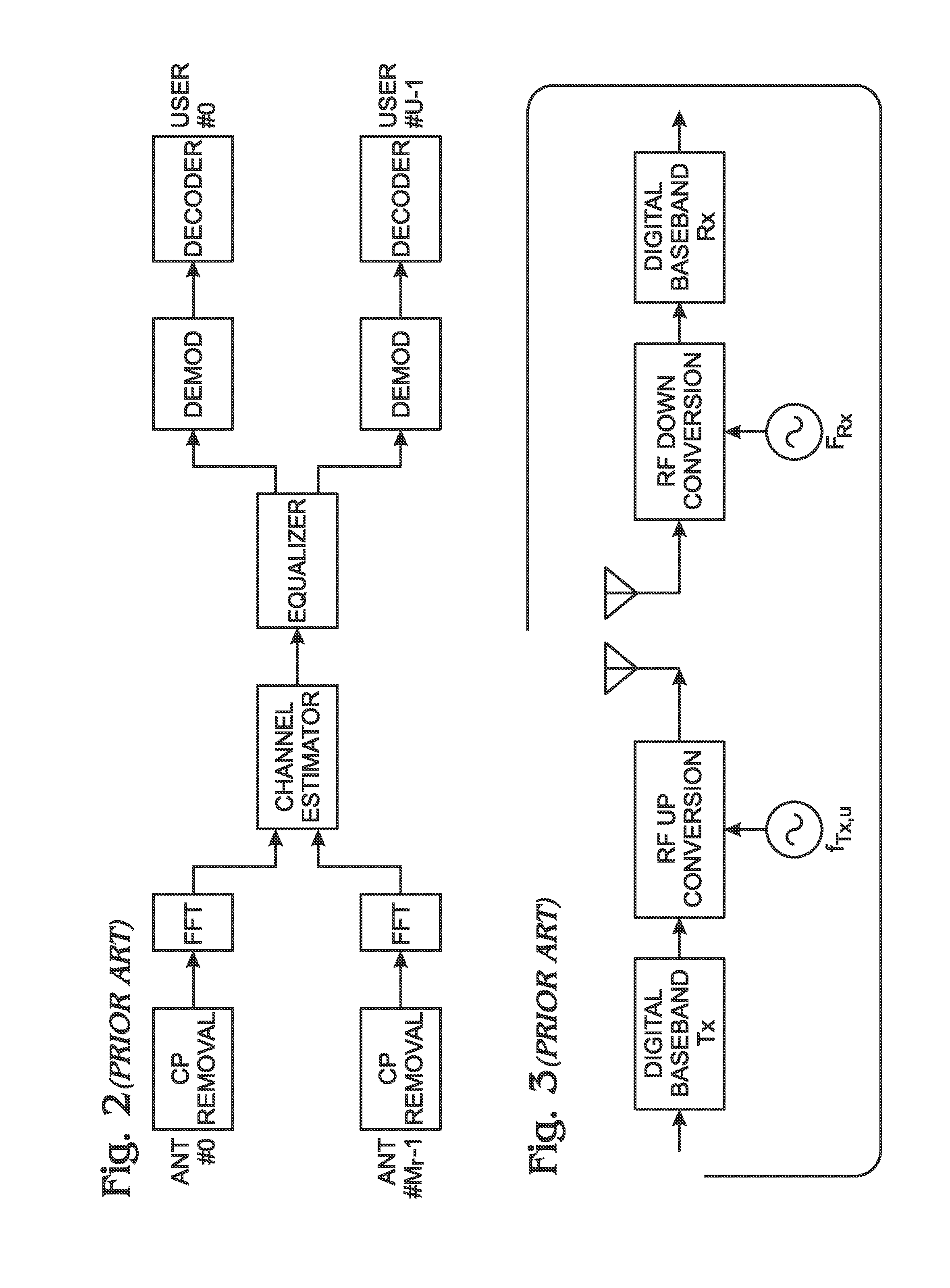
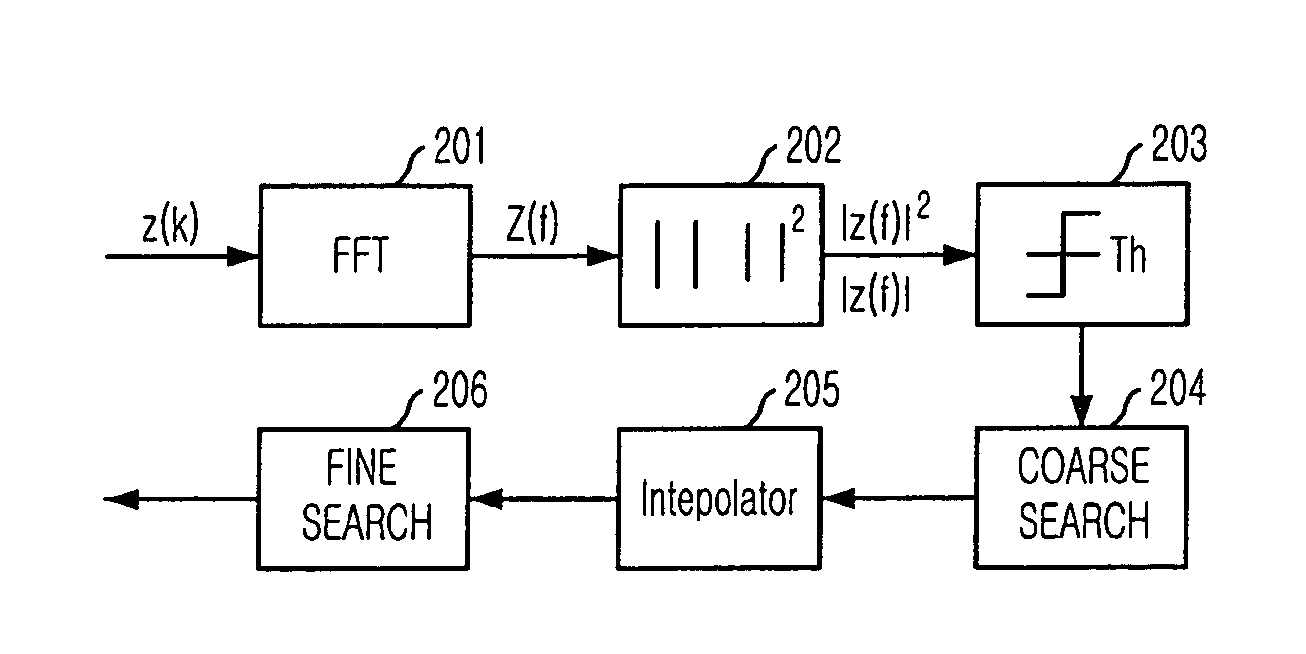
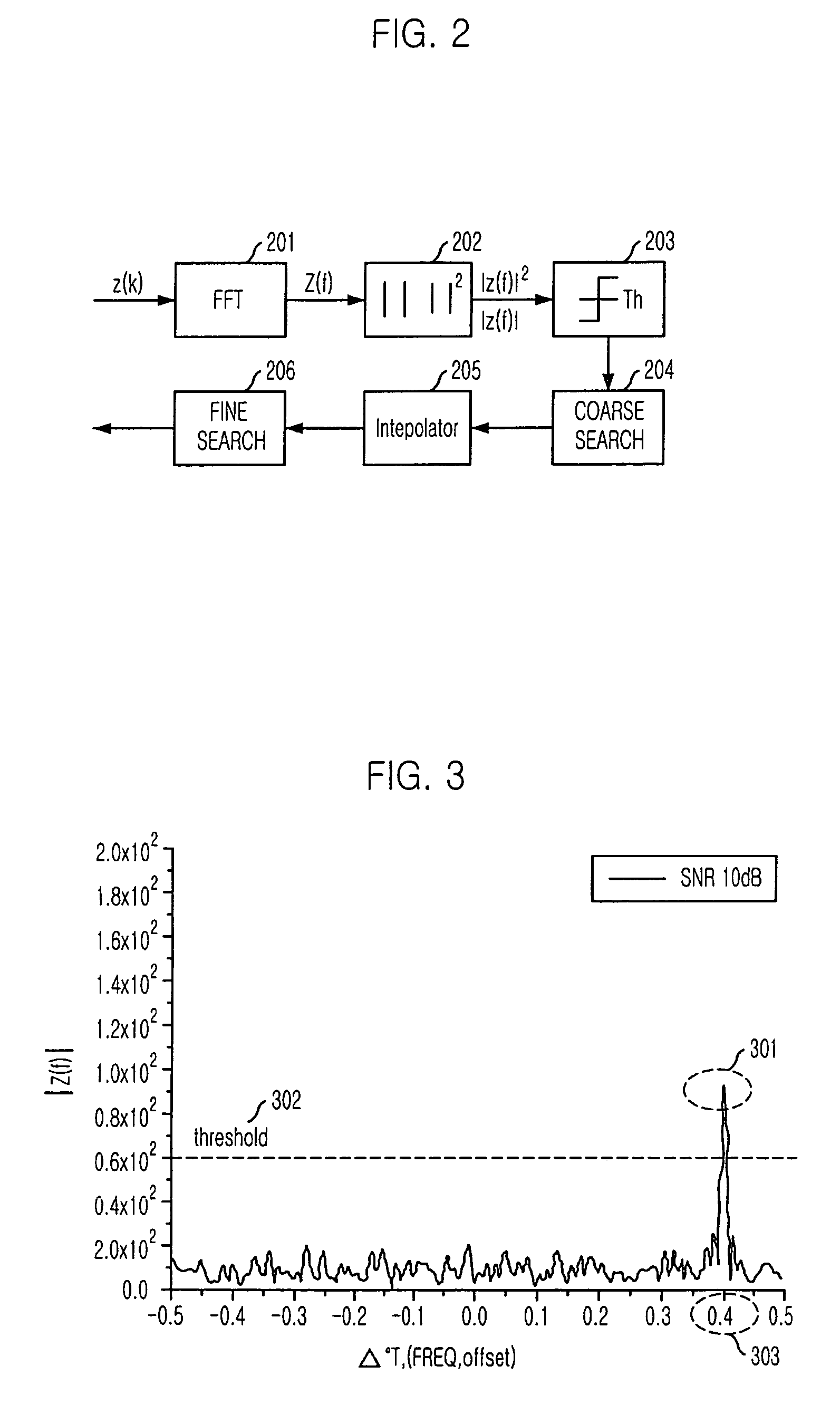
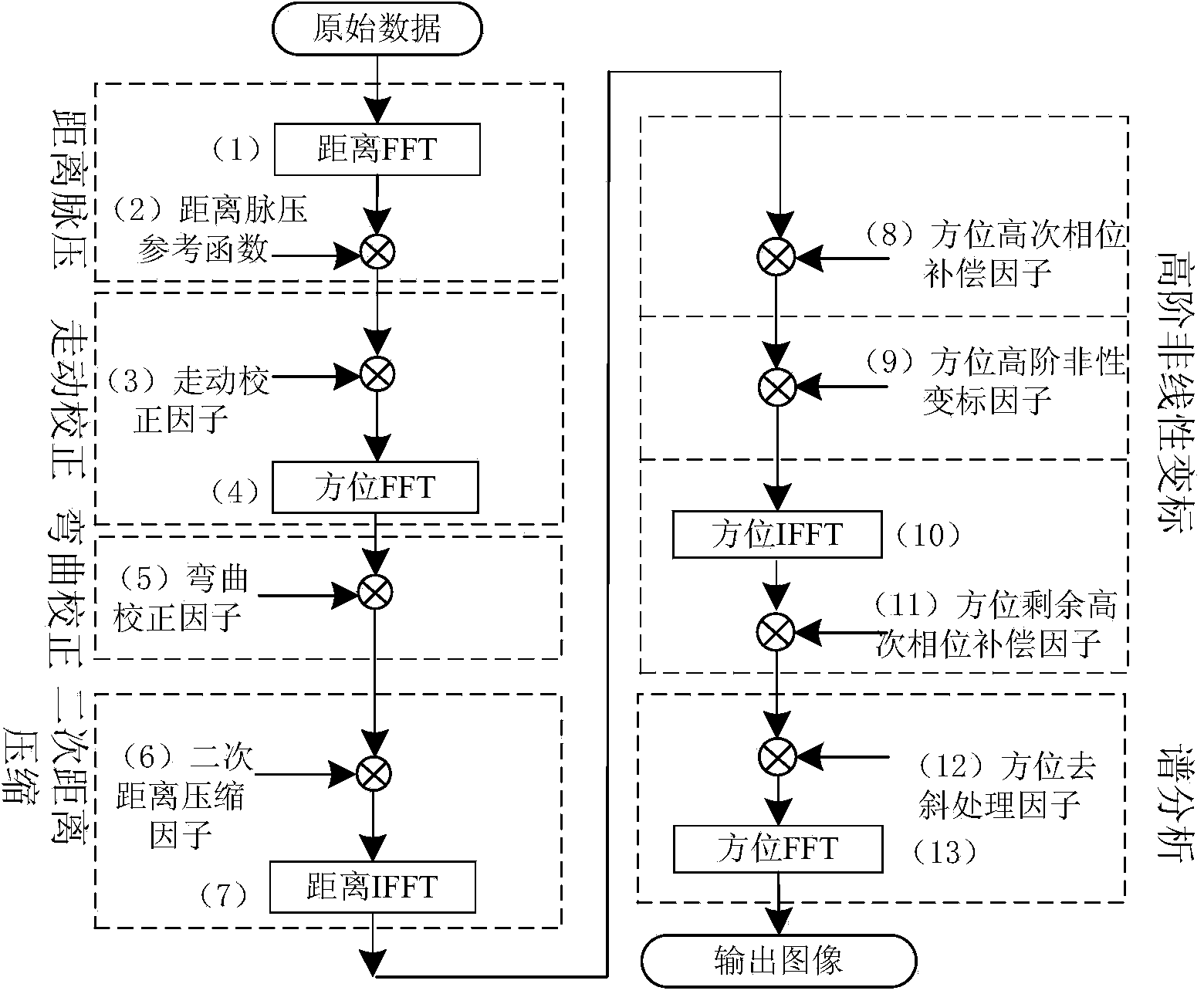
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2814 results about "Doppler frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
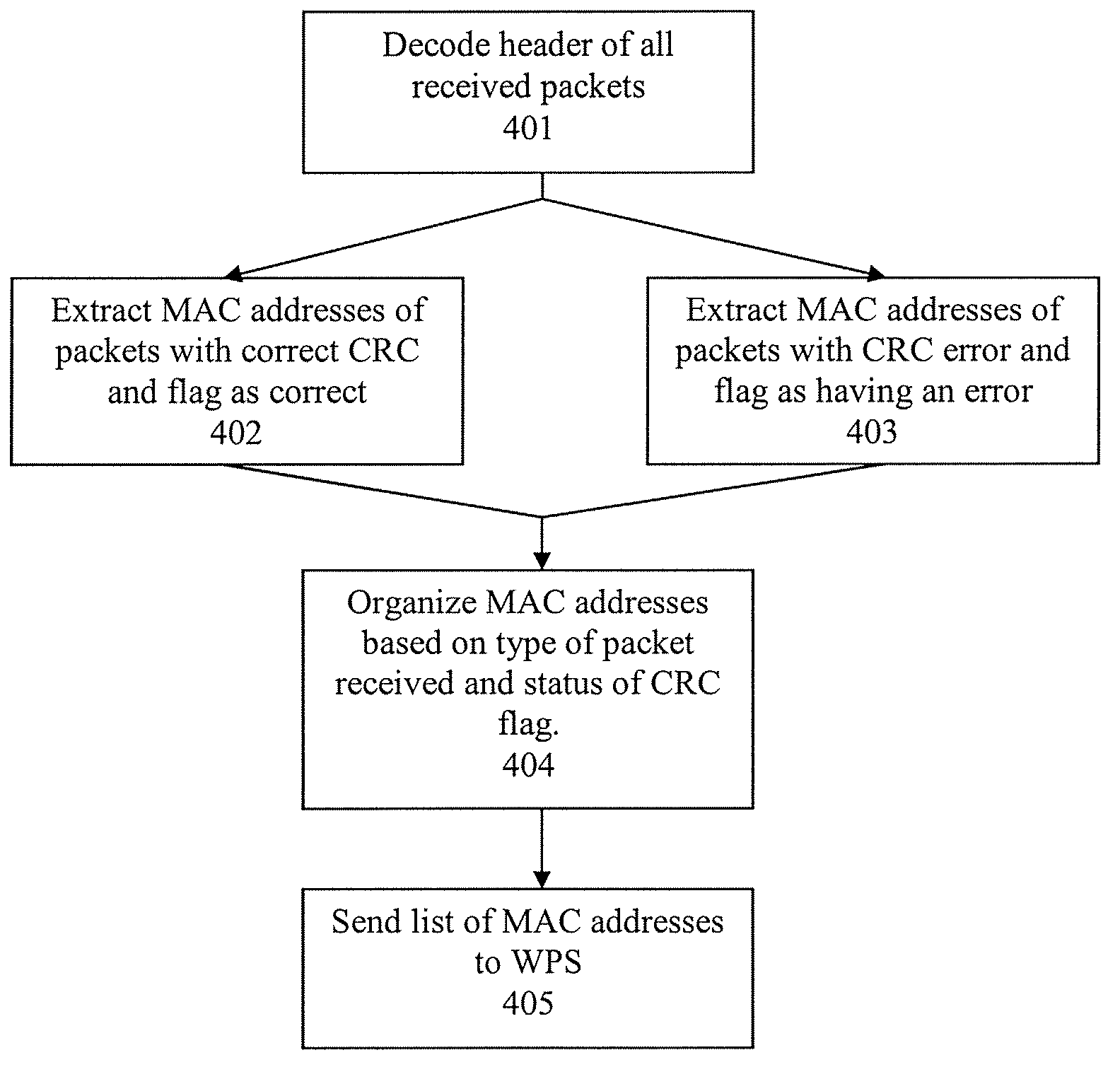
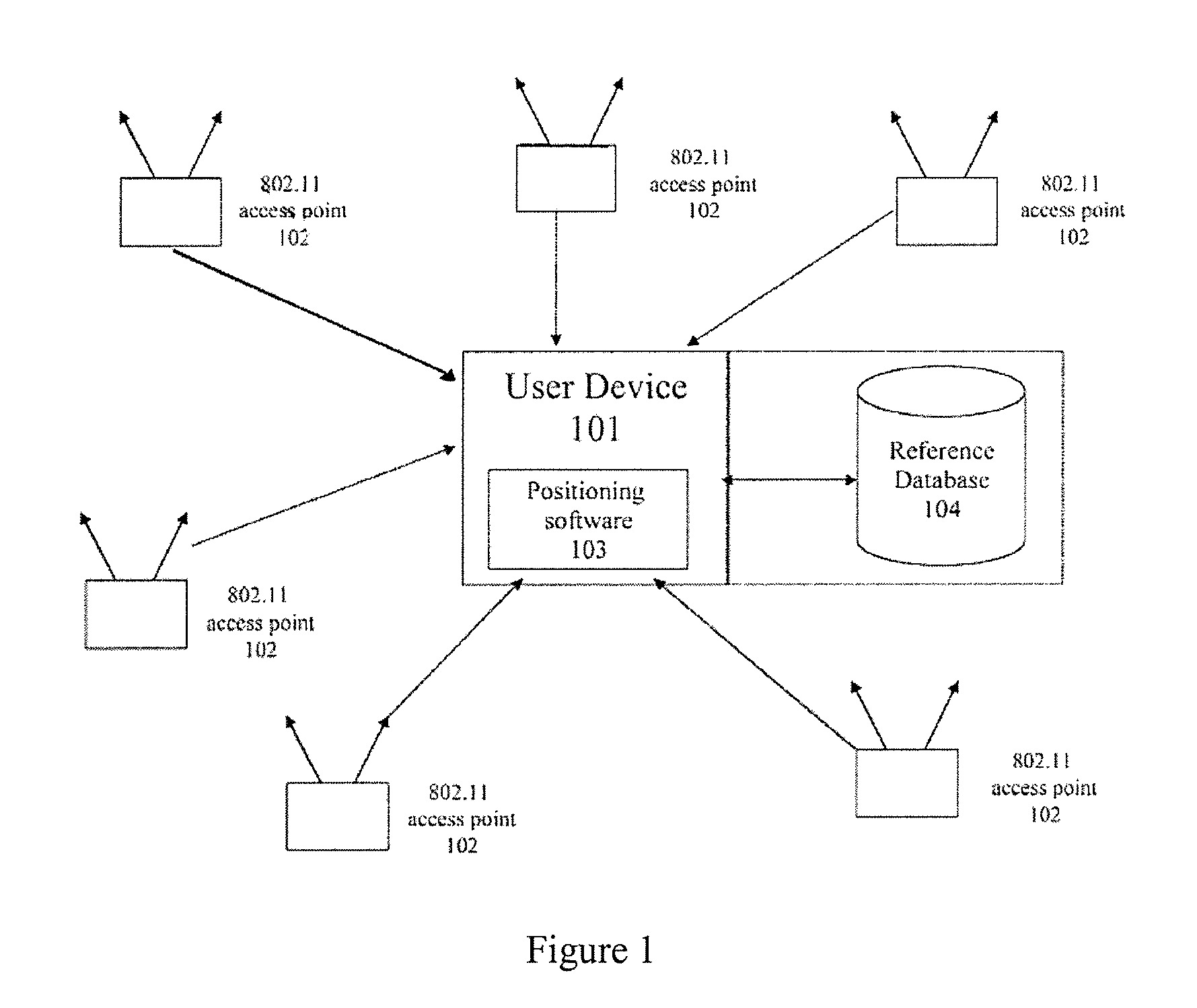
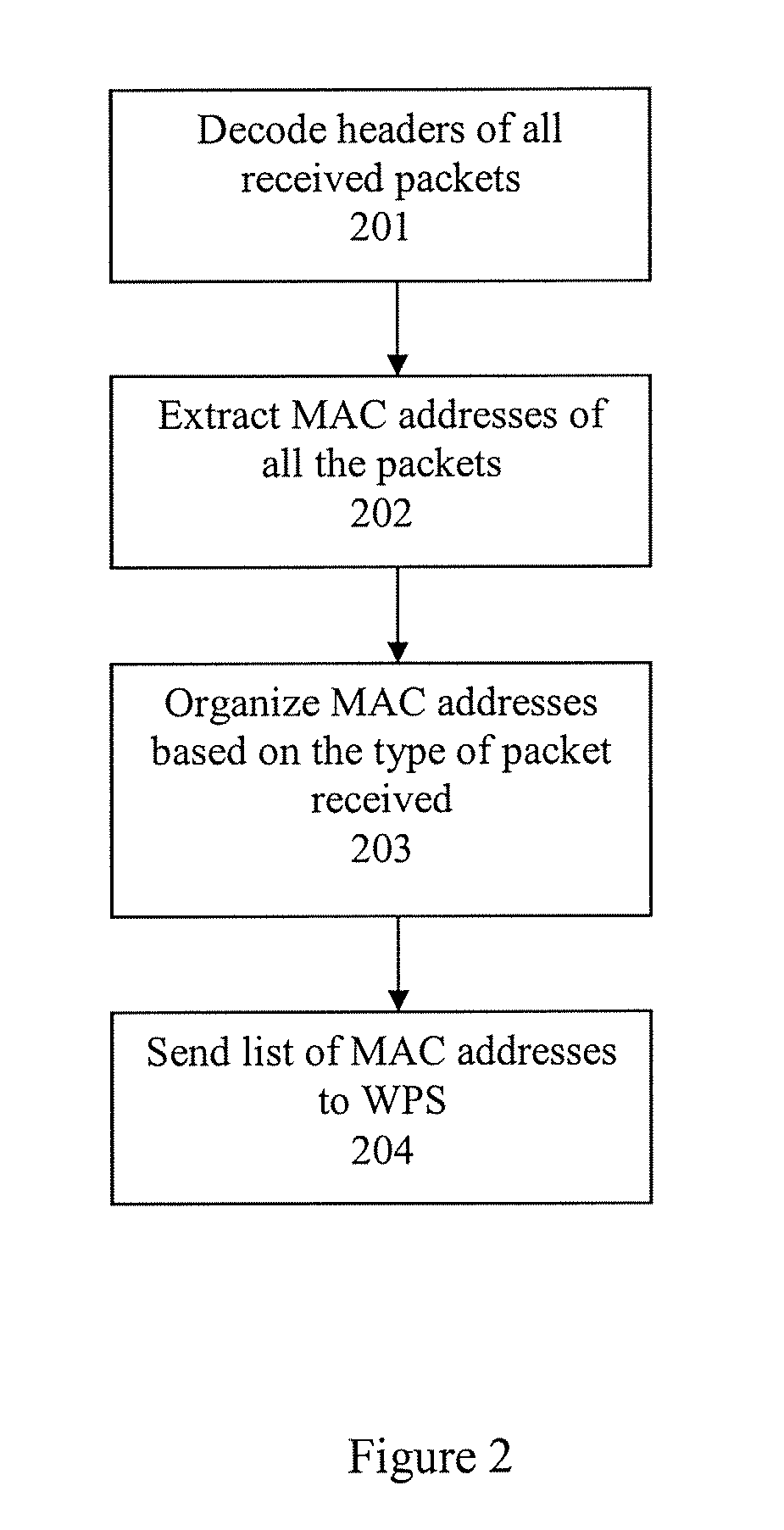
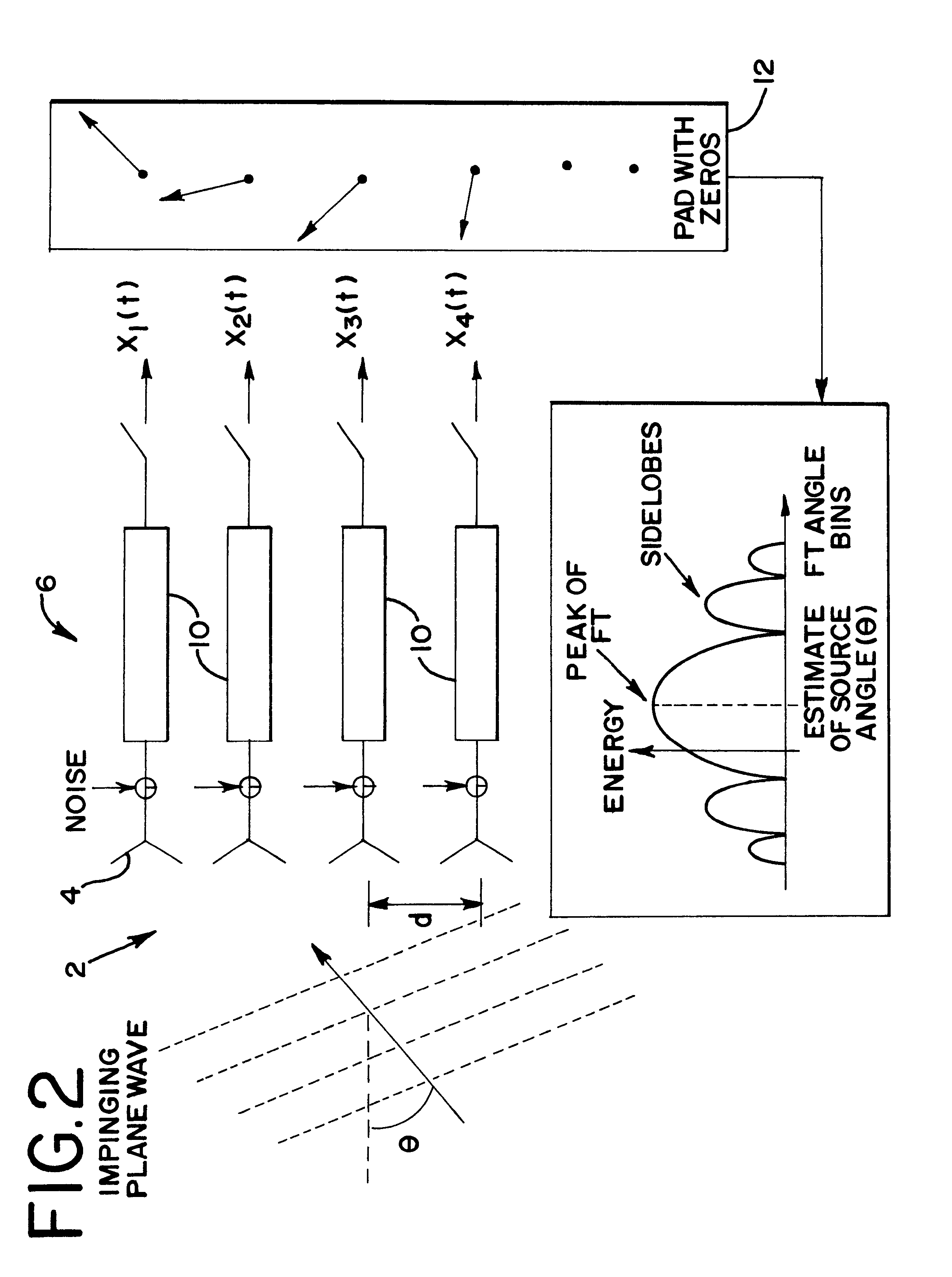
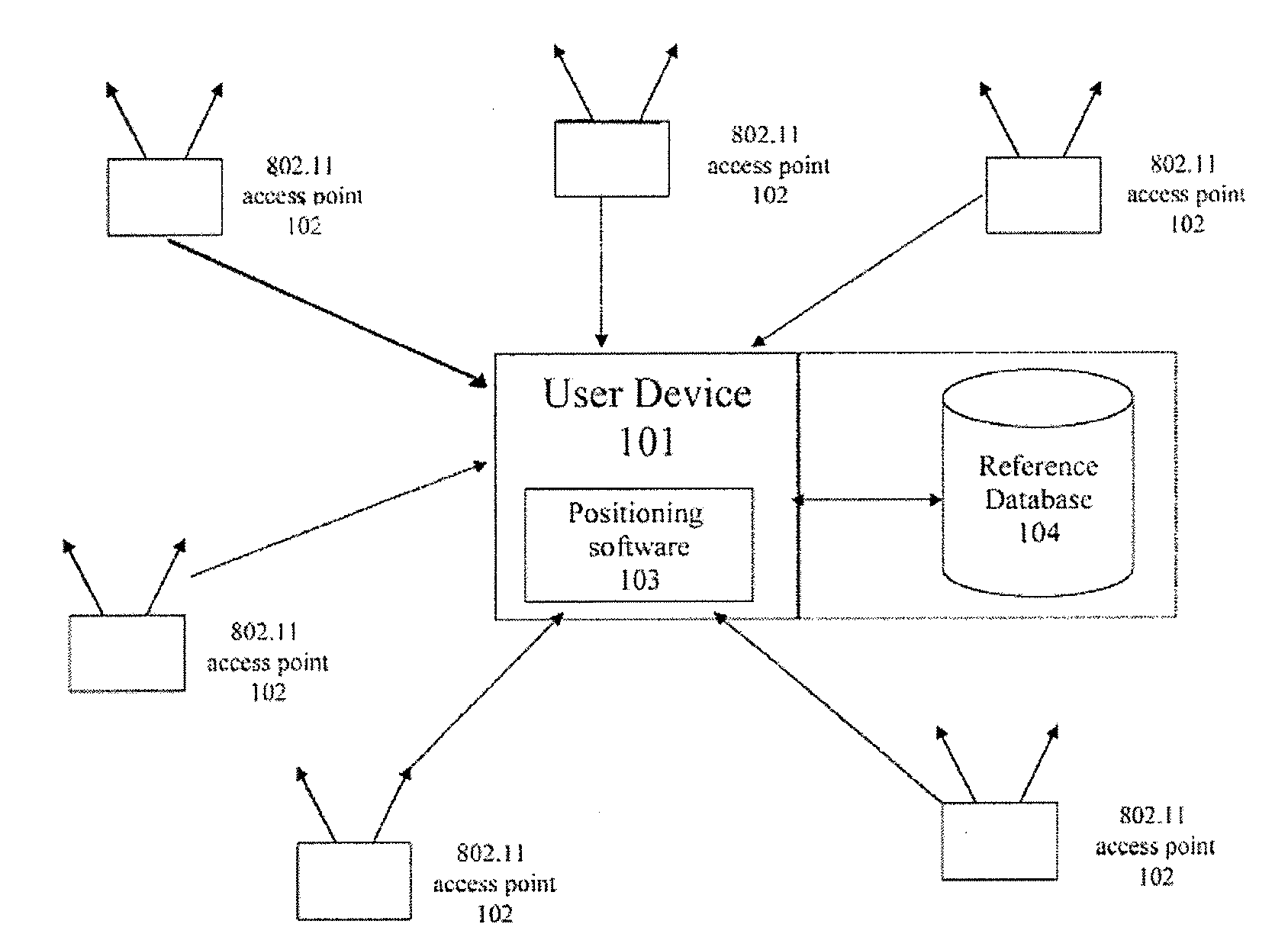
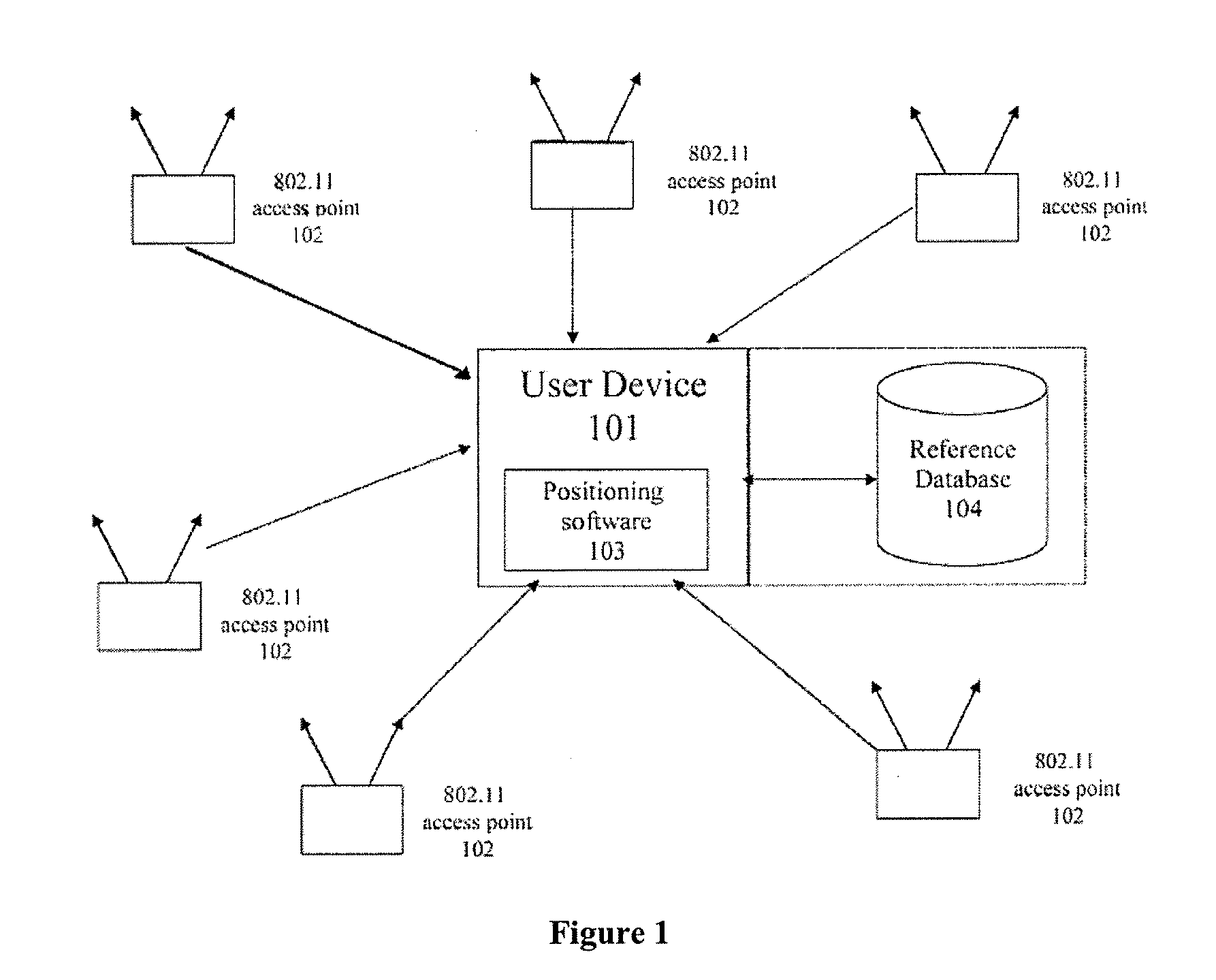
System and method of improving sampling of WLAN packet information to improve estimates of Doppler frequency of a WLAN positioning device
ActiveUS7768963B2Enhanced informationIncrease frequencyDirection finders using radio wavesNetwork topologiesReceived signal strength indicationComputer module
Systems and methods of improving sampling of WLAN packet information to improve estimates of Doppler frequency of a WLAN positioning device. A device estimates the position of itself. The device includes a WLAN radio module for receiving WLAN signals transmitted by WLAN APs in range of said device, extraction logic for extracting information from said received WLAN signals to identify the WLAN APs, and logic to cooperate with a WLAN-based positioning system to estimate the position of the device based at least in part on the extracted information identifying the WLAN APs in the range of said device. The WLAN radio module includes logic for measuring multiple received signal strength indicator (RSSI) values for sufficiently long WLAN packets to increase the sampled rate of RSSI of WLAN packets from WLAN APs and to thereby improve an estimate of the Doppler frequency of said device.
Owner:SKYHOOK WIRELESS
Miniature radio-acoustic sounding system for low altitude wind and precipitation measurements
InactiveUS6856273B1Improve accuracyRainfall/precipitation gaugesVolume/mass flow measurementTransceiverLength wave
The present invention is directed to a radio-acoustic sounding system for providing wind measurements at altitudes of 100 meters or less. Wind measurements are obtained by transmitting a pulse of audio frequency energy through one or more volumes corresponding to the coverage area of one or more radio frequency transceivers. The frequency of the audio pulse is selected to have a wavelength that is one-half the wavelength of the electromagnetic energy transmitted by the antenna or antennas. By monitoring a return radio frequency signal at selected times following the transmission of the audio pulse, wind data is obtained at selected altitudes. Wind speed and direction can be obtained by observing the Doppler frequency shift of return radio frequency signals, or by observing the amplitude of the return radio frequency signals. In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, precipitation measurements may be made by transmitting a radio frequency signal at the same radio frequency as is used in connection with wind measurements, and observing return radio frequency signals.
Owner:BOGNAR JOHN A
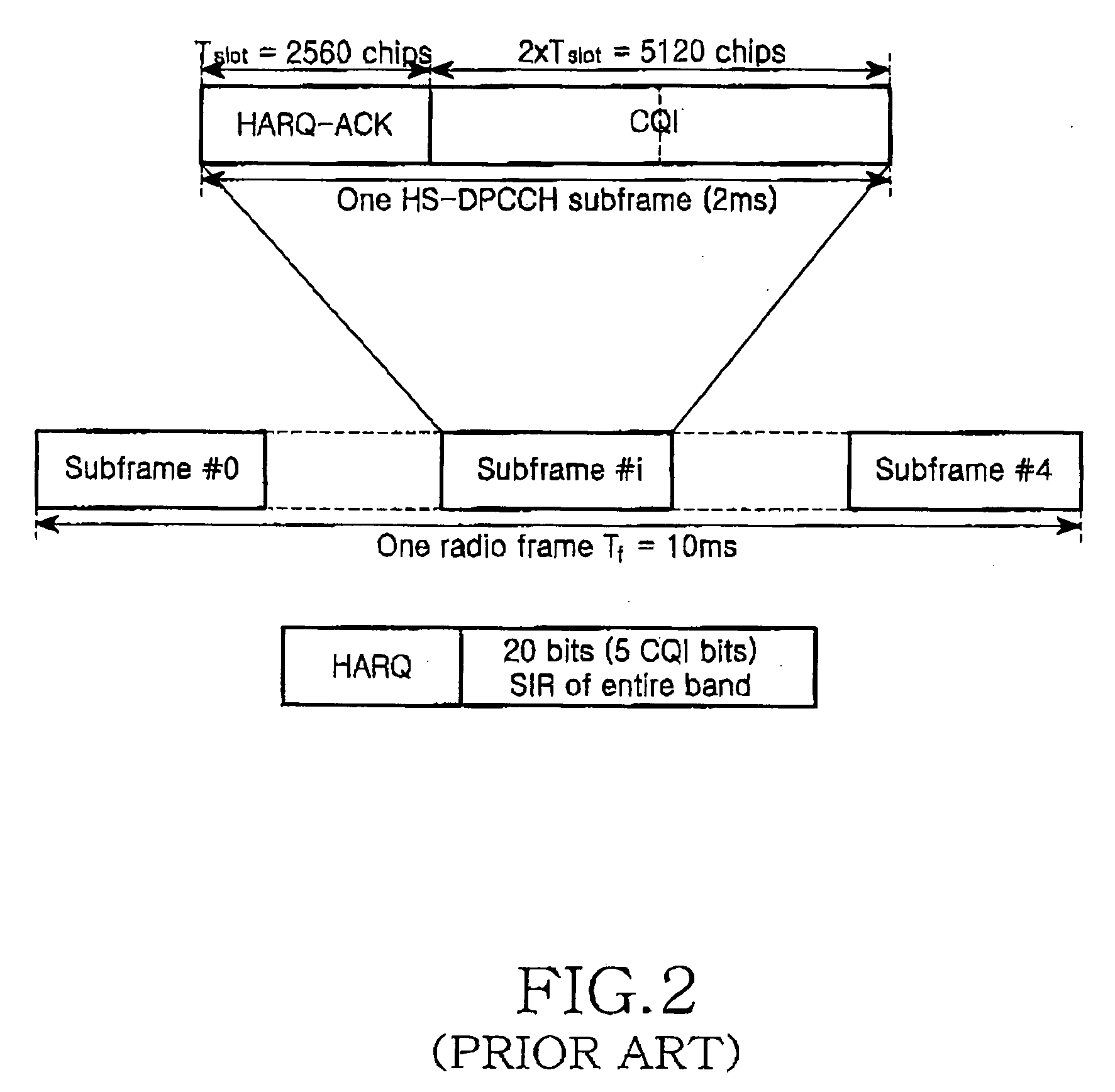
