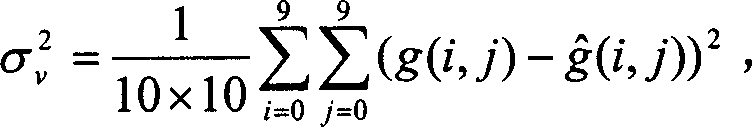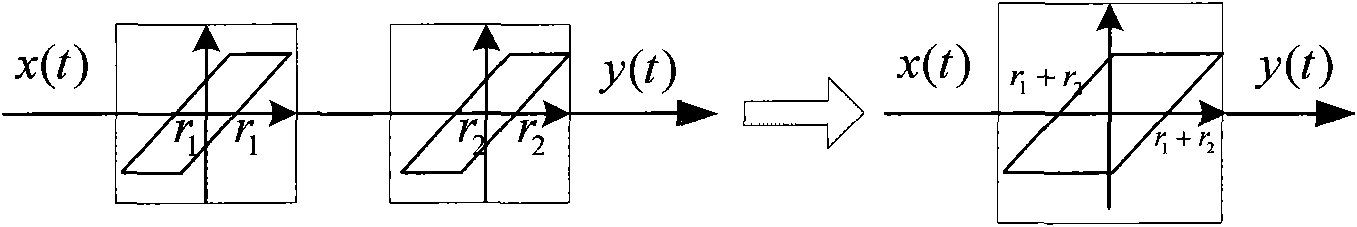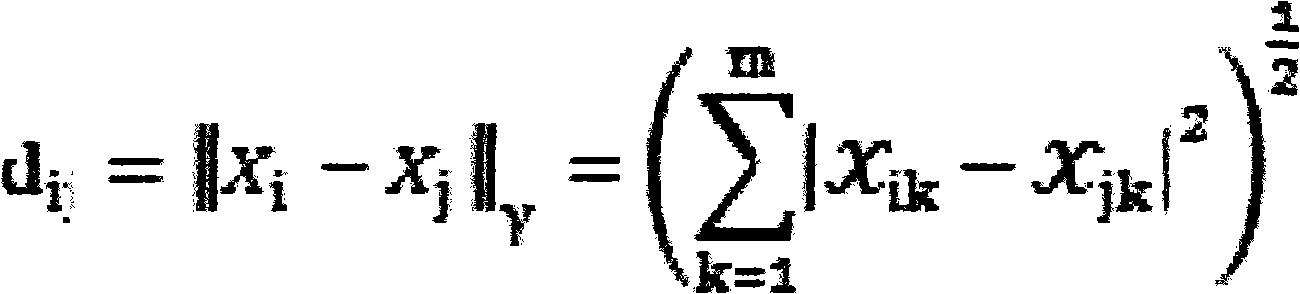Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
274 results about "Kernel adaptive filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
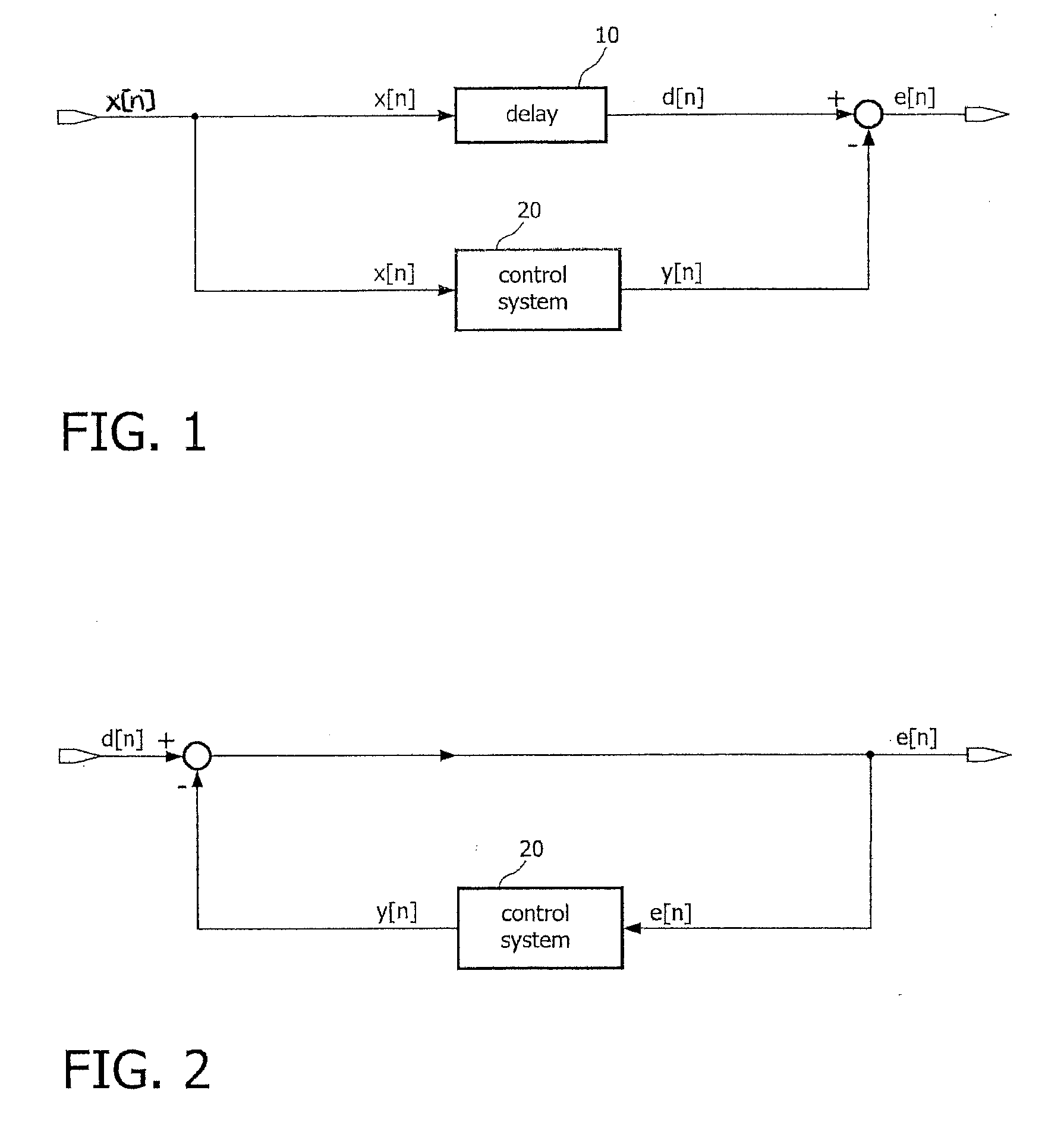
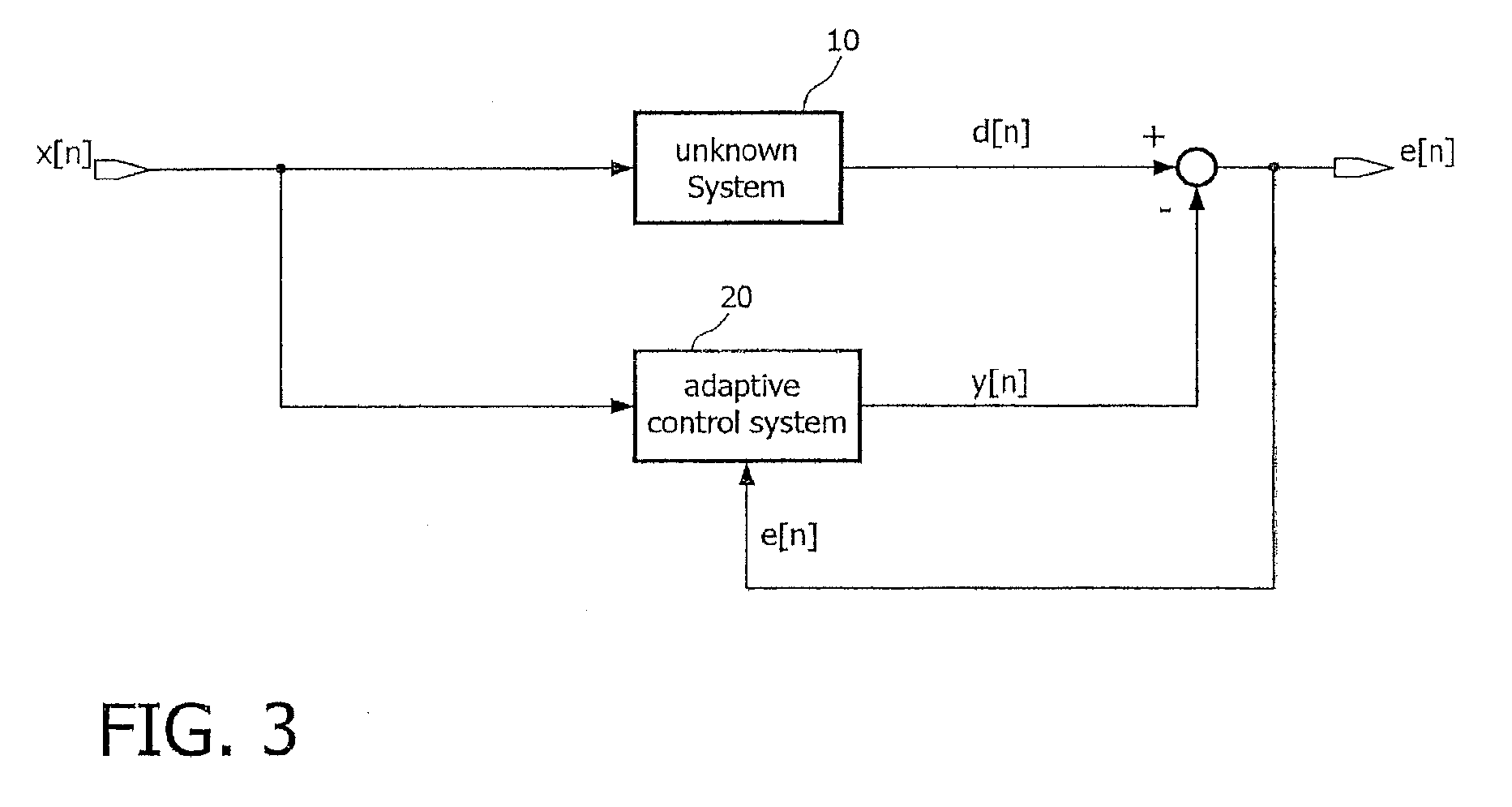
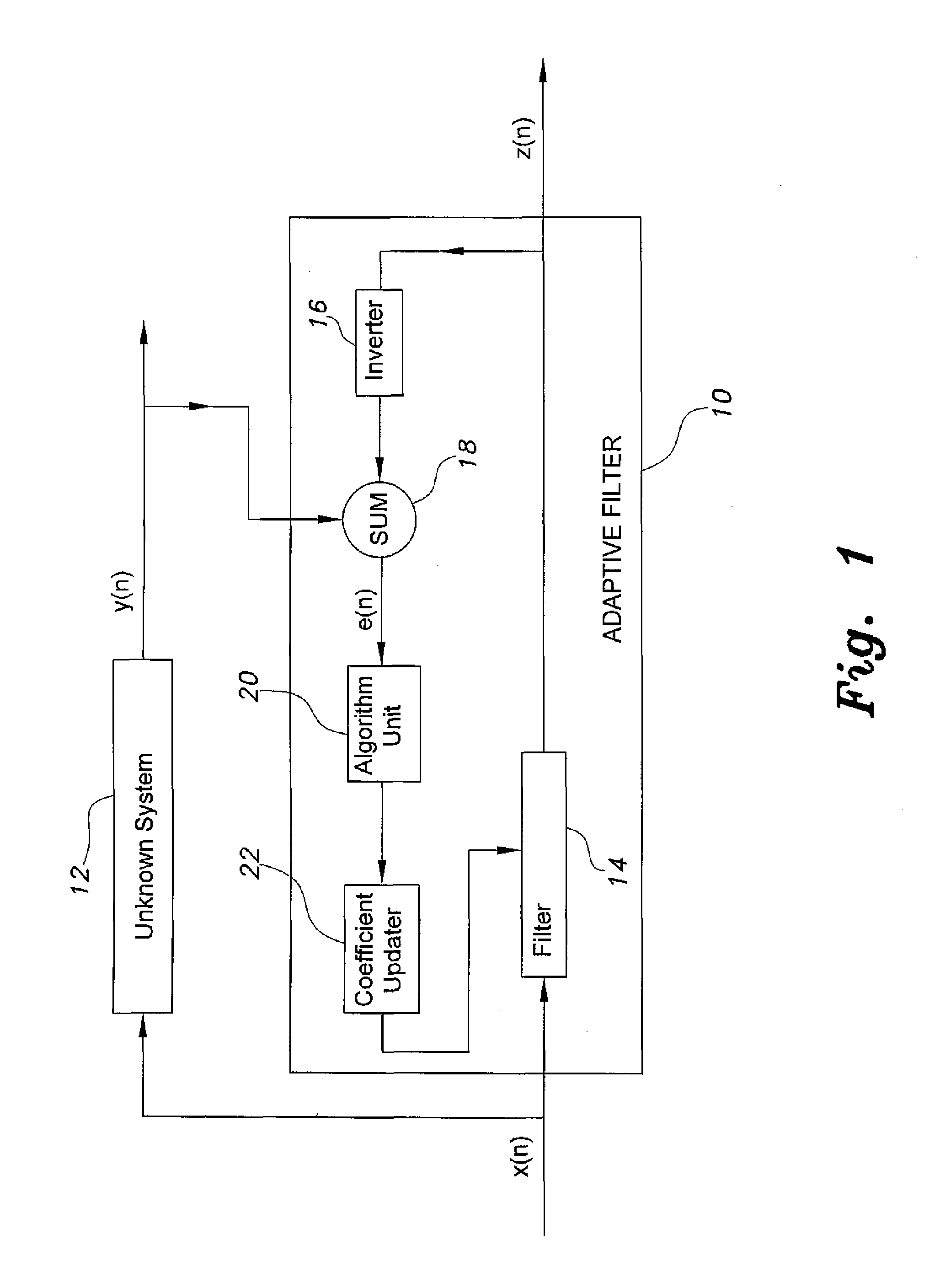
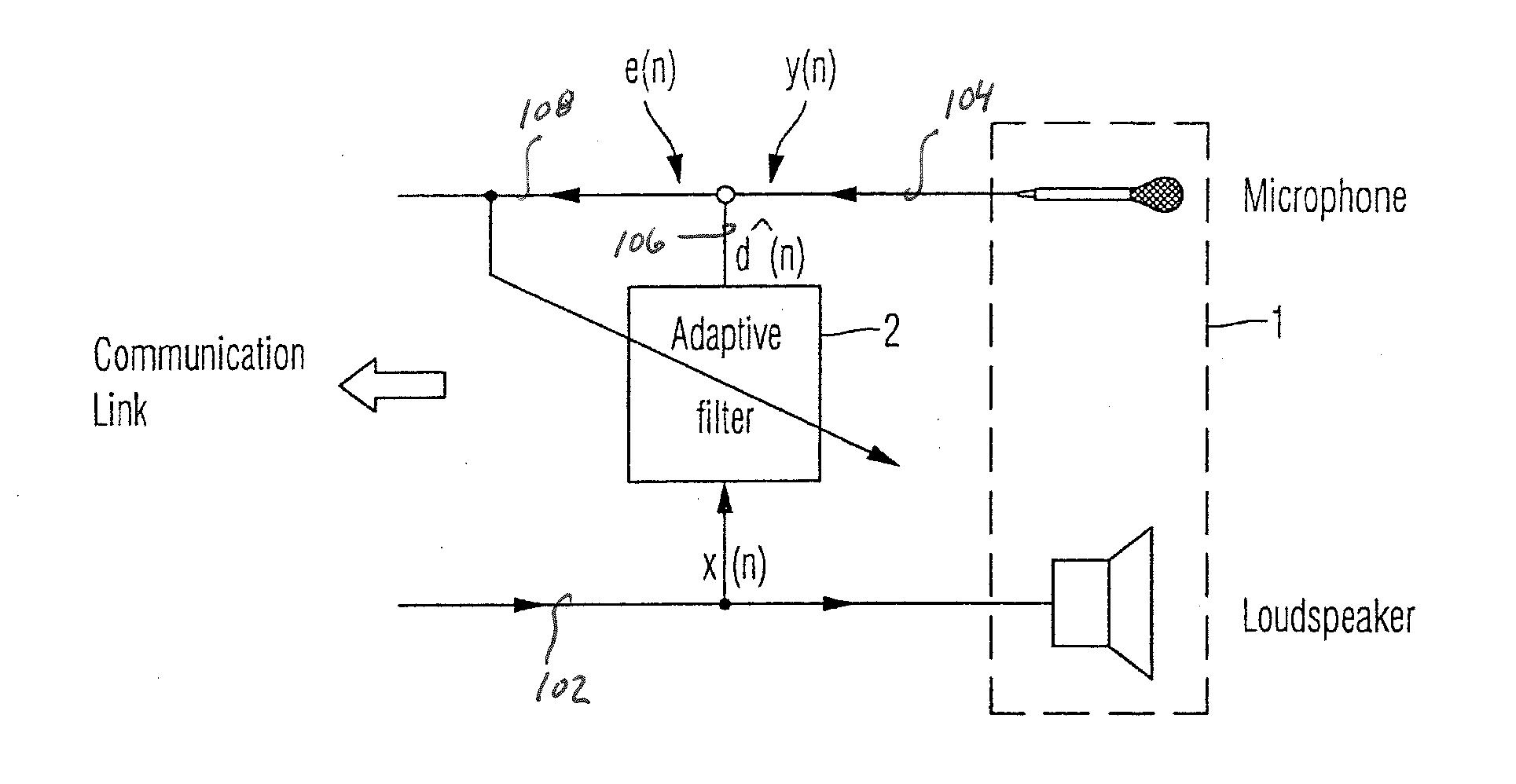
In signal processing, a kernel adaptive filter is a type of nonlinear adaptive filter. An adaptive filter is a filter that adapts its transfer function to changes in signal properties over time by minimizing an error or loss function that characterizes how far the filter deviates from ideal behavior. The adaptation process is based on learning from a sequence of signal samples and is thus an online algorithm. A nonlinear adaptive filter is one in which the transfer function is nonlinear.
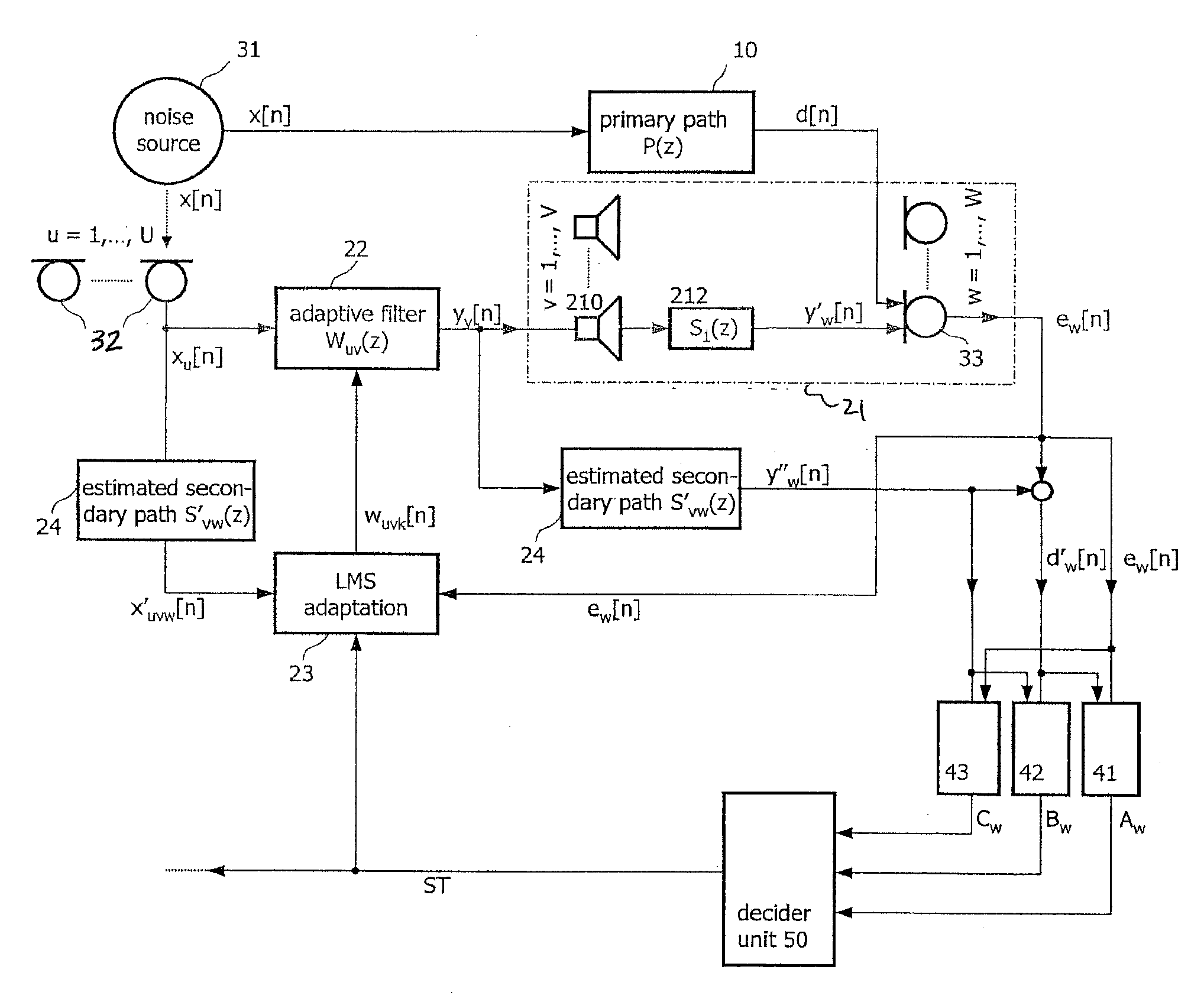
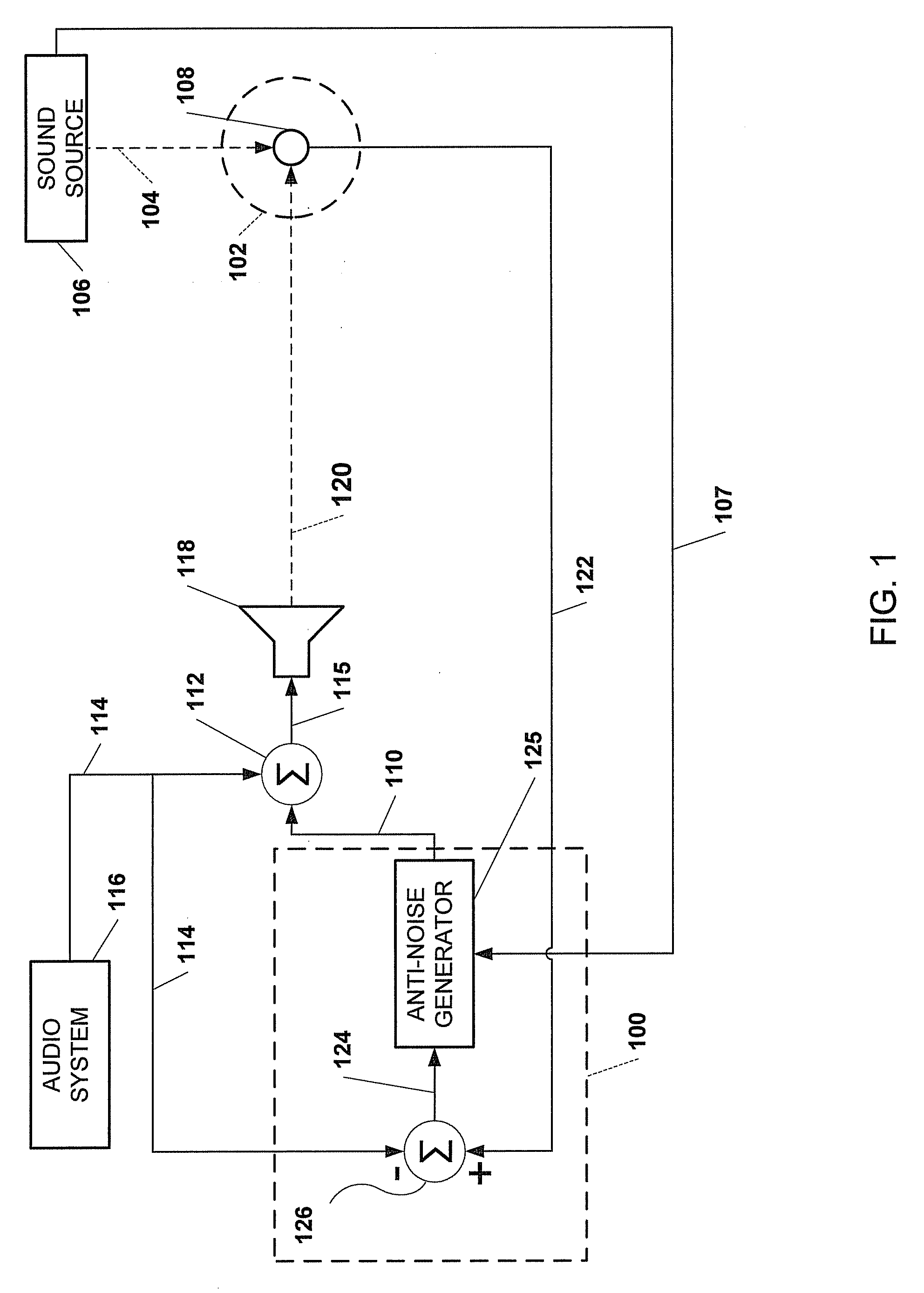
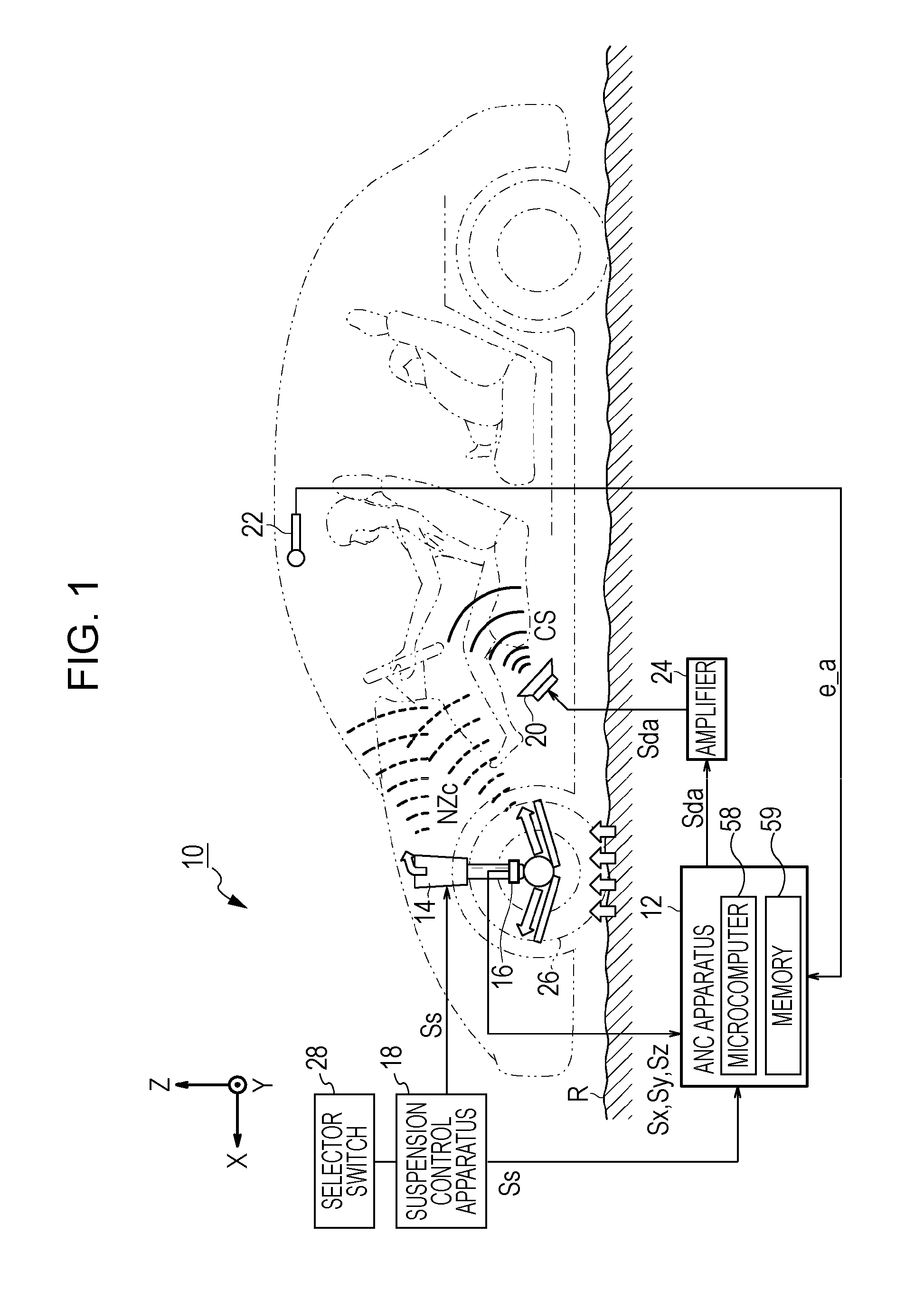
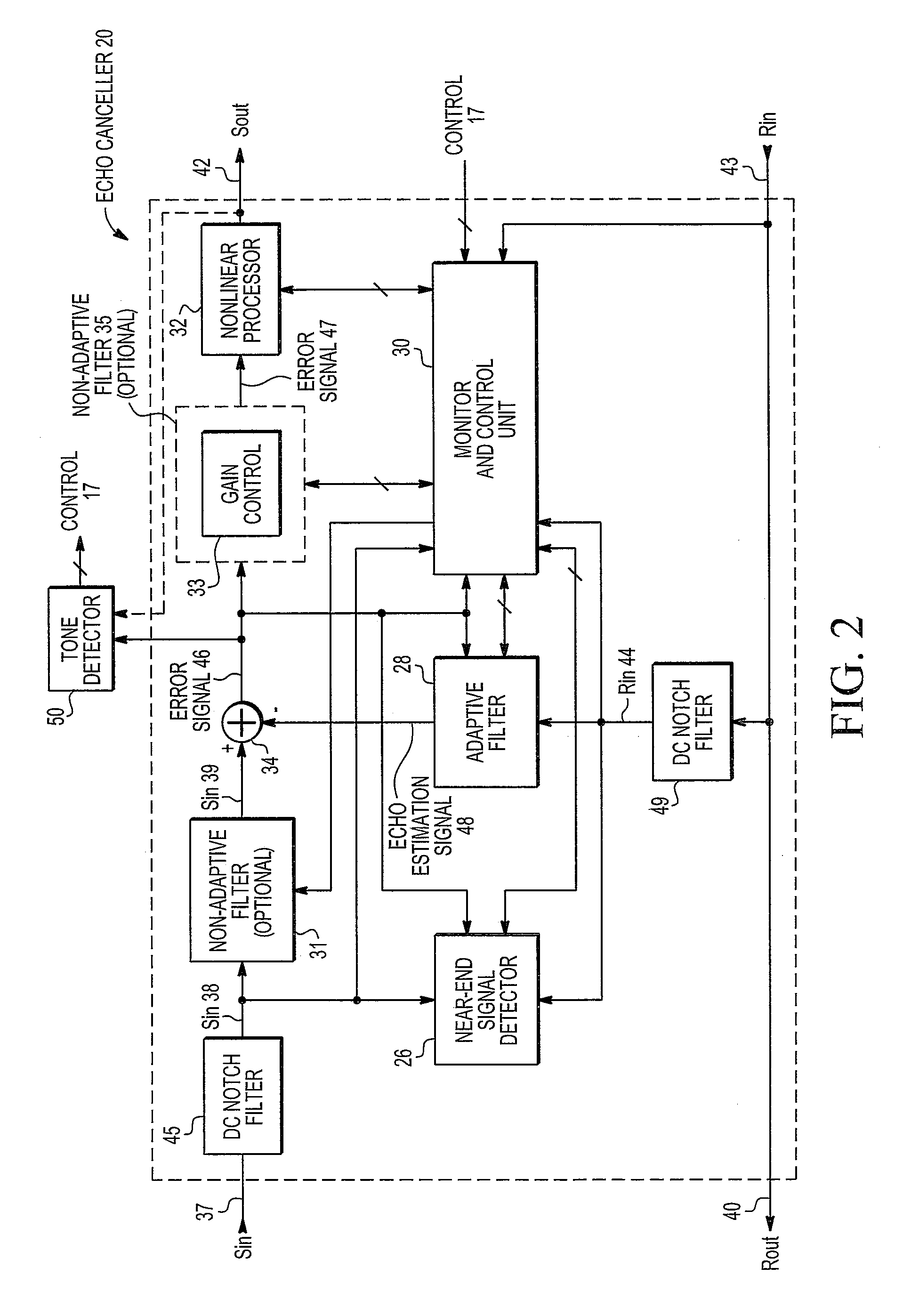
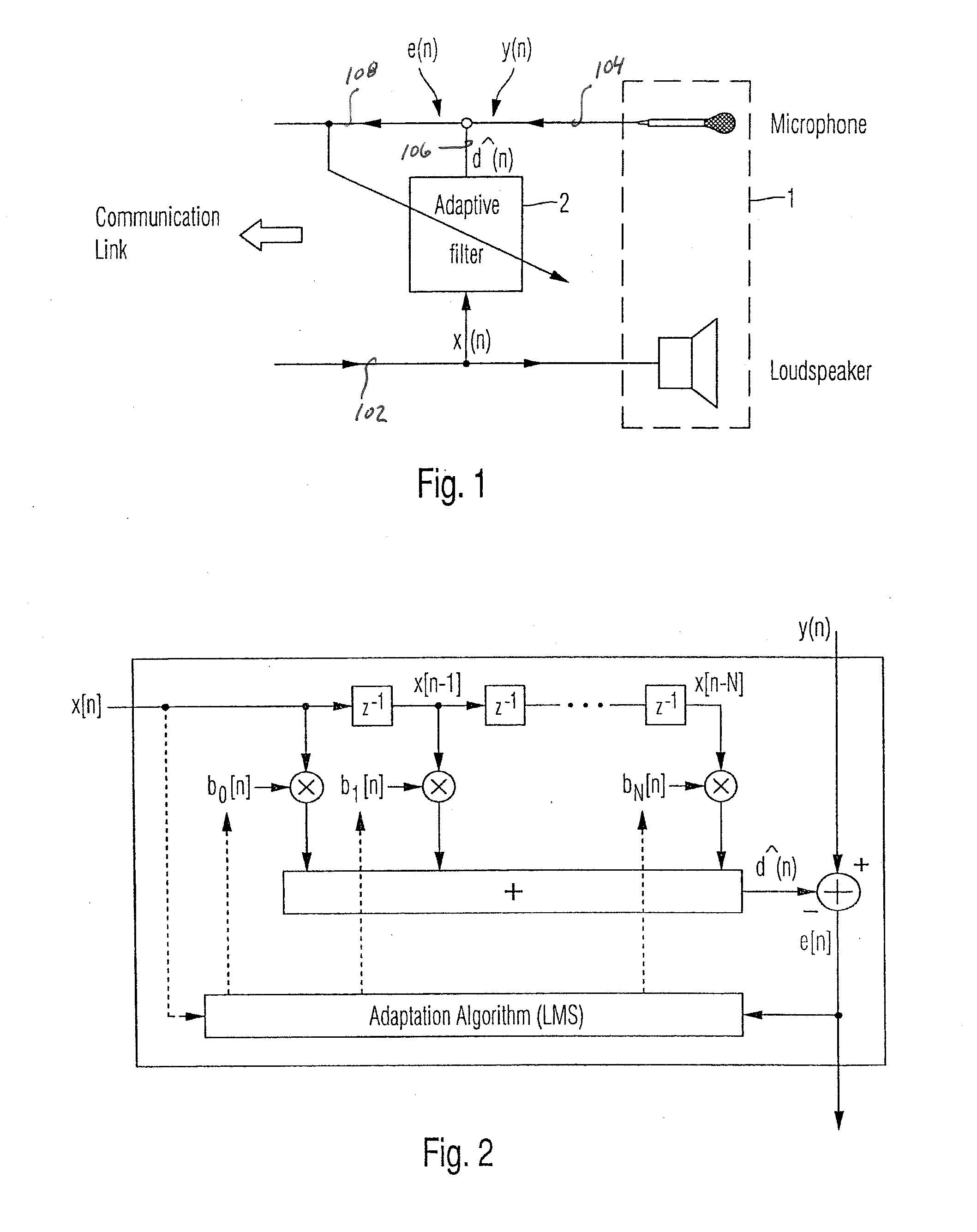
Adaptive noise control system
ActiveUS20100014685A1Improve robustnessImprove stabilityEar treatmentNoise generationNoise controlControl system
An active noise cancellation system that reduces, at a listening position, power of a noise signal radiated from a noise source to the listening position. The system includes an adaptive filter, at least one acoustic actuator and a signal processing device. The adaptive filter receives a reference signal representing the noise signal, and provides a compensation signal. The at least one acoustic actuator radiates the compensation signal to the listening position. The signal processing device evaluates and assesses the stability of the adaptive filter.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Quiet zone control system
An active noise control system generates an anti-noise signal to drive a speaker to produce sound waves to destructively interfere with an undesired sound in a quiet zone. The anti-noise signal is generated with an adaptive filter having filter coefficients. The coefficients of the adaptive filter may be adjusted based on a first filter adjustment from a first listening region, and a second filter adjustment from a second listening region. A first weighting factor may be applied to the first filter adjustment, and a second weighting factor may be applied to the second filter adjustment. The first and second weighting factors may dictate the location and size of the quiet zone as being outside or partially within at least one of the first listening region and the second listening region.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
