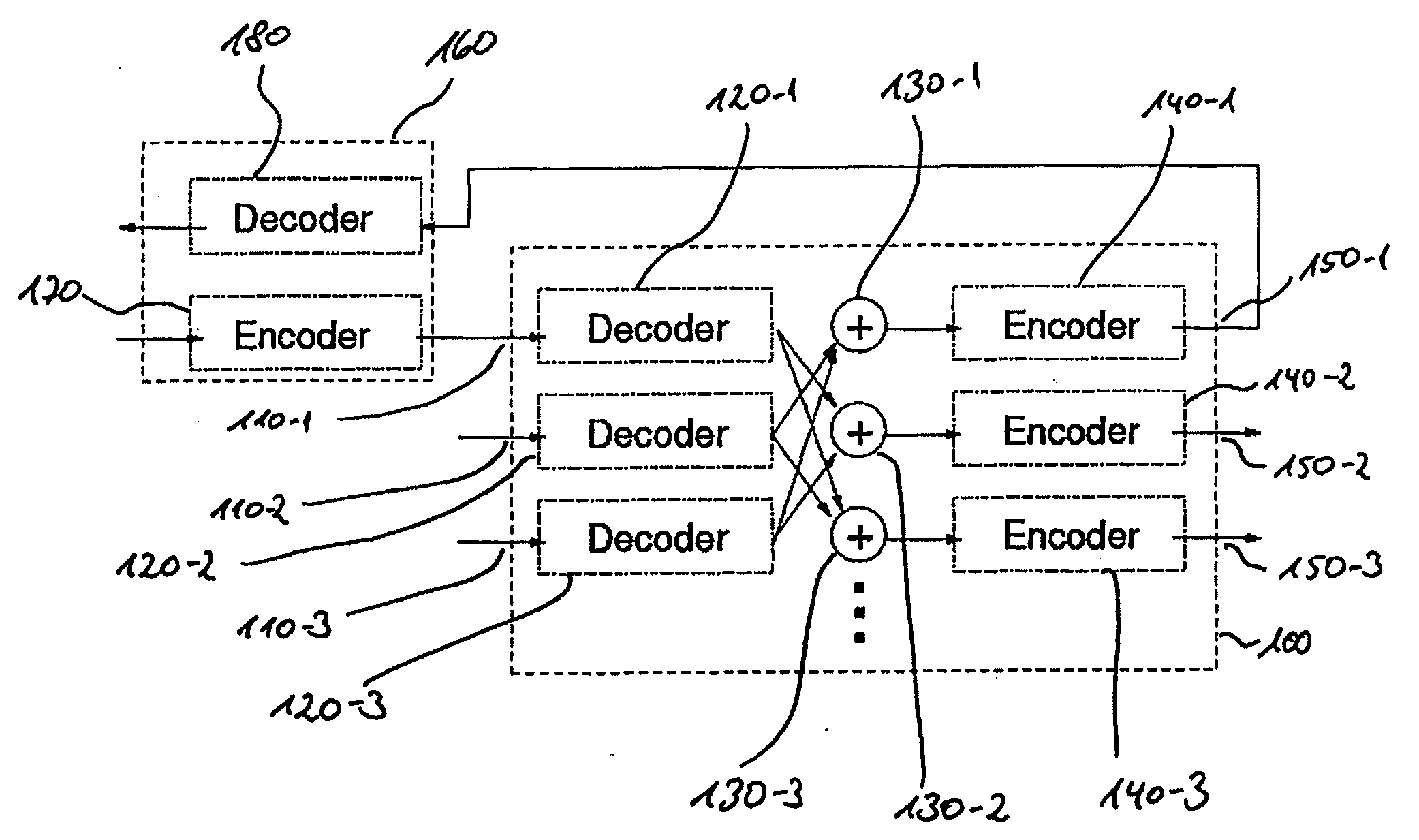
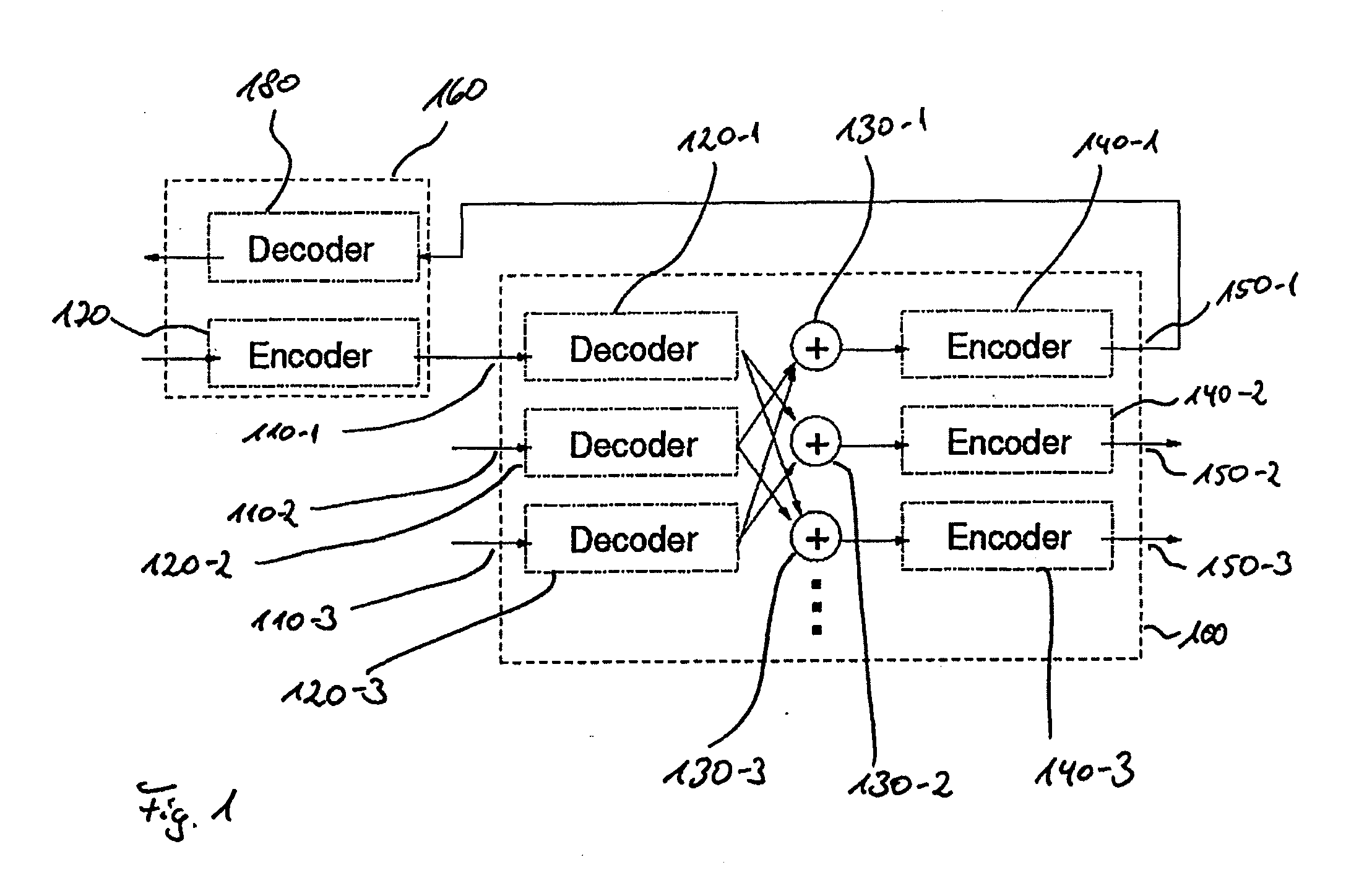
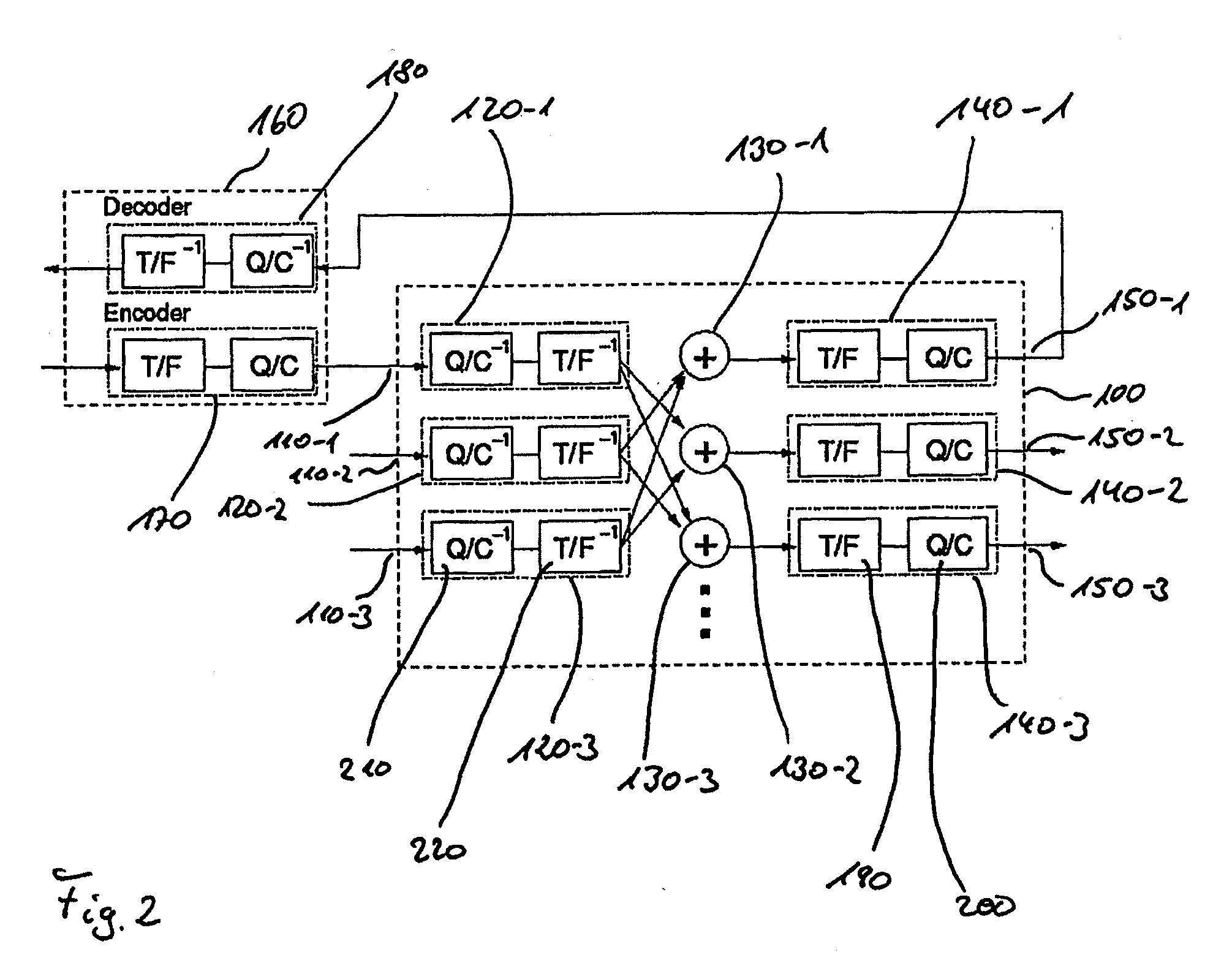
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
448 results about "Spectral domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
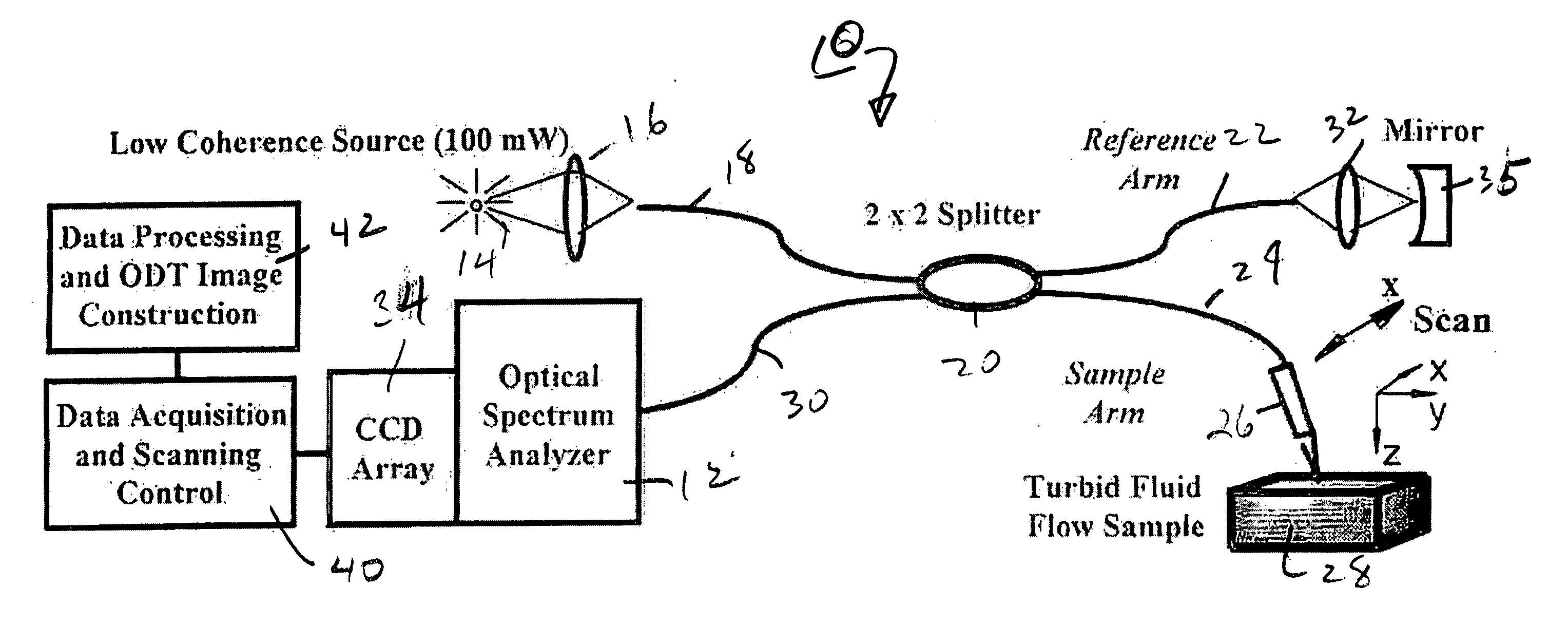
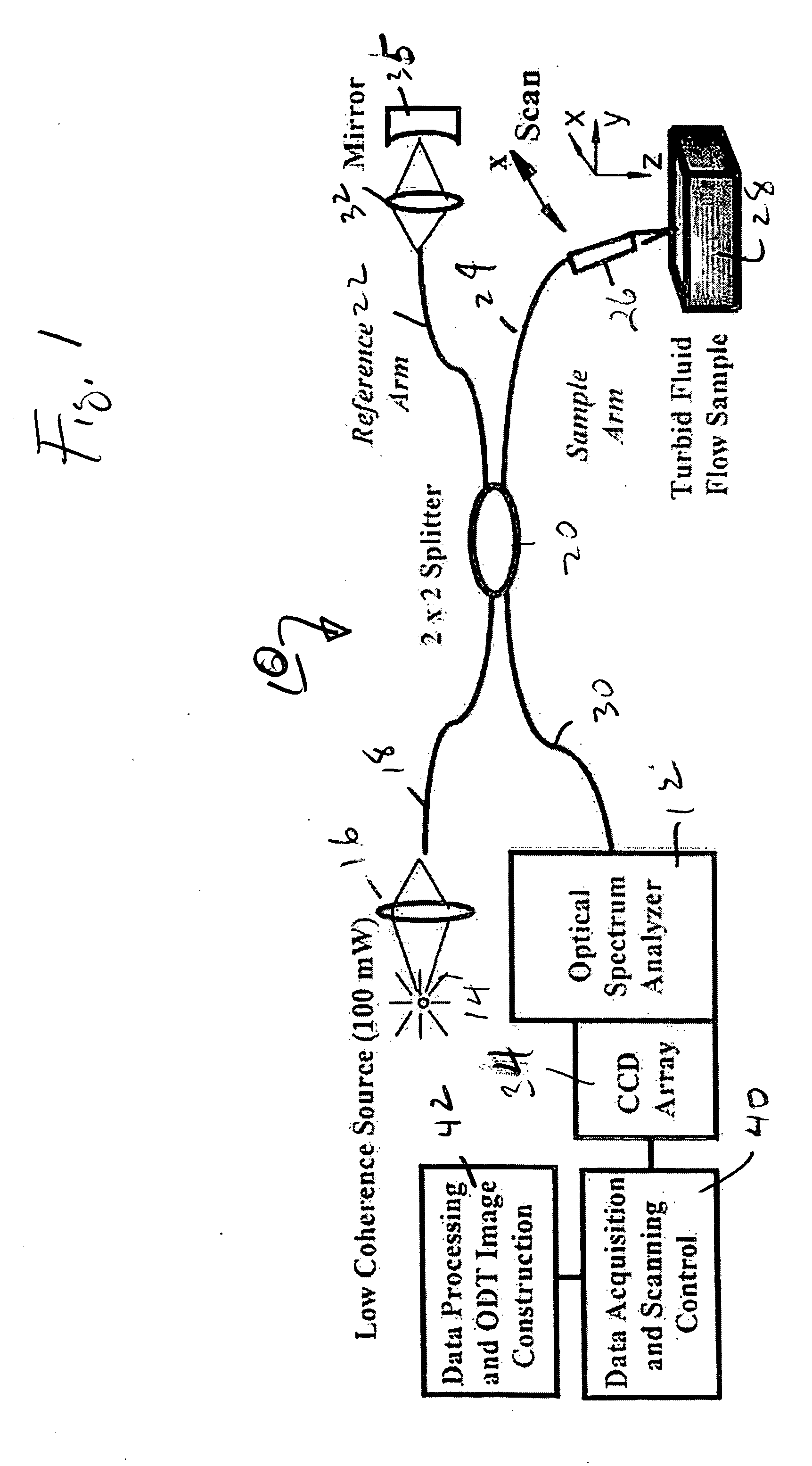
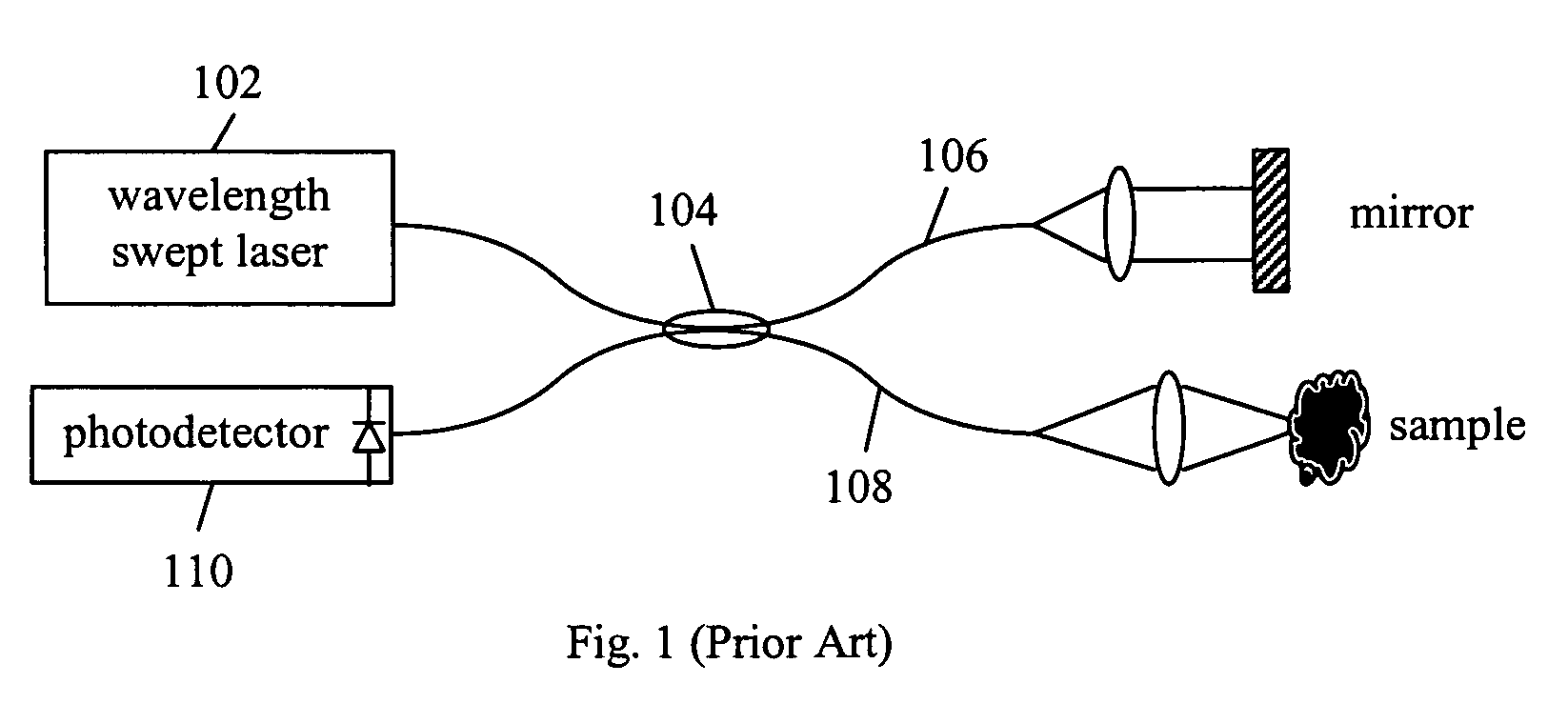
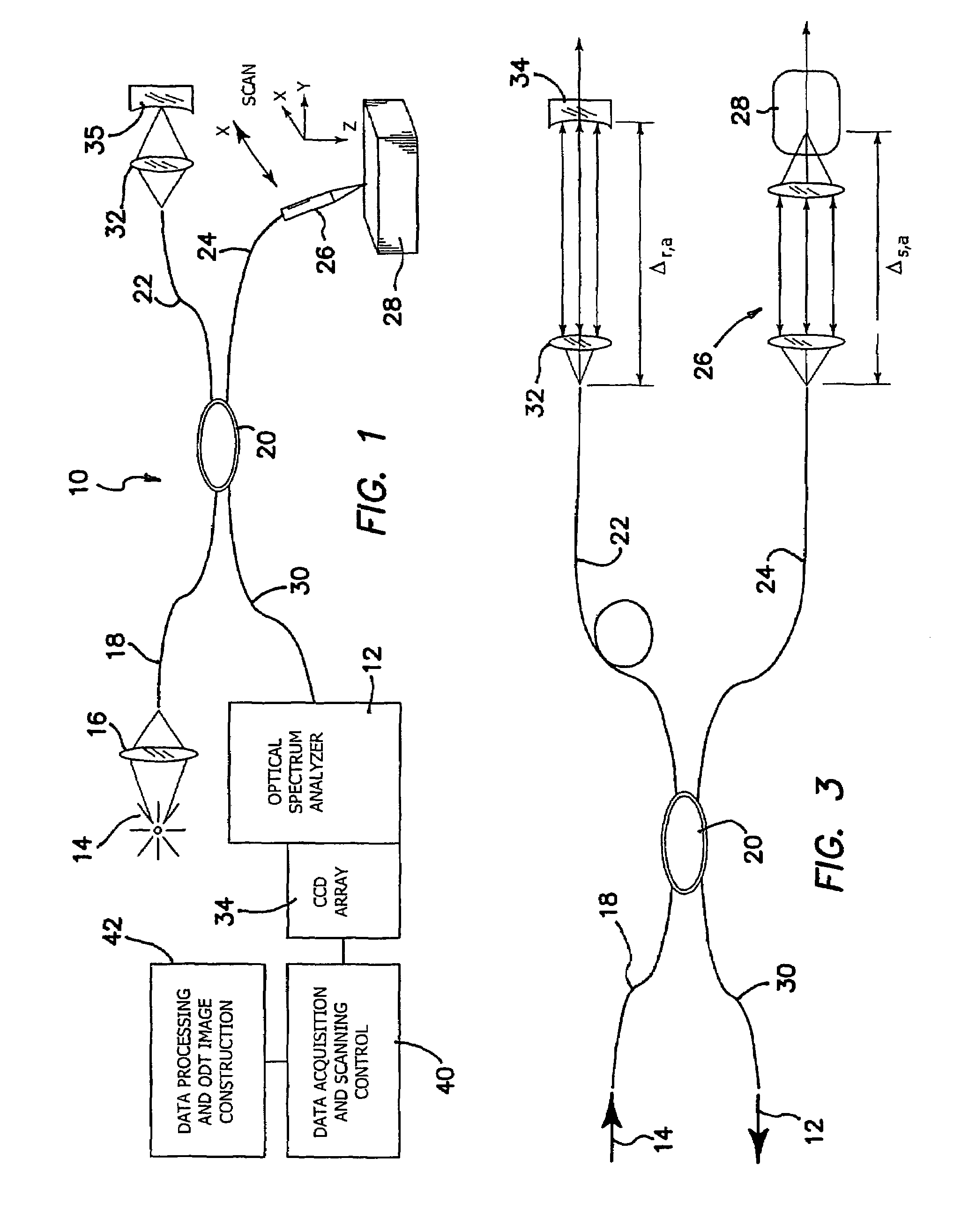
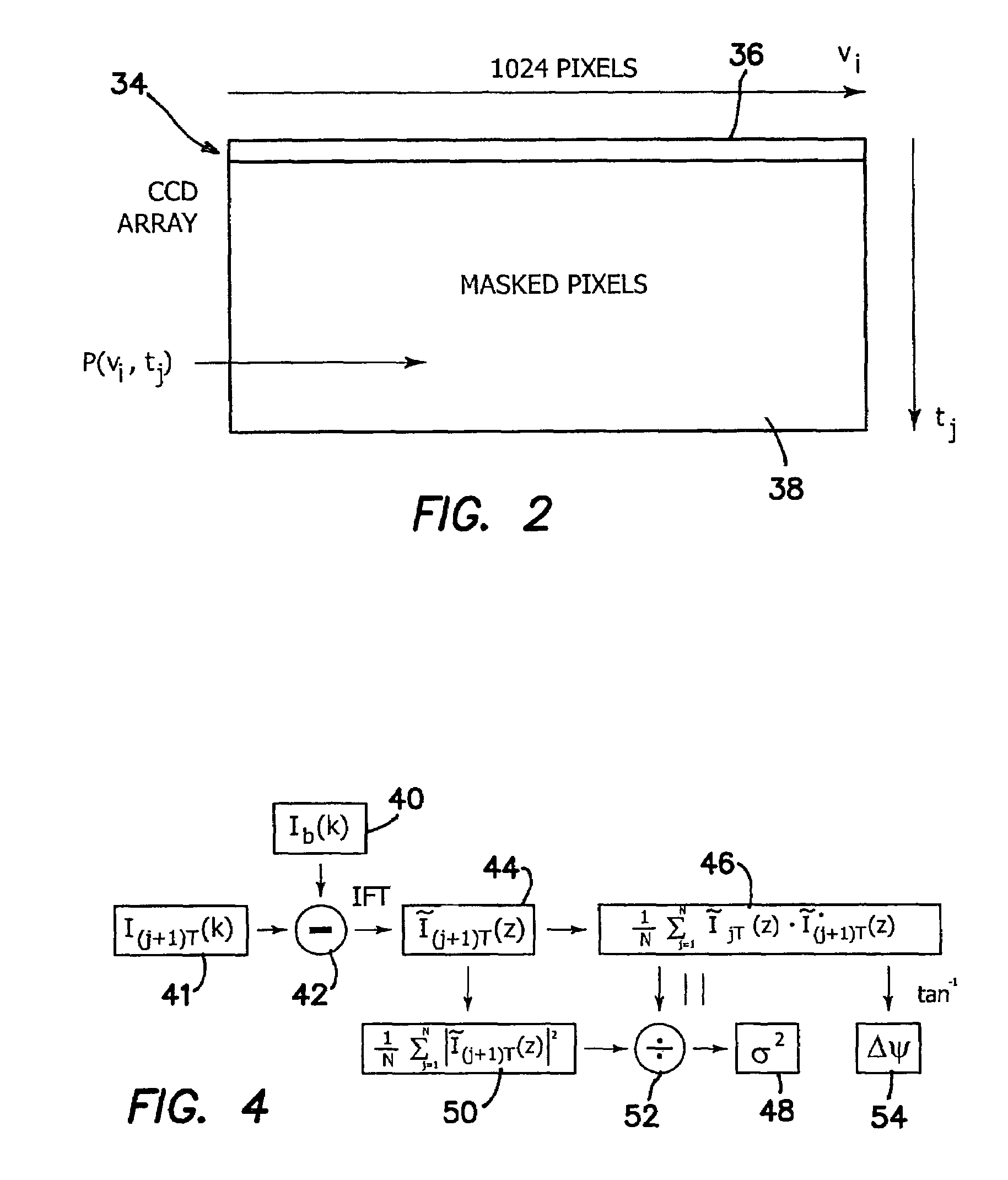
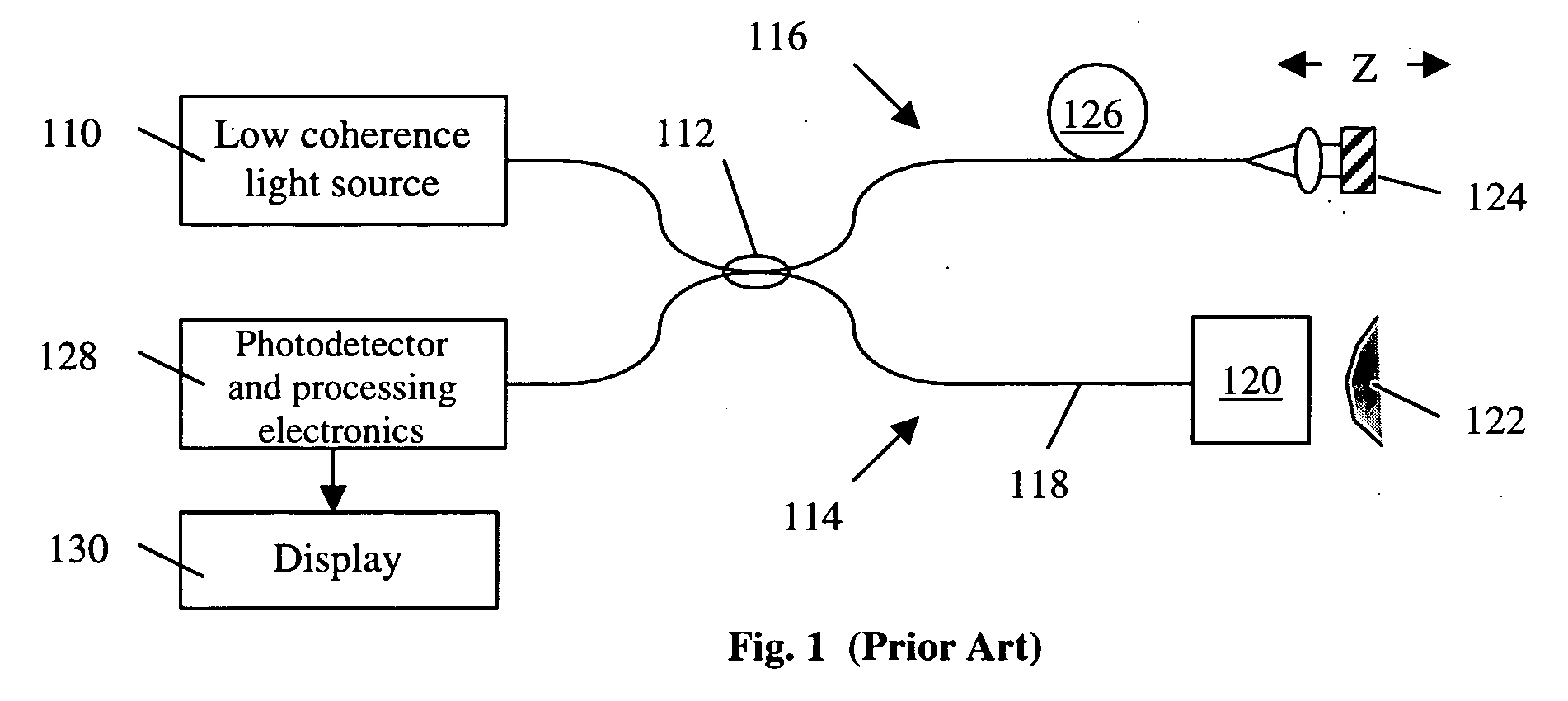
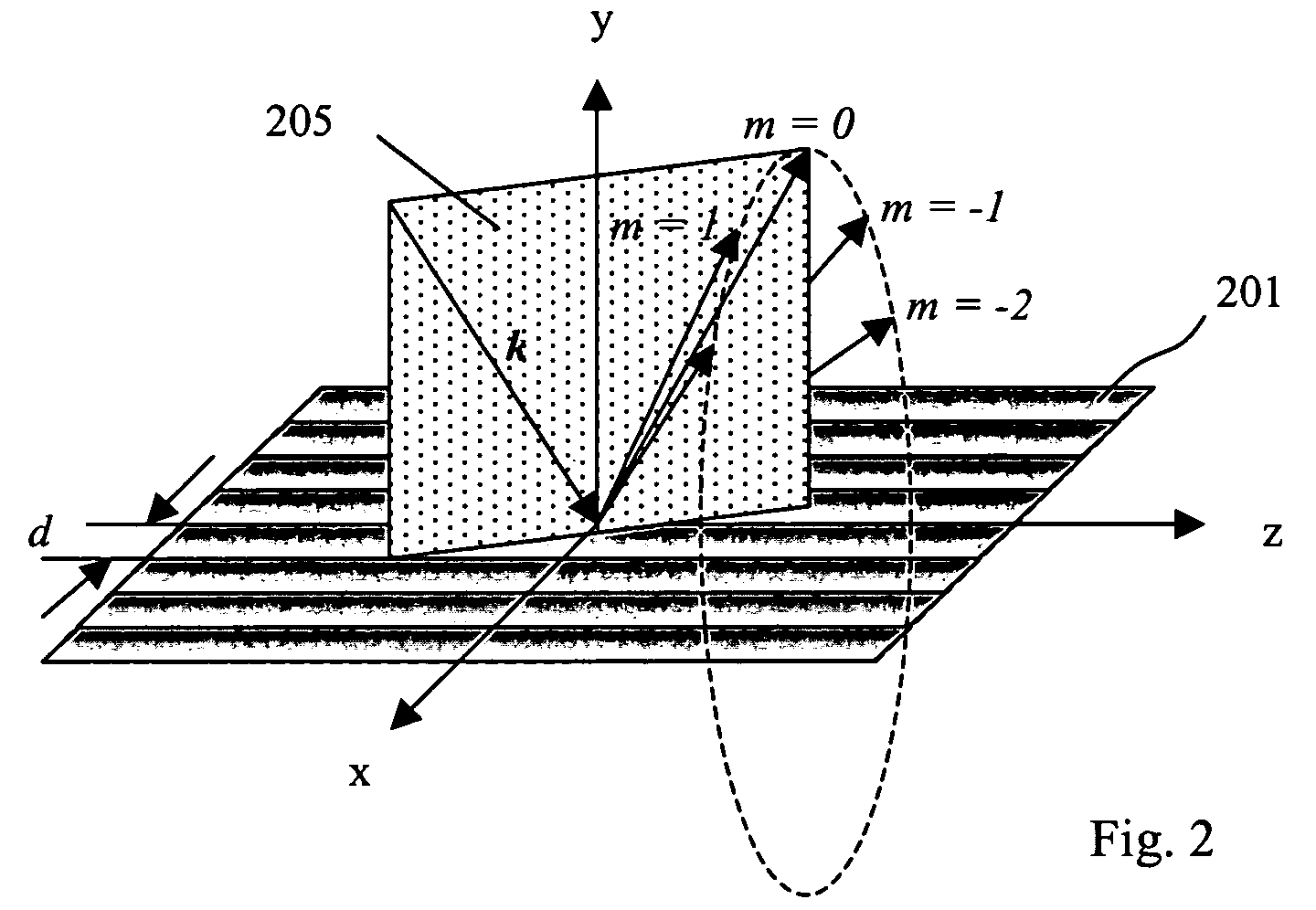
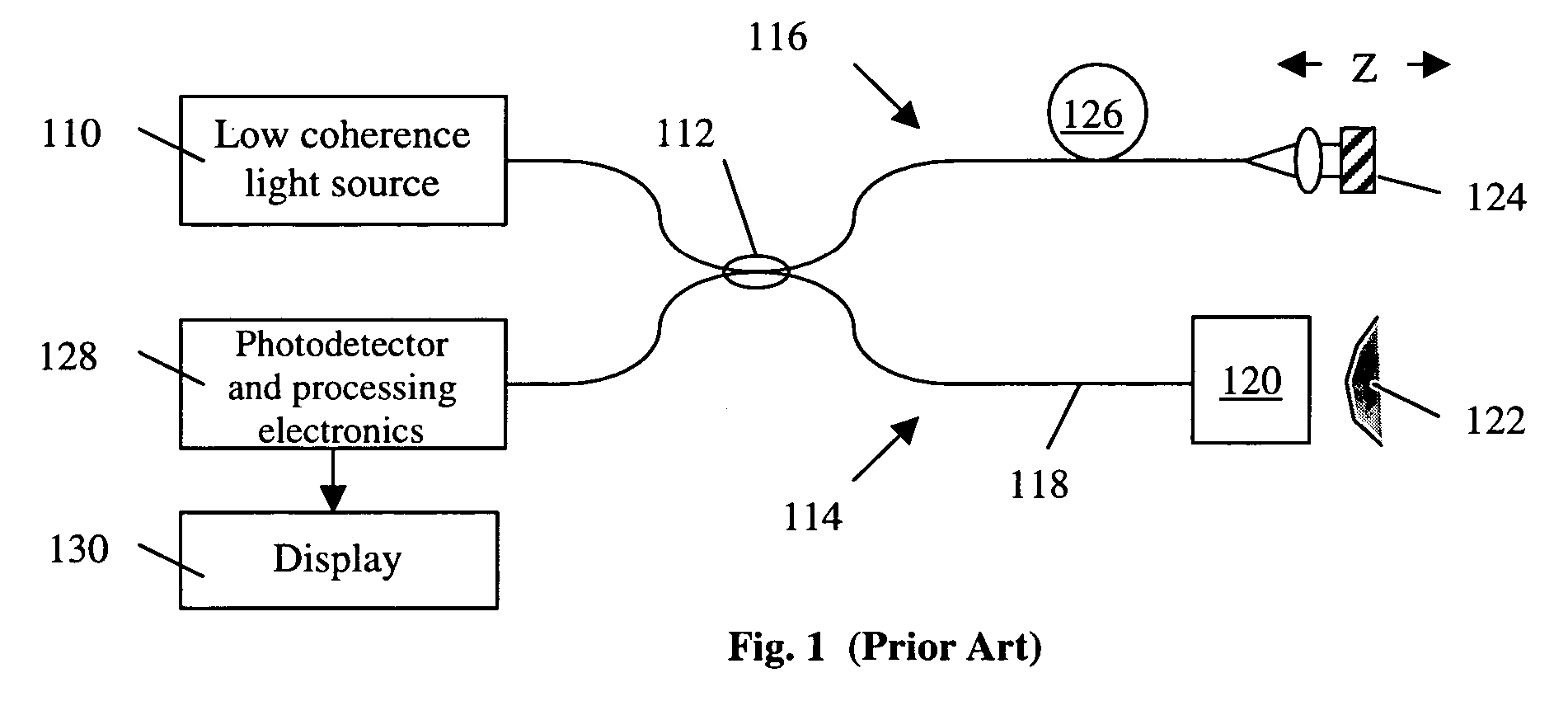
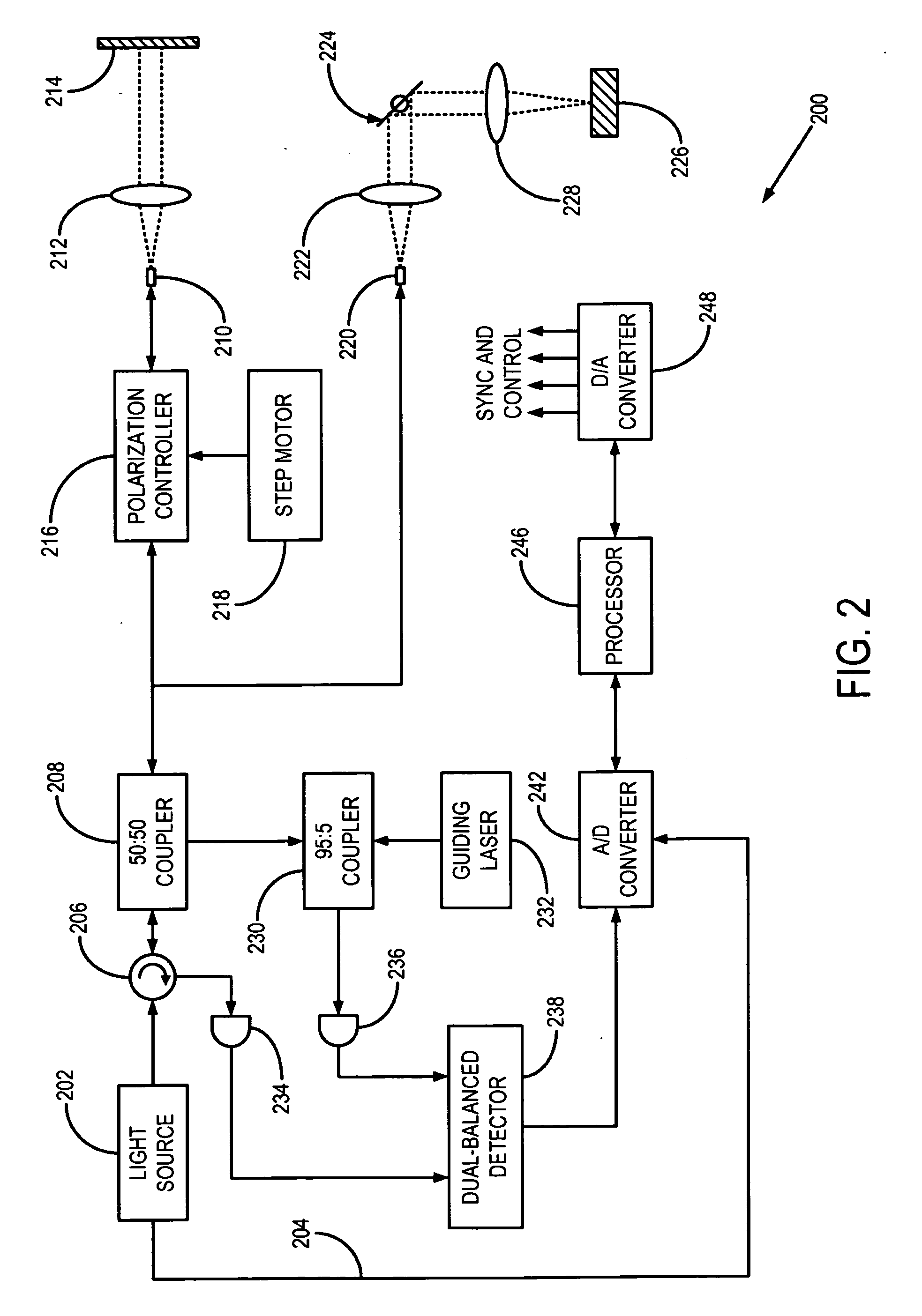
High speed spectral domain functional optical coherence tomography and optical doppler tomography for in vivo blood flow dynamics and tissue structure
ActiveUS20050171438A1Accurate settingImprove system sensitivityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsBlood flowIn vivo
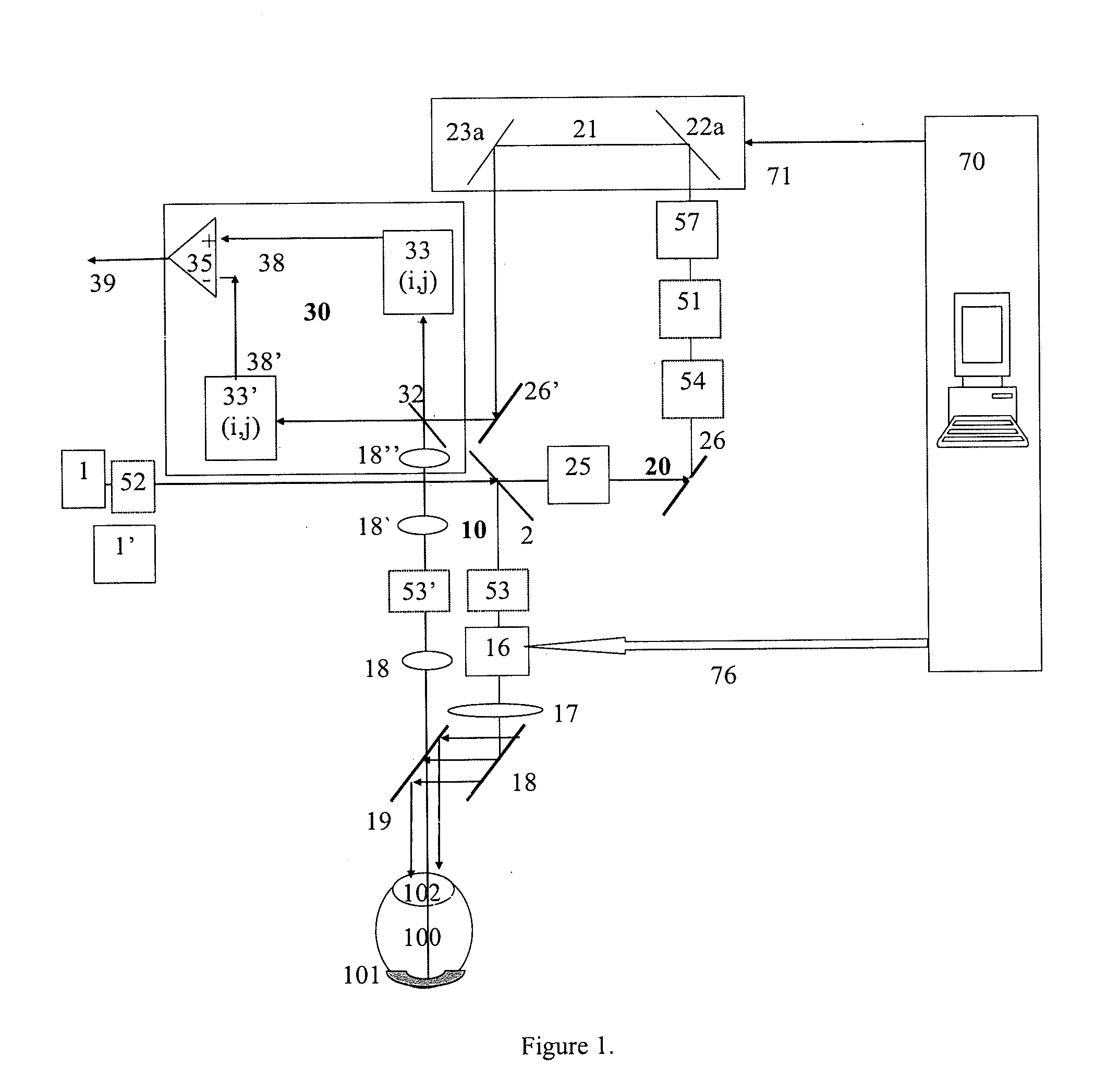
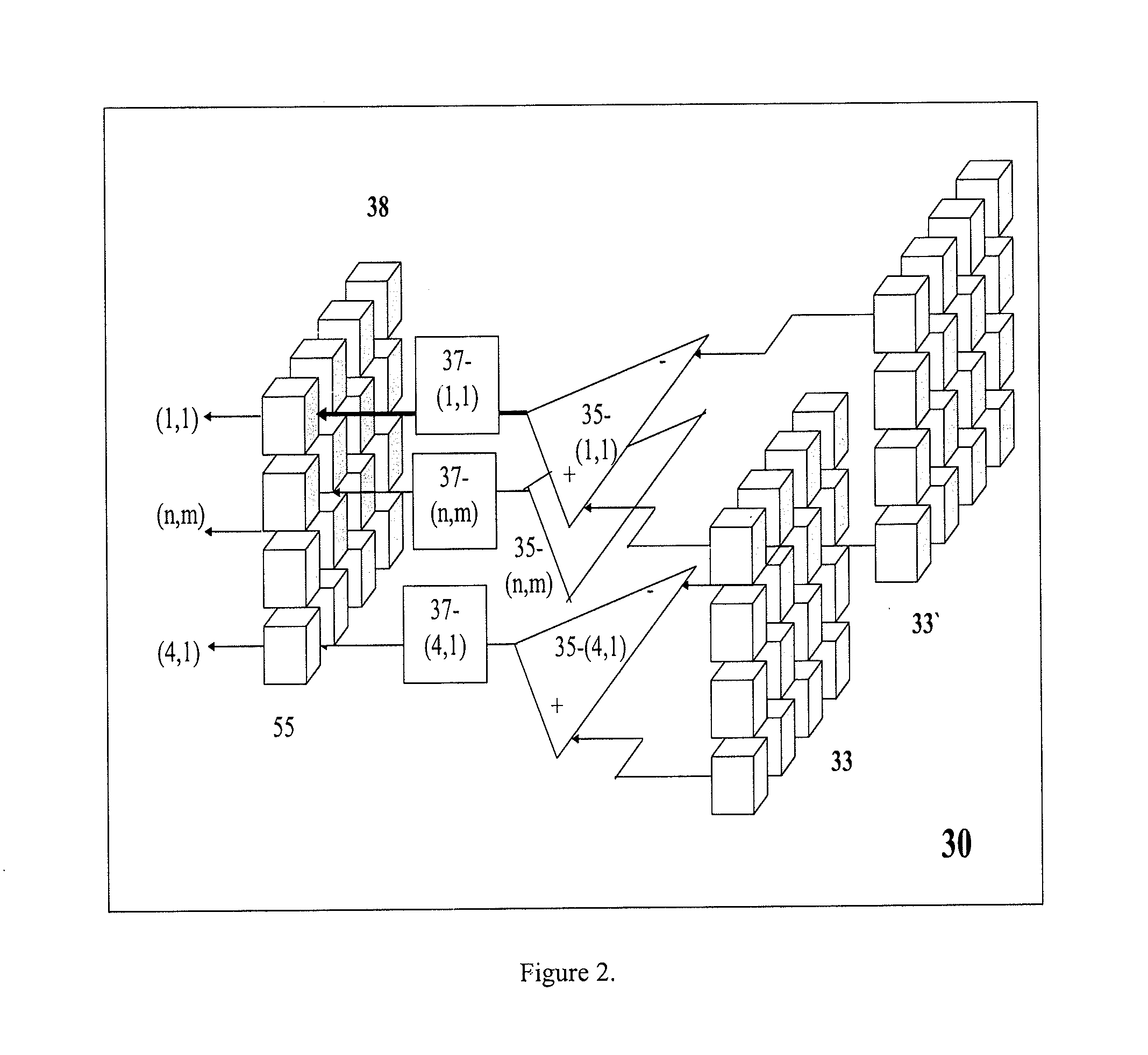
A method for tomographic imaging comprises the steps of providing a source of at least partially coherent radiation and a frequency-swept laser source through an interferometer; phase modulating the radiation in the interferometer at a modulation frequency for elimination of DC and autocorrelation noises as well as the mirror image; detecting interference fringes of the radiation backscattered from the sample into the interferometer to obtain a spectral signal; transforming the spectral signal of the detected backscattered interference fringes to obtain a time and location dependent signal, including the Doppler shift and variance, at each pixel location in a data window; and generating a tomographic image of the fluid flow in the data window and of the structure of the scanned fluid flow sample in the data window from the time and location dependent signal. The apparatus comprises a system for tomographic imaging operating according to the above method.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
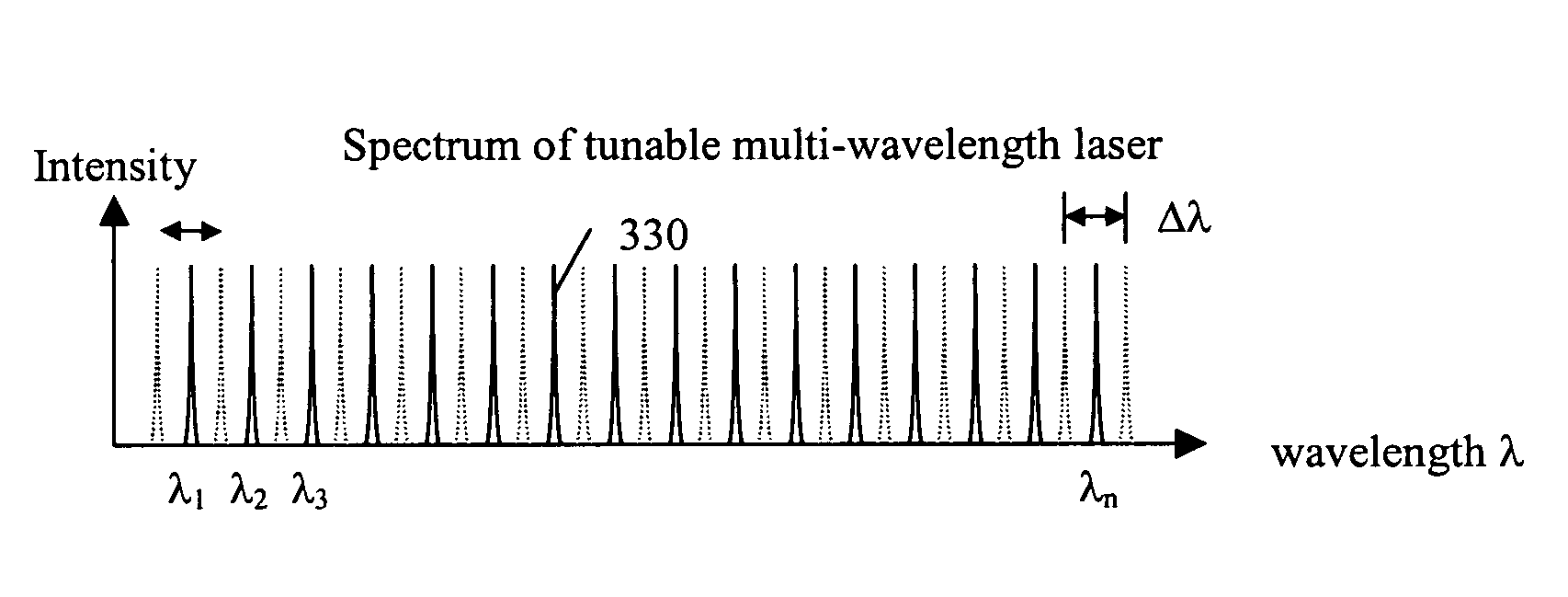
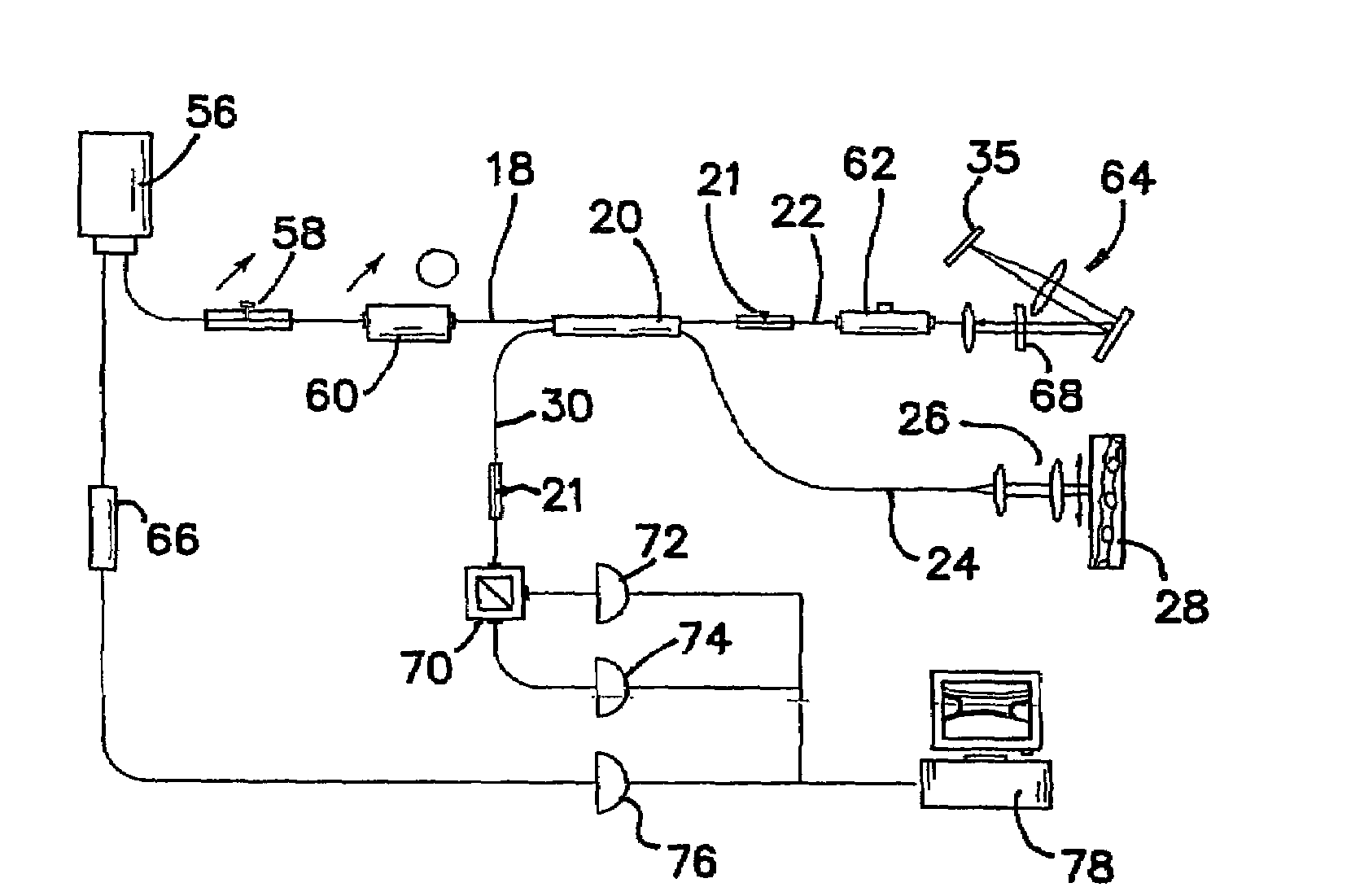
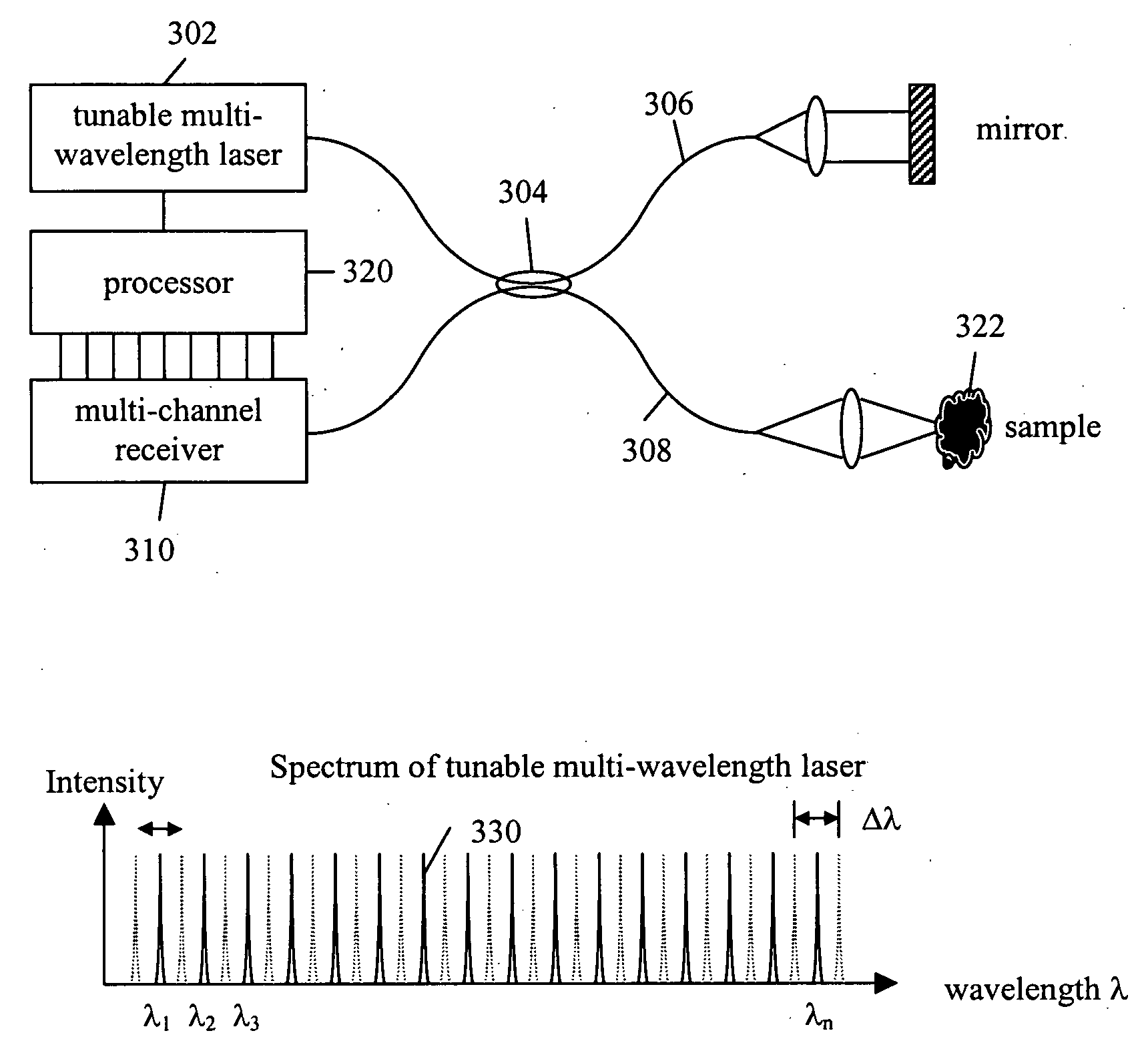
Fourier domain optical coherence tomography employing a swept multi-wavelength laser and a multi-channel receiver
ActiveUS7391520B2Low costIncrease in the speed of each axial scanInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansSpectral domainLasing wavelength
The present invention is an alternative Fourier domain optical coherence system (FD-OCT) and its associated method. The system comprises a swept multi-wavelength laser, an optical interferometer and a multi-channel receiver. By employing a multi-wavelength laser, the sweeping range for each lasing wavelength is substantially reduced as compared to a pure swept single wavelength laser that needs to cover the same overall spectral range. The overall spectral interferogram is divided over the individual channels of the multi-channel receiver and can be re-constructed through processing of the data from each channel detector. In addition to a substantial increase in the speed of each axial scan, the cost of invented FD-OCT system can also be substantially less than that of a pure swept source OCT or a pure spectral domain OCT system.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
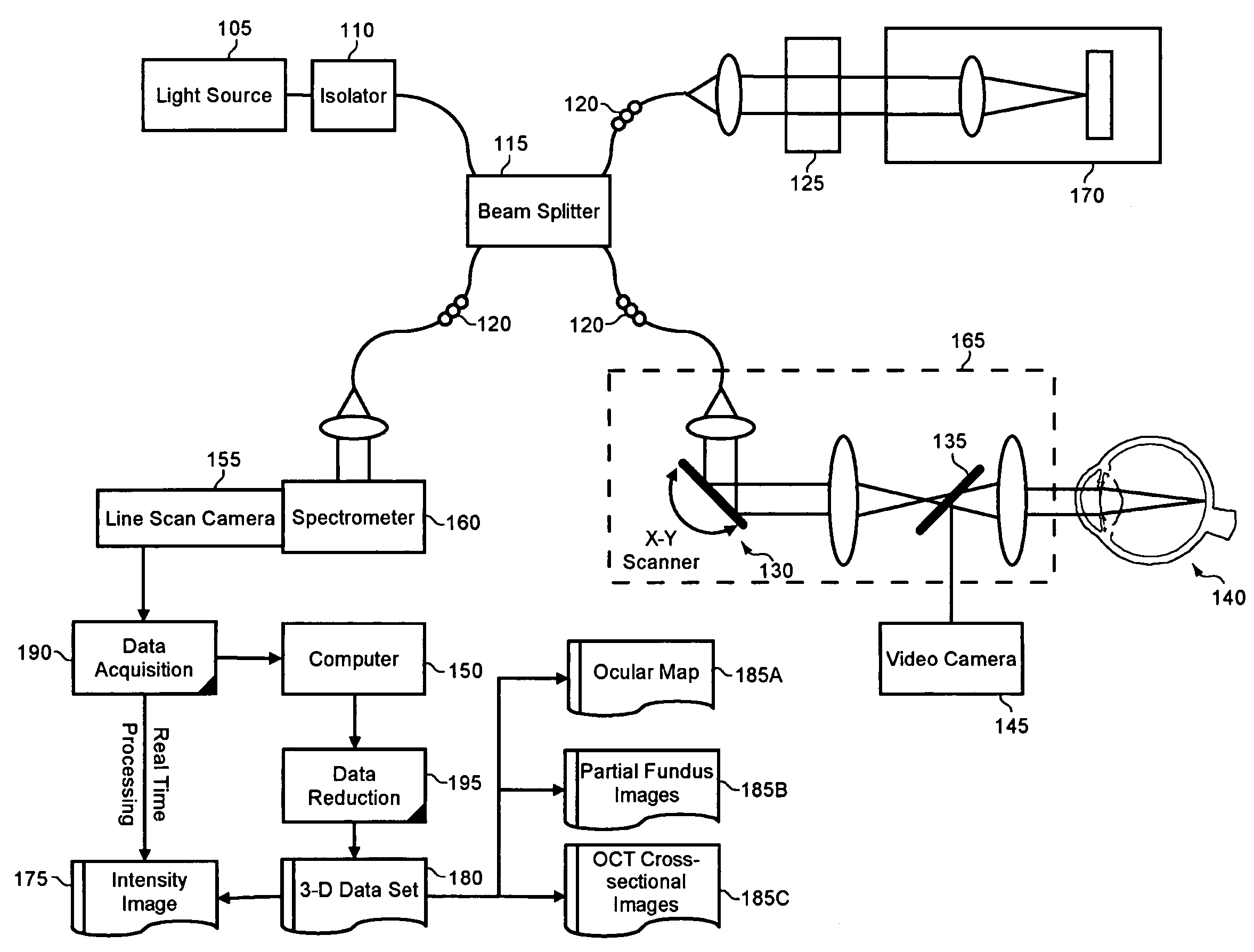
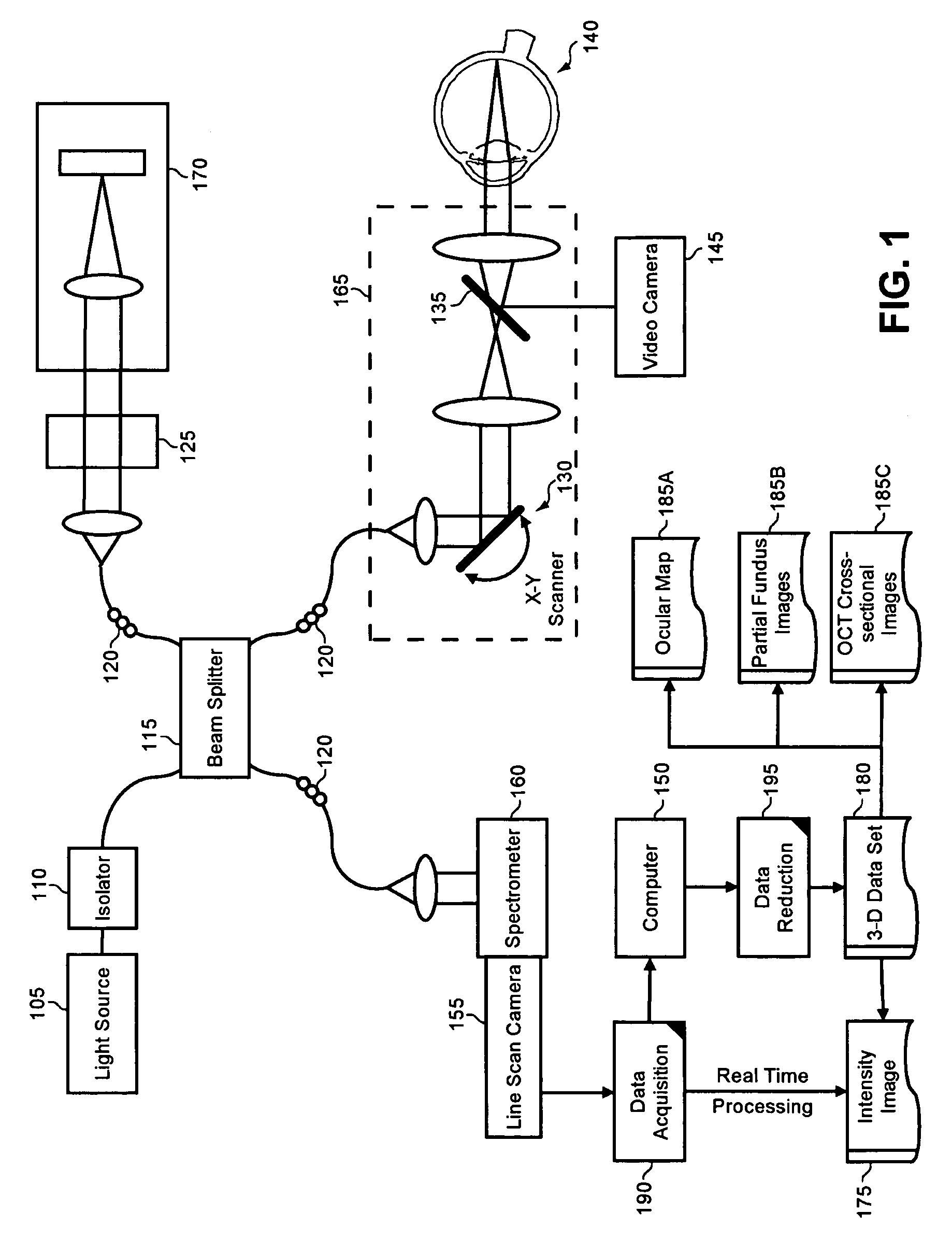
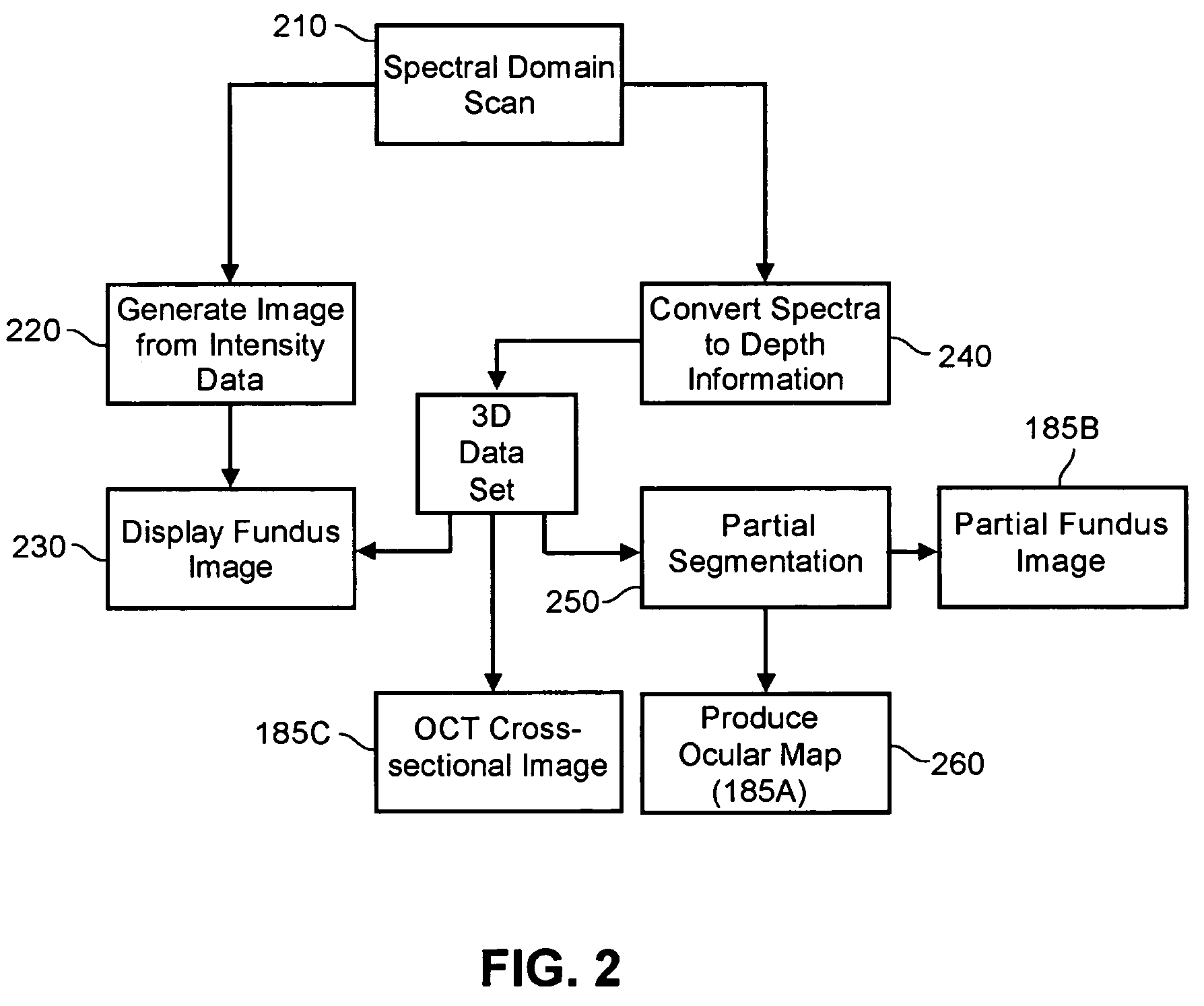
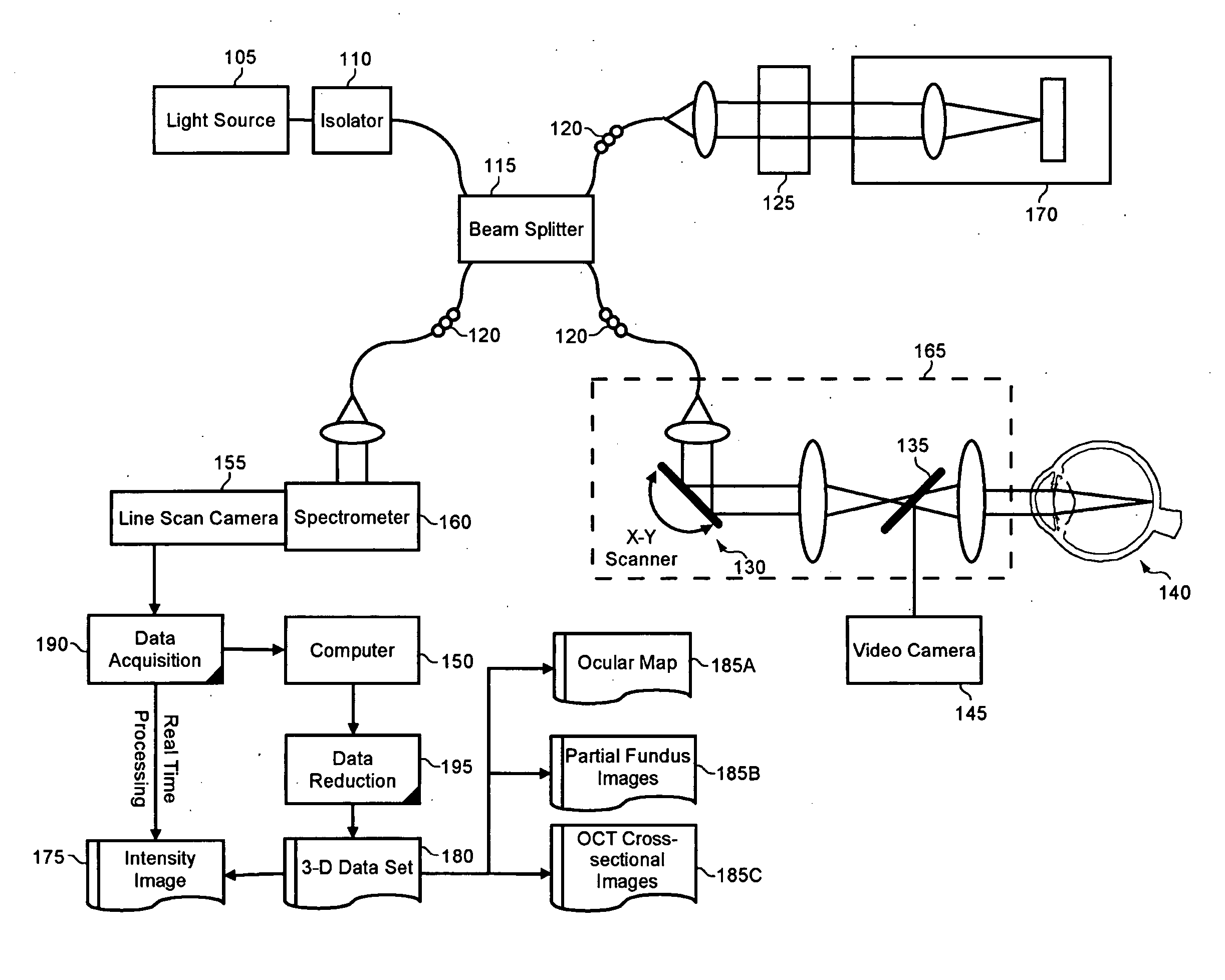
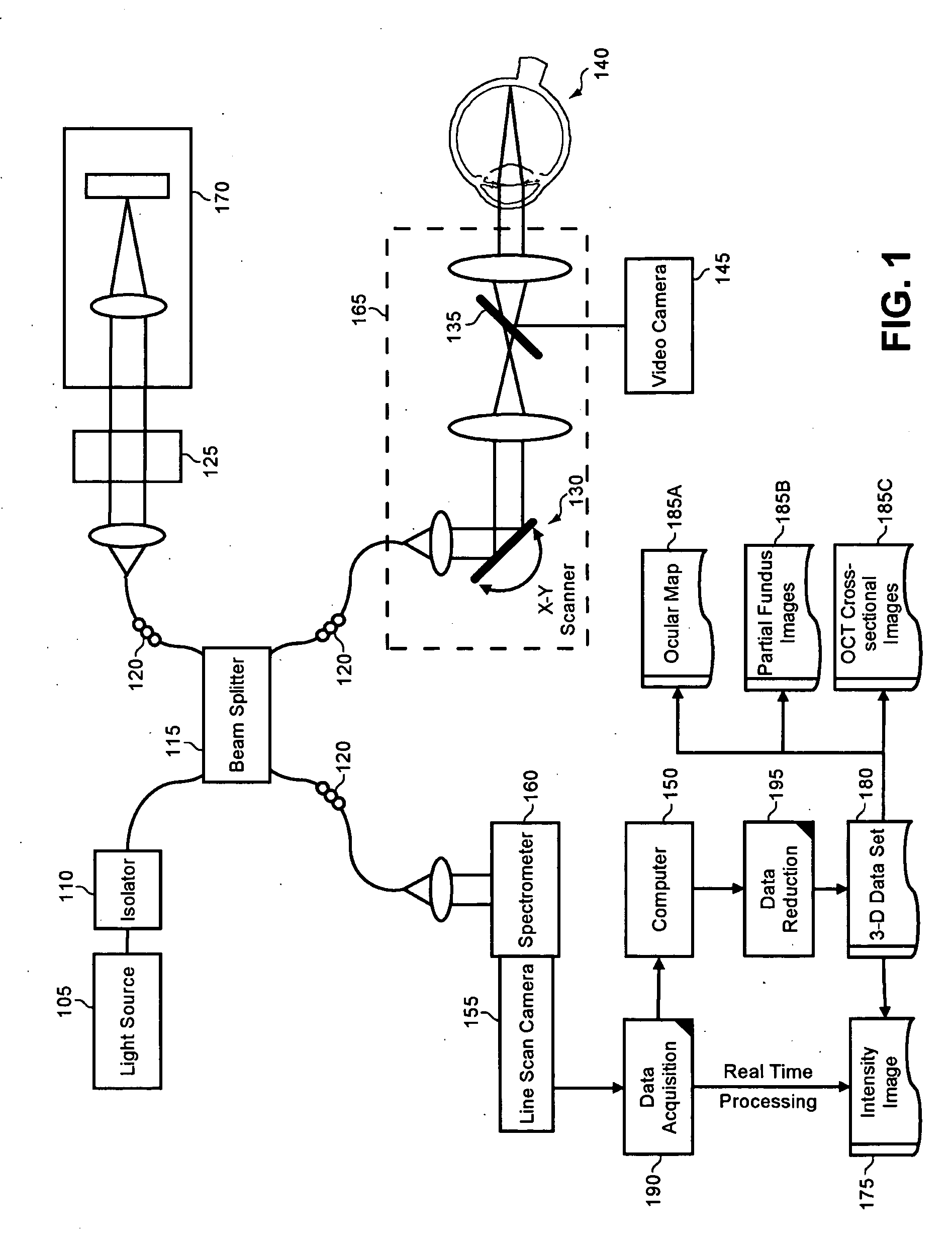
Enhanced optical coherence tomography for anatomical mapping
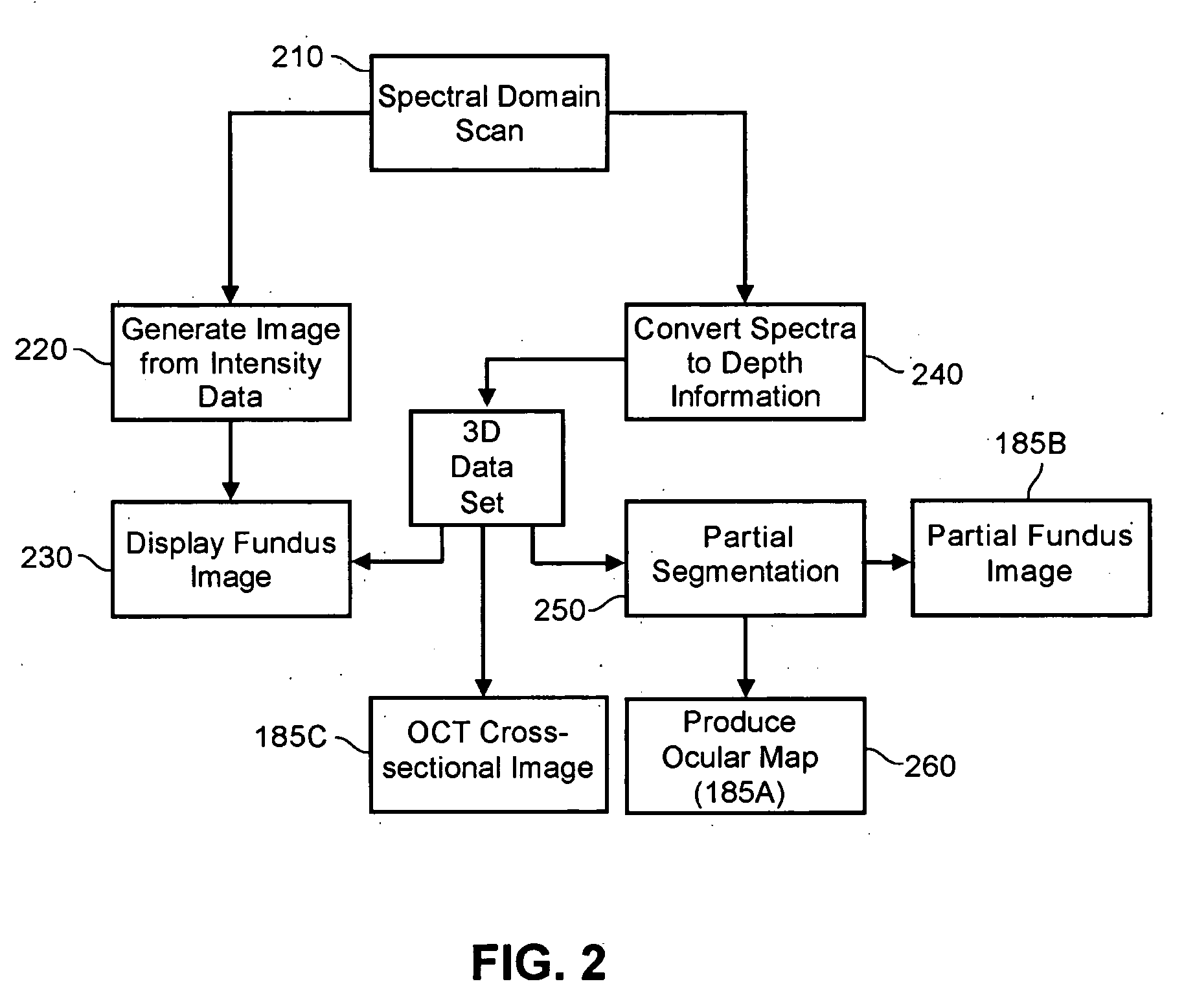
