Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1655 results about "Noise control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Noise control or noise mitigation is a set of strategies to reduce noise pollution or to reduce the impact of that noise, whether outdoors or indoors.
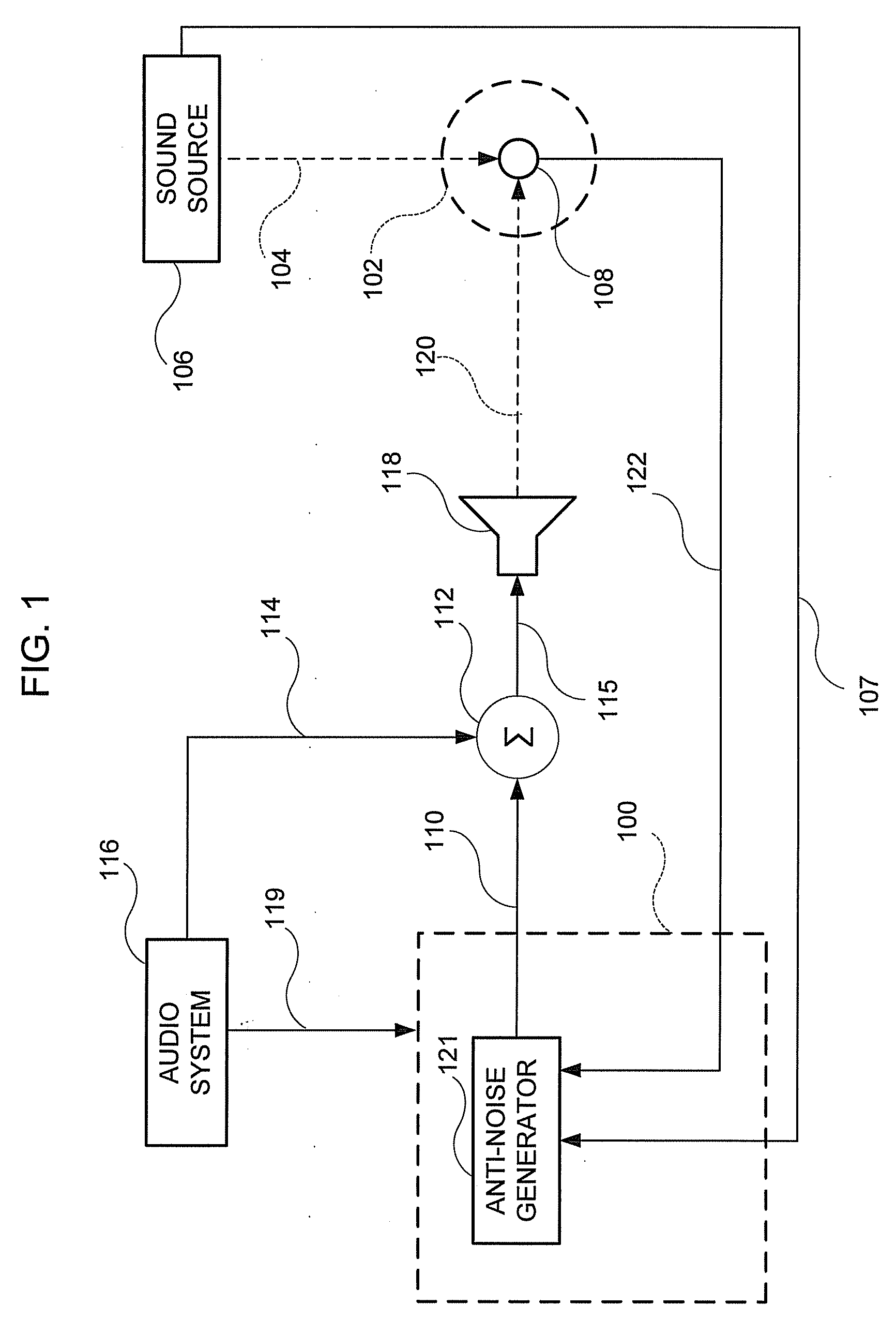
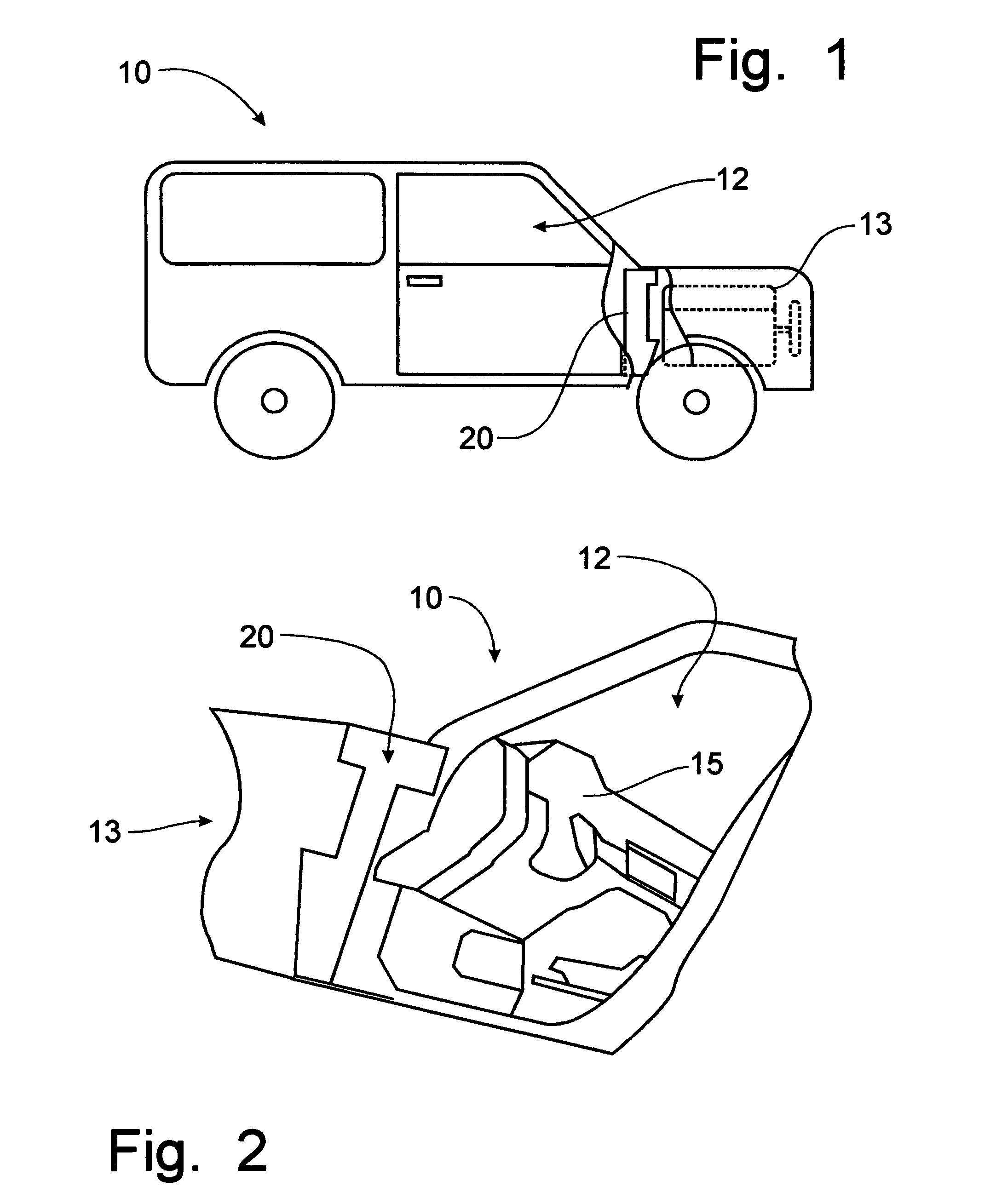
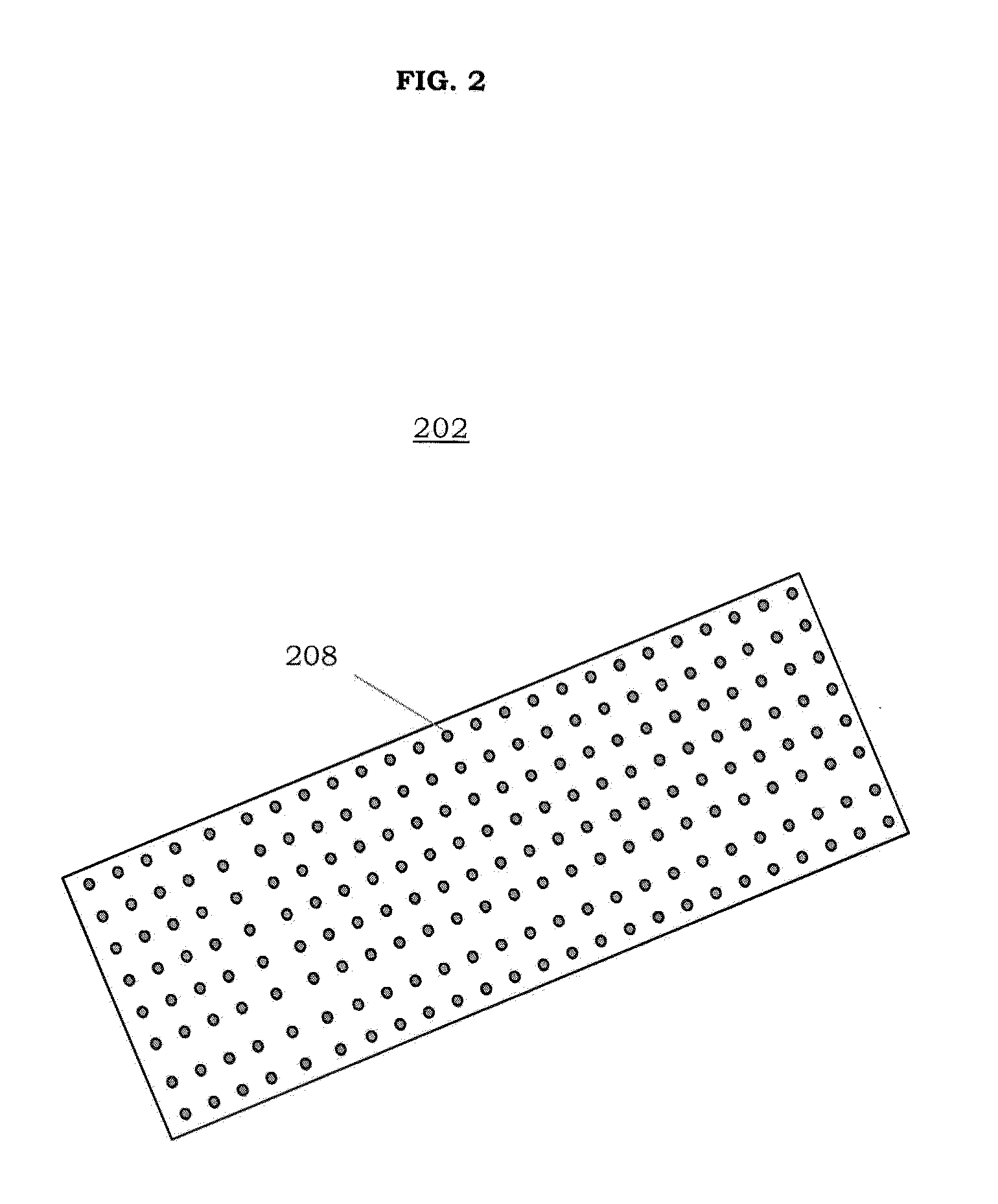
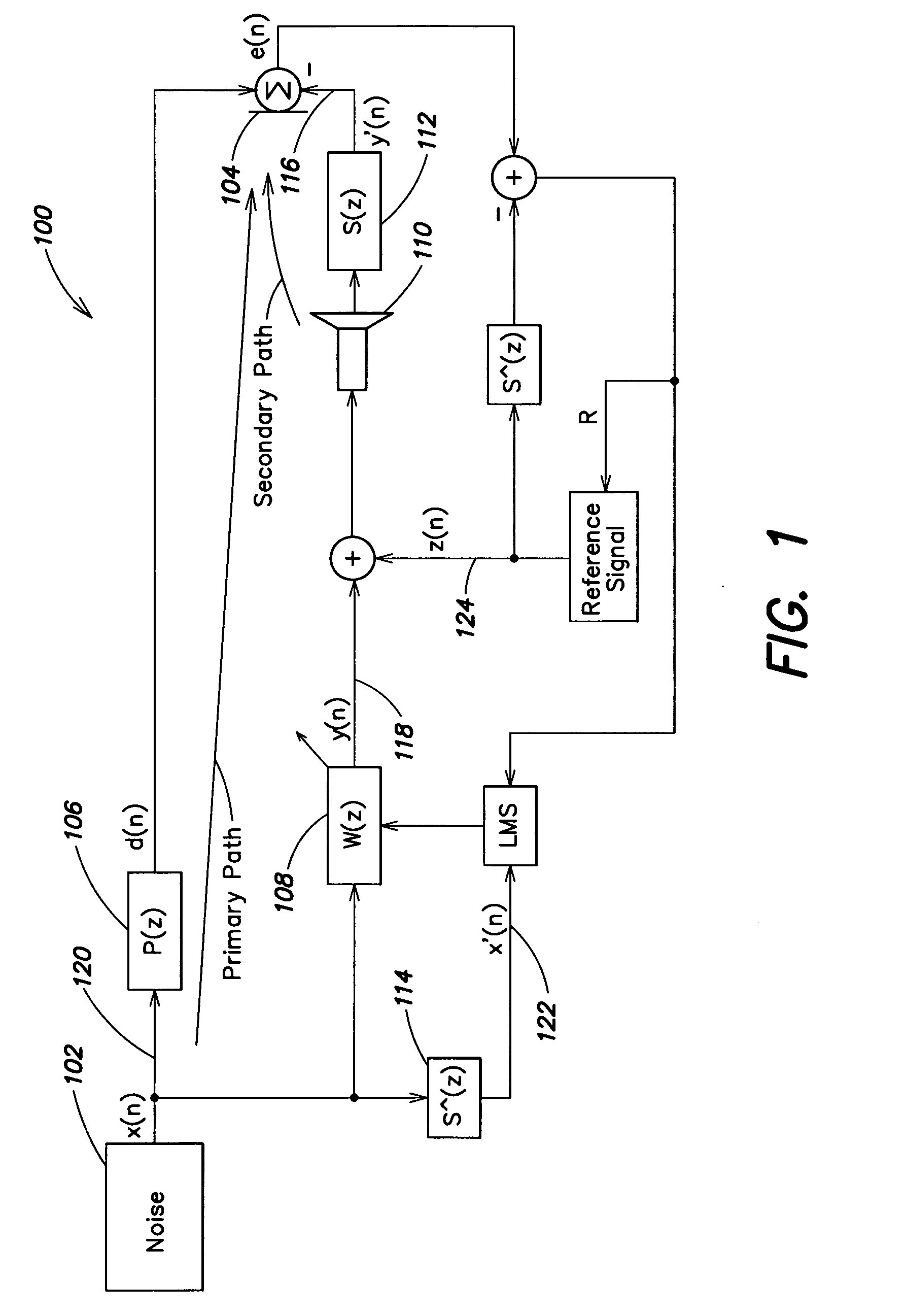
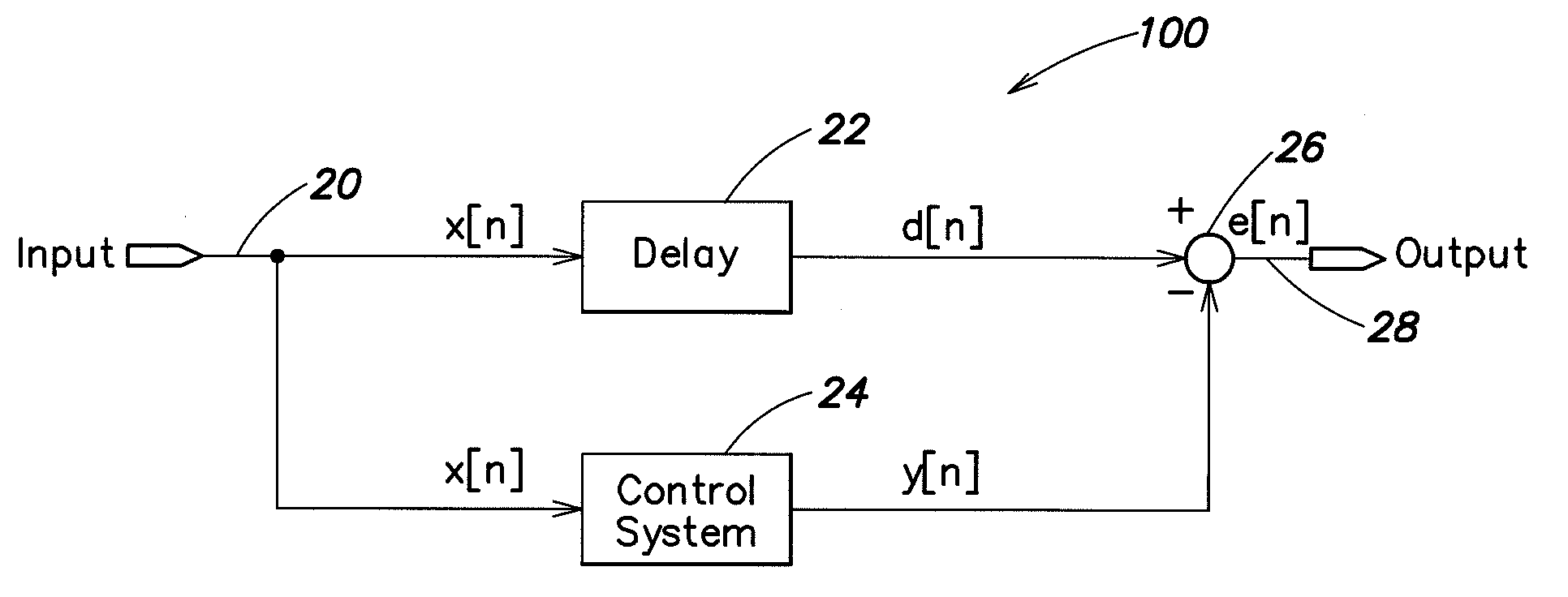
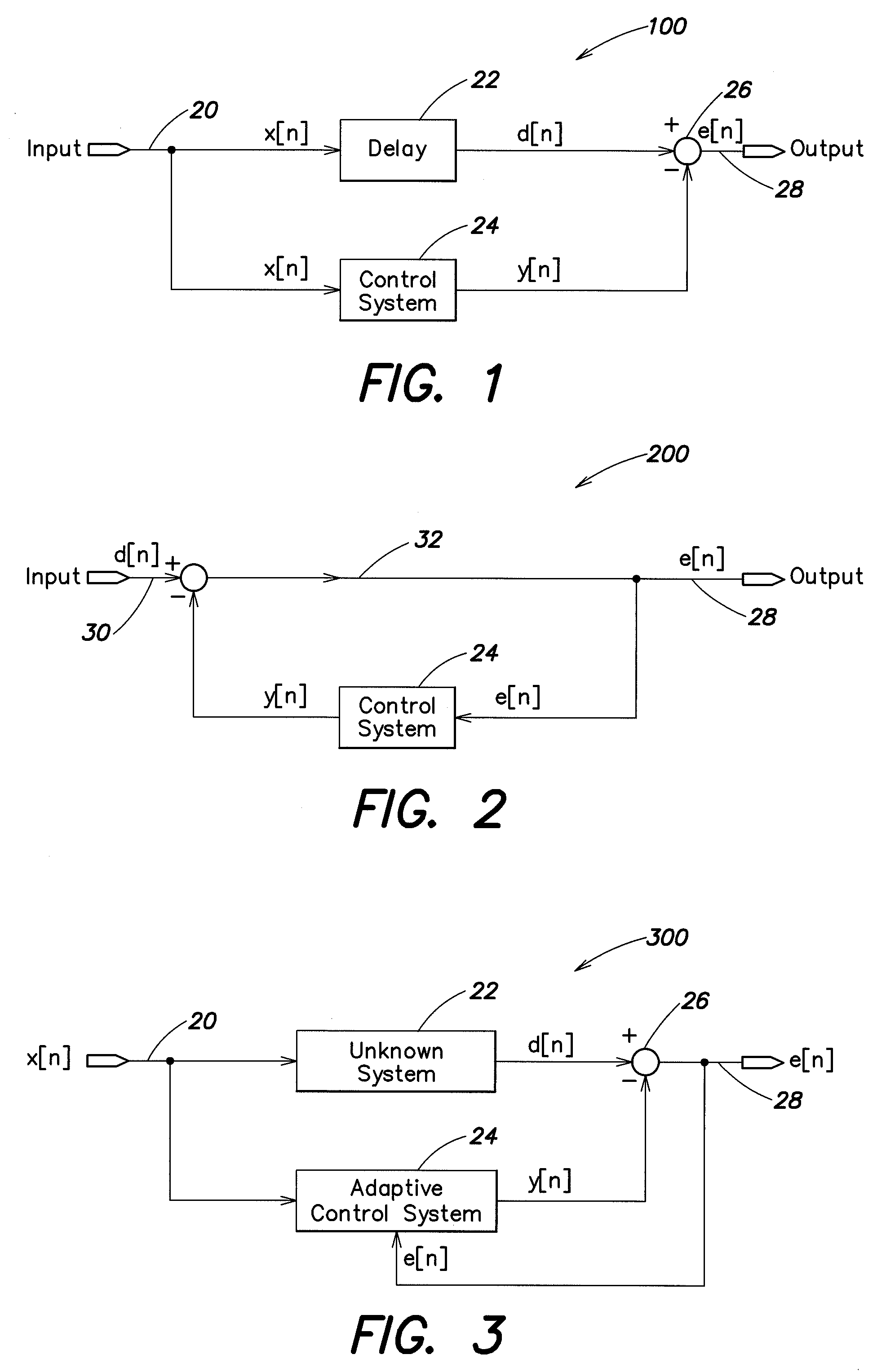
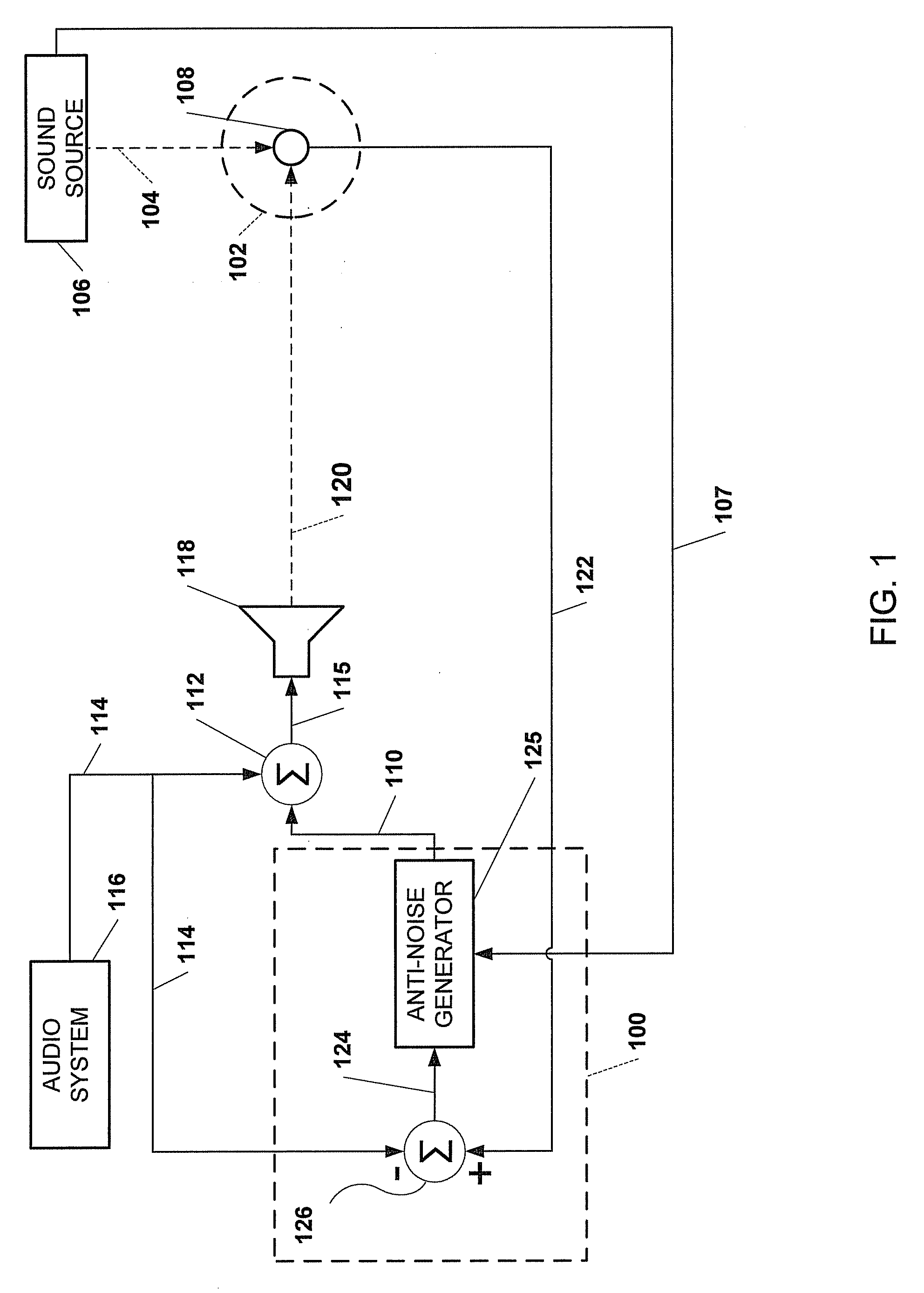
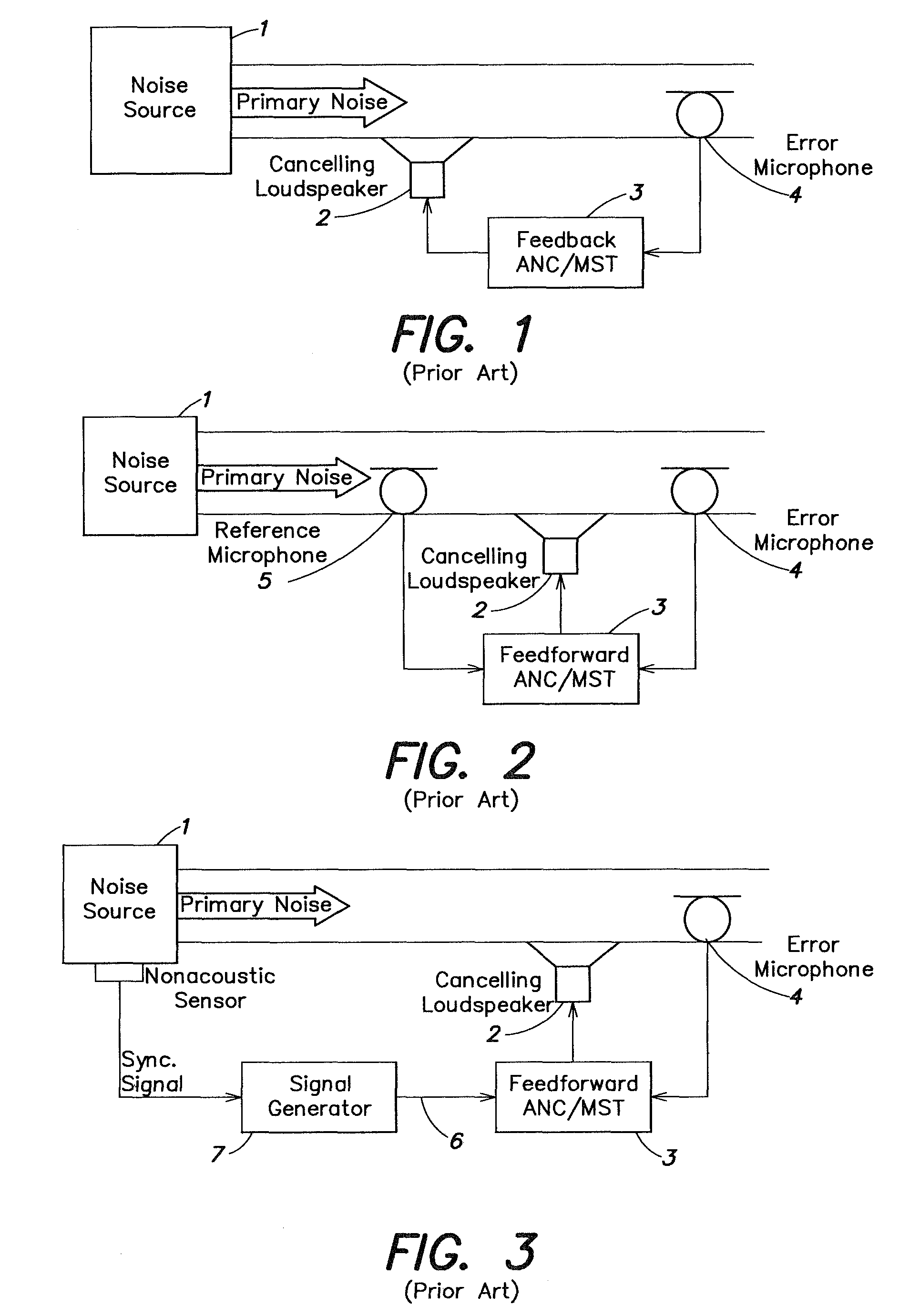
Adaptive noise control system
ActiveUS20100014685A1Improve robustnessImprove stabilityEar treatmentNoise generationNoise controlControl system
An active noise cancellation system that reduces, at a listening position, power of a noise signal radiated from a noise source to the listening position. The system includes an adaptive filter, at least one acoustic actuator and a signal processing device. The adaptive filter receives a reference signal representing the noise signal, and provides a compensation signal. The at least one acoustic actuator radiates the compensation signal to the listening position. The signal processing device evaluates and assesses the stability of the adaptive filter.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Active noise tuning system
ActiveUS20050207585A1Improved noise suppressionEar treatmentSpeech analysisNoise controlControl signal
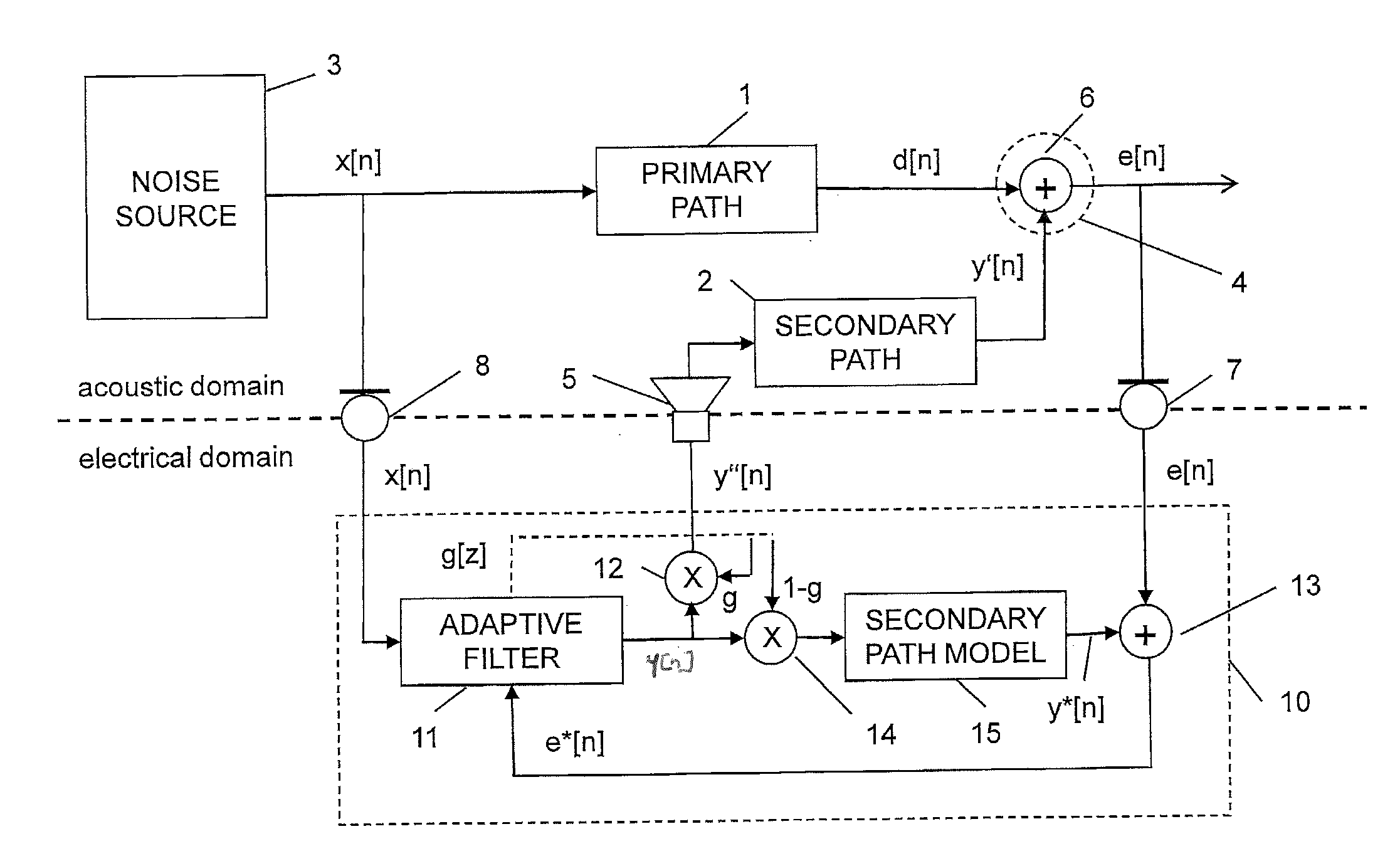
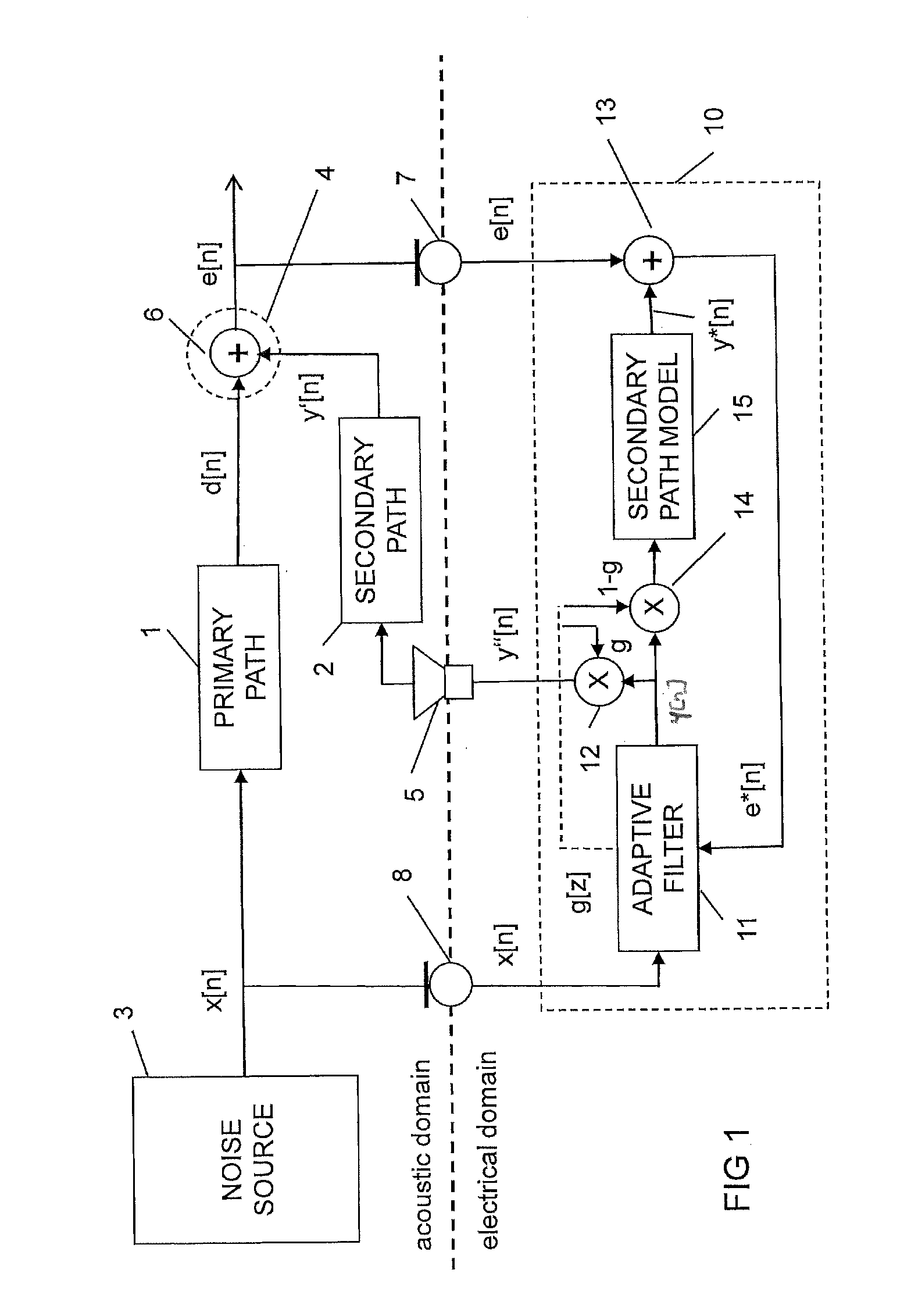
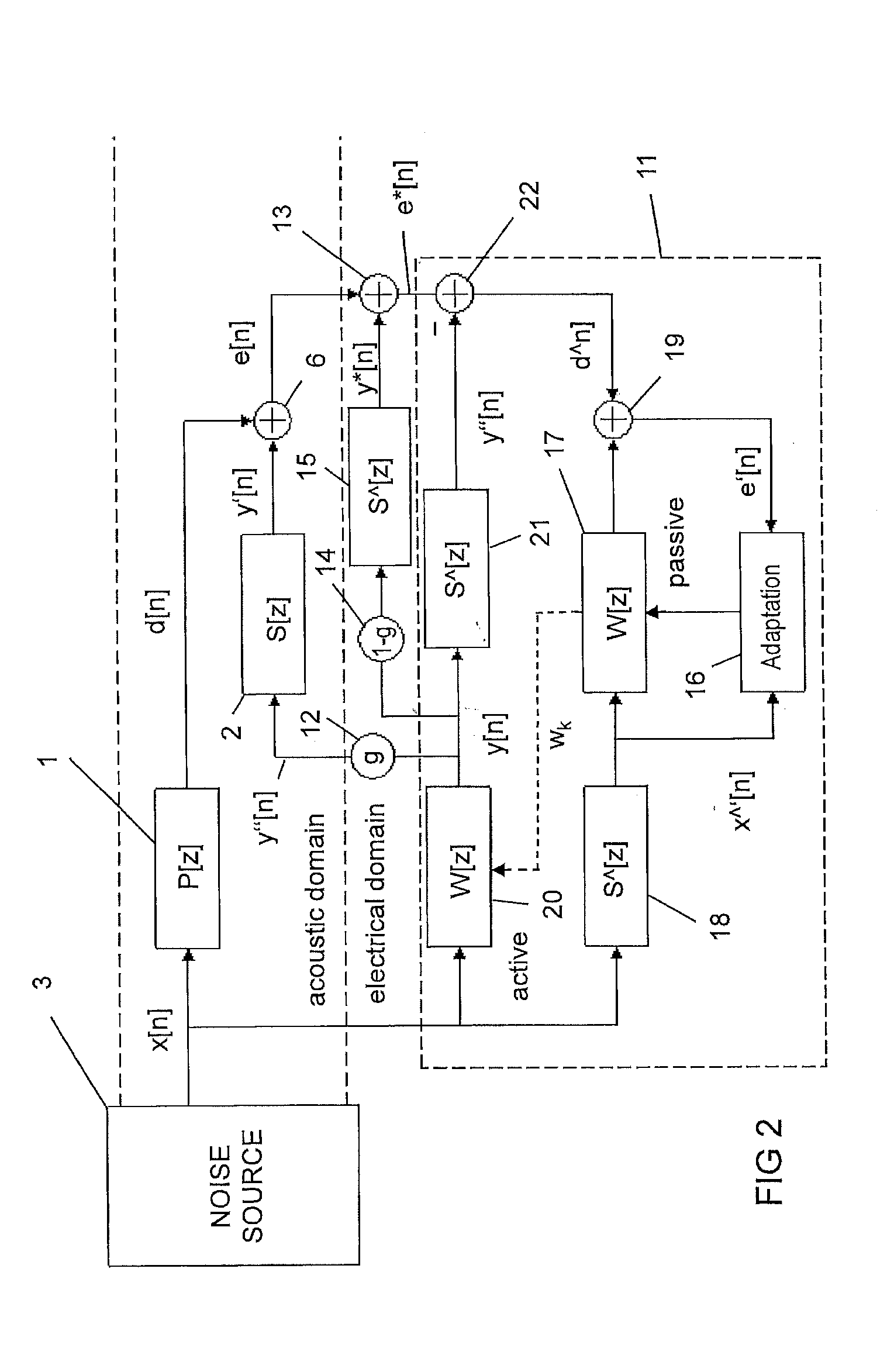
Active noise control system and method for controlling an acoustic noise generated by a noise source at a listening location, in which system and method sound is picked up in the surroundings of the listening location by a sound sensor; an electrical noise signal which corresponds to the acoustic noise of the noise source is generated and filtered adaptively in accordance with control signals. The adaptively filtered noise signal is irradiated into the surroundings of the listening location by a sound reproduction device, where a secondary path transfer function extends between the sound reproduction device and sound sensor. The noise signal is filtered with a transfer function that models the secondary path transfer function. The signals which provided by the sound sensor after first filtering serve as control signals for the adaptive filtering.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Active noise control system
ActiveUS20080181422A1Reduce and cancel unwanted noise signalLower Level RequirementsEar treatmentNoise generationNoise controlEngineering
An active control of an unwanted noise signal at a listening site radiated by a noise source uses a reference signal that has an amplitude and / or frequency such that it is masked for a human listener at the listening site by the unwanted noise signal and / or a wanted signal present at the listening site in order to adapt for the time-varying secondary path in a real time manner such that a user doesn't fell disturbed by an additional artificial noise source.
