Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
97 results about "Intravascular imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
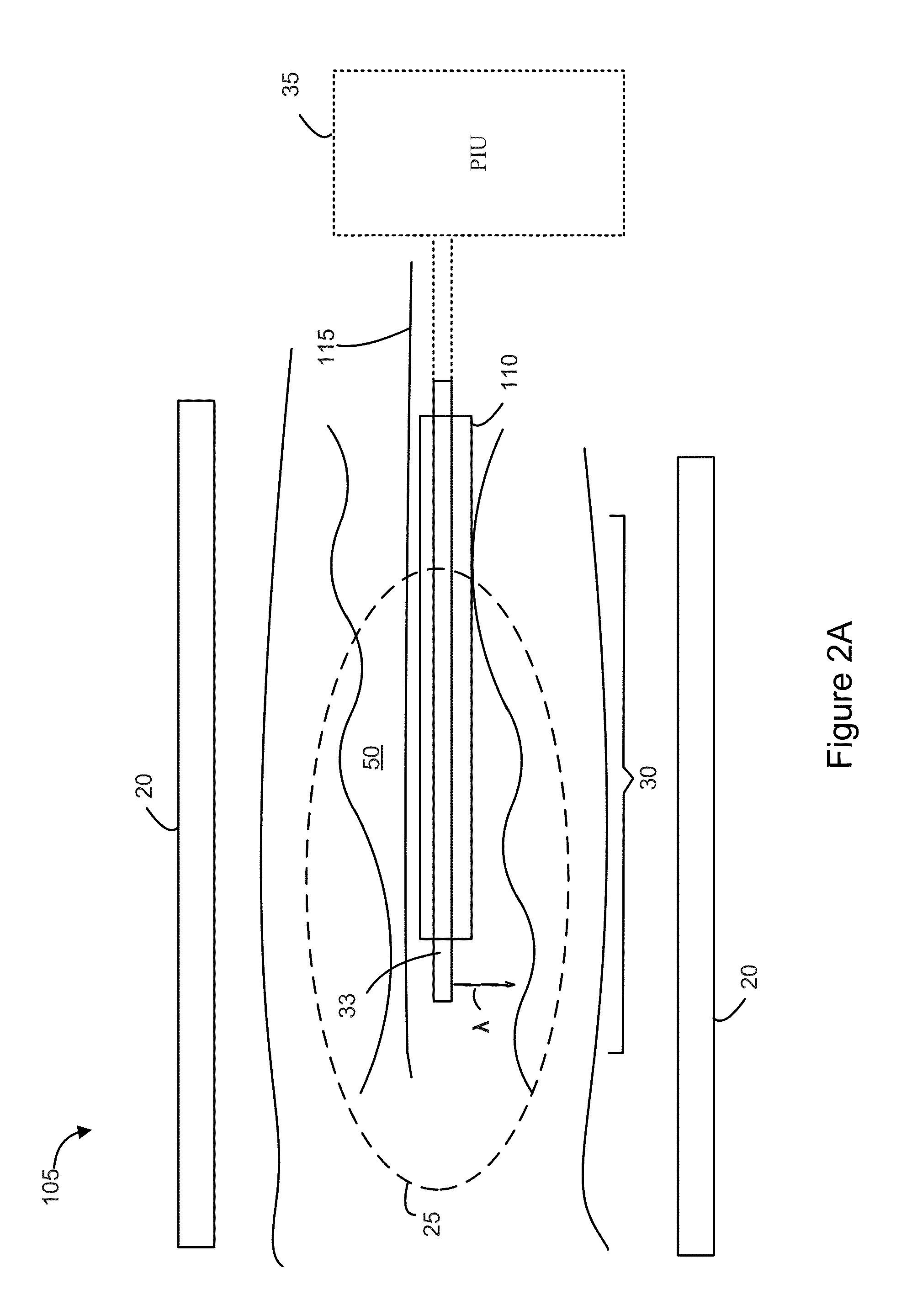
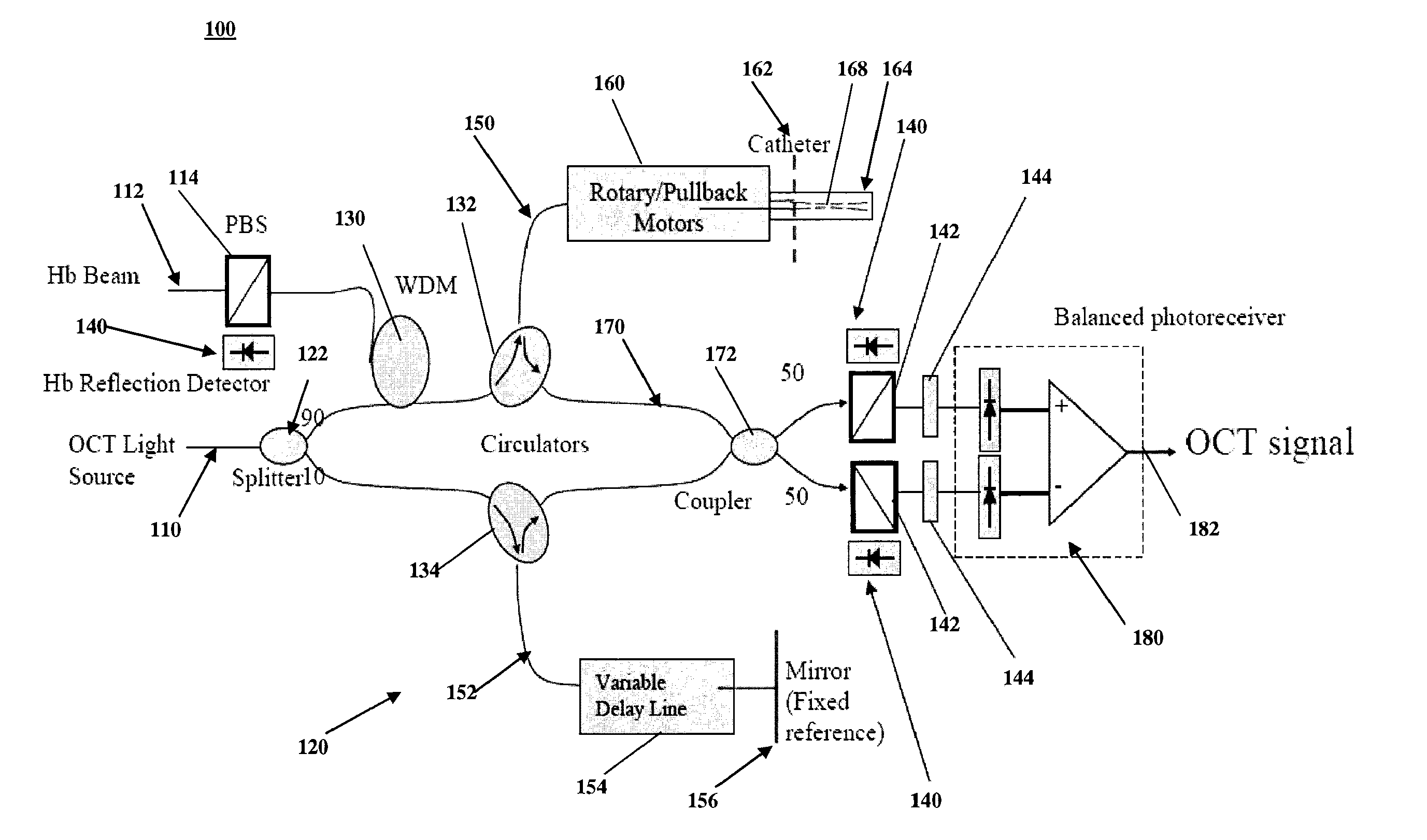
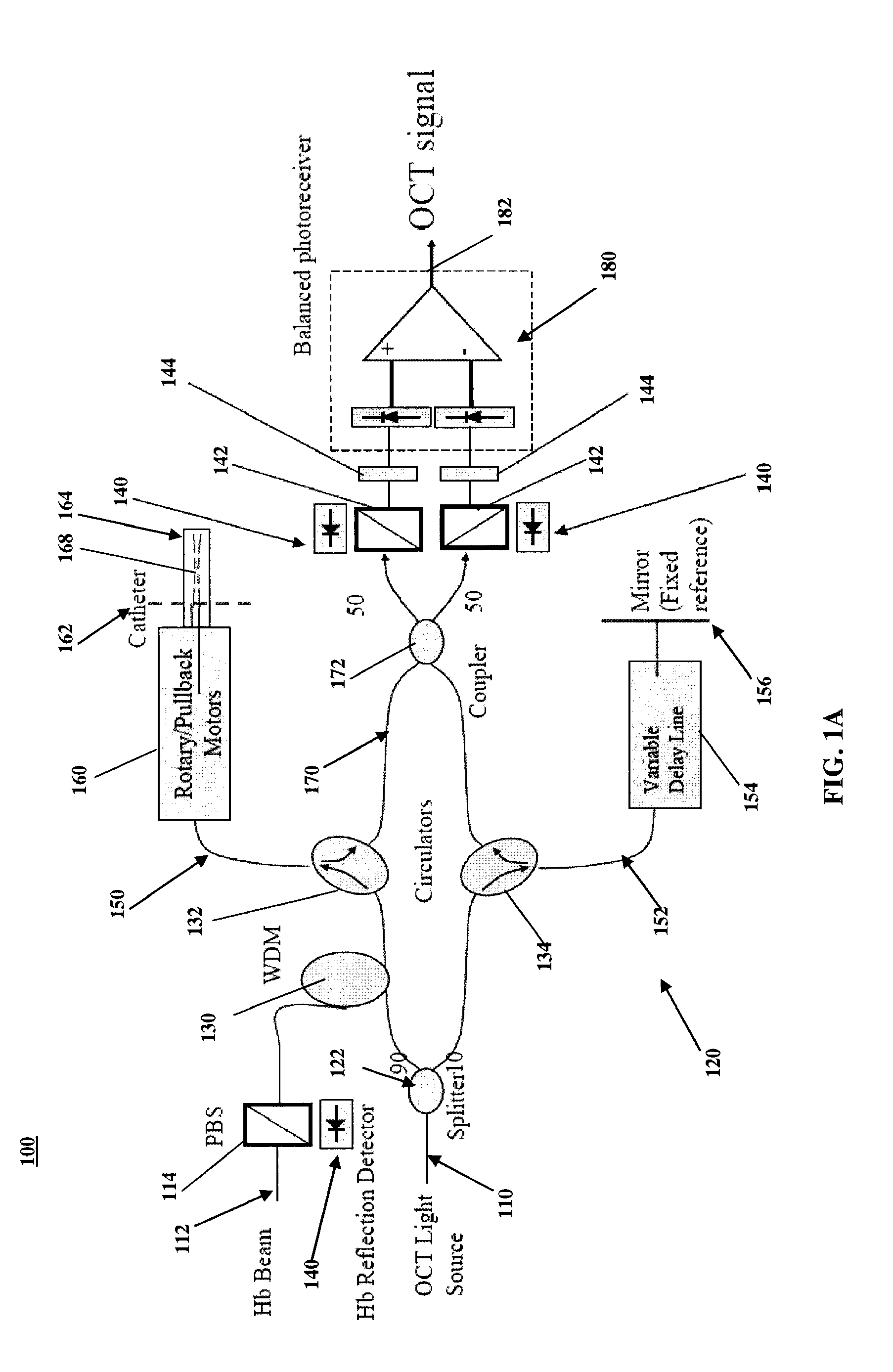
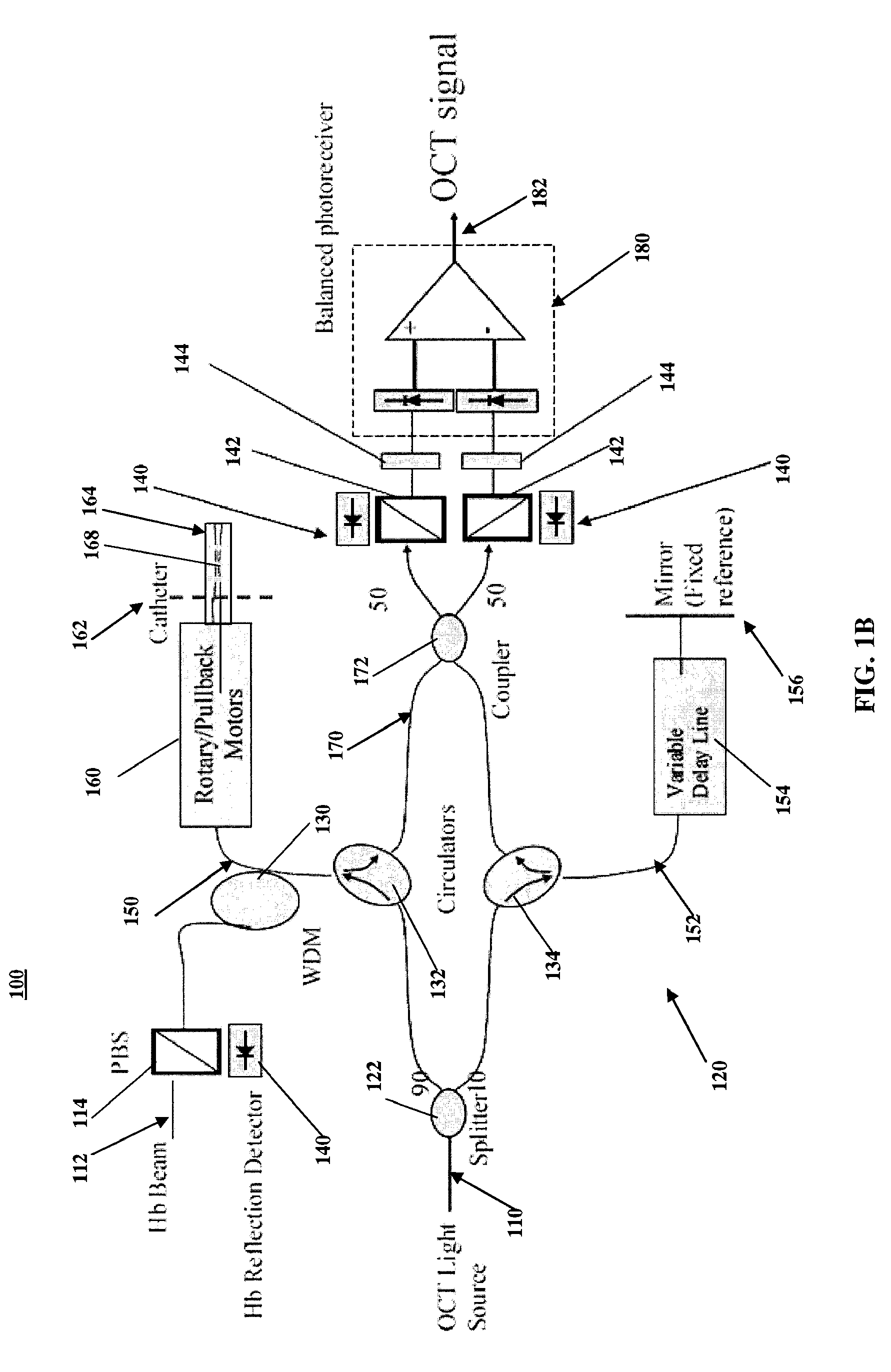
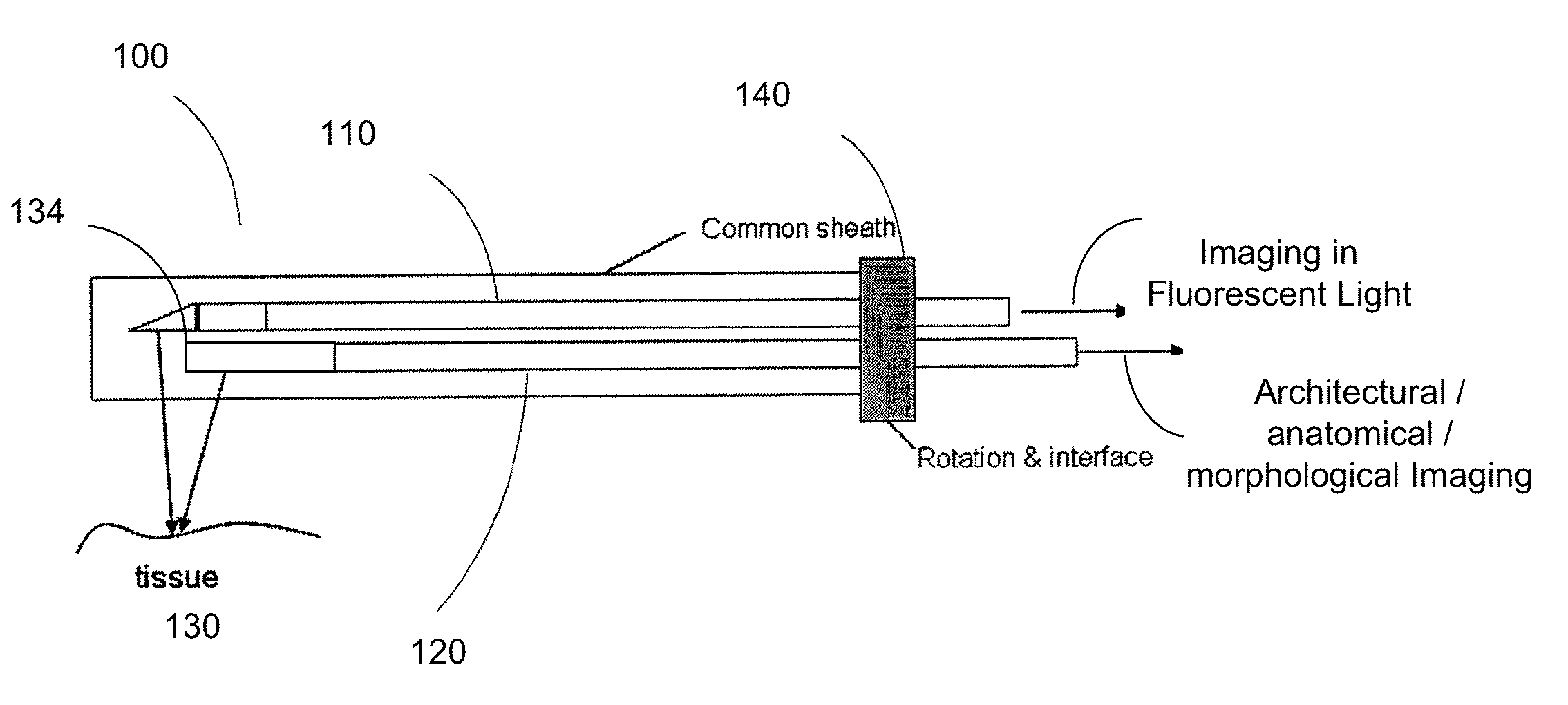
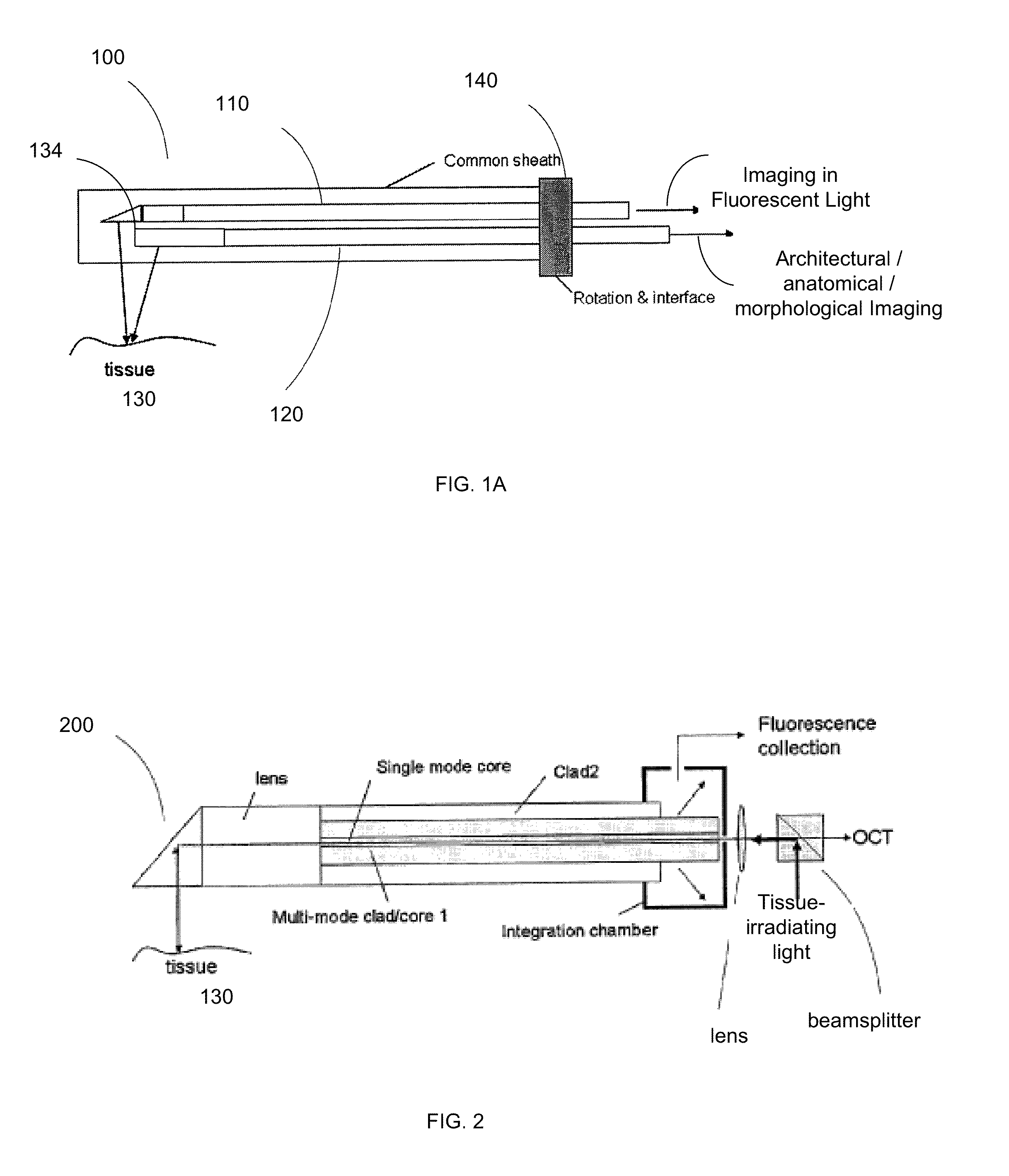
Intravascular imaging is a catheter based system that allows physicians such as interventional cardiologists to acquire images of diseased vessels from inside the artery. Intravascular imaging provides detailed and accurate measurements of vessel lumen morphology, vessel size, extension of diseased artery segments, vessel size and plaque characteristics. Examples of intravascular imaging modalities are intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) and Intracoronary Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT or IVOCT).