Method and apparatus for controlling transmission of channel quality information according to characteristics of a time-varying channel in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS20050191965A1Guaranteed normal transmissionEnergy efficient ICTSignal allocationTelecommunicationsInformation transmission
A method and apparatus for efficiently transmitting channel quality information on a radio channel in a mobile communication system are provided. The reporting cycle of channel quality information is changed adaptively according to time-varying characteristics associated with the Doppler frequency of a radio channel or the variation of the channel quality information. Therefore, the channel quality information is efficiently transmitted. Also, the decrease of unnecessary frequent information transmissions reduces an uplink interference power level and power consumption in user equipment (UE), as well.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
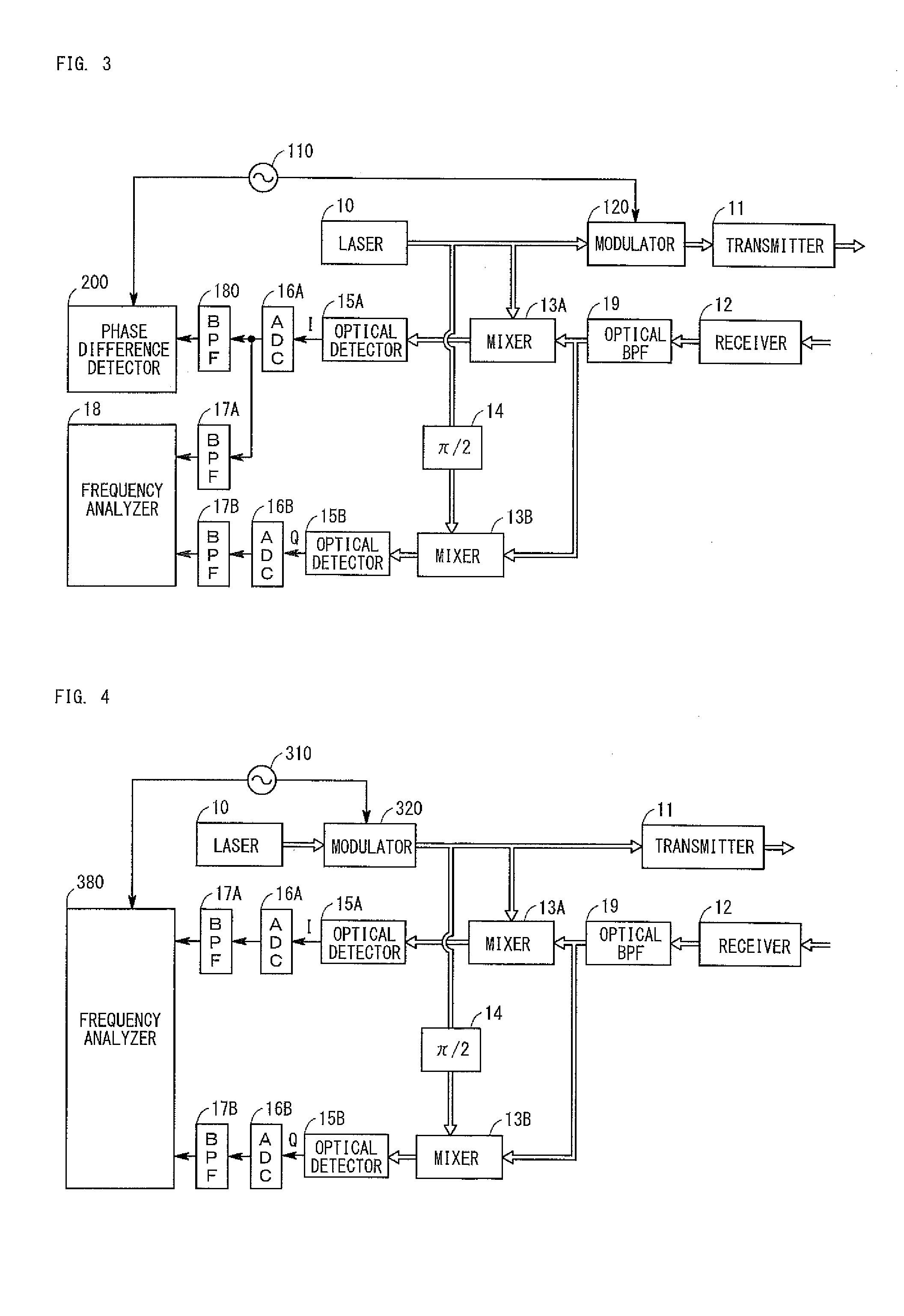
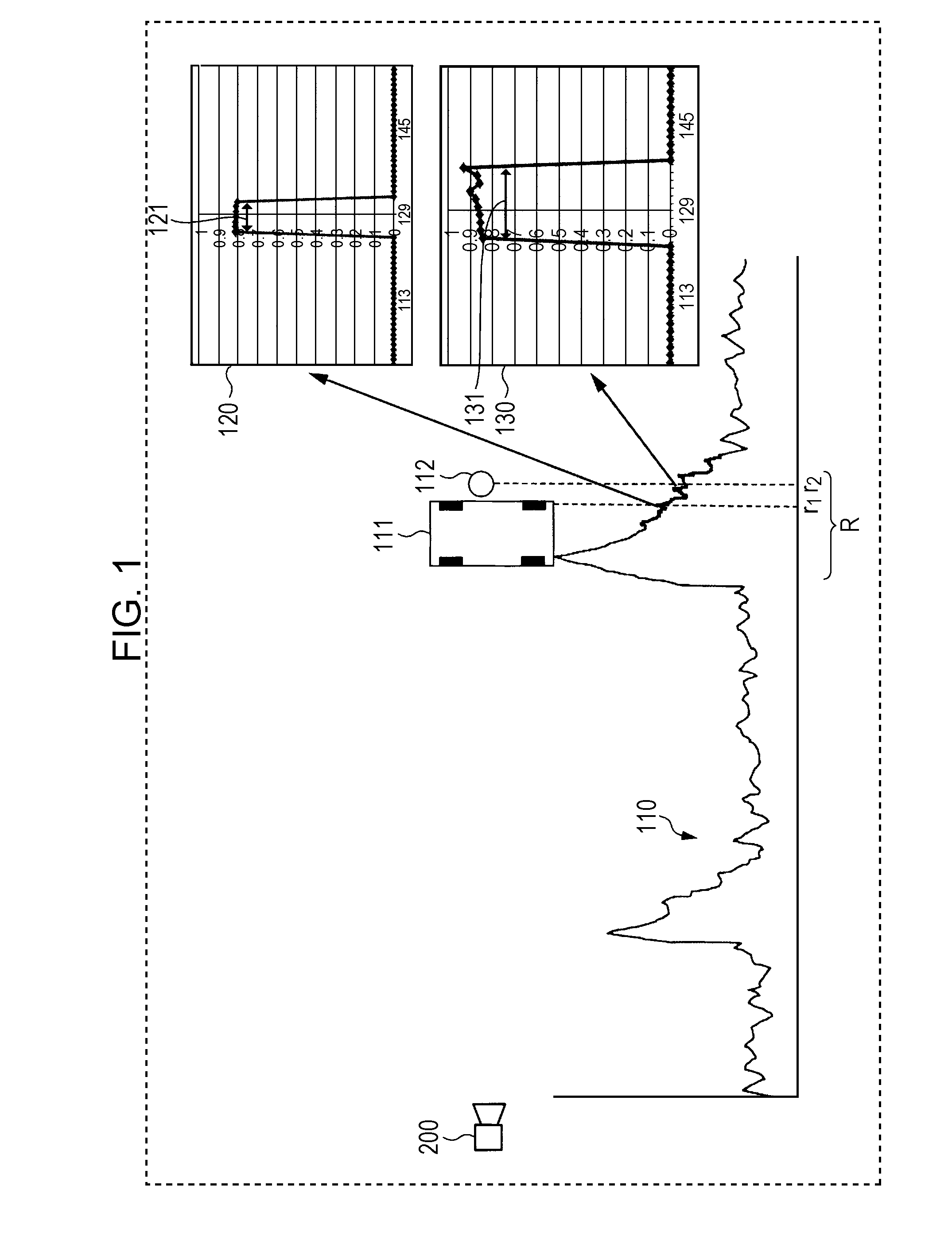
Radar apparatus and method of determining sign of velocity
ActiveUS20150185244A1Low costHigh sensitivityOptical rangefindersDevices using time traversedFrequency spectrumRadar
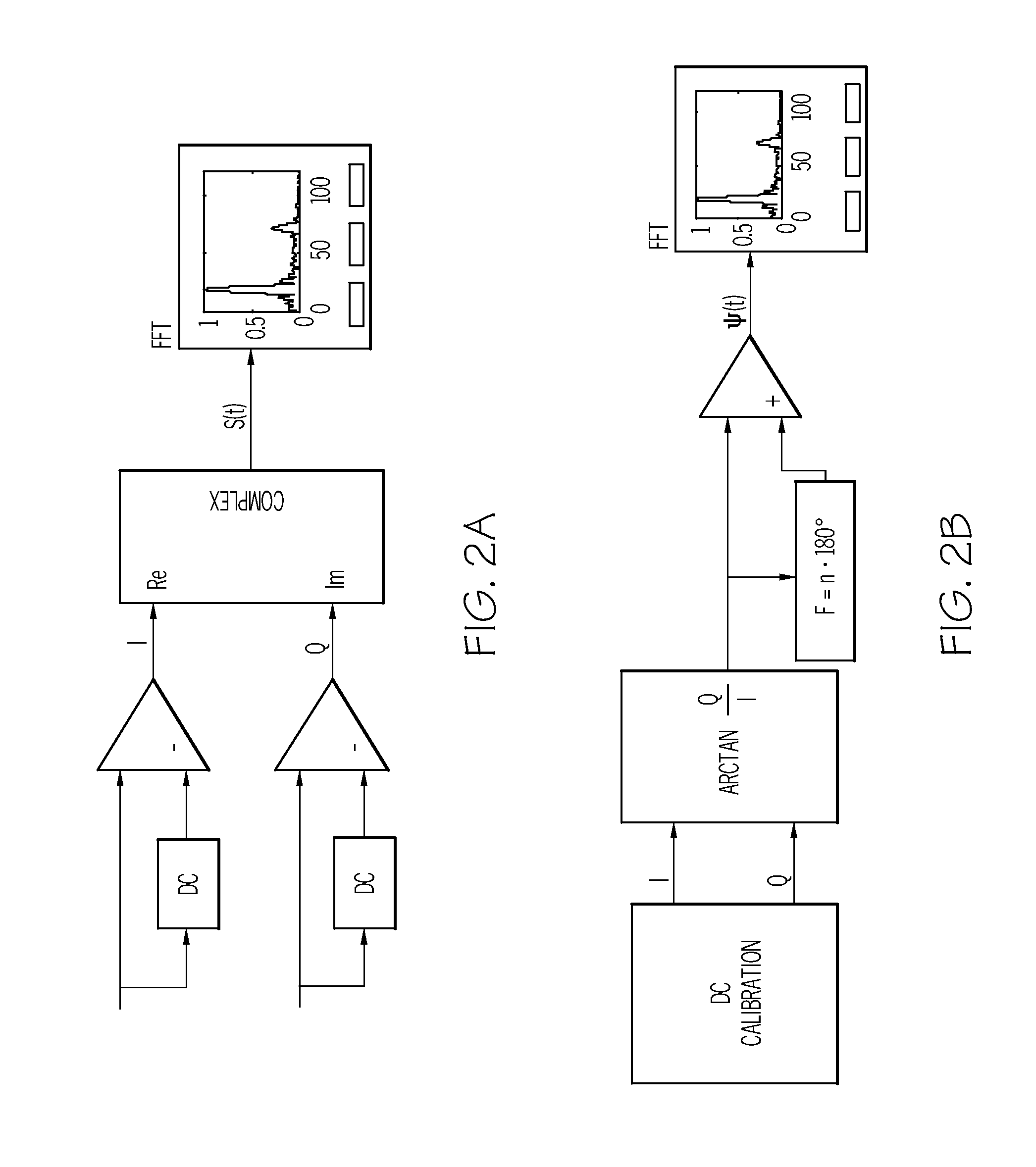
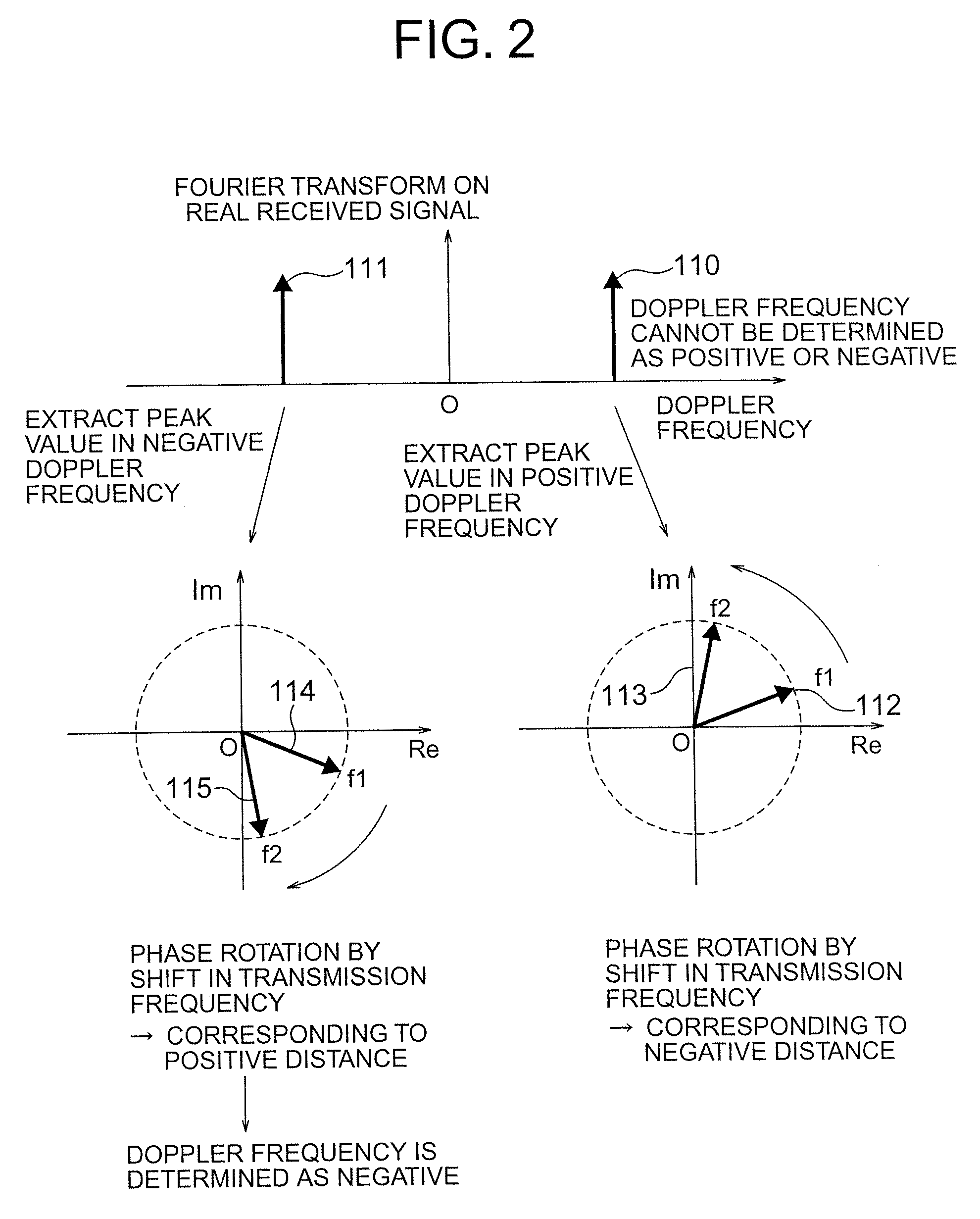
A radar apparatus which can simply determine the sign of velocity of an object is provided. Laser light reflected by the object undergoes quadrature optical heterodyne detection performed by mixers, optical detectors, and a π / 2 phase shifter, whereby I and Q component signals are output. A frequency analyzer performs FFT on a complex signal composed of the I component signal (real part) and the Q component signal (imaginary part) to thereby obtain its frequency spectrum. Since the frequency spectrum is calculated without being folded back even in a region where the frequency is negative, the sign of the Doppler frequency fd can be determined. When the Doppler frequency fd is positive, the sign of the velocity of the object is a direction toward the radar apparatus. When the Doppler frequency fd is negative, the sign of the velocity of the object is a direction away from the radar apparatus.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
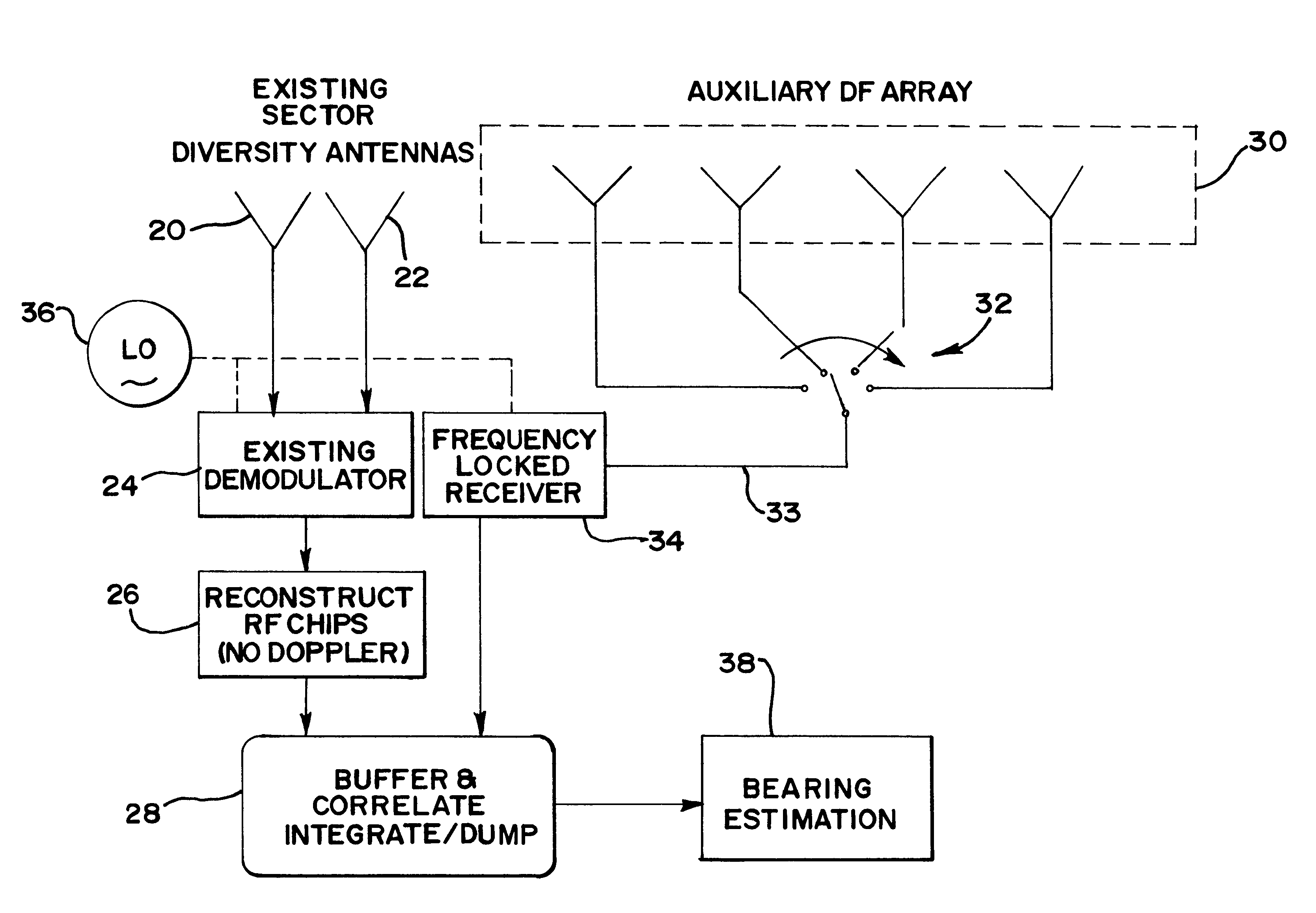
Position location method and apparatus for a mobile telecommunications system
InactiveUS6489923B1Limited bandwidthEasy CalibrationRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsBeacon systems using radio wavesRelative phaseDirectional antenna
In a cellular mobile telecommunications system the position of a mobile station can be estimated in terms of its bearing and range from a cell site. A multi-element direction finding antenna at the cell site receives signals from the mobile station and a receiver circuit estimates the bearing using the relative phase of signals received at different antenna elements and estimates the range by measuring round trip delay of signals to and from the mobile station. Motion of the mobile station can introduce errors into the bearing estimate due to frequency offset and frequency spread when element sampling is non-simultaneous. Compensation for these errors is introduced by using signal samples successively received at the same antenna element to estimate Doppler frequency offset and spread. It is necessary to ensure accurate calibration of the direction finding antenna and the receiver circuit. This is done by injecting calibration signals into the circuit near the antenna or into the antenna itself from a near field probe. Other aspects of calibration, such as antenna position, are calibrated using a remote beacon. A beacon emulating a mobile station but at a fixed, known location, or a beacon at an adjacent cell site may be used.
