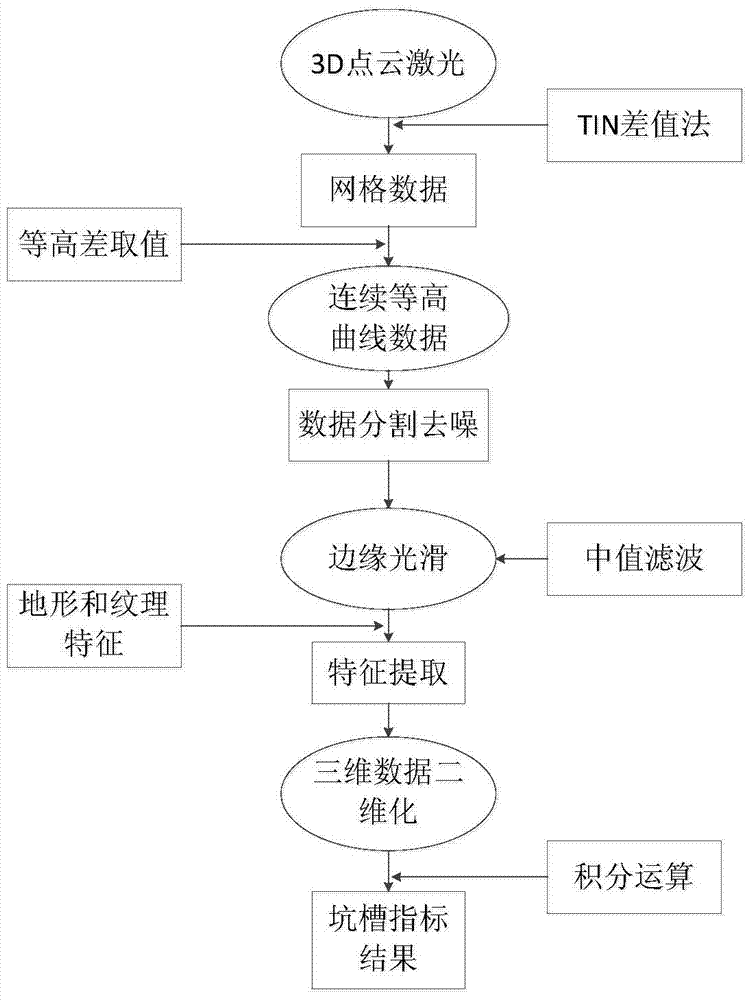
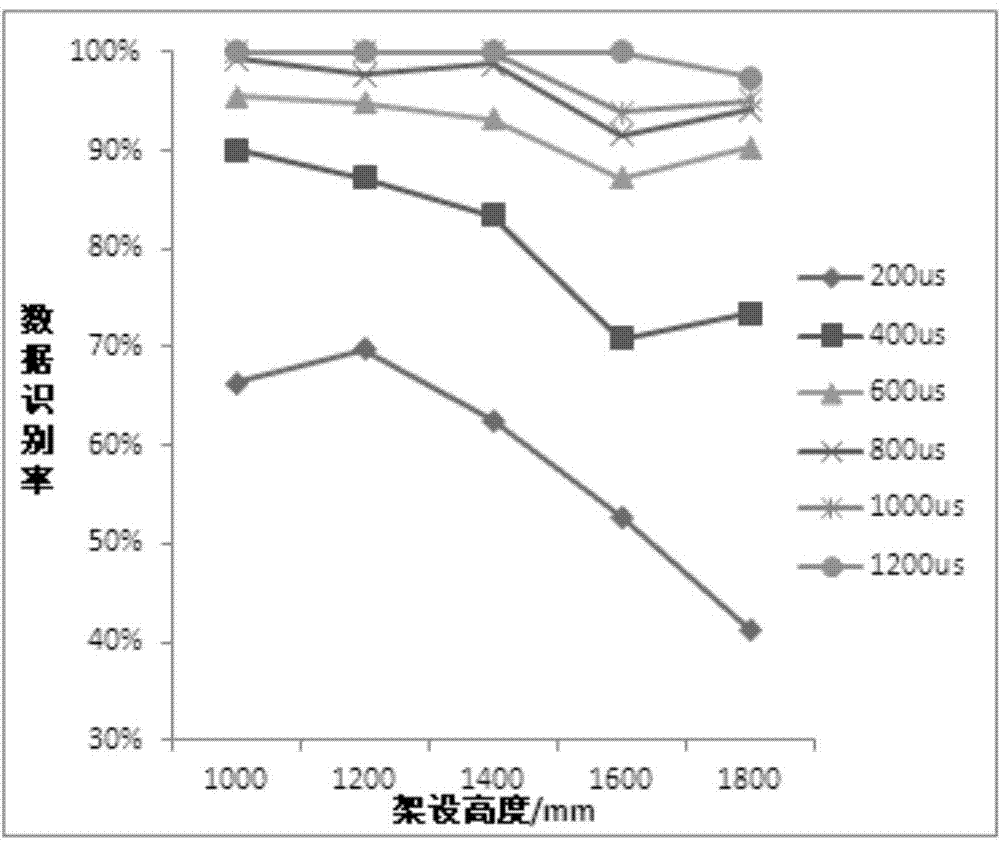
Pit slot three-dimensional index extracting and calculating method based on 3D line laser equipment
The invention discloses a pit slot three-dimensional index extracting and calculating method based on 3D line laser equipment. The pit slot three-dimensional index extracting and calculating method comprises the following steps: firstly, making a plurality of regular simulation pit slots with different depths and different areas, calibrating parameters affecting a recognition rate of the 3D line laser equipment to obtain an optimal parameter combination; secondly, recognizing and calculating depth, area and volume indexes of a pit slot under the optimal parameter combination; finally, performing a reliability test on the reliability of detecting equipment and a detecting method. The pit slot three-dimensional index extracting and calculating method disclosed by the invention basically can meet a requirement of an actual pit slot test under existing equipment, and provides a reliable method for extracting and calculating three-dimensional indexes of the pit slot.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
