Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
223 results about "Initialization vector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
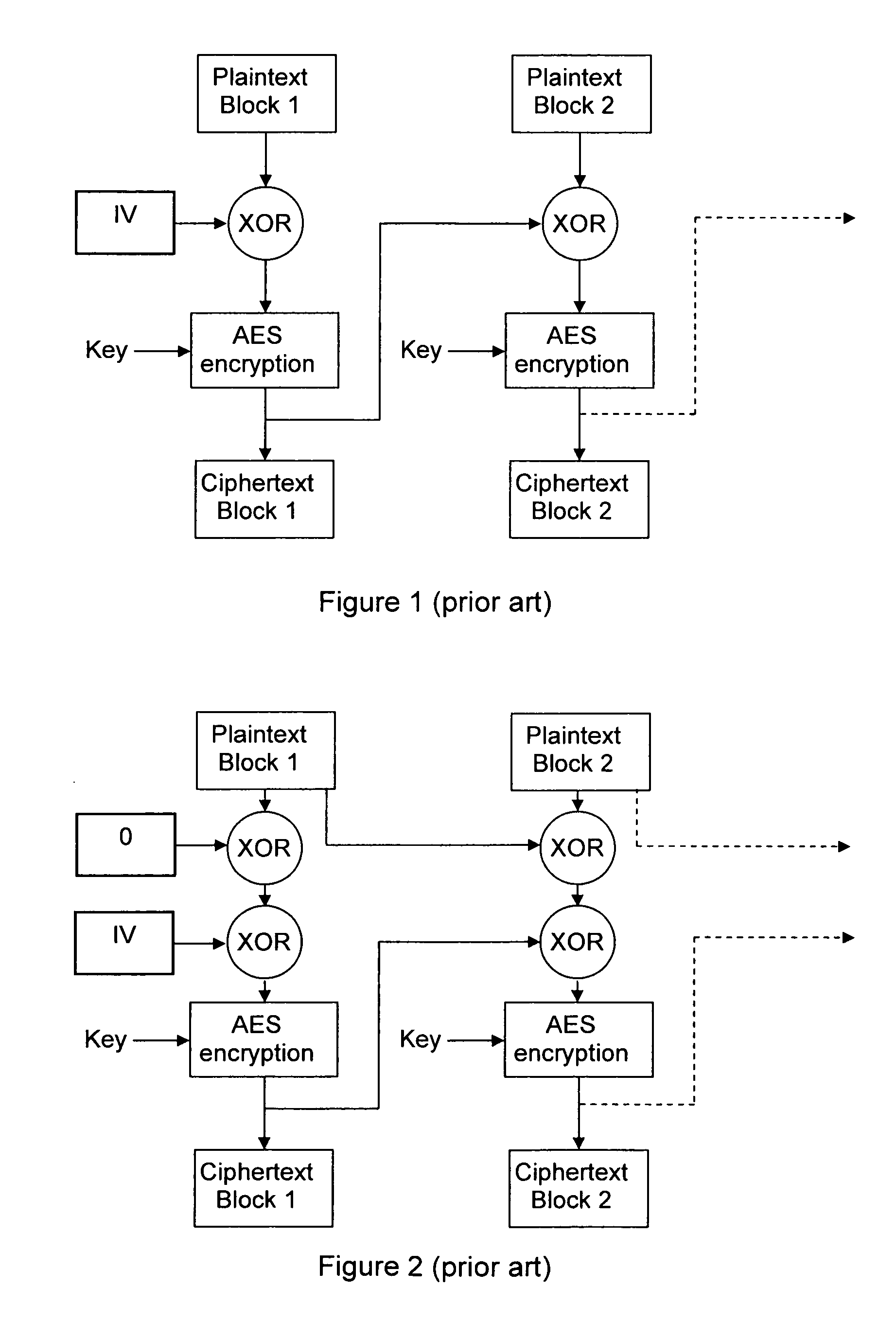
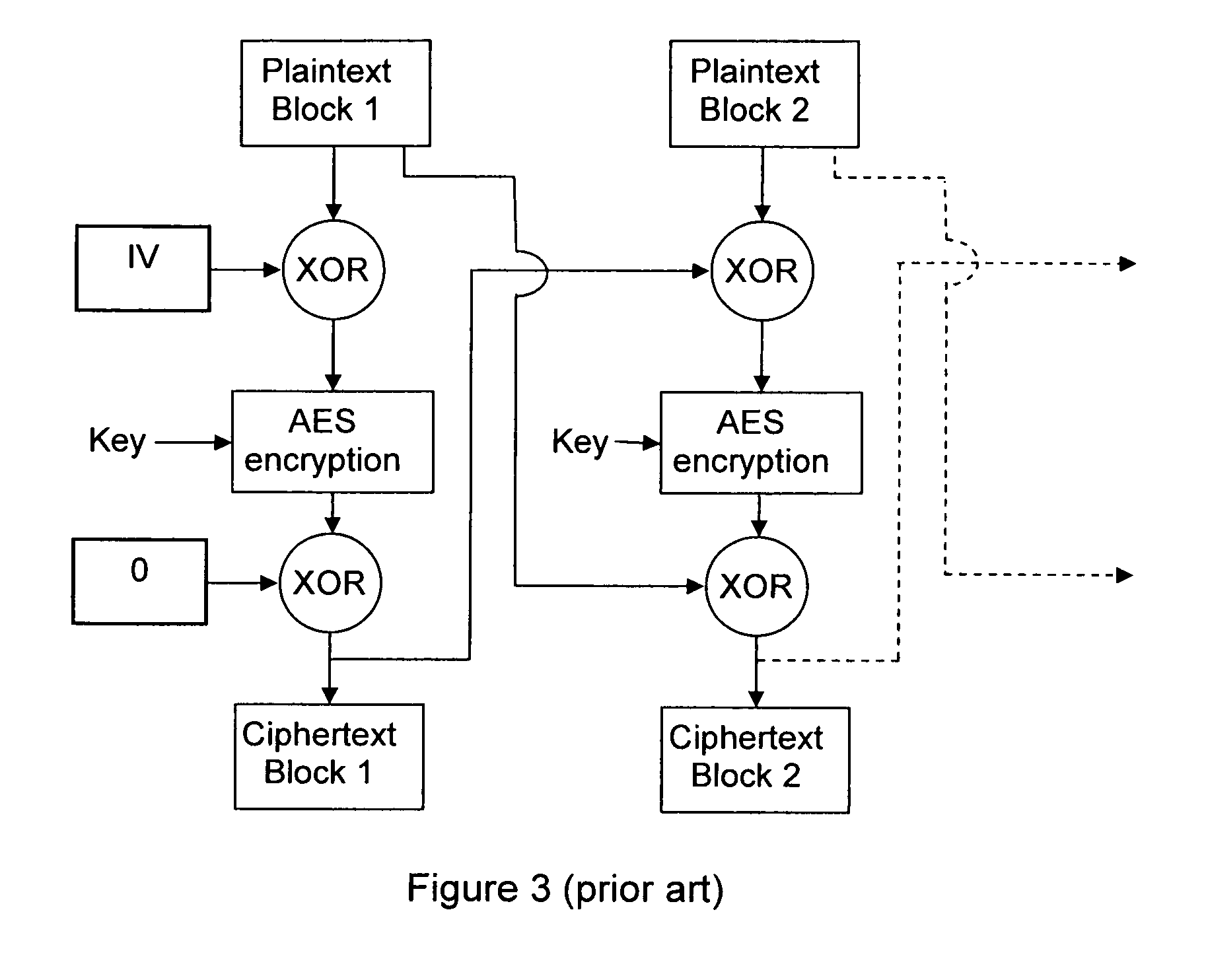
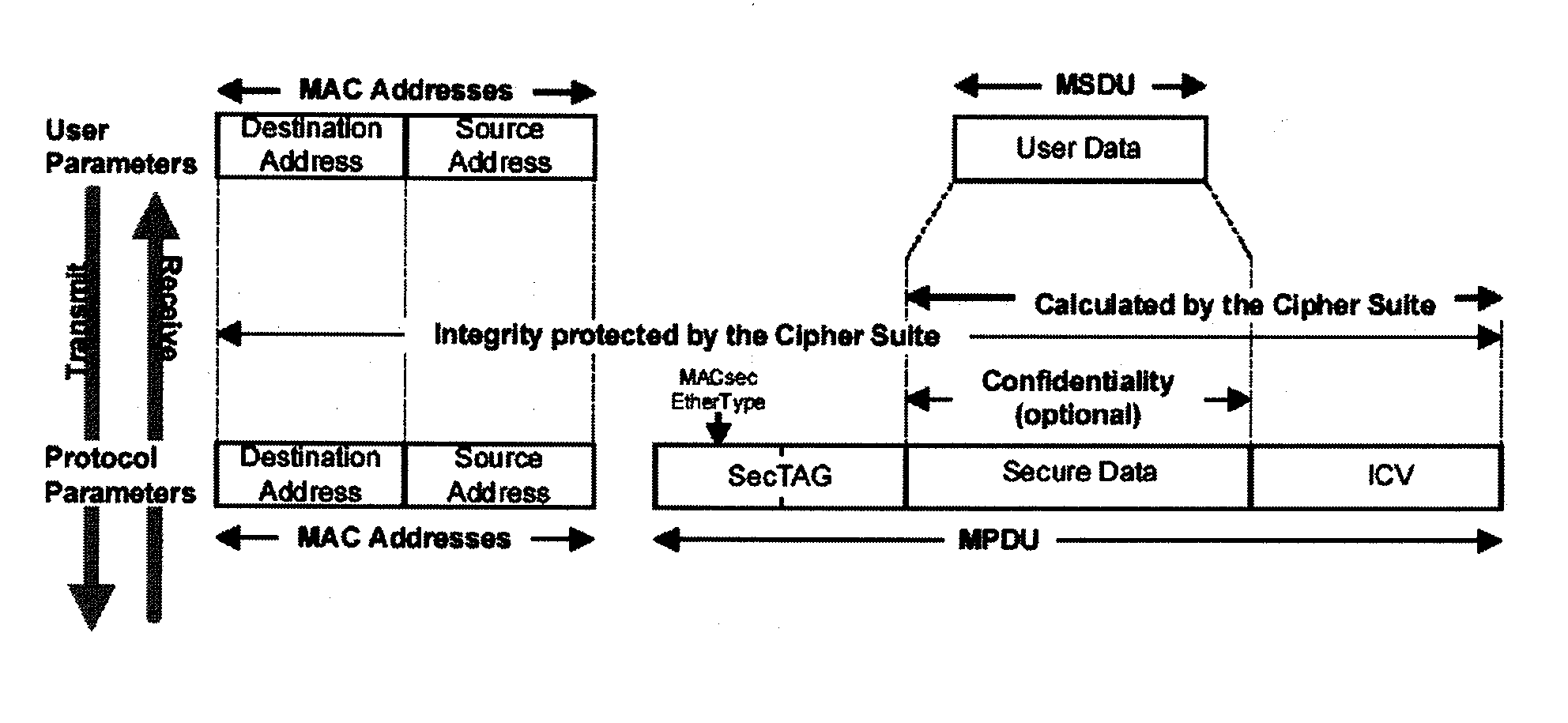
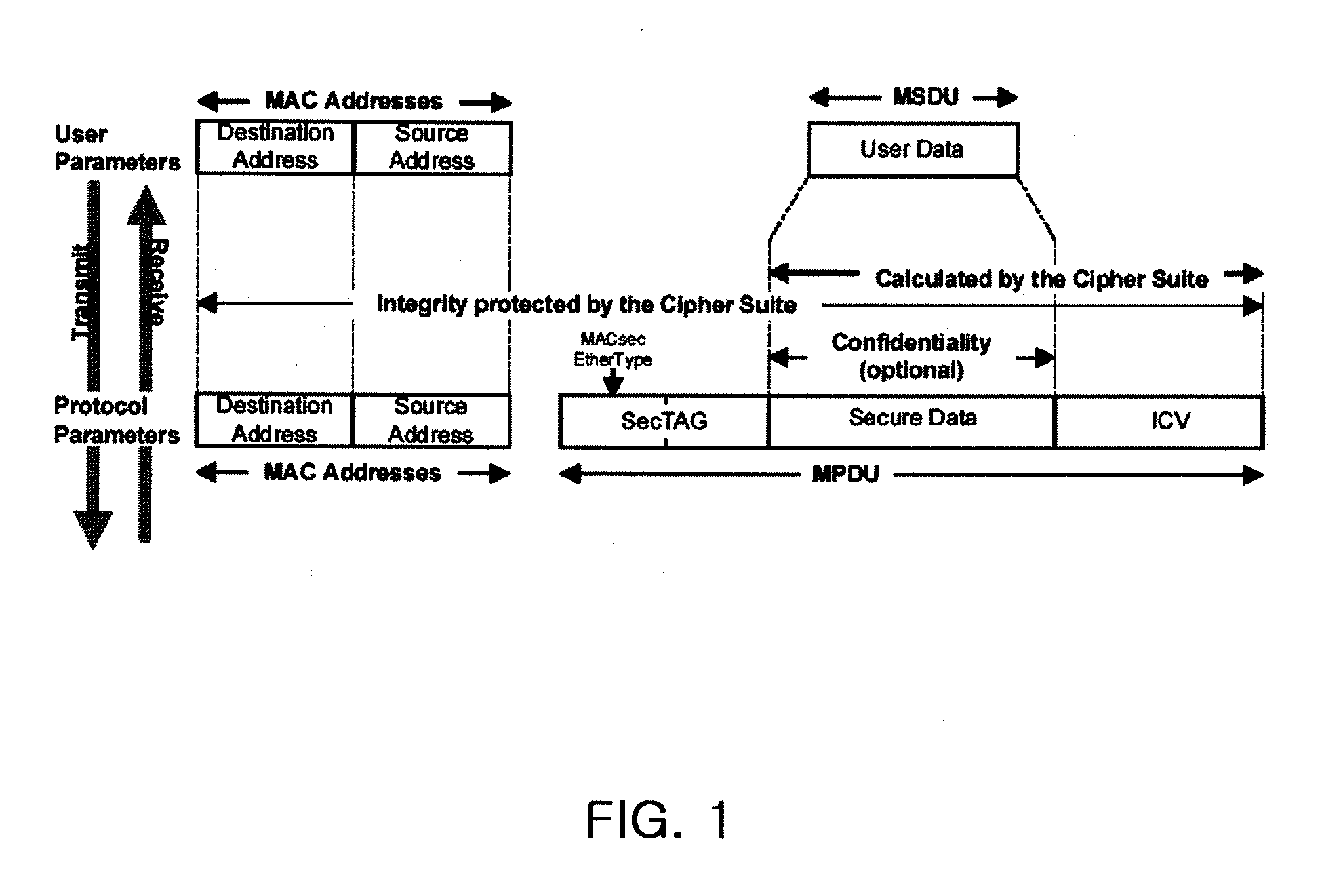
In cryptography, an initialization vector (IV) or starting variable (SV) is a fixed-size input to a cryptographic primitive that is typically required to be random or pseudorandom. Randomization is crucial for encryption schemes to achieve semantic security, a property whereby repeated usage of the scheme under the same key does not allow an attacker to infer relationships between segments of the encrypted message. For block ciphers, the use of an IV is described by the modes of operation. Randomization is also required for other primitives, such as universal hash functions and message authentication codes based thereon.
Financial transaction network
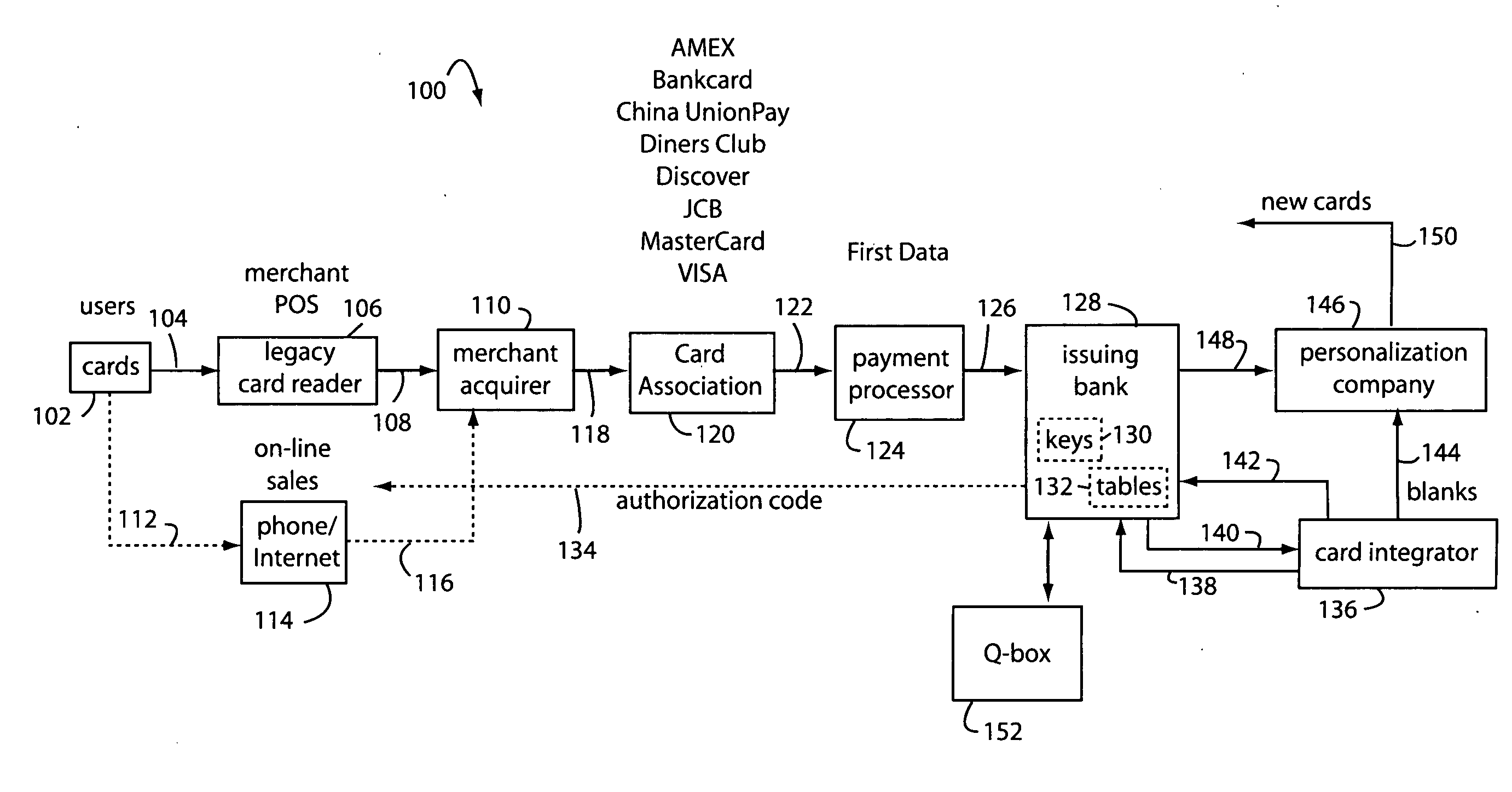
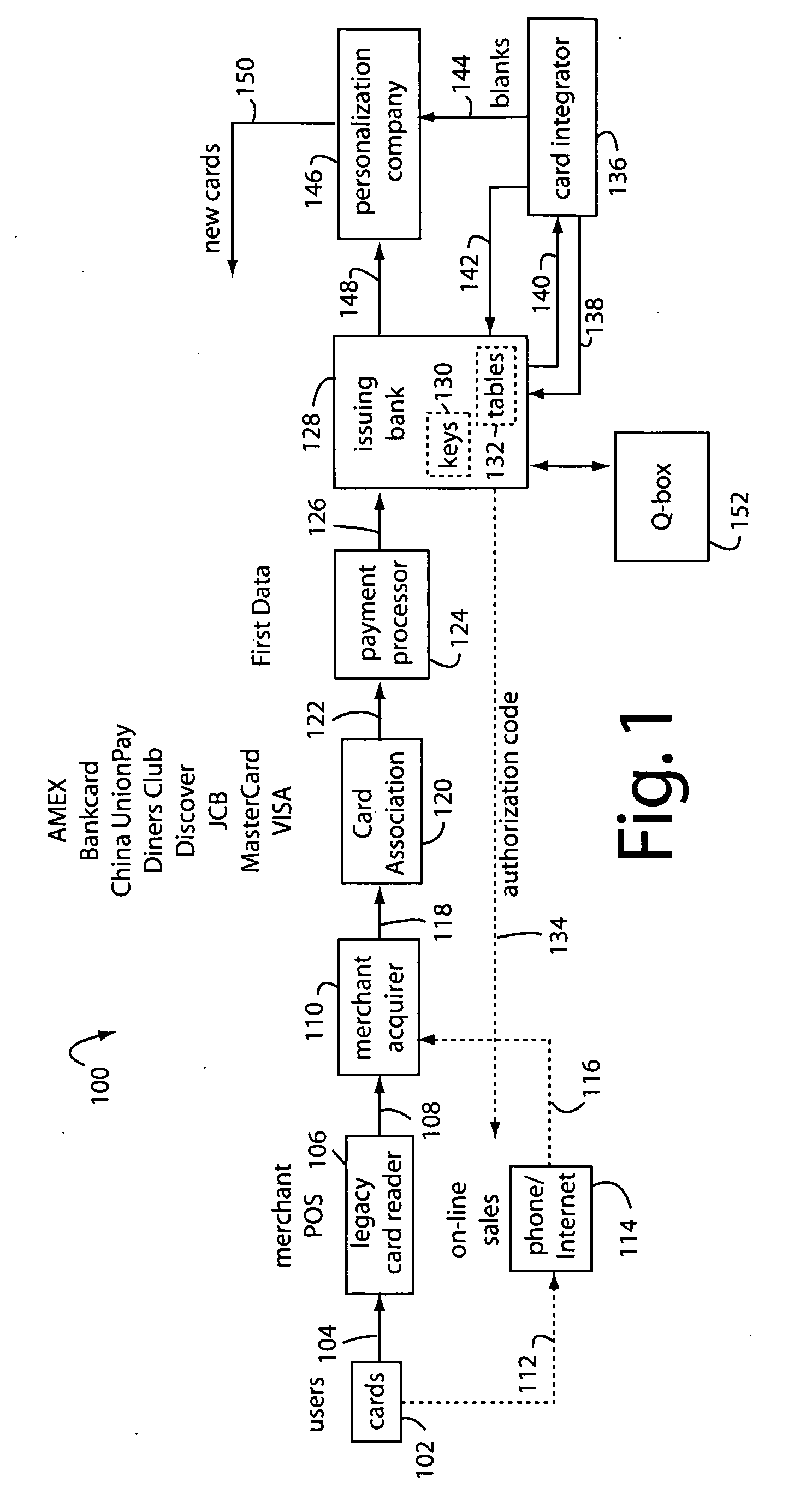
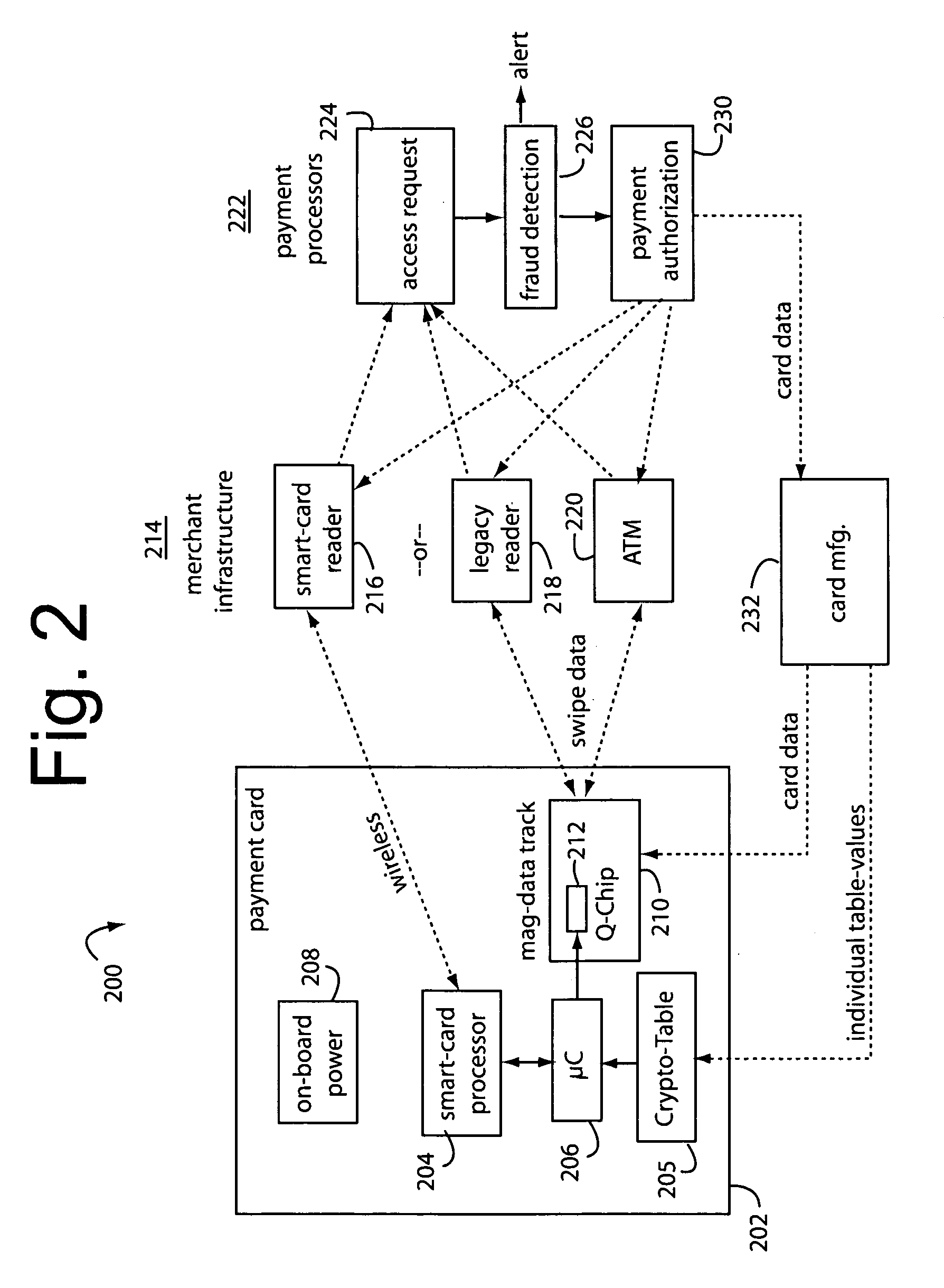
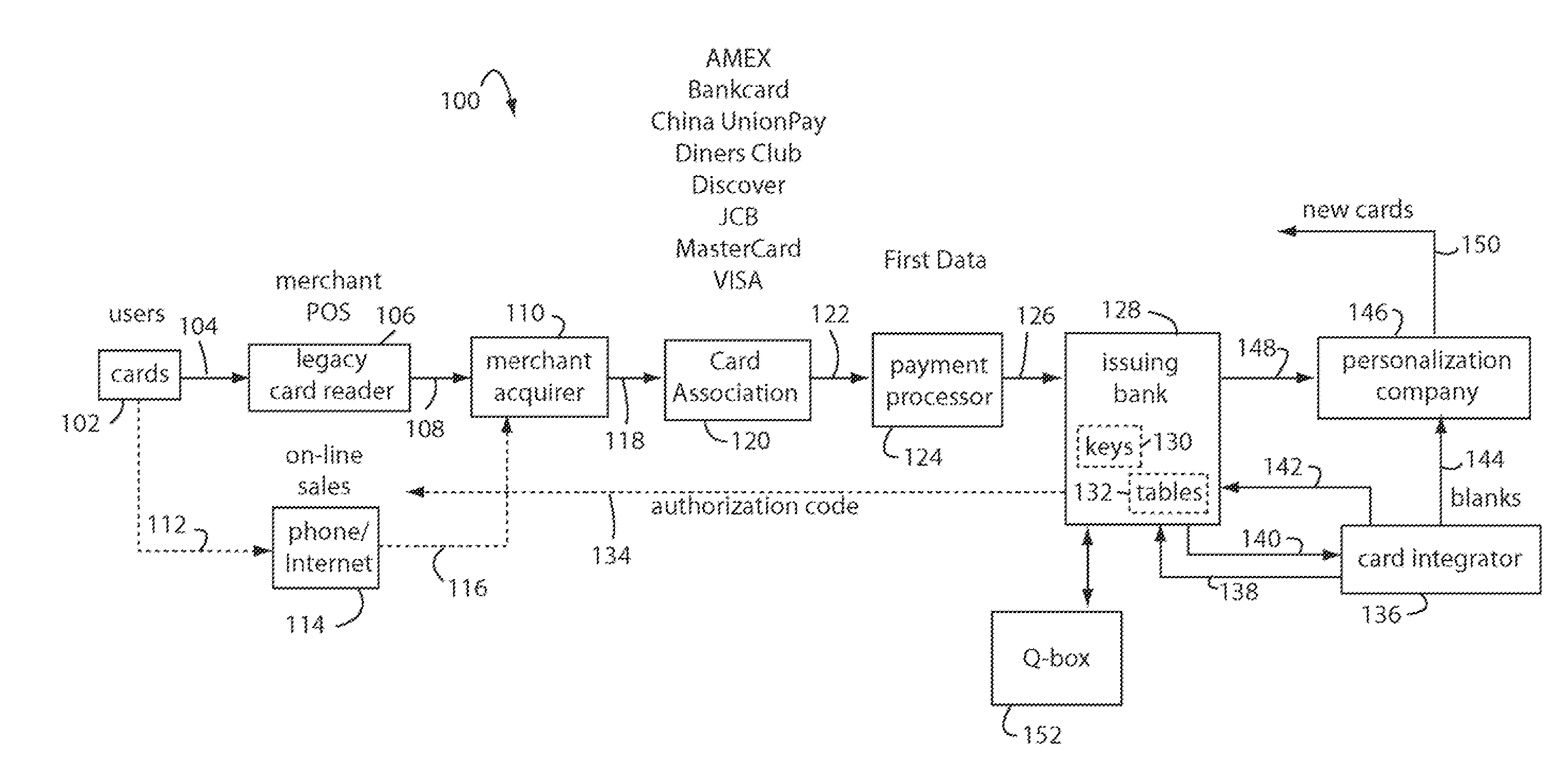
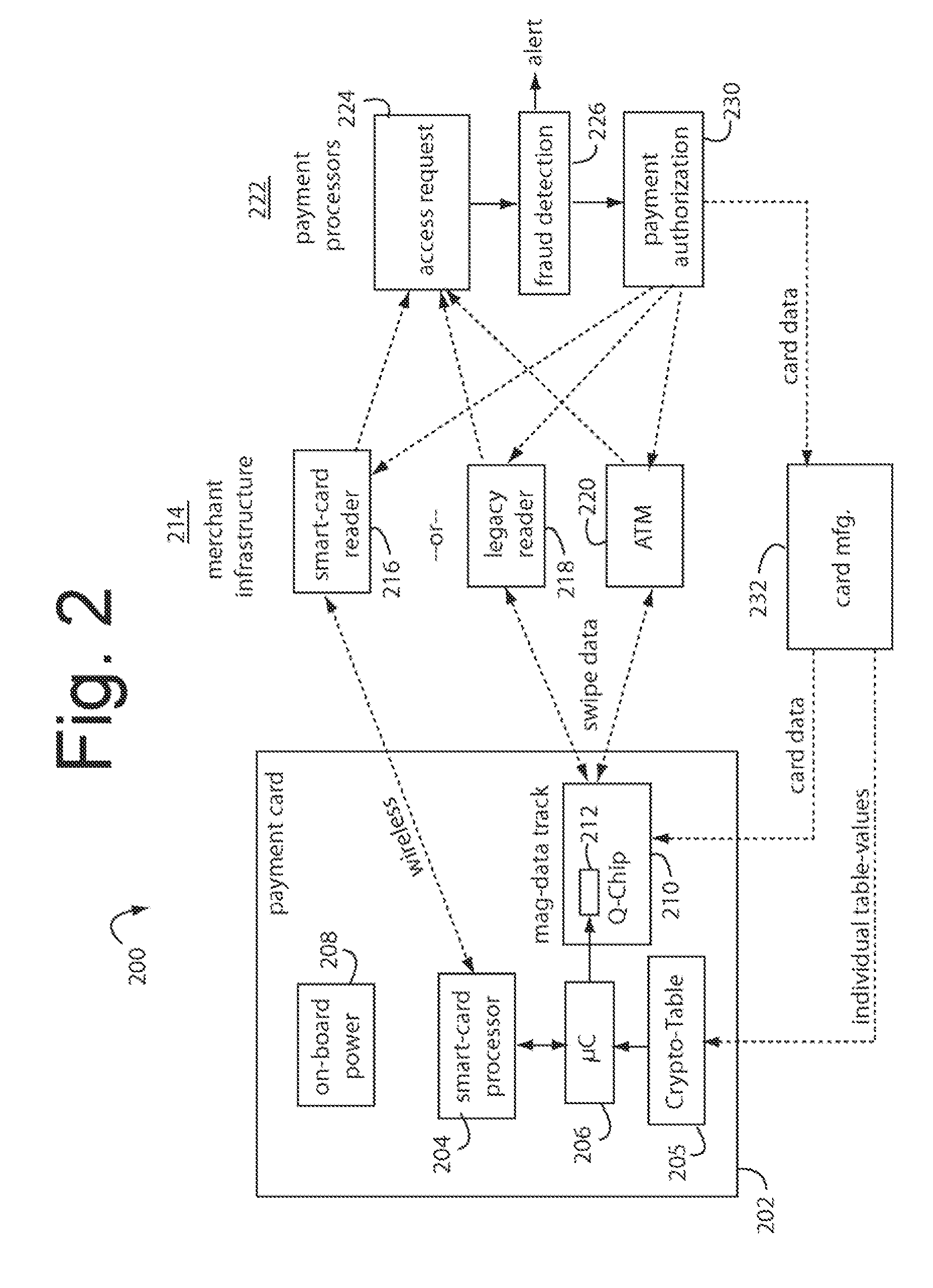
The manufacture and control of payment cards used in consumer financial transactions circulates a population of payments cards with user identification and account access codes. Each use of an individual card produces a variation of its user access code according to an encryption program seeded with encryption keys or initialization vectors. A portion of the magnetic stripe is made dynamic with a Q-Chip magnetic MEMS device. The job of personalizing payment cards with the user identification and account access codes is outsourced to a personalization company. The encryption keys and initialization vectors are kept private from the personalization company by using the encryption program to generate tables of computed results. Respective ones of the tables of computed results are sent for loading by the personalization company into new members of the population of payments cards. New payment cards are manufactured and distributed that include and operate with the tables of computed results.
Owner:FITBIT INC
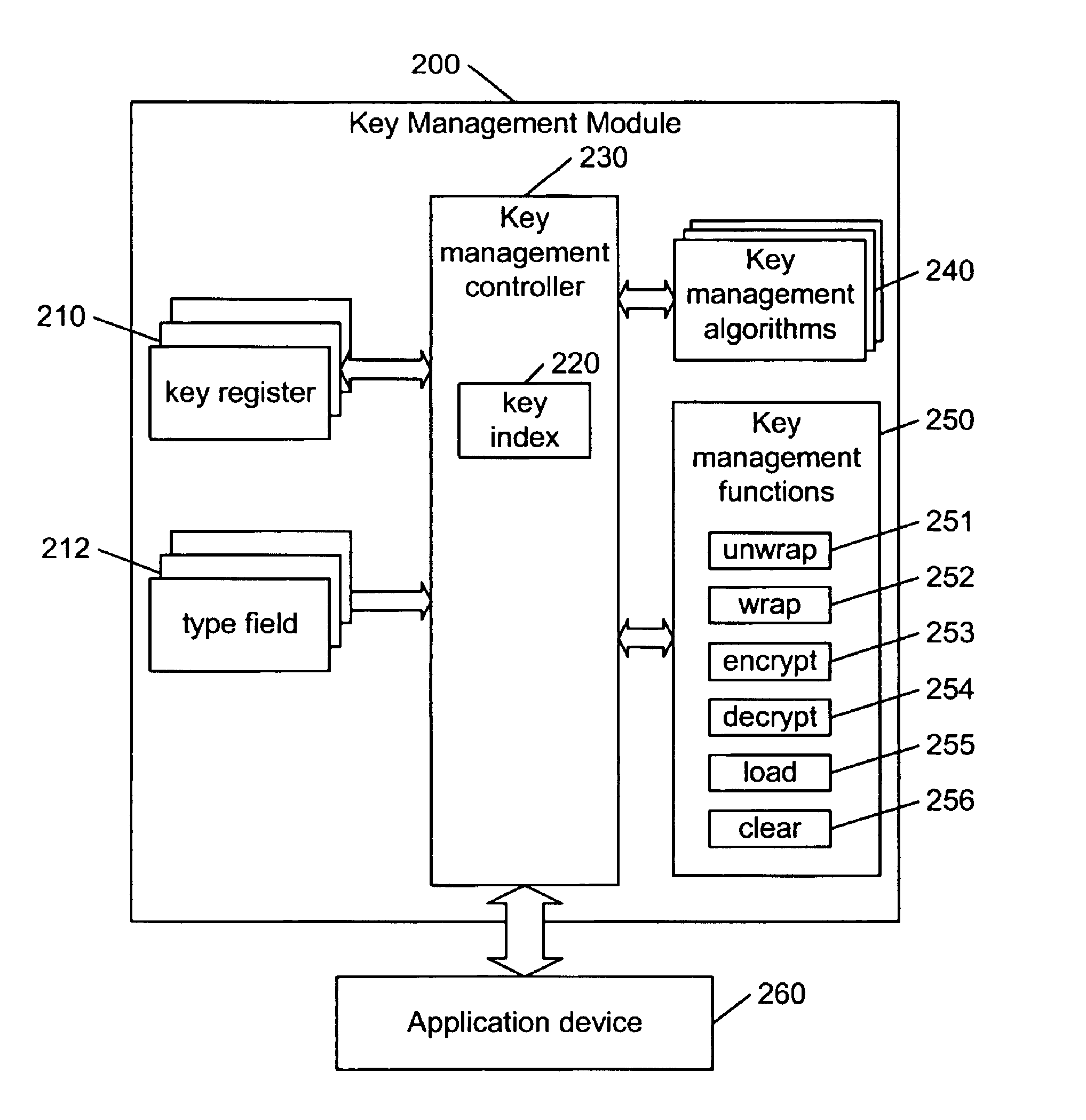
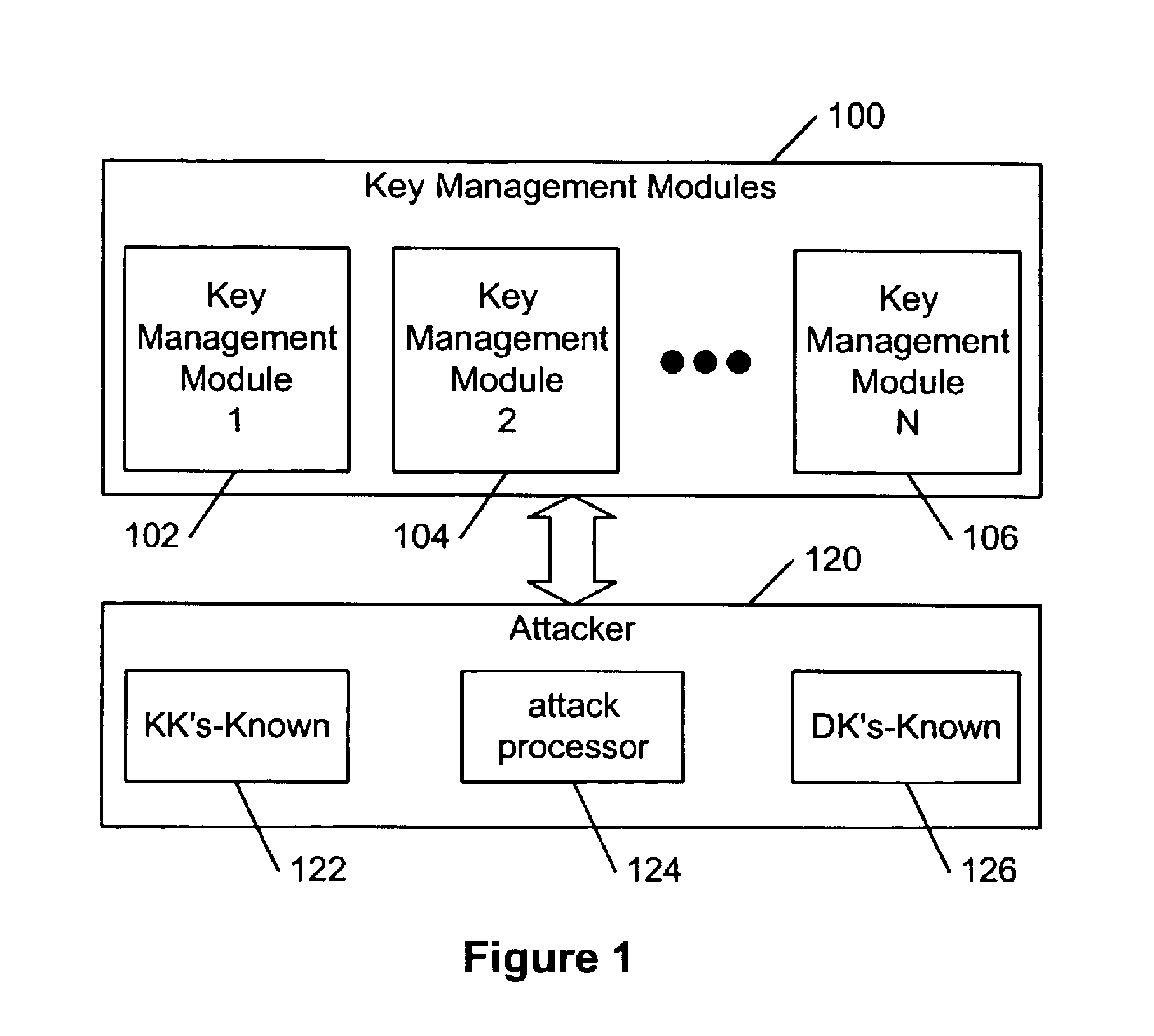
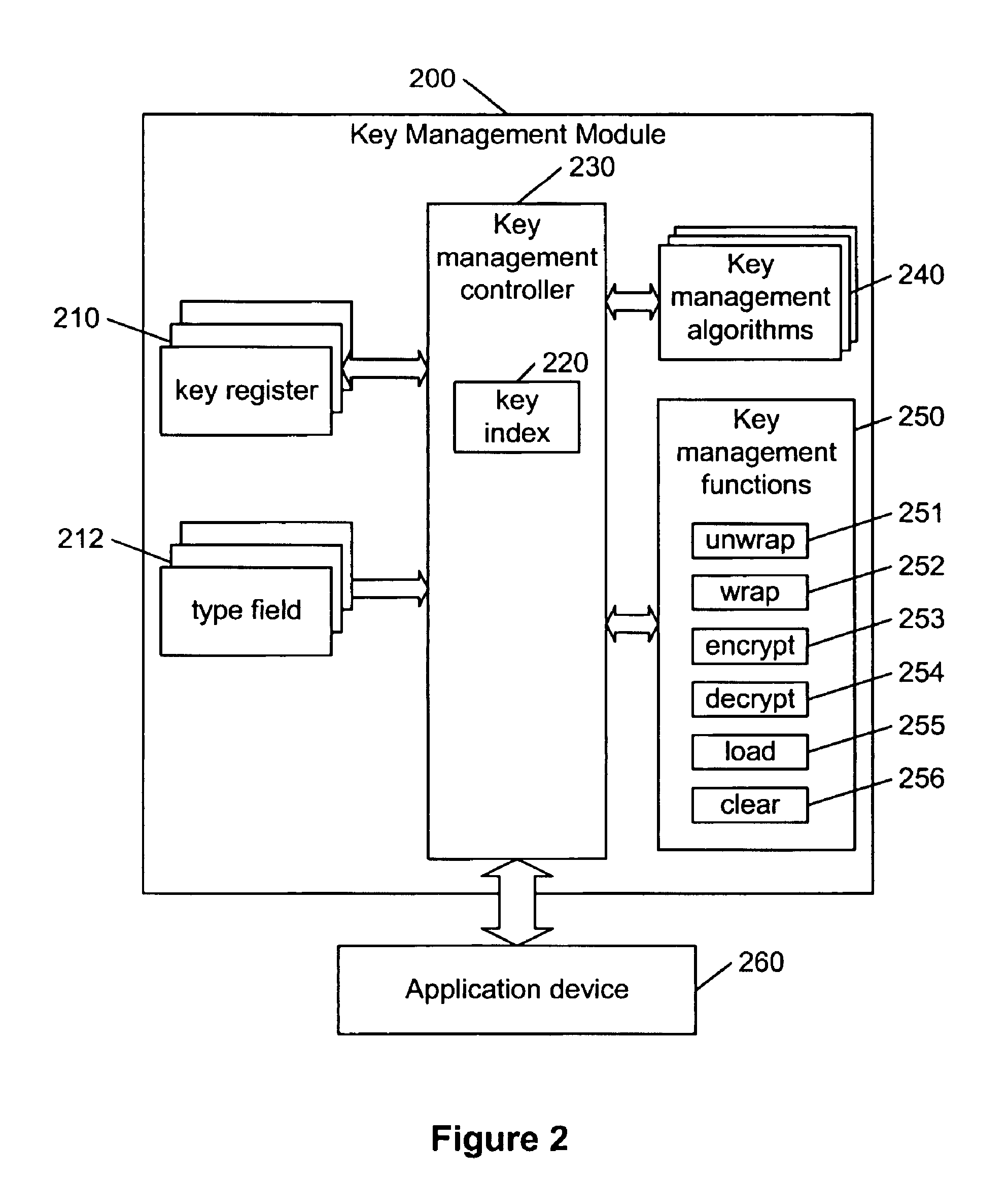
Hierarchical key management encoding and decoding
InactiveUS6907127B1Simple designSeparate applicationKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsExclusive orInitialization vector