Owner:APPLE INC
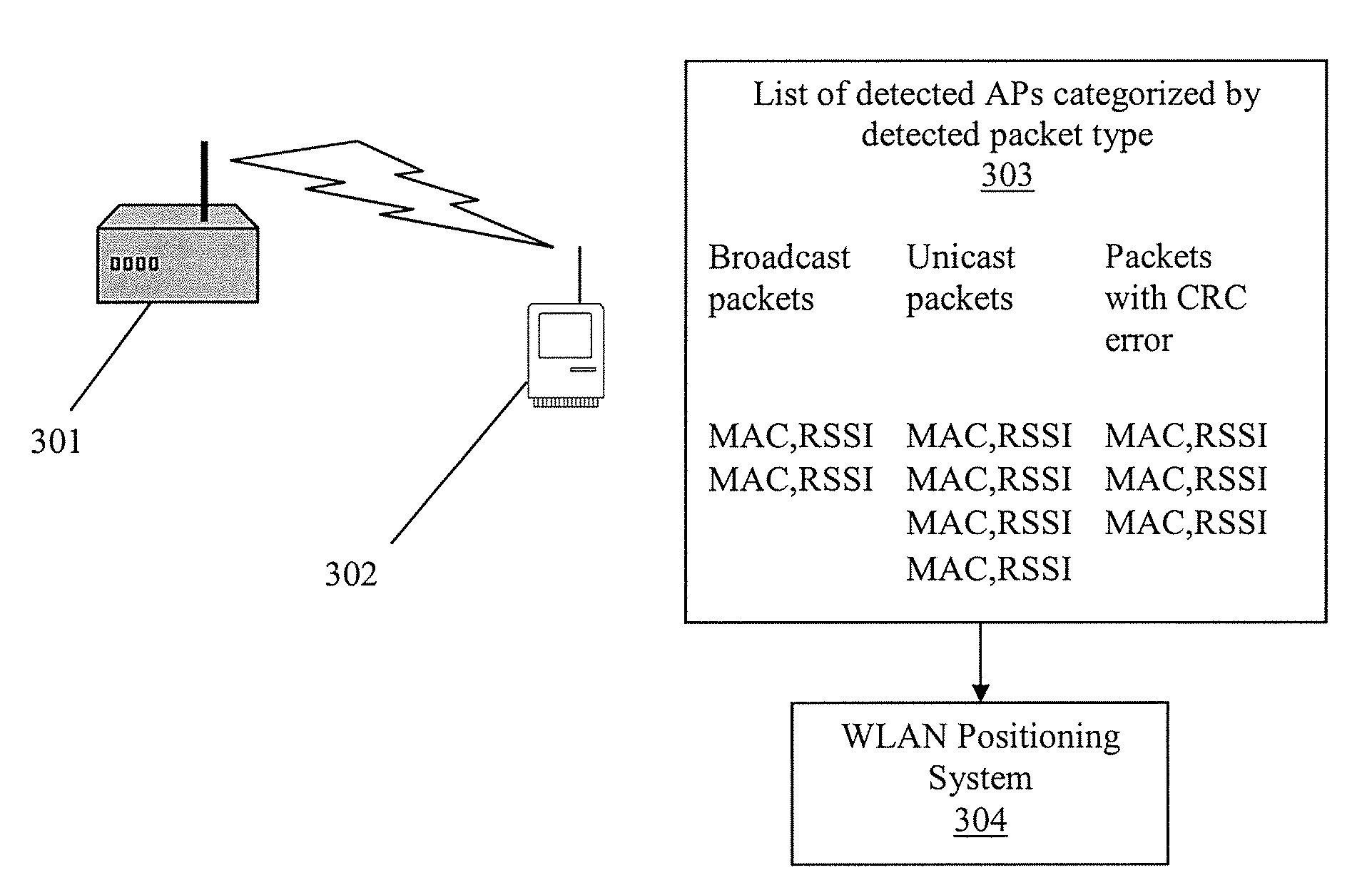
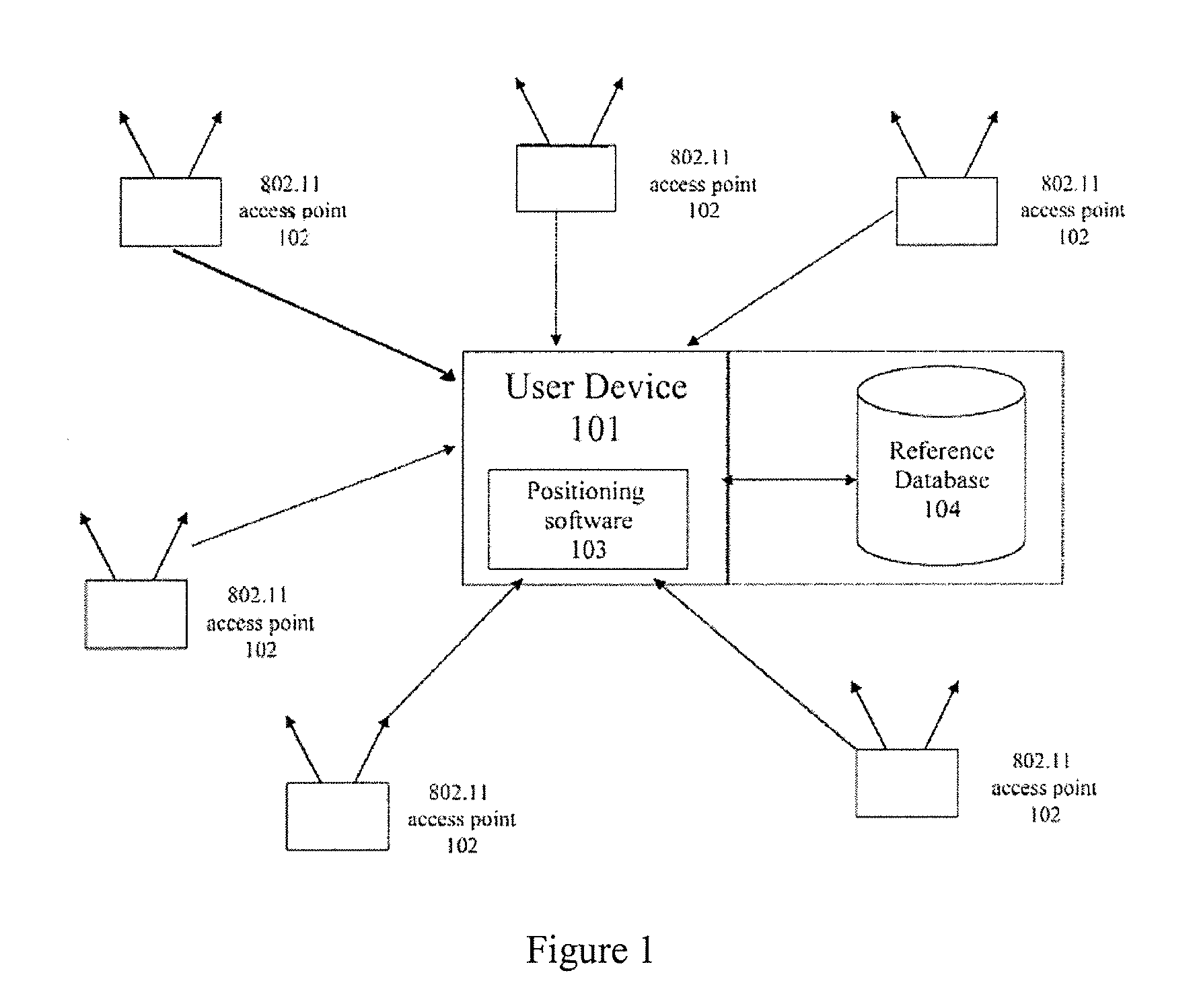
System and method of improving sampling of WLAN packet information to improve estimates of doppler frequency of a WLAN positioning device
ActiveUS20080008120A1Enhanced informationIncrease frequencyNetwork topologiesPosition fixationReceived signal strength indicationComputer module
Systems and methods of improving sampling of WLAN packet information to improve estimates of Doppler frequency of a WLAN positioning device. A device estimates the position of itself. The device includes a WLAN radio module for receiving WLAN signals transmitted by WLAN APs in range of said device, extraction logic for extracting information from said received WLAN signals to identify the WLAN APs, and logic to cooperate with a WLAN-based positioning system to estimate the position of the device based at least in part on the extracted information identifying the WLAN APs in the range of said device. The WLAN radio module includes logic for measuring multiple received signal strength indicator (RSSI) values for sufficiently long WLAN packets to increase the sampled rate of RSSI of WLAN packets from WLAN APs and to thereby improve an estimate of the Doppler frequency of said device.
Owner:SKYHOOK WIRELESS
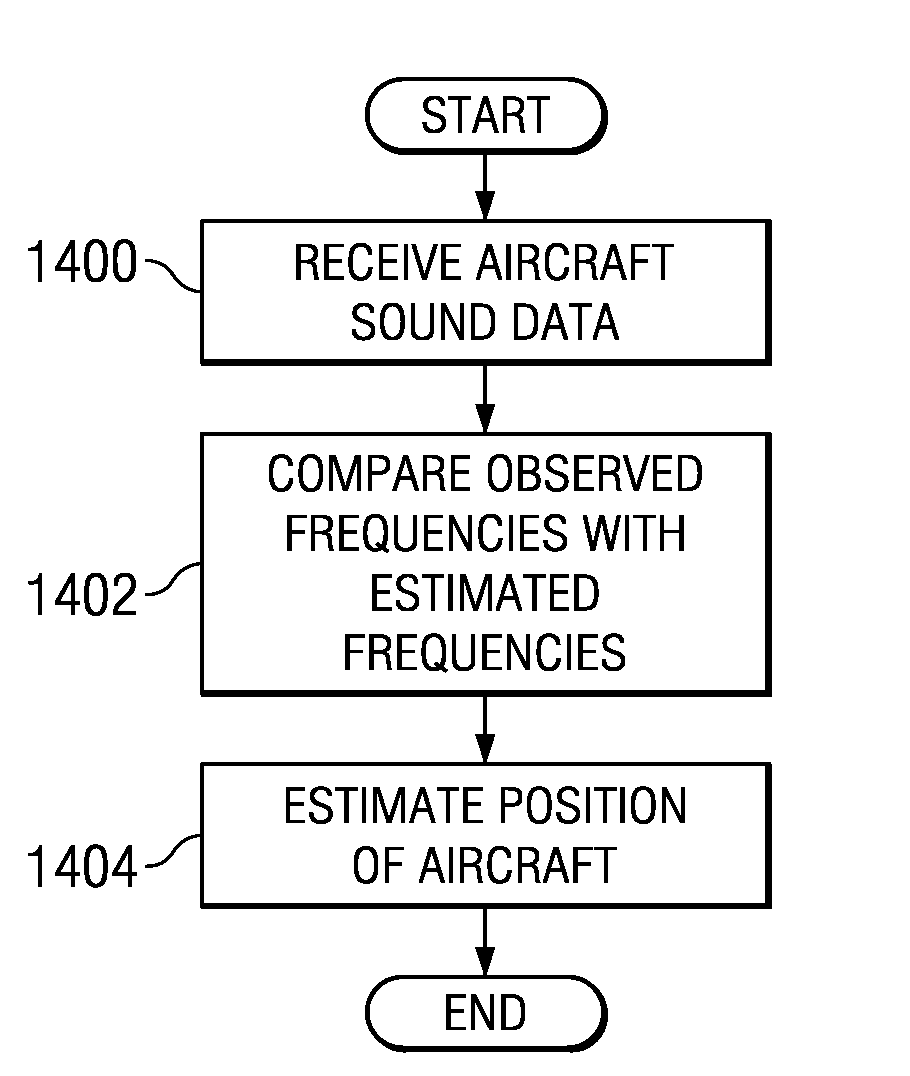
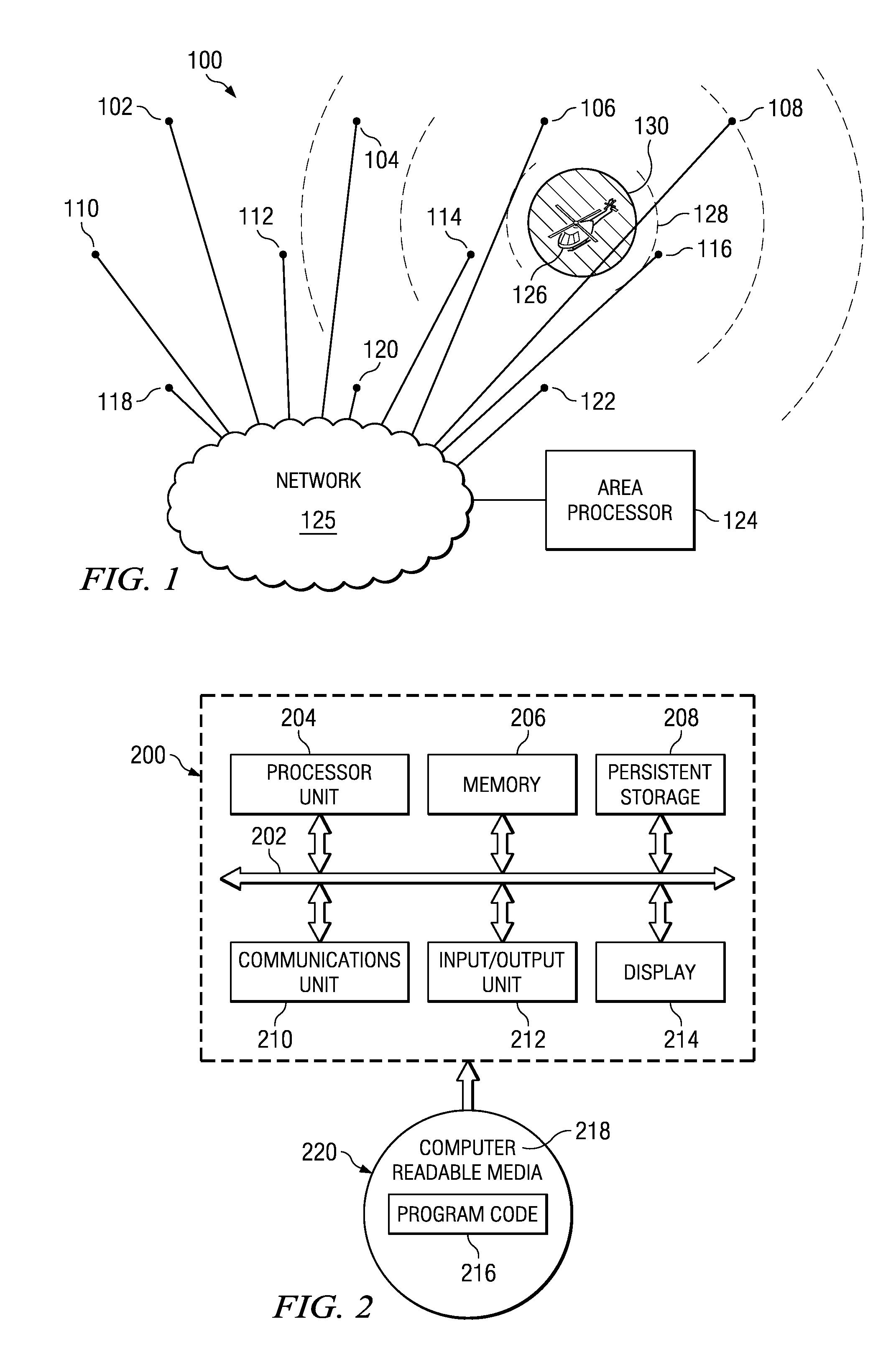
Acoustic wide area air surveillance system
ActiveUS20090257314A1Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationLocation detectionWide area
A method and apparatus for detecting an aircraft. The method is provided for wide area tracking of aircraft. An acoustic emission of the aircraft is detected from a plurality of locations. A position of the aircraft at a set of times is estimated by comparing a set of harmonically related Doppler shifted frequencies for the acoustic emission to an expected zero Doppler shifted frequency of the aircraft to form an estimated position. The position of the aircraft and a heading of the aircraft are tracked using the estimated position. The aircraft type is classified based on the corresponding set of zero Doppler frequencies at each acoustic sensor.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Methods and systems for stationary user detection in a hybrid positioning system
This disclosure describes methods and systems for stationary user detection in a hybrid location system. In some embodiments, the method for determining whether a satellite enabled device is stationary by measuring the Doppler frequency of received satellite signals can include acquiring satellite measurements from at least two satellites, wherein the satellite measurements include Doppler frequency measurements, acquiring a rough estimate of location of the satellite enabled device and calculating an internal frequency offset of satellite enabled device.
