Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
932 results about "Spectral component" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
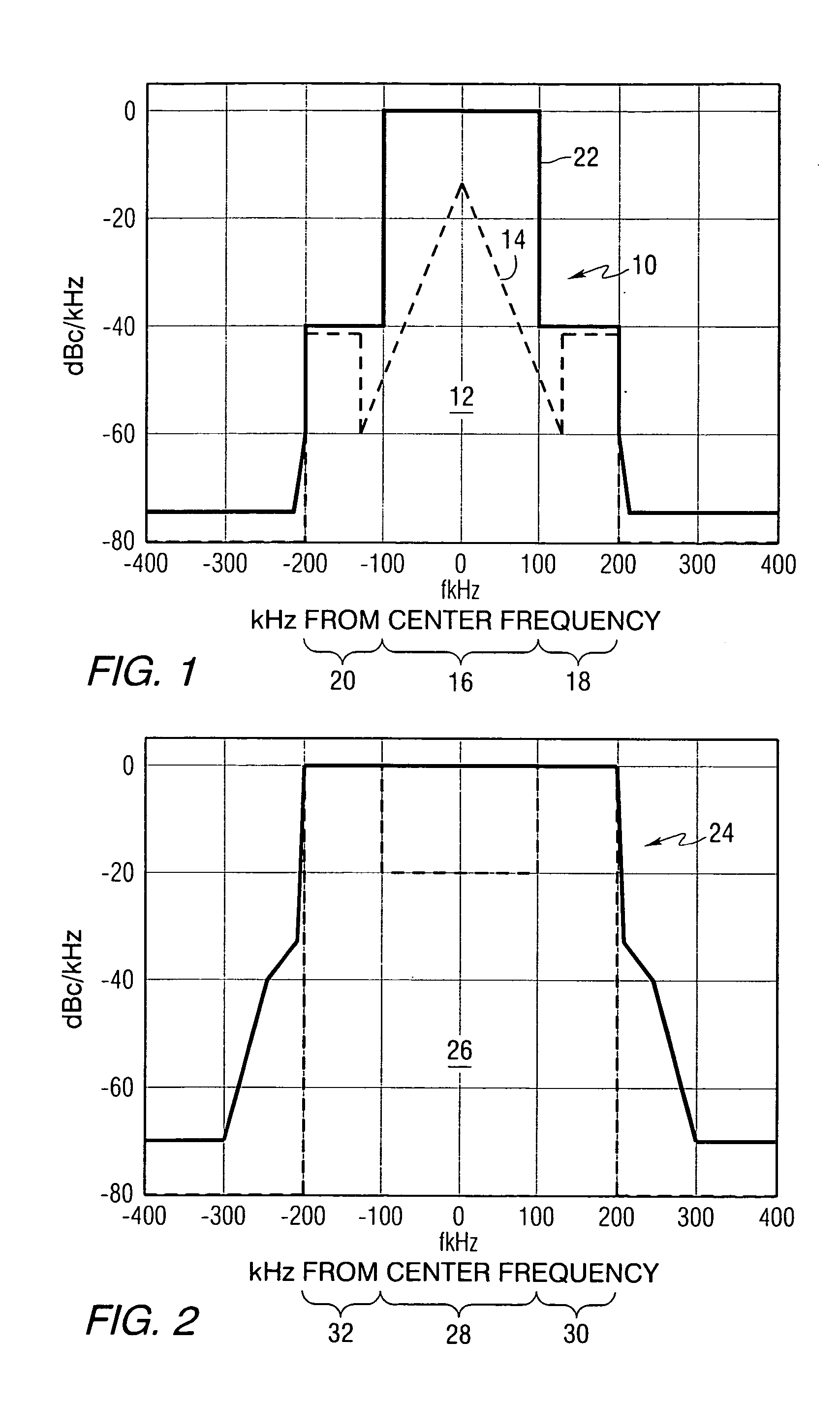
In telecommunications, spectral component is any of the waves that range outside the interval of frequencies assigned to a signal. Any waveform can be disassembled into its spectral components by Fourier analysis or Fourier transformation. The length of a pulse thereby is determined by its complex spectral components, which include not just their relative intensities, but also the relative positions (spectral phase) of these spectral components.
Broadband frequency translation for high frequency regeneration
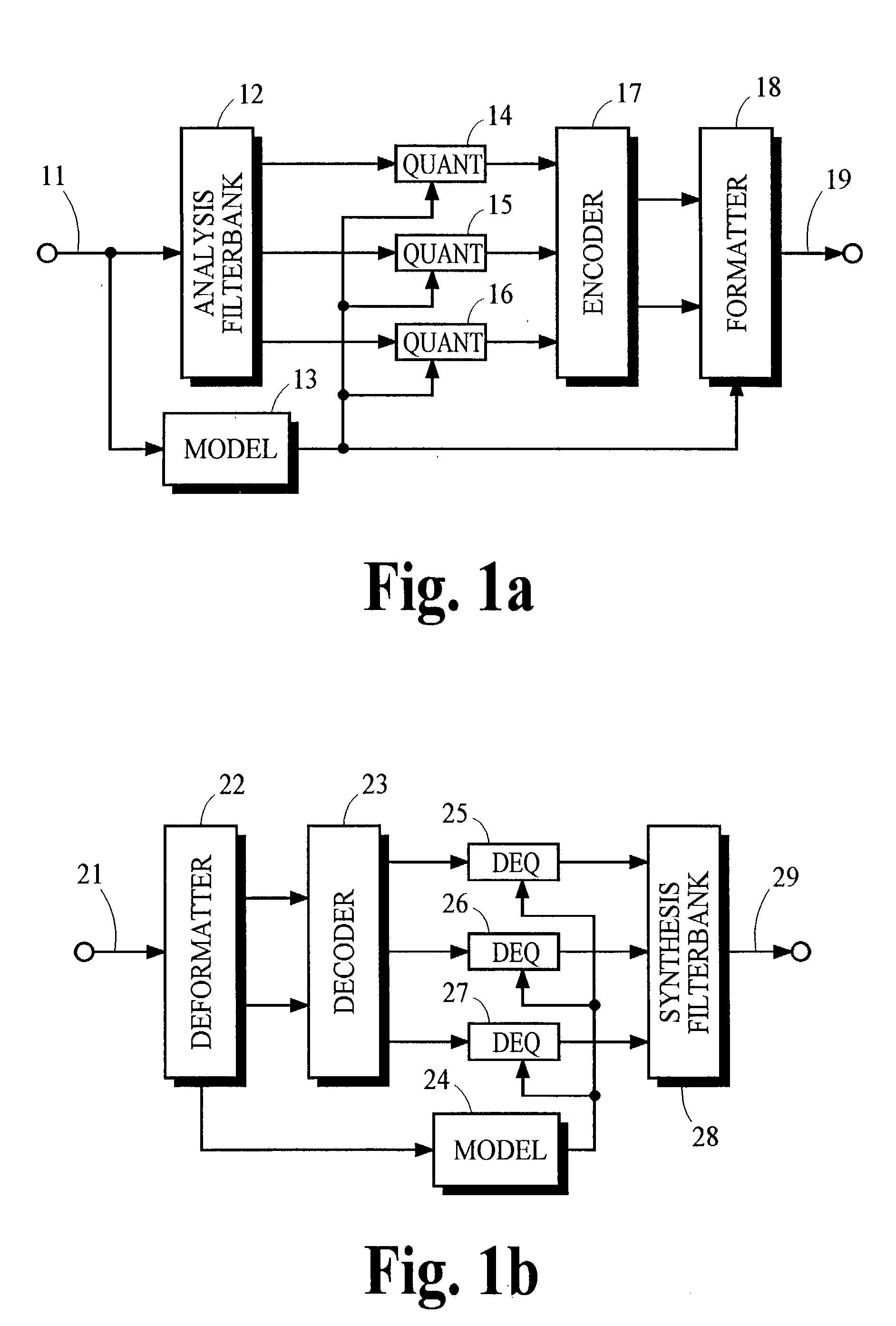
InactiveUS20030187663A1Reduce in quantityMaintaining perceived qualitySpeech analysisFrequency spectrumAudio signal flow
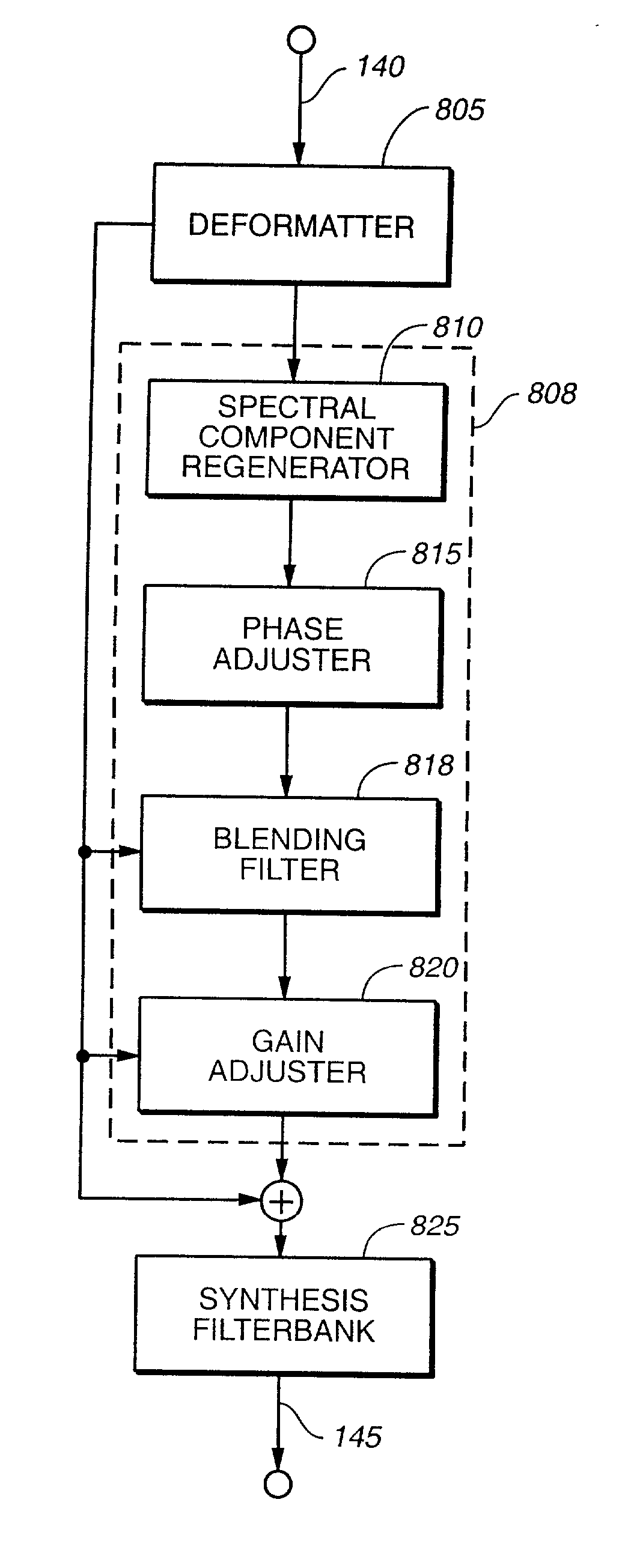
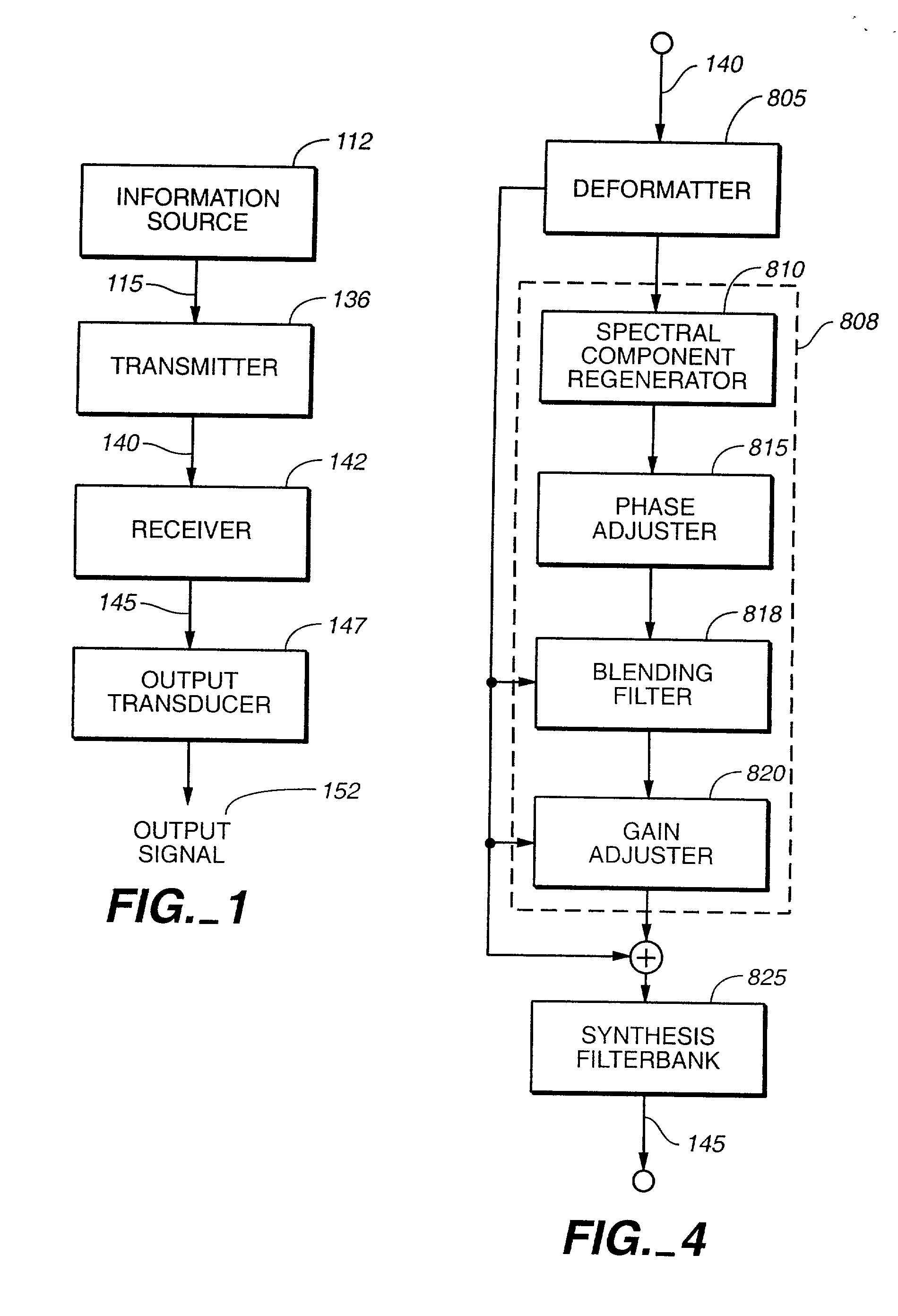
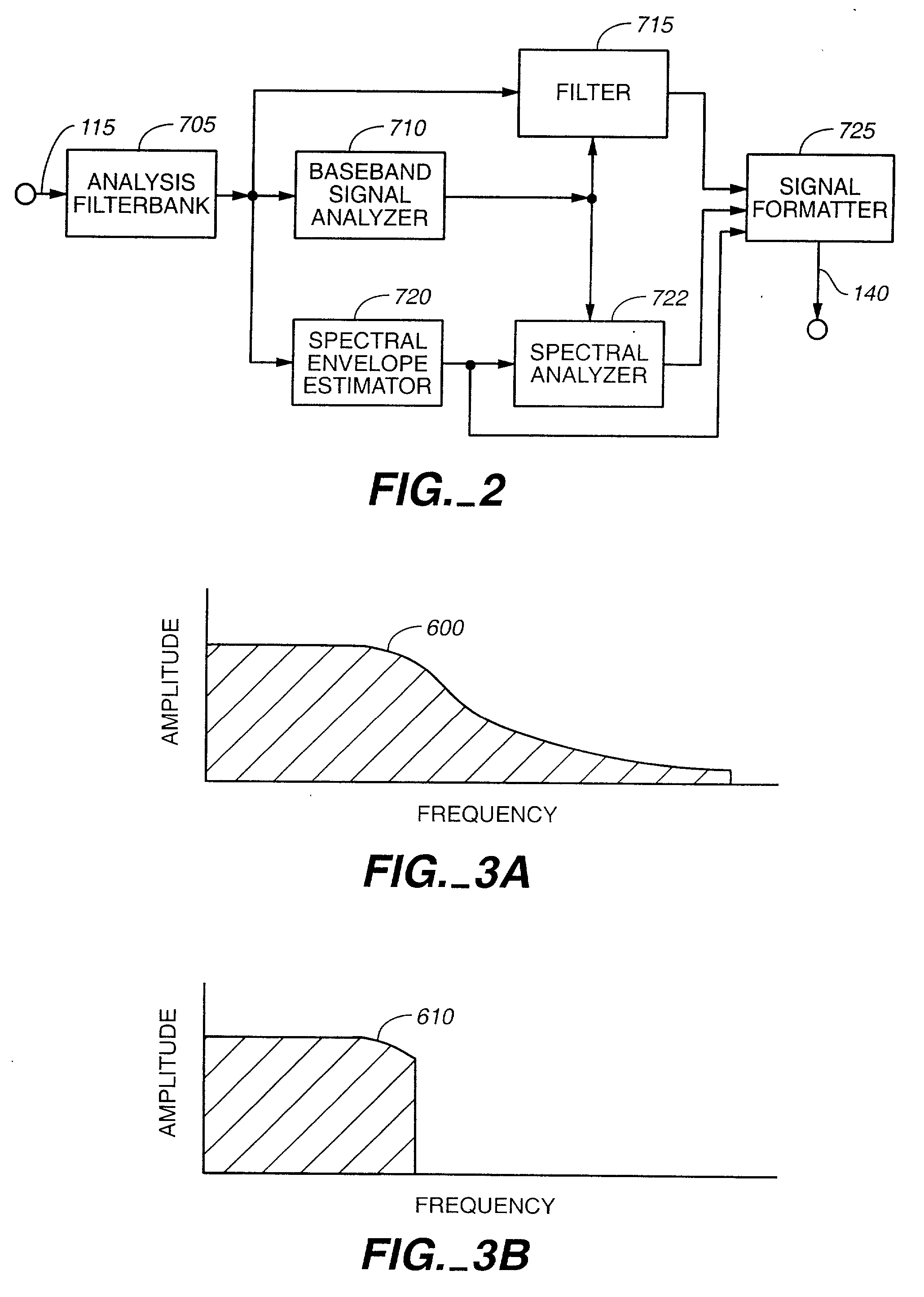
An audio signal is conveyed more efficiently by transmitting or recording a baseband of the signal with an estimated spectral envelope and a noise-blending parameter derived from a measure of the signal's noise-like quality. The signal is reconstructed by translating spectral components of the baseband signal to frequencies outside the baseband, adjusting phase of the regenerated components to maintain phase coherency, adjusting spectral shape according to the estimated spectral envelope, and adding noise according to the noise-blending parameter. Preferably, the transmitted or recorded signal also includes an estimated temporal envelope that is used to adjust the temporal shape of the reconstructed signal.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
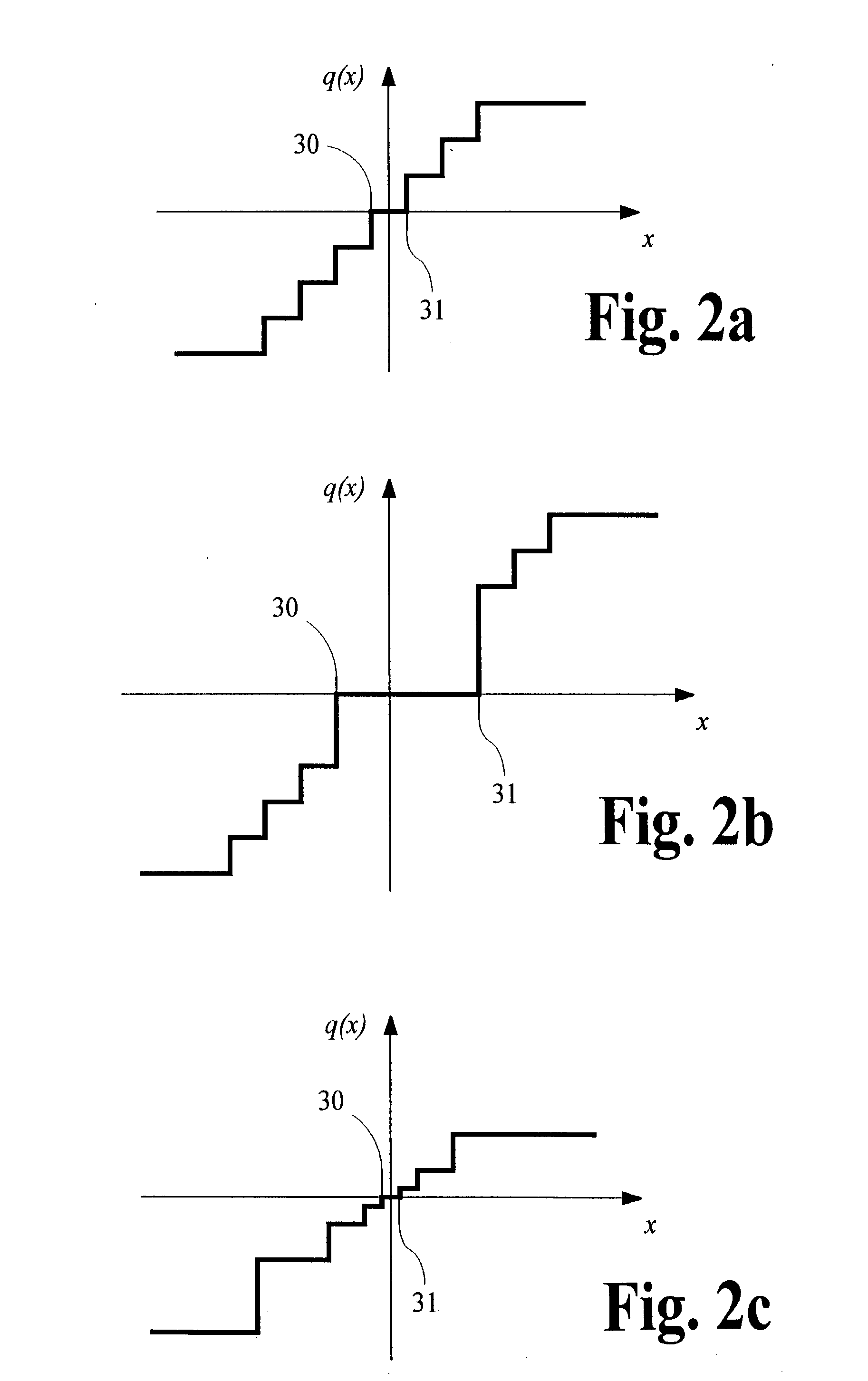
Audio coding system using spectral hole filling
ActiveUS20030233234A1Improve perceived qualityReducing and avoiding degradationCode conversionSpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumAudio frequency
Audio coding processes like quantization can cause spectral components of an encoded audio signal to be set to zero, creating spectral holes in the signal. These spectral holes can degrade the perceived quality of audio signals that are reproduced by audio coding systems. An improved decoder avoids or reduces the degradation by filling the spectral holes with synthesized spectral components. An improved encoder may also be used to realize further improvements in the decoder.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
In-situ method of analyzing cells
InactiveUS6165734AWidespread samplingEasy to masterRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryHistological stainingBiology
A method of in situ analysis of a biological sample comprising the steps of (a) staining the biological sample with N stains of which a first stain is selected from the group consisting of a first immunohistochemical stain, a first histological stain and a first DNA ploidy stain, and a second stain is selected from the group consisting of a second immunohistochemical stain, a second histological stain and a second DNA ploidy stain, with provisions that N is an integer greater than three and further that (i) if the first stain is the first immunohistochemical stain then the second stain is either the second histological stain or the second DNA ploidy stain; (ii) if the first stain is the first histological stain then the second stain is either the second immunohistochemical stain or the second DNA ploidy stain; whereas (iii) if the first stain is the first DNA ploidy stain then the second stain is either the second immunohistochemical stain or the second histological stain; and (b) using a spectral data collection device for collecting spectral data from the biological sample, the spectral data collection device and the N stains are selected such that a spectral component associated with each of the N stains is collectable.
