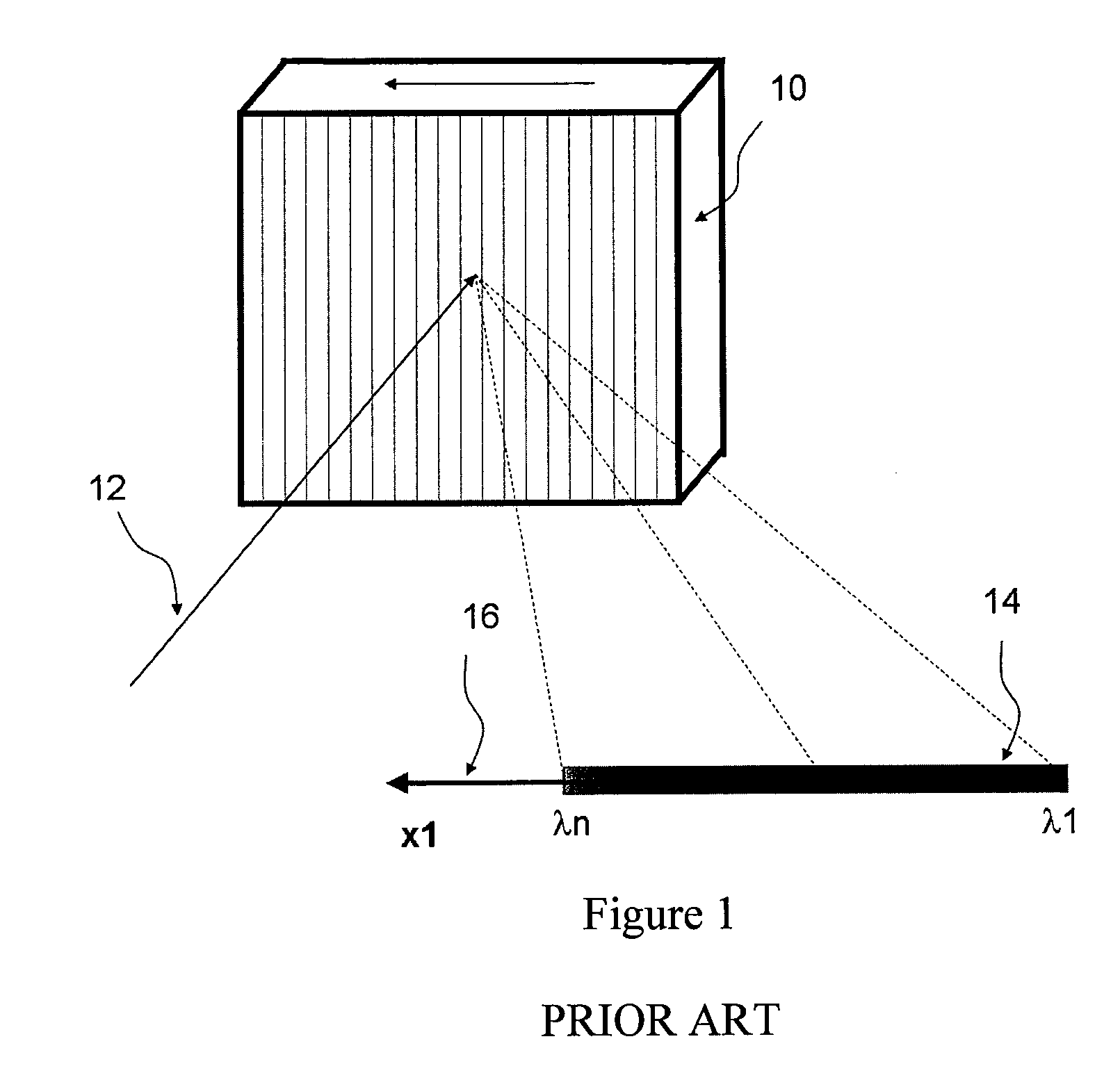
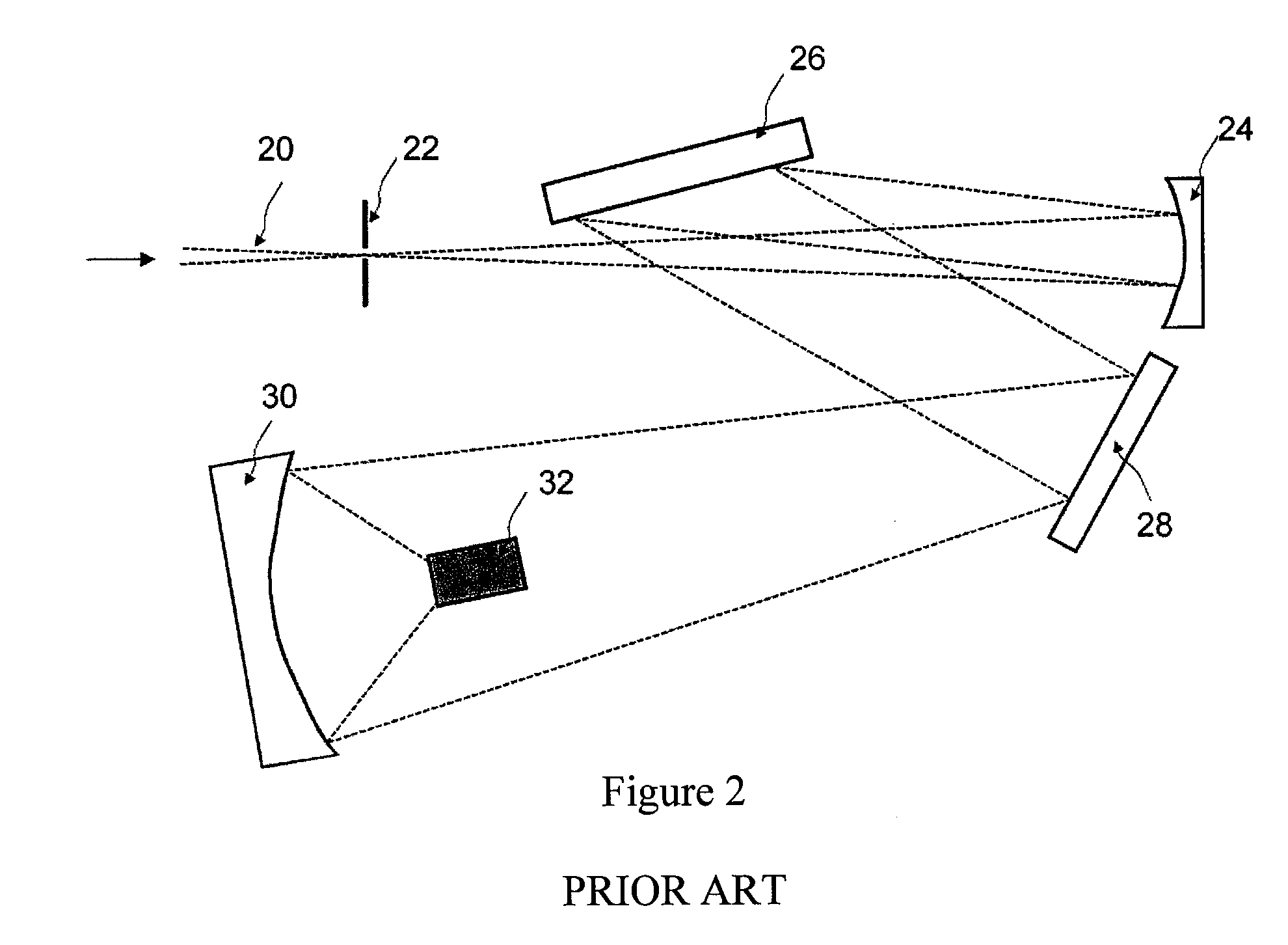
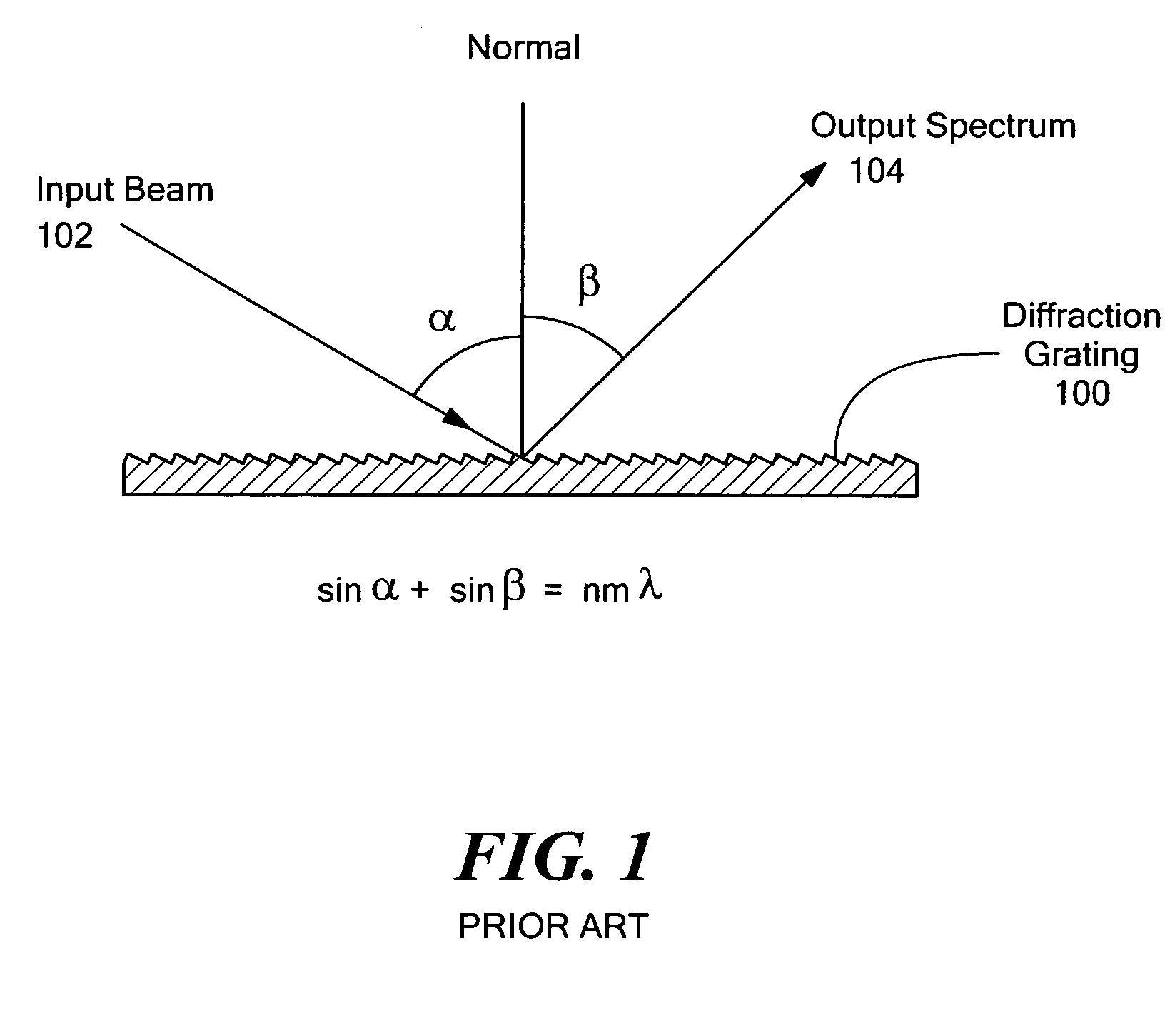
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1324results about "Spectrum generation using diffraction elements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
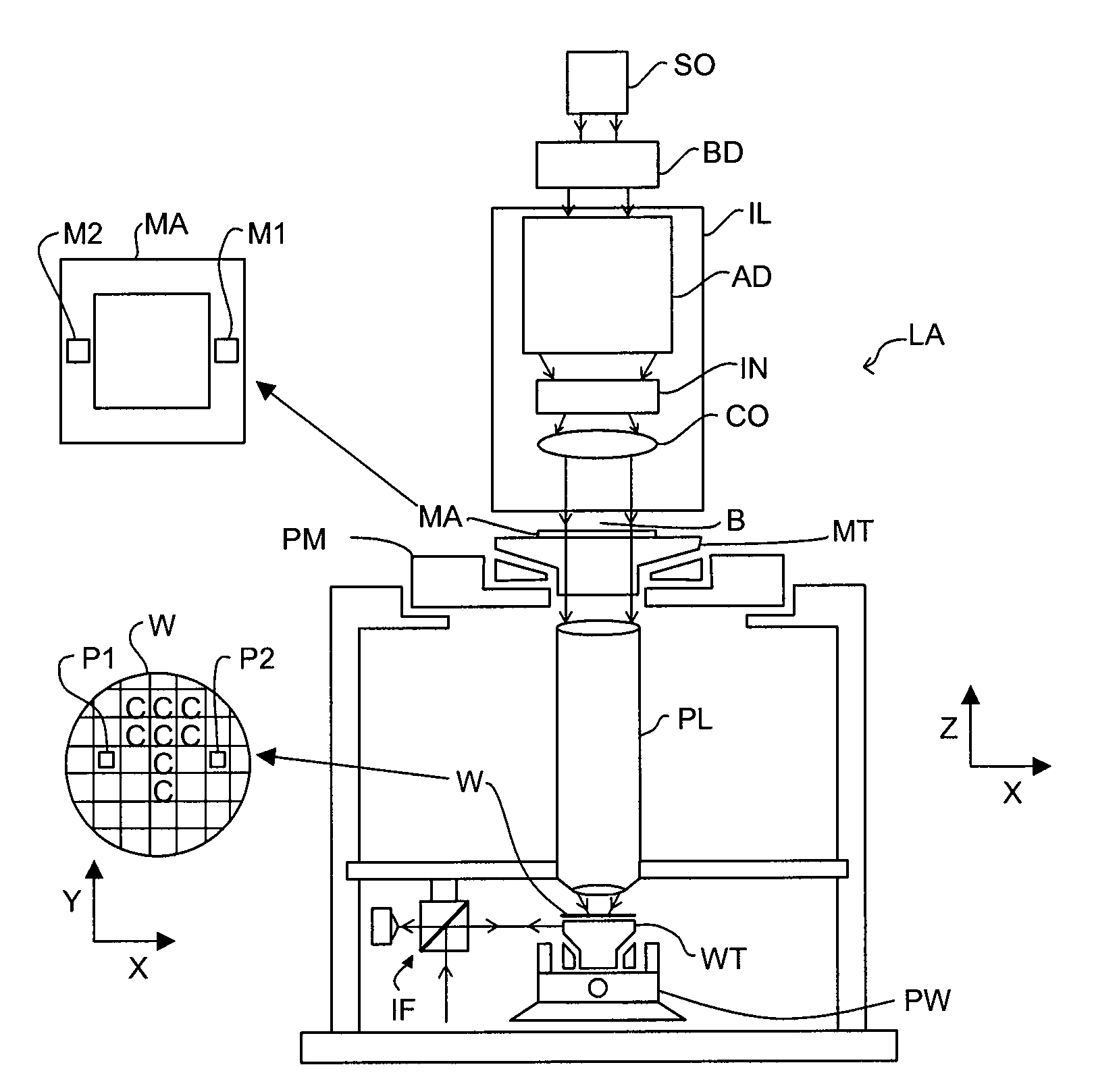
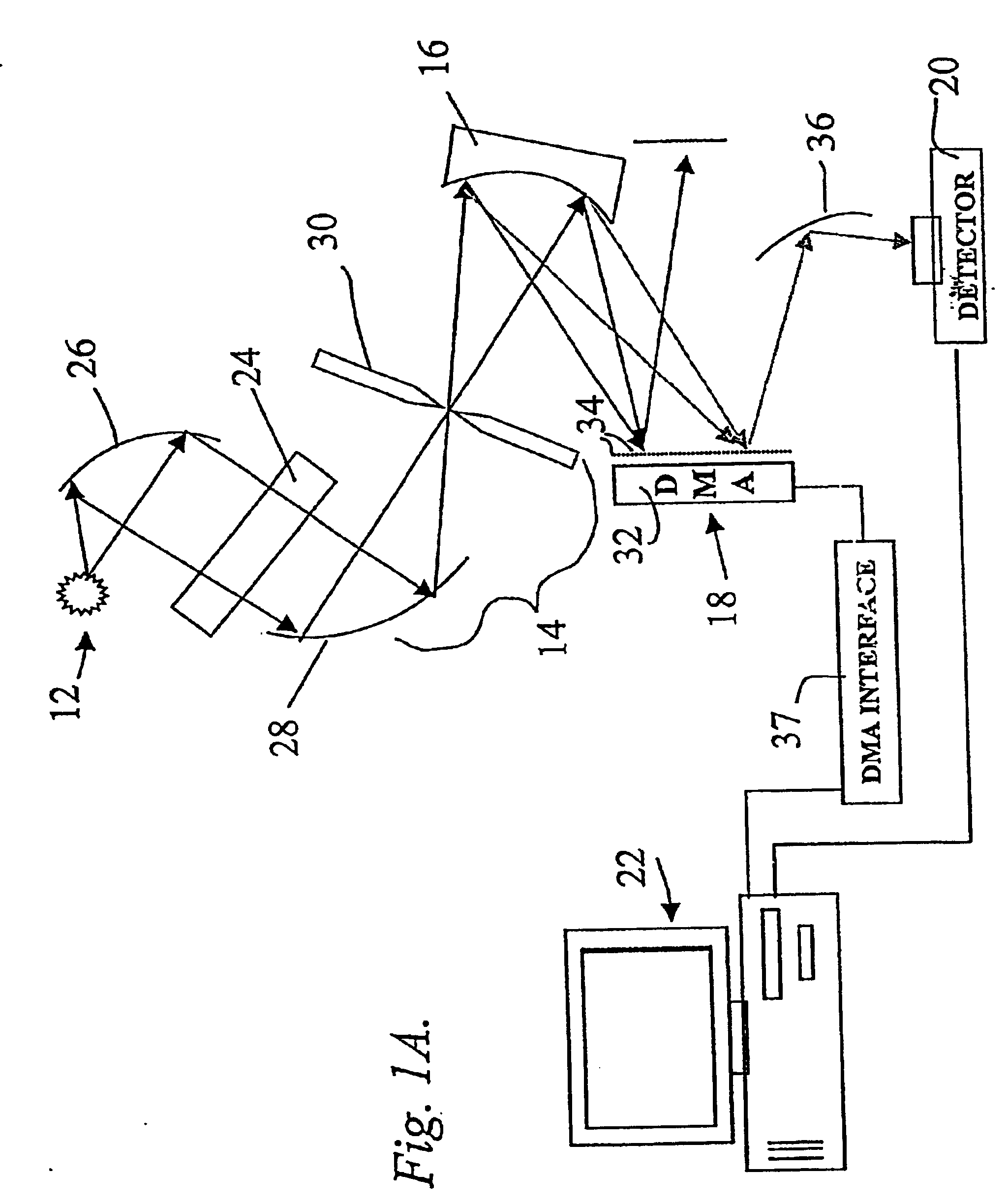
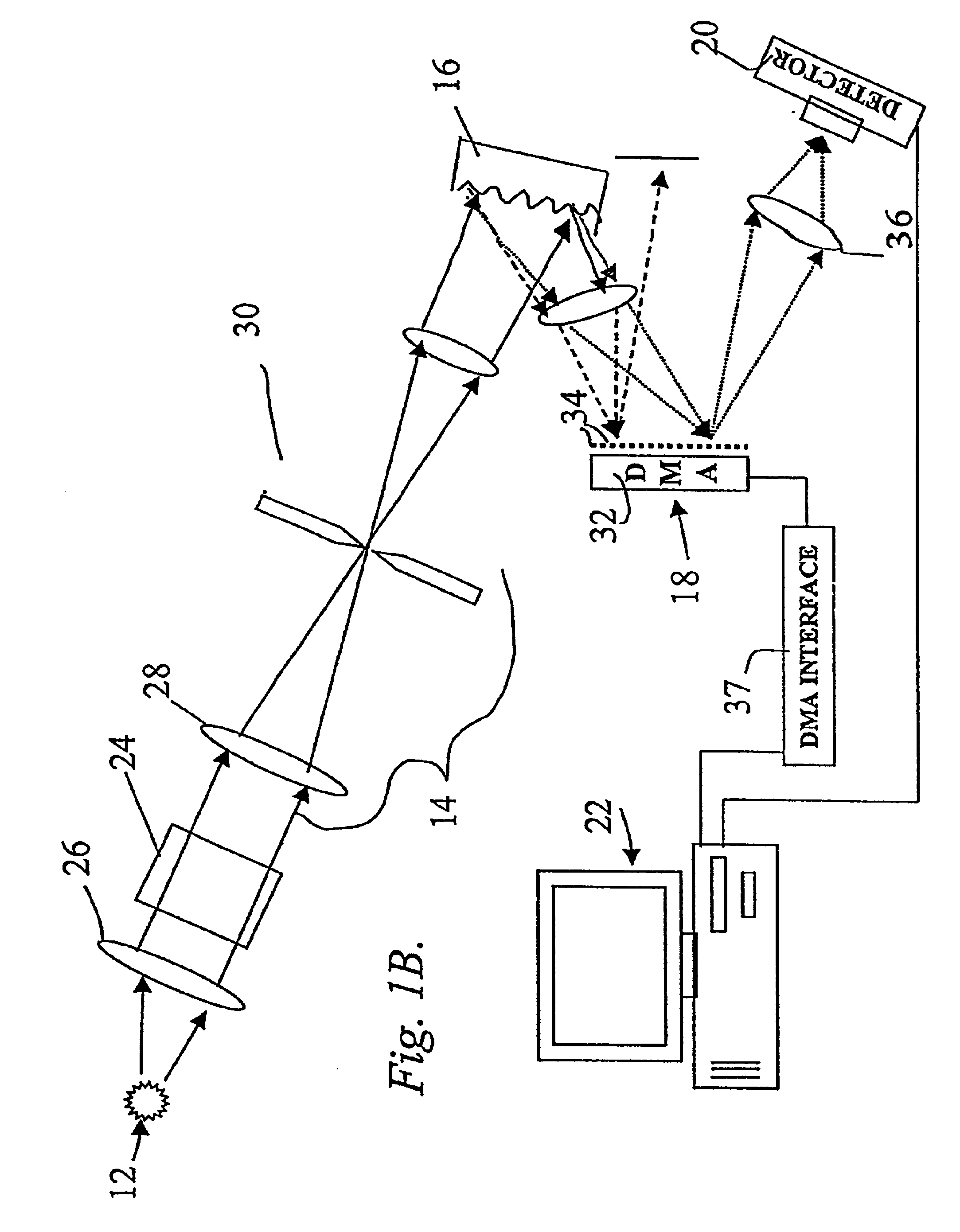
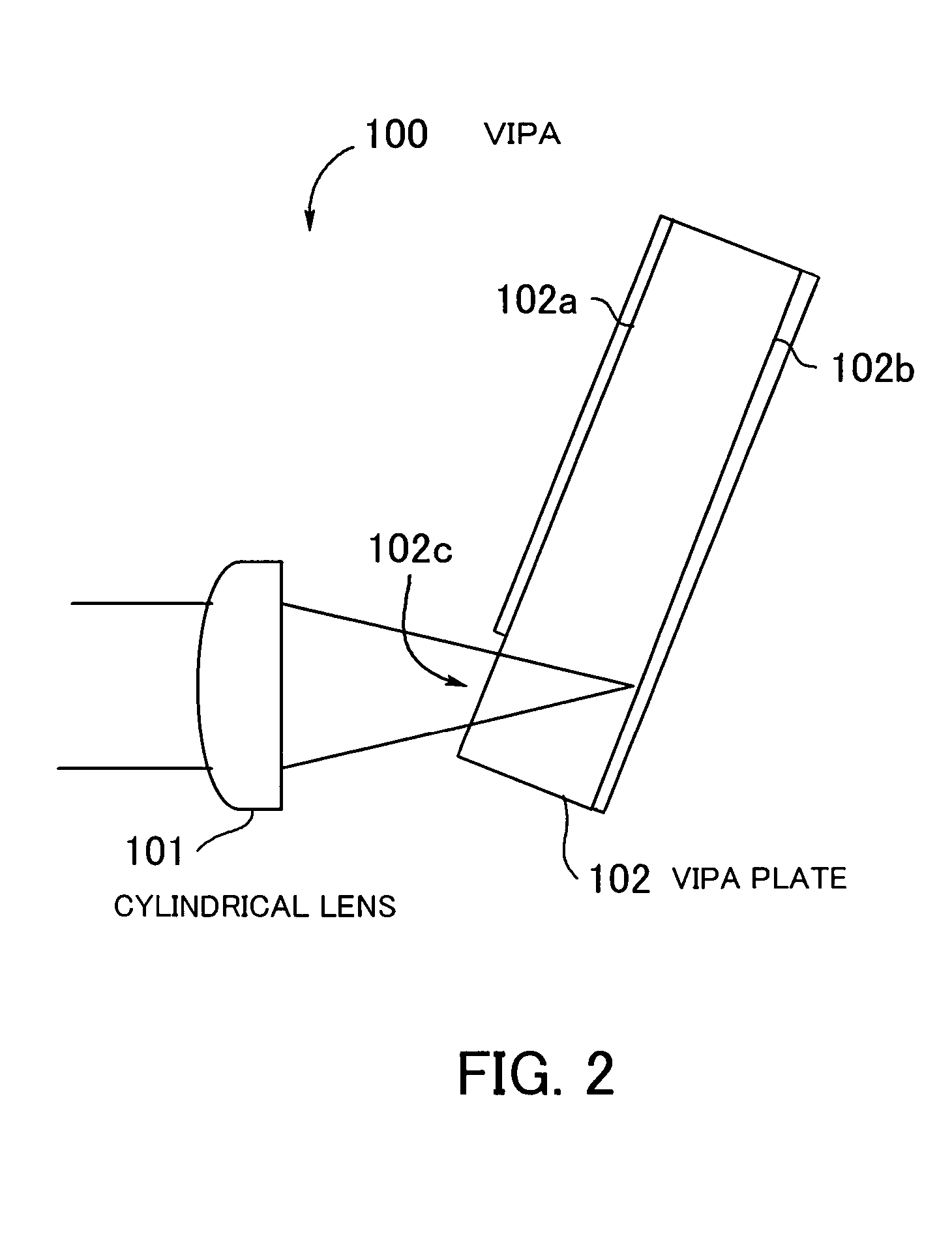
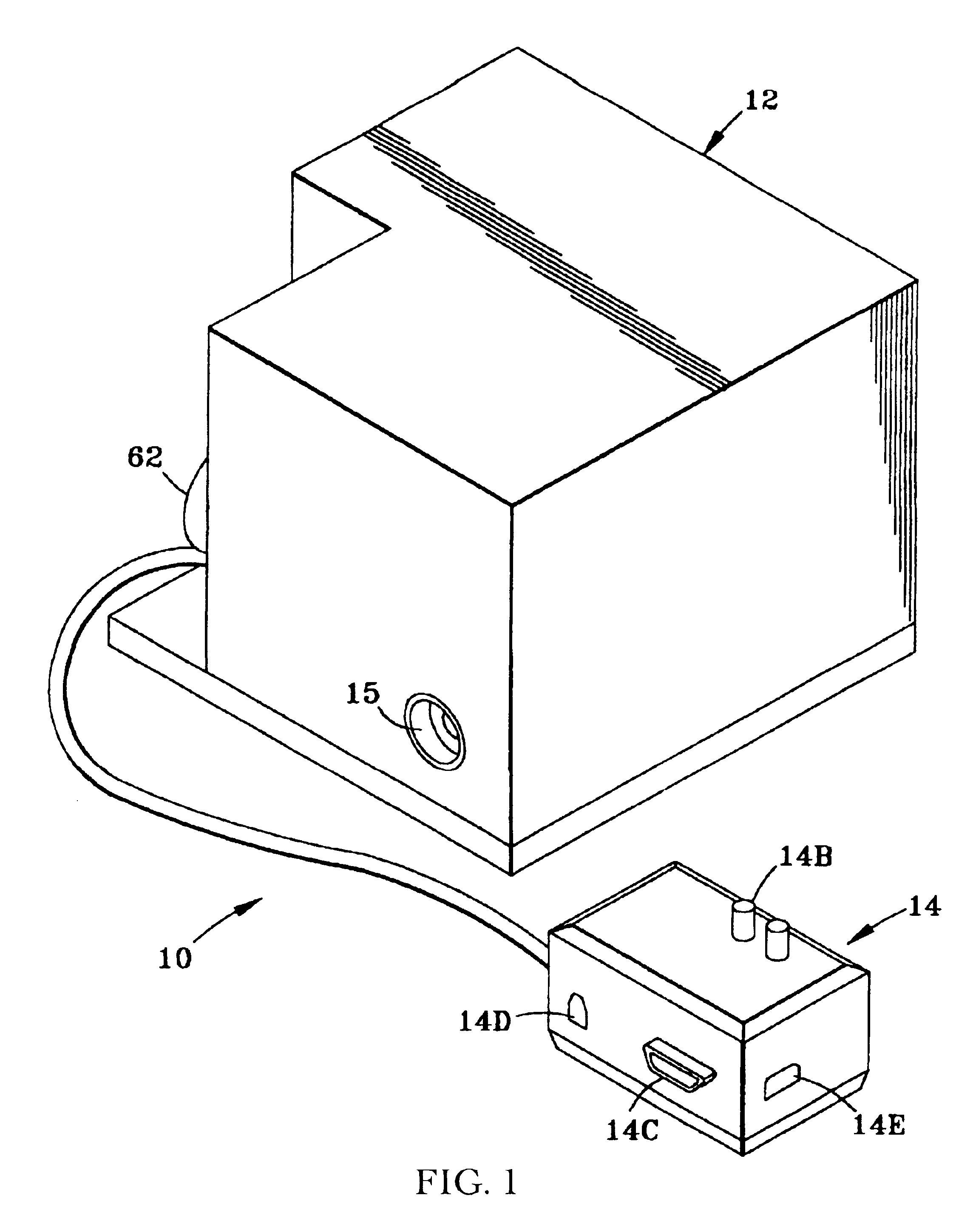
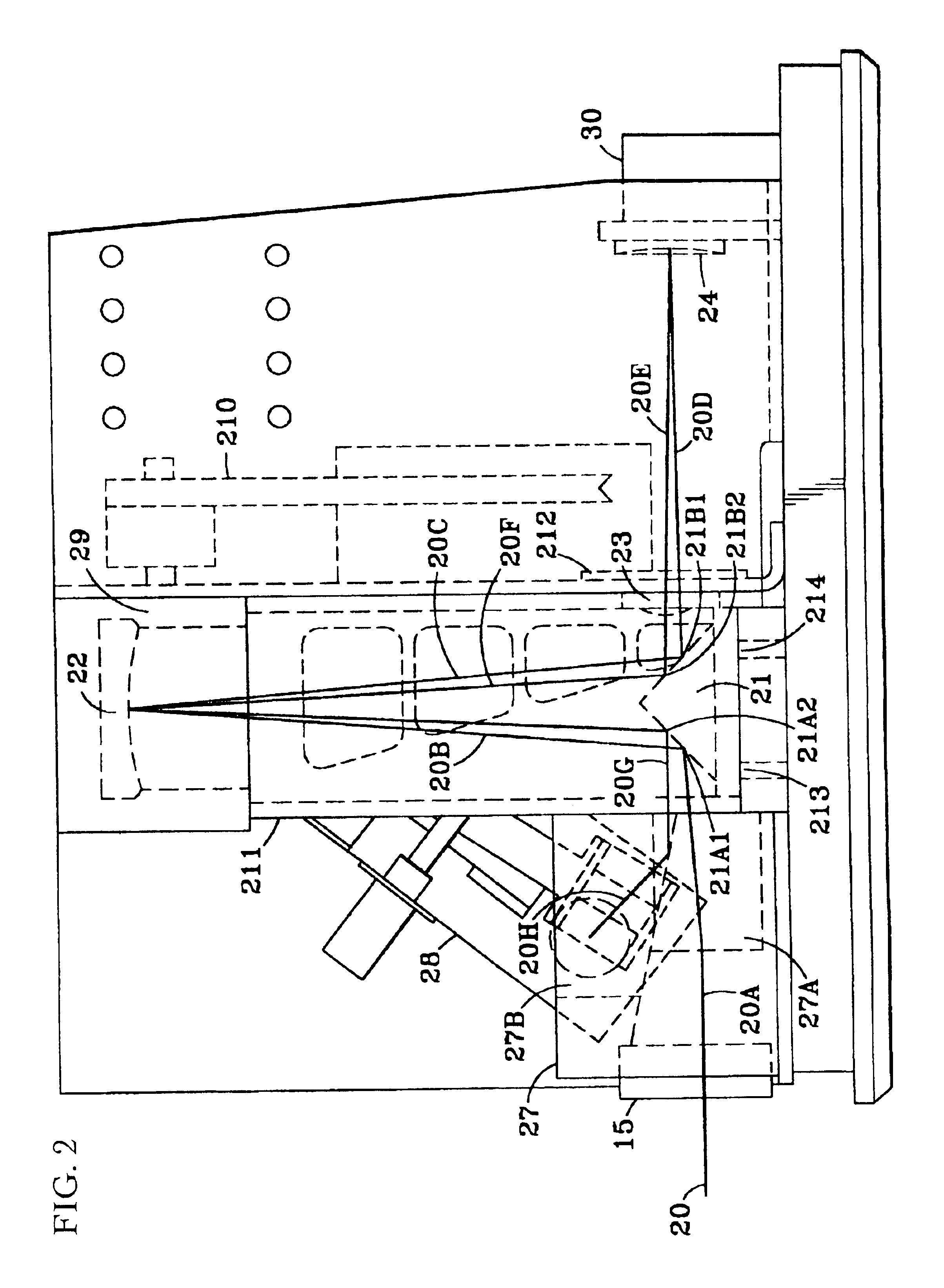
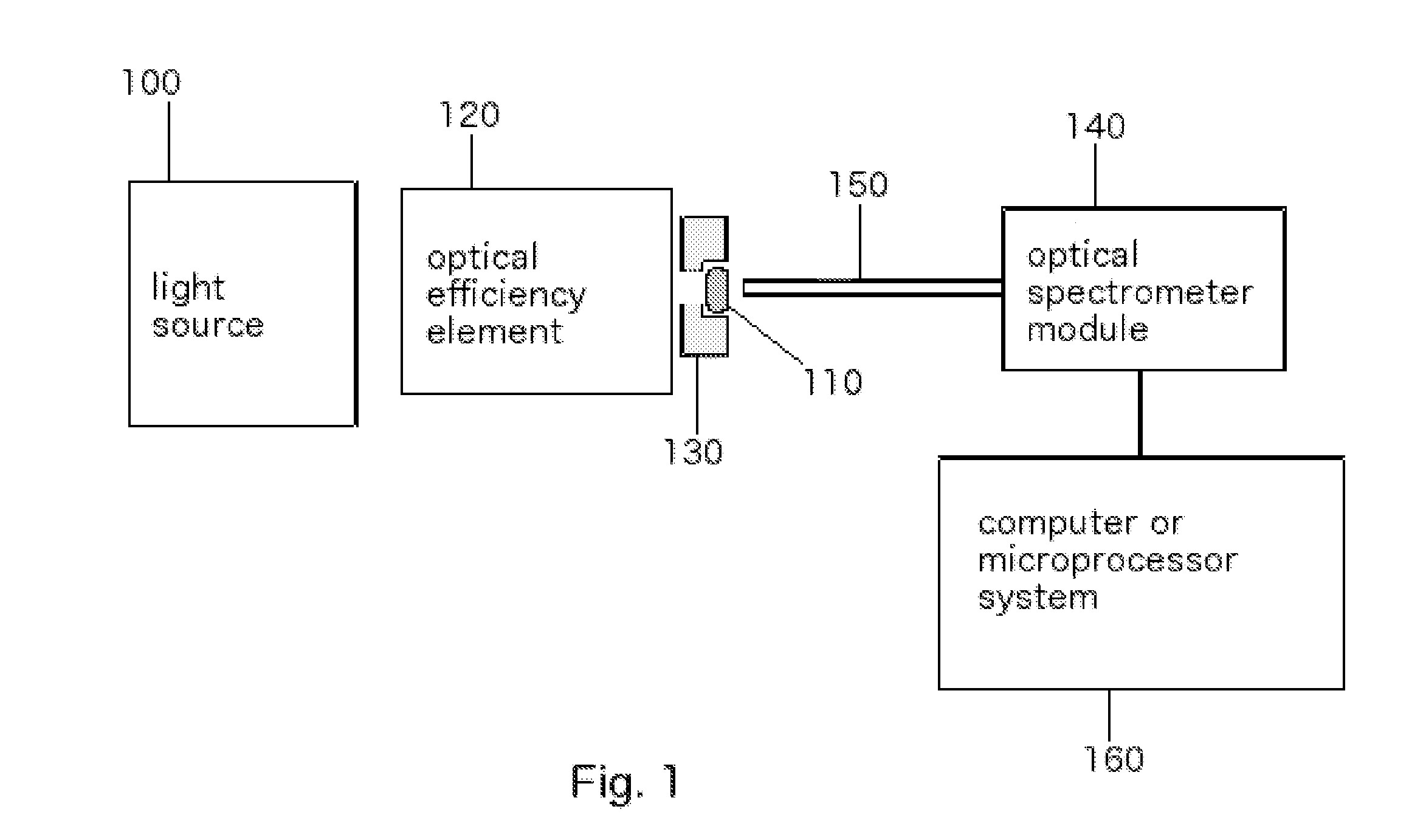
Inspection Apparatus, Lithographic Apparatus, Lithographic Processing Cell and Inspection Method
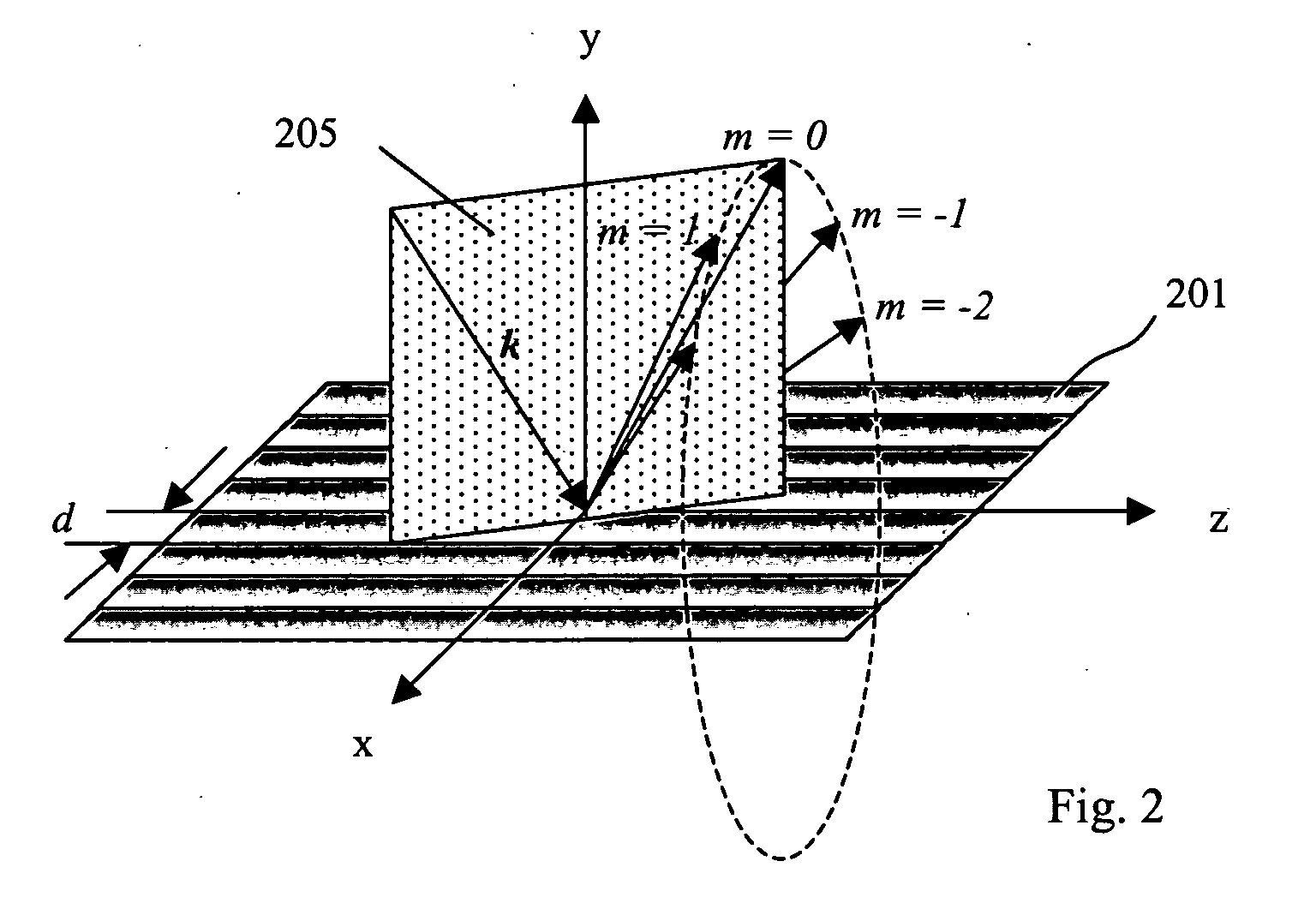
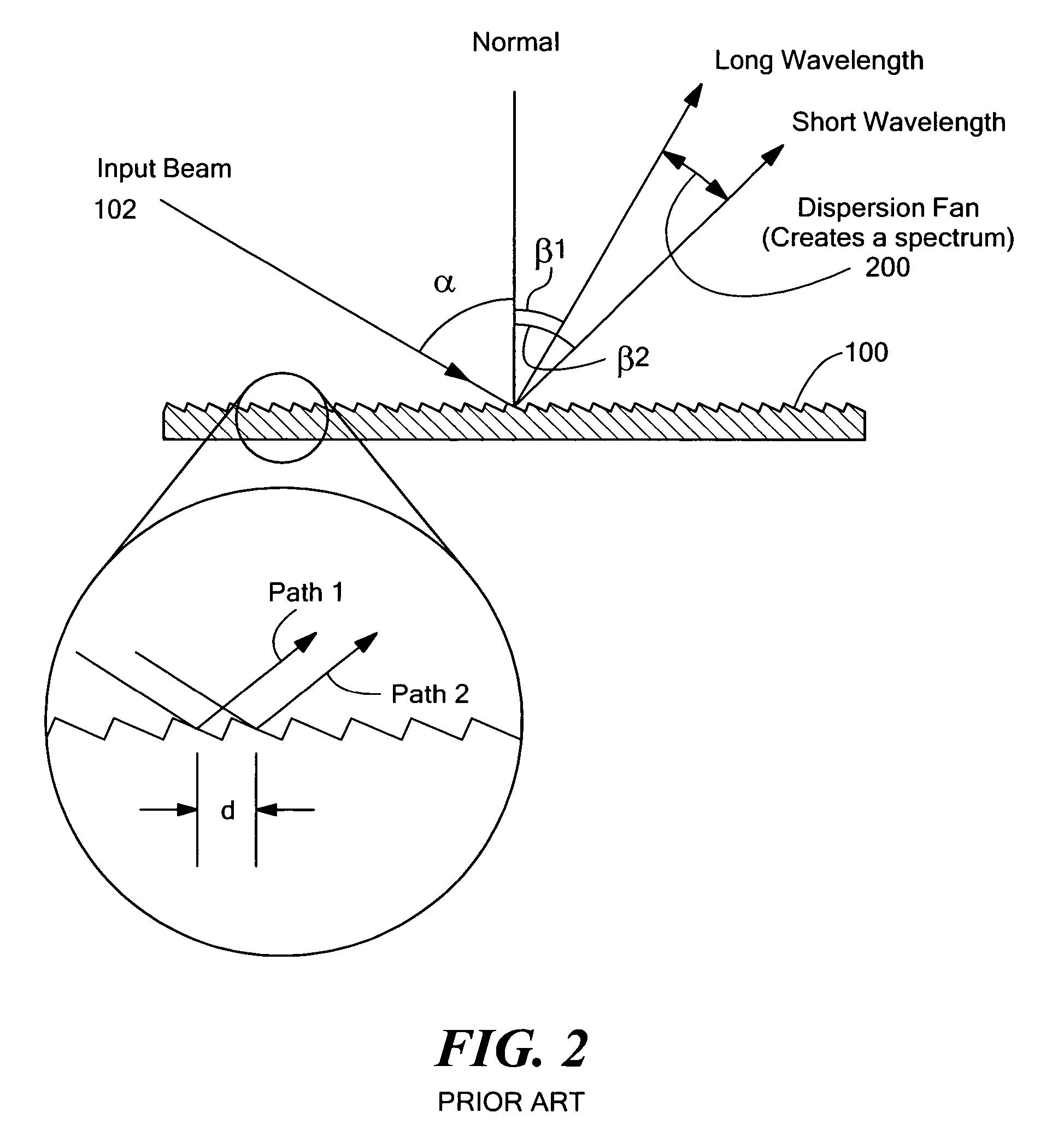
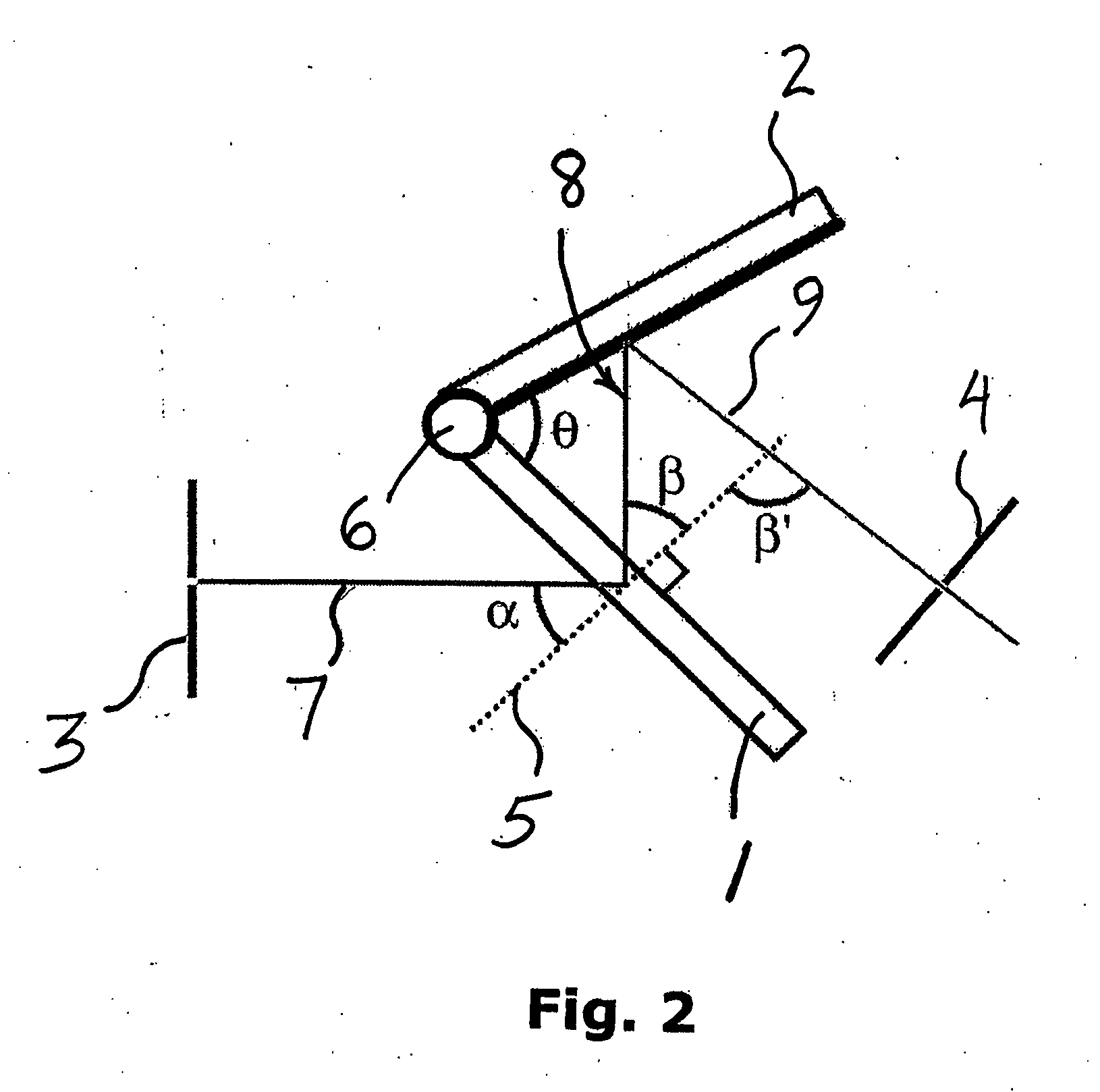
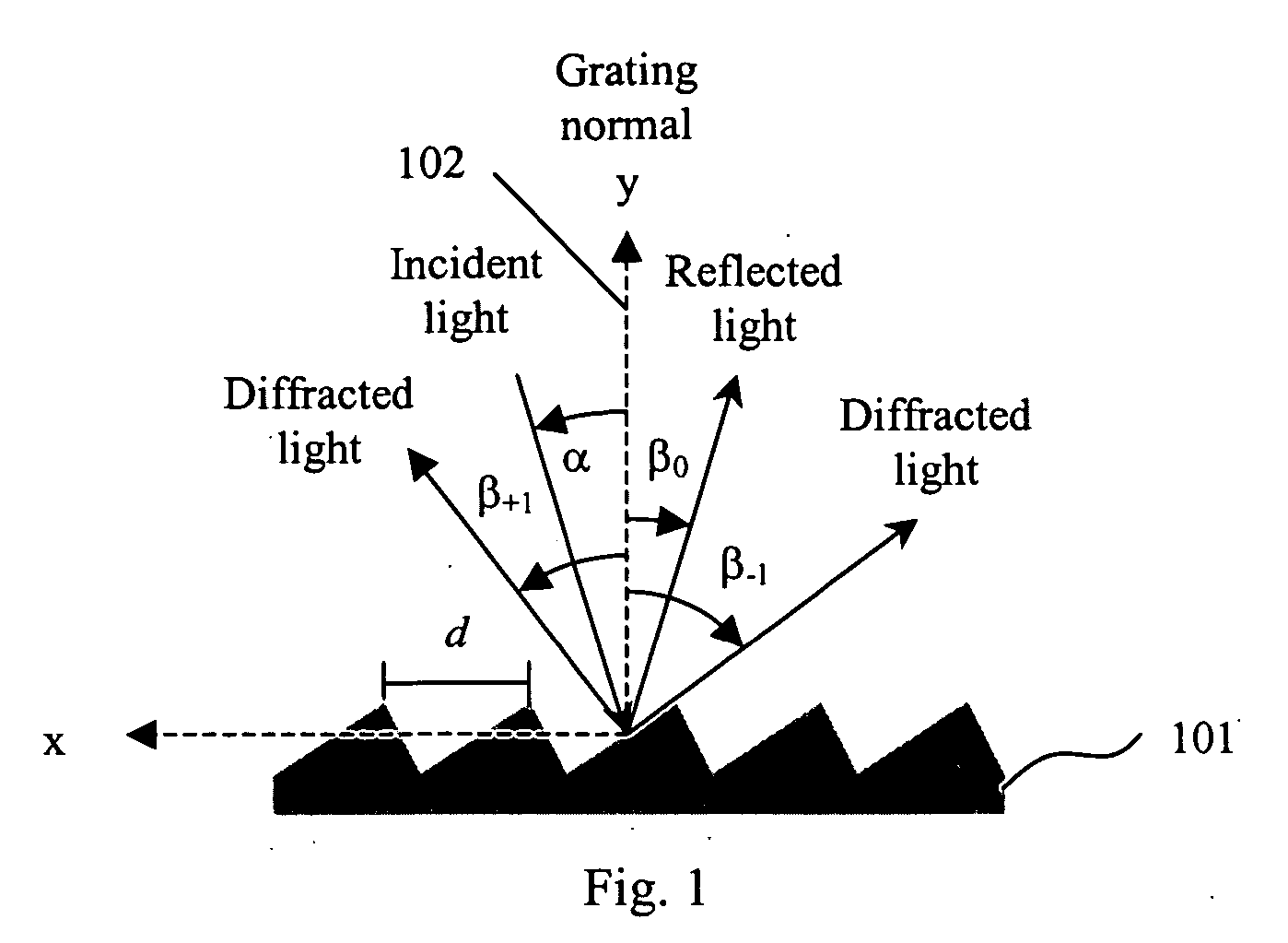
ActiveUS20100201963A1Increase the number ofPossible to separateRaman/scattering spectroscopySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsFour quadrantsZeroth order
For angular resolved spectrometry a radiation beam is used having an illumination profile having four quadrants is used. The first and third quadrants are illuminated whereas the second and fourth quadrants aren't illuminated. The resulting pupil plane is thus also divided into four quadrants with only the zeroth order diffraction pattern appearing in the first and third quadrants and only the first order diffraction pattern appearing in the second and third quadrants.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
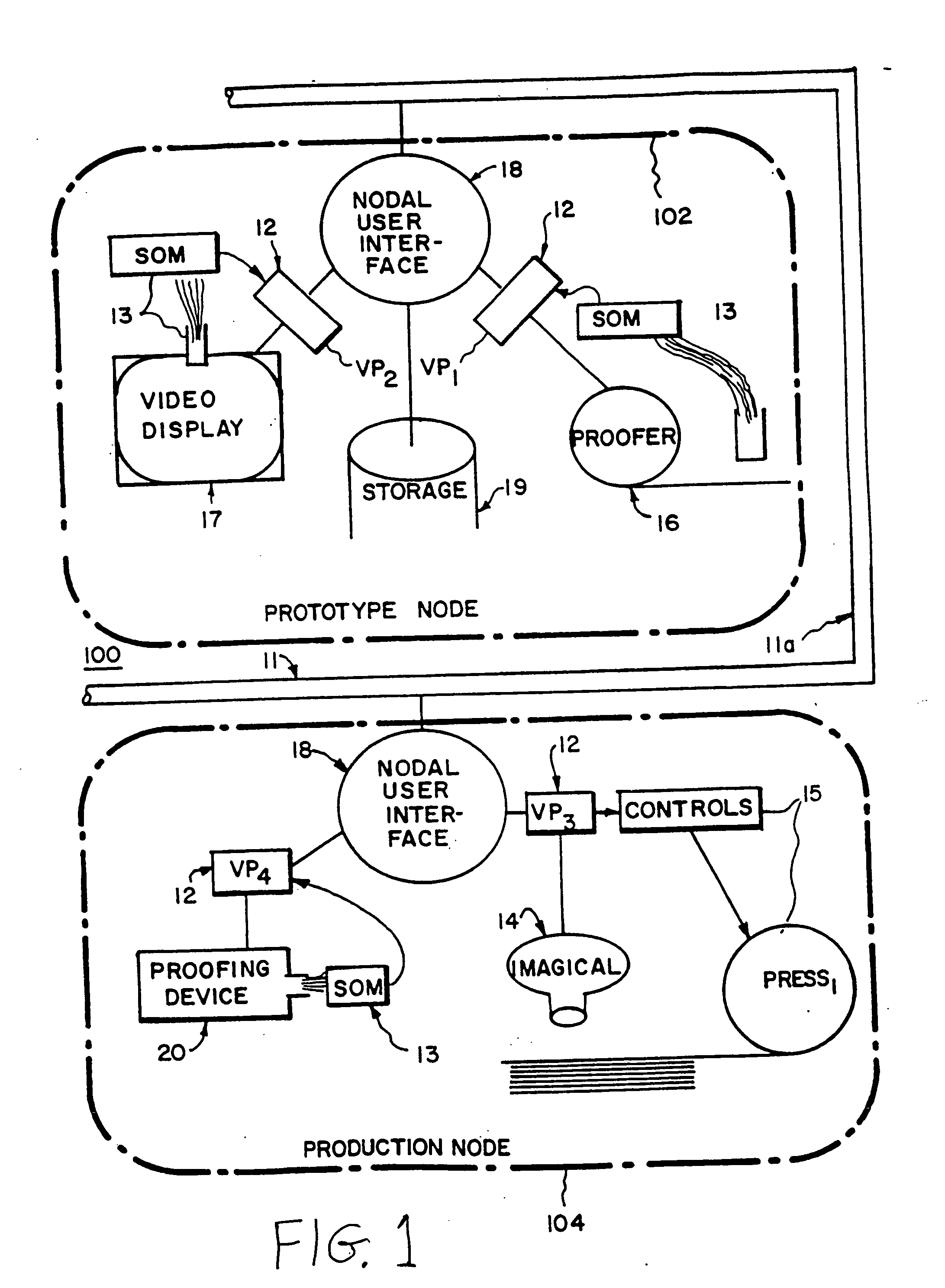
Color calibration of color image rendering devices
InactiveUS20060280360A1Increase heightImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageComputer graphics (images)
Color calibration of color image rendering devices, such as large color displays, which operate by either projection or emission of images, utilize internal color measurement instrument or external color measurement modules locatable on a wall or speaker. A dual use camera is provided for a portable or laptop computer, or a cellular phone, handset, personal digital assistant or other handheld device with a digital camera, in which one of the camera or a display is movable with respect to the other to enable the camera in a first mode to capture images of the display for enabling calibration of the display, and in a second mode for capturing image other than of the display. The displays may represent rendering devices for enabling virtual proofing in a network, or may be part of stand-alone systems and apparatuses for color calibration. Improved calibration is also provided for sensing and correcting for non-uniformities of rendering devices, such as color displays, printer, presses, or other color image rendering device.
Owner:RAH COLOR TECH
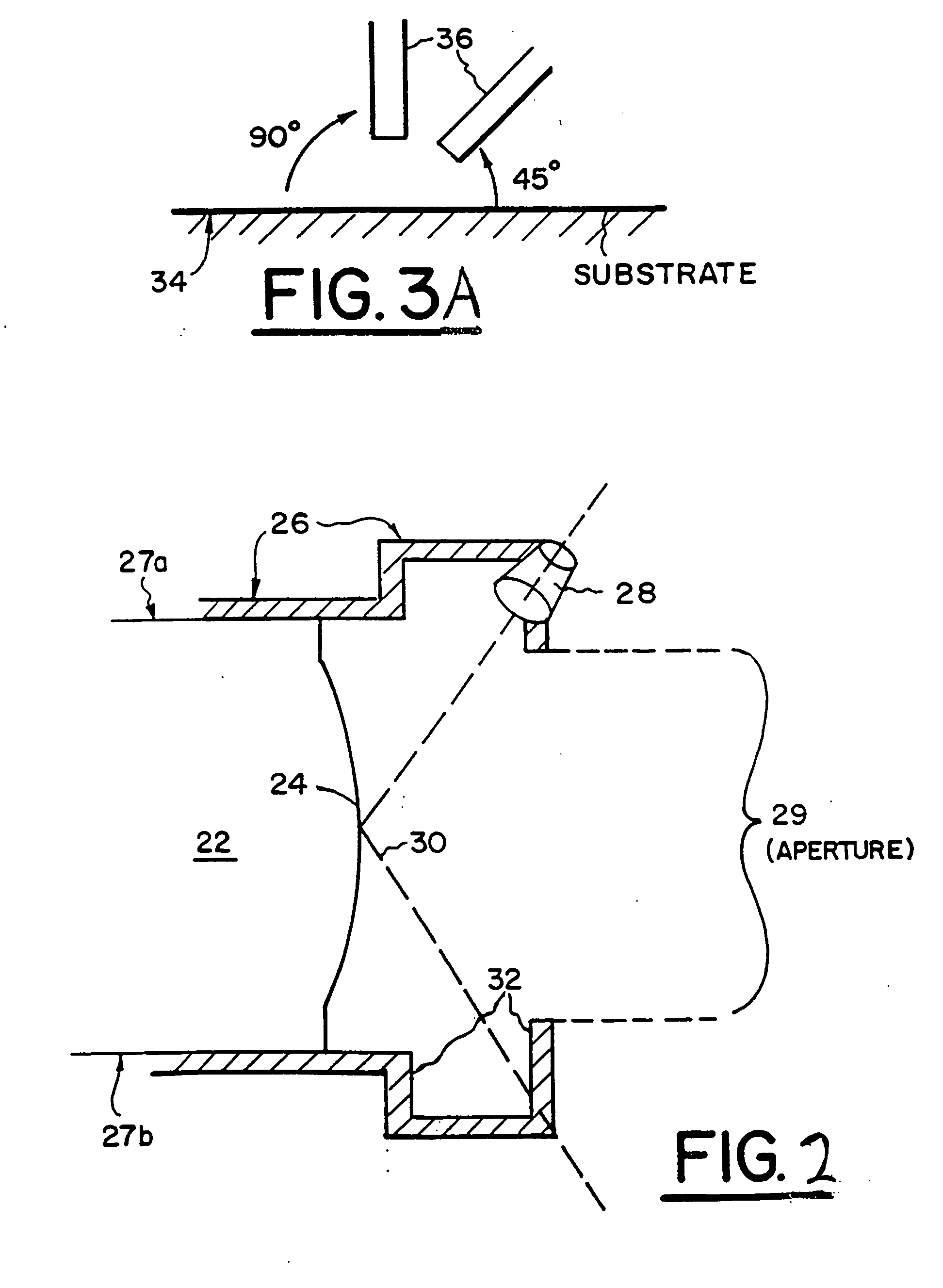
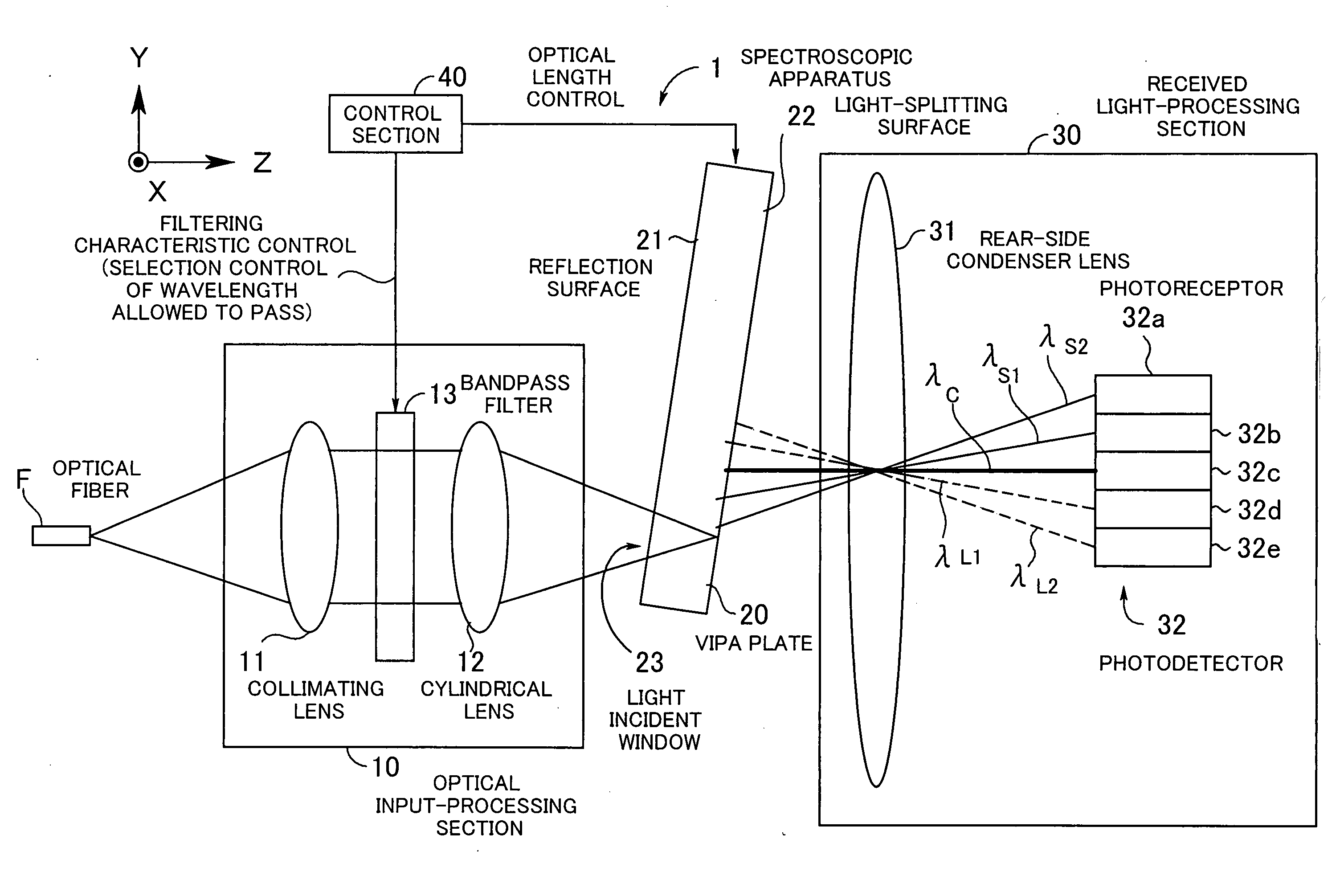
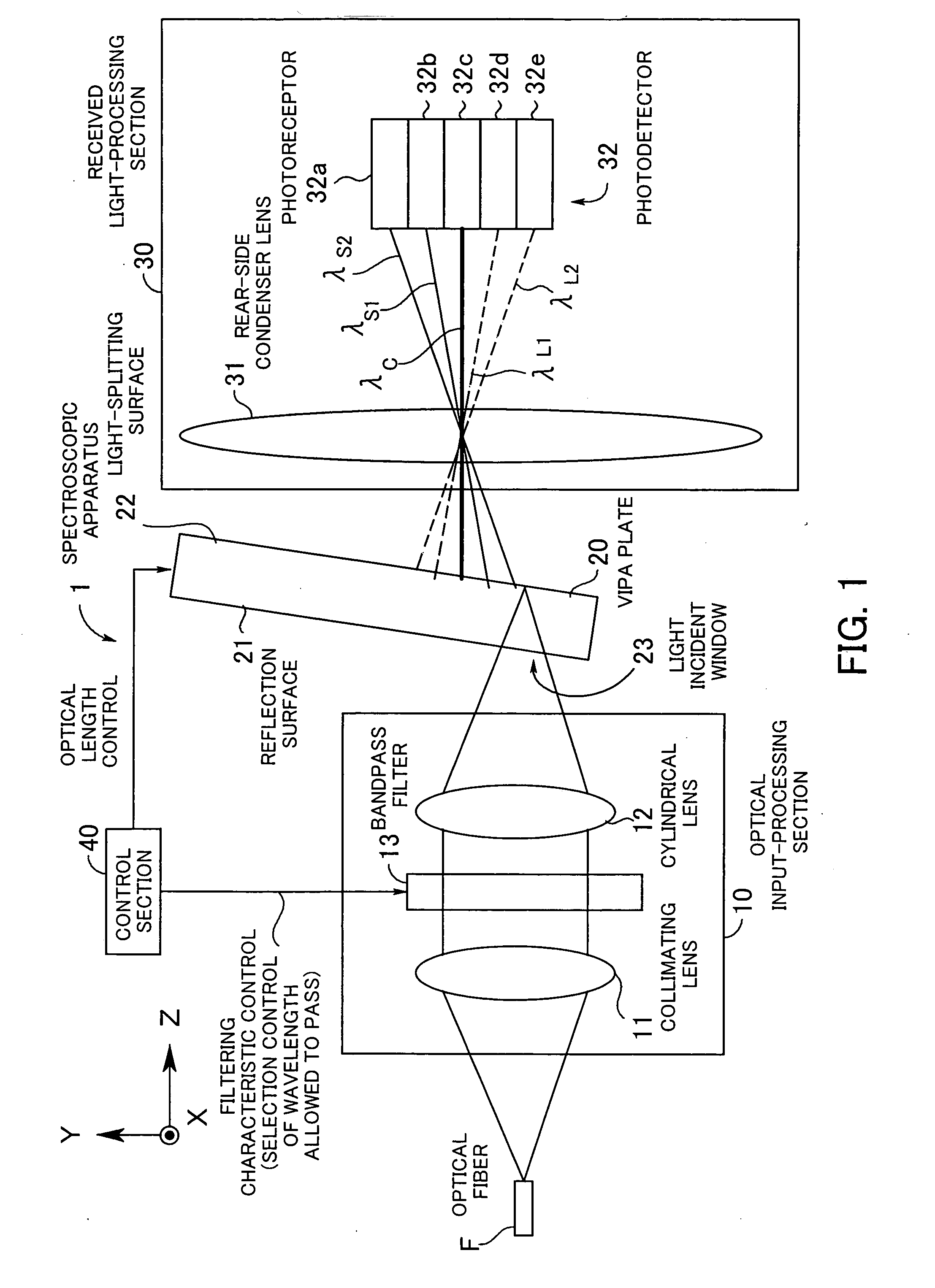
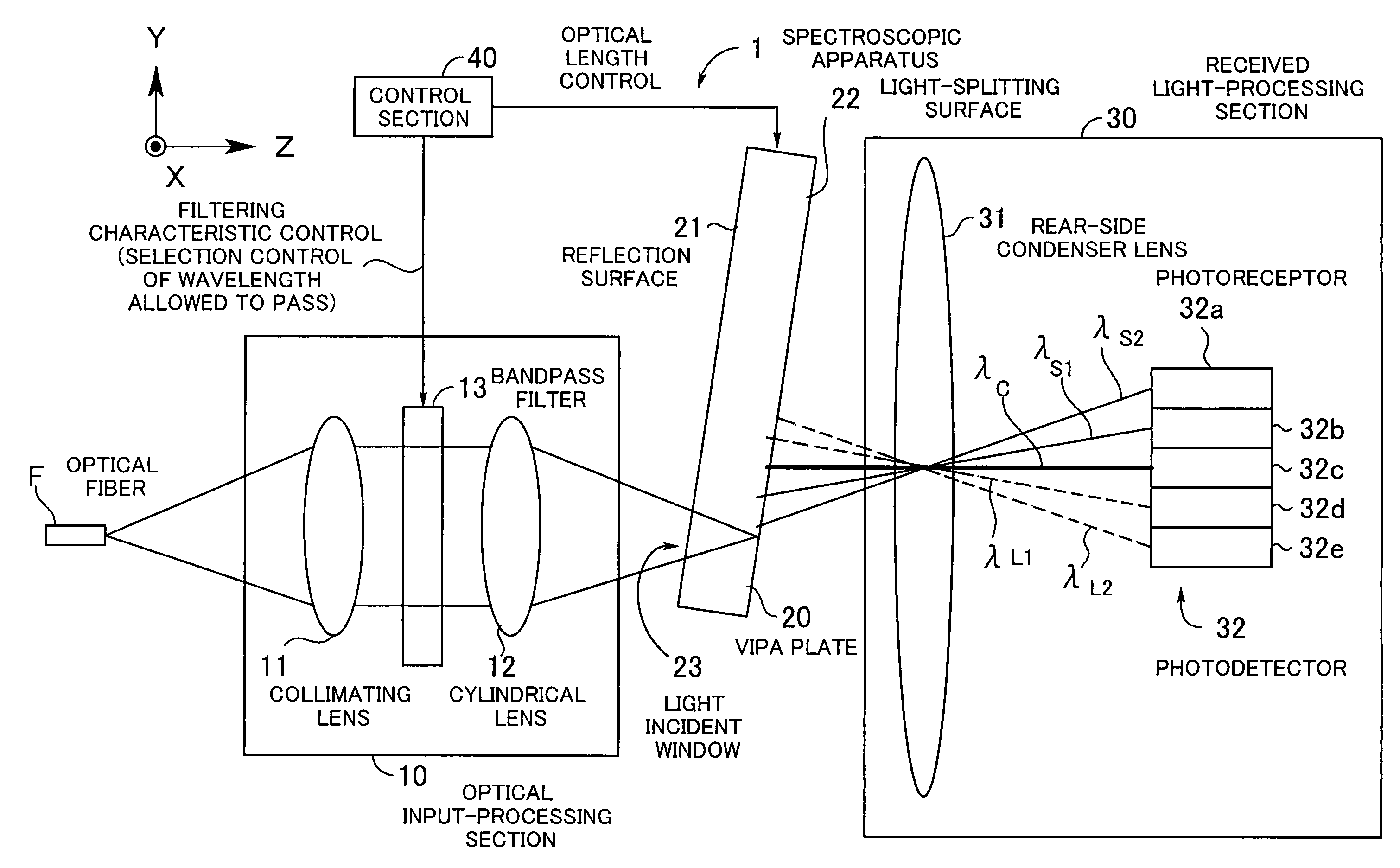
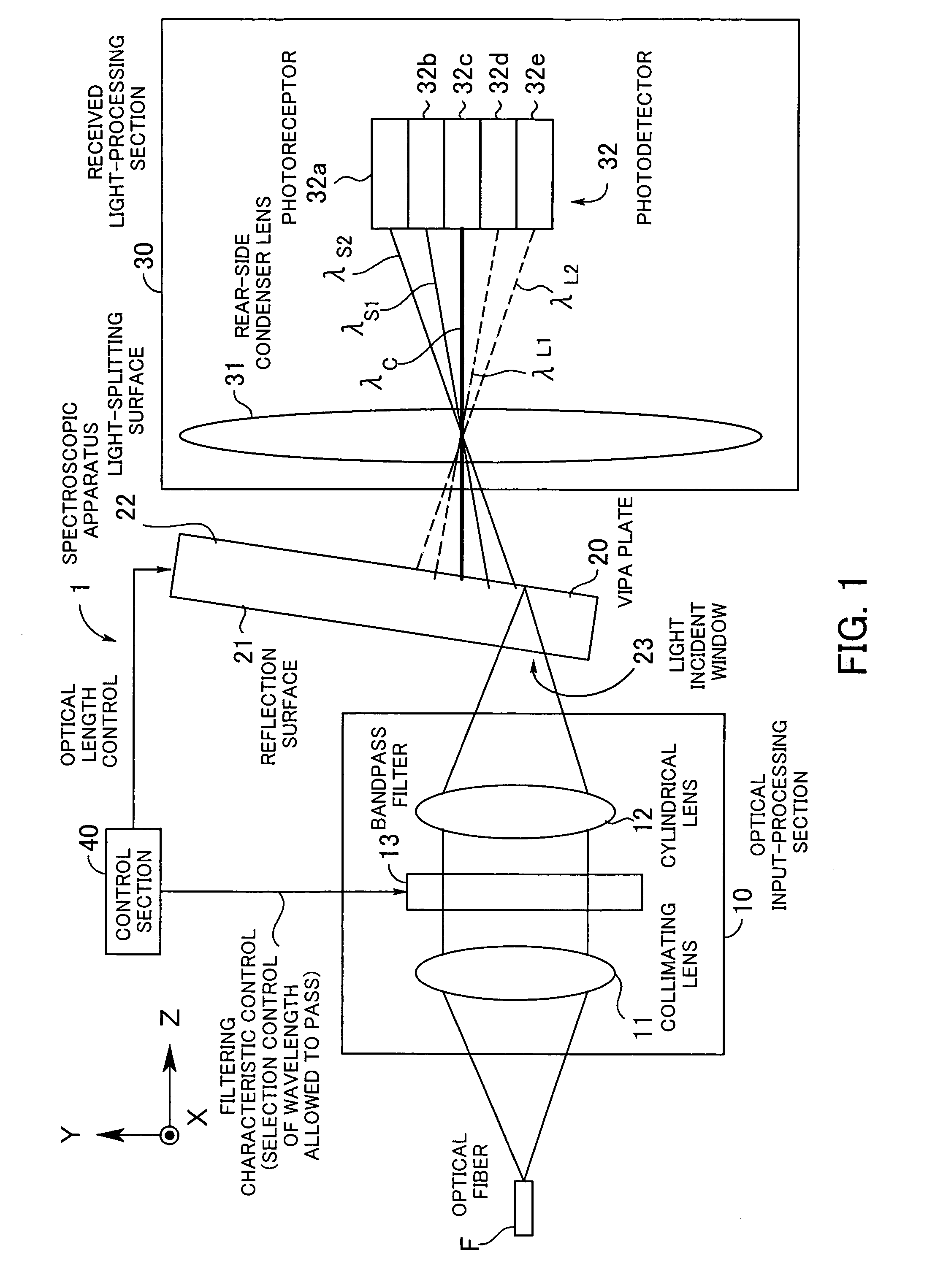
Spectroscopic apparatus
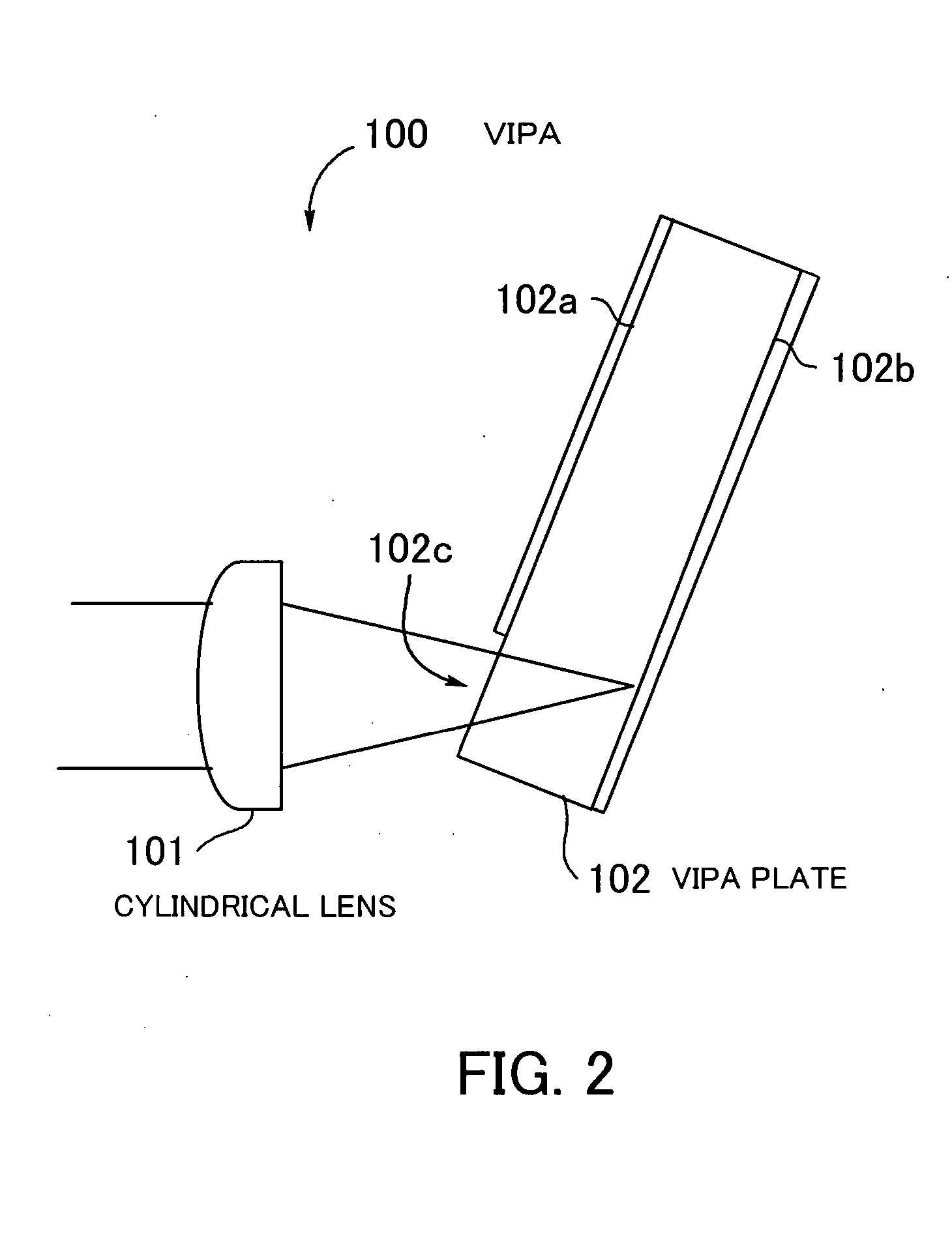
InactiveUS20050046837A1Small sizeLarge angular dispersionRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryBandpass filteringLight beam