The present invention discloses a construction for key management module functionality which provides for secure encoding and decoding of messages which are up to two blocks long. A method for generating an encoded value having a first encoded value part and a second encoded value part from an unencoded value having a first unencoded value part and a second unencoded value part, comprising the steps of: obtaining an initialization vector; and generating the first and second encoded value parts. The first encoded value part is generated by: generating a first result by encrypting the first unencoded value part; generating a second result by performing an exclusive or operation on the first result and the second unencoded value part; generating a third result by performing an exclusive or operation on the second result and the initialization vector; generating a fourth result by encrypting the third result; generating a fifth result by performing an exclusive or operation on the fourth result and the first unencoded value part; and encrypting the fifth result. The second encoded value part is generated by encrypting the second result.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Remote authentication and transaction signatures
InactiveUS20140189359A1Simple ideaUser identity/authority verificationCommunication interfaceSmart card
Authentication devices and methods for generating dynamic credentials are disclosed. The authentication devices include a communication interface for communicating with a security device such as a smart card. A dynamic credential such as a one-time password (OTP) or a message authentication code (MAC) may be generated by receiving from a server an encrypted initialization seed encrypted with an asymmetric encryption algorithm using a public key of a public / private key pair, submitting the encrypted initialization seed to a security device, decrypting at the security device the encrypted initialization seed with a private key of the public / private key pair, returning the decrypted initialization seed to the authentication device, deriving at the authentication device a secret credential generation key from the decrypted initialization seed, and generating the dynamic credential by combining a dynamic variable with the secret credential generation key using a symmetric cryptographic dynamic credential generation algorithm.
