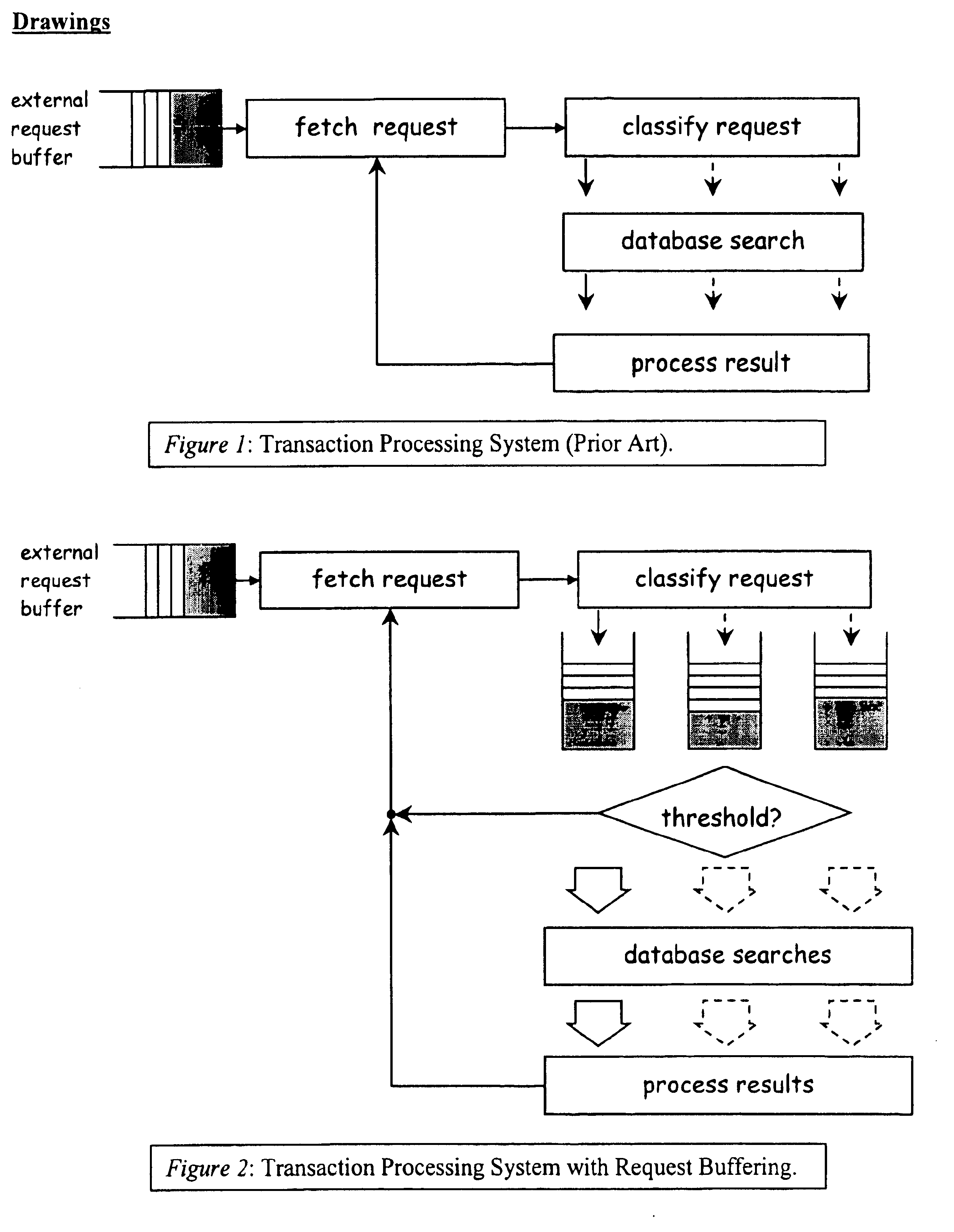
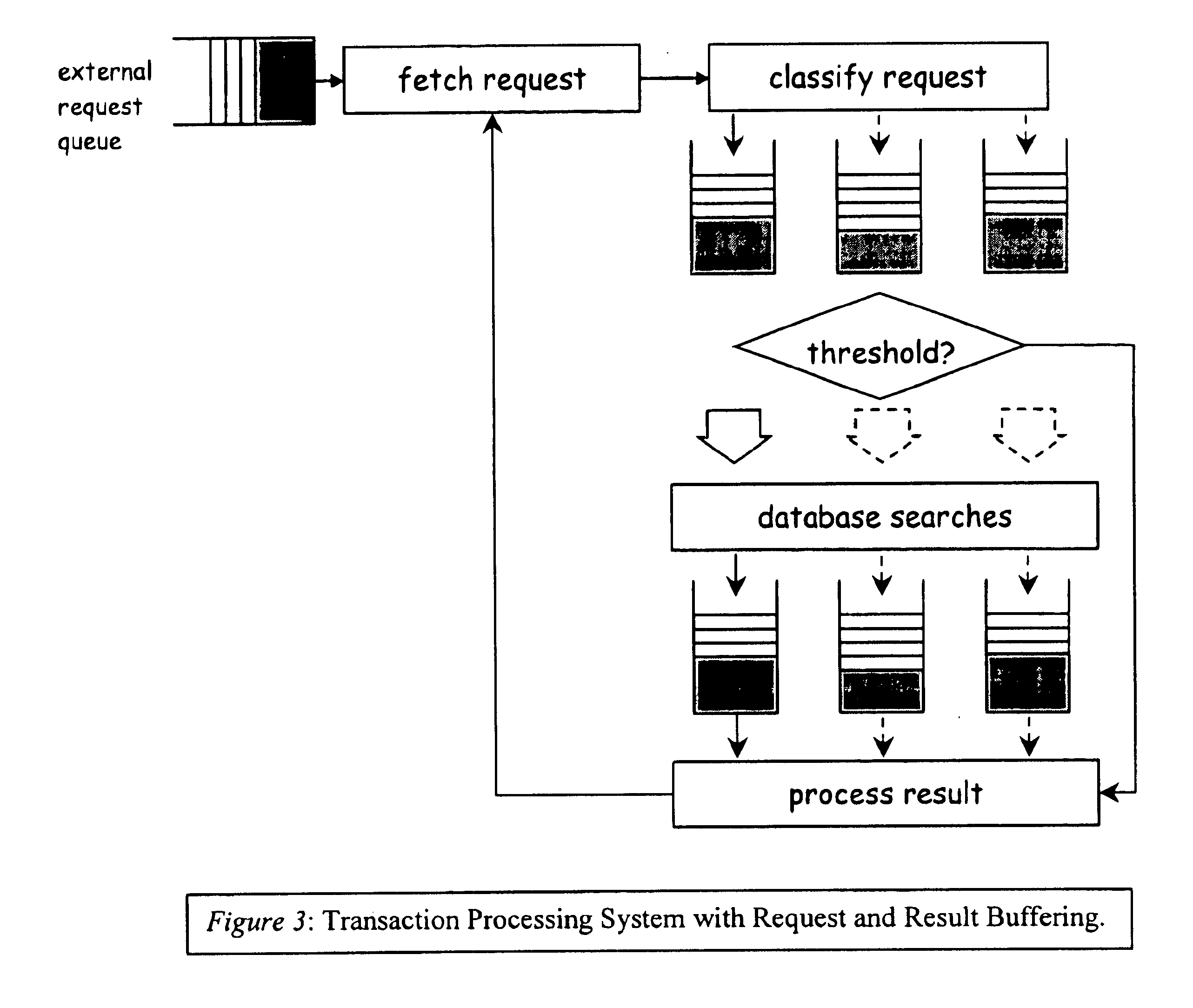
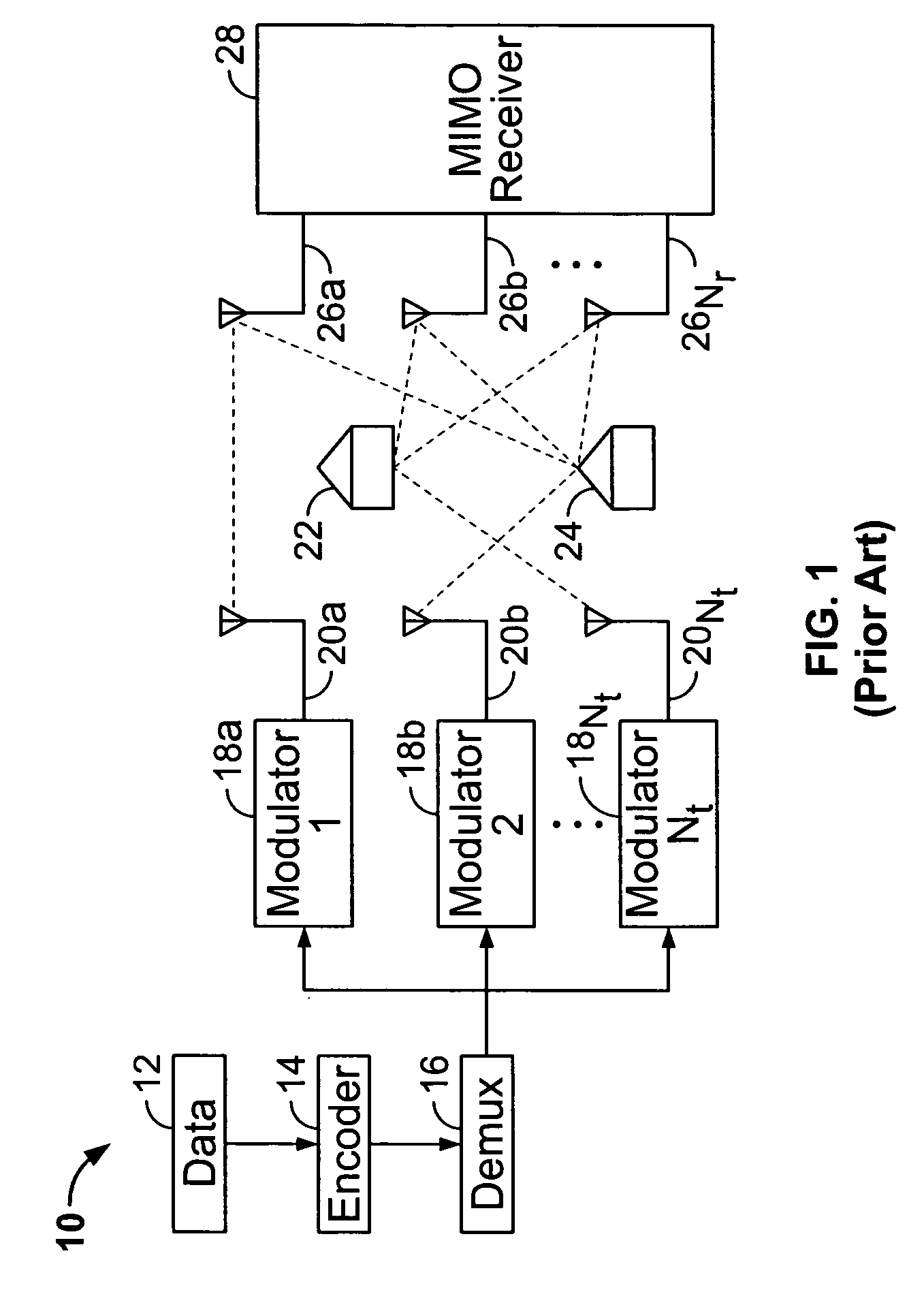
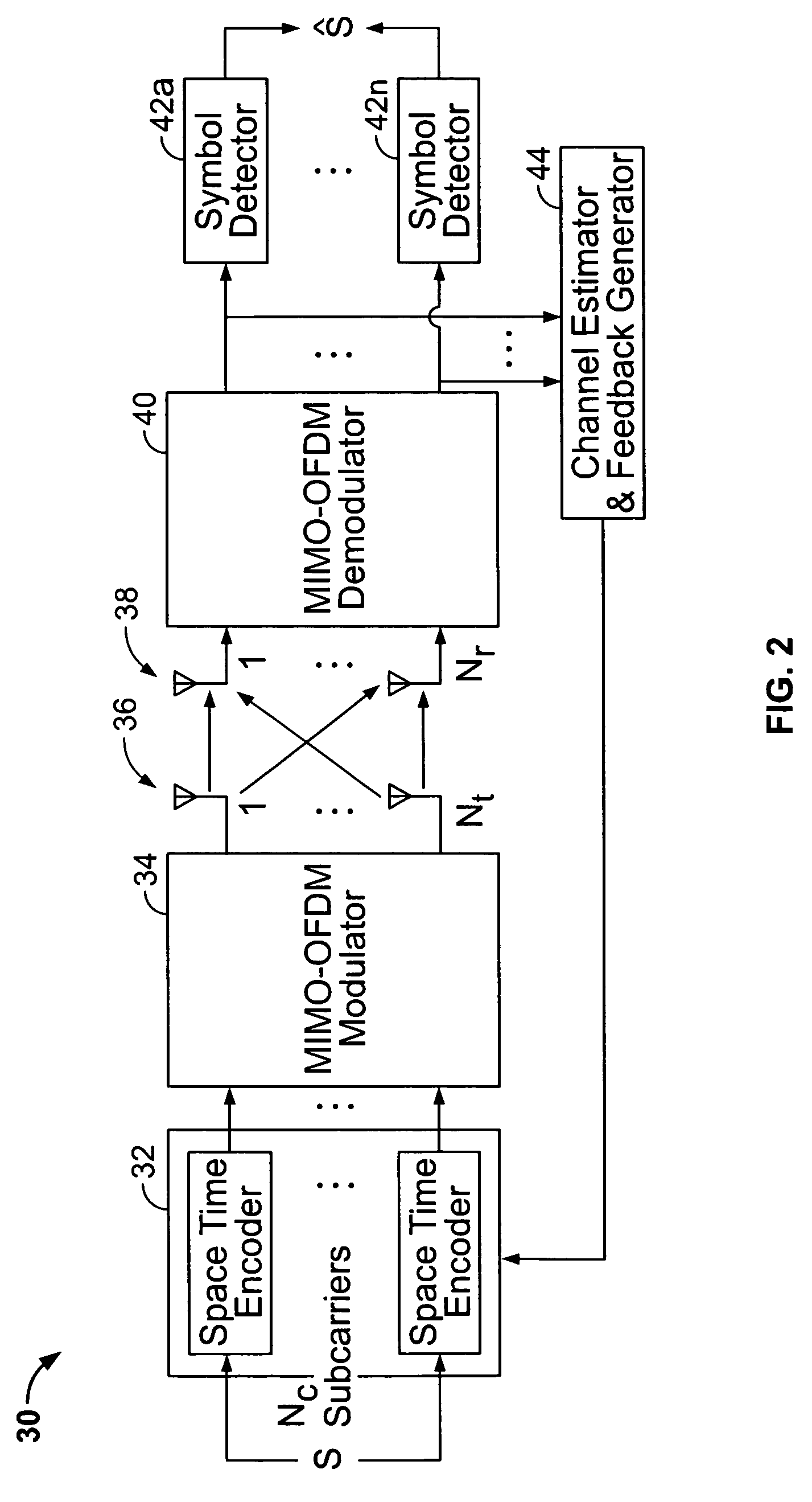
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
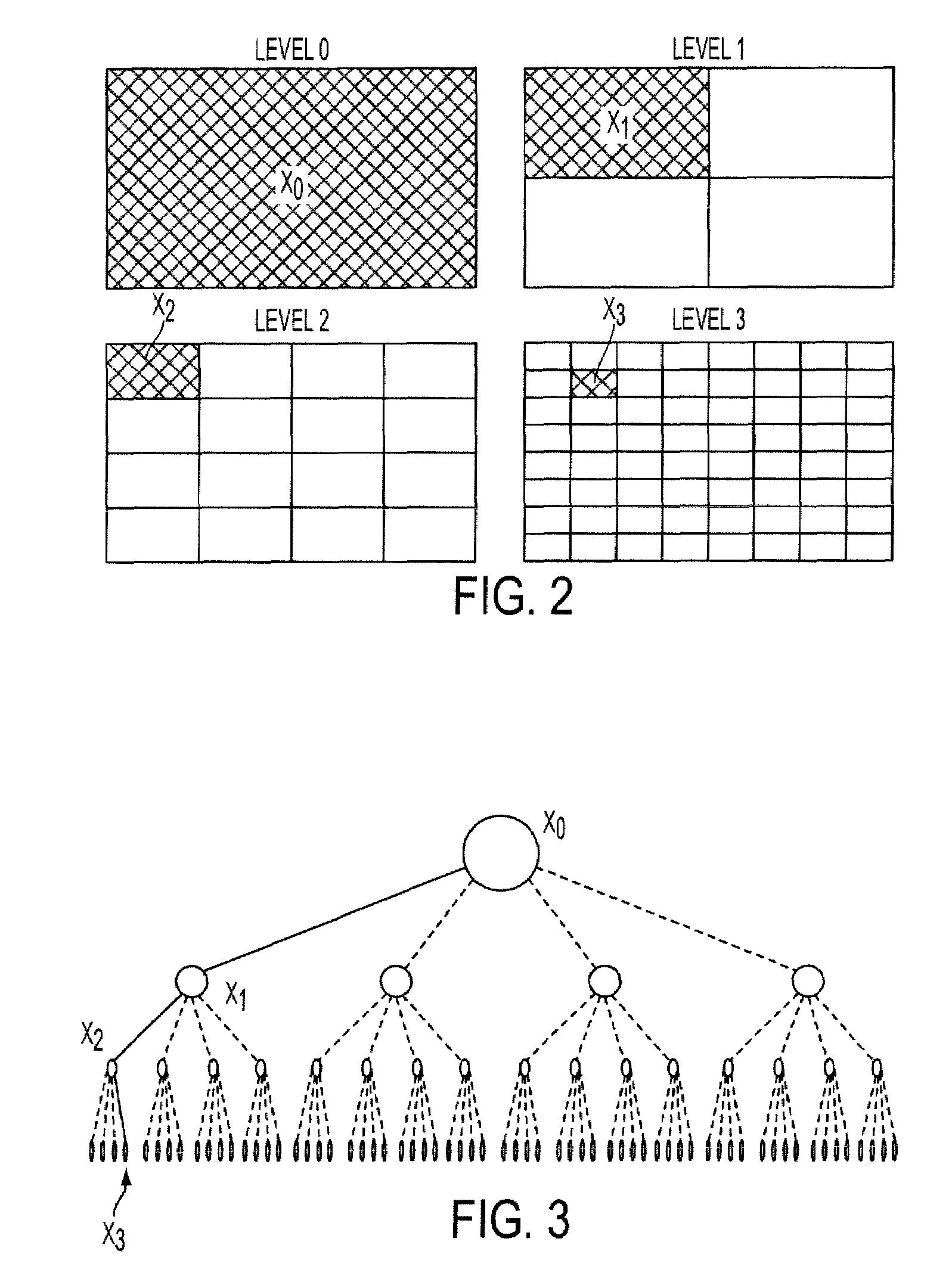
2239 results about "Recursion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Recursion (adjective: recursive) occurs when a thing is defined in terms of itself or of its type. Recursion is used in a variety of disciplines ranging from linguistics to logic. The most common application of recursion is in mathematics and computer science, where a function being defined is applied within its own definition. While this apparently defines an infinite number of instances (function values), it is often done in such a way that no loop or infinite chain of references can occur.