Owner:APPLE INC
Adaptive noise control system
An active noise cancellation system includes an adaptive filter, a signal source, an acoustic actuator, a microphone, a secondary path and an estimation unit. The adaptive filter receives a reference signal representing noise, and provides a compensation signal in response to the received reference signal. The signal source provides a measurement signal. The acoustic actuator radiates the compensation signal and the measurement signal to the listening position. The microphone receives a first signal that is a superposition of the radiated compensation signal, the radiated measurement signal, and the noise signal at the listening position, and provides a microphone signal in response to the received first signal. The secondary path includes a secondary path system that represents a signal transmission path between an output of the adaptive filter and an output of the microphone. The estimation unit estimates a transfer characteristic of the secondary path system in response to the measurement signal and the microphone signal.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
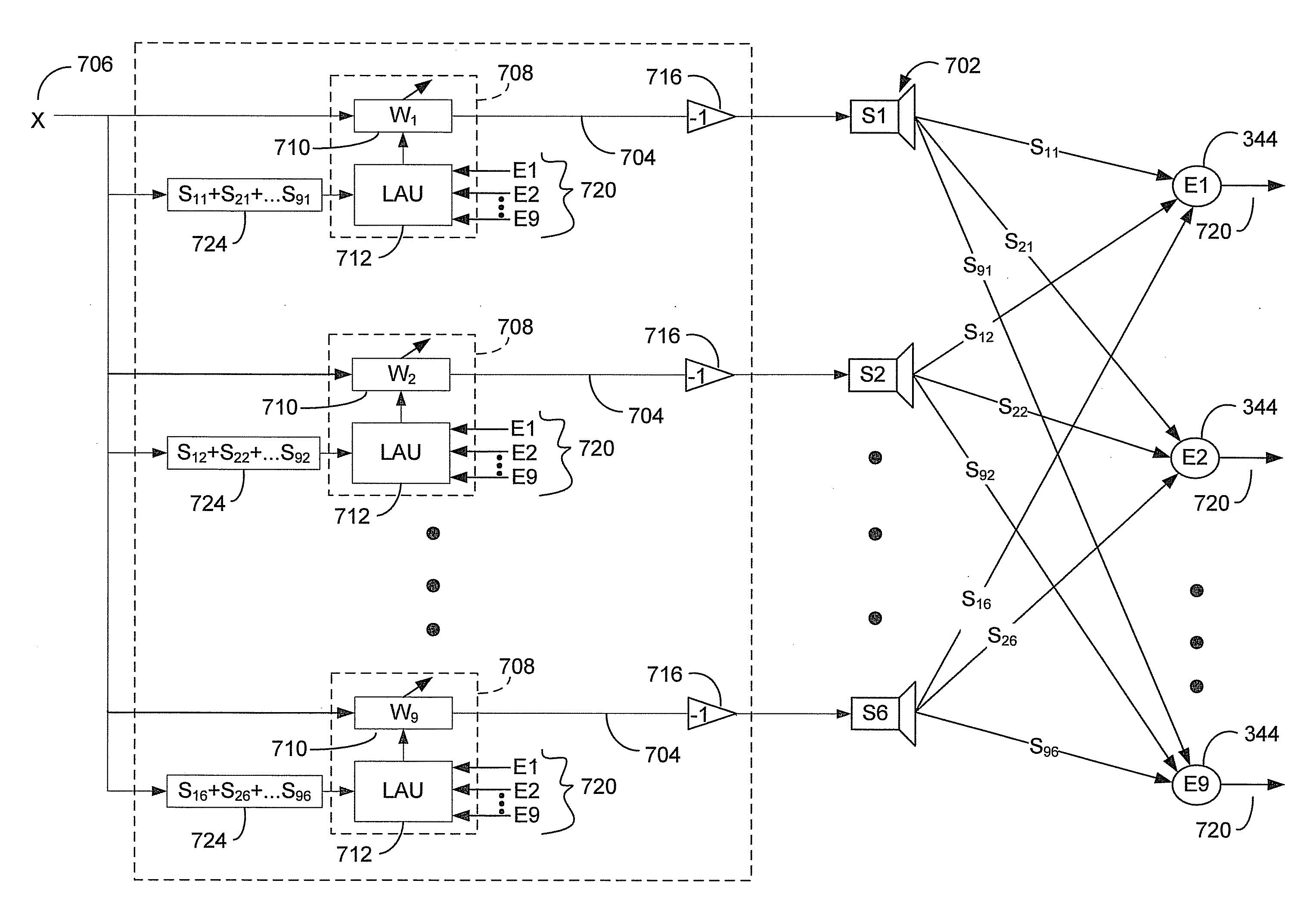
Quiet zone control system
An active noise control system generates an anti-noise signal to drive a speaker to produce sound waves to destructively interfere with an undesired sound in a quiet zone. The anti-noise signal is generated with an adaptive filter having filter coefficients. The coefficients of the adaptive filter may be adjusted based on a first filter adjustment from a first listening region, and a second filter adjustment from a second listening region. A first weighting factor may be applied to the first filter adjustment, and a second weighting factor may be applied to the second filter adjustment. The first and second weighting factors may dictate the location and size of the quiet zone as being outside or partially within at least one of the first listening region and the second listening region.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
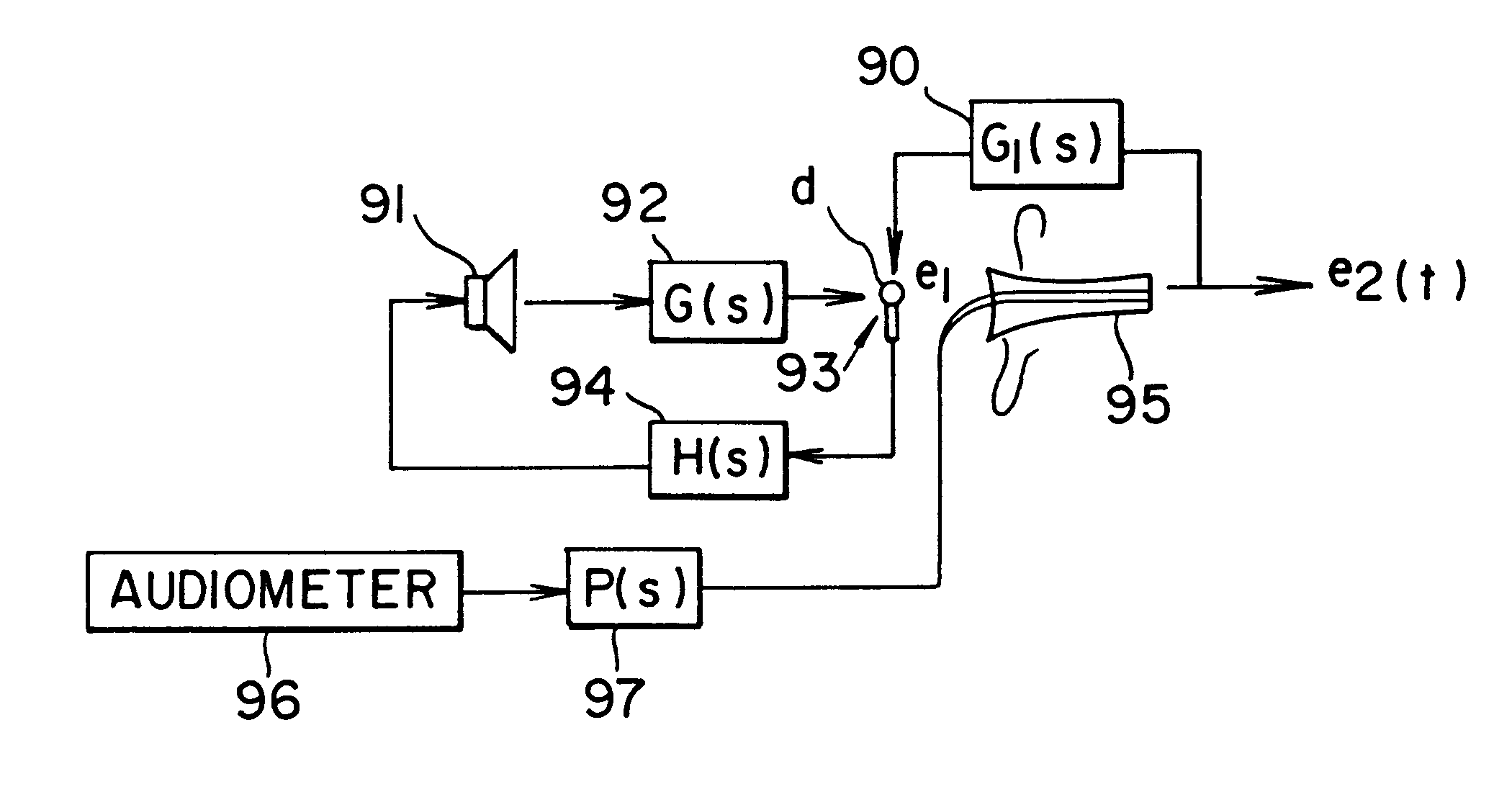
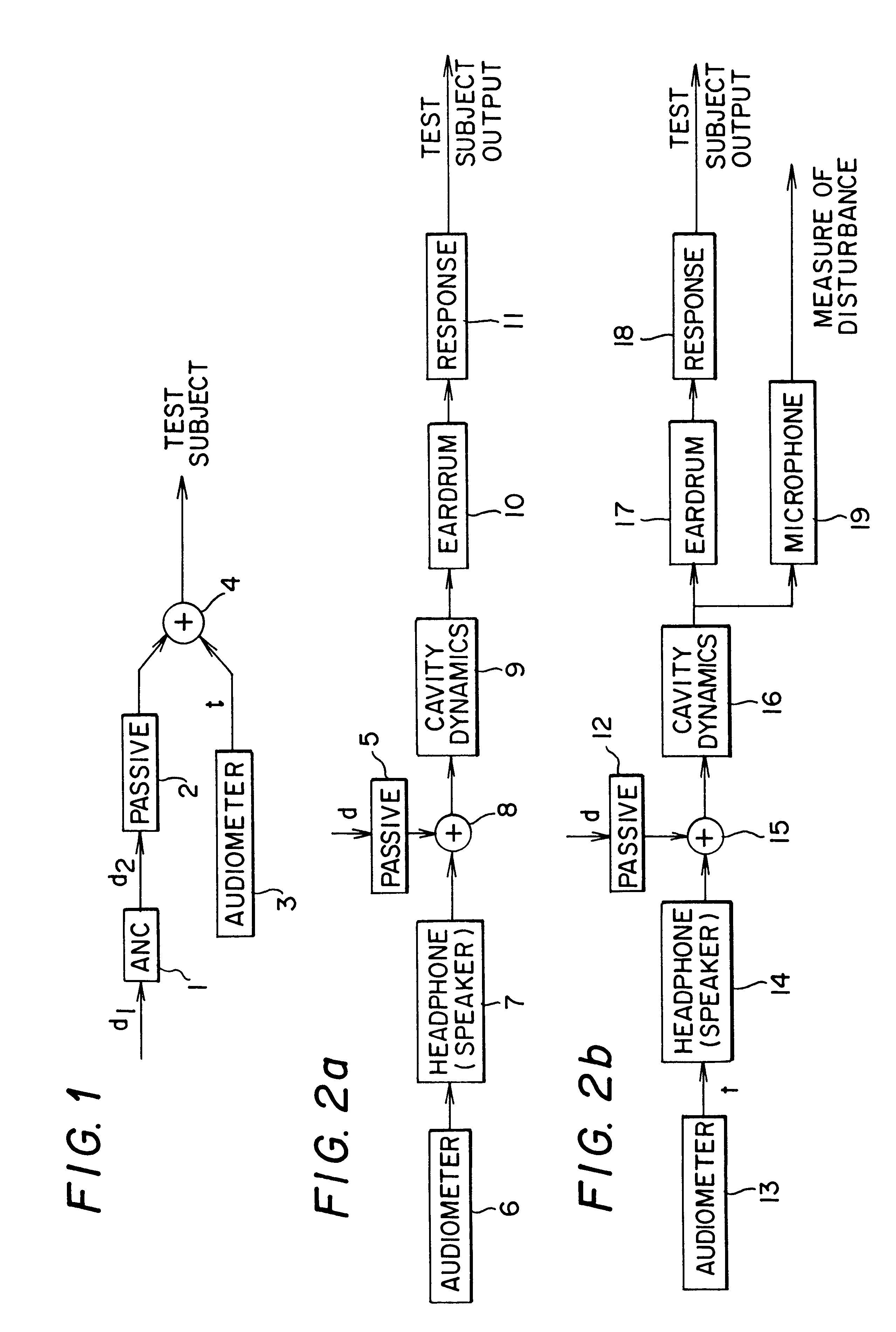
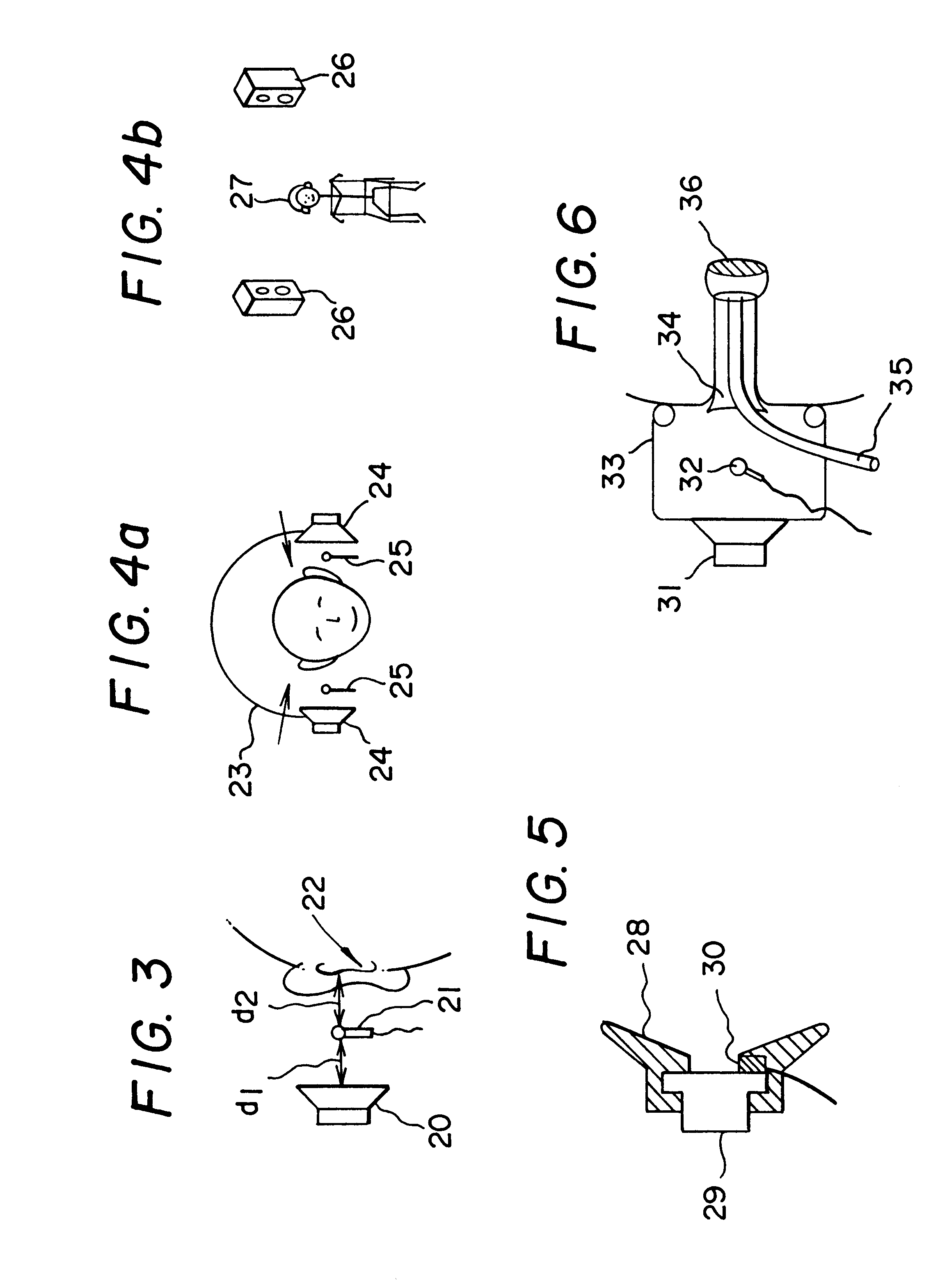
Active noise reduction for audiometry
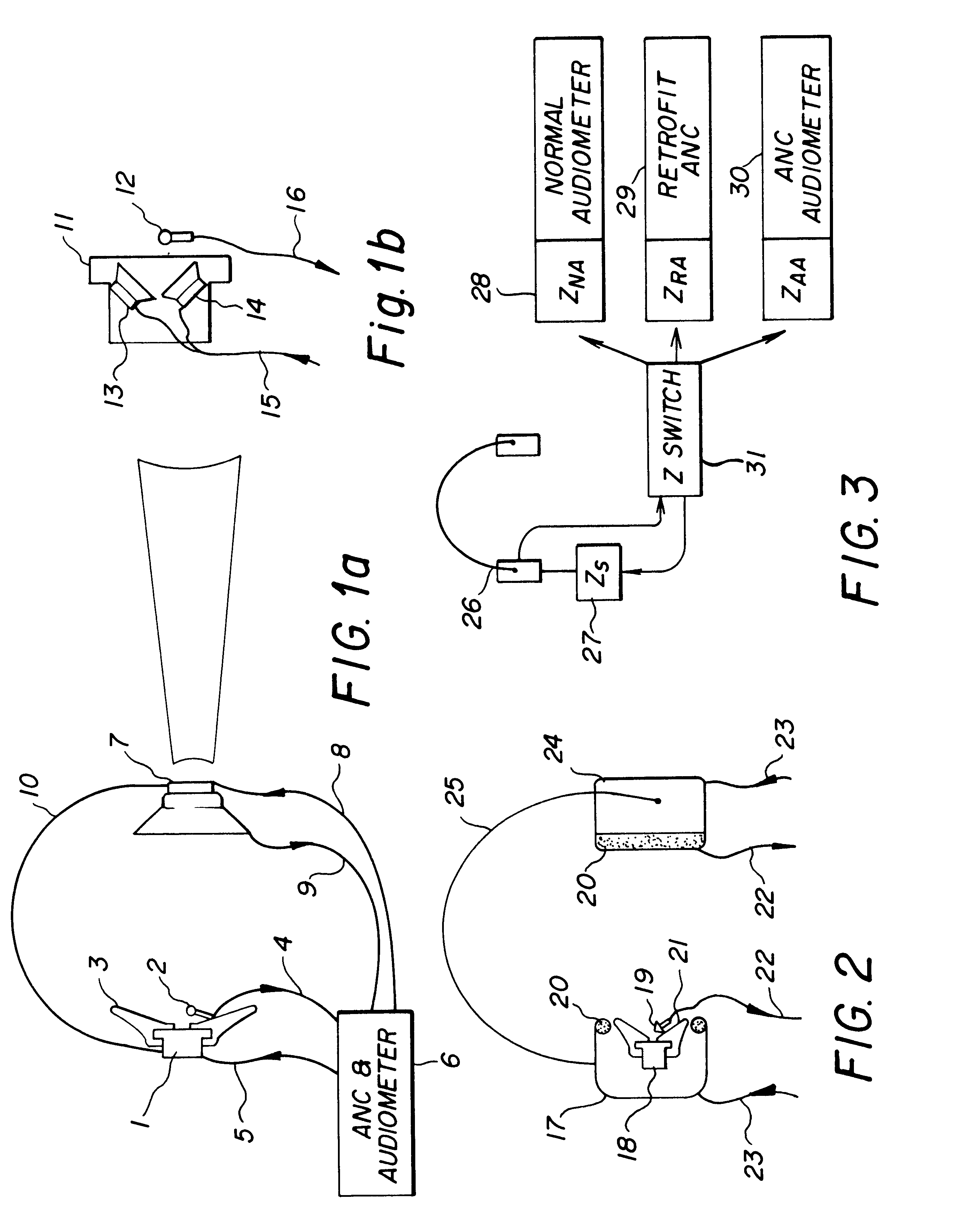
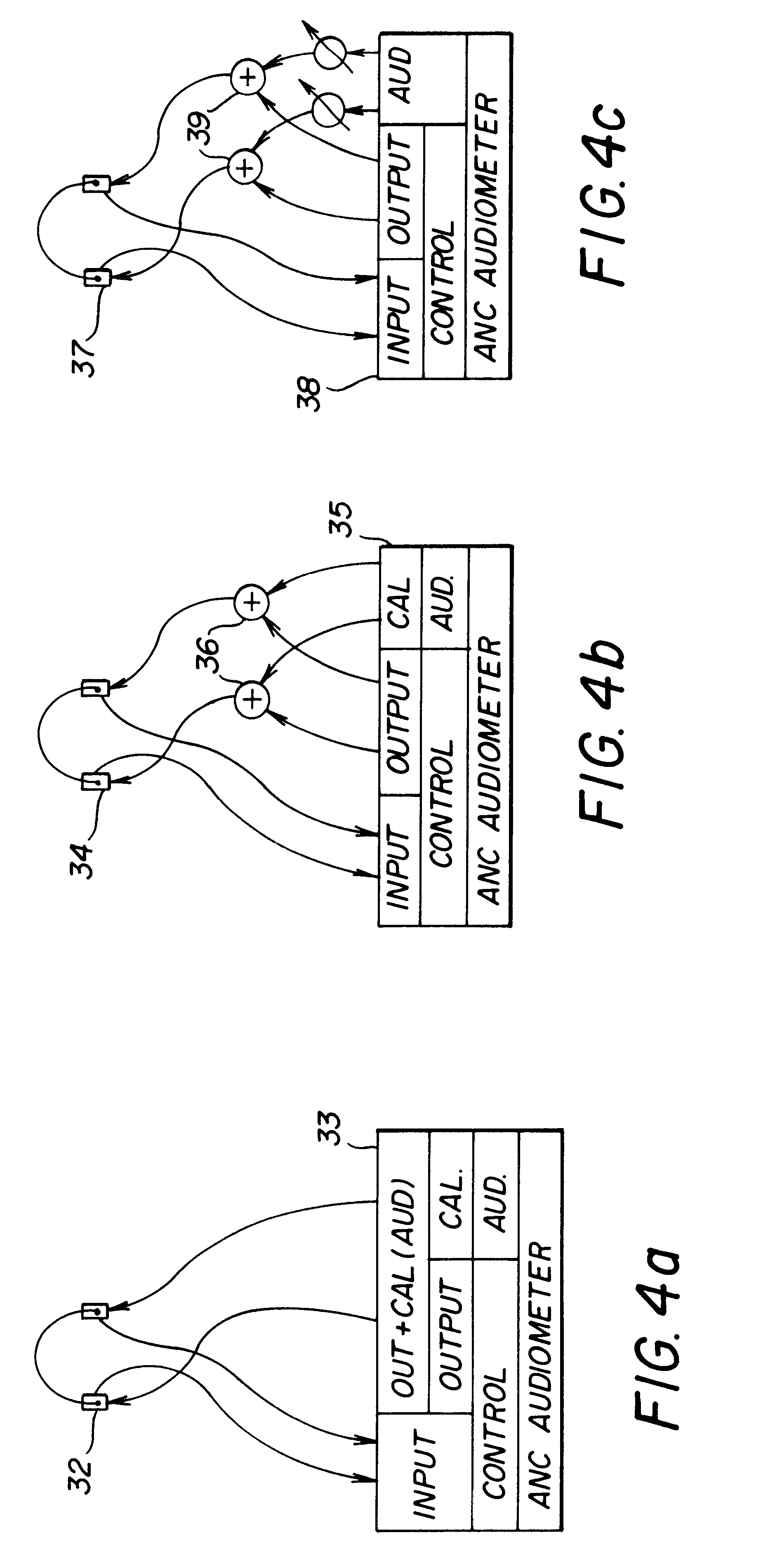
InactiveUS6396930B1Maximize noise control performanceAccurate comparisonEar treatmentAudiometeringNoise controlNoise field
The technology of active noise reduction (ANR) is incorporated into audiometry testing in a variety of formats. Analog feedback, digital feedback, adaptive feedforward, and adaptive feedback noise control schemes are presented for use in audiometry to reduce the ambient noise heard by the test subject, allowing subject testing in higher ambient noise fields. Audiometer test signals are appropriately compensated so the test results are accurate and comply with existing calibration standards for audiometers. Existing audiometry headphone technologies are modified so that ANR can be accomplished while satisfying existing standards for audiometric testing. Embodiments are also defined for alternate headphone arrangements that may not conform to current (1997) audiometric testing standards but provide sufficient performance advantages to warrant new standards for audiometry testing in the future.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
