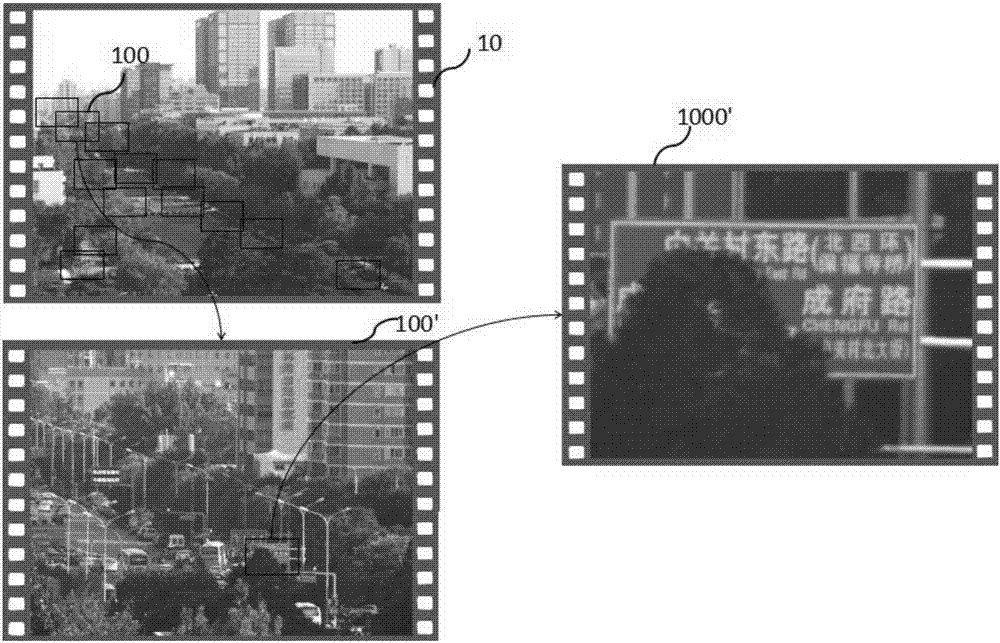
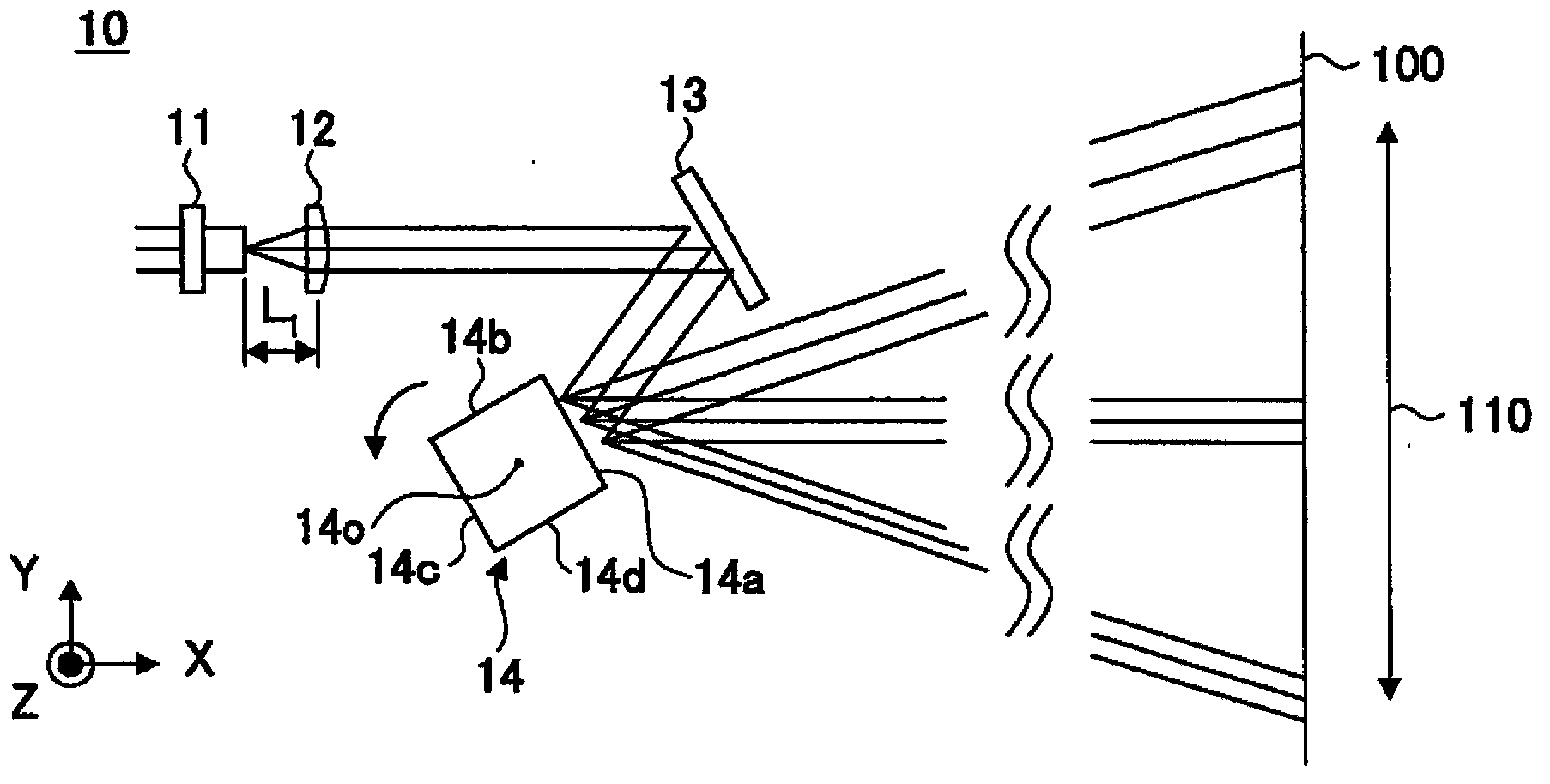
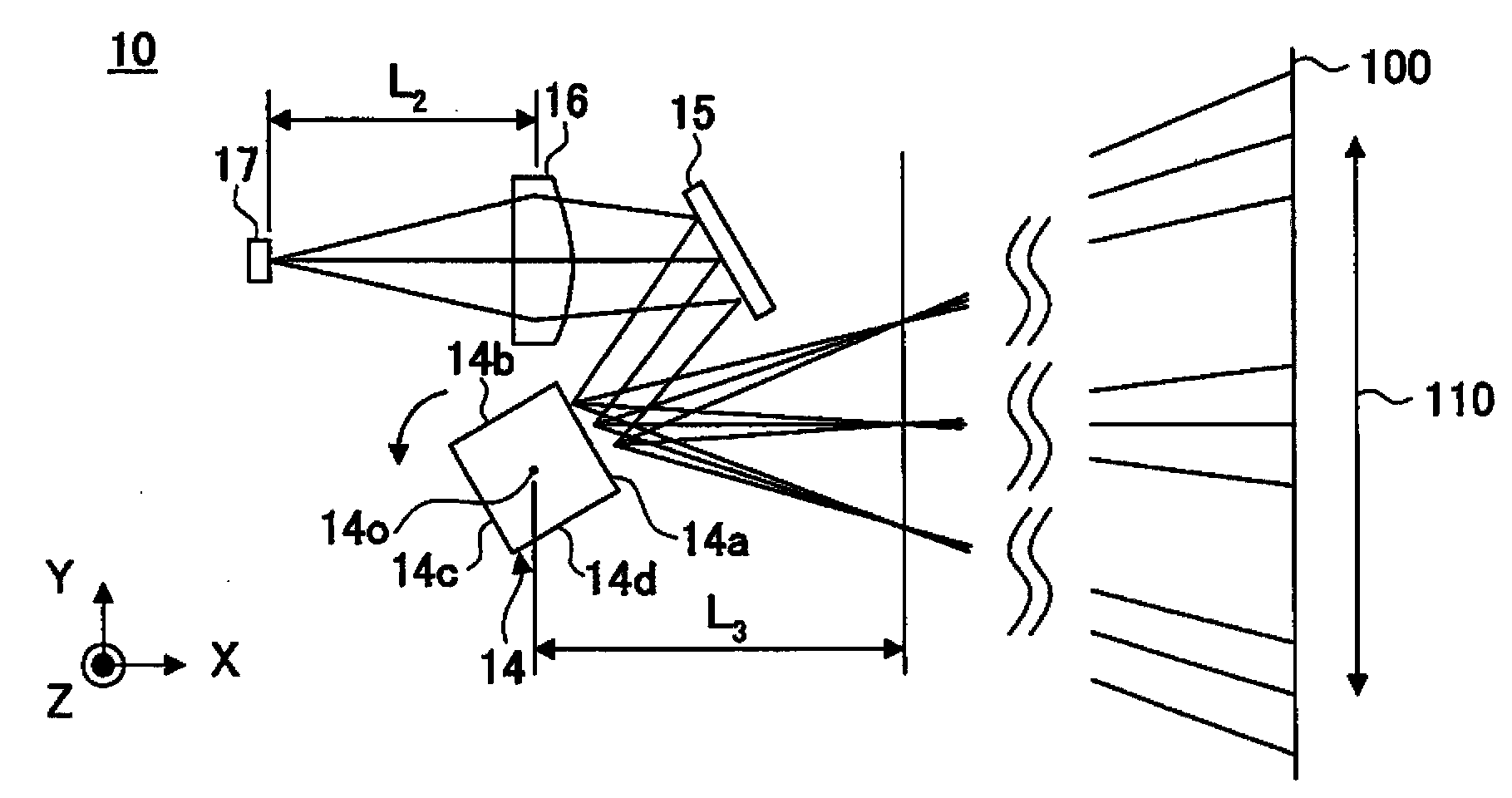
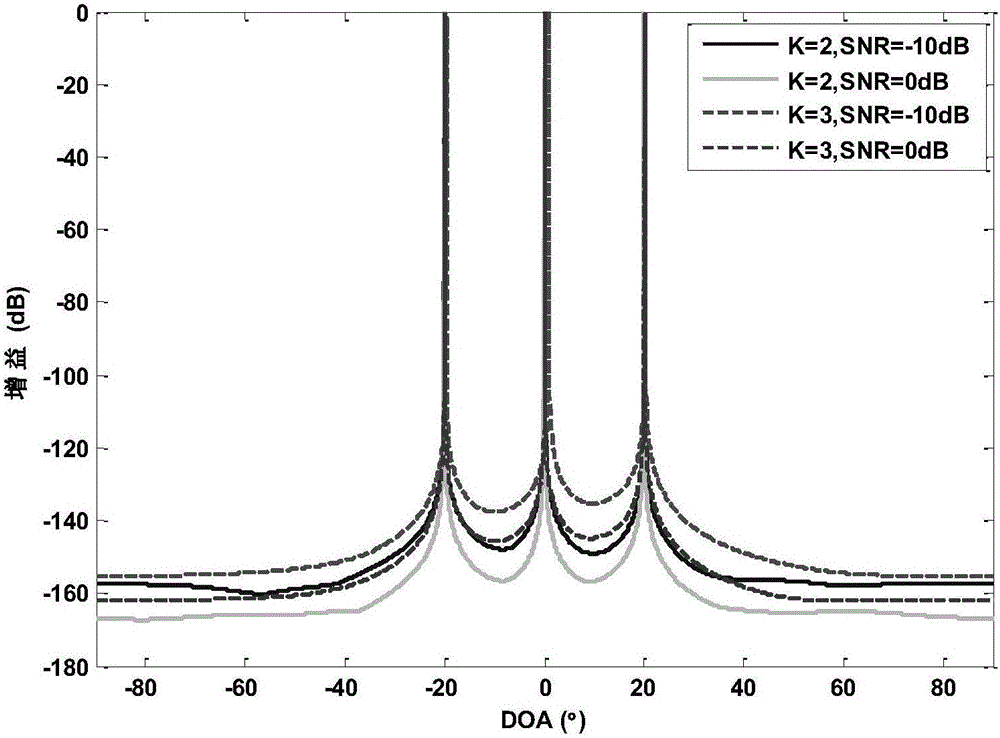
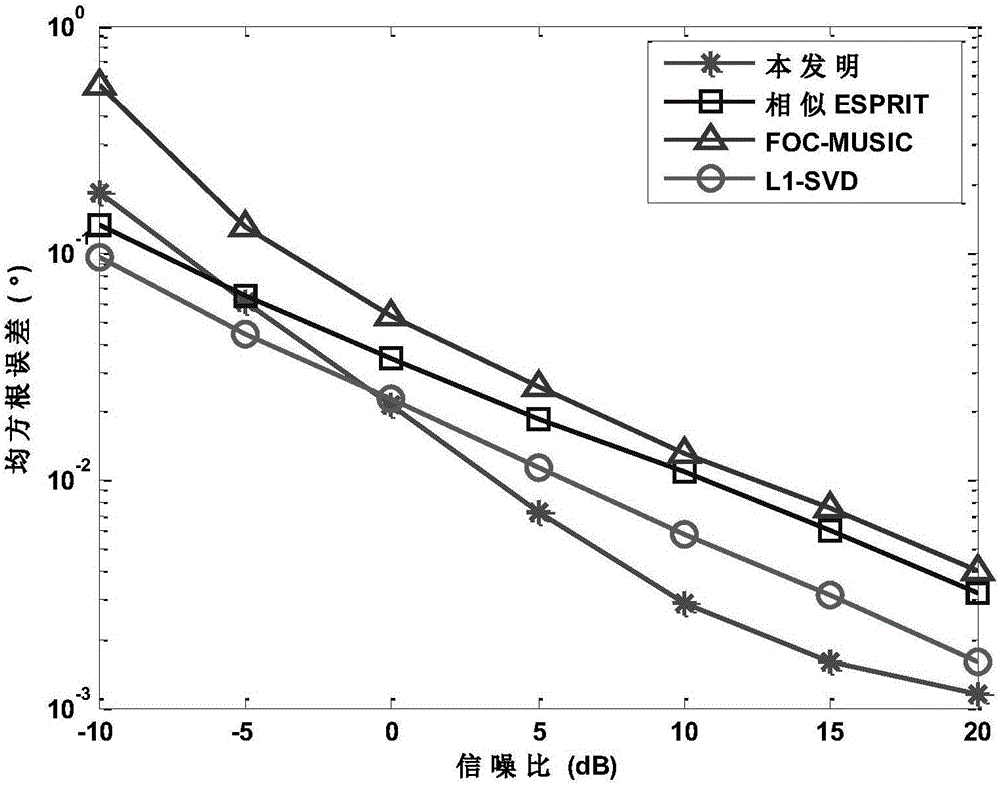
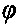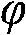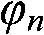Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
276results about How to "Improve angular resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
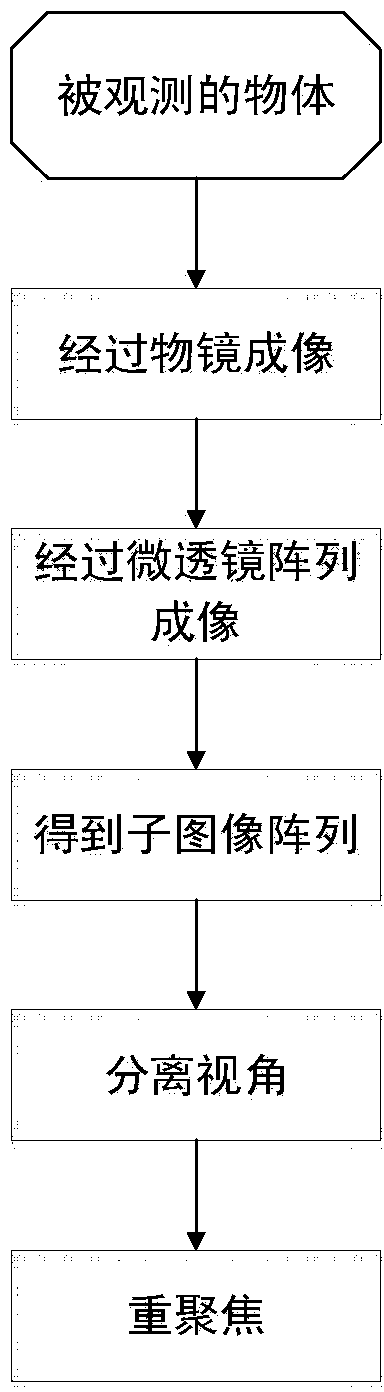
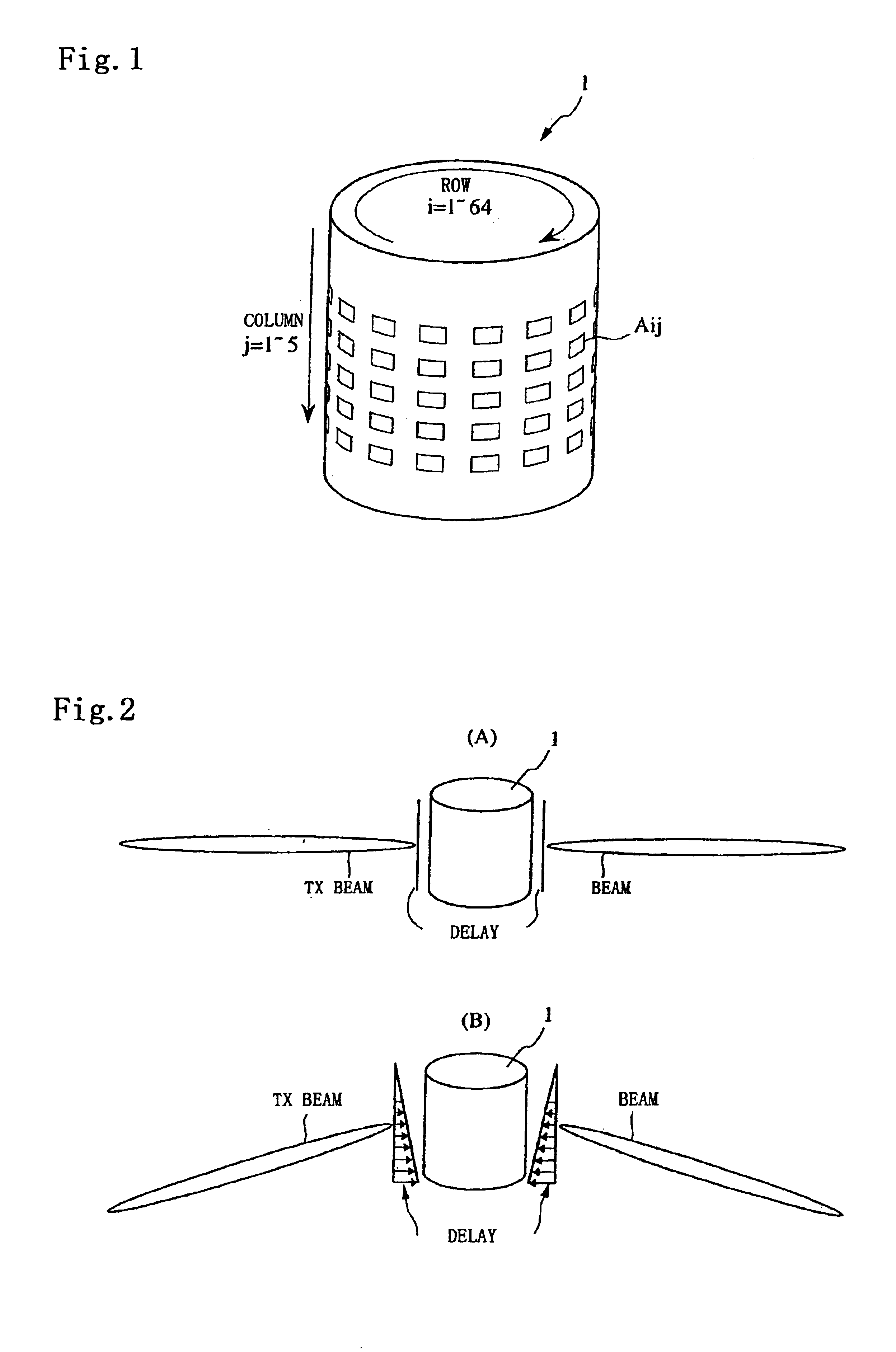
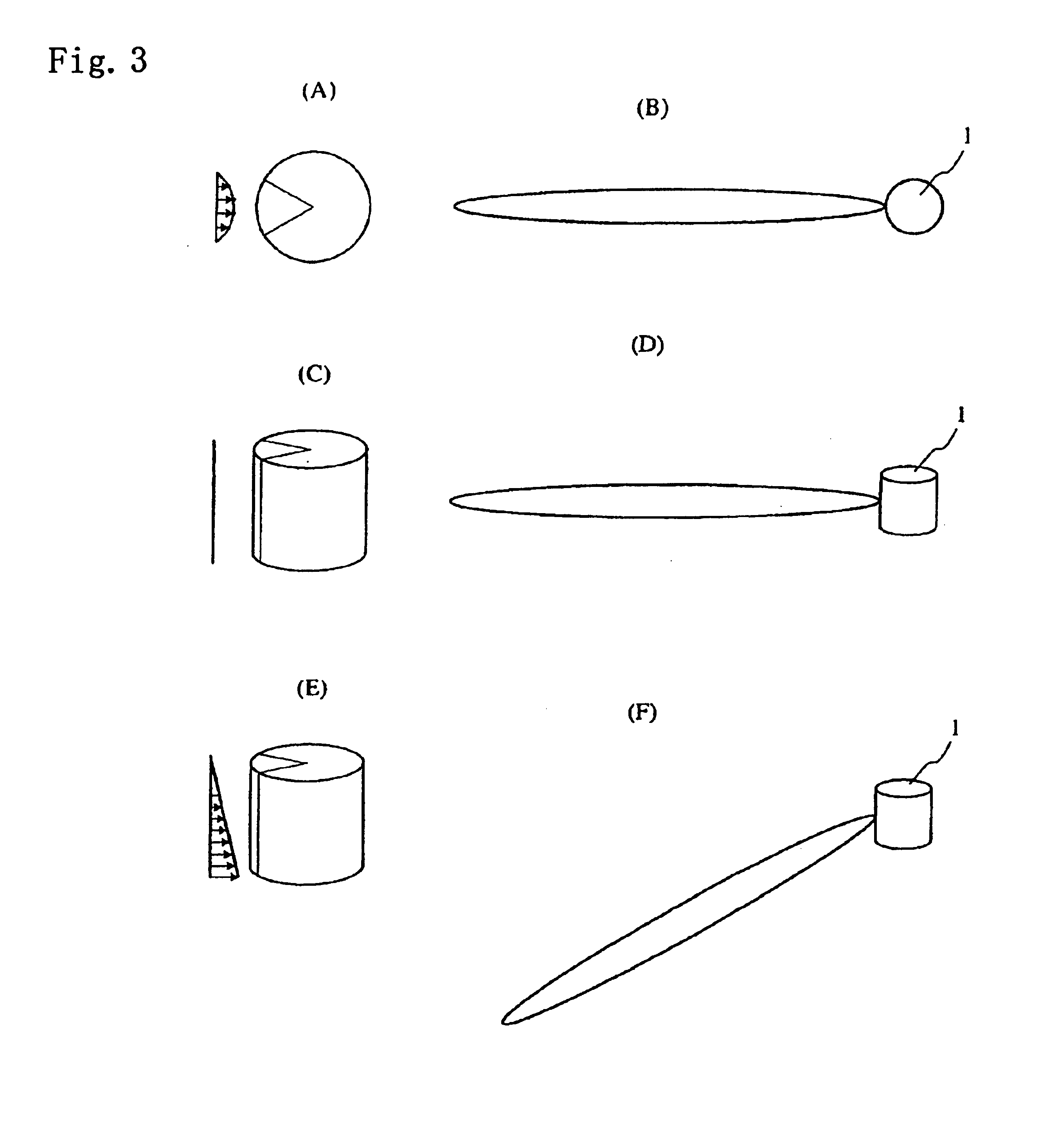
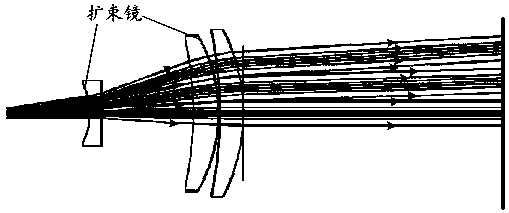
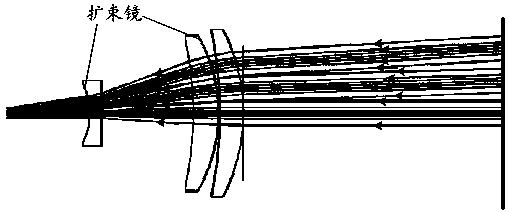
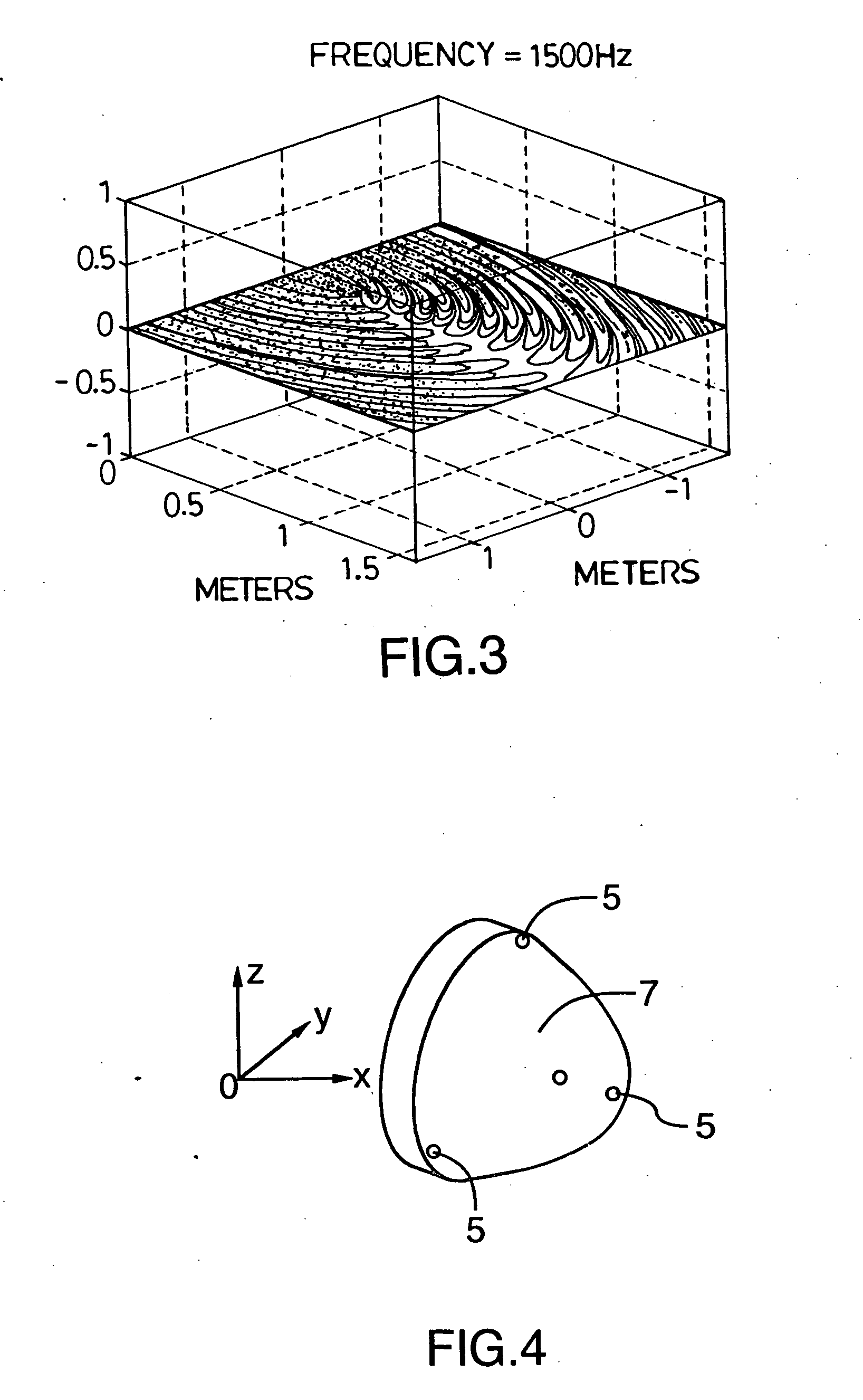
Multiscale Optical System
ActiveUS20100171866A1Low costImproved optical imagingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSpatial correlationCamera lens
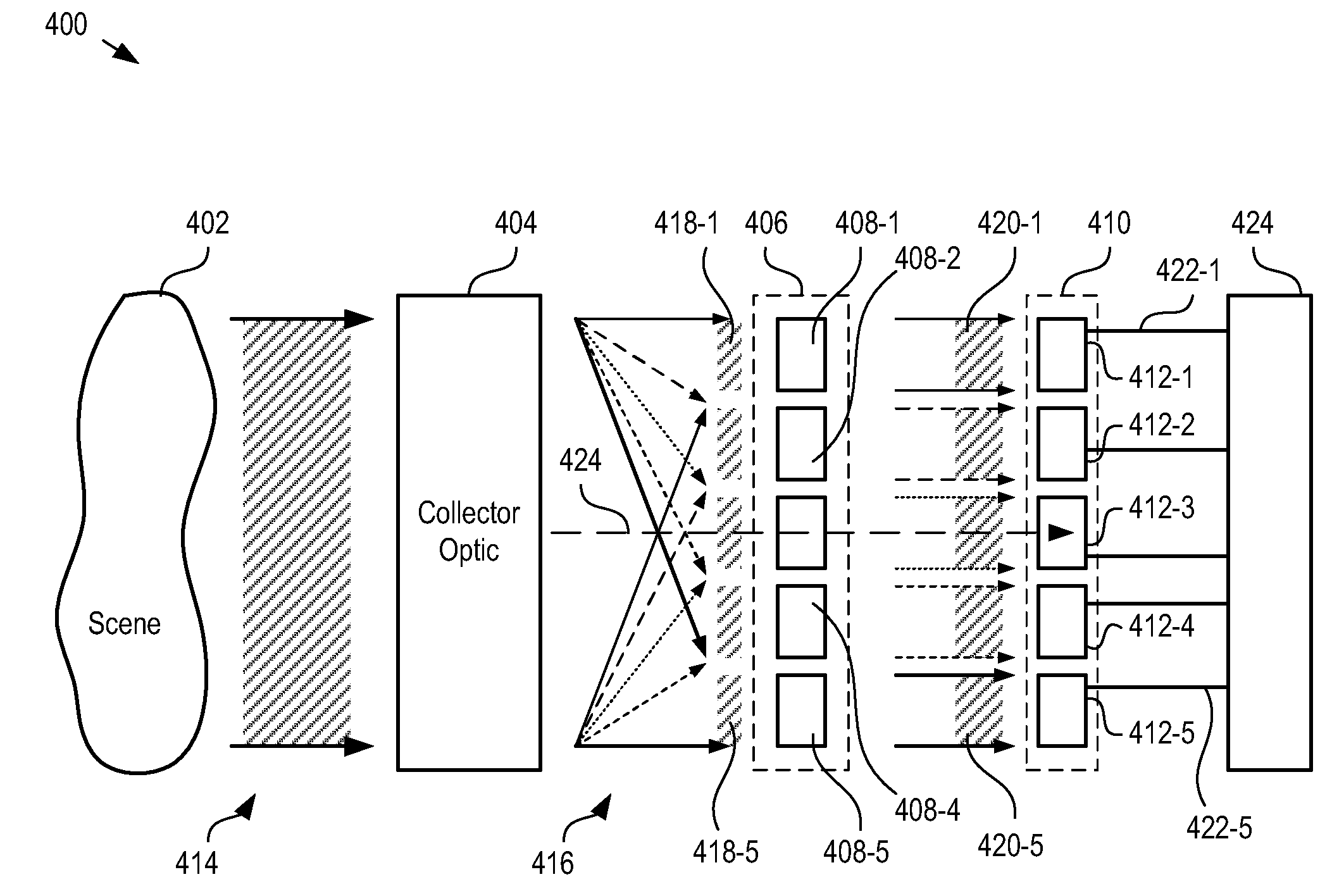
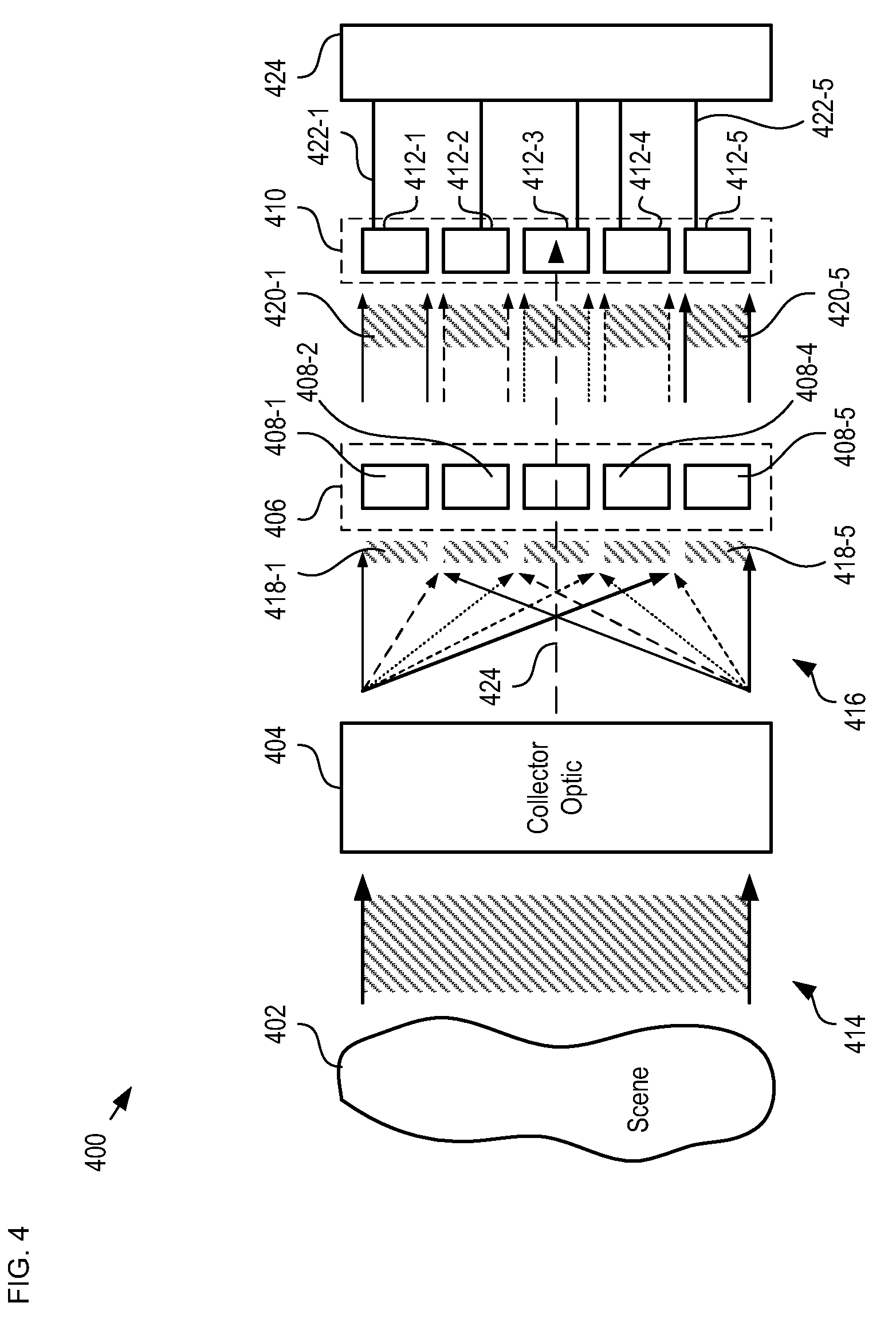
A means of enabling an imaging lens system that overcomes some of the costs and disadvantages of the prior art is disclosed. A lens system in accordance with the present invention reduces or eliminates one or more aberrations of an optical input by separating image collection functionality from image processing functionality. As a result, each function can be performed without compromising the other function. An embodiment of the present invention comprises a collection optic that provides a first optical field, based on light from a scene, to a processing optic that comprises a plurality of lenslets. The processing optic tiles the first optical field into a plurality of second optical fields. Each lenslet receives a different one of the plurality of second optical fields, reduces at least