Owner:APPLIED SPECTRAL IMAGING
Apparatus and method for providing information for at least one structure
A spectrally encoded endoscopic probe having high resolution and small diameter comprising at least one flexible optical fiber; an energy source; a grating through which said energy is transmitted such that the energy spectrum is dispersed; a lens for focusing the dispersed energy spectrum onto a sample such that the impingement spot for each wavelength is a separate position on the sample, the wavelength spectrum defining a wavelength encoded axis; means for mechanically scanning the sample with focused energy in a direction perpendicular to the wavelength encoded axis; a means for receiving energy reflected from the sample; and, a means for detecting the received reflected energy. The probe grating and lens delivers a beam of multi-spectral light having spectral components extending in one dimension across a target region and which is moved to scan in another direction. The reflected spectrum is measured to provide two dimensional imaging of the region.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
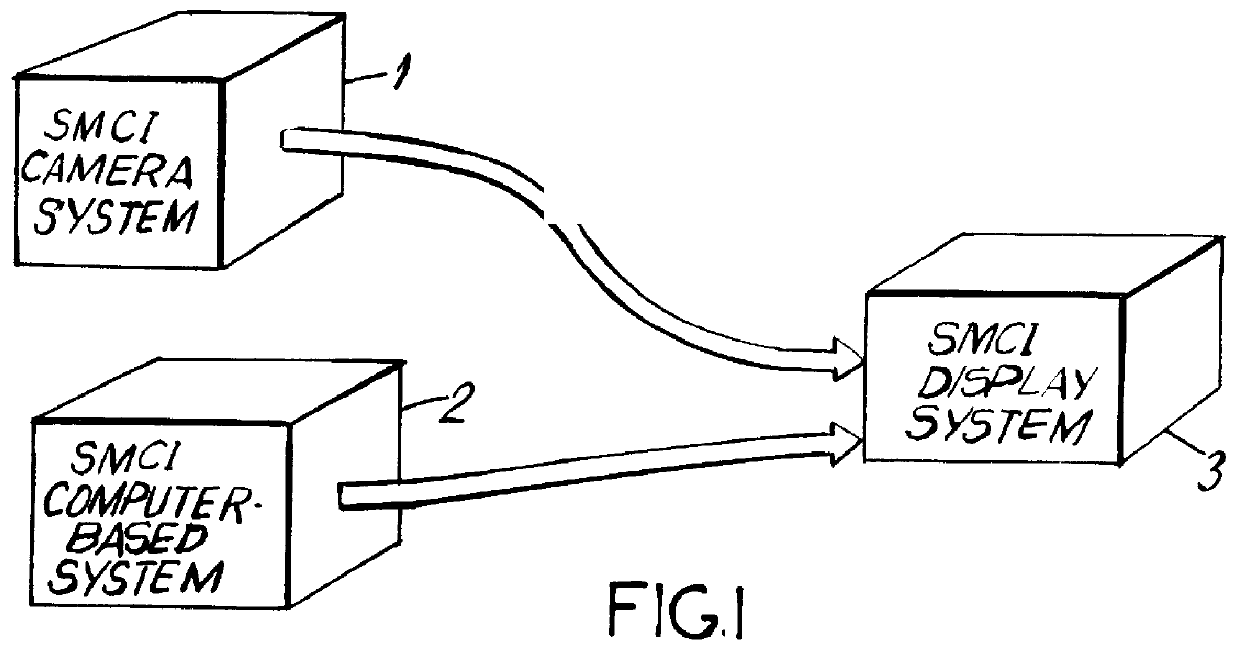
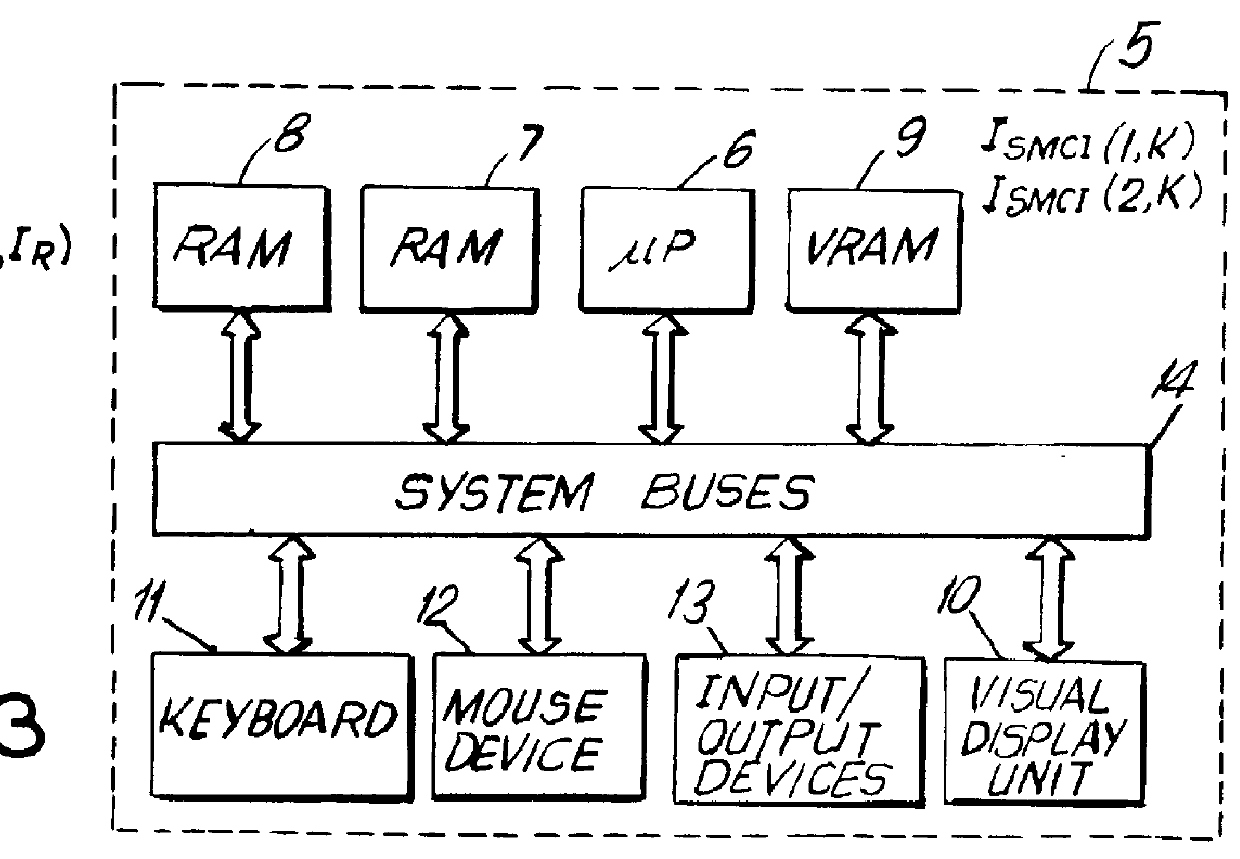
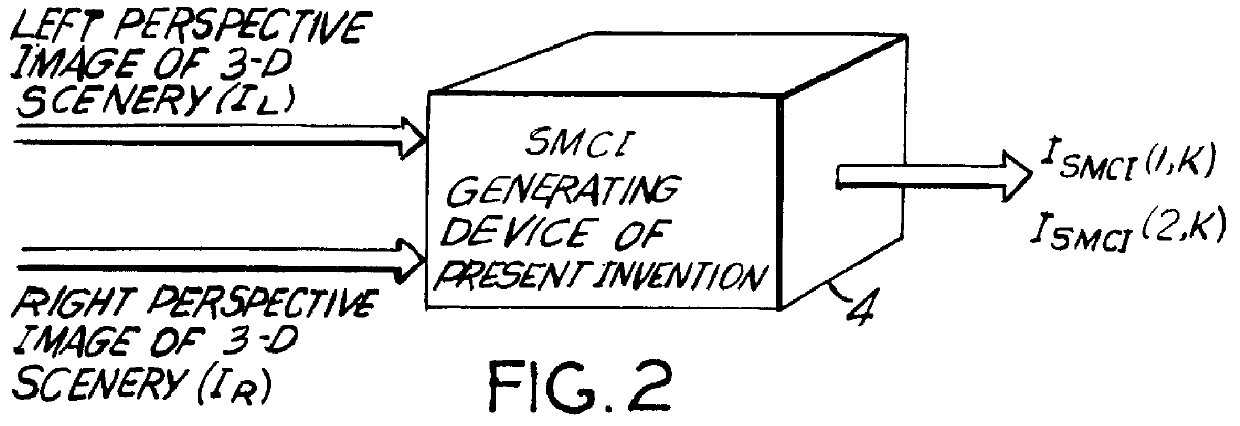
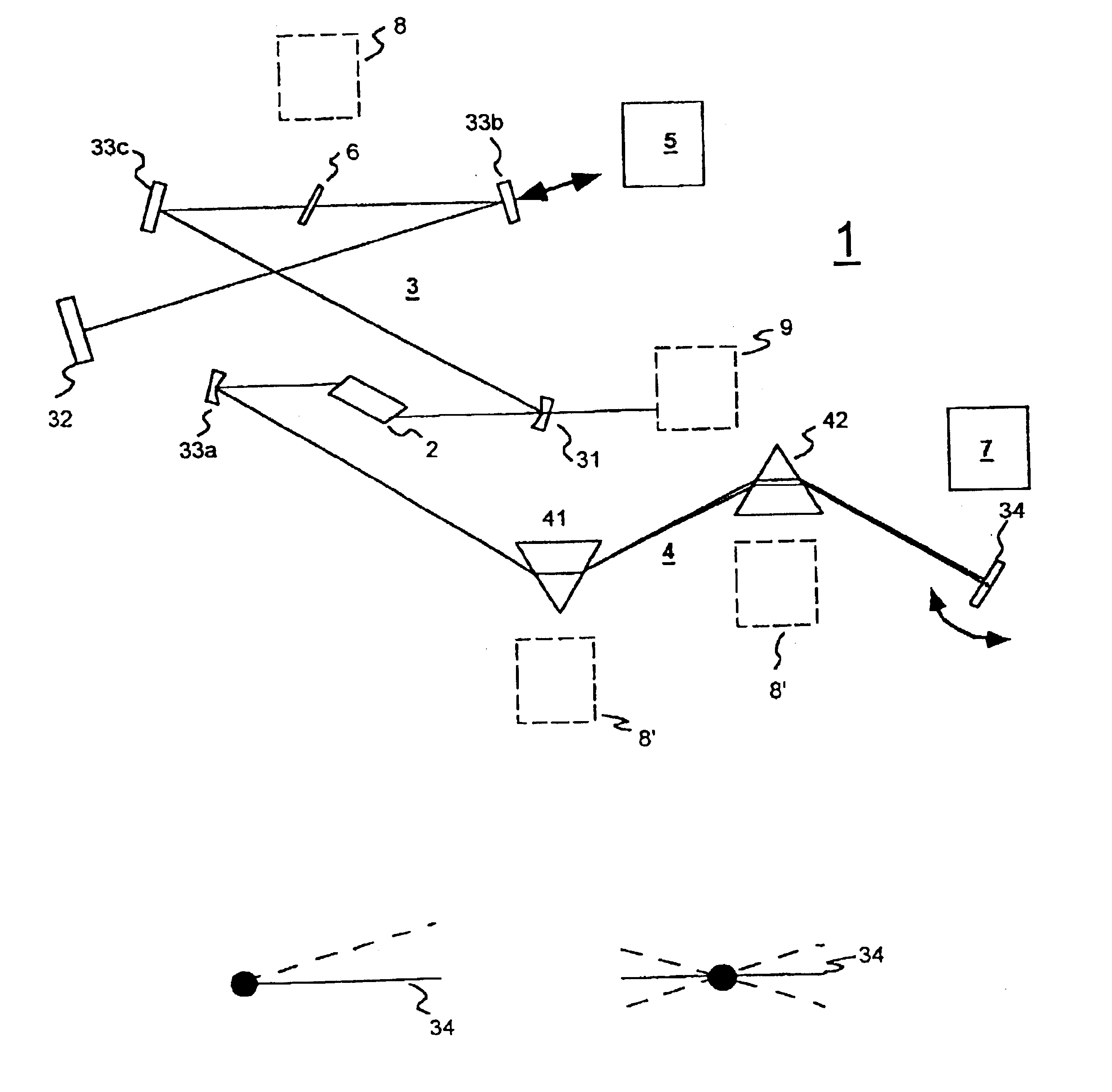
System and method for producing and displaying spectrally-multiplexed images of three-dimensional imagery for use in flicker-free stereoscopic viewing thereof
InactiveUS6111598AEasy to useColor television detailsDigital video signal modificationColor imageFrequency spectrum
A Method and apparatus is provided for producing and displaying pairs of spectrally-multiplexed gray-scale or color images of 3-D scenery for use in stereoscopic viewing thereof. In one illustrative embodiment of the present invention, pairs of spectrally-multiplexed color images of 3-D scenery are produced using a camera system records left and right color perspective images thereof and optically processes the spectral components thereof. In another illustrative embodiment of the present invention, pairs of spectrally-multiplexed color images of 3-D imagery are produced within a computer-based system which generates left and right perspective images thereof using computer graphic processes, and processes the pixel data thereof using pixel-data processing methods of the present invention. Thereafter, produced pairs of spectrally-multiplexed images can be recorded on diverse recording mediums, and accessed by the display system of the present invention for real-time display on diverse display surfaces including, for example, flat-panel liquid-crystal display (LCD) surfaces, CRT display surfaces, projection display screen surfaces, and electro-luminescent panel display surfaces. In the various illustrative embodiments of the display system, stereoscopic viewing of 3-D imagery is facilitated by wearing electrically passive or electrically-active light polarizing spectacles during the image display process of the present invention.
Owner:REVEO
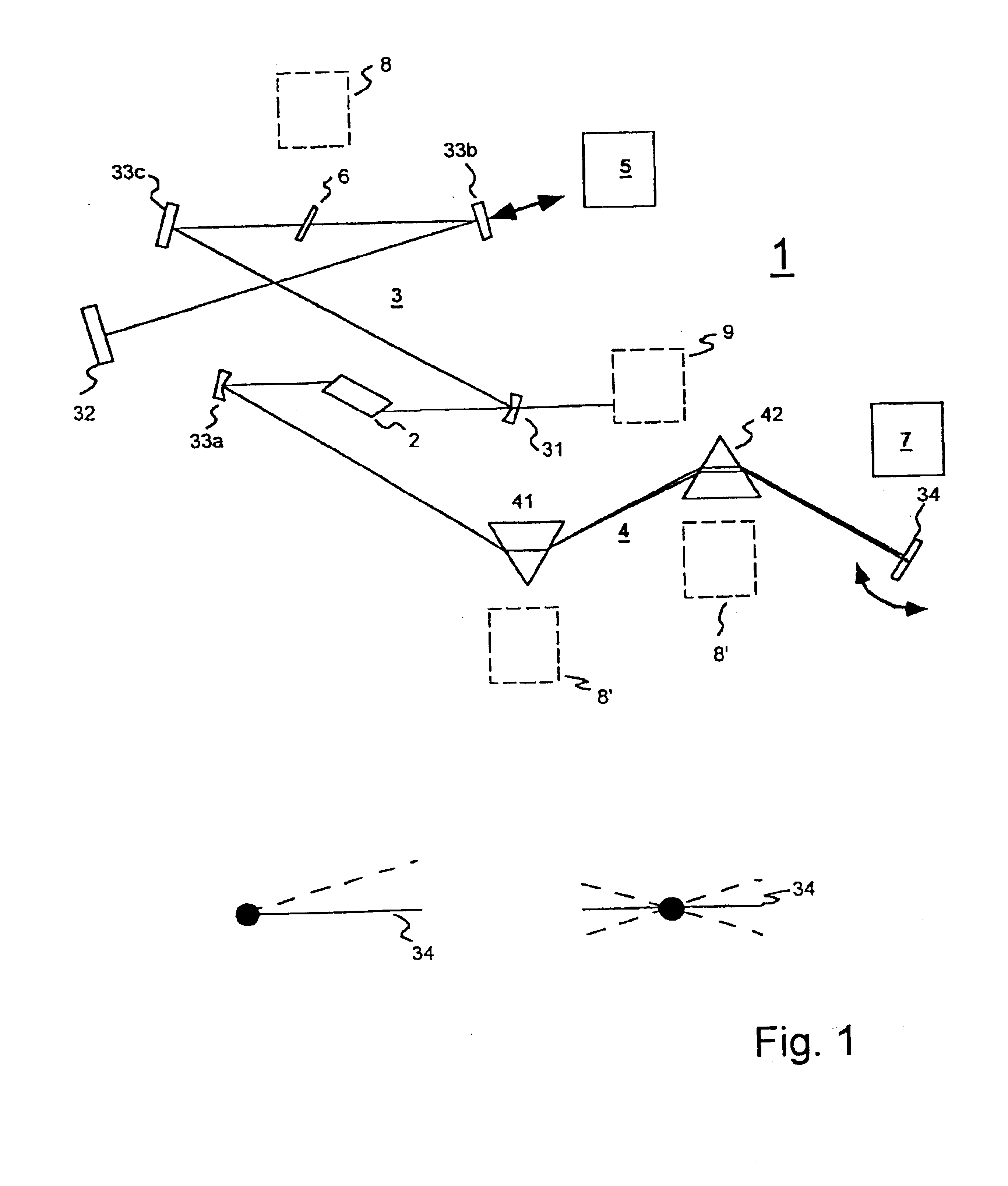
Generation of stabilized, ultra-short light pulses and the use thereof for synthesizing optical frequencies
InactiveUS6785303B1Optical measurementsMaterial analysis by optical meansLinear dispersionOptical frequencies
A process for operation of a laser device (1) is described, whereby circulating light pulses each comprising spectral components according to a plurality of longitudinal modes of a resonator configuration (3) are generated in the resonator configuration (3) and subjected to a compensation of group velocity dispersion, and a predetermined linear dispersion is introduced into the light path of the resonator configuration (3), so that at least one mode has a predetermined frequency and / or the mode distance between the modes has a predetermined value. Furthermore, regulations for stabilizing the laser device on the basis of this process and applications of the regulations for the generation for stabilized, ultra-short light pulses, generation of optical frequencies and in the frequency and / or time measuring technique as well as in the spectroscopy are described.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
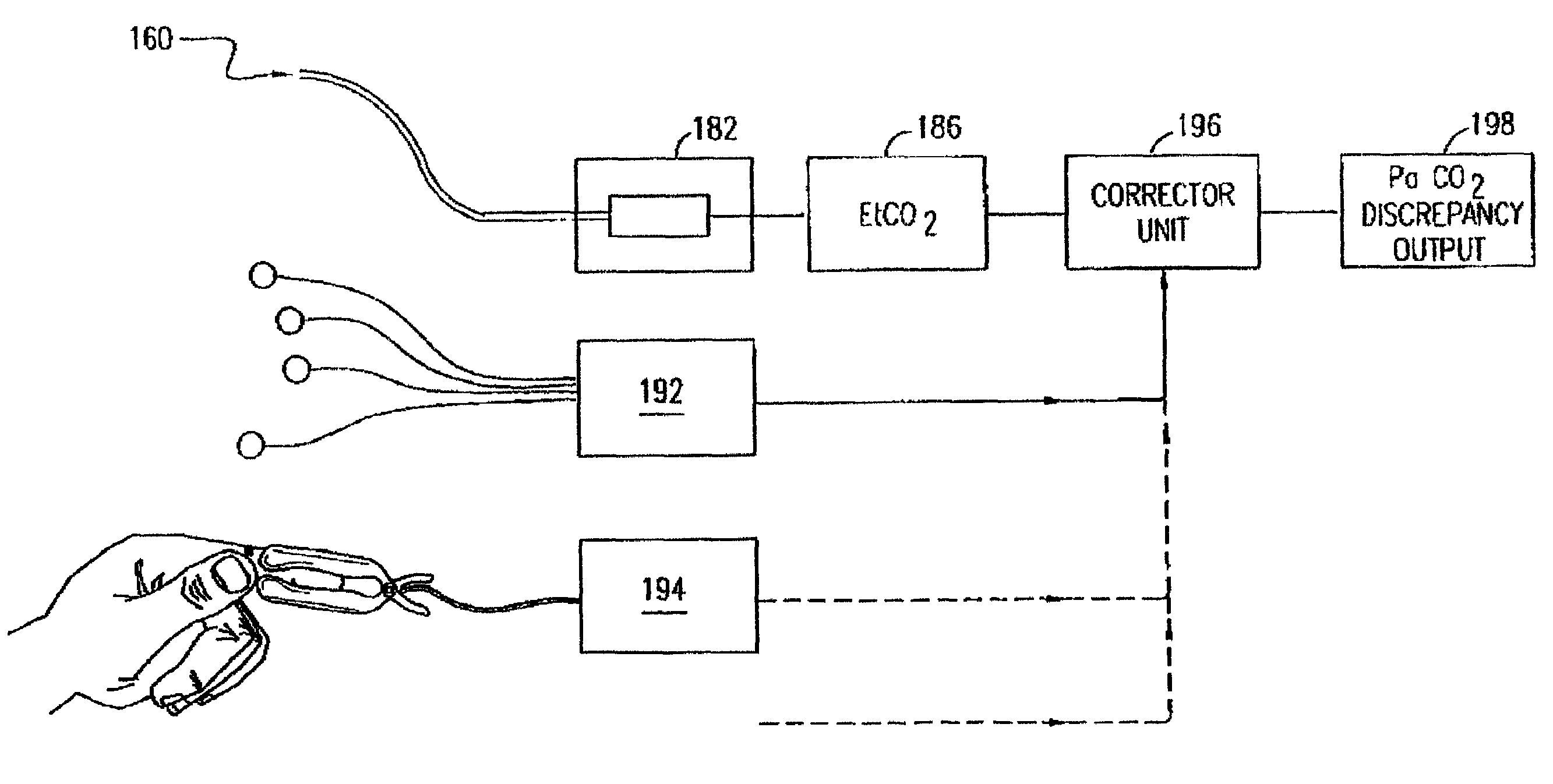
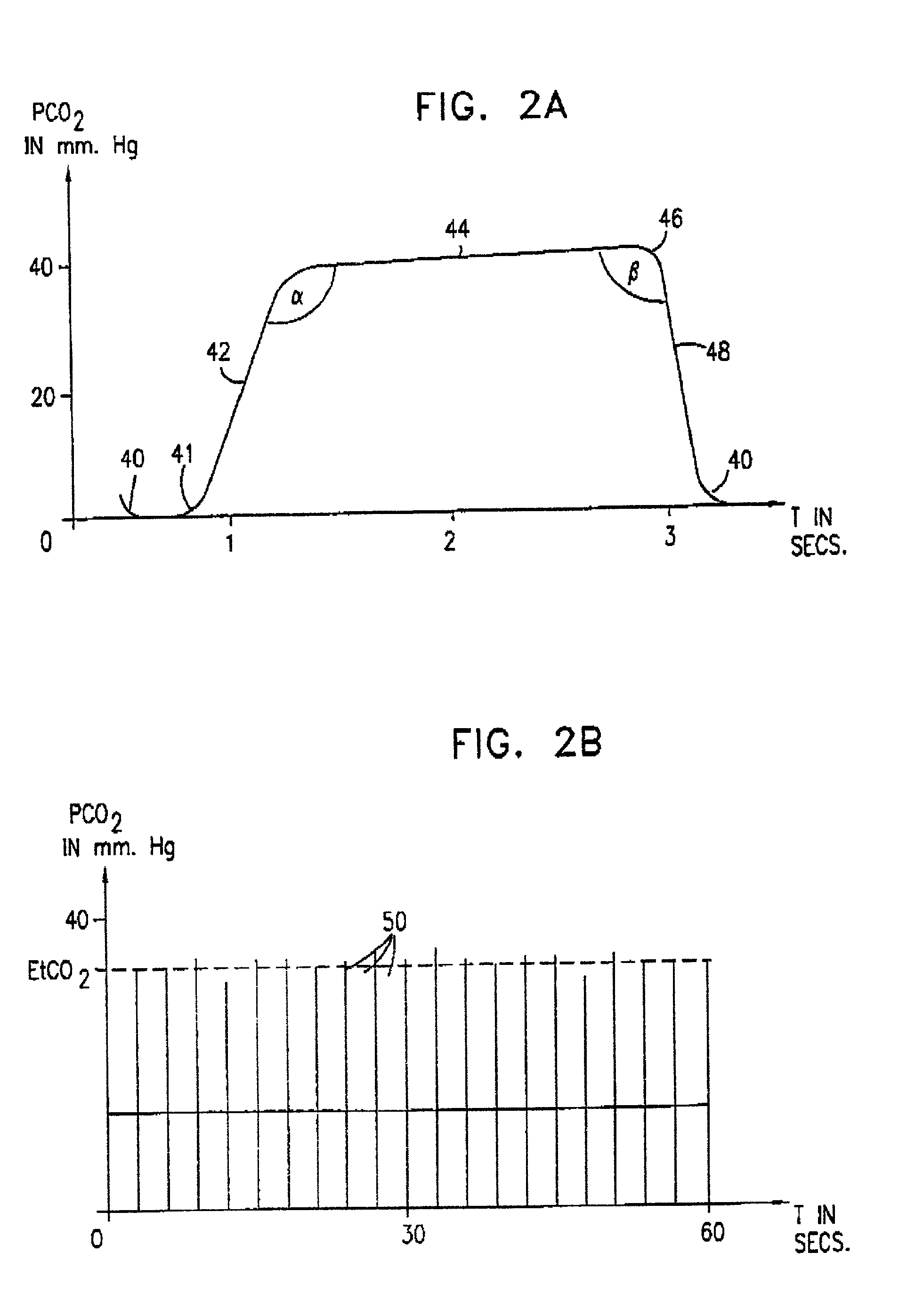
Waveform interpreter for respiratory analysis
InactiveUS6997880B2More informationAccurate diagnosisRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsWaveform analysisTime domain
A capnograph which performs an analysis of the breath waveforms measured by the carbon dioxide sensor, interprets the results of this analysis, and outputs to the operator diagnostic information about the respiratory status of the patient, or about the adequacy of the breathing support provided to the patient. The instrument compares a number of parameters characteristic of the waveforms of the patient's breath with an internal library of the values of those parameters expected from normal waveforms stored in its memory. These parameters may either relate to specific features of the waveform in the time domain, or may characterize spectral components of the waveform in the frequency domain. The capnographic waveform analysis may be combined with further non-invasive measurements in order to provide an indication of the deviation of the value of EtCO2 from PaCO2.
Owner:ORIDION MEDICAL 1987
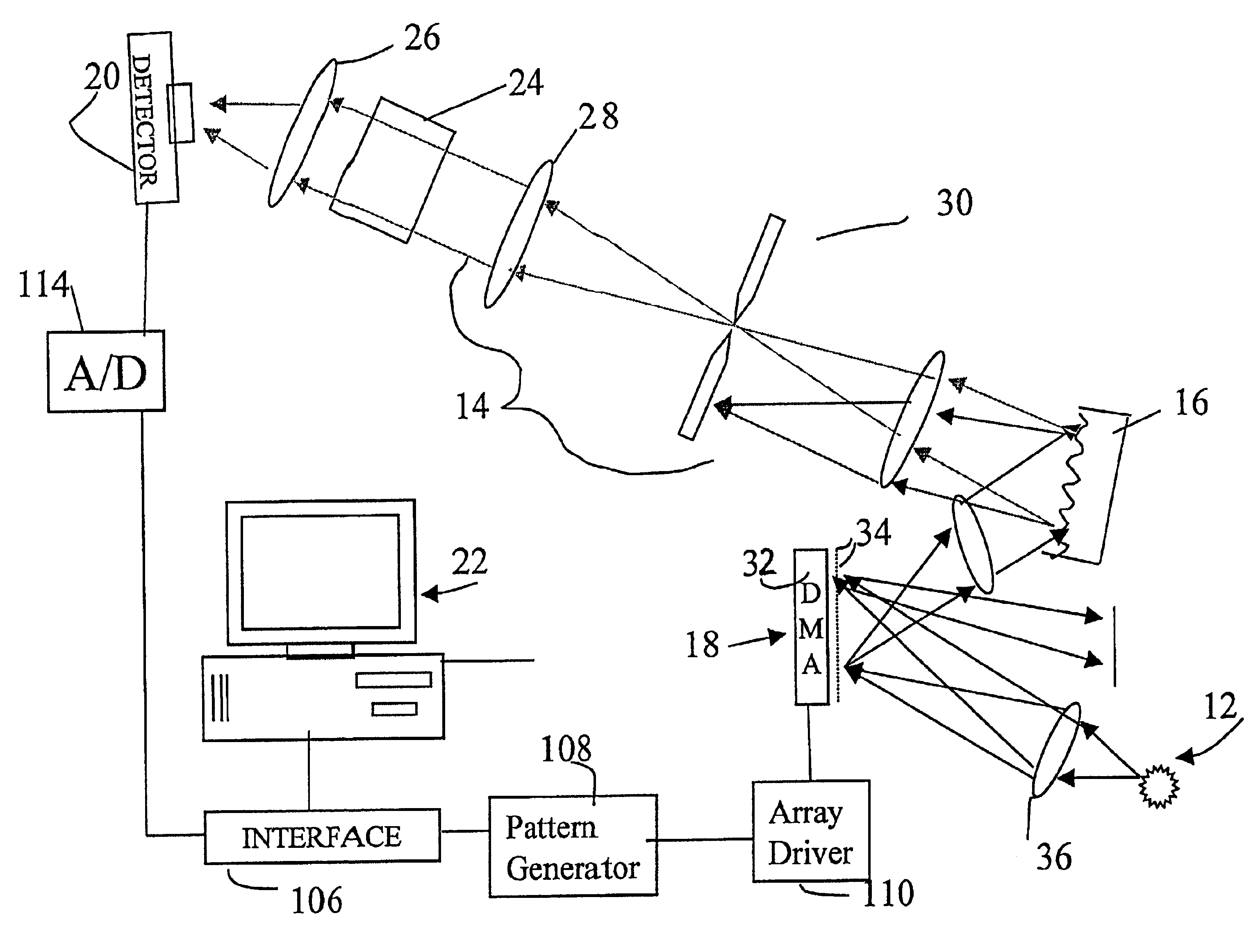
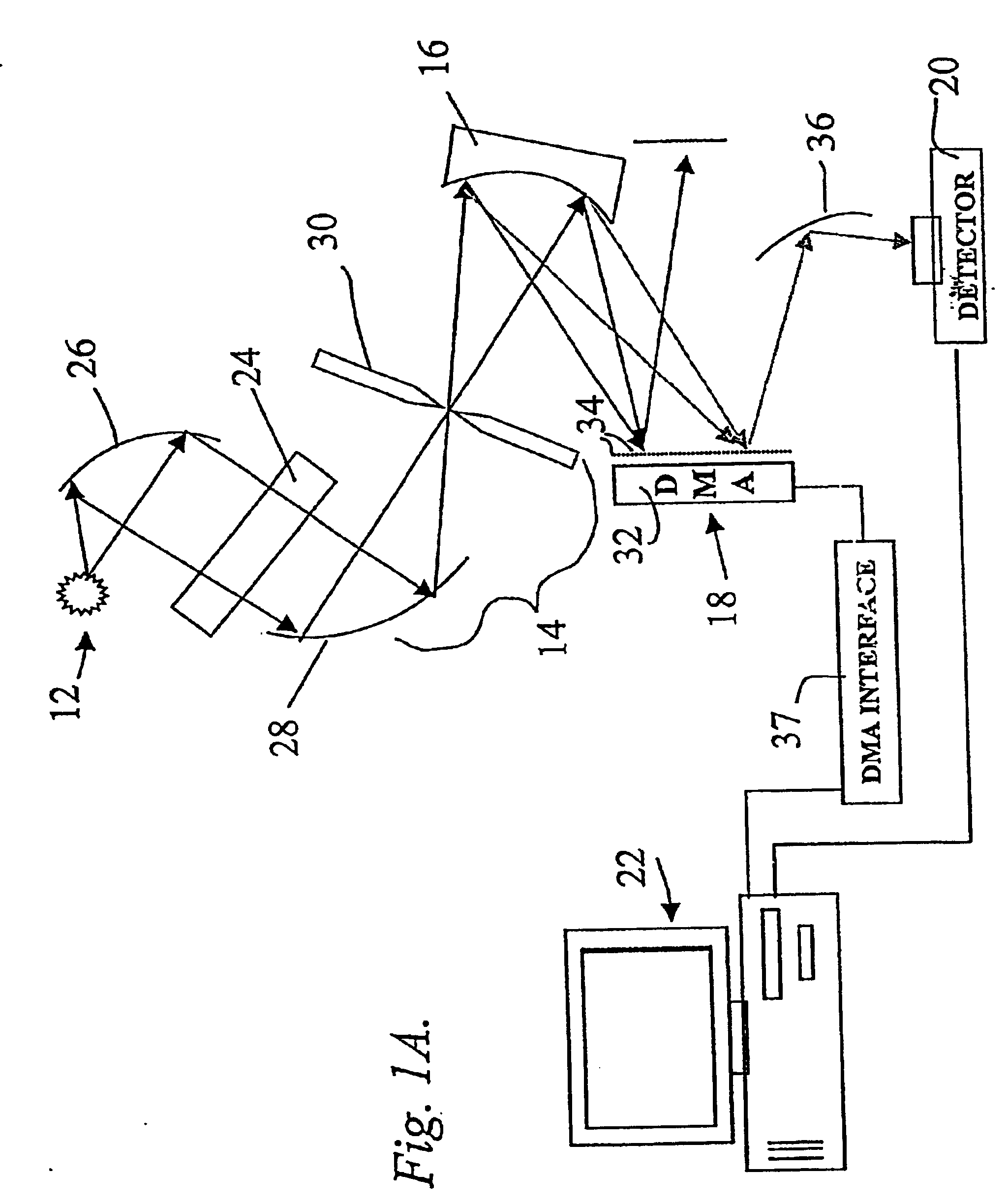
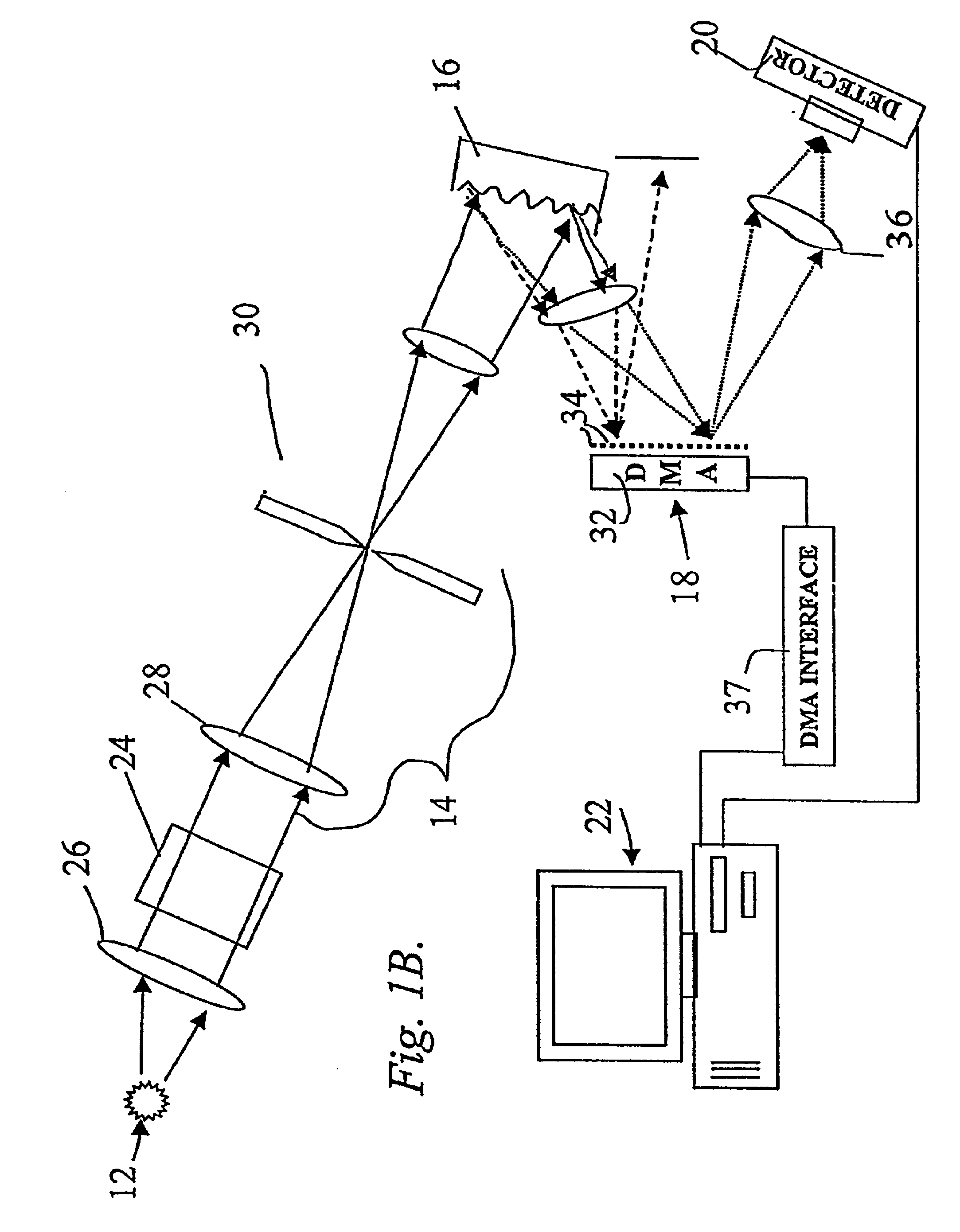
System and method for encoded spatio-spectral information processing
InactiveUS6859275B2Less sensitive to ambient noiseEasy to operateRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsInformation processingLength wave
Encoded spatio-spectral information processing is performed using a system having a radiation source, wavelength dispersion device and two-dimensional switching array, such as digital micro-mirror array (DMA). In one aspect, spectral components from a sample are dispersed in space and modulated separately by the switching array, each element of which may operate according to a predetermined encoding pattern. The encoded spectral components can then be detected and analyzed. In a different aspect, the switching array can be used to provide a controllable radiation source for illuminating a sample with radiation patterns that have predetermined characteristics and separately encoded components. Various applications are disclosed.