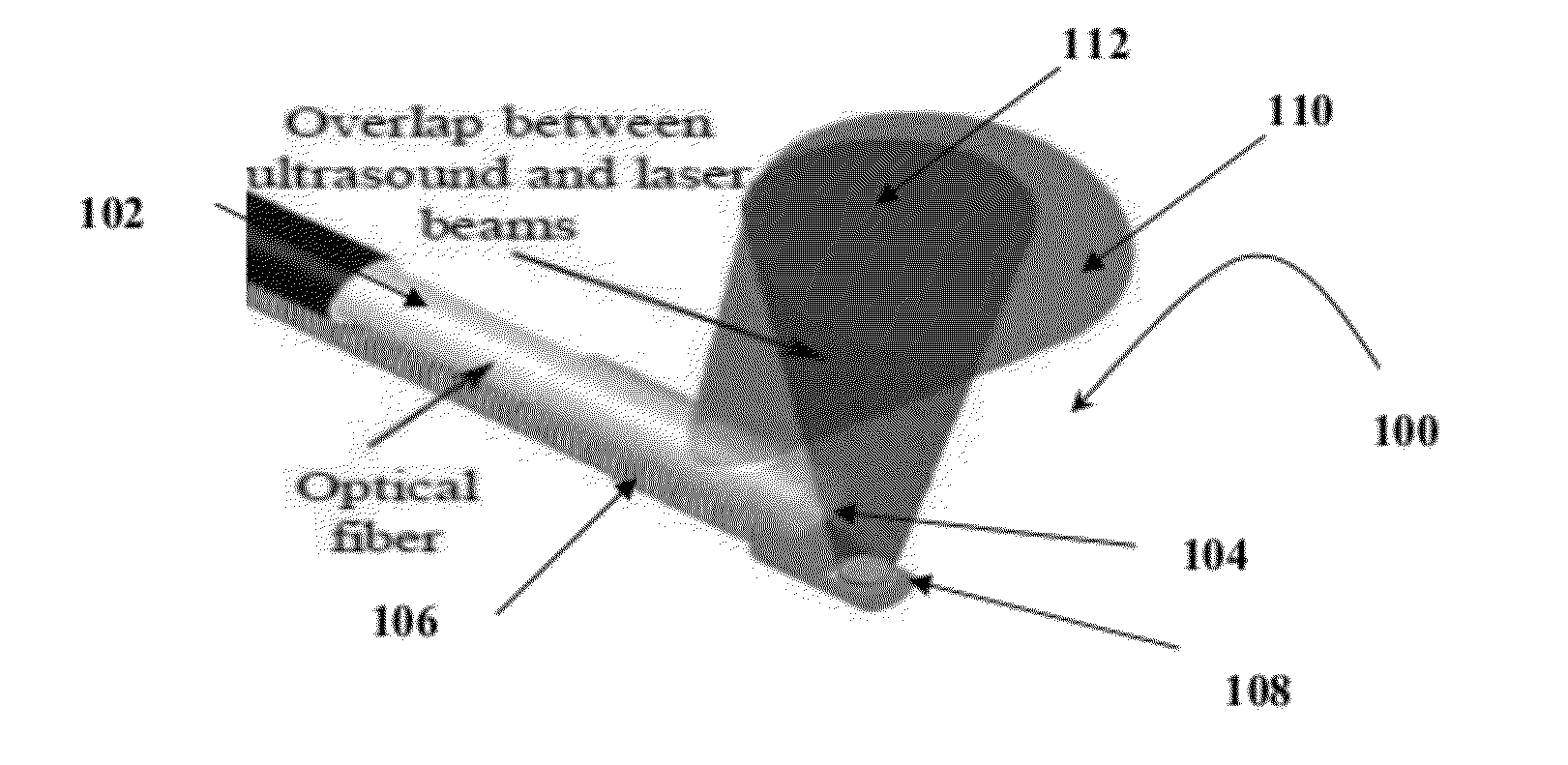
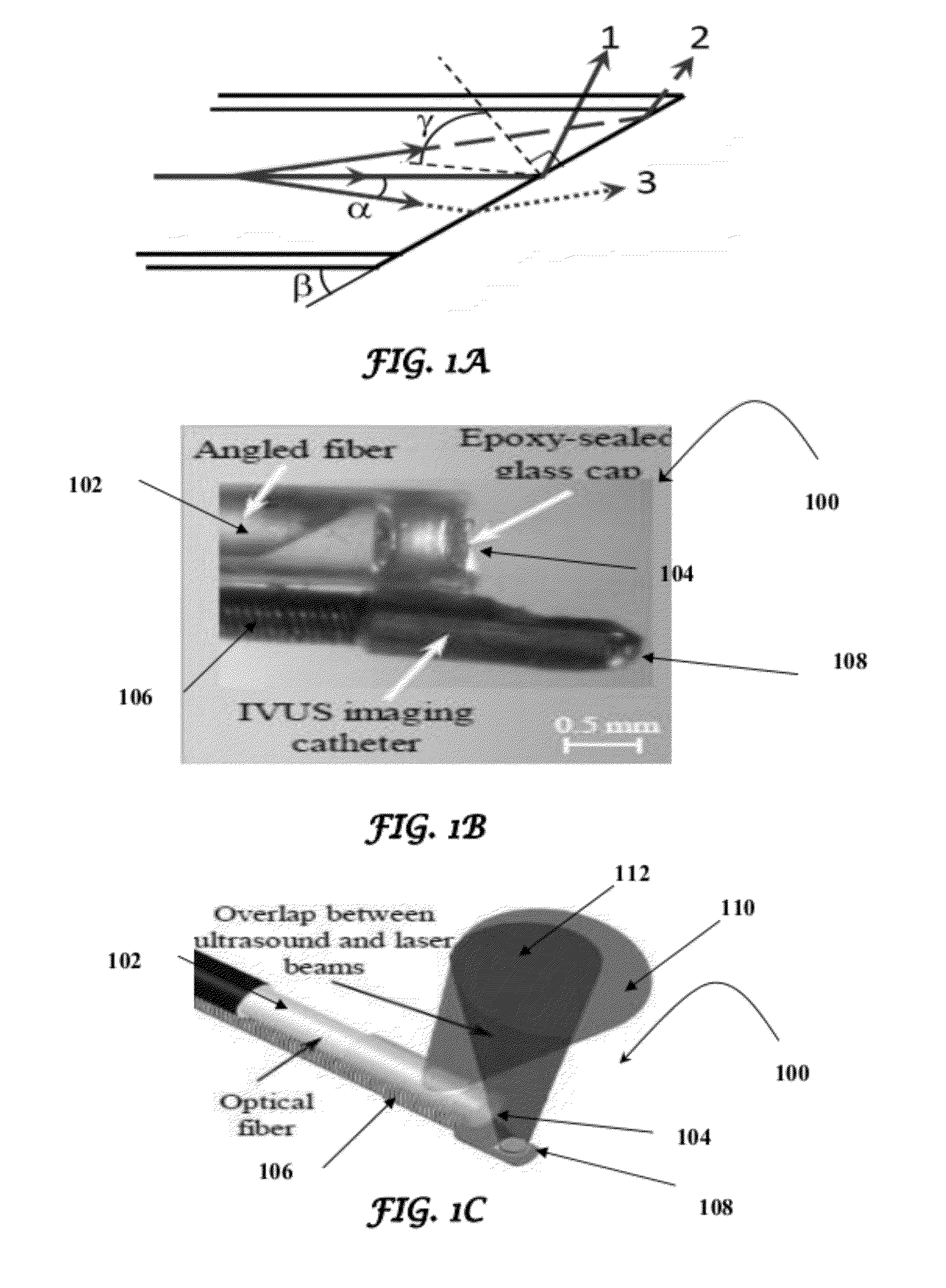
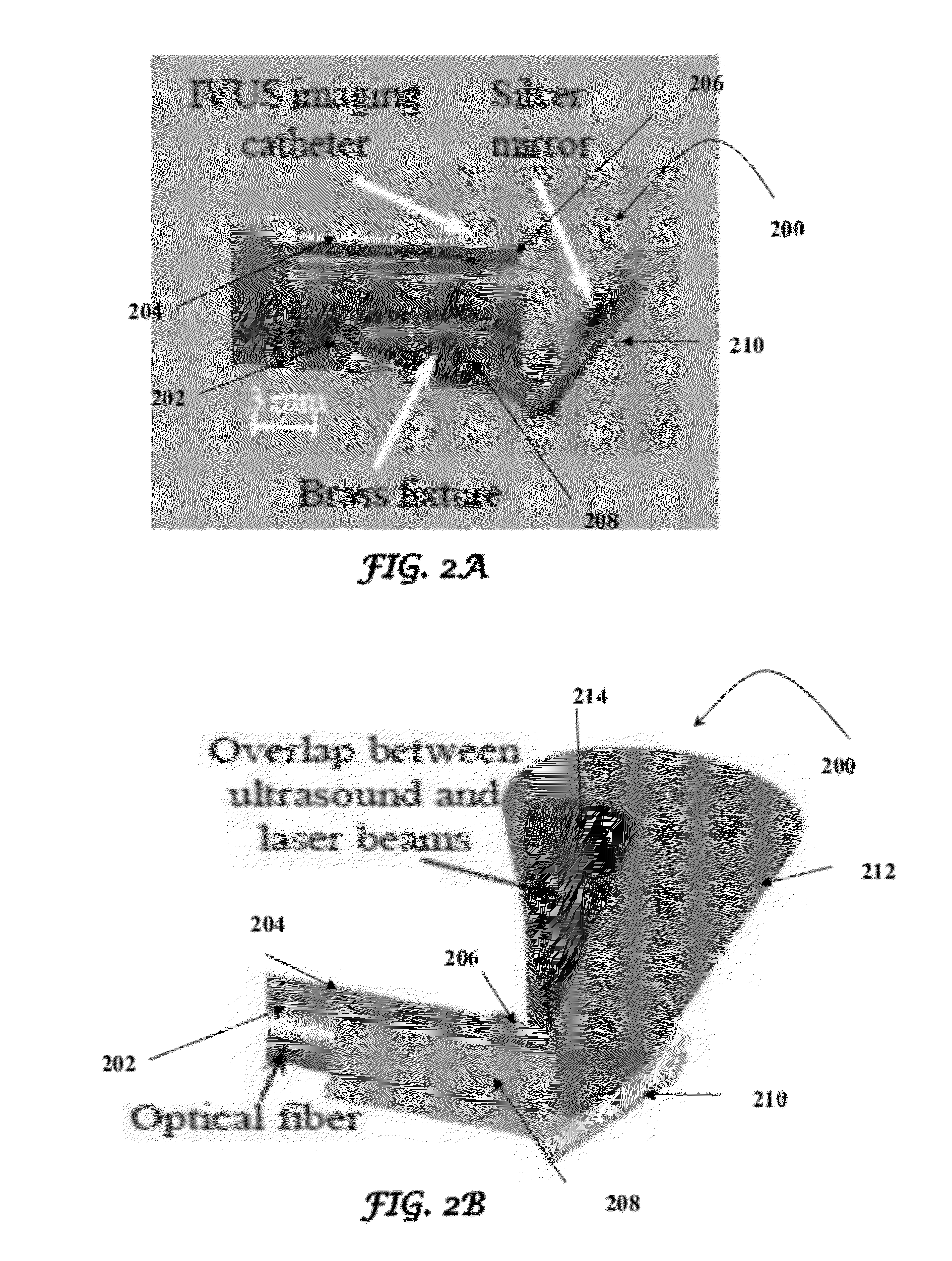
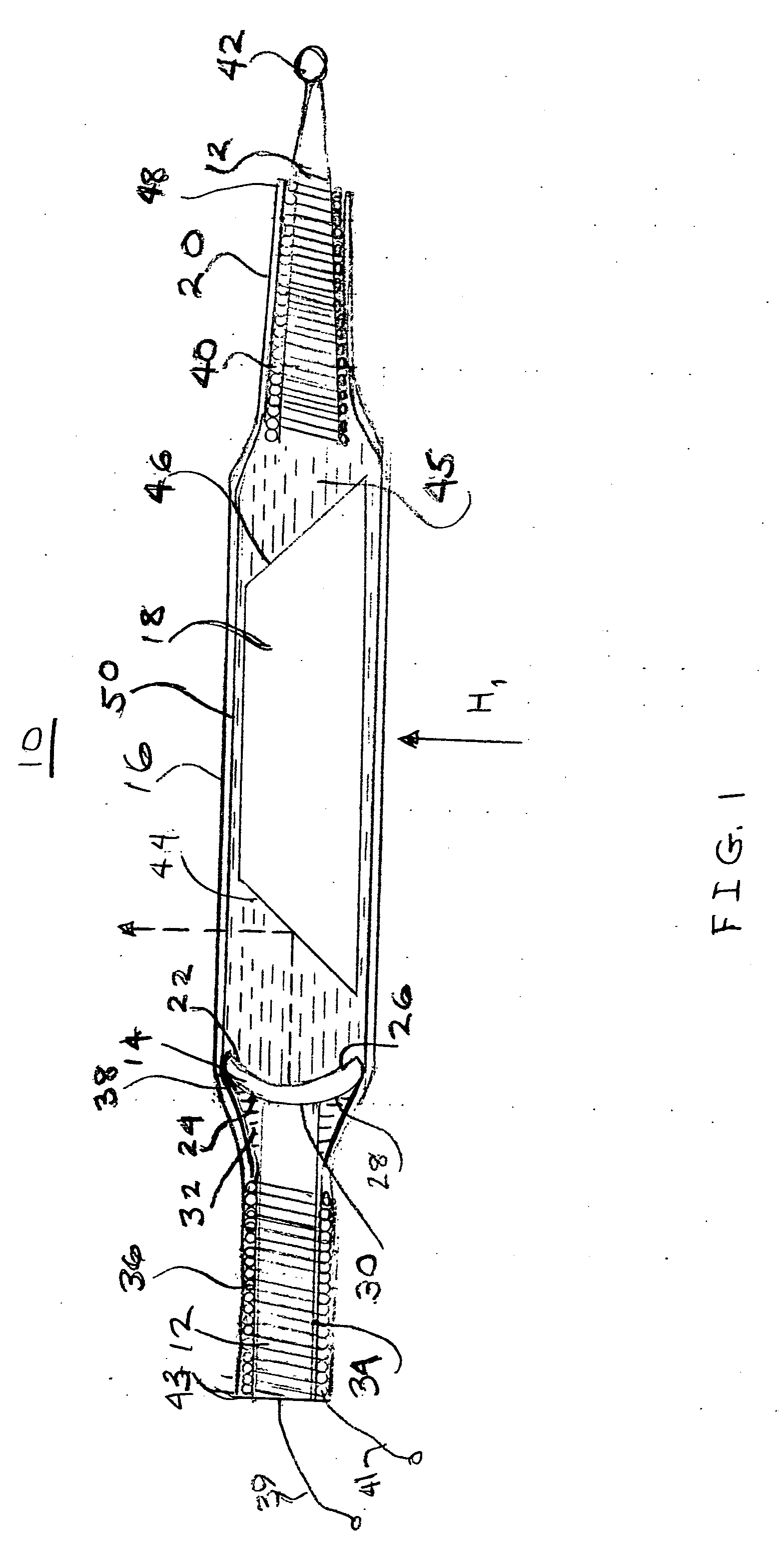
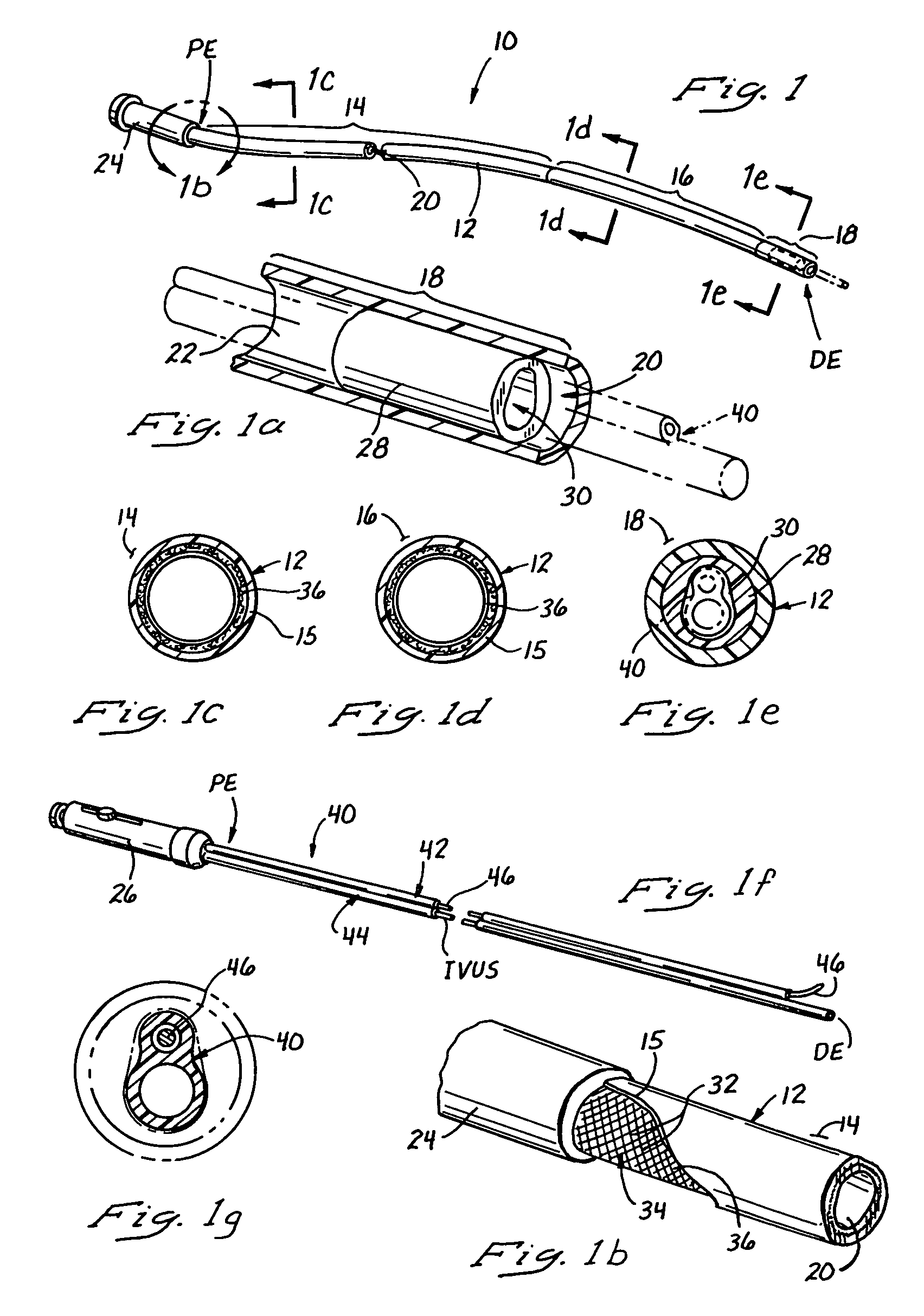
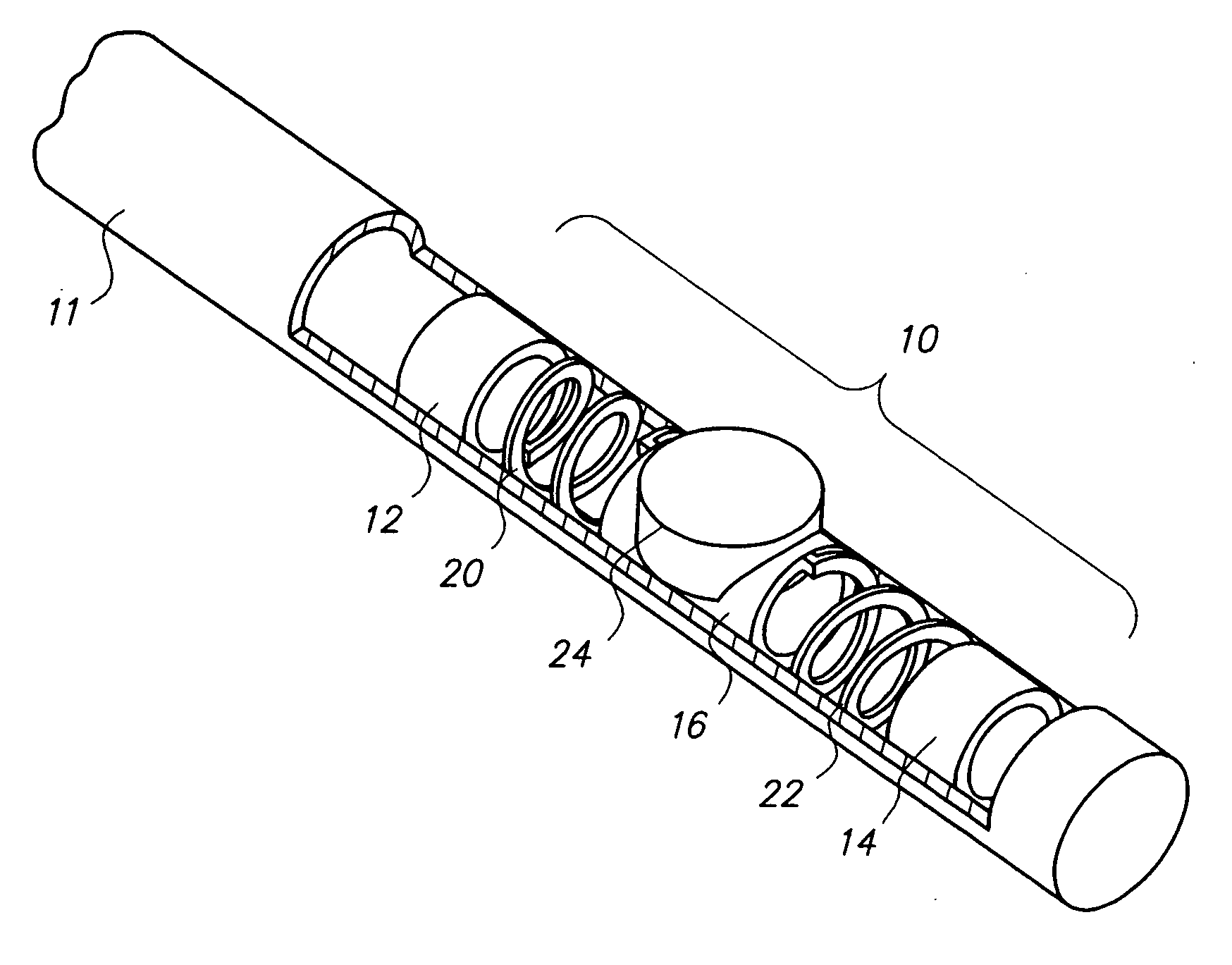
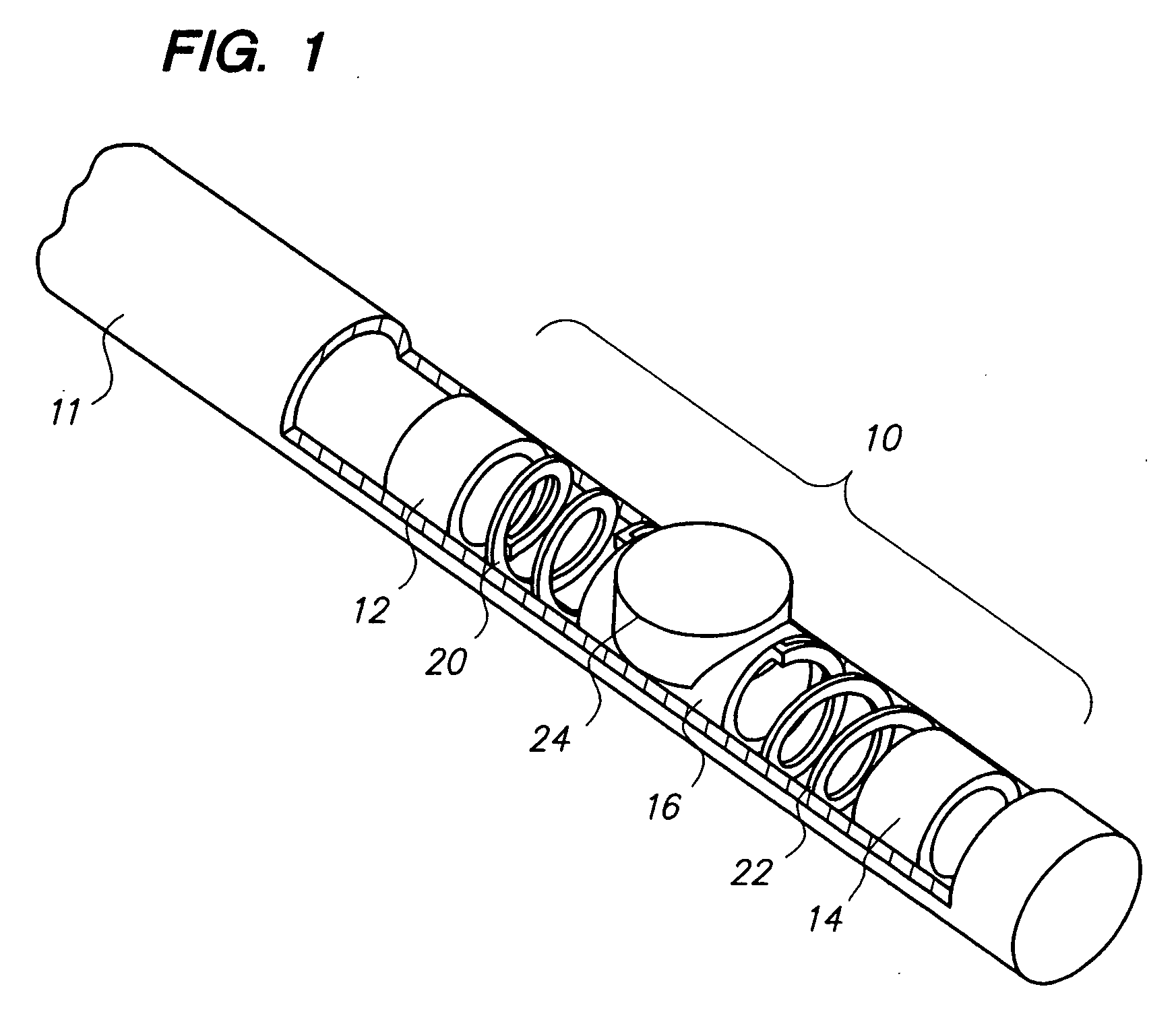
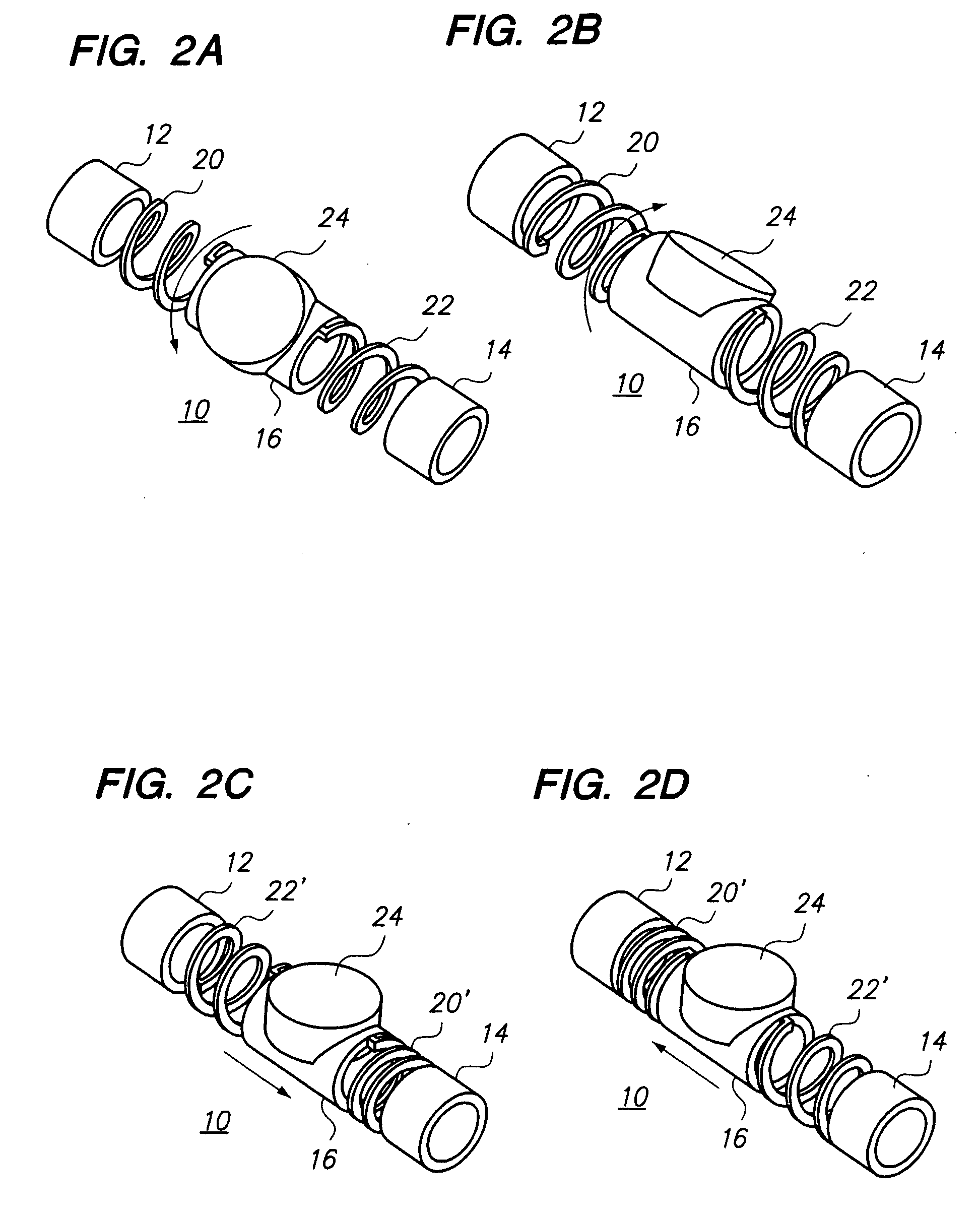
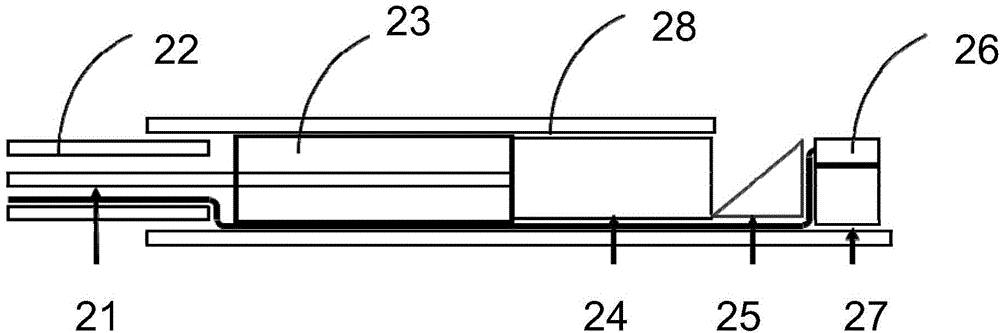
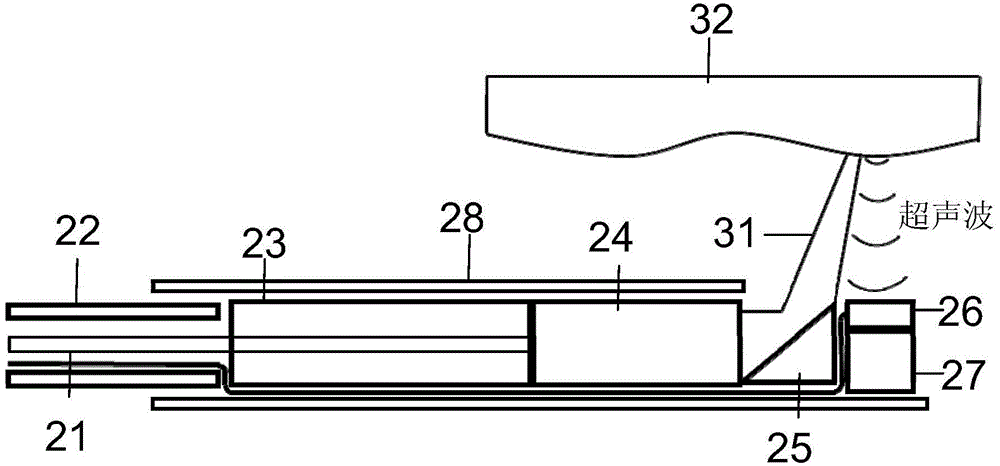
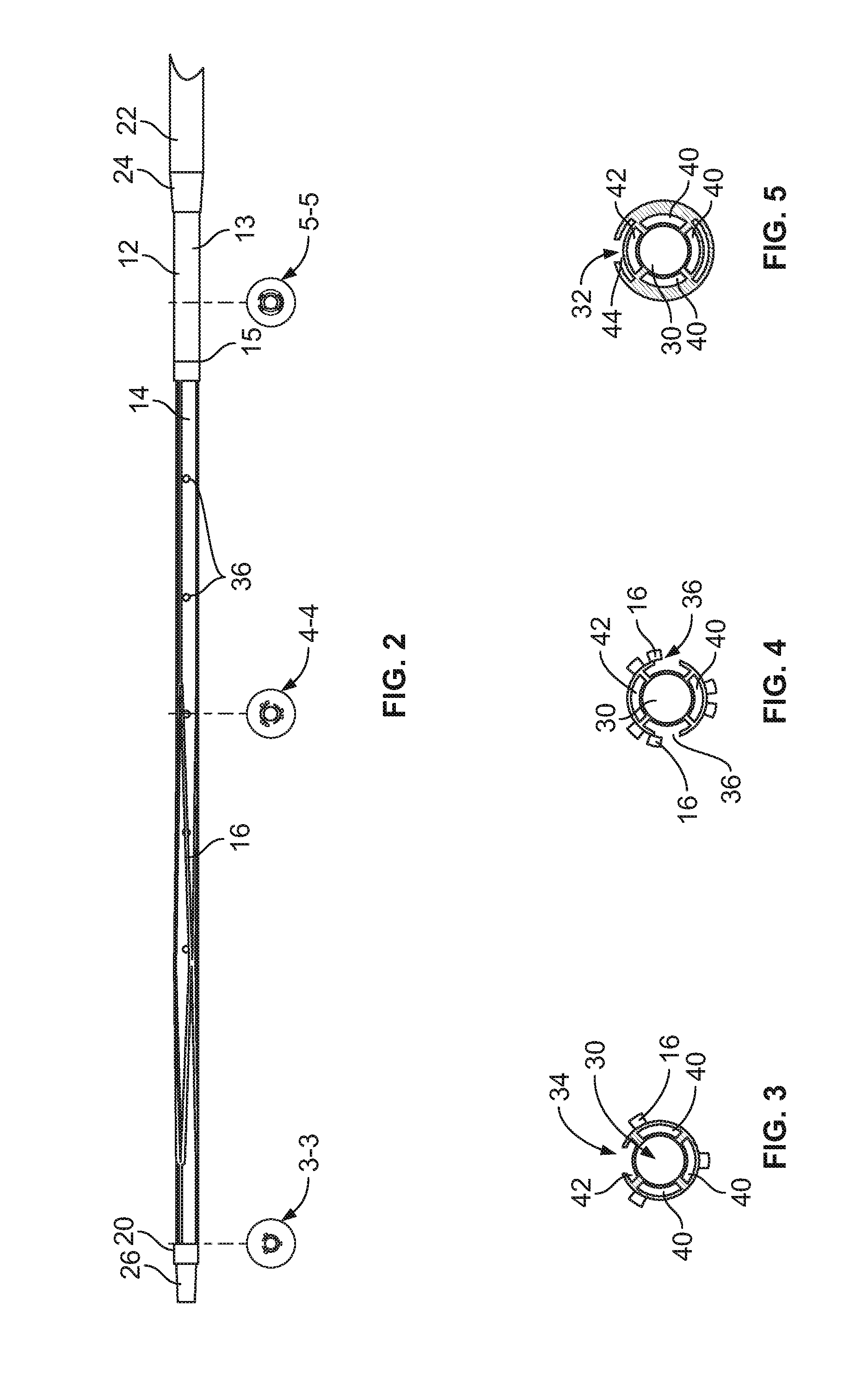
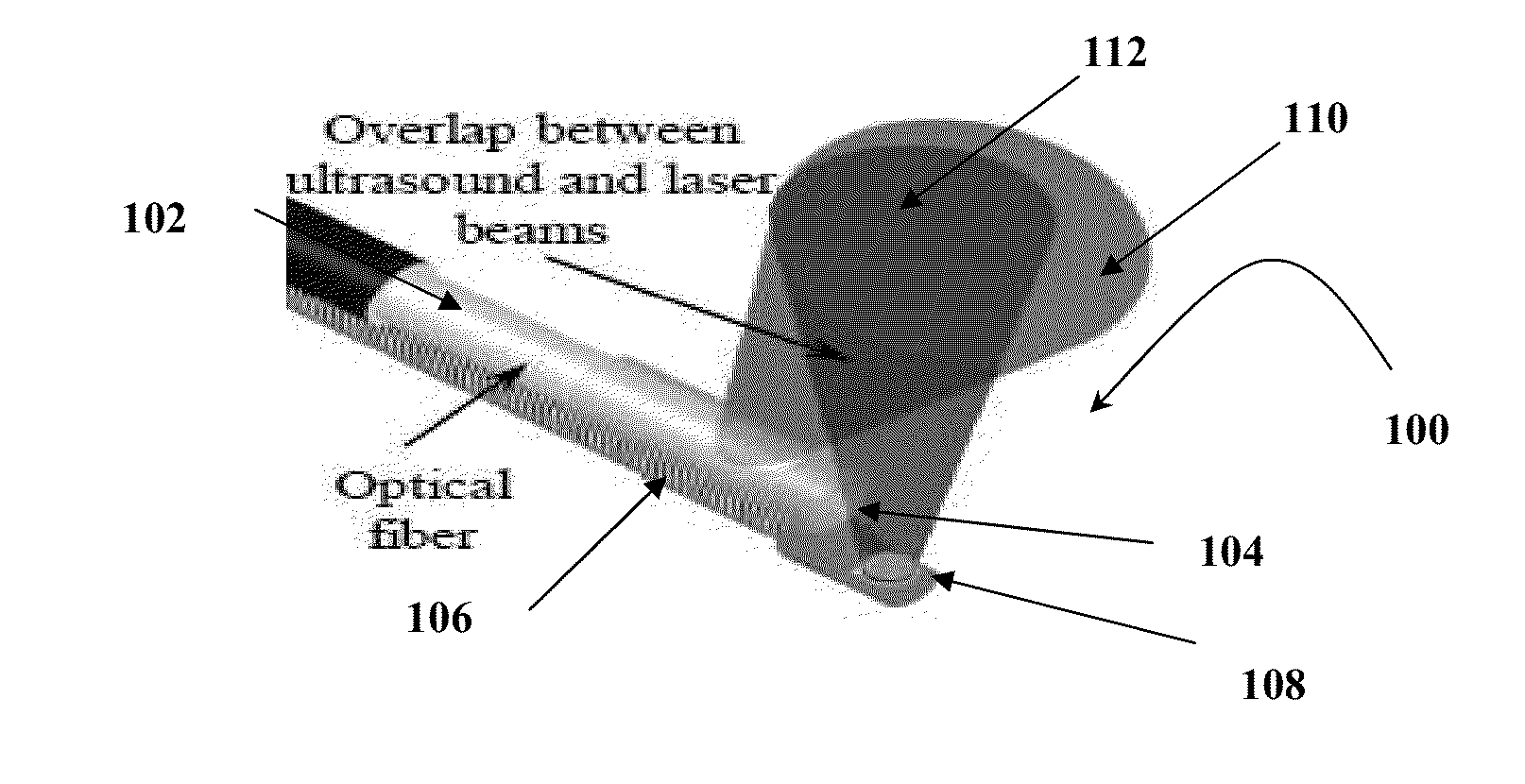
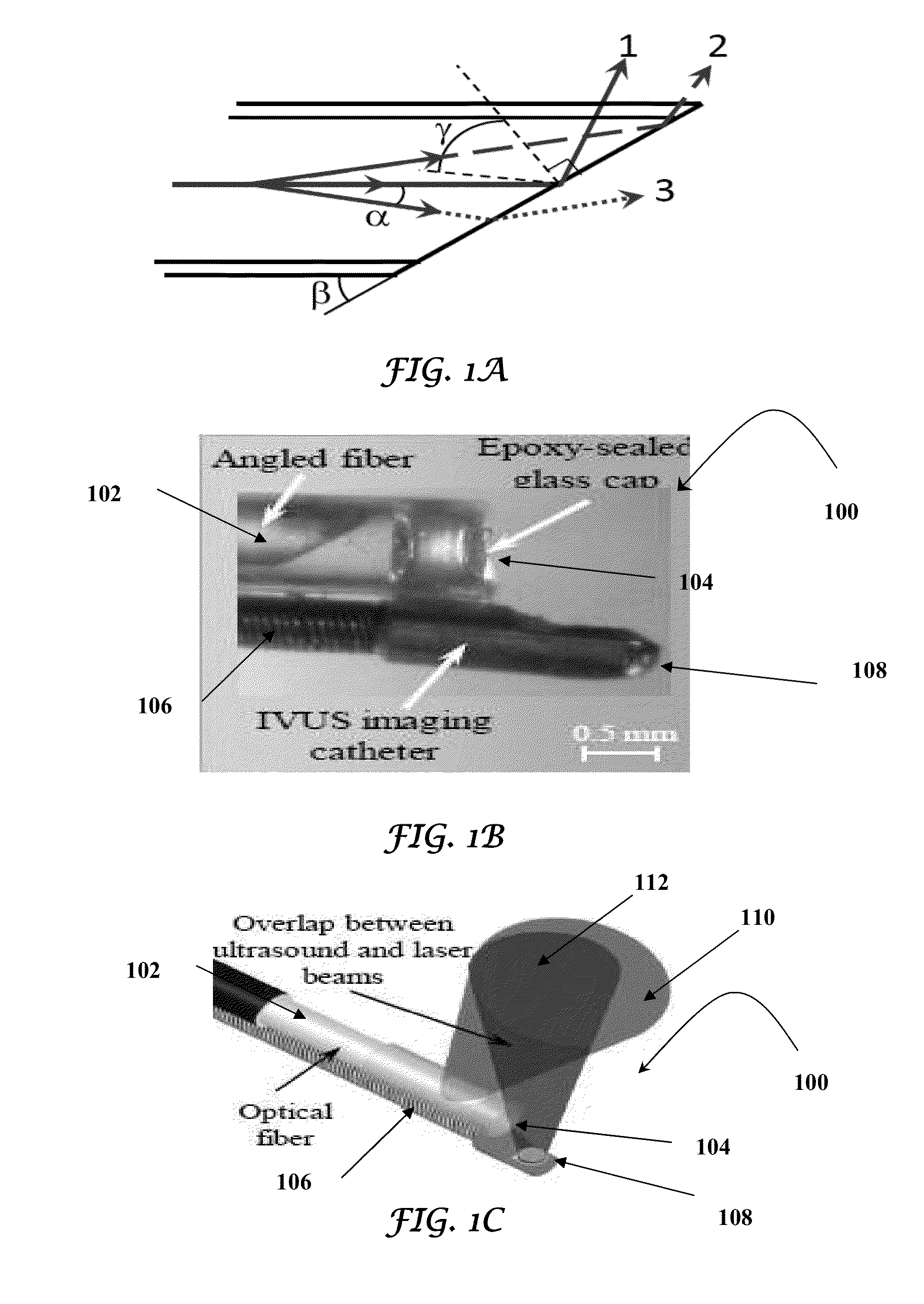
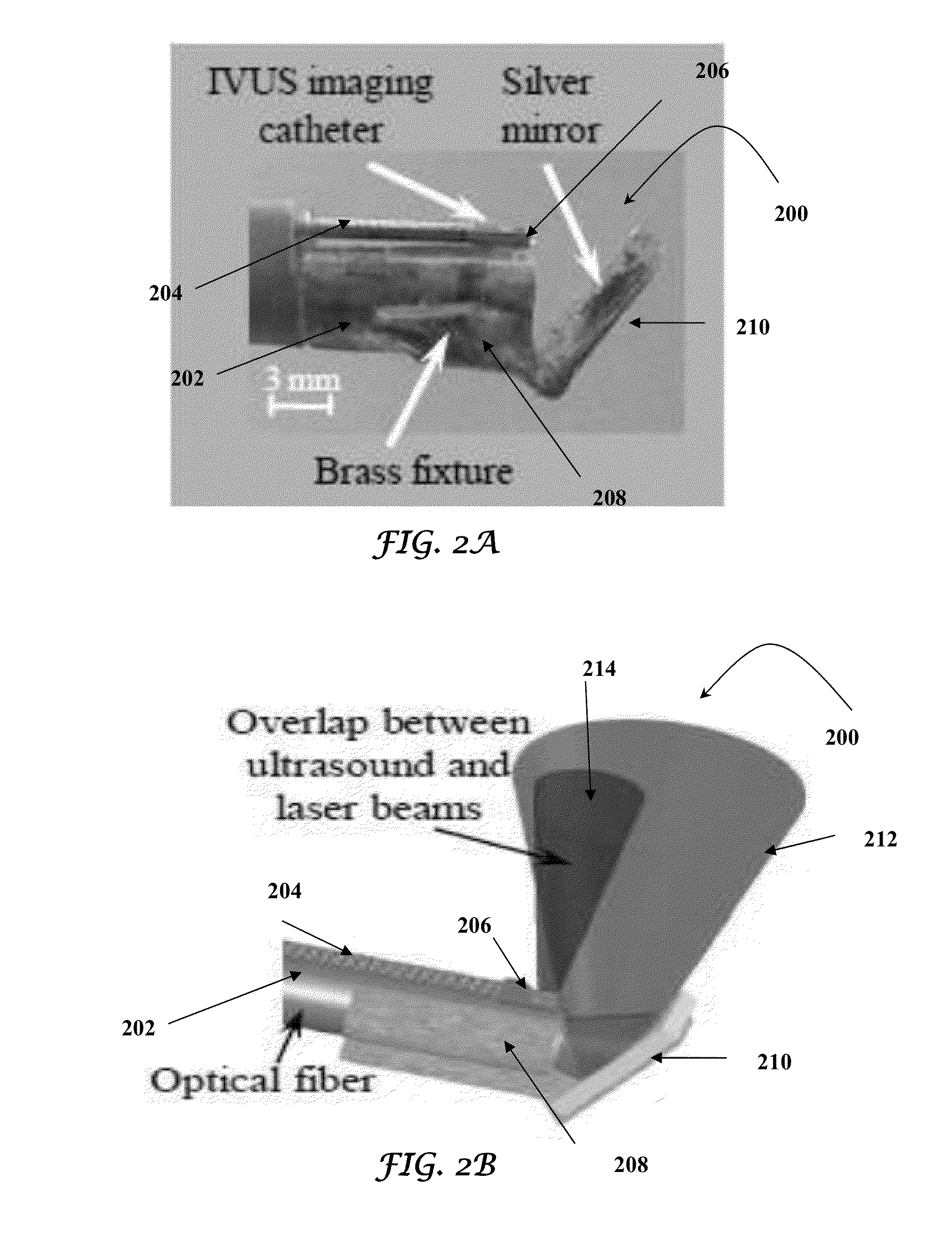
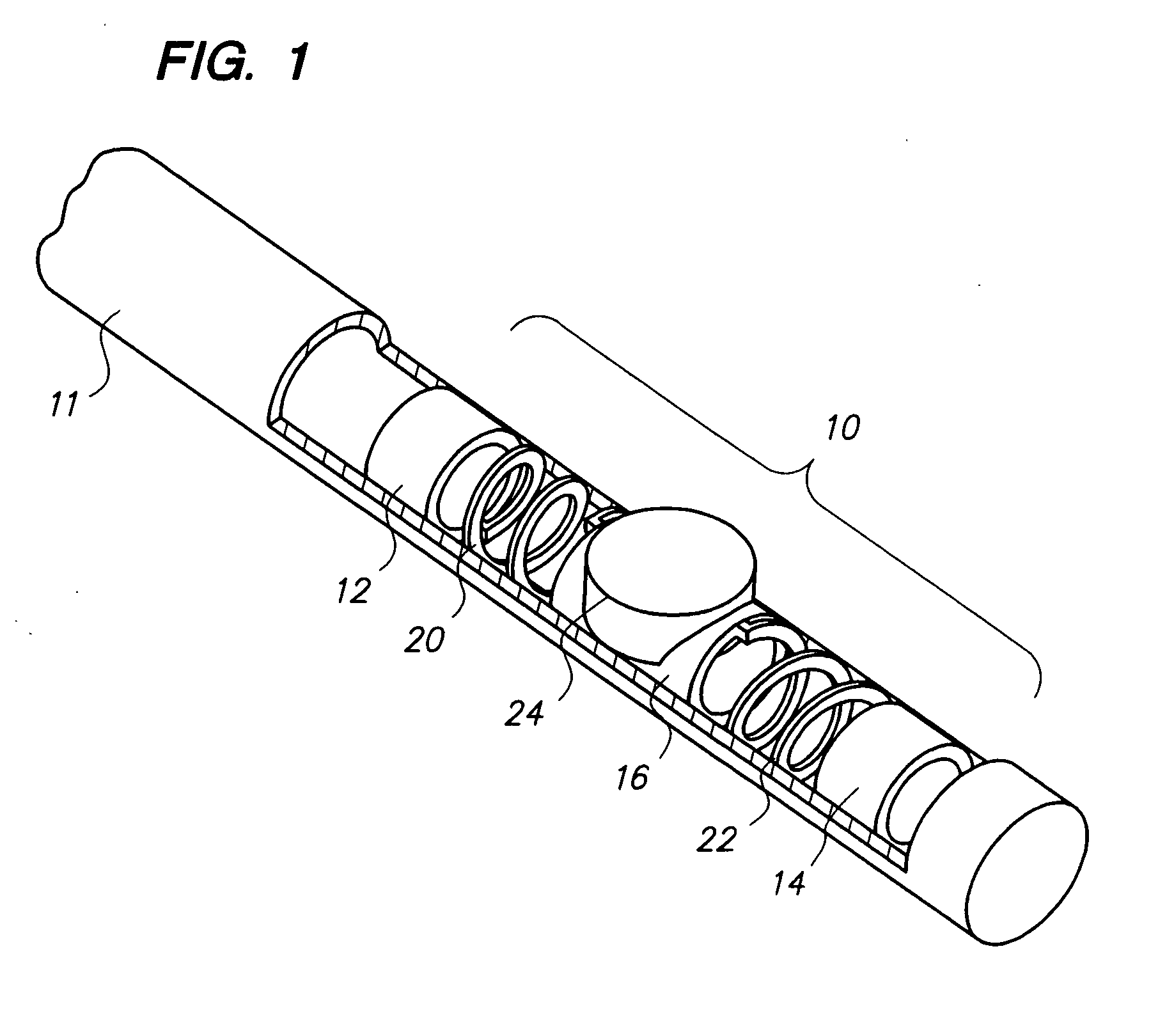
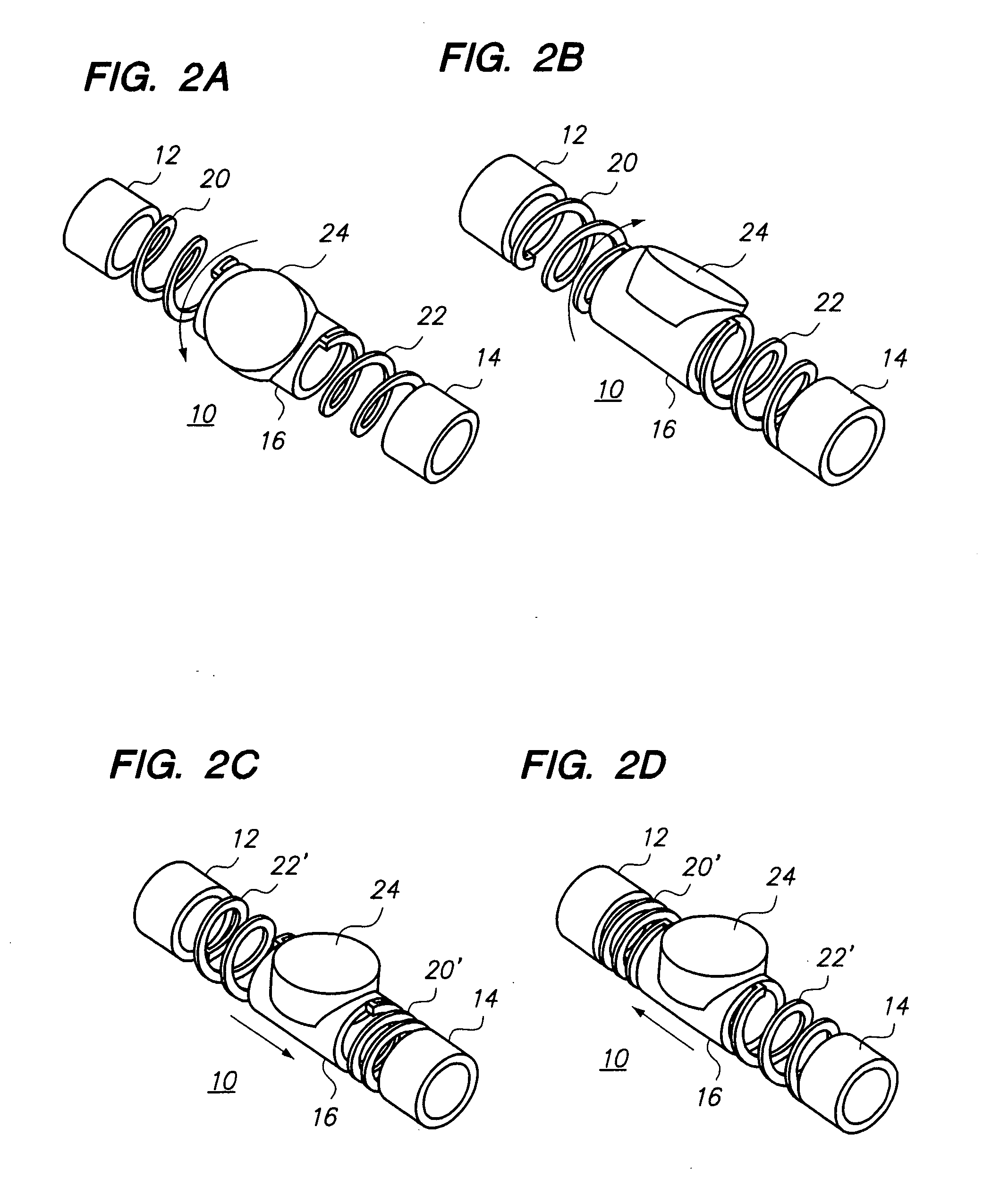
Catheter for intravascular ultrasound and photoacoustic imaging
InactiveUS20120271170A1Protect partsAvoid mechanical damageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasonic sensorElastography
A design and a fabrication method for an intravascular imaging and therapeutic catheters for combined ultrasound, photoacoustic, and elasticity imaging and for optical and / or acoustic therapy of hollow organs and diseased blood vessels and tissues are disclosed in the present invention. The invention comprises both a device—optical fiber-based intravascular catheter designs for combined IVUS / IVPA, and elasticity imaging and for acoustic and / or optical therapy—and a method of combined ultrasound, photoacoustic, and elasticity imaging and optical and / or acoustic therapy. The designs of the catheters are based on single-element catheter-based ultrasound transducers or on ultrasound array-based units coupled with optical fiber, fiber bundles or a combination thereof with specially designed light delivery systems. One approach uses the side fire fiber, similar to the one utilized for biomedical optical spectroscopy. The second catheter design uses the micro-optics in the manner of a probe for optical coherent tomography.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Apparatus and method for intravascular imaging
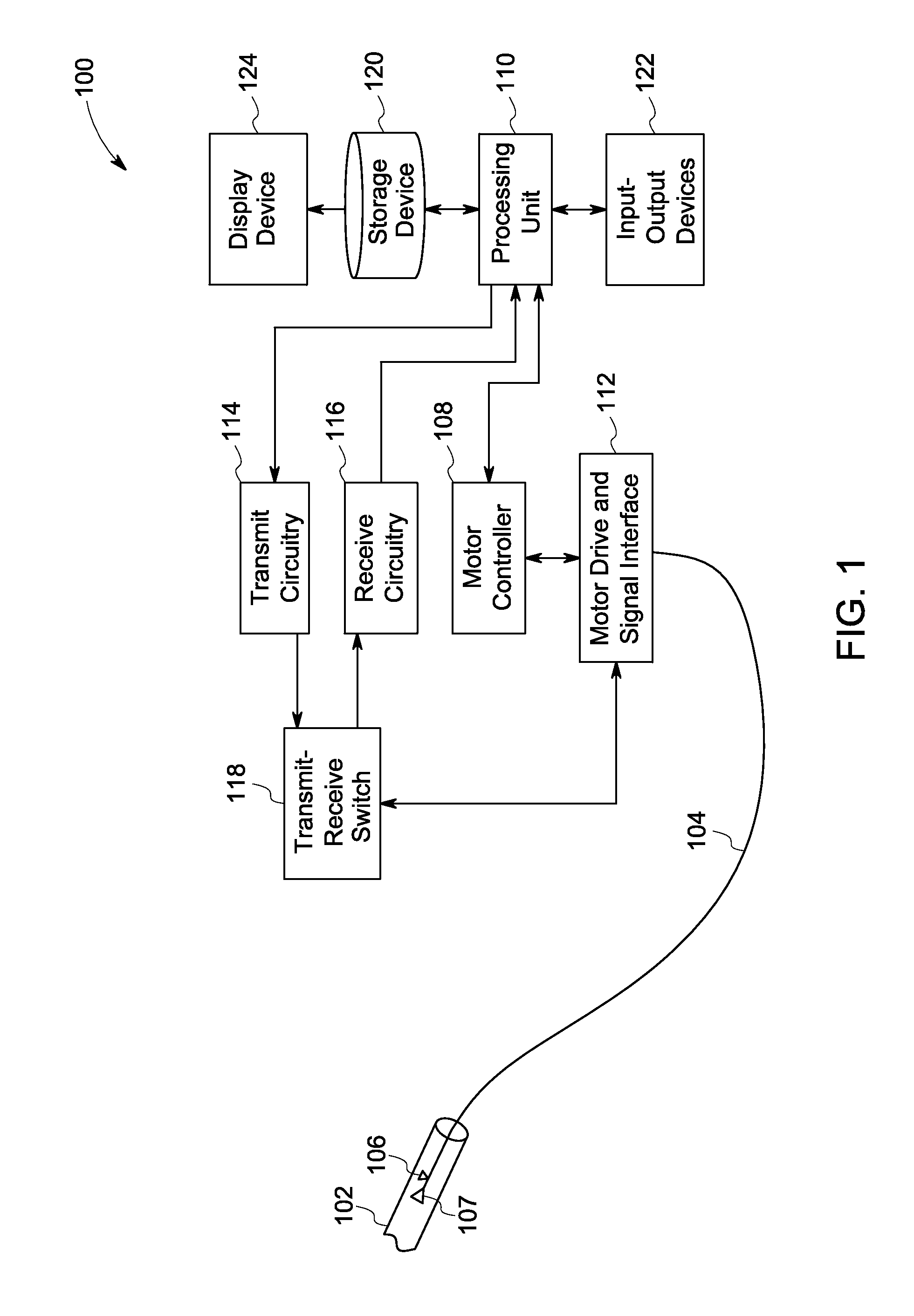
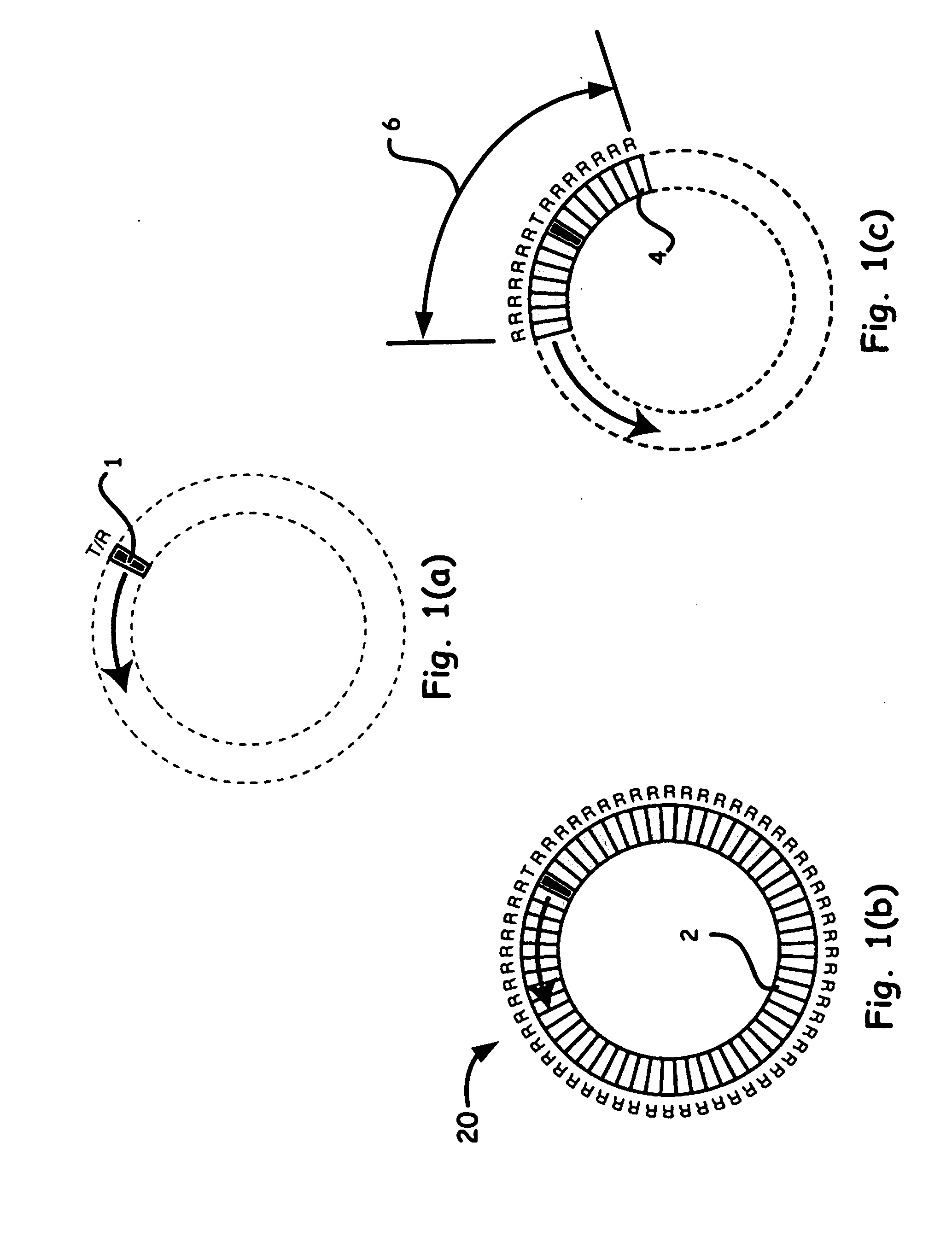
A method and apparatus for intravascular imaging utilizes a rotating magnetic field generated outside of the patient's body to cause a substantially synchronous rotation of an ultrasonic signal inside the patient's body.
Owner:MARTINELLI MICHAEL A
Vascular Data Processing and Image Registration Systems, Methods, and Apparatuses
ActiveUS20140270436A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementDiagnostic Radiology ModalityImaging modalities
In part, the invention relates to processing, tracking and registering angiography images and elements in such images relative to images from an intravascular imaging modality such as, for example, optical coherence tomography (OCT). Registration between such imaging modalities is facilitated by tracking of a marker of the intravascular imaging probe performed on the angiography images obtained during a pullback. Further, detecting and tracking vessel centerlines is used to perform a continuous registration between OCT and angiography images in one embodiment.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Full Circumferential Scanning Oct Intravascular Imaging Probe Based On Scanning Mems Mirror
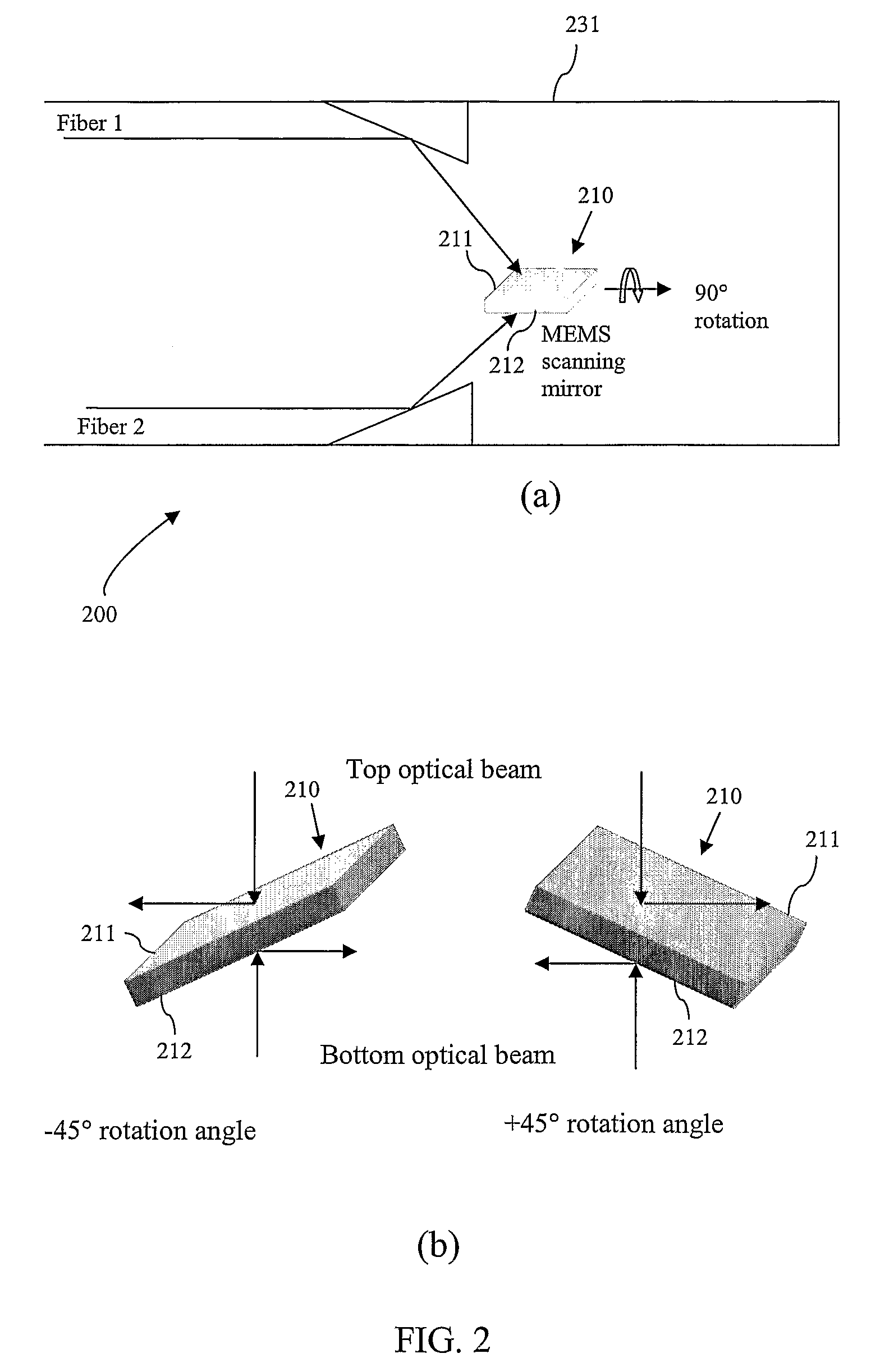
An optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging probe 500 comprises a reference arm, and a sample arm which are both preferably disposed in a hollow outer tube 515. The sample arm comprises a MEMS scanning mirror 210 disposed inside and secured to the tube 515 for providing lateral scanning of a first and second optical beam provided. The scanning mirror has a highly reflective top 211 and highly reflective bottom surface 212, wherein the first beam is incident on the top surface and the second beam is incident on the bottom surface. The scanning mirror 210 is rotatable through at least 90° along a first axis to provide 180° scanning on each of its surfaces to cover a full 360° circumferential view of a sample to be imaged.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Methods for intravascular imaging and flushing
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
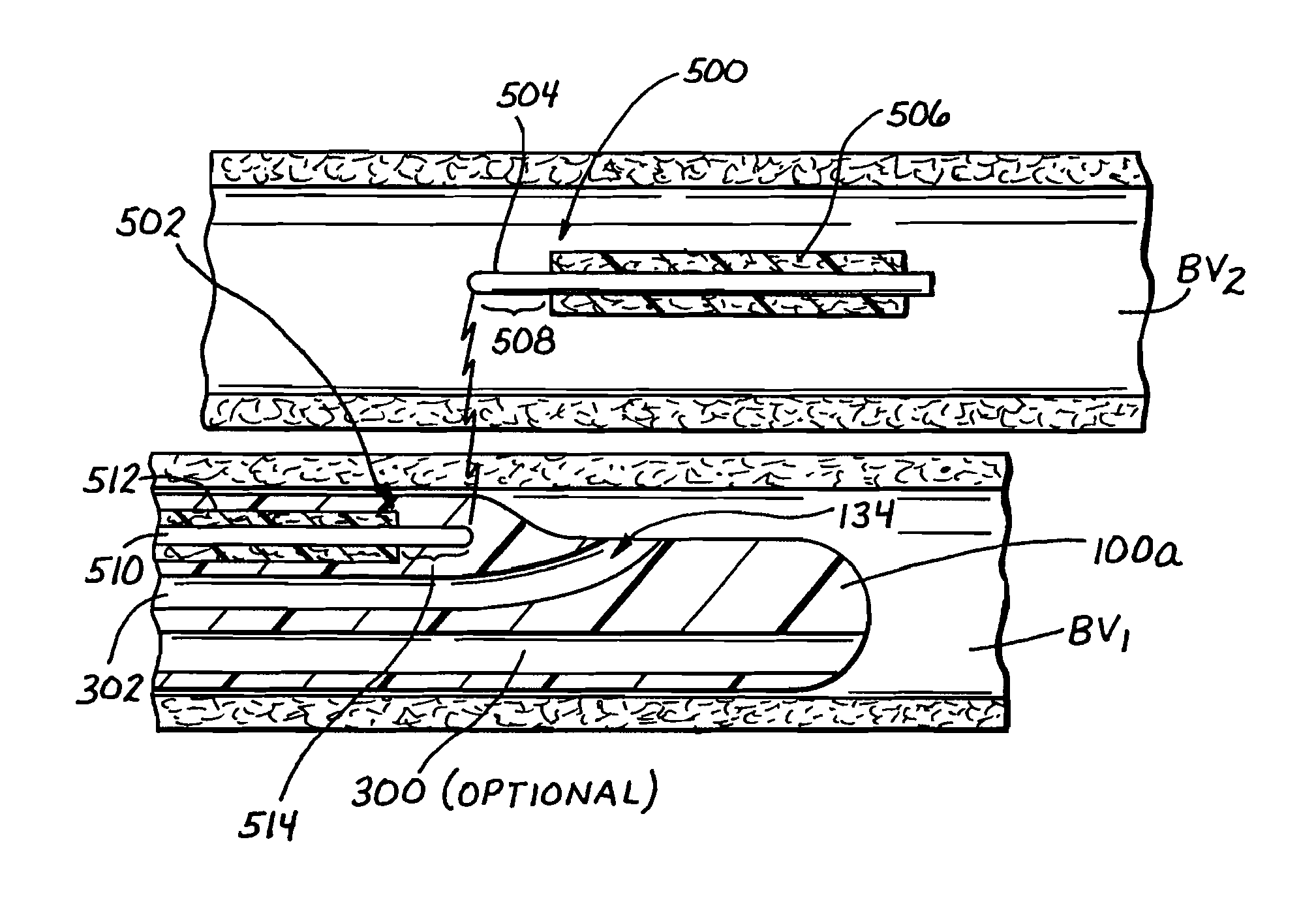
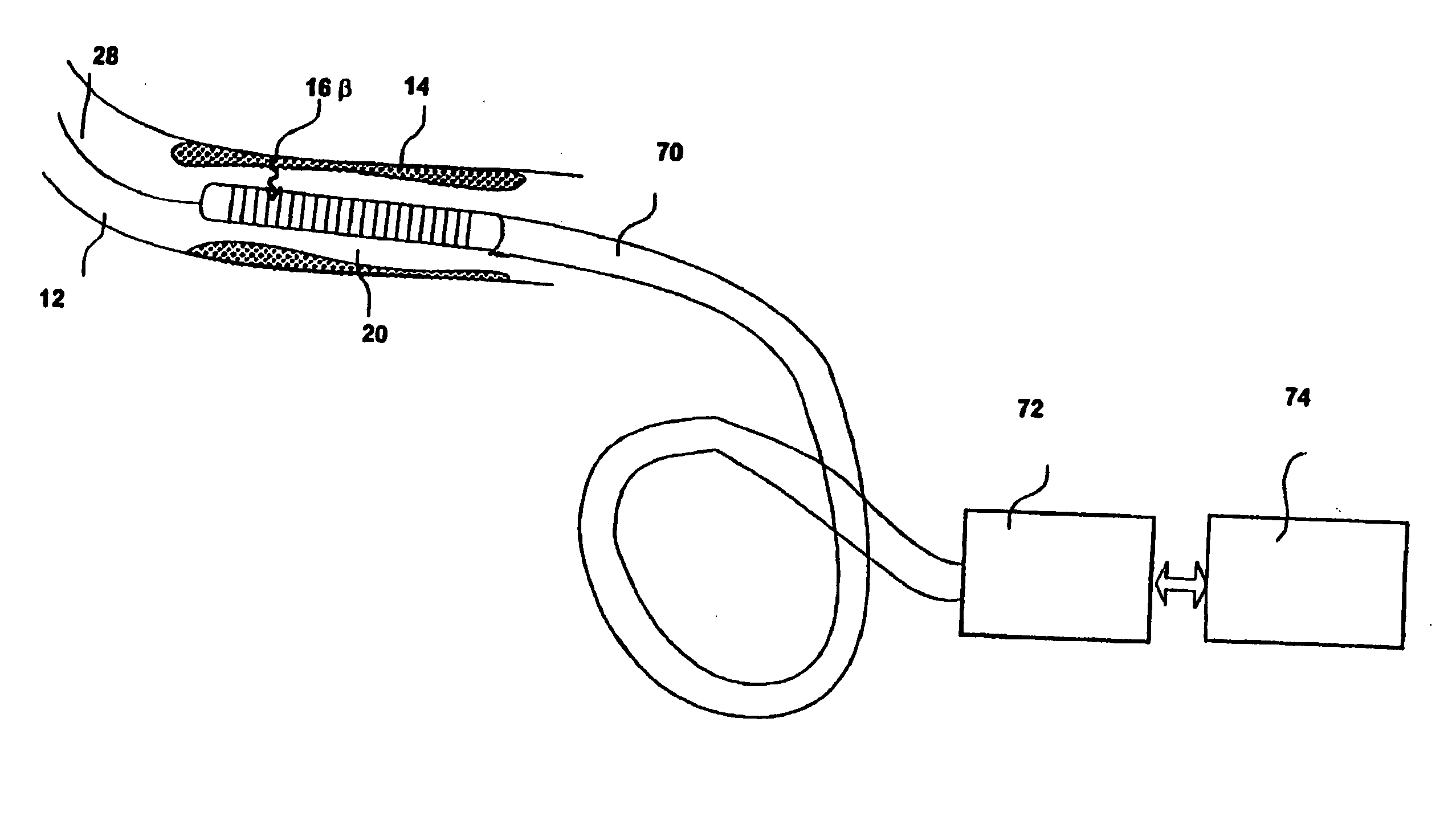
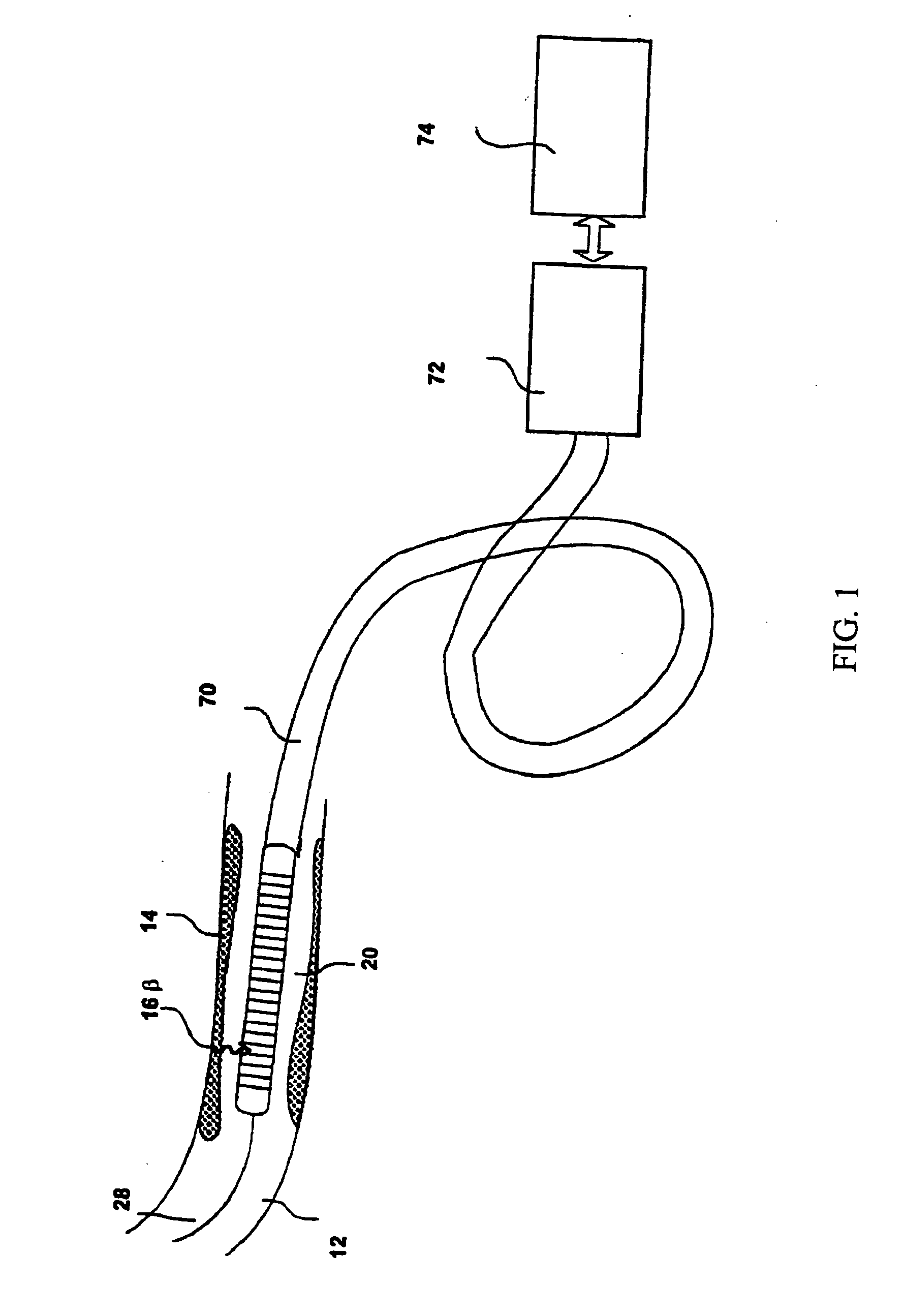
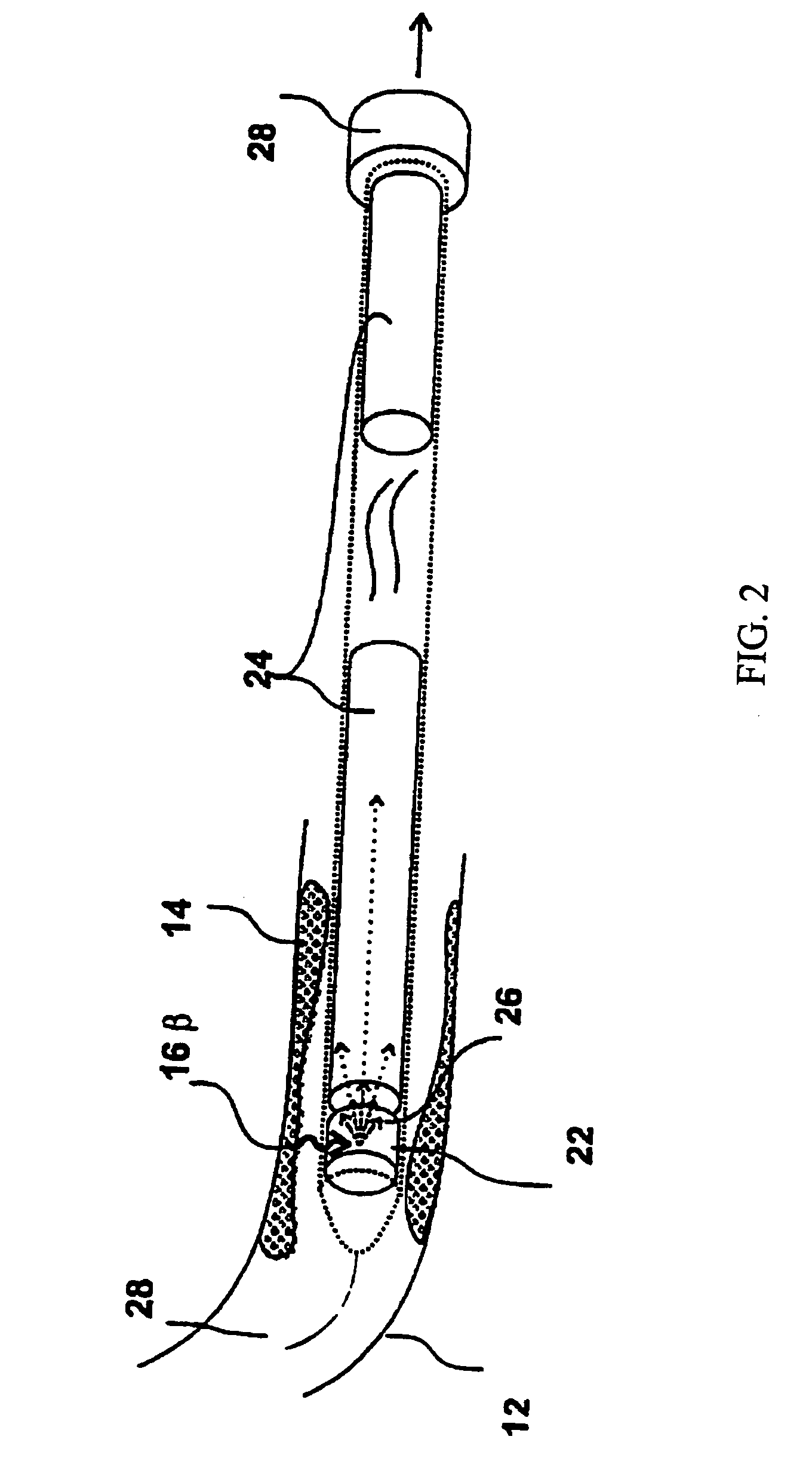
Catheters and related devices for forming passageways between blood vessels or other anatomical structures
InactiveUS7648517B2Precise rotation controlPrecise positioningUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCannulasAnatomical structuresDistal portion
The inventions described in this patent application include i) a torqueable introducer sheath which is useable in conjunction with a transvascular passageway forming catheter to effect precise rotational control of the catheter; ii) an anchorable guide catheter which is useable in conjunction with an intravascular imaging catheter and a transvascular passageway-forming catheter to effect precise positioning and aiming of the passageway-forming catheter; iii) a passageway forming catheter having a torqueable proximal portion to facilitate precise rotational positioning of the distal portion of the catheter; iv) a deflectable-tipped passageway forming catheter, v) various markers and other apparatus useable in conjunction with any of the passageway-forming catheters to facilitate precise positioning and aiming of the catheter, and vi) an apparatus which may be formed within a catheter to prevent a member, apparatus of flow of material from being inadvertently advanced through a lumen of the catheter.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
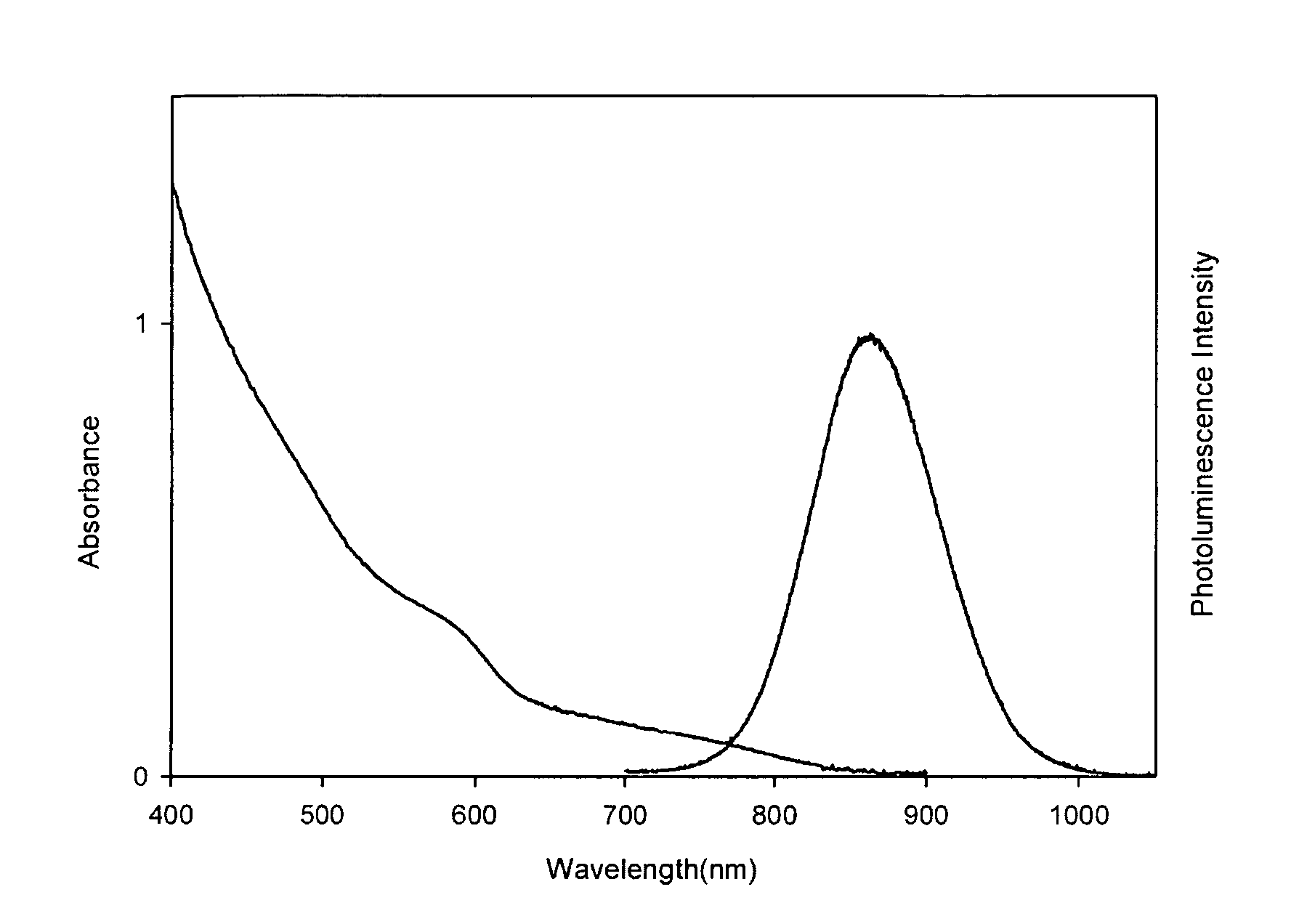
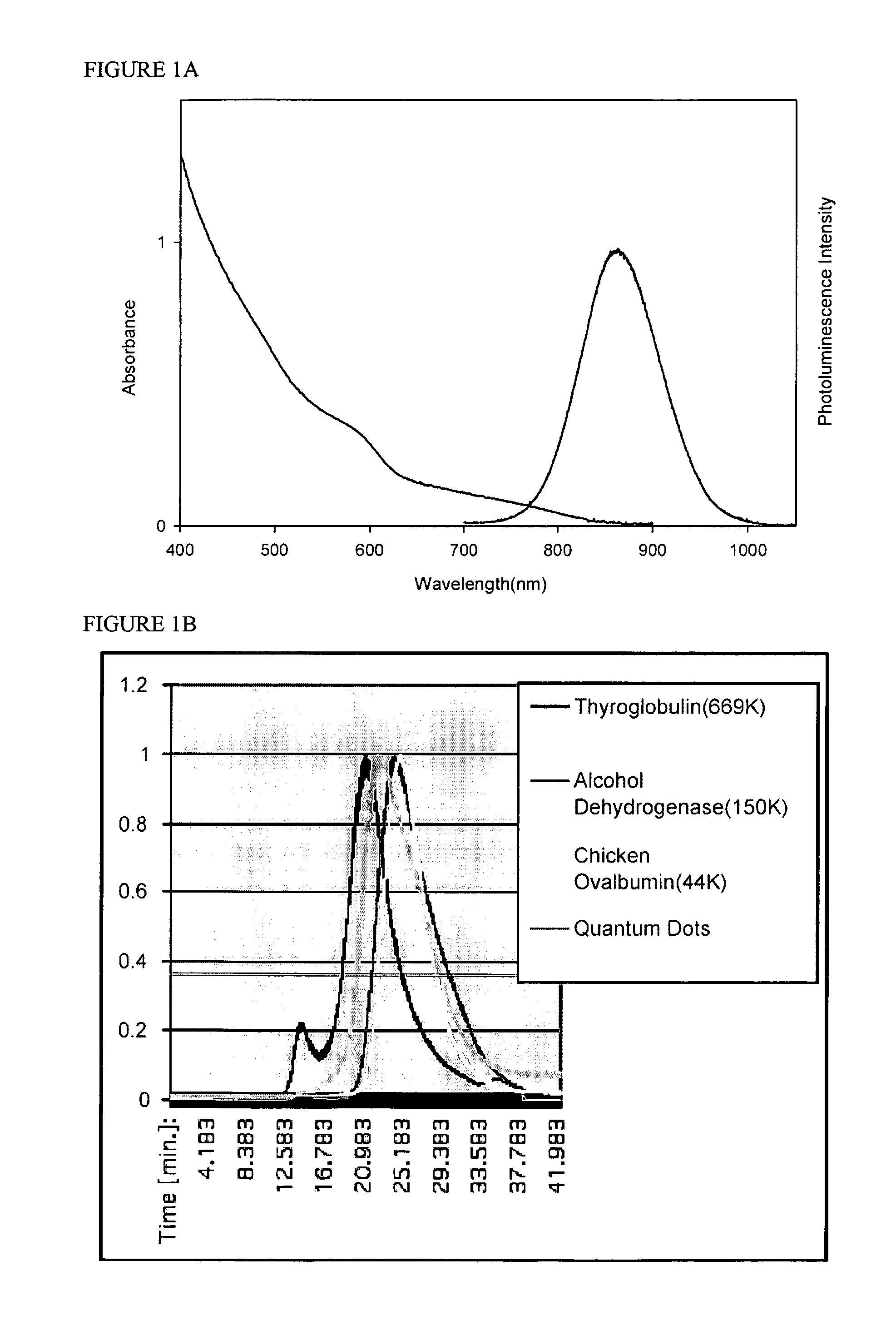
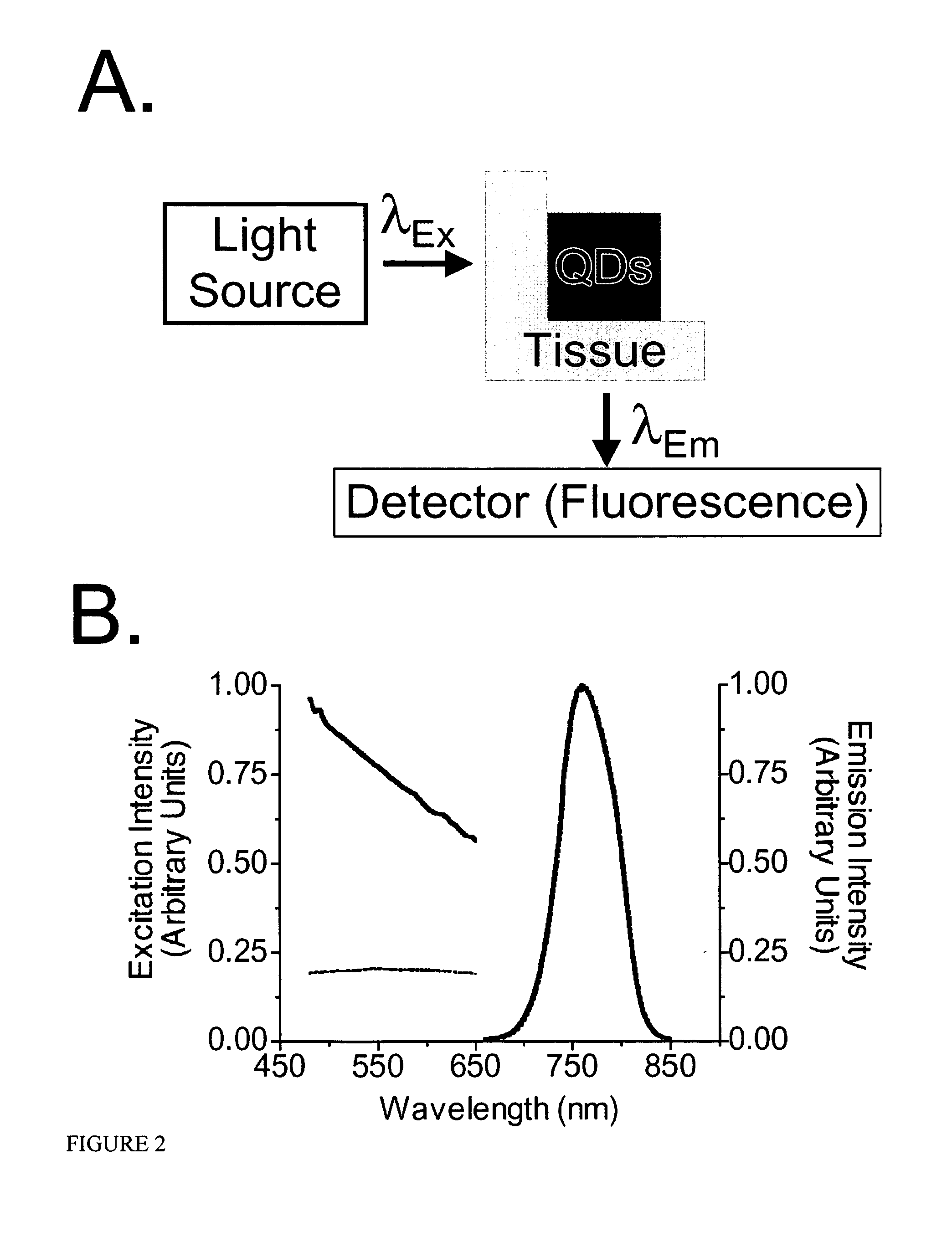
Materials and methods for near-infrared and infrared intravascular imaging
InactiveUS20050020922A1Short time windowEnhance the imageDiagnostics using lightSolid-state devicesSemiconductor nanocrystalsSemiconductor
Vasculature can be imaged with emissive semiconductor nanocrystals, for example, in the near infrared.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC +1
Catheters and related devices for forming passageways between blood vessels or other anatomical structures
InactiveUS8753366B2Precise rotation controlPrecise positioningUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCannulasAnatomical structuresDistal portion
The inventions described in this patent application include i) a torqueable introducer sheath which is useable in conjunction with a transvascular passageway forming catheter to effect precise rotational control of the catheter; ii) an anchorable guide catheter which is useable in conjunction with an intravascular imaging catheter and a transvascular passageway-forming catheter to effect precise positioning and aiming of the passageway-forming catheter; iii) a passageway forming catheter having a torqueable proximal portion to facilitate precise rotational positioning of the distal portion of the catheter; iv) a deflectable-tipped passageway forming catheter, v) various markers and other apparatus useable in conjunction with any of the passageway-forming catheters to facilitate precise positioning and aiming of the catheter, and vi) an apparatus which may be formed within a catheter to prevent a member, apparatus of flow of material from being inadvertently advanced through a lumen of the catheter.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Vascular data processing and image registration systems, methods, and apparatuses
