Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
972results about How to "Reduce conflict" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Masonry cement having higher strength and water retention
InactiveCN101182139AHigh strengthSolve the difficult problem of preparing high-strength grade building mortarSolid waste managementCelluloseLower grade
The invention discloses a masonry cement with high strength and water retention. According to the weight percentage, the masonry cement consists of 21-98.99 percent of porland cement clinker, 0-50 percent of blending materials, 1-12 percent of gypsum, 0.01-2 percent of cellulose ether and 0-15 percent of other additives. With the cellulose ether of high water retention material added, the water retention of the masonry cement is greatly improved. At the same time, through breaking through the limitation that the using amount of the blending materials in the original masonry cement is not less than 50 percent, the using amount of the blending materials is lowered to be 50 percent below to improve the strength of novel masonry cement. The strength of the prepared masonry cement is high, and the masonry cement with the strength grades of 12.5, 22.5, 52.5R, 62.5, 62.5R, etc. can be made. The hard problems of using low-grade blending materials to produce masonry cement with high water retention and using low- grade strength masonry cement of 12.5 and 22.5 to produce high-grade strength building mortar are solved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
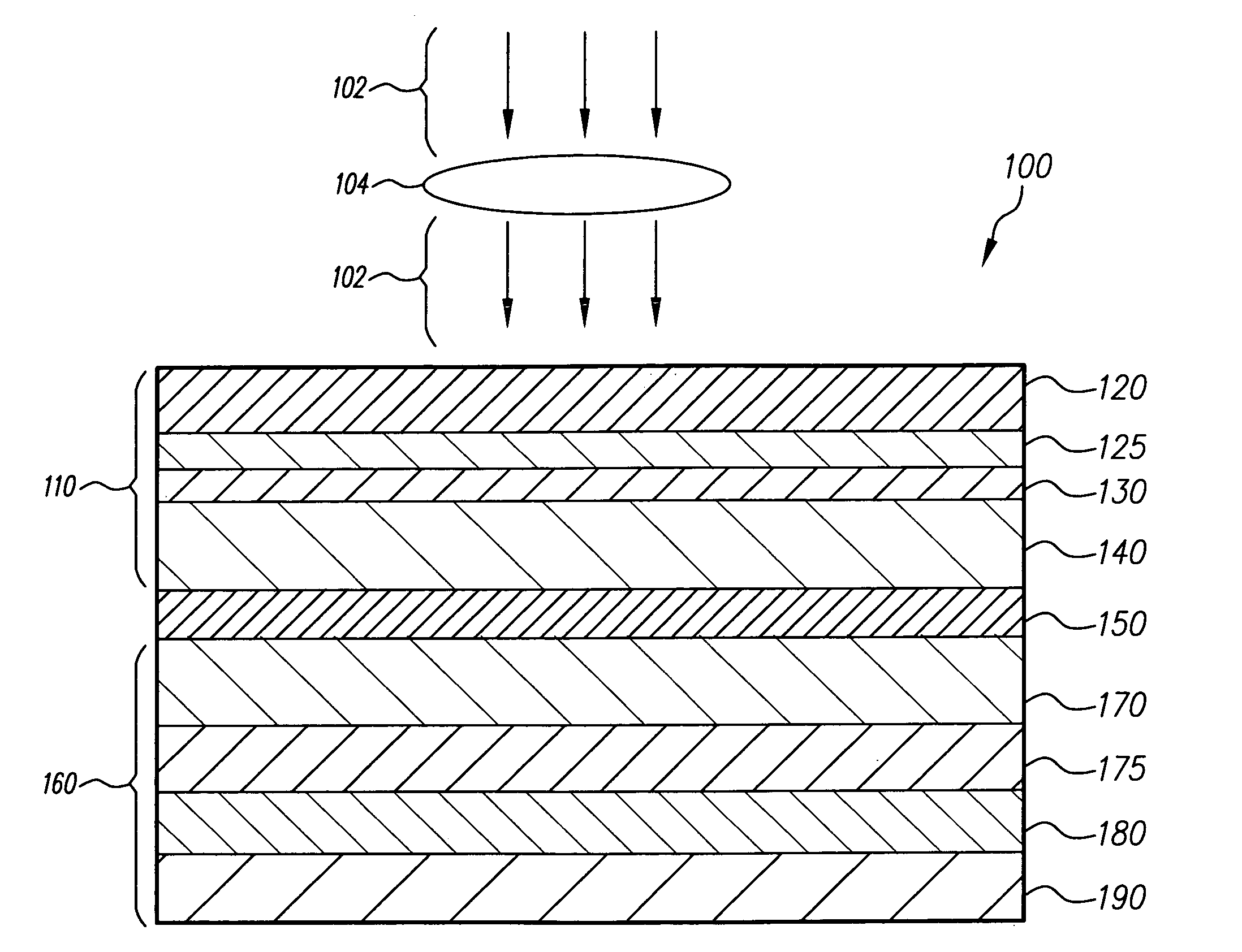
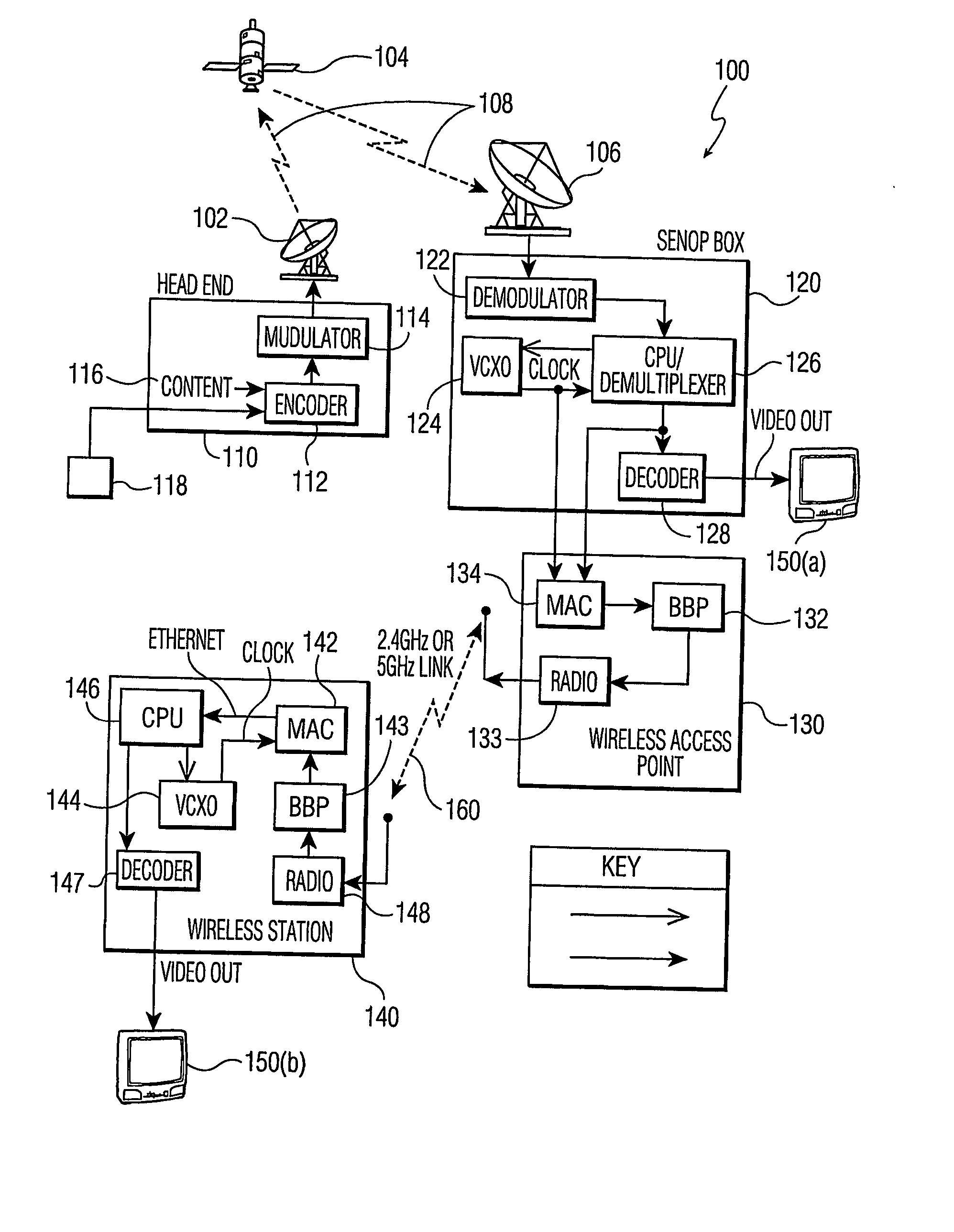
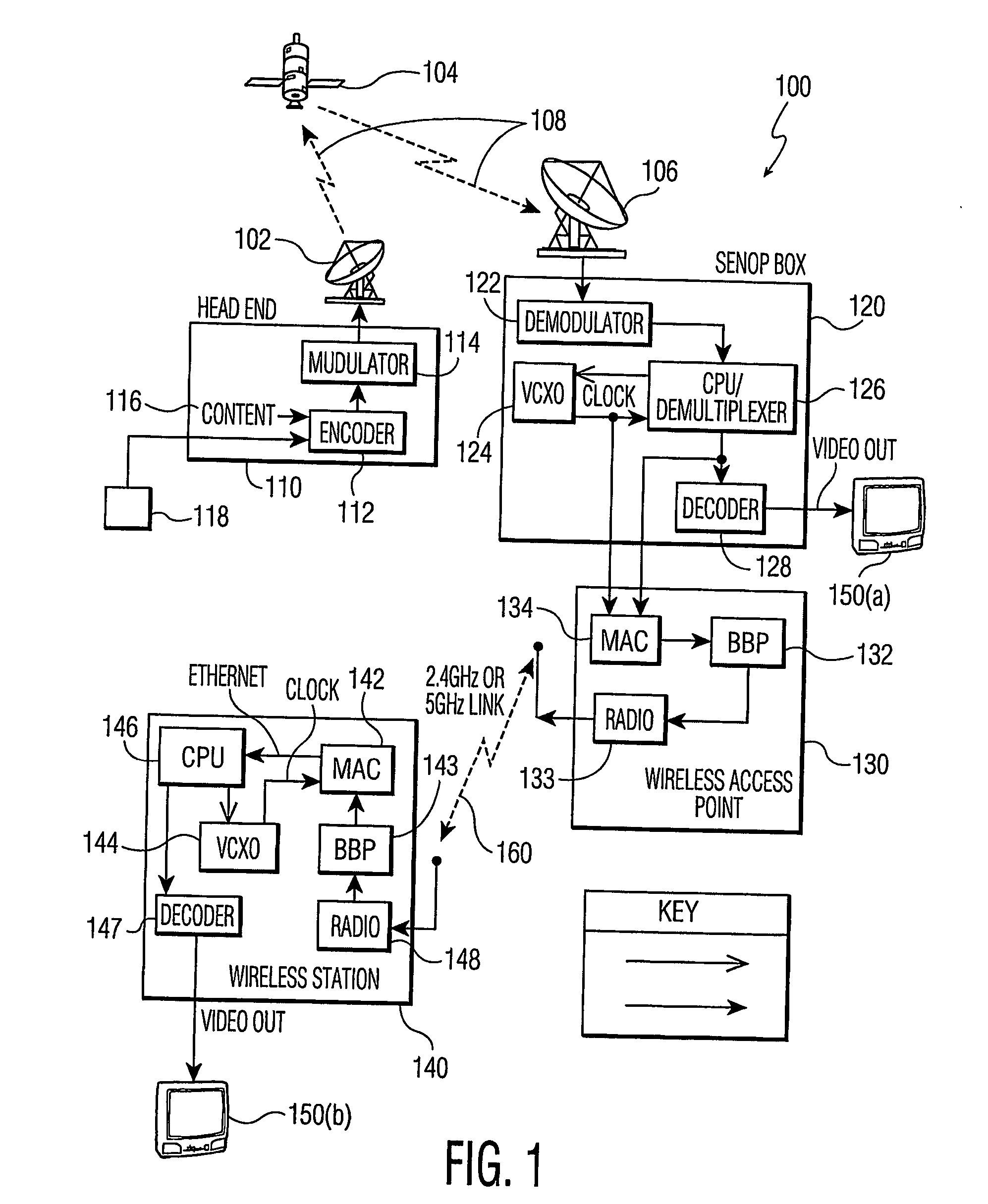
Apparatus for asymmetric dual-screen digital radiography
ActiveUS20080011960A1High detective quantum efficiencyClear imagingSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSoft x rayFluorescence
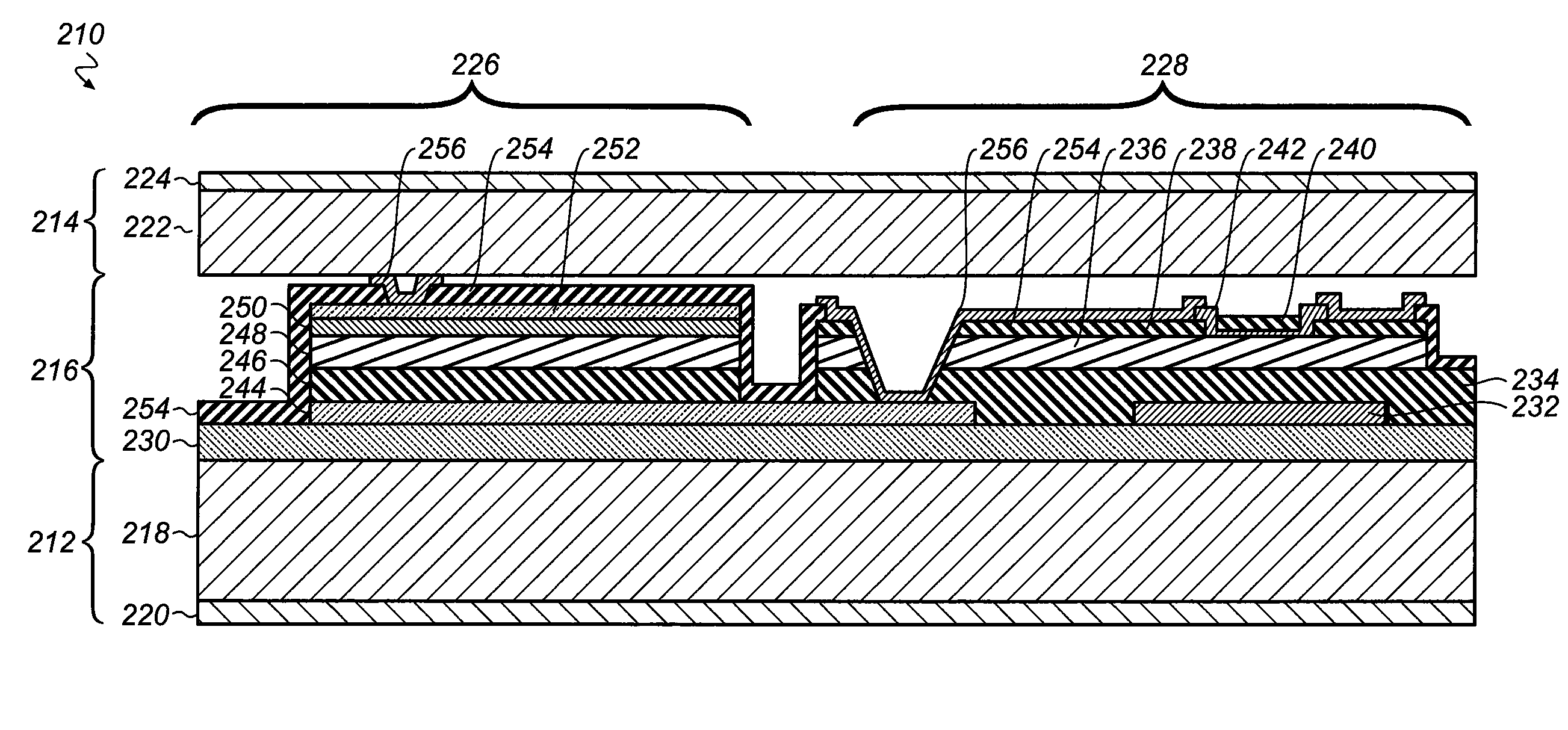
The present invention relates to radiographic imaging apparatus for taking X-ray images of an object. In various two-panel radiographic imaging apparatus configurations, a front panel and back panel have substrates, arrays of signal sensing elements and readout devices, and passivation layers. The front and back panels have scintillating phosphor layers responsive to X-rays passing through an object produce light which illuminates the signal sensing elements to provide signals representing X-ray images. The X-ray apparatus has means for combining the signals of the X-ray images to produce a composite X-ray image. Furthermore, the composition and thickness of the scintillating phosphor layers are selected, relative to each other, to improve the diagnostic efficacy of the composite X-ray image. Alternatively, a radiographic imaging apparatus has a single panel having arrays of signal sensing elements and readout devices and scintillating phosphor layers that are disposed on both sides of a single substrate. The present invention further relates to various embodiments of indirect dual-screen DR flat-panel imager apparatus that provide single-exposure dual energy imaging.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
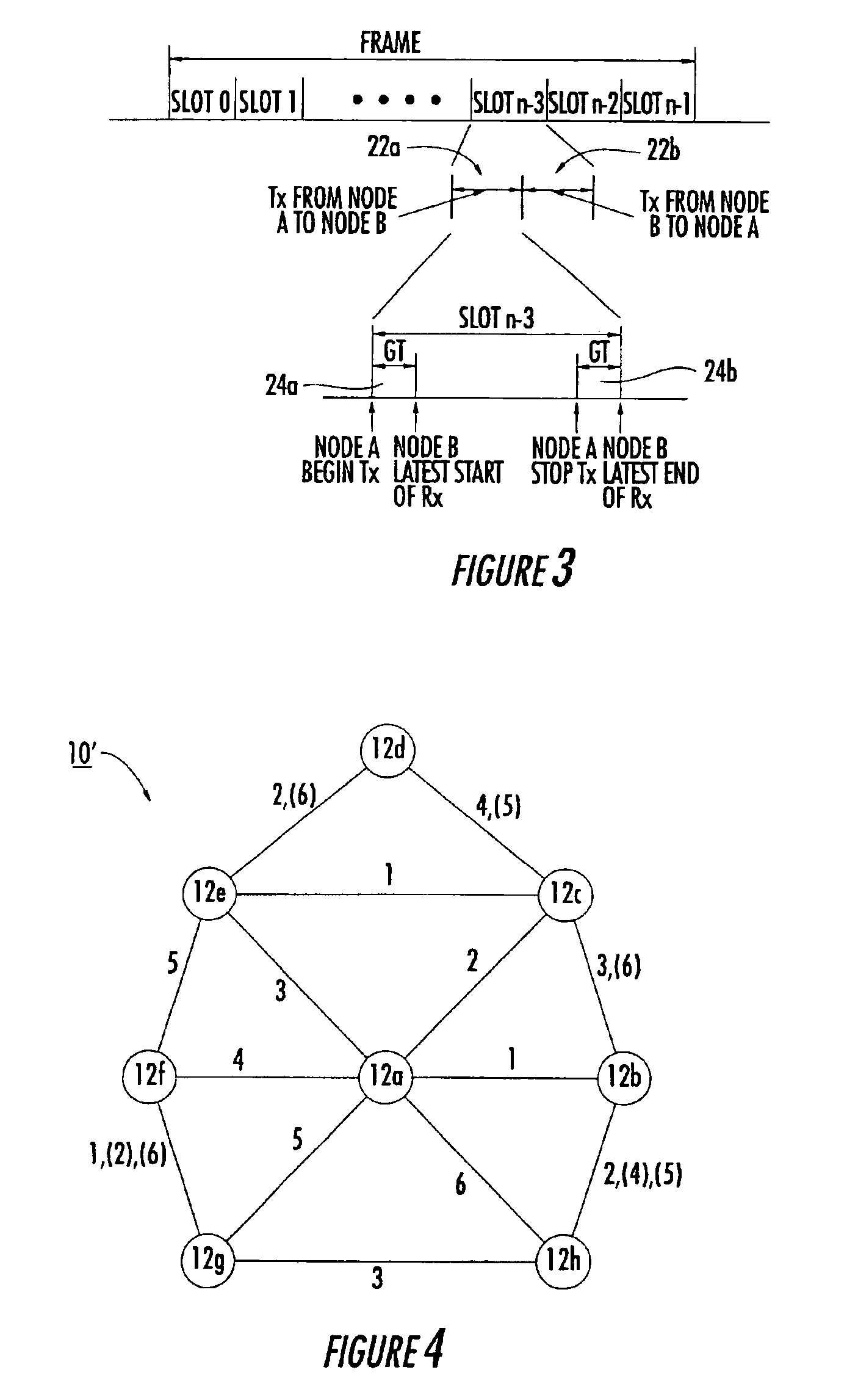
Wireless communication system with enhanced time slot allocation and interference avoidance/mitigation features and related methods
InactiveUS6958986B2Reduce the impact of interferenceMinimize disruptionSpatial transmit diversityError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCommunications systemTelecommunications link
A wireless communication network may include a plurality of mobile nodes each including a wireless transceiver and a controller for controlling the wireless transceiver. The controller may also be for scheduling a respective semi-permanent time slot to establish a communication link with neighboring mobile nodes for transmitting data therebetween, where the data has different priority levels. The controller may also determine respective link utilization metrics for each data priority level for each communication link, and schedule demand assigned time slots for establishing additional communication links with the neighboring mobile nodes for transmitting data therebetween based upon the link utilization metrics and data priority levels. The wireless communication network may also provide enhanced interference avoidance and / or mitigation features in certain embodiments.