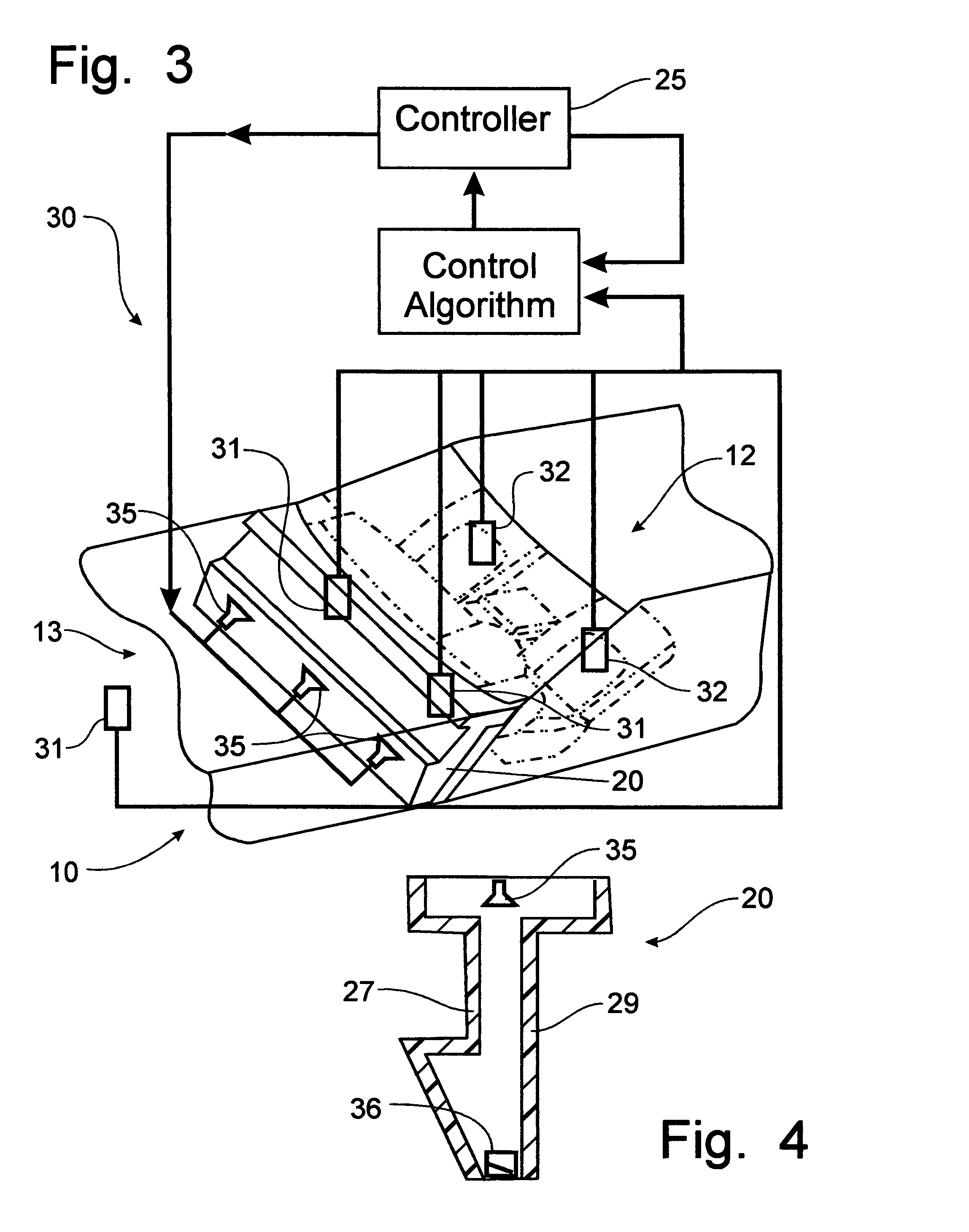
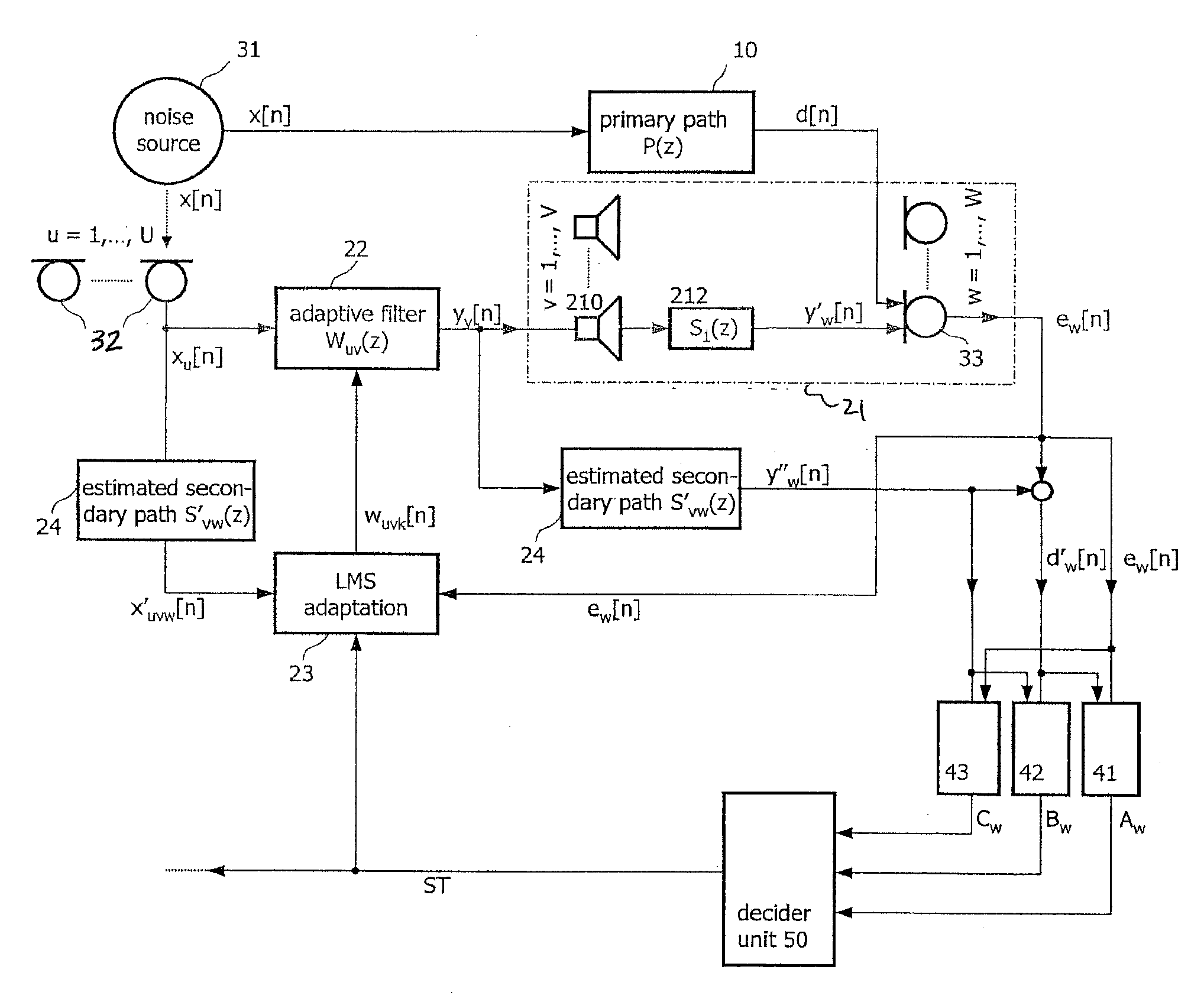
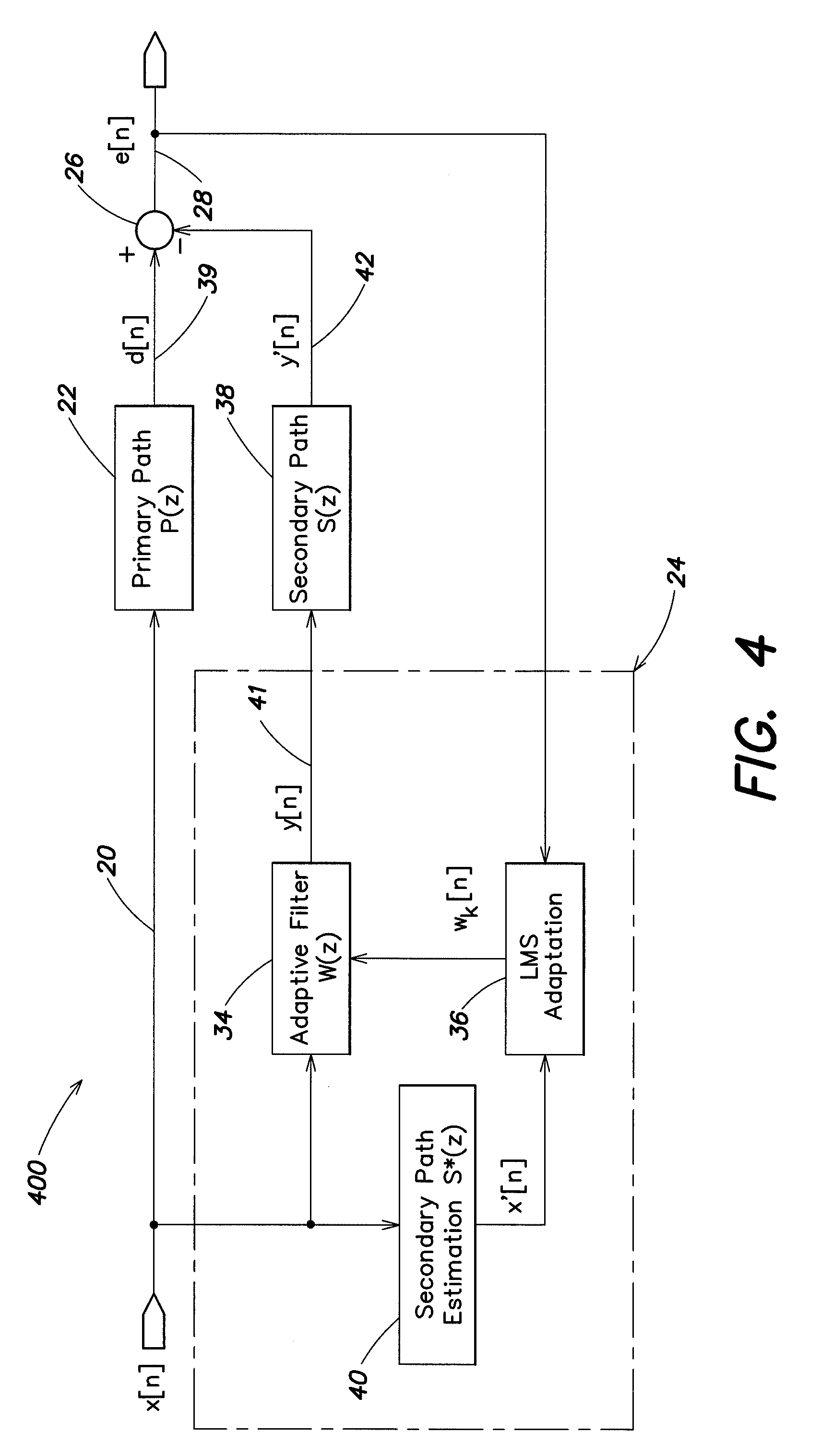
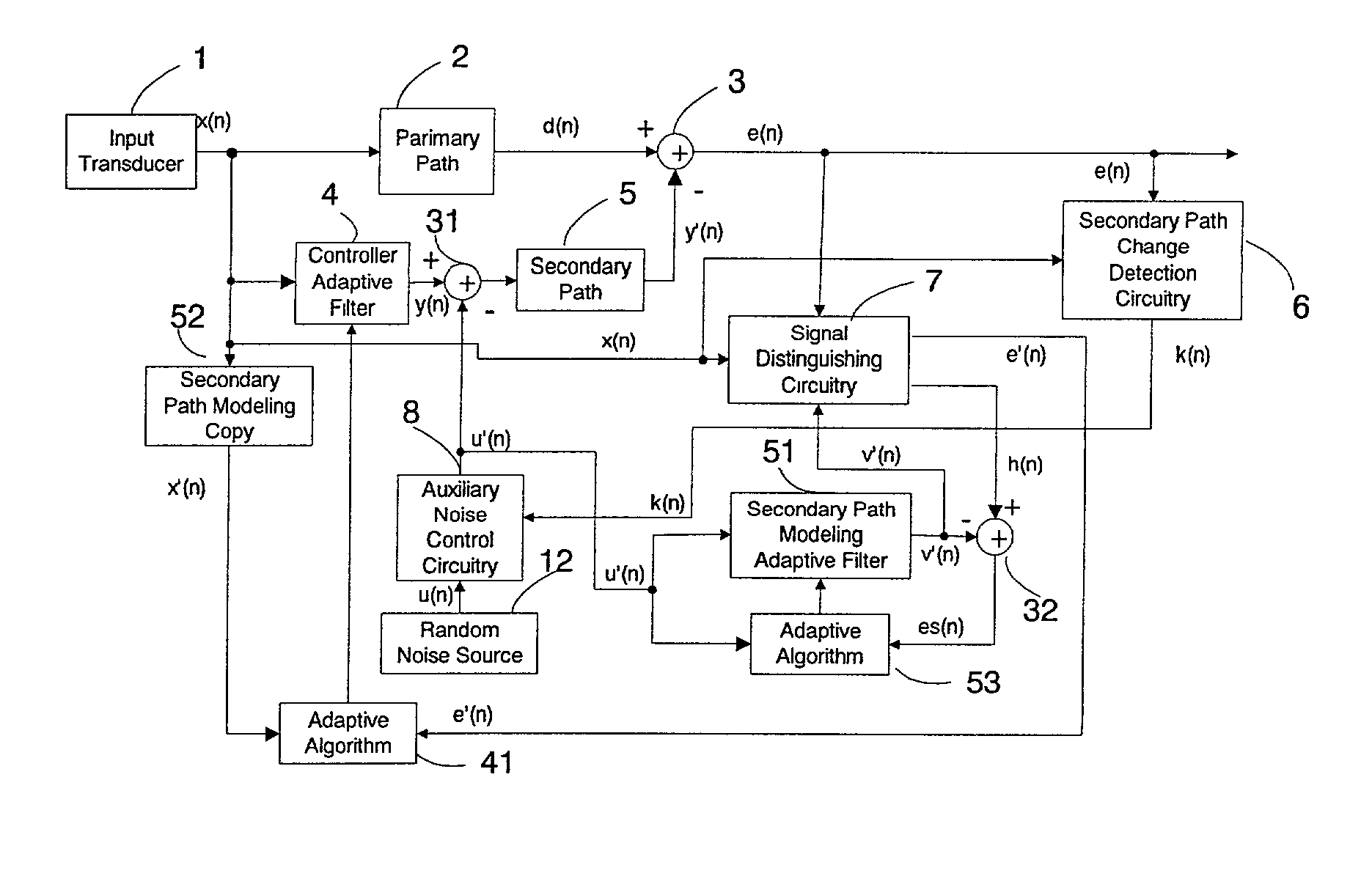
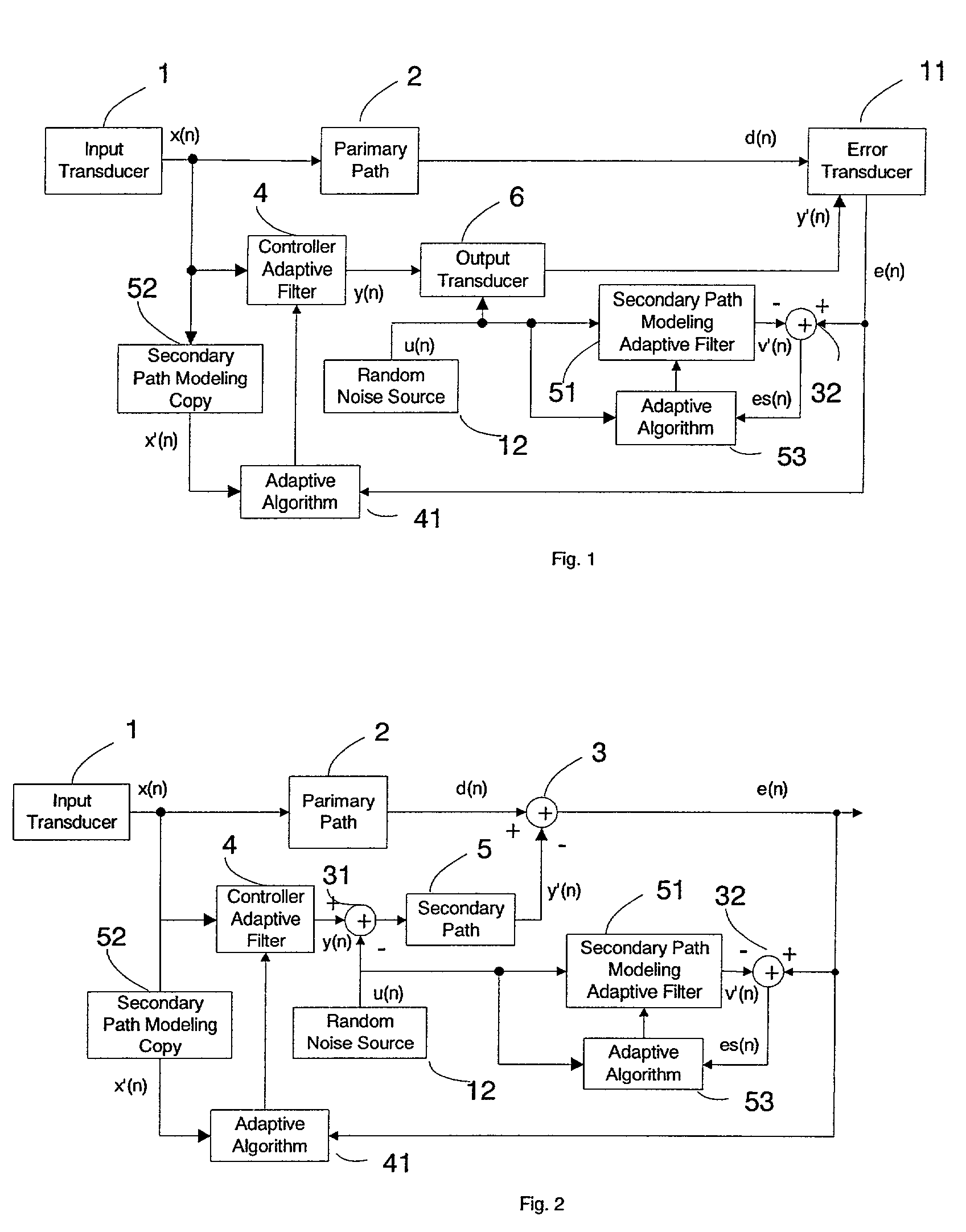
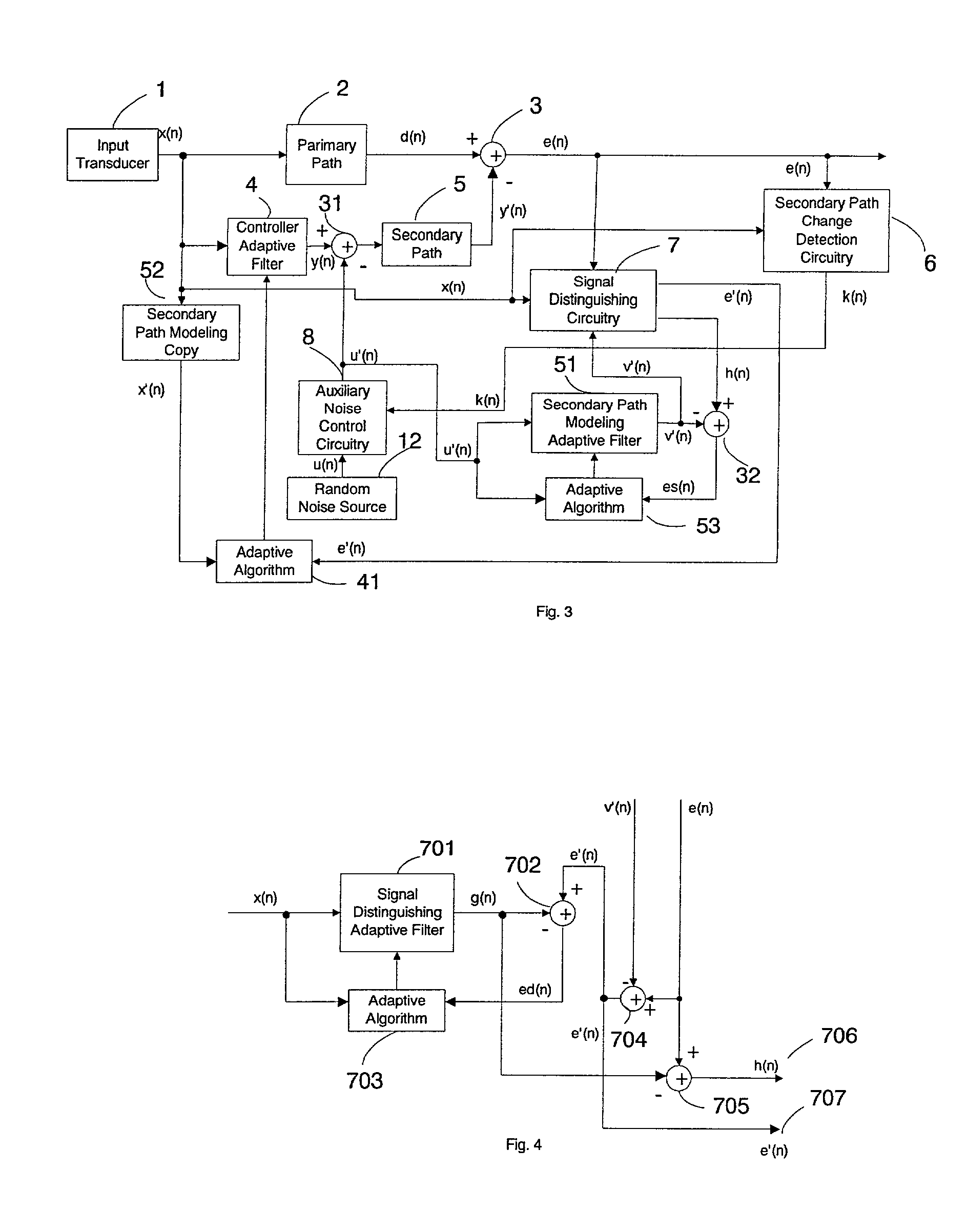
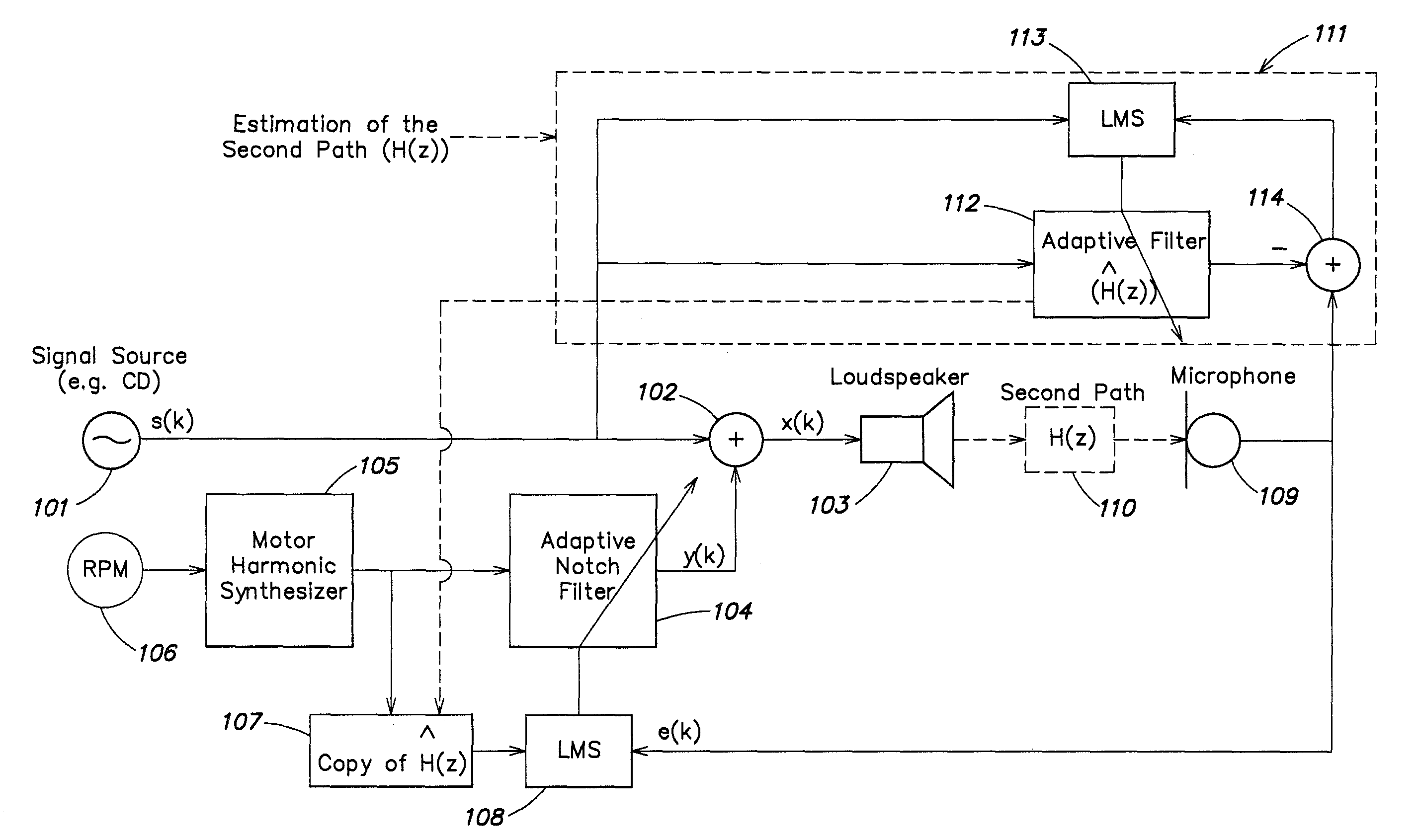
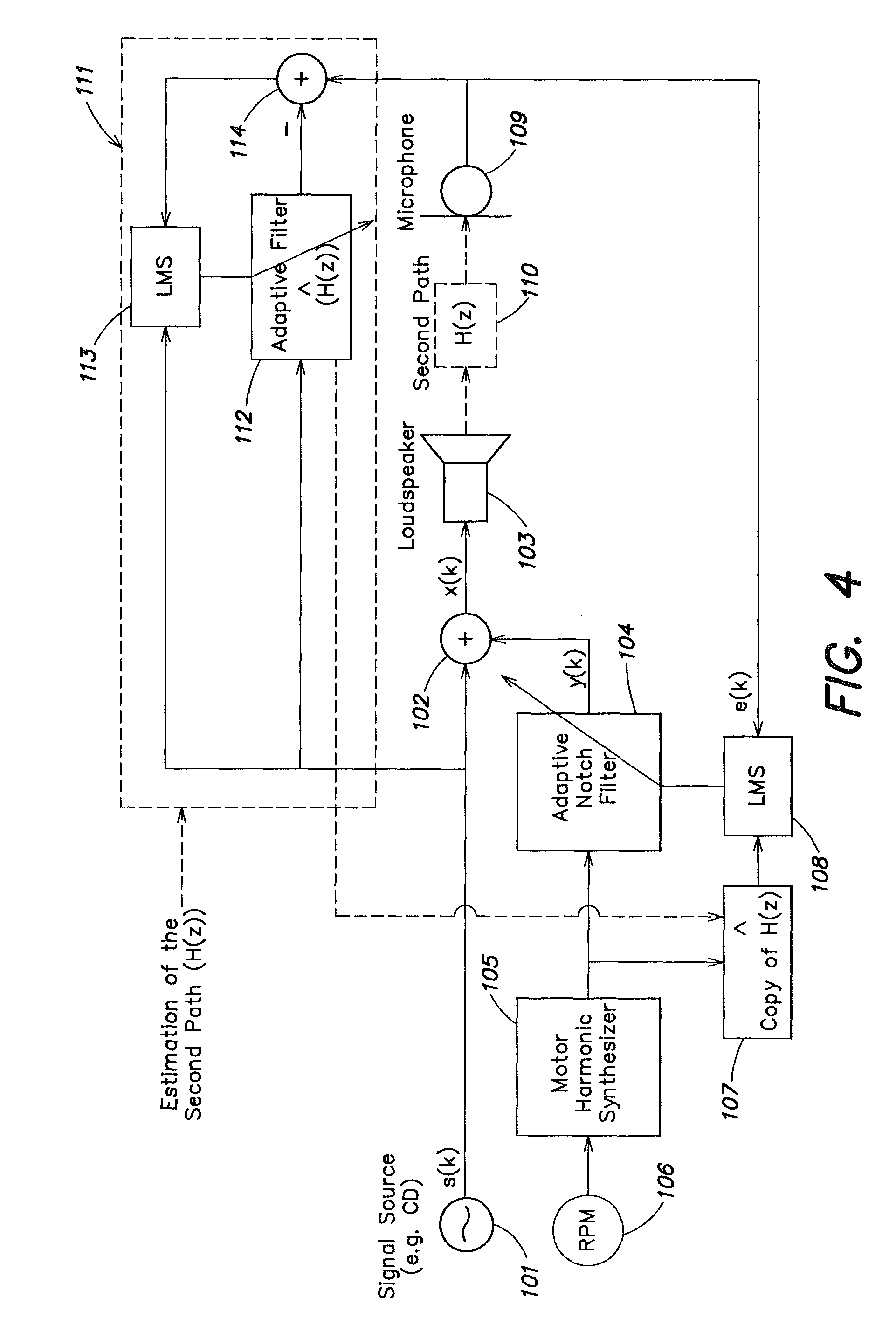
Active noise control system with on-line secondary path modeling
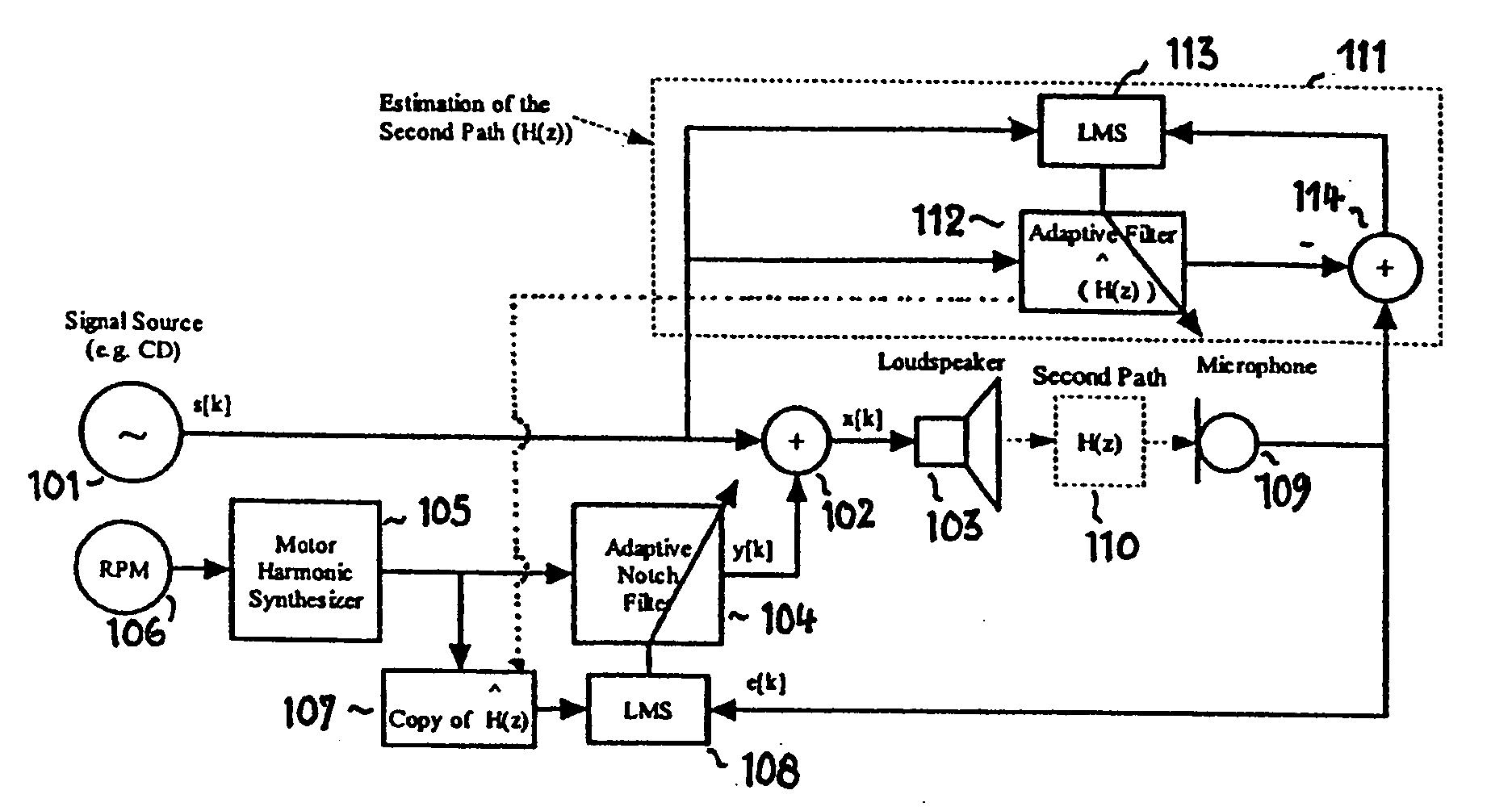
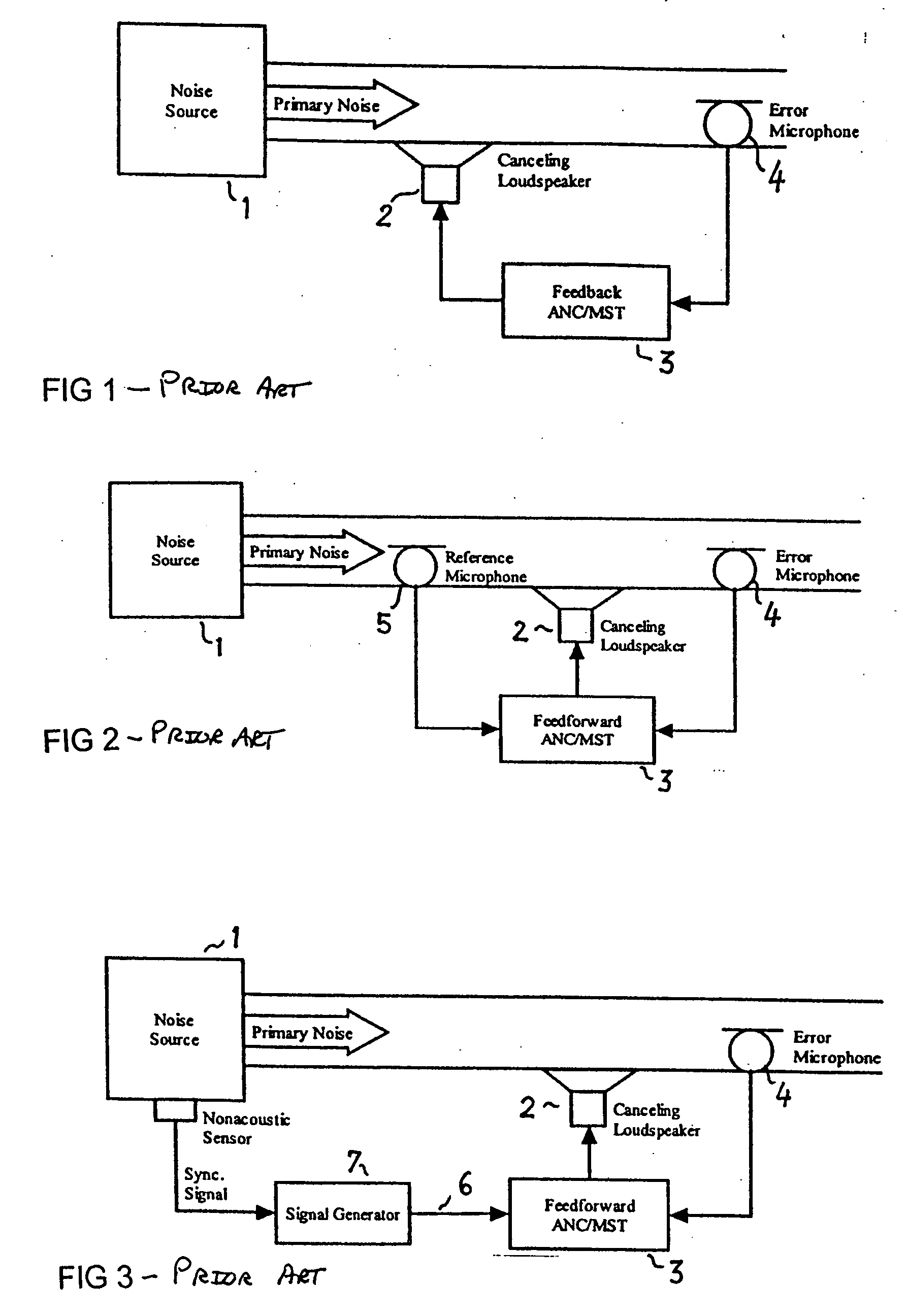
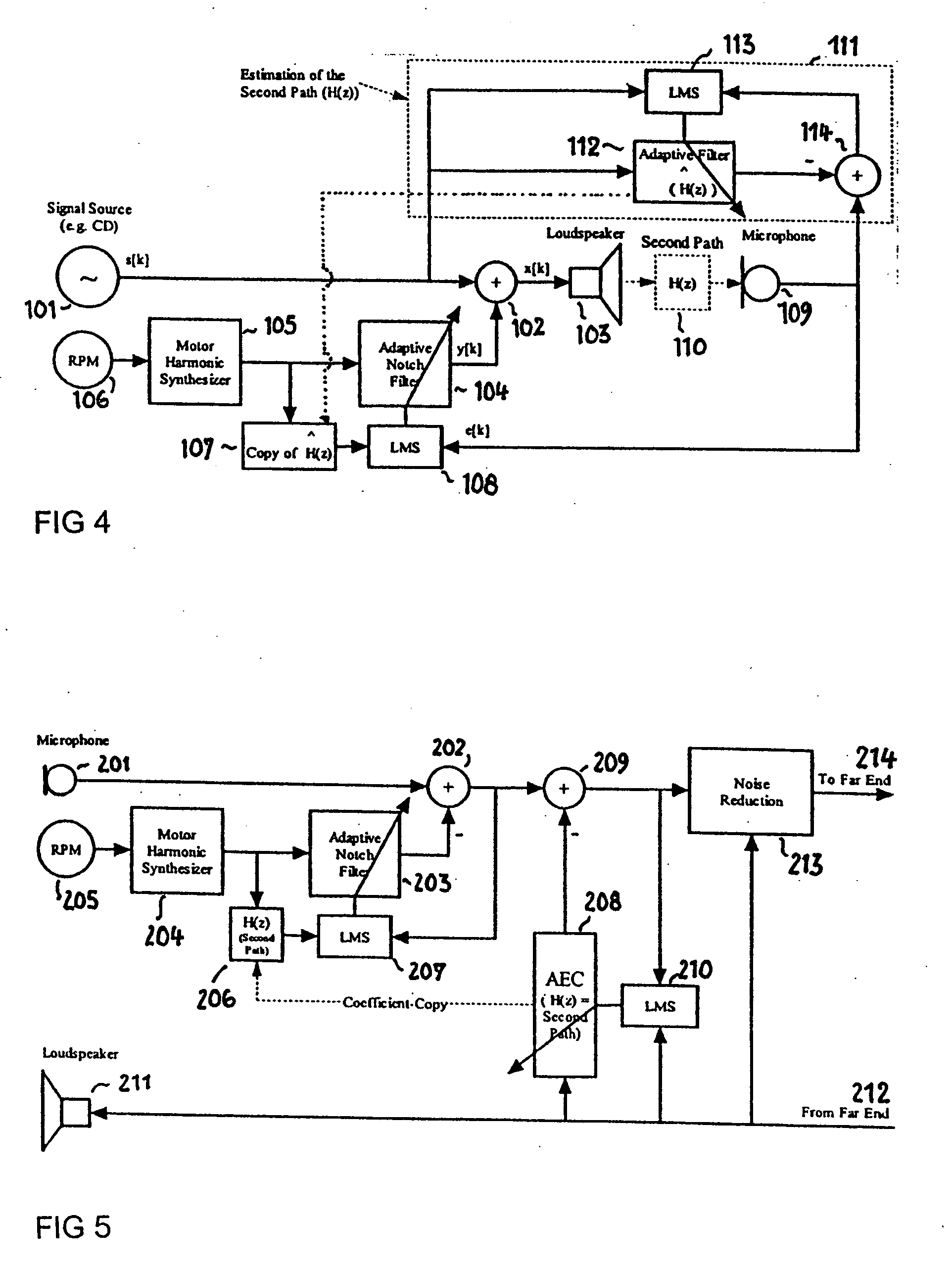
An active noise control system is provided to specify an input transducer, an error transducer, an output transducer and an active noise controller for generating an anti-phase canceling acoustic signal to attenuate an input noise and to output a reduced noise. The active noise control system also performs on-line secondary path modeling. For this purpose the active noise control system comprises, in addition to known systems, a secondary path change detection circuitry (6), a signal distinguishing circuitry (7) and an auxiliary noise control circuitry (8), all of them being used to model said secondary path. FIG. 3
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
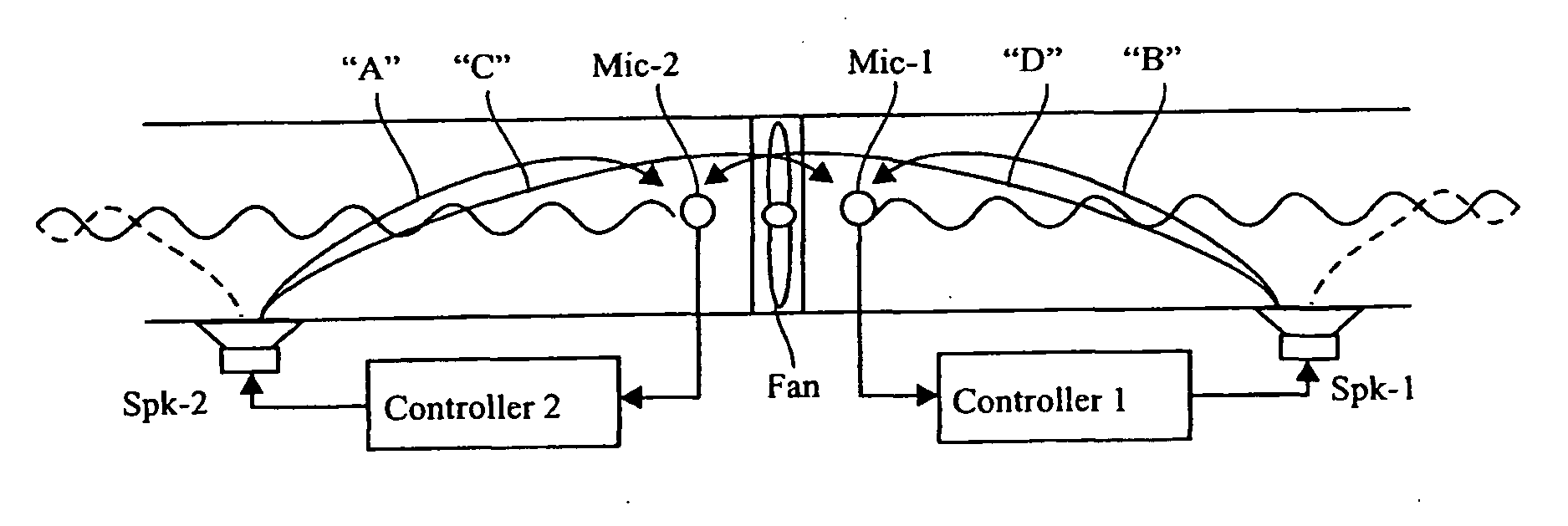
Quiet fan incorporating active noise control (ANC)
ActiveUS20100028134A1Reduce cross echoEar treatmentPump componentsUltrasound attenuationNoise control
An active noise control (ANC) system may be implemented to both sides of a fan, such that both directions of the noise emitting are treated to reduce the overall noise. The impact on airflow is minimal, and the technique is very effective in a broad range of low frequencies. Passive sound-absorbing materials may be included for attenuation of high frequencies. The resulting quiet fan produces a low level of noise compared to any other device based on fan, which produces the same capacity of airflow. The quiet fan may be incorporated in any mechanical system which requires airflow induction such as: computers, air conditioners, machines, and more.
Owner:SILENTIUM LTD
Active noise control algorithm that requires no secondary path identification based on the SPR property
InactiveUS20100284546A1Reduce vibration and noiseReduce residual noise powerEar treatmentNoise generationNoise controlControl system