A spectroscopic apparatus which is compact in size and performs high-precision light-splitting with a large angular dispersion. An optical input-processing section outputs a filtered transmitted light, using a bandpass filter that transmits only wavelength bands at one period of an input light, and collects the filtered transmitted light to generate a collected beam. An optic includes a first reflection surface and a second reflection surface which are high but asymmetric in reflectivity, and causes the collected beam incident thereon to undergo multiple reflections within an inner region between the first reflection surface and the second reflection surface, to thereby cause split beams to be emitted via the second reflection surface. A received light-processing section performs received light processing of the beams emitted from the optic. A control section variably controls at least one of a filter characteristic of the bandpass filter and an optical length through the optic.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
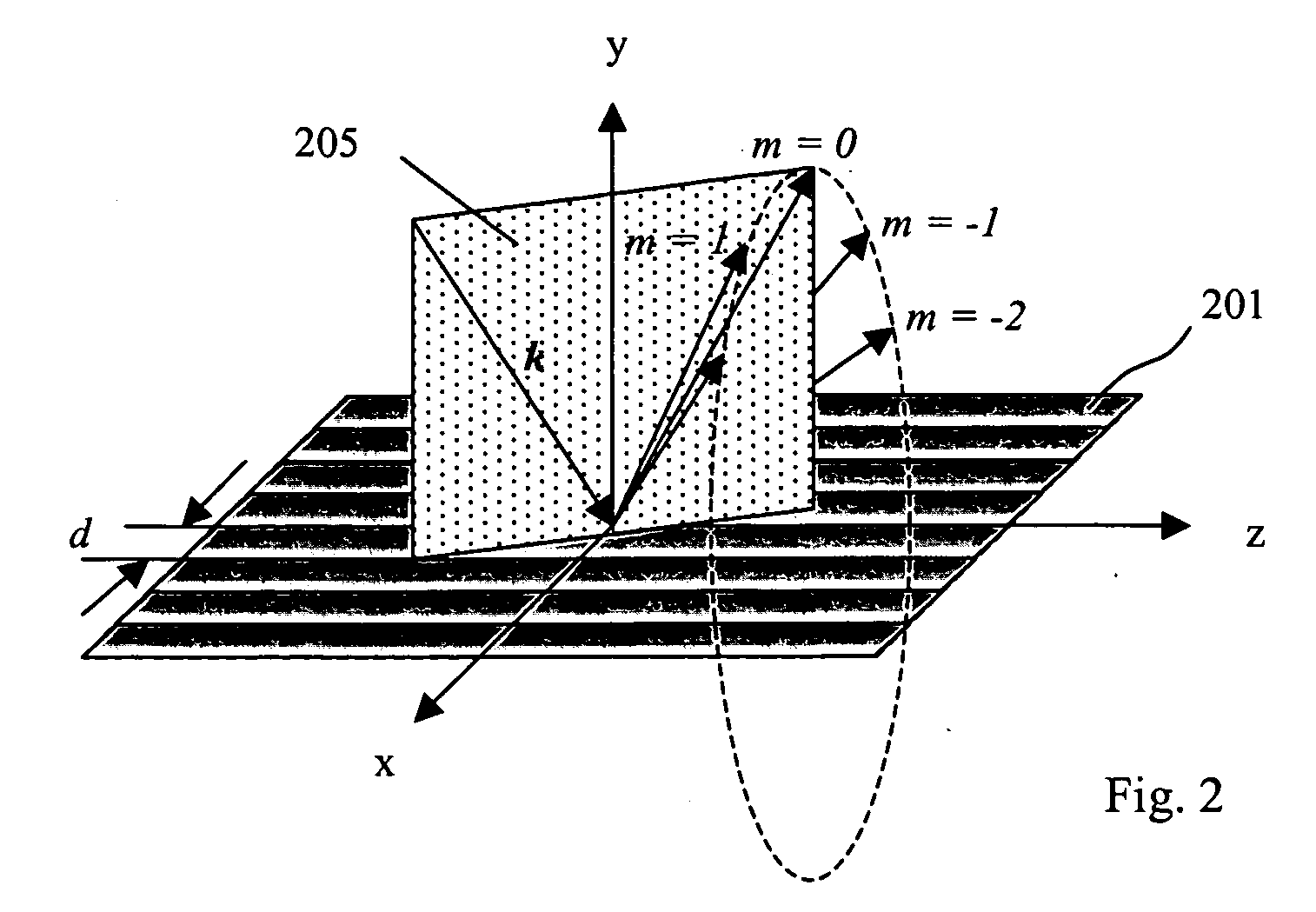
Cross-dispersed spectrometer in a spectral domain optical coherence tomography system
InactiveUS7342659B2Eliminating spatial order overlapReduce non-linearityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationTwo dimensional detectorGrating
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
Apparatus for obtaining information for a structure using spectrally-encoded endoscopy teachniques and methods for producing one or more optical arrangements
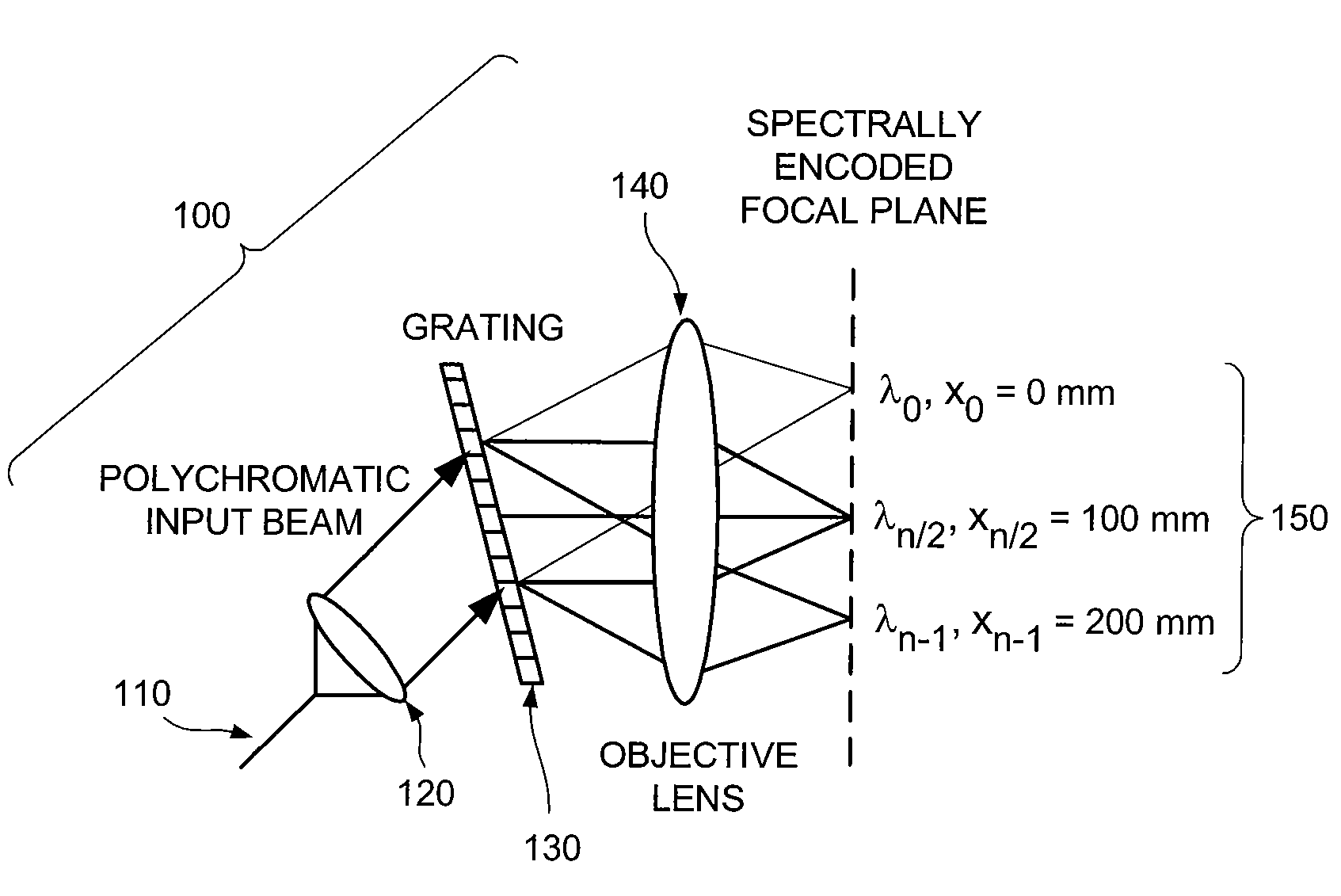
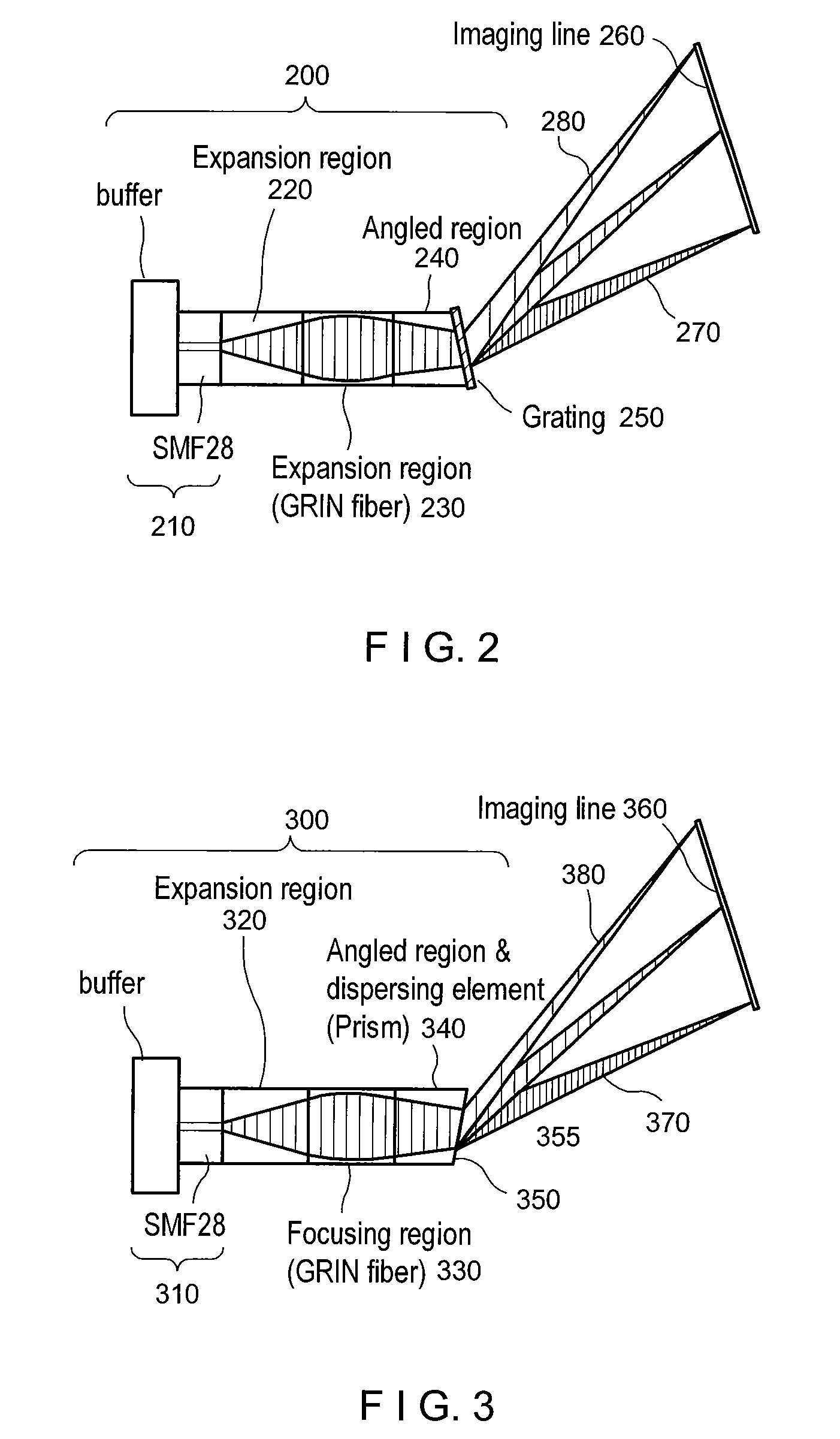
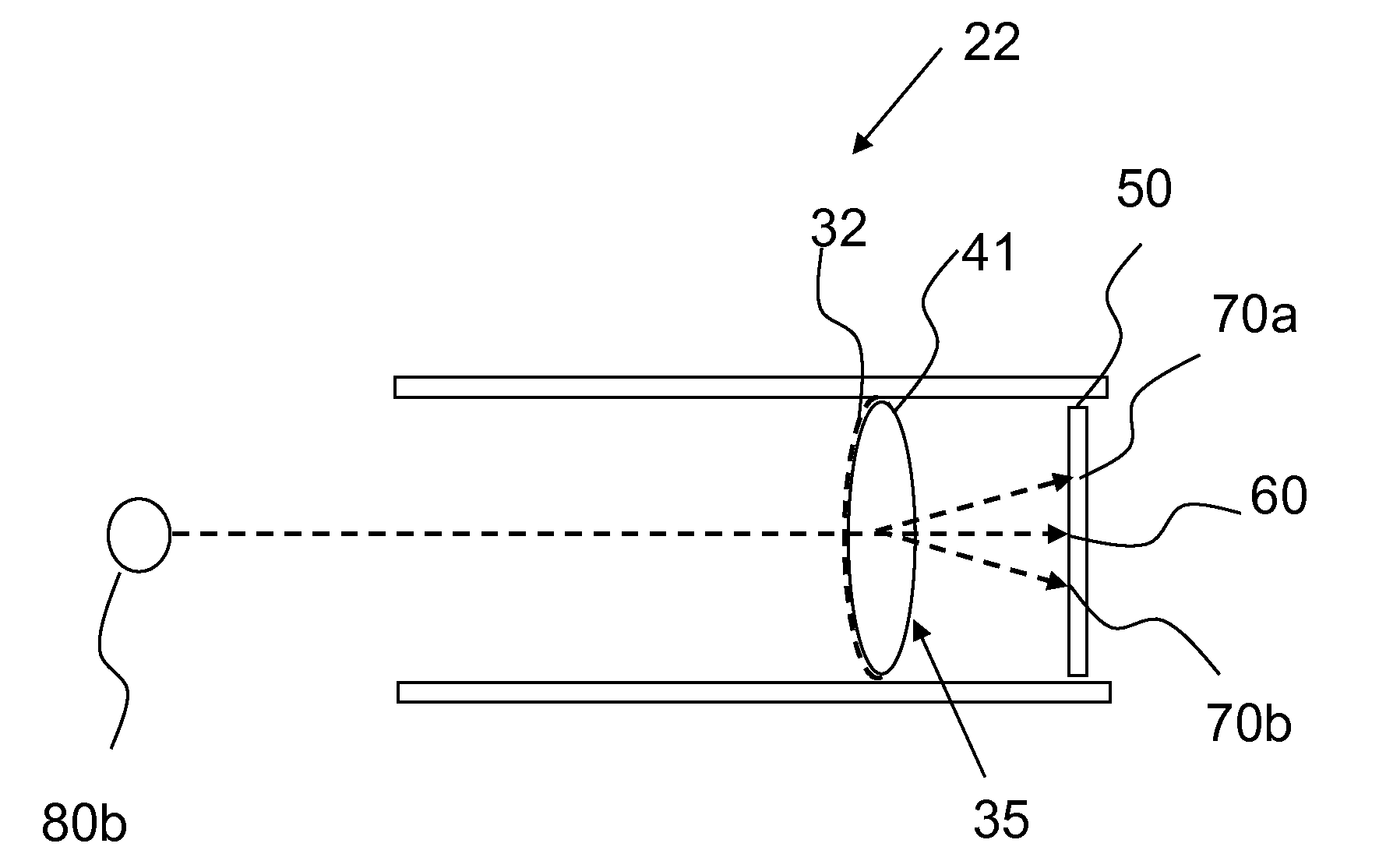
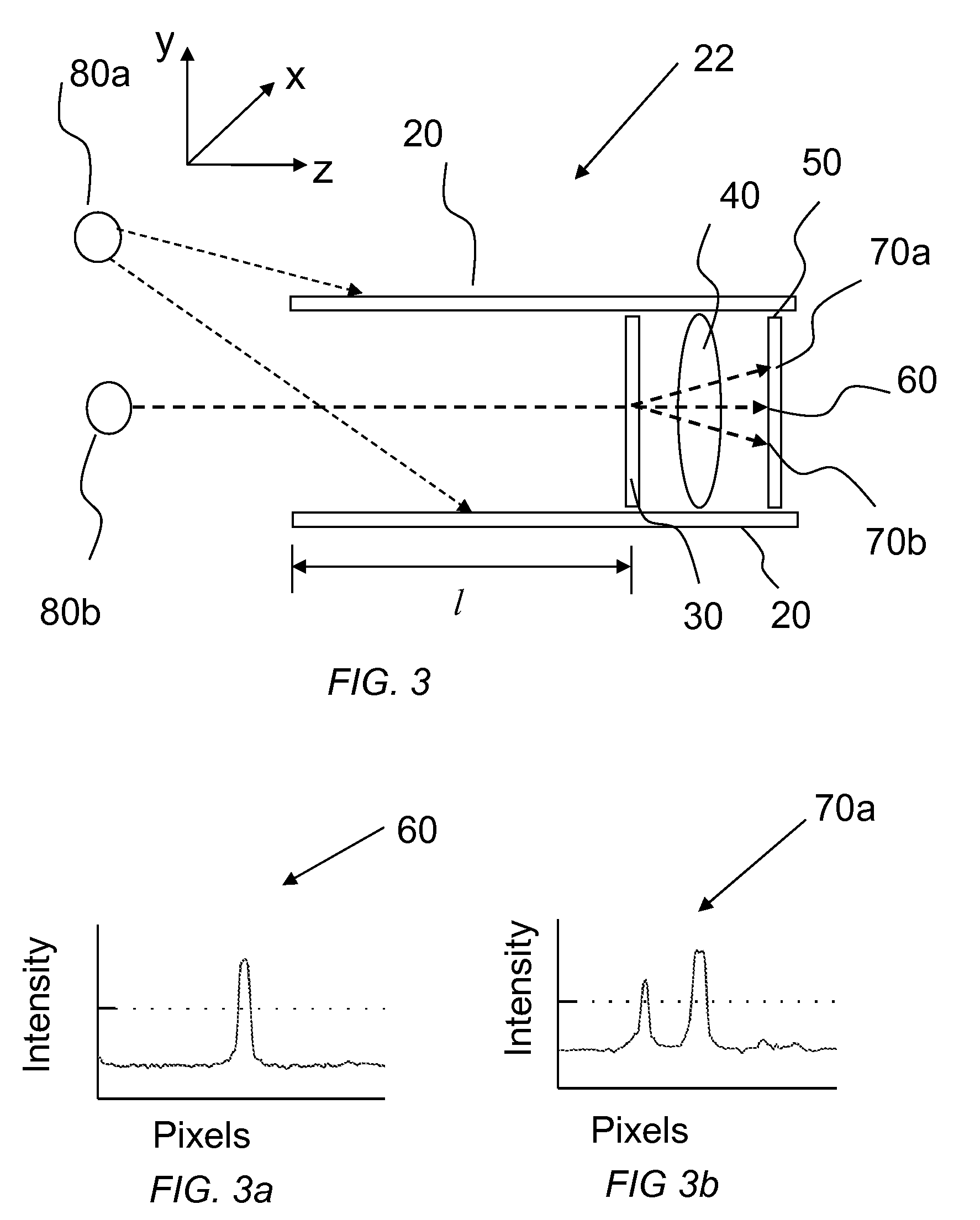
ActiveUS20070188855A1Improve collection efficiencyMinimizing speckleEdge grinding machinesSpectrum generation using diffraction elementsFiberEngineering
Exemplary apparatus for obtaining information for a structure can be provided. For example, the exemplary apparatus can include at least one first optical fiber arrangement which is configured to transceive at least one first electromagnetic radiation, and can include at least one fiber. The exemplary apparatus can also include at least one second focusing arrangement in optical communication with the optical fiber arrangement. The second arrangement can be configured to focus and provide there through the first electromagnetic radiation. Further, the exemplary apparatus can include at least one third dispersive arrangement which is configured to receive a particular radiation which is the first electromagnetic radiation and / or the focused electromagnetic radiation, and forward a dispersed radiation thereof to at least one section of the structure. At least one end of the fiber can be directly connected to the second focusing arrangement and / or the third dispersive arrangement. In addition, an exemplary embodiment of a method for producing an optical arrangement can be provided. For example, a first set of optical elements having a first size in a first configuration and a second set of optical elements in cooperation with the second set and having a second size in a second configuration can be provided. The first and second sets can be clamped into a third set of optical elements. The third set can be polished, and a further set of optical elements may be deposited on the polished set.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Cross-dispersed spectrometer in a spectral domain optical coherence tomography system
InactiveUS20060164639A1Eliminating spatial order overlapReduce non-linearityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationTwo dimensional detectorGrating
