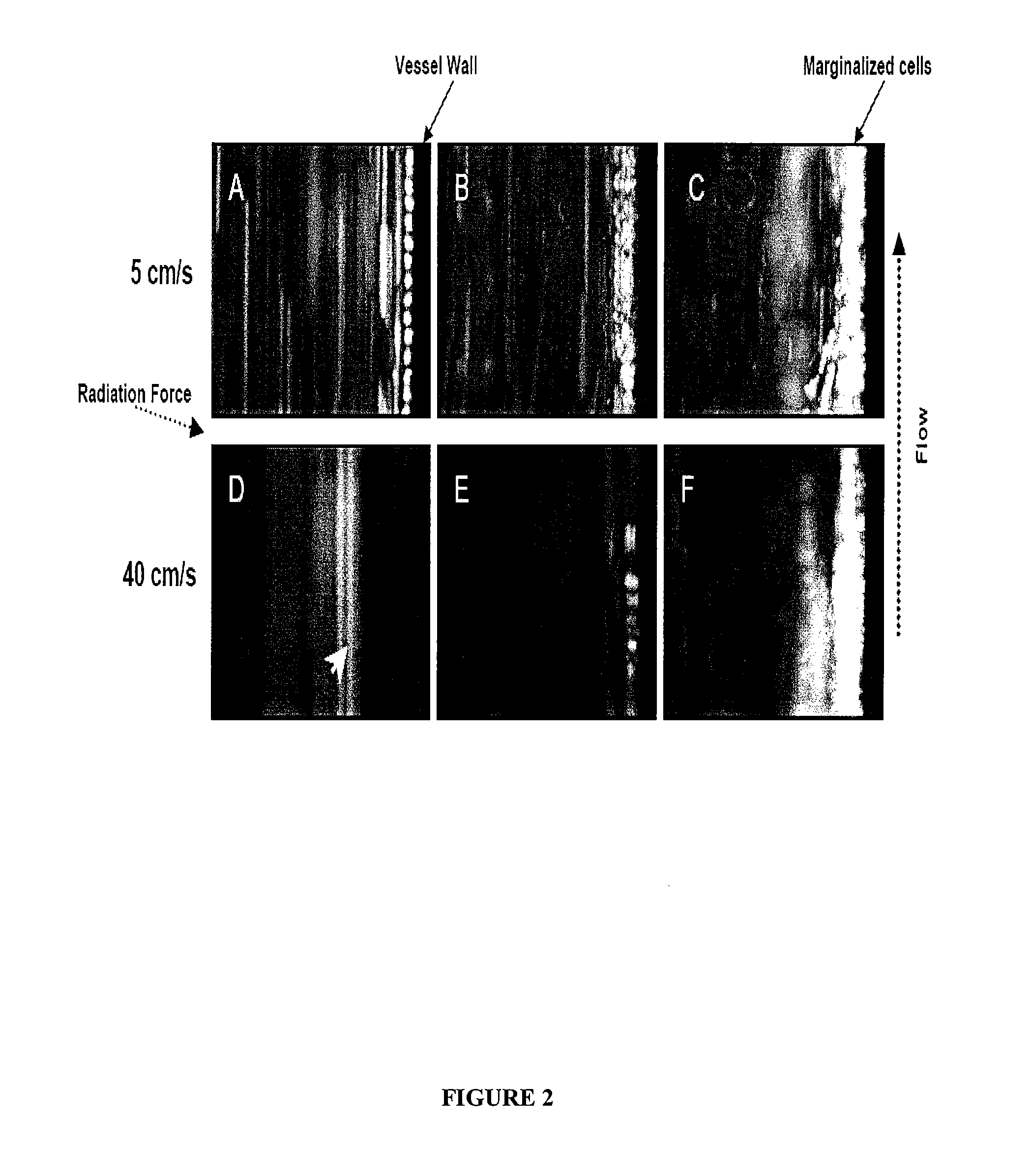
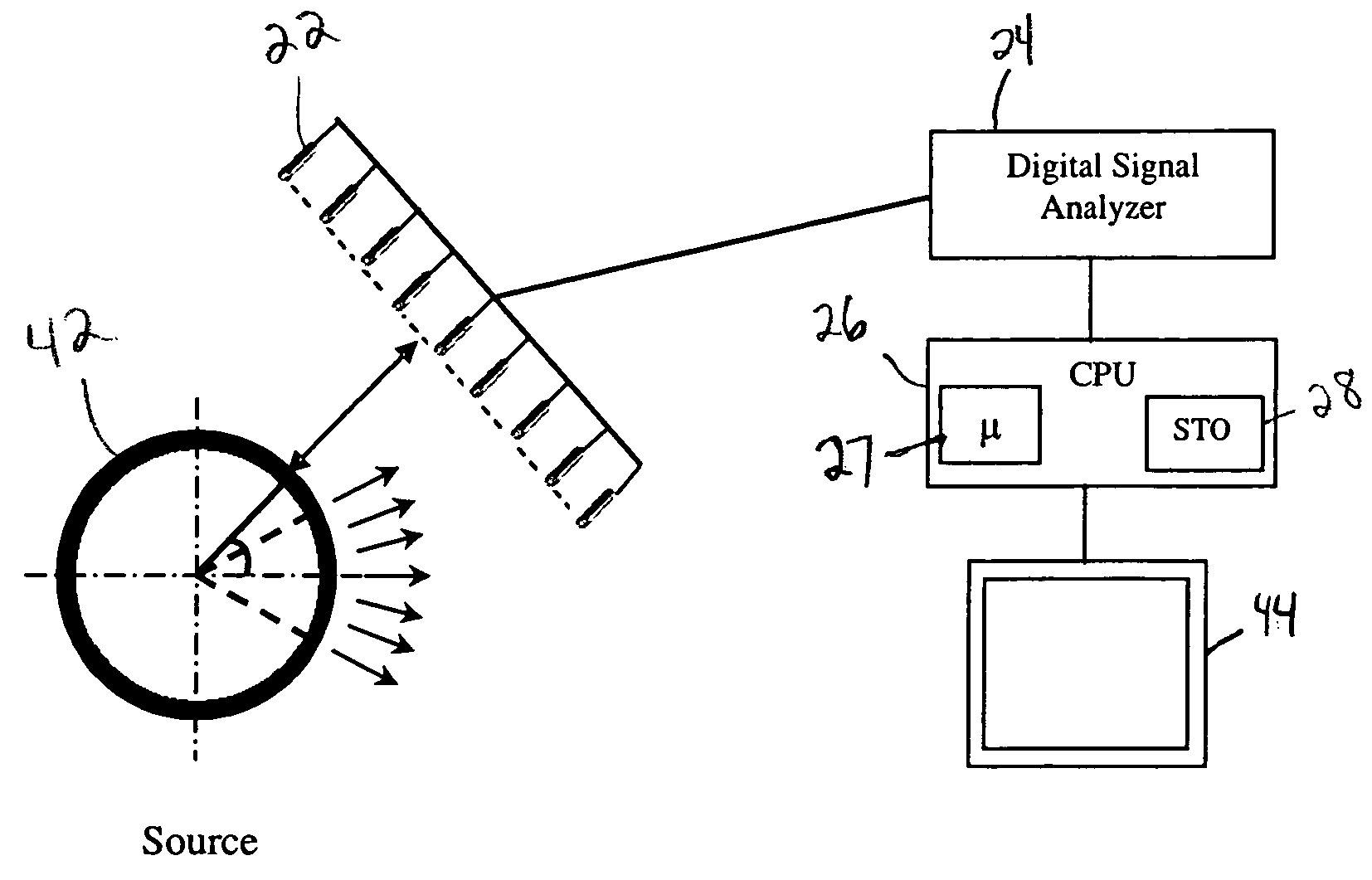
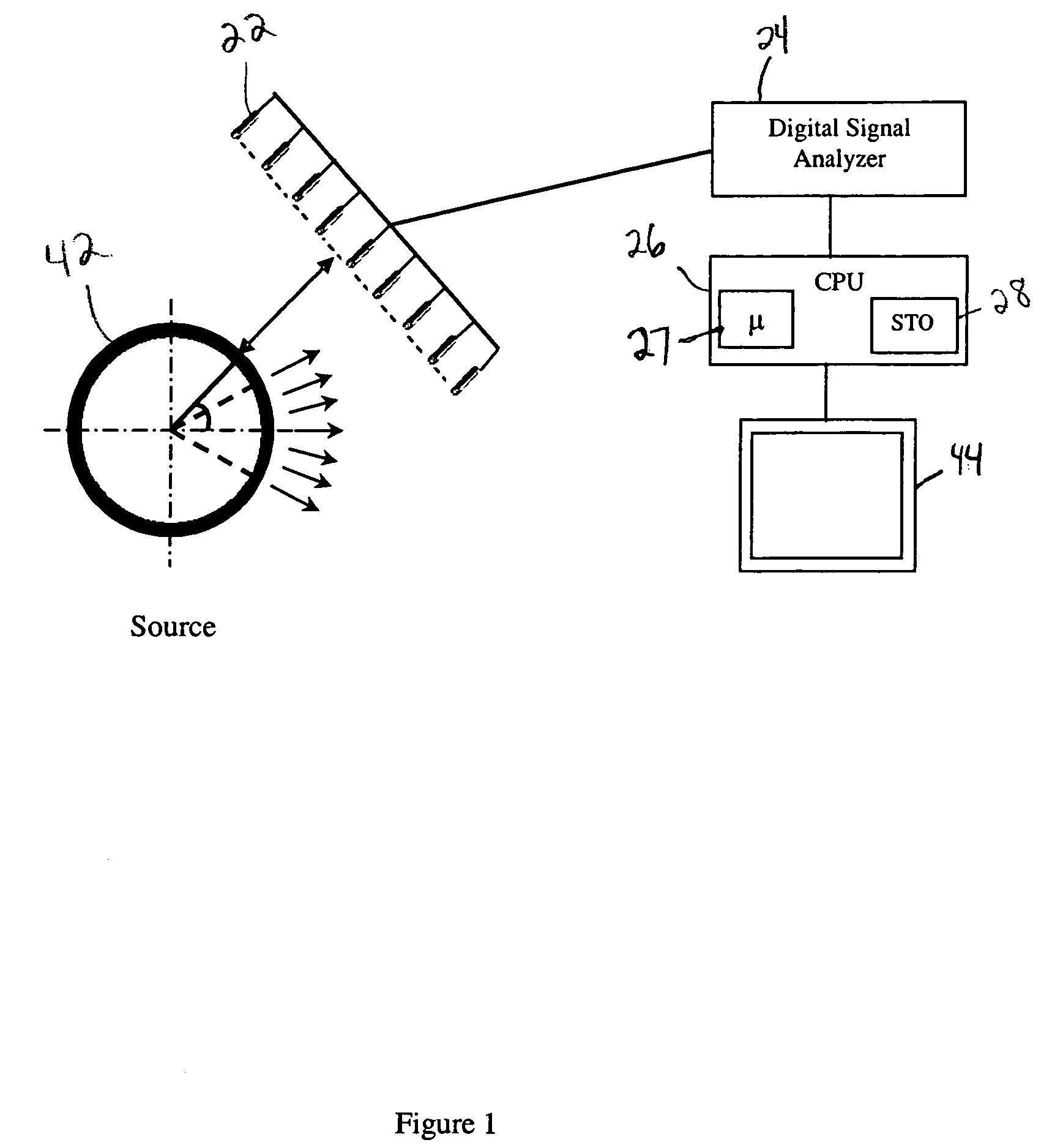
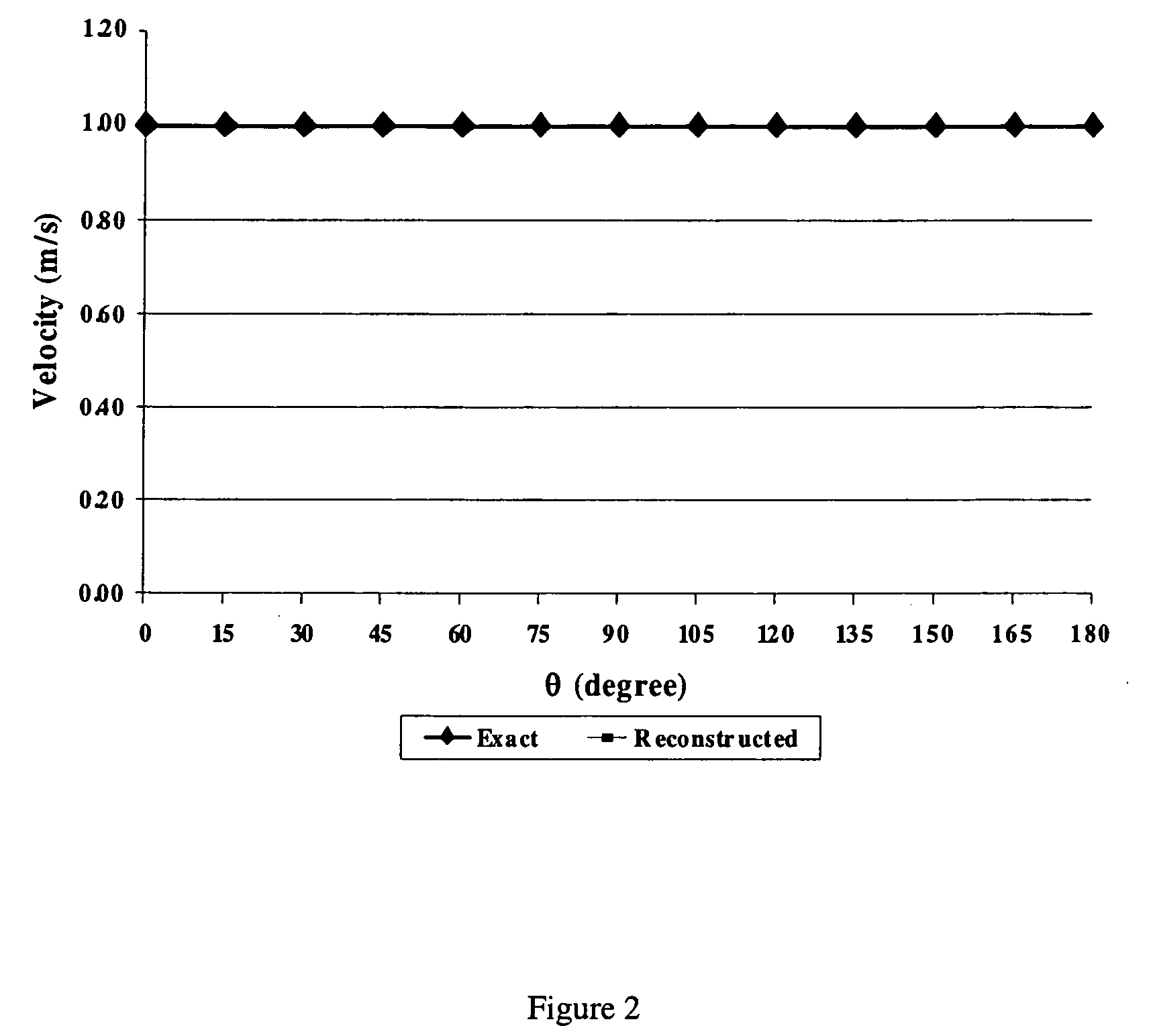
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
319 results about "Acoustic radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
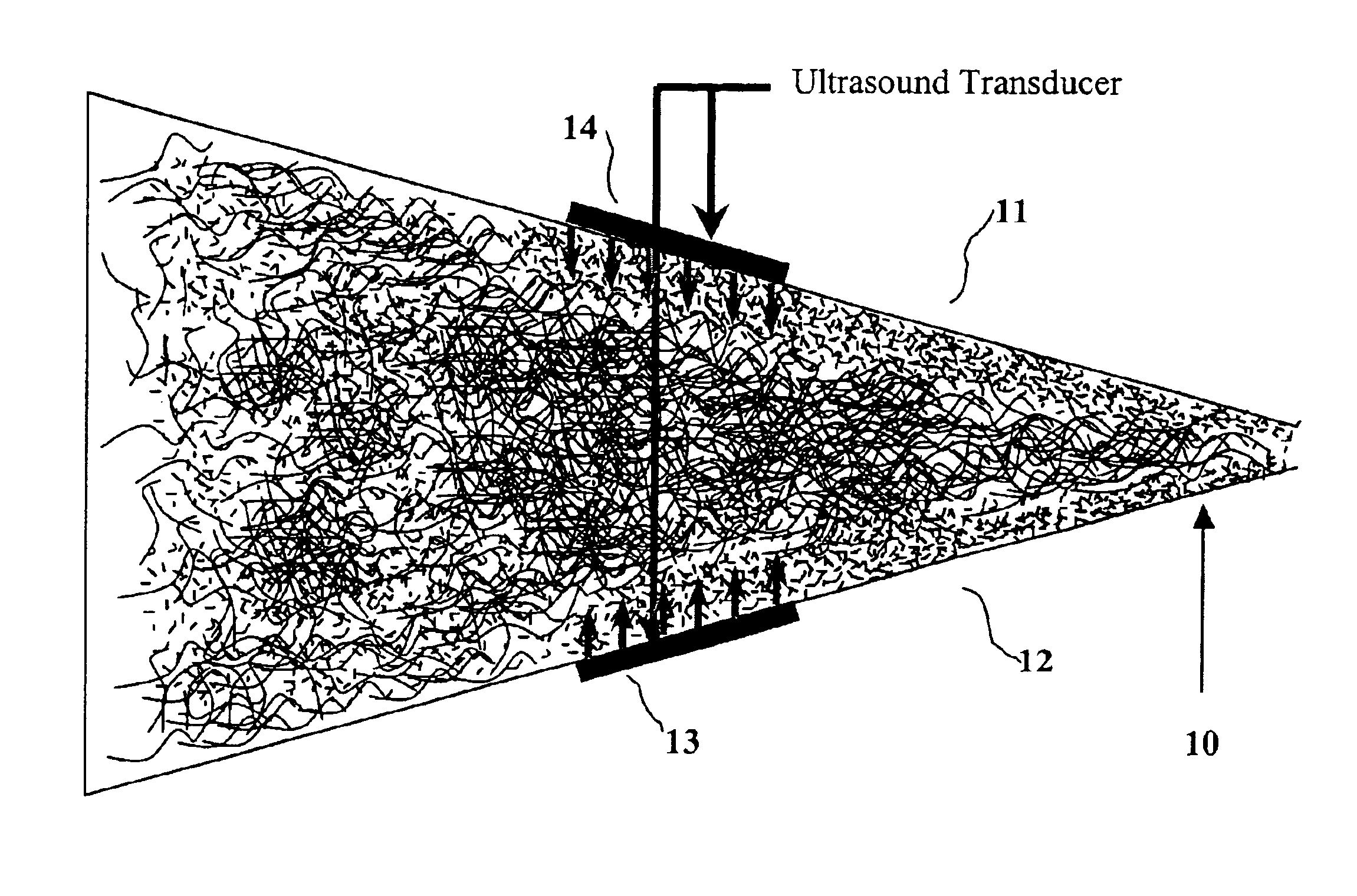
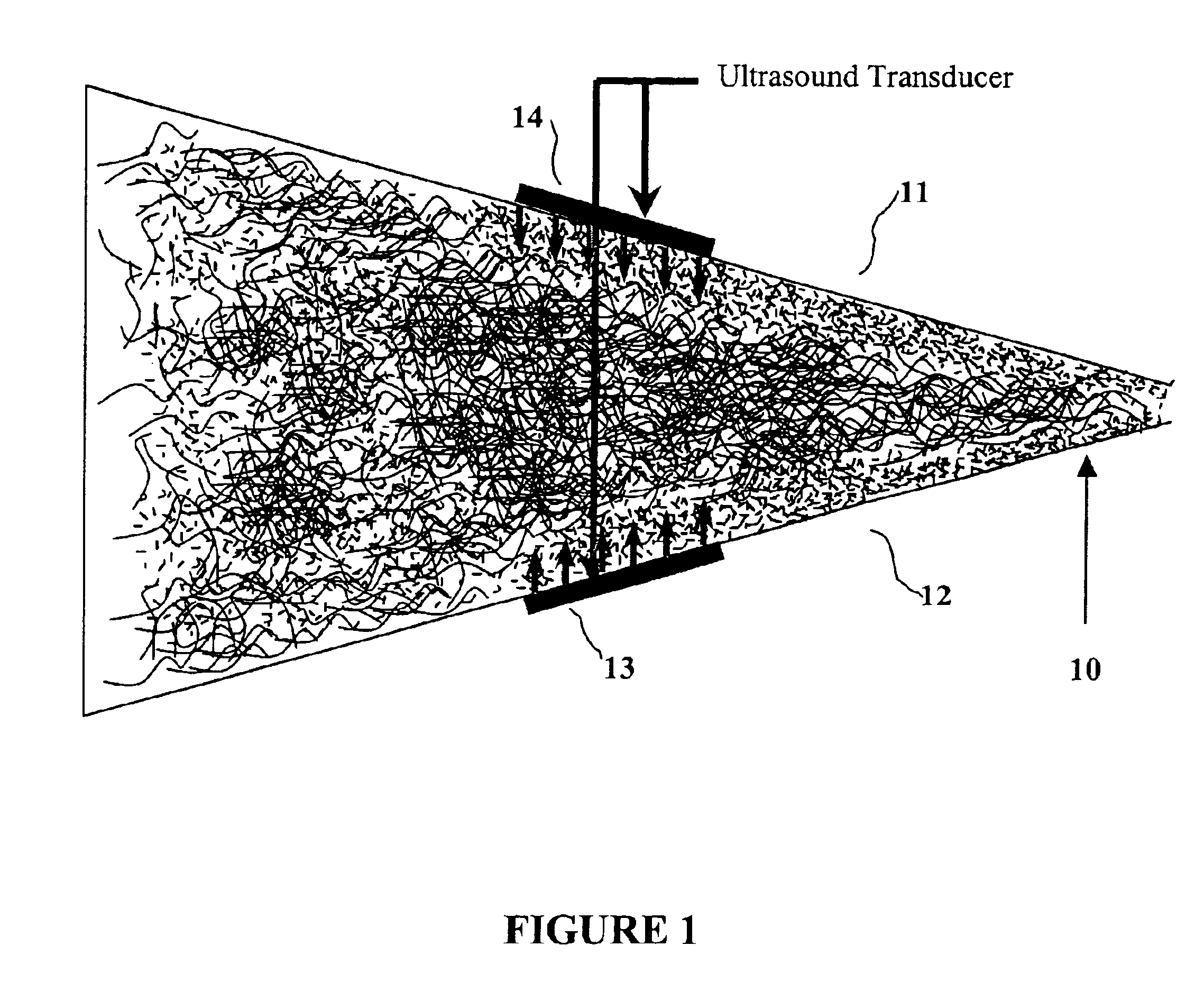
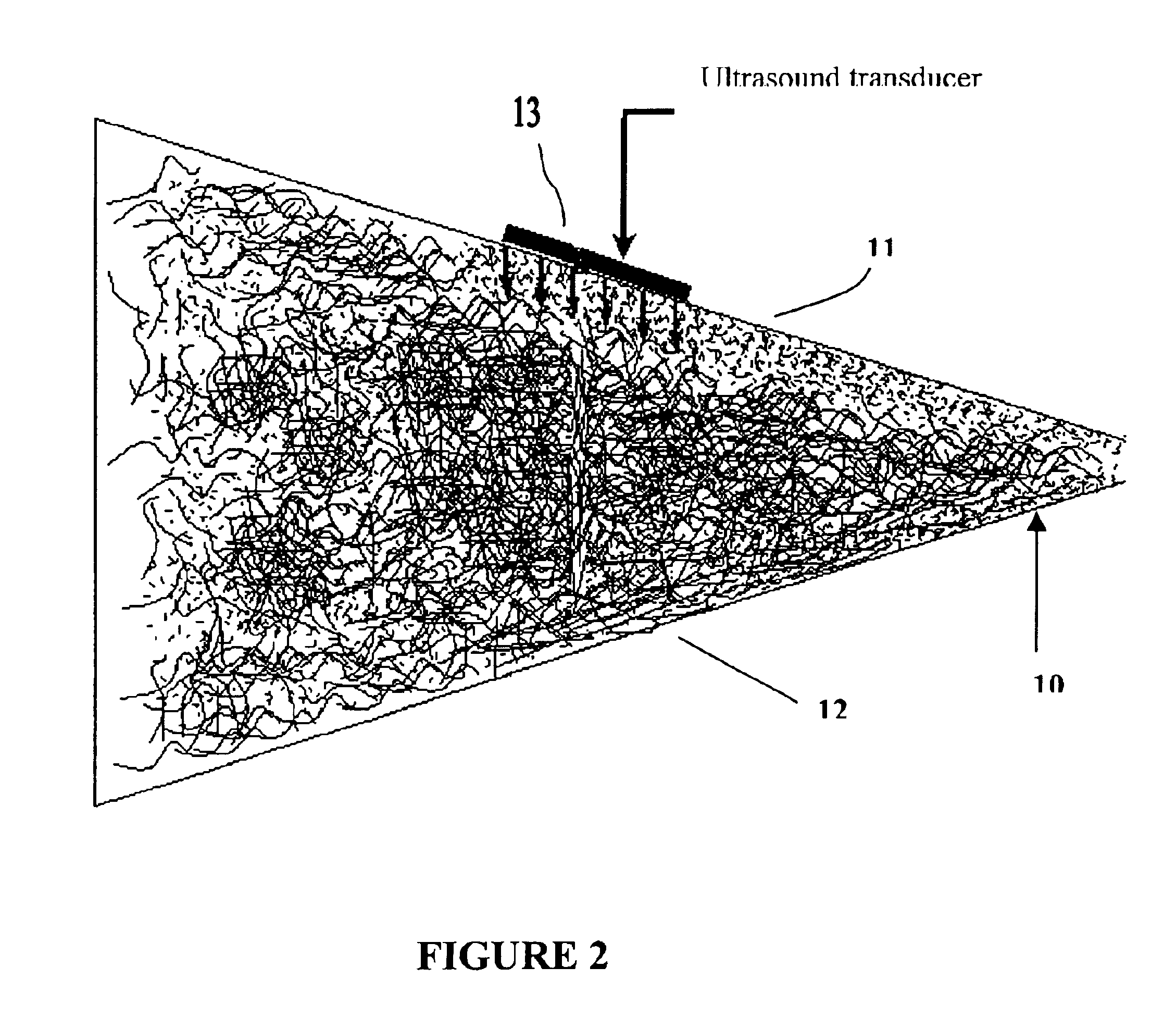
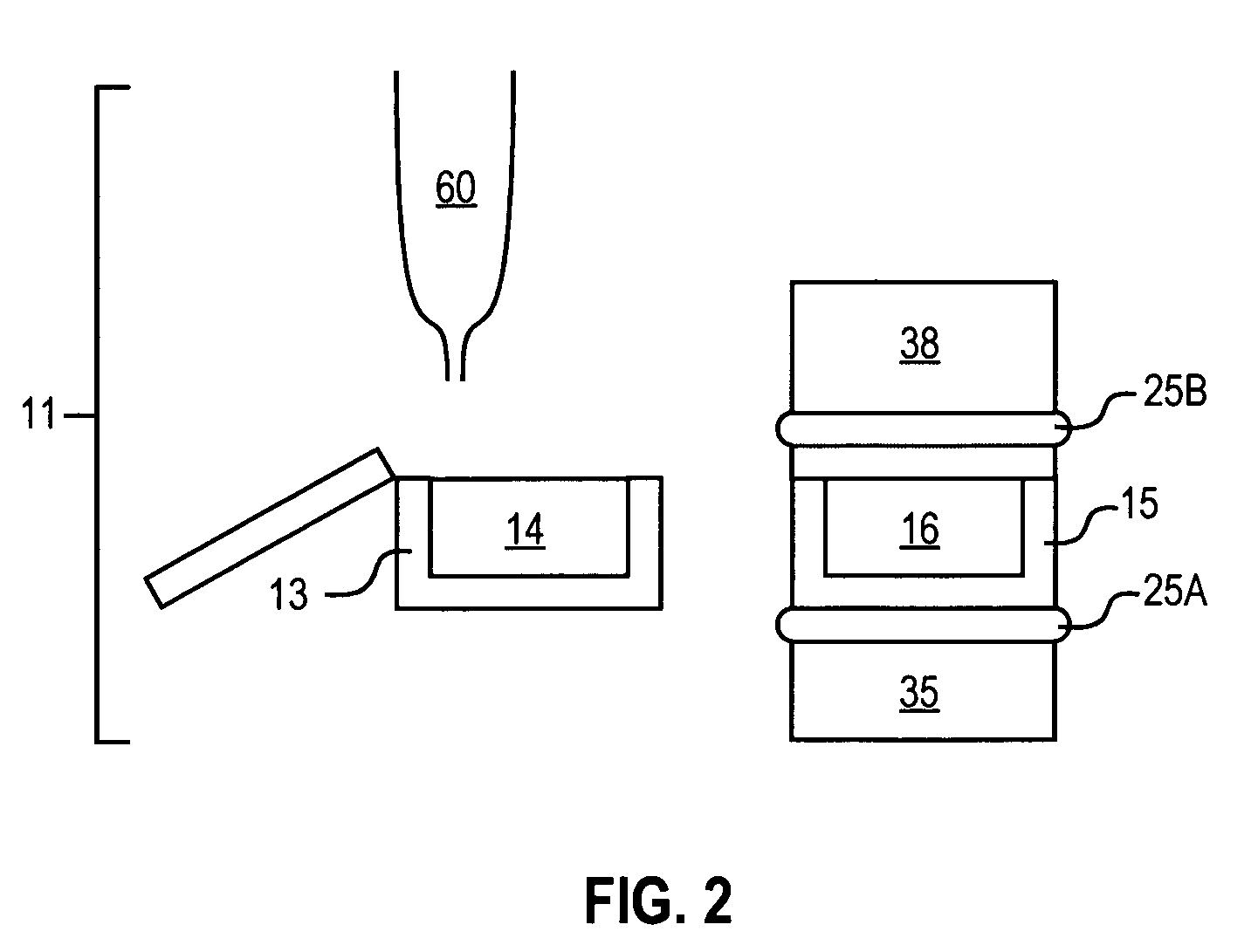
The acoustic radiations or auditory radiations are structures found in the brain, in the ventral cochlear pathway, a part of the auditory system. Acoustic radiation arising in the medial geniculate nucleus and end in primary auditory cortex (transverse temporal gyri). Lesions to the auditory radiations could be a cause of cortical deafness.
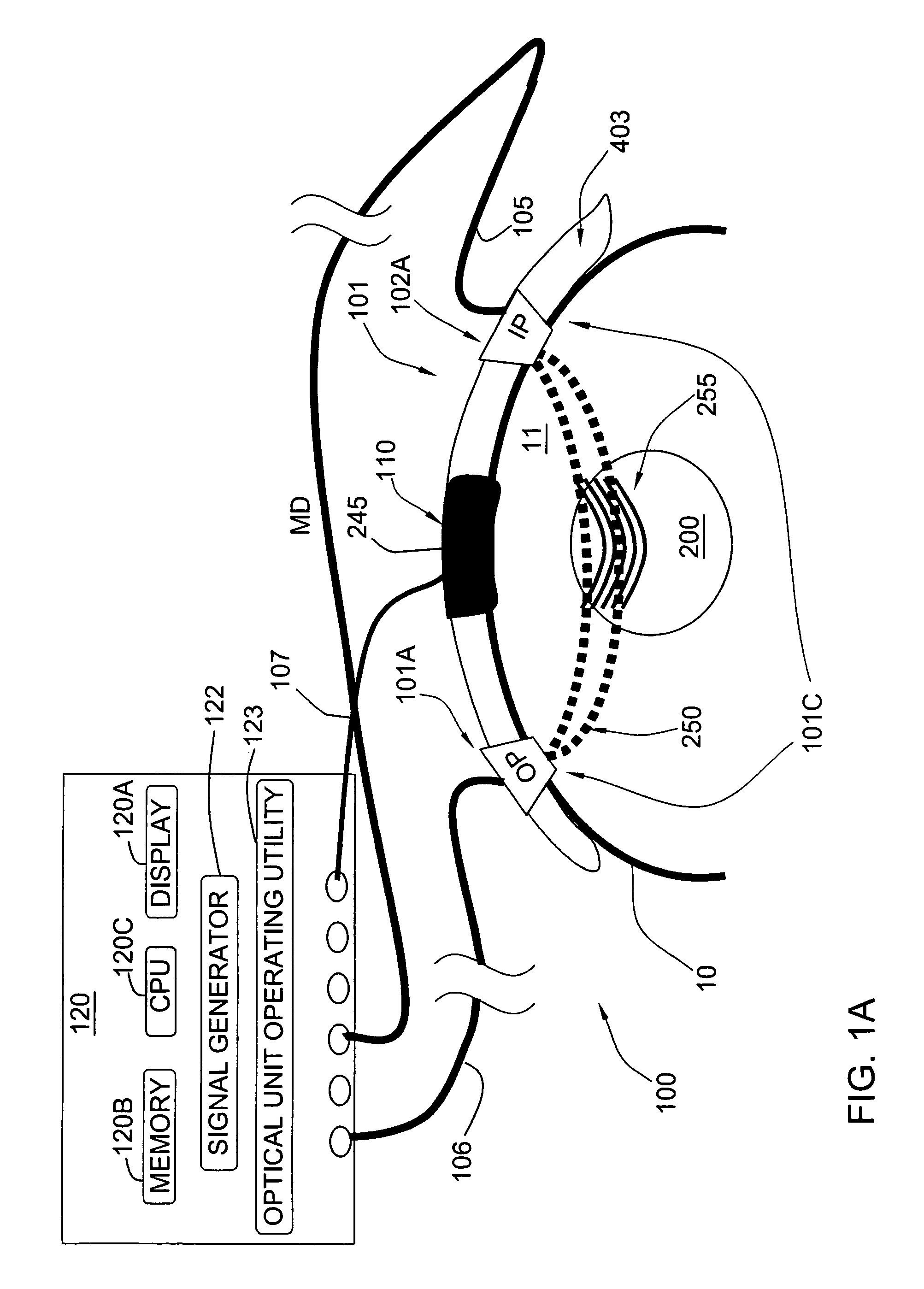
Photoacoustic analyzer of region of interest in a human body
InactiveUS7515948B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioSafer light energyAuscultation instrumentsDiagnostic recording/measuringAuditory radiationHuman body
A method and apparatus are presented for non-invasively monitoring at least one characteristic of a region of interest in a body. The body is illuminated by pulsed light to induce a photoacoustic effect. Acoustic radiation is detected, and measured data indicative thereof is generated. The photoacoustic effect is controlled by carrying out at least one of the following: providing the pulsed light of at least two different wavelength, analyzing the measured data to determine time variations of at least one predetermined parameter of a time dependent acoustic signal for each of wavelength, and determining oxygen saturation level in the region of interest; and operating a plurality of acoustic elements configured for detection of the acoustic radiation, to thereby define a focal volume for acoustic radiation detection to match dimensions of the region of interest.
Owner:ORNIM
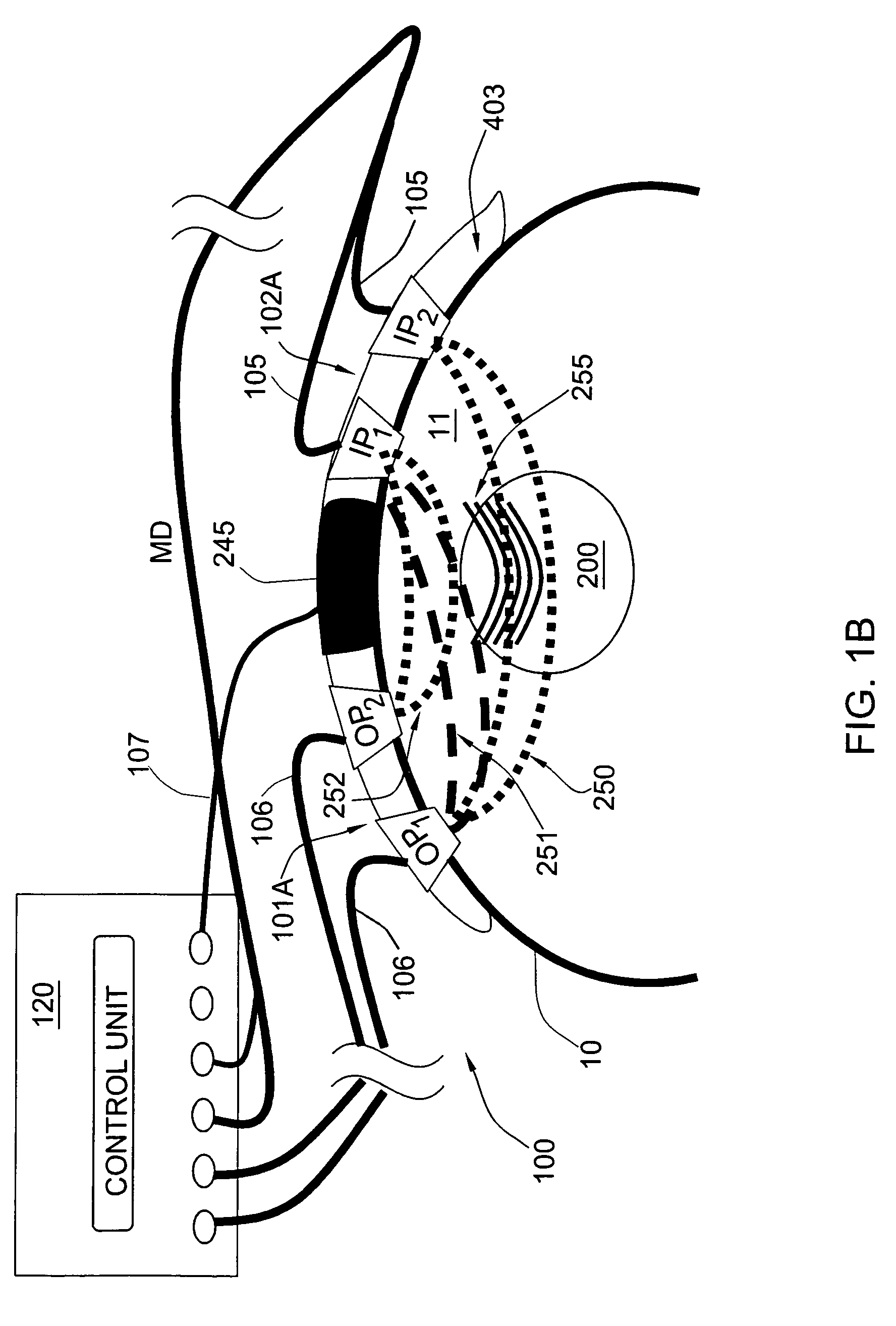
Real-time monitoring and control of hifu therapy in multiple dimensions
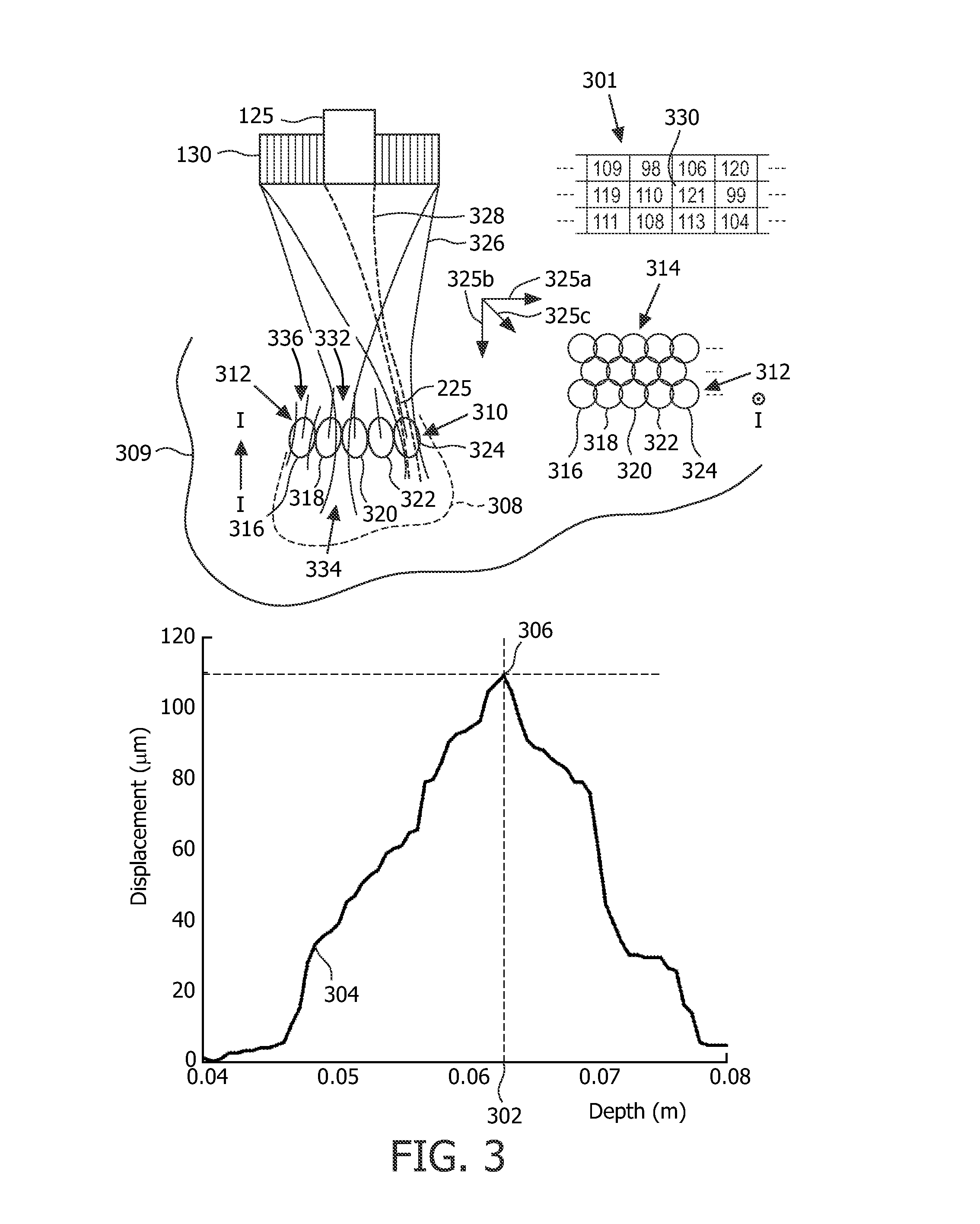
InactiveUS20130096597A1Reliable indicatorAccurate and fast and low-cost and simple and convenient techniqueUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyAuditory radiationMechanical property
