Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
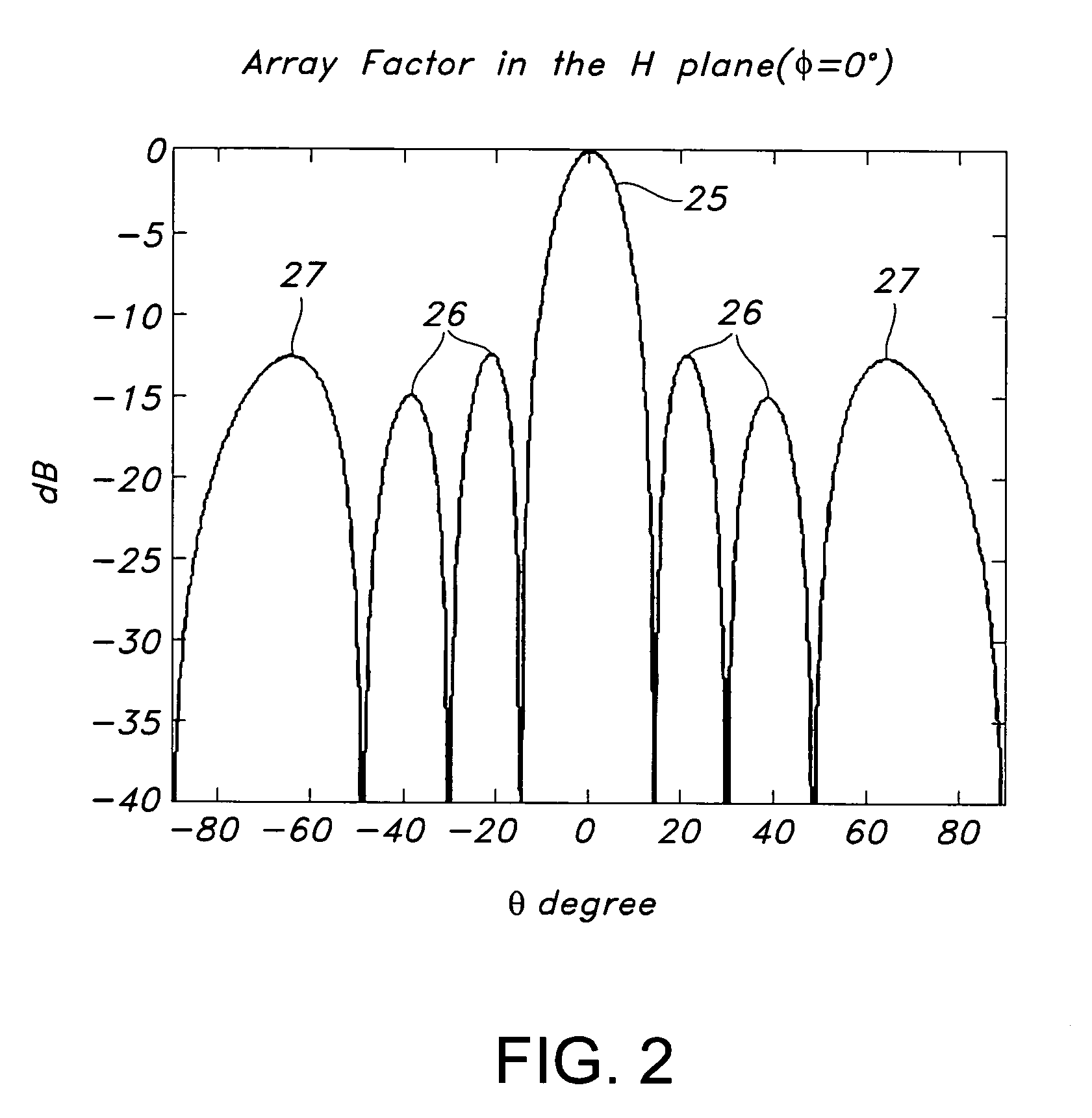
367 results about "Grating lobe" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
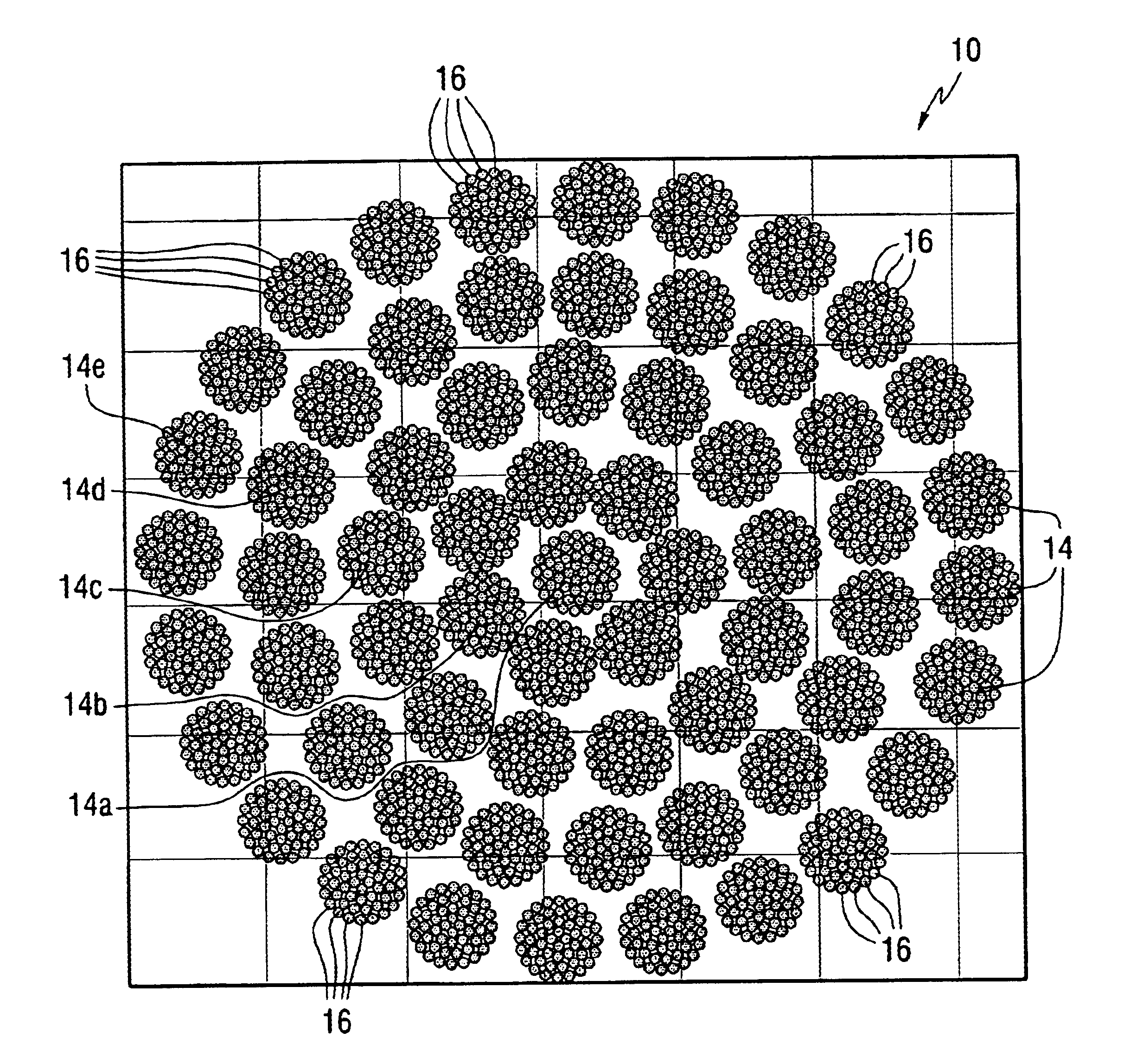
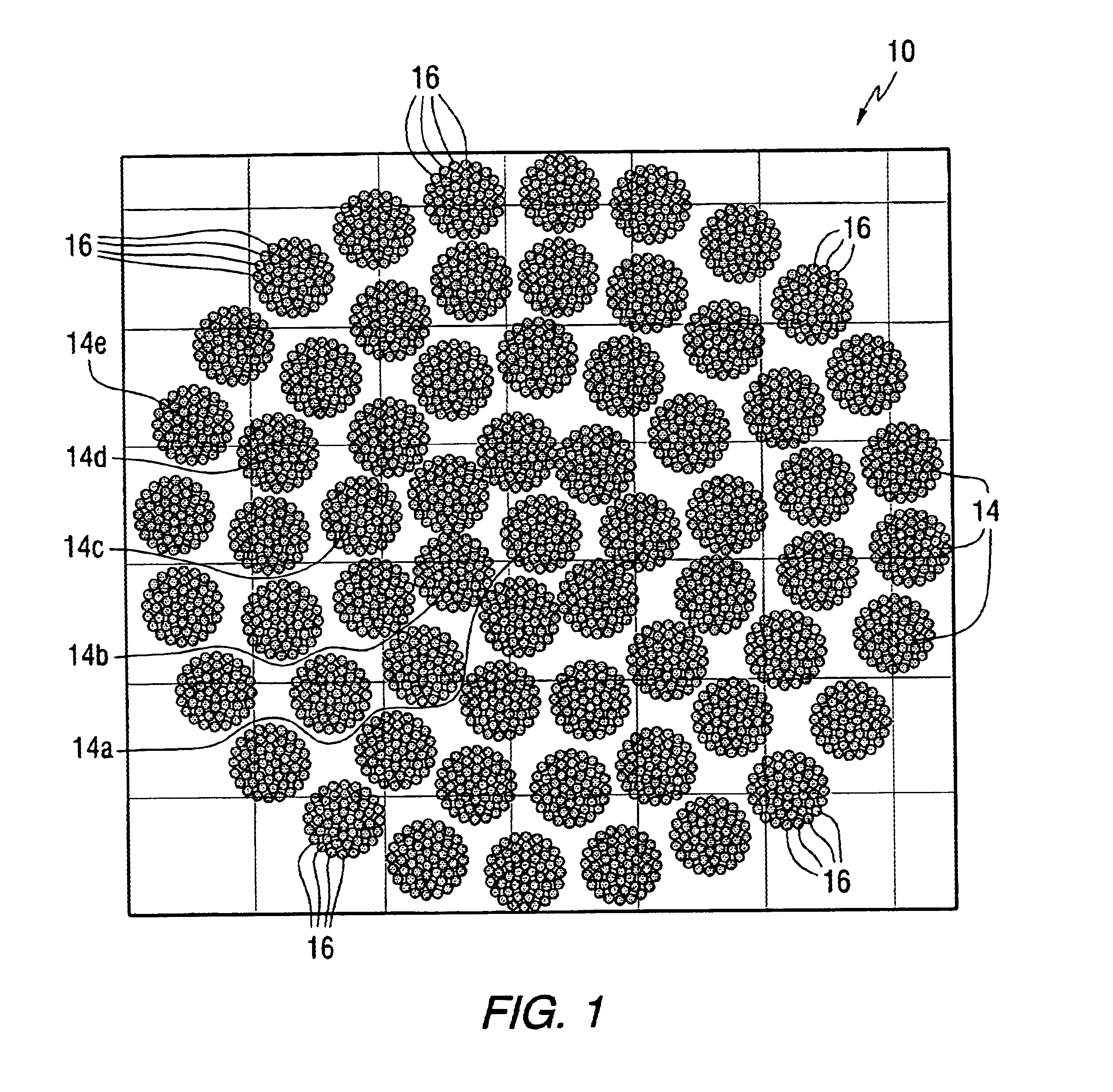
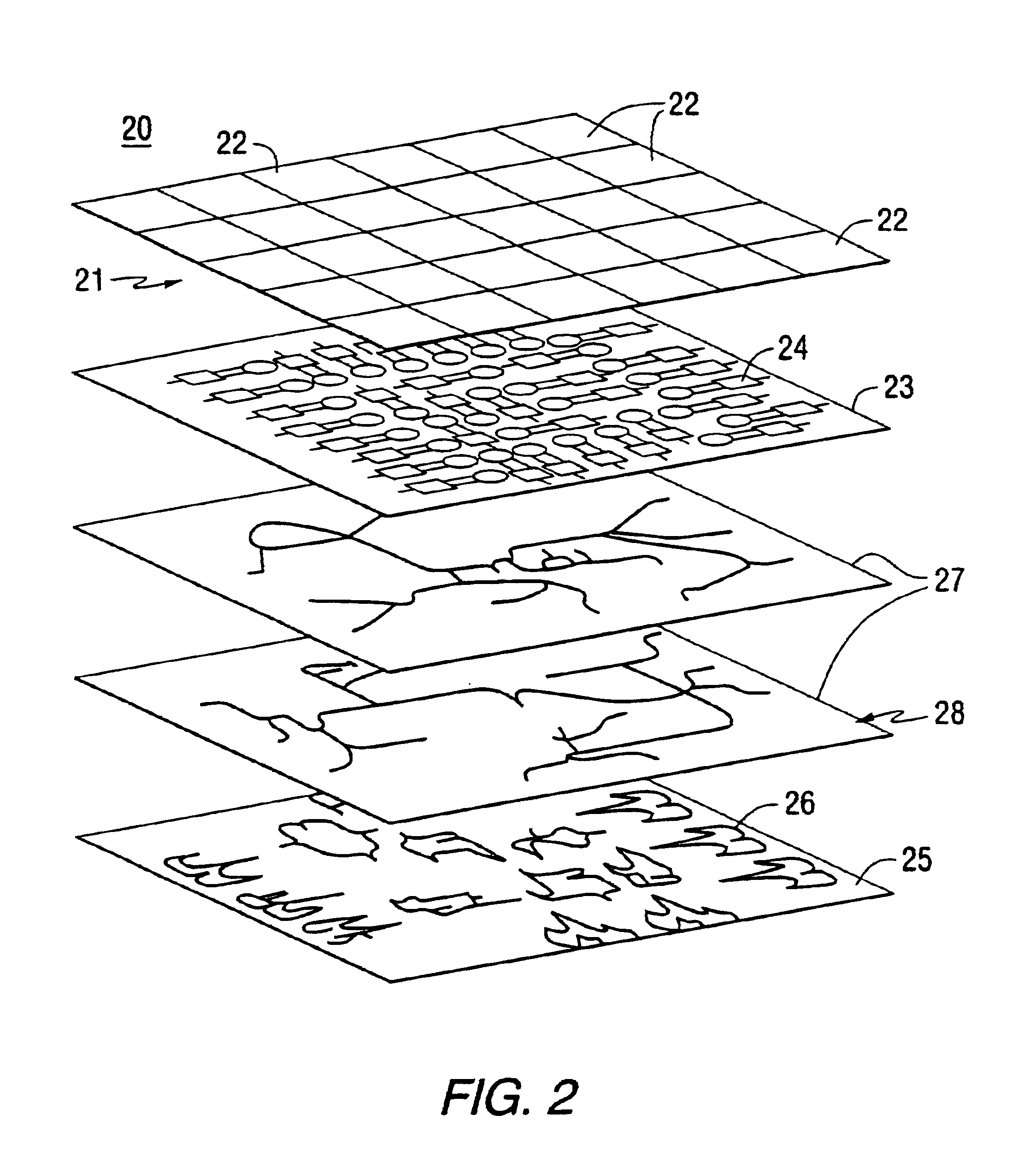
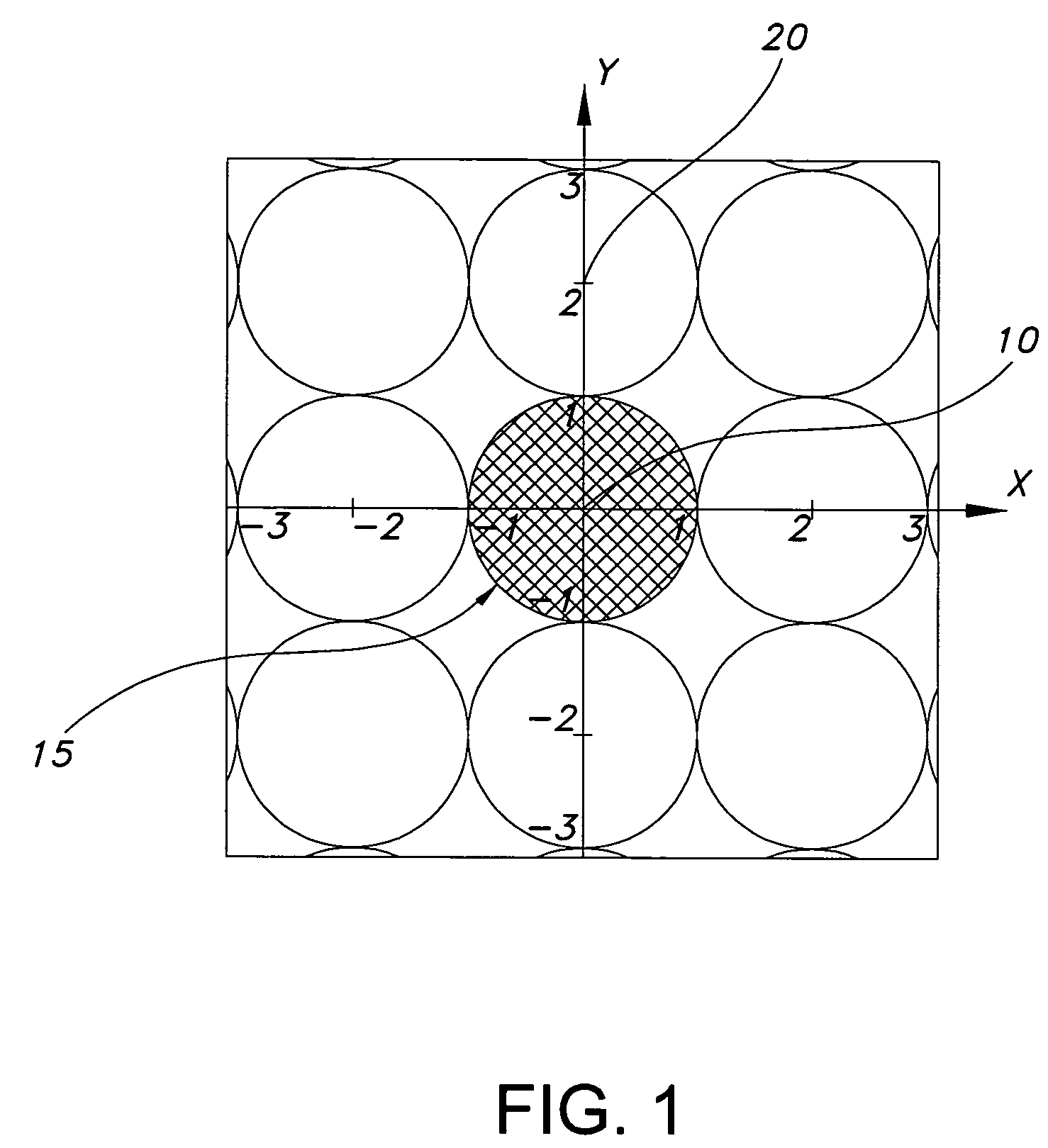
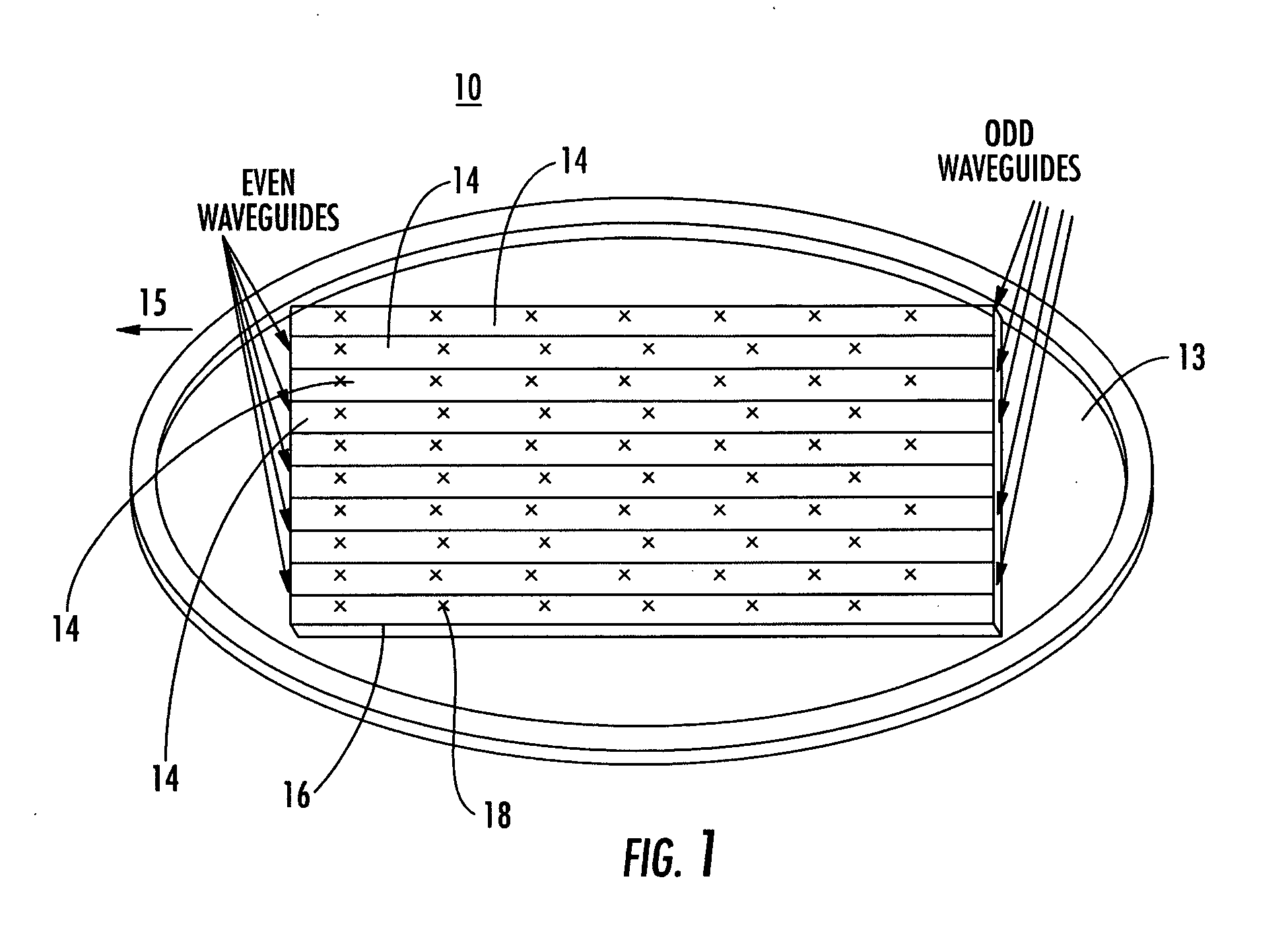
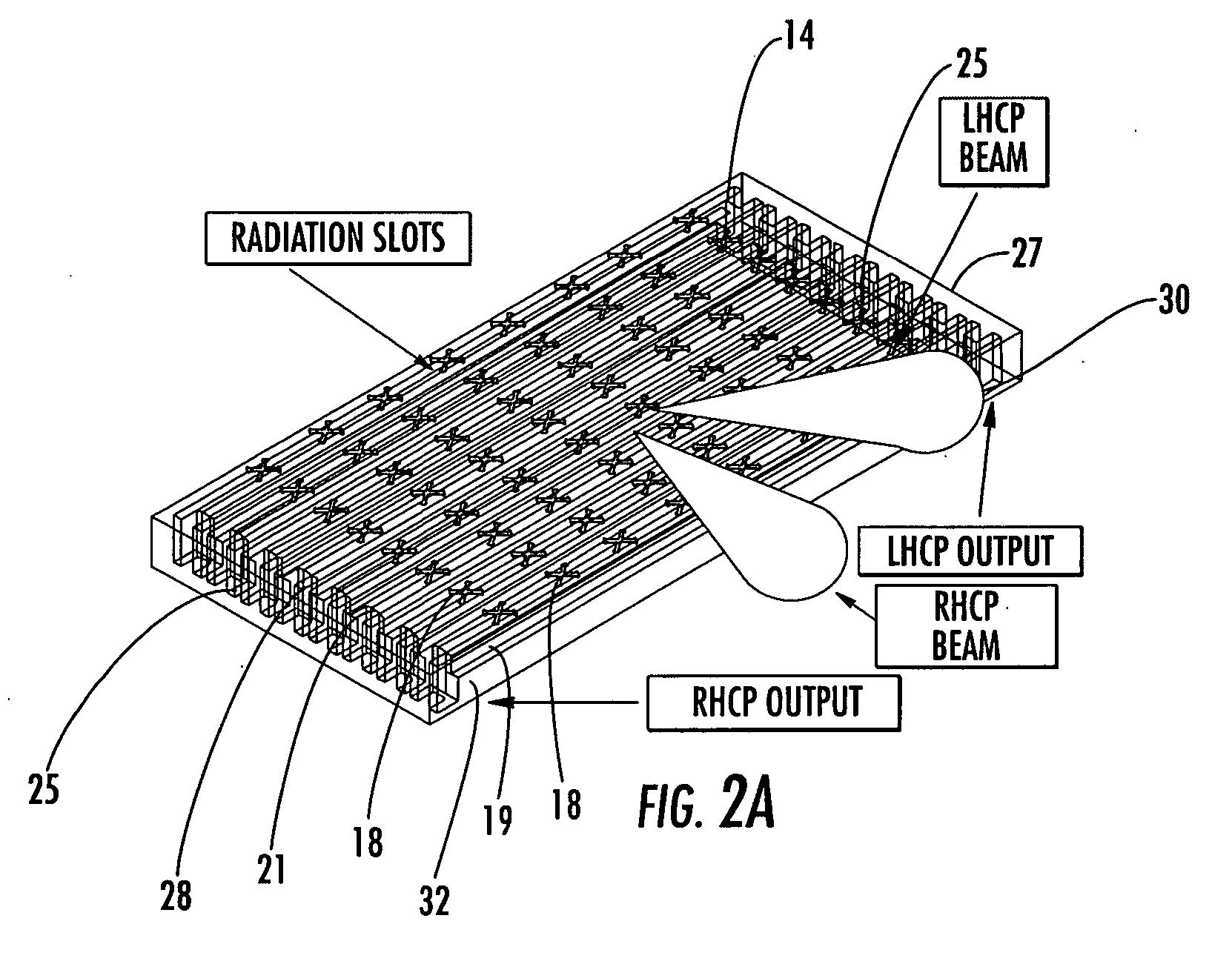
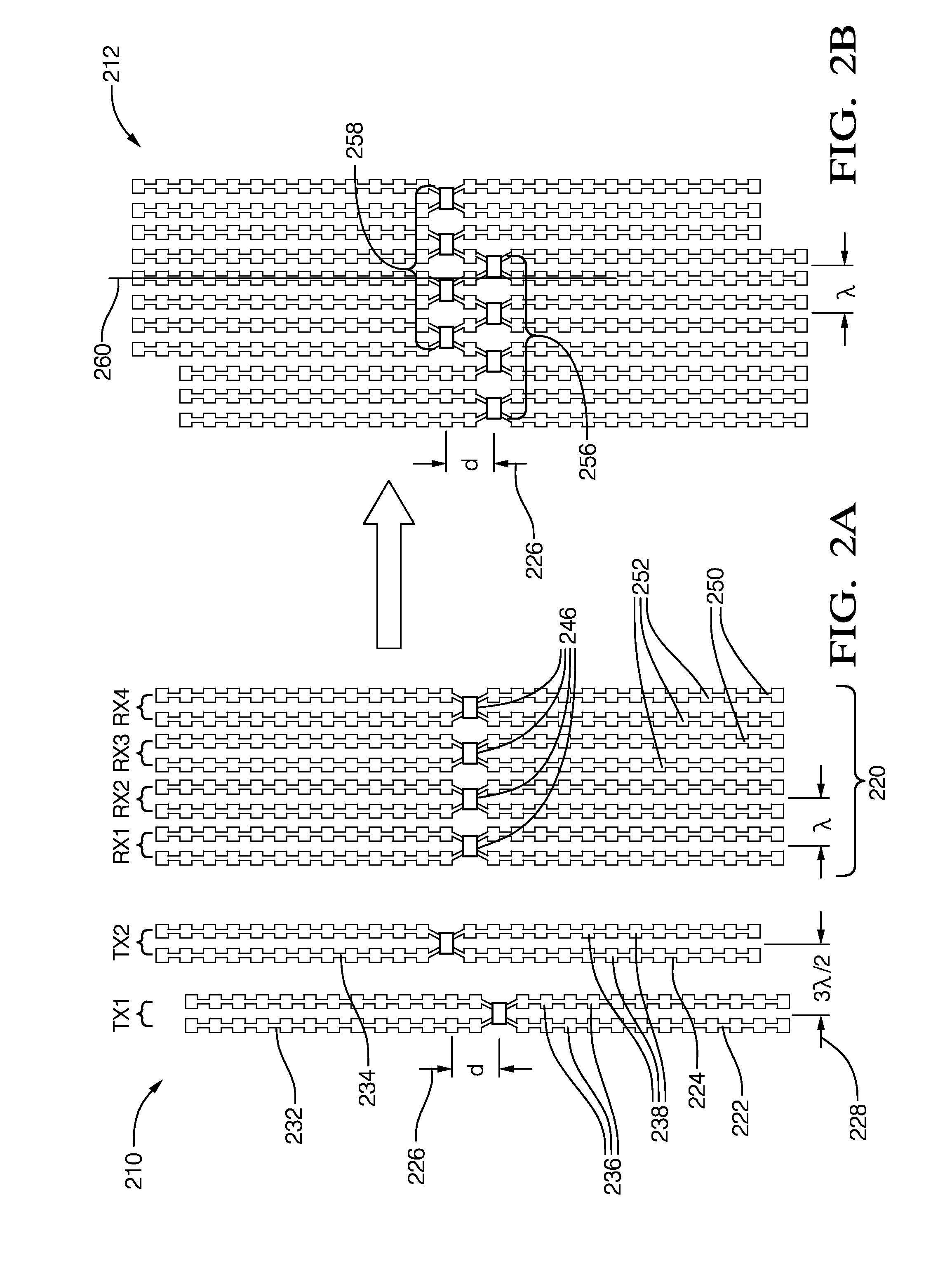
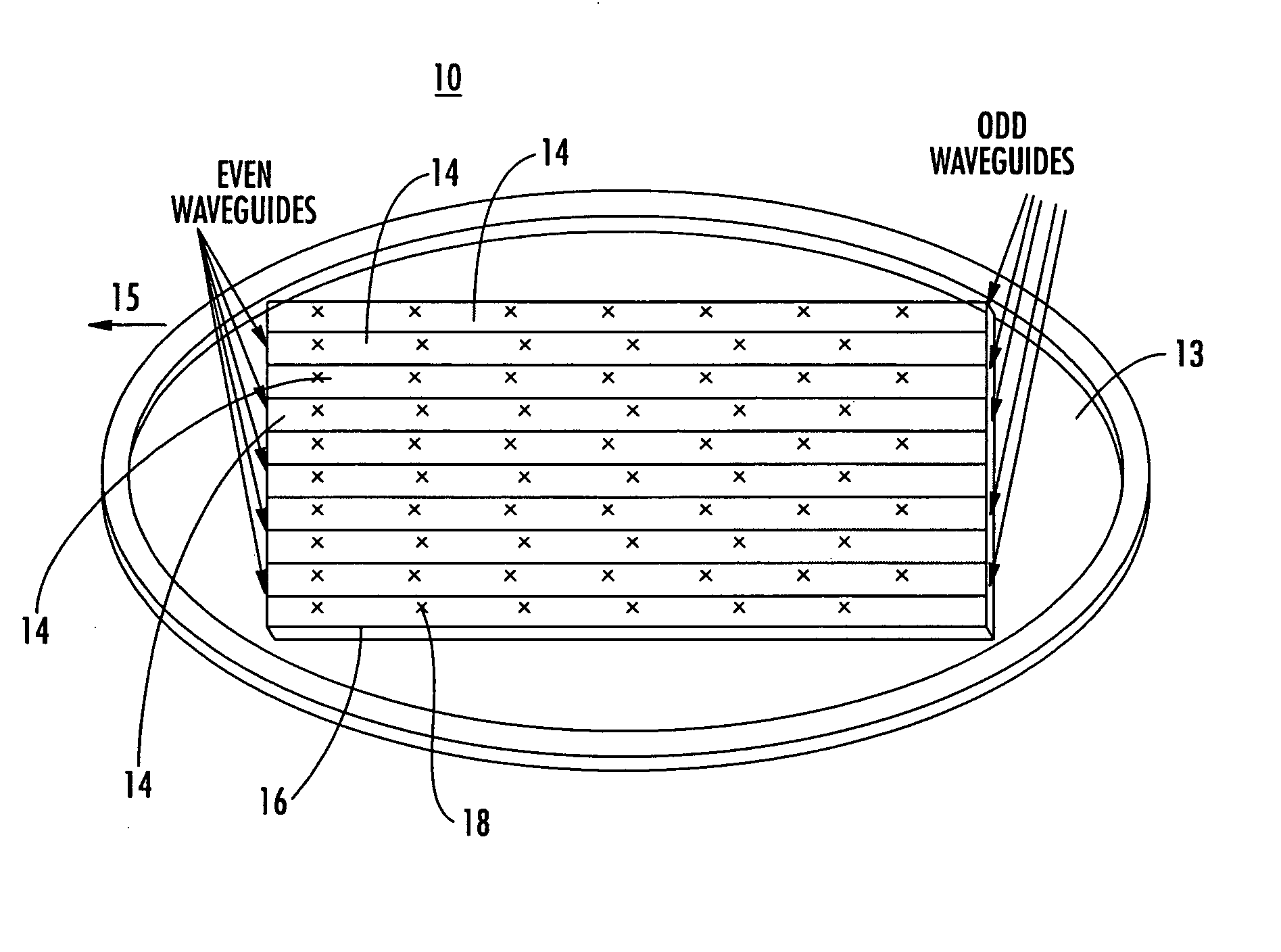
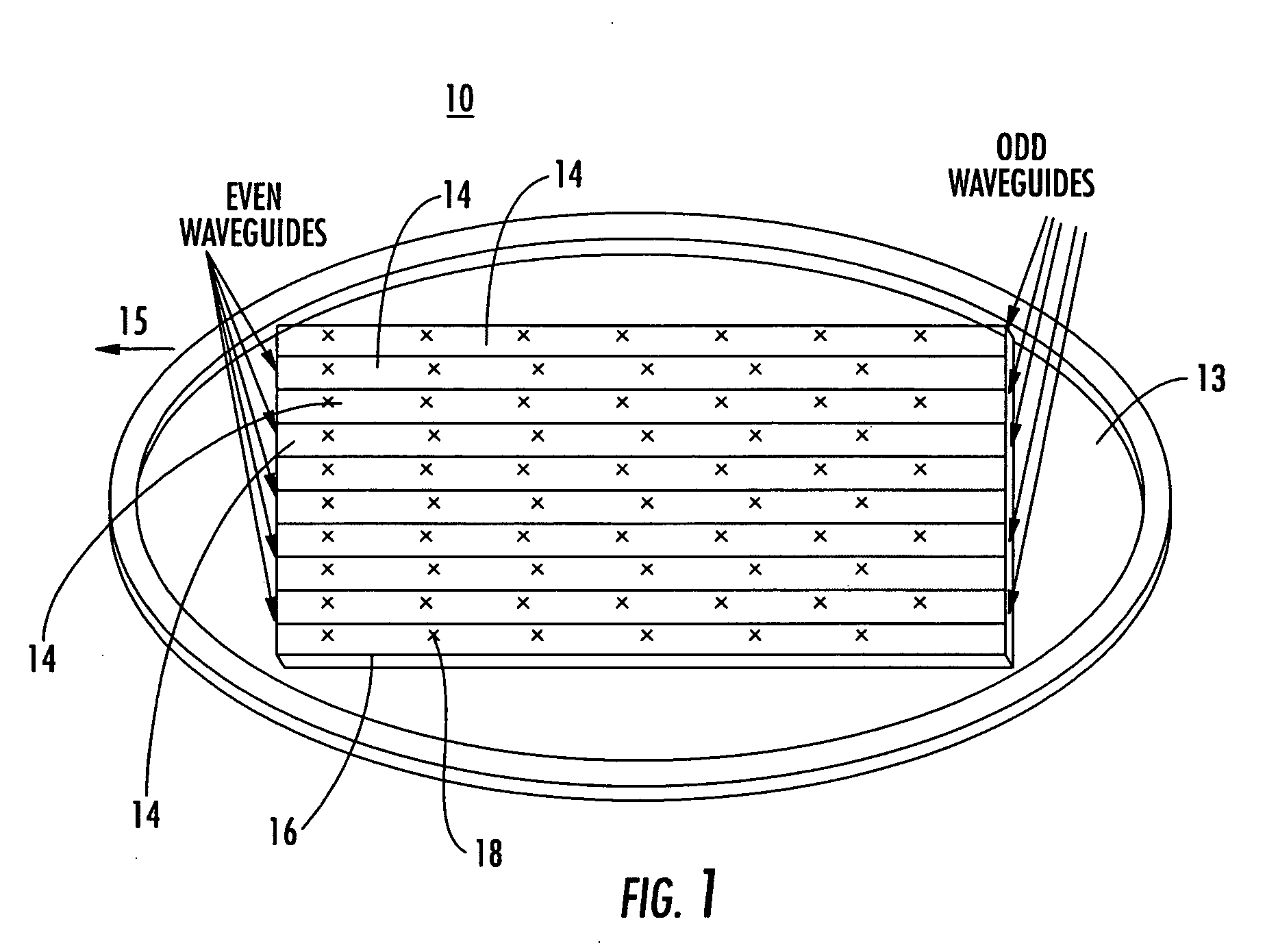
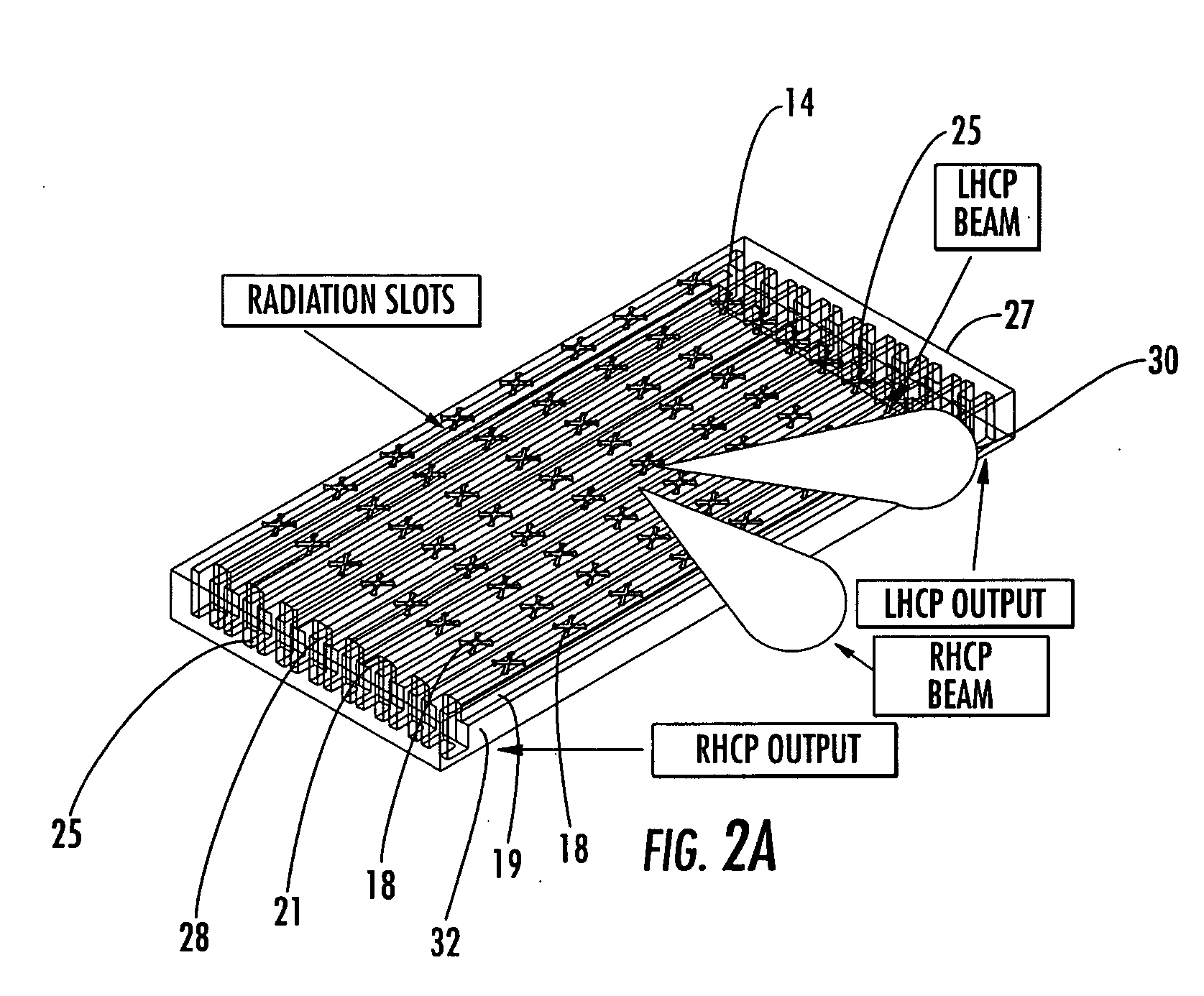
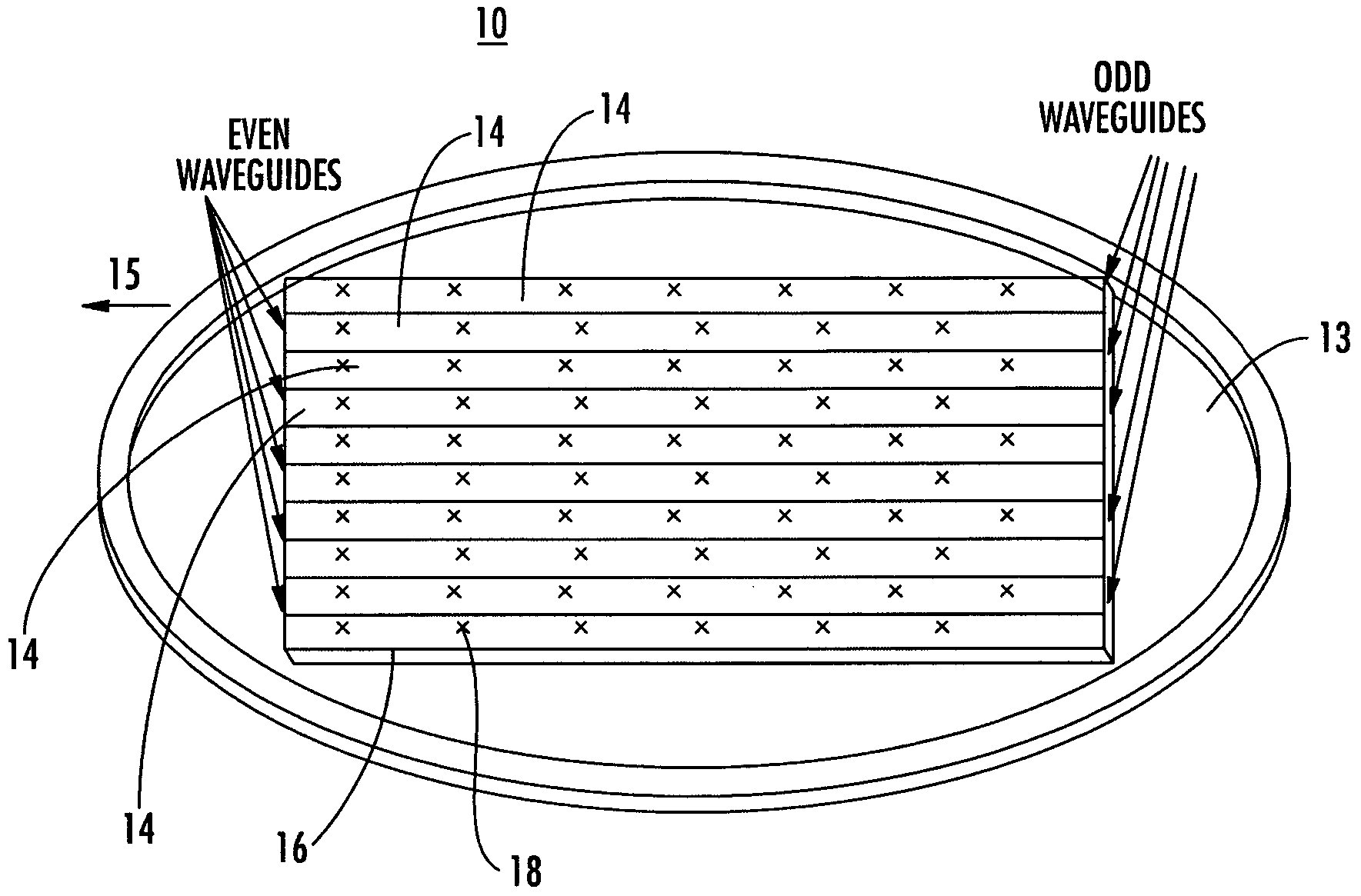
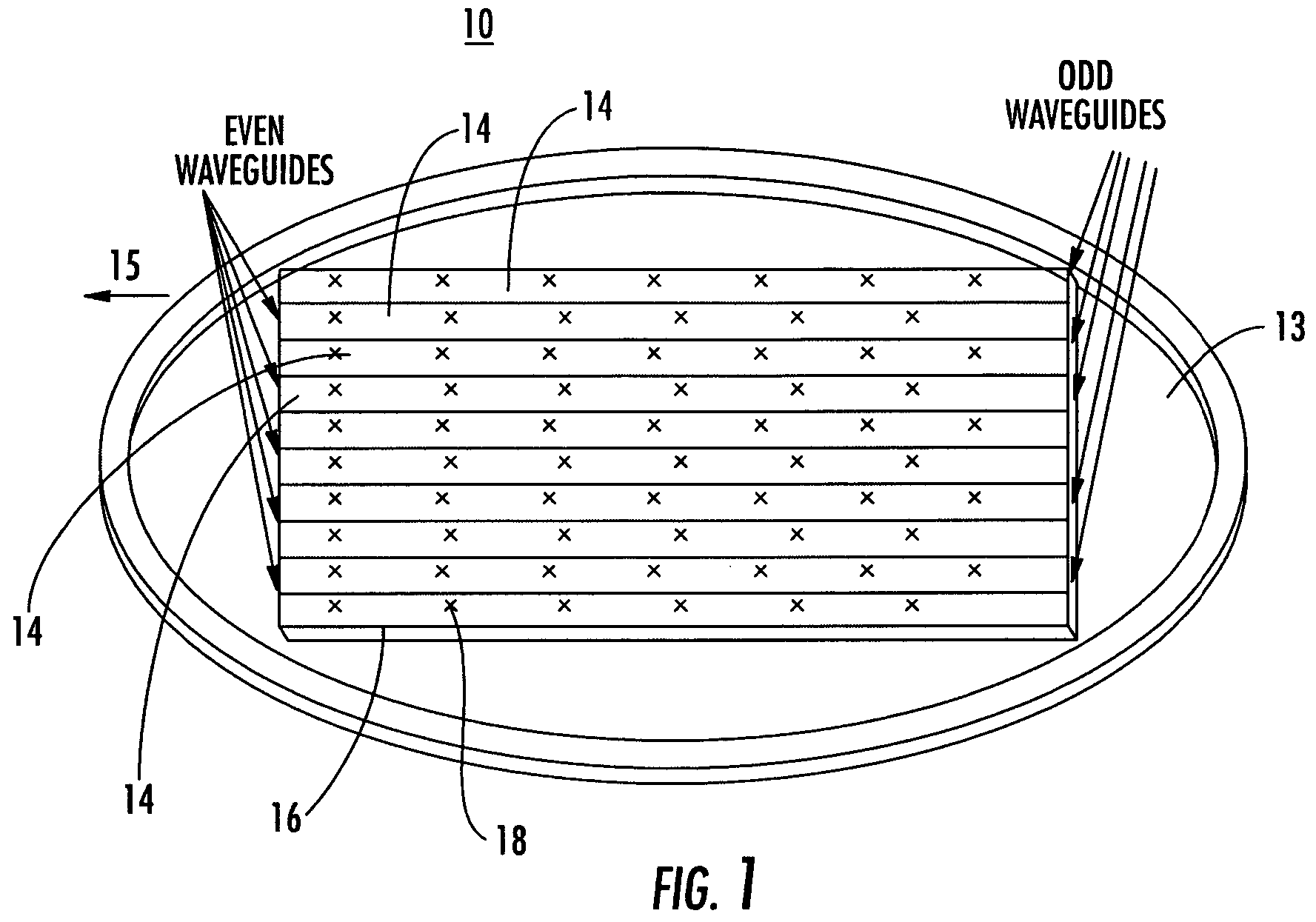
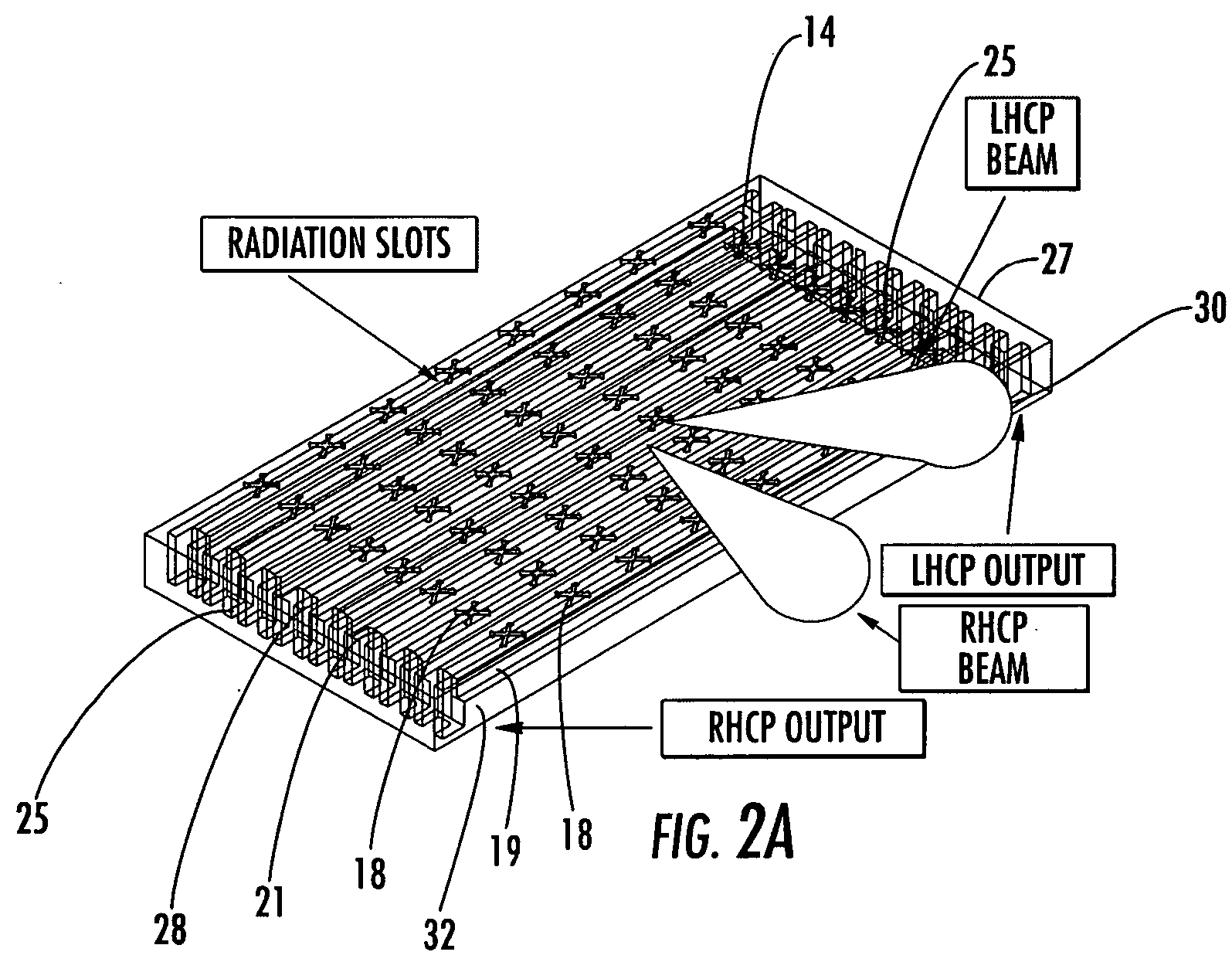
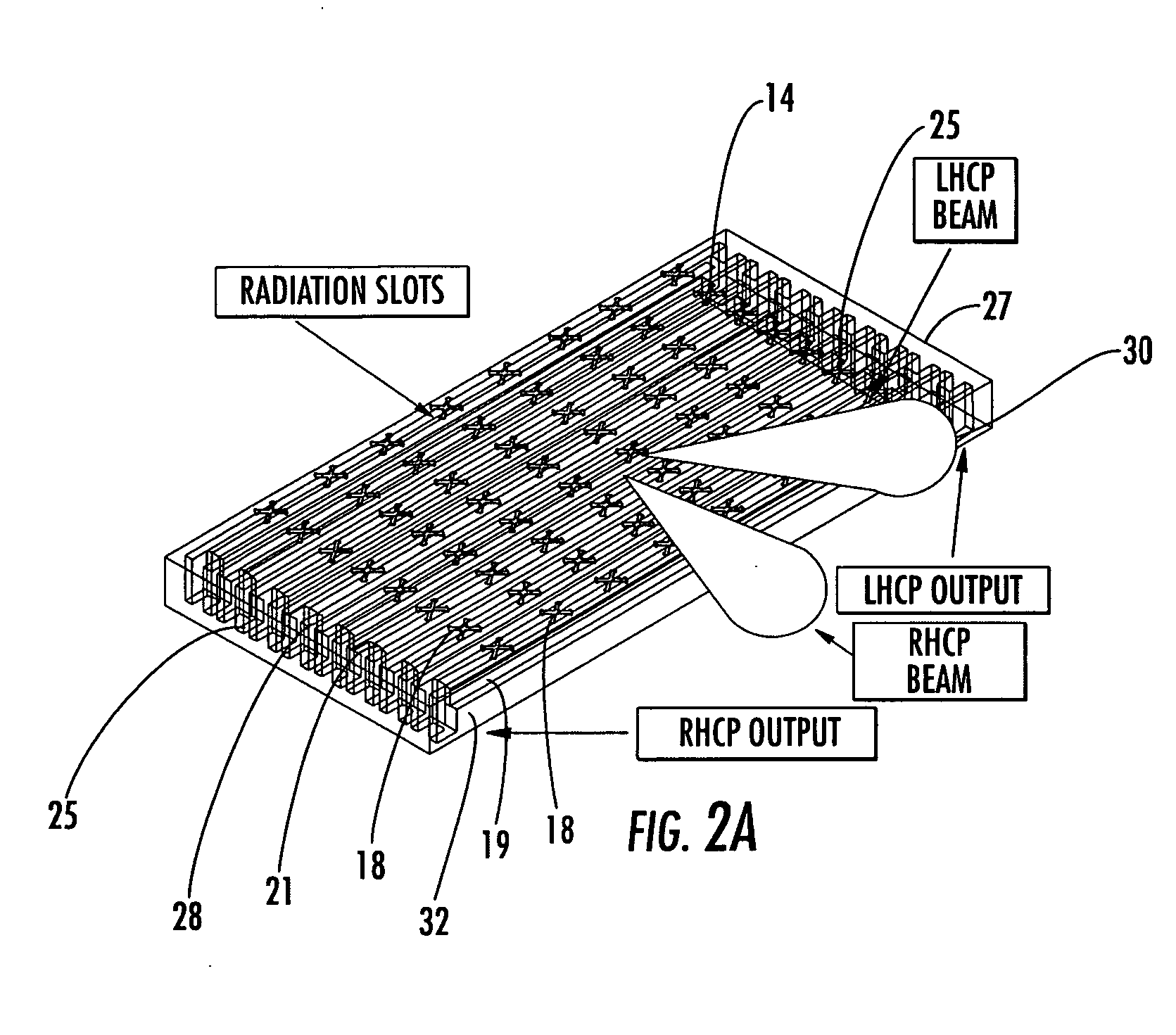
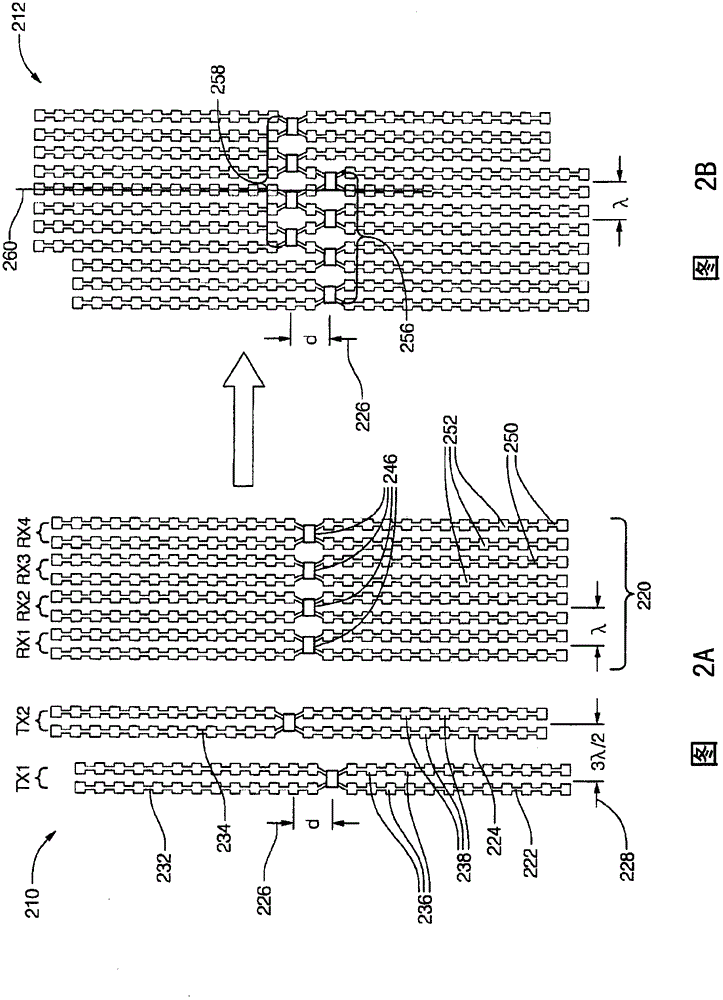
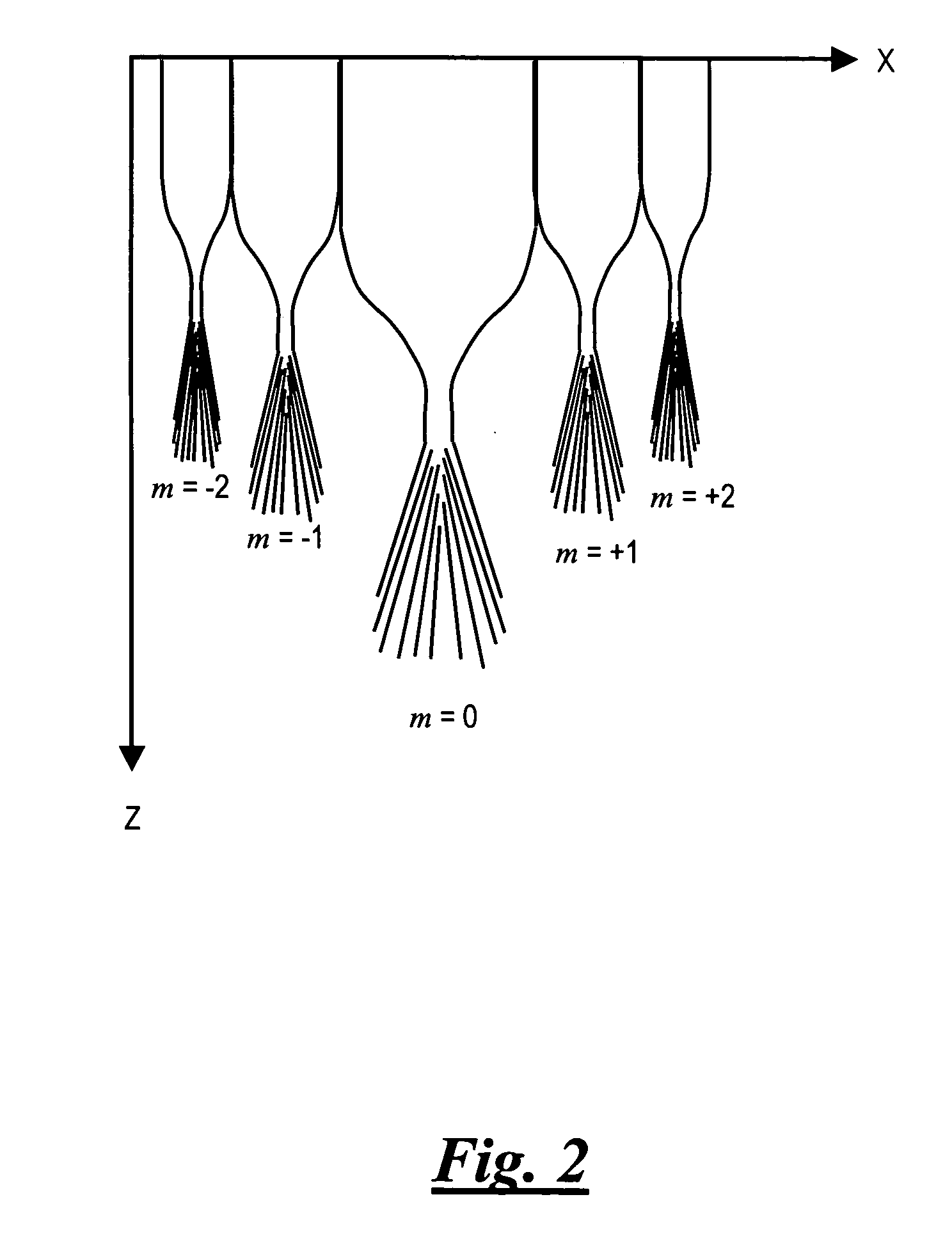
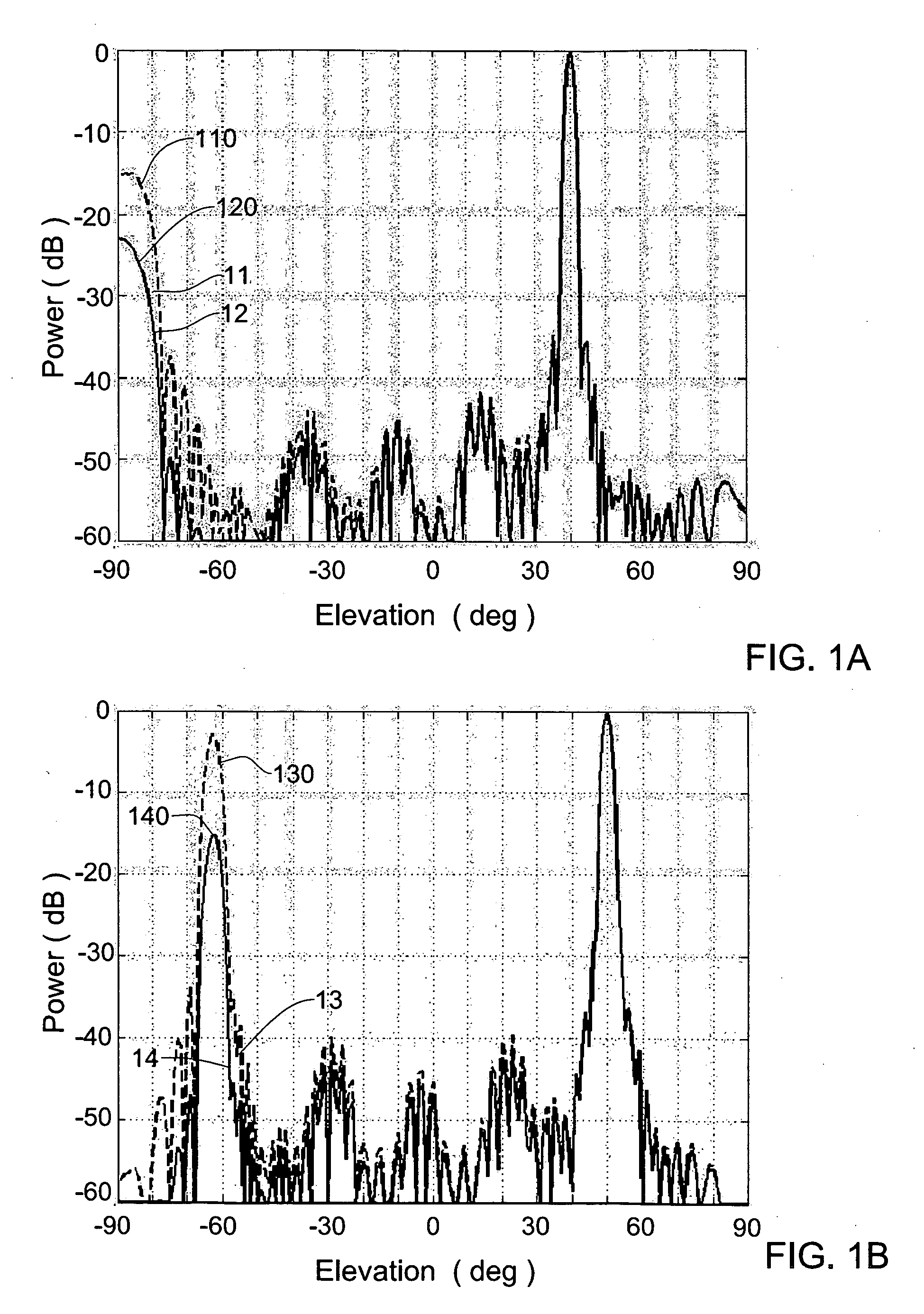
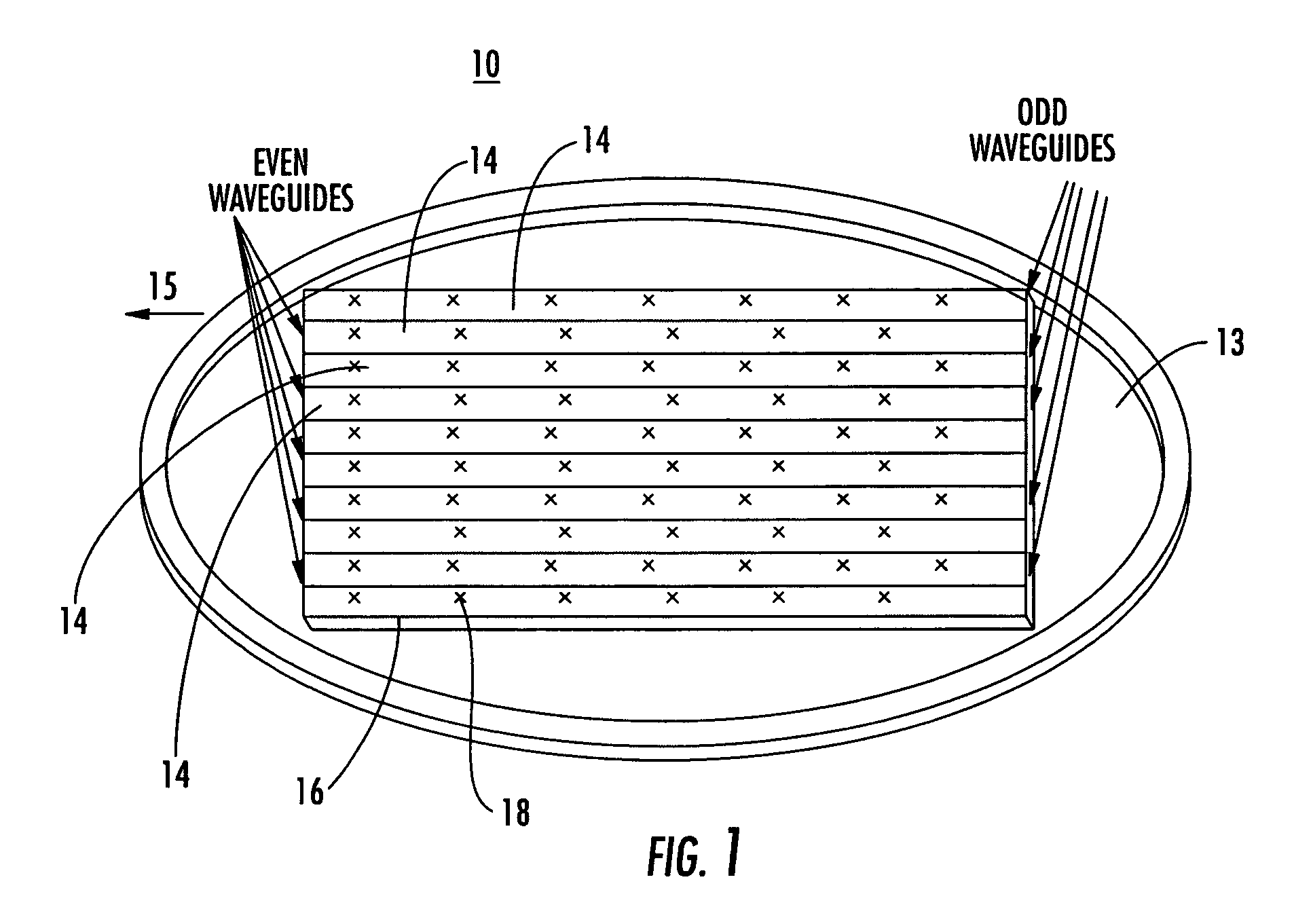
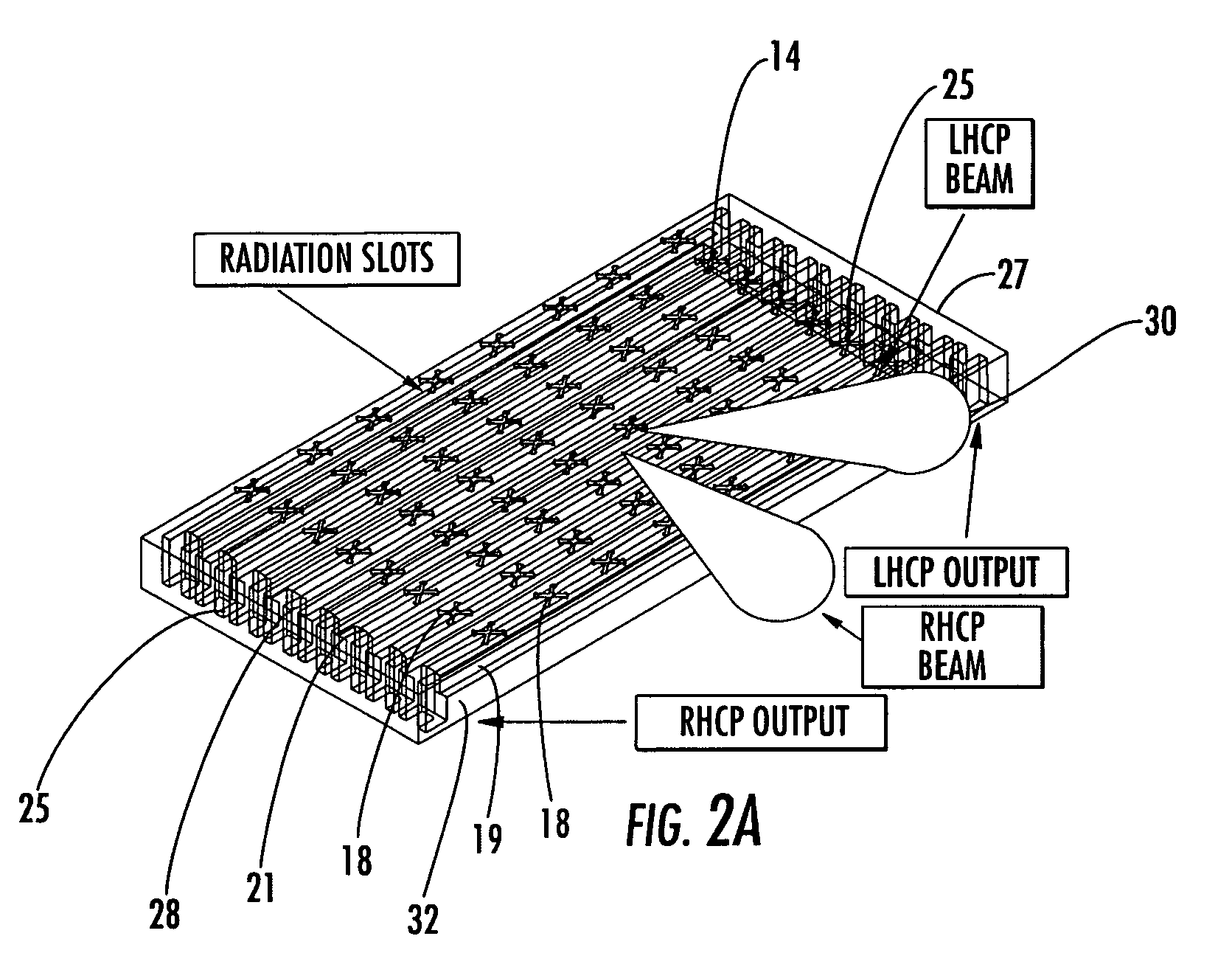
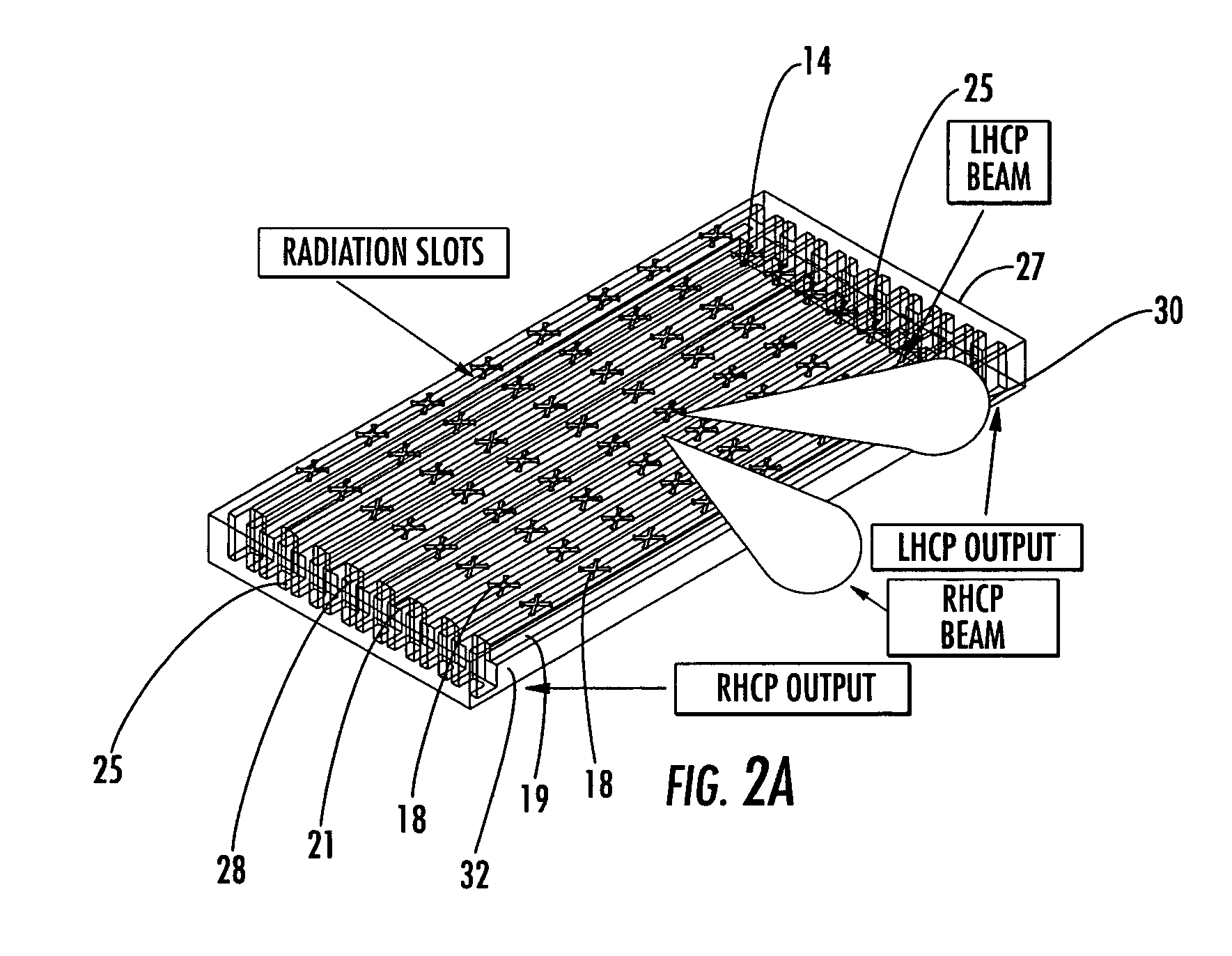
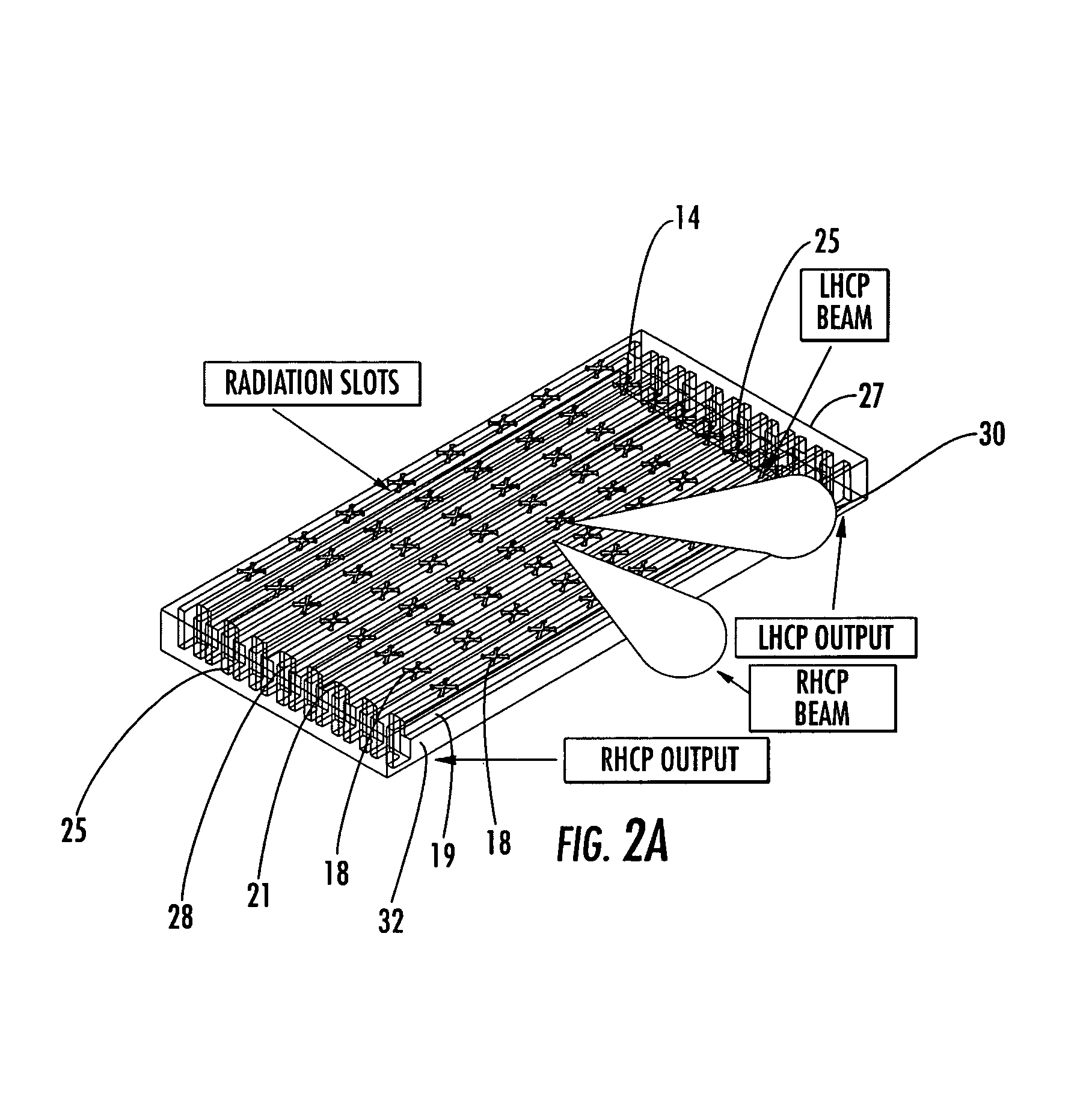
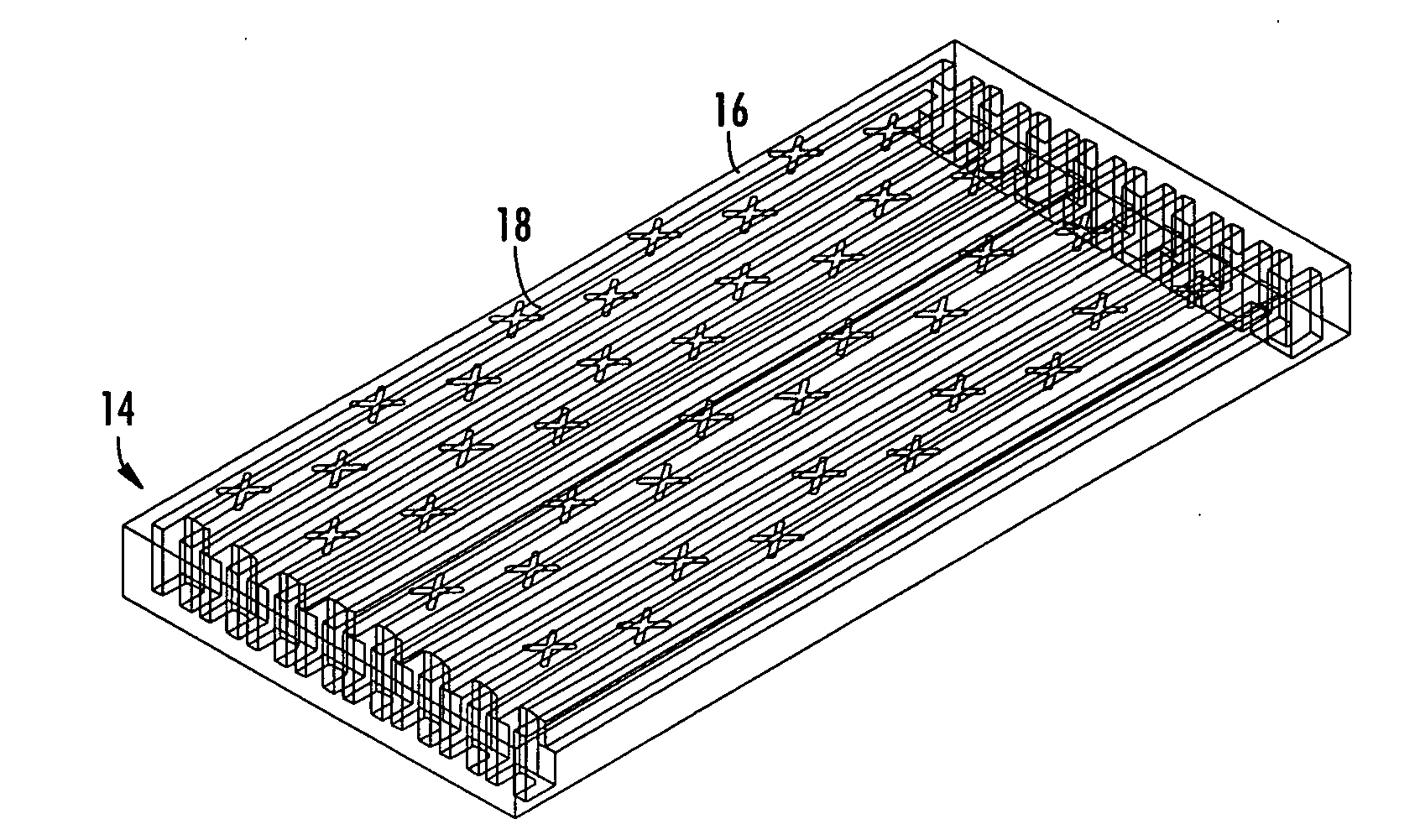
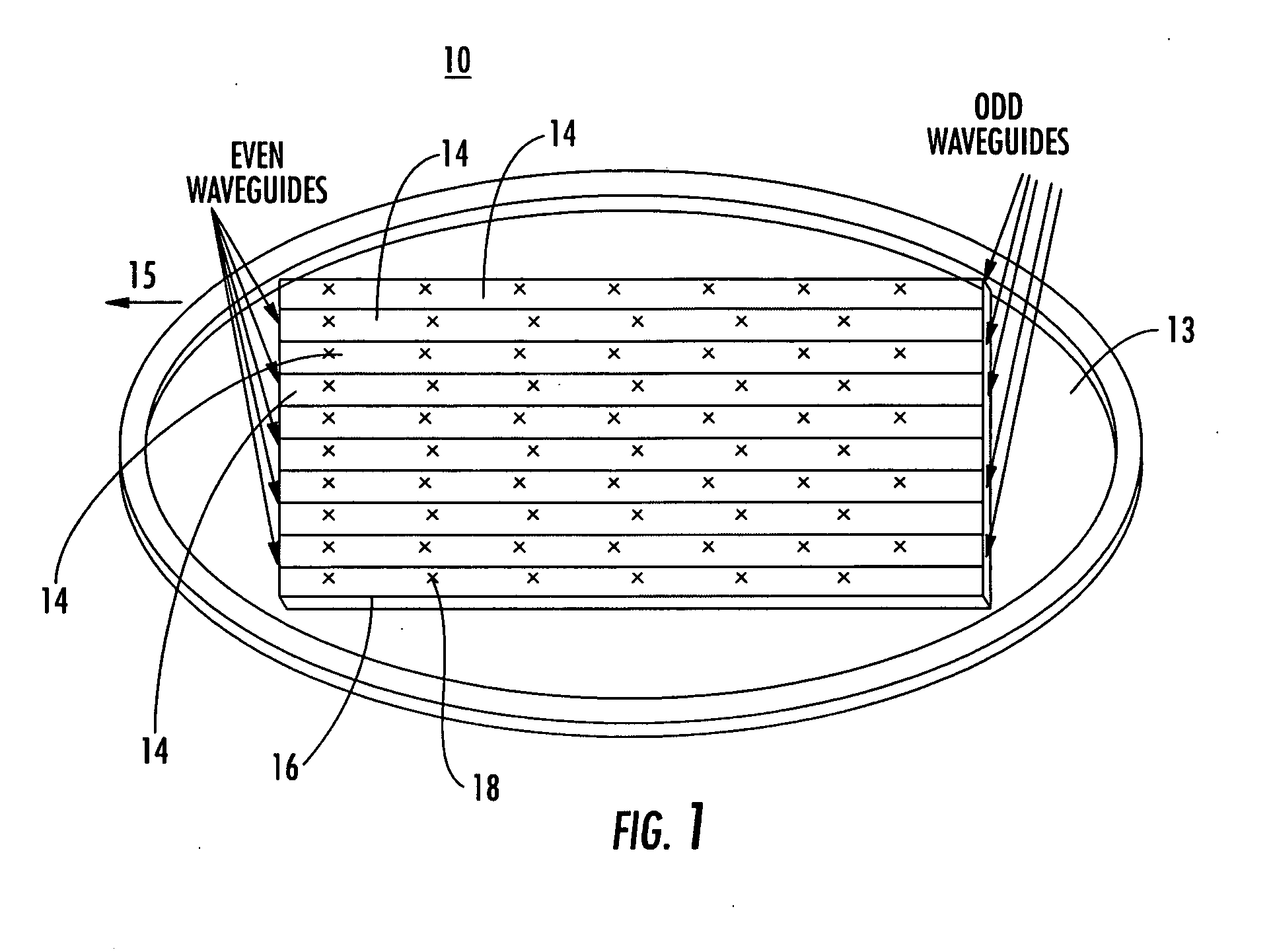
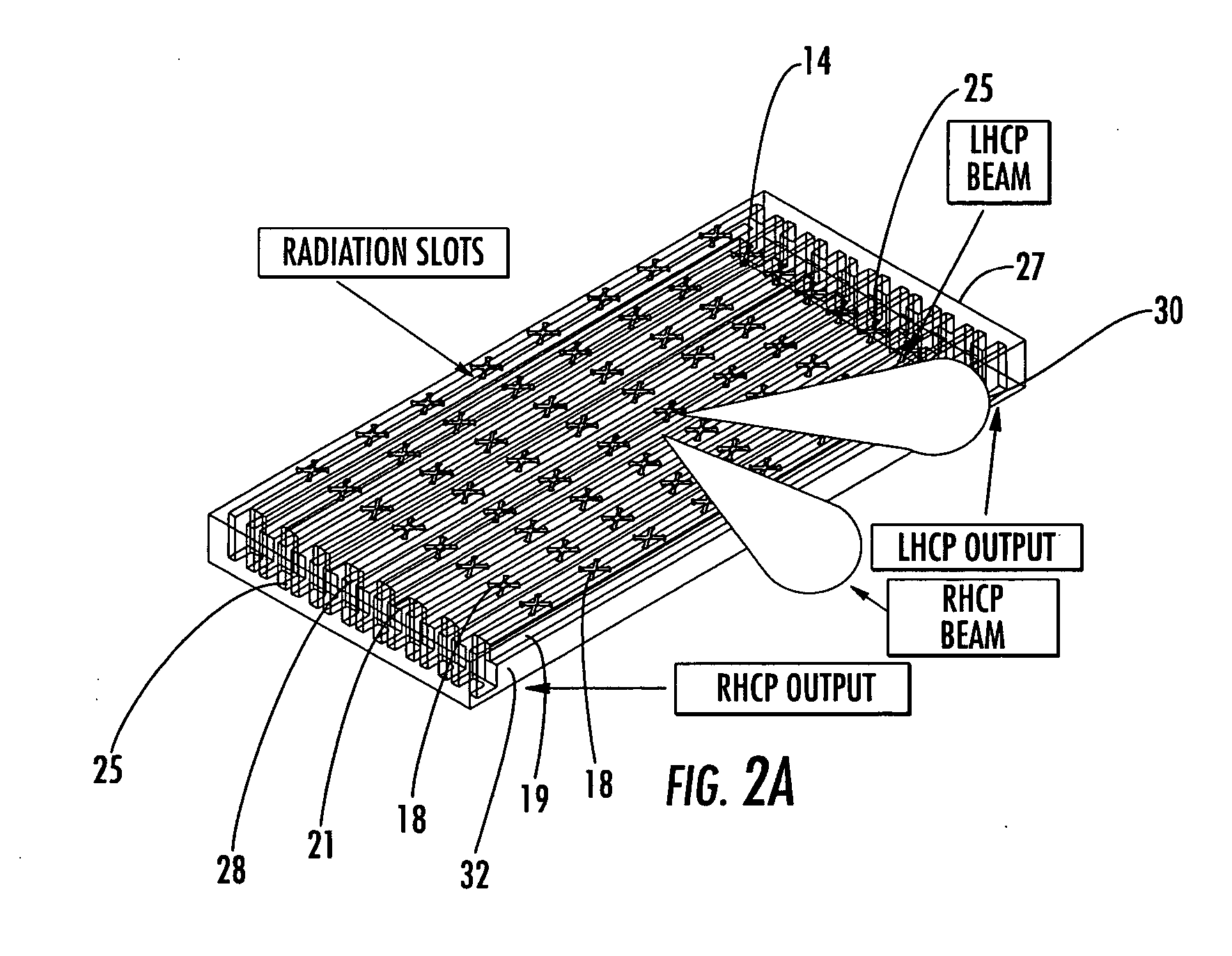
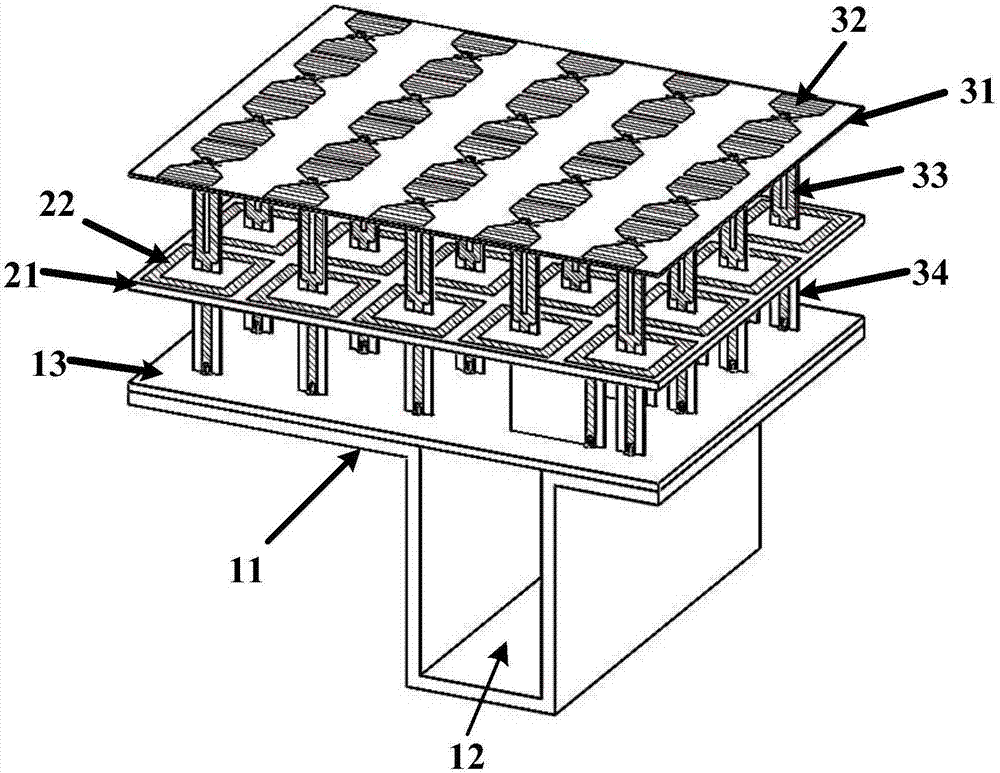
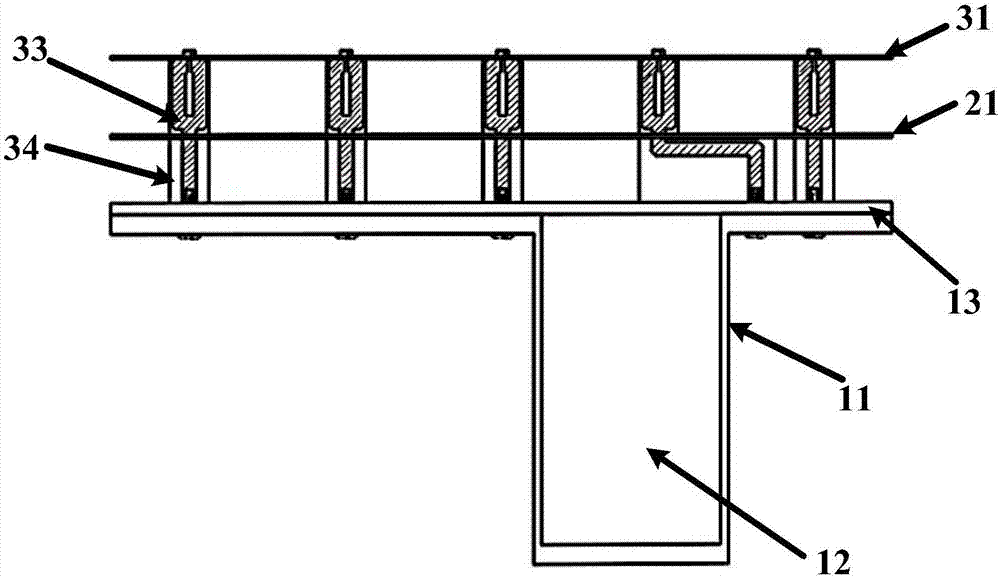
Antenna arrays formed of spiral sub-array lattices
InactiveUS6842157B2Improve bindingWider antenna bandwidthSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringGrating lobe