Owner:STINGRAY IP SOLUTIONS LLC
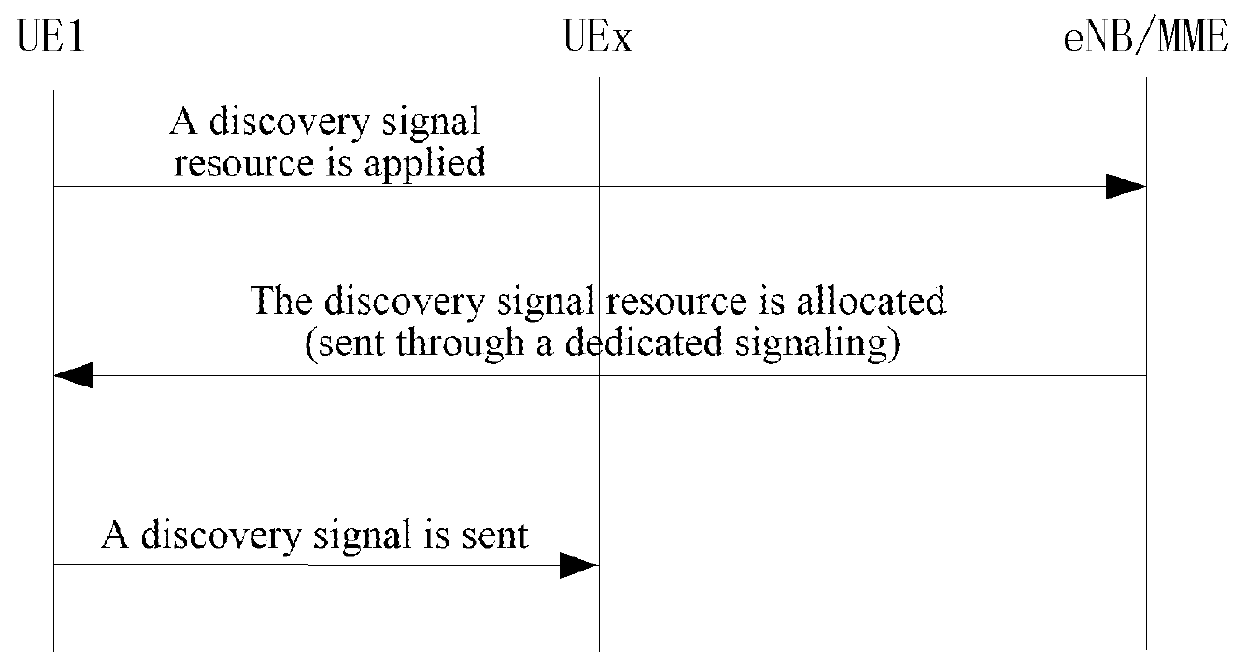
Device-to-Device (D2D) Discovery Method, Base Station, And User Equipment
ActiveUS20160057604A1Reduce conflictImprove reliabilityAssess restrictionWireless commuication servicesDevice to deviceTime frequency domain
A device-to-device (D2D) discovery method, an eNodeB and a user equipment are disclosed. The method includes: a user equipment acquiring discovery signal resources allocated by an eNodeB (eNB) to the user equipment, wherein the discovery signal resources include time-frequency domain resources used for sending or monitoring a discovery signal; and when the user equipment performs a D2D discovery operation, sending or monitoring the discovery signal according to acquired discovery signal resources to perform D2D discovery.
Owner:XIAN ZHONGXING NEW SOFTWARE
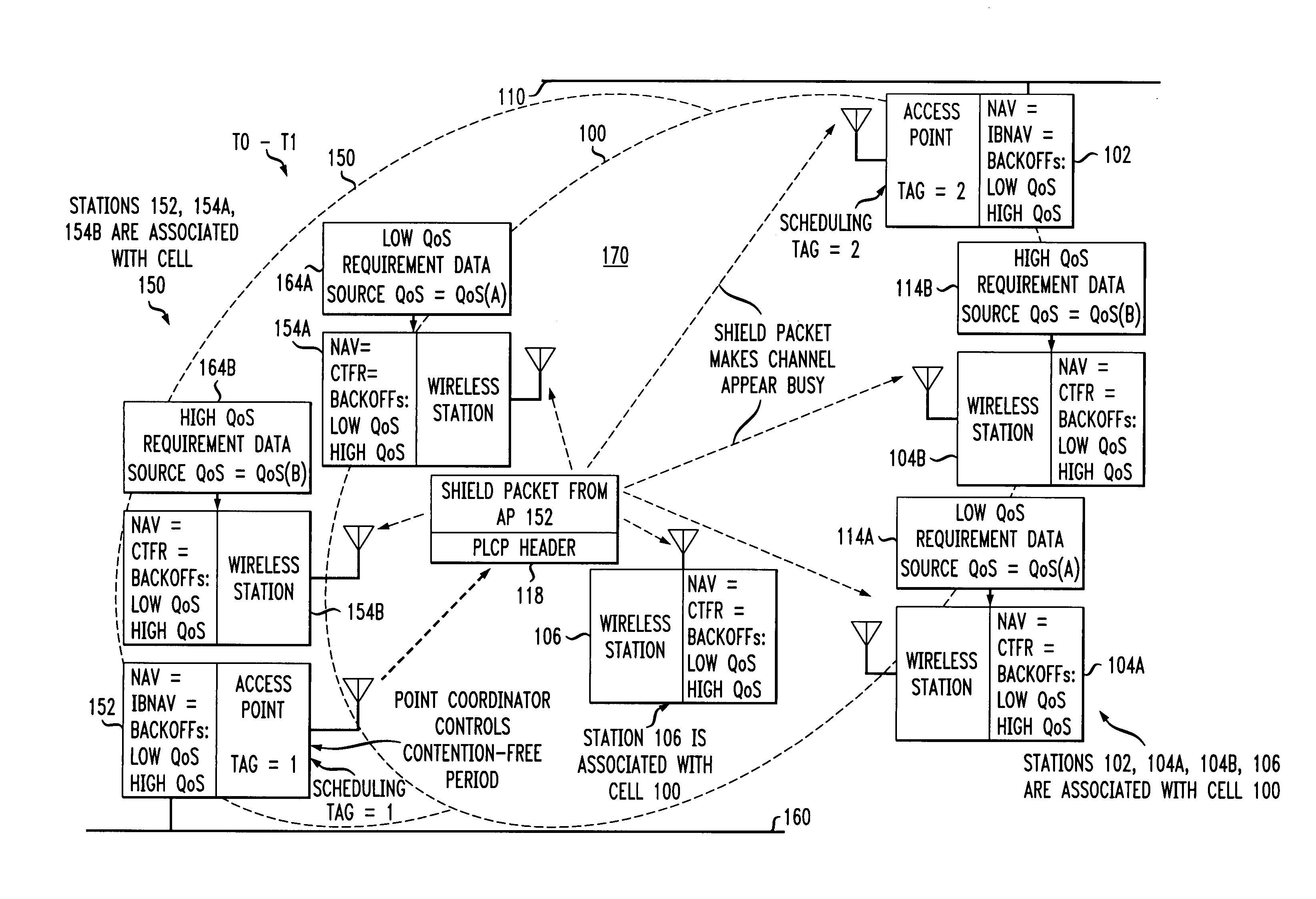
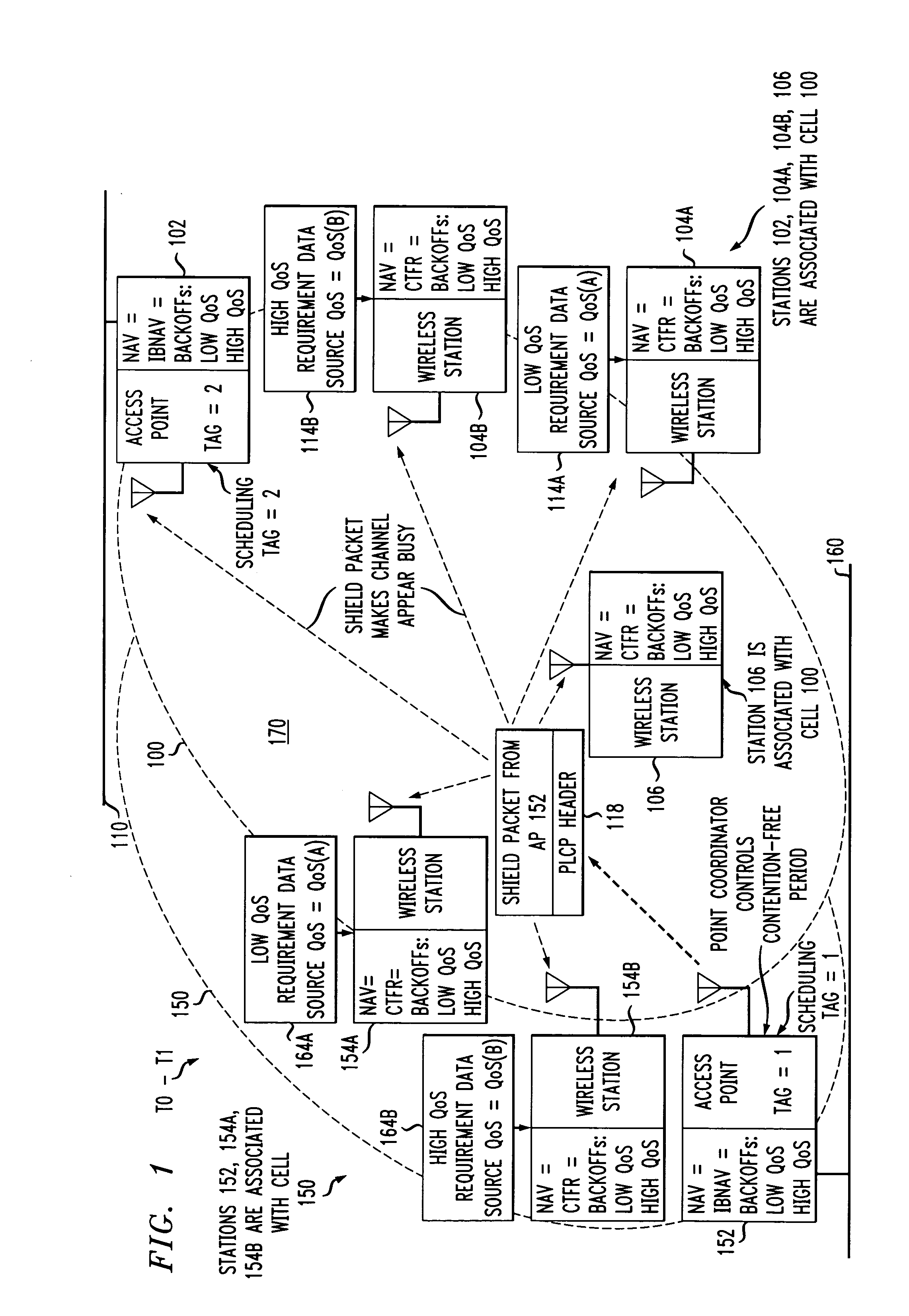
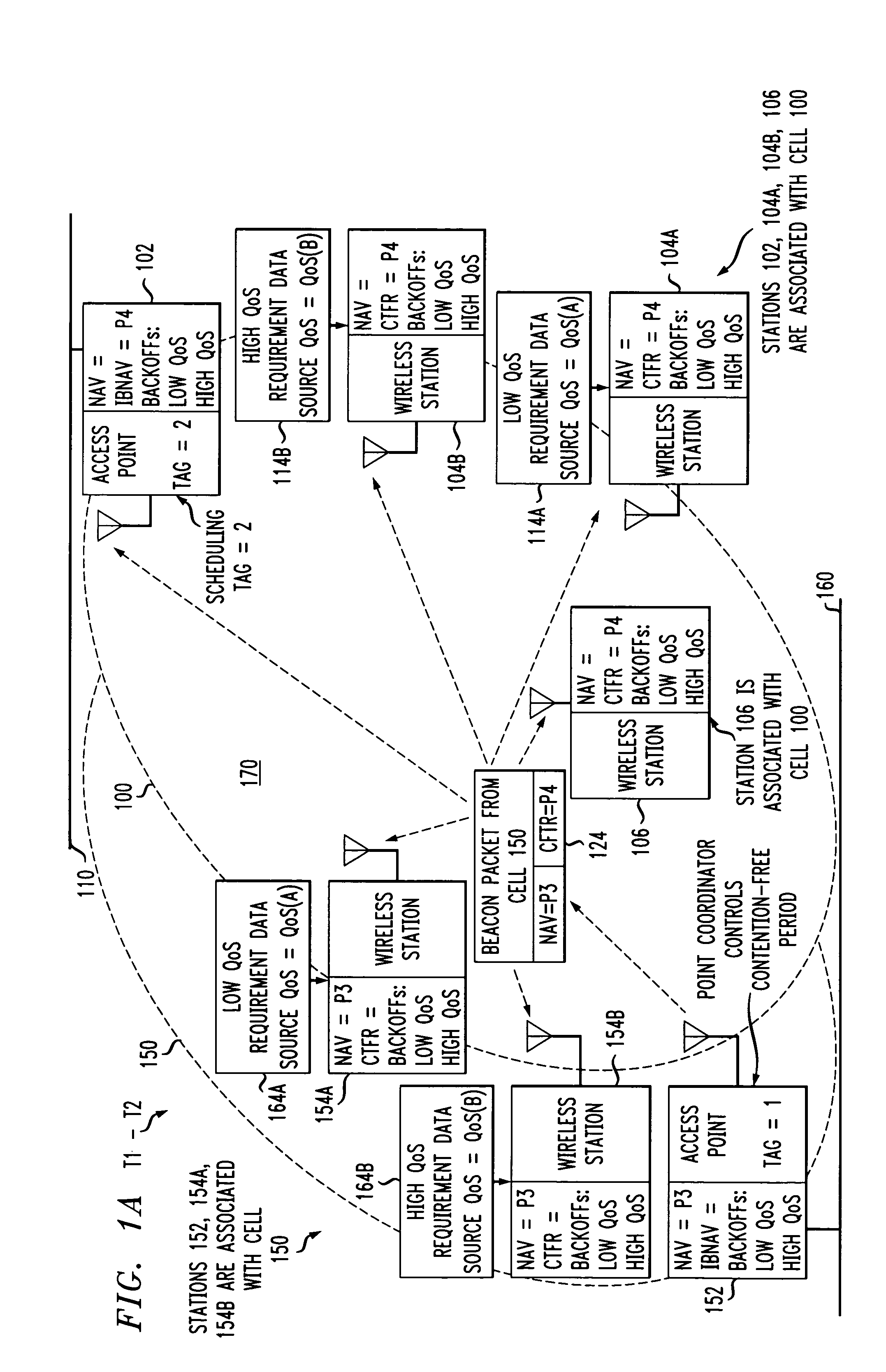
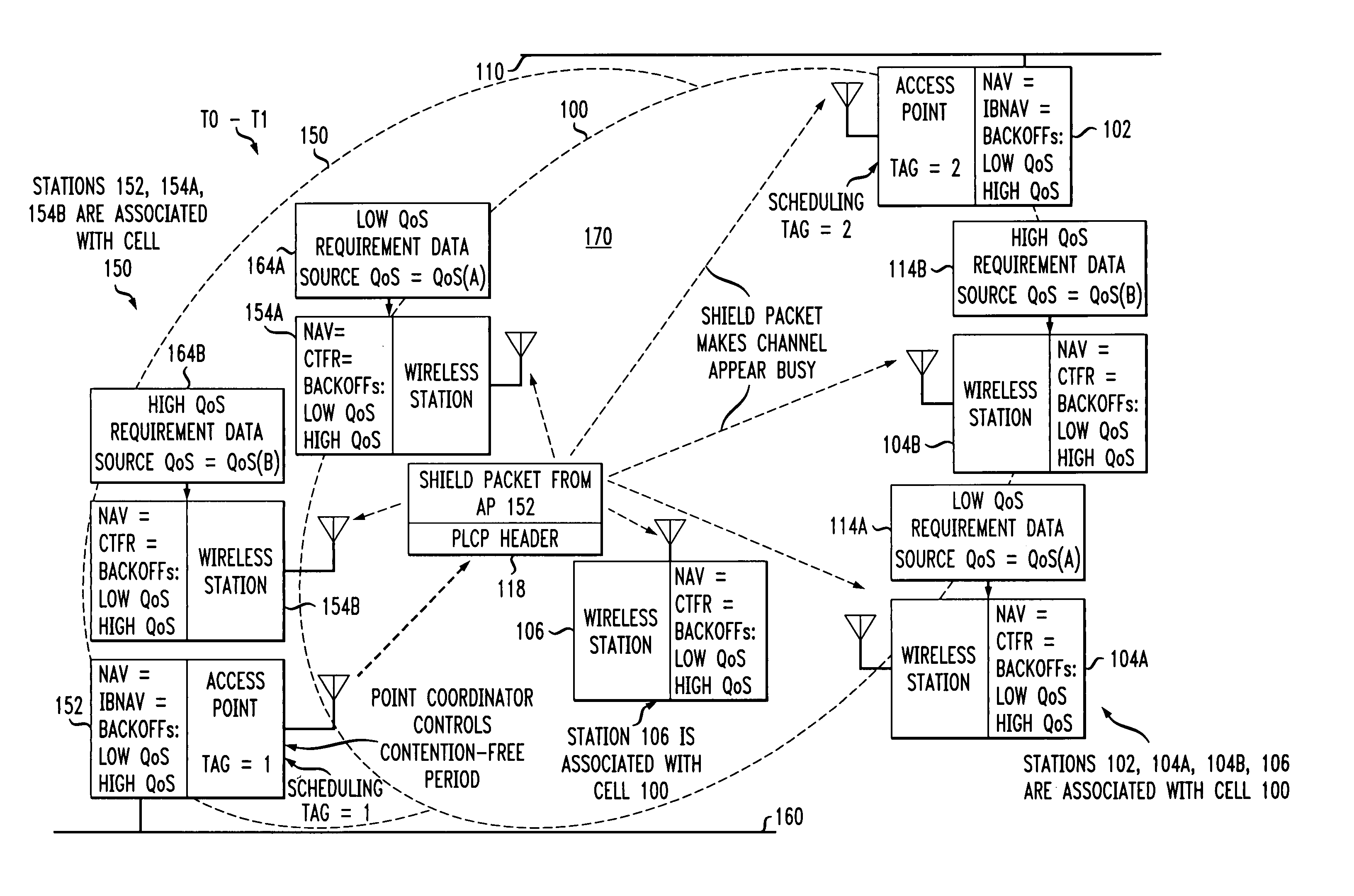
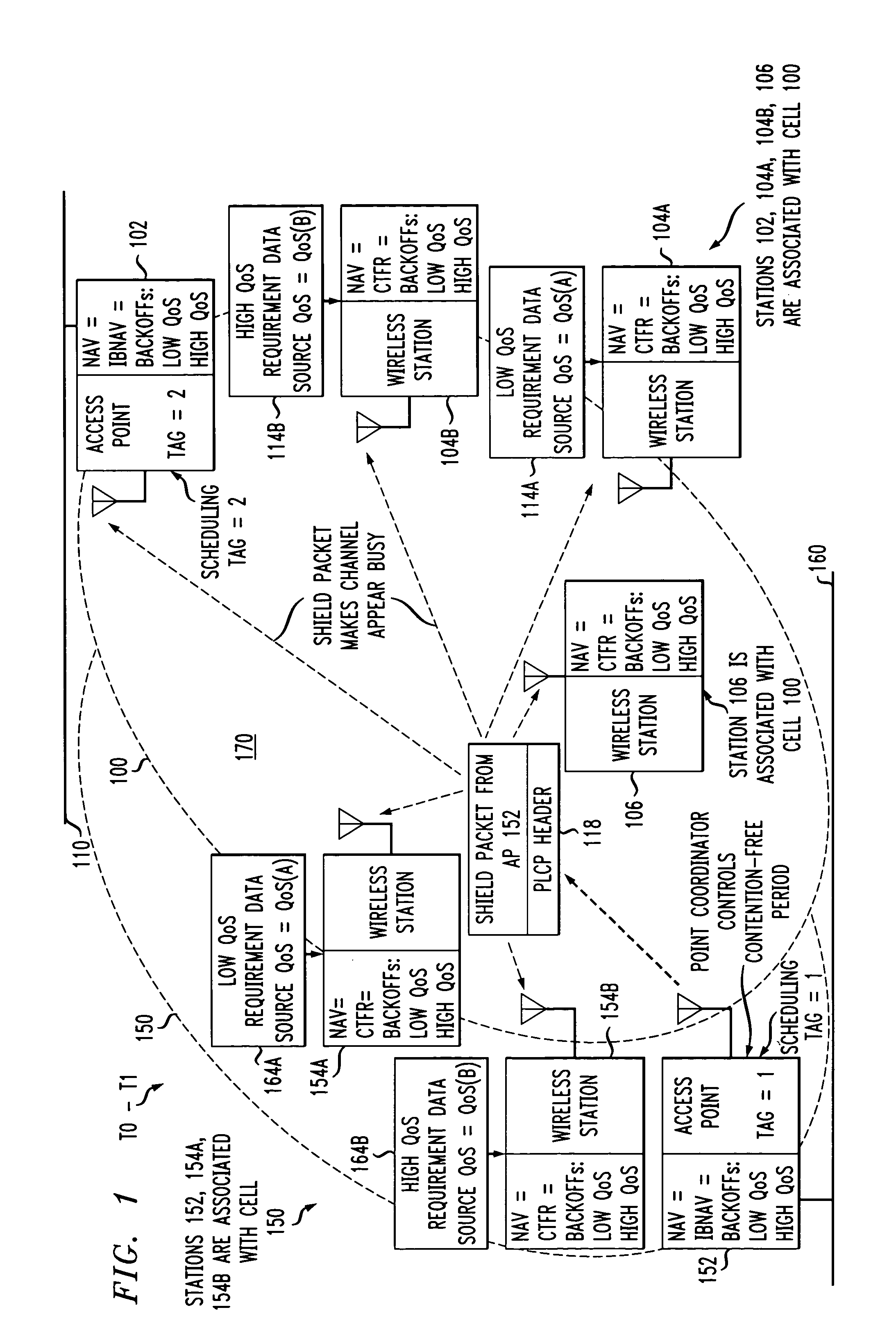
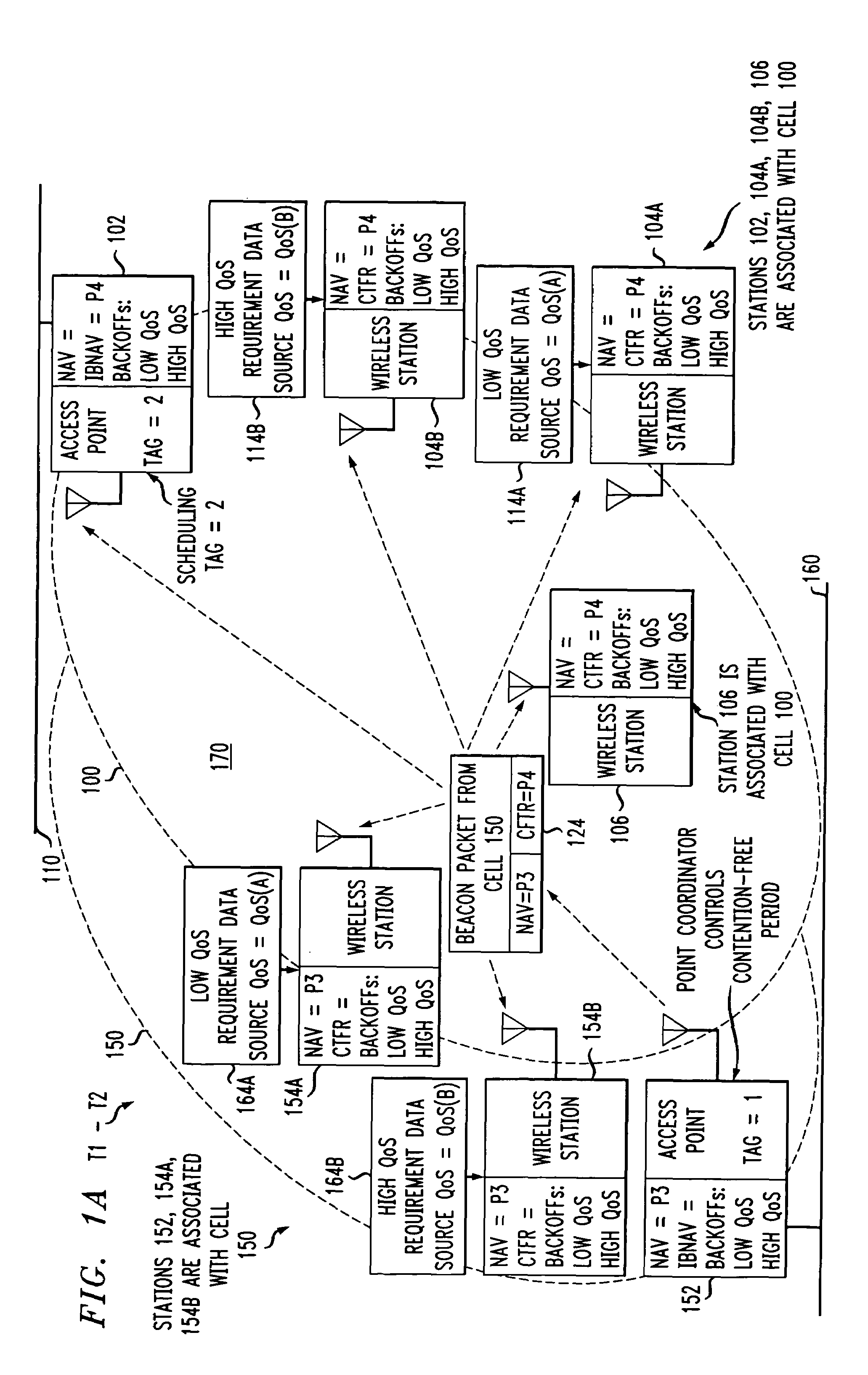
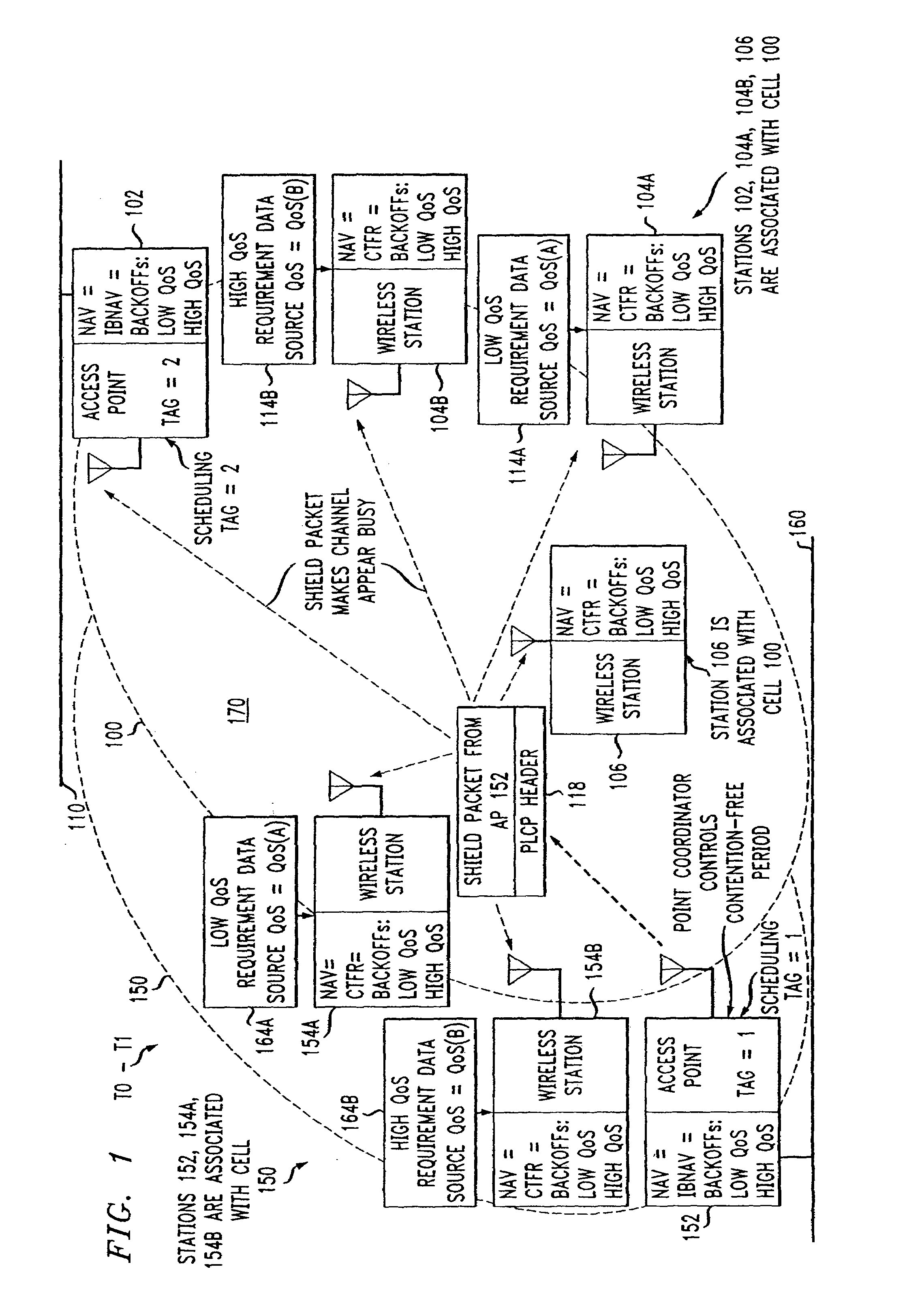
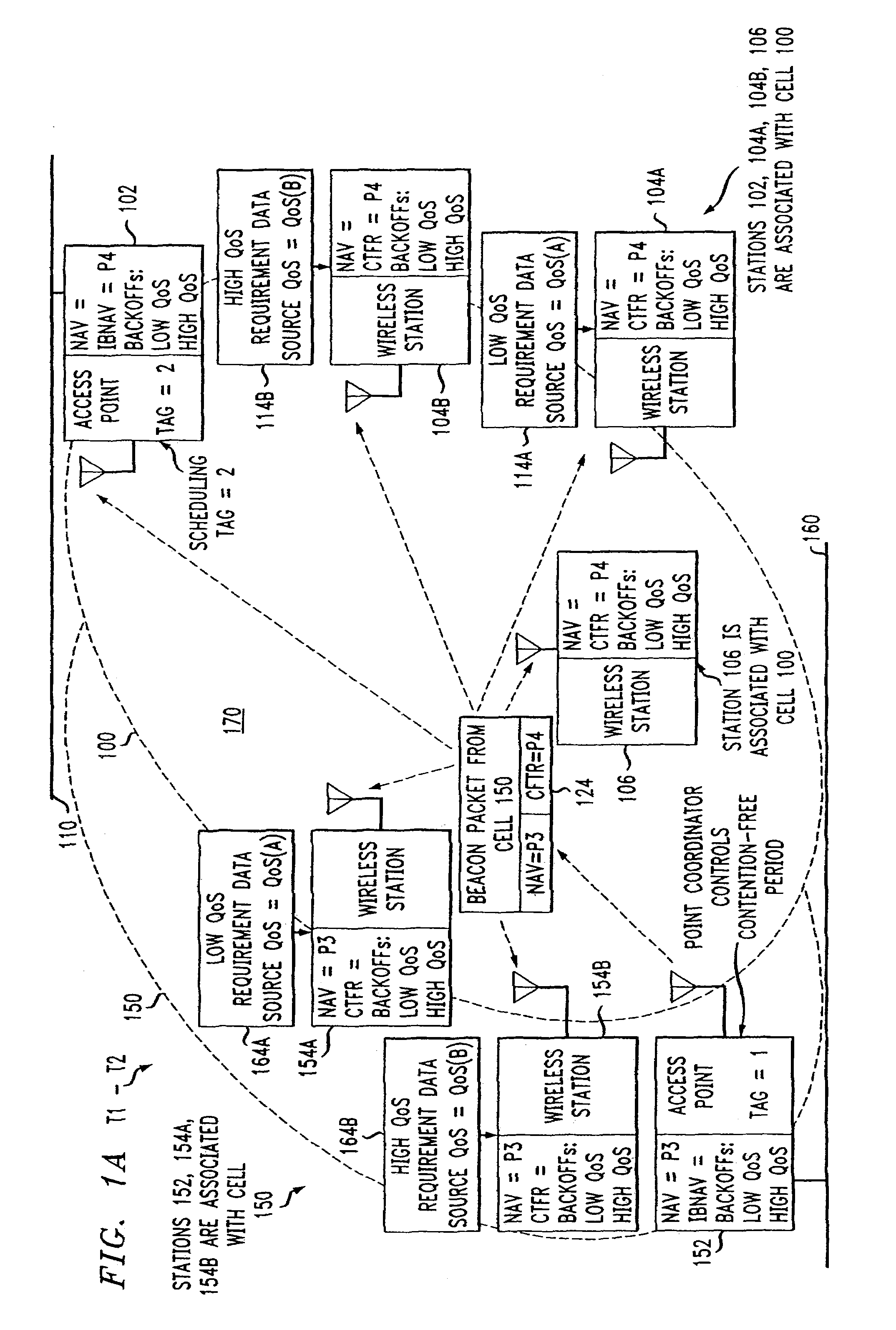
Access method for periodic contention-free sessions
ActiveUS7180905B2Reduce distractionsReduce conflictSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of serviceAccess method
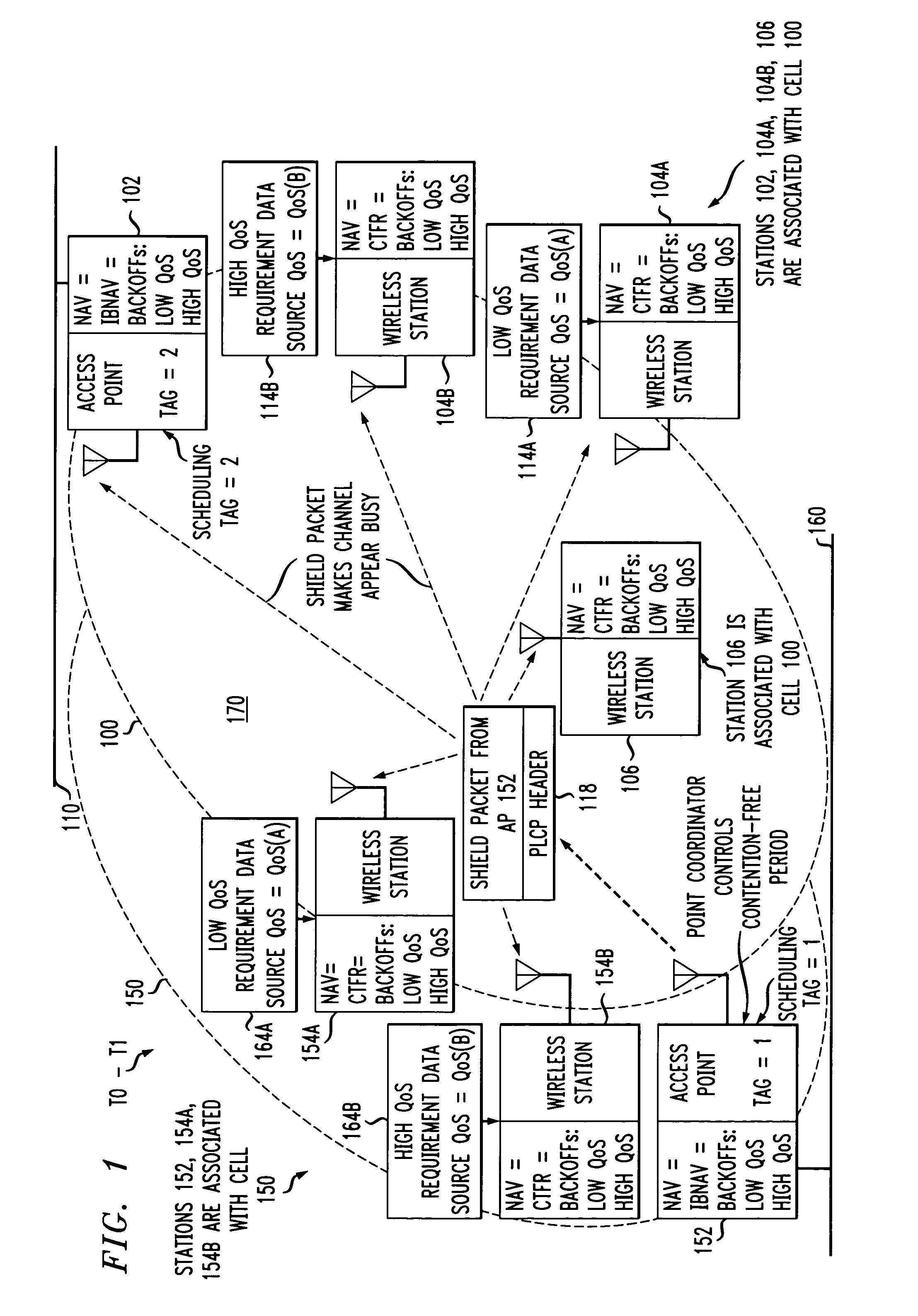
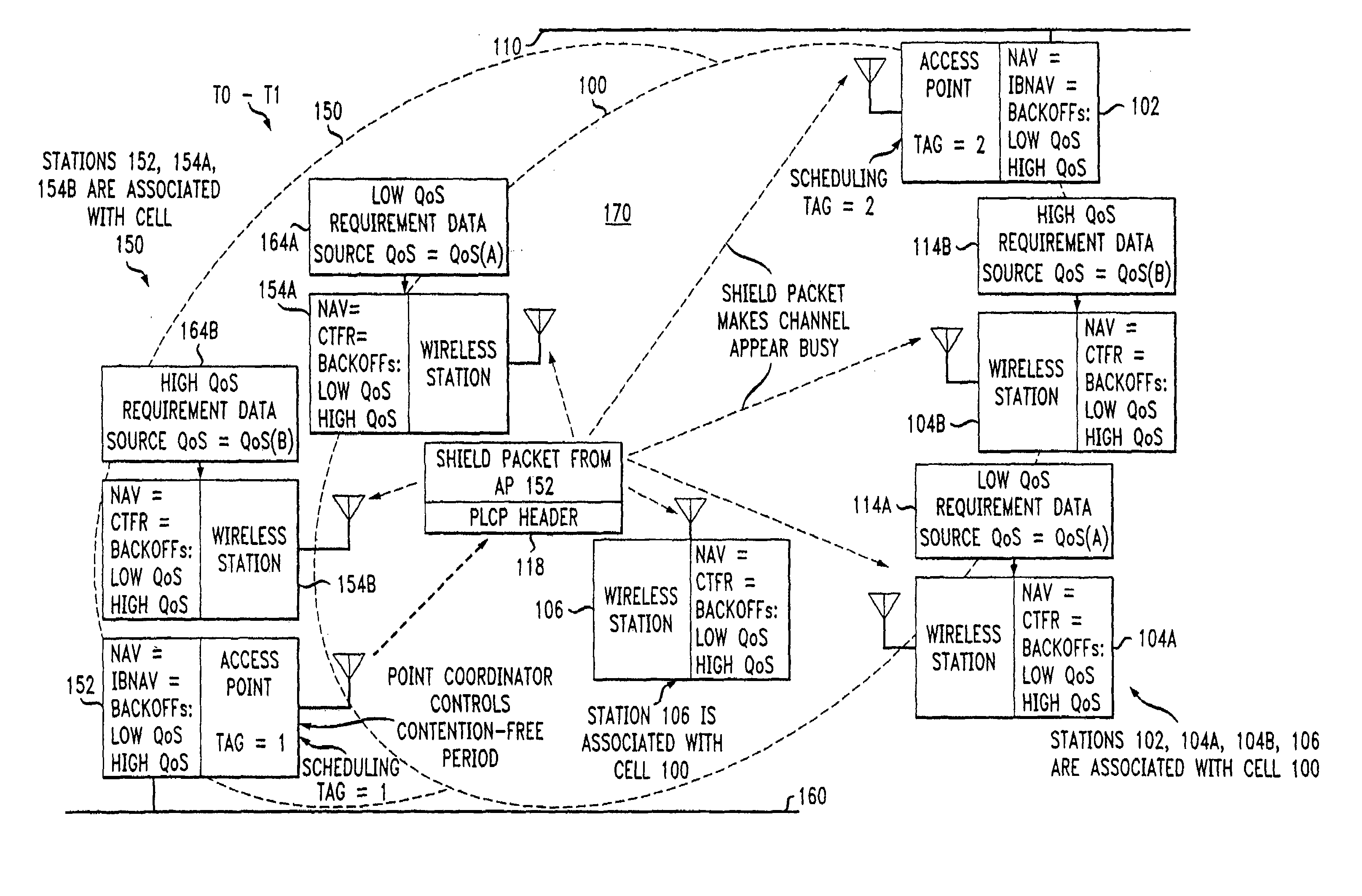
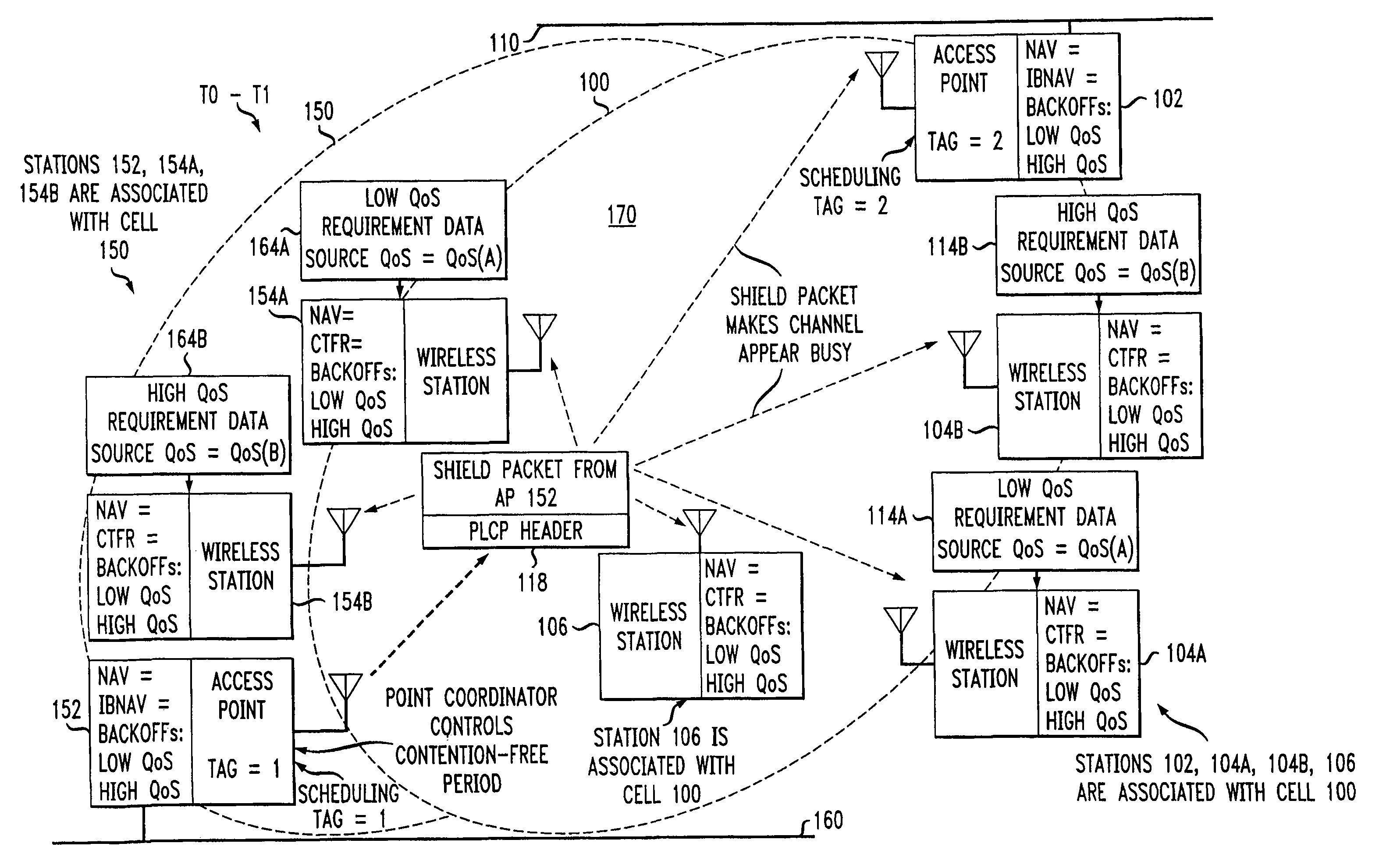
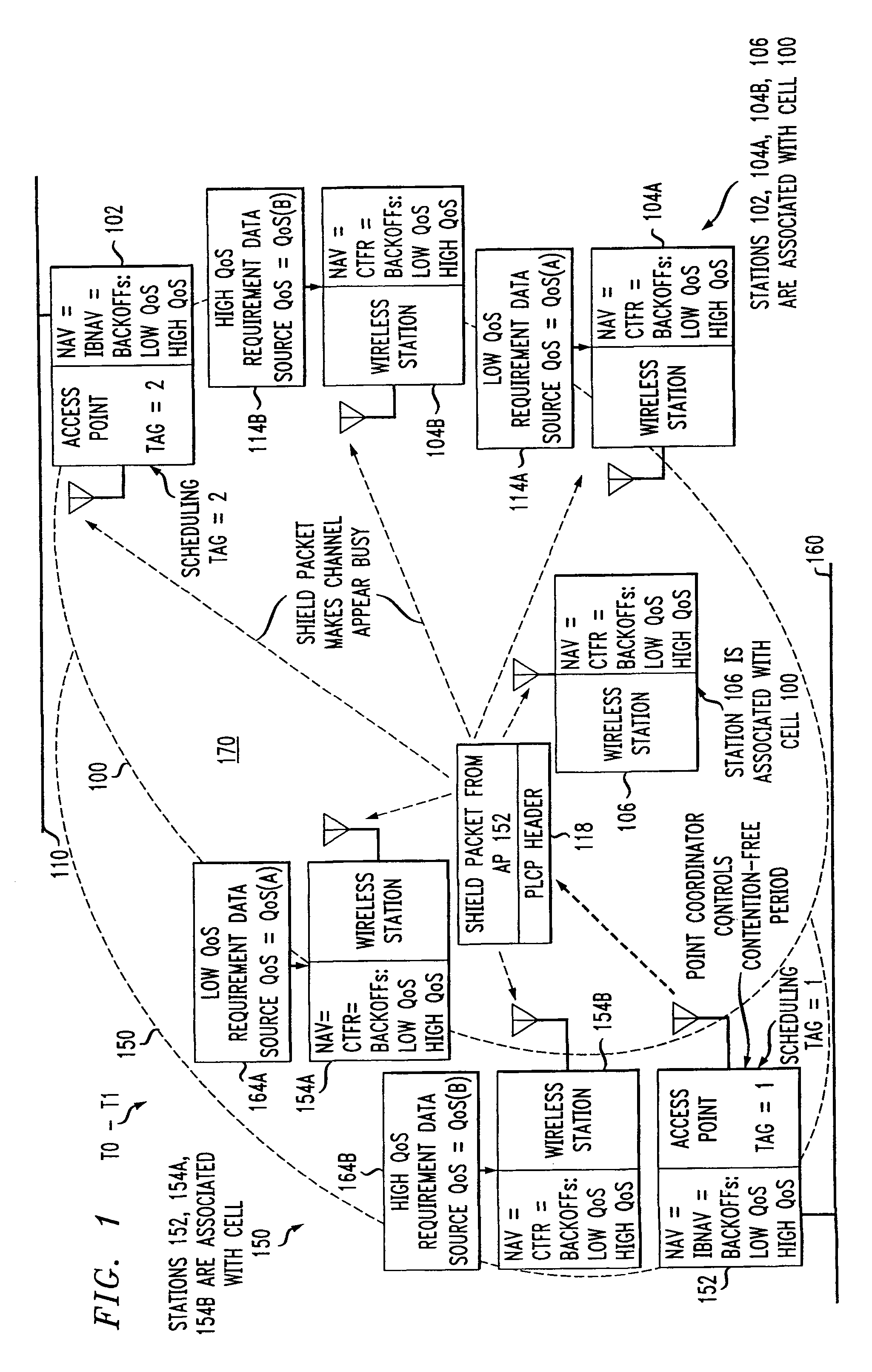
An access method for periodic contention-free sessions (PCFS) reduces interference between overlapping first and second wireless LAN cells contending for the same medium. Each cell includes a respective plurality of member stations and an access point (AP) station. The access method for periodic contention-free sessions (PCFS) includes a fixed cycle time that reduces conflicts with PCFS from other cells. The PCFS from several cells are repeated in cycles of cycle period (CP), which is the contention-free period (CFP) of an access point times a factor that is a function of the number of overlapping cells. Periodic contention-free sessions (PCFSs) are generated, one from each overlapping cell. PCFS transmission attempts occur at the fixed specified time spacing following the start of the previous cycle. Each active AP sets a timer at CP and a PCFS is initiated