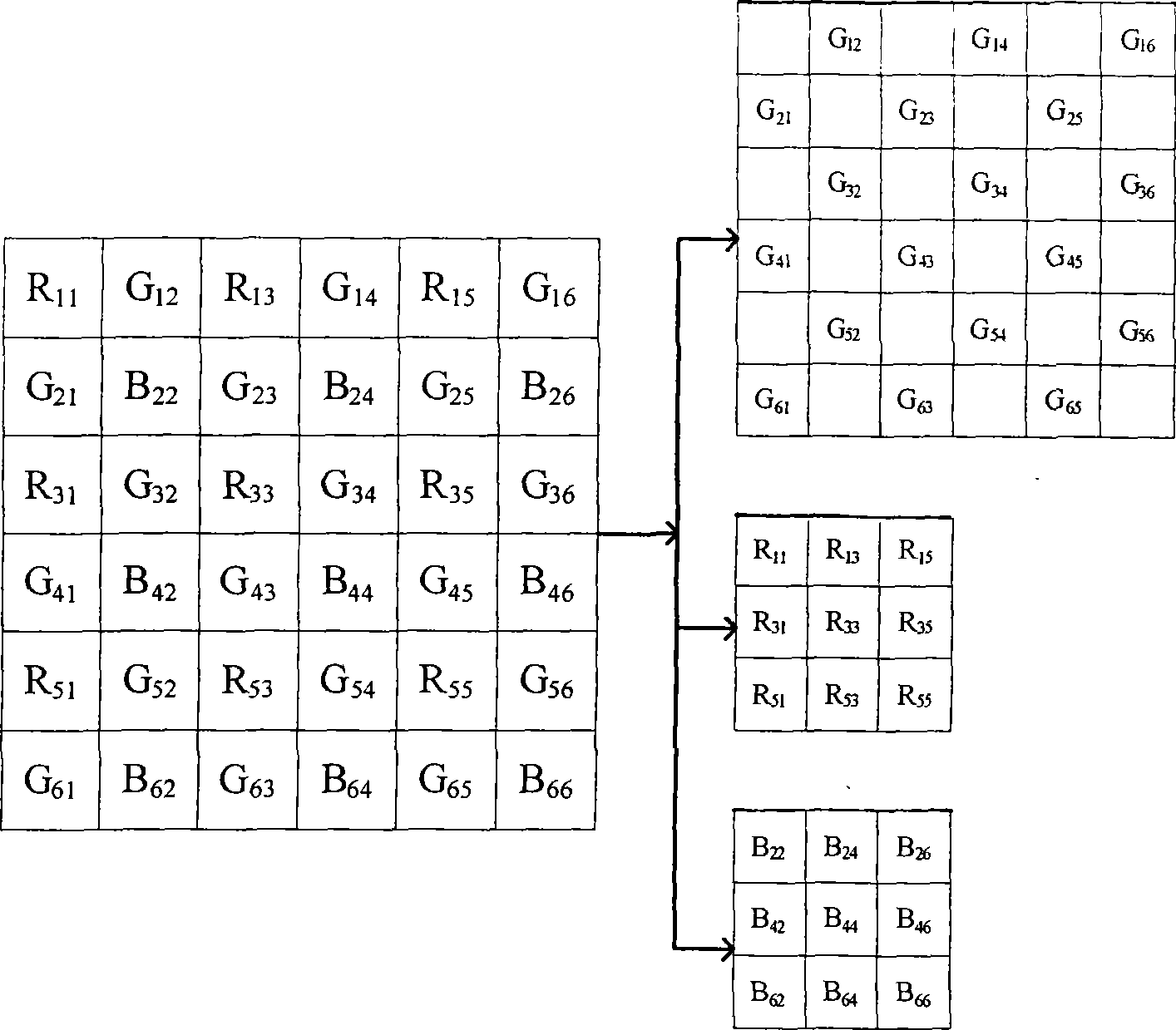Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
235 results about "Lossless coding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
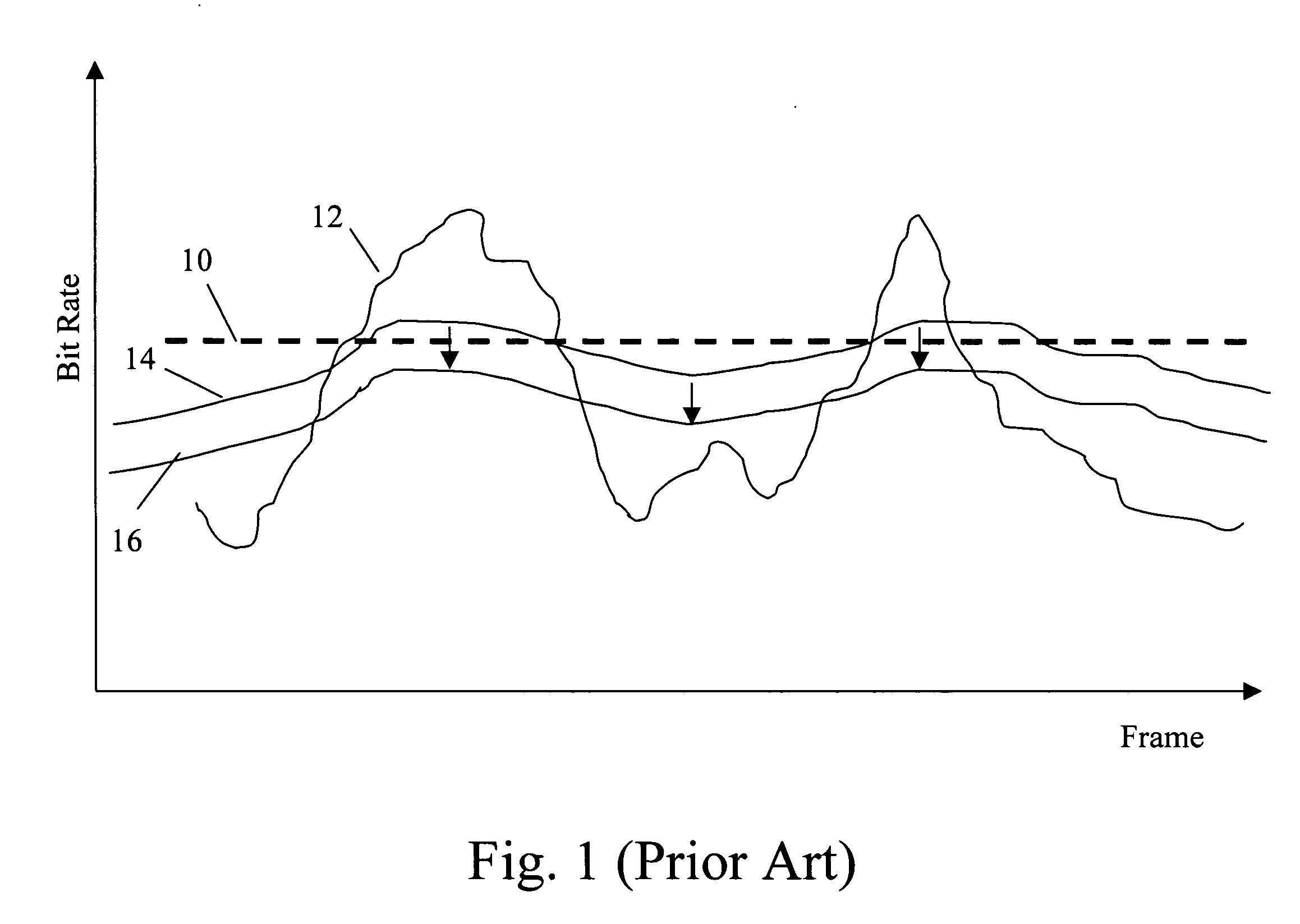
Lossless coding Coding in which no information whatsoever is lost during the encoding (or decoding) process. Generally, encryption and decryption are lossless, as is channel coding. Strictly, data compaction is lossless, while data compression is not, but the latter term is often used for the former.
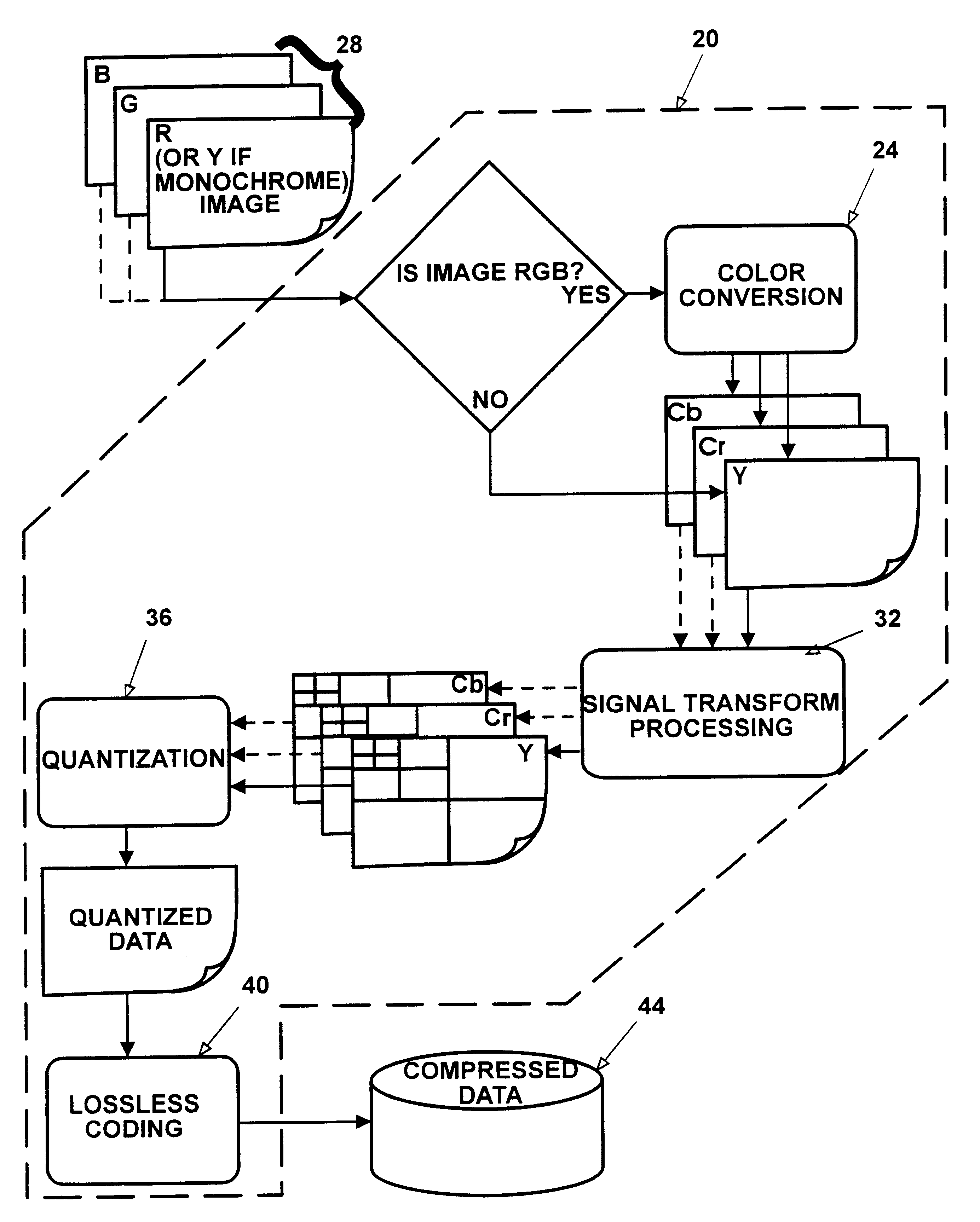
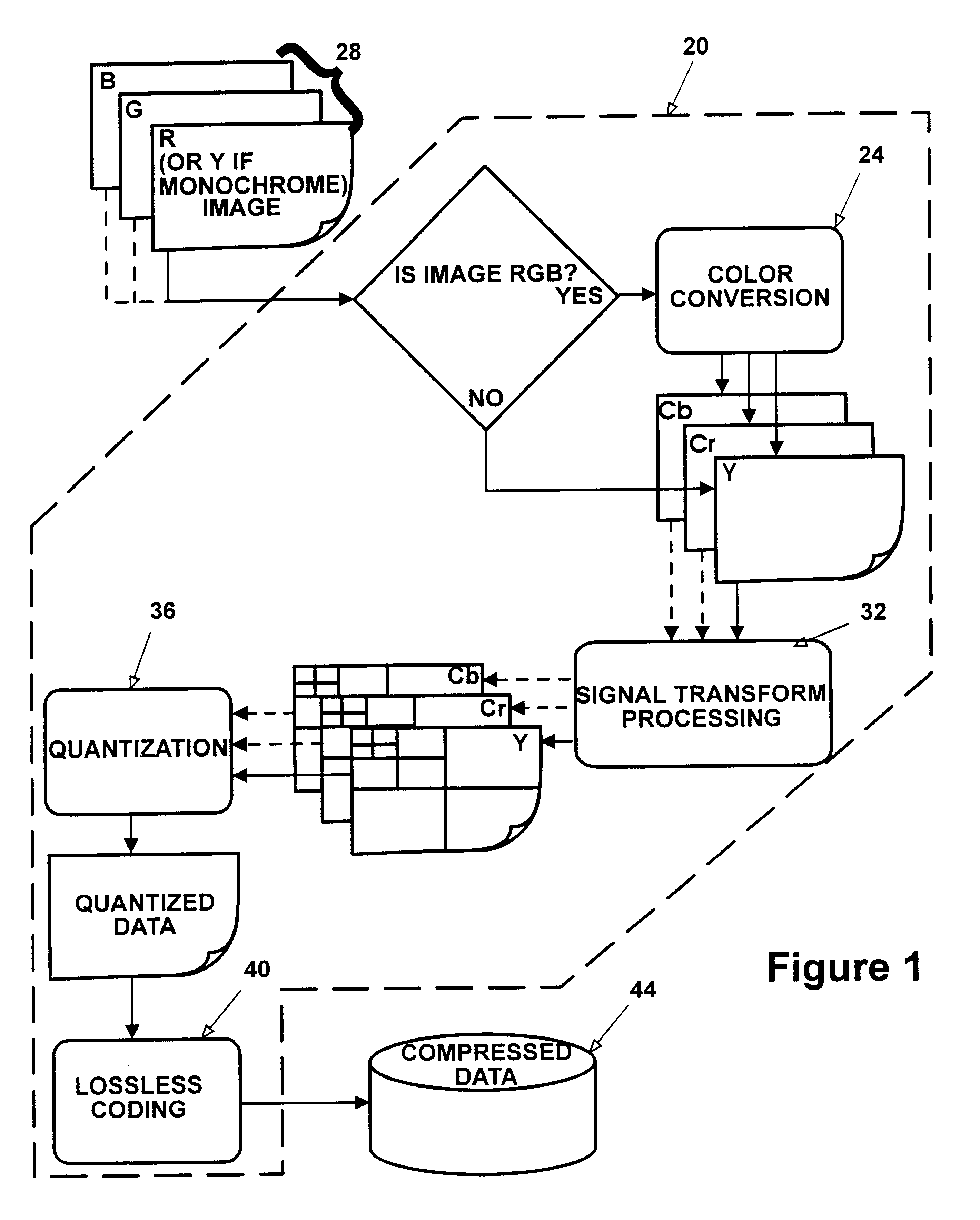
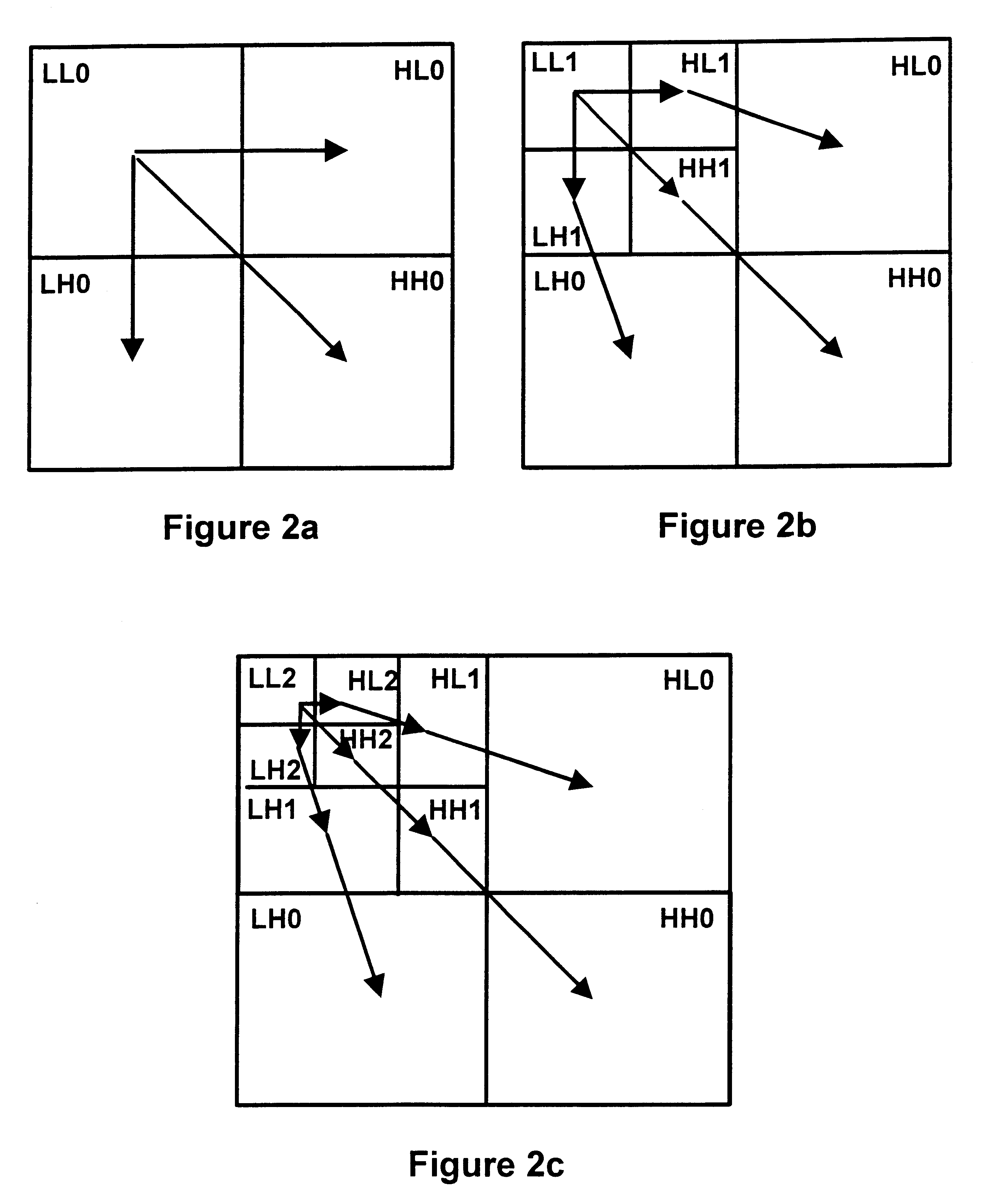
Method apparatus and system for compressing data that wavelet decomposes by color plane and then divides by magnitude range non-dc terms between a scalar quantizer and a vector quantizer
InactiveUS6865291B1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData compressionImaging quality
An apparatus and method for image data compression performs a modified zero-tree coding on a range of image bit plane values from the largest to a defined smaller value, and a vector quantizer codes the remaining values and lossless coding is performed on the results of the two coding steps. The defined smaller value can be adjusted iteratively to meet a preselected compressed image size criterion or to meet a predefined level of image quality, as determined by any suitable metric. If the image to be compressed is in RGB color space, the apparatus converts the RGB image to a less redundant color space before commencing further processing.