one localized aberration in its received second optical field, and provides the corrected optical field to a different one of plurality of photodetectors whose collective output is used to form a spatially correlated sub-image of that corrected optical field. The sub-images are readily combined into a spatially correlated image of the scene.
Owner:APPLIED QUANTUM TECH +1
Broadband signal DOA estimation method based on co-prime array
ActiveCN106324558AHigh-resolutionEasy to detectDirection findersSparse constraintSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
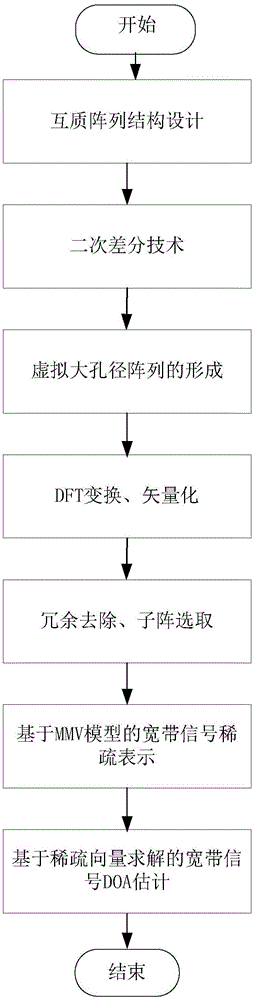
The invention discloses a broadband signal DOA estimation method based on a co-prime array, and the method comprises the steps: S1, designing a co-prime array structure through an antenna; S2, carrying out the sampling and discrete Fourier transform of a broadband signal received by an antenna in the co-prime array, and obtaining a frequency domain signal output model; S3, calculating an autocorrelation matrix of the frequency domain signal output model, carrying out the vectorization of the frequency domain signal output model, and obtaining a new signal model; S4, carrying out the processing of the new signal model, and obtaining a spatial smooth covariance matrix of the broadband signal; Sa5, dividing a space domain grid, constructing a dictionary, carrying out the sparse representation of the spatial smooth covariance matrix through employing the dictionaries of a plurality of frequency points of the broadband signal, and forming a multi-measurement-vector sparse representation model of a plurality of dictionaries of the broadband signal; S6, achieving the arrival direction estimation of the broadband signal in a mode of solving