when the timer expires. The timer is then reset to CP and this starts a new cycle. Contention transmissions are attempted by stations based on their assigned priority. If a channel is busy at the designated start time for transmitting a PCFS, the PCFS is shortened by the time lost. Interleaving PCFSs and CFSs reduces conflicts with CFSs from other cells. To lessen the contention between APs of different cells, each station's Network Allocation Vector (NAV) and Inter-BSS Network Allocation Vector (IBNAV) is updated by an increased value of the next CFS length, the increment being the inter-BSS contention period (IBCP). APs will attempt to access the channel during the IBCP only for transmitting a PCFS, while they will wait for the NAV and IBNAV expirations before attempting to transmit a CFS. Interleaving PCFSs and CFSs also enables maintaining quality of service (QoS).
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
A novel masonry cement
The invention discloses a novel type of masonry cement, which comprises silicate cement clinker aggregate, mixed material, gypsum, cellulose ether, grinding aid, dispersant emulsion powder, water reducing agent, air-entrainer, quick-setting agent, retarders, instant coagulant, thixotropy lubricating agent, defoaming agent, hydrophobing agent, starch ether, plumping agent, shrinkage reduction agent, exciting agent, pigment and fabric.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Fixed deterministic post-backoff for cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) contention-free sessions
ActiveUS7245604B2Reduce conflictSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementIdle timeTimer
A cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) method is disclosed which includes Fixed Deterministic Post-Backoff. Fixed deterministic post-backoff reduces conflicts between access points of overlapping cells. Contention-free sessions (CFSs) can be generated, one from each overlapping cell. Each active access point engages in a fixed deterministic post-backoff. A fixed deterministic backoff delay (Bkoff times a fixed number of idle time slots) is used by all access points, with the value of Bkoff being greater than the number of overlapping cells. The Bkoff should be large enough to enable the traffic that needs to be accommodated by the channel. Each access point has a backoff timer that is