A spectral-domain optical coherence tomography system using a cross-dispersed spectrometer is disclosed. The interfered optical signal is dispersed by a grating into several orders of diffraction, and these orders of diffraction are separated by an additional dispersive optical element. The spectral interferogram is recorded by a set of linear detector arrays, or by a two-dimensional detector array.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
Optical computational system
In optical filter systems and optical transmission systems, an optical filter compresses data into and / or derives data from a light signal. The filter way weight an incident light signal by wavelength over a predetermined wavelength range according to a predetermined function so that the filter performs the dot product of the light signal and the function.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC +1
Method and apparatus for spectrum analysis and encoder
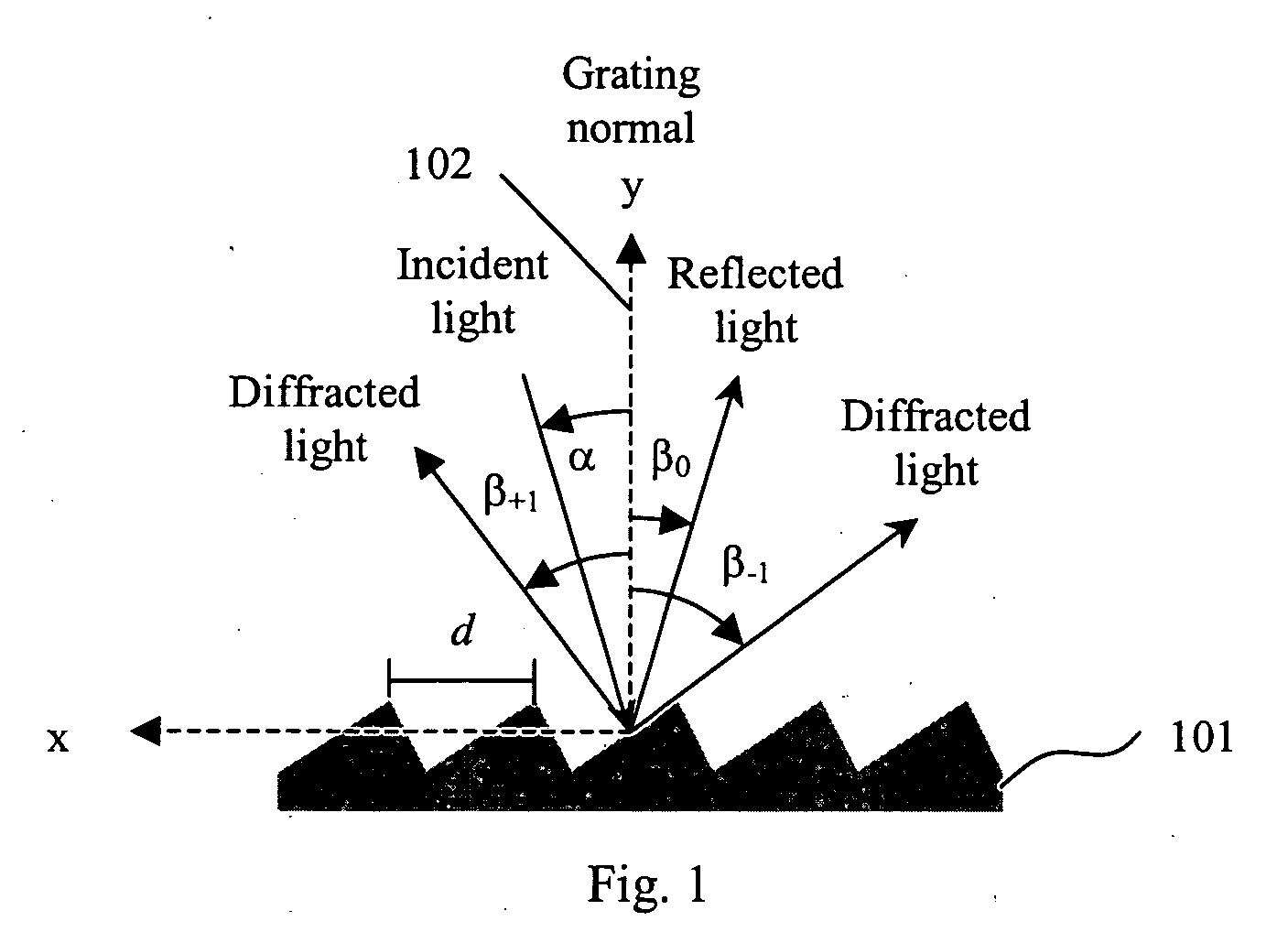
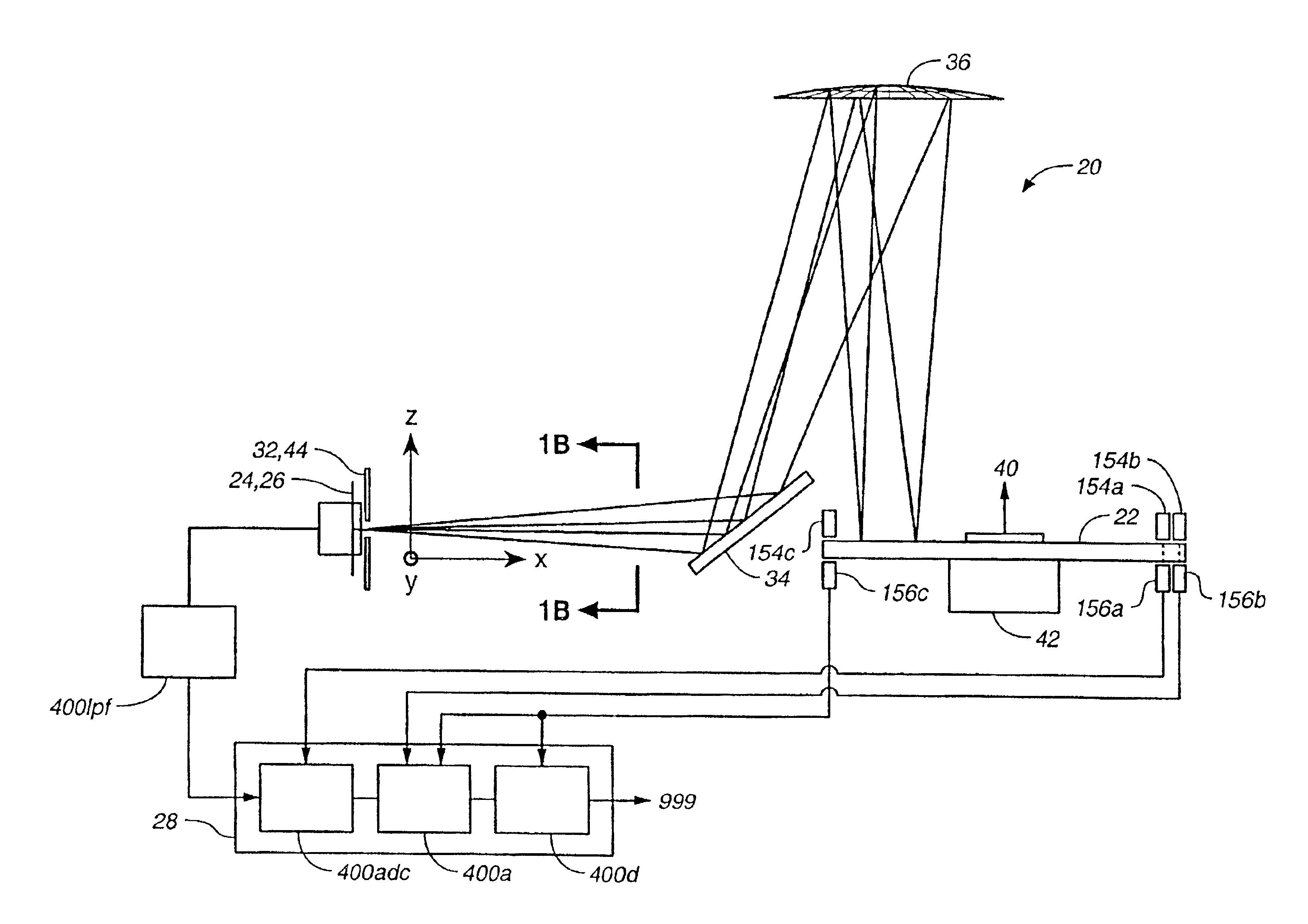
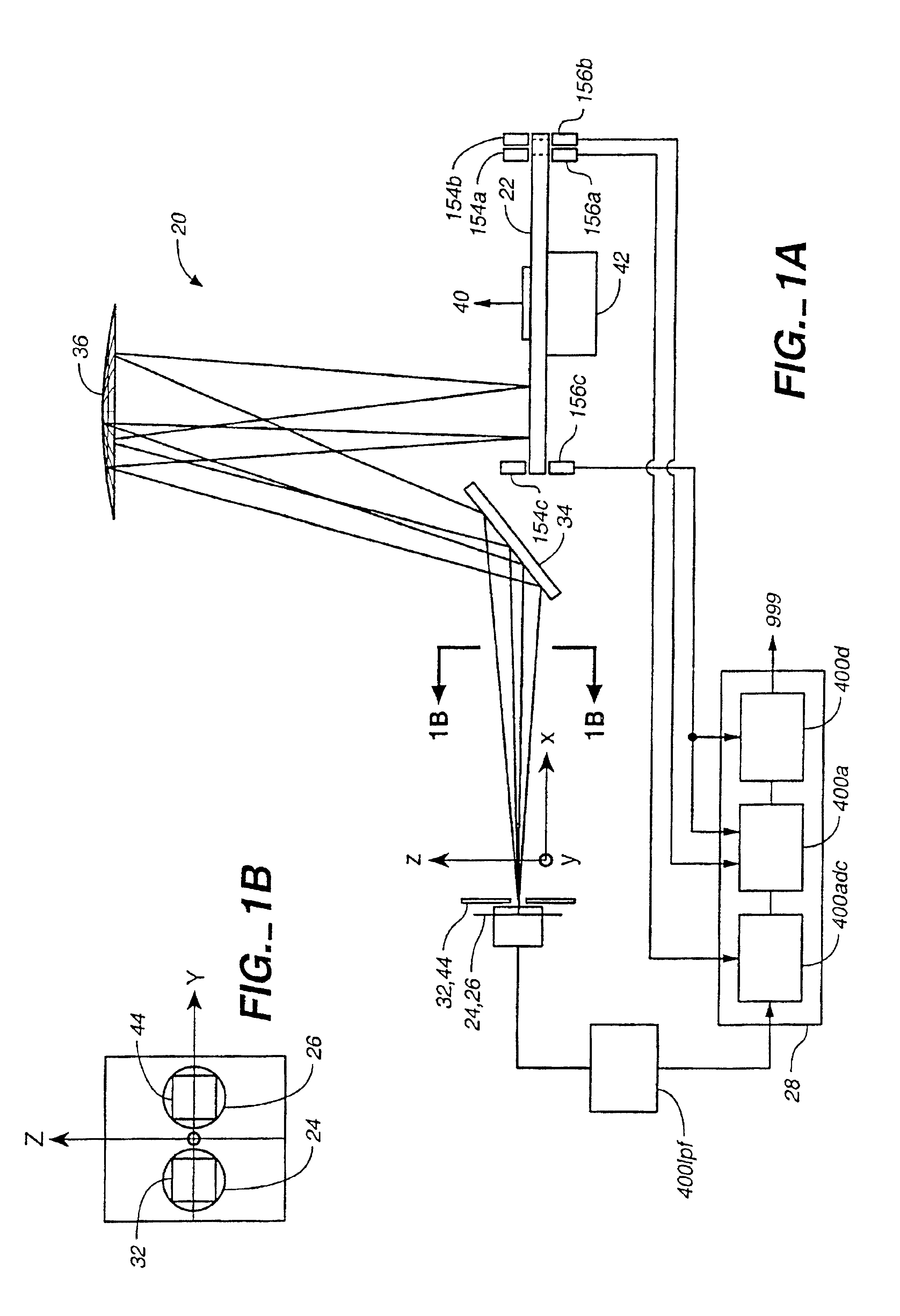
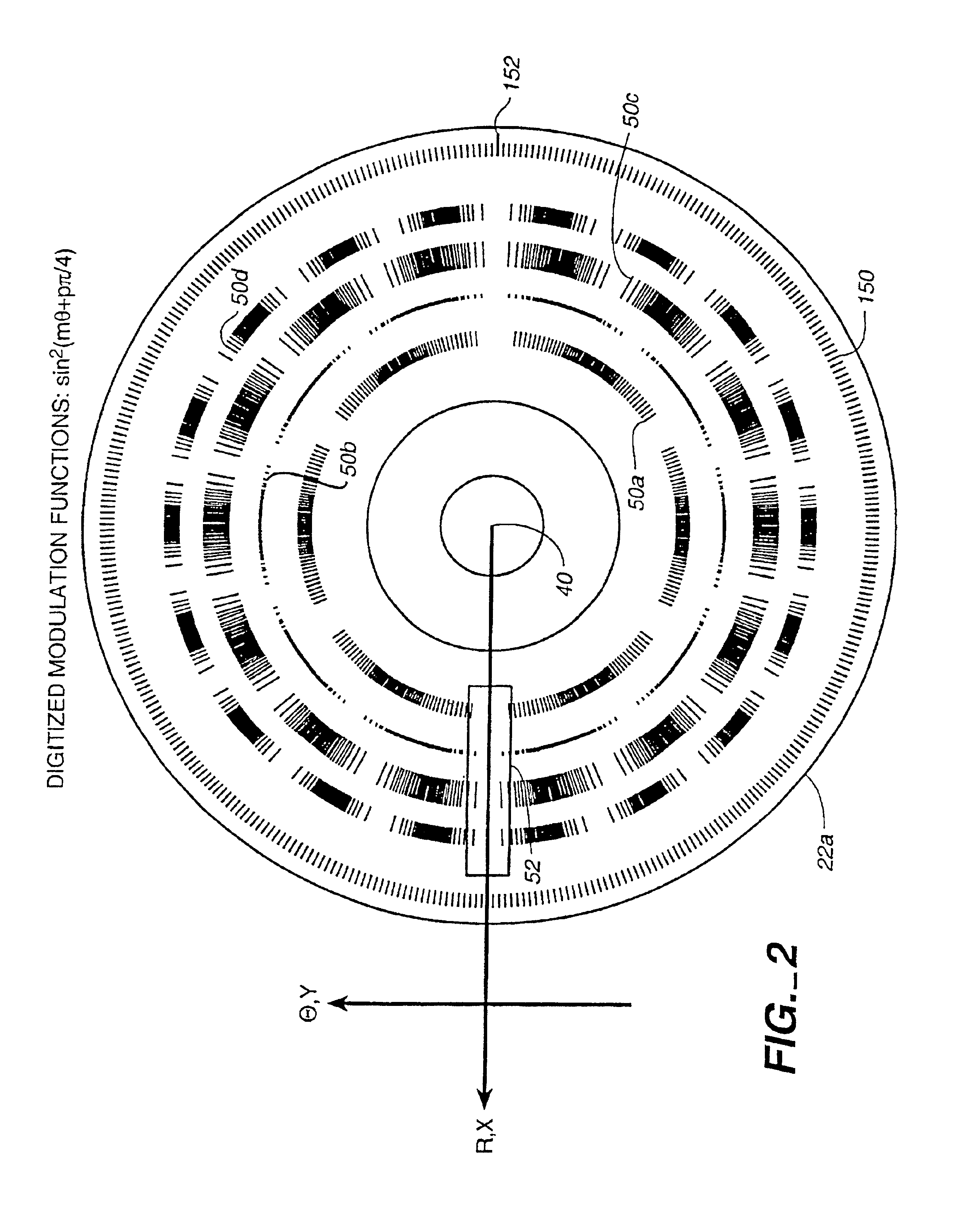
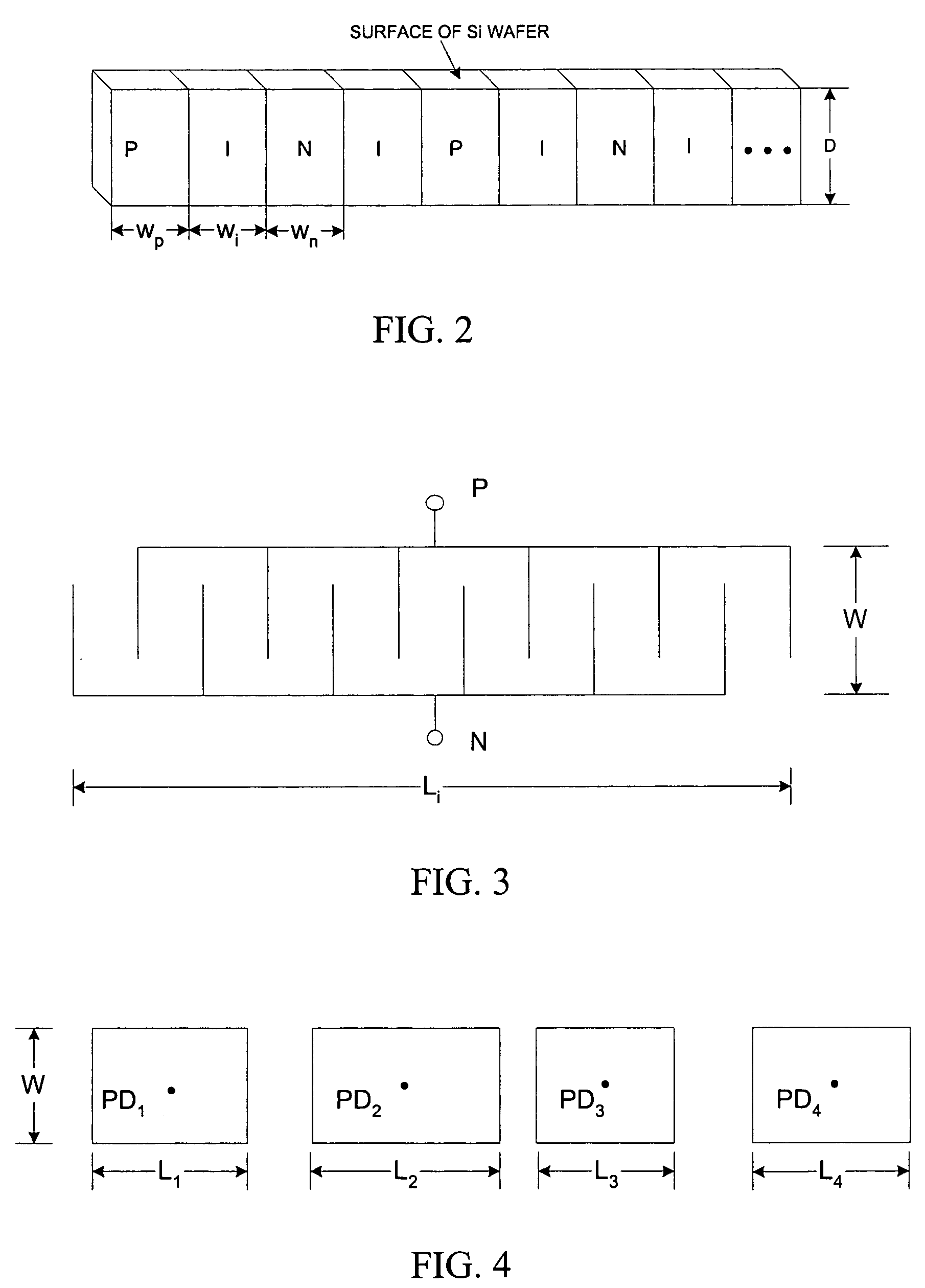
InactiveUS6897952B1Increase motor speedReduce motor speedRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsModulation functionFrequency spectrum
A disc serving as a spatial radiation modulator has dispersed radiation filters thereon. Each filter has a transmittance or reflectance modulation function of the form sin2(mθ+pπ / 4), where m is a positive integer and p has one of the four values 0, 1, 2, 3. A radiation beam including selected wavelength components is diffracted into an elongated image dispersed according to wavelength. Different wavelength components are focused onto different filters on the modulator and are encoded by corresponding filters. Since the modulation functions of the filters are orthogonal to one another, it is possible to extract the amplitude of each wavelength component after it has been encoded or modulated by corresponding filter from the total detected signal during one measurement.
Owner:MUDLOGGING SYST
System and method for encoded spatio-spectral information processing
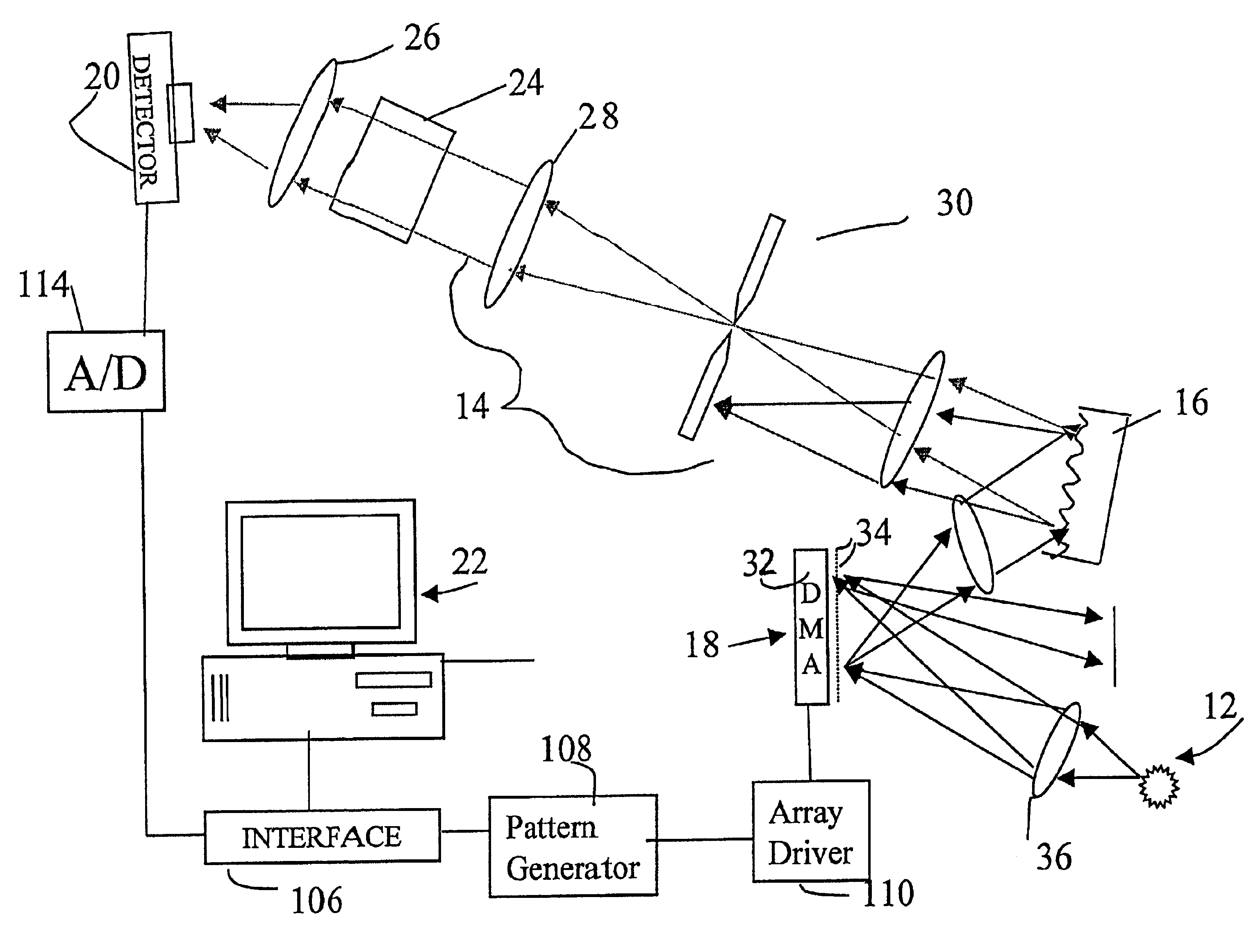
InactiveUS6859275B2Less sensitive to ambient noiseEasy to operateRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsInformation processingLength wave
Encoded spatio-spectral information processing is performed using a system having a radiation source, wavelength dispersion device and two-dimensional switching array, such as digital micro-mirror array (DMA). In one aspect, spectral components from a sample are dispersed in space and modulated separately by the switching array, each element of which may operate according to a predetermined encoding pattern. The encoded spectral components can then be detected and analyzed. In a different aspect, the switching array can be used to provide a controllable radiation source for illuminating a sample with radiation patterns that have predetermined characteristics and separately encoded components. Various applications are disclosed.
Owner:PLAIN SIGHT SYST
Spectroscopic apparatus
InactiveUS7304798B2Small sizeHigh-precision light-splittingRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryBandpass filteringLight beam
