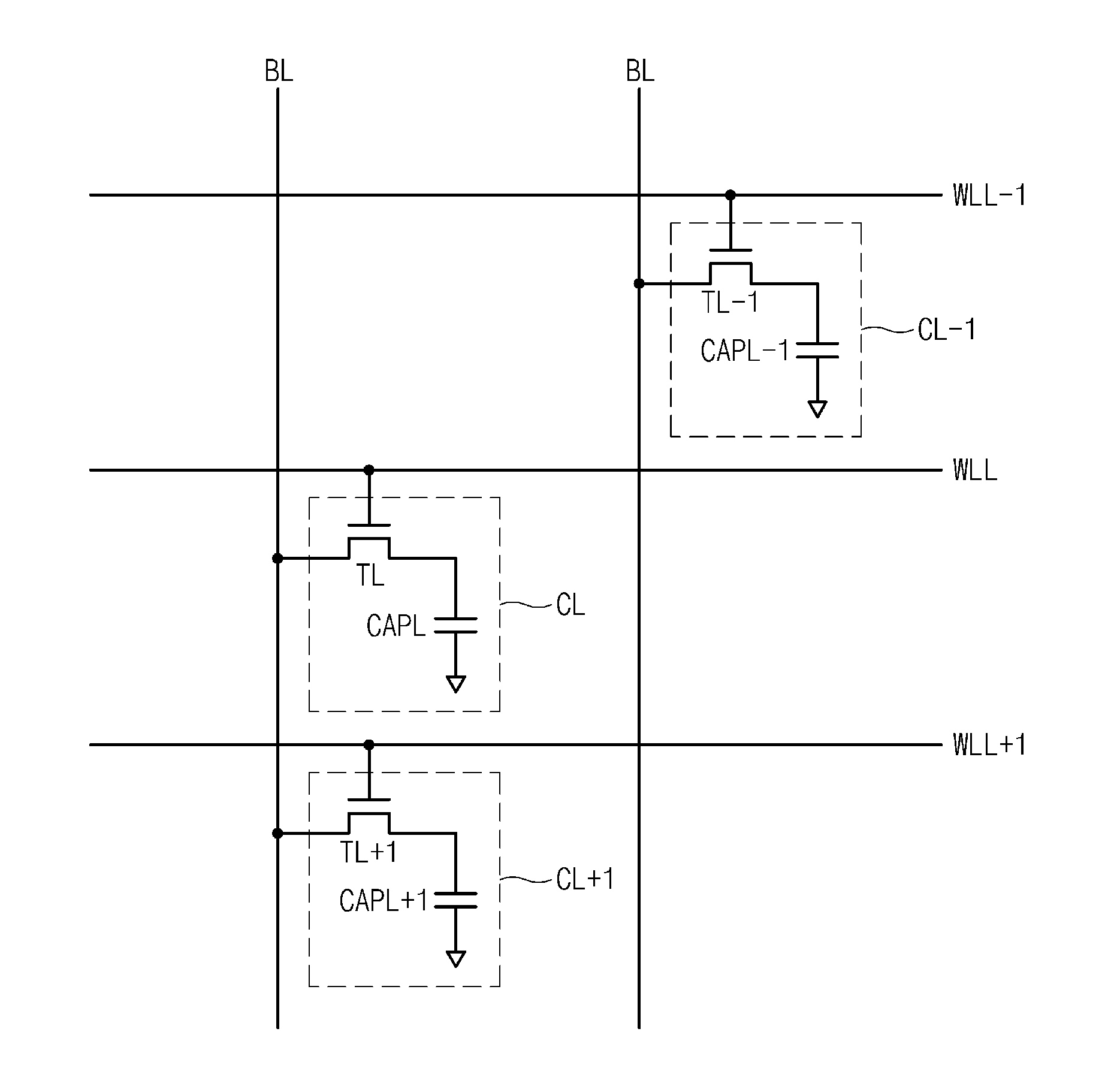Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
611 results about "Address control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
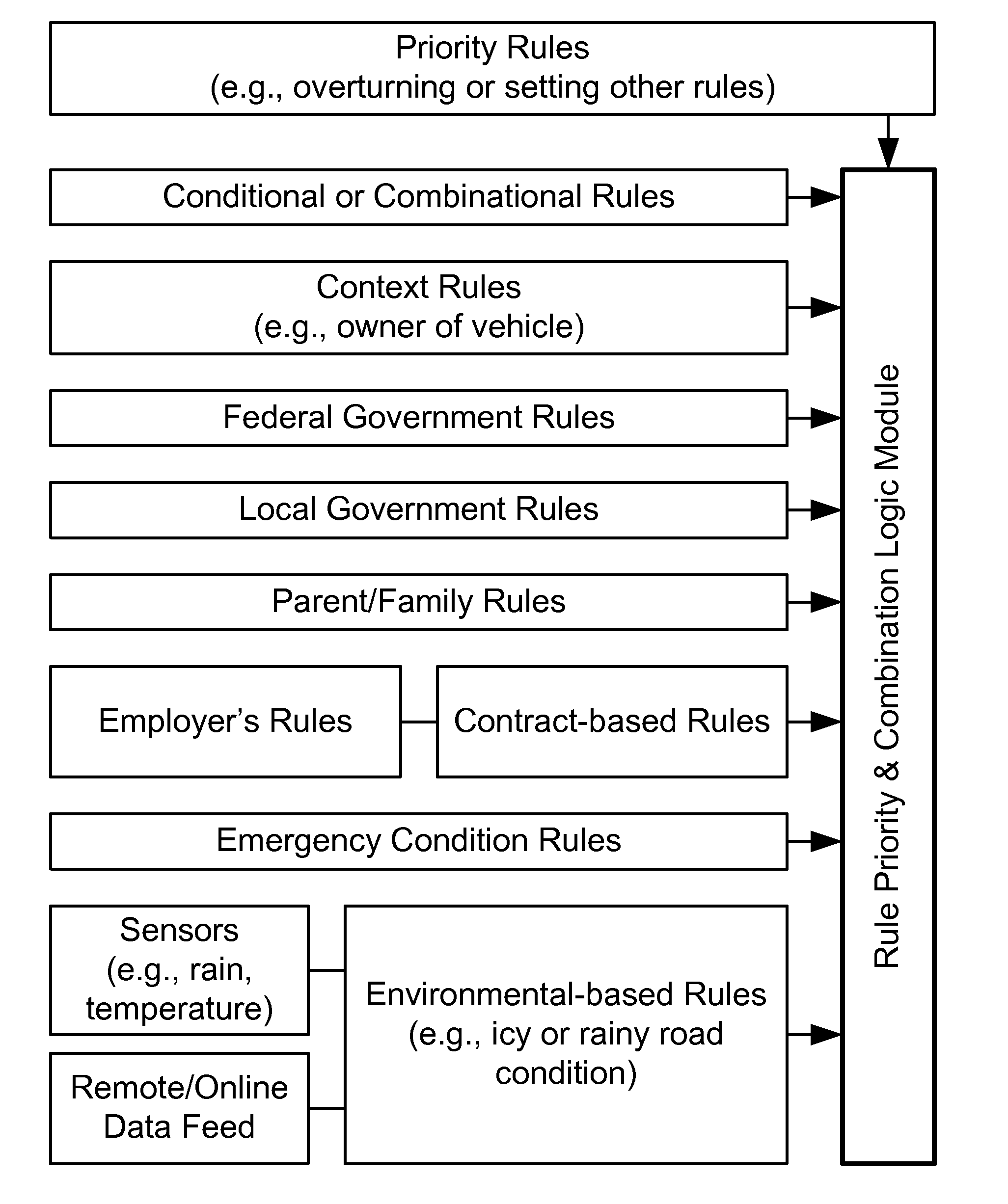
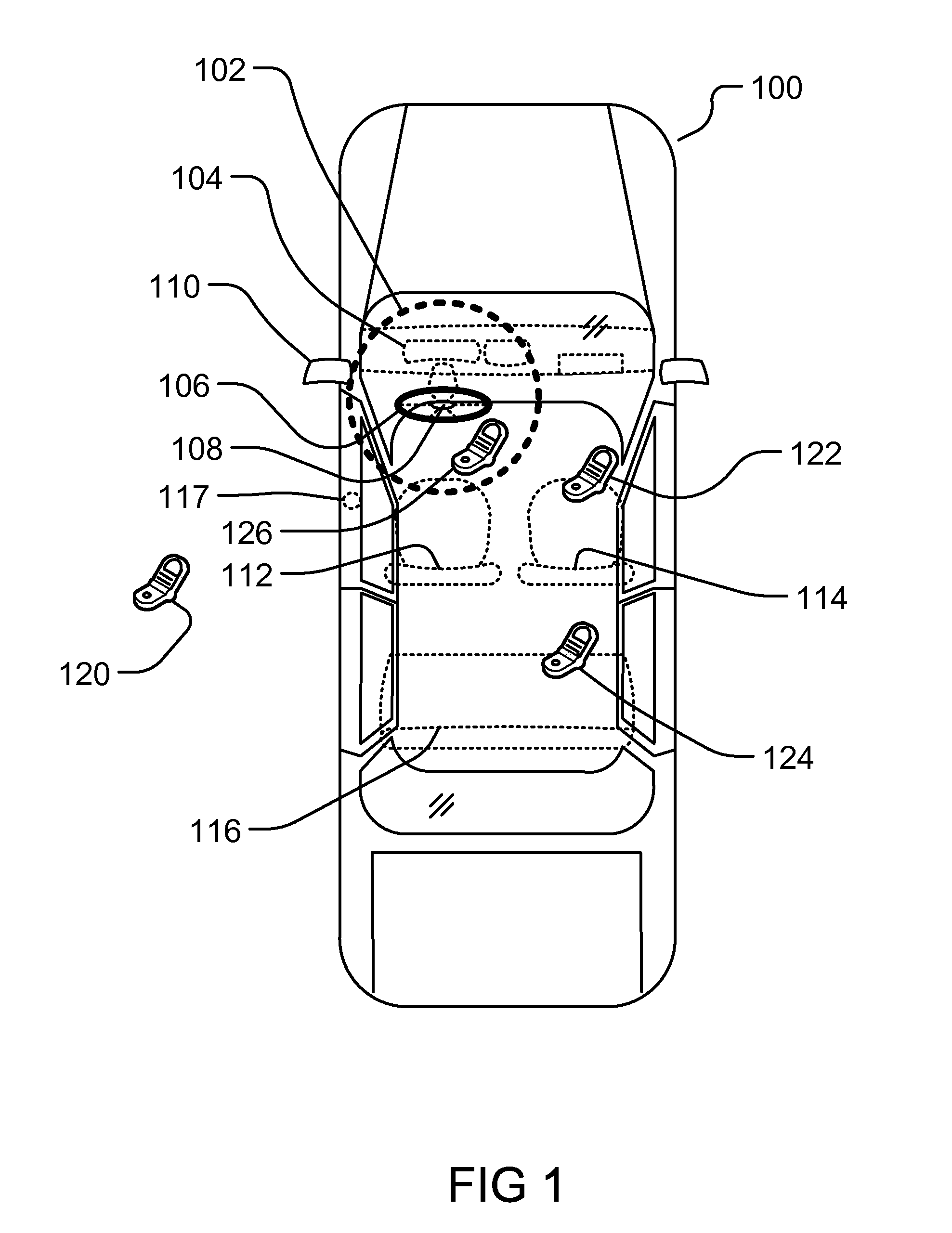
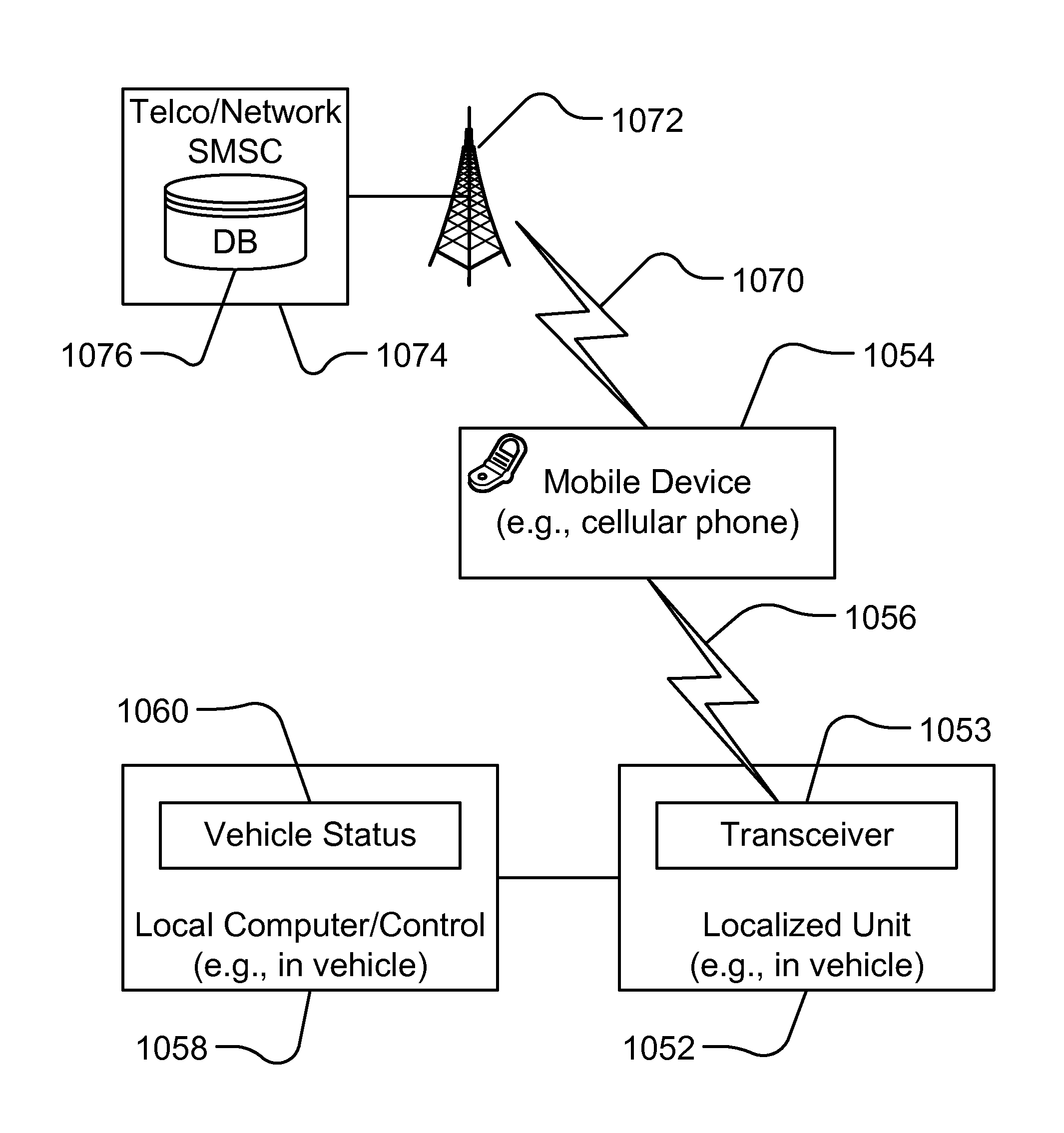
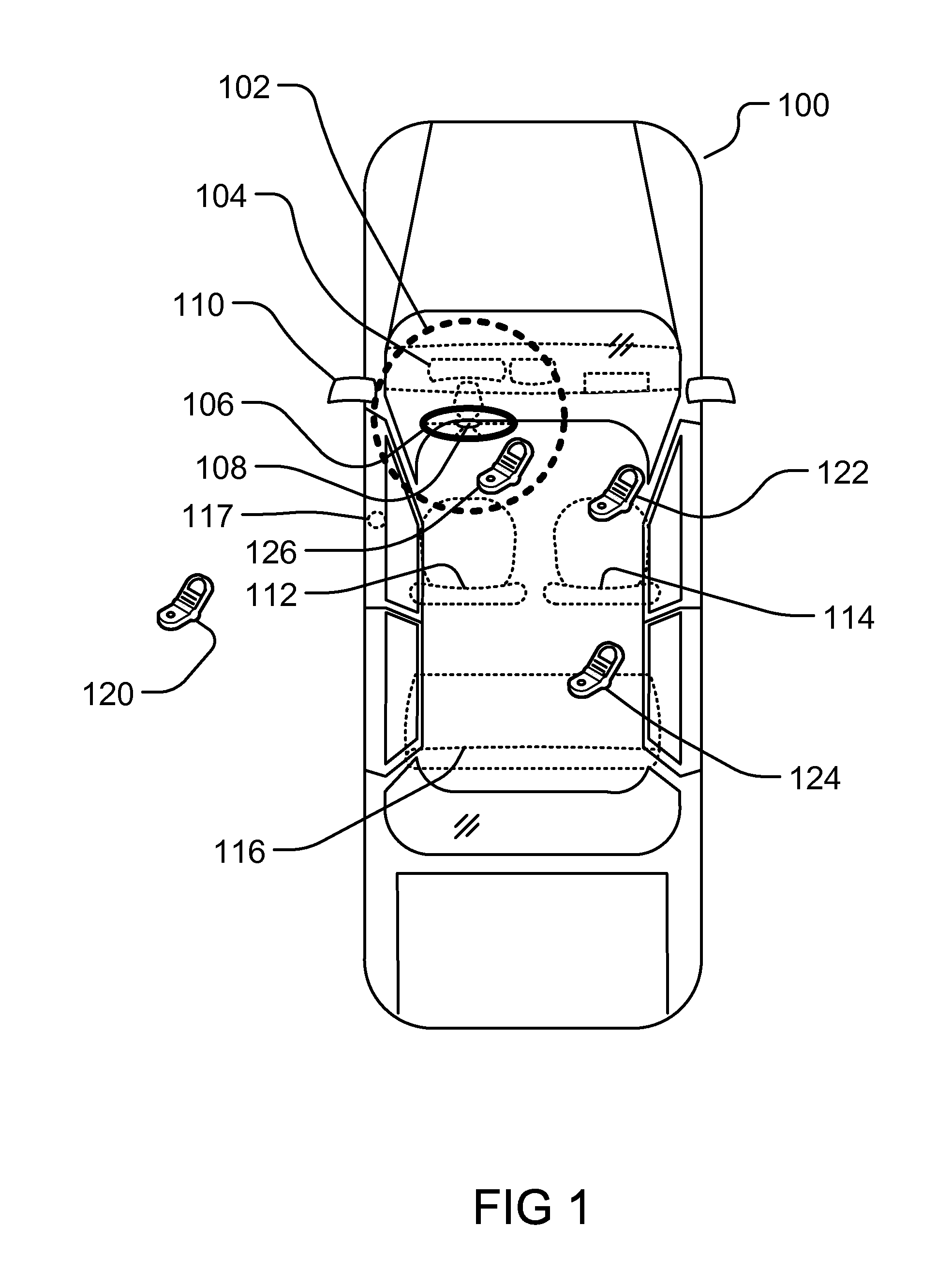
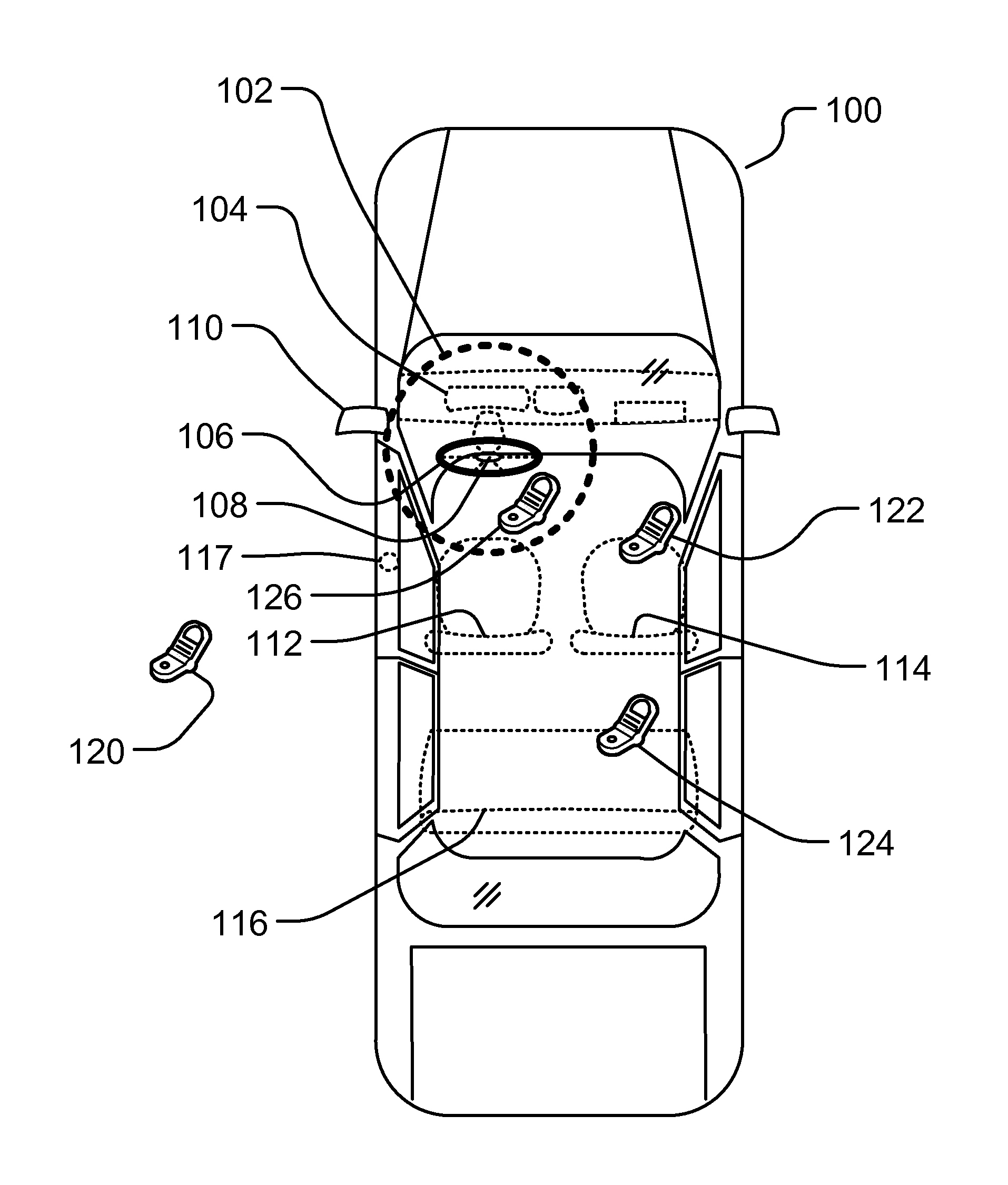
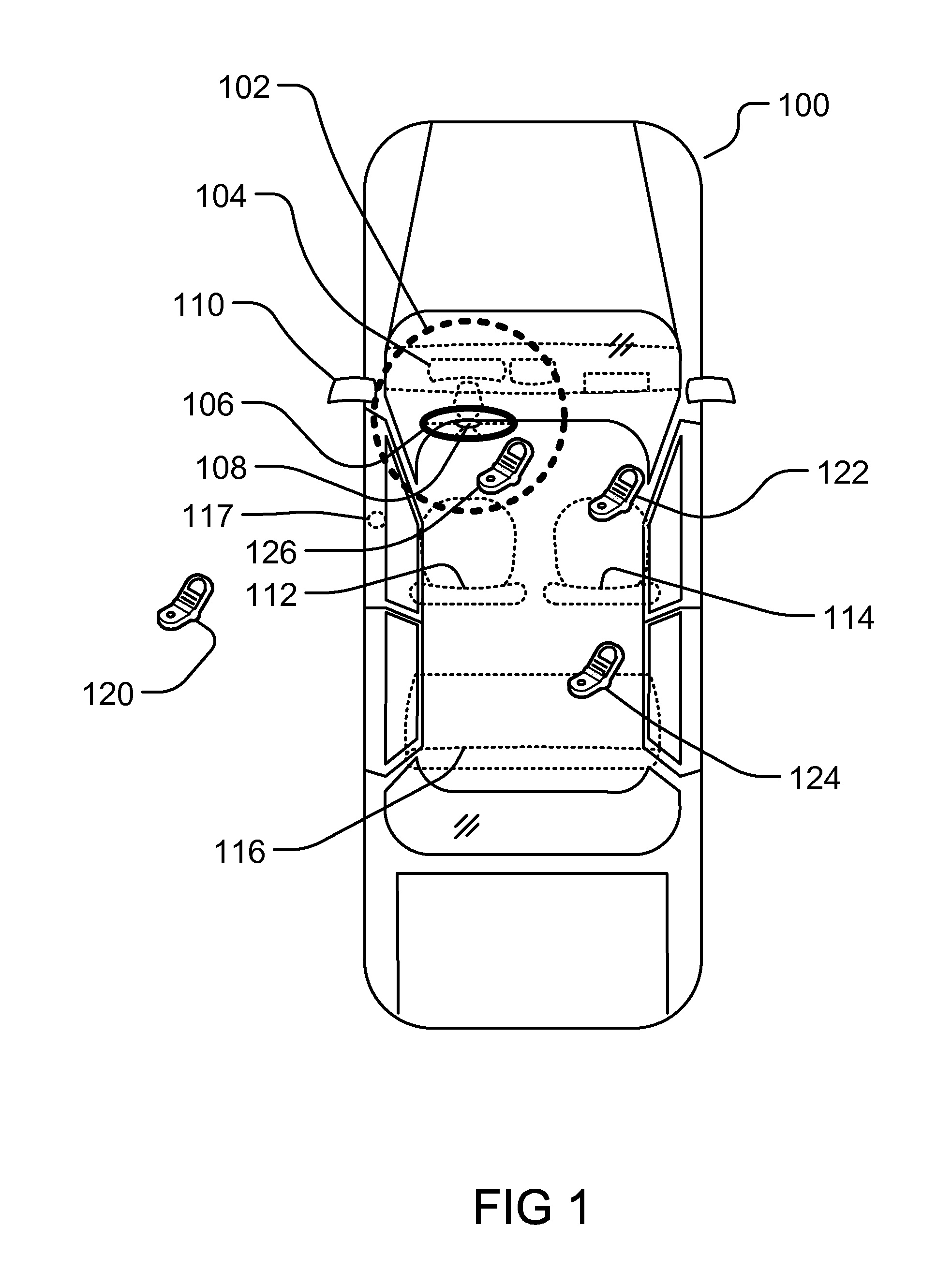
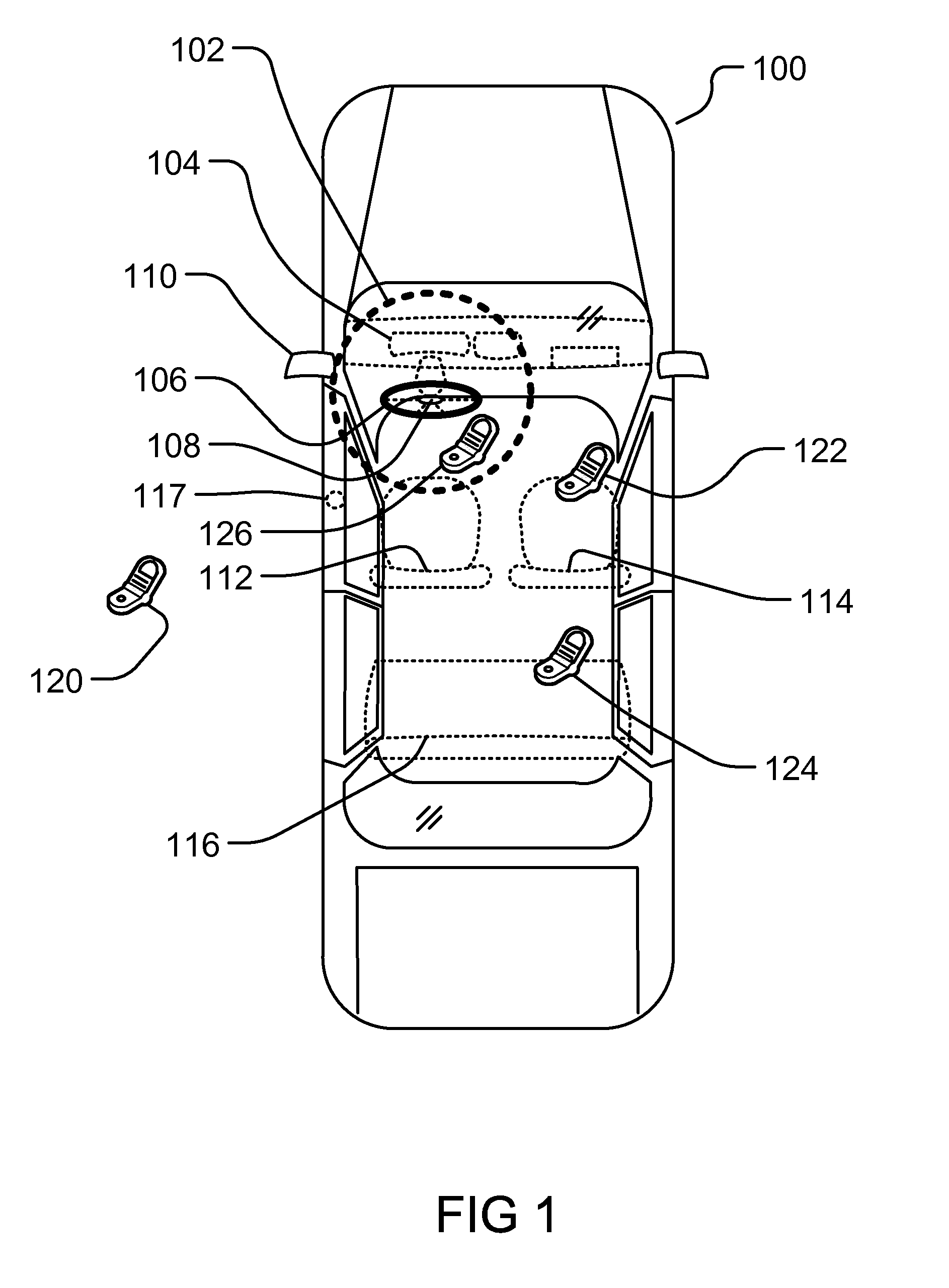
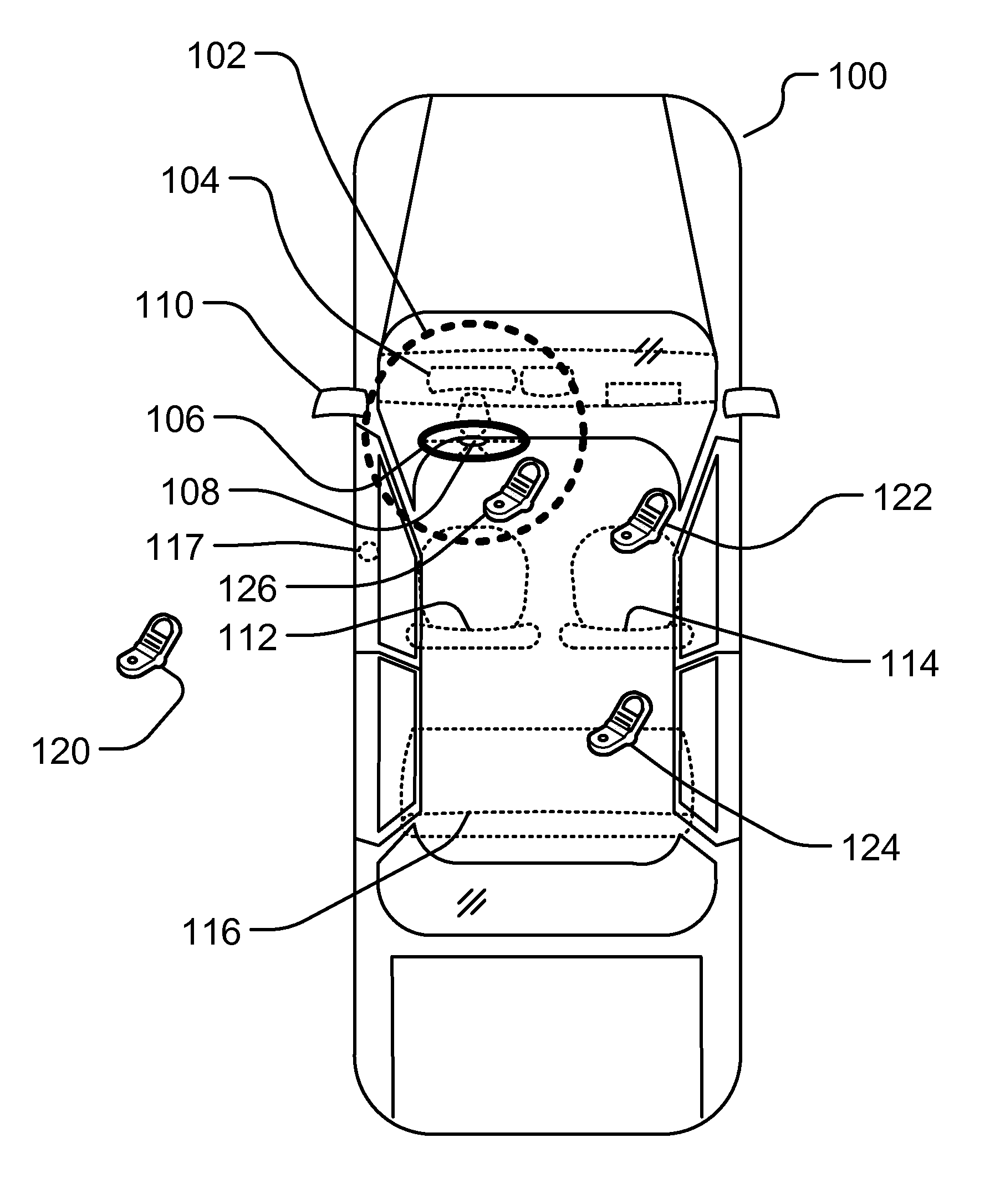
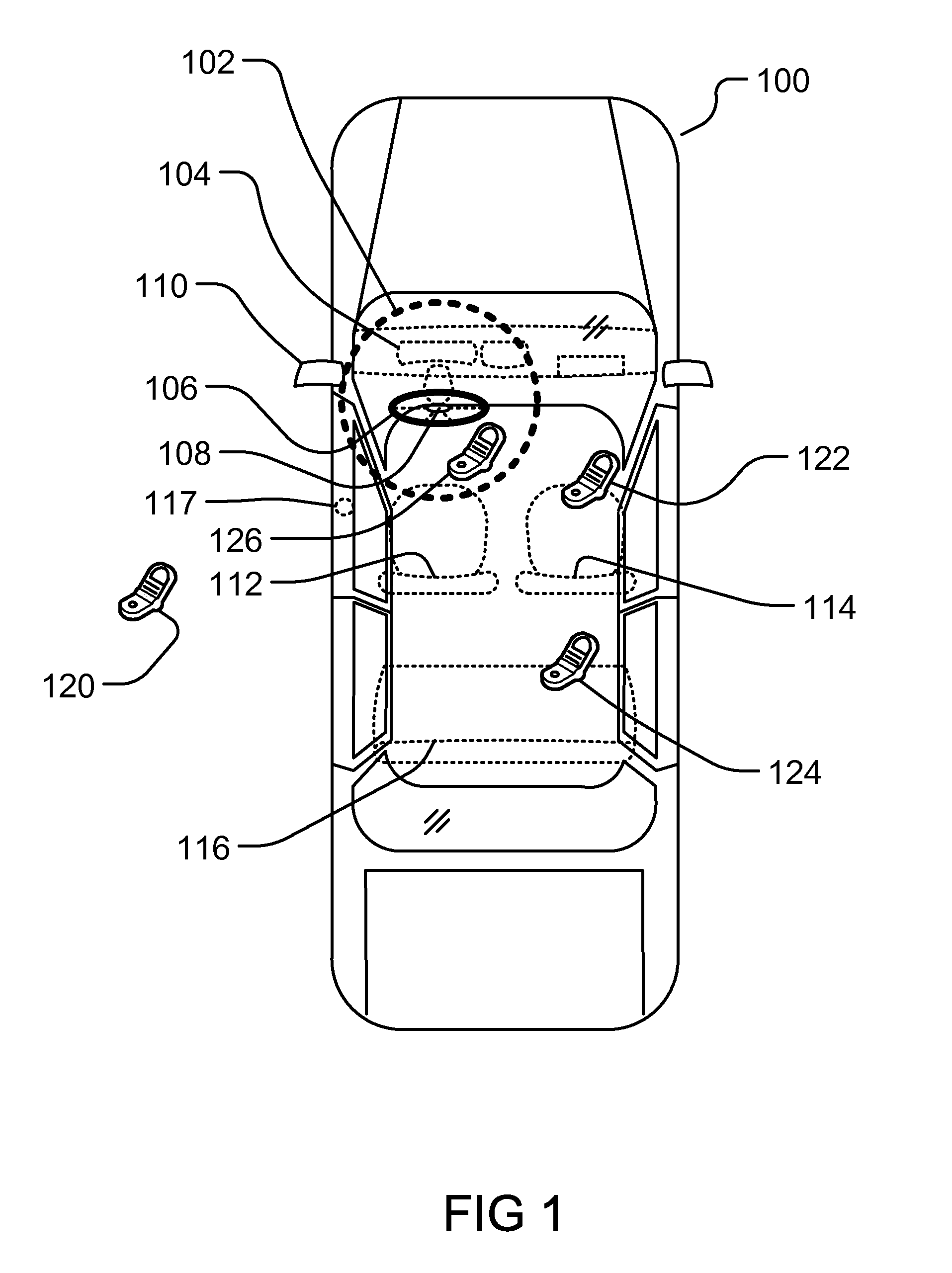
Controlling Mobile Device Functions
ActiveUS20110105097A1Limited abilityAutomatically disabling the texting ability of mobile deviceService provisioningReceivers monitoringDistractionAddress control
This provides for controlling mobile device functions and features. For example, it limits or disables the use of some of mobile device features which could cause distraction to the user, when the user is engaged in another activity. In an example, it enables other mobile device features based on occurrence of events related to the user or environment. Another example addresses controlling the mobile device features, such as SMS, while the user is in a vehicle or driving. Another example restricts the ability of the driver of a vehicle to text, while the vehicle is in motion, by automatically disabling the texting ability of mobile device within and around the perimeter of the driver's seat. Other variations, examples, improvements, detection mechanisms, models, techniques, calculations, verification mechanisms, and features are also described in details.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Controlling Mobile Device Functions
ActiveUS20110195699A1Limited abilityAutomatically disabling the texting ability of mobile deviceAssess restrictionSpecial service for subscribersDistractionDriver/operator
This provides for controlling mobile device functions and features, along with systems incorporating these devices and methods. For example, it limits or disables the use of some of mobile device features which could cause distraction to the user, when the user is engaged in another activity. In an example, it enables other mobile device features based on occurrence of events related to the user or environment. Another example addresses controlling the mobile device features, such as SMS, while the user is in a vehicle or driving. Another example restricts the ability of the driver of a vehicle to text, while the vehicle is in motion, by automatically disabling the texting ability of mobile device within and around the perimeter of the driver's seat. Other variations, examples, improvements, detection mechanisms, models, techniques, calculations, verification mechanisms, and features are also described in details.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
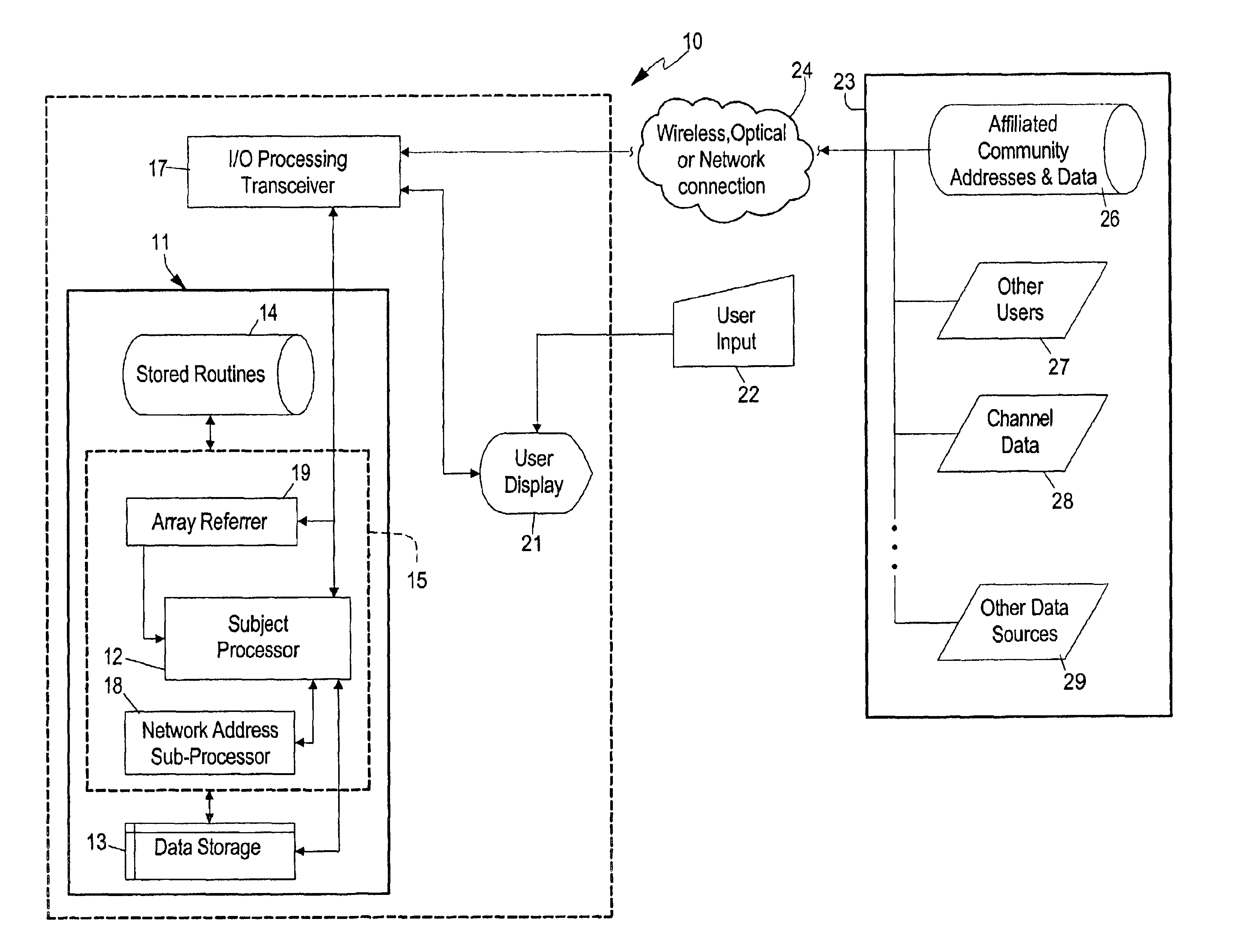
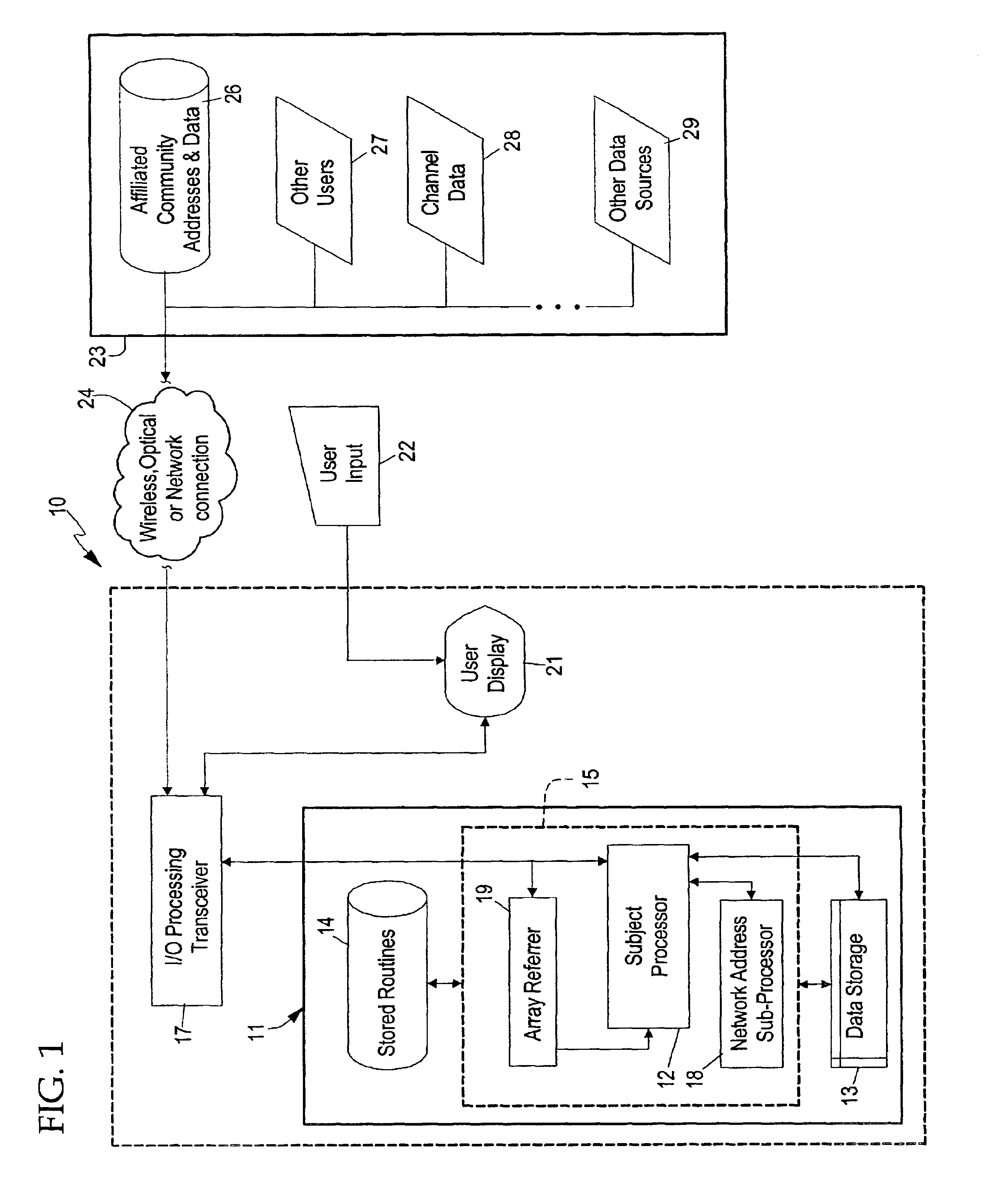
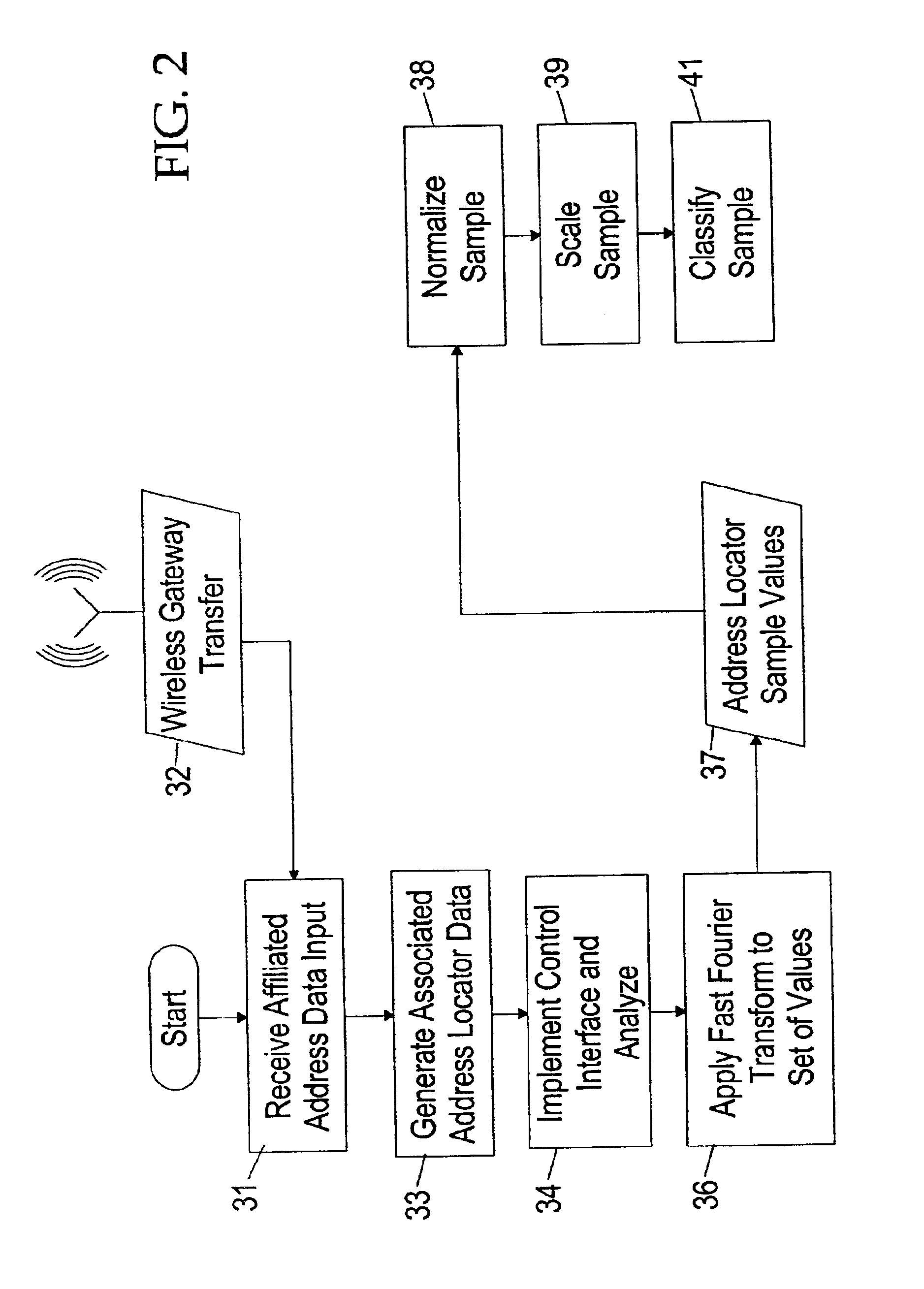
System and method for efficiently accessing affiliated network addresses from a wireless device
InactiveUS6873610B1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsHigh speed memoryNetwork addressing
A system and method for a wireless device to efficiently access affiliated addresses across linked topical communities, such as an Internet WebRing, through a wireless gateway. The invention includes a processing unit running on a wireless device controlled by an affiliated address control program. The processing unit includes a processing unit with a subject processor, a program store for holding an apparatus control program, a network address sub-processor, an address array referrer, an input mechanism, a display device for selecting retrieved affiliated addresses, and a high speed memory for holding site address selectors and associated content buffer. The wireless device communicates with a network via conventional wireless communication means which provides a path for updating the content buffer and array referrer, as well as transference of other types of sensory data. Means for predicting search failures is also integrated into the apparatus control program of the processing unit. Data received from the wireless gateway is statistically preprocessed then supplied to a processor called a network address sub-processor. The system then incorporates sorted affiliated addresses into the system on the wireless device to make possible a real-time detector system for a wireless device accessing content through a wireless gateway. The system may be offered as a service benefit for wireless device subscription or as a per occurrence chargeable item for a wireless subscriber. The system relieves the standard “hit-or-miss” method for affiliated address selection and site address storage and retrieval.