A antenna array (20) includes a plurality of periodic or aperiodic arranged sub-arrays (22). Each sub-array (22) includes a plurality of antenna elements (32) arranged in the form of a spiral (30). The sub-arrays (22) can comprise various spiral shapes to provide the required physical configuration and operational parameters to the antenna array (20). The elements (32) of each sub-array (22) are arranged to minimize the number of such elements (32) that intersect imaginary planes perpendicular to the spiral and passing through the spiral center. Such an orientation of the elements (32) minimizes grating lobes in the antenna pattern.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
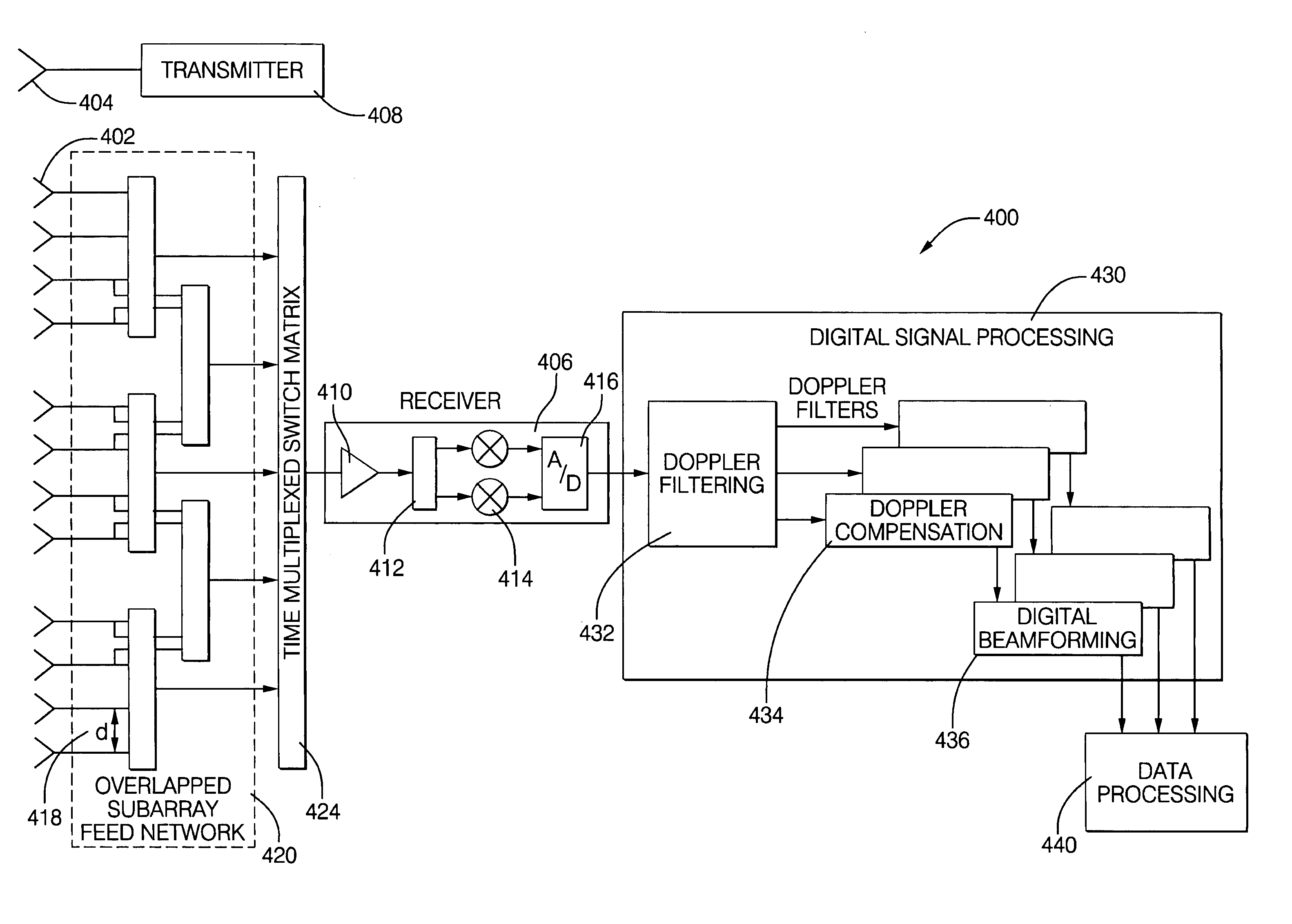
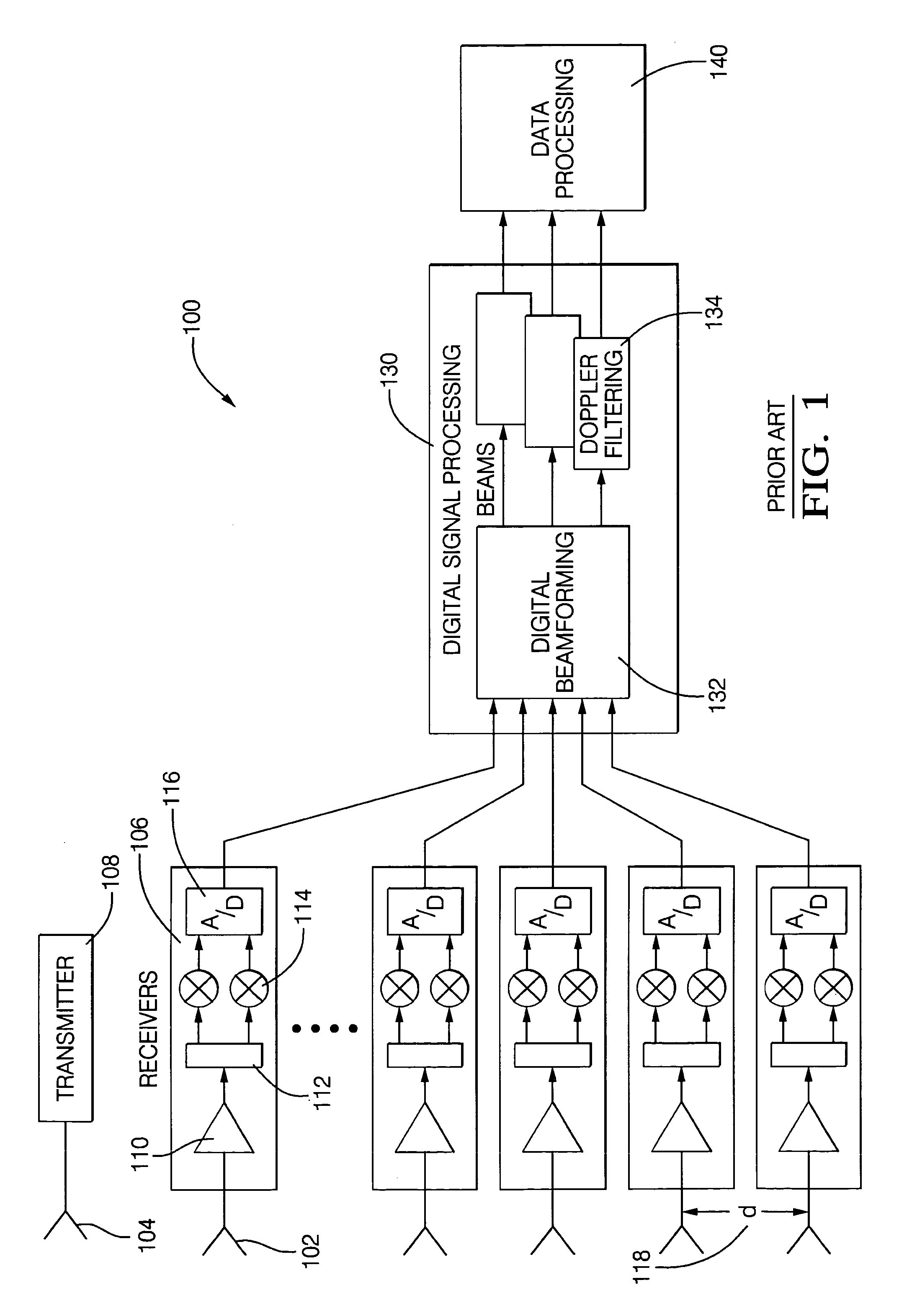
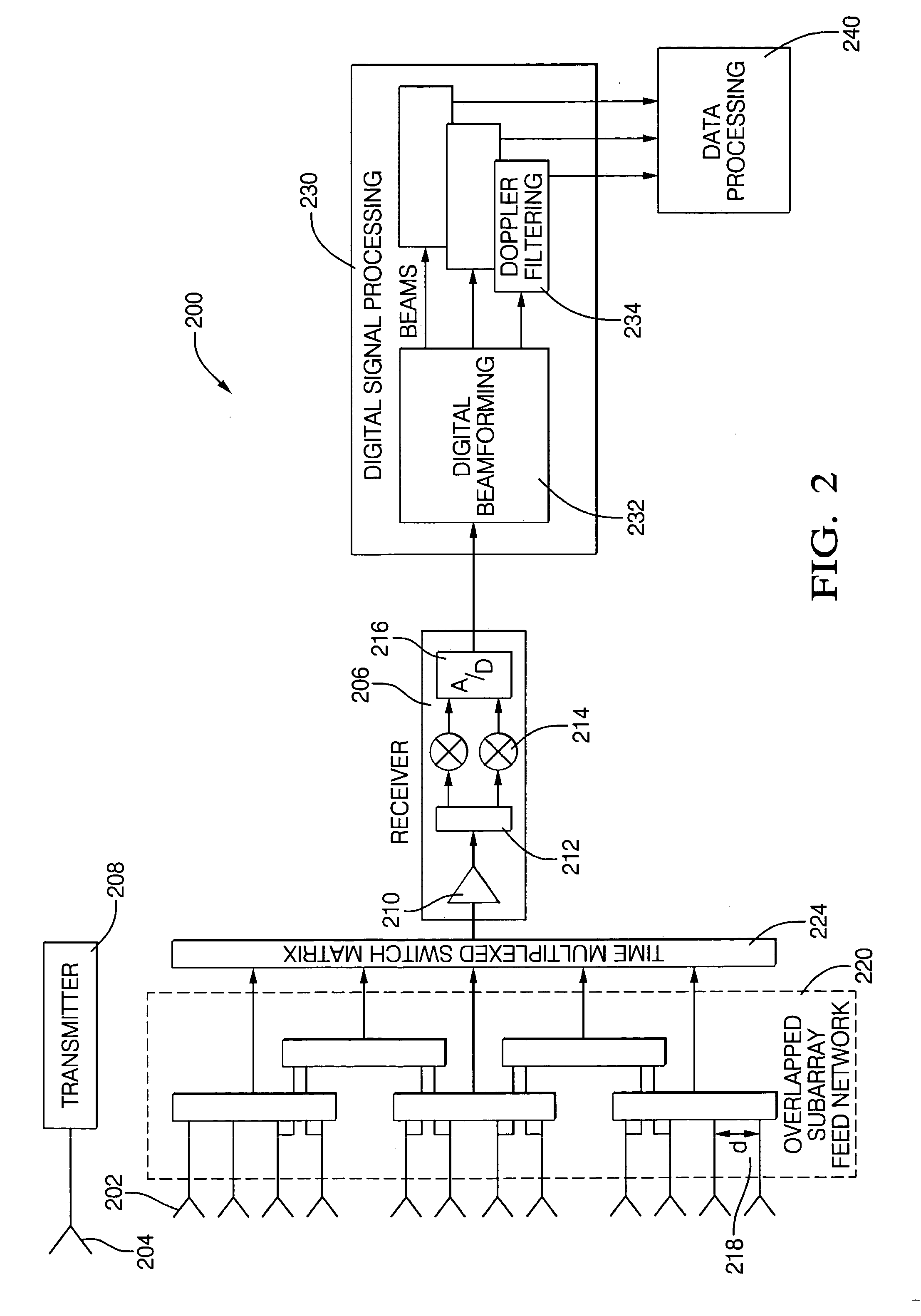
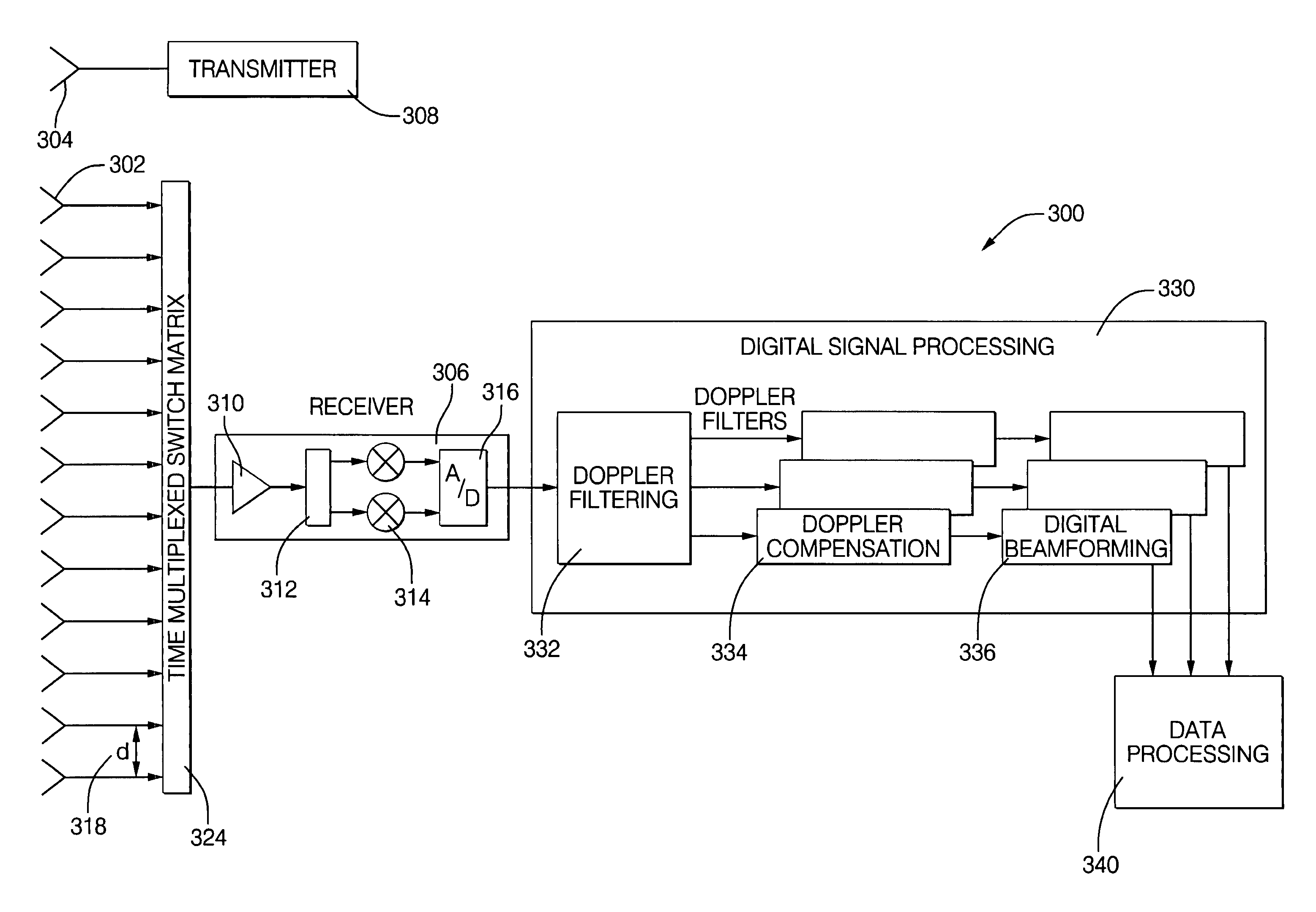
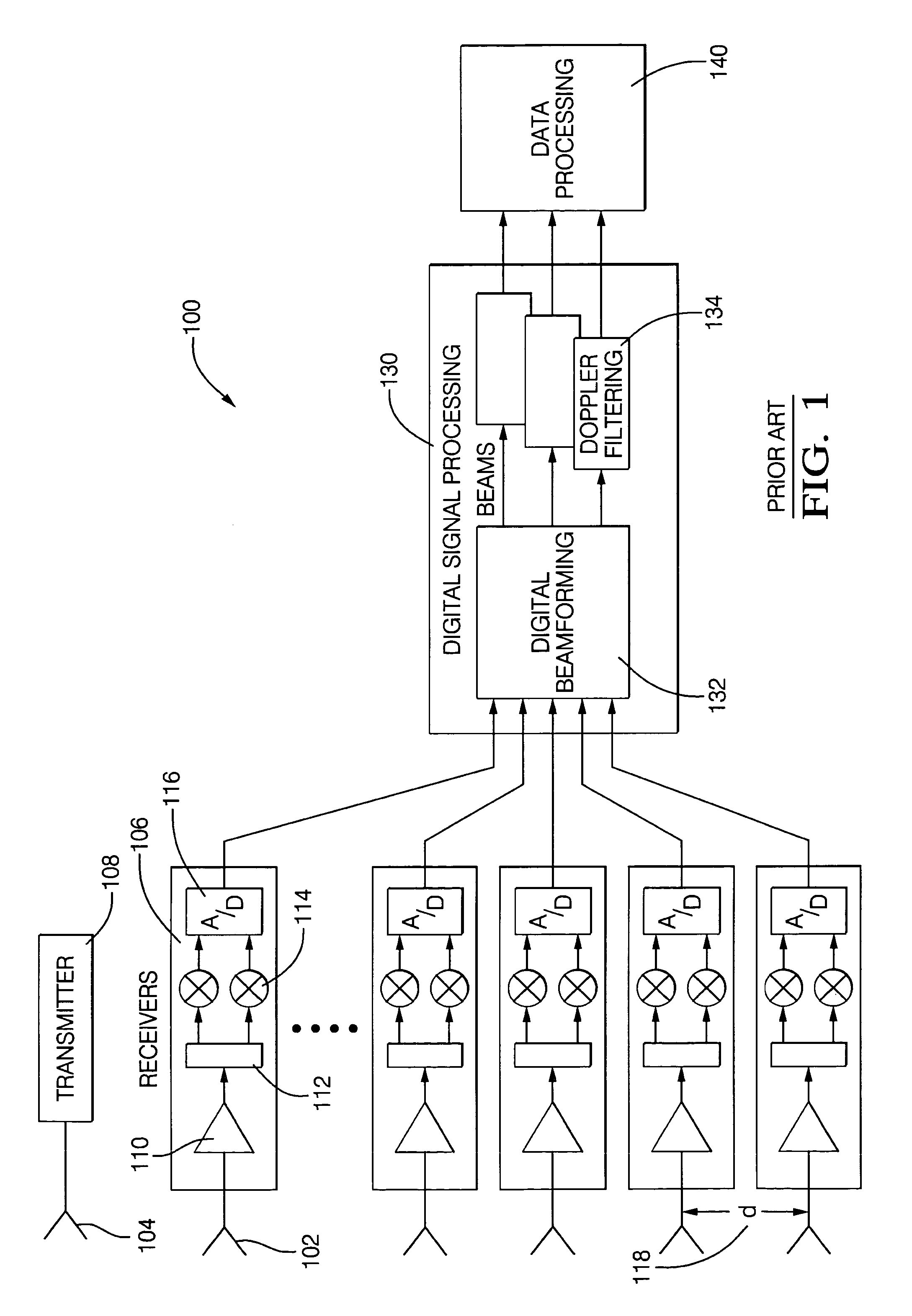
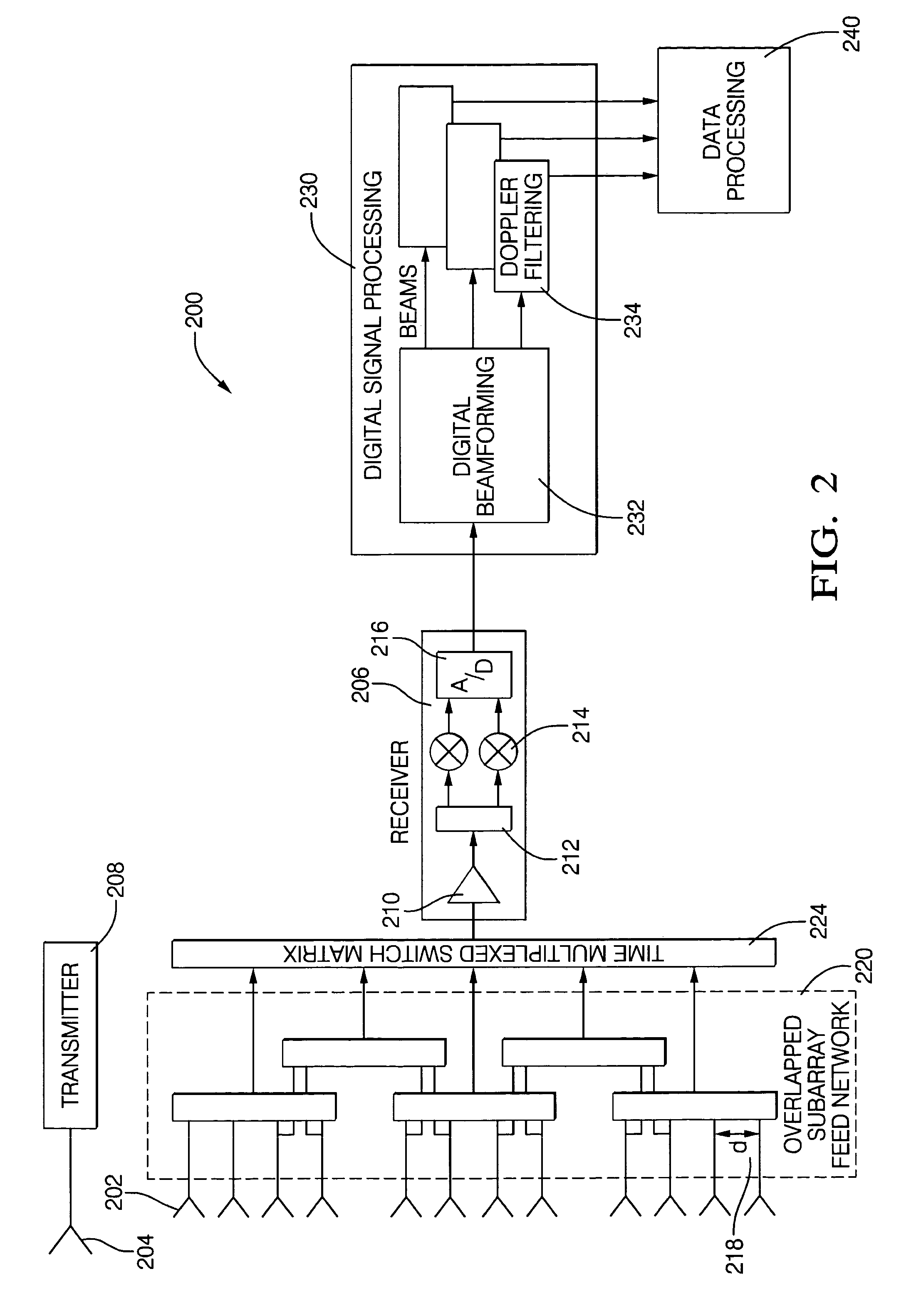
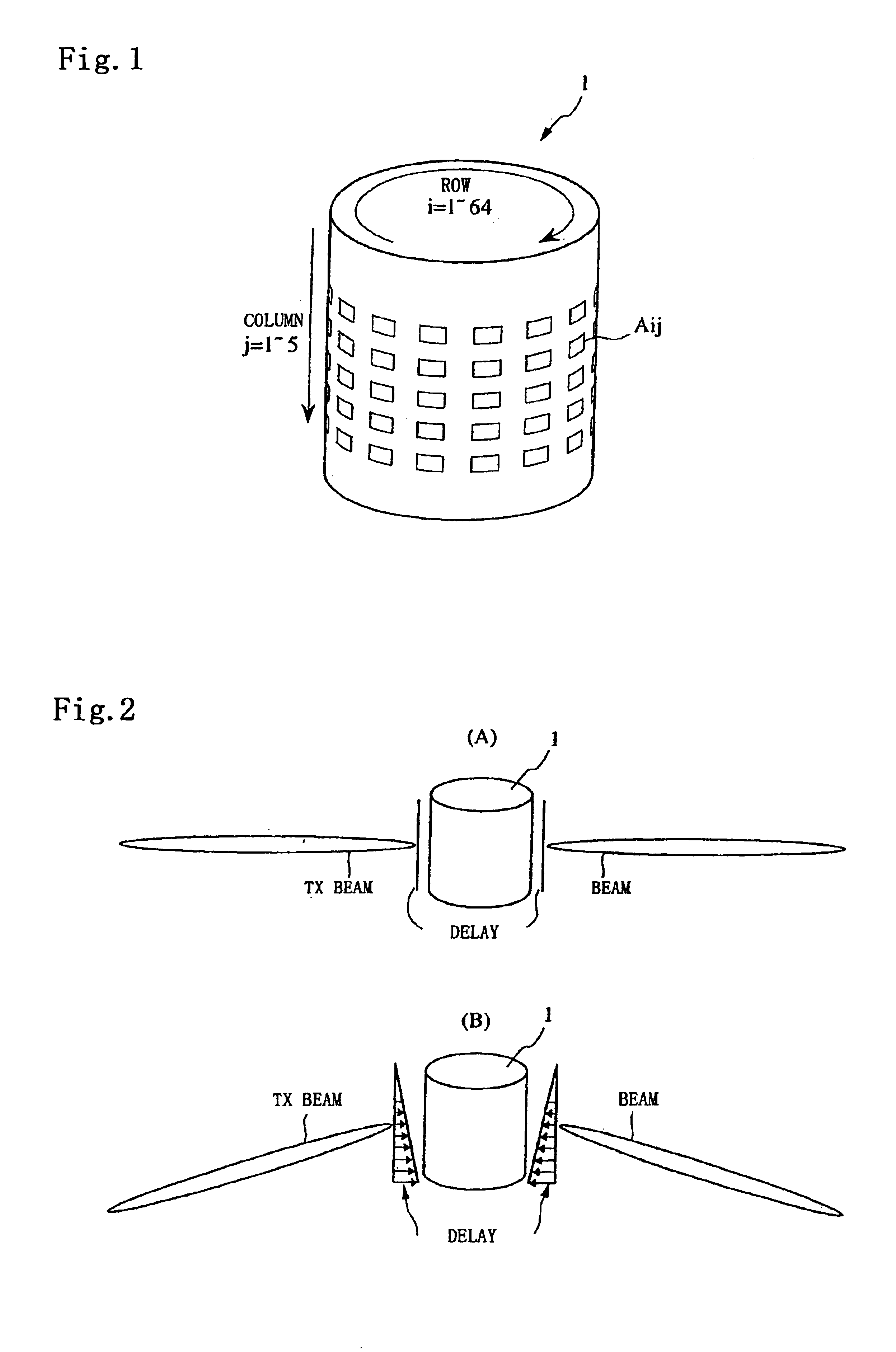
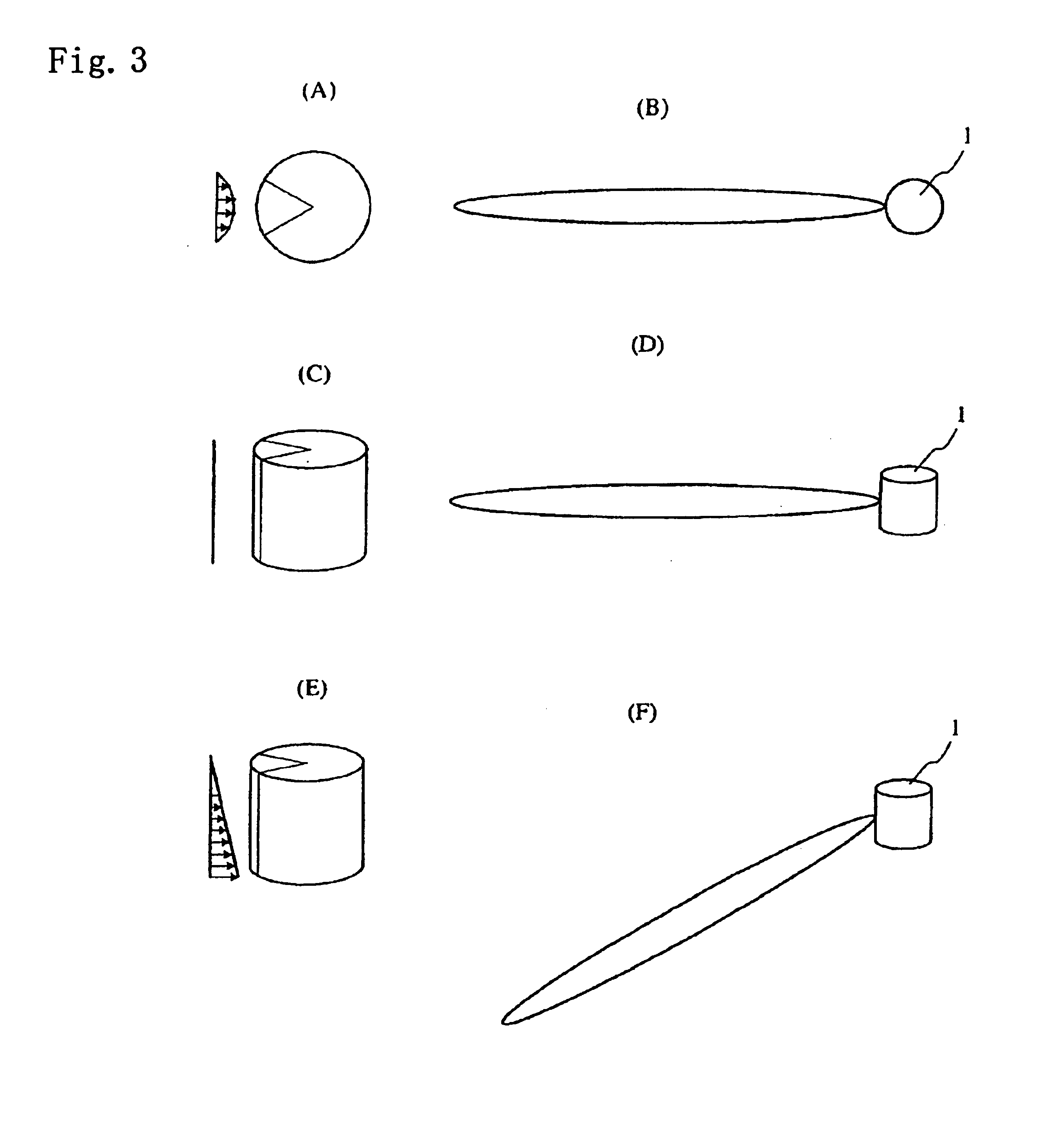
Digital beamforming for an electronically scanned radar system
ActiveUS20070001897A1Improve performanceLow costParticular array feeding systemsRadio transmissionRadar systemsGrating lobe
Digital beamforming is provided for use with electronically scanned radar. In an aspect, the present invention provides enhanced sensitivity, wide angle or field of view (FOV) coverage with narrow beams, minimized number of receivers, reduced sidelobes, eliminated grating lobes and beam compensation for target motion. In an aspect, the present invention employs a uniform overlapped subarray feed network, a time multiplexed switch matrix, and a restructured digital signal