A control system for reducing noise or vibration in a target zone. The noise or vibration is produced by a source and transferred to the target zone by a main path. The control system is provided with an actuator, at least one error sensor and a controller. The actuator is positioned to deliver actuated signals into at least a portion of the target zone. The at least one error sensor monitors the residual noise or vibration power in the target zone and produces an error signal representative thereof. The controller receives a reference signal representative of noise or vibration produced by the source, and the error signal representative of the residual noise power in the target zone. The controller analyzes sub-bands of the reference signal and the error signal without identification of a secondary path, and provides drive signals to the actuator to cause the actuator to deliver the actuated signals into the target zone so as to reduce the residual noise power in the target zone.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
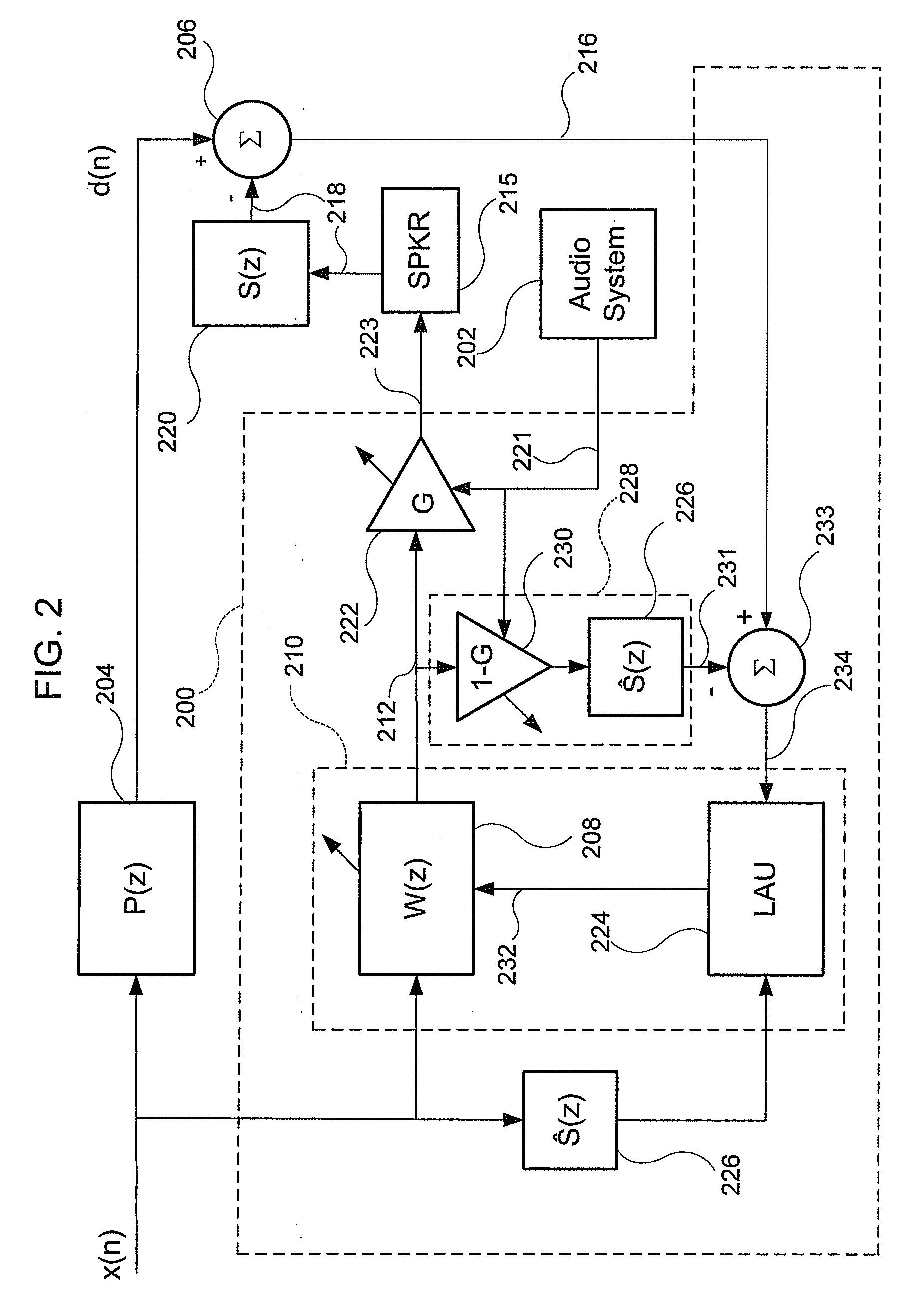
Adaptive noise control
ActiveUS20110305347A1Reduce the required powerEar treatmentNoise generationNoise controlAdaptive filter
Adaptive noise control for reducing power of an acoustic noise signal radiated from a noise source to a listening position comprises providing an electrical reference signal correlated with the acoustic noise signal; filtering the electrical reference signal with an adaptive filter to provide an electrical output signal; multiplying the electrical output signal of the adaptive filter by a gain factor to provide a first electrical compensation signal; filtering and multiplying the electrical output signal of the adaptive filter by the inverse of the gain factor to provide a second electrical compensation signal, the second gain factor being equal to 1 subtracted by the first gain factor; radiating the first electrical compensation signal to the listening position with an acoustic transducer; sensing a residual electrical error signal at the listening position; adding the second electrical compensation signal to the electrical error signal to provide a compensated error signal; and adapting filter coefficients of the adaptive filter as a function of the compensated error signal and the reference signal.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
System for active noise control with audio signal compensation
ActiveUS20100124336A1Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsNoise controlEngineering
An active noise control system generates an anti-noise signal to drive a speaker to produce sound waves to destructively interfere with an undesired sound in a targeted space. The speaker is also driven to produce sound waves representative of a desired audio signal. Sound waves are detected in the target space and a representative signal is generated. The representative signal is combined with an audio compensation signal to remove a signal component representative of the sound waves based on the desired audio signal and generate an error signal. The active noise control adjusts the anti-noise signal based on the error signal. The active noise control system converts the sample rates of an input signal representative of the undesired sound, the desired audio signal, and the error signal. The active noise control system converts the sample rate of the anti-noise signal.