Owner:WDE
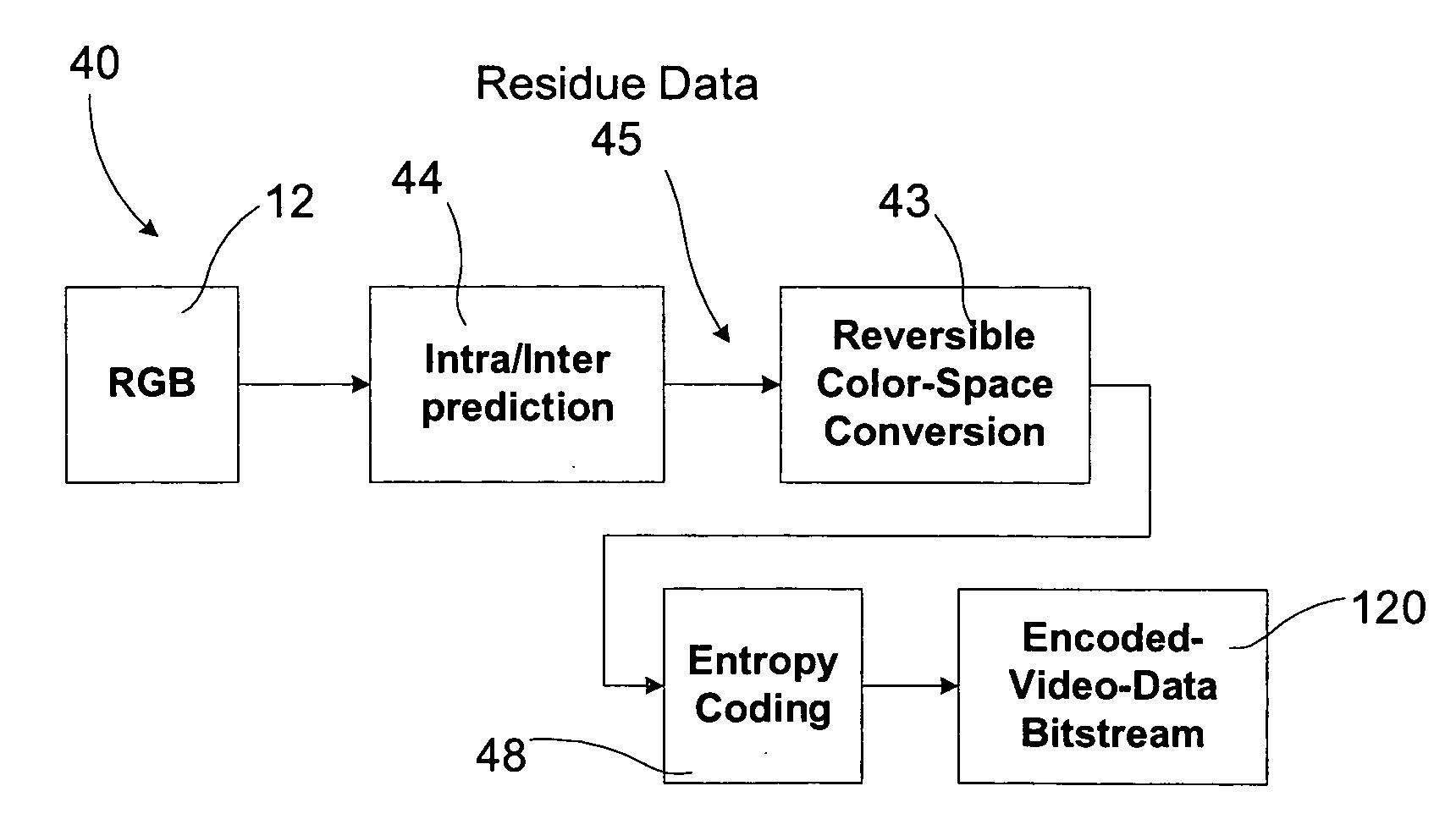
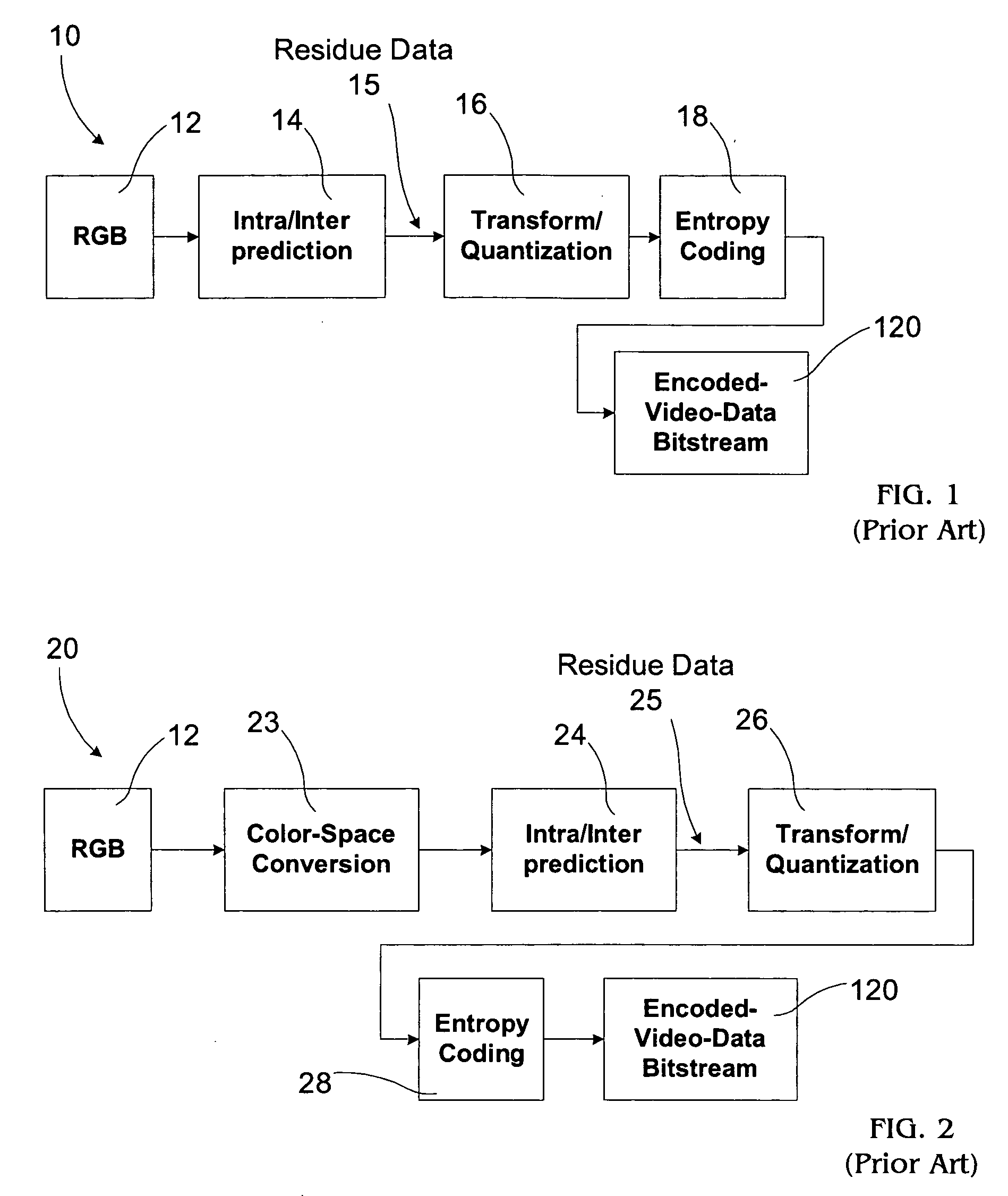
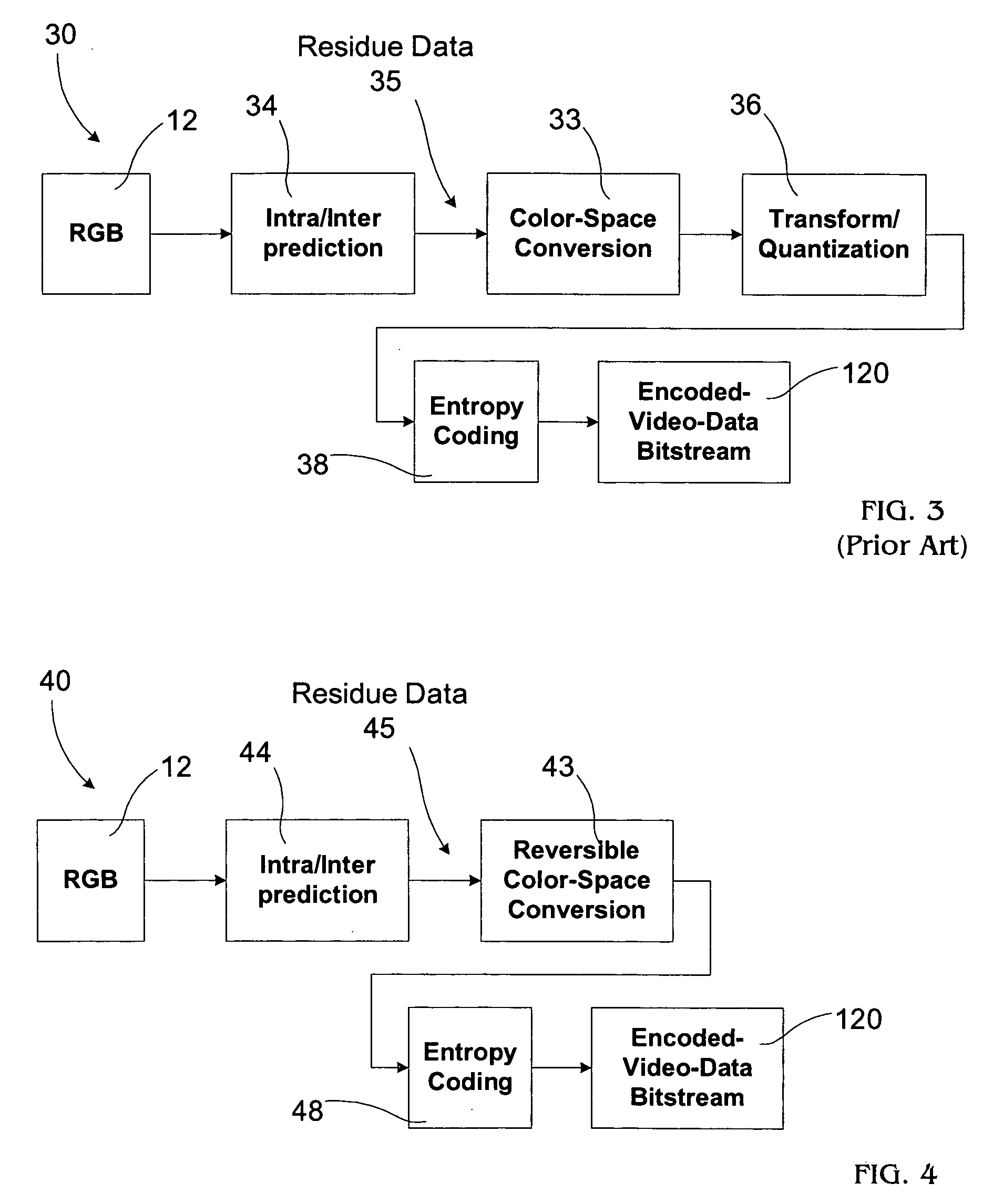
Video coding with residual color conversion using reversible YCoCg
InactiveUS20050259730A1Improve coding efficiencyHigh color fidelityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionLossless codingFrame based
A video coding algorithm supports both lossy and lossless coding of video while maintaining high color fidelity and coding efficiency using an in-loop, reversible color transform. Accordingly, a method is provided to encode video data and decode the generated bitstream. The method includes generating a prediction-error signal by performing intra / inter-frame prediction on a plurality of video frames; generating a color-transformed, prediction-error signal by performing a reversible color-space transform on the prediction-error signal; and forming a bitstream based on the color-transformed prediction-error signal. The method may further include generating a color-space transformed error residual based on a bitstream; generating an error residual by performing a reversible color-space transform on the color-space transformed error residual; and generating a video frame based on the error residual.