processor. Antenna channels share a receiver, rather than maintain a dedicated receiver for each antenna element, as in conventional systems. In an aspect, Doppler / frequency filtering is performed on each antenna element or subarray output prior to digital beamforming. Further, Doppler compensation is employed following Doppler / frequency filtering, followed by digital beamforming.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Multi-band wide-angle scan phased array antenna with novel grating lobe suppression
ActiveUS7034753B1Minimize mechanical blockageMinimize mutual couplingParticular array feeding systemsSimultaneous aerial operationsMulti bandRadiating element
A multi-band wide-angle scan phased array antenna with novel grating lobe suppression has a first plurality of radiation elements for radiating a first frequency arranged in a rectangular configuration. A second plurality of radiation elements for radiating second frequency are arranged in a rectangular frame around the first radiation elements. A third plurality of radiation elements for radiating third frequency are arranged in a rectangular frame around the second radiation elements. The radiation elements are apertures that are λ / 2 of an operating frequency in size. The radiation elements may also be arranged in square, circular, or elliptical configurations.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Digital beamforming for an electronically scanned radar system
ActiveUS7474262B2Improve performanceLow costParticular array feeding systemsRadio transmissionRadar systemsEngineering
Digital beamforming is provided for use with electronically scanned radar. In an aspect, the present invention provides enhanced sensitivity, wide angle or field of view (FOV) coverage with narrow beams, minimized number of receivers, reduced sidelobes, eliminated grating lobes and beam compensation for target motion. In an aspect, the present invention employs a uniform overlapped subarray feed network, a time multiplexed switch matrix, and a restructured digital signal processor. Antenna channels share a receiver, rather than maintain a dedicated receiver for each antenna element, as in conventional systems. In an aspect, Doppler / frequency filtering is performed on each antenna element or subarray output prior to digital beamforming. Further, Doppler compensation is employed following Doppler / frequency filtering, followed by digital beamforming.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
System and method for ultrasound therapy using grating lobes
ActiveUS7806839B2Accomplished more efficientlyOvercome limitationsUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesPhase shiftedTransducer
A system and method for medical treatment of tissue using ultrasound. The system comprises a probe having an array of transducer elements, an ultrasound waveform generator adapted to generate at least one electrical ultrasound signal, and a plurality of phase controls, each coupled to the ultrasound waveform generator and adapted to generate from the electrical ultrasound signal a phase-shifted drive signal that is coupled to an associated transducer element. The drive signal is effective to control grating lobe foci emitted by the array. The method employs the system.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