A spectroscopic apparatus which is compact in size and performs high-precision light-splitting with a large angular dispersion. An optical input-processing section outputs a filtered transmitted light, using a bandpass filter that transmits only wavelength bands at one period of an input light, and collects the filtered transmitted light to generate a collected beam. An optic includes a first reflection surface and a second reflection surface which are high but asymmetric in reflectivity, and causes the collected beam incident thereon to undergo multiple reflections within an inner region between the first reflection surface and the second reflection surface, to thereby cause split beams to be emitted via the second reflection surface. A received light-processing section performs received light processing of the beams emitted from the optic. A control section variably controls at least one of a filter characteristic of the bandpass filter and an optical length through the optic.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical apparatus of a stacked design, and method of producing same
ActiveUS20090262346A1Precise and simple alignmentHigh precisionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptoelectronicsPhysics
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Apparatus and method for cross axis parallel spectroscopy
ActiveUS20090273777A1Cascading convenienceImprove dynamic rangeRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySpectroscopyElectromagnetic radiation
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
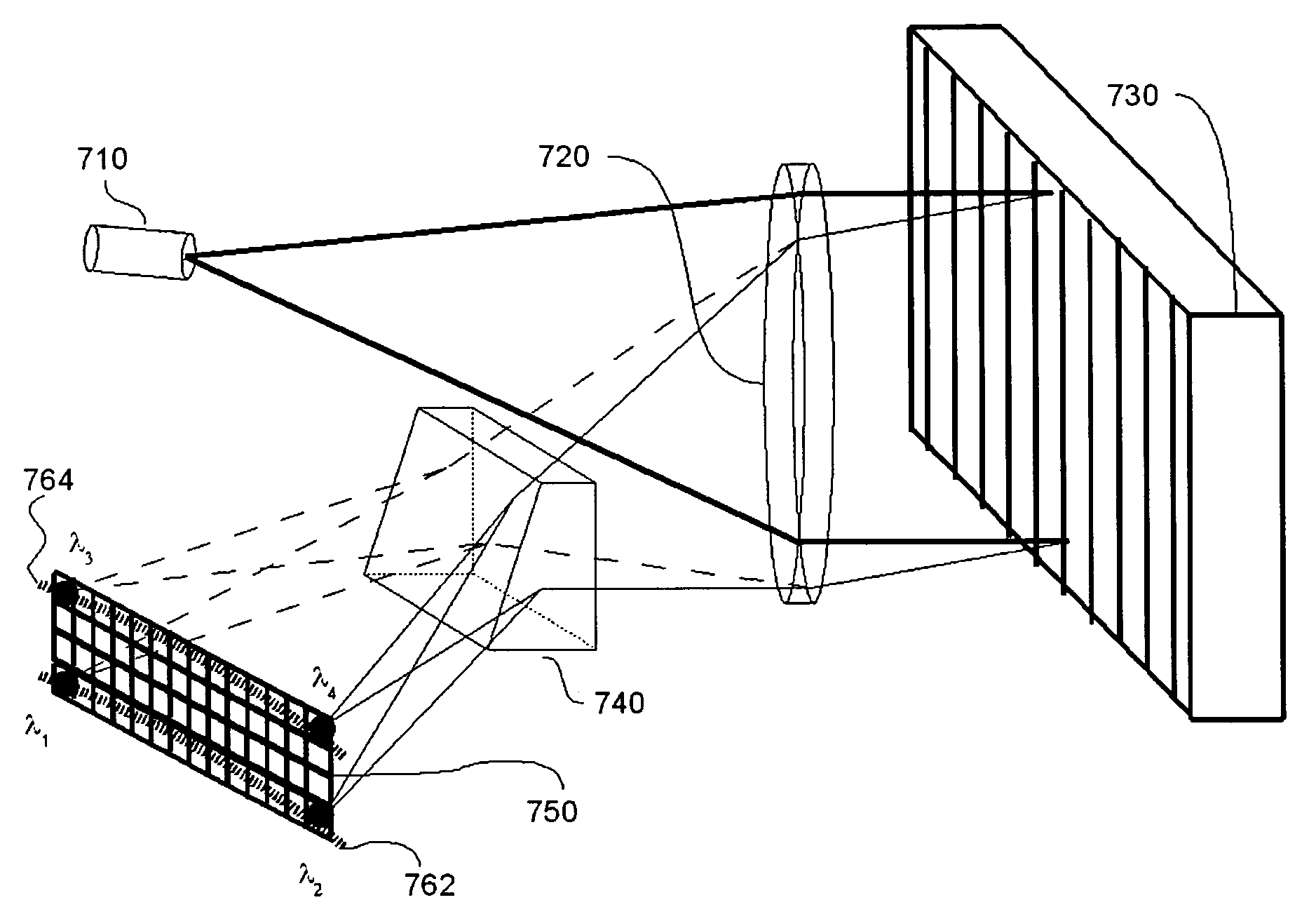
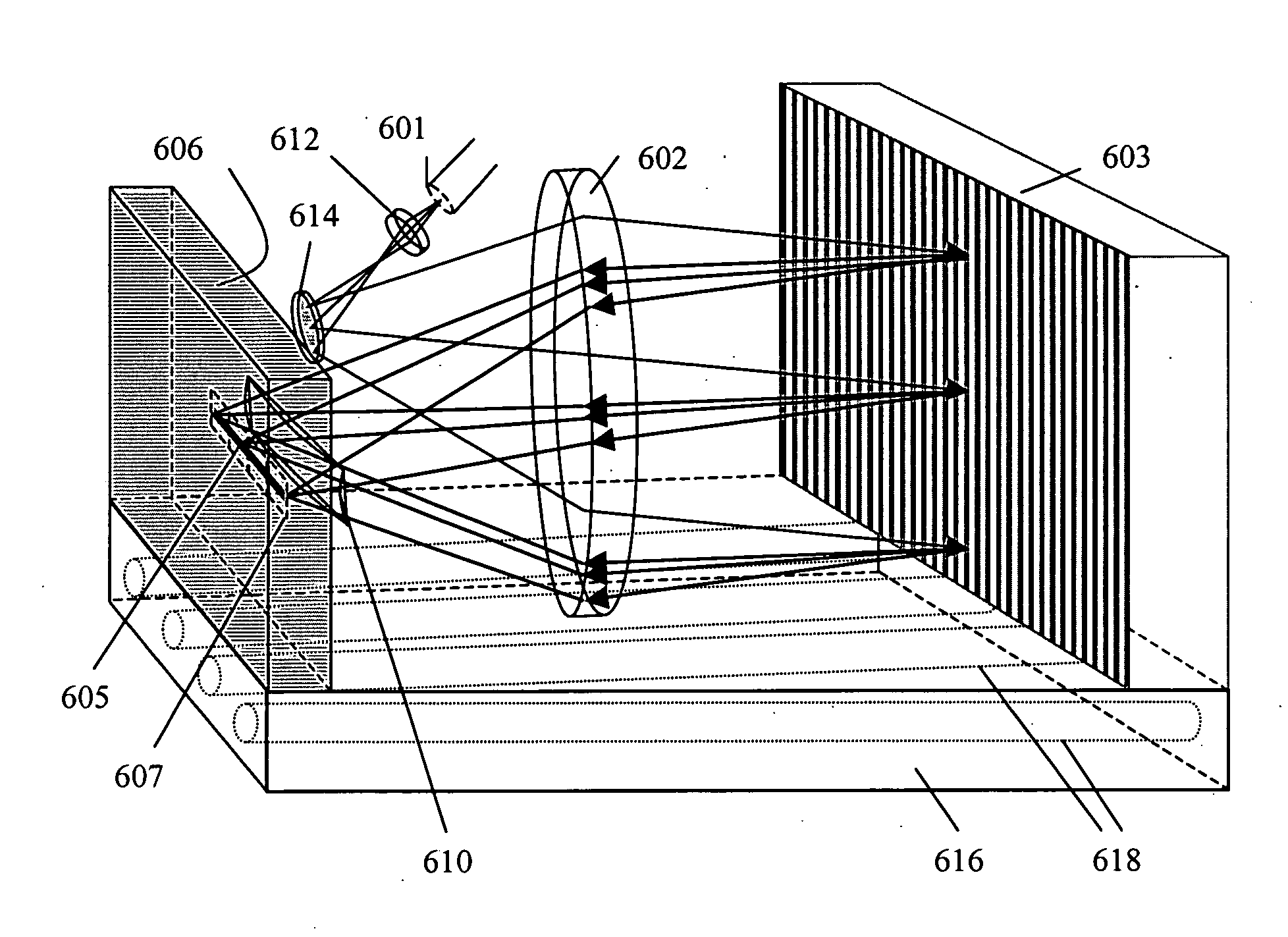
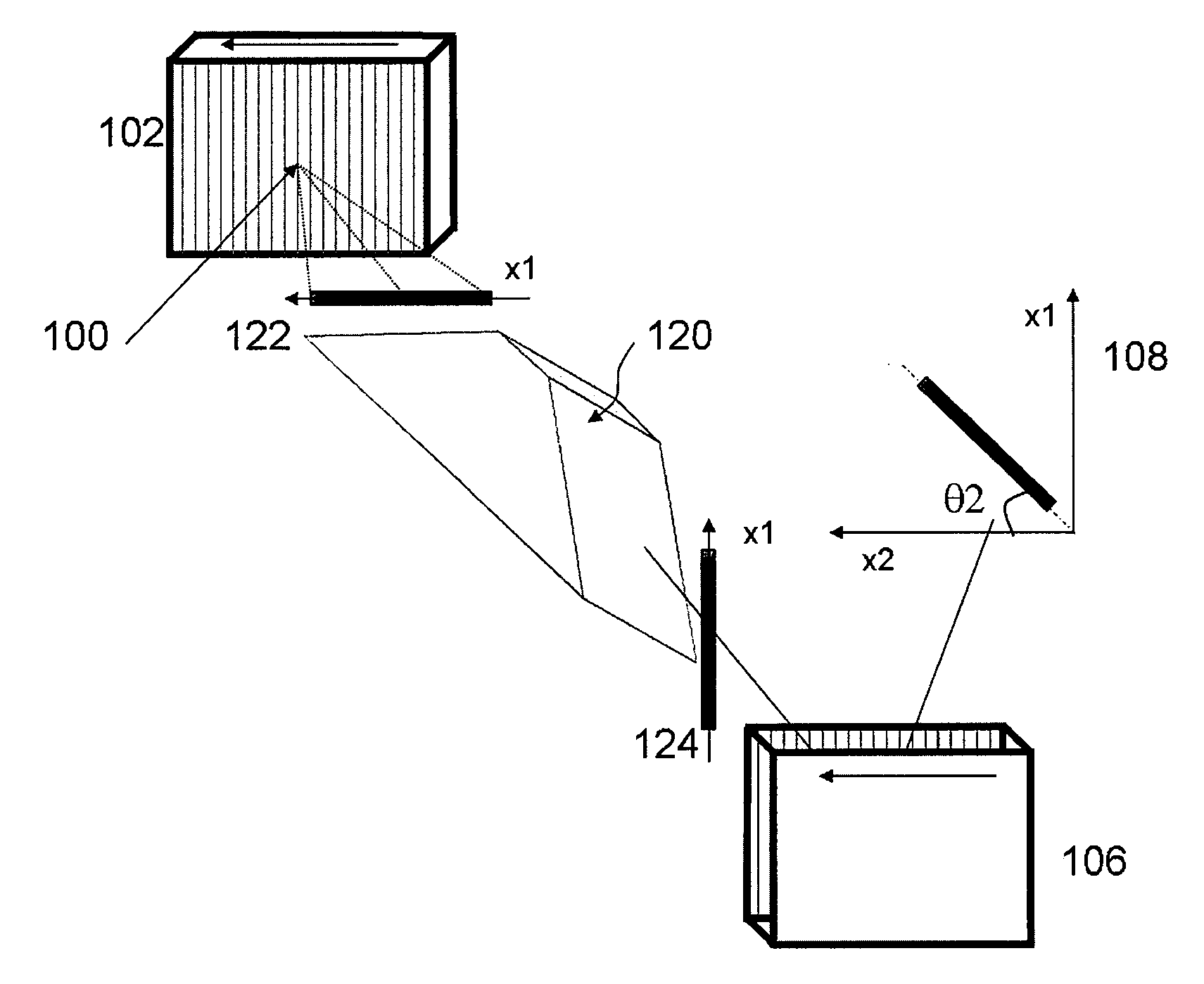
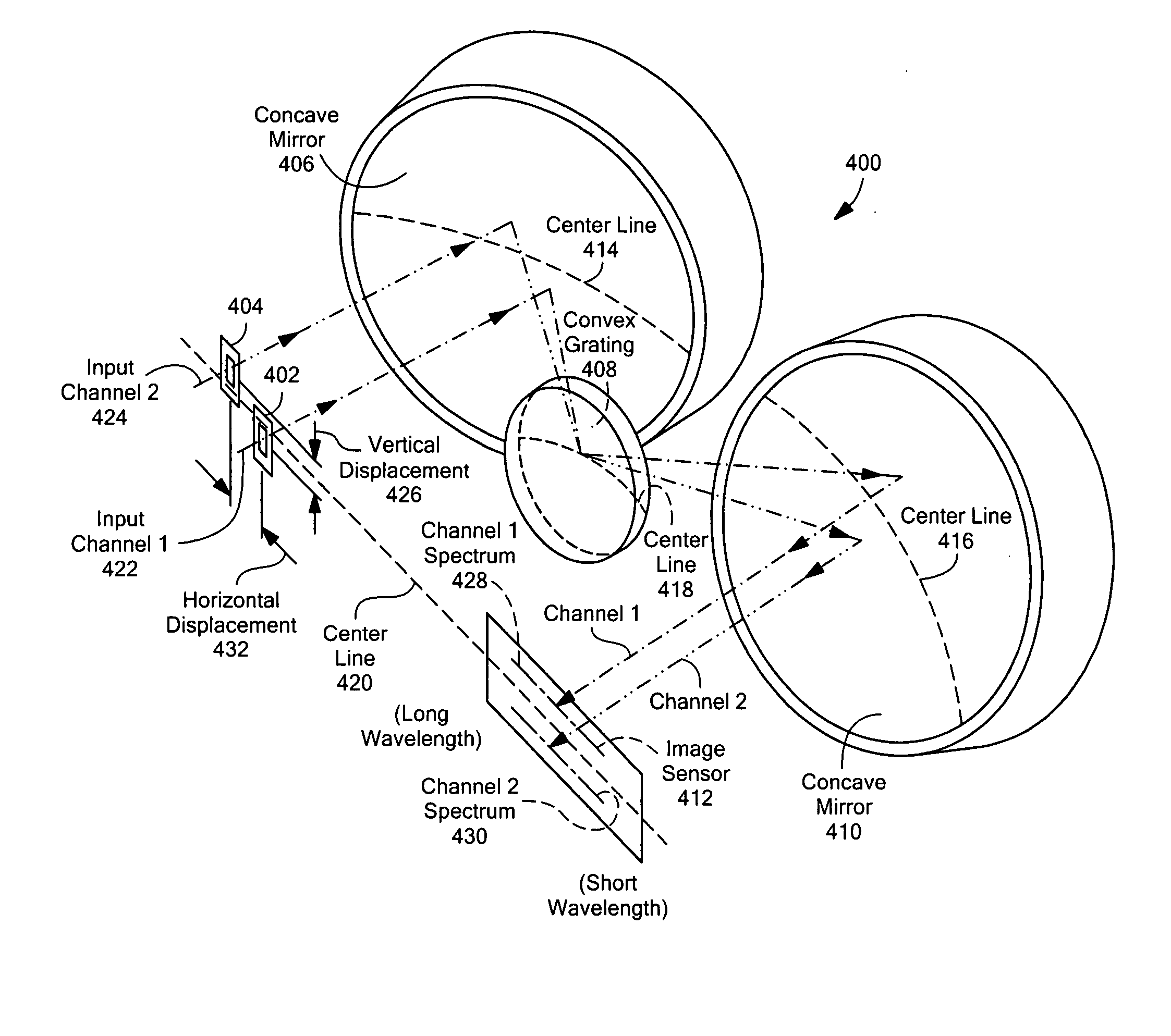
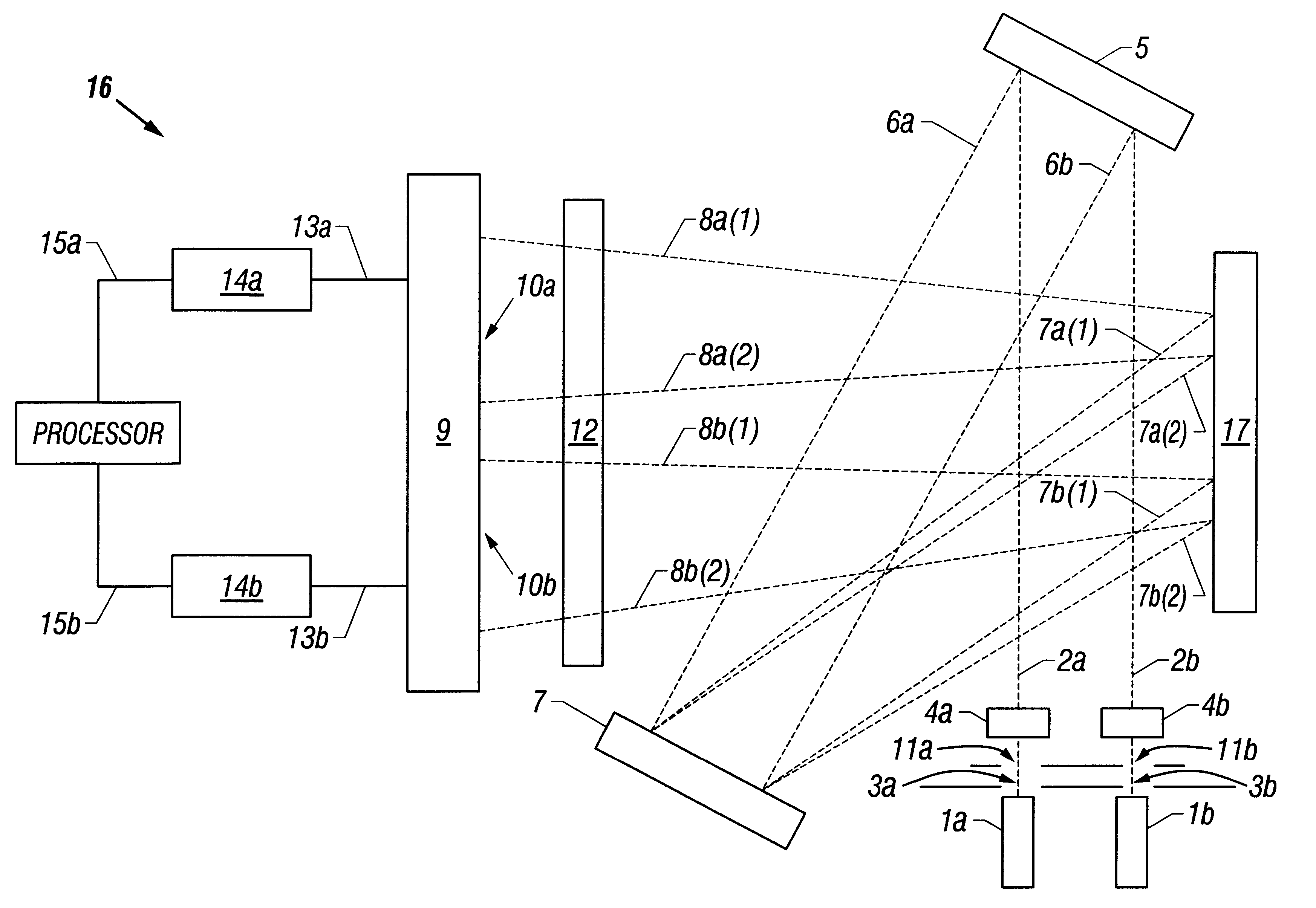
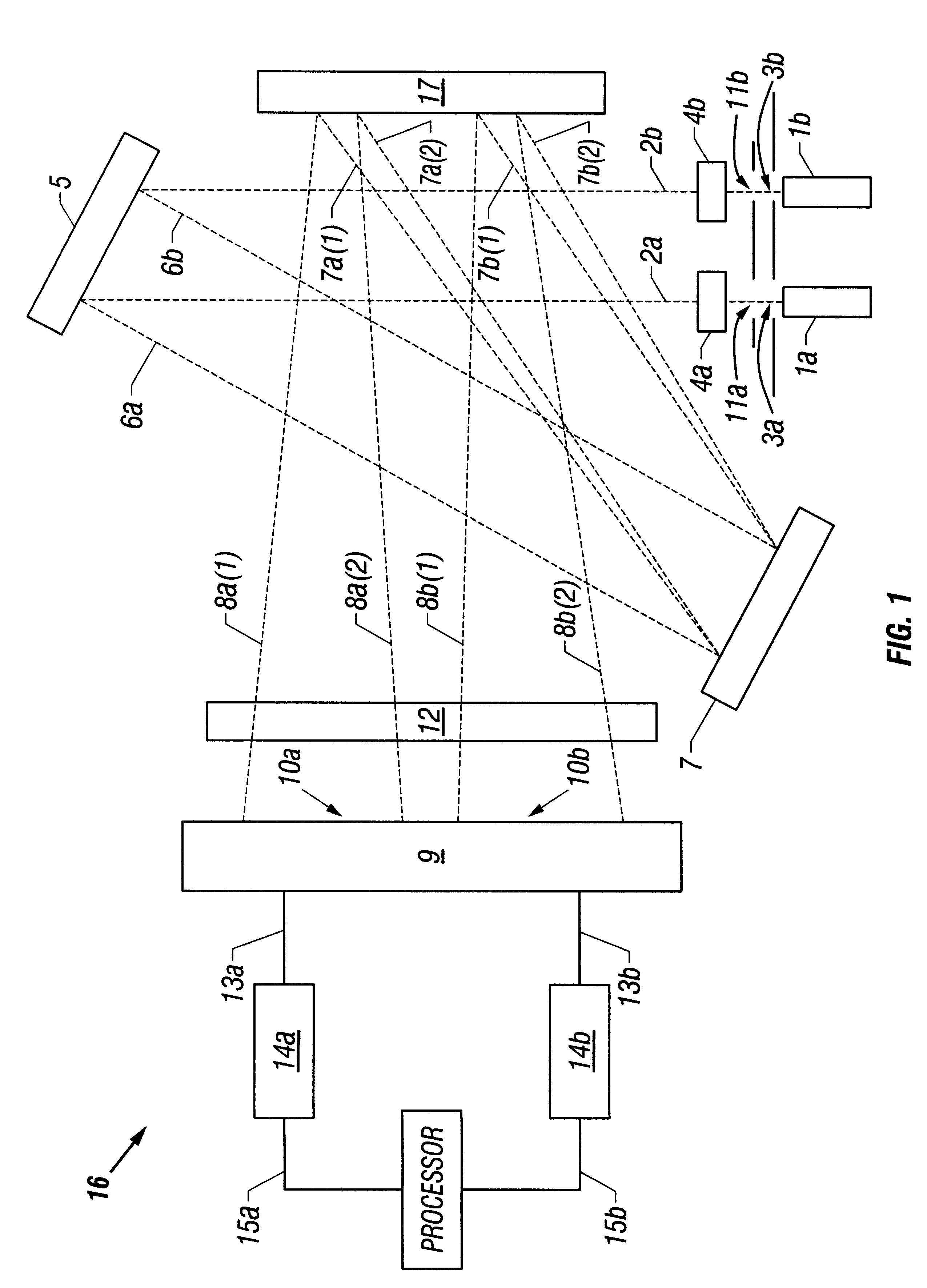
Multi-channel, multi-spectrum imaging spectrometer
A multi-spectrum, multi-channel imaging spectrometer includes two or more input slits or other light input devices, one for each of two or more input channels. The input slits are vertically and horizontally displaced, with respect to each other. The vertical displacements cause spectra from the two channels to be vertically displaced, with respect to each other, on a single image sensor on a stationary image plane. The horizontal displacements cause incident light beams from the respective input channels to strike a convex grating at different respective incidence angles and produce separate spectra having different respective spectral ranges. A retroflective spectrometer includes a convex grating that, by diffraction, disperses wavelengths of light at different angles and orders approximately back along an incident light beam. A single concave mirror reflects both the input channel and the dispersed spectrum. A prism, set of mirrors, beam splitters or other optical element(s) folds the input channel(s) of a spectrometer to enable the input(s) to be moved away from the plane of the image sensor, thereby enabling a large camera or other device to be attached to the spectrometer without blocking the input(s). A mounting mechanism enables a curved optical element to be adjusted through lateral and transverse translations, without requiring a gimbal mount.
Owner:HEADWALL PHOTONICS
Color calibration of color image rendering devices
