Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
398 results about "Modulation function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
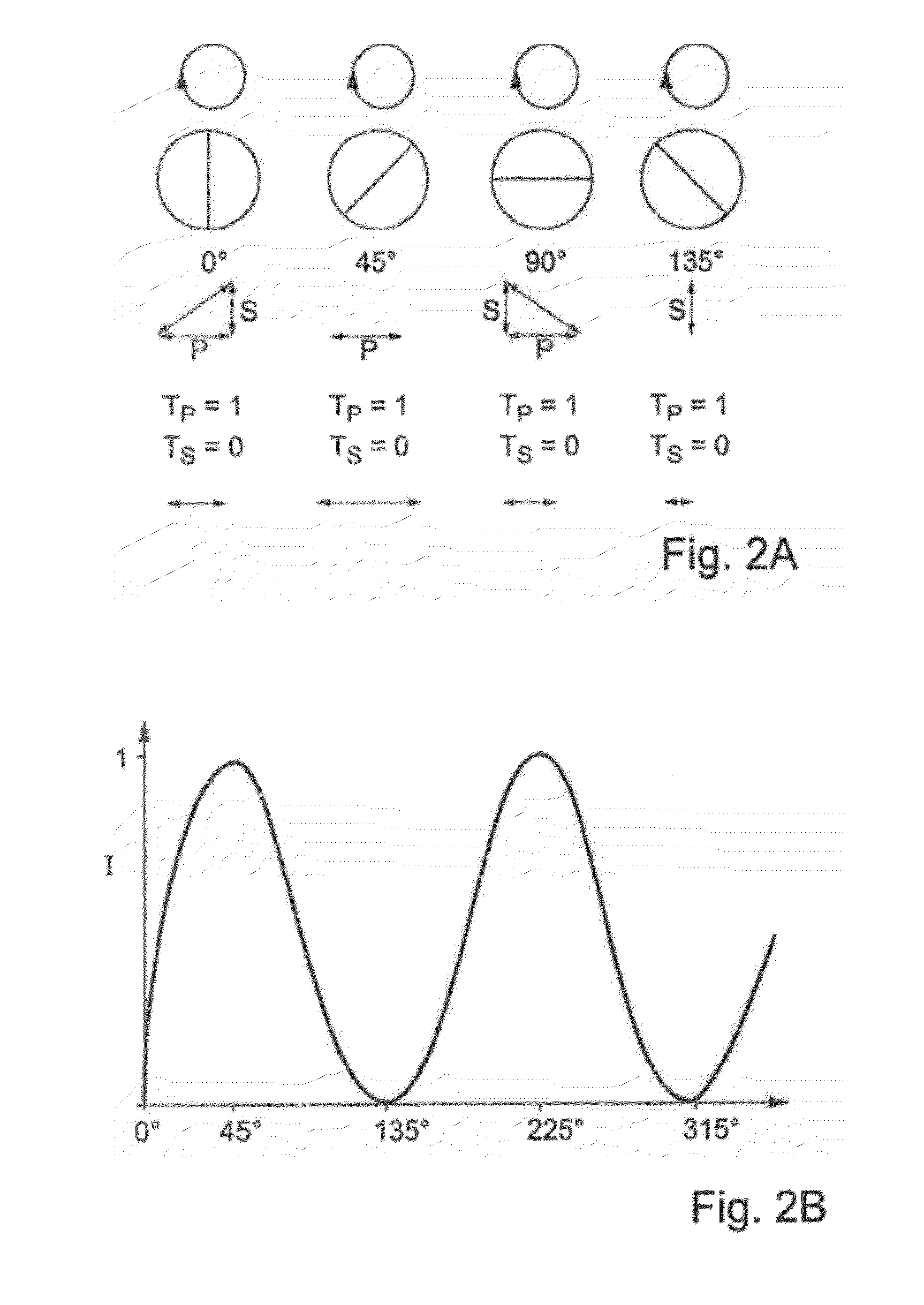
The modulation transfer function (MTF) is the spatial frequency response of an imaging system or a component. It is the contrast at a given spatial frequency relative to low frequencies.
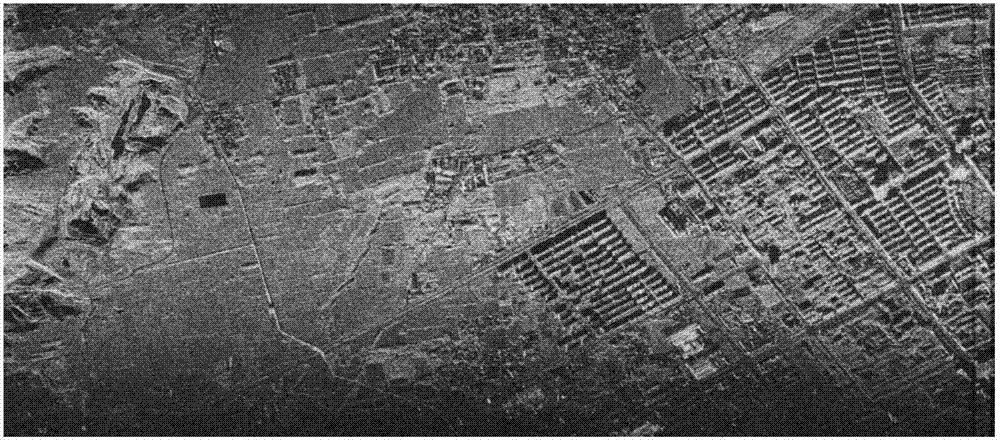
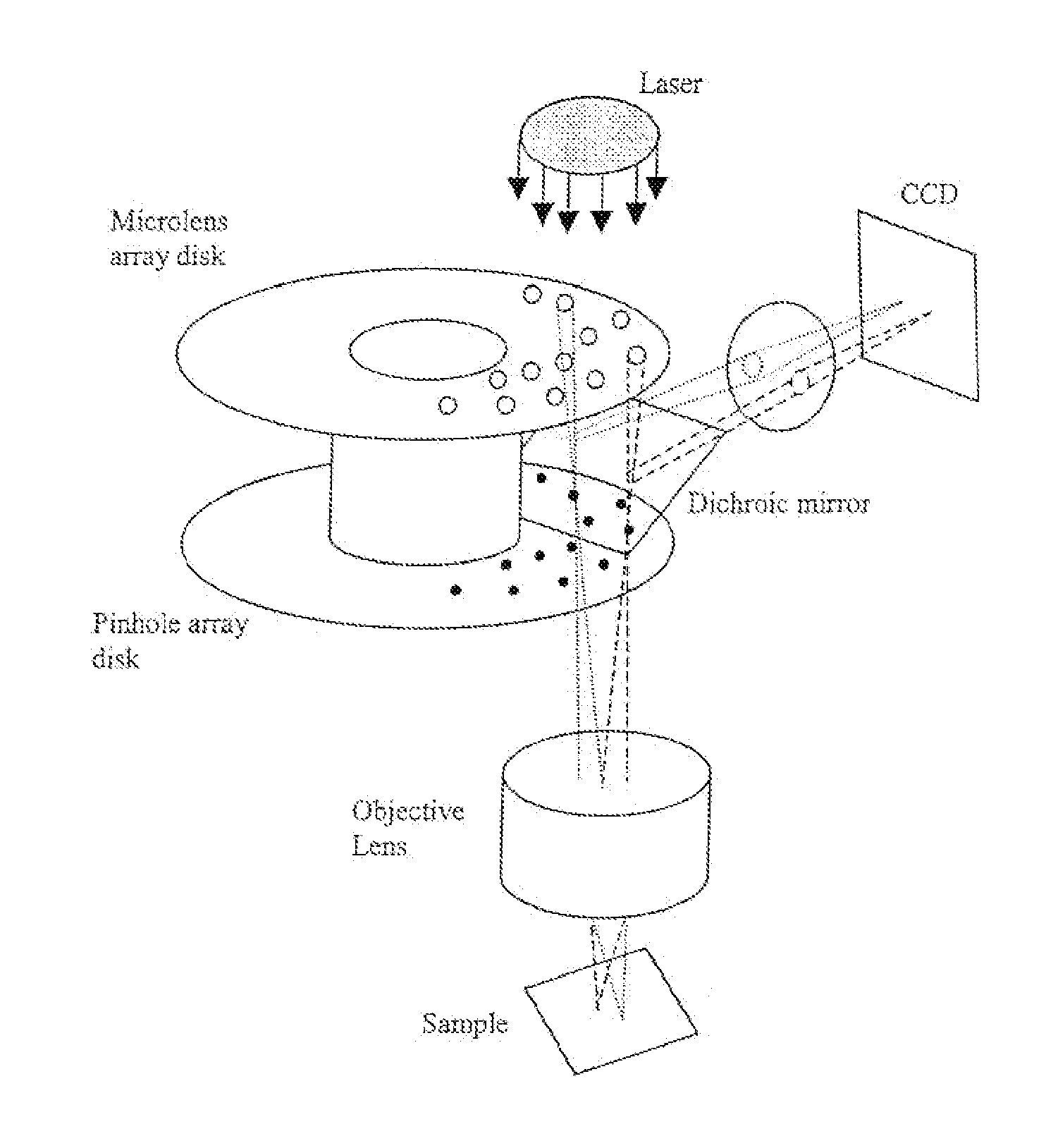
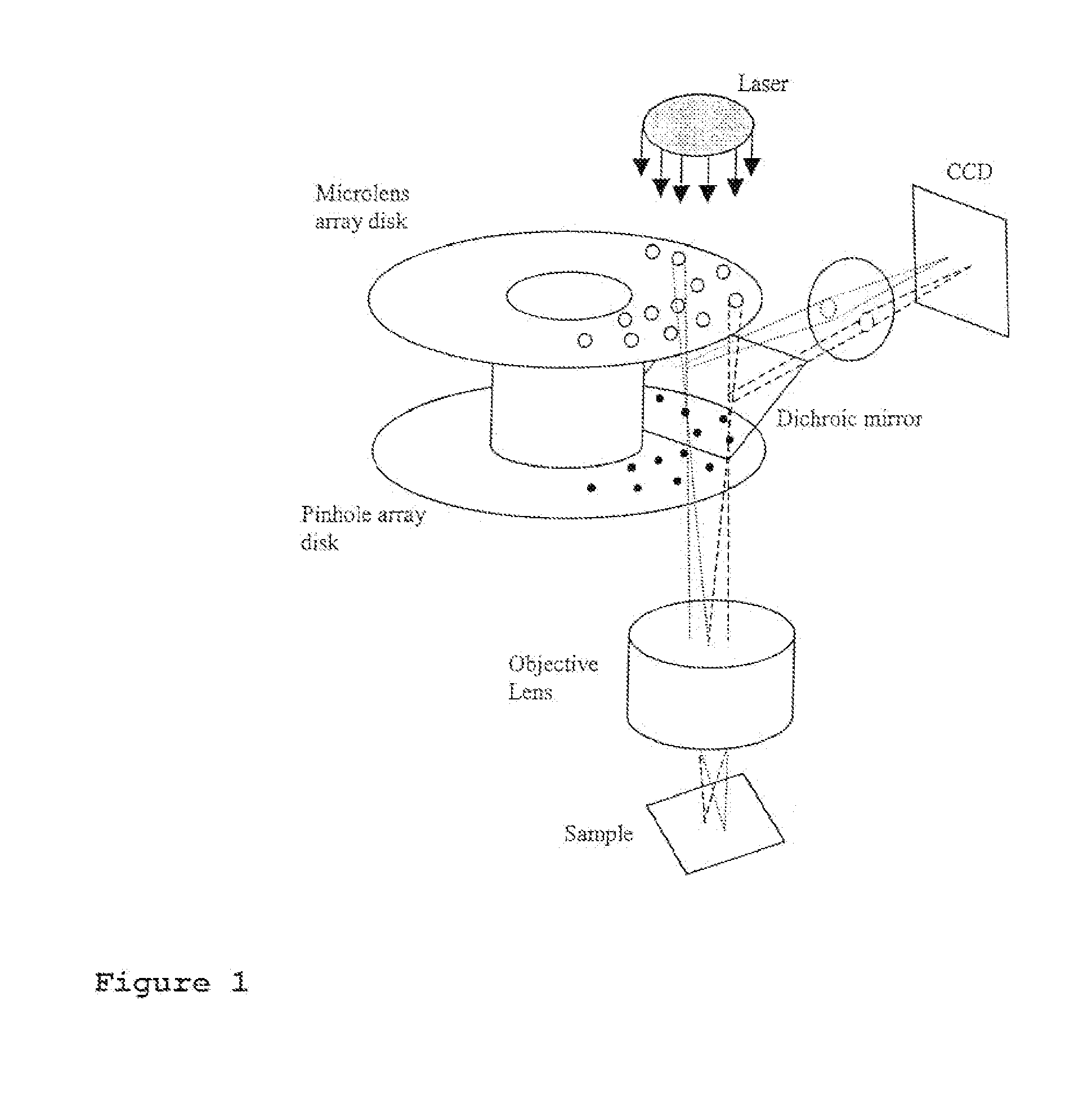
Computational imaging system
InactiveUS8212914B2Television system detailsSolid-state devicesModulation functionIntermediate image
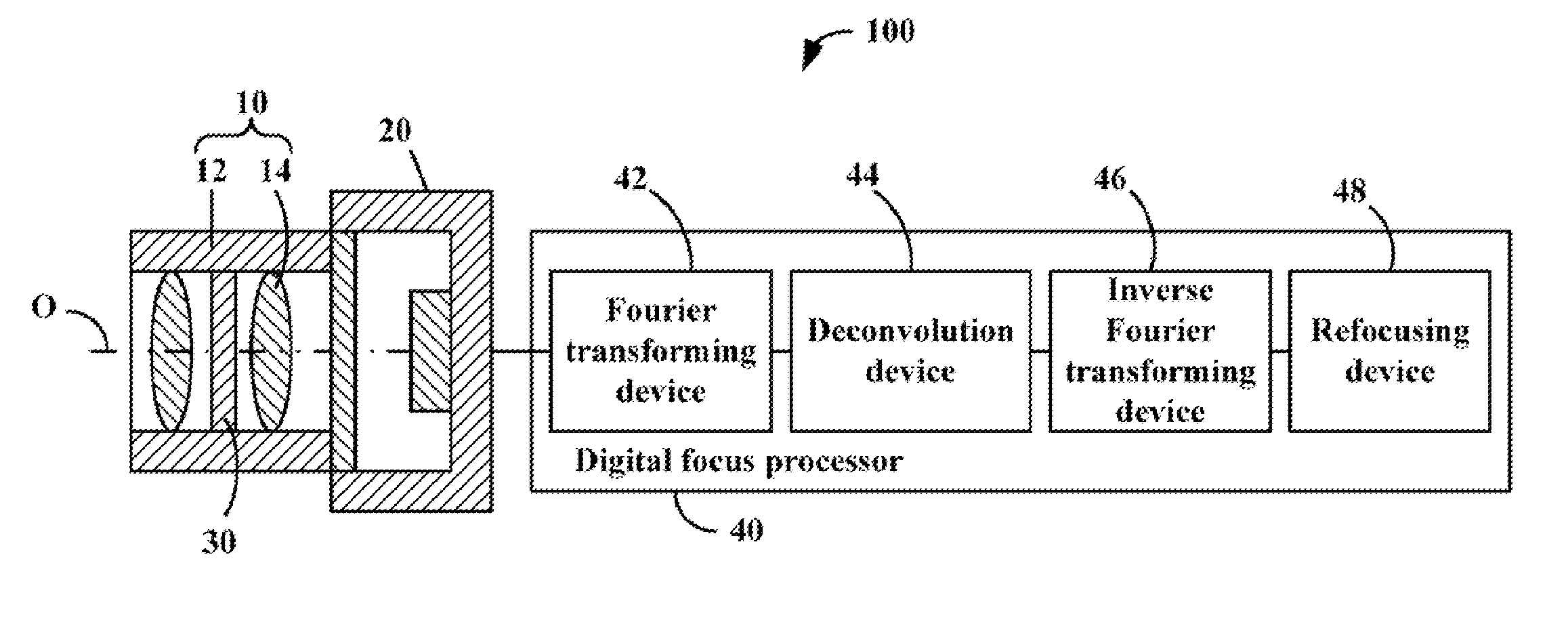
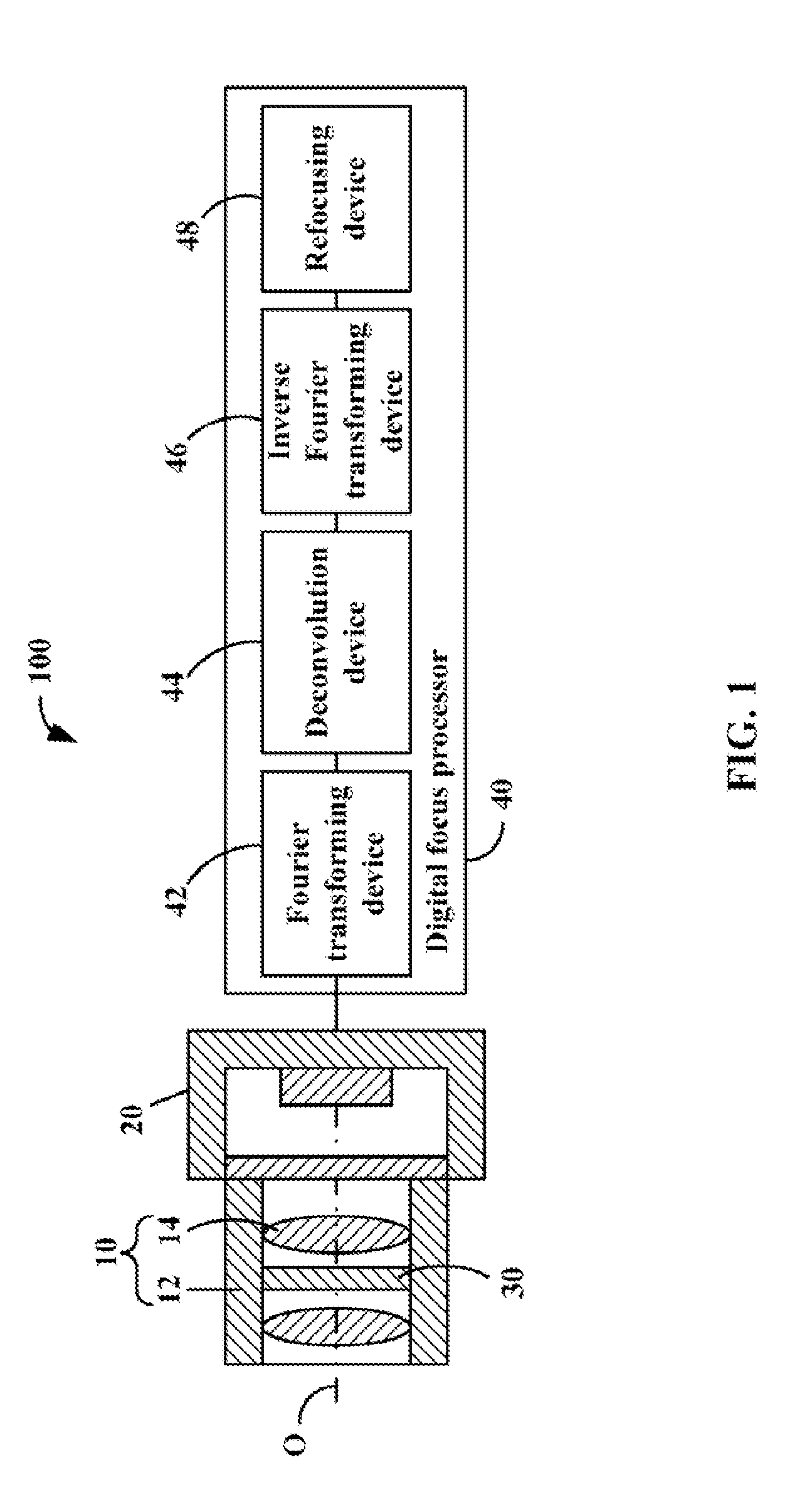
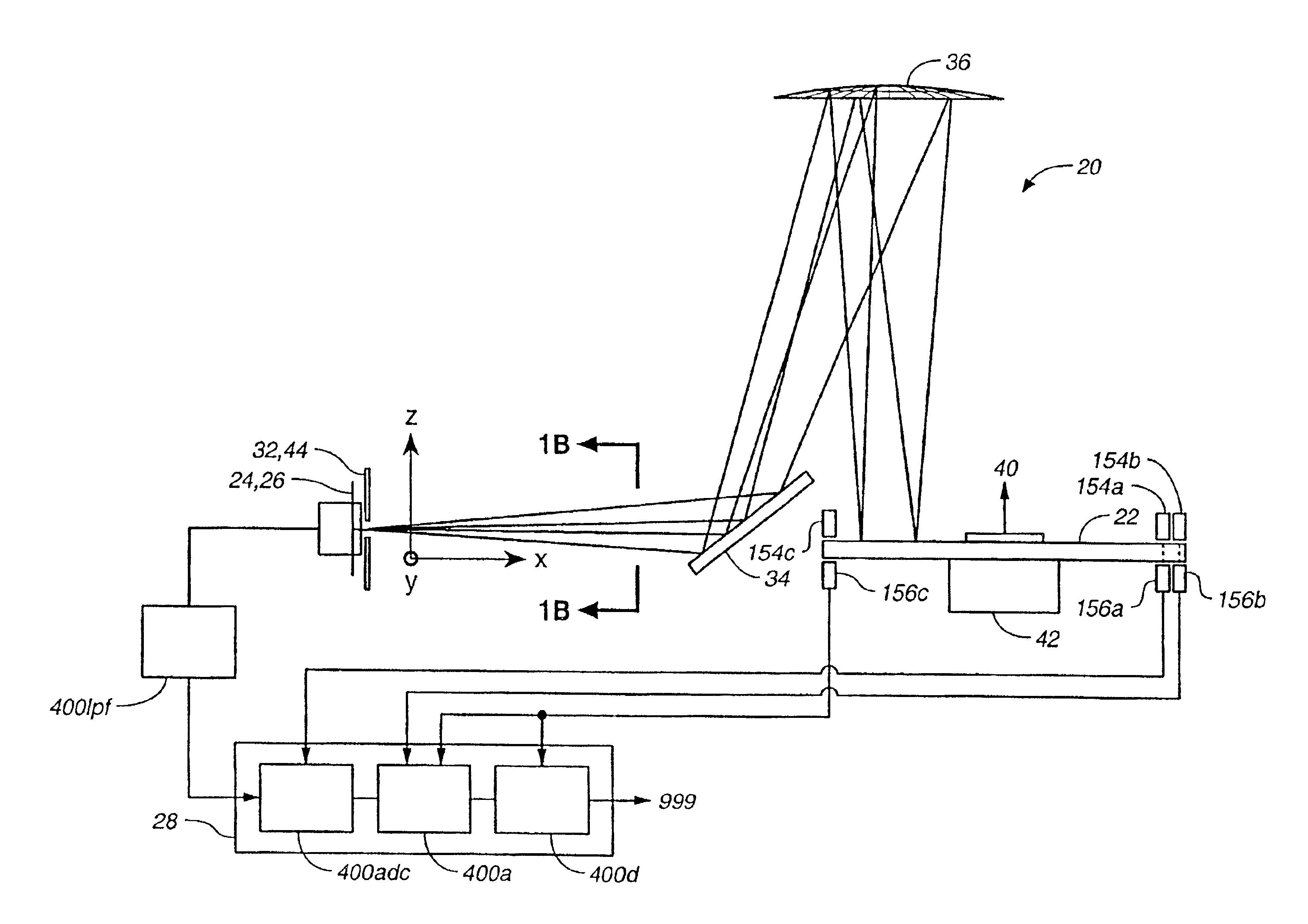
An imaging sub-system, a liquid crystal (LC) element, and a digital focus processor are provided. The LC element is placed in the light path of the imaging sub-system, functioning as the aperture of the imaging sub-system, and includes a periodically patterned electrode which is patterned according to a periodical modulation function and configured to blur an intermediate image captured by the imaging sub-system by applying a controllable voltage thereto. The digital focus processor is configured to deconvolute the periodical modulation function to remove the blur away from the intermediate image and determine an all-in-focus real image.