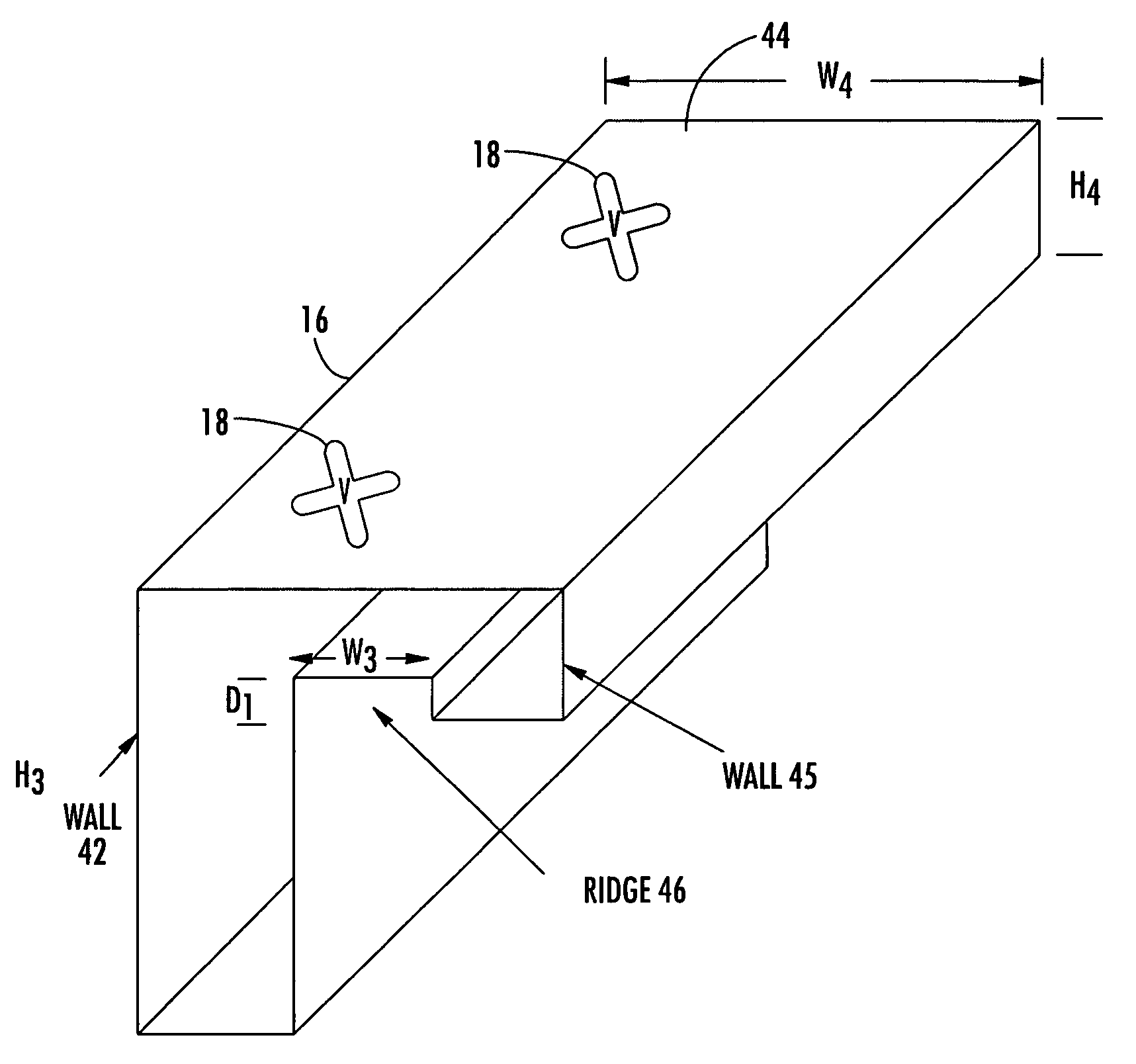
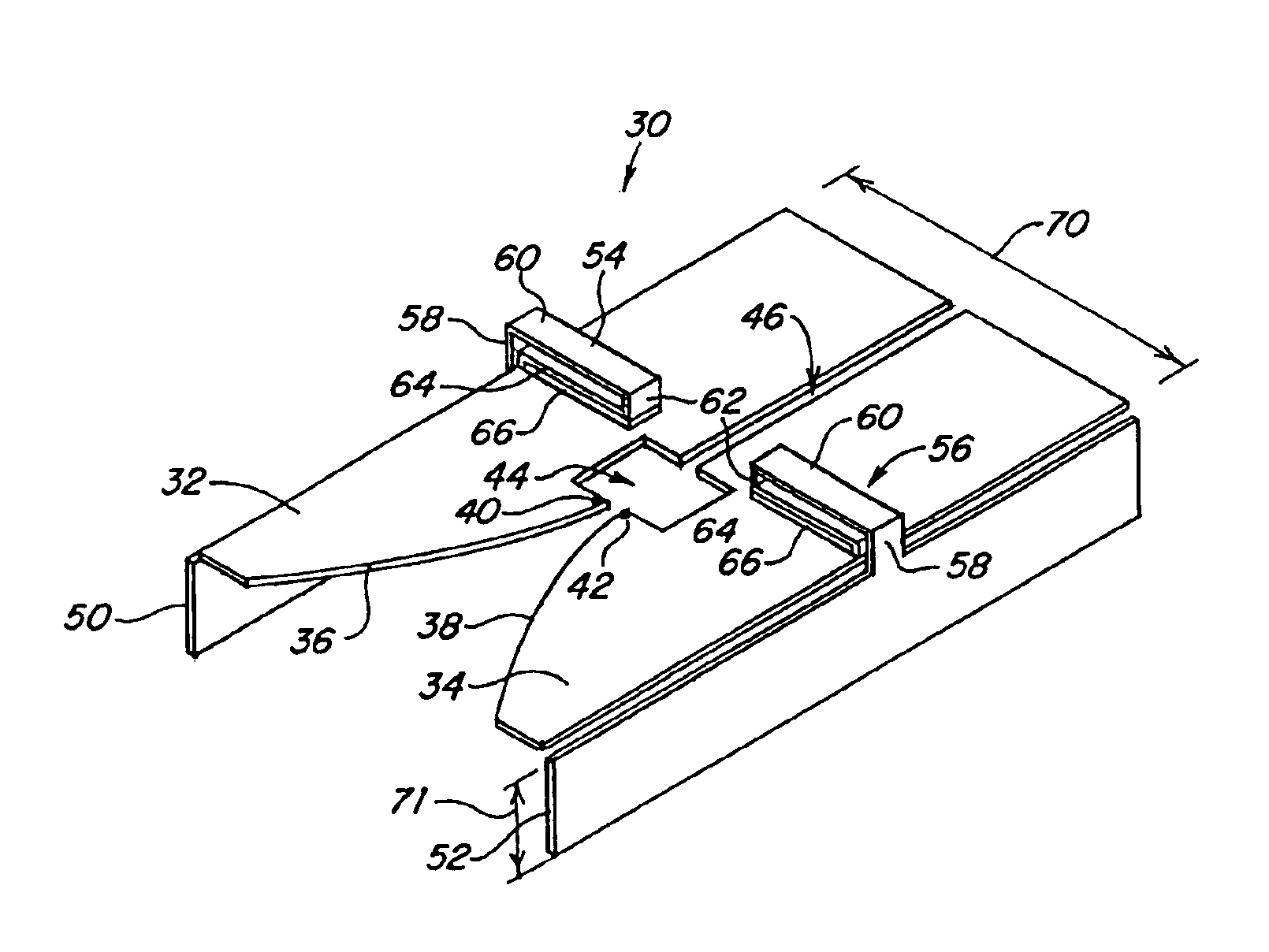
Vehicle mounted satellite antenna system with ridged waveguide
ActiveUS20060132374A1Low axle ratioImprove efficiencyAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesLinear waveguide fed arraysAxial ratioRidge waveguides
The present invention relates to a vehicle mountable satellite antenna as defined in the claims which is operable while the vehicle is in motion. The satellite antenna of the present invention can be installed on top of (or embedded into) the roof of a vehicle. The antenna is capable of providing high gain and a narrow antenna beam for aiming at a satellite direction and enabling broadband communication to vehicle. The present invention provides a vehicle mounted satellite antenna which has low axial ratio, high efficiency and has low grating lobes gain. The vehicle mounted satellite antenna of the present invention provides two simultaneous polarization states. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a ridged waveguide instead of a conventional rectangular waveguide to alleviate the effects of grating lobes. The ridge waveguide provides a ridged section longitudinally between walls forming the waveguide. A plurality of radiating elements are formed in a radiating surface of the ridged waveguide.