Owner:MOBULAR TECH
System and method for maintaining translation look-aside buffer (TLB) consistency
InactiveUS6105113AMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationVirtual memoryMemory address
A system and method for maintaining consistency between translational look-aside buffers (TLB) and page tables. A TLB has a TLB table for storing a list of virtual memory address-to-physical memory address translations, or page table entries (PTES) and a hardware-based controller for invalidating a translation that is stored in the TLB table when a corresponding page table entry changes. The TLB table includes a virtual memory (VM) page tag and a page table entry address tag for indexing the list of translations The VM page tag can be searched for VM pages that are referenced by a process. If a referenced VM page is found, an associated physical address is retrieved for use by the processor. The TLB controller includes a snooping controller for snooping a cache-memory interconnect for activity that affects PTEs. The page table entry address tag can be searched by a search engine in the TLB controller for snooped page table entry addresses. The TLB controller includes an updating module for invalidating or updating translations associated with snooped page table entry addresses. Translations in TLBs are thus updated or invalidated through hardware when an operating system changes a PTE, without intervention by an operating system or other software.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Controlling mobile device functions
ActiveUS8145199B2Limited abilityAutomatically disabling the texting ability of mobile deviceAssess restrictionSpecial service for subscribersDistractionAddress control
This provides for controlling mobile device functions and features, along with systems incorporating these devices and methods. For example, it limits or disables the use of some of mobile device features which could cause distraction to the user, when the user is engaged in another activity. In an example, it enables other mobile device features based on occurrence of events related to the user or environment. Another example addresses controlling the mobile device features, such as SMS, while the user is in a vehicle or driving. Another example restricts the ability of the driver of a vehicle to text, while the vehicle is in motion, by automatically disabling the texting ability of mobile device within and around the perimeter of the driver's seat. Other variations, examples, improvements, detection mechanisms, models, techniques, calculations, verification mechanisms, and features are also described in details.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
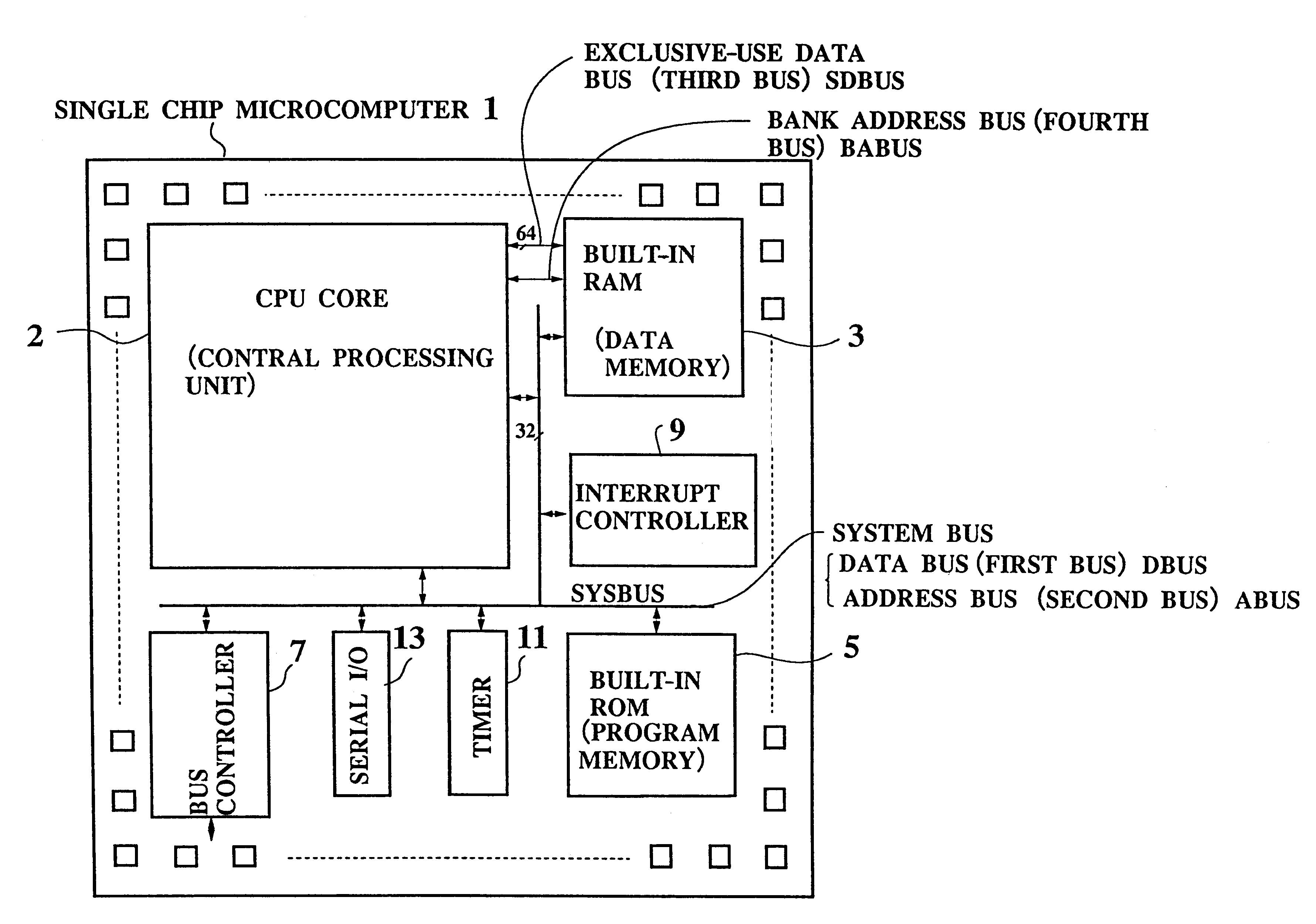
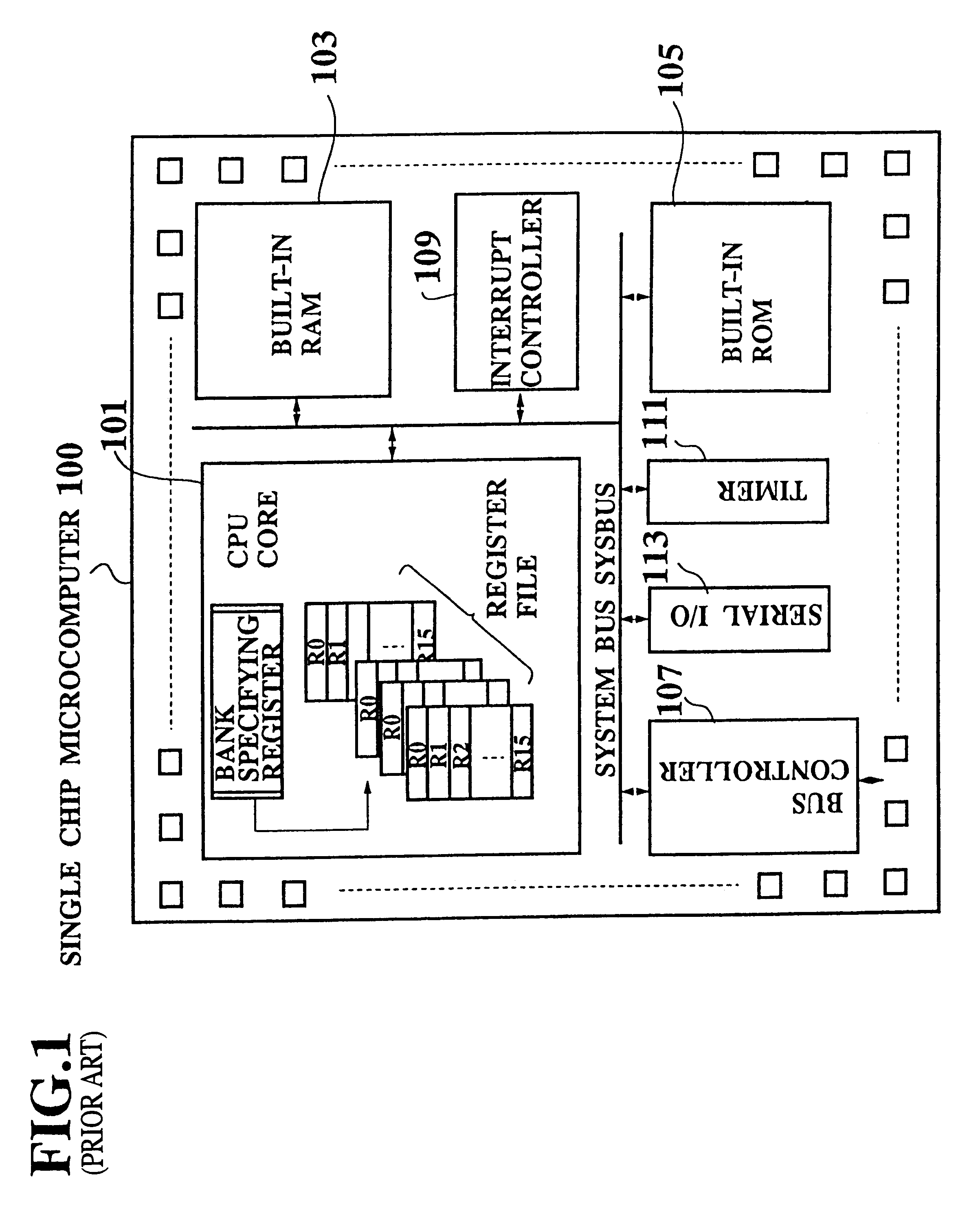
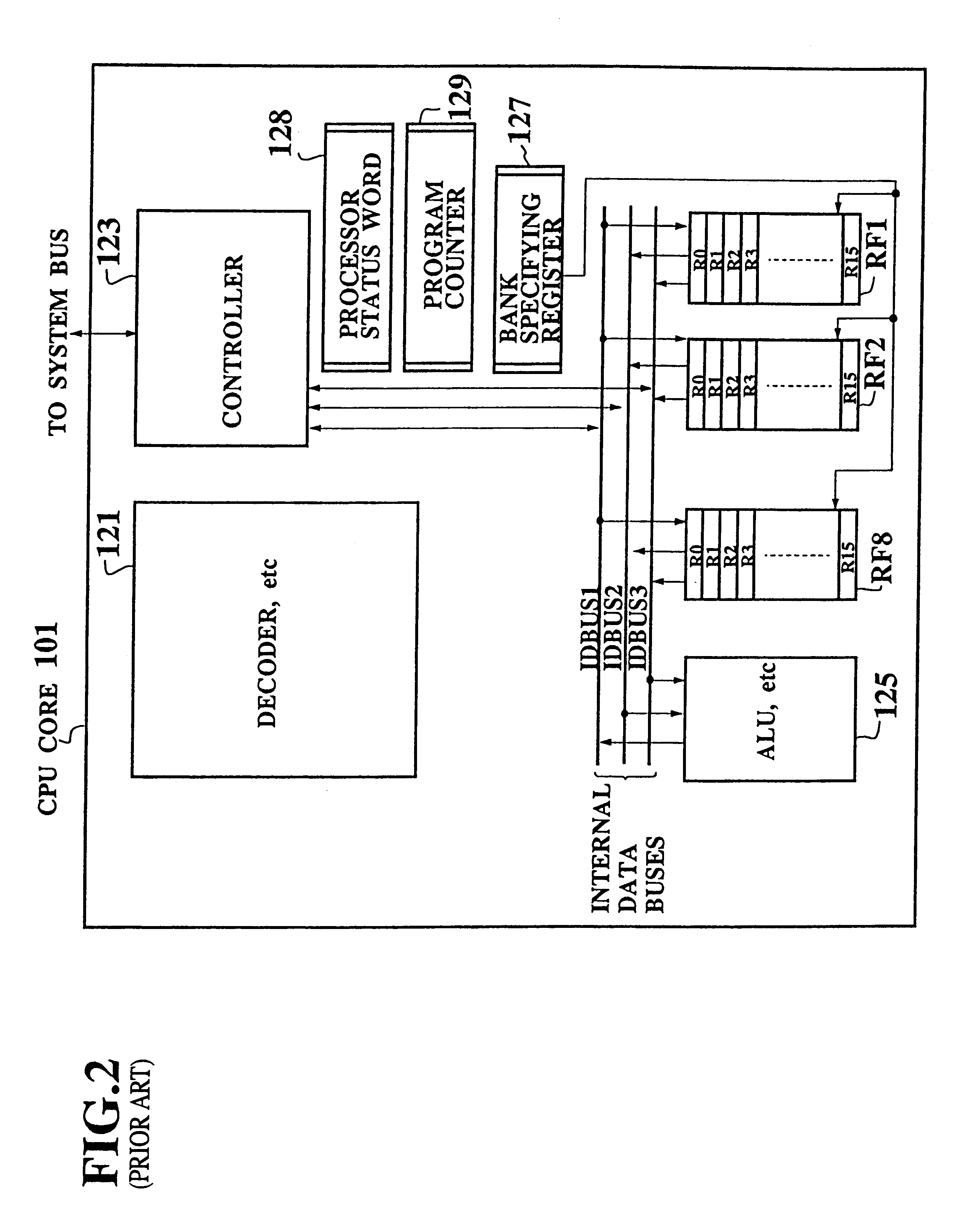
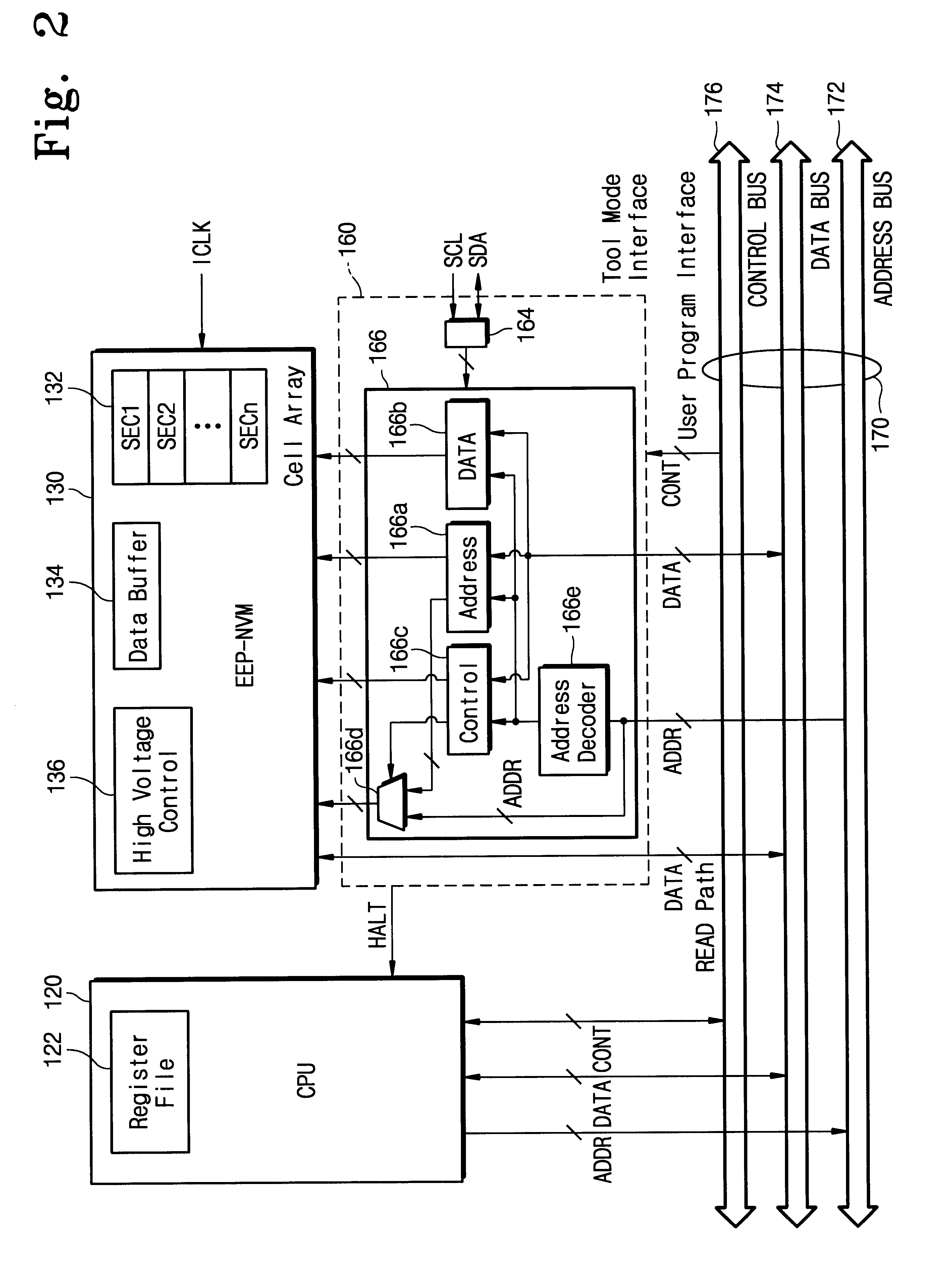
Single chip microcomputer having a dedicated address bus and dedicated data bus for transferring register bank data to and from an on-line RAM
InactiveUS6223279B1Efficiently chip spaceData transferArchitecture with single central processing unitSpecial data processing applicationsGeneral purposeProcessor register