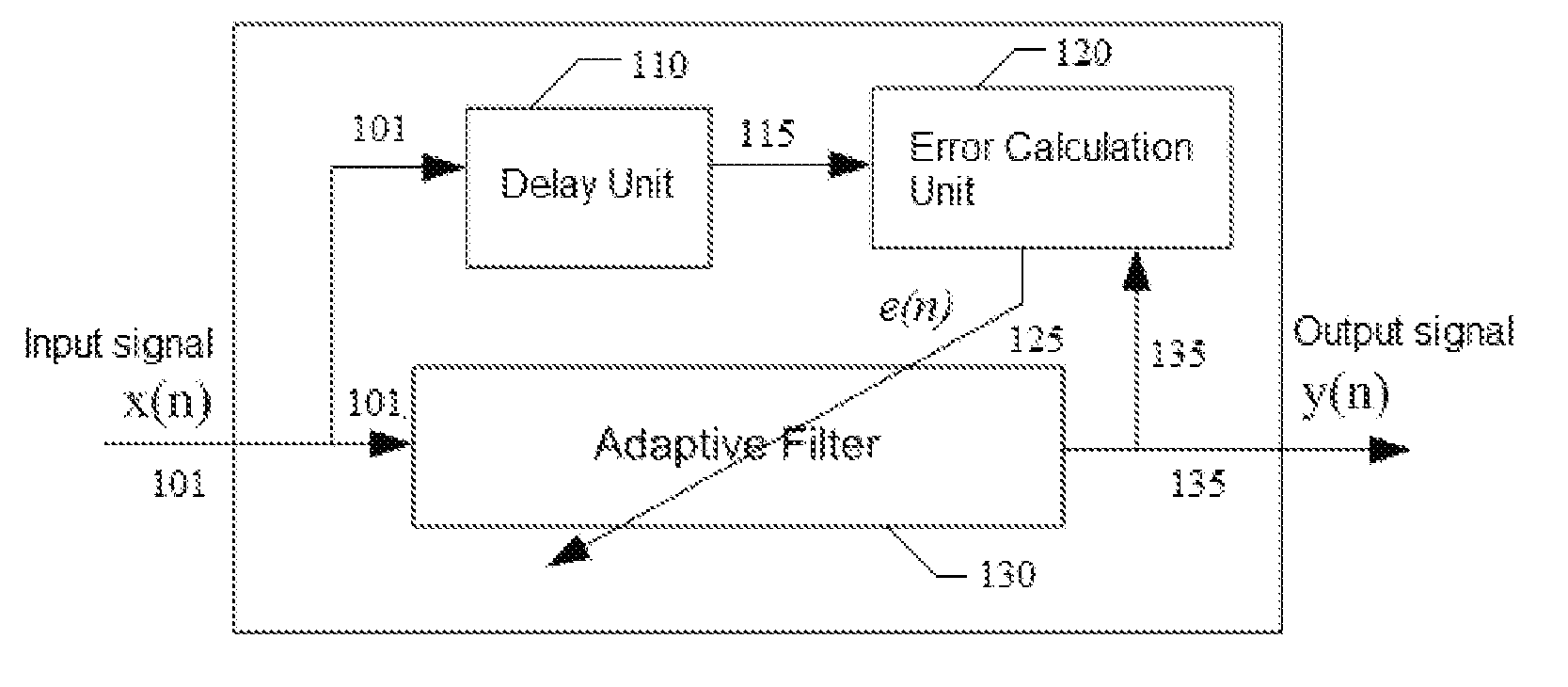
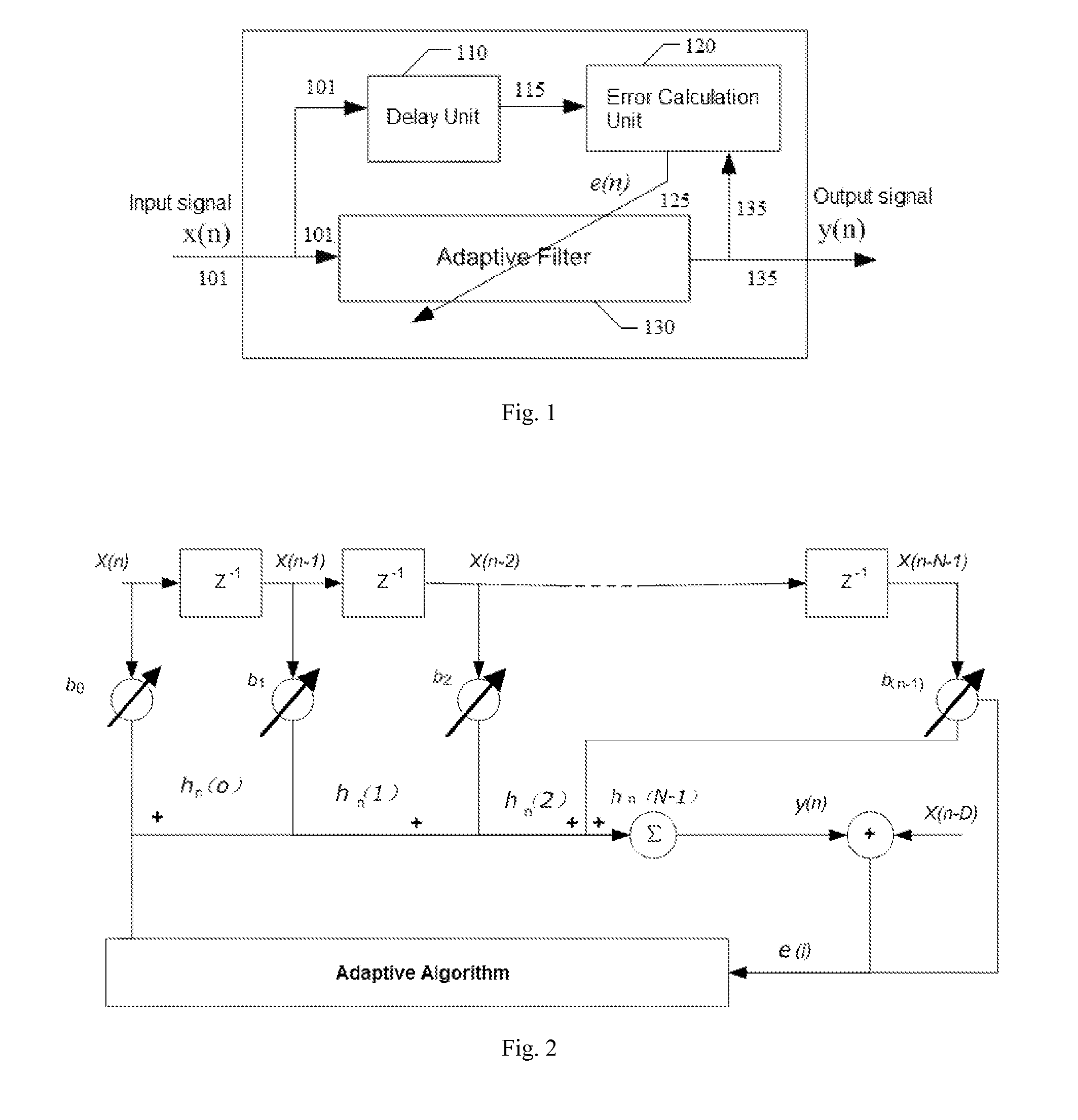
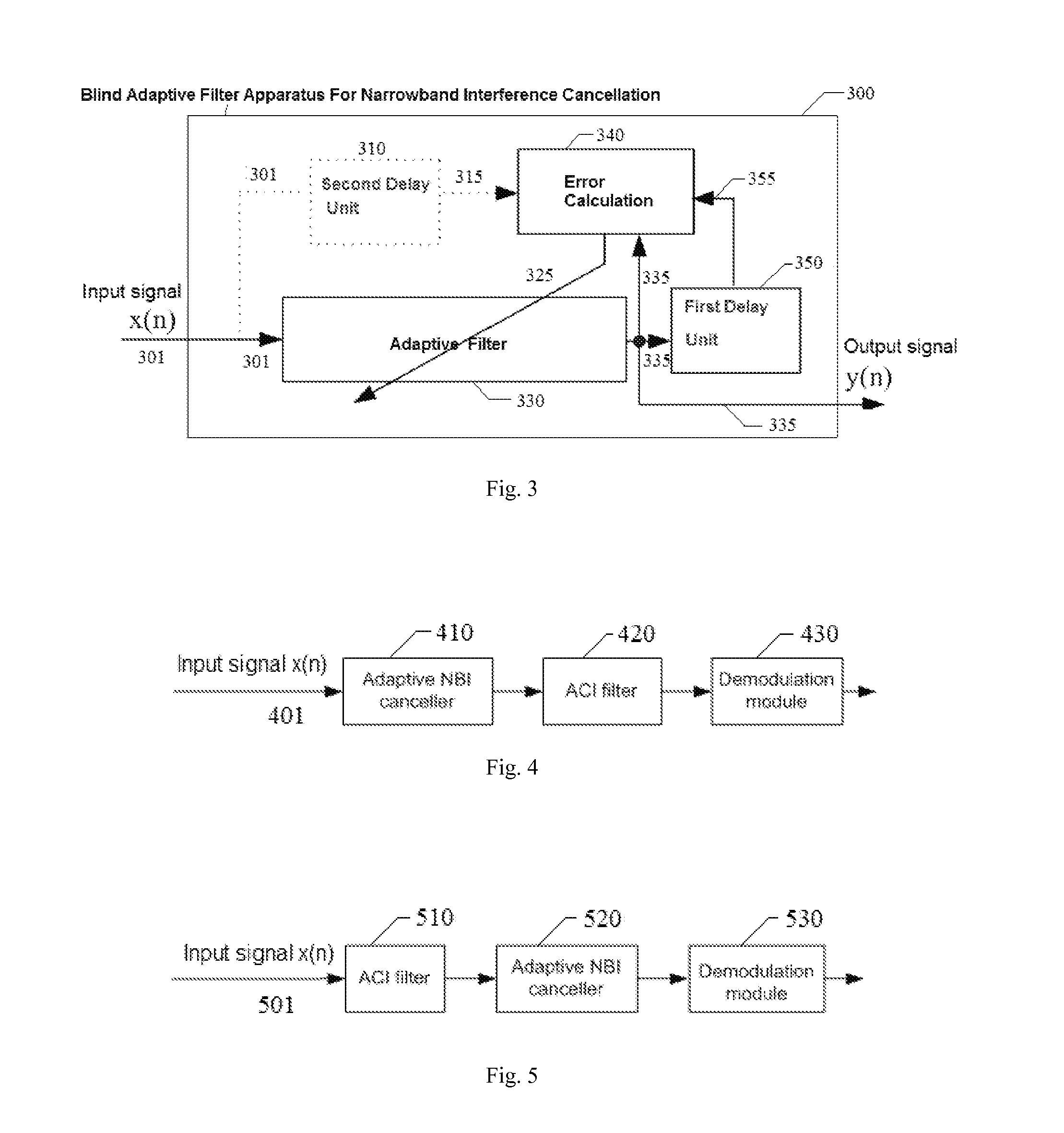
Blind adaptive filter for narrowband interference cancellation
ActiveUS20110305306A1Wide applicationError preventionDigital adaptive filtersSelf adaptiveSweep rate
The present invention relates to a blind adaptive filter for narrowband interference cancellation, which includes an adaptive filter, a delay unit coupled to the adaptive filter for generating a delayed signal with a predetermined delay length from the output signal of the adaptive filter, and an error calculation unit coupled to the adaptive filter and the delay unit. The error calculation unit compares the output signal from the adaptive filter and the delayed signal from the delay unit to extract error information, and feedback the first error information to the adaptive filter. The first error information is formed of a transfer function including a number of coefficients, and used to adjust the adaptive filter and remove interference in the next input signal. The disclosed technique is also applicable in wideband receivers, as well as resisting multiple strong narrowband interferences having a frequency sweep rate of tens of milliseconds.
Owner:MONTAGE TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
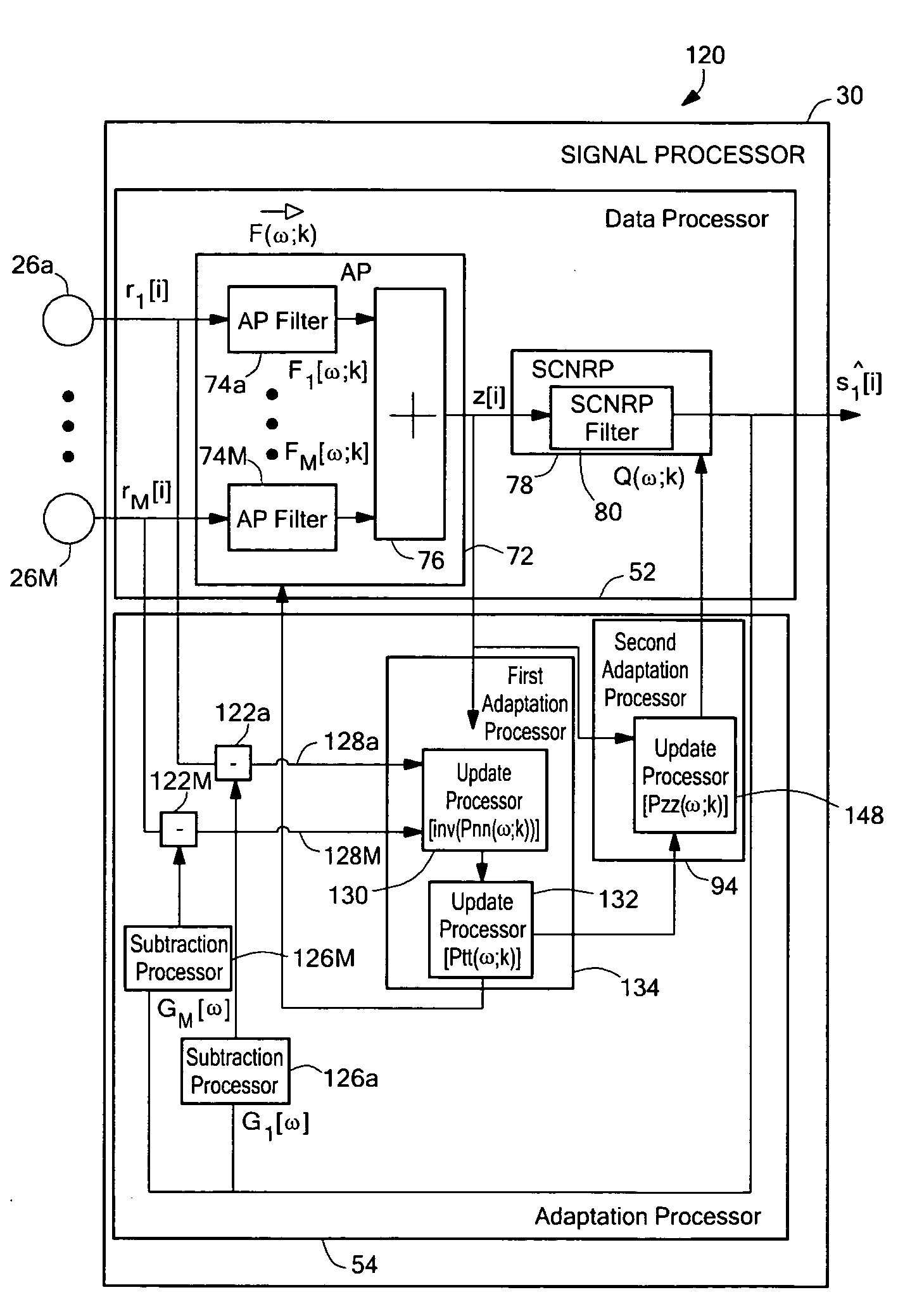
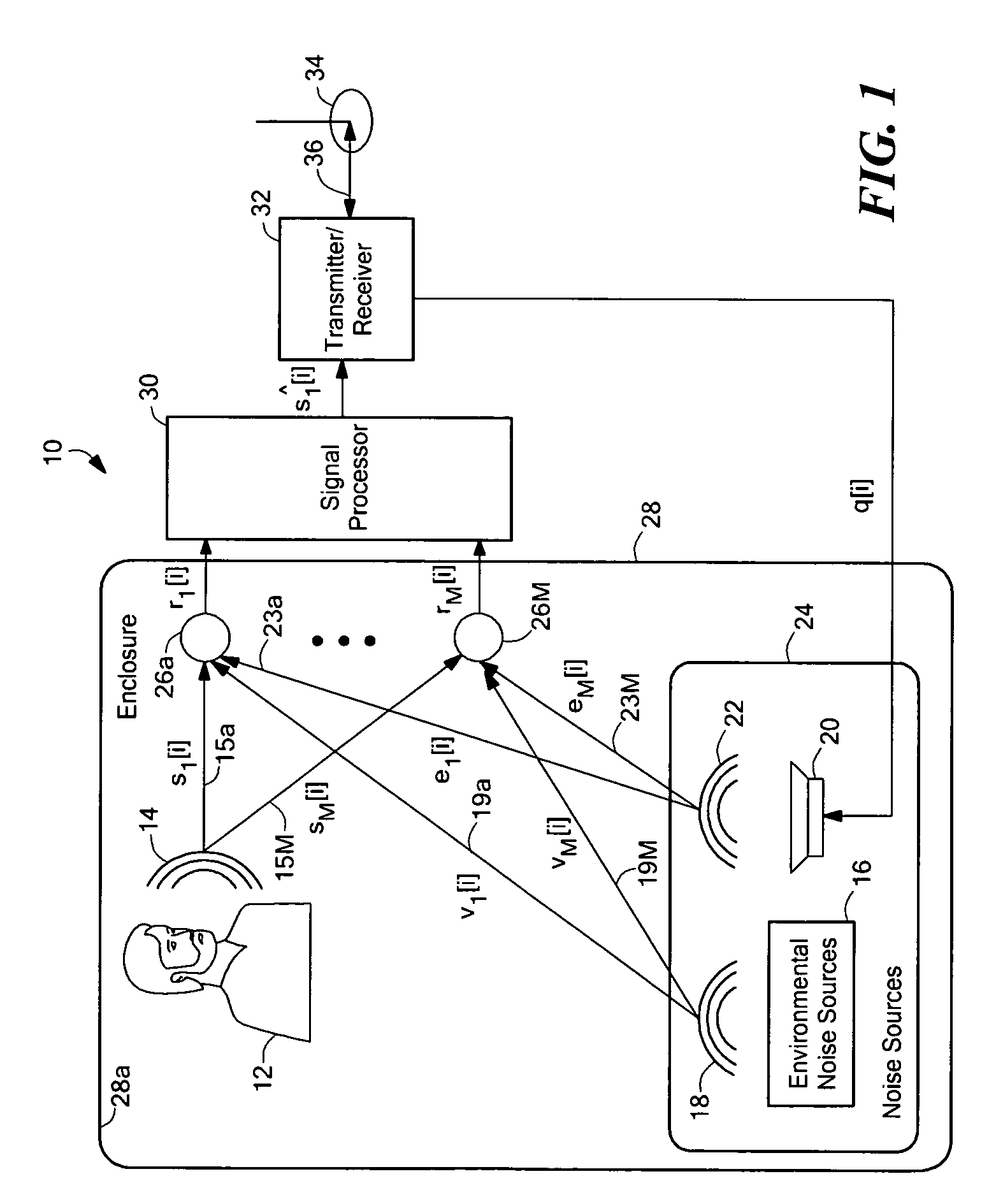
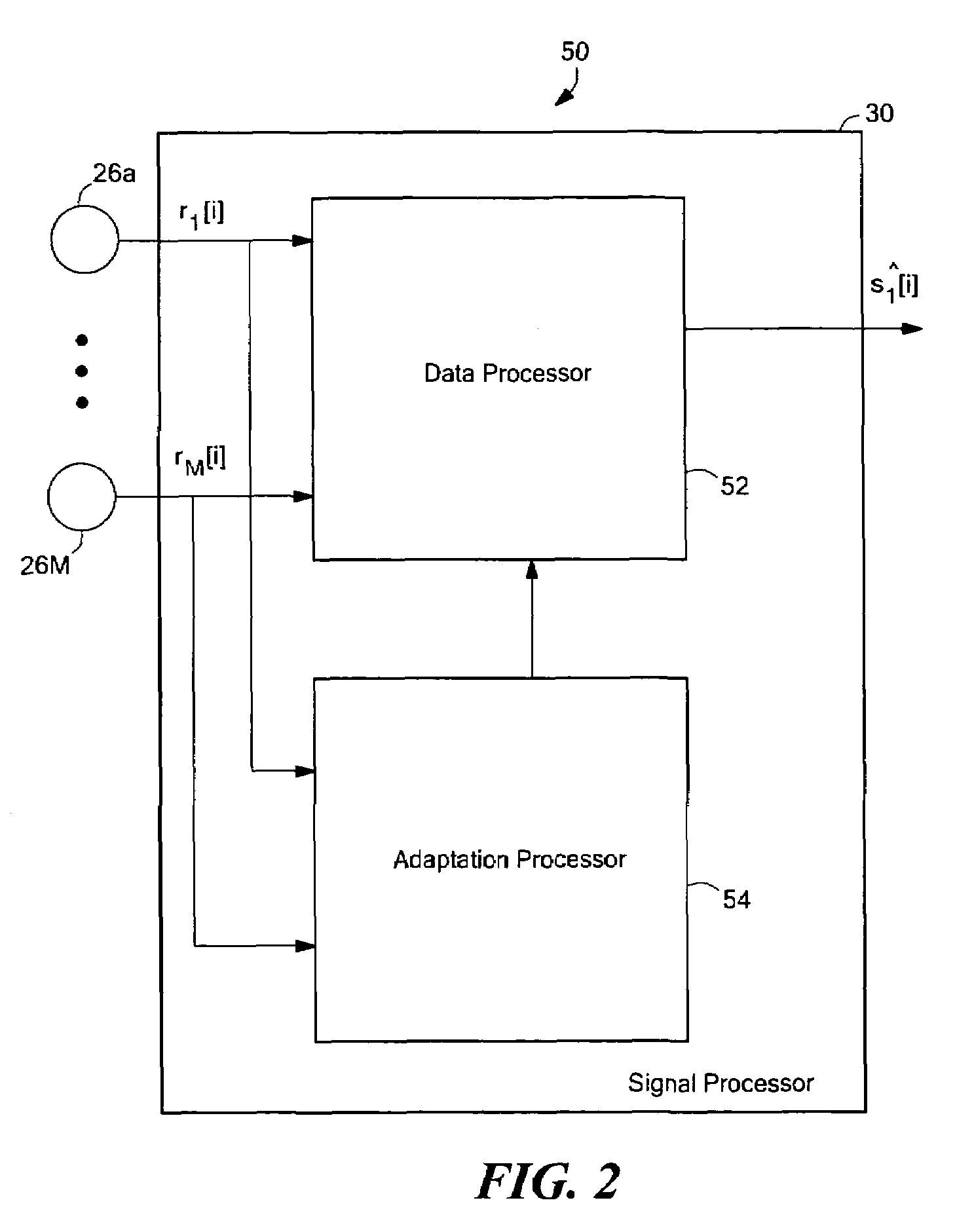
System and method for noise reduction having first and second adaptive filters
ActiveUS7162420B2Improve speech clarityGood estimateMultiple-port networksEar treatmentNoise reductionSelf adaptive
An apparatus and method for noise reduction employ a first processor having one or more channels, each channel comprising a respective first processor filter, and each channel configured to receive a respective one of one or more input signals. The first processor is configured to provide an intermediate output signal. The apparatus and method further employ a second processor including a second processor filter configured to receive the intermediate output signal and to provide a noise-reduced output signal. The apparatus and method further employ a first adaptation processor coupled to the first processor and a second adaptation processor coupled to the second processor. In some embodiments, an echo canceling processor reduces an echo portion associated with the noise-reduced output signal. In some embodiments, a response of the first filter portion and of the second filter portion are dynamically adapted.