Owner:RENDA TRUST
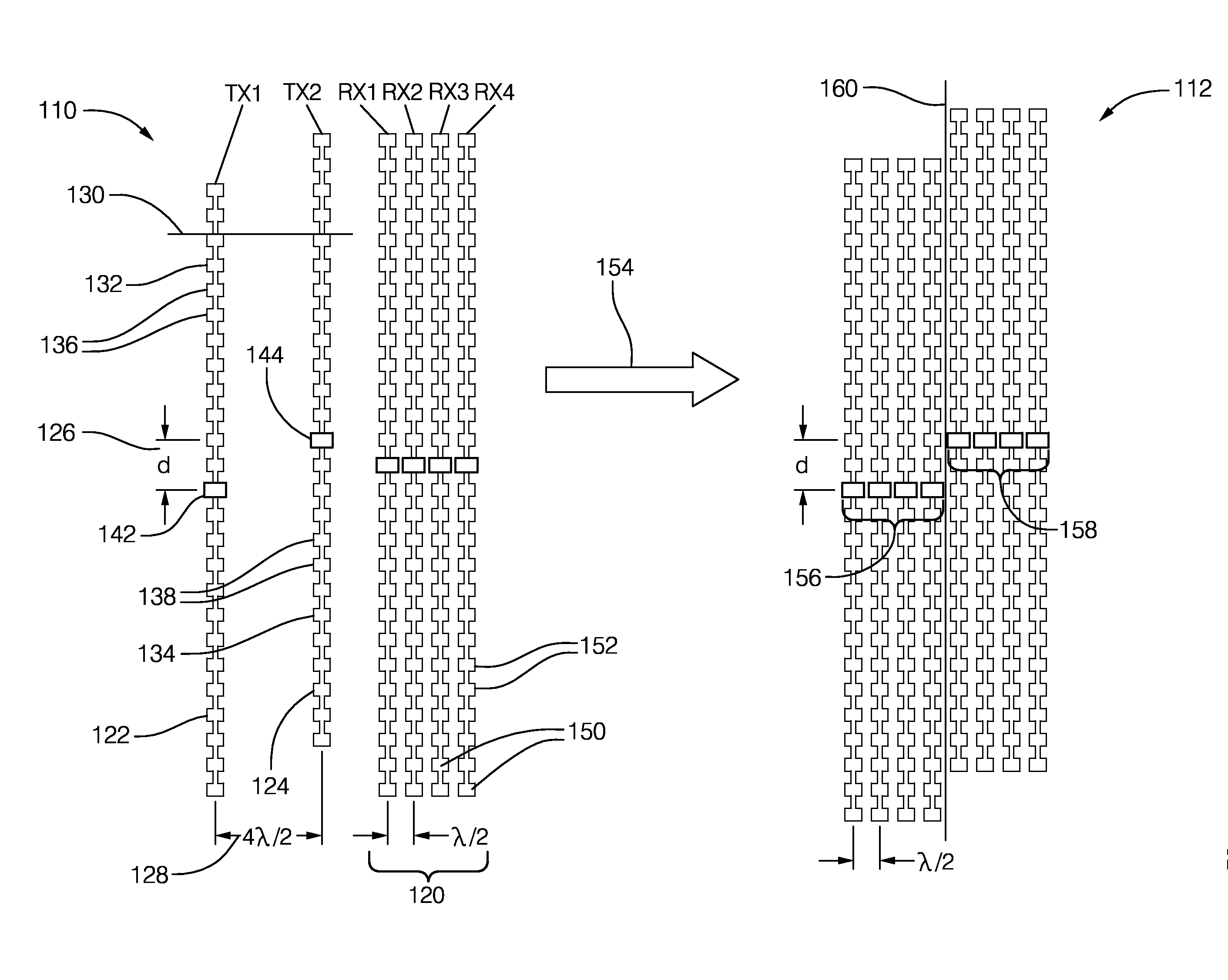
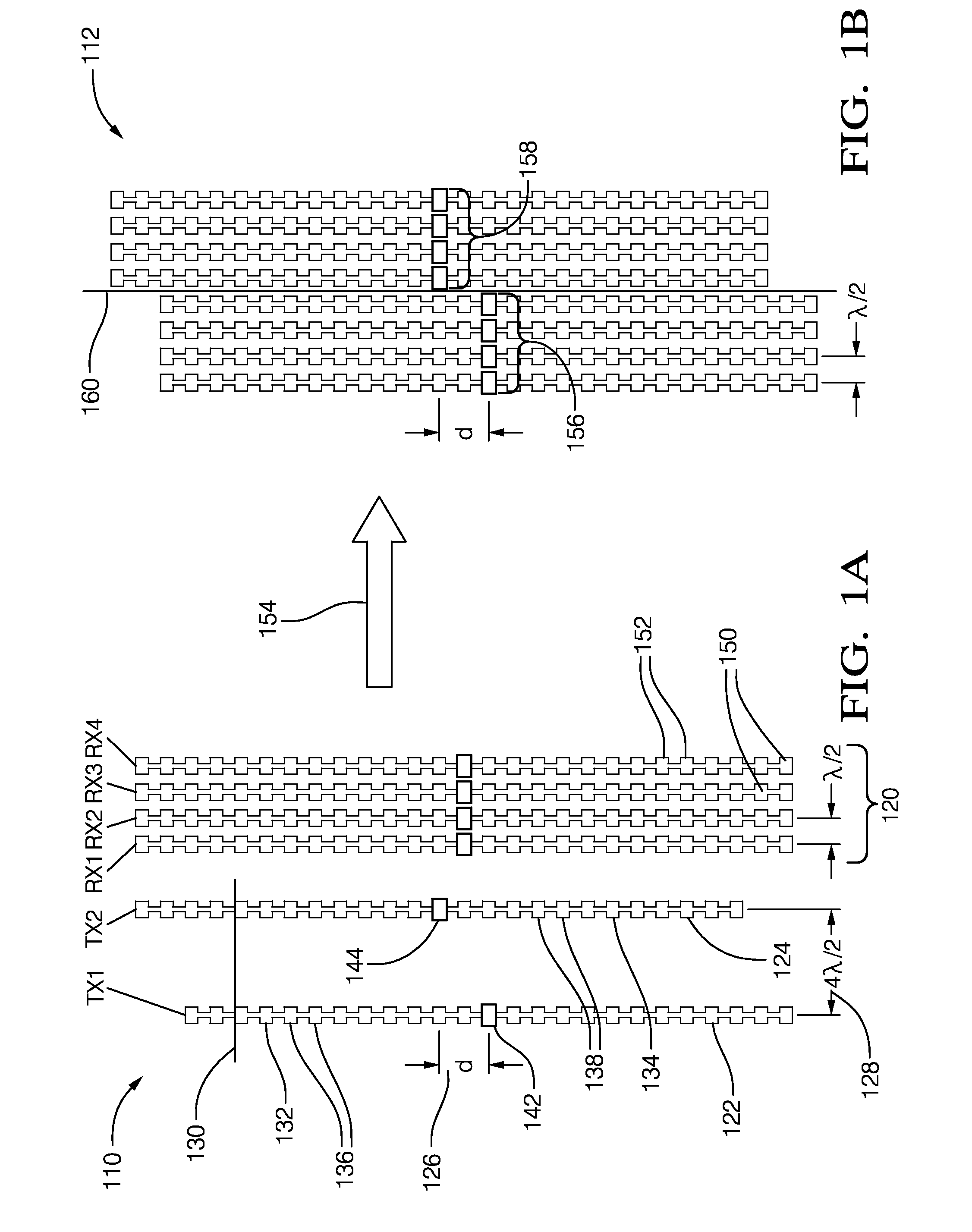
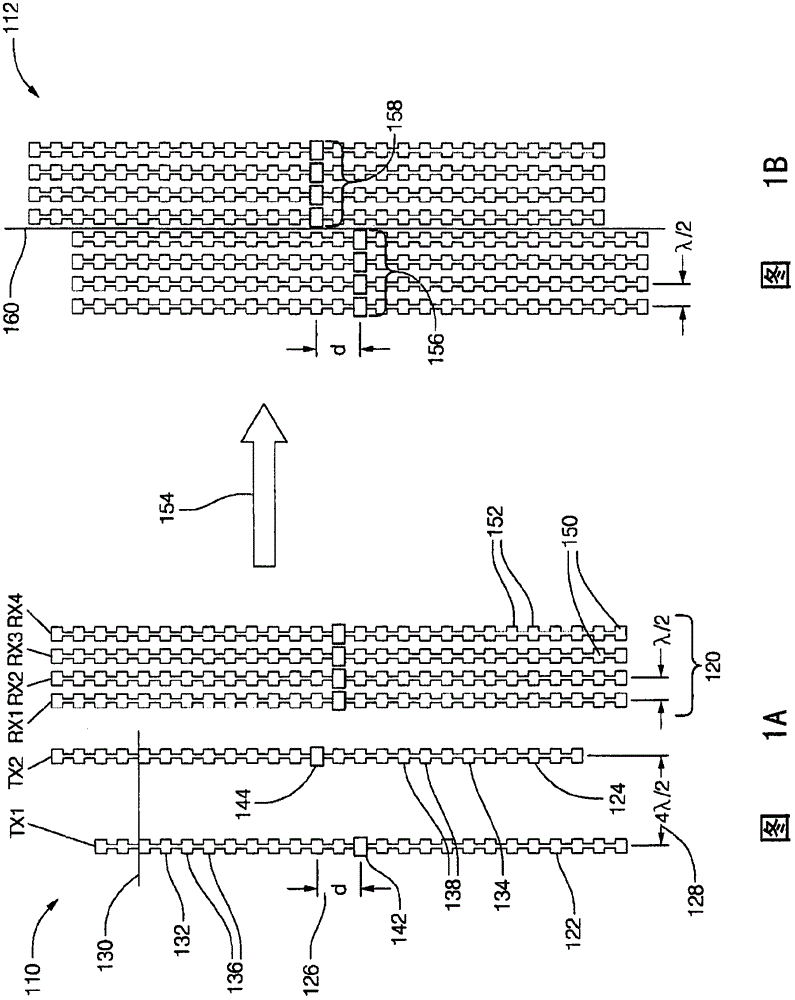
MIMO antenna with improved grating lobe characteristics
A multiple input multiple output (MIMO) antenna for a radar system that includes a first transmit antenna, a second transmit antenna, and a receive antenna. The first transmit antenna is configured to emit a first radar signal toward a target. The first transmit antenna is formed of a first vertical array of radiator elements. The second transmit antenna is configured to emit a second radar signal toward the target. The second transmit antenna is formed of a second vertical array of radiator elements distinct from the first vertical array. The receive antenna is configured to detect radar signals reflected by a target toward the receive antenna. The receive antenna is formed of a plurality of paired vertical arrays of detector elements.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Vehicle mounted satellite antenna embedded within moonroof or sunroof
InactiveUS20050146478A1Low axle ratioImprove efficiencyAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesPolarised antenna unit combinationsAxial ratioIn vehicle
The present invention relates to a vehicle mountable satellite antenna as defined in the claims which is operable while the vehicle is in motion. The satellite antenna of the present invention can be installed on top of (or embedded into) the roof of a vehicle. The antenna is capable of providing high gain and a narrow antenna beam for aiming at a satellite direction and enabling broadband communication to vehicle. The present invention provides a vehicle mounted satellite antenna which has low axial ratio, high efficiency and has low grating lobes gain. The vehicle mounted satellite antenna of the present invention provides two simultaneous polarization states.
Owner:RENDA TRUST
Vehicle mounted satellite antenna system with ridged waveguide
ActiveUS7202832B2Low axle ratioImprove efficiencyAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesLinear waveguide fed arraysAxial ratioRidge waveguides
Owner:RENDA TRUST
Microphone array with physical beamforming using omnidirectional microphones
An array of microphones is provided wherein the microphones are positioned at the ends of cavities within a diffracting structure. The cavity depth, width, and shape are optimised to provide high directivity without grating lobes, at frequencies for which the distance between microphones is greater than half the acoustic wavelength.
Owner:MITEL
Vehicle mounted satellite antenna system with inverted L-shaped waveguide
ActiveUS20050146477A1Low axle ratioImprove efficiencyAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesLinear waveguide fed arraysAxial ratioWaveguide
The present invention relates to a vehicle mountable satellite antenna as defined in the claims which is operable while the vehicle is in motion. The satellite antenna of the present invention can be installed on top of (or embedded into) the roof of a vehicle. The antenna is capable of providing high gain and a narrow antenna beam for aiming at a satellite direction and enabling broadband communication to vehicle. The present invention provides a vehicle mounted satellite antenna which has low axial ratio, high efficiency and has low grating lobes gain. The vehicle mounted satellite antenna of the present invention provides two simultaneous polarization states. In one embodiment, an inverted L-shaped waveguide has a first wall extending vertically downward from a top surface. The top surface can include a ridge portion. The top surface includes a plurality of radiating elements for forming a radiating surface.
Owner:RENDA TRUST
Method and apparatus for ultrasound compound imaging with combined fundamental and harmonic signals
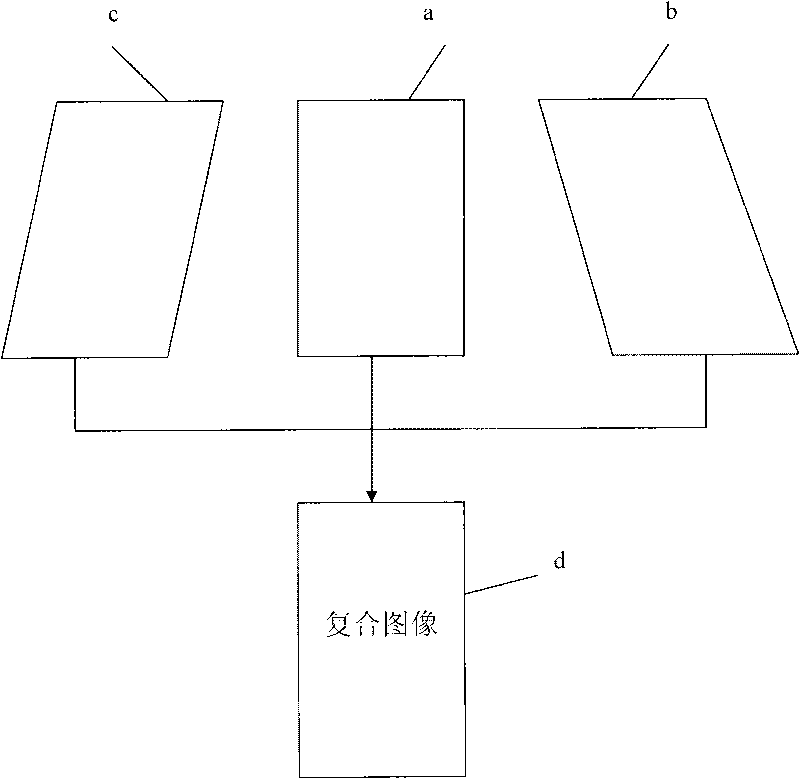
ActiveUS20050101865A1Improved compounding imagingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSteering angleSonification
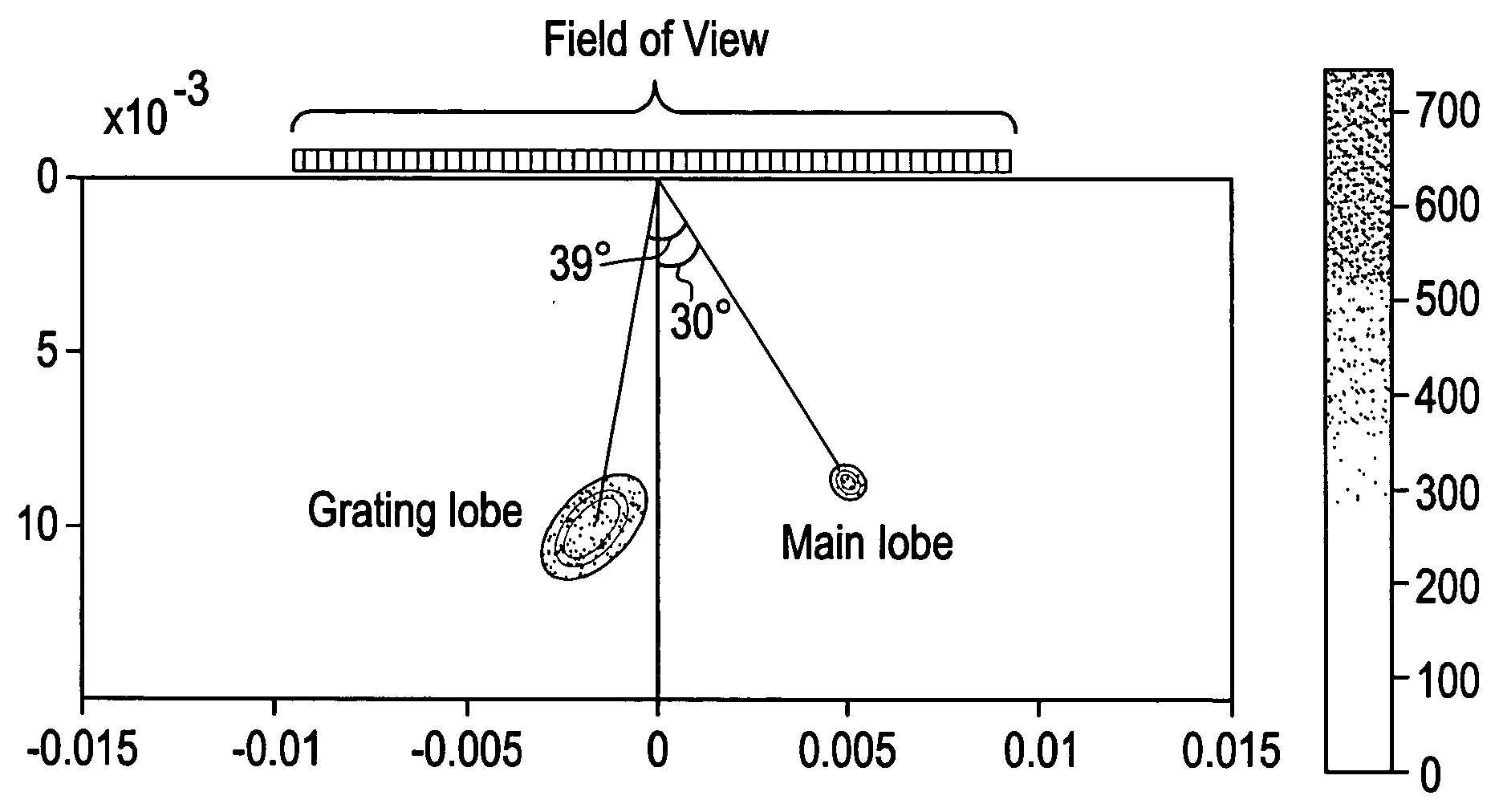
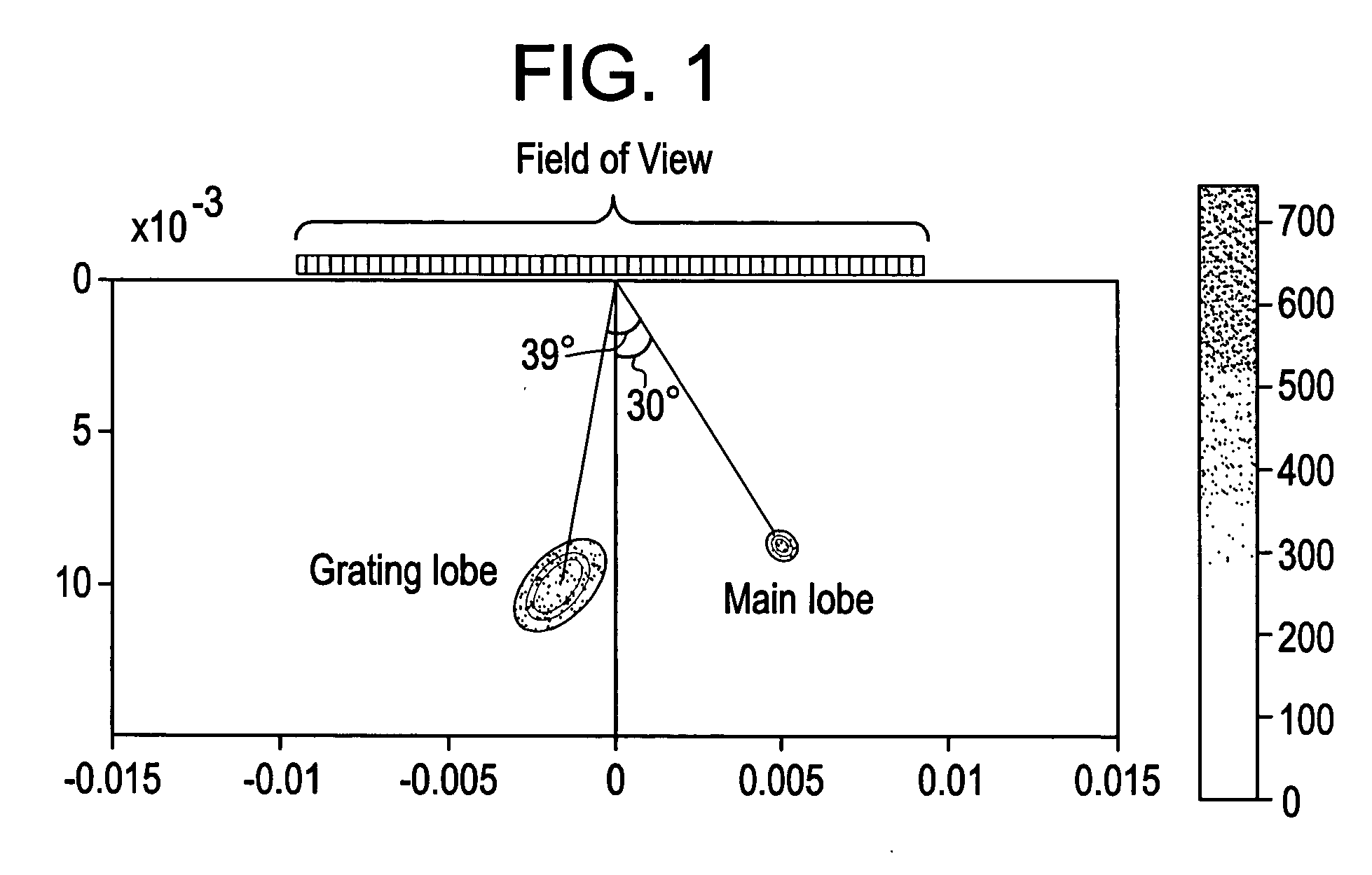
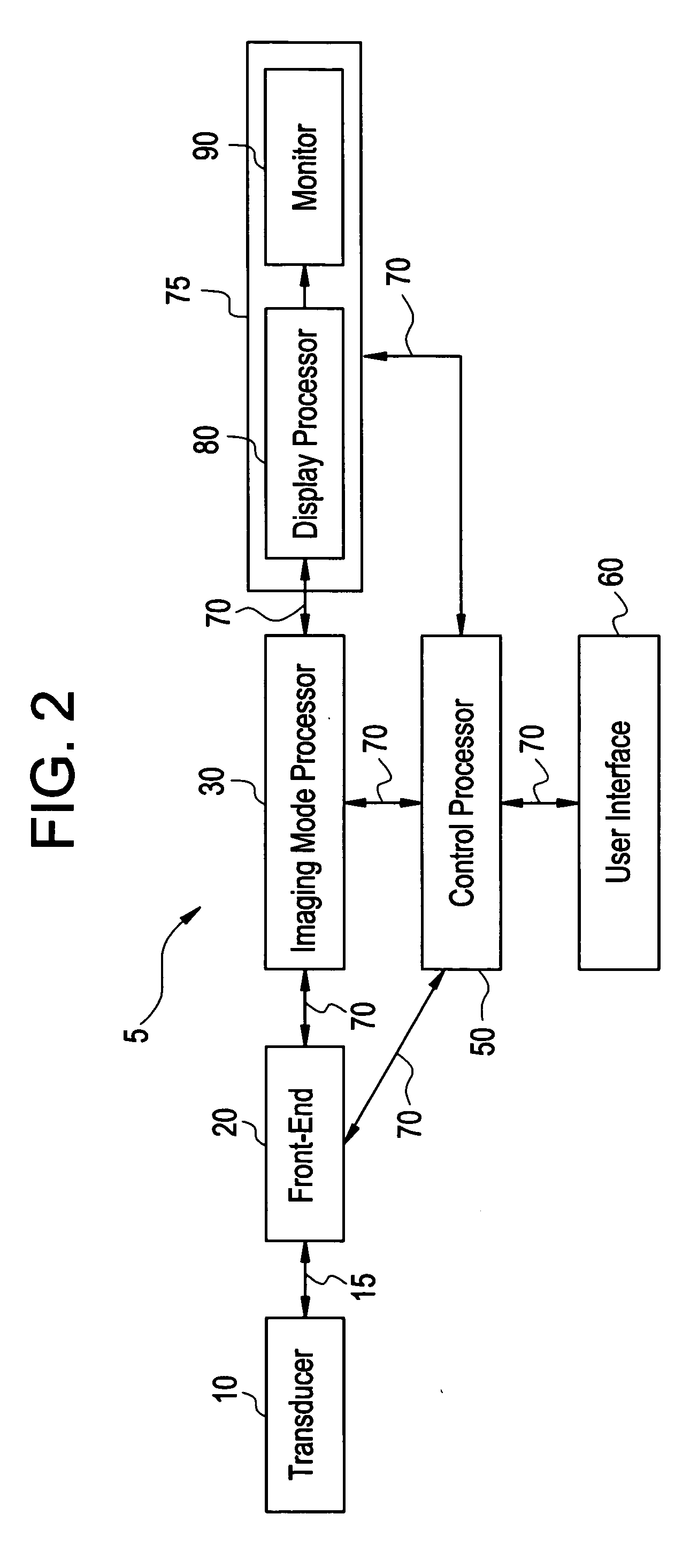
Certain embodiments include a system and method for improved compound imaging using a plurality of imaging modes. In an embodiment, a plurality of echo signals are received in response to a plurality of beams formed based on different imaging modes corresponding to different steering angles, such as steered or non-steered angles. The plurality of echo signals is compounded to form a compound image. In an embodiment, the imaging mode includes at least one of harmonic, fundamental, coded harmonic, and variable frequency imaging. Parameters may be generated for the plurality of beams formed based on different imaging modes corresponding to different steering angles. Additionally, the parameters may be stored. The echo signals may be filtered. Imaging mode may be controlled based on steering angle. Employing different imaging modes based on steering angles for spatial compound imaging helps reduce grating lobe artifacts while improving speckle reduction effect.
Owner:G E MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL
Ultrasonic imaging method and device
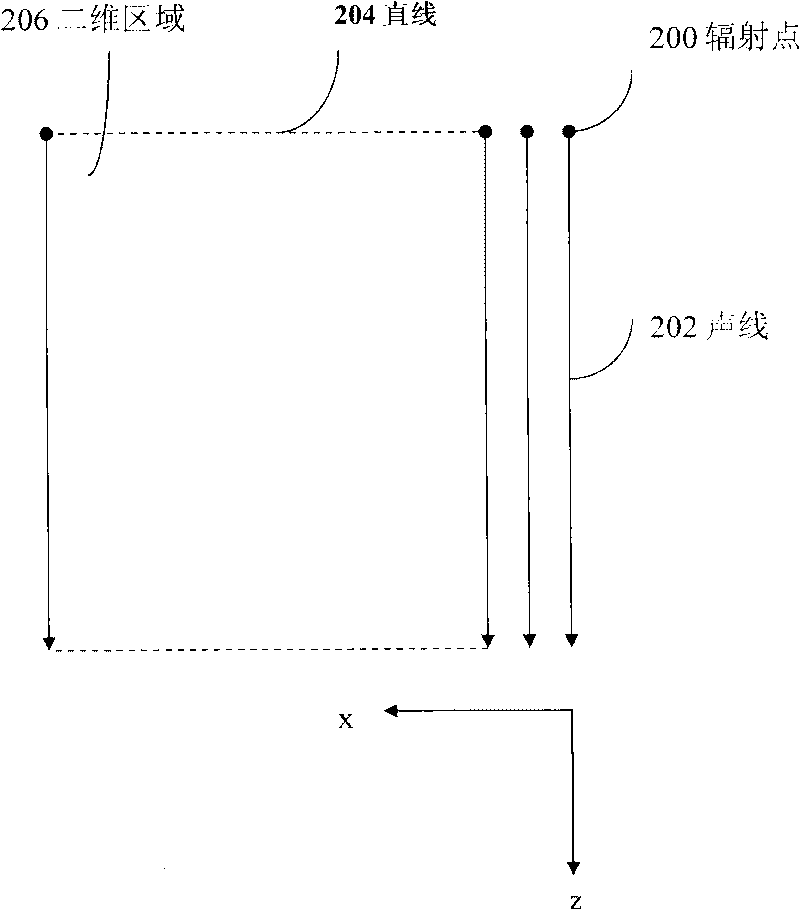
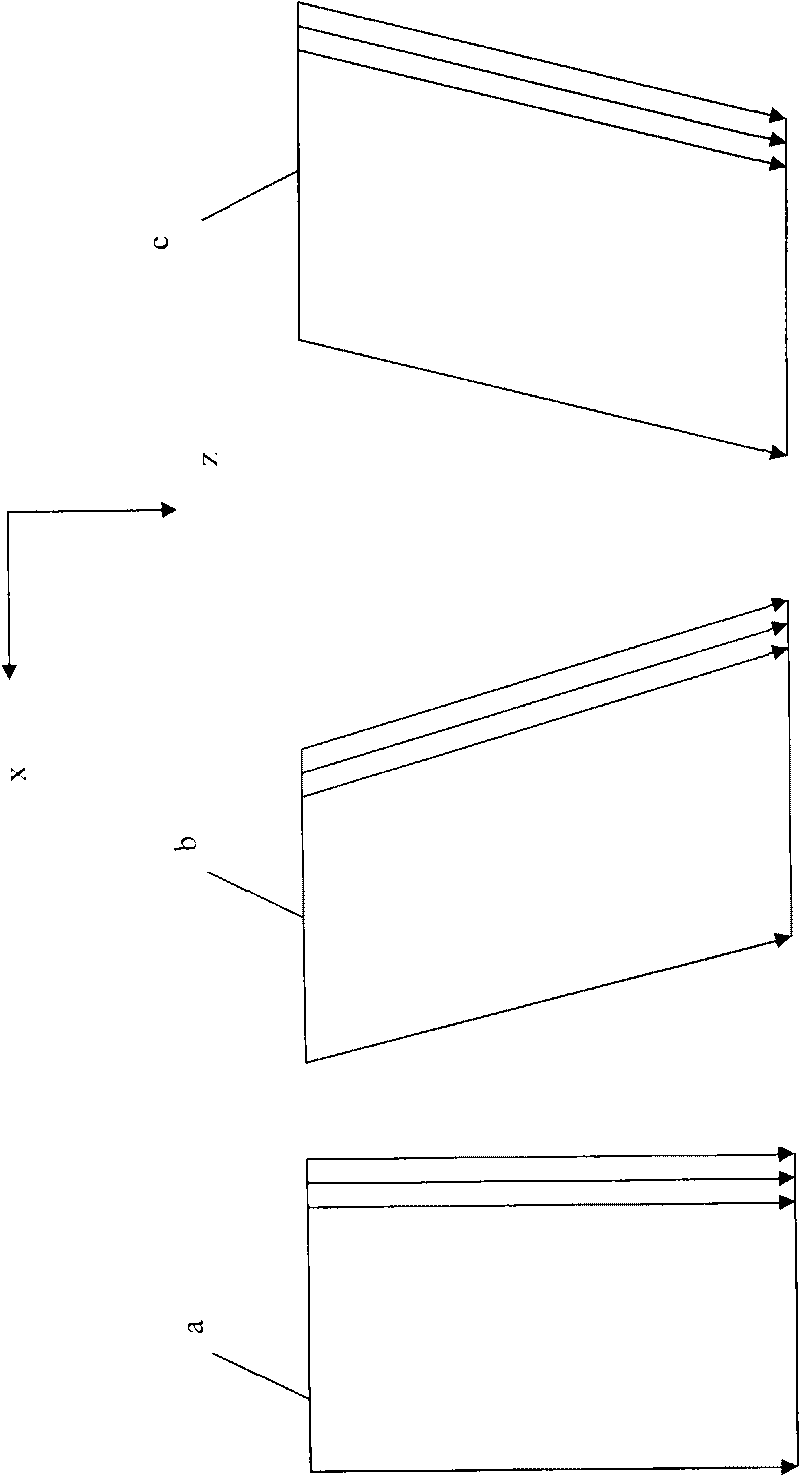
InactiveCN101744639AHigh resolutionGood mirror reflection profileUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsMirror reflectionSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention relates to ultrasonic imaging method and device, in particular to ultrasonic imaging method and device for acquiring a composite ultrasonic image by using a space and frequency composite technology. By using the space and frequency composite technology, frames observable from a plurality of angles are acquired by a Tx / Rx frequency and beam deflection angles which can be configured by a user and the frames are compounded to form a composite image with high resolution and favorable mirror reflection contour. Because the frequency in the invention can be flexibly configured along with the deflection angles, the invention can further widen the allowable range of the beam deflection angles and lower less resolution to a certain extent to restrict the side lobes and the grating lobes of the deflection frames and weaken spot noise and clutter, thereby improving the visibility, the signal-to-noise ratios of the tested tissue and needle and the texture appearance and smoothening the edges.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Mimo antenna with improved grating lobe characteristics
InactiveCN104901022AAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesIndividually energised antenna arraysRadar systemsMimo antenna
A multiple input multiple output (MIMO) antenna (110, 210, 410, 510, 610, 710) for a radar system that includes a first transmit antenna (122, 222, 422, 522, 622, 722), a second transmit antenna (124, 224, 424, 524, 624, 724), and a receive antenna (120, 220, 420, 520, 620, 720). The first transmit antenna is configured to emit a first radar signal toward a target. The first transmit antenna is formed of a first vertical array (132, 232) of radiator elements (136, 236). The second transmit antenna is configured to emit a second radar signal toward the target. The second transmit antenna (110) is formed of a second vertical array (134, 234) of radiator elements (136, 236) distinct from the first vertical array (132). The receive antenna is configured to detect radar signals reflected by a target toward the receive antenna. The receive antenna is formed of a plurality of paired vertical arrays (250) of detector elements (252).