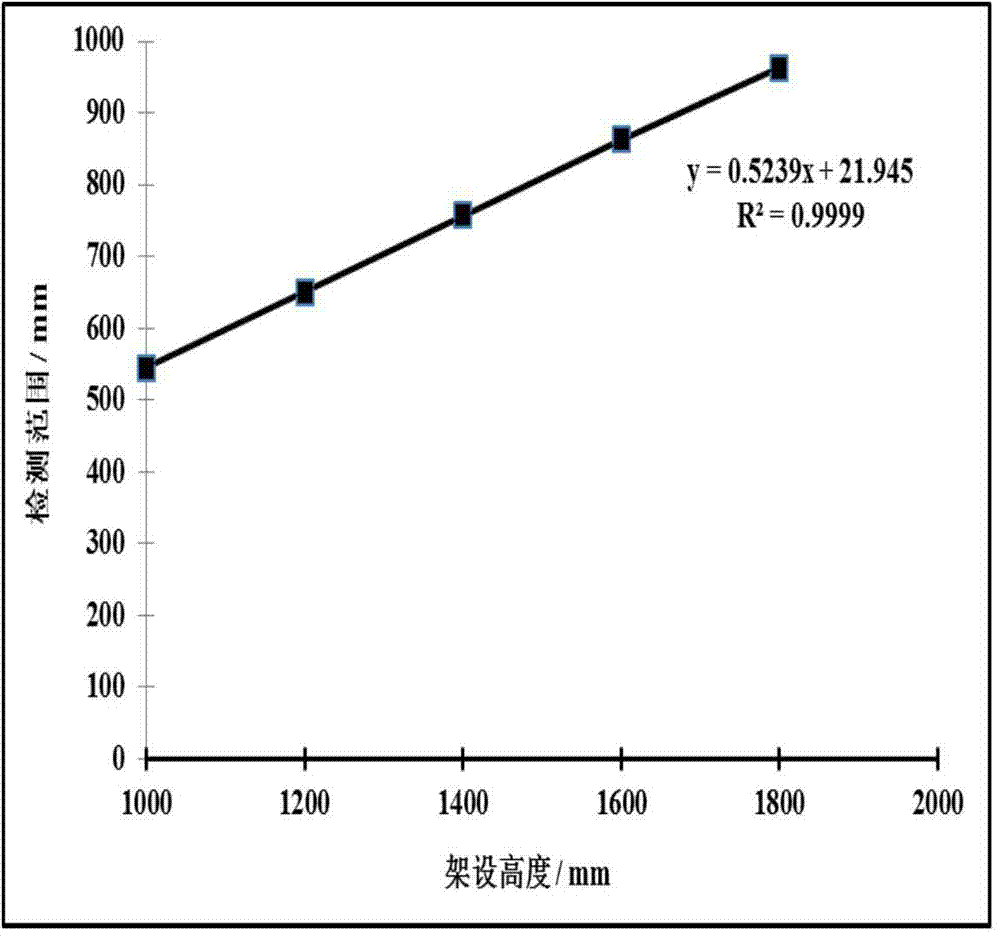
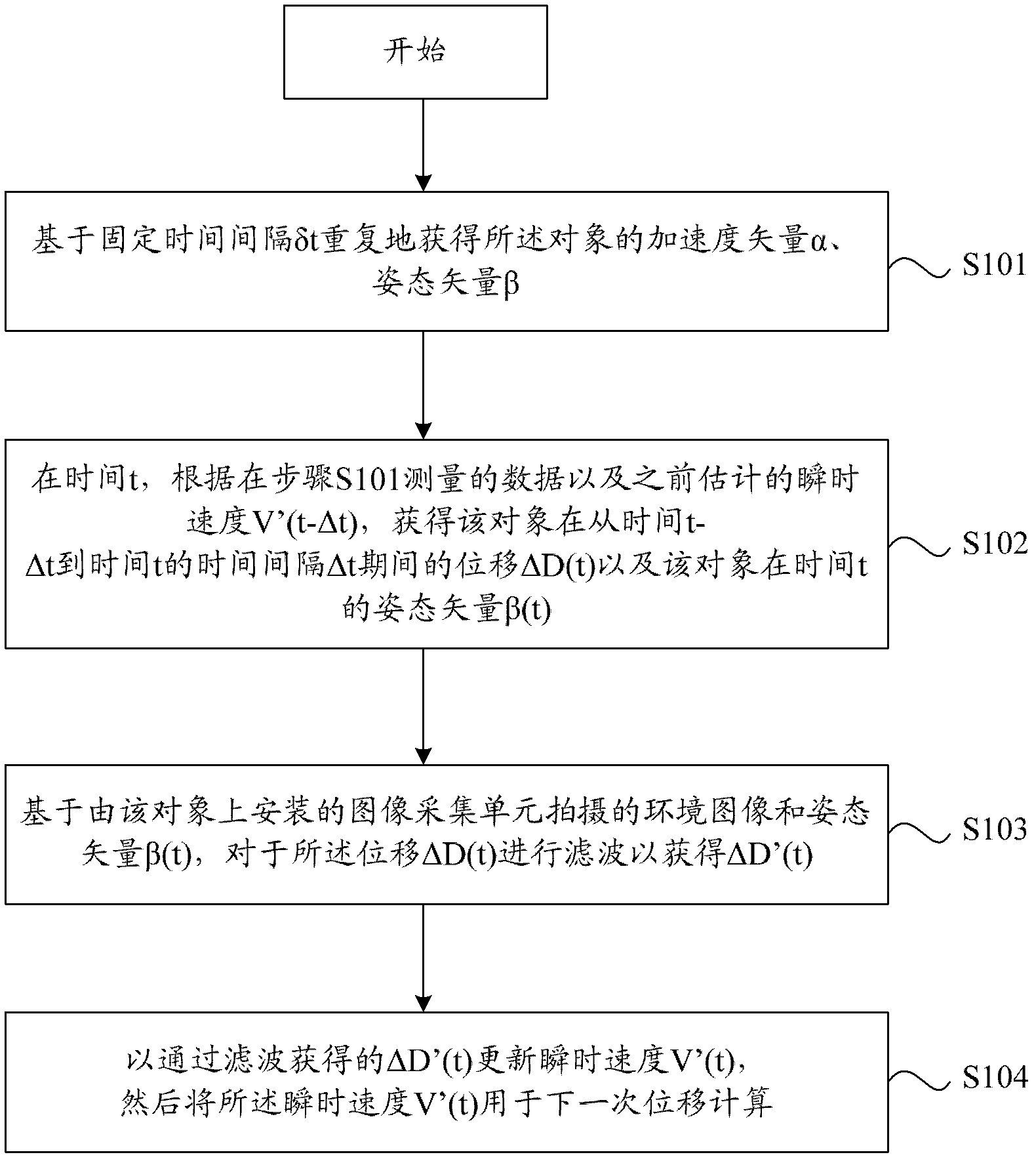
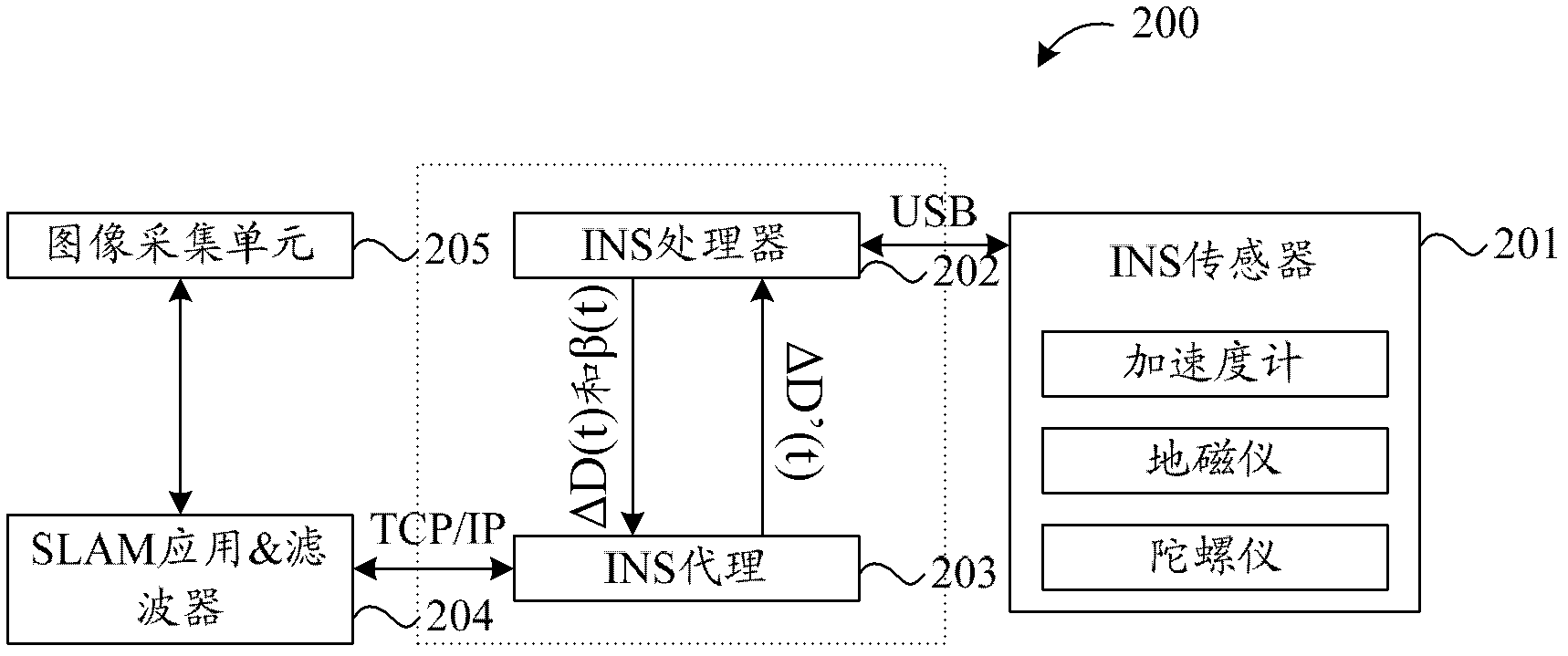
Method and device for displacement computing and method and device for simultaneous localization and mapping
ActiveCN103105852AImprove performanceImprove stabilityComplex mathematical operationsPosition/course control in two dimensionsComputing MethodologiesSimultaneous localization and mapping
The invention discloses a method and a device for simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM). A method for displacement computing comprises the steps of repeatedly acquiring an acceleration vector alpha and a gesture vector beta of a movable object (such as a robot or a handheld device) based on a fixed time interval delta t, obtaining displacement of the object during the time interval delta t from time of t-delta t to time of t according to measured data and instantaneous speed V' (t-delta t) estimated in advance and obtaining a gesture vector beta (t) of the movable object during the time of t, wherein delta t = n*delta t, n belongs to N, estimating displacement according to data collected by a three-dimensional camera installed on the movable