Energy is transferred (336) to cause a mechanical property of biological tissue to change, as in ablation. An effect of the transferring is examined in more than one spatial dimension to, for example, make an ablation halting decision for a treatment region, i.e., line (312) or layer (314), or for a location (316) within the region. Halting decisions can be based on lesion-central and / or lesion-peripheral longitudinal displacement of treated tissue evaluated in real time against a characteristic curve. Steering in the azimuthal and / or elevation direction is afforded by, for example, linear, or 2D, multi-channel ultrasound arrays for therapy and imaging. Protocols includable are region-wide scanning (SI 010) and location-by-location completion for both (HIFU) therapy and tracking (acoustic-radiation-forced-based) displacement of treated tissue. Fine, location- to-location monitoring can be used for relatively inhomogeneous tissue; whereas, quicker, sparser and more generalized monitoring (1 100, 1200) can be employed for relatively homogeneous tissue.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Particle Quantifying Systems and Methods Using Acoustic Radiation Pressure
ActiveUS20090042310A1Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAcoustic radiation pressurePhysics
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
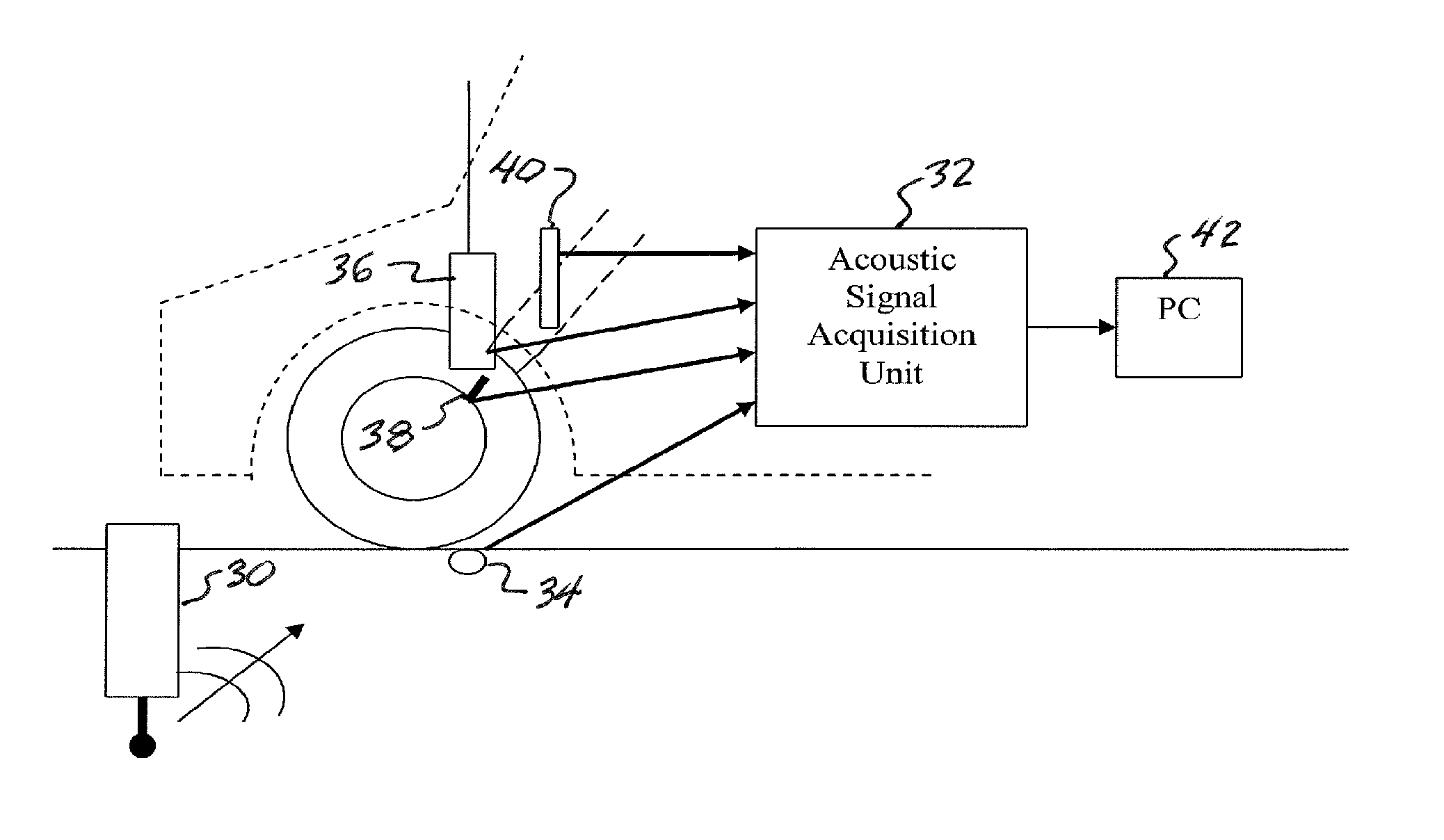
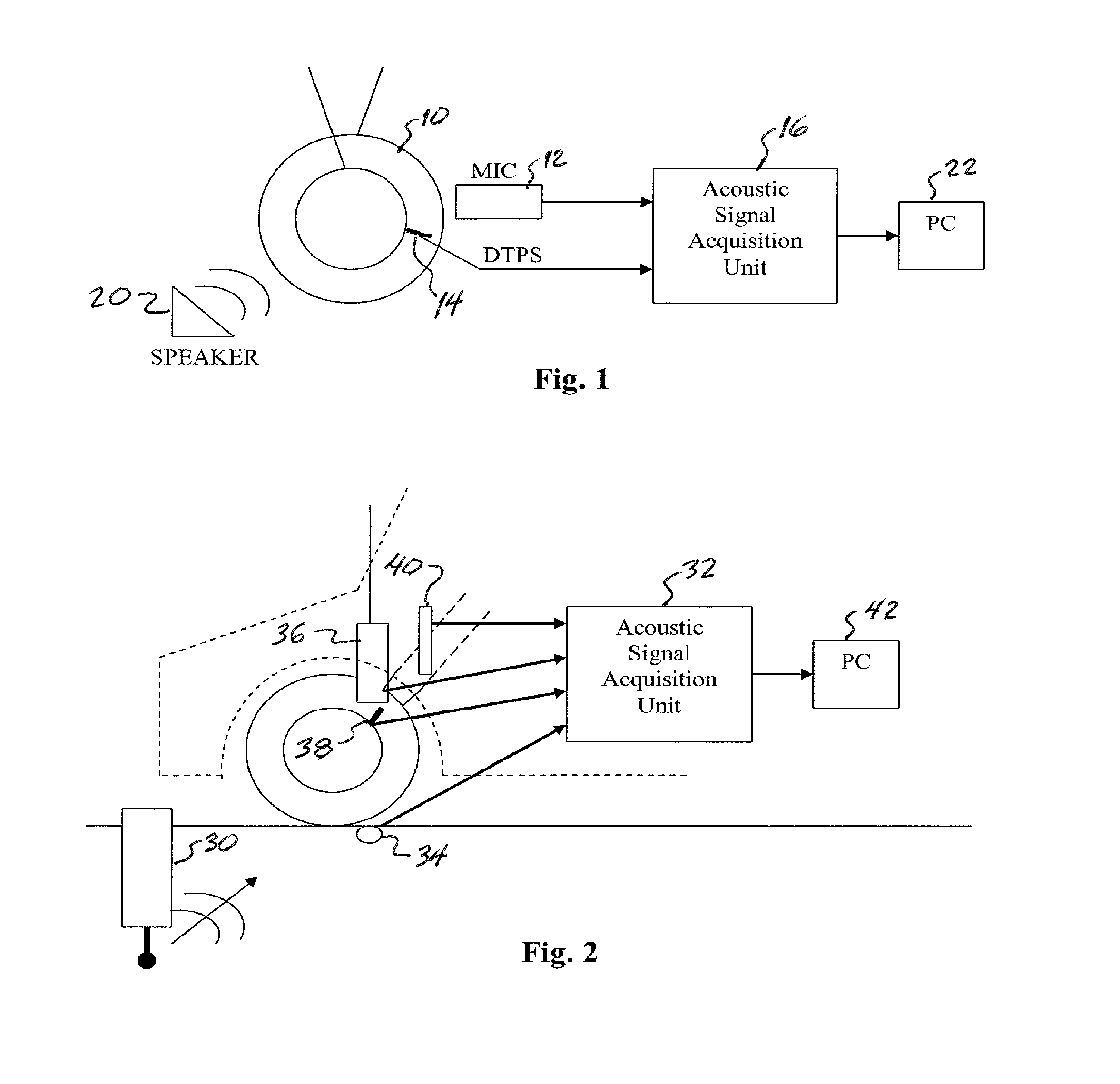
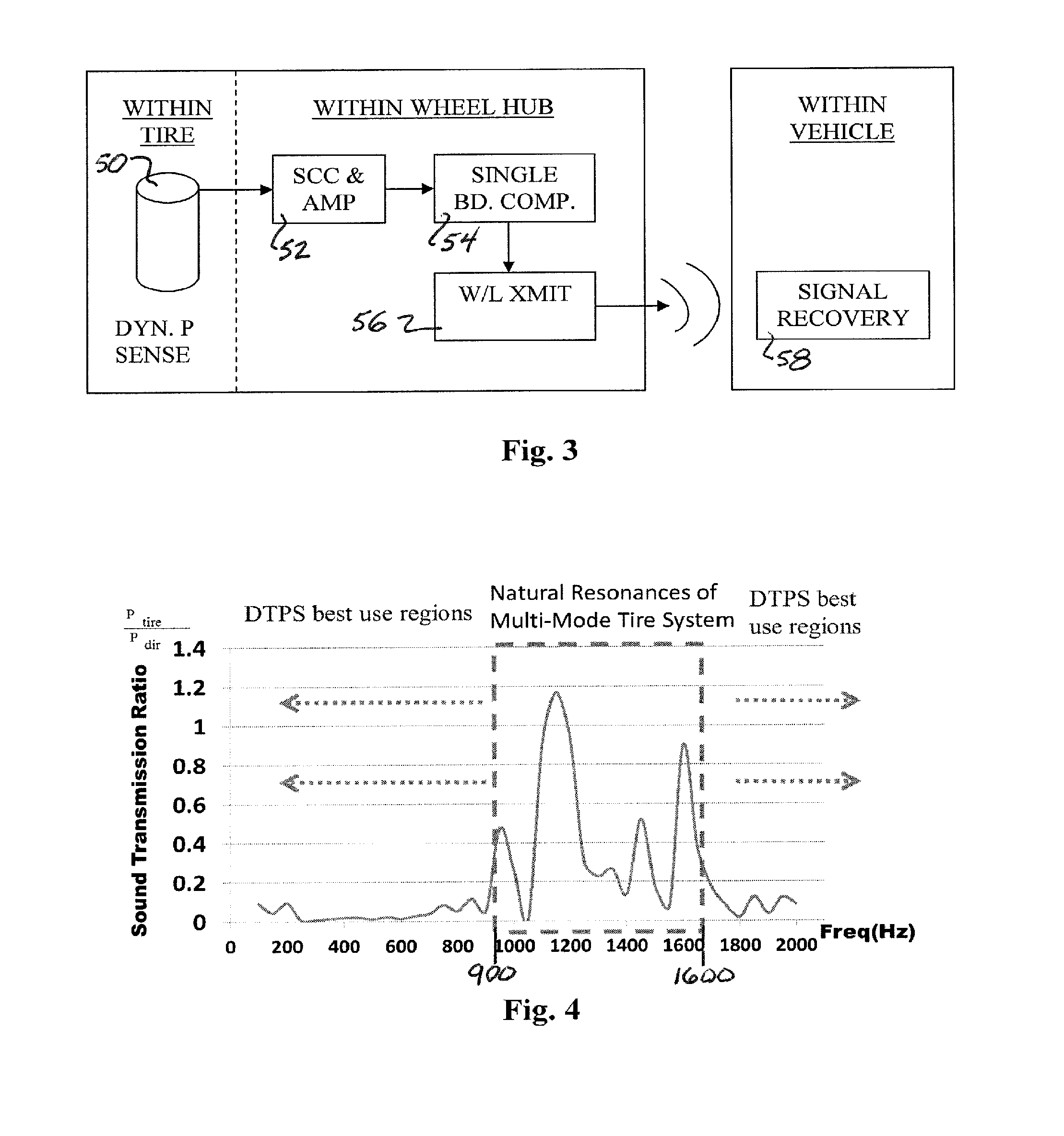
Real-time wireless dynamic tire pressure sensor and energy harvesting system
ActiveUS20140070935A1Quick testImprove detection accuracyBatteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAuditory radiationEnergy harvester
An instantaneous / real-time wireless dynamic tire pressure sensor (DTPS) for characterizing pavement qualities and for detecting surface and subsurface pavement defects under normal driving conditions. Signal processing provides quantitative assessment of surface conditions. DTPS includes a vehicle tire valve stem-mounted pressure sensor and wheel hub-mounted signal conditioning, amplification, and transmitting circuitry. A signal processing computer within the vehicle is wirelessly coupled to the hub-mounted circuitry. Tire pressure changes caused by ground vibration excitation from the interaction between the tire and pavement at normal driving speeds are detected. When acoustic radiation from a surface wave is significantly stronger than acoustic noise, subsurface information can be extracted. An energy harvester based on strong magnetostatic coupling between a high permeability core solenoid, fixed proximate a vehicle wheel, and a bias magnet array, fixedly mounted in conjunction with a dust shield, can provide power the DIPS.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Noninvasive Measurements in a Human Body