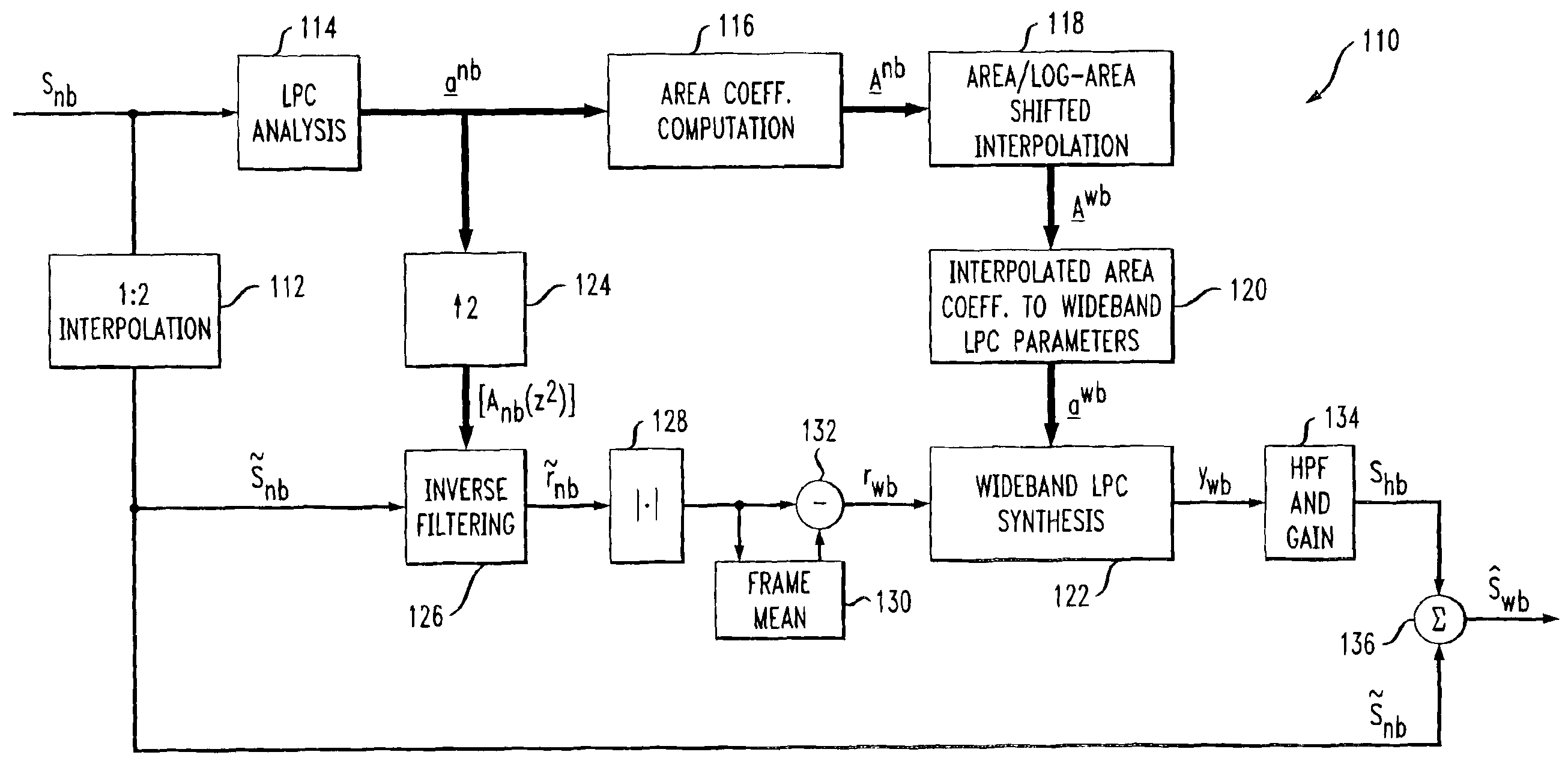
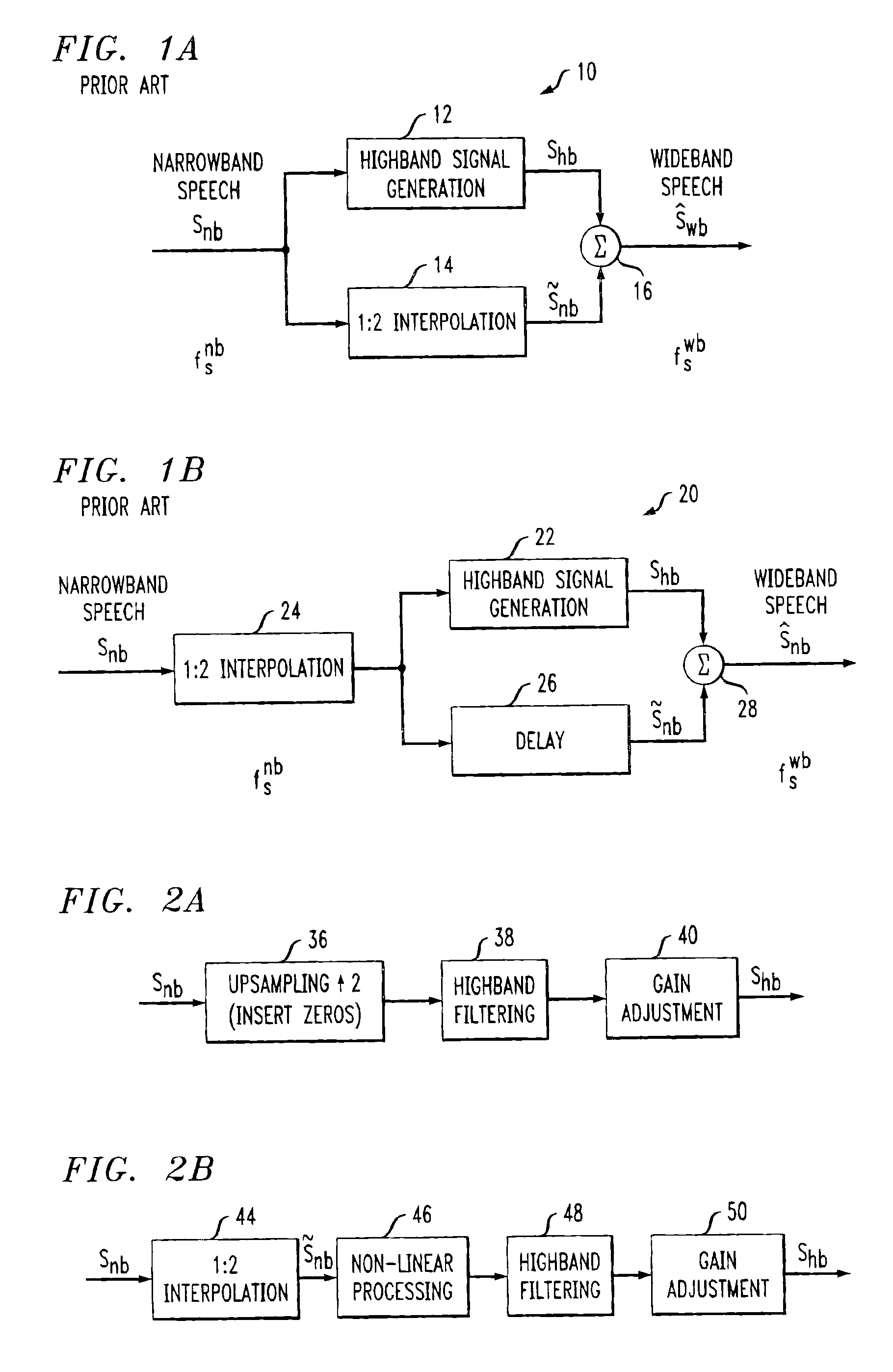
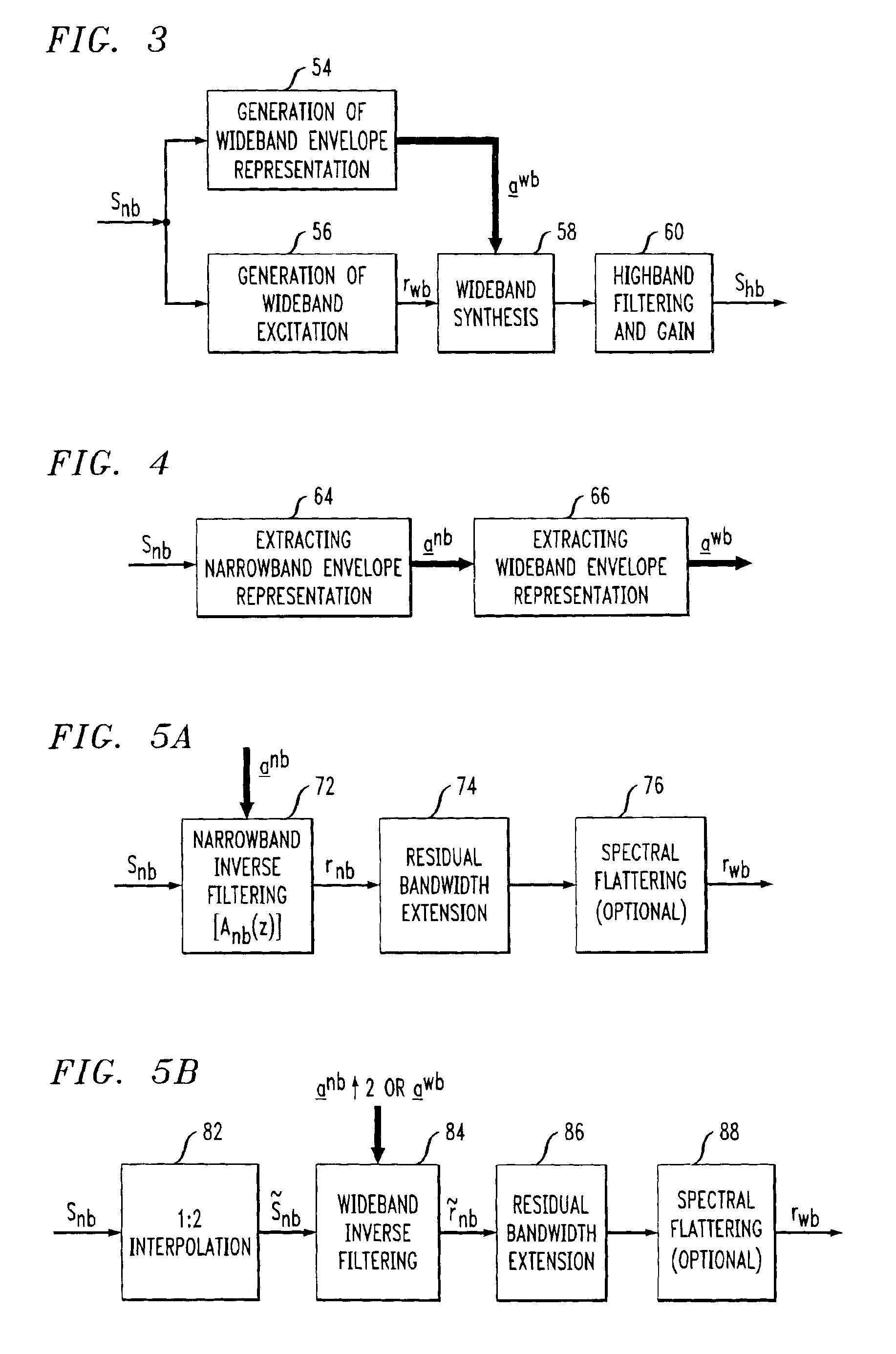
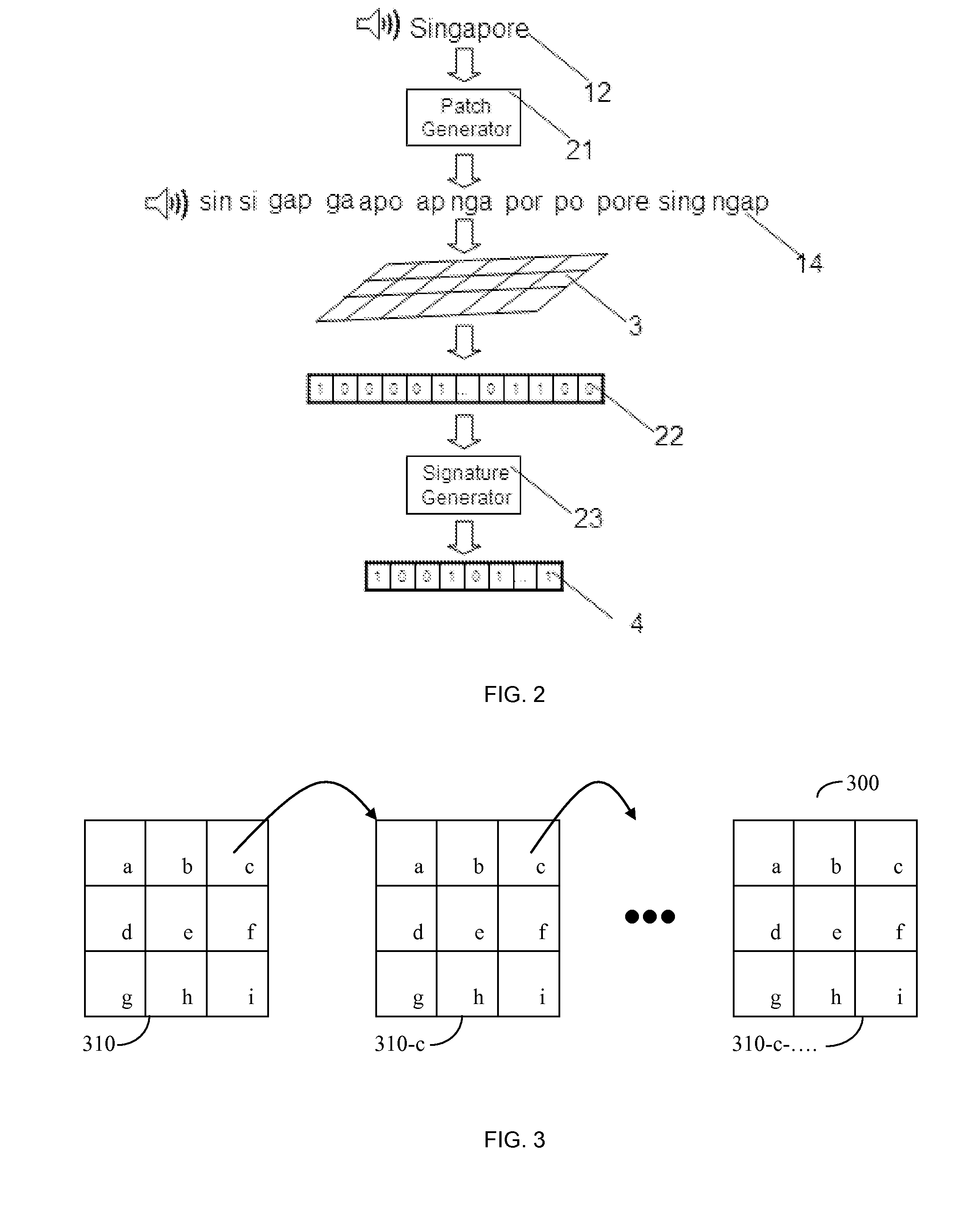
System for bandwidth extension of Narrow-band speech
InactiveUS6895375B2Quality improvementEasy to useDigital computer detailsElectric digital data processingNarrowband speechLinear prediction coefficient
A system and method are disclosed for extending the bandwidth of a narrowband signal such as a speech signal. The method applies a parametric approach to bandwidth extension but does not require training. The parametric representation relates to a discrete acoustic tube model (DATM). The method comprises computing narrowband linear predictive coefficients (LPCs) from a received narrowband speech signal, computing narrowband partial correlation coefficients (parcors) using recursion, computing Mnb area coefficients from the partial correlation coefficient, and extracting Mwb area coefficients using interpolation. Wideband parcors are computed from the Mwb area coefficients and wideband LPCs are computed from the wideband parcors. The method further comprises synthesizing a wideband signal using the wideband LPCs and a wideband excitation signal, highpass filtering the synthesized wideband signal to produce a highband signal, and combining the highband signal with the original narrowband signal to generate a wideband signal. In a preferred variation of the invention, the Mnb area coefficients are converted to log-area coefficients for the purpose of extracting, through shifted-interpolation, Mwb log-area coefficients. The Mwb log-area coefficients are then converted to Mwb area coefficients before generating the wideband parcors.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
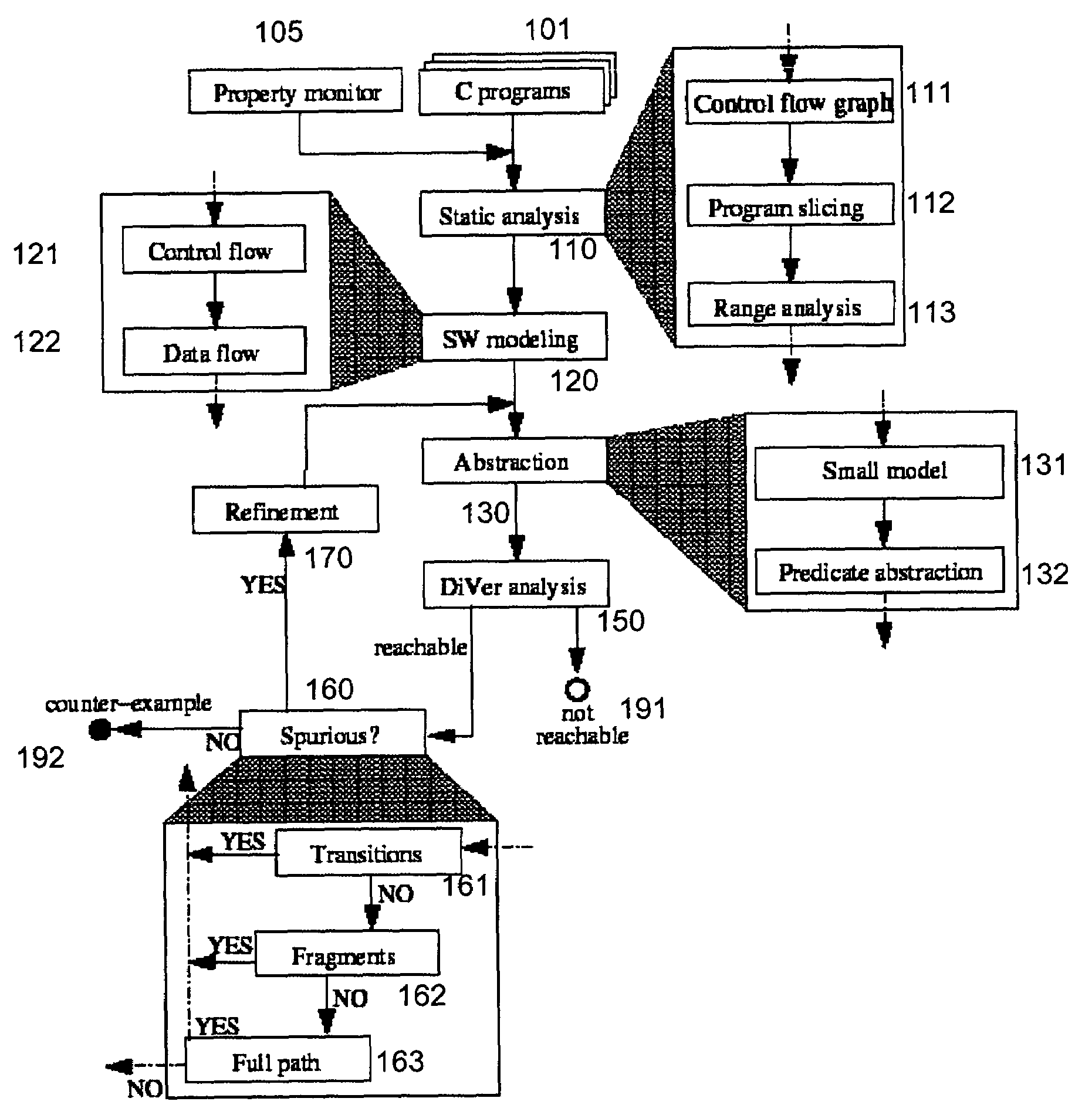
System and method for modeling, abstraction, and analysis of software
ActiveUS7346486B2Improve verification efficiencyImprove translationError detection/correctionComputation using non-denominational number representationBasic blockSoftware
A system and method is disclosed for formal verification of software programs that advantageously translates the software, which can have bounded recursion, into a Boolean representation comprised of basic blocks and which applies SAT-based model checking to the Boolean representation.
Owner:NEC CORP
Flexible polar encoders and decoders
Modern communication systems must cope with varying channel conditions and differing throughput constraints. Polar codes despite being the first error-correcting codes with an explicit construction to achieve the symmetric capacity of memoryless channels are not currently employed against other older coding protocols such as low-density parity check (LDPC) codes as their performance at short / moderate lengths has been inferior and their decoding algorithm is serial leading to low decoding throughput. Accordingly techniques to address these issues are identified and disclosed including decoders that decode constituent codes without recursion and / or recognize classes of constituent directly decodable codes thereby increasing the decoder throughput. Flexible encoders and decoders supporting polar codes of any length up to a design maximum allow adaptive polar code systems responsive to communication link characteristics, performance, etc. whilst maximizing throughput. Further, designers are provided flexibility in implementing either hardware or software implementations.
Owner:POLAR TECH
Methods and systems for generating natural language descriptions from data
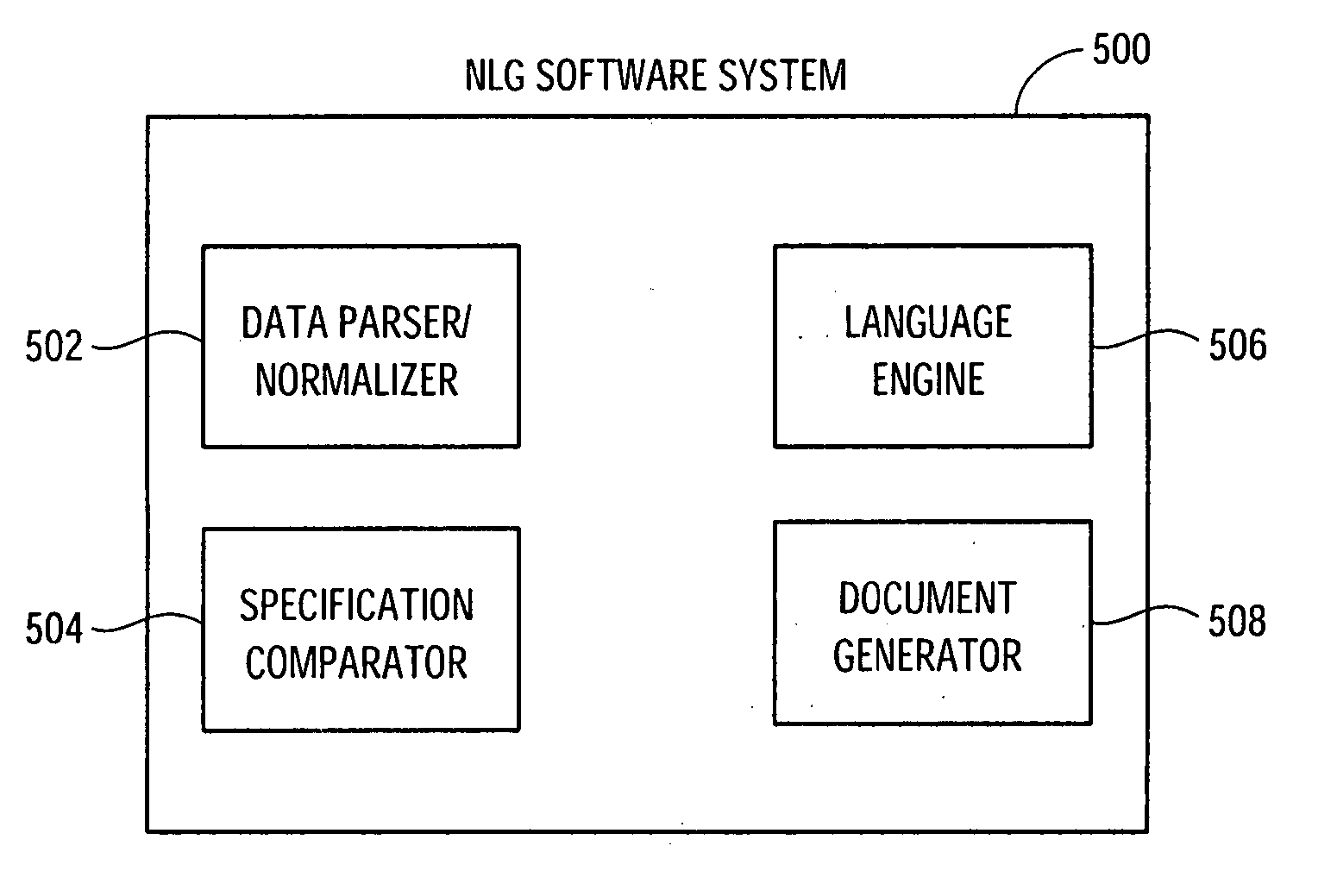
ActiveUS20060178868A1Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsDocumentation generatorSoftware system
The invention is directed to a natural language generation (NLG) software system that generates rich, content-sensitive human language descriptions based on unparsed raw domain-specific data. In one embodiment, the NLG software system may include a data parser / normalizer, a comparator, a language engine, and a document generator. The data parser / normalizer may be configured to retrieve specification information for items to be described by the NLG software system, to extract pertinent information from the raw specification information, and to convert and normalize the extracted information so that the items may be compared specification by specification. The comparator may be configured to use the normalized data from the data parser / normalizer to compare the specifications of the items using comparison functions and interpretation rules to determine outcomes of the comparisons. The language engine may be configured to cycle through all or a subset of the normalized specification information, to retrieve all sentence templates associated with each of the item specifications, to call the comparator to compute or retrieve the results of the comparisons between the item specifications, and to recursively generate every possible syntactically legal sentence associated with the specifications based on the retrieved sentence templates. The document generator may be configured to select one or more discourse models having instructions regarding the selection, organization and modification of the generated sentences, and to apply the instructions of the discourse model to the generated sentences to generate a natural language description of the selected items.
Owner:CLASSIFIED VENTURES
Method and apparatus for prefetching recursive data structures
InactiveUS6848029B2Improve cache hit ratioPotential throughput of the computer systemMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationApplication softwareCache hit rate
Computer systems are typically designed with multiple levels of memory hierarchy. Prefetching has been employed to overcome the latency of fetching data or instructions from or to memory. Prefetching works well for data structures with regular memory access patterns, but less so for data structures such as trees, hash tables, and other structures in which the datum that will be used is not known a priori. The present invention significantly increases the cache hit rates of many important data structure traversals, and thereby the potential throughput of the computer system and application in which it is employed. The invention is applicable to those data structure accesses in which the traversal path is dynamically determined. The invention does this by aggregating traversal requests and then pipelining the traversal of aggregated requests on the data structure. Once enough traversal requests have been accumulated so that most of the memory latency can be hidden by prefetching the accumulated requests, the data structure is traversed by performing software pipelining on some or all of the accumulated requests. As requests are completed and retired from the set of requests that are being traversed, additional accumulated requests are added to that set. This process is repeated until either an upper threshold of processed requests or a lower threshold of residual accumulated requests has been reached. At that point, the traversal results may be processed.