object and the gesture vector beta (t), carrying out filtering on the displacement delta D (t) to obtain delta D' (t), and then achieving construction of a three-dimensional map, updating the instantaneous speed V' (t) according to obtained delta D' (t) obtained through filtering, and using the instantaneous speed V' (t) for next synchronization displacement and mapping computing.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) LTD
Method for calculating random floating state of ship on basis of STL model
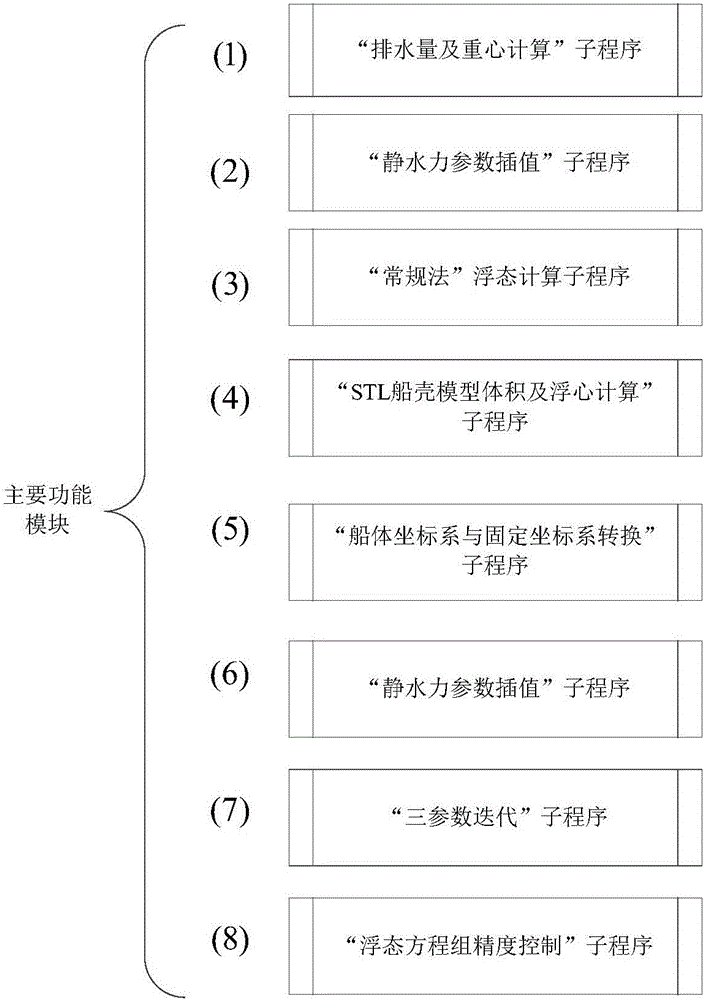
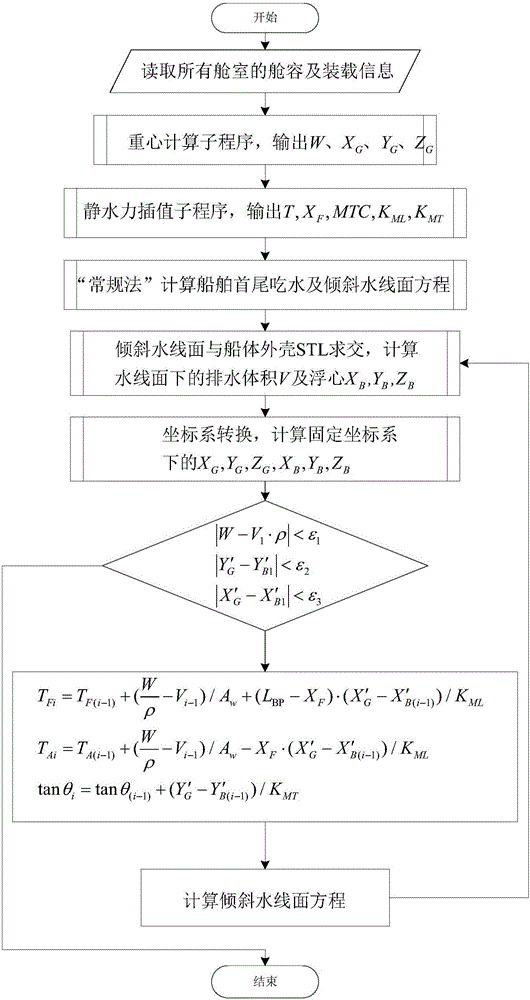
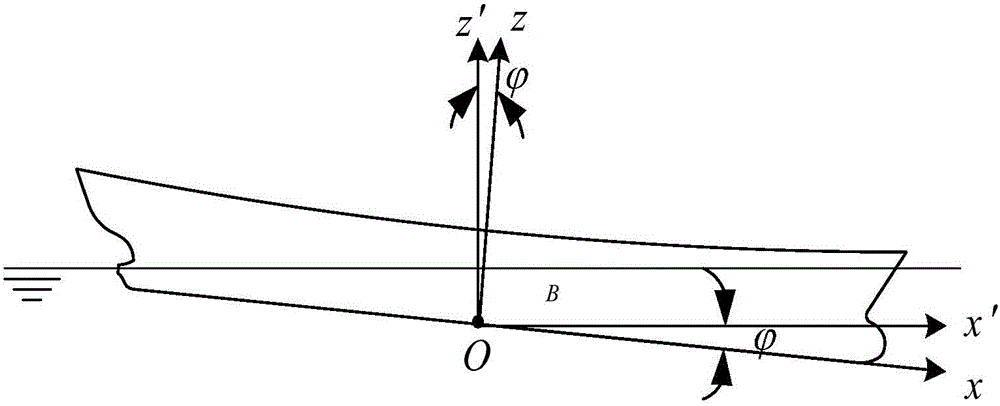
ActiveCN105825061ASimple 3D data formatCalculation speedInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsComputing MethodologiesLithographic artist
The invention discloses a method for calculating a random floating state of a ship on the basis of an STL (Stereo Lithography) model. The method comprises the following steps of calculating a midship draft TM, a heeling angle tangent value tan(Theta) and a trimming angle tangent value of the ship according to a conventional method; determining an equation of an inclined waterplane according to the