Owner:PLAIN SIGHT SYST
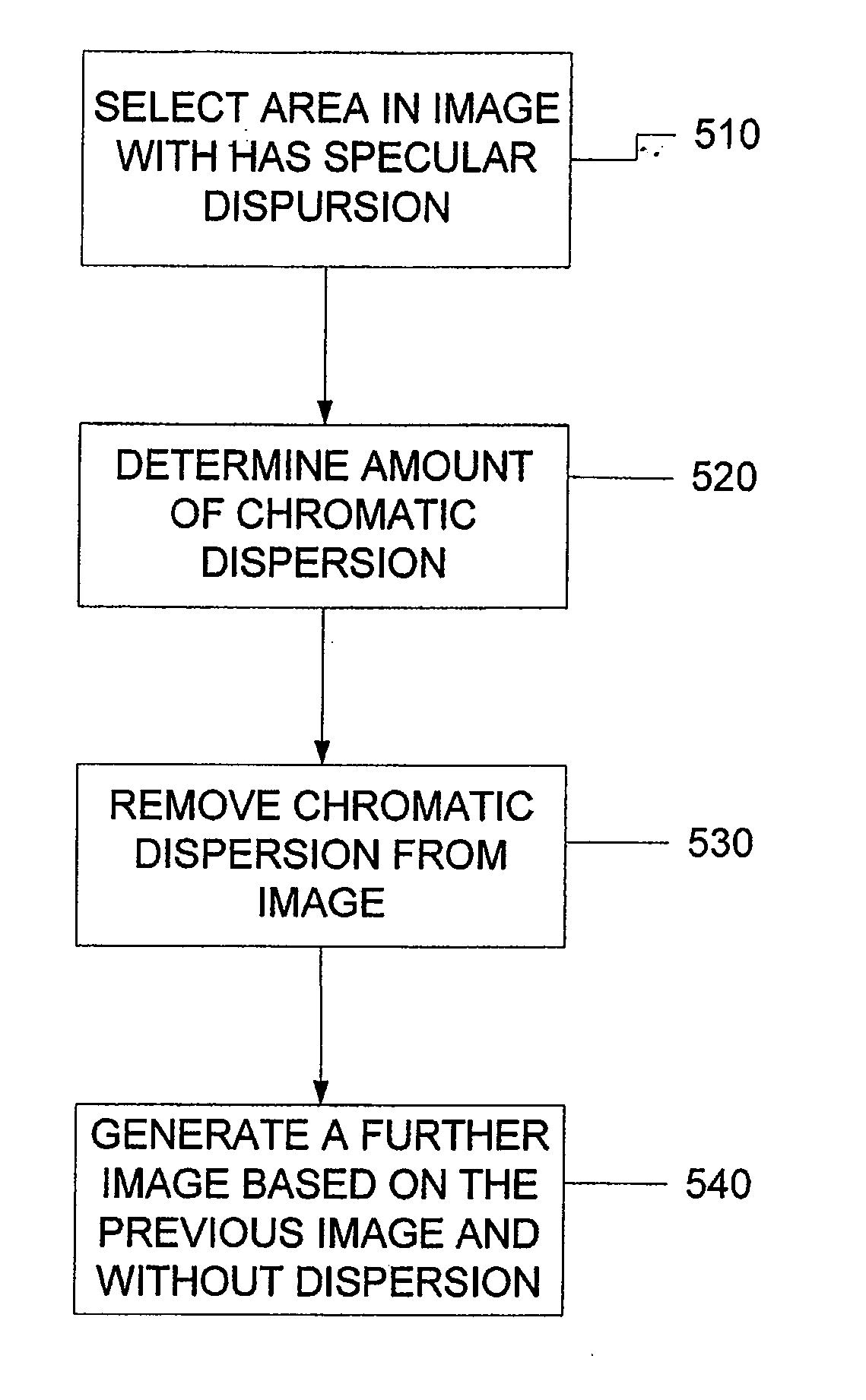
Process, System And Software Arrangement For A Chromatic Dispersion Compensation Using Reflective Layers In Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Imaging
ActiveUS20090196477A1Compensation for dispersionEasy to implementRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFrequency spectrumReflective layer
A system, process and software arrangement are provided to compensate for a dispersion in at least one portion of an image. In particular, information associated with the portion of the image is obtained. The portion of the image can be associated with an interference signal that includes a first electromagnetic radiation received from a sample and a second electromagnetic radiation received from a reference. The dispersion in the at least one portion of the image can be compensated by controlling a phase of at least one spectral component of the interference signal.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Hybrid multi-channel/cue coding/decoding of audio signals
ActiveUS7292901B2Low bandwidthReduce amountPseudo-stereo systemsSpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumAudio signal flow
Part of the spectrum of two or more input signals is encoded using conventional coding techniques, while encoding the rest of the spectrum using binaural cue coding (BCC). In BCC coding, spectral components of the input signals are downmixed and BCC parameters (e.g., inter-channel level and / or time differences) are generated. In a stereo implementation, after converting the left and right channels to the frequency domain, pairs of left- and right-channel spectral components are downmixed to mono. The mono components are then converted back to the time domain, along with those left- and right-channel spectral components that were not downmixed, to form hybrid stereo signals, which can then be encoded using conventional coding techniques. For playback, the encoded bitstream is decoded using conventional decoding techniques. BCC synthesis techniques may then apply the BCC parameters to synthesize an auditory scene based on the mono components as well as the unmixed stereo components.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
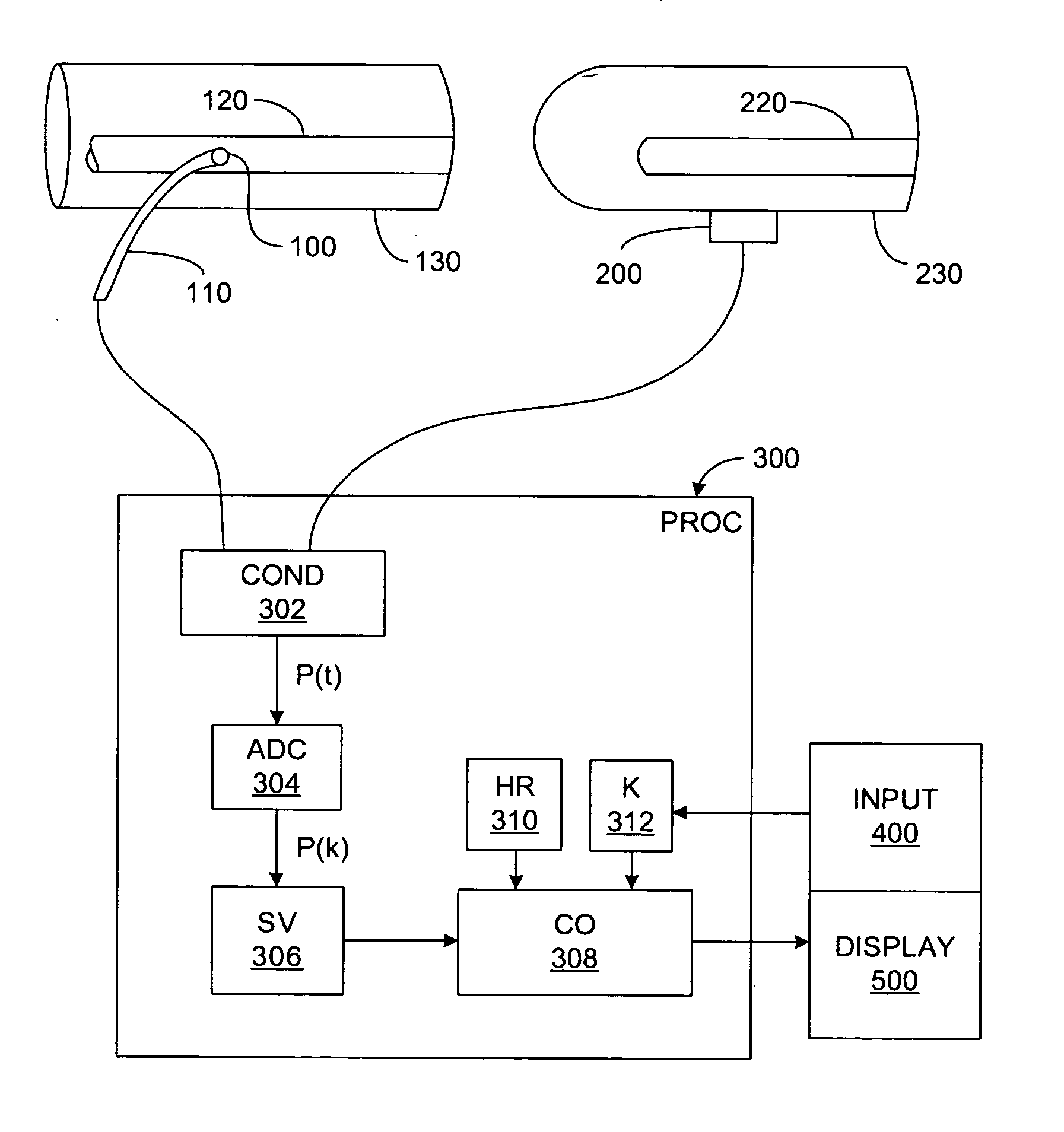
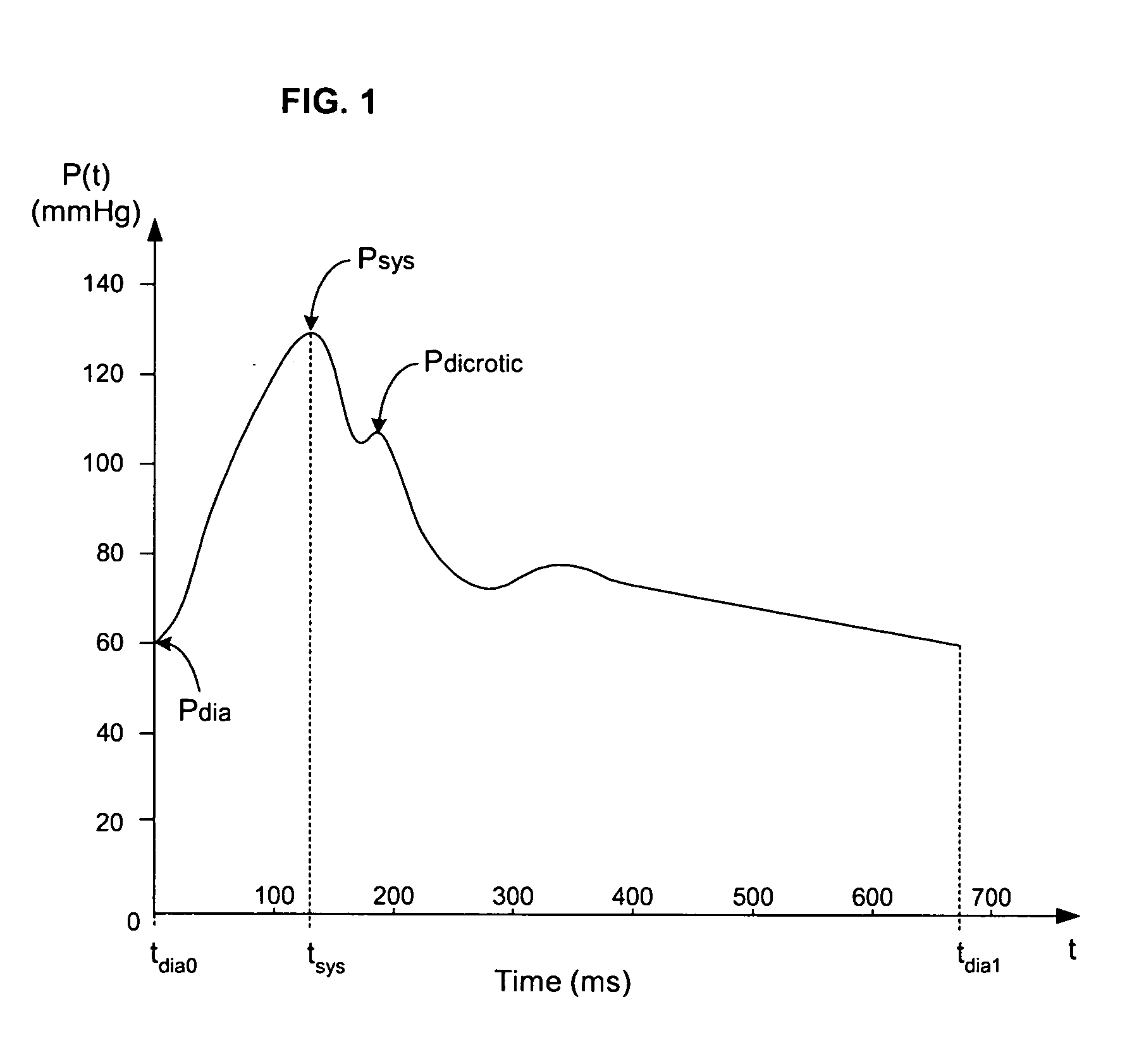
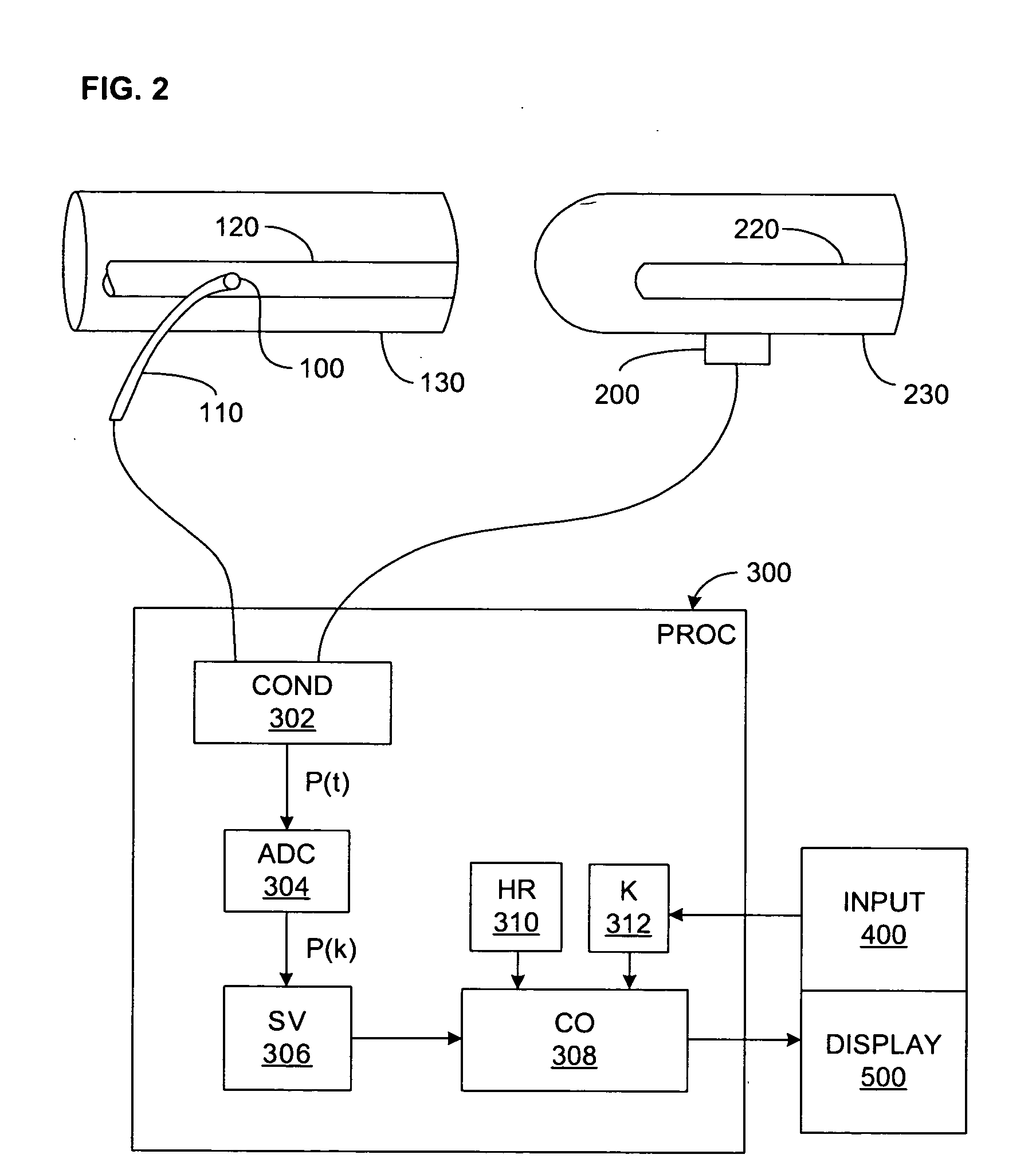
Pressure-based system and method for determining cardiac stroke volume
ActiveUS20050124903A1Potent effectEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterArterial pressure waveformDecreased mean arterial pressure
Cardiac stroke volume (SV) of a subject is estimated as a function of a value derived from a measured arterial pressure waveform. The value may be the standard deviation, or a function of the difference between maximum and minimum pressure values, or a function of either the maximum value of the first time derivative or the absolute value of the minimum of the first time derivative of the pressure waveform, or both, or a function of the magnitude of one or more spectral components of the pressure waveform at a frequency corresponding to the heart rate. Cardiac output is then estimated as the product of the subject's heart rate and SV, scaled by a calibration constant. Arterial pressure may be measured invasively or non-invasively.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
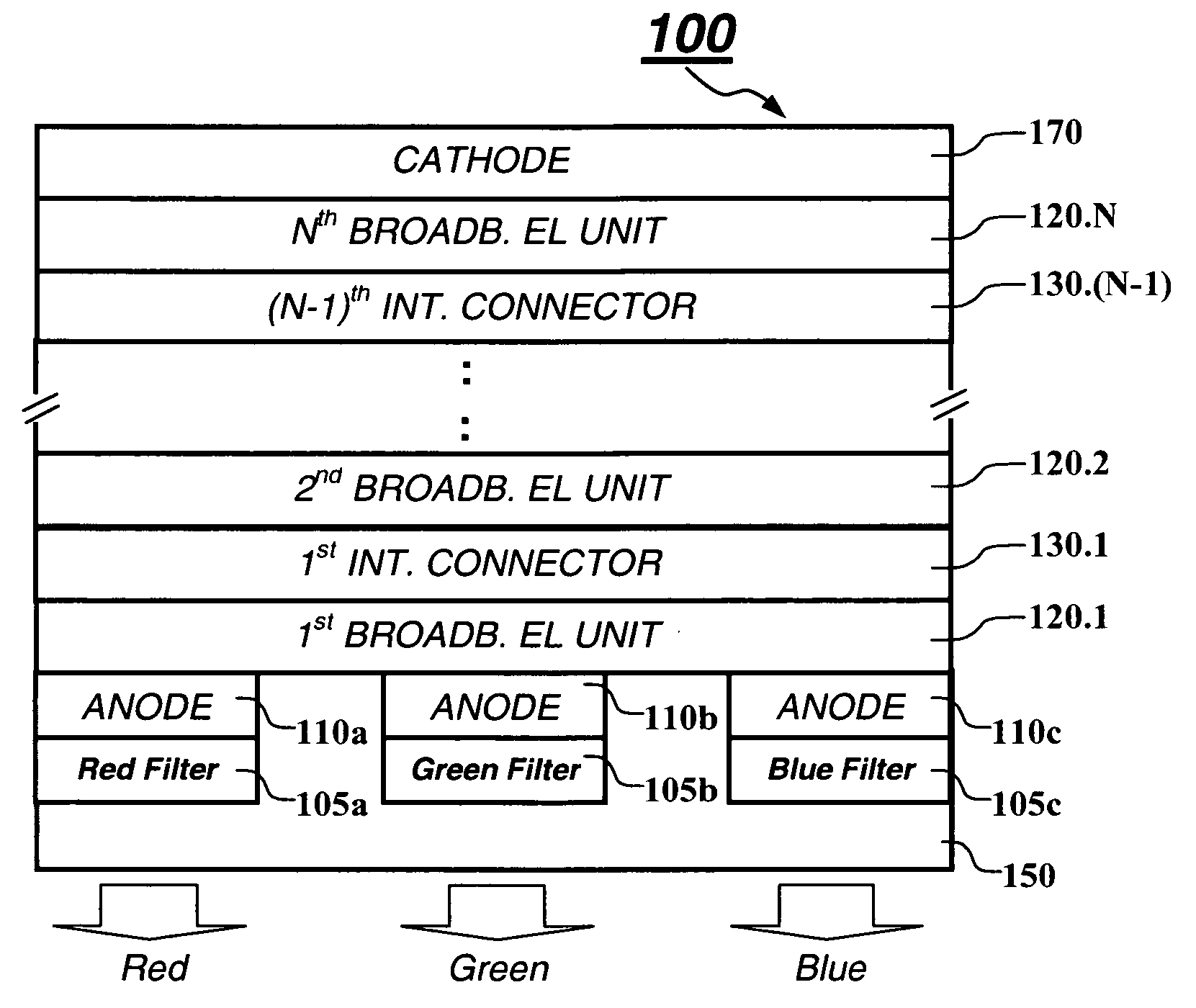
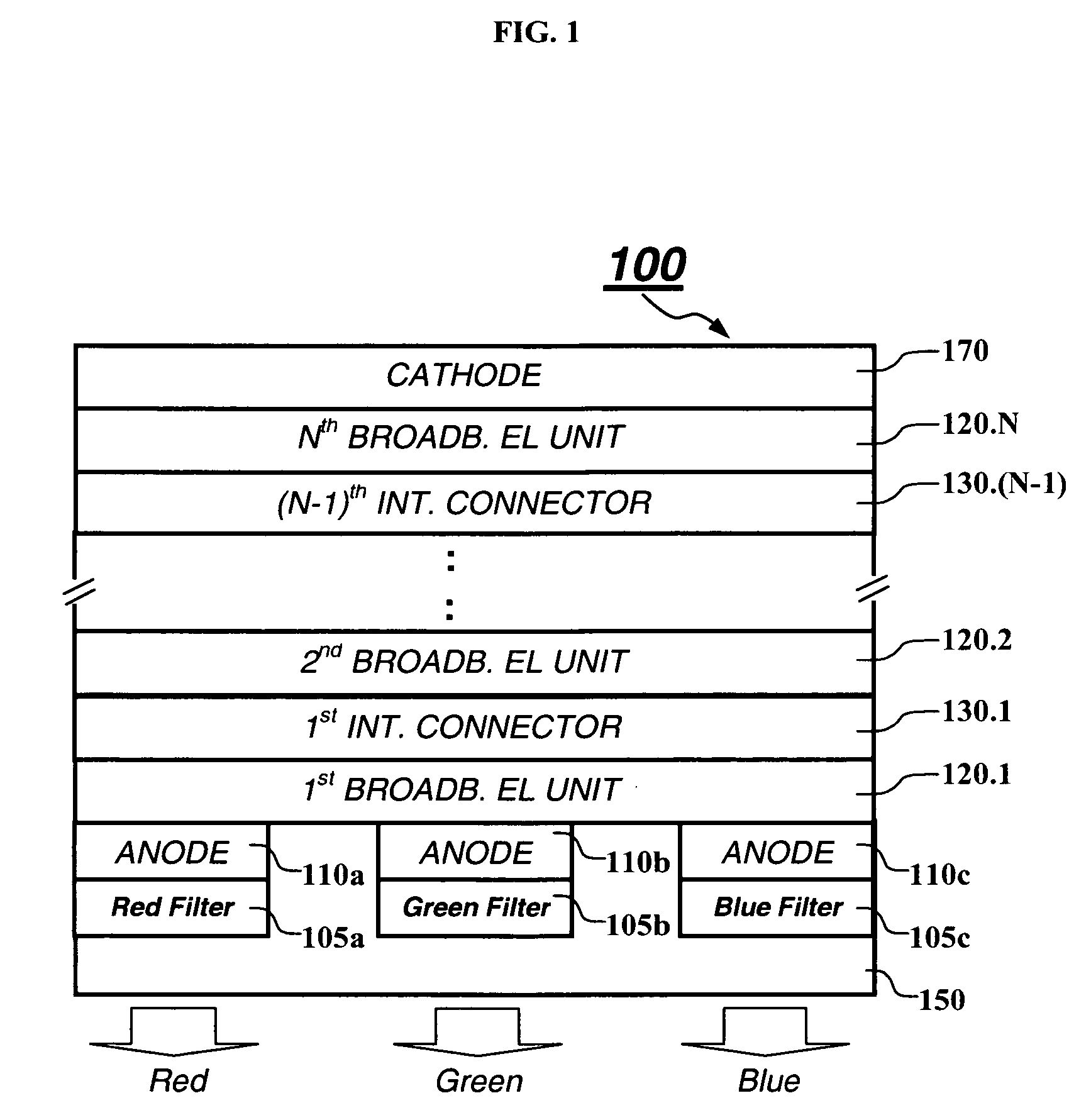
White light tandem OLED display with filters
ActiveUS20070001587A1EffectiveImprove color gamutDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsPeak valueBroadband
A tandem OLED device having spaced electrodes includes broadband light-emitting units disposed between the electrodes that produce different emission spectra and each light-emitting unit produces light that has multiple spaced peak spectral components, and an intermediate connector disposed between each of the light-emitting units. The device also includes an array of at least three different color filters associated with the device which receives light from the broadband light-emitting units, the band pass of each of the color filters being selected to produce different colored light, wherein the full width at about half maximum of at least one of such spaced peak spectral components produced by each emitting unit is within the band pass of a color filter, and wherein each of the at least three different color filters receives at least one spaced peak spectral component having a full width at about half maximum that is within its band pass.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