counted down using the shortest interframe space possible, typically the Priority Interframe Space (PIFS). A contention-free session (CFS) is initiated when the backoff timer expires, and it is then reset to the value of Bkoff to start a new cycle. A cycle is measured in terms of idle time slots instead of a fixed time interval. Contention-based transmissions can be attempted by an access point or other stations in the cell using their assigned priority while the access point is counting down its backoff timer. A new access point can get started and resolve possible collisions by a small random backoff. Subsequent contention-free sessions (CFSs) will not conflict, given an existing sequence of non-conflicting CFSs, since the follower access point's backoff delay exceeds that of the leader's by at least one times the fixed number of idle time slots. In this manner, contention-free sessions can be conducted without interference in the first and second cells.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
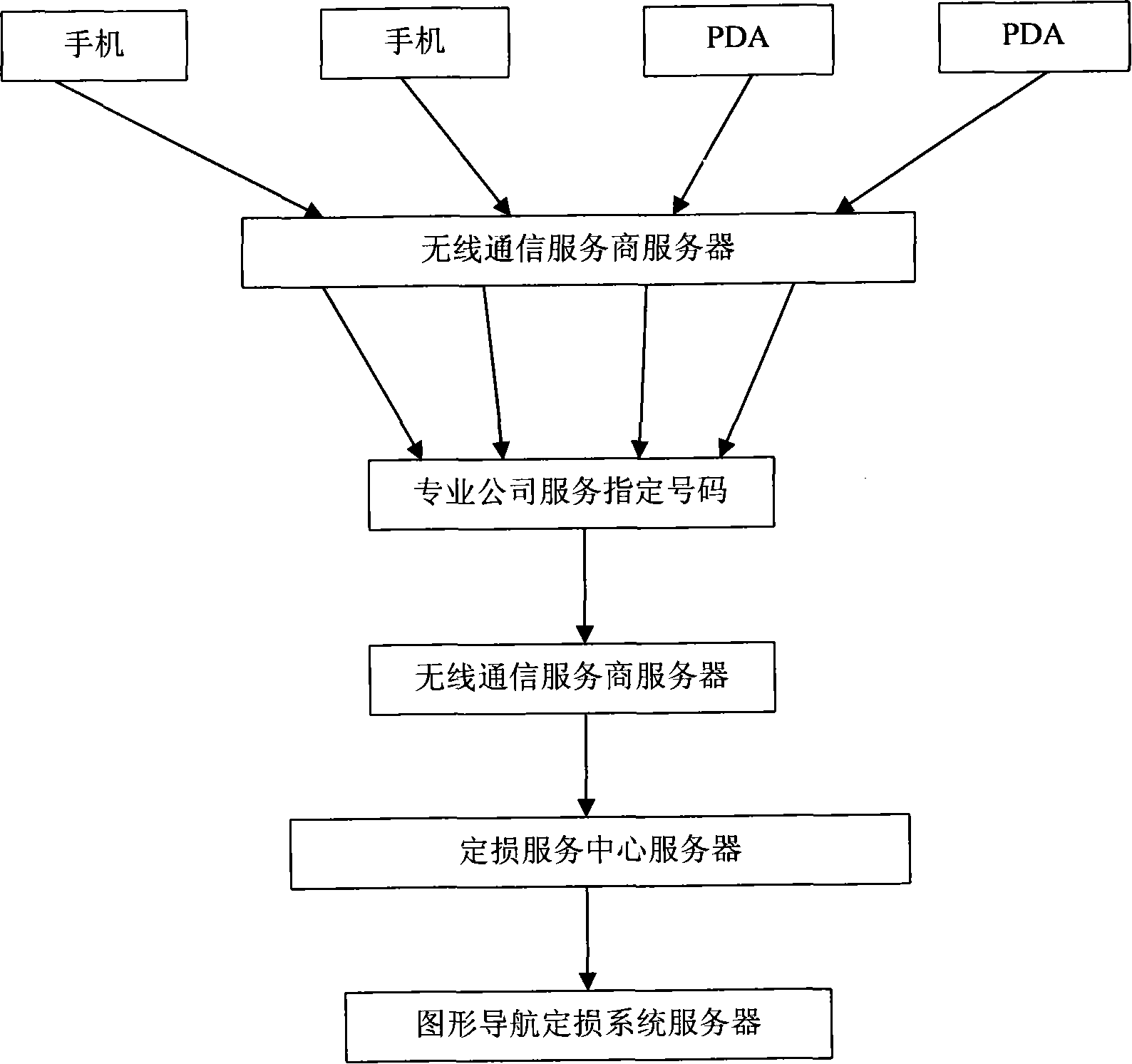
Car damage identification method based on mobile communication terminal or network terminal
InactiveCN101242379ASolve the road occupation problemRealization of fixed lossData processing applicationsData switching networksNetwork terminationRelevant information
The invention discloses a vehicle loss determination method based on mobile communication terminal or network terminal, comprising the steps that: after a traffic accident, a party transmits an image of the damaged part and related information of a vehicle to a loss determination service center by wireless communication network; the loss determination center analyzes the image of the damaged part and related information of the vehicle, determinates the loss by a loss determination system; and the loss determination service center submits the loss determination result to the party by wireless commutation network. The party transmits the image of the damaged part and related information of the vehicle to the loss determination service center by wireless communication network, the loss determination service center determinates the loss by the loss determination system, and submits the result to the party by wireless communication network, therefore the invention is capable of assuring instantaneity, reasonability and precision of loss determination.