Owner:F POSZAT HU
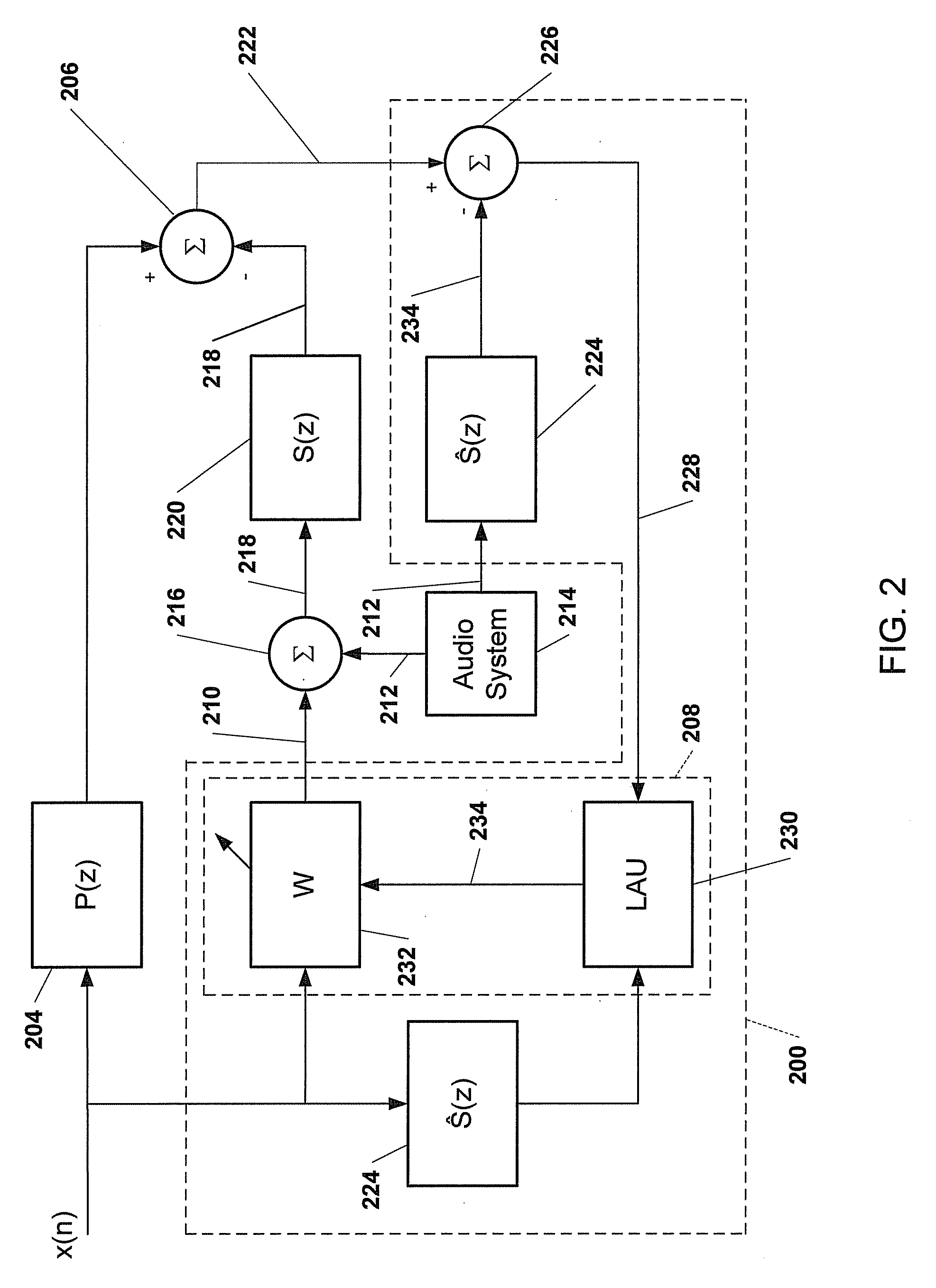
Advanced periodic signal enhancement
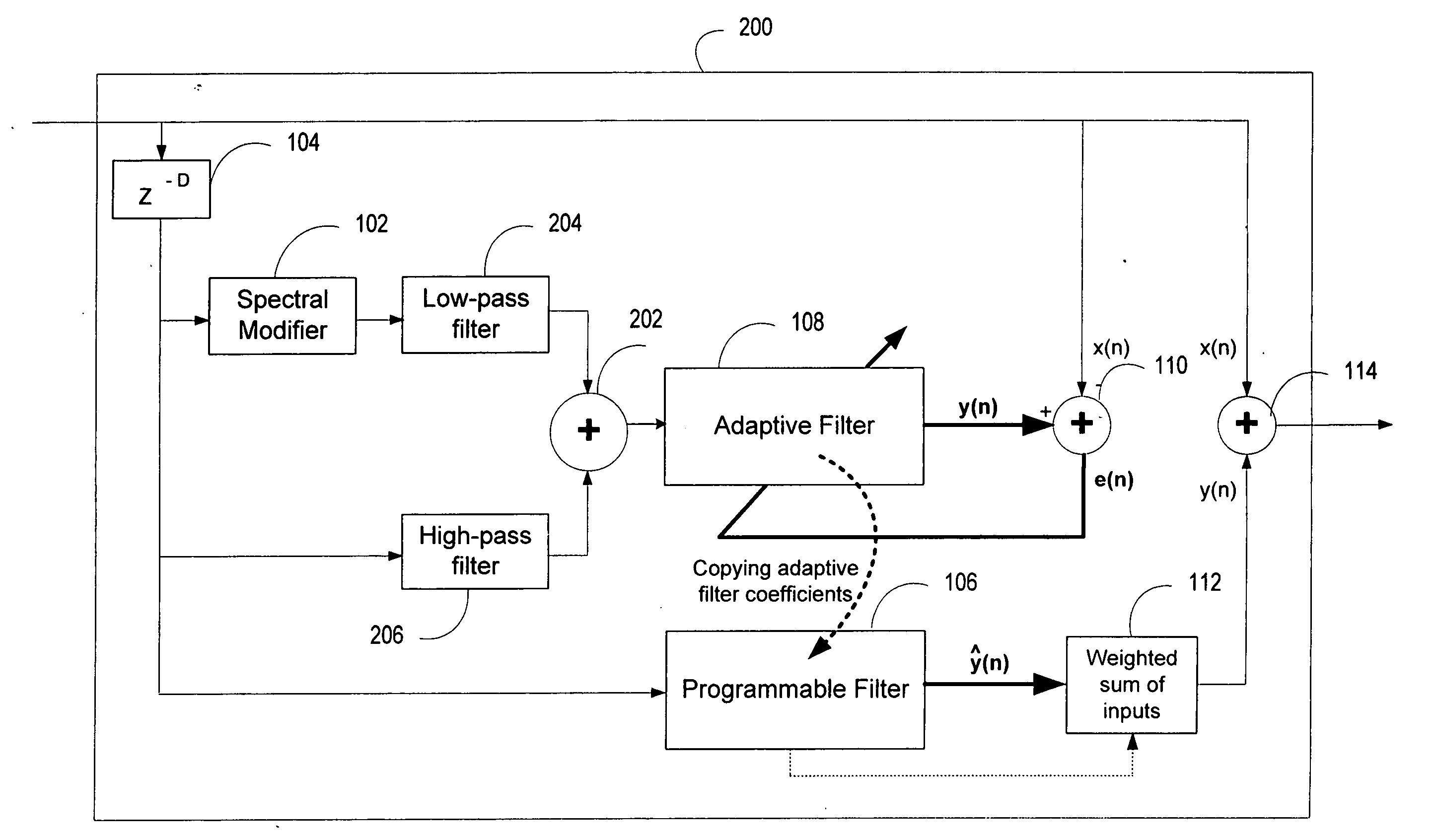
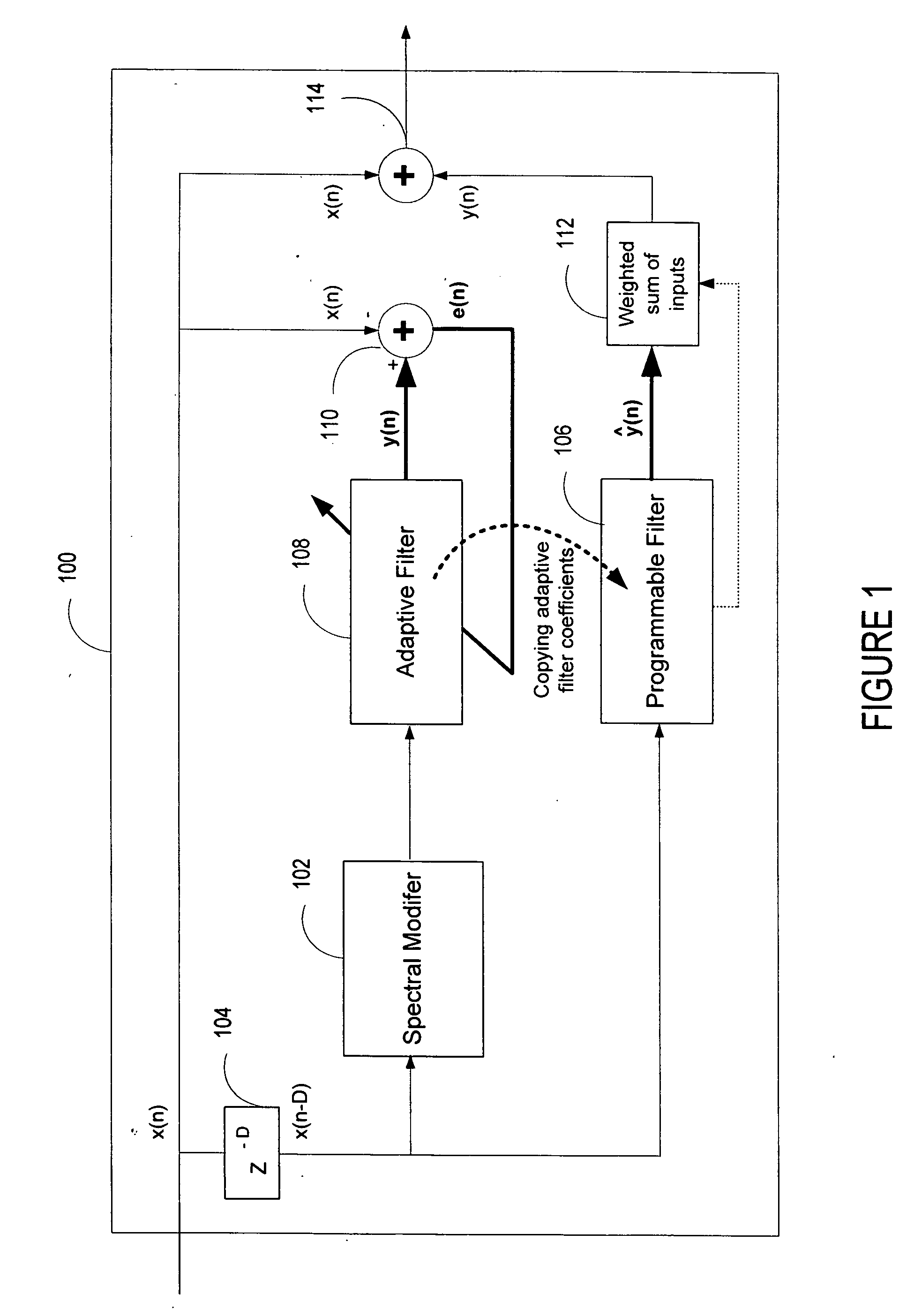
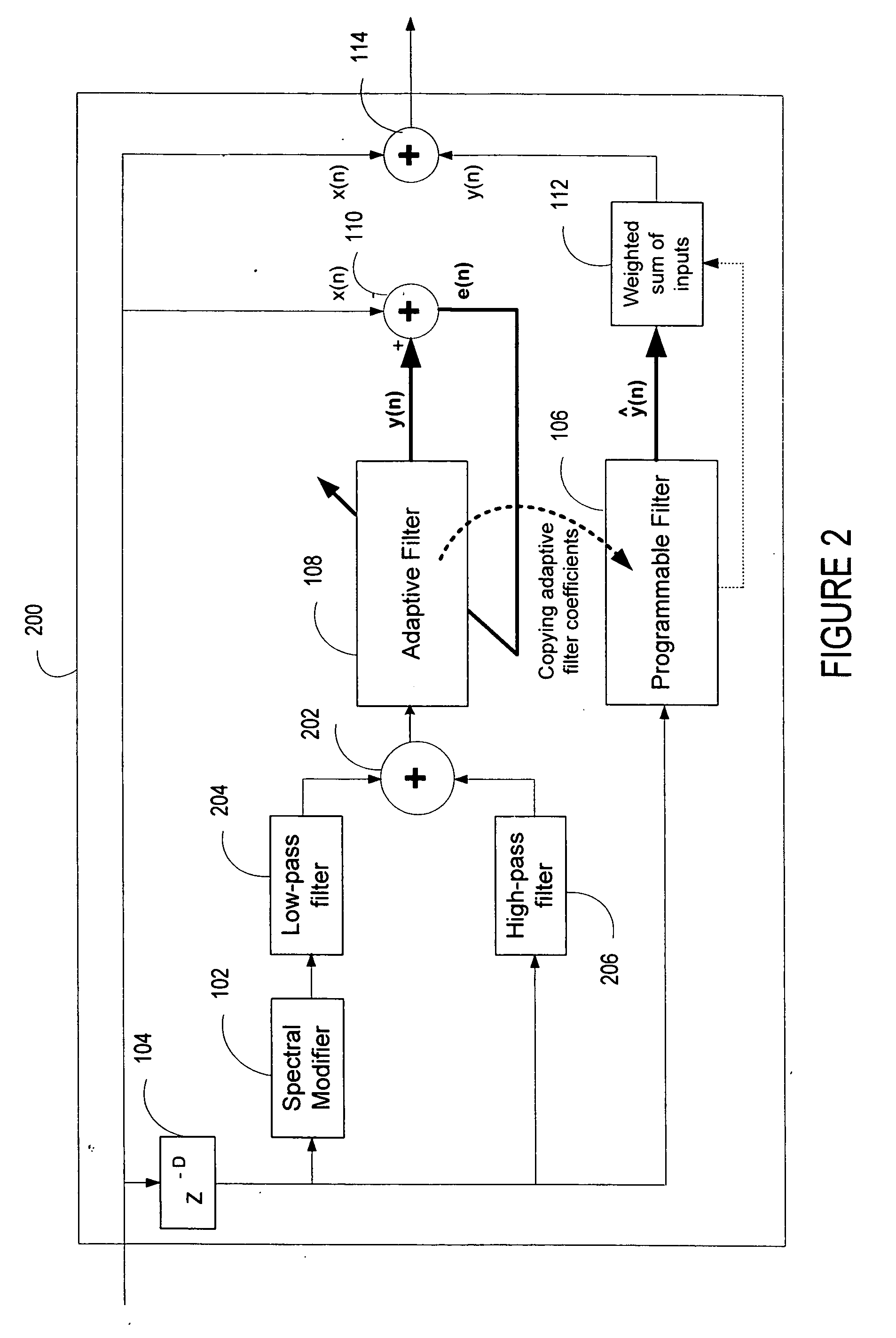
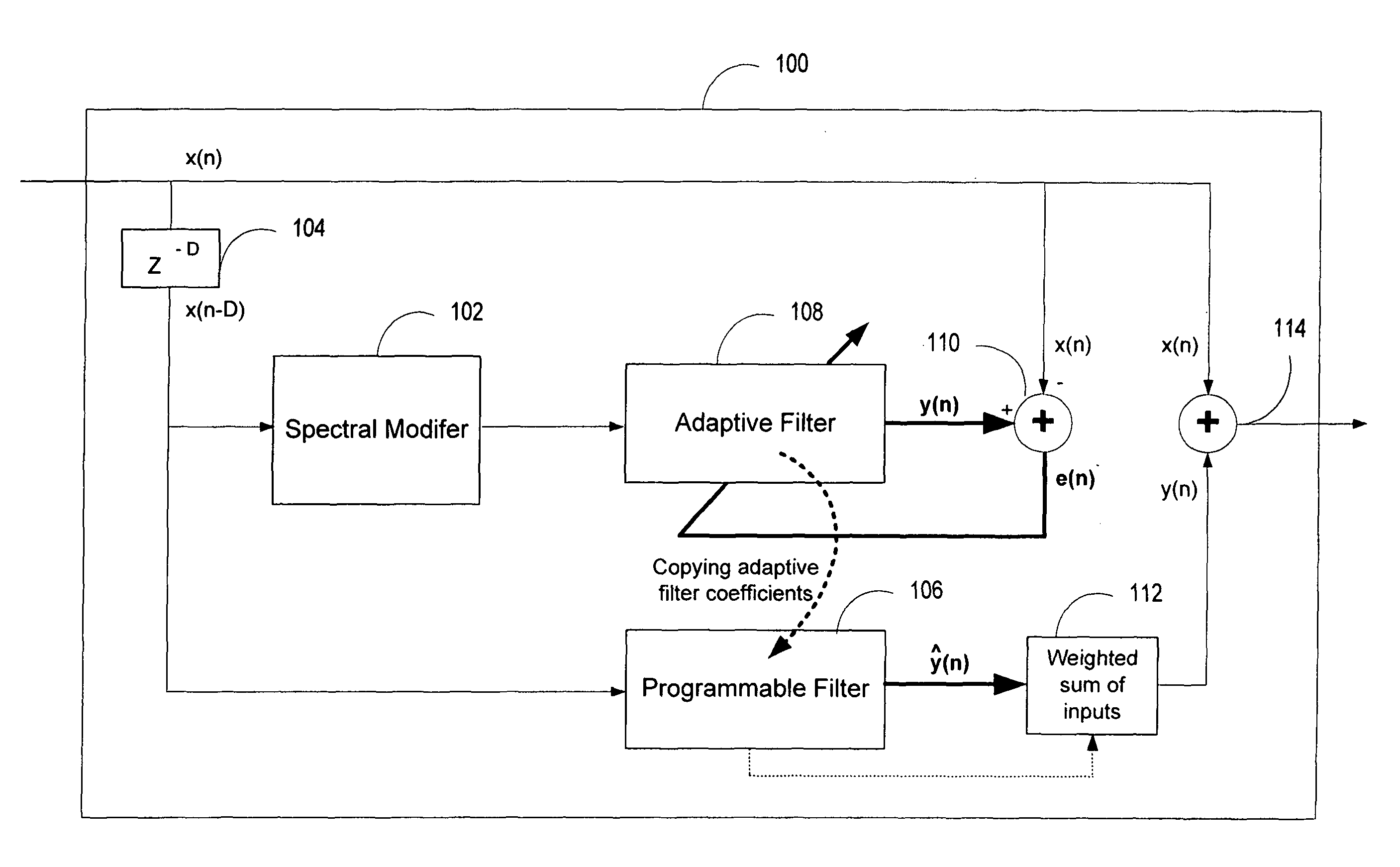
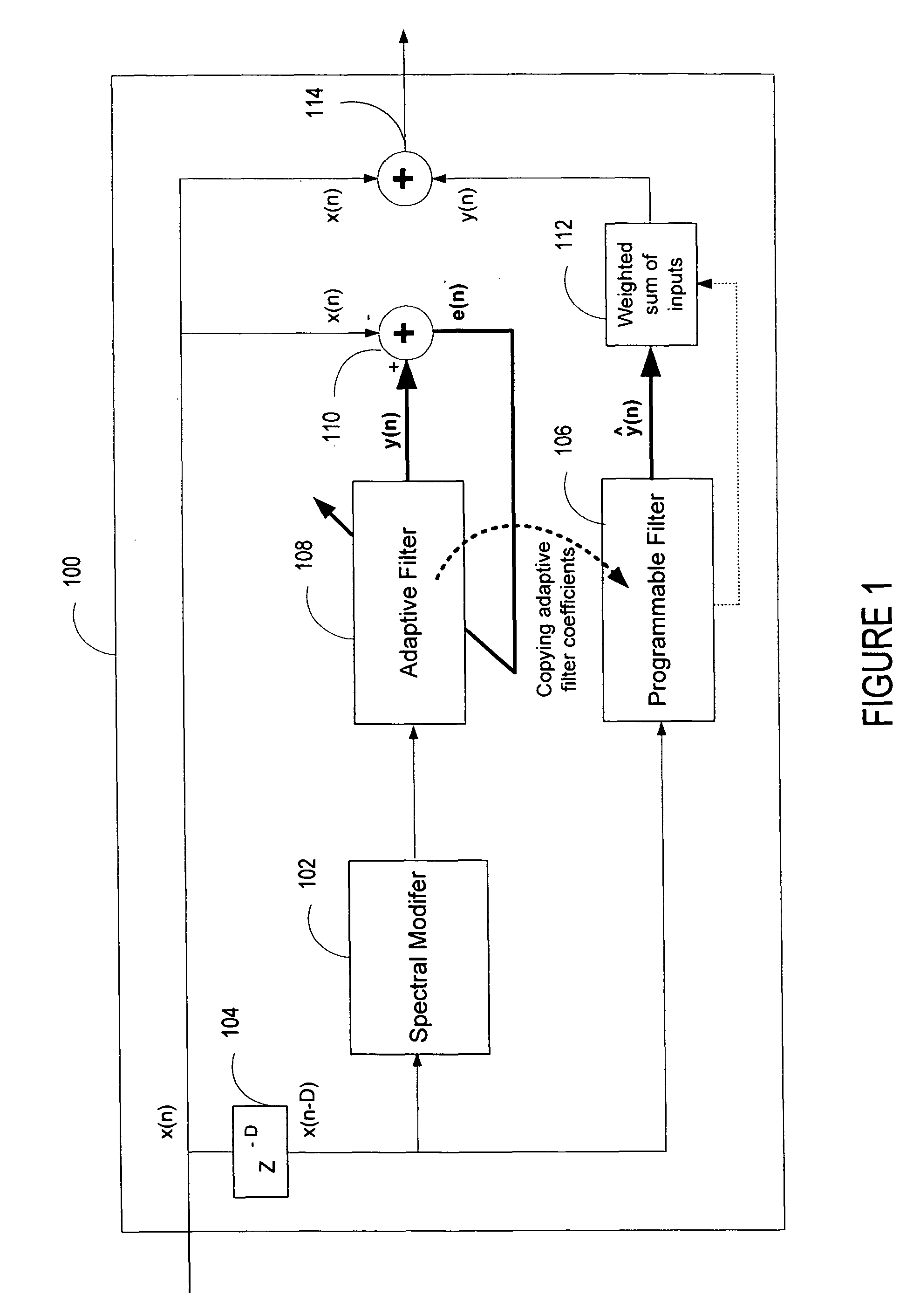
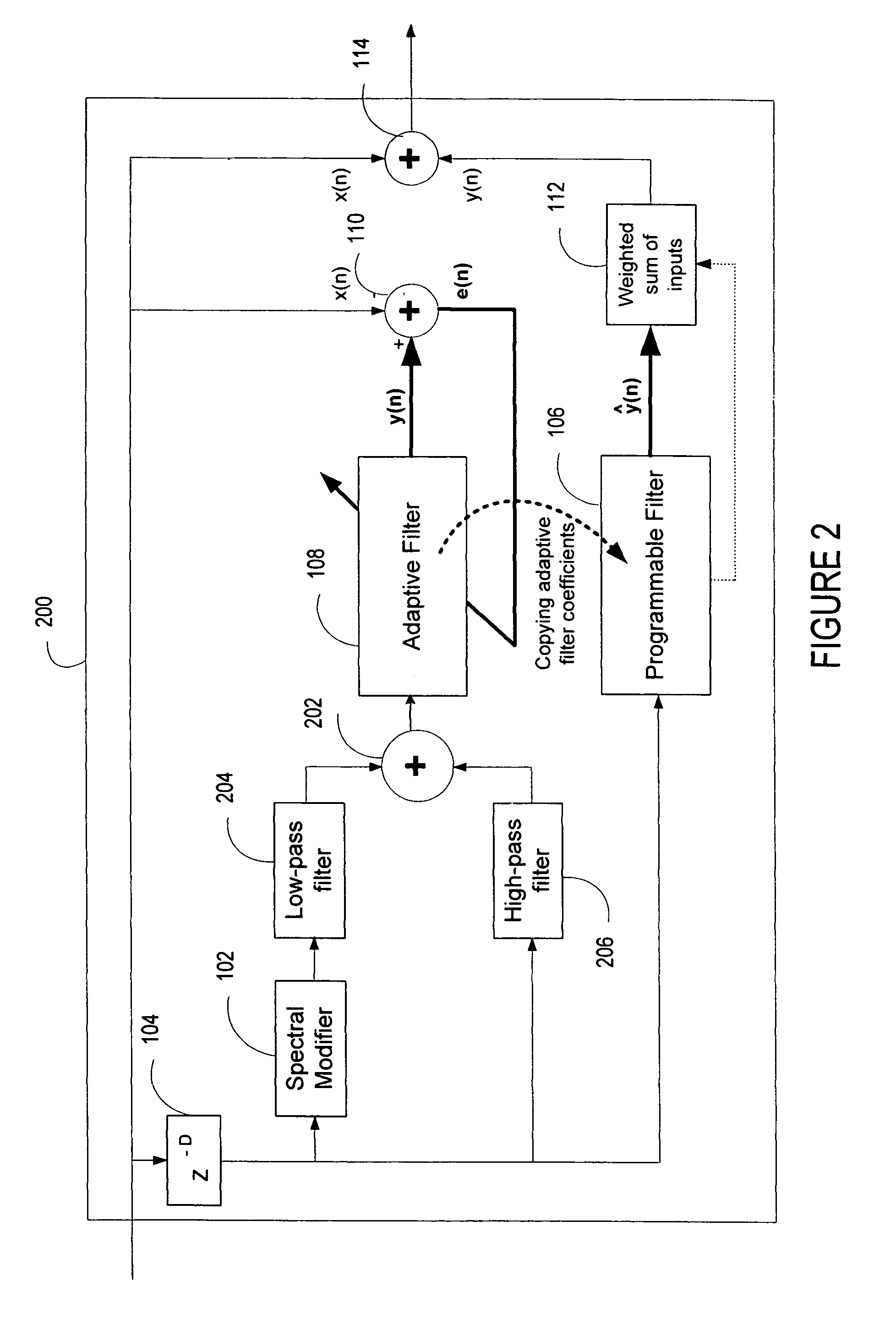
ActiveUS20060136199A1Improve processing qualityFlatten spectral character of background noiseAdaptive networkSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumProgrammable filters
An enhancement system improves the perceptual quality of a processed speech. The system includes a delay unit that delays a signal received through a discrete input. A spectral modifier linked to the delay unit is programmed to substantially flatten the spectral character of a background noise. An adaptive filter linked to the spectral modifier adapts filter characteristics to match a response of a non-delayed signal. A programmable filter is linked to the delay unit. The programmable filter has a transfer function functionally related to a transfer function of the adaptive filter.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
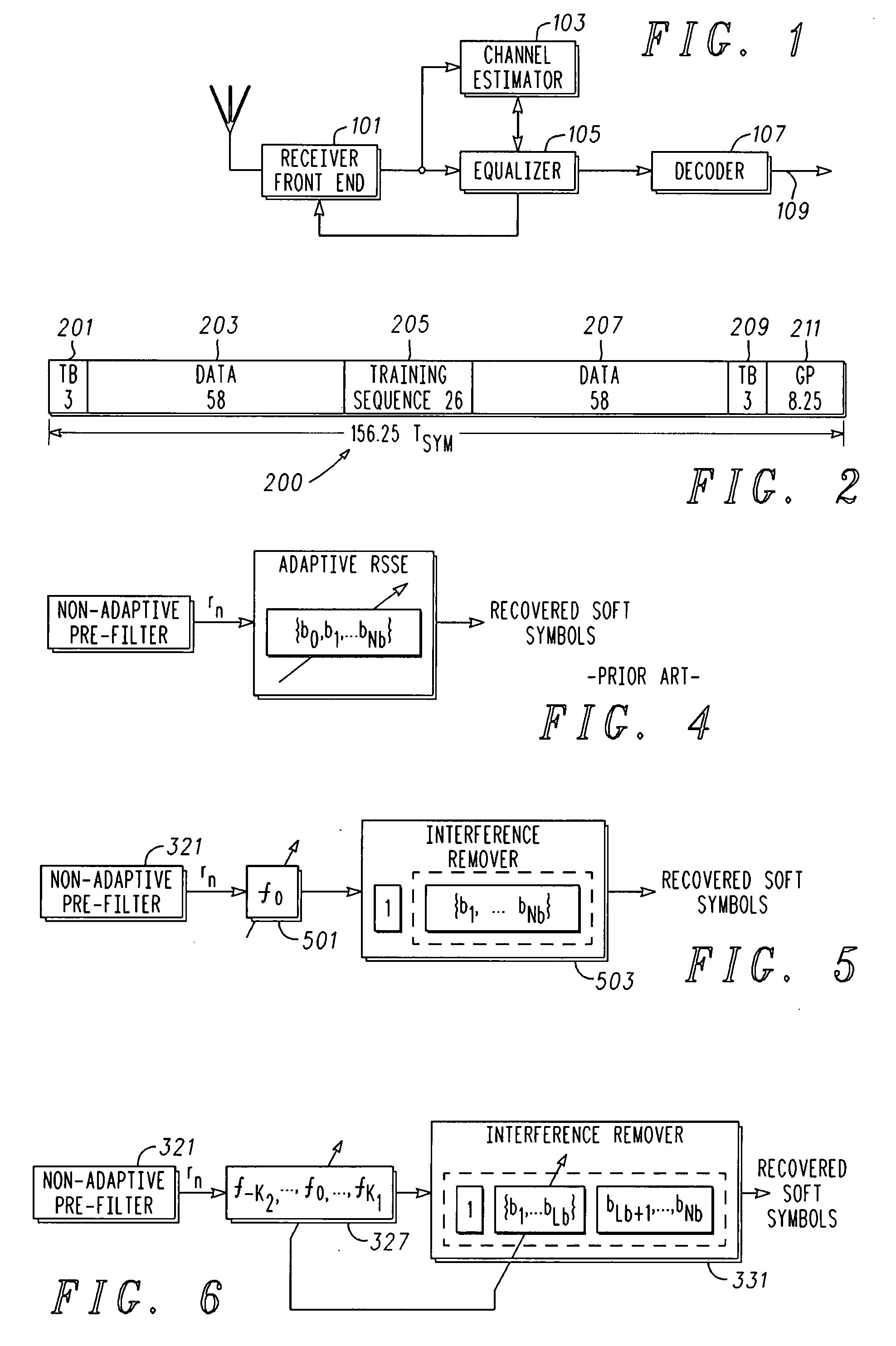
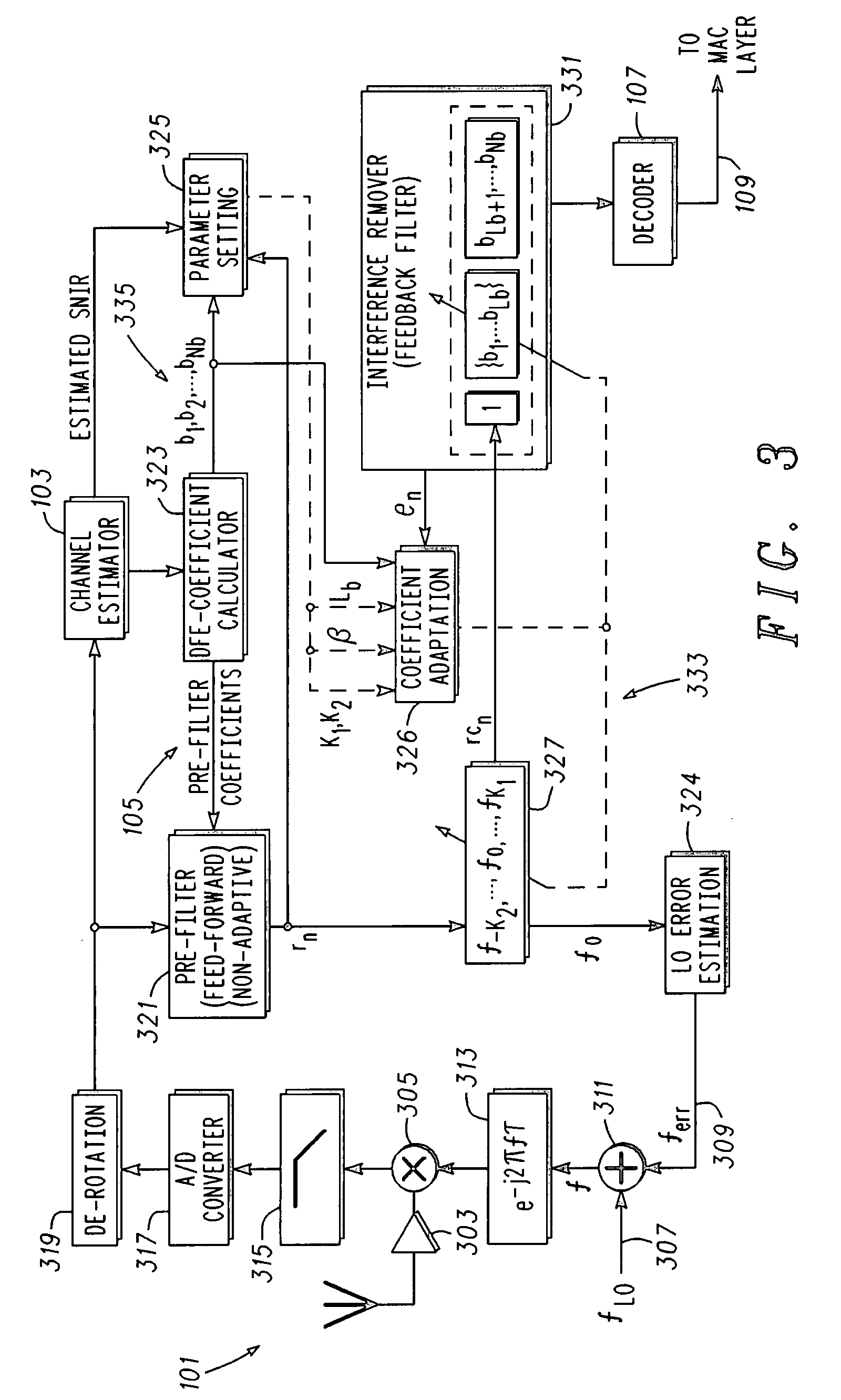
Adaptive equalizer for communication channels
Adaptive equalizers for a communication channel and corresponding methods of equalizing are described. The adaptive equalizer includes: a fixed pre-filter configured to be coupled to a received signal and provide a pre-filter signal; an adaptive filter coupled to and configured to compensate the pre-filter signal for changes in phase and amplitude; and an interference remover coupled to the adaptive filter and configured to reduce interference in the received signal.