A single chip microcomputer comprises a central processing unit (CPU) 2, a on-chip RAM 3, a on-chip ROM 5, a first bus DBUS for connecting the CPU, RAM, and ROM with one another and transferring data between them, a second bus ABUS for passing address data corresponding to the data passed through the first bus, a third bus SDBUS for connecting the CPU 2 with the RAM 3 and transferring data between them, the number of bits of the third bus SDBUS being larger than that of the first bus DBUS, and a fourth bus BABUS for connecting the CPU 2 with the RAM 3 and passing address data corresponding to the data passed through the third bus SDBUS. The CPU 2 has a data memory RF serving as general purpose registers for providing internal data to the third bus SDBUS, and a bank specifying register BP for holding positional data of a mapping region in the RAM 3 where the contents of the data memory RF are mapped and providing the positional data to the fourth bus BABUS. The RAM 3 has a memory cell array 31, a bank address control circuit 35 connected to the fourth bus BABUS, for generating a real address according to the contents of the bank specifying register BP (BP0, BP1), and a selection circuit 37 for selecting the real address generated by the bank address control circuit 35, or the address provided through the second bus ABUS.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
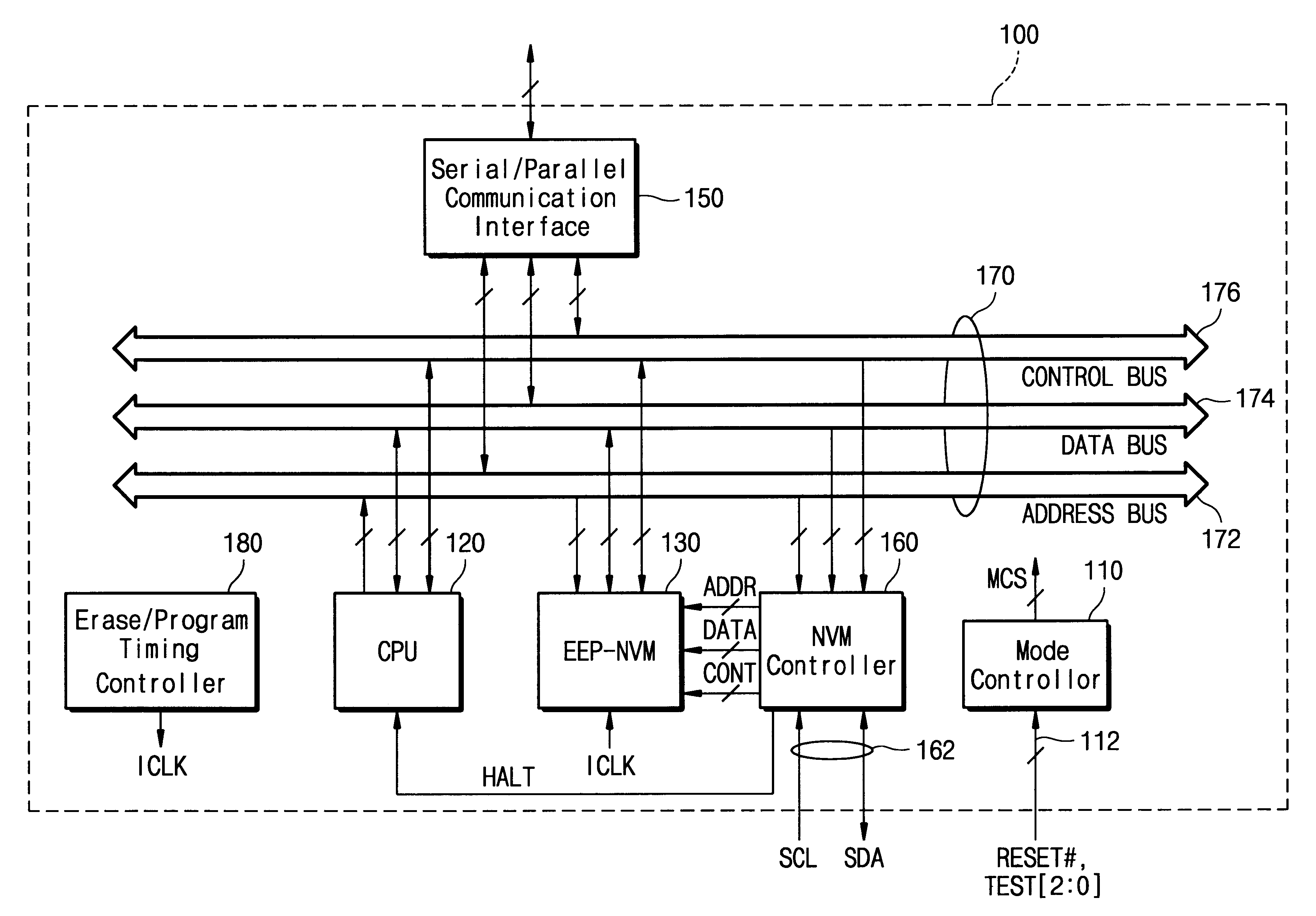
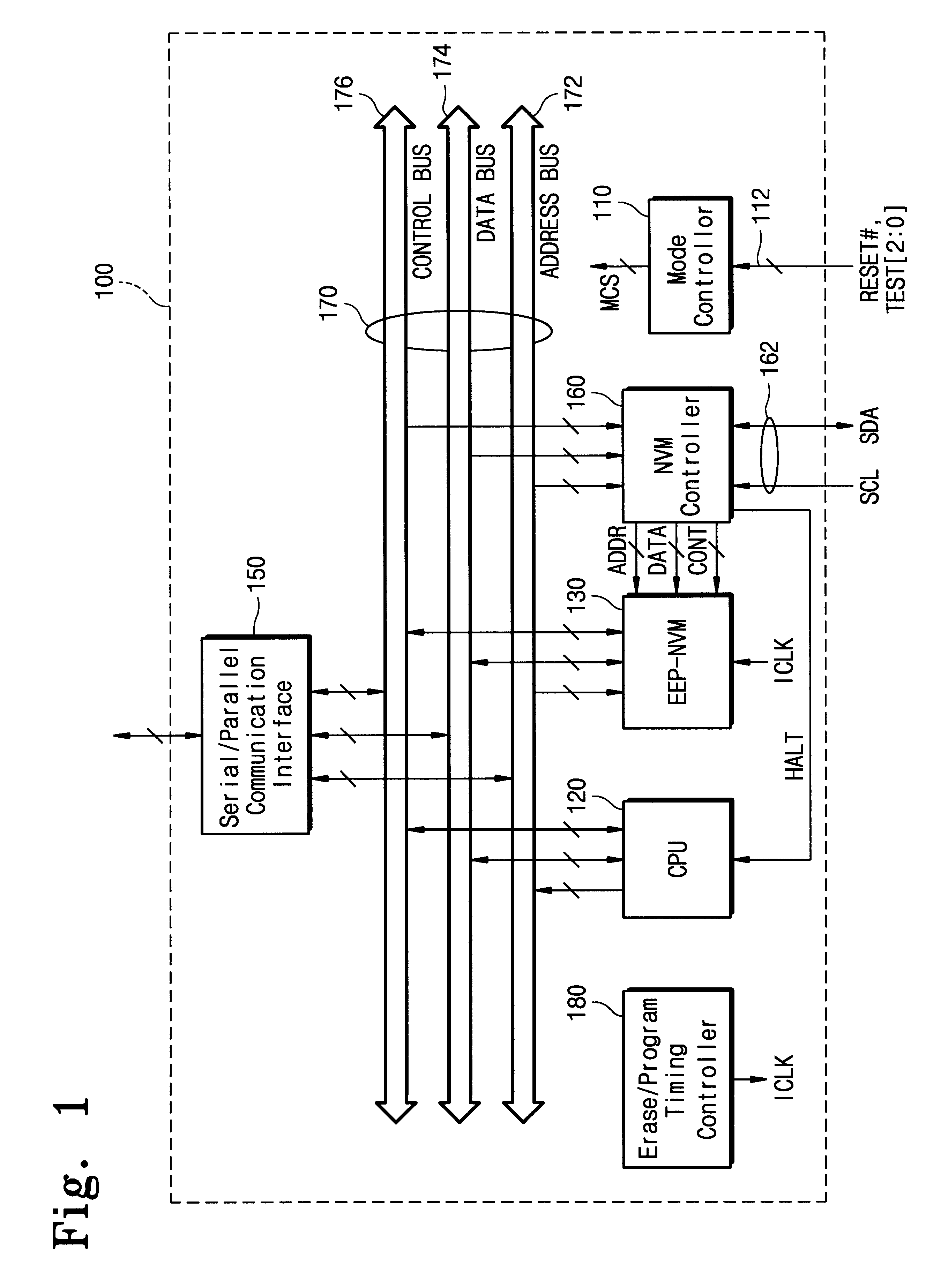
Single-chip data processing apparatus incorporating an electrically rewritable nonvolatile memory and method of operating the same
InactiveUS6839774B1Reduce chip sizeLow costEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementMicrocontrollerCommunication interface
A microcontroller includes an electrically erasable and programmable nonvolatile memory and a memory controller for controlling the nonvolatile memory. Upon writing a control program for the microcontroller and data into the nonvolatile memory pursuant to an externally provided NVM command or an internally issued program command, a CPU of the microcontroller does not intervene in controlling the nonvolatile memory. Particularly, in a programming mode set by the external program command, CPU, buses, and communication interfaces of the microcontroller are deactivated. Further, the memory controller receives a NVM command, an address and data from outside of the microcontroller for controlling an operation of the nonvolatile memory based on the NVM command and the address without intervention of the CPU.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
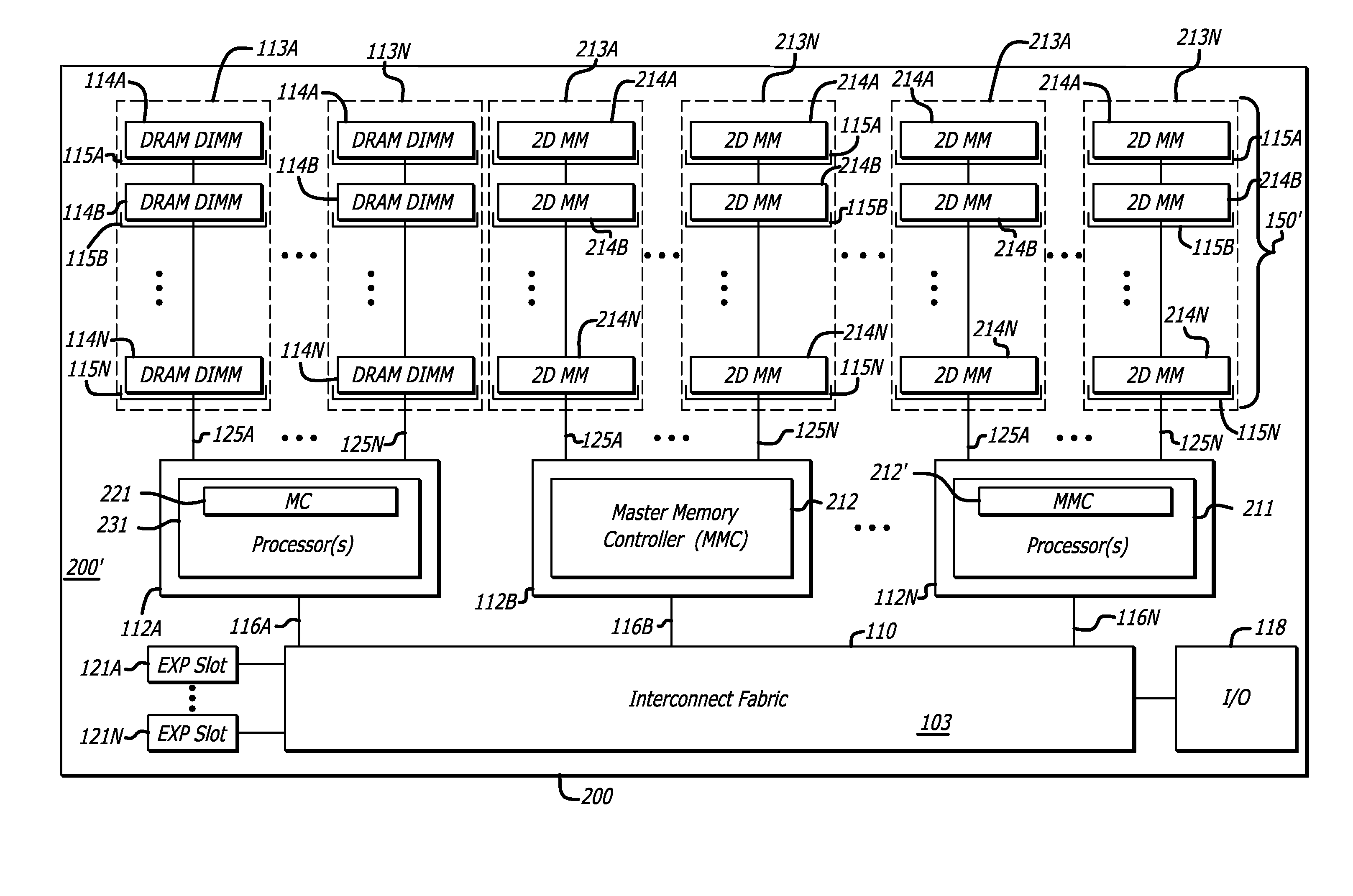
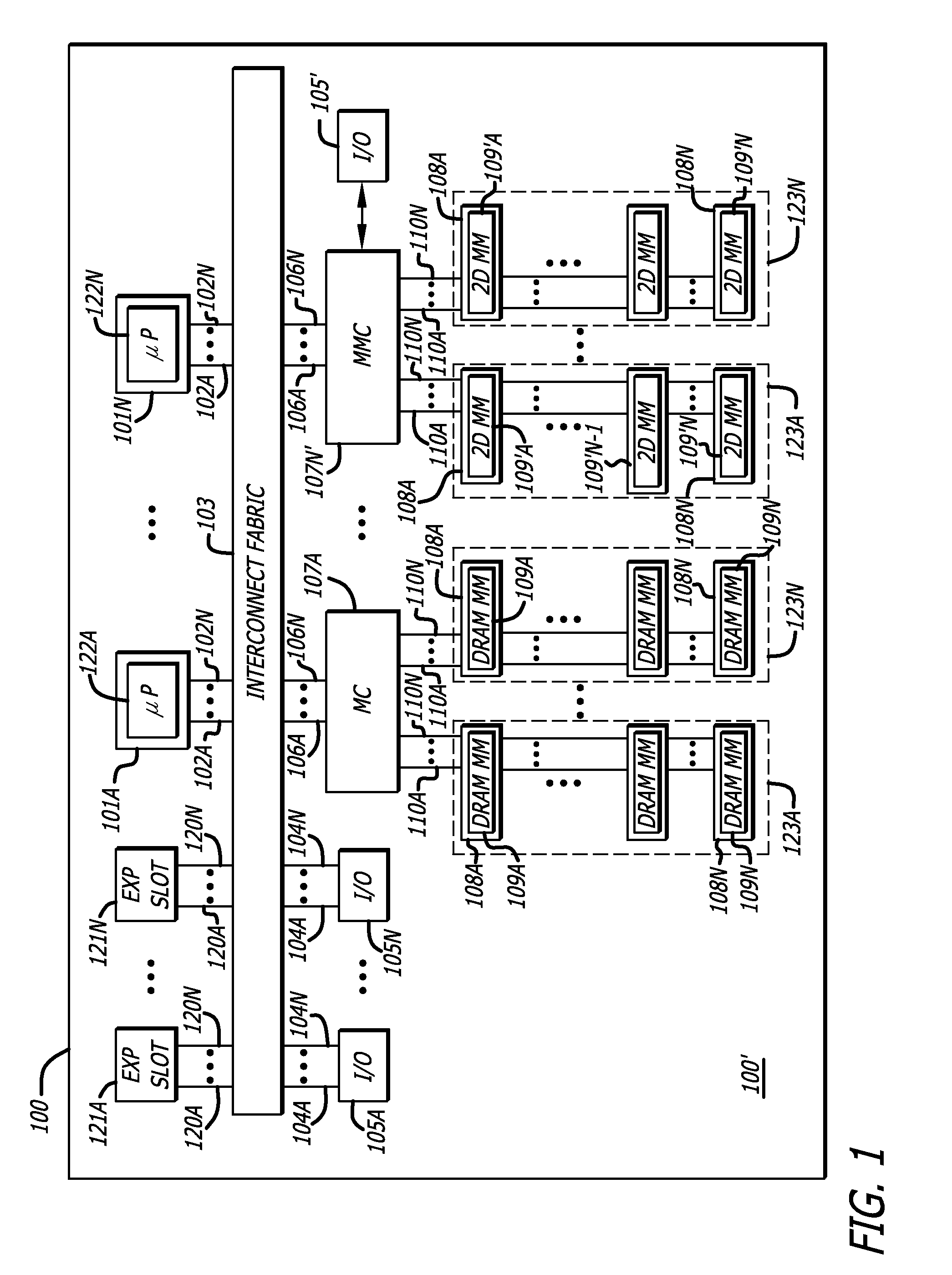
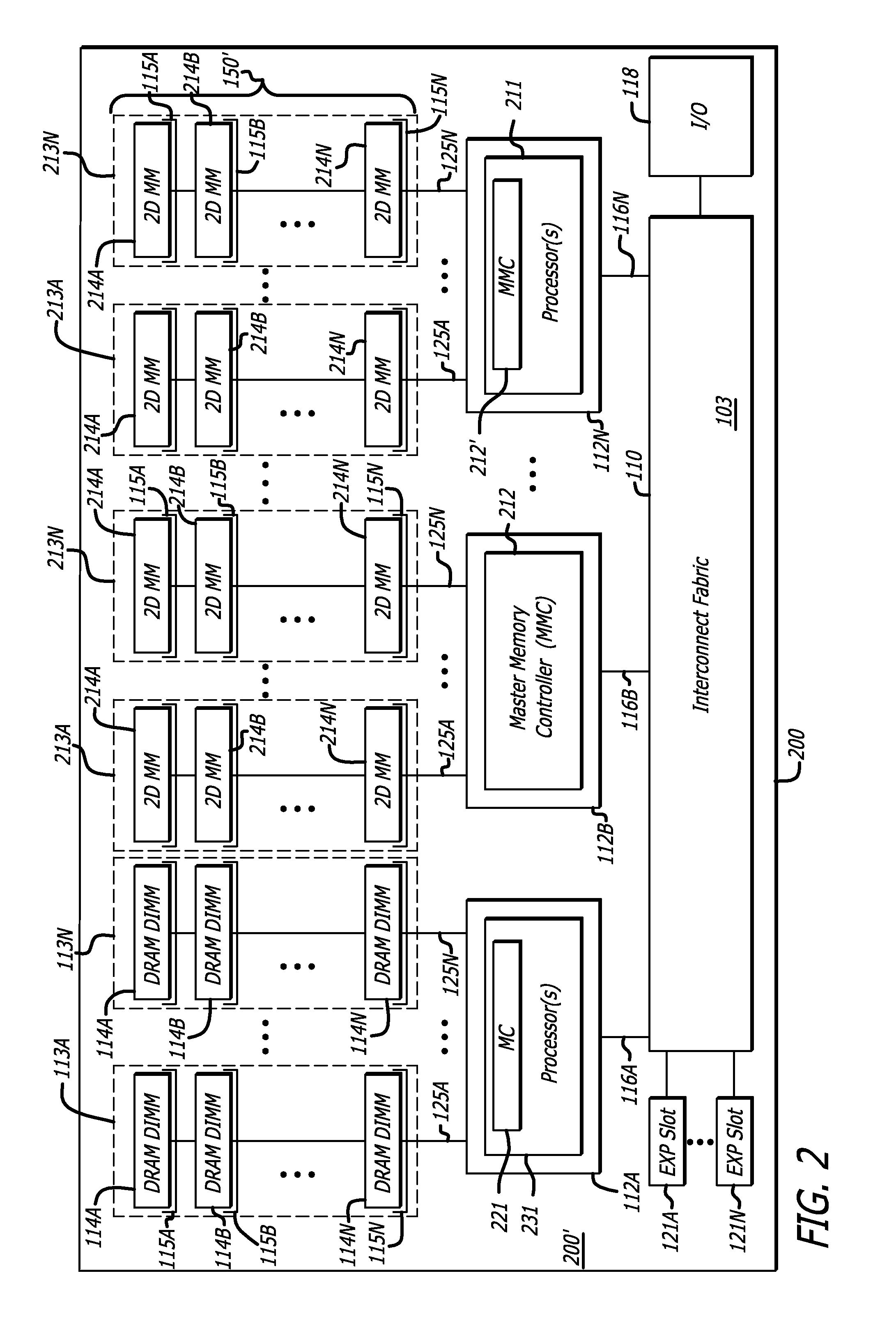
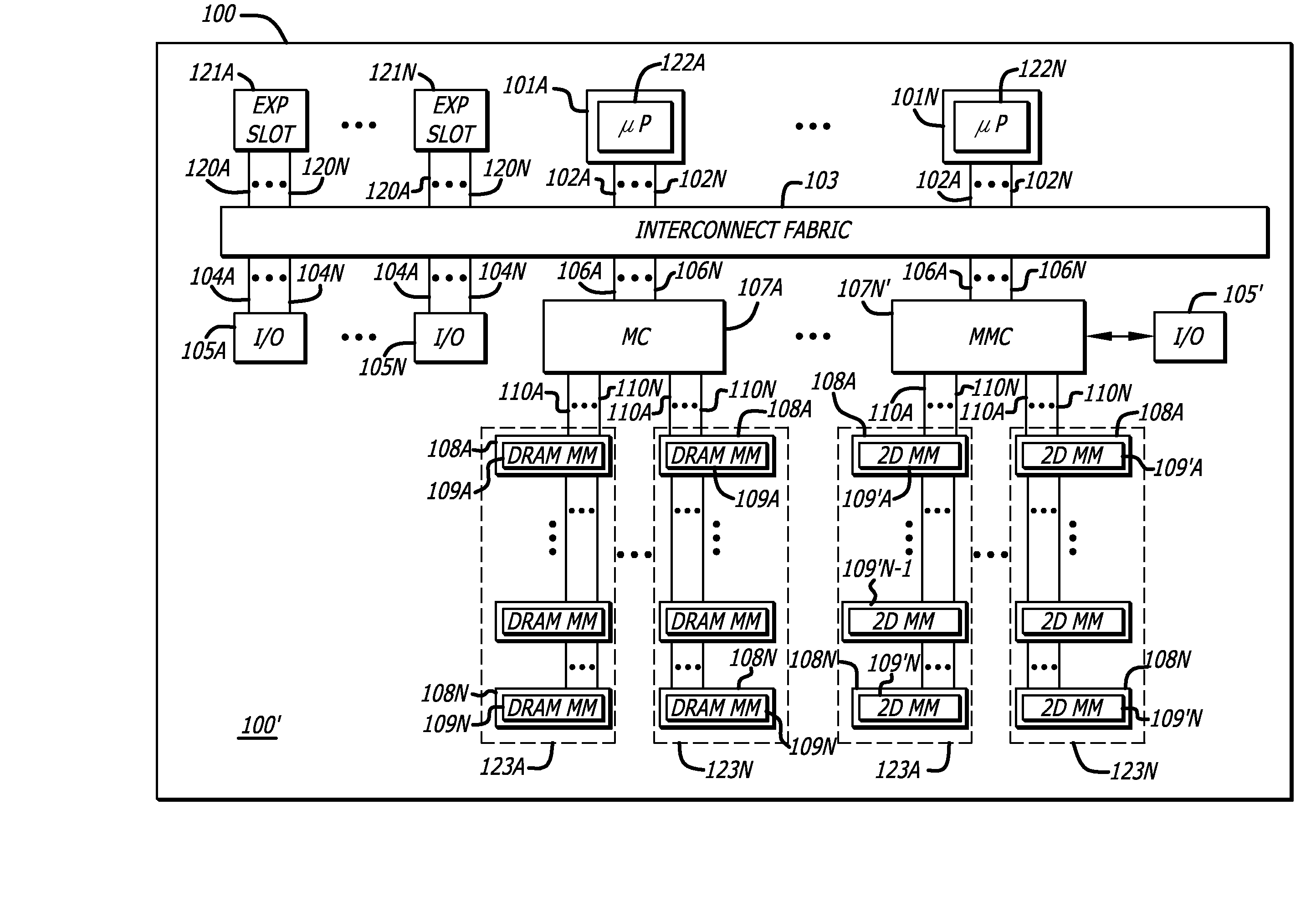
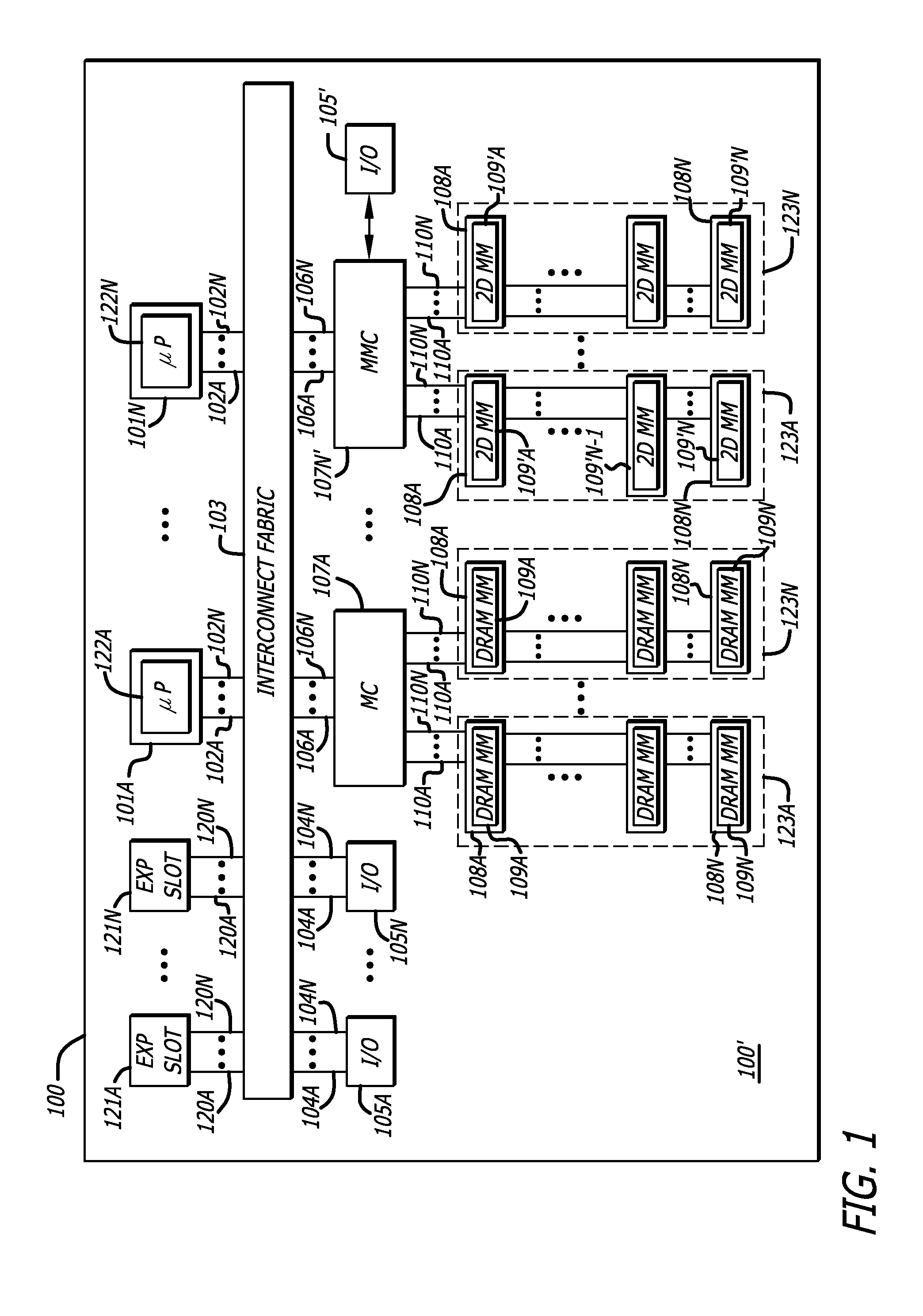
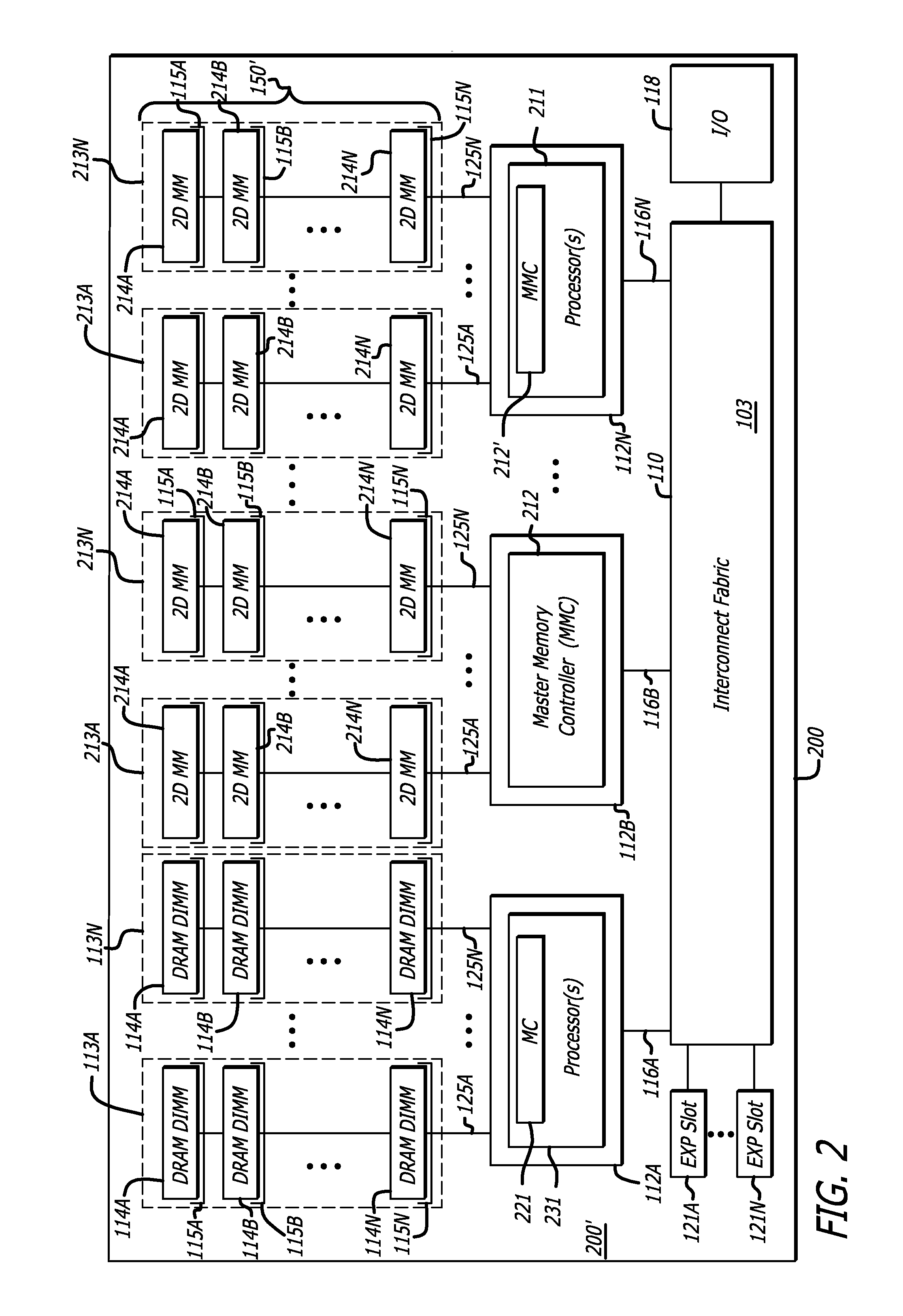
Methods and apparatus for two-dimensional main memory
ActiveUS20090254689A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTMemory controllerAddress control
In one embodiment of the invention, a memory module is disclosed including a printed circuit board with an edge connector; an address controller coupled to the printed circuit board; and a plurality of memory slices. Each of the plurality of memory slices of the memory module includes one or more memory integrated circuits coupled to the printed circuit board, and a slave memory controller coupled to the printed circuit board and the one or more memory integrated circuits. The slave memory controller receives memory access requests for the memory module from the address controller. The slave memory controller selectively activates one or more of the one or more memory integrated circuits in the respective memory slice in response to the address received from the address controller to read data from or write data into selected memory locations in the memory integrated circuits.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
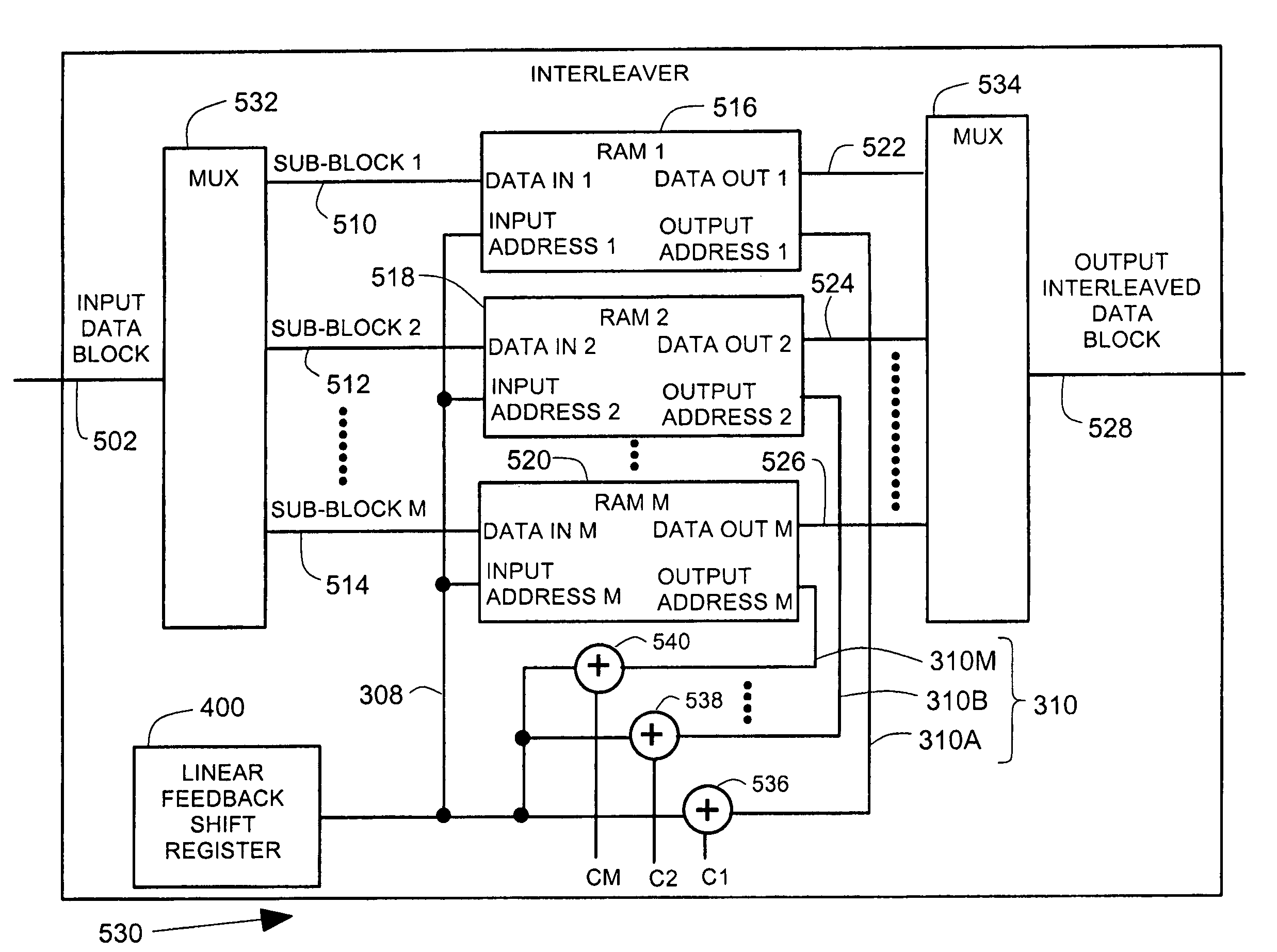
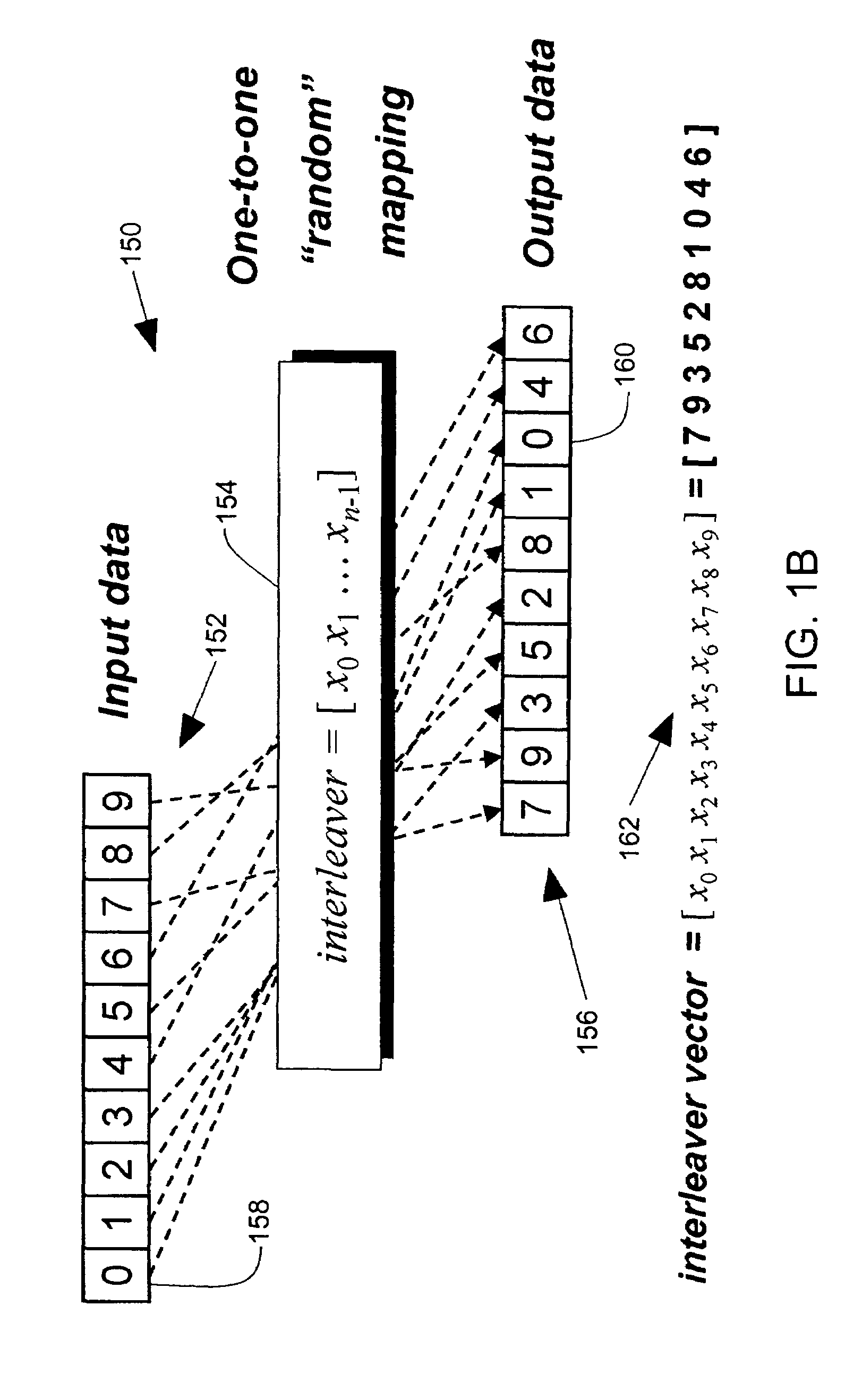
Low complexity pseudo-random interleaver
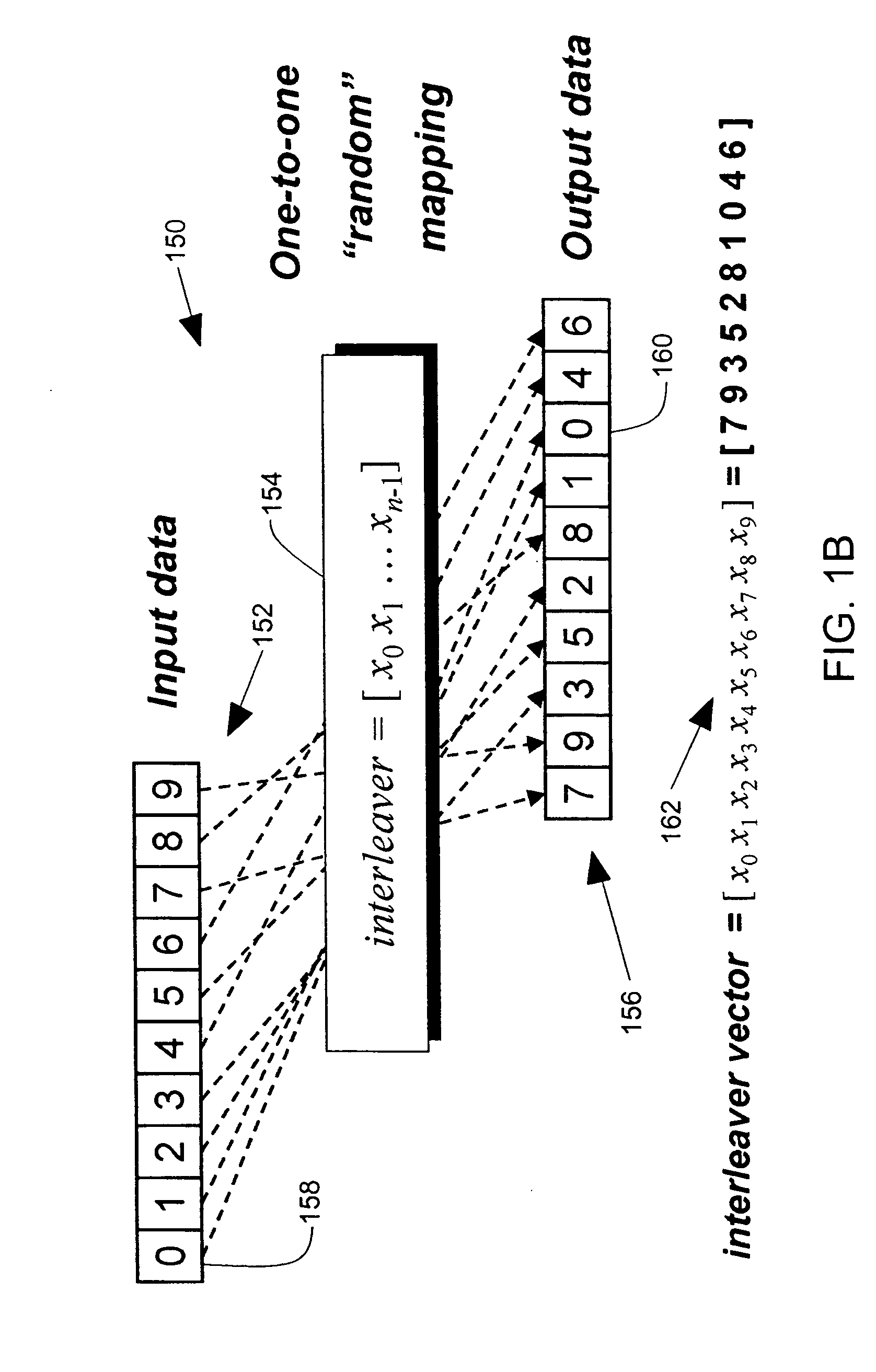
An interleaver has an input multiplexer that receives a data sequence at an interleaver input and that separates the data sequence into multiple data sub-blocks. The interleaver has a linear feedback shift register that generates an input address sequence. The interleaver has adder circuits that generate output address sequences associated with each data sub-block. The interleaver has memory that stores the data sub-blocks at addresses controlled by the input address sequence. The memory reproduces each data sub-block in an interleaved sequence controlled by the associated output address sequence. The interleaver has an output multiplexer that assembles the interleaved sequences to provide an interleaver output.