A system, method and apparatus for anatomical mapping utilizing optical coherence tomography. In the present invention, 3-dimensional fundus intensity imagery can be acquired from a scanning of light back-reflected from an eye. The scanning can include spectral domain scanning, as an example. A fundus intensity image can be acquired in real-time. The 3-dimensional data set can be reduced to generate an anatomical mapping, such as an edema mapping and a thickness mapping. Optionally, a partial fundus intensity image can be produced from the scanning of the eye to generate an en face view of the retinal structure of the eye without first requiring a full segmentation of the 3-D data set. Advantageously, the system, method and apparatus of the present invention can provide quantitative three-dimensional information about the spatial location and extent of macular edema and other pathologies. This three-dimensional information can be used to determine the need for treatment, monitor the effectiveness of treatment and identify the return of fluid that may signal the need for re-treatment.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
High speed spectral domain functional optical coherence tomography and optical doppler tomography for in vivo blood flow dynamics and tissue structure
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Arrangements, systems and methods capable of providing spectral-domain polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography
InactiveUS20070038040A1Improve measurement reliabilityHigh sensitivityPolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsSpectral domainTomography
Systems, arrangements and methods for separating an electromagnetic radiation and obtaining information for a sample using an electromagnetic radiation are provided. In particular, the electromagnetic radiation can be separated into at least one first portion and at least one second portion according to at least one polarization and at least one wave-length of the electromagnetic radiation. The first and second separated portions may be simultaneously detected. Further, a first radiation can be obtained from the sample and a second radiation may be obtained from a reference, and the first and second radiations may be combined to form a further radiation, with the first and second radiations being associated with the electro-magnetic radiation. The information is provided as a function of first and second portions of the further radiations that have been previously separated and can be analyzed to extract birefringent information characterizing the sample.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
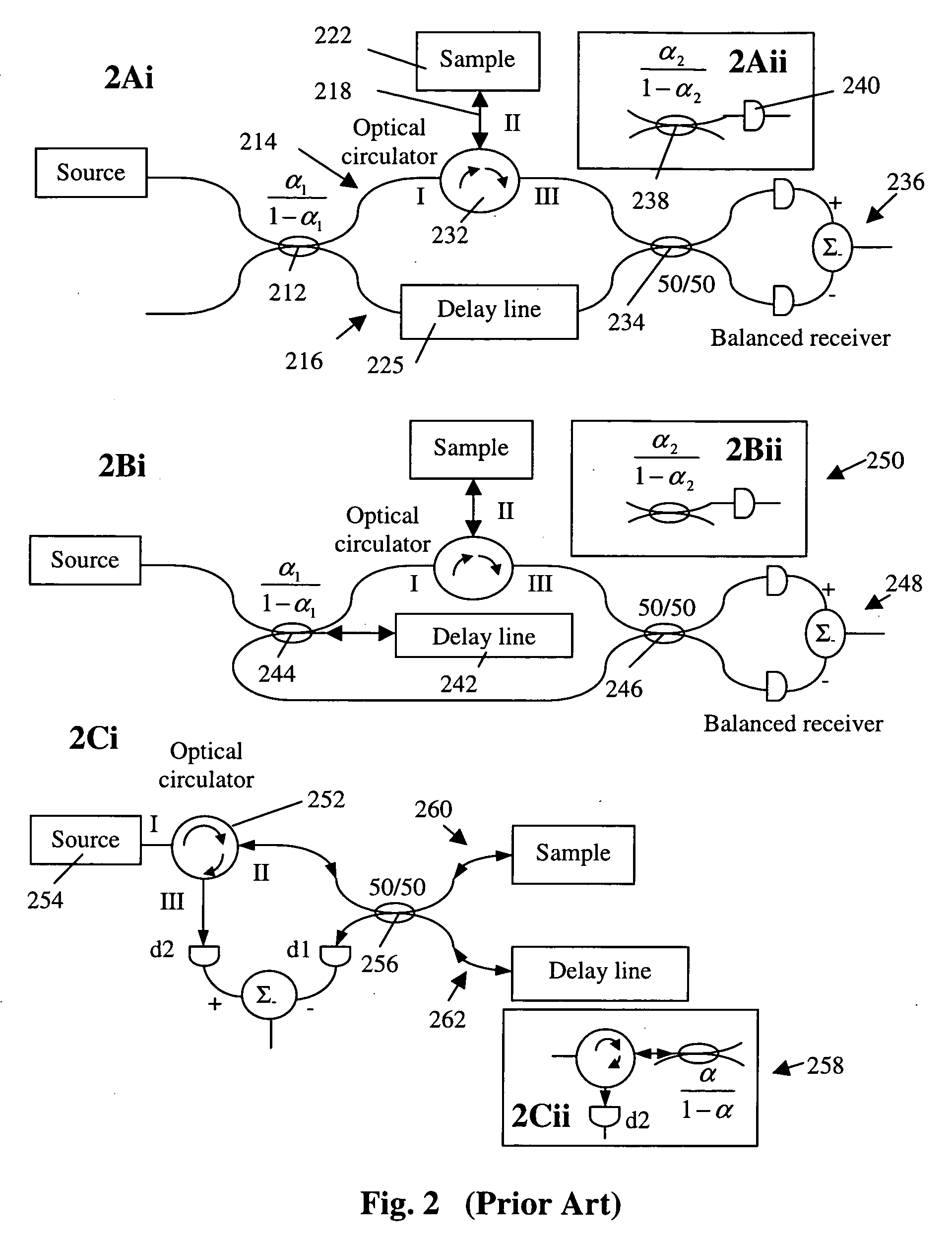
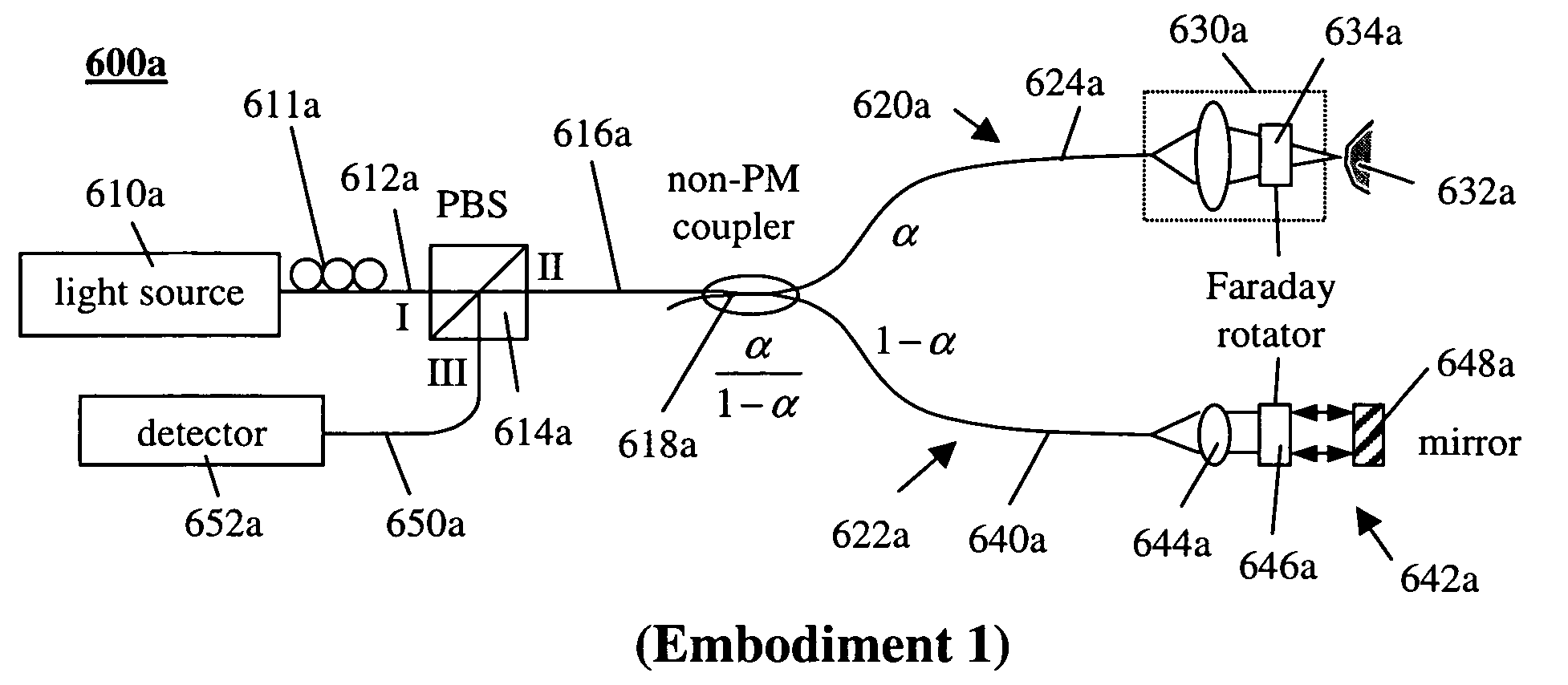
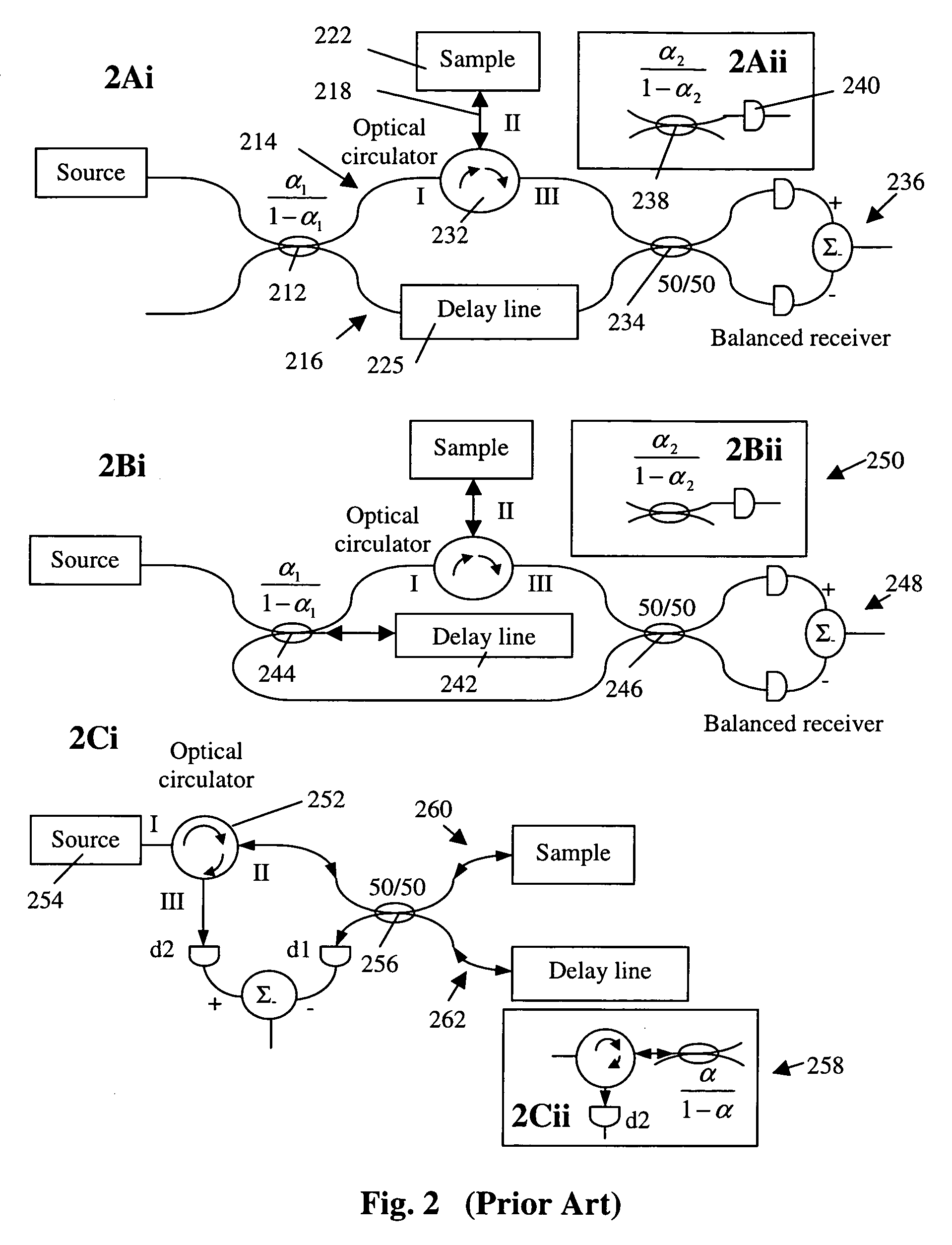
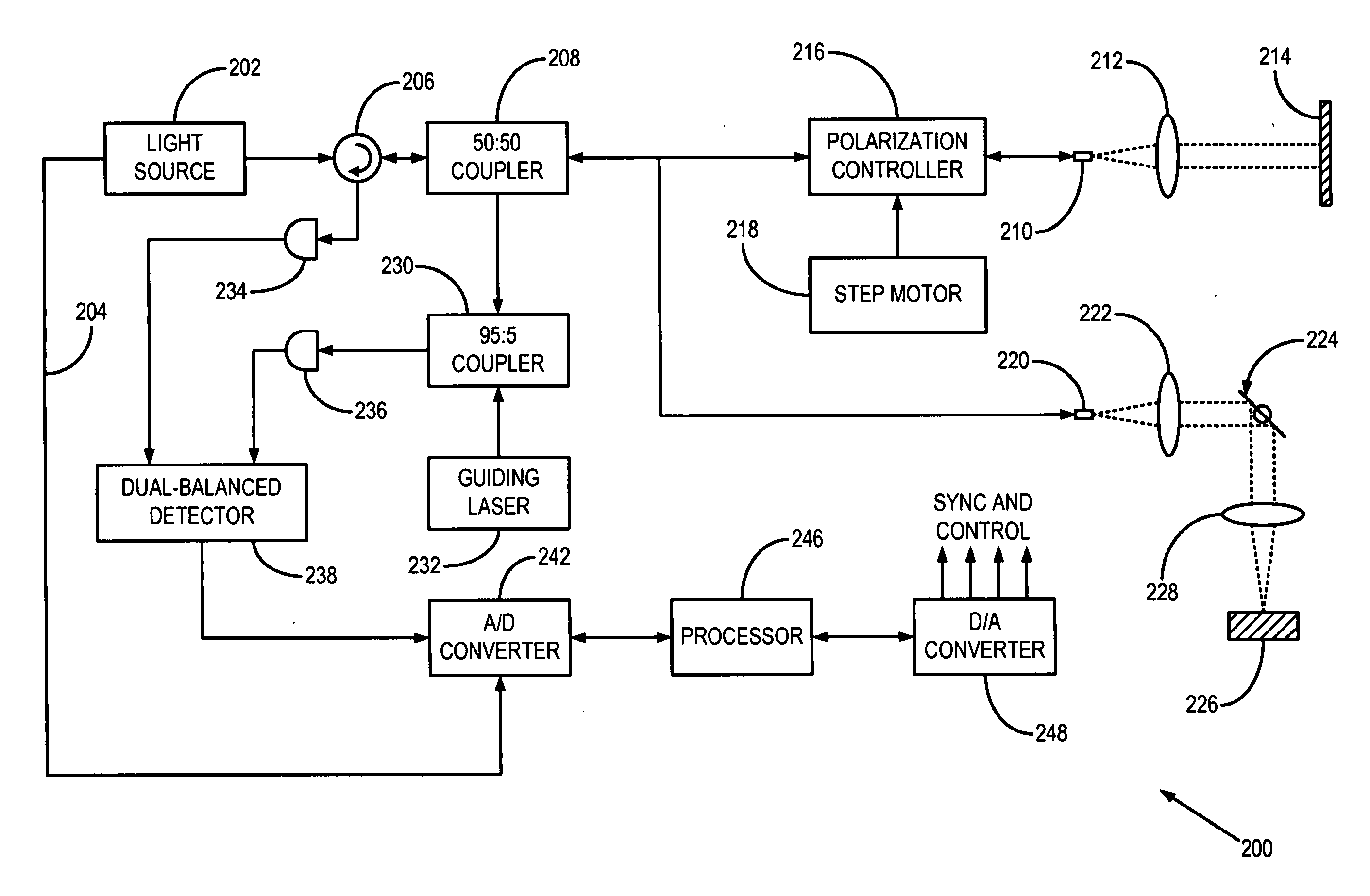
Simple high efficiency optical coherence domain reflectometer design
ActiveUS20050213103A1Reduce system costLow costReflectometers dealing with polarizationInterferometersBeam splitterDetector array
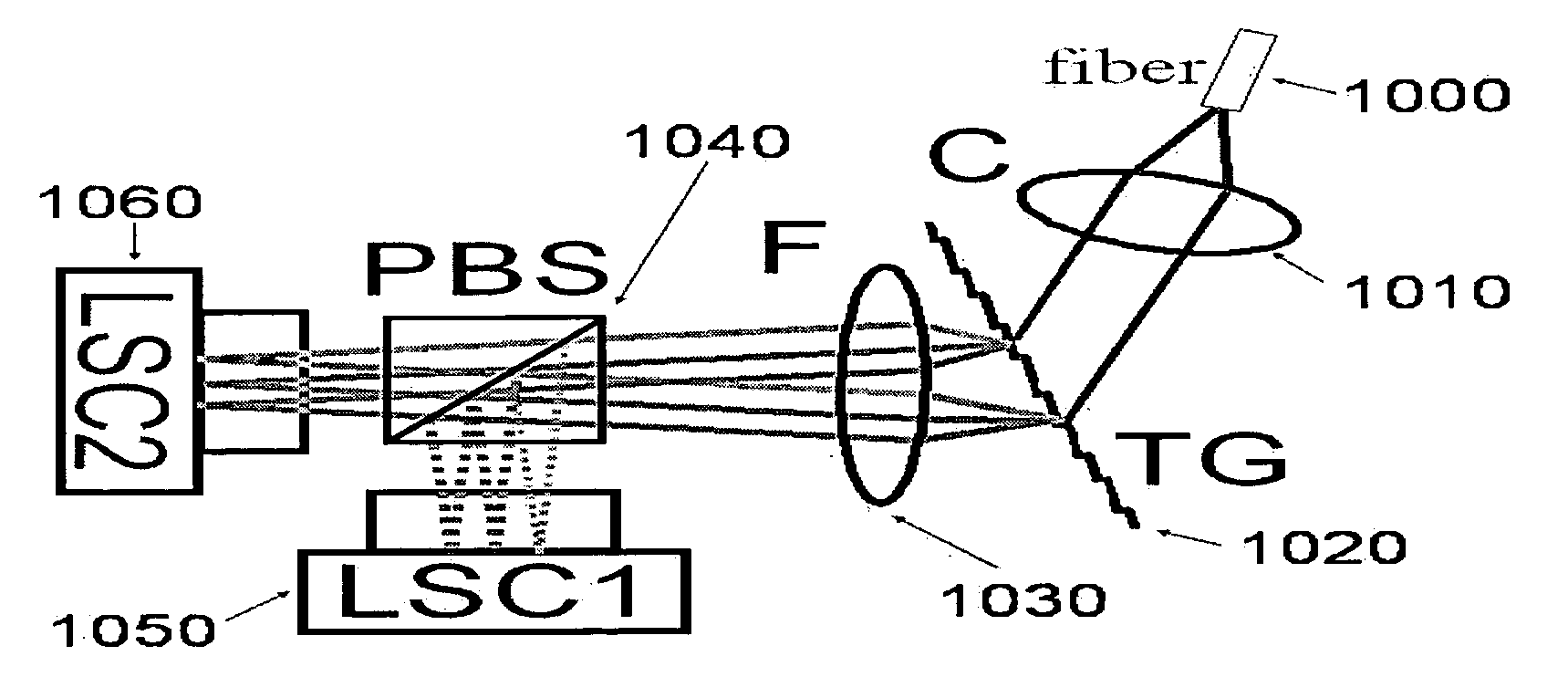
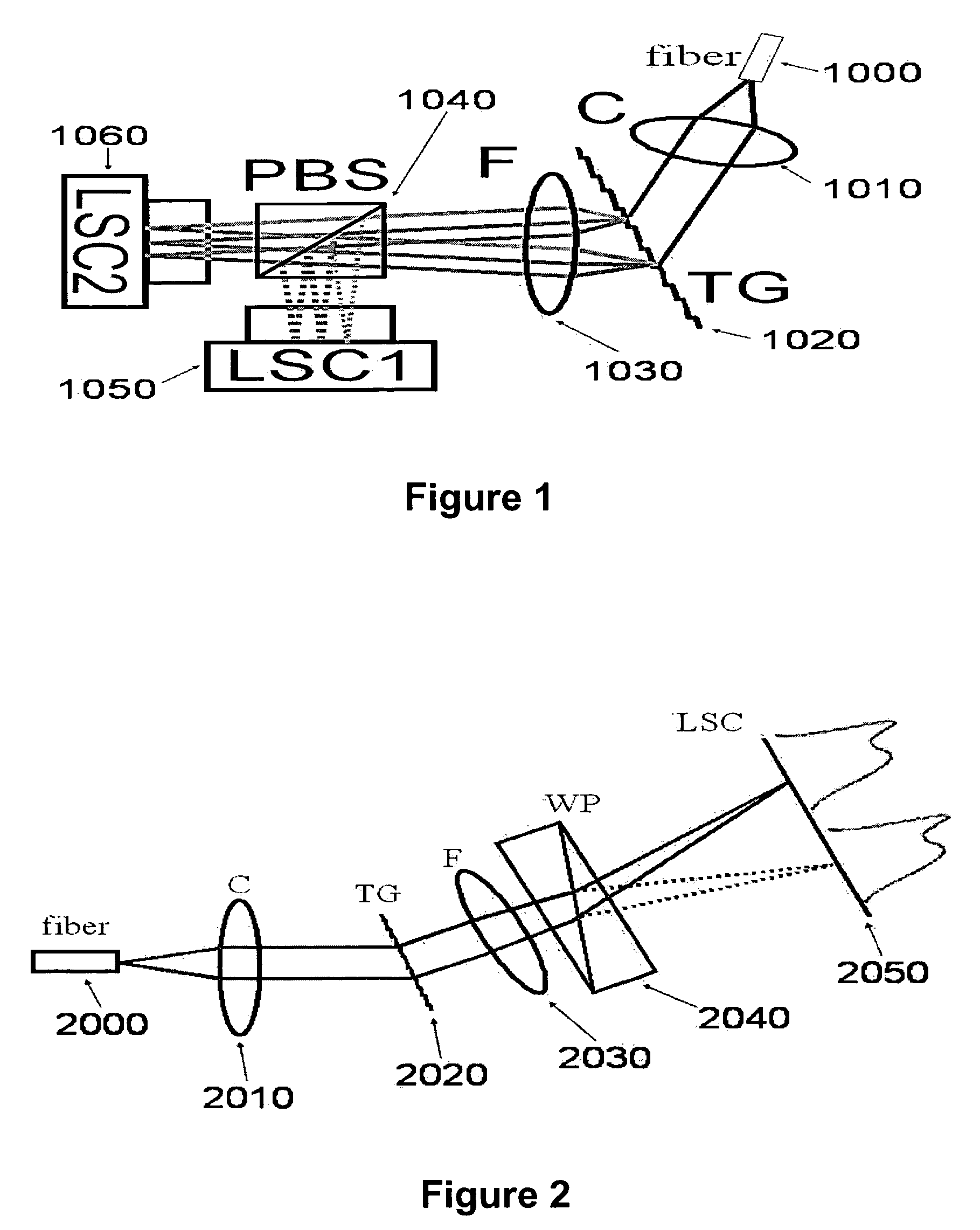
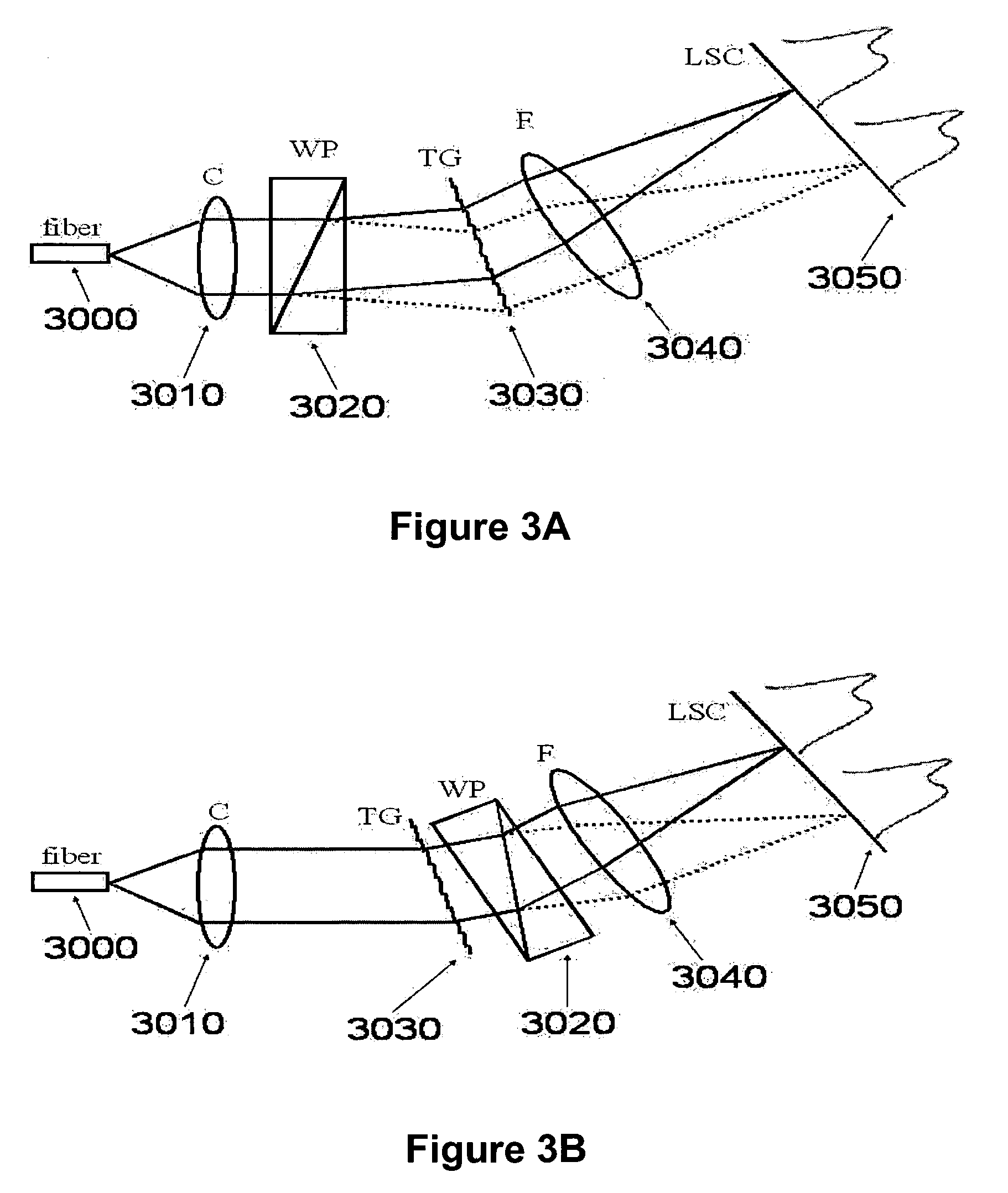
The present invention discloses simple and yet highly efficient configurations of optical coherence domain reflectometry systems. The combined use of a polarizing beam splitter with one or two polarization manipulator(s) that rotate the returned light wave polarization to an orthogonal direction, enables one to achieve high optical power delivery efficiency as well as fixed or predetermined output polarization state of the interfering light waves reaching a detector or detector array, which is especially beneficial for spectral domain optical coherence tomography. In addition, the system can be made insensitive to polarization fading resulting from the birefringence change in the sample and reference arms. Dispersion matching can also be easily achieved between the sample and the reference arm for high resolution longitudinal scanning.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
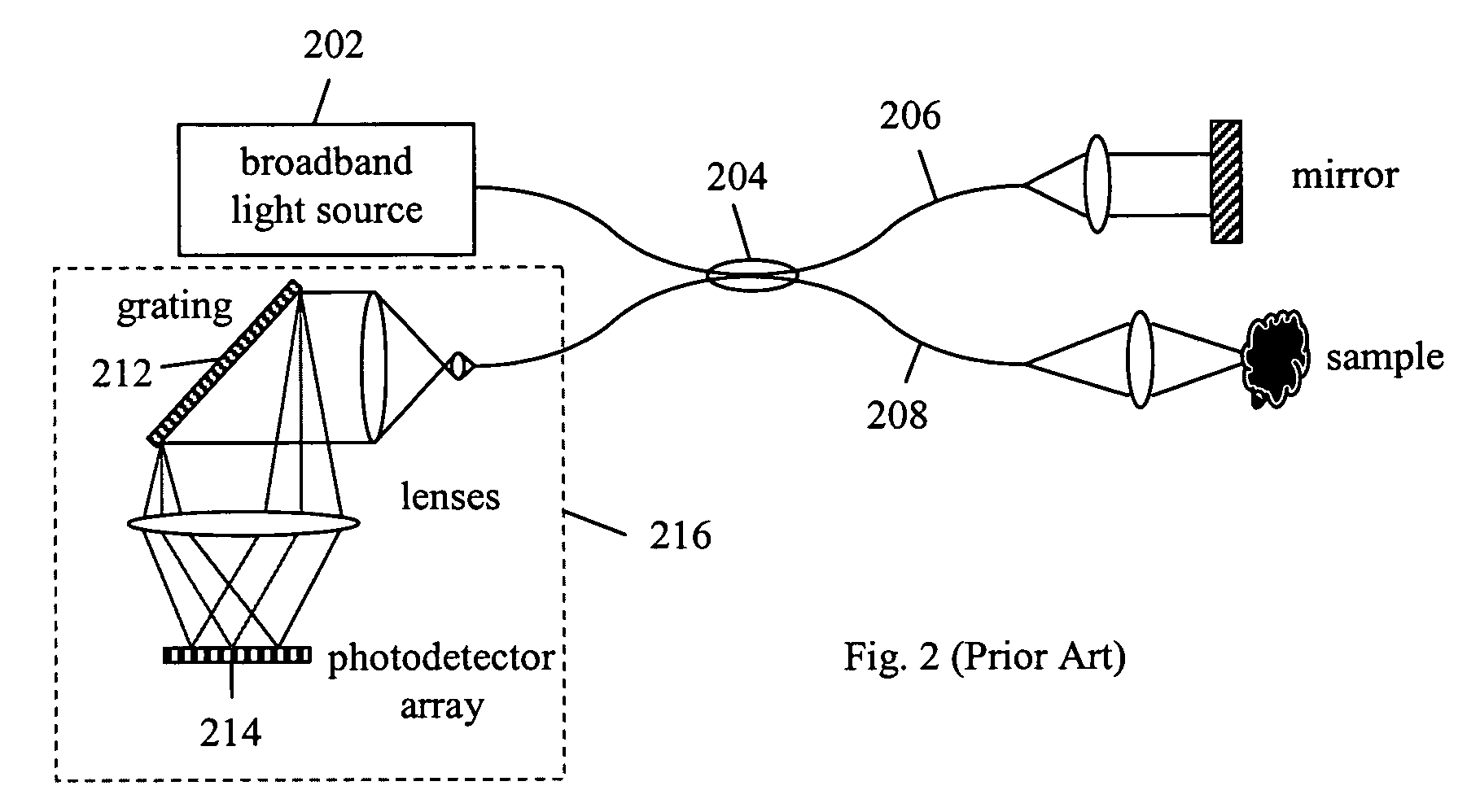
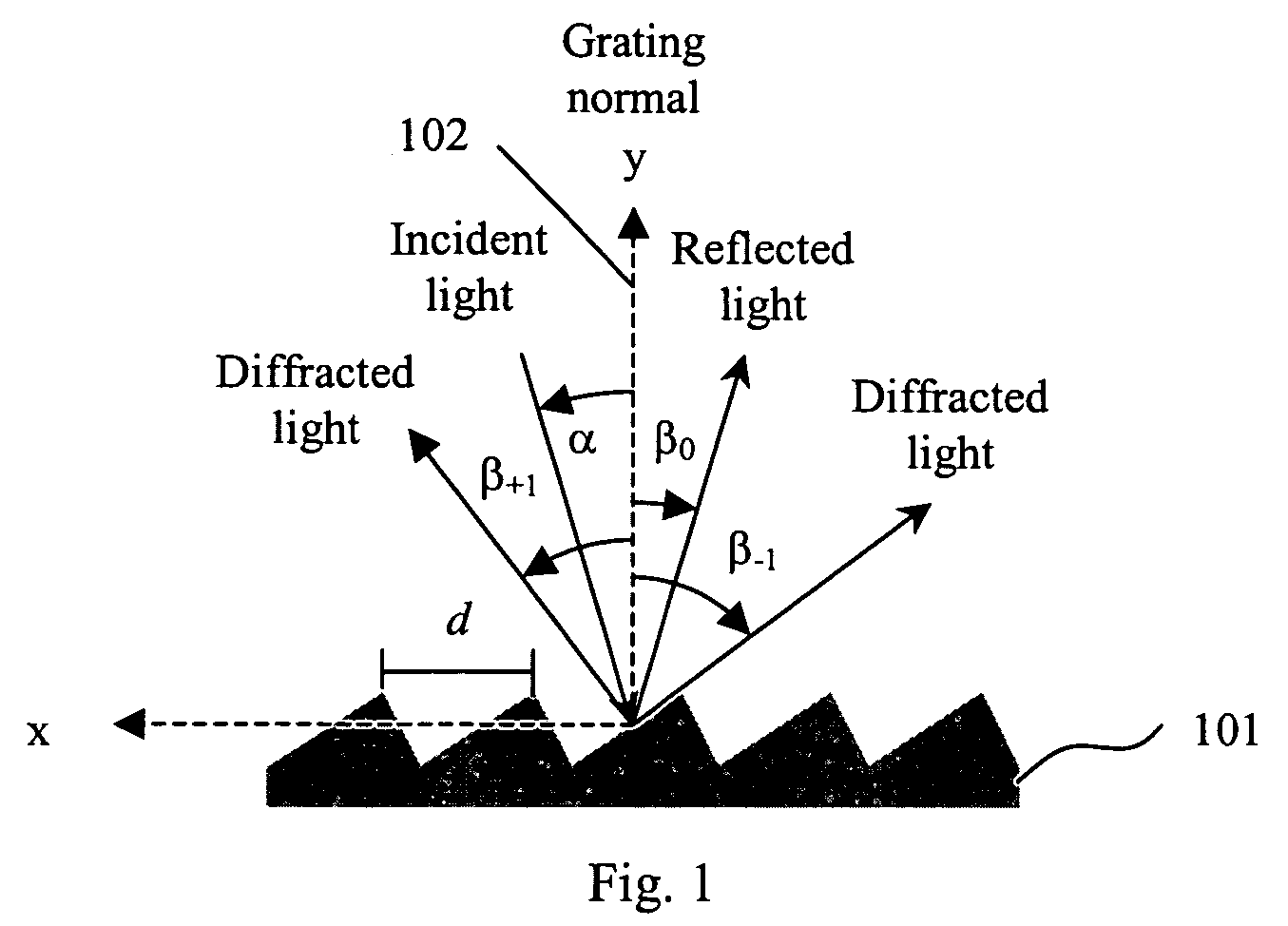
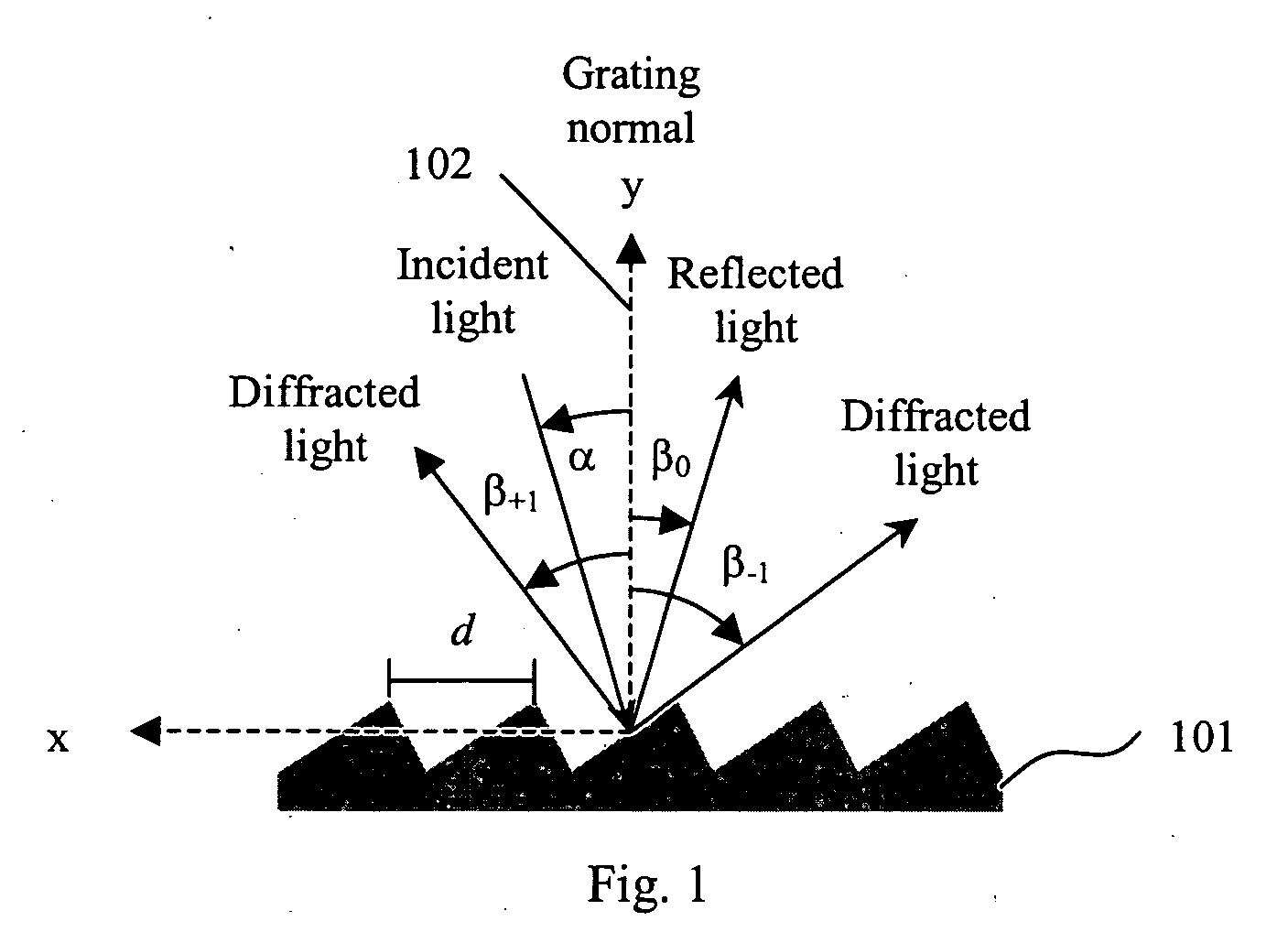
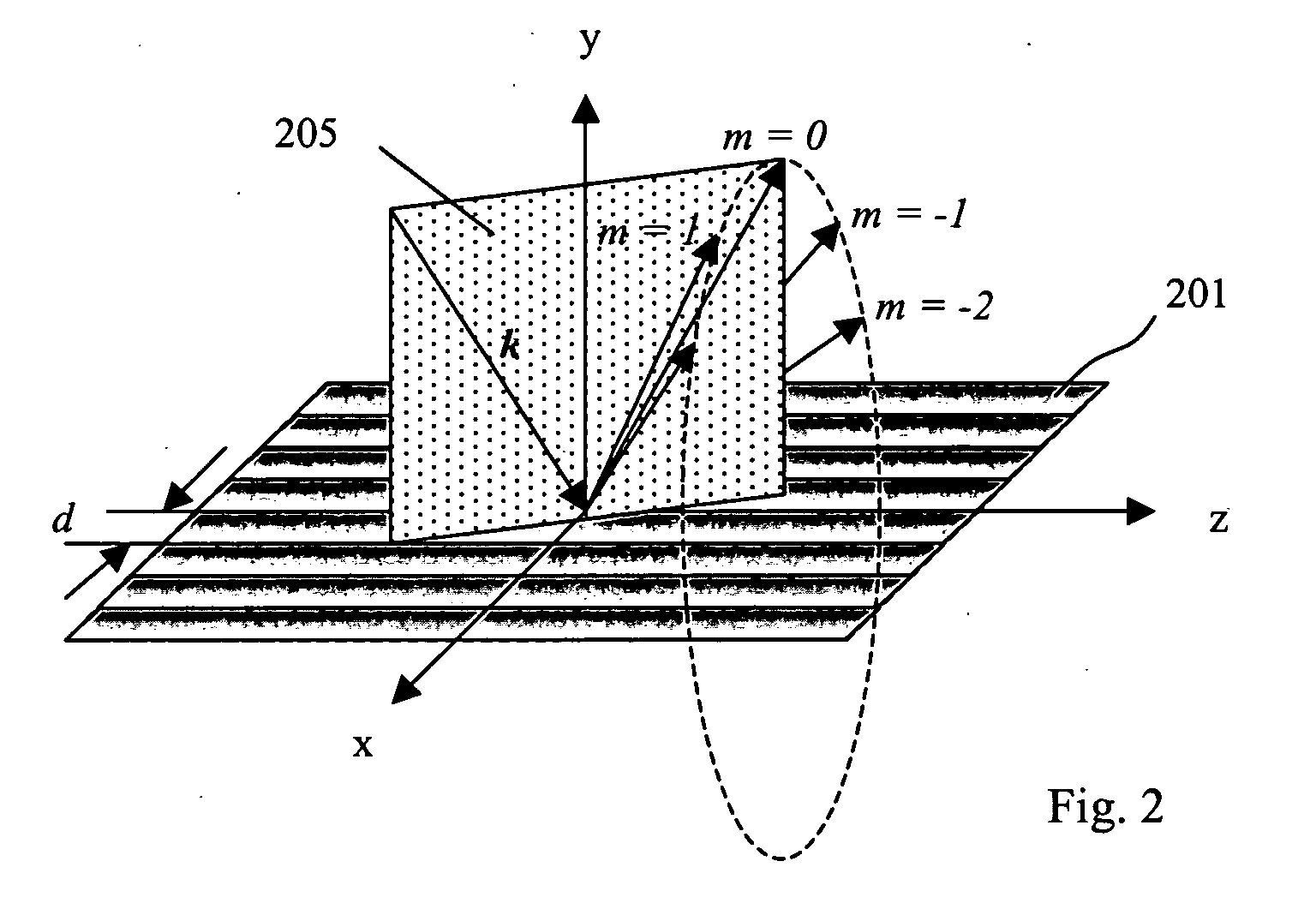
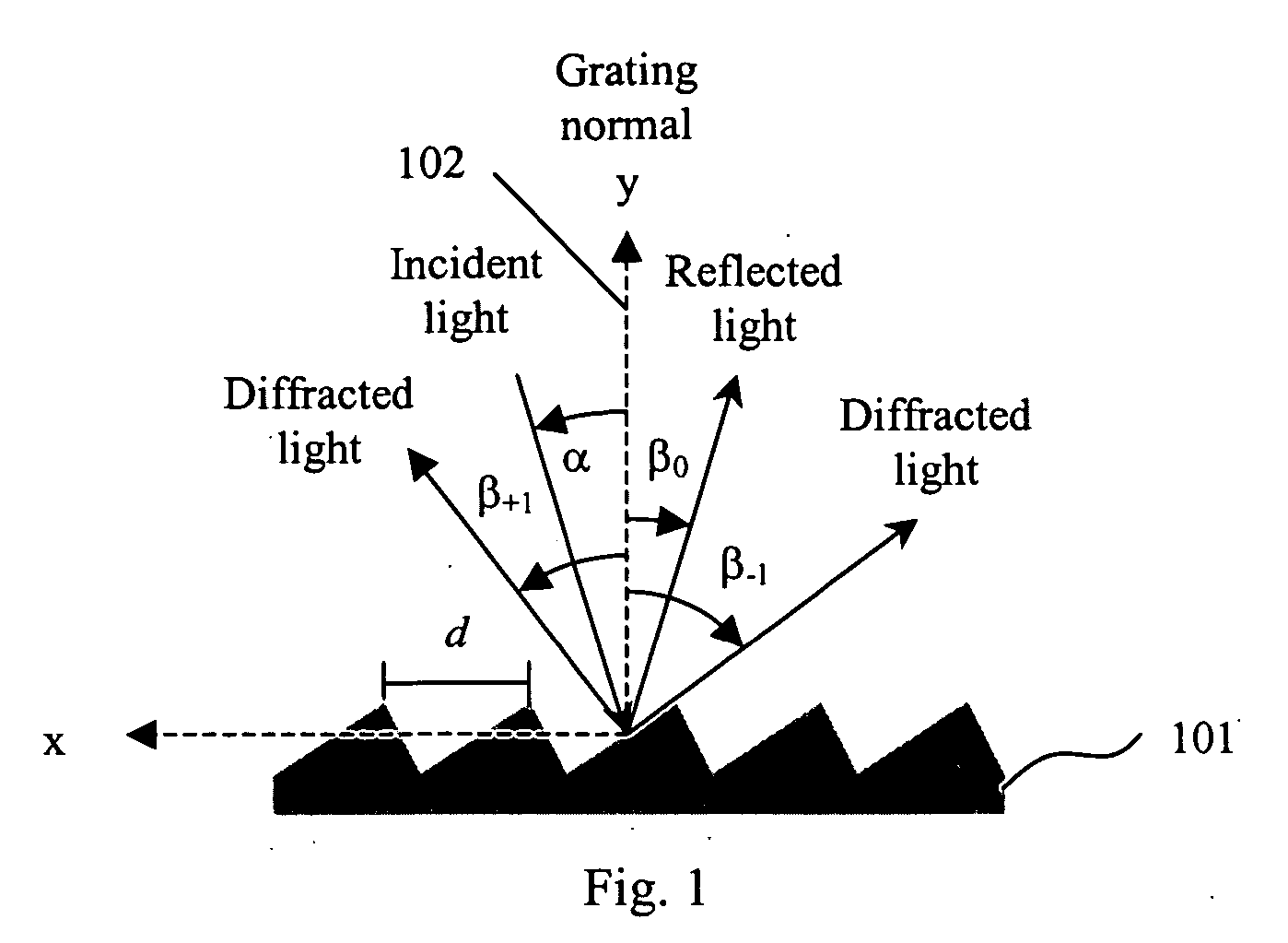
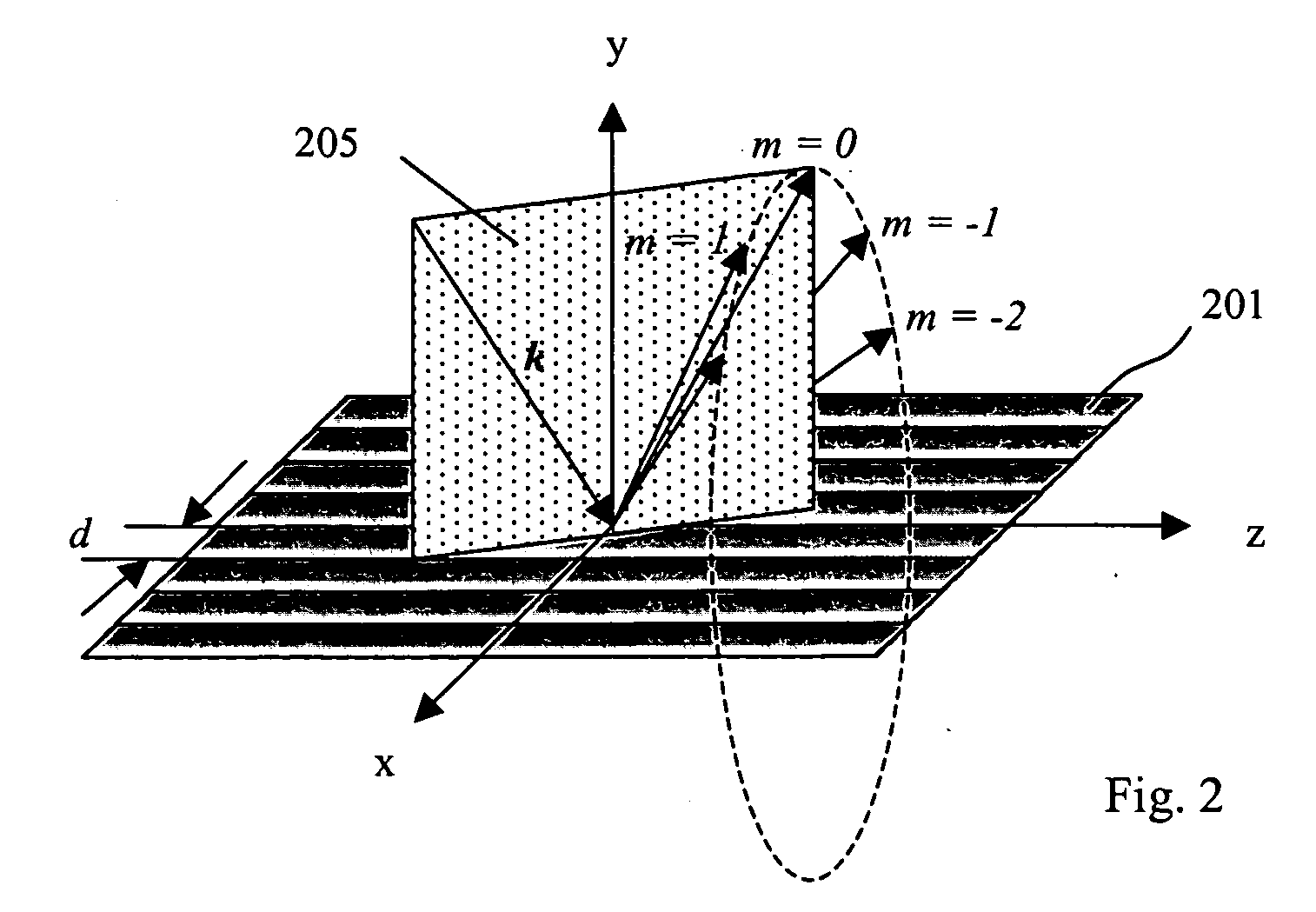
Cross-dispersed spectrometer in a spectral domain optical coherence tomography system