Owner:APPLE INC
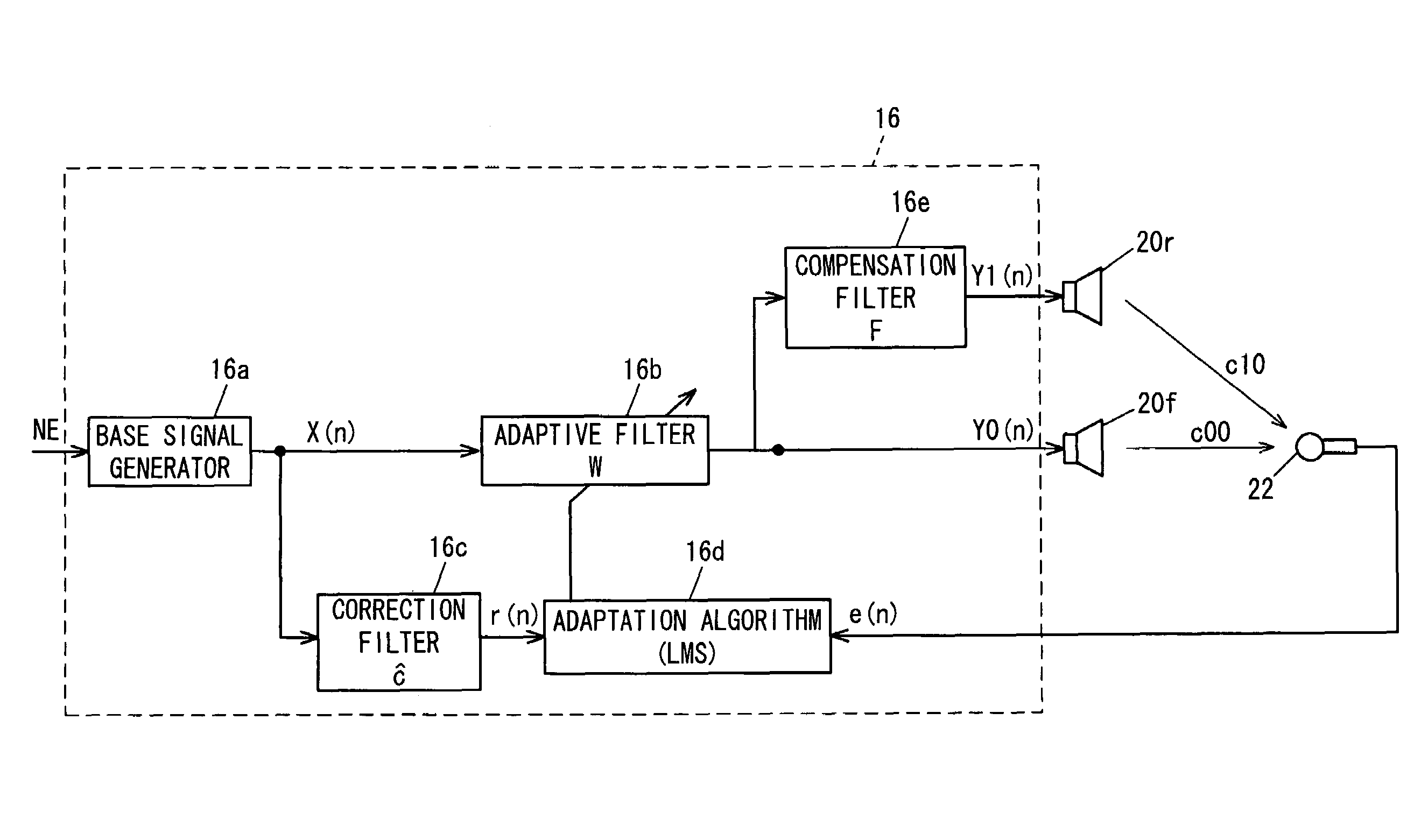
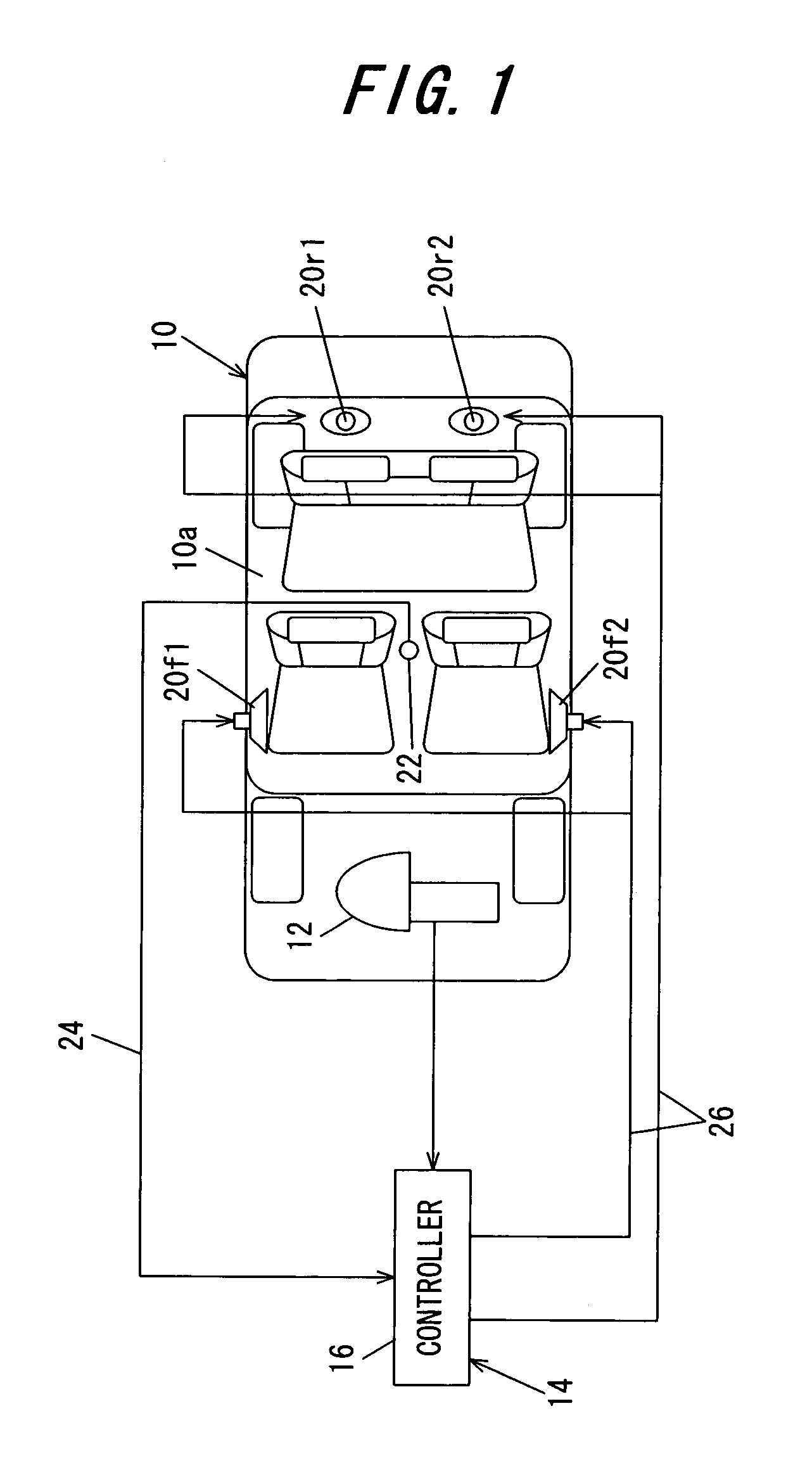
Active noise cancellation system
ActiveUS7536018B2Reduce noiseIncrease the number ofVibration measurement in fluidAdaptive networkControl signalEngineering
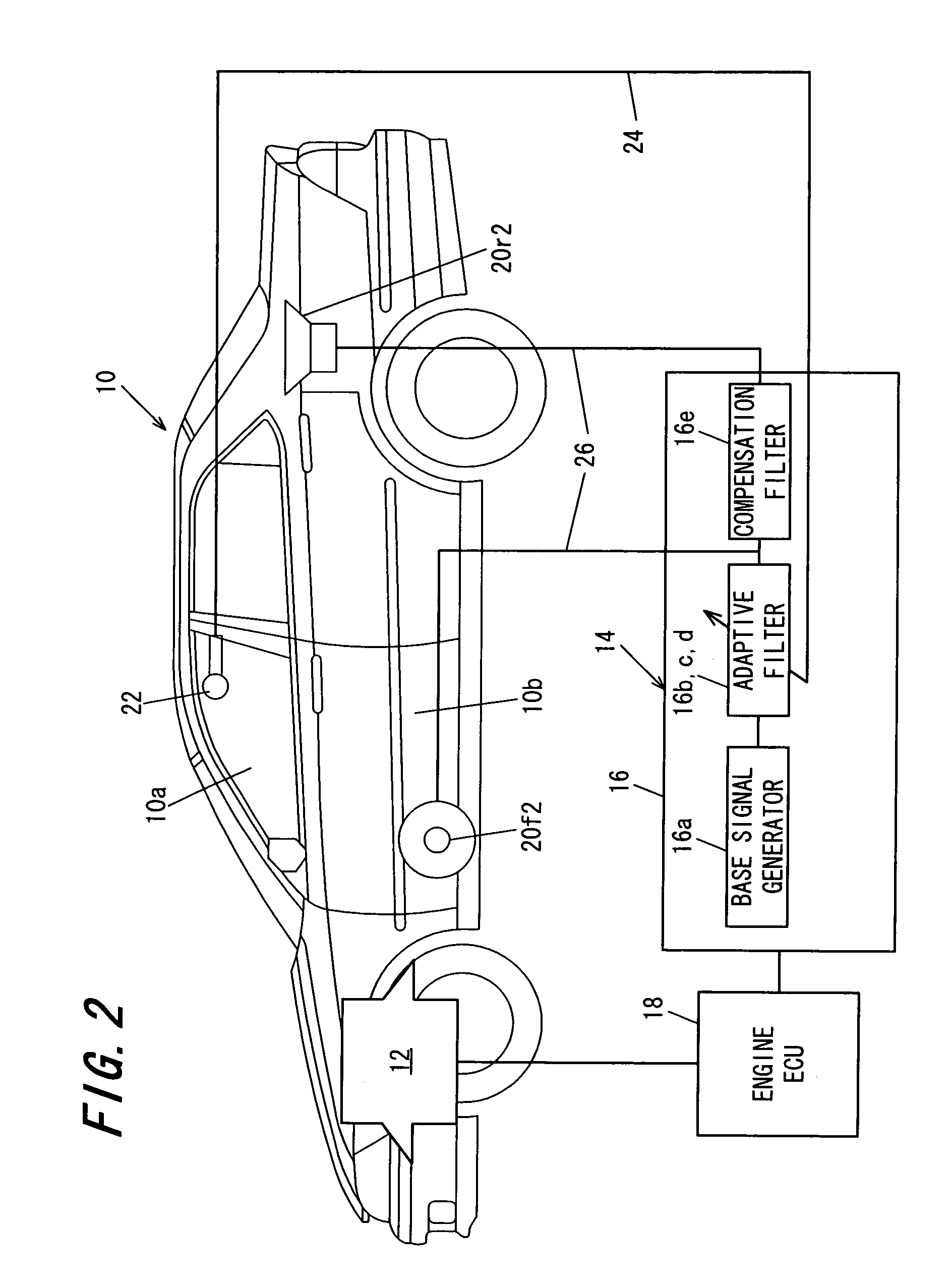
In an active noise cancellation system having an adaptive filter that outputs a control signal, first and second speakers that emit a canceling signal generated based on the control signal, a microphone that detects an error signal, a correction filter that corrects the base signal by a correction value to generate a reference signal and a filter coefficient updater that successively updates the adaptive filter coefficient based on the error signal and reference signal such that the error signal is minimized, the correction value of the correction filter is set to a sum obtained by adding the transfer characteristic from the first speaker to the microphone, and a product obtained by multiplying the transfer characteristic from the second speaker to the microphone by the prescribed value, thereby enabling to reduce the number of microphones and avoid the increase in parts, the amount of work to provide complicated wiring to the microphones, and the computational load involved in updating the adaptive filter coefficient, while enabling to maintain an area in which noise can be reduced to the same level as that obtained before reducing the number of microphones.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
Adaptive filtering for FMCW interference mitigation in PMCW radar systems
ActiveUS9791564B1Improve performanceReduce the impact of interferenceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsSelf adaptive
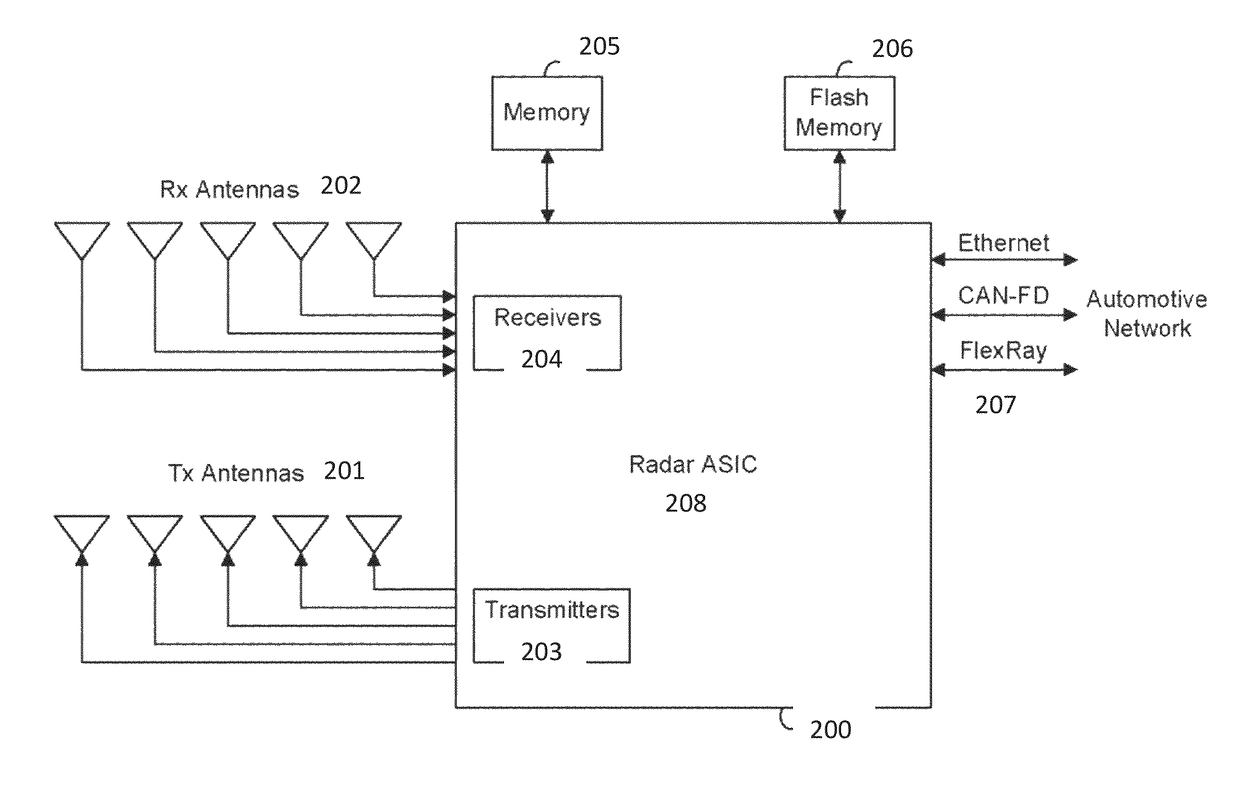
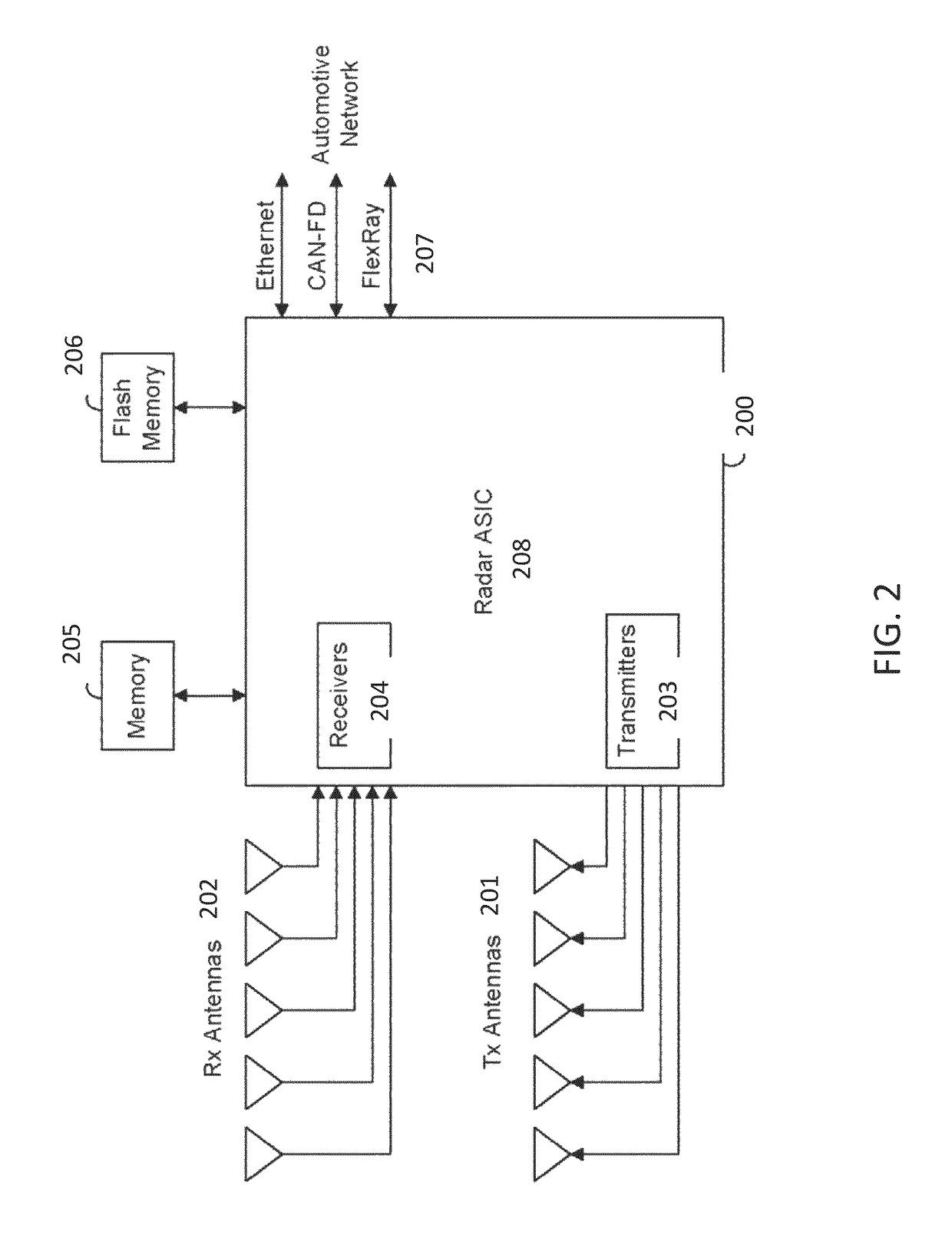
A radar sensing system for a vehicle includes a transmitter configured for installation and use on a vehicle and able to transmit radio signals. The radar sensing system also includes a receiver and a processor. The receiver is configured for installation and use on the vehicle and able to receive radio signals. The received radio signals include transmitted radio signals that are reflected from objects in the environment. The received radio signals further include radio signals transmitted by at least one other radar system. The processor samples the received radio signals to produce a sampled stream. The processor is configured to control an adaptive filter. Responsive to the processor, the adaptive filter is configured to filter the sampled stream, such that the radio signals transmitted by the at least one other radar system are removed from the received radio signals.
Owner:UHNDER INC
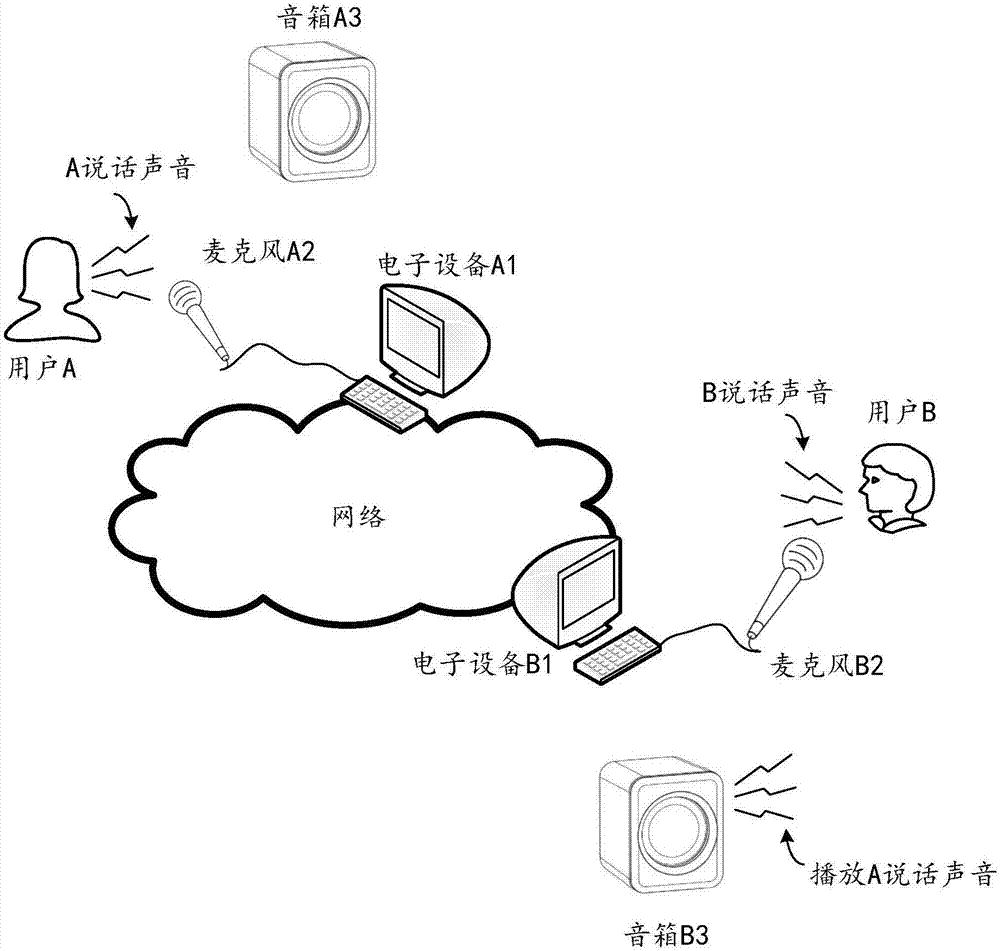
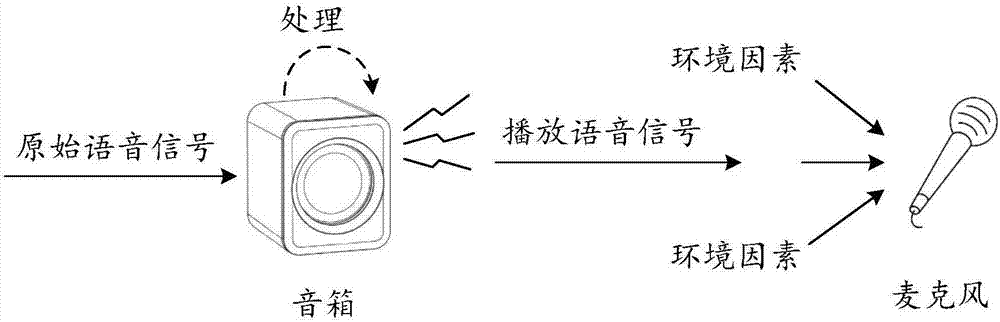
Echo cancellation method, echo cancellation device, conference tablet computer and computer storage medium
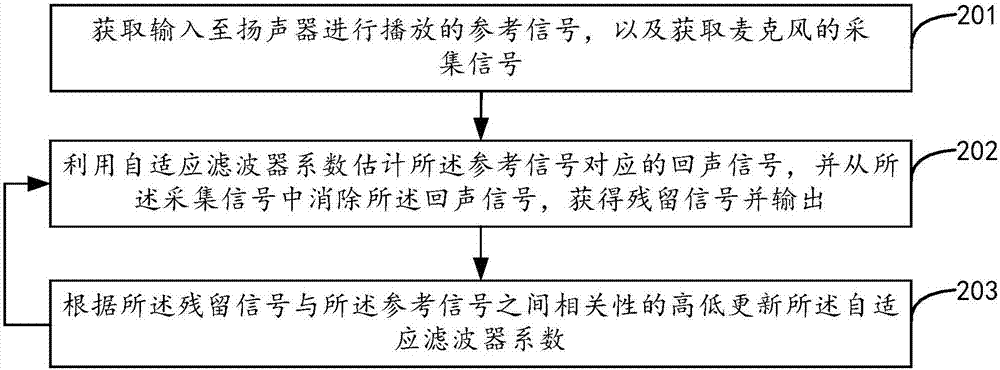
ActiveCN107123430ATimely updateEasy to updateTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpeech analysisTablet computerSelf adaptive
The invention relates to an echo cancellation method, an echo cancellation device, a conference tablet computer and a computer storage medium. The method comprises steps: reference signals inputted to a loudspeaker for playback are acquired, and acquisition signals of a microphone are acquired; coefficients of an adaptive filter are acquired, and the adaptive filter coefficients are used for estimating echo signals corresponding to the reference signals; the echo signals are canceled from the acquisition signals, and residual signals are acquired and outputted; and according to the relativity between the residual signals and the reference signals, the coefficients of the adaptive filter are updated. The embodiment creatively adjusts the coefficients of the adaptive filter through the relativity between the residual signals and the reference signals, echo cancellation can be carried out to an extremely large degree, updating on the coefficients of the adaptive filter only needs to be added on the basis of the traditional algorithm, and the newly-added cost is low.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SHIYUAN ELECTRONICS CO LTD
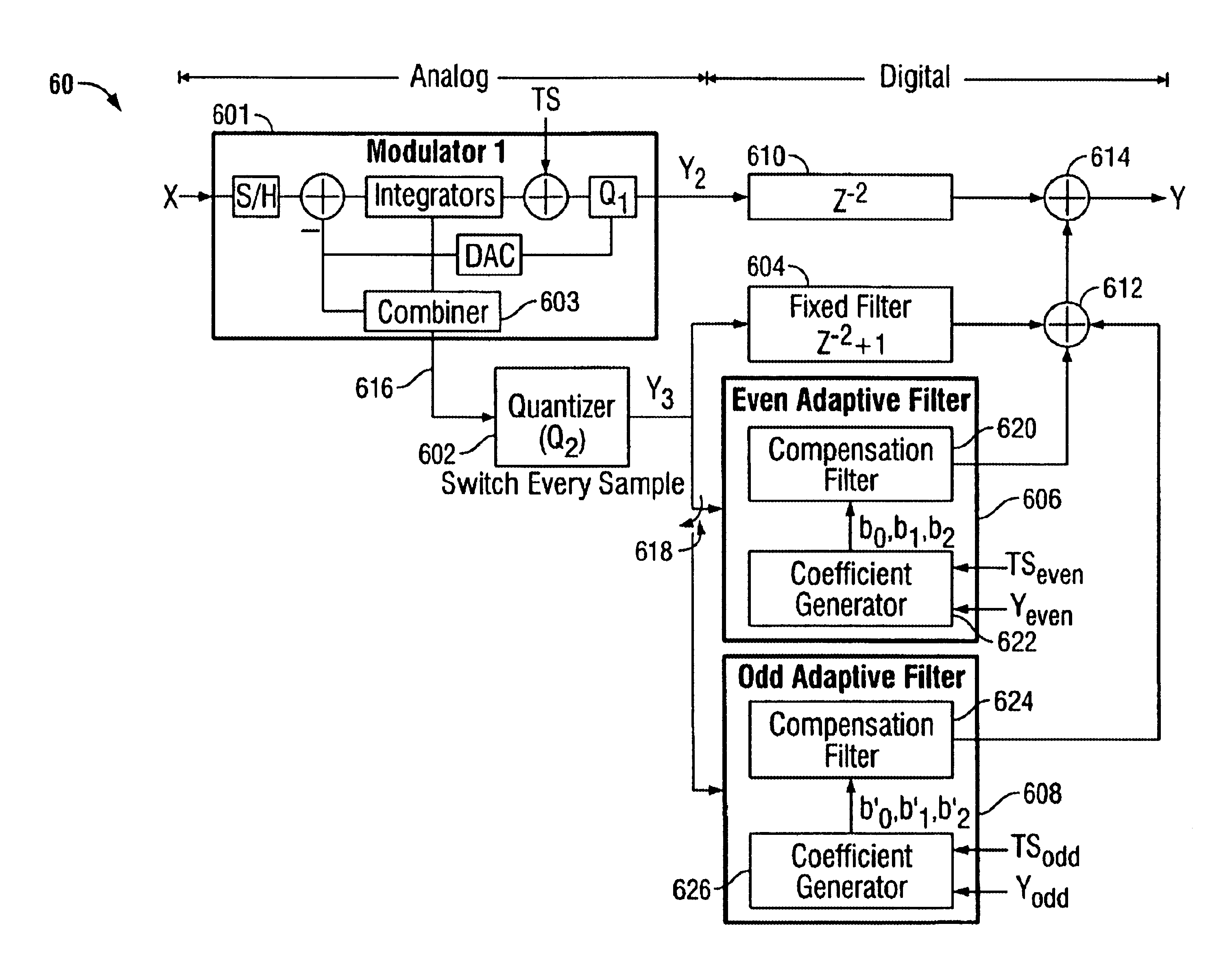
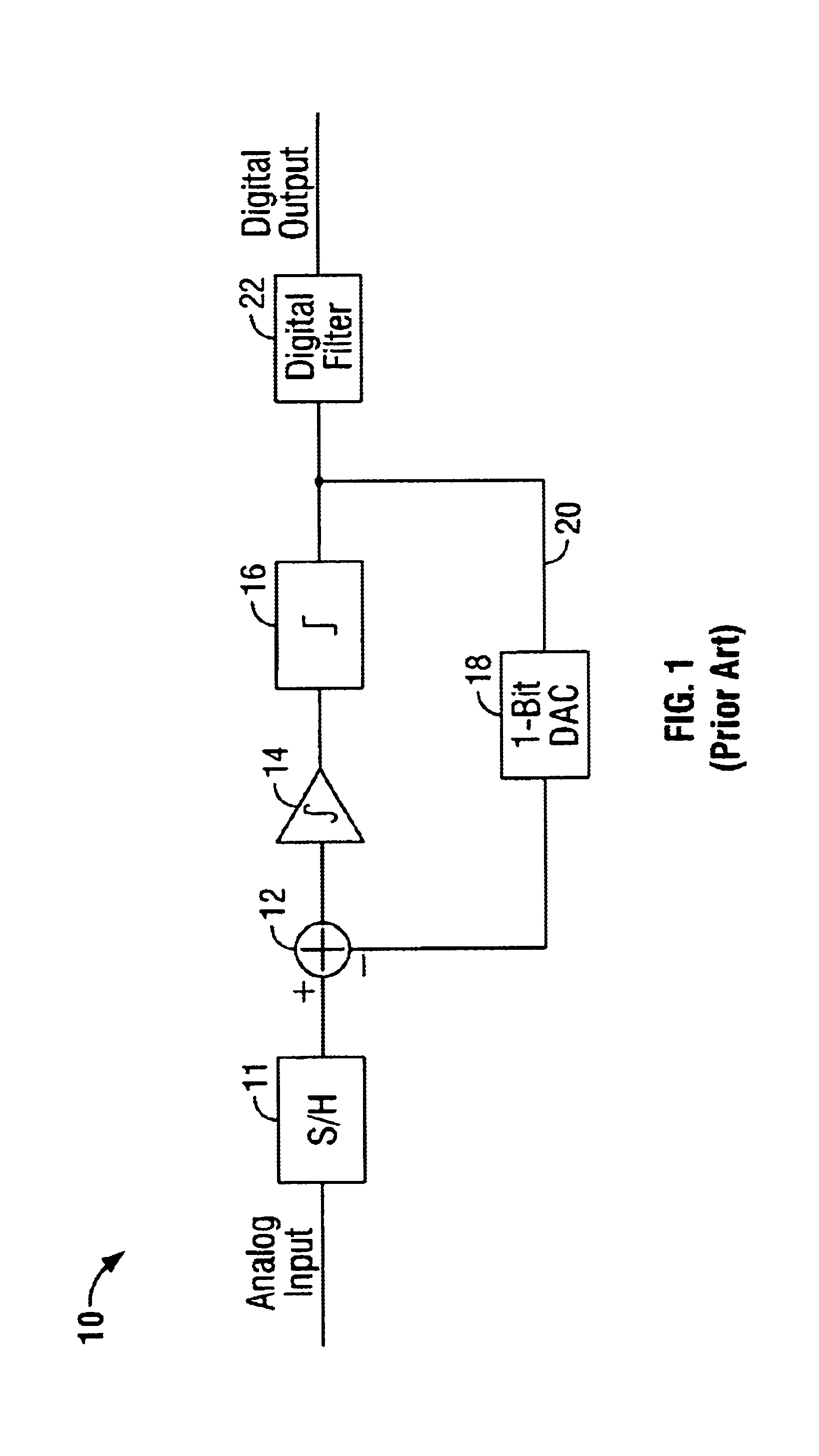
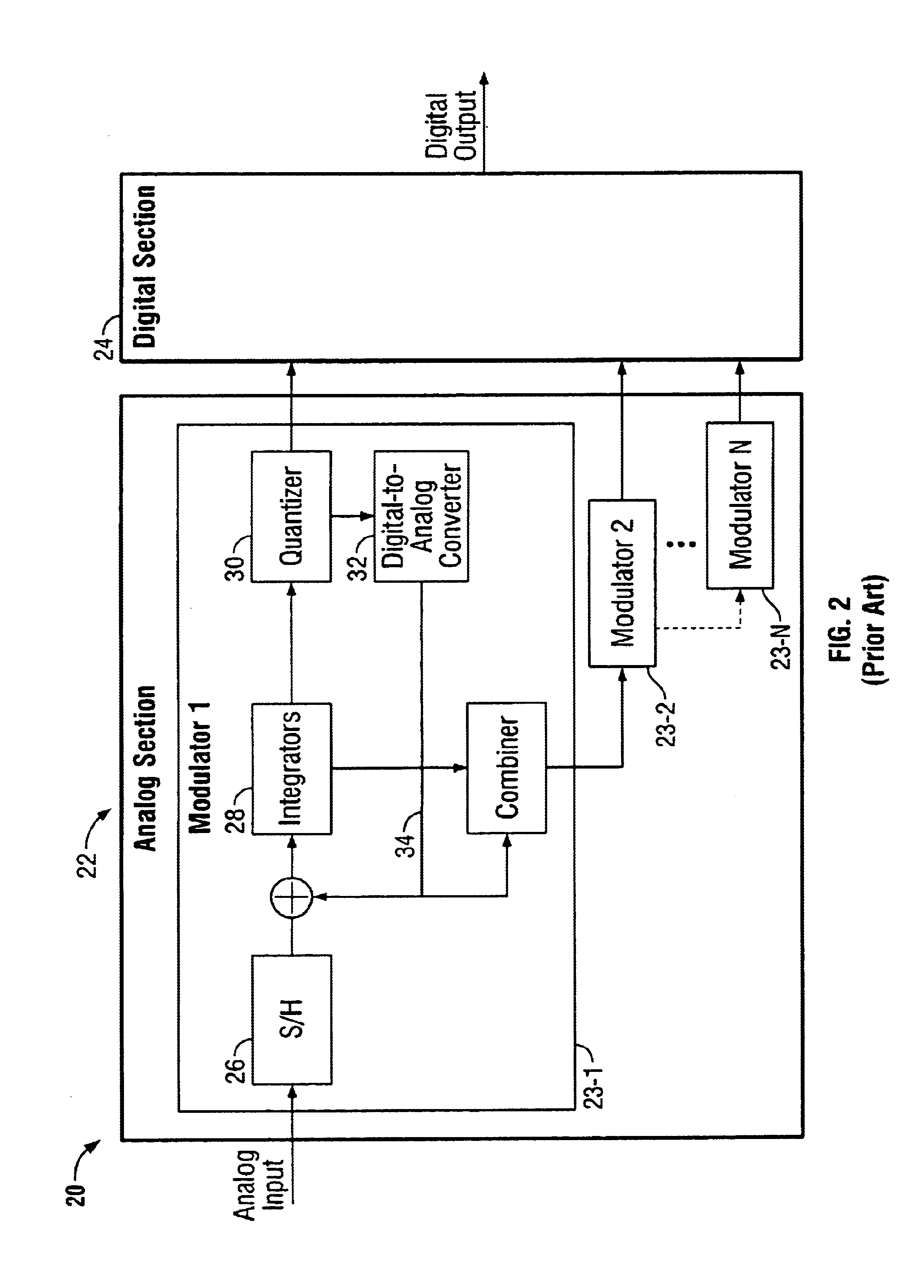
Interleaved digital correction for MASH delta-sigma ADC
InactiveUS6873281B1Improved signal-to-noise ratio performanceAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsClock rateEngineering
Methods of and apparatuses for optimizing quantization noise cancellation in multi-phase sampled MASH ADCs are disclosed. A test signal is combined with quantization noise produced by a delta-sigma modulator. Two parallel adaptive filters (i.e. even and odd filters) are configured to receive respective even and odd samples of a digital output signal of a MASH ADC analog modulator. Adaptive coefficients for the even adaptive filter are derived from correlation results between the even samples of the test signal and associated even samples of the final digital output signal. Similarly, adaptive coefficients for the odd adaptive filter are derived from correlation results between the odd samples of the test signal and associated odd samples of the final digital output signal. Using the adaptive coefficients, the even and odd adaptive filters are able to independently compensate for analog variations in the two paths. Fixed, slowly varying, and clock rate variations may all be tracked out using the methods and apparatus of the present invention.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
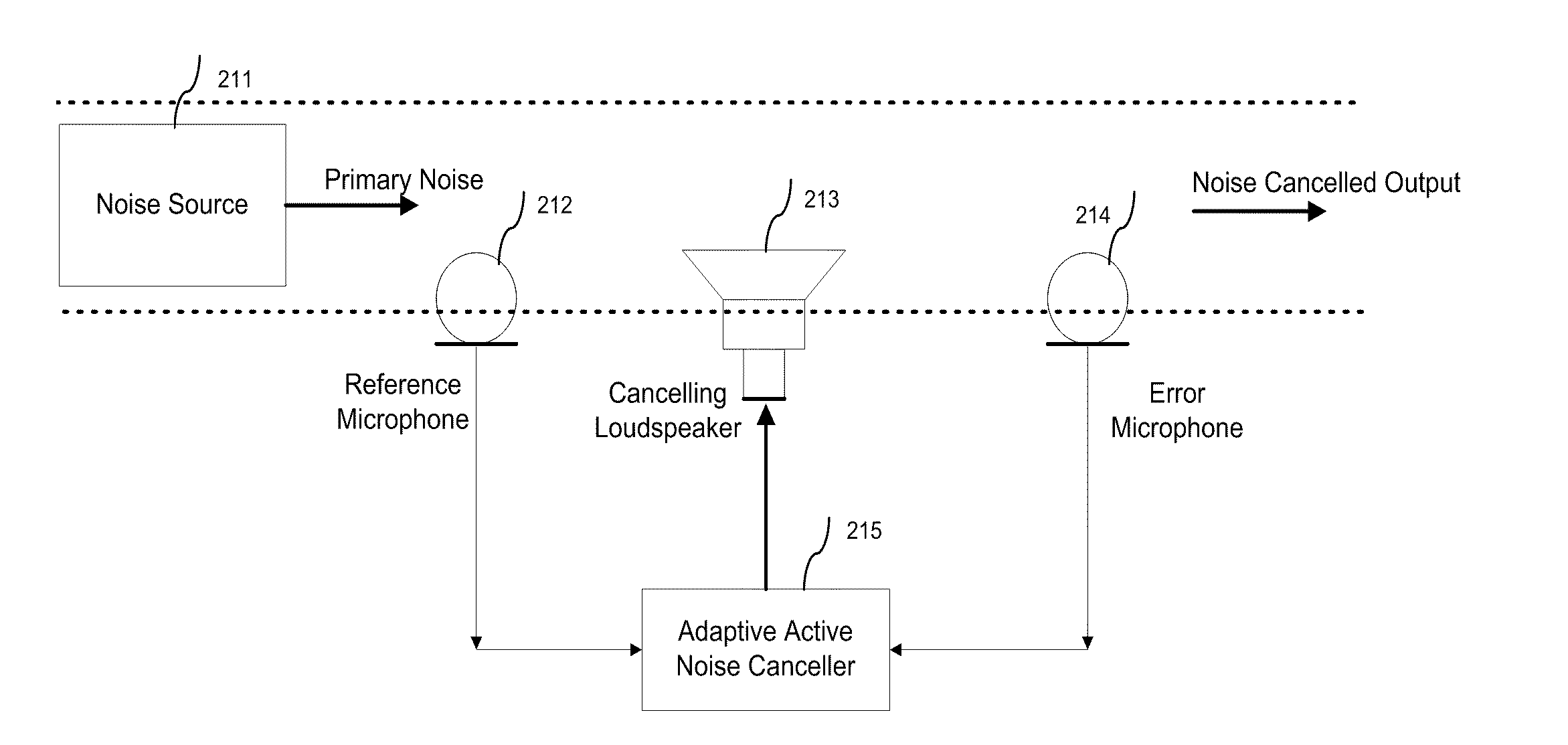
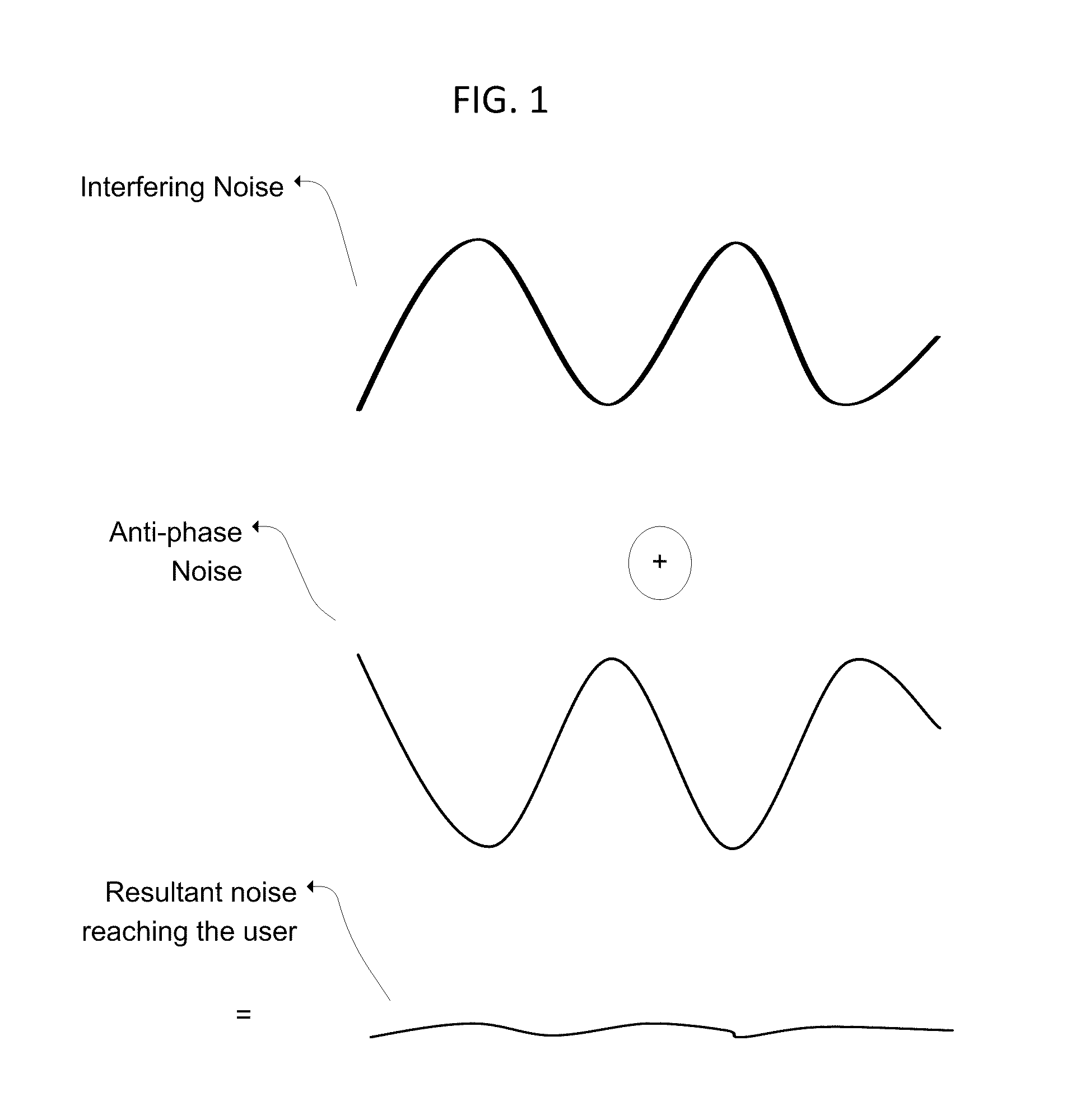
Active Noise Control in Mobile Devices
InactiveUS20110091047A1Ability to detect and reduce different level of background noiseComputationally inexpensiveEar treatmentNoise generationNoise controlMean square
A three dimensional area of quiet is created by an active noise cancellation system comprising a reference microphone receiving background noise and sending the noise signal to an adaptive active noise canceller. An adaptive filter system using weights updated by a least mean squares method or other method generates an anti-phase signal which is broadcasted to counteract the background noise. The resulting residual noise or residual signal is sent back to the adaptive active noise canceller to reset the weights of the adaptive filter.