Owner:BEIJING AUTOMOTIVE INFORMATION TECH
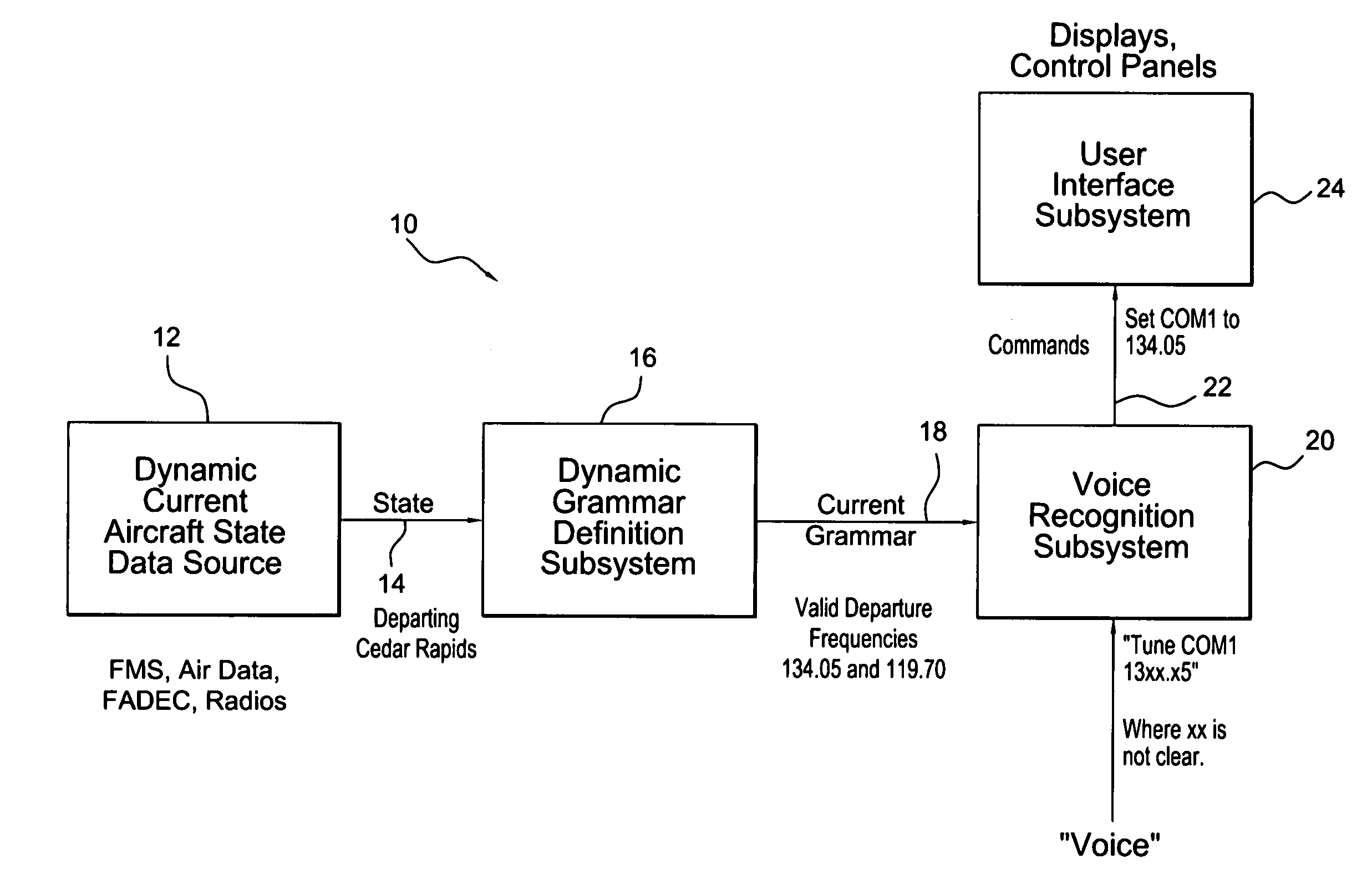
Avionics system for providing commands based on aircraft state
An avionics system includes a dynamic grammar definition subsystem configured to receive and analyze dynamic, current aircraft state data and provide an enhanced set of recognizable current grammar data based on the aircraft state data. A voice recognition subsystem is configured to receive the current grammar data from the dynamic grammar definition subsystem and utilize the current grammar data to provide commands in response to a user's voice input based on the aircraft's dynamic, current state.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
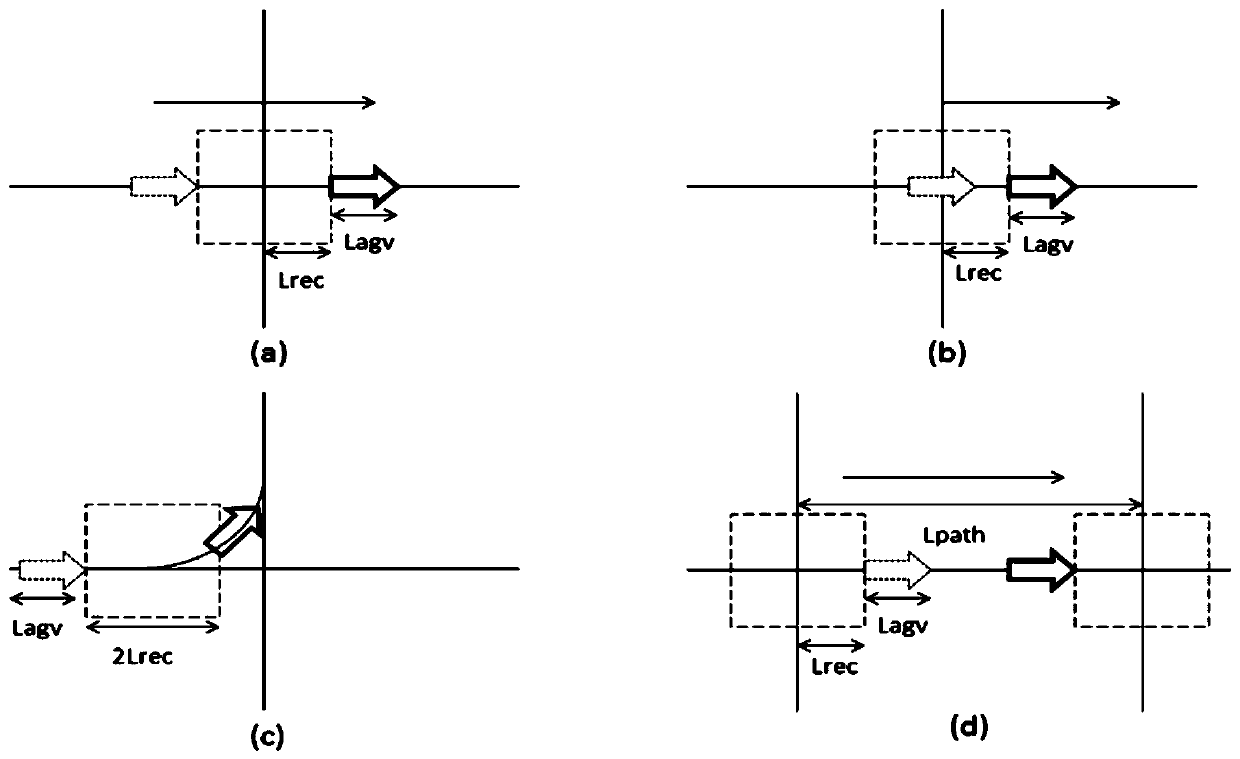
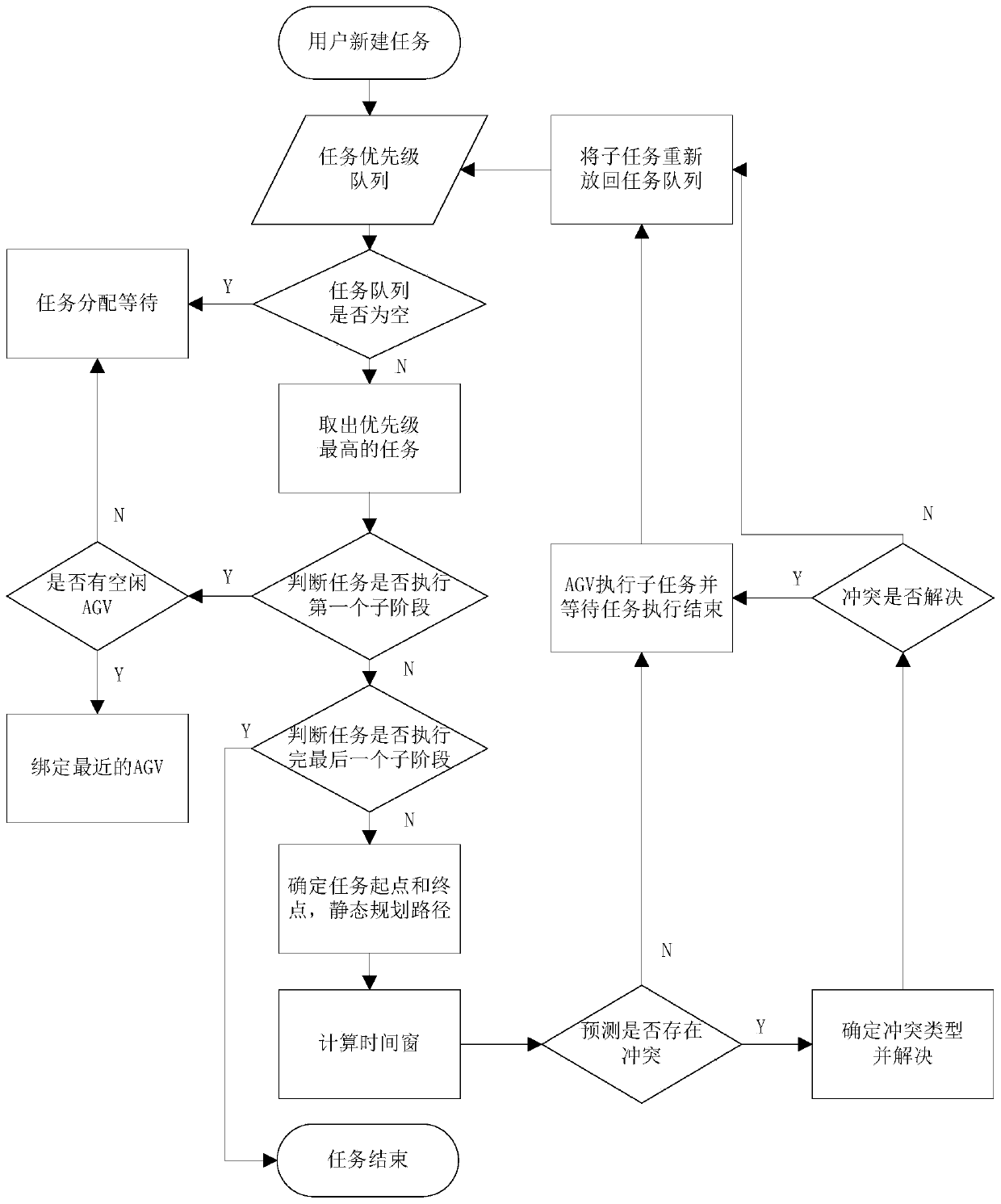
Time window-based task segmentation multi-AGV path planning algorithm
InactiveCN110174111AReduce mistakesImprove efficiencyNavigational calculation instrumentsElectric/hybrid propulsionCalculation errorTask segmentation
The invention relates to a path planning method, and specifically relates to a time window-based task segmentation multi-AGV path planning algorithm. The method comprises steps of first, generating anAGV working environment model; second, generating a task, and decomposing the task into multiple secondary stages according to different task types; and third, assigning the task by a task assigningmodule according to task priorities, picking the task out by a scheduling system from a high-priority queue, then determining which stage the task is in, if the task is not executed, assigning the task to closest AGV by using an improved A* algorithm, and setting the task state in first secondary stage; if the task is in the second or after stages, and planning a non-conflict shortest path for theAGV bound with the task by using the time widow algorithm by the scheduling system. Shortest and fastest paths are planned by using the improved A* algorithm and time window algorithm, so that the working efficiency is improved and calculation errors are reduced.
Owner:山东华锐智能技术有限公司
Method and apparatus for bandwidth provisioning in a wlan
InactiveUS20060153117A1Eliminate requirementsReduce distractionsNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesTime informationBroadcasting
The invention provides for a receiver transmitter comprising: a plurality of logical access points; for downloading a duration into a mobile terminal in accordance with an access point determination of the maximum amount of time information linked with a downlink broadcast traffic to deliver all the broadcast / multicast information in a single communication stream. The invention also provides for a method of broadcast / multicast frames “Duration” are set to values in order to deliver all the broadcast / multicast information in a single communication stream eliminating the requirement for contending for the medium for each broadcast / multicast frame transmission. This pseudo-reservation of the wireless medium can also be made periodic for enabling broadcast / multicast services.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Method for Opportunistic Computing
InactiveUS20080005332A1Overcome disadvantagesReduce conflictDigital computer detailsProgram controlComputing MethodologiesApplication software
In a method of dynamically changing a computation performed by an application executing on a digital computer, the application is characterized in terms of slack and workloads of underlying components of the application and of interactions therebetween. The application is enhanced dynamically based on predictive models generated from the characterizing action and on the dynamic availability of computational resources. Strictness of data consistency constraints is adjusted dynamically between threads in the application, thereby providing runtime control mechanisms for dynamically enhancing the application.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Staggered startup for cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) contention-free sessions
ActiveUS7277415B2Reduce conflictSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsWireless lan
A staggered startup method and system for a cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) system reduce interference between overlapping first and second wireless LAN cells contending for the same medium. Each cell includes a respective plurality of member stations. A first member station in the first cell coordinates a periodic sequence of first contention-free sessions. Each contention-free session includes multiple bursts with other member stations in the first cell. The first member station retains control of the medium by using interframe spaces sufficiently short between the bursts so that the multiple bursts appear to contending stations to be a single instance of activity in the medium during a session until an end of a session. A second member station in the second cell listens to the activity in the medium and detects an end to one of the first contention-free sessions indicated by an interval longer than a PIFS idle interval following an end to the activity in the medium. The second member station then sets a post-backoff delay to periodically transmit a minimal interval after the first contention-free sessions of the first member station. The second member station coordinates in the second cell a periodic sequence of second contention-free sessions. In this manner, contention-free sessions are interleaved on a periodic basis in the first and second cells.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