Owner:APPLE INC
Noise control device
ActiveUS20100150367A1Lower latencyReduce the impactEar treatmentTransducer circuit dampingNoise controlNoise detection
A noise control device according to the present invention is capable of reducing noises respectively arriving in a plurality of spaces which are acoustically independent from each other. The noise control device comprises: sound output means, which are respectively provided in the plurality of spaces so as to respectively correspond to the plurality of spaces, each for outputting a sound to a corresponding space; noise detection means, which is provided in at least one of the plurality of spaces, for detecting a noise arriving in the at least one of the plurality of spaces; and signal generation means which is a single means for generating, based on the noise detected by one of the noise detection means, a cancellation signal for canceling the noise, and outputting the generated cancellation signal to each of the plurality of sound output means.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Active noise control system
InactiveUS7062049B1Noise can be canceled outEasy to getEar treatmentNoise generationTrunk compartmentNoise control
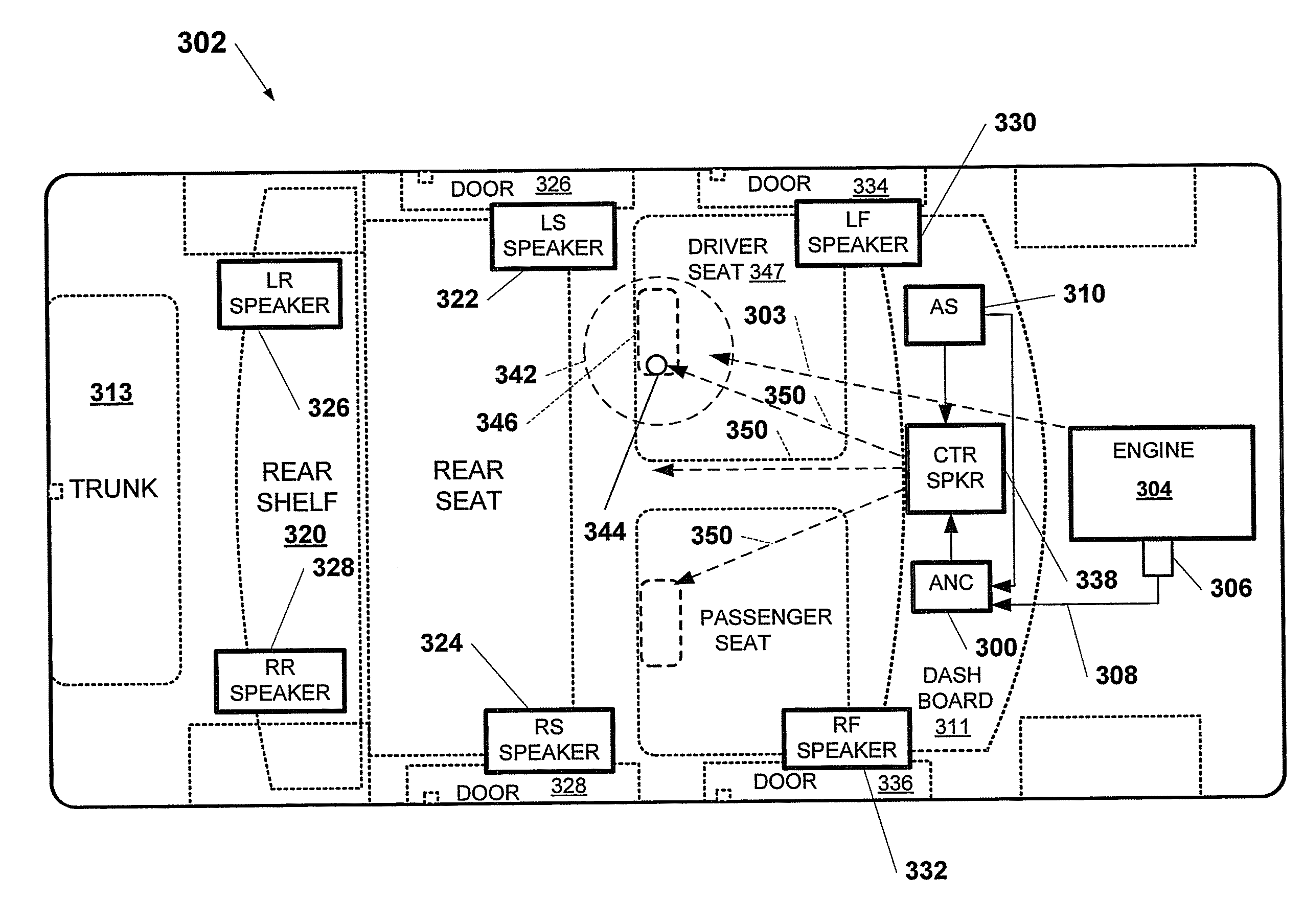
An active noise control system is capable of canceling out noise in the passenger compartment of a vehicle based on low-frequency road noise. The active noise control system has a feed-forward control unit for being supplied with reference signals highly correlated to noise from a noise source and generating a noise cancellation signal which is out of phase to noise in the passenger compartment of the vehicle, and a canceling sound generating unit disposed in the passenger compartment for generating a noise canceling sound in response to the noise cancellation signal from said feed-forward control unit. The active noise control system also has microphones for generating reference signals which are positioned respectively near the base of the front seat, near the center of a roof, and within a trunk compartment, i.e., respectively at vibrational antinodes of a primary or secondary acoustic normal mode of the passenger compartment in the longitudinal direction thereof. Output signals from the microphones are supplied as the reference signals.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
Secondary Path Modeling for Active Noise Control
ActiveUS20080144853A1Noise minimizationSampled-variable control systemsEar treatmentNoise controlMaximum difference
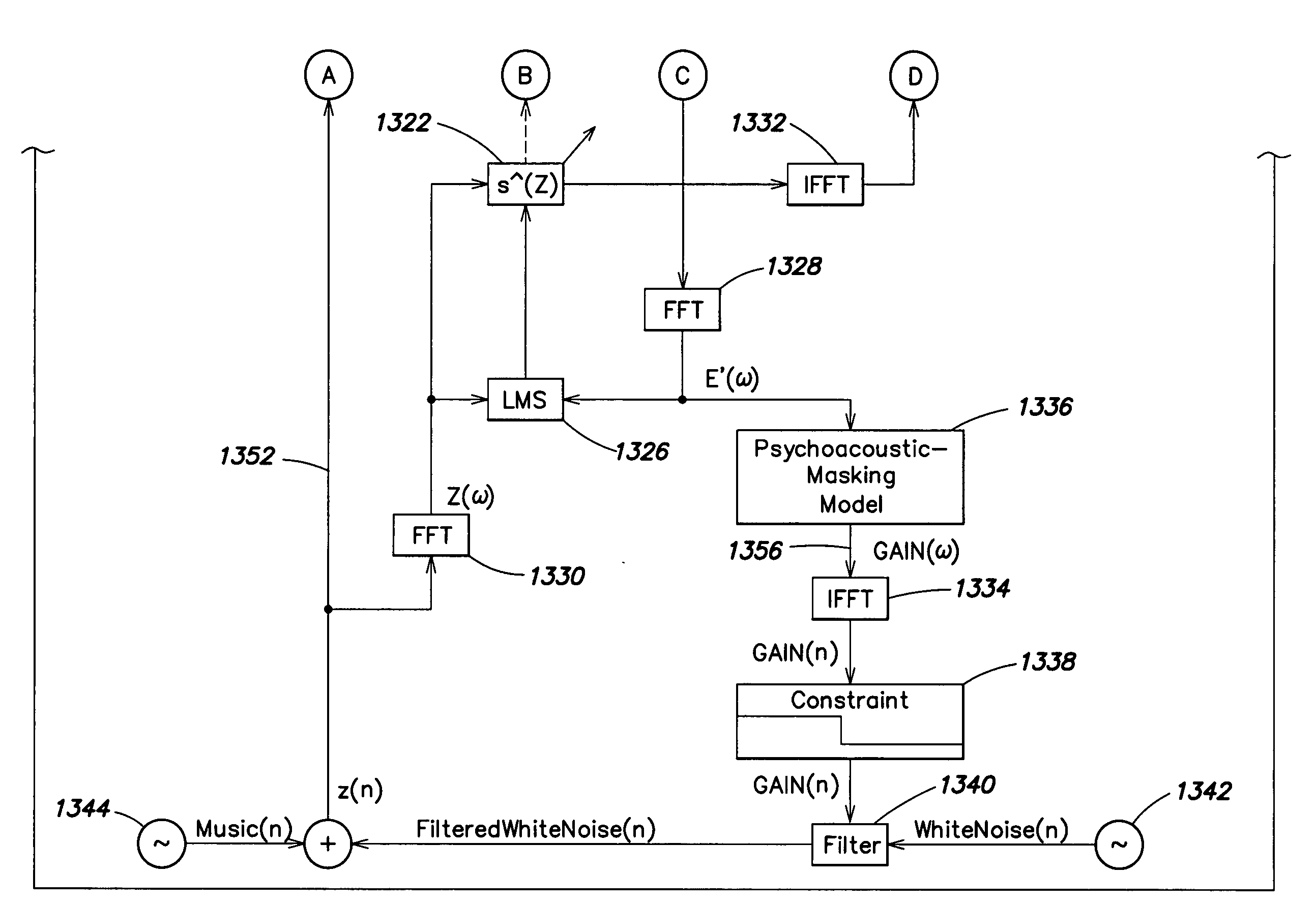
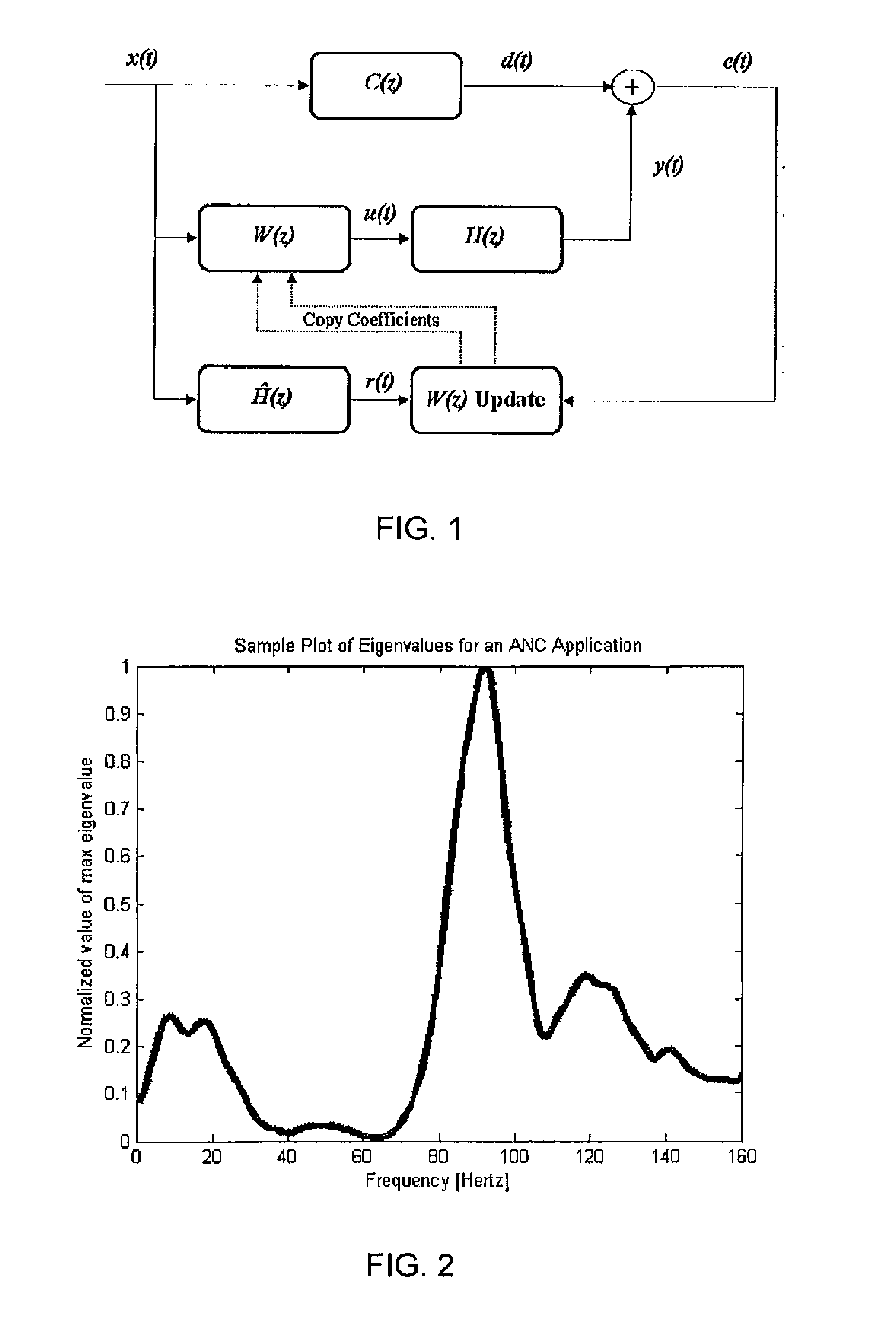
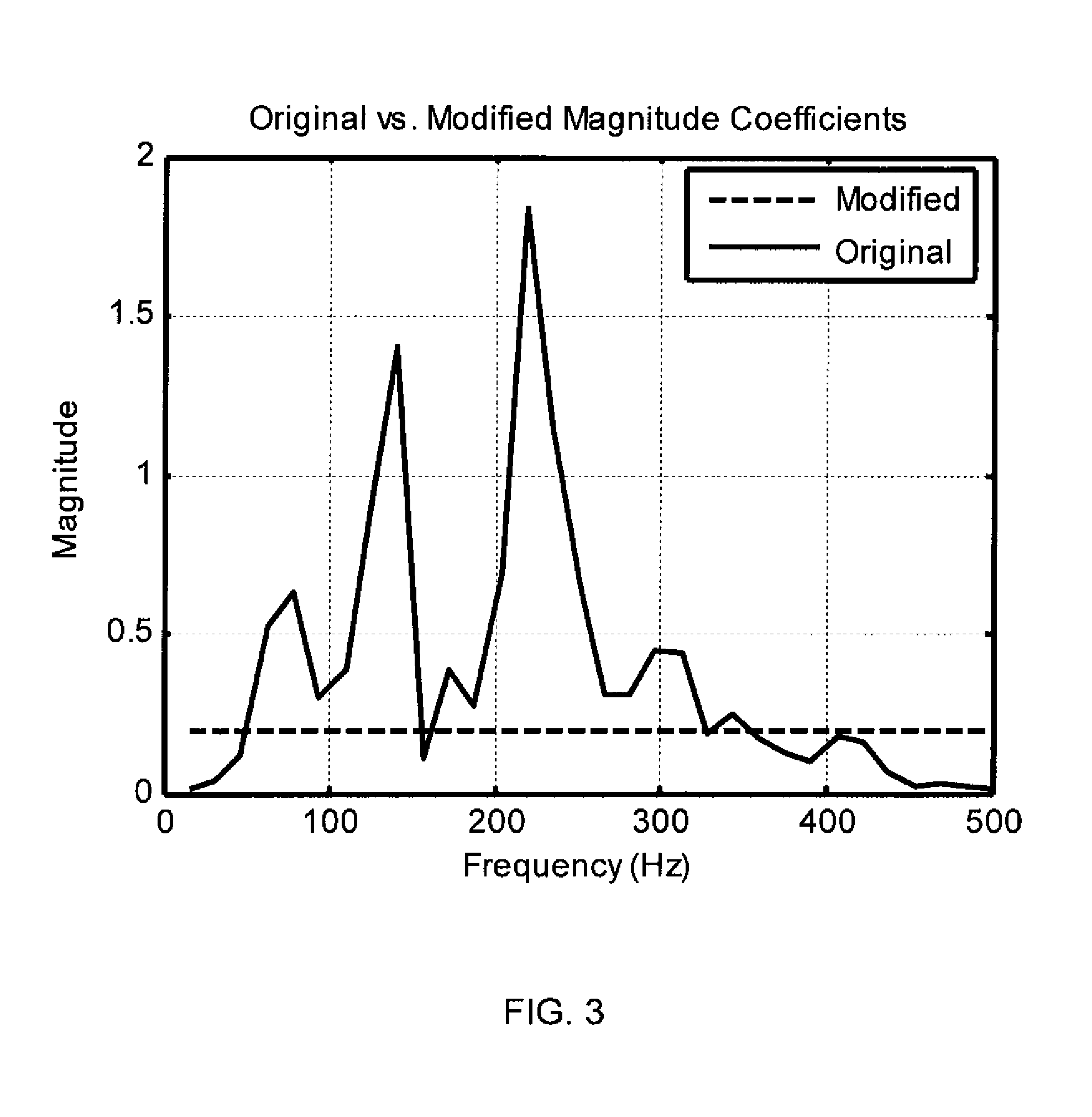
Methods for modeling the secondary path of an ANC system to improve convergence and tracking during noise control operation, and their associated uses are provided. In one aspect, for example, a method for modeling a secondary path for an active noise control system is provided. Such a method may include receiving a reference signal, filtering the reference signal with an initial secondary path model to obtain a filtered reference signal, calculating an autocorrelation matrix from the filtered reference signal, and calculating a plurality of eigenvalues from the autocorrelation matrix. The method may further include calculating a maximum difference between the plurality of eigenvalues and iterating a test model to determine an optimized secondary path model having a plurality of optimized eigenvalues that have a minimized difference that is less than the maximum difference of the plurality of eigenvalues, such that the optimized secondary path model may be utilized in the active noise control system.
Owner:BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIV
Active noise tuning system
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
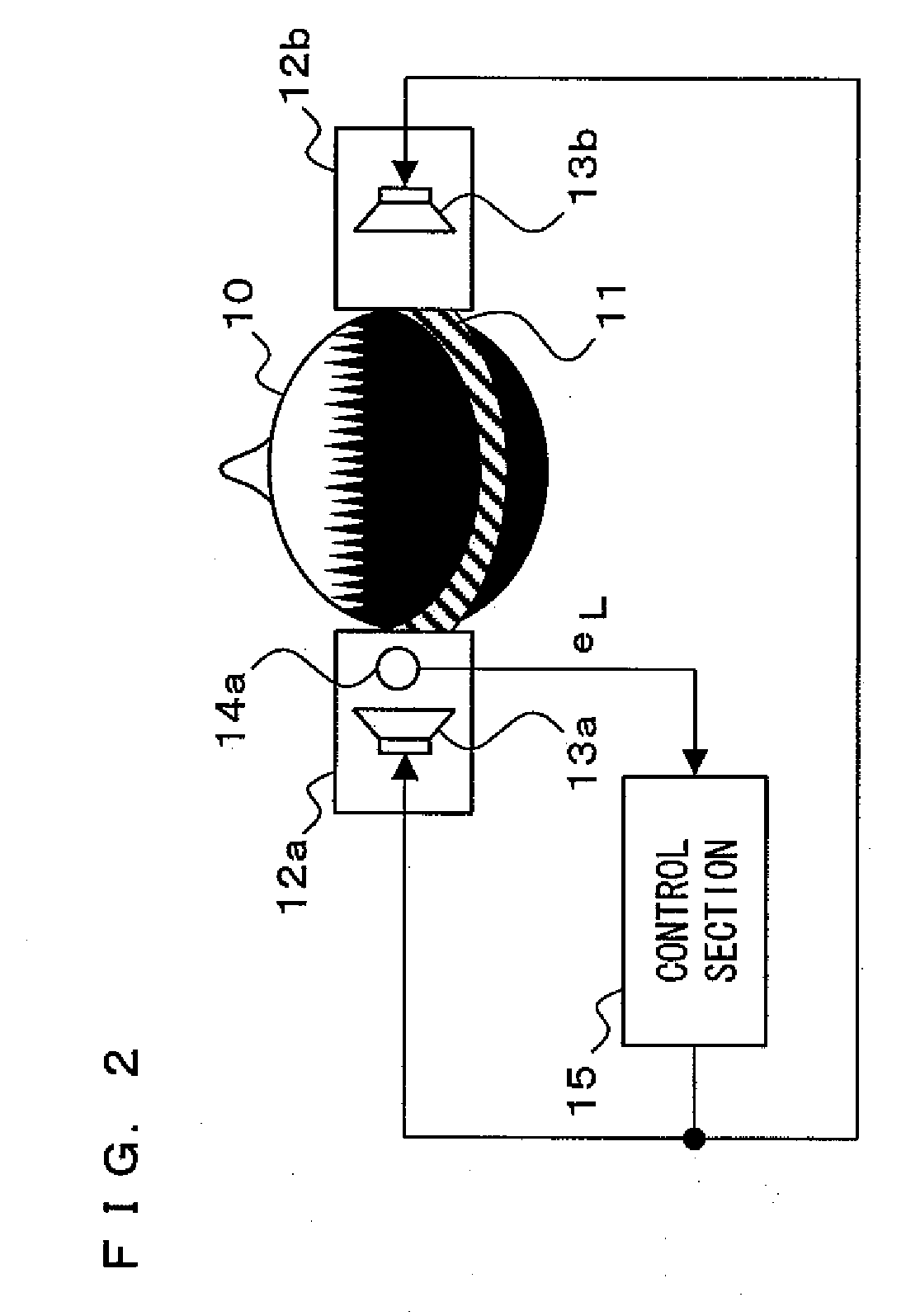
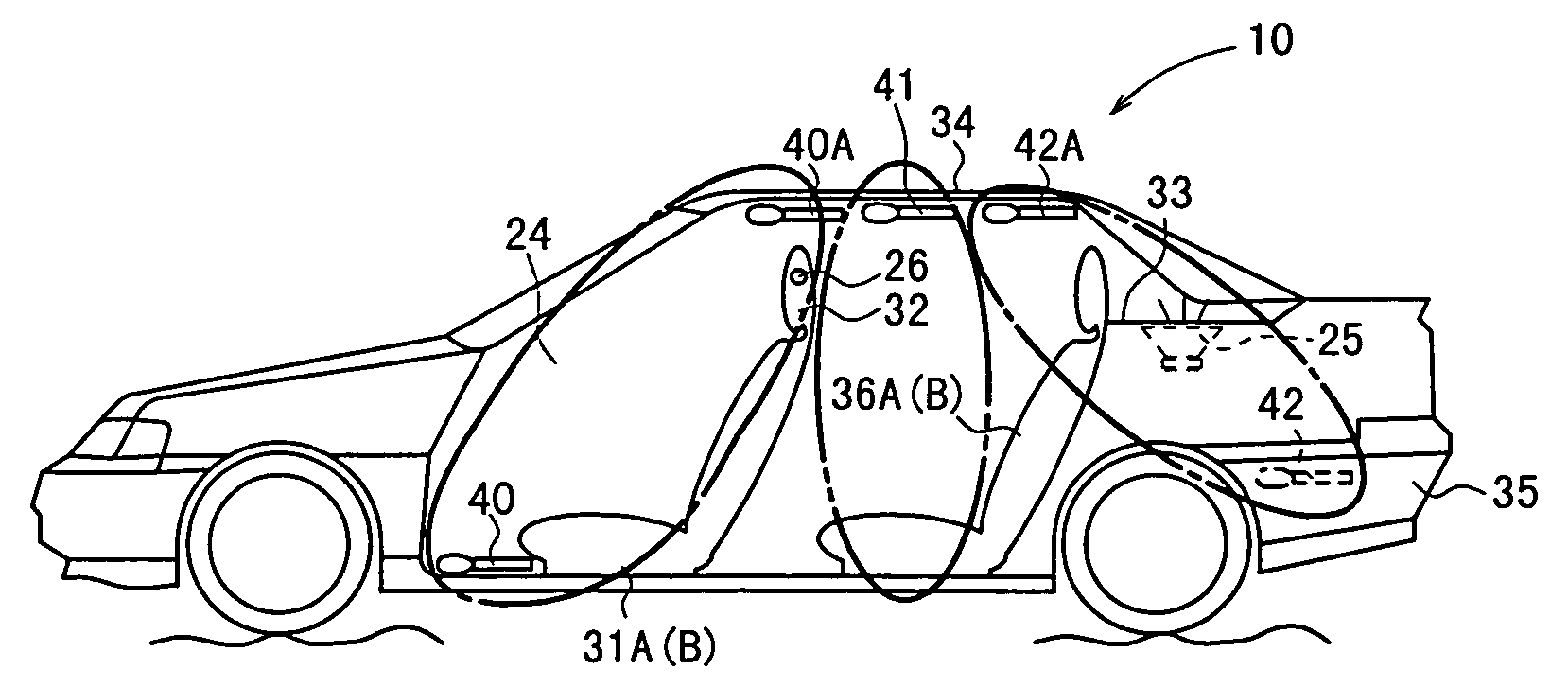
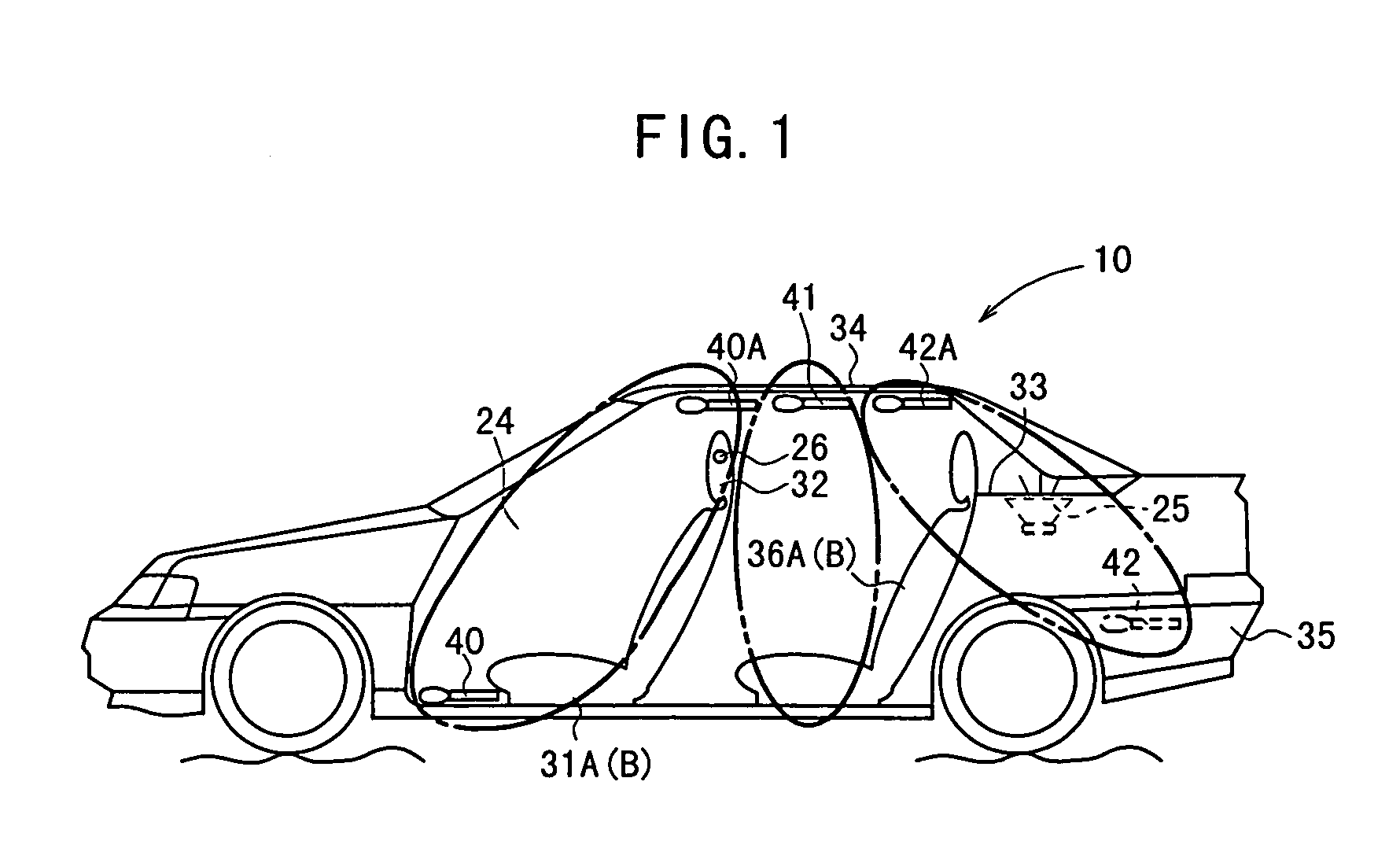
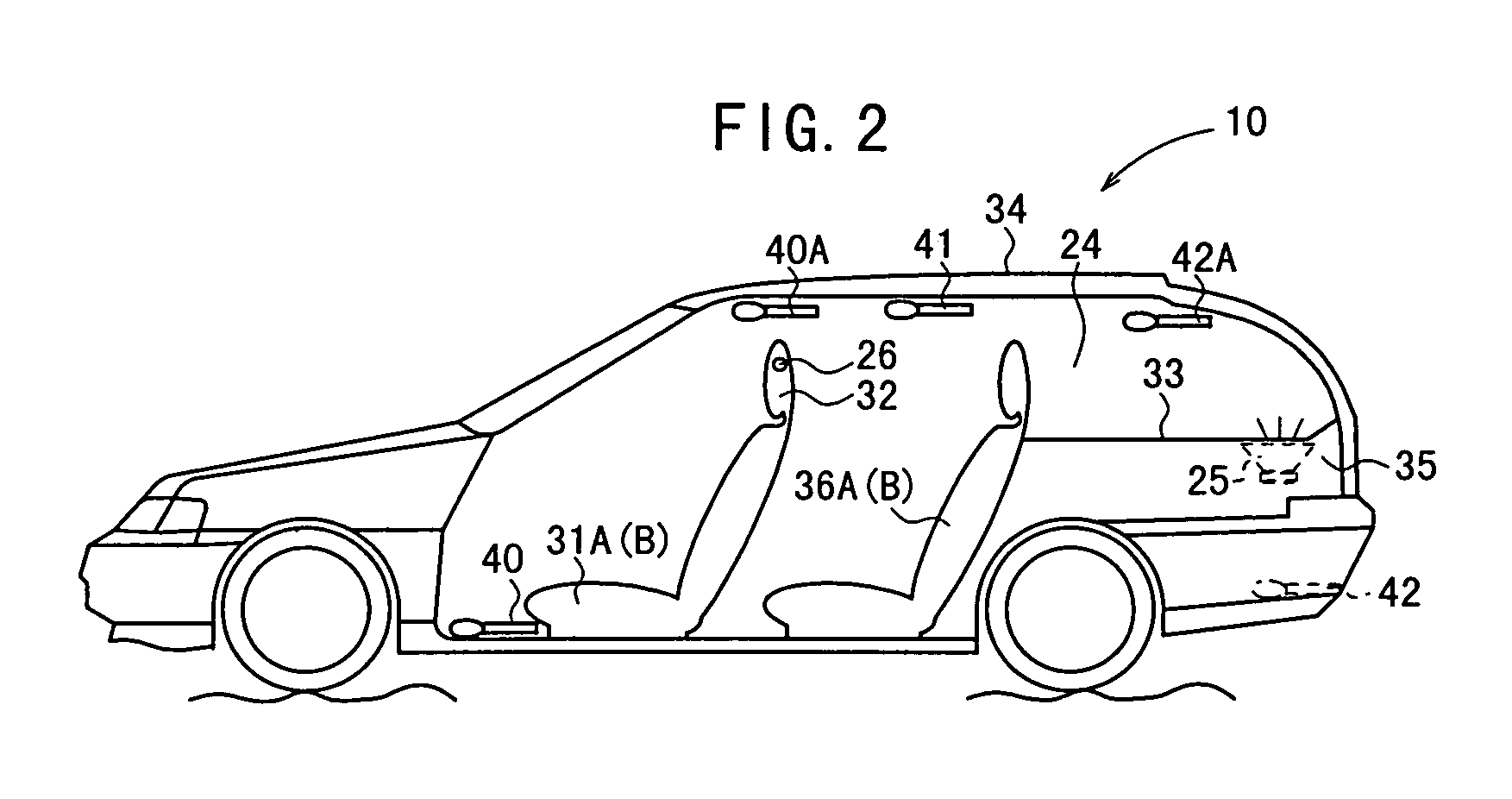
[feedback active noise controlling circuit and headphone]
InactiveUS20050249355A1Reduce noiseImprove reception qualityEar treatmentHeadphones for stereophonic communicationNoise controlEngineering
A feedback active noise cancellation headphone is disclosed. A plurality of microphone sensors are disposed in front of the left and the right speakers of the headphone for improving the sound reception quality of the microphone sensors, so that the active noise controlling circuit generates an inverse phase soundwave accurately for countering the low frequency noise, and further to improve the noise reduction performance of the active noise cancellation headphone.