Owner:SHARP LAB OF AMERICA INC
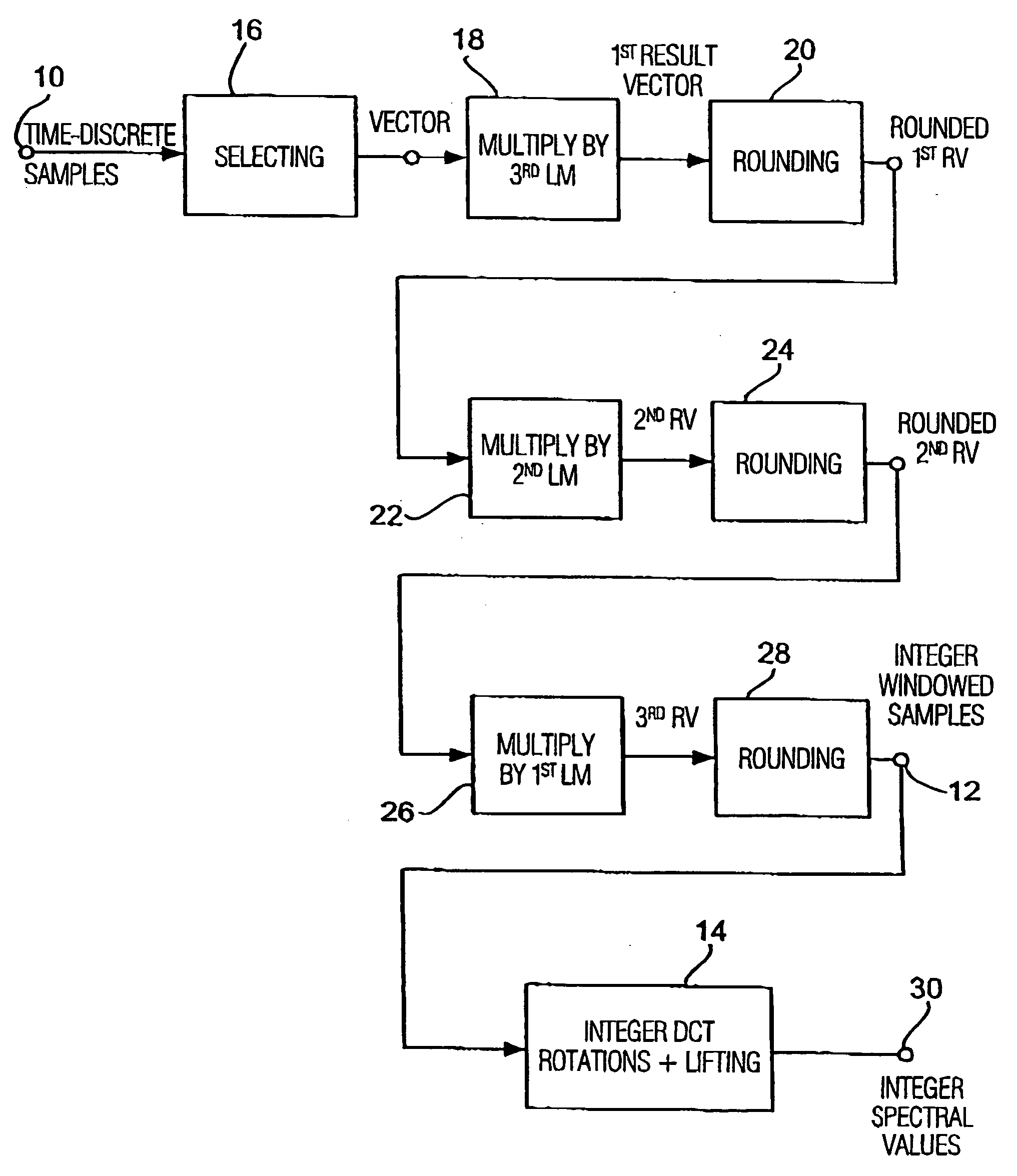
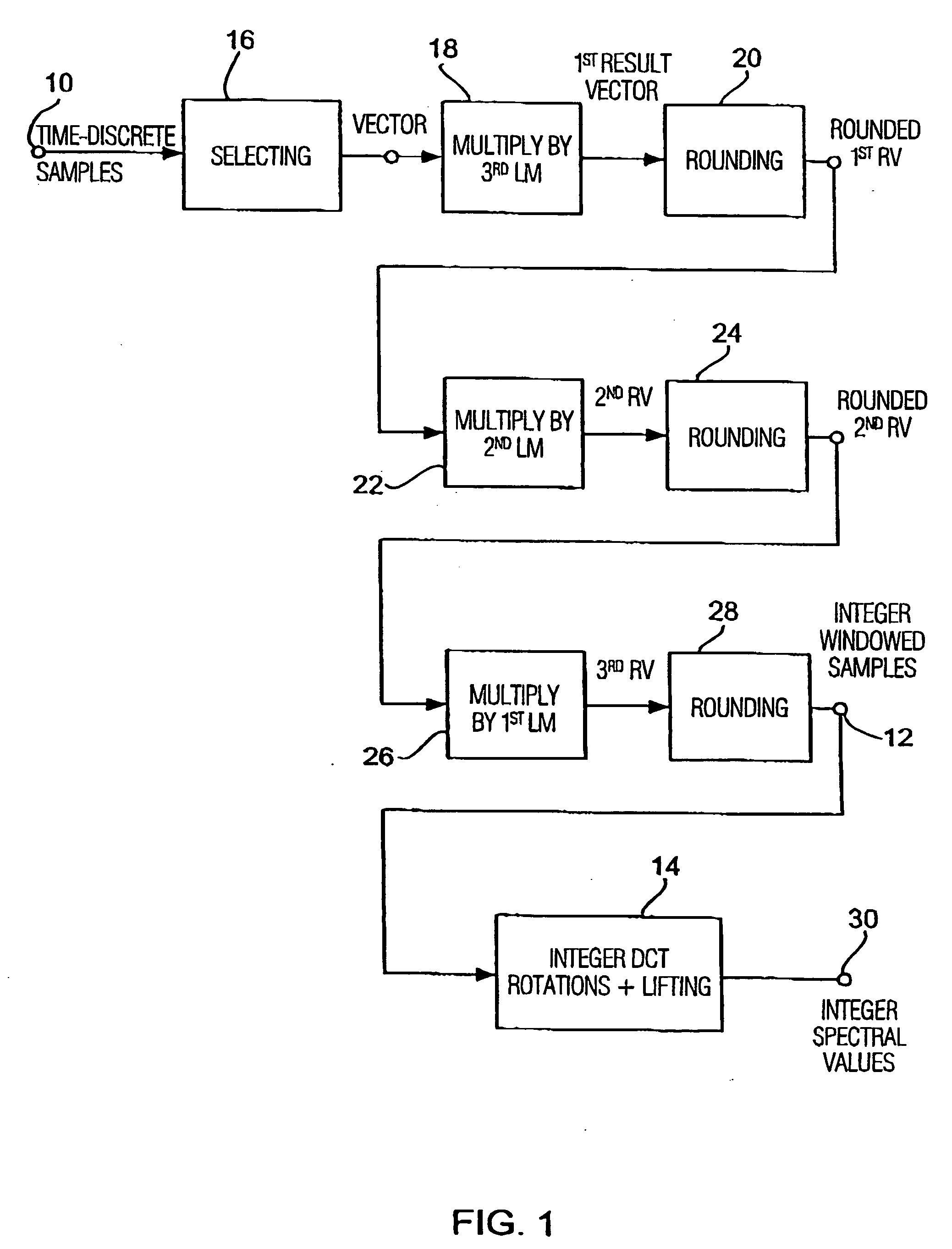
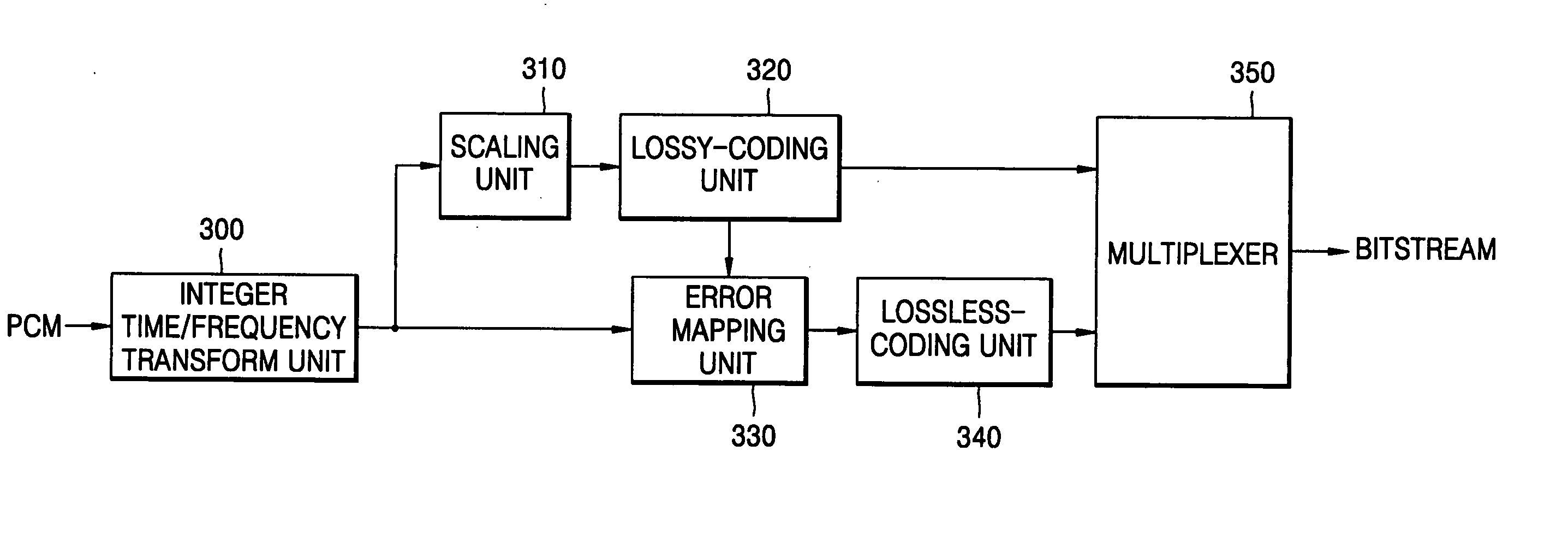
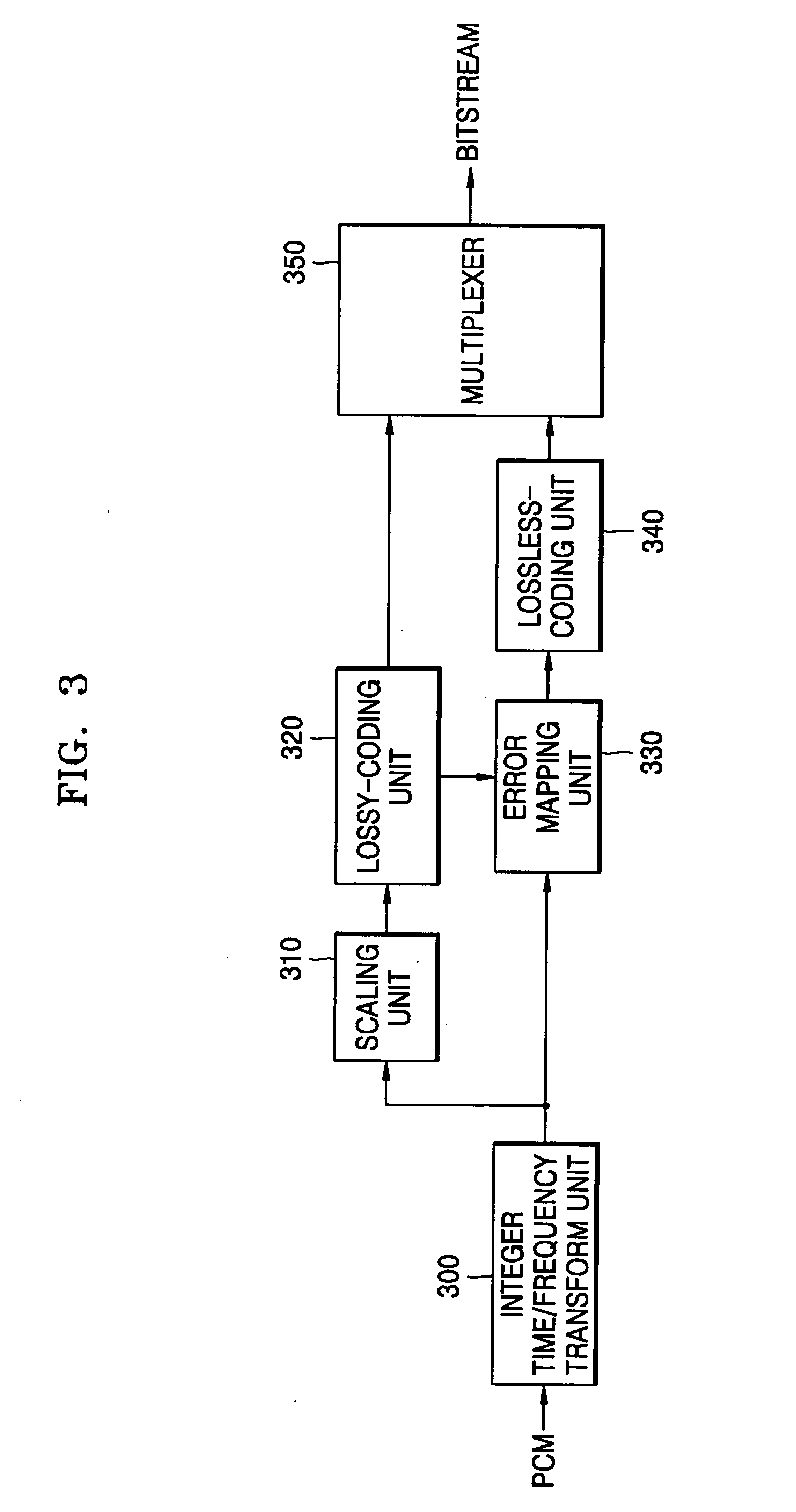
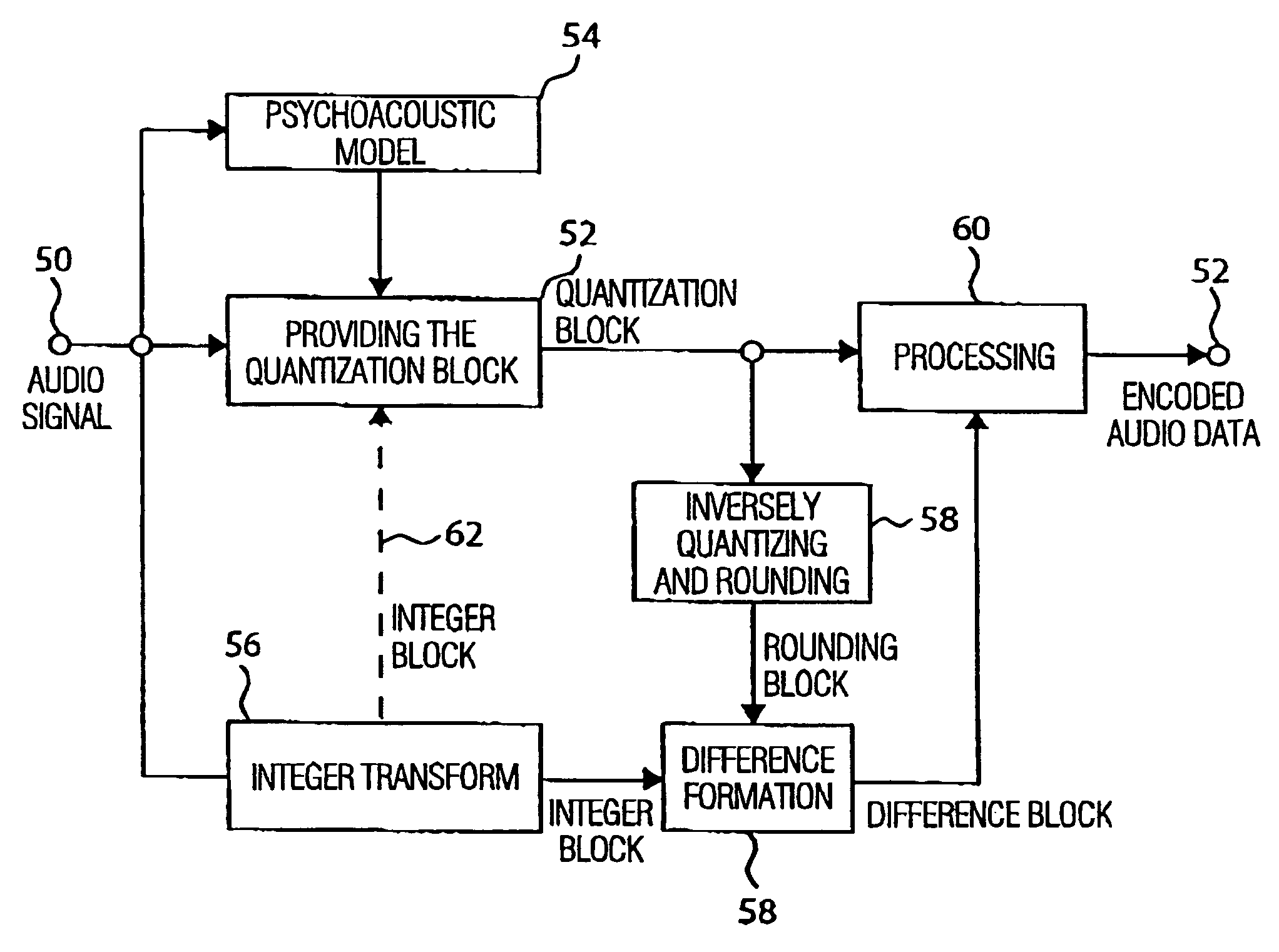
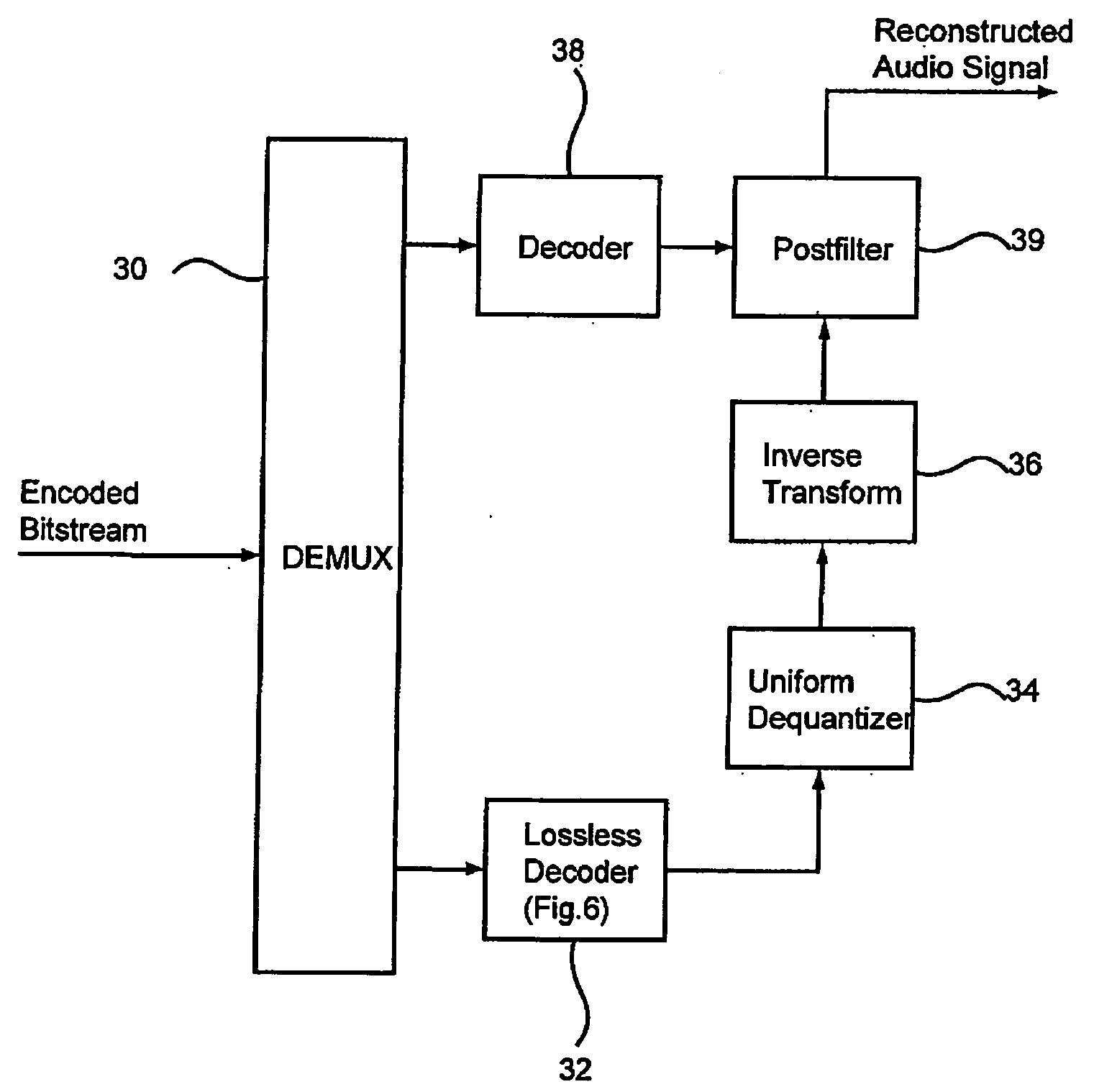
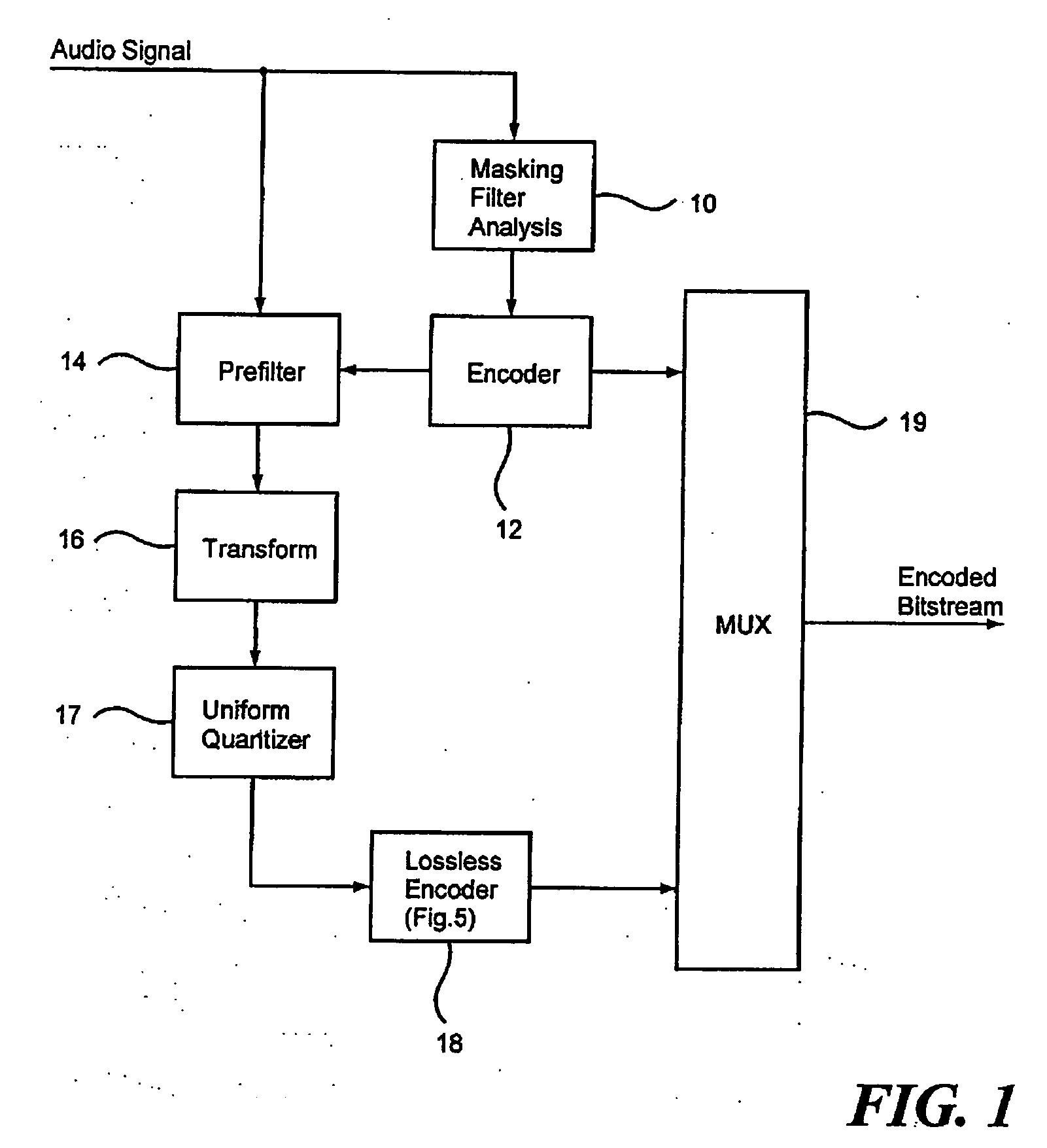
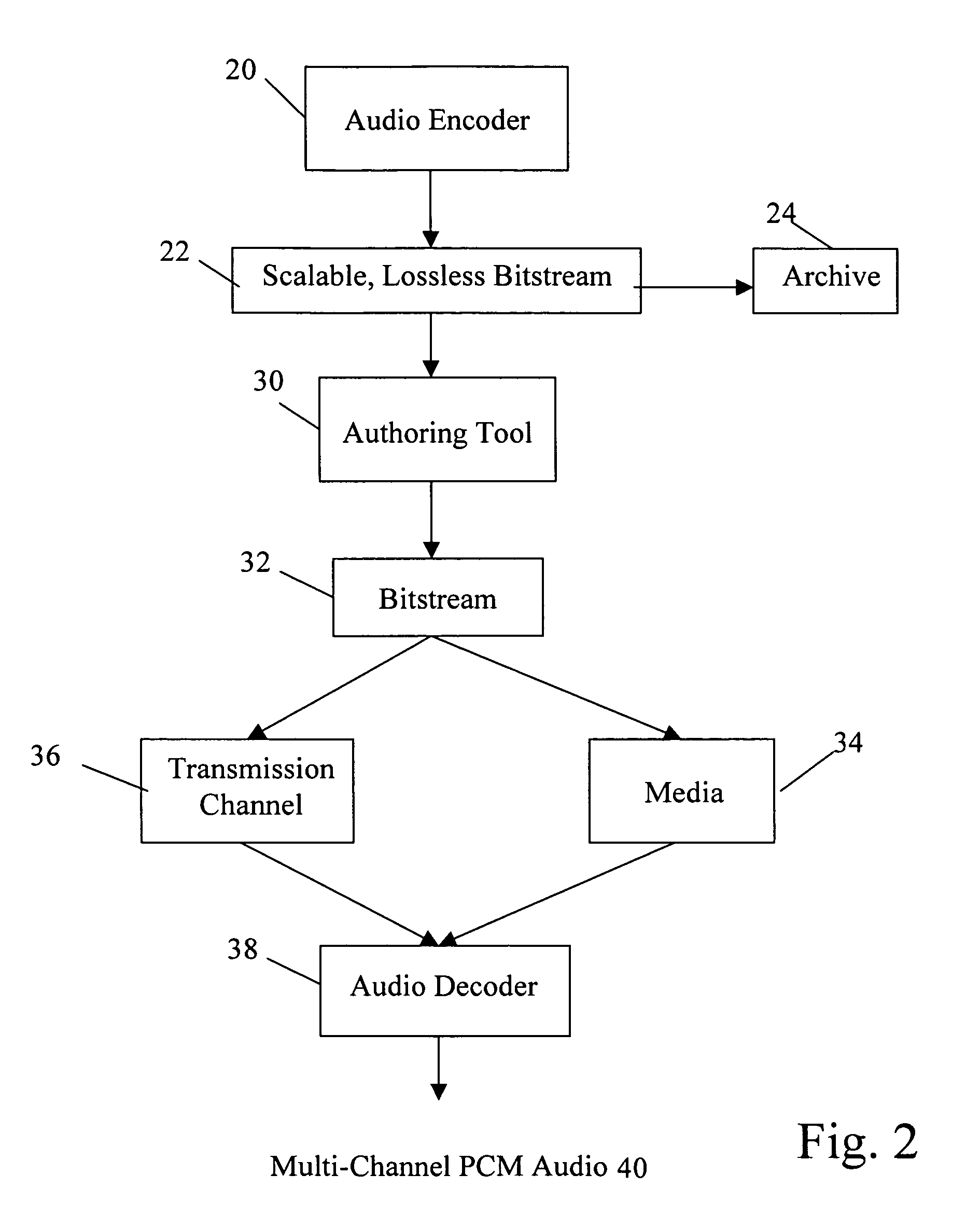
Apparatus and method for coding a time-discrete audio signal and apparatus and method for decoding coded audio data
A time-discrete audio signal is processed to provide a quantization block with quantized spectral values. Furthermore, an integer spectral representation is generated from the time-discrete audio signal using an integer transform algorithm. The quantization block having been generated using a psychoacoustic model is inversely quantized and rounded to then form a difference between the integer spectral values and the inversely quantized rounded spectral values. The quantization block alone provides a lossy psychoacoustically coded / decoded audio signal after the decoding, whereas the quantization block, together with the combination block, provides a lossless or almost lossless coded and again decoded audio signal in the decoding. By generating the differential signal in the frequency domain, a simpler coder / decoder structure results.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
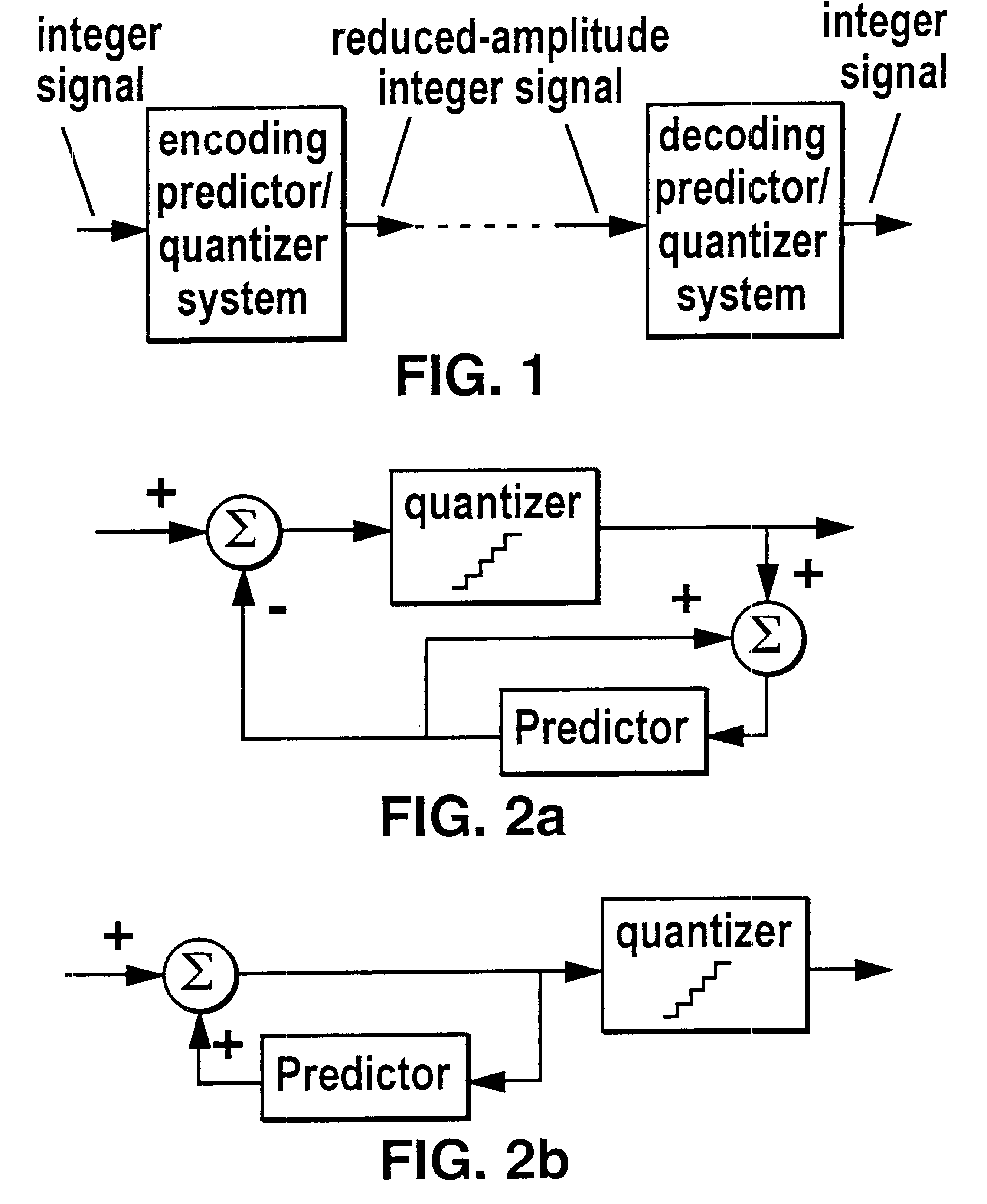
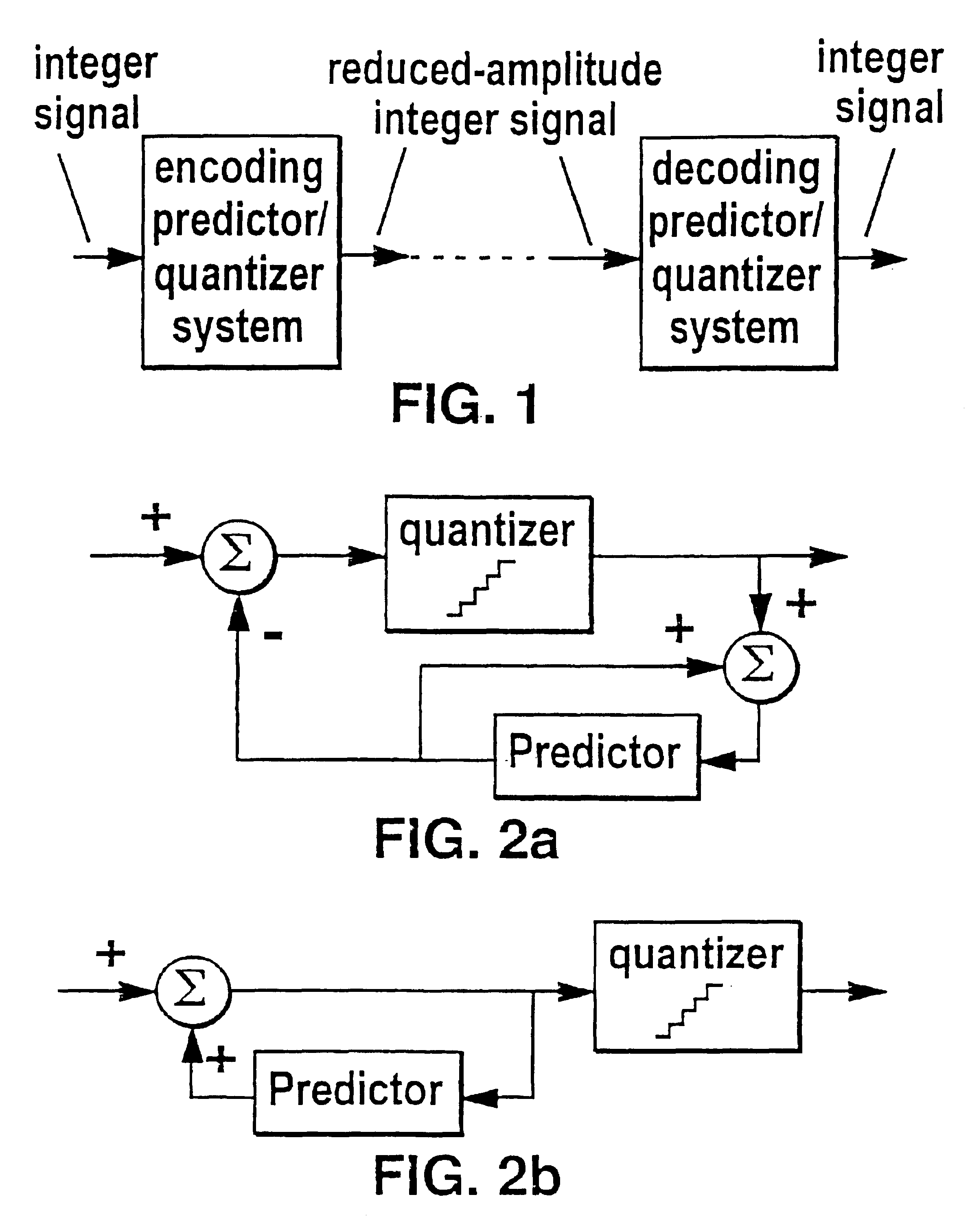
Lossless coding method for waveform data
InactiveUS6664913B1Preserve integrityAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsLossless codingSampling instant
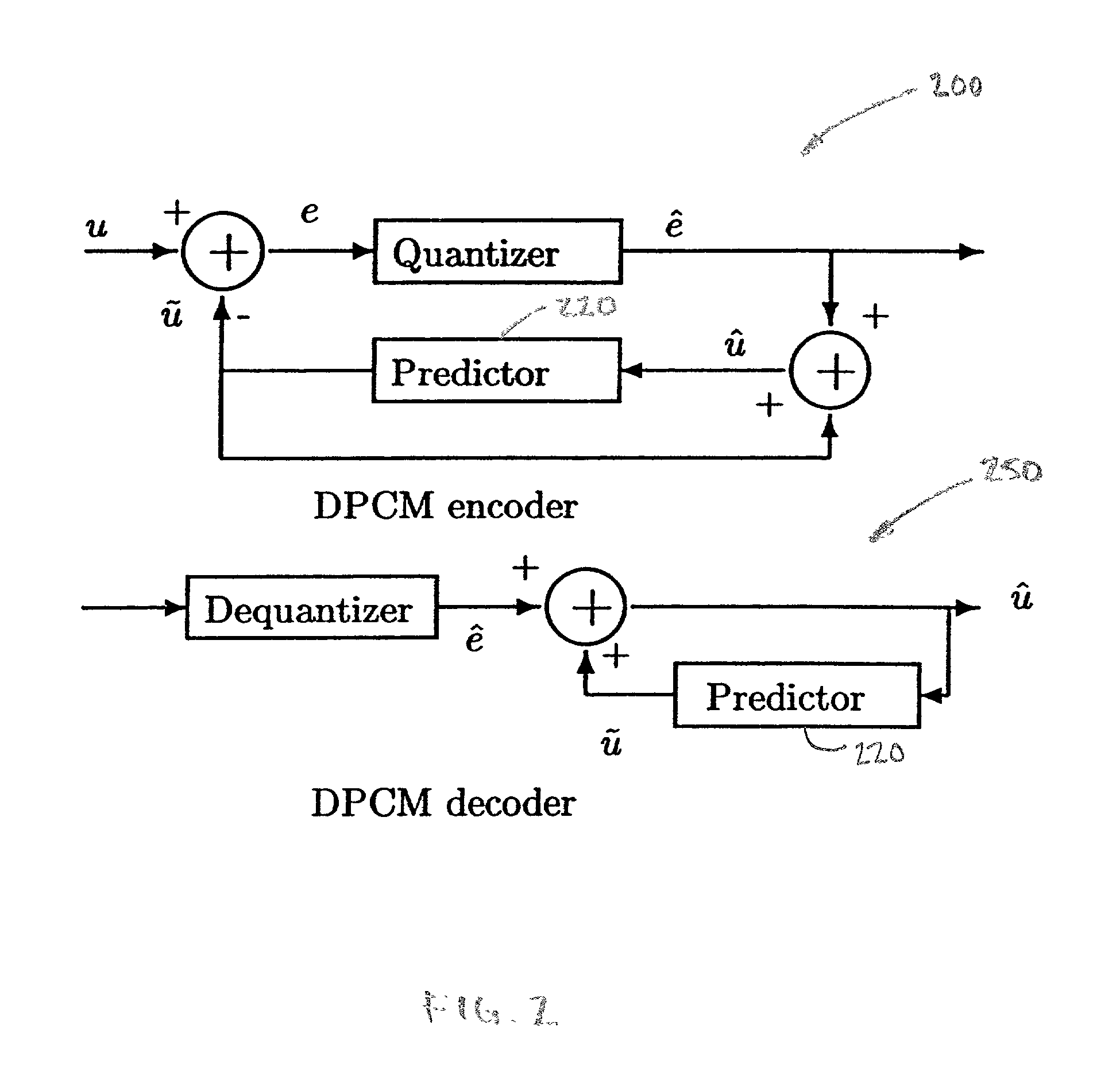