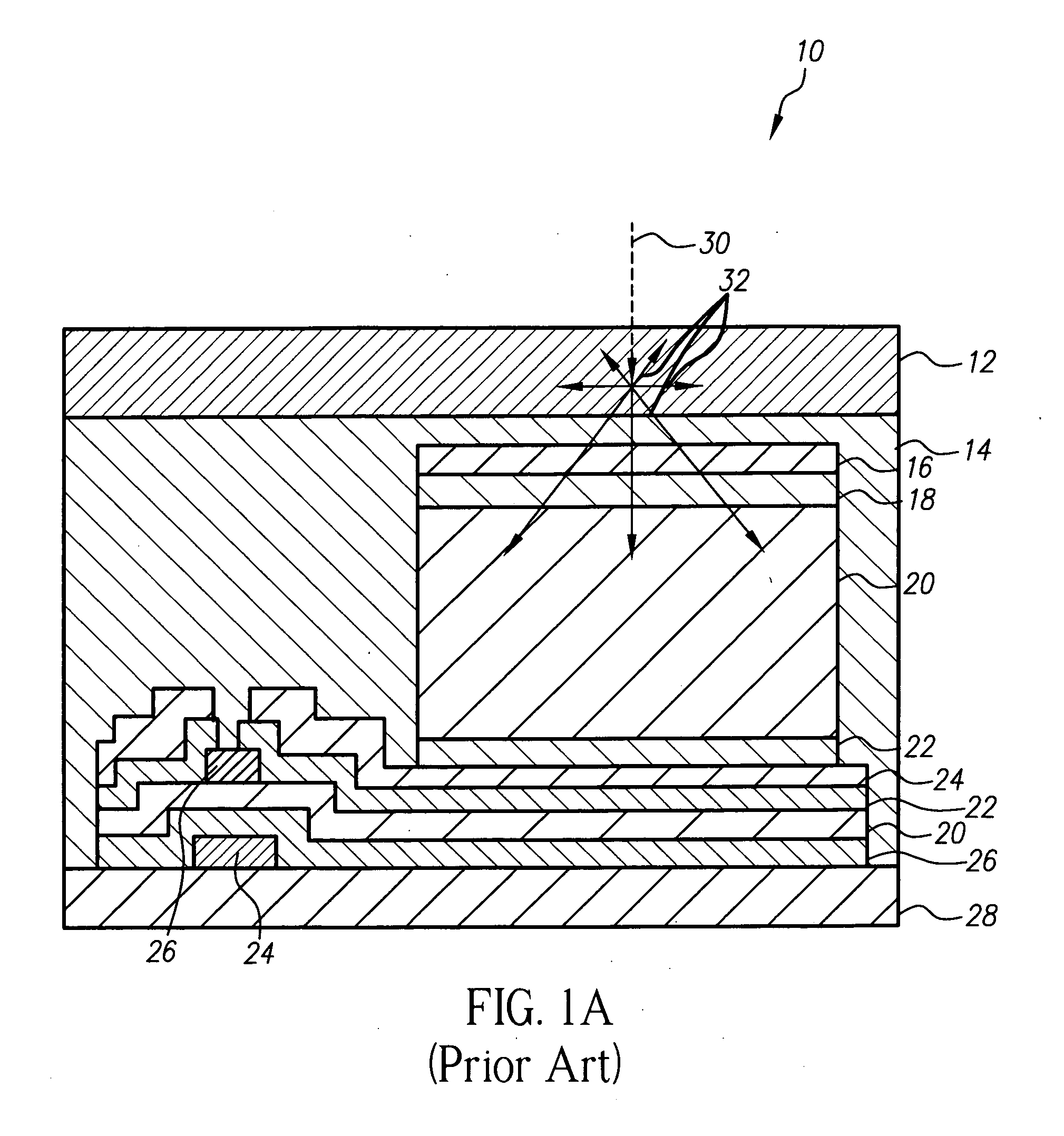
Dual-screen digital radiographic imaging detector array
ActiveUS7569832B2Quality improvementClear imagingTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesPhosphorDetector array
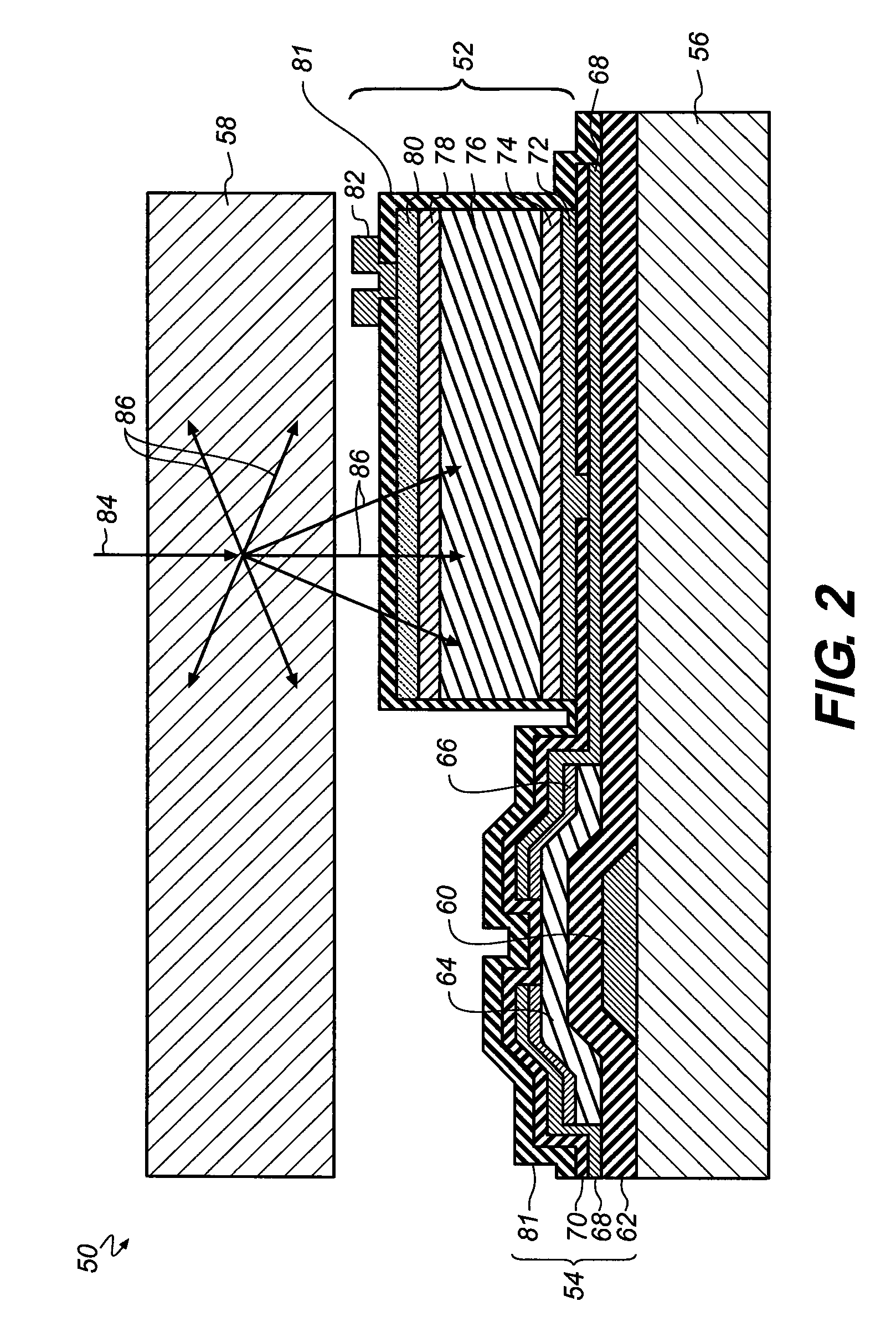
A radiographic imaging device has a first scintillating phosphor screen having a first thickness and a second scintillating phosphor screen having a second thickness. A transparent substrate is disposed between the first and second screens. An imaging array formed on a side of the substrate includes multiple photosensors and an array of readout elements.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
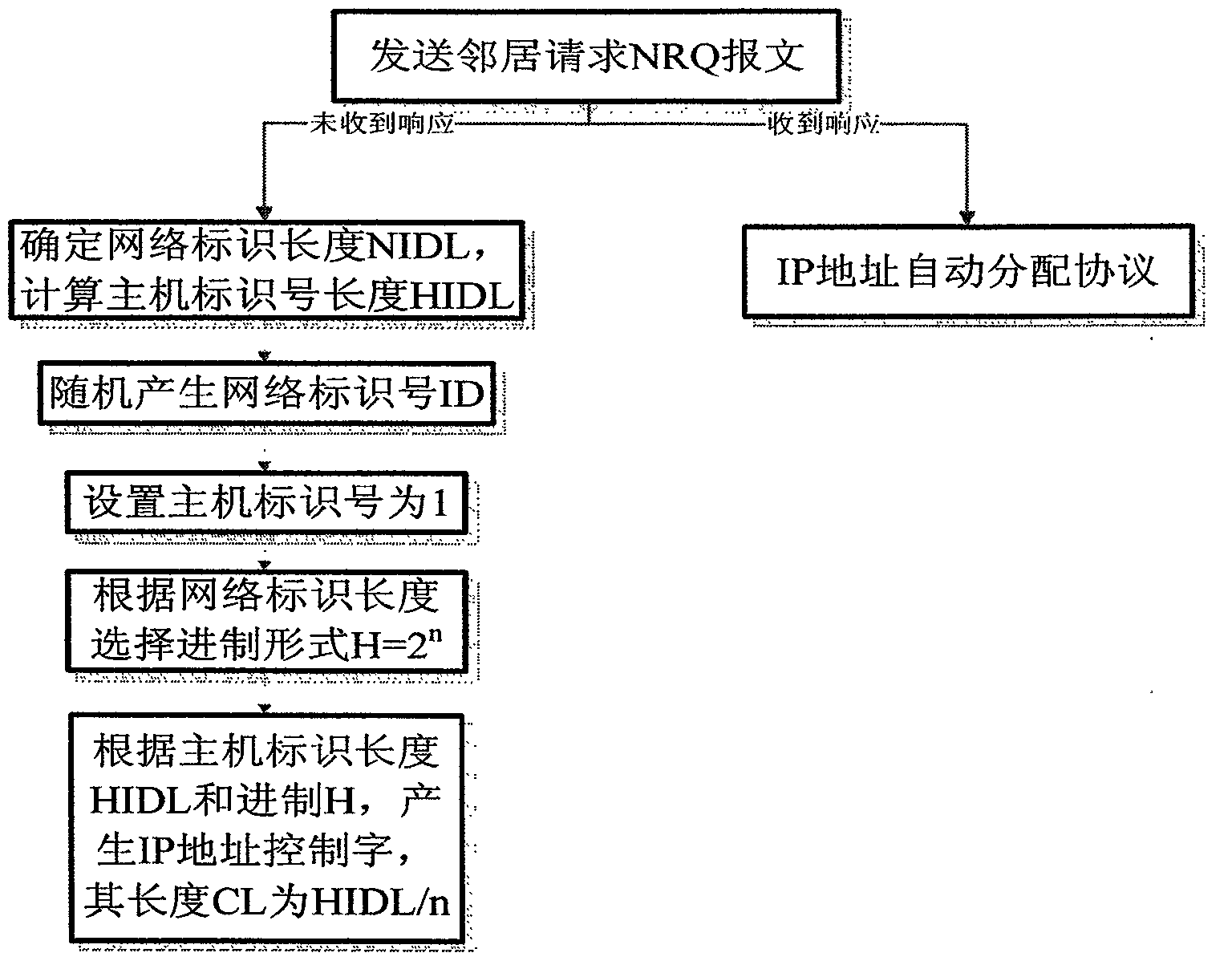
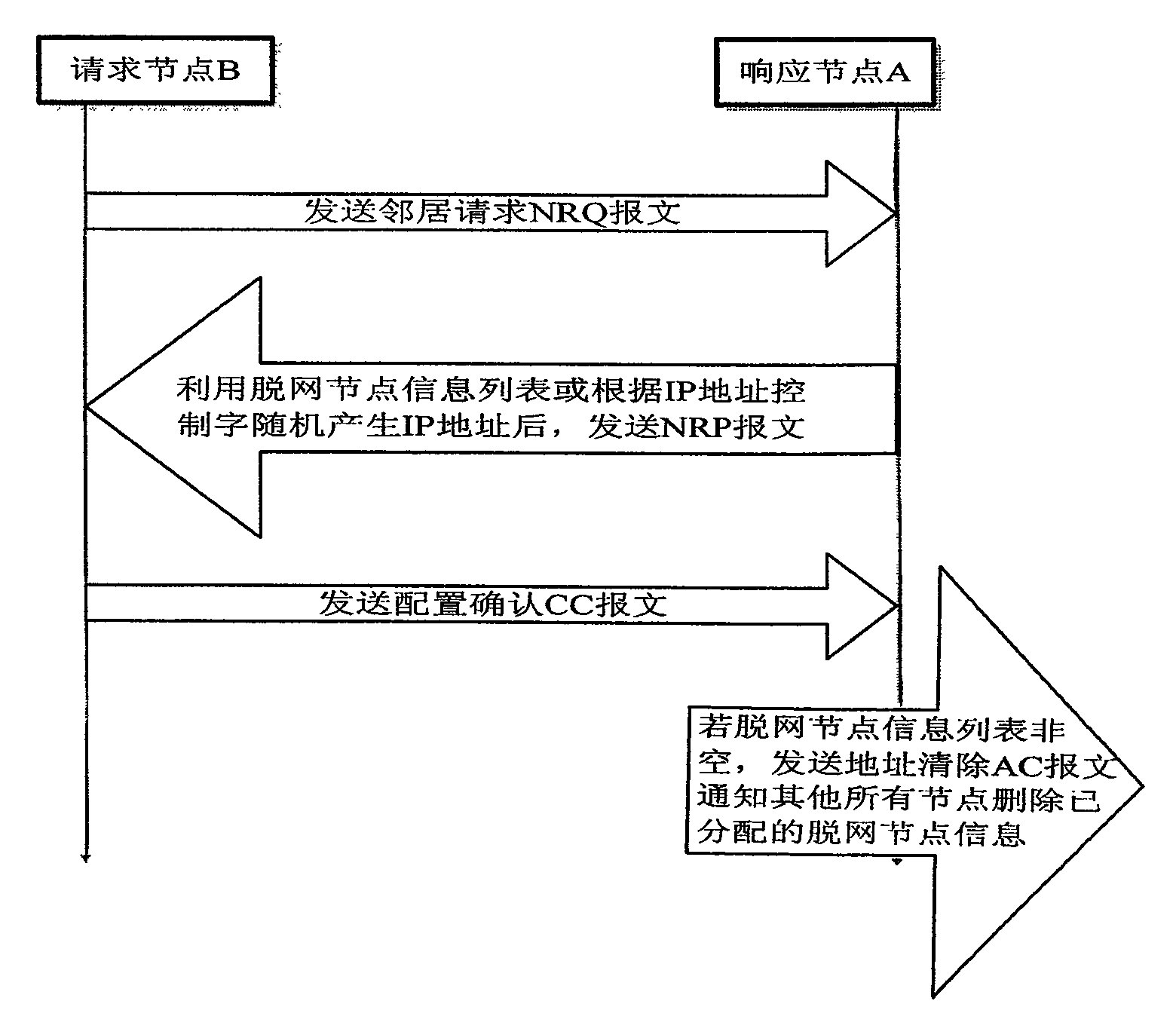
Auto-allocation method of addresses of mobile ad hoc networks
InactiveCN101600156ANo address conflictReduce conflictNetwork topologiesWireless network protocolsIp addressResource consumption
An auto-allocation method of addresses of mobile ad hoc networks adopts an IP address stratified allocation mode based on neighbour proxy collision-free detection, address allocation information is provided with hereditary property; usable IP address control word which can become long is adopted to control the process of IP address allocation; the method comprises mobile ad hoc network address initialization configuration, an IP address auto-allocation protocol, an IP address allocation control process, an IP address trunking protocol, an IP address pool recover protocol, network merger and transformation and network partitioning and transformation; the invention adopts the IP address stratified allocation mode based on neighbour proxy collision-free detection, the address allocation information is provided with hereditary property, the usable IP address control word which can become long is adopted to flexibly control the allocation process of IP address space, thus effectively avoiding address allocation conflict, dispensing with address conflict detection, improving address allocation efficiency, reducing use of multicast or broadcast message in the process of address allocation, lowering resource consumption, and being applicable to allocation of IP addresses of multiple versions.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
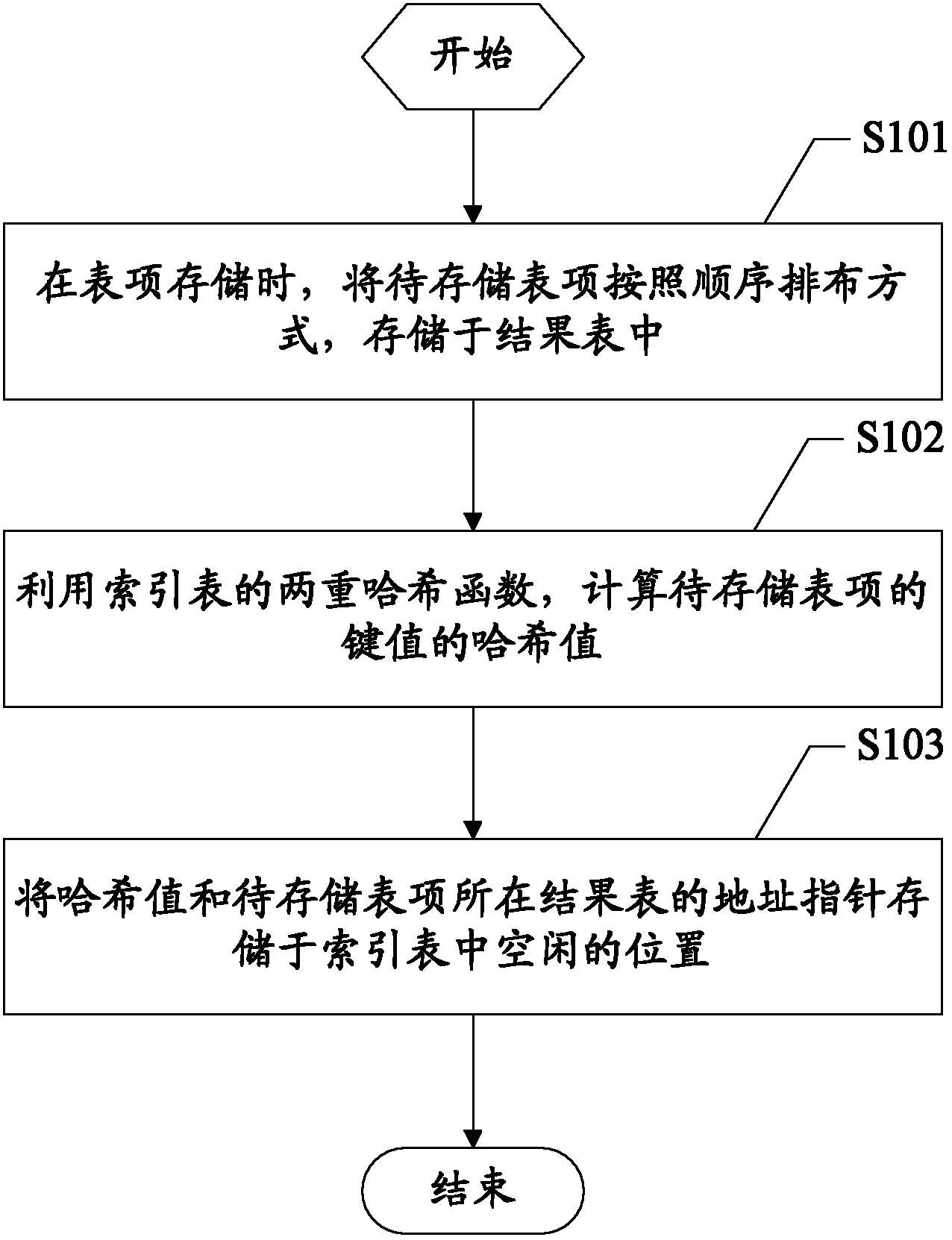
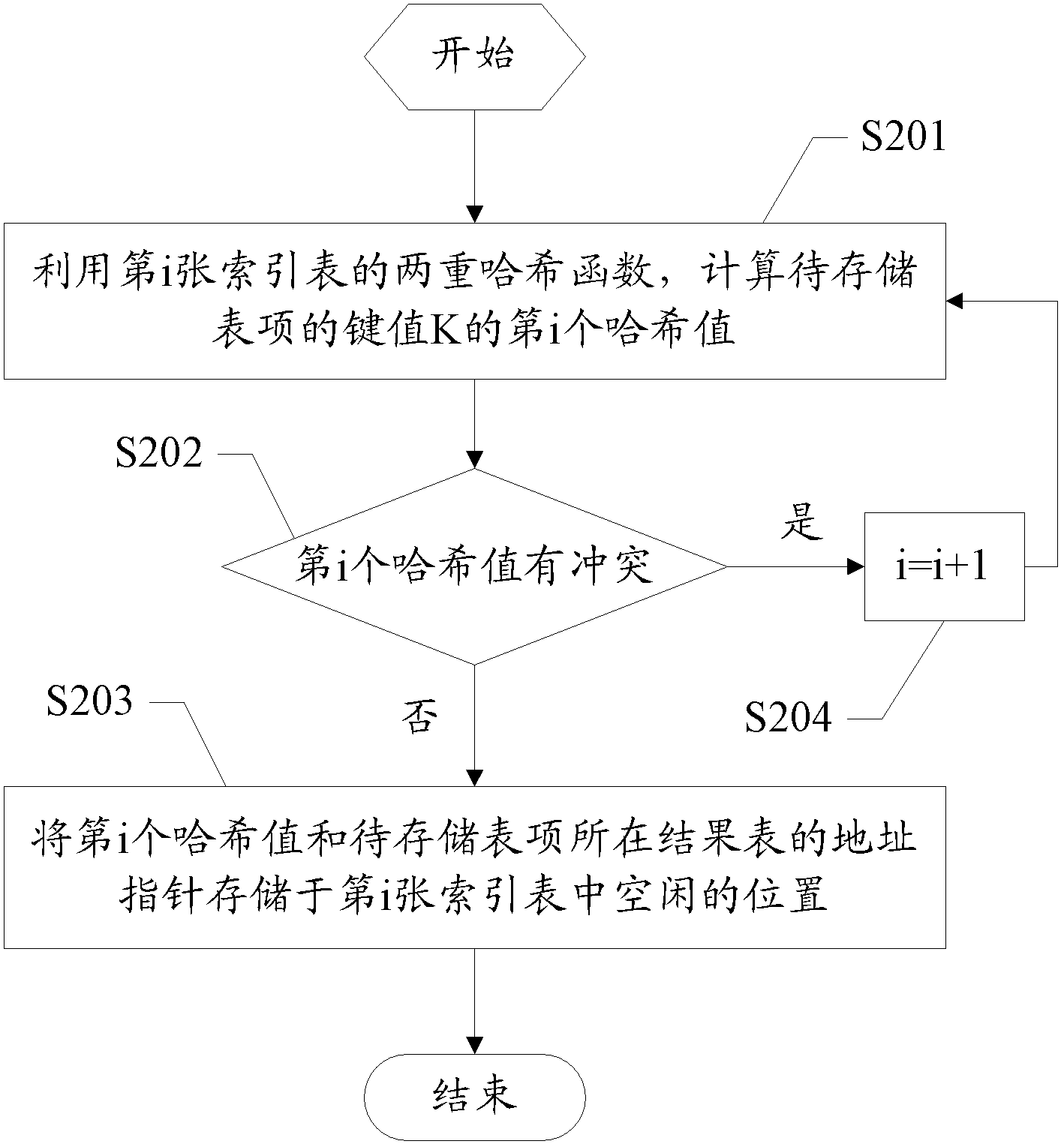
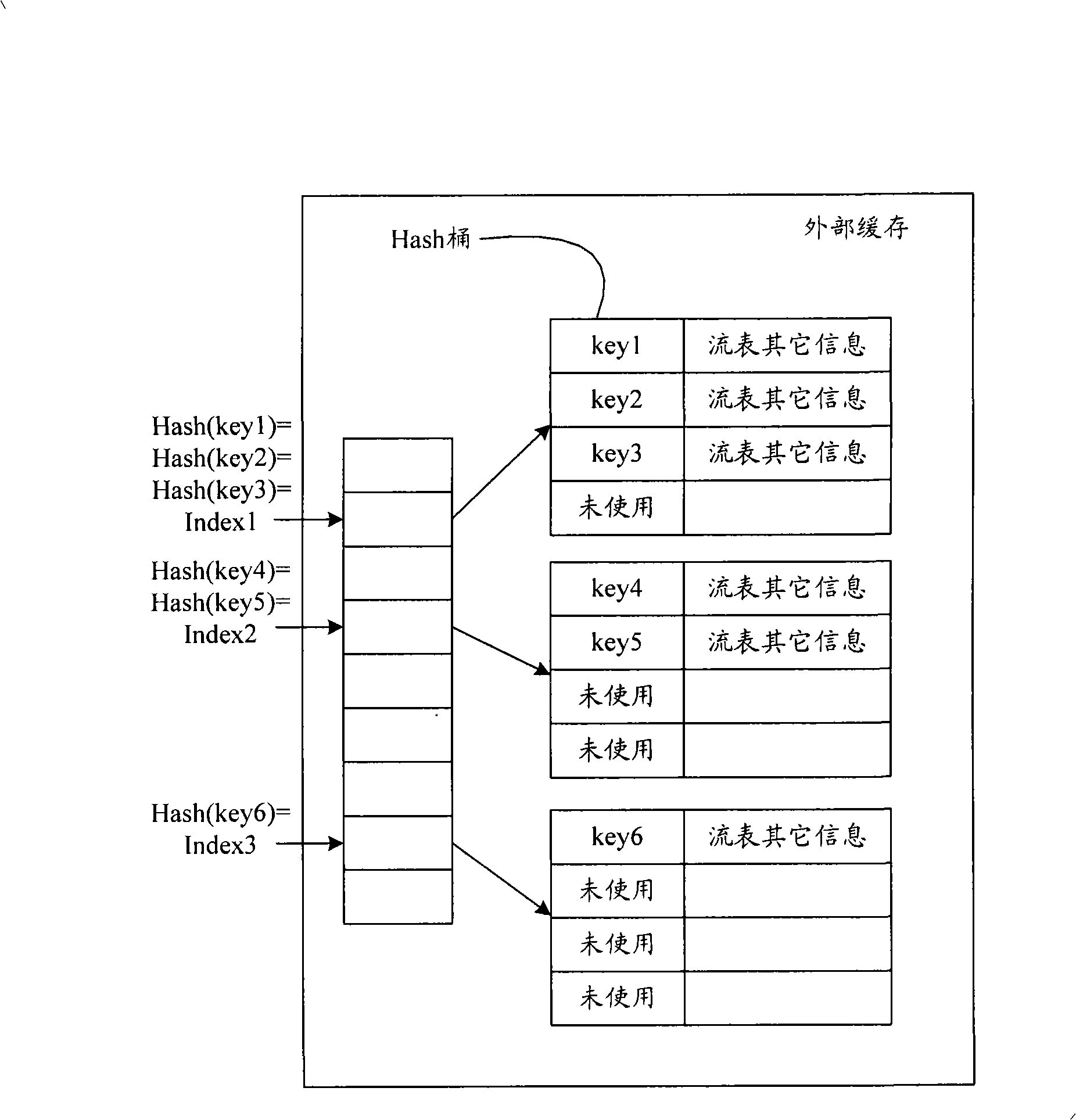
Method and device for processing table items based on Hash table
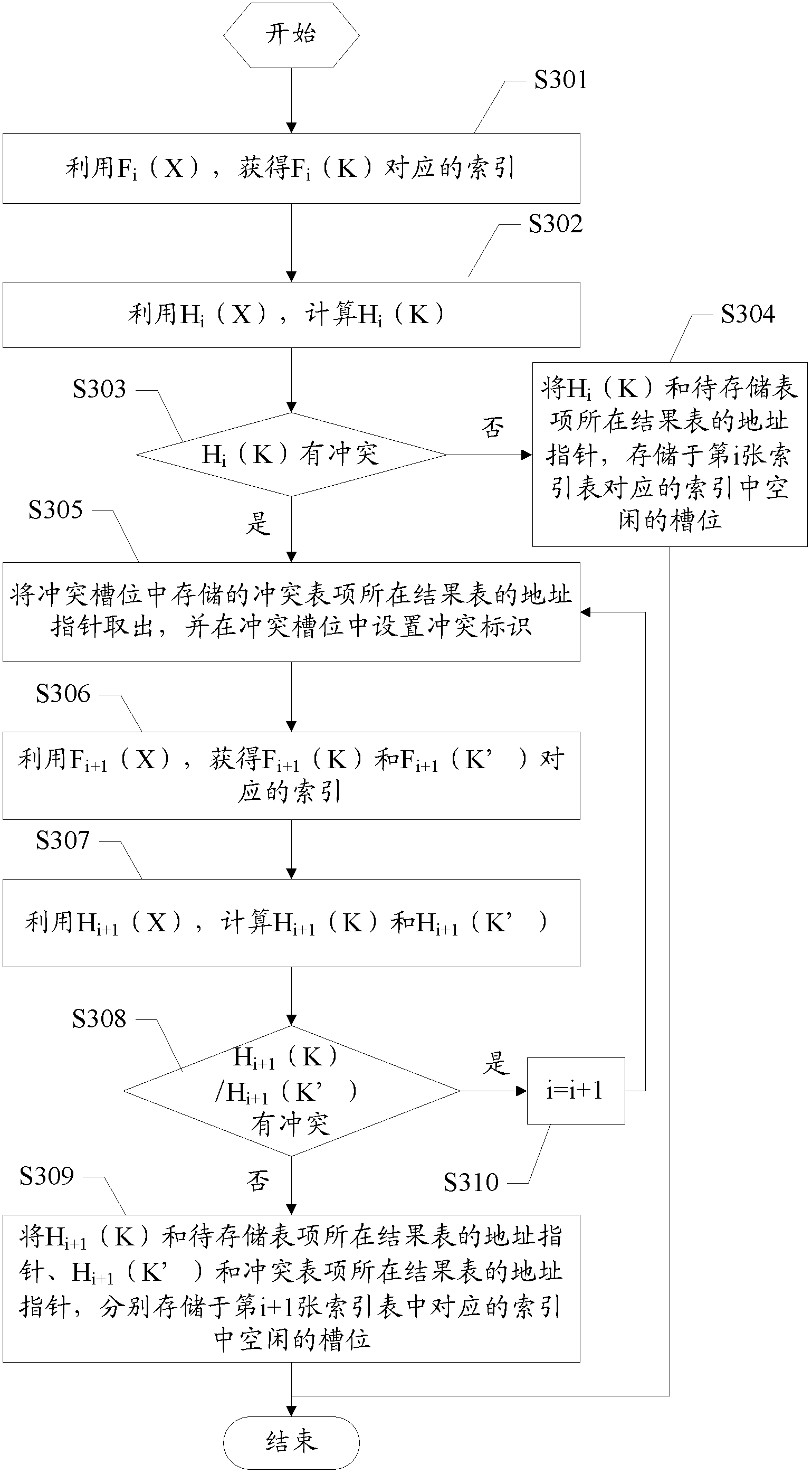
ActiveCN102682116AIncrease storage capacityImprove space utilizationSpecial data processing applicationsTheoretical computer scienceAccess frequency
The invention discloses a method and a device for processing table items based on a Hash table. The method comprises the steps of: during table item storage, storing table items to be stored in a result table in a sequential arrangement manner; calculating Hash values of key values of the table items to be stored by using dual Hash functions of an index table; and storing the Hash values and address pointers of the result table of the table items to be stored at idle positions in the index table. According to the invention, while lower access frequency and higher inquiry speed are guaranteed, the clause memory capacity of the service table items is increased effectively, the capacity of the Hash table for supporting possible services is increased, high spatial utilization rate is achieved for the Hash table, in addition, the probability of conflicts is reduced, and thus, the performance and the capacity of the Hash table are balanced.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Financial data processing method and device based on blockchain and electronic equipment
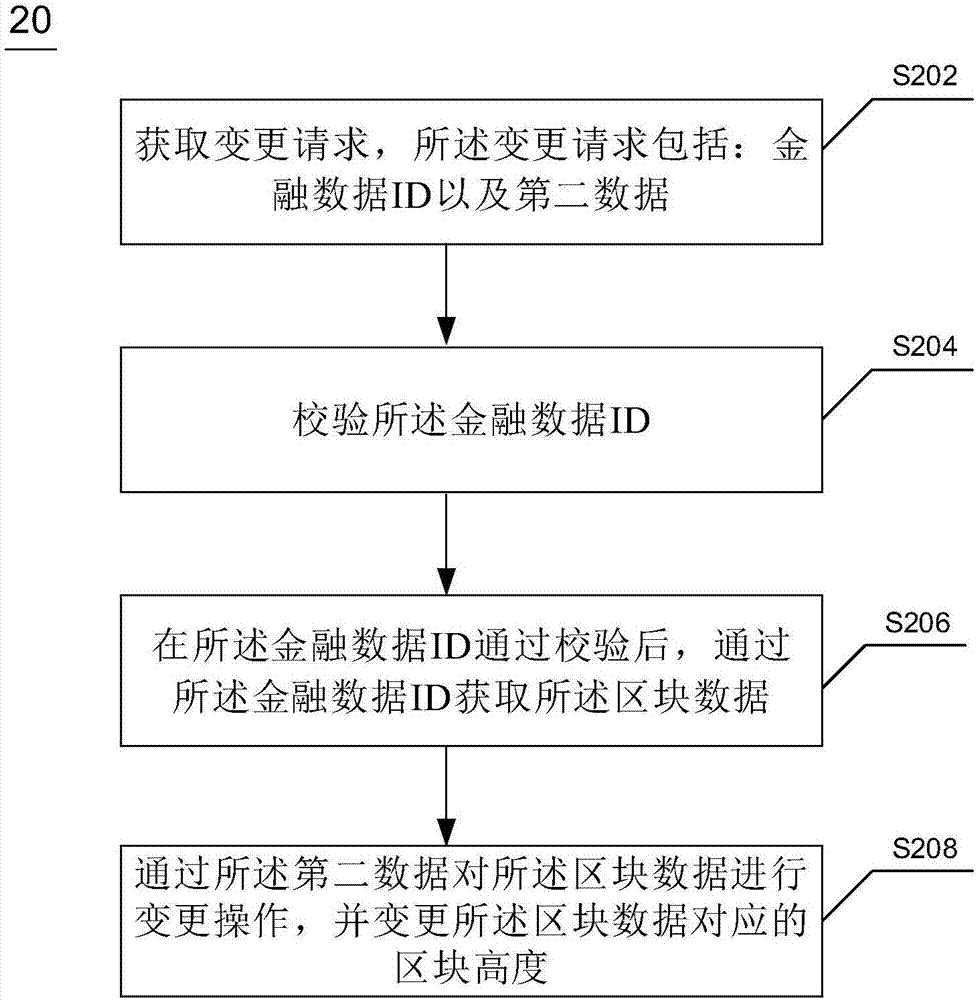
ActiveCN106991165AEase conflictMitigate conflicts between execution operationsFinanceSpecial data processing applicationsBlockchainMachine learning
The invention discloses a financial data processing method and device based on the blockchain and electronic equipment. The method includes the steps that financial data is received and verified; Hash processing is conducted on the verified financial data to generate financial data ID; financial status data is generated according to the financial data; the financial data, the financial status data and the financial data ID are encapsulated to generate block data and block height. By means of the financial data processing method and device based on the blockchain and the electronic equipment, the conflict between financial data variability and blockchain execution singleness can be alleviated.
Owner:JINGDONG TECH HLDG CO LTD
Clinical method and system for patient to acquire right to know medical treatment
InactiveCN102004862AShorten the timeUnderstand and monitor the diagnosis and treatment processSpecial data processing applicationsDatabase serverComputer terminal
The invention relates to a clinical method and a clinical system for a patient to acquire right to know medical treatment, and belongs to the technical field of information. The system comprises a patient terminal, a platform server, a hospital information system (HIS) interface server, a database server, a doctor work station and a network, and is characterized in that: the patient terminal, the platform server, the HIS interface server, the database server and the doctor work station are connected with one another through the network; and the HIS interface server is connected with an HIS through the network and acquires diagnosis and treatment data. The patient logs in the platform server through the patient terminal, and the platform server verifies the identity of the patient, acquires data from the database server and the HIS interface server and sends the data to the patient terminal. Multiple kinds of related information is provided for the patient, the problem of unequal doctor and patient information is solved, the patient acquires the right to know the medical treatment, and doctor and patient conflicts are furthest reduced.