ActiveUS9351698B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementDiagnostic Radiology ModalityImaging modalities
In part, the invention relates to processing, tracking and registering angiography images and elements in such images relative to images from an intravascular imaging modality such as, for example, optical coherence tomography (OCT). Registration between such imaging modalities is facilitated by tracking of a marker of the intravascular imaging probe performed on the angiography images obtained during a pullback. Further, detecting and tracking vessel centerlines is used to perform a continuous registration between OCT and angiography images in one embodiment.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
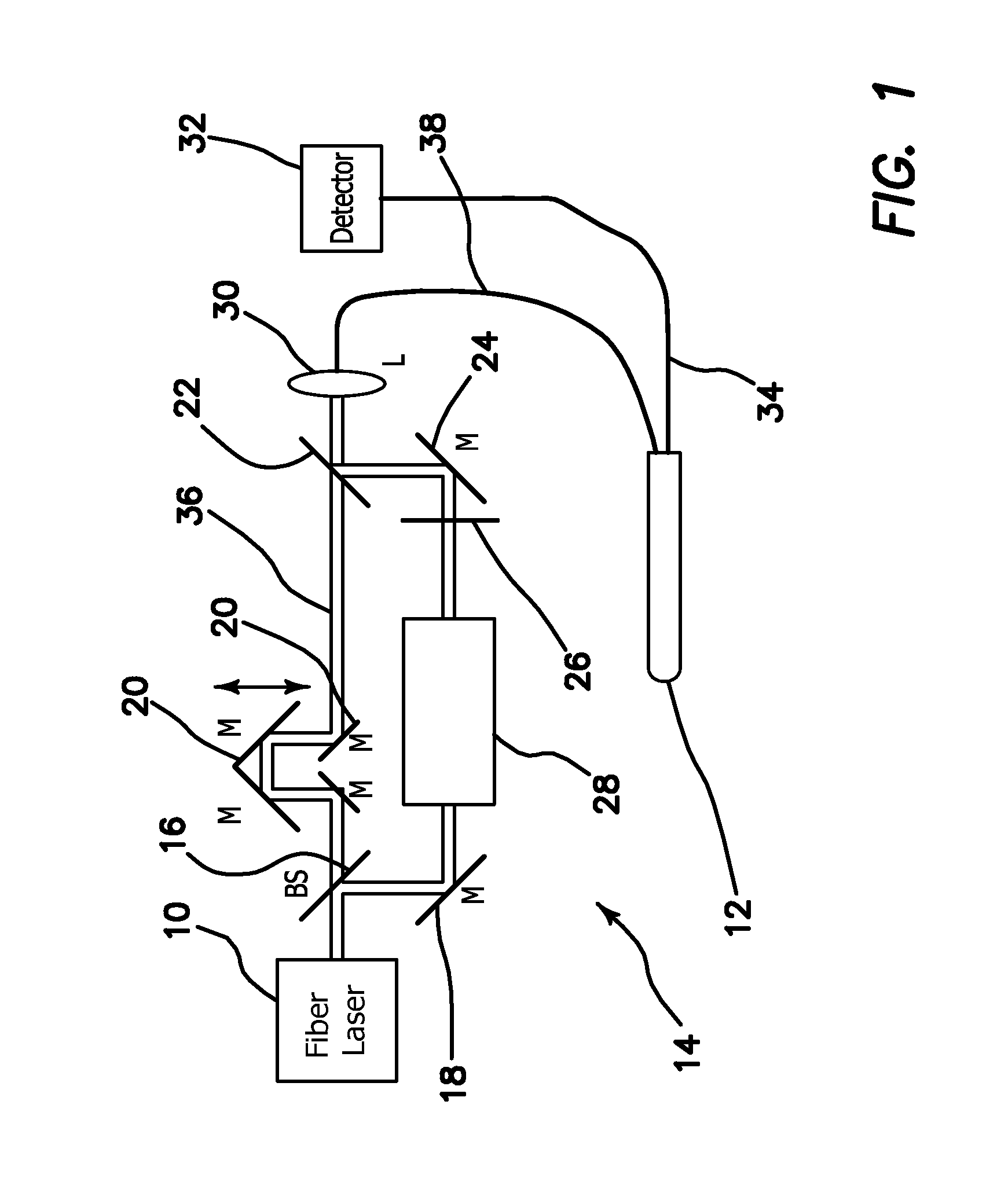
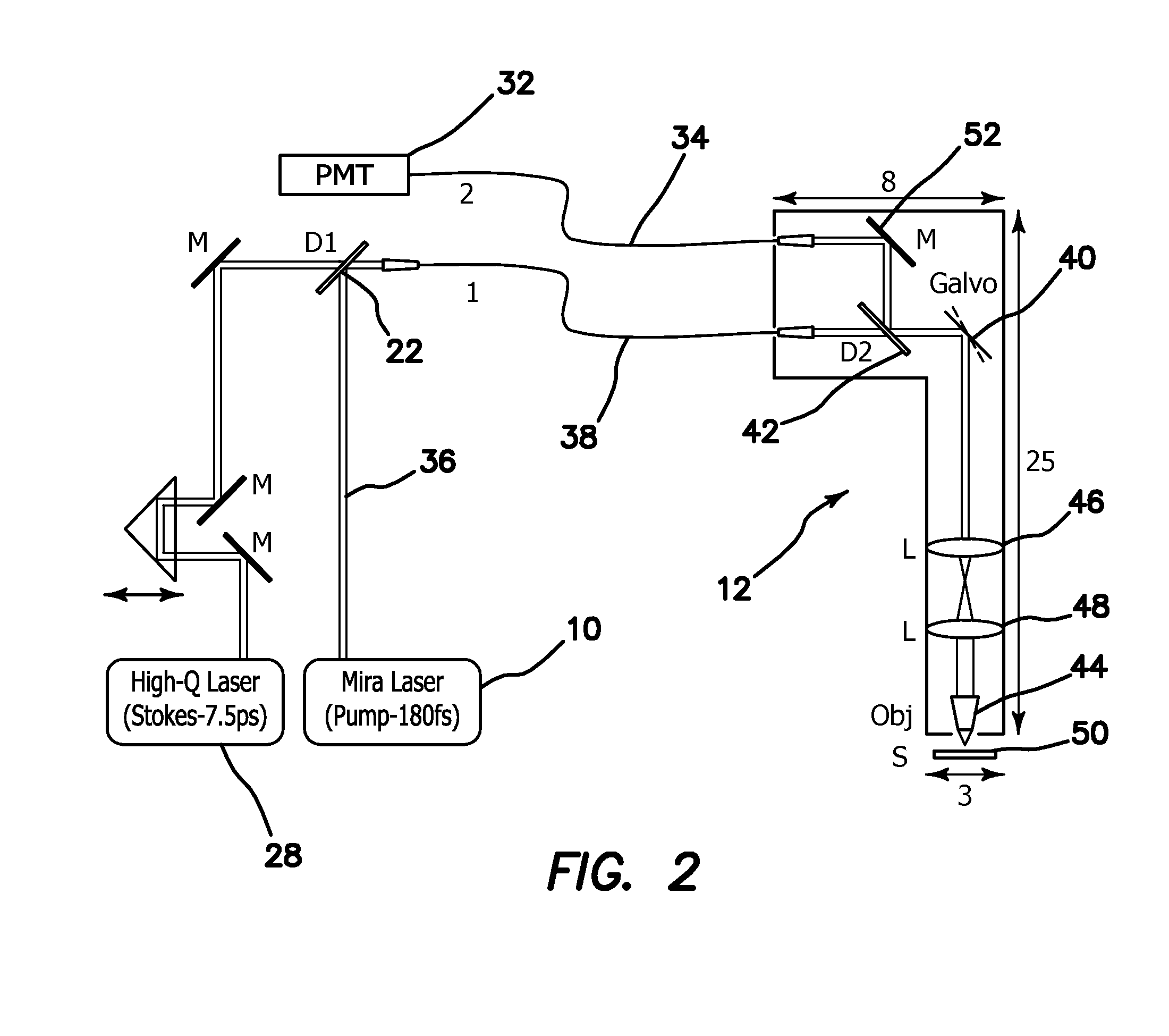
System and Method for Efficient Coherence Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering Endoscopic and Intravascular Imaging and Multimodal Imaging
ActiveUS20110282166A1Complicate interpretationEliminate the problemRadiation pyrometryEndoscopesFiberStokes component
A fiber-delivered probe suitable for CARS imaging of thick tissues is practical. The disclosed design is based on two advances. First, a major problem in CARS probe design is the presence of a very strong anti-Stokes component in silica delivery fibers generated through a FWM process. Without proper spectral filtering, this component affects the CARS image from the tissue sample. The illustrated embodiments of the invention efficiently suppress this spurious anti-Stokes component through the use of a separate fiber for excitation delivery and for signal detection, which allows the incorporation of dichroic optics for anti-Stokes rejection. Second, the detection of backscattered CARS radiation from the sample is optimized by using a large core multi mode fiber in the detection channel. This scheme produces high quality CARS images free of detector aperture effects. Miniaturization of this fiber-delivered probe results in a practical handheld probe for clinical CARS imaging.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
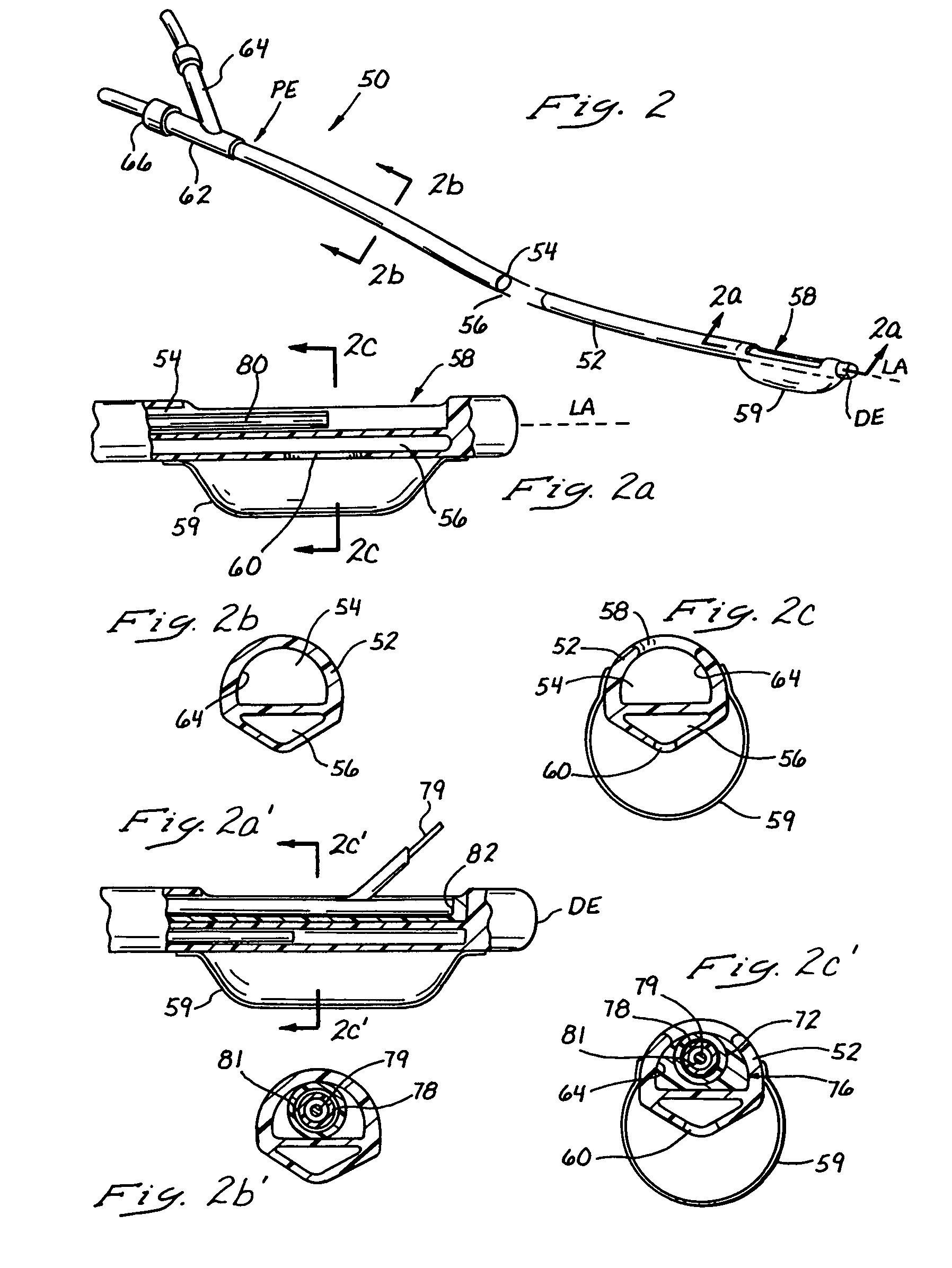
Intravascular imaging device and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060041199A1High sensitivityEasy diagnosisUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryProbe typeMolecular imaging
The invention is directed to a probe-type imaging device useful to visualize interior surfaces, e.g., the lumen of blood vessels. Specifically, the probe-type device is particularly useful for direct tissue imaging in the presence or absence of molecular imaging agents.
Owner:ELMALEH DAVID R
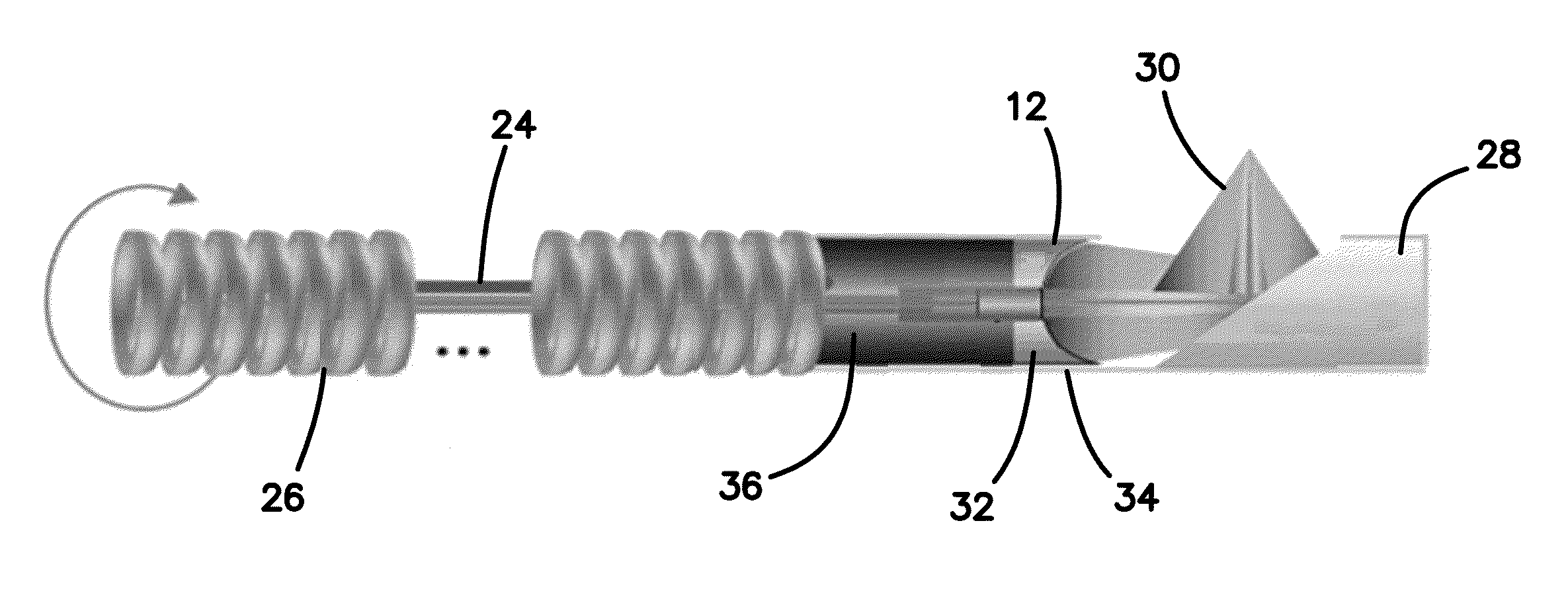
Miniature actuator mechanism for intravascular imaging
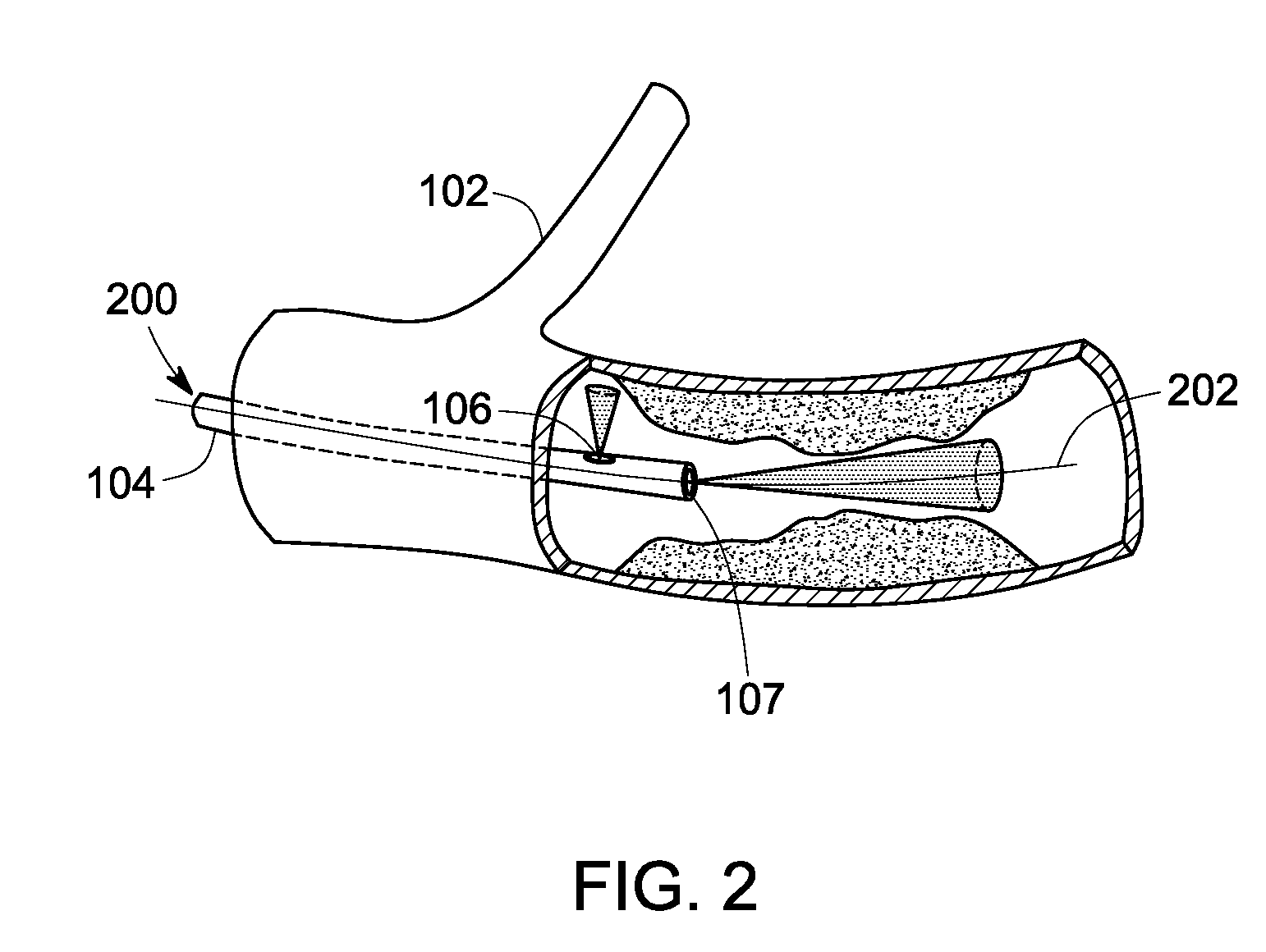