InactiveUS7342659B2Eliminating spatial order overlapReduce non-linearityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationTwo dimensional detectorGrating
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
Fourier domain optical coherence tomography employing a swept multi-wavelength laser and a multi-channel receiver
ActiveUS20070002327A1Low costIncrease in the speed of each axial scanRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySpectral domainLasing wavelength
The present invention is an alternative Fourier domain optical coherence system (FD-OCT) and its associated method. The system comprises a swept multi-wavelength laser, an optical interferometer and a multi-channel receiver. By employing a multi-wavelength laser, the sweeping range for each lasing wavelength is substantially reduced as compared to a pure swept single wavelength laser that needs to cover the same overall spectral range. The overall spectral interferogram is divided over the individual channels of the multi-channel receiver and can be re-constructed through processing of the data from each channel detector. In addition to a substantial increase in the speed of each axial scan, the cost of invented FD-OCT system can also be substantially less than that of a pure swept source OCT or a pure spectral domain OCT system.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
Cross-dispersed spectrometer in a spectral domain optical coherence tomography system
InactiveUS20060164639A1Eliminating spatial order overlapReduce non-linearityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationTwo dimensional detectorGrating
A spectral-domain optical coherence tomography system using a cross-dispersed spectrometer is disclosed. The interfered optical signal is dispersed by a grating into several orders of diffraction, and these orders of diffraction are separated by an additional dispersive optical element. The spectral interferogram is recorded by a set of linear detector arrays, or by a two-dimensional detector array.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
Simple high efficiency optical coherence domain reflectometer design
ActiveUS7126693B2Improve efficiencySimple configurationReflectometers dealing with polarizationInterferometersBeam splitterDetector array
The present invention discloses simple and yet highly efficient configurations of optical coherence domain reflectometry systems. The combined use of a polarizing beam splitter with one or two polarization manipulator(s) that rotate the returned light wave polarization to an orthogonal direction, enables one to achieve high optical power delivery efficiency as well as fixed or predetermined output polarization state of the interfering light waves reaching a detector or detector array, which is especially beneficial for spectral domain optical coherence tomography. In addition, the system can be made insensitive to polarization fading resulting from the birefringence change in the sample and reference arms. Dispersion matching can also be easily achieved between the sample and the reference arm for high resolution longitudinal scanning.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
Enhanced optical coherence tomography for anatomical mapping
ActiveUS20060119858A1Enhanced anatomical mappingReduction in total information contentEye diagnosticsUsing optical meansData setSpectral domain
A system, method and apparatus for anatomical mapping utilizing optical coherence tomography. In the present invention, 3-dimensional fundus intensity imagery can be acquired from a scanning of light back-reflected from an eye. The scanning can include spectral domain scanning, as an example. A fundus intensity image can be acquired in real-time. The 3-dimensional data set can be reduced to generate an anatomical mapping, such as an edema mapping and a thickness mapping. Optionally, a partial fundus intensity image can be produced from the scanning of the eye to generate an en face view of the retinal structure of the eye without first requiring a full segmentation of the 3-D data set. Advantageously, the system, method and apparatus of the present invention can provide quantitative three-dimensional information about the spatial location and extent of macular edema and other pathologies. This three-dimensional information can be used to determine the need for treatment, monitor the effectiveness of treatment and identify the return of fluid that may signal the need for re-treatment.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