In a method of lossless processing of an integer value signal in a prediction filter which includes a quantiser, a numerator of the prediction filter is implemented prior to the quantiser and a denominator of the prediction filter is implemented recursively around the quantiser to reduce the peak data rate of an output signal. In the lossless processor, at each sample instant, an input to the quantiser is jointly responsive to a first sample value of a signal input to the prediction filter, a second sample value of a signal input to the prediction filter at a previous sample instant, and an output value of the quantiser at a previous sample incident. In a preferred embodiment, the prediction filter includes noise shaping for affecting the output of the quantiser.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
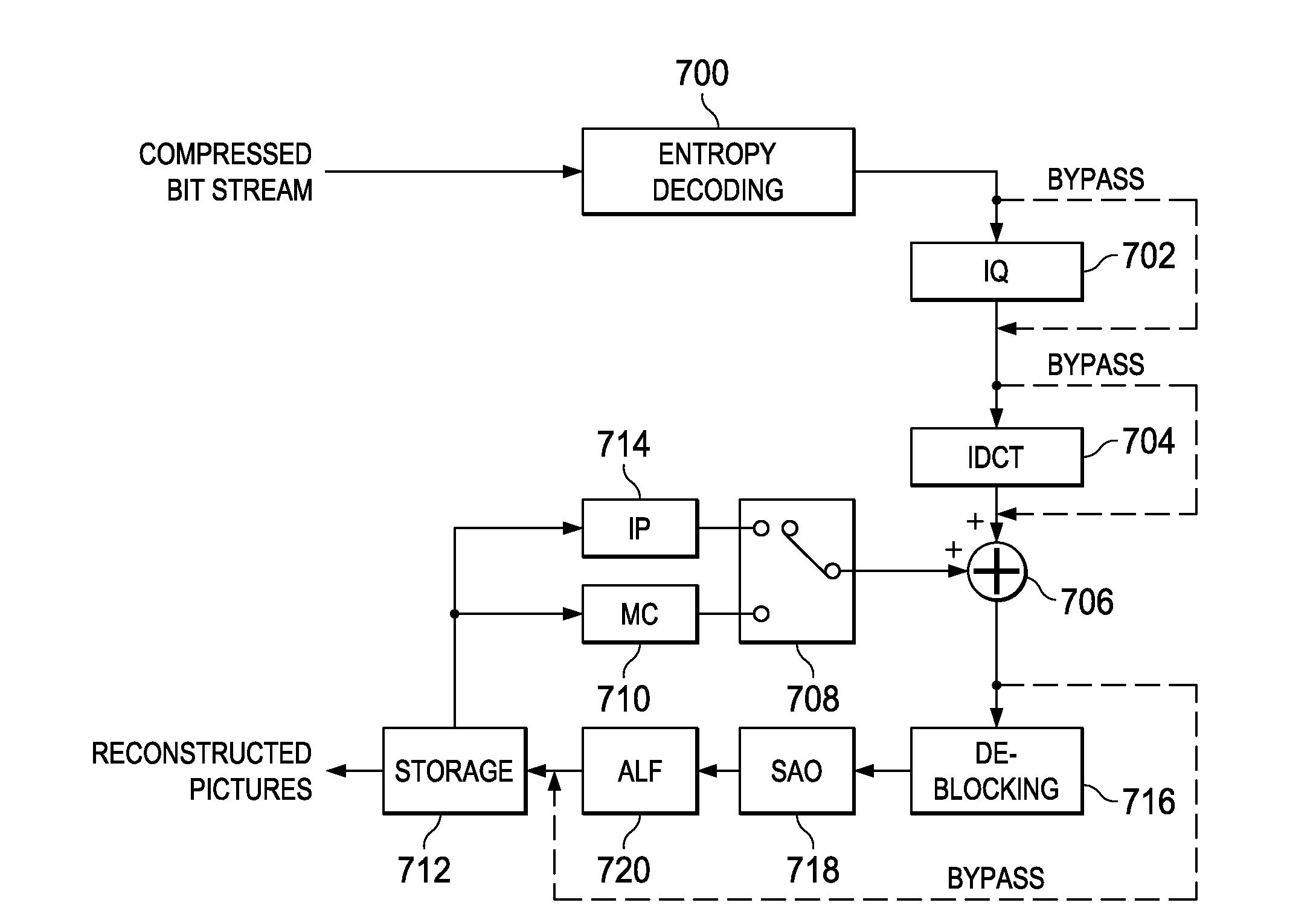
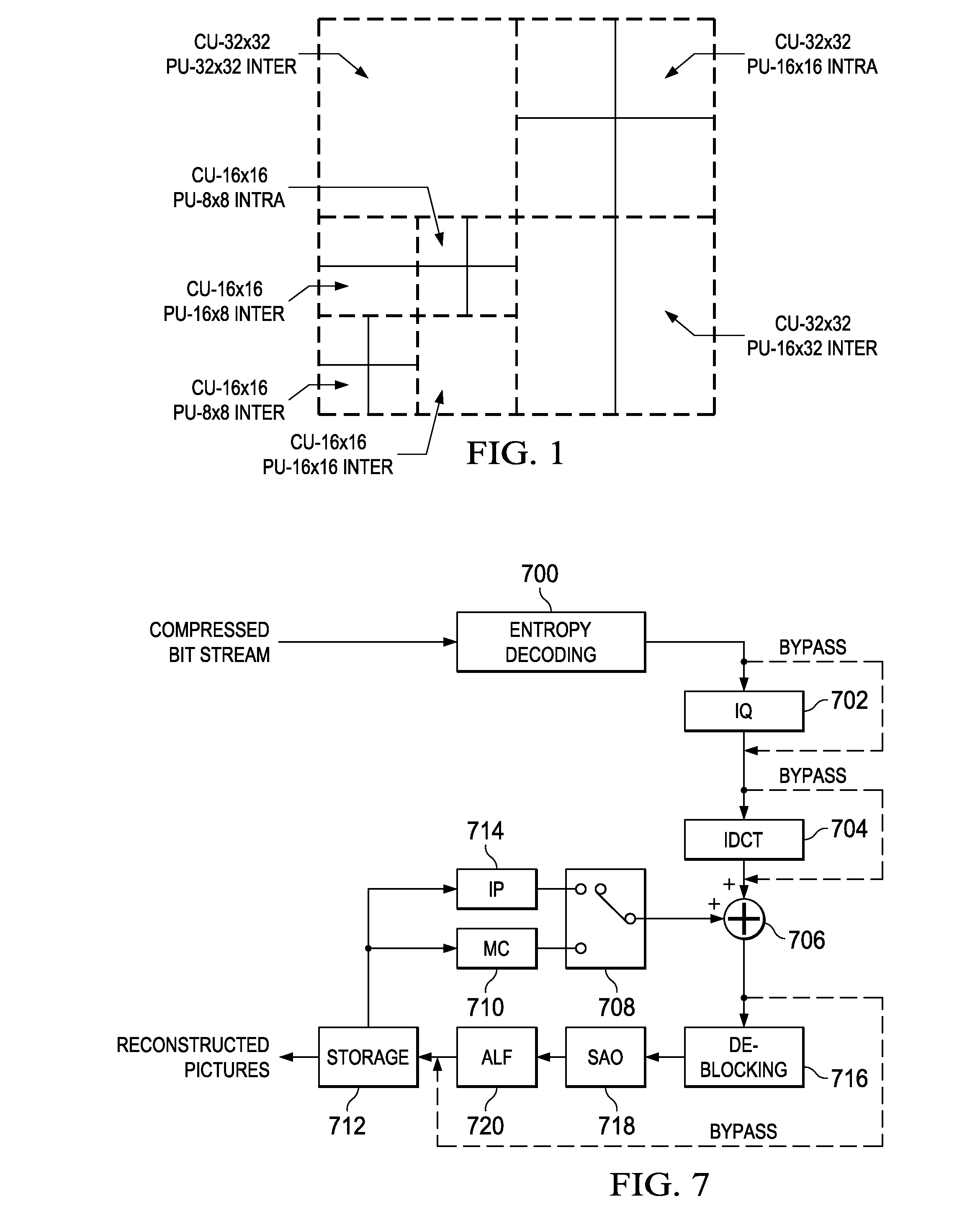
Method and System for Lossless Coding Mode in Video Coding
ActiveUS20130077696A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionLossless codingVideo bitstream
A method for coding a video sequence is provided that includes encoding a portion of a picture in the video sequence in lossless coding mode, and signaling a lossless coding indicator in a compressed bit stream, wherein the lossless coding indicator corresponds to the portion of a picture and indicates whether or not the portion of the picture is losslessly coded. A method for decoding a compressed video bit stream is provided that includes determining that lossless coding mode is enabled, decoding a lossless coding indicator from the compressed video bit stream, wherein the lossless coding indicator corresponds to a portion of a picture in the compressed video bit stream and indicates whether or not the portion of the picture is losslessly coded, and decoding the portion of the picture in lossless coding mode when the lossless coding indicator indicates the portion of the picture is losslessly coded.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