Owner:DIGITAL CACHE LLC +1
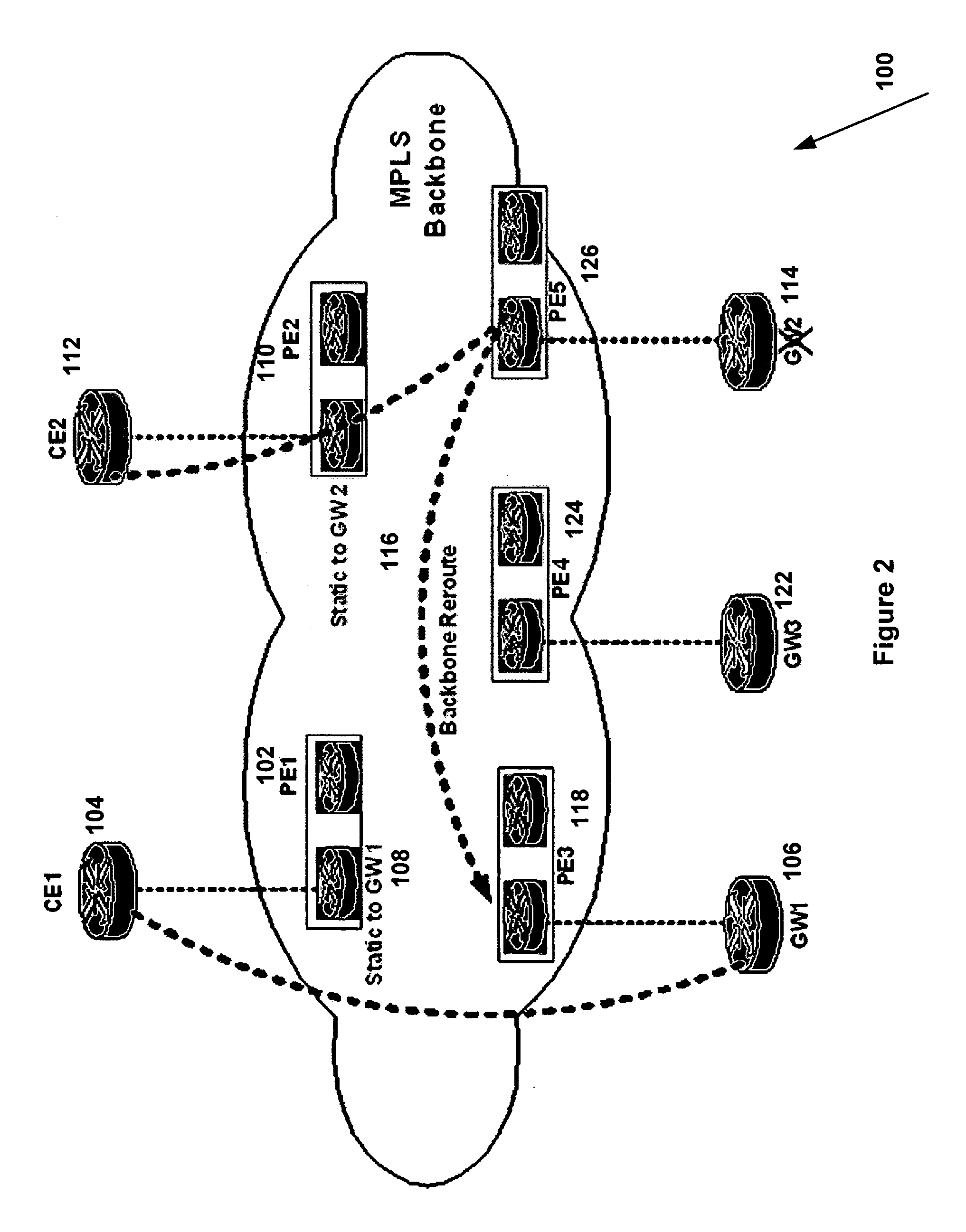
System and method for forwarding traffic data in an MPLS VPN
InactiveUS20080080517A1Data switching by path configurationTraffic capacityTelecommunications network
The present invention provides a system and method for forwarding traffic data in a MPLS VPN network within a telecommunications network. The method comprise a technique for gateway selection in the MPLS VPN by using a combination of recursive floating static routes in the PE routers and conditional route advertisements from the gateway CE routers. This method allows for choice of gateway on a per-PE per-VRF basis.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
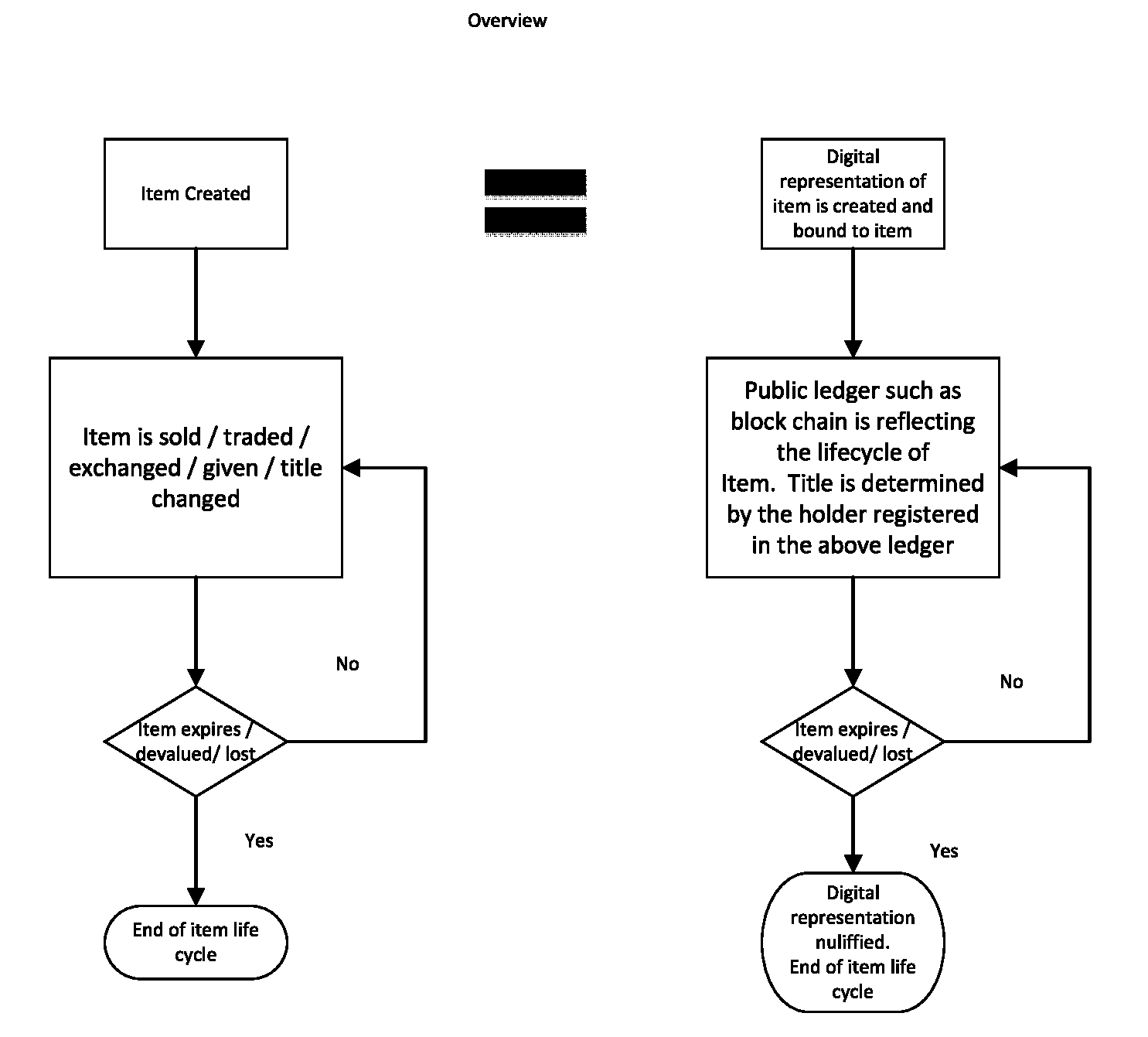
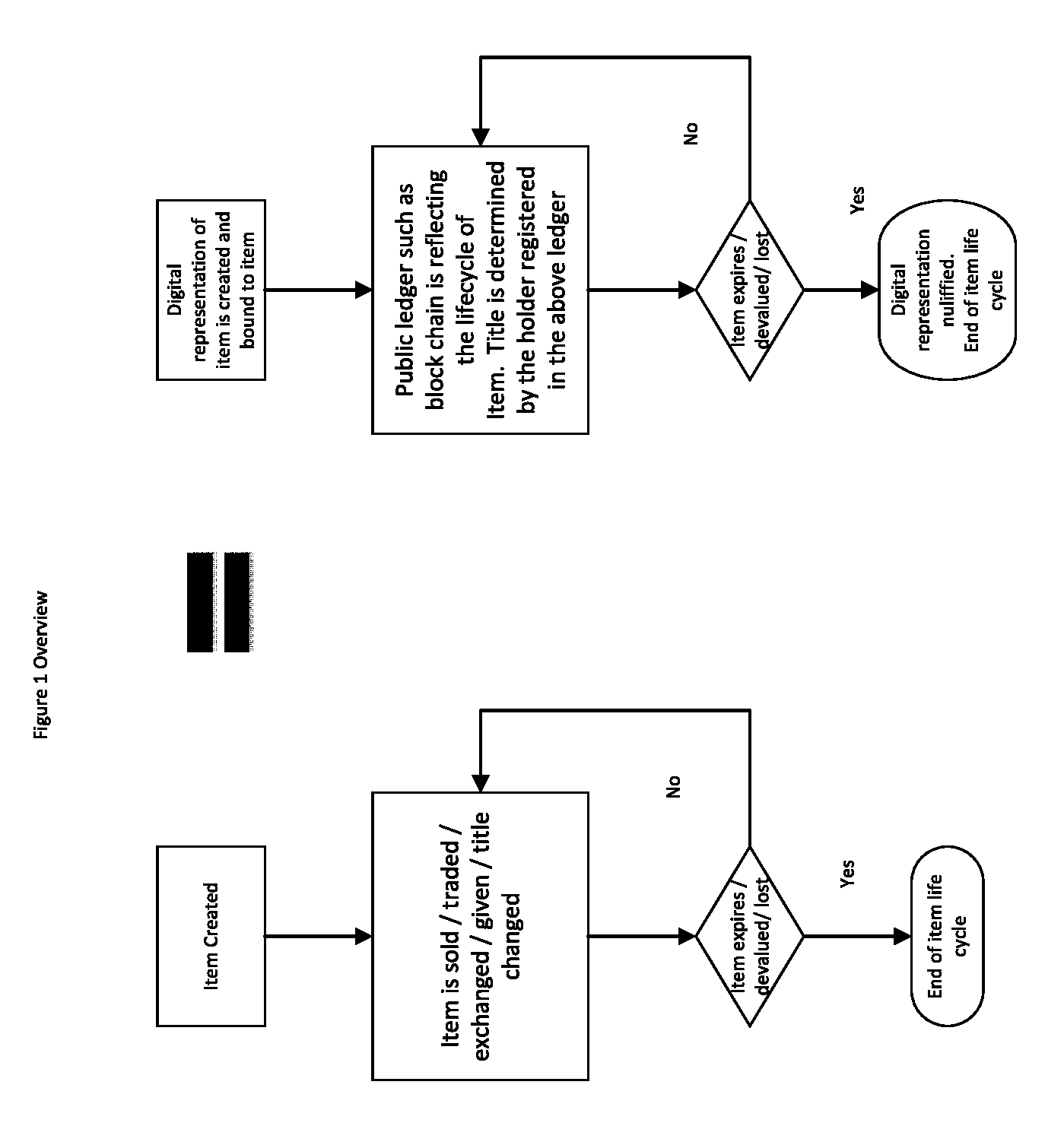
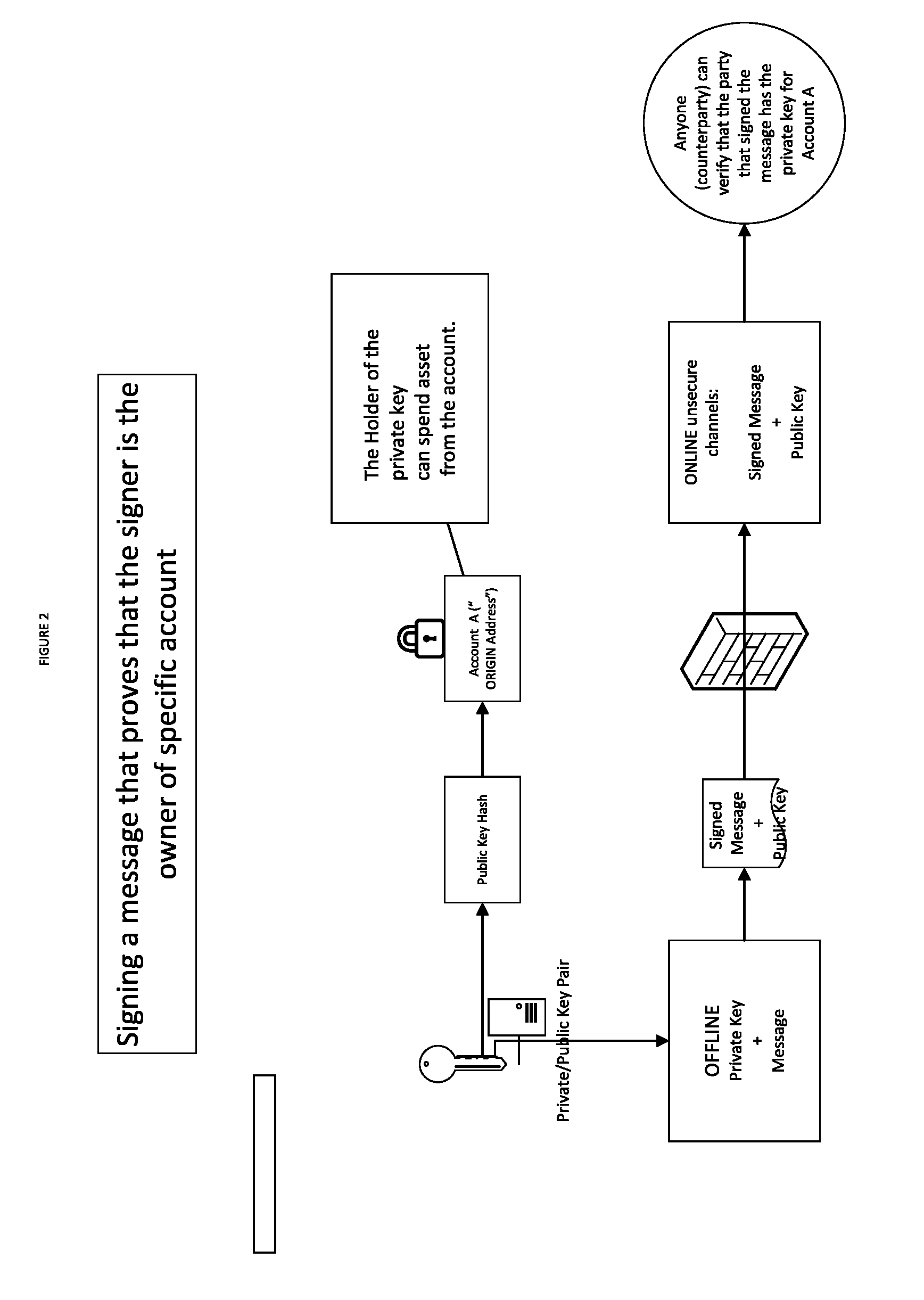
Method, System and Program Product for Tracking and Securing Transactions of Authenticated Items over Block Chain Systems.
InactiveUS20160217436A1Tracking chainRead-only accessPayment circuitsProtocol authorisationDigital currencyTransaction data
A method, system and program product comprise accessing a system having a digital currency infrastructure. At least three user addresses are created. Rules for filtering acceptable transactions on the system are prepared in form of recursion base and recursion steps. Items are initiated on the system according to the defined rules. The assets transaction data is transferred to the system wherein the system links asset data and the parties to the transaction according to the said rules.
Owner:BRAMA DROR SAMUEL
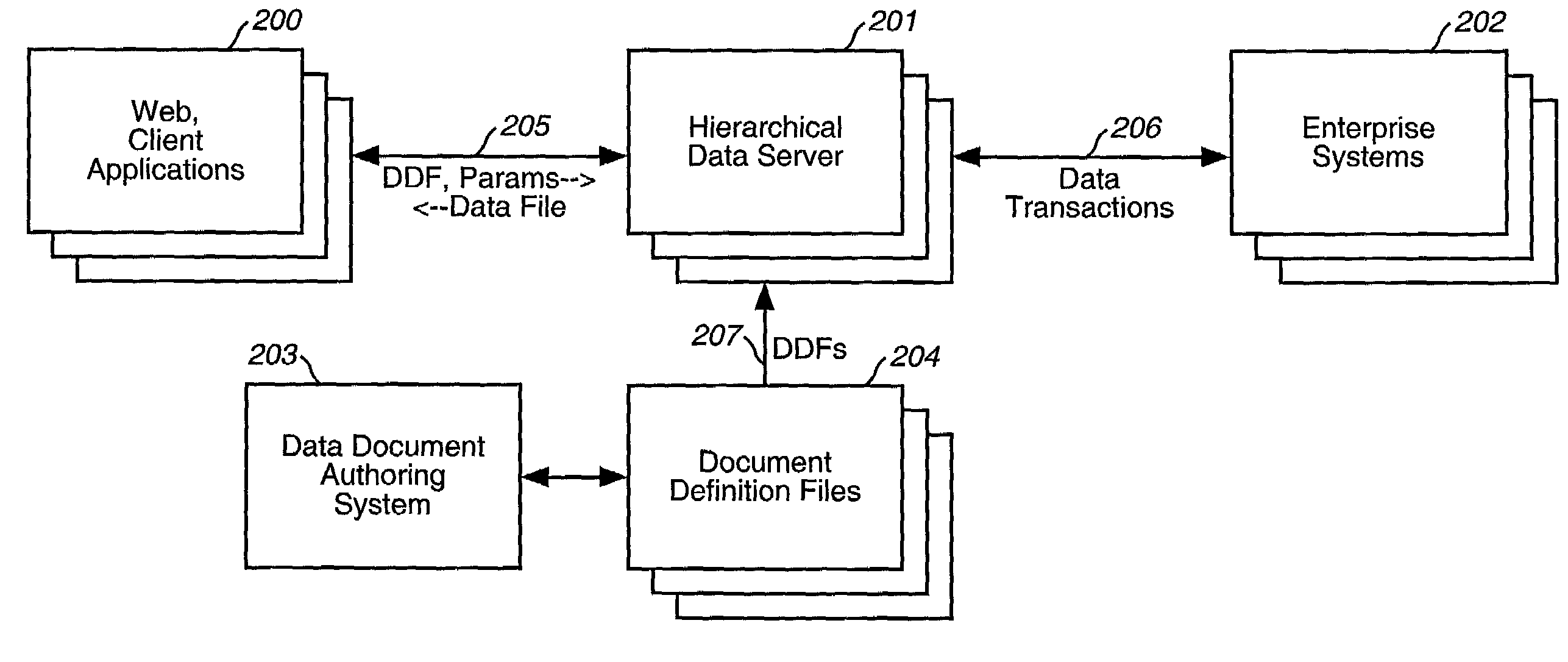
Dynamic, hierarchical data exchange system
InactiveUS7165073B2Overcome limitationsOptimize locationData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalRelational algebraData operations
A computer system provides the ability to construct and edit a Data Definition File (DDF) containing hierarchically related elements of data, some of which are dynamic in that they must execute in order to produce or retrieve data. A client computer system having knowledge of a DDF appropriate for its uses sends a request to a server, which contains or can retrieve the DDF requested by the client. The request contains parameters used by the server to customize the resulting keyed data file for the client's purposes. Upon receipt of the request, the server copies the DDF into a coupled memory, performs requested parameter substitutions, and executes dynamic elements to produce resulting data elements. The process is repeated recursively for all elements of the hierarchical structure, until no dynamic elements remain, then the resulting keyed data file is returned to the client for its uses. Data elements may be derived from a plurality of sources, and these sources may be combined and manipulated using a plurality of data operations, including relational algebra or structured query language, enabling joins and merges between multiple sources and formats. An Authoring System is provided which assists in the construction and validation of DDFs.
Owner:X AWARE
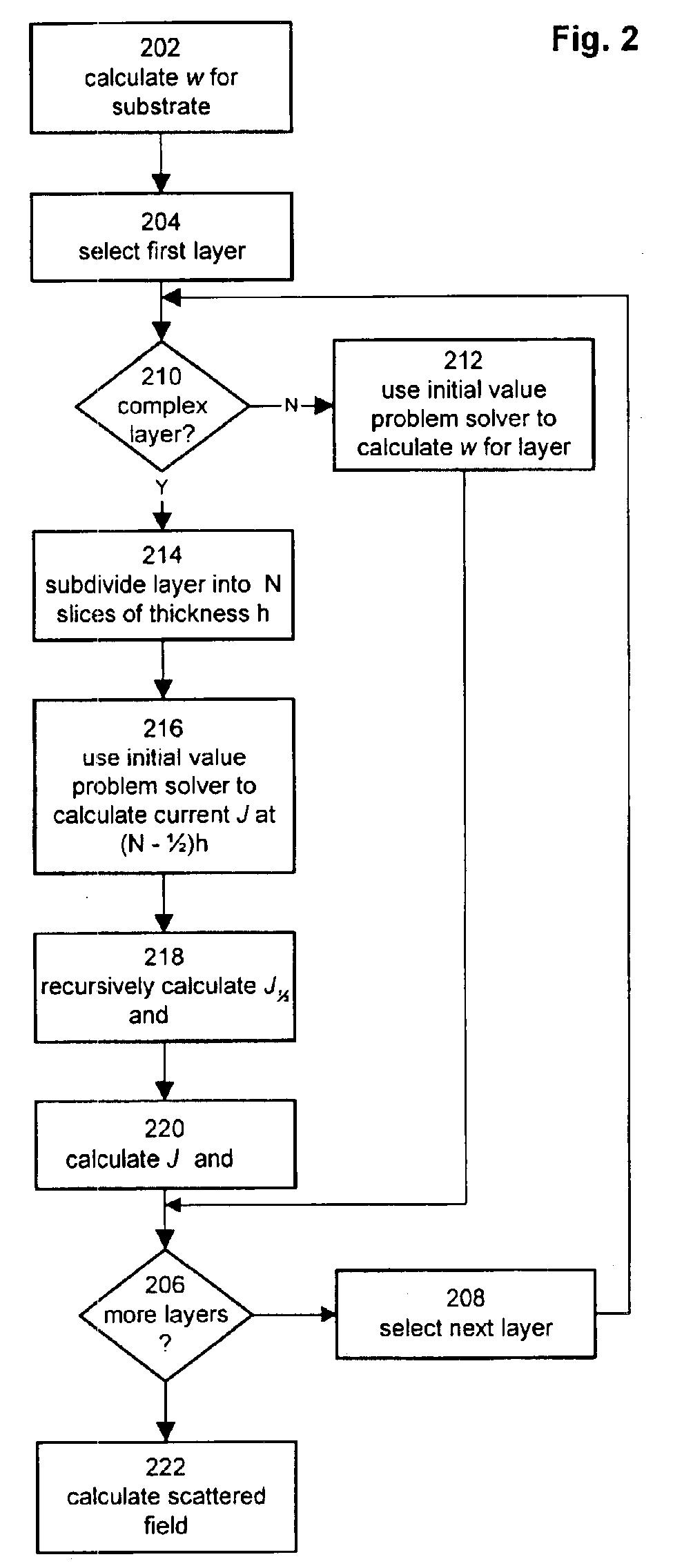
CD metrology analysis using a finite difference method
ActiveUS6919964B2Directly computeSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetrologyDirect evaluation
A method for modeling diffraction includes constructing a theoretical model of the subject. A numerical method is then used to predict the output field that is created when an incident field is diffracted by the subject. The numerical method begins by computing the output field at the upper boundary of the substrate and then iterates upward through each of the subject's layers. Structurally simple layers are evaluated directly. More complex layers are discretized into slices. A finite difference scheme is performed for these layers using a recursive expansion of the field-current ratio that starts (or has a base case) at the lowermost slice. The combined evaluation, through all layers, creates a scattering matrix that is evaluated to determine the output field for the subject.
Owner:THERMA WAVE INC
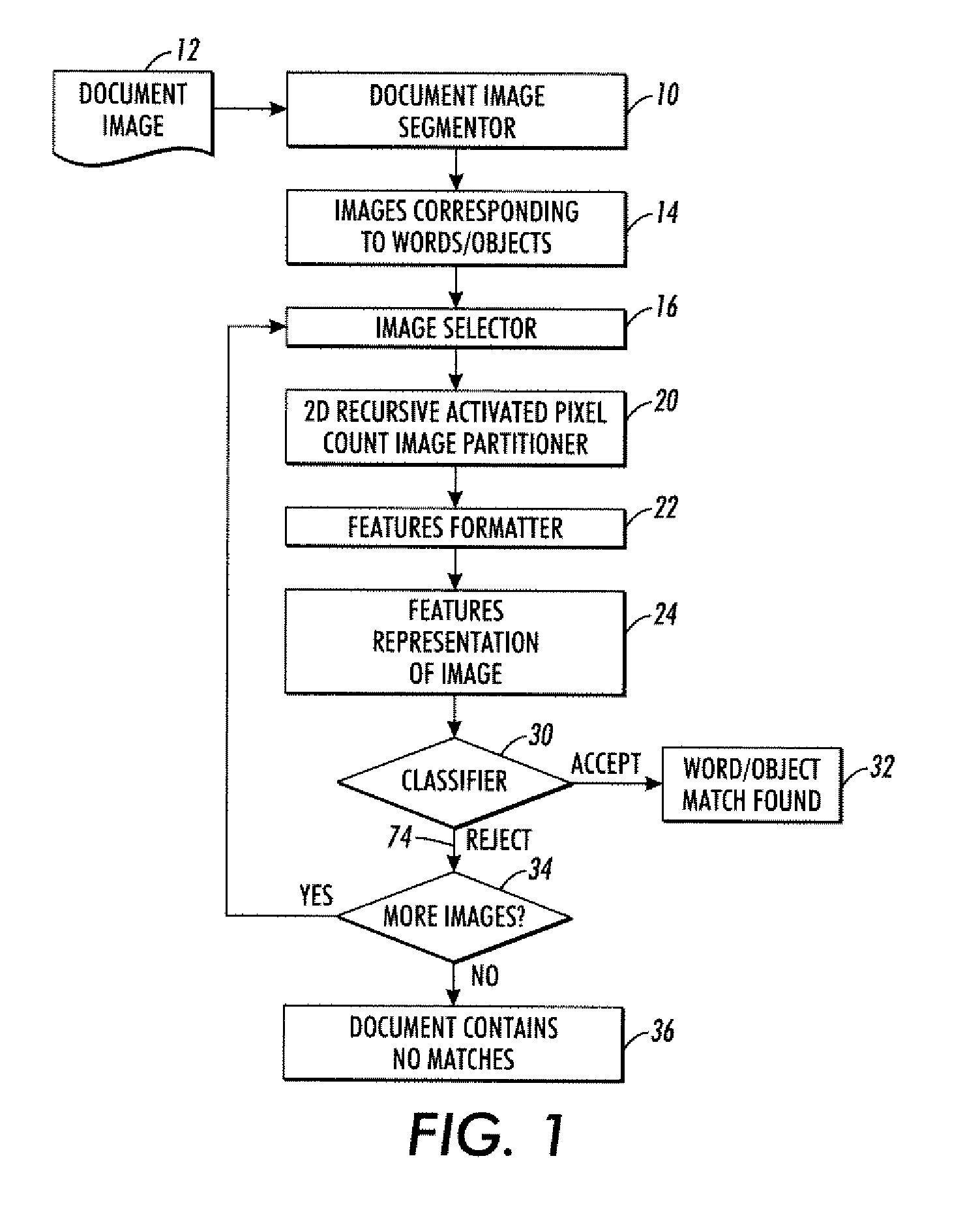
Features generation and spotting methods and systems using same
An image partitioner is configured to find a partition point that divides a received image into four sub-images each having a pre-selected activated pixel count. A recursion processor is configured to (i) apply the image partitioner to an input image to generate a first partition point and four sub-images and to (ii) recursively apply the image partitioner to at least one of the four sub-images for at least one recursion iteration to generate at least one additional partition point. A formatter is configured to generate a features representation of the input image in a selected format. The features representation is based at least in part on the partition points. The features representation can be used in various ways, such as by a classifier configured to classify the input image based on the features representation.
Owner:XEROX CORP
System and method for recursive path analysis of dbms procedures
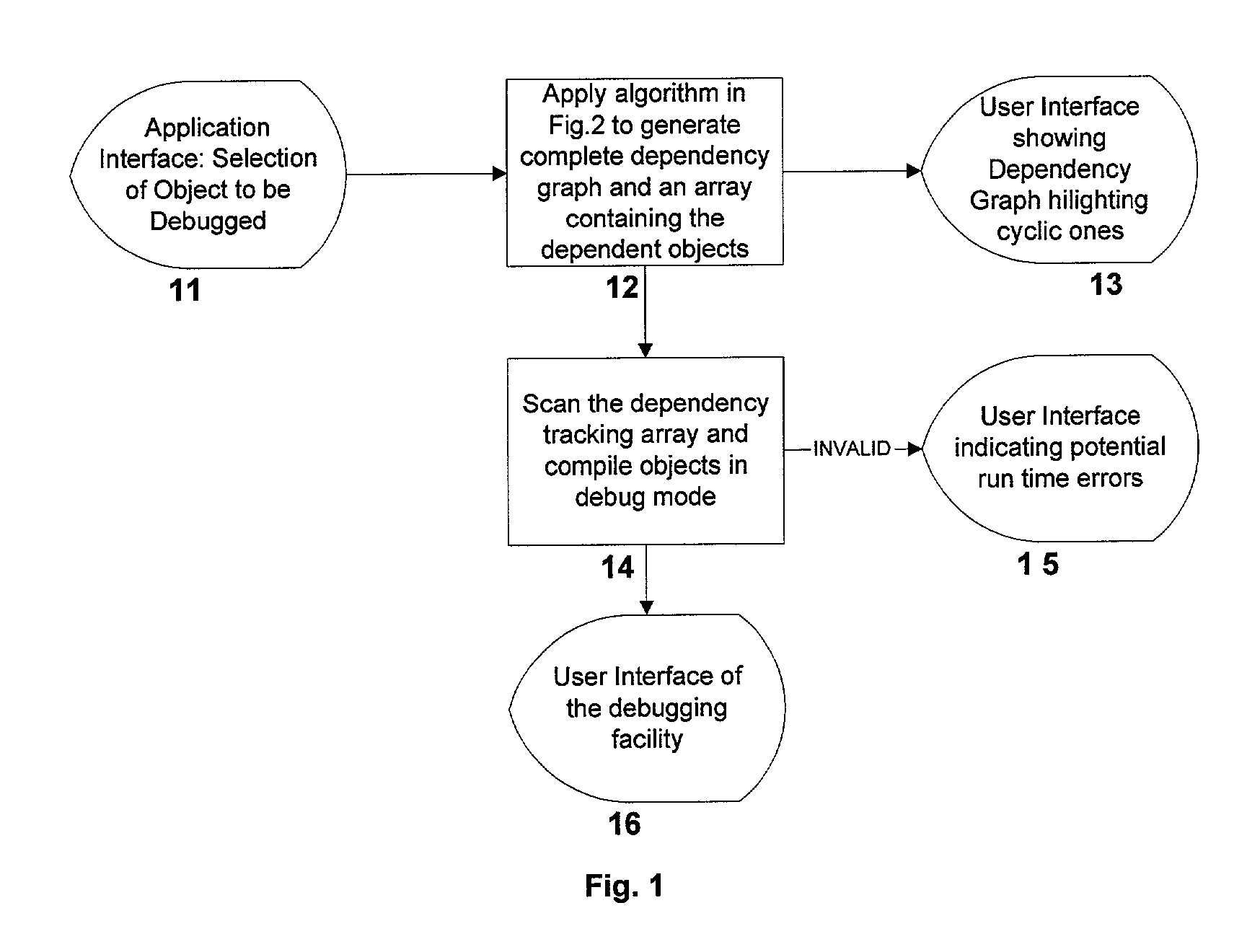
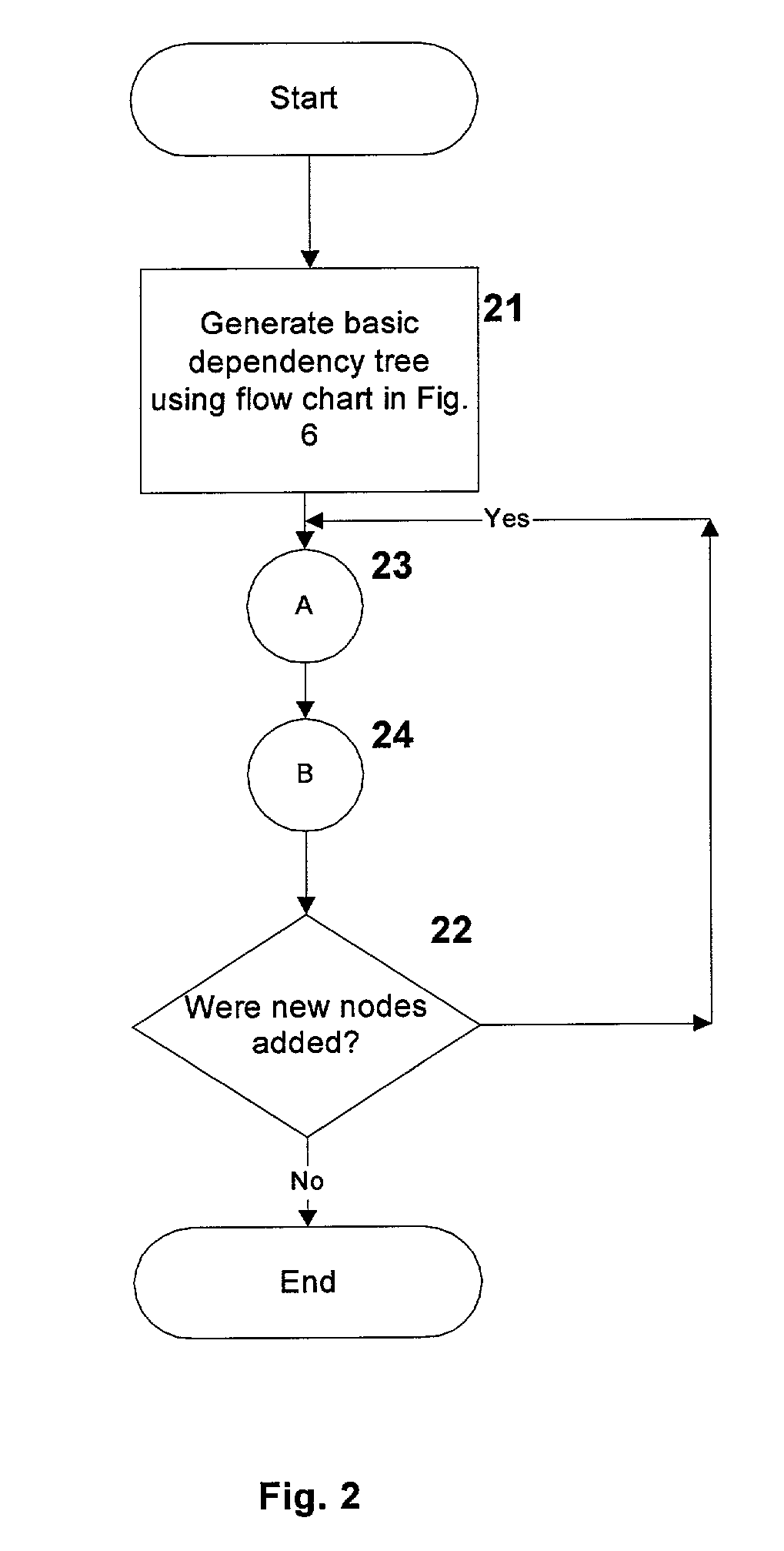
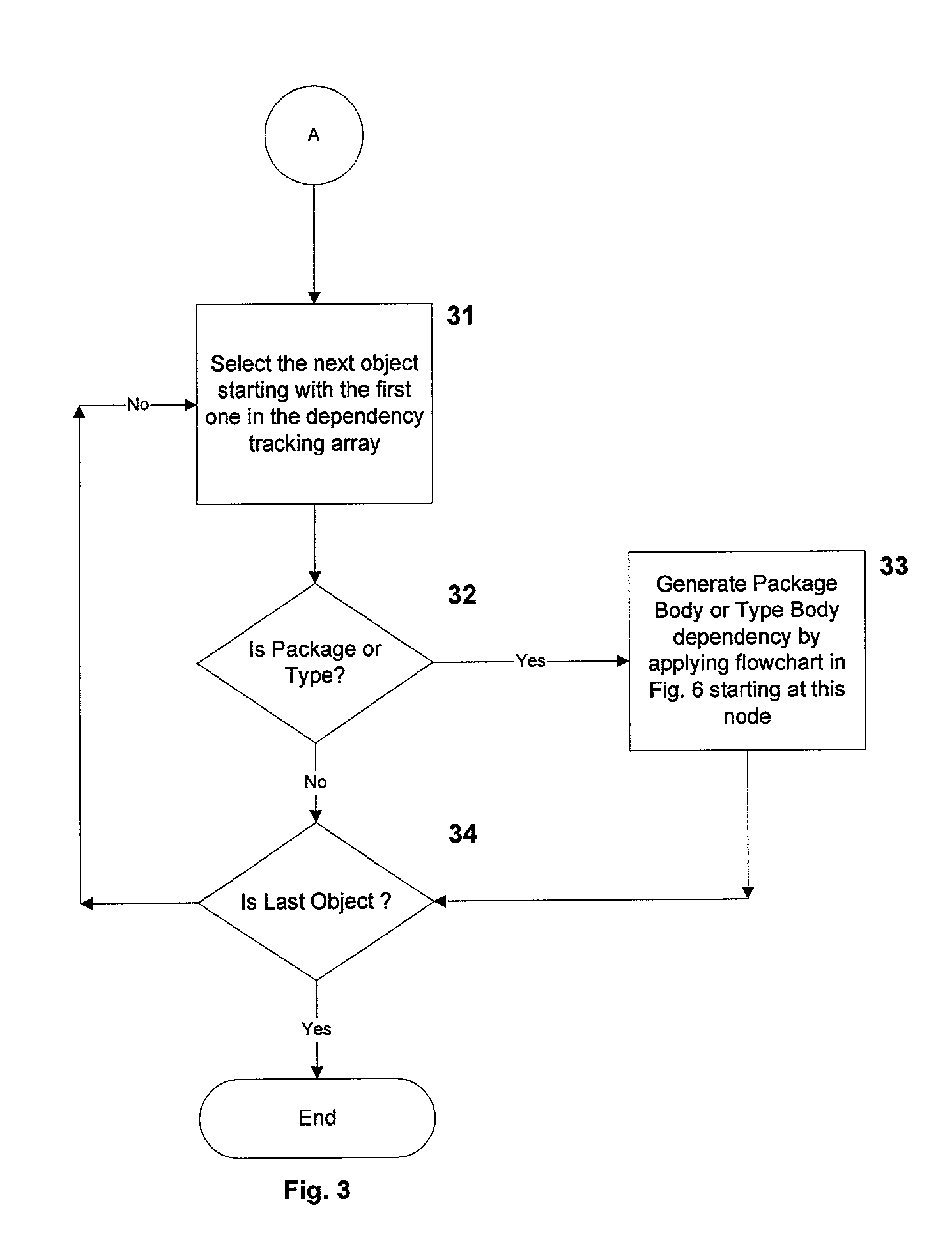
InactiveUS20010049682A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsTrack algorithmDependency graph
A system, method and database development tool are disclosed for automatically generating the complete dependency graph for use in debugging stored code objects in a database, by using a recursive dependency tracking algorithm which takes into consideration the indirect dependencies on triggers as well as the dependencies on implementations of object oriented code objects which are represented as separate objects in the database catalog.