midship draft, a heeling angle and a trimming angle; calculating a ship body displacement volume V under the waterplane and buoyancy coordinates (XB, YB, ZB); calculating barycentric coordinates (X'G, YG', Z'G) and buoyancy center coordinates (X'B, YB', ZB') of the ship under a fixed coordinate system; judging whether floating state equations meet a balance condition or not; performing three-parameter iterative calculation according to a fore draft, an aft draft and the heeling angle if the floating state equations do not meet the balance condition. The invention provides a three-parameter iterative method for calculating the floating state of the ship under any loading condition on the basis of the STL model, which has the features that the transverse inclination and longitudinal inclination of the ship can be calculated simultaneously, the method is suitable for any floating state of the ship, and the calculation precision is improved. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the calculation quantity is reduced, the displacement volume and buoyancy center of the ship under any floating state are only calculated, and a program is strong and stable.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Comprehensive risk priority number calculating method for architecture
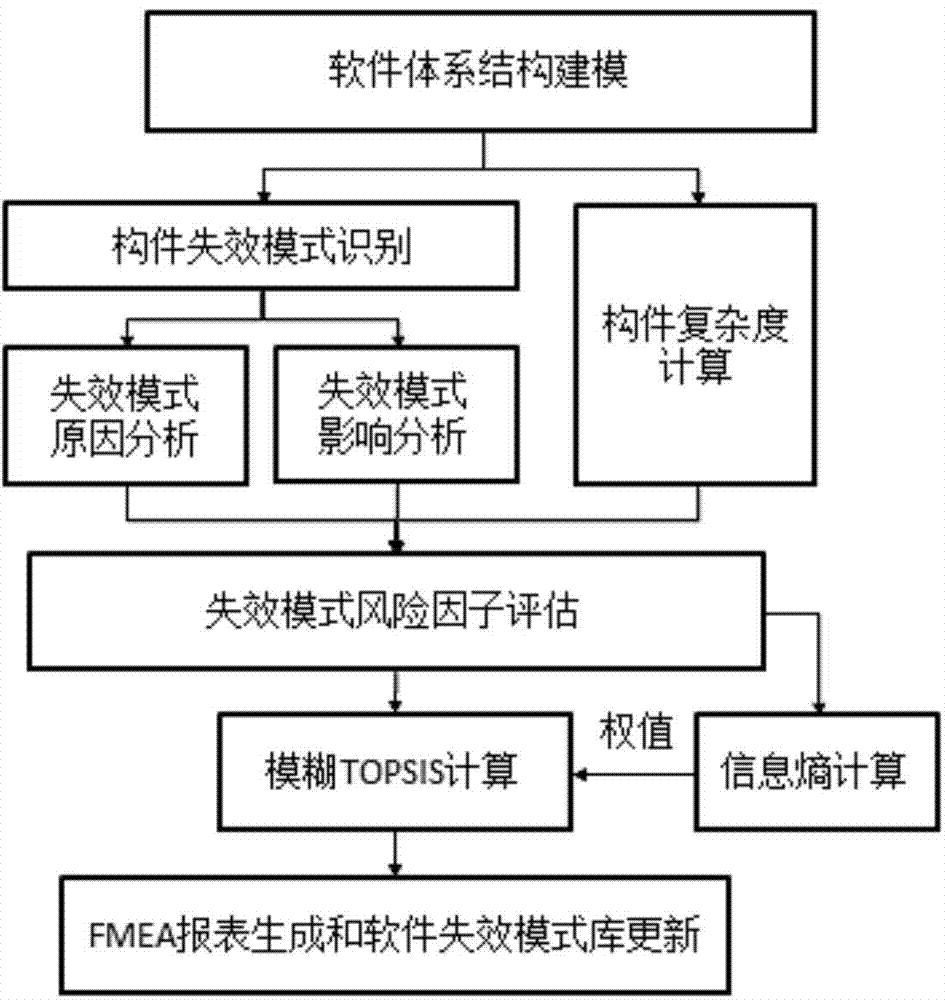
ActiveCN104750979AAccurate and reliable assessment resultsAvoid the problem of inaccurate subjective semantic description boundariesSpecial data processing applicationsCOLA (software architecture)Computing Methodologies
The invention provides a comprehensive risk priority number calculating method for architecture. Three risk factors (the appearance frequency, the severity degree and the discovery index) in FMEA are evaluated in the mode that fuzzy numbers are utilized in software architecture in a leveled mode; the appearance frequency and the discovery index are determined through component complexity and expertise, and the weights of different risk factors are distinguished through the conception of information entropy; through the conceptions of a positive ideal solution and a negative ideal solution in a TOPSIS method, a more reasonable and accurate risk priority number rank is obtained; in this way, a comprehensive software-failing mode risk factor evaluation technology for the architecture is achieved. By means of the comprehensive risk