InactiveUS20080312533A1Facilitate noninvasive measurementContinuous informationBlood flow measurement devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringHuman bodyAuditory radiation
A measurement system and method are presented for use for non-invasive measurements in a human body. Acoustic radiation is applied to a certain illuminated region in the body, with at least two different conditions of the applied radiation achievable by varying at least one characteristic of the acoustic radiation. Light scattered from the body part is detected, and measured data indicative of detected photons tagged and untagged by the acoustic radiation is generated. The measured data is analyzed to extract therefrom a data portion corresponding to the tagged photons and being therefore associated with a light response of said certain region, thereby enabling determination of tissue properties of said certain region based on a relation between the measured data portions corresponding to the at least two different operating conditions.
Owner:OR NIM MEDICAL
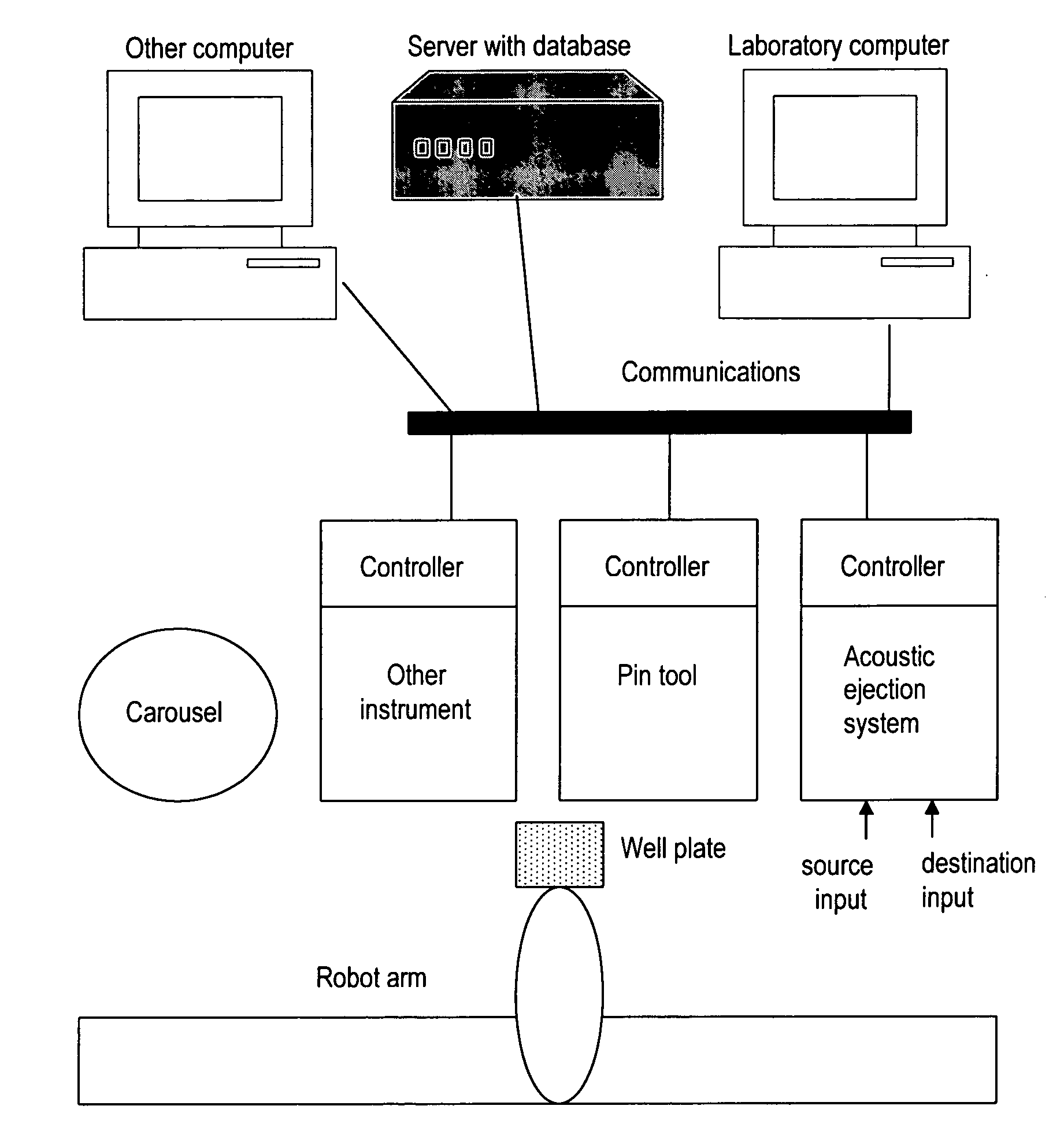
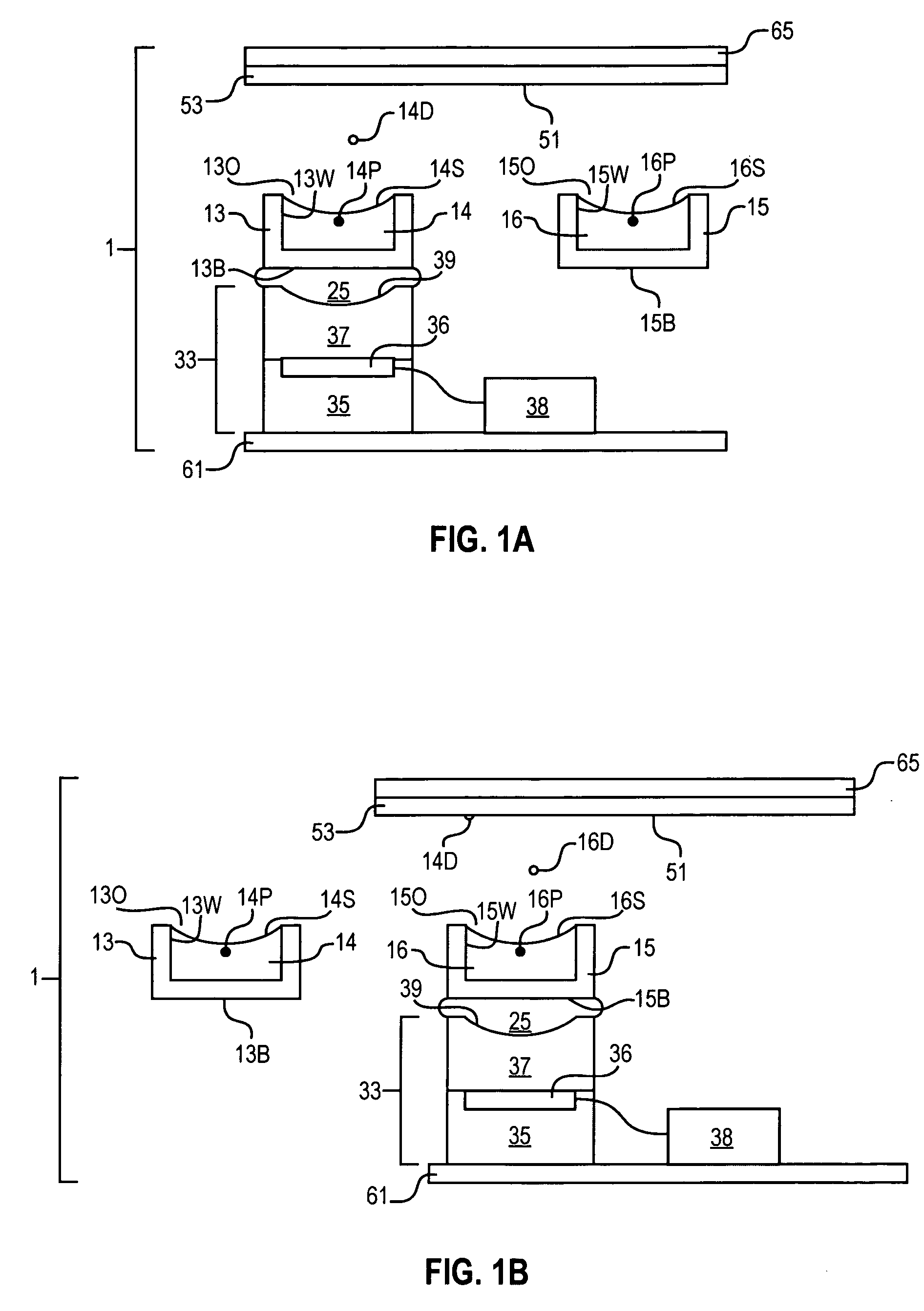
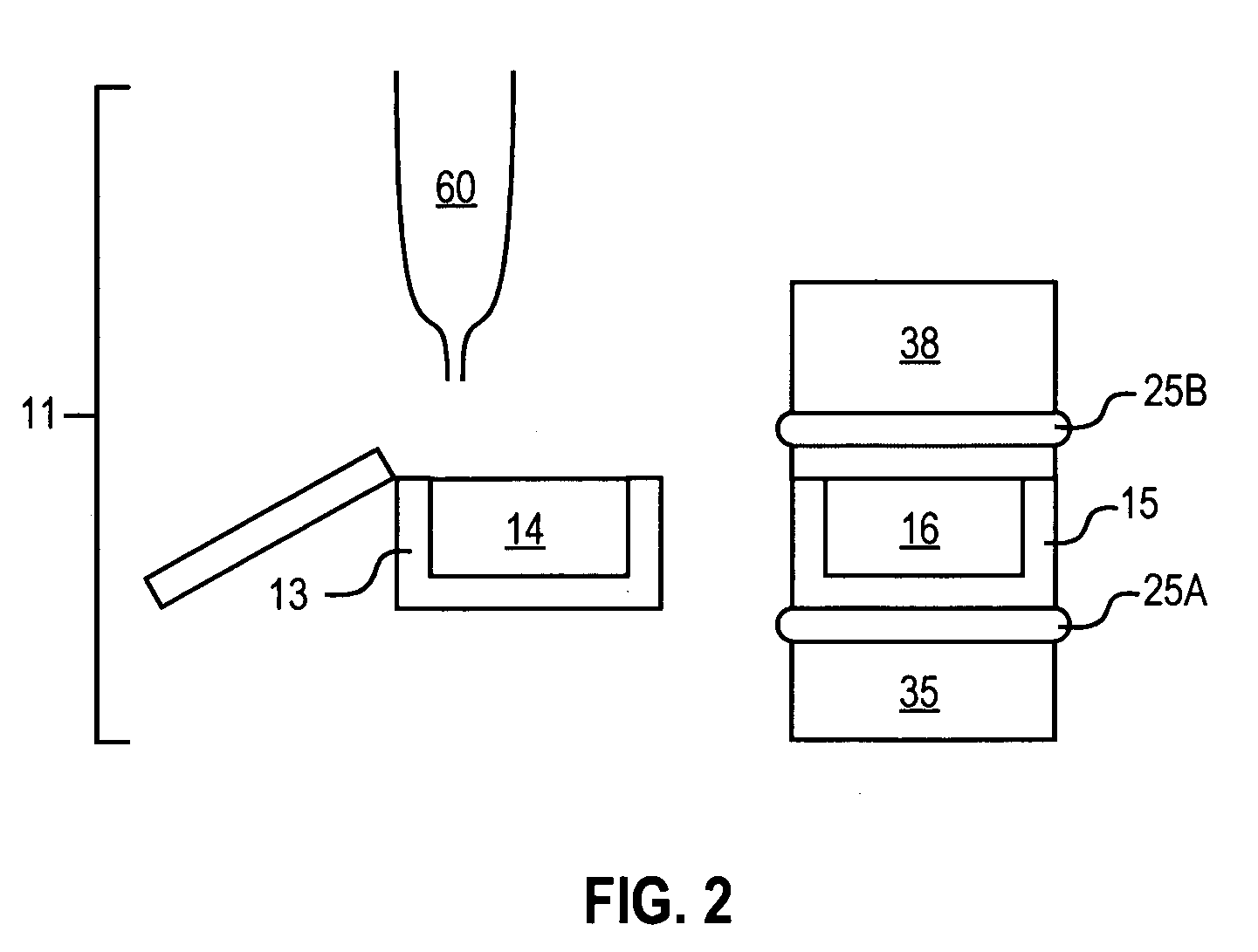
Acoustic assessment of fluids in a plurality of reservoirs
InactiveUS6938995B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFlow propertiesAuditory radiationCoupling
The invention provides devices and methods for acoustically assessing the contents of a plurality of reservoirs that are typically provided as an array. An acoustic radiation generator is employed for generating acoustic radiation having an image field of a size sufficient to interrogate a plurality of selected reservoirs at one time. The generator is placed in acoustic coupling relationship via a fluid acoustic coupling medium to the selected reservoirs, and acoustic radiation generated by the generator is transmitted through the coupling medium, an exterior surface of the selected reservoirs, and the selected reservoirs. A characteristic of the transmitted acoustic radiation is analyzed so as to assess the contents of each of the selected reservoirs. Fluid may be ejected from the selected reservoirs according to the assessment. Optionally, a means is provided for removing fluid acoustic coupling medium from the exterior surface after acoustic assessment.