The present invention relates to a new intravascular imaging device based on a Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) actuator mechanism embedded inside an elongate member such as a guide wire or catheter. The present invention utilizes a novel SMA mechanism to provide side-looking imaging by providing movement for an ultrasound transducer element. This novel SMA actuator mechanism can be easily fabricated in micro-scale, providing an advantage over existing imaging devices because it offers the ability to miniaturize the overall size of the device, while the use of multiple transducer crystals maximizes field of view. Also disclosed are methods of using the same.
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
Vascular data processing and image registration systems, methods, and apparatuses
In part, the invention relates to processing, tracking and registering angiography images and elements in such images relative to images from an intravascular imaging modality such as, for example, optical coherence tomography (OCT). Registration between such imaging modalities is facilitated by tracking of a marker of the intravascular imaging probe performed on the angiography images obtained during a pullback. Further, detecting and tracking vessel centerlines is used to perform a continuous registration between OCT and angiography images in one embodiment.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Intravascular imaging system and method
ActiveCN104545811AHigh repetition rateTake advantage ofUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgerySonificationTransceiver
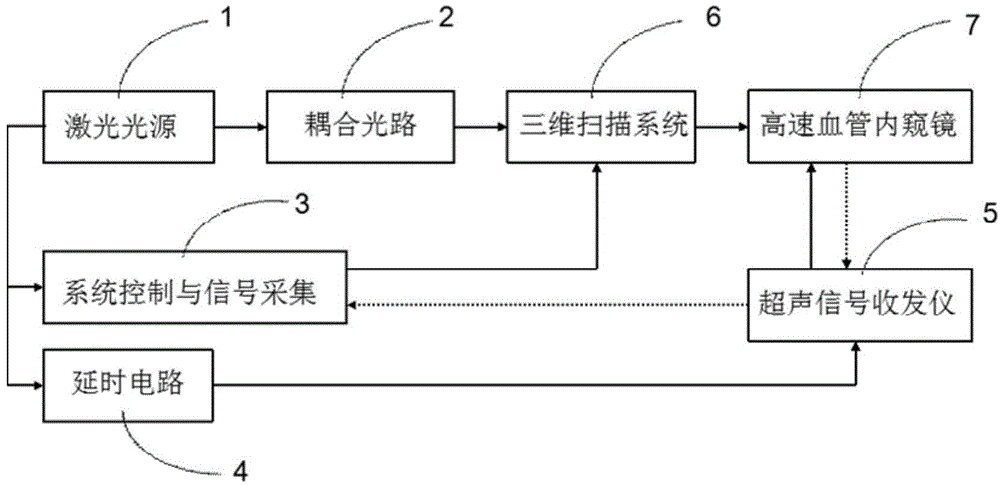
The invention provides an intravascular imaging system and method. The intravascular imaging system comprises a laser source, a coupling optical path, a signal acquisition and control system, a time-delay circuit, an ultrasonic signal transceiver, a three-dimensional scanning system and an opto-acoustic / ultrasonic vascular endoscope device; pulse laser emitted by the laser source is guided into the opto-acoustic / ultrasonic vascular endoscope device through the coupling optical path and the three-dimensional scanning system; the pulse laser obliquely enters to a vascular wall to excite an opto-acoustic signal; a synchronous triggering signal emitted by the laser source enters the ultrasonic signal transceiver; the ultrasonic signal transceiver is used for controlling the opto-acoustic / ultrasonic vascular endoscope device to emit and receive the ultrasonic signal according to the synchronous triggering signal; the signal acquisition and control system is used for receiving the opto-acoustic signal and the ultrasonic signal from the opto-acoustic / ultrasonic vascular endoscope device through the ultrasonic signal transceiver and carrying out three-dimensional reconstruction according to the opto-acoustic signal and the ultrasonic signal to generate a three-dimensional image and a cross section image of intravascular tissues. According to the intravascular imaging system and method, the imaging speed can be improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Integrated Multimodality Intravascular Imaging System that Combines Optical Coherence Tomography, Ultrasound Imaging, and Acoustic Radiation Force Optical Coherence Elastography
ActiveUS20150351722A1Low costImproved prognosisOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryBiomechanicsMechanical property