Owner:王兴强
RFID management system for site construction worker safety
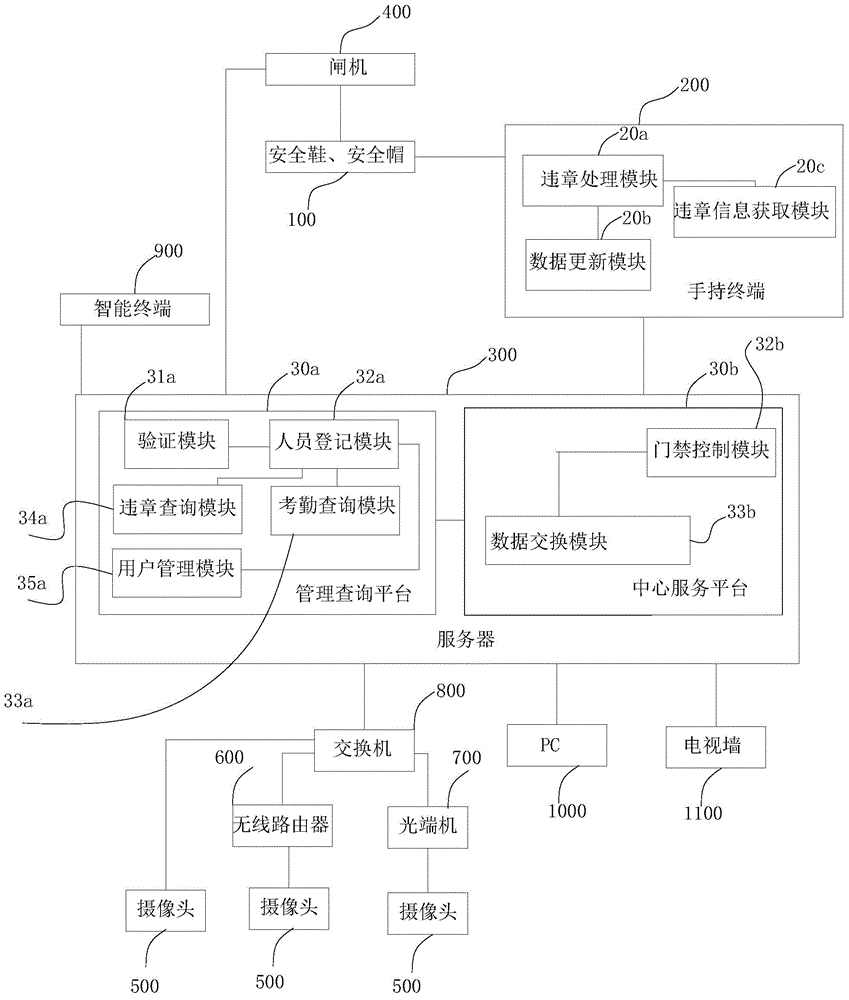
InactiveCN104700211ACrack liquidityCracking difficultyCo-operative working arrangementsResourcesWireless routerHand held
The invention discloses an RFID management system for site construction worker safety. The RFID management system comprises a pair of safety shoes, a safety helmet, a gate, a camera, a wireless router, an optical transmitter and receiver, an interchanger, a hand-held terminal, an intelligent terminal, a server, a PC and a television wall; the safety shoes, safety helmet, gate and hand-held terminal are connected in a wireless mode through an RFID mode; the hand-held terminal, intelligent terminal, gate and server are connected in a wireless mode; the interchanger, television wall, PC and server have communication connection; the camera is electrically connected with the wireless router and optical transmitter and receiver; the wireless router, optical transmitter and receiver and interchanger are electrically connected; the hand-held terminal comprises a violation information acquiring module, a violation processing module and a data updating module; the violation processing module is connected with the data updating module; the server comprises a management inquiry platform and a central service platform; the management inquiry platform is connected with the central service platform; the management inquiry platform comprises a verification module, a personnel registration module, an attendance inquiry module, a violation inquiry module and a user management module.
Owner:SHANGHAI JINNENG SAFETY TECH
Access method for periodic contention-free sessions
InactiveUS7773625B2Reduce conflictReduce distractionsSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementAccess methodWireless lan
An access method for periodic contention-free sessions (PCFS) reduces interference between overlapping first and second wireless LAN cells contending for the same medium. Each cell includes a respective plurality of member stations and an access point (AP) station. The access method for periodic contention-free sessions (PCFS) includes a fixed cycle time that reduces conflicts with PCFS from other cells. The PCFS from several cells are repeated in cycles of cycle period (CP), which is the contention-free period (CFP) of an access point times a factor that is a function of the number of overlapping cells. Periodic contention-free sessions (PCFSs) are generated, one from each overlapping cell. PCFS transmission attempts occur at the fixed specified time spacing following the start of the previous cycle. Each active AP sets a timer at CP and a PCFS is initiated when the timer expires. The timer is then reset and starts a new cycle.
Owner:AT & T INTPROP II LP
Methanol gasoline for vehicle
The invention discloses an energy-efficient, environment-friendly and high-efficient and low-cost automobile methanol gasoline. The methanol gasoline consists of (calculated by weight percent) gasoline (20-48 percent), methanol (30-70 percent), light hydrocarbon (5-15 percent) and additives (5-7 percent); the additives in the automobile methanol gasoline consists of (calculated by weight percent) solubilizer (1.5-5 percent), anti-oxidant (0.05-0.2 percent), antifreezing agent (0.5-1.0 percent), heat-value increasing agent (0.5-1.0 percent), plasticizer (0.05-0.5 percent), antioxidant (0.05-0.2 percent), stabilizer (0.2-0.8 percent) and antiseptic agent (0.2-1.0 percent). The raw materials required by the automobile methanol gasoline are available from extensive resources and the price is low; suitable for mass production and the production process is very simple; besides, the production is not restricted by seasons or scale.
Owner:上海龙津石油有限公司
V2X communication method and apparatus in Internet of Vehicles
InactiveCN107040960AImprove power efficiencyReduce conflictPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementResource poolThe Internet
The invention provides a V2X communication method and apparatus in the Internet of Vehicles. The method comprises the following steps: determining a resource pool for V2X communication according to resource configuration parameters; selecting sending resources in the sending resources contained in the resource pool, and using the sending resources to send a first V2X communication signal; and / or, selecting receiving resources in the receiving resources contained in the resource pool, and using the receiving resources to receive a second V2X communication signal. By adoption of the V2X communication method and apparatus, the problems of low power consumption efficiency of end-to-end communication of the Internet of Vehicles, communication resource conflict and network congestion in the prior art are solved, and thus the effects of improving the power consumption efficiency of the end-to-end communication of the Internet of Vehicles, and relieving the communication resource conflict and the network congestion are realized.