Owner:COMP ASSOC THINK INC
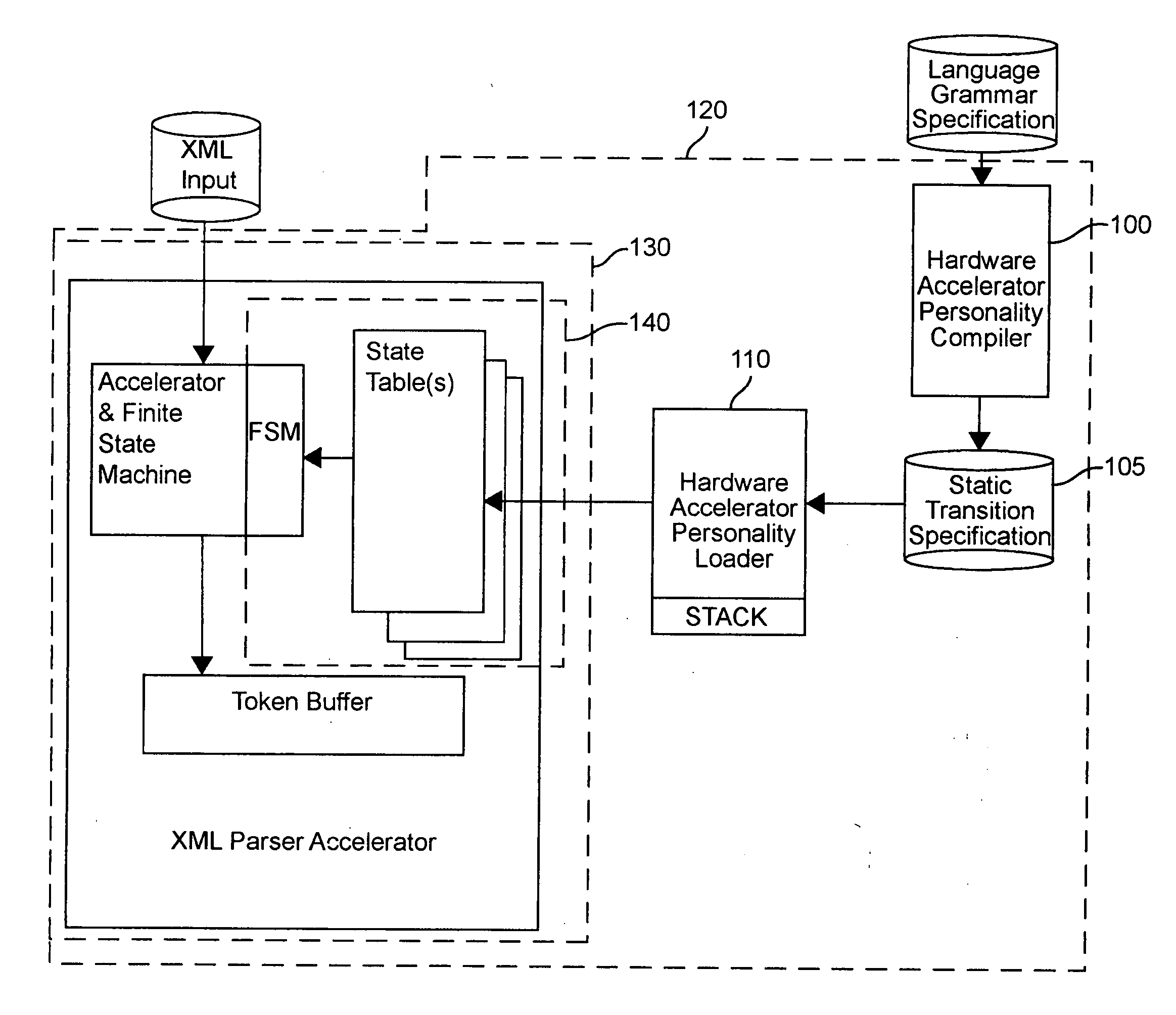
Hardware accelerator personality compiler
InactiveUS20040172234A1Software engineeringSpecial data processing applicationsState switchingAutomaton
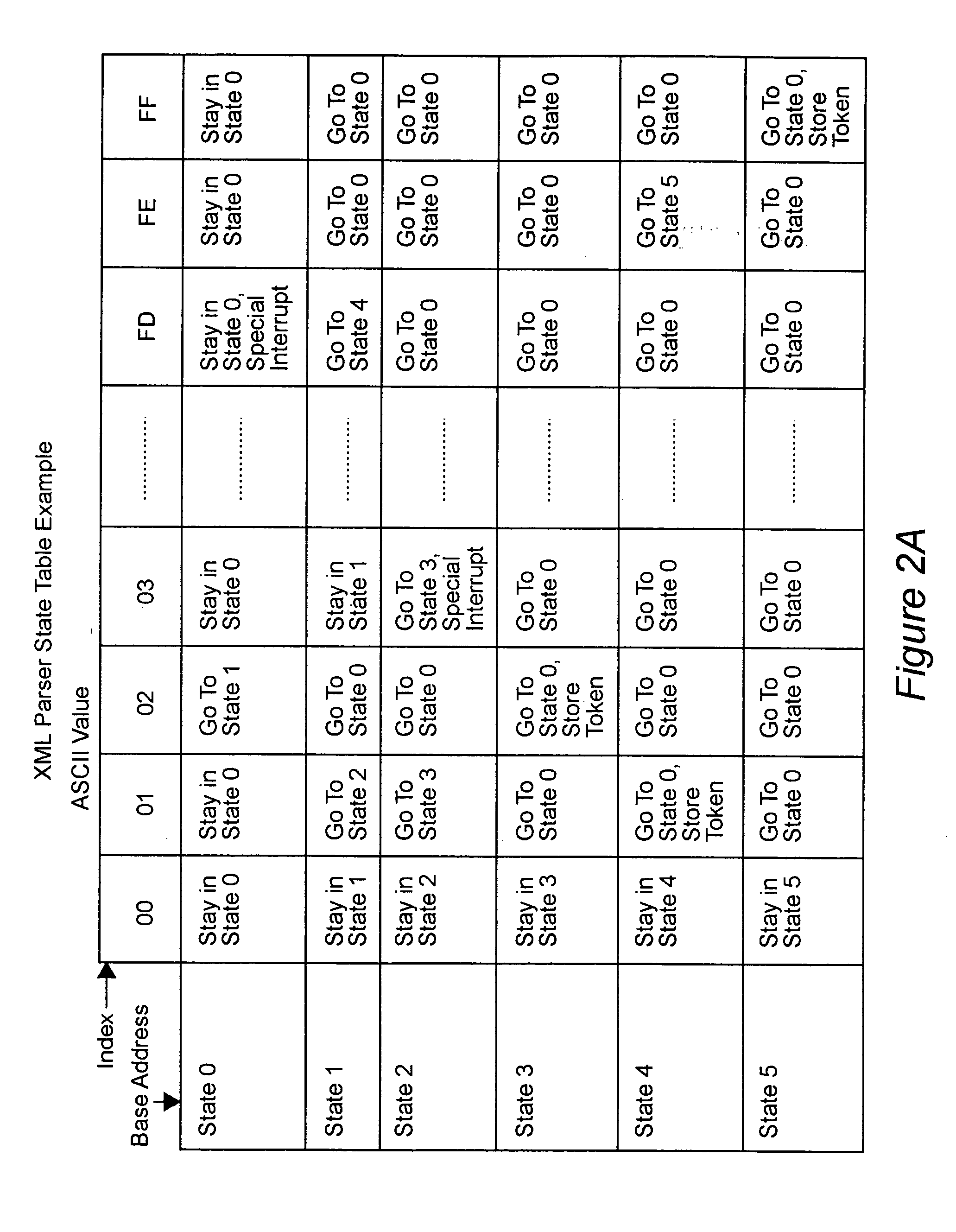
Error-free state tables are automatically generated from a specification of a group of desired performable functions, such as are provided in a programming language in a formal notation such as Backus-Naur form or a derivative thereof by discriminating tokens corresponding to respective performable functions, identifications, arguments, syntax, grammar rules, special symbols and the like. The tokens may be recursive (e.g. infinite), in which case they are transformed into a finite automata which may be deterministic or non-deterministic. Non-deterministic finite automata are transformed into deterministic finite automata and then into state transitions which are used to build a state table which can then be stored or, preferably, loaded into a finite state machine of a hardware parser accelerator to define its personality.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Method and system for high resolution, ultra fast 3-d imaging
InactiveUS20090016642A1Add depthHigh displacement accuracyTelevision system detailsImage analysisImage resolutionUltra fast
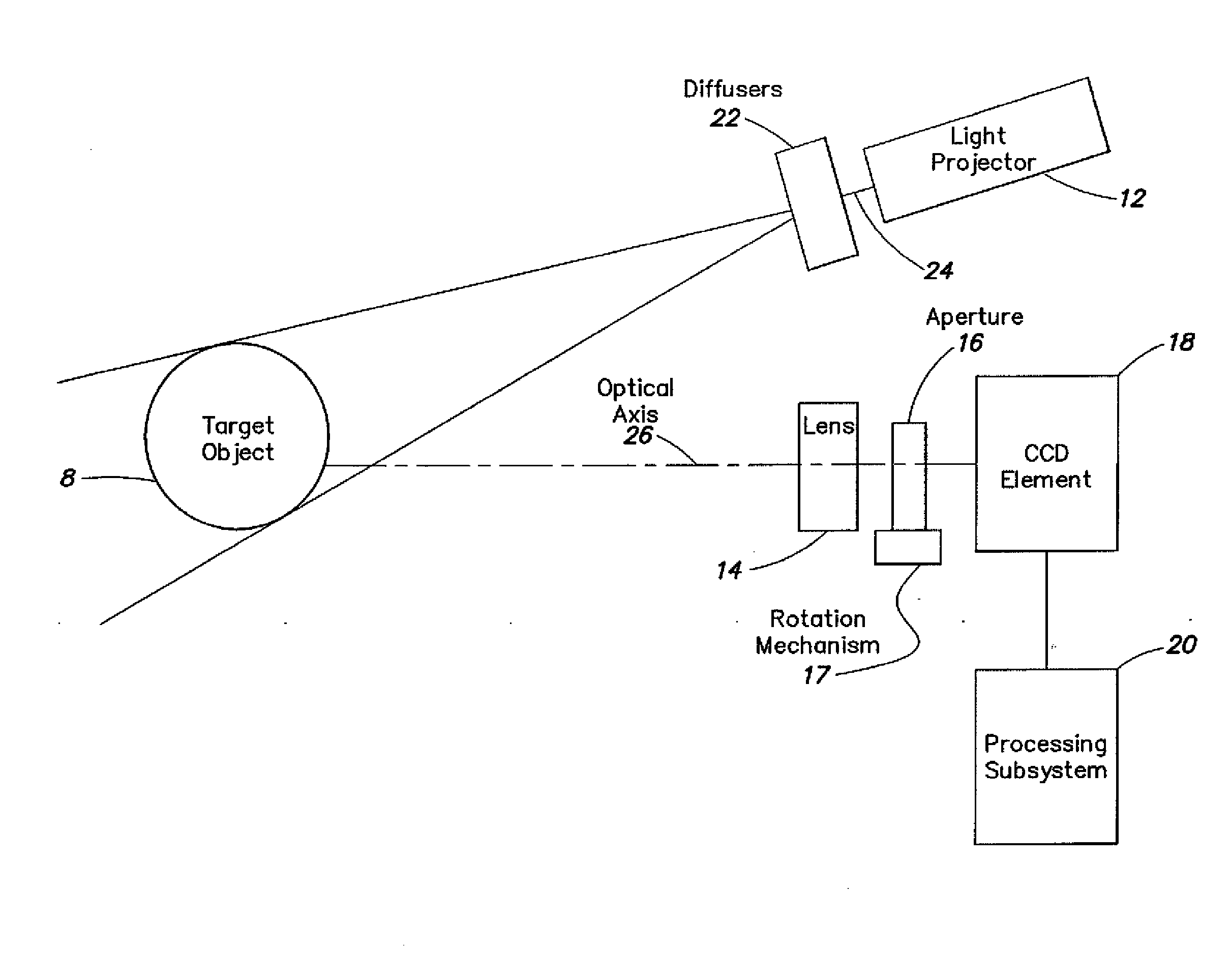
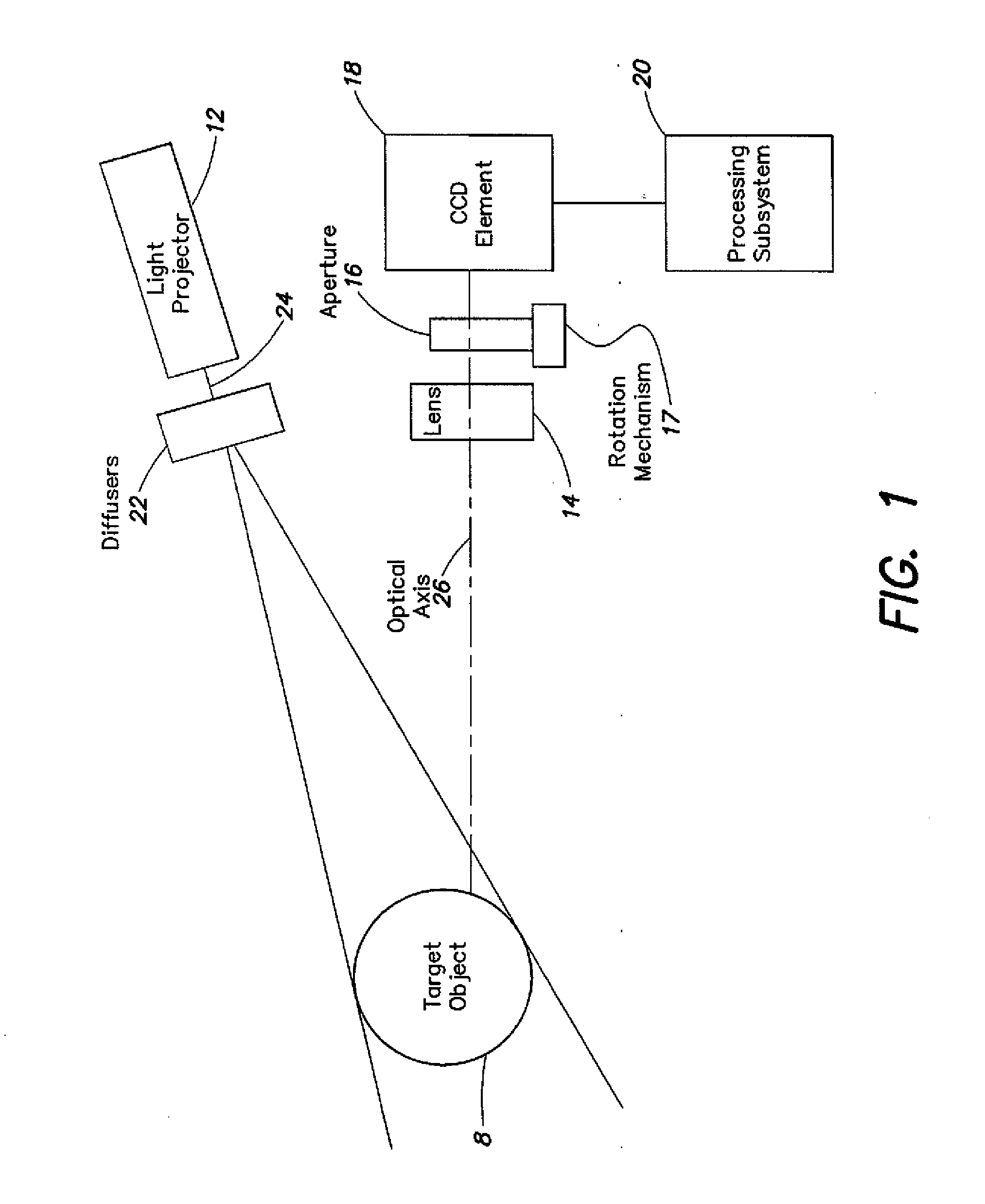
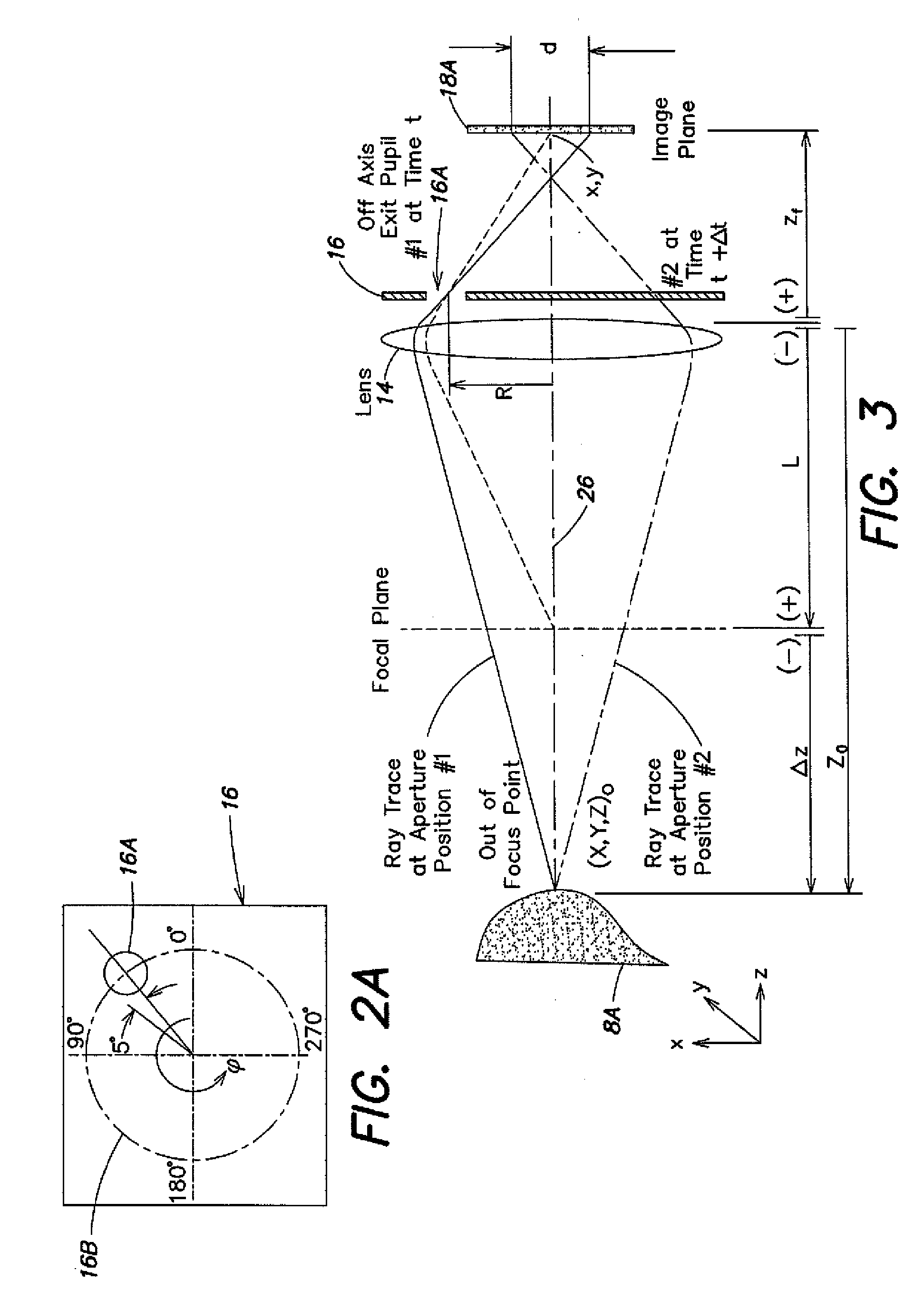
A high-speed three-dimensional imaging system includes a single lens camera subsystem with an active imaging element and CCD element, and a correlation processing subsystem. The active imaging element can be a rotating aperture which allows adjustable non-equilateral spacing between defocused images to achieve greater depth of field and higher sub-pixel displacement accuracy. A speckle pattern is projected onto an object and images of the resulting pattern are acquired from multiple angles. The images are locally cross-correlated using a sparse array image correlation technique and the surface is resolved by using relative camera position information to calculate the three-dimensional coordinates of each locally correlated region. Increased resolution and accuracy are provided by recursively correlating the images down to the level of individual points of light and using the Gaussian nature of the projected speckle pattern to determine subpixel displacement between images. Processing is done at very high-speeds by compressing the images before they are correlated. Correlation errors are eliminated during processing by a technique based on the multiplication of correlation table elements from one or more adjacent regions.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
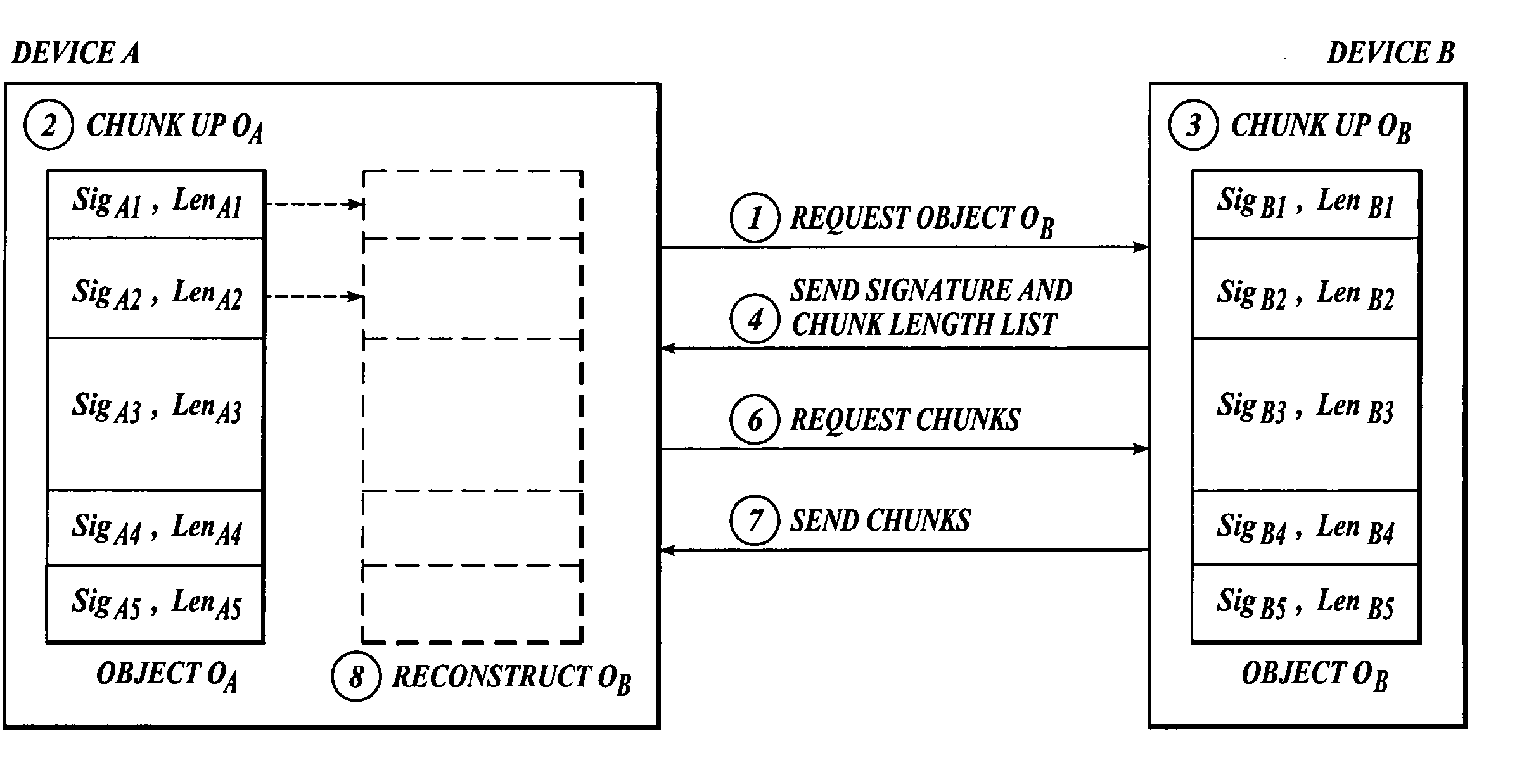
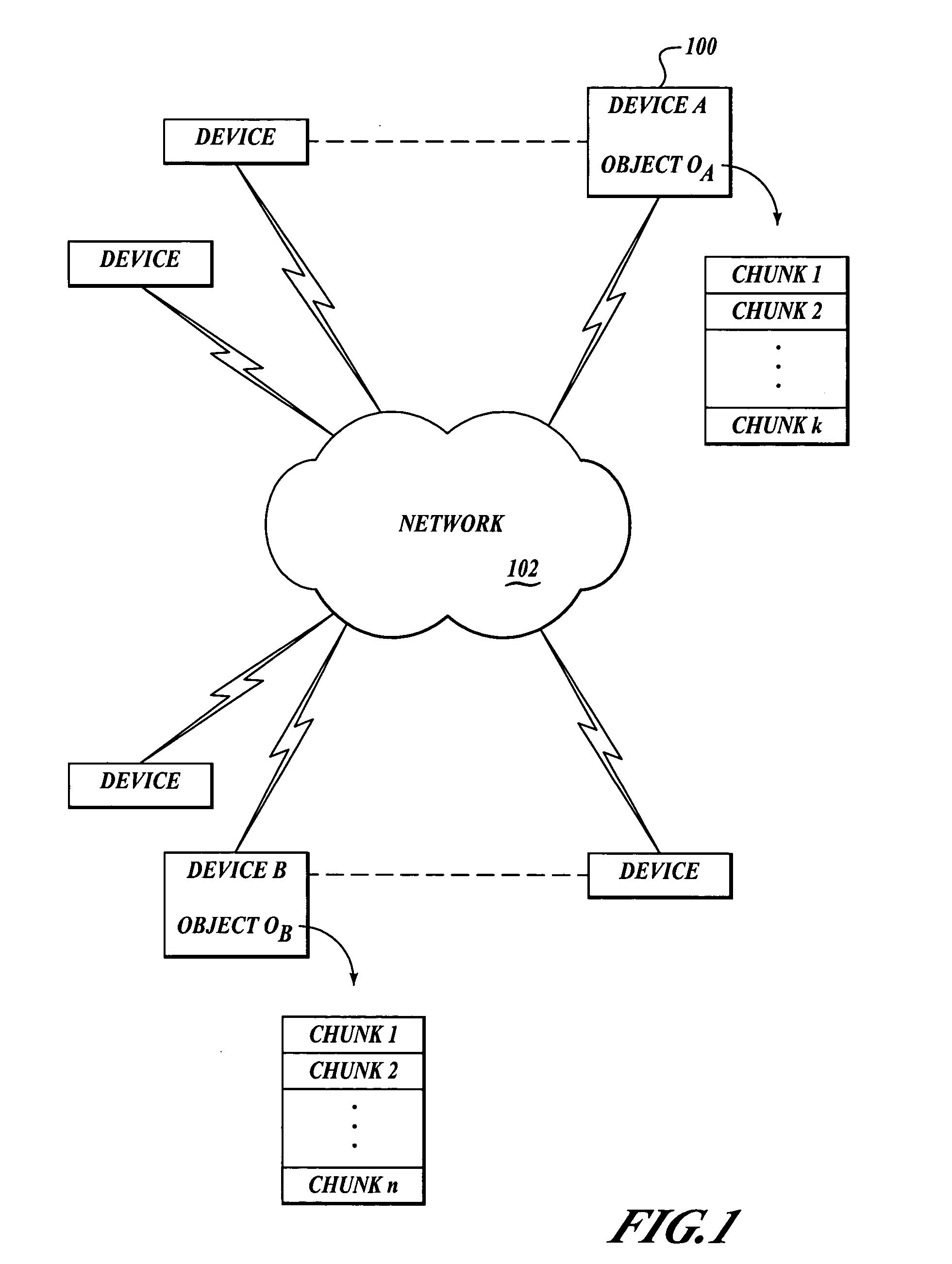
Efficient algorithm and protocol for remote differential compression
A method and system are related to updating objects over limited bandwidth networks. Objects are updated between two or more computing devices using remote differential compression (RDC) techniques such that required data transfers are minimized. In one aspect, efficient large object transfers are achieved by recursively applying the RDC algorithm to its own metadata; a single or multiple recursion step(s) may be used in this case to reduce the amount of metadata sent over the network by the RDC algorithm. Objects and / or signature and chunk length lists can be chunked by locating boundaries at dynamically determined locations. A mathematical function evaluates hash values associated within a horizon window relative to potential chunk boundary. The described method and system is useful in a variety of networked applications, such as peer-to-peer replicators, email clients and servers, client-side caching systems, general-purpose copy utilities, database replicators, portals, software update services, file / data synchronization, and others.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
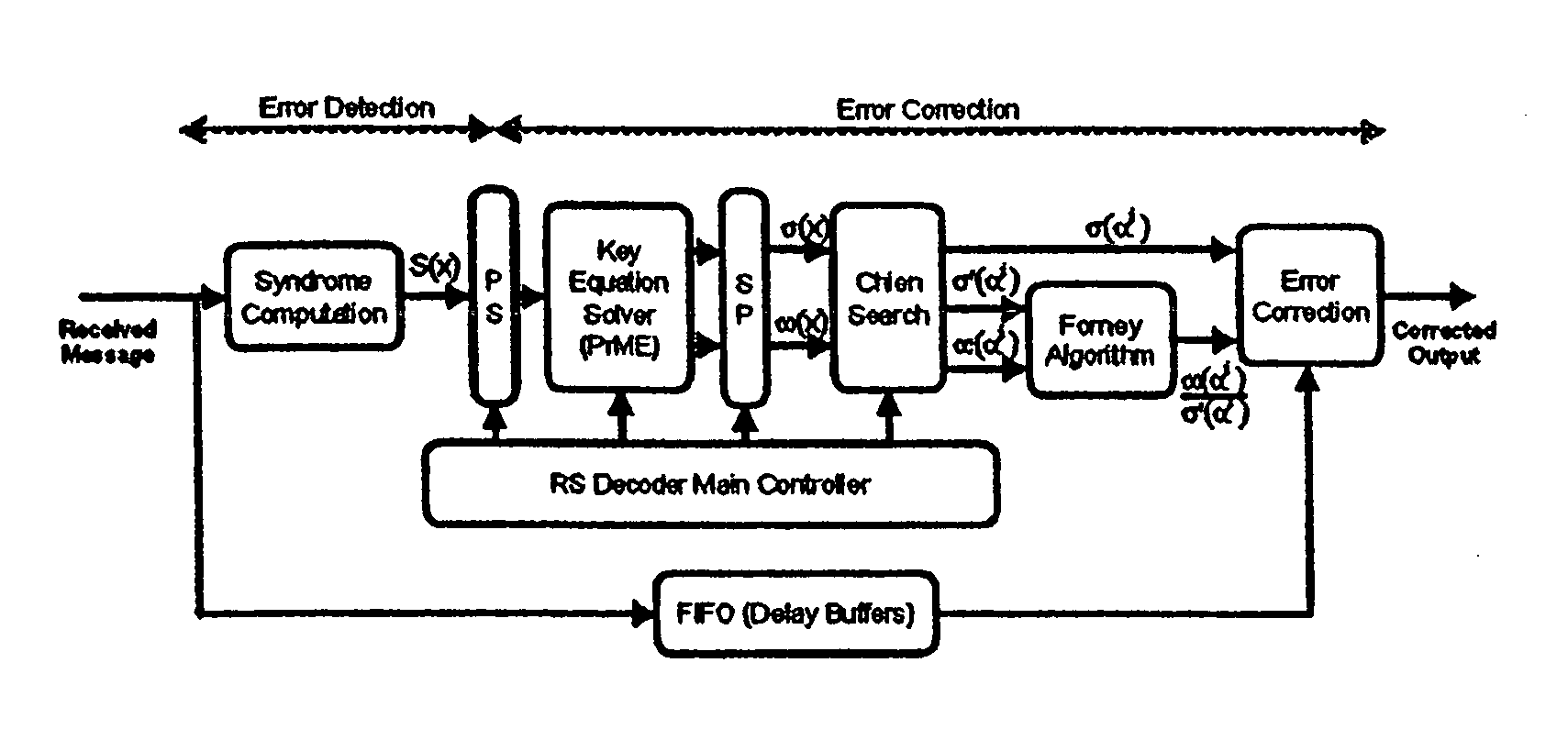
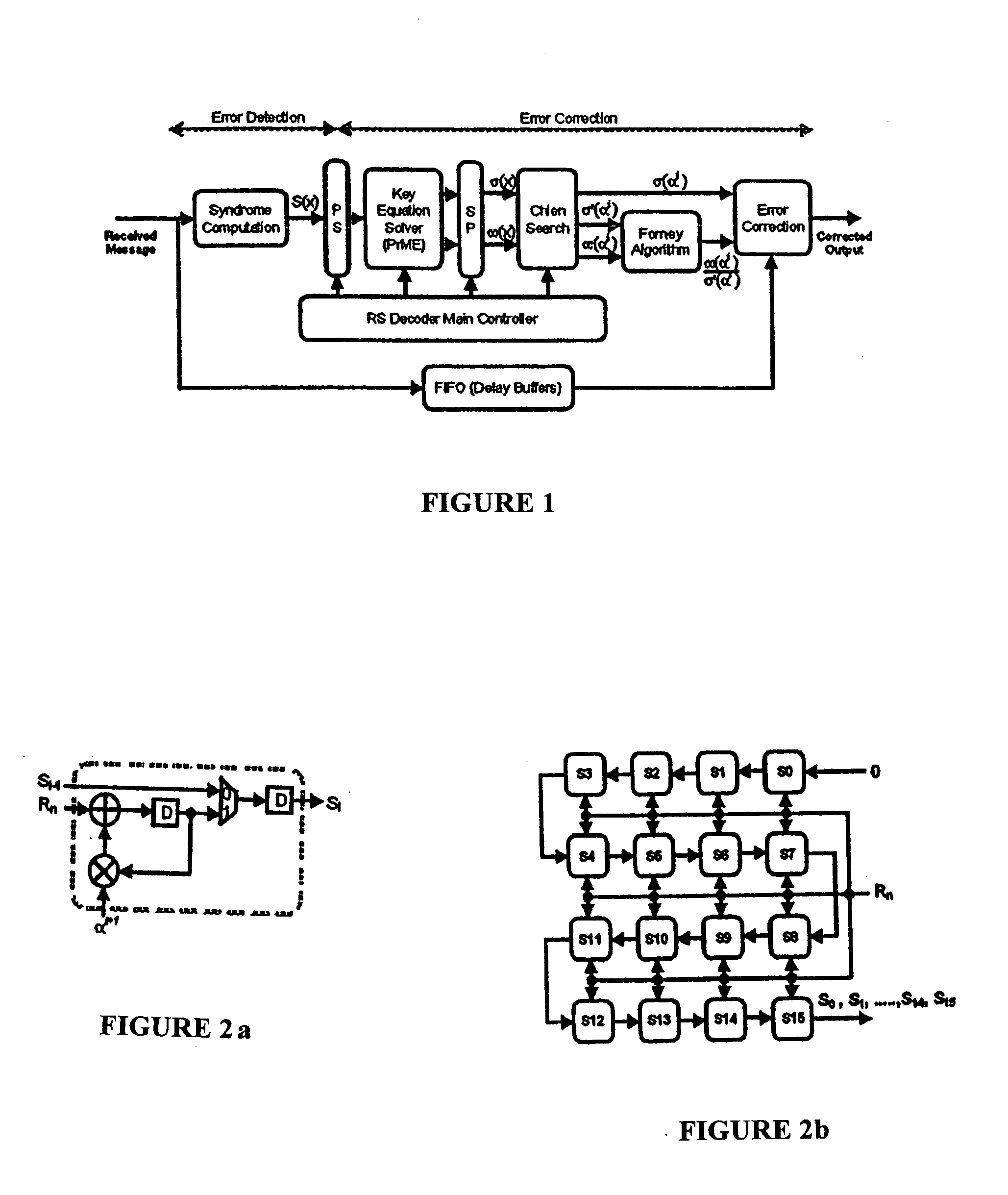
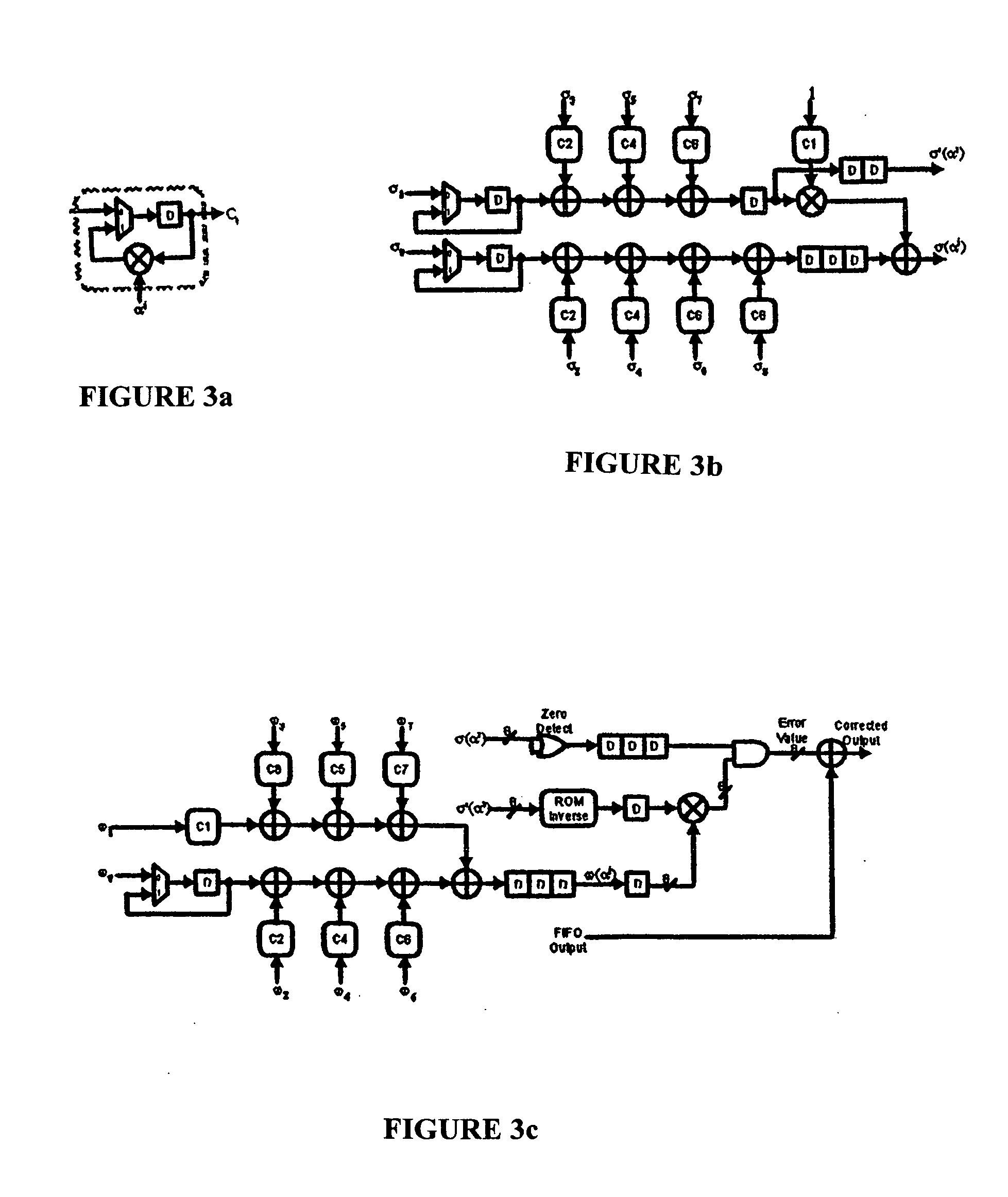
Reed-solomon decoder systems for high speed communication and data storage applications
InactiveUS20060059409A1Effective and reliable error correction functionalityReduce complexityCode conversionCoding detailsModem deviceHigh rate
A high-speed, low-complexity Reed-Solomon (RS) decoder architecture using a novel pipelined recursive Modified Euclidean (PrME) algorithm block for very high-speed optical communications is provided. The RS decoder features a low-complexity Key Equation Solver using a PrME algorithm block. The recursive structure enables the low-complexity PrME algorithm block to be implemented. Pipelining and parallelizing allow the inputs to be received at very high fiber optic rates, and outputs to be delivered at correspondingly high rates with minimum delay. An 80-Gb / s RS decoder architecture using 0.13-μm CMOS technology in a supply voltage of 1.2 V is disclosed that features a core gate count of 393 K and operates at a clock rate of 625 MHz. The RS decoder has a wide range of applications, including fiber optic telecommunication applications, hard drive or disk controller applications, computational storage system applications, CD or DVD controller applications, fiber optic systems, router systems, wireless communication systems, cellular telephone systems, microwave link systems, satellite communication systems, digital television systems, networking systems, high-speed modems and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