priority number calculating method, at the initial software design stage, developers are helped to find out potential design defects in a system, and therefore the subsequent software development quality is guaranteed.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
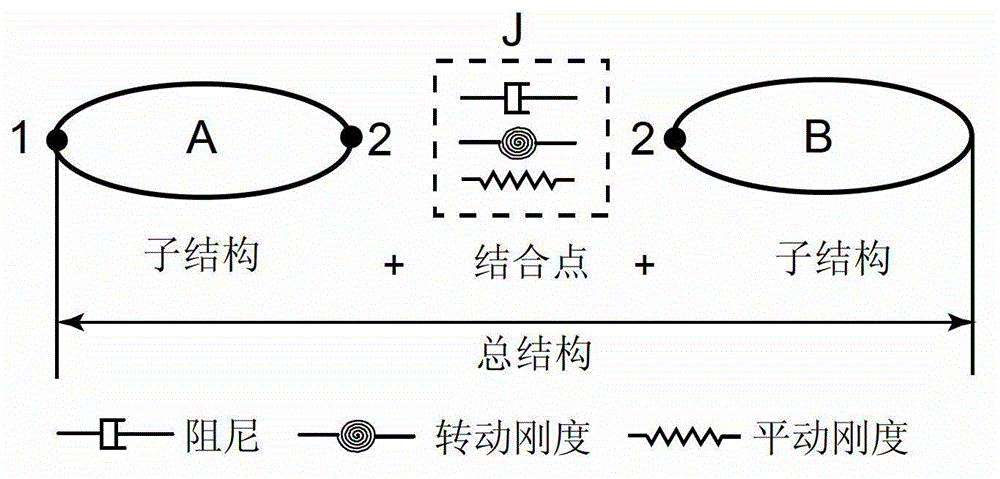
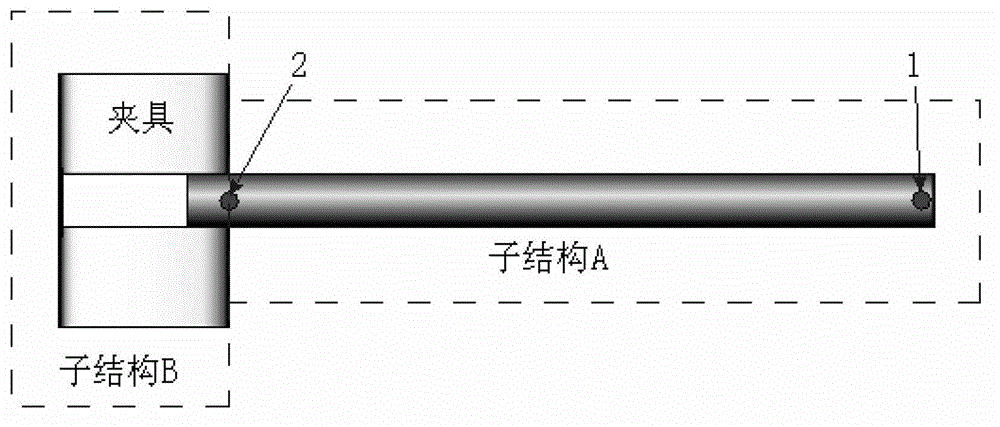
Rotational freedom frequency response function computing method of complex mechanical structure
ActiveCN102880803AAccurate modelingAvoid measuringSpecial data processing applicationsComputing MethodologiesRotational freedom
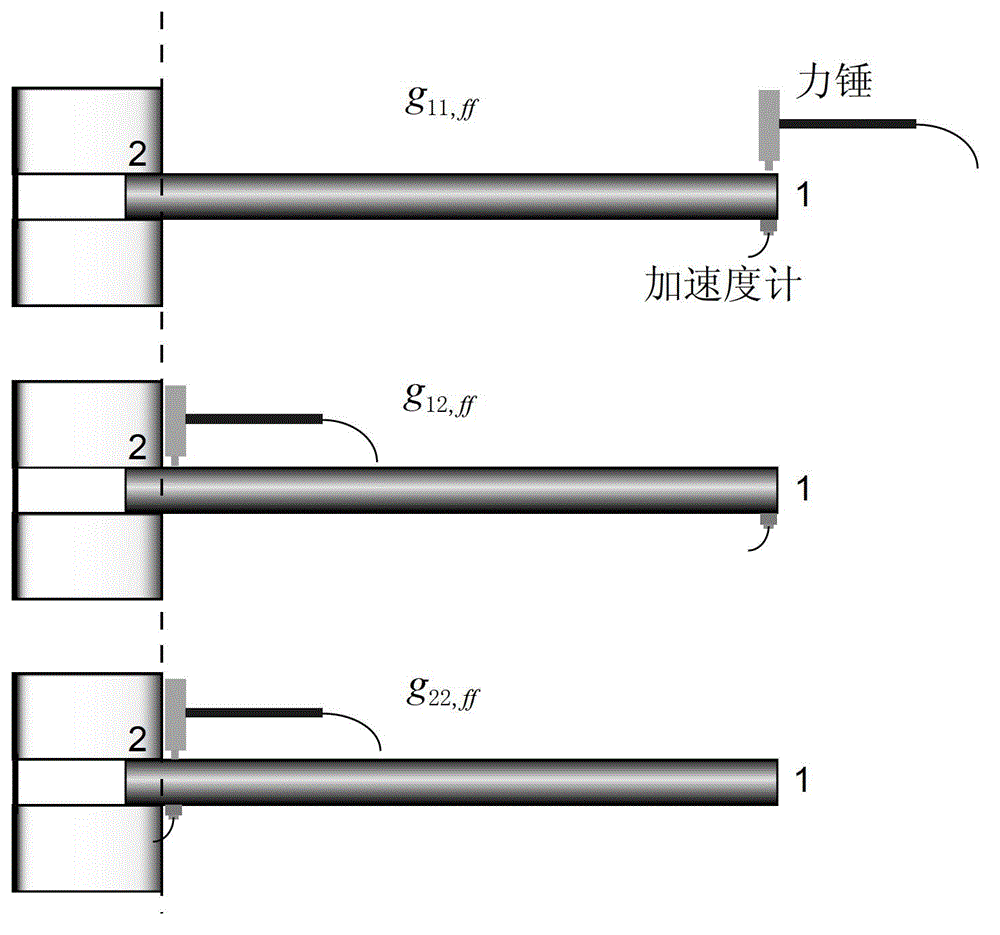
The invention relates to a rotational freedom frequency response function estimation method based on the response coupling technology. The method is mainly suitable for estimation of rotational freedom frequency response function in a complex mechanical structure. The method includes: utilizing the receptance coupling technology, estimating rotational freedom frequency response function according to needs, decomposing the complex mechanical structure into a substructure A and a substructure B, choosing a first measuring point, at a position convenient for measuring, on the