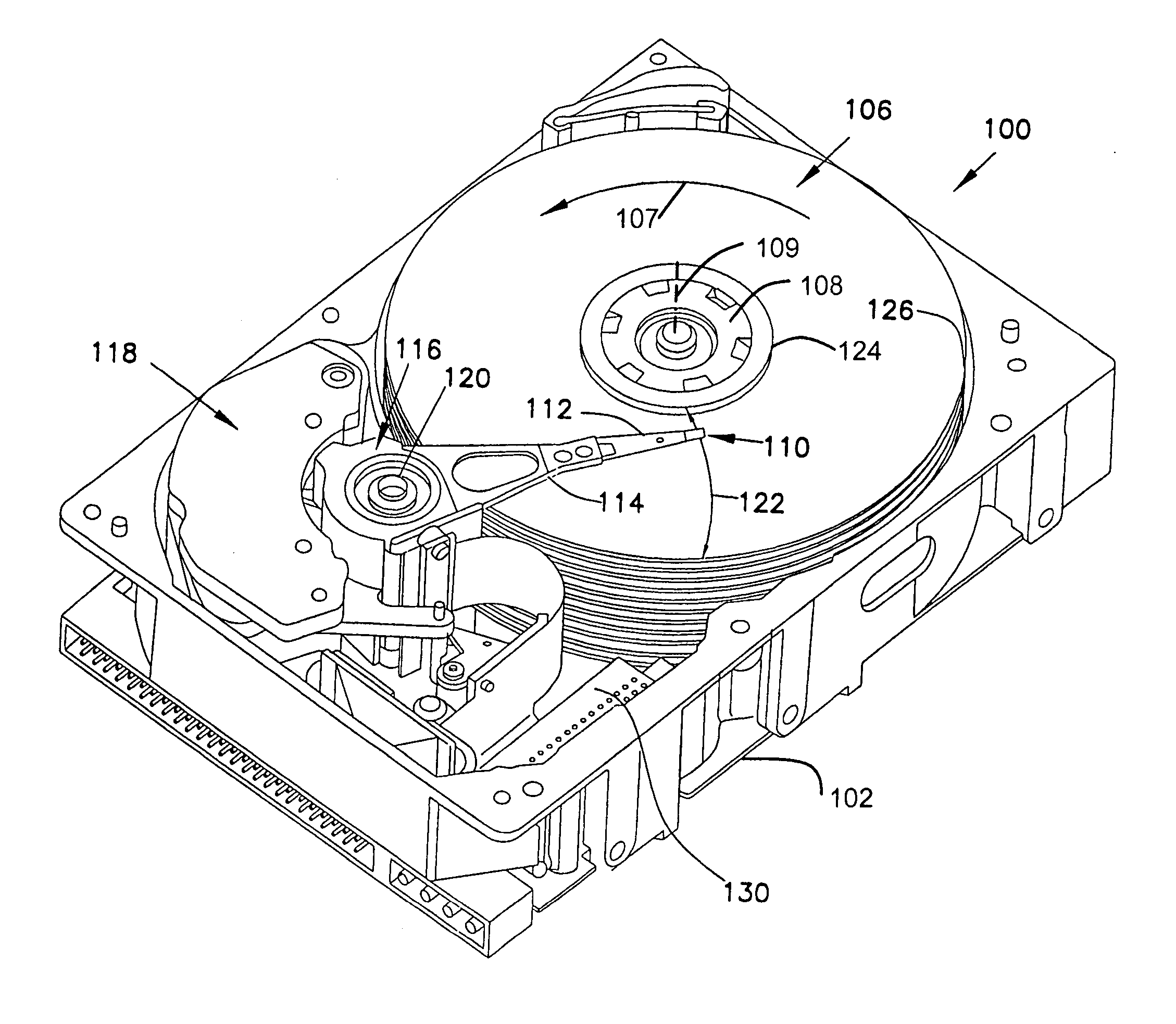
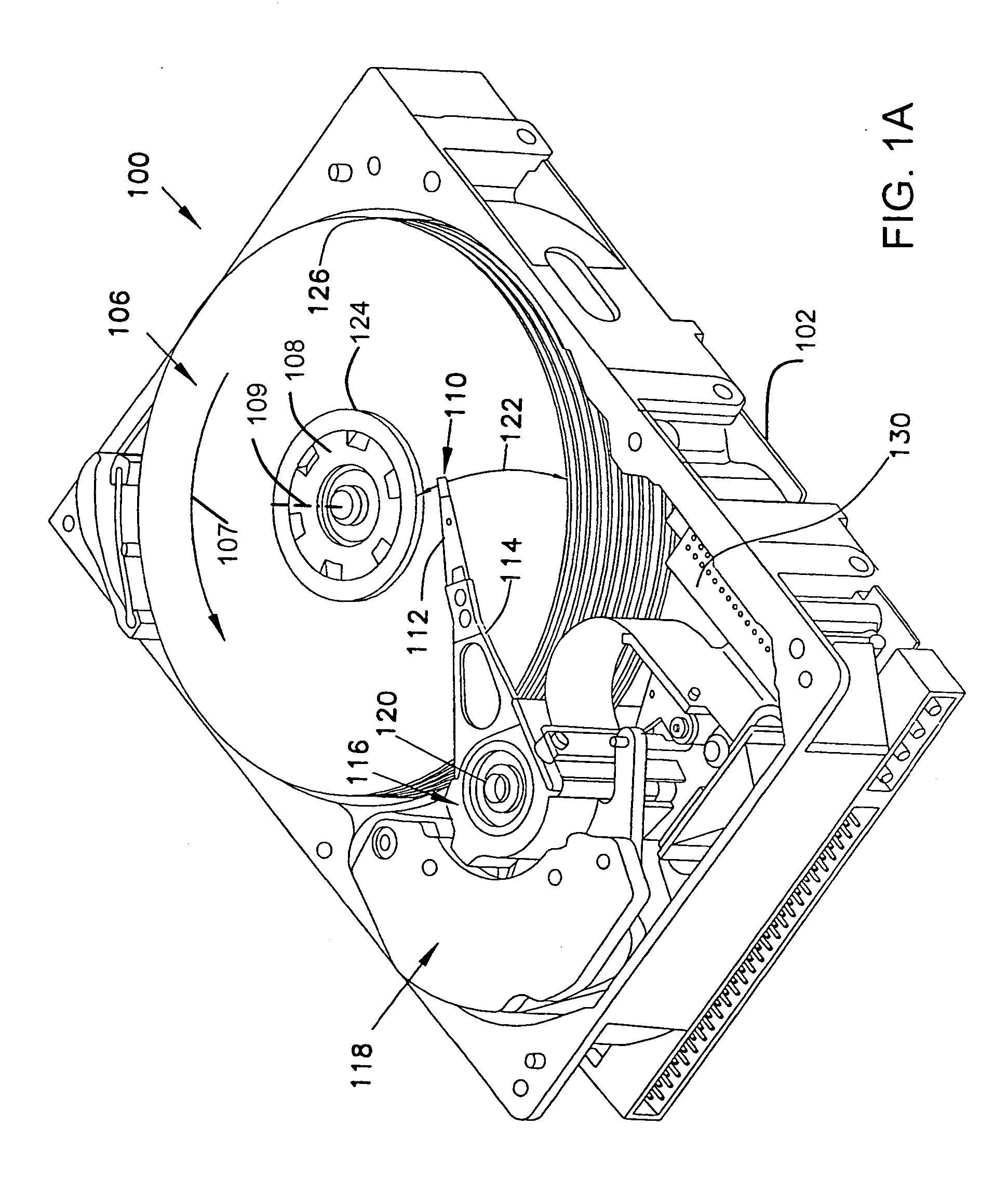
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
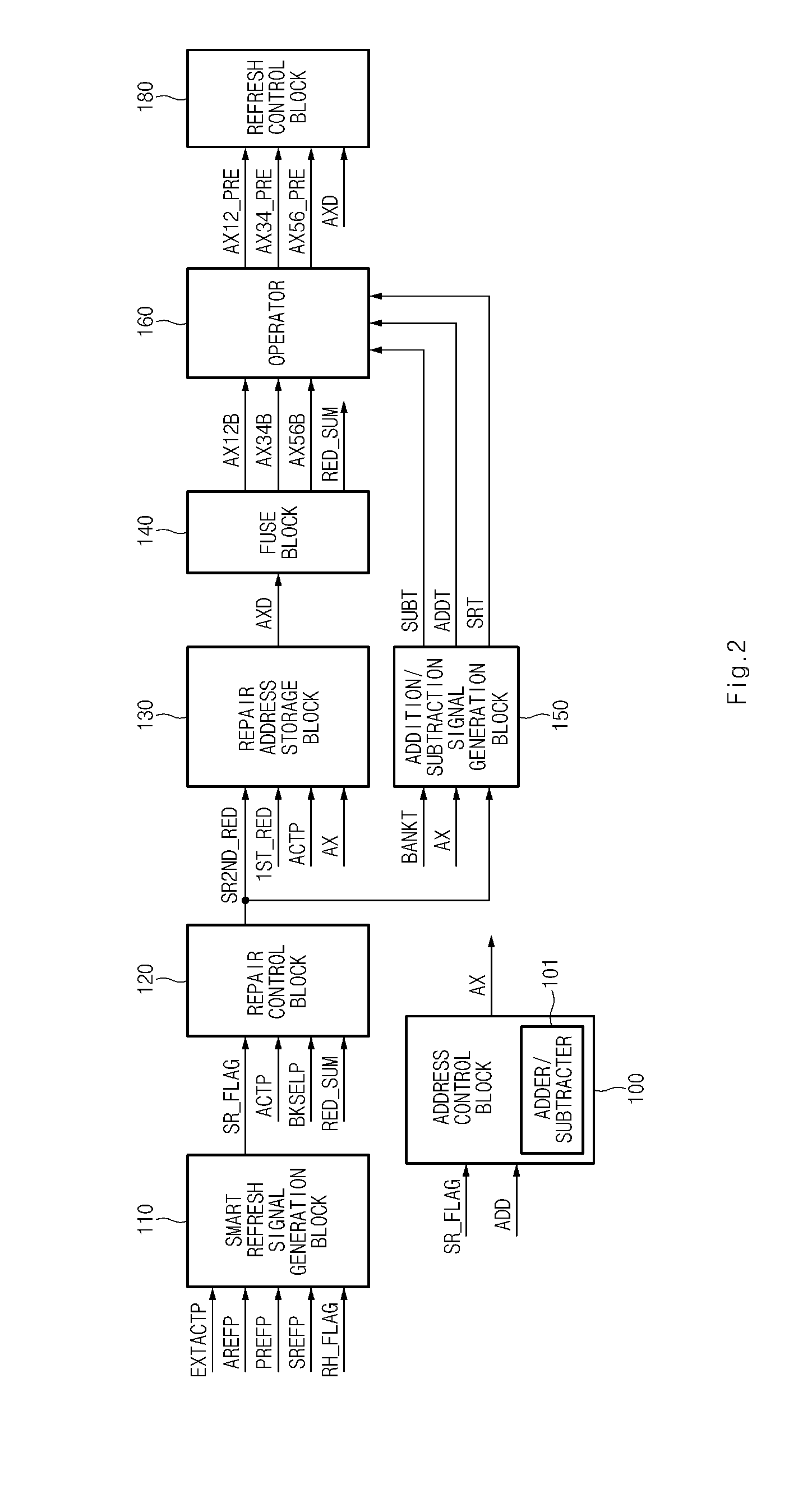
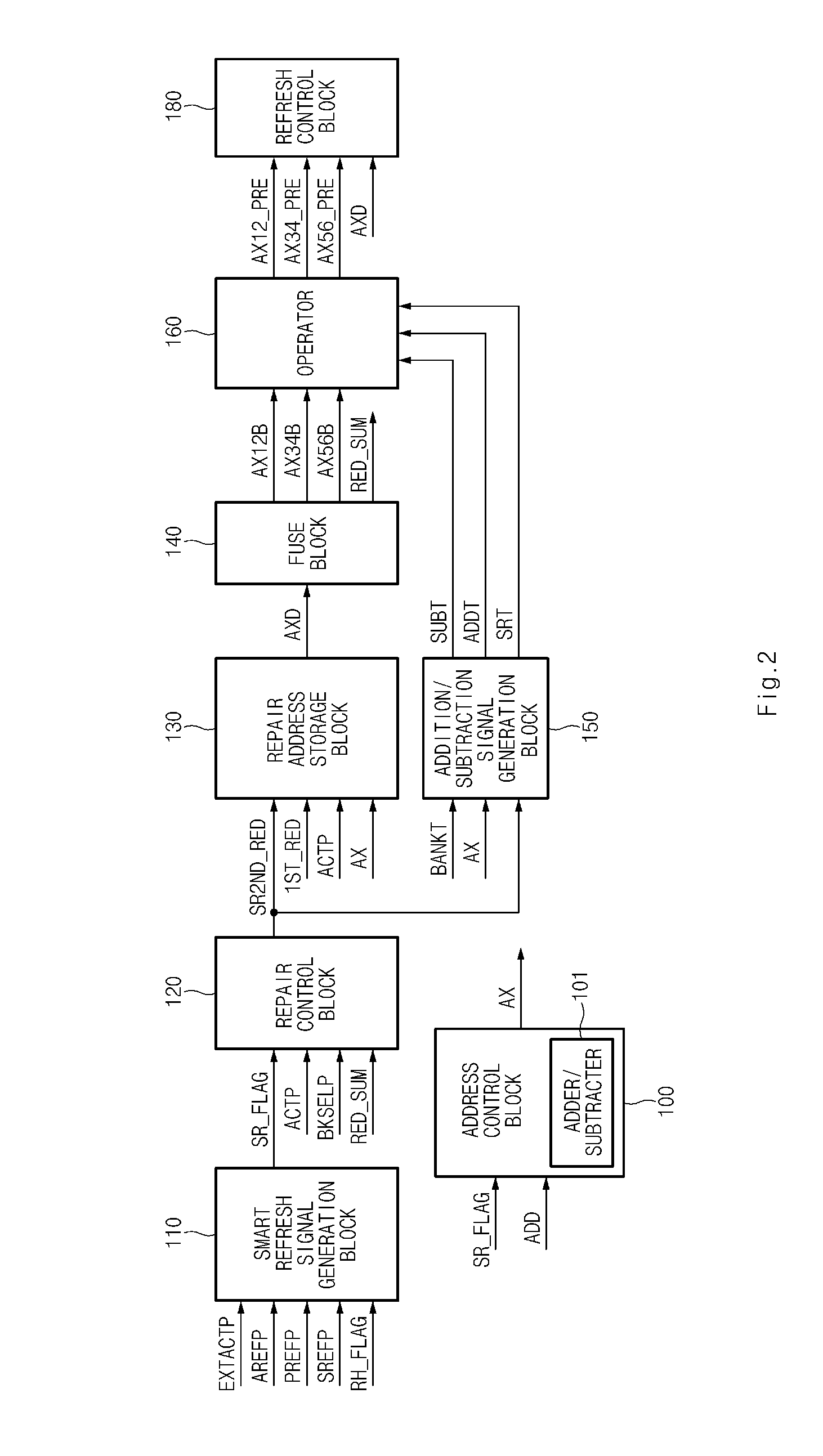
Smart refresh device
A smart refresh device includes an address control block configured to determine whether a specific row address is a row hammer address, and invert a first row hammer address and perform an addition / subtraction of an address; a repair control block configured to determine whether the row hammer address is a repaired address and output a stored repair address as a second repair control signal; a repair address storage block configured to store an output address of the address control block and output a stored address as a latch address; a fuse block configured to output a repair signal representing information on a repair address to the repair control block, and output a decoding signal according to the latch address; and an operator configured to add and subtract the decoding signal according to an addition signal and a subtraction signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
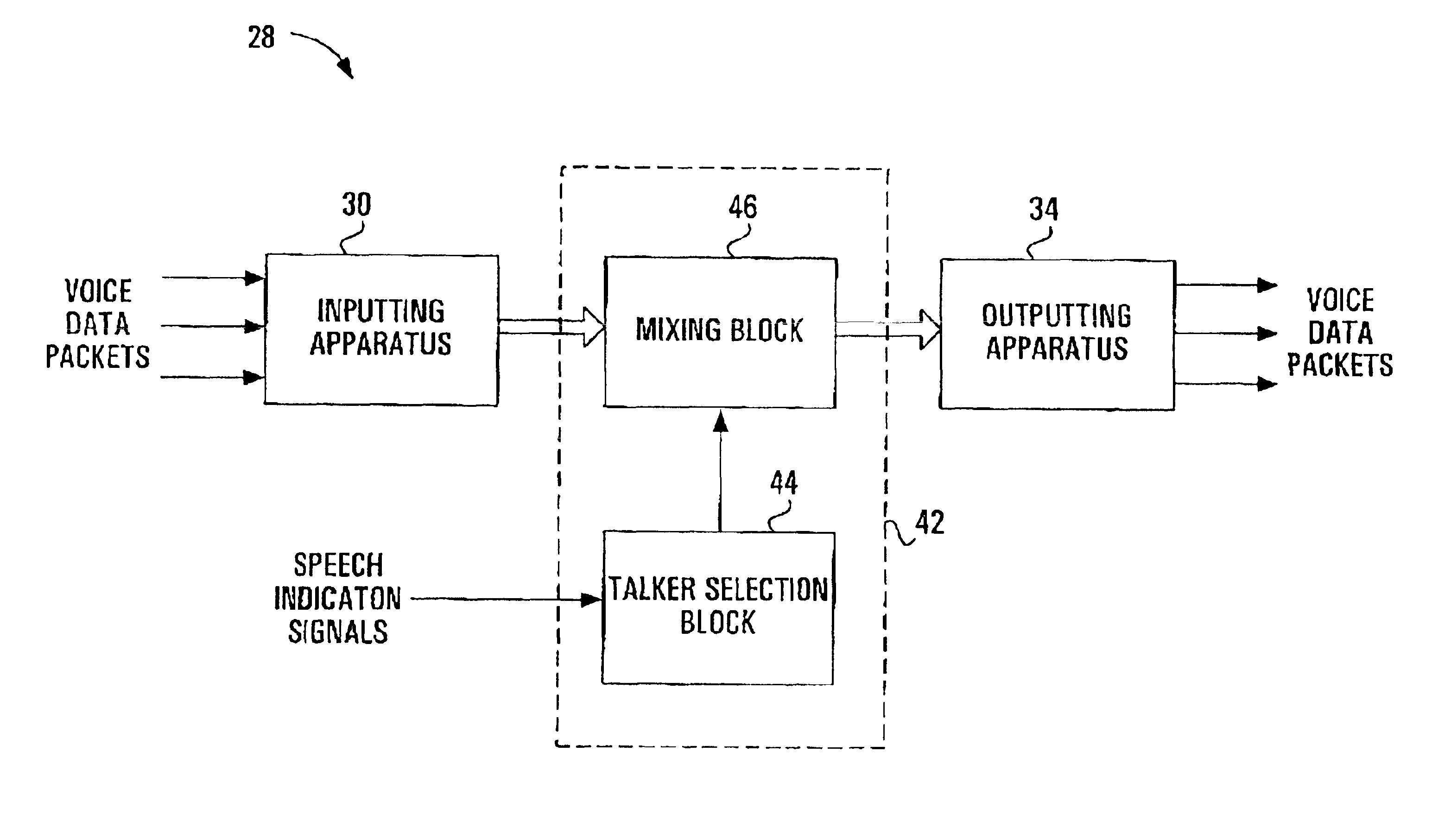
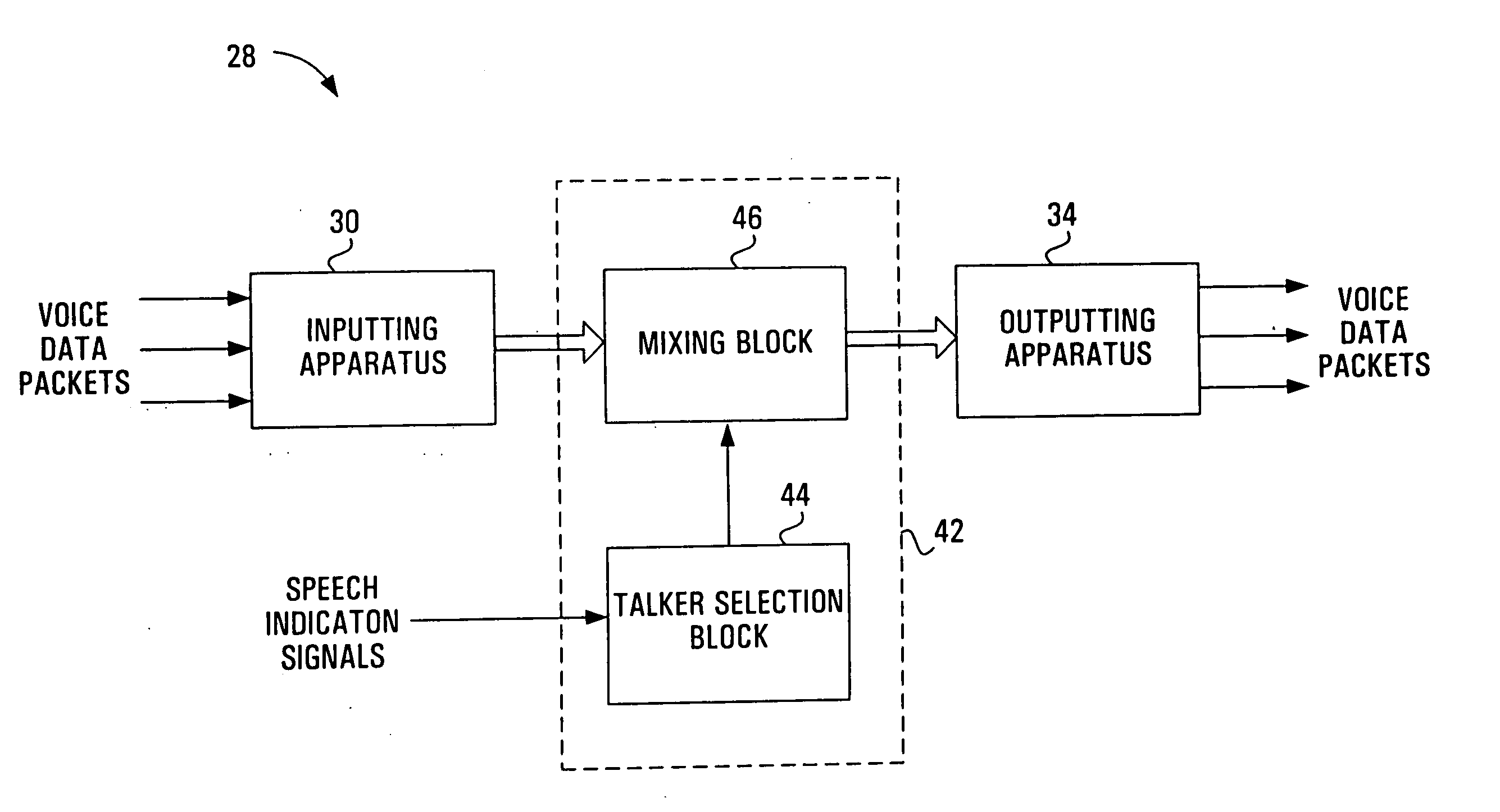
Apparatus and method for packet-based media communications
InactiveUS6956828B2Reduce the amount requiredLower latencyMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationControl signalTranscoding
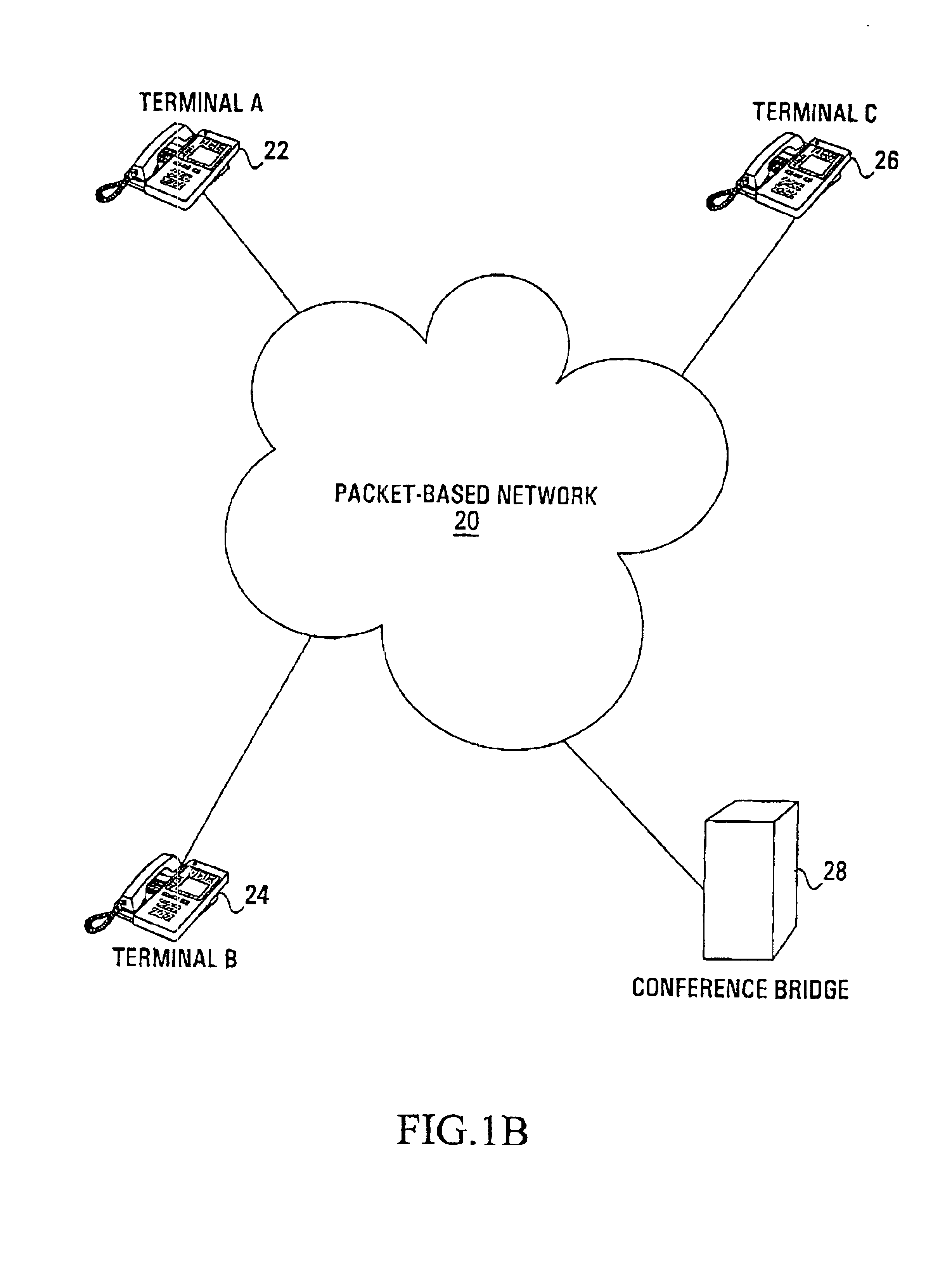
The performance of a voice conference using a packet-based conference bridge can be improved with a number of modifications. In one modification, the conference bridge receives speech indication signals from the individual packet-based terminals within the voice conference, these speech indication signals then being used by the conference bridge to select the talkers within the voice conference. This removes the need for speech detection techniques within the conference bridge, hence decreasing the required processing power and the latency within the conference bridge. In another modification, the conference bridge sends addressing control signals to the individual packet-based terminals selected as talkers, these addressing control signals directing the terminals selected as talkers to directly transmit their voice data packets to the other terminals within the voice conference. This direct transmission of voice data packets can reduce transcoding and latency within the network. These two modifications could further be combined, resulting in a conference bridge that receives speech indication signals, selects the talkers for the voice conference and outputs addressing control signal to the talkers. In this case, the advantages of the two modifications are gained as well as additional capacity advantages resulting from no voice signals actually traversing the conference bridge.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
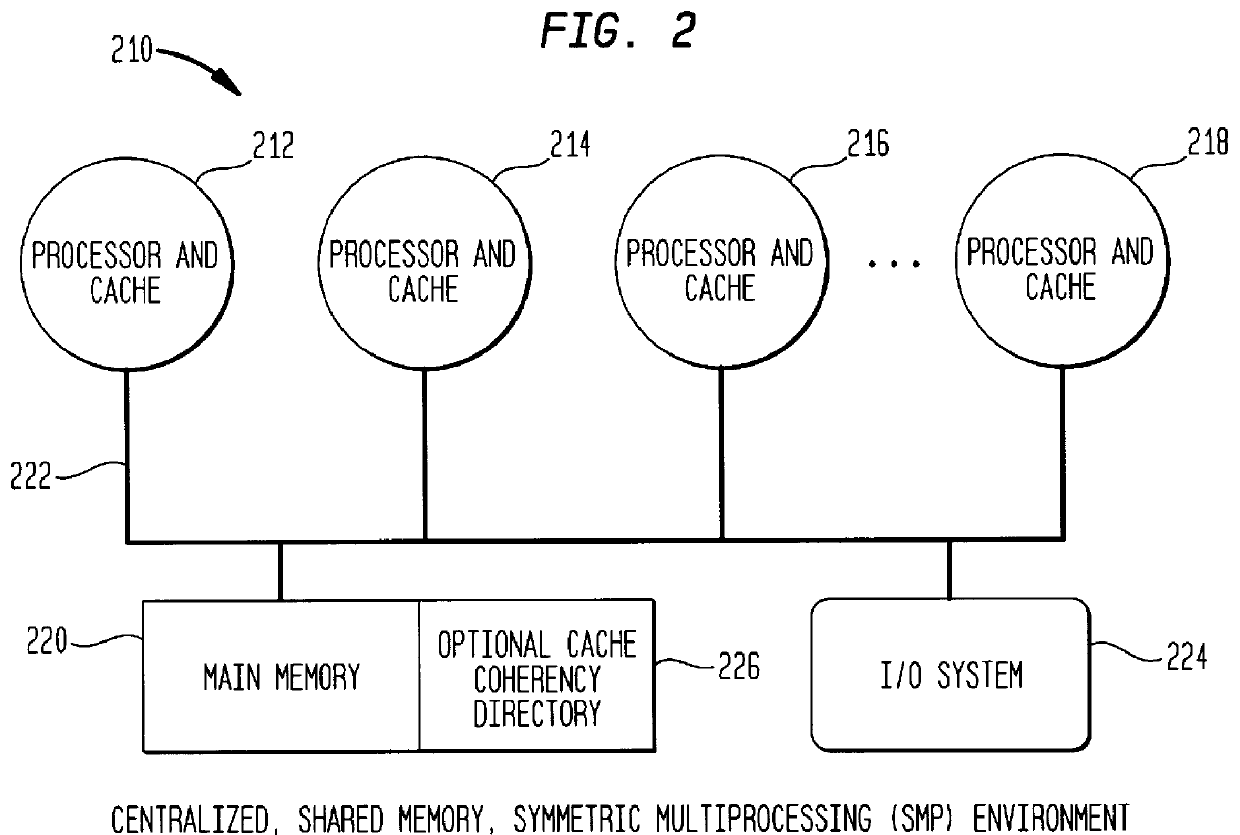
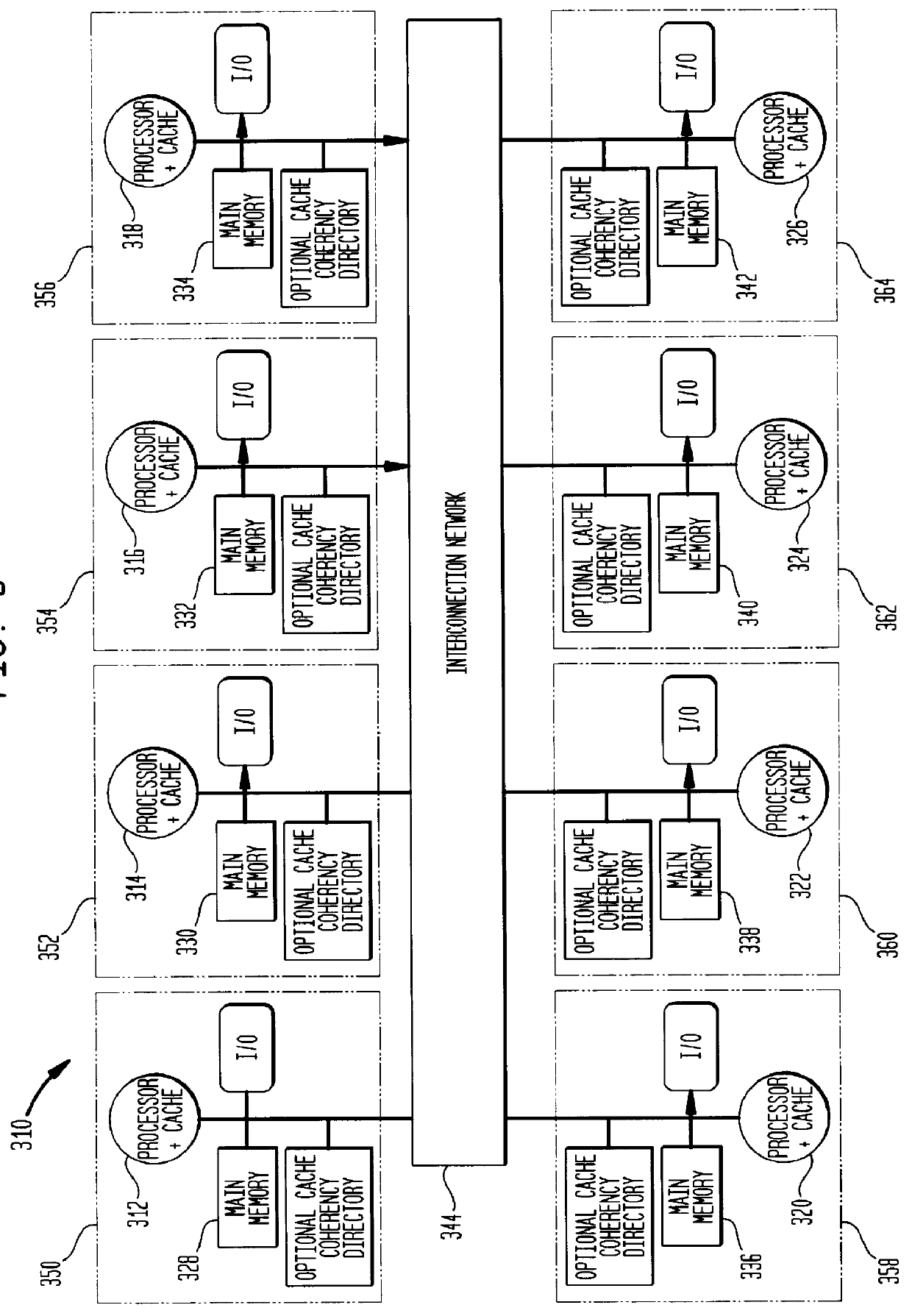
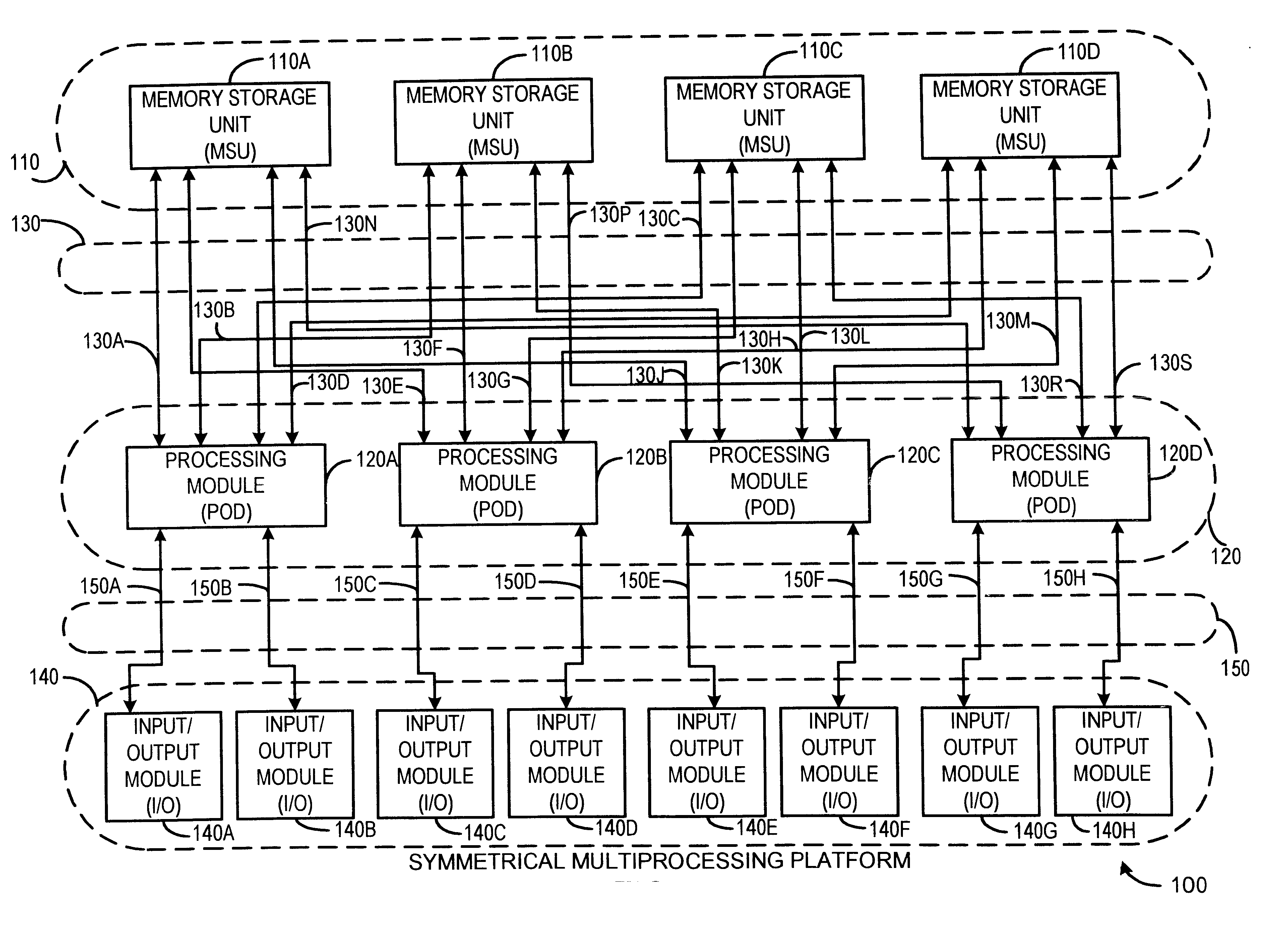
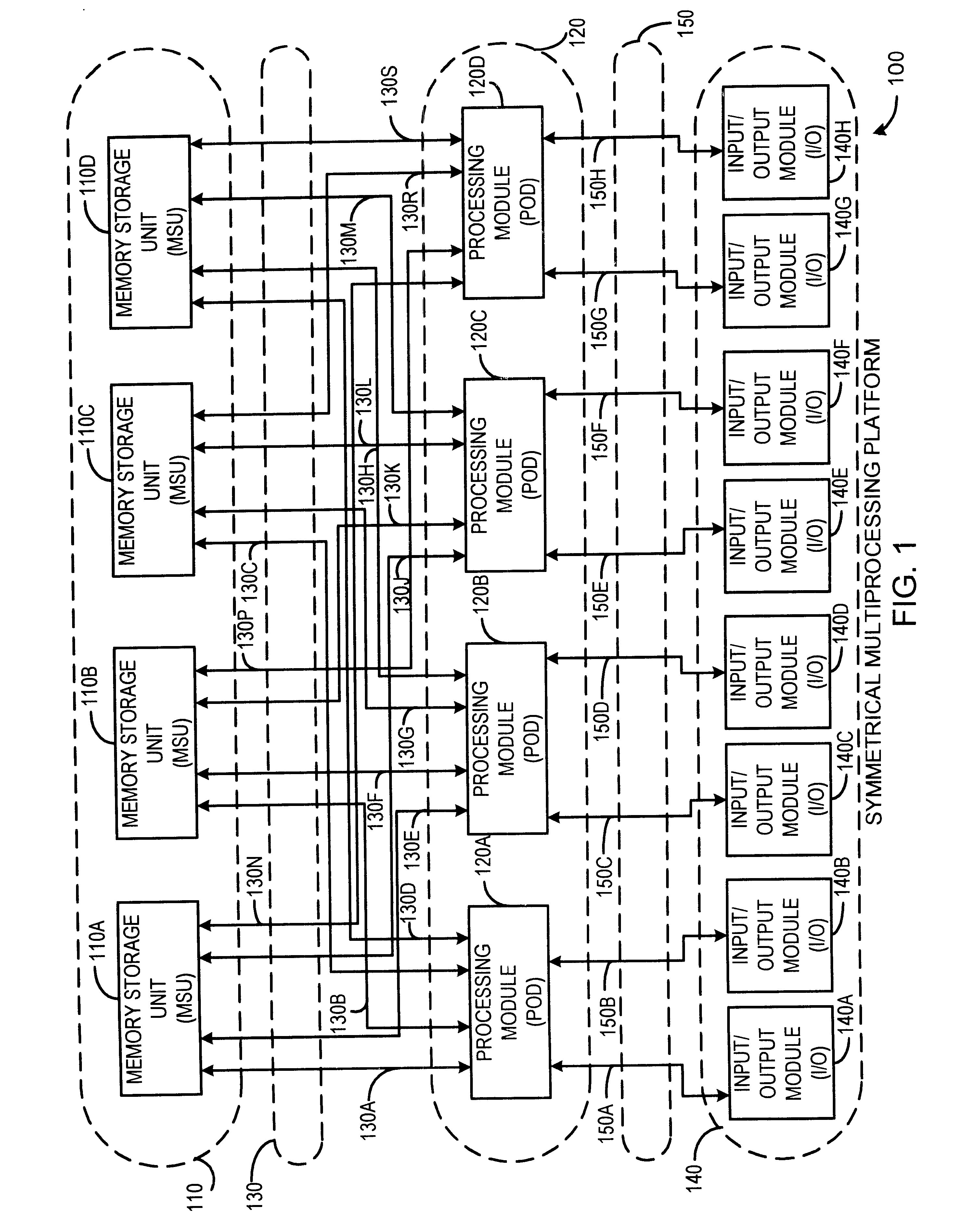
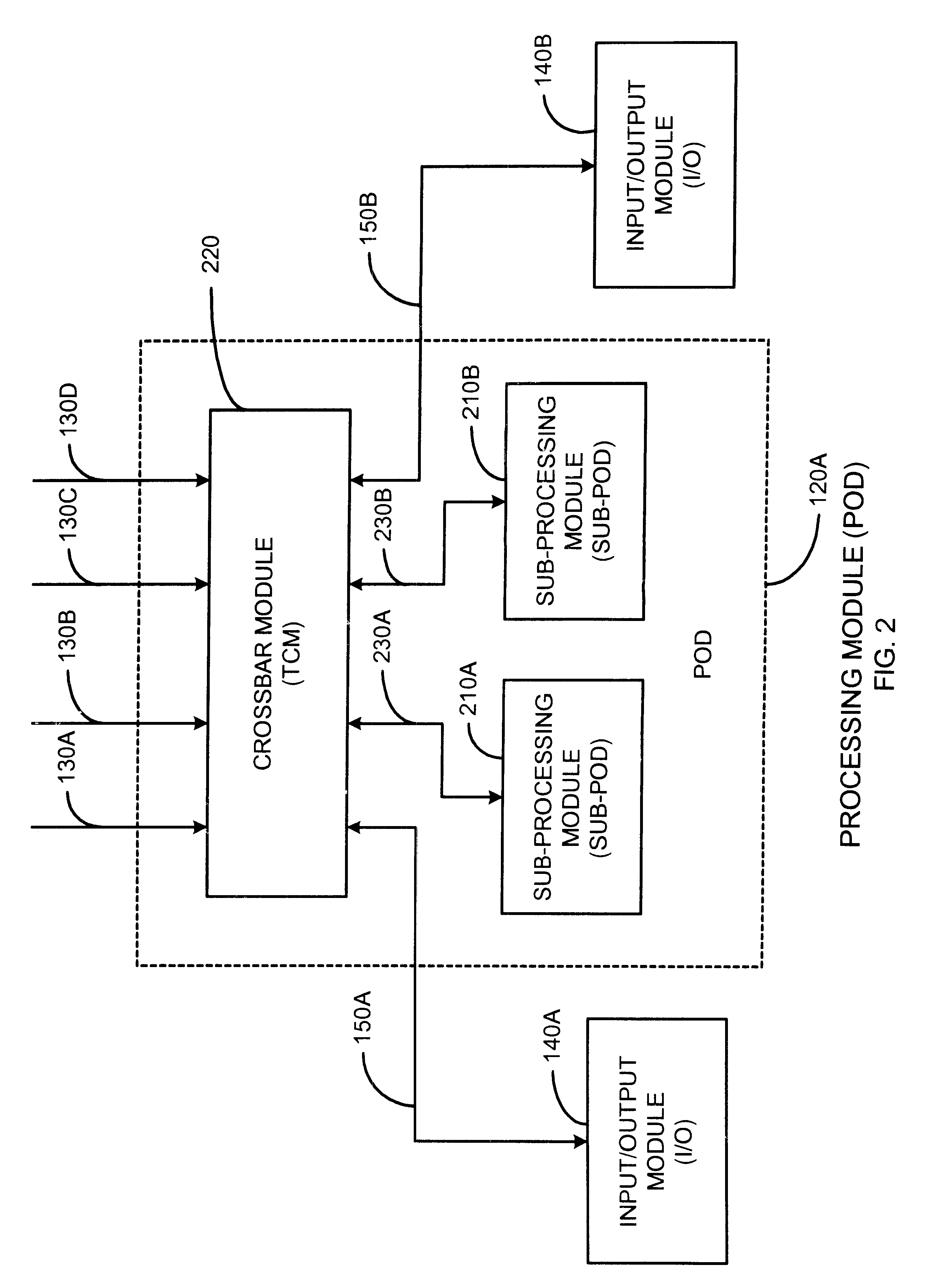
High-speed memory storage unit for a multiprocessor system having integrated directory and data storage subsystems
InactiveUS6415364B1Easy to manageImprove system throughputMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInput/output processes for data processingHigh speed memoryImpact system
A high-speed memory system is disclosed for use in supporting a directory-based cache coherency protocol. The memory system includes at least one data system for storing data, and a corresponding directory system for storing the corresponding cache coherency information. Each data storage operation involves a block transfer operation performed to multiple sequential addresses within the data system. Each data storage operation occurs in conjunction with an associated read-modify-write operation performed on cache coherency information stored within the corresponding directory system. Multiple ones of the data storage operations may be occurring within one or more of the data systems in parallel. Likewise, multiple ones of the read-modify-write operations may be performed to one or more of the directory systems in parallel. The transfer of address, control, and data signals for these concurrently performed operations occurs in an interleaved manner. The use of block transfer operations in combination with the interleaved transfer of signals to memory systems prevents the overhead associated with the read-modify-write operations from substantially impacting system performance. This is true even when data and directory systems are implemented using the same memory technology.