Owner:ONESPAN NORTH AMERICA INC
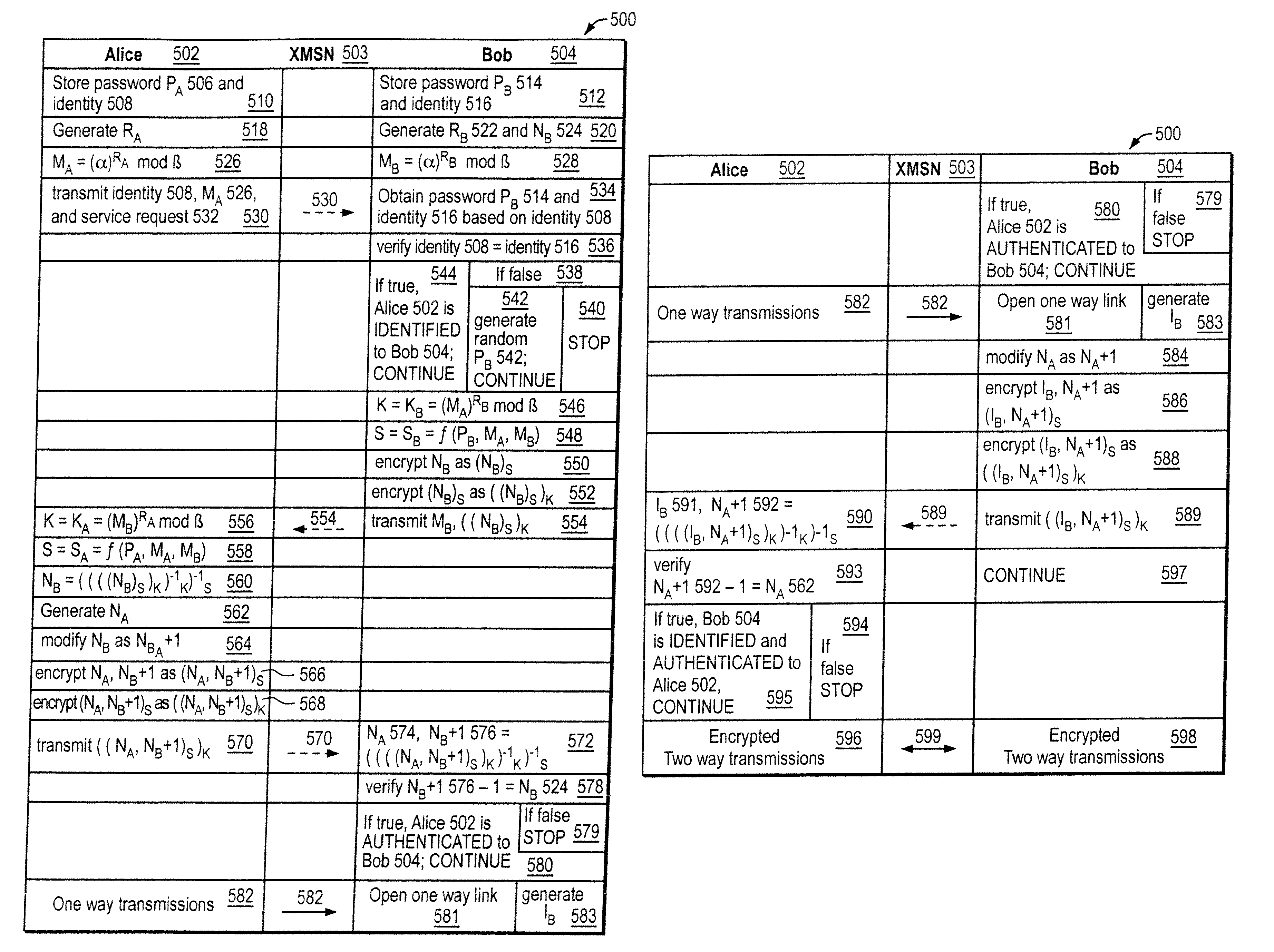
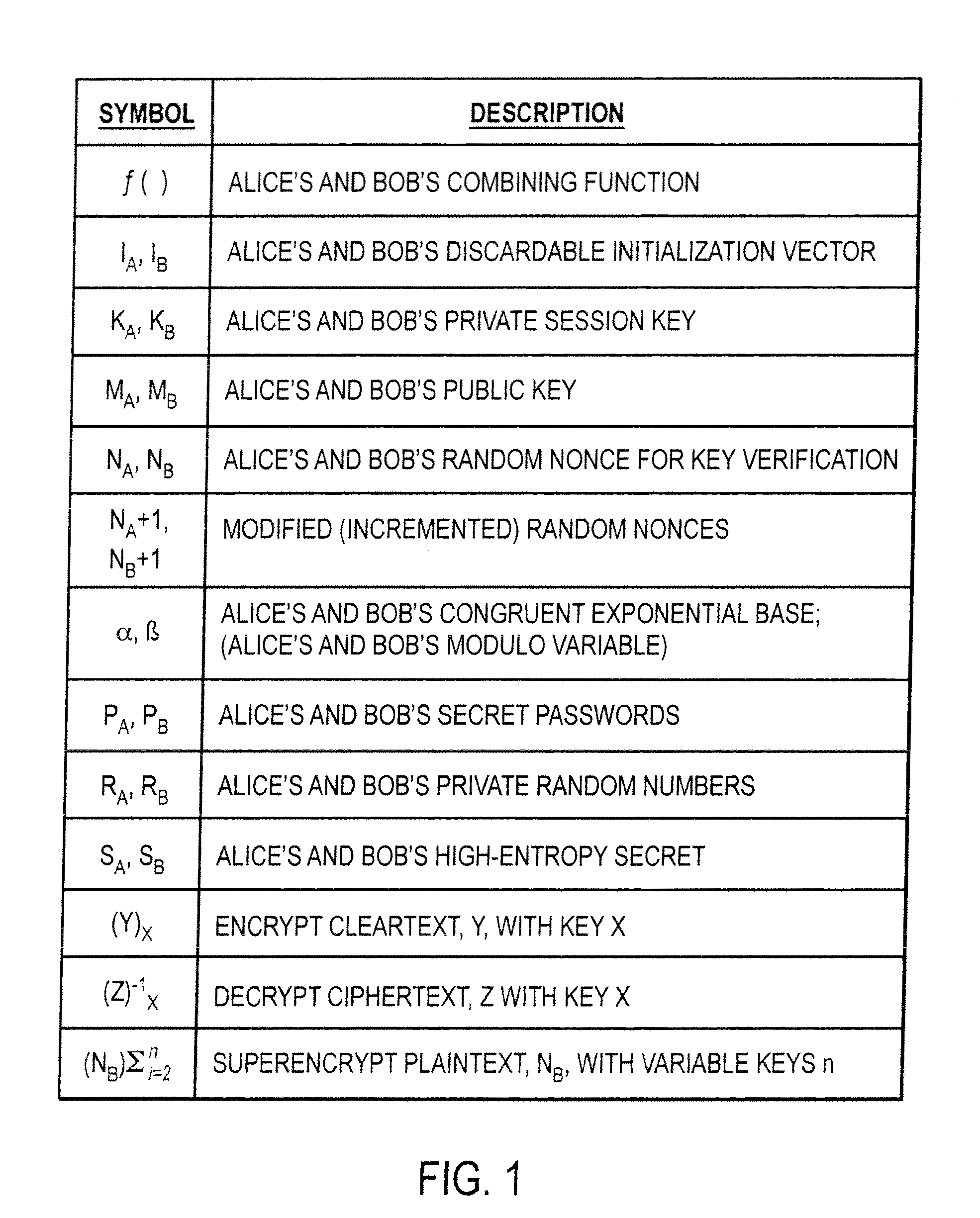
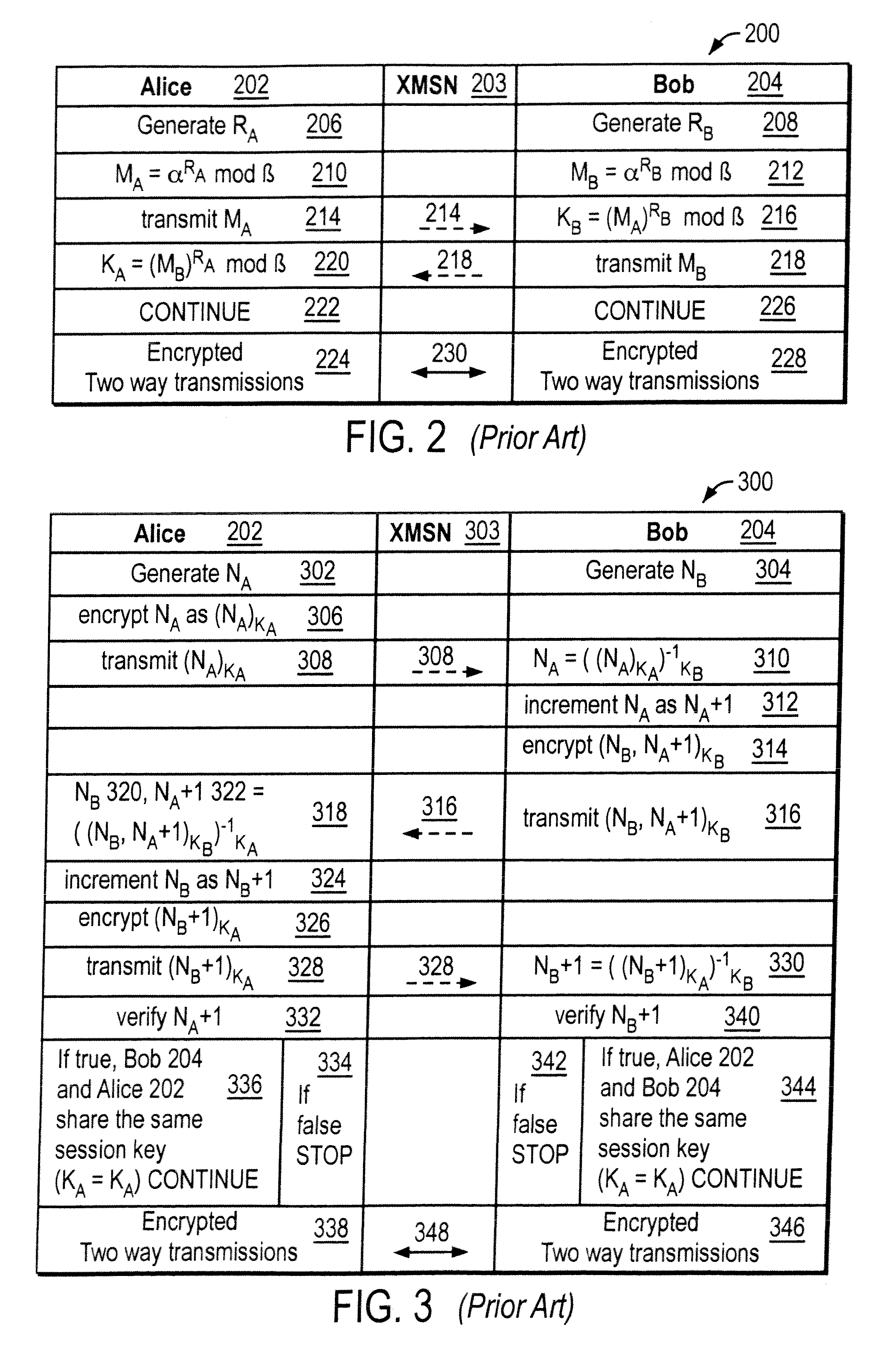
Mutually authenticated secure key exchange (MASKE)
InactiveUS7424615B1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationKey exchangeTelecommunications link
The invention provides a cryptographic method which includes receiving at a first entity a second public key MA. At least one of a first session key KB and a first secret SB may be generated based on the second public key MA. A first random nonce NB may be generated which may be encrypted with at least one of the first session key KB and the first secret SB to obtain an encrypted random nonce. The encrypted random nonce may be transmitted from the first entity. In response to transmitting the encrypted random nonce, the first computer may receive a data signal containing a modification of the first random nonce NB+1. If the modification of the first random nonce NB+1 was correctly performed, then at least one of (i) opening a communication link at the first computer, and (ii) generating a first initialization vector IB is performed.
Owner:APPLE INC
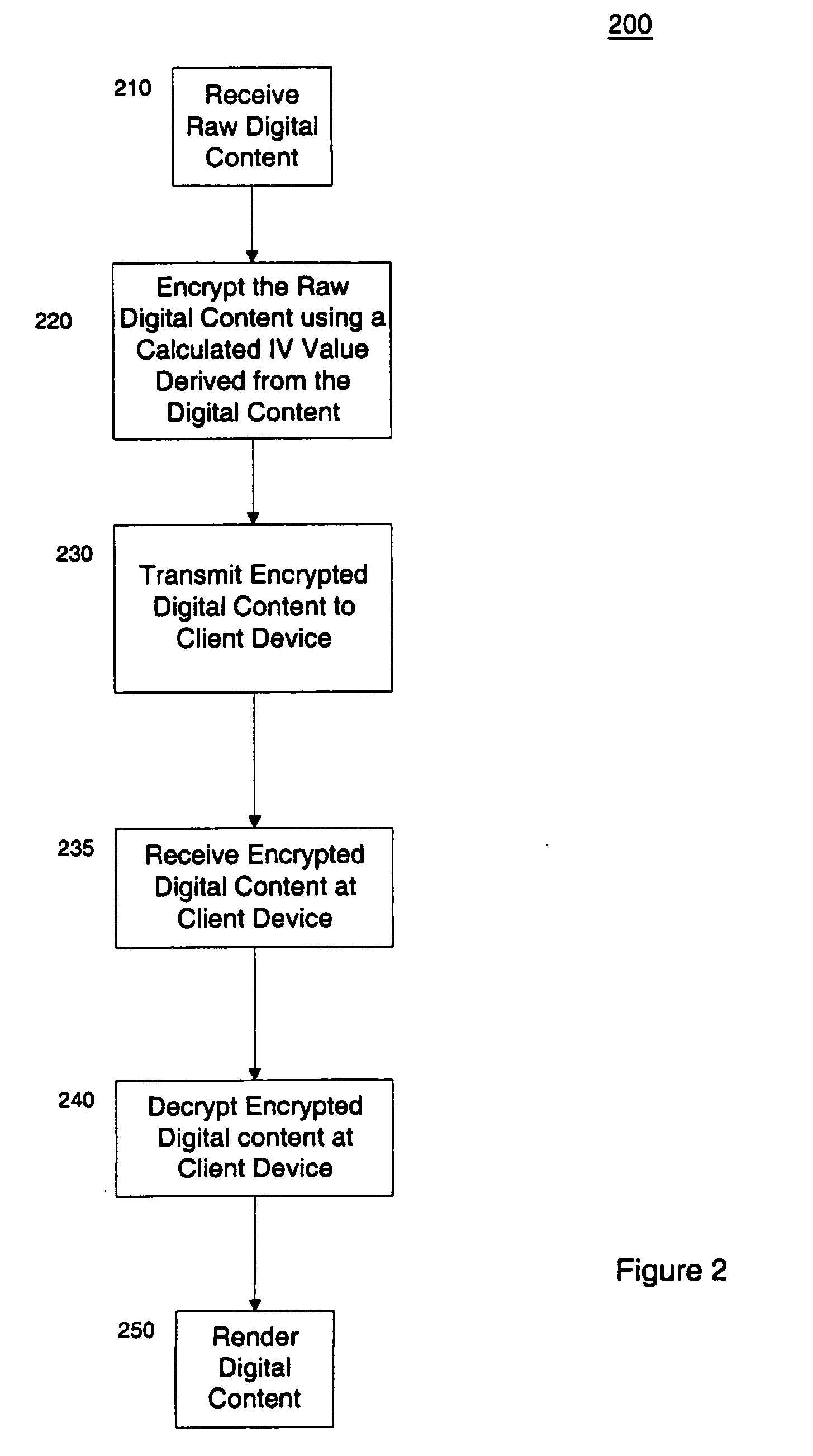
Protection of digital content using block cipher crytography
InactiveUS7055039B2Synchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesDigital contentInitialization vector
Protection of digital content using a specific application of block cipher cryptography is described. The digital content is encrypted using an encryption key and a calculated initialization vector. The digital content includes a plurality of strides of data and each stride includes a string of data to be encrypted and a block of data to be encrypted. The calculated initialization vector to be used to encrypt the block of data is derived from the string of data in the stride to be encrypted. Furthermore, the initialization vector is calculated by performing an exclusive disjunction function on a seed value and the string of data for each stride.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
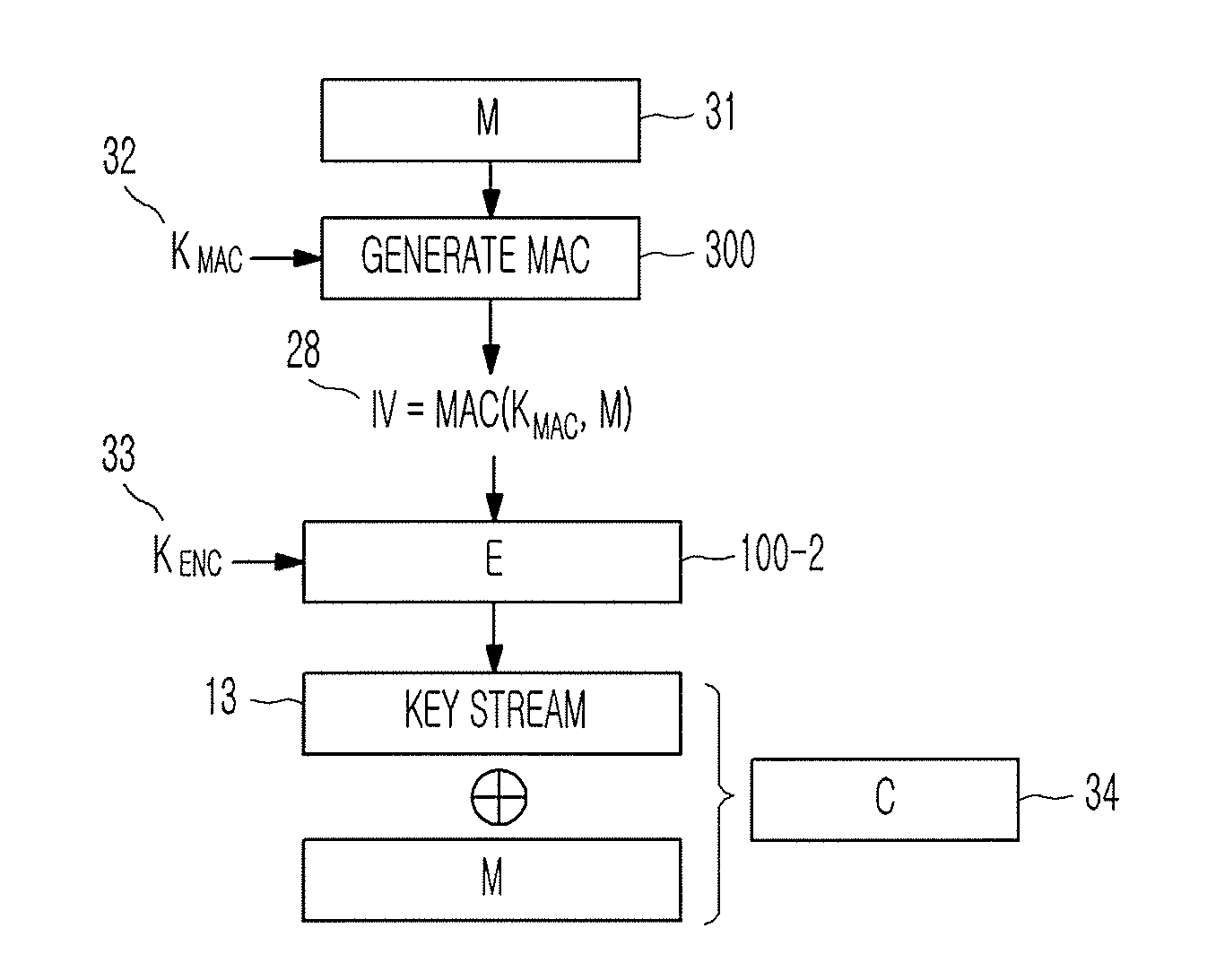
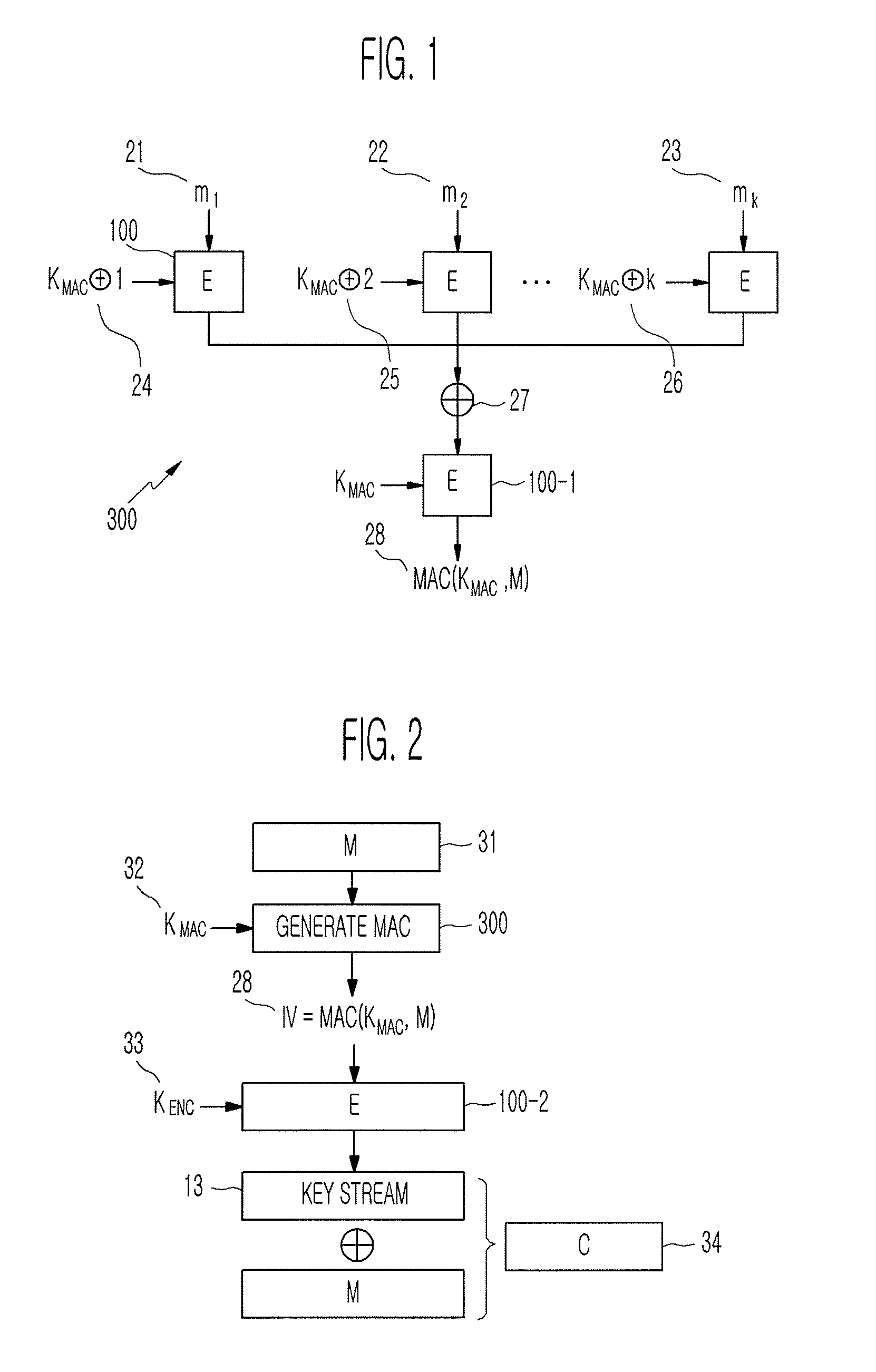
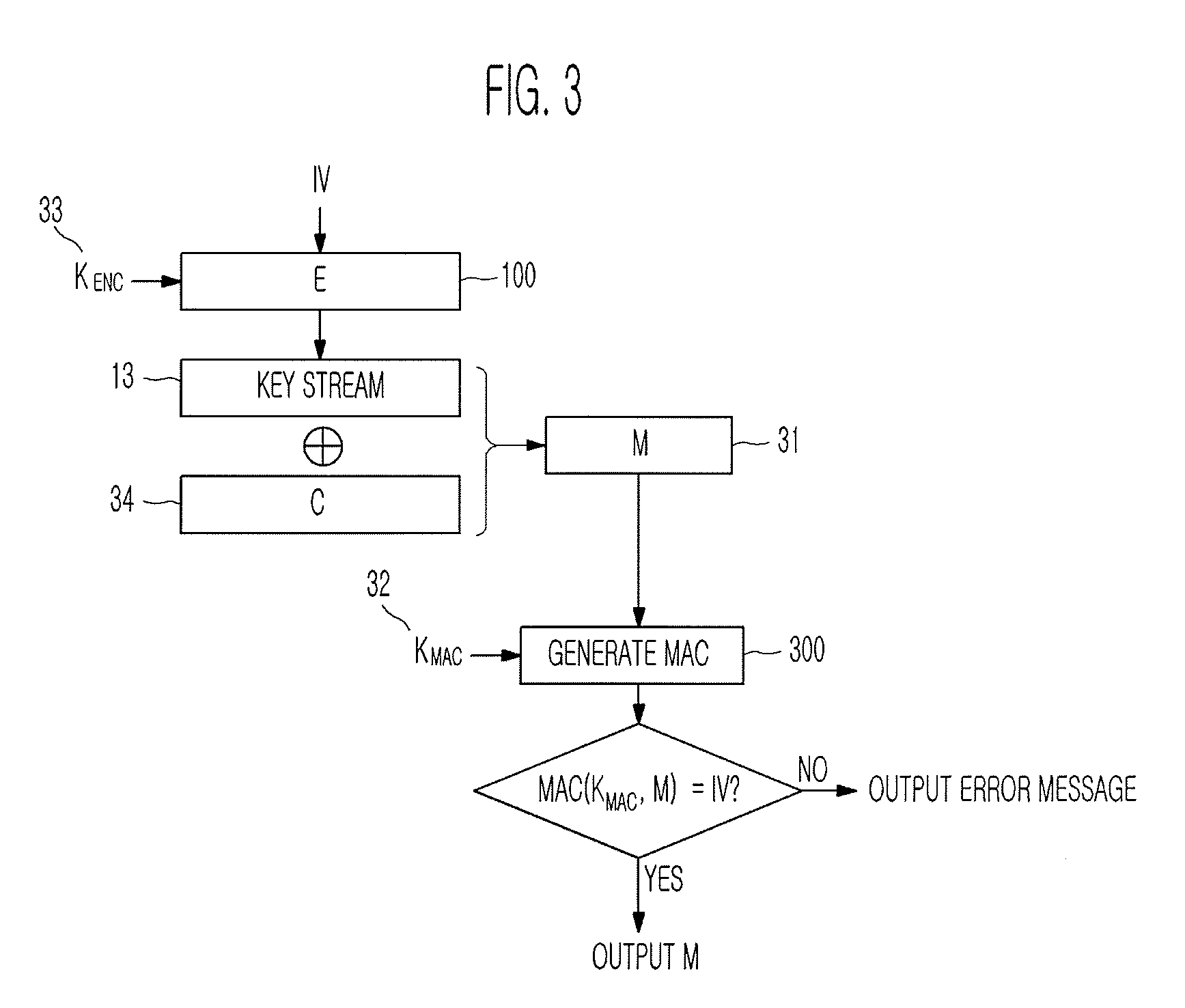
Method of generating message authentication code using stream cipher and authentication/encryption and authentication/decryption methods using stream cipher
InactiveUS20080112561A1Secret communicationSecuring communicationComputer hardwareHash-based message authentication code
Provided are a method of generating a Message Authentication Code (MAC) using a stream cipher, and authentication / encryption and authentication / decryption methods using a stream cipher.According to the methods, authentication / encryption is performed using a MAC generated using a stream cipher as an initialization vector of the stream cipher. Therefore, it is unnecessary to use a random number generation algorithm to generate the initialization vector, and thus implementation efficiency can be improved.In addition, upon generation of a MAC, a plurality of key stream generators perform computation for a plurality of message blocks, respectively. Therefore, the message blocks are computed in parallel at a time, and thus computation efficiency is excellent.