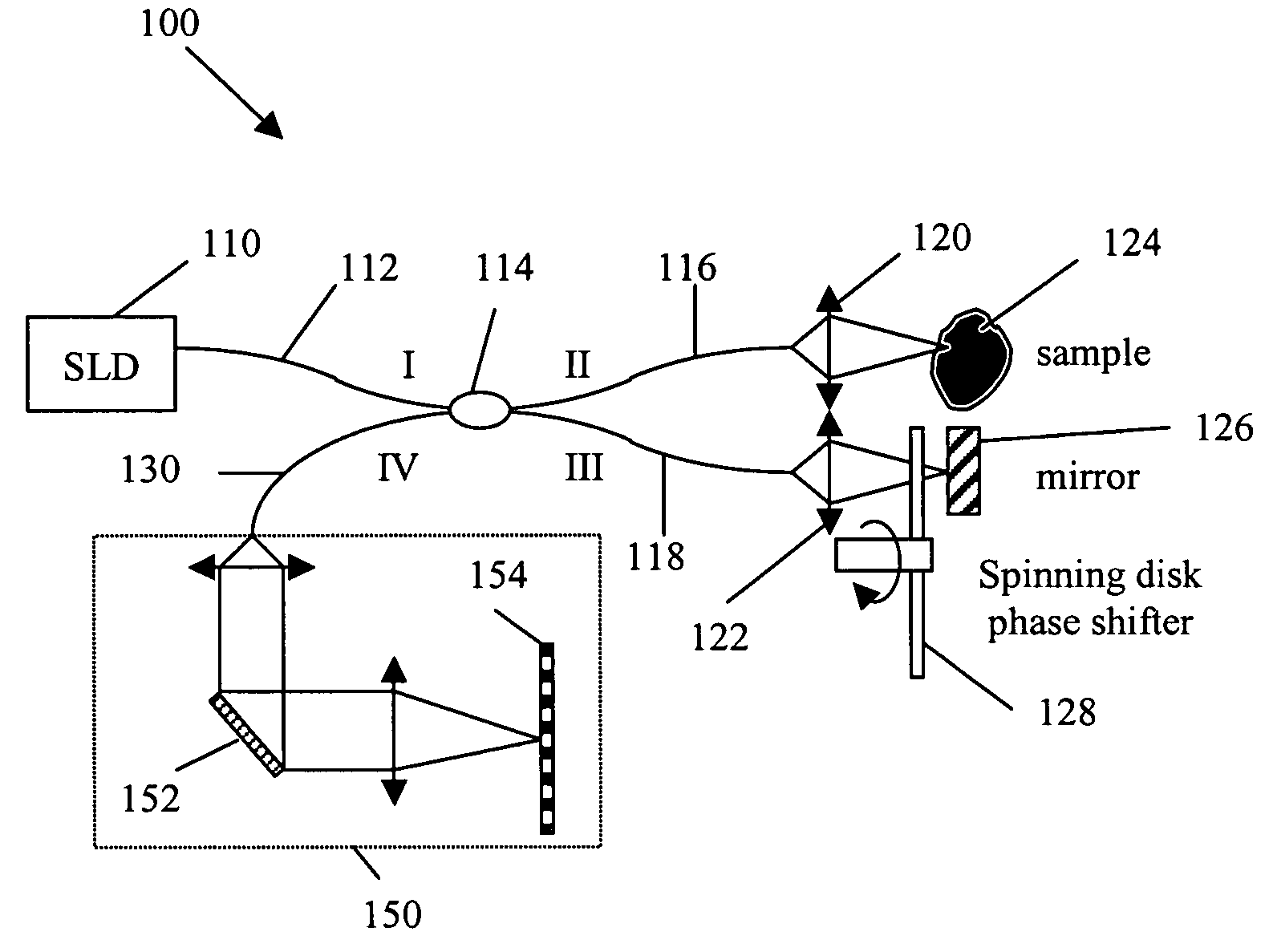
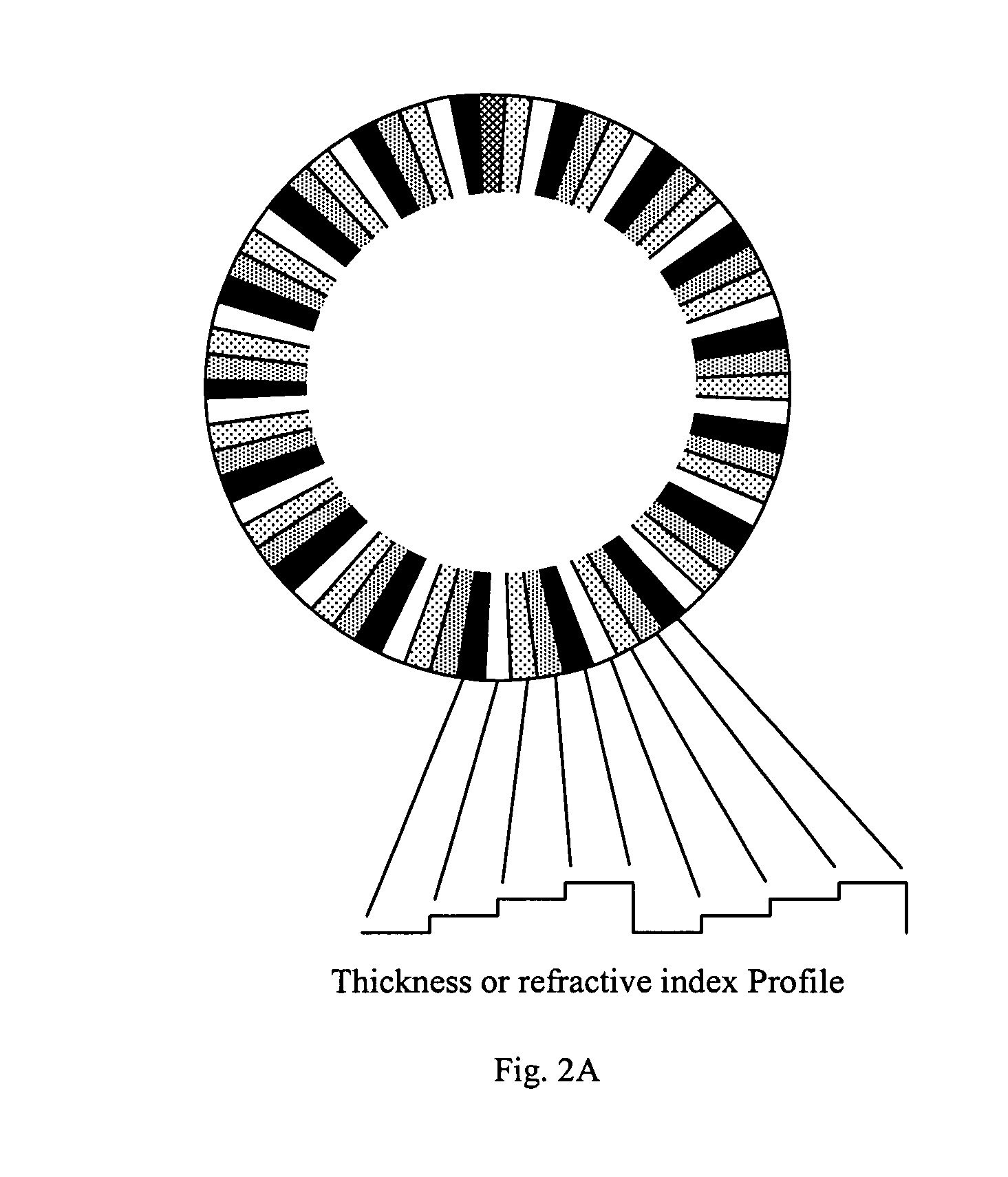
Patterned spinning disk based optical phase shifter for spectral domain optical coherence tomography
InactiveUS7433046B2Low costSolve the slow scanning speedInterferometersEye diagnosticsPhase shiftedPhase retardation
A low cost patterned spinning disk is disclosed for achieving relatively rapid discrete optical phase shifts for an optical beam. The invention is particularly useful in a spectral domain optical coherence tomography system. The disk contains stepped patterns of different heights and / or refractive index distribution such that as it spins, an optical beam passing through or being reflected by the disk will experience different discrete optical phase delays. The disk can be operated as a phase shifter or it can be operated in synchronization with an intensity modulating chopper disk or a direct intensity modulation of the light source. The disk can also contain intensity modulating patterns such that both phase shifting and intensity modulation can be achieved at the same time. Various possible methods are also disclosed for the fabrication of the disk.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
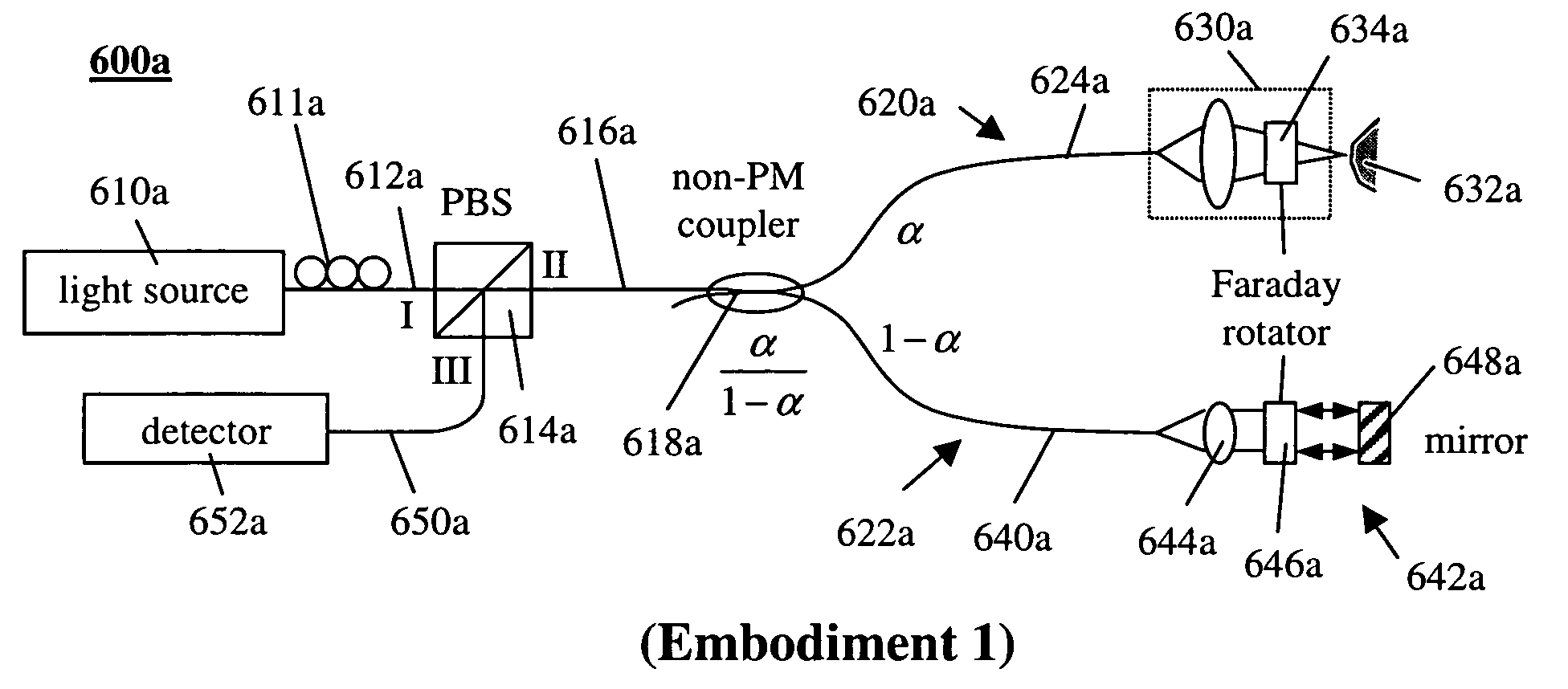
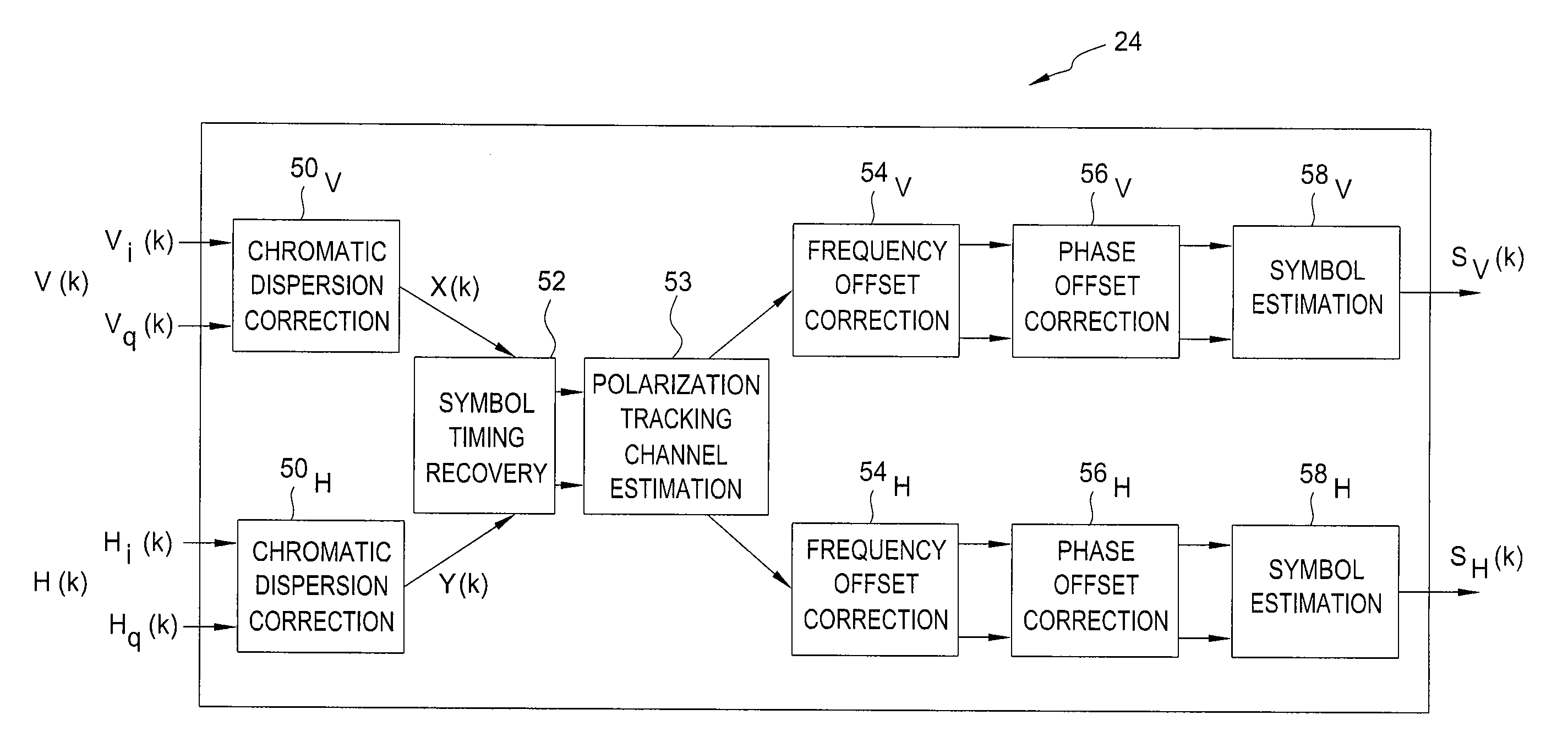
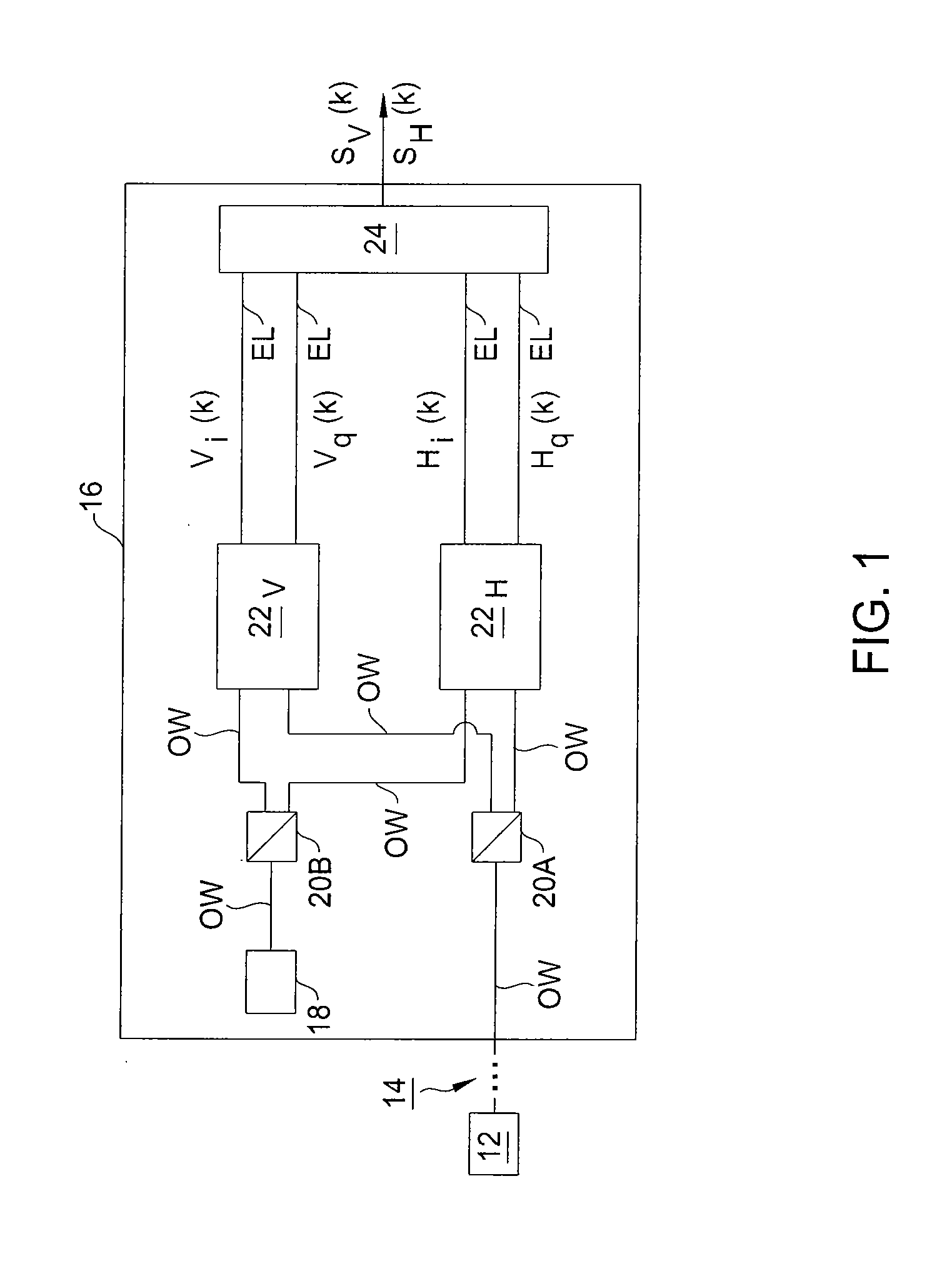
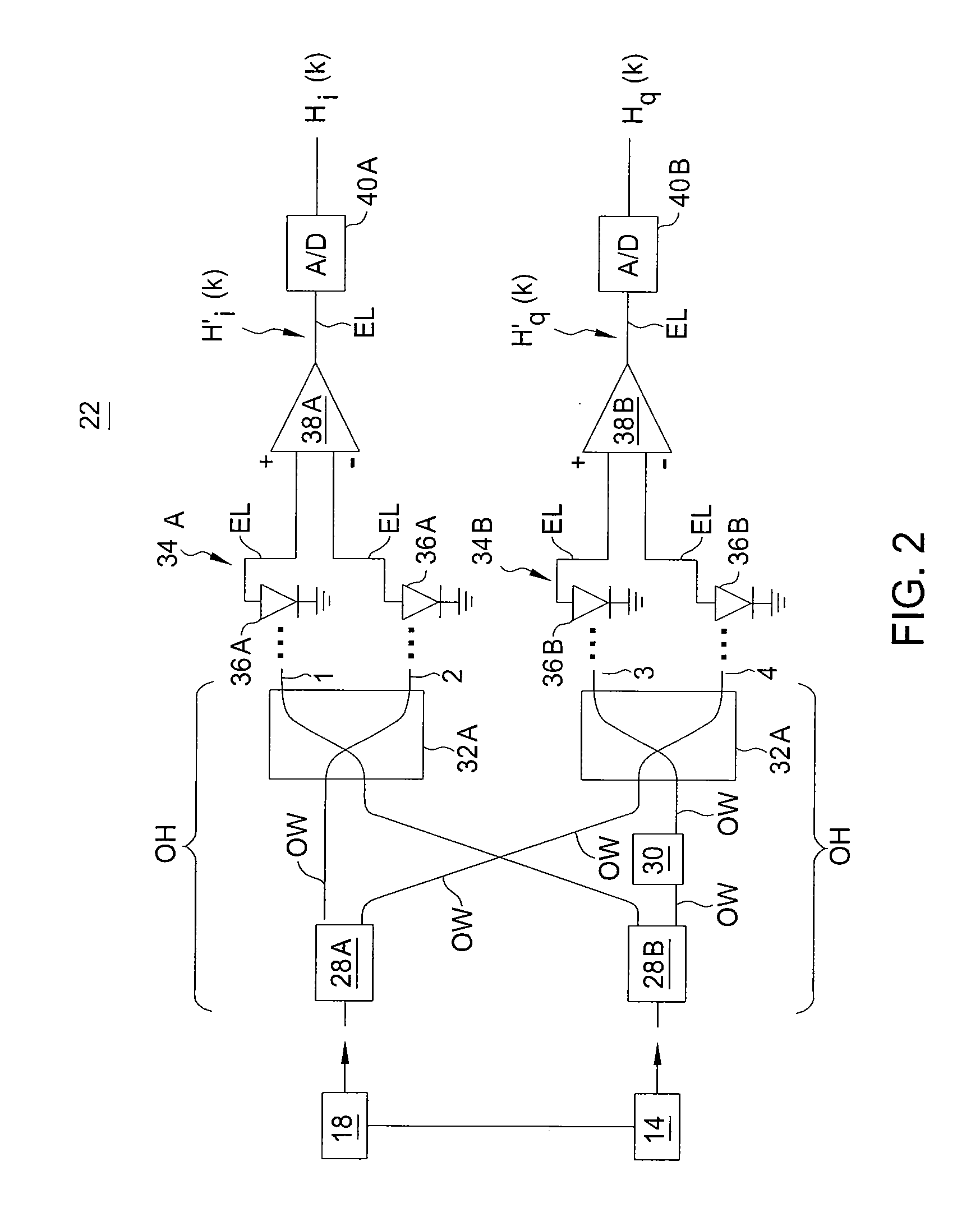
Symbol Timing Recovery in Polarization Division Multiplexed Coherent Optical Transmission System
ActiveUS20100329677A1Polarisation multiplex systemsElectromagnetic receiversDigital signal processingMultiplexing
A method, apparatus and system for providing clock and data recovery in a receiver for receiving a high speed coherent polarization division multiplexed optical signal using a digital signal processing block including a spectral domain spatial combiner are provided.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
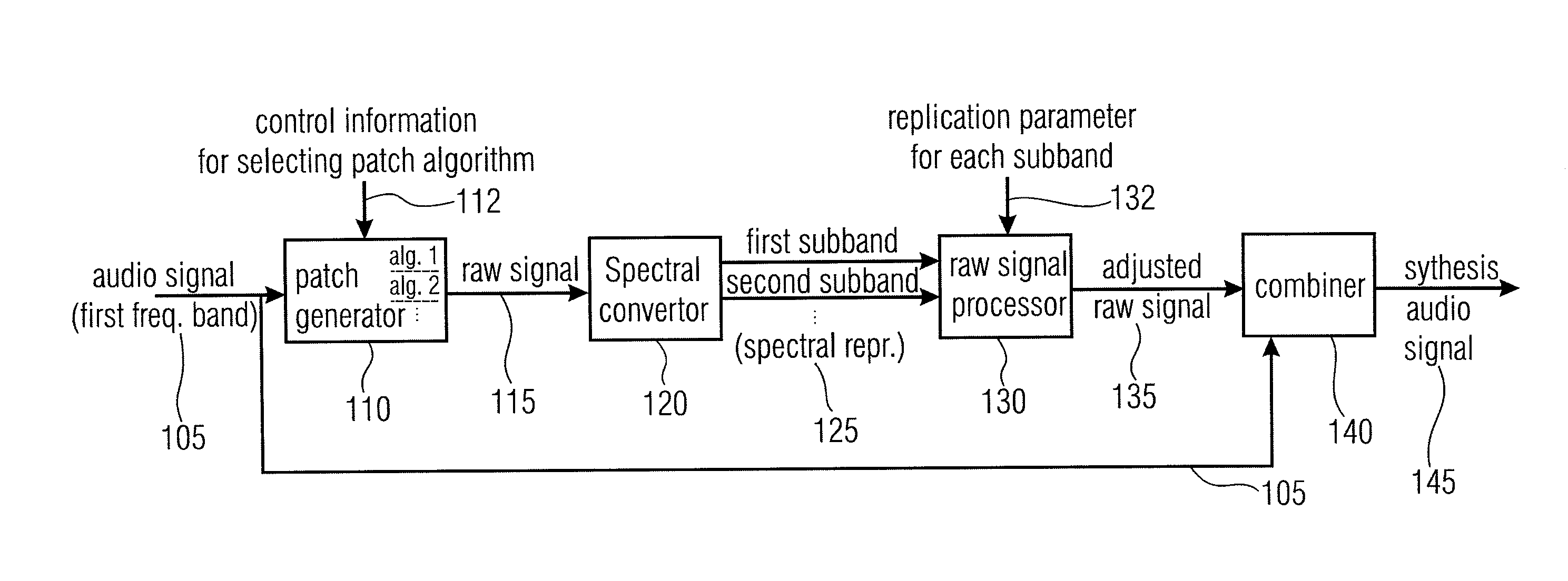
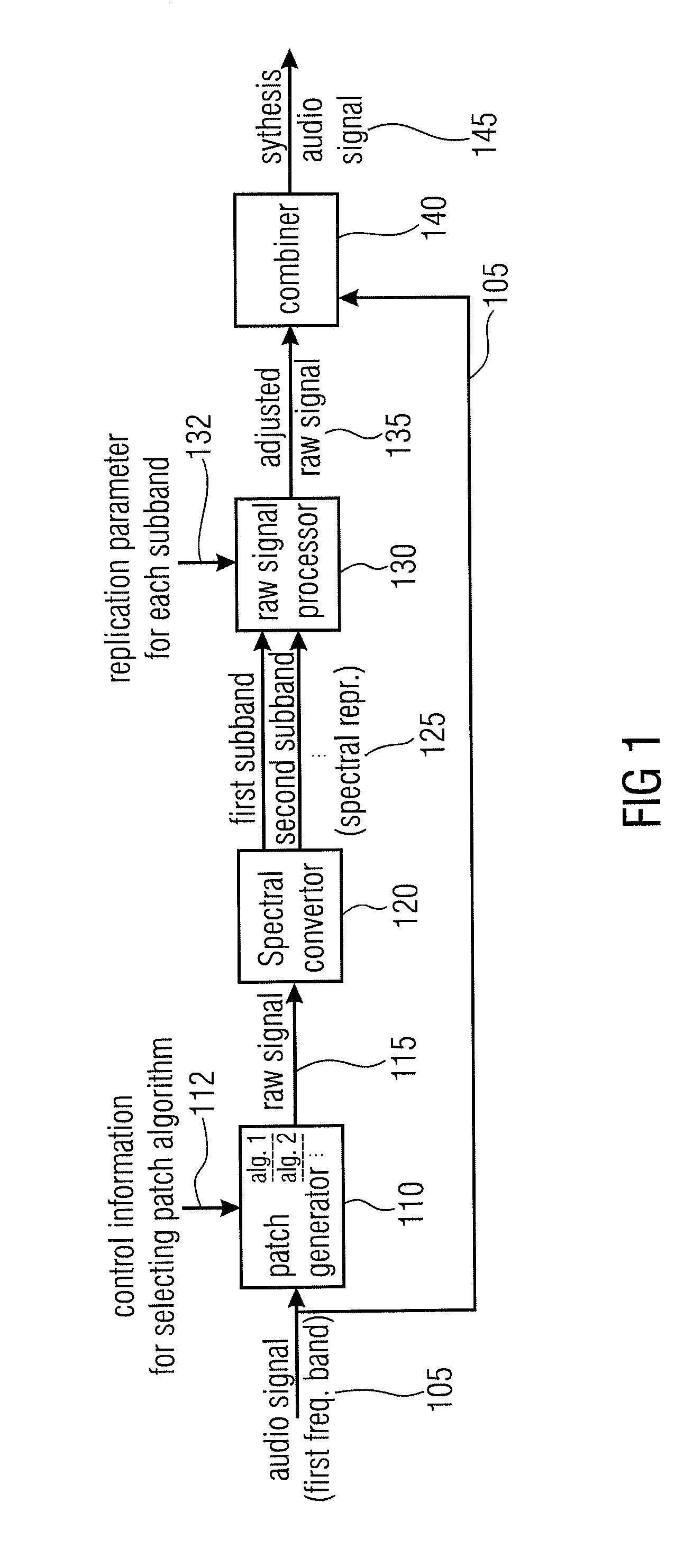
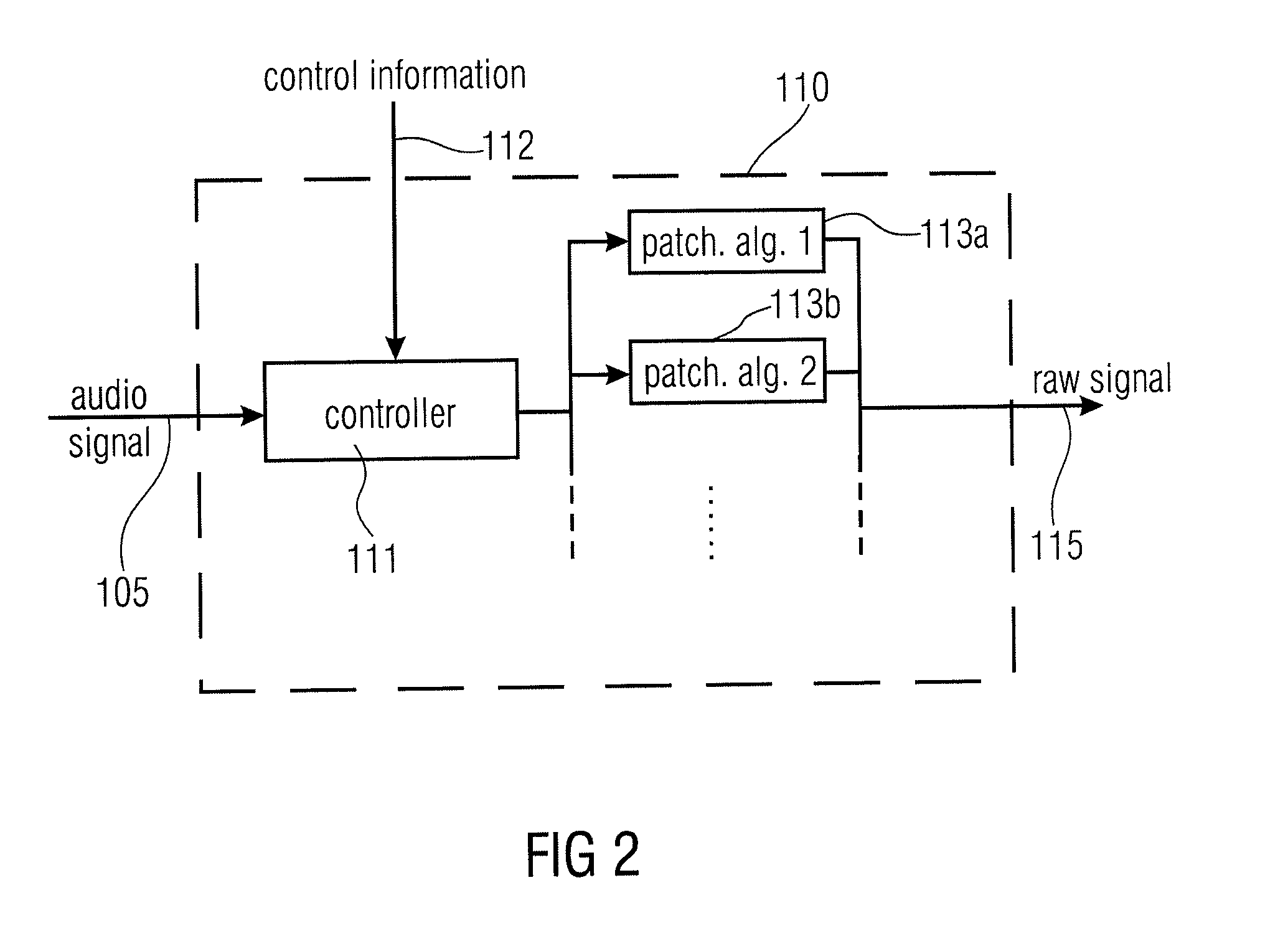
Audio Signal Synthesizer and Audio Signal Encoder
ActiveUS20110173006A1Quality improvementAvoid artifactsSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumSpectral domain
An audio signal synthesizer generates a synthesis audio signal having a first frequency band and a second synthesized frequency band derived from the first frequency band and comprises a patch generator, a spectral converter, a raw signal processor and a combiner. The patch generator performs at least two different patching algorithms, each patching algorithm generating a raw signal. The patch generator is adapted to select one of the at least two different patching algorithms in response to a control information. The spectral converter converts the raw signal into a raw signal spectral representation. The raw signal processor processes the raw signal spectral representation in response to spectral domain spectral band replication parameters to obtain an adjusted raw signal spectral representation.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
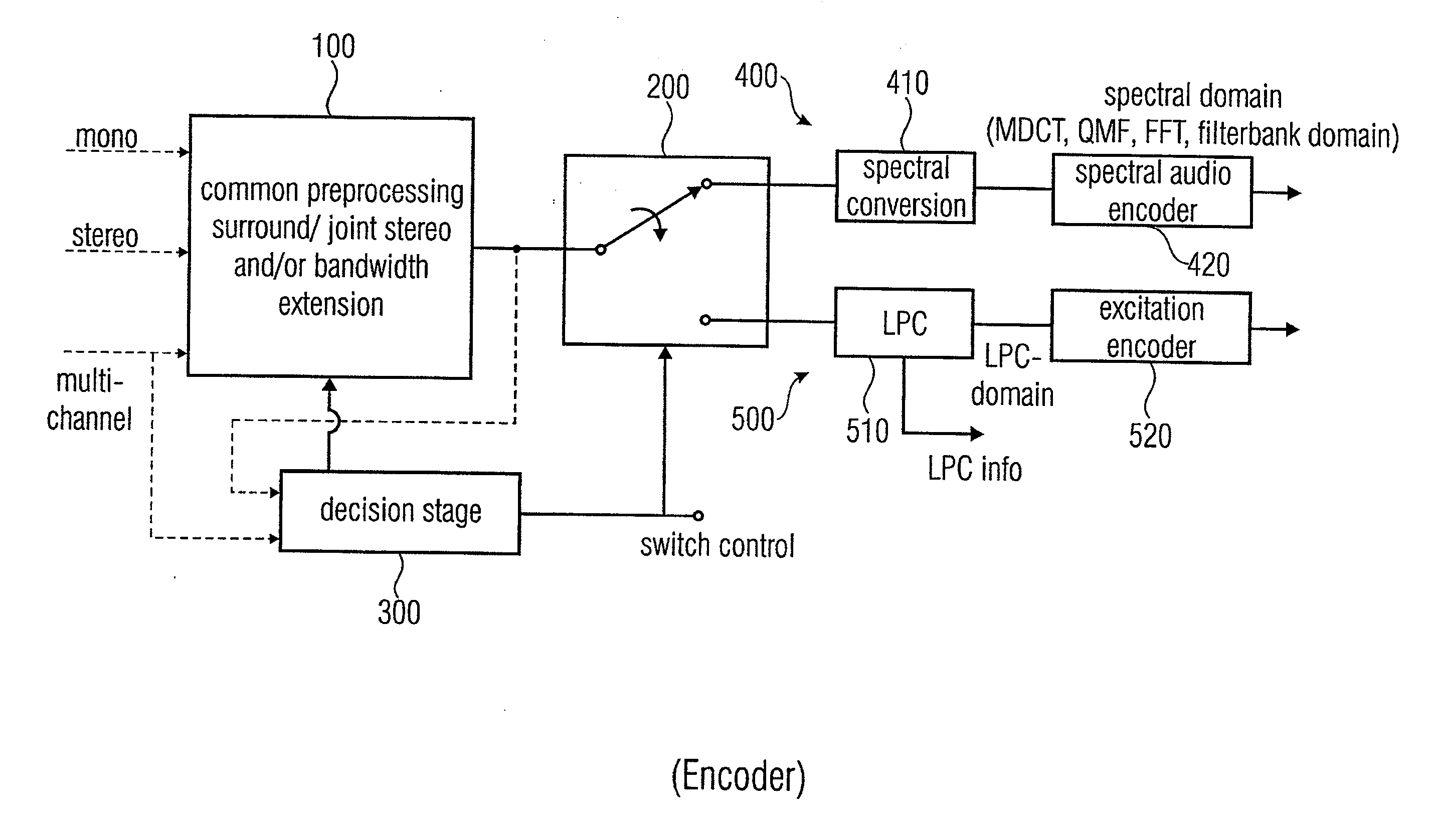
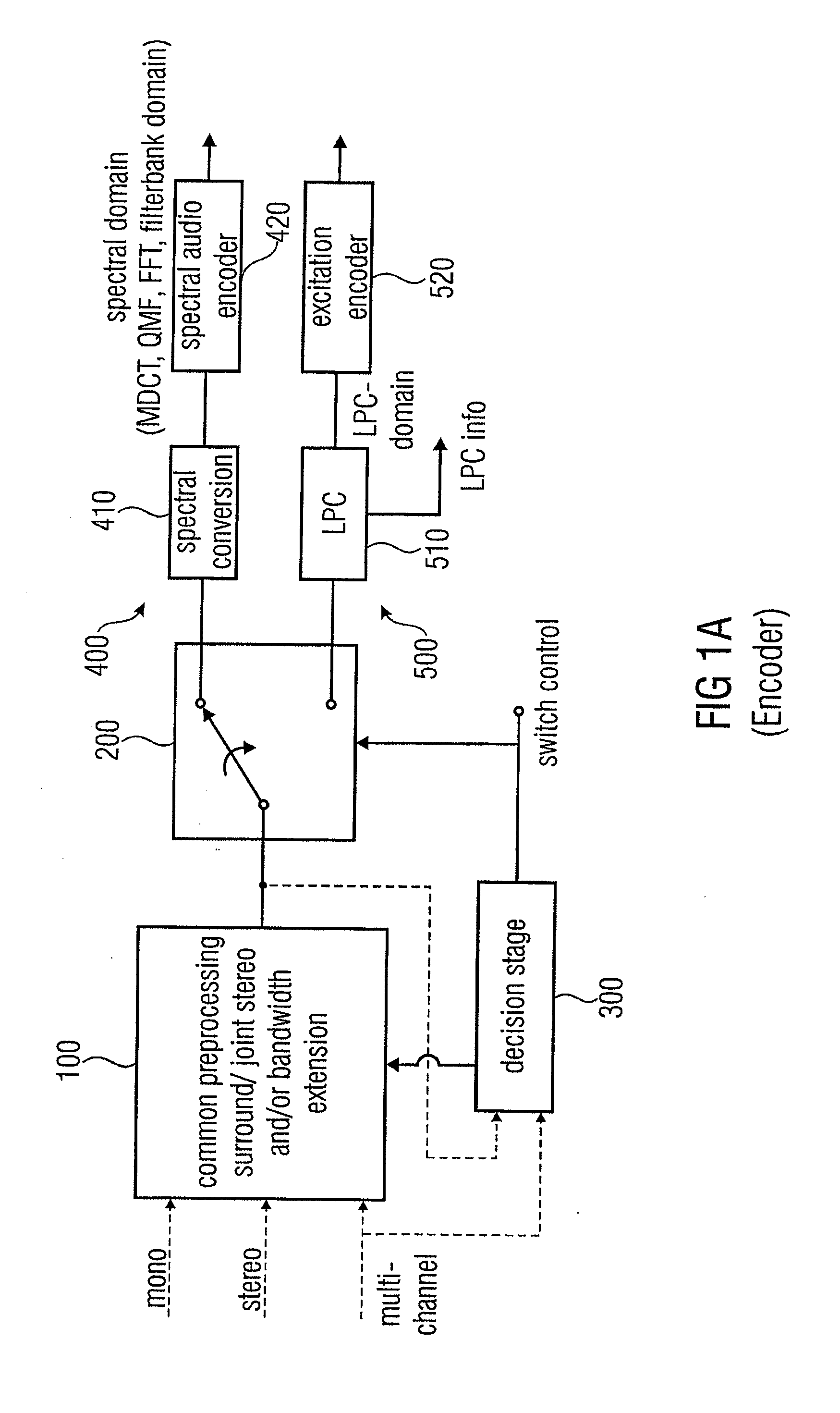
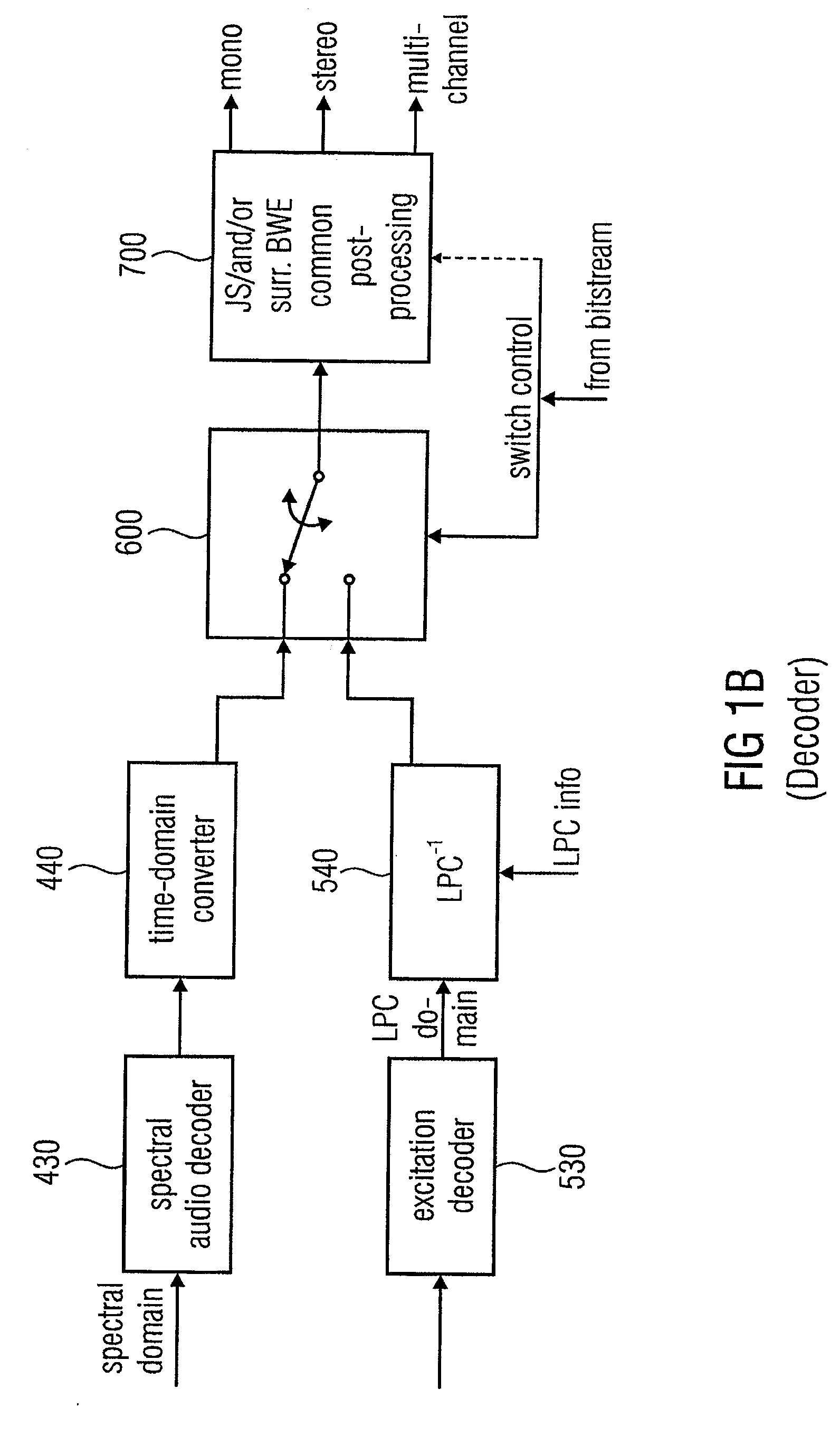
Low Bitrate Audio Encoding/Decoding Scheme with Common Preprocessing
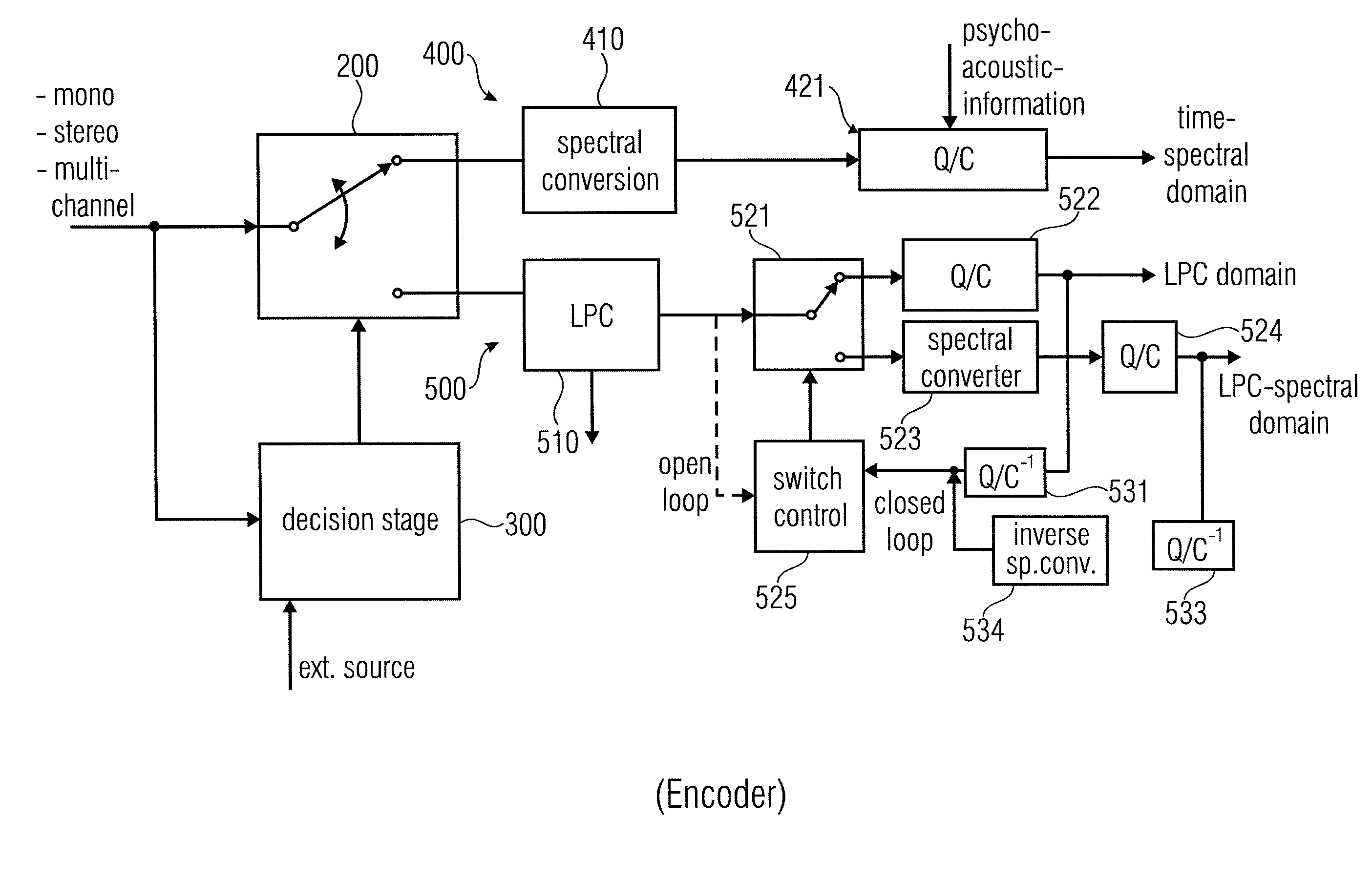
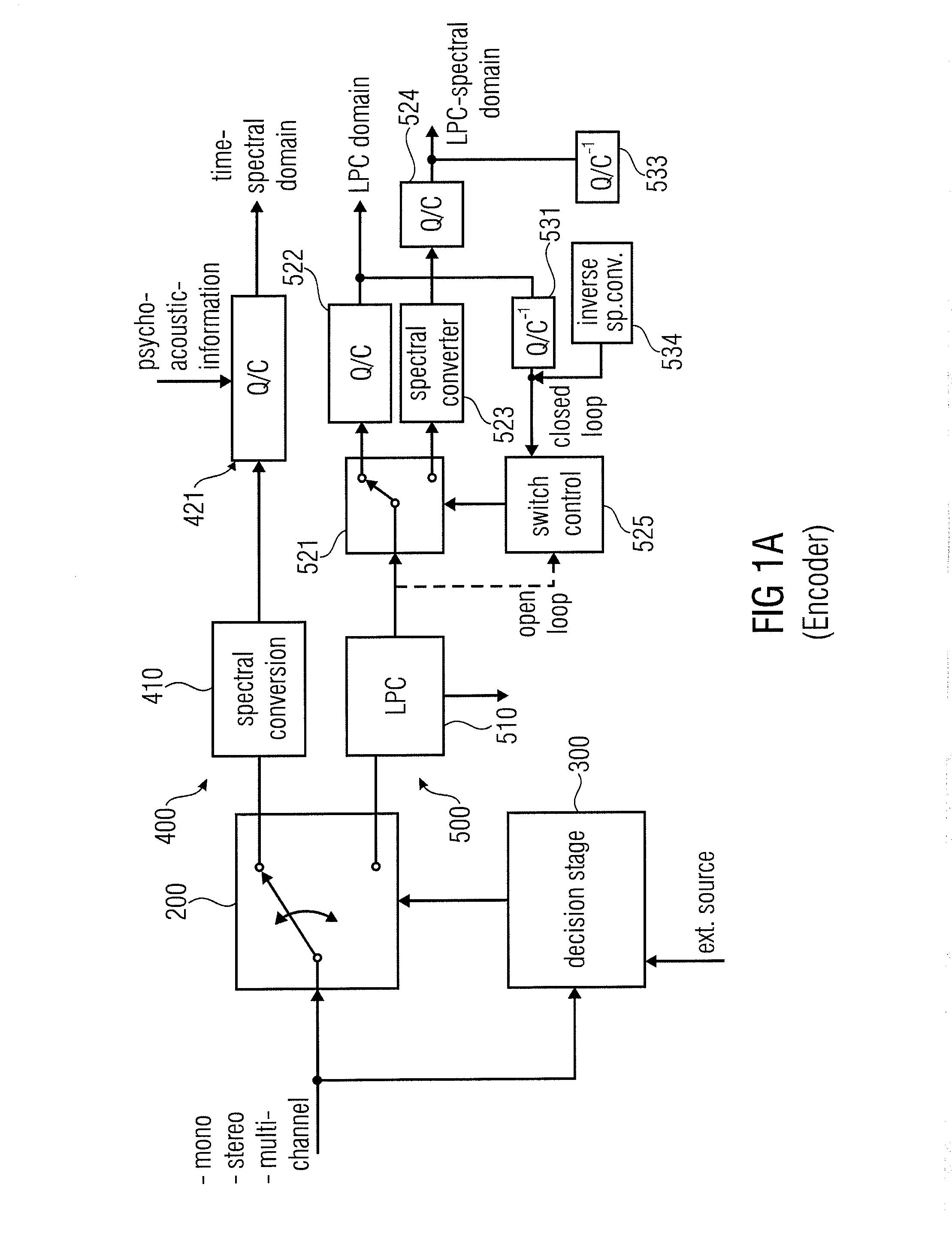
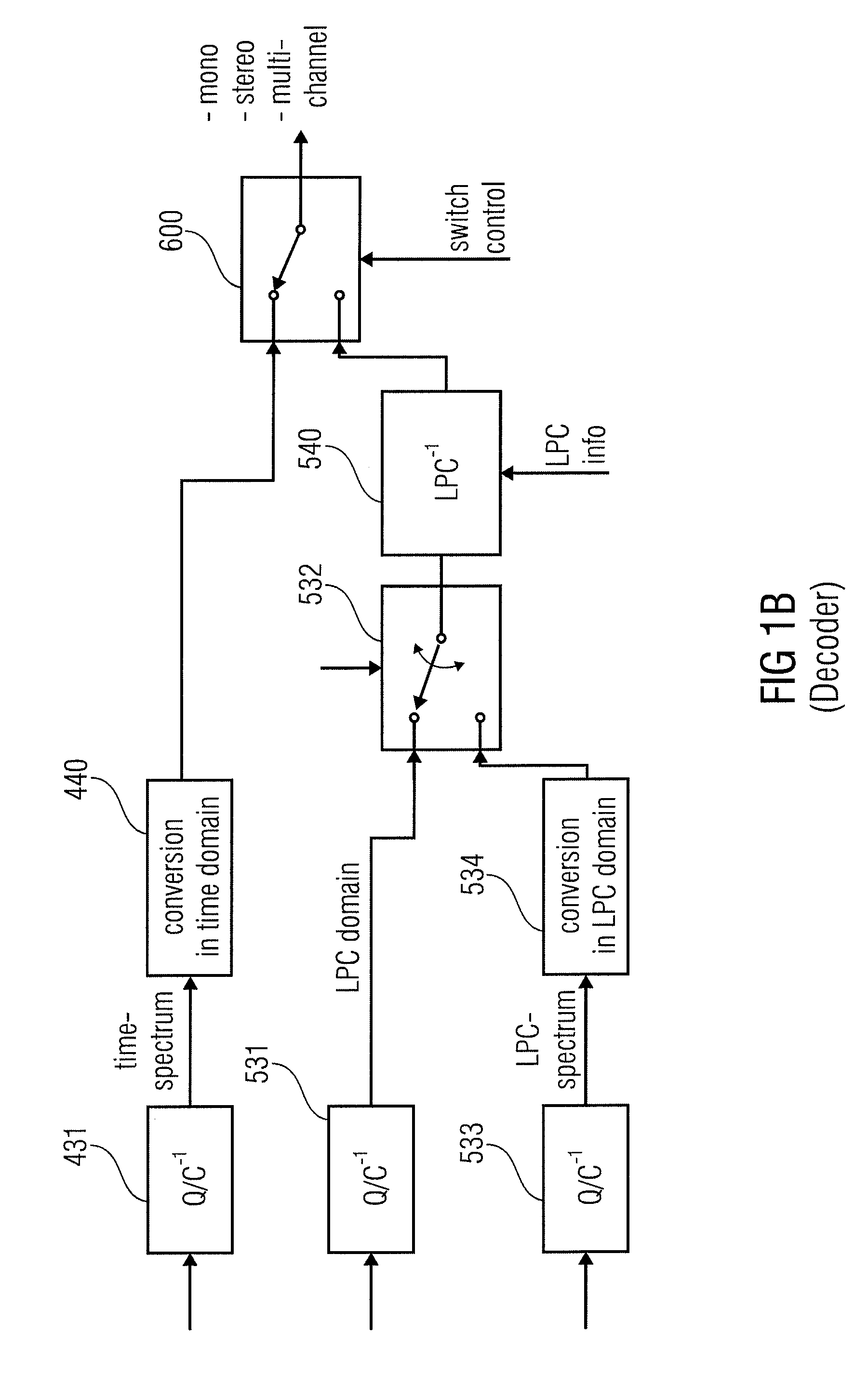
ActiveUS20110200198A1Save amountSave of area consumptionSpeech analysisStereophonic arrangmentsTime domainFrequency spectrum