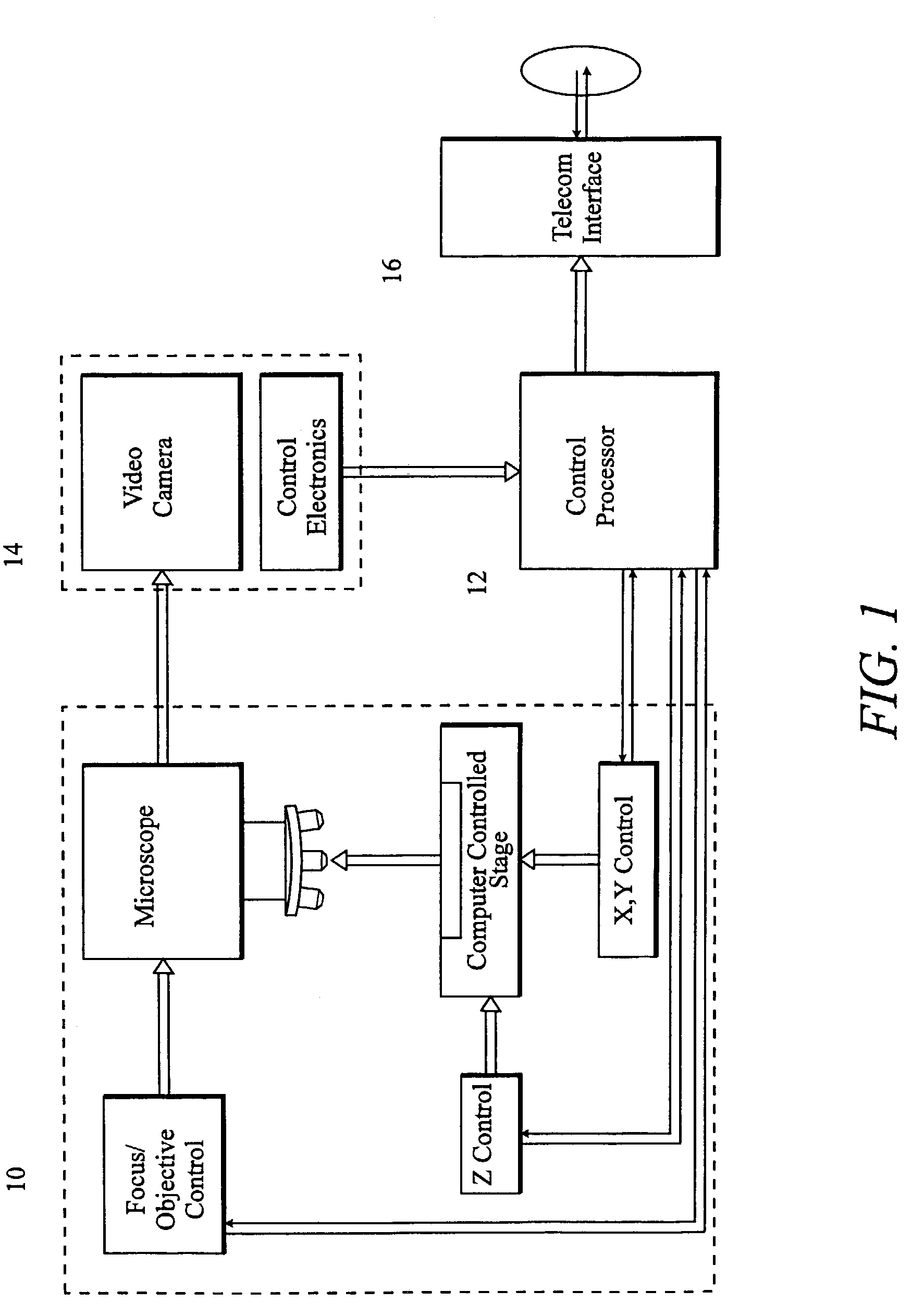
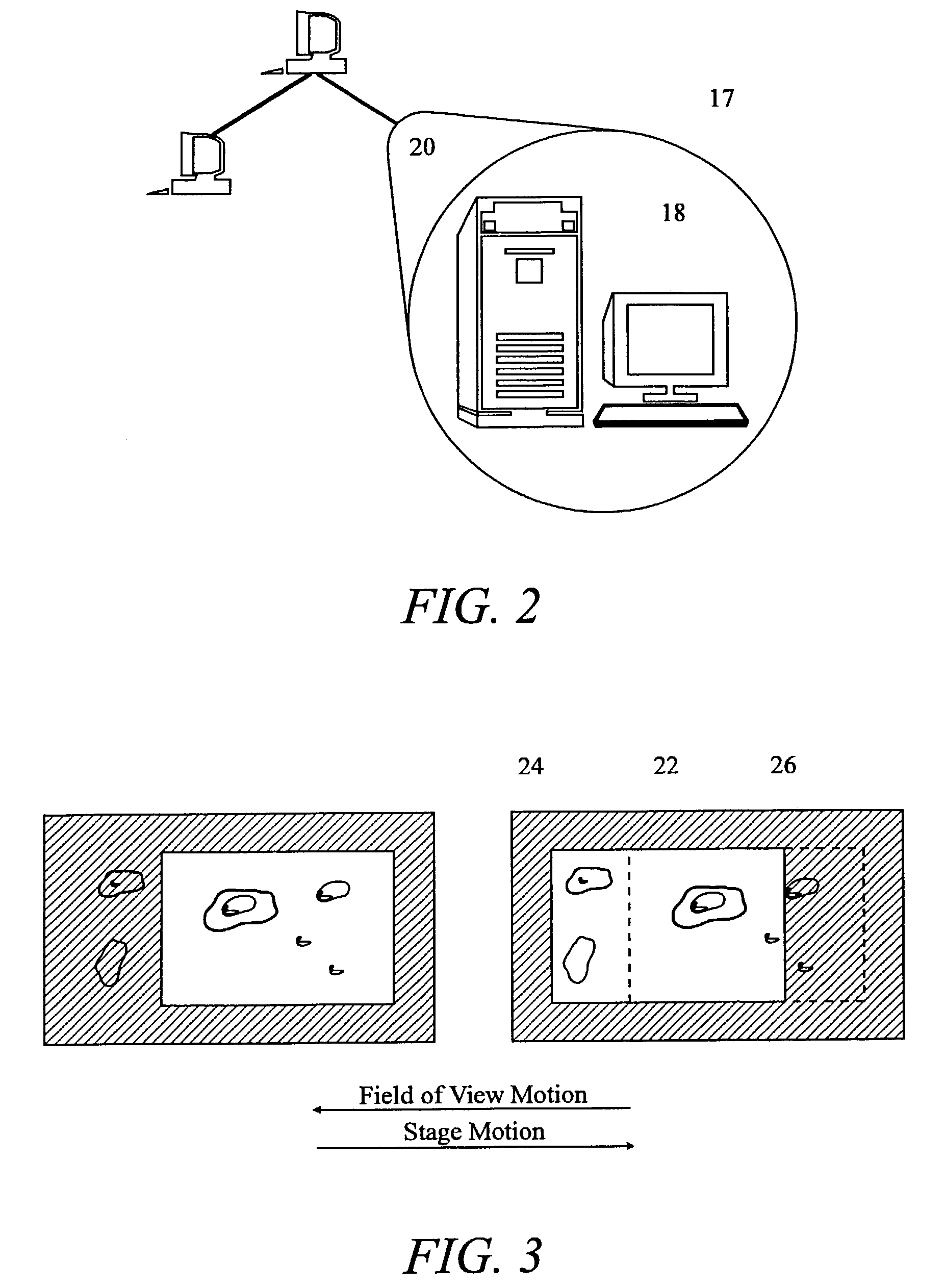
Compression packaged image transmission for telemicroscopy
InactiveUS7224839B2Medical communicationCharacter and pattern recognitionLossless codingHigh resolution imaging
A system and method for visual image compression and transmission offers significant bandwidth conservation while retaining high resolution imaging capability. Videograpic images are decomposed into detail levels, and images are delivered to a remote site display at a level of detail proportional to the perception level of a viewer. Images are transformed, quantized, coded and queued for transmission in accordance with their level of image detail. Image detail layers are transmitted as an inverse function of image displacement speed and as a direct function of image magnification. Images are constructed vertically with each additional queueing layer providing additional image detail. Higher priority layers are lossy encoded, while the lowest priority layers (highest detail levels) are losslessly encoded.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROIMAGING AIS
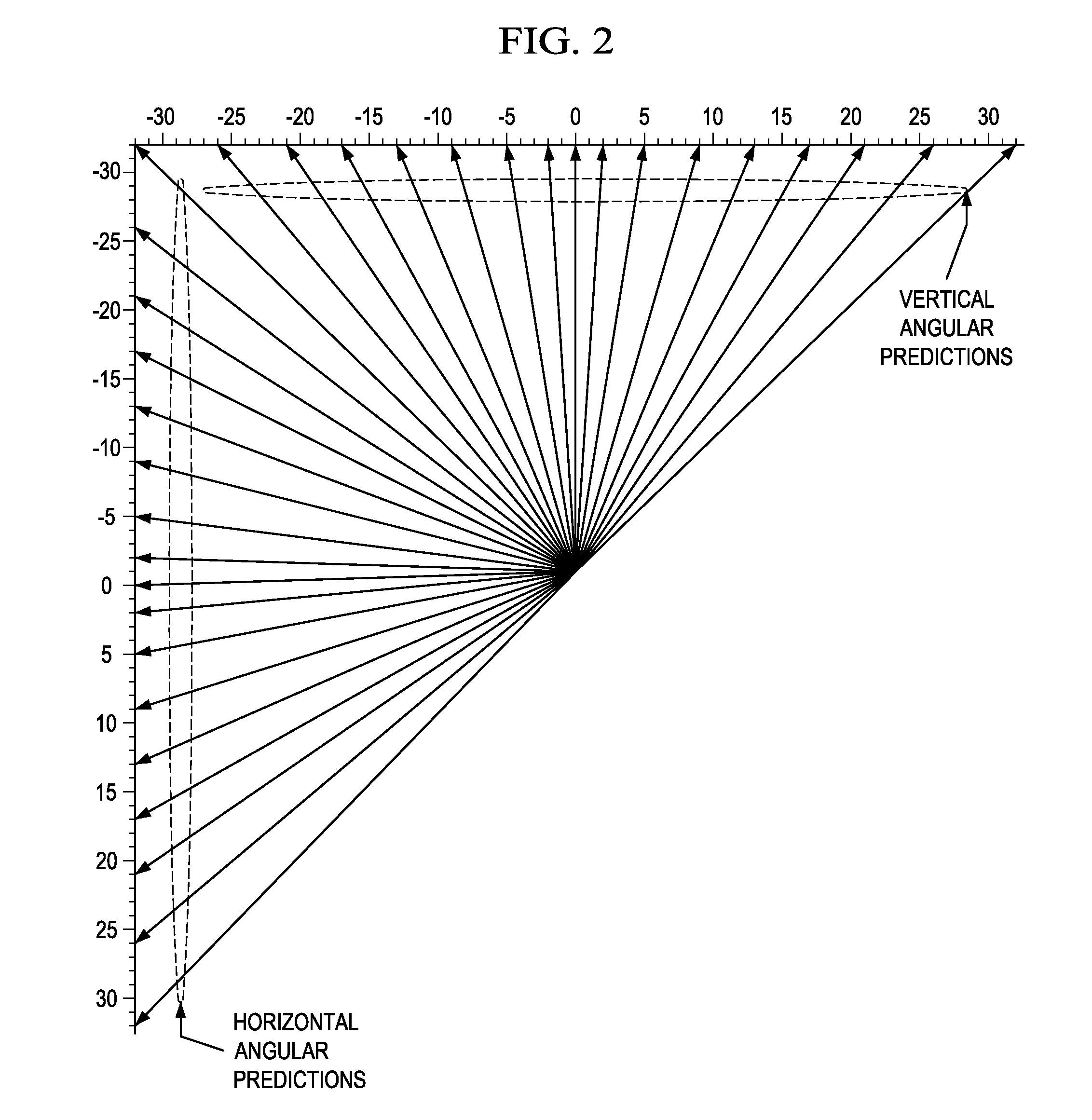
Sample-Based Angular Intra-Prediction in Video Coding
ActiveUS20130101036A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionLossless codingReference sample
A method for processing a prediction unit (PU) to generate predicted samples is provided that includes computing predicted samples for samples of the PU using sample-based angular intra-prediction (SAP) when lossless coding is enabled for the PU, and computing predicted samples for the samples of the PU using block-based angular intra-prediction when lossless coding is not enabled for the PU. Computation of the predicted using SAP includes determining an intra-prediction angle for the PU, and computing a predicted sample for each sample of the samples in the PU based on linear interpolation of two reference samples adjacent to the sample, wherein the two reference samples are selected according to the intra-prediction angle.