Owner:LABCYTE
Acoustic control of the composition and/or volume of fluid in a reservoir
InactiveUS6932097B2Efficient transportFunctional valve typesLarge containersAuditory radiationEngineering
The invention provides a device for controlling the composition and / or volume of a fluid within a reservoir. The device includes a reservoir adapted to contain at least one fluid, a means for monitoring a characteristic of the fluid contained in the reservoir, and a means for introducing additional fluid into the reservoir according to the fluid characteristic monitored by the monitoring means. The device also includes an acoustic generator for generating acoustic radiation. A dispensing means may be provided as well. Other devices and methods that use acoustic radiation to control the composition and / or volume of a fluid within a reservoir are included.
Owner:LABCYTE
Acoustic assessment of characteristics of a fluid relevant to acoustic ejection
InactiveUS20050212869A1Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAuditory radiationAcoustic energy
Methods are provided for analyzing characteristics of fluids in the context of an acoustic ejection system. Such a system has a controller, an acoustic radiation generator, and a coupling medium coupling the radiation to a reservoir holding fluid. The methods can use acoustic radiation to both perturb a surface of the fluid in the reservoir and analyze the effect of the perturbation. The methods may use information about prior fluids. The methods of the invention can determine physical characteristics such as speed of sound and viscosity. The methods also include ways to determine a level of acoustic energy suitable to eject a droplet. Preferably the methods are executed automatically under control of programming of a controller of an acoustic ejection system.
Owner:LABCYTE
Computerized ultrasound risk evaluation system
InactiveUS7285092B2Improve comfortOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsAuditory radiationSonification
A method and system for examining tissue are provided in which the tissue is maintained in a position so that it may be insonified with a plurality of pulsed spherical or cylindrical acoustic waves. The insonifying acoustic waves are scattered by the tissue so that scattered acoustic radiation including a mix of reflected and transmitted acoustic waves is received. A representation of a portion of the tissue is then derived from the received scattered acoustic radiation.
Owner:DELPHINUS MEDICAL TECH
System and method for noninvasively monitoring conditions of a subject
InactiveUS7541602B2Easy to measureHigh resolution measurementDiagnostics using lightScattering properties measurementsAuditory radiationElectromagnetic radiation
A method and system are presented for use in determining one or more parameters of a subject. A region of interest of the subject is irradiated with acoustic tagging radiation, which comprises at least one acoustic tagging beam. At least a portion of the region of interest is irradiated with at least one electromagnetic beam of a predetermined frequency range. Electromagnetic radiation response of the at least portion of the region of interest is detected and measured data indicative thereof is generated. The detected response comprises electromagnetic radiation tagged by the acoustic radiation. This enables processing of the measured data indicative of the detected electromagnetic radiation response to determine at least one parameter of the subject in a region corresponding to the locations in the medium at which the electromagnetic radiation has been tagged by the acoustic radiation, and outputting data indicative of the at least one determined parameter.
Owner:OR NIM MEDICAL
System and method for noninvasively monitoring conditions of a subject
InactiveUS20080296514A1Easy to measureHigh resolution measurementDiagnostics using lightElectric discharge tubesAuditory radiationElectromagnetic radiation
A method and system are presented for use in determining one or more parameters of a subject. A region of interest of the subject is irradiated with acoustic tagging radiation, which comprises at least one acoustic tagging beam. At least a portion of the region of interest is irradiated with at least one electromagnetic beam of a predetermined frequency range. Electromagnetic radiation response of the at least portion of the region of interest is detected and measured data indicative thereof is generated. The detected response comprises electromagnetic radiation tagged by the acoustic radiation. This enables processing of the measured data indicative of the detected electromagnetic radiation response to determine at least one parameter of the subject in a region corresponding to the locations in the medium at which the electromagnetic radiation has been tagged by the acoustic radiation, and outputting data indicative of the at least one determined parameter.
Owner:OR NIM MEDICAL
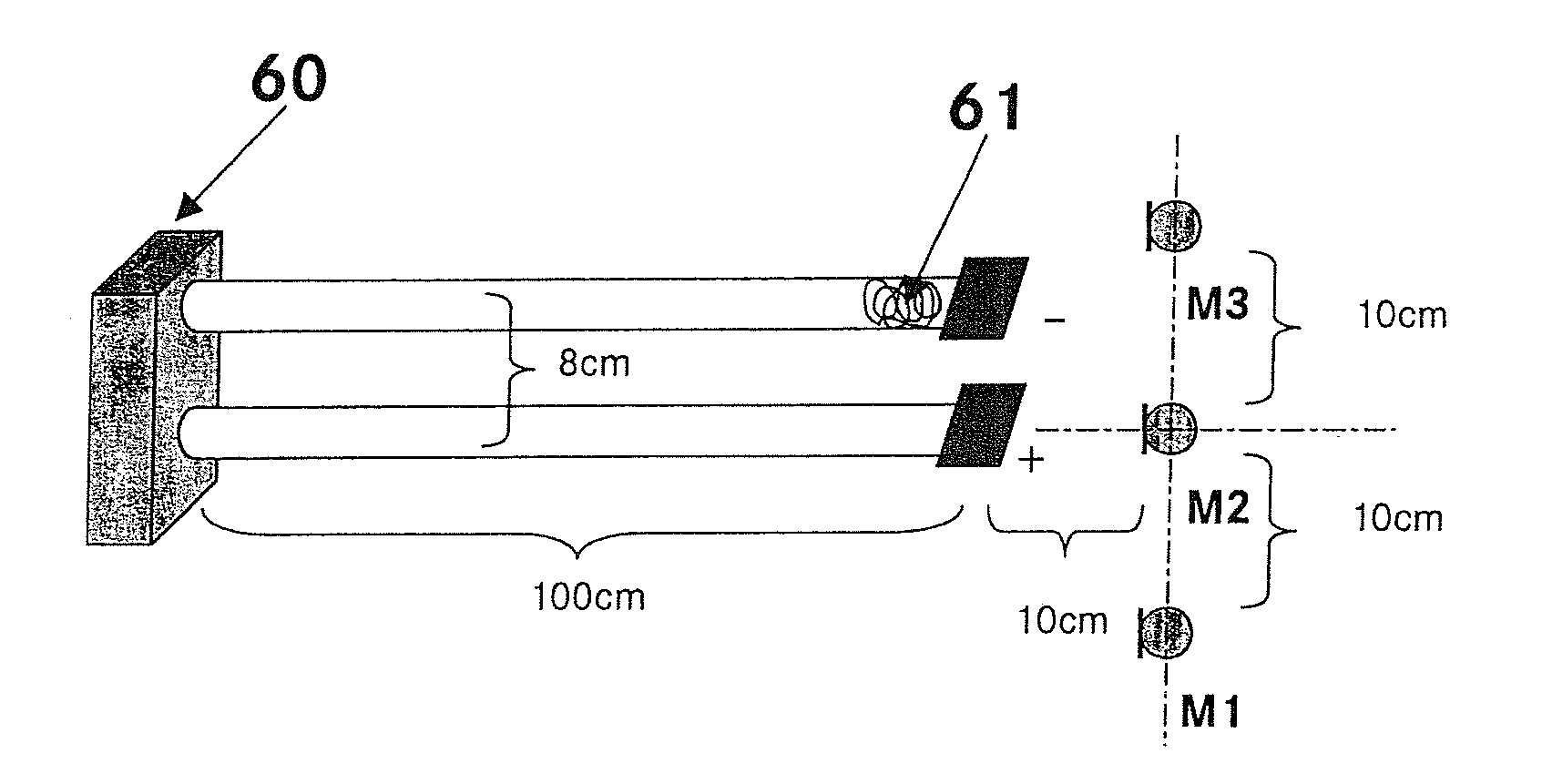
Method of making a stratified paper
The present invention provides a method making stratified paper by redistributing the pulp suspension inside the headbox nozzle using acoustic radiation waves. Acoustic radiation forces fractionate fibers based on fiber radius. The acoustic radiation waves separate the fibers by pushing the coarse and longer fibers to the inner area while fines and smaller fibers remain in the outer area. This has a similar effect of multi-layer stratification headbox, and provides paper with a smoother surface.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
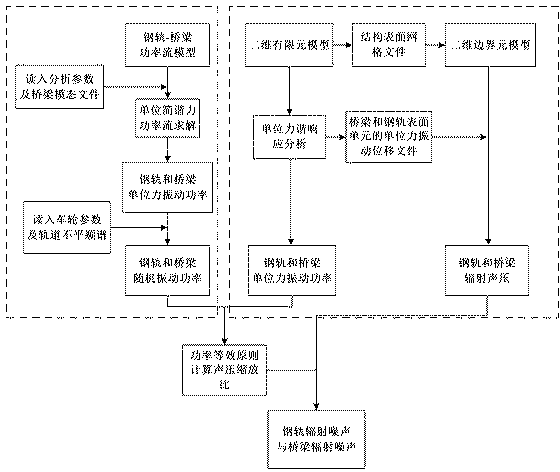
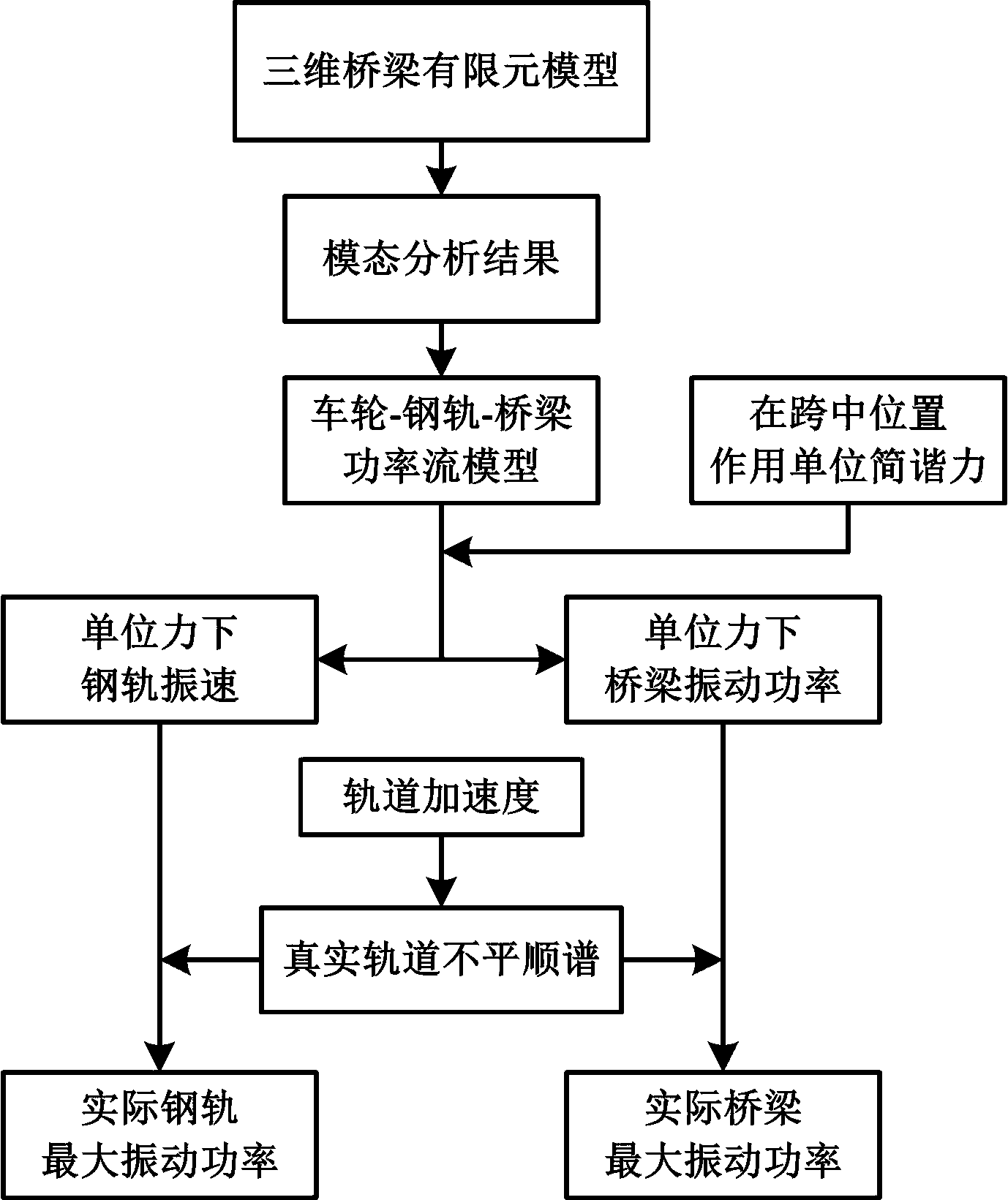
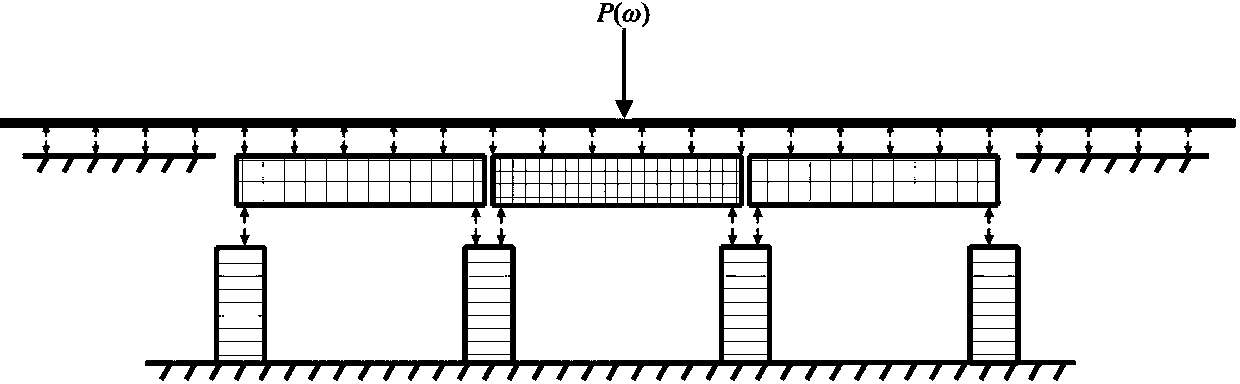
Power flow-boundary element model based elevated rail traffic vibratory-noise simulating and predicting method
InactiveCN104036087ASimulation is accurateHigh simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAuditory radiationElement model
The invention relates to a power flow-boundary element model based elevated rail traffic vibratory-noise simulating and predicting method. The power flow-boundary element model based elevated rail traffic vibratory-noise simulating and predicting method comprehensively considers bridge noise and steel-rail noise of the medium-frequency range (200-1000Hz) in elevated rail traffic, and is higher in noise prediction accuracy than that of a method only considering bridge noise or steel-rail noise. The method includes firstly establishing a rail- bridge system power flow model, calculating input power of bridges and vibration speed of steel rails when harmonic force units different in frequency act on the steel rails; secondly, calculating wheel-rail contact force spectrum under a wheel-rail-bridge coupling system through a wheel-rail combination roughness spectrum so as to obtain vibration states of the bridges and the steel rails under the action of random wheel-rail force; thirdly, respectively establishing an acoustic-radiation two-dimension finite-element-boundary element weak-coupling model for the bridges and the steel rails, and calculating vibration power and radiation sound field under the action of the harmonic force units at different frequencies; finally, acquiring practical vibration power by the power flow method and vibration power by the finite-element-boundary element model, scaling field-point sound pressure under the action of unit force to obtain the bridge noise, the steel-rail noise and the total noise thereof.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Acoustic assessment of characteristics of a fluid relevant to acoustic ejection
InactiveUS7354141B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAuditory radiationAcoustic energy
Owner:LABCYTE
Acoustic assessment of fluids in a plurality of reservoirs
InactiveUS7900505B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFlow propertiesAuditory radiationEngineering
The invention provides devices and methods for acoustically assessing the contents in a plurality of reservoirs. Each reservoir has a portion adapted to contain a fluid, and an acoustic radiation generator is positioned in acoustic coupling relationship to each of the reservoirs. Acoustic radiation generated by the acoustic radiation generator is transmitted through at least the portion of each reservoir to an analyzer. The analyzer is capable of analyzing a characteristic of the transmitted acoustic radiation and optionally correlating the characteristic to a property of the reservoirs' contents. The invention is particularly suited for assessing the contents of a plurality of reservoirs to allow for accuracy and control over the dispensing of fluids therefrom.
Owner:LABCYTE
Piezoelectric ultrasonic transducer
InactiveCN101121165AIncrease powerImprove efficiencyMechanical vibrations separationSound producing devicesAuditory radiationUltrasonic sensor
The invention relates to a high-power radial vibration piezoelectric ultrasonic transducer suitable for liquid ultrasonic treatment under normal pressure and high pressure. The purpose of the present invention is to provide a high structural strength, high power density, which can generate uniform sound radiation in the radial direction of 360°, aiming at the defects of low structural strength and low power density of existing ultrasonic transducers, It is a high-power radial vibration piezoelectric ultrasonic transducer especially suitable for liquid ultrasonic treatment under normal pressure and high pressure. The invention comprises a piezoelectric ceramic disc, a prestressed annular cover plate, a cylinder body, an insulating vibration-isolating ring pad and an end cover, wherein a through hole is arranged on the piezoelectric ceramic disc, and the side of the piezoelectric ceramic disc and the prestressed annular cover plate The composite disk piezoelectric transducer is formed by radial compounding. Several composite disk piezoelectric transducer units whose geometric parameters are consistent with the radial resonance frequency are connected in electrical parallel, and are closely fixed on the inner wall of the cylinder at equal intervals. An insulating vibration-isolating ring pad is arranged between two adjacent composite disc piezoelectric transducer units.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for acoustically ejecting a droplet of fluid from a reservoir by an acoustic fluid ejection apparatus
The invention provides apparatuses and methods for acoustically ejecting the fluid from a reservoir contained in or disposed on a substrate. The reservoir has a portion adapted to contain a fluid, and an acoustic radiation generator is positioned in acoustic coupling relationship to the reservoir. Acoustic radiation generated by the acoustic radiation generator is transmitted through at least the portion of the reservoir to an analyzer. The analyzer is capable of determining the energy level of the transmitted acoustic radiation and raising the energy level of subsequent pulses to a level sufficient to eject fluid droplets from the reservoir. The invention is particularly suited for delivering fluid from a plurality of reservoirs in an accurate and efficient manner.