An audio encoder has a common preprocessing stage, an information sink based encoding branch such as spectral domain encoding branch, a information source based encoding branch such as an LPC-domain encoding branch and a switch for switching between these branches at inputs into these branches or outputs of these branches controlled by a decision stage. An audio decoder has a spectral domain decoding branch, an LPC-domain decoding branch, one or more switches for switching between the branches and a common post-processing stage for post-processing a time-domain audio signal for obtaining a post-processed audio signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Low Bitrate Audio Encoding/Decoding Scheme Having Cascaded Switches
An audio encoder has a first information sink oriented encoding branch such as a spectral domain encoding branch, a second information source or SNR oriented encoding branch such as an LPC-domain encoding branch, and a switch for switching between the first encoding branch and the second encoding branch, wherein the second encoding branch has a converter into a specific domain different from the spectral domain such as an LPC analysis stage generating an excitation signal, and wherein the second encoding branch furthermore has a specific domain coding branch such as LPC domain processing branch, and a specific spectral domain coding branch such as LPC spectral domain processing branch, and an additional switch for switching between the specific domain coding branch and the specific spectral domain coding branch. An audio decoder has a first domain decoder such as a spectral domain decoding branch, a second domain decoder such as an LPC domain decoding branch for decoding a signal such as an excitation signal in the second domain, and a third domain decoder such as an LPC-spectral decoder branch and two cascaded switches for switching between the decoders.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
Method for depth resolved wavefront sensing, depth resolved wavefront sensors and method and apparatus for optical imaging
ActiveUS20110134436A1Less sensitive to reflectionAll optics layout more compactInterferometersUsing optical meansWavefront sensorConfocal
Methods and devices are disclosed for acquiring depth resolved aberration information using principles of low coherence interferometry and perform coherence gated wavefront sensing (CG-WFS). The wavefront aberrations is collected using spectral domain low coherence interferometry (SD-LCI) or time domain low coherence interferometry (TD-LCI) principles. When using SD-LCI, chromatic aberrations can also be evaluated. Methods and devices are disclosed in using a wavefront corrector to compensate for the aberration information provided by CG-WFS, in a combined imaging system, that can use one or more channels from the class of (i) optical coherence tomography (OCT), (ii) scanning laser ophthalmoscopy, (iii) microscopy, such as confocal or phase microscopy, (iv) multiphoton microscopy, such as harmonic generation and multiphoton absorption. In particular, a swept source (SS) is used that drives both an OCT channel and a coherence gated wavefront sensor, where:a) both channels operate according to SS-OCT principles;b) OCT channel integrates over at least one tuning scan of the swept source to provide a TD-OCT image of the object;c) CG-WFS integrates over at least one tuning scan of the swept source to provide an en-face TD-OCT mapping of the wavefront.For some implementations, simultaneous and dynamic aberration measurements / correction with the imaging process is achieved. The methods and devices for depth resolved aberrations disclosed, will find applications in wavefront sensing and adaptive optics imaging systems that are more tolerant to stray reflections from optical interfaces, such as reflections from the microscope objectives and cover slip in microscopy and when imaging the eye, the reflection from the cornea.