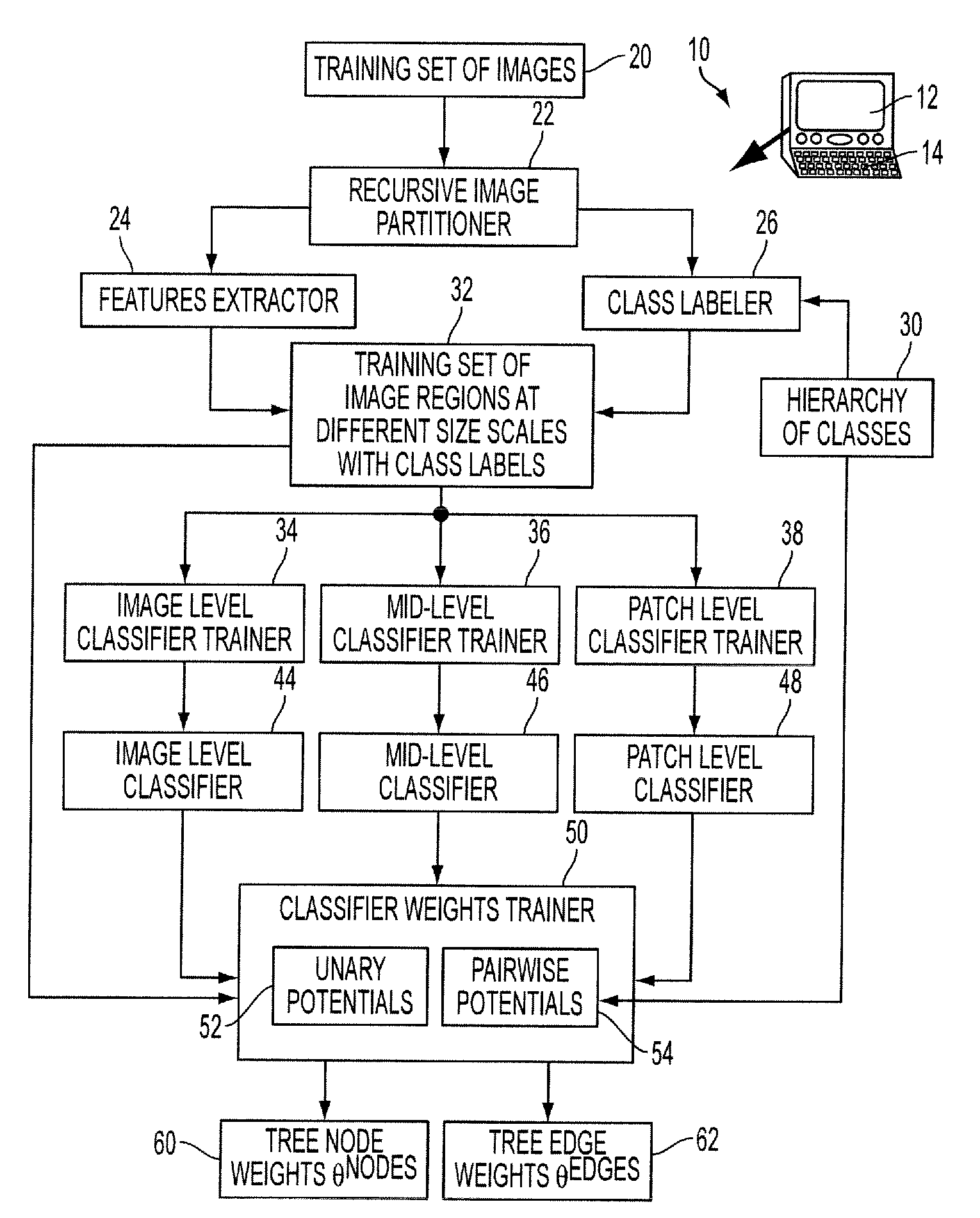
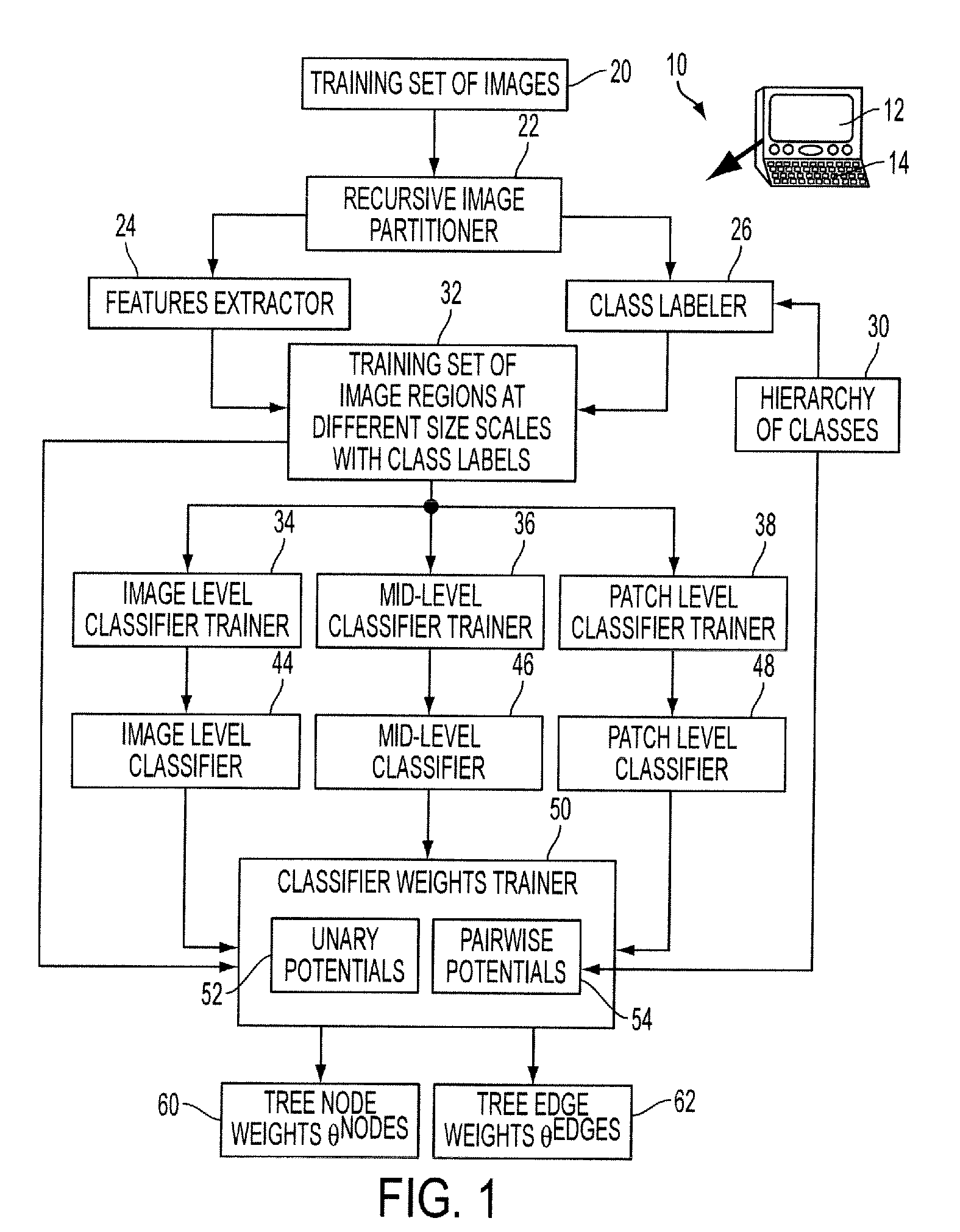
Consistent hierarchical labeling of image and image regions
Classification of image regions comprises: recursively partitioning an image into a tree of image regions having the image as a tree root and at least one image patch in each leaf image region of the tree, the tree having nodes defined by the image regions and edges defined by pairs of nodes connected by edges of the tree; assigning unary classification potentials to nodes of the tree; assigning pairwise classification potentials to edges of the tree; and labeling the image regions of the tree of image regions based on optimizing an objective function comprising an aggregation of the unary classification potentials and the pairwise classification potentials.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method and apparatus of a self-configured, model-based adaptive, predictive controller for multi-zone regulation systems
InactiveUS20110022193A1Easy to addPrecise processingSampled-variable control systemsTravelling carriersHorizonPlastic injection molding
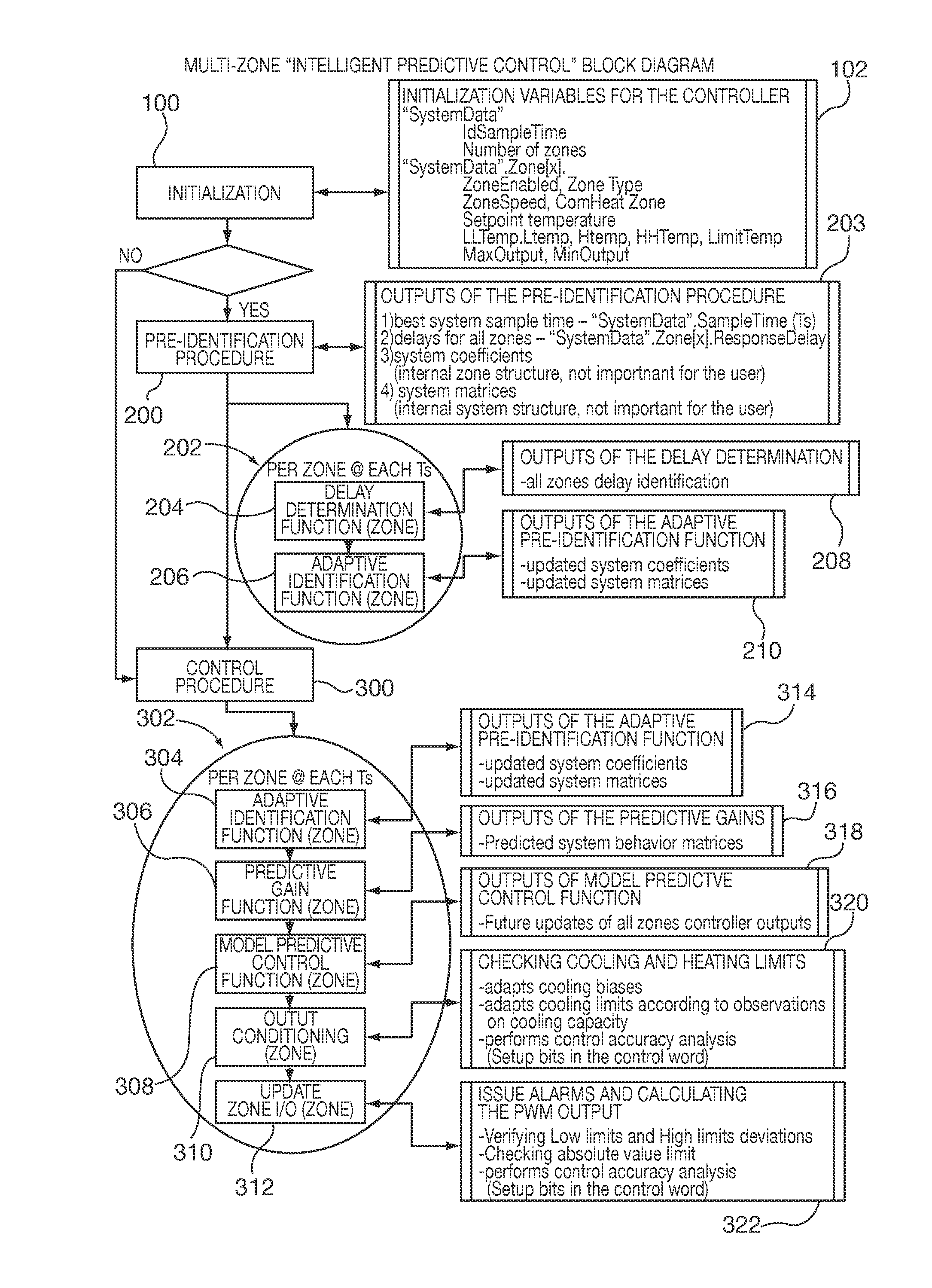
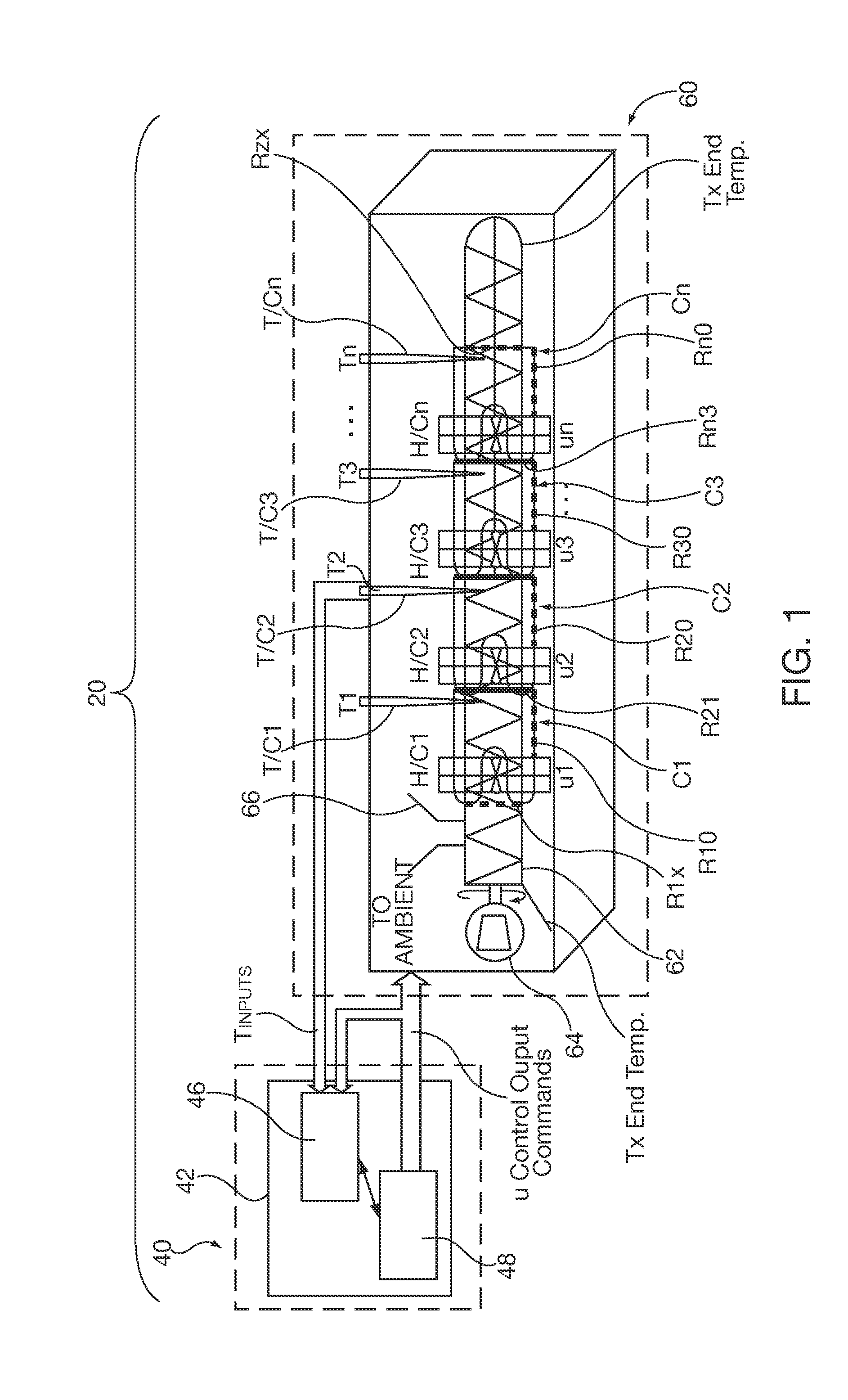
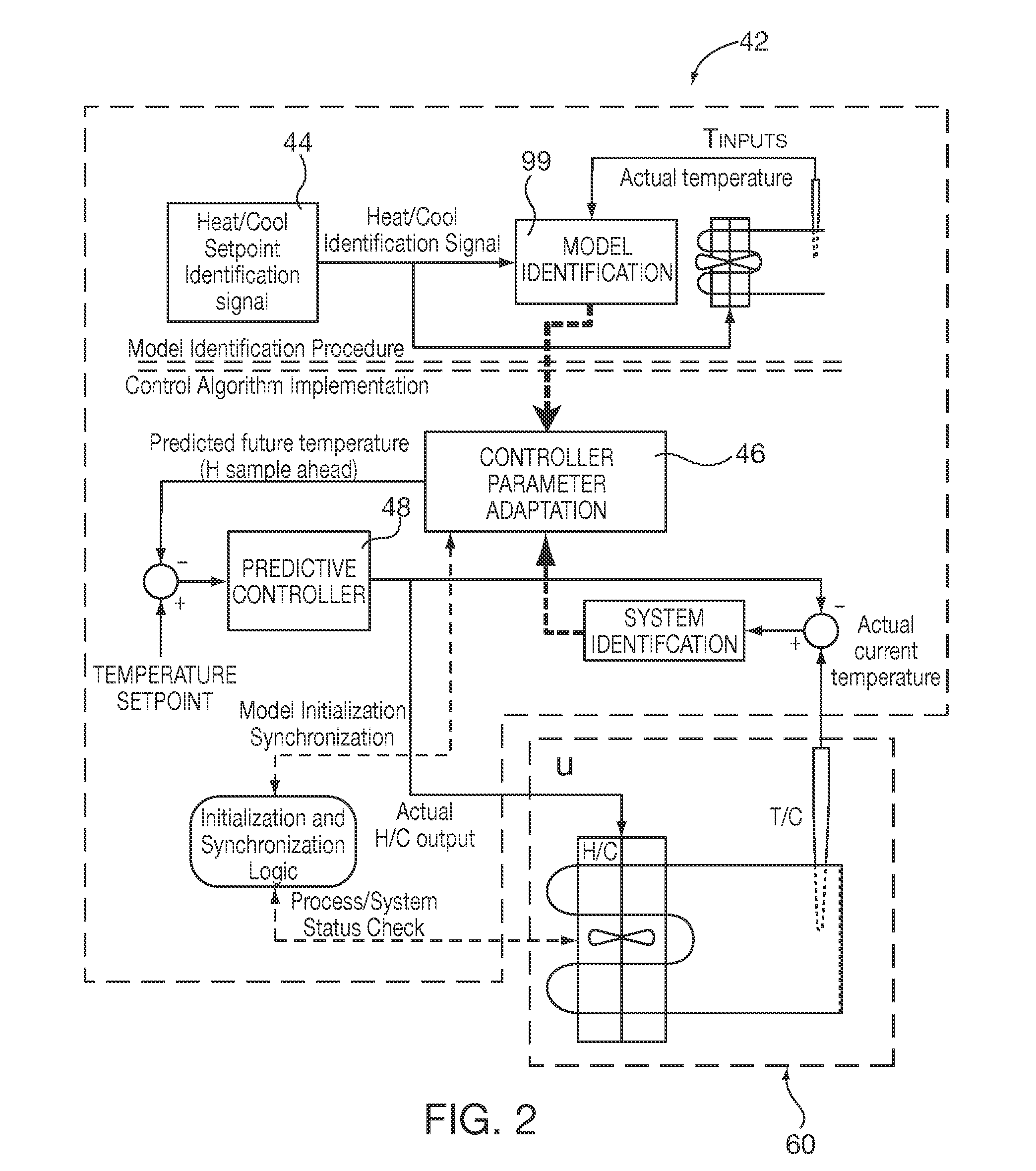
A control system simultaneously controls a multi-zone process with a self-adaptive model predictive controller (MPC), such as temperature control within a plastic injection molding system. The controller is initialized with basic system information. A pre-identification procedure determines a suggested system sampling rate, delays or “dead times” for each zone and initial system model matrix coefficients necessary for operation of the control predictions. The recursive least squares based system model update, control variable predictions and calculations of the control horizon values are preferably executed in real time by using matrix calculation basic functions implemented and optimized for being used in a S7 environment by a Siemens PLC. The number of predictions and the horizon of the control steps required to achieve the setpoint are significantly high to achieve smooth and robust control. Several matrix calculations, including an inverse matrix procedure performed at each sample pulse and for each individual zone determine the MPC gain matrices needed to bring the system with minimum control effort and variations to the final setpoint. Corrective signals, based on the predictive model and the minimization criteria explained above, are issued to adjust system heating / cooling outputs at the next sample time occurrence, so as to bring the system to the desired set point. The process is repeated continuously at each sample pulse.
Owner:SIEMENS IND INC
Binary prediction tree modeling with many predictors and its uses in clinical and genomic applications
The statistical analysis described and claimed is a predictive statistical tree model that overcomes several problems observed in prior statistical models and regression analyses, while ensuring greater accuracy and predictive capabilities. Although the claimed use of the predictive statistical tree model described herein is directed to the prediction of a disease in individuals, the claimed model can be used for a variety of applications including the prediction of disease states, susceptibility of disease states or any other biological state of interest, as well as other applicable non-biological states of interest. This model first screens genes to reduce noise, applies k-means correlation-based clustering targeting a large number of clusters, and then uses singular value decompositions (SVD) to extract the single dominant factor (principal component) from each cluster. This generates a statistically significant number of cluster-derived singular factors, that we refer to as metagenes, that characterize multiple patterns of expression of the genes across samples. The strategy aims to extract multiple such patterns while reducing dimension and smoothing out gene-specific noise through the aggregation within clusters. Formal predictive analysis then uses these metagenes in a Bayesian classification tree analysis. This generates multiple recursive partitions of the sample into subgroups (the “leaves” of the classification tree), and associates Bayesian predictive probabilities of outcomes with each subgroup. Overall predictions for an individual sample are then generated by averaging predictions, with appropriate weights, across many such tree models. The model includes the use of iterative out-of-sample, cross-validation predictions leaving each sample out of the data set one at a time, refitting the model from the remaining samples and using it to predict the hold-out case. This rigorously tests the predictive value of a model and mirrors the real-world prognostic context where prediction of new cases as they arise is the major goal.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
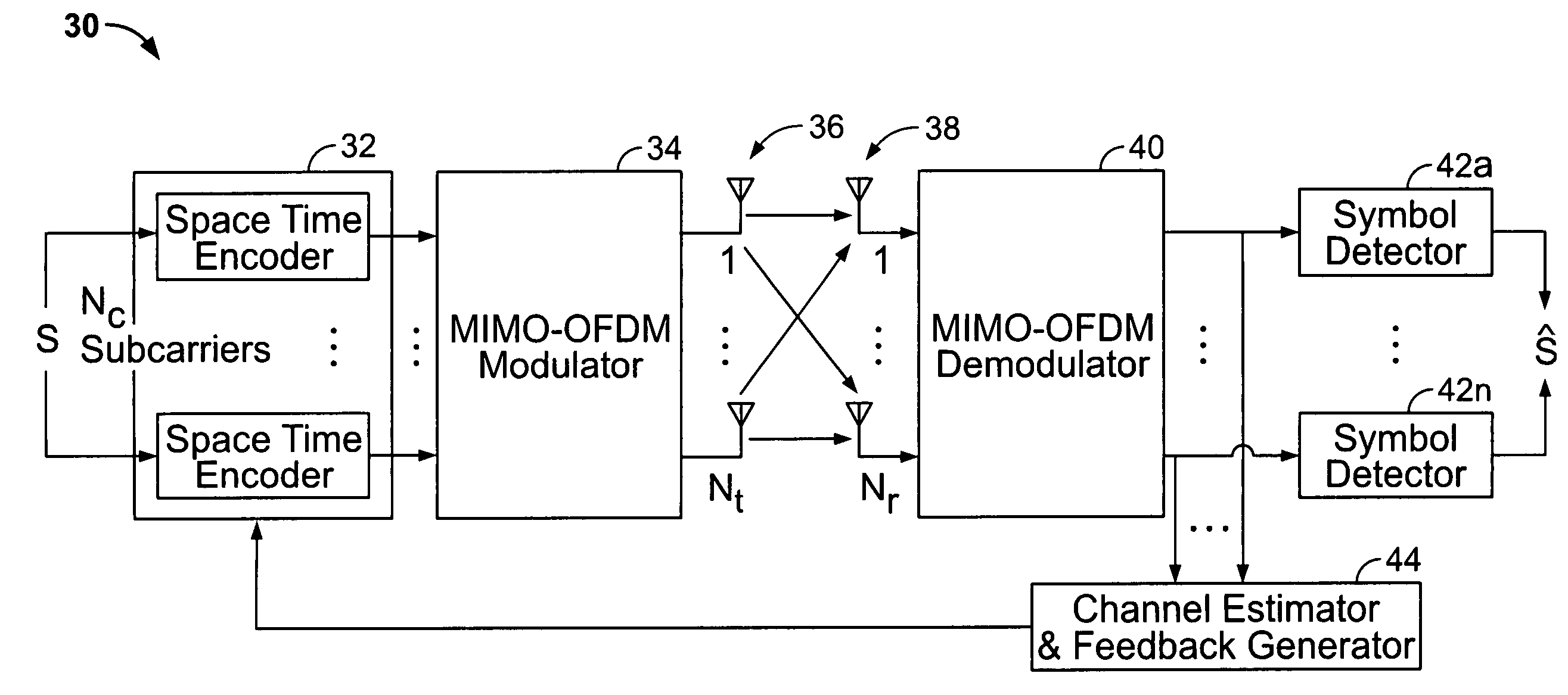
Recursive and trellis-based feedback reduction for MIMO-OFDM with rate-limited feedback