Owner:NAINFOX CO LTD
Financial transaction network security
InactiveUS20070100754A1Eliminate disintermediationSecure networkComputer security arrangementsDebit schemesPersonalizationFinancial transaction
A business model for the manufacture and control of payment cards used in consumer financial transactions circulates a population of payments cards with user identification and account access codes. Each use of an individual card produces a variation of its user access code according to an encryption program seeded with encryption keys or initialization vectors. A portion of the magnetic stripe is made dynamic with a Q-Chip magnetic MEMS device. The job of personalizing payment cards with the user identification and account access codes is outsourced to a personalization company. The encryption keys and initialization vectors are kept private from the personalization company by using the encryption program to generate tables of computed results. Respective ones of the tables of computed results are sent for loading by the personalization company into new members of the population of payments cards. New payment cards are manufactured and distributed that include and operate with the tables of computed results.
Owner:FITBIT INC
Method and Apparatus of Providing the Security and Error Correction Capability for Memory Storage Devices
InactiveUS20090125726A1Improve securityEnhance error correction capabilityMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRead-only memoriesComputer moduleInitialization vector
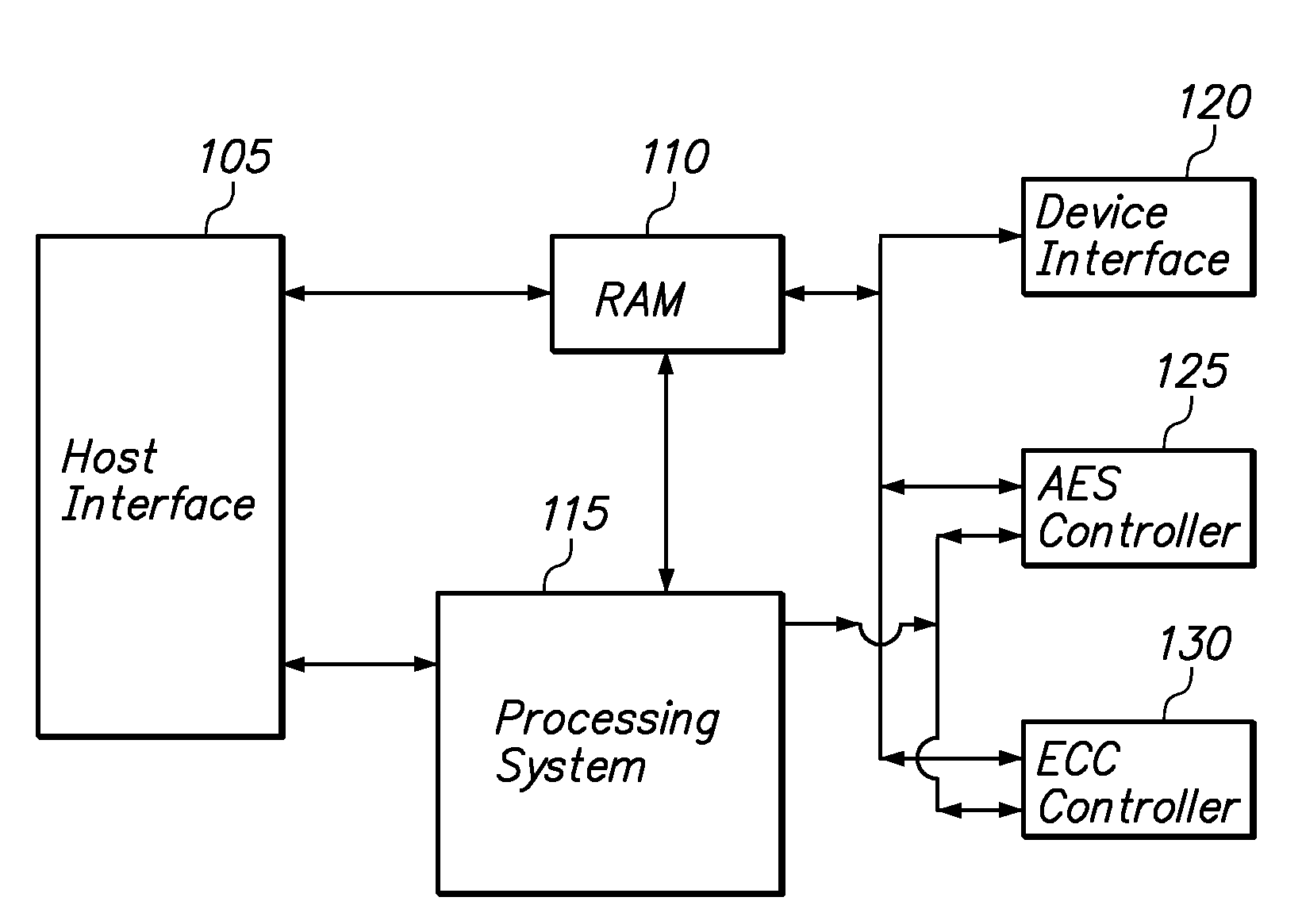
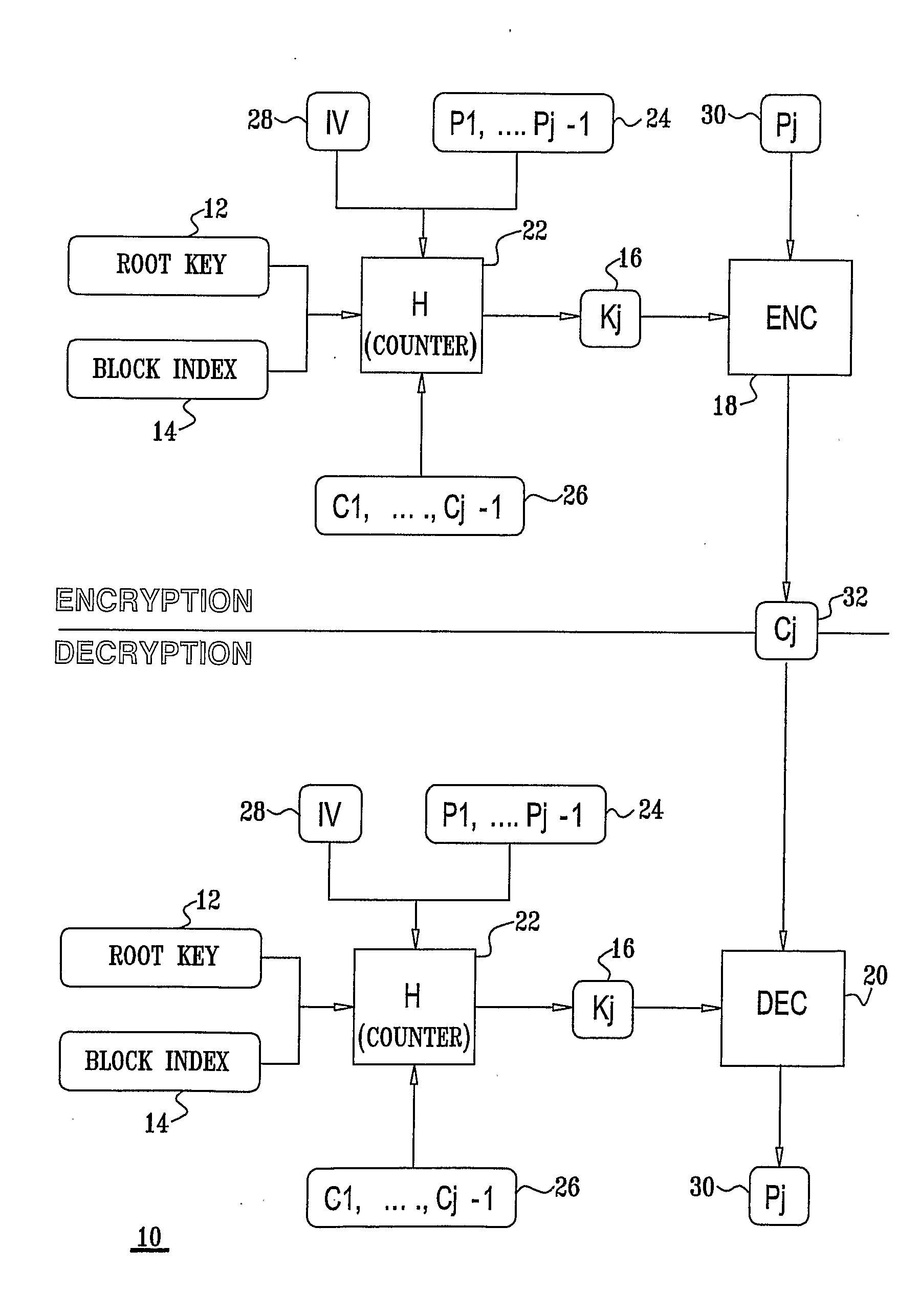
A method and apparatus of configuring the byte structure of a memory storage device, including a flash memory device, to enhance the security and error correction capability is described. In one embodiment, the method includes increasing the security of data stored in the storage device by encrypting data with a unique initialization vector and storing the initialization vector in the storage device. The method also includes using a unique initialization vector for encrypting data, to be stored in each datablock, each time data are encrypted. In one embodiment, the apparatus includes an AES controller that includes encryption and decryption modules to encrypt and decrypt data prior to writing data to or reading from the storage device. The apparatus also includes an encoder module and decoder circuits to encode and decode data prior to writing or reading from memory storage devices. The apparatus optionally includes a state machine that generates and provides the initialization vector and also activates different components of AES controller and ECC module depending on the operation of the device.
Owner:MCM PORTFOLIO LLC
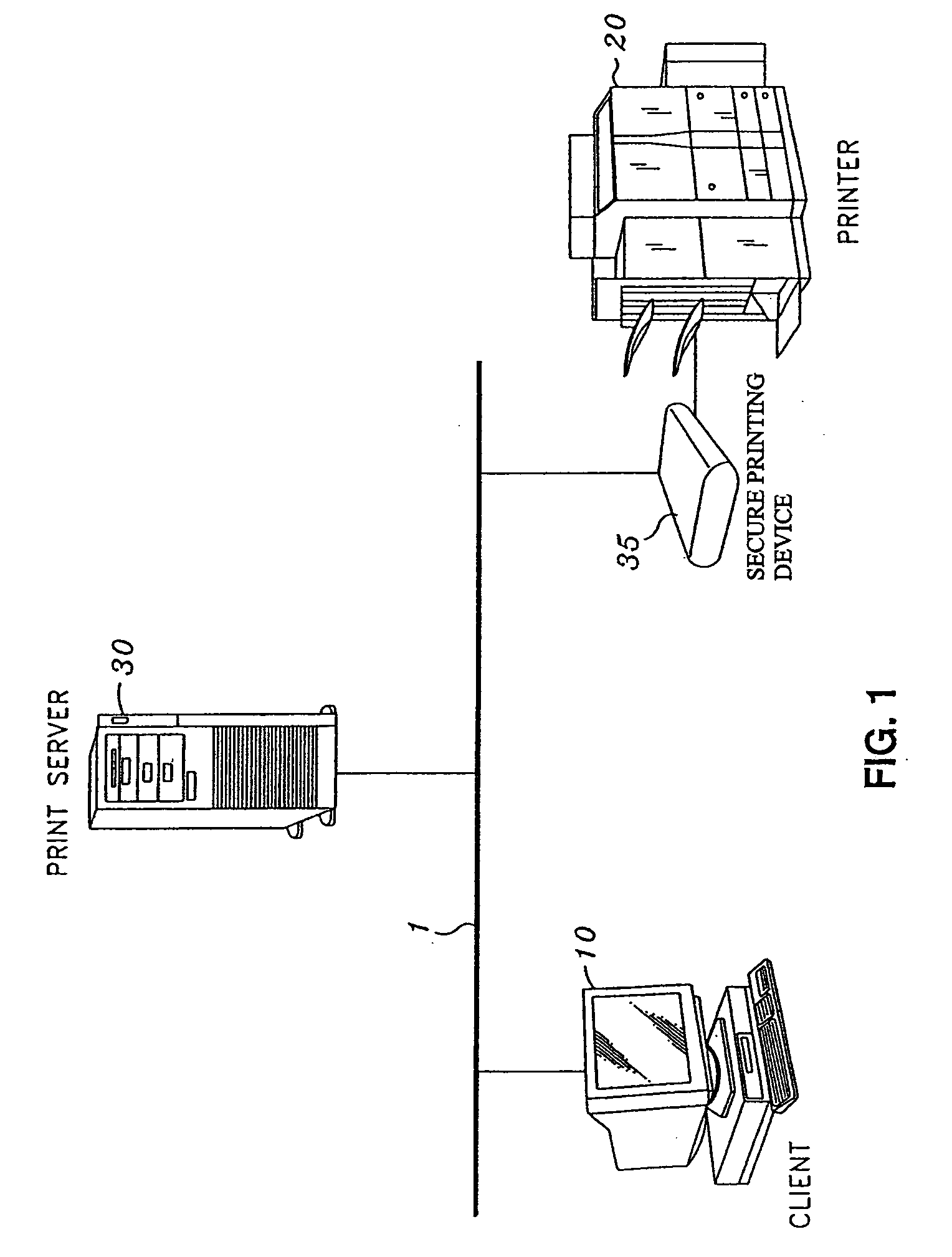
Secure file format
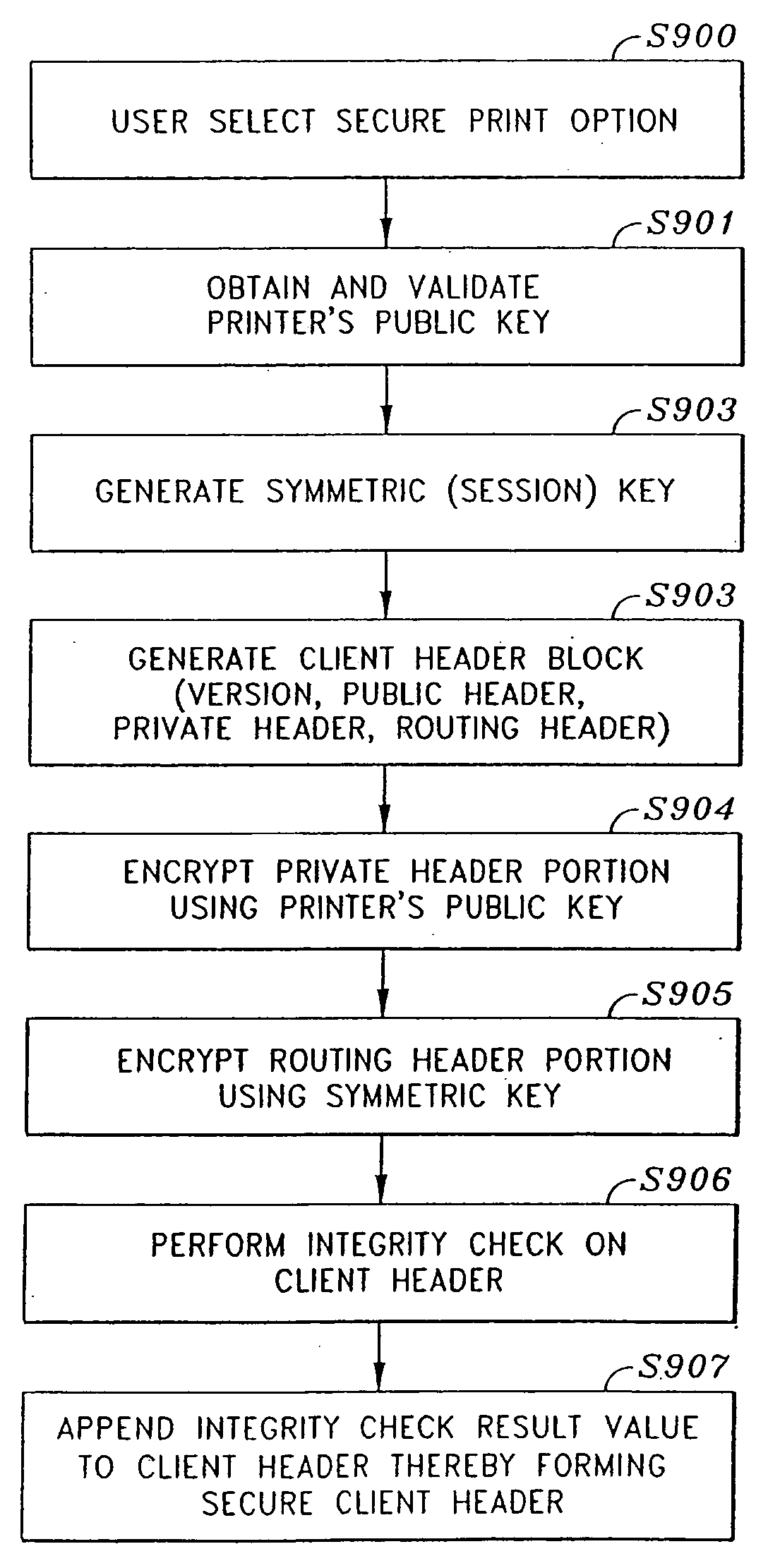
A file format for a secure file for use with a block cipher or a stream cipher, the secure file having a secure client header and a data block appended to the secure client header. The client header has a client information block comprised of a public information block, a private information block and an initialization vector. At least a portion of the private information block is encrypted, and a client information block integrity check value is appended to the client information block, the client information block integrity check value being obtained by performing an integrity check on the client information block. The data block is preferably encrypted and is comprised of a plurality of encrypted data blocks each appended with its own respective integrity check result value. Each of the plurality of data blocks and their respective integrity check result values are obtained by dividing the encrypted data block into n encrypted data blocks, performing an integrity check on a first one of the n encrypted data blocks and the client information integrity check result value appended to the client information block, so as to obtain a first encrypted data block integrity check result value, appending the first encrypted data block integrity check result value to the first encrypted data block, and repeatedly performing, for each of the subsequent n encrypted data blocks, an integrity check on the subsequent encrypted data block and an integrity check result value appended to a previous one of the n encrypted data blocks, so as to obtain an integrity check result value for the subsequent encrypted data block, and appending the subsequent integrity check result value to the subsequent encrypted data block.