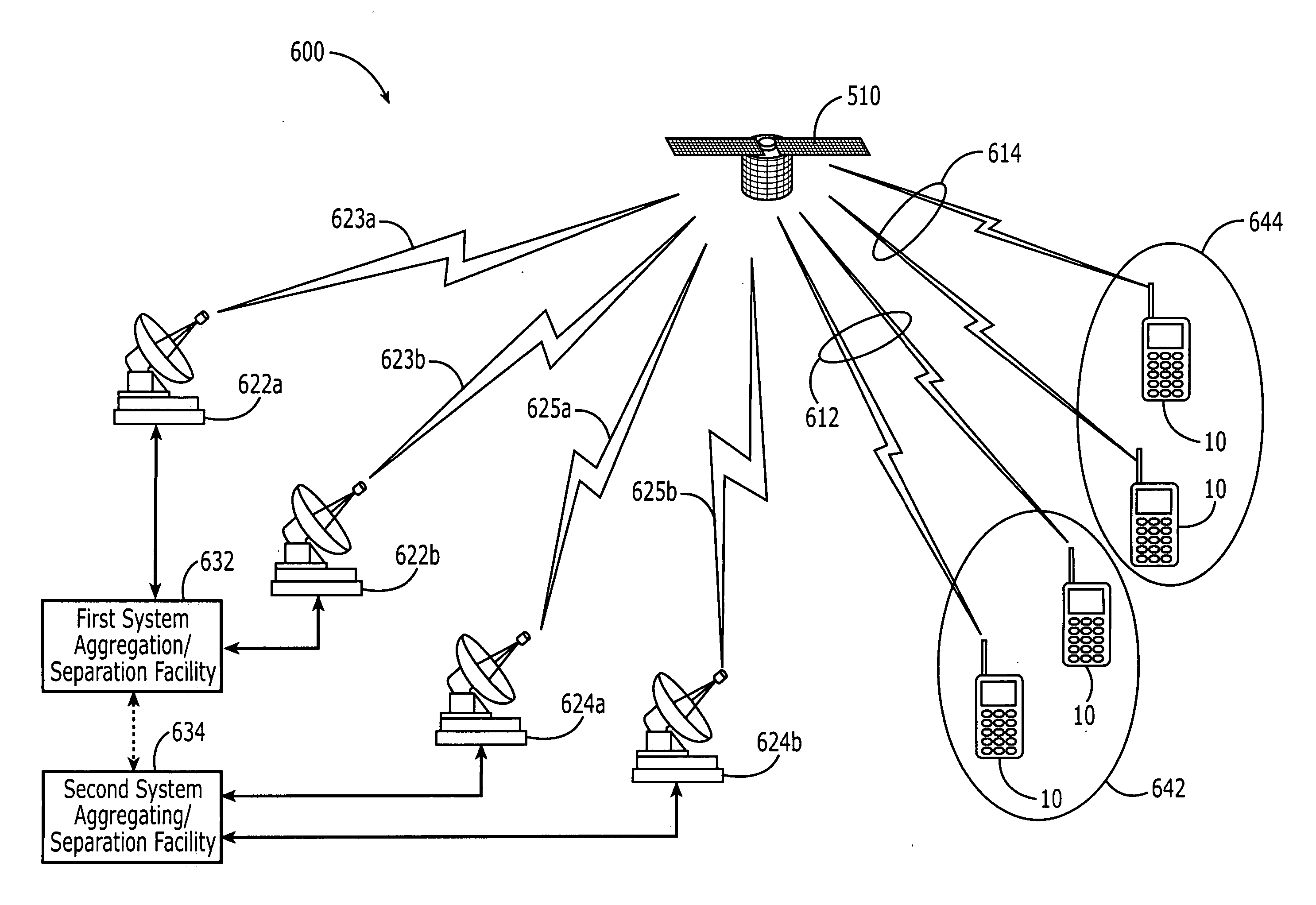
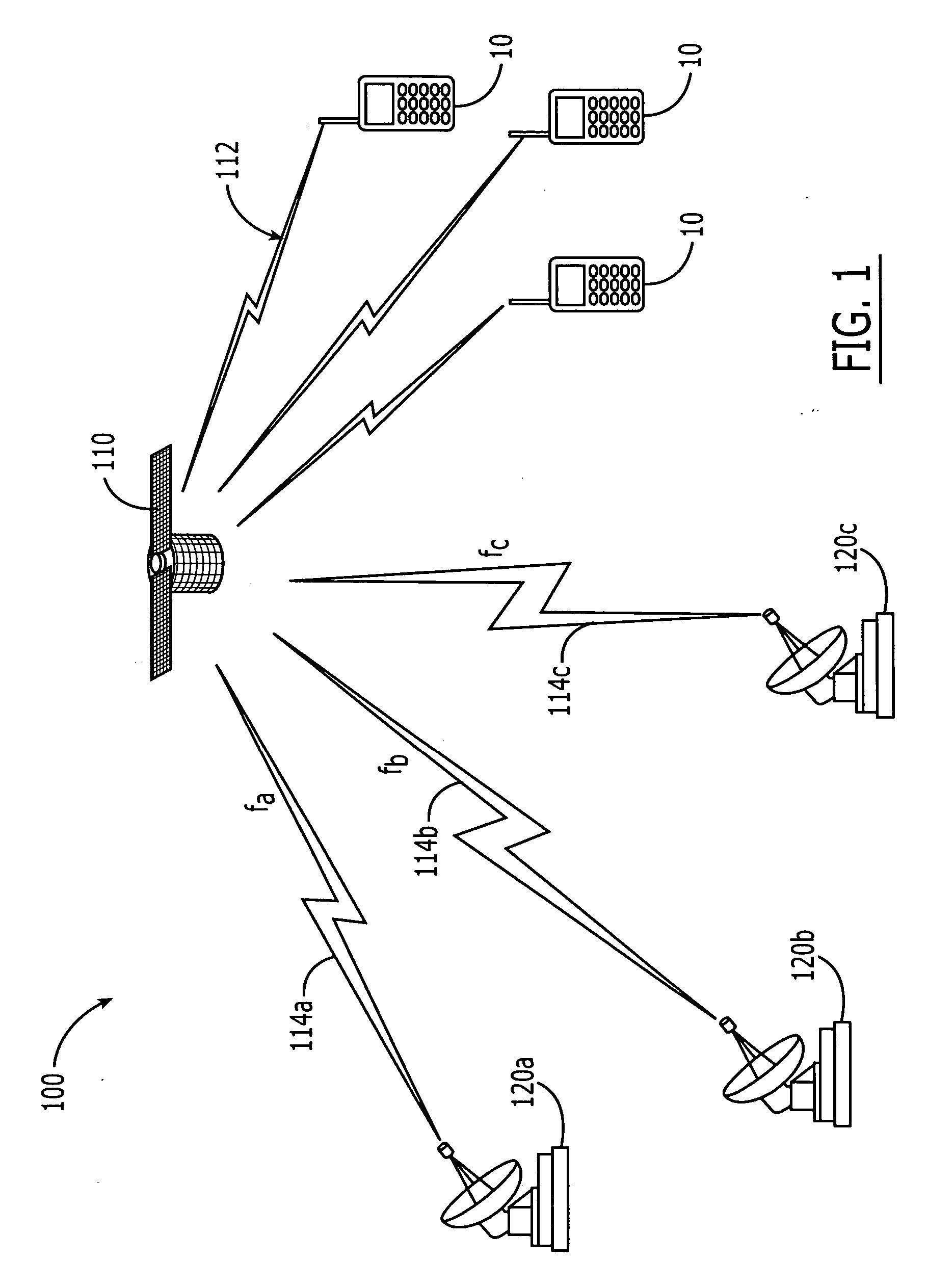
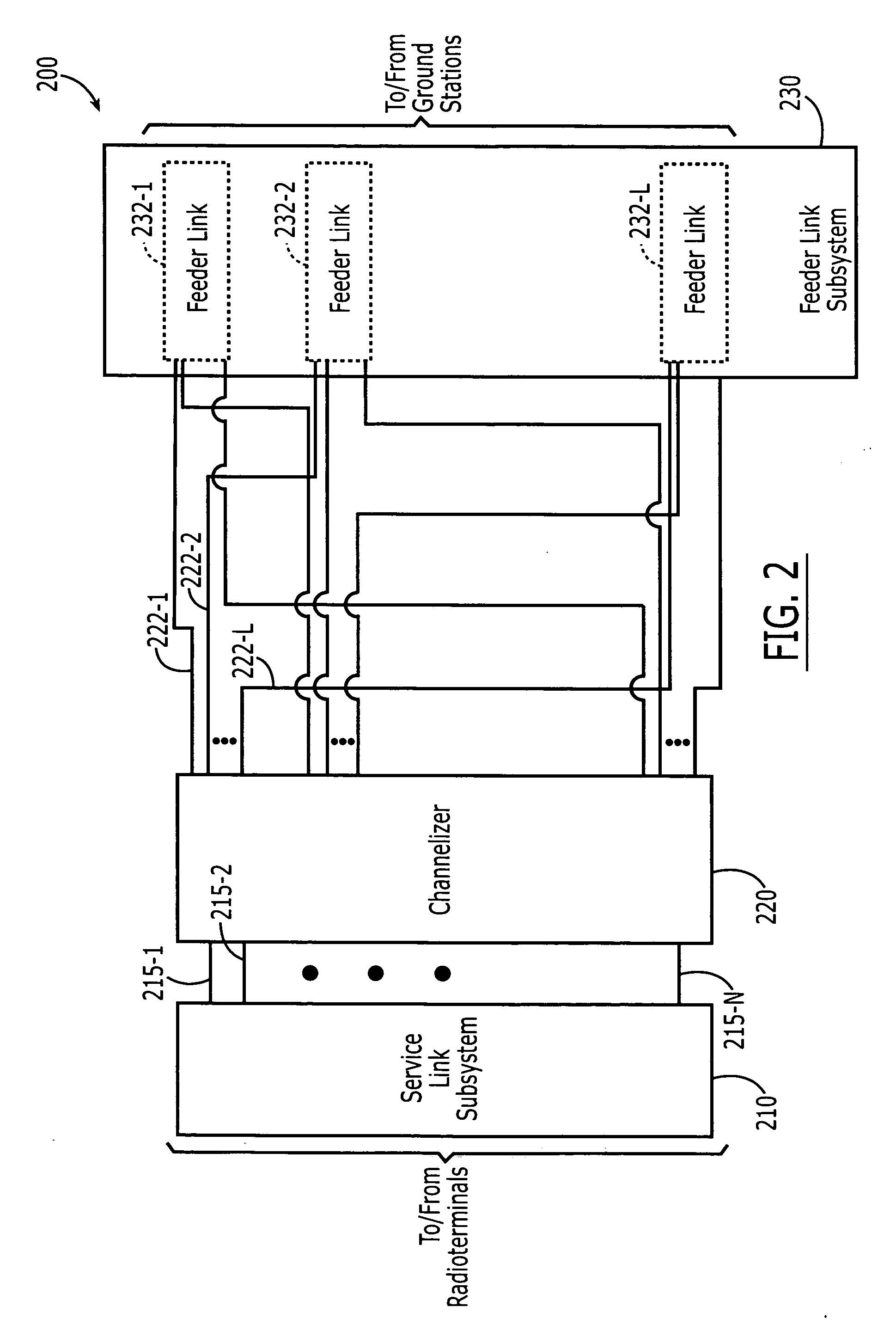
Satellite communications systems and methods with distributed and/or centralized architecture including ground-based beam forming
ActiveUS20060205347A1Active radio relay systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemAntenna element
A space-based component (SBC) of a communications system includes a service link subsystem including a plurality of service link antenna elements configured to provide service links with radioterminals and a feeder link subsystem configured to provide respective feeder links to / from respective processing facilities. The SBC further includes a channelizer configured to map different spectral components of a signal received at the SBC via a service link antenna element to different feeder links.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
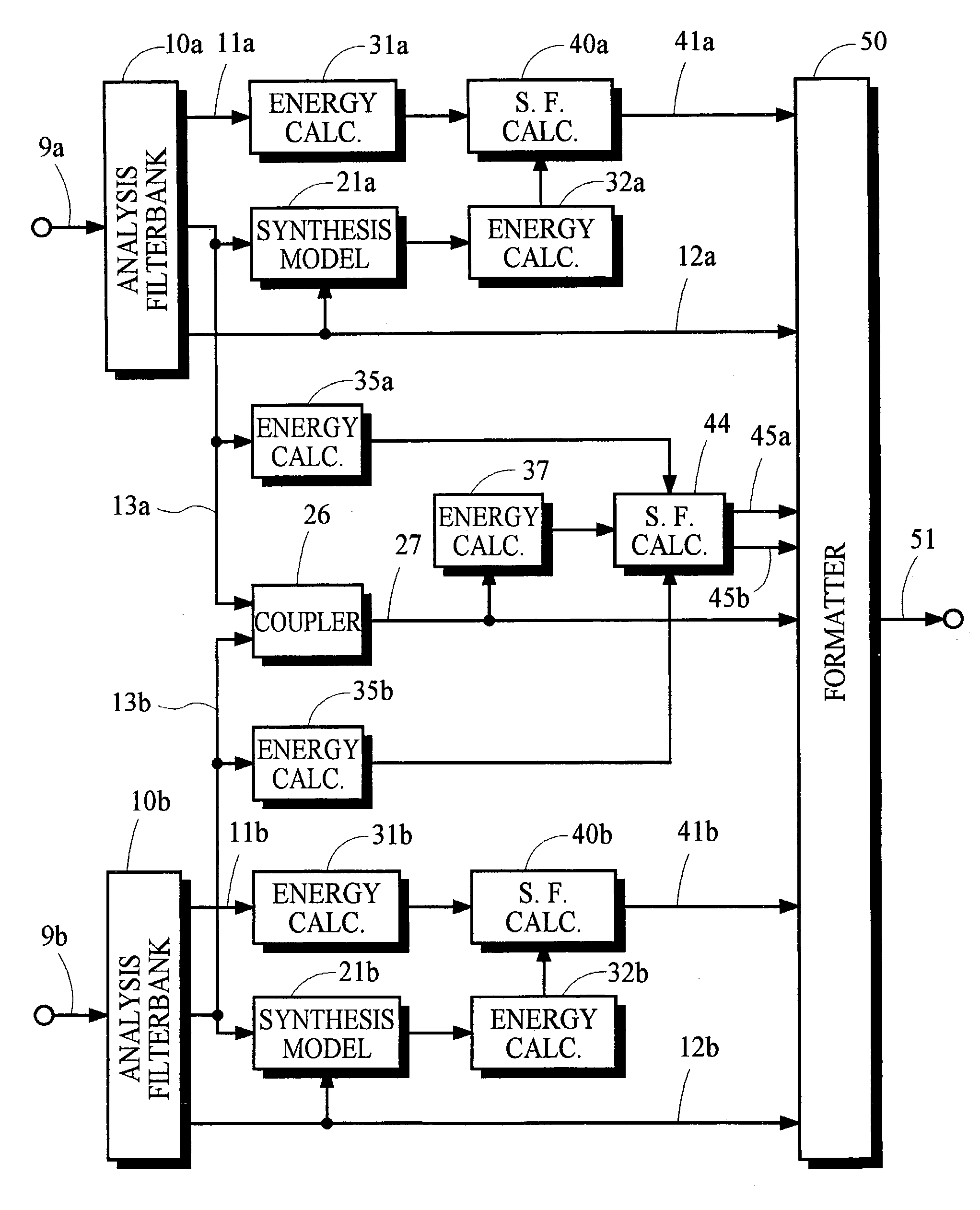
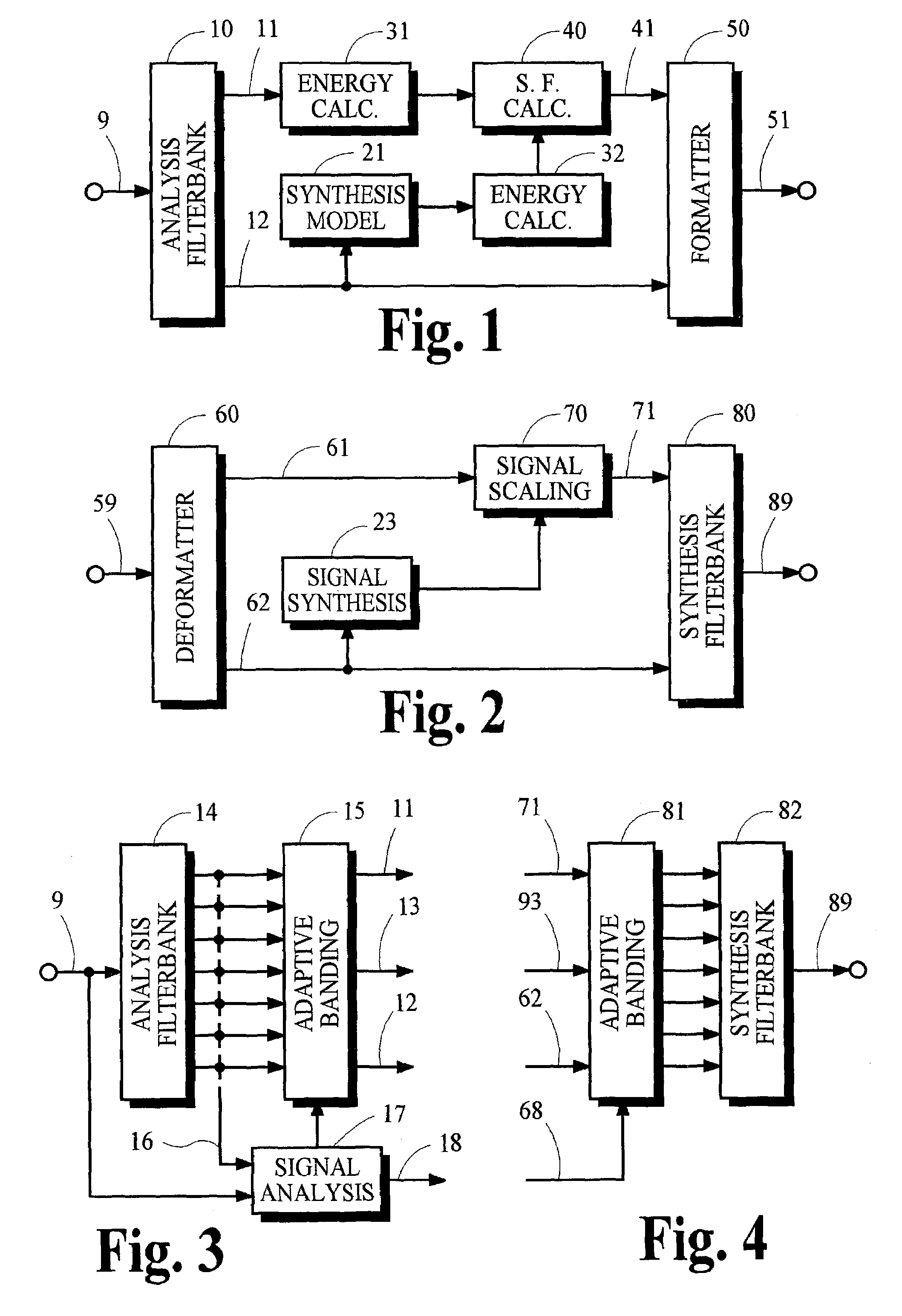
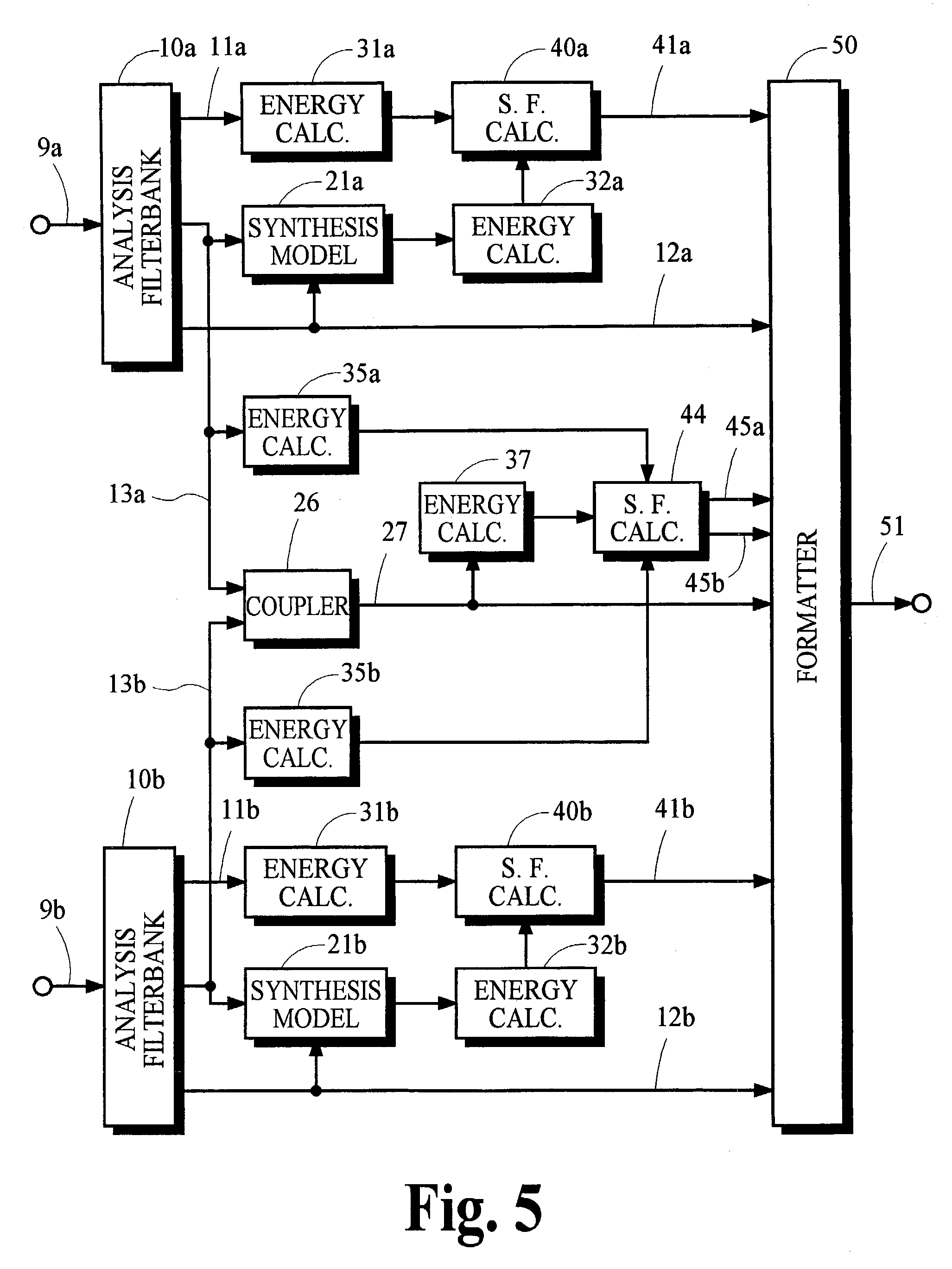
Audio coding systems and methods using spectral component coupling and spectral component regeneration
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and apparatus providing imager pixel array with grating structure and imager device containing the same
ActiveUS20070298533A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum efficiencyGrating
An imager pixel array capable of separating and detecting the spectral components of an incident light without the use of a color filter array. The imager pixel array employs a grating layer which allows one or more spectral components of incident light to be transmitted therethrough, but diffracts other spectral components of the incident light. Both the transmitted and diffracted spectral components can be sensed by photosensors in the imager pixel array and used in subsequent data processing, thereby improving the quantum efficiency of the imager device. The grating layer can be formed of first and second materials each having a refractive index which are substantially the same at a predetermined wavelength.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
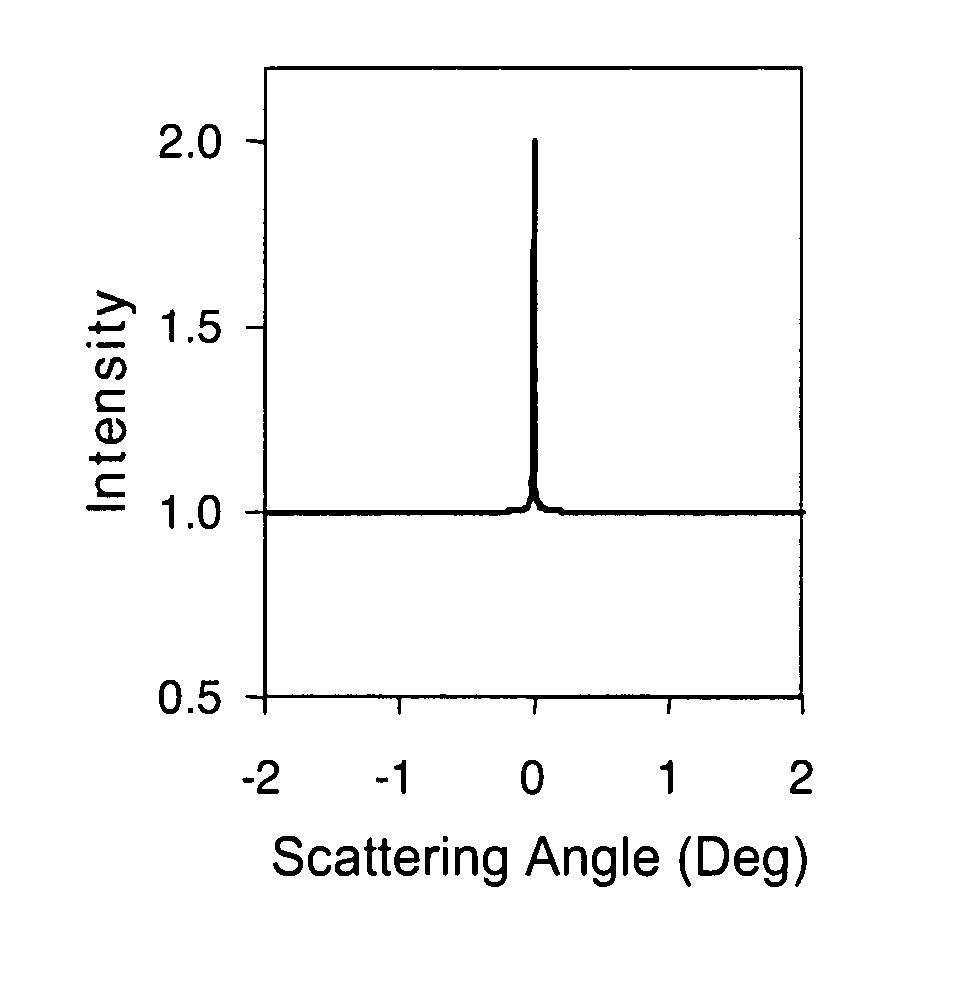
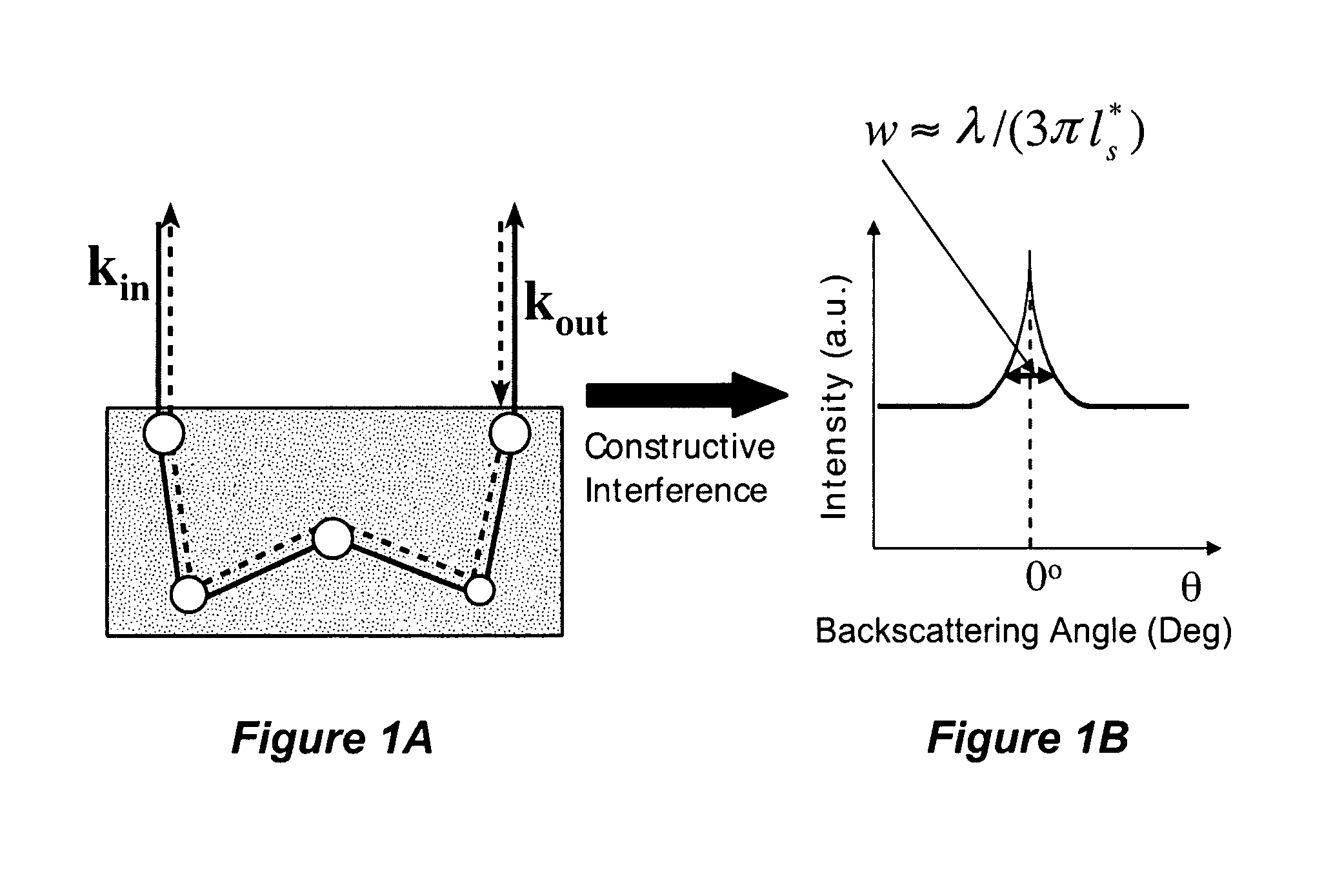
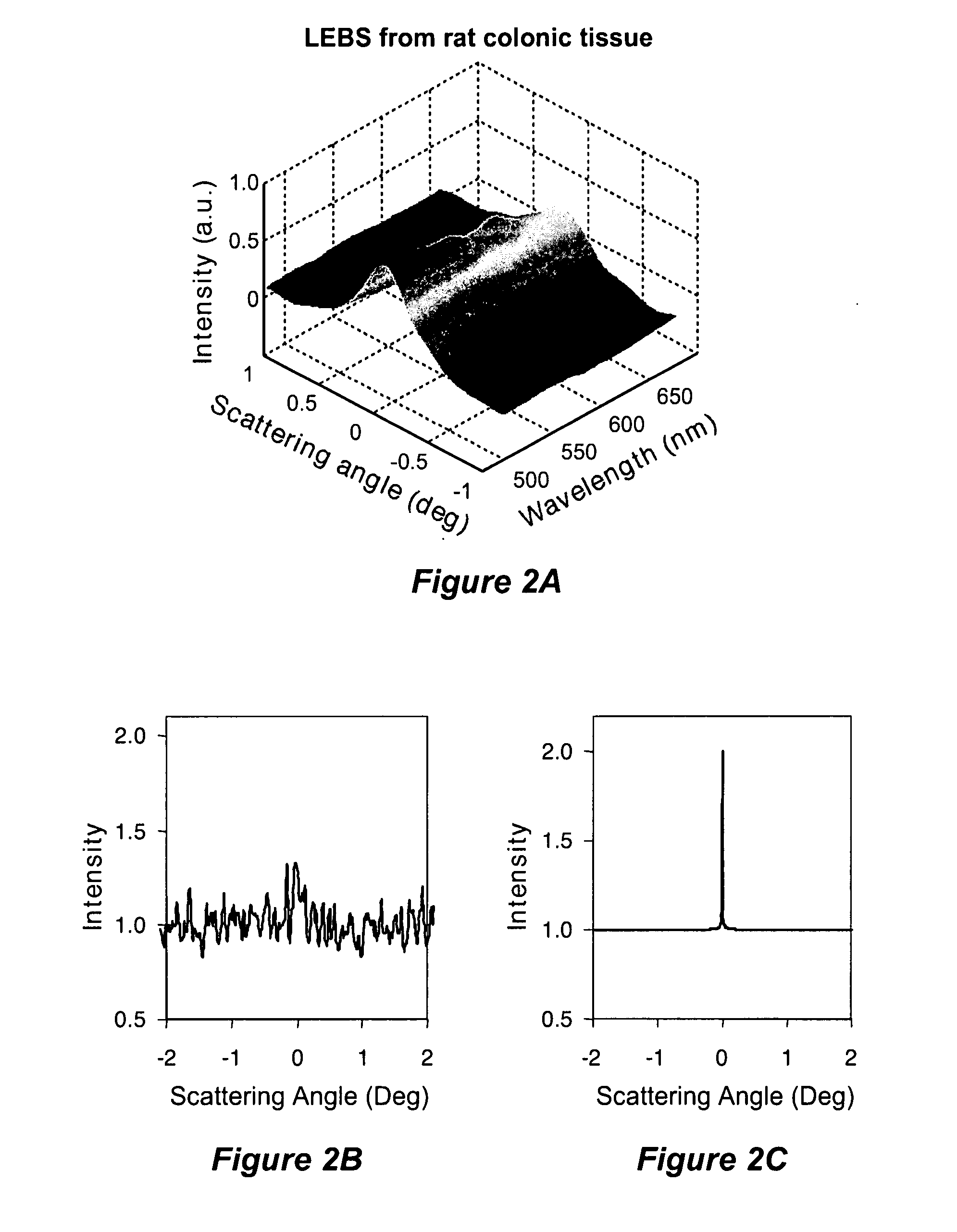
Systems, methods, and apparatuses of low-coherence enhanced backscattering spectroscopy
InactiveUS20080037024A1Raman/scattering spectroscopyScattering properties measurementsSpectroscopyIn vivo
Systems, methods, and apparatuses of low-coherence enhanced backscattering spectroscopy are described within this application. One embodiment includes providing incident light comprising at least one spectral component having low coherence, wherein the incident light is to be illuminated on a target object in vivo. An intensity of one or more of at least one spectral component and at least one angular component of backscattering angle of backscattered light is recorded, wherein the backscattered light is to be backscattered from illumination of the incident light on the target object and wherein the backscattering angle is an angle between incident light propagation direction and backscattered light propagation direction. The intensity of the at least one spectral component and the at least one backscattering angle of backscattered light is analyzed, to obtain one or more optical markers of the backscattered light, toward evaluating said properties.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
Light Sources Adapted to Spectral Sensitivity of Diurnal Avians and Humans
ActiveUS20110228515A1Improve welfareImprove lifetime developmentElectrical apparatusAnimal housingLight-emitting diodeVisual perception
Various apparatus and associated methods involve a light source that provides light at wavelengths that substantially correlate to local maxima in the spectral sensitivity of a diurnal avian. In an illustrative example, the light source may output light primarily in wavelength bands that are not substantially absorbed by colored oil droplets and / or visual pigment in at least one type of cone in the eye of a diurnal avian. In some embodiments, the light source may include a light-emitting diode (LED) light source. Exemplary light sources may output spectral components to illuminate diurnal avians with local maxima of intensity at wavelengths that substantially correspond to local maxima in a spectral sensitivity visual response characteristic of the diurnal avians.