InactiveUS20070297529A1Reduce feedbackMaintain performanceModulated-carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsCarrier signalDynamic programming
Techniques are provided for reducing feedback while maintaining performance in a MIMO-OFDM system. The disclosed techniques employ finite-rate feedback methods that uses vector quantization compression. The disclosed methods / techniques generally involve: receiving a plurality of symbols from a plurality of sub-carriers at a receiver; selecting a plurality of indices of codewords corresponding to a codebook of pre-coding weighting matrices for the sub-carriers based on vector quantization compression of the codewords; and transmitting the selected indices over a wireless channel to a transmitter. Finite state vector quantization feedback makes use of a finite state vector quantizer (FSVQ), which is a recursive vector quantizer (VQ) with a finite number of states. In finite state vector quantization feedback, optimal precoding matrices (beamforming vectors) are selected sequentially across subcarriers. In a trellis-based feedback method, the optimal precoding matrices are selected at the same time for all subcarriers by searching for the optimum choice of matrices along a trellis using the Viterbi algorithm (dynamic programming).
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
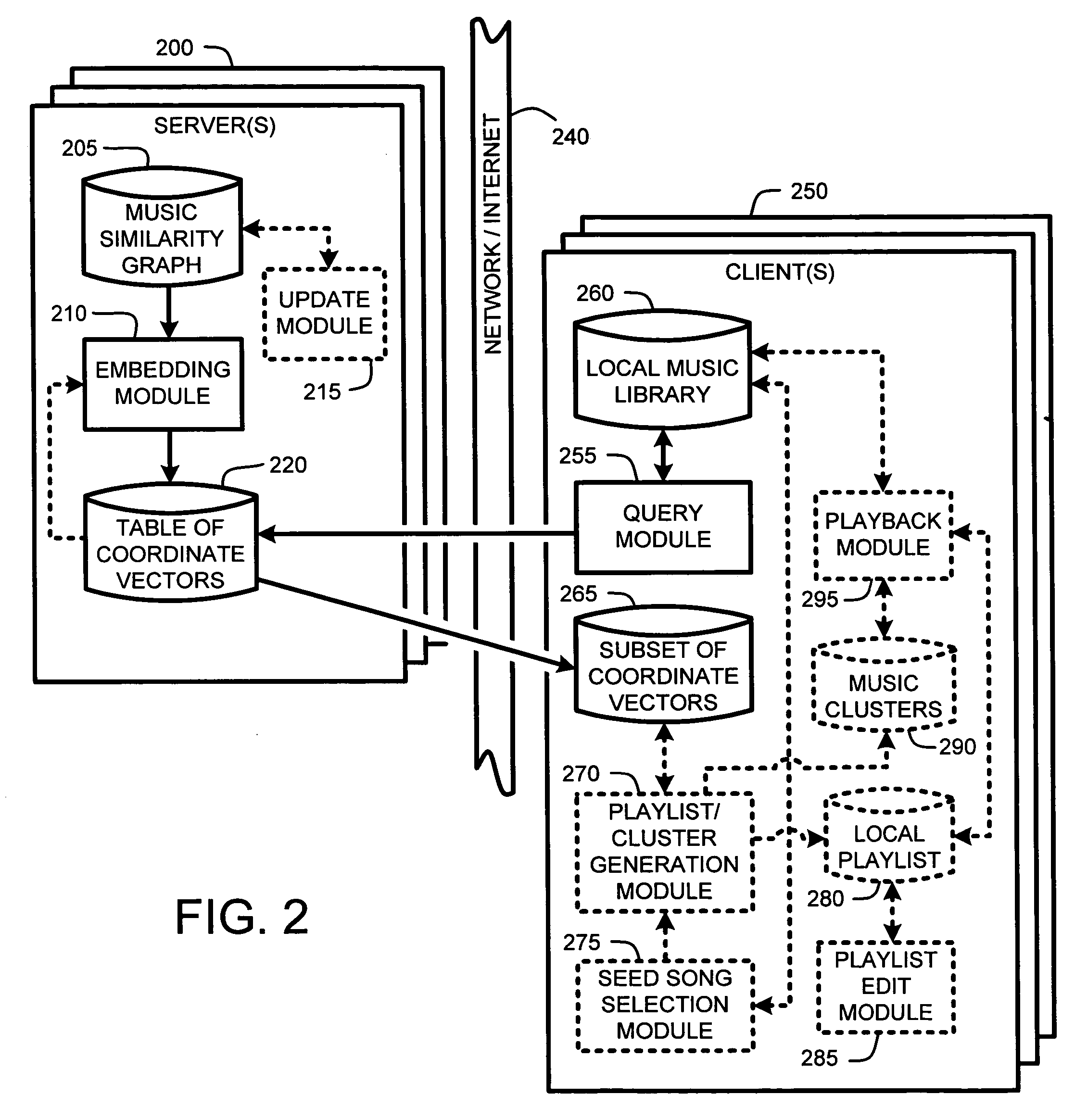
Client-based generation of music playlists via clustering of music similarity vectors
InactiveUS20060112098A1Easy to updateLimited amountMetadata audio data retrievalElectrophonic musical instrumentsPattern recognitionGraphics
A “Music Mapper” automatically constructs a set coordinate vectors for use in inferring similarity between various pieces of music. In particular, given a music similarity graph expressed as links between various artists, albums, songs, etc., the Music Mapper applies a recursive embedding process to embed each of the graphs music entries into a multi-dimensional space. This recursive embedding process also embeds new music items added to the music similarity graph without reembedding existing entries so long a convergent embedding solution is achieved. Given this embedding, coordinate vectors are then computed for each of the embedded musical items. The similarity between any two musical items is then determined as either a function of the distance between the two corresponding vectors. In various embodiments, this similarity is then used in constructing music playlists given one or more random or user selected seed songs or in a statistical music clustering process.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
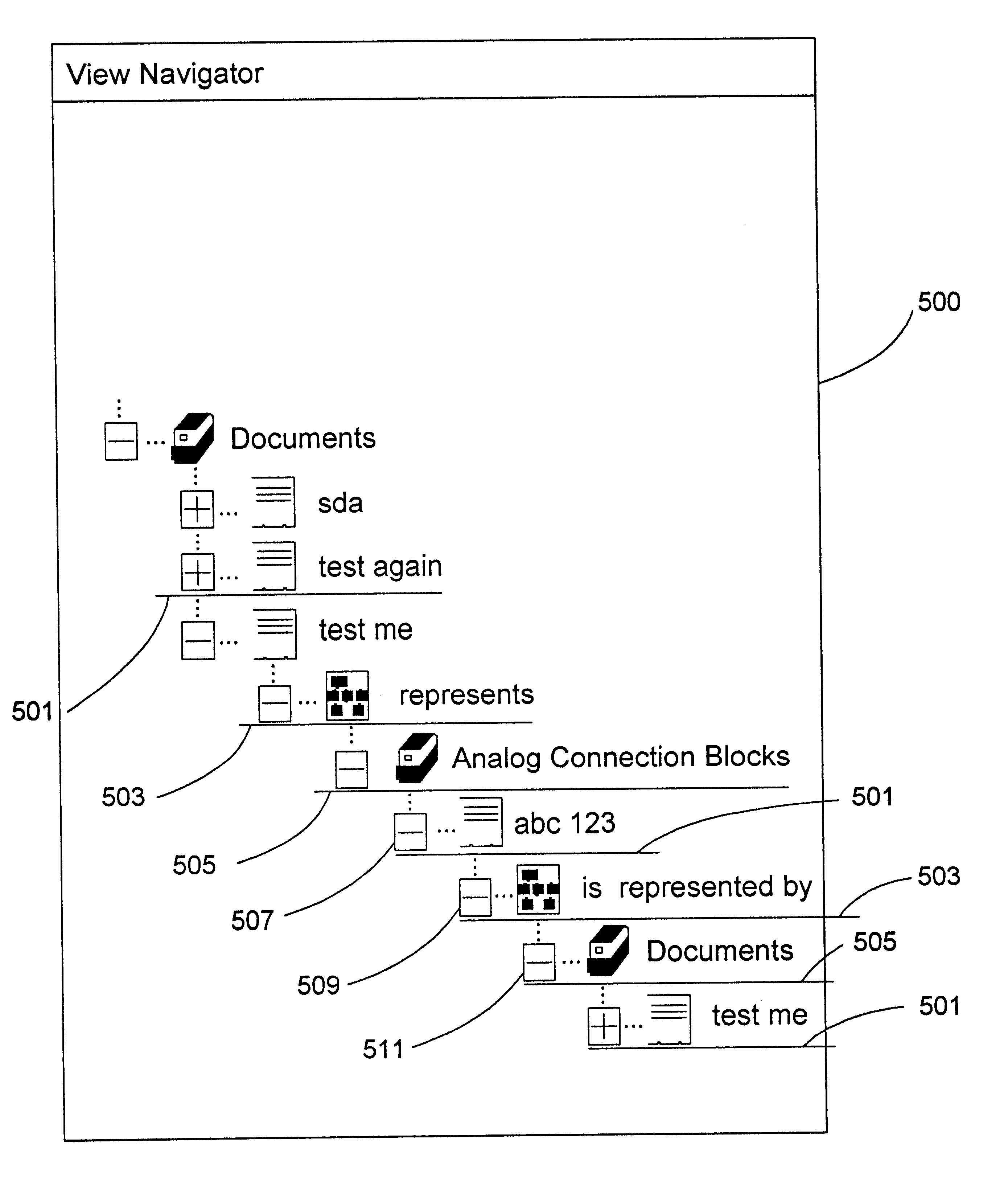
View navigation for creation, update and querying of data objects and textual annotations of relations between data objects
InactiveUS6618733B1EffectivelySave storage spaceData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsCustomer relationship managementOperational system
A method (and corresponding database system) for displaying in a view window information characterizing semantics of relations between objects. For each given relation between at least one subject object and at least one direct object, bi-directional modifier data is stored that represents first text characterizing semantics of a relationship of the at least one first object to the at least one second object, and represents second text characterizing semantics of a relationship of the at least one second object to the at least one first object. In response to predetermined user input associated with an object node displayed in the view window, a set of relations whose at least one subject object or at least one direct object is associated with the object node is identified. For at least one relation in the set of relations, the view window is updated to include a second node comprising a graphical representation of: the first text of the given relation in the event that the given object is a subject object in the given relation, or the second text of the given relation in the event that the given object is a direct object in the given relation. The second node may be a relation node associated with a given relation, or a mixed node associated with a relation-type pair. In response to predetermined input with a second node, the second node may be expanded to identify and display one or more object nodes (identifying direct object(s) of relations derived from expansion of a subject object associated therewith or identifying subject object(s) of relations derived from expansion of a direct object associated therewith). Preferably, this expansion routine is recursive in nature.The method (and database system) of the present invention may be used in a wide assortment of software applications, including enterprise applications (such as e-business applications, supply chain management applications, customer relationship management applications, decision support applications), the file system in operating systems, web browsers, e-mail applications and personal information management applications. Importantly, the method (and database system) provides an easy, user friendly and efficient mechanism to define, view and query the organization of the data elements (and the relationships therebetween) stored and accessed in such software applications, in a manner that conveys the real-world meaning of such relationships.