Owner:CANON KK
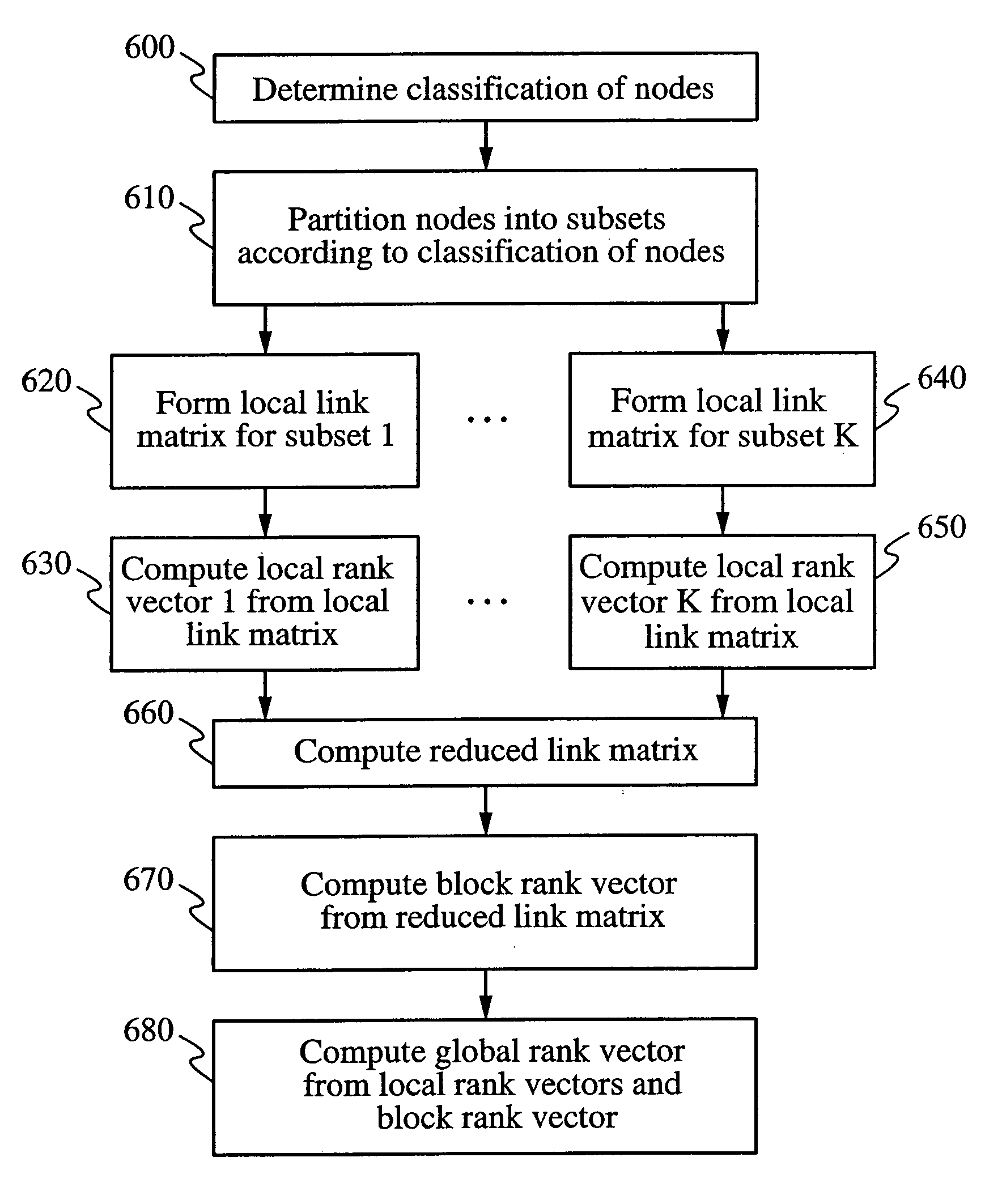
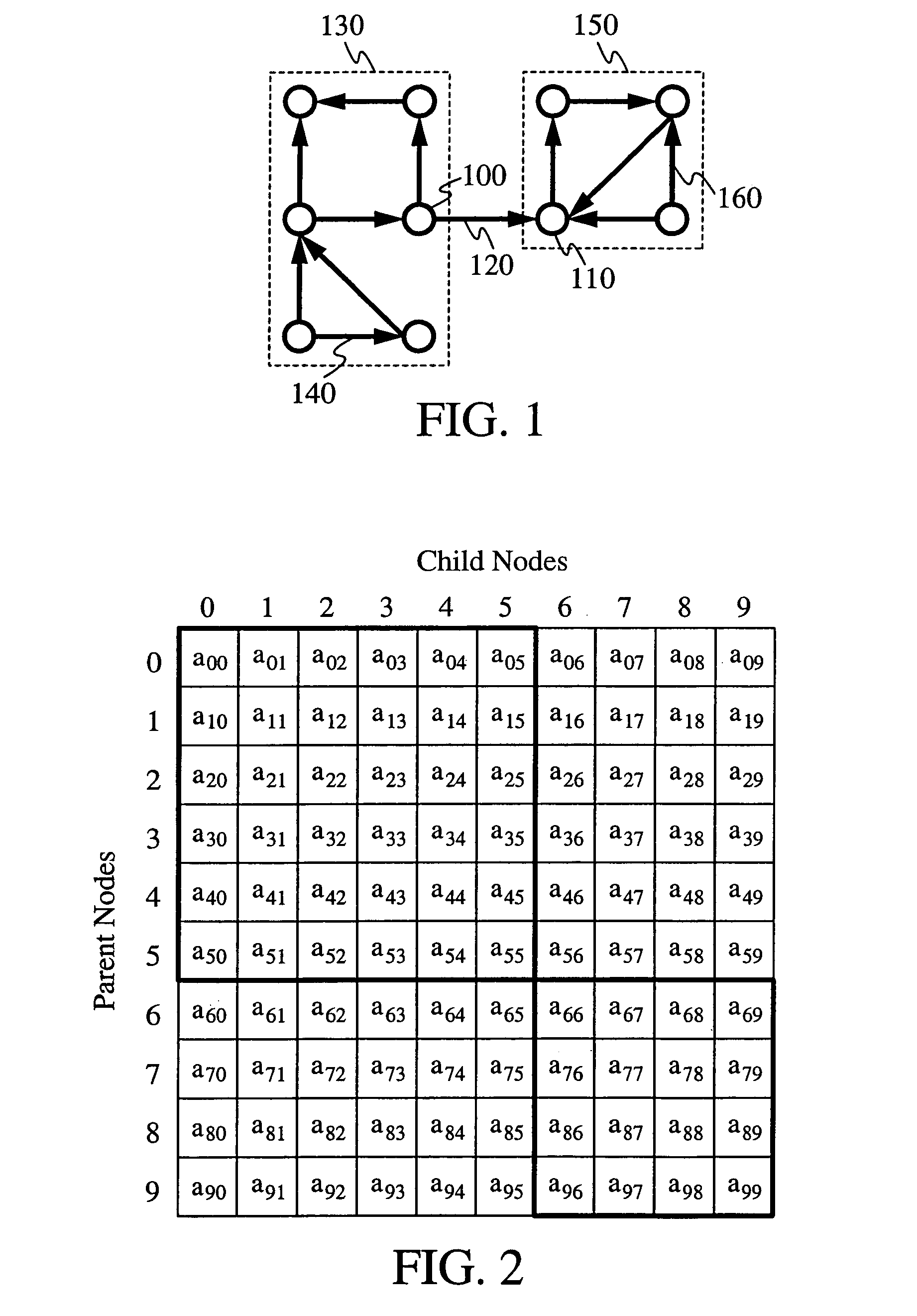
Methods for ranking nodes in large directed graphs
InactiveUS7216123B2Increase speedSimple calculationData processing applicationsWeb data indexingDirected graphDistributed Computing Environment
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
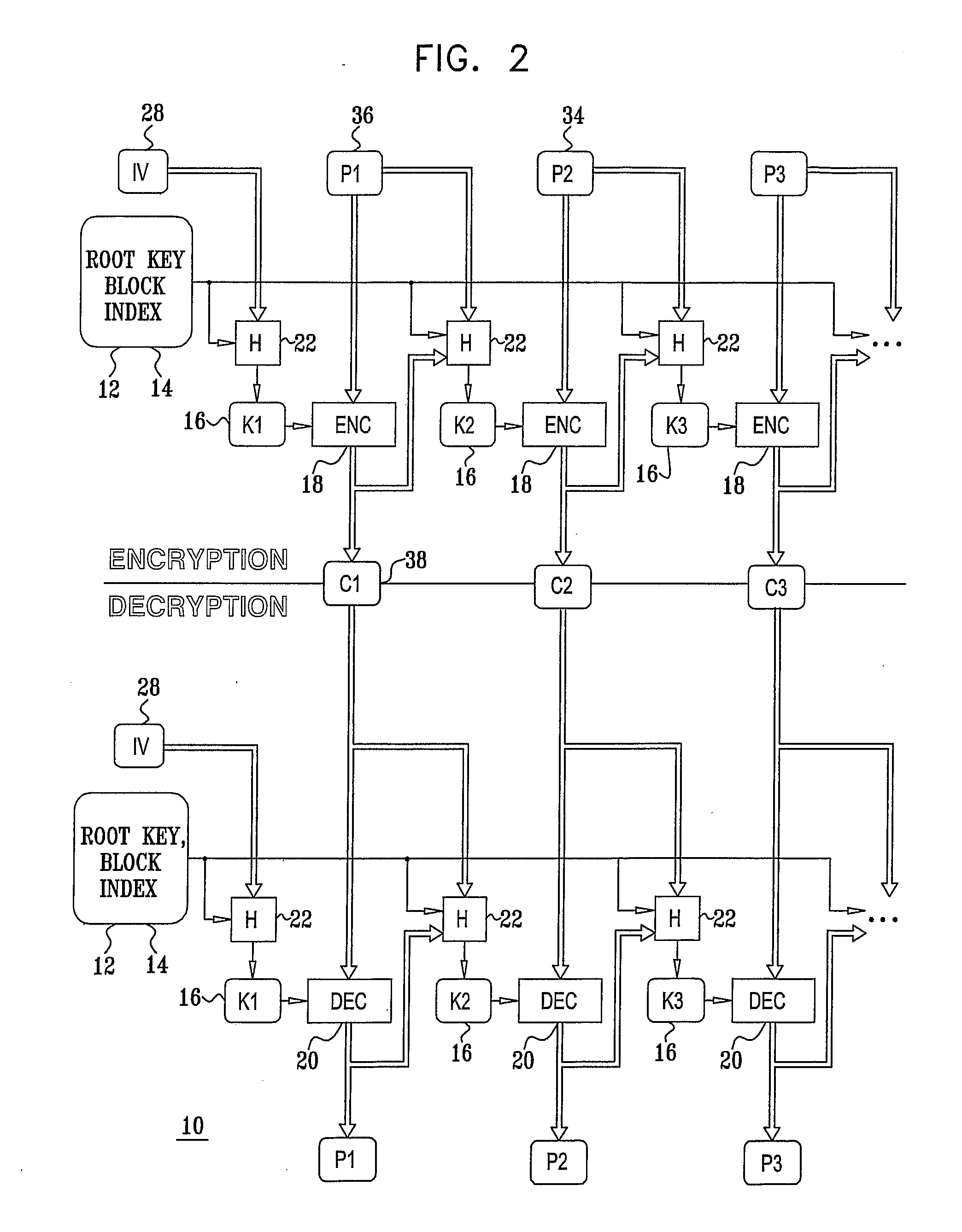
Method and System for Usage of Block Cipher Encryption
InactiveUS20090080647A1Reduce speedStrengthens the cipher against cryptanalysisEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesSecret communicationComputer hardwarePlaintext
A block cipher system for encrypting a plurality of blocks from plaintext to ciphertext, each of the blocks being associated with a constant root key, the system including an encryption key module to determine an input key for each of blocks based on a function having a plurality of inputs including the root key and an initialization vector, for a first one of the blocks, and the plaintext of at least one of the blocks which was previously encrypted and the root key, for the blocks other than the first block, and an encryption module to encrypt each of the blocks based on the input key determined for each of the blocks, respectively. Related apparatus and methods also included.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
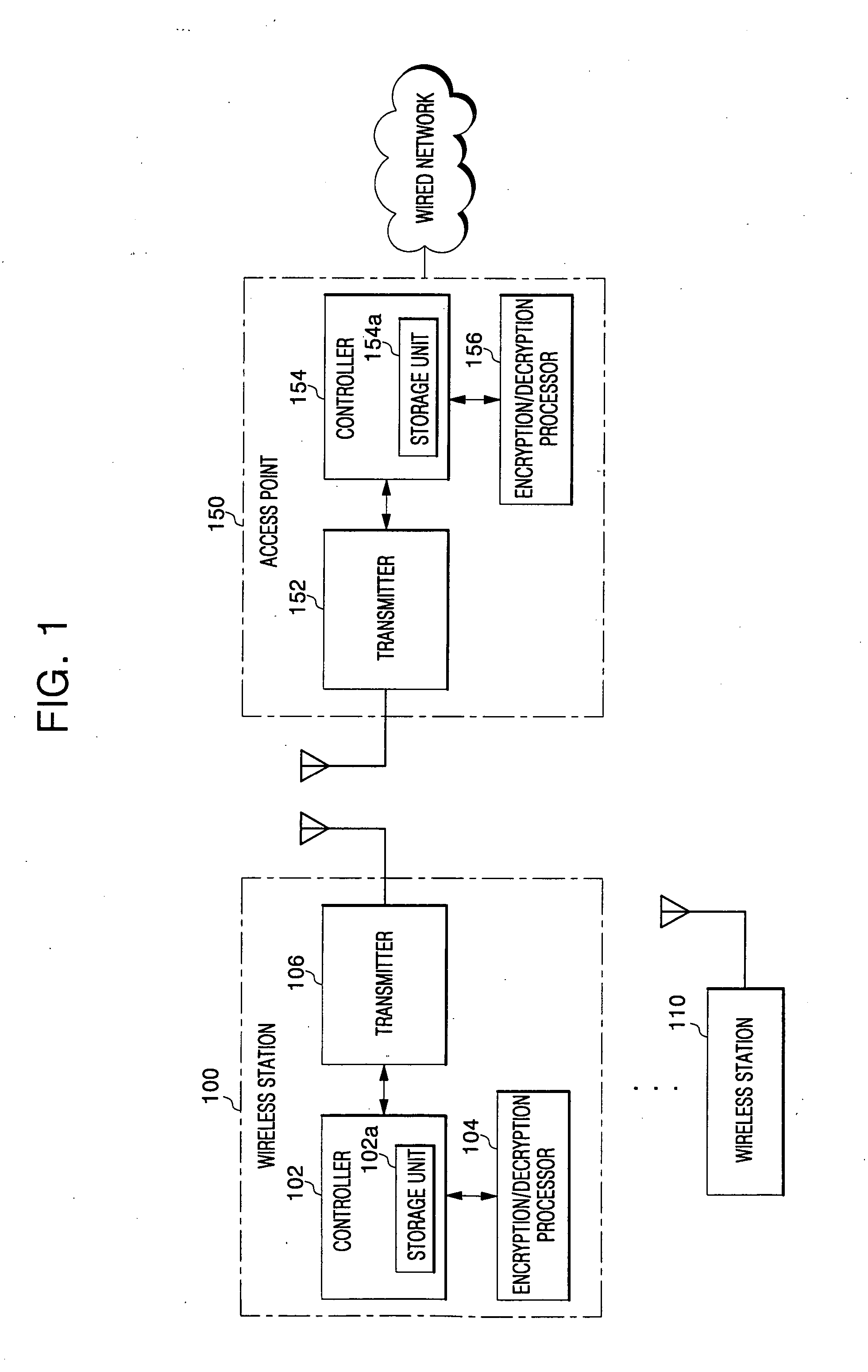
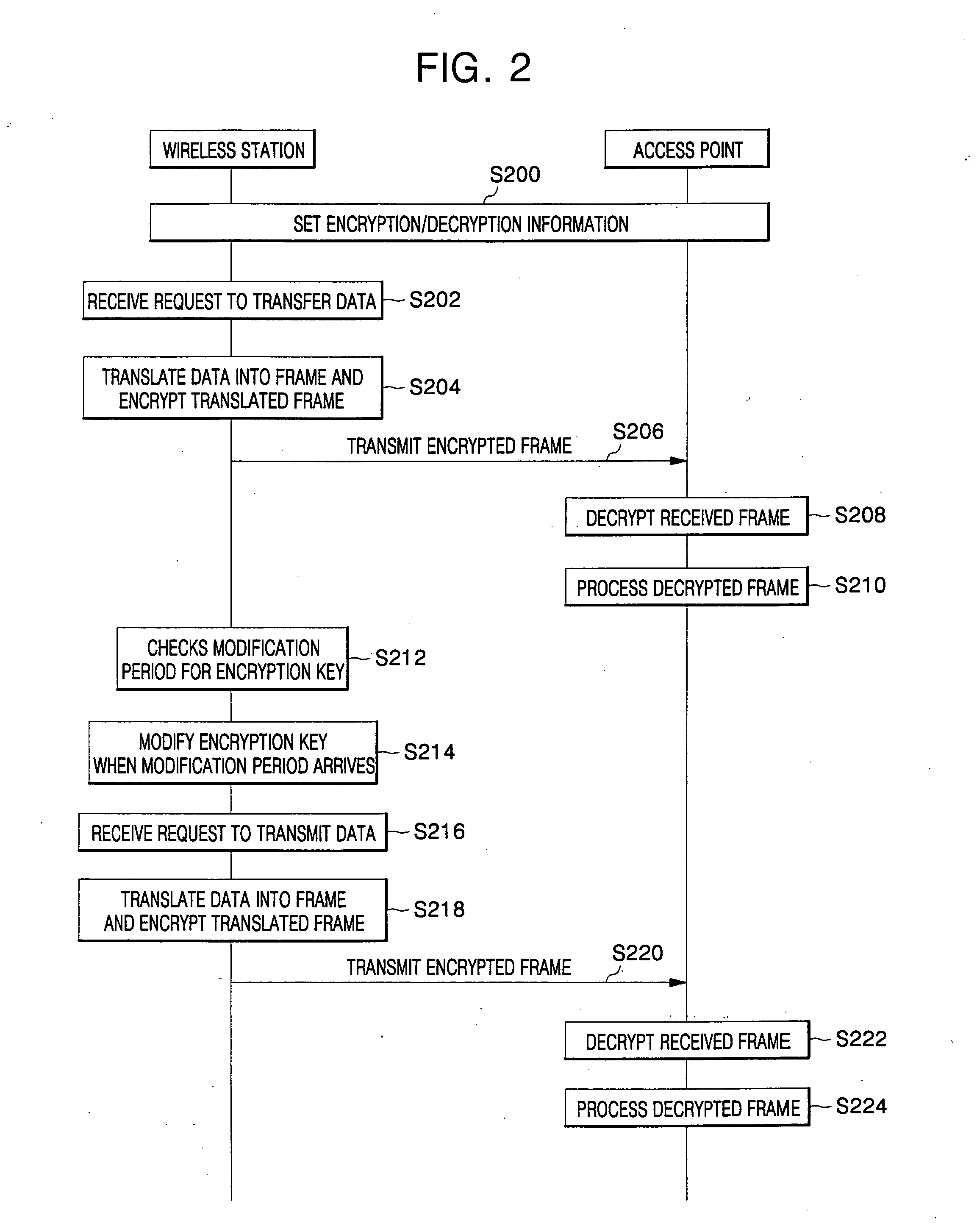
Data security in wireless network system
InactiveUS20060153375A1Lighting and heating apparatusUnauthorized memory use protectionWireless transmissionInitialization vector
For data protection in a wireless network system, a frame, including its Medium Address Control (MAC) header and payload, is encrypted with an initialization vector modified at each set state in a wireless network system, such that wirelessly transmitted data is prevented from being exposed to unauthorized users.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
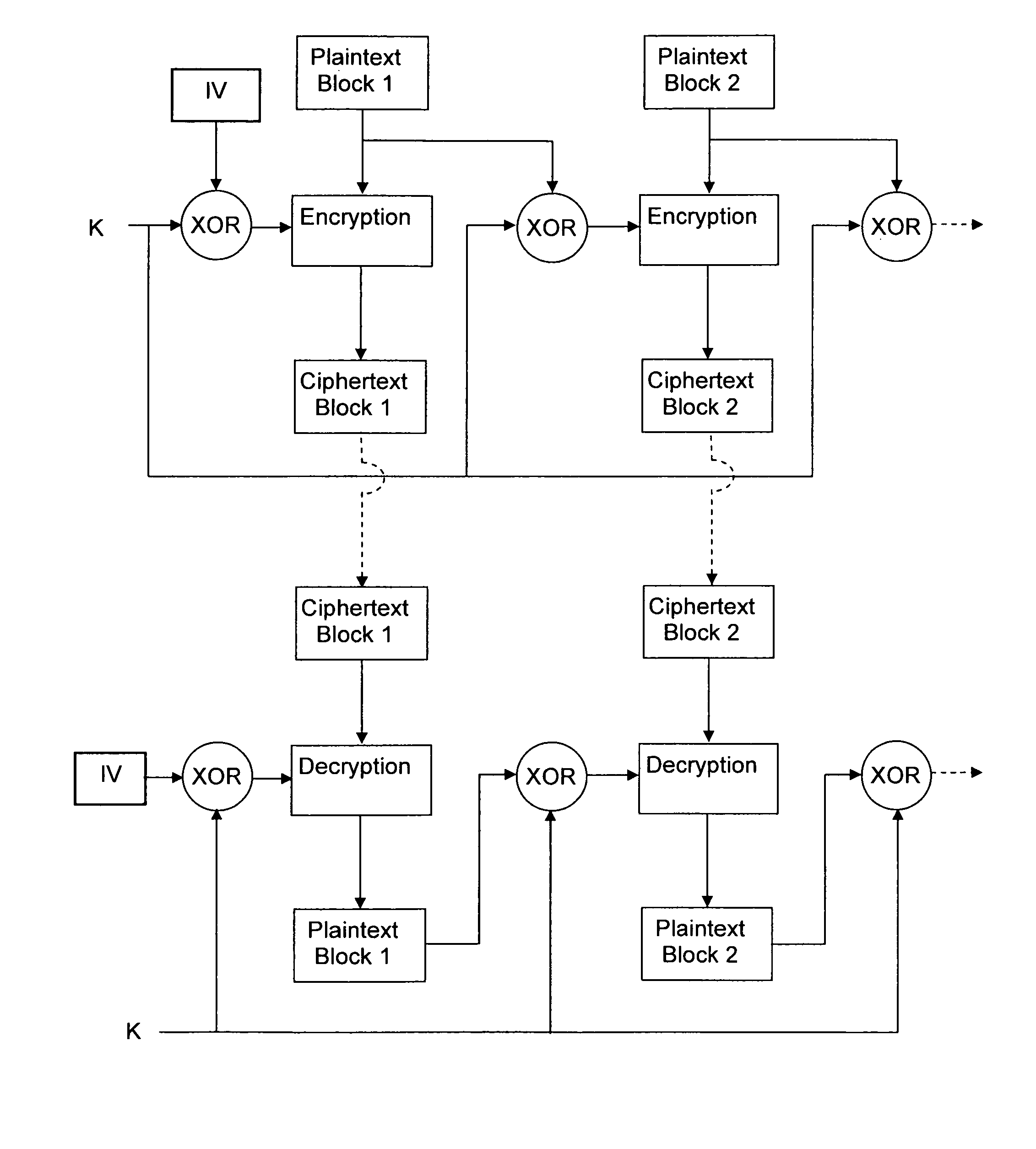
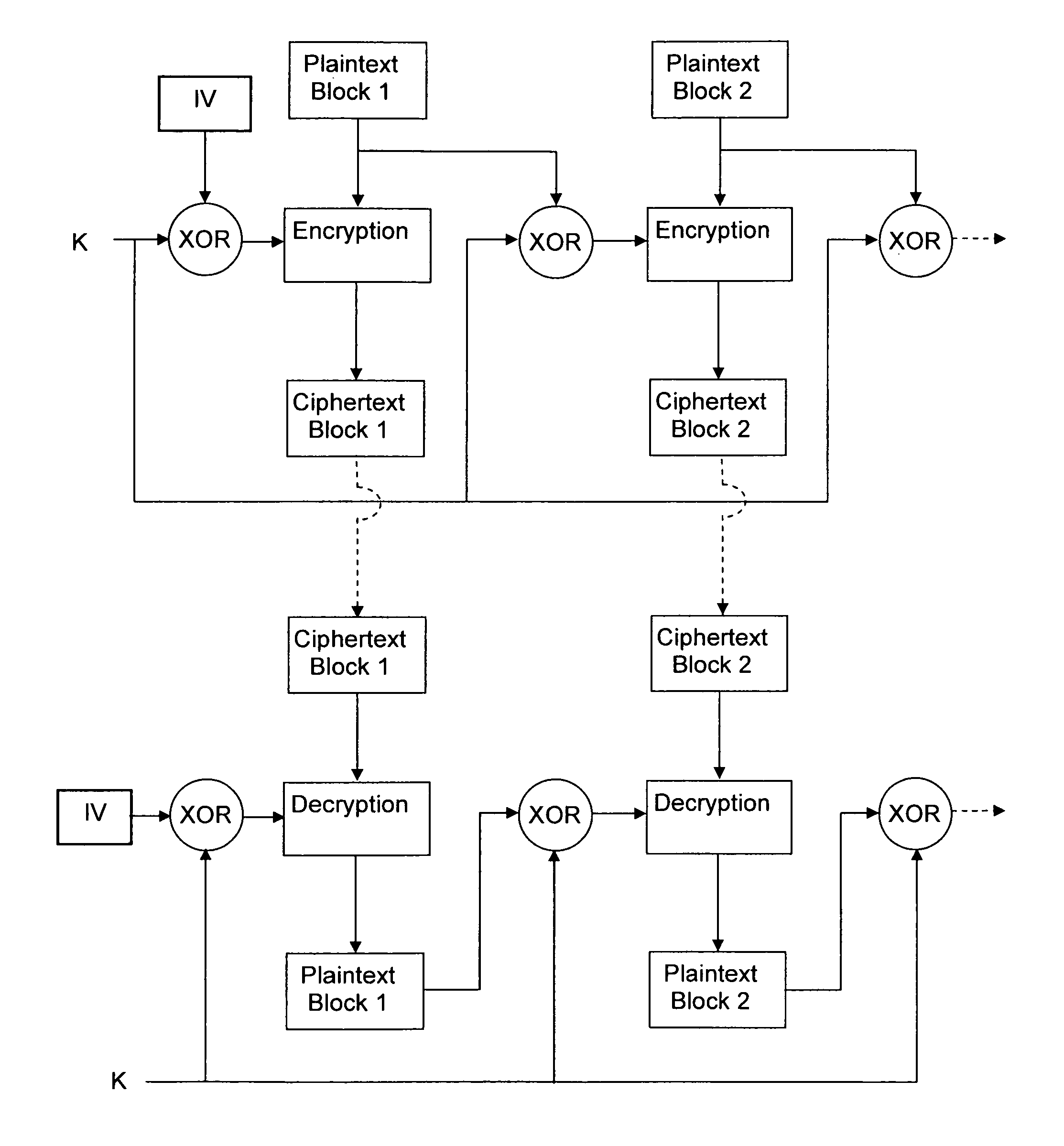
Methods and devices for a chained encryption mode
InactiveUS8259934B2Data stream serial/continuous modificationSecret communicationPlaintextComputer hardware
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Information-processing apparatus, control method, program and recording medium
InactiveUS20050094805A1Improve securitySecurity along a transmission line between a host and a drive can be improvedTelevision system detailsSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesInformation processingHash function
A 4-byte LBA (logical block address) specified in a read command is supplied to first and second IV (initialization vector) generation units. The initialization-vector generation units each extend the LBA to data with a size of 16 bytes by applying typically a hash function to the LBA. The first initialization-vector generation unit outputs the data with a size of 16 bytes to an encryption unit as an initialization vector IV. On the other hand, the second initialization-vector generation unit outputs the data with a size of 16 bytes to a decryption unit as an initialization vector IV. The encryption unit encrypts input data by using the initialization vector IV and a session key Ks received from a first authentication-processing unit. On the other hand, the decryption unit decrypts input data by using the initialization vector IV and the session key Ks received from a second authentication-processing unit. In this way, data can be encrypted and decrypted by using the initialization vector IV. The present invention can be applied to a personal computer and a drive, which exchange data with each other by way of a predetermined interface.