Owner:SKYHOOK WIRELESS
Obstacle and terrain avoidance sensor
InactiveUS20040178943A1Improve elevation accuracyHigh resolutionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionClassical mechanicsLight beam
A method of terrain mapping and / or obstacle detection for aircraft, comprising: (a) transmitting a non-scanning beam that illuminates the terrain and / or obstacles; (b) receiving a Doppler shifted signal that is Doppler frequency shifted by an amount dependent on an angle between a line of flight of the aircraft and scatterers that reflect the transmitted beam; (c) determining the angle from the Doppler frequency; (d) determining the range of at least some of said scatterers; and (e) determining the azimuth and elevation of the scatterers.
Owner:RODRADAR LTD
Digital beamforming for an electronically scanned radar system
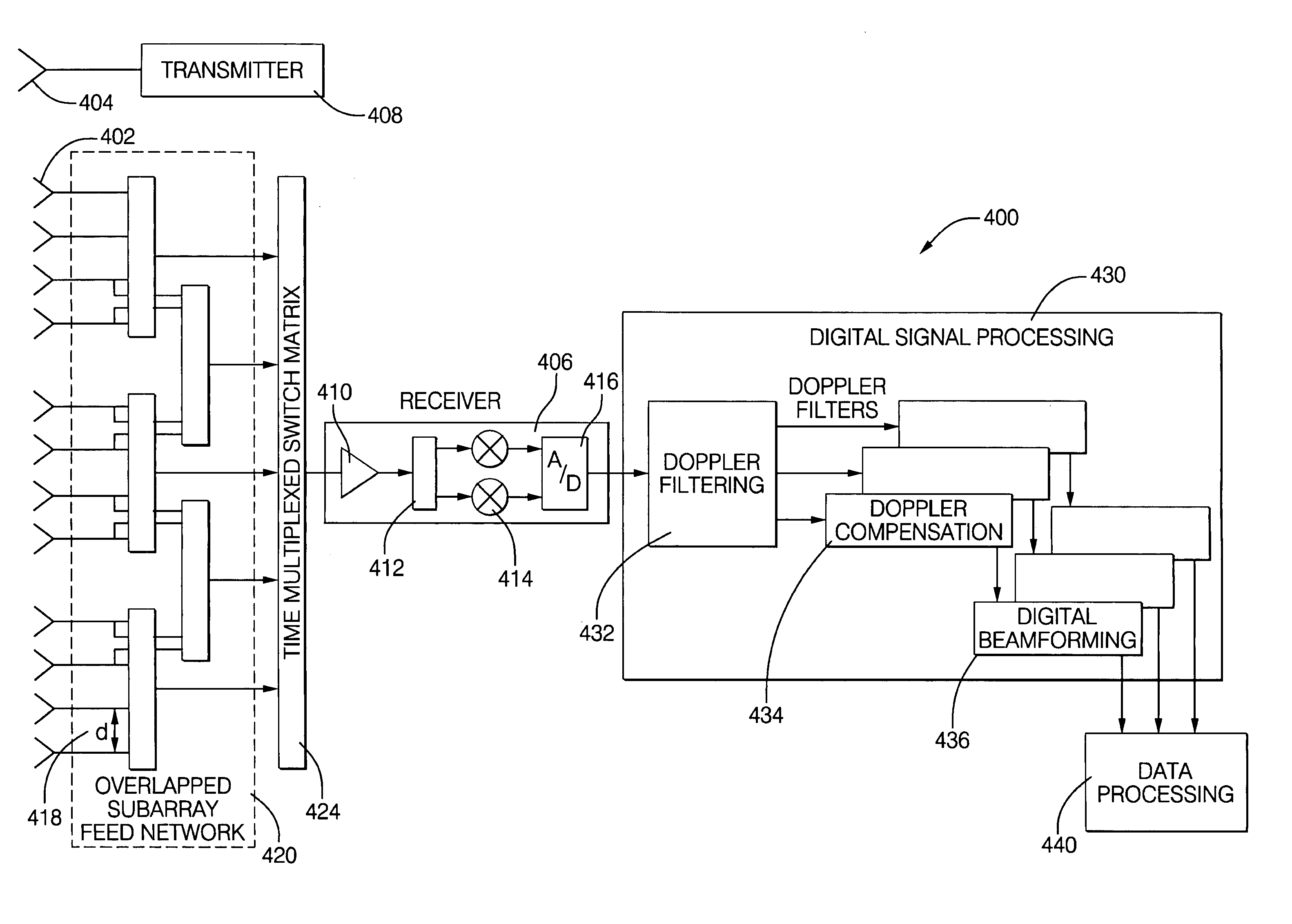
ActiveUS20070001897A1Improve performanceLow costParticular array feeding systemsRadio transmissionRadar systemsGrating lobe
Digital beamforming is provided for use with electronically scanned radar. In an aspect, the present invention provides enhanced sensitivity, wide angle or field of view (FOV) coverage with narrow beams, minimized number of receivers, reduced sidelobes, eliminated grating lobes and beam compensation for target motion. In an aspect, the present invention employs a uniform overlapped subarray feed network, a time multiplexed switch matrix, and a restructured digital signal processor. Antenna channels share a receiver, rather than maintain a dedicated receiver for each antenna element, as in conventional systems. In an aspect, Doppler / frequency filtering is performed on each antenna element or subarray output prior to digital beamforming. Further, Doppler compensation is employed following Doppler / frequency filtering, followed by digital beamforming.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Millimeter wave quick frequency conversion radar target simulator
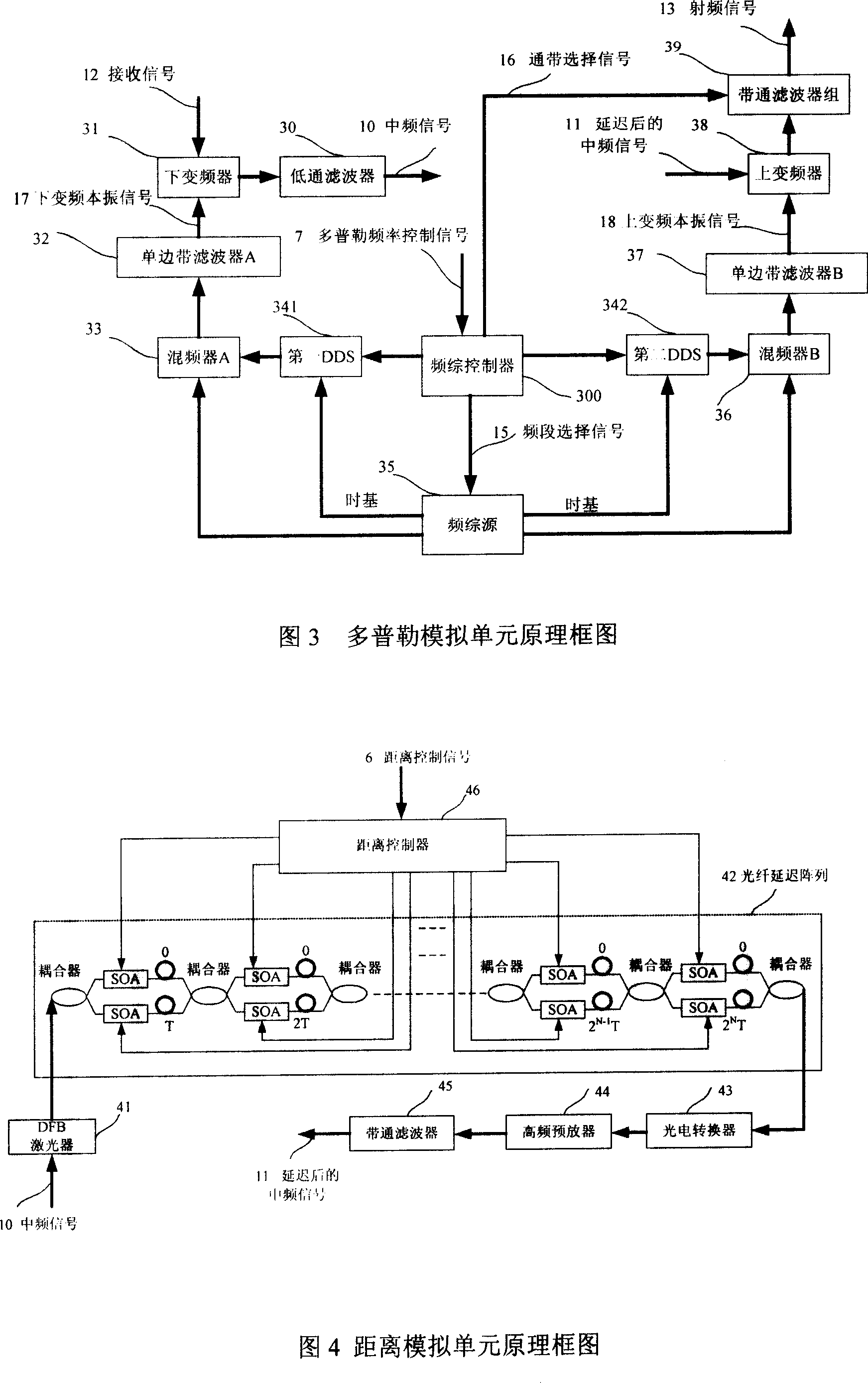
InactiveCN101082667ALow costImprove confidentialityCosmonautic condition simulationsSimulatorsFrequency changerBandpass filtering
The invention discloses a frequency-change radar goal emulator of millimeter wave, which comprises the following parts: control unit, transceiver unit, Doppler analog unit, distant analog unit and amplitude analog unit, wherein the radar signal enters into the Doppler analog unit through transceiver unit, which produces middle-frequency signal through lower frequency-changer and low-pass filter of the Doppler analog unit; the upper frequency-changer and band-pass filter group of Doppler analog unit produces RF signal; the difference of local oscillator frequency of upper and lower frequency-changers analogs the Doppler frequency shift of goal; the RF signal generates launching signal through changing the echo amplitude of goal simulated by amplitude analog unit, which is transmitted by transceiver unit; the control unit transmits control signal for other four units according to the analog parameter such as input distance, speed and amplitude; the radar signal passes the emulator to provide an analog signal with Doppler frequency shift, signal amplitude fluctuation and distant delay to radar, which provides estimating platform for working property testing for radar.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Radar moving target radon-fractional Fourier transform long-time phase-coherent accumulation detection method
ActiveCN103176178AEffective accumulationImprove complex (noise) ratioWave based measurement systemsRadar signal processingConstant false alarm rate
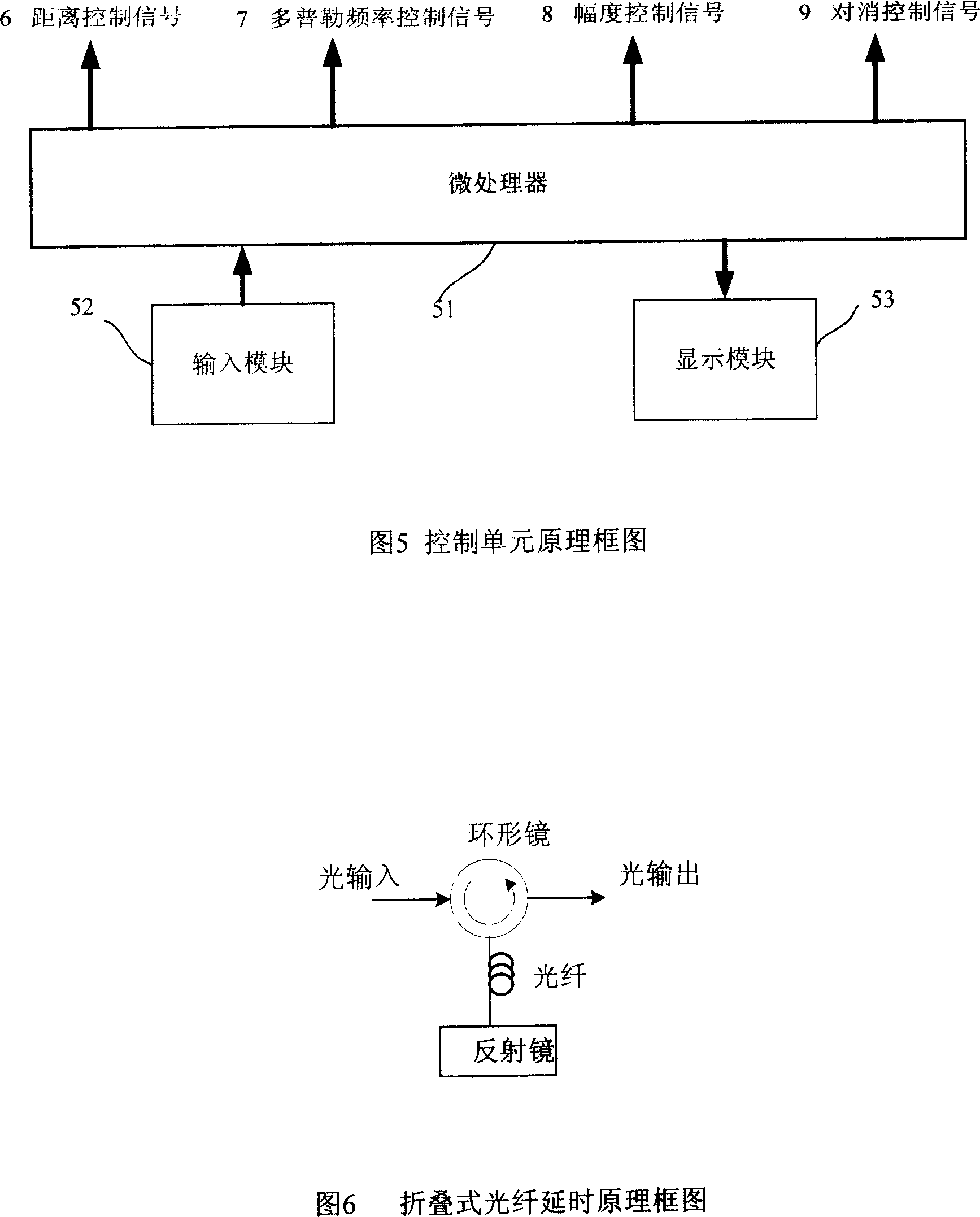
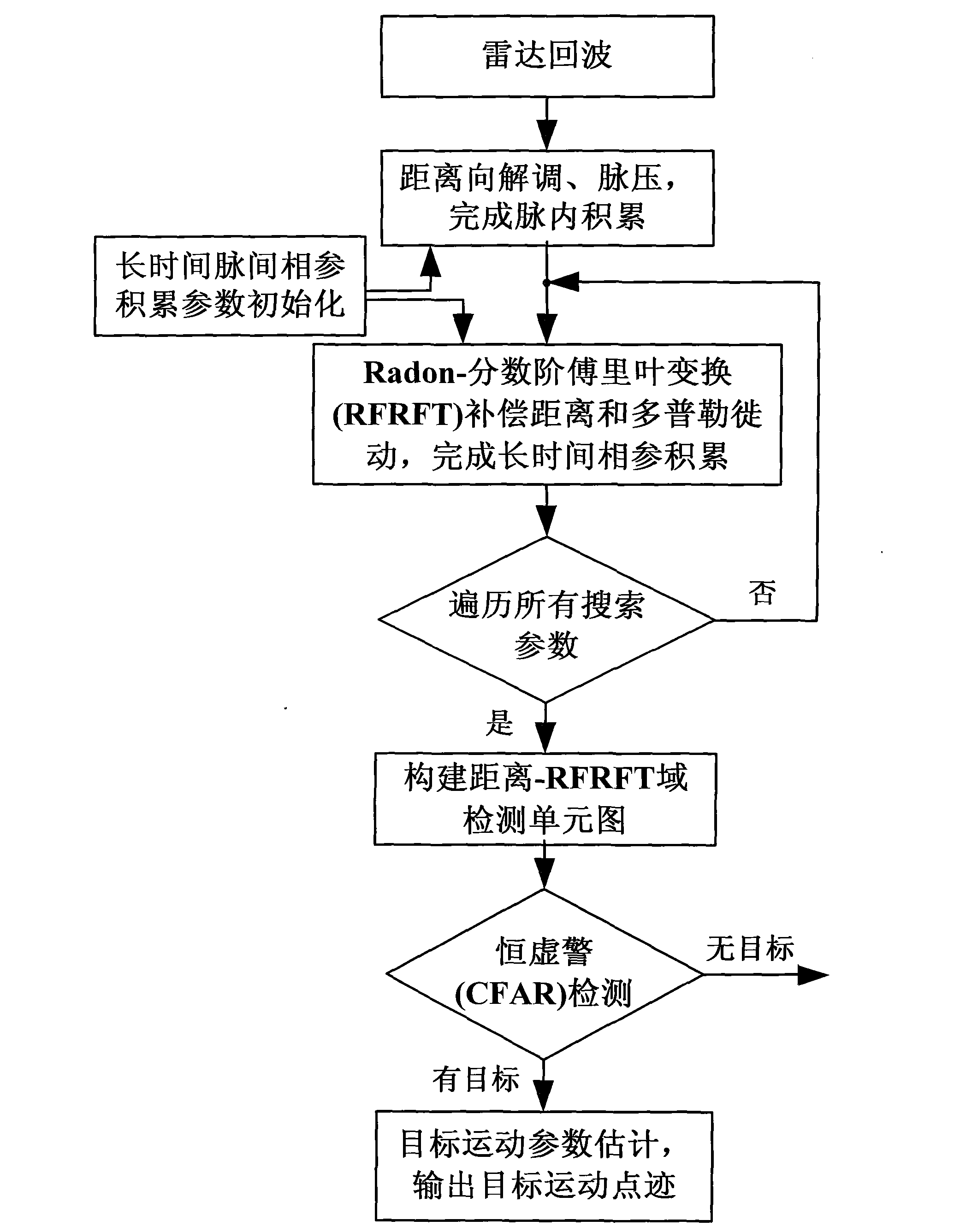
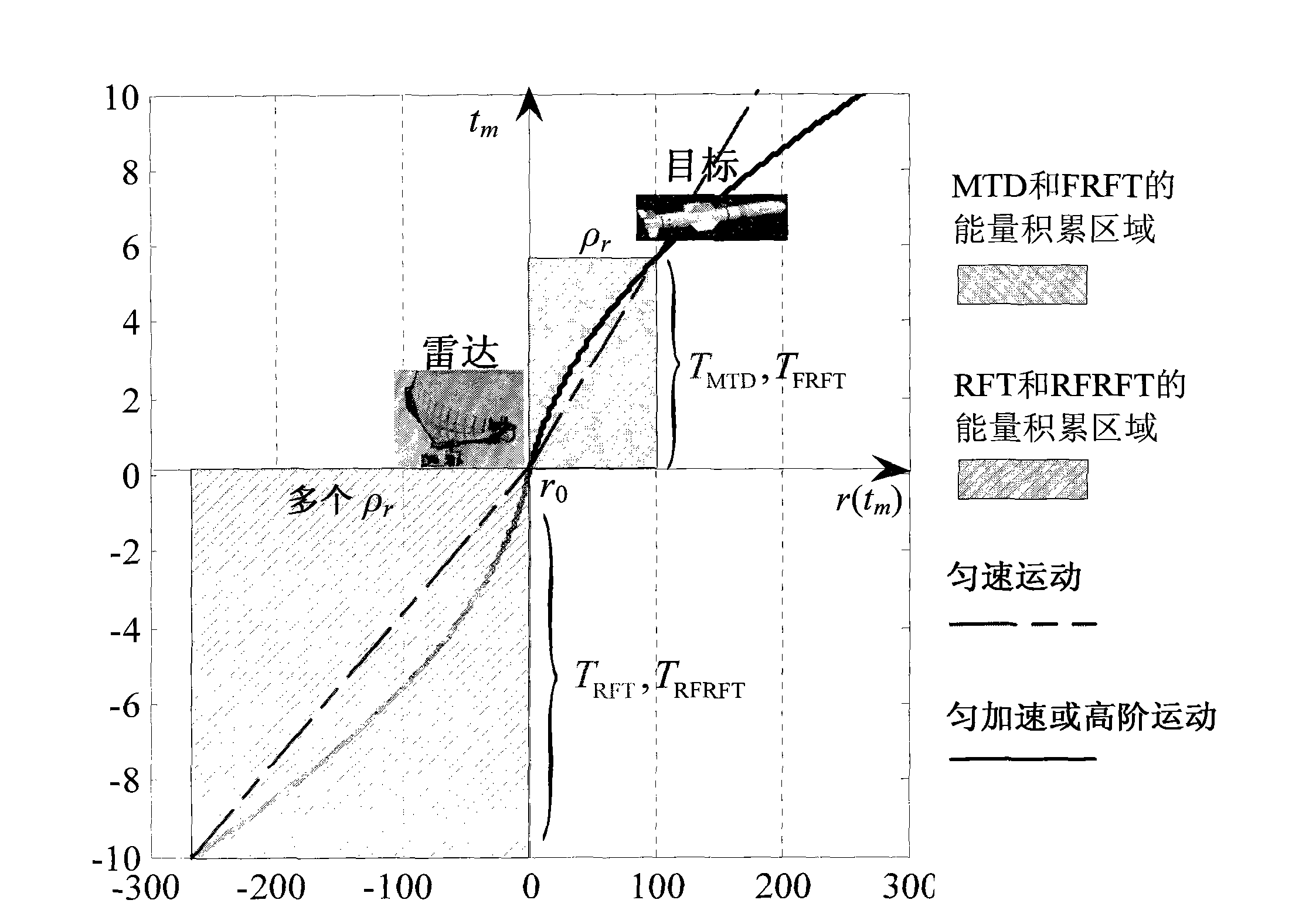
The invention relates to a radar moving target Radon-fractional Fourier transform (RFRFT) long-time phase-coherent accumulation detection method, and belongs to the technical field of radar signal processing and detection. The radar moving target Radon-fractional Fourier transform long-time phase-coherent accumulation detection method includes steps of 1), performing range demodulation and pulse pressure for radar echo to complete intra-pulse accumulation; 2), initializing parameters; 3), completing long-time inter-pulse phase-coherent accumulation by RFRFT compensation distance and Doppler frequency migration; 4), traversing all search parameters and creating a distance-RFRFT domain detection unit graph; 5), performing constant false alarm rate detection for the detection unit graph; and 6), estimating movement parameters of a target and outputting movement point traces. The radar moving target Radon-fractional Fourier transform long-time phase-coherent accumulation detection method has the advantages that amplitude information and phase information of the echo of the moving target are simultaneously utilized for long-time phase-coherent accumulation, the distance and the Doppler frequency migration in a long-time accumulation procedure are compensated, background clutter and noise are effectively suppressed, an accumulation gain is increased, dim moving targets in the heavy cluster can be detected, the movement point traces of the target can be acquired, and the method has popularization and application value.