Owner:REVELINK
Lossless coding method for waveform data
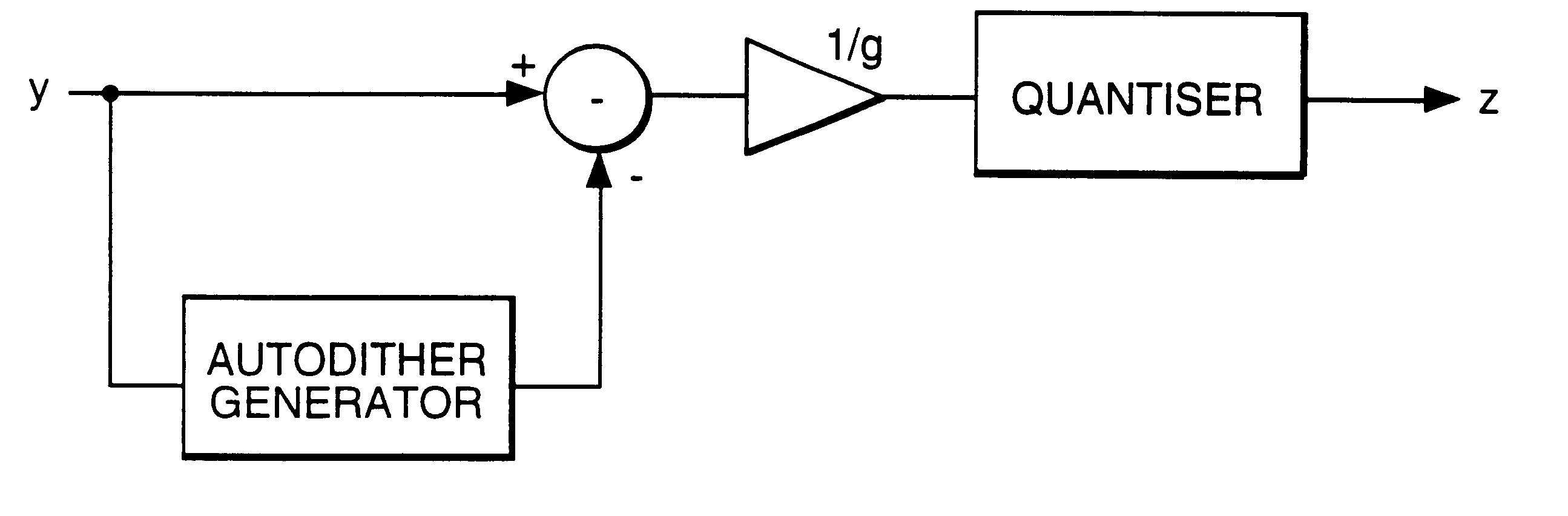
InactiveUS6664913B1Preserve integrityAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsLossless codingSampling instant
In a method of lossless processing of an integer value signal in a prediction filter which includes a quantiser, a numerator of the prediction filter is implemented prior to the quantiser and a denominator of the prediction filter is implemented recursively around the quantiser to reduce the peak data rate of an output signal. In the lossless processor, at each sample instant, an input to the quantiser is jointly responsive to a first sample value of a signal input to the prediction filter, a second sample value of a signal input to the prediction filter at a previous sample instant, and an output value of the quantiser at a previous sample incident. In a preferred embodiment, the prediction filter includes noise shaping for affecting the output of the quantiser.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
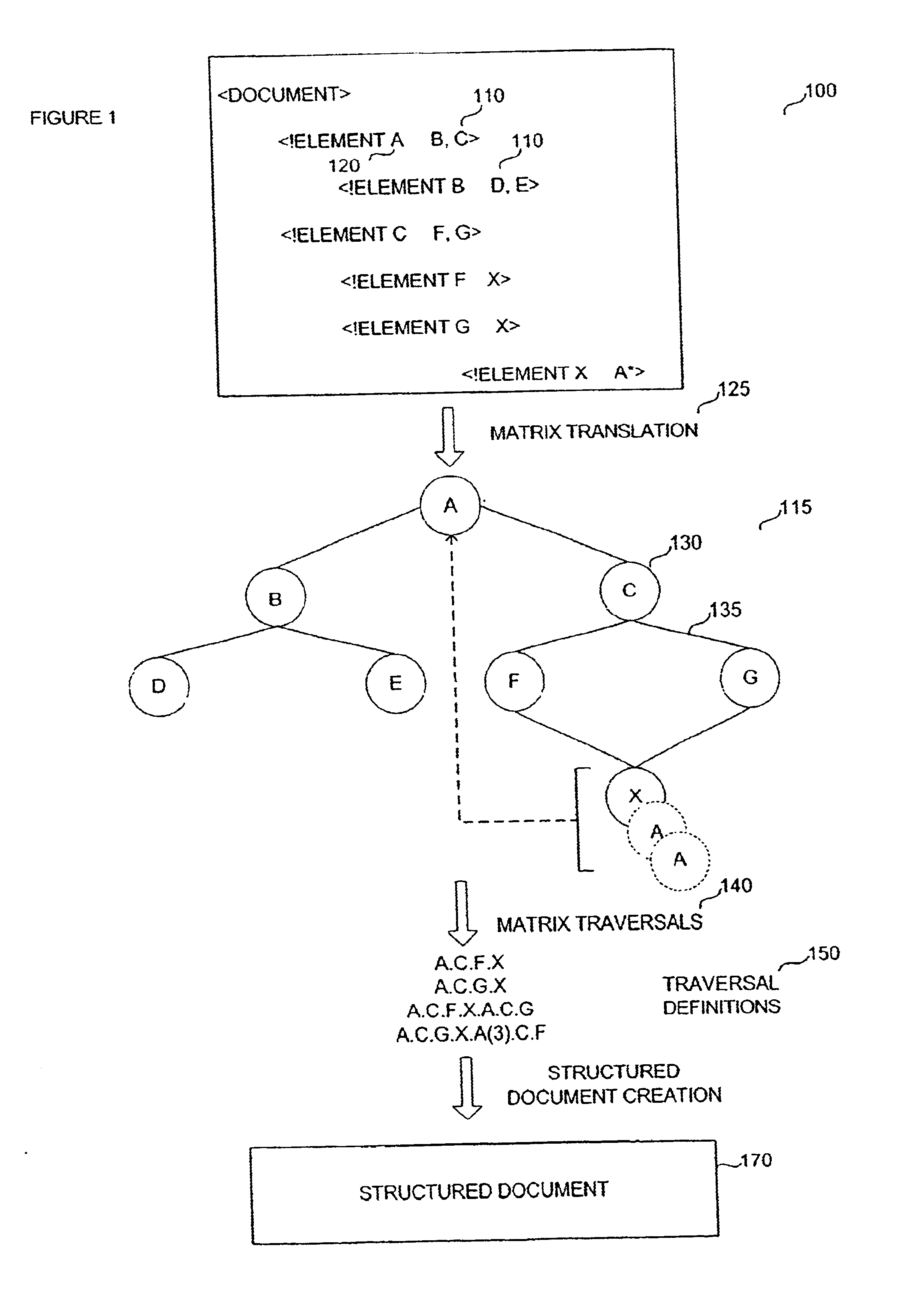
System and method for dynamic generation of structured documents
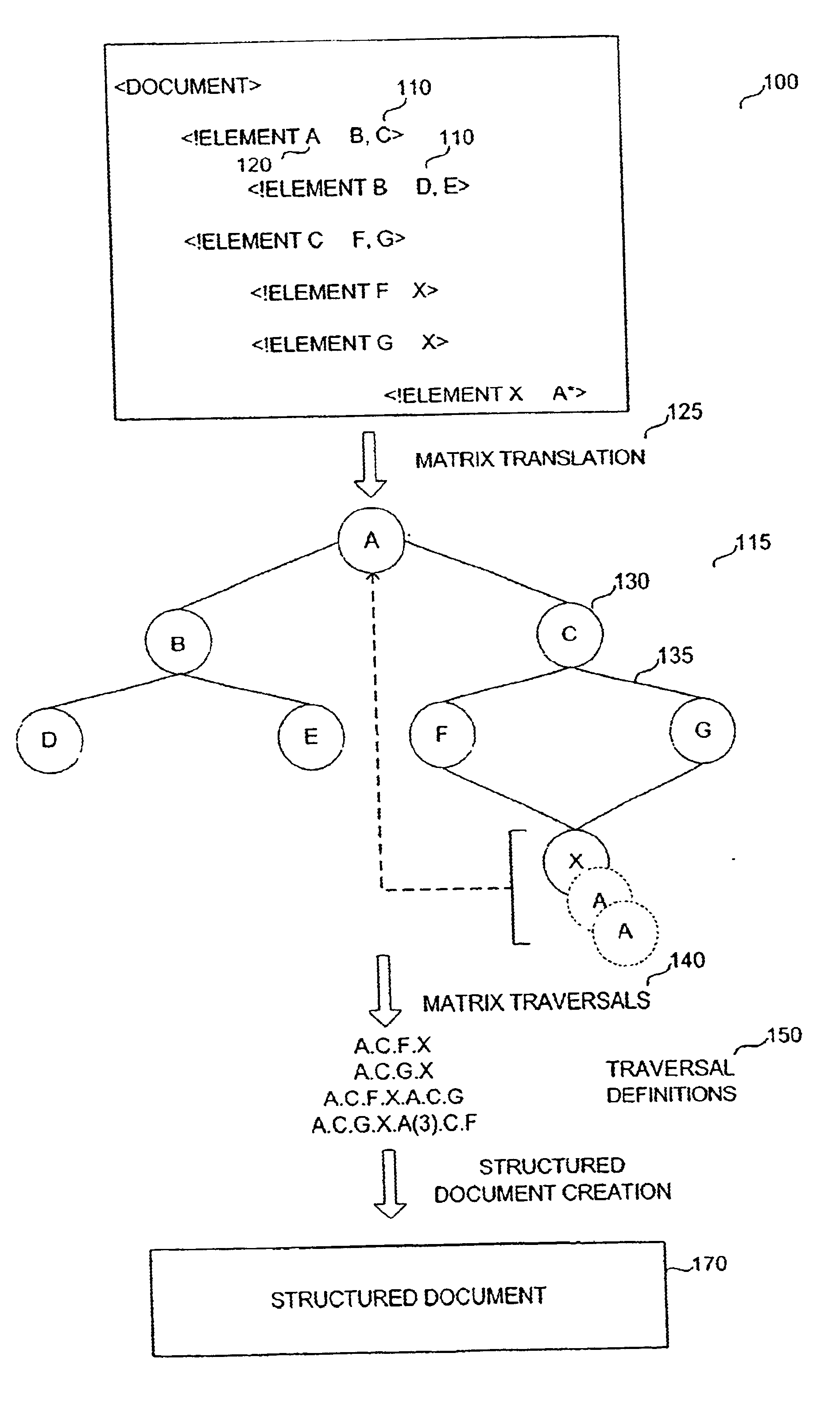
InactiveUS6912538B2Reduced database table configuration requirementReduce complexityData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDocument preparationExtensible markup
A method and apparatus for representing complex data schemas and generating type validated output documents in a markup language. The methods apply to transforming document type definitions into extensible markup language coded information that can readily accommodate logical constraints imposed by recursion or repetition within the DTD structure. Furthermore, non-determinism arising from repetition or recursion in a data schema is resolved by traversal path coding using a matrix representation of the data schema.
Owner:STAPEL KEVIN +1
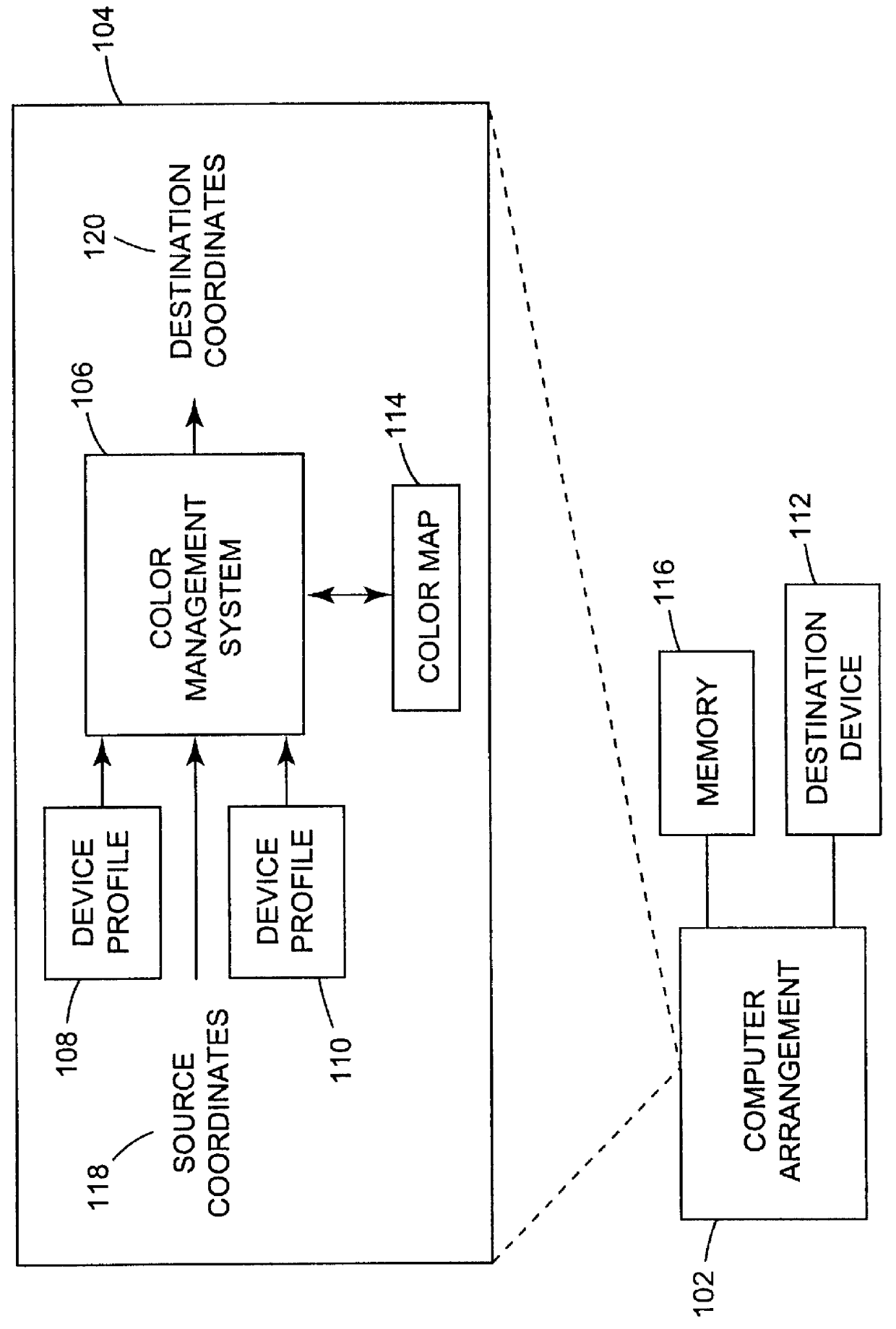
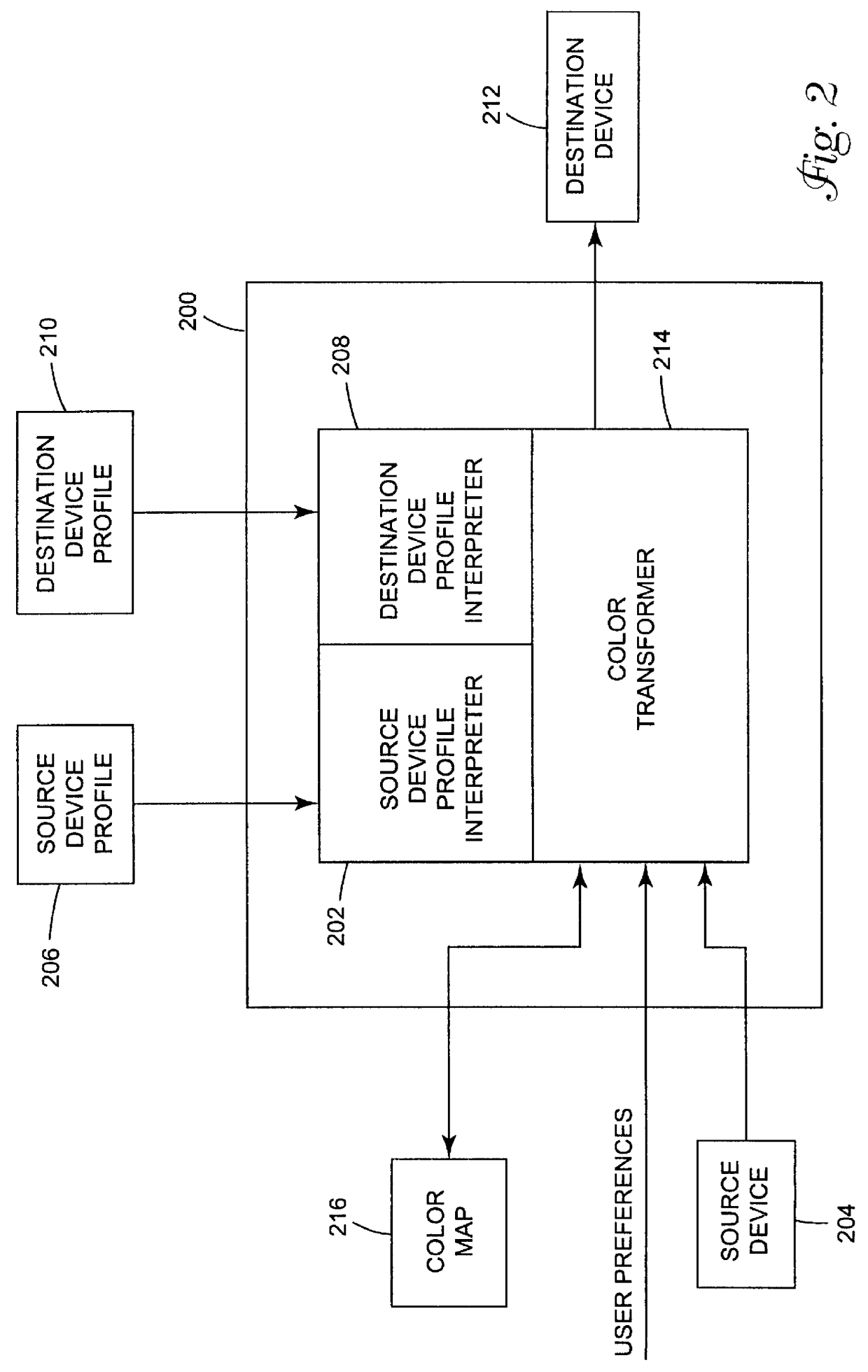
Arrangement for mapping colors between imaging systems and method therefor
A color mapping method is used in transforming colors between color imaging systems. The method includes using forward transformation profiles that characterize the color imaging systems to generate respective sets of device-independent color values for the color imaging systems. Color conversions are calculated by recursively reducing differences between the respective sets of device-independent color values. Based on these color conversions, a color map is constructed that describes a relationship between the color imaging systems.
Owner:KODAK POLYCHROME GRAPHICS
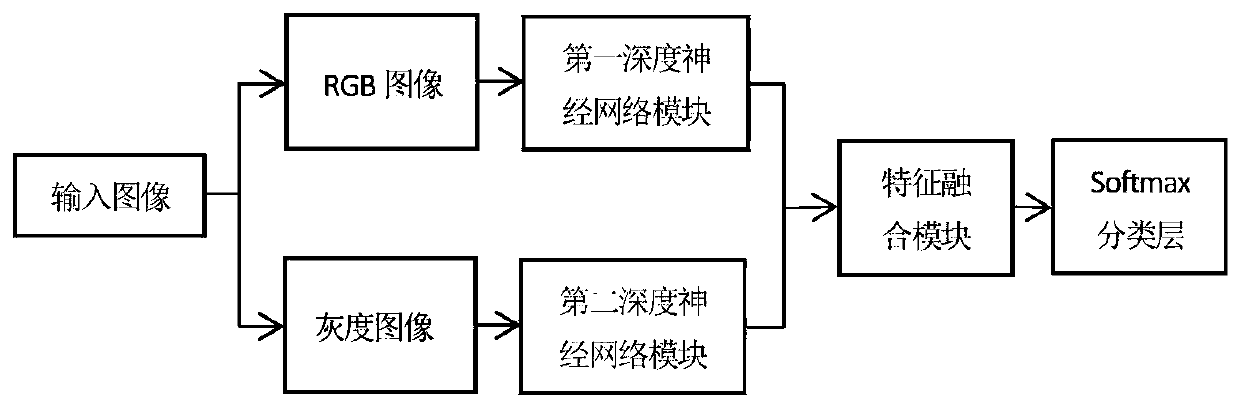
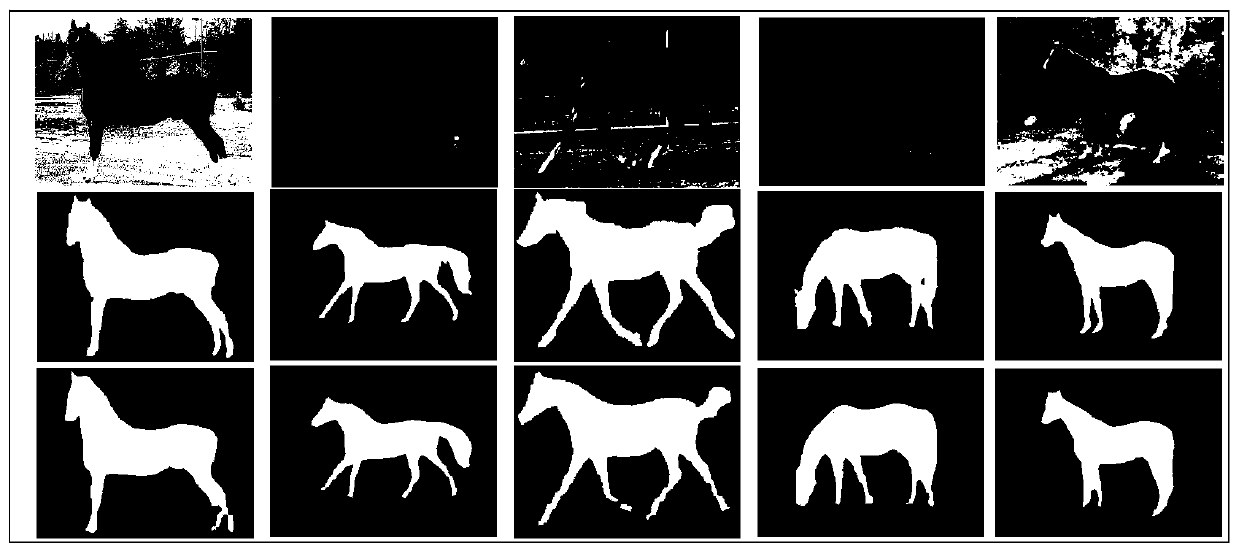
An image semantic segmentation method based on deep learning
ActiveCN109711413ARich coordinate featuresImprove generalization abilityInternal combustion piston enginesCharacter and pattern recognitionData setRgb image
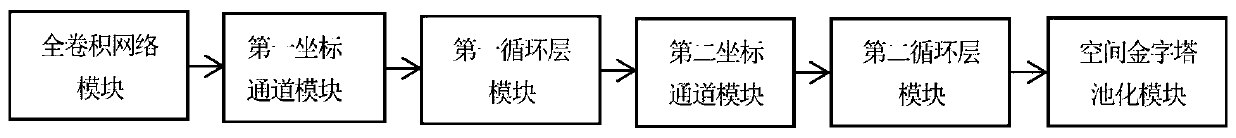
The invention discloses an image semantic segmentation method based on deep learning. The method comprises four parts of data set processing, deep semantic segmentation network construction, deep semantic segmentation network training and parameter learning, and semantic segmentation on a test image. The RGB image and the gray level image of the input image are used as the input of the network model, the edge information of the gray level image is fully utilized, and the richness degree of input characteristics is effectively increased; a convolutional neural network and a bidirectional threshold recursion unit are combined, and more context dependency relationships and global feature information are captured on the basis of learning image local features; coordinate information is added tothe feature map through the first coordinate channel module and the second coordinate channel module, the coordinate features of the model are enriched, the generalization ability of the model is improved, and a semantic segmentation result with high resolution and accurate boundary is generated.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Internet security analysis system and process
InactiveUS6996845B1Memory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionWeb siteSecurity analysis
An automated Web security analysis system and process identifies security vulnerabilities in a target Internet Web site by parsing through the target Web site to search for a predetermined list of common security vulnerabilities. The process is recursive, exploiting information gathered throughout the process to search for additional security vulnerabilities. A prioritized list of detected security vulnerabilities is then presented to a user, including preferably a list of recommendations to eliminate the detected security vulnerabilities.