Owner:SONY CORP
Methods and devices for a chained encryption mode
InactiveUS20100150344A1Data stream serial/continuous modificationMultiple keys/algorithms usageComputer hardwarePlaintext
An encryption chaining mode takes plaintext block N, generates encryption key N by combining, preferably by XOR, encryption key N−1 and plaintext block N−1 and encrypts plaintext block N using an encryption algorithm with encryption key N to output ciphertext block N. Encryption key for the first plaintext block is generated by XOR-ing a random Initialization vector and a random initialization key K. In a preferred embodiment, initialization key K is subkeys resulting from a key schedule algorithm and encryption key N−1 is only one of the subkeys. Encryption key for the first plaintext block is generated by XOR-ing a random Initialization vector and one subkey resulting from a key schedule algorithm. Also provided is a corresponding decryption method, an encryption device, a decryption device.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
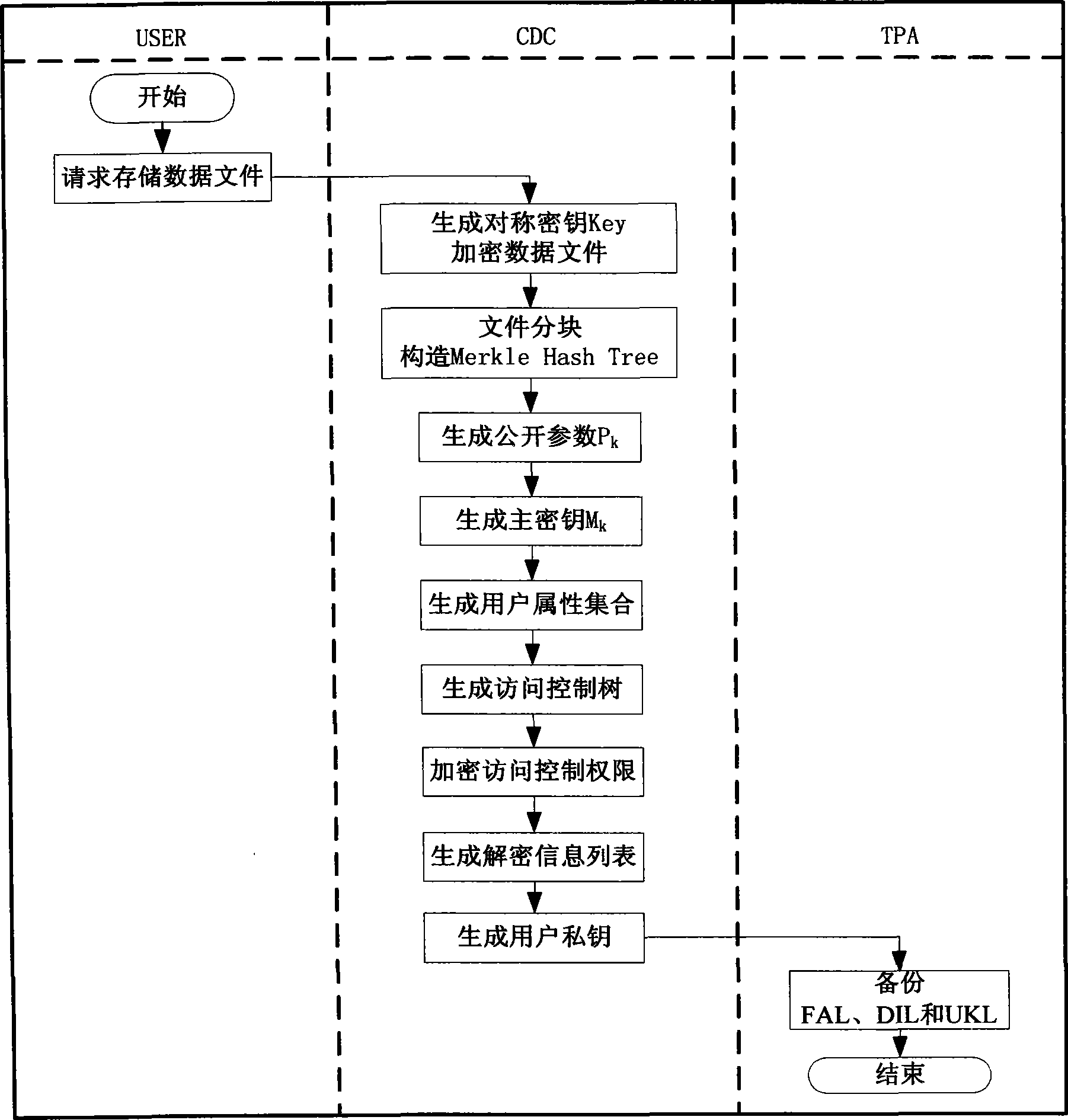
Access control method base on attribute encryption algorithm
InactiveCN103220291AAvoid re-encryption workIncrease rate of permission changesUser identity/authority verificationData filePaper document
The invention discloses an access control method base on an attribute encryption algorithm. The method includes an initialization step; a data document access step and an access authority limit changing step. Advantages which are possessed based on the attribute encryption algorithm in a distributed environment are utilized to effectively solve the problem such as that a deciphering party is not fixed under a cloud computing environment, and the problem exists in a data file sharing aspect. Safe access to a data file in the cloud computing environment is supported, and meanwhile problems in aspects such as revocation of user permission and data misreading of a user are fully considered.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
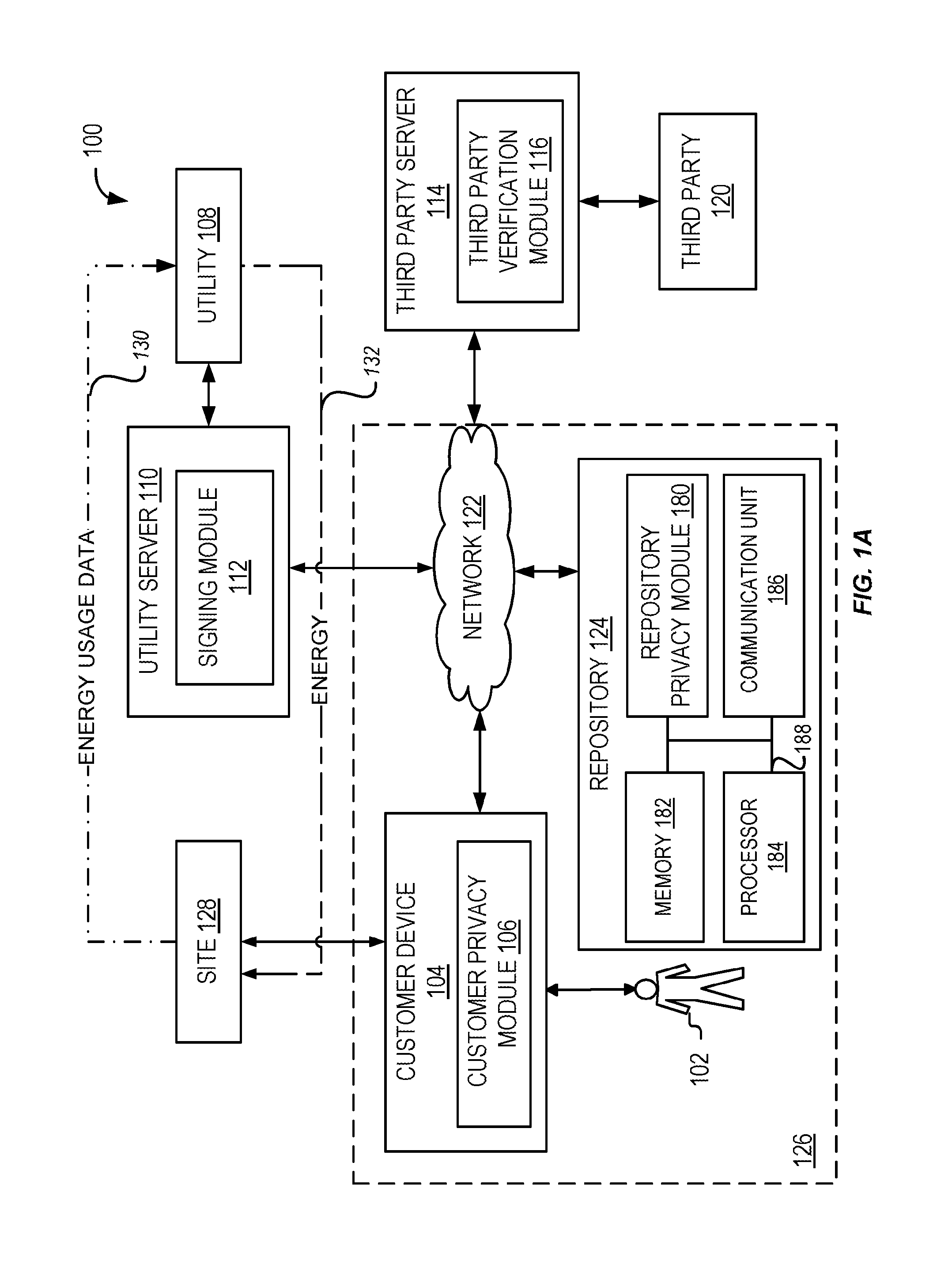
Energy usage data management
ActiveUS20150128283A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationDigital signatureInitialization vector
A method including receiving energy usage data representative of energy usage of a customer during a particular time period. The energy usage data is sign with a digital signature of a utility. The method includes receiving input of a customer effective to select a data block of the energy usage data. The method includes redacting the selected data block from the energy usage data in response to the input. The method includes calculating a hash value for the redacted data block using a per-customer key that is unique to the customer, an initialization vector, and a counter. The method includes replacing in the energy usage data the redacted data block with the calculated hash value corresponding to the redacted data block.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and system to provide security implementation for storage devices
InactiveUS20080114994A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationUnauthorized memory use protectionLogical block addressingInitialization vector
In one embodiment, method that can be performed on a system, is provided to security implementations for storage devices. In one embodiment, the method comprises providing a separate encryption seed for each of a plurality of separate addressable blocks of a non-volatile storage device, wherein a common encryption method is to encrypt data to be stored on the plurality of separate addressable blocks. In one embodiment, the storage device is a portable storage device. In one embodiment, encryption seed is an Initialization Vector (IV). In one embodiment, the encryption seeds comprise at least one of a media serial number and a logical block address corresponding to the respective block of the non-volatile storage device. In an alternative embodiment, the method further comprises storing at least a part of the separate encryption seed of the separate blocks of the non-volatile storage device within the respective blocks of the storage device.
Owner:MCM PORTFOLIO LLC
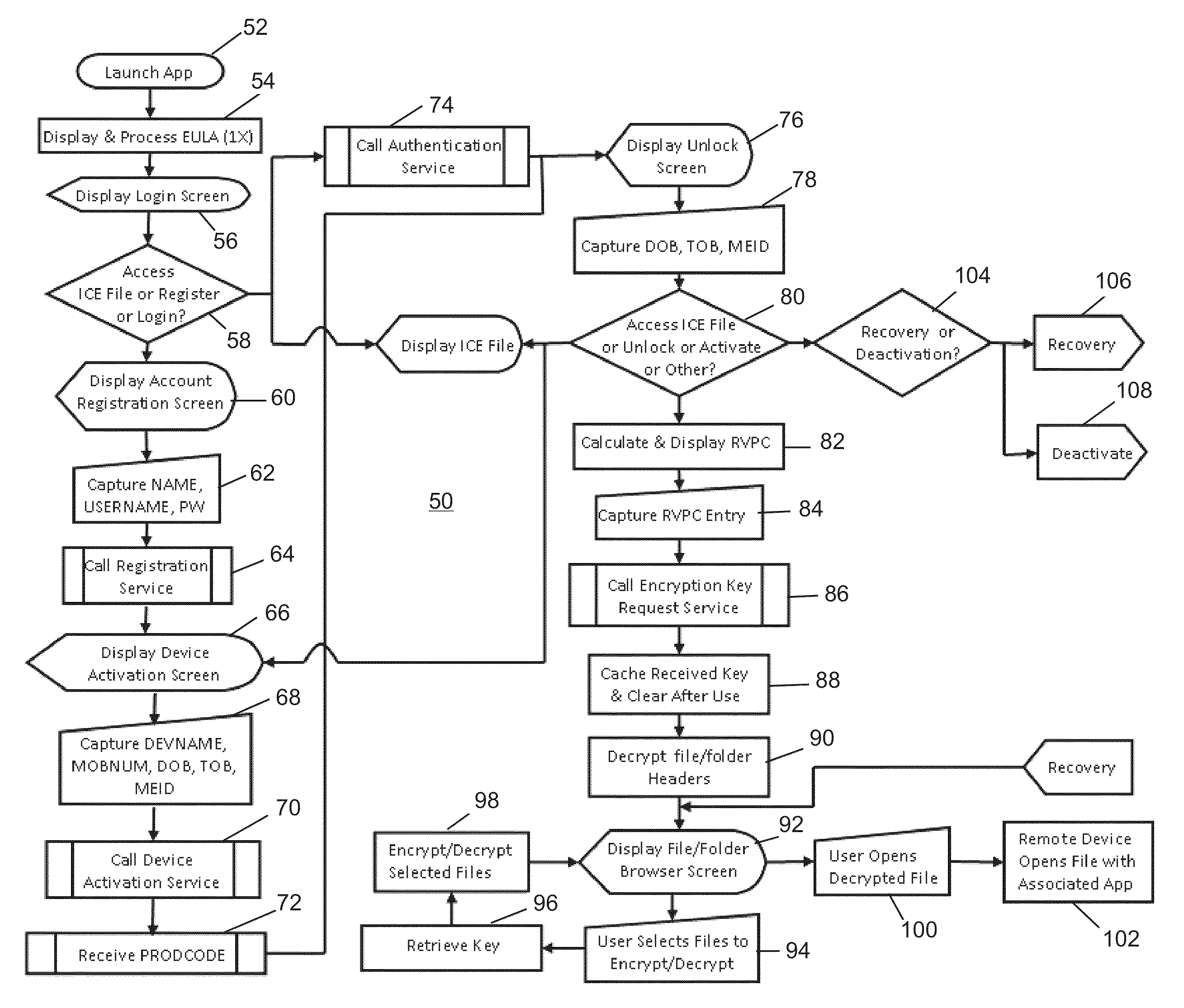
Remote device secure data file storage system and method
ActiveUS8930700B2Low costKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesData fileInitialization vector
A remote device secure data file storage system and method of securely storing data files at a remote device, includes a host system having a database and a plurality of remote devices, each connected with the host system by a communication network. Each remote device and the host system is programmed with a time-based cryptography system that generates an encryption key (RVK) and initialization vector (IV) for encrypting and decrypting data on the remote device. The time-based cryptography system generates the encryption key (RVK) as a function of a parameter (PDPT) that is a function of a personal date (PD) and personal time (PT) of the user. The personal date and personal time of the user being a function of personal data entered by the user on the remote device. The personal date (PD) is a function of the date of birth (DOB) of the user and the personal time (PT) is a function of the time of birth (TOB) of the user.
Owner:WIELOPOLSKI RICHARD J
Secure financial transaction network
Owner:FITBIT INC
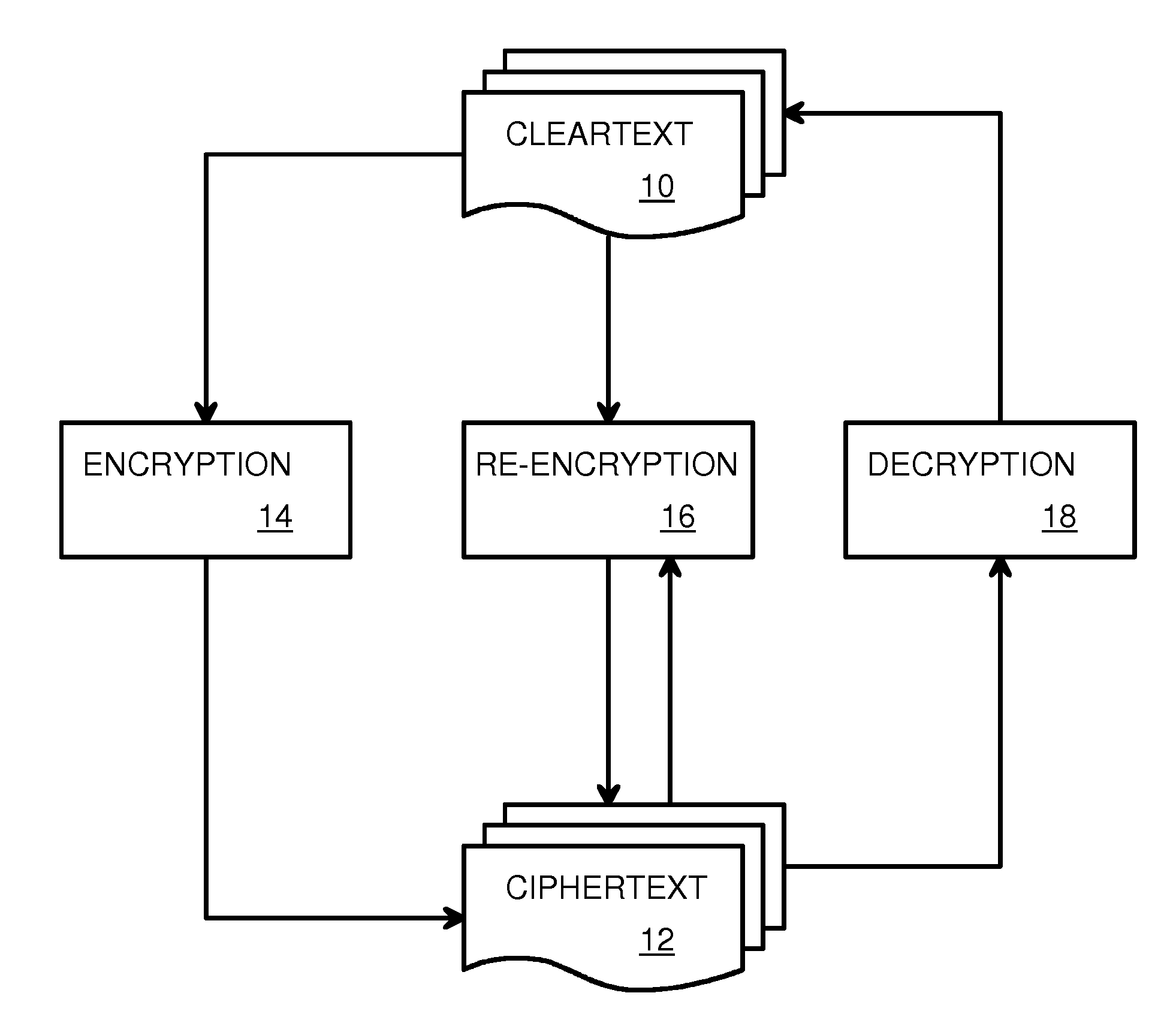
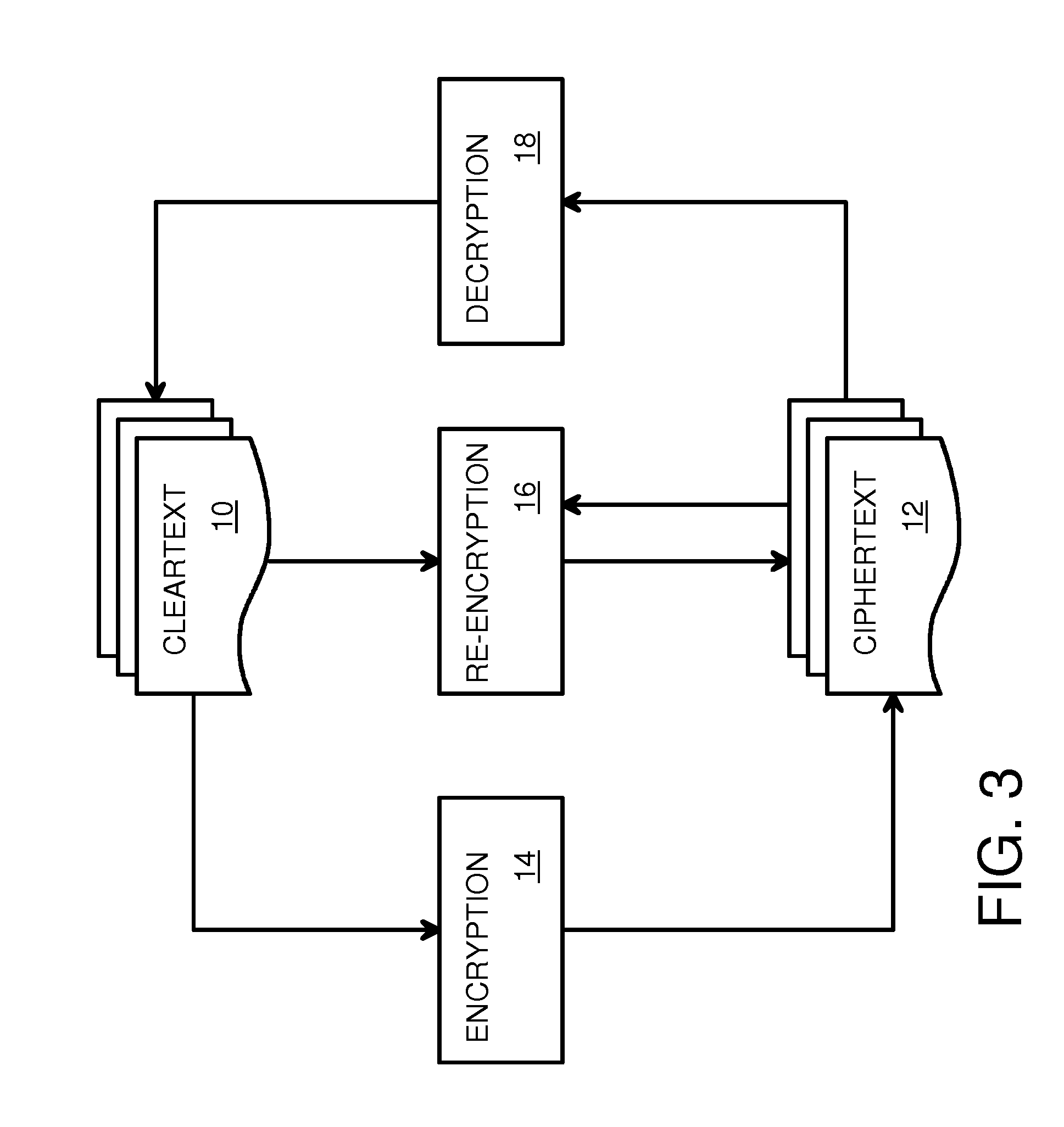
Partial CipherText Updates Using Variable-Length Segments Delineated by Pattern Matching and Encrypted by Fixed-Length Blocks
ActiveUS20140355754A1Data stream serial/continuous modificationSecret communicationComputer hardwareCiphertext
A re-encryptor compares hashed digests of updated segments and original segments to located changed segments that must be re-encrypted. A new initialization vector is input to a block cipher engine for each changed segment. Since only changed segments need to be re-encrypted, transmission bandwidth to remote encrypted storage may be reduced. The amount of cipher text that is changed by a single update is reduced to a segment. Segments have a variable length and are bound by bits matching a segment delimiter. Each segment may have many fixed-length blocks that are encrypted by the block cipher engine with the same initialization vector for that segment. The segment delimiter is a randomly-generated word that is included with the initialization vectors in the metadata. Variable-length segments limit update disruption of the cipher text while fixed-length blocks are more efficiently encrypted. Combining segments and blocks provides for better re-encryption of updates.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Protection of digital content using block cipher crytography
InactiveUS20060159266A1Synchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesDigital contentInitialization vector
Protection of digital content using a specific application of block cipher cryptography is described. The digital content is encrypted using an encryption key and a calculated initialization vector. The digital content includes a plurality of strides of data and each stride includes a string of data to be encrypted and a block of data to be encrypted. The calculated initialization vector to be used to encrypt the block of data is derived from the string of data in the stride to be encrypted. Furthermore, the initialization vector is calculated by performing an exclusive disjunction function on a seed value and the string of data for each stride.