Owner:NAVAL AVIATION UNIV
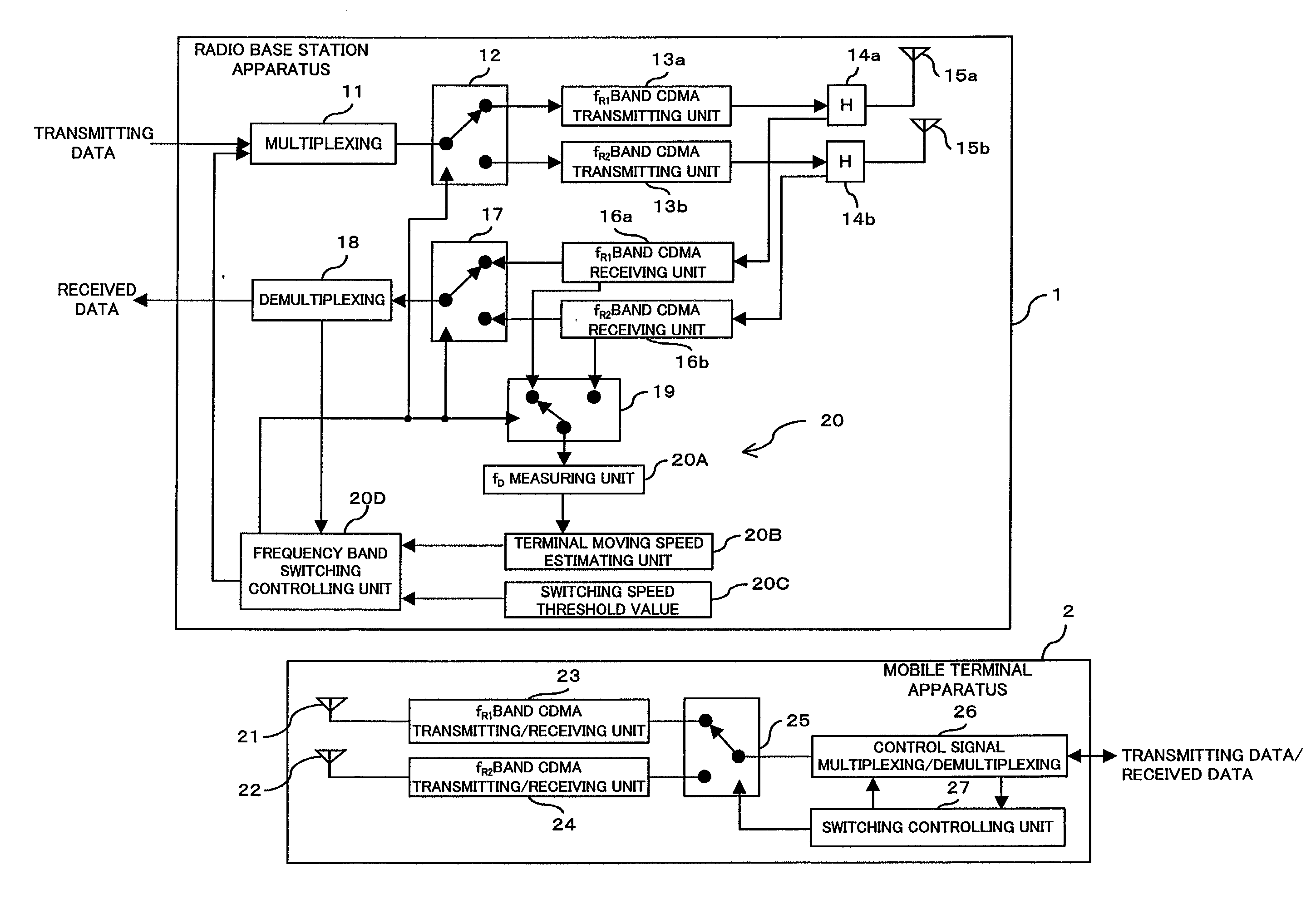
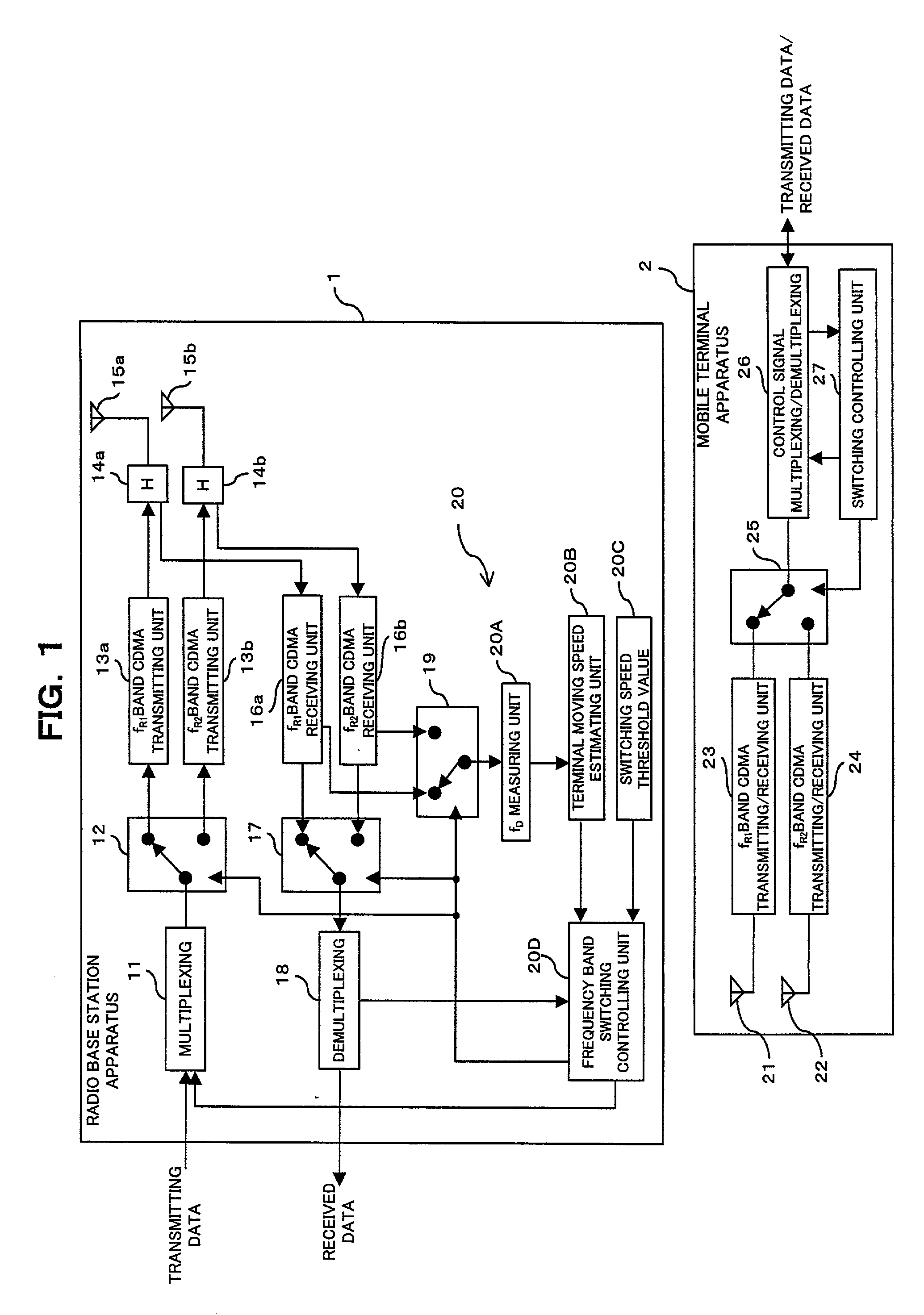
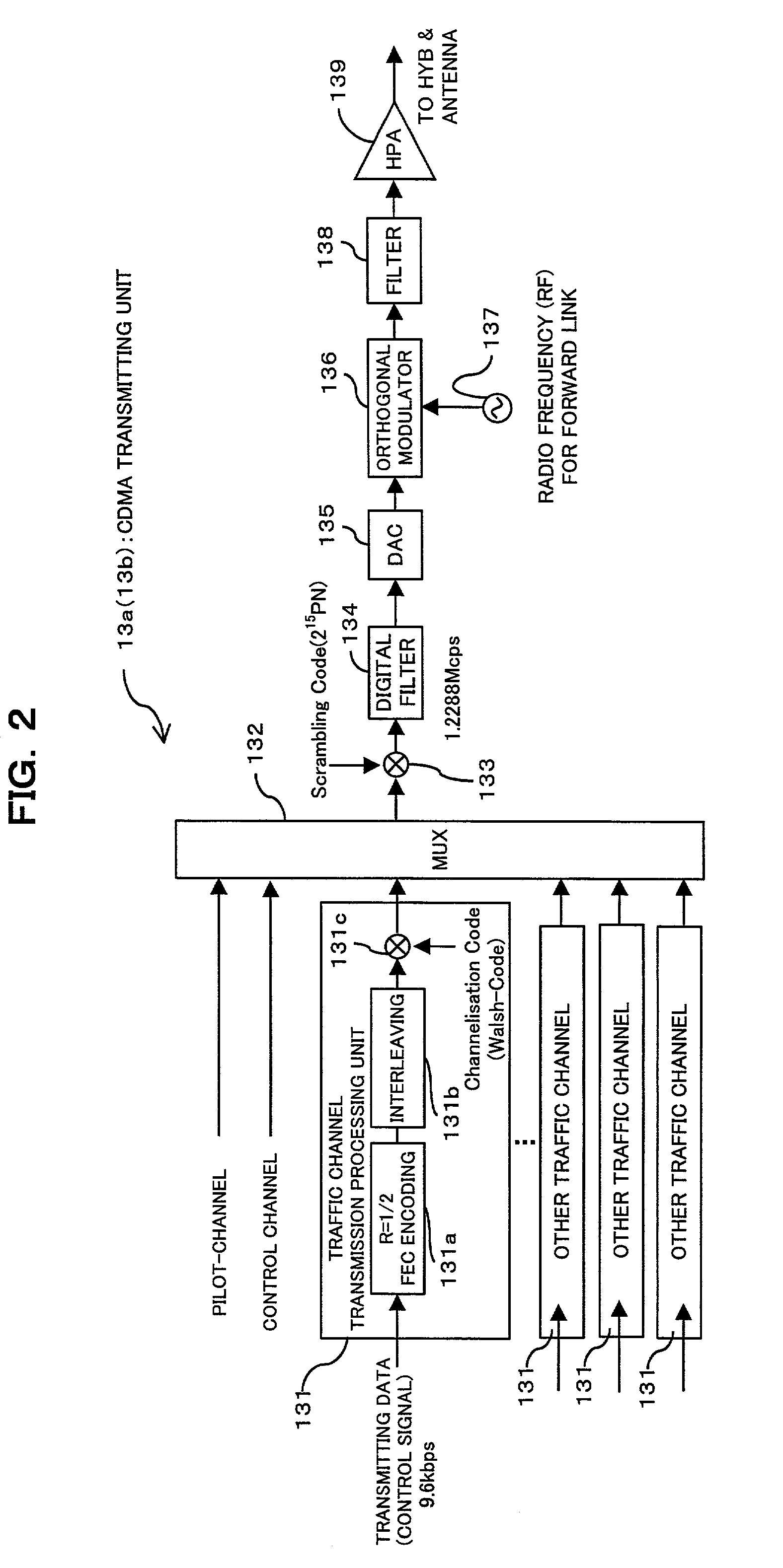
Mobile communication system, and a radio base station, a radio apparatus and a mobile terminal
InactiveUS20030064729A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionLow speedLow frequency band
A mobile communication system comprises a detecting unit to detect information concerning a moving speed of a mobile terminal, and a selection controlling unit to select a use frequency in a higher frequency band when the speed information detected by the detecting unit is a higher speed, while selecting the use frequency in a lower frequency band when the detected information is a lower speed, and assigning it to the mobile terminal. In a mobile communication system in which a relationship between a terminal moving speed (Doppler frequency) and transmission quality degradation is non-monotonous, the communication quality can be improved and the channel capacity can be increased.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Radar apparatus and object sensing method
A radar apparatus includes an antenna that receives echo signals, each of the echo signals being a radar signal reflected by one or more objects; a Doppler-frequency acquirer that acquires Doppler frequencies at each range bin from the received echo signals; a direction correlation power-value calculator that calculates direction correlation power values for respective combinations of the Doppler frequencies and at least one of a distance to the one or more objects and an arrival direction of the echo signals, each direction correlation power value indicating a strength of a corresponding echo signal; and a normalized direction correlation-value calculator that calculates, for the respective combinations, normalized direction correlation values, each normalized direction correlation value indicating a probability of the arrival direction of the corresponding echo signal.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
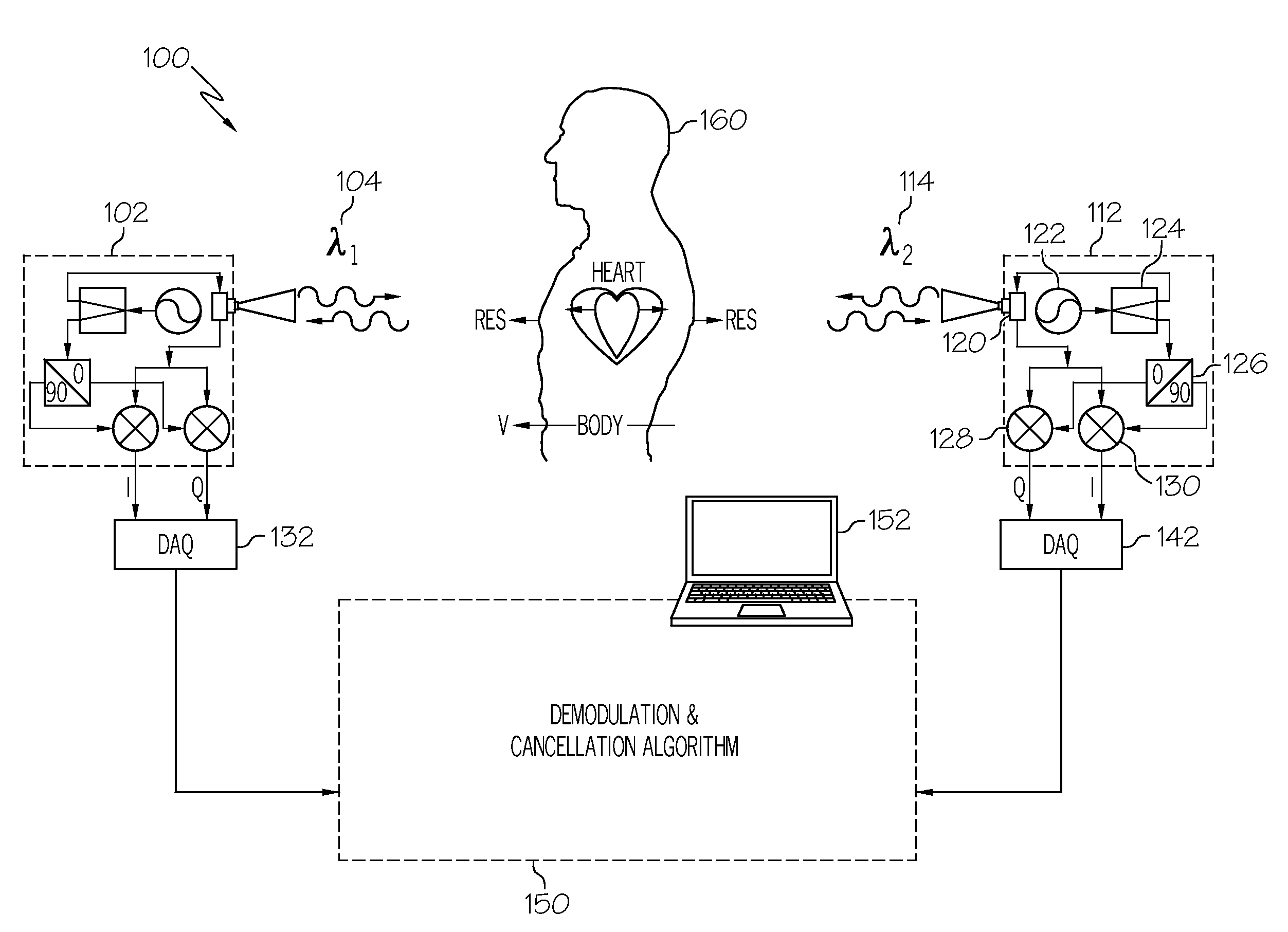
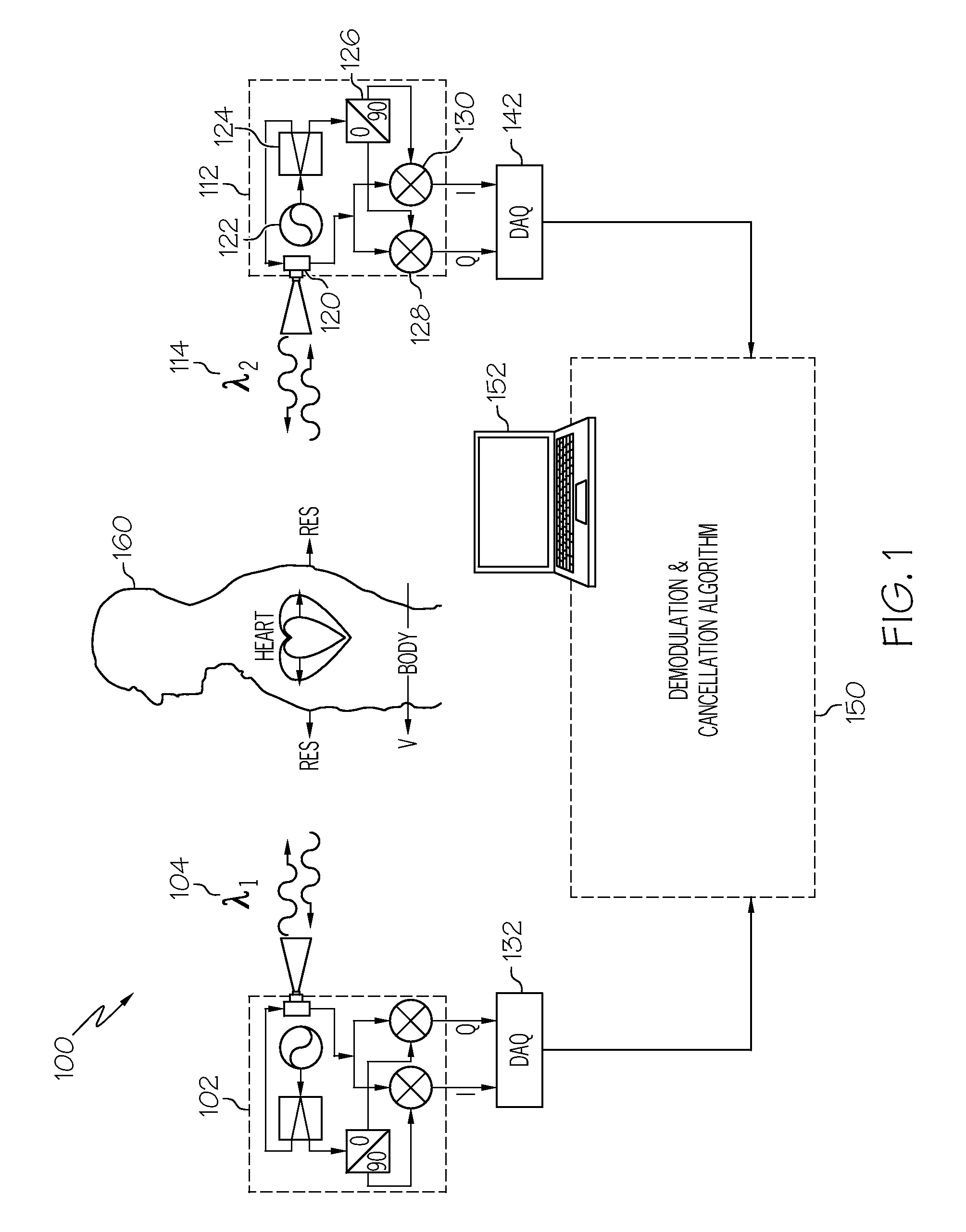
Random Body Movement Cancellation for Non-Contact Vital Sign Detection
ActiveUS20100198083A1Noise can be canceled outAccurate measurementMedical communicationTelemedicineTransceiverVital sign detection
A method and system for cancelling body movement effect for non-contact vital sign detection is described. The method begins with sending on a first electromagnetic wave transceiver a first electromagnetic signal with a first frequency to a first side of a body, such as a person or animal. Simultaneously using a second electromagnetic wave transceiver a second electromagnetic signal is sent with a second frequency to a second side of a body, wherein the first frequency and the second frequency are different frequencies. A first reflected electromagnetic signal reflected back in response to the first electromagnetic wave on the first transceiver is received and a first baseband complex signal is extracted. Likewise a second reflected electromagnetic signal reflected back in response to the second electromagnetic wave on the second transceiver is received and a second baseband complex signal is extracted. The first baseband complex signal is mathematically combined with the second baseband complex signal to cancel out a Doppler frequency drift therebetween to yield a periodic Doppler phase effect.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
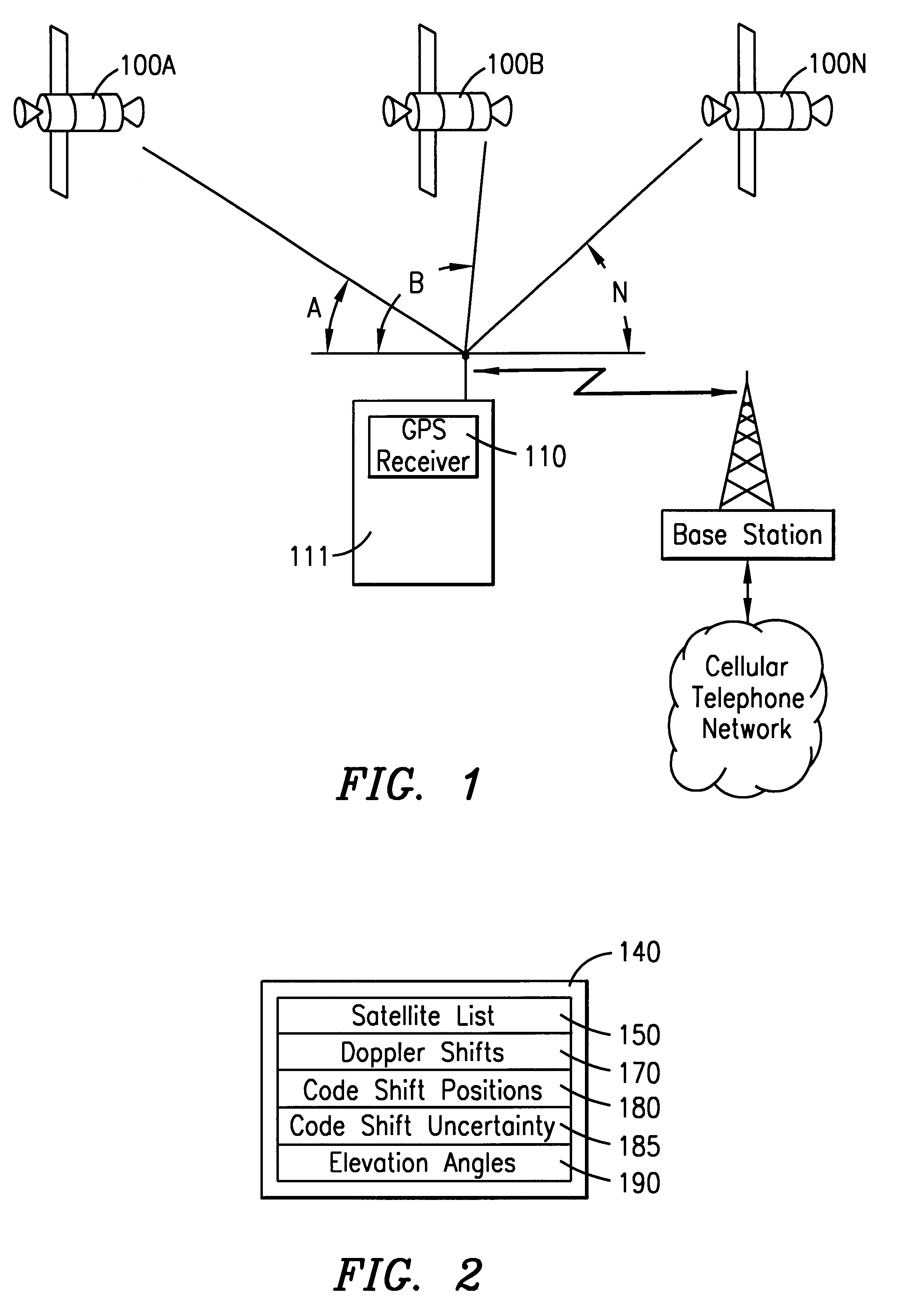
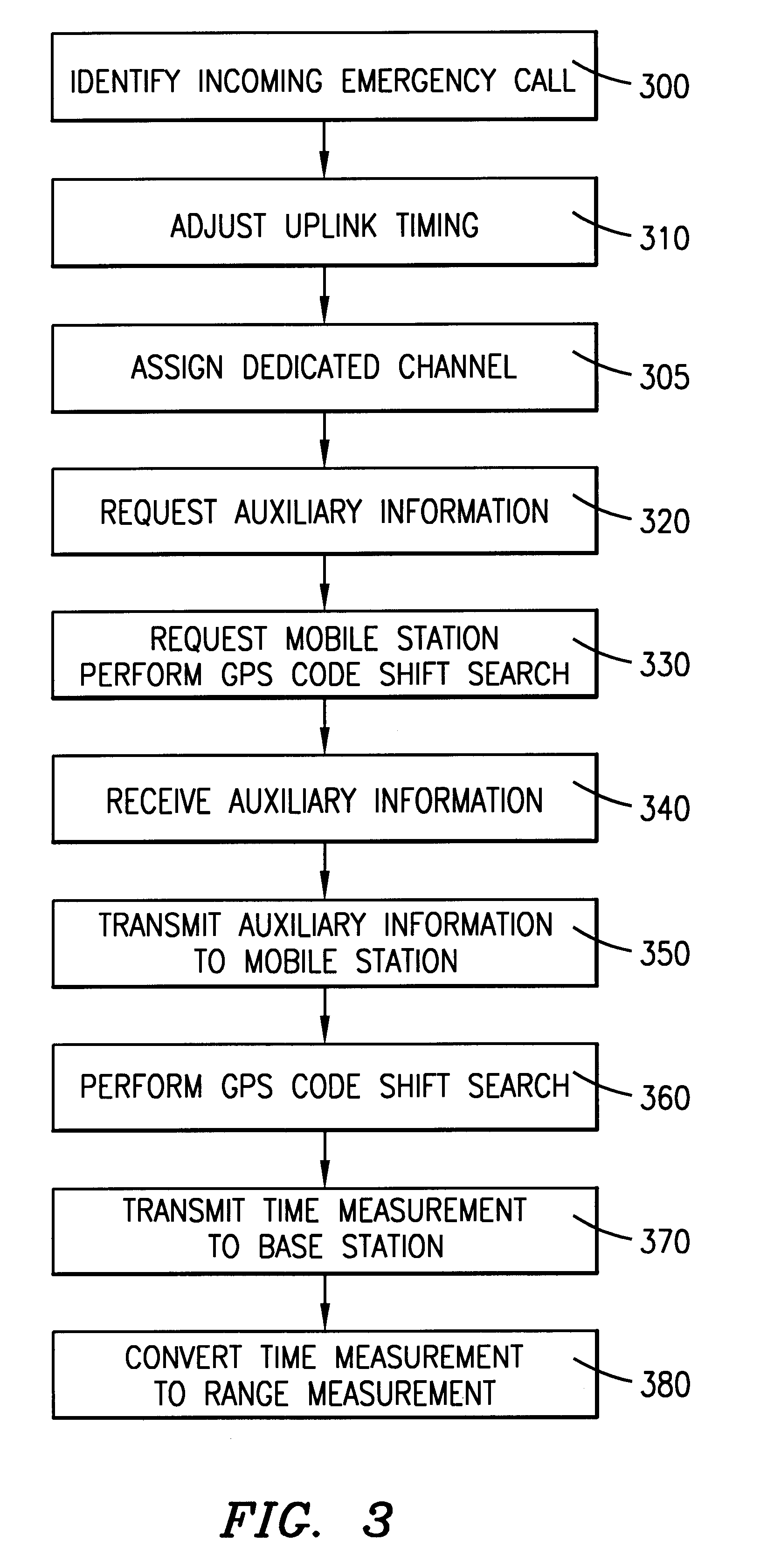
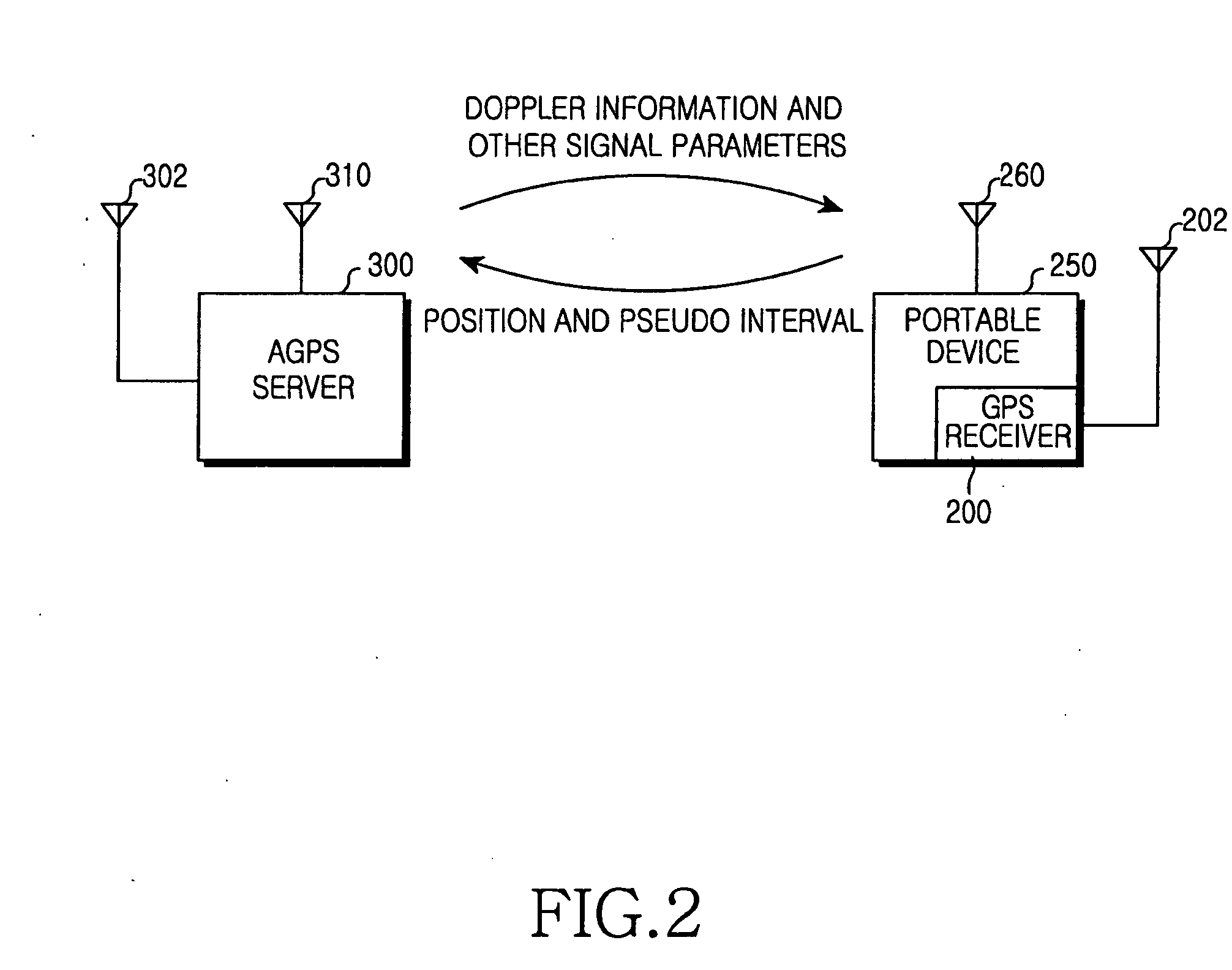