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
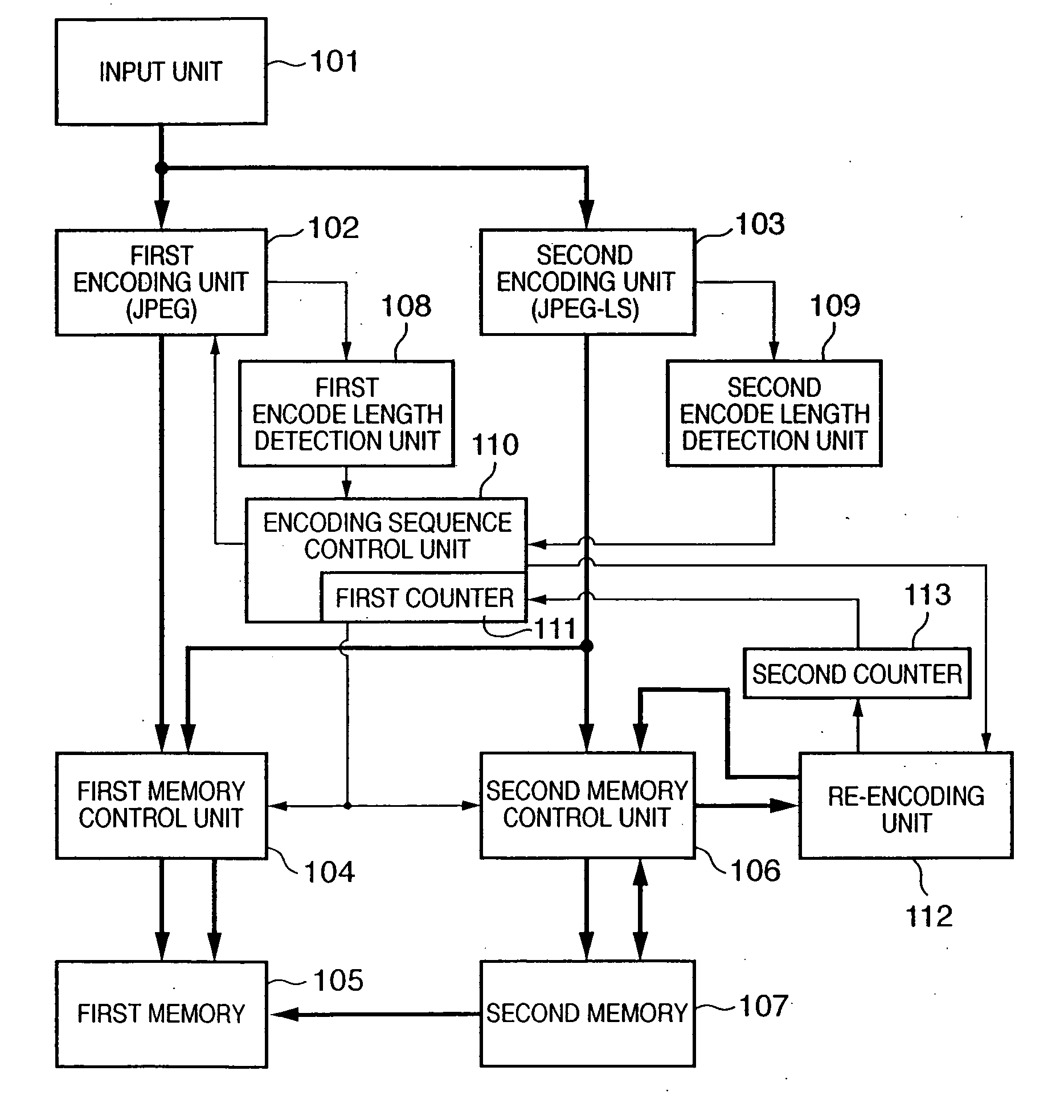
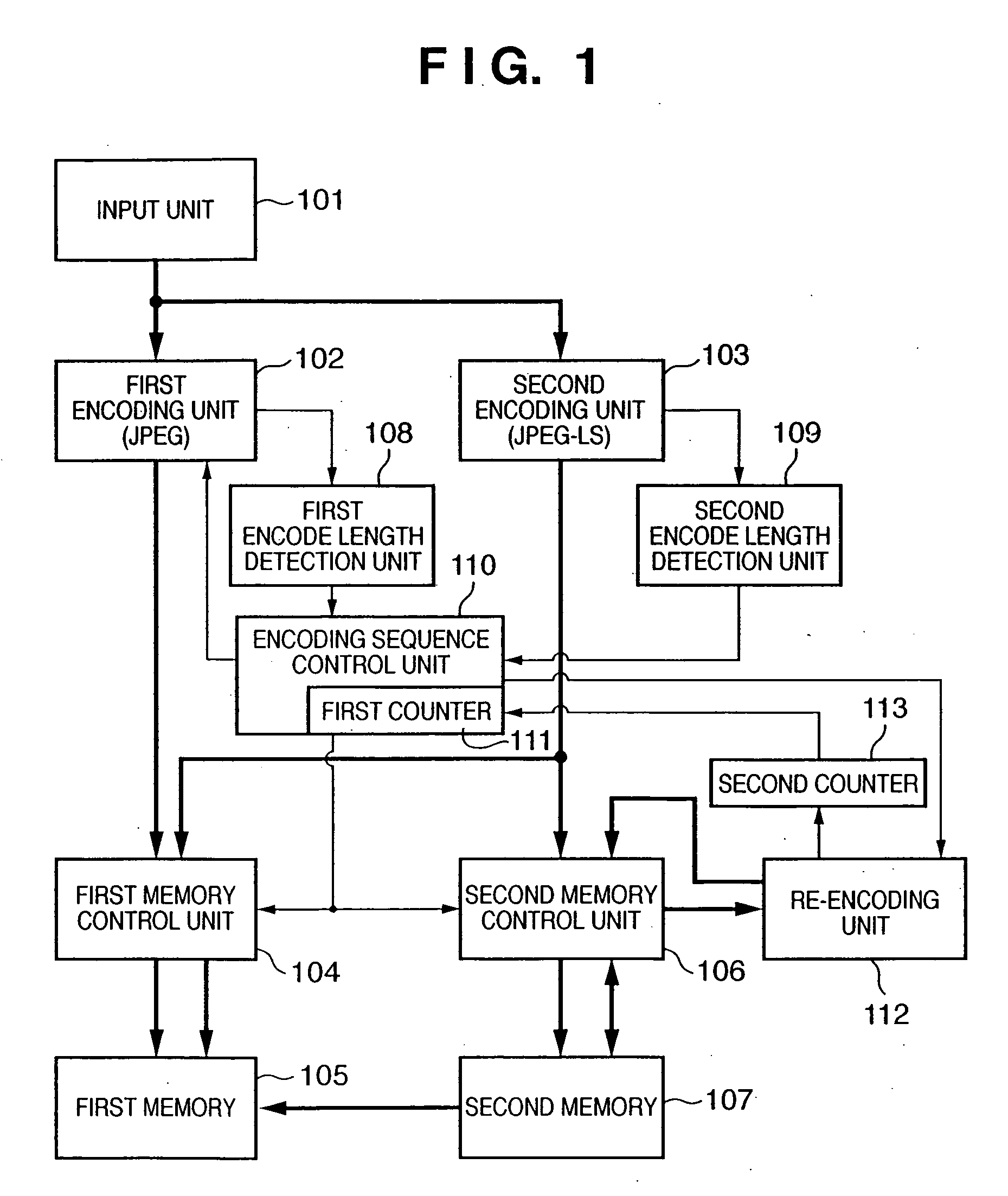
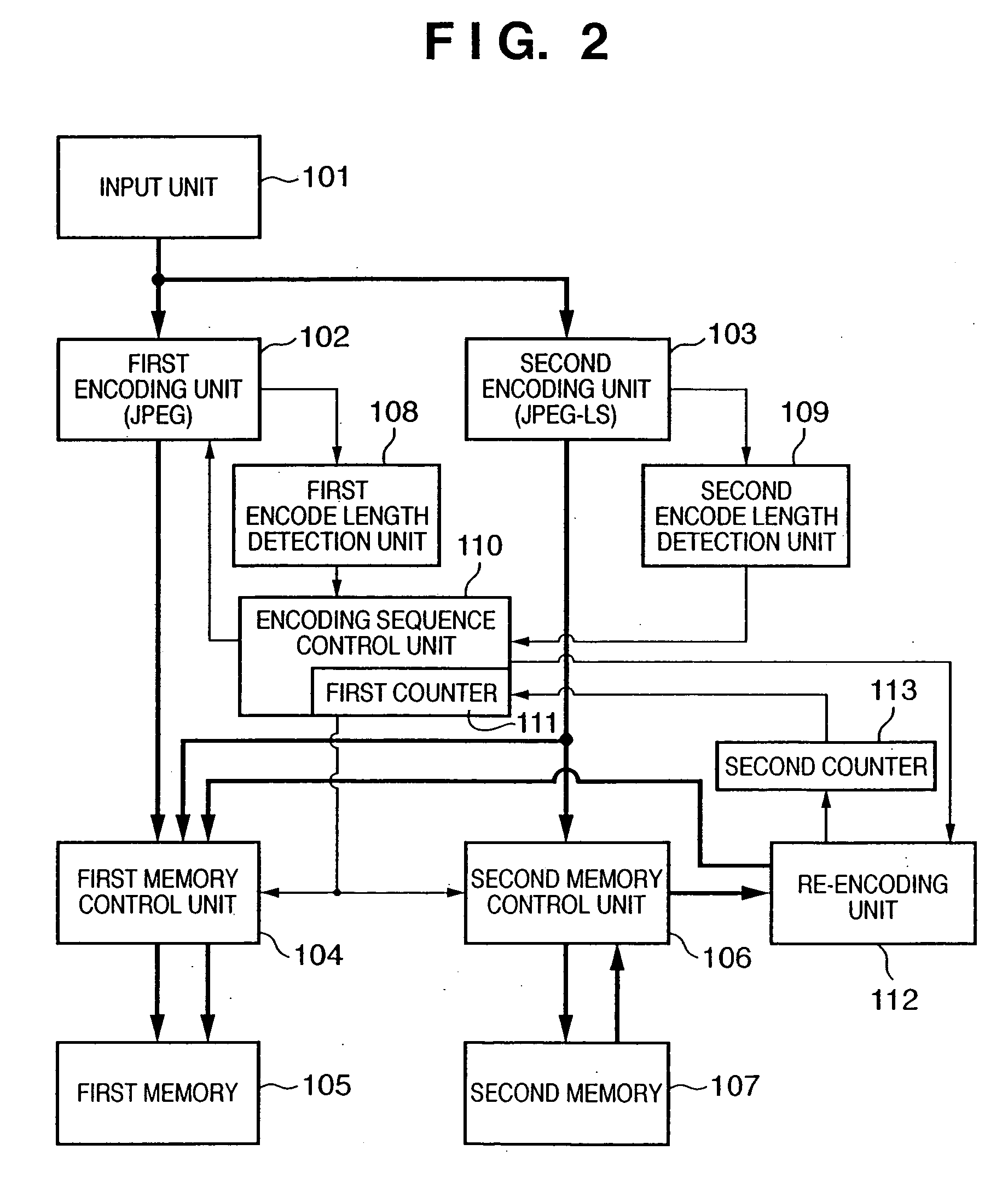
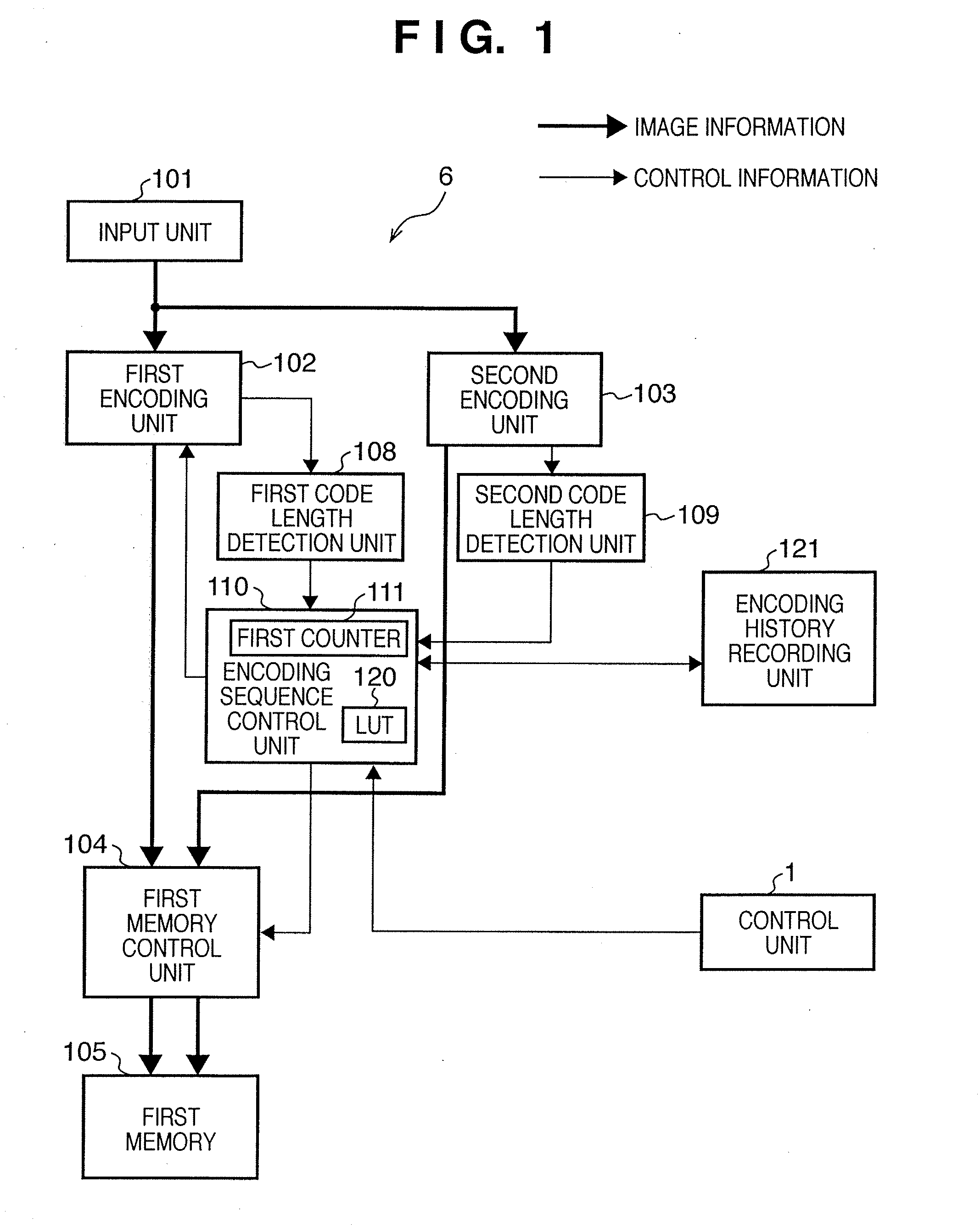
Image encoding apparatus and method, computer program, and computer-readable storage medium
According to this invention, encoded data of a target data amount is generated by one image input operation while both lossless encoding and lossy encoding are adopted. For this purpose, a first memory stores encoded data of a shorter encode length among encoded data generated by a first encoding unit which performs lossy encoding and encoded data generated by a second encoding unit which performs lossless encoding. A second memory stores encoded data from a second encoding unit. When an encoding sequence control unit determines that the encoded data amount in the first memory has exceeded the target data amount, the encoding sequence control unit discards data in the first memory, sets a quantization parameter for a higher compression ratio for the first encoding unit, and causes the first encoding unit to execute encoding. Encoded data before the encoded data amount is determined to have exceeded the target data amount is re-encoded by a re-encoding unit.
Owner:CANON KK
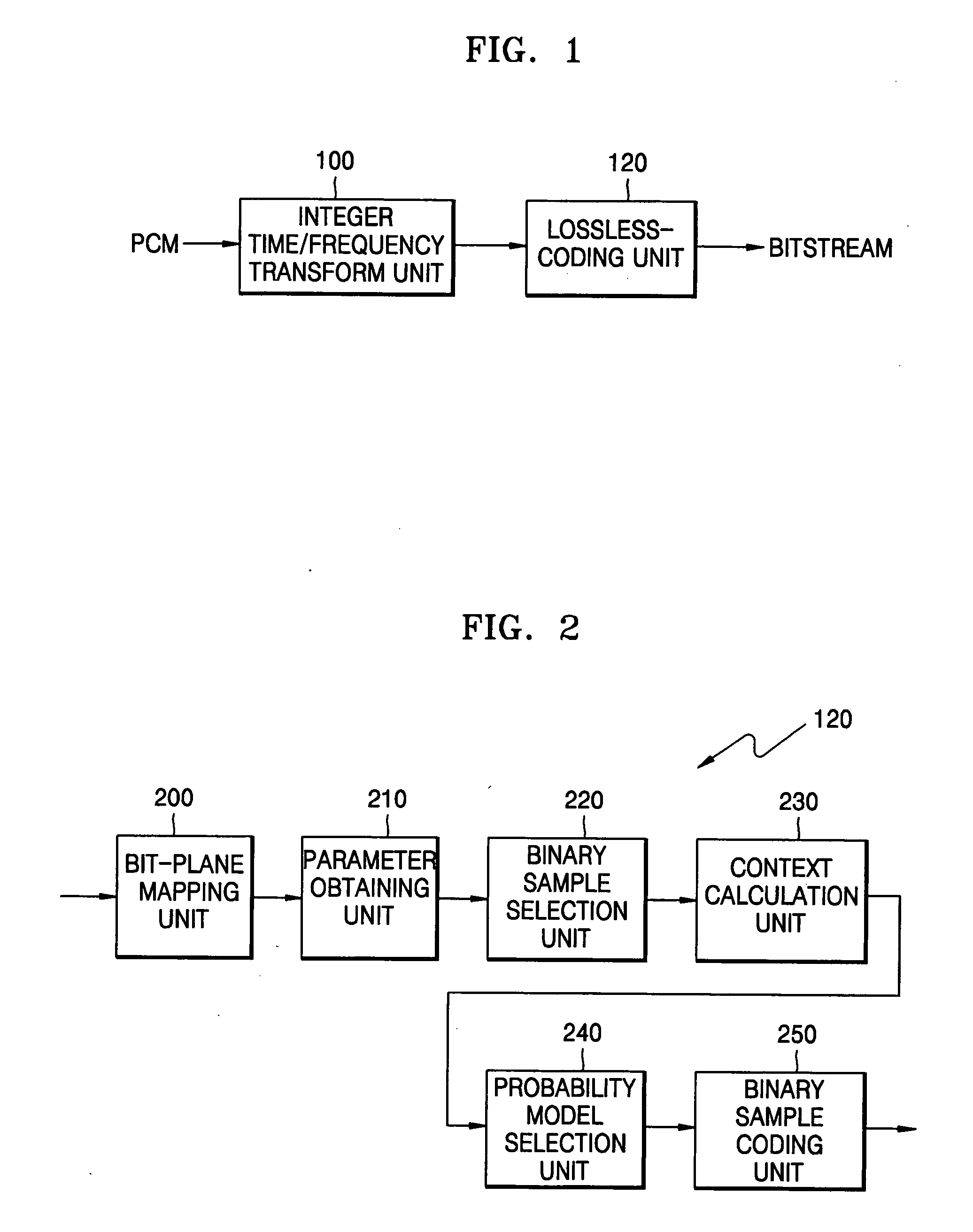
Lossless audio coding/decoding method and apparatus
InactiveUS20050203731A1Increase the compression ratioColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionProbit modelBit plane
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
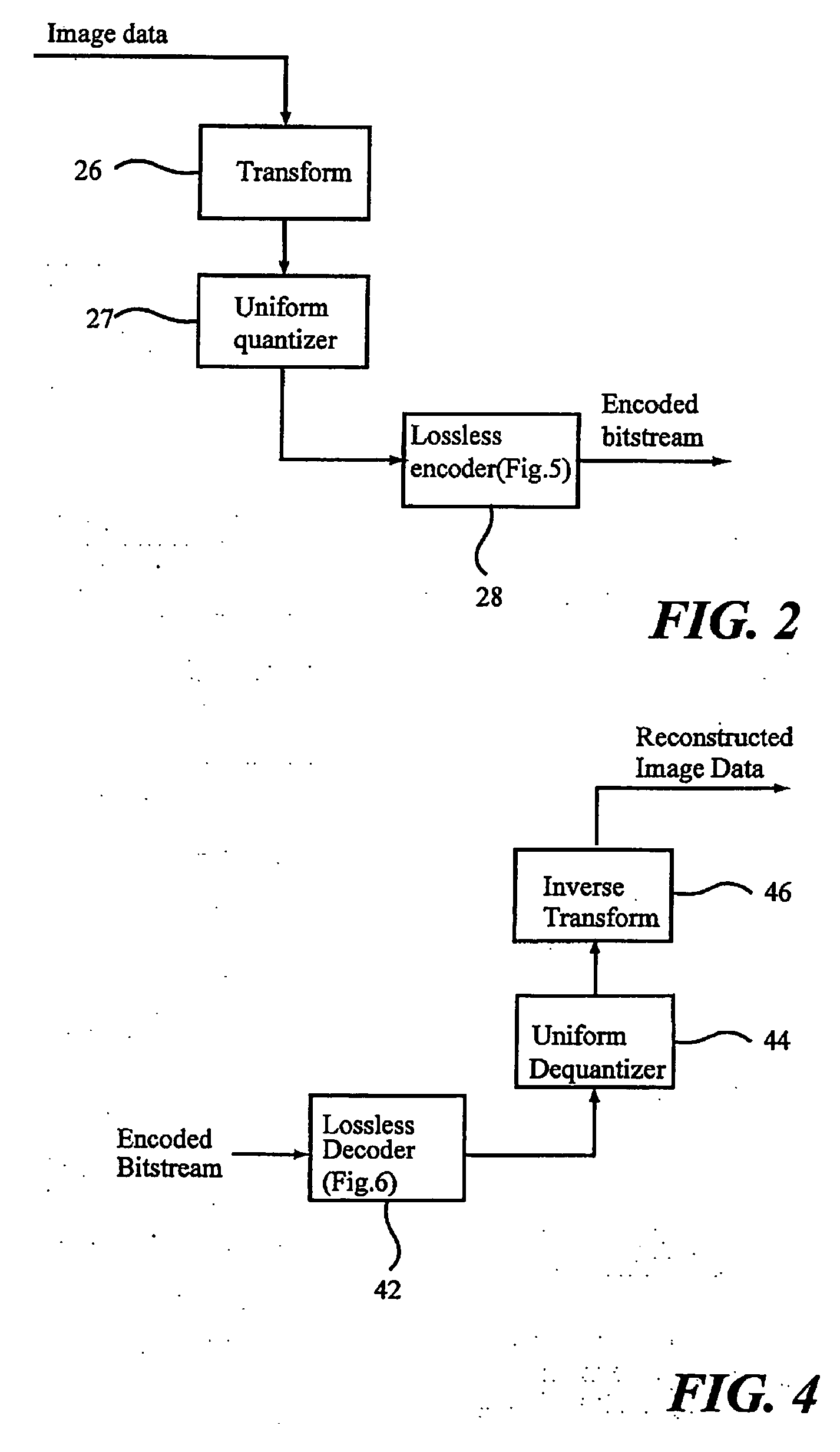