Owner:GOLD CHARM LTD
Method and apparatus for spectrum analysis and encoder
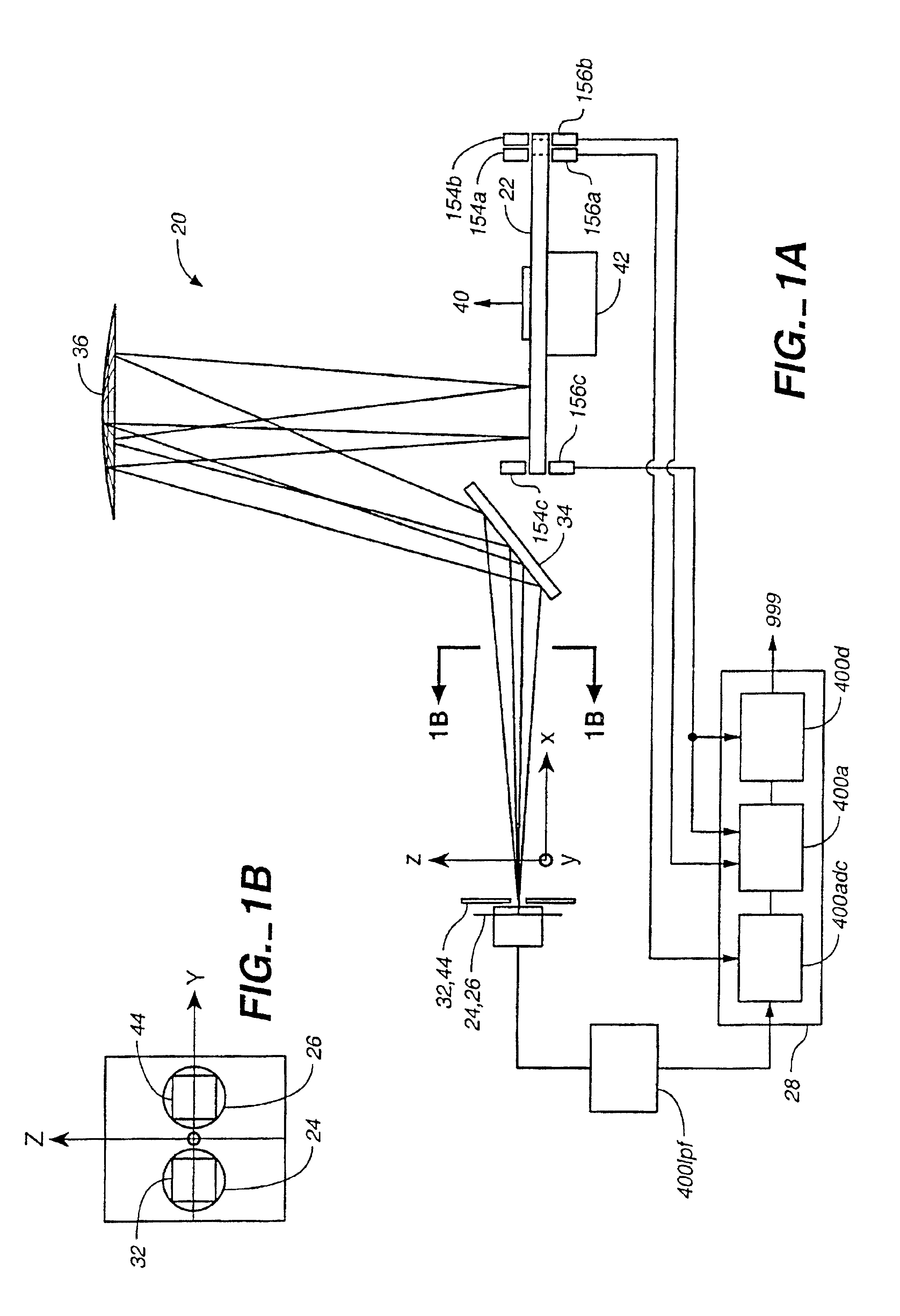
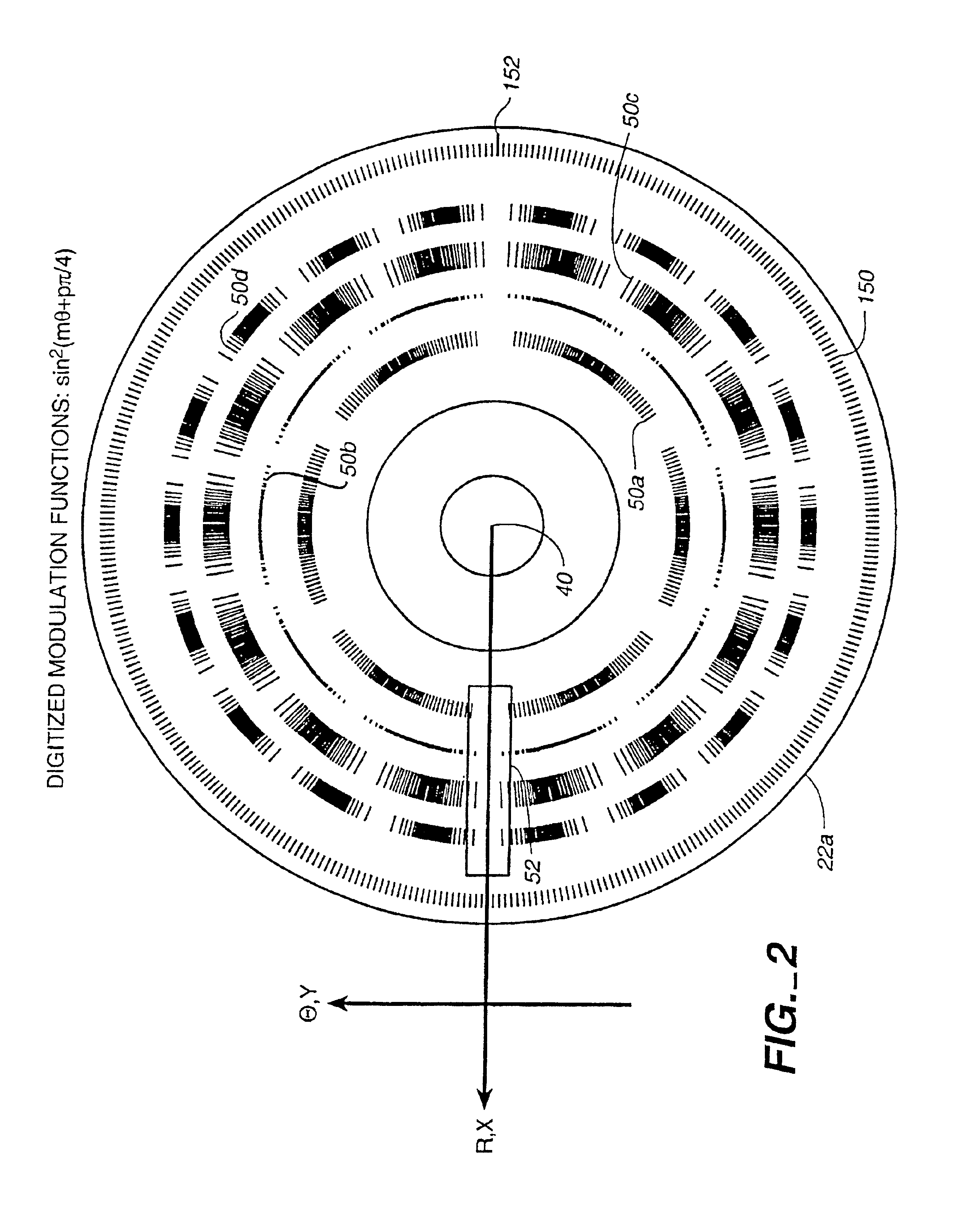
InactiveUS6897952B1Increase motor speedReduce motor speedRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsModulation functionFrequency spectrum
A disc serving as a spatial radiation modulator has dispersed radiation filters thereon. Each filter has a transmittance or reflectance modulation function of the form sin2(mθ+pπ / 4), where m is a positive integer and p has one of the four values 0, 1, 2, 3. A radiation beam including selected wavelength components is diffracted into an elongated image dispersed according to wavelength. Different wavelength components are focused onto different filters on the modulator and are encoded by corresponding filters. Since the modulation functions of the filters are orthogonal to one another, it is possible to extract the amplitude of each wavelength component after it has been encoded or modulated by corresponding filter from the total detected signal during one measurement.
Owner:MUDLOGGING SYST
Surgical implement detector utilizing a radio-frequency identification marker
InactiveUS7307530B2Control moreSevere possibilitySurgeryElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingModulation functionEngineering
A radio-frequency surgical implement detection system detects surgical implements in a surgical wound during and at the completion of a surgical procedure. Surgical implements, including surgical sponges or laparotomy pads, gauze pads and metallic surgical instruments, are individually attached to a non battery-powered, encapsulated radio-frequency marker. The marker comprises an integrated chip having a burnt-in memory code, which is broadcast through an antenna using a modulated carrier frequency. The code is received by an interrogating antenna of a detector. The interrogating antenna provides a power pulse, which is received by the antenna of the radio-frequency marker. The power pulse charges a capacitor, which proves power for the read function, carrier frequency modulation function and broadcast function of the integrated chip, permitting each marker-containing implement to be specifically identified.
Owner:FABIAN CARL E
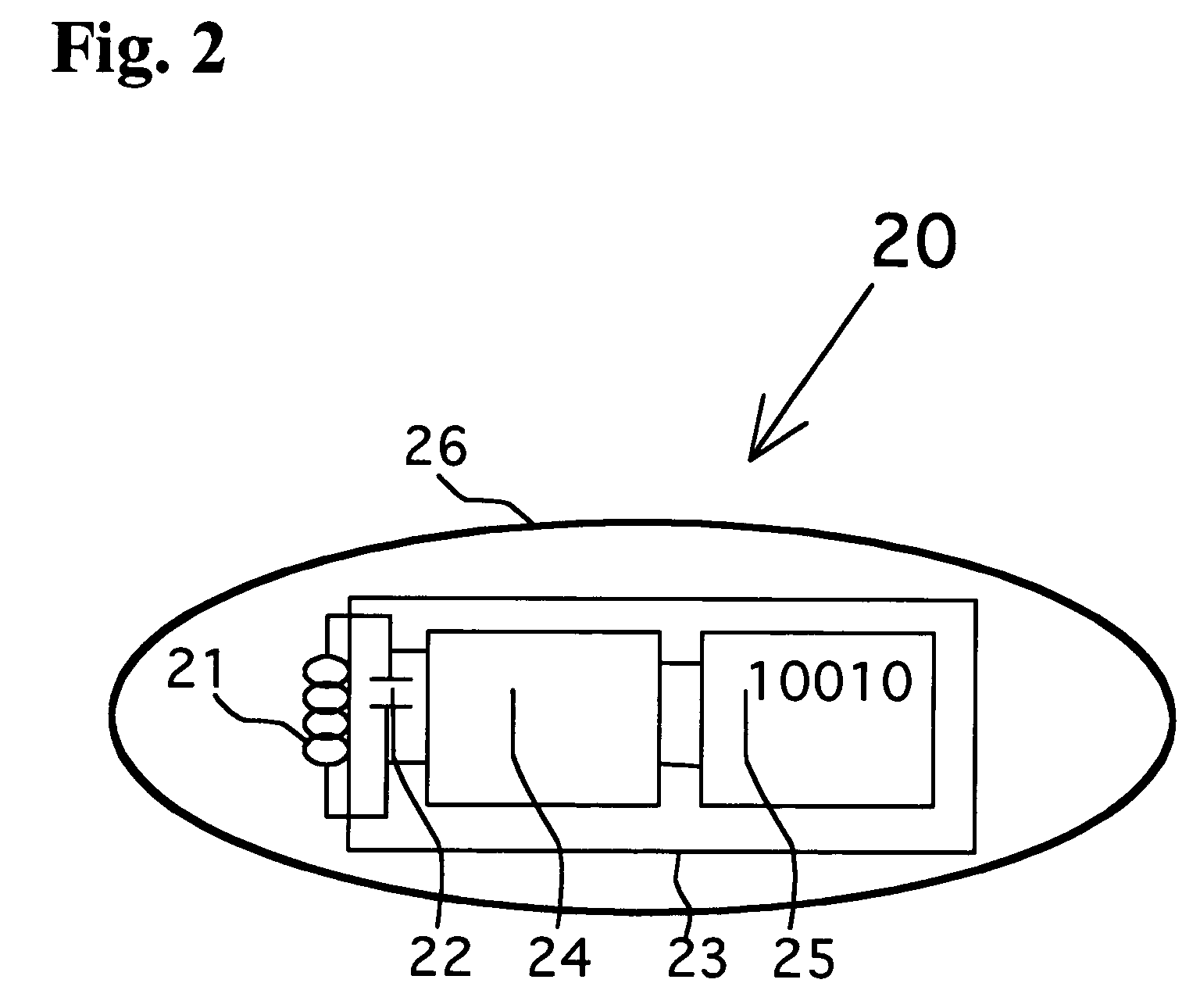
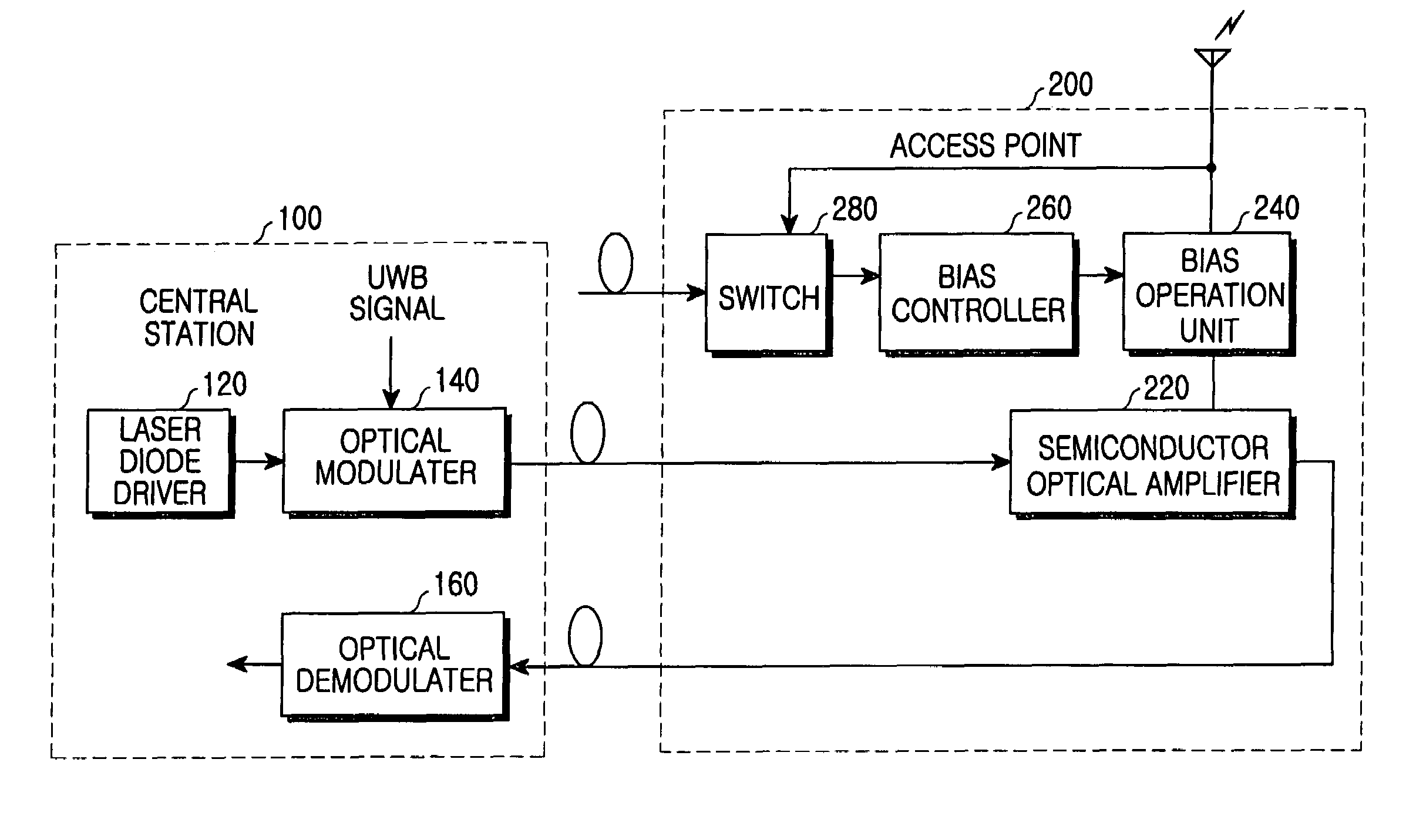
Access point for constructing optical fiber-based high-speed wireless network system
InactiveUS7349633B2Small sizeReduce manufacturing costTime-division optical multiplex systemsNetwork topologiesModulation functionNetworked system