Owner:SIGNIFY NORTH AMERICA CORP
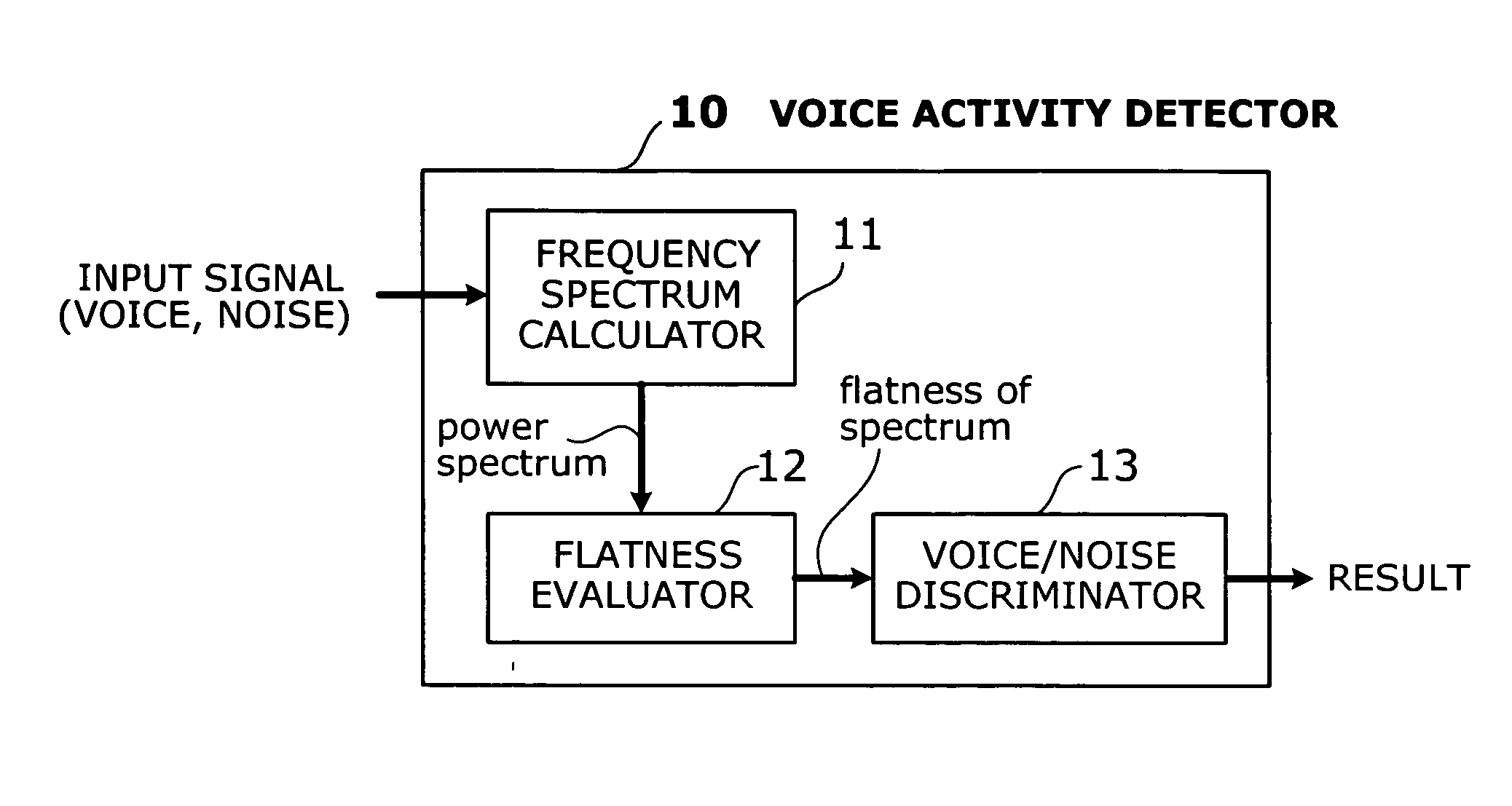
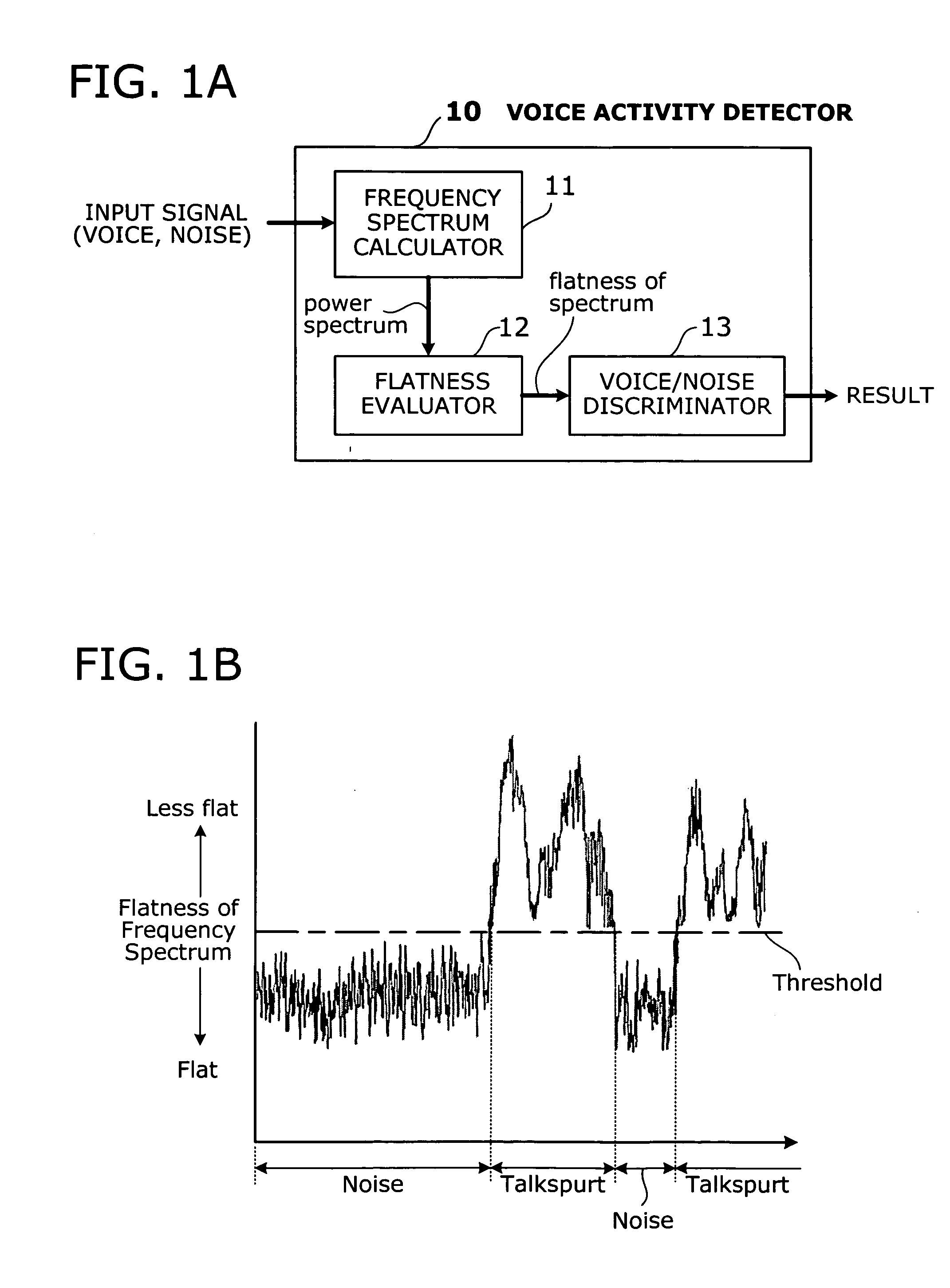
Voice activity detector based on spectral flatness of input signal
InactiveUS20050108004A1Quality improvementImprove accuracyEcho effect reductionSubstation equipmentDiscriminatorVoice communication
A voice activity detector that detects talkspurts in a given signal at a high accuracy, so as to improve the quality of voice communication. A frequency spectrum calculator calculates frequency spectrum of a given input signal. A flatness evaluator evaluates the flatness of this power spectrum by, for example, calculating the average of power spectral components and then adding up the differences between those components and the average. The resultant sum of differences, in this case, is used as a flatness factor of the spectrum. A voice / noise discriminator determines whether the input signal contains a talkspurt or not, by comparing the flatness factor of the frequency spectrum with a predetermined threshold.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
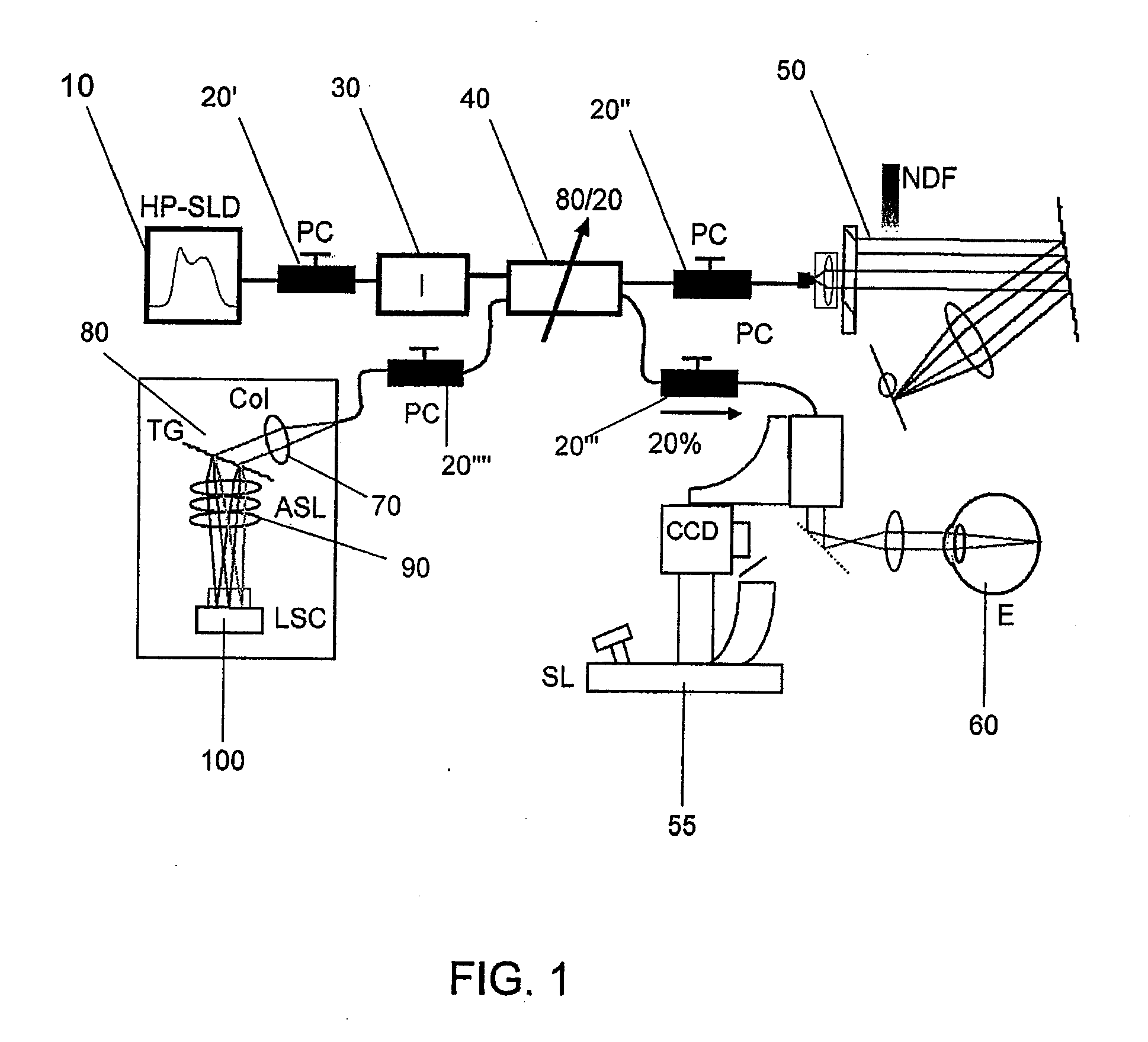
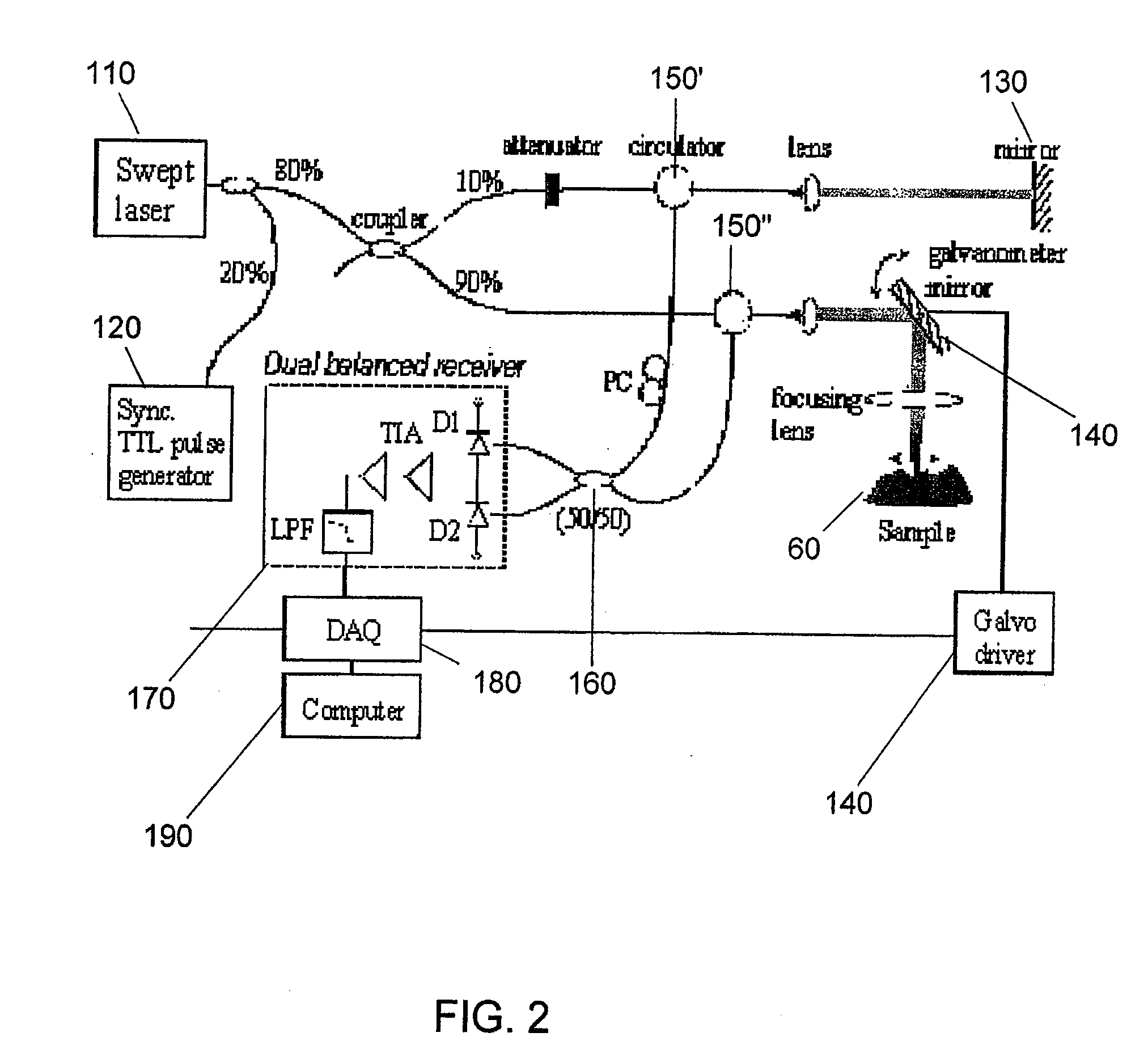
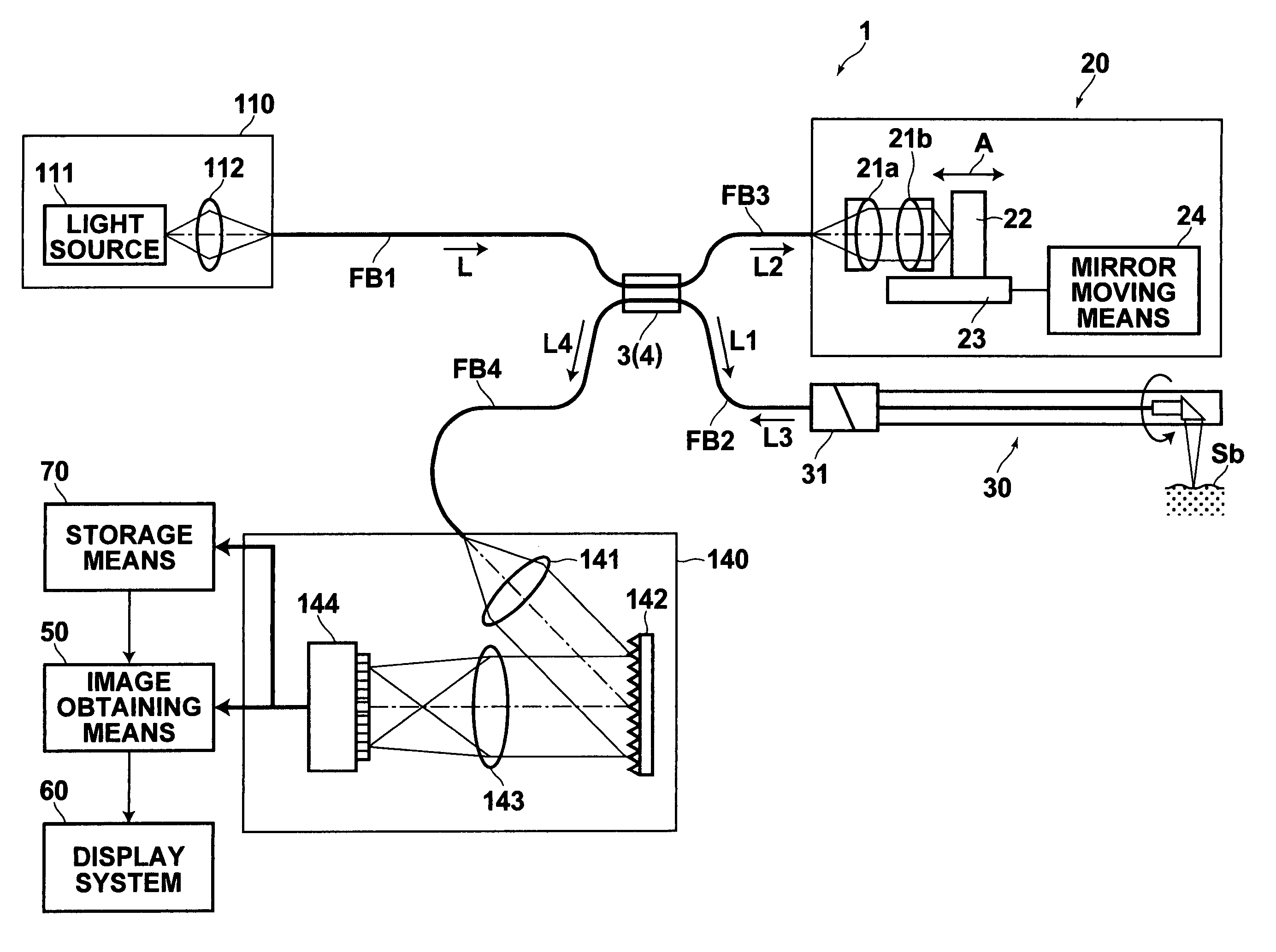
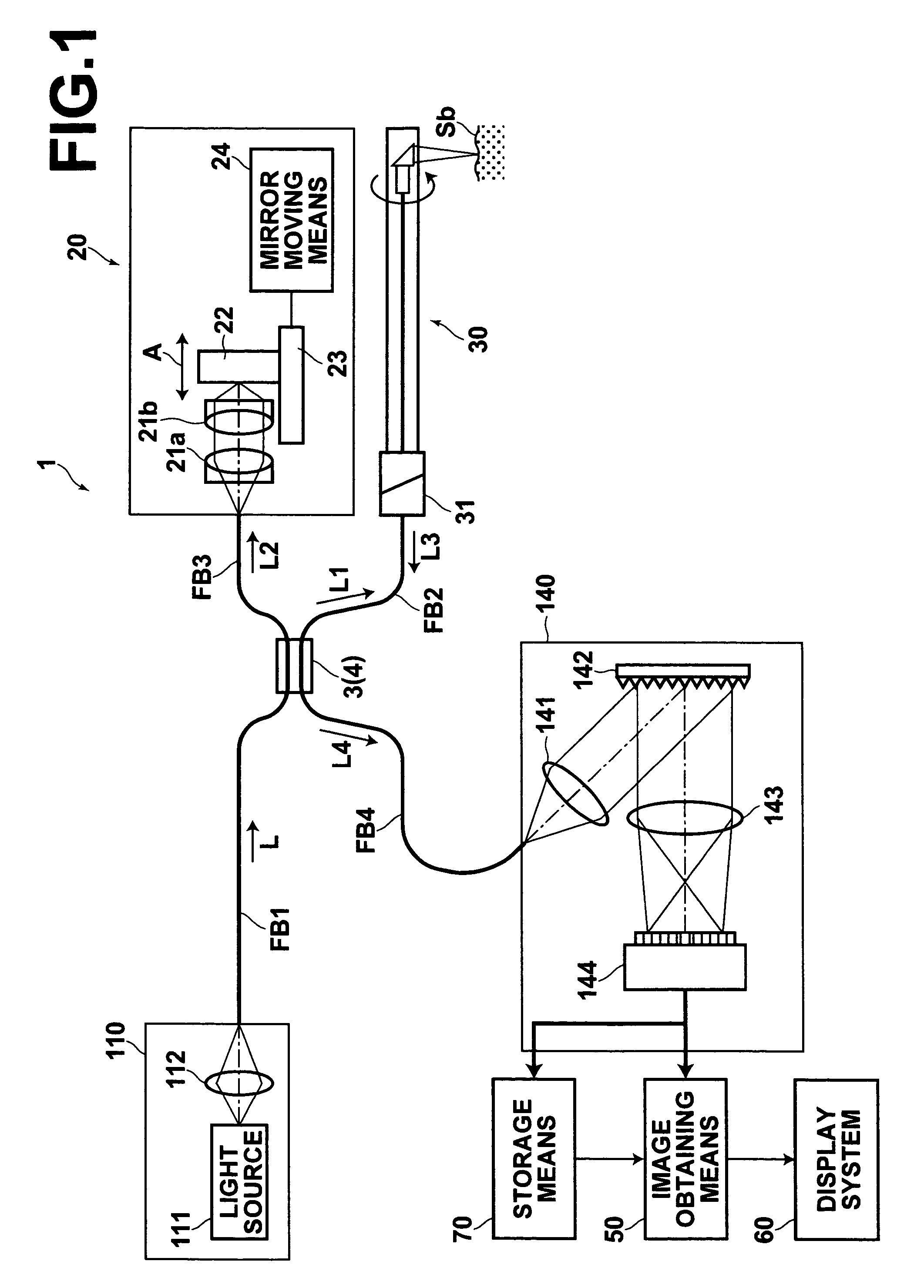
Optical tomography method and optical tomography system
ActiveUS7542145B2Accurate imagingAccurate tomographic image can be stably obtainRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryOptical tomographyTomographic image
Light emitted from a light source is divided into measuring light and reference light. The reflected light from the object and the reference light are superposed. Interference light of the reflected light and reference light which have been superposed is detected. Intensities of the reflected light in a plurality of positions in the direction of depth of the object are detected on the basis of the frequency and the intensity, and a tomographic image of the object is obtained on the basis of the intensity of the reflected light in each position in the direction of depth. A compensating signal is obtained by removing the spectral components of the measuring light from an interference signal obtained by detection of the interference light, and the compensating signal is provided for detection of the intensities of the reflected light after a Gaussian transform.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Distributed strain and temperature discrimination in polarization maintaining fiber
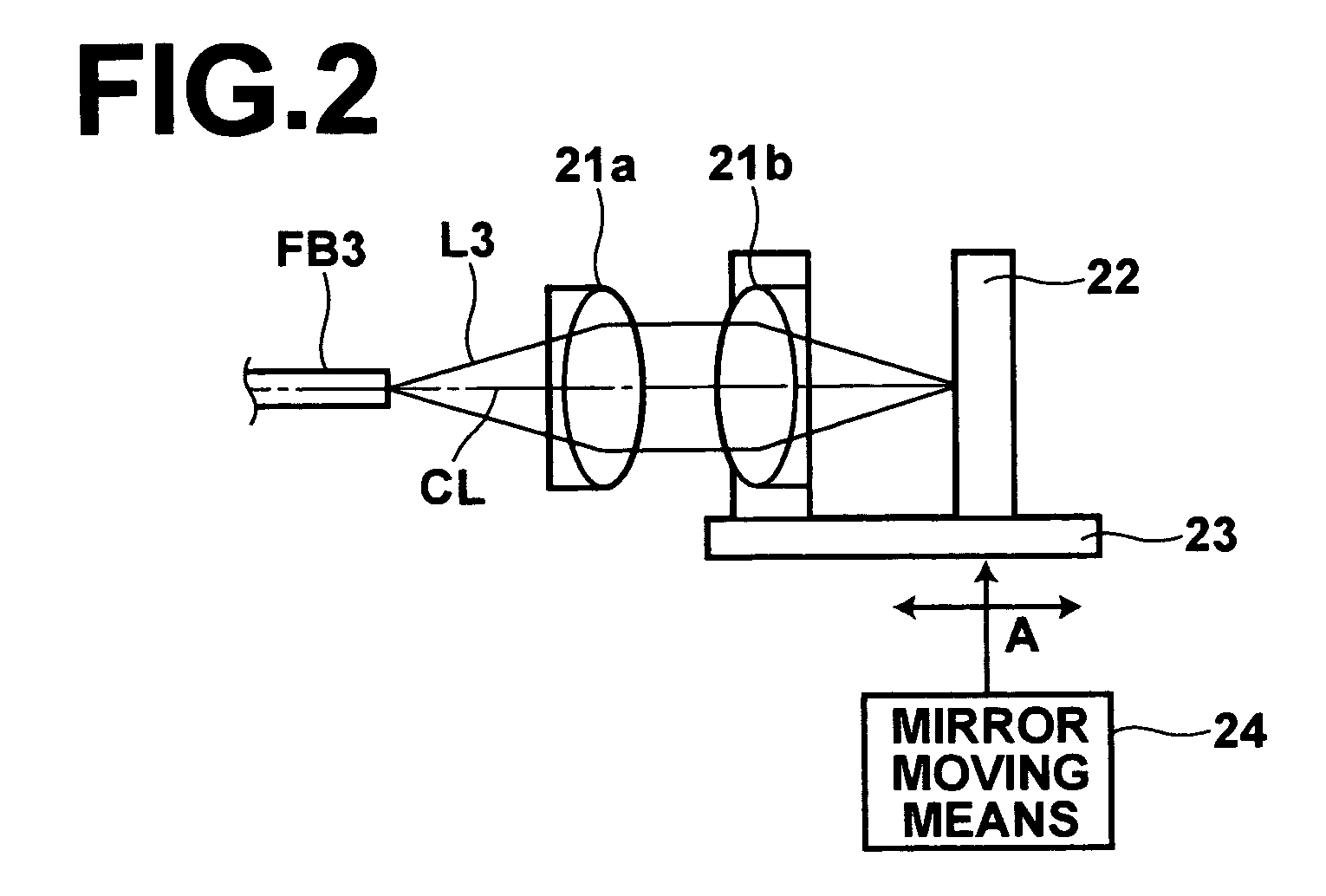
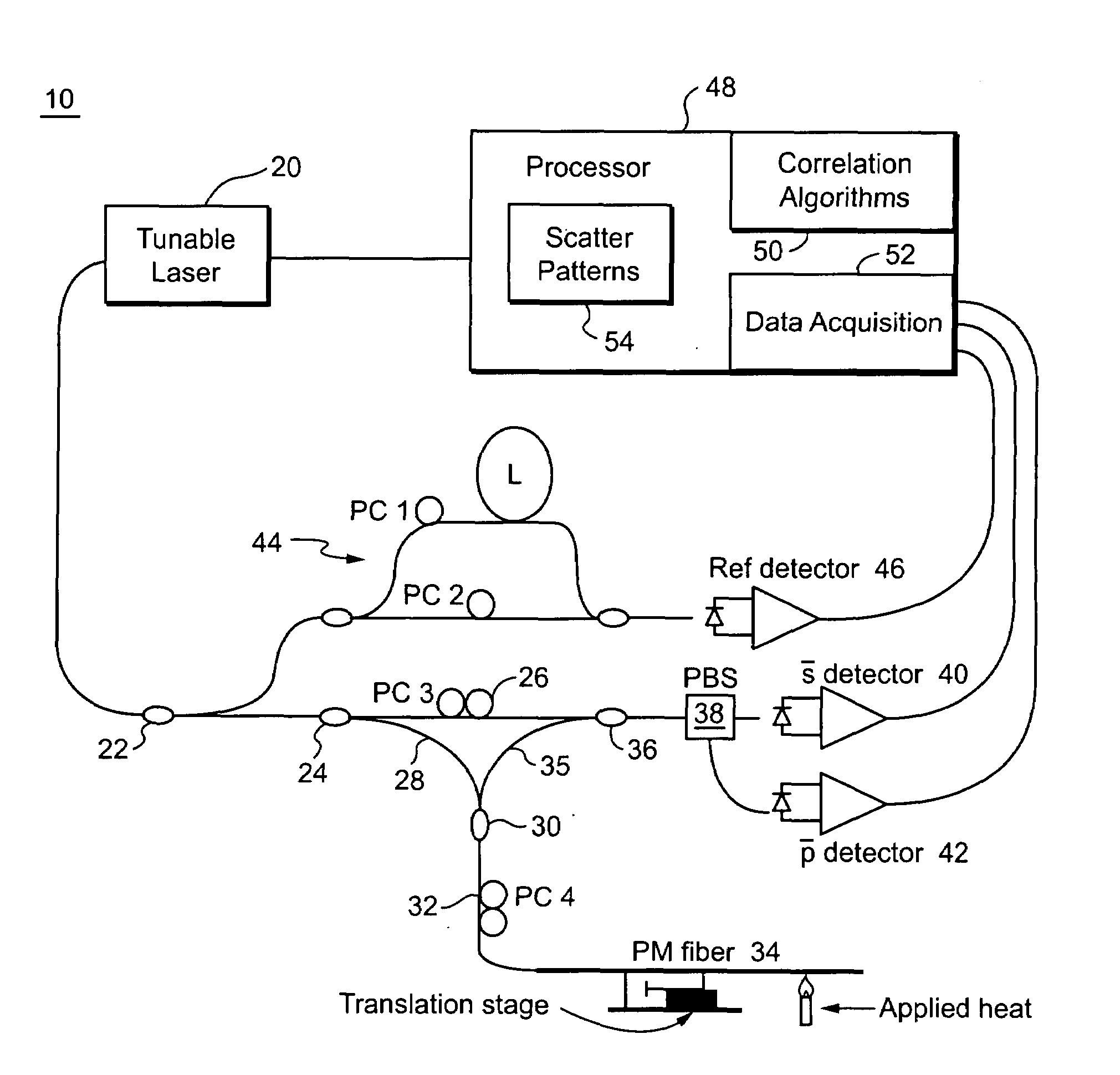
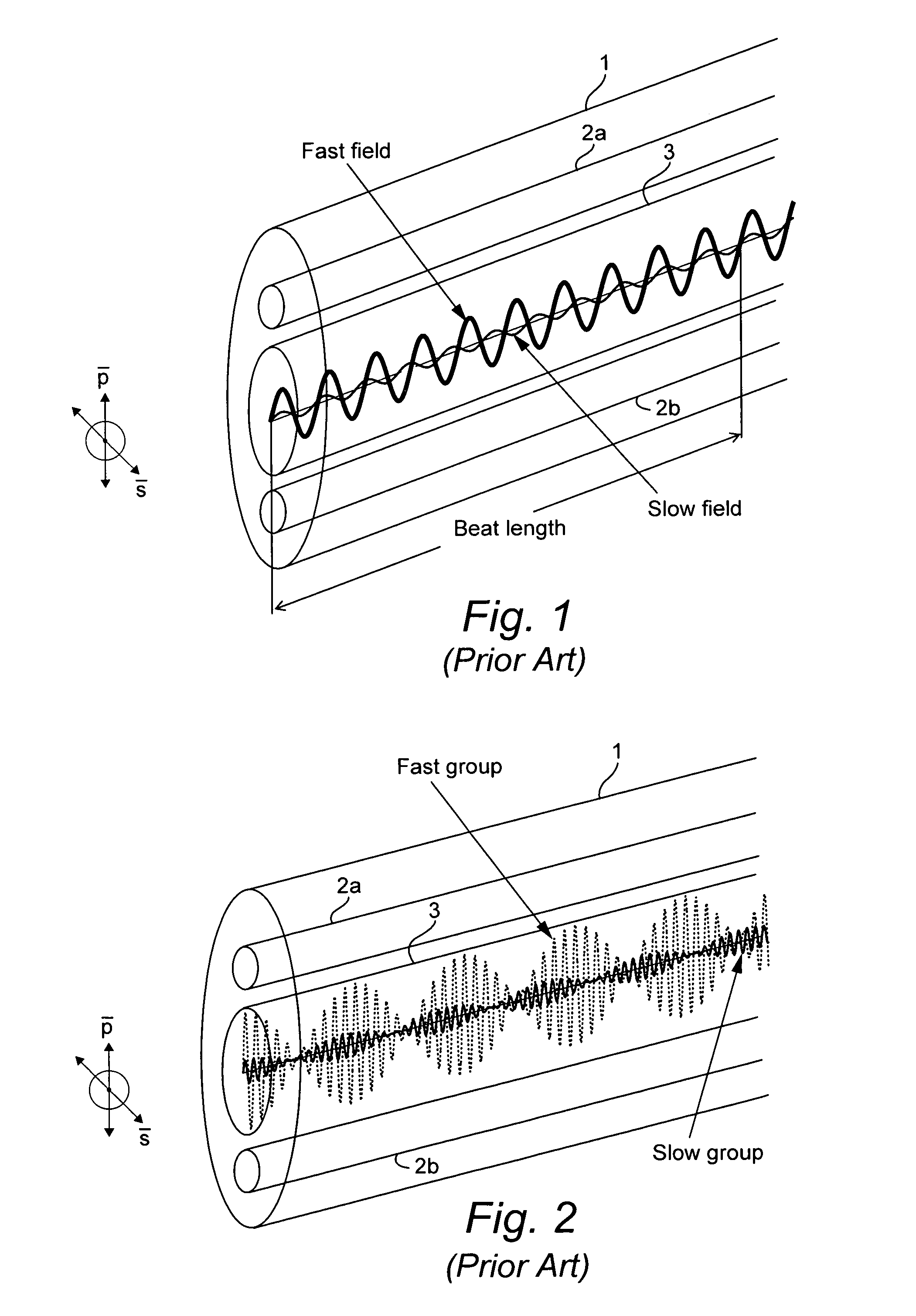
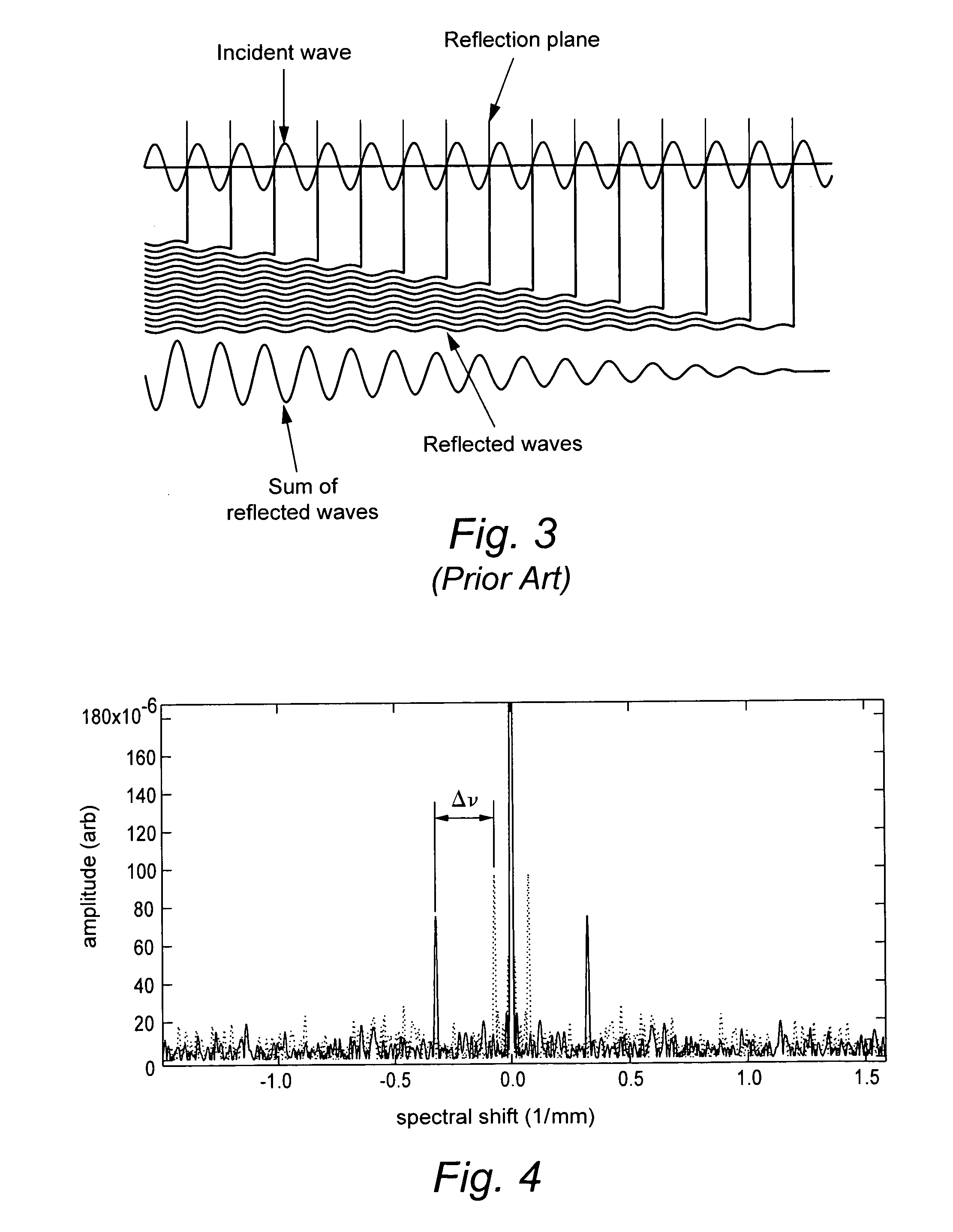
ActiveUS7538883B2Force measurement by measuring optical property variationMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberSpectral response
A portion of a polarization maintaining (PM) optical fiber having two polarization states is analyzed. First and second spectral responses of the PM fiber portion are determined. In a preferred implementation, the spectral responses are determined using Optical Frequency Domain Reflectometry (OFDR). Each polarization state of the PM fiber portion has a corresponding spectral component in the first spectral response. First and second spectral analyses of the PM fiber portion are performed using the first and second spectral responses. Based on those spectral analyses of the PM fiber portion, a first physical characteristic affecting the PM fiber portion is determined that is distinct from a second different physical characteristic affecting the fiber portion. Example physical characteristics include temperature and strain. An output signal related to the first physical characteristics affecting the fiber portion is provided, e.g., for display, further processing, etc.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Green light-emitting microcavity OLED device using a yellow color filter element