Owner:CHAVANNE PIERRE +7
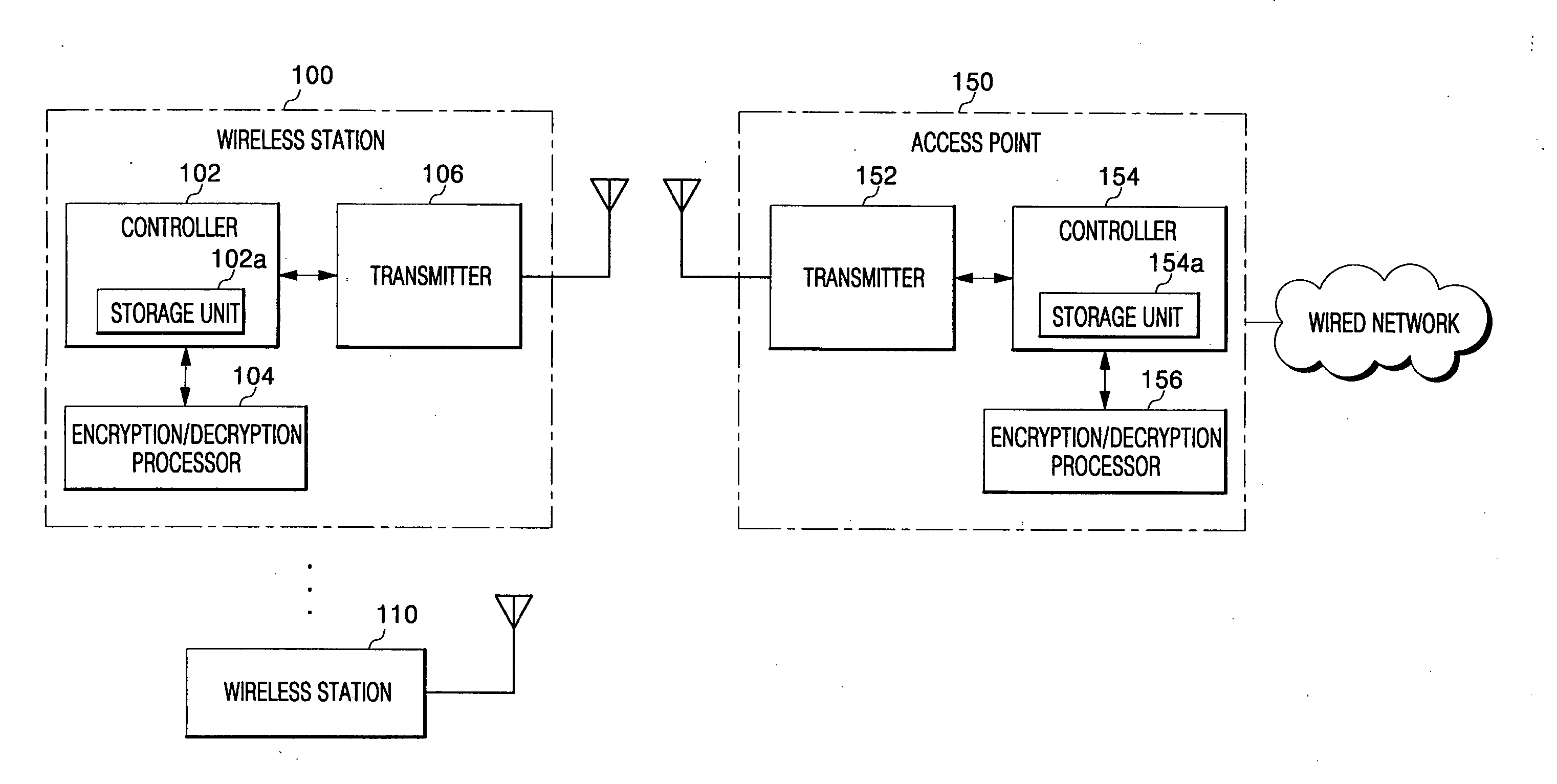
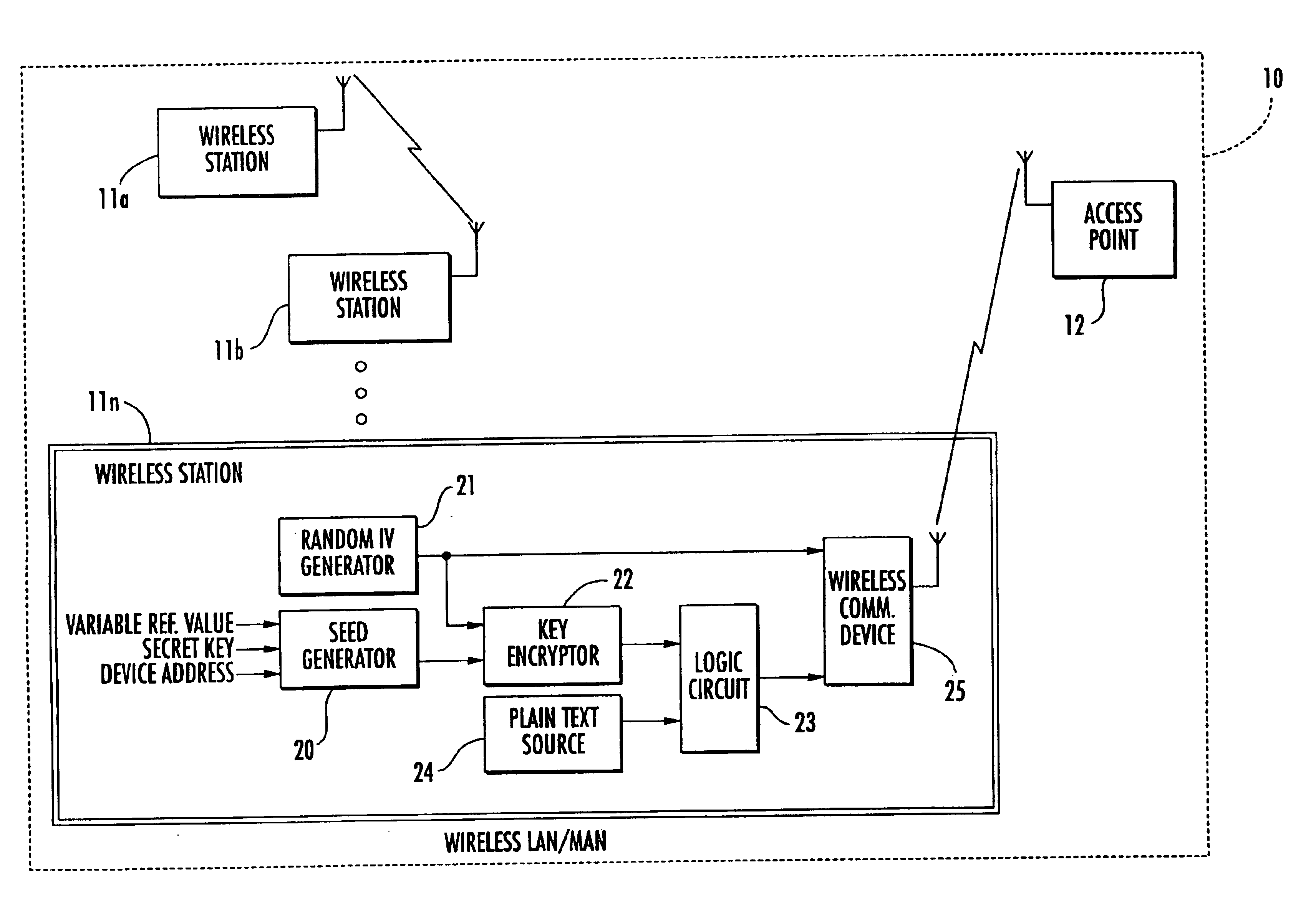
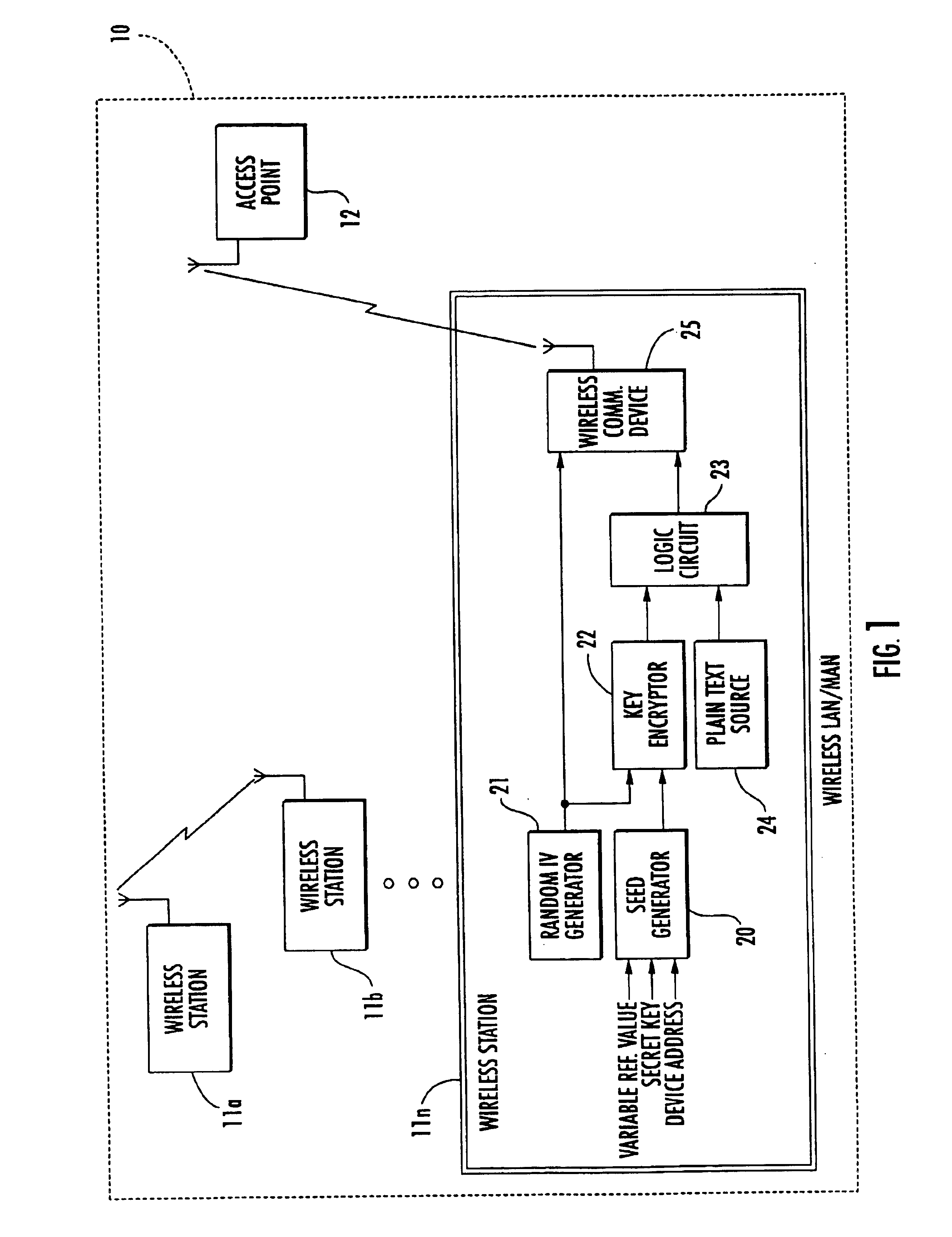
Secure wireless local or metropolitan area network and related methods
InactiveUS6931132B2Improve security featuresIncrease in sizeKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usagePlaintextCiphertext
A secure wireless local or metropolitan area network and data communications device therefor are provided, where the device transmits plain text in an encrypted message including cipher text and an initialization vector. The device may include a seed generator for performing a one-way algorithm using a secret key, a device address, and a changing reference value for generating a seed. Further, a random initialization vector (IV) generator may be included for generating a random IV, and a key encryptor may generate a key sequence based upon the seed and the random IV. Additionally, a logic circuit may be included for generating cipher text based upon the key sequence and plain text, and a wireless communications device may be connected to the logic circuit and the random IV generator for wirelessly transmitting the encrypted message.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
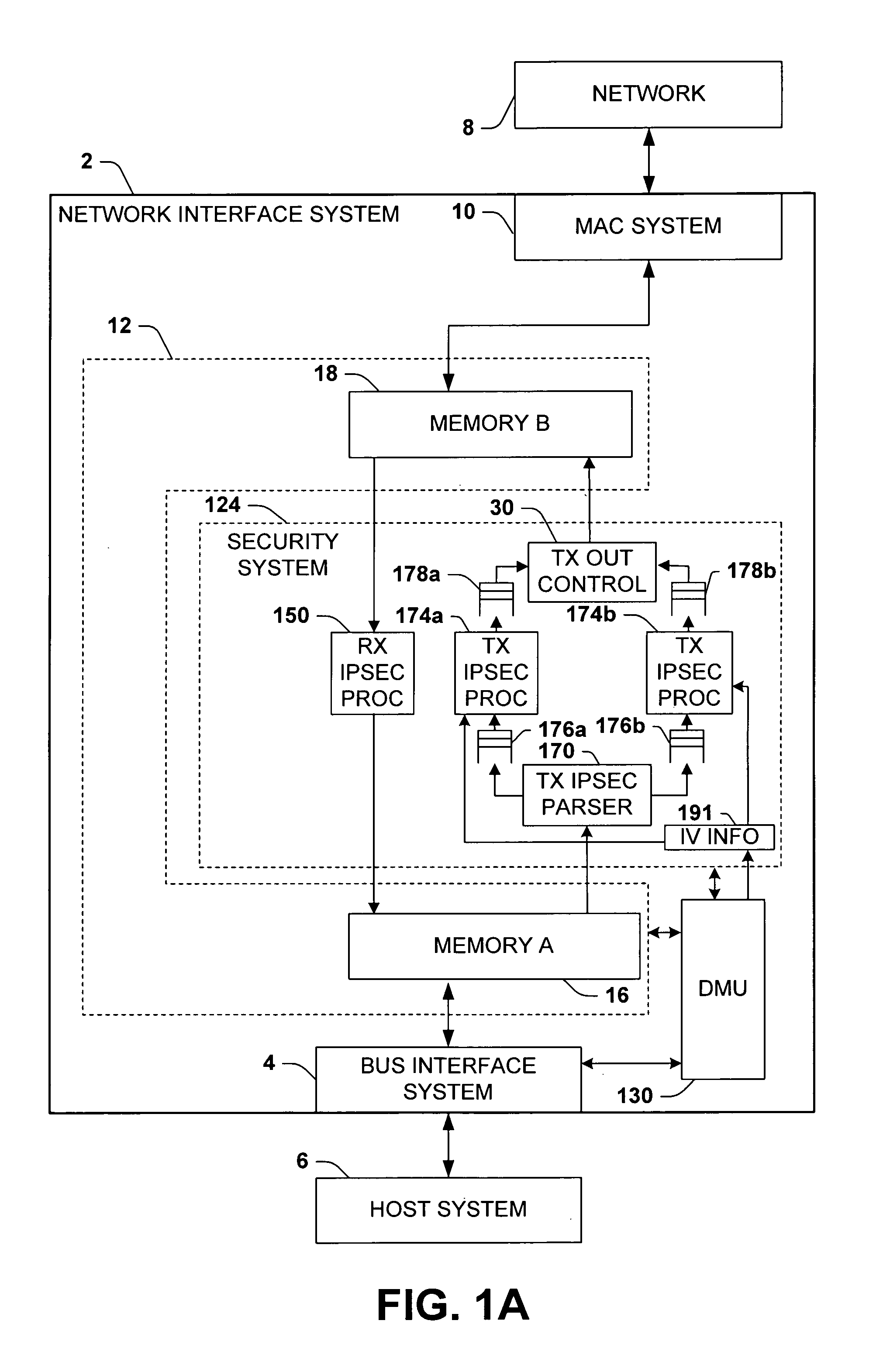
Methods and apparatus for passing initialization vector information from software to hardware to perform IPsec encryption operation
InactiveUS7826614B1Improve network transmission speedWell formedSecret communicationSecuring communicationNetwork connectionBus interface
A network interface system is presented for interfacing a host system with a network, including a bus interface system, a media access control system, a memory system, a security system, and a descriptor management system, wherein the descriptor management system obtains initialization vector information from the host system and provides the initialization vector information to the security system. A method of encrypting outgoing data in a network interface system is provided, comprising providing initialization vector information from a descriptor to a security system in a network interface system, selectively encrypting or authenticating outgoing data using the security system, and selectively employing an initialization vector from the outgoing data to perform CBC encryption of the outgoing data according to the initialization vector information.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method for controlling security channel in MAC security network and terminal using the same
InactiveUS20070133791A1Reduce system loadSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesDigital data processing detailsSecurity associationInitialization vector
A method for controlling a security channel for reducing system load by extending the use period of a security association key is provided. In this method, an upper bit initial value of an initialization vector of an encryption algorithm and a using range thereof are shared between a transmitting side and a receiving side when a security channel is created. Then, a secure association is created between a transmitting side and a receiving side by setting an association number, a next packet number which is a lower bit value of an initialization vector, and a secure association key. Afterward, a packet number is modified whenever a frame is transmitted until all of packet numbers are used. When all packet numbers are used, the upper bit value of the initialization vector changes.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
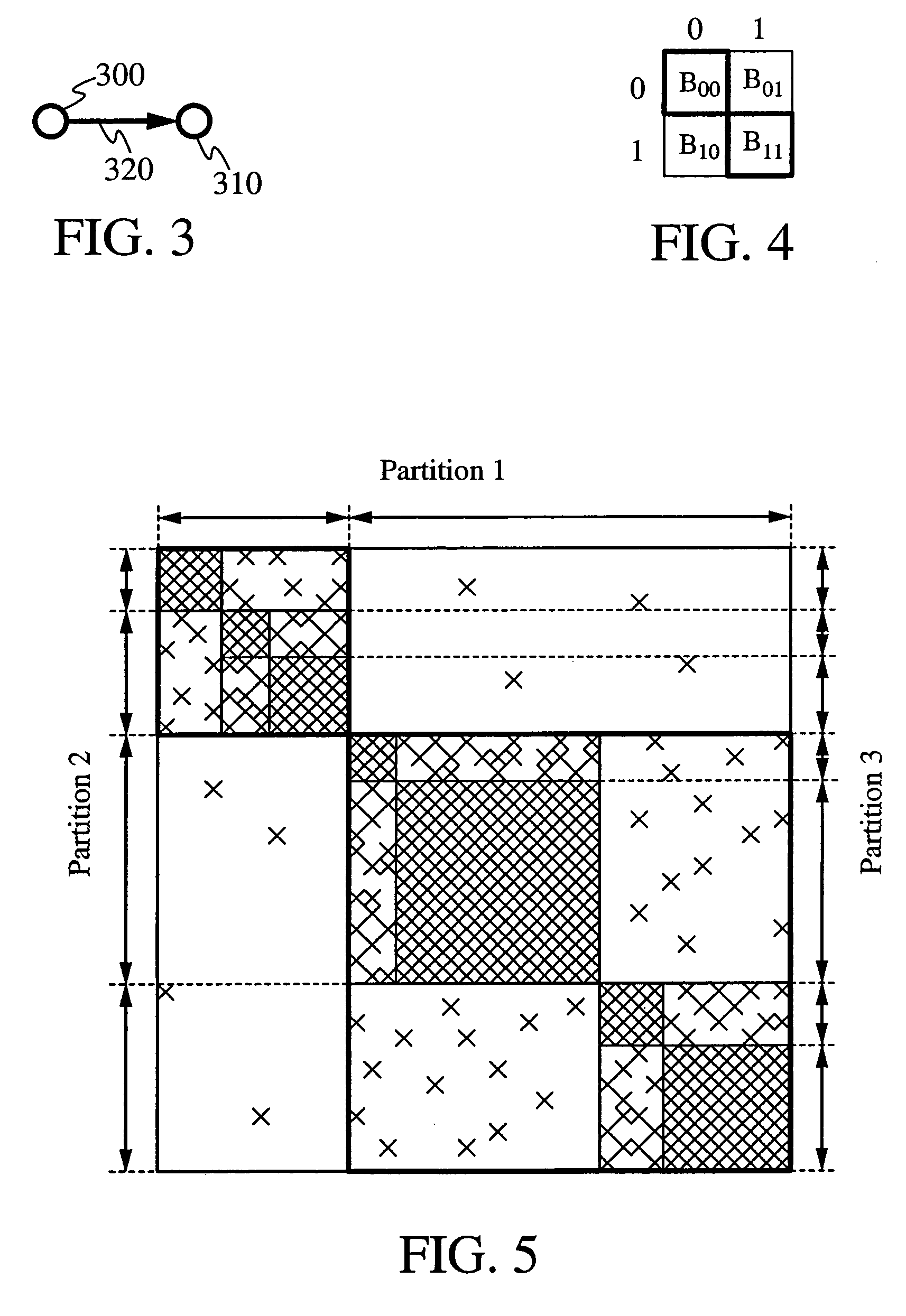
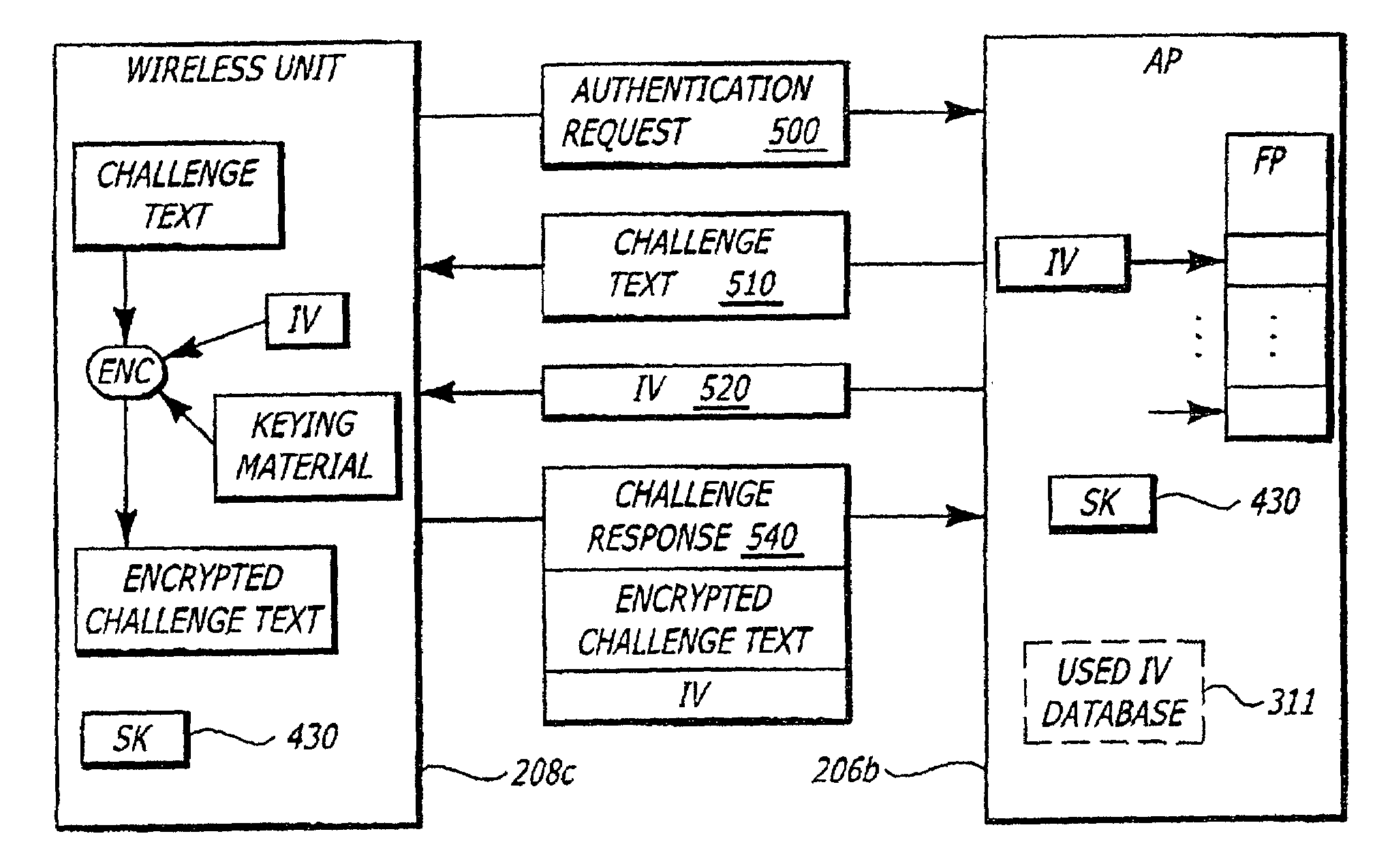
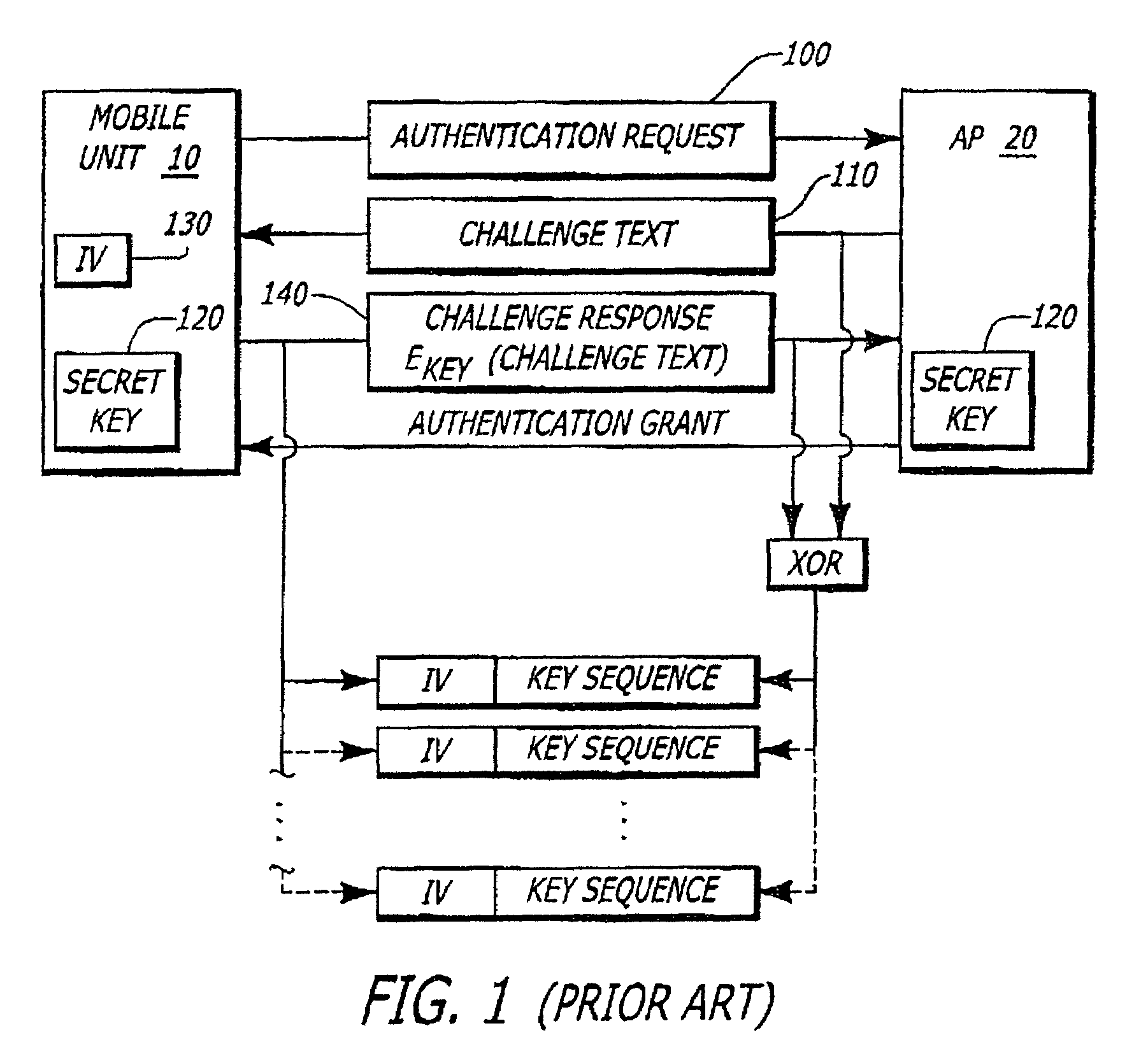
Wireless LAN WEP initialization vector partitioning scheme
InactiveUS7039190B1Reduce the possibilityPrevent replay attacksNetwork topologiesSecret communicationInitialization vectorWireless lan
In one embodiment, an authentication method features the generation of an initialization vector at a first electronic device and the determination at the first electronic device whether the initialization vector falls within a first group of initialization vectors. The first group includes a plurality of initialization vectors solely used in connection with an authentication sequence. Information is encrypted using in part the initialization vector for return to a second electronic device if the initialization vector falls within the first group.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Method and system for encrypting/decrypting payload content of an OTN frame
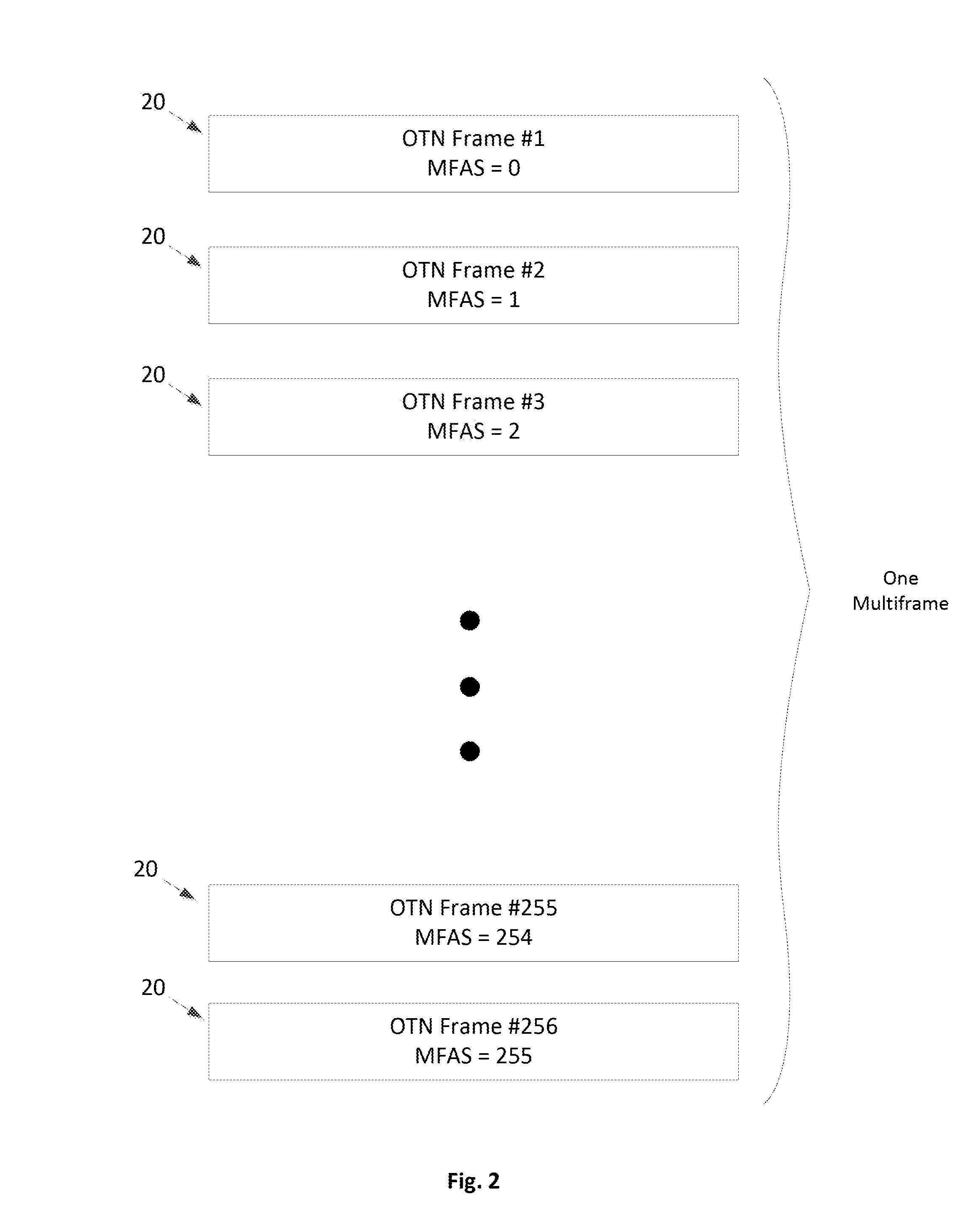