Color calibration of color image rendering devices, such as large color displays, which operate by either projection or emission of images, utilize internal color measurement instrument or external color measurement modules locatable on a wall or speaker. A dual use camera is provided for a portable or laptop computer, or a cellular phone, handset, personal digital assistant or other handheld device with a digital camera, in which one of the camera or a display is movable with respect to the other to enable the camera in a first mode to capture images of the display for enabling calibration of the display, and in a second mode for capturing image other than of the display. The displays may represent rendering devices for enabling virtual proofing in a network, or may be part of stand-alone systems and apparatuses for color calibration. Improved calibration is also provided for sensing and correcting for non-uniformities of rendering devices, such as color displays, printer, presses, or other color image rendering device.
Owner:RAH COLOR TECH
Compact edge illuminated diffractive display
ActiveUS9075184B2Thin form factorCladded optical fibreSpectrum generation using diffraction elementsTotal internal reflectionLight guide
Owner:DIGILENS
Spectral instrument using multiple non-interfering optical beam paths and elements for use therewith
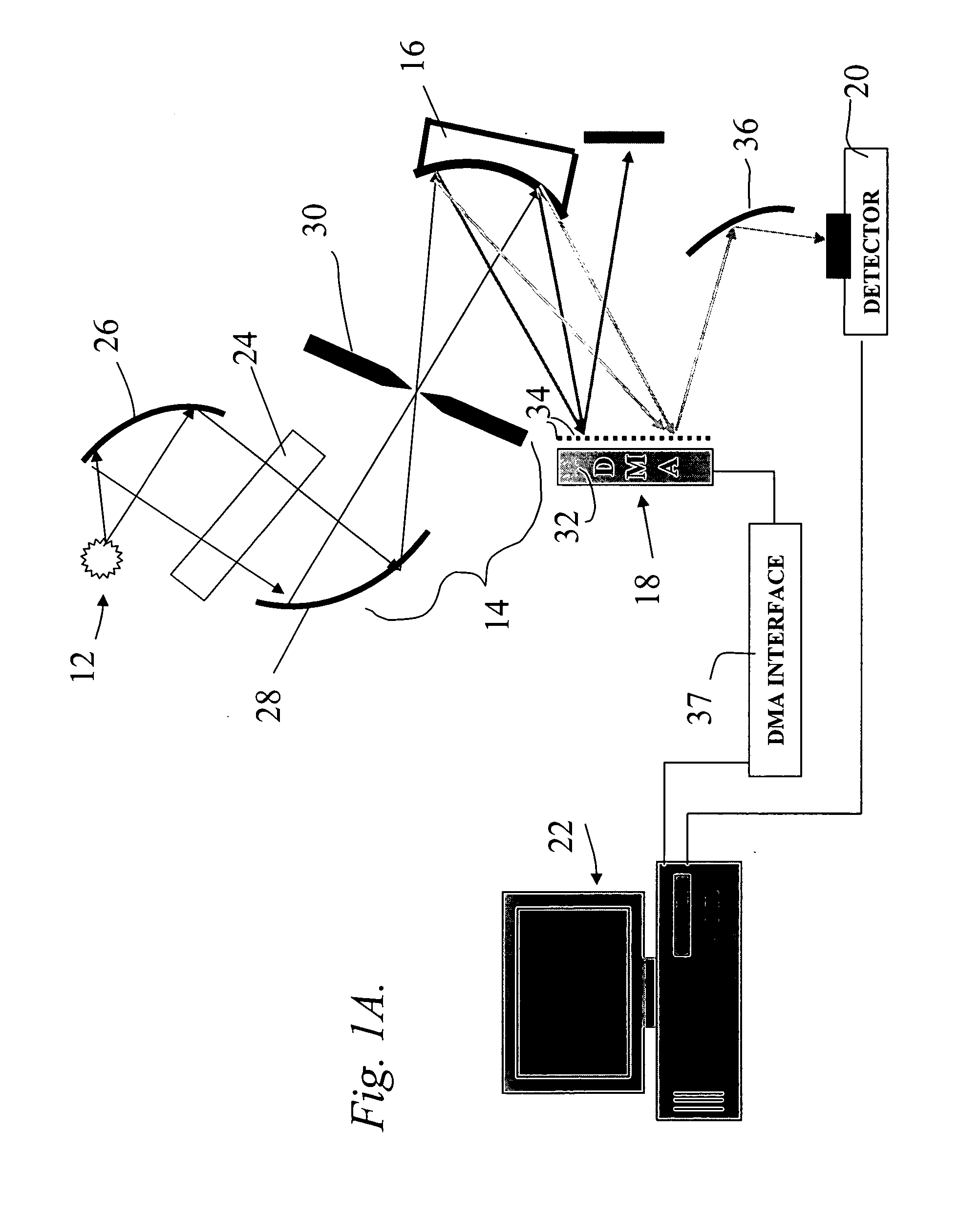
InactiveUS6714298B2Good dispersionReduce dispersionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationAngle of incidencePrism
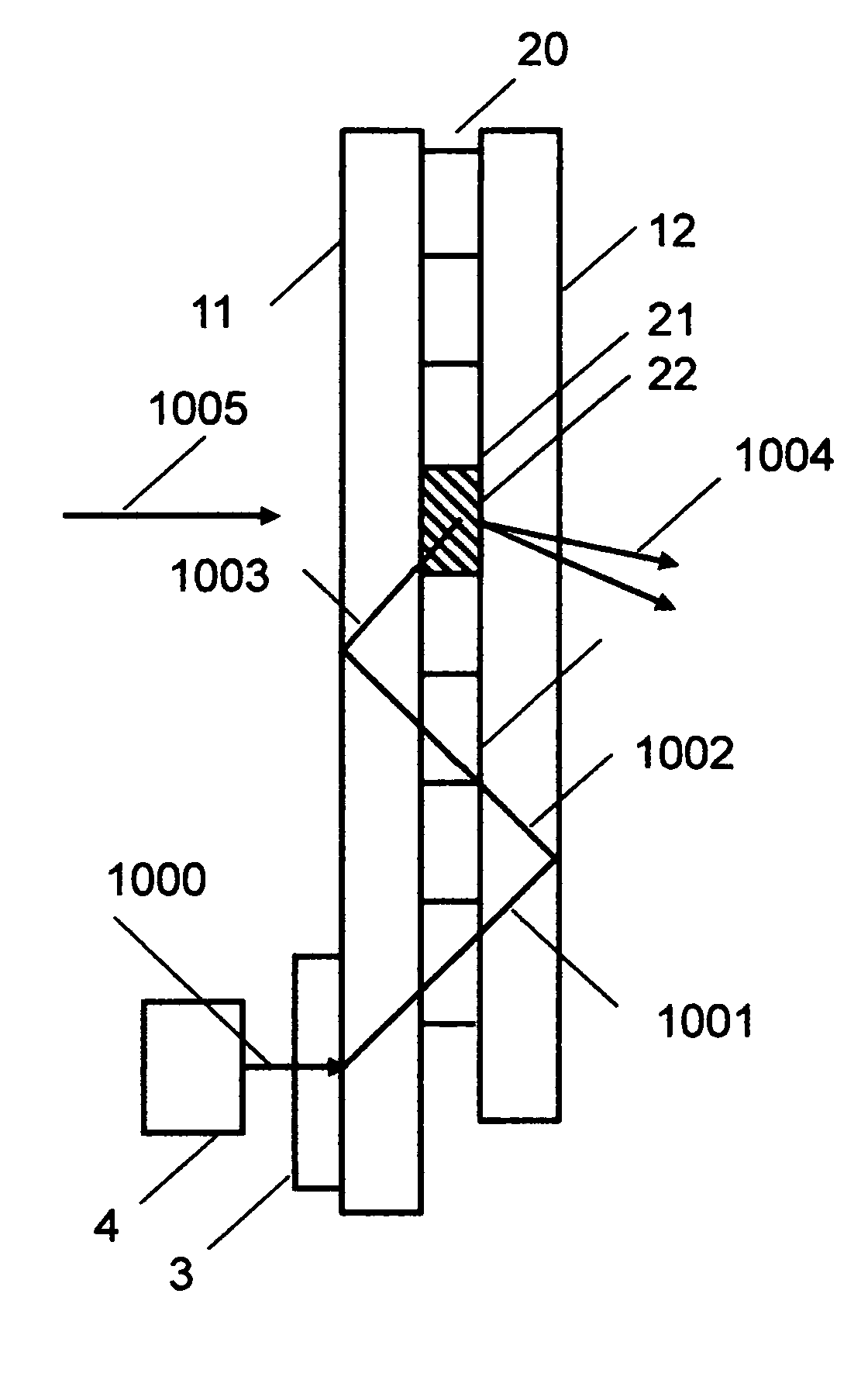
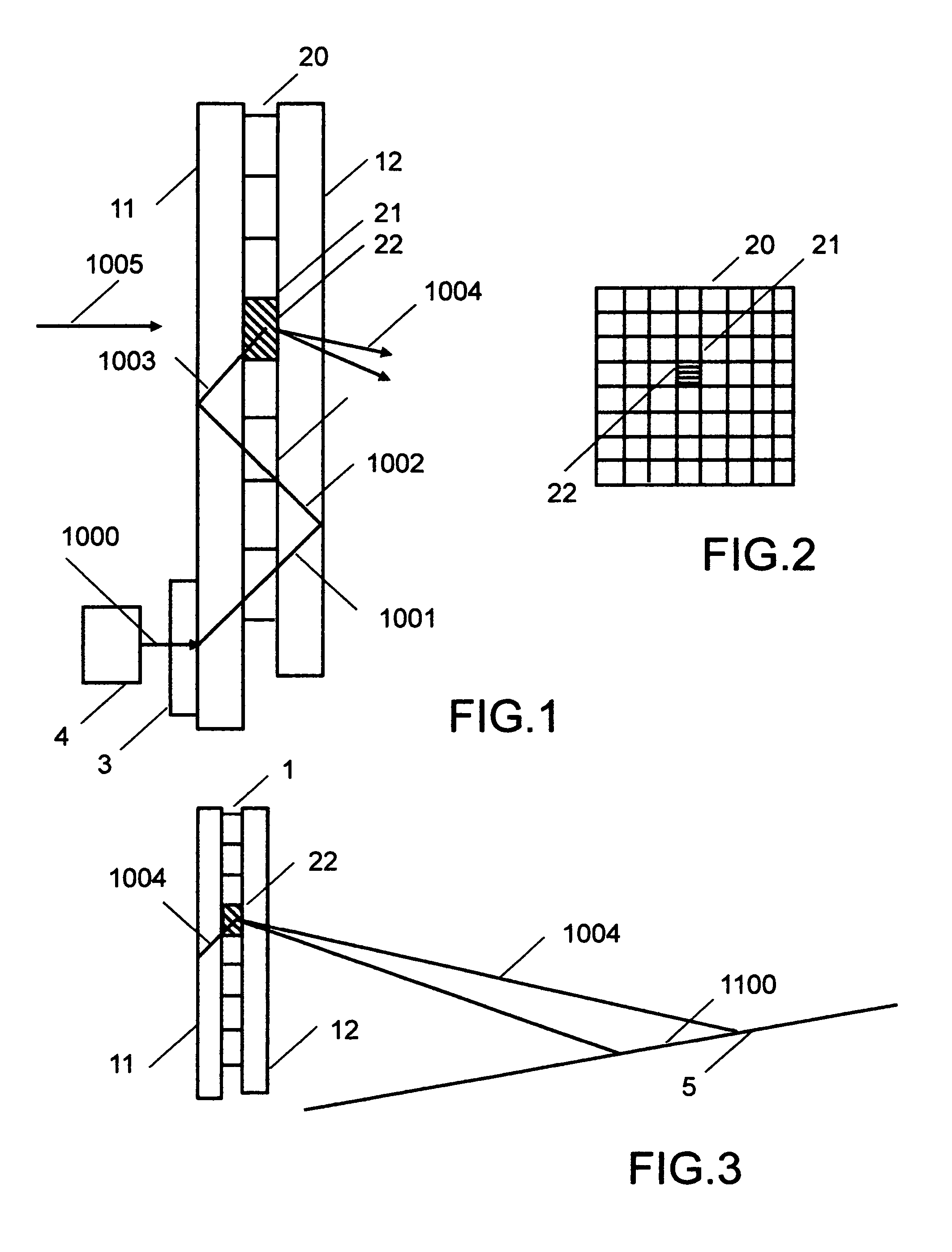
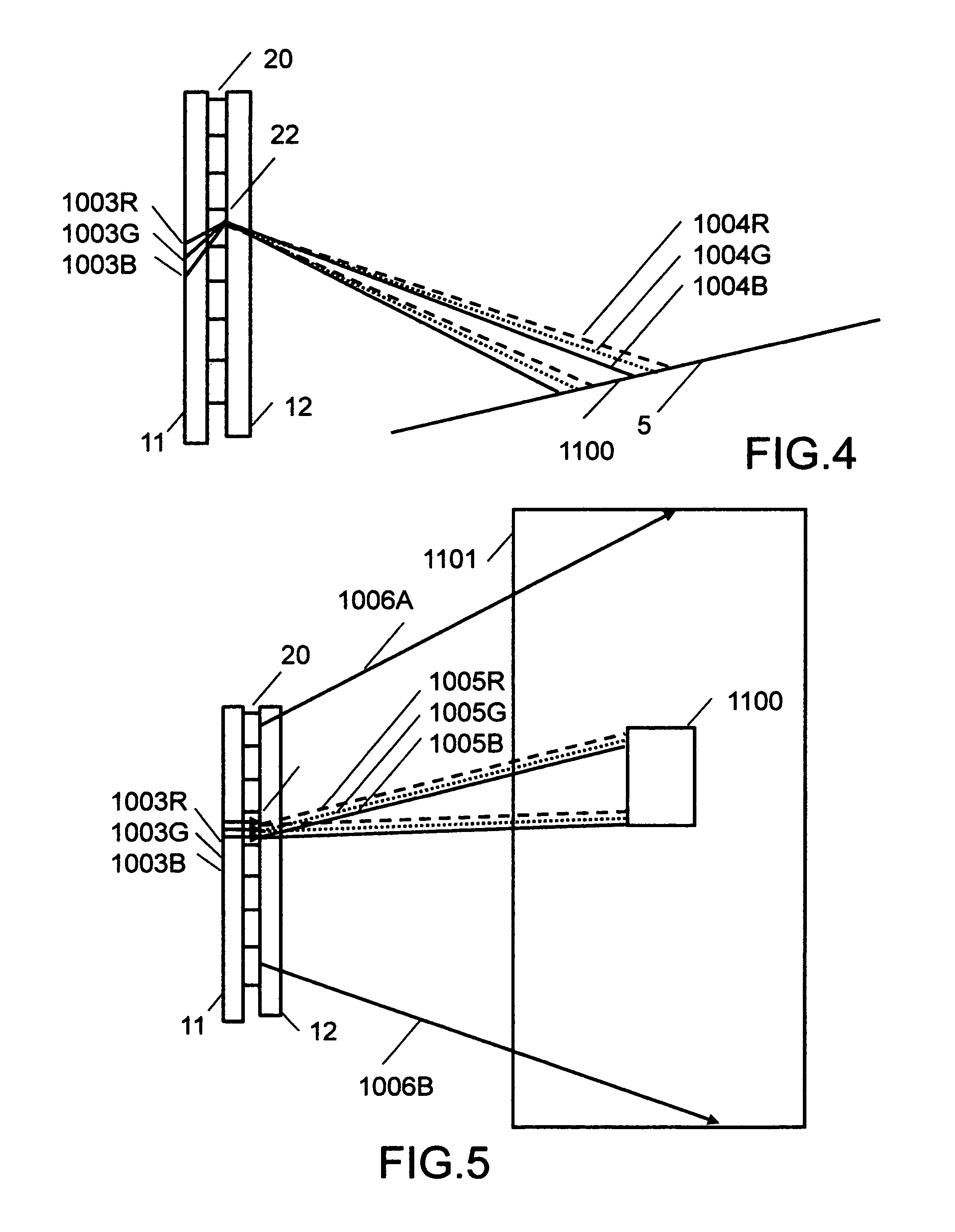
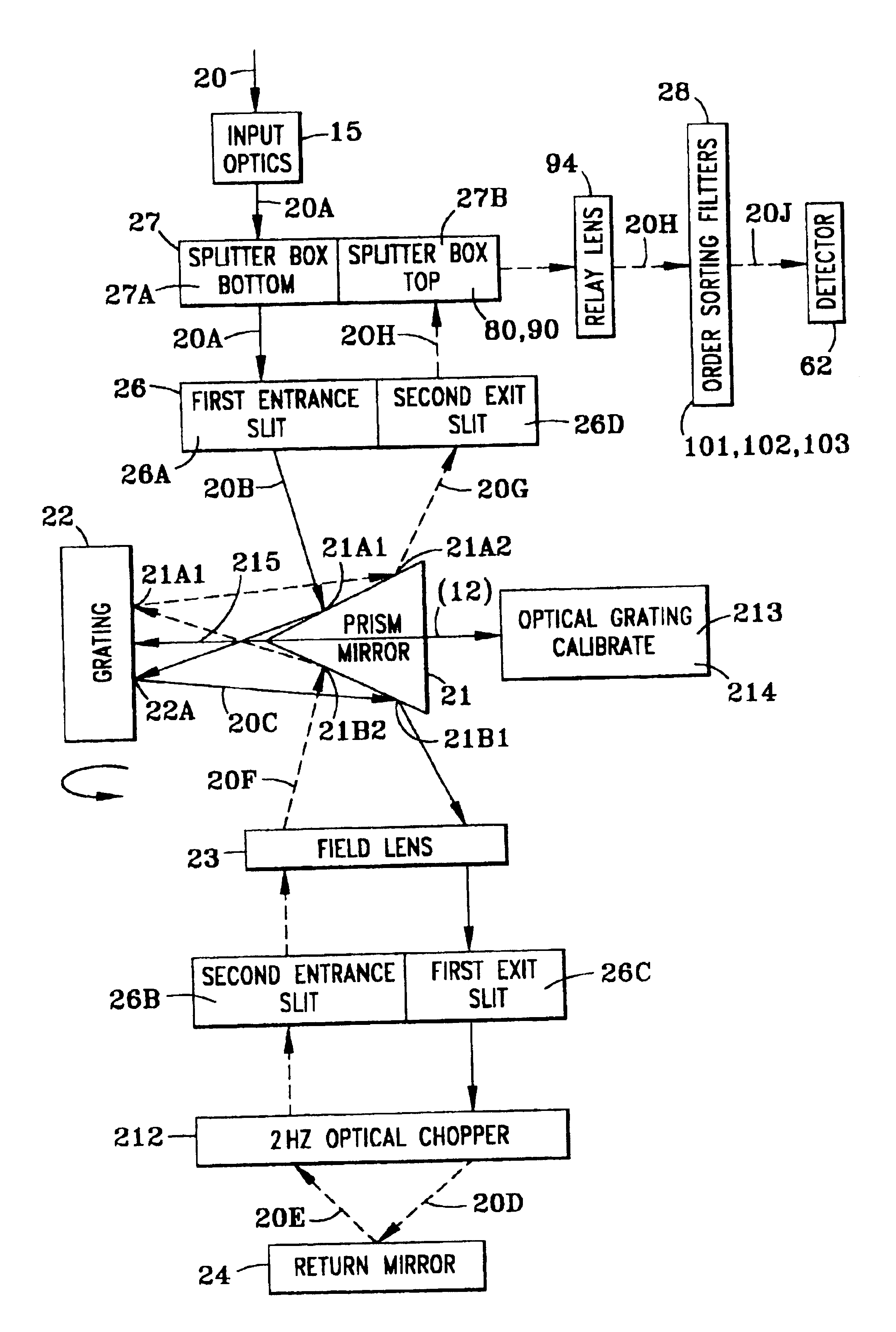
A spectrometer, or a spectral instrument using multiple non-interfering optical beam paths and special optical elements. The special optical elements for use with the instrument are used for directing the optical beam and / or altering the form of the beam. The instrument has the potential, depending upon the totality of the optical components incorporated into the instrument, to be a monochromator, a spectroradiometer, a spectrophotometer and a spectral source. The spectral instrument may further be a part of the spectral system. The system may include the spectral instrument, a power module and means for remote control of the instrument. Such remote control may be by use of a personal computer or a control system dedicated to the control, measurement and analysis of the collected information. The multiple non-interfering beam paths are created using specially designed optical elements such as a diffraction grating, a splitter box, a zero back-lash drive system for movement of the grating element. The orientation of and a physical / spatial relationship between the field lenses, slits, return mirror, reflecting prism, turning lenses all define the multiple, preferably two paths. Particularly, there is a double pass through the grating to increase dispersion, reduce scatter while maintaining a perfect temperature independent spectral match for the second pass. Using the same grating twice reduces scatter by about a factor of 1000, increases the dispersion by a factor of two, and eliminates any temperature-related mechanical spectral drift which often is present with two separate monochromators. Because of the specially designed grating structure, the grating can cause the concurrent diffraction of a plurality of incident optical beams, each of which beams have different angles of incidence and different angles of reflection. The path of the incident and the reflected beam to and from the grating is "off-axis". That is, the beams going to and from the grating do not use the optical axis of the grating structure.