An OLED device having green emitting regions disposed over a substrate, and wherein each green emitting region includes one or more light-emitting layer(s), a reflector and a semitransparent reflector respectively disposed on opposite sides of the light-emitting layer(s) and arranged to resonate light produced by such layers such that the light has a substantial green spectral component, and a yellow color filter element disposed in relationship to each green emitting region to produce green light.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
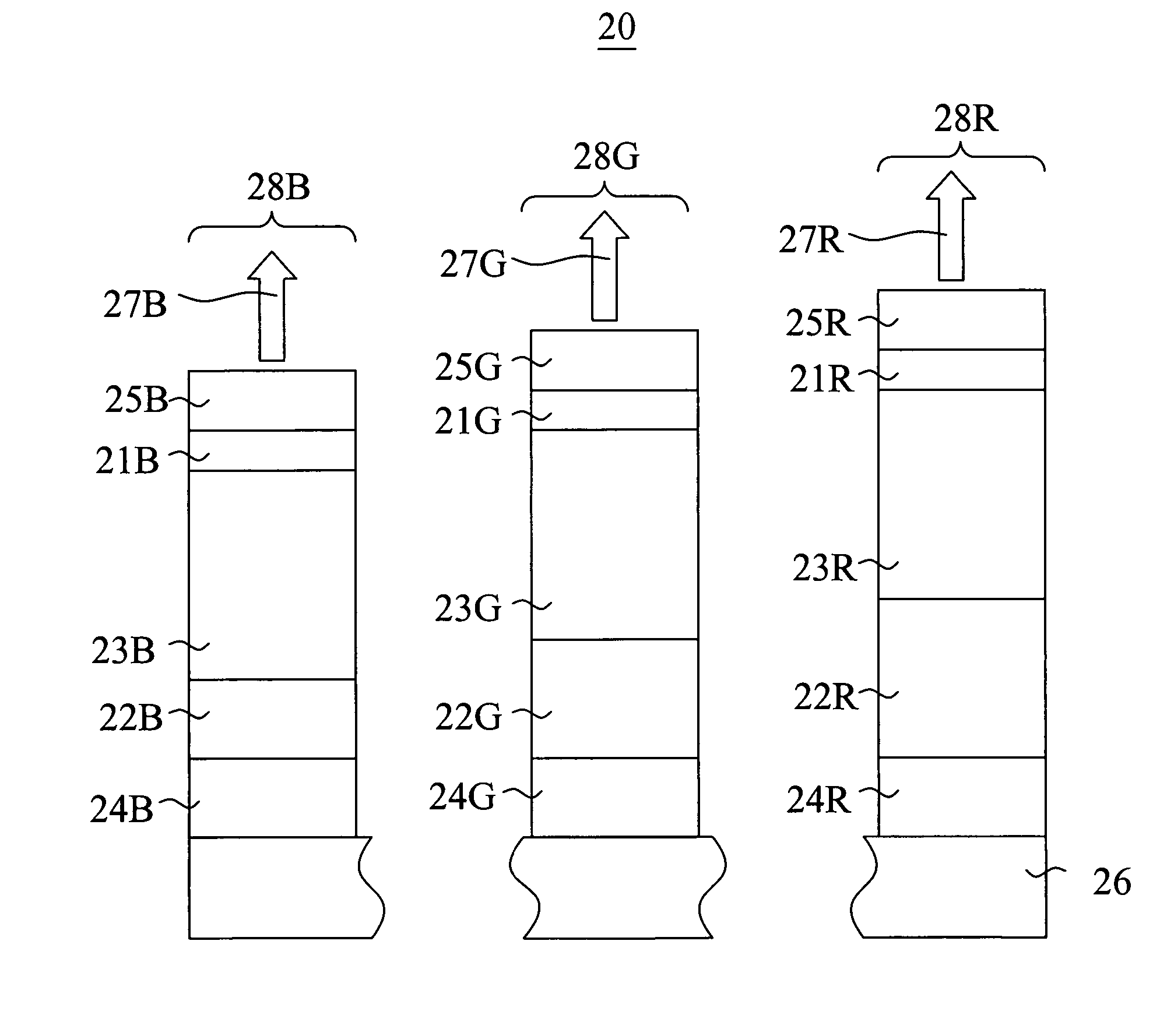
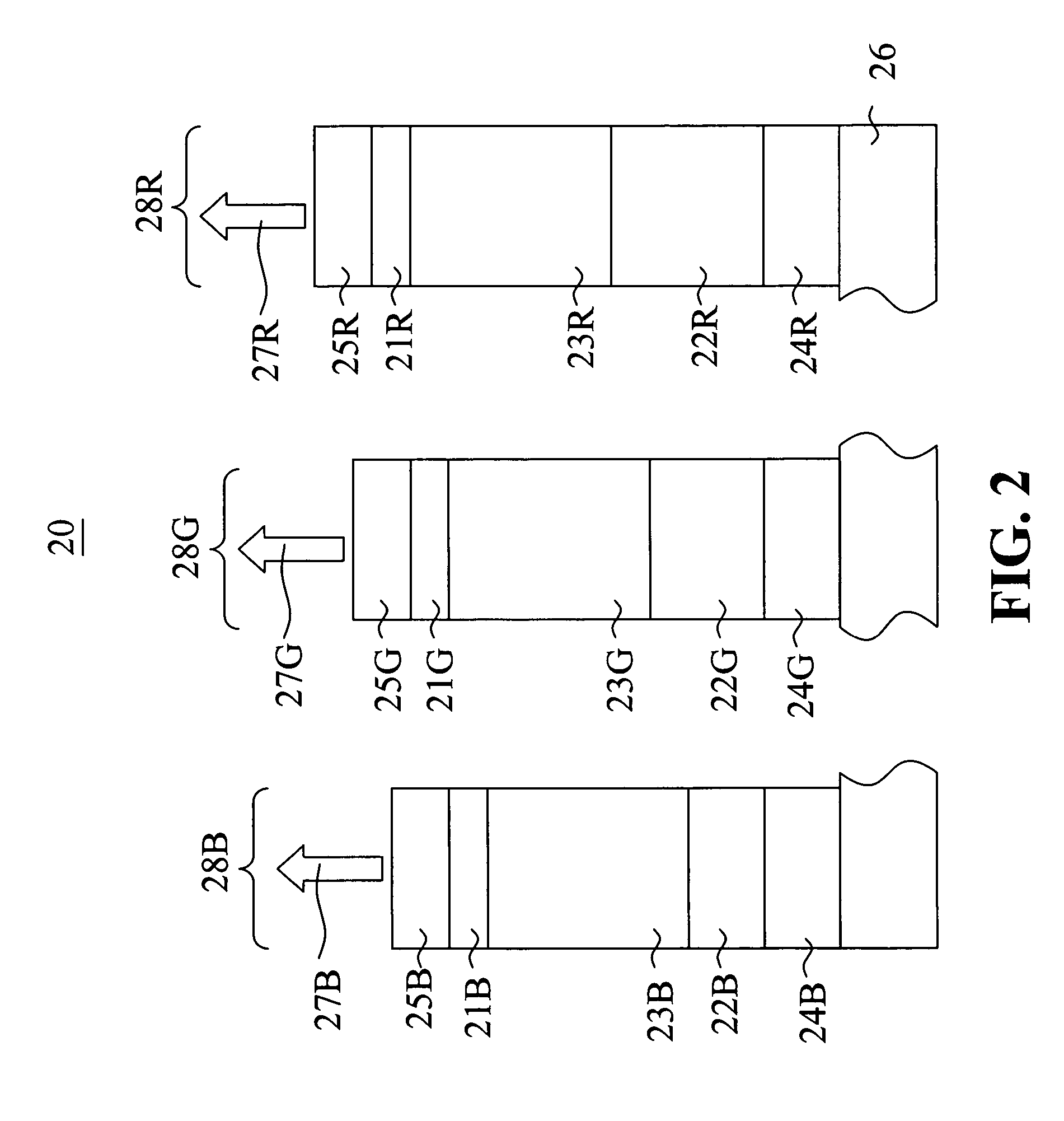
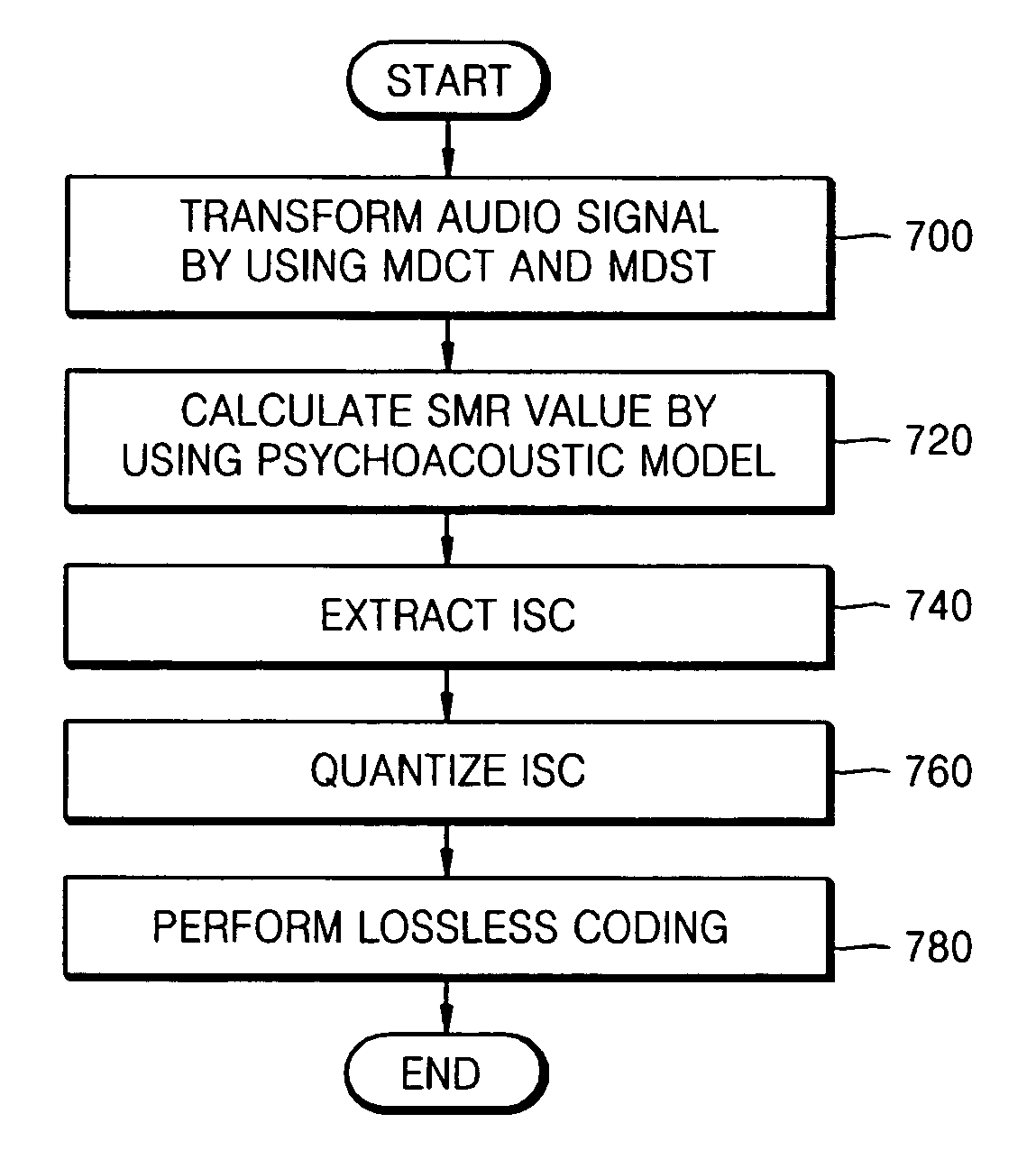
Method and apparatus to extract important spectral component from audio signal and low bit-rate audio signal coding and/or decoding method and apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20070016404A1Broadcast information characterisationBroadcast circuit arrangementsDecoding methodsFrequency spectrum
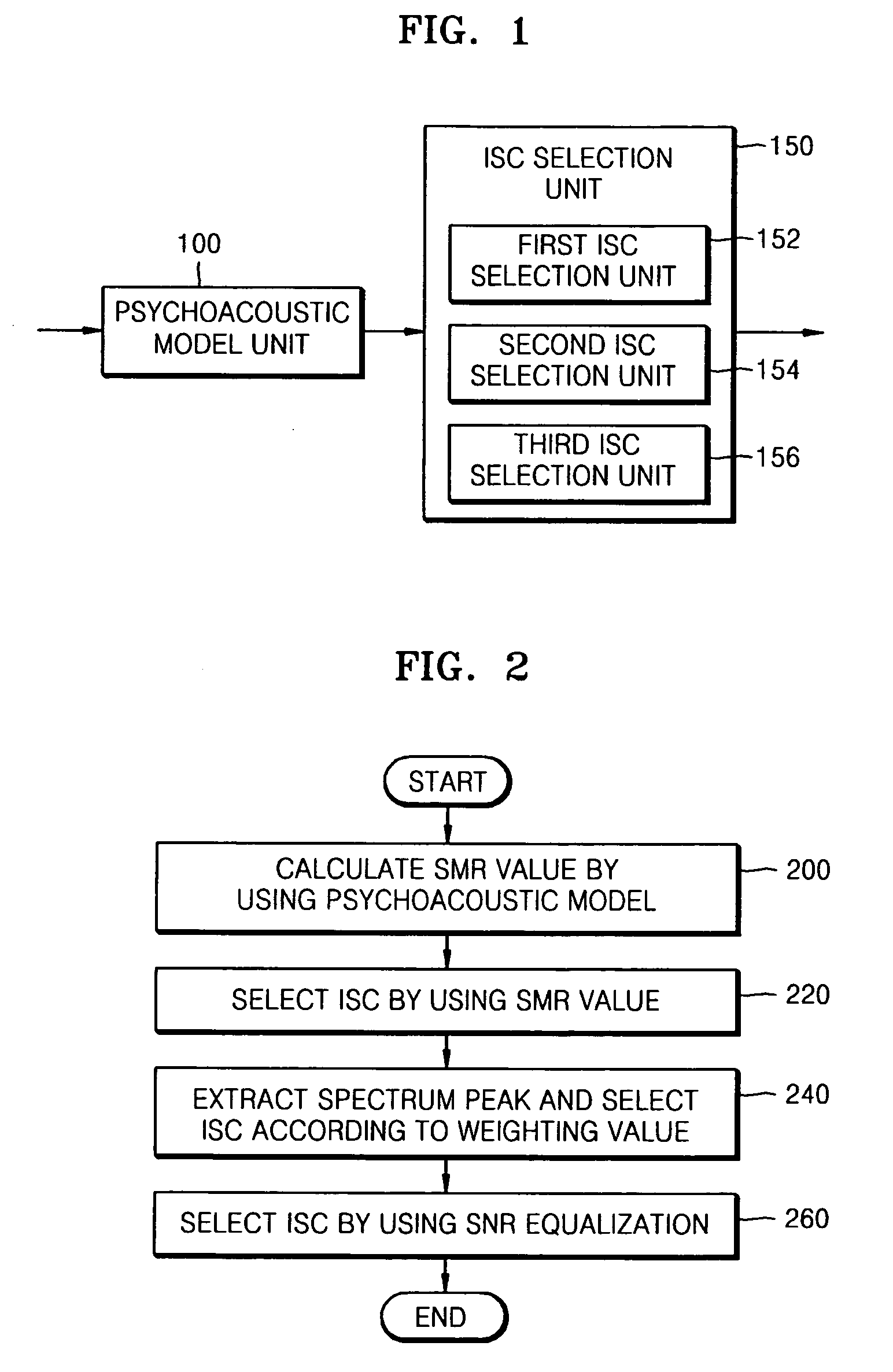
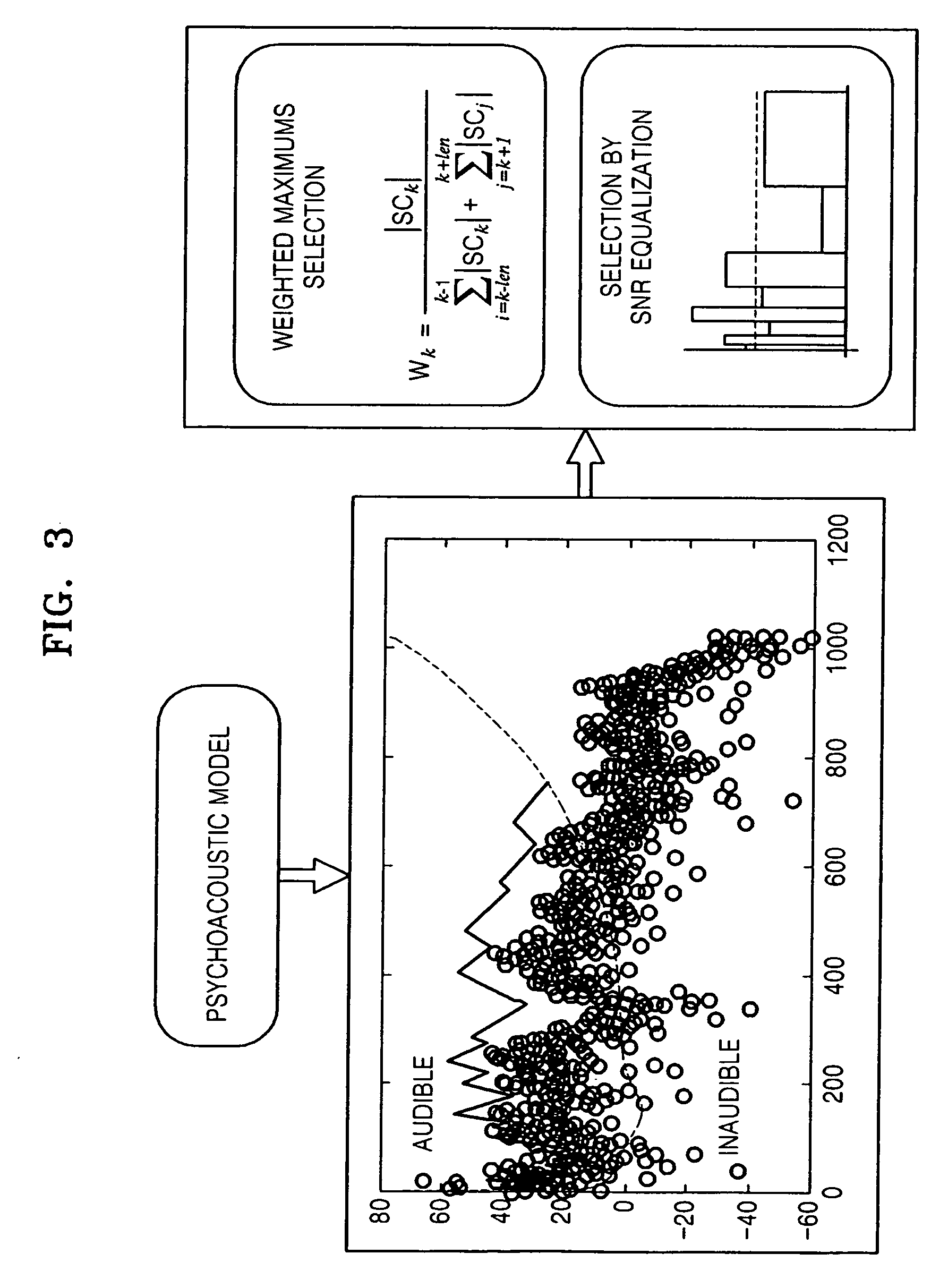
An method and apparatus to extract an audio signal having an important spectral component (ISC) and a low bit-rate audio signal coding / decoding method using the method and apparatus to extract the ISC. The method of extracting the ISC includes calculating perceptual importance including an SMR (signal-to-mark ratio) value of transformed spectral audio signals by using a psychoacoustic model, selecting spectral signals having a masking threshold value smaller than that of the spectral audio signals using the SMR value as first ISCs, and extracting a spectral peak from the audio signals selected as the ISCs according to a predetermined weighting factor to select second ISCs. Accordingly, the perceptual important spectral components can be efficiently coded so as to obtain high sound quality at a low bit-rate. In addition, it is possible to extract the perceptual important spectral component by using the psychoacoustic model, to perform coding without phase information, and to efficiently represent a spectral signal at a low bit-rate. In addition, the methods and apparatus can be employed in all the applications requiring a low bit-rate audio coding scheme and in a next generation audio scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
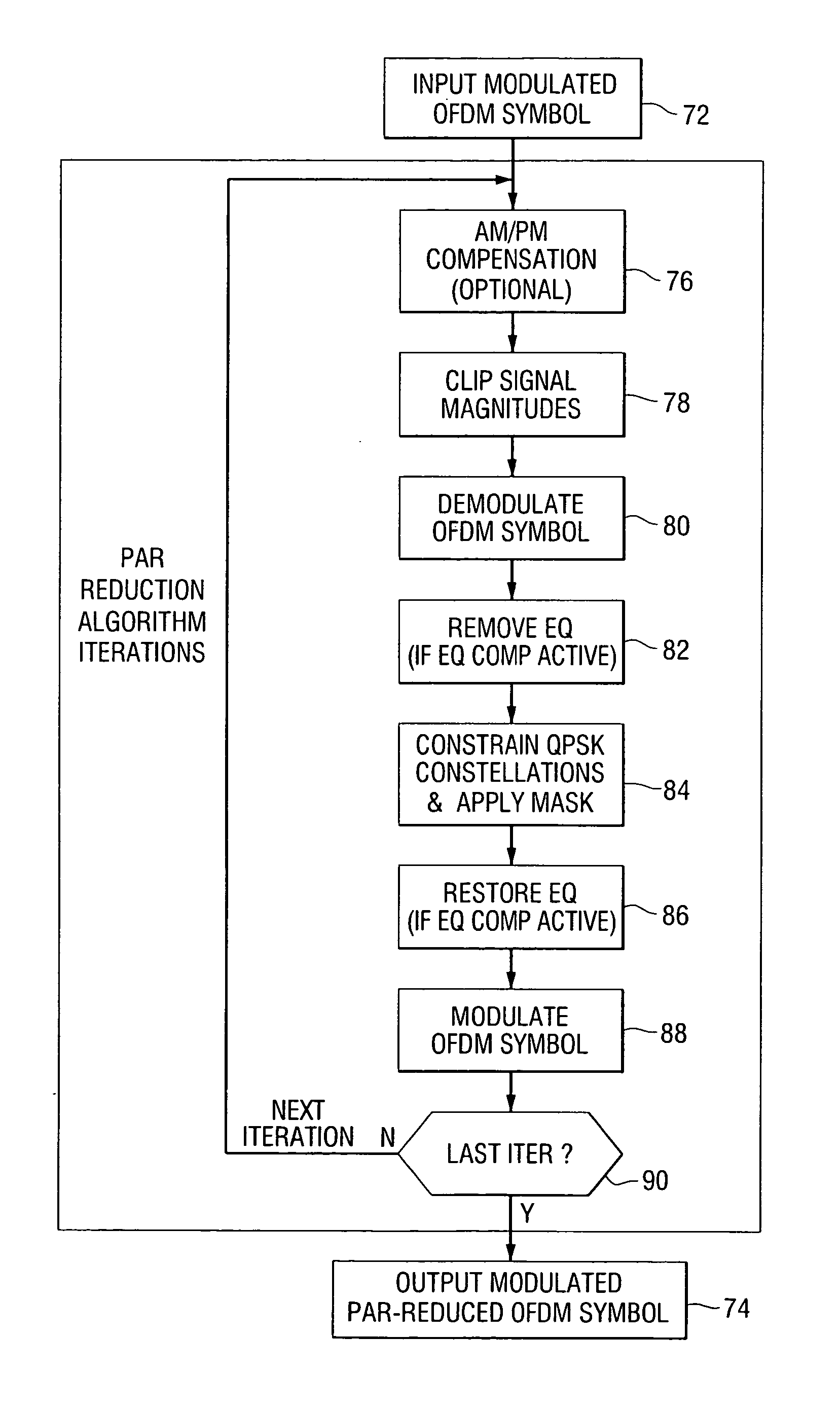
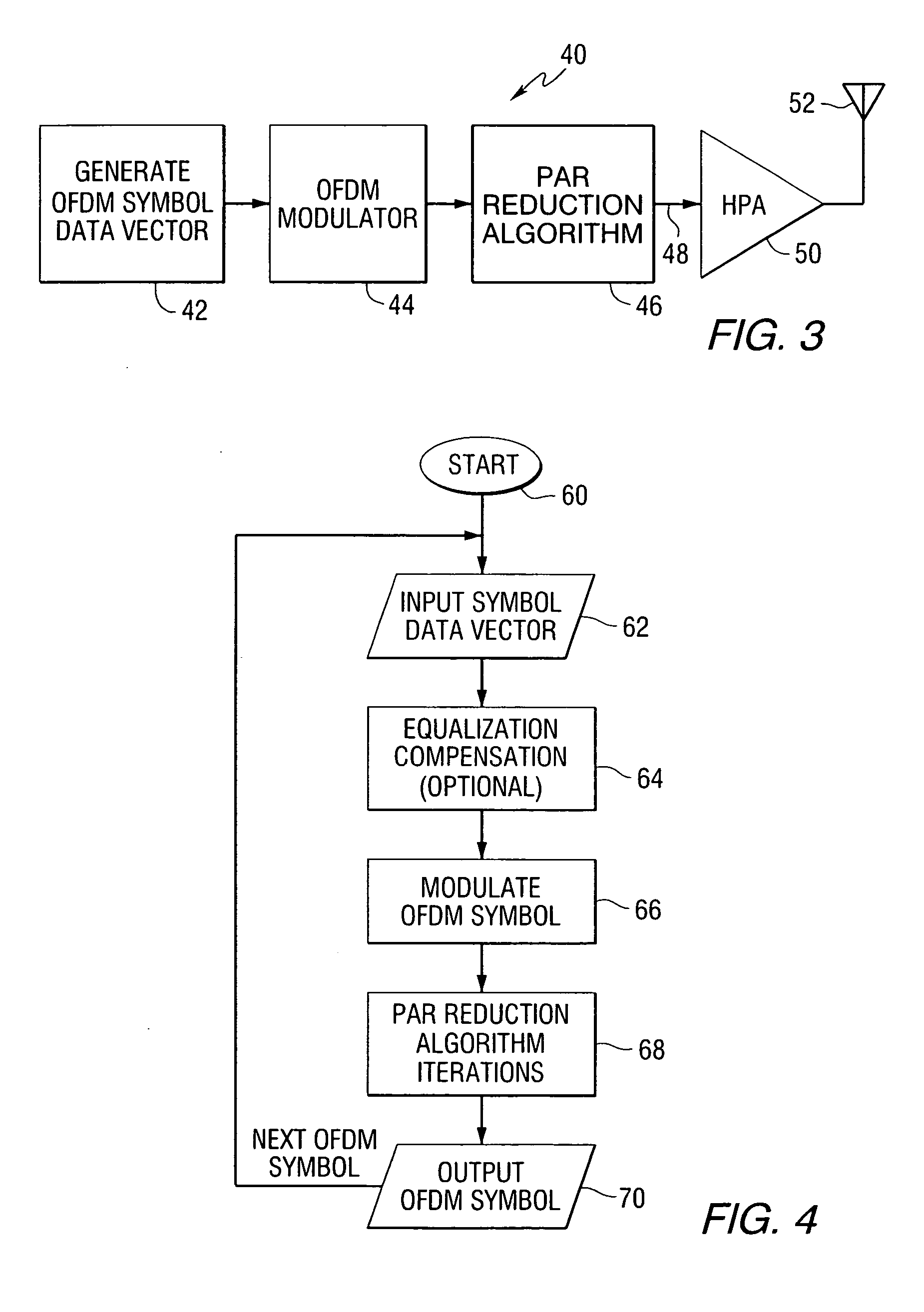
Peak-to-average power reduction for FM OFDM transmission
ActiveUS20050169411A1Reducing peak-to-average power ratioMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsCarrier signalPeak value
A method of reducing peak-to-average power ratio in an OFDM signal comprises the steps of modulating a set of subcarriers with a set of data symbol vectors to produce a first modulated signal, limiting the magnitude of the first modulated signal to produce a first limited modulated signal, demodulating the first limited modulated signal to recover distorted input symbol vectors, constraining the distorted input symbol vectors to values greater than or equal to a minimum threshold value to produce constrained data symbol vectors, constraining out-of-band spectral components to lie within a predetermined mask, and remodulating the constrained data symbol vectors. A transmitter that performs the method is also included.
Owner:IBIQUITY DIGITAL CORP
Audio decoding apparatus and method for band expansion with aliasing suppression