An access point in an optical fiber-based high-speed optical wireless network is disclosed. The access point includes an antenna for receiving communication requirement signals, a switch for selectively outputting a corresponding signal according to the communication requirement signals, a bias control unit for selectively outputting bias current with variable intensity according to whether an output of the signal from the switch exists or not, on the basis of a threshold current; a bias operation unit for outputting input signals to the antenna when an input bias current is smaller than the threshold current and for outputting signals received by the antenna when an input bias current is larger than the predetermined threshold current, and a semiconductor optical amplifier for selectively performing an optical detection function of converting optical signals, which have been received through a first optical fiber from an central station, into electrical signals and sending the converted electrical signals to the bias operation unit, when a current smaller than the threshold current is input to the bias operation unit, and an optical modulation function of transmitting signals output from the bias operation unit through a second optical fiber to the central station, when a current larger than the threshold current is input to the bias operation unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
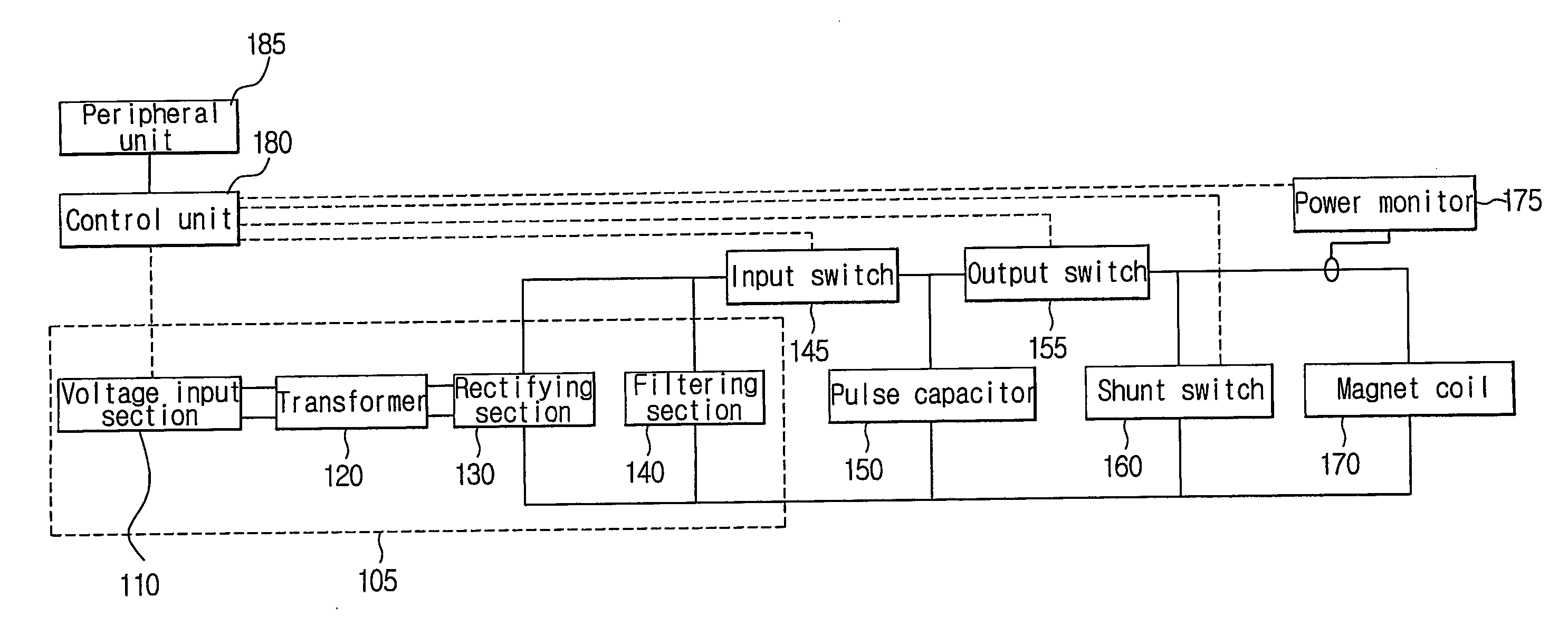
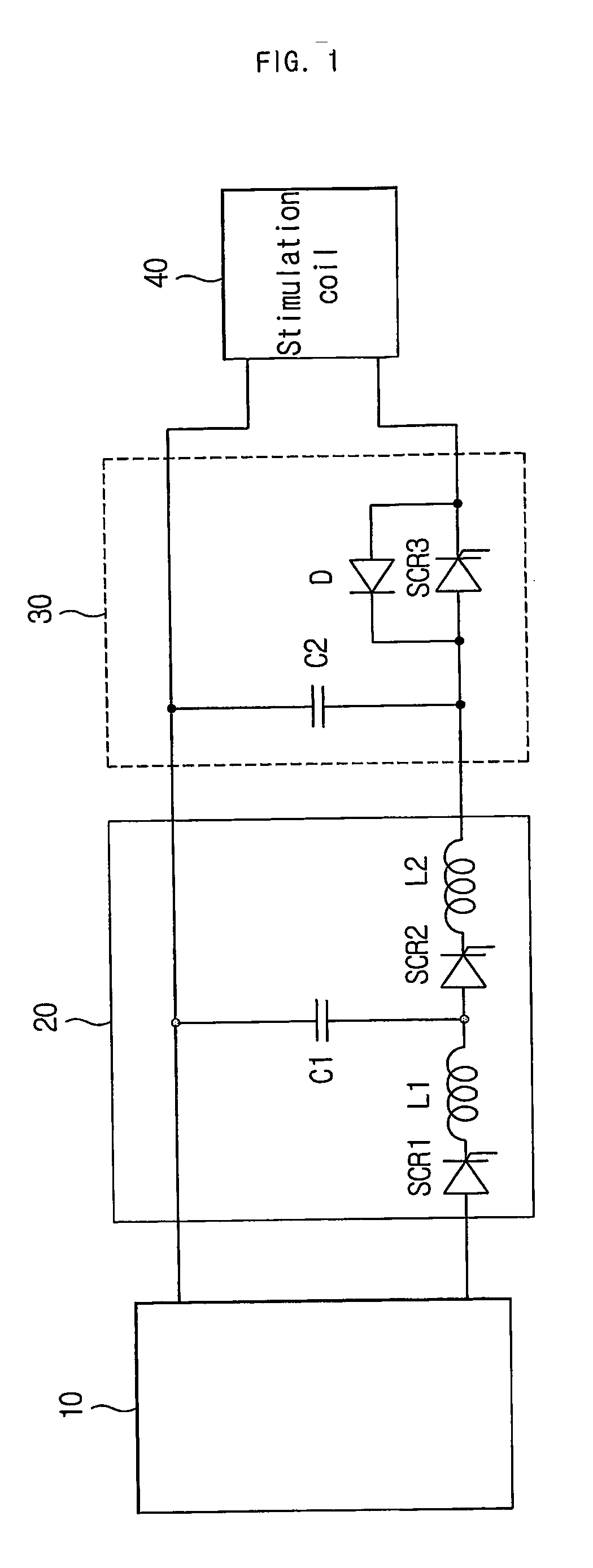
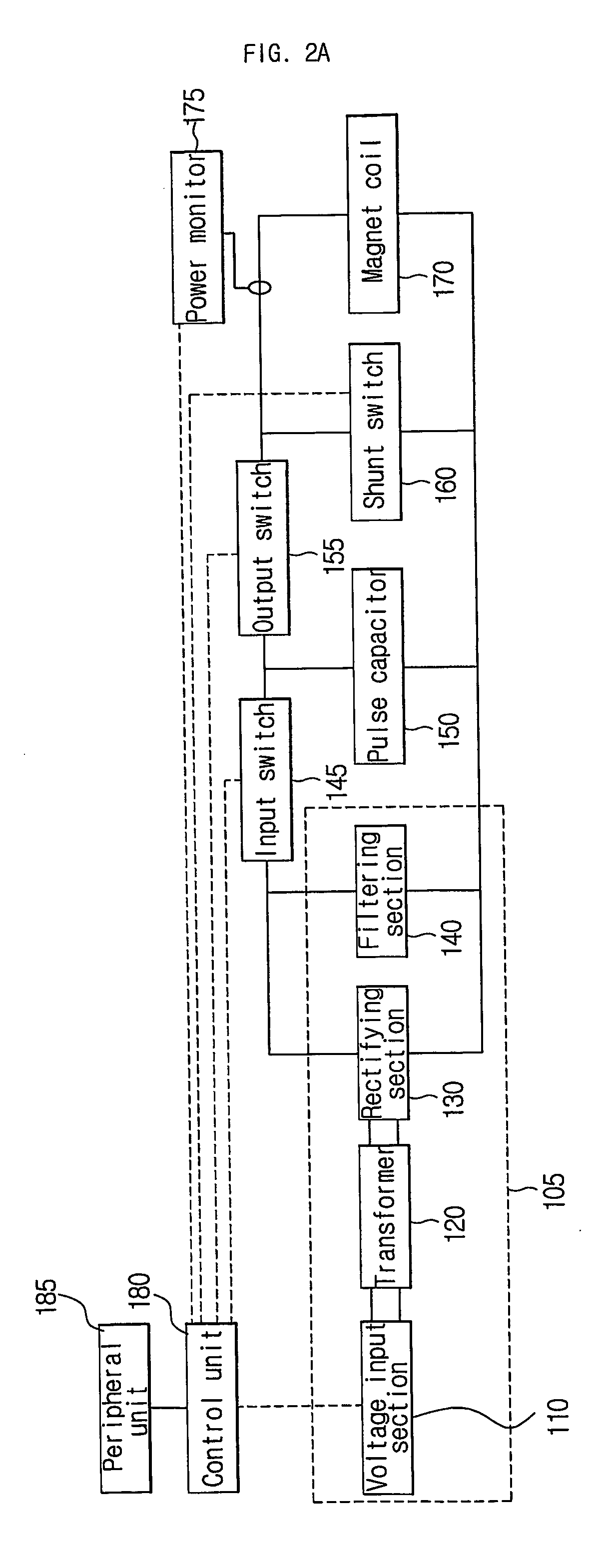
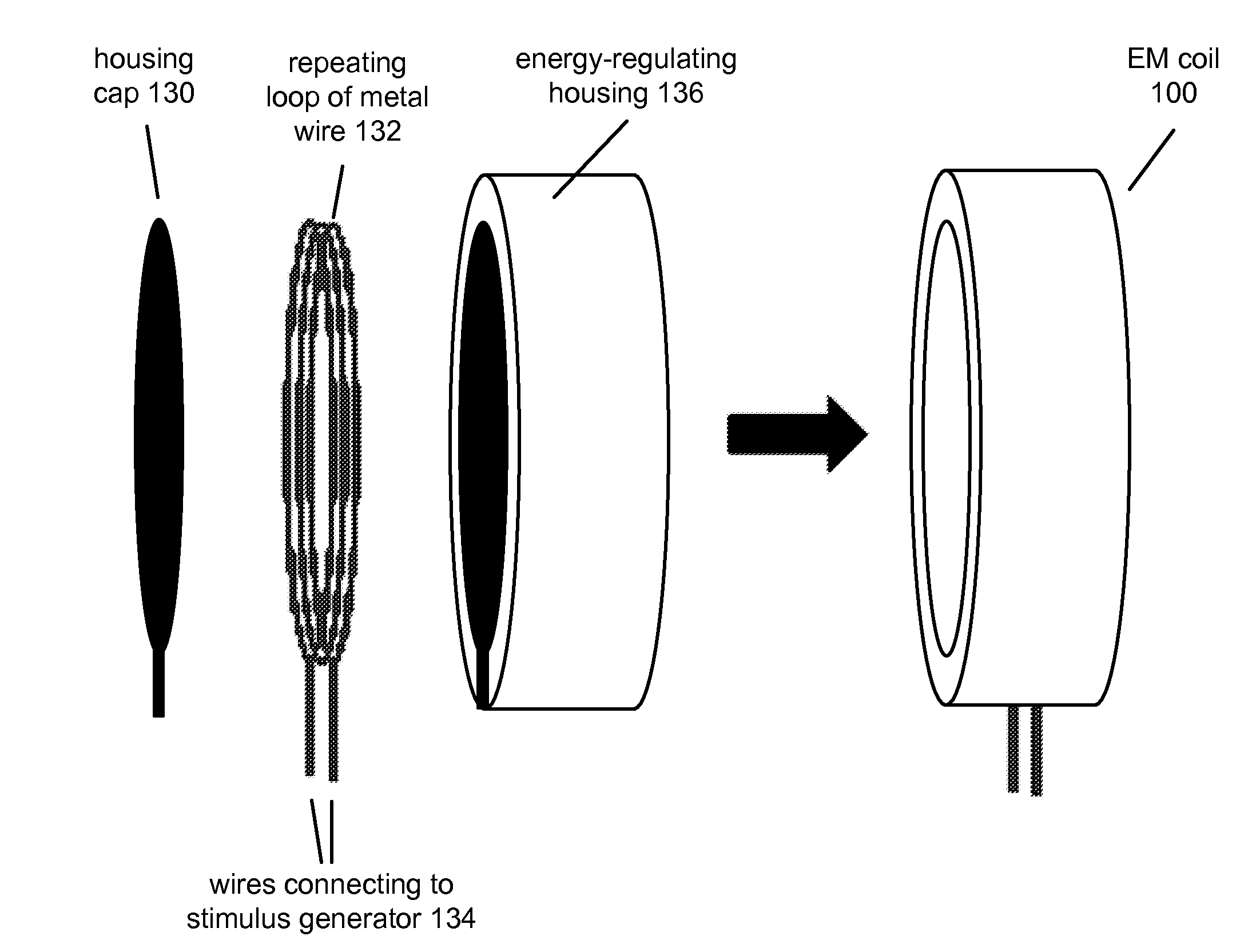
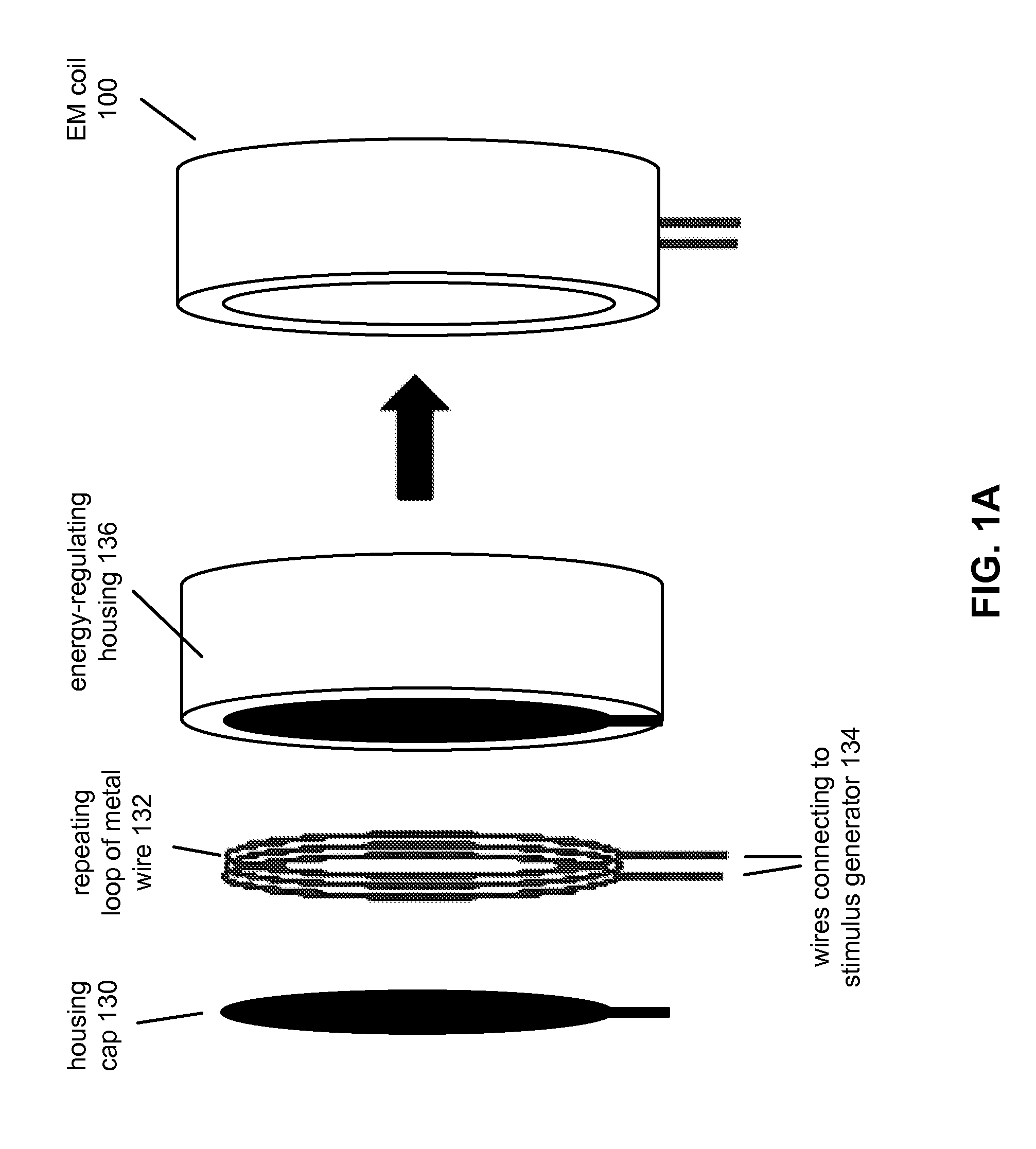
Apparatus and method for creating pulse magnetic stimulation having modulation function
InactiveUS20060187607A1Efficiently transferring energyEnergy efficiencyElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsModulation functionVoltage source
An apparatus for creating pulse magnetic stimulation, having a modulation function, according to the present invention, comprises: a driving voltage supplying section for converting AC voltage input from a voltage source into DC voltage having a predetermined magnitude; a capacitor section for accumulating electric charge in accordance with the DC voltage; an input switch section for controlling the accumulation of electric charge in the capacitor section; a coil for generating magnetic flux in accordance with current generated by both-end voltage corresponding to the electric charge accumulated in the capacitor section; an output switch section for controlling discharge of the electric charge accumulated in the capacitor section through the coil; and a shunt switch section for lowering magnetic energy stored in the coil and voltage stored in the capacitor section into a ground level to obtain a pulse magnetic field. In this pulse-magnetic-stimulation creating apparatus having a modulation function according to the present invention, it is possible to efficiently transfer energy on the basis of current compliance of a patient and impedance of biologic tissue for therapeutic applications.