Owner:RYER DAMOND V
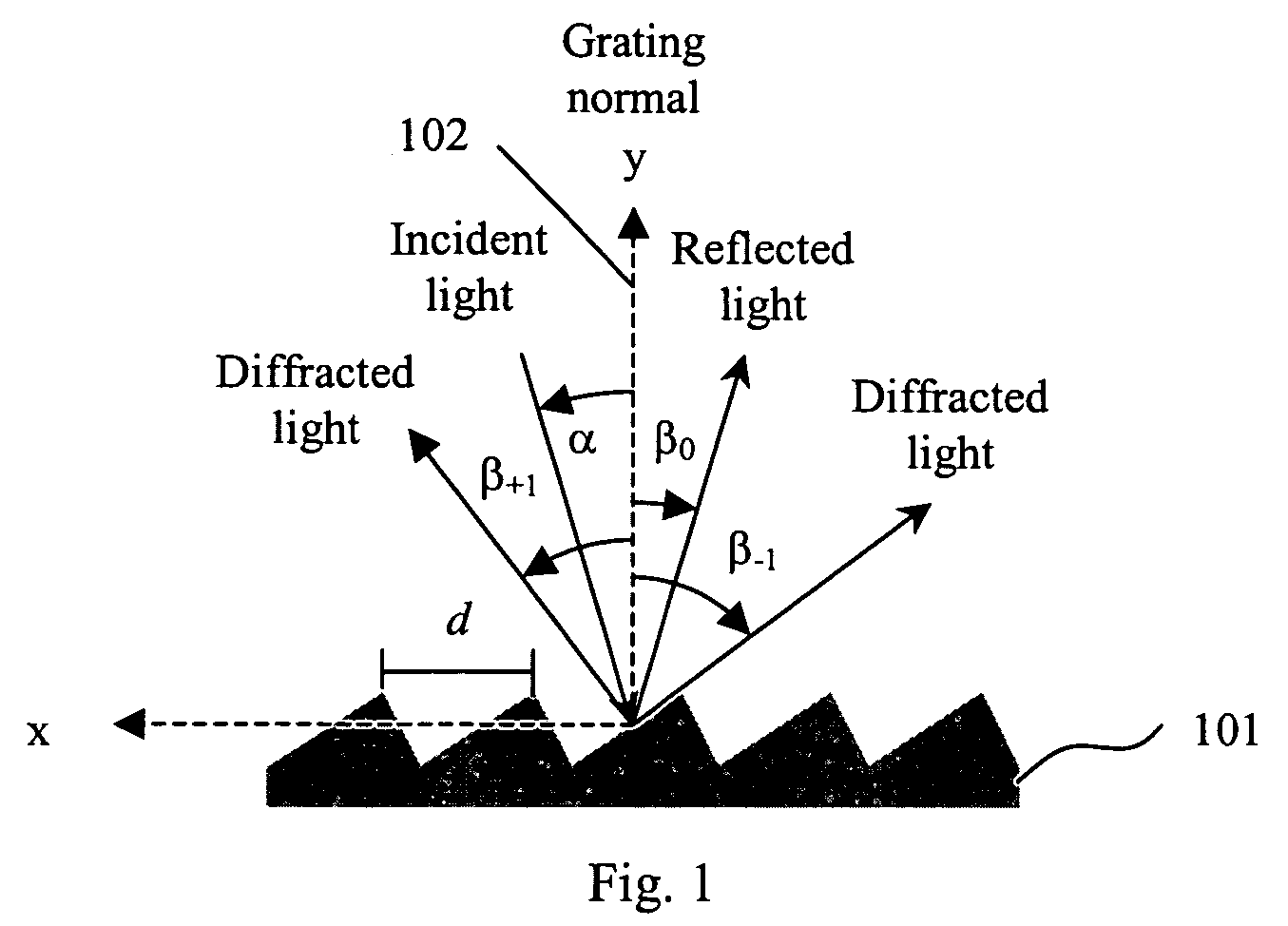
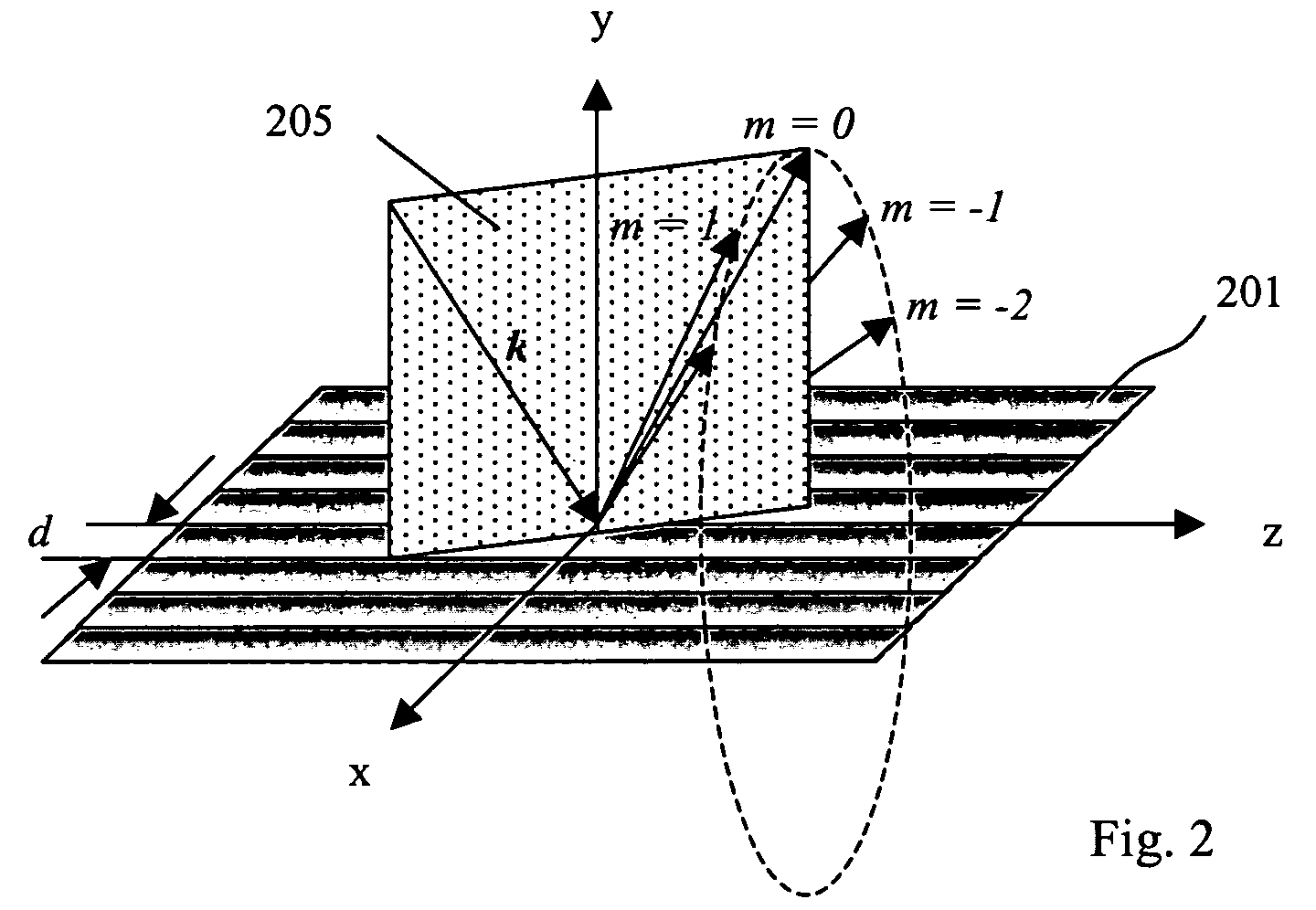
Angle-tunable transmissive grating
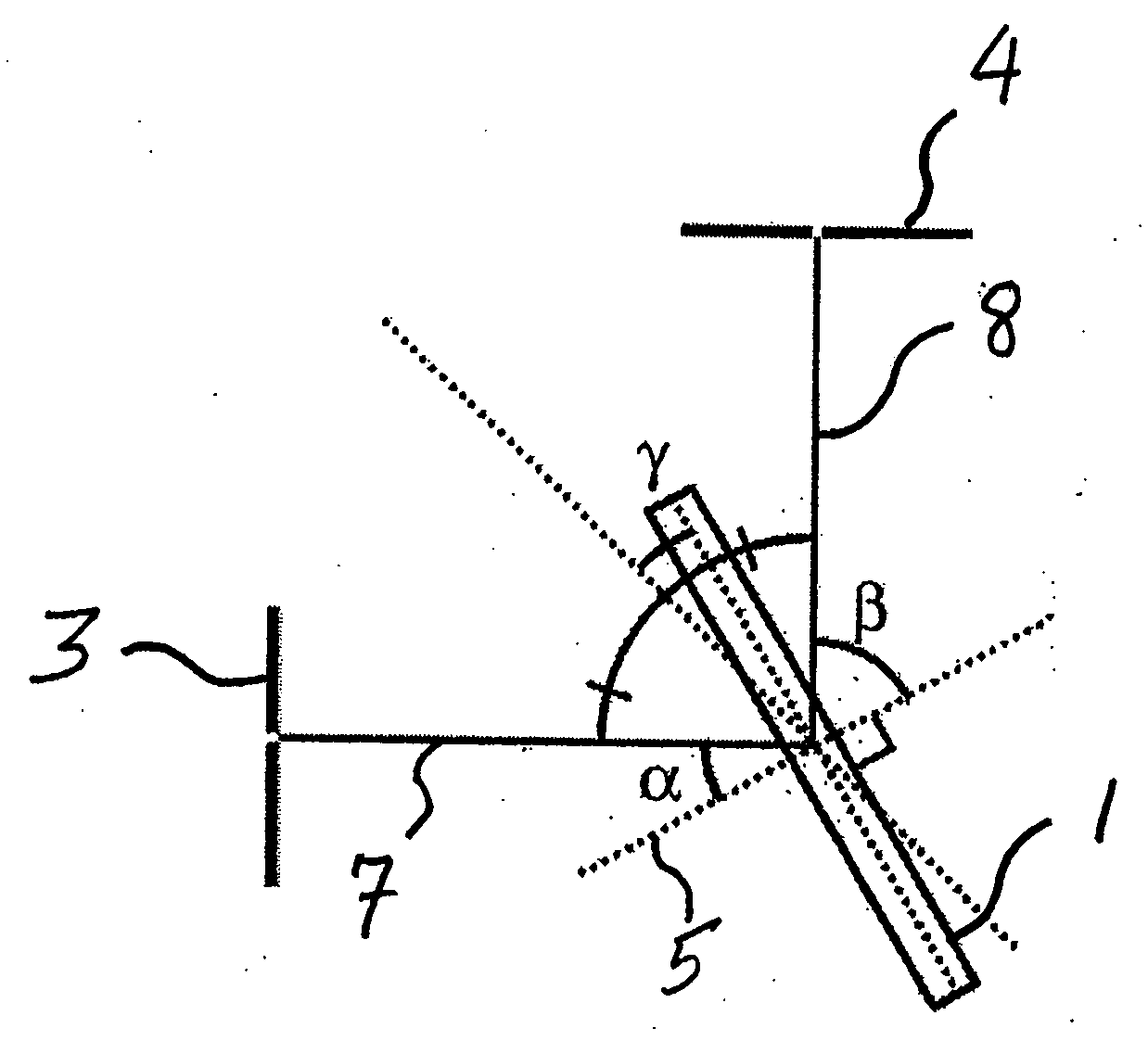
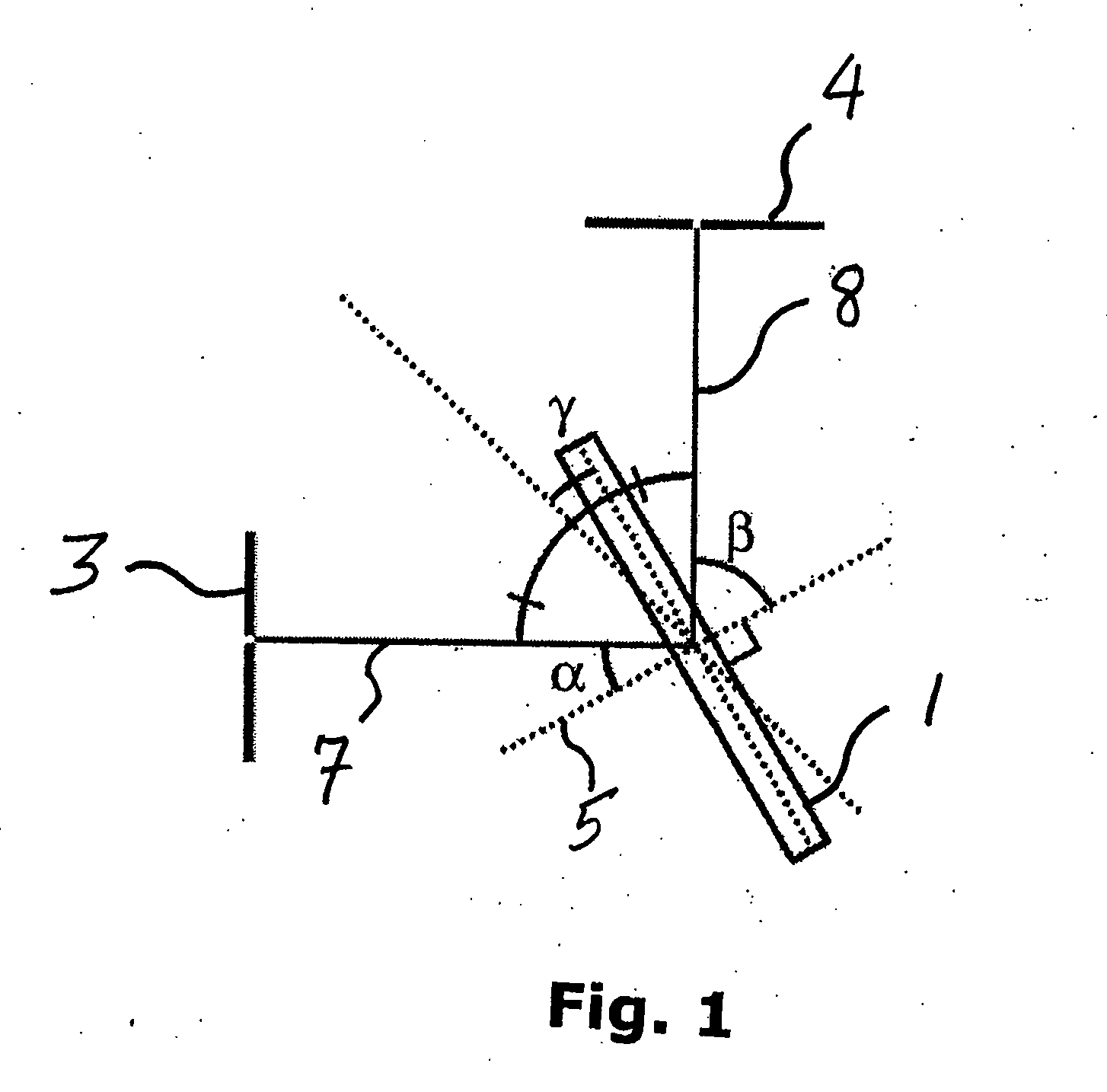
InactiveUS20070160325A1High spectral purityHigh Power Handling CapabilitySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsOptical resonator shape and constructionRotational axisGrating
A tunable transmissive grating comprises a transmissive dispersive element, a reflective element, and an angle θ formed between the two elements. A first optical path is formed according to the angle θ, wherein light dispersing from the dispersive element is directed onto the reflective element and reflects therefrom. At least one element is rotatable about a rotational center to cause a second optical path and thereby tune the wavelength of the light reflecting from the reflective element. Both elements can be rotatable together around a common rotational center point according to certain embodiments, and / or each element can be independently rotated around a rotational axis associated only with that element. According to some embodiments, the relative angle θ formed between the elements is held constant; however, in other embodiments θ can vary.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Film mapping system
ActiveUS20050046850A1Radiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsLight beamElectromagnetic radiation
Owner:SVT ASSOCS
Detection and classification of light sources using a diffraction grating
A system mounted in a vehicle for classifying light sources. The system includes a lens and a spatial image sensor. The lens is adapted to provide an image of a light source on the spatial image sensor. A diffraction grating is disposed between the lens and the light source. The diffraction grating is adapted for providing a spectrum. A processor is configured for classifying the light source as belonging to a class selected from a plurality of classes of light sources expected to be found in the vicinity of the vehicle, wherein the spectrum is used for the classifying of the light source. Both the image and the spectrum may be used for classifying the light source or the spectrum is used for classifying the light source and the image is used for another driver assistance application.
Owner:MOBILEYE VISION TECH LTD
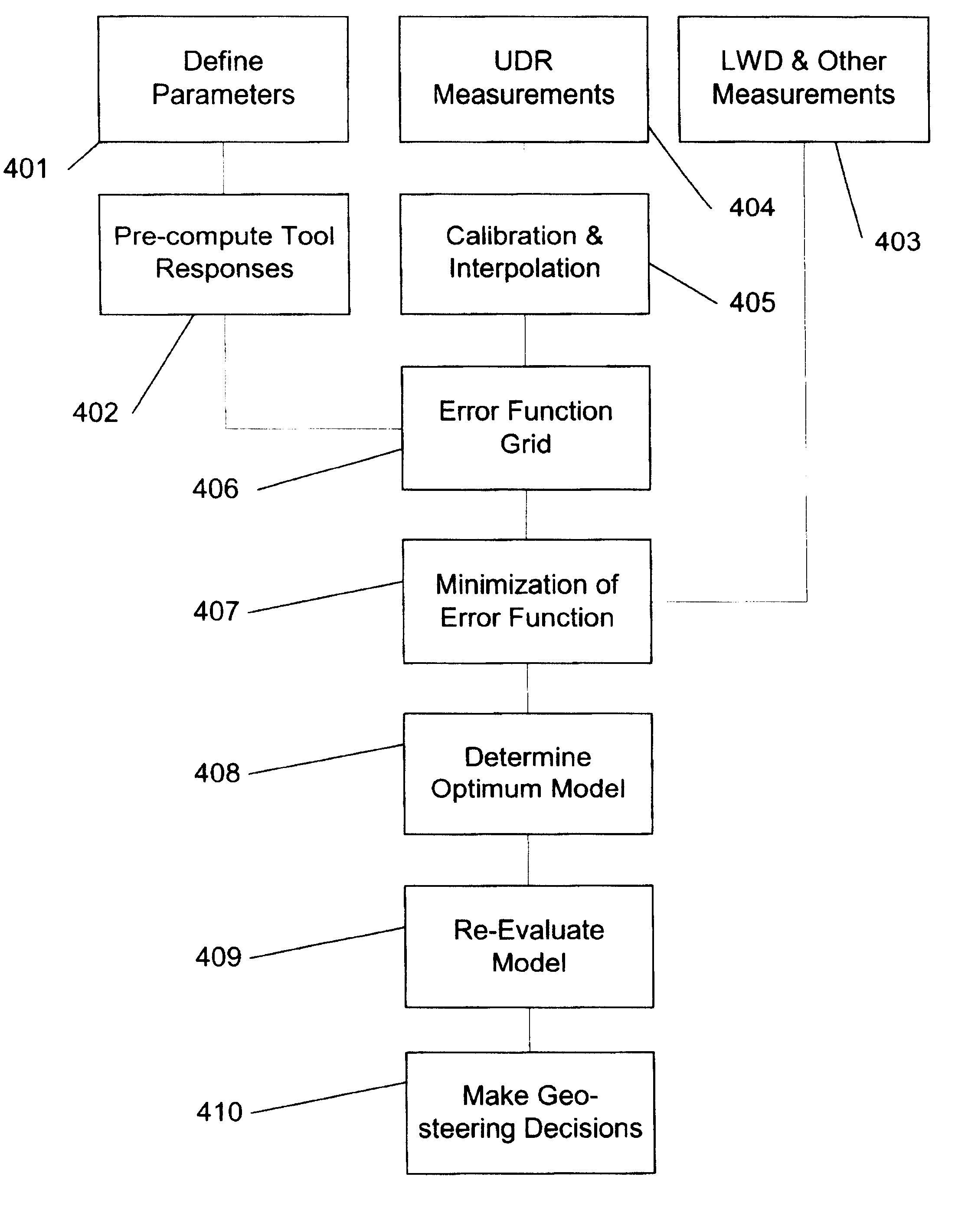
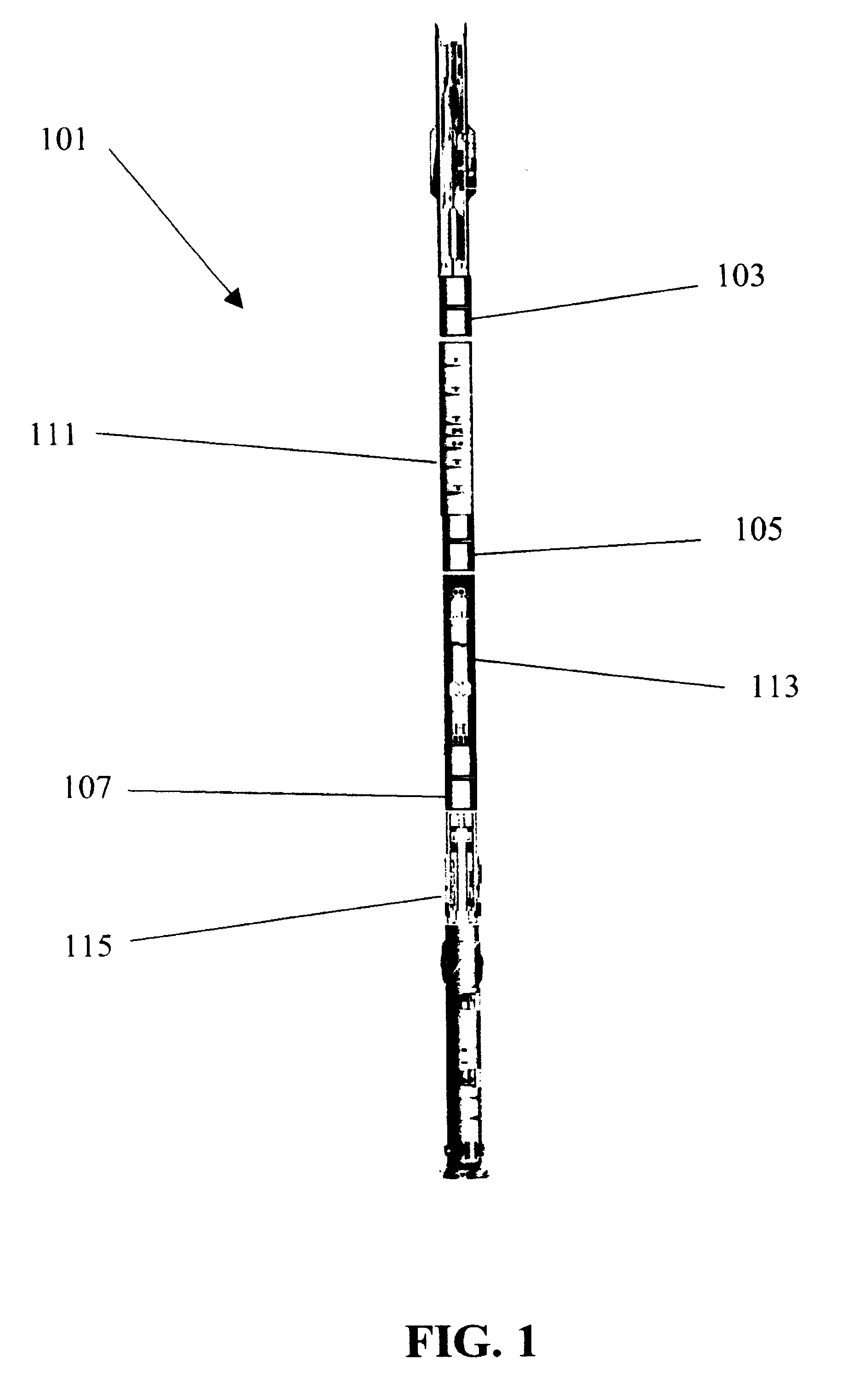
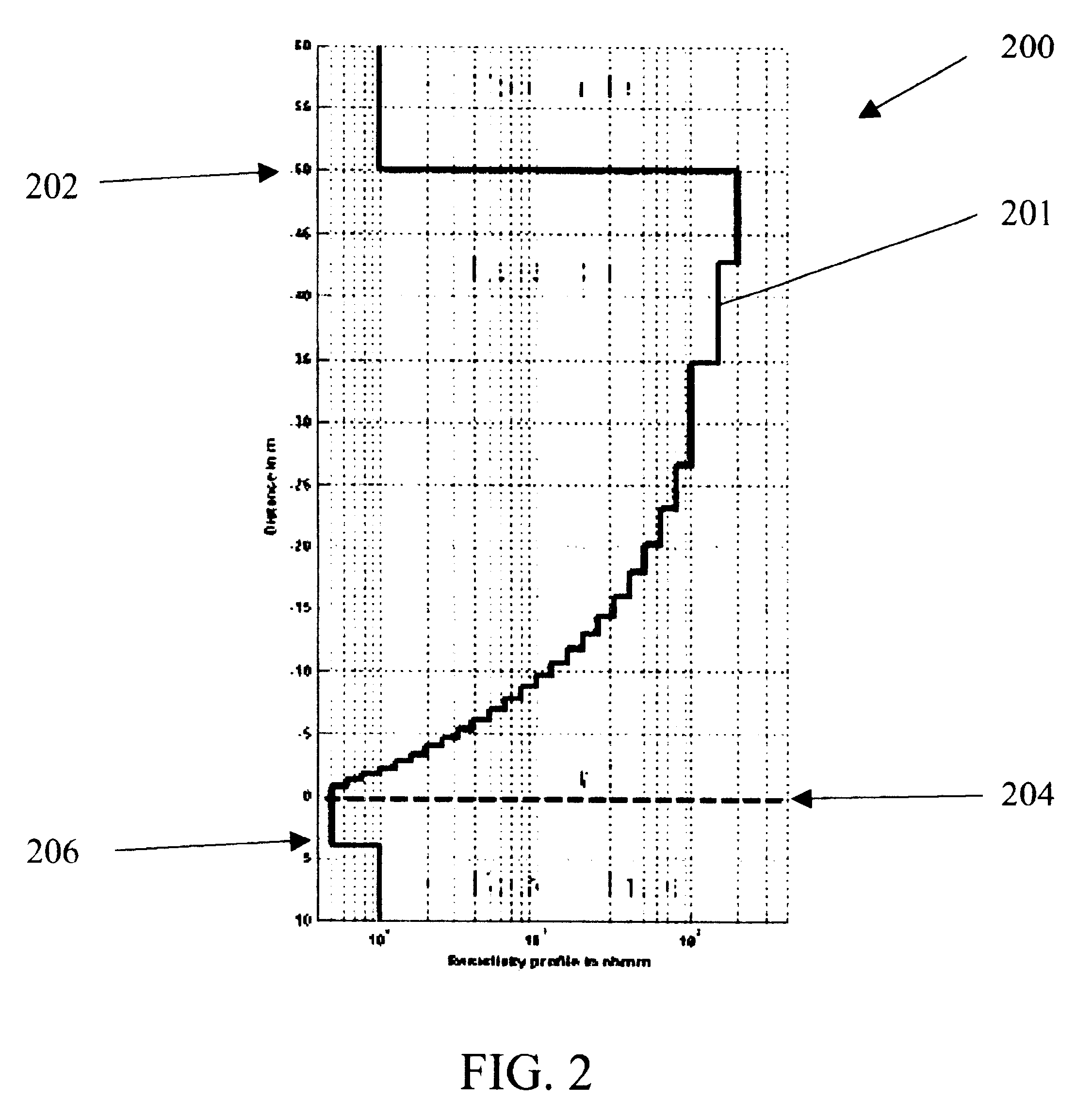
Systems for deep resistivity while drilling for proactive geosteering
A method for geosteering while drilling a formation includes generating a plurality of formation models for the formation, where each of the plurality of the formation models includes a set of parameters and a resistivity tool therein and locations of the resistivity tool differ in the plurality of the formation models. The method may also include computing predicted tool responses for the resistivity tool in the plurality of formation models, acquiring resistivity measurements using the resistivity tool in the formation, and determining an optimum formation model based on a comparison between the actual tool response and the predicted tool responses. The method may also include steering a bottom home assembly based on the optimum formation model.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
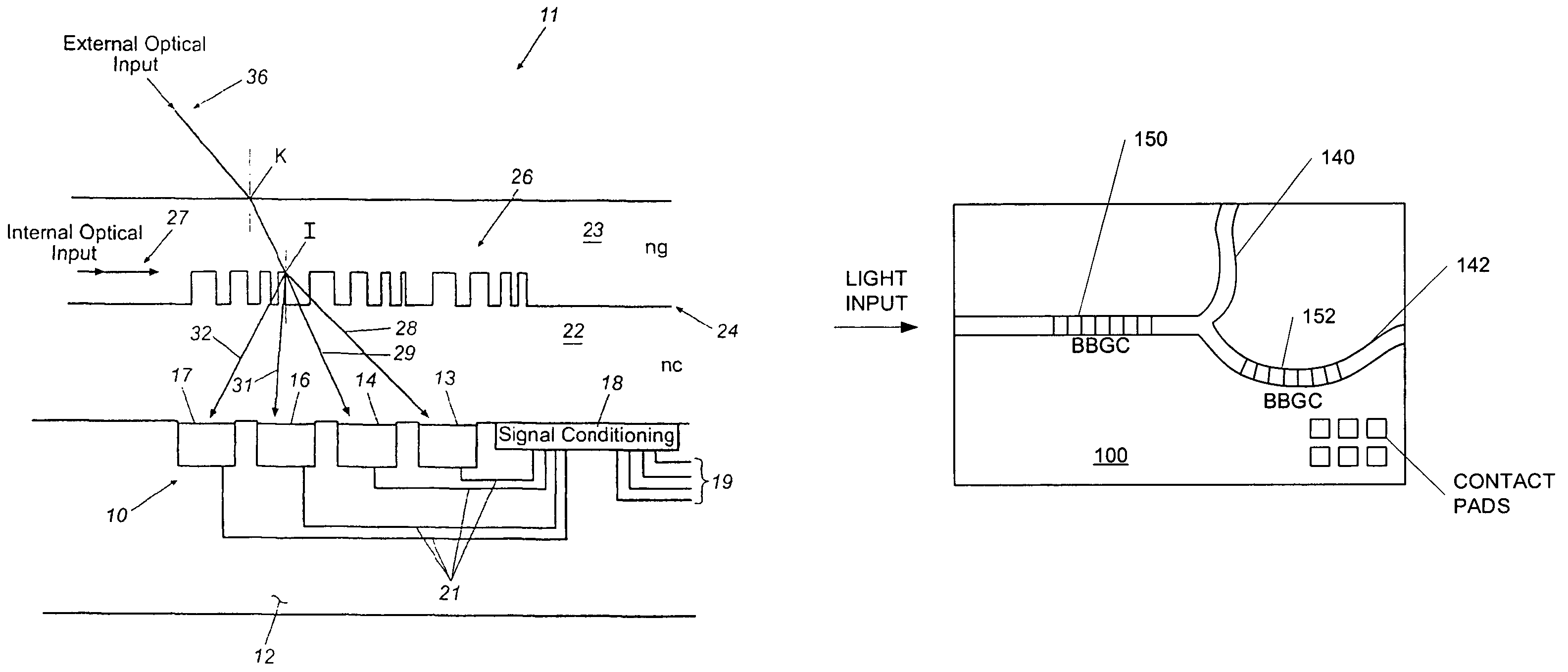
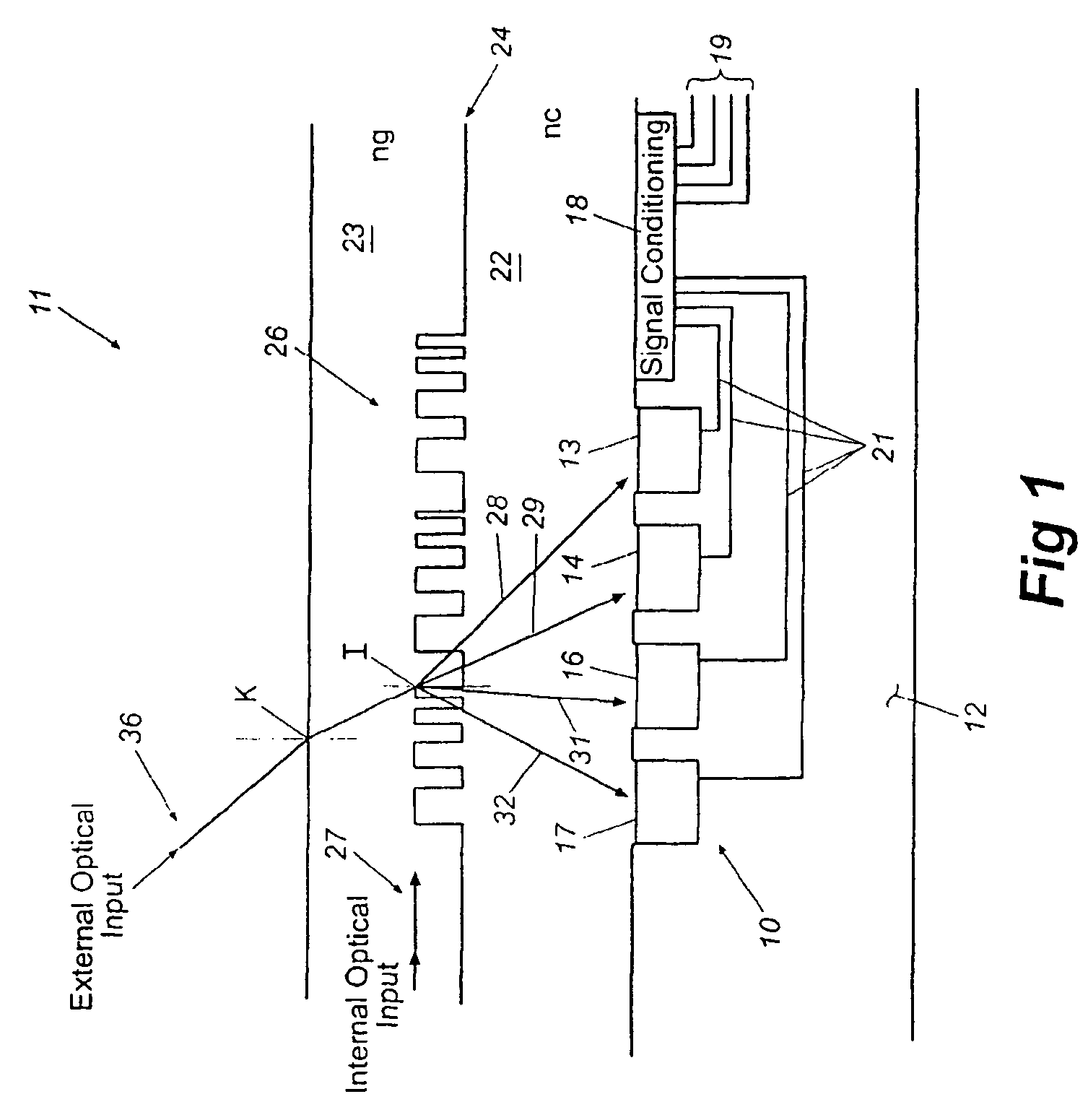
Integrated optical multiplexer and demultiplexer for wavelength division transmission of information
InactiveUS7050675B2High intensity optical signalFast data throughputRadiation pyrometryFinal product manufactureGratingWaveguide
A multiplexer / demultiplexer is provided for optical interconnection between electronic components on an integrated circuit chip. The multiplexer / demultiplexer includes a substrate formed with an array of photo emitters / detectors and conditioning electronics coupled thereto. A first layer of optically transparent material is formed on the substrate overlying the emitters / detectors and a second layer of optically transparent material, functioning as an optical waveguide, is formed on the first layer. A binary blazed grating is formed at the interface of the two layers. For multiplexing, discrete wavelength optical signals are modulated with data, emitted by the emitters, intercepted by the binary blazed grating, and multiplexed into a polychromatic beam for transmission through the waveguide. For demultiplexing, the discrete wavelengths are separated by the binary blazed grating and directed to corresponding detectors. The conditioning electronics receive and demodulate the output of the detectors to extract data, and format the data for communication with electronic components.