Owner:PODOLEANU ADRIAN +1
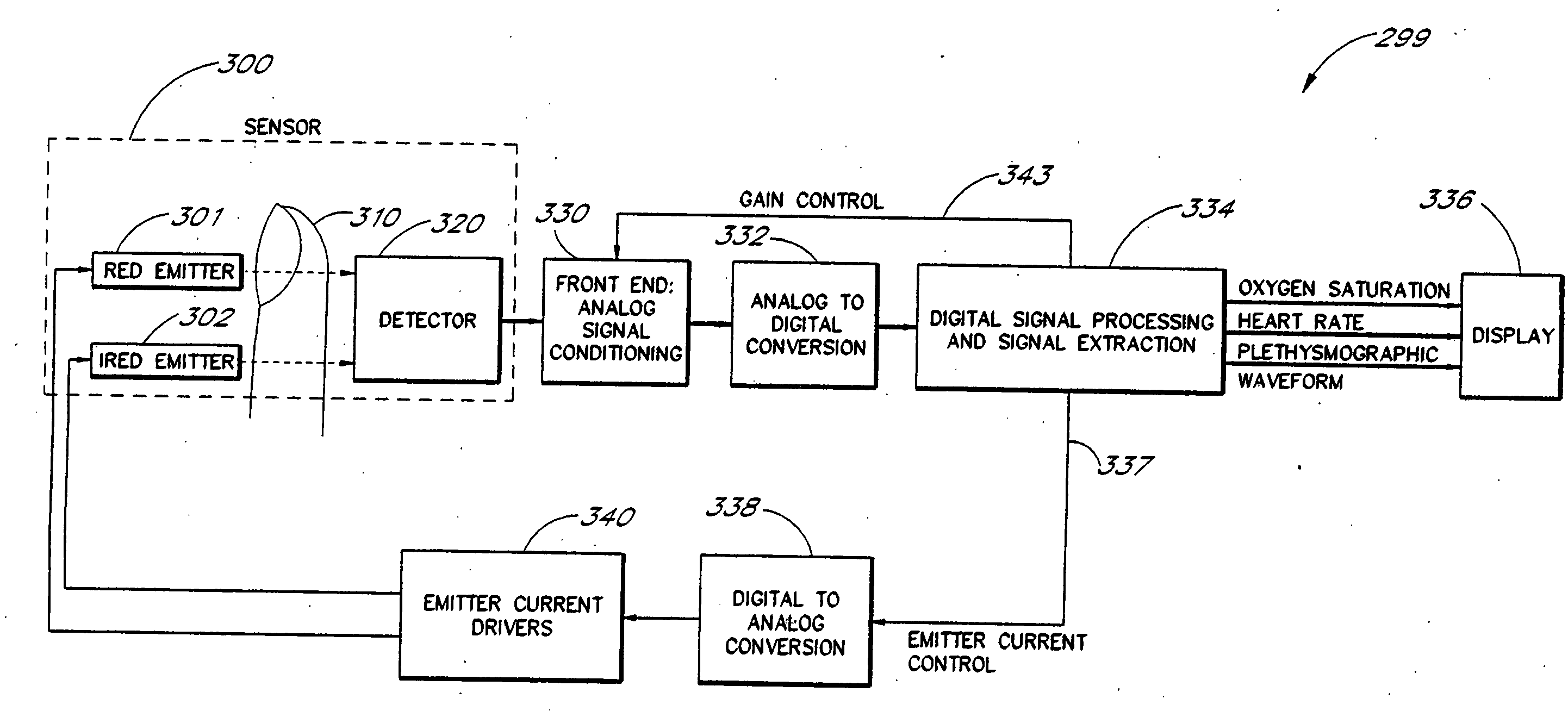
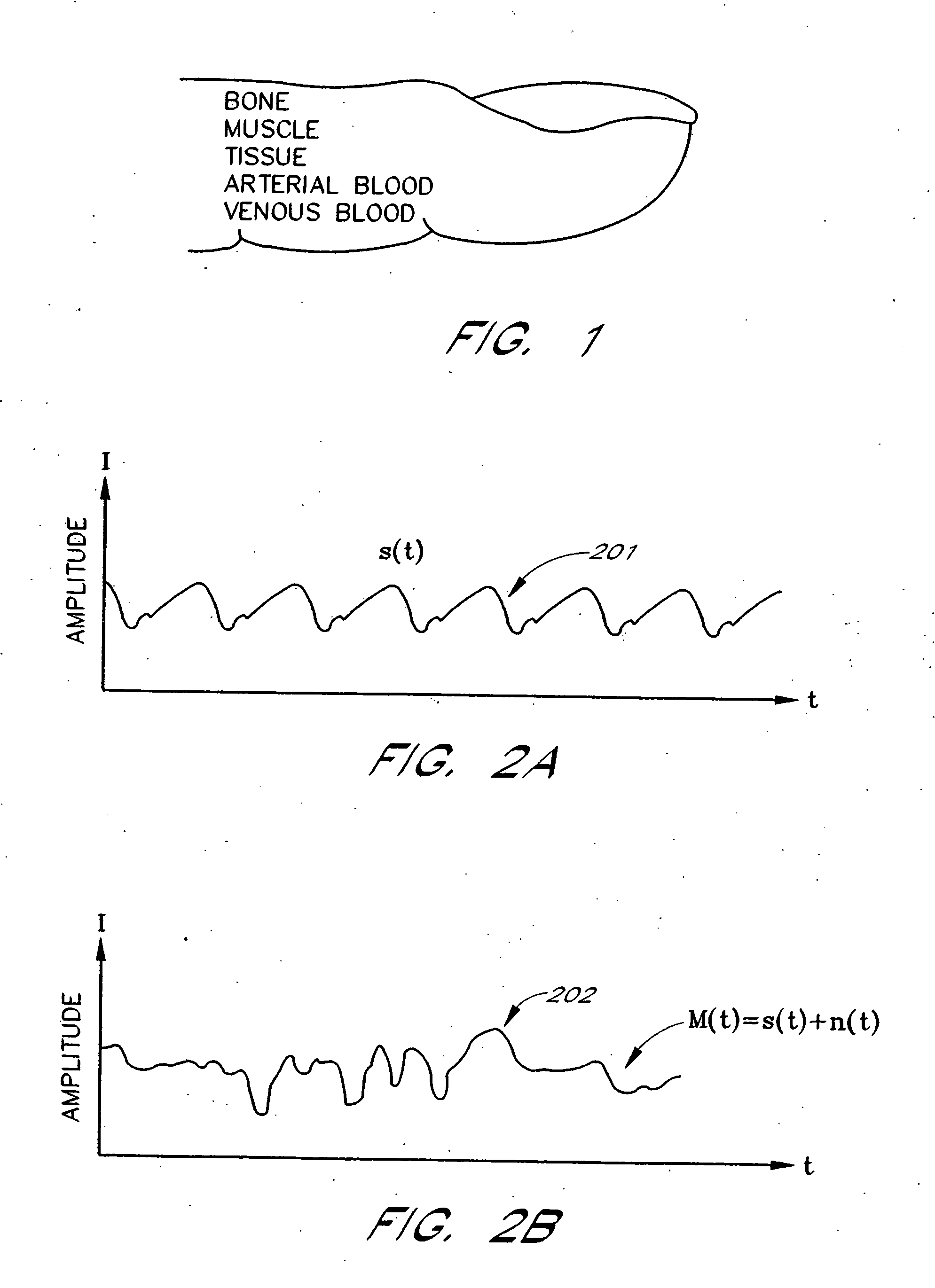
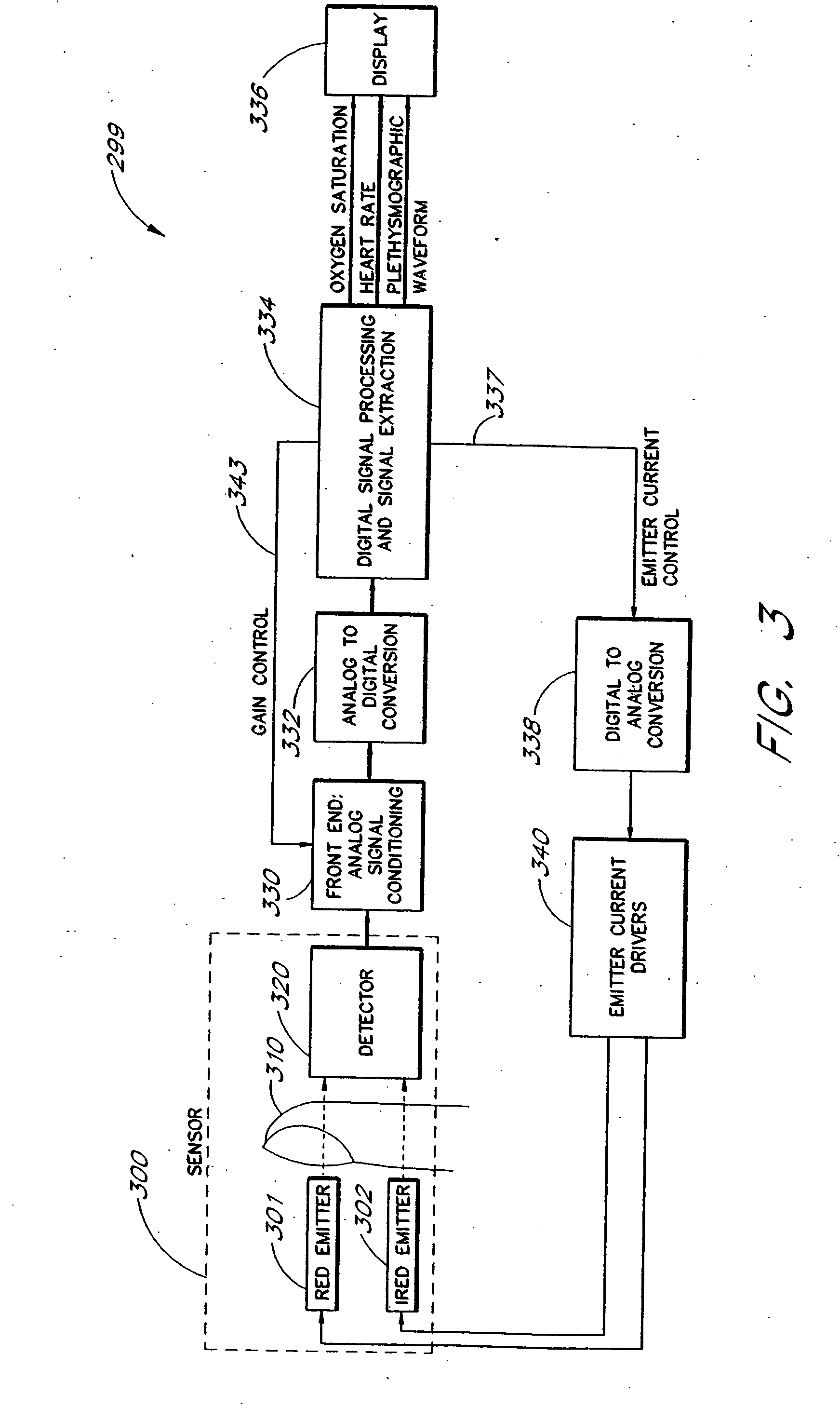
Signal processing apparatus and method
A method and an apparatus to analyze two measured signals that are modeled as containing desired and undesired portions such as noise, FM and AM modulation. Coefficients relate the two signals according to a model defined in accordance with the present invention. In one embodiment, a transformation is used to evaluate a ratio of the two measured signals in order to find appropriate coefficients. The measured signals are then fed into a signal scrubber which uses the coefficients to remove the unwanted portions. The signal scrubbing is performed in either the time domain or in the frequency domain. The method and apparatus are particularly advantageous to blood oximetry and pulserate measurements. In another embodiment, an estimate of the pulserate is obtained by applying a set of rules to a spectral transform of the scrubbed signal. In another embodiment, an estimate of the pulserate is obtained by transforming the scrubbed signal from a first spectral domain into a second spectral domain. The pulserate is found by identifying the largest spectral peak in the second spectral domain.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
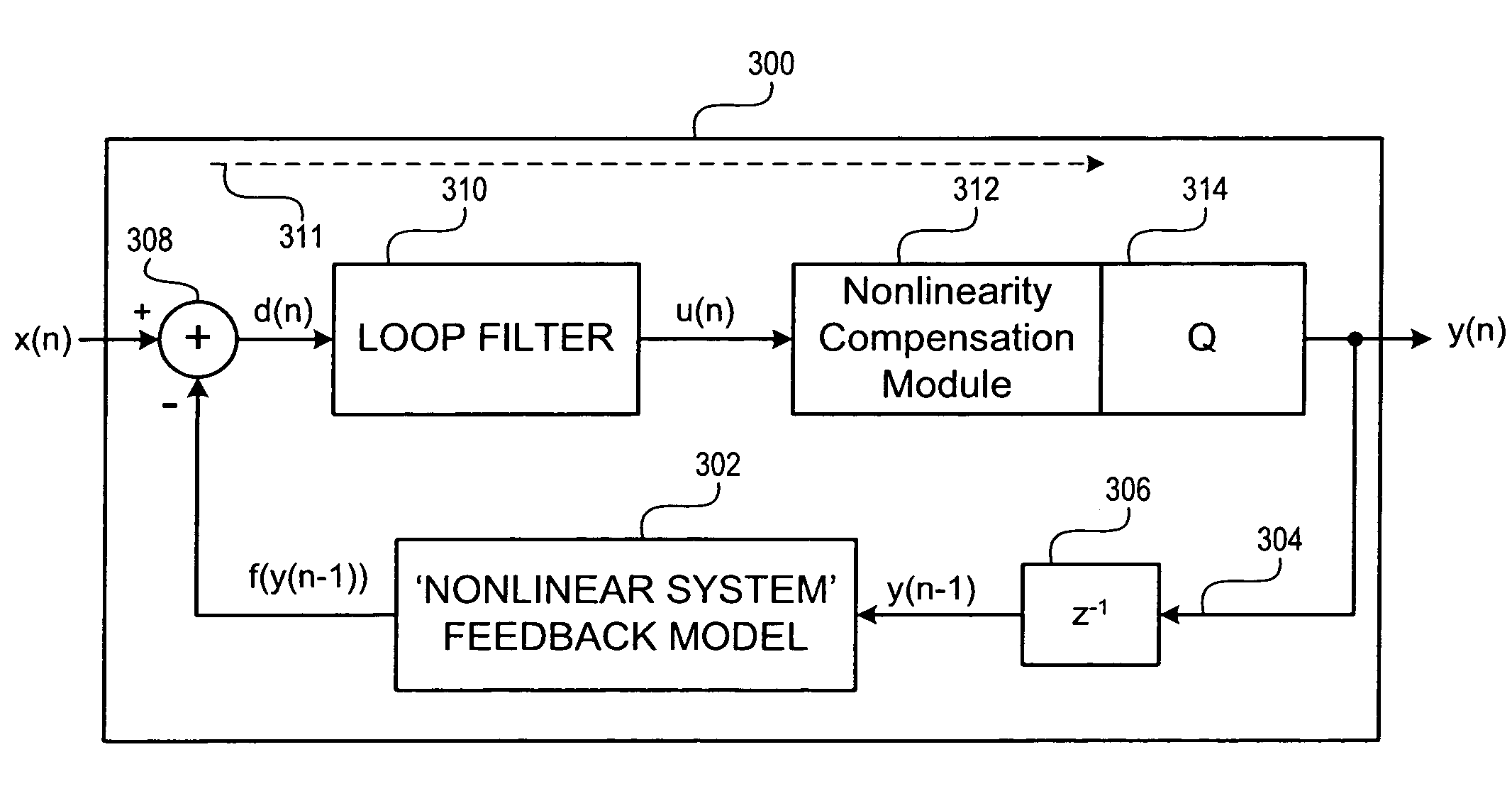
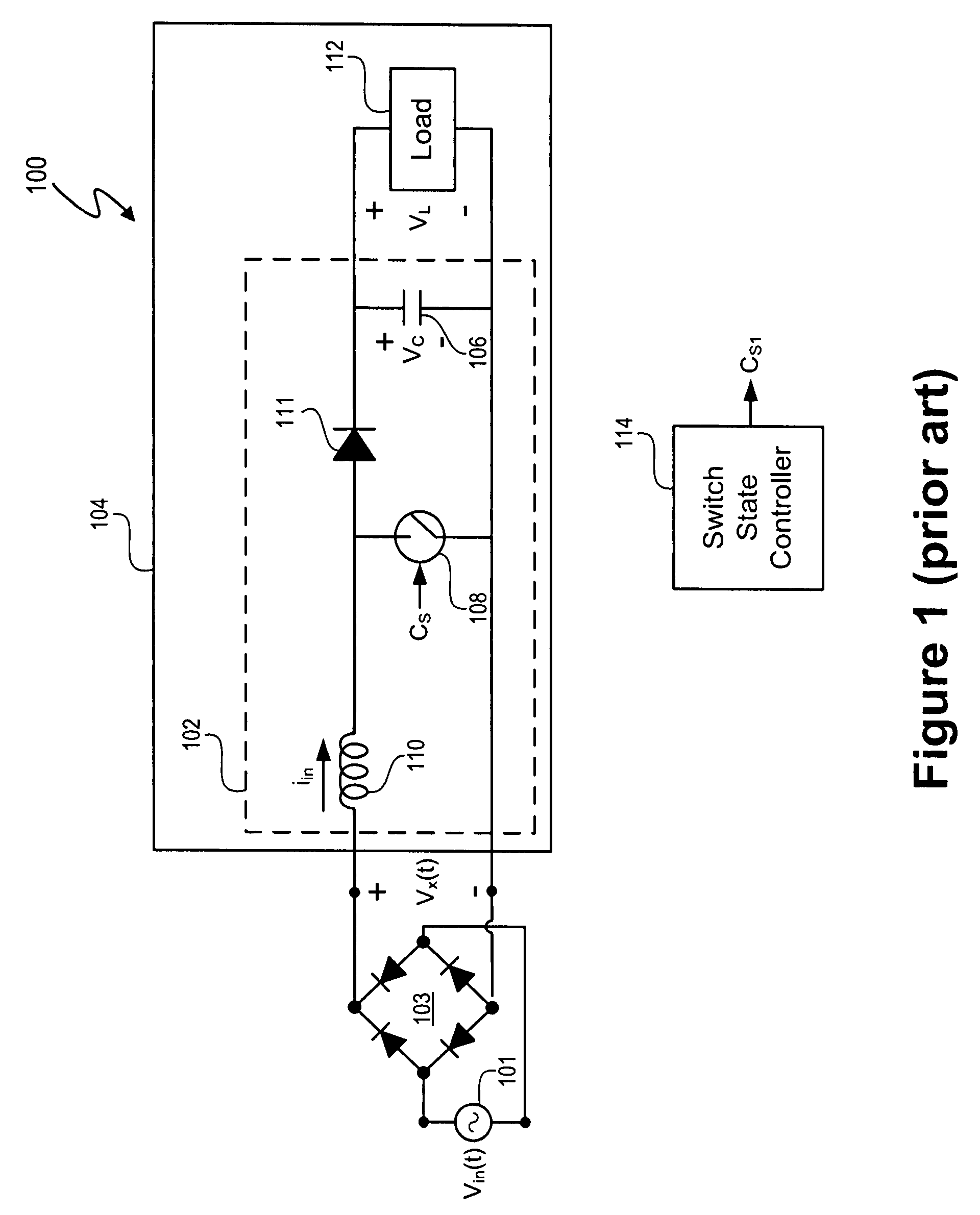
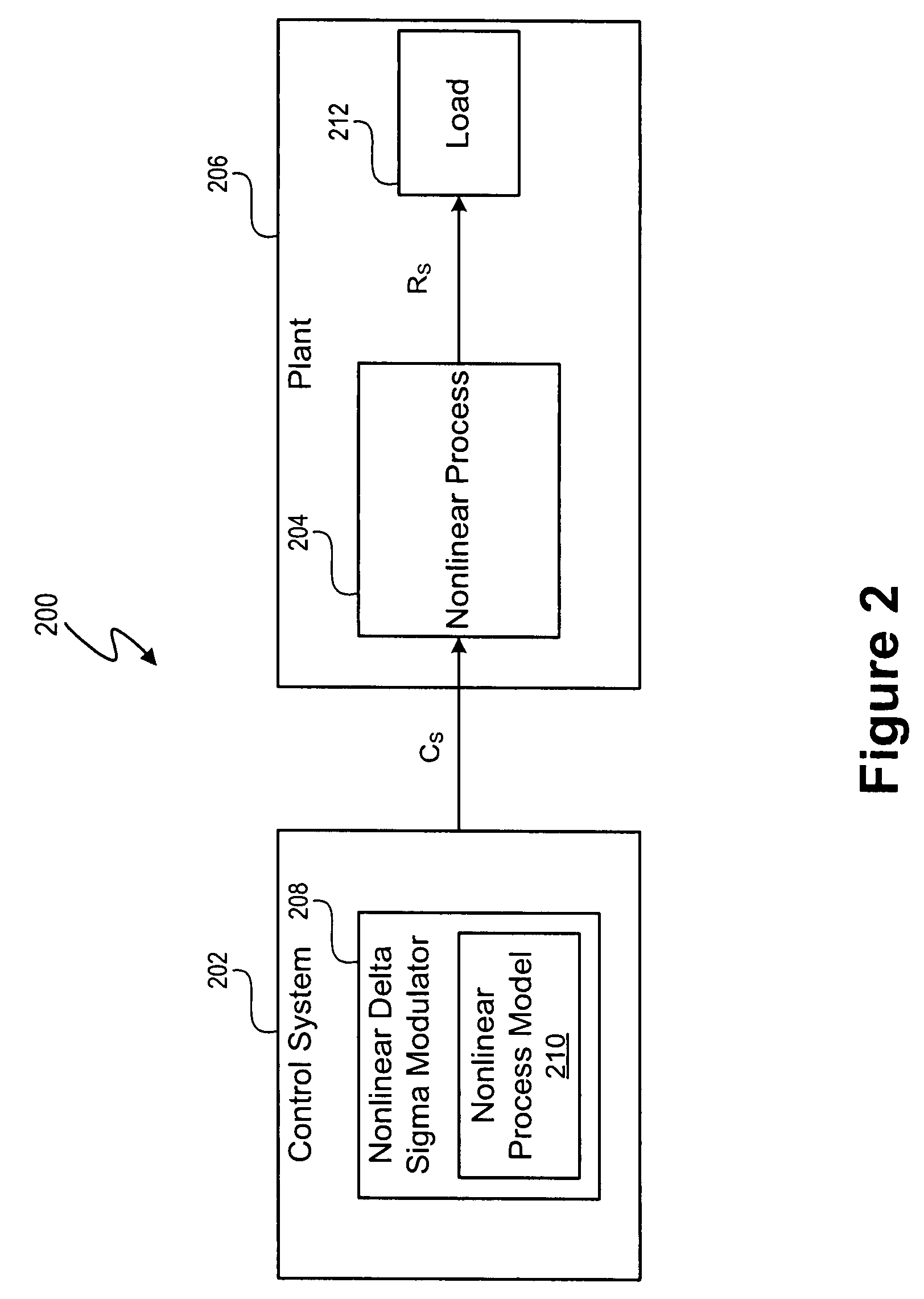
Control system using a nonlinear delta-sigma modulator with nonlinear process modeling
ActiveUS7554473B2Electric signal transmission systemsEfficient power electronics conversionNonlinear resistorFrequency spectrum
A control system includes a nonlinear delta-sigma modulator, and the nonlinear delta-sigma modulator includes a nonlinear process model that models a nonlinear process in a signal processing system, such as a nonlinear plant. The nonlinear delta-sigma modulator includes a feedback model that models the nonlinear process being controlled and facilitates spectral shaping to shift noise out of a baseband in a spectral domain of a response signal of the nonlinear process. In at least one embodiment, the nonlinear delta-sigma modulator is part of a control system that controls power factor correction and output voltage of a switching power converter. The control system controls the pulse width and period of a control signal to control power factor correction and the output voltage level. In at least one embodiment, the nonlinear delta-sigma modulator generates a signal to control the pulse width of the control signal.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
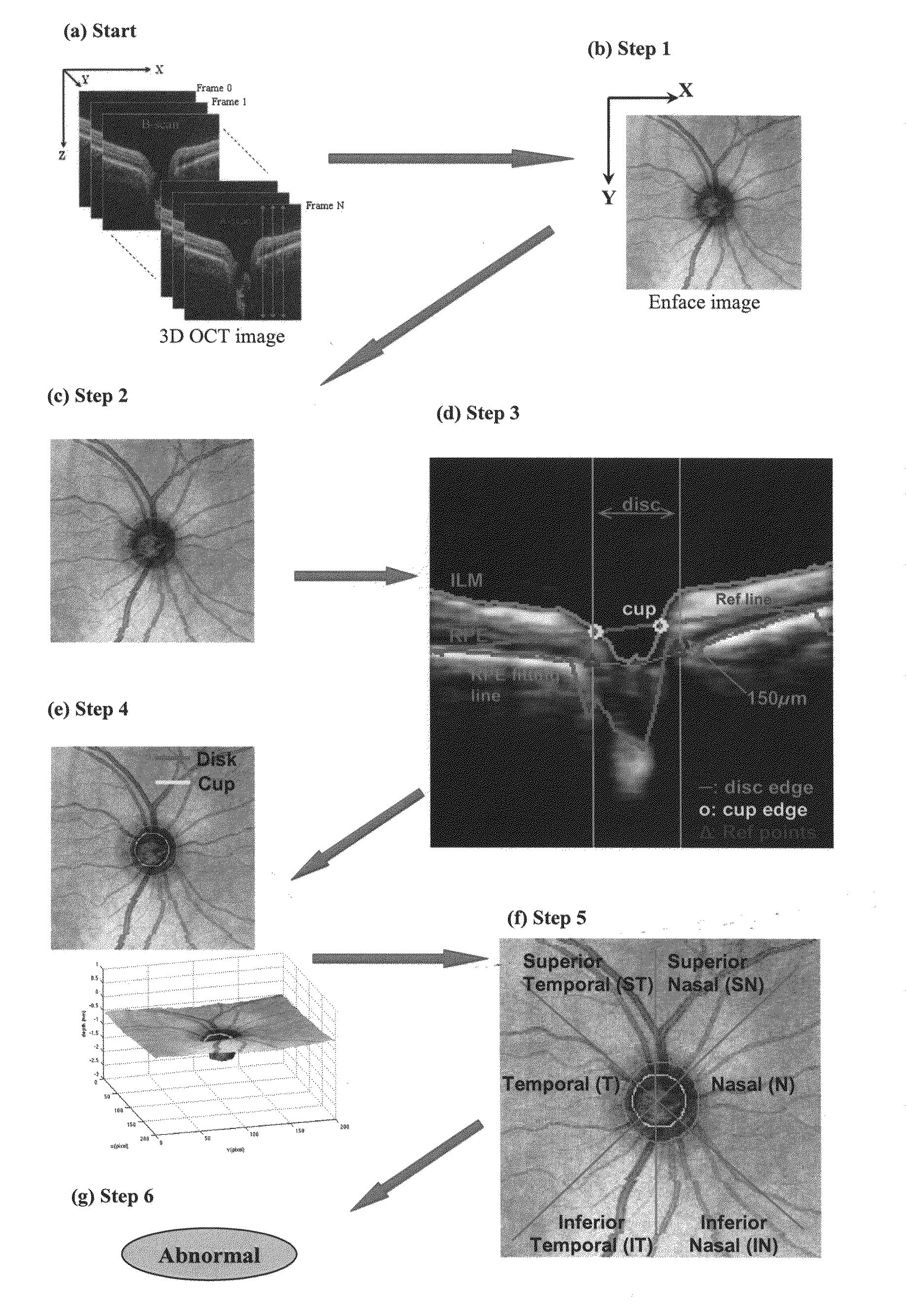
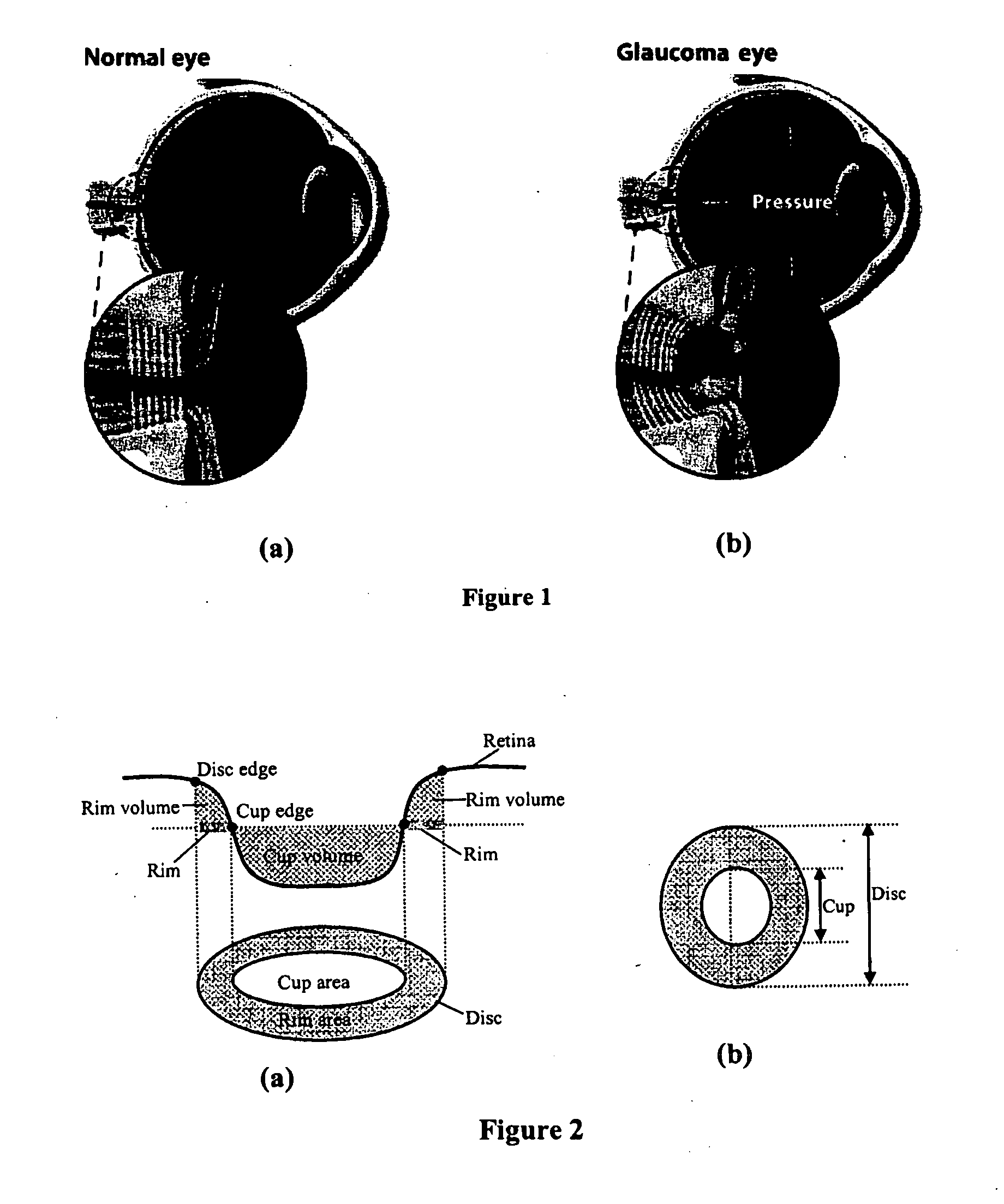
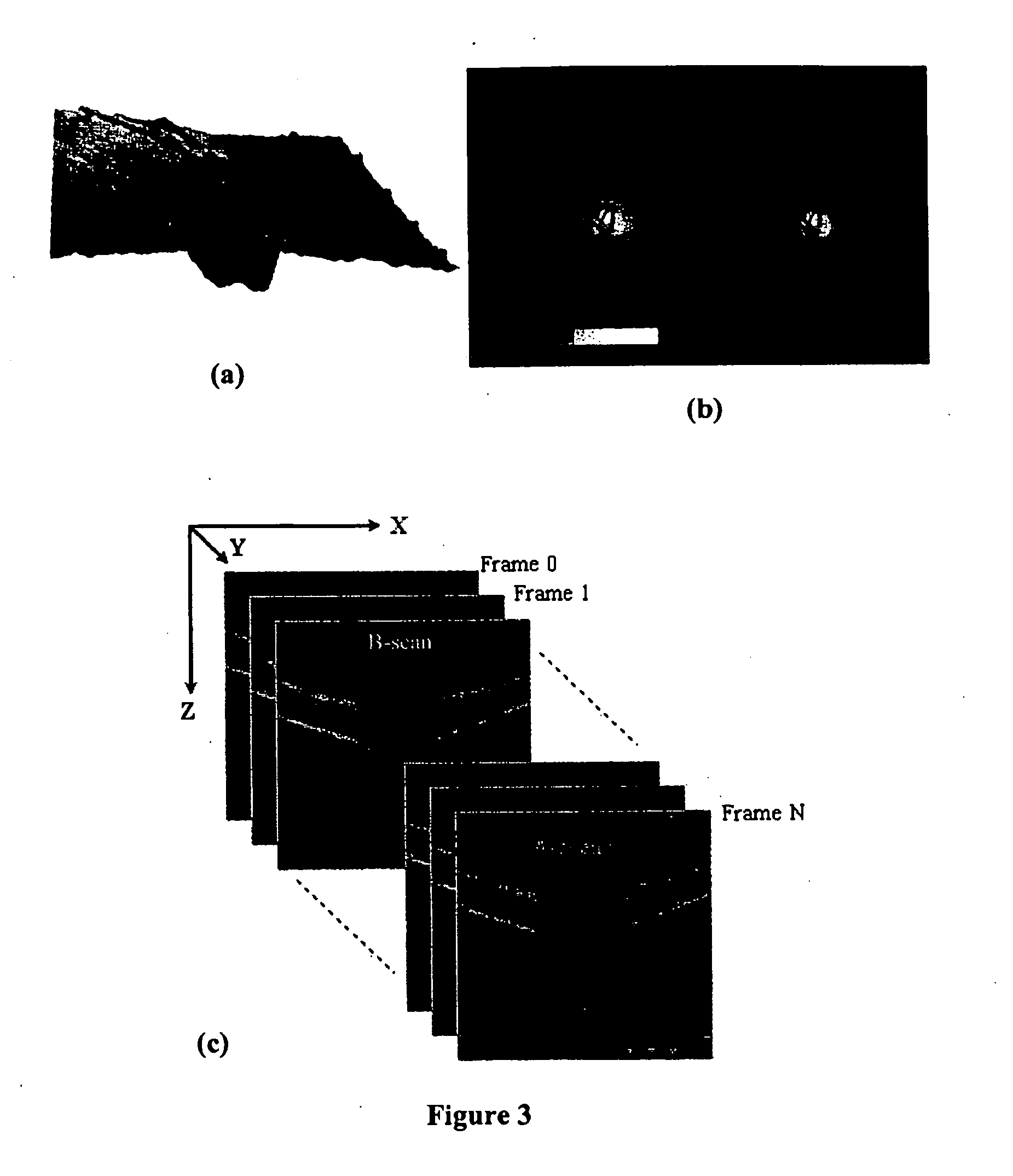
Automated assessment of optic nerve head with spectral domain optical coherence tomography
A fully automated optic nerve head assessment system, based on spectral domain optical coherence tomography, provides essential disc parameters for clinical analysis, early detection, and monitoring of progression.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
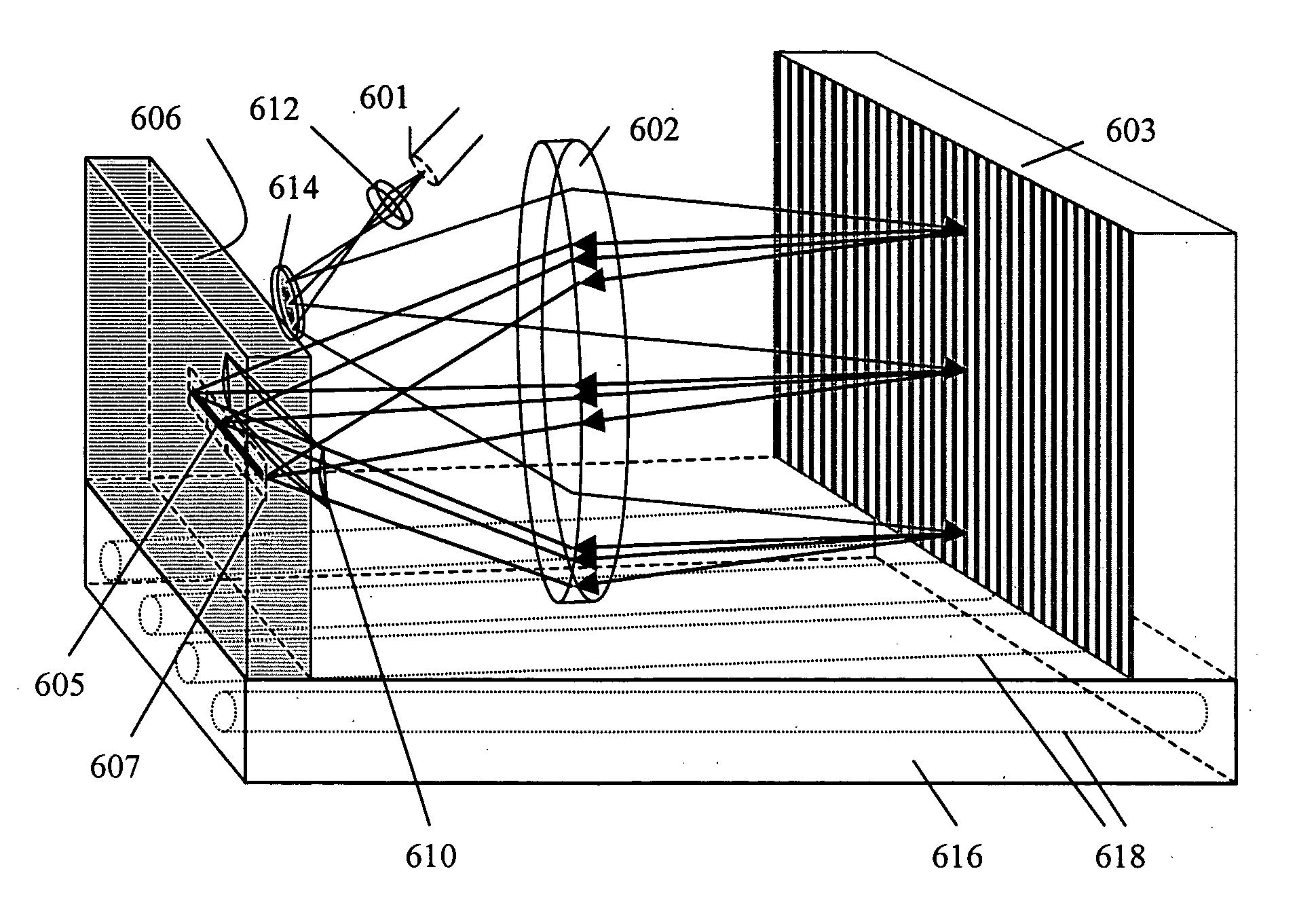
Littrow spectrometer and a spectral domain optical coherence tomography system with a littrow spectrometer
ActiveUS20070030483A1Reduce non-linearityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSpectral domainDetector array
A compact conical diffraction Littrow spectrometer is disclosed. The distortion of the conically diffracted spectral component beams is compensated and as a result, the diffracted spectral beams can still be focused into a substantially straight line to shine onto a detector array. A spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) system incorporating a Littrow spectrometer or a spectrometer having one or more shared focusing element(s) and an SD-OCT system incorporating a spectrometer that is substantially polarization independent are also disclosed.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
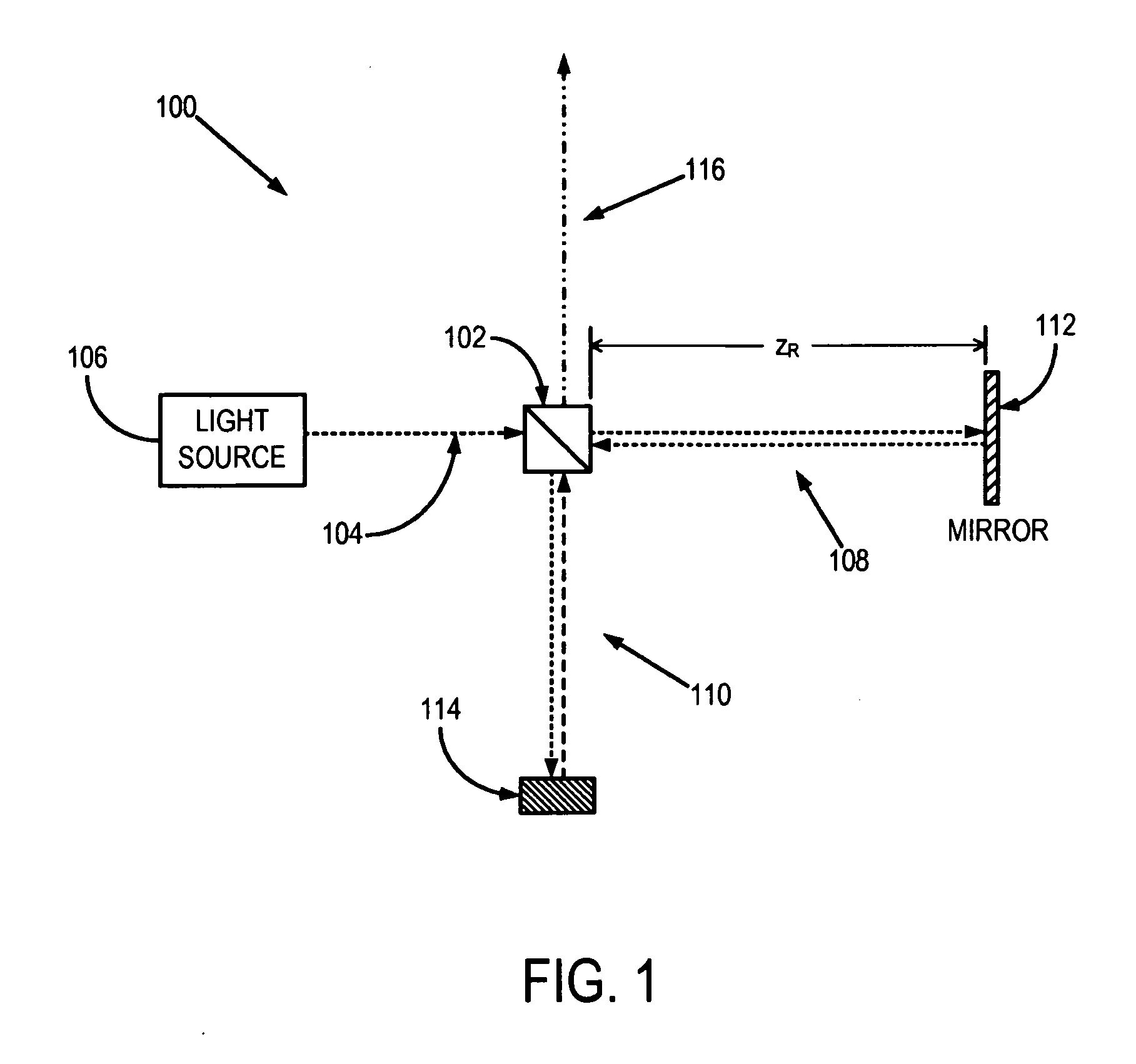
System and method for calibrated spectral domain optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry
InactiveUS20130182259A1Robust to phase errorImprove dynamic rangeRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySpectral domainTomography
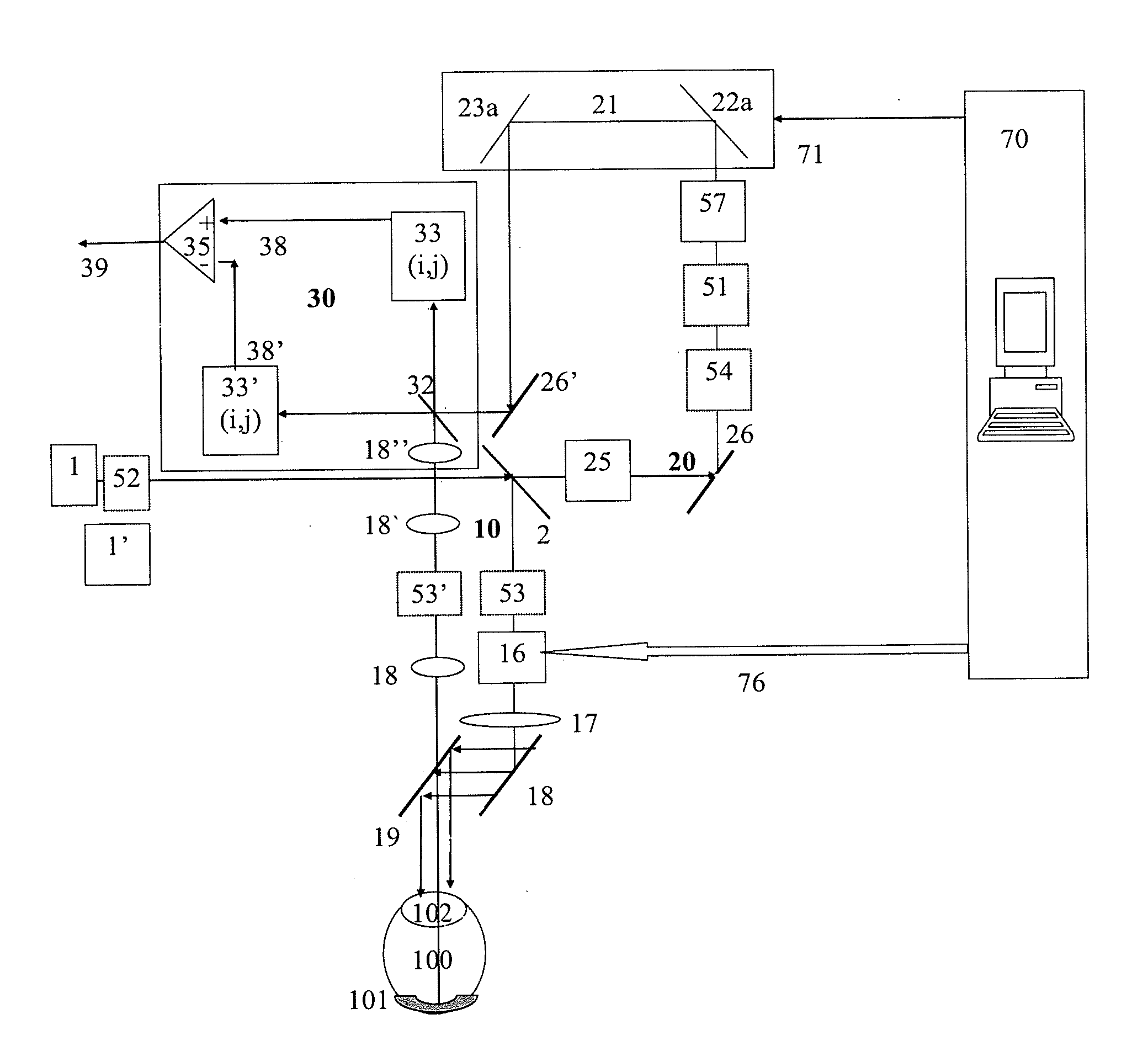