a sparse inverse problem through the joint sparse constraint of the sparse representation coefficients of the plurality of dictionaries. The method can improve the estimation precision of the direction angle of the broadband signal under the condition of low signal to noise ratio, and reduces the direction finding error.
Owner:东北大学秦皇岛分校
Head-mounted displaying of magnified images locked on an object of interest
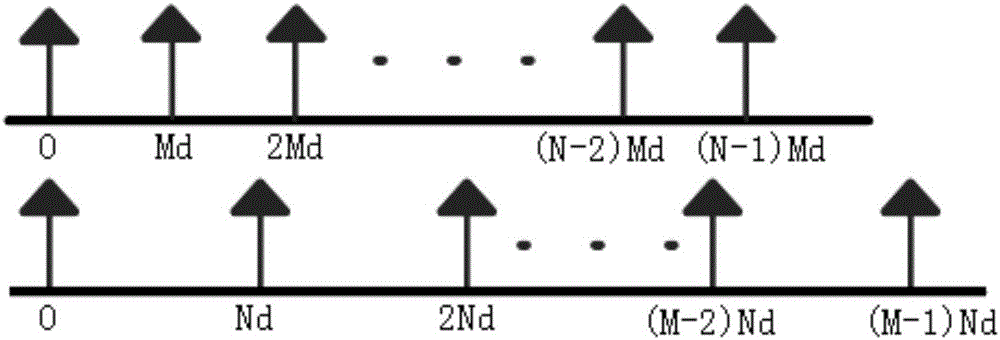
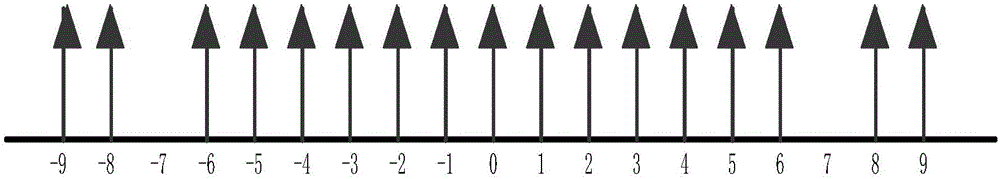
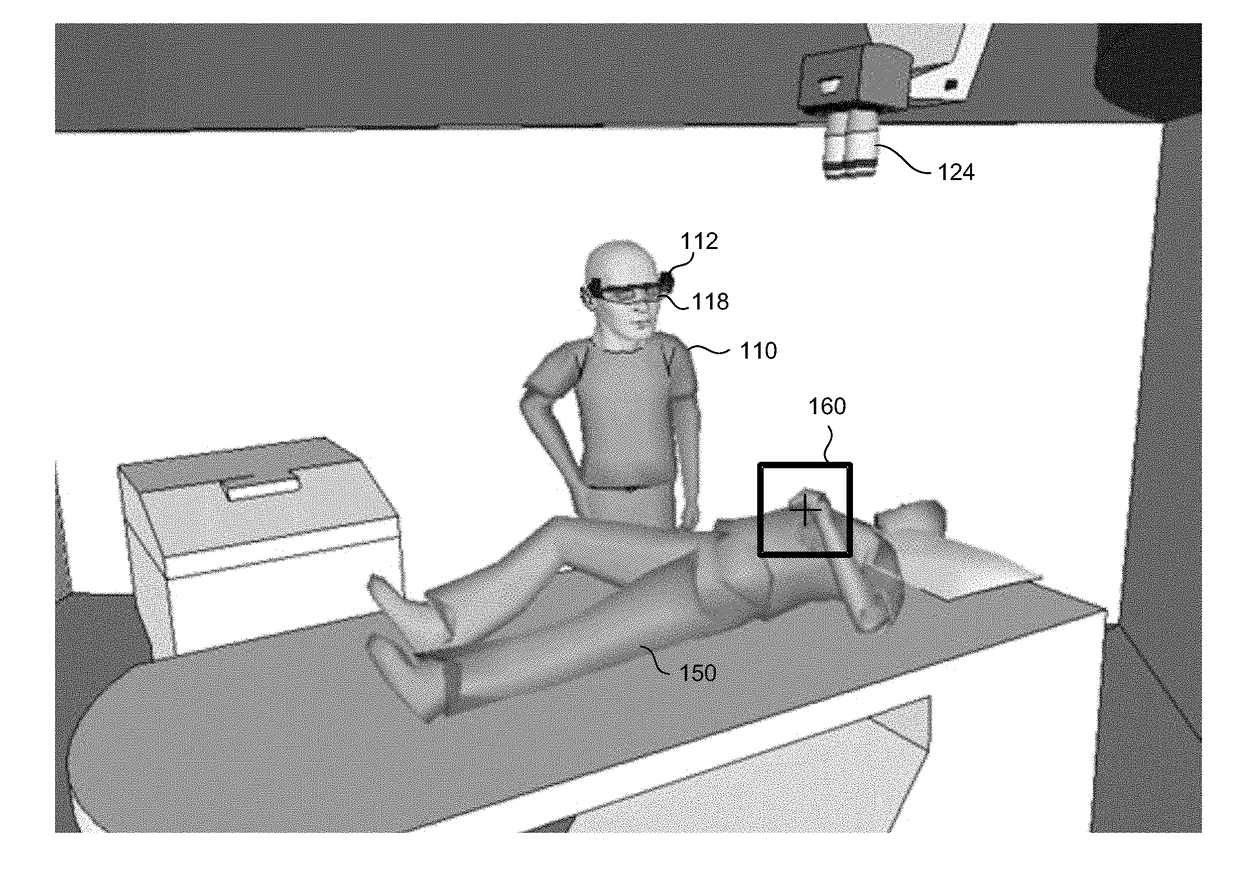
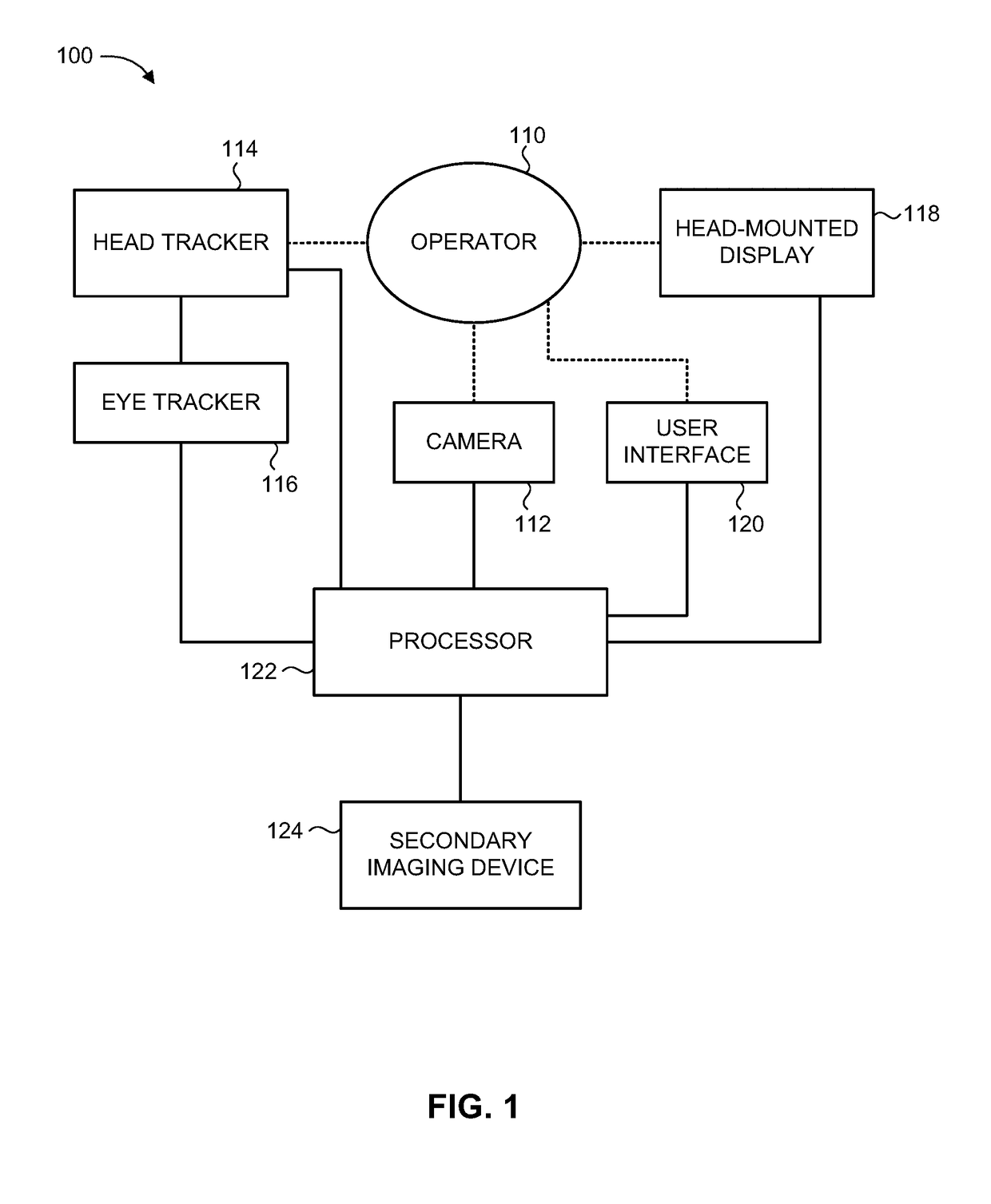
ActiveUS20170318235A1Increase and decrease magnification factorImprove angular resolutionTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionHead movementsImaging processing
System and method for presenting magnified images locked onto object of interest in operator environment. A camera disposed on head of operator captures images of scene, where camera moves in conjunction with head movements. A head tracker detects the operator LOS by detecting at least head orientation. A processor obtains designated coordinates of object of interest in scene, and determines relative angle between detected operator LOS and object. The processor determines coordinates of object in acquired images, and applies image processing for fine stabilization of images based on previous images so as to compensate for operator head movements. The processor rescales an image region surrounding object of interest, in accordance with at least one display parameter, to produce respective magnified image frames of object. A head-mounted display displays the magnified images to operator such that object of interest appears in a defined position on display regardless of operator head movements.