Owner:NOISE FREE WIRELESS
Advanced periodic signal enhancement
ActiveUS7716046B2Improve processing qualityFlatten spectral character of background noiseAdaptive networkSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumProgrammable filters
An enhancement system improves the perceptual quality of a processed speech. The system includes a delay unit that delays a signal received through a discrete input. A spectral modifier linked to the delay unit is programmed to substantially flatten the spectral character of a background noise. An adaptive filter linked to the spectral modifier adapts filter characteristics to match a response of a non-delayed signal. A programmable filter is linked to the delay unit. The programmable filter has a transfer function functionally related to a transfer function of the adaptive filter.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
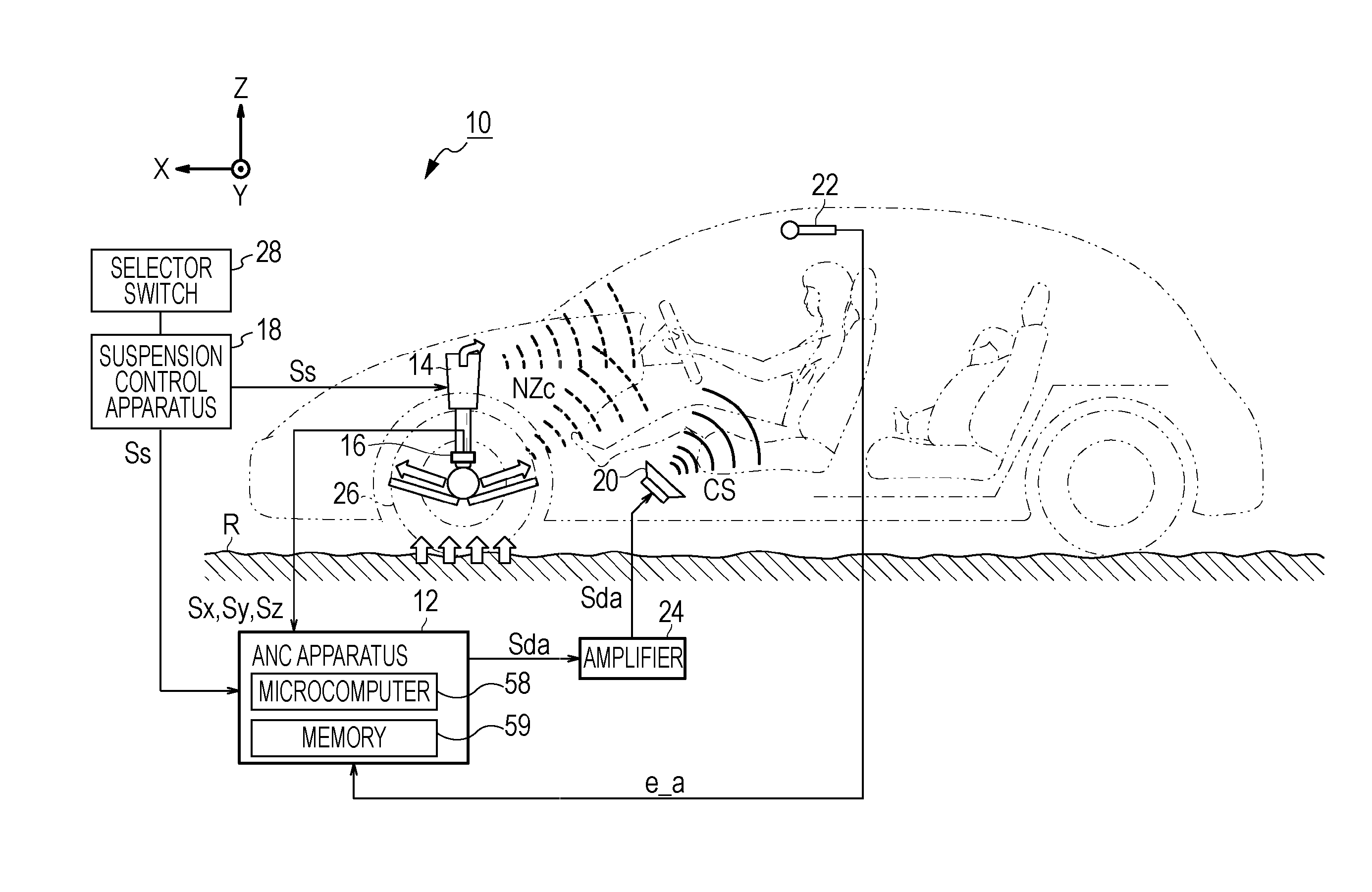
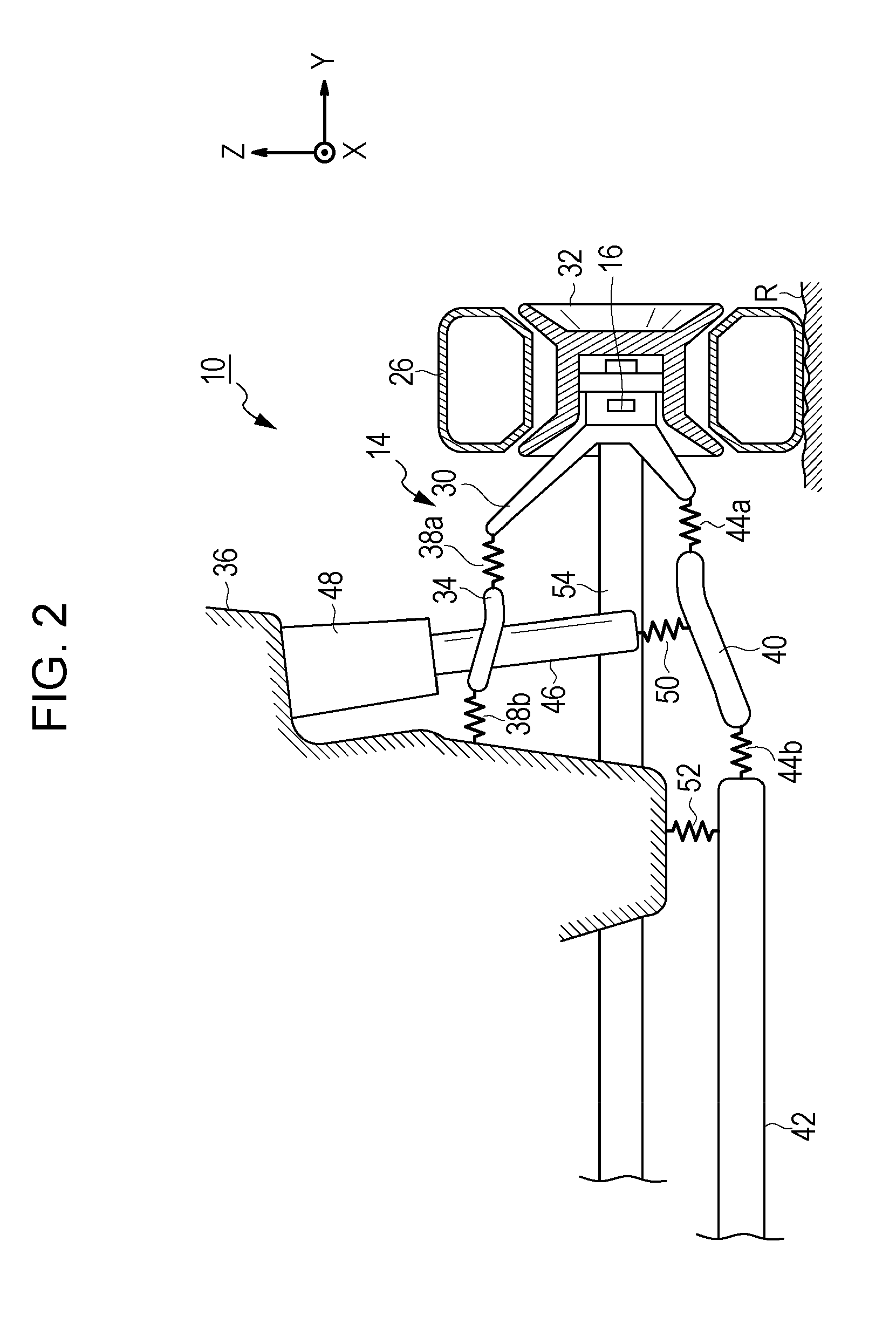
Active noise control apparatus
InactiveUS20110142248A1Minimize error signalError signalEar treatmentNoise generationNoise controlNormal mode
An active noise control apparatus includes a road surface input detector, a reference signal generator, an adaptive filter, a noise-cancellation sound generator, an error detector, a reference signal corrector, a filter coefficient updating unit, a transfer characteristic variation detector, and an update amount controller. The transfer characteristic variation detector is configured to detect a variation in transfer characteristic between the road surface input detector and the error detector. The update amount controller is configured to increase an amount of updating of a filter coefficient to a value greater than a value that is used in a normal mode in accordance with the variation in transfer characteristic detected by the transfer characteristic variation detector.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
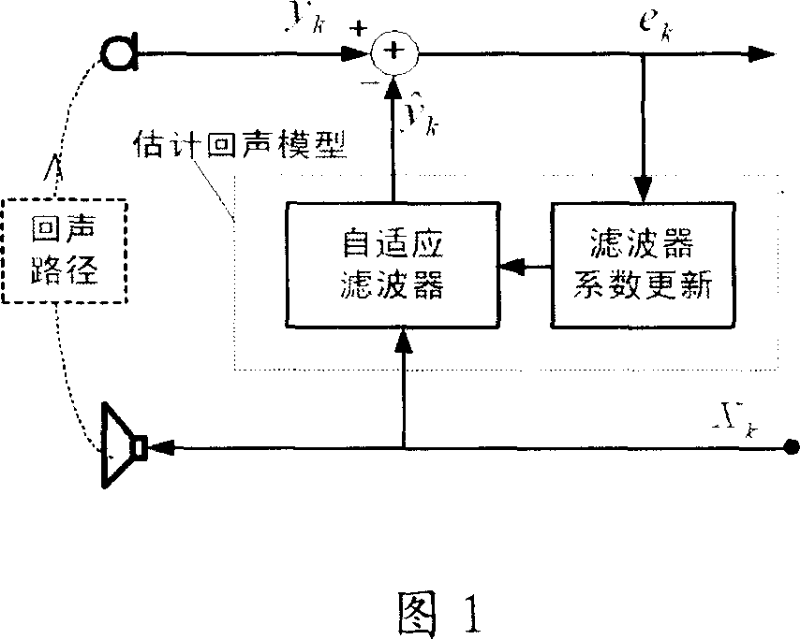
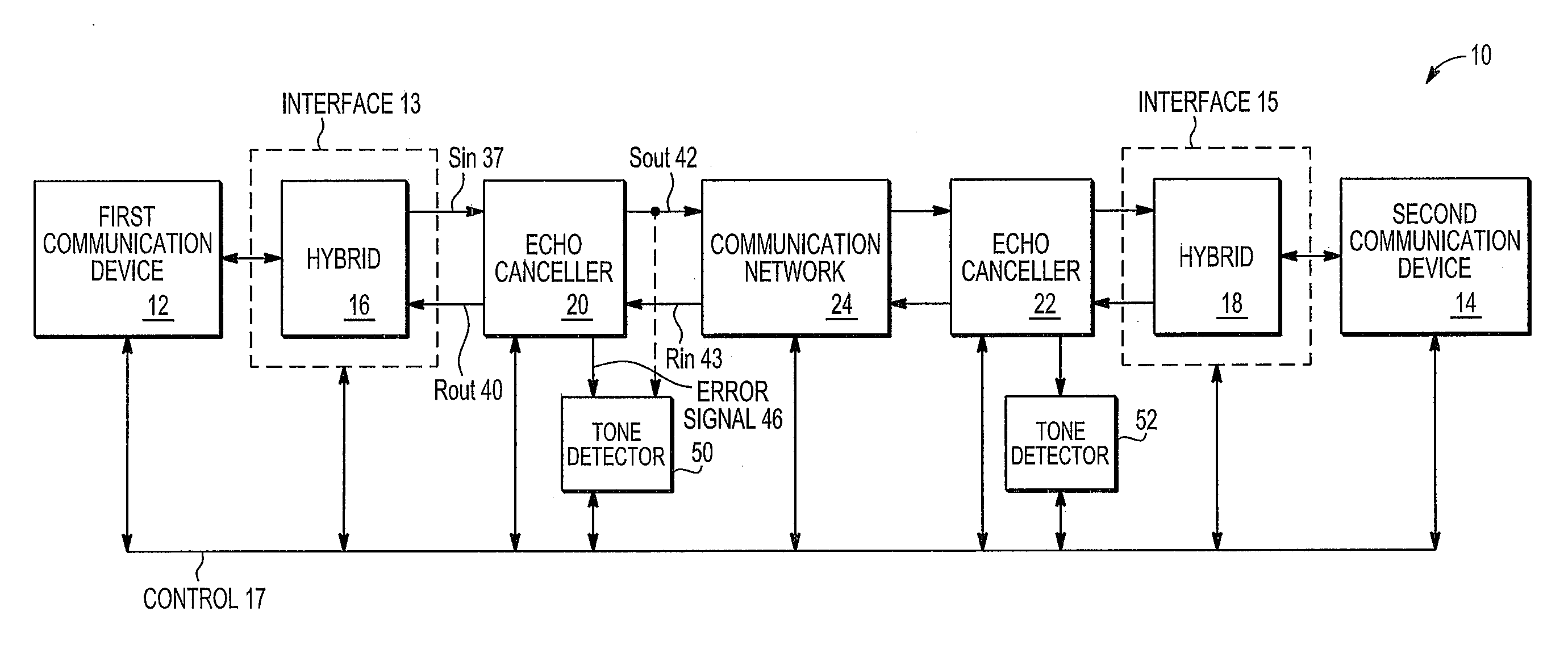
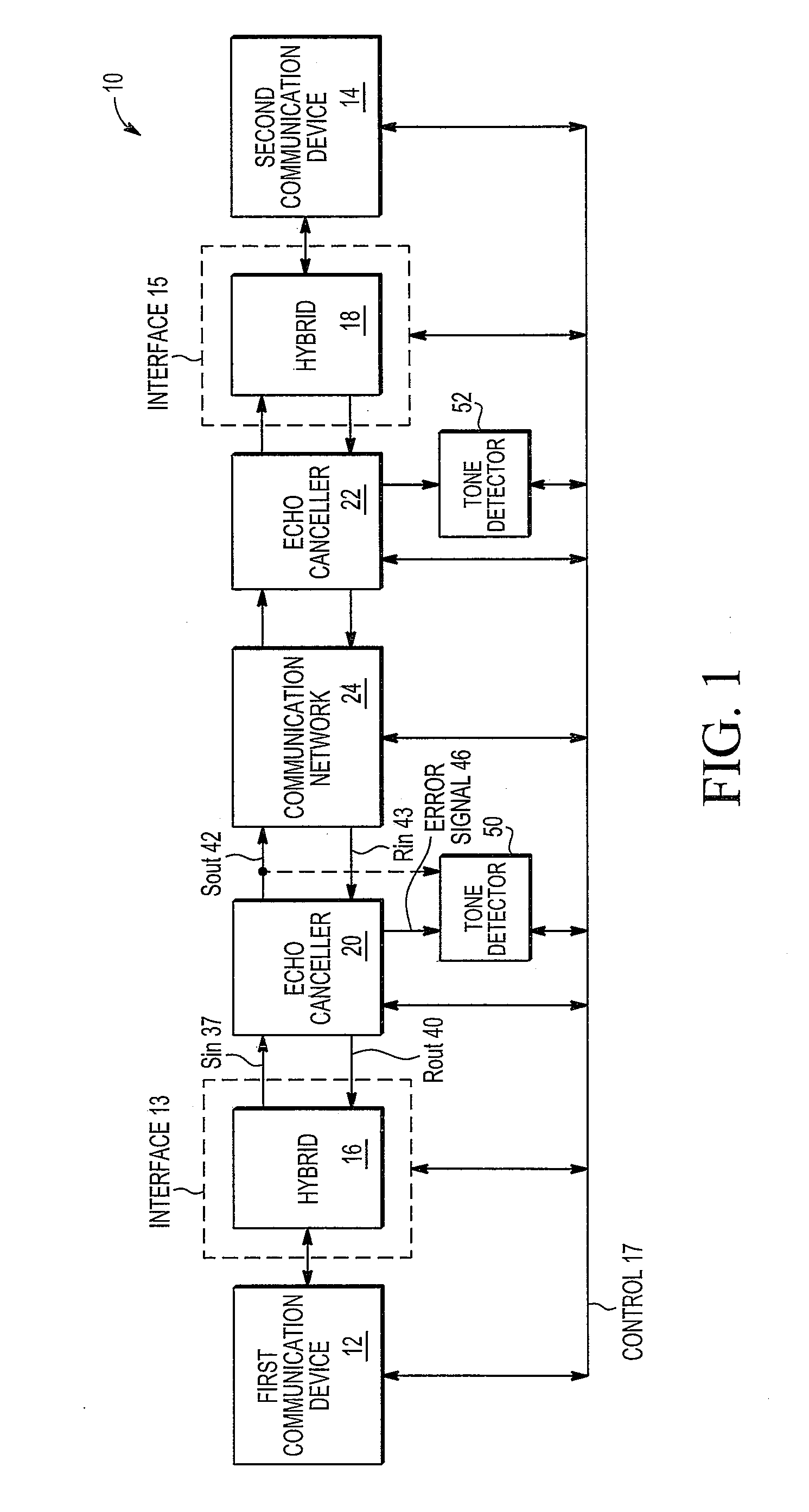
Echo eliminator and echo cancellation method
InactiveCN101043560ASmall amount of calculationFast convergenceTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpeech analysisLinear prediction codingData stream
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
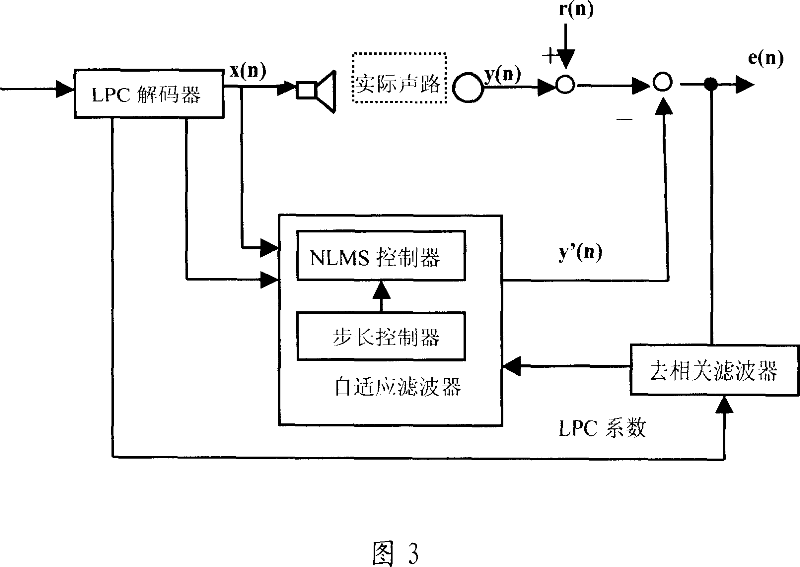
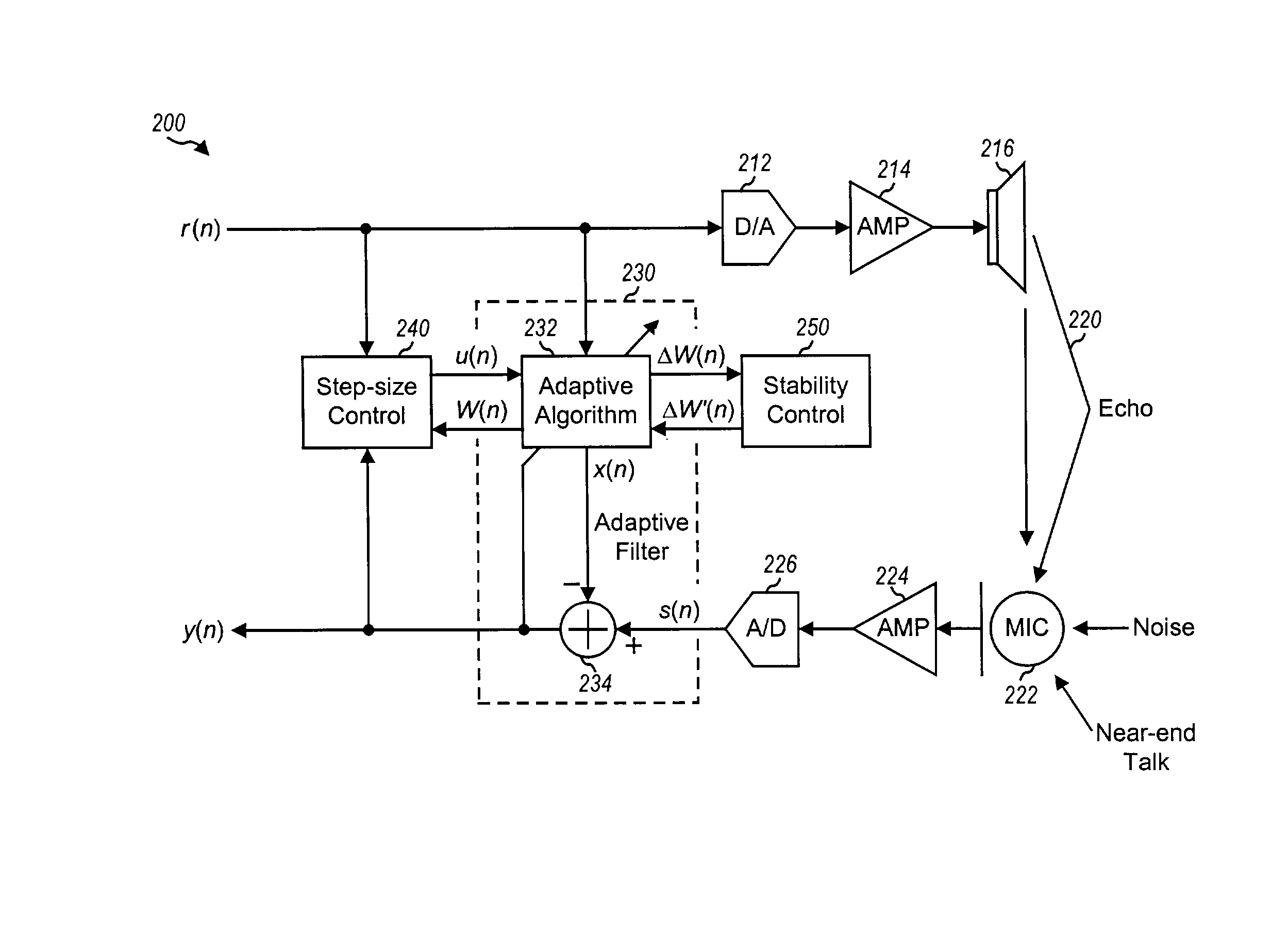
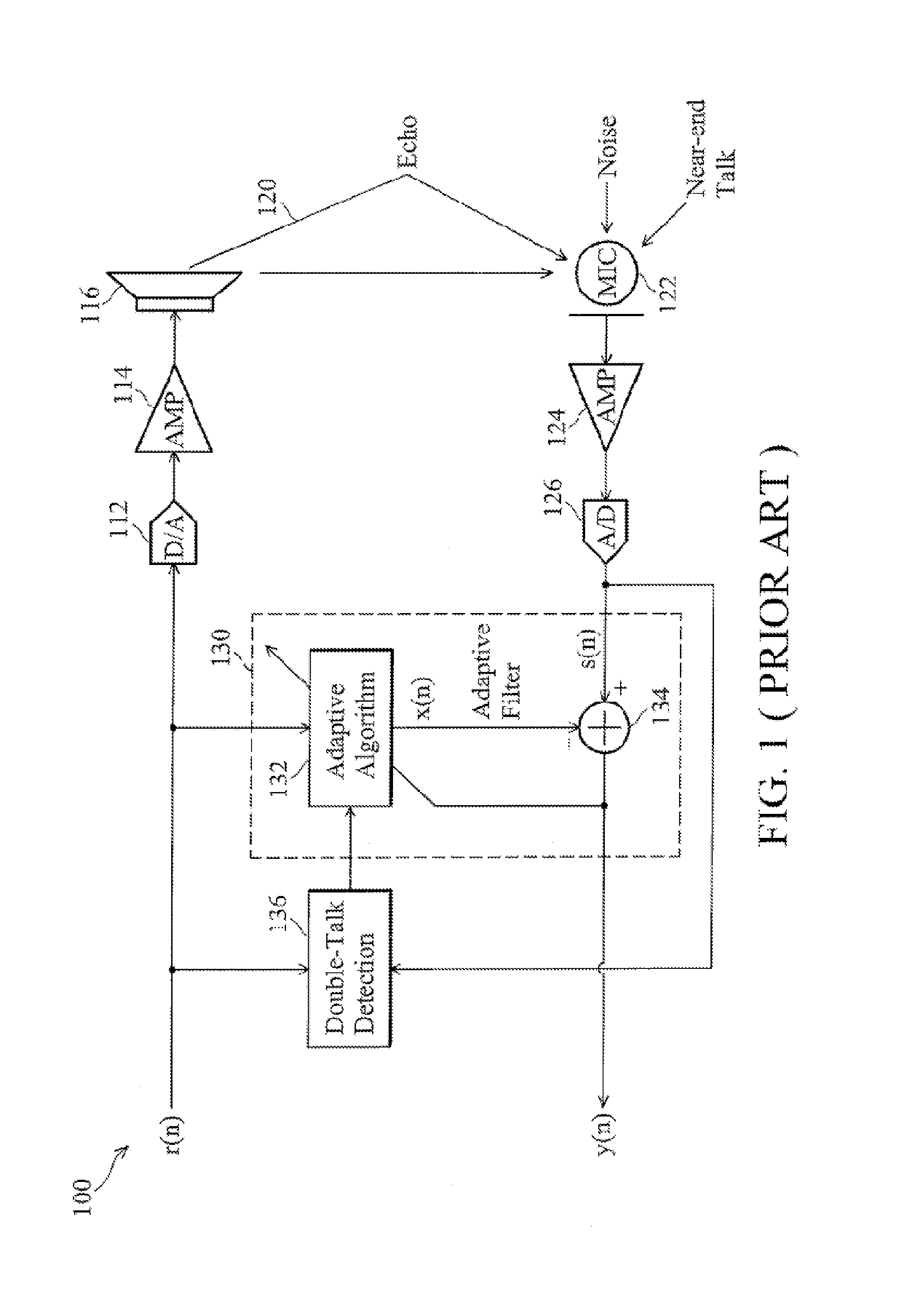
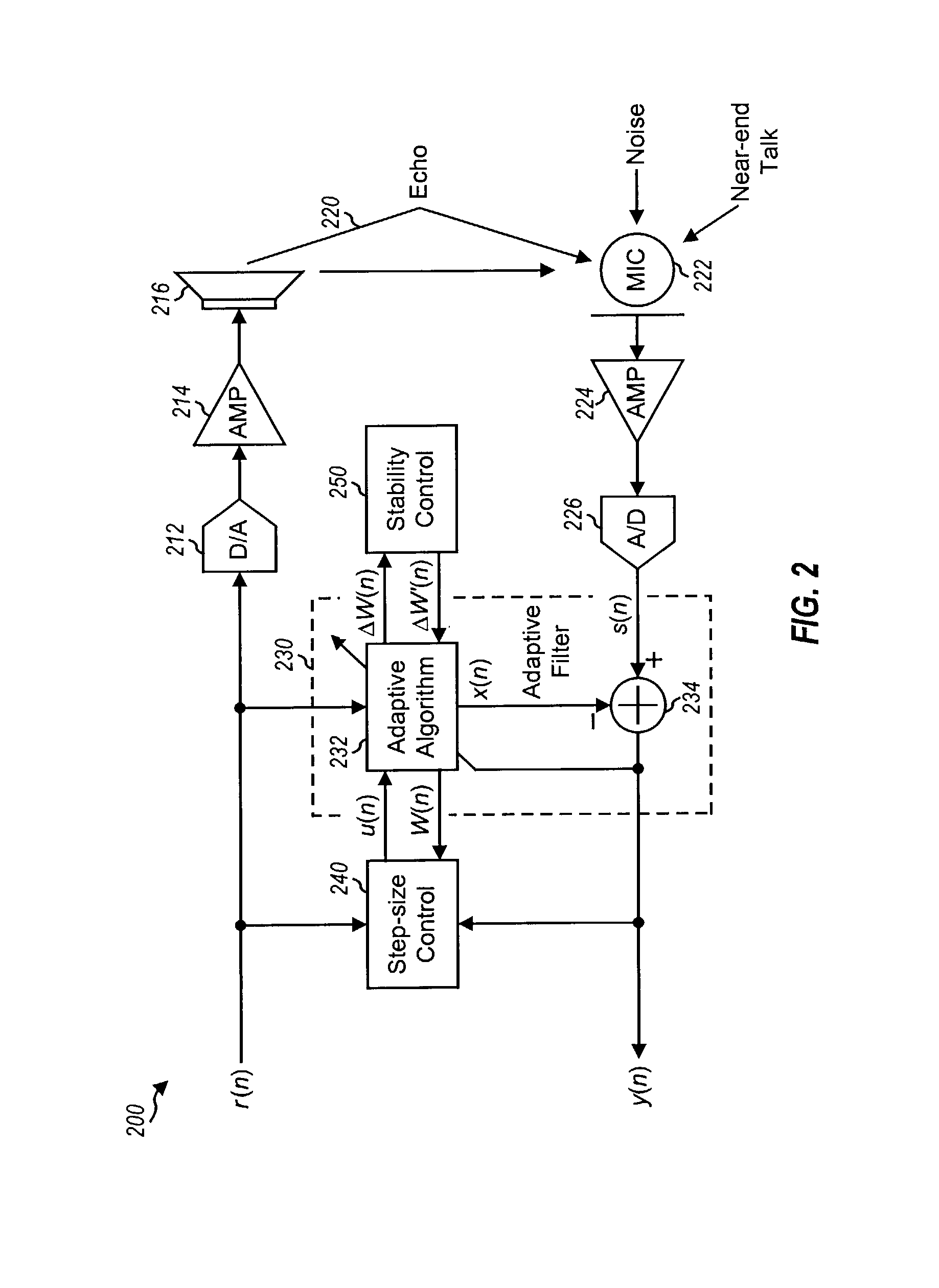
Acoustic echo cancellation with adaptive step size and stability control
ActiveUS7333605B1Improve echo cancellation effectAvoid harmful effectsTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsLine-transmissionInstabilitySelf adaptive
An acoustic echo canceller having an adaptive filter, a step size control unit, and (optionally) a stability control unit. The adaptive filter derives an estimate of the echo in a near-end signal using a digital filter (e.g., a FIR filter) and further cancels the echo estimate from the near-end signal to provide an output signal. The step size control unit derives step sizes to be used to adjust the coefficients of the digital filter. The step sizes are determined based on the characteristics of a reference signal and the output signal and (optionally) the characteristics of the coefficients. For example, the step size is set proportional to the reference signal amplitude, inversely proportional to the output signal amplitude, and based on a difference in the coefficient power at two different time instants. The stability control unit constrains the adjustments to the coefficients to prevent instability.