Systems and methods for enhancing spectral domain optical coherence tomography (OCT] are provided. In particular, a system and method for calibration of spectral interference signals using an acquired calibration signal are provided. The calibration signal may be logarithmically amplified to further improve the accuracy of the calibration. From the calibration signal, a series of more accurate calibration data are calculated. An acquired spectral interference signal is calibrated using these calibration data. Moreover, systems that include logarithmic amplification of the spectral interference signal and variable band-pass filtering of the spectral interference signal are provided. Such systems increase the dynamic range and visualization capabilities relative to conventional spectral domain OCT systems.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
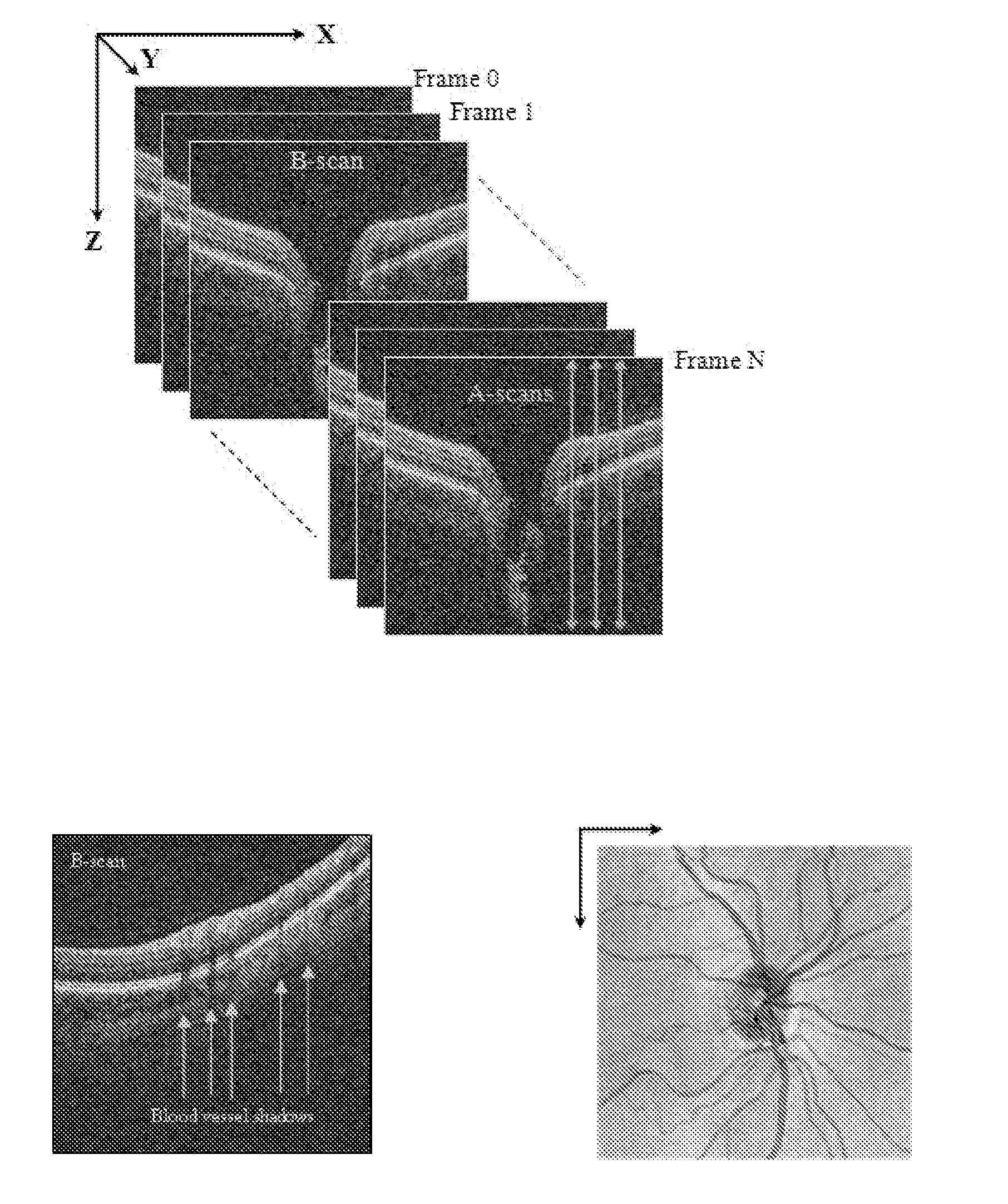
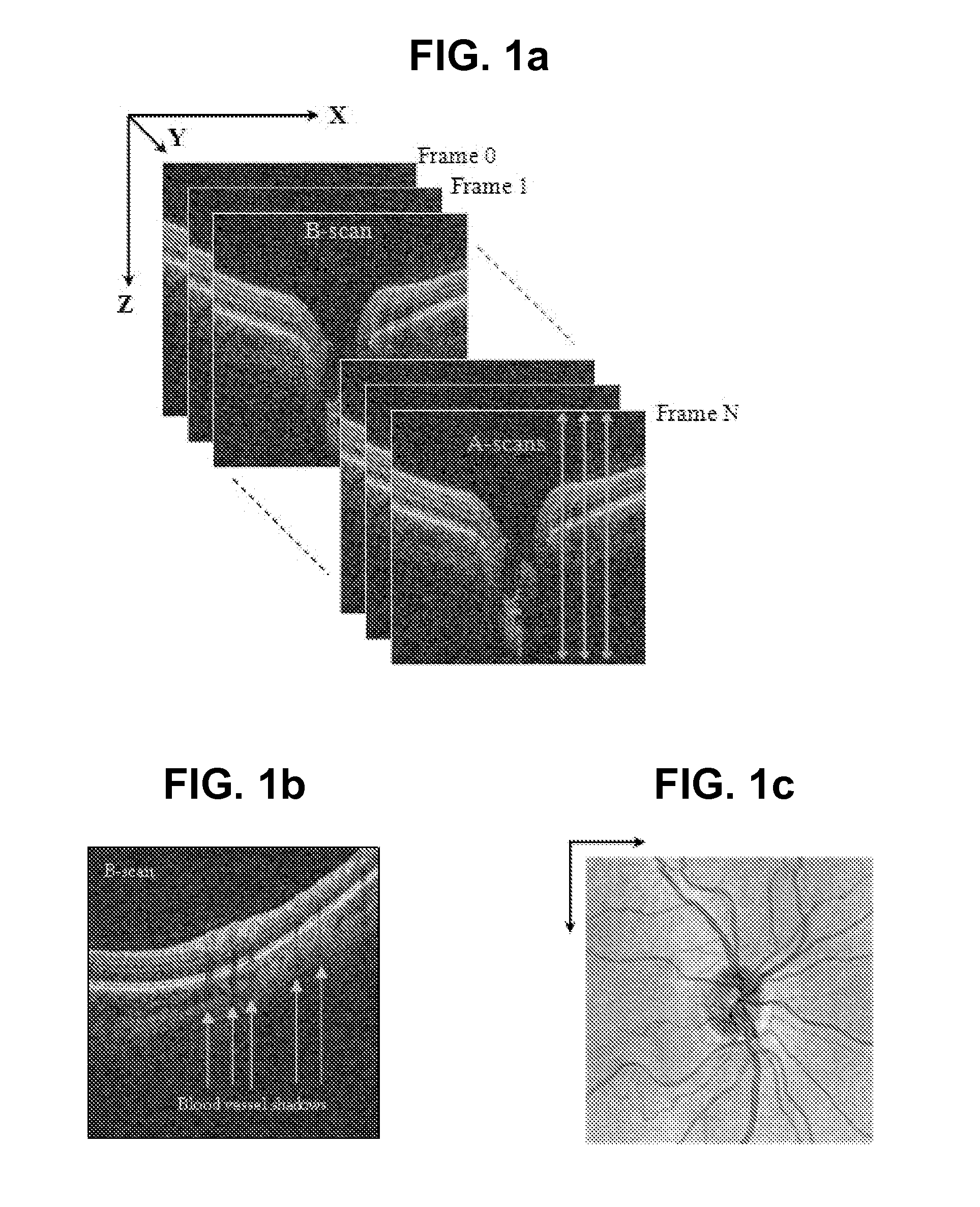
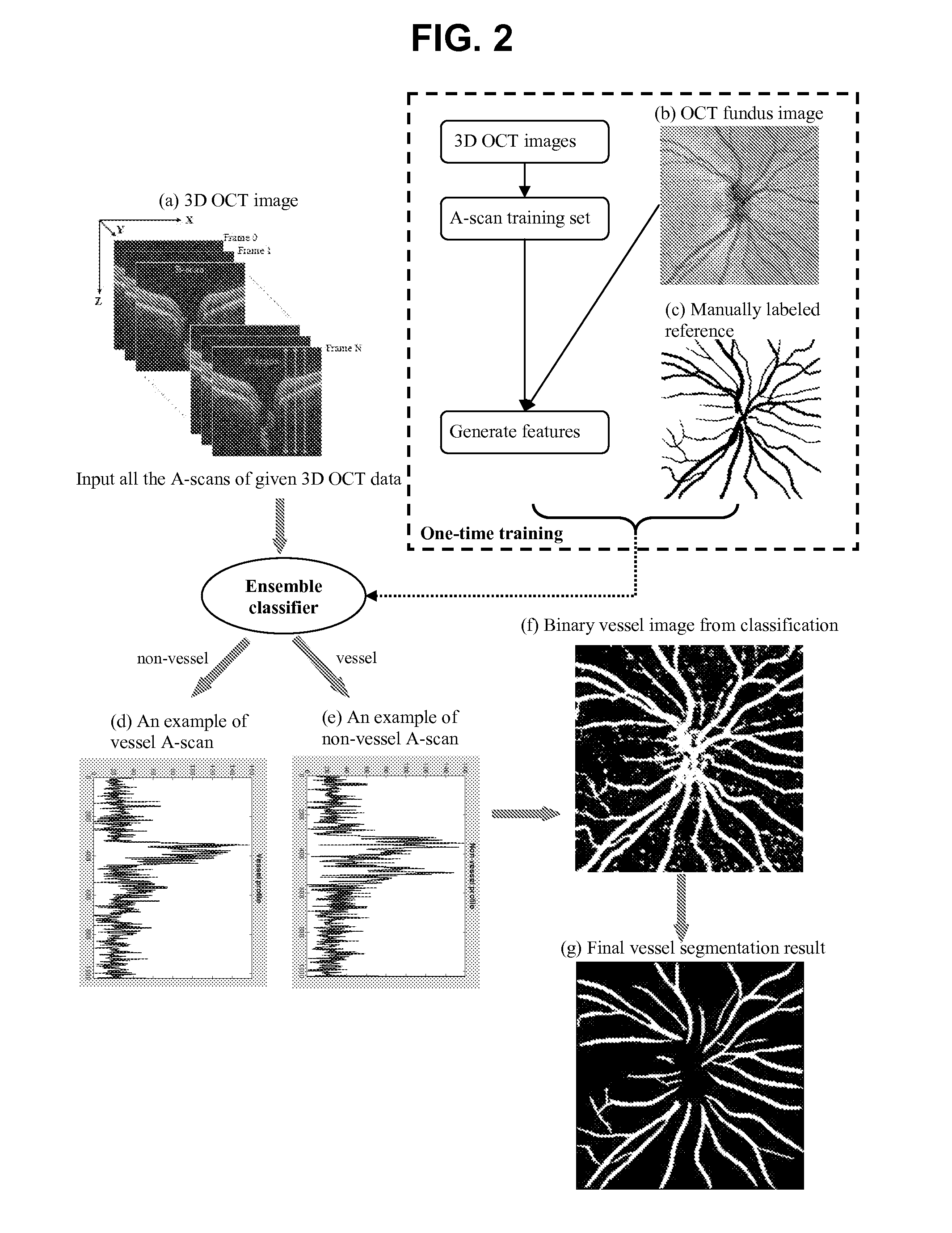
Blood vessel segmentation with three dimensional spectral domain optical coherence tomography
ActiveUS20120213423A1Precise patternImage enhancementImage analysisStudy methodsRetinal image registration
In the context of the early detection and monitoring of eye diseases, such as glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy, the use of optical coherence tomography presents the difficulty, with respect to blood vessel segmentation, of weak visibility of vessel pattern in the OCT fundus image. To address this problem, a boosting learning approach uses three-dimensional (3D) information to effect automated segmentation of retinal blood vessels. The automated blood vessel segmentation technique described herein is based on 3D spectral domain OCT and provides accurate vessel pattern for clinical analysis, for retinal image registration, and for early diagnosis and monitoring of the progression of glaucoma and other retinal diseases. The technique employs a machine learning algorithm to identify blood vessel automatically in 3D OCT image, in a manner that does not rely on retinal layer segmentation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Apparatus for Mixing a Plurality of Input Data Streams
An apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention for mixing a first frame of a first input data stream and a second frame of a second input data stream has a processing unit adapted to generate an output frame, wherein the output frame has output spectral data describing a lower part of an output spectrum up to an output cross-over frequency, and wherein the output frame further has output SBR-data describing a higher part of the output spectrum above the output cross-over frequency by way of energy-related values in an output time / frequency grid resolution. The processing unit is further adapted such that the output spectral data corresponding to frequencies below a minimum value of cross-over frequencies of the first frame, the second frame and the output cross-over frequency is generated in a spectral domain and the output SBR-data corresponding to frequencies above a maximum value of cross-over frequencies of the first and second frames and the output cross-over frequency is processed in a SBR-domain.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
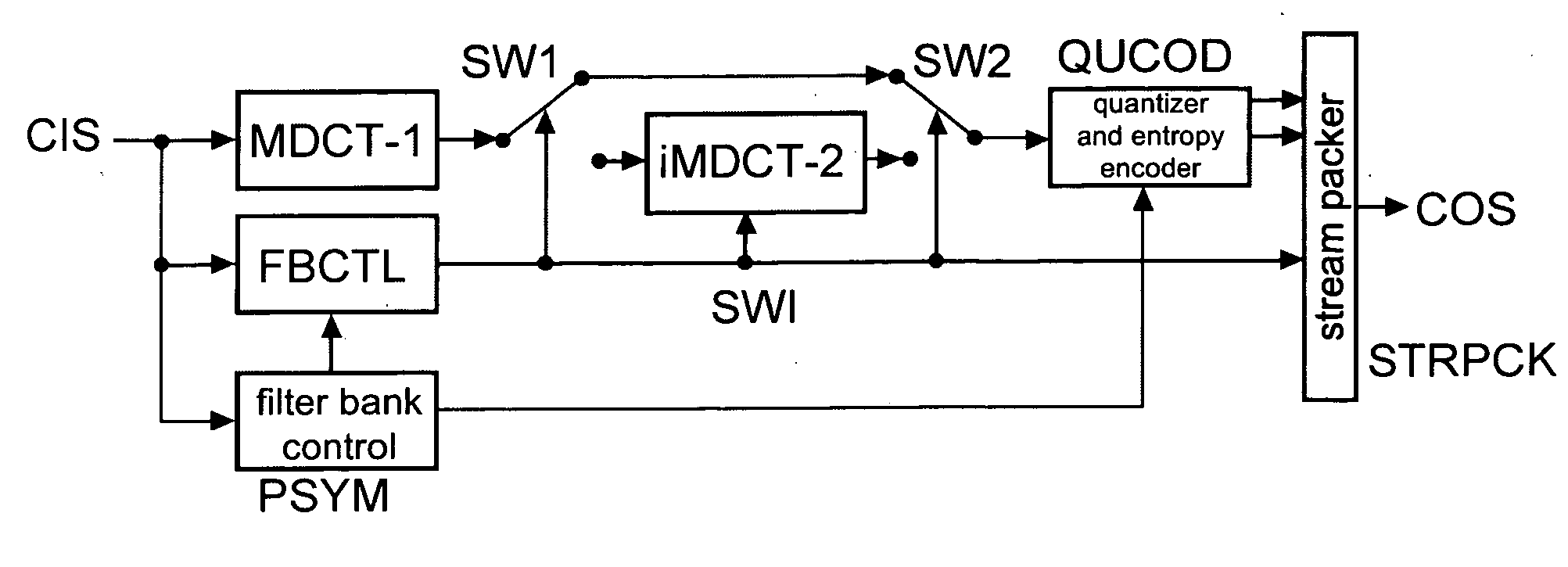
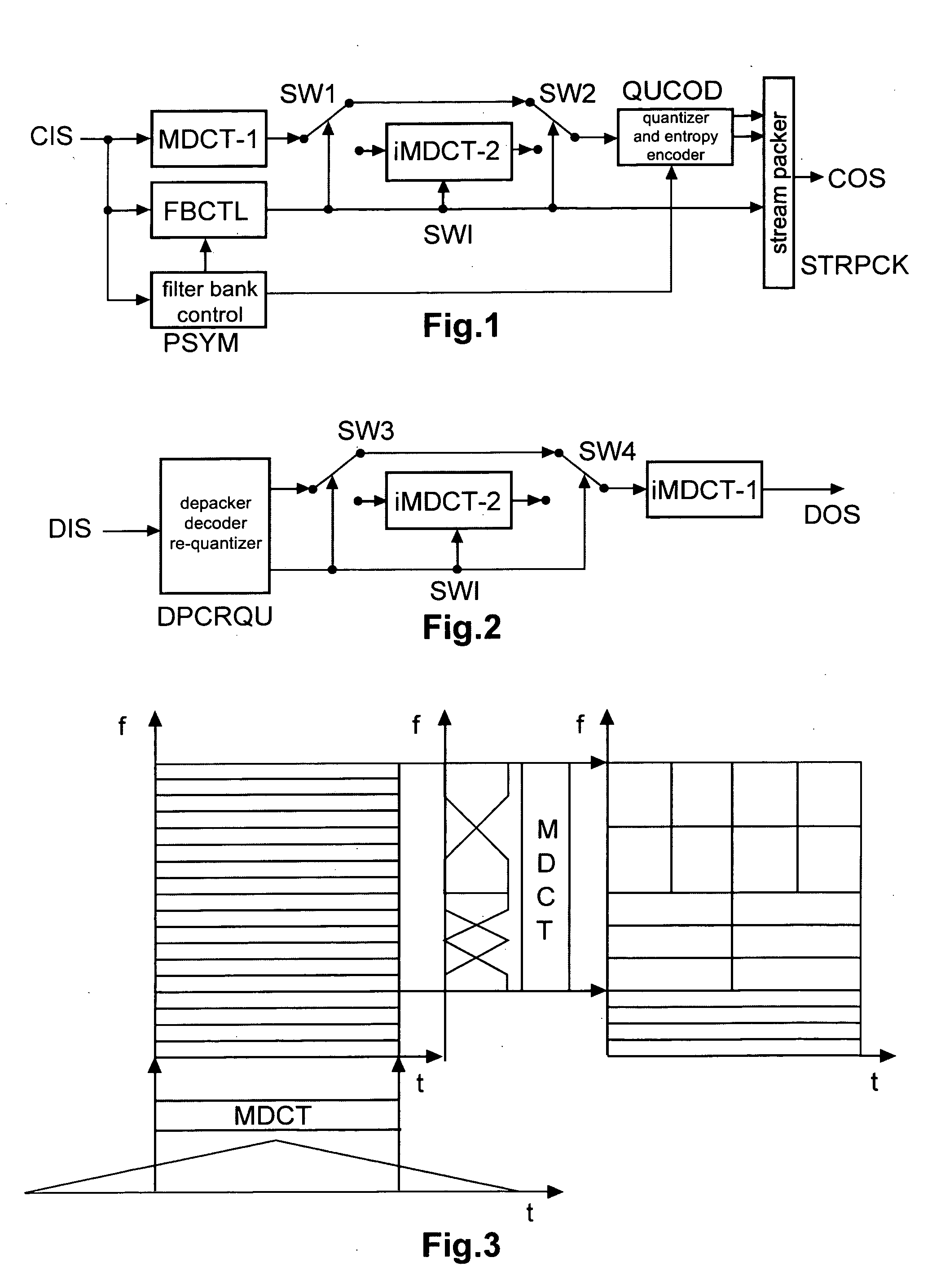
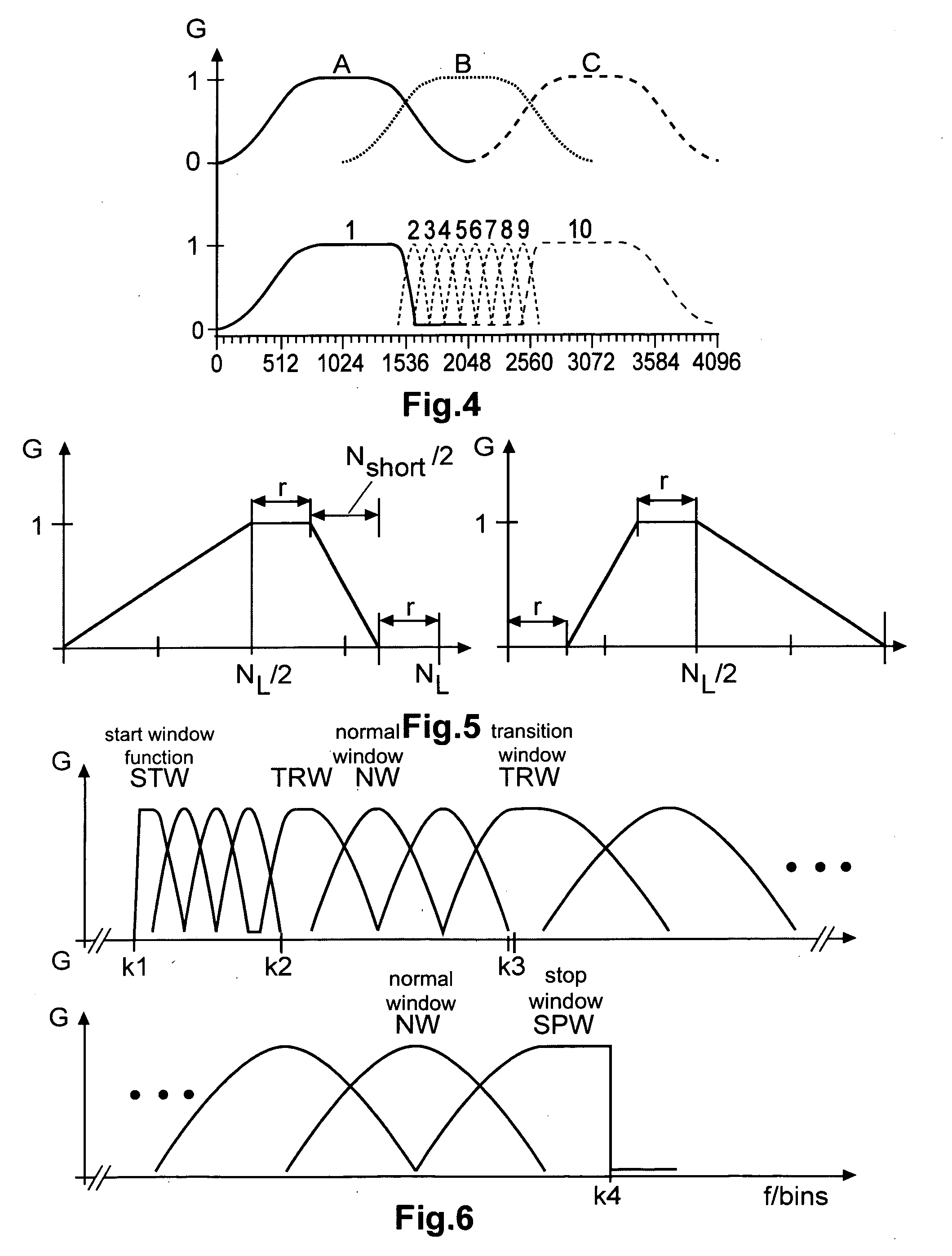
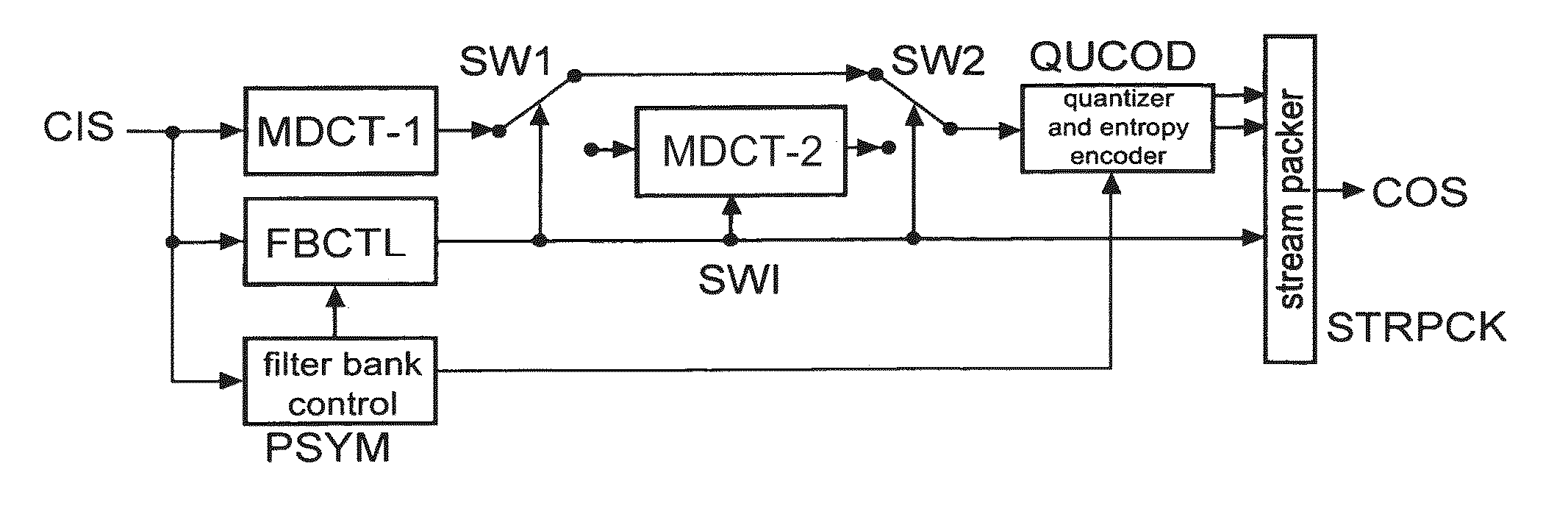
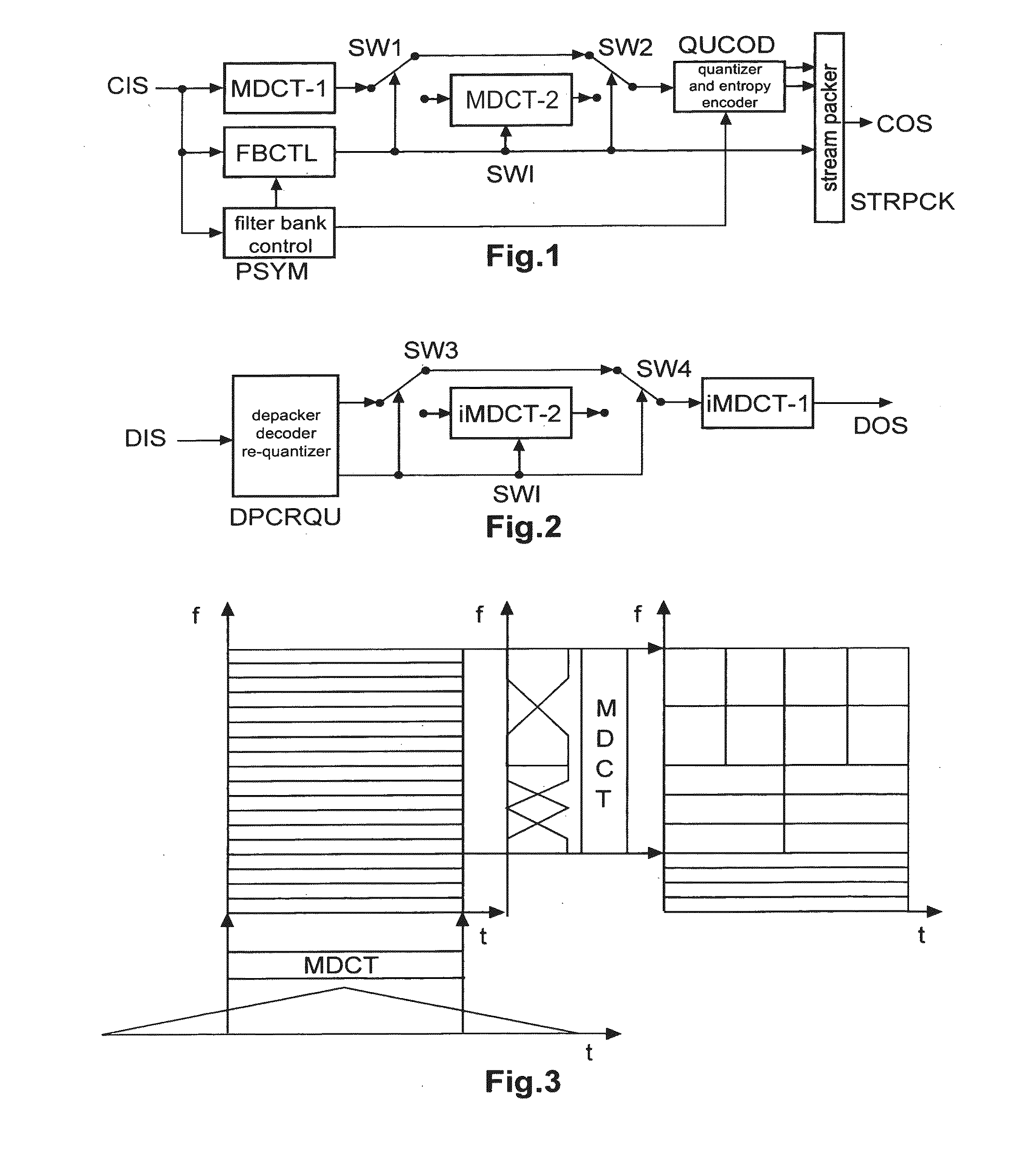
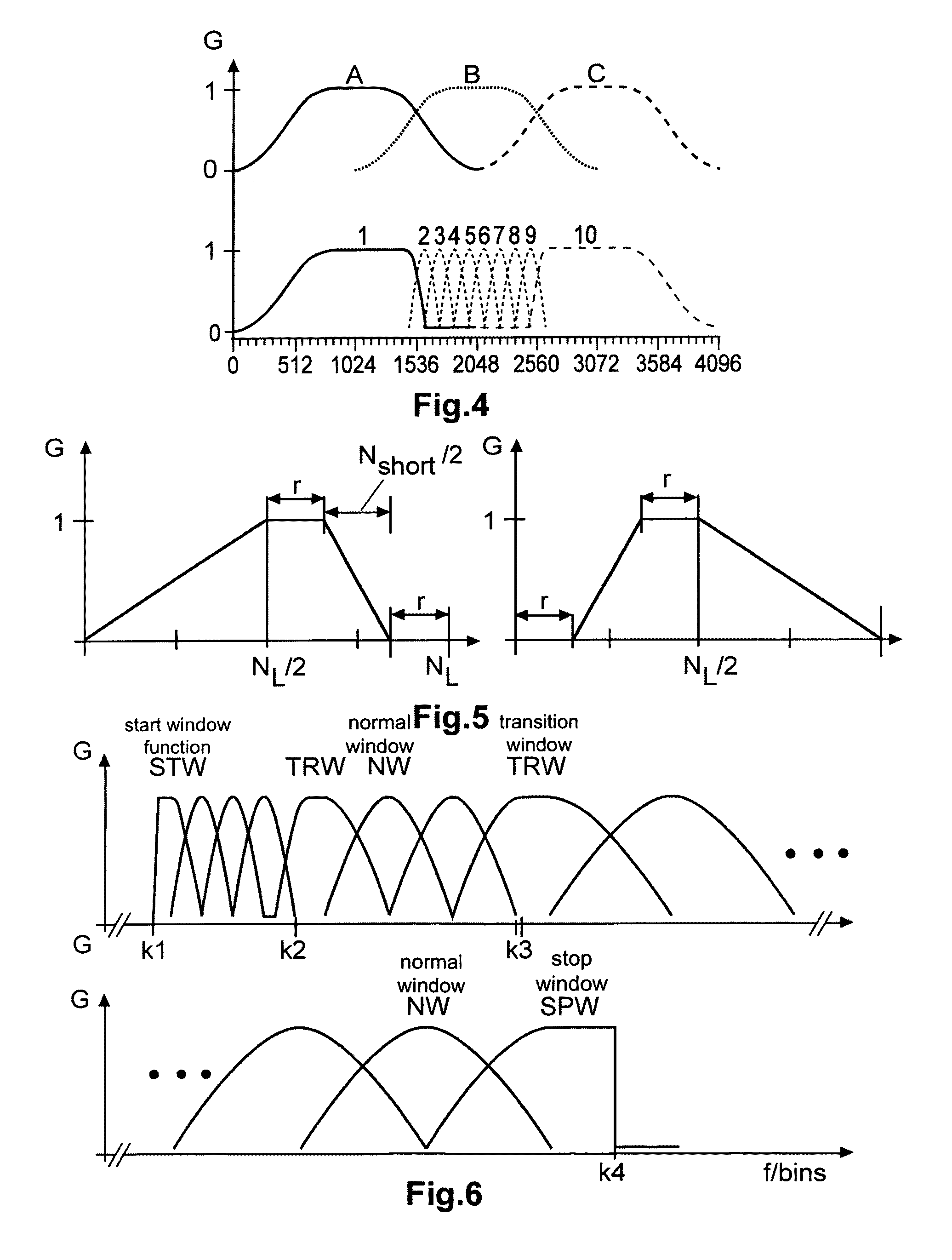
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding an audio signal using adaptively switched temporal resolution in the spectral domain
ActiveUS20090012797A1Quality improvementReduce encoding delaySpeech synthesisTemporal resolutionFrequency spectrum
Perceptual audio codecs make use of filter banks and MDCT in order to achieve a compact representation of the audio signal, by removing redundancy and irrelevancy from the original audio signal. During quasi-stationary parts of the audio signal a high frequency resolution of the filter bank is advantageous in order to achieve a high coding gain, but this high frequency resolution is coupled to a coarse temporal resolution that becomes a problem during transient signal parts by producing audible pre-echo effects. The invention achieves improved coding / decoding quality by applying on top of the output of a first filter bank a second non-uniform filter bank, i.e. a cascaded MDCT. The inventive codec uses switching to an additional extension filter bank (or multi-resolution filter bank) in order to re-group the time-frequency representation during transient or fast changing audio signal sections. By applying a corresponding switching control, pre-echo effects are avoided and a high coding gain and a low coding delay are achieved.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding an audio signal using adaptively switched temporal resolution in the spectral domain