InactiveUS7058571B2Quality improvementCode conversionSpeech synthesisFrequency spectrumComputer science
A wideband, high quality audio signal is decoded with few calculations at a low bitrate. Unwanted spectrum components accompanying sinusoidal signal injection by a synthesis subband filter built with real-value operations are suppressed by inserting a suppression signal to subbands adjacent to the subband to which the sine wave is injected. This makes it possible to inject a desired sinusoid with few calculations.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
Apparatus for photodynamic therapy and photodetection
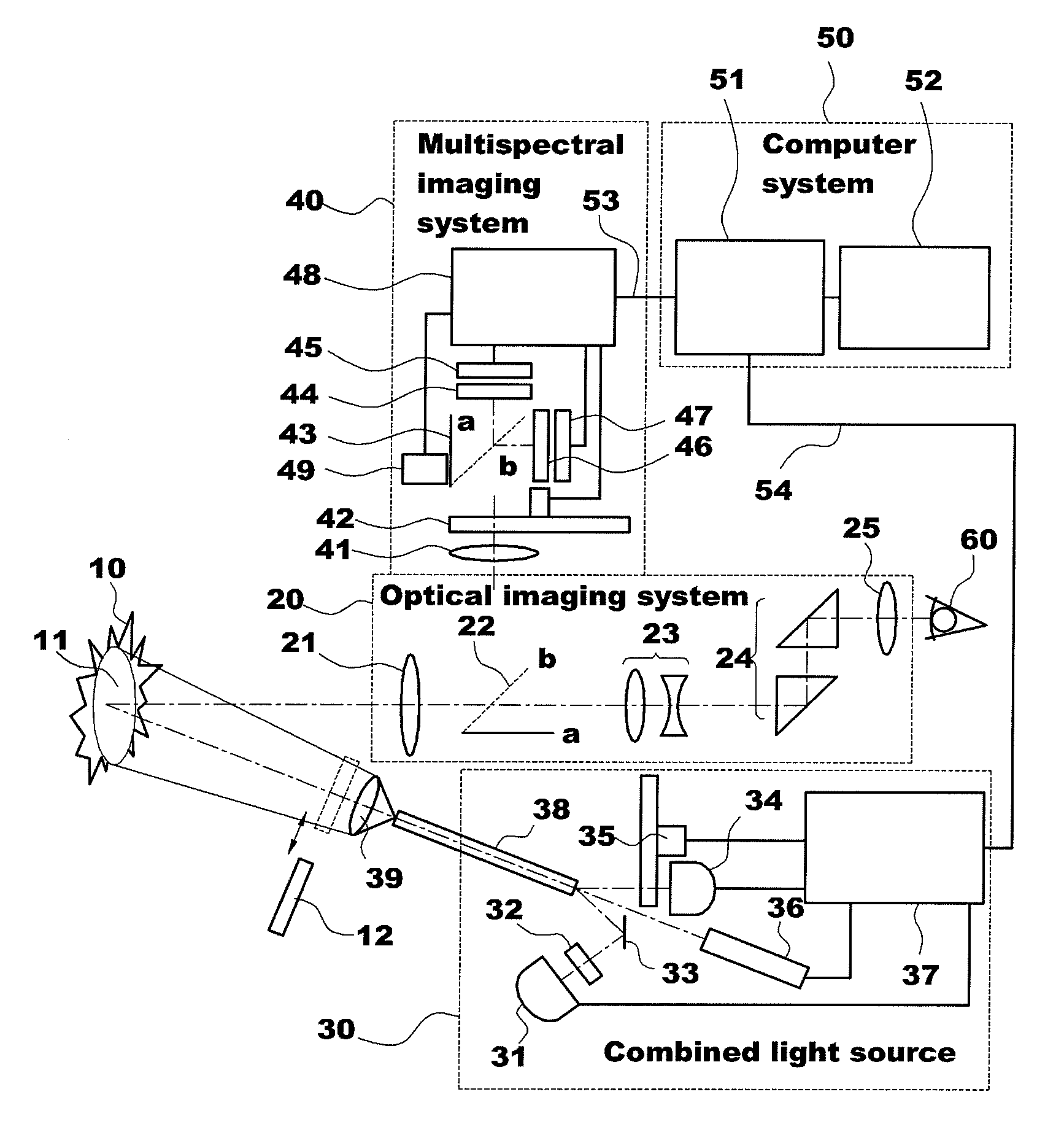
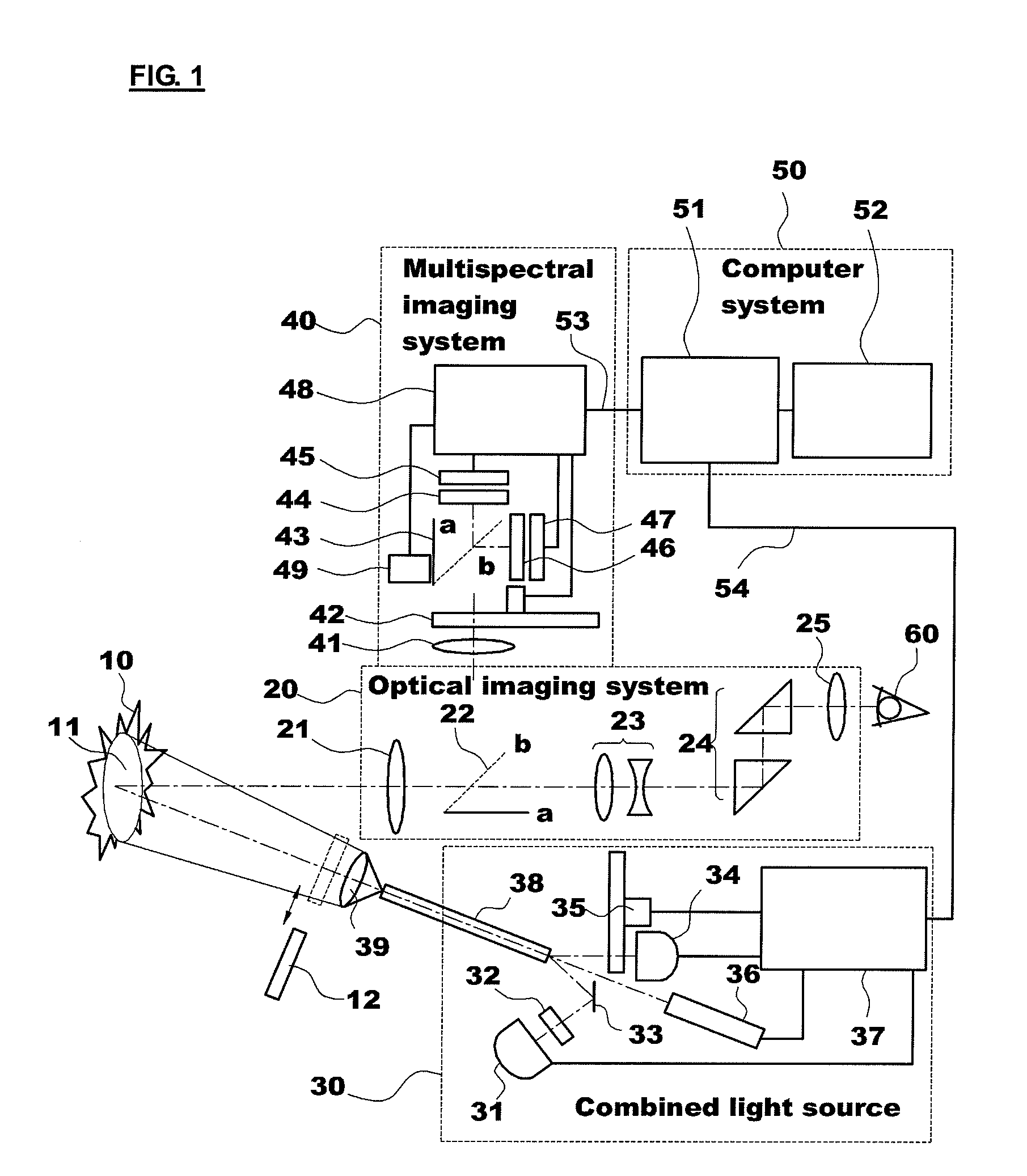
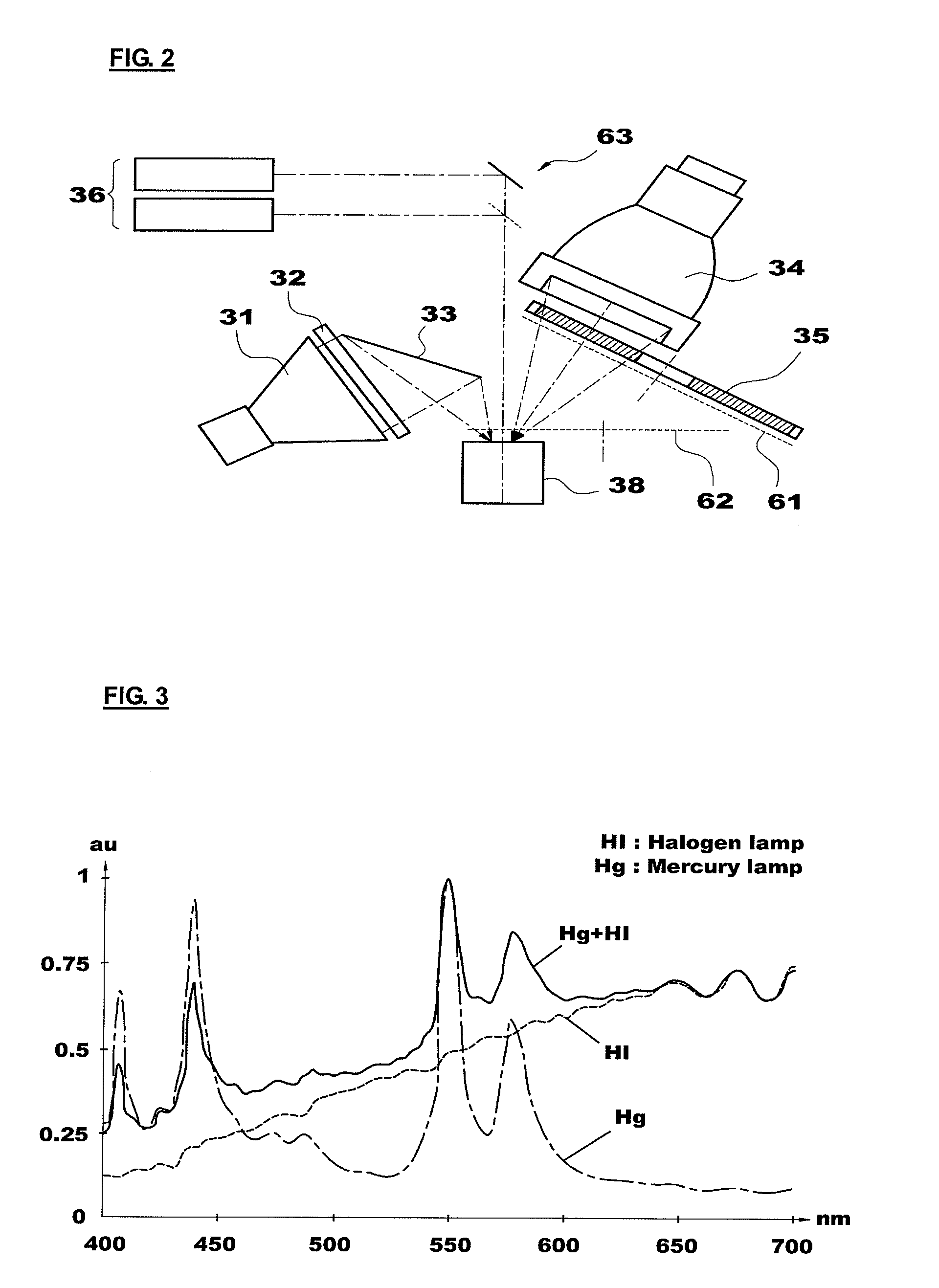
ActiveUS20100145416A1Effective therapyRaman/scattering spectroscopyDiagnostics using lightDiseaseFluorescence
The present invention provides an apparatus for photodynamic therapy and fluorescence detection, in which a combined light source is provided to illuminate an object body and a multispectral fluorescence-reflectance image is provided to reproduce various and complex spectral images for an object tissue, thus performing effective photodynamic therapy for various diseases both outside and inside of the body.For this purpose, the present invention provides an apparatus for photodynamic therapy and photodetection, which provides illumination with light of various wavelengths and multispectral images, the apparatus including: an optical imaging system producing an image of an object tissue and transmitting the image to a naked eye or an imaging device; a combined light source including a plurality of coherent and non-coherent light sources and a light guide guiding incident light emitted from the light sources; a multispectral imaging system including at least one image sensor; and a computer system outputting an image of the object tissue to the outside. Thus, the apparatus for photodynamic therapy and photodetection of the present invention can effectively perform the photodynamic therapy and photodetection by means of the combined light source capable of irradiating light having various spectral components to an object tissue and the multispectral imaging system capable of obtaining images from several spectral portions for these various spectral ranges at the same time, thus improving the accuracy of diagnosis and efficiency of the photodynamic therapy.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
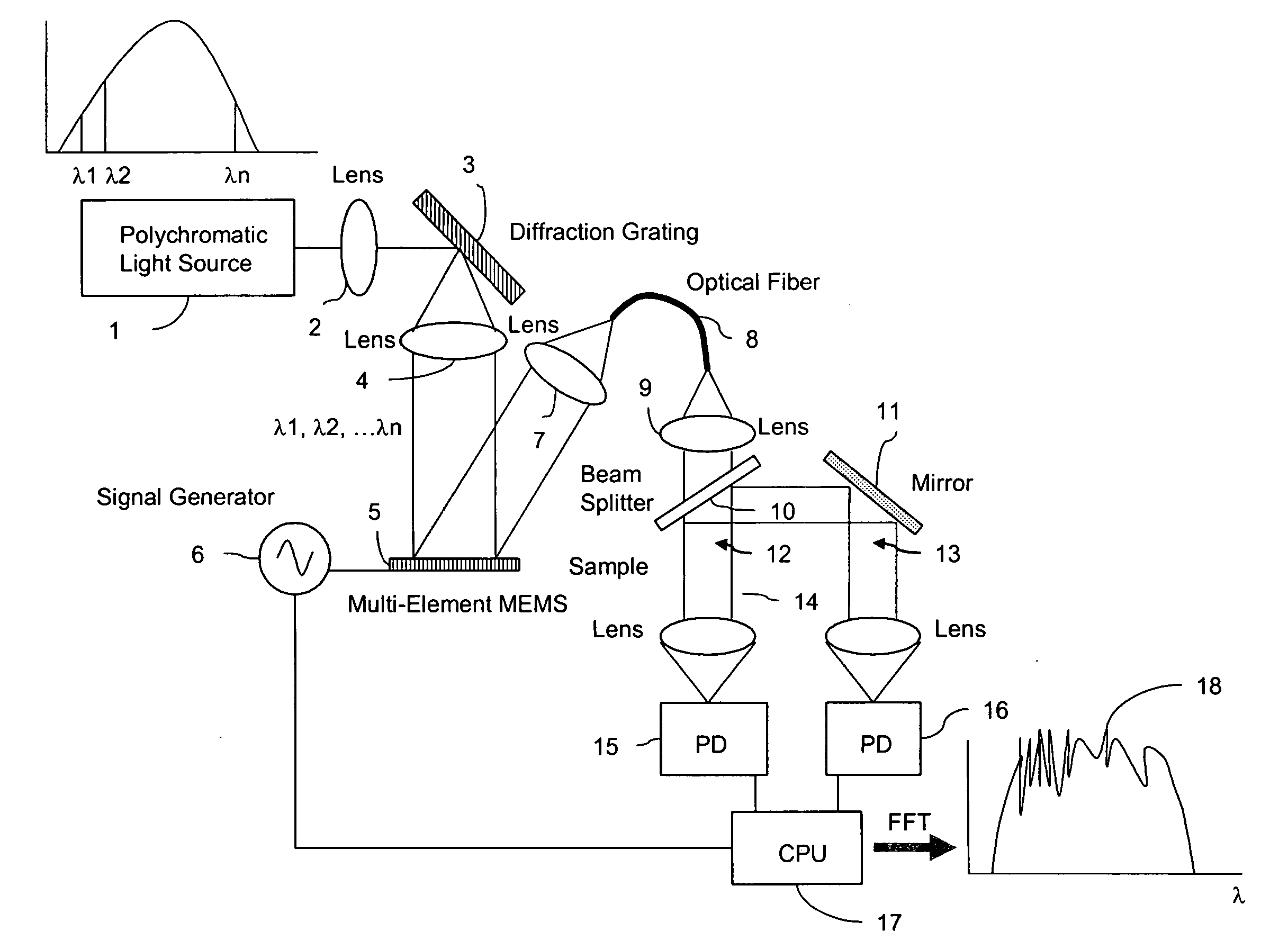
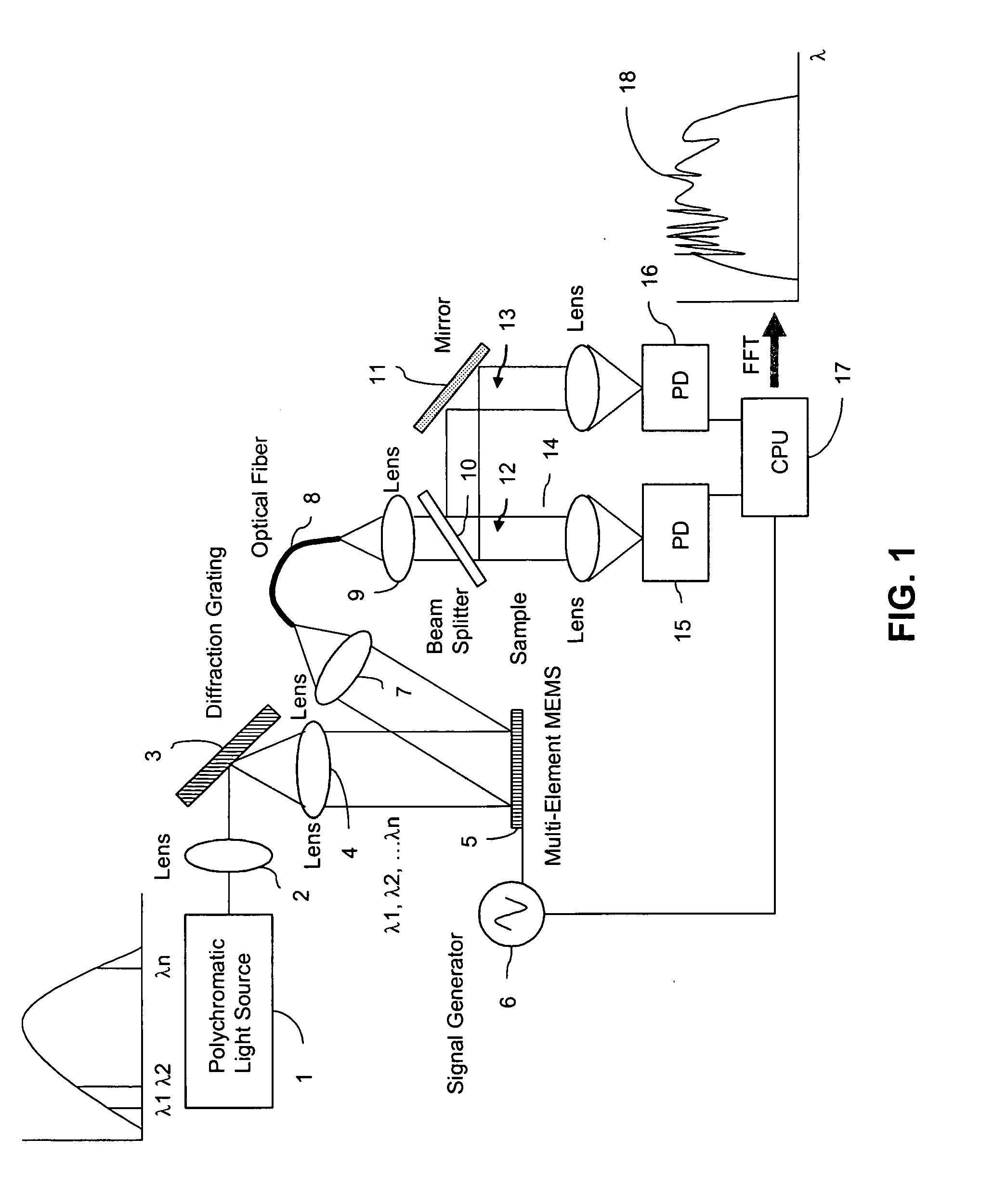
Fourier transform spectrometer apparatus using multi-element mems
InactiveUS20050185179A1Low costHigh enough speedRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationGratingPhotovoltaic detectors
A Fourier Transform (FT) spectrometer apparatus uses multi-element MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical-Systems) or D-MEMS (Diffractive Micro-Electro-Mechanical-Systems) devices. A polychromatic light source is first diffracted or refracted by a dispersive component such as a grating or prism. The dispersed beam is intersected by a multi-element MEMS apparatus. The MEMS apparatus encodes each spectral component thereof with different time varying modulation through corresponding MEMS element. The light radiation is then spectrally recombined as a single beam. The beam is further split into to a reference beam and a probe beam. The probe light is directed to a sample and then the transmitted or reflected light is collected. Both the reference beam and probe beam are detected by a photo-detector. The detected time varying signal is analyzed by Fourier transformation to resolve the spectral components of the sample under measurement.