Owner:MO SEUNG KEE
Absolute optical encoder with long range intensity modulation on scale
ActiveUS8309906B2Improved absolute encoderRaise the ratioElectric signal transmission systemsMaterial analysis by optical meansModulation functionOptical density
An encoder configuration comprises a dual-modulation scale track pattern that provides a first intensity modulation component for producing periodic signals, and a second intensity modulation component for producing a long-range absolute signal. The dual-modulation scale track pattern increases the range-to-resolution ratio of the encoder without the use of additional scale tracks that would increase the width of the encoder components. The long-range signal may be encoded in the dual-modulation scale track pattern either by varying certain dimensions of pattern elements included in the scale track or by superimposing a layer including an optical density variation along on the track on pattern elements of similar areas. In either case, the net offset and / or amplitude levels of the associated signals are modified along the scale track. These modified offset and / or amplitude levels provide the basis for the long-range absolute signal.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
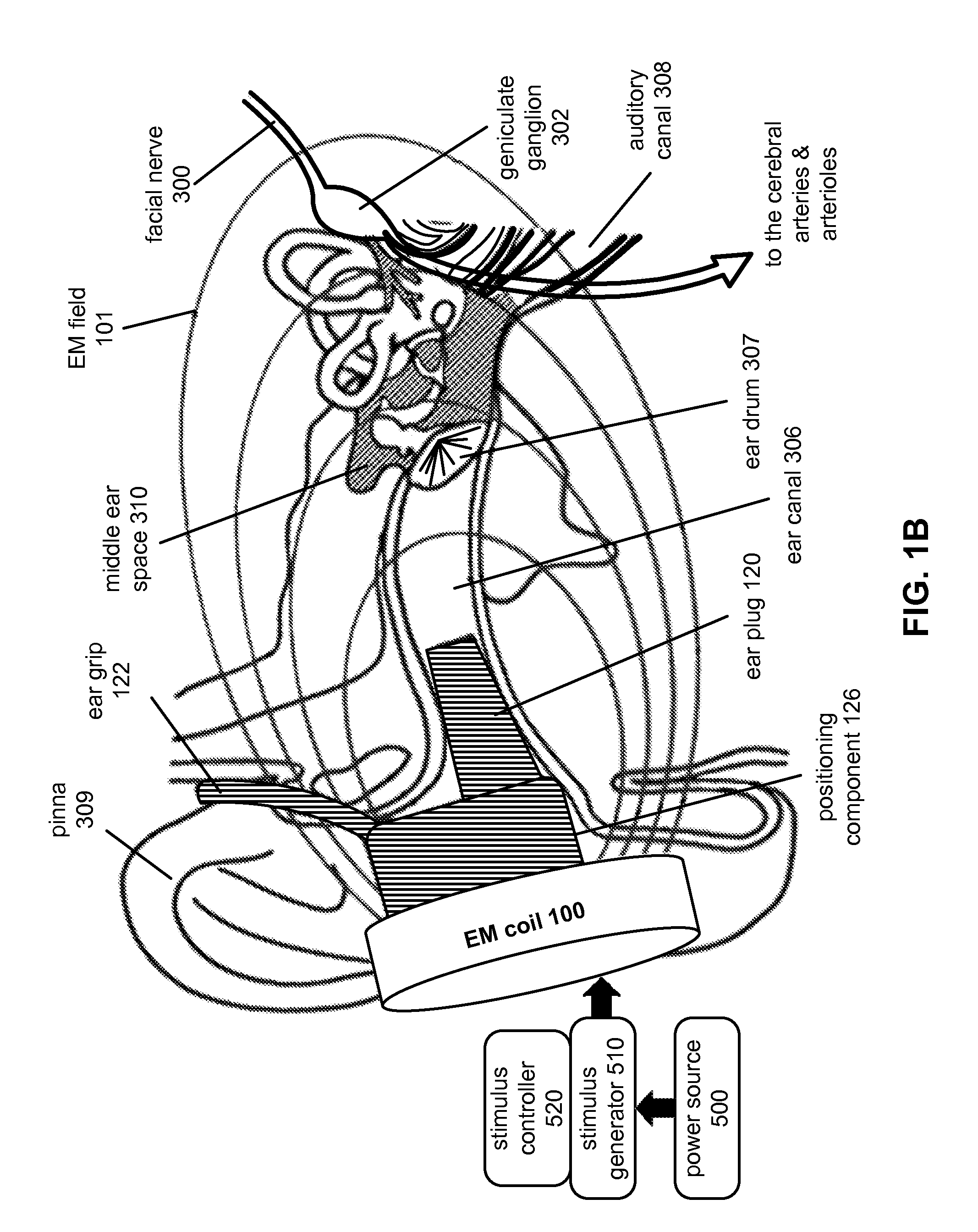
Modulating Function of Neural Structures Near the Ear
ActiveUS20130150653A1Increase blood flowIncrease cerebral blood flowUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyNervous systemModulation function
Stimulation of the facial nerve system (e.g., electrically, electromagnetically, etc.) in ischemic stroke patients will cause dilation of occluded arteries and dilation of surrounding arteries, allowing for blood flow to circumvent the obstruction and reach previously-deprived tissue. The device approaches the facial nerve and its branches in the vicinity of the ear. In use, the device can be inserted into the ear canal and / or placed in proximity to the ear in order to stimulate the facial nerve system non-invasively (e.g., using an electromagnetic field). The device can be used in the emergency treatment of acute stroke or chronically variations for long-term maintenance of blood flow to the brain and stroke prevention. Additional embodiments of the device may be adapted for use on different regions of the body.
Owner:NERVIVE
Acoustic wave device with modulation functionality
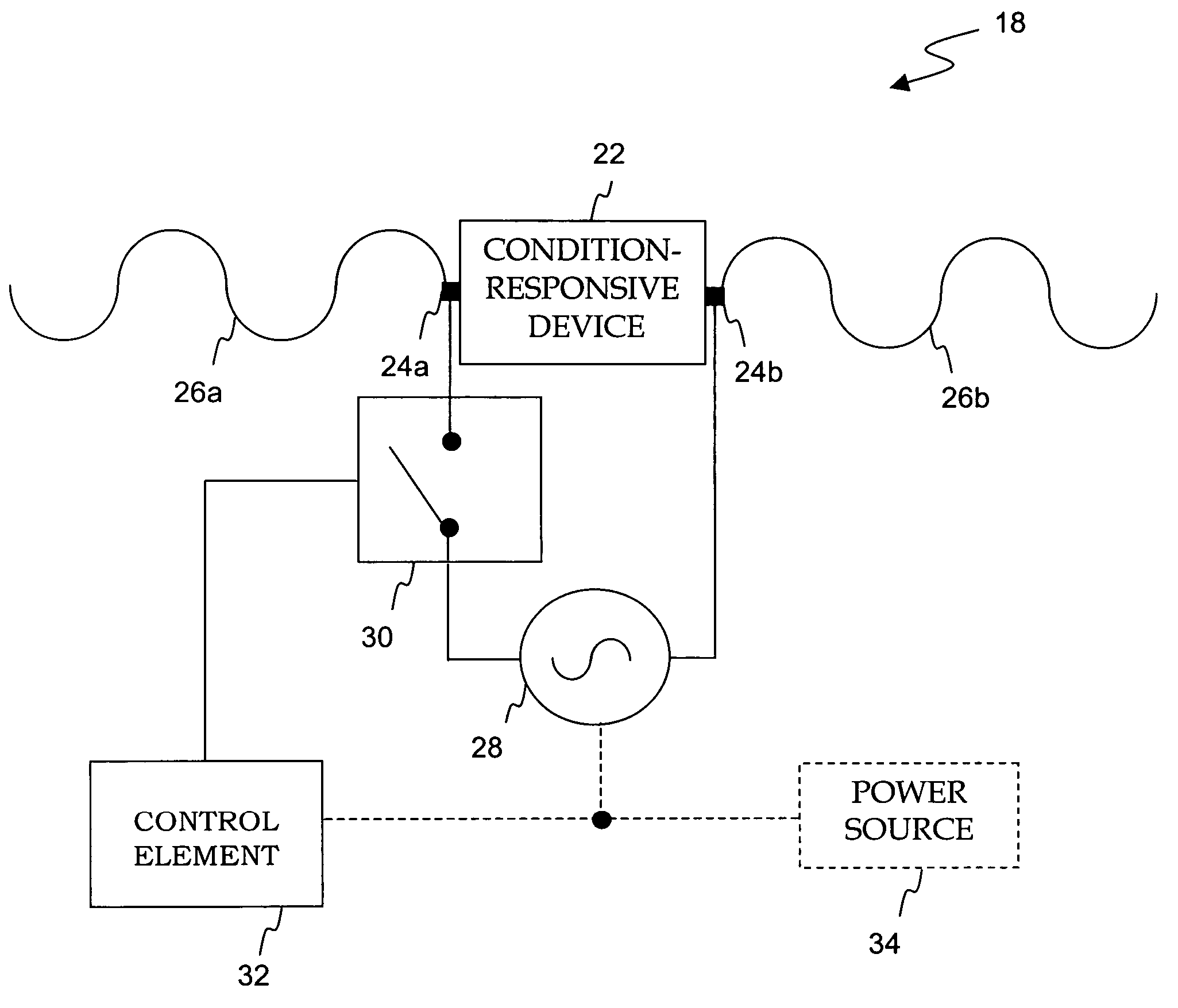
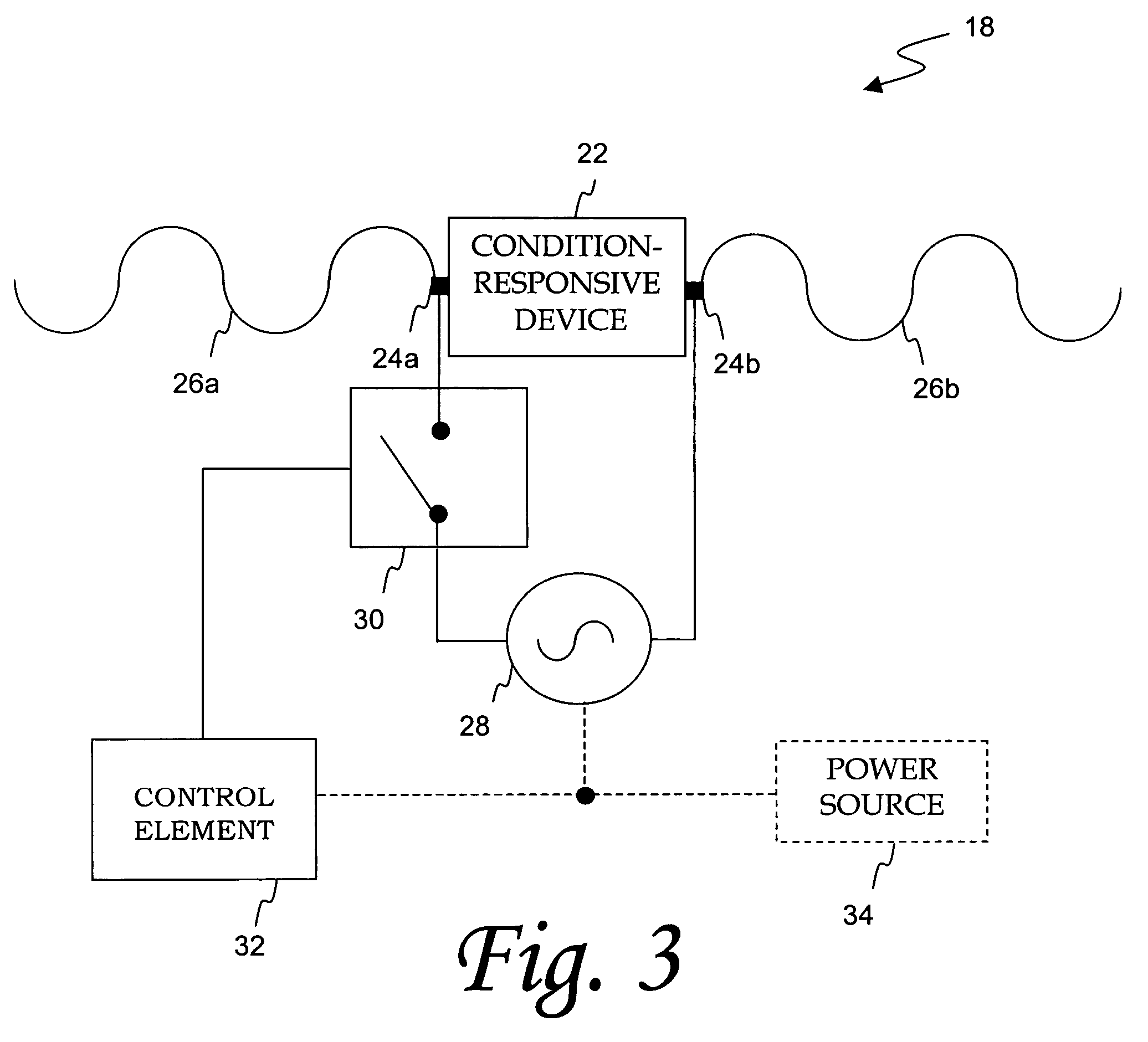
InactiveUS7116213B2Reduced Power RequirementsEliminate needTyre measurementsAlarmsDigital dataMicrocontroller
An electronics assembly for integration with a tire structure or in another environment includes a condition-responsive device, an RF source, an antenna, and at least one controllable switching element. The condition-responsive device may comprise at least one acoustic wave resonator that is configured for monitoring such parameters as pressure and temperature within a tire or associated wheel assembly environment. The frequency and bandwidth of the RF source is preferably inclusive of the respective resonant frequency bands for each acoustic wave resonator. An antenna may also be connected to the condition-responsive device for facilitating the transmission of electric signals generated therein. In some embodiments, a switching element is coupled between the condition-responsive device and the RF source. Selective control of such switching element results in the modulation of data on the RF carrier, causing the condition-responsive device to transmit both sensed condition information as well as some other predefined digital data signal. Another controllable switching element may be provided in parallel with the condition-responsive device to selectively cloak the device for predetermined amounts of time, thus offering an anti-collision solution for multiple transmitting condition-responsive devices. The switching elements and corresponding control elements may respectively correspond to such devices as a field-effect transistor with a programmable microcontroller input or as an RFID transponder.