A method of using an integrated intraluminal imaging system includes an optical coherence tomography interferometer (OCT), an ultrasound subsystem (US) and a phase resolved acoustic radiation force optical coherence elastography subsystem (PR-RAF-OCE). The steps include performing OCT to generate a returned optical signal, performing US imaging to generate a returned ultrasound signal, performing PR-ARF-OCE to generate a returned PR-ARF-OCE signal by generating a amplitude modulated ultrasound beam or chirped amplitude modulated ultrasound beam to frequency sweep the acoustic radiation force, measuring the ARF induced tissue displacement using phase resolved OCT method, and the frequency dependence of the PR-ARF-OCE signal, processing the returned optical signal, the returned ultrasound signal and the measured frequency dependence of the returned PR-ARF-OCE optical coherence elastographic signal to quantitatively measure the mechanical properties of the identified tissues with both spectral and spatial resolution using enhanced materials response at mechanically resonant frequencies to distinguish tissues with varying stiffness, to identify tissues with different biomechanical properties and to measure structural and mechanical properties simultaneously.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods for Computing Coronary Physiology Indexes Using a High Precision Registration Model
InactiveUS20190110776A1Improve accuracyHigh registrationImage enhancementImage analysisArterial blood flowCoronary physiology
Owner:QUANJING HENGSHENG BEIJING SCI & TECH CO LTD
Full circumferential scanning OCT intravascular imaging probe based on scanning MEMS mirror
An optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging probe 500 comprises a reference arm, and a sample arm which are both preferably disposed in a hollow outer tube 515. The sample arm comprises a MEMS scanning mirror 210 disposed inside and secured to the tube 515 for providing lateral scanning of a first and second optical beam provided. The scanning mirror has a highly reflective top 211 and highly reflective bottom surface 212, wherein the first beam is incident on the top surface and the second beam is incident on the bottom surface. The scanning mirror 210 is rotatable through at least 90° along a first axis to provide 180° scanning on each of its surfaces to cover a full 360° circumferential view of a sample to be imaged.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
High-precision matching model-based method for calculating coronary artery parameters
ActiveCN107730540AImprove practicalityThe calculation result is accurateImage enhancementImage analysisCoronary arteriesComputing Methodologies
The invention discloses a high-precision matching model-based method for calculating coronary artery parameters. According to the method, firstly, the angiography imaging means and the intravascular imaging means of a coronary vessel part are acquired. After that, an angiography image and an intravascular image are matched to form a high-precision matching model. The blood flow amount, the blood fractional Flow Reserve (FFR) and the microcirculation resistance index of microcirculatory resistance (IMR) of coronary vessels are calculated on the basis of the high-precision matching model. According to the method for calculating the coronary parameter blood flow, the blood flow reserve score and the microcirculation resistance index, the high-precision matching model of images is acquired through two ways, namely the angiography imaging means and the intravascular imaging means. The calculation result of the method is more accurate than the image of either the angiography imaging means orthe intravascular imaging means alone, so that the method is high in practicability.