Owner:LAB9
Active noise control apparatus
InactiveUS20080240457A1Lighten the computational burdenReduce manufacturing costEar treatmentNoise generationNoise controlControl signal
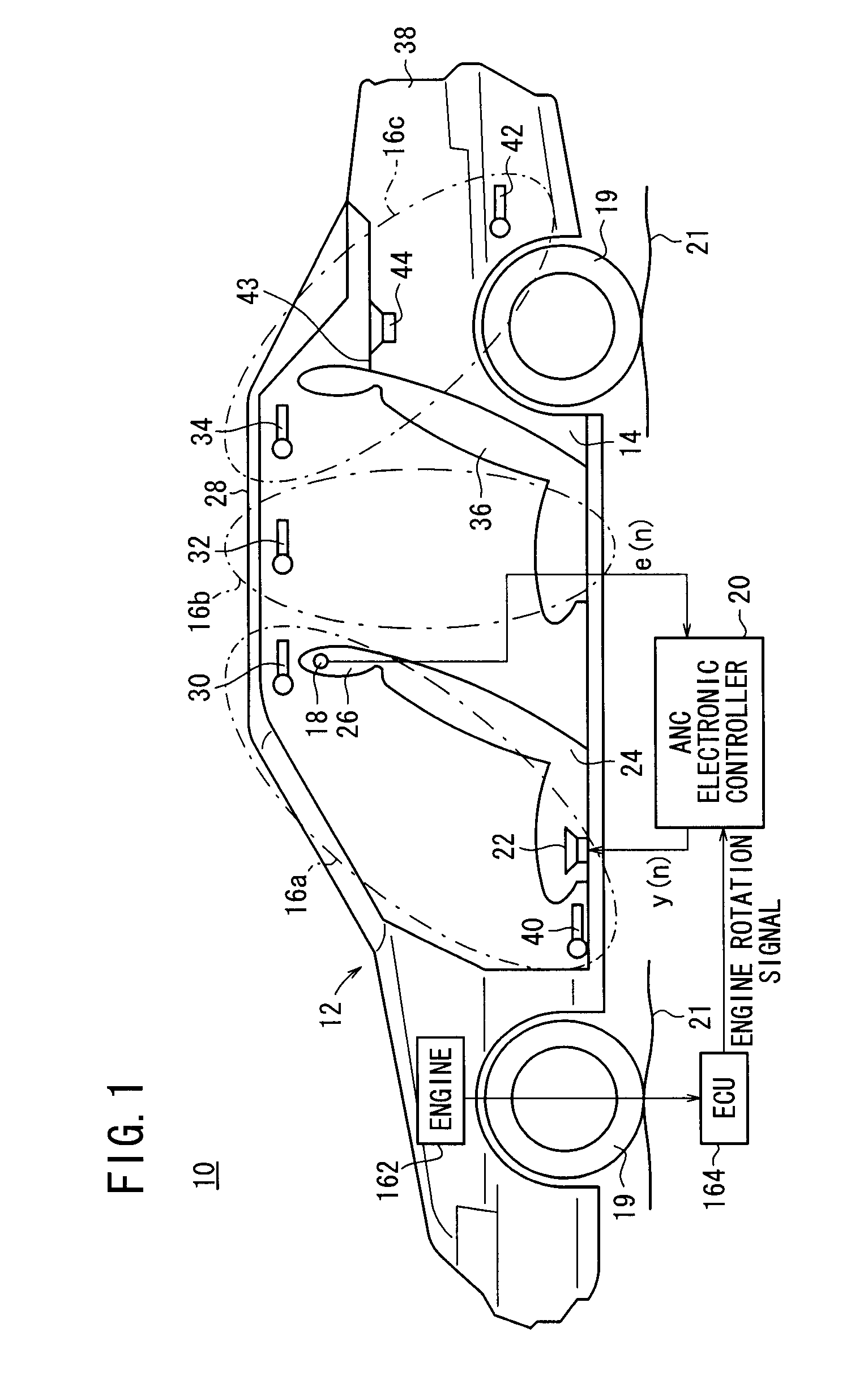
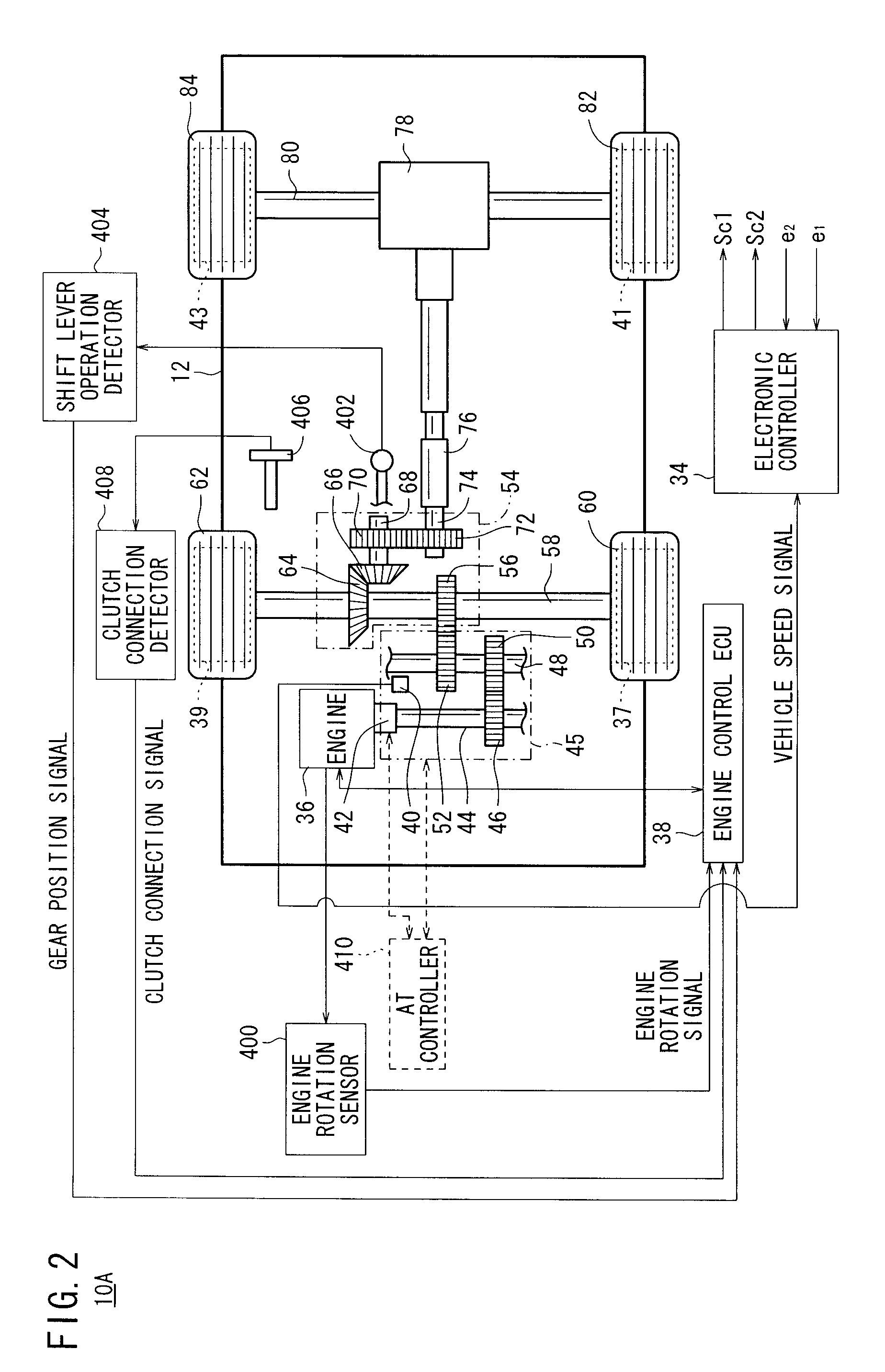
A subtractor subtracts an echo canceling signal Ĉ·yl(n−1) from a canceling error signal e(n) to estimate a residual noise to be silenced at the position of a microphone, and outputs a first basic signal x1(n) representing the residual noise. A first control circuit section generates a first control signal y1(n) based on the first basic signal x1(n) and a second basic signal x2(n) that is generated by delaying the first basic signal x1(n) by a time Z−n. A second circuit section generates a second control signal y2(n) based on the first basic signal x1(n) and an engine rotation signal.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
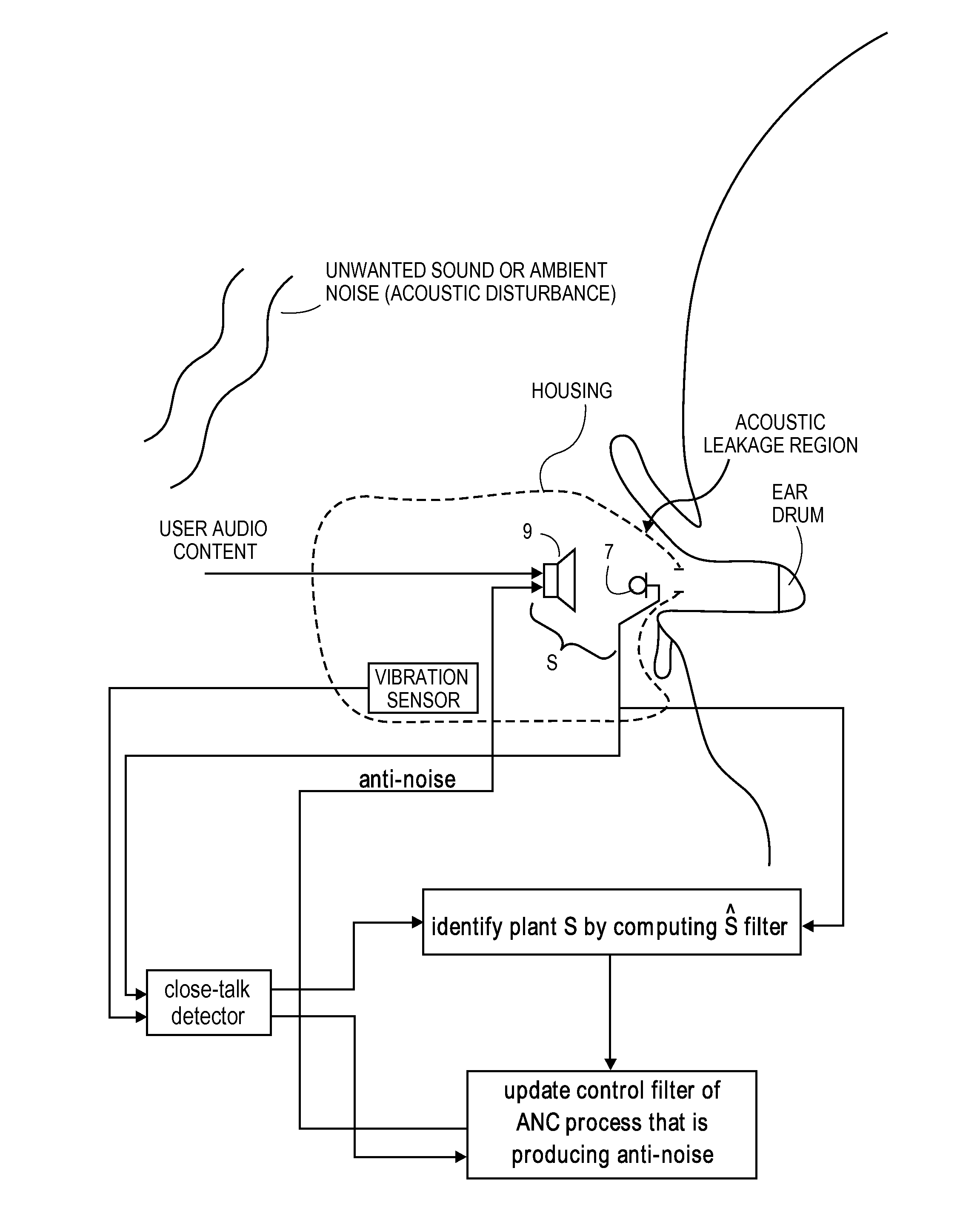
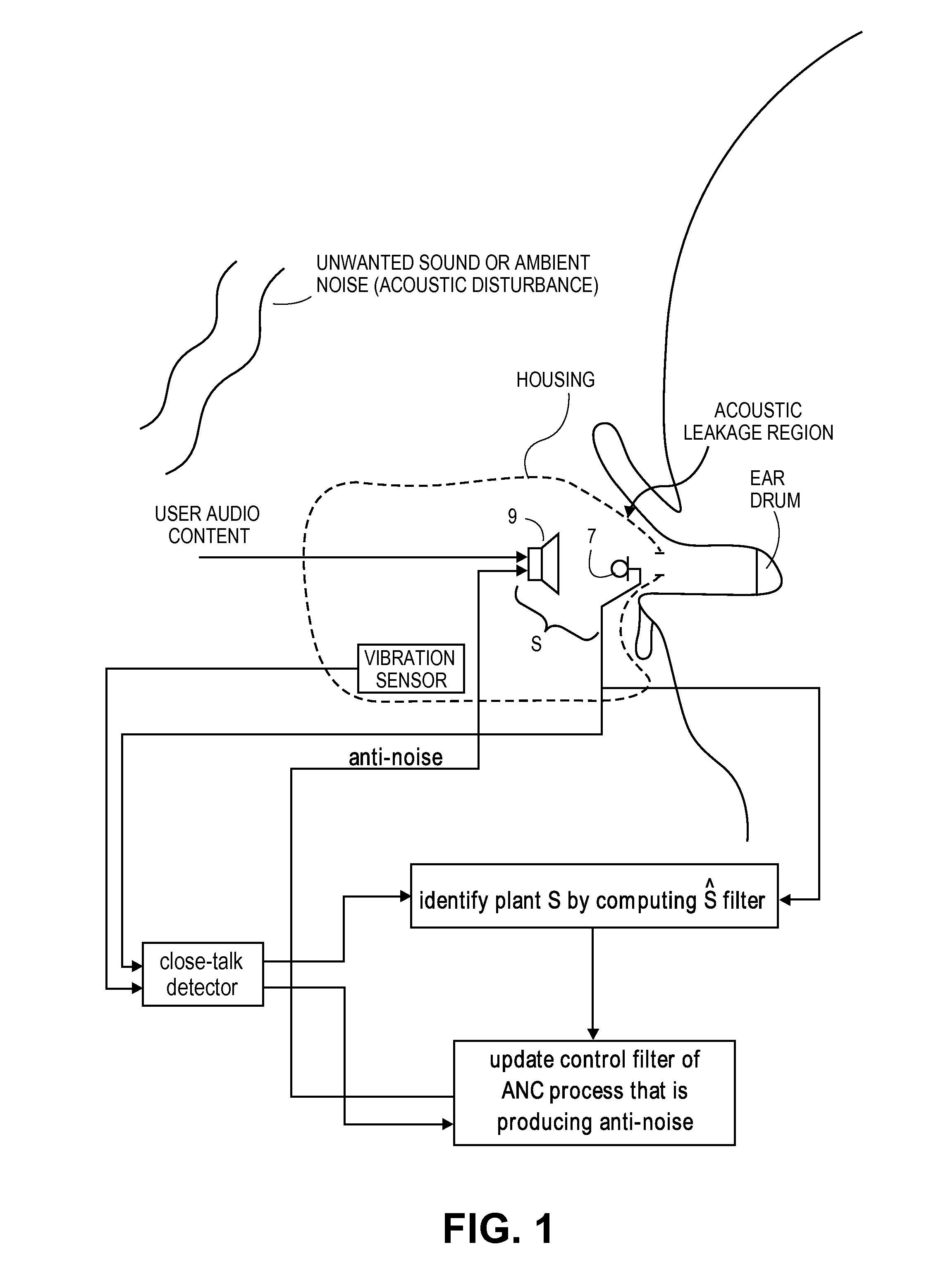
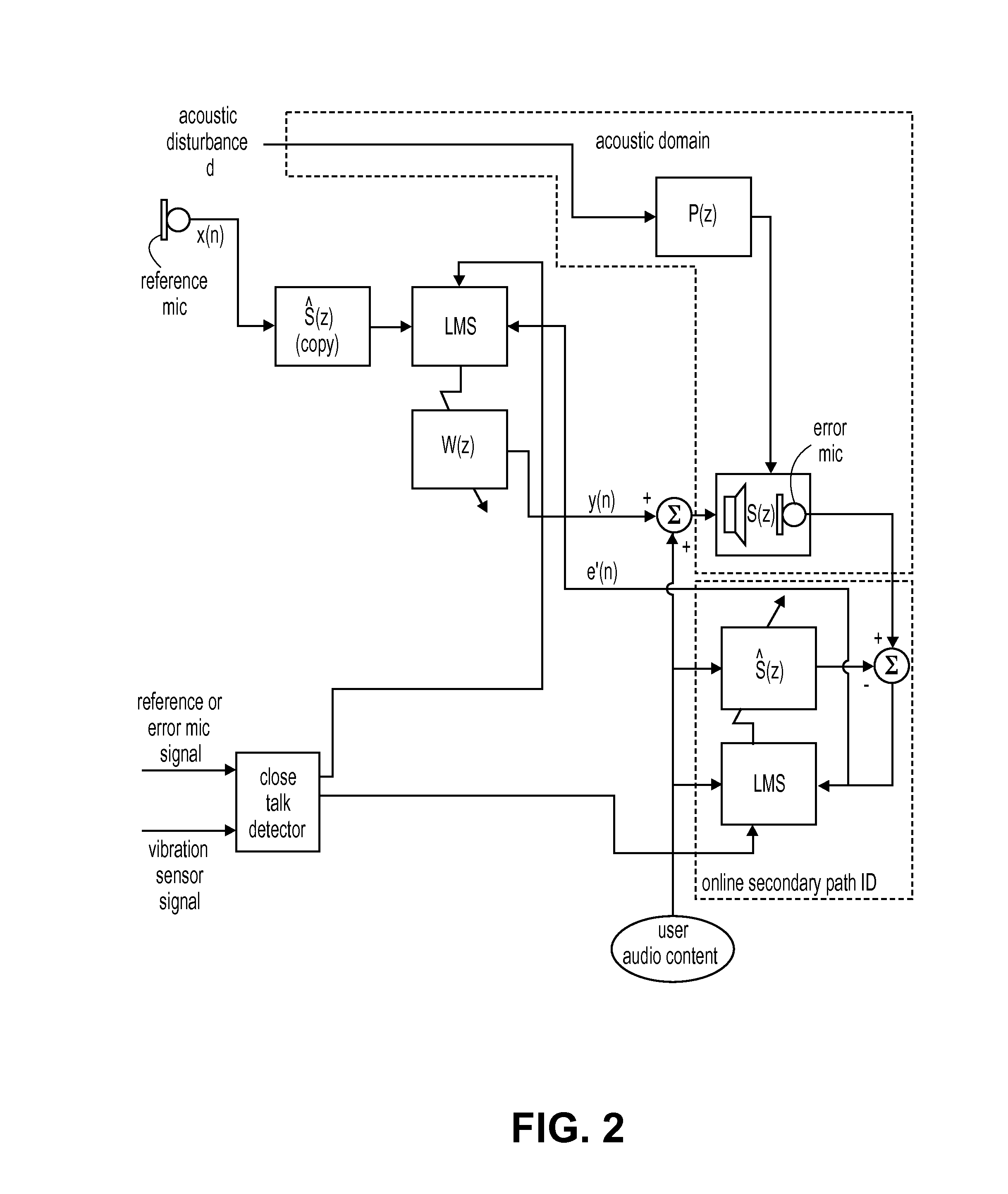
Close-talk detector for personal listening device with adaptive active noise control
A close-talk detector detects a near-end user's speech signal, while an adaptive ANC process is running, and in response helps prevent the filter coefficients of an adaptive filter of the ANC process from being corrupted, thereby reducing the risk of the adaptive filters diverge. Upon detecting speech using a vibration sensor signal and one or more microphone signals, the detector asserts a signal that slows down, or even freezes or halts, the adaptation of the adaptive filter. The signal may be de-asserted when no more speech is being detected, thereby allowing the adaptive ANC process to resume its normal rate adaptation of the filter. The detector may continuously operate in this manner during the call, as the user talks and then pauses and then resumes talking. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:APPLE INC
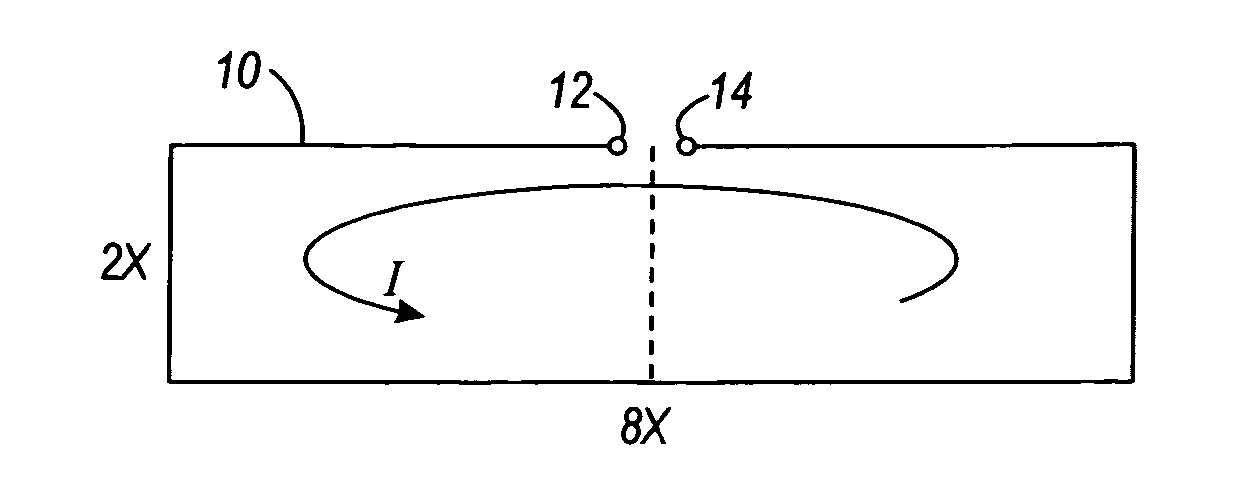
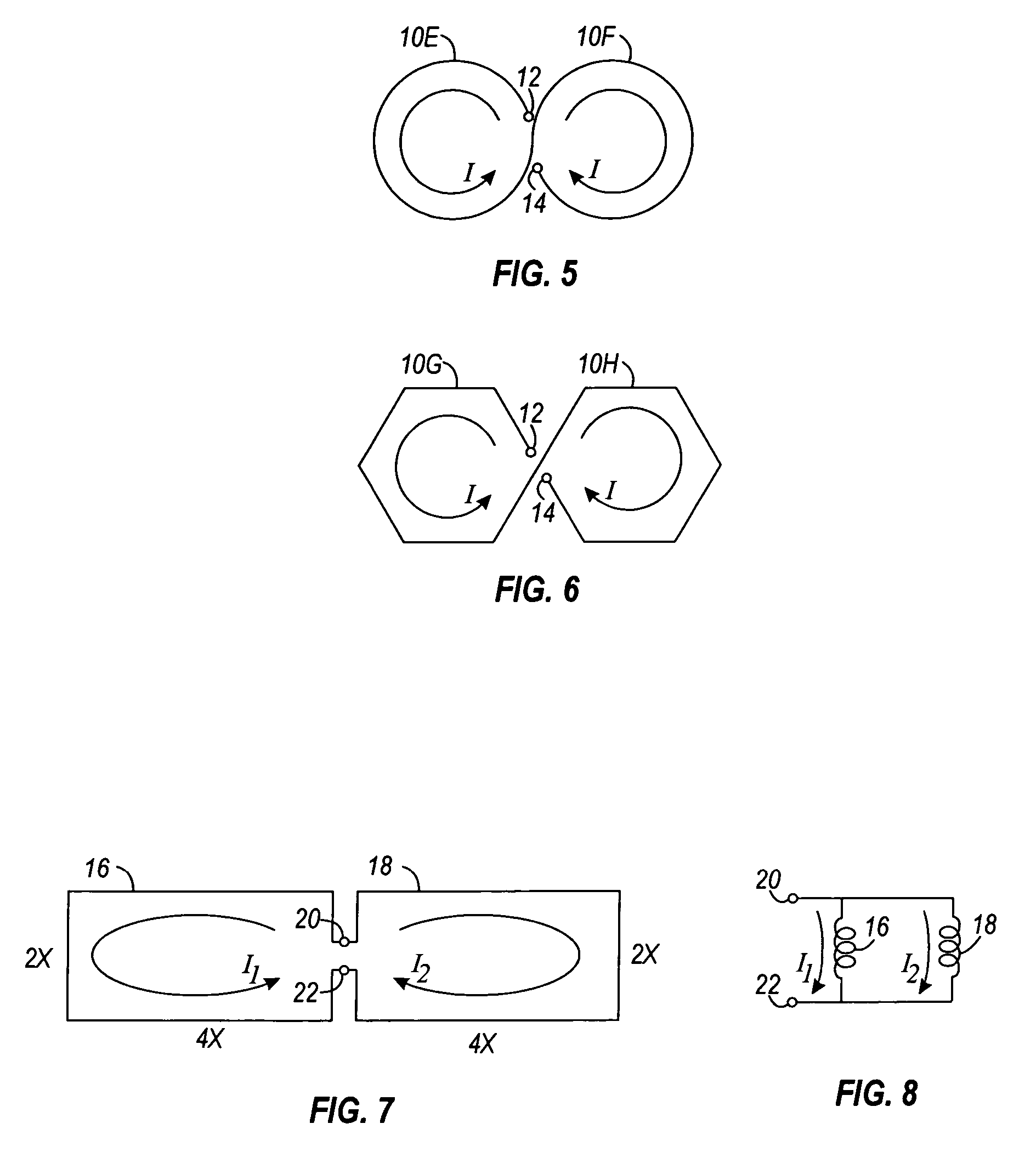
Magnetically differential inductors and associated methods
InactiveUS20060226943A1Interference minimizationMaximize cancellationElectromagnets without armaturesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNoise controlInductor
A method and apparatus is provided for use in an integrated circuit or printed circuit board for reducing or minimizing interference. An inductance is formed using two or more inductors coupled together and configured such that current flows through the inductors in different directions, thus at least partially canceling magnetic fields. When designing a circuit, the configuration of the inductors, as well as the relative positions of portions of the circuit, can be tweaked to provide optimal interference or noise control.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
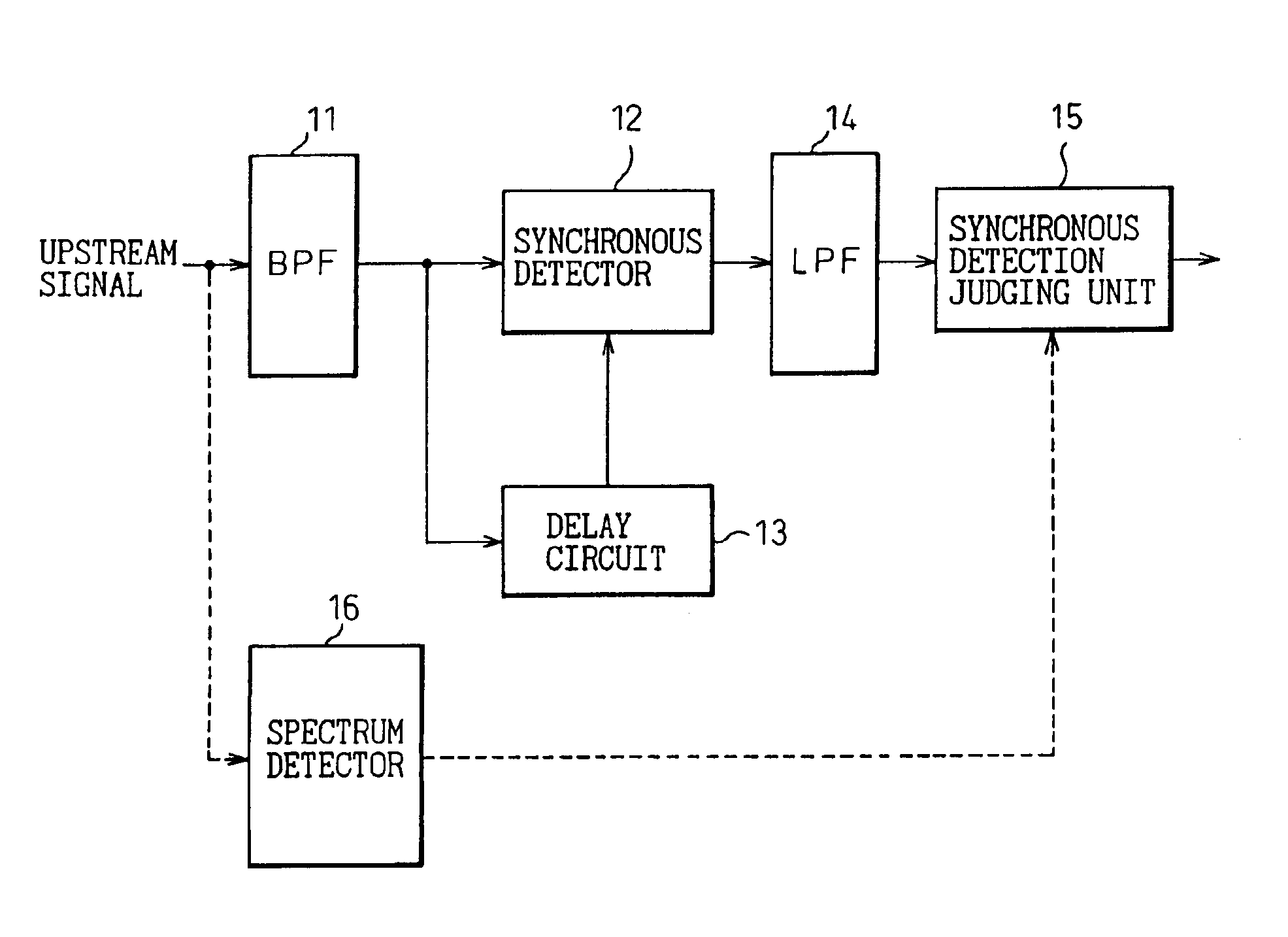
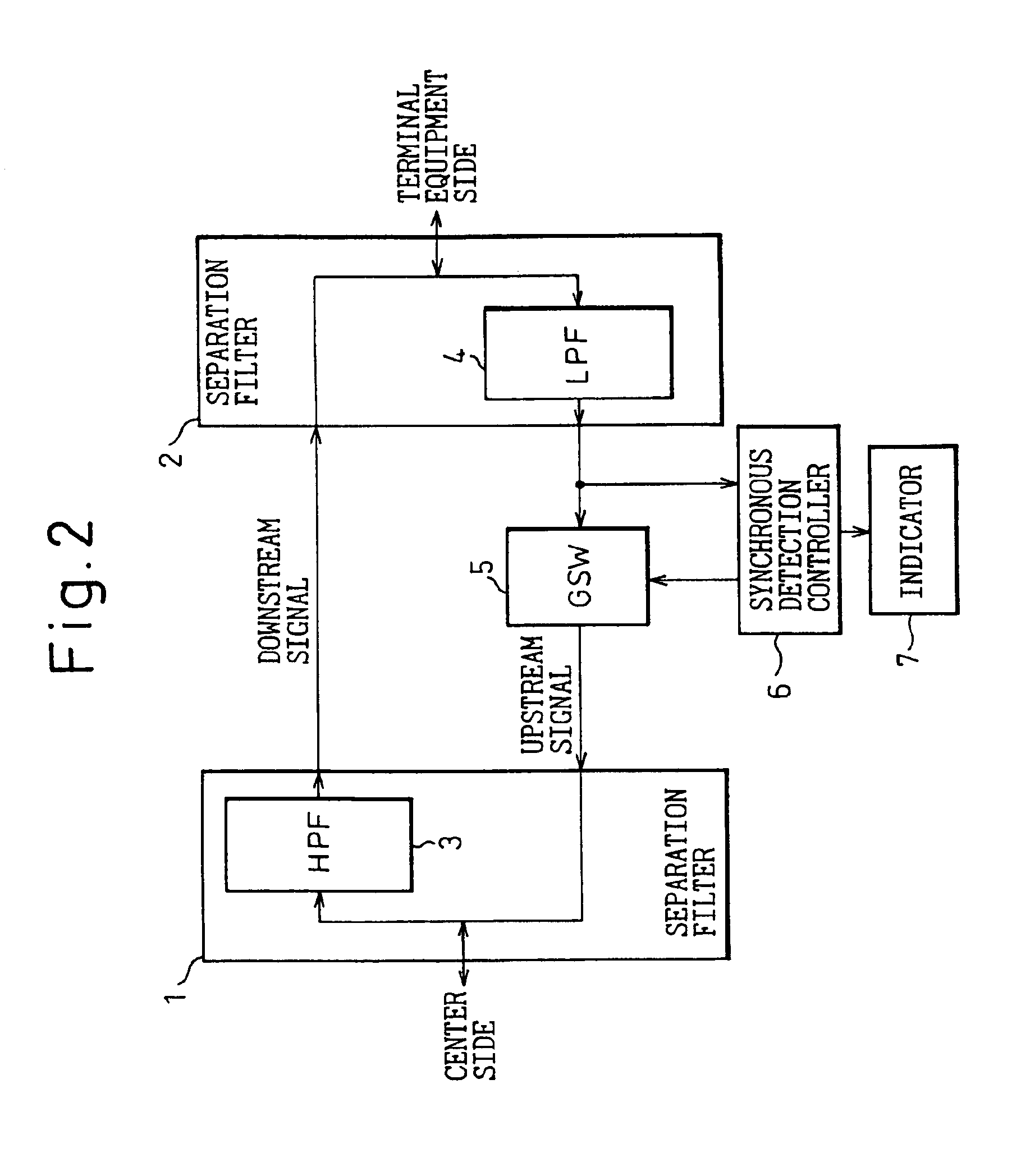
Ingress noise control system and ingress noise blocking device
InactiveUS6868552B1Eliminate the effects ofRepeater circuitsTwo-way working systemsNoise controlLow-pass filter
The present invention concerns an ingress noise control system and an ingress noise blocking device which are used in a cable system to suppress ingress noise. In the cable system providing two-way communication using different frequency bands for transmission of upstream and downstream signals, the ingress noise control system includes, within a distribution unit, a two-way amplification unit, etc. provided in an upstream signal transmission path, a synchronous detection controller 6 for synchronously detecting the upstream signal transmitted from terminal equipment and separated by a low-pass filter 4 in a second separation filter 2, a gate switch circuit 5 which is turned on by the synchronous detection controller 6 to pass the upstream signal only when the upstream signal is synchronously detected, and an indicator 7 for indicating the on / off state of the gate switch circuit 5.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD +1