Owner:SPI DYNAMICS HEADQUARTERS
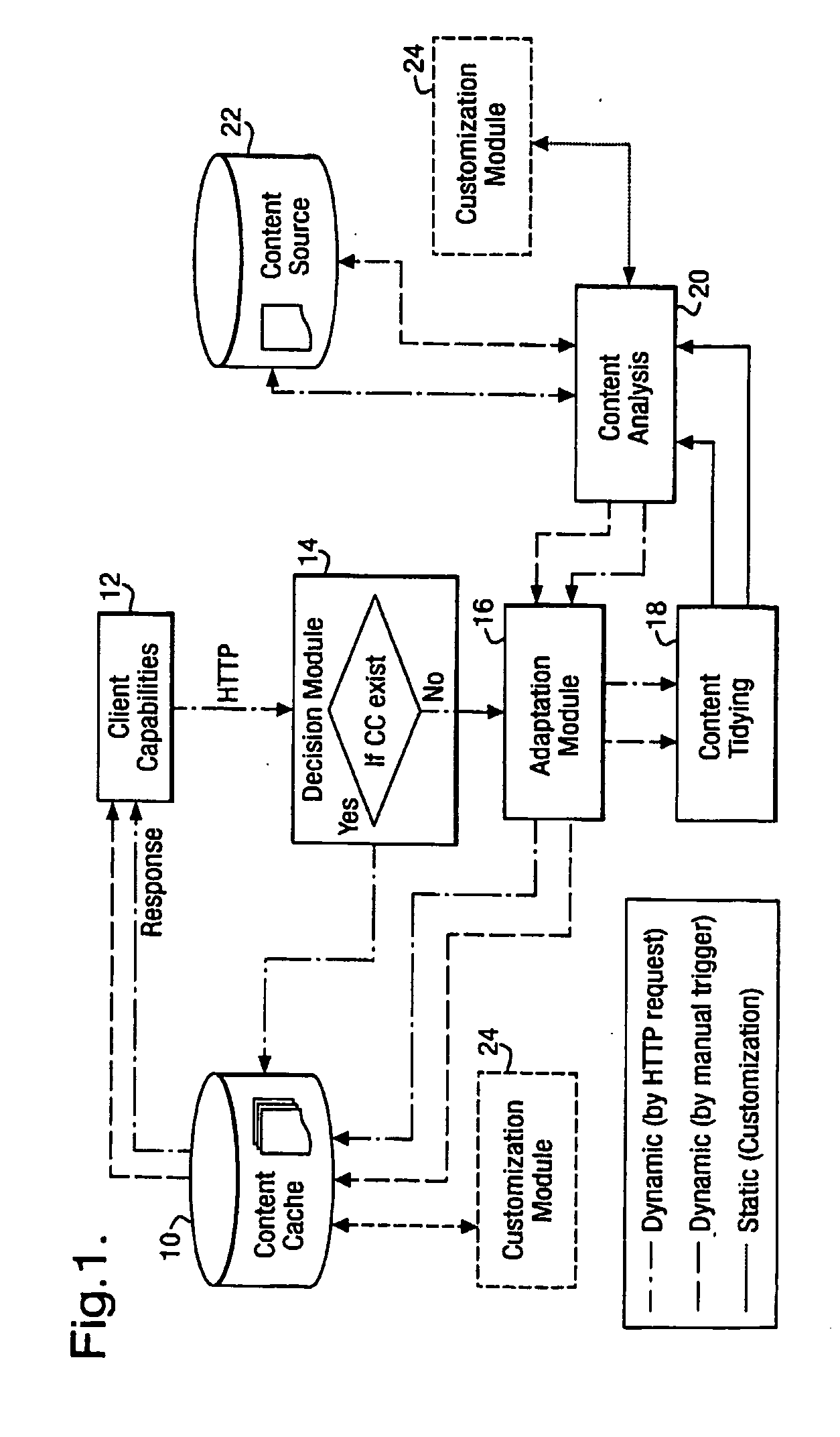
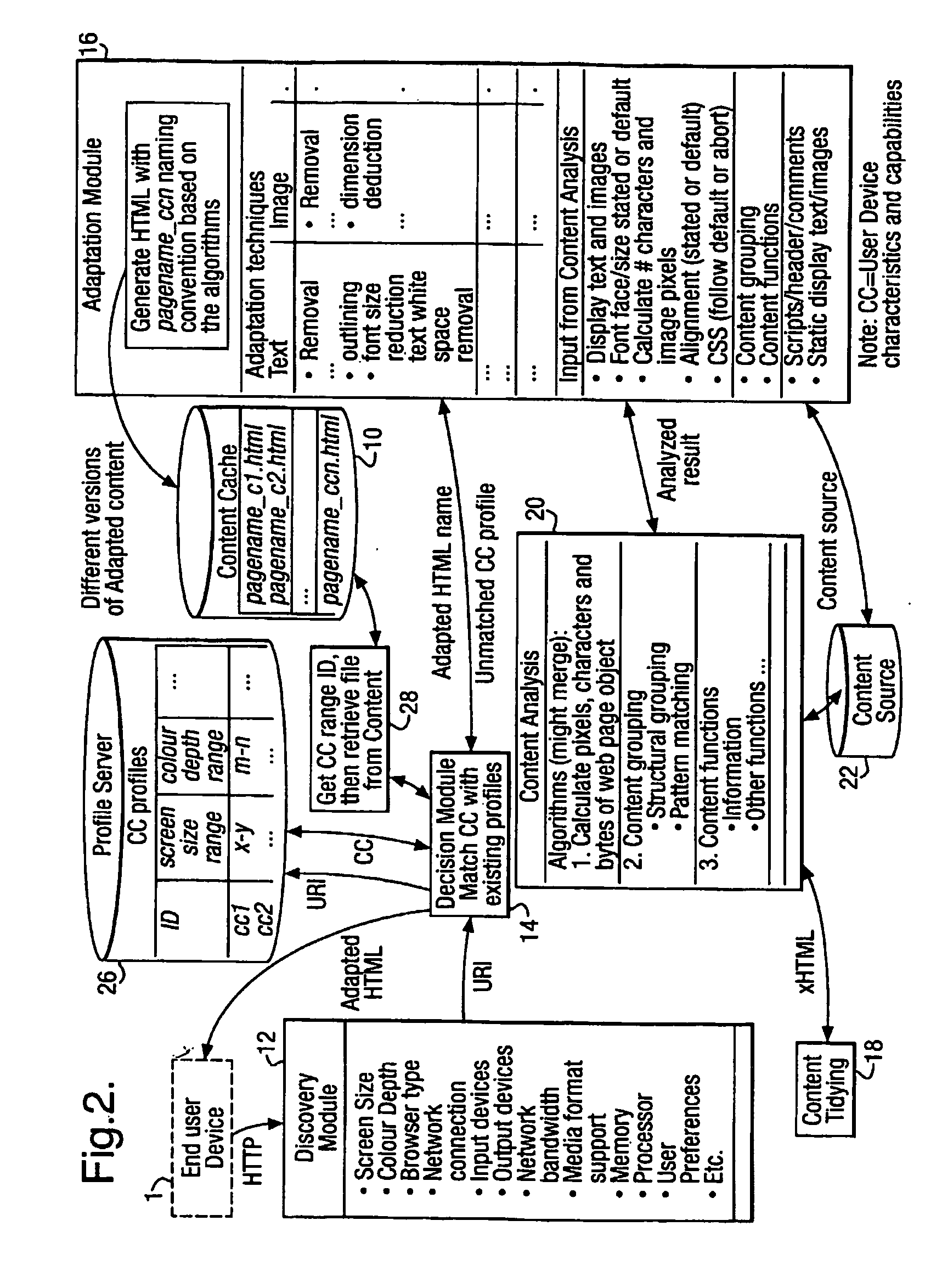
Web content adaptation process and system
InactiveUS20070083810A1Reducing/increasing sizeMinimal amountSpecial data processing applicationsWeb data browsing optimisationComputer graphics (images)Display device
An apparatus and method for adapting web page content are described. The adaptation of web page content for display on smaller intended display devices often requires the splitting of the content over a number of smaller pages. The apparatus and method relate to a procedure which integrates the process of splitting the content with applying transformations (for example, reducing the font size, images, etc) so as to optimise this process. The procedure is carried out systematically over the entire web page content, recursively splitting the content into smaller and smaller portions whilst simultaneously alternating this with various transformations so as to minimise the amount of white space visible on the smaller pages. Additionally, the preferred embodiment also tracks the transformations which have been applied to the objects and ensures consistency by applying them later to any similar objects.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
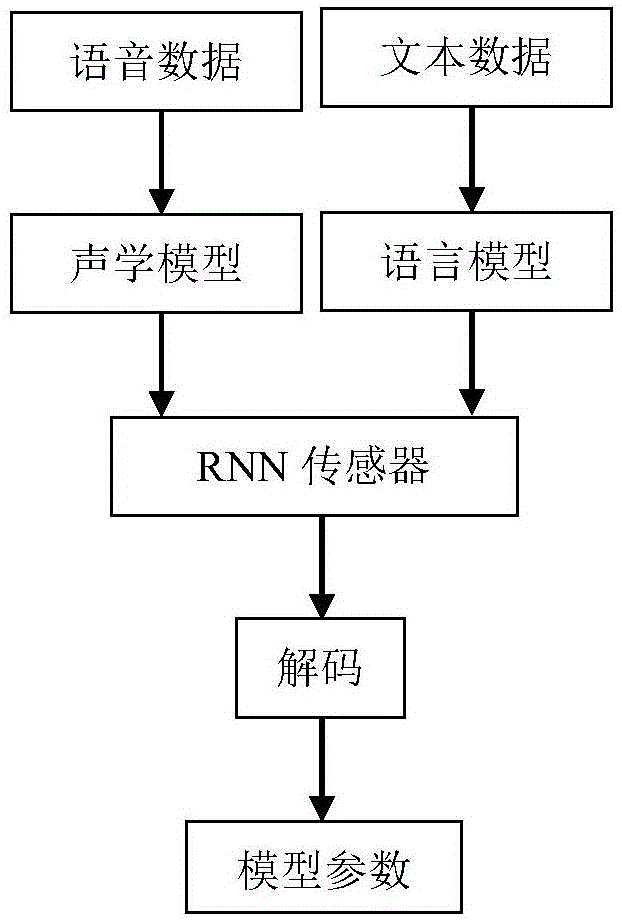
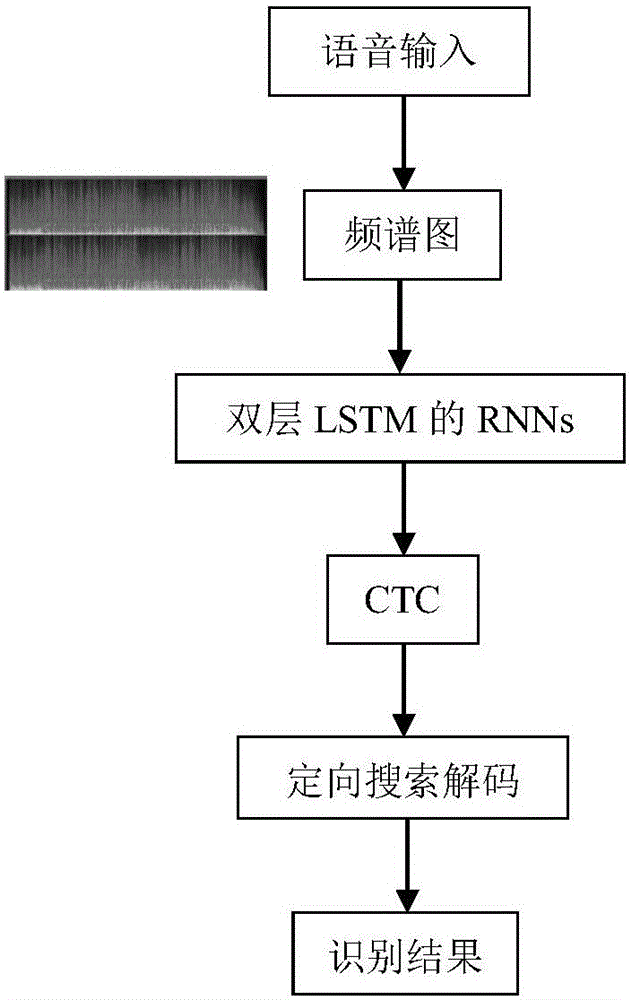
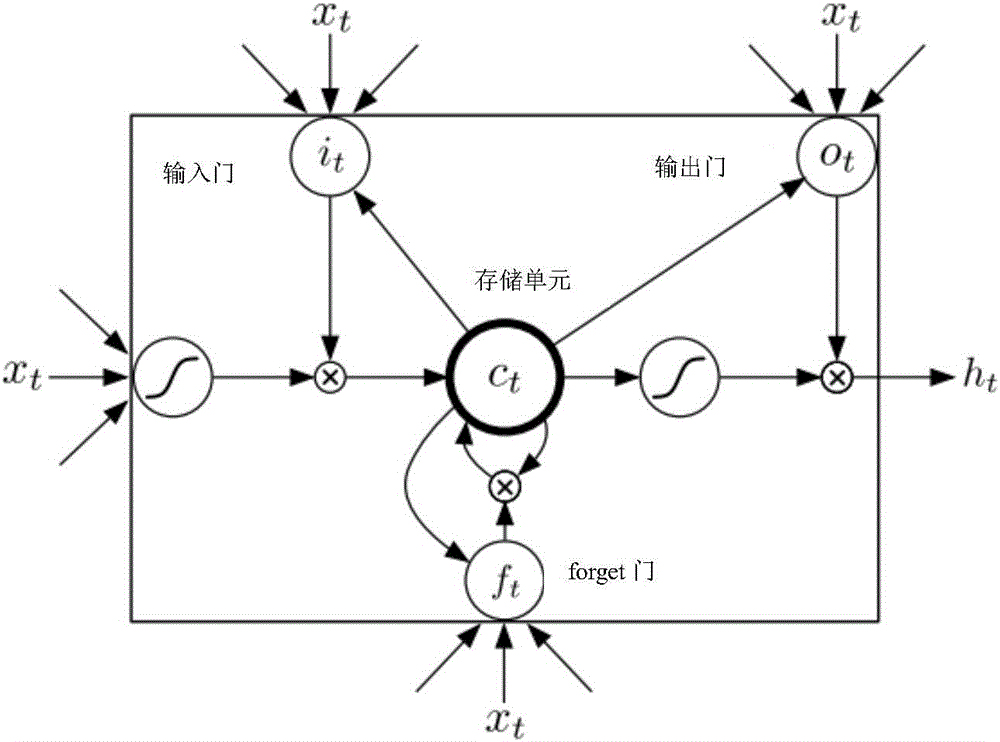
Voice identification method using long-short term memory model recurrent neural network
The invention discloses a voice identification method using a long-short term memory model recurrent neural network. The voice identification method comprises training and identification. The training process comprises steps of introducing voice data and text data to generate a commonly-trained acoustic and language mode, and using an RNN sensor to perform decoding to form a model parameter. The identification process comprises steps of converting voice input to a frequency spectrum graph through Fourier conversion, using the recursion neural network of the long-short term memory model to perform orientational searching decoding and finally generating an identification result. The voice identification method adopts the recursion neural network (RNNs) and adopts connection time classification (CTC) to train RNNs through an end-to-end training method. These LSTM units combining with the long-short term memory have good effects and combines with multi-level expression to prove effective in a deep network; only one neural network model (end-to-end model) exits from a voice characteristic (an input end) to a character string (an output end) and the neural network can be directly trained by a target function which is a some kind of a proxy of WER, which avoids to cost useless work to optimize an individual target function.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEITESHI TECH
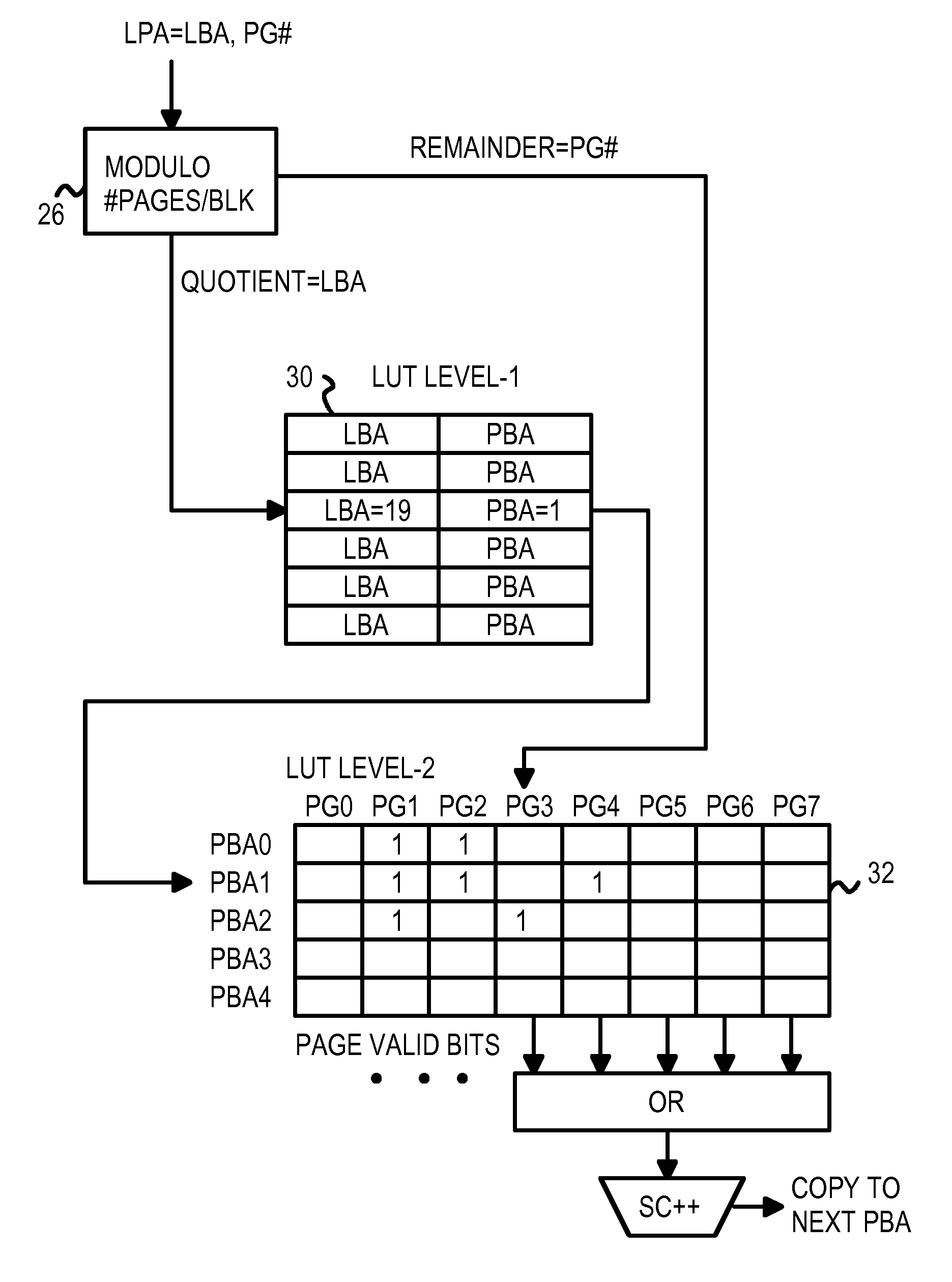
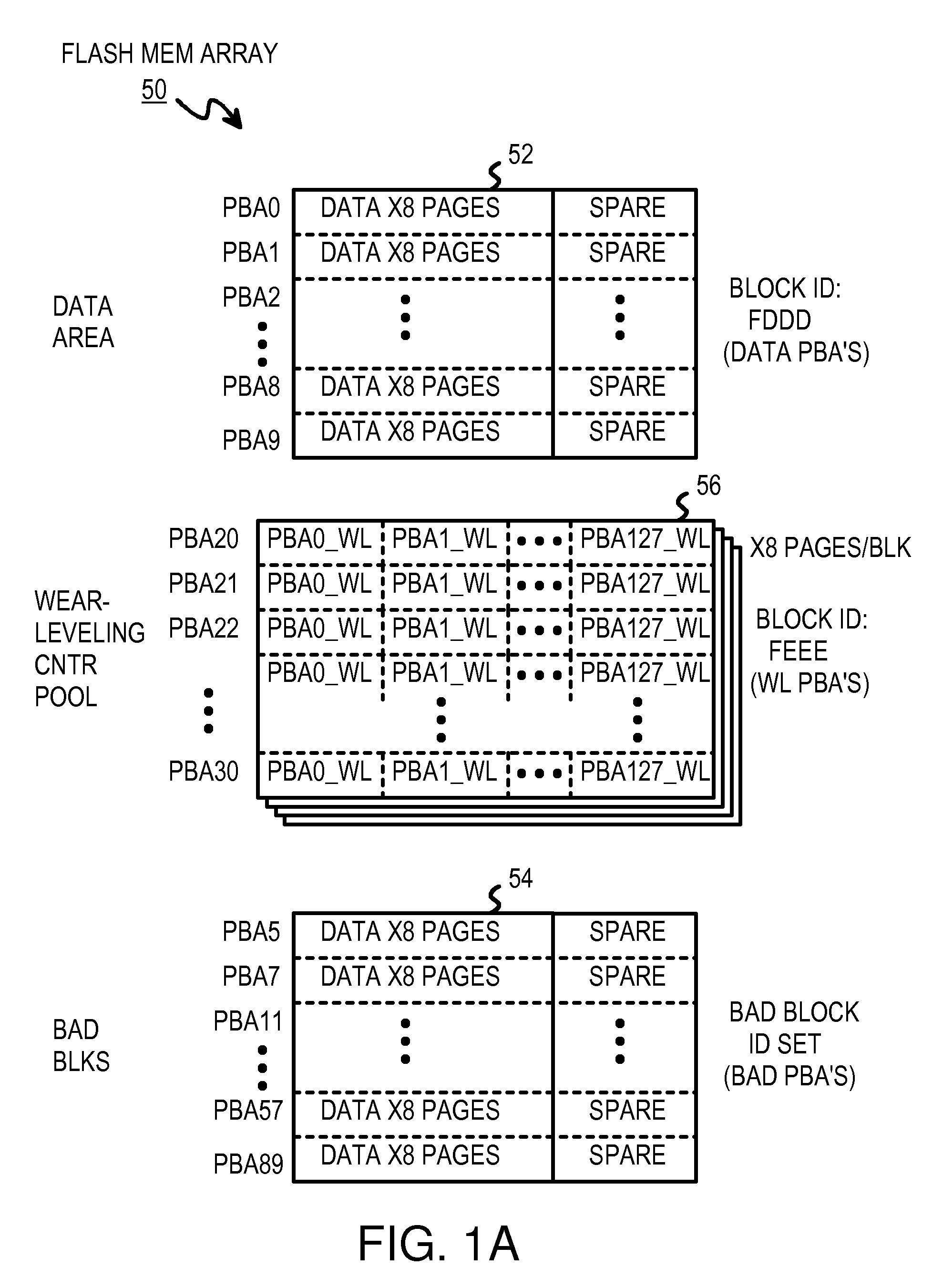
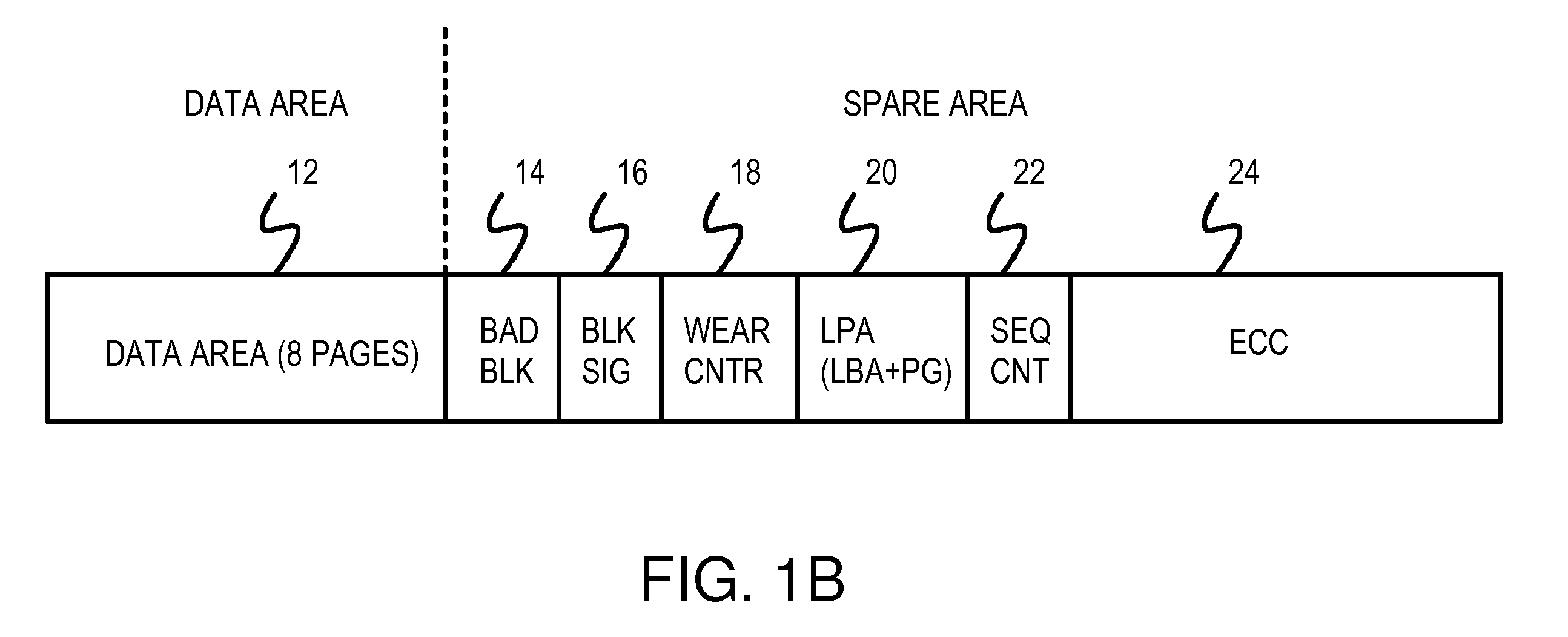
Two-level RAM lookup table for block and page allocation and wear-leveling in limited-write flash-memories
InactiveUS7660941B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesLogical block addressingRandom access memory
A restrictive multi-level-cell (MLC) flash memory prohibits regressive page-writes. When a regressive page-write is requested, an empty block having a low wear-level count is found, and data from the regressive page-write and data from pages stored in the old block are written to the empty block in page order. The old block is erased and recycled. A two-level look-up table is stored in volatile random-access memory (RAM). A logical page address from a host is divided by a modulo divider to generate a quotient and a remainder. The quotient is a logical block address that indexes a first-level look-up table to find a mapping entry with a physical block address that selects a row in a second-level look-up table. The remainder locates a column in the row in the second-level look-up table. If any page-valid bits above the column pointed to by the remainder are set, the write is regressive.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com