Owner:FORTEMEDIA
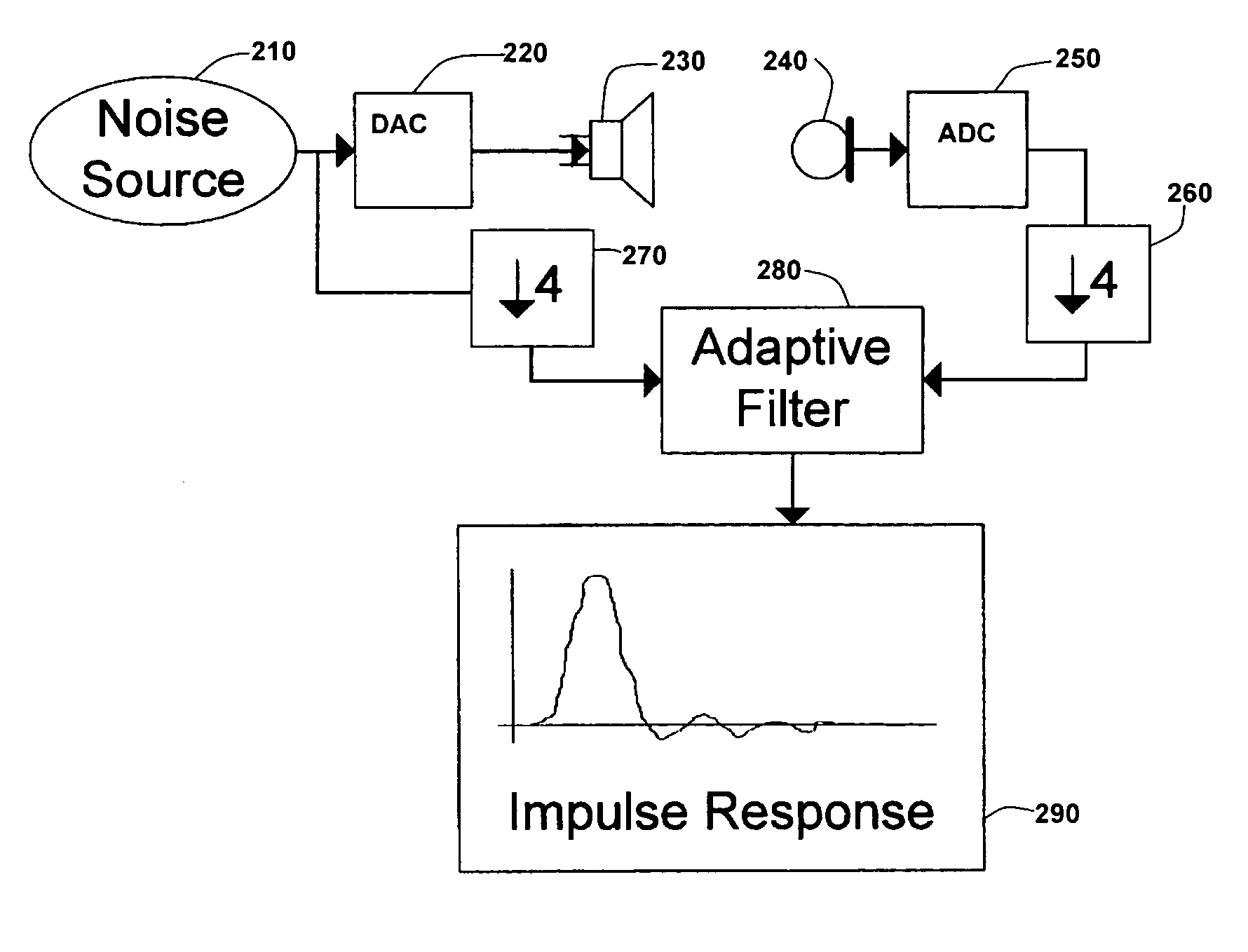
Speaker distance measurement using downsampled adaptive filter
InactiveUS20060062398A1Easy to measureLess susceptible to noiseStereophonic circuit arrangementsUsing reradiationMean squareImage resolution
A downsampled adaptive filter is used to find the impulse response of a home theater system. Downsampling yields higher maximum measurable distance for given filter length. By using a Least-Mean-Square (LMS) adaptive filter, almost anything can be used as the source noise. While downsampling may decrease the resolution of the distance measurement, Adaptive Filtering allows a much broader range of test signals, as opposed to MLS (Maximum Length Sequence) in which the test signal defines the technique (a pseudo-random Maximum Length Sequence.)
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
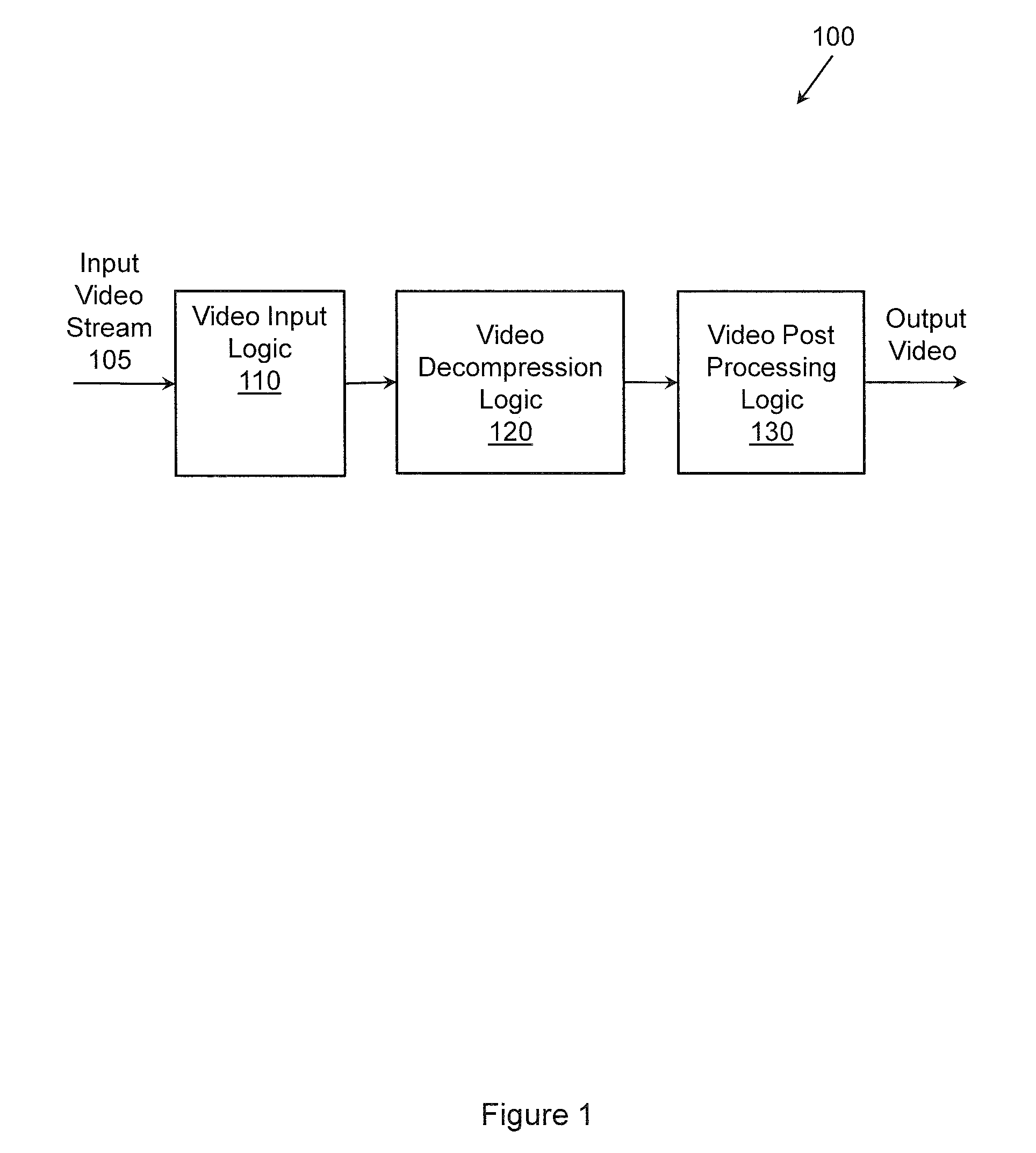
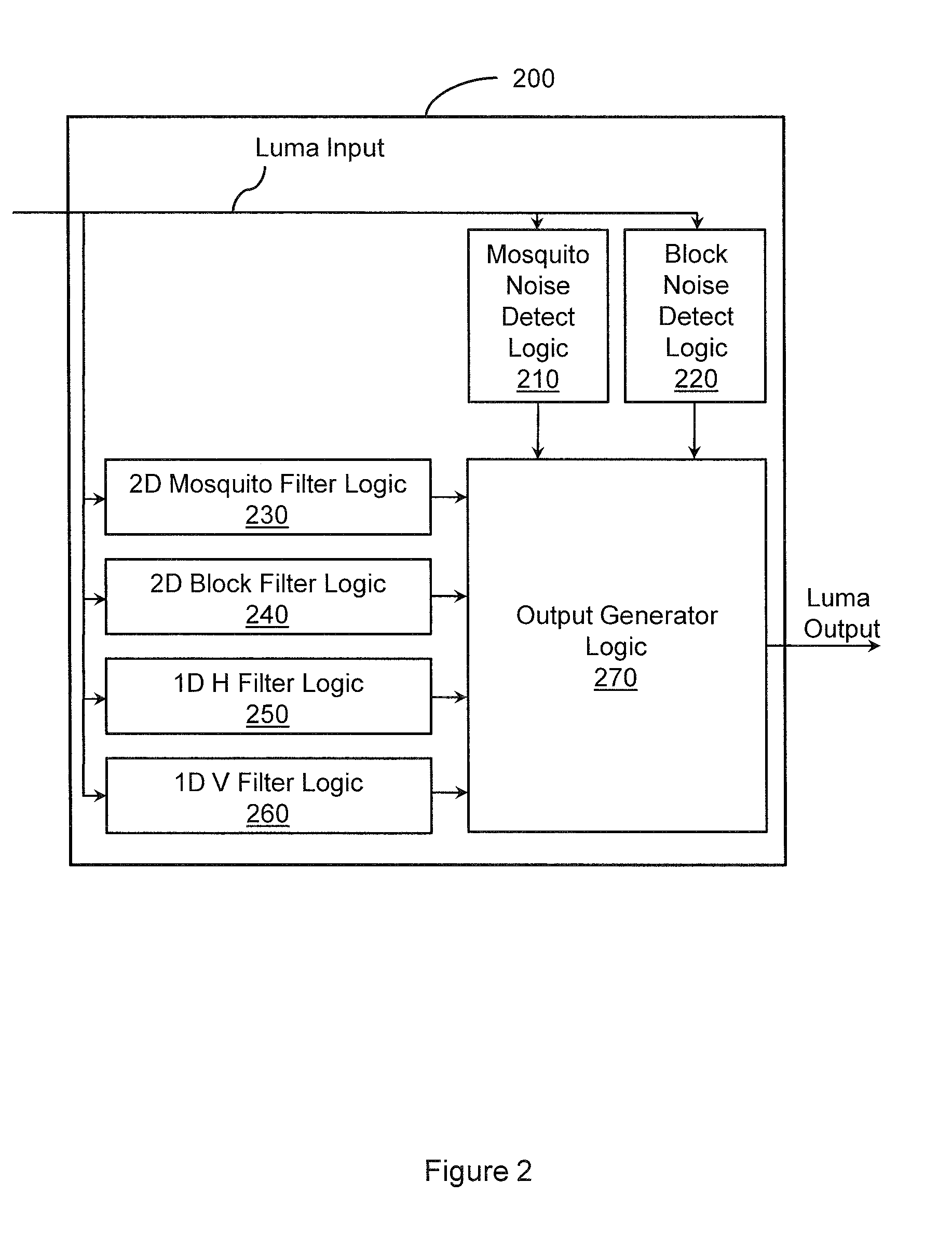
Reducing digital image noise
ActiveUS20100060749A1Improve image qualityReduce artifactsImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionCompression artifact
Devices, systems, methods, and other embodiments associated with reducing digital image noise are described. In one embodiment, a method includes determining, on a per pixel basis, mosquito noise values associated with pixels of a digital image. The method determines, on a per pixel basis, block noise values associated with the digital image. The method filters the digital image with a plurality of adaptive filters. A compression artifact in the digital image is reduced. The compression artifact is reduced by combining filter outputs from the plurality of adaptive filters. The filter outputs are combined based, at least in part, on the mosquito noise values and the block noise values.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC +1
Techniques for Updating Filter Coefficients of an Adaptive Filter
ActiveUS20110261948A1Two-way loud-speaking telephone systemsLine-transmissionImpulse responseSelf adaptive
A technique for updating filter coefficients of an adaptive filter includes filtering a signal with an adaptive filter, whose filter coefficients are grouped into filter blocks. In this case a number of the filter blocks is less than or equal to a number of the filter coefficients. During each update period, the filter coefficients for less than all of the filter blocks are updated based on a network echo path impulse response.
Owner:NXP USA INC
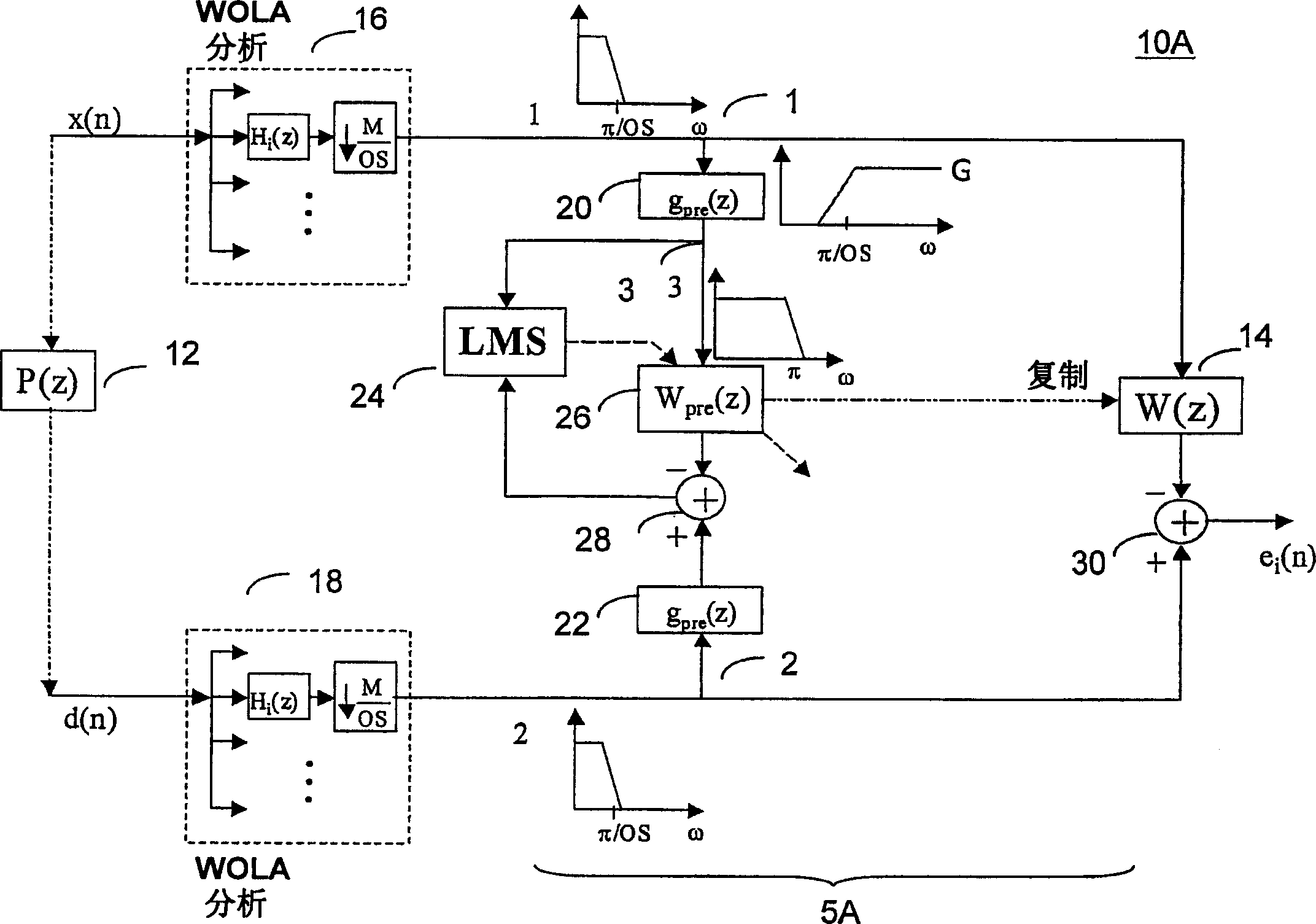
Method and system for processing subband signals using adaptive filters
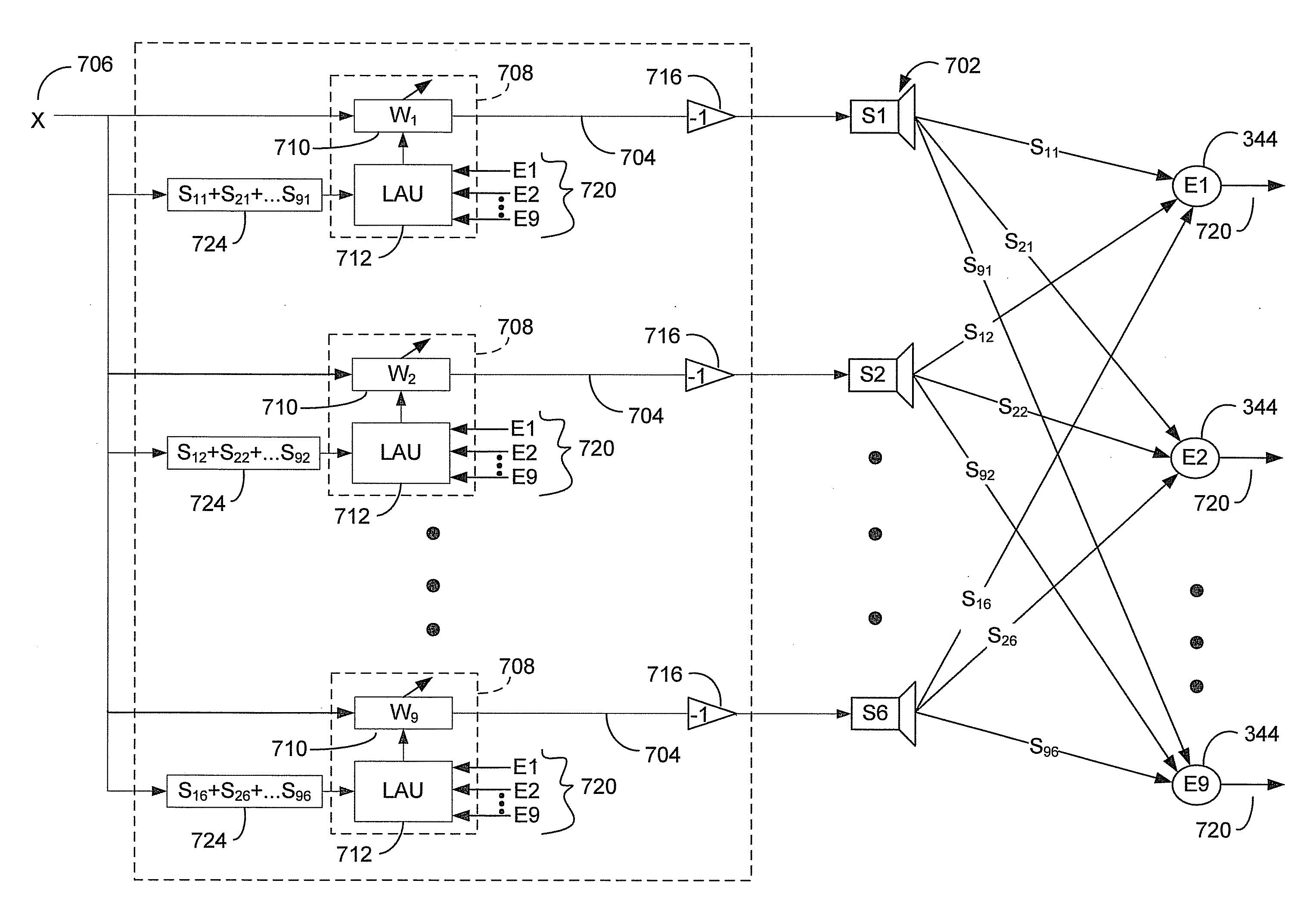
A method and system for processing subband signals using adaptive filters is provided. The system is implemented on an oversampled WOLA filterbank. Inputs signals are oversampled. The system includes an adaptive filter for each subband, and the functionality of improving the convergence properties of the adaptive filter. For example, the convergence property is improved by whitening the spectra of the oversampled subband signals and / or affine projection algorithm. The system is applicable to echo and / or noise cancellation. Adaptive step size control, adaptation process control using Double-Talk detector may be implemented. The system may further implement a non-adaptive processing for reducing uncorrelated noise and / or cross-talk resistant adaptive noise cancellation.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Adaptive filtering
InactiveCN101971632AHigh precisionImprove adaptabilityTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationVideo encodingEngineering
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
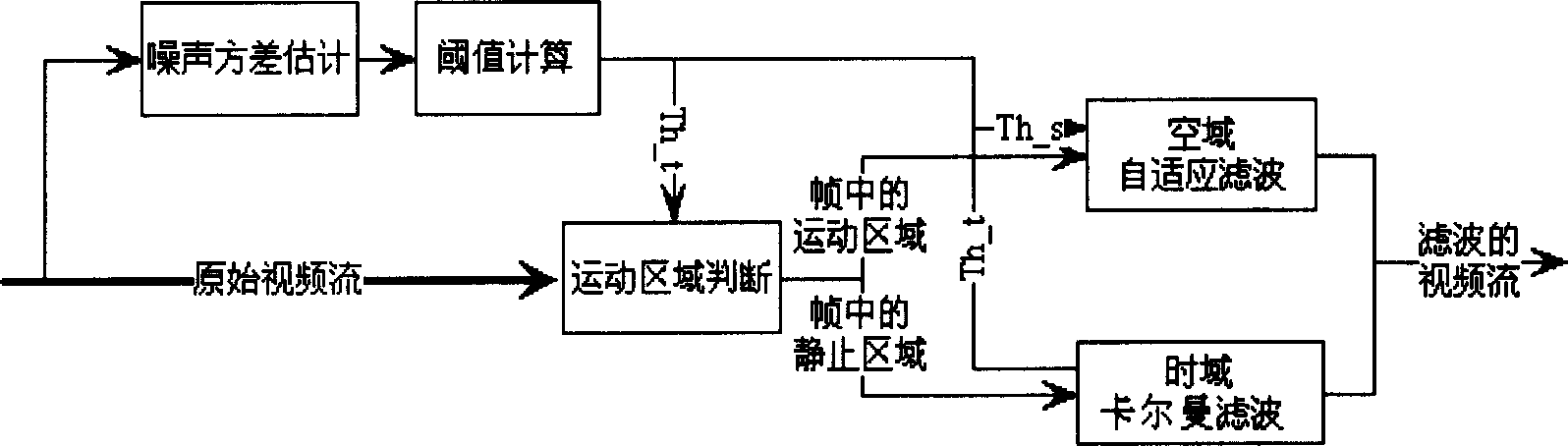
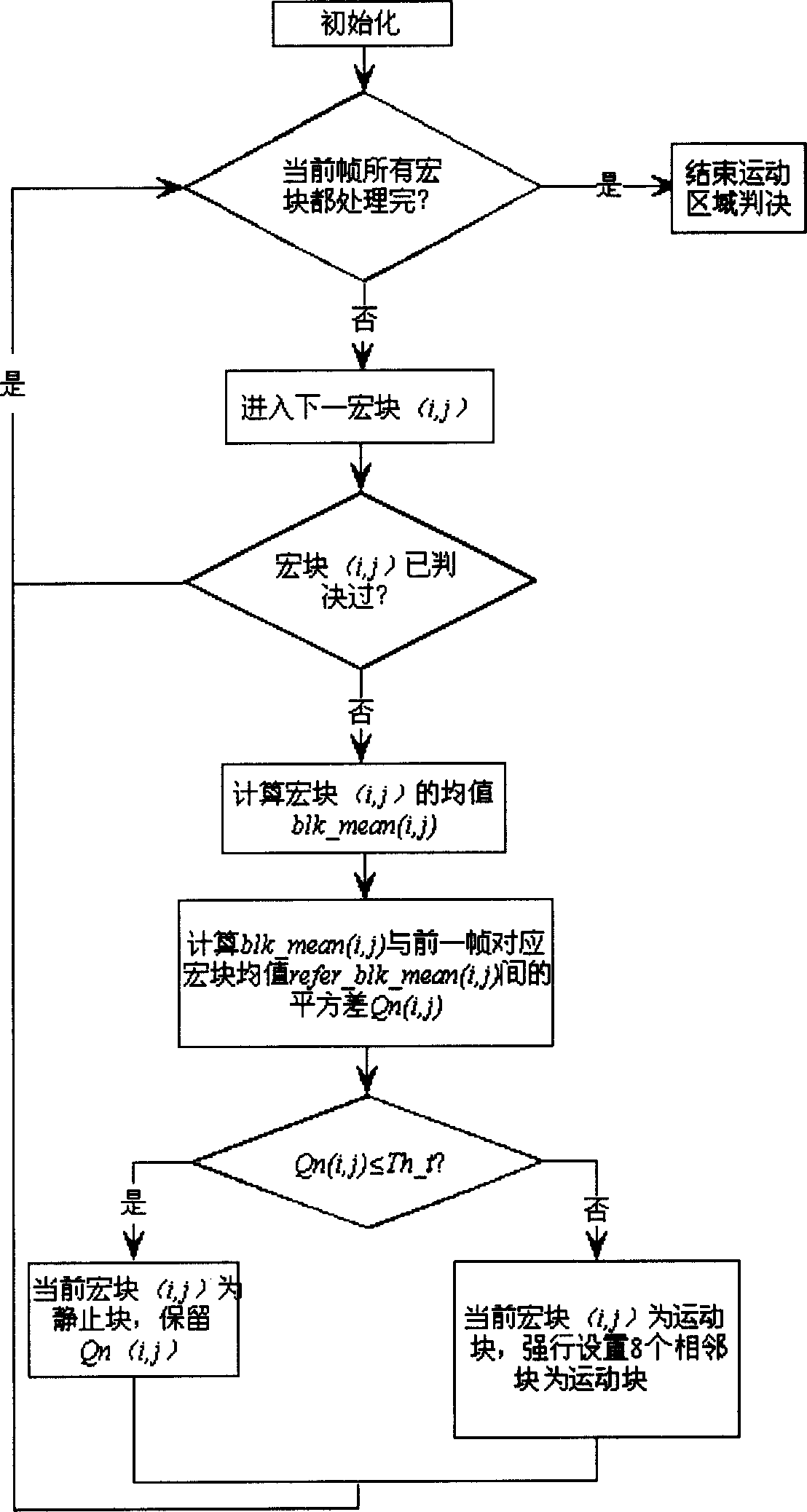
Video image noise reducing method based on moving detection and self adaptive filter
InactiveCN1901620AAvoid damageReduce computational costTelevision system detailsColor television detailsTime domainPattern recognition
This invention discloses a method for reducing noises based on motion test and adaptive filter including: 1, estimating the noise variance based on input video images and computing the threshold value of an adaptive filter, 2, applying a motion test based a macroblock to segment the motion-background region, 3, applying time domain Kallman filtering in a static region for process, 4, applying an empty domain to filter adaptively in the motion region, which avoids the complex computation of motion estimation and compensation to either secure the process result in static regions or the filter result in motion regions.