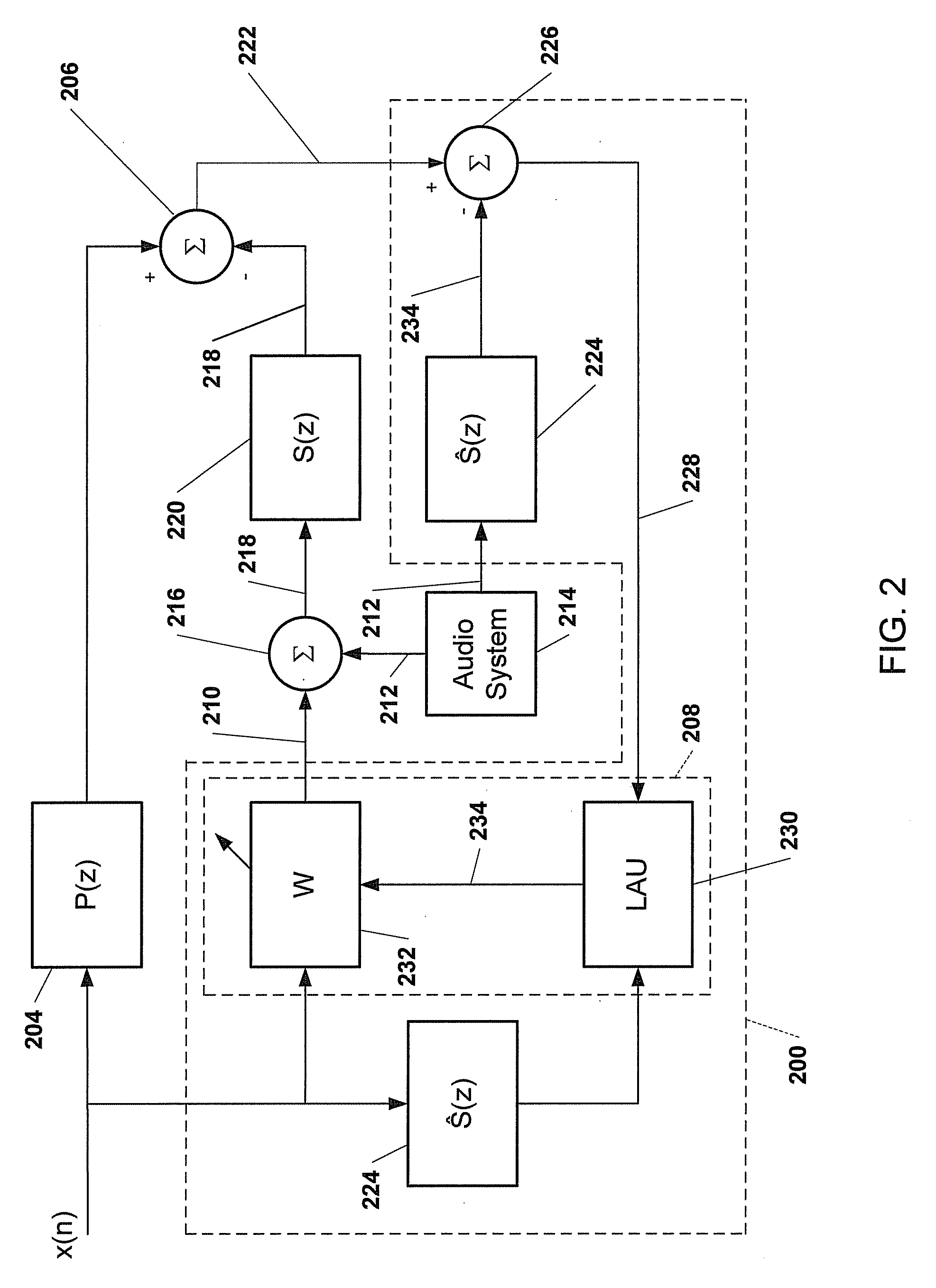
System for active noise control based on audio system output
An active noise control (ANC) system is configured to generate at least one anti-noise signal configured to drive a speaker to generate sound waves to destructively interfere with an undesired sound present in a target space. The at least one anti-noise signal is adjusted based an output signal of an audio system. The at least one anti-noise signal may be adjusted based on at least one of a volume level of the audio system, a power level of at least one predetermined frequency or frequency range of the output signal of the audio system, frequency content of an output signal of the audio system. The ANC system receives an error signal to adjust generation of the at least one anti-noise signal. The error signal is adjusted to compensate for adjustment of the at least one anti-noise signal based on the output signal of the audio system.
Owner:APPLE INC
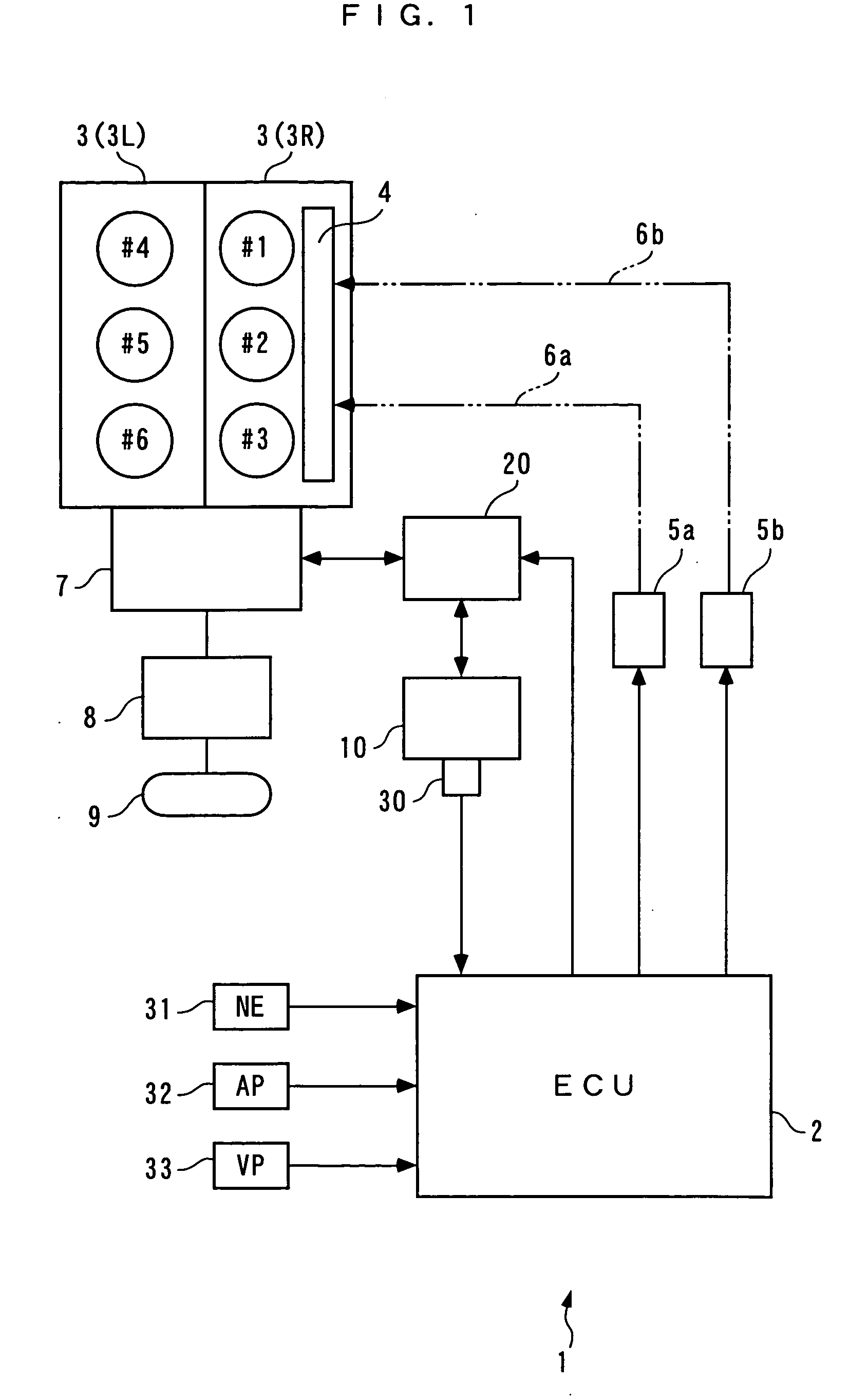
Control system for variable-cylinder internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20060107919A1Improve fuel economyReduce vibrationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesNoise controlControl system
A control system for a variable-cylinder internal combustion engine, which is capable of attaining excellent fuel economy by executing a partial-cylinder operation mode as long as possible, while suppressing vibration and noise during the partial-cylinder operation mode. A control system switches the operation mode of a variable-cylinder internal combustion engine between an all-cylinder operation mode in which all of a plurality of cylinders (#1 to #3, and #4 to #6) are put in operation, and a partial-cylinder operation mode in which some (#1 to #3) of the plurality of cylinders are deactivated. During the partial-cylinder operation mode, the control system 1 calculates a degree-of-continuation parameter SDTQCSNH indicative of a degree of continuation of a state where detected load TQECMDF on the engine is within a predetermined range of load between a first reference value TQCSNH and a second reference value TQCSEH smaller than the first reference value (steps 10 to 13), and determines whether or not the operation mode should be switched to the all-cylinder operation mode, based on the degree-of-continuation parameter SDTQCSNH (step 14).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
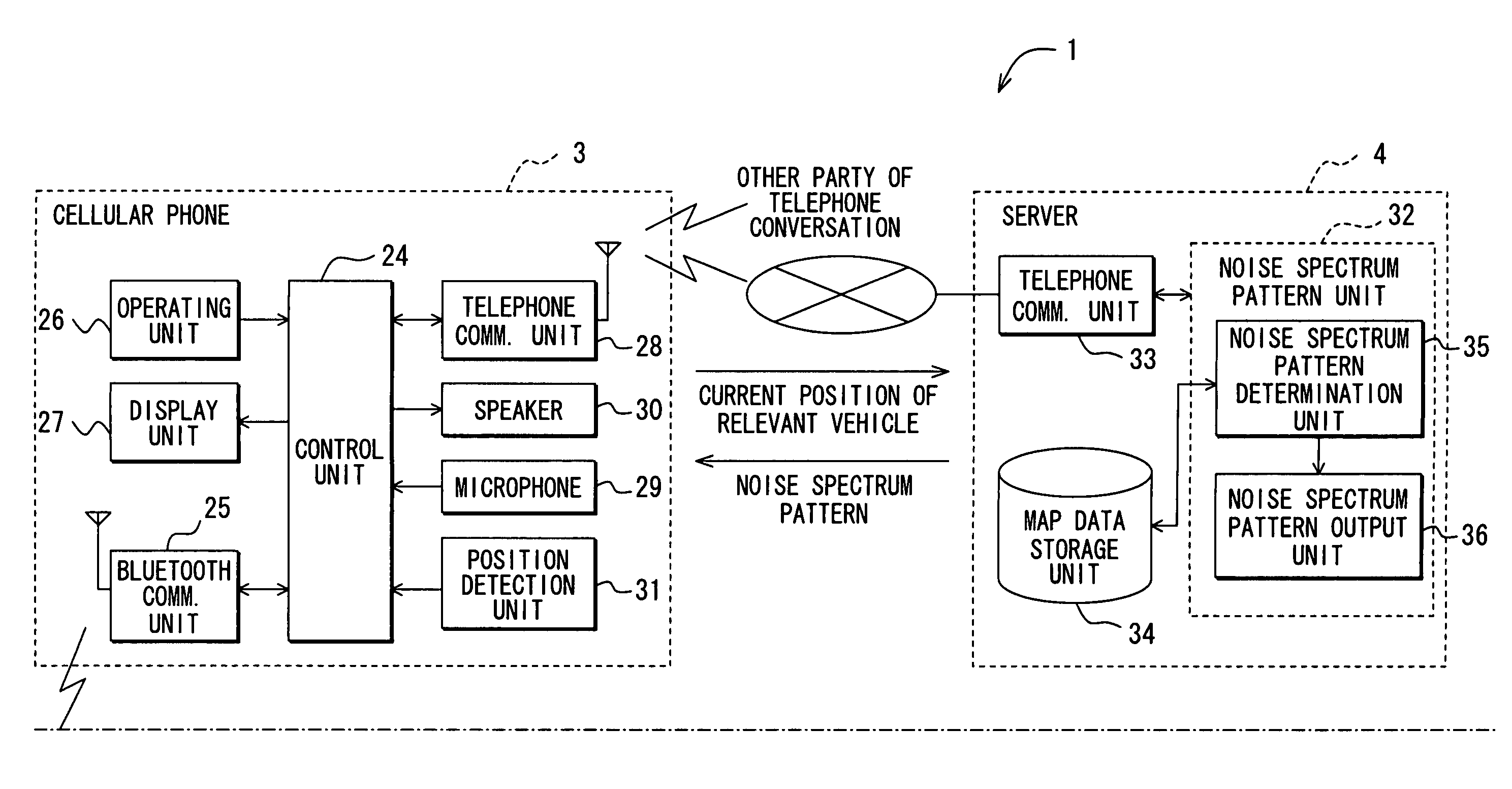
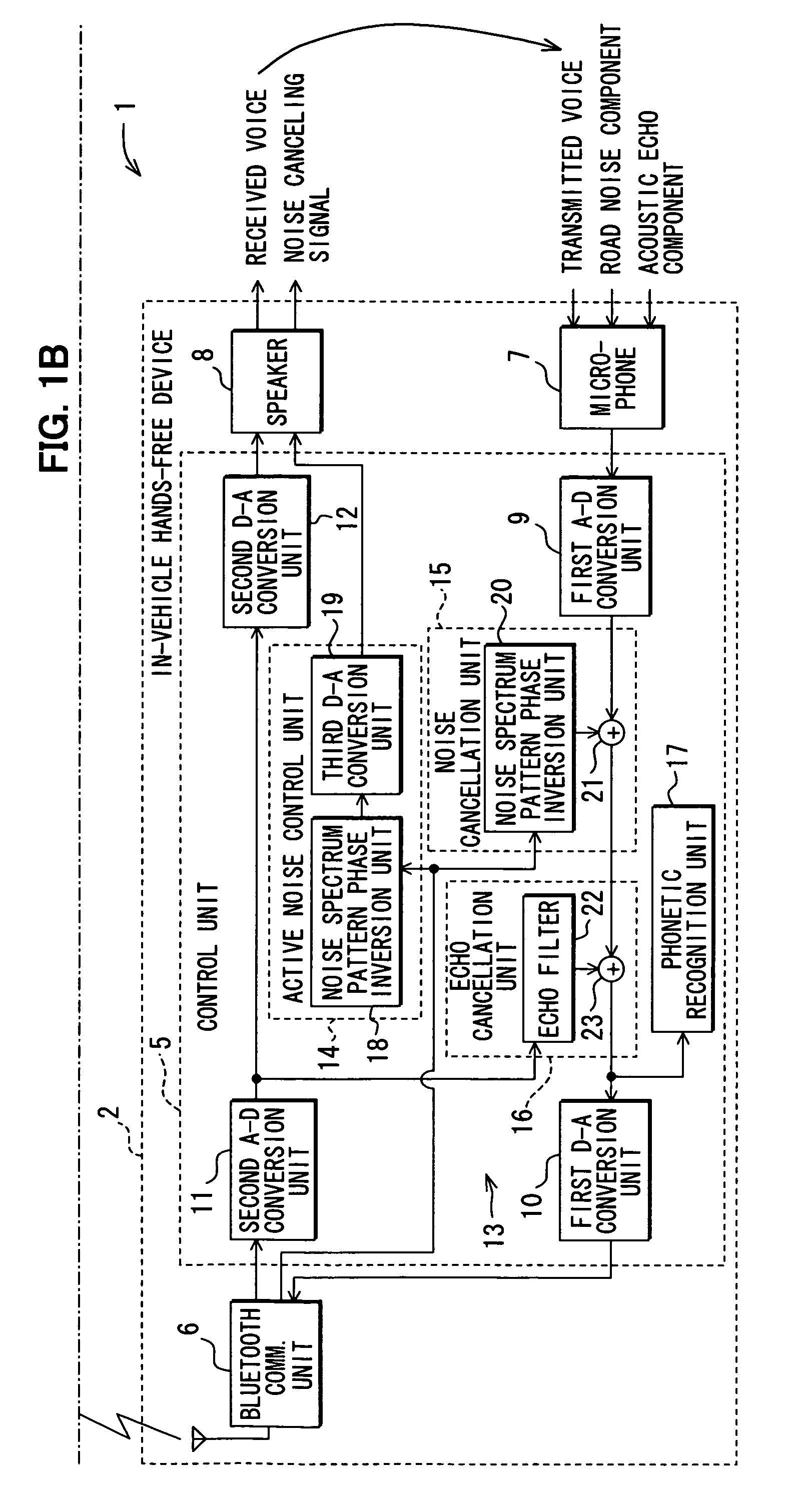
Communicating road noise control system, in-vehicle road noise controller, and server
Road noise is reduced without locally storing noise spectrum patterns for determination or without detecting the present position of a vehicle from the device. An in-vehicle hands-free device causes a cellular phone to detect the present position of the vehicle and transmit the position to a server. The server determines a noise spectrum pattern corresponding to the road surface on which the vehicle is presently running. The noise spectrum pattern is based on the present position of the vehicle received from the in-vehicle hands-free device and road information. The server transmits the noise spectrum pattern to the in-vehicle hands-free device whereupon a noise canceling signal is superimposed on a received signal. The noise canceling signal is based on an inverted noise spectrum pattern that is obtained by inverting the phase of the noise spectrum pattern. The resulting composite signal is output from a speaker.