Owner:MICHELIN RECH & TECH SA
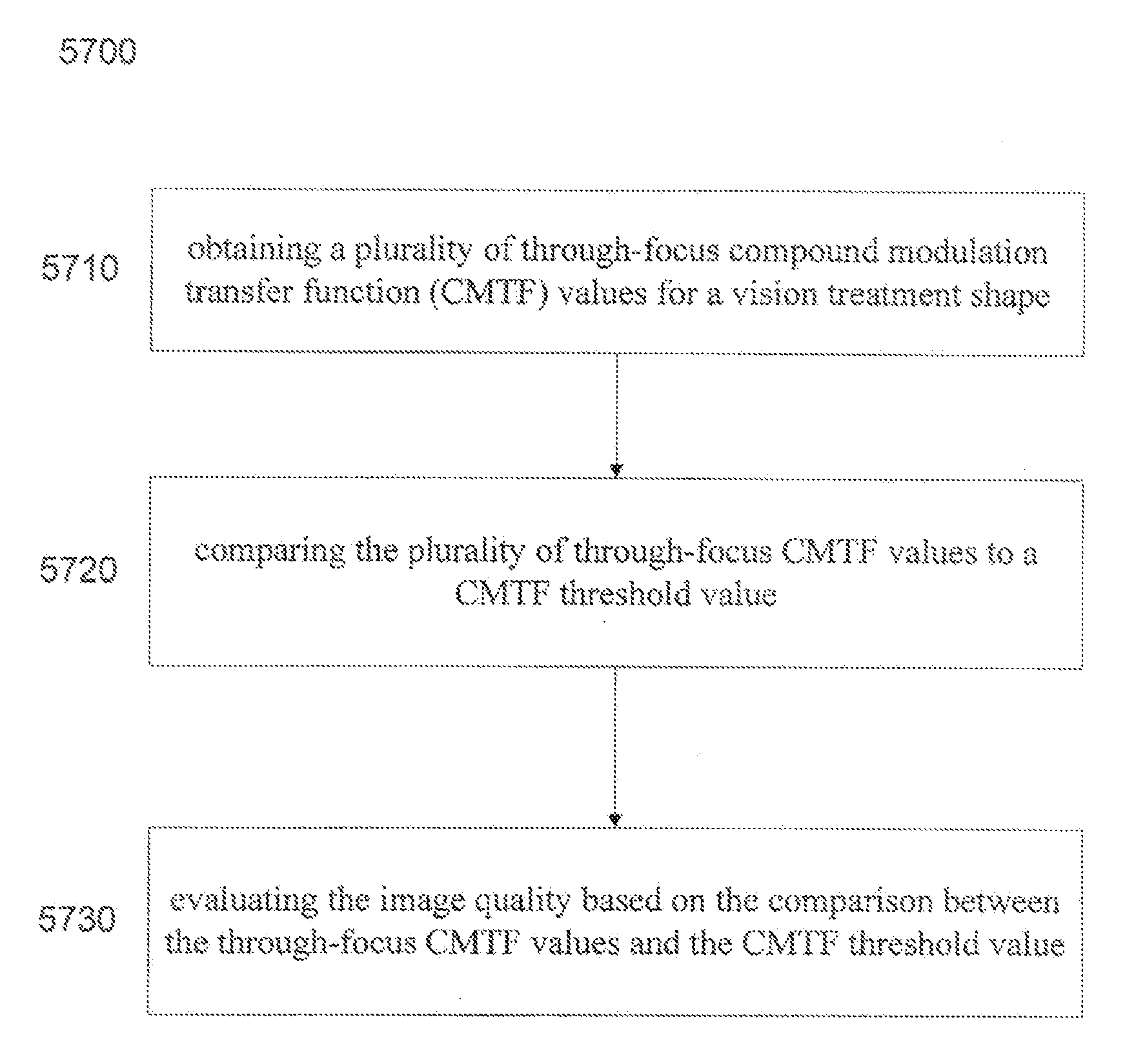
Compound modulation transfer function for laser surgery and other optical applications
InactiveUS20120033182A1Mitigates presbyopiaMitigates and treats vision conditionLaser surgeryEye diagnosticsModulation functionLaser surgery
Methods, devices, and systems establish an optical surface shape that mitigates or treats a vision condition in a patient. An optical surface shape for a particular patient can be determined using a set of patient parameters for the specific patient by using a compound modulation transfer function (CMTF). The compound modulation transfer function can include a combination of modulation transfer functions (MTF's) at a plurality of distinct frequencies.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
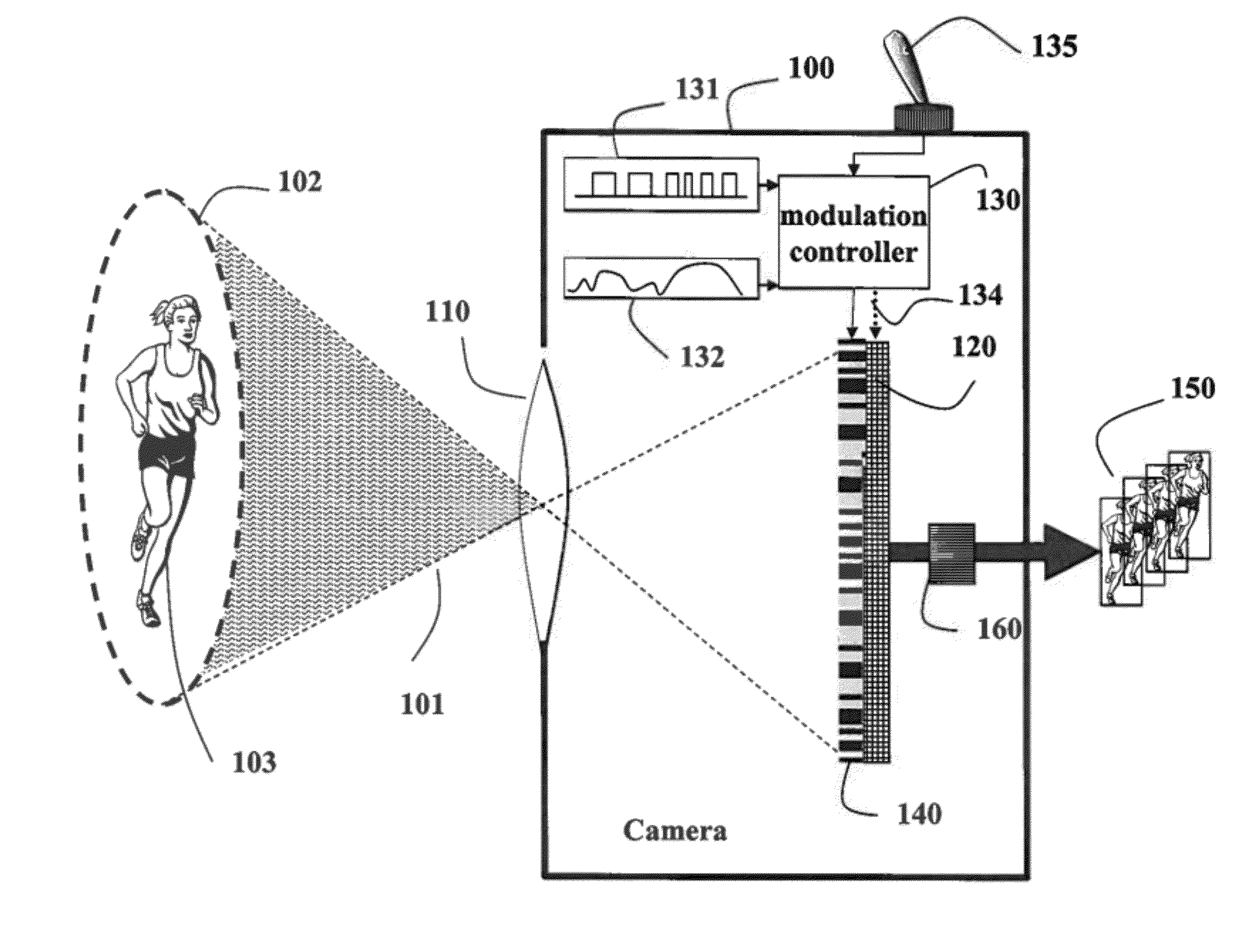
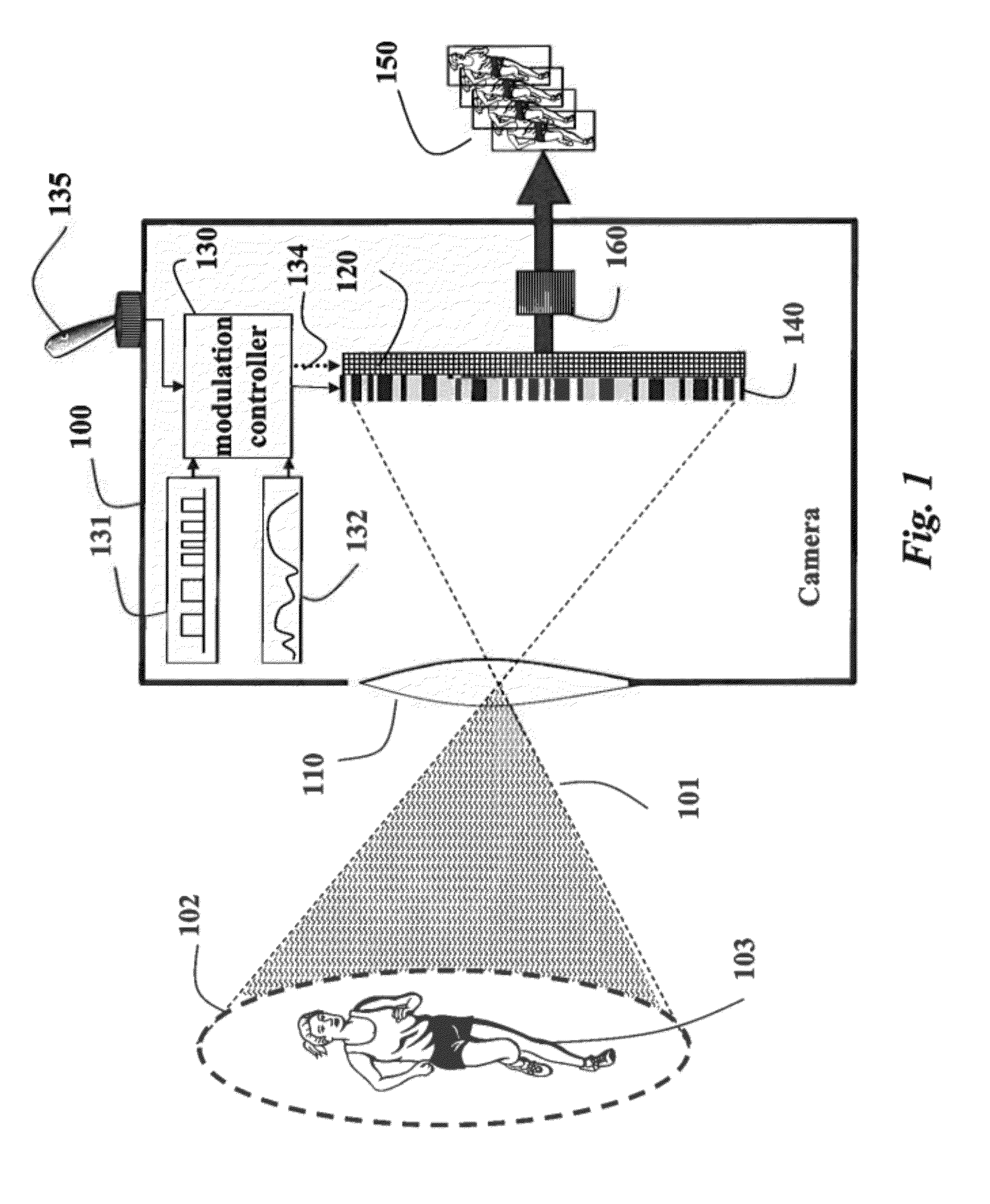
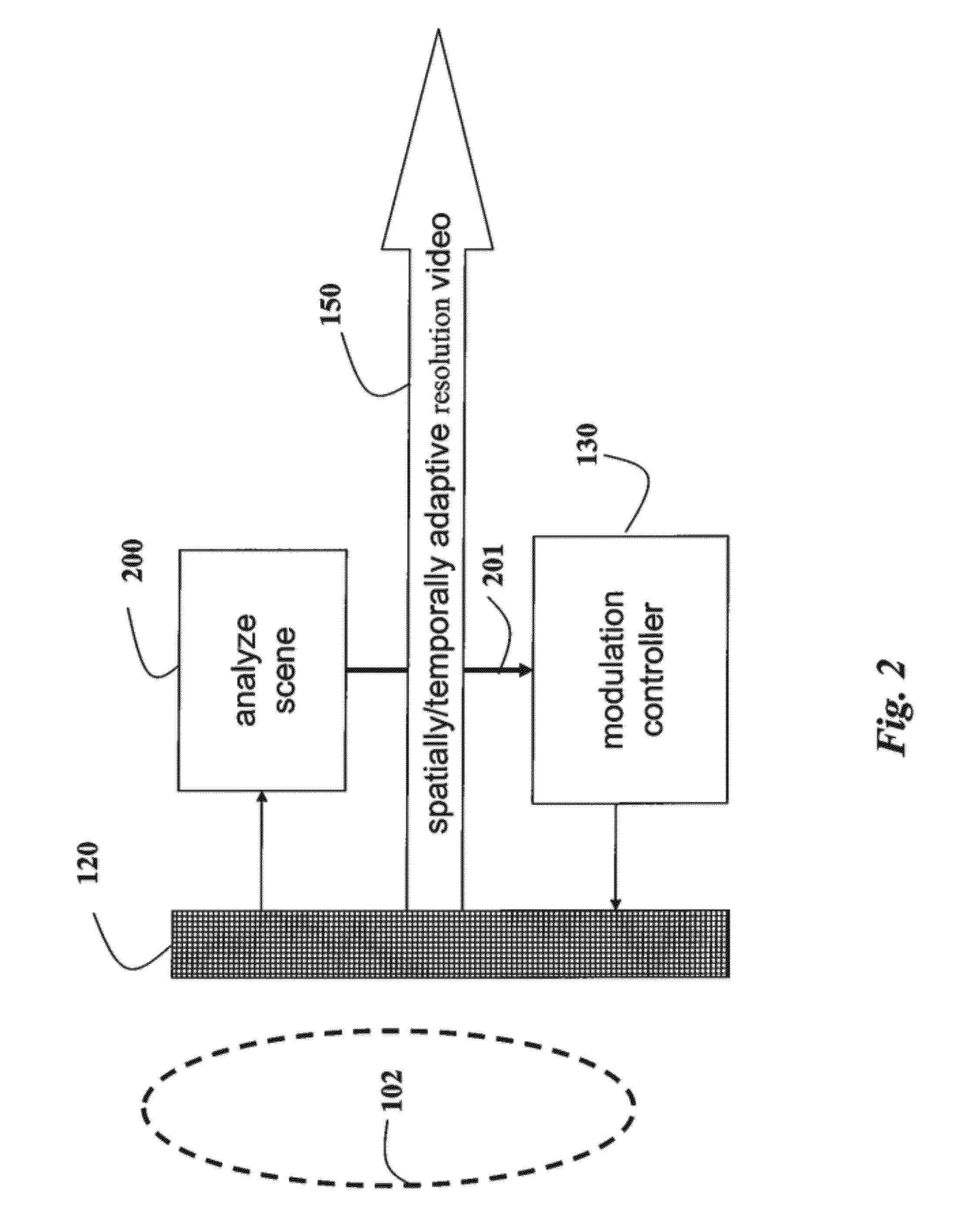
Programmable Camera and Video Reconstruction Method
InactiveUS20120162457A1Mask pixel resolutionTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionModulation functionImage resolution
A camera for acquiring a sequence of frames of a scene as a video includes a sensor with an array of sensor pixels. Individual sensor pixels are modulated by corresponding modulation functions while acquiring each frame of the video. The modulation can be performed by a transmissive or reflective masked arranged in an optical path between the scene and the senor. The frames can be reconstructed to have a frame rate and spatial resolution substantially higher than a natural frame rate and a spatial resolution of the camera.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
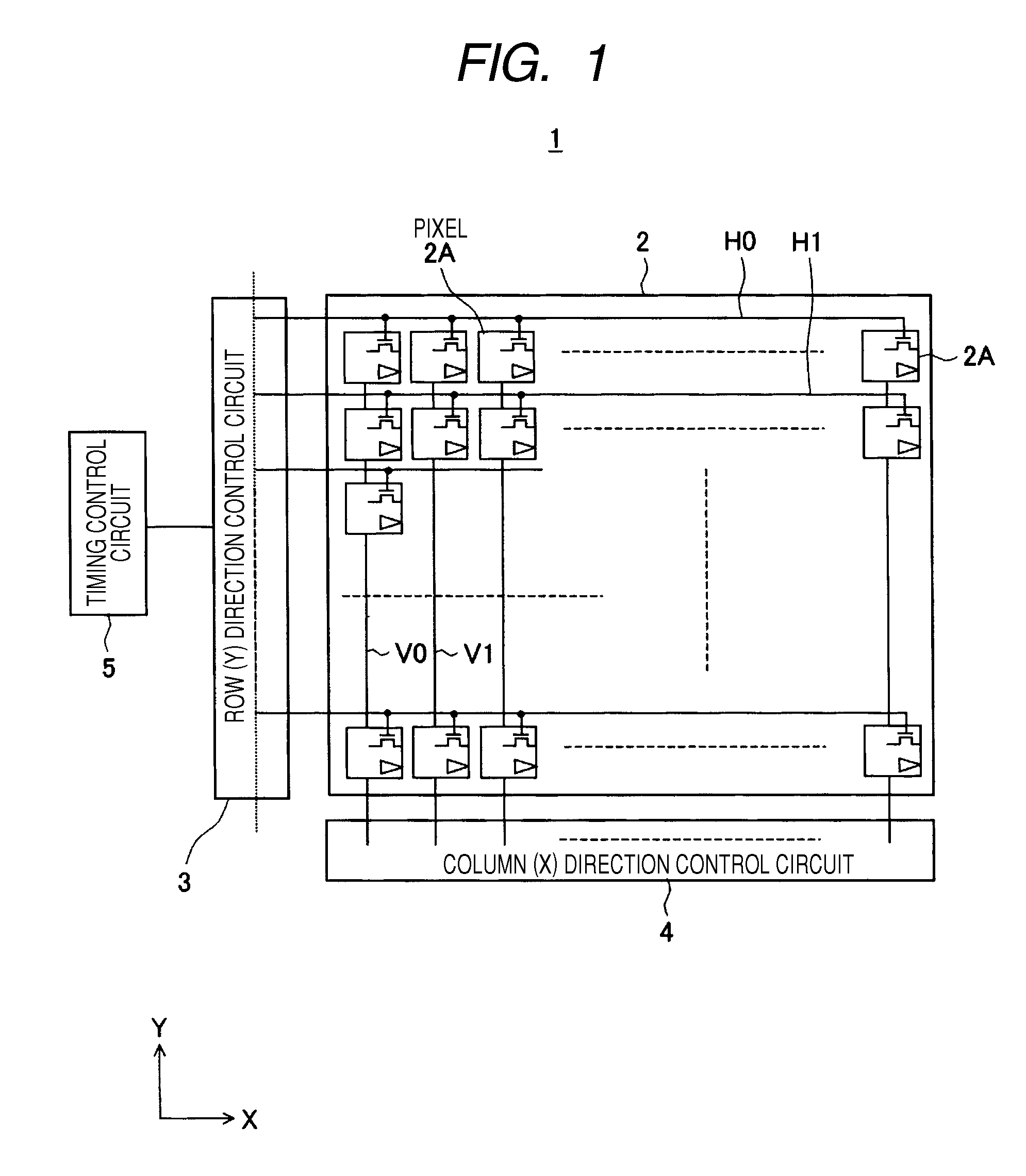
Solid-state imaging device and camera
ActiveUS20090153708A1Performed quickly and efficientlyImprovement of pixel sizeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsModulation functionPhotoelectric conversion
A solid-state imaging device includes pixel cells that are formed on a substrate having a first substrate surface side, on which light is irradiated, and a second substrate surface side, on which elements are formed, and separated by an adjacent cell group and an element separation layer for each of the pixel cells or with plural pixel cells as a unit. Each of the pixel cells has a first conductive well formed on the first substrate surface side and a second conductive well formed on the second substrate surface side. The first conductive well receives light from the first substrate surface side and has a photoelectric conversion function and a charge accumulation function for the received light. A transistor that detects accumulated charges in the first conductive well and has a threshold modulation function is formed in the second conductive well.
Owner:SONY CORP
Multi-channel nuclear magnetic resonance radio frequency signal transmitter
ActiveCN102724162AImplement parallel launchIndividually control the modulation methodMultiple carrier systemsMeasurements using magnetic resonanceQuadrature modulatorModulation function
The invention discloses a multi-channel nuclear magnetic resonance radio frequency signal transmitter which comprises a baseband signal modulation module, an orthometric up-conversion module and a radio frequency signal generation module, wherein the baseband signal modulation module comprises a field programmable gate array control module and a direct digital signal synthesizer; the orthometric up-conversion module comprises a power splitter, an orthometric modulator, a variable gain amplifier and the like; the radio frequency signal generation module supplies a local oscillation signal to the orthometric up-conversion module; and at least one baseband signal modulation module is arranged, and the orthometric up-conversion module is connected with the baseband signal modulation module and in the same number with the baseband signal modulation module. According to the multi-channel nuclear magnetic resonance radio frequency signal transmitter, the sole control and the parallel transmission of a plurality of paths of radio frequency signals are realized; all modulation functions are realized in a single-chip direct digital synthesizer (DDS), so that the integrated level of a system is improved; the radio frequency transmission of broadband can be carried out, and the full-range coverage of the signals is realized; and an orthogonal modulation system is adopted in the generation of the radio frequency signals, so that the mirror image frequency band is effectively suppressed, and the radio frequency power utilization rate is improved.
Owner:ウーハン ジョンケ ニウジン マグネティック レゾナンス テクノロジー カンパニー リミテッド
Making method of fermentation-type ready-to-eat red oil chili thick broad-bean sauce
InactiveCN103766862AGreat tasteFood ingredient functionsFood preparationReady to eatModulation function
The invention discloses a making method of fermentation-type ready-to-eat red oil chili thick broad-bean sauce, and belongs to the field of non-staple food processing. The making method of the fermentation-type ready-to-eat red oil chili thick broad-bean sauce takes high-quality salty thick broad-bean sauce, bright red four-flat head chilis produced at the north slope of Tianshan mountain and chick pea meal as main raw materials. The processing method comprises the following steps: carrying out temperature control fermentation, inoculating lactic acid bacteria, adding aspergillus oryzae, inoculating for a second time, processing the finished product and the like. The prepared fermentation-type ready-to-eat red oil chili thick broad-bean sauce is rich in sauce flavor, spicy in mouthfeel and slightly sweet, has flower fragrance, can be directly eaten, and is very palatable and rich in nutrition. The fermentation-type ready-to-eat red oil chili thick broad-bean sauce is rich in components such as vitamins, trace elements and amino acid. The sauce body has natural deep red color, and has very good color modulation function besides seasoning.
Owner:XINJIANG YUANYE FOOD
Measurement of ion mobility spectra
ActiveUS20090236514A1High mobility resolutionHigh detection sensitivityTime-of-flight spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionLow noiseModulation function
The invention relates to measuring the mobility spectra of ions with ion mobility spectrometers (IMS). The invention provides an analog modulation of the ion current of an IMS ion source with a continuous modulation function, the instantaneous frequency of which temporally varies across a large frequency range, and a generation of the mobility spectrum from the measured ion current by a correlation analysis with the modulation pattern. The modulation can, for example, be produced by the gating grid, which is usually present. The analog modulation removes many of the difficulties which occur with square-wave modulation and leads to a surprisingly stable evaluation which is relatively insensitive to noisy signals and produces a high mobility resolution at very low noise.
Owner:BRUKER OPTICS GMBH & CO KG
Differactive micro-structure color wavelength division device
InactiveUS20050062928A1Enhance optical operational efficiencyHigh aspect ratioPicture reproducers using projection devicesDiffraction gratingsColor imageSurface phase
A diffractive micro-structure color wavelength division device makes use of diffraction theory, binary optics theory, and operation of phase iteration algorithm to its complex two-dimensional surface phase micro-structure. The color wavelength division device has a multi-wavelength modulation function and is capable of wavelength division and focus, thereby resulting in structural simplification and enhancement of light utilized efficiency of a color image system.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Measurement method and measurement system for measuring birefringence
ActiveUS20120092669A1High precision measurementPhotomechanical apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansModulation functionLight beam
A method measuring the birefringence of an object. A measurement beam having a defined input polarization state is generated, the measurement beam being directed onto the object. Polarization properties of the measurement beam after interaction with the object are detected in order to generate polarization measurement values representing an output polarization state of the measurement beam after interaction with the object. The input polarization state of the measurement beam is modulated into at least four different measurement states in accordance with a periodic modulation function of an angle parameter α, and the polarization measurement values associated with the at least four measurement states are processed to form a measurement function dependent on the angle parameter α. A two-wave portion of the measurement function is determined and analysed in order to derive at least one birefringence parameter describing the birefringence, preferably by double Fourier transformation of the measurement function.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Three-dimensional structure metamaterial
ActiveCN102983407ASimple preparation processReduce processing costsRadiating element housingsWaveguide type devicesMicro structureModulation function
The invention discloses a three-dimensional structure metamaterial which comprises at least one layer of forming base material and at least one flexible function layer arranged on the surface of the forming base material. Each flexible function layer comprises a flexible substrate formed by at least one flexible sub-substrate and a plurality of manmade micro-structures corresponding to electromagnetic waves and arranged on the surface of each flexible sub-substrate. The three-dimensional structure metamaterial has an electromagnetic wave modulation function. The three-dimensional structure metamaterial is simple in manufacturing process and low in processing cost, process precision is controlled simply, and the three-dimensional structure metamaterial can replace various structure parts provided with complex curved surfaces and needing to have a certain electromagnetic modulation functions and can also be attached to various structure parts provided with the complex curved surfaces to achieve the required electromagnetic modulation functions. Besides, the three-dimensional structure metamaterial has good electromagnetic response and wide application range in a curved surface expanding and electromagnetic partition mode.