Owner:UNISYS CORP
Memory modules for two-dimensional main memory
In one embodiment of the invention, a memory module is disclosed including a printed circuit board with an edge connector; an address controller coupled to the printed circuit board; and a plurality of memory slices. Each of the plurality of memory slices of the memory module includes one or more memory integrated circuits coupled to the printed circuit board, and a slave memory controller coupled to the printed circuit board and the one or more memory integrated circuits. The slave memory controller receives memory access requests for the memory module from the address controller. The slave memory controller selectively activates one or more of the one or more memory integrated circuits in the respective memory slice in response to the address received from the address controller to read data from or write data into selected memory locations in the memory integrated circuits.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
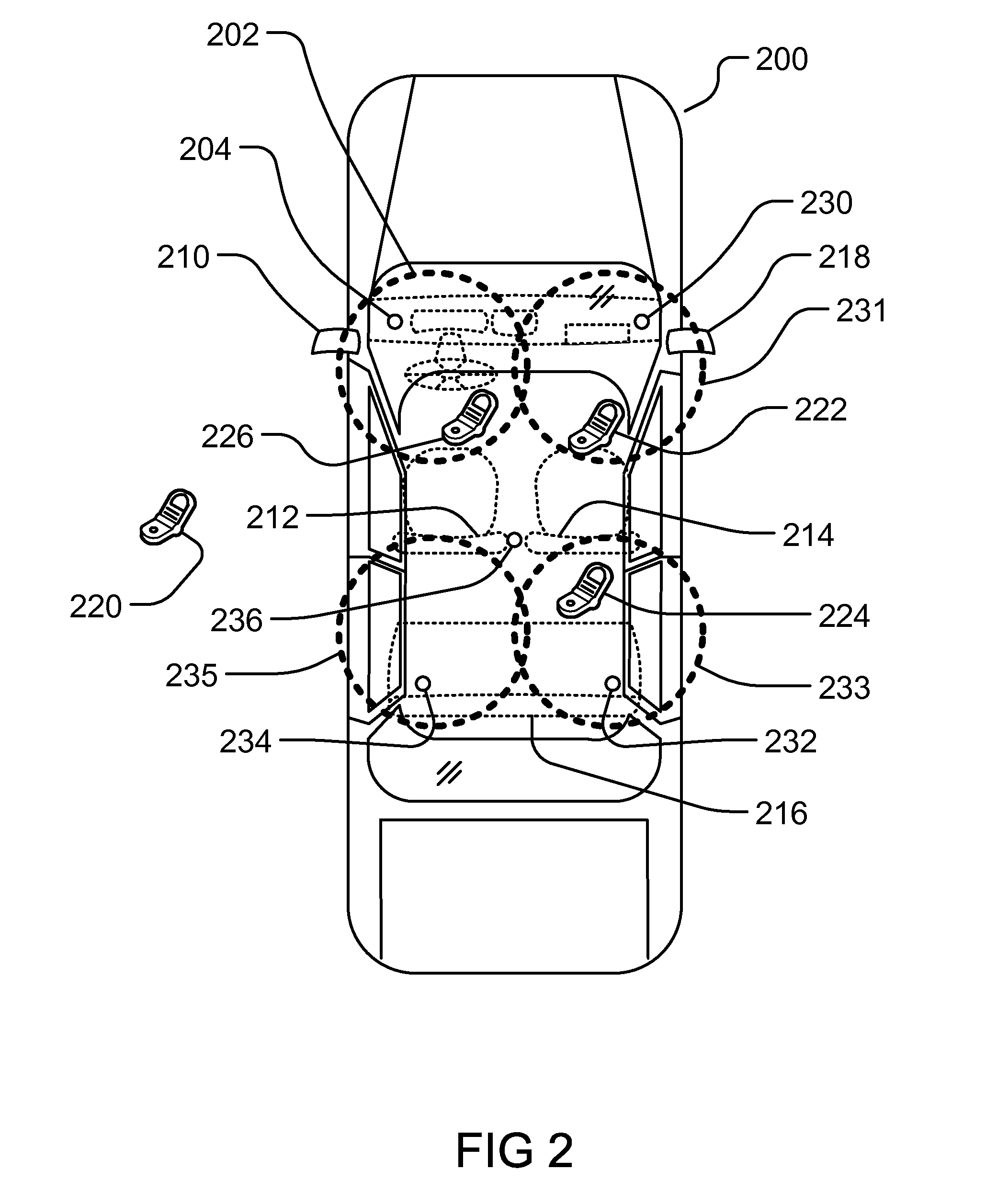
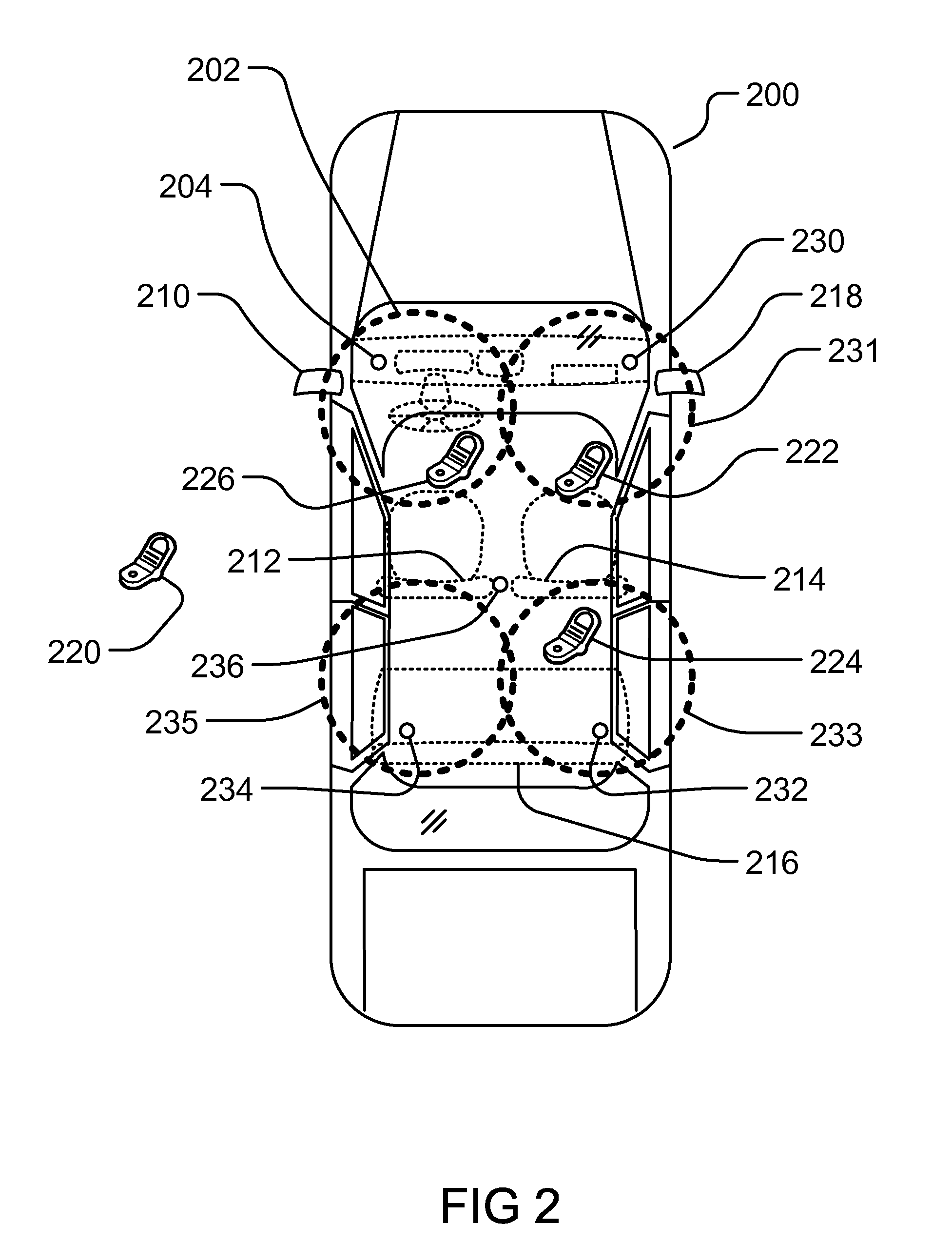
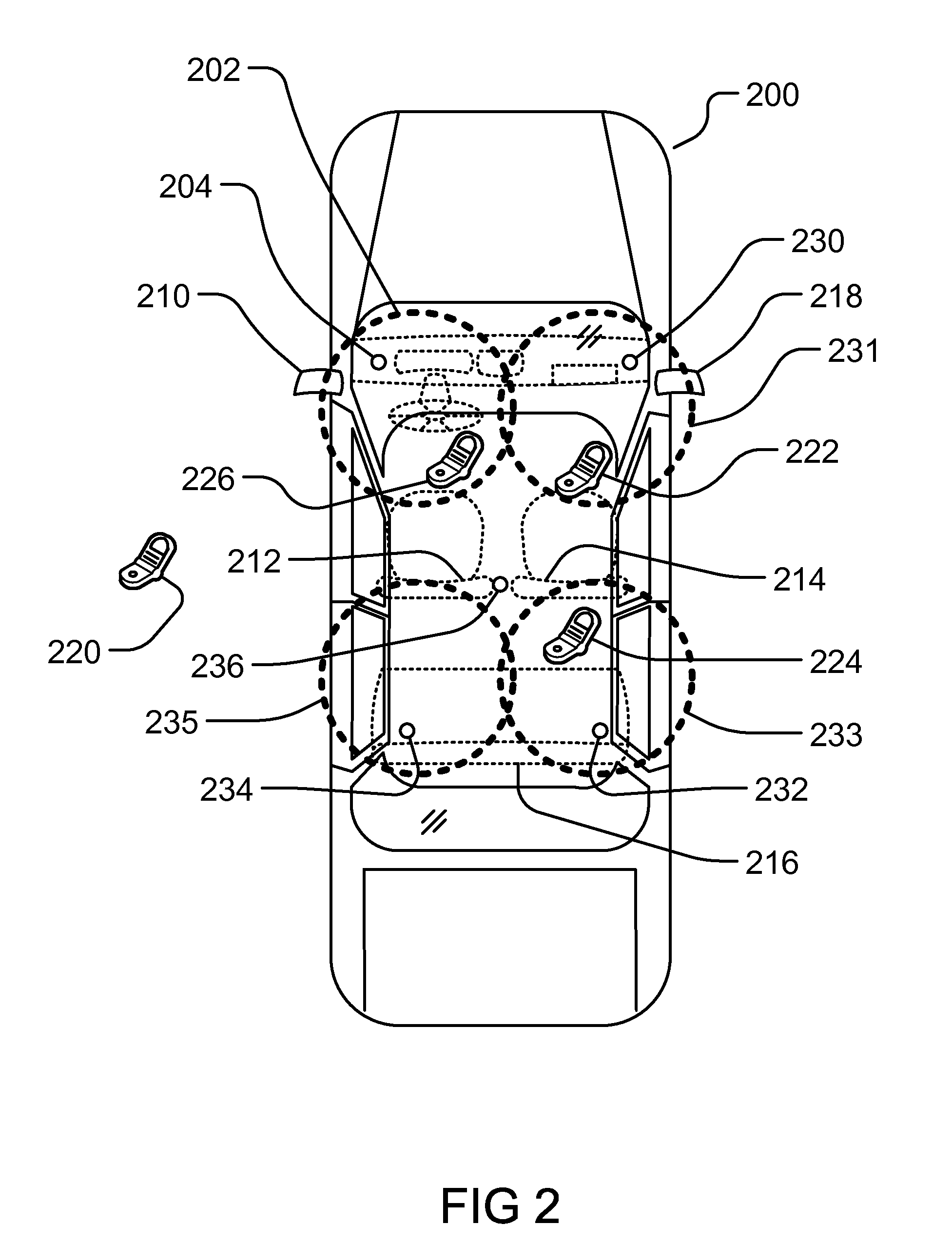
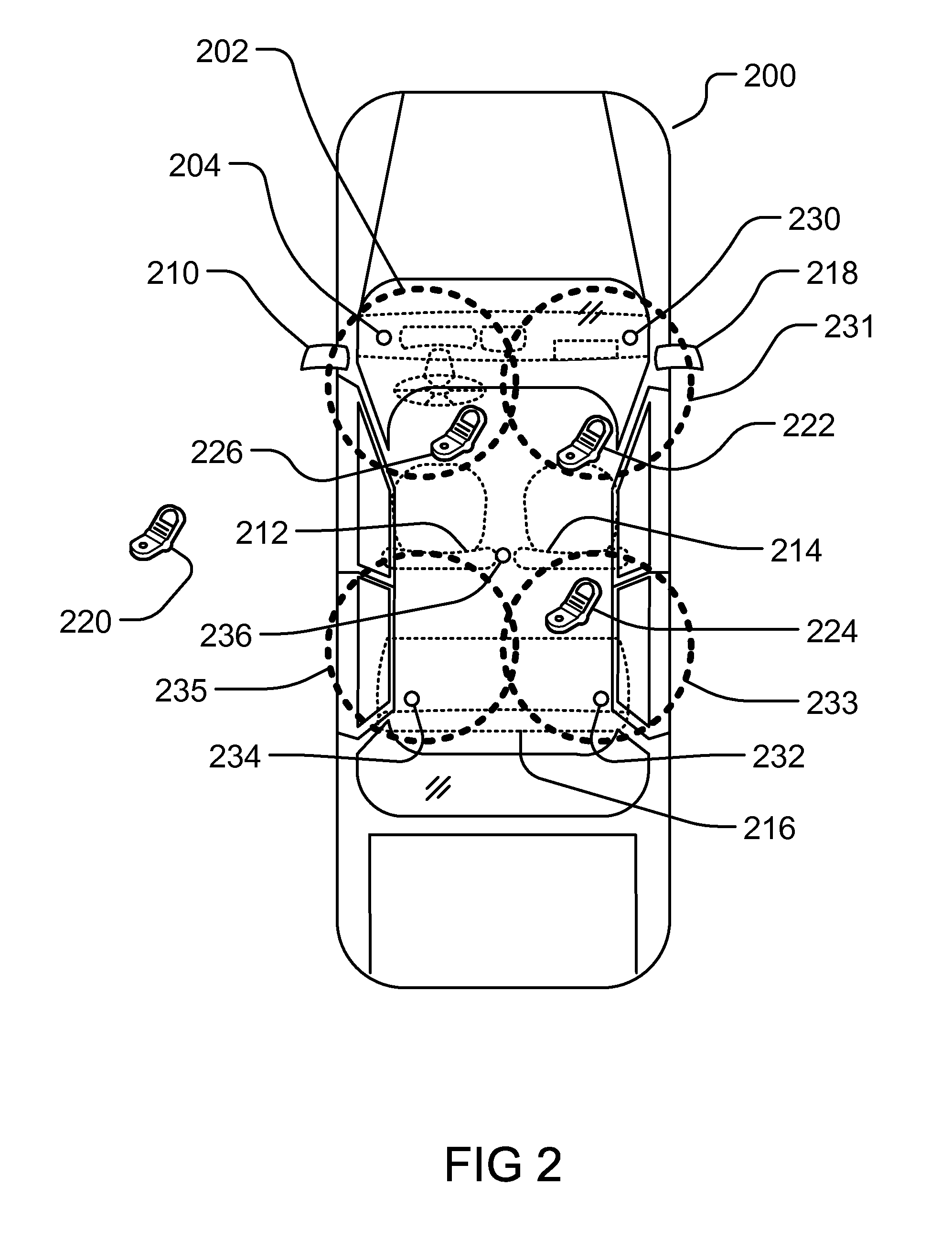
Method and System for Dynamic Configuration for Mobile Communication Device Functions
ActiveUS20120214470A1Limited abilityAutomatically disabling the texting ability of mobile deviceService provisioningReceivers monitoringDistractionAddress control
This provides for controlling mobile device functions and features. For example, it limits or disables the use of some of mobile device features which could cause distraction to the user, when the user is engaged in another activity. In an example, it enables other mobile device features based on occurrence of events related to the user or environment. Another example addresses controlling the mobile device features, such as SMS, while the user is in a vehicle or driving. Another example restricts the ability of the driver of a vehicle to text, while the vehicle is in motion, by automatically disabling the texting ability of mobile device within and around the perimeter of the driver's seat. Other variations, examples, improvements, detection mechanisms, models, techniques, calculations, verification mechanisms, and features are also described in details.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
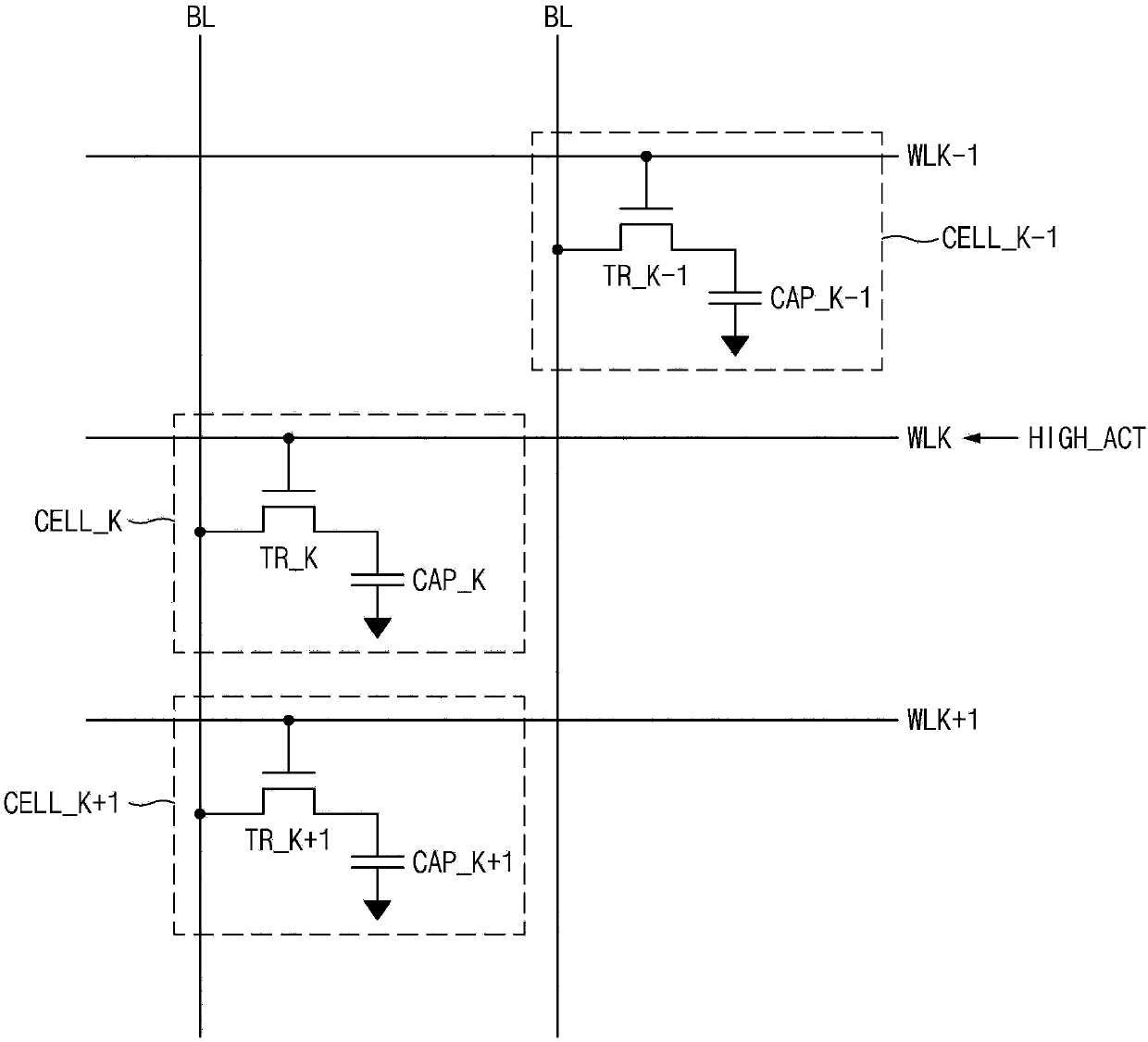
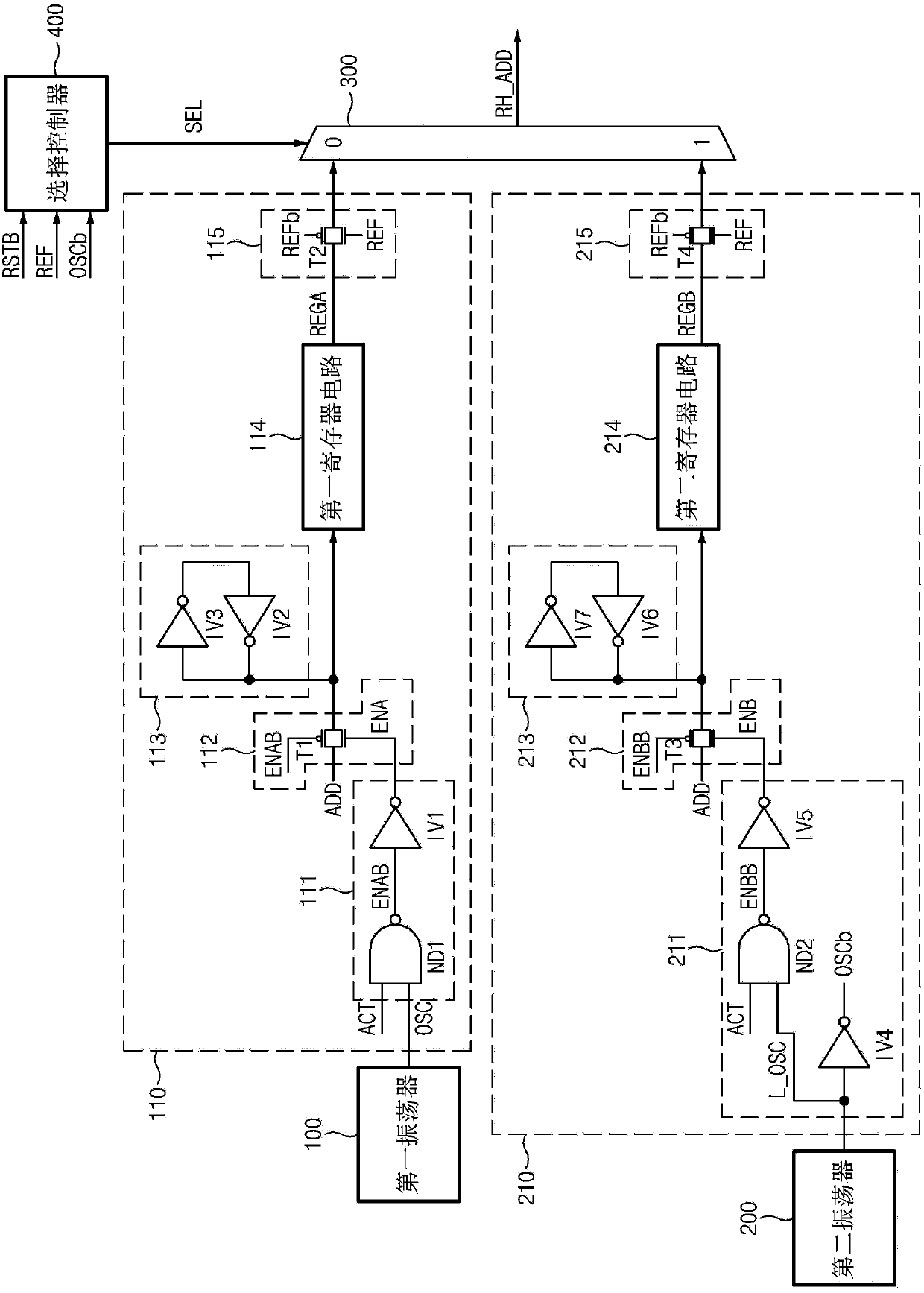
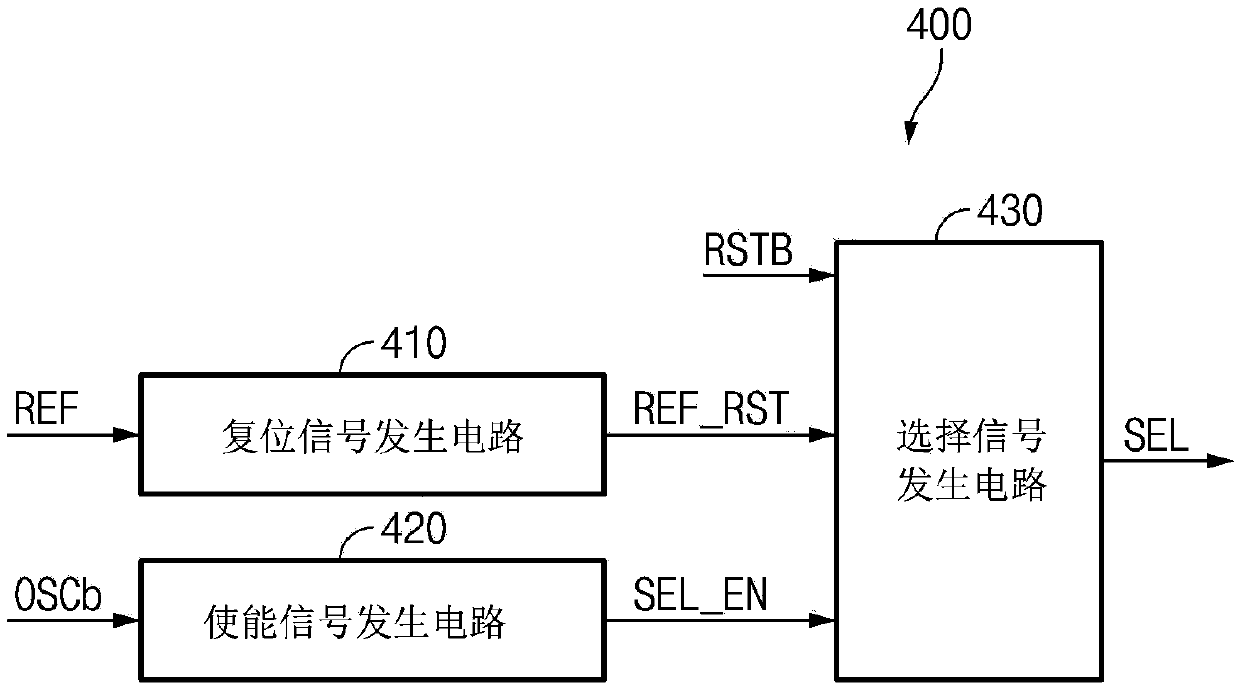
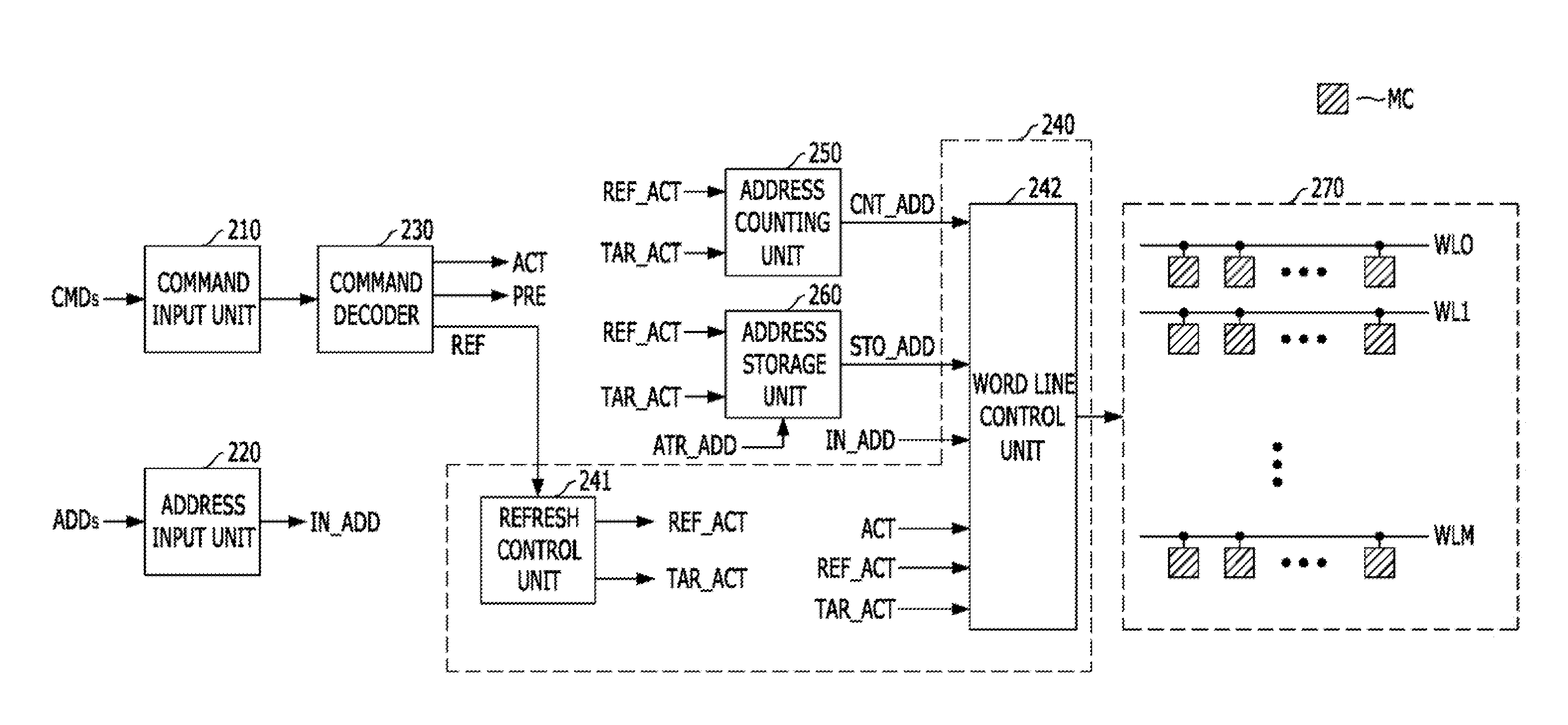
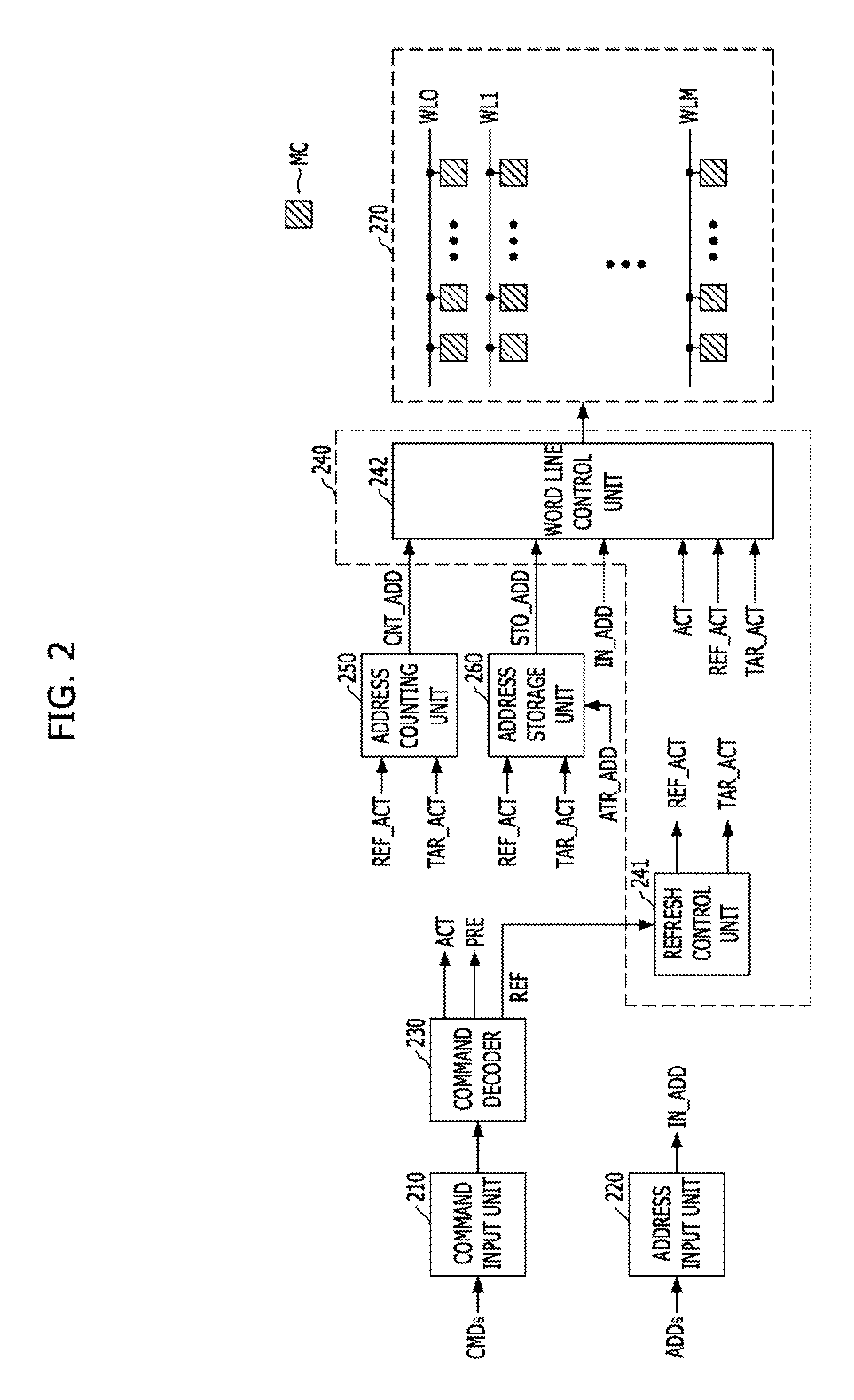
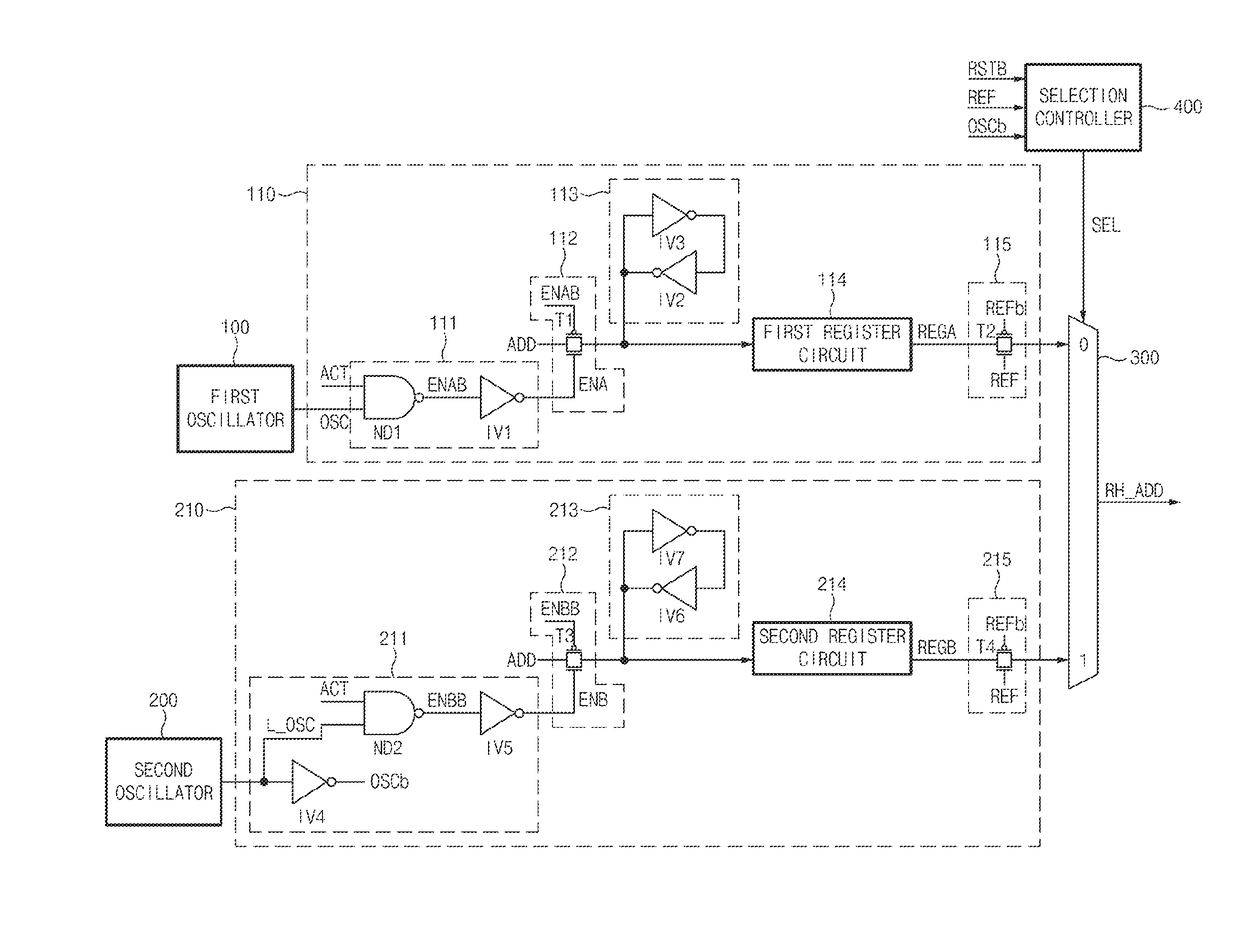
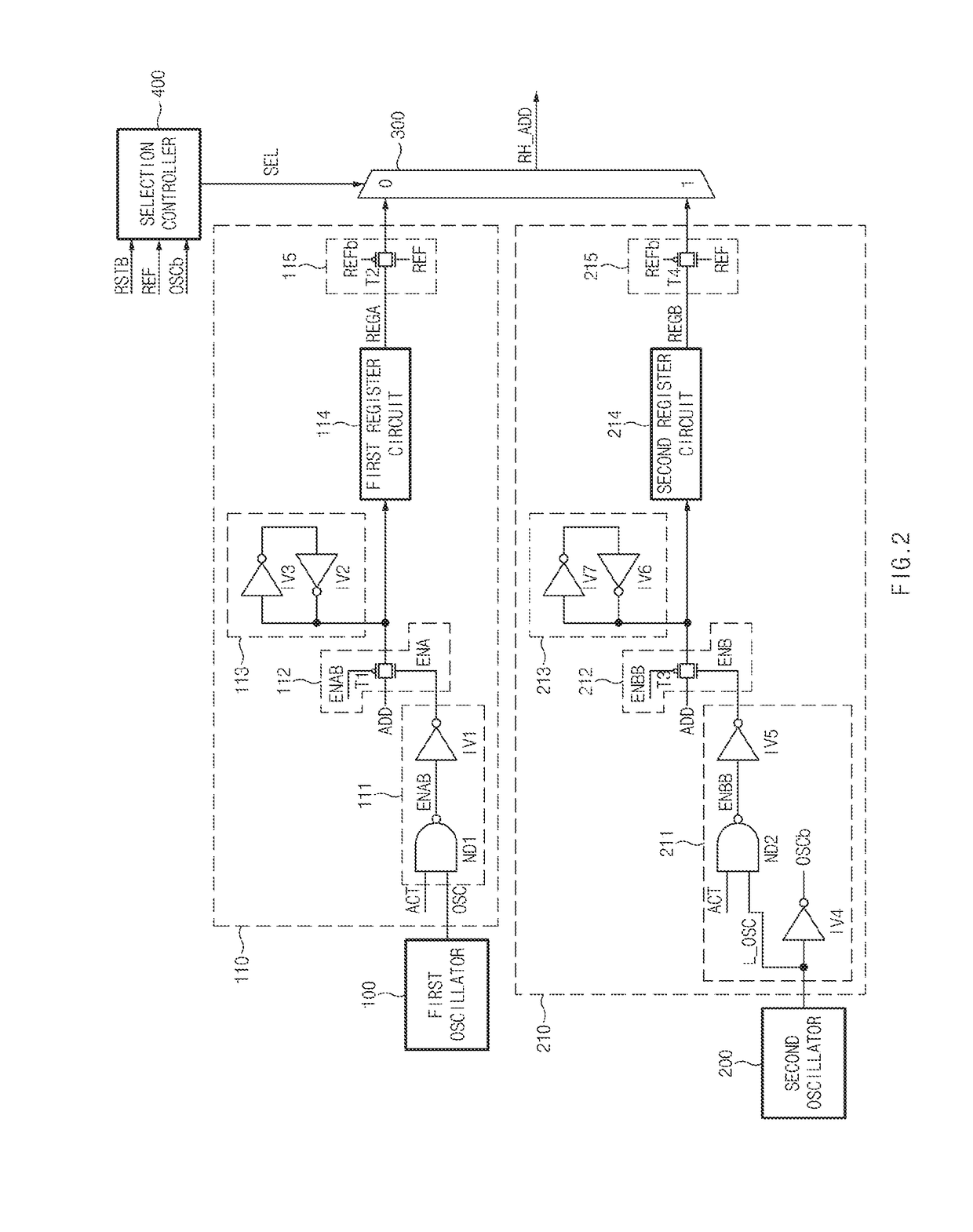
Refresh control device
A refresh control device may include a first oscillator configured to generate a first oscillation signal, a second oscillator configured to generate a second oscillation signal having a different cycle from the first oscillation signal, a first address controller configured to latch an address in response to the first oscillation signal, and output the latched address when a refresh signal is enabled. The refresh control device may also include a second address controller configured to latch the address in response to the second oscillation signal, and output the latched address when the refresh signal is enabled. Further included may be a selector configured to select any one of the output of the first address controller and the output of the second address controller in response to a selection signal, and output the selected output as a row hammer address.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
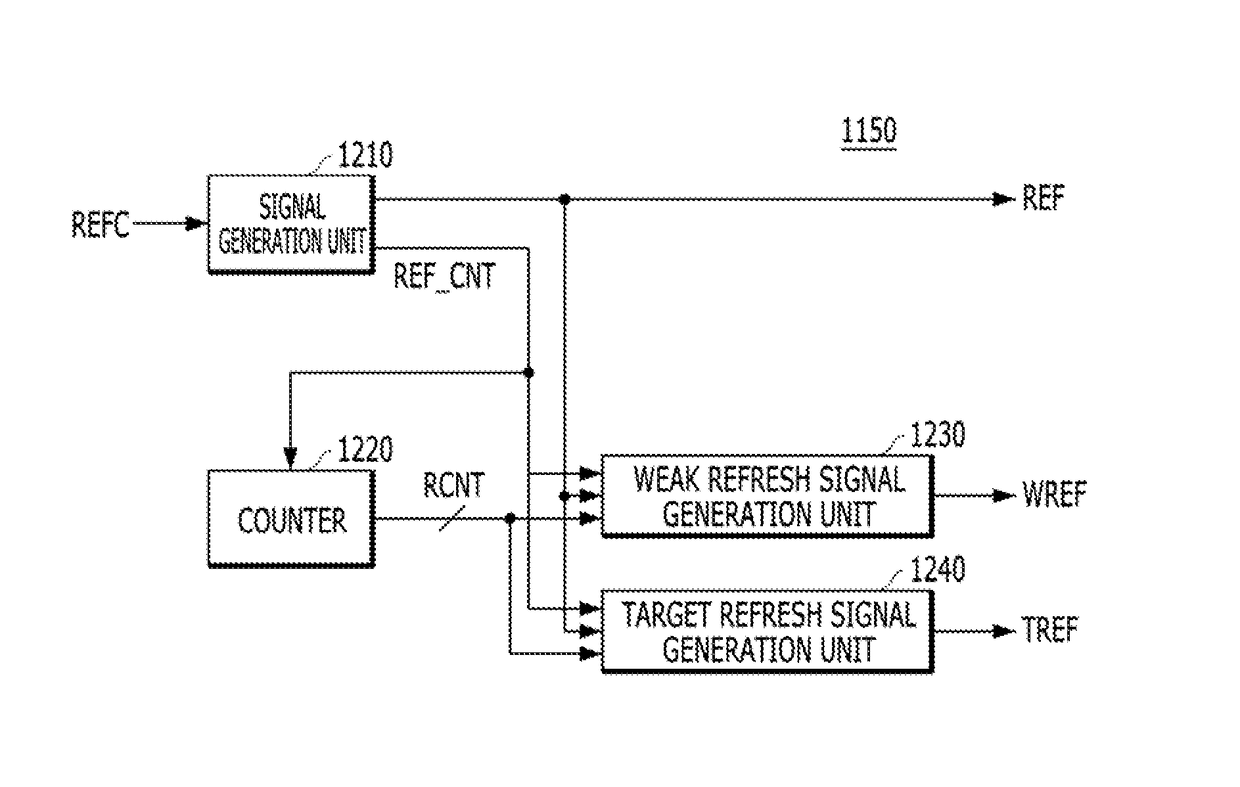
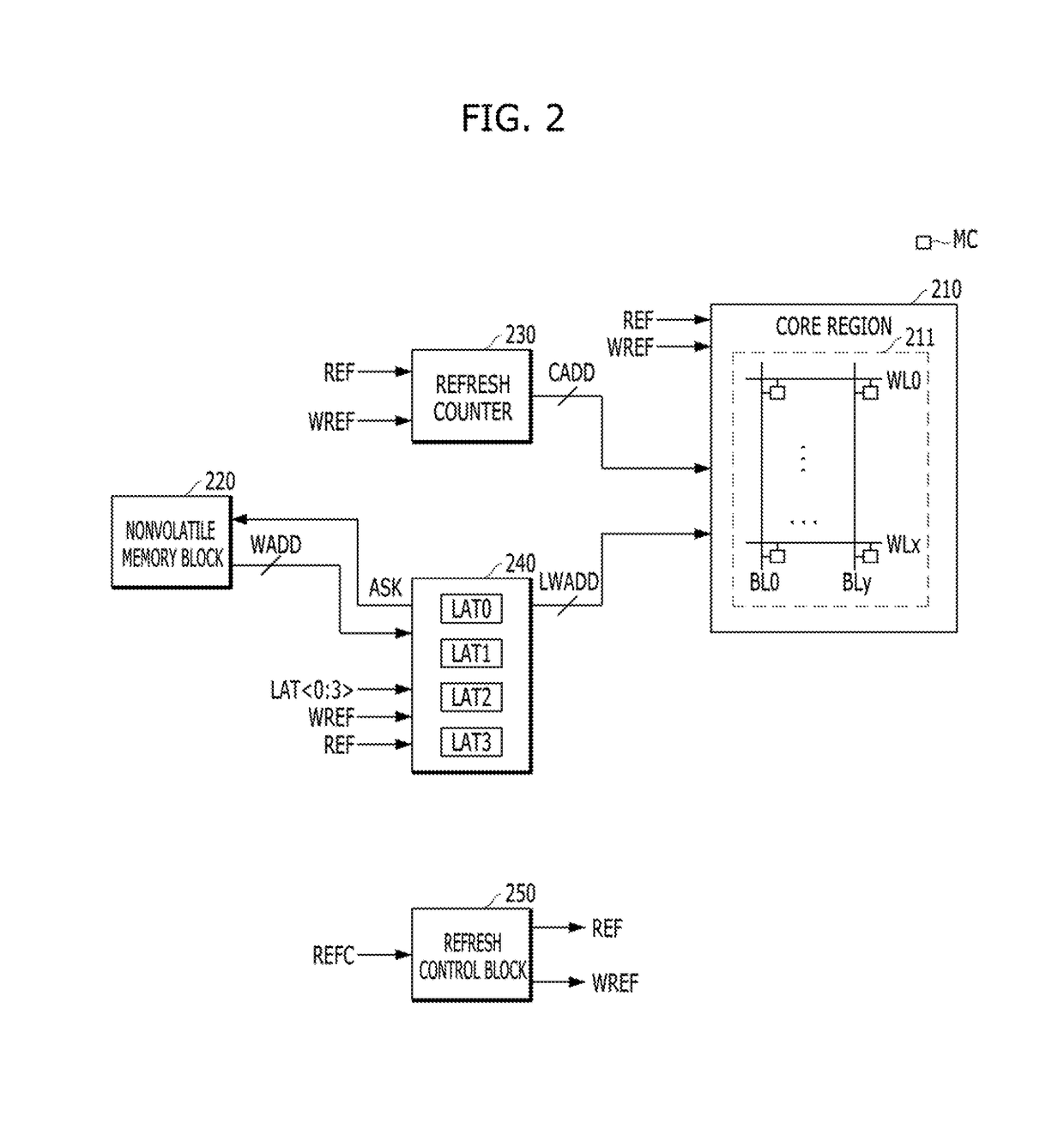
Memory device and method of refreshing the same
ActiveUS9646672B1Improve refresh operationImprove operationRead-only memoriesDigital storageAddress controlComputer science