Owner:ELBIT SYST LTD
Laser radar and working method thereof
ActiveCN108226899AImprove angular resolutionExpand field of viewWave based measurement systemsRadarBeam splitting
The invention provides a laser radar and a working method thereof. The laser radar comprises a transmitting device, a beam splitting device, a galvanometer and a receiving device, wherein the transmitting device is used for transmitting a first laser beam to a to-be-detected object; the beam splitting device is used for splitting the first laser beam into a plurality of second laser beams, and thepropagation directions of the multiple second laser beams are different; the galvanometer comprises a first reflecting surface, the first reflecting surface is used for reflecting the second laser beams, the galvanometer is provided with a first rotary shaft and is rotated around the first rotary shaft, and an included angle between the first rotary shaft and a normal line of the first reflectingsurface is greater than zero; the receiving device is used for receiving echo beams reflected by the to-be-detected object. The laser radar has the advantage that the larger field angle can be obtained through smaller rotation angle of the galvanometer.
Owner:HESAI TECH CO LTD
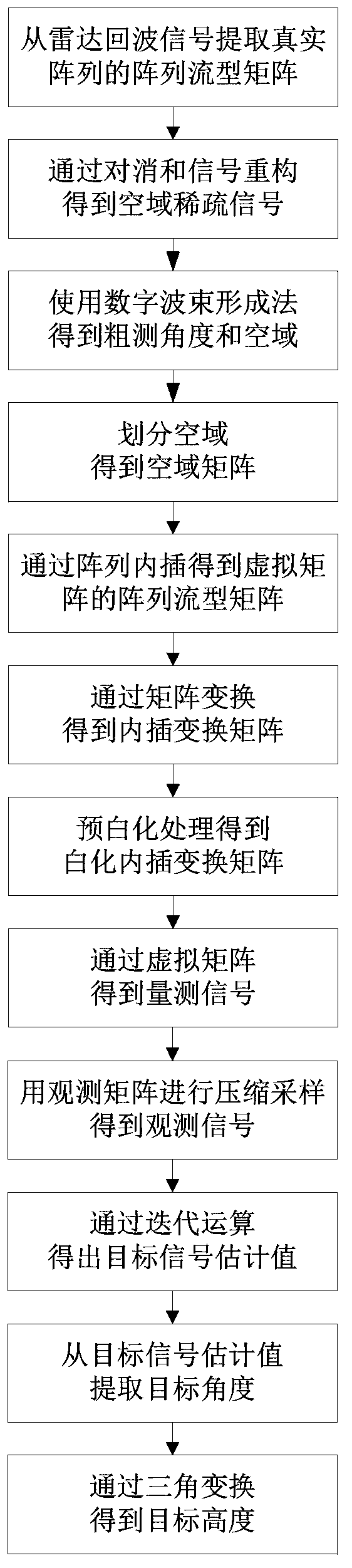
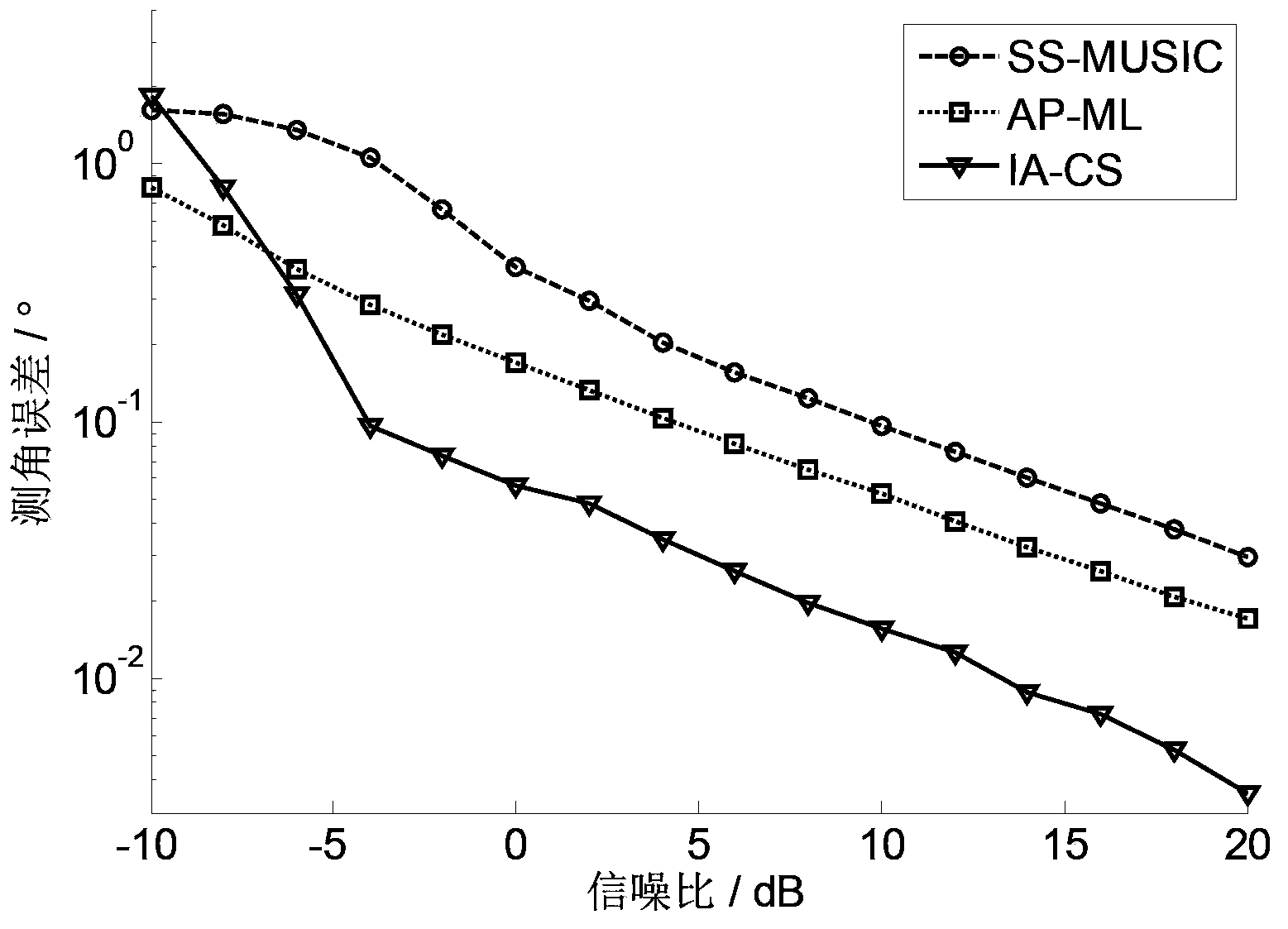
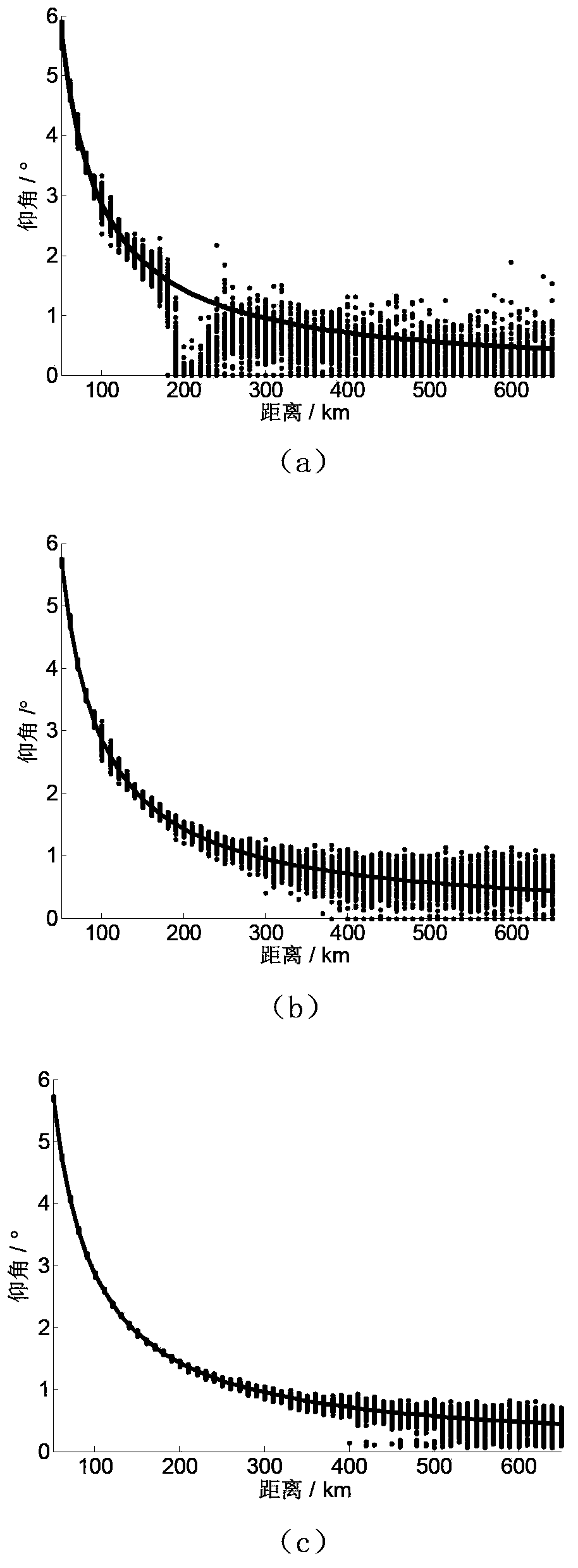
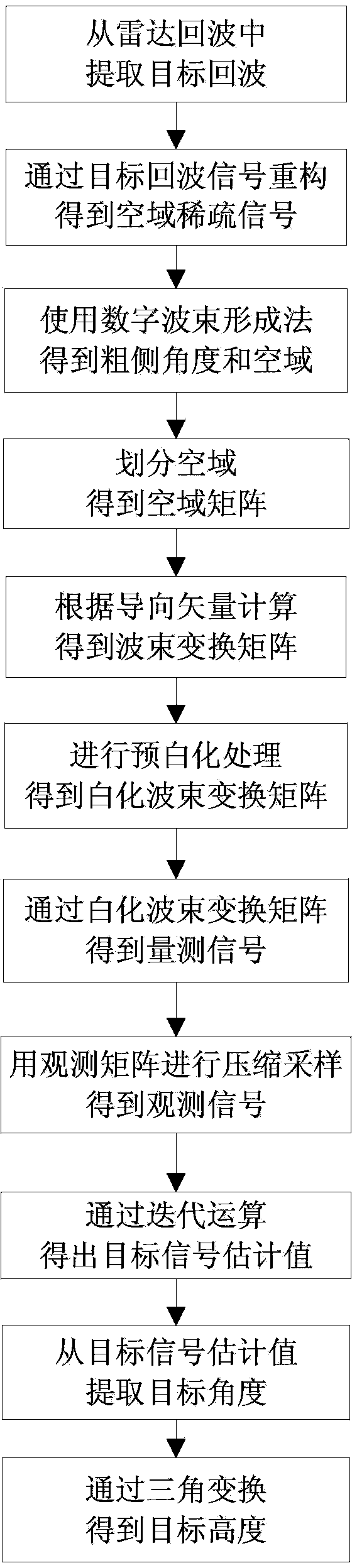
Meter wave radar height measurement method based on array interpolation compression perception
ActiveCN103353595AReduce sidelobeImprove performanceWave based measurement systemsTarget signalRadar
The invention discloses a height measurement method based on an array interpolation compression perception. The height measurement method mainly aims at solving a low elevation height measurement problem under a multipath environment, and especially under low signal to noise ratio and less snapshot environments. The method comprises the following steps of extracting a target signal from a radar echo; acquiring a spatial-domain sparse signal through cancellation and signal reconstruction; using a wave beam formation method to obtain a rough measurement target angle; according to the rough measurement angle, acquiring the spatial domain and dividing the spatial domain; using the array interpolation to acquire a virtual array; according to a matrix transformation relation, acquiring an interpolation transformation matrix and carrying out prewhitening processing on the interpolation transformation matrix; using a whitening interpolation transformation matrix and an observation matrix to acquire an observation signal; using a whitening interpolation transformation matrix and observation signal iteration operation to acquire a target signal estimation value; extracting a target angle from the target signal estimation value so as to acquire a target height. By using the method of the invention, sampling points of the target signal and computation intensity are obviously reduced; sidelobes of a signal power spectrum and a space spectrum are effectively reduced; the method can be used in target tracking.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
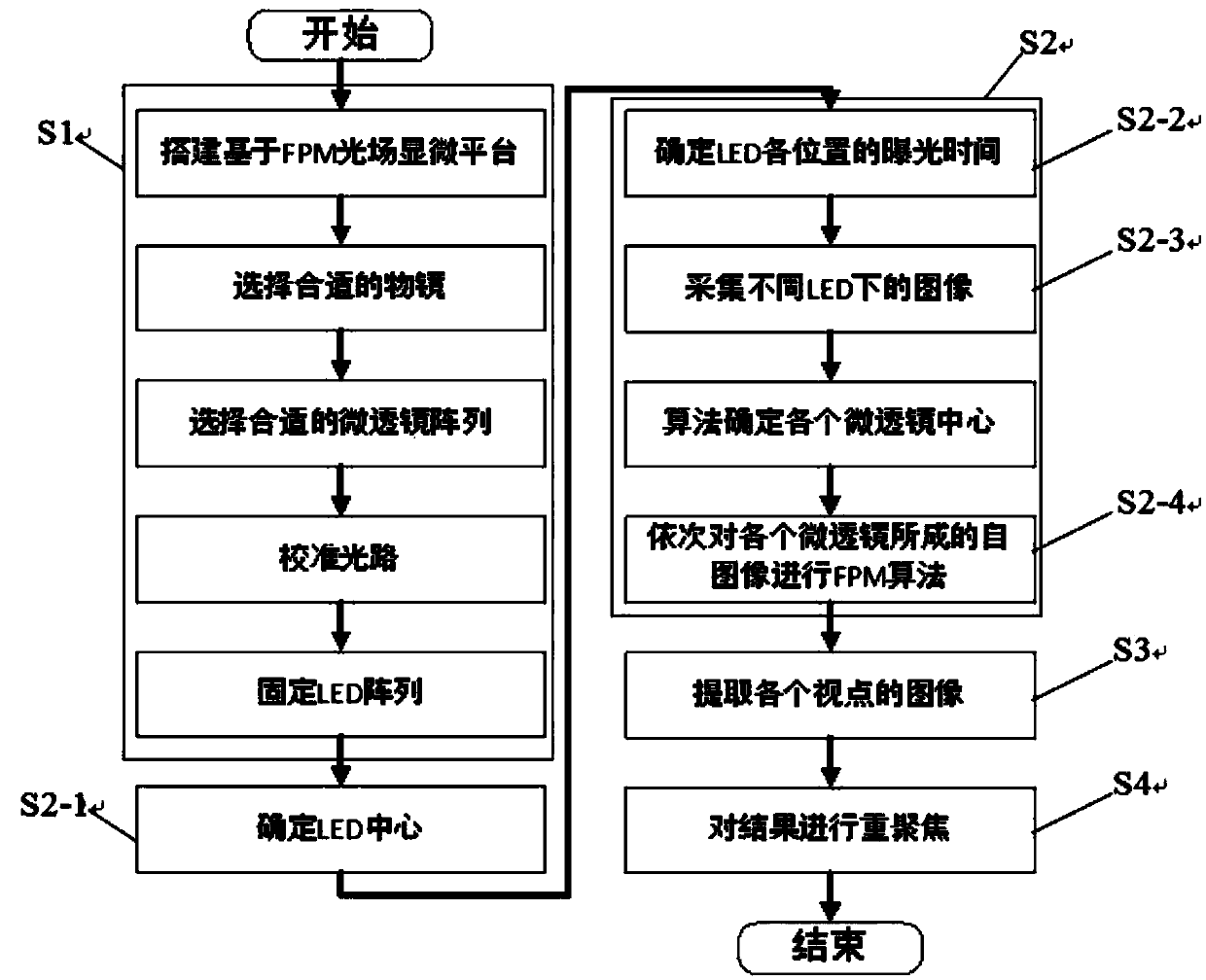
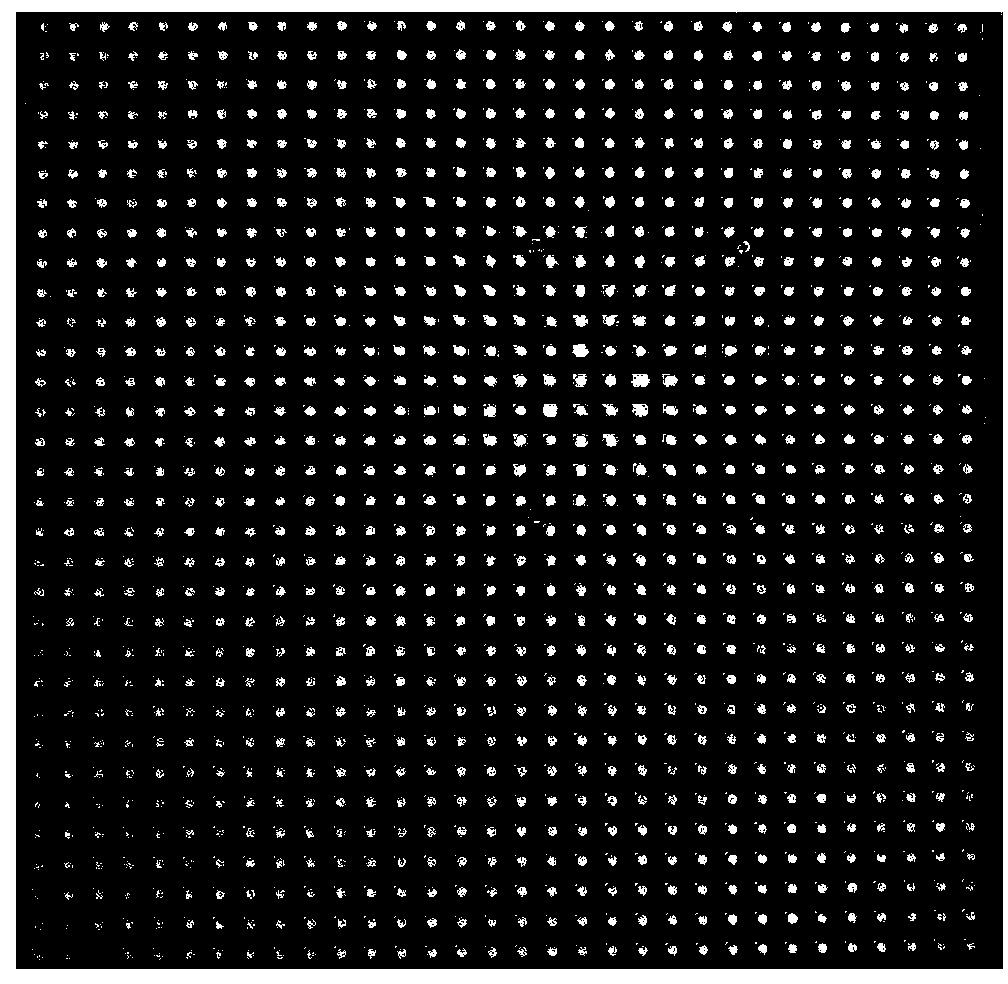
Light field microscopical method based on FPM
ActiveCN104181686AHigh-resolutionPromote reconstructionMicroscopesImage resolutionComputational physics
A light field microscopical method based on FPM includes the following steps of building a light field microscopical platform based on FPM, collecting high-definition wide-vision images through the light field microscopical platform based on FPM, carrying out view separation on the obtained high-definition wide-vision images, and obtaining wanted results through refocusing by means of results of view separation. Light field information is collected by means of a light field microscope based on an FPM algorithm, definition of each microlens image in the light field microscope is improved, angle definition is improved, the collected light field information is enriched, and a better three-dimensional structure can be reconstructed for an object.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Wave beam space domain meter wave radar height measurement method based on compressed sensing
ActiveCN103353596AReduce sidelobeImprove angle measurement accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Target signal