ActiveUS20160301669A1Synchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesInitialization vectorOptical Transport Network
The present disclosure relates to a system and method of encrypting and decrypting Optical Transport Network (OTN) payload content. A transmitter of the system includes a series of ordered encryption keys and a counter for generating an initialization vector to be combined with one of the encryption keys for encrypting the OTN payload content. A receiver of the system includes a series of ordered decryption keys and a counter for generating an initialization vector to be combined with one of the decryption keys for decrypting the encrypted OTN payload content. The system synchronizes switching, at the transmitter and the receiver, the encryption and decryption keys to the next keys in each series. The system also synchronizes the counters for generating the same initialization vector at the transmitter and the receiver.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOLUTIONS (US) INC
Method for increasing calculation speed of SMP cluster system through MPI and OpenMP in hybrid parallel mode
ActiveCN104461467AReduce synchronizationAvoid interactionConcurrent instruction executionCalculation errorInitialization vector
The invention discloses a method for increasing the calculation speed of an SMP cluster system through an MPI and an OpenMP in a hybrid parallel mode. The method comprises the steps that the number of MPI processes which can be called and the number of OpenMP threads are determined according to the number of calculation nodes and the number of usable CPU kernels in the nodes; an existing sub sparse matrix, a sub initial vector, a block vector and the maximum calculation tolerance are read in each process; a multi-thread compiling instruction is started for each process; circulation calculation of a precondition conjugate gradient method is conducted on all the processes, and the number of OpenMP barriers in circulation calculation is only three; if calculation errors are smaller than an allowable value, circulation is over, and otherwise circulation continues; calculation results of all the processes are reduced, and solutions of questions are output; when parallel calculation is conducted, firstly, MPI processes are started, multi-process decomposition is conducted on the questions, parallel among the nodes is started, each MPI process is allocated to one calculation node, and information is exchanged between the processes trough message transmission; then, in each MPI process, OpenMP guidance instructions are used for establishing one set of threads, and the threads are allocated to different processors of the calculation nodes to conduct parallel execution.
Owner:INST OF SOFTWARE APPL TECH GUANGZHOU & CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
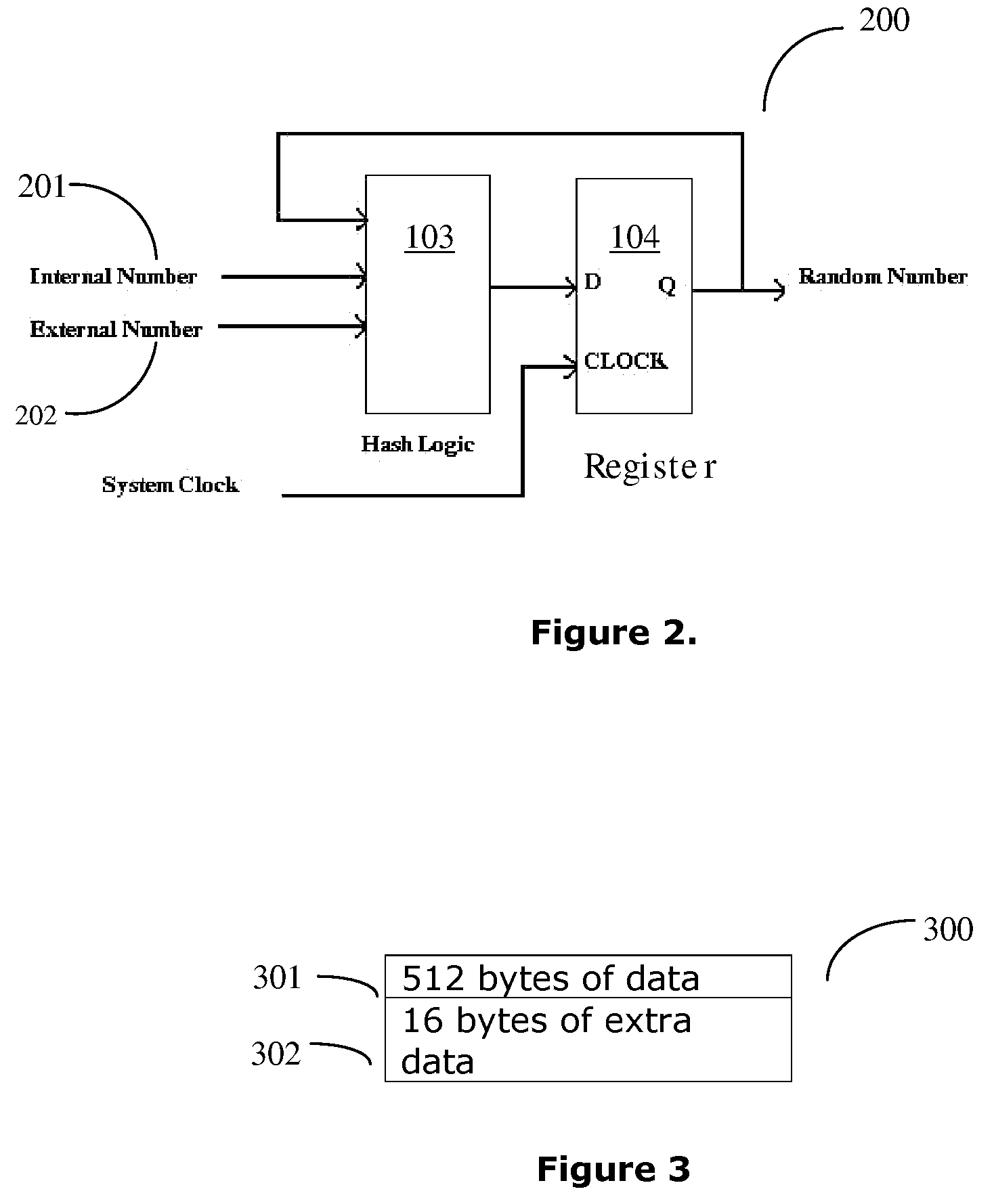
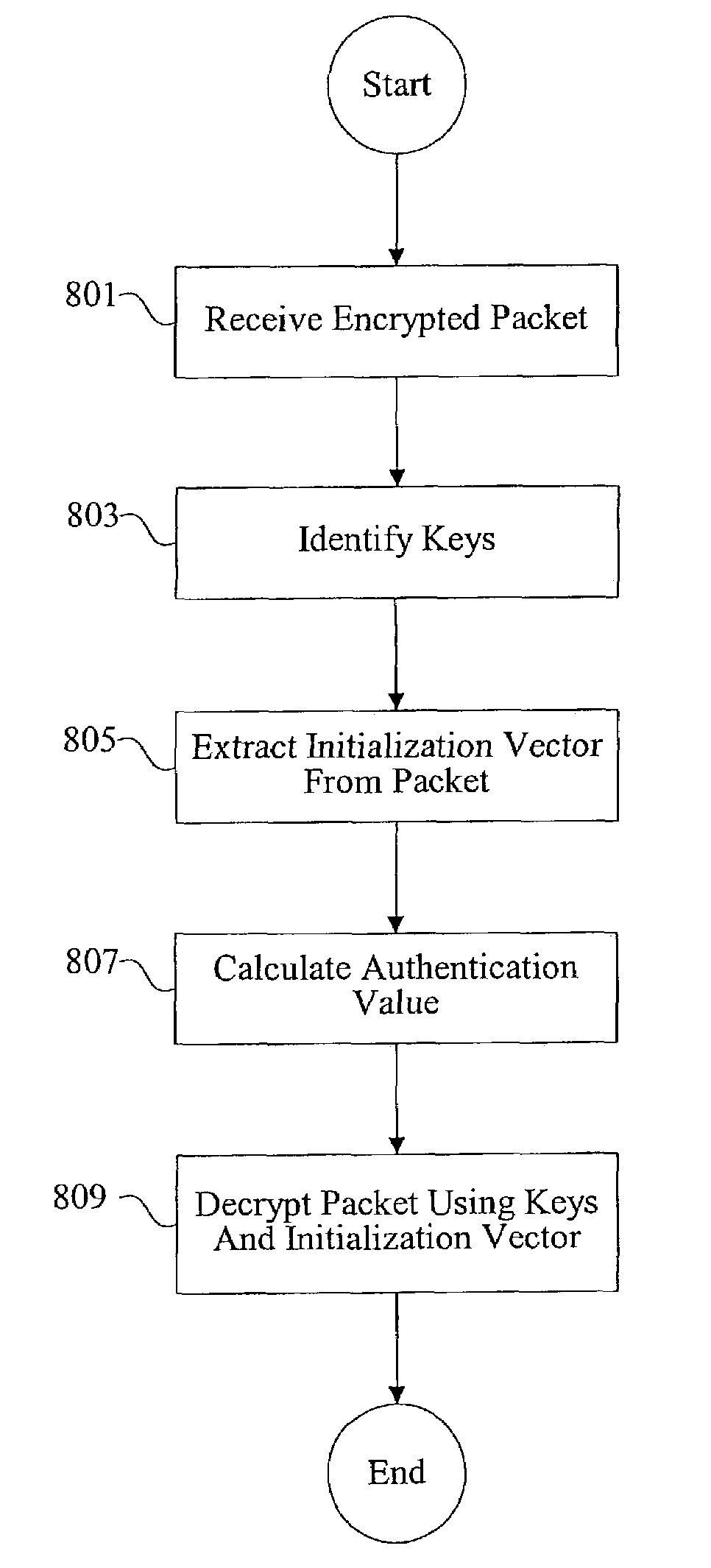
Methods and apparatus for initialization vector processing
InactiveUS7274792B2Synchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesMultiple keys/algorithms usageInitialization vector
Methods and apparatus are provided for using explicit initialization vectors in both encryption and decryption processing. In one example, a sender generates an initialization vector, identifies cryptographic keys, encrypts data using the initialization vectors and the cryptographic keys, and transmits the encrypted data in a packet along with the initialization vector. A receiver identifies cryptographic keys, extracts the initialization vector from the received packet, and decrypts the encrypted data using the cryptographic keys and the initialization vector extracted from the received packet.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Hard-disc fan-area data enciphering and deciphering method and system
InactiveCN1936870AImprove securityPrevent leakageUnauthorized memory use protectionSecuring communicationProgrammable read-only memoryTransfer procedure
This invention discloses an encryption and decryption method for data in hardware. It consists of several steps: obtain the key by reading data from the ROM; obtain the original key by the expending mechanism; operate the logic address and the sequence number and shift the result to get the address key; encryption on the address key by the original key to form a key flow; encryption and decryption on transmitting data. This invention could enhance data security on storage device and protect them from missing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG XUNBO INFORMATION ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com