Method and apparatus for communicating auxilliary information and location information between a cellular telephone network and a global positioning system receiver for reducing code shift search time of the receiver
A method and apparatus for communicating auxiliary information between a cellular telephone network and a GPS receiver positioned within a mobile station and identifying the location of the mobile station. A dedicated channel between the mobile station and the network is assigned by the network and uplink timing between the mobile station and the network is adjusted. The network requests auxiliary information and also requests the GPS receiver to perform a GPS code shift search at a common reference time. Upon receiving the auxiliary information, the network transmits the auxiliary information to the GPS receiver which then performs the GPS code shift search. The GPS receiver incorporates a bank of correlators and accumulators to perform multiple parallel searches for various Doppler frequency shifts resulting from a moving GPS receiver. The mobile station subsequently transmits the location information to the cellular telephone network.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
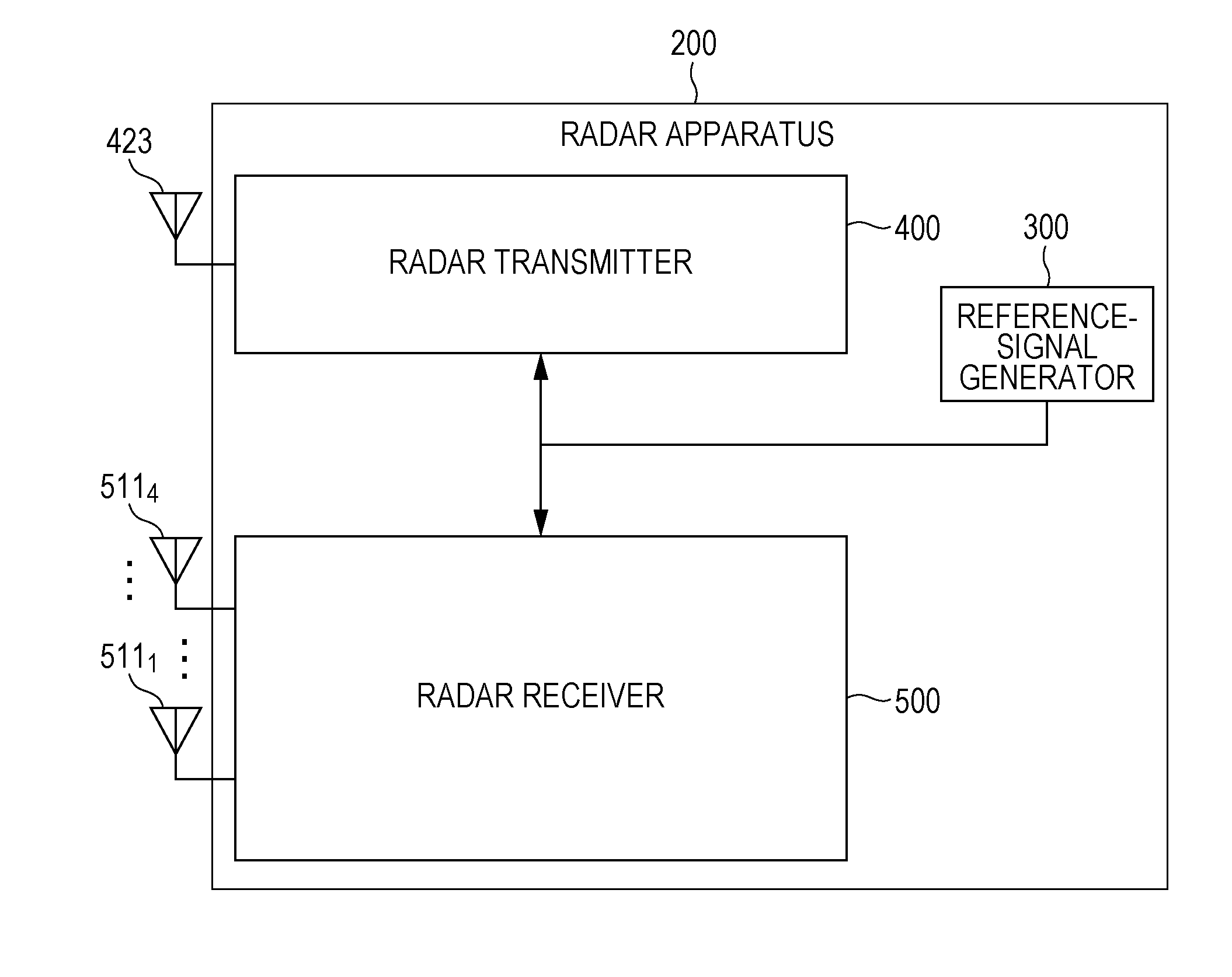
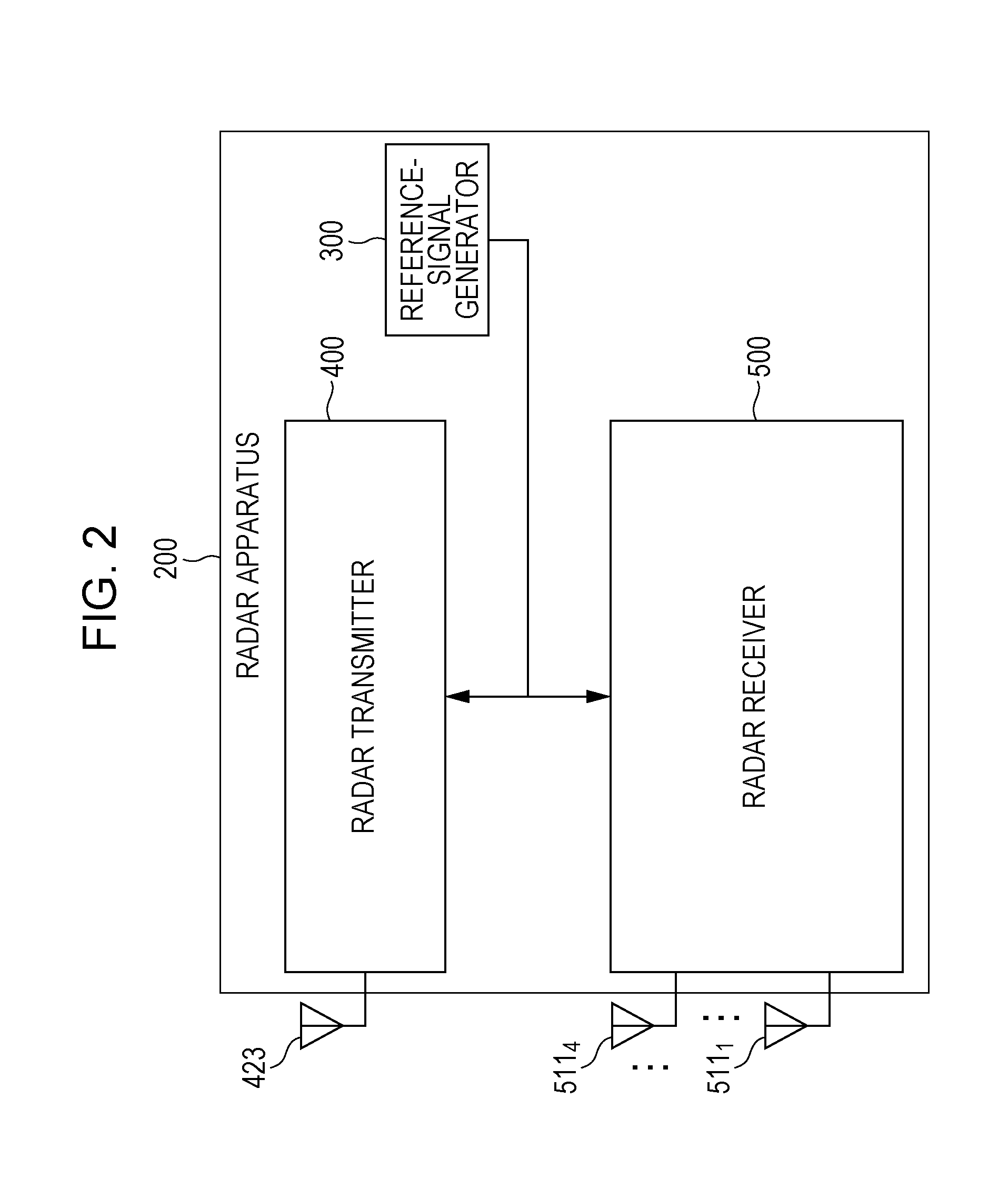
Radar device
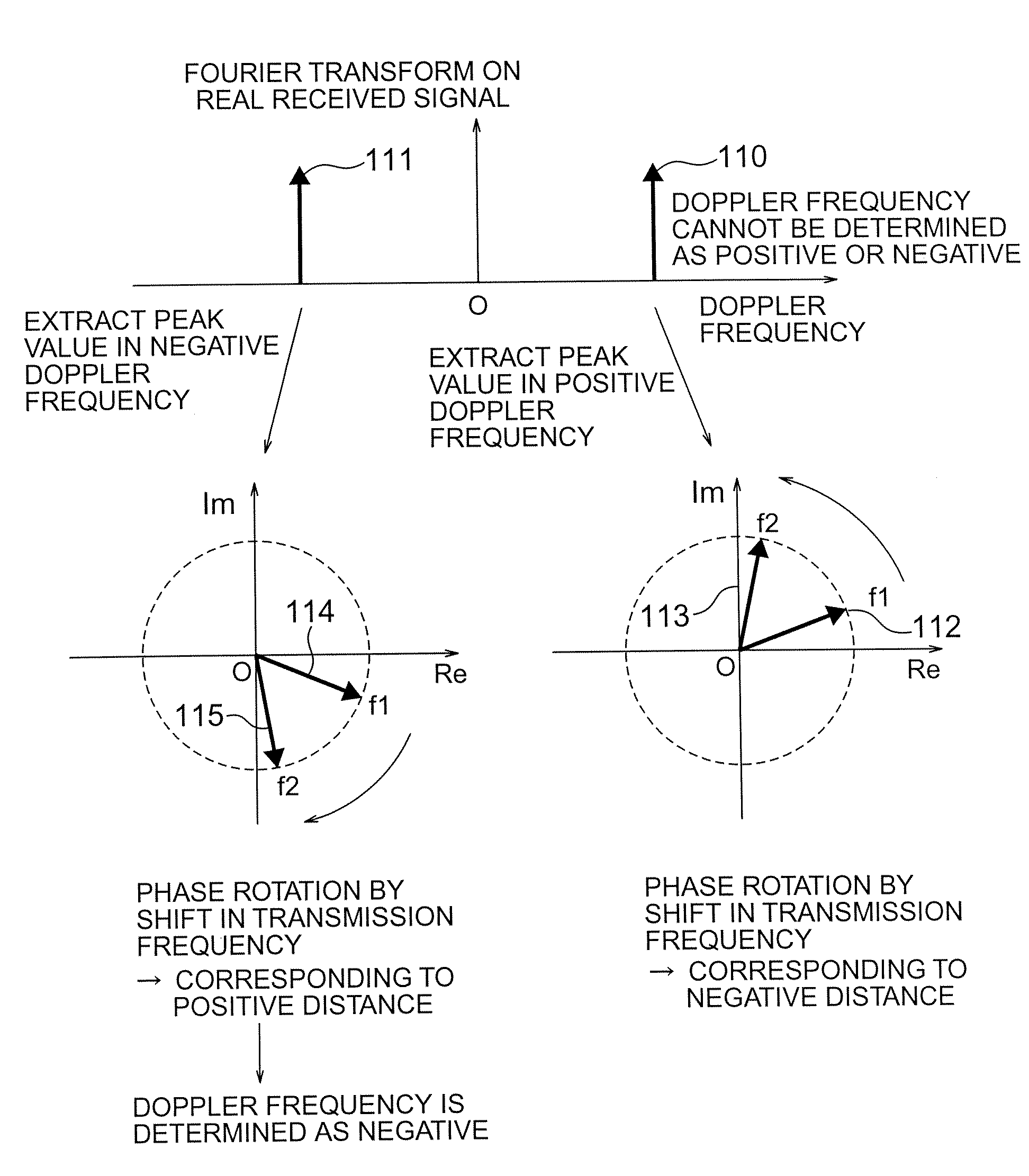
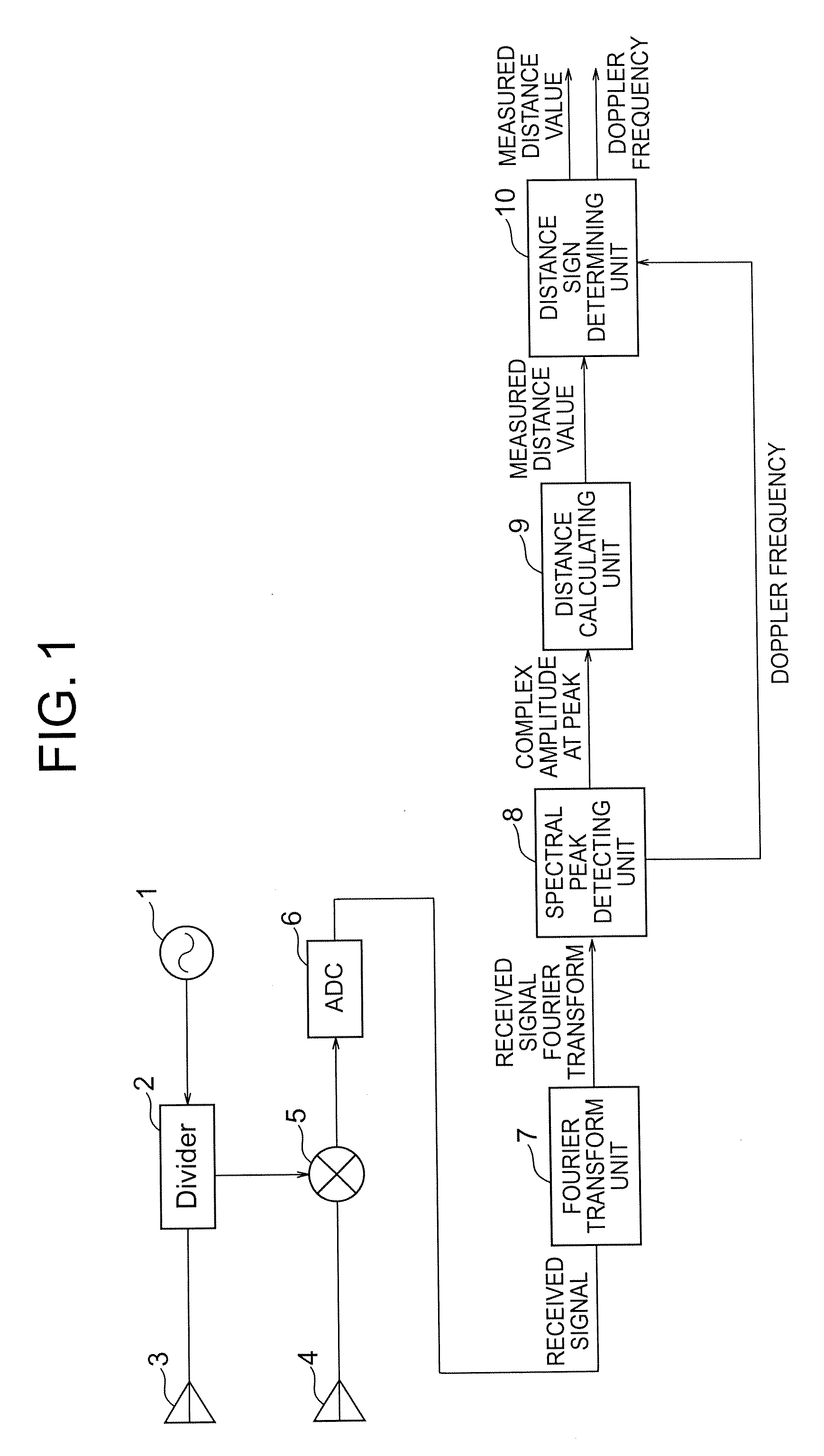
A radar device includes: an oscillator for generating a wave at a plurality of transmission frequencies; a transmitting antenna; a receiving antenna; a receiver for generating a real received signal; a Fourier transform unit for performing a Fourier transform on the real received signal in a time direction; a spectral peak detecting unit for receiving an input of a result of the Fourier transform to extract peak complex signal values of Doppler frequency points having a maximum amplitude; a distance calculating unit for storing the peak complex signal values and for calculating a distance to a reflecting object based on the stored peak complex signal values to output the obtained distance as a measured distance value; and a distance sign determining unit for determining validity of the measured distance value and for outputting the measured distance value and the Doppler frequency according to a result of determination.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
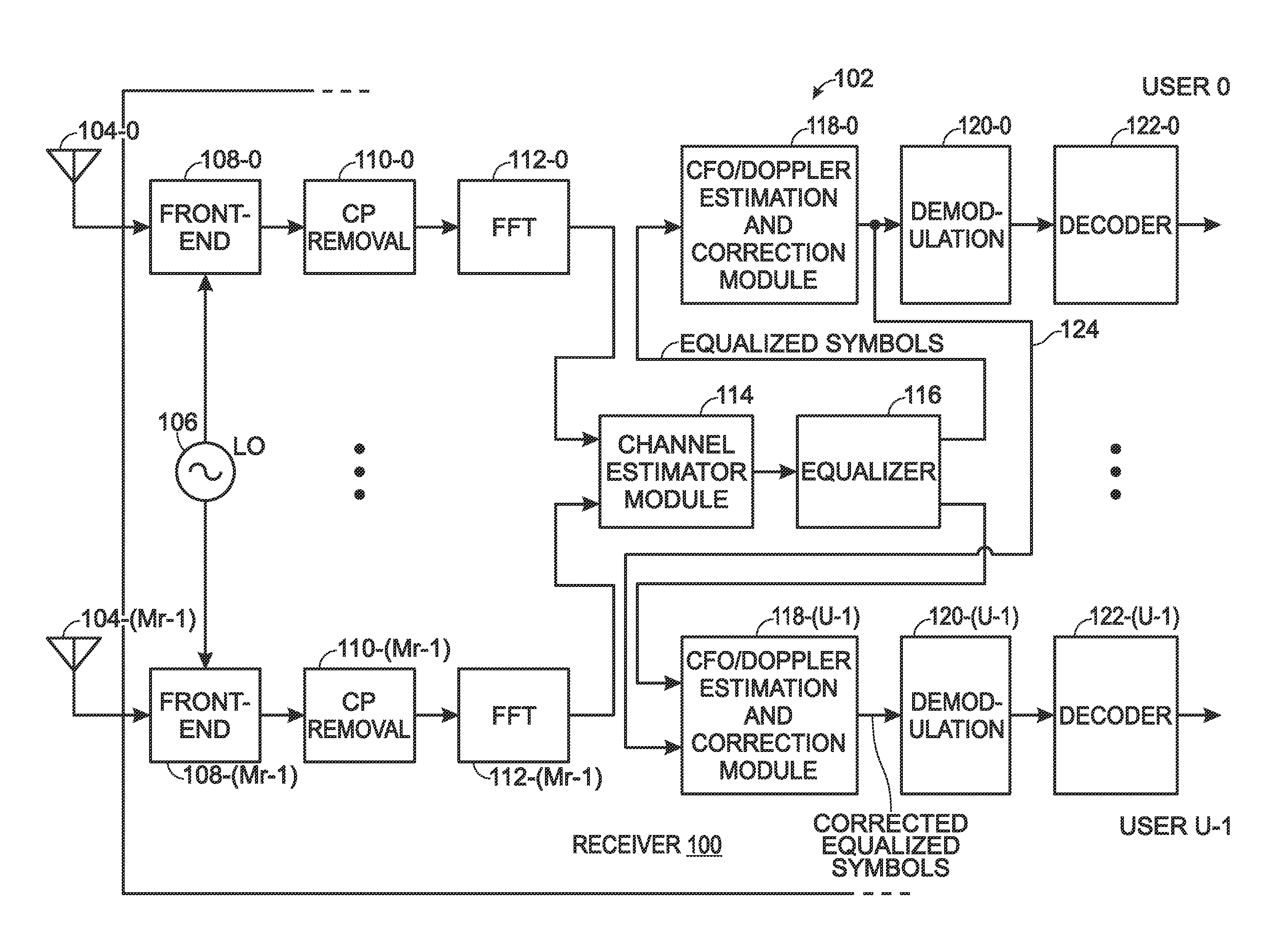
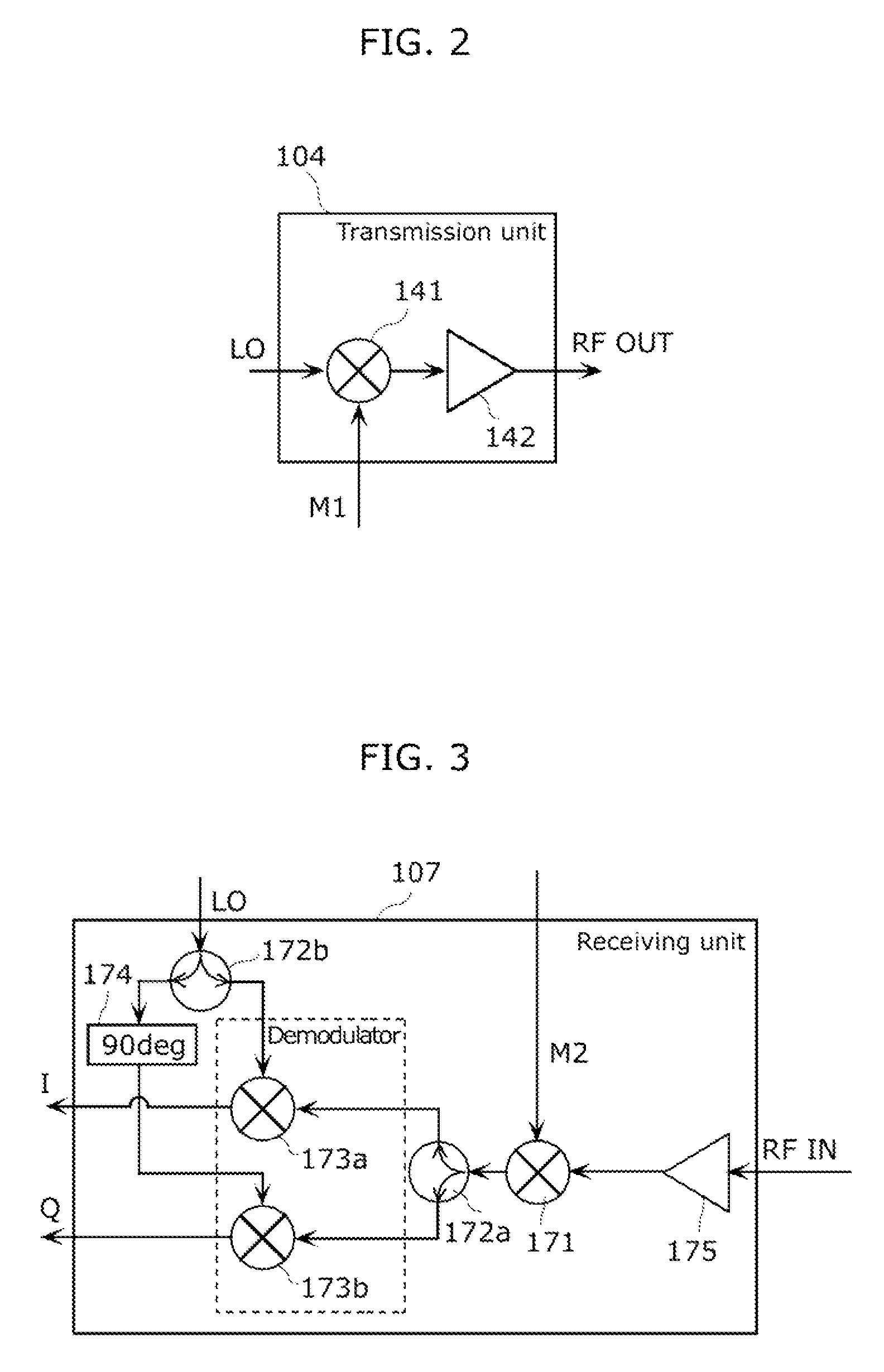
Carrier frequency offset and doppler frequency estimation and correction for OFDMA and SC-FDMA
ActiveUS8416759B1Improve performanceSynchronisation arrangementAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCarrier frequency offsetLocal oscillator
A system and method are provided for carrier frequency offset (CFO) and Doppler frequency estimation and correction for Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) and Single Carrier-Frequency-Division Multiple Access (SC-FDMA) signals in a wireless communications receiver. The receiver is capable of accepting a plurality of multicarrier signals transmitted simultaneously from a plurality of transmitters, with overlapping carrier frequencies and orthogonal reference signals. For each multicarrier signal, a channel estimate is performed and the channel is equalized. Then, a frequency offset is estimated between the transmit carrier frequency of each multicarrier signal and a receiver local oscillator frequency using either the phase rotation of data constellations as a function of time or the phase rotation of channel estimates as a function of time. The receiver supplies the CFO / Doppler frequency estimates and corrects the equalized symbols prior to demodulation.