ActiveUS8095359B2Quality improvementReduce encoding delaySpeech synthesisTemporal resolutionFrequency spectrum
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
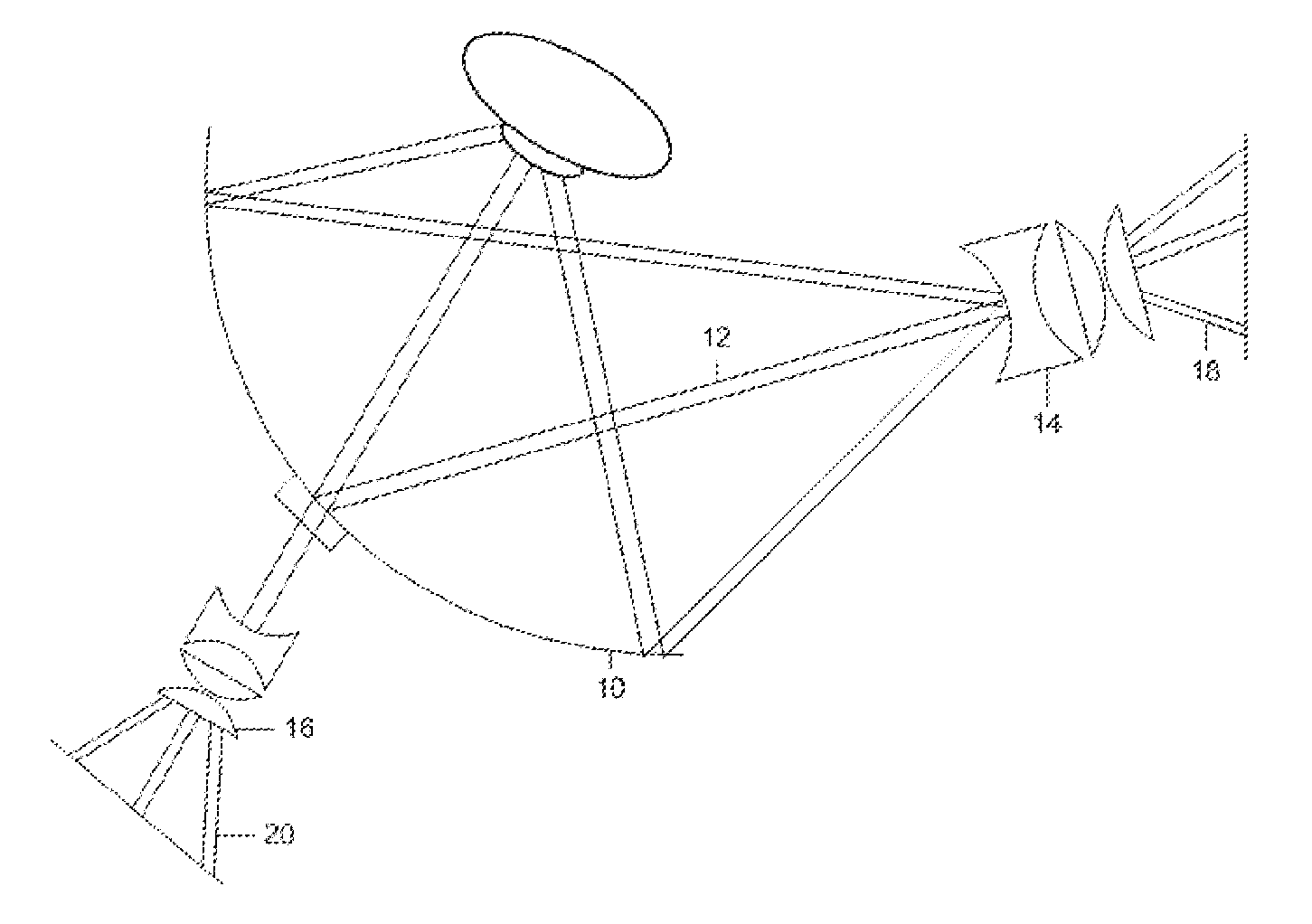
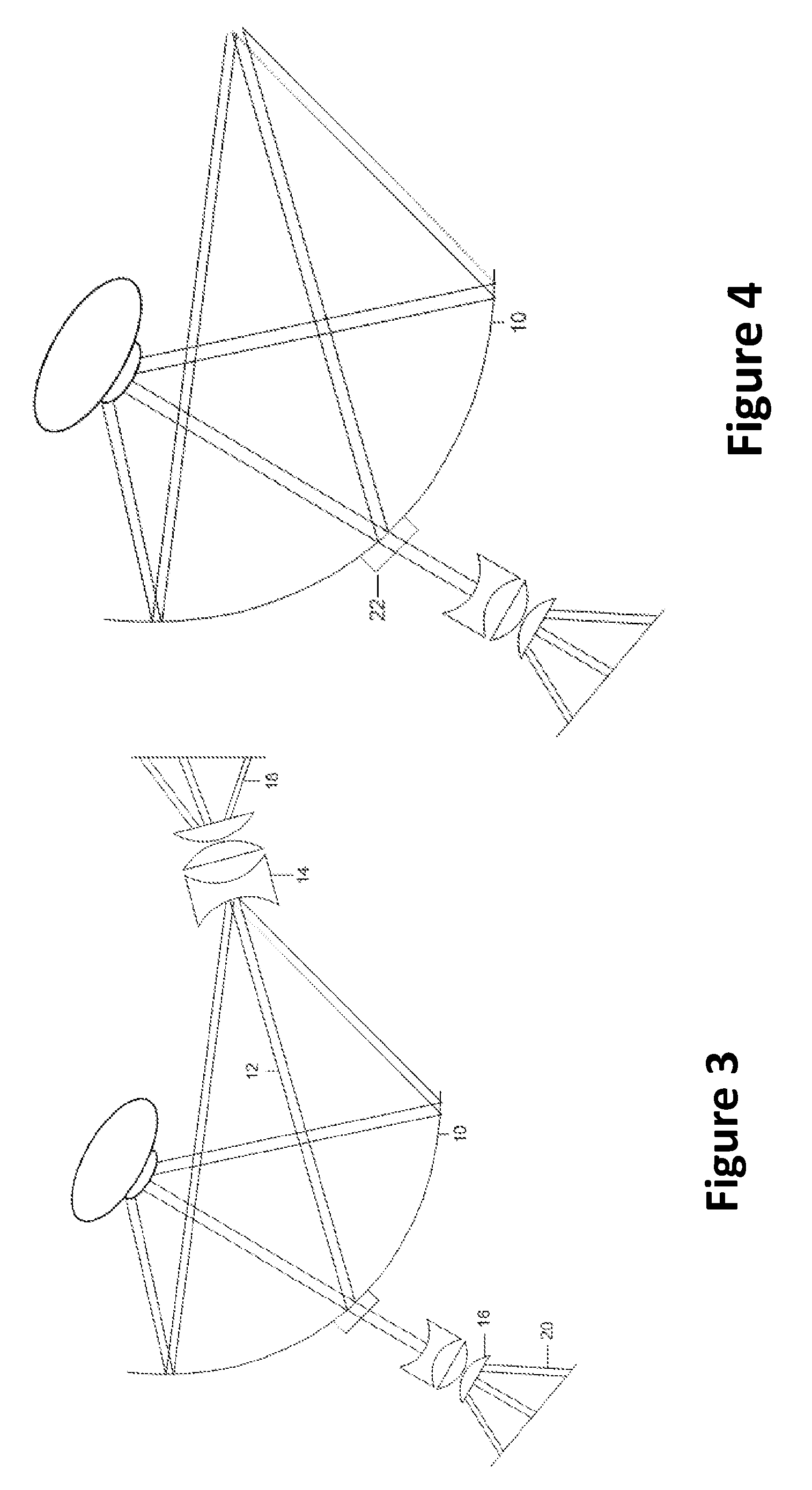
Non-contact optical coherence tomography imaging of the central and peripheral retina
ActiveUS20100328606A1Simplifies taking imageEliminate timeOthalmoscopesPeripheral retinaSpectral domain
A system for imaging of the central and peripheral retina, includes one of a concave mirror and an elliptical mirror having an axis and being configured to rotate around the axis and a scanner configured to using a spectral domain optical coherence tomography system to obtain a non-contact wide angle OCT-image of a large portion of the central and peripheral retina.
Owner:PEYMAN GHOLAM A
Endoscopic imaging system in bulk optics biopsy spectral coverage OCT
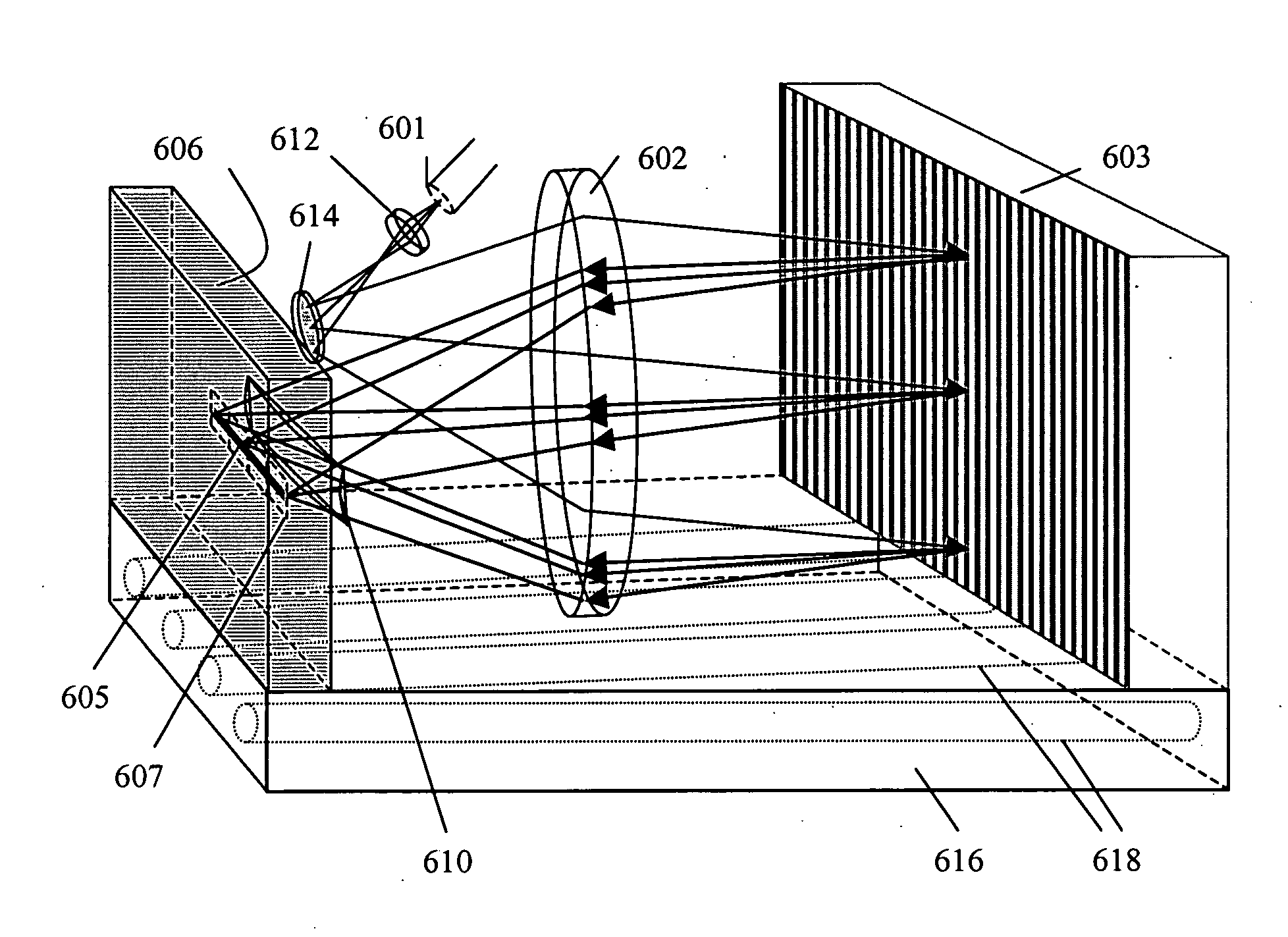
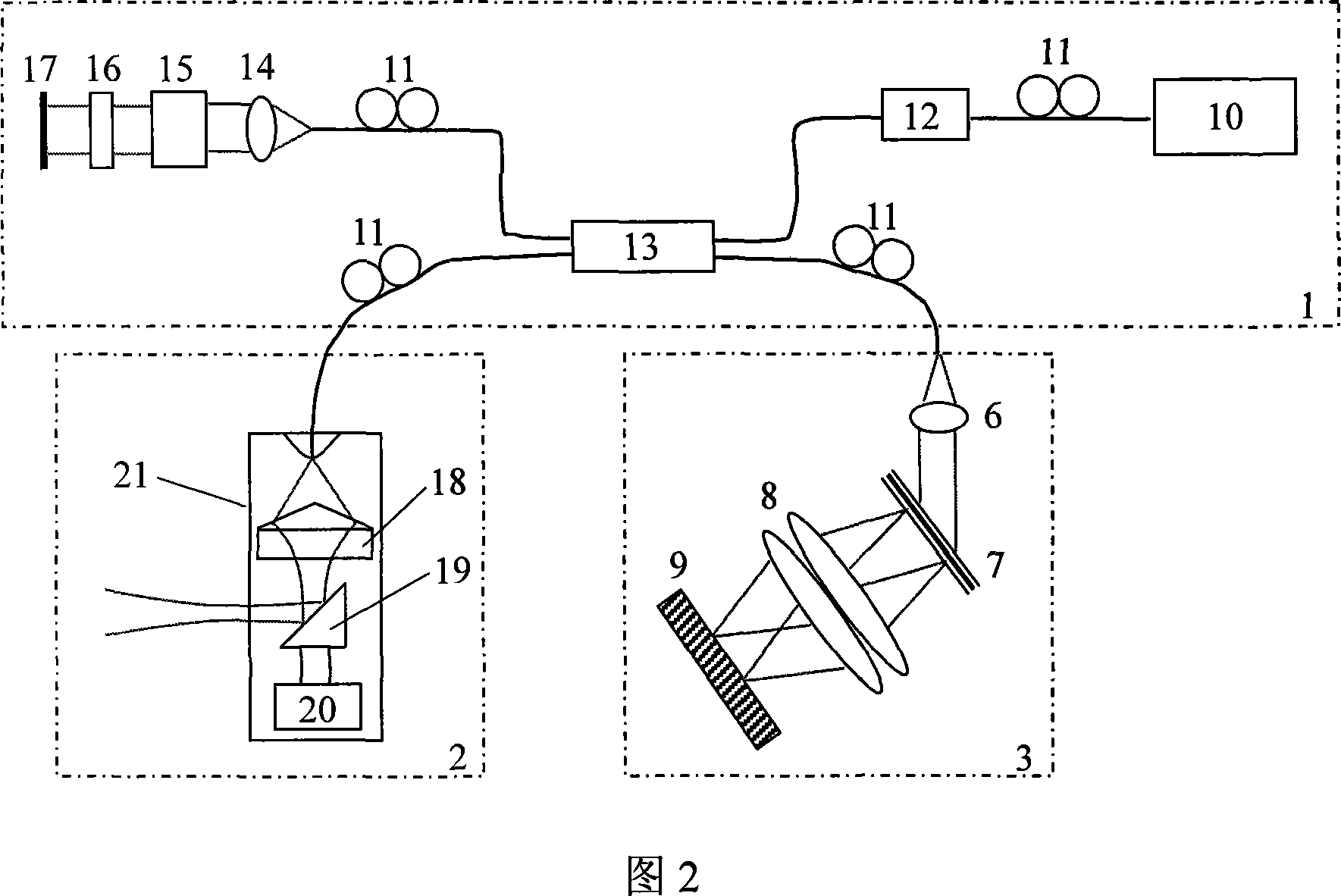
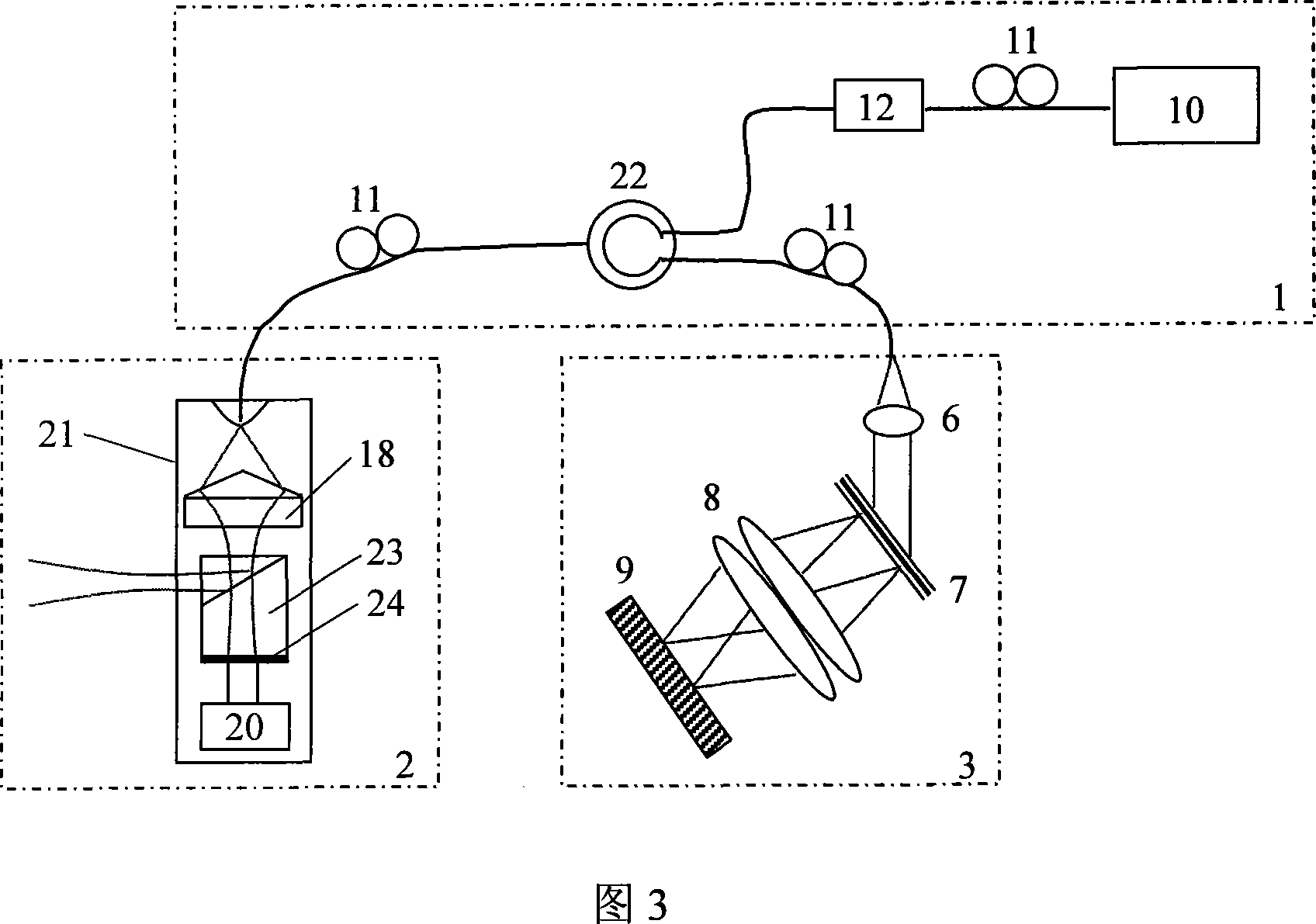
InactiveCN101032390ASolve the problem that dynamic focus cannot be used to ensure lateral resolutionQuality of reliefEndoscopesDiagnostic recording/measuringBeam splitterPrism
The present invention discloses one kind of spectral-domain optical coherent tomography endoscopic image system for in vivo optical biopsy, and the system includes one fiber optical interferometer, one imaging probe, one detection unit, one image acquiring card and one computer. The detection unit has grating spectrograph for high imaging speed, and the imaging probe has axial axicon lens and inside rotating right angle prism or circularly symmetric beam splitter combined to ensure high transverse resolution in the whole depth range, so as to realize circularly scanning endoscopic imaging. The present invention proposes two embodiments of circularly scanning probe and their corresponding system structures. The present invention may be applied in the optical endoscopic biopsy and analytic study of oral cavity, respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
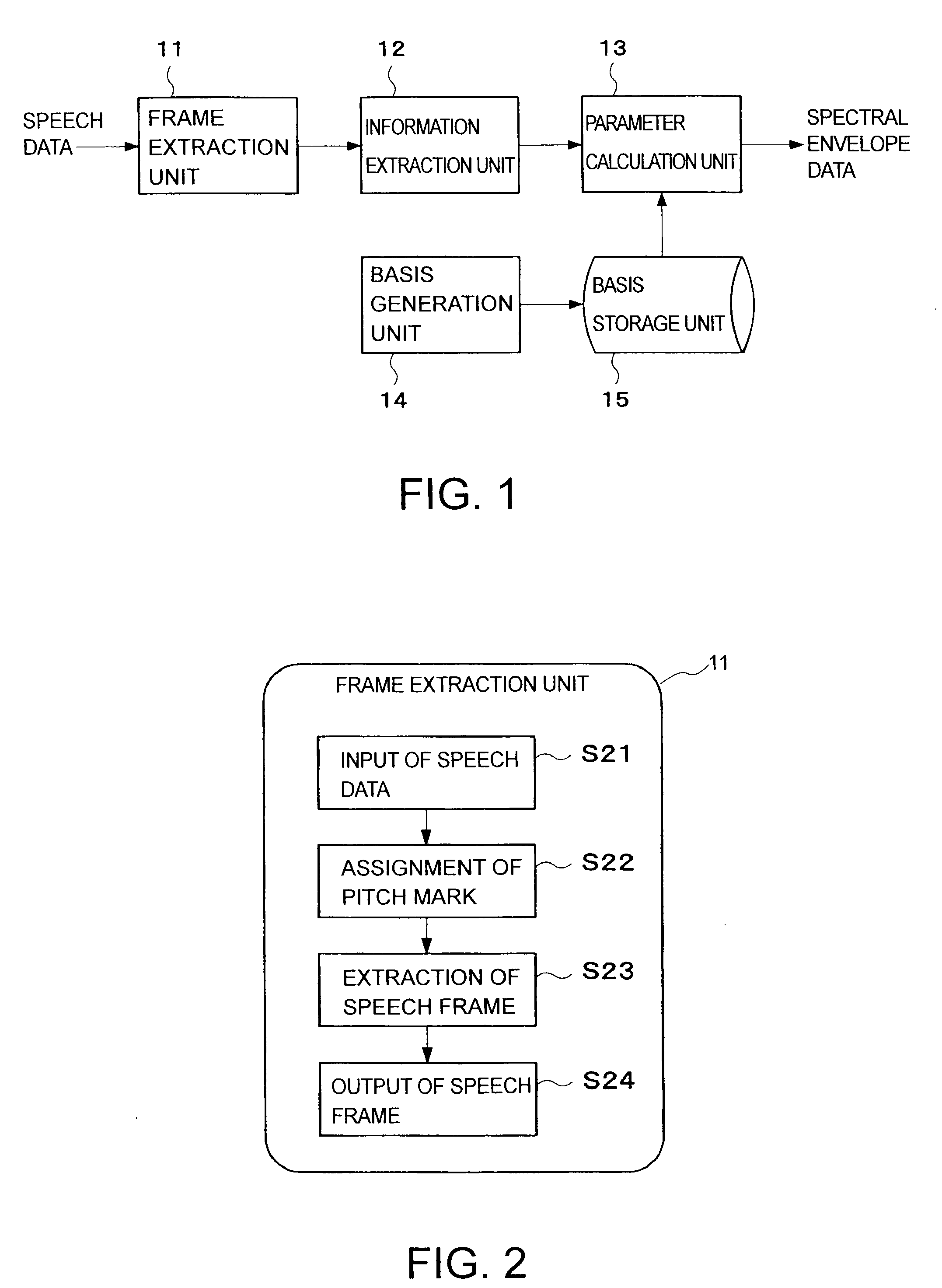
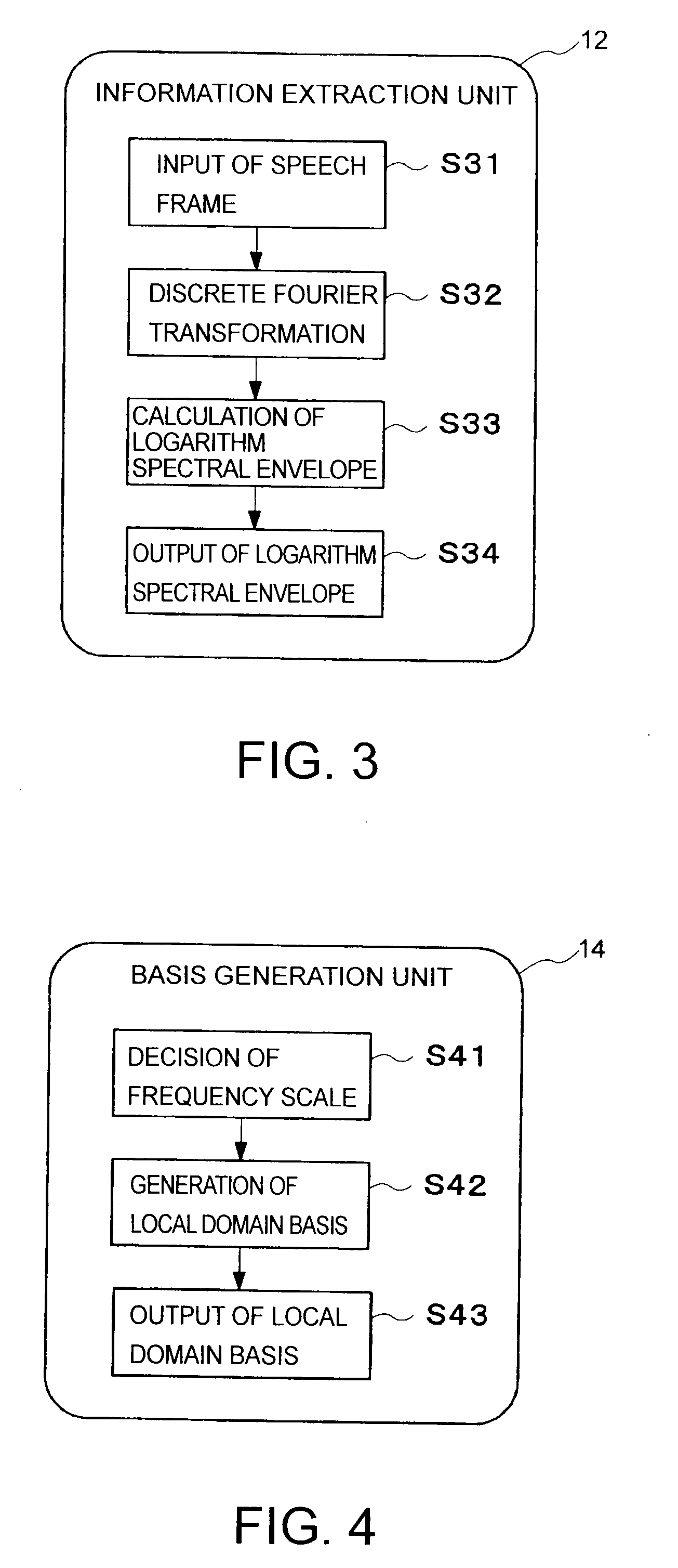
Speech processing apparatus and speech synthesis apparatus
ActiveUS20090144053A1Quality improvementEasy execution of processingSpeech synthesisFine structureFrequency spectrum
An information extraction unit extracts spectral envelope information of L-dimension from each frame of speech data. The spectral envelope information does not have a spectral fine structure. A basis storage unit stores N bases (L>N>1). Each basis is differently a frequency band having a maximum as a peak frequency in a spectral domain having L-dimension. A value corresponding to a frequency outside the frequency band along a frequency axis of the spectral domain is zero. Two frequency bands of which two peak frequencies are adjacent along the frequency axis partially overlap. A parameter calculation unit minimizes a distortion between the spectral envelope information and a linear combination of each basis with a coefficient by changing the coefficient, and sets the coefficient of each basis from which the distortion is minimized to a spectral envelope parameter of the spectral envelope information.
Owner:TOSHIBA DIGITAL SOLUTIONS CORP
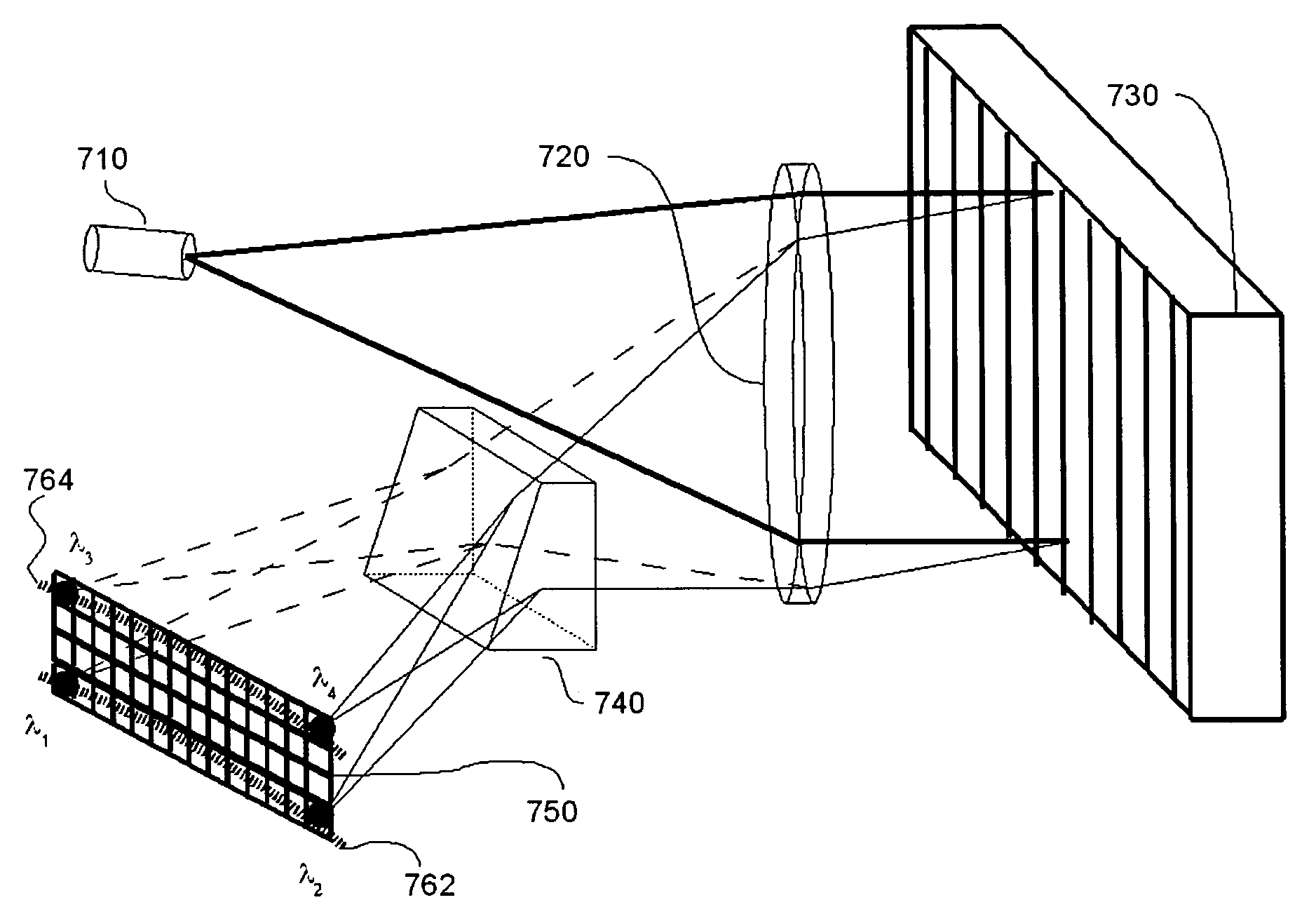
High resolution 3-d spectral domain optical imaging apparatus and method
ActiveUS20160345820A1Improved high resolution optical imageProvide usageReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansSensor arrayDepth of field
Methods and apparatus are presented for obtaining high-resolution 3-D images of a sample over a range of wavelengths, optionally with polarisation-sensitive detection. In preferred embodiments a spectral domain OCT apparatus is used to sample the complex field of light reflected or scattered from a sample, providing full range imaging. In certain embodiments structured illumination is utilised to provide enhanced lateral resolution. In certain embodiments the resolution or depth of field of images is enhanced by digital refocusing or digital correction of aberrations in the sample. Individual sample volumes are imaged using single shot techniques, and larger volumes can be imaged by stitching together images of adjacent volumes. In preferred embodiments a 2-D lenslet array is used to sample the reflected or scattered light in the Fourier plane or the image plane, with the lenslet array suitably angled with respect to the dispersive axis of a wavelength dispersive element such that the resulting beamlets are dispersed onto unique sets of pixels of a 2-D sensor array.
Owner:CYLITE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com