Owner:DENSO CORP
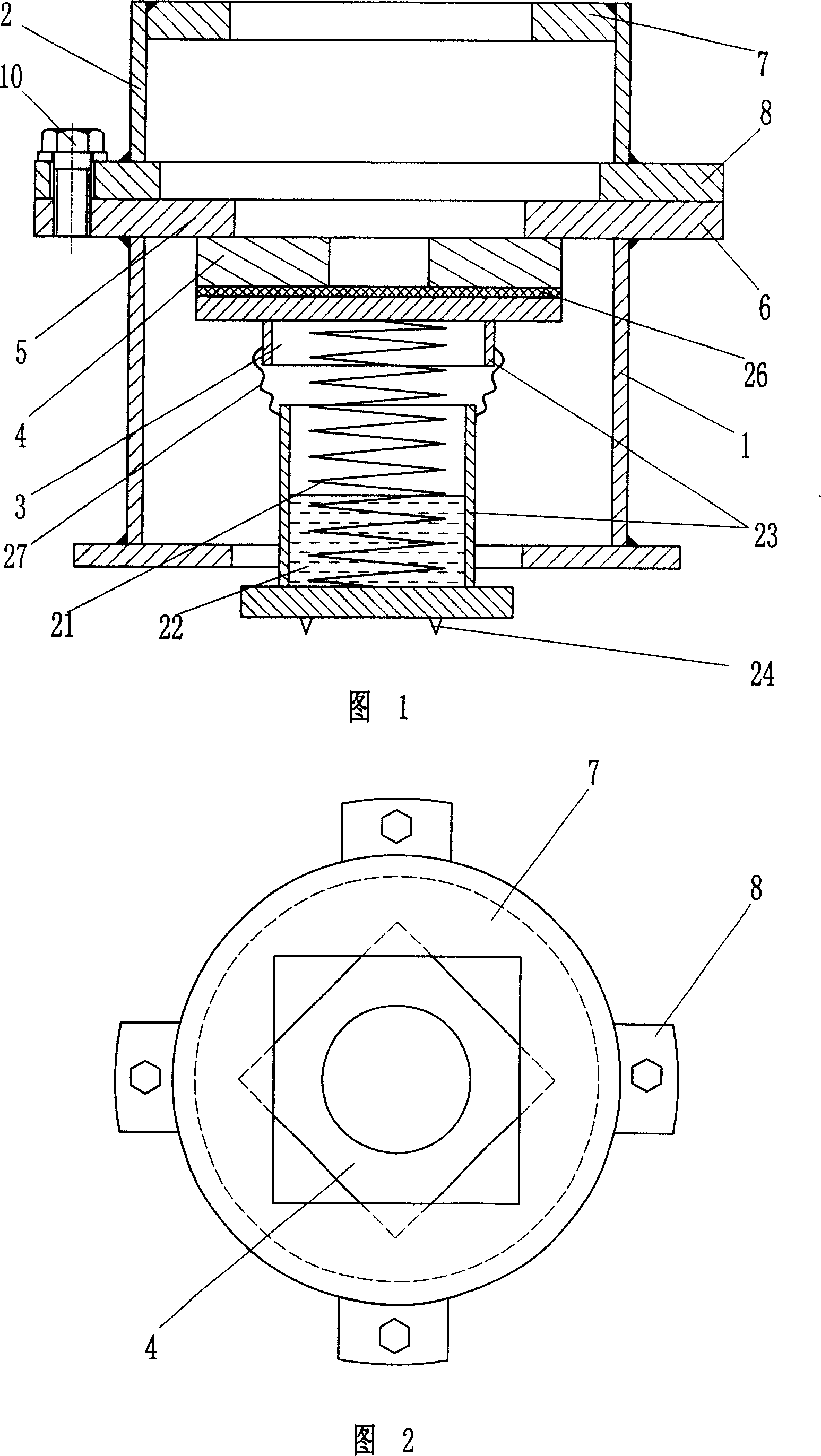
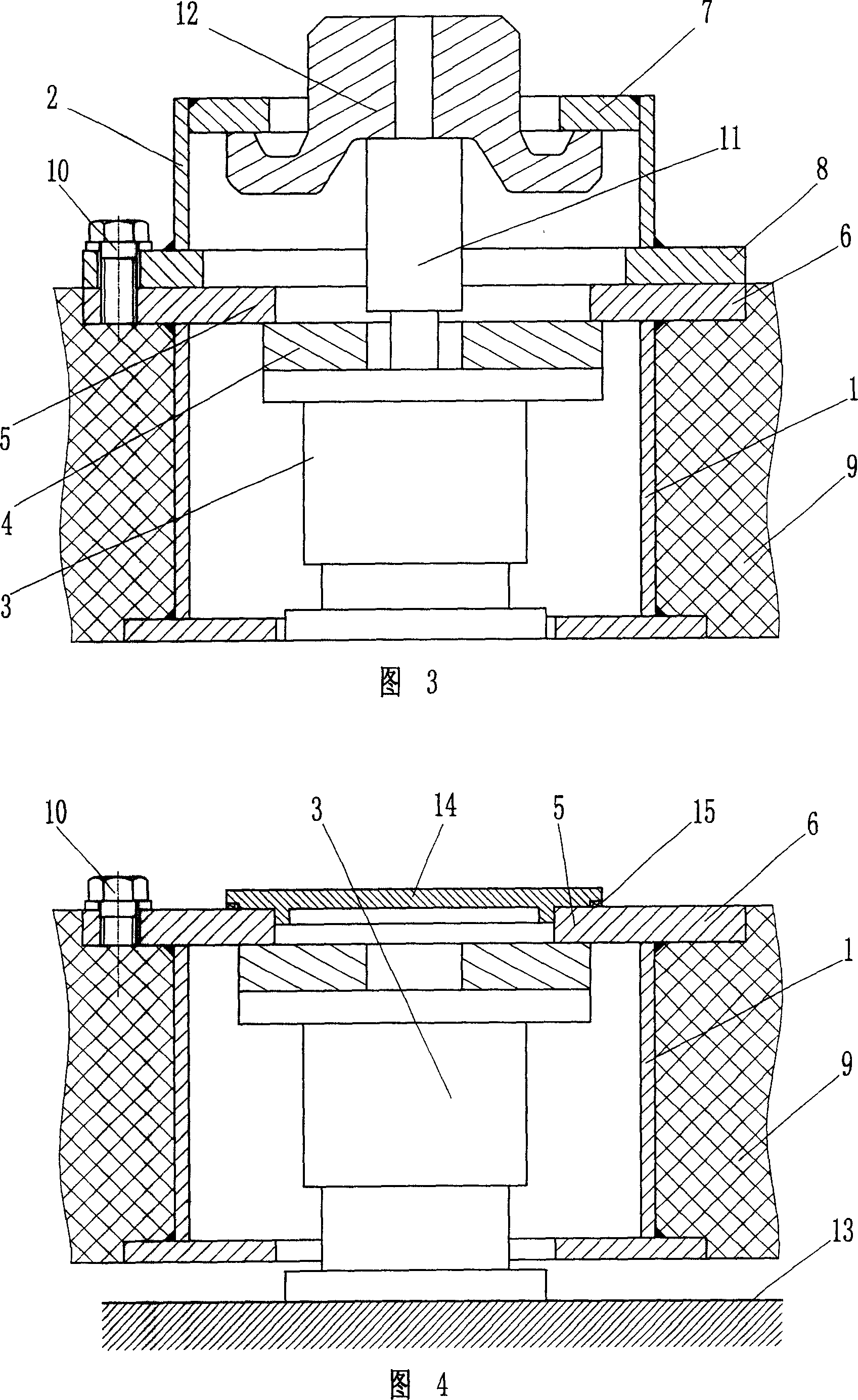
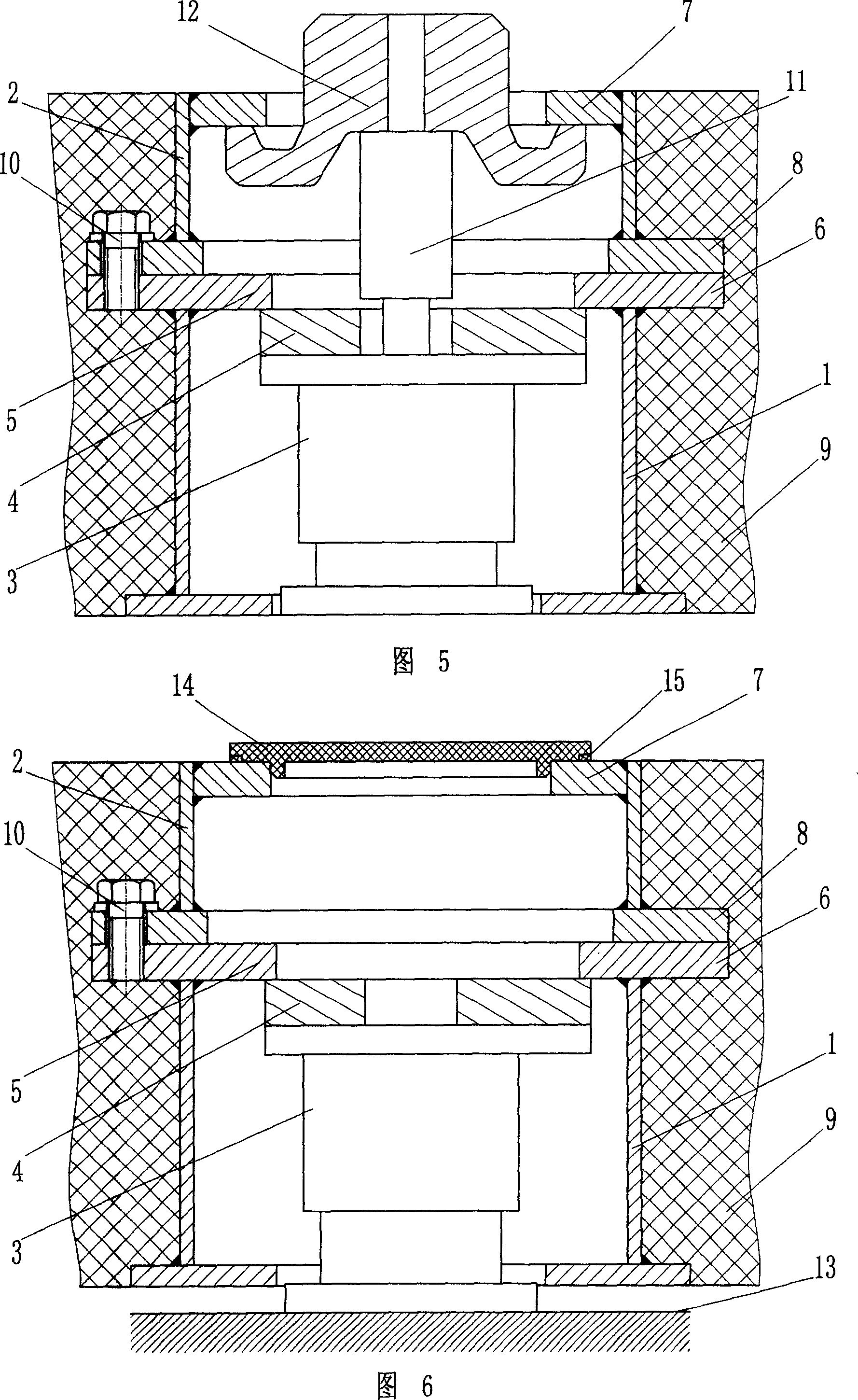
Split vibration-isolation device and use
ActiveCN101024981AShorten the processing cycleImprove the rapid response ability of supplyProtective foundationRailway tracksNoise controlEngineering
The invention belongs to the vibration and noise control field, especially relating to a vibration isolating device for rail vehicle, comprising: connecting sleeve and spring vibration isolator, where the connecting sleeve is equipped with support stop and lift stop and comprises upper and lower sleeves, a splitting connecting structure is arranged between the upper and lower sleeves, the support stop is arranged at the upper part of the lower sleeve and the lift stop is arranged at the lower part of the upper sleeve. And the invention has features of compact and reasonable structure, low cost, enlarging the application range of under-roadbed vibration isolating devices, strong practicality, and having both economic and environmental protection effects, able to be applied to thinner rail floating slabs.
Owner:尹学军 +1
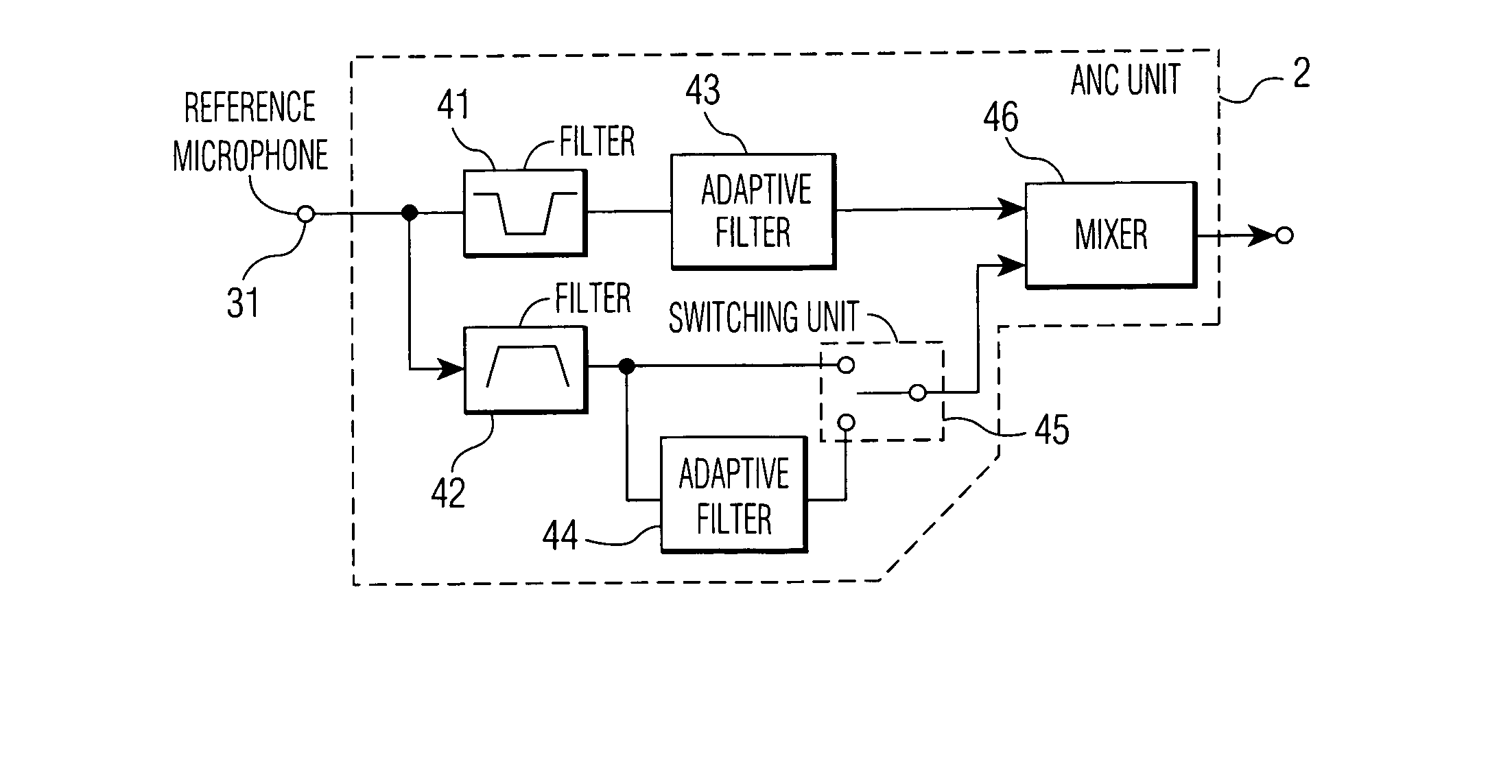
Noise reduction apparatus
An active noise control system includes a source unit for generating regenerative signals, an ANC unit for processing signals so as to actively cancel noise, sensors for detecting the information on the inside and outside of a vehicle, a vehicle interior voice discriminating unit for discriminating voice of conversation generated in the vehicle interior, an amplifier for amplifying the signals processed by ANC unit and reproducing transducers for reproducing the signals amplified by the amplifier.
Owner:SOLBERG CREATIONS +1
Vehicular active noise control system
ActiveUS20080292110A1Reliably canceling out driveline noiseWeight and costEar treatmentNoise generationNoise controlAdaptive filter
A frequency detecting circuit estimates the frequency fp of a propeller shaft based on the frequency fc of vehicle speed pulses, and calculates a control frequency fp′ which is a harmonic of the frequency fp. A basic signal generator generates a basic cosine wave signal xp1 and a basic sine wave signal xp2 of the control frequency fp′. Adaptive filters and an adder generate a control signal Scp for canceling a driveline noise produced in a passenger compartment by the propeller shaft. A speaker outputs a canceling sound based on the control signal Scp into the passenger compartment.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Active noise reduction audiometric headphones
InactiveUS6532296B1Reduce cavity volumeReduce the cushioning forceEar treatmentAudiometeringNoise controlAudiometry test
Active noise reduction headphones for audiometry where the earphone portion of said headphones has a cavity volume greater than 6 cc and including an acoustic-electric sensing means and an electro-acoustic transducing means which are used cooperatively and which has additional passive noise control means in the form of a circumaural seal around the ear for improving high frequency noise control performance, the headphone having a summing junction for combining the active noise reduction signal and an audiometry test signal.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Method and apparatus for a fan noise controller
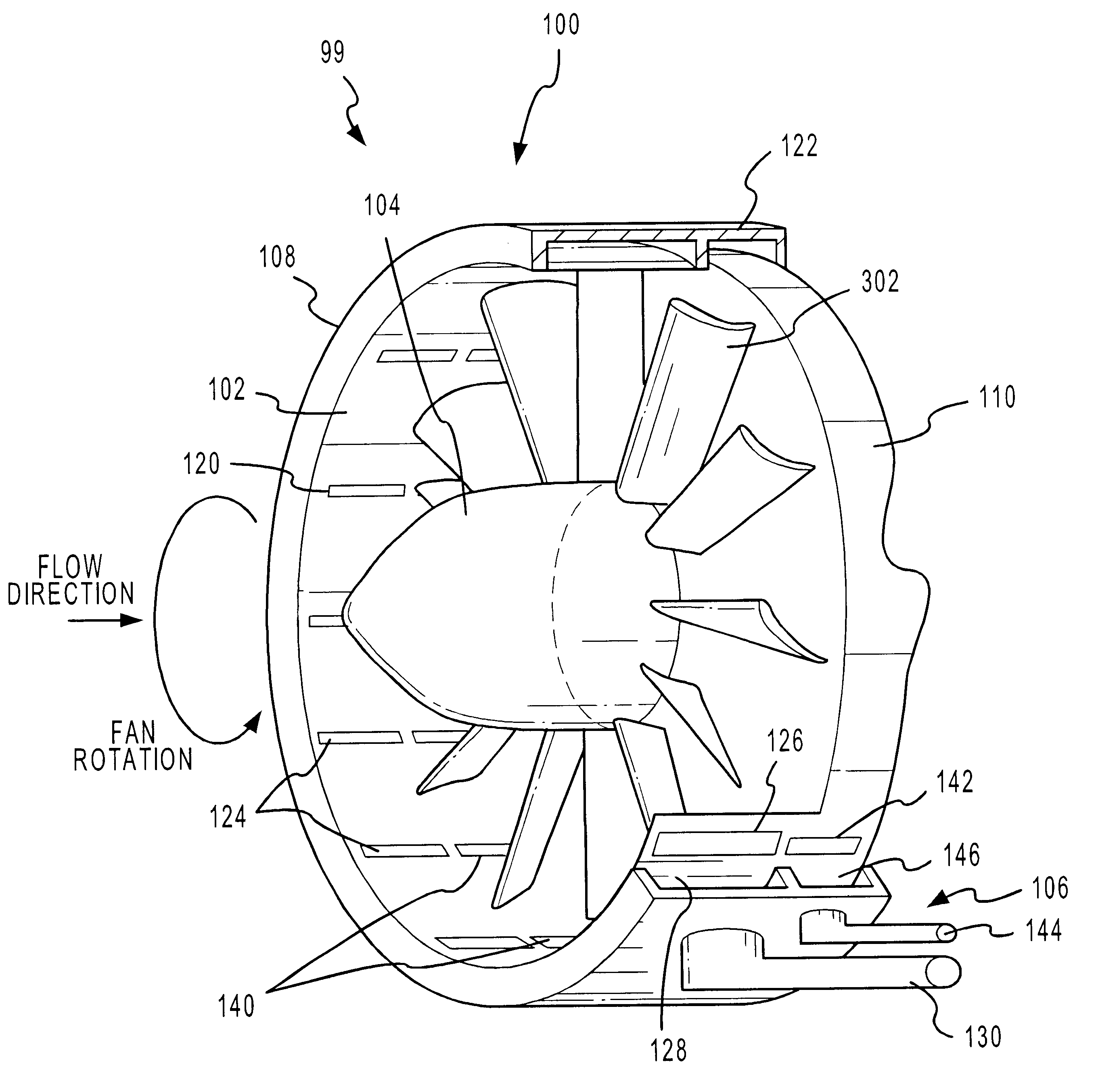
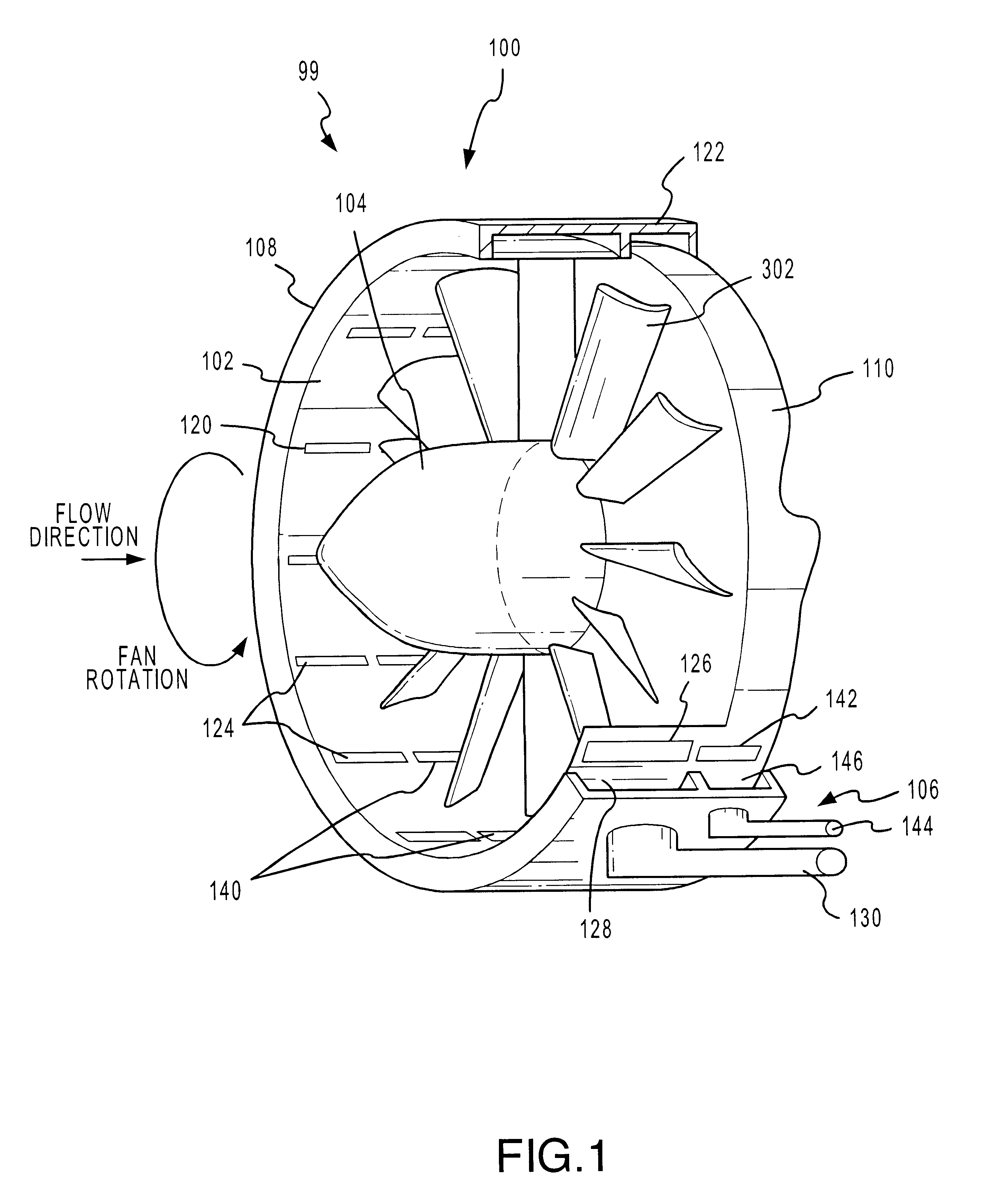
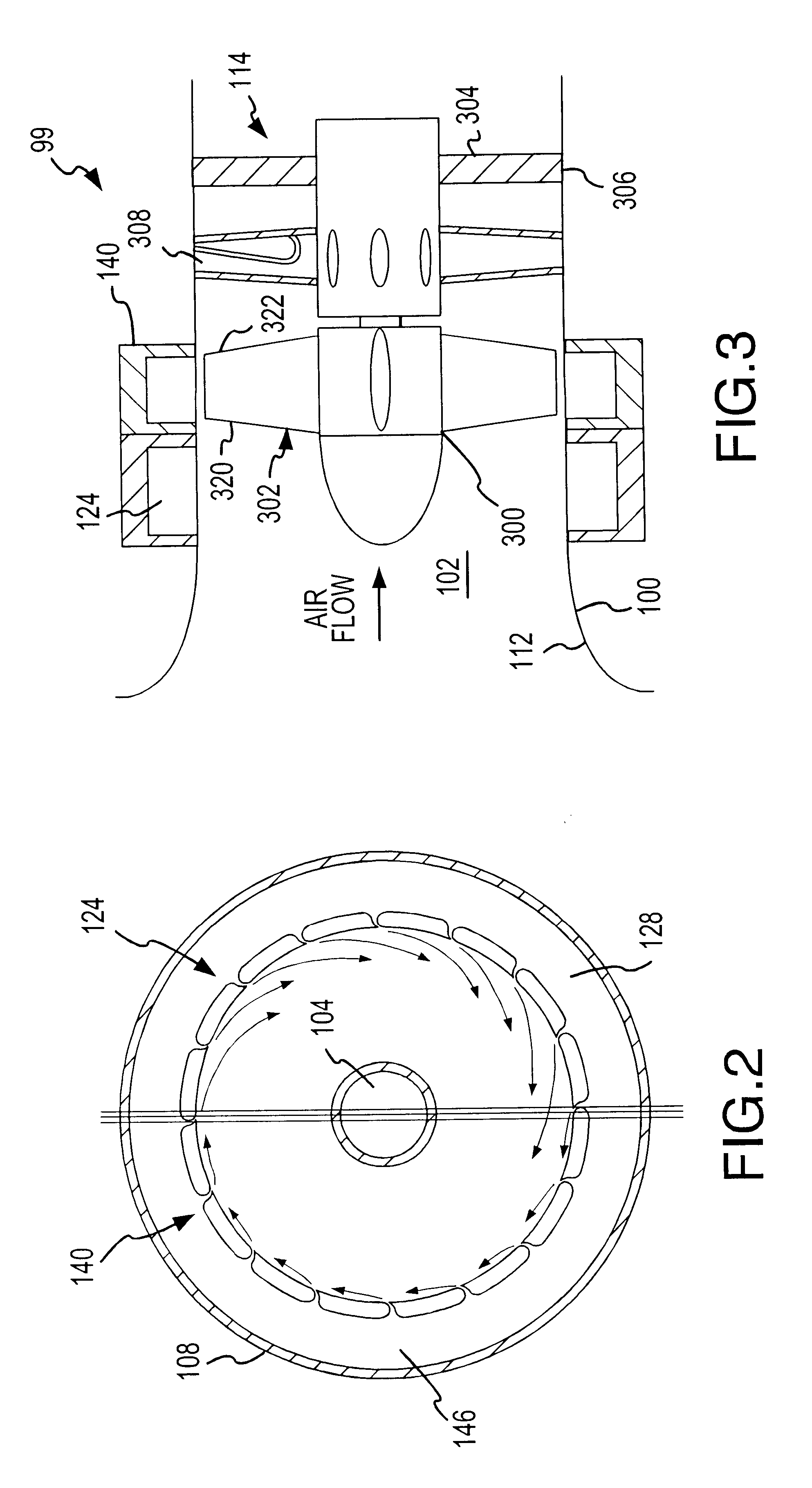
A fan system, such as a turbofan, marine propeller, or a cooling fan, includes a fan noise control system for reducing noise generated by the fan system. The noise control system may be configured to reduce either broadband noise, blade-passage noise, or both. In particular, the fan noise control system suitably includes a pre-swirl generator configured to provide a layer of fluid upstream from the fan blades. The layer swirls in the direction of the fan's rotation, reducing the angular velocity differential between the fan blades and the incident fluid. In addition, the fan noise control system may also include a fluid seal generator configured to create a fluid barrier between the fan blade tips and the interior surface of the fluid flow channel. The fluid seal inhibits leakage flow between the fan blade tips and the interior surface as well as the formation of blade vortices. By minimizing the blade wake and the blade tip vortices without adding solid surfaces, noise tends to diminish.
Owner:MCDONNELL DOUGLAS
Multi-chamber noise control system
A noise control system is operable within a box-like structure provided by the dual bulkhead plenum of the vehicle dashboard positioned within the transfer path along which the noise is being transmitted from the source of the generated noise to the receiver of the noise in the passenger compartment of an automobile. The plenum is divided into discrete chambers into each of which is provided a counter noise generating apparatus to create a counteracting noise offsetting the noise generated at the source. The acoustic resonance of the chambers amplifies the noise control energy. The geometry of the individual chambers can be varied to optimize the packaging and sound control or shaping strategy. The sound energy permitted to pass through the plenum to the driver's side of the passenger compartment can be tuned to be different than the noise received in the passenger's side.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Acoustic metamaterial architectured composite layers, methods of manufacturing the same, and methods for noise control using the same
ActiveUS20150279345A1Improving noise reductionImproving sound absorbent efficiencySound proofingSound producing devicesMicro perforated plateNoise control
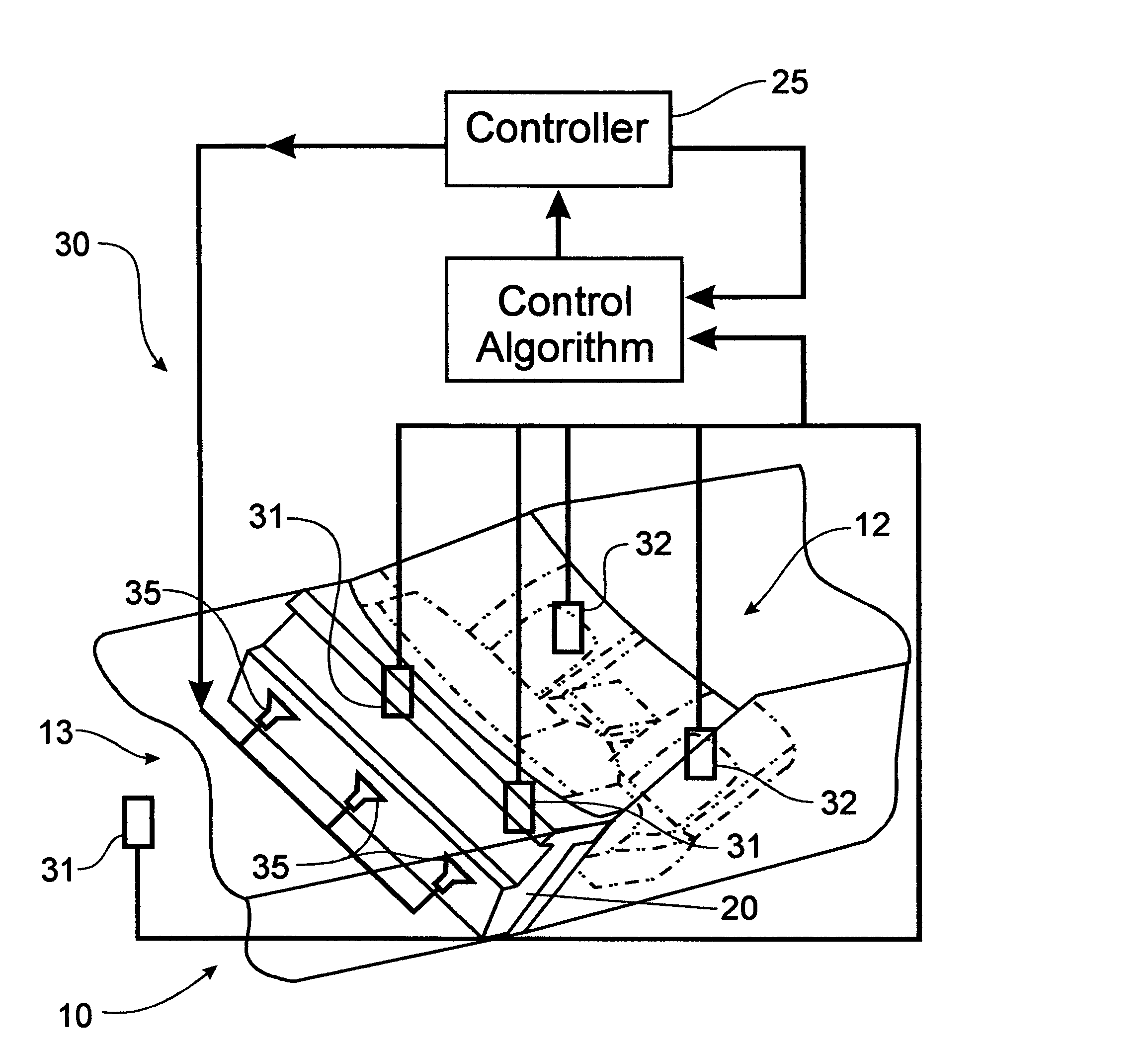
An acoustic metamaterial layered composite for noise control may include a plurality of micro-perforated plates alternately and periodically arranged with a plurality of absorbent layers and optional air gaps. The plurality of micro-perforated plates may be in a form of a periodically arranged stack and include perforations extending therethrough. Each of the plurality of absorbent layers is formed of a poroelastic material. The metamaterial layered composite noise control device is designed using the metamaterial acoustics transformation approach for optimized noise control.
Owner:ACOUSTIC METAMATERIALS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

![[feedback active noise controlling circuit and headphone] [feedback active noise controlling circuit and headphone]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/cbdbabcc-f5d4-495a-aef9-61bd6646b6a7/US20050249355A1-20051110-D00000.png)
![[feedback active noise controlling circuit and headphone] [feedback active noise controlling circuit and headphone]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/cbdbabcc-f5d4-495a-aef9-61bd6646b6a7/US20050249355A1-20051110-D00001.png)
![[feedback active noise controlling circuit and headphone] [feedback active noise controlling circuit and headphone]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/cbdbabcc-f5d4-495a-aef9-61bd6646b6a7/US20050249355A1-20051110-D00002.png)