Owner:QUANJING HENGSHENG BEIJING SCI & TECH CO LTD
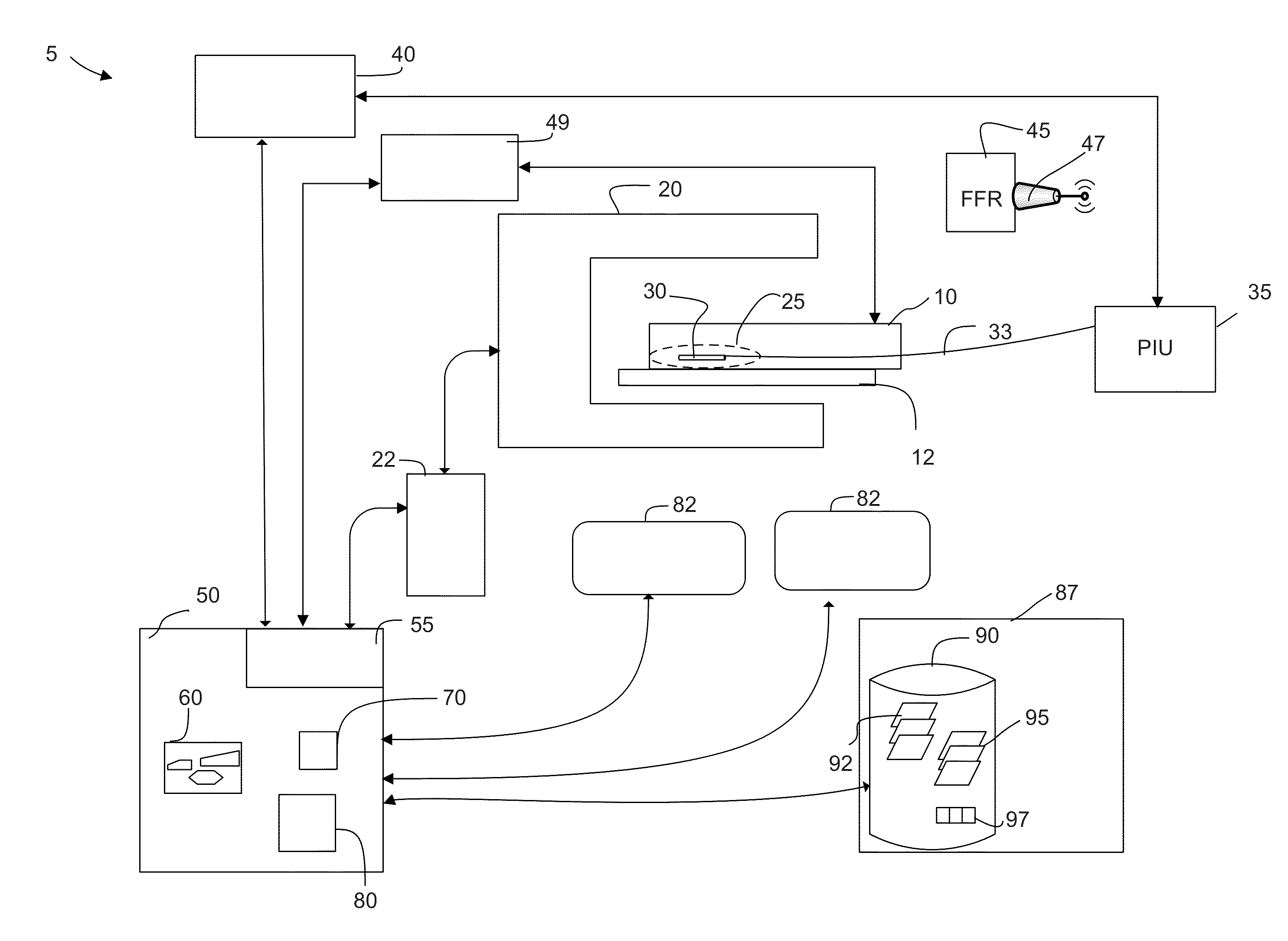
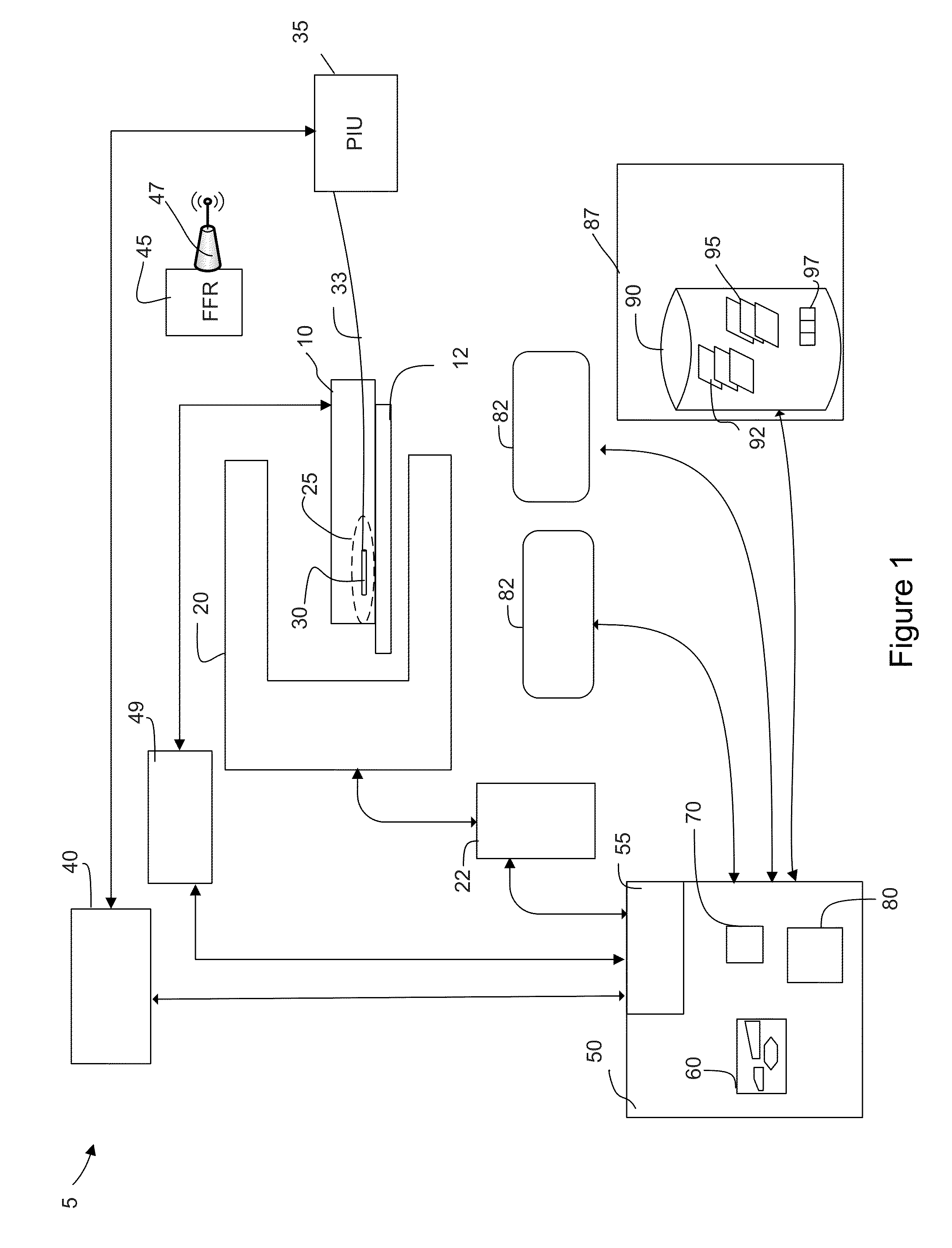
Hybrid systems and methods for multi-modal acquisition of intravascular imaging data and counteracting the effects of signal absorption in blood
ActiveUS20160228097A1Blood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasound attenuationHybrid system
A multi-modal catheter combining at least NIRF and IVUs imaging channels used to reveal integrated biological and structural features of a lumen intravascularly imaged through flowing blood in vivo and corrected for distance-related attenuation and / or scattering parameters of in vivo blood to compensate for discovered overestimation of the degree of in-vivo-blood attenuation of NIRF signal Enhancing the sensitivity of detection of vascular injury and / or plaque deposition beyond the capability of a standalone IVUS imaging as a result of the use of such corrected catheter.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
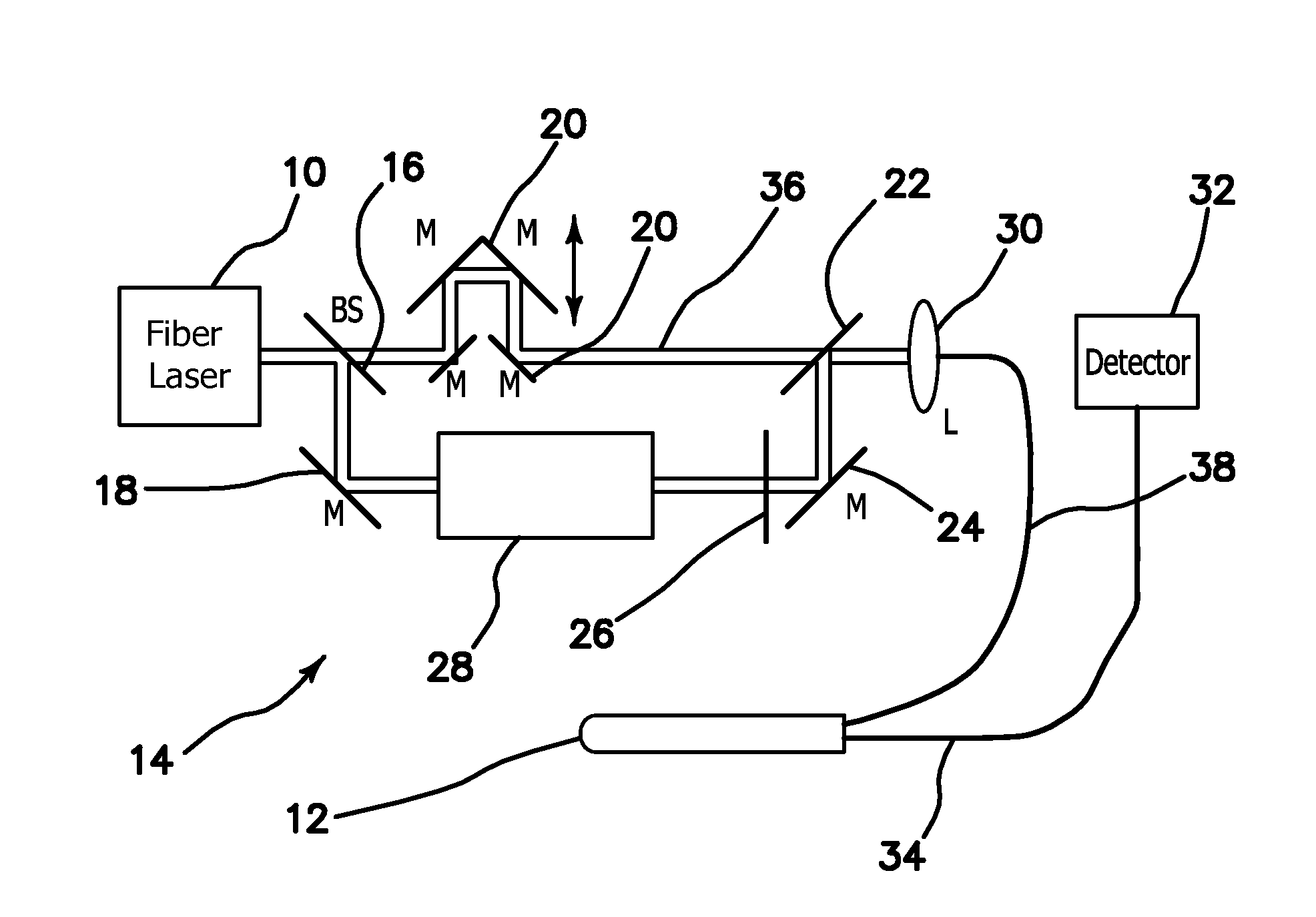
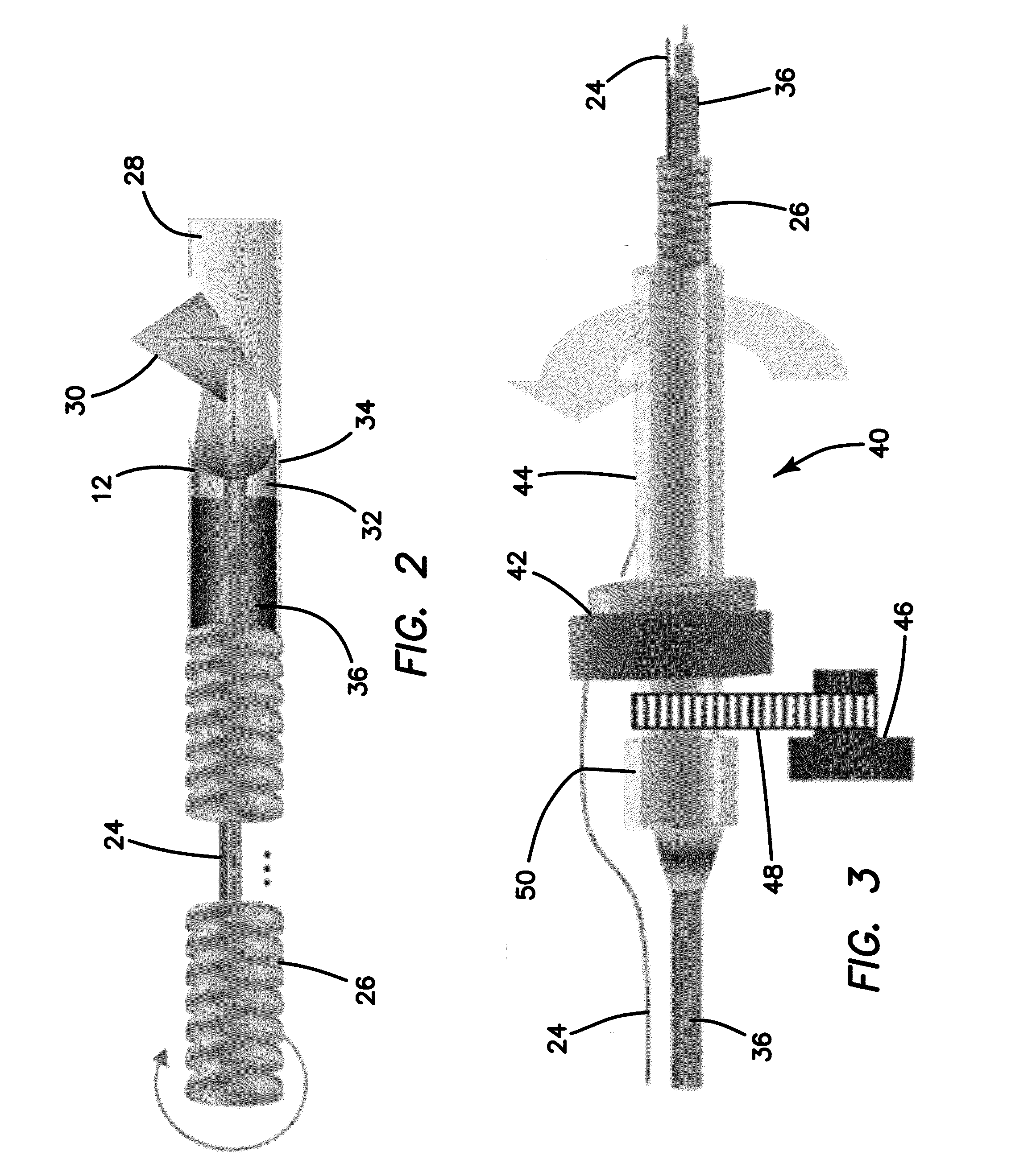
Endovascular Optical Coherence Tomography Device
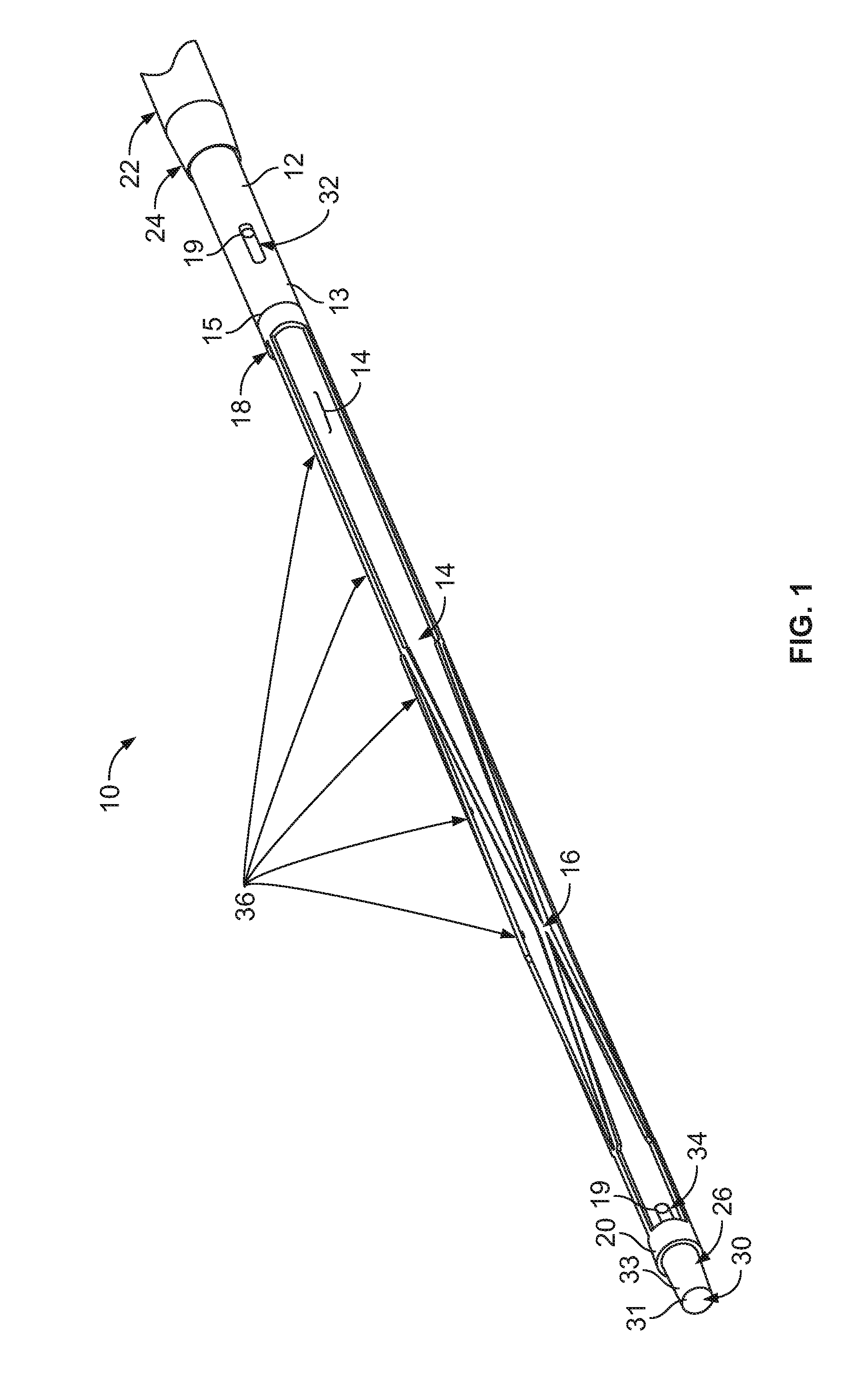
InactiveUS20110009741A1Free from mechanical damageIncreased torsional stiffnessCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringMedicineImage resolution
An endovascular OCT probe is included in an endovascular access device for intravascular imaging. The probe includes a hollow coil wire defining an axial lumen of the endovascular access device. A single mode optical fiber for transmitting light is disposed in the axial lumen of the hollow coil wire so that translation and rotation of the hollow coil wire carrying the optical fiber within the endovascular access device is stabilized for scanning endovascular tissue with at least 5 microns resolution. An optic element directs light from and into the optical fiber at a distal tip of the optical fiber and is coupled to or fixed to the distal end of the optical fiber. The optic element and the distal end of the optical fiber is disposed within a glass ferule to protect it from damage.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Catheters and Related Devices for Forming Passageways Between Blood Vessels or Other Anatomical Structures
InactiveUS20100094259A1Precise rotation controlPrecise positioningUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCannulasAnatomical structuresDistal portion
The inventions described in this patent application include i) a torqueable introducer sheath which is useable in conjunction with a transvascular passageway forming catheter to effect precise rotational control of the catheter; ii) an anchorable guide catheter which is useable in conjunction with an intravascular imaging catheter and a transvascular passageway-forming catheter to effect precise positioning and aiming of the passageway-forming catheter; iii) a passageway forming catheter having a torqueable proximal portion to facilitate precise rotational positioning of the distal portion of the catheter; iv) a deflectable-tipped passageway forming catheter, v) various markers and other apparatus useable in conjunction with any of the passageway-forming catheters to facilitate precise positioning and aiming of the catheter, and vi) an apparatus which may be formed within a catheter to prevent a member, apparatus of flow of material from being inadvertently advanced through a lumen of the catheter.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
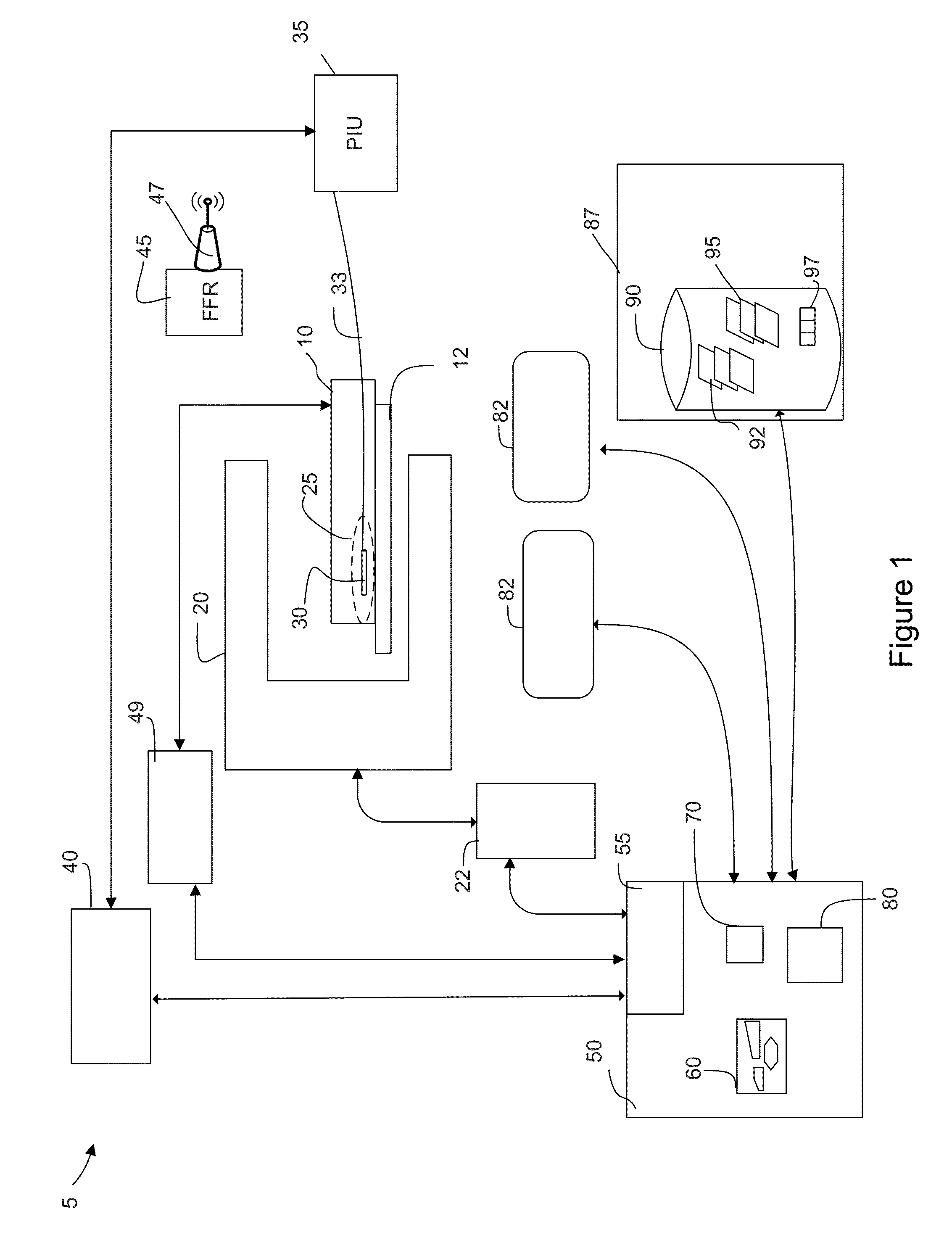
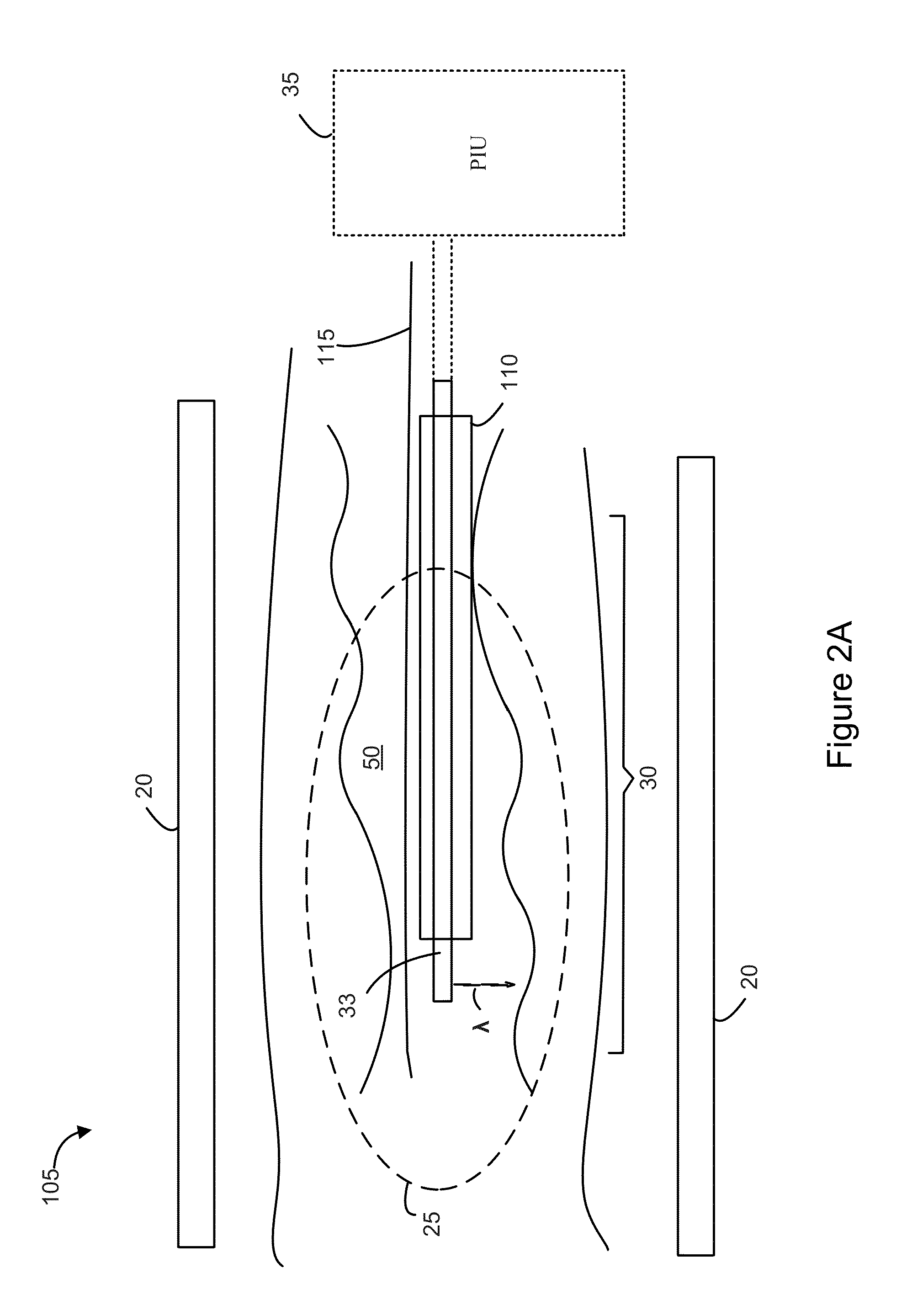
Methods and systems for intravascular imaging and flow measurement
Methods, systems and non-transitory computer readable media that store instructions executable by one or more processors for performing an interventional procedure are presented. One or more pulses are delivered to an intravascular region of interest (ROI) in a subject using at least one image sensor and at least one forward-looking flow sensor disposed at a distal end of an integrated intravascular device. Further, one or more images corresponding to the ROI are reconstructed using imaging signals received in response to the pulses delivered by the image sensor. Additionally, one or more flow characteristics corresponding to the ROI are determined based on the signals received in response to the pulses delivered by the flow sensor. The determined flow characteristics are used for computing one or more functional parameters corresponding to the ROI. An assessment of the subject may be provided based on the reconstructed images and / or the functional parameters.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ivc filter catheter with imaging modality
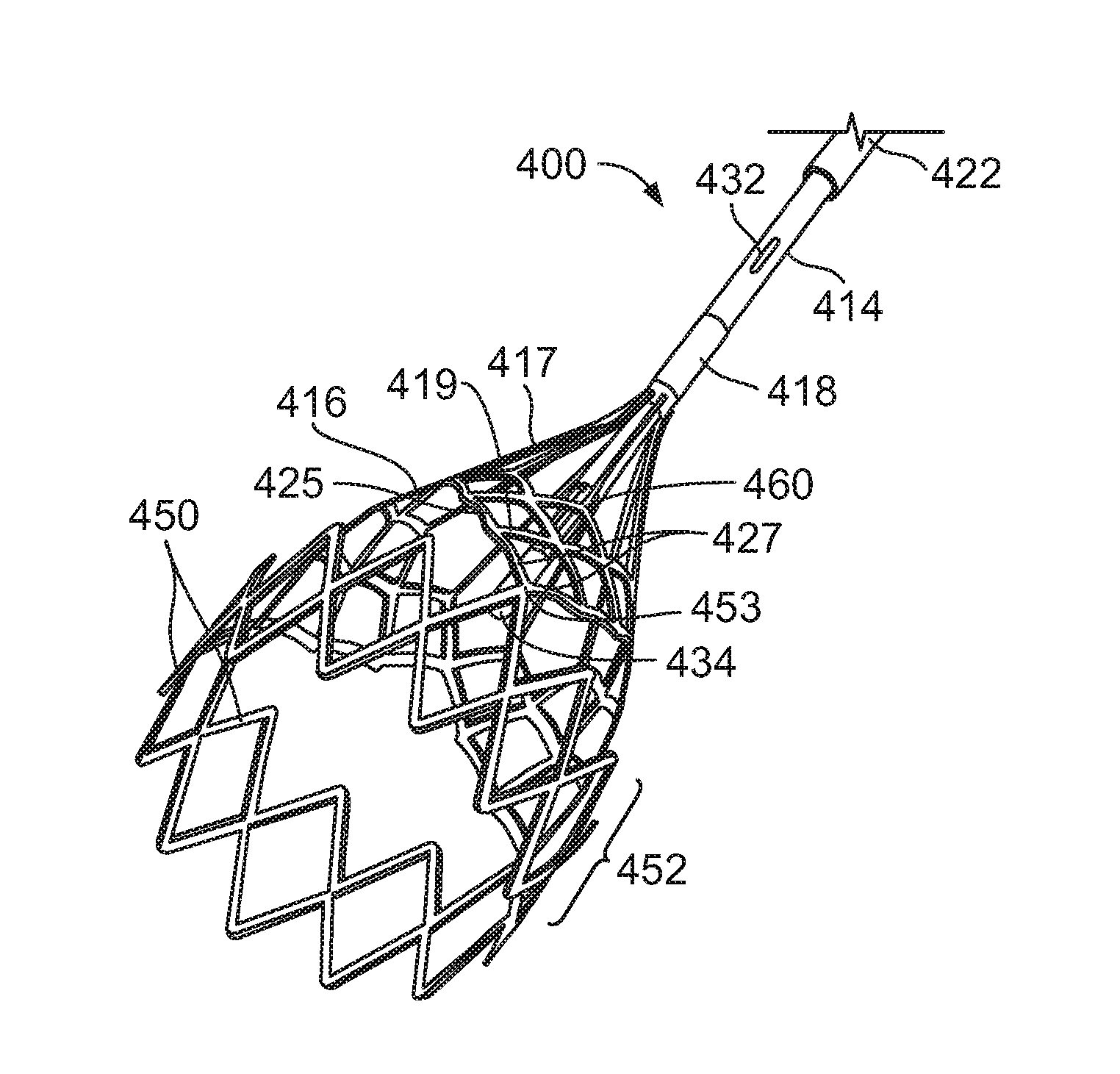
ActiveUS20130190803A1Easy to optimizeEnhance the imageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMulti-lumen catheterImaging modalitiesIvc filter
A combined multi-lumen central access catheter and an embolic filter, further comprising an imaging modality to facilitate intravascular imaging of the filter.