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
System and method for medical treatment using ultrasound
ActiveUS20050277853A1Overcome limitationsEfficient ablationUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesElectricityPhase shifted
A system and method for medical treatment of tissue using ultrasound. The system comprises a probe having an array of transducer elements, an ultrasound waveform generator adapted to generate at least one electrical ultrasound signal, and a plurality of phase controls, each coupled to the ultrasound waveform generator and adapted to generate from the electrical ultrasound signal a phase-shifted drive signal that is coupled to an associated transducer element. The drive signal is effective to control grating lobe foci emitted by the array. The method employs the system.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
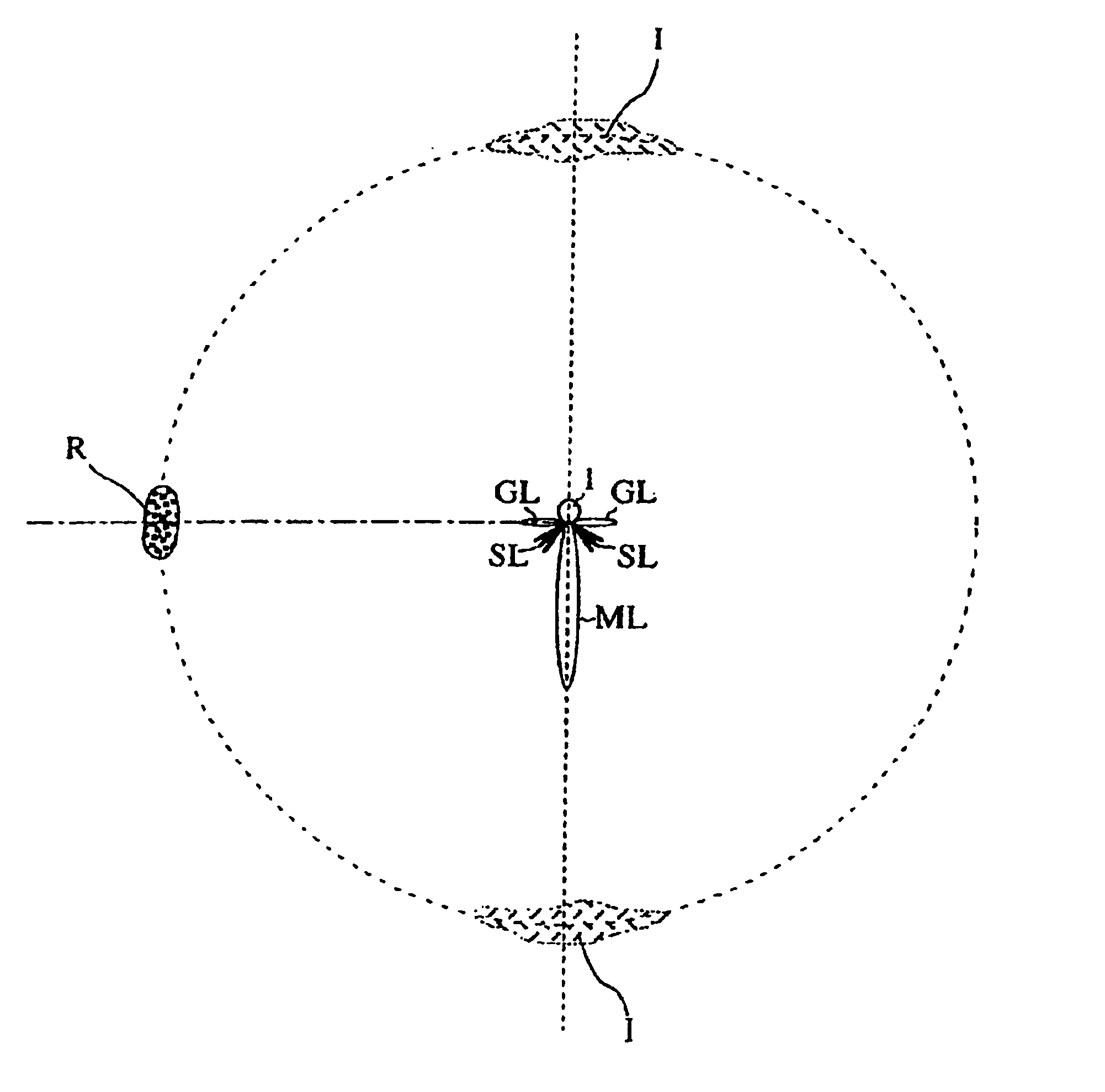
Automatically tracking scanning sonar
InactiveUS6778468B1Improve angular resolutionIncrease in scale of hardwareMechanical vibrations separationAcoustic wave reradiationSonarSound sources
The invention provides an ultrasonic transmit-receive apparatus which solves a false image problem caused by grating lobes and side lobes and offers high bearing resolution without increasing in the scale of hardware or in manufacturing cost. Using a transducer having multiple transducer elements arranged on a surface of the transducer along its circumferential direction, the apparatus emits ultrasonic waves in directionally varying frequency bands and receives echo signals from specified angular directions while selecting the frequency from one direction to another. In a Doppler transmission method, for example, the apparatus drives the individual transducer elements in such a manner that the ultrasonic waves emitted by the transducer elements are equivalent to ultrasonic waves emitted from an imaginary moving sound source moving within a circle enclosed by the multiple transducer elements arranged along the circumferential direction, so that the transducer elements emit ultrasonic signals at directionally varying Doppler shift frequencies.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
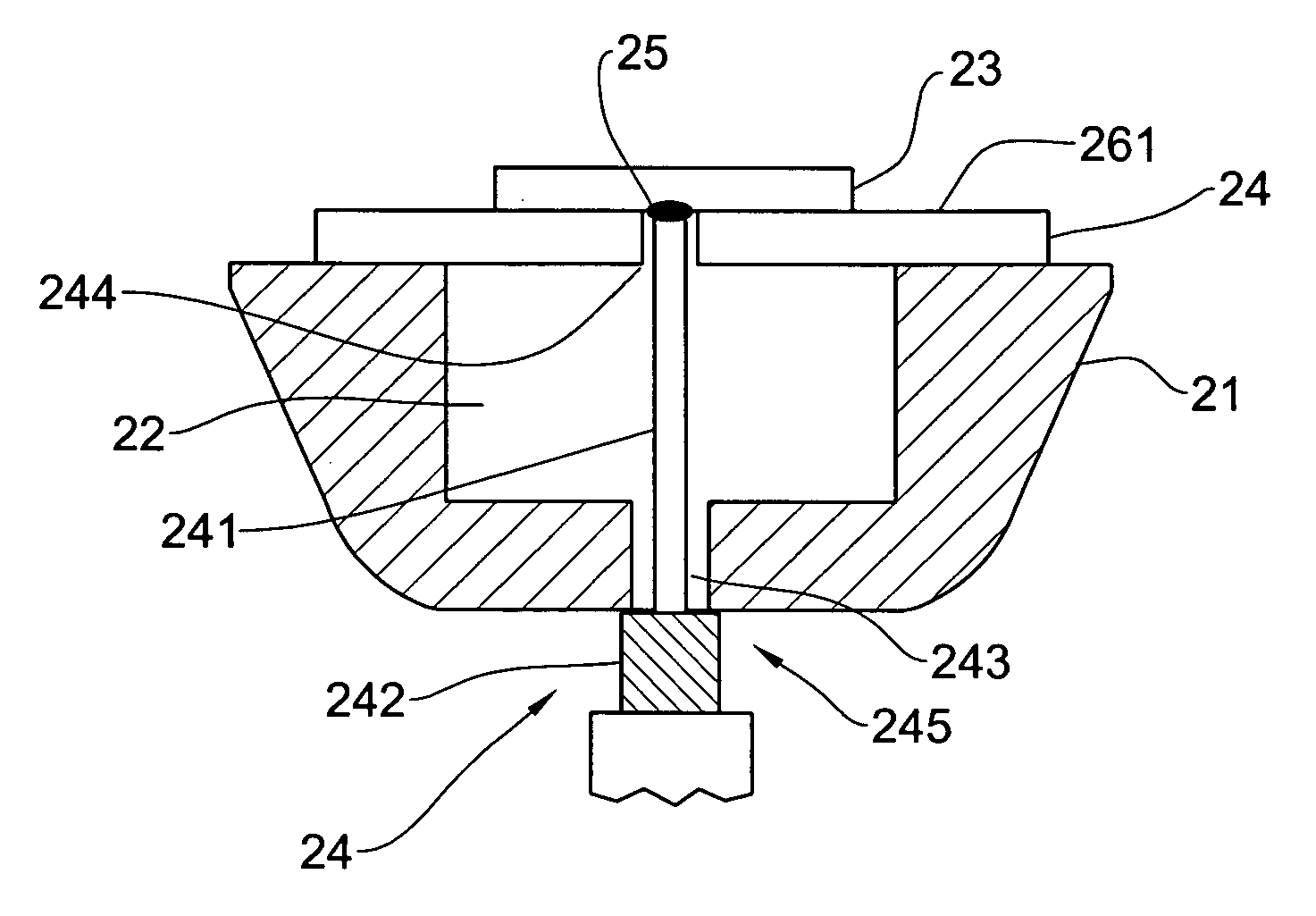
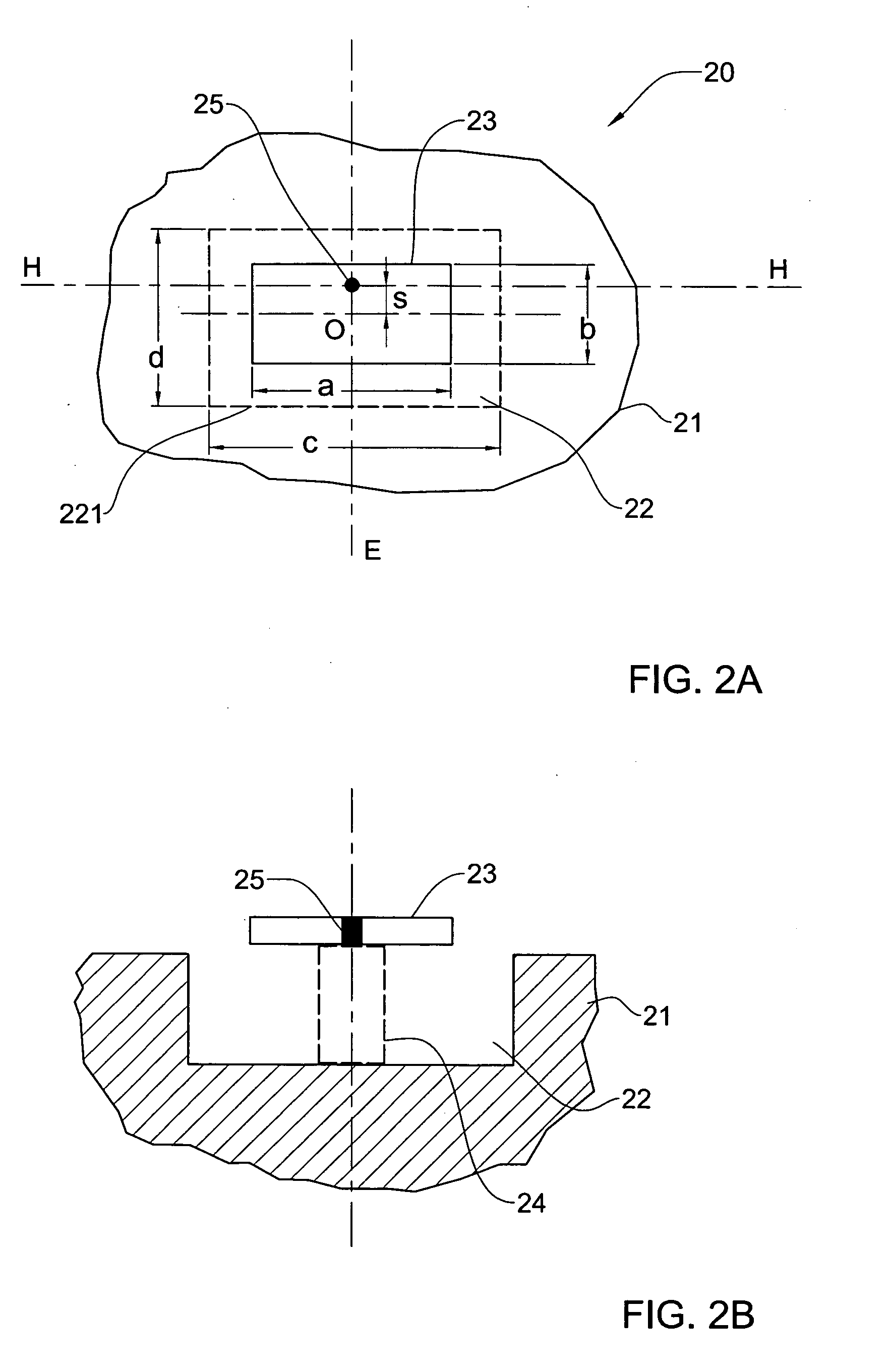
Patch antenna element and application thereof in a phased array antenna
ActiveUS20070132642A1Easy and efficient to manufactureDurable and reliable constructionAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsGround planeAntenna element
A method of suppressing grating lobes generated in a radiating pattern of a phased array antenna, and a patch antenna element for use in the phased array antenna are described. The phased array antenna is formed from a plurality of symmetrical patch antenna elements spaced apart at a predetermined distance from each other. Each patch antenna element is configured for producing an asymmetrical radiation pattern. The antenna element includes a conductive ground plane, a radiating patch backed by a cavity and arranged in cavity aperture, and a feed arrangement. The patch antenna element is configured such that a dimension of the radiating patch along the E-plane of the antenna element is less than the dimension of the cavity aperture by a first predetermined value selected to provide an asymmetrical radiation pattern of the patch antenna element. To provide a required degree of the asymmetry of said radiation pattern, a dimension of the radiating patch along the H-plane should be less than the dimension of the cavity aperture along said H-plane by a second predetermined value.
Owner:ELTA SYST LTD
High power microwave radial line slit array antenna
InactiveCN103151620AImprove radiation efficiencyInhibitionAntenna arraysRadiating element housingsWave structureMicrowave
The invention relates to a high power microwave radial line slit array antenna which comprises a coaxial input waveguide, a radial line leaky wave waveguide and an antenna housing, wherein an output port of the coaxial input waveguide is connected with an input port of the radial line leaky wave waveguide, and an output port of the radial line leaky wave waveguide is sealed through the antenna housing. Microwaves are inputted through a coaxial over-mode waveguide in a transverse electronic and magnetic (TEM) mode, folding conversion is carried out through a double layer radial line waveguide, and microwave radial inner feedback is achieved on a waveguide upper layer. Slit unit arrays arranged on an antenna aperture cut a radial electric field, distant field same-phase superimposed circular polarization radian is achieved, the whole axial dimension is small, and the structure is compact. Due to action of a radial line slow wave structure, the wavelength of the radial line waveguide is reduced, and generation of slit array grating lobes is restrained. Due to the fact that a high order reflection mode excited by a wide slit array is restrained through a reflection offset spiral groove in a lower layer waveguide, the whole antenna has high radiant efficiency. Due to the improvement on the slit unit structure and vacuum sealing of the antenna housing, the whole radiating system has high power capacity, and application requirements in the high power microwave field can be met.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Double-frequency double-circular polarization common-caliber antenna array for two-dimensional phase control scanning
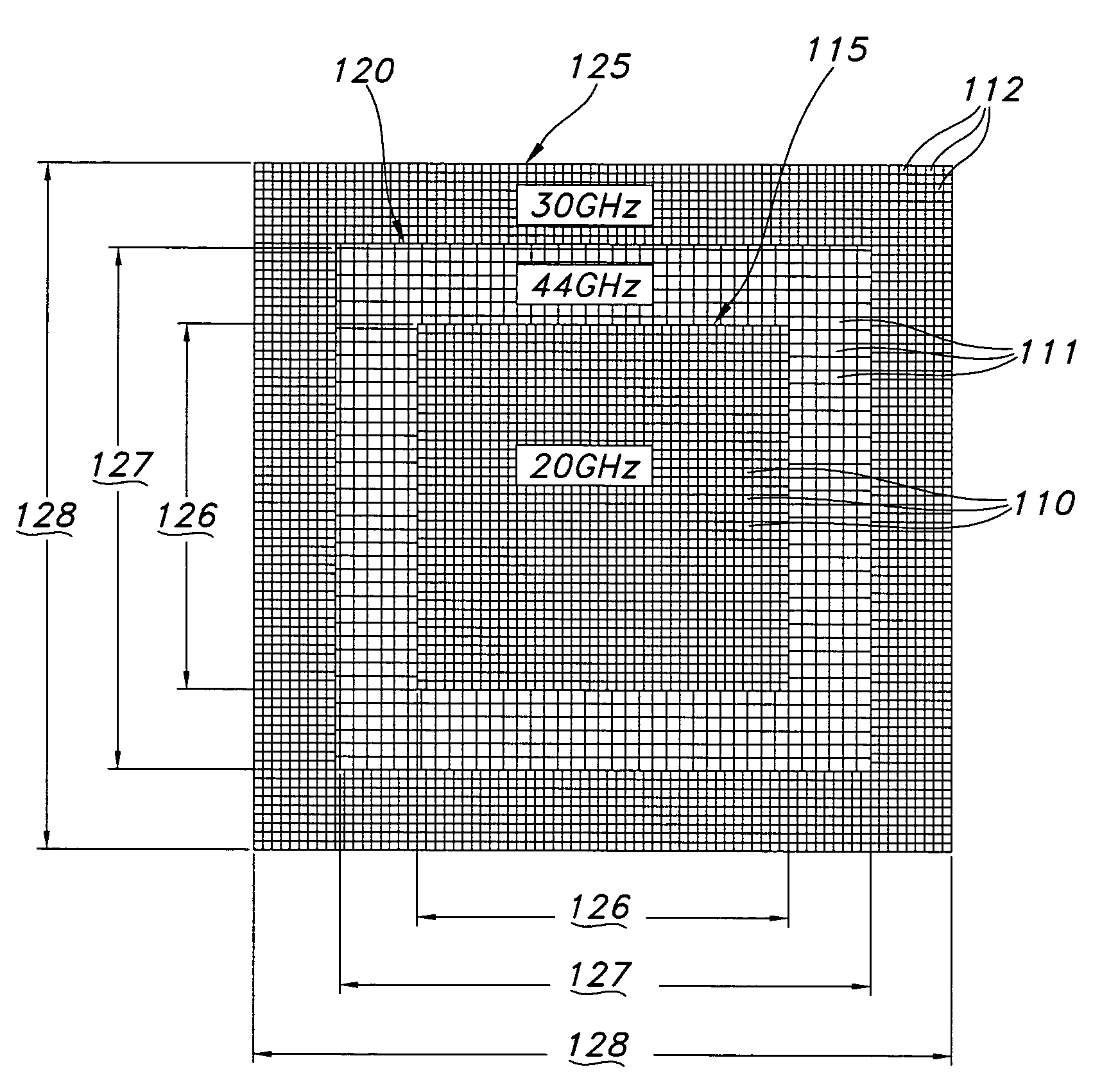
ActiveCN103762425AReduce interactionCompact structurePolarised antenna unit combinationsResonant antennasPhase controlDouble frequency
The invention relates to a double-frequency double-circular polarization common-caliber antenna array for two-dimensional phase control scanning, wherein the antenna array covers a Ka-frequency range and a Ku-frequency range. At the overlapping portion of the two frequency ranges, a basic composition unit of the antenna array is formed by encircling of eight Ka-frequency range metal radiation sheets around one Ku-frequency range metal radiation sheet. At the edge portion, intervals of Ku-frequency range metal radiation sheet need to be adjusted to form an array with a compact layout, thereby effectively reducing a minor lobe and inhibiting a grating lobe. And antennas with different frequency ranges use metal radiation sheets with different polarization modes to form a double-circular polarization state, thereby improving the polarization isolation of the common-caliber antennas. According to the invention, on the basis of the reasonable layout, the antennas with the Ka-frequency range and the Ku-frequency range can be integrated into one caliber; and the mutual influence is minimized by using the means of array optimization and polarization isolation and the like. The antenna array is suitable for various two-dimensional phase control array antenna systems with low-profile requirement and compact structure and two-dimensional phase scanning with the large scanning angle can be realized.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
Vehicle mounted satellite antenna system with inverted L-shaped waveguide
ActiveUS6977621B2Low axle ratioImprove efficiencyAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesLinear waveguide fed arraysAxial ratioWaveguide
The present invention relates to a vehicle mountable satellite antenna as defined in the claims which is operable while the vehicle is in motion. The satellite antenna of the present invention can be installed on top of (or embedded into) the roof of a vehicle. The antenna is capable of providing high gain and a narrow antenna beam for aiming at a satellite direction and enabling broadband communication to vehicle. The present invention provides a vehicle mounted satellite antenna which has low axial ratio, high efficiency and has low grating lobes gain. The vehicle mounted satellite antenna of the present invention provides two simultaneous polarization states. In one embodiment, an inverted L-shaped waveguide has a first wall extending vertically downward from a top surface. The top surface can include a ridge portion. The top surface includes a plurality of radiating elements for forming a radiating surface.
Owner:RENDA TRUST
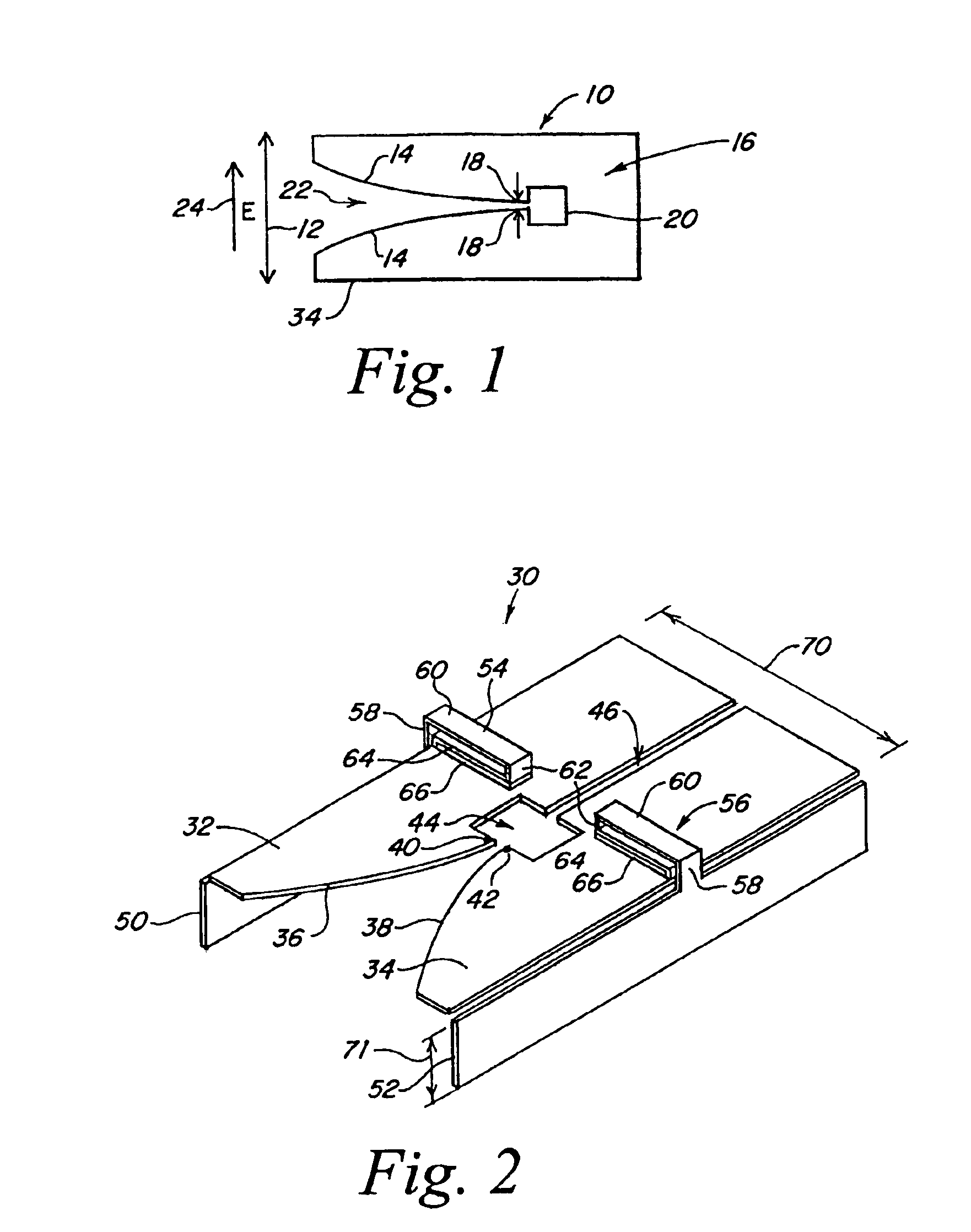
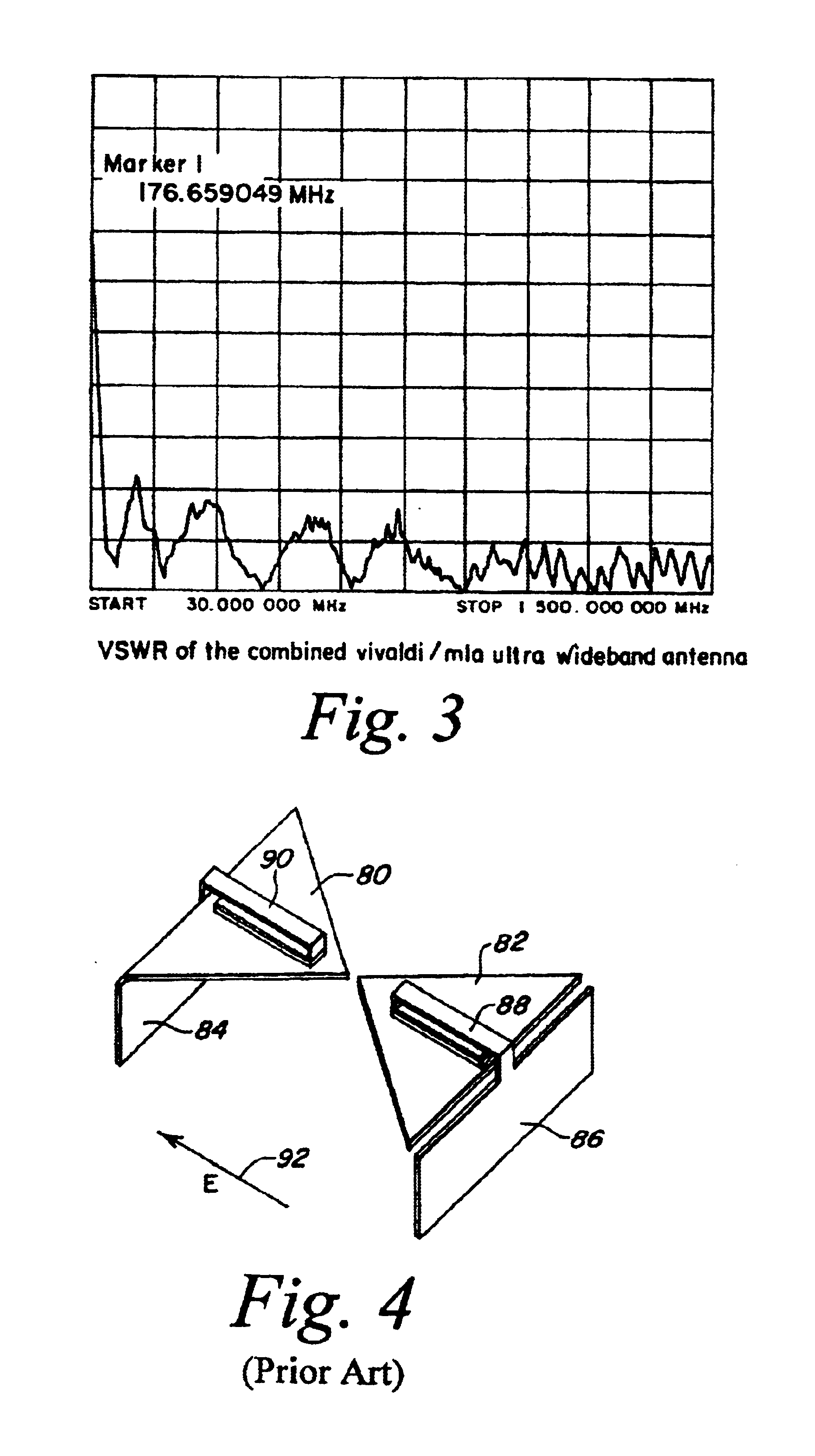
Combined ultra wideband Vivaldi notch/meander line loaded antenna
InactiveUS6900770B2Rule out the possibilityGrating lobeAntenna feed intermediatesSeparate antenna unit combinationsSINGLE LOBEUltra-wideband
The combination of a Vivaldi slot and a meander line loaded antenna is provided which exhibits an ultra wideband characteristic with the Vivaldi notch expanding the high end and with the meander line loaded antenna portion reducing the low frequency cut-off. When these antennas are arrayed, this array exhibits a single lobe and an ultra wide 100:1 bandwidth. The Vivaldi notch portion of the antenna accommodates the higher frequencies, whereas the meander line loaded antenna portion of the antenna accommodates the lower frequencies, there being a smooth transition region between the Vivaldi and meander line portions of the antenna and no discontinuity. In one embodiment, the antenna is made to work between 50 MHz and 1500 MHz with a VSWR less than 3:1. The Vivaldi notch meander line combination assures that for an array one does not have a separation of the elements more than a 0.5 wavelength at the highest frequency, thus to eliminate the possibility of creating grating lobes. As one goes down in frequency to {fraction (1 / 50)} of the highest frequency, the 0.5 wavelength is divided by 50. This means that antenna element spacing is 0.01 wavelength at the low frequency end, clearly below that separation which would cause grating lobes. In short, the generation of grating lobes at the high end is prevented because the antenna element spacing is less than a 0.5 wavelength, with the situation improving as one goes down in frequency.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION ELECTRONICS INTEGRATION
Vehicle mounted satellite antenna system with in-motion tracking using beam forming
InactiveUS7391381B2Low axle ratioImprove efficiencyRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesAxial ratioAzimuth direction
The present invention relates to a vehicle mountable satellite antenna as defined in the claims which is operable while the vehicle is in motion. The satellite antenna of the present invention can be installed on top of (or embedded into) the roof of a vehicle. The antenna is capable of providing high gain and a narrow antenna beam for aiming at a satellite direction and enabling broadband communication to vehicle. The present invention provides a vehicle mounted satellite antenna which has low axial ratio, high efficiency and has low grating lobes gain. The vehicle mounted satellite antenna of the present invention provides two simultaneous polarization states. In one embodiment, a hybrid mechanic and electronic steering approach provides a more reasonable cost and performance trade-off. The antenna aiming in the elevation direction is achieved via control of an electronic beamforming network. The antenna is mounted on a rotatable platform under mechanical steering and motion control for aiming the antenna in the azimuth direction. Such approach significantly reduces the complexity and increases the reliability of the mechanical design. The antenna height is compatible to the two-dimensional electronic steering phased-array antenna. Additionally, the number of the electronic processing elements required is considerably reduced from that of the conventional two-dimensional electronic steering phased-array antenna, thereby allowing for low cost and large volume commercial production. The present invention provides electronically generated left, right, up, and down beams for focusing the antenna beam toward the satellite while the vehicle is moving. All of the beams are simultaneously available for use in the motion beam tracking. This provides much faster response and less signal degradation.