Owner:北京伟世万联科技有限公司
Audio processing apparatuses
ActiveUS8249862B1Cancel any interferenceSpeech analysisTransmission noise suppressionSelf adaptiveComputer science
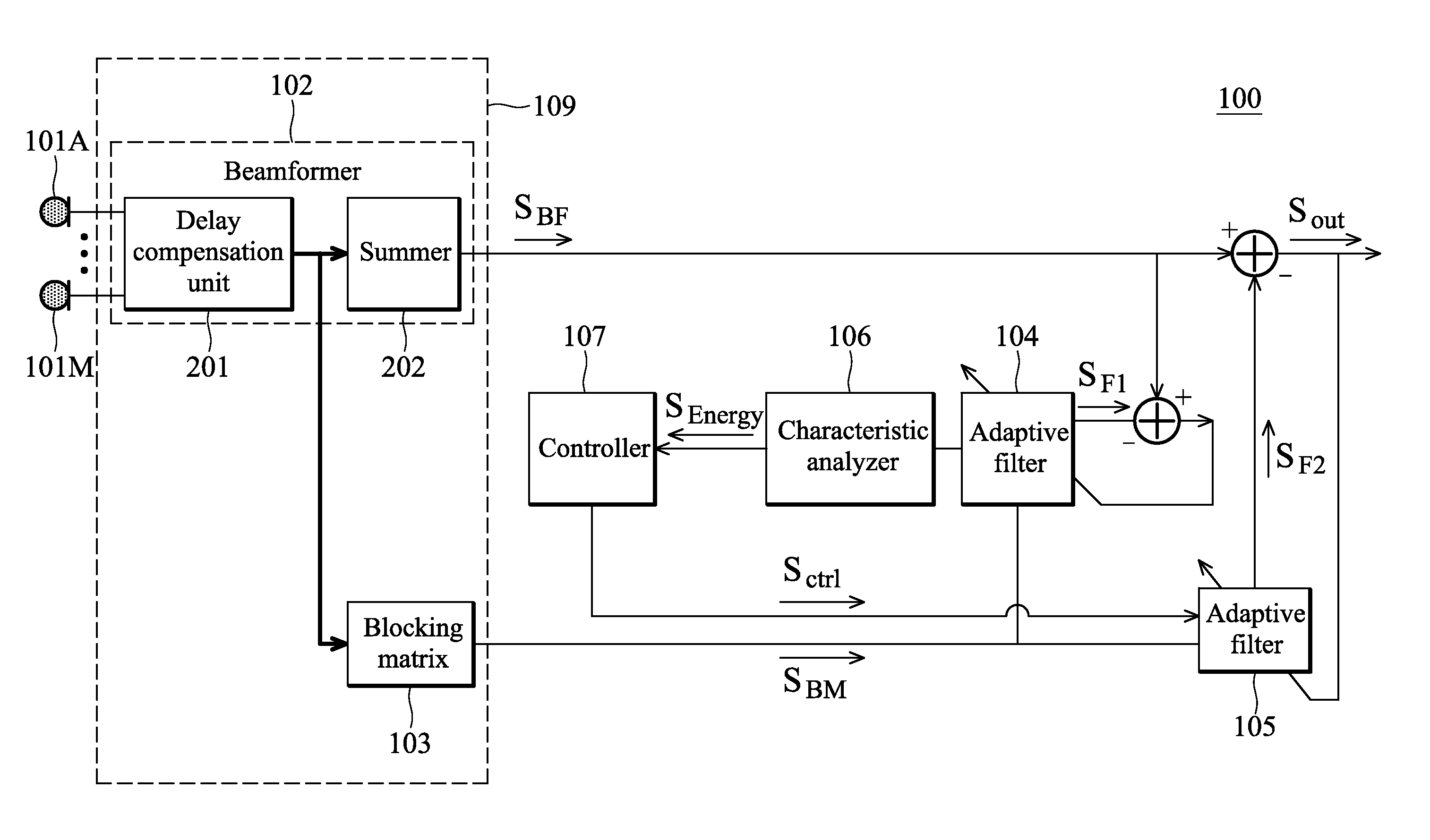
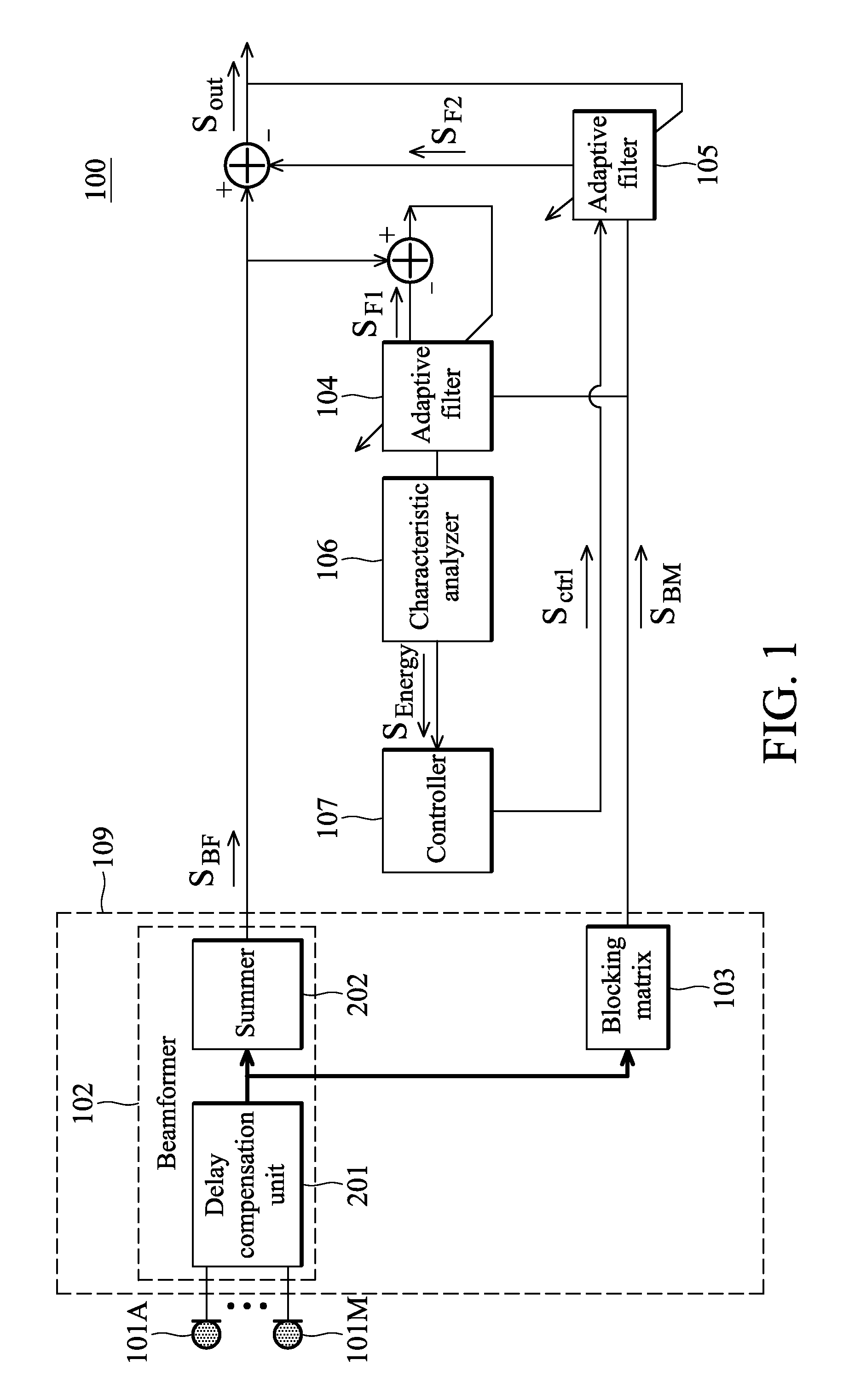
An audio processing apparatus is provided. A beamformer receives input signals and processes the input signals to generate a first processed signal. The input signals include at least one of a source signal and interference. A blocking matrix receives the input signals and operates to cancel the source signal from the input signals to generate a second processed signal. A first adaptive filter has adaptable first filter coefficients, generates a first filtered signal approximating the interference according to the first and second processed signals and continuously adapts the first filter coefficients according to the first filtered signal and the first processed signal. A second adaptive filter has adaptable second filter coefficients, generates a second filtered signal approximating the interference according to the first and second processed signals and selectively adapts the second filter coefficients according to the first filter coefficients and an output signal.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Backlash self-adaptive filter and method for modeling and compensating hysteresis thereof
InactiveCN101977034AEffective compensation for hysteretic nonlinearitySimple design methodAdaptive networkHysteresisElectricity
The invention relates to a Backlash self-adaptive filter and a method for modeling and compensating the hysteresis thereof, belonging to the technical field of modeling and control of hysteresis non-linear systems. The filter comprises a summator module, an error calculating module, a plurality of self-adaptive weighting modules and a plurality of Backlash operator modules with the same width. The whole designing scheme avoids using a hysteresis item and is only related with current inputs, meanwhile, the hysteresis non-linearity can be reflected, and the modeling effect is more precise; and the self-adaptive inverse control of the filter can effectively compensate the hysteresis non-linearity of a piezoelectric ceramic actuator. The self-adaptive filter and the modeling and self-adaptive inverse control method based on the filter can be applied to systems having the characteristics of hysteresis non-linearity, such as intelligent materials of magnetostrictive materials, excitation motors, piezoelectric chips, piezoelectric ceramics, and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
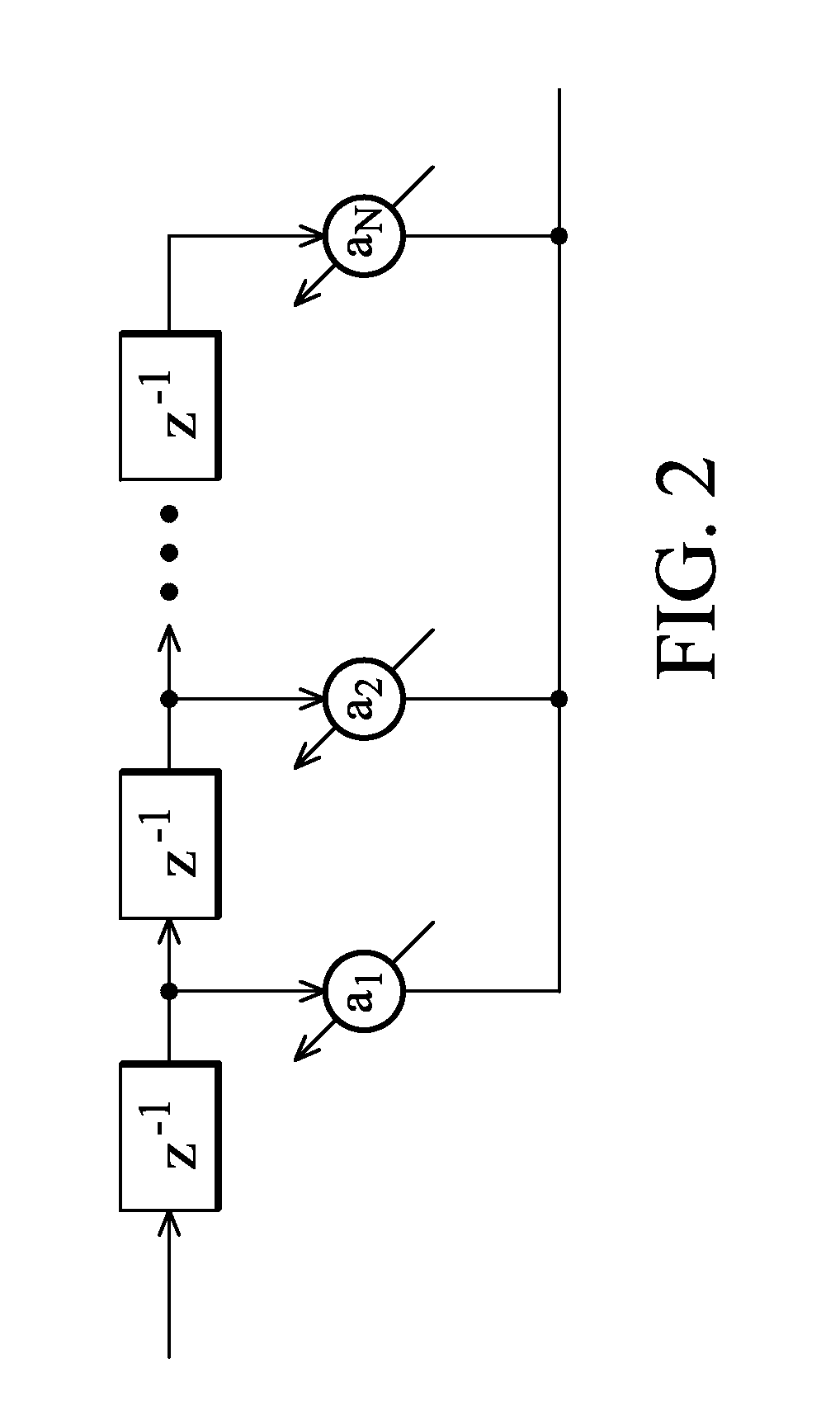
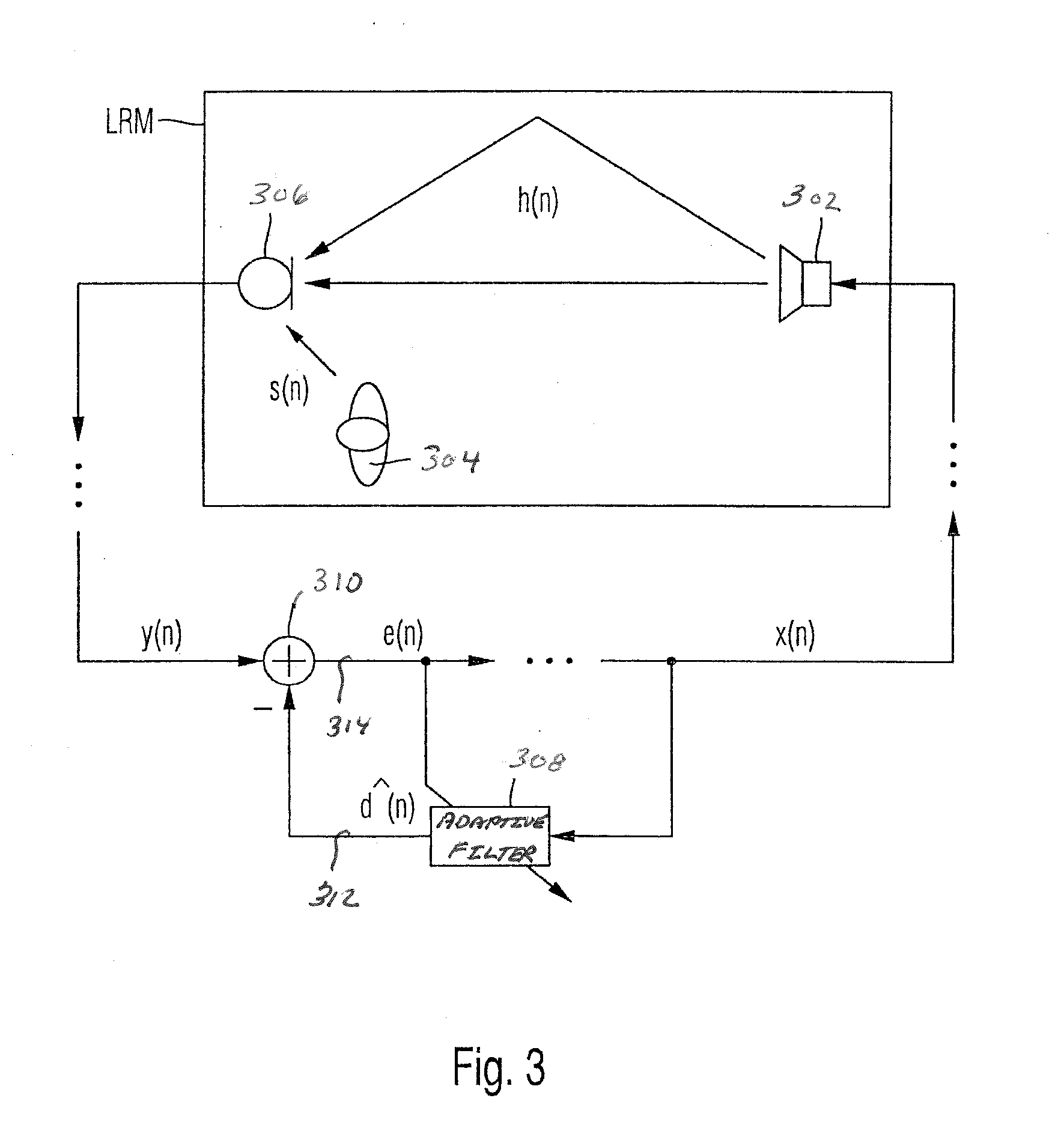
Digital filter adaptively learning filter coefficient
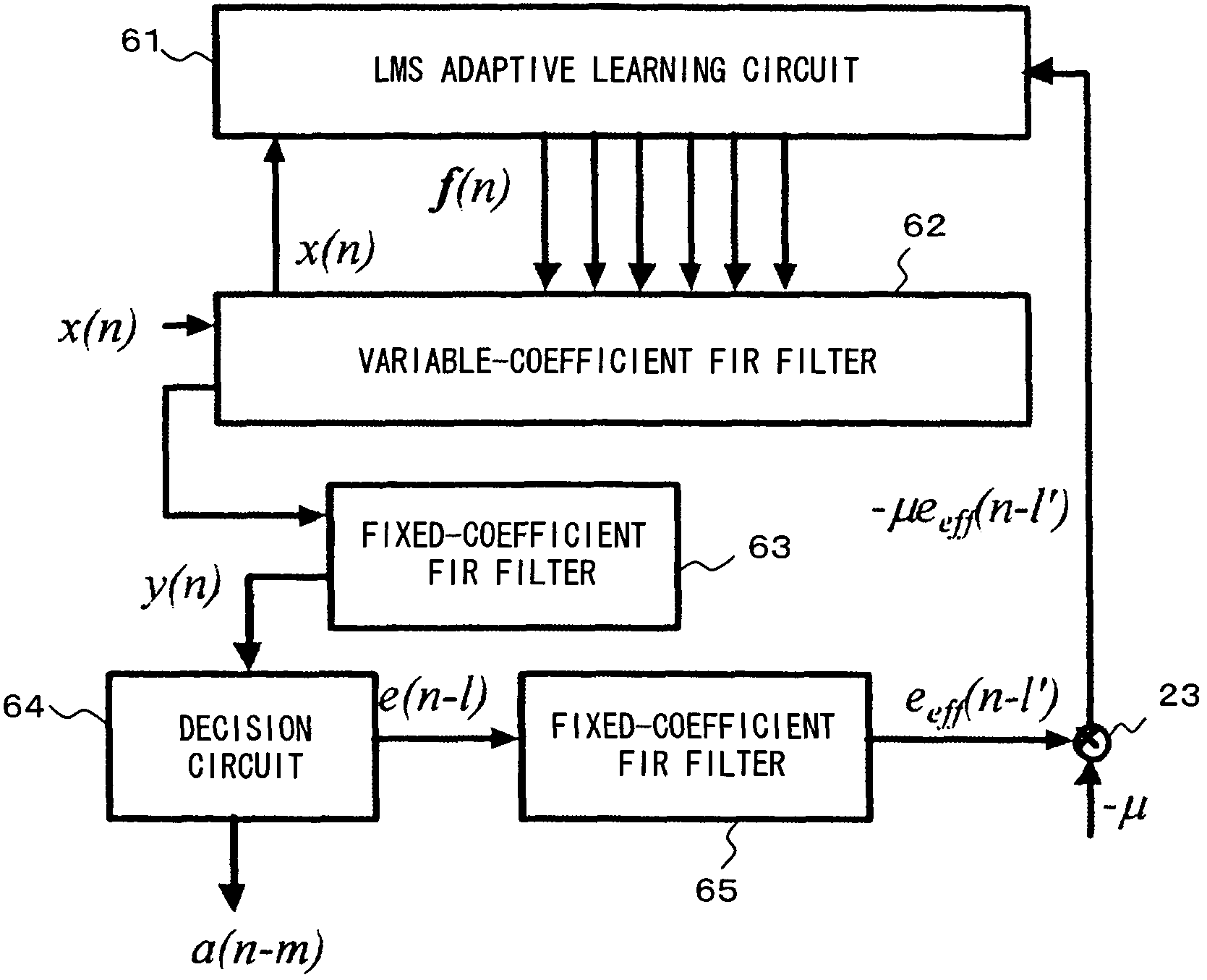
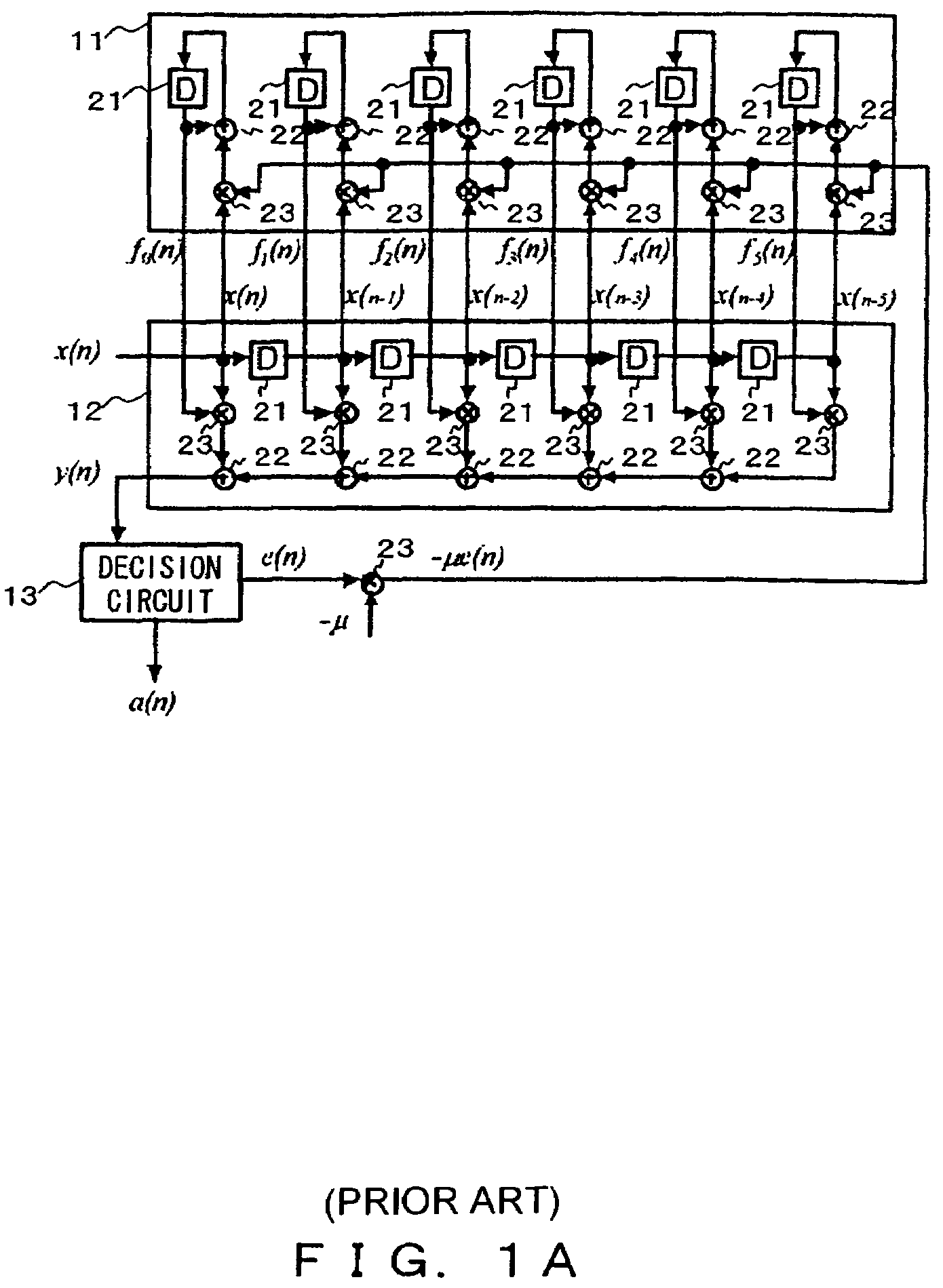
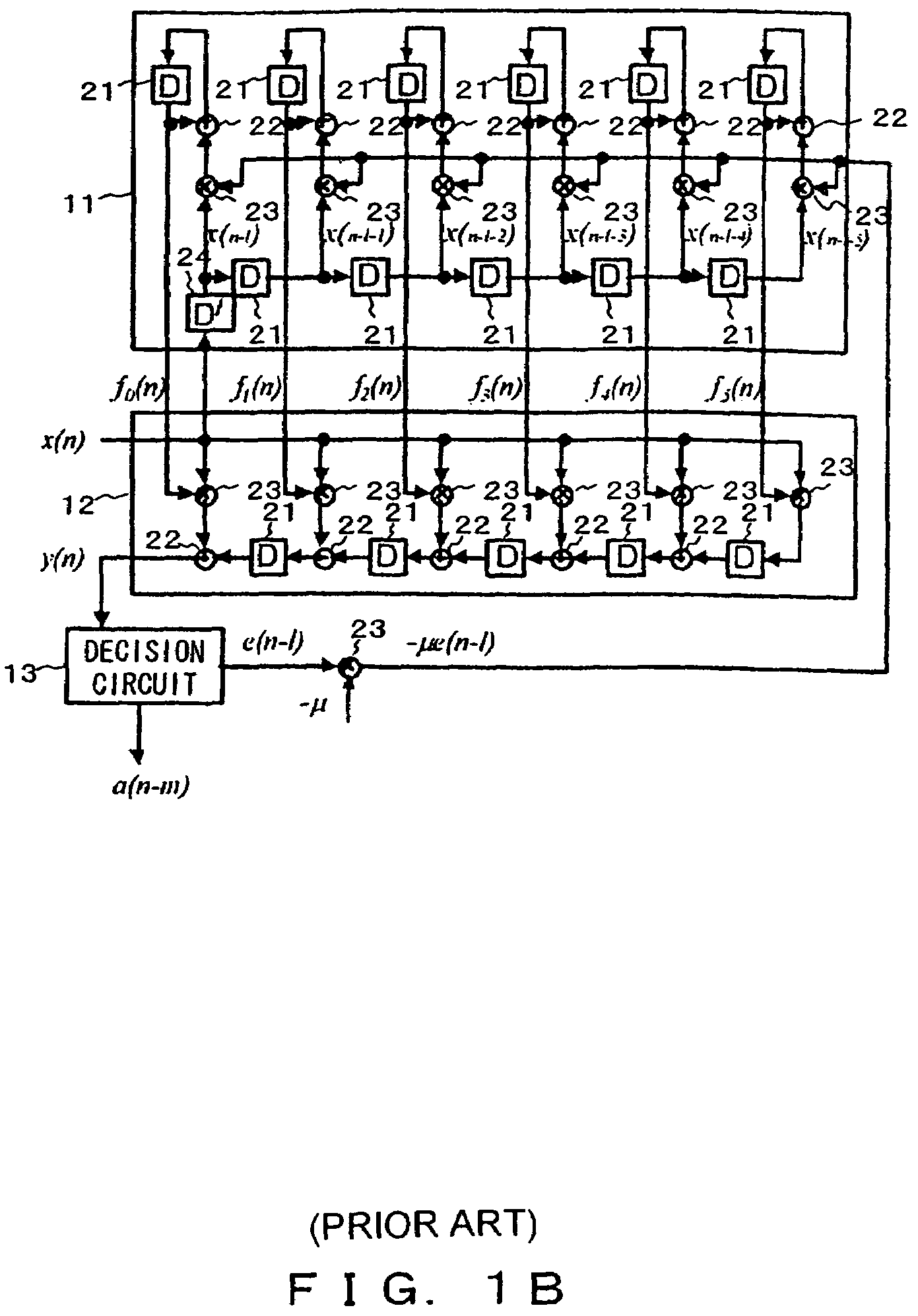
InactiveUS7421017B2Good coefficientMultiple-port networksDigital technique networkTarget signalLinear filter
A linear filter feeds back an error signal generated using the output of an adaptive filter to a learning circuit. The learning circuit learns the coefficients of the adaptive filter using the error signal. The coefficients of the linear filter are determined depending on the generation method of a target signal for error minimization. In a signal interpolation type timing recovery digital filter, the coefficients of an inverse interpolation filter are determined in such a way as to minimize an error of a signal after interpolation.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
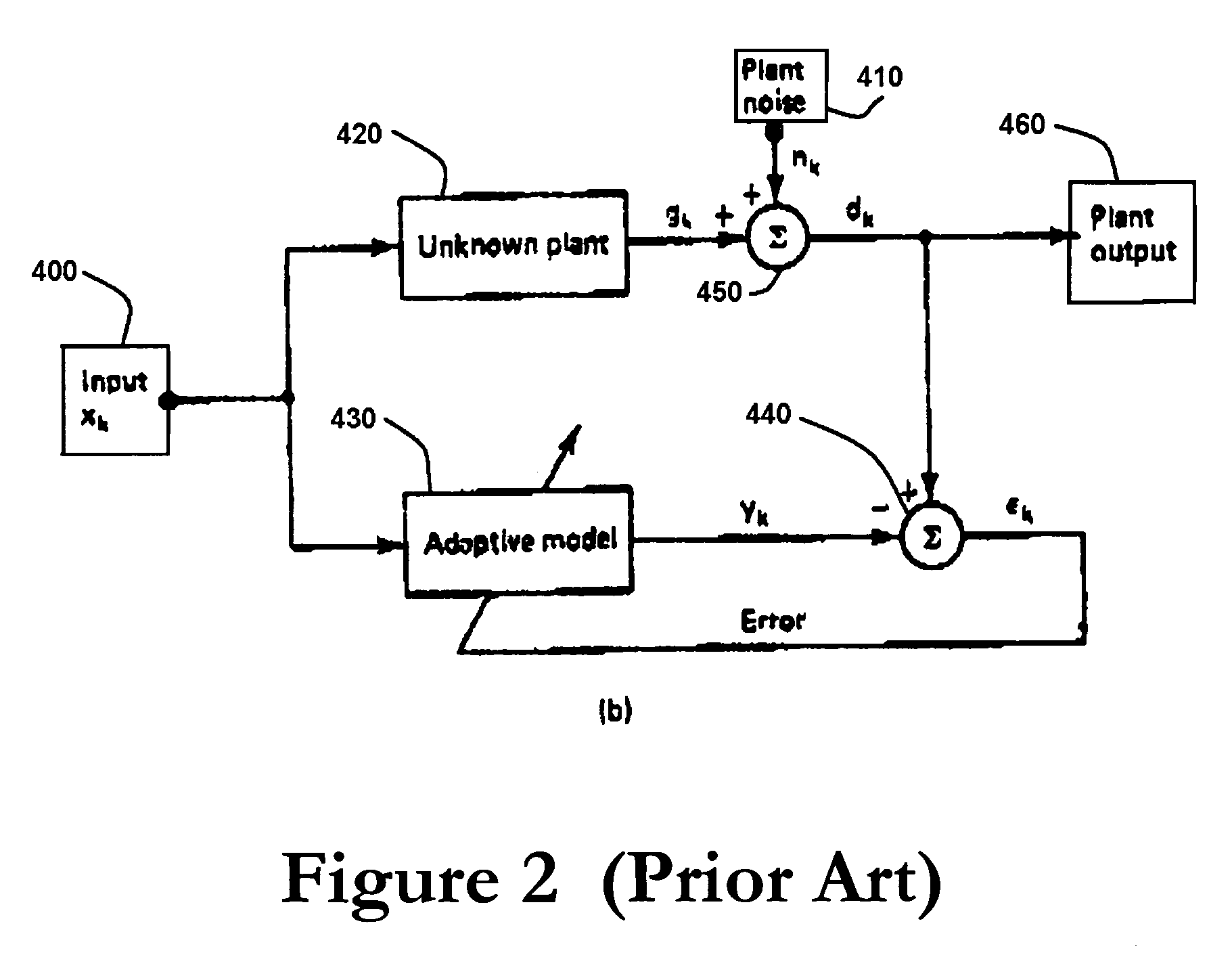
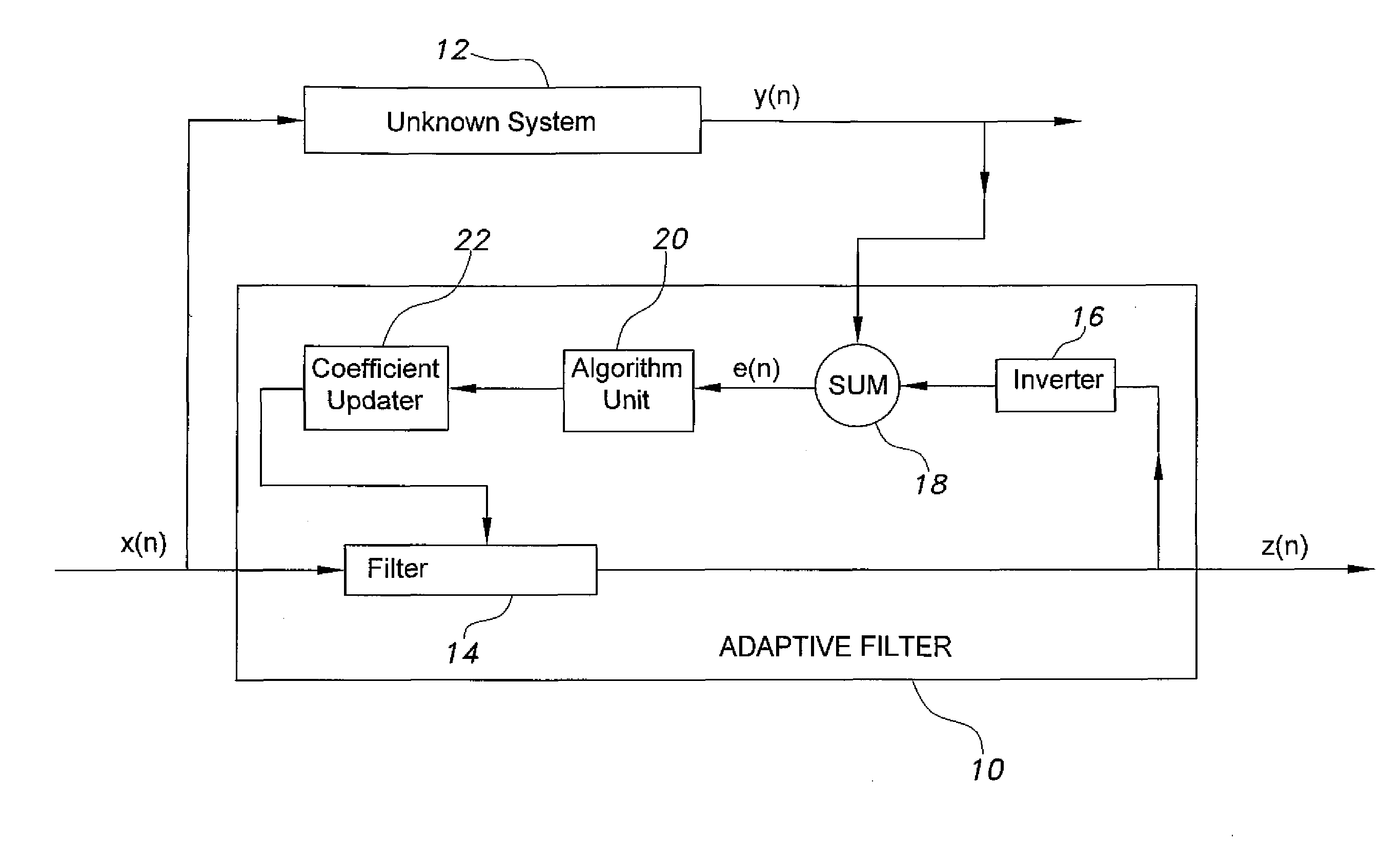
Adaptive filter for system identification
InactiveUS20140310326A1Improve performanceReadily apparentAdaptive networkComplex mathematical operationsFir systemMean square
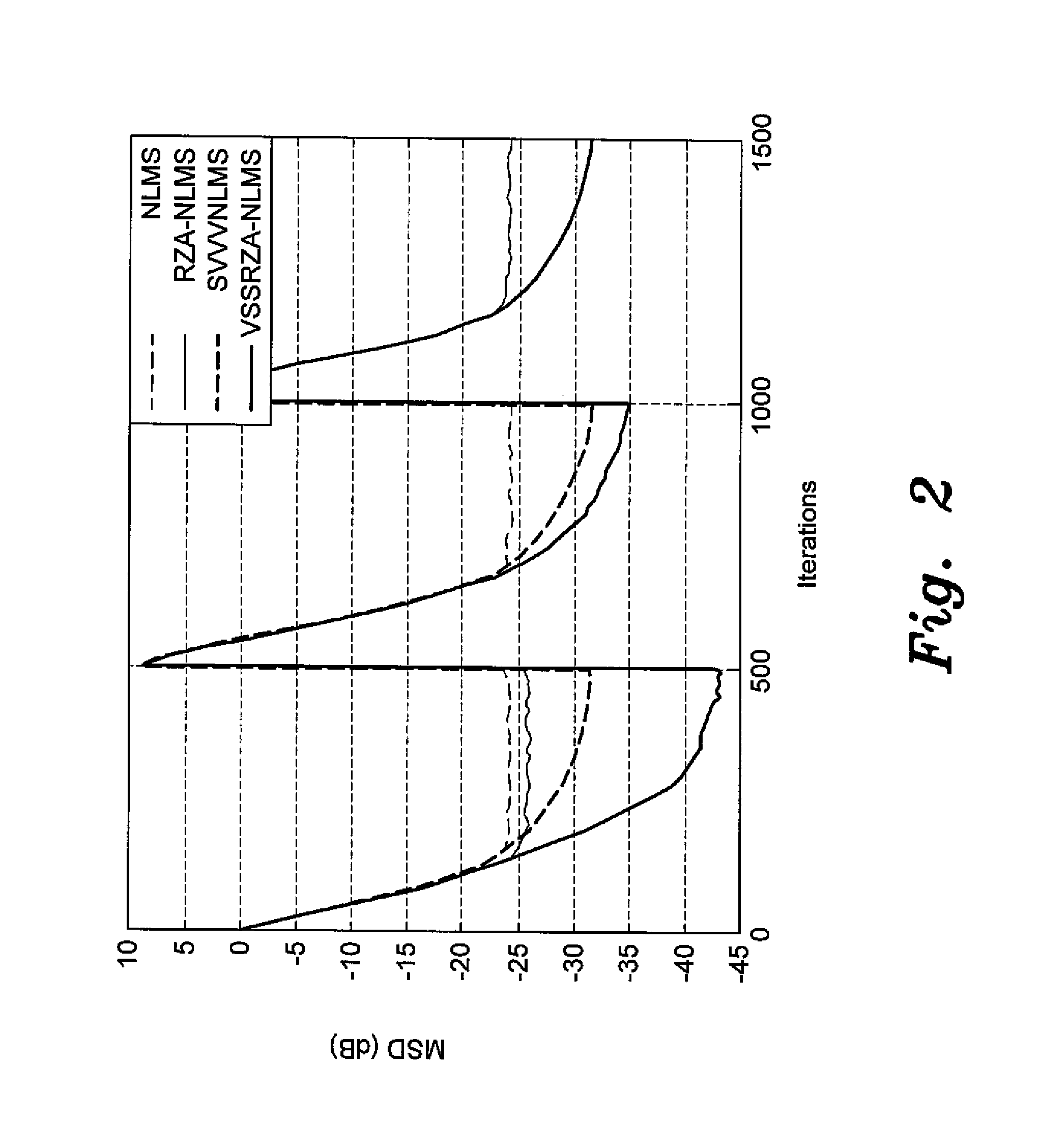
The adaptive filter for system identification is an adaptive filter that uses an algorithm in the feedback loop that is designed to provide better performance when the unknown system model has sparse input, i.e., when the filter has only a few non-zero coefficients, such as digital TV transmission channels and echo paths. In a first embodiment, the algorithm is the Normalized Least Mean Square (NLMS) algorithm in which the filter coefficients are updated at each iteration according to:w(i+1)=w(i)+μ(i)e(i)uT(i)u(i)2,where the step size μ is varied according to μ(i+1)=αμ(i)+γ|e(i)|. In a second embodiment, the algorithm is a Reweighted Zero Attracting LMS (RZA-LMS) algorithm in which the filter coefficients are updated at each iteration according to:w(i+1)=w(i)+μ(i)e(i)uT(i)u(i)2-ρsgn(w(i))1+ɛw(i),where the step size μ is varied according to μ(i+1)=αμ(i)+γ|e(i)|. The adaptive filter may be implemented on a digital signal processor (DSP), an ASIC, or by FPGAs.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Adaptive GDFE
ActiveUS20060276918A1Minimize error propagation effectImprove performanceMultiple-port networksModulated-carrier systemsSpatial correlationCommunications system
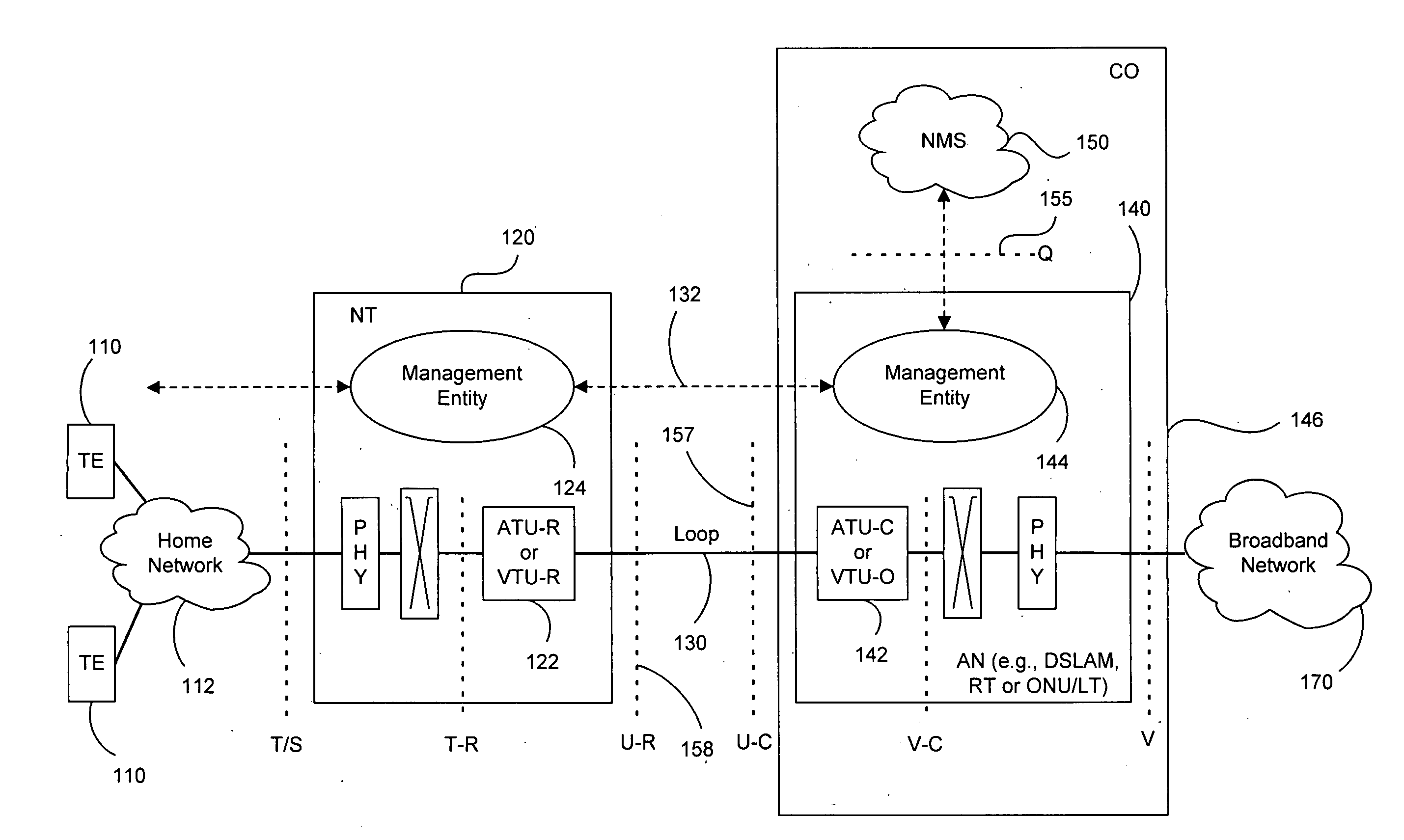
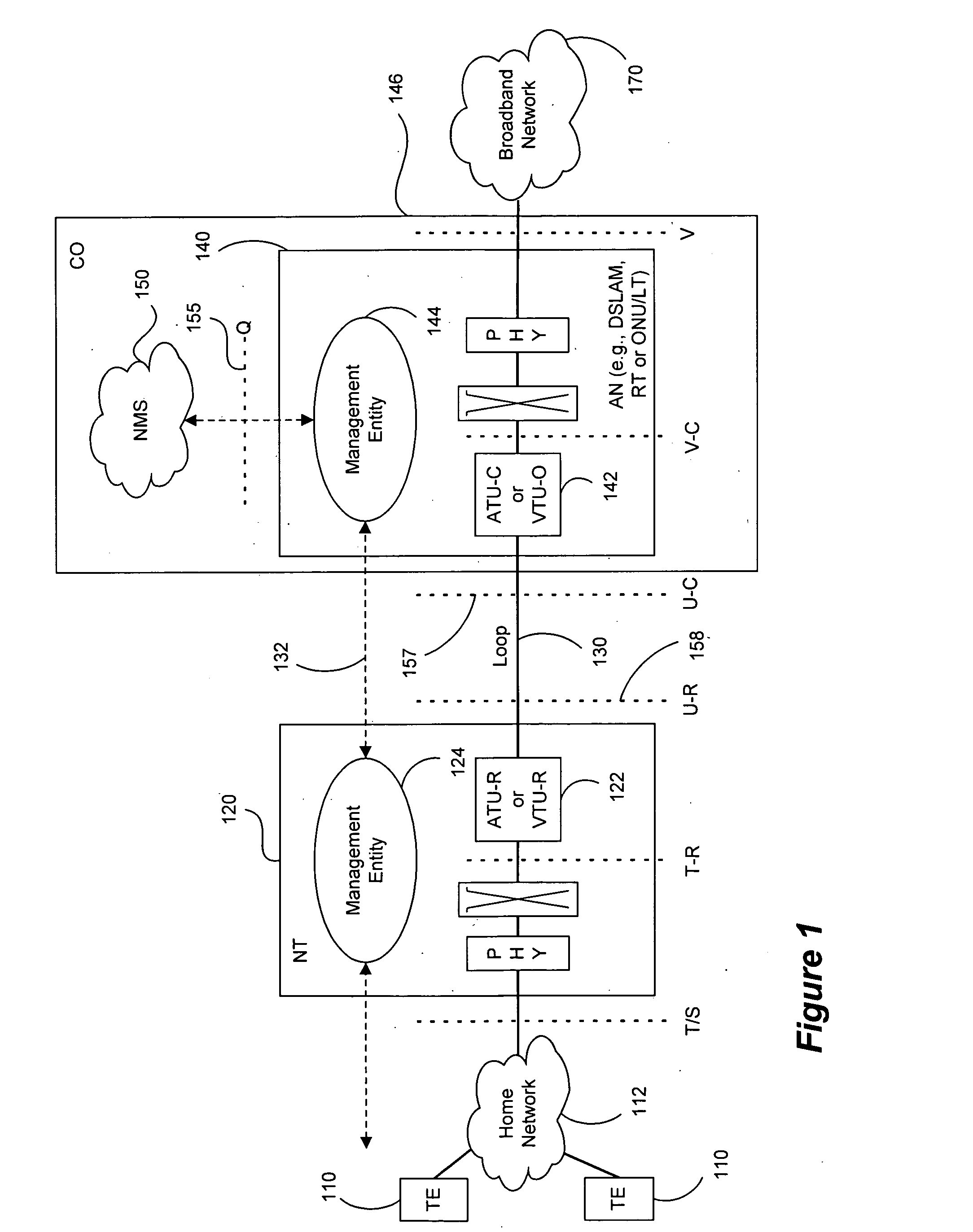