Owner:ADVANCED INTERFACES GEORGIA
Devices and method for spectral measurements
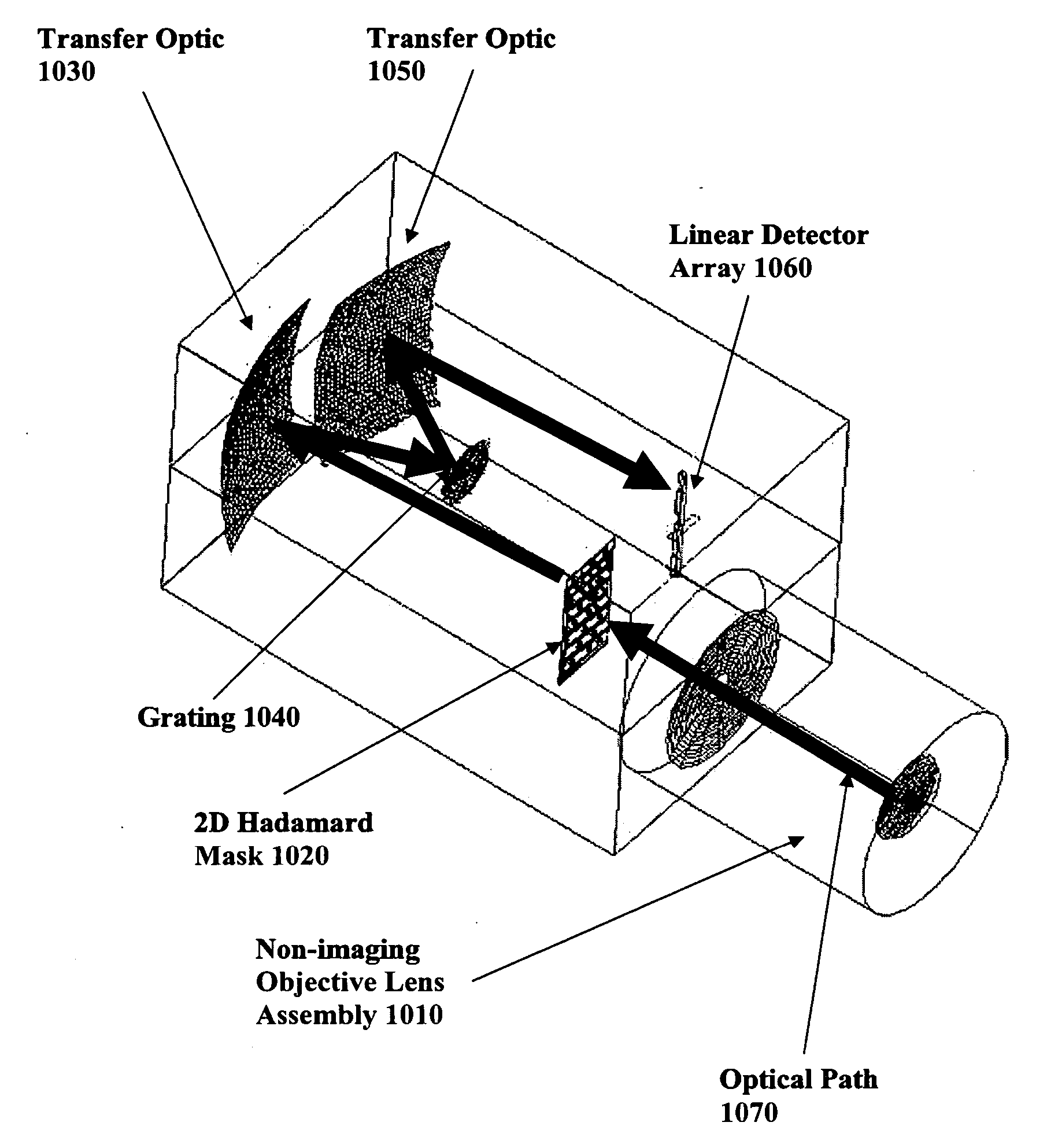
InactiveUS20050243312A1Quick collectionImprove throughputRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsMeasurement deviceFtir spectra
A spectral measurement device comprising an entrance aperture for receiving an electromagnetic energy and a mask located at the entrance aperture in the form of a two-dimensional encodement pattern. An optical element conditions the electromagnetic energy received from the mask for presentation to the spectral dispersion element and the and a spectral dispersion element disperses the electromagnetic energy in one or more dimensions. Additionally, the optical element conditions the dispersed electromagnetic energy onto an array of detector elements.
Owner:PLAIN SIGHT SYST
Optical analyzer for identification of materials using reflectance spectroscopy
ActiveUS20130256534A1Reduce manufacturing costSmall sizeRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsFast measurementChemical composition
Owner:INNOVATIVE SCI TOOLS
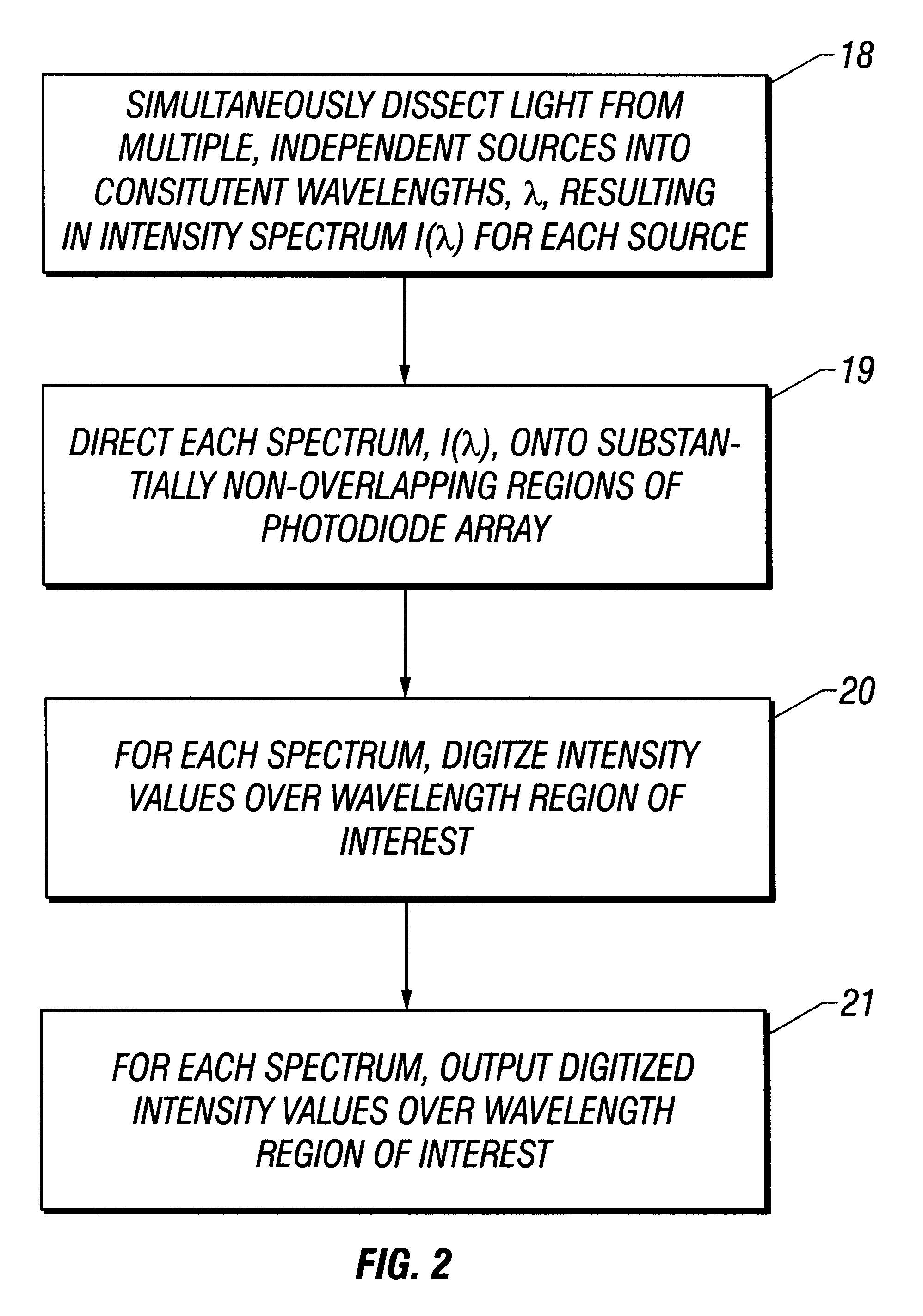
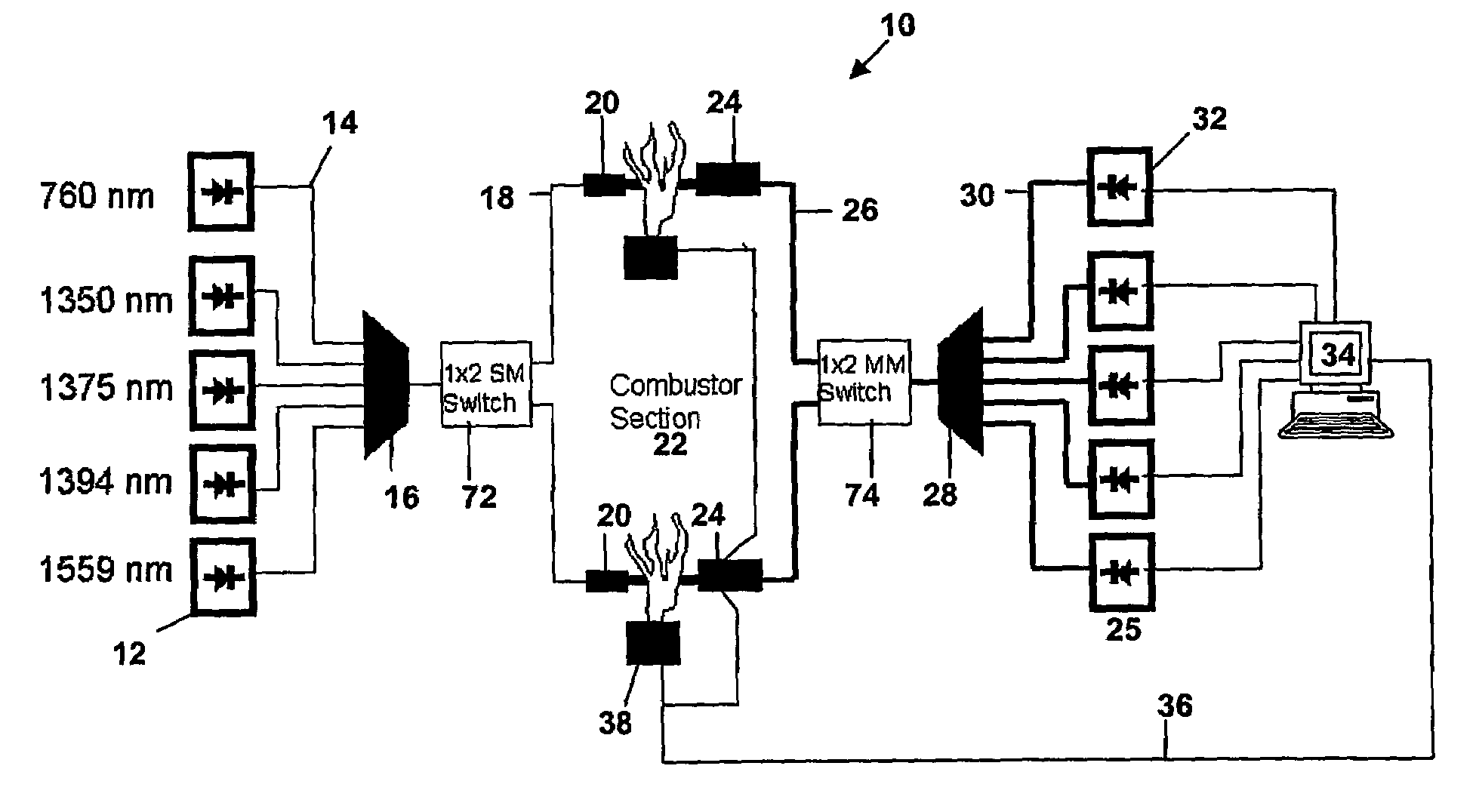
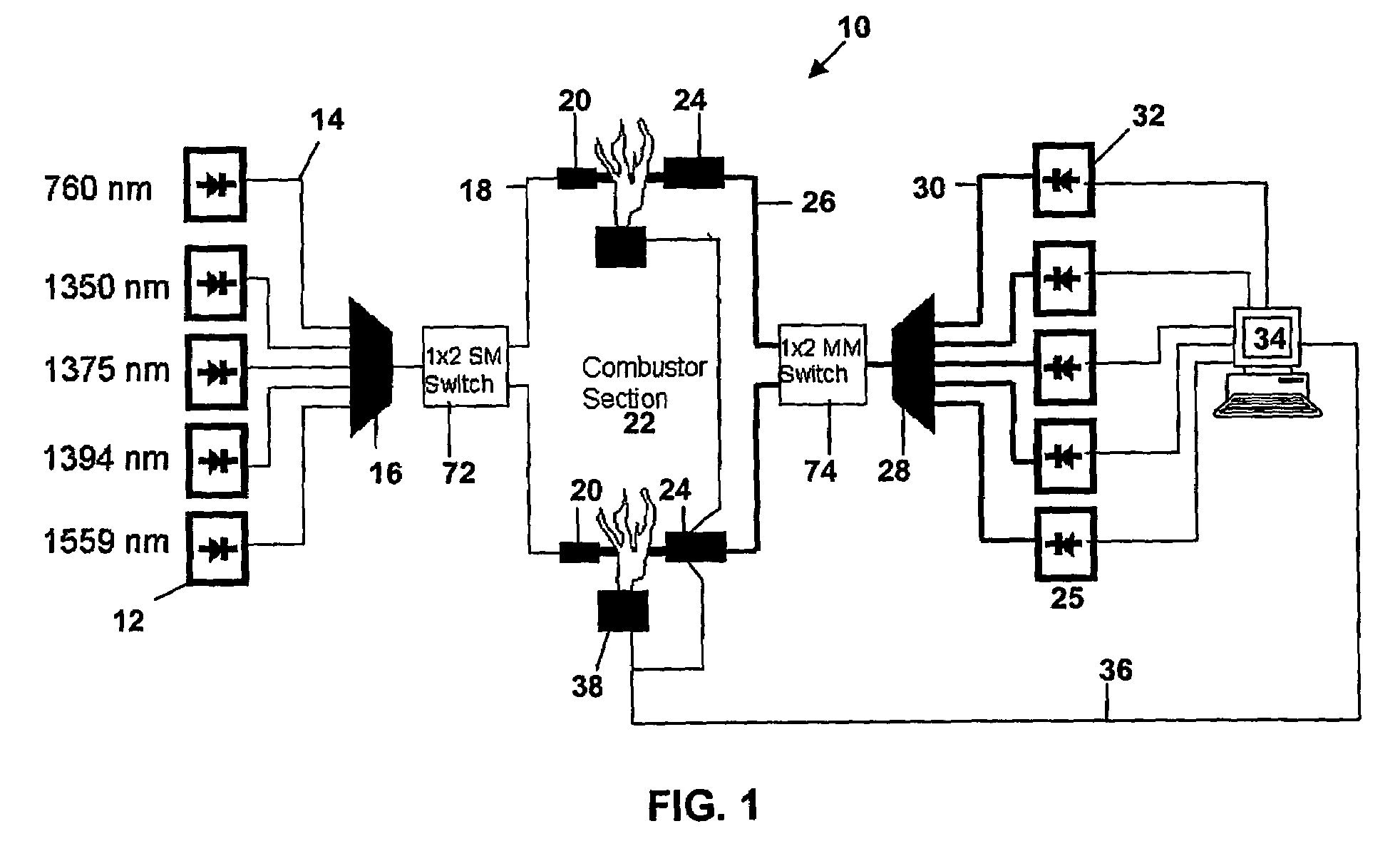
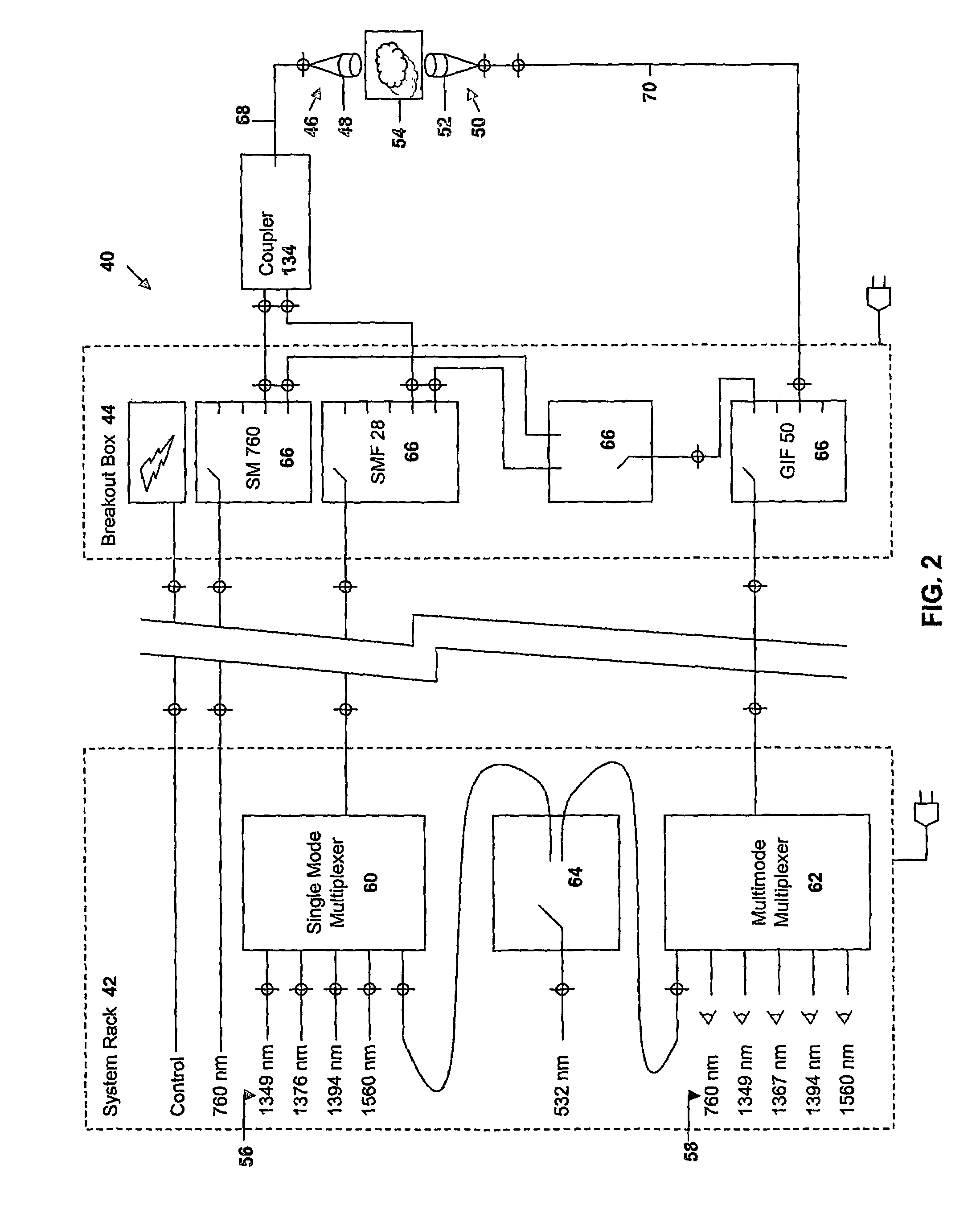
Spectrometer configured to provide simultaneous multiple intensity spectra from independent light sources
A spectrometer for providing multiple, simultaneous spectra from independent light sources is described characterized in that light from the multiple sources is directed to different portions of a diffraction grating, and the wavelength components of the resultant spectra are directed to at least one receptor.
Owner:FILMETRICS
Method and apparatus for the monitoring and control of combustion
ActiveUS7248755B2Noise minimizationEfficiently transmitting signalRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsCombustion chamberLaser light
Owner:ONPOINT TECHNOLOGIES LLC
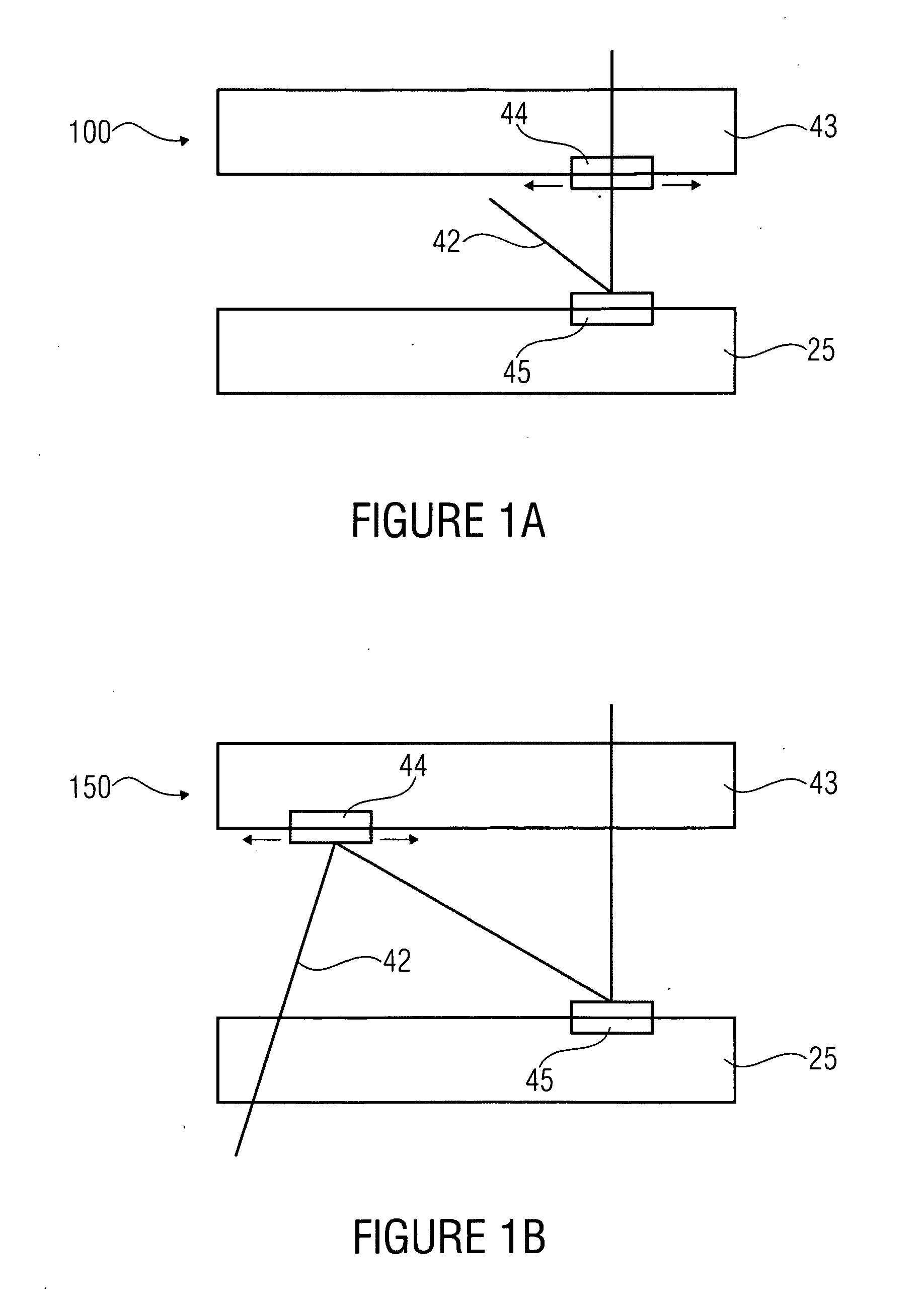
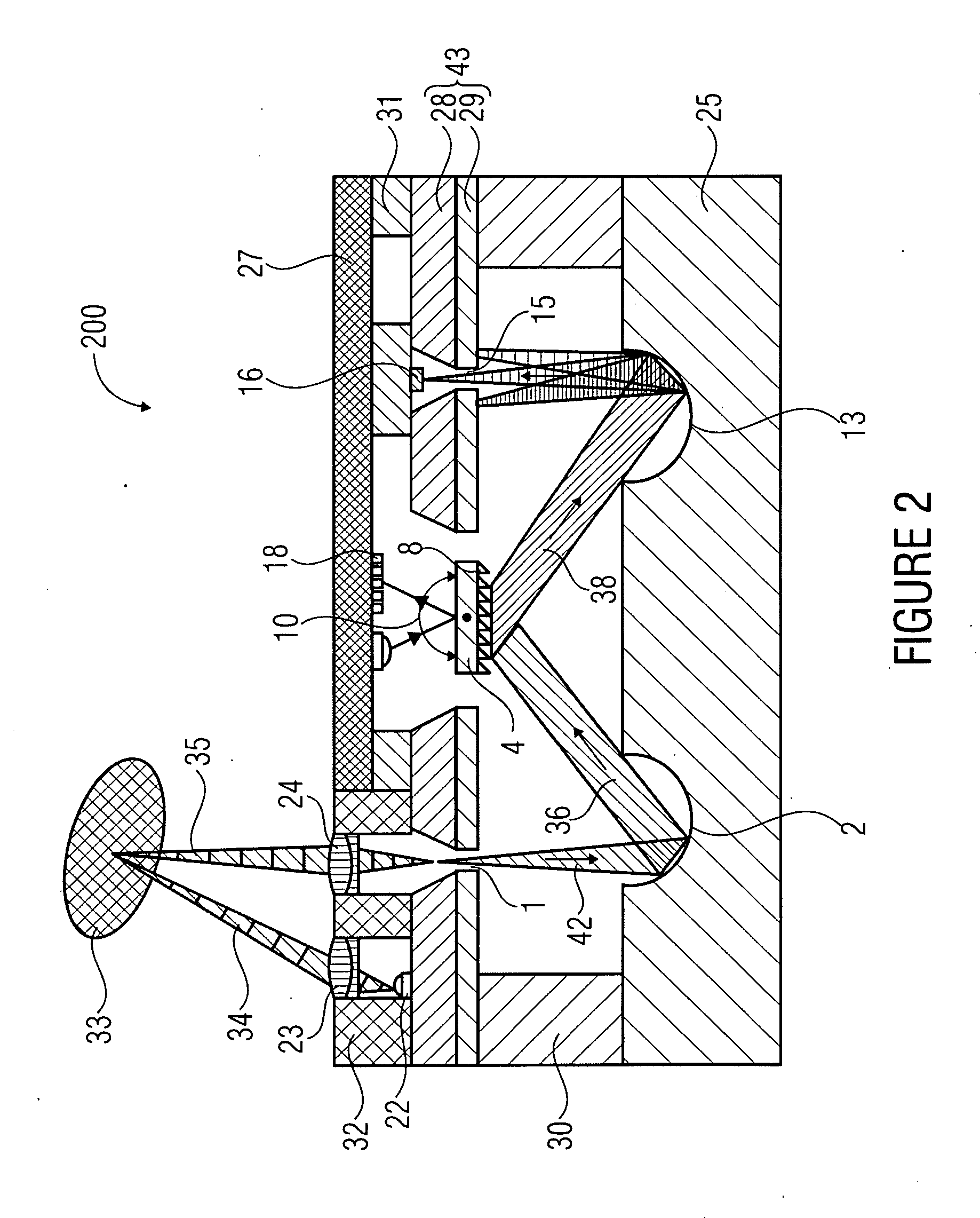
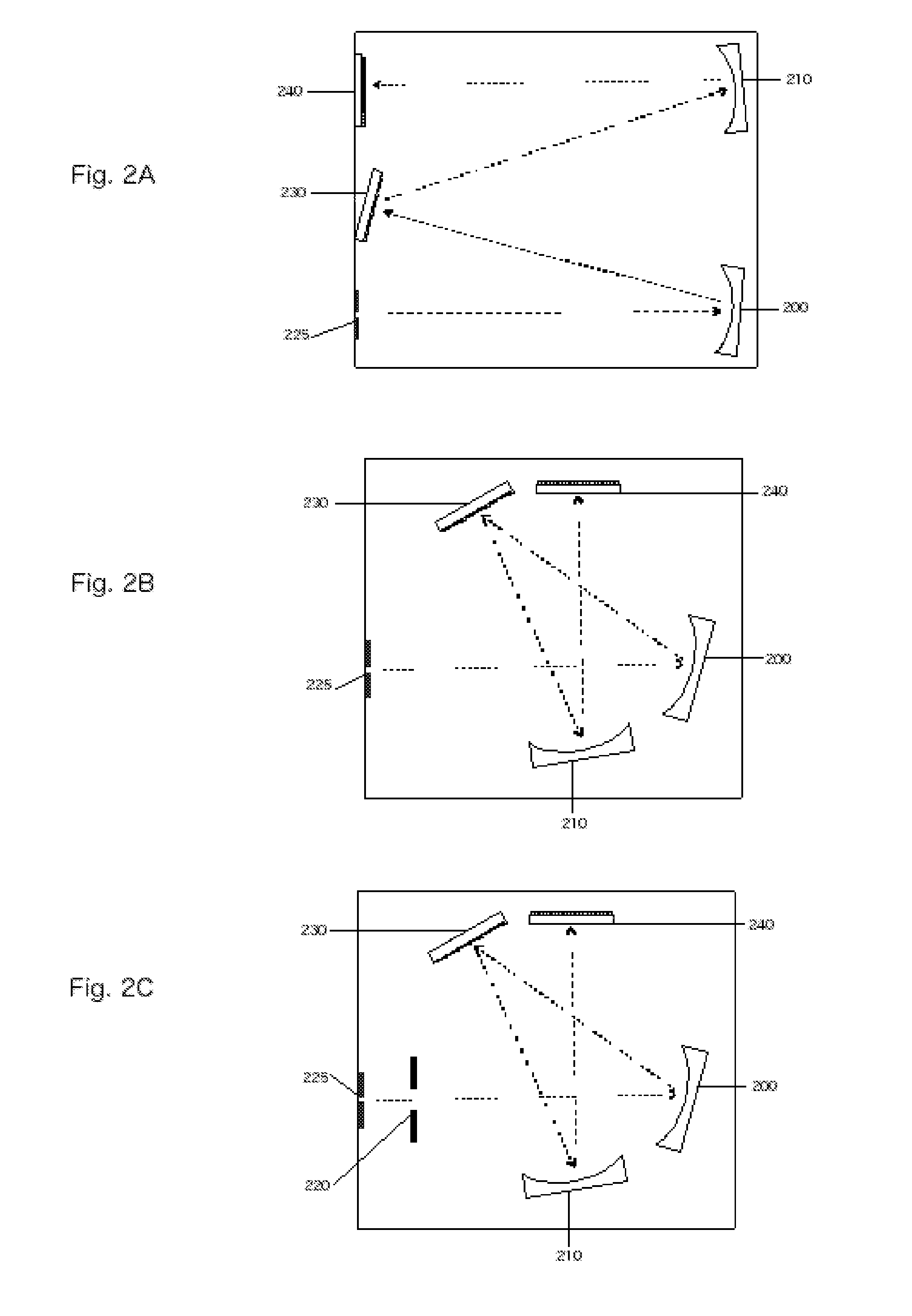
Littrow spectrometer and a spectral domain optical coherence tomography system with a littrow spectrometer
ActiveUS20070030483A1Reduce non-linearityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSpectral domainDetector array
A compact conical diffraction Littrow spectrometer is disclosed. The distortion of the conically diffracted spectral component beams is compensated and as a result, the diffracted spectral beams can still be focused into a substantially straight line to shine onto a detector array. A spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) system incorporating a Littrow spectrometer or a spectrometer having one or more shared focusing element(s) and an SD-OCT system incorporating a spectrometer that is substantially polarization independent are also disclosed.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
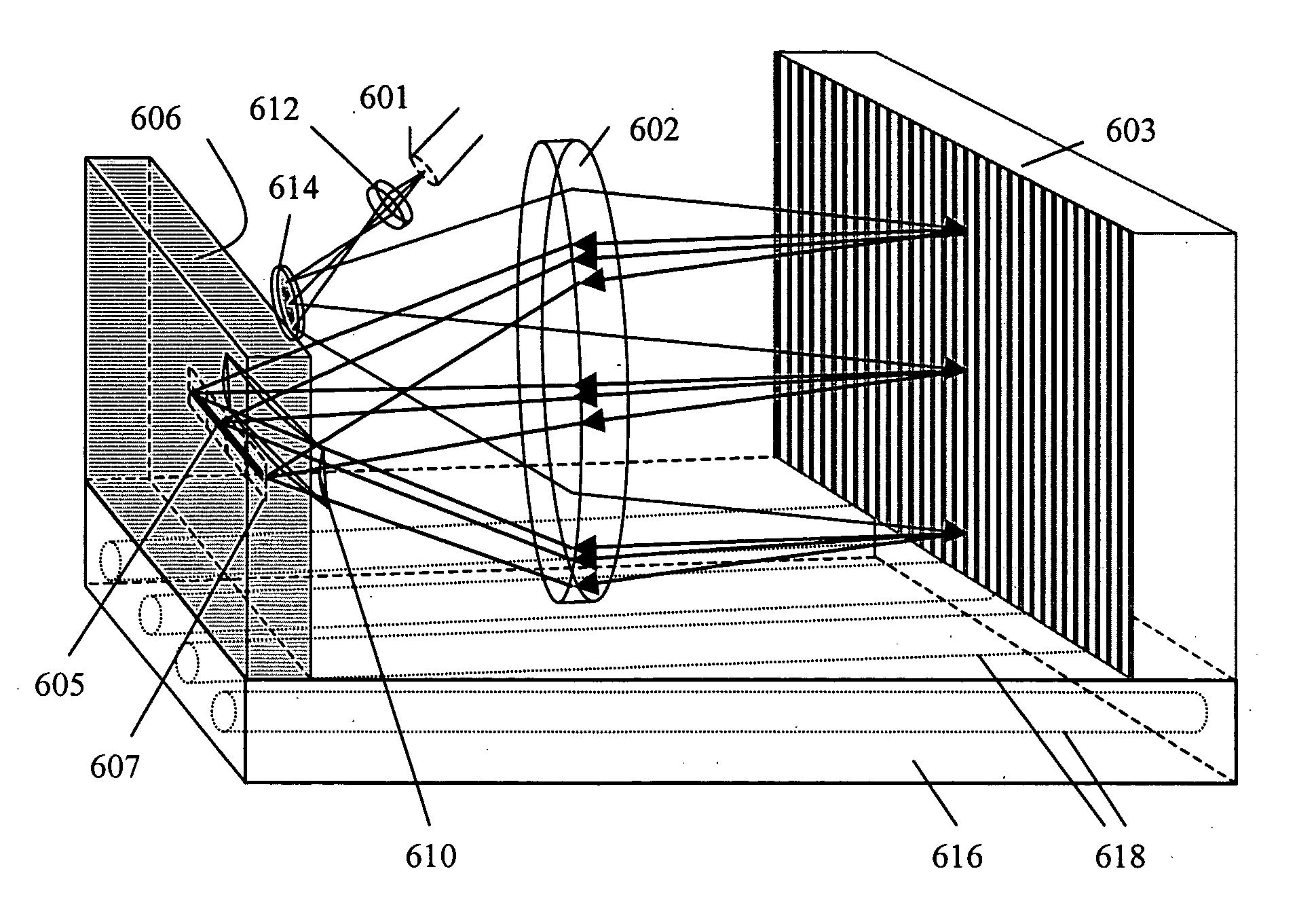
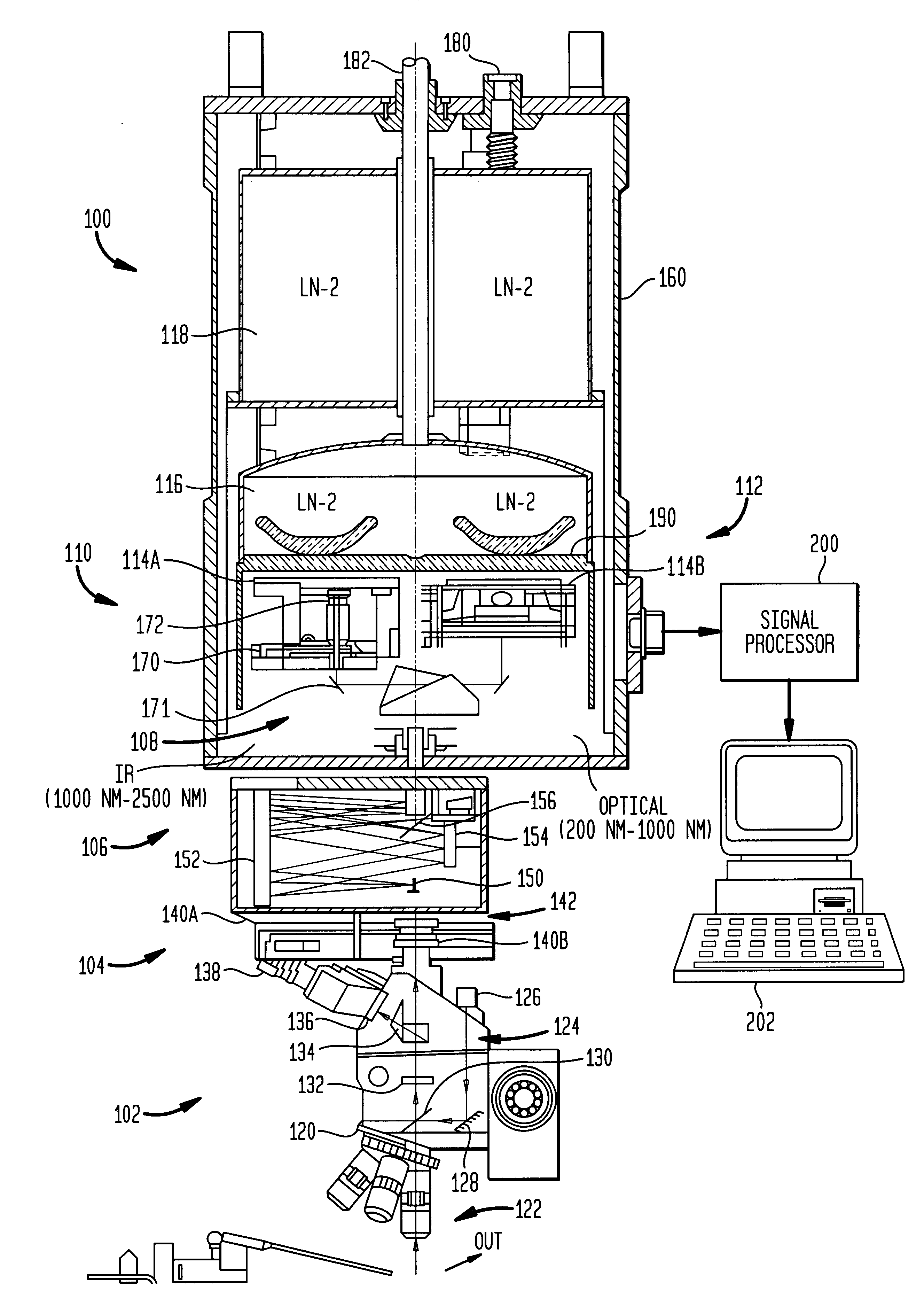
Multiwavelength imaging and spectroscopic photoemission microscope system
InactiveUS6222187B1Wide of electromagnetic emissionReduce the temperatureEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryBeam splitterSpectrograph
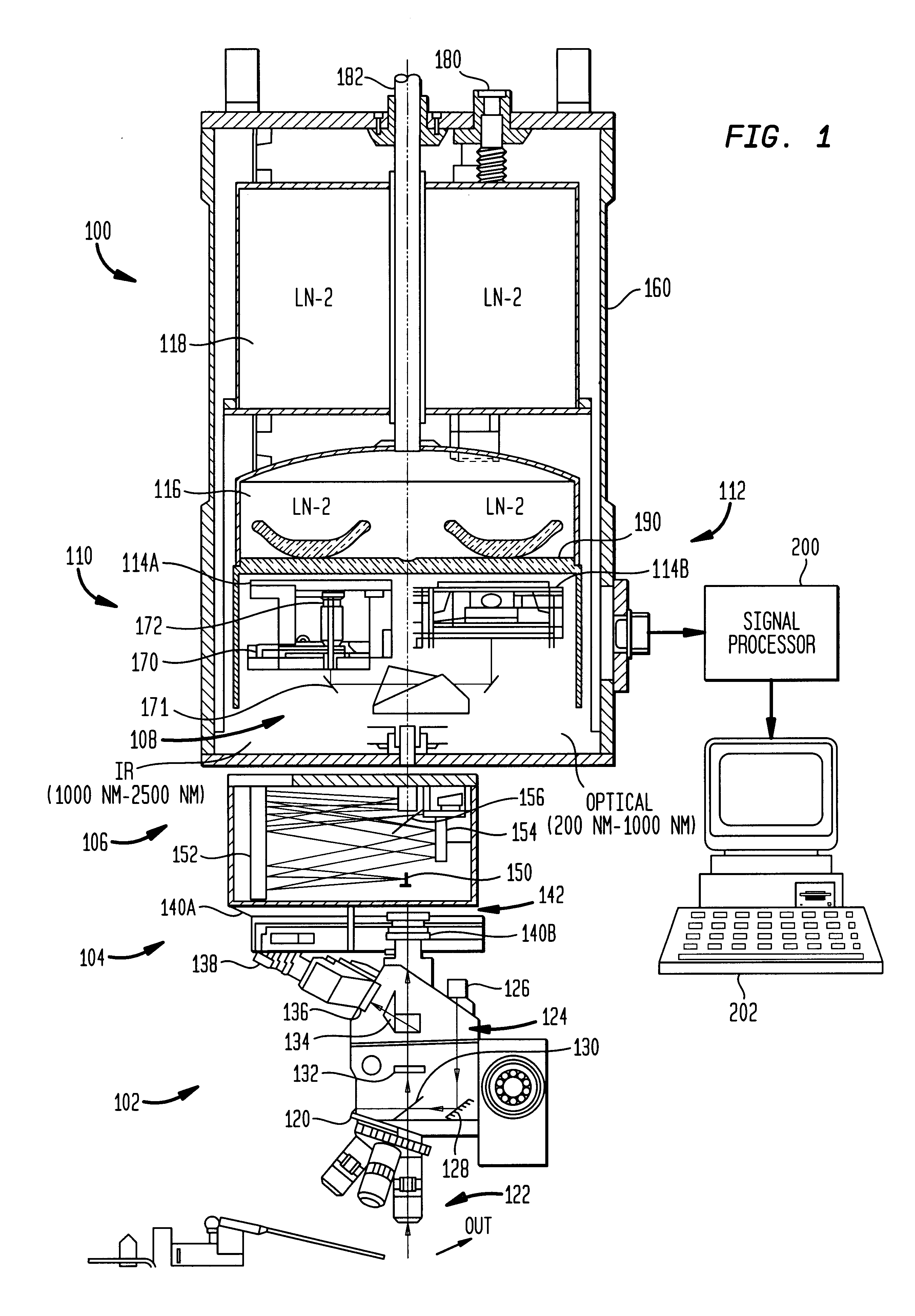
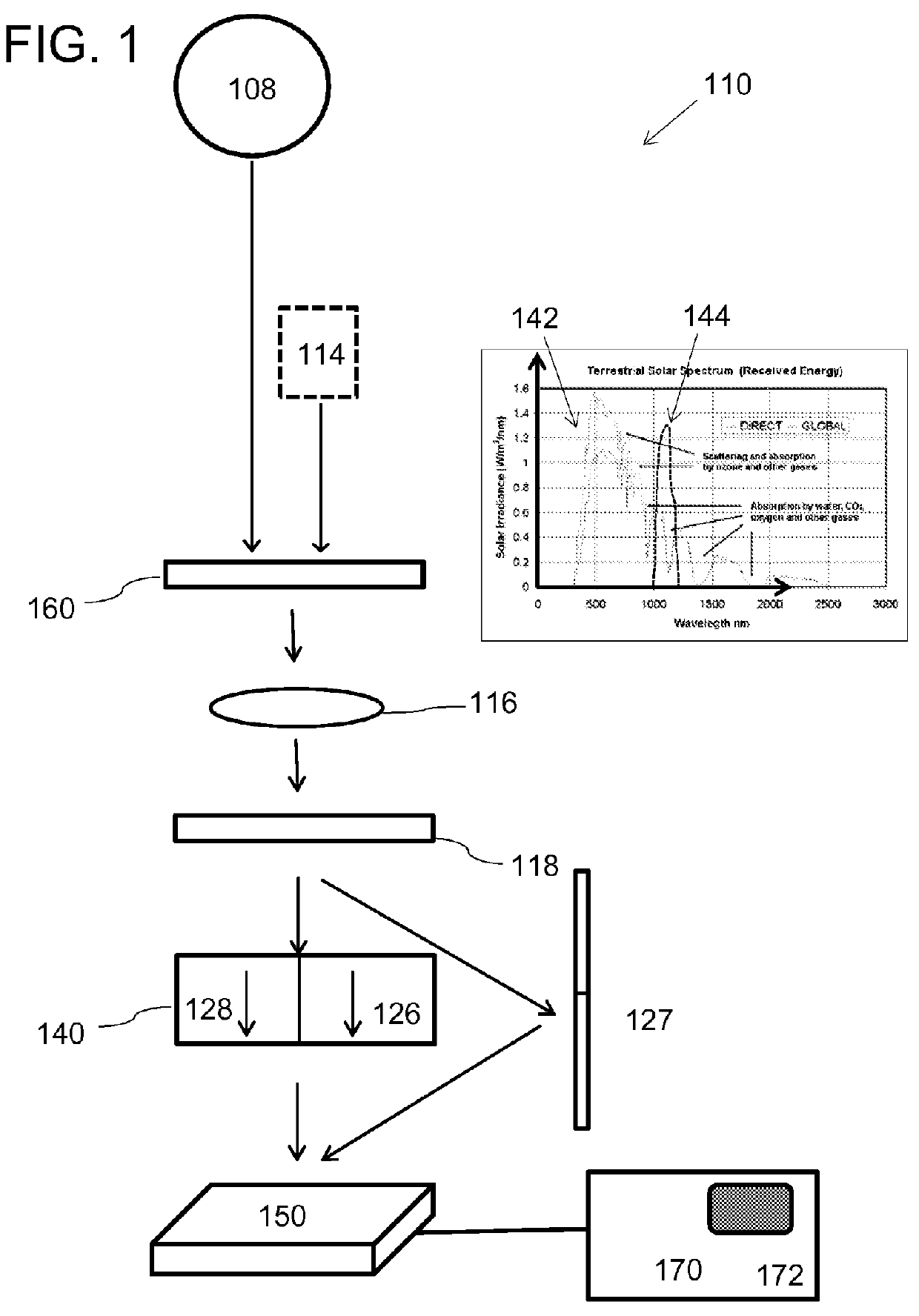