The invention discloses a wave beam space domain meter wave radar height measurement method based on compressed sensing and relates to low elevation height measurement under the condition that a signal to noise ratio is low and snapshots are less. A realization process is characterized in that a target signal is extracted from a radar echo and rough measurement of the elevation is performed so that the space domain theta where a target signal elevation is located is obtained; the space domain theta is divided into P parts, wave beam formation is performed in the space domain theta so as to obtain a wave beam transformation matrix B and prewhitening is performed on the wave beam transformation matrix B so as to obtain a whitening wave beam transformation matrix T; receiving data is projected to the whitening wave beam transformation matrix so as to obtain a wave beam domain measurement signal z and an observation matrix phi carries out compression sampling on the z so as to obtain an observation signal y; iterative operation of the whitening wave beam transformation matrix T and the observation signal y is used to obtain a target signal estimation value; a target angle is extracted from the target signal estimation value so as to obtain the target height. By using the method of the invention, sampling points of the target signal and operands are reduced; sidelobes of a signal power spectrum and a space spectrum are effectively reduced; height measurement precision under the low signal to noise ratio is increased; the method can be used in target positioning.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
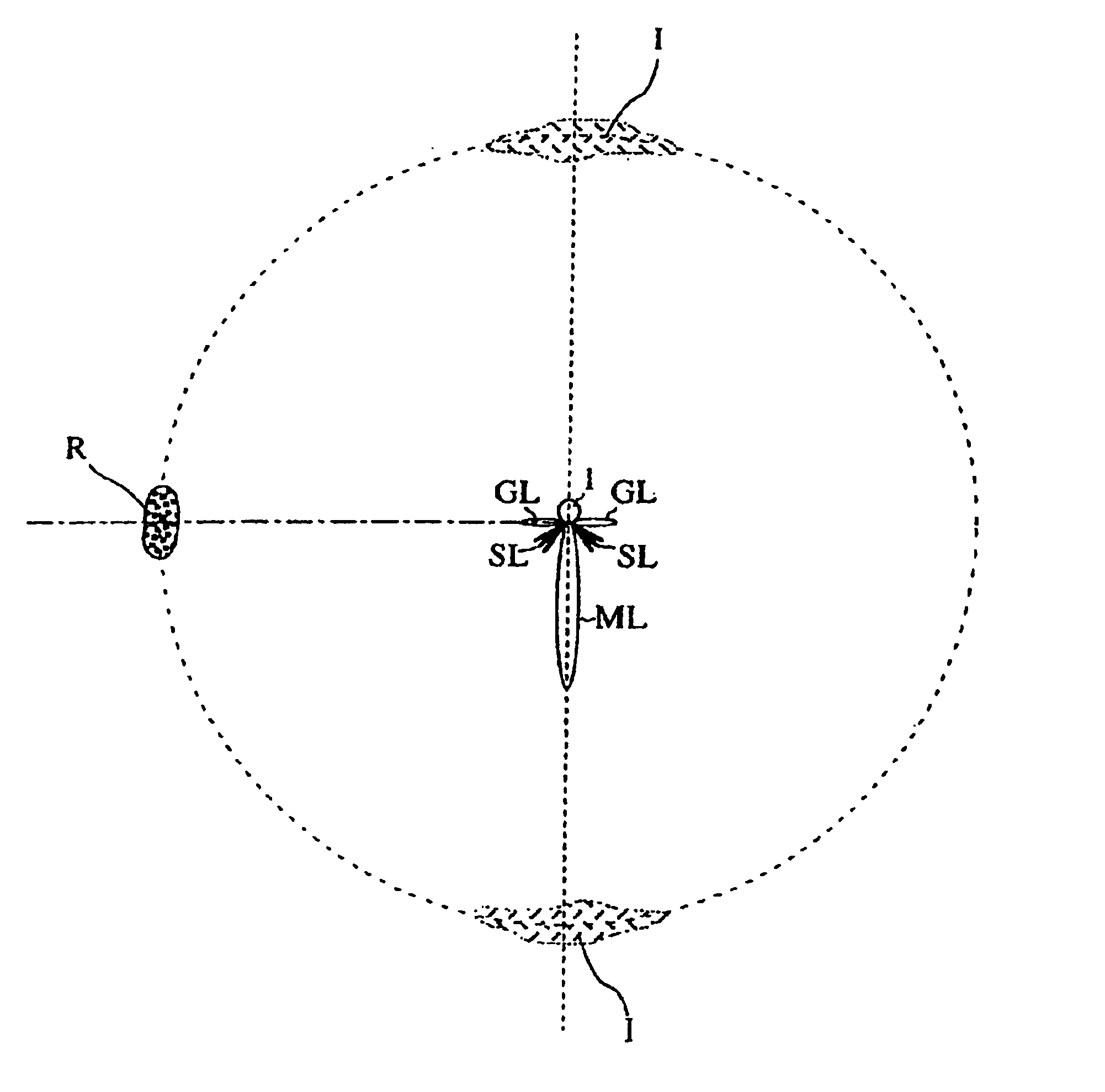
Automatically tracking scanning sonar
InactiveUS6778468B1Improve angular resolutionIncrease in scale of hardwareMechanical vibrations separationAcoustic wave reradiationSonarSound sources
The invention provides an ultrasonic transmit-receive apparatus which solves a false image problem caused by grating lobes and side lobes and offers high bearing resolution without increasing in the scale of hardware or in manufacturing cost. Using a transducer having multiple transducer elements arranged on a surface of the transducer along its circumferential direction, the apparatus emits ultrasonic waves in directionally varying frequency bands and receives echo signals from specified angular directions while selecting the frequency from one direction to another. In a Doppler transmission method, for example, the apparatus drives the individual transducer elements in such a manner that the ultrasonic waves emitted by the transducer elements are equivalent to ultrasonic waves emitted from an imaginary moving sound source moving within a circle enclosed by the multiple transducer elements arranged along the circumferential direction, so that the transducer elements emit ultrasonic signals at directionally varying Doppler shift frequencies.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
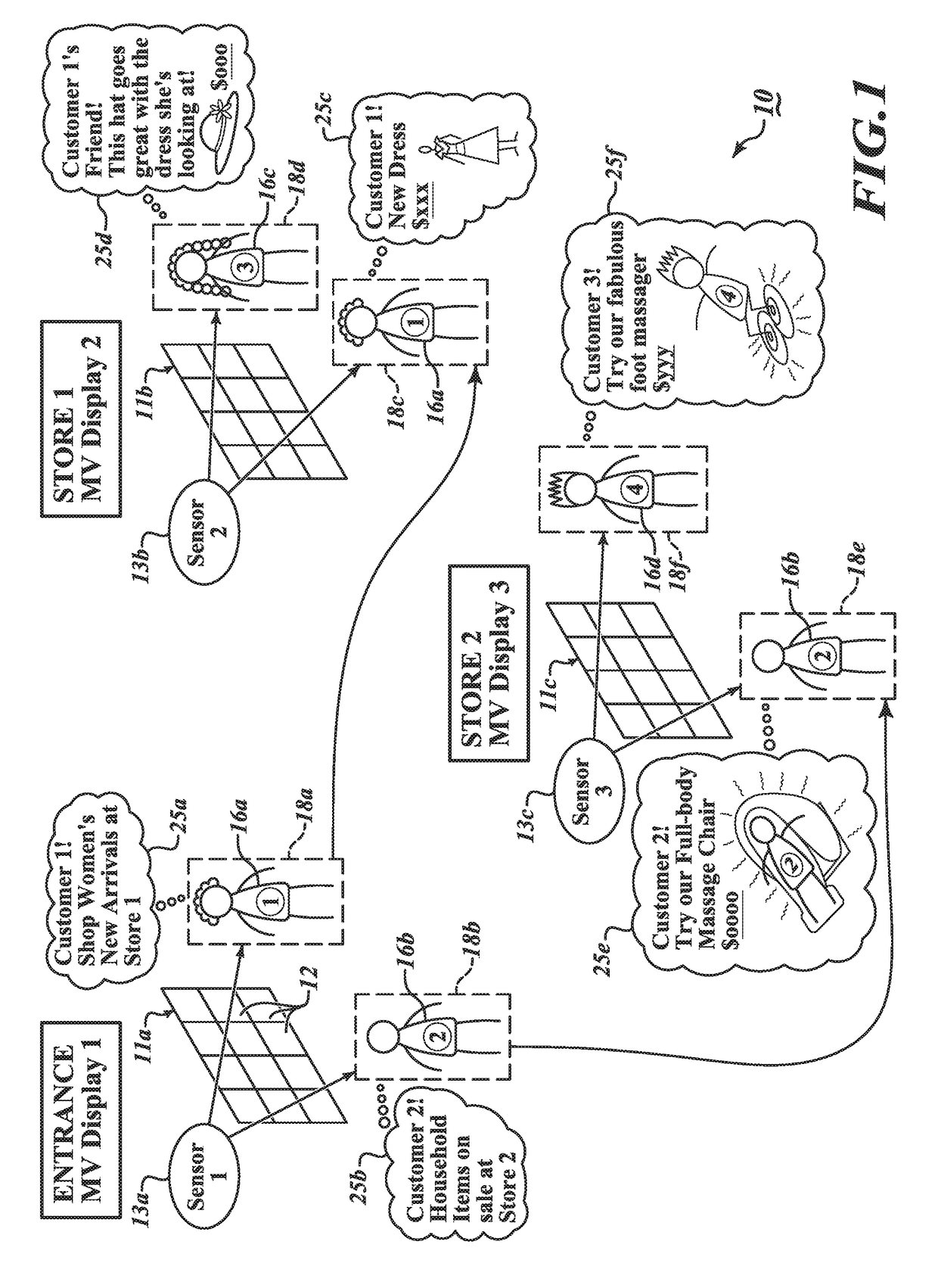
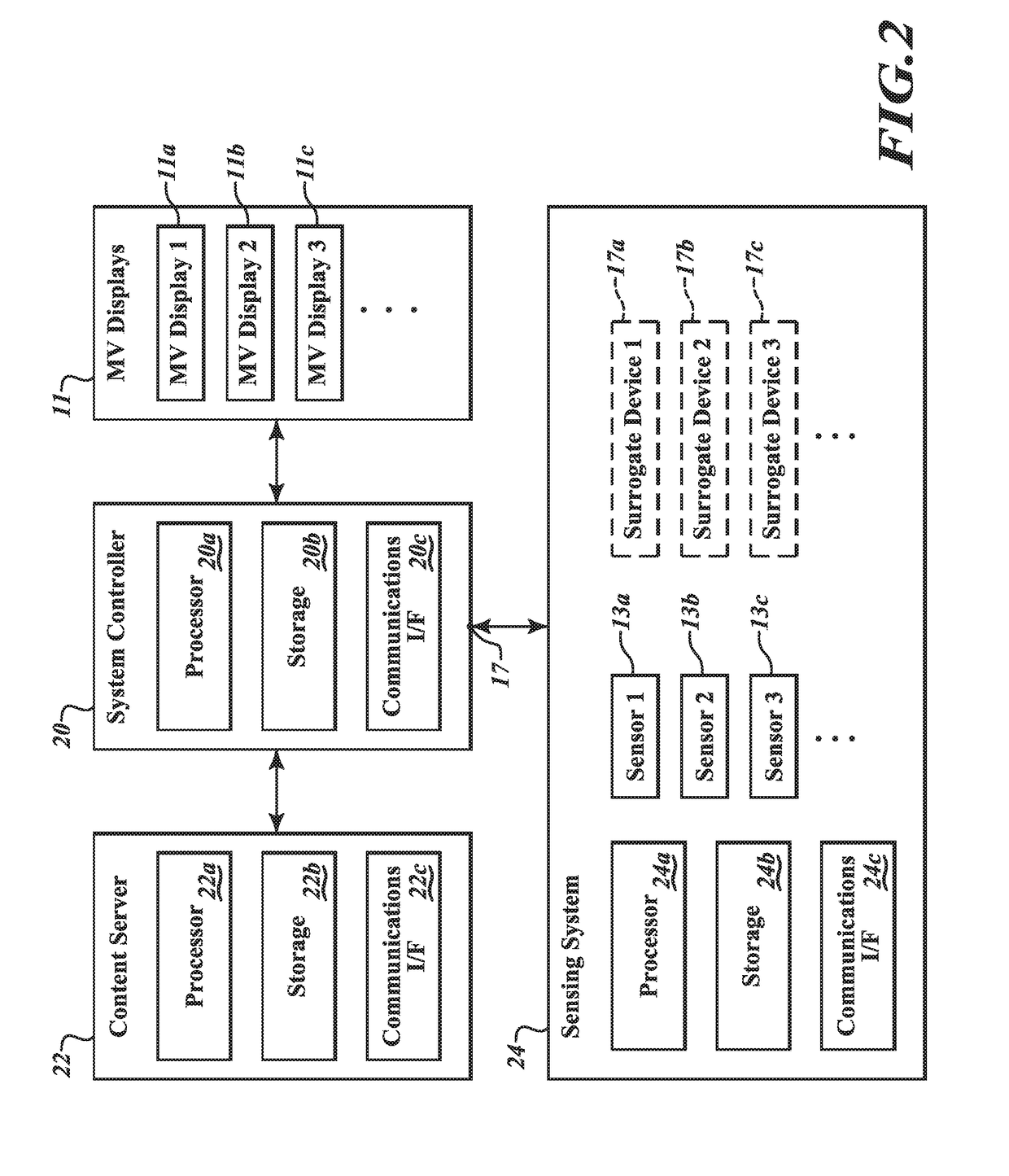
Multi-view advertising system and method
ActiveUS20190019218A1Increase valueImprove angular resolutionAdvertisingDisplay meansTargeted advertisingSystem controller
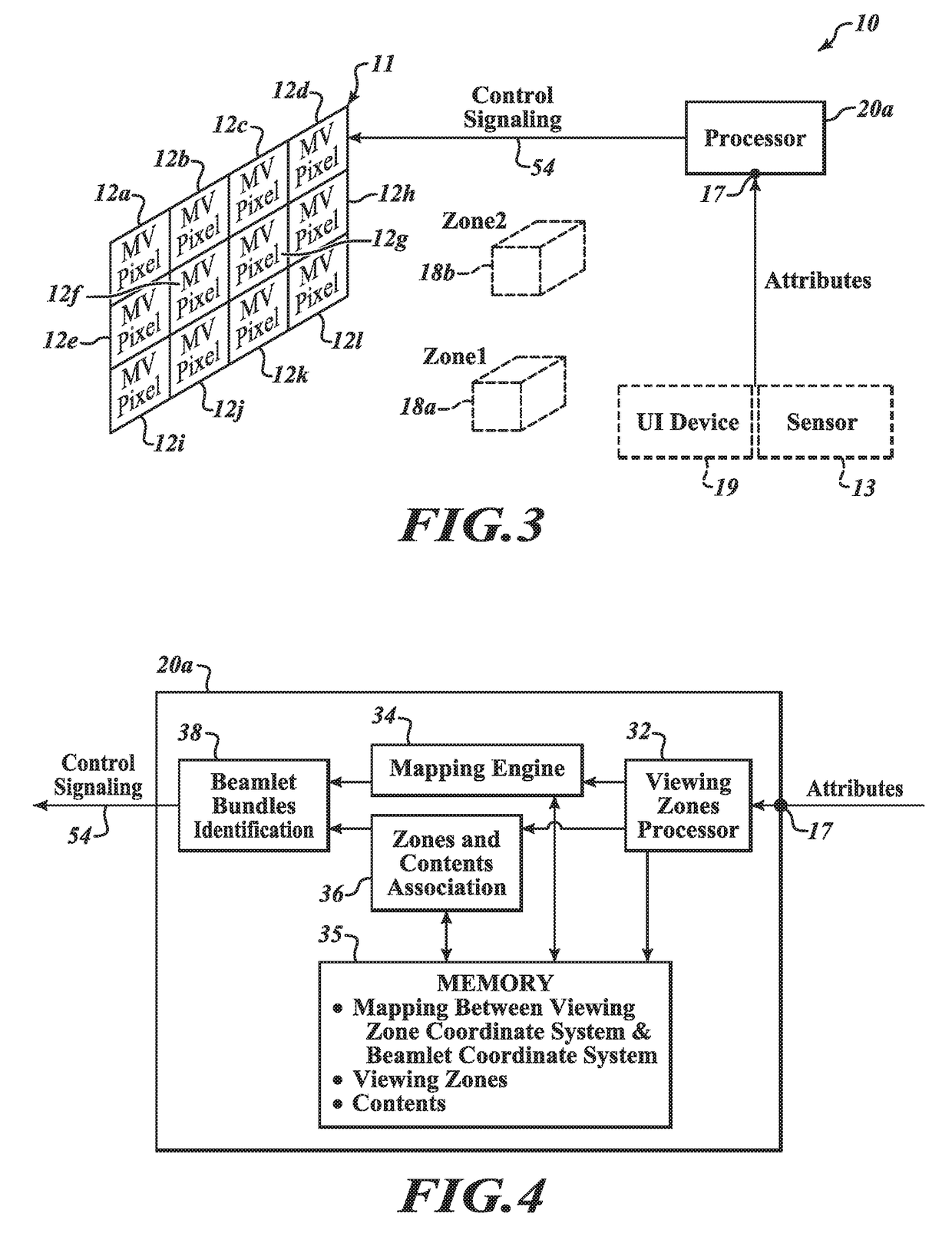
A multi-view (MV) advertising system includes an MV display including one or more MV pixels, each configured to emit beamlets in different directions in a beamlet coordinate system. The MV advertising system receives, via an input node, a first attribute of a first viewer or of a first viewing zone and, optionally, a second attribute of a second viewer or of a second viewing zone. The MV advertising system controller defines the first and second viewing zones relative to the MV display in a viewing zone coordinate system, determines a mapping that translates between the viewing zone coordinate system and the beamlet coordinate system, associates first and second targeted advertising contents with the first and second viewing zones based at least on the first and second attributes, and controls the MV display to project first and second images generated from the first and second targeted advertising contents to the first and second viewers at the first and second viewing zones, respectively.
Owner:MISAPPLIED SCI INC
Light field projection method used for scene illumination recovery
InactiveCN104156916AReduce demandLow priceLighting applicationsImage enhancementPoint lightOptical measurements