Adaptive generalized decision feedback equalization (GDFE) allows variations in one or more channels and noise of a multi-line / multi-channel communication system to be tracked. Such tracking can be used in vector upstream (one-sided) situations in communication systems such as ADSL and VDSL, among others. The GDFE may be separated into adaptive and static portions and / or components. Either a feedforward section or a feedback section (or both) can be separated to create a static component and an adaptive component. The adaptive components adjust to the instantaneous channel and noise changes (for example, using the instantaneous errors and simple LMS algorithms). When the channel and noise do not exhibit any time-variation, the adaptive filters can zero themselves. Local updating of adaptive feedforward and / or feedback filters addresses rapid changes to the spatial correlation of noise and / or changes to the multi-line channel (for example, time-variation due to temperature changes, component variations, mechanical stress, and other reasons), without disruption to separate static feedforward and / or feedback filters supplied by a controller, such as a DSL optimizer or the like that can assist by doing the heavier calculations and providing vectoring information and data to the DSL line components. An efficient implementation is provided of any triangularization of the binder channel that characterizes multi-user vectored-DMT DSL. Adaptation also allows correction of any inaccuracy in initially or previously reported crosstalk transfer functions and noise spatial correlation.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
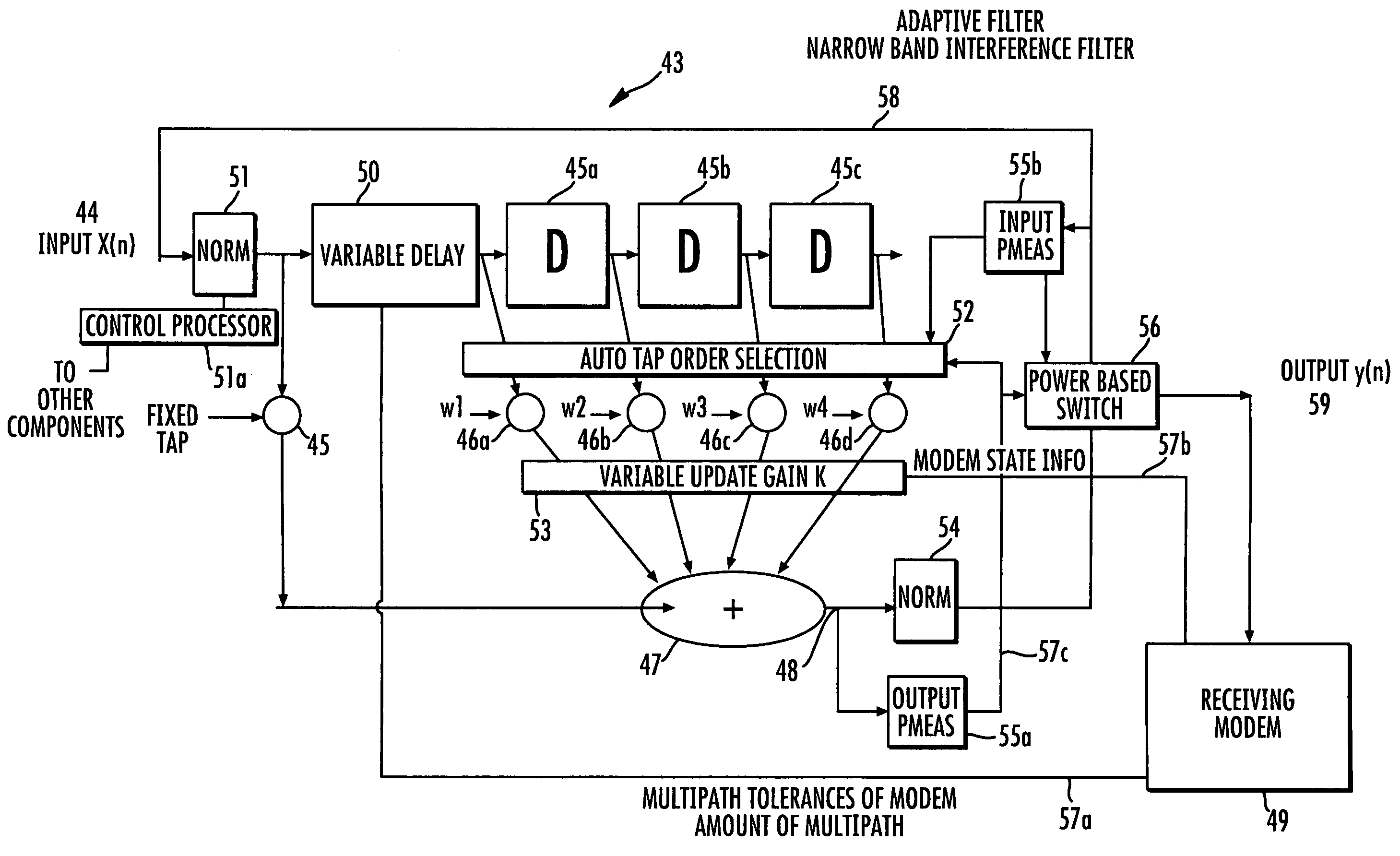
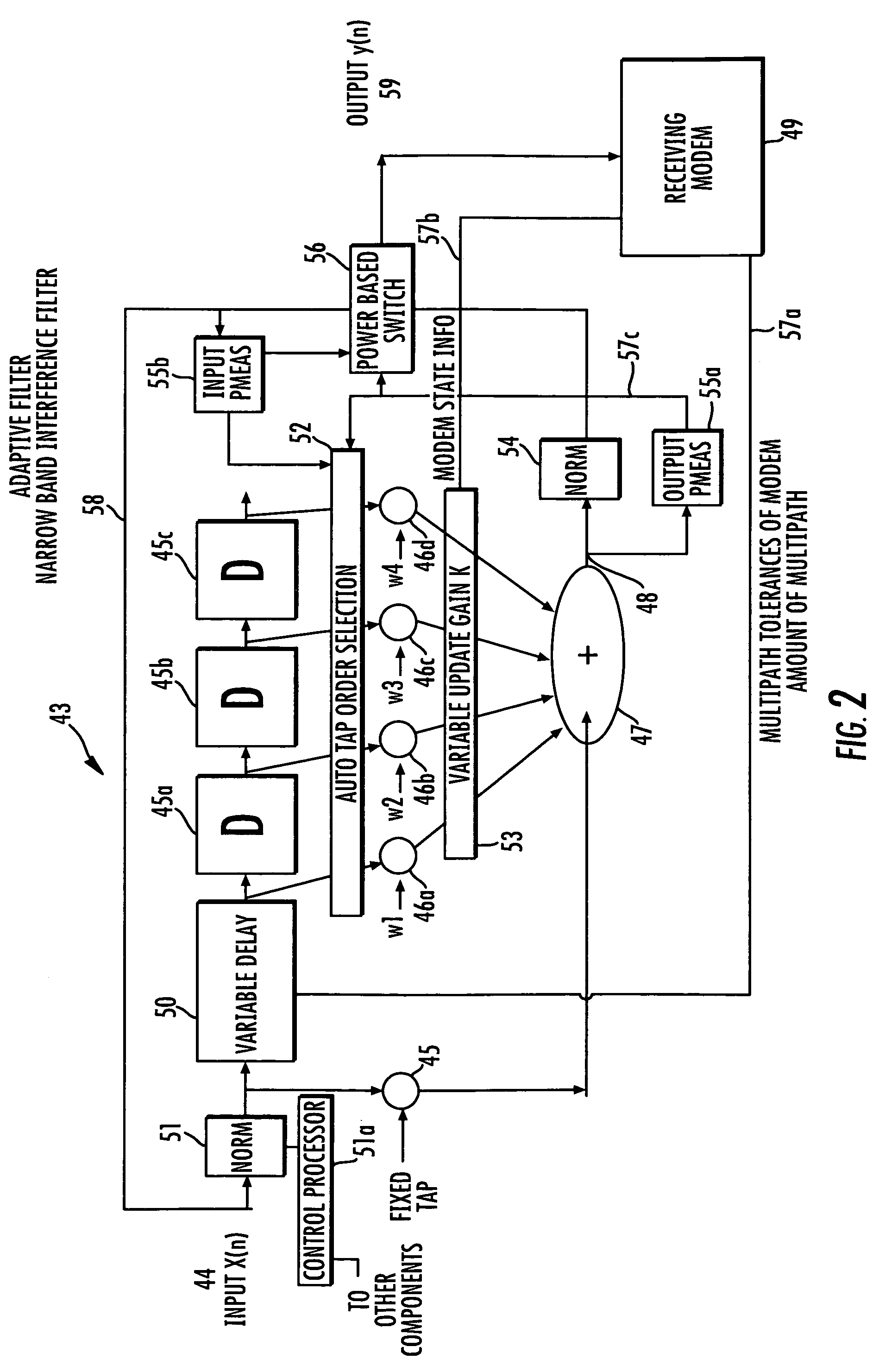
Communications system using adaptive filter that is selected based on output power
ActiveUS7860200B2Reduce errorsImprove performanceMultiple-port networksError preventionCommunications systemMeasuring output
Owner:HARRIS GLOBAL COMM INC
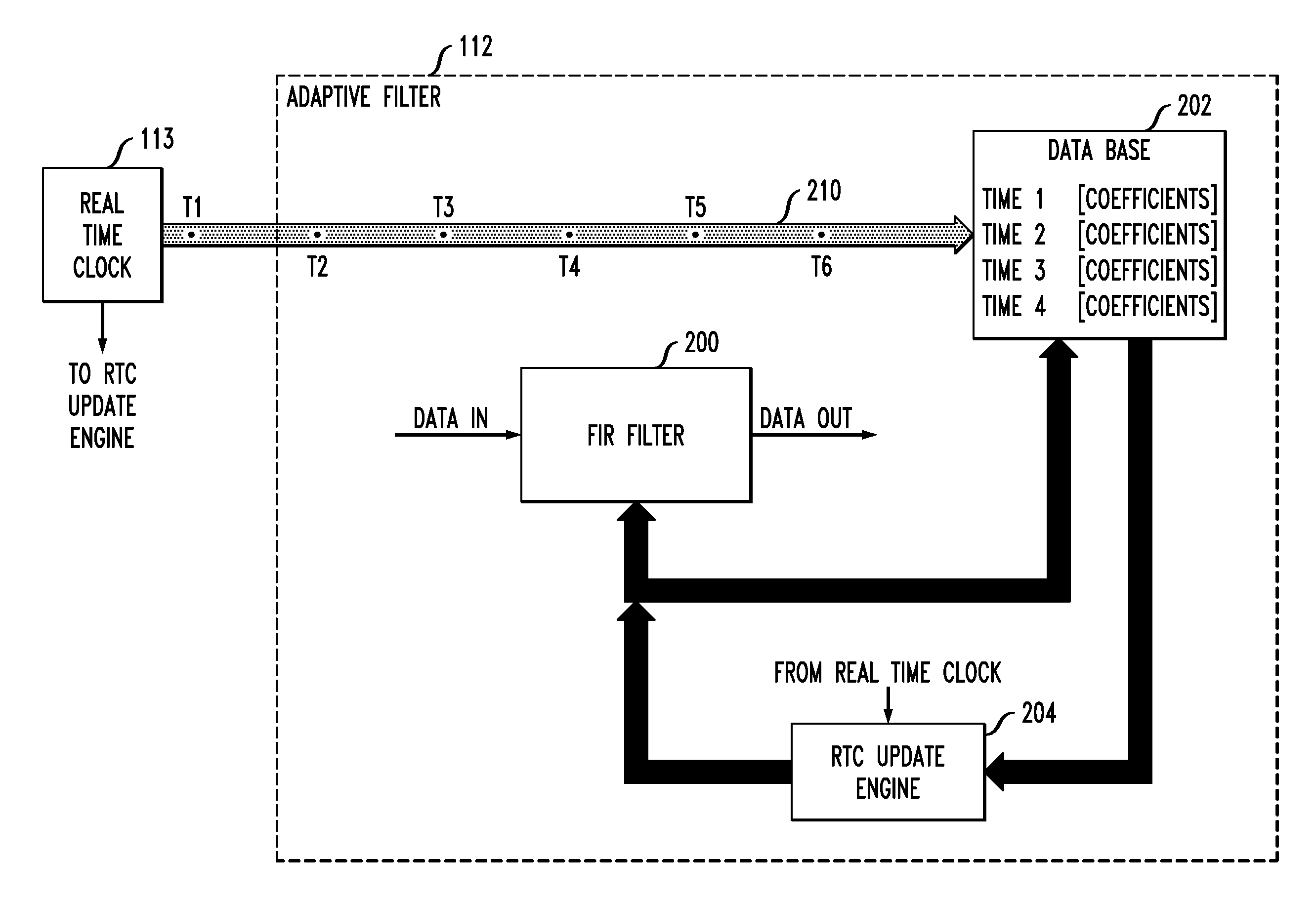
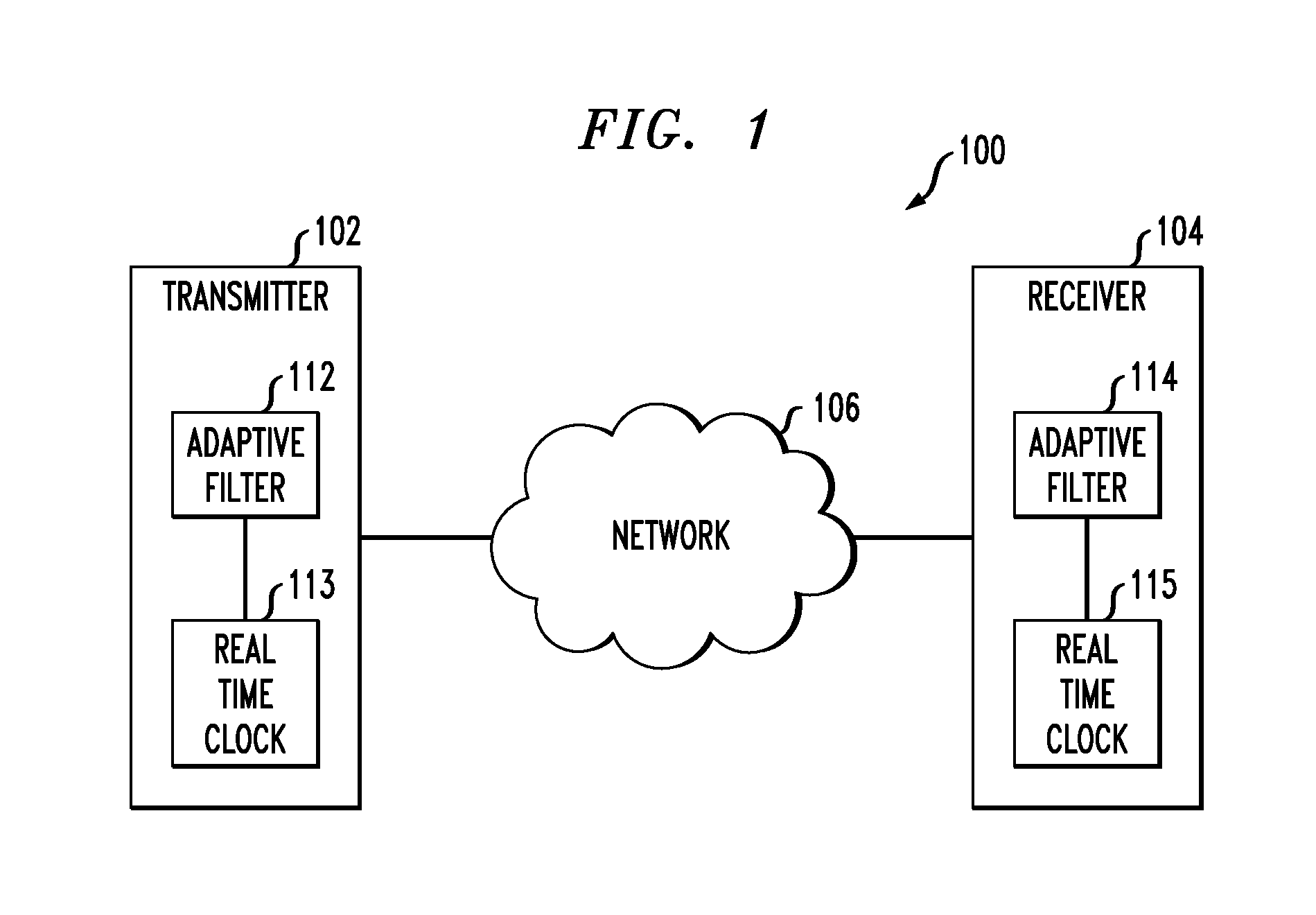
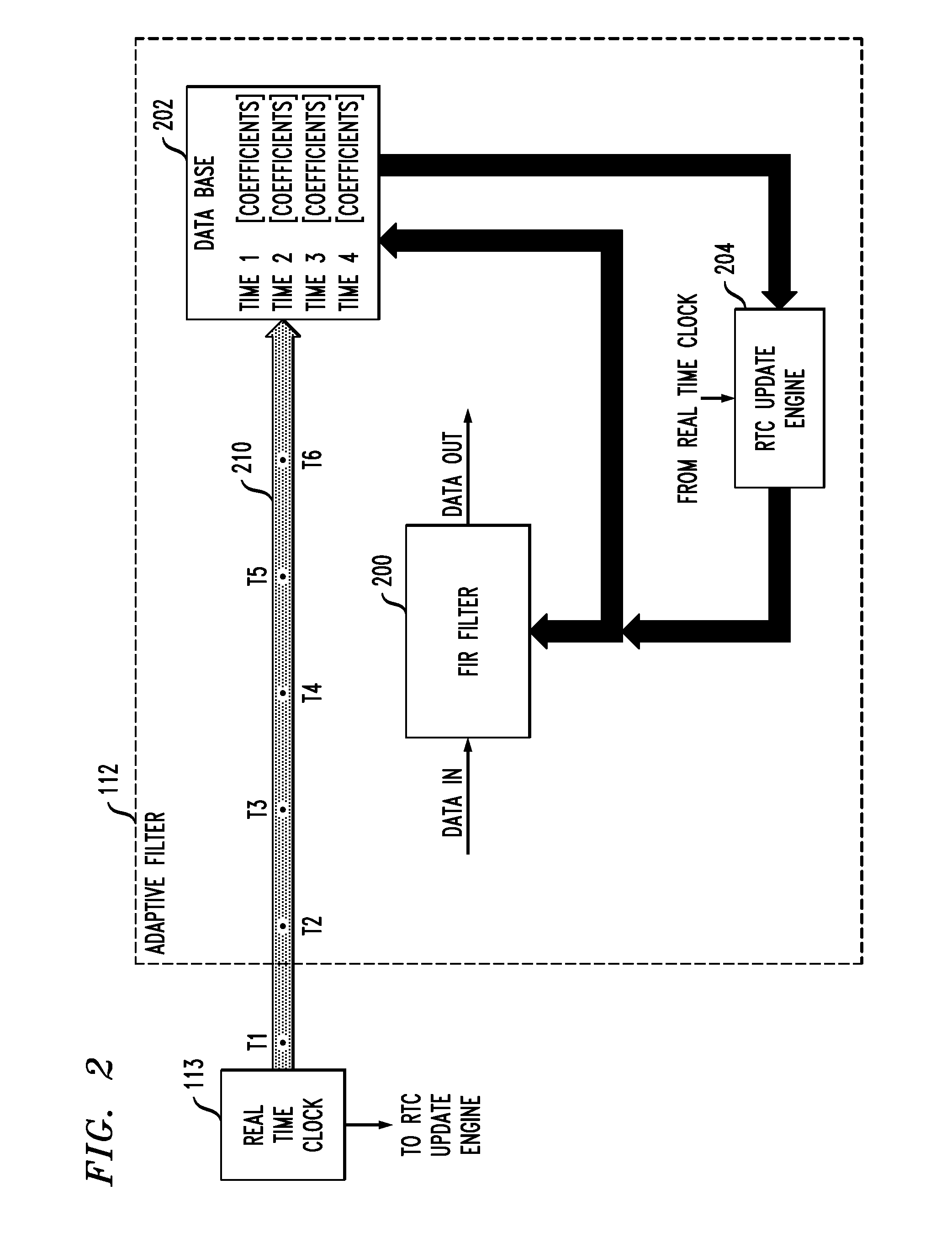
Adaptive filter with coefficient determination based on output of real time clock
InactiveUS20130076433A1Improvement in adaptive filtering performanceImprove filtering effectAdaptive networkBaseband system detailsReal-time clockCommunications system
An adaptive filter implemented in a communication system transmitter or receiver has a real time clock associated therewith, and one or more coefficients of the adaptive filter are determined based at least in part on an output of the real time clock. For example, the adaptive filter may comprise a coefficient update engine and a memory for storing a plurality of sets of adaptive filter coefficients in association with respective time indicators derived from the output of the real time clock, with the coefficient update engine being configured to determine a particular one of the sets of filter coefficients for use by the adaptive filter based at least in part on one or more of the time indicators. The time indicators may comprise respective time stamps generated based on the output of the real time clock at respective times at which the corresponding sets of coefficients are determined.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
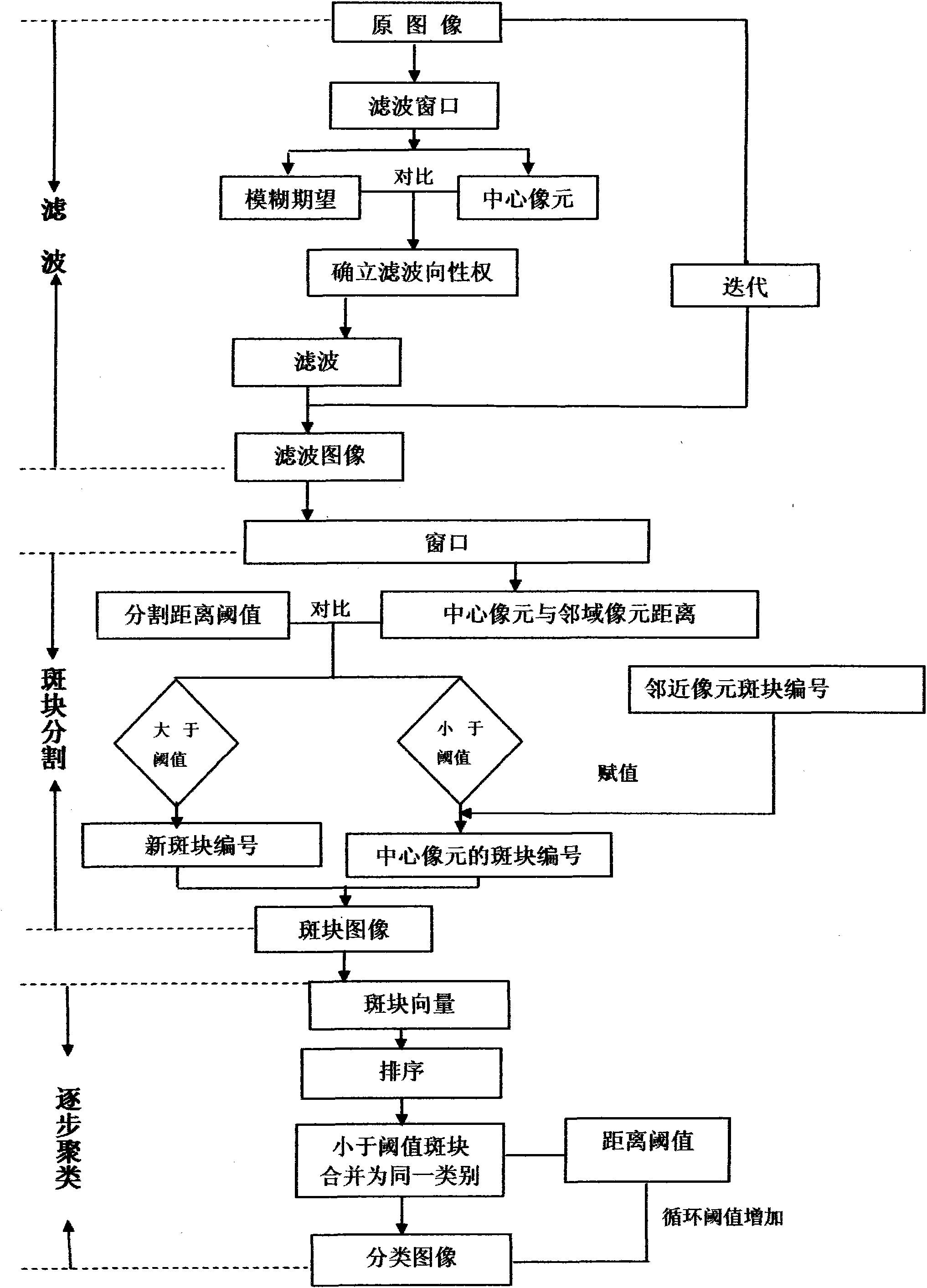
Acoustic echo cancellation
An input signal is supplied to a loudspeaker-room-microphone system having a transfer function and that provides an output signal. An adaptive filter unit models the transfer function of the loudspeaker-room-microphone system and provides an approximated output signal, where the output signal and the approximated output signal are subtracted from each other to provide an error signal. The modeling of the transfer function of the loudspeaker-room-microphone system in the adaptive filter comprises transforming the input signal and the error signal from the time domain into the spectral domain; delaying of the input signal in the frequency domain to generate multiple differently delayed input signals in the frequency domain; adaptive filtering of each one of the multiple differently delayed input signals in the frequency domain according to the error signal in the spectral domain; summing up of the filtered differently delayed input signals in the frequency domain to generate the approximated output signal in the frequency domain; and transforming the approximated output signal from the spectral domain into the time domain.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
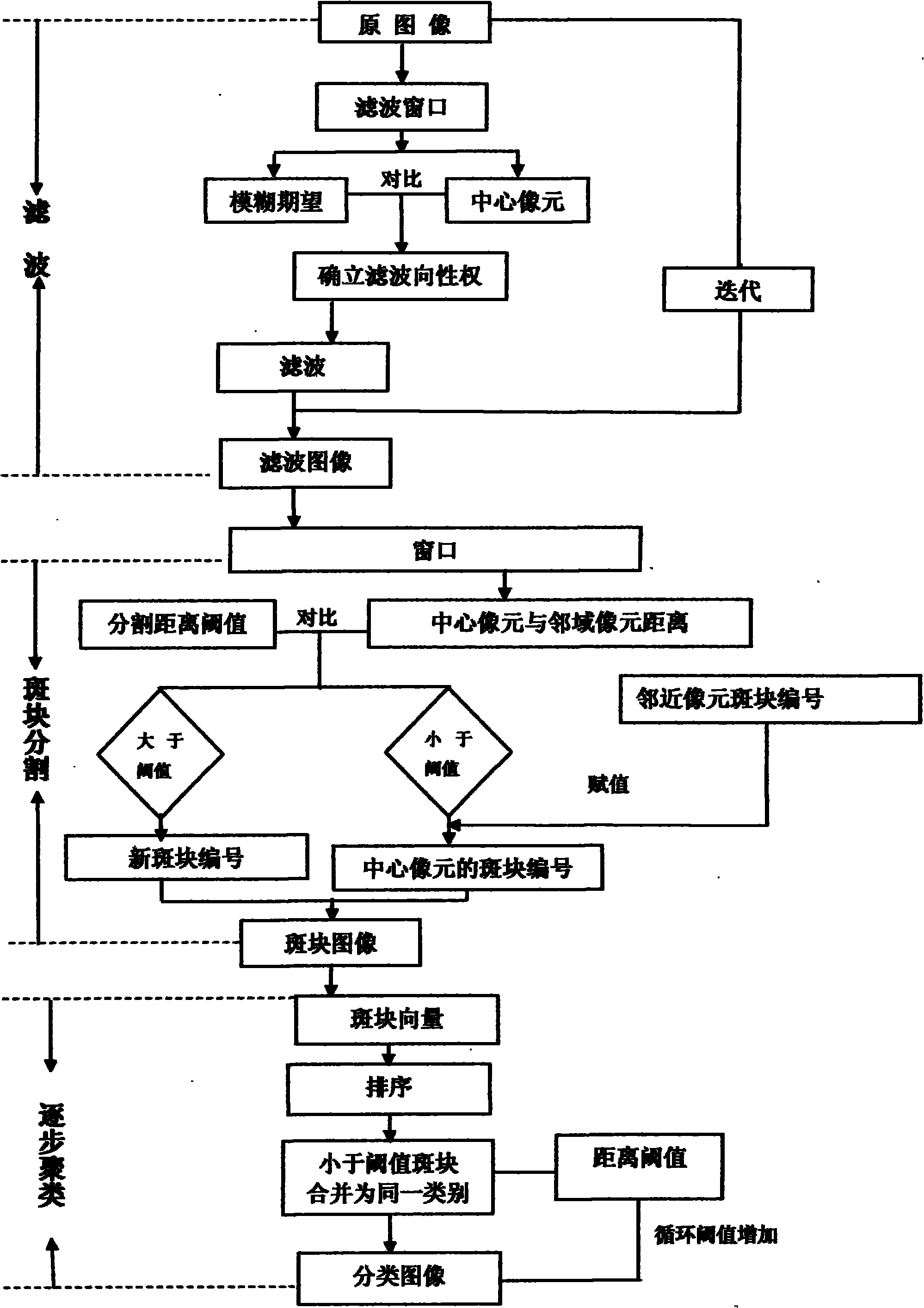
Method for automatically segmenting multi-band image by adaptive filter
The invention discloses a method for automatically segmenting a multi-band image by an adaptive filter. The method realizes automatic fine segmentation of the multi-band image by using a good adaptive mechanism, neighborhood fuzzy category determination and safe neighborhood threshold segmentation. The entire process mainly comprises the following steps of: (1) designing the filter; (2) segmenting the image (segmenting patches); (3) combining the minimum drafting area of patches (combining small patches); and (4) gradually clustering (classified variable and clustering algorithm). The method has the advantages of dynamic adjustment, adaptive selection of vector spatial direction, adaptive selection of weight and rapid convergence of an iterative process based on adaptive increase of a fuzzy region and capability of realizing anisotropic adaptive filtering and regional fuzzy increase.
Owner:董永平 +6
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com