Owner:MACOM CONNECTIVITY SOLUTIONS LLC
General signal generator for radar target simulation
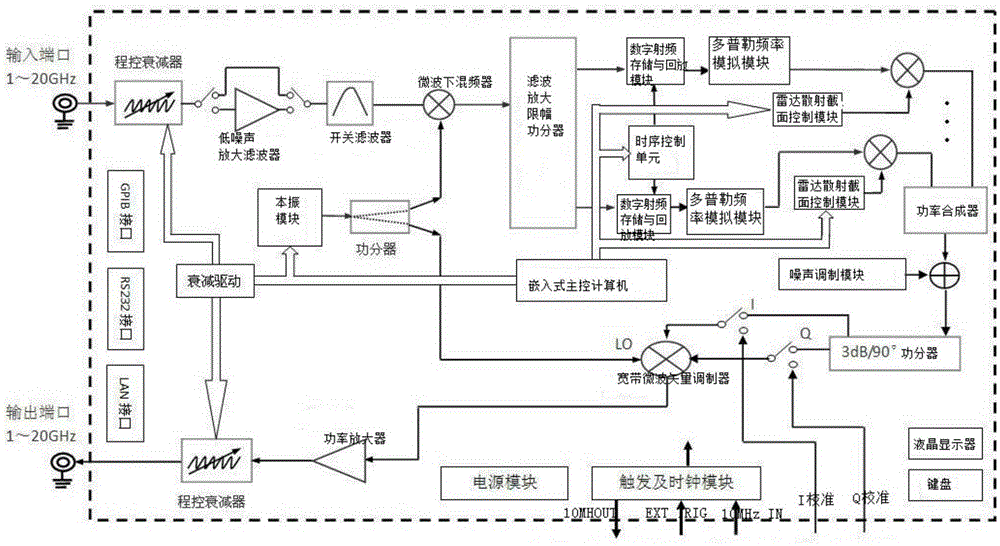
InactiveCN105403870AControllable distanceEasy to control speedWave based measurement systemsSequence controlRadar systems
The invention, which relates to the technical field of the radar target simulation, discloses a general signal generator for radar target simulation. With the signal generator, a defect that the existing radar target signal generator is based on a special-purpose signal generator and only serve a radar system with a specific type in terms of frequency band coverage and function setting and thus the application range is limited can be solved. The signal generator comprises an embedded main control computer, a timing sequence control unit, an attenuation drive, a local oscillation module, a filtering, amplifying and limiting amplitude power divider, a plurality of digital radio frequency storage and playback modules, a plurality of Doppler frequency simulation modules, a radar cross section control module, a noise modulation module, a microwave down mixer, and IQ up mixing unit and the like. The output terminal of the microwave down mixer is connected with the filtering, amplifying and limiting amplitude power divider; the multiple digital radio frequency storage and playback modules are connected to the filtering, amplifying and limiting amplitude power divider; and the output terminal of each digital radio frequency storage and playback module is connected with one Doppler frequency simulation module.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
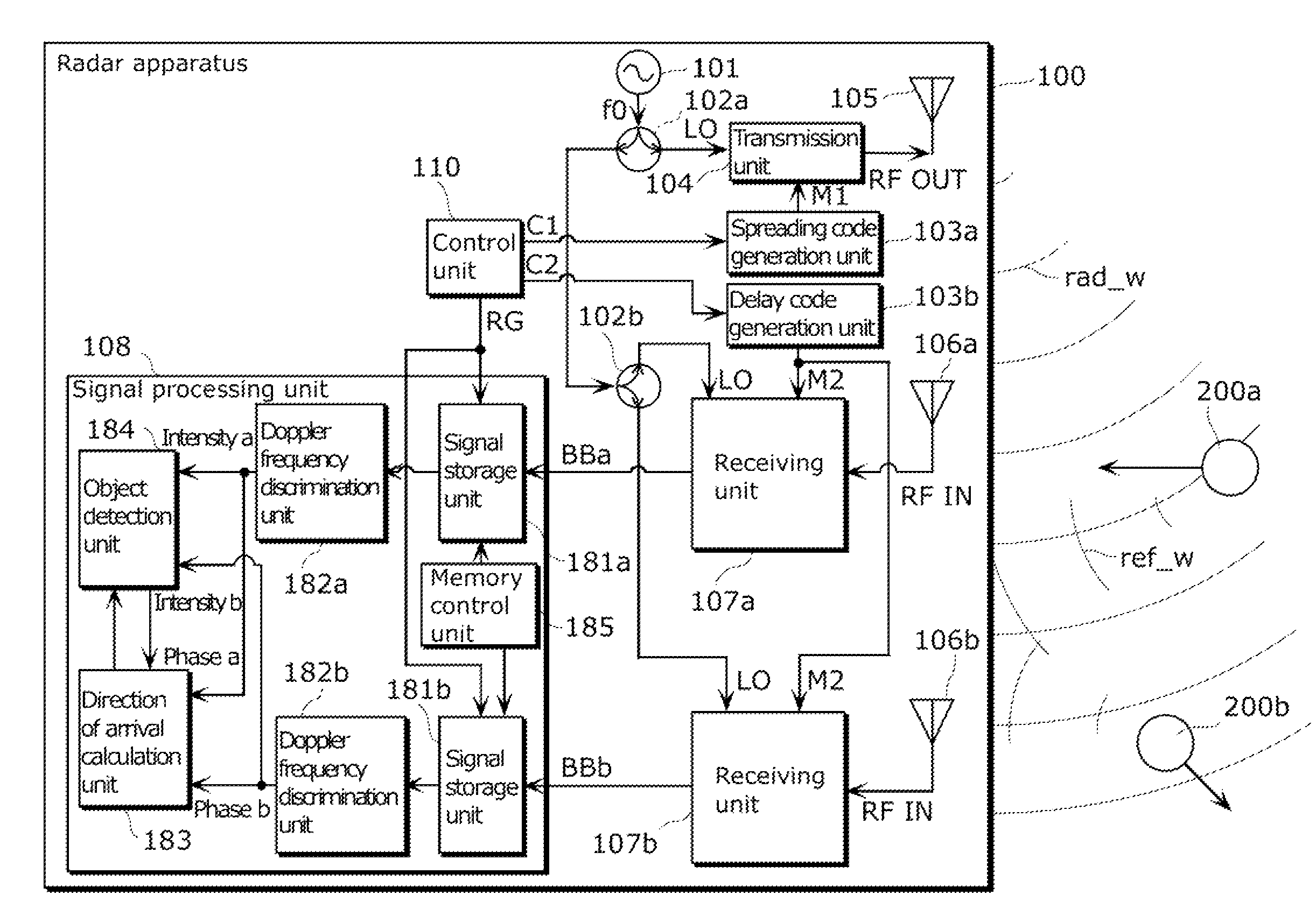
Radar imaging apparatus, imaging method, and program thereof
InactiveUS8686894B2Function increaseDirection findersRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEngineeringRange gate
A radar imaging apparatus includes: (i) a delay code generation unit which repeats, for M scan periods, scan processing of generating, using a transmission code, N delay codes in a scan period for scanning N range gates having mutually different distances from the radar imaging apparatus; (ii) a signal storage unit which stores, in association with a range gate and a scan period, a baseband signal; (iii) a memory control unit which repeatedly writes, in the signal storage unit, for the M scan periods, N demodulated signals corresponding to a single scan period, and reads out a group of M demodulated signals corresponding to mutually different scan periods; (iv) a Doppler frequency discrimination unit which performs frequency analysis on demodulated signals having the same range gate; and (v) a direction of arrival calculation unit which estimates a direction of a target.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and apparatus for radar signal processing
A radar apparatus and method for determining the range to and velocity of at least one object comprising, transmitting a plurality of RF signals, each comprising a particular frequency and being transmitted during a particular unique finite period, the plurality of signals collectively comprising at least one first subset of signals having the same frequency and at least one second subset of signals having different frequencies, receiving the plurality of signals after reflection from an object, determining a phase difference between each of the signals and the corresponding reflected signal, each piece of phase difference information herein termed a sample, organizing the samples in two-dimensions wherein, in a first dimension, all samples have the same frequency and, in a second dimension, all consecutive samples are separated from each other by a fixed time interval; processing the samples in the first dimension to determine a phase rotation frequency corresponding to the samples in the first dimension, the phase rotation frequency comprising a Doppler frequency for the at least one object, processing the samples in the second dimension to determine a second phase rotation frequency corresponding to the samples in the second dimension; the phase rotation frequency comprising Doppler frequency and range frequency for the at least one object; comparing the first phase rotation frequency to the second phase rotation frequency to distinguish range frequency from Doppler frequency of the at least one object; and converting the Doppler frequency to a velocity of the object and converting the range frequency to a range of the object.
Owner:VEONEER US LLC
Position location method and apparatus for a mobile telecommunications system
InactiveUS6778130B1Limited bandwidthEasy CalibrationRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsBeacon systems using radio wavesRelative phaseDirectional antenna
In a cellular mobile telecommunications system the position of a mobile station can be estimated in terms of its bearing and range from a cell site. A multi-element direction finding antenna at the cell site receives signals from the mobile station and a receiver circuit estimates the bearing using the relative phase of signals received at different antenna elements and estimates the range by measuring round trip delay of signals to and from the mobile station. Motion of the mobile station can introduce errors into the bearing estimate due to frequency offset and frequency spread when element sampling is non-simultaneous. Compensation for these errors is introduced by using signal samples successively received at the same antenna element to estimate Doppler frequency offset and spread. It is necessary to ensure accurate calibration of the direction finding antenna and the receiver circuit. This is done by injecting calibration signals into the circuit near the antenna or into the antenna itself from a near field probe. Other aspects of calibration, such as antenna position, are calibrated using a remote beacon. A beacon emulating a mobile station but at a fixed, known location, or a beacon at an adjacent cell site may be used.
Owner:APPLE INC
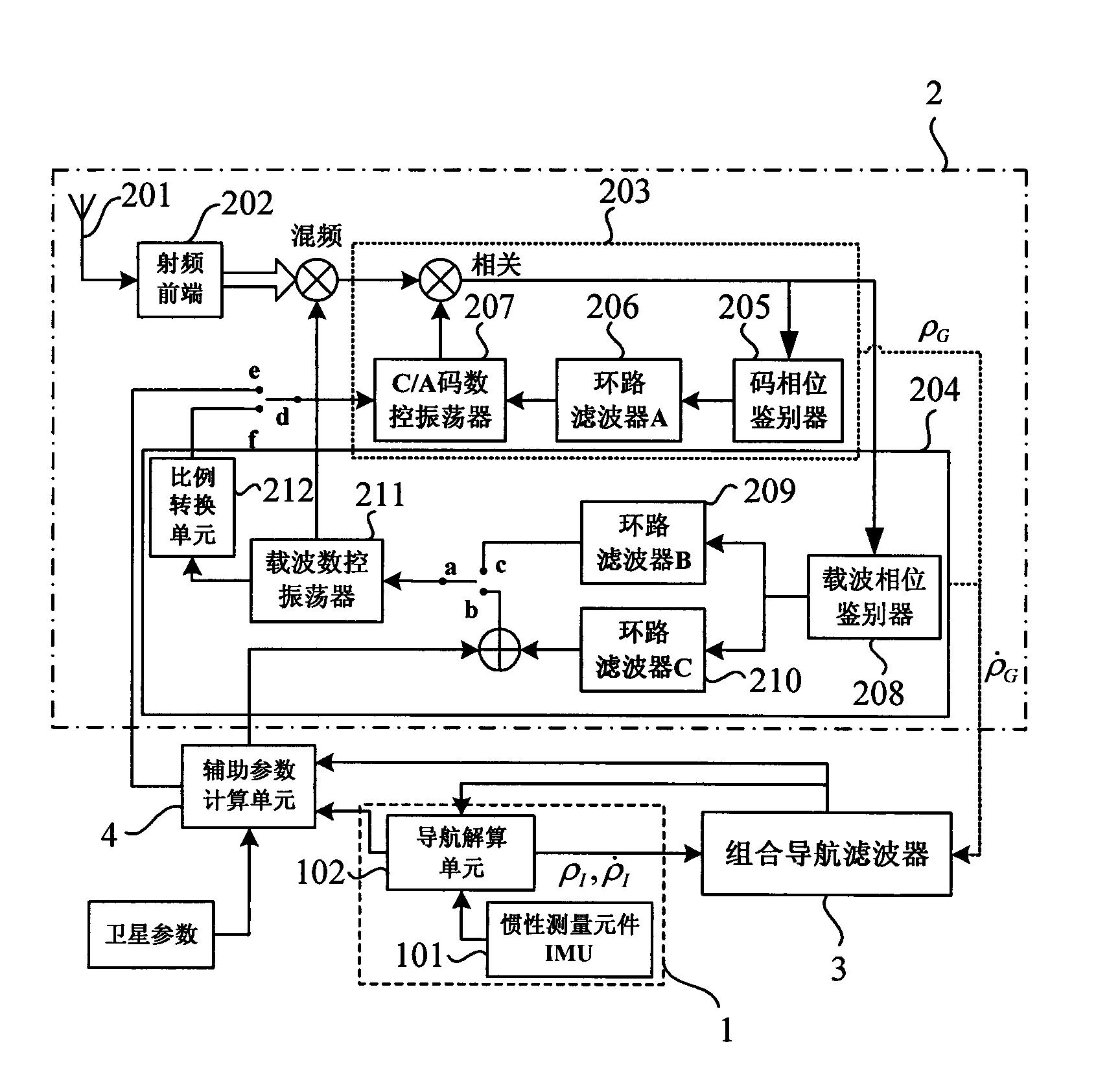
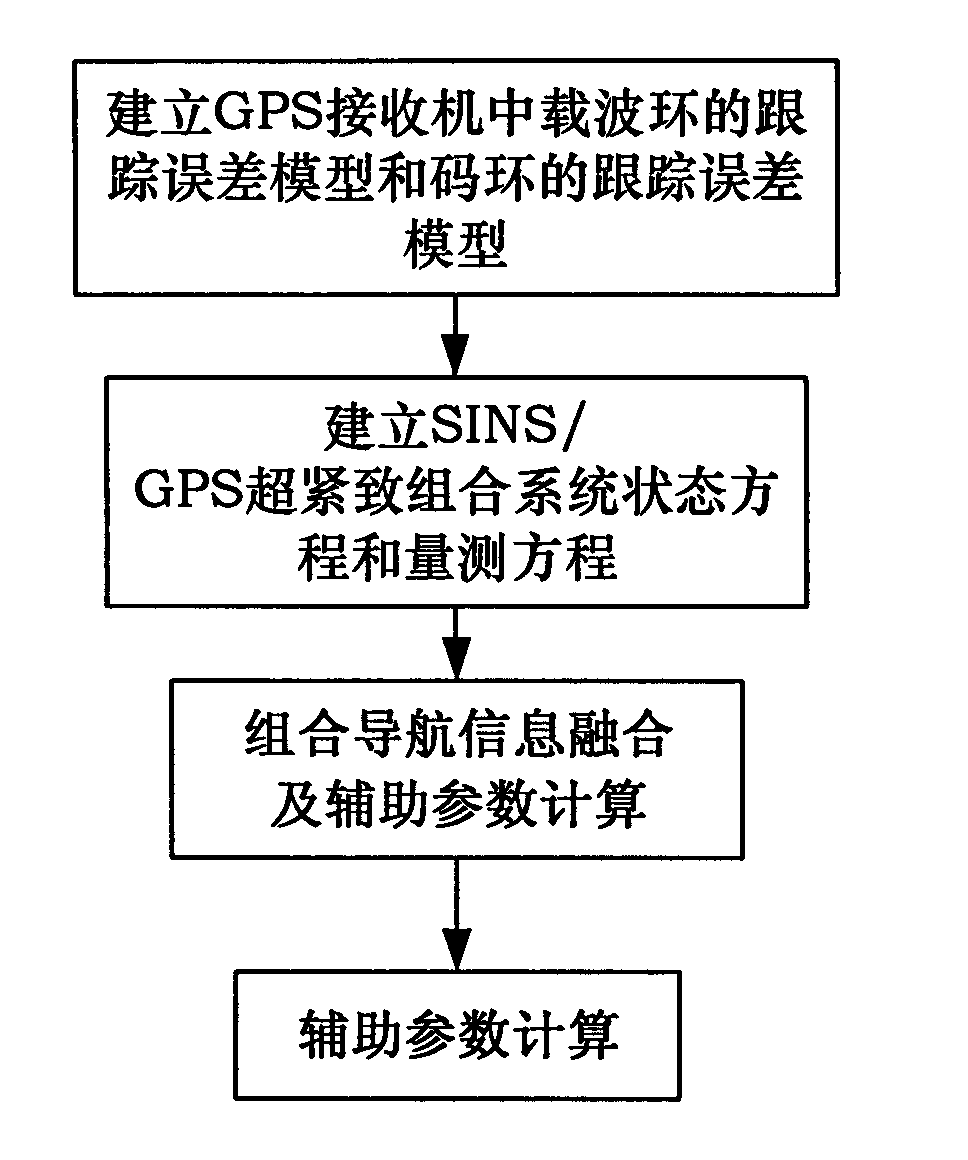
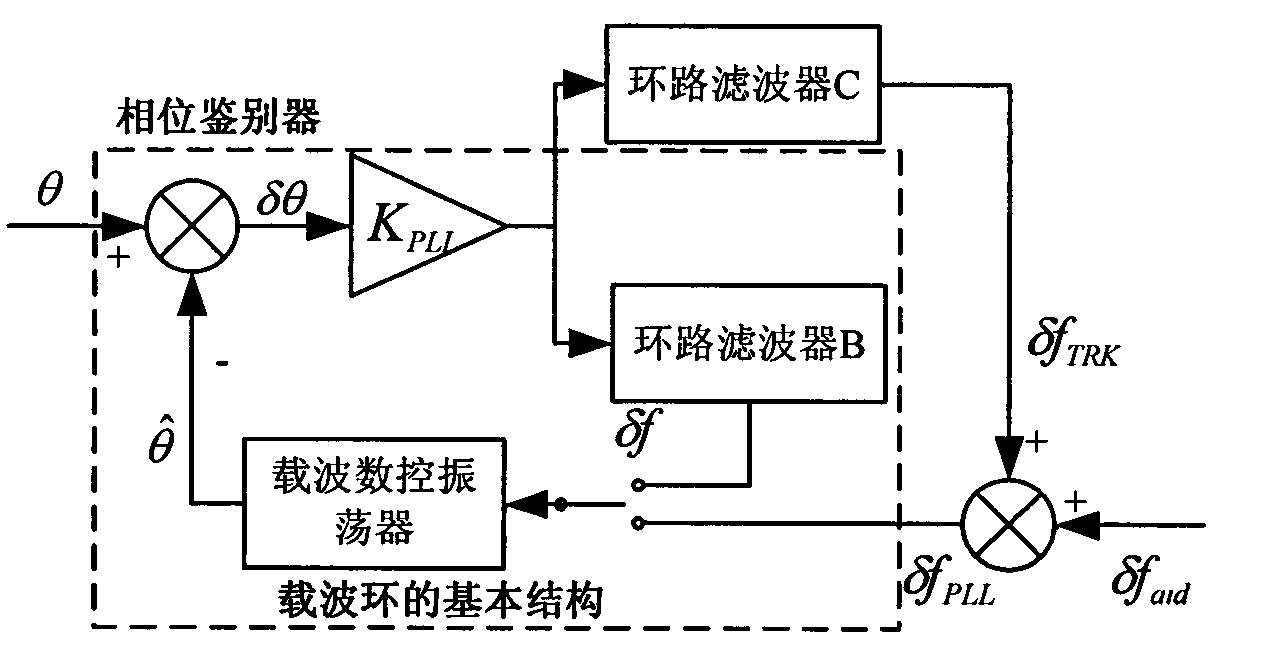
SINS/GPS super-compact integrated navigation system and implementing method thereof
InactiveCN101666650AIncrease equivalent bandwidthReduce dynamic tracking rangeBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationCarrier signalGps receiver
The invention discloses an SINS / GPS super-compact integrated navigation system and an implementing method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: the doppler frequency assistance is provided for a GPS carrier loop by using the velocity information of a strapdown inertial navigation system, therefore, the loop equivalent bandwidth is increased, the influence of the carrier dynamic stateon the carrier loop is lowered, and the noise suppression capability is improved by reducing the bandwidth of a filter; meanwhile, in order to eliminate the correlation between the pseudo-range rate error and the inertial navigation error, a carrier loop tracking error model is obtained by establishing the relationship between the carrier tracking error and the inertial navigation speed error, andthe influence of the carrier tracking error is subduced in the measurement equation; and in addition, the carrier frequency is adjusted according to the output error estimation information, and the tracking accuracy of the carrier loop is enhanced. The invention can effectively enhance the noise suppression capability and the dynamic tracking performance of the tracking loop and enhance the tracking accuracy of a GPS receiver and the navigation accuracy of the integrated navigation system under strong interference and high dynamic circumstance.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Frequency offset estimating method and receiver employing the same