substructure A, and choosing a second measuring point on a joint surface of the substructure A and the substructure B; utilizing the hammer impact excitation method to measure frequency response function of three translational freedom degrees, and solving a frequency response function matrix on the joint surface of the substructure A and the substructure B; and calculating to obtain all frequency response functions at the two measuring points related to rotational freedom. The rotational freedom frequency response function estimation method based on the response coupling technology is convenient to implement and accurate in calculation result and provides another effective technology for estimation of rotational freedom frequency response function.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Electronic equipment spare part configuration and calculation method based on reliability model
ActiveCN104462755AIncrease computing read and write overheadAvoid frequent reading and writingSpecial data processing applicationsComputing MethodologiesFailure rate
The invention provides an electronic equipment spare part configuration and calculation method based on a reliability model. The method comprises the steps that (1) according to the condition of equipment support resources and the requirement of an equipment user, the minimum acceptance value of the optimized spare part supportability probability is determined, and basic configuration parameters of spare part configuration and calculation are determined according to the work stress condition and the physical structure of the equipment; (2) the mutual relation of all mold components is analyzed when the equipment completes a task, the reliability logic relation of the mold components is analyzed, the reliability model is built, and the total failure rate of the mold components is calculated according to a mathematical model corresponding to the reliability model; (3) an iteration model of the spare part configuration and calculation is constructed, and the number of spare parts, needing to be configured, of a component is obtained. Precision of spare part configuration is achieved, the reliability model and reliability predicted data are combined, and the number of the spare parts can be configured effectively and precisely. 0.
Owner:中国船舶重工集团公司第七二六研究所
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com