A multiwavelength imaging and spectroscopic photoemission microscope system (100) which simultaneously provides images in a broad range of the electromagnetic spectrum, such as between 200 nm-1000 nm (optical or visible light) and 1000 nm-500 nm (infrared light). The multiwavelength imaging and spectroscopic photoemission microscope system comprises a microscope (102), a spectrometer (106), a beam splitter (108), a first spectrum focal plane array (110) including an appropriate photodiode (114A), a second spectrum focal plane array (120) including an appropriate photodiode (114B), and a cryogenic vessel (160) to maintain relevant portions of the system at a very low temperature. The invention may be used in failure analysis of integrated circuits and in semiconductor and low temperature physics.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Ambient light assisted spectroscopy
ActiveUS20160033328A1Radiation pyrometryPolarisation spectroscopyBroadband light sourceControl channel
A spectroscopic device, which may be a handheld spectroscopic light source, which uses ambient light as a primary broadband light source, but which may be supplemented with an auxiliary light source to supplement band regions which may be deficient in the broad band source. The spectroscopic device makes use of a number of parallel control channels to monitor for sufficient light and to compensate for variations in the input light levels.
Owner:INTEGRATED PLASMONICS CORP
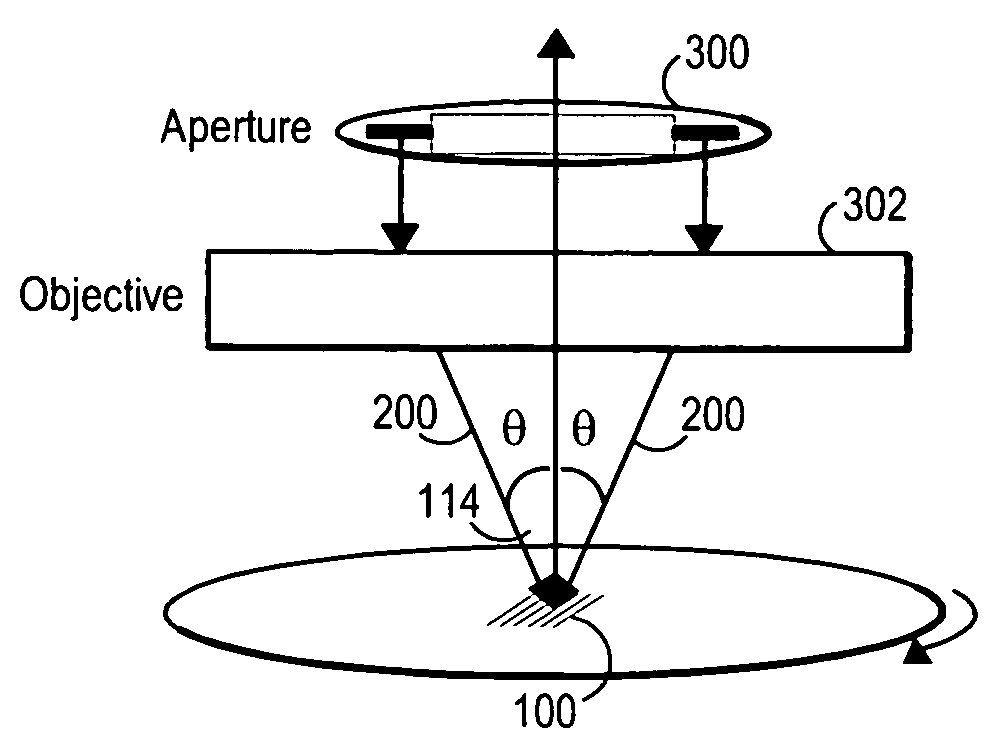
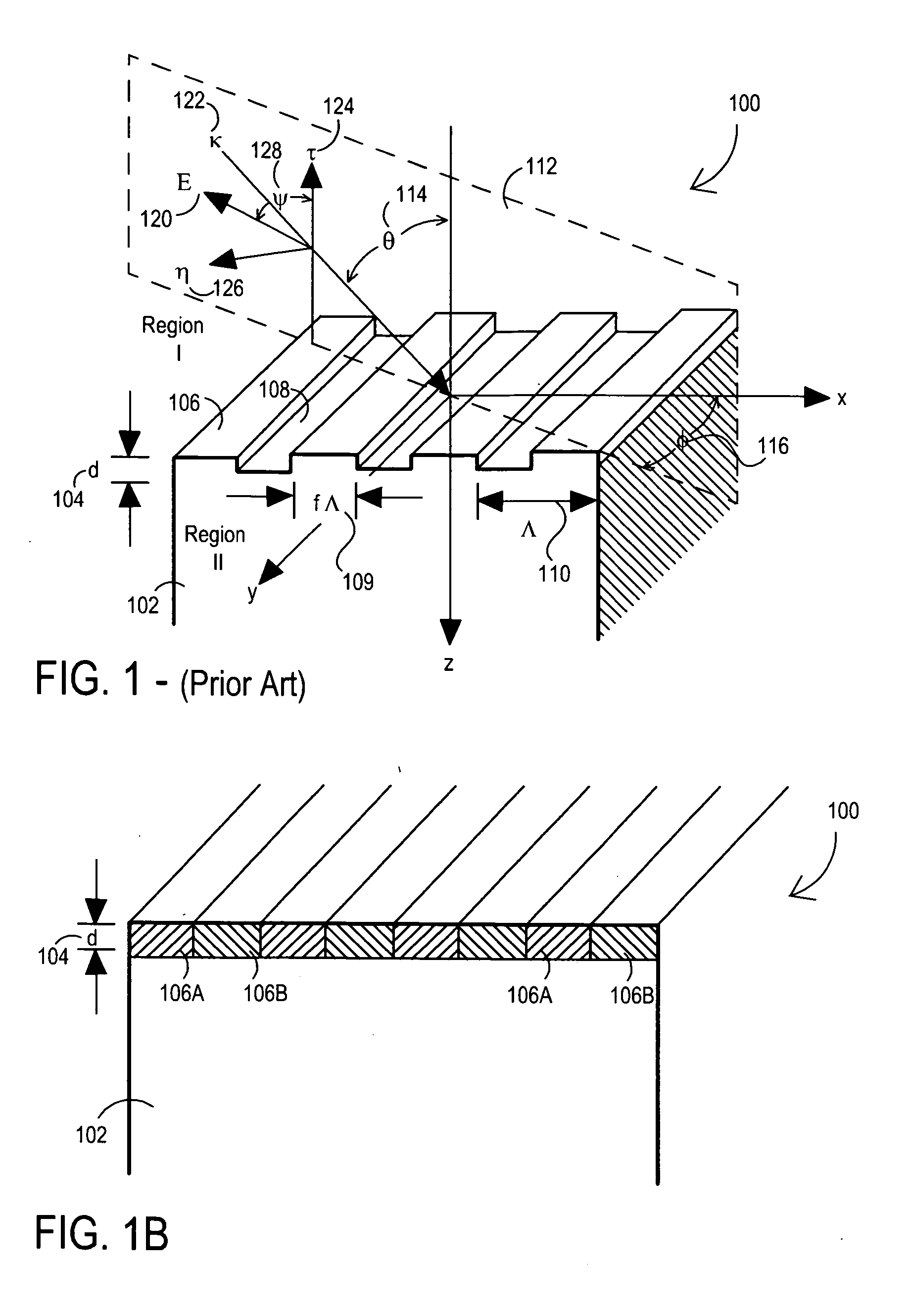
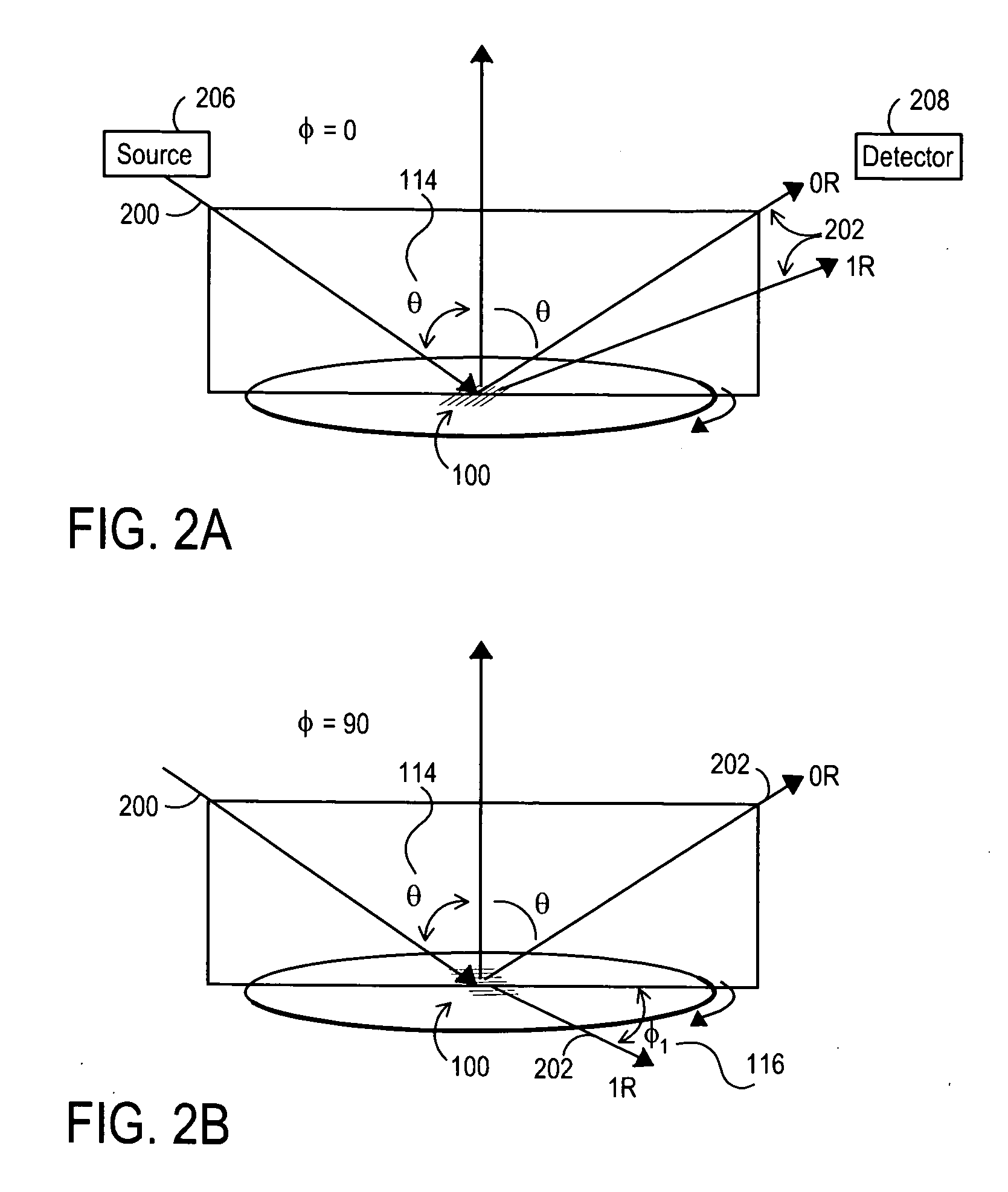
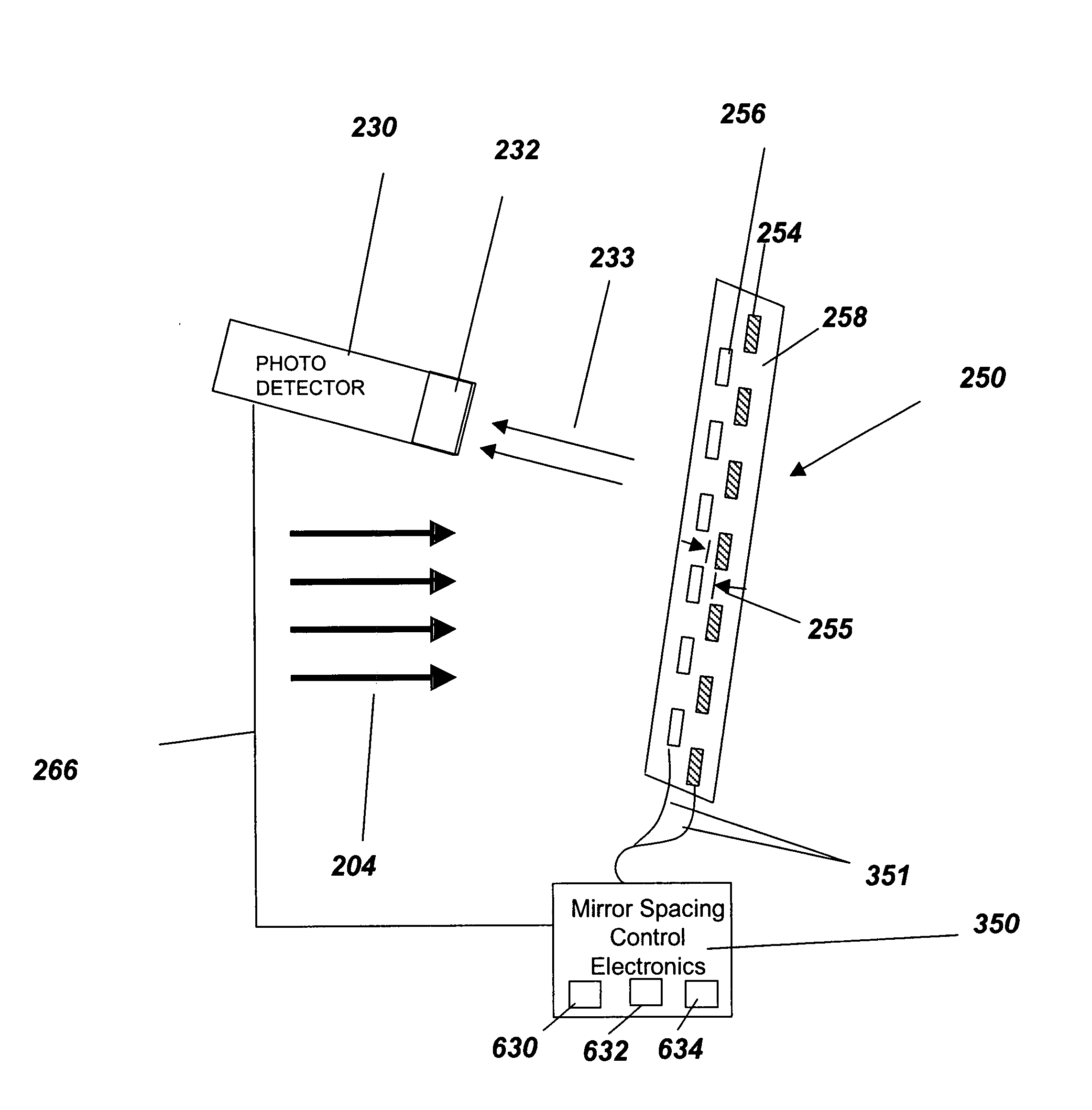
Method and apparatus for optically measuring periodic structures using orthogonal azimuthal sample orientations
InactiveUS20080129986A1Increase computing speedReduce computing timeAngle measurementRadiation pyrometryGratingAngle of incidence
An optical metrology apparatus for measuring periodic structures using multiple incident azimuthal (phi) and polar (theta) incident angles is described. One embodiment provides the enhanced calculation speed for the special case of phi=90 incidence for 1-D (line and space) structures, which has the incident plane parallel to the grating lines, as opposed to the phi=0 classical mounting, which has incident plane perpendicular to the grating lines. The enhancement reduces the computation time of the phi=90 case to the same order as the corresponding phi=0 case, and in some cases the phi=90 case can be significantly faster. One advantageous configuration consists of two measurements for each sample structure, one perpendicular to the grating lines and one parallel. This provides additional information about the structure, equivalent to two simultaneous angles of incidence, without excessive increase in computation time. Alternately, in cases where the computation for phi=90 is faster than the corresponding phi=0 incidence, it may be advantageous to measure parallel to the grating lines only. In the case where two sets of incident angles are used, the incident light can be polarized to provide a total of four sets of data—Rs0, Rp0, Rs90, Rp90—for each incident polar angle, all from the same structure.
Owner:JORDAN VALLEY SEMICON
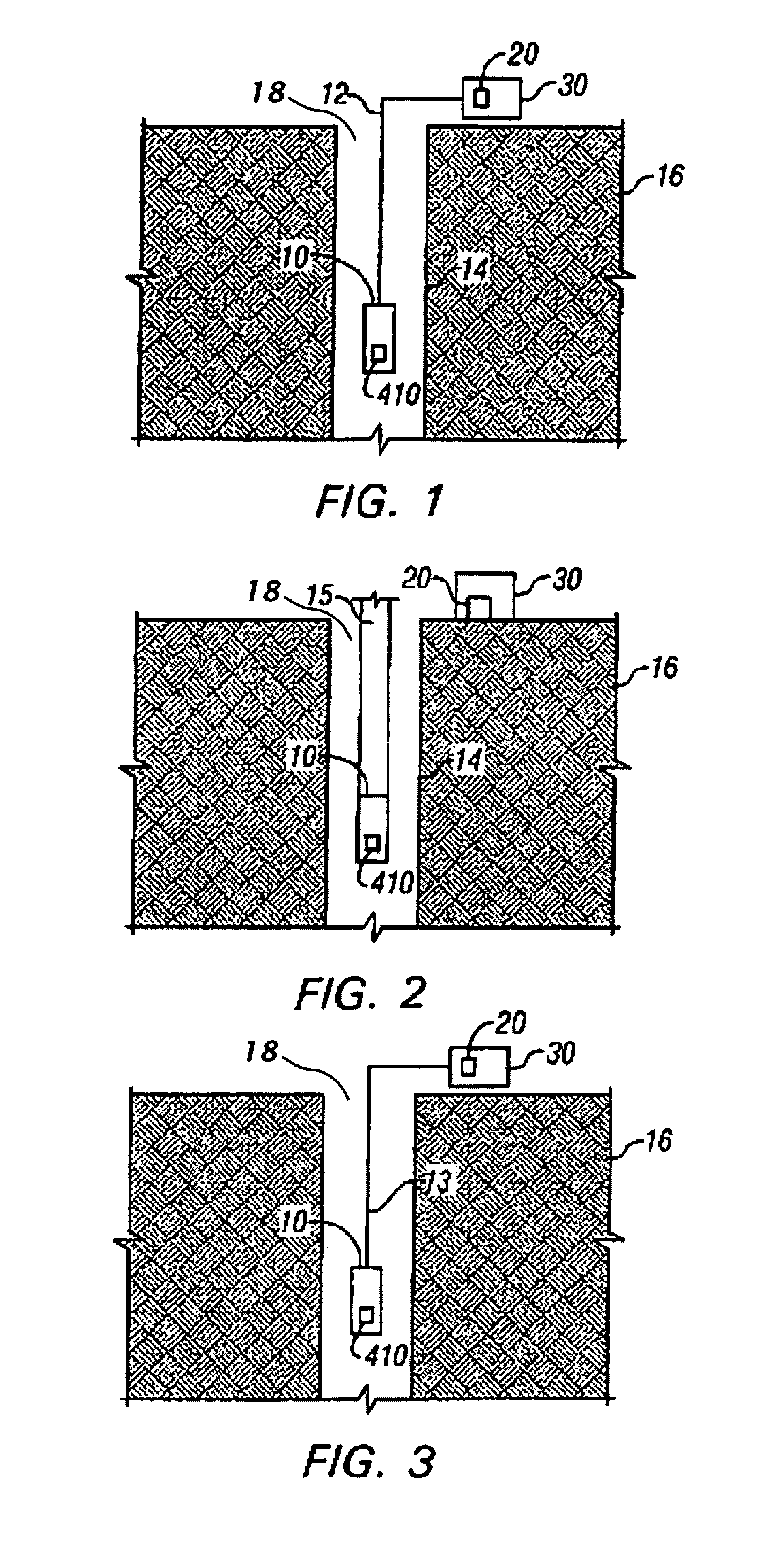
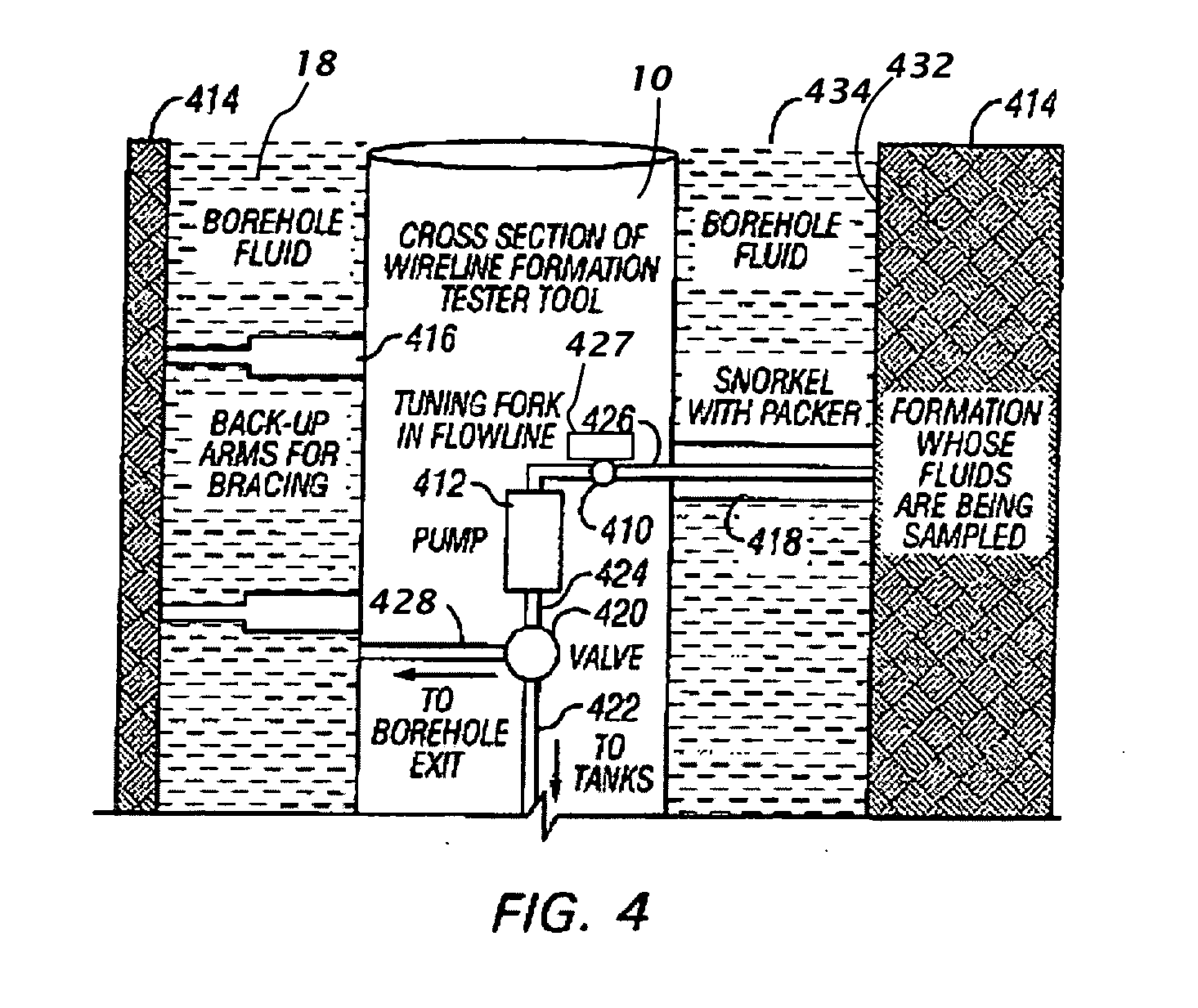
Method and apparatus for estimating a property of a fluid downhole
ActiveUS20070159625A1High resolutionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationGratingPhotovoltaic detectors
A method and apparatus are provided for determining a property of a fluid downhole by using a tunable optical grating to collect a fluid's spectrum over a wavelength region of interest. A property of the fluid is estimated from spectra that are obtained from light that has interacted with the fluid and then been reflected off of the tunable optical grating onto a photodetector.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com