Owner:ZTE CORP
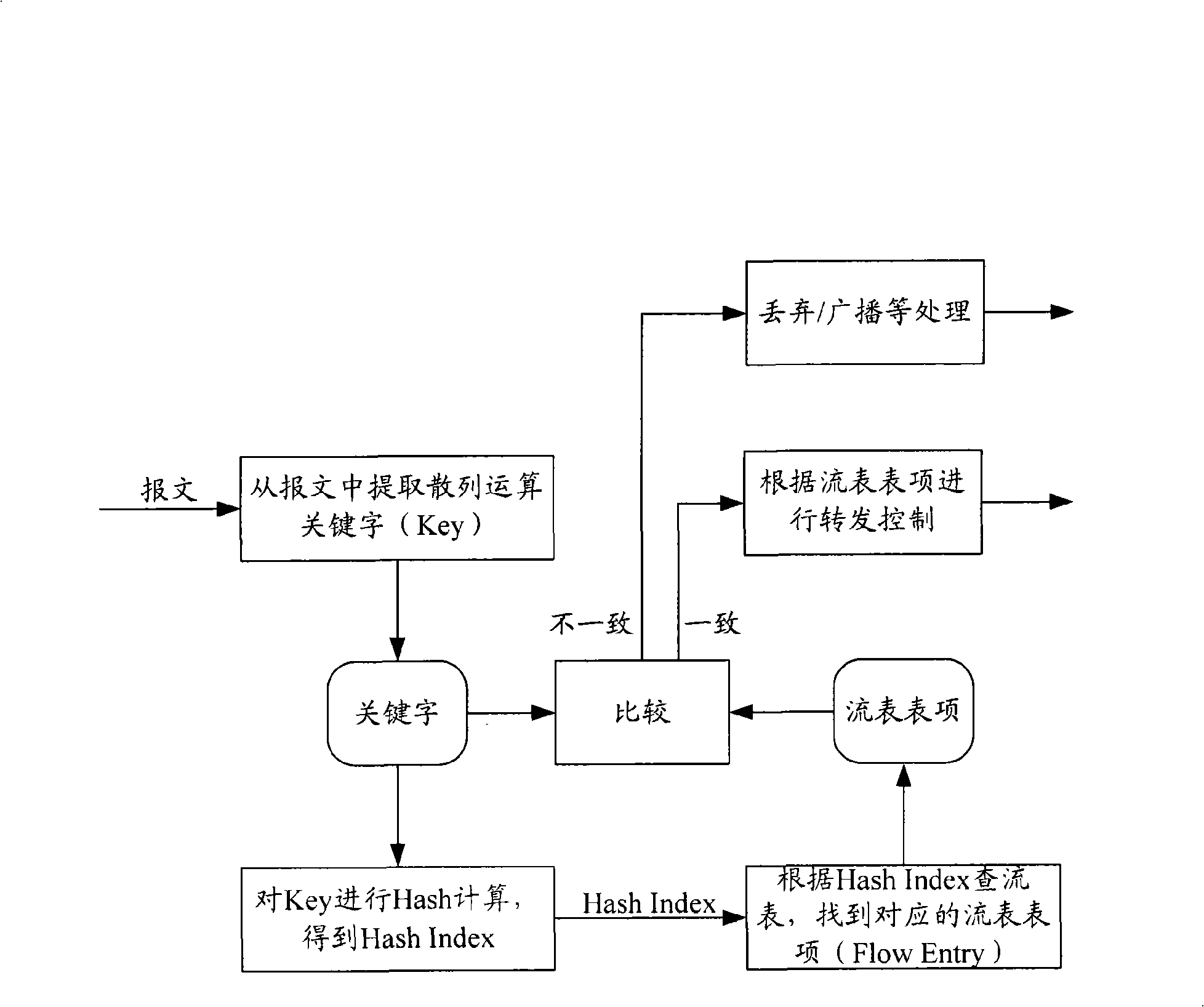
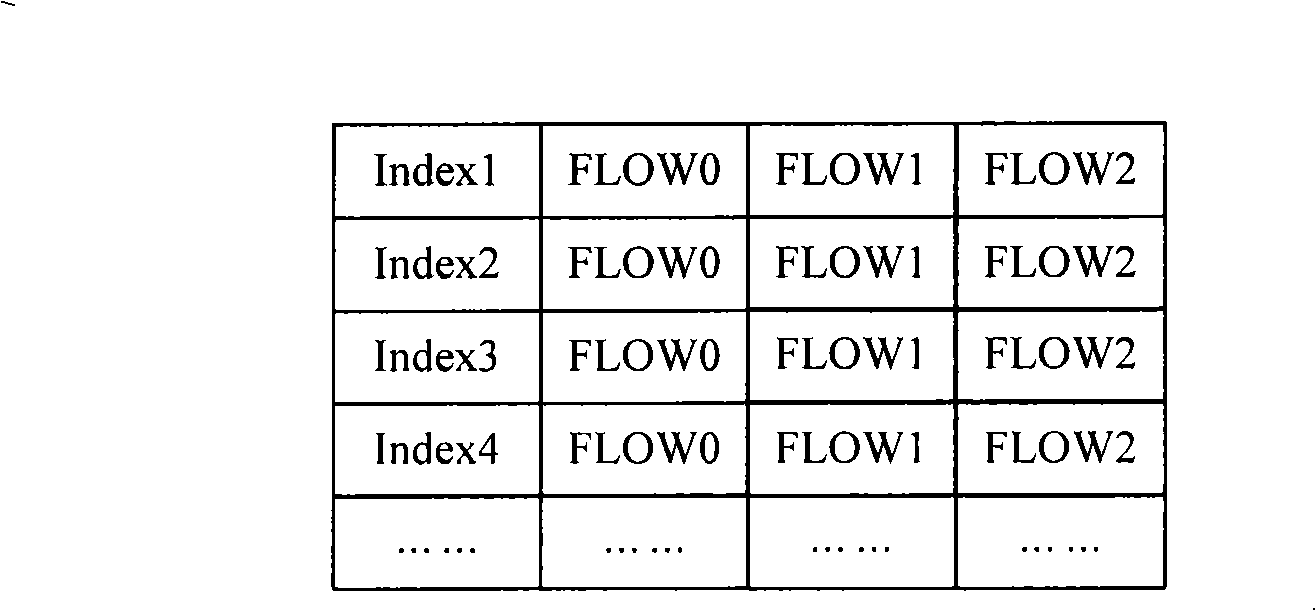
Flow stream searching method and device
ActiveCN101540723AFast searchQuick searchData switching networksSpecial data processing applicationsOperating system
The invention discloses a flow stream searching method and a device. The method comprises the following steps of: setting a pre-searching table in internal cache of a chip, adopting the pre-searching table to record key words and corresponding relation of Index thereof, and calling part of fields which only record the key words as Flow value when recording. The recording position of the Flow value of the key words corresponds to the recording position of flow table entry corresponding to the key words in a Hash barrel. When searching the needed flow table entry for message, the invention can determine the recording position of the needed flow table entry in the external cache according to the position of Index obtained by carrying out Hash operation on the key words of the message and the Flow value matched with the key words of the message in the pre-search table entry, and obtain the needed flow table entry only by needing to access the external cache for once, thus achieving the purpose of fast search.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for transmitting uplink data having low latency in wireless communication system
ActiveCN106465401ADelay minimizationSatisfy process delayNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemLatency (engineering)
The present specification provides a method for transmitting uplink data (UL data) requiring a low latency in a wireless communication system. The method performed by a terminal comprises the steps of: receiving control information related to a contention based PUSCH zone from a base station; and transmitting uplink data to the base station on the basis of the received control information. The contention based PUSCH zone is a resource area where uplink data of the terminal can be transmitted without allocation of a UL grant from the base station. Further, in order to distinguish between kinds of specific procedures performed by the terminal, the control information includes procedure-distinguishing information allocated for each kind of the specific procedures.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Network interface device
ActiveUS20070208854A1Reduce conflictDelay minimizationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityNetwork interface device
There are methods and apparatus, including computer program products, for defining a policy including a set of rules for a packet forwarding device by receiving information sufficient to enable a first rule related to one of security or traffic management to be defined, and based on the received information, enabling a corresponding second rule related to the other one of security or traffic management to be defined.
Owner:BARRACUDA NETWORKS
Staggered startup for cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) contention-free sessions
ActiveUS20080013515A1Reduce conflictSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsWireless lan
Owner:AT & T INTPROP II LP
Multi-business supporting network switching device and implementation method therefor
InactiveCN105337883AReduce conflictReduce competitionData switching networksComputer architectureTime delays
The invention relates to a multi-business supporting network switching device and an implementation method therefor. The device employs a multi-level CLOS switching configuration, and an input unit, an output unit and a switching unit are respectively provided with a buffer memory. The device can process a multi-business flow, and can achieve switching according to the business characteristics. The device can generate quick flow control in a congestion scene through the output unit, wherein the quick flow control acts on an input end, thereby reducing the congestion stress on the output end, and reducing the congestion degree of a central level. The device can reduce the input flow of a fault plane in a link fault scene through a load balancing scheme, and alleviates the congestion of the switching unit. An output unit package ordering method is employed, thereby reducing the design complexity of the switching unit. A data package cell load balancing method of the input unit is employed for enabling the time difference among cells to be small, thereby reducing the time delay of a data package, and reducing the size of the ordering and recombination buffer memory of an output end.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
System and method for gestation of sows in large pen gestation facilities
InactiveUS8132538B1Reduce conflictEasy accessPasturing equipmentAnimal housingGestationContinuous flow
A sow management system makes use of separate Trickle Feeding and loafing areas separated by a one way gate or gates to establish a general continuous flow of sows through an interrogator apparatus where an RFID tag for each sow is read to determine if such sow should be returned to the general Trickle Feeding area or at least two other possible areas through automatic gating controlled by computer means sensitive to RFID tagging of the sows.
Owner:SCHICK PAUL H +1
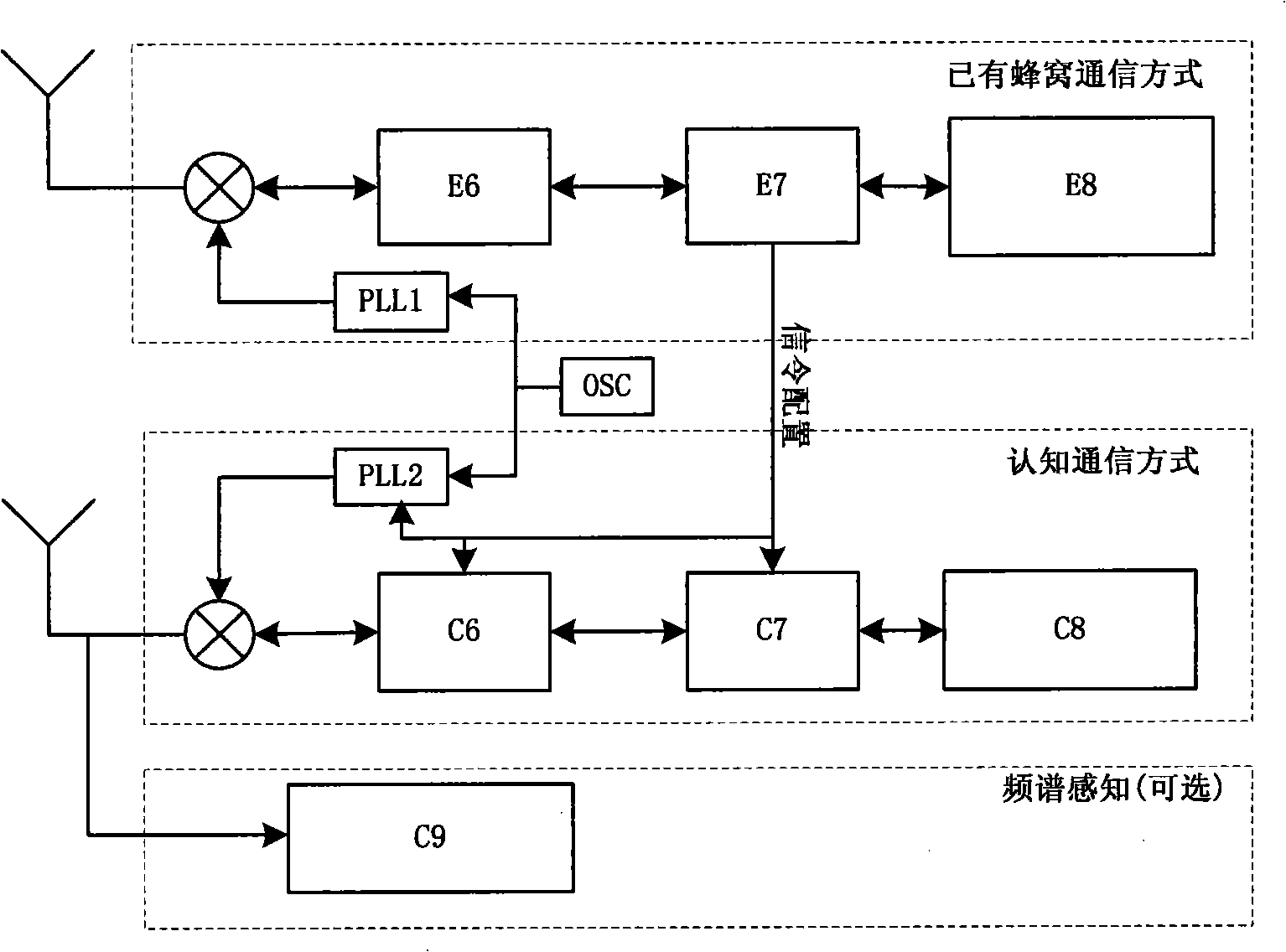
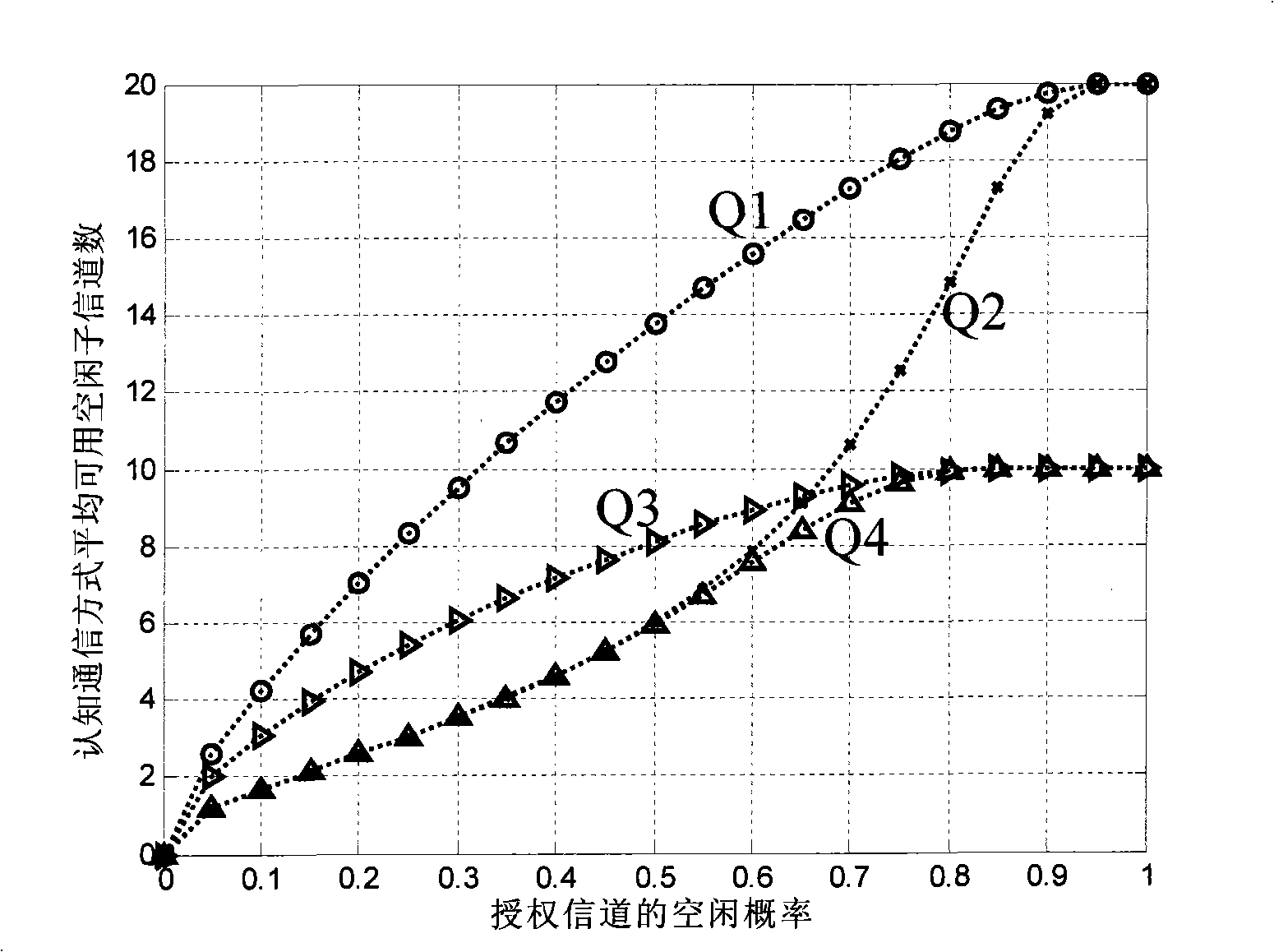
Method for implementing frequency spectrum cavity-pocket efficient utilization based on existing honeycomb communication signaling transmission
InactiveCN101330461ATake advantage ofReduce conflictMulti-frequency code systemsData switching networksCellular communication systemsHoneycomb
The invention discloses a method for realizing effective utilization of spectrum holes based on available cellular communication signaling, which is characterized in that the available cellular communication mode and the cognitive communication mode adopt a same clock source, a user terminal keeps the synchronization of the carrier frequency and the frame timing of the cognitive communication mode by locking on the carrier frequency and the frame timing of the available cellular communication mode. Signaling messages for allocating the frequency point, the bandwidth and the perceived spectrum holes of the cognitive communication mode are added in the available cellular communication signaling. A base station determines the cognitive manner including working parameters of the frequency, the bandwidth and the perceived spectrum holes based on the perception result, and notifies a terminal in time via the signaling of the available cellular communication mode. The terminal allocates the cognitive communication mode thereof according to the effective time. The perceived spectrum results interact among base stations, and the user terminal transmits and reports the perceived spectrum information to the base stations via the signaling of the available cellular communication mode. The method can effectively adopt cognitive radio technology in the radio cellular communication system, take full use of spectrum holes resource, and reduce possible conflicts with authorized users.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Base station, signal transmitting method of the same, communication system comprising thereof
InactiveUS20160234763A1Reduce conflictConflict with other base stations will be reducedModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionVIT signalsEngineering
An exemplary embodiment of the present information discloses a base station which transmits a discovery reference signal (DRS) in an unlicensed band, including: a transmission control unit which sets different timings to transmit the DRS for each of a plurality of channels; and a communication unit which transmits the DRS to the outside through the plurality of channels based on the set timing.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com