Owner:KUANG CHI INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Fourier transform chip spectrometer based on integrated light technique
ActiveCN102207459ASensitive assayFast and Sensitive Absorption SpectroscopyPhase-affecting property measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsModulation functionLighting spectrum
The invention discloses a Fourier transform chip spectrometer based on integrated light technique, comprising an integrated optical waveguide chip having electro-optic modulation function. Light from a light source enters the integrated optical waveguide chip through a fiber transmission coupler, and waveguide light from the chip enters an optical waveguide interferometer through a sensitive window interval. The interferometer outputs signals to a photoelectric detector. A voltage function generator is used for applying voltages varying with time between two modulated electrodes of the optical waveguide interferometer, the photoelectric detector is used for real-time measuring the change of the signal strength of the interferometer varying with the modulated voltage, and a signal processing chip connected with the photoelectric detector and the voltage function generator at same time is used for rapidly processing Fourier transform on the signals of the interferometer to obtain an incident light spectrum. The Fourier transform chip spectrometer provided by the invention can determine visible-infrared light absorbing spectra of solids, liquid, even monomolecular adsorption layers in the sensitive window, and determine fluorescence spectra of fluorescent substances in the sensitive window, with the advantages of strong anti-interference capability, and is suitable for rapid on-site quantitative determination.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
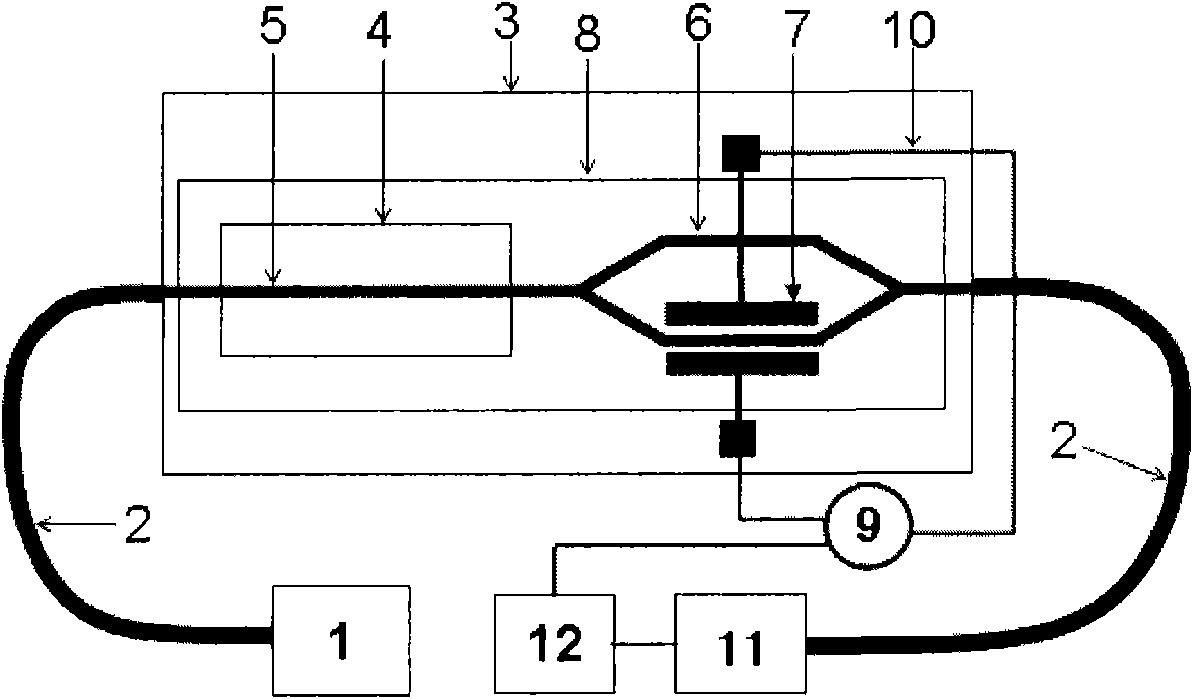
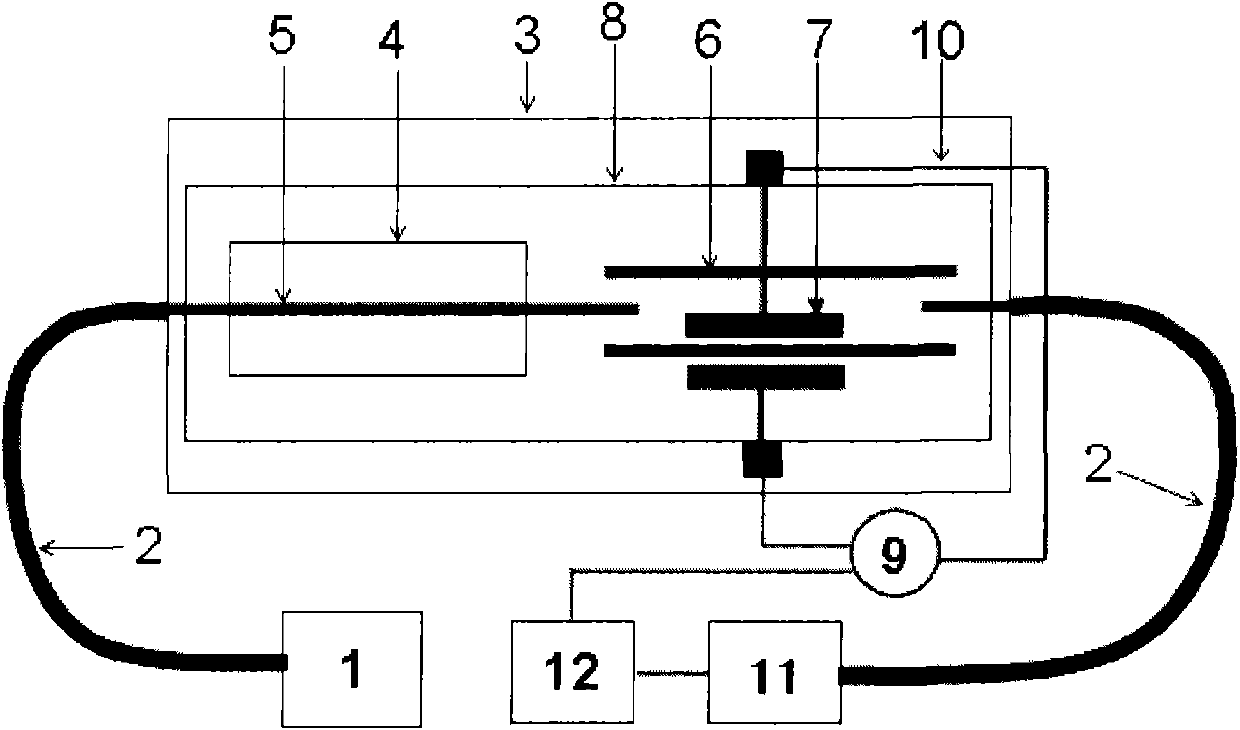
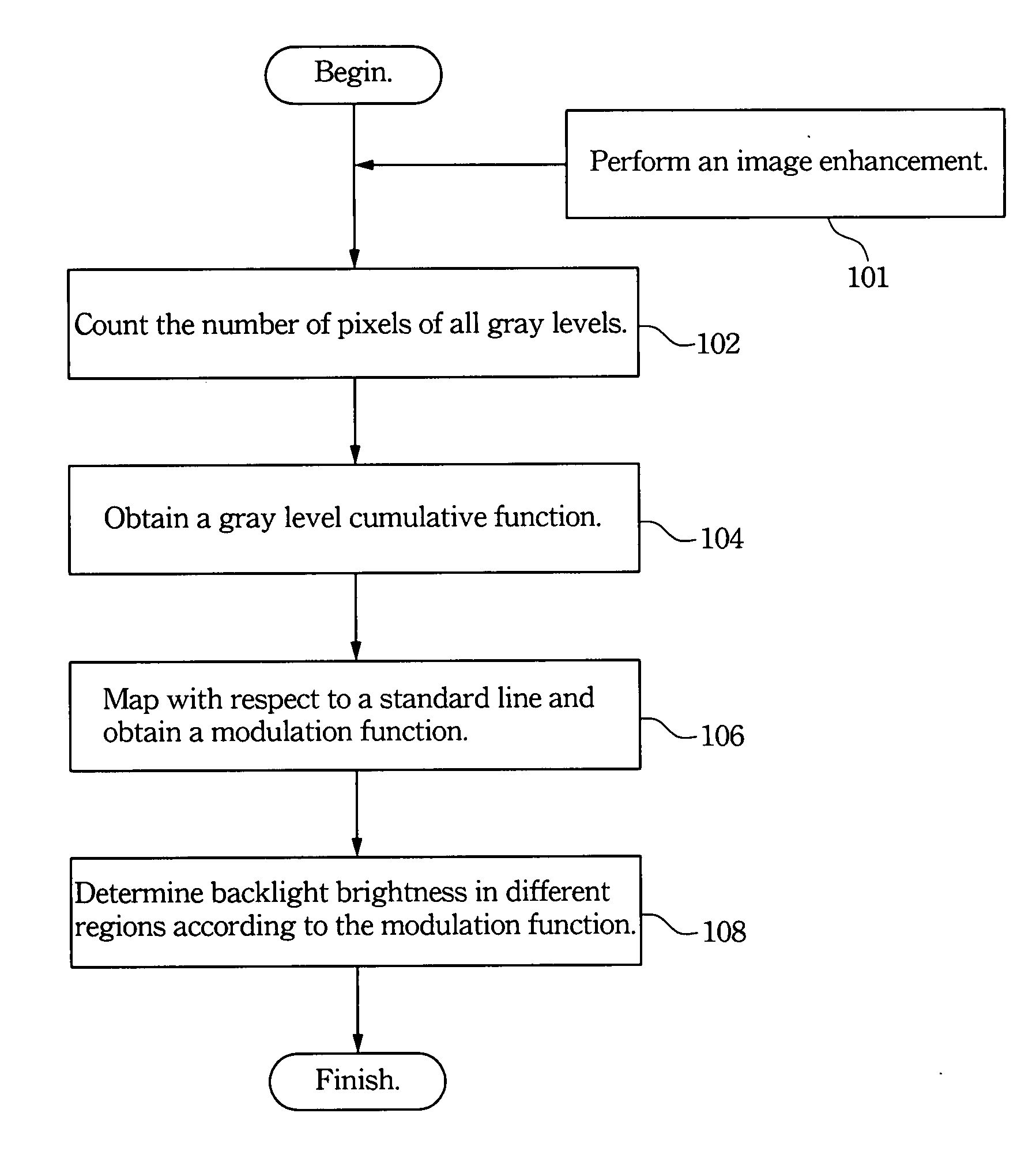
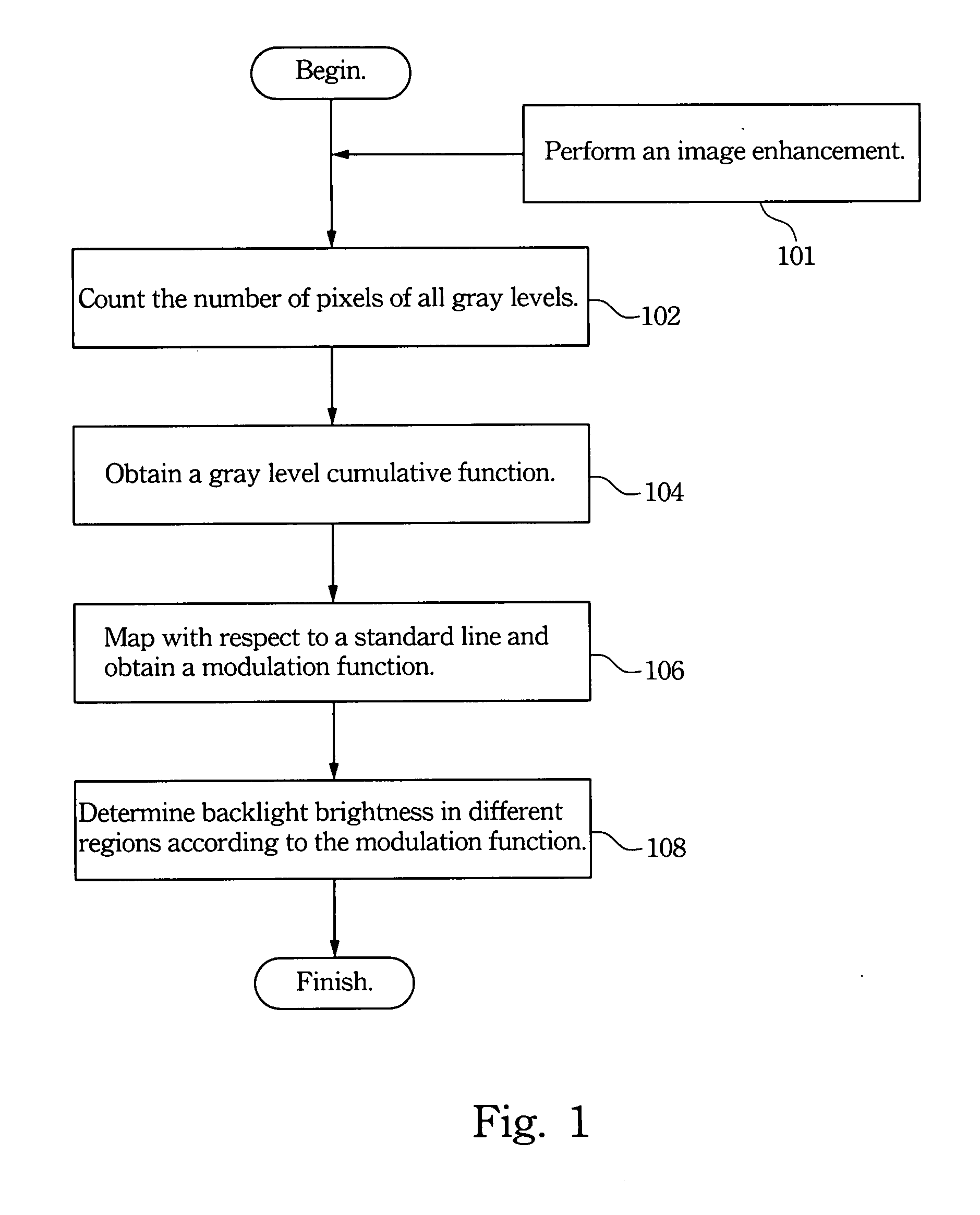
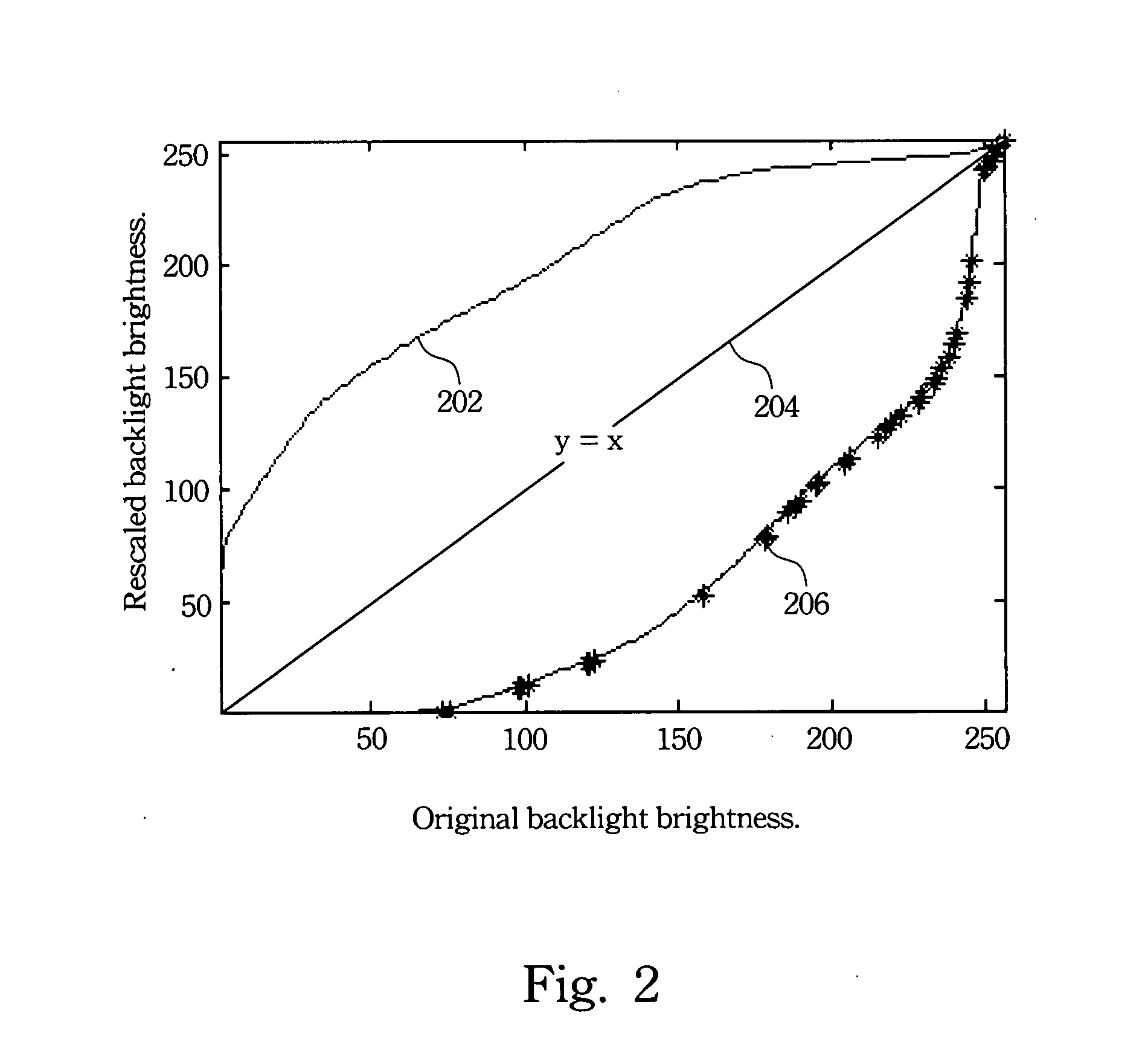
Backlight control method for high dynamic range LCD
A cumulative function of image is obtained according to its gray levels of pixels. This function is then mapped to obtain a backlight modulation function according to a reference line. The backlight brightness provided for different regions of the liquid crystal display are decided by the backlight modulation function while displaying the images.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
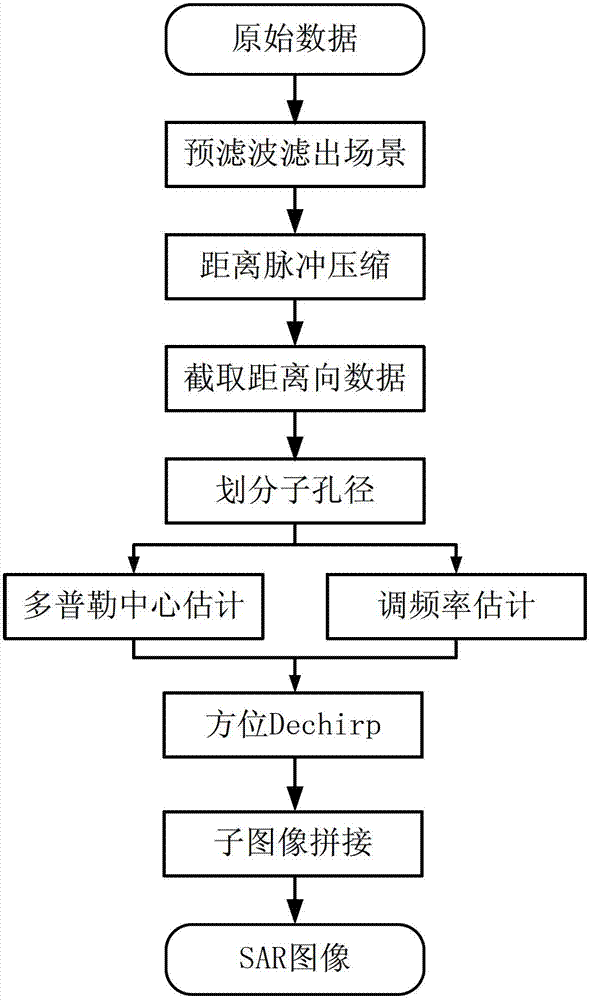
Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imaging method based on field programmable gate array (FPGA)
ActiveCN103197317AHigh degree of parallel processingFast signal processingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture sonarModulation function
The invention discloses a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imaging method based on field programmable gate array (FPGA). The SAR imaging method based on the FPGA mainly solves the problems that an existing system is complex in structure and slow in data processing speed. The SAR imaging method based on the FPGA comprises the following steps: calling a multiplying unit in the FPGA, conducting fast Fourier transform (FFT) operation after multiplying each array of distance direction data and hamming window data after quantification, finishing distance pulse pressure; calculating a scene central location of the distance direction by inertia parameters, intercepting the distance direction data; transposing acquired data by interception, realizing to store aperture data based on direction; estimating a Doppler central value and a Doppler frequency modulation rate based on inertia navigation parameters; constructing a Doppler frequency shift function, a Doppler frequency modulation function and a direction hamming window function based on the estimated Doppler central value and the Doppler frequency modulation rate; conducting FFT operation by multiplying each array of the direction data after finishing the distance impulse pressure with the Doppler frequency shift function, the Doppler frequency modulation function and the direction hamming window function, and acquiring final imaging data. The SAR imaging method based on the FPGA has the advantages of simplifying an SAR imaging system structure, improving processing speed, and capable of being used in the SAR imaging under a missile-borne module.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
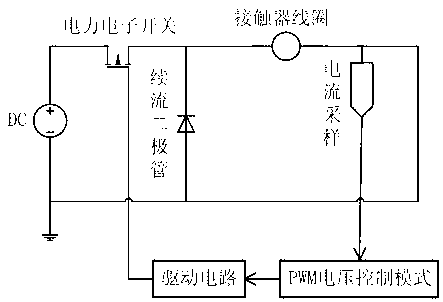
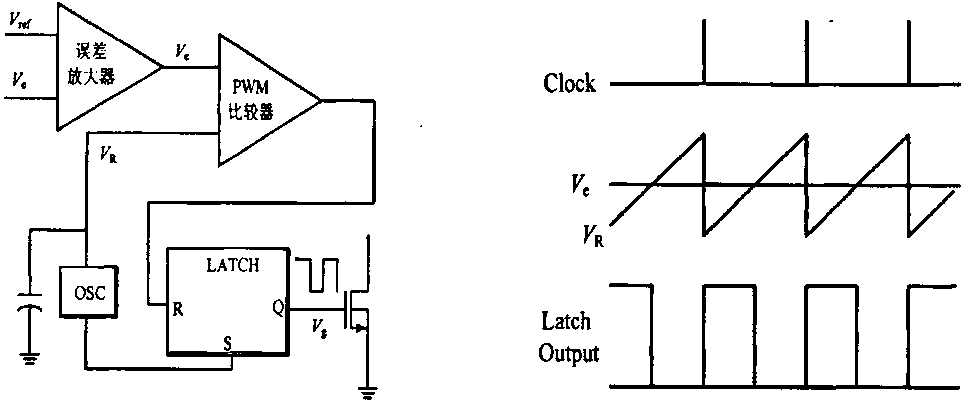
Alternating current contactor intelligent control module with high speed pulse width modulation function
The invention relates to an alternating current contactor intelligent control module with a high speed pulse width modulation function. The alternating current contactor intelligent control module comprises an alternating current / direct current (AC / DC) power supply, the AC / DC power supply supplies power for an alternating current contactor coil sequentially through a rectification filter circuit and an electronic power switch, and the alternating current contactor intelligent control module further comprises a voltage sampling circuit, a single chip microcomputer control system, a double-way digital-analog (DA) switching circuit, a sawtooth wave generating circuit, a square wave clock signal, a high speed pulse width modulator, a bootstrap circuit, a compensating circuit, a switching point detection circuit, a hall current sensor, a follow current circuit, a low voltage maintaining loop and an automatic constant voltage / constant current switching circuit. According to the alternating current contactor intelligent control module with the high speed pulse width modulation function, a novel Buck structure is used as a coil power level topology, orders of a power level circuit are lowered, a system is easy to stabilize, the compensating circuit is easy to design, the hall current sensor is used for current sampling, the impedance characteristic of a coil power level circuit is not changed, advantages of high accuracy, isolation characteristics, large bandwidth and the like of a current sensor are fully utilized, and closed-loop control with the isolation characteristics is formed.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