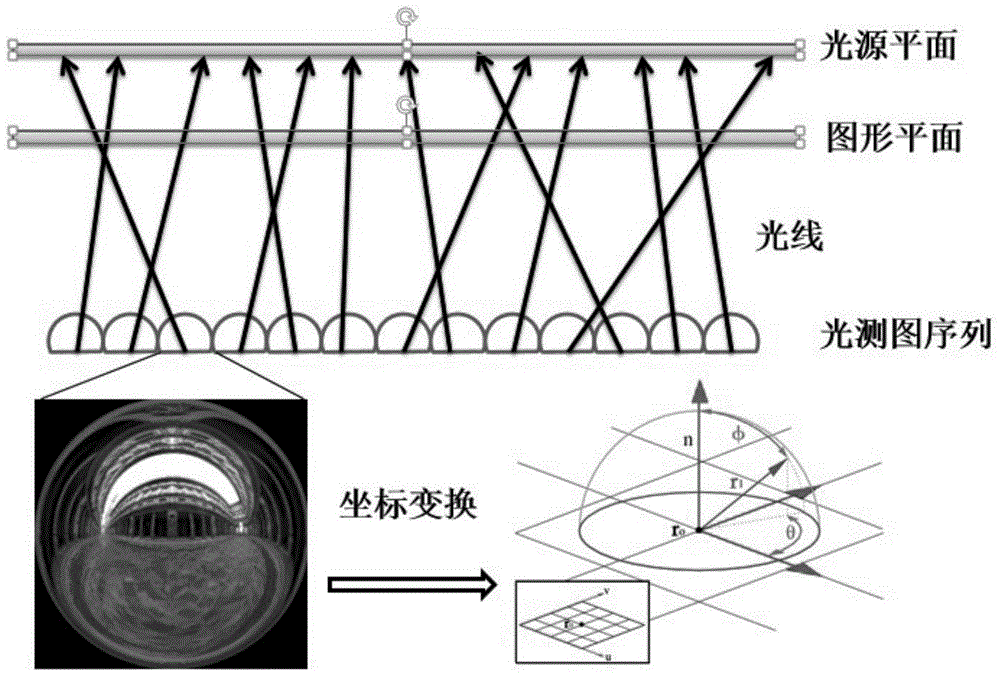
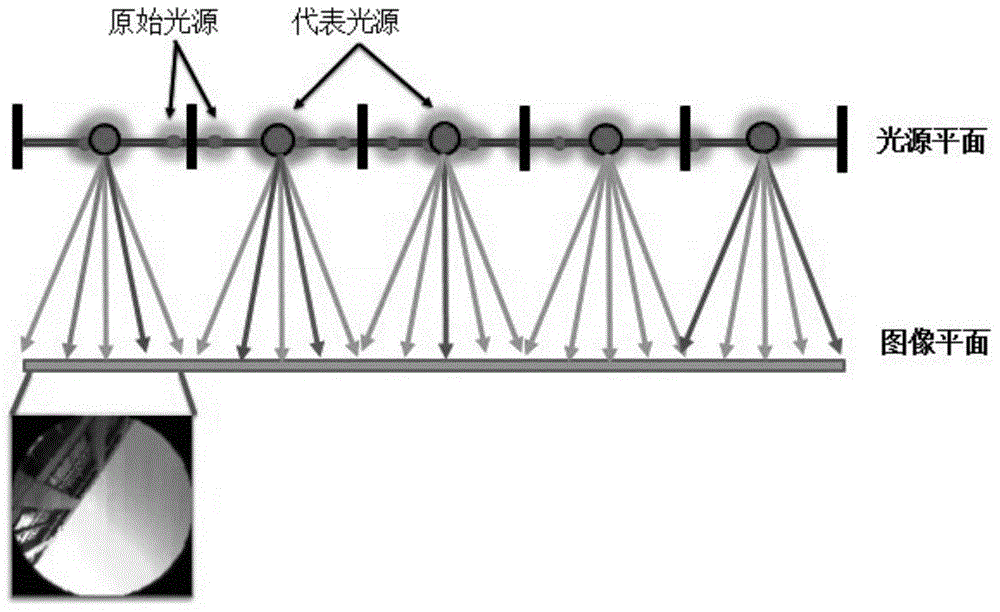
The invention discloses a light field projection method used for scene illumination recovery, and belongs to the technical field of virtual reality. In the method, a device adopting a projector and a lens array is designed to perform the light field projection, light field data is converted into a light field to perform projection, and the scene illumination is recovered. The method comprises the following specific steps: firstly, converting a sampled optical measurement image sequence into the four-dimensional light field expression of the scene illumination; then, clustering point light sources on a light source plane, generating projection sub-images for all the point light sources clustered, and performing distortion correction and image stitching; finally, after geometric calibration and luminance calibration, adopting a projector to project the projected images on the lens array, and refracting light rays on the other side through lenses to form a plane light field, so as to recover the illumination of an original scene. The illumination recovered by adopting the method has higher realness, higher space freedom degree and higher practicability. The method is applicable to the illumination application fields such as video and film special effects and stage lighting control.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Multilayer liquid crystal-based projection type three-dimensional display device and method
InactiveCN102692805AImprove scalabilityLarge amount of informationProjectorsStereoscopic photographyLiquid-crystal displayLighting system
The invention discloses a multilayer liquid crystal-based projection type three-dimensional display device. The three-dimensional display device comprises a backlight illumination system, a plurality of layers of liquid crystal display panels, a lens array and a directional scattering screen, which are sequentially arranged along the direction of an optical path, and also comprises a controller connected with each layer of liquid crystal display panel respectively. The invention also discloses a three-dimensional display method, which comprises the following steps of: resolving a three-dimensional scene required to be displayed into projected images, performing combination to form display images, transmitting the display images into each layer of liquid crystal display panel respectively, converging and projecting projected and displayed image sources which are products of pixel information of the liquid crystal display panels to the directional scattering screen by using corresponding lenses, and forming images at specified spatial positions. High-resolution three-dimensional display is realized by utilizing the superposition of the pixel information of the liquid crystal display panels.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Hybrid camera array based light field video imaging system and video processing method
ActiveCN107959805AAvoid defectsImprove angular resolutionTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationHigh definition tvLight-field camera
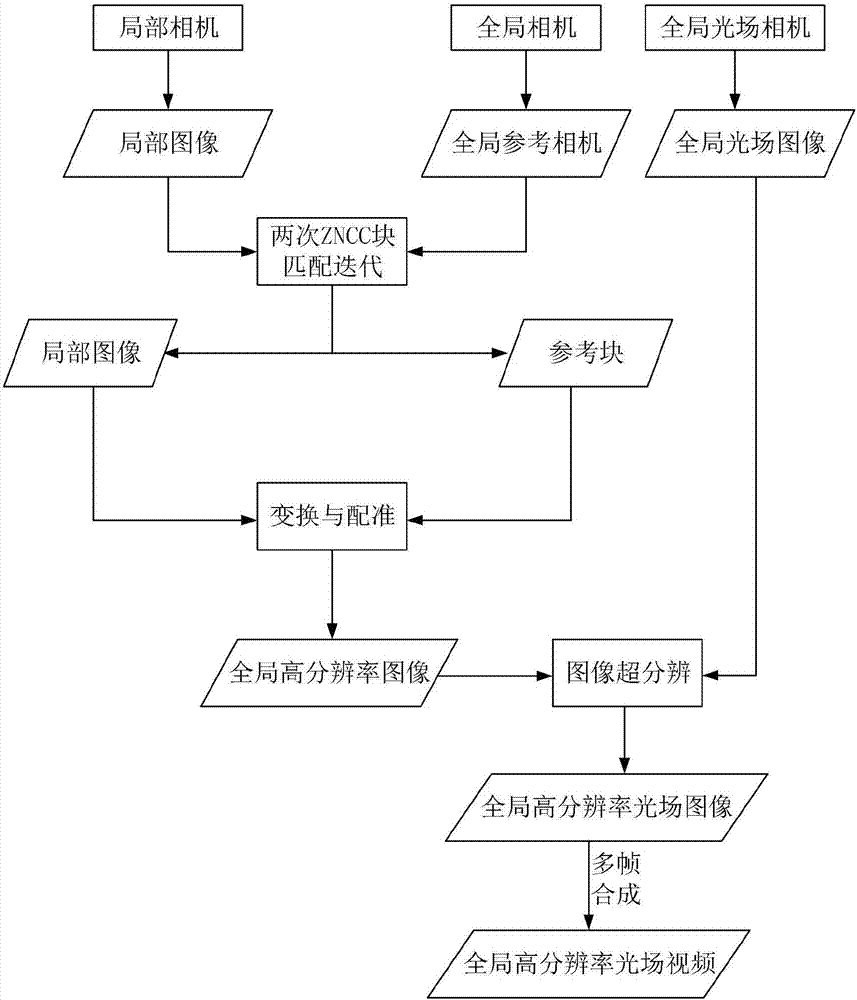
The invention discloses a hybrid camera array based light field video imaging system and video processing method. The system includes a control cloud deck, an image processing unit, a storage unit anda hybrid camera array. The hybrid camera array includes a global camera, a global light field camera and a plurality of local cameras used for collecting a global low resolution reference video, a global light field video and a plurality of local high definition videos of one scene synchronously. The image processing unit performs following treatment on a reference image, a global light field image and a plurality of high definition images of each group taken at the same moment: performing block matching on the local images with the reference image, converting the local images to corresponding blocks of the reference image based on matching results and obtaining a global high definition image; based on the global high definition image, performing super-resolution on the global light fieldimage so as to obtain a global high resolution light field image; combining all frames of global high resolution light field images into a global high resolution light field video.