InactiveUS7616710B2Carrier regulationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsCarrier signalHardware complexity
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Missile-borne SAR sub-aperture forward squint high-order nonlinear chirp scaling imaging method
ActiveCN103901428AMeet real-time processing needsAccurate 2D SpectrumSpecial data processing applicationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar signal processingEcho signal
The invention belongs to the field of radar signal processing, and discloses a missile-borne SAR sub-aperture forward squint high-order nonlinear chirp scaling imaging method. According to the method, missile-borne SAR forward squint high-order nonlinear chirp scaling imaging is achieved through sub-aperture data, and the method can be used for SAR imaging of airborne platforms or missile-borne platforms. The method mainly includes the steps of firstly, conducting distance pulse pressure and time domain walking correction on an echo signal; secondly, converting the signal into the two-dimensional frequency domain, conducting frequency domain migration correction and secondary compression, and compensating for the high order phase in the orientation direction; thirdly, leading high-order nonlinear chirp scaling disturbance factors into the orientation frequency domain, and correcting the space variability of the Doppler frequency modulation and the high-order terms in the orientation direction; fourthly, focusing an image on the orientation frequency domain through spectrum analysis. The method solves the problem of decoupling of distance orientation and the orientation focus depth problem caused by time domain walking correction, and the method can meet the requirements for different scenes and high resolution and can be used for the field of ground mapping and other fields.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
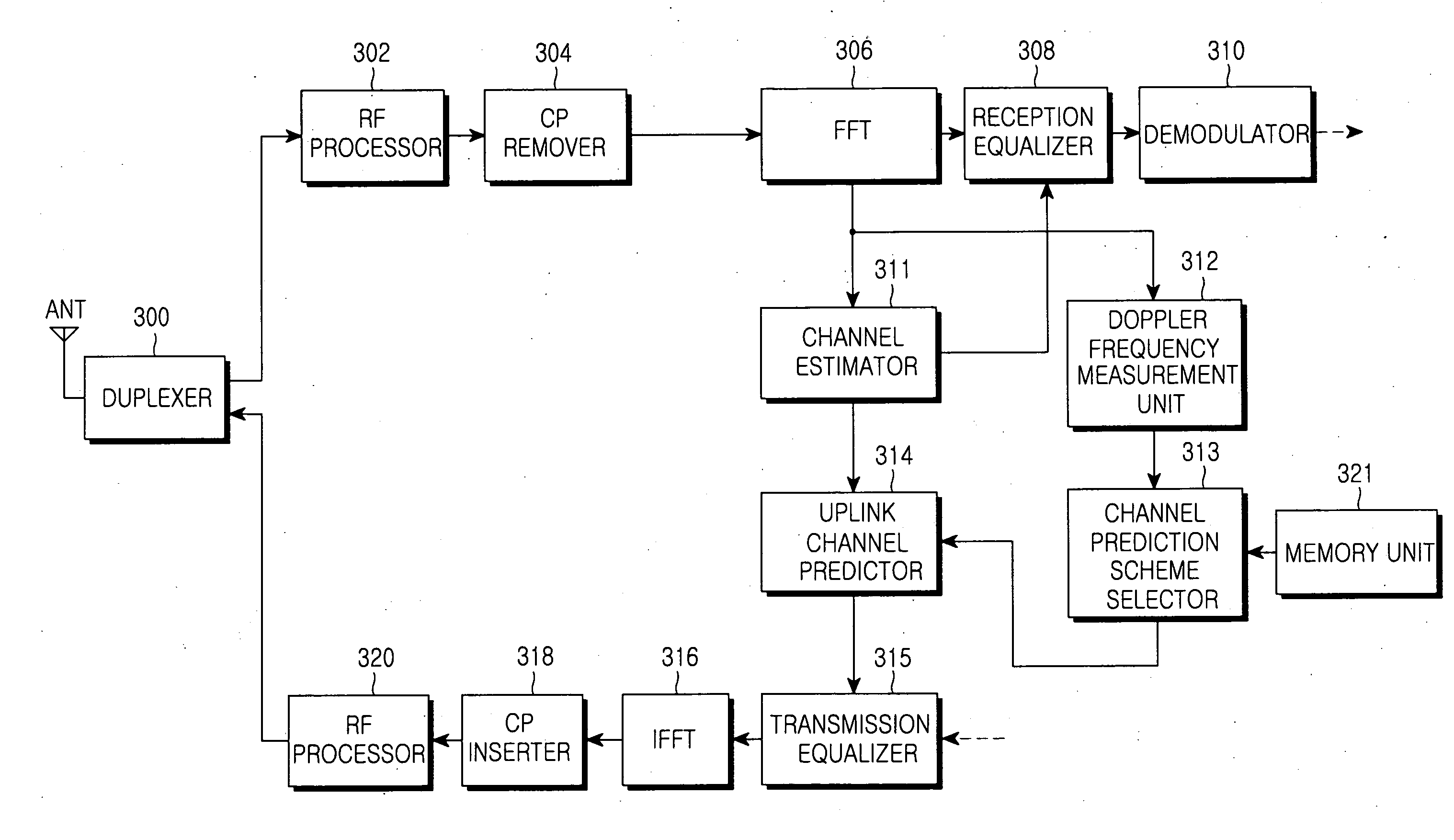
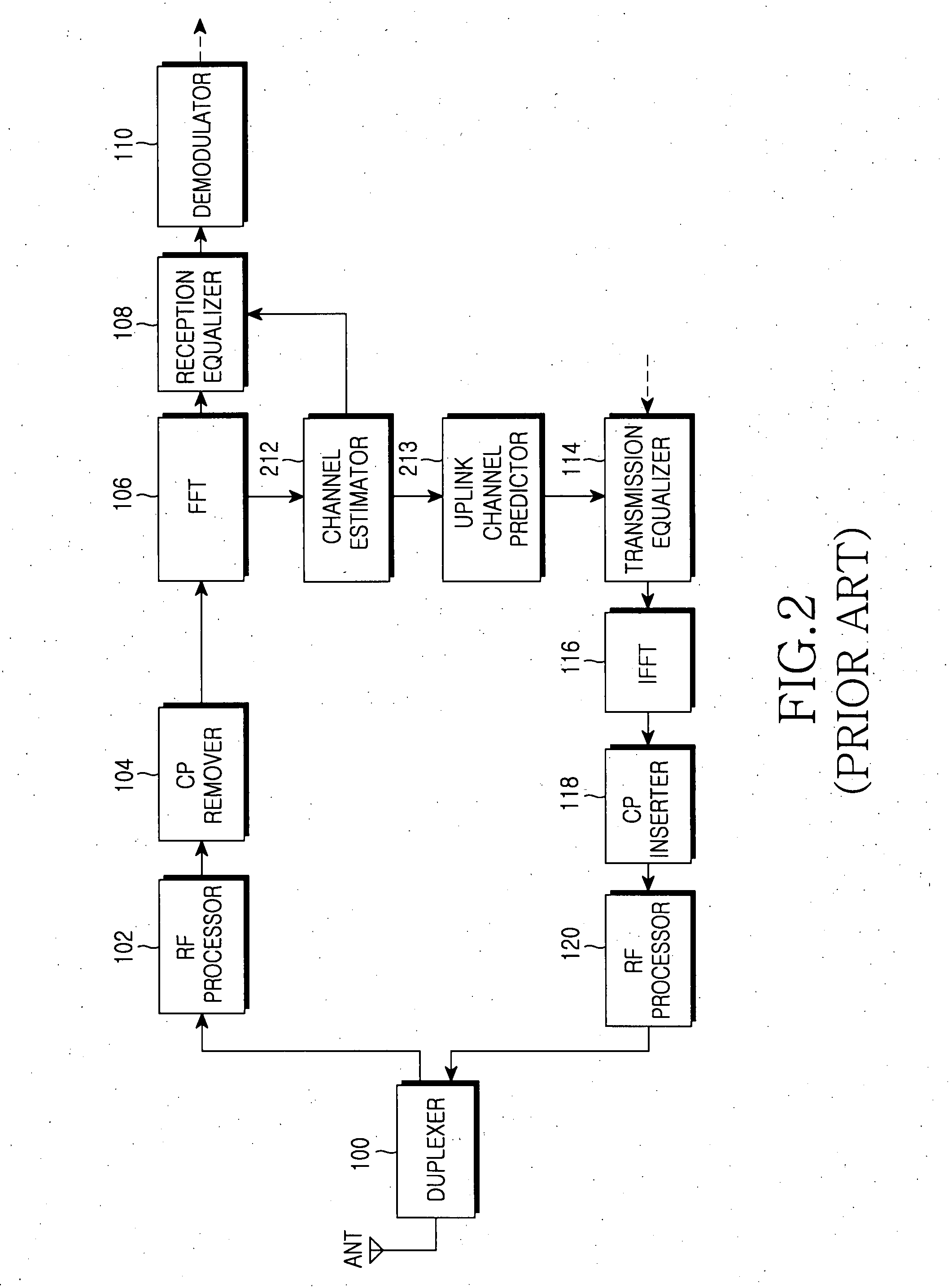
Adaptive channel prediction apparatus and method for performing uplink pre-equalization depending on downlink channel variation in OFDM/TDD mobile communication system
ActiveUS20070211747A1Carrier regulationTime-division multiplexMobile communication systemsEqualization
Disclosed are an apparatus and a method for changing a channel prediction depending on the degree of downlink channel variation in predicting an uplink channel for uplink pre-equalization. N number of Doppler frequency ranges are set according to uplink channel variation degrees, and channel prediction schemes corresponding to the respective Doppler frequency ranges are established. A Doppler frequency is measured from a signal received over a downlink channel, and the Doppler frequency range, within which the measured Doppler frequency is included, is determined from among the Doppler frequency ranges. The channel prediction scheme established corresponding to the determined Doppler frequency is selected, and the uplink pre-equalization is performed by using the selected channel prediction scheme. This enables uplink pre-equalization that is suitable for a channel varying with a terminal's moving speed or other channel environments.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
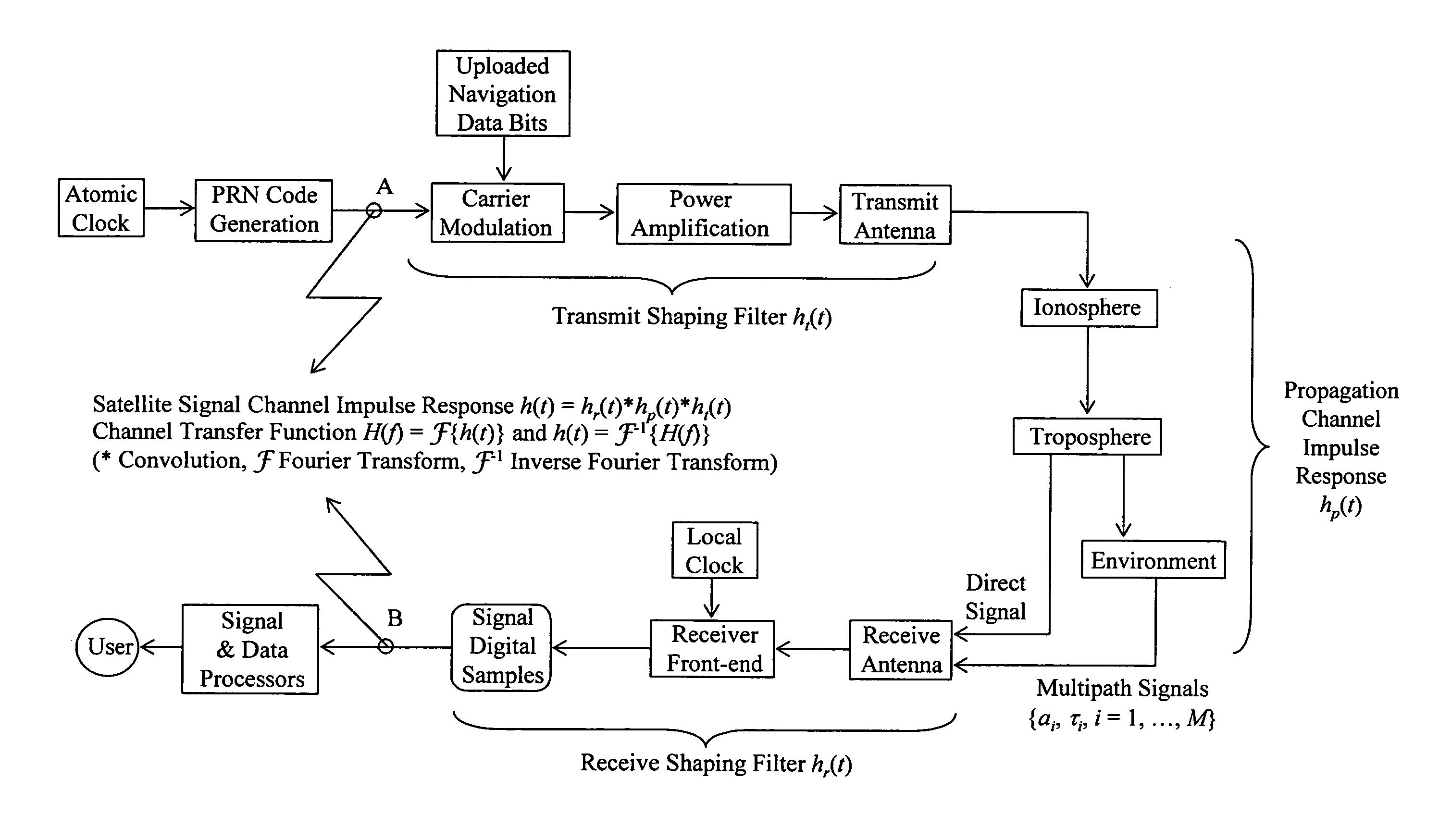
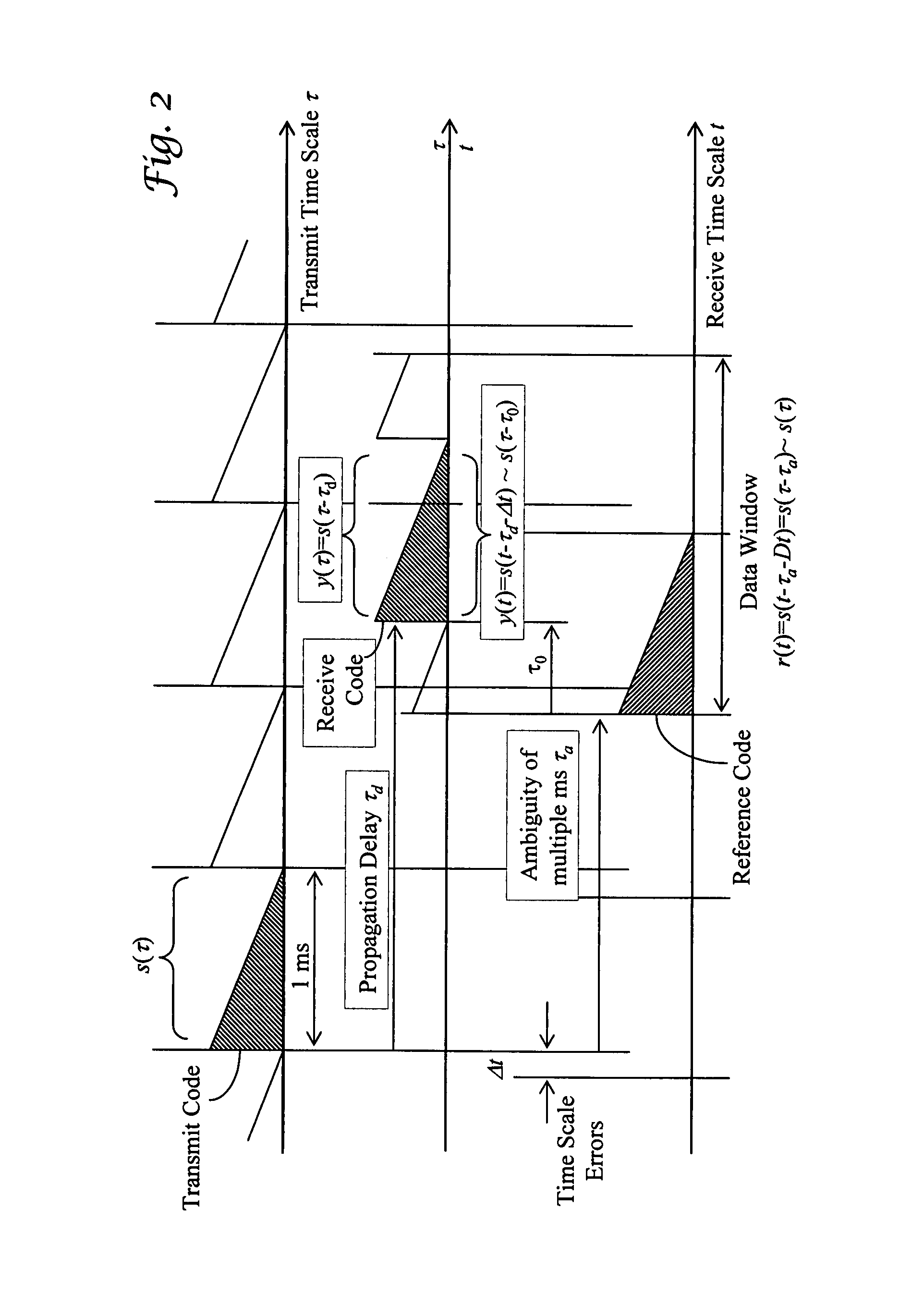
Global navigation satellite system (GNSS) receivers based on satellite signal channel impulse response
A Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receiver and associated method for the reception and processing of GNSS signals. The GNSS receiver includes an antenna and an analog front-end to intercept the incoming radio-frequency signal and to convert it to an appropriate intermediate frequency for digital sampling. A baseband signal processor is organized into functionally identical channels, each dynamically assigned to a different satellite visible. The baseband signal processor processes the signal samples to generate the satellite signal channel impulse response for a number of Doppler frequency shifts. This results in a two-dimensional delay-Doppler map of satellite signal responses from which the baseband signal processor extracts the code time and carrier phase and frequency parameters as well as navigation data for timing, positioning, and environment mapping in the data processor.
Owner:YANG CHUN
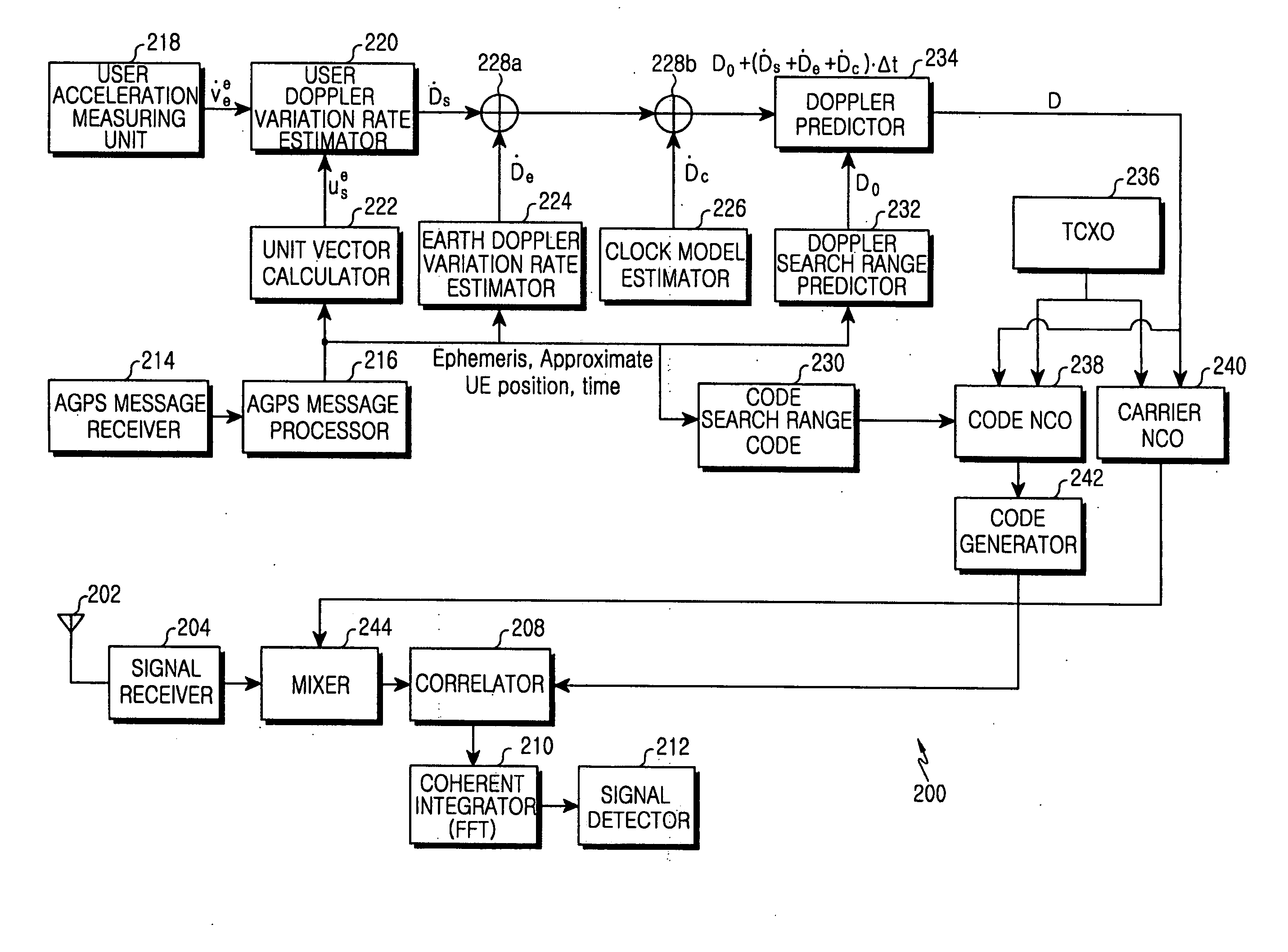
High sensitivity GPS receiver and method for compensating for doppler variation
InactiveUS20060012515A1Reception sensitivity is degradedMeasure Doppler variationPosition fixationRadio transmissionGps receiverCarrier signal
A global positioning system (GPS) receiver and method are provided for compensating for Doppler variation to accurately detect GPS signals in an environment in which intensities of the GPS signals received from GPS satellites are very low. A user acceleration measuring unit measures an acceleration vector of the terminal with respect to a center of the Earth. A user Doppler variation rate estimator estimates a user Doppler variation rate of each GPS satellite due to acceleration of the terminal by making use of the measured acceleration vector. A Doppler predictor predicts a Doppler frequency according to the estimated user Doppler variation rate. Code and carrier frequency signal generators compensate codes and carriers of GPS satellites to be correlated with signals received therefrom by making use of the predicted Doppler frequency.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Obstacle and terrain avoidance sensor
A method and apparatus for terrain mapping and / or obstacle detection for aircraft, including (a) transmitting a non-scanning beam that illuminates the terrain and / or obstacles; (b) receiving a Doppler shifted signal that is Doppler frequency shifted by an amount dependent on an angle between a line of flight of the aircraft and scatterers that reflect the transmitted beam; (c) determining the angle from the Doppler frequency; (d) determining the range of at least some of said scatterers; and (e) determining the azimuth and elevation of the scatterers.
Owner:RODRADAR LTD
Radio communication apparatus and transfer rate decision method
ActiveUS20050128976A1Transmission rate can be optimizedImprove accuracyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDecision methodsMobile station
A transmission rate determining method that enables assignment of transmission rate (modulation scheme and coding rate) to be optimized with high accuracy in the AMC technique. In the method, in abase station, Doppler frequency detector 117 detects the Doppler frequency (moving speed) of each mobile station. MCS assignment section 125 corrects a relational expression of MCS (coding rate and modulation scheme) and CIR based on the Doppler frequency (moving speed) obtained in Doppler frequency detector 117, for example, corrects a threshold in CIR, and determines MCS optimal for CIR report value. Results of assignment in MCS assignment section 125 are output to coding section 101 and modulation section 103.
Owner:INVT SPE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com