Owner:LABCYTE
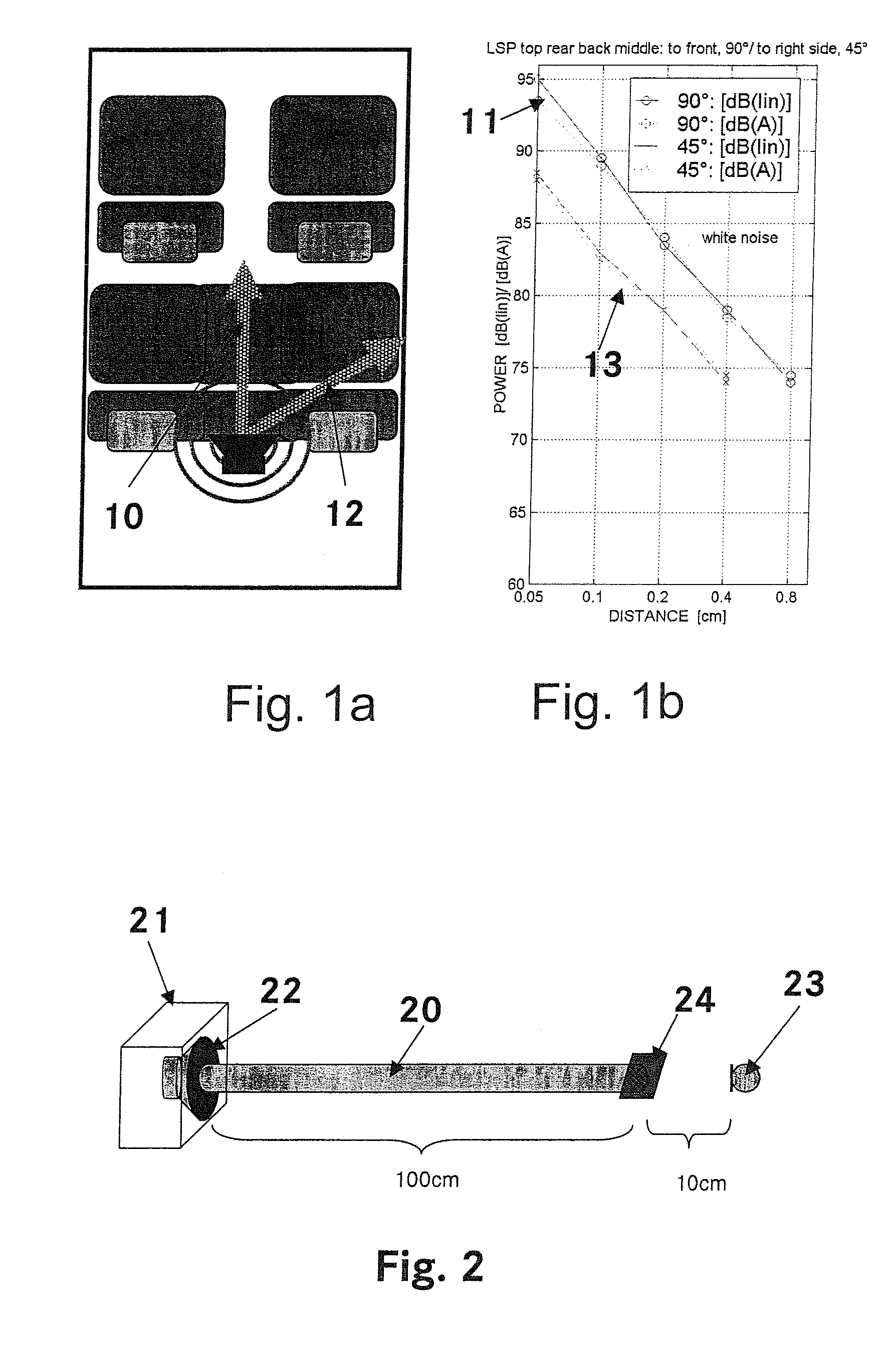
Acoustic sound routing in vehicles
InactiveUS7508952B2Reduce resonance effectVehicle seatsLoudspeaker screensAuditory radiationSound sources
To ensure the same high quality of acoustic radiation from audio systems on each seat of current vehicles, an acoustic device is provided for generating audio signals, which allows sound sources to be integrated into the area located near the headrest of a vehicle seat such that the volume can be regulated in an individual manner without unduly disturbing the other passengers in a vehicle. The headrest does not comprise any loudspeakers, thus is safe regarding accident protection. The acoustic near field at the headrest is generated by means of a sound channel. The loudspeaker is disposed inside the backrest or under the seat, for example, while the sound channel terminates in the headrest. Tuned pipes, the end of which is adjusted to the acoustic impedance of the clearance zone, are used as a sound channel.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
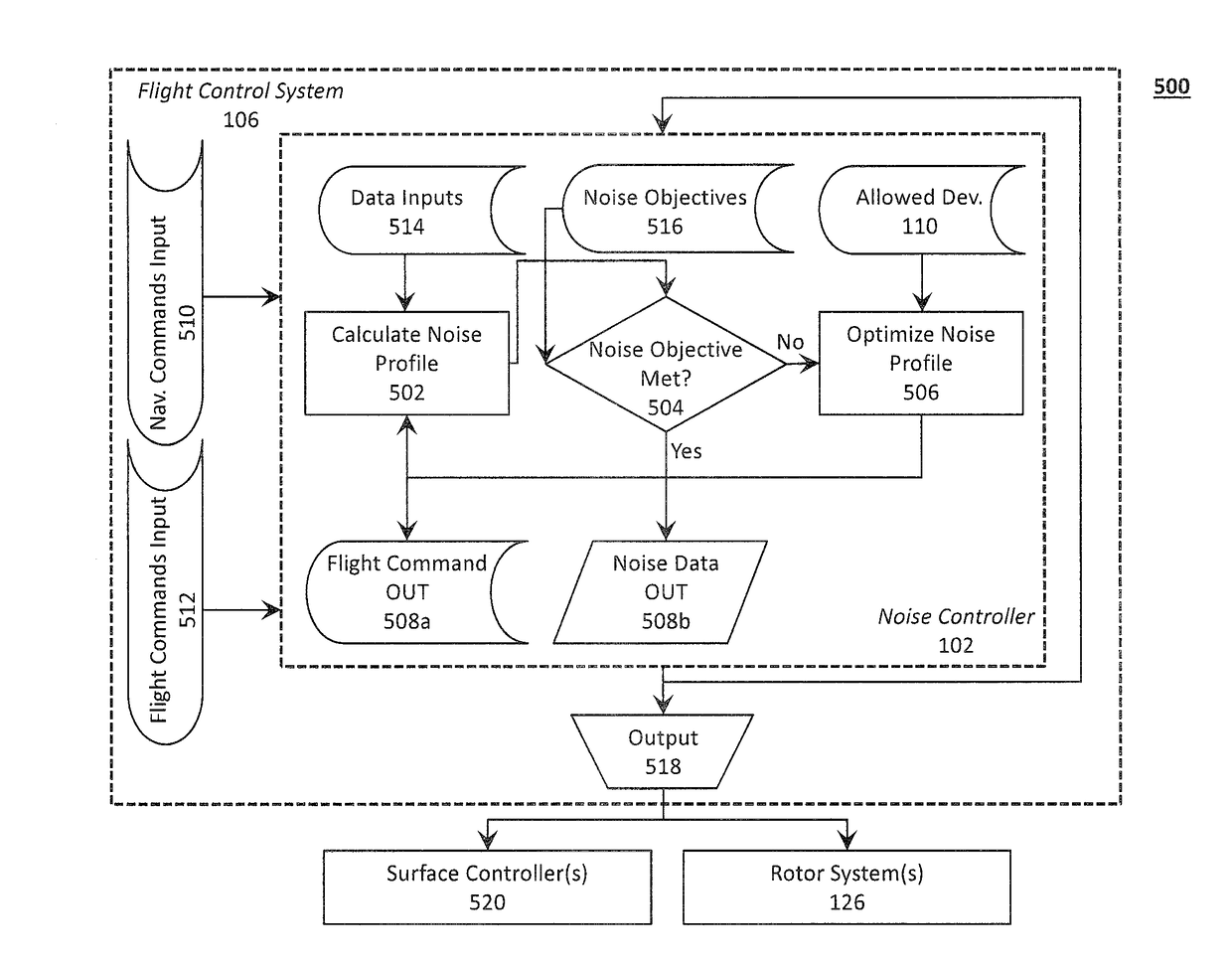
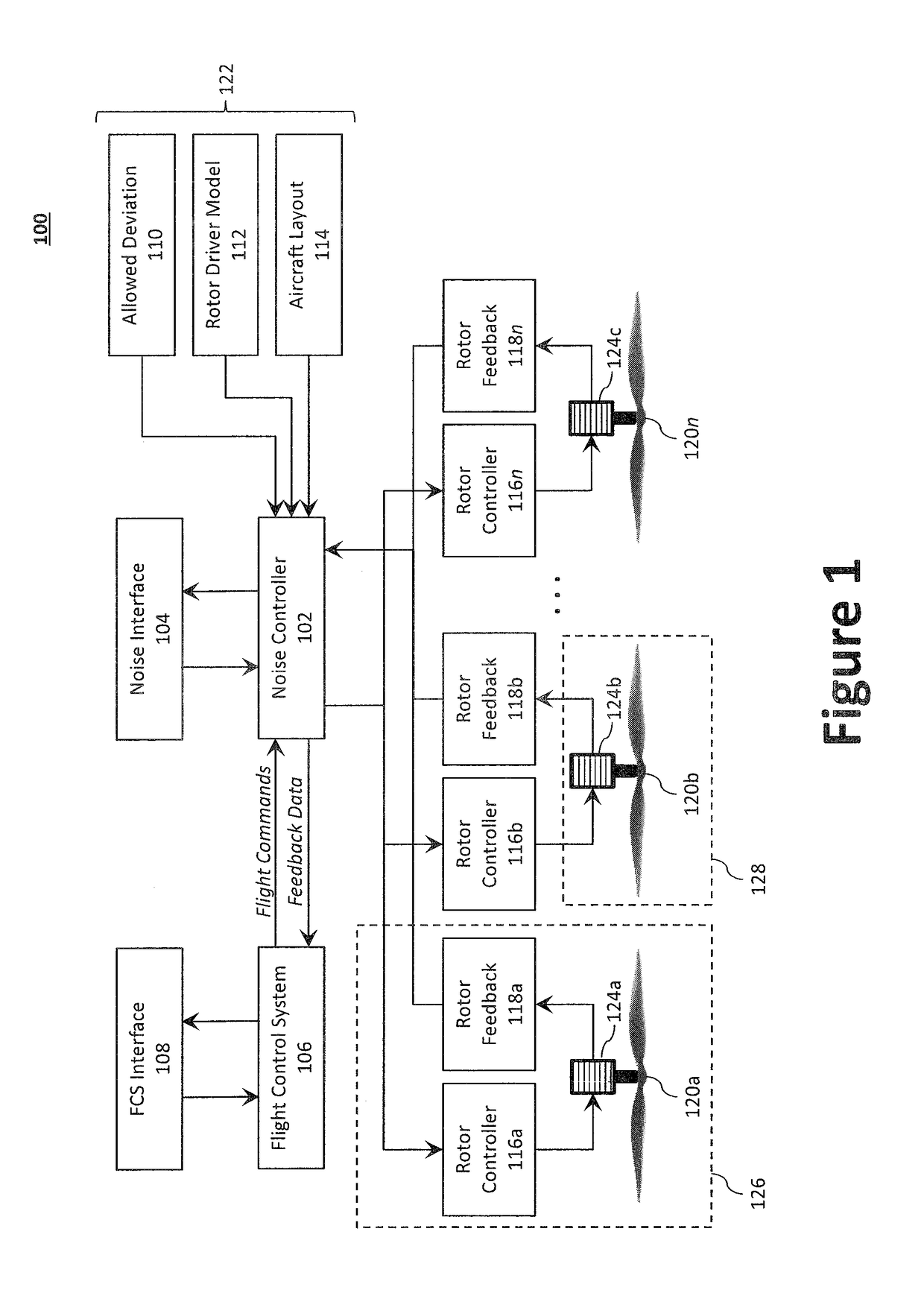
Systems and Methods for Acoustic Radiation Control
ActiveUS20180319491A1Diminishing detectabilityPropellersUnmanned aerial vehiclesAuditory radiationNoise control
Disclosed is a system for controlling acoustic radiation from an aircraft. The system comprising a plurality of rotor systems (one or more) and a noise controller configured to regulate acoustic radiation from the plurality of rotor systems. The noise controller can be configured to regulate a commanded flight setting from the flight control system and to output a regulated flight setting to the plurality of rotor systems. Based on the regulated flight setting, the plurality of rotor systems are configured to generate, individually and in aggregate, acoustic radiation having a target acoustic behavior. The target acoustic behavior may be achieved using beamforming techniques to, for example, change the directionality of acoustic radiation from the plurality of rotor systems, or otherwise tune the acoustic radiation to reduce detectability and / or annoyance.
Owner:AURORA FLIGHT SCI CORP
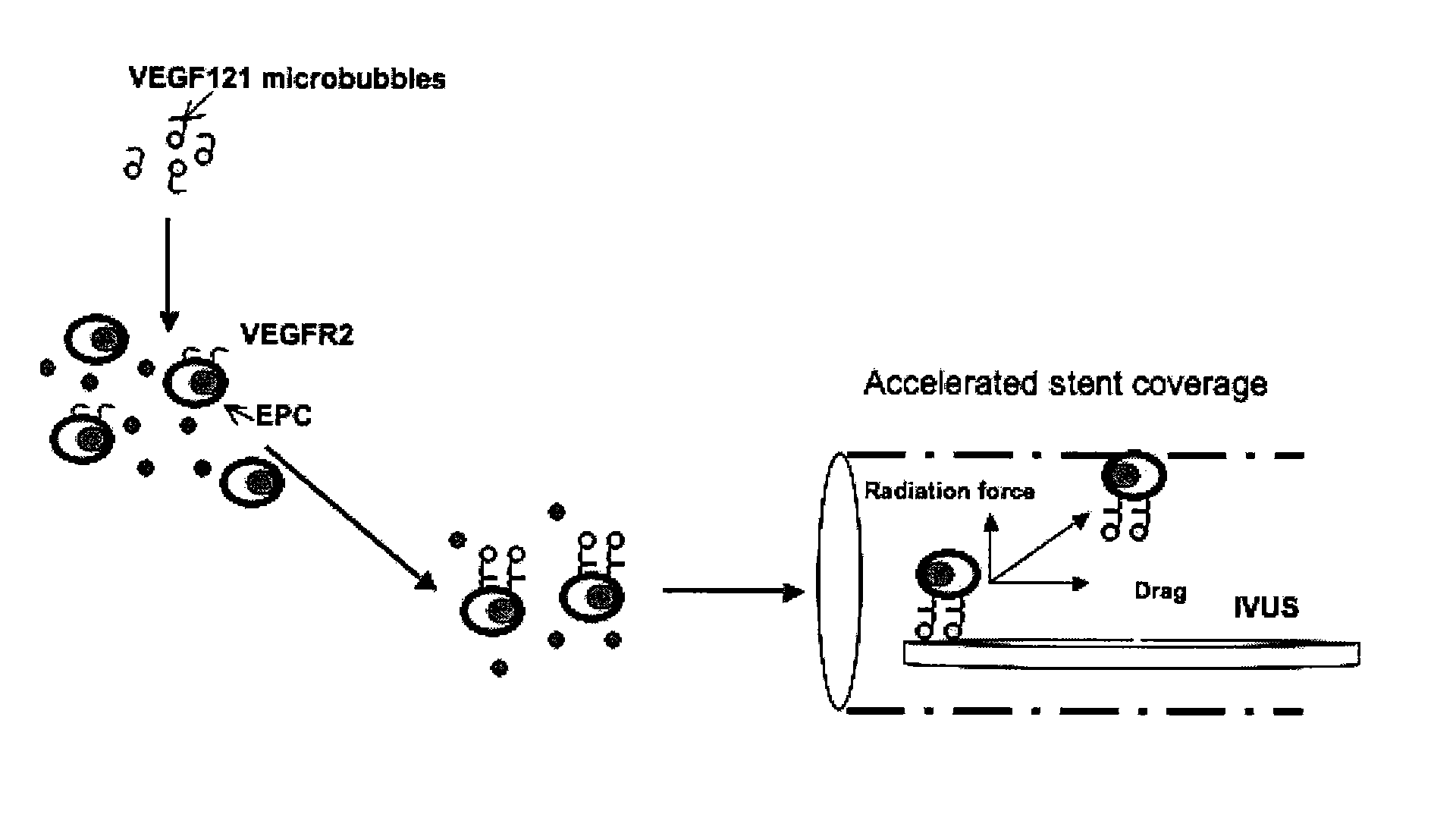
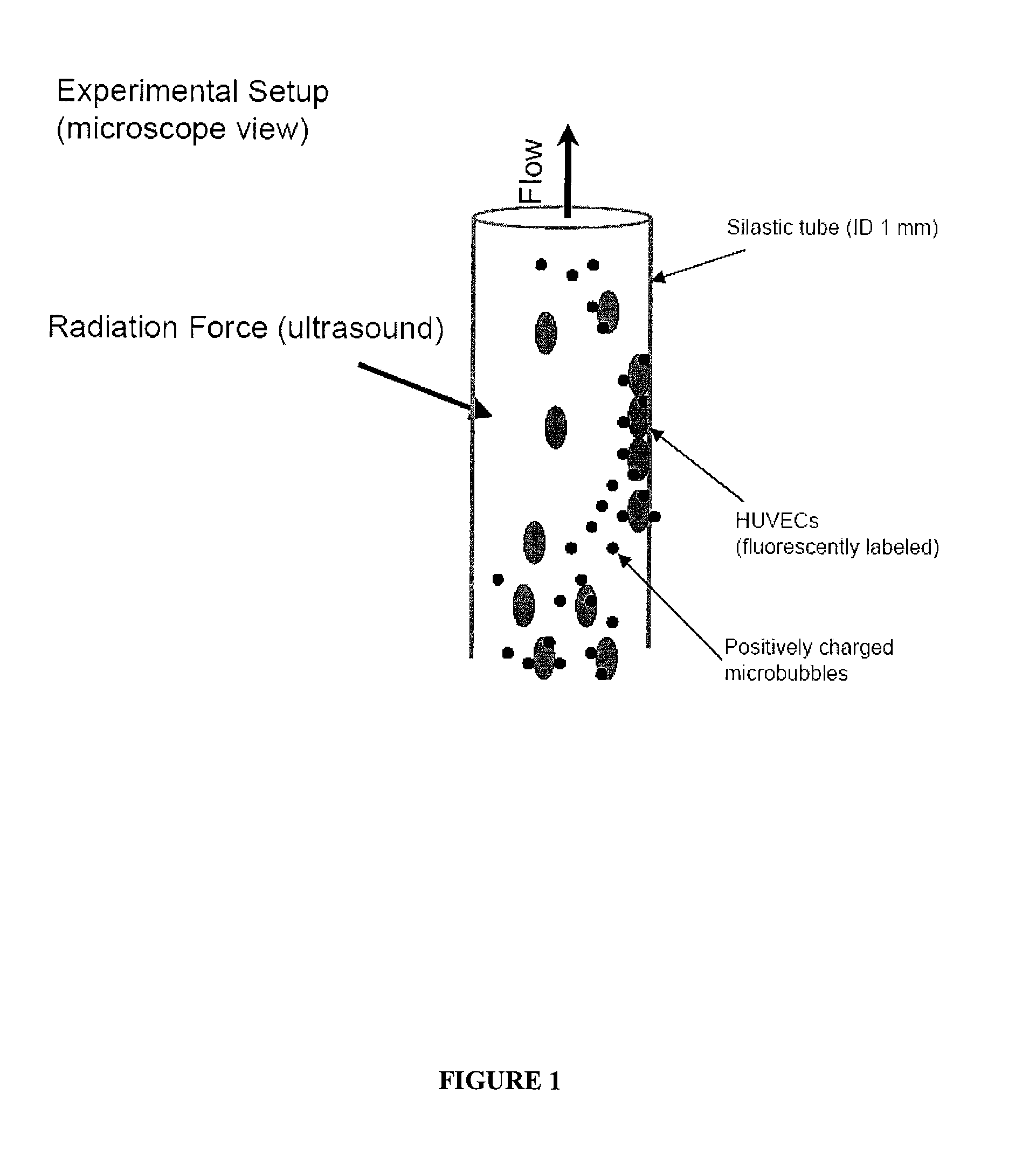
Directed Cell-Based Therapy Using Microbubble Tagged Cells
ActiveUS20110208113A1Promote tissue growthImprove satisfactionBiocideUltrasound therapyAuditory radiationProgenitor
The disclosed technology describes compositions and methods useful for providing cell based therapy. For example, one embodiment of cell based therapy involves the regeneration of injured tissue and / or promoting wound healing. Certain embodiments provide improved therapeutic compositions using microbubbles by delivering biological progenitor cells to the injured tissues. The administration of the microbubbles is directed by acoustic radiation forces that interact with embodiments of microbubbles comprising an acoustically active gas. As such, a high efficiency of progenitor cell delivery to injured tissue is realized. One advantage of this technique over targeted delivery of pharmaceutical compounds, is that the delivered progenitors cells may be derived from the patient (i.e., personalized therapy), thereby avoiding side effects, allergic reactions, and overall problems associated with refractive drug responses.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