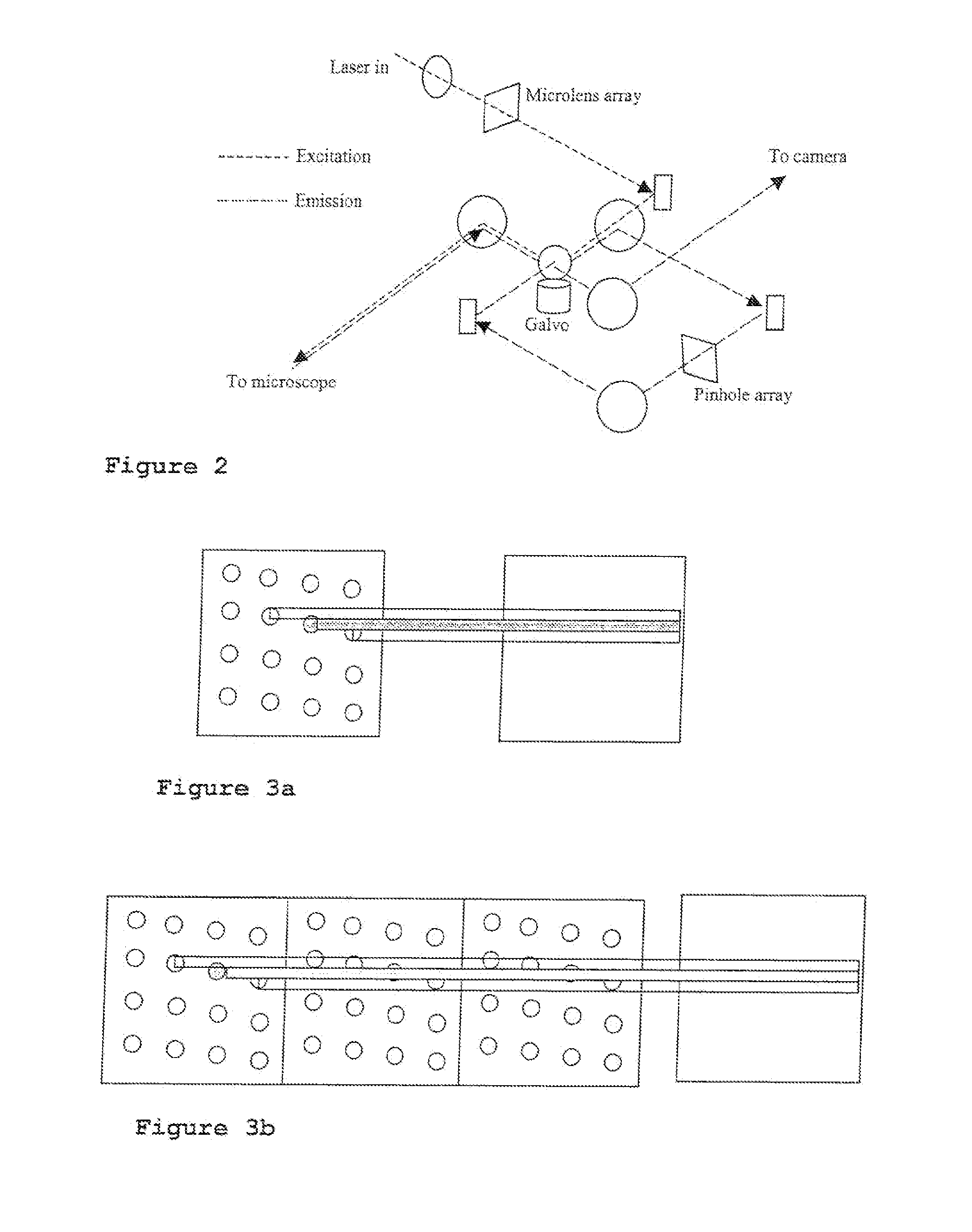
Laser confocal scanning microscope and methods of improving image quality in such microscope
InactiveUS20080037114A1High strengthReduce appearance problemsMicroscopesModulation functionImaging quality
According to a first embodiment the invention provides for increasing the throughput and reducing the striping due to imperfections in the microlens and / or confocal aperture arrays of a Laser Confocal Scanning Microscope by increasing the number of repeat patterns in the microlens and confocal aperture arrays to more than one, and incorporating an intensity modulation function that ensures constant integrated image intensities at the image detector independent of the instantaneous speed of scanning. According to a second embodiment the invention provides for reducing the striping in a Laser Confocal Scanning Microscope by introducing a second galvanometer mirror such that the emitted laser light beam is descanned at the image (sample) plane. According to embodiments three to five, striping in a Laser Confocal Scanning Microscope is also reduced by destroying coherency in the emitted light beam by insertion of a small angle diffuser, by flattening the Gaussian intensity distribution of the emitted laser light beam and changing the characteristics of the beam expander. According to embodiment six the invention provides for changing the degree of confocality of a Laser Confocal Scanning Microscope by inserting a mechanism that offers a range of selectable confocal aperture sizes.
Owner:VISITECH INT LTD
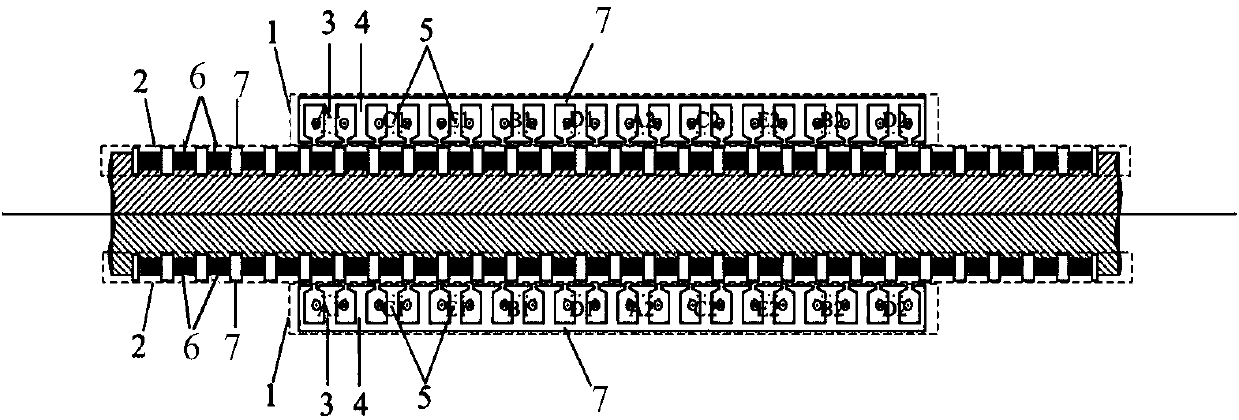
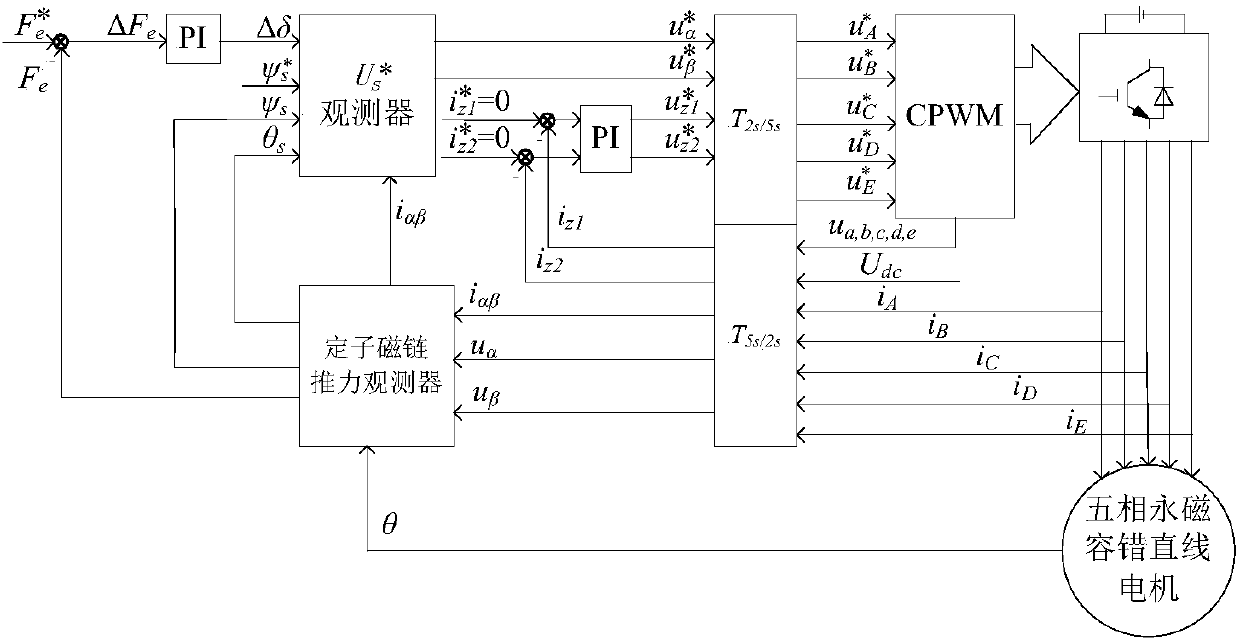
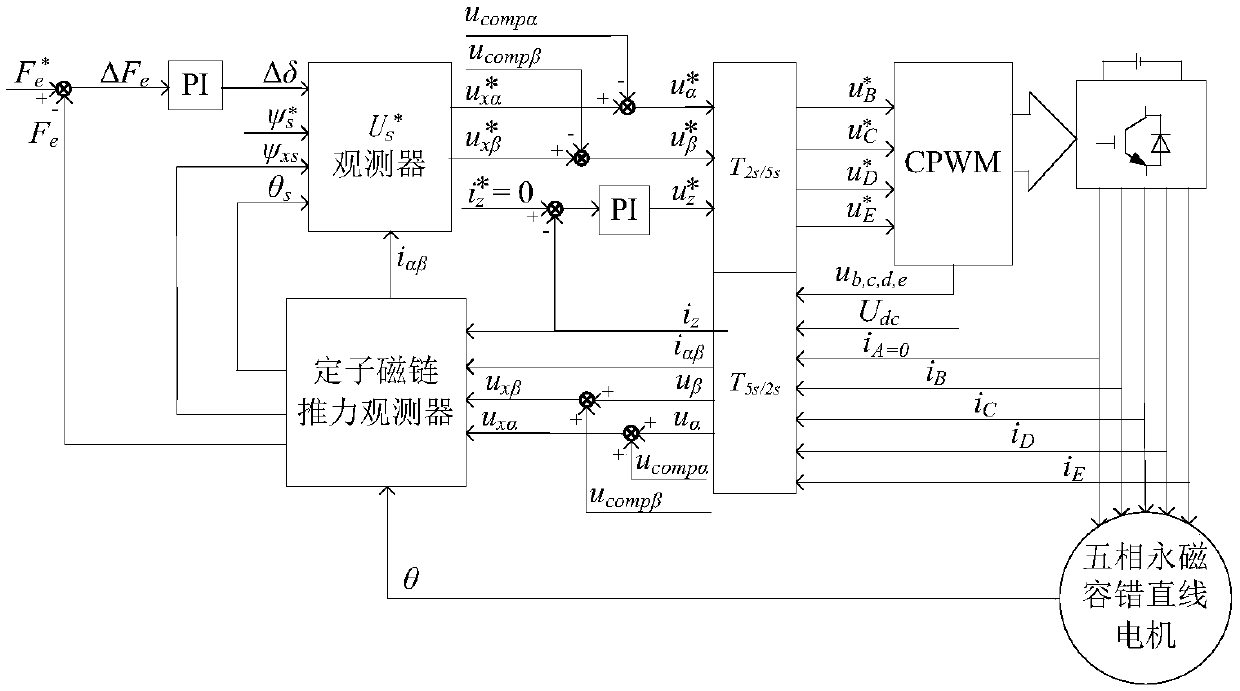
One-phase open-circuit fault-tolerant direct thrust control method for five-phase permanent magnet linear motor
InactiveCN108306571AIncreased complexitySave memory resourcesElectric motor controlVector control systemsPhase currentsModulation function
The invention discloses a one-phase open-circuit fault-tolerant direct thrust control method for a five-phase permanent magnet linear motor. Firstly, a Clark transform matrix and an inverse matrix thereof are derived based on fault-tolerant phase current. On the above basis, a stator flux linkage on alpha-beta is derived, a stator virtual flux linkage is defined according to the requirements of acircular stator flux linkage trajectory, and thus the voltage compensation on alpha-beta is derived. The stator actual voltage on the alpha-beta is derived by a modulation function of a voltage sourceinverter, and voltage is combined with voltage compensation and stator current, and a stator virtual flux linkage and thrust are observed by a stator flux observer and a thrust observer. Then statorvirtual target votlage is calculated according to given thrust, a given stator flux linkage amplitude and the observed stator virtual flux linkage and thrust. Finally, the stator actual voltage is calculated by the voltage and the voltage compensation, and the motor is controlled by the voltage by the voltage source inverter. According to the method, a thrust fluctuation caused by a motor failureis suppressed, and more importantly, the dynamic performance and steady state performance are consistent with that in a normal condition.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Microelectromechanical modulation device and microelectromechanical modulation device array, and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20060066931A1Reduce oscillationShorten the timeNon-linear opticsOptical elementsModulation functionEngineering
A microelectromechanical modulation device comprising: a movable portion, which is supported to be elastically and bi-directionally displaced and which has a modulation function; and a plurality of driving sources operative to apply a physical action force to said movable portion, wherein when said movable portion is displacement-driven in a first direction, a physical action force for suppressing oscillation of said movable portion is applied to said movable portion in a second direction different from the first direction by said drive sources while said movable portion is transited in the first direction.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
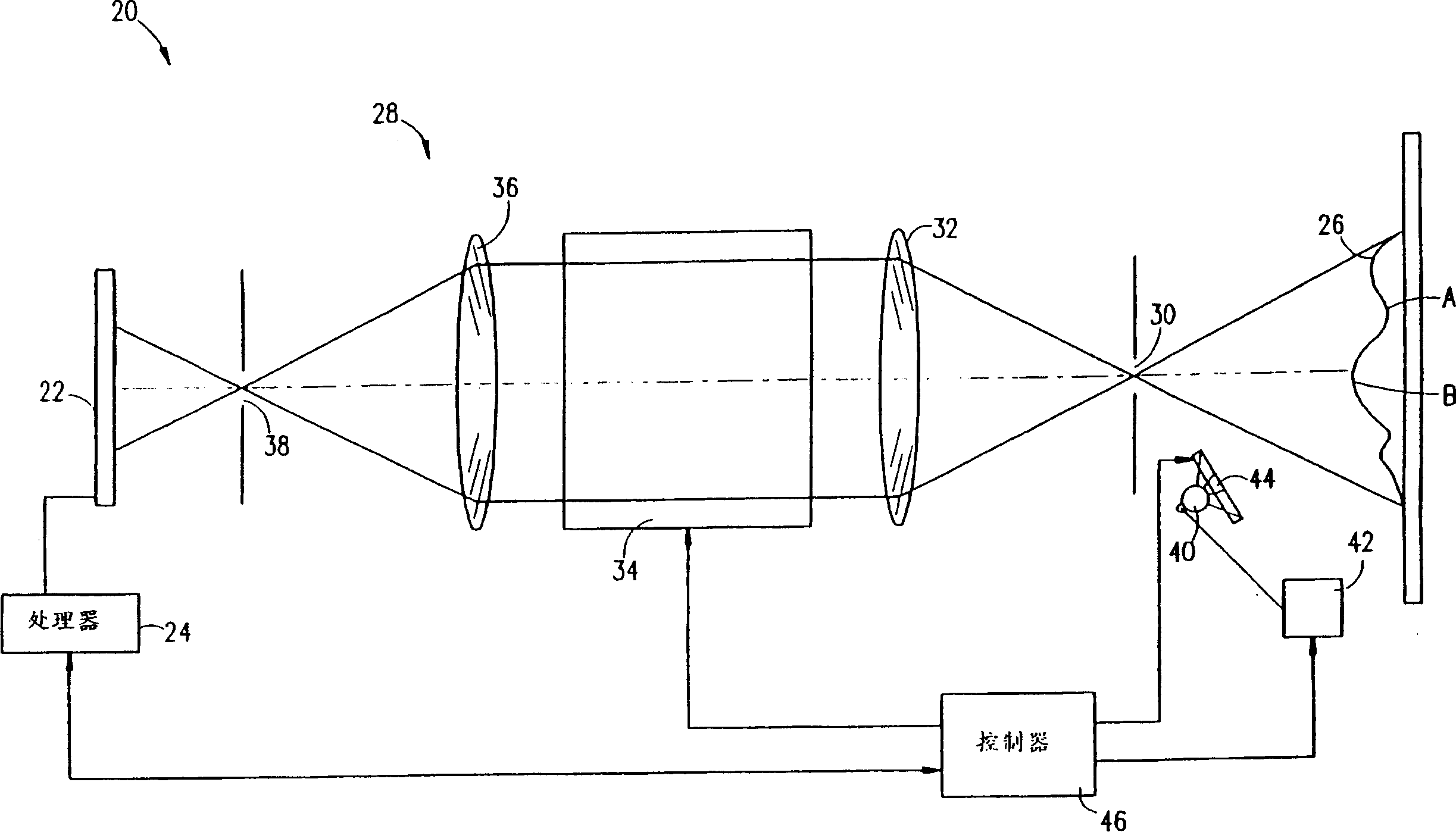
Method and apparatus for generating range subject distance image
Apparatus for creating an image indicating distances to objects in a scene, including a modulated source of radiation, having a first modulation function, which directs radiation toward a scene; a detector which detects radiation from the scene, modulated by a second modulation function, and generates, responsive to the detected modulated radiation, signals responsive to the distance to regions of the scene; and a processor which forms an image having an intensity value distribution indicative of the distance of objects from the apparatus, and a controller modulates at least one of the first and second modulation functions based on the intensity value distribution indicative formed by the processor.