Owner:BEIJING ZOHETEC CO LTD
Optical measurement device and vehicle
ActiveCN103576209AImprove angular resolutionOptical rangefindersPhotometryLight beamOptical measurements
Disclosed is an optical measurement device including a first light source, an optical element that condenses a light beam emitted from the first light source, a light irradiator that irradiates the light beam onto an object; and a photo detector that detects reflected light or scattered light of the light beam from the object through an imaging system, the light beam being irradiated onto the object, wherein a first optical path length from the first light source to a first conjugate image of the first light source by the optical element is different from a second optical path length from the photo detector to a second conjugate image of the photo detector by the imaging system at least in a first direction.
Owner:RICOH KK
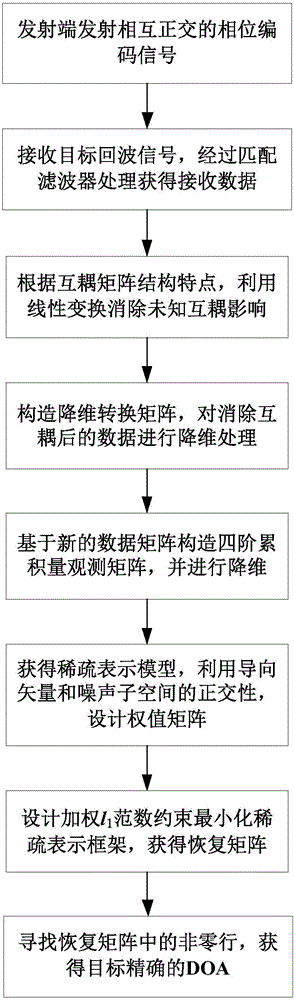
Four-order cumulant sparse representation-based MIMO (multiple-input-multiple-output) radar direction of arrival estimation method under mutual coupling condition
InactiveCN105974366ASuppress color noiseImprove angular resolutionWave based measurement systemsRadar systemsMultiple input
The invention belongs to the monostatic MIMO (multiple-input-multiple-output) radar system technical field and relates to a four-order cumulant sparse representation-based MIMO (multiple-input-multiple-output) radar direction of arrival estimation method under a mutual coupling condition. The method of the invention comprises the following steps that: a transmitting array transmits mutually-orthogonal phase encoding signals, a receiving end carries out matched filtering on the phase encoding signals so as to obtain receiving data, and the influence of unknown mutual coupling is eliminated through linear transform based on the strap-shaped symmetric Toeplitz structures of the mutual coupling matrixes of the transmitting array and the receiving array; and a dimension reduction conversion matrix is constructed to carry out dimension reduction processing on mutual coupling-eliminated data, and a four-order cumulant matrix of a special form is constructed based on a new data matrix. According to the method of the invention, since the four-order cumulant technique and a weighted sparse representation framework are adopted, colored noises are successfully inhibited. The method of the invention can achieve accurate direction of arrival estimation under a Gaussian color noise condition, and has higher angular resolution and better angle estimation performance.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Laser radar system, laser radar point cloud data processing method and readable medium
InactiveCN108267746AReduce complexityImprove angular resolutionElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadar systemsPoint cloud
The invention relates to a laser radar system, a laser radar point cloud data processing method and a readable medium. The laser radar system comprises a scanning module and a plurality of laser transmitting and receiving modules; the scanning module is suitable for reflecting laser pulse signals into a space, and receiving laser pulse echo signals reflected by a space obstacle; each laser transmitting and receiving module emits laser to the scanning module with a preset angle corresponding to the laser transmitting and receiving module; and fields of view corresponding to at least two laser transmitting and receiving modules have an overlapping region. With the above laser radar system adopted, the angular resolution of a laser radar can be improved at a lower cost and with lower system processing complexity.
Owner:HESAI TECH CO LTD
Laser radar and control method thereof, and automatic driving device
ActiveCN110632618AMeet diverse detection needsIncrease the ranging distanceElectromagnetic wave reradiationPosition/course control in two dimensionsRadarOptoelectronics
The embodiment of the invention relates to the technical field of laser detection, and discloses a laser radar, a control method thereof and an automatic driving device. The laser radar comprises a first transceiving module for transmitting first exiting laser and receiving first reflected laser; a first scanning module for deflecting the first exiting laser and for receiving the first reflected laser, deflecting the first reflected laser and emitting the deflected laser to the first transceiving module; a beam expanding module for expanding and collimating the first exiting laser passing through the first scanning module and emitting the first exiting laser to a first detection area, and for converging the received first reflected laser in a beam shrinking manner and emitting the first reflected laser to the first scanning module; a second transceiving module for transmitting second exiting laser and receiving second reflected laser; and a second scanning module for enabling the second exiting laser to emit to a second detection area, and for receiving the second reflected laser, deflecting the second reflected laser and emitting the second reflected laser to the second transceiving module. Through the mode disclosed by the embodiment of the invention, the ranging capability of the laser radar is improved.
Owner:SUTENG INNOVATION TECH CO LTD
Security monitoring system
InactiveCN110719442AAccurate judgmentImplement active detectionClosed circuit television systemsBurglar alarmPoint cloudMonitoring system
The invention discloses a security monitoring system which comprises at least one laser radar, a control module and at least one camera module. Each laser radar is provided with a preset target detection area; the laser radar is used for obtaining first point cloud data based on a laser radar coordinate system; the control module is connected with the at least one laser radar, and is used for converting the first point cloud data into second point cloud data under a space coordinate system and carrying out obstacle identification according to the second point cloud data, and determining the coordinates of the obstacle in the space coordinate system according to the third point cloud data of the obstacle in the space coordinate system when the obstacle is identified; the control module is further connected with at least one camera module and used for controlling the camera modules to acquire images of the obstacles according to the coordinates of the obstacles in the space coordinate system. According to the security and protection monitoring system provided by the invention, accurate illegal intrusion monitoring on the perimeter of a large-range area is realized.
Owner:LEISHEN INTELLIGENT SYST CO LTD
Virtual array antenna based angle estimation method for improving accuracy
ActiveCN104698430AHigh precisionImprove angular resolutionRadio wave finder detailsMillimeter wave communication systemsEstimation methods
The invention discloses a virtual array antenna based angle estimation method for improving accuracy. The virtual array antenna based angle estimation method is used for a large-scale uniform linear array based millimeter wave communication system, and the sparse characteristics of millimeter wave channels and a compressing reconstruction algorithm are utilized to estimate an antenna transmitting angle and an arrival angle of each channel of multiple channels by adding a plurality of virtual array elements on antenna arrays at the receiving end and the transmitting end. By means of the virtual array antenna based angle estimation method, the angle estimation accuracy can be improved, pilot frequency sequence expenditure can be reduced, and antenna array hardware change is not needed.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
MIMO radar distance-angle two-dimensional super-resolution imaging algorithm
ActiveCN104020469AImprove real-time performanceReduce complexityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImage resolutionMathematical model
The invention relates to a MIMO radar distance-angle two-dimensional super-resolution imaging algorithm. The algorithm comprises the following steps: step 1, establishing a mathematic model for MIMO radar imaging; step 2, performing pulse compression by use of a multi-waveform self-adaptive pulse compression method, obtaining a distance image of an observation scene, and realizing separation of emitted waveforms to obtain a receiving signal of a MIMO radar virtual array; and step 3, at a virtual array end, performing orientation focusing on echo signals of different distance units by use of a super-resolution space spectrum estimation algorithm to finish high-resolution distance-angle two-dimensional focusing imaging.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Embattling method of logarithmic spiral array antennas
InactiveCN101931124AIncrease cell spacingLarge apertureLogperiodic antennasHelical antennasPhase differenceArray element
The invention discloses an embattling method of logarithmic spiral array antennas. An antenna array uses N logarithmic spirals to embattle; a single logarithmic spiral line function is as follows: r=e, and an antenna unit is displaced on the logarithmic spiral line function r=e, wherein (r, phi) is a position coordinate of any point on the logarithmic spiral line under polar coordinates, r is a distance from the point to an original point (unit: wavelength), namely a relative wavelength number, phi is an angle relative to a polar axis (0 degree), and a is a parameter of the logarithmic spiral line function and is an optimizable constant for designing the array; the antenna unit n on each logarithmic spiral is arranged at the position of phi n along the spiral line function; the phase difference between adjacent units is delta phi; N spiral lines rotate 360 degrees / N rounding a rotating shaft in turn; r of the initial starting point of each logarithmic spiral line is the same; the phase position of the initial starting point of the first starting point on each spiral line is phi0; m array elements are respectively arranged on each spiral line from the initial starting point at an interval of delta phi; one array element can be placed at the center of the array, namely original point, or not; when the parameter a, delta phi and phi0 are determined, an array manifold is determined; and the total antenna unit number of N logarithmic spiral arrays is Nm+1.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Low-complexity receiving and transmitting angle joint estimation method for non-circular signal double-base MIMO radar
InactiveCN103983952AMany degrees of freedomStrong parameter identification abilityMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSignal subspaceEngineering
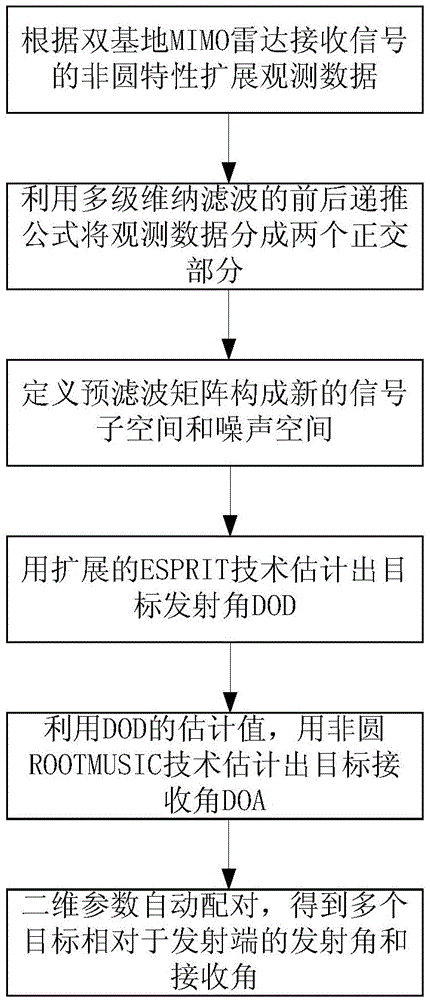
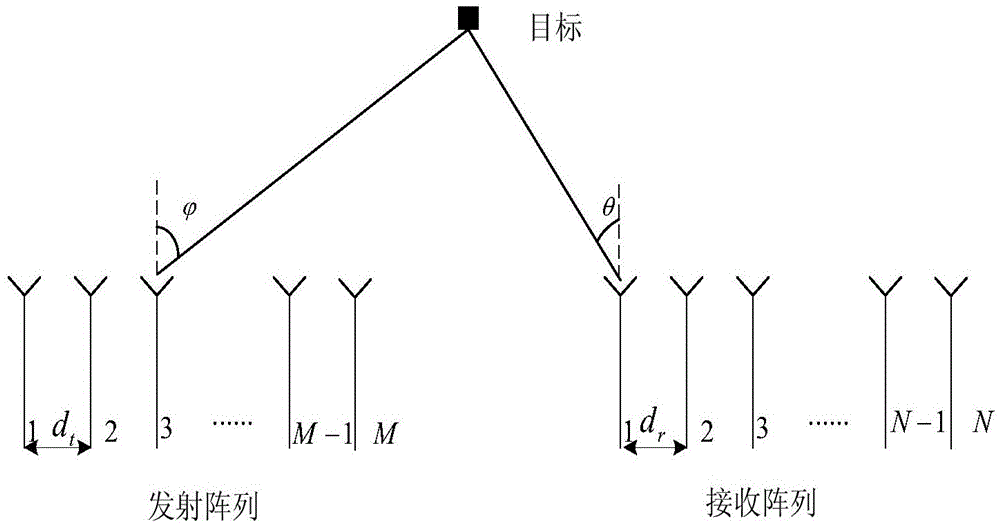
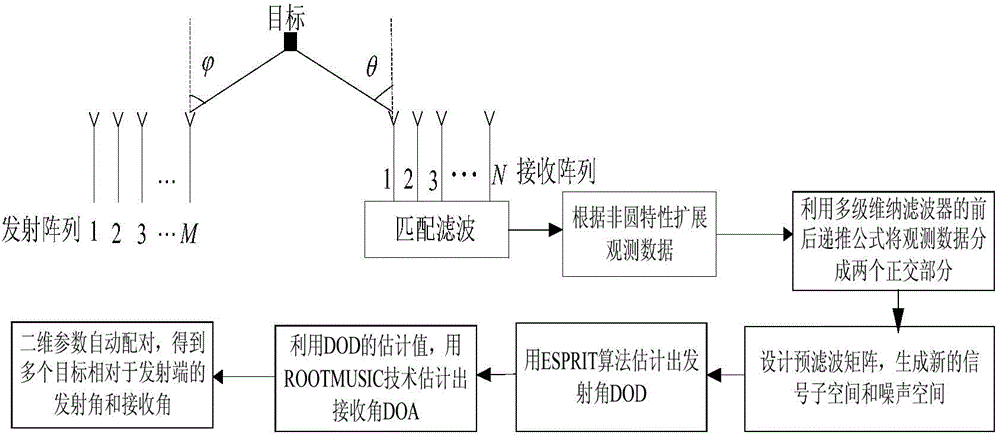
The invention provides a low-complexity receiving and transmitting angle joint estimation method for non-circular signal double-base MIMO radar. Firstly, observation data are extended according to the non-circular characteristic of received signals of the MIMO radar, and a virtual array element of the MIMO radar is amplified by one time. Secondarily, the observation data are divided into two orthogonal portions according to the front-to-back recursion formula of multi-stage Wiener filtering, the two orthogonal portions serve as desired signals of a next stage of multi-stage Wiener filtering and observation data vectors respectively, and then a new signal subspace and a new noise space are formed through pre-filtering matrixes. Finally, the target transmission angle DOD is estimated according to the extended ESPRIT, the target reception angle DOA is estimated according to the estimated value of the DOD and the non-circular ROOTMUSIC technology, and two-dimension parameters of the DOD and two-dimension parameters of the DOA are automatically paired to obtain the target transmission angles, relative to the transmission end, of many targets and target reception angles, relative to the reception end, of the targets. According to the method, the virtual aperture of the MIMO radar is increased according to the non-circular signal characteristic, maximization of the recognized targets is achieved, the algorithm complexity is low, and additional pairing processes are not needed.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
High precision beamsteerer based on fixed beamforming approach beampatterns
ActiveUS20050201204A1Improve angular resolutionReasonable error robustnessTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSensor arrayOptimal weight
A beamsteerer for broadband energy source location, comprising an array of sensors, each for generating a signal vector within one of a plurality of sectors in a domain of interest, and a beamformer for receiving and multiplying each signal vector by a set of optimal weight vectors to generate a plurality of beampatterns, each of the beampatterns being characterized by a null having high angular resolution, and detecting the source by selecting a maximum steering index.