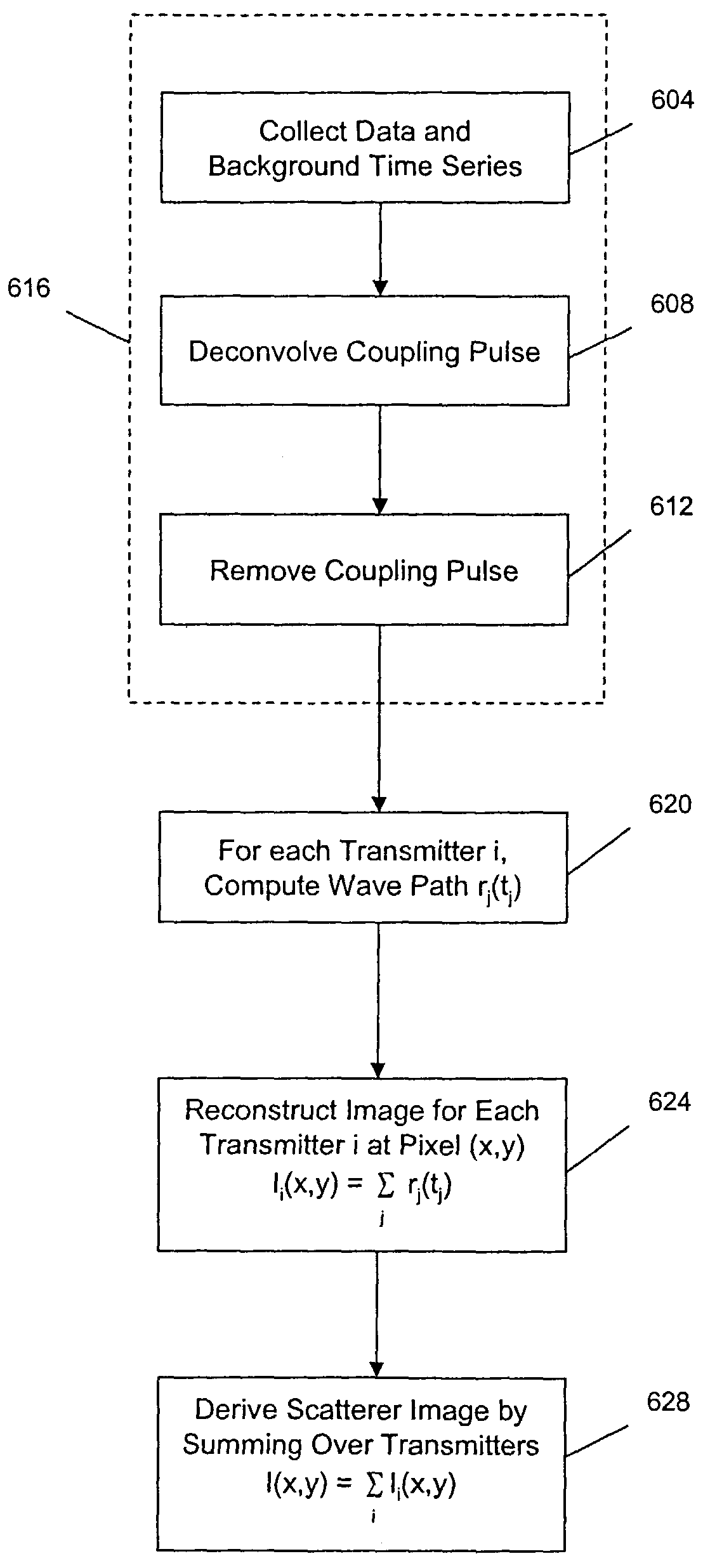
Reconstruction of transient acoustic radiation from a finite object subject to arbitrarily time-dependent excitation
ActiveUS20050150299A1Vibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAcoustic radiationTime domain
General algorithms are developed for reconstructing the acoustic field generated by an arbitrary object subject to an arbitrarily time-dependent excitation. These algorithms enable one to visualize a time-domain acoustic pressure wave as it travels through three-dimensional space. Such a tool can be used to diagnose general noise sources and transmission since in engineering applications most structures are subject to arbitrarily time-dependent excitations. To facilitate the derivations of the temporal solutions, we make use of Laplace transform and expand the acoustic pressure in terms of the spherical Hankel functions and the spherical harmonics. The expansion coefficients are settled by solving an over-determined system of equations obtained by matching the assumed-form solutions to the measured acoustic pressures. To obtain a general expression for a temporal kernel, we replace the spherical Hankel functions by polynomials in s, recast the infinite integral in the inverse Laplace transform as a contour integral in the complex s-plane, and evaluate it via residue theorem. Once this is done, the transient acoustic quantities anywhere including a source surface can be obtained by convoluting the temporal kernels with respect to measured acoustic pressures.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
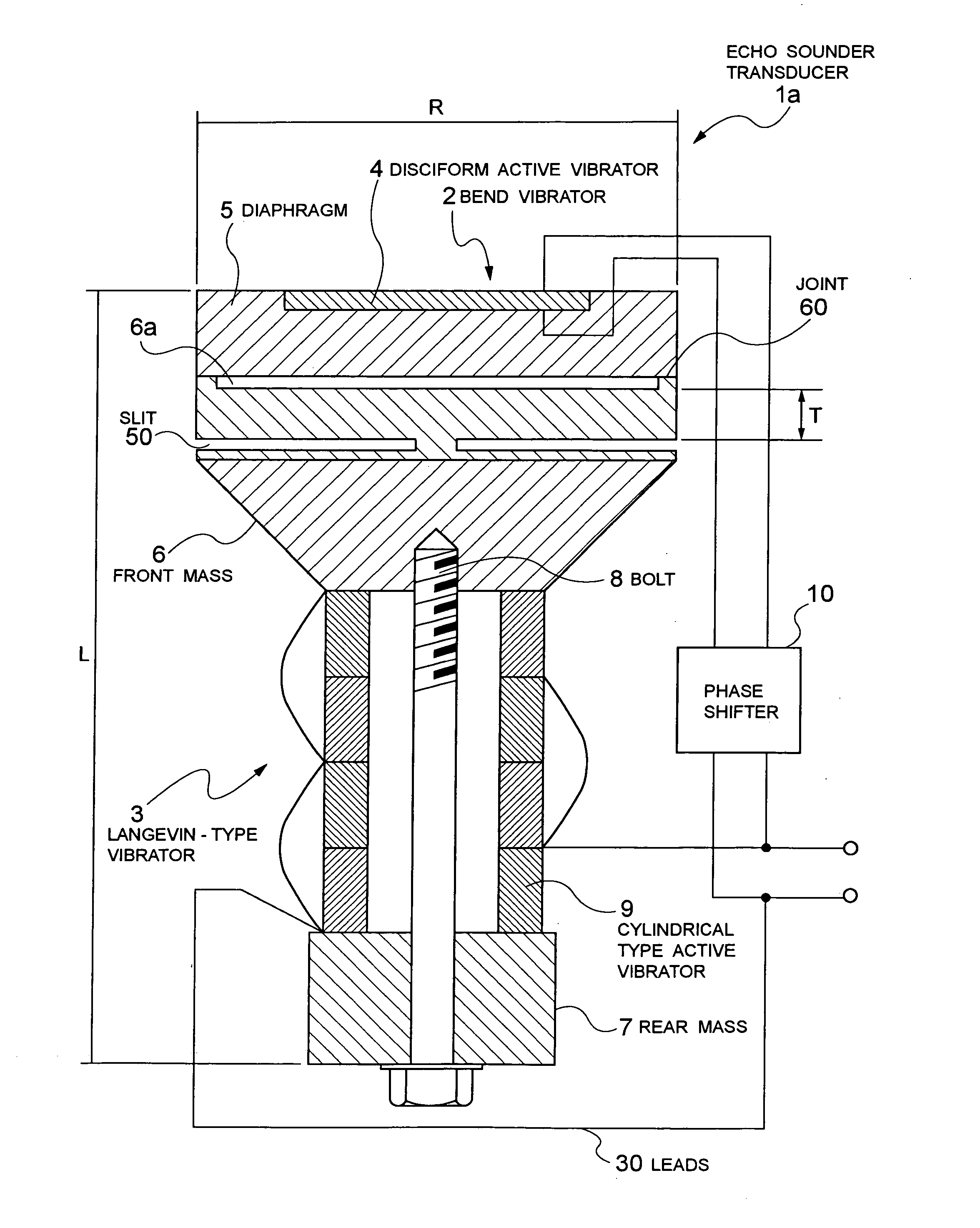
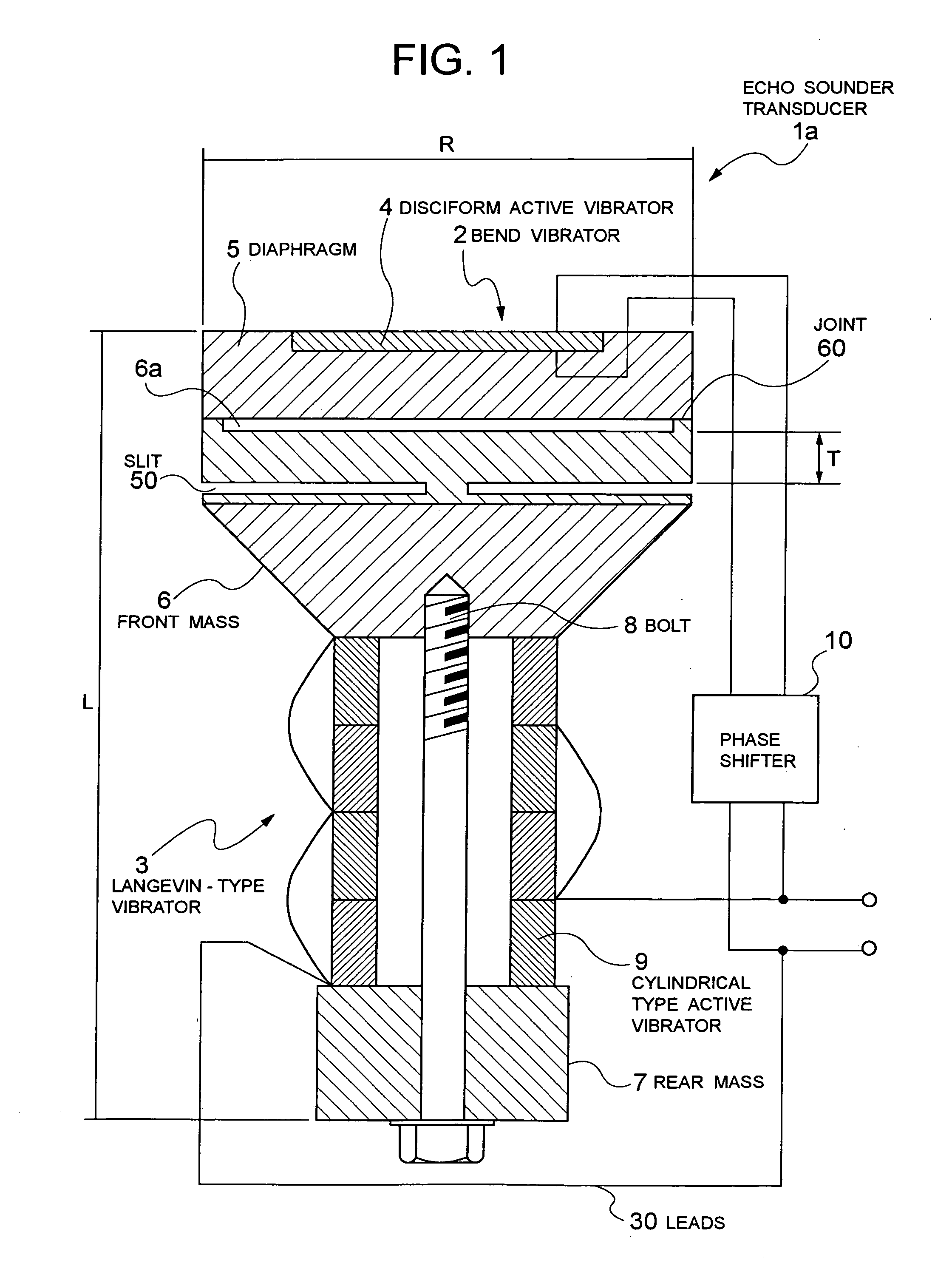
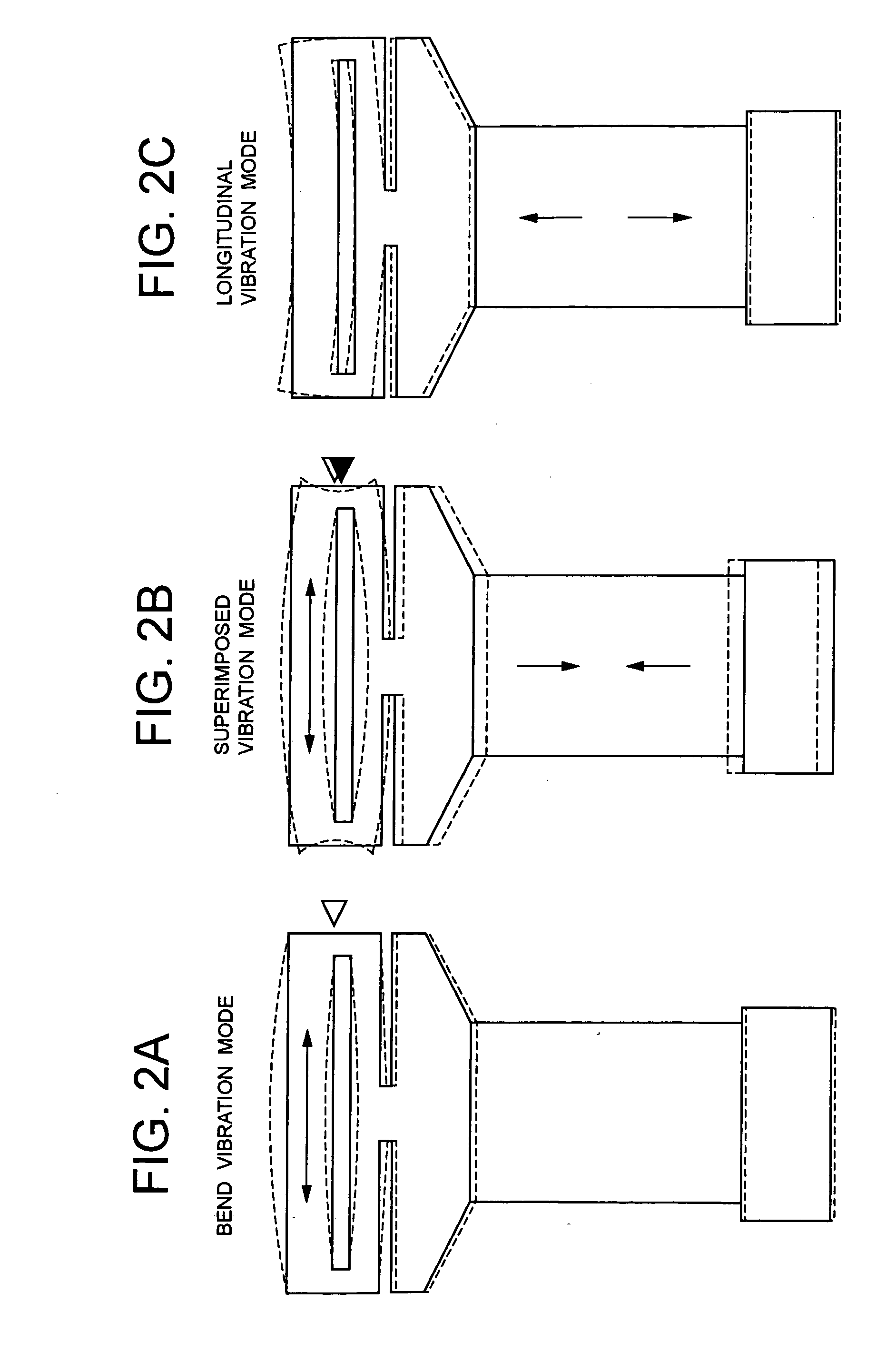
Echo sounder transducer
ActiveUS20060001334A1Increase the frequency bandIncrease the sound pressure levelPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive resonant transducersAuditory radiationTransducer
The present invention achieves the wideband operation of a bolted Langevin-type echo sounder transducer by enabling low frequency operation with securing a sound pressure level above a certain level without changing the external dimensions of the echo sounder transducer. This is an echo sounder transducer includes a Langevin-type vibrator having a front mass and a rear mass, and a cylindrical active vibrator which is sandwiched between the front mass and rear mass, a bend vibrator constituted of a diaphragm arranged in an acoustic radiation surface section of the front mass of the Langevin-type vibrator, and a disc type active vibrator fixed to the diaphragm. This has such structure that a slit, communicating from an outer peripheral side face toward an axial center, is provided on the circumference in the side of the lower portion of the front mass of the Langevin-type vibrator toward the rear mass.