A memory device includes a plurality of memory cells; a nonvolatile memory block suitable for simultaneously sensing one or more programmed weak addresses, and sequentially transmitting the sensed weak addresses; a weak address control block suitable for latching the weak addresses transmitted from the nonvolatile memory block, and outputting sequentially the latched weak addresses in a weak refresh operation; and a refresh control block suitable for controlling the memory cells corresponding to the counting address to be refreshed, in a normal refresh operation, and controlling the memory cells corresponding to the weak address to be refreshed, in the weak refresh operation.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Data security in wireless network system
InactiveUS20060153375A1Lighting and heating apparatusUnauthorized memory use protectionWireless transmissionInitialization vector
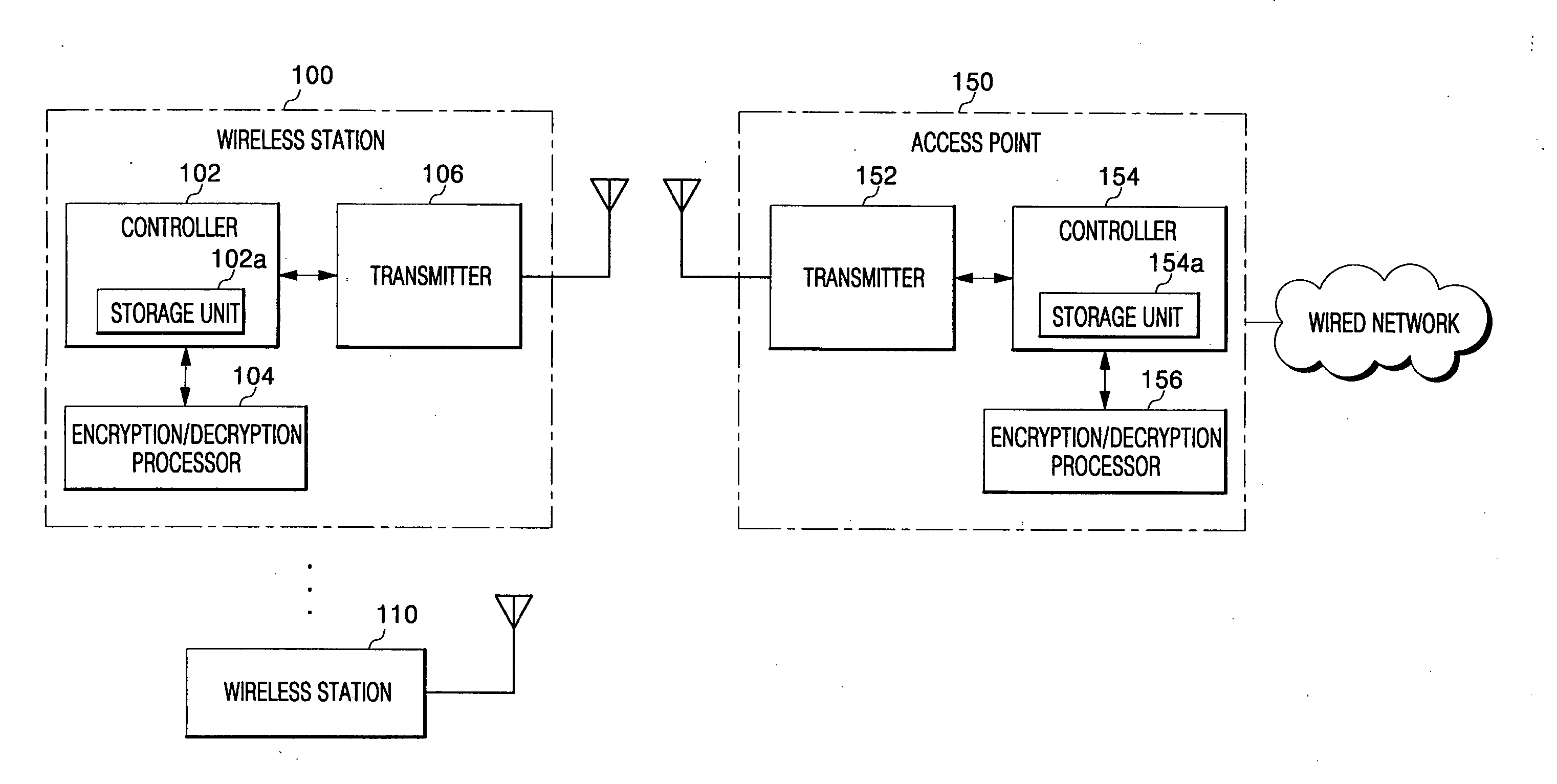
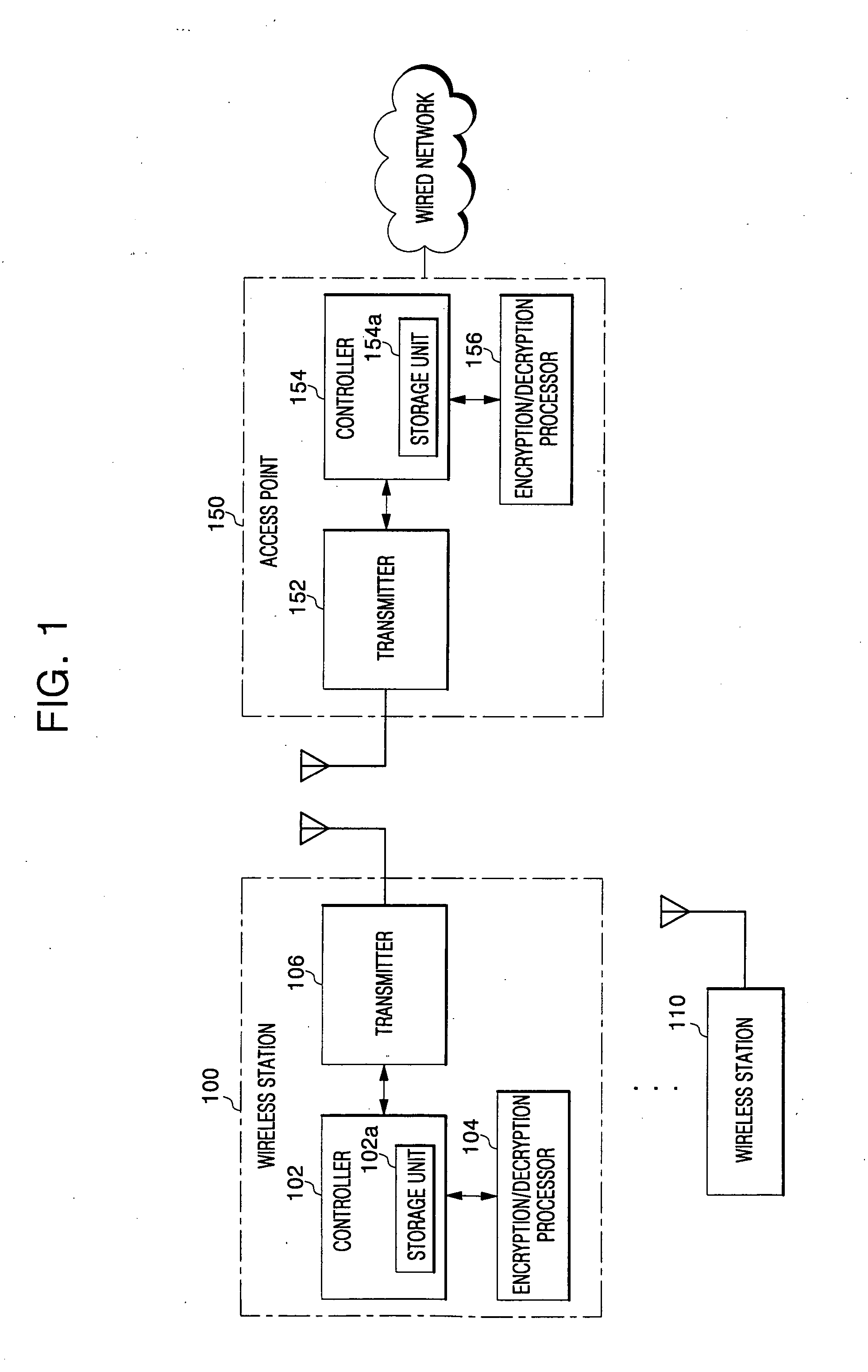
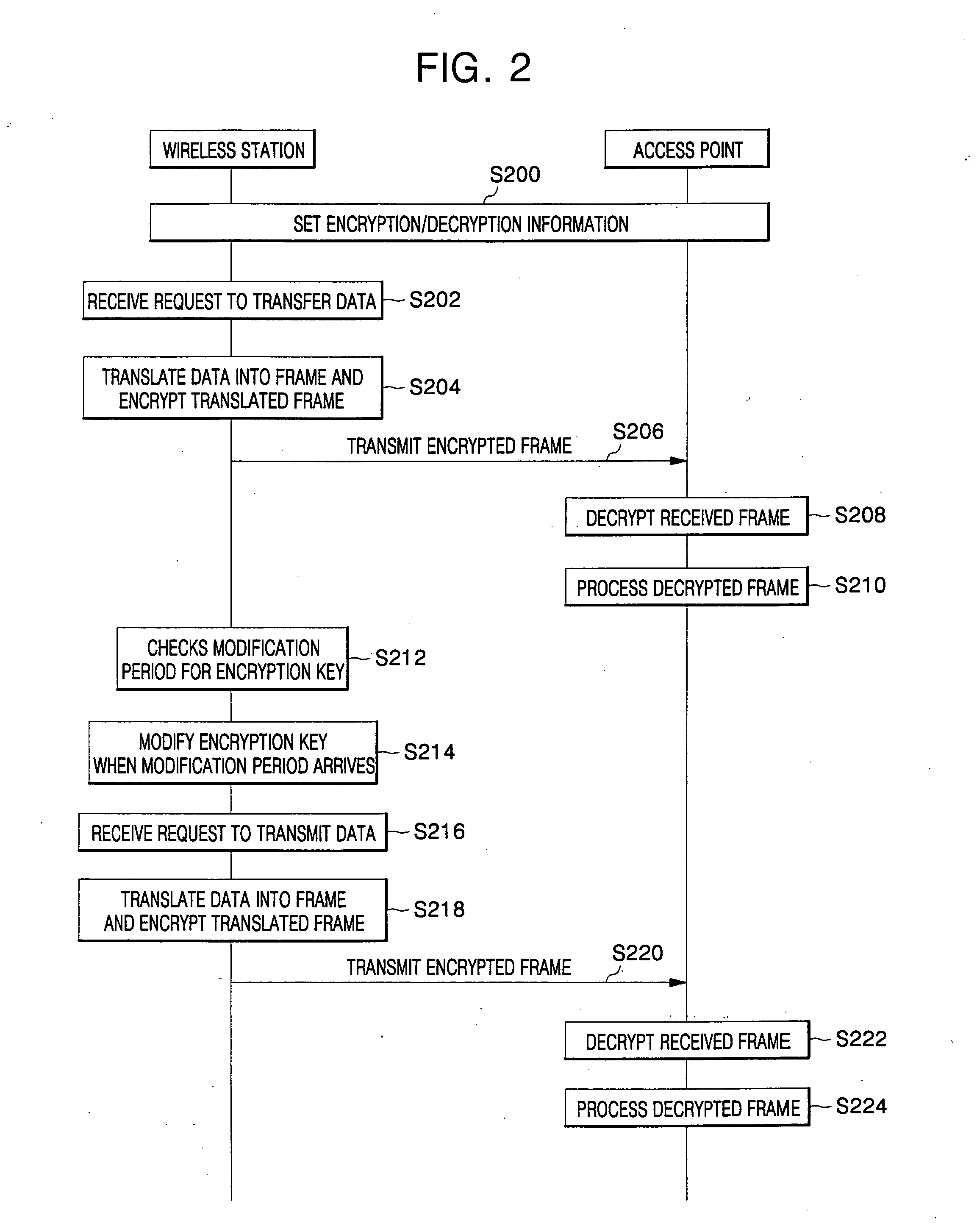
For data protection in a wireless network system, a frame, including its Medium Address Control (MAC) header and payload, is encrypted with an initialization vector modified at each set state in a wireless network system, such that wirelessly transmitted data is prevented from being exposed to unauthorized users.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
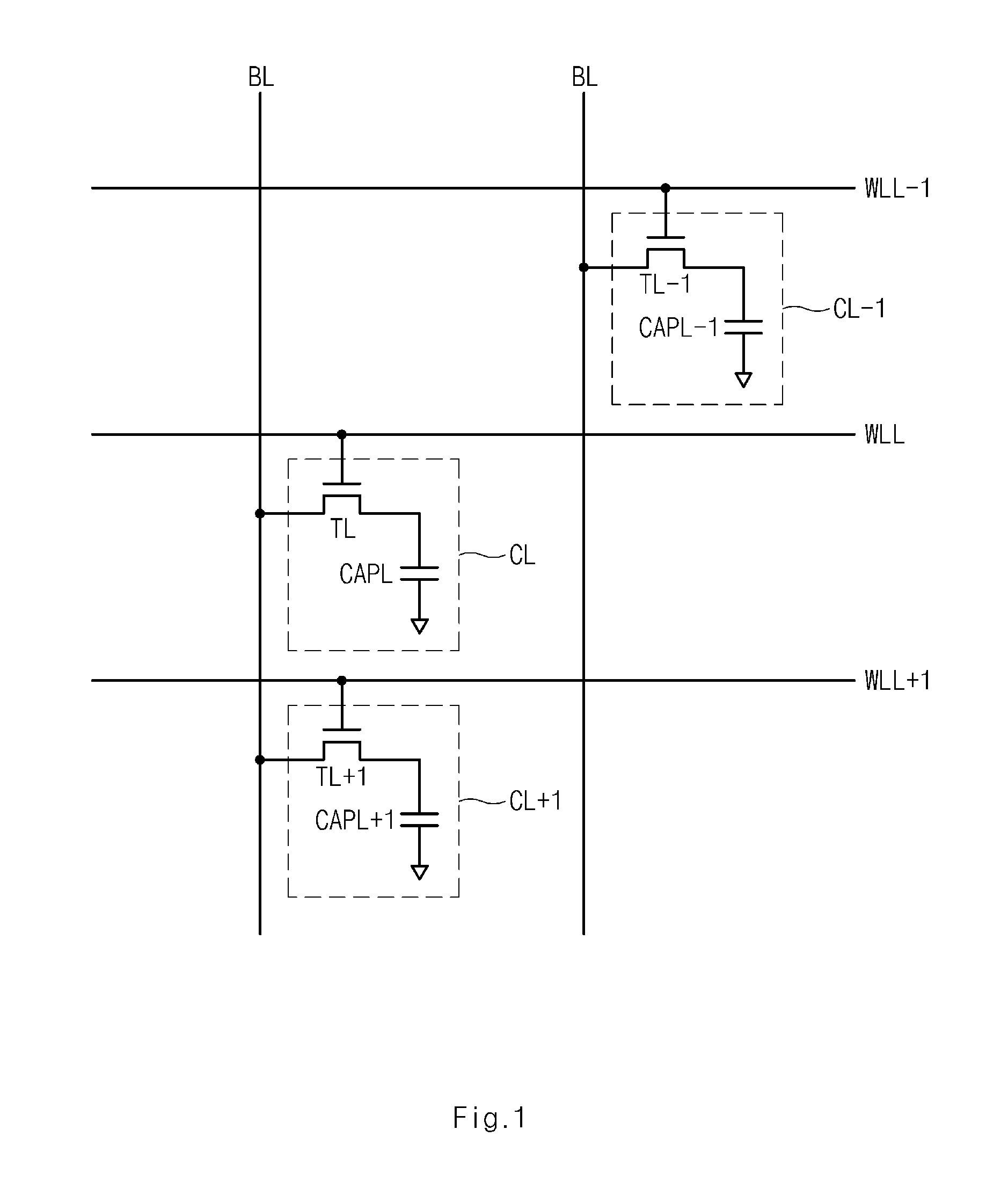
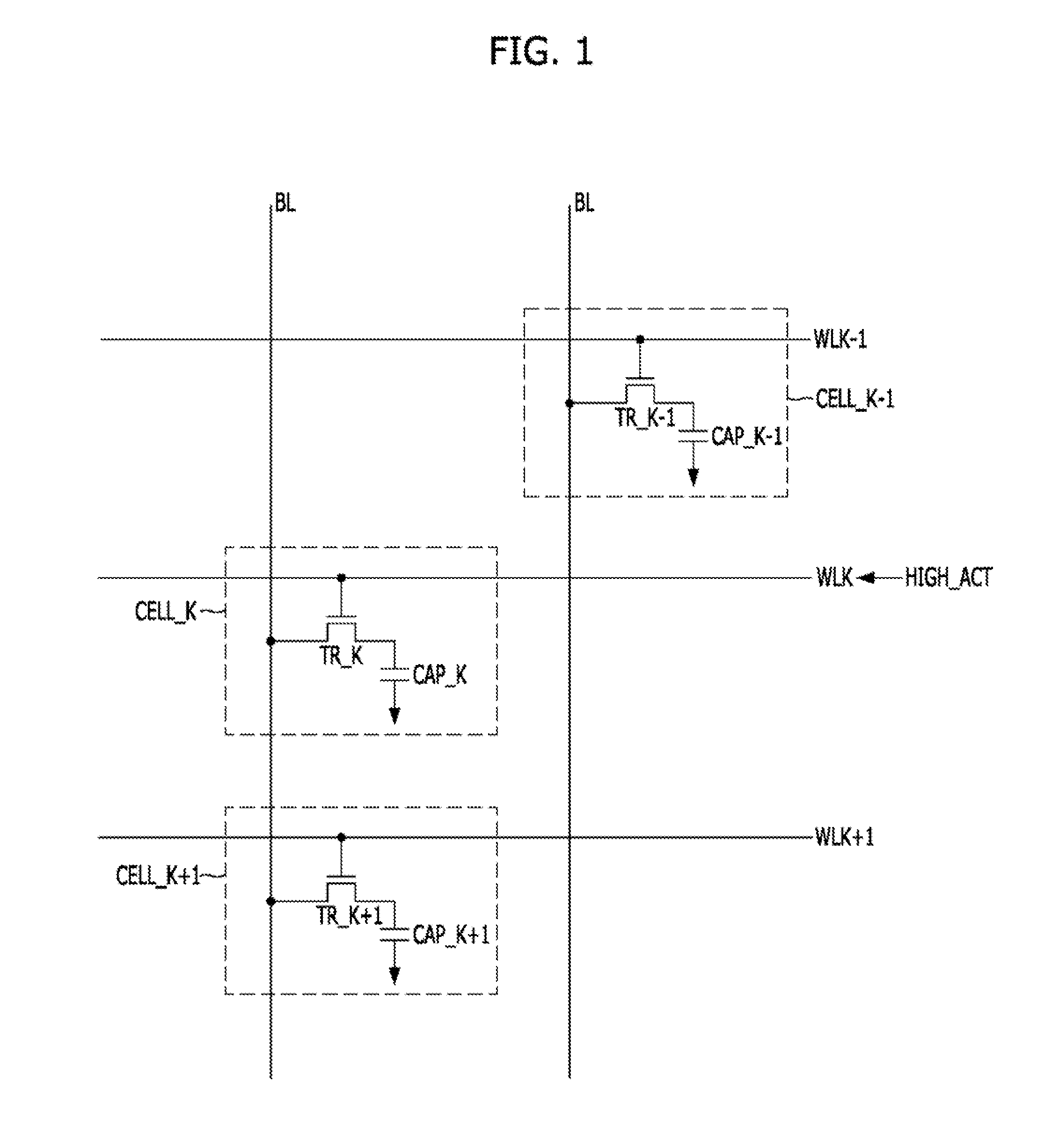
Memory and memory system including the same
A memory includes a plurality of word lines each coupled to one or more memory cells, an address storage unit suitable for storing an address of a word line selected for access by a control unit among the plurality of word lines at a first time point; and the control unit suitable for sequentially refreshing the plurality of word lines in response to application of a refresh command, refreshing one or more adjacent word lines adjacent to a word line corresponding to the address stored in the address storage unit in response to every Nth application of the refresh command where N is a natural number and selecting one or more of the plurality of word lines for access, wherein the first time point is included in time section other than a refresh section in which the control unit refreshes one or more word lines in response to application of the refresh command.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Equipment, method and system for implementing identification of embedded device address sequence
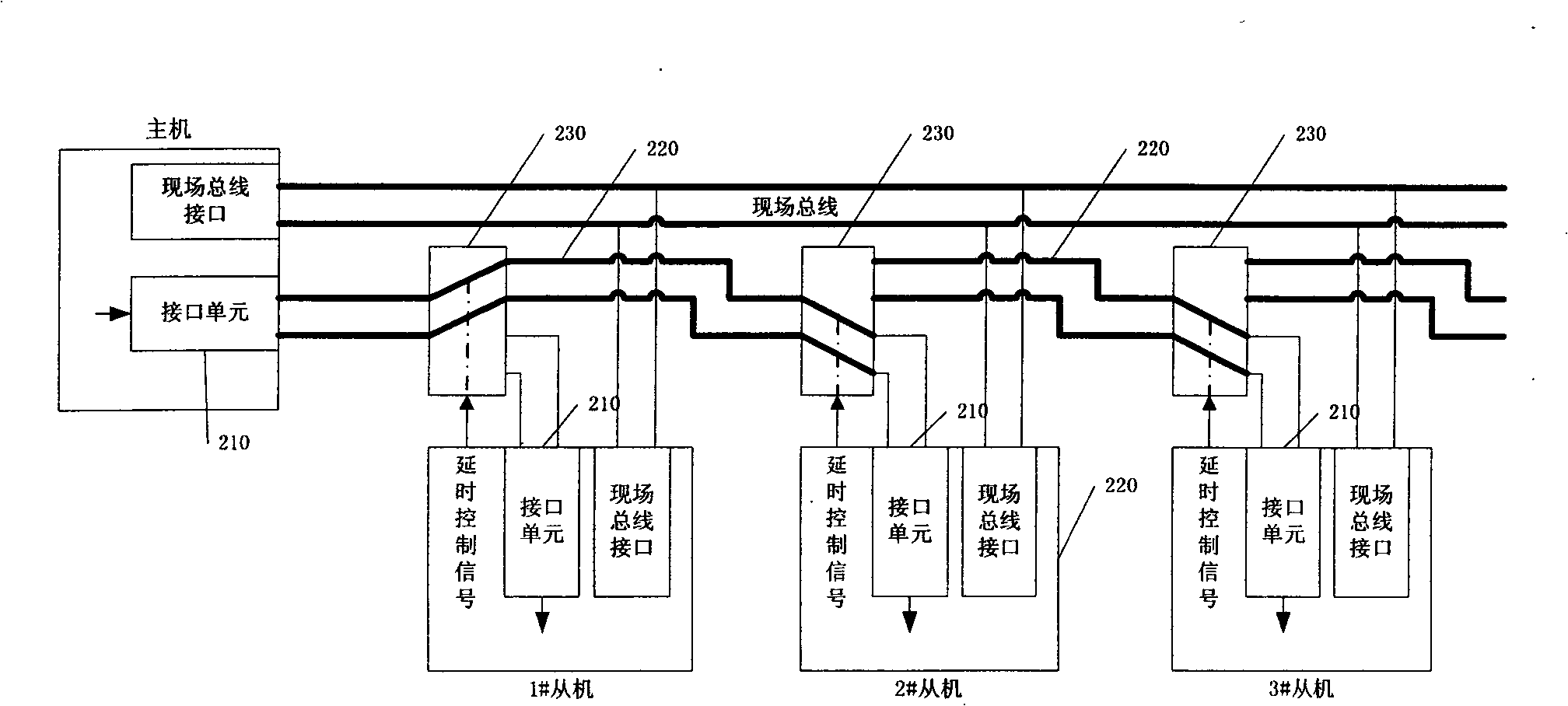
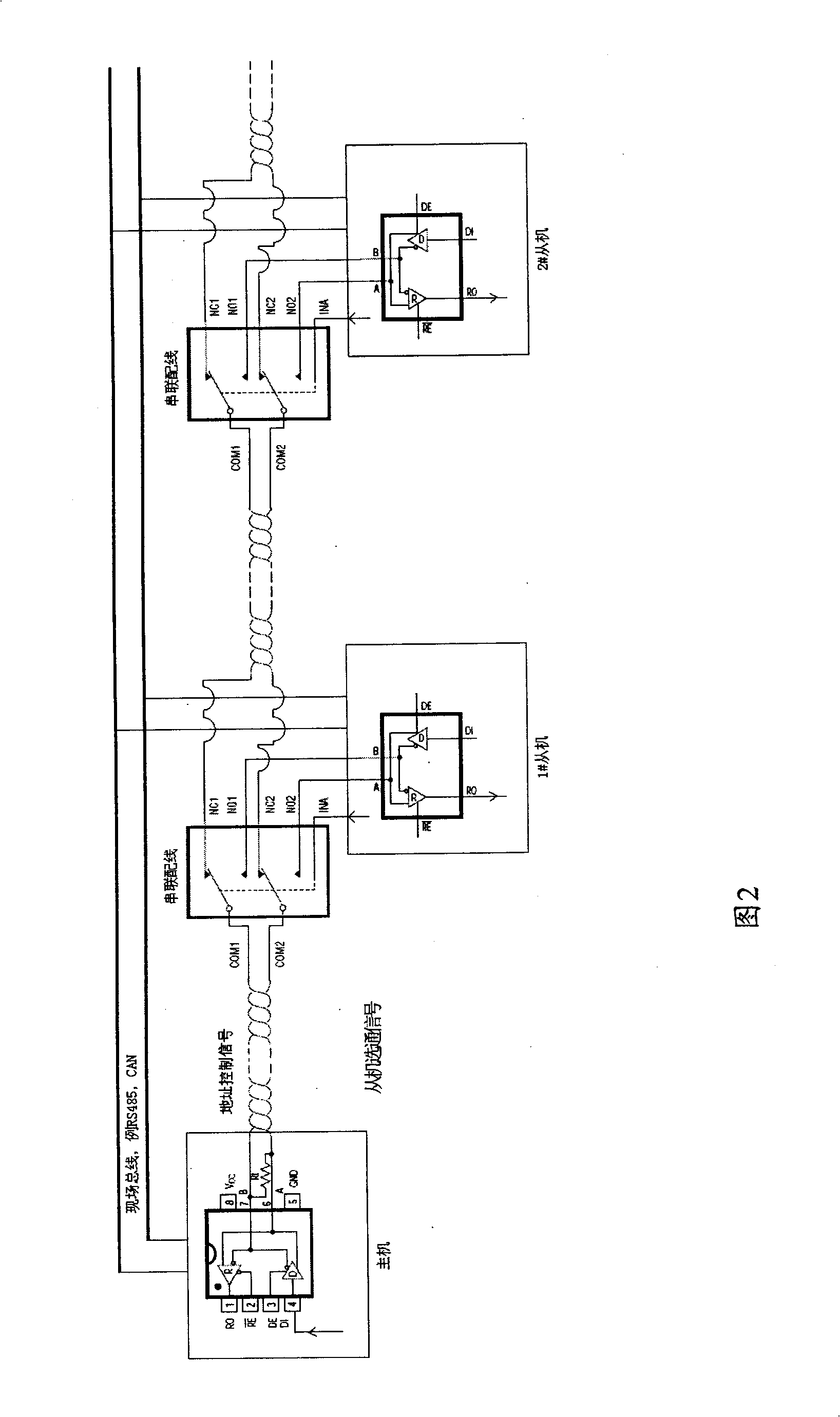
ActiveCN101355482AAvoid repetitionSolve the problem of automatic sequence recognitionTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlControl signalAddress control
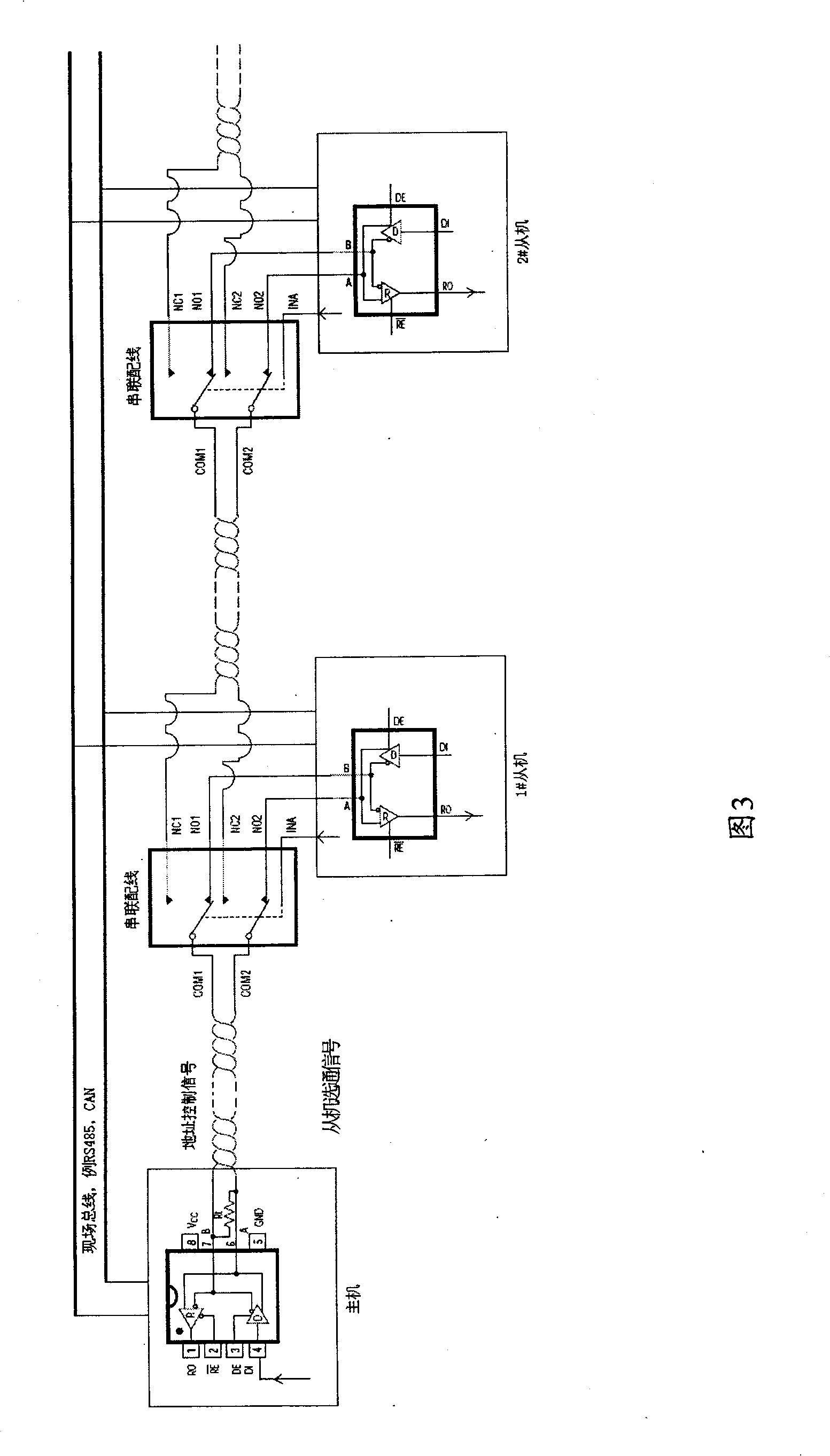
The invention discloses a device, a method and a system for realizing address order identification of an embedded device. In the system, all devices are connected through field buses, and are connected in series in turn through interface units arranged on the devices to form an address control signal transmission line for transmitting a slave strobe signal; moreover, every two devices are in cascade connection through a controllable connection unit, and the control end of each controllable connection unit is correspondingly connected with the output end of a delayed control signal of one device; and each controllable connection unit is used to keep or cut off the connection of a device and the address control signal transmission line according to the delayed control signal output by the device connected with the unit. The device, the method and the system solve the problems of bus conflict or identification error, and the like caused by the address loss of the device, realize automatic order identification and allocation of the address during putting the device into service, and are suitable for a network in which no communication is carried out among slave devices.