Owner:MITEL
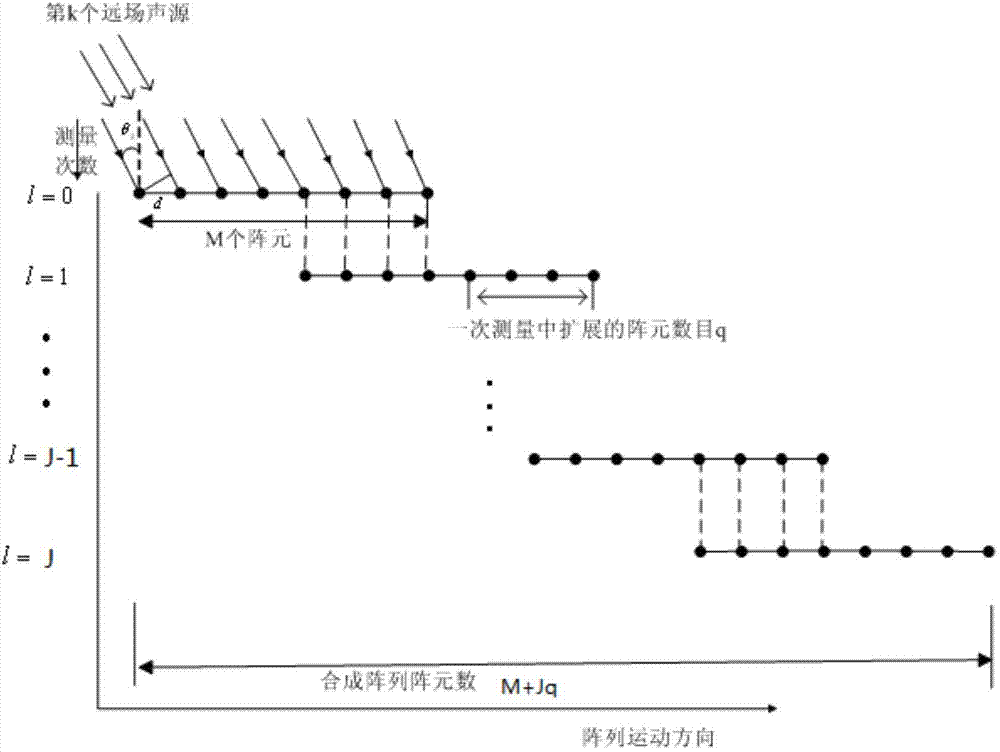
Underwater motion array multi-target detection and position estimation integrated method
InactiveCN104330787AImprove angular resolutionEasy to detectAcoustic wave reradiationContinuous measurementArray gain
The invention relates to an underwater motion array multi-target detection and position estimation integrated method which is characterized by according to a motion array signal model, obtaining a twice-continuous-measurement reception data formula and obtaining phase correction factors; carrying out matrix-form block partitioning on the motion array signal model; by utilizing the synthetic aperture technique and utilizing the phase correction factors, extending a physical array into a virtual array and reconstituting the block matrixes into data matrixes to form MVDR spatial spectrum, and obtaining a detection threshold value through on-site noise study; and obtaining spectrum peak number above the detection threshold value which is regarded as the target number, and the angle corresponding to the spectrum peak is the azimuth angle of an incidence target. The method fully utilizes the underwater motion array synthetic aperture technique to improve array gain and angular resolution, and utilizes an MVDR spatial spectrum function for reflecting signal energy to determine the number of the targets and method; and compared with coherent signals, the detection performance of the method under low signal to noise ratio is obviously superior to that of the conventional method, detection threshold is reduced, farther detection distance is achieved, and position estimation value can be given.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
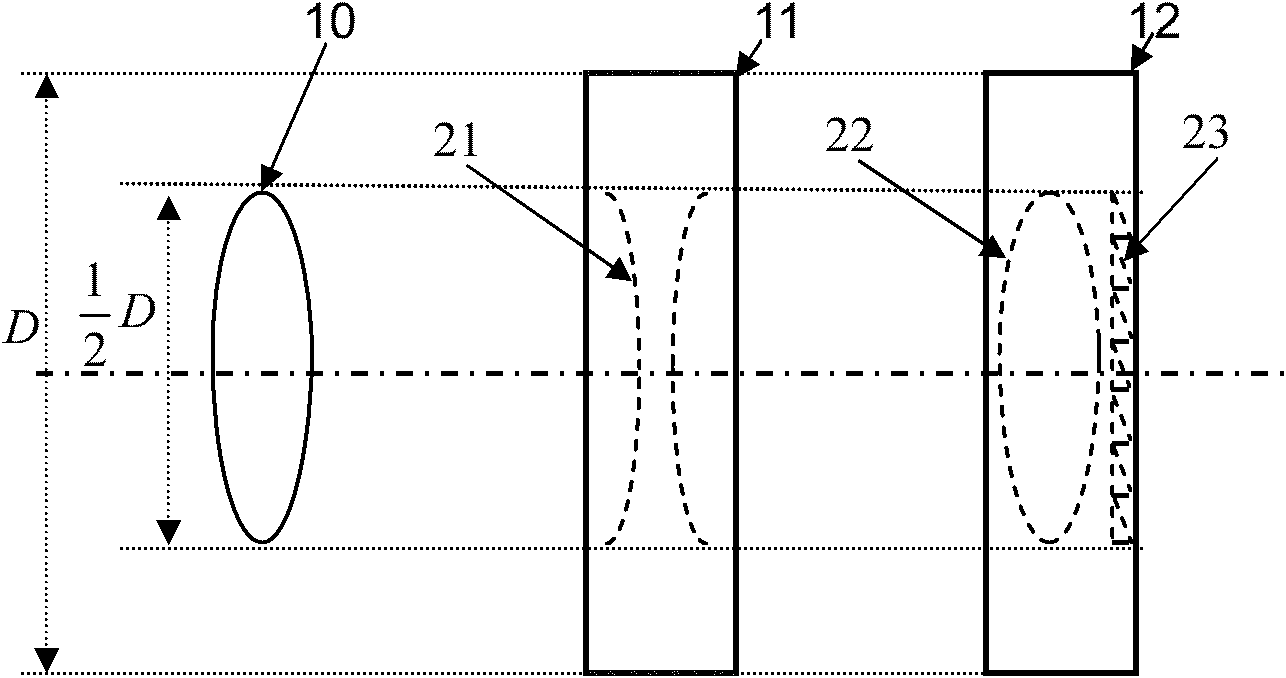
Large-angle, continuous and high-resolution beam deflection scanning device based on liquid crystal optical phased array and scanning method
InactiveCN102073186ARealize large angle deflection scanningImprove angular resolutionNon-linear opticsOptical elementsImage resolutionInformation storage
The present invention relates to a large-angle, continuous and high-resolution beam deflection scanning device based on a liquid crystal optical phased array and a scanning method, relating to the technical field of crossing of liquid crystal optics, applied optics and diffractive optics and solving the problem of the prior art that only small-angle beam deflection scanning can be realized. An angle resolution can reach the diffraction limit or higher while large-angle beam deflection scanning is achieved. The large-angle beam deflection scanning is achieved through a liquid crystal lens or aliquid crystal lens array formed with a lens layer or a lens array layer and two liquid crystal optical phased array layers. A blazed grating phase is added on the liquid crystal optical phased arrayfor beam emergence to realize continuous beam deflection scanning. Finally, the large-angle and continuous beam deflection scanning can be achieved. The device and the method have significant prospects of application in free-space optical communication, laser radars, optical tweezers, laser direct writing, optical interconnection, projection display, optical information storage and other fields.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Long distance high resolution laser active imaging device and method based on spatial coding
ActiveCN106405572AImprove angle measurement accuracyImprove angular resolutionElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser rangingMeasurement device
The invention provides a long distance high resolution laser active imaging device and method based on spatial coding. The device comprises a laser light source, a two-dimensional laser scanning mirror fixed to the light emitting end of the laser light source, a target fixed to a two-dimensional laser scanning lens area, an imaging lens fixed to a target reflection optical path, a photoelectric array detector fixed to the imaging lens imaging optical path, a scanning lens rotation angle measurement device connected to the laser scanning lens, a space decoding and laser distance measurement module connected to the photoelectric array detector through a conductive wire, a computer connected to the space decoding and laser distance measurement module and the scanning lens rotation angle measurement device through conductive wires, and a laser controller connected to the laser light source through a conductive wire. The invention also discloses an image method of the device. In the condition of ensuring high resolution, the detection distance is expanded.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Balancing machine for vehicle wheels with analog to digital conversion and adjustable sampling frequency
InactiveUS20080053223A1Quality and precision of takenIncrease angular resolutionStatic/dynamic balance measurementBalancing machineA d converter
The upgraded balancing machine for vehicle wheels comprise a supporting frame for gripping and rotation means for gripping and rotating a wheel to be balanced around a rotation axis, a first sensor for detecting the unbalance of the wheel with respect to the rotation axis suitable for generating a first analog signal, a second sensor for detecting at least one portion of the profile of the wheel suitable for generating a second analog signal, at least one analog to digital converter associated with at least one of the first and the second detection sensors and suitable for converting at least one of the first and the second analog signal into a corresponding digital signal, a processing and control unit associated with the conversion device and suitable for processing the digital signal, and an adjustment unit for adjusting the sampling frequency of at least one of the first and the second analog signals associated with the conversion device. The adjustment unit responds to a first signal generated by a shaft encoder, and responds to a programmable timer, so that the frequency of the sampling operation can be altered.
Owner:SICAM SRL
Broad band coherent source azimuth estimating method based on data reconstruction
InactiveCN102621527AImprove angular resolutionSuperior Position Estimation PerformanceSpecial data processing applicationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Decomposition
The invention provides a broad band coherent source azimuth estimating method based on data reconstruction, which includes the steps as follows: (1) carrying out subband decomposition on the broadband array received data; (2) selecting the lowest frequency of the broadband signal as the focusing frequency and utilizing the spatial data construction formula to focus all the subband data on one frequency; (3) calculating the covariance matrixes of all the focused subband data, improving the covariance matrixes through the matrix conjugate rearrangement principle, and finding the mean value of the improved covariance matrixes of all the focused subband data as the final covariance matrix; (4) achieving the spatial spectrum estimation of the final covariance matrix through the MVDR algorithm, so as to obtain the azimuth information of the broad band coherent source. The broad band coherent source azimuth estimating method not only has higher angular resolution under low signal-to-noise ratio and less snapshots, but also can overcome the instability of the MVDR algorithm under the high low signal-to-noise ratio without the need of processing the angular resolution and the like; and the broad band coherent source azimuth estimating method has better azimuth estimating performance.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Laser radar acquisition and ranging apparatus and working method thereof
InactiveCN105572683ARealize acquisitionRealize full-angle signal acquisitionElectromagnetic wave reradiationImage resolutionLaser scattering
The present invention belongs to the laser radar field and provides a laser radar acquisition and ranging apparatus. The laser radar acquisition and ranging apparatus includes a laser output device which is used for outputting collimated laser, a laser scattering device which is arranged on the laser path of the laser output device and is used for scattering the collimated laser to 360-degree ring-shaped laser, and image sensing devices which are arranged around the laser output device and can receive laser signals reflected by a measured object in an all-direction manner. With the laser radar acquisition and ranging apparatus adopted, 360-degree full-angle signal acquisition can be realized, and angle resolution and scanning frequency can be improved.
Owner:LEISHEN INTELLIGENT SYST CO LTD
X-ray diffraction apparatus and X-ray diffraction method
InactiveCN101403713AReduced radiation intensityImprove angular resolutionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayLattice plane
In an X-ray diffraction method using the parallel beam method, an X-ray parallel beam (24) is incident on a sample (26), and diffracted X-rays (28) from the sample (26) are reflected at a mirror (18) and thereafter detected by an X-ray detector (20). The reflective surface (19) of the mirror (18) has a shape of an equiangular spiral that has a center located on the surface of the sample (26). A crystal lattice plane that causes reflection is parallel to the reflective surface (19) at any point on the reflective surface (19). The X-ray detector (20) is one-dimensional position sensitive in a plane parallel to the diffraction plane. A relative positional relationship between the mirror (18) and the X-ray detector (20) is determined so that reflected X-rays (40) from different points on the reflective surface (19) of the mirror (18) reach different points on the X-ray detector (20) respectively. This X-ray diffraction method is superior in angular resolution, and is small in X-ray intensity reduction, and is simple in structure.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
Towed linear array sonar subarray error mismatching estimation method
ActiveCN108845325AReduce positioning errorsImprove robustnessAcoustic wave reradiationImage resolutionDisplacement error
The invention discloses a towed linear array sonar subarray error mismatching estimation method, aims to realize reduction of the positioning error and can obtain the accurate orientation estimate andthe higher angle resolution. The method is characterized in that in an array manifold matrix model, a real full array manifold matrix is represented as linear combination of the displacement error amount of each subarray and the error amount of each subarray contributed to the full array manifold matrix; the position error between subarrays is introduced to a direction finding model, for a full array model with subarray displacement mismatching, the Bayesian rule is utilized to establish a data fusion model, a subarray position error vector and the target true azimuth are simultaneously solved, according to data collected by fused sensor nodes, the Bayesian algorithm is utilized to estimate the subarray displacement error and the direction of arrival to obtain the likelihood function of amulti-shot observation value; the azimuth estimate and the displacement error estimate of the root mean square error changing with the SNR are obtained through utilizing the posterior function.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com