Owner:BIO2MEDICAL
Intravascular photoacoustic-optical coherence tomography-near-infrared multi-mode imaging device and method
InactiveCN108618758ASolve technical problems that are difficult to detectSimplify testing proceduresDiagnostics using spectroscopyCatheterDouble-clad fiberControl system
The invention discloses an intravascular photoacoustic-optical coherence tomography-near-infrared multi-mode imaging device and method. The device comprises a computer, a photoacoustic imaging system,an optical coherence tomography system, a near-infrared optical imaging system, an optical fiber combiner, a double-cladding optical fiber photoelectric combination slip ring, a three-dimensional motion control system and a miniature endoscopic probe. On the one hand, the photoacoustic imaging system, the optical coherence tomography system and the near-infrared optical imaging system are connected to the computer; on the other hand, double-cladding optical fibers are disposed on the double-cladding optical fiber photoelectric combination slip ring through the optical fiber combiner and thenconnected to the miniature endoscope probe, and the double-cladding optical fiber photoelectric combination slip ring is disposed on a three-dimensional motion detection system. Integration of three intravascular imaging methods of photoacoustic imaging, OCT imaging and near-infrared optical imaging is achieved, detection procedures are simplified, the detection difficulty is reduced, and the situation that work is conducted by means of the three imaging methods simultaneously can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
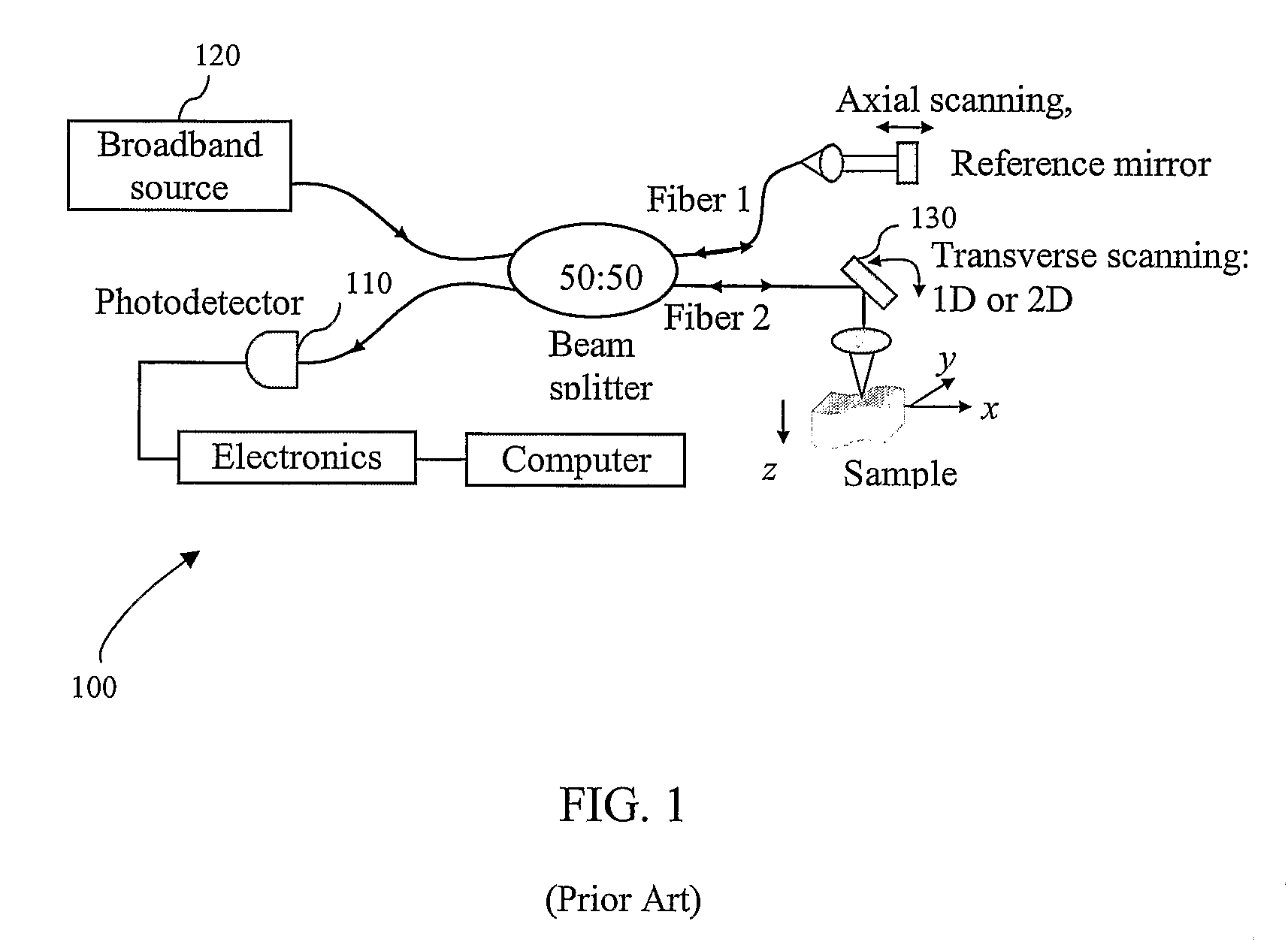
Radial reflection diffraction tomography
A wave-based tomographic imaging method and apparatus based upon one or more rotating radially outward oriented transmitting and receiving elements have been developed for non-destructive evaluation. At successive angular locations at a fixed radius, a predetermined transmitting element can launch a primary field and one or more predetermined receiving elements can collect the backscattered field in a "pitch / catch" operation. A Hilbert space inverse wave (HSIW) algorithm can construct images of the received scattered energy waves using operating modes chosen for a particular application. Applications include, improved intravascular imaging, bore hole tomography, and non-destructive evaluation (NDE) of parts having existing access holes.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Calibration and image processing devices, methods and systems
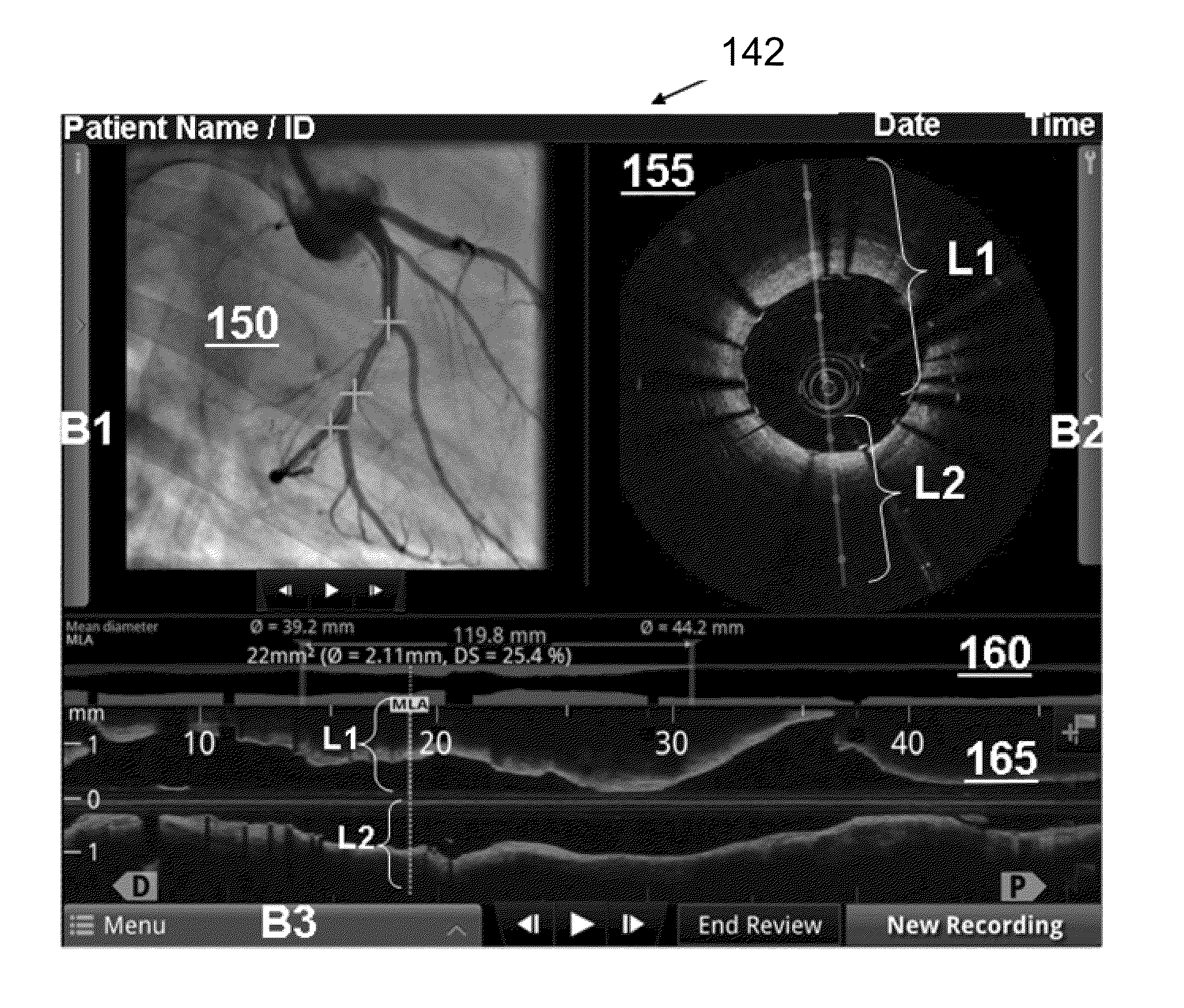
In part, the invention relates to systems and methods of calibrating a plurality of frames generated with respect to a blood vessel as a result of a pullback of an intravascular imaging probe being pullback through the vessel. A calibration feature disposed in the frames that changes between a subset of the frames can be used to perform calibration. Calibration can be performed post-pullback. Various filters and image processing techniques can be used to identify one or more feature in the frames including, without limitation, a calibration feature, a guidewire, a side branch, a stent strut, a lumen of the blood vessel, and other features. The feature can be displayed using a graphic user interface.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Catheter for intravascular ultrasound and photoacoustic imaging
InactiveUS8932223B2Protect partsAvoid mechanical damageOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryElastographyUltrasonic sensor
A design and a fabrication method for an intravascular imaging and therapeutic catheters for combined ultrasound, photoacoustic, and elasticity imaging and for optical and / or acoustic therapy of hollow organs and diseased blood vessels and tissues are disclosed in the present invention. The invention comprises both a device—optical fiber-based intravascular catheter designs for combined IVUS / IVPA, and elasticity imaging and for acoustic and / or optical therapy—and a method of combined ultrasound, photoacoustic, and elasticity imaging and optical and / or acoustic therapy. The designs of the catheters are based on single-element catheter-based ultrasound transducers or on ultrasound array-based units coupled with optical fiber, fiber bundles or a combination thereof with specially designed light delivery systems. One approach uses the side fire fiber, similar to the one utilized for biomedical optical spectroscopy. The second catheter design uses the micro-optics in the manner of a probe for optical coherent tomography.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Miniature actuator mechanism for intravascular optical imaging
The present invention relates to a new intravascular imaging device based on a Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) actuator mechanism embedded inside an elongate member such as a guide wire or catheter. The present invention utilizes a novel SMA mechanism to provide side-looking imaging by providing movement for an optical coherence tomography (OCT) element. This novel SMA actuator mechanism can be easily fabricated in micro-scale, providing an advantage over existing imaging devices by offering the ability to miniaturize the overall size of the device. Because the device does not require a rotating shaft or fiber optic along the length of the catheter, it also allows for a more flexible catheter or guide wire, and provides room for other interventional devices. The device simplifies the manufacture and operation of OCT by allowing a straight fiber optic directed by an independent, oscillating reflector or prism controlled by the actuator mechanism located only in the distal tip of the device. A variation uses the actuator mechanism to rotate only the distal end of the optical fiber, eliminating the need to spin the entire fiber via a remote mechanism. Also disclosed are methods of using the same.
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
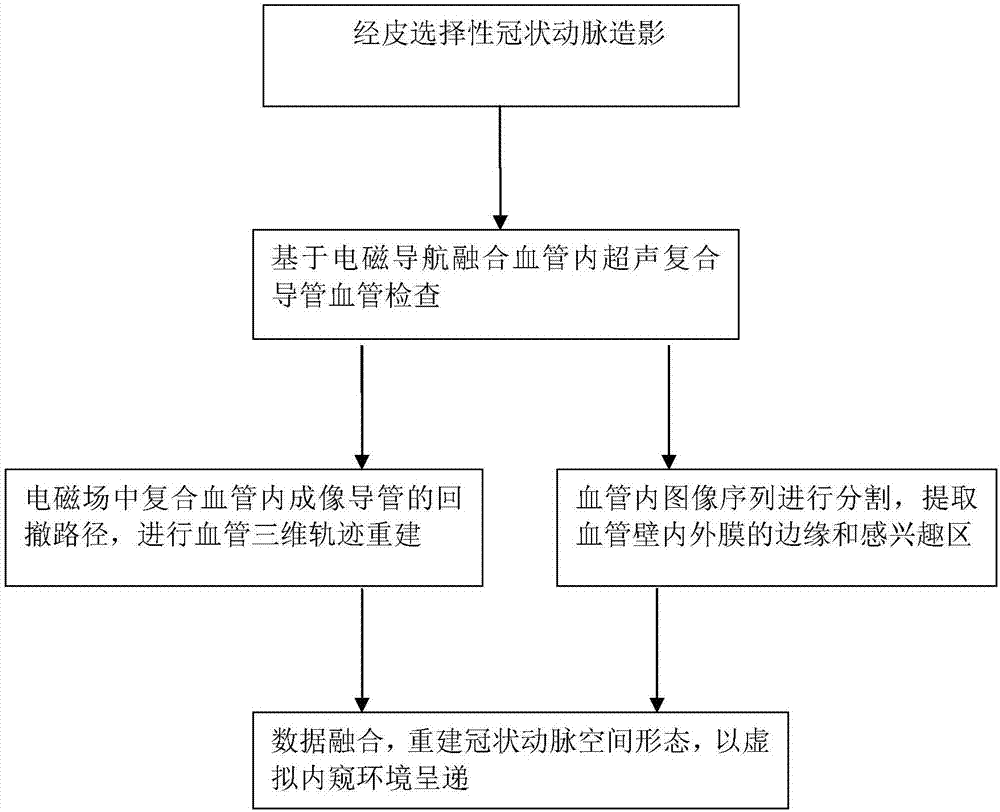
Intravascular virtual endoscope imaging system based on electromagnetic positioning composite conduit and working method of system
ActiveCN107019513AAvoid warpingHigh electromagnetic positioning accuracyOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryInformation processingCatheter
The invention relates to an intravascular virtual endoscope imaging system based on an electromagnetic positioning composite conduit and a working method of the system. The intravascular virtual endoscope imaging system comprises an electromagnetic positioning tracking module, a composite intravascular imaging conduit module and a positioning information processing and composite image presenting module, wherein the composite intravascular imaging conduit module is used for acquiring intravascular images; the electromagnetic positioning tracking module is used for acquiring a movement track of the composite intravascular imaging conduit module inside blood vessels, and used for transmitting the movement track to the positioning information processing and composite image presenting module, then correction and fusion of the intravascular images and the positioning information is implemented, and blood vessel spatial information is represented in a virtual endoscope environment. Relatively precise bases are provided for diagnosis on vasculopathy.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV QILU HOSPITAL +1
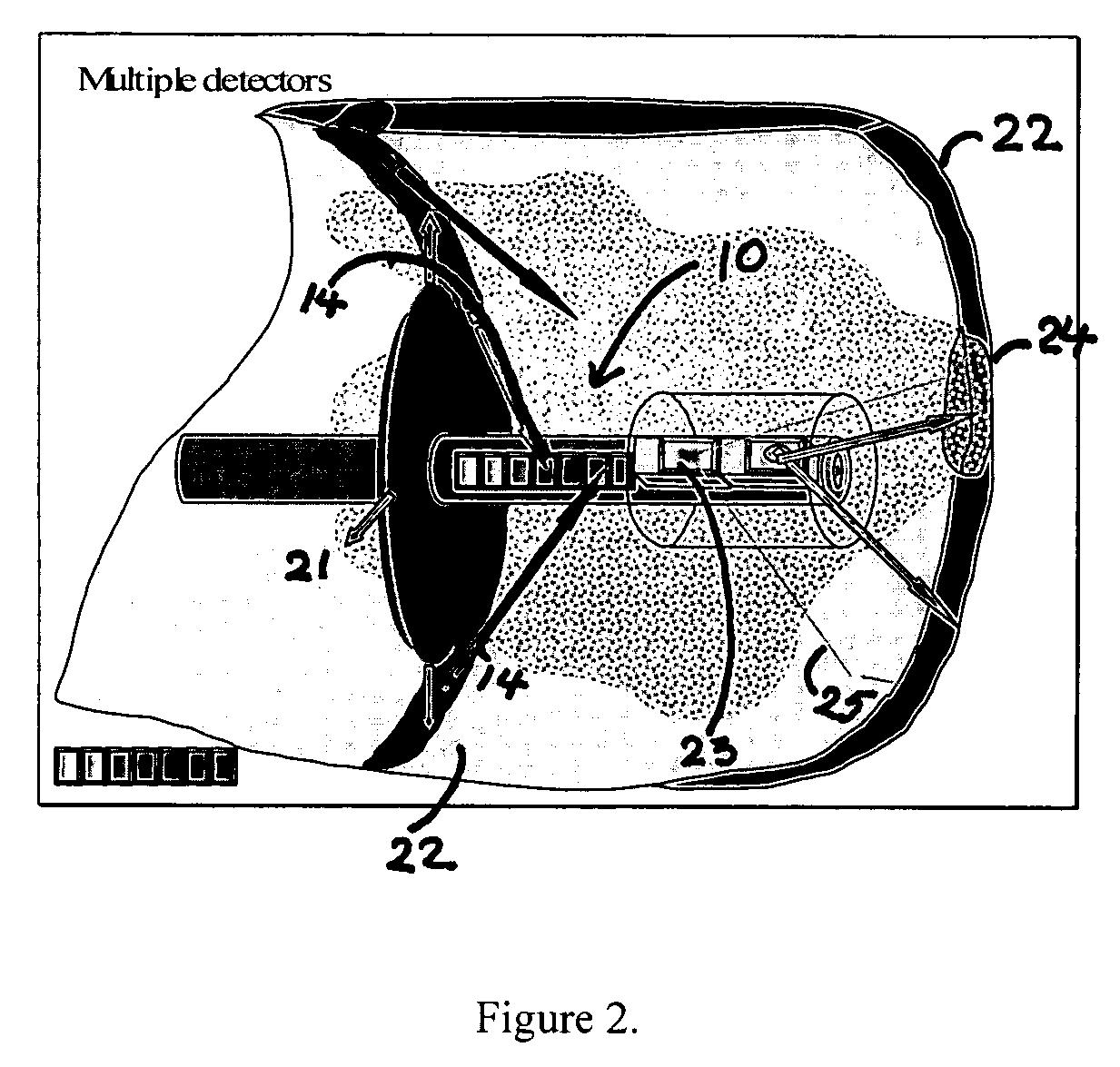
Intravascular imaging detector
InactiveUS20060178577A1Addressing Insufficient SensitivitySolve the low detection efficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBlood vesselIntravascular imaging
An apparatus for intravascular imaging to detect and characterize early stage, unstable coronary arty plaques. The detector works by identifying and localizing plaque-binding beta-emitting radiopharmaceuticals.
Owner:CMR NAVISCAN CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com