Owner:ZTE CORP
RAM-incorporated driver, and display unit and electronic equipment using the same
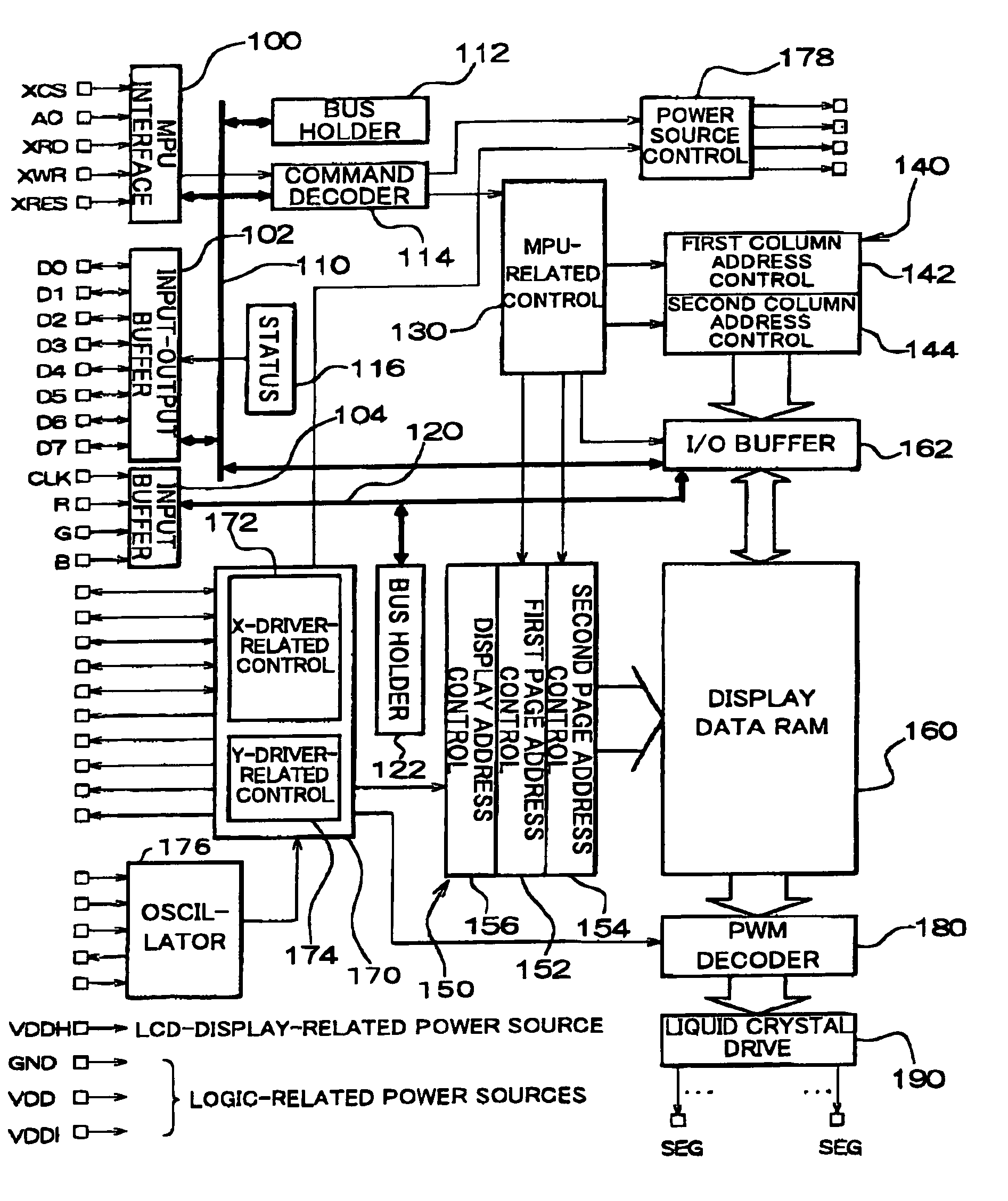
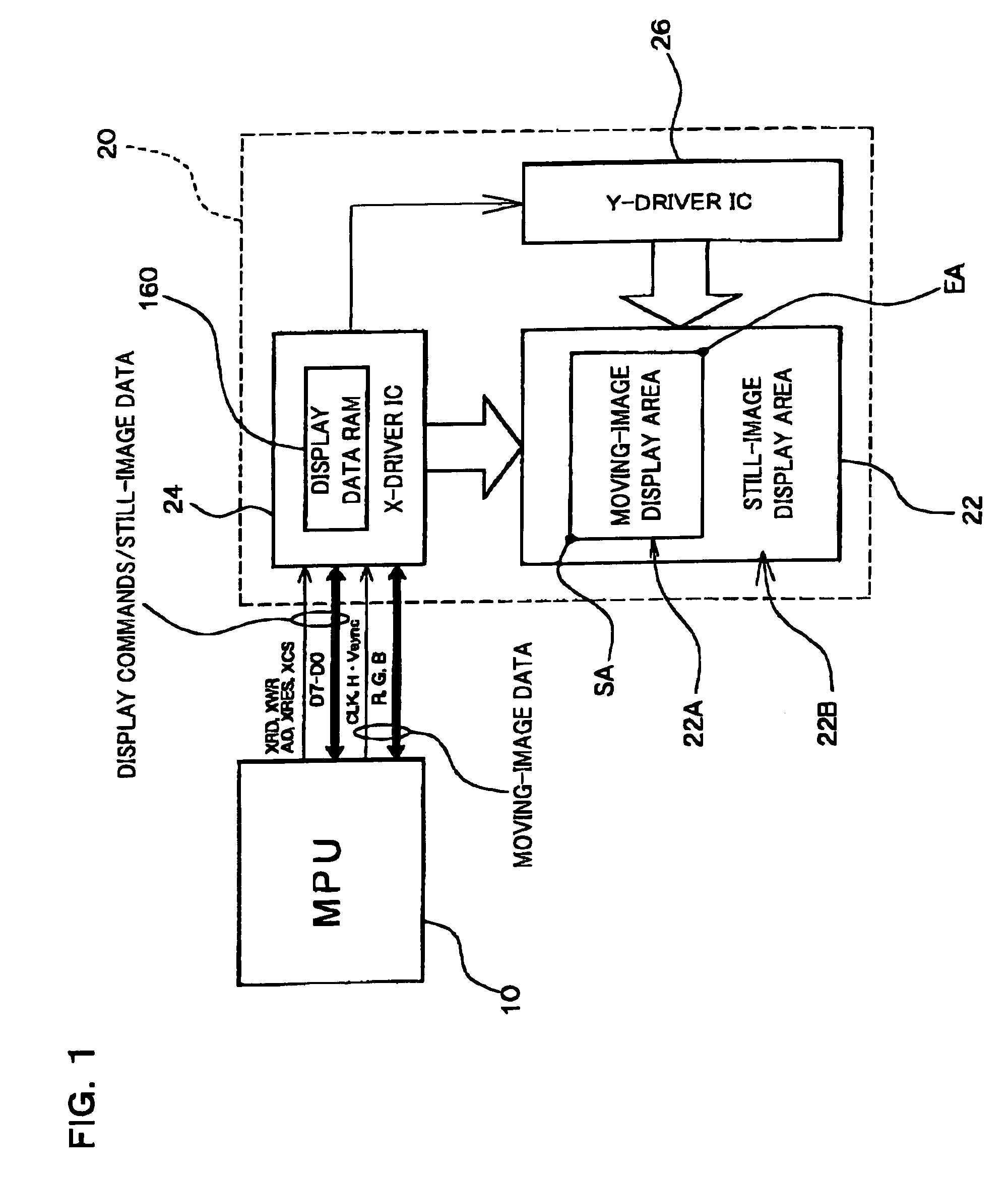
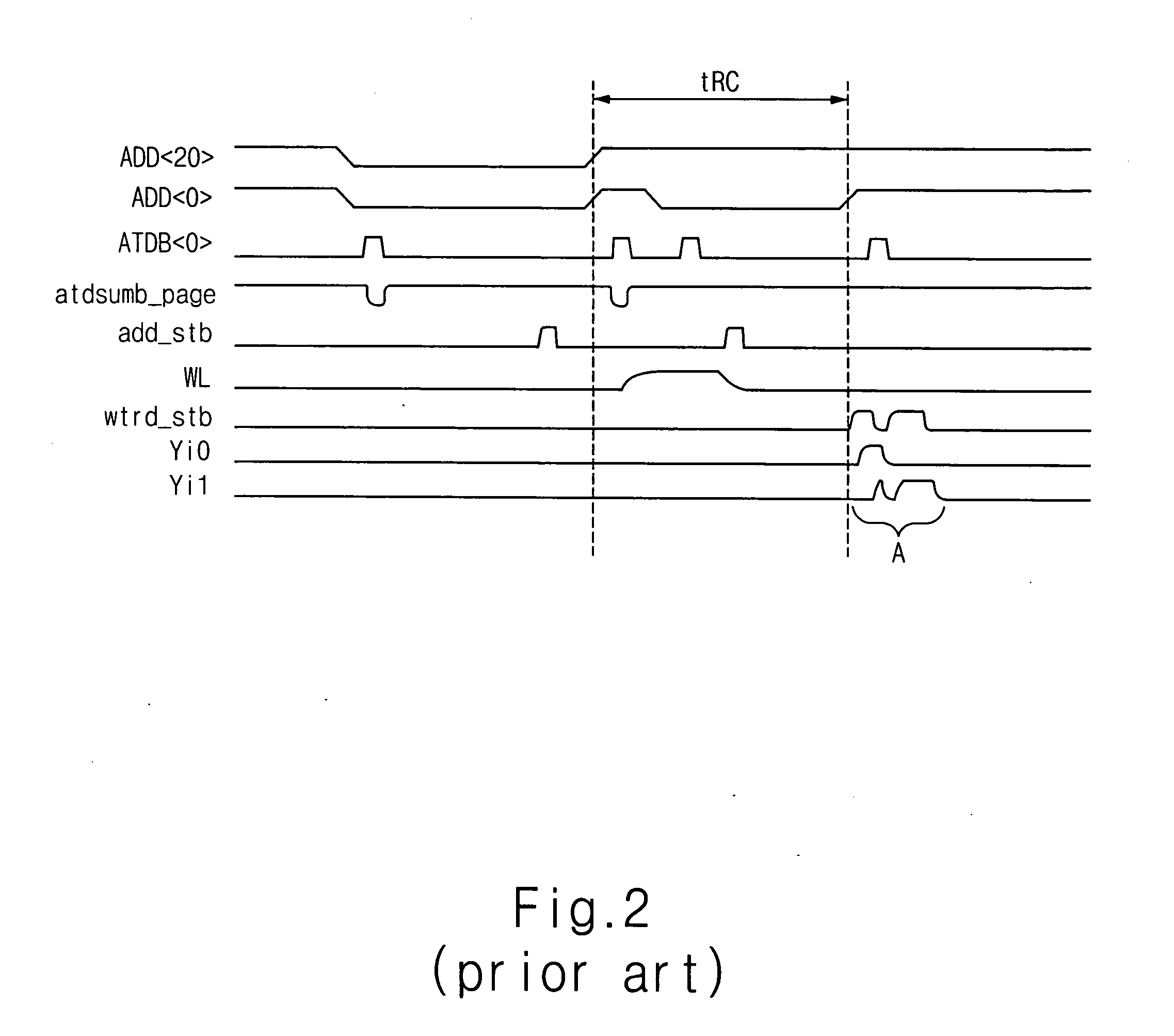
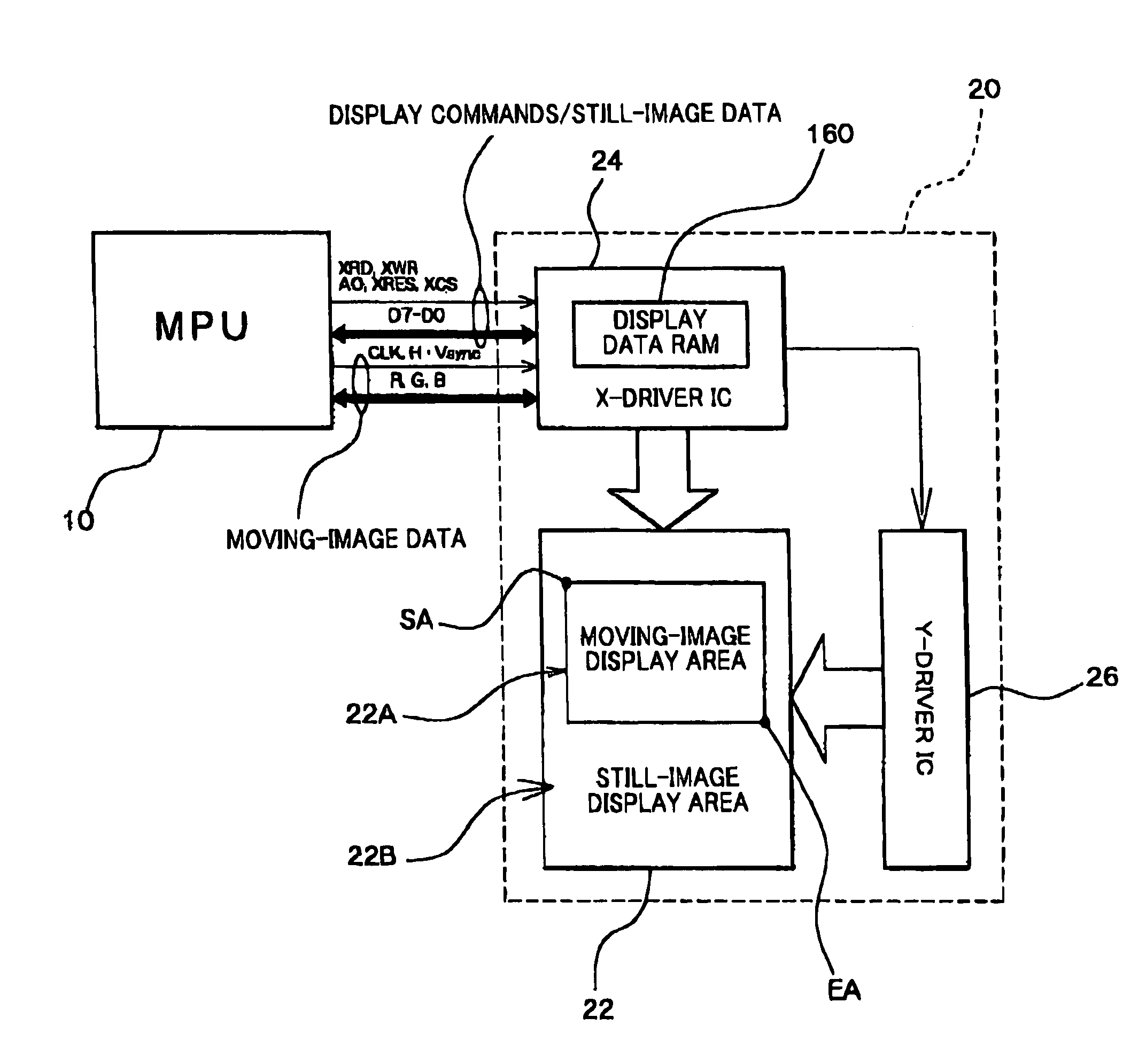
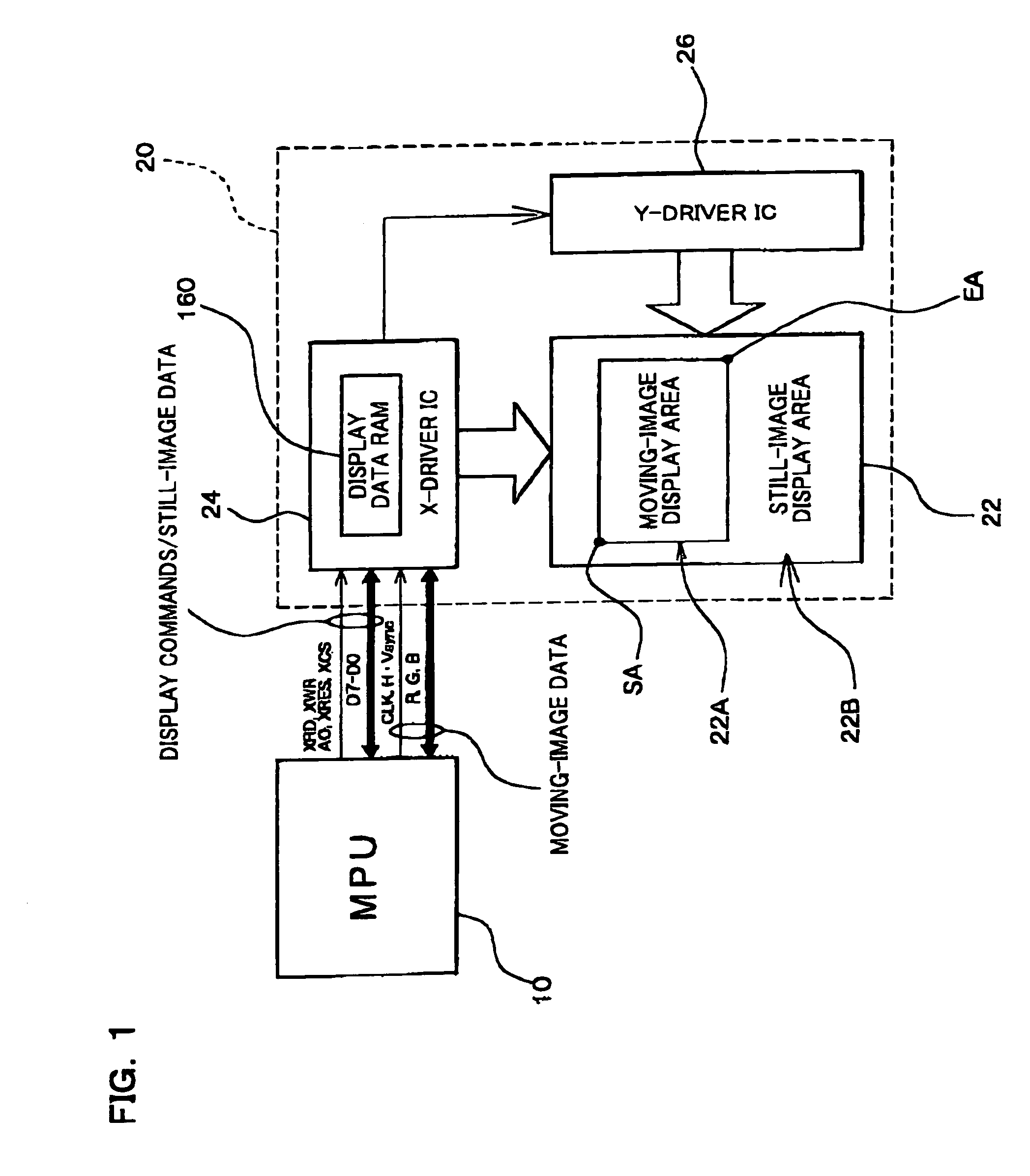
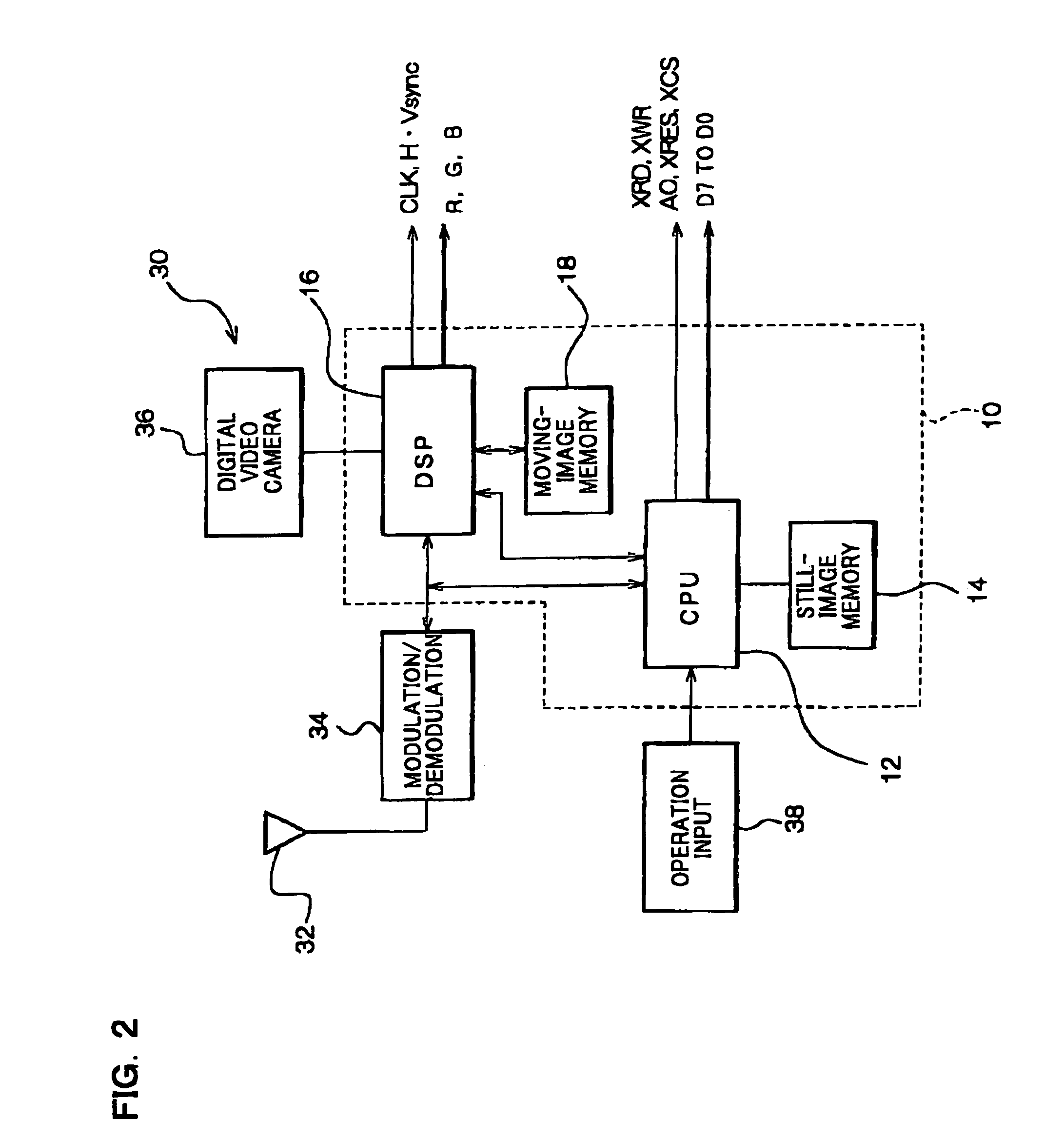
The present invention provides a RAM-incorporated driver that enables the writing of moving-image data to a RAM simultaneously with the writing of still-image data to the RAM. The RAM-incorporated X-driver IC can include first and second bus lines for transferring still-image data and moving-image data from an MPU, a RAM for storing the still-image data and moving-image data, first column and page address control circuits for specifying column and page addresses in RAM for writing still-image data, second column and page address control circuits for specifying column and page addresses in RAM for writing moving-image data, an MPU-related control circuit for controlling each of the address control circuits, based on commands from the MPU, a display address control circuit for controlling the reading of still-image data and moving-image data stored in the RAM, as display data, and a driver-related control circuit for controlling the display address control circuit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Apparatus and method for packet-based media communications
InactiveUS20050185602A1Reduce the amount requiredReduced transcodingMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationControl signalTranscoding
The performance of a voice conference using a packet-based conference bridge can be improved with a number of modifications. In one modification, the conference bridge receives speech indication signals from the individual packet-based terminals within the voice conference, these speech indication signals then being used by the conference bridge to select the talkers within the voice conference. This removes the need for speech detection techniques within the conference bridge, hence decreasing the required processing power and the latency within the conference bridge. In another modification, the conference bridge sends addressing control signals to the individual packet-based terminals selected as talkers, these addressing control signals directing the terminals selected as talkers to directly transmit their voice data packets to the other terminals within the voice conference. This direct transmission of voice data packets can reduce transcoding and latency within the network. These two modifications could further be combined, resulting in a conference bridge that receives speech indication signals, selects the talkers for the voice conference and outputs addressing control signal to the talkers. In this case, the advantages of the two modifications are gained as well as additional capacity advantages resulting from no voice signals actually traversing the conference bridge.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
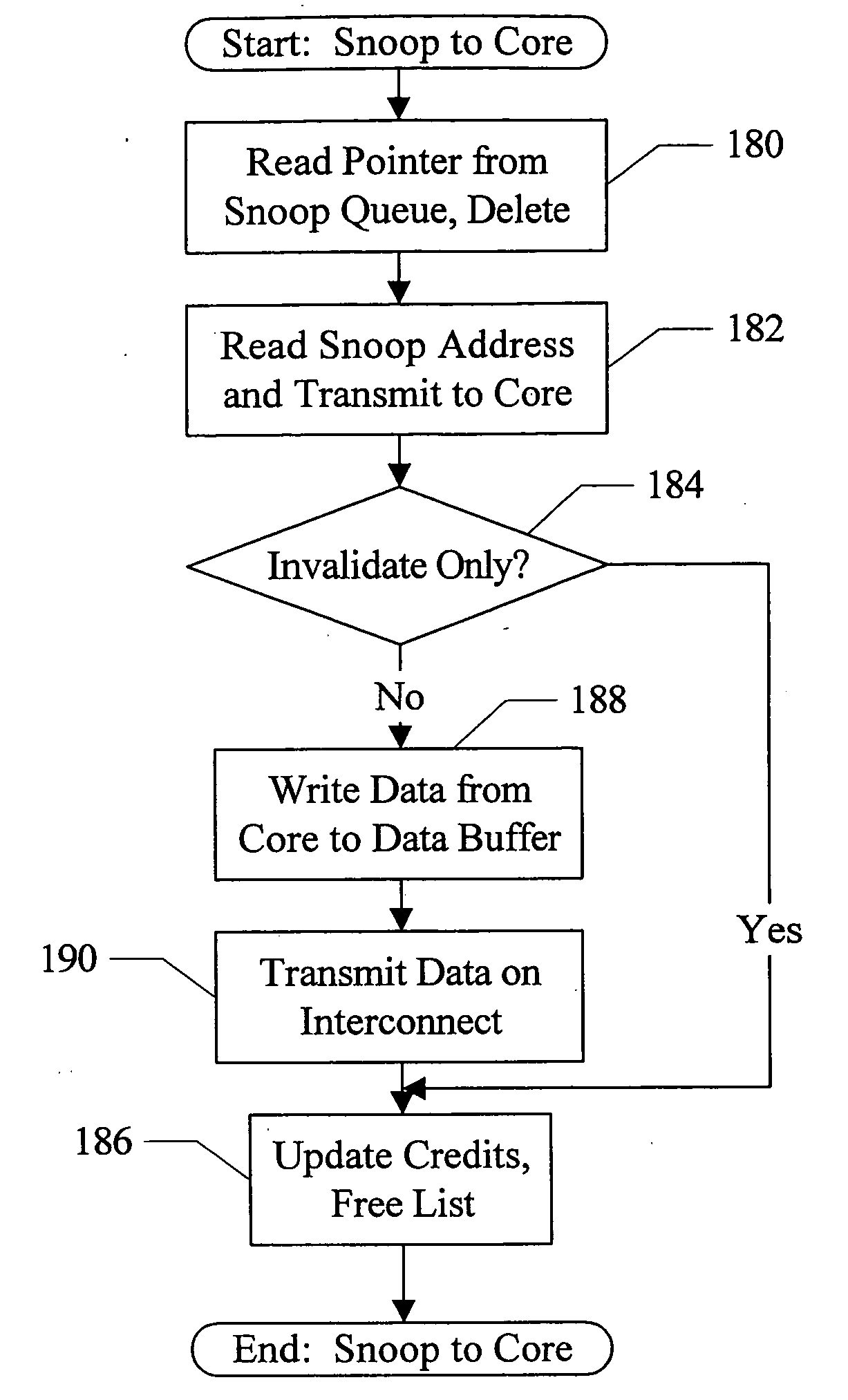
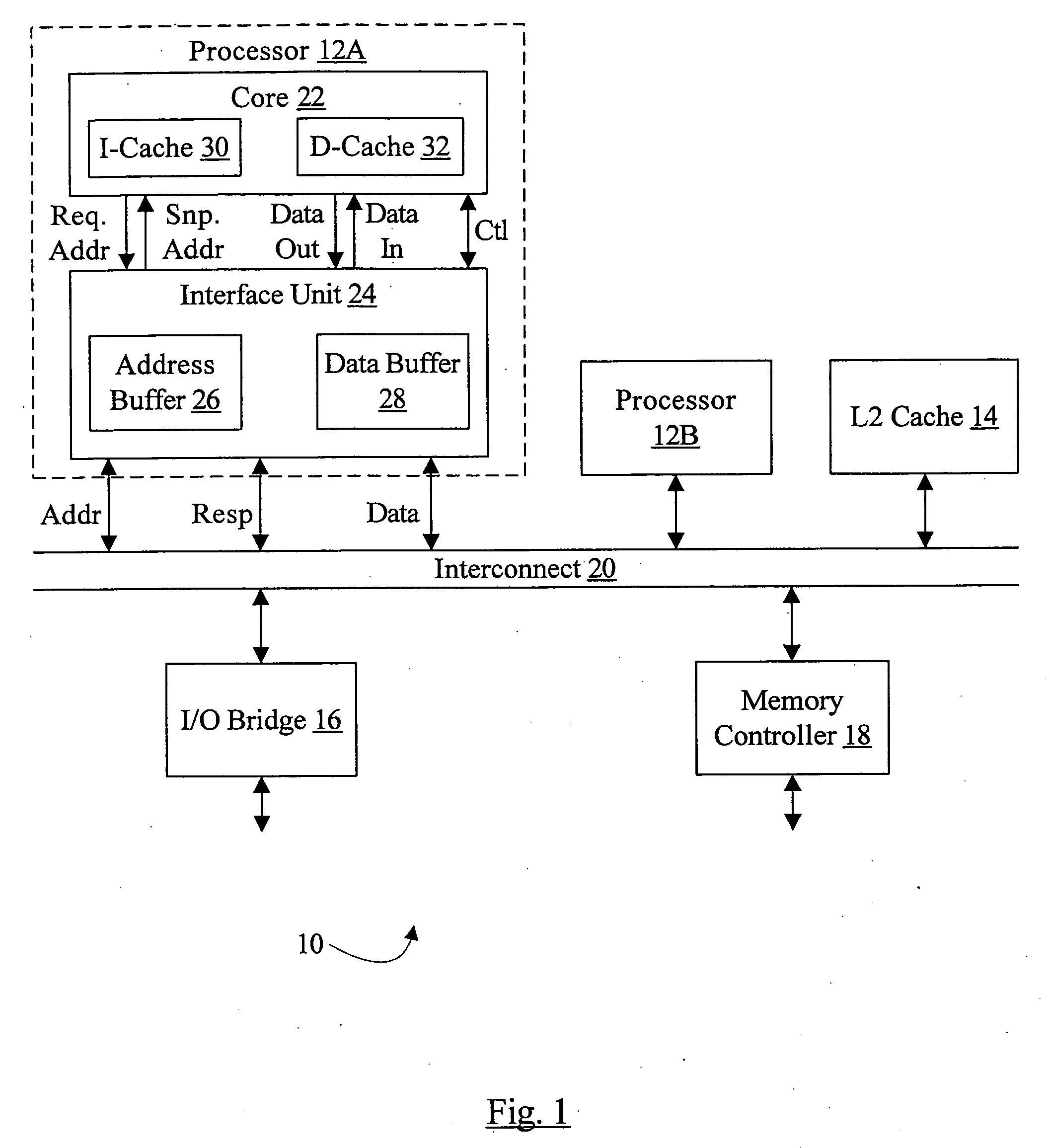
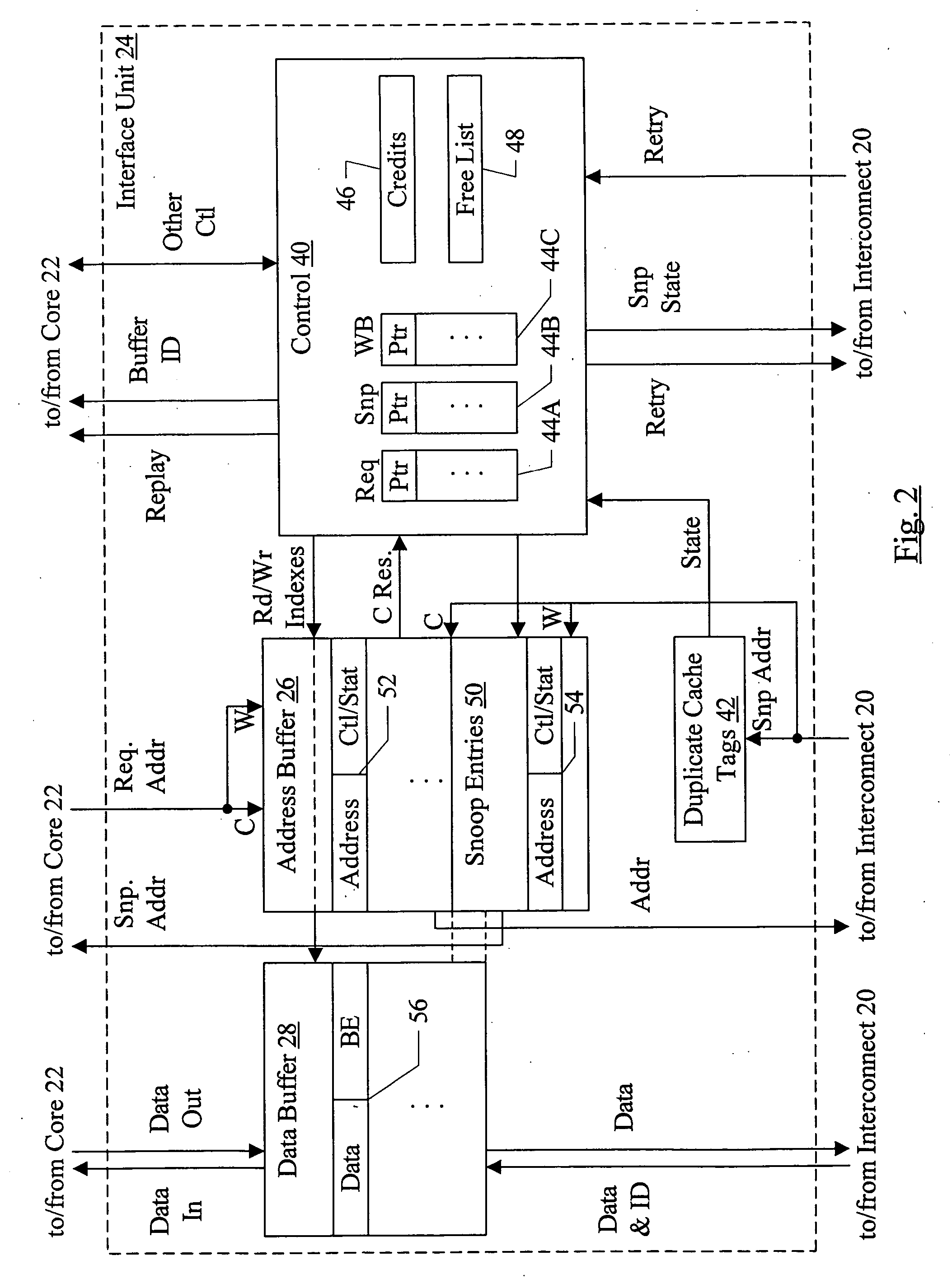
Combined buffer for snoop, store merging, load miss, and writeback operations
In one embodiment, an interface unit comprises an address buffer and a control unit coupled to the address buffer. The address buffer is configured to store addresses of processor core requests generated by a processor core and addresses of snoop requests received from an interconnect. The control unit is configured to maintain a plurality of queues, wherein at least a first queue of the plurality of queues is dedicated to snoop requests and at least a second queue of the plurality of queues is dedicated to processor core requests. Responsive to a first snoop request received by the interface unit from the interconnect, the control unit is configured to allocate a first address buffer entry of the address buffer to store the first snoop request and to store a first pointer to the first address buffer entry in the first queue. Responsive to a first processor core request received by the interface unit from the processor core, the control unit is configured to allocate a second address buffer entry of the address buffer to store the first processor core request and to store a second pointer to the second address buffer entry in the second queue.