Owner:NEC CORP
Acoustic wave guidance in a vehicle
InactiveUS20060056650A1Reduce resonance effectAdequate shockVehicle seatsLoudspeaker screensAuditory radiationSound sources
The aim of the invention is to ensure the same high quality of acoustic radiation from audio systems on each seat of current vehicles. Said aim is achieved by a novel acoustic device for generating audio signals, which allows sound sources to be integrated into the area located near the headrest of a vehicle seat such that the volume can be regulated in an individual manner without unduly disturbing the other passengers in a vehicle, who hear the audio signals to a significantly reduced extent. The headrest does not comprise any loudspeakers, thus offering good creative possibilities regarding accident protection and design. The acoustic near field at the headrest is generated by means of a sound line. The loudspeaker is disposed inside the backrest or under the seat, for example, while the sound line terminates in the headrest. Tuned pipes, the end of which is adjusted to the acoustic impedance of the clearance zone, are used as a sound line.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
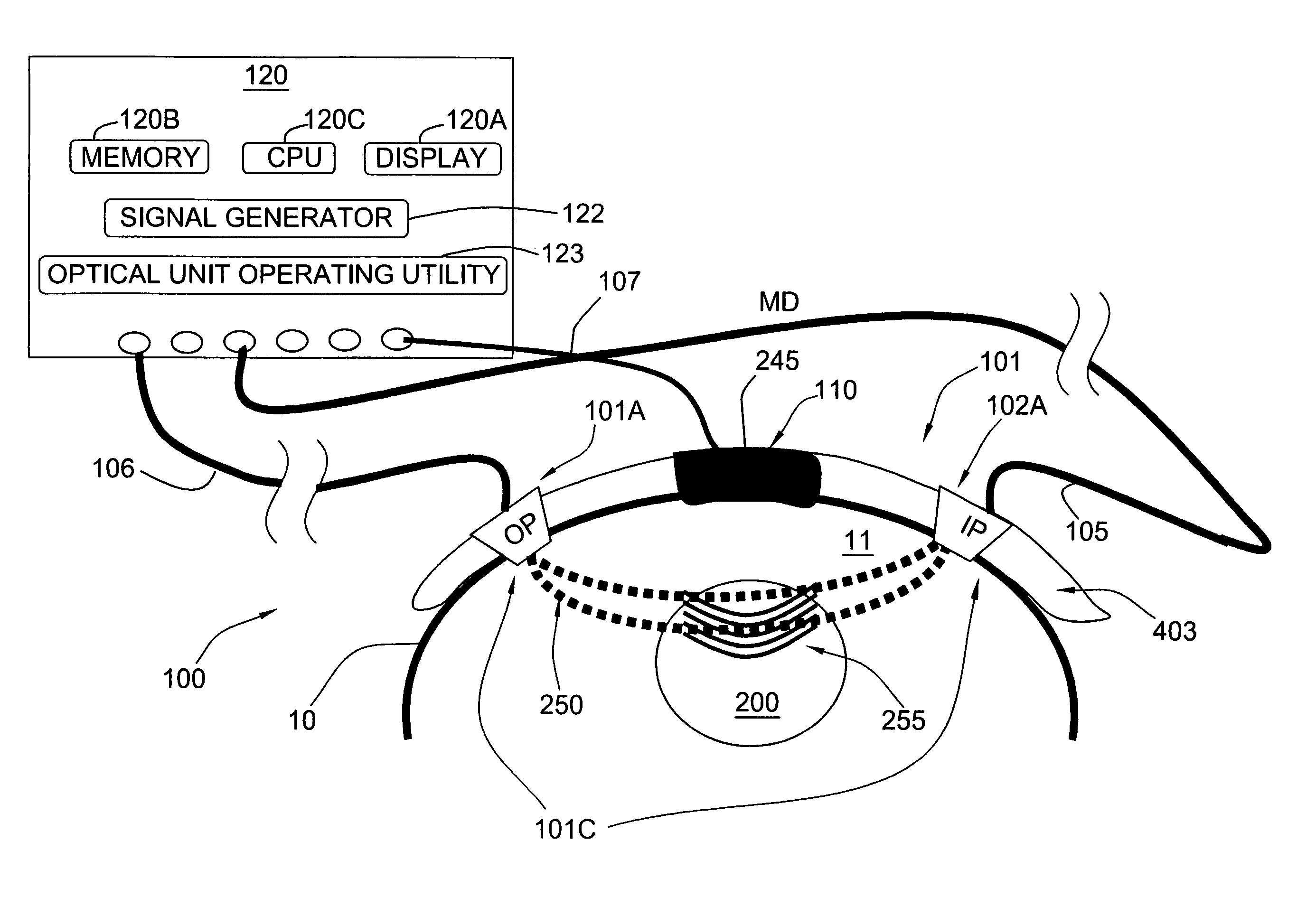
Medical ultrasound device with force detection
ActiveUS20120165669A1Minimal space requirementMitigate, alleviate or eliminate oneUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasonographyAuditory radiation
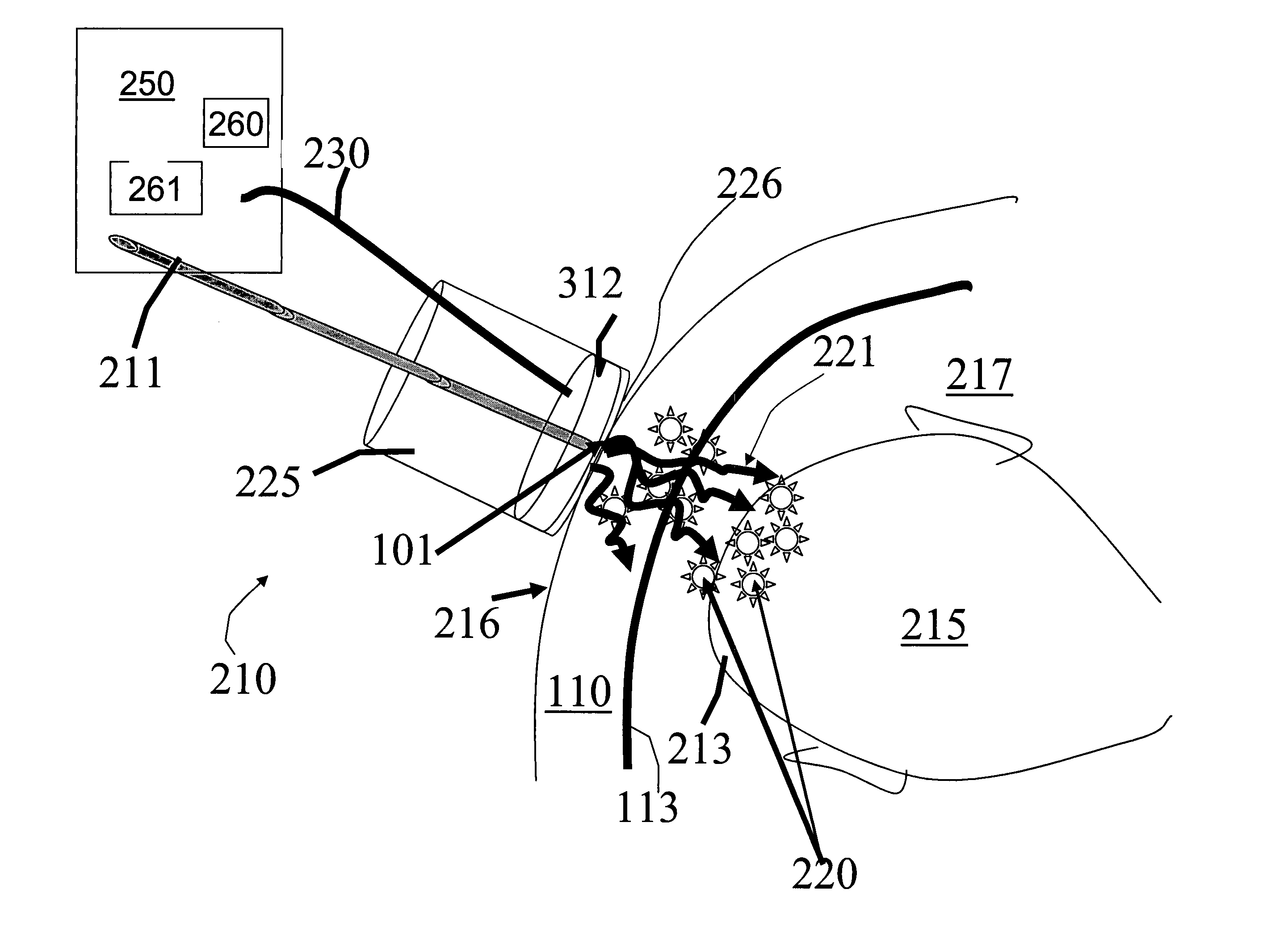
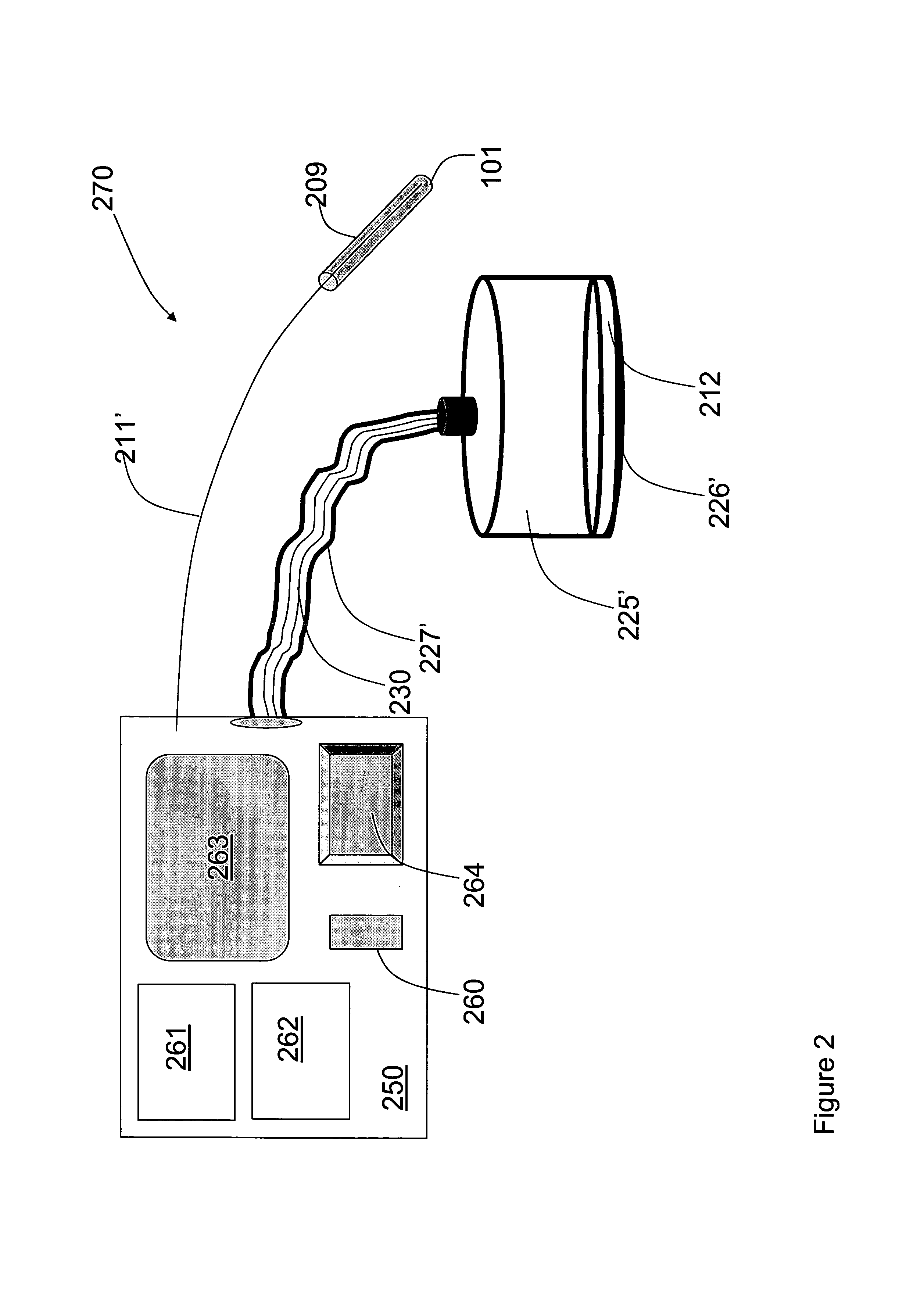
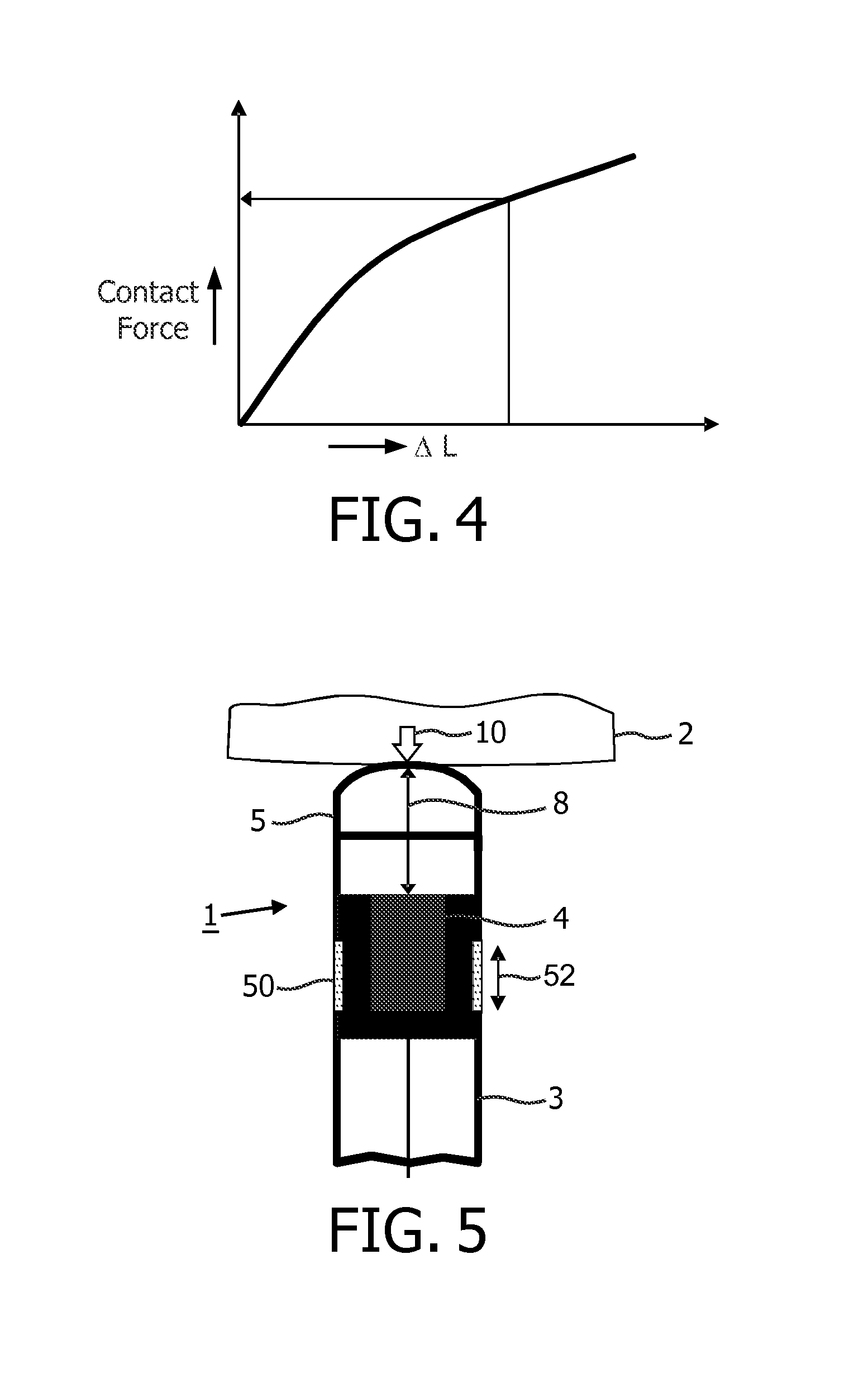
A medical ultrasound device is disclosed. The device comprises an elongated body having a proximal end and a distal end region (1). One or more ultrasound transducers (4) for generating acoustic radiation are positioned in the distal end region, inside the elongated body. A transmission element (5) which is substantially transparent to acoustic radiation is positioned in the radiation path of the acoustic radiation, and a controller unit is operatively connected to the ultrasound transducer. The transmission element and the one or more ultrasound transducers are mounted so that an acoustic path length (8) between the transmission element (5) and the ultrasound transducer (4) varies with contact force (10) imposed to the distal end region. The controller unit detects the acoustic path length between the ultrasound transducer and the transmission element and determines the contact force from the detected acoustic path length. In an embodiment, the medical device is an ultrasound RF ablation catheter.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Piezoelectric underwater sound transducer acoustic radiation mode measurement method and system
InactiveCN103743469AAddressed issue where reconstruction accuracy was often much lower than acoustic pressure reconstruction accuracyPrevent leakageSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementAuditory radiationSound pressure
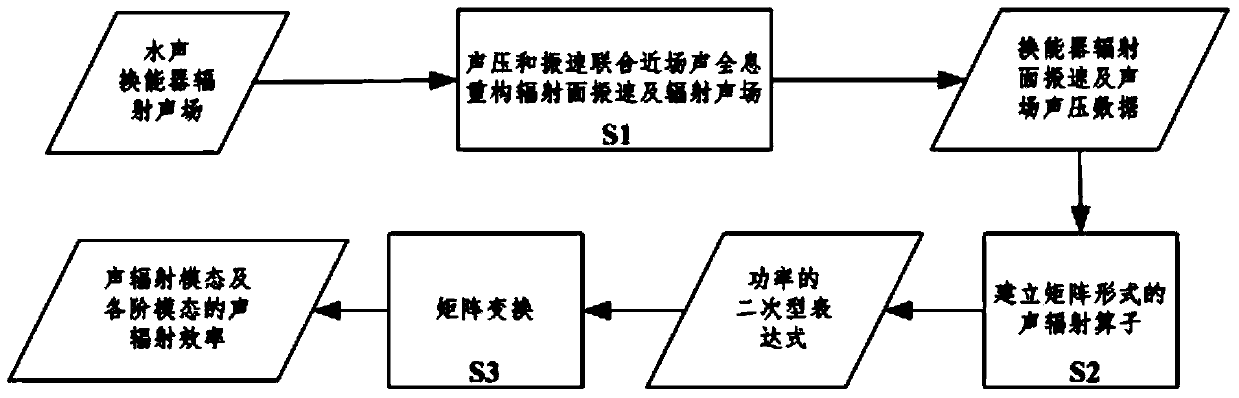
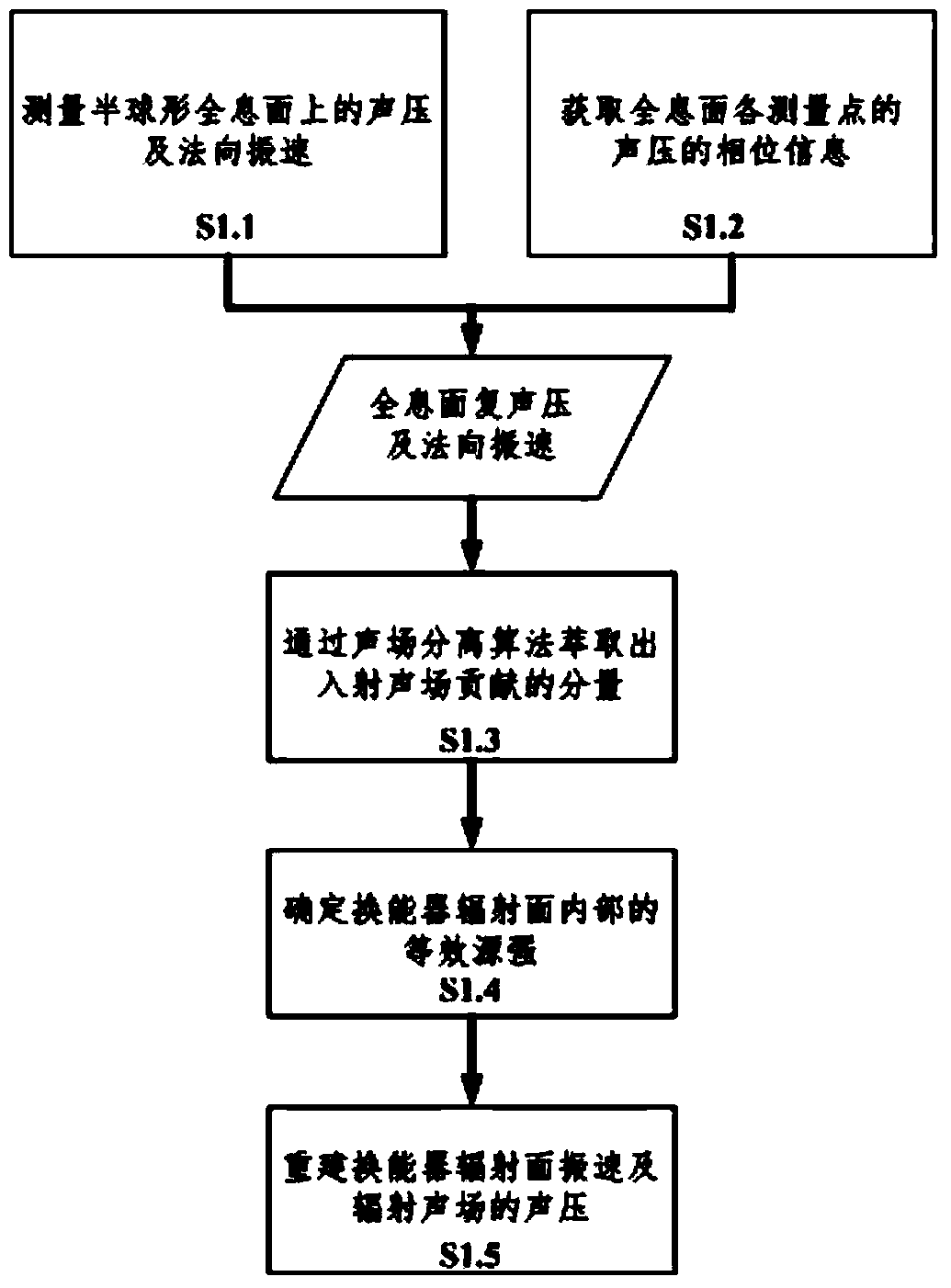
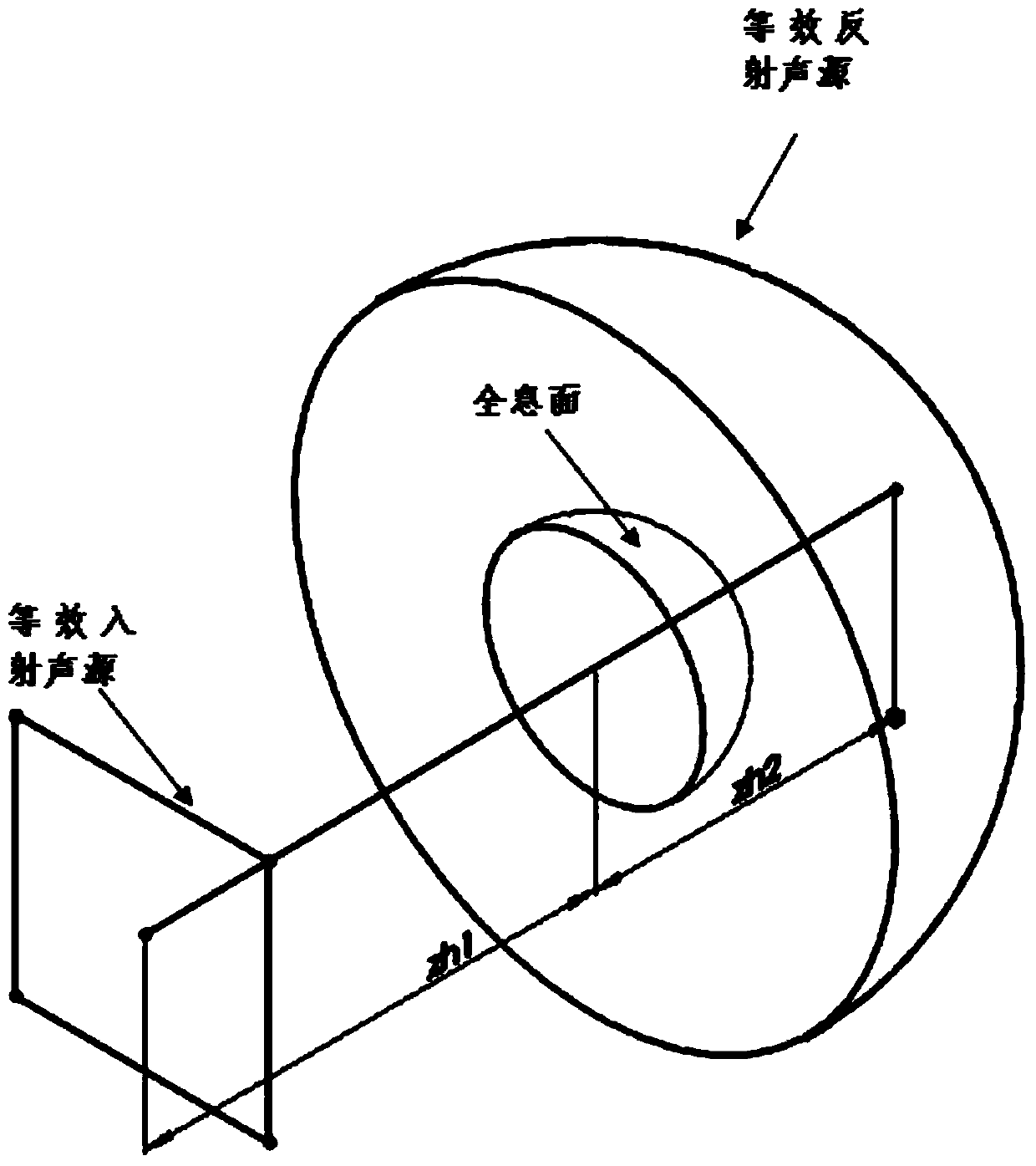
The invention provides a piezoelectric underwater sound transducer acoustic radiation mode measurement method and system based on combination near-field acoustical holography. In the method, the combination near-field acoustical holography is utilized to reestablish sound field, sound pressure and radiation surface vibration velocity; on the basis of an acoustic radiation operator matrix obtained based on measurement data and with the sound field radiation theory being combined, the acoustic radiation power of a piezoelectric underwater sound transducer is expressed to be a positive definite quadric form; and positive definite and conjugate performance of the matrix are utilized to obtained an acoustic radiation mode of the structure. The system comprises a glass water tank, an industrial control computer with PXI bus, a transducer excitation module based on the PXI bus, a sound pressure and vibration velocity acquisition module and a three-dimensional motion platform. The method and system in the invention break the limitation that acoustic radiation mode in the current complex underwater structure can only be solved numerically, provide a new idea for research on the piezoelectric underwater sound transducer, and also provide basis for structure optimization of the piezoelectric underwater sound transducer.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
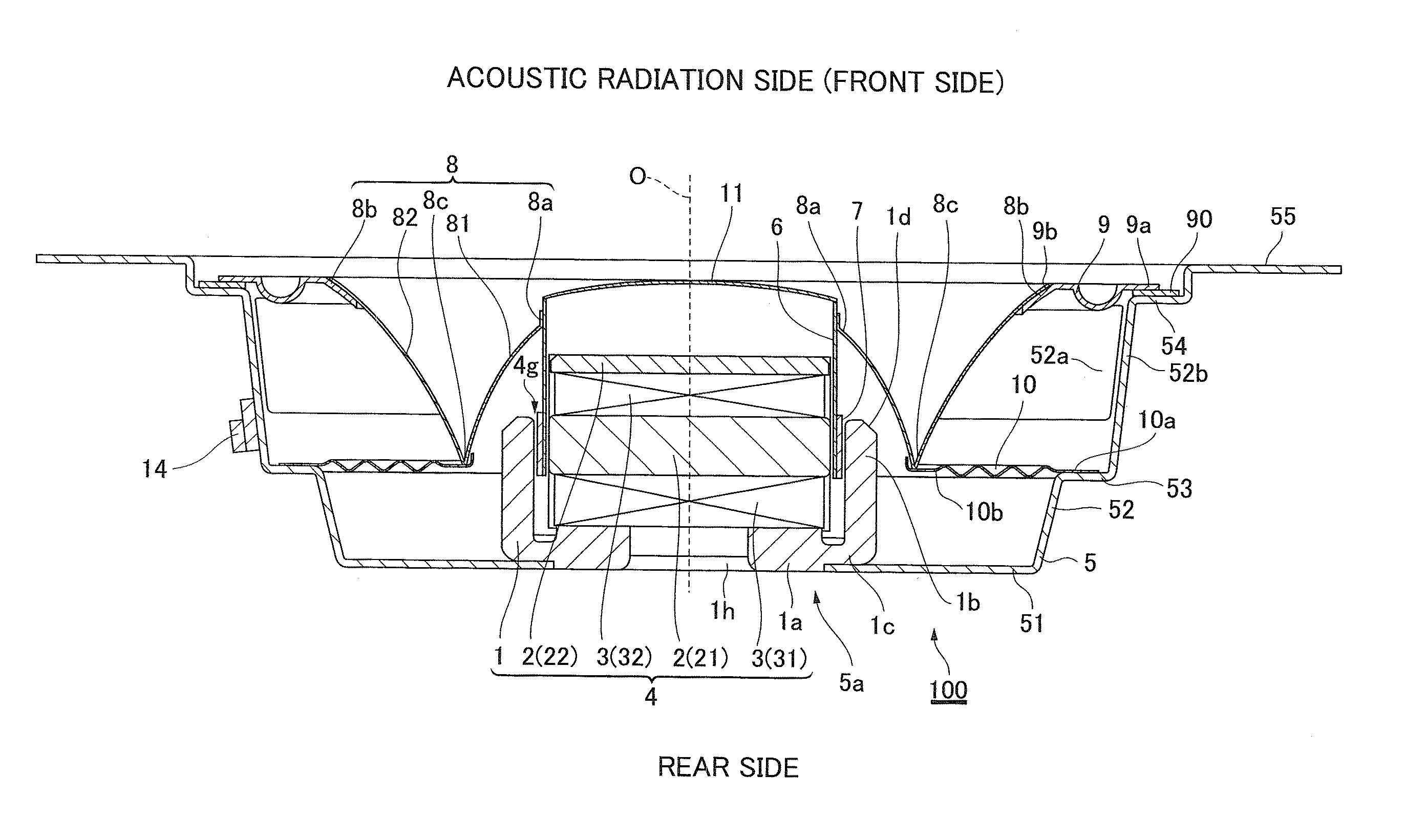
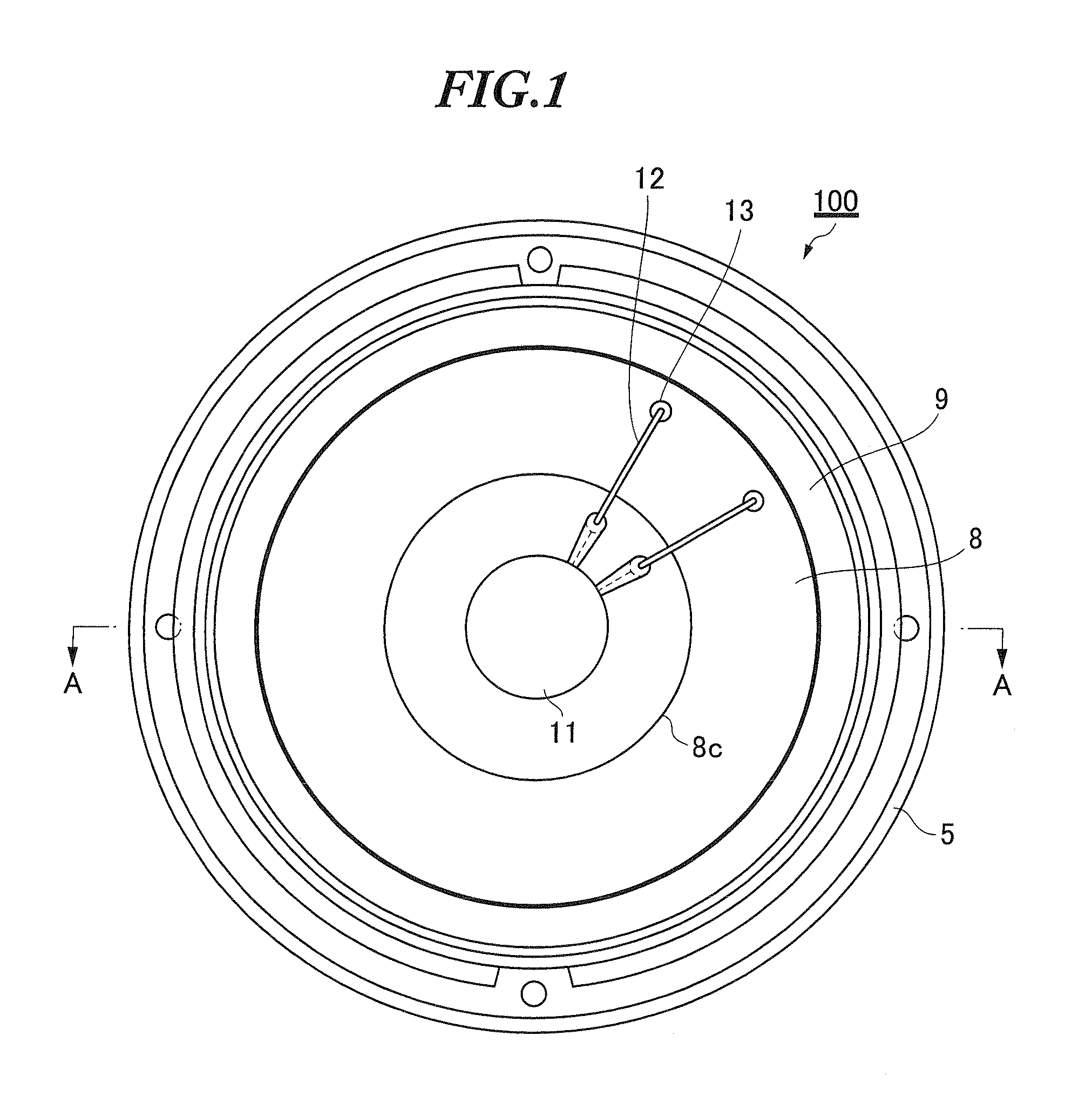
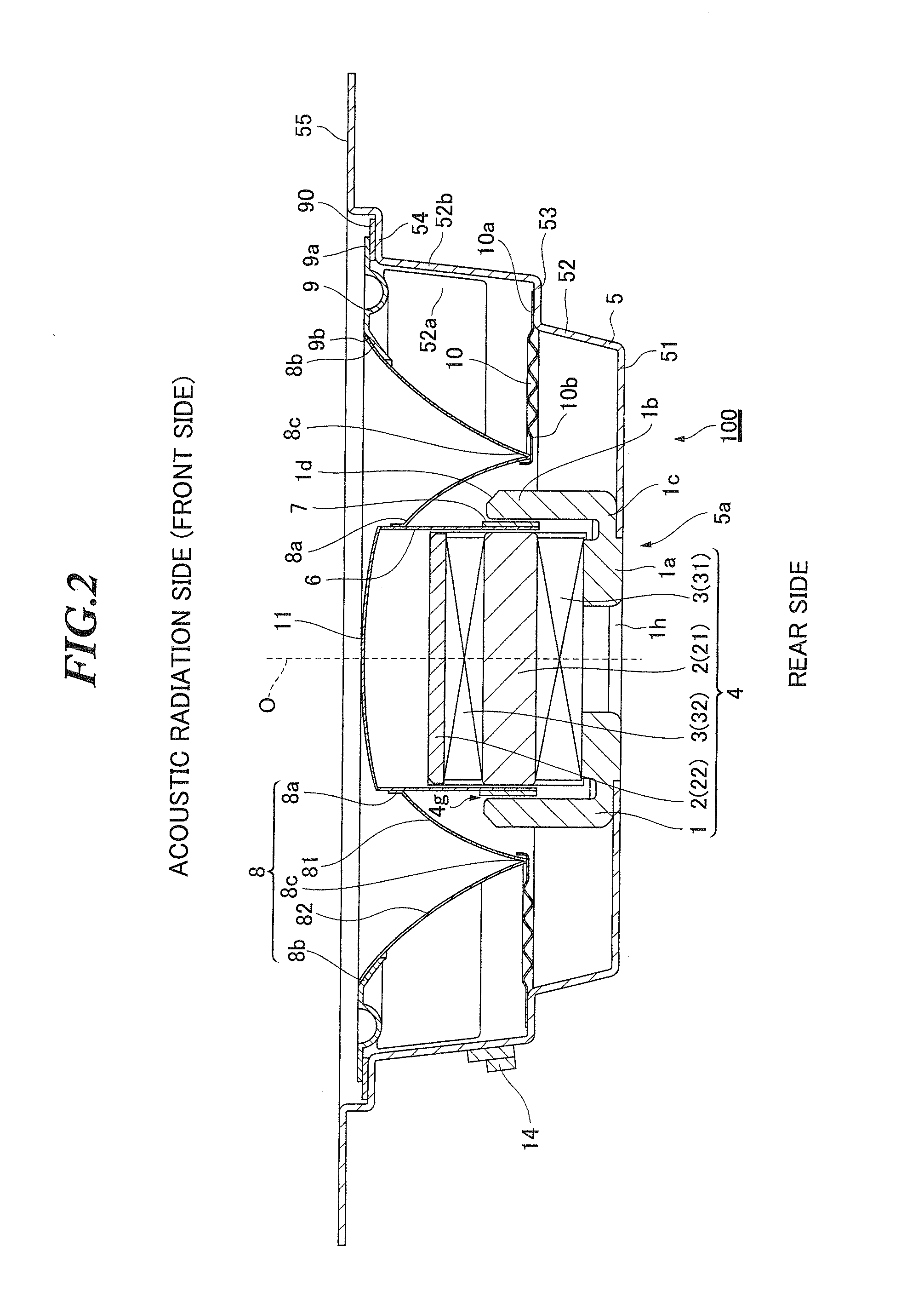
Speaker device
InactiveUS20100208934A1Quality improvementHigh-quality reproductionNon-planar diaphragms/conesTransducer circuitsBobbinEngineering
Owner:PIONEER CORP +1
Noninvasive measurements in a human body
InactiveUS8423116B2Easy to measureEasy to operateBlood flow measurement devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringHuman bodyAuditory radiation