Owner:RENDA TRUST
Vehicle mounted satellite antenna embedded within moonroof or sunroof
InactiveUS7227508B2Low axle ratioImprove efficiencyAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesPolarised antenna unit combinationsAxial ratioEngineering
Owner:RENDA TRUST
Vehicle mounted satellite antenna system with in-motion tracking using beam forming
InactiveUS20050146476A1Low axle ratioImprove efficiencyRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesAxial ratioAzimuth direction
The present invention relates to a vehicle mountable satellite antenna as defined in the claims which is operable while the vehicle is in motion. The satellite antenna of the present invention can be installed on top of (or embedded into) the roof of a vehicle. The antenna is capable of providing high gain and a narrow antenna beam for aiming at a satellite direction and enabling broadband communication to vehicle. The present invention provides a vehicle mounted satellite antenna which has low axial ratio, high efficiency and has low grating lobes gain. The vehicle mounted satellite antenna of the present invention provides two simultaneous polarization states. In one embodiment, a hybrid mechanic and electronic steering approach provides a more reasonable cost and performance trade-off. The antenna aiming in the elevation direction is achieved via control of an electronic beamforming network. The antenna is mounted on a rotatable platform under mechanical steering and motion control for aiming the antenna in the azimuth direction. Such approach significantly reduces the complexity and increases the reliability of the mechanical design. The antenna height is compatible to the two-dimensional electronic steering phased-array antenna. Additionally, the number of the electronic processing elements required is considerably reduced from that of the conventional two-dimensional electronic steering phased-array antenna, thereby allowing for low cost and large volume commercial production. The present invention provides electronically generated left, right, up, and down beams for focusing the antenna beam toward the satellite while the vehicle is moving. All of the beams are simultaneously available for use in the motion beam tracking. This provides much faster response and less signal degradation.
Owner:RENDA TRUST
Double frequency dual polarization wide angle scanning co-aperture phased array antenna
InactiveCN107579347AEnables wide-angle scanningSimple structureRadiating elements structural formsIndividually energised antenna arraysDirect communicationGrating lobe
The invention discloses a double frequency dual polarization wide angle scanning co-aperture phased array antenna. The antenna comprises a low frequency antenna unit and a high frequency antenna unit;the high and low frequency antennas respectively work in different work modes, a radiation aperture of each low frequency antenna unit and a sub array of the high frequency antenna are conformal, sothe finally acquired co-aperture array can realize double frequency bands, dual polarization and wide angle scanning; the low frequency antenna is a connection chamber antenna, a metal floor is with achamber, for avoiding influence of height inconsistency of the metal floor on work performance of the high frequency antenna, a reflection surface employs a selection surface with resistance frequency when the high and low frequency antennas are conformal; feed of the two-frequency band antennas are in common ground to the metal floor, feed ground connection of the high frequency antenna can be direct connection or direct communication with the metal floor through a capacitor, a resistor and an inductor. The antenna is advantaged in that double frequency dual polarization can be realized in aco-aperture antenna form, wide angle scanning can be realized without grating lobe, the structure is simple, and the antenna is easy to process and assemble.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
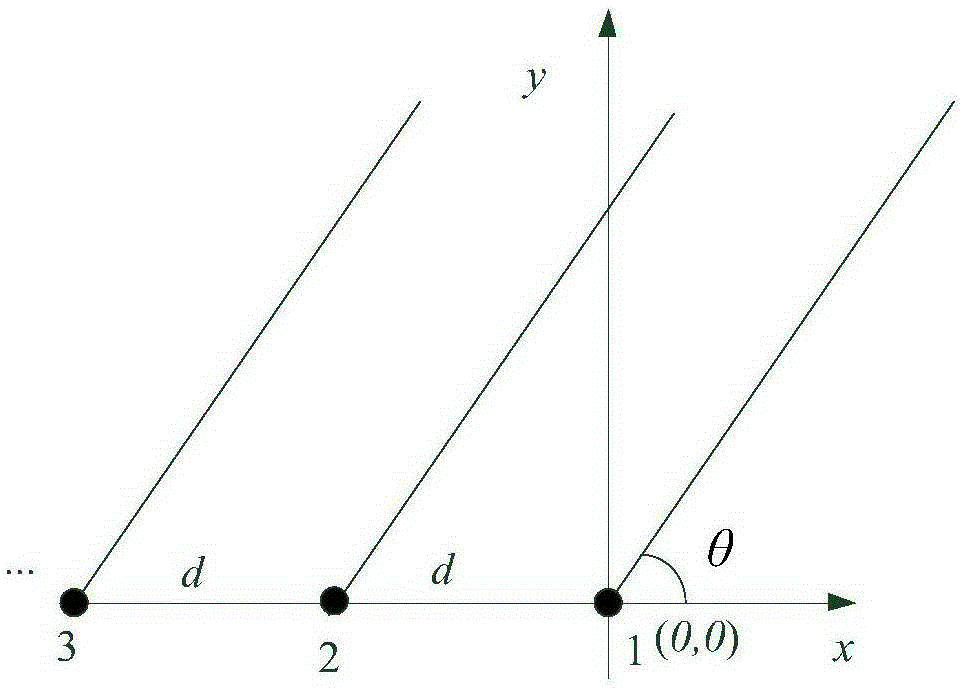
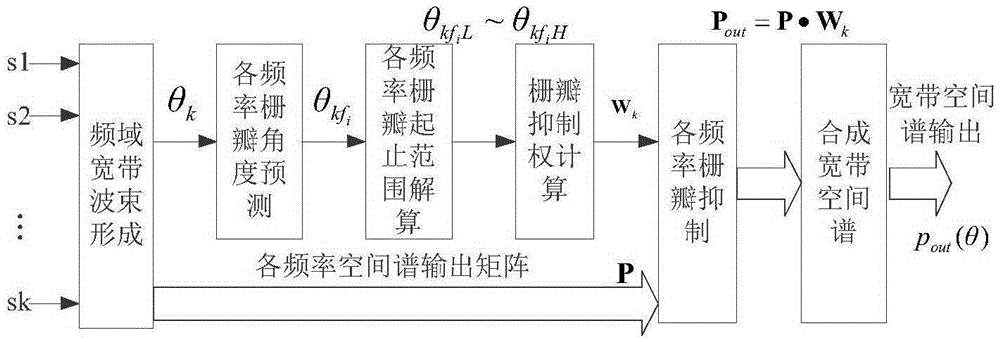
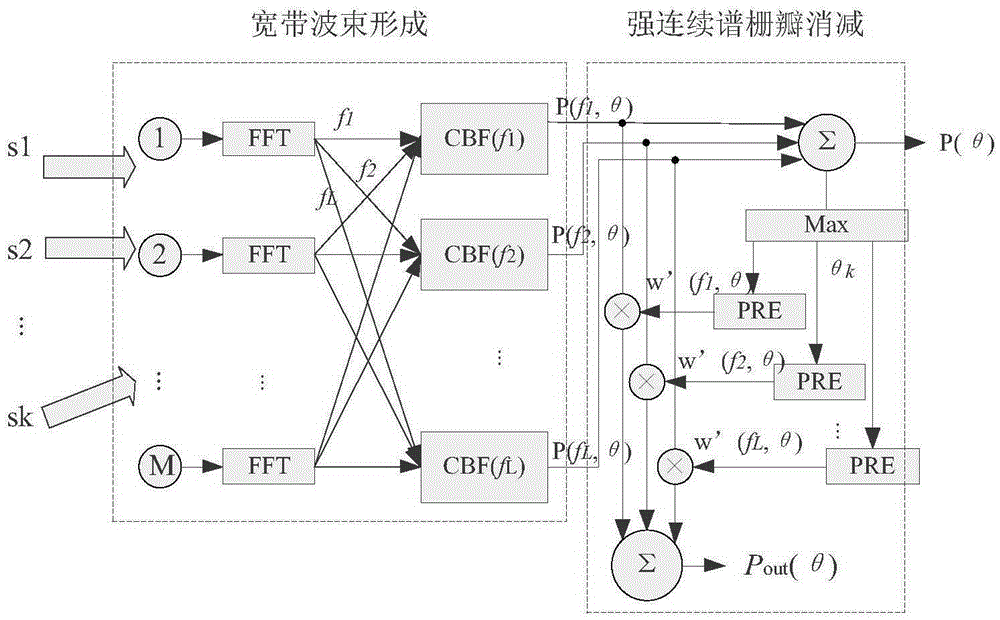
Sparse array broadband beamforming grating lobe suppressing method
ActiveCN105334508AImprove practicalityLow application costWave based measurement systemsWeight coefficientTarget signal
The invention provides a sparse array broadband beamforming grating lobe suppressing method. The method comprises a step 1 of performing frequency-domain broadband beamforming on array signals received by multiple array elements of a sparse array; a step 2 of predicting a grating lobe angle by using the orientation [theta]k of a strong interference target signal obtained in the step 1; a step 3 of resolving the start-stop range of the grating lobe of each frequency point according to the grating lobe angle [theta]kfj obtained in the step 2 and the main lobe width of each frequency point; a step 4 of computing a grating lobe suppression weight coefficient matrix Wk according to a grating lobe range obtained in the step 3; and a step 5 of suppressing the gratin lobe by using the grating lobe suppression weight coefficient matrix Wk obtained in the step 4 and a spatial spectrum output matrix P of each frequency point obtained in the step 1; and a step 6 of adding the spatial spectrum output matrix Pout after the grating lobe suppression in order to perform broadband spatial spectrum synthesis. The method solves broadband beamforming grating lobe influences caused by a common equal-interval sparse array and is used in signal processing field.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Element Reduction In Phased Arrays With Cladding
ActiveUS20080094300A1Particular array feeding systemsProtective material radiating elementsEngineeringArray element
Grating lobe free scanning in a phased array with sparse element spacing is obtained by restricting the maximum scan angle for elements in the array, and cladding the array. Array elements may be integrated into the cladding.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Reconfigurable antenna array and associated method of use
ActiveUS20180102593A1Narrow bandwidthMeet different requirementsSimultaneous aerial operationsPolarisation/directional diversityReconfigurable antennaPolarization diversity
A reconfigurable antenna array capable of utilizing a common antenna aperture which can cover a wide frequency range in a continuous way. With the basic antenna element based on a slot-ring and using a self similar structure approach and RE' switches, the antenna array operates without grating lobes. The antenna array exhibits polarization diversity and single-side radiation capability. When varactors are implemented into the array, the antenna array can cover the frequency range by continuously tuning the center frequency with a relatively narrow instantaneous bandwidth.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Method for suppressing uniform ultra-sparse array antenna beam pointing fuzziness
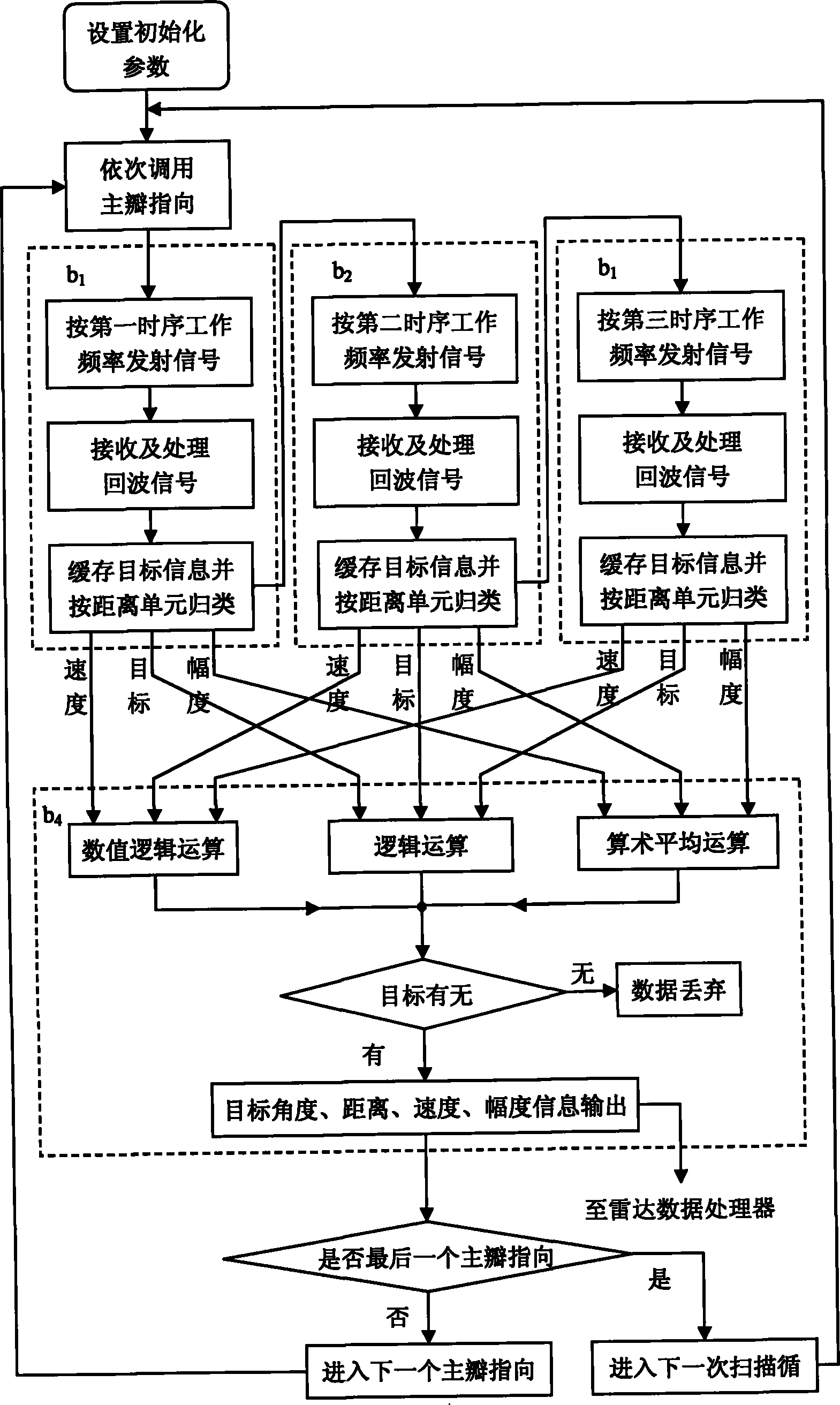
InactiveCN101813764ARemove blurReduce adverse effectsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPulse numberArray element
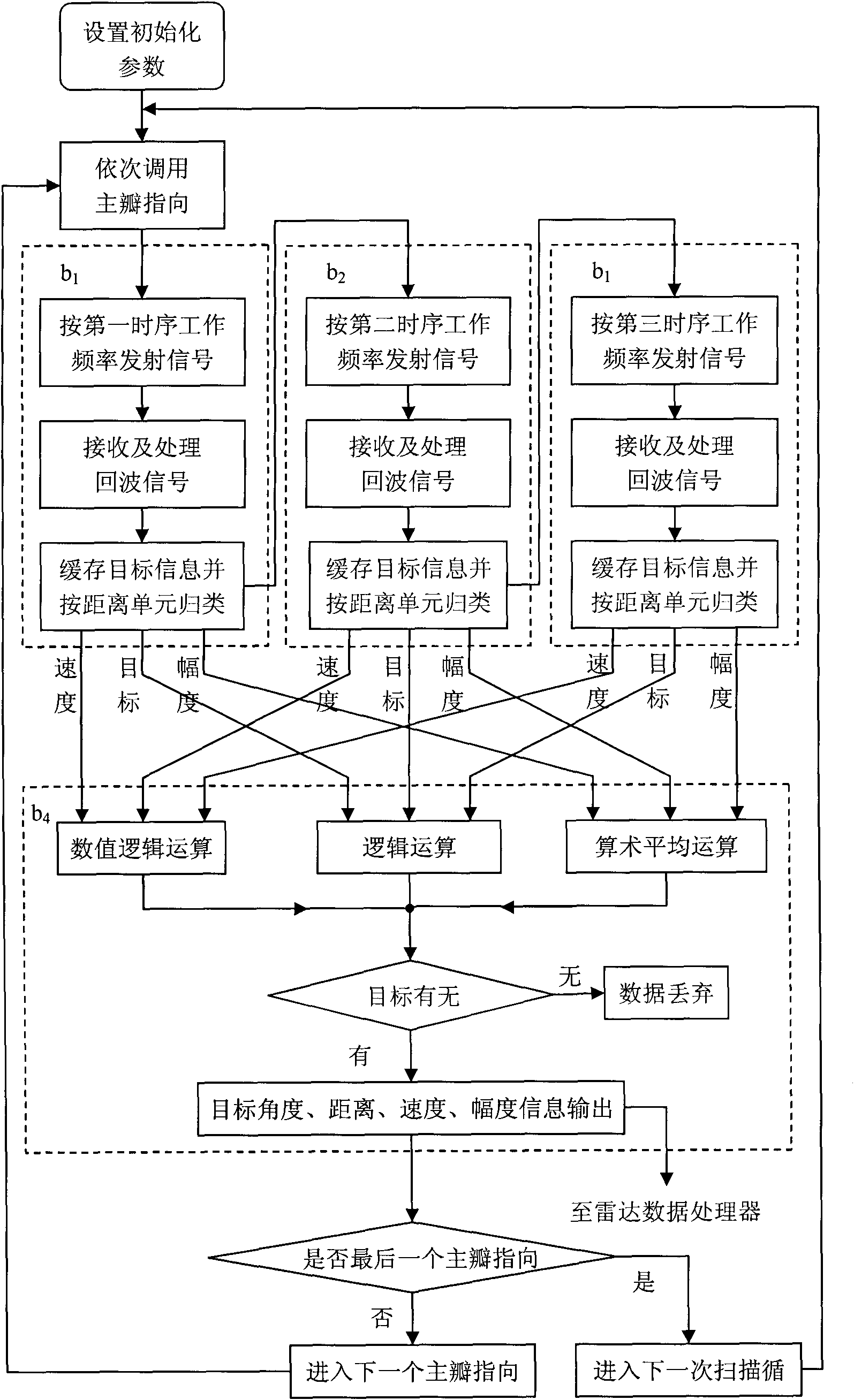
The invention belongs to a method for processing uniform ultra-sparse array antenna beam pointing fuzziness in the radar technology. The method comprises the steps of; performing initialization processing; performing directional transmission and reception by a first main lobe according to the set reference working frequency and two associated working frequency and pulse number in turn and performing comprehensive processing on the acquired three groups of target information so as to determine the existence of the target and removing pointing fuzziness caused by a grating lobe; when the target exists, inputting the angle and distance, speed and magnitude value of the target into a radar data processor together; and then repeatedly performing the processing on other main lobes so as to finish detection of the target on the pointing position of each main lobe. In the method, the angle range without grating lobe fuzziness is two times wider than that of two pieces of background technology and the array element number is reduced by over 50 percent, so that the method for the suppressing the uniform ultra-sparse array antenna beam pointing fuzziness is characterized in that: adverse impact of the grating lobe on the radar measured angle can be removed to the full extent; the antenna array element number and corresponding channel number of large-aperture uniform array radar are effectively reduced; the system cost is reduced, the application range is enlarged, and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Passive distribution SAR (synthetic aperture radar) imaging process method based on double-stage multi-resolution reconstruction
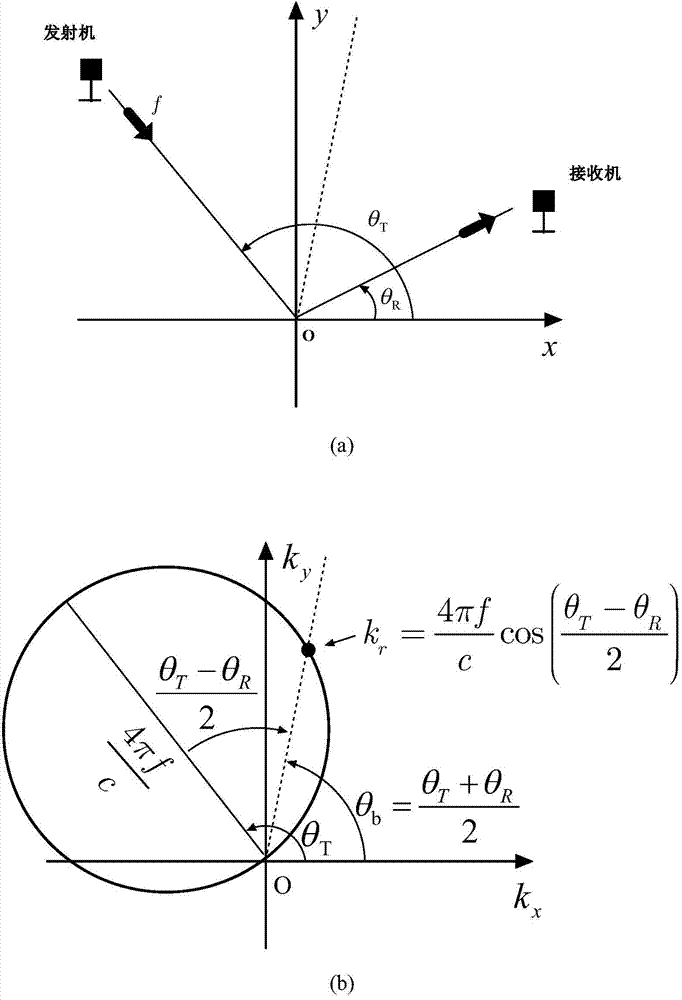
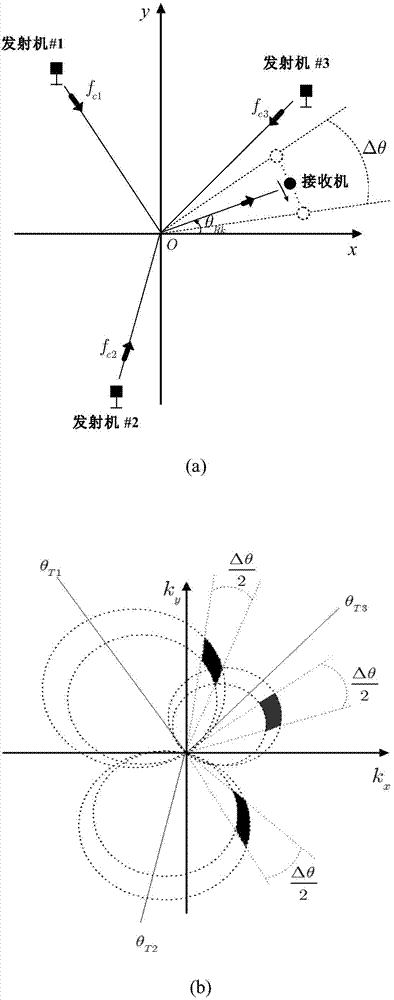
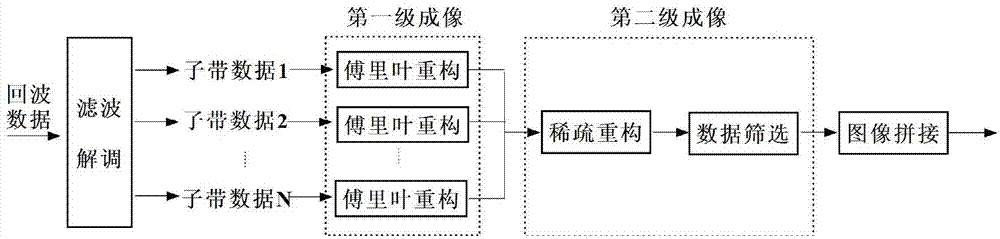
InactiveCN103941256AOvercome the grating lobe effectImprove computing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarReconstruction method
The invention relates to a passive distribution SAR imaging process method based on double-stage multi-resolution reconstruction and belongs to the technical field of SAR imaging signal processing methods. The method comprises the following steps of, firstly, performing filtering and modulation on target echo signals received by an airborne receiver, separating out the target echo signals from different radiation sources and modulating the target echo signals to a base band; secondly, processing various channel signals separated out in the first step through the Fourier reconstruction algorithm to obtain the coarse-resolution images of a target; thirdly, for the coarse-resolution images obtained in the second step, obtaining the high-definition image of the target in every coarse-definition pixel unit among the images through a sparse reconstruction method; lastly, obtaining the high-definition image of a whole scene through data screening and image splicing. The passive distribution SAR imaging process method based on the double-stage multi-resolution reconstruction can solves the grating lobe problem due to sparse sampling and meanwhile has higher computation efficiency compared with traditional sparse reconstruction methods.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com