Owner:MAJKROSOFT INT KHLDGZ
Rapid super-resolution micro-imaging method and device
InactiveCN104614318AFast imagingSimple structureMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicro imagingModulation function
The invention discloses a rapid super-resolution micro-imaging method which comprises the following steps: modulating a first light beam and a second light beam according to corresponding modulation functions; combining the light beams into a path of light by using a beam splitter prism; radiating to the surface of a sample; collecting signal light emitted from different scanning points of the sample to be detected; dividing the signal light into two bundles, wherein the first light beam and the second light beam are imaged simultaneously; controlling the fragrance of the first light beam to be v, by taking the fragrance v as a reference signal, extracting signal light intensity I1(x, y) corresponding to the first light beam from one bundle of the signal light according to the reference signal, and by taking intensity of the other bundle of the signal light as I0(x, y), calculating the signal light intensity I2(x, y)=I0(x, y)-I1(x, y) corresponding to the second light beam, and achieving super-resolution imaging by using final effective signal light intensity I (x, y), wherein x and y are two-dimensional coordinates of the scanning points. The invention further discloses a rapid super-resolution micro-imaging device. As conventional respective imaging of hollow spots and solid spots is converted into simultaneous imaging, the scanning speed is accelerated while the transverse resolution is not changed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Compound modulation transfer function for laser surgery and other optical applications
ActiveUS8911086B2Mitigates and treats vision conditionMitigates presbyopiaLaser surgeryEye diagnosticsModulation functionLaser surgery
Methods, devices, and systems establish an optical surface shape that mitigates or treats a vision condition in a patient. An optical surface shape for a particular patient can be determined using a set of patient parameters for the specific patient by using a compound modulation transfer function (CMTF). The compound modulation transfer function can include a combination of modulation transfer functions (MTF's) at a plurality of distinct frequencies.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
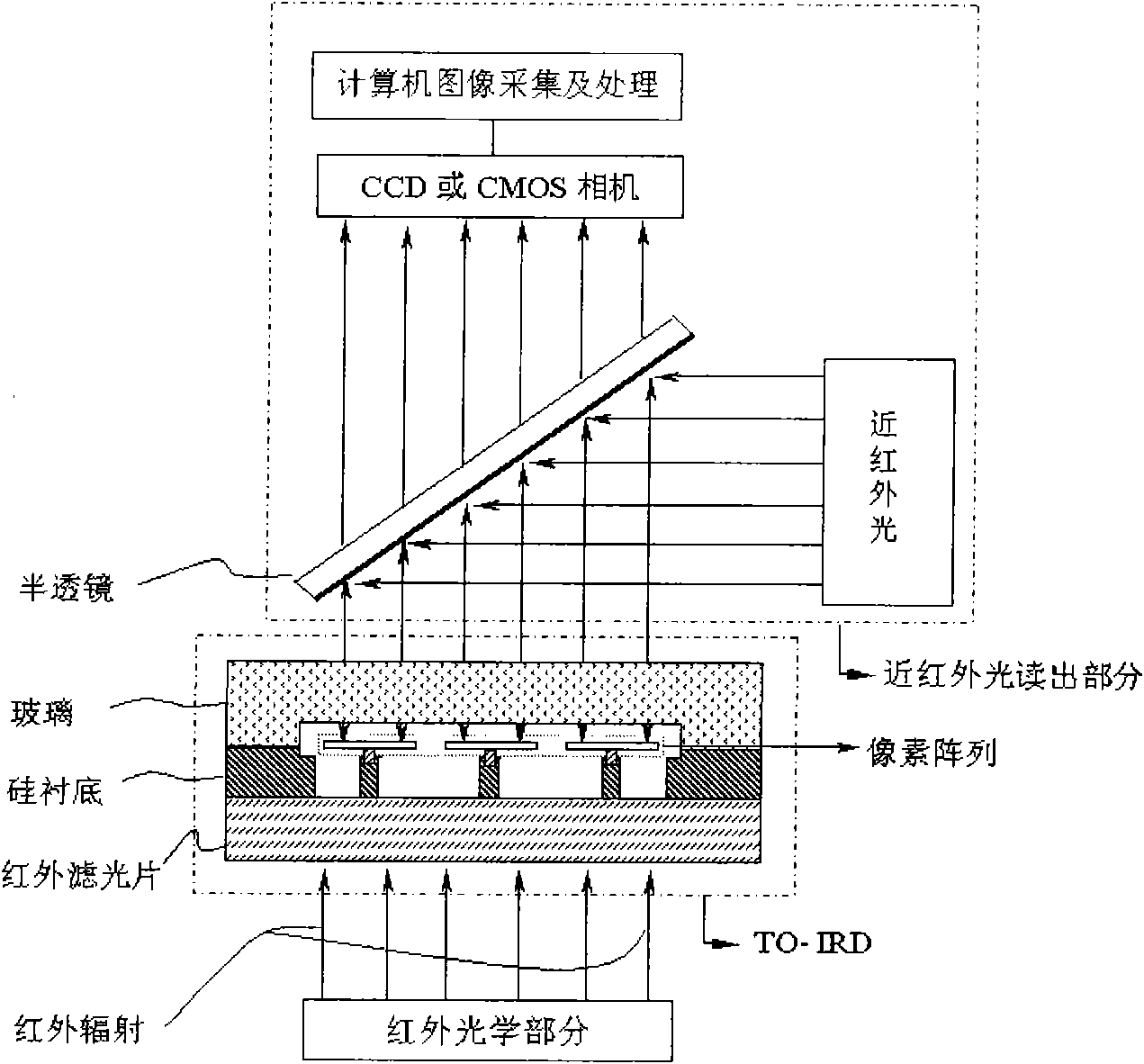
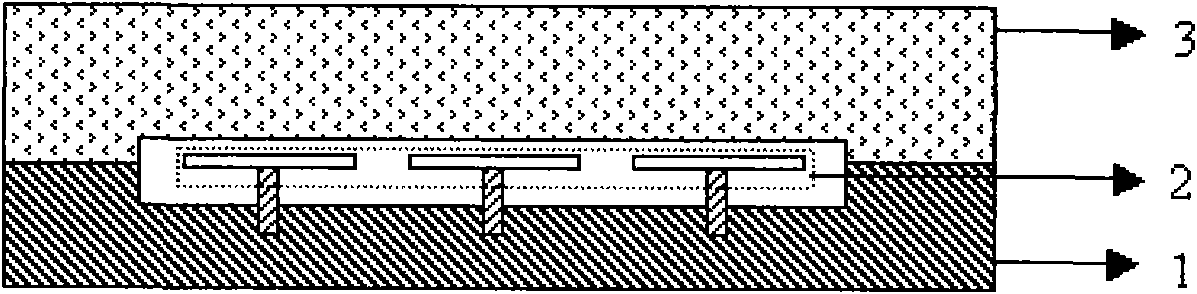
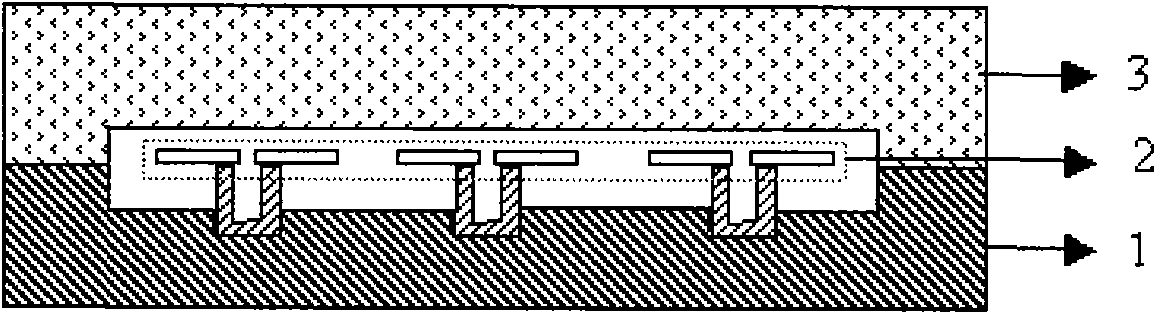
Thermo-optical infrared detector and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101566502ASimple structureReduce manufacturing difficultyTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesModulation functionAbsorption rate
The invention relates to a thermo-optical infrared detector and a preparation method thereof, and is characterized in that the infrared detector consists of a silicon substrate, a pixel array arranged on the silicon substrate and a glass bonded with the silicon substrate; alternatively, the infrared detector consists of a silicon substrate, a pixel array arranged on the silicon substrate, a glass bonded with the silicon substrate and an infrared filter bonded with the silicon substrate. In the TO-IRD, a special heat-insulation structure and a process design are used for preparing a heat insulation column with high height standing on the silicon substrate, thus improving the heat insulation performance of the TO-IRD; in a pixel film system, by designing and preparing a special infrared absorbing layer, the absorption rate of the TO-IRD to the infrared radiation is improved; furthermore, the modulation function of the TO-IRD to the readout beam is not affected; and the vacuum encapsulation of the device is realized by the bonding of silicon glass or bonding of infrared filter in vacuum.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
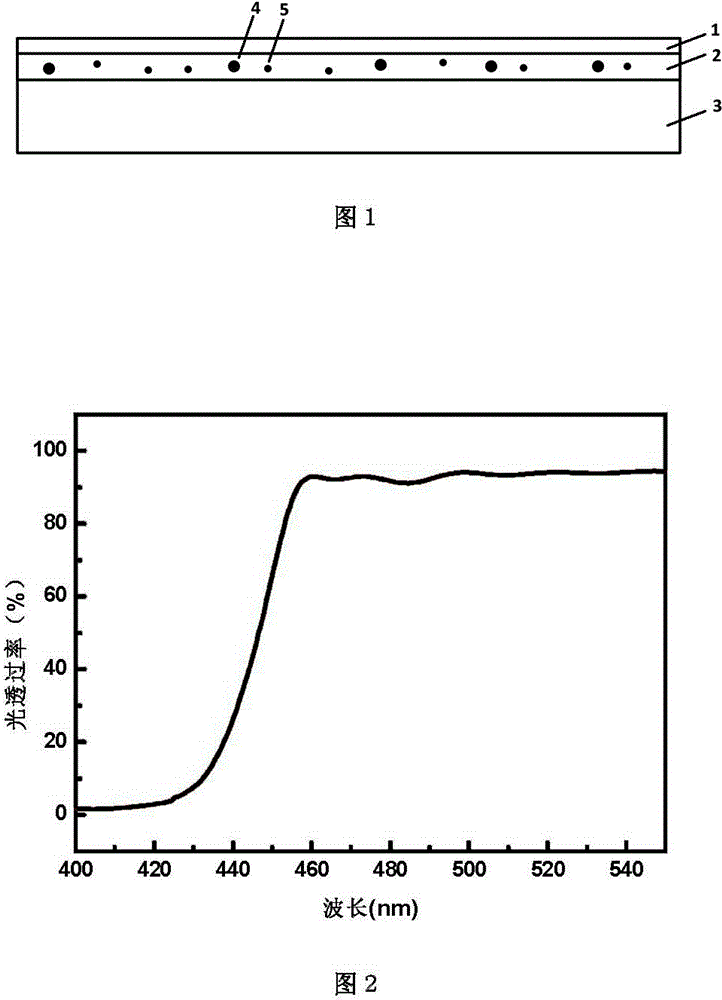
Dichroic optical filter fluorescence-enhanced light guide plate and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104536078AWith light guideFunctionalLuminescent paintsLight guides with fluorescent dopantsModulation functionFluorescence
The invention relates to a dichroic optical filter fluorescence-enhanced light guide plate which is used for an LED backlight module. The dichroic optical filter fluorescence-enhanced light guide plate is composed of a dichroic optical fiber 1, a fluorescence layer 2 and a light guide plate body 3. The fluorescence layer 2 is located between the dichroic optical fiber 1 and the light guide plate body 3. The invention further relates to a manufacturing method of the dichroic optical filter fluorescence-enhanced light guide plate. By means of the dichroic optical filter fluorescence-enhanced light guide plate, the wide gamut can be obtained with the low cost, and meanwhile the problems that due to the fact that light emitted by quantum dots is absorbed by the quantum dots, the brightness is reduced, and red shift of an emission spectrum is caused are avoided. Meanwhile, the manufacturing method is easy to implement, and the obtained dichroic optical filter fluorescence-enhanced light guide plate further has the light guide and white light modulation functions.
Owner:GUANGDONG POLY OPTOELECTRONICS
Optical Modulators With Controllable Chirp
InactiveUS20110222813A1Small capacitive loadCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsModulation functionEngineering
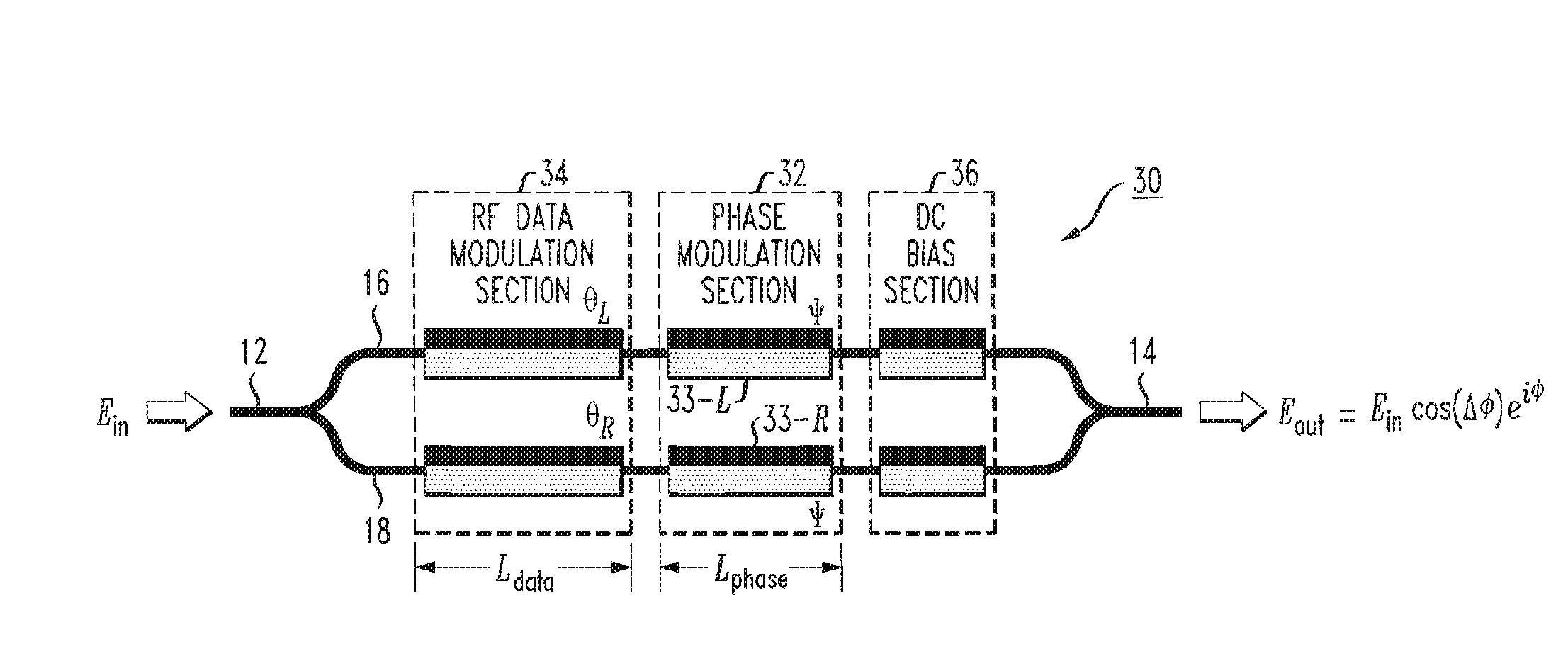
A semiconductor-based optical modulator is presented that includes a separate phase control section to adjust the amount of chirp present in the modulated output signal. At least one section is added to the modulator configuration and driven to create a pure “phase” signal that will is added to the output signal and modify the eiφ term inherent in the modulation function. The phase modulation control section may be located within the modulator itself (with one segment on each arm, driven by the same input signal), or may be disposed “outside” of the modulator on either the input waveguiding section or the output waveguiding section. The phase control section may be formed to comprise multiple segments (of different lengths), with the overall phase added to the propagating signal controlled by selecting the different segments to be energized to impart a phase delay to a signal propagating through the energized section(s).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com