Owner:METROHM SPECTRO INC
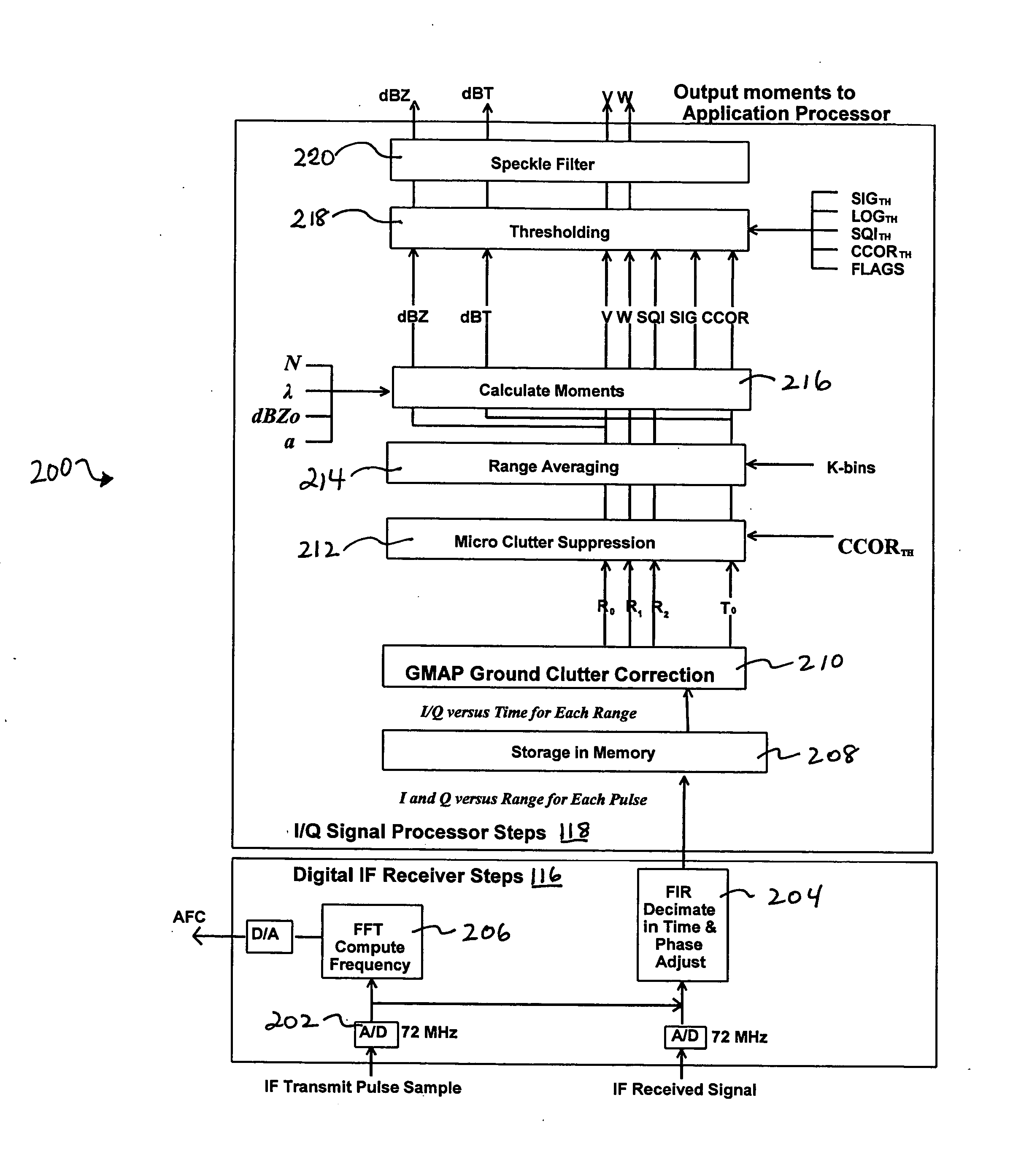
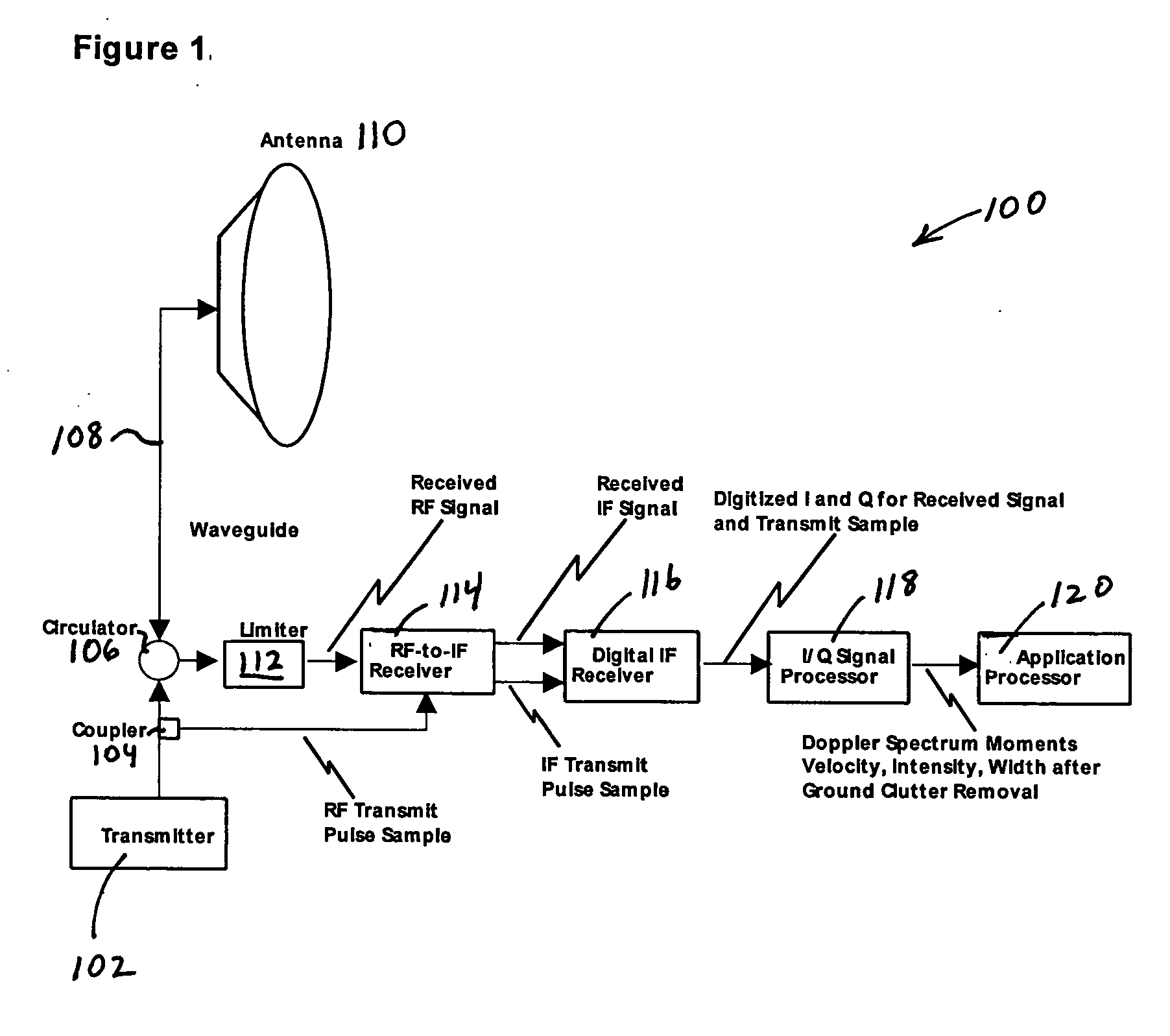
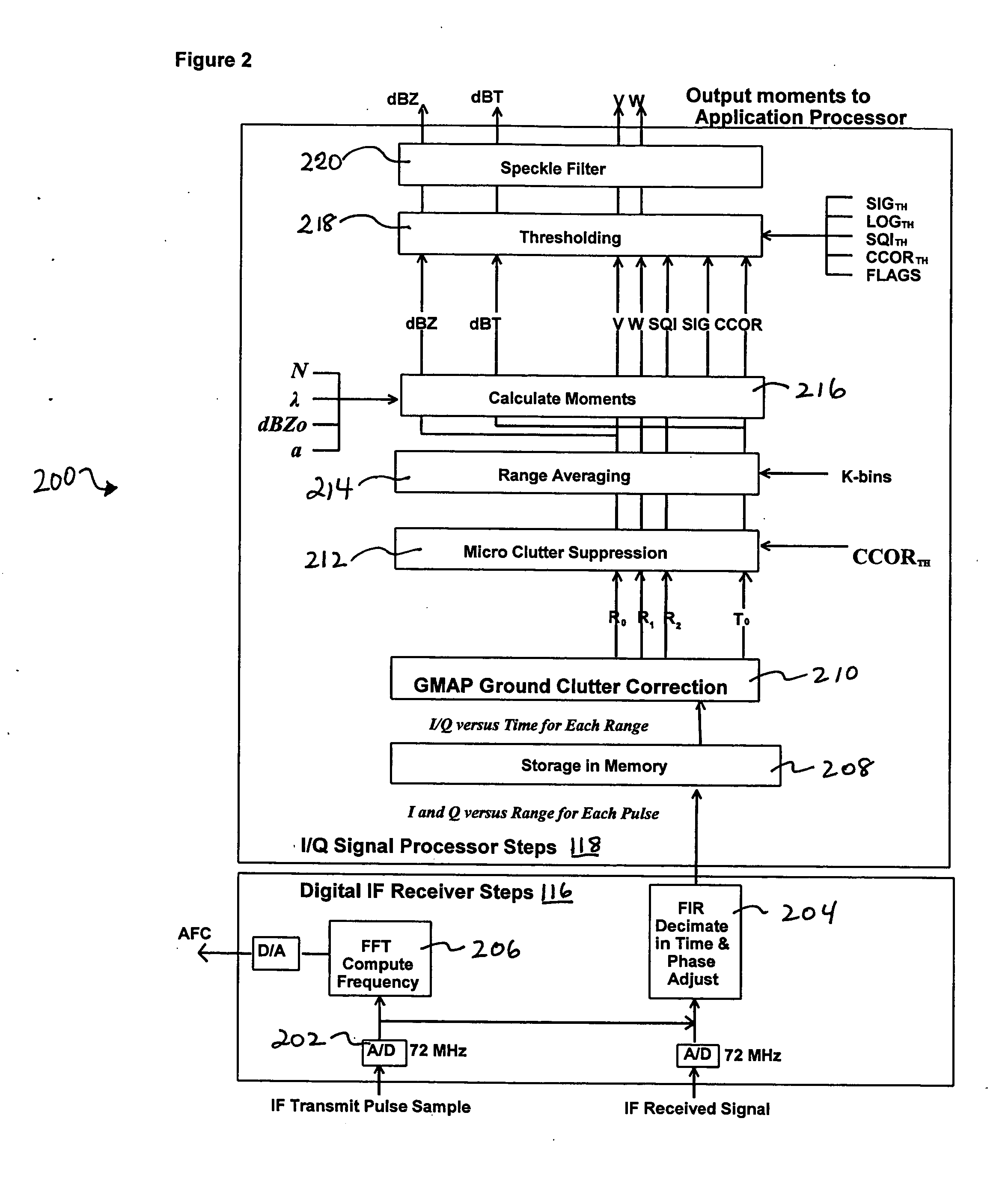
System and method for processing data in weather radar
ActiveUS20080001808A1Reduce varianceEliminate clutterRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationWeather radarFrequency spectrum
Systems and methods that adapt to the weather and clutter in a weather radar signal and apply a frequency domain approach that uses a Gaussian clutter model to remove ground clutter over a variable number of spectral components that is dependent on the assumed clutter width, signal power, Nyquist interval and number of samples. A Gaussian weather model is used to iteratively interpolate over the components that have been removed, if any, thus restoring any overlapped weather spectrum with minimal bias caused by the clutter filter. The system uses a DFT approach. In one embodiment, the process is first performed with a Hamming window and then, based on the outcome, the Hamming results are kept or a portion of the process is repeated with a different window. Thus, proper windows are utilized to minimize the negative impact of more aggressive windows.
Owner:SIGMET
Natural fiber span reflectometer providing a virtual phase signal sensing array capability
ActiveUS20060028636A1Low costMaterial analysis by optical meansBurglar alarmRayleigh scatteringFrequency spectrum
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
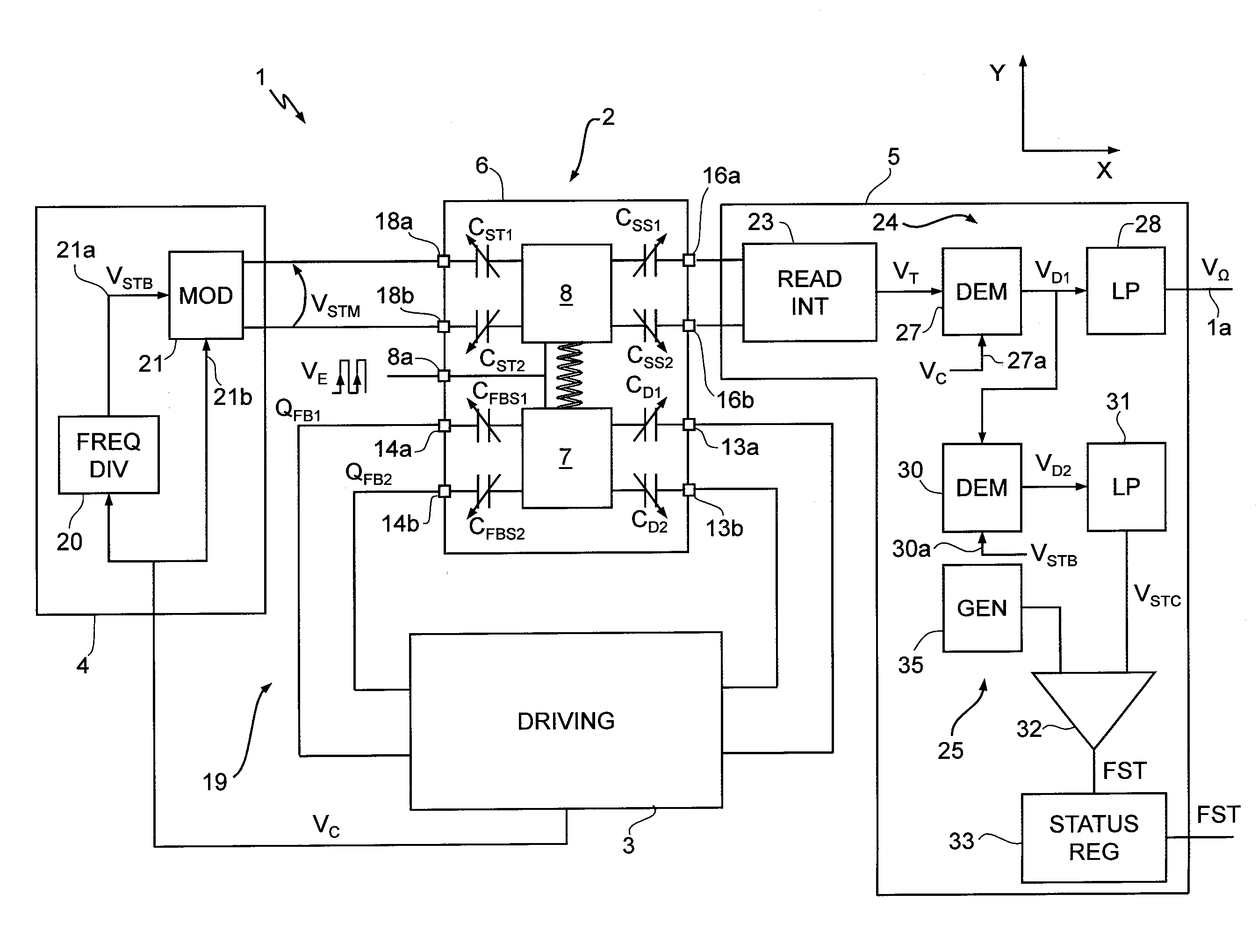
Microelectromechanical gyroscope with continuous self-test function, and method for controlling a microelectromechanical gyroscope
ActiveUS20110146402A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsCapacitanceFrequency spectrum
A microelectromechanical gyroscope includes a body and a sensing mass, which is movable with a degree of freedom in response to rotations of the body about an axis. A self-test actuator is capacitively coupled to the sensing mass for supplying a self-test signal. The capacitive coupling causes, in response to the self-test signal, electrostatic forces that are able to move the sensing mass in accordance with the degree of freedom at an actuation frequency. A sensing device detects transduction signals indicating displacements of the sensing mass in accordance with the degree of freedom. The sensing device is configured for discriminating, in the transduction signals, spectral components that are correlated to the actuation frequency and indicate the movement of the sensing mass as a result of the self-test signal.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
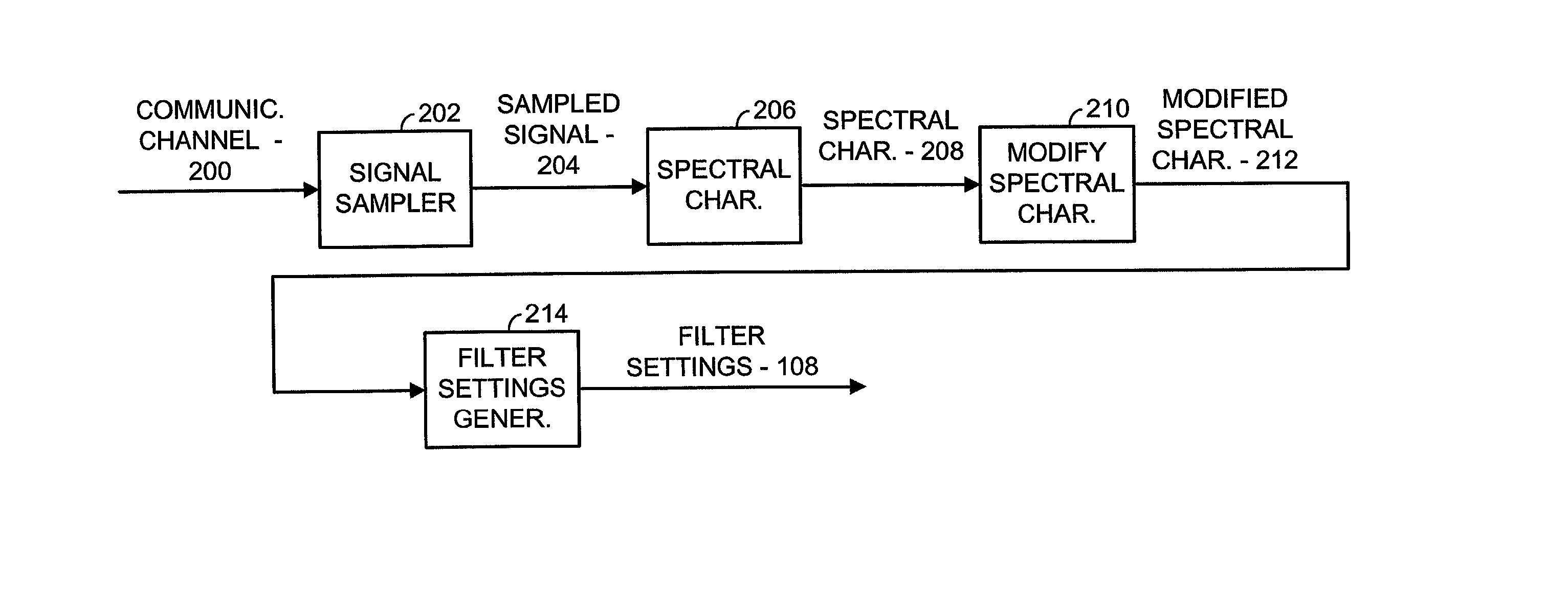
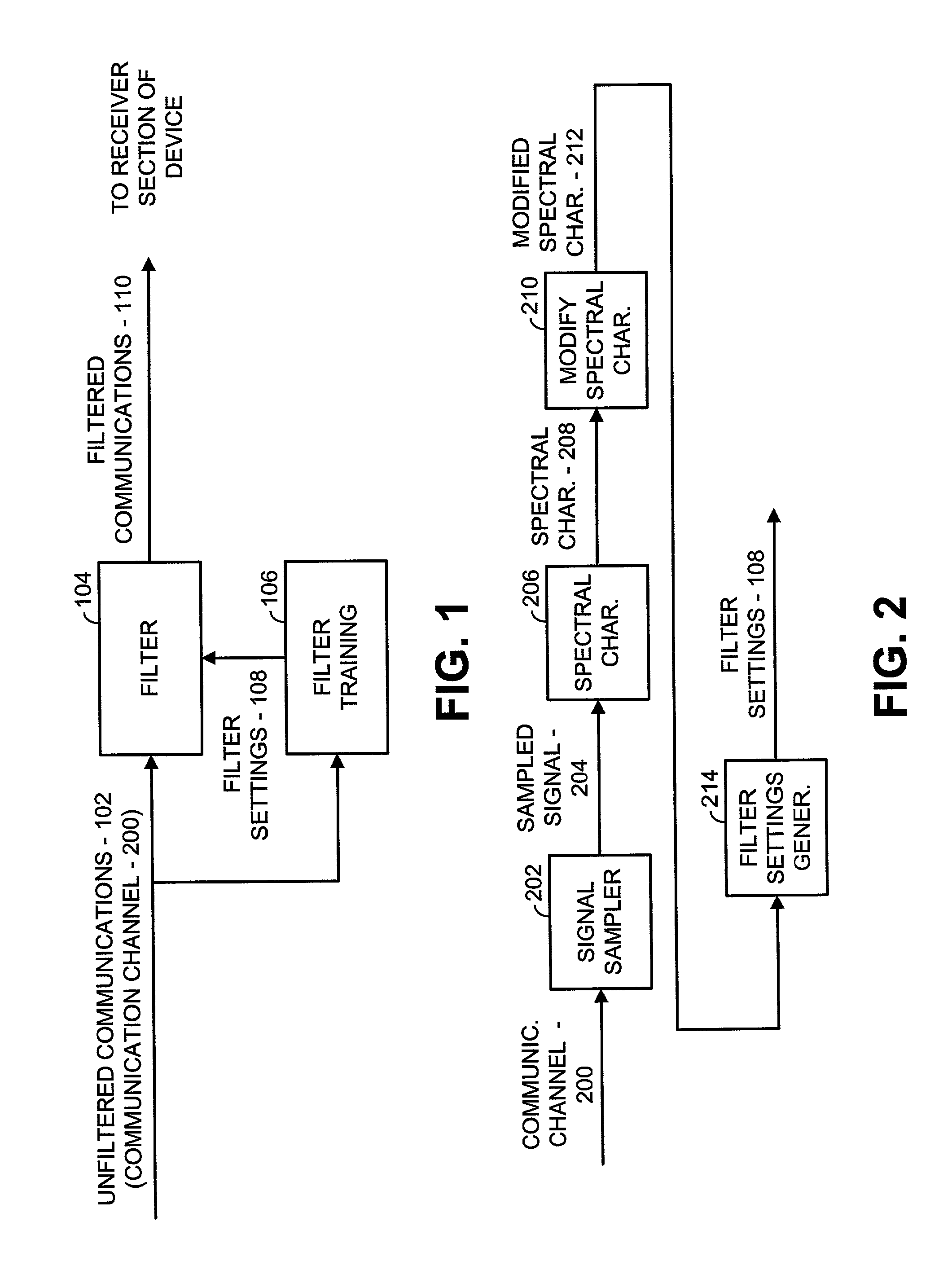
Method for whitening colored noise in a communication system
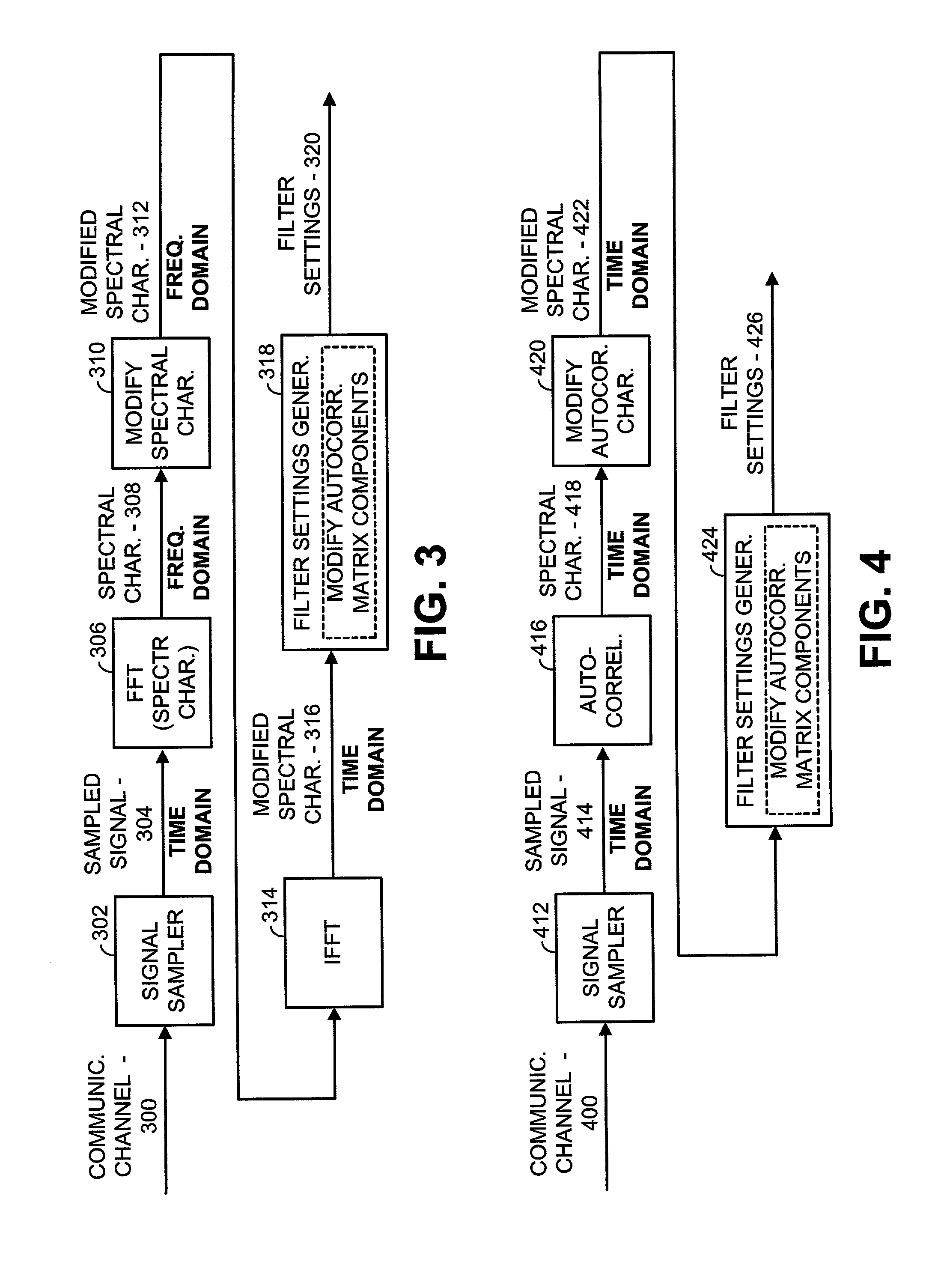
InactiveUS20020126778A1Improve propertiesImprove data throughputLine-faulsts/interference reductionAmplitude demodulation detailsTime domainFrequency spectrum
A filter settings generation operation includes sampling colored noise present at the input of a receiver to produce a sampled signal. The sampled signal is spectrally characterized across a frequency band of interest to produce a spectral characterization of the sampled signal. This spectral characterization may not include a signal of interest. The spectral characterization is then modified to produce a modified spectral characterization. Filter settings are then generated based upon the modified spectral characterization. Finally, the input present at the receiver is filtered using the filter settings when the signal of interest is present to whiten colored noise that is present with the signal of interest. In modifying the spectral characterization, pluralities of spectral components of the spectral characterization are independently modified to produce the modified spectral characterization. Modifications to the spectral characterization may be performed in the frequency domain and / or the time domain. Particular modifications include amplifying spectral components, weighting spectral components based upon prior spectral components, and averaging spectral components with prior spectral components.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com