Owner:APPLE INC
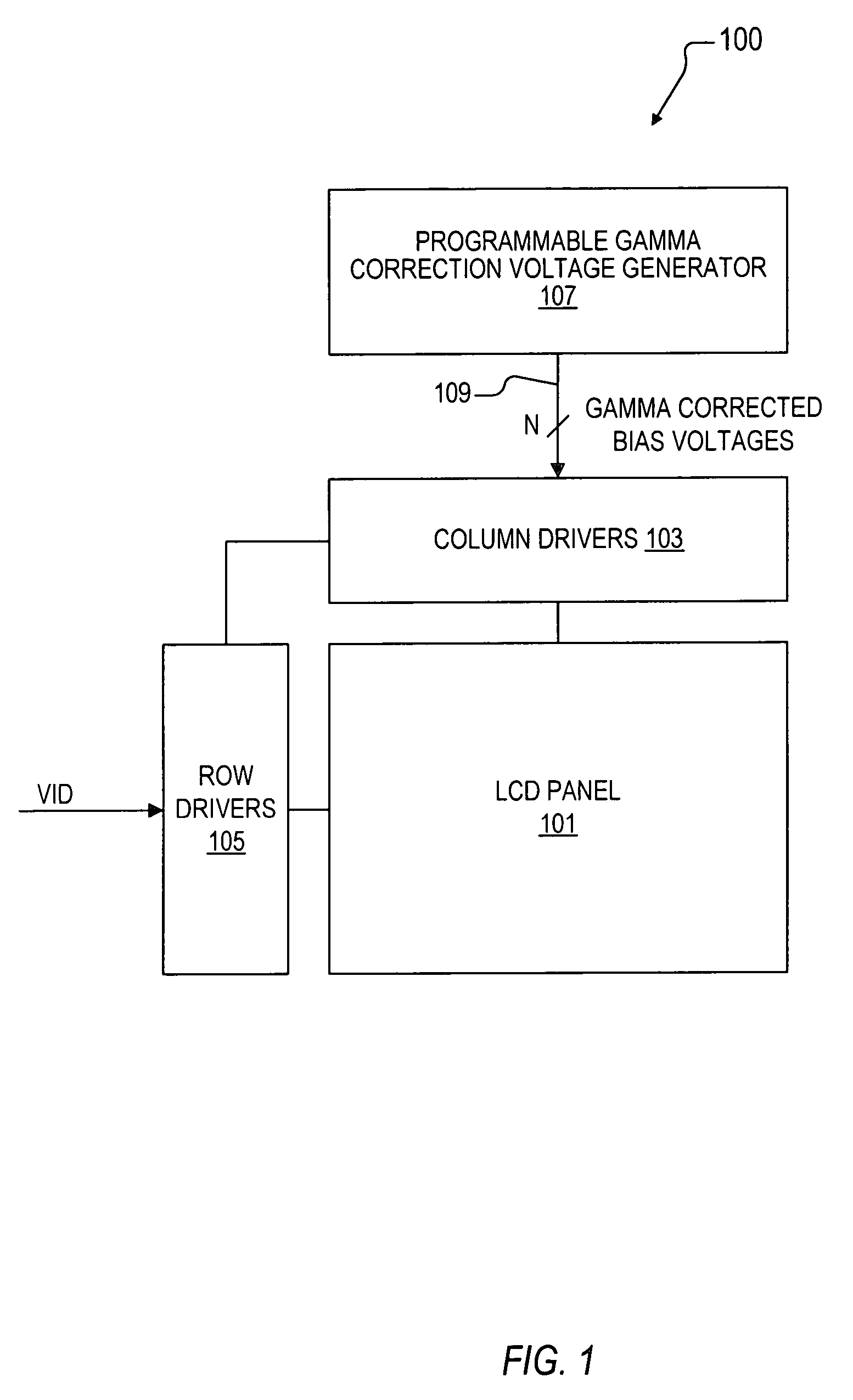
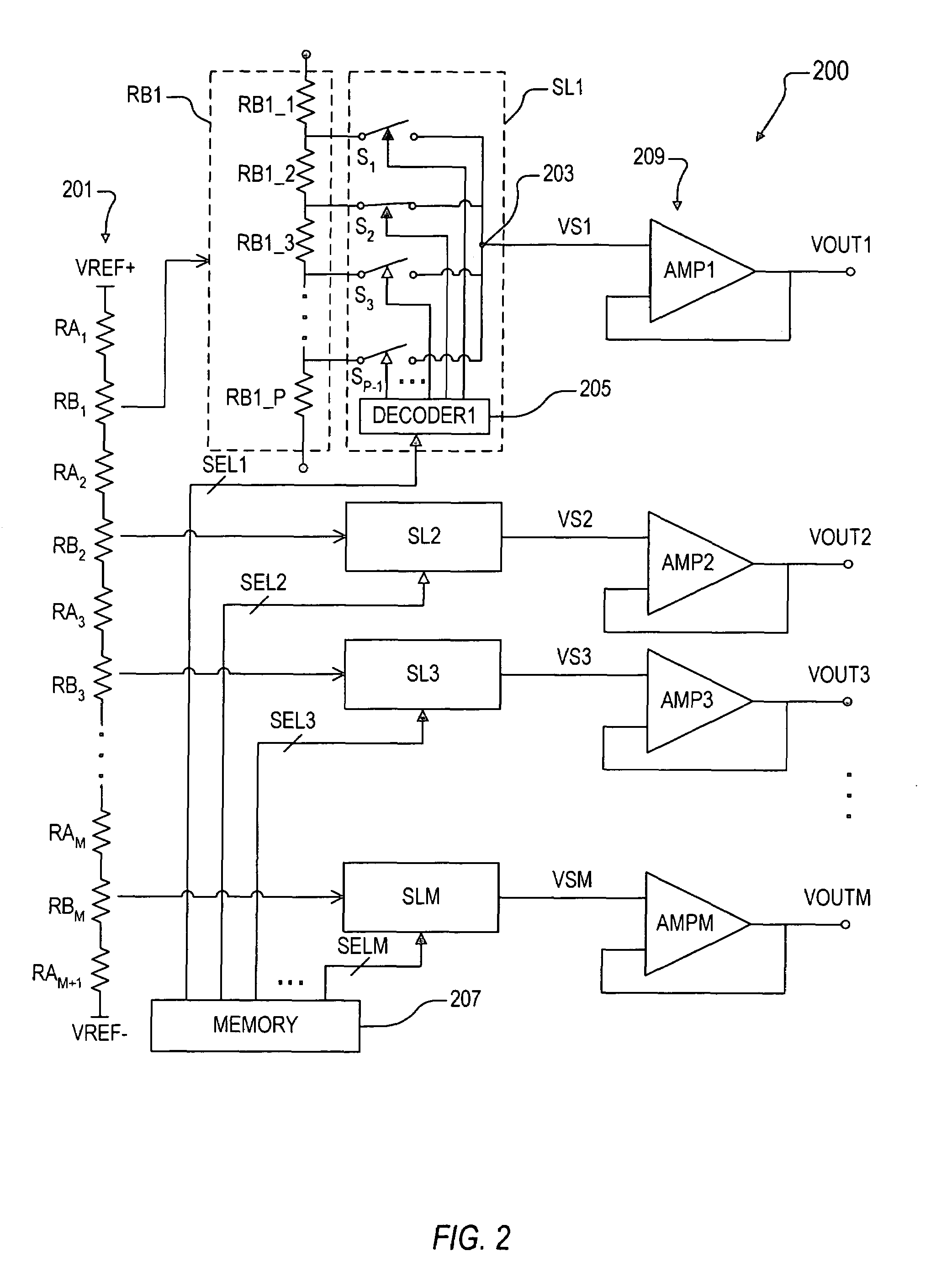
Multiple channel programmable gamma correction voltage generator
InactiveUS7446747B2Increase temperatureExtension of timeTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage generator
A multiple channel programmable gamma correction voltage generator including a resistor ladder, buffers, select logic, and a programmable non-volatile memory device. The memory provides select values indicative of one or more stored gamma correction values. The resistor ladder includes adjustable tap resistors distributed along the resistor ladder. The adjustable tap resistors provide multiple tap voltages distributed according to the gamma correction value. The buffers receive the tap voltages and provide gamma correction voltages. The select logic selects tap points of the adjustable tap resistors to select the tap voltages based on the select values stored in the memory. Additional resistors and switch logic may be included to enable re-positioning of the adjustable tap resistor within the resistor ladder. Latches and address control may be provided on the memory to enable programming and selection of multiple gamma correction values.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
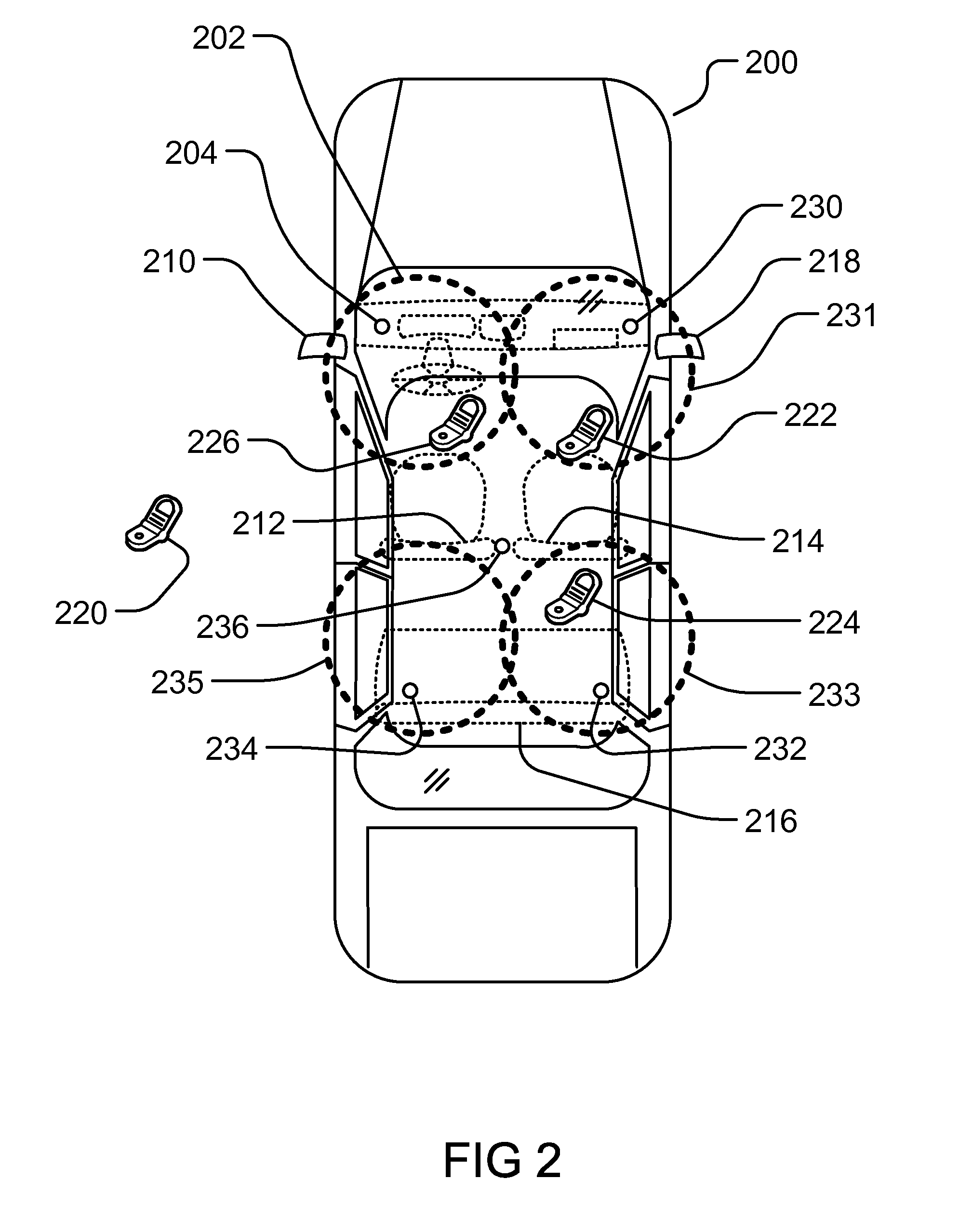
Method and System for Using Multiple Transceivers for Controlling Mobile Communication Device Functions
ActiveUS20120214471A1Limited abilityAutomatically disabling the texting ability of mobile deviceService provisioningReceivers monitoringDistractionDriver/operator
This provides for controlling mobile device functions and features. For example, it limits or disables the use of some of mobile device features which could cause distraction to the user, when the user is engaged in another activity. In an example, it enables other mobile device features based on occurrence of events related to the user or environment. Another example addresses controlling the mobile device features, such as SMS, while the user is in a vehicle or driving. Another example restricts the ability of the driver of a vehicle to text, while the vehicle is in motion, by automatically disabling the texting ability of mobile device within and around the perimeter of the driver's seat. Other variations, examples, improvements, detection mechanisms, models, techniques, calculations, verification mechanisms, and features are also described in details.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Low complexity pseudo-random interleaver
An interleaver has an input multiplexer that receives a data sequence at an interleaver input and that separates the data sequence into multiple data sub-blocks. The interleaver has a linear feedback shift register that generates an input address sequence. The interleaver has adder circuits that generate output address sequences associated with each data sub-block. The interleaver has memory that stores the data sub-blocks at addresses controlled by the input address sequence. The memory reproduces each data sub-block in an interleaved sequence controlled by the associated output address sequence. The interleaver has an output multiplexer that assembles the interleaved sequences to provide an interleaver output.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Refresh control device
ActiveUS20180090199A1Reducing a refresh failMemory architecture accessing/allocationData resettingRow hammerAddress control
A refresh control device may include a first oscillator configured to generate a first oscillation signal, a second oscillator configured to generate a second oscillation signal having a different cycle from the first oscillation signal, a first address controller configured to latch an address in response to the first oscillation signal, and output the latched address when a refresh signal is enabled. The refresh control device may also include a second address controller configured to latch the address in response to the second oscillation signal, and output the latched address when the refresh signal is enabled. Further included may be a selector configured to select any one of the output of the first address controller and the output of the second address controller in response to a select signal, and output the selected output as a row hammer address.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Smart refresh device
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
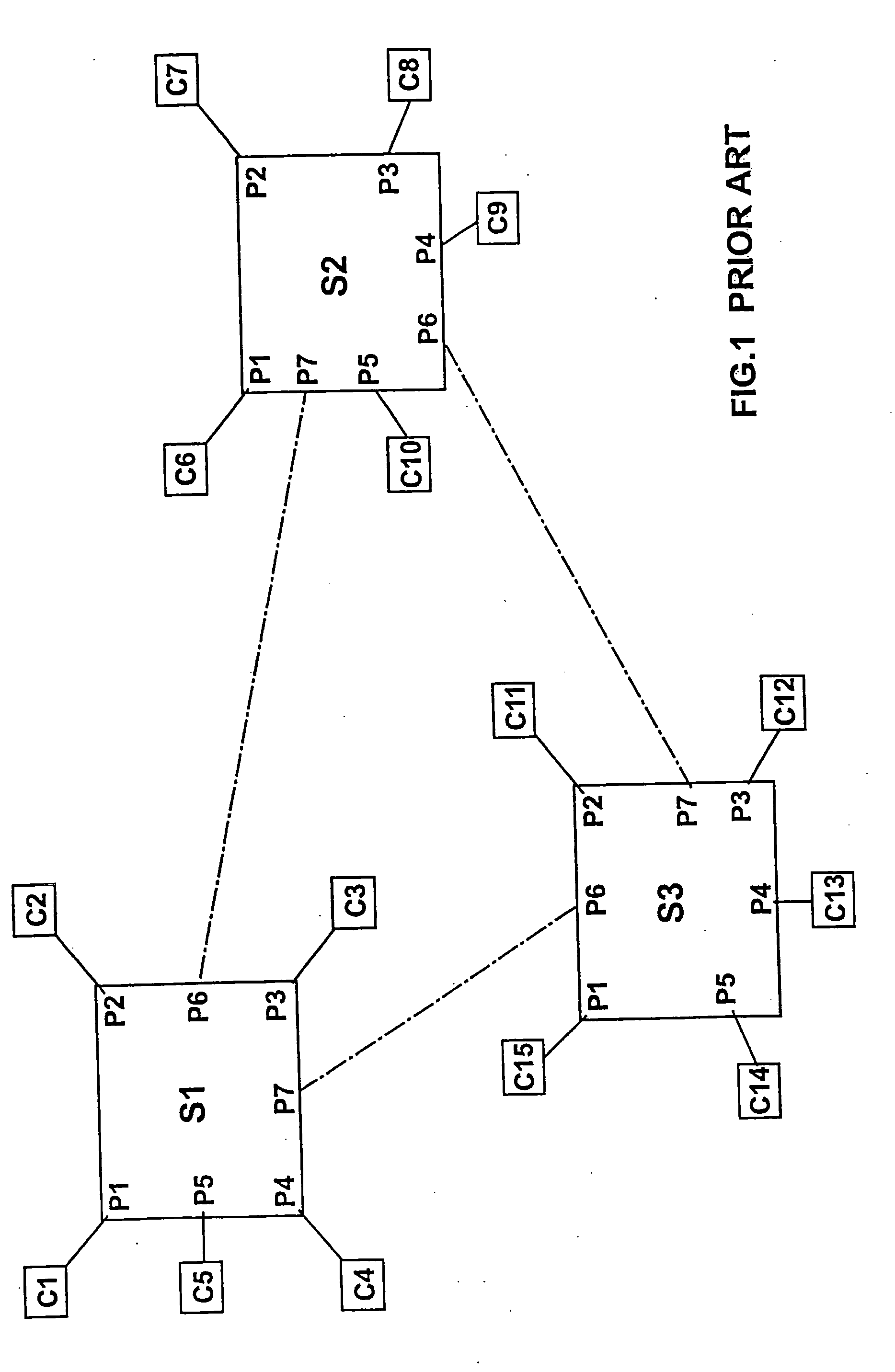
Vlan protocol
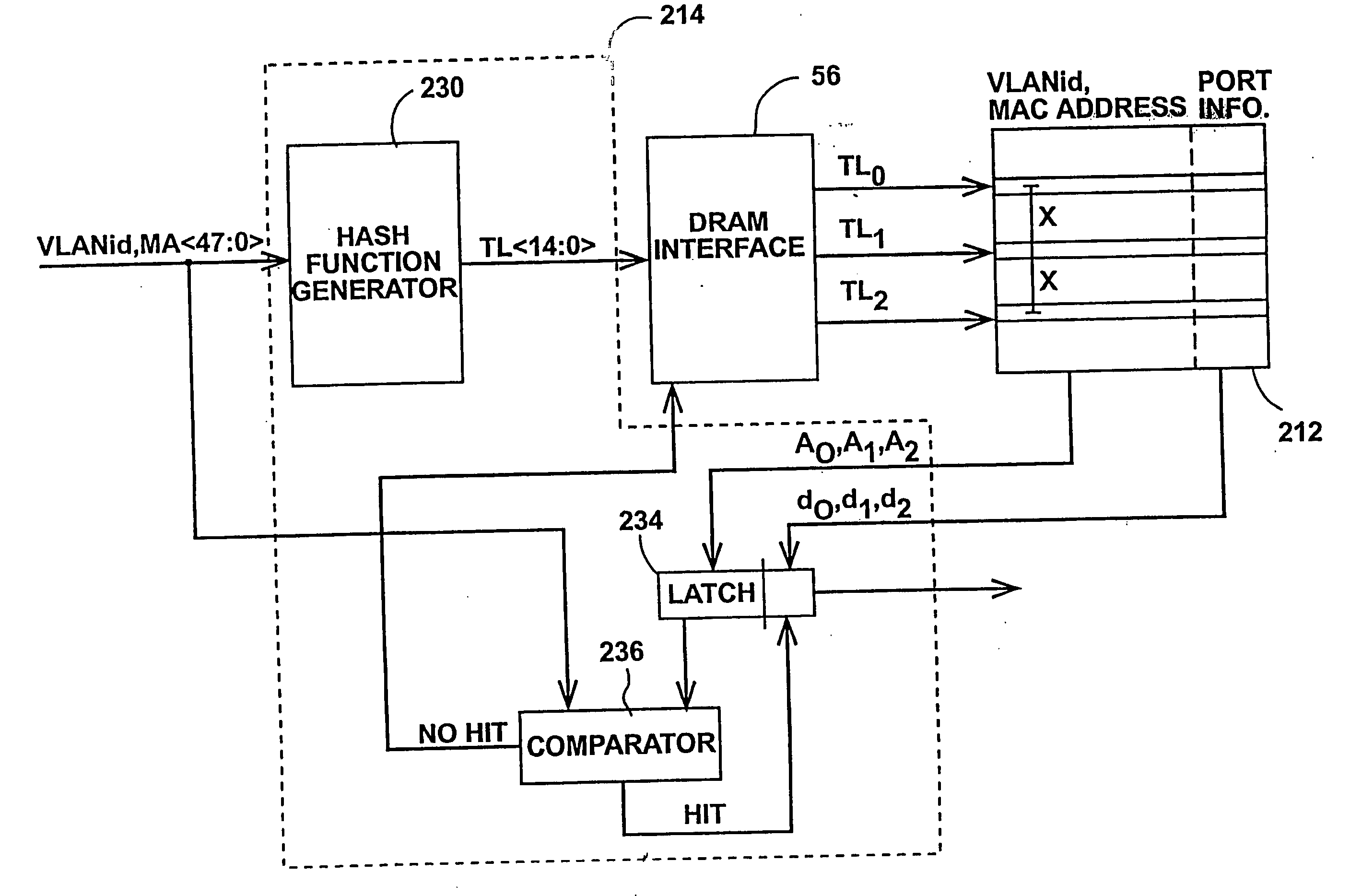
A generally full-wire throughput, switching Ethernet controller used within an Ethernet network of other switching Ethernet controllers connected together by a bus. The controller comprises a plurality of ports including at least one bus port associated with ports connected to other switching Ethernet controllers. A hash table stores MAC addresses and VLAN ids of ports within said Ethernet network. A hash table address control hashes the MAC address and VLAN id of a packet to initial hash table location values, changes the hash table location values by a fixed jump amount if the address and VLAN id values stored in said initial hash table location do not match the received address and VLAN id, and provides at least an output port number of the port associated with the received address and VLAN id. A storage buffer includes a multiplicity of contiguous buffers in which to temporarily store said packet.
Owner:MARVELL ISRAEL MISL
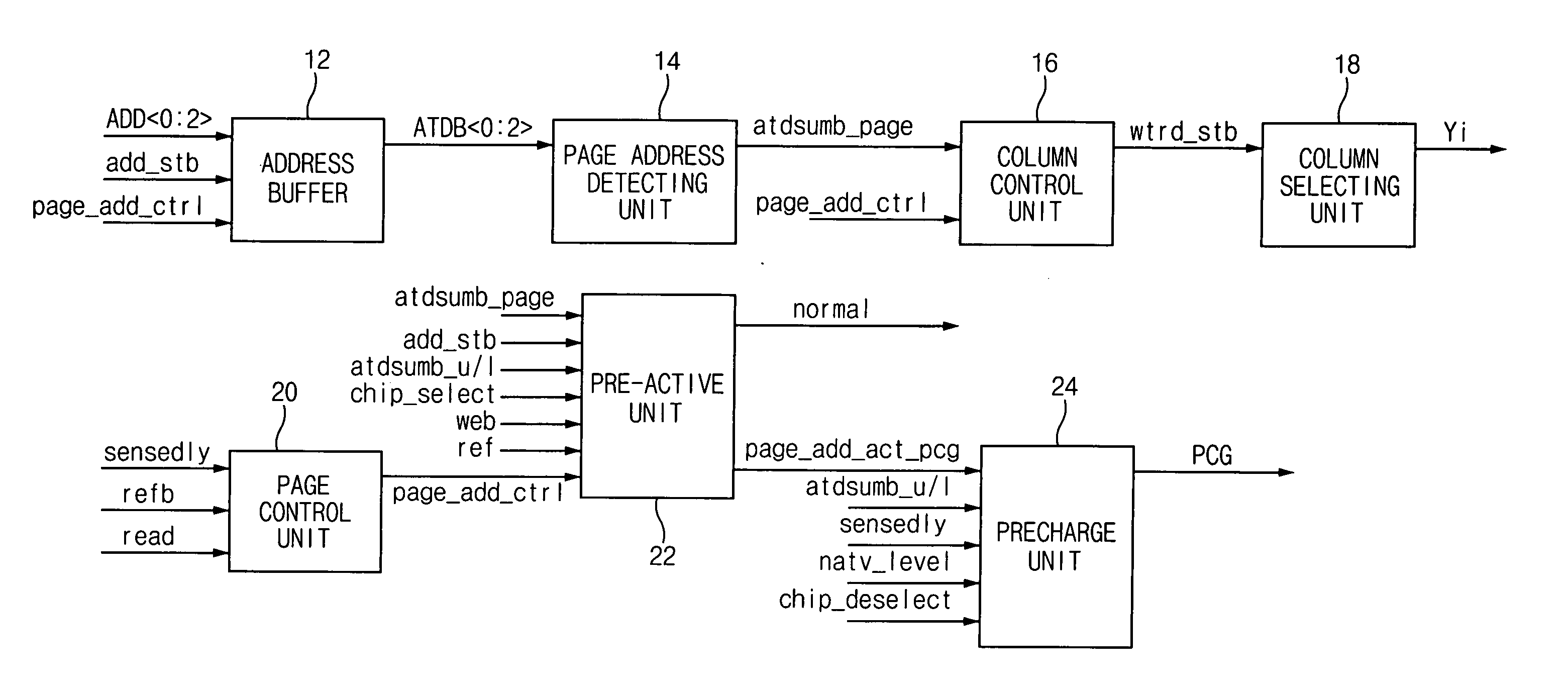
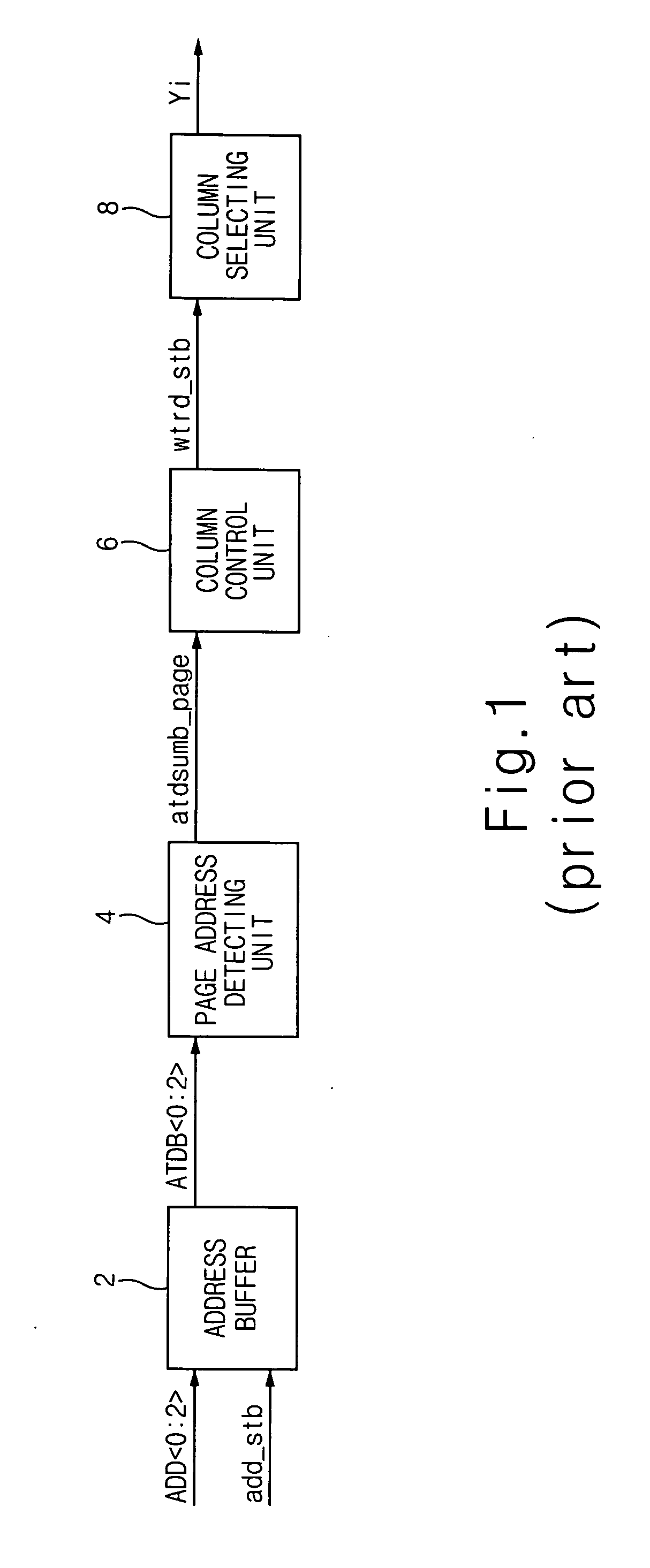
Page access circuit of semiconductor memory device
Abstract of the Disclosure A page access circuit of a semiconductor memory device is normally operated even when a page address toggles at any timing in a page mode. The page access circuit comprises an address buffer, a column control unit, a page control unit, a pre-active unit and a precharge unit. The column control unit is controlled by the page address control signal. The page control unit controlled by a sense detecting signal is adapted and configured to generate the page address control signal. The pre-active unit controlled by the page address control signal is adapted and configured to generate a mode identification signal in response to the page address transition detecting signal. The precharge unit is adapted and configured to perform a selective precharge operation in response to the mode identification signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Ram-incorporated driver, and display unit and electronic equipment using the same
InactiveUS7050032B2Reduce loadOperation efficiency can be improvedCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital storageData validationSerial transfer
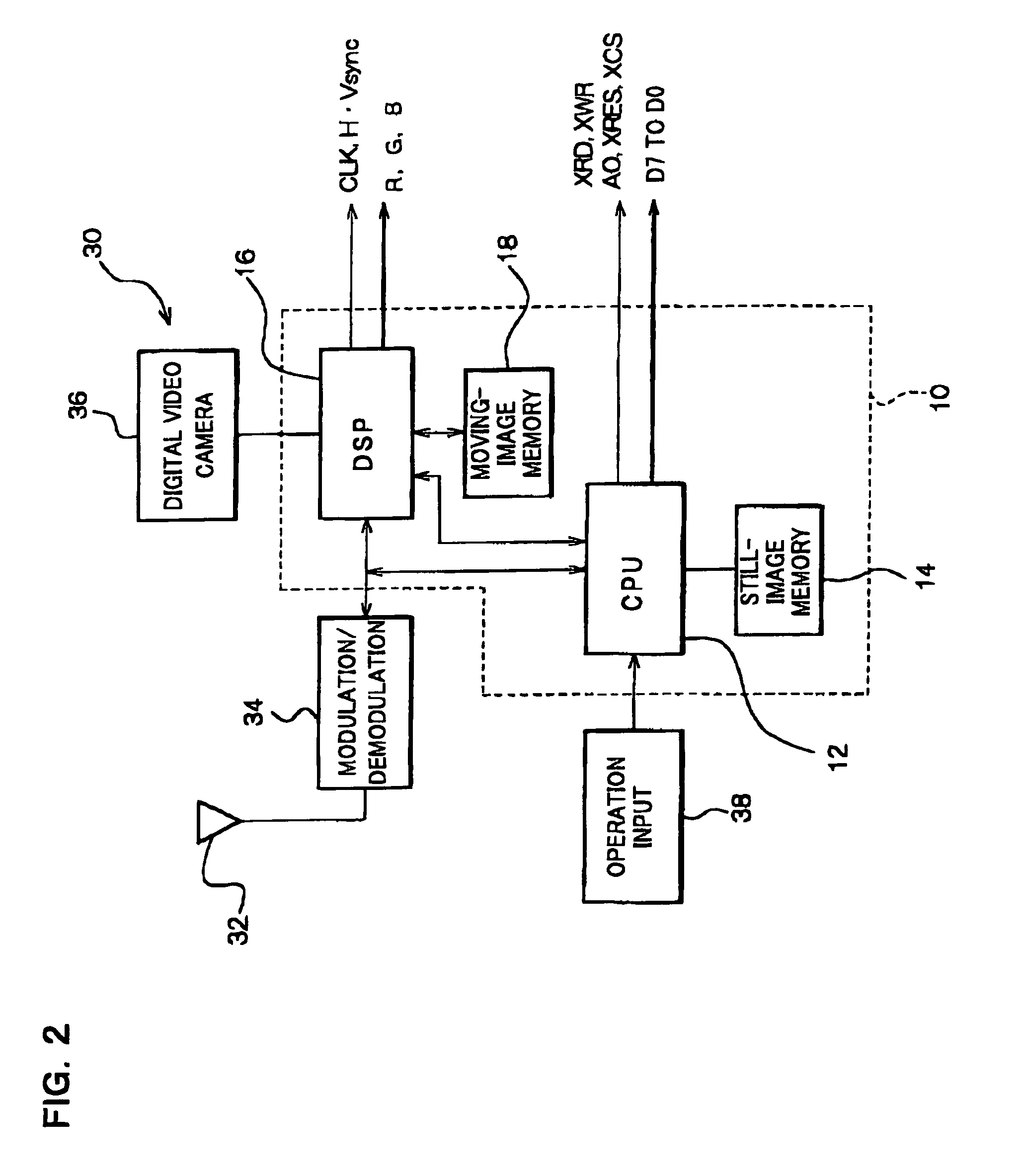
The present invention provides a RAM-incorporated driver that enables the writing of moving-image data to a RAM simultaneously with the writing of still-image data to a RAM, at a reduced energy consumption. The RAM incorporated X-driver IC receives still-image data from an MPU and moving-image data that is input by a separate system through a high-speed serial transfer line in accordance with the LVDS standard. An LVDS reception circuit suppresses the consumption of a steady current by which the differential input receiver operates, based on a data validation signal that becomes active when transfer data on the high-speed serial data transfer line from the MPU becomes valid. The still-image data and moving-image data that is received by separate systems is written to a RAM through first and second bus lines, respectively. Reading of still-image data and moving-image data, which is stored in a RAM, as display data is controlled by a display address control circuit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com