A measurement system and method are presented for use for non-invasive measurements in a human body. Acoustic radiation is applied to a certain illuminated region in the body, with at least two different conditions of the applied radiation achievable by varying at least one characteristic of the acoustic radiation. Light scattered from the body part is detected, and measured data indicative of detected photons tagged and untagged by the acoustic radiation is generated. The measured data is analyzed to extract therefrom a data portion corresponding to the tagged photons and being therefore associated with a light response of said certain region, thereby enabling determination of tissue properties of said certain region based on a relation between the measured data portions corresponding to the at least two different operating conditions.
Owner:OR NIM MEDICAL
Method and apparatus for combined diagnostic and therapeutic ultrasound system incorporating noninvasive thermometry, ablation control and automation
A method for treating a medical pathology includes receiving a first set of acoustic radiation scattered by a volume of tissue containing at least a portion of the medical pathology and thereafter, changing a temperature of the volume of tissue. The method also includes thereafter, receiving a second set of acoustic radiation scattered by the volume of tissue and localizing the portion of the medical pathology from the first and second sets of received acoustic radiation. Localizing the portion of the medical pathology comprises identifying the medical pathology from differences in the first and second sets of received acoustic radiation resulting from the change in temperature. The method also includes insonifying the portion of the medical pathology with sufficient energy to damage the portion of the medical pathology.
Owner:DELPHINUS MEDICAL TECH
Acoustic determination of properties of reservoirs and of fluids contained therein
InactiveUS20050092058A1Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSamplingAuditory radiationCoupling
The invention provides devices and methods for acoustically determining the properties of the contents of one or more reservoirs in a plurality of reservoirs. Each reservoir is adapted to contain a fluid. An acoustic radiation generator can be positioned in acoustic coupling relationship to each of the reservoirs. Acoustic radiation generated by the acoustic radiation generator is transmitted through each reservoir to an analyzer. The analyzer is capable of analyzing a characteristic of the transmitted acoustic radiation and optionally correlating the characteristic to a property of the reservoirs' contents. Properties that may be determined include volume, temperature, and composition. The invention is particularly suited to determining the properties of the contents of a plurality of reservoirs to allow for accuracy and control over the dispensing of fluids therefrom.
Owner:LABCYTE
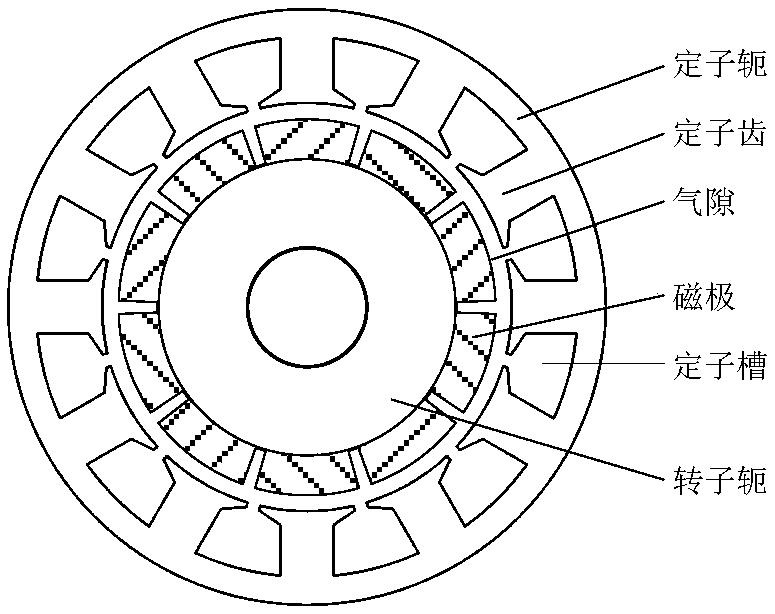
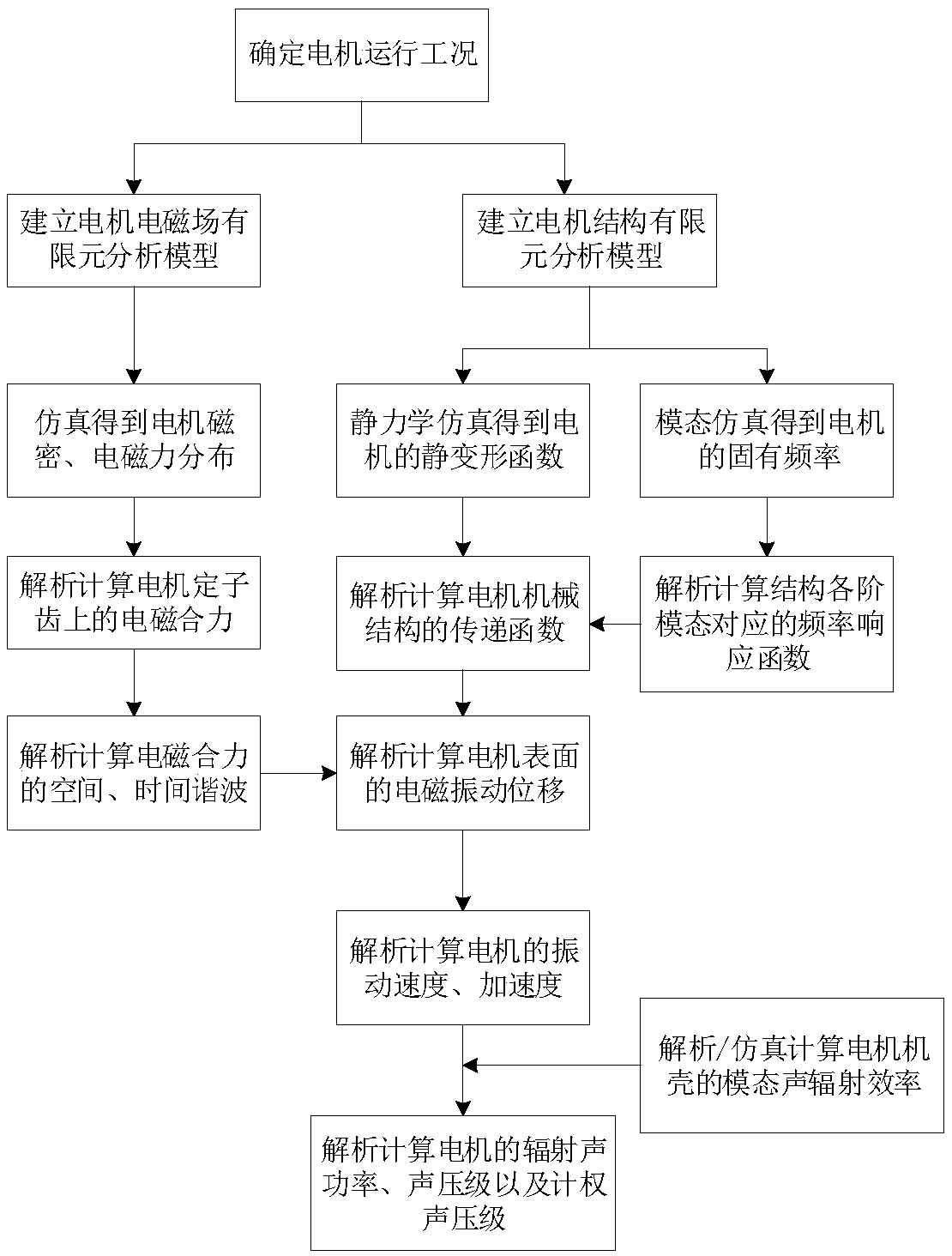
A calculation method of electromagnetic vibration noise of electric machine
ActiveCN109214125AHigh precisionImprove computing efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAuditory radiationFrequency response
The invention discloses a method for calculating the electromagnetic vibration noise of a motor, which comprises the following steps: calculating the distribution of the electromagnetic force densityof the motor according to the operation condition of the motor, and calculating the static deformation and the natural frequency of the motor respectively; according to the distribution of the electromagnetic force density, the electromagnetic resultant force on the stator teeth of the motor is calculated, and the time-space harmonic of the electromagnetic resultant force is calculated. The frequency response function of the motor structure corresponding to each vibration mode is calculated according to the natural frequencies of each vibration mode corresponding to each spatial order of the electromagnetic force, and the transfer function of the motor mechanical structure is calculated according to the static deformation function and the frequency response function. The vibration displacement of the motor surface is calculated according to the time-space harmonics and the transfer function. The modal acoustic radiation efficiency of the motor housing is obtained, and the electromagnetic vibration noise of the motor is calculated according to the modal acoustic radiation efficiency and vibration displacement. In the process of analyzing the vibration and noise of the motor, the invention ensures that the calculation accuracy meets the precision requirement, and reduces the calculation amount to avoid consuming a large amount of calculation resources.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com