Multiresolution lossless/lossy compression and storage of data for efficient processing thereof
InactiveUS6021224AEfficient storage and retrievalEasy retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingLossless codingImage resolution
Data representing, for instance, an image is lossily encoded, and a residual of the data is losslessly encoded. The lossily encoded data and the losslessly encoded residual provide a losslessly compressed data representation of the original data. The losslessly compressed data is then organized and stored on a storage system according to one or more criteria selected for the particular losslessly encoded data to be organized. This enables the efficient retrieval and processing of the compressed data, including retrieval of portions of the compressed data.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method for coding a time-discrete audio signal to obtain coded audio data and for decoding coded audio data
A time-discrete audio signal is processed to provide a quantization block with quantized spectral values. Furthermore, an integer spectral representation is generated from the time-discrete audio signal using an integer transform algorithm. The quantization block having been generated using a psychoacoustic model is inversely quantized and rounded to then form a difference between the integer spectral values and the inversely quantized rounded spectral values. The quantization block alone provides a lossy psychoacoustically coded / decoded audio signal after the decoding, whereas the quantization block, together with the combination block, provides a lossless or almost lossless coded and again decoded audio signal in the decoding. By generating the differential signal in the frequency domain, a simpler coder / decoder structure results.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Lossless coding method for waveform data
In a method of lossless processing of an integer value signal in a prediction filter which includes a quantiser, a numerator of the prediction filter is implemented prior to the quantiser and a denominator of the prediction filter is implemented recursively around the quantiser to reduce the peak data rate of an output signal. In the lossless processor, at each sample instant, an input to the quantiser is jointly responsive to a first sample value of a signal input to the prediction filter, a second sample value of a signal input to the prediction filter at a previous sample instant, and an output value of the quantiser at a previous sample incident. In a preferred embodiment, the prediction filter includes noise shaping for affecting the output of the quantiser.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Lossless encoding and decoding of digital data
ActiveUS20080112632A1Shorter code wordEasy to compressPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionDigital dataLossless coding
The disclosure relates to encoding and decoding of digital data, and in particular to lossless arithmetic encoding and decoding of digital data representing audio, image or video data. A probability density function used for lossless arithmetic encoding of digital data is controlled by employing one or more parameters that changes over the set of data to be encoded. A parametric model in the form of an envelope function describes the spread of quantization indices derived from the data in a transform domain. By transmitting the one or more parameters together with the arithmetically encoded data, a receiving decoder may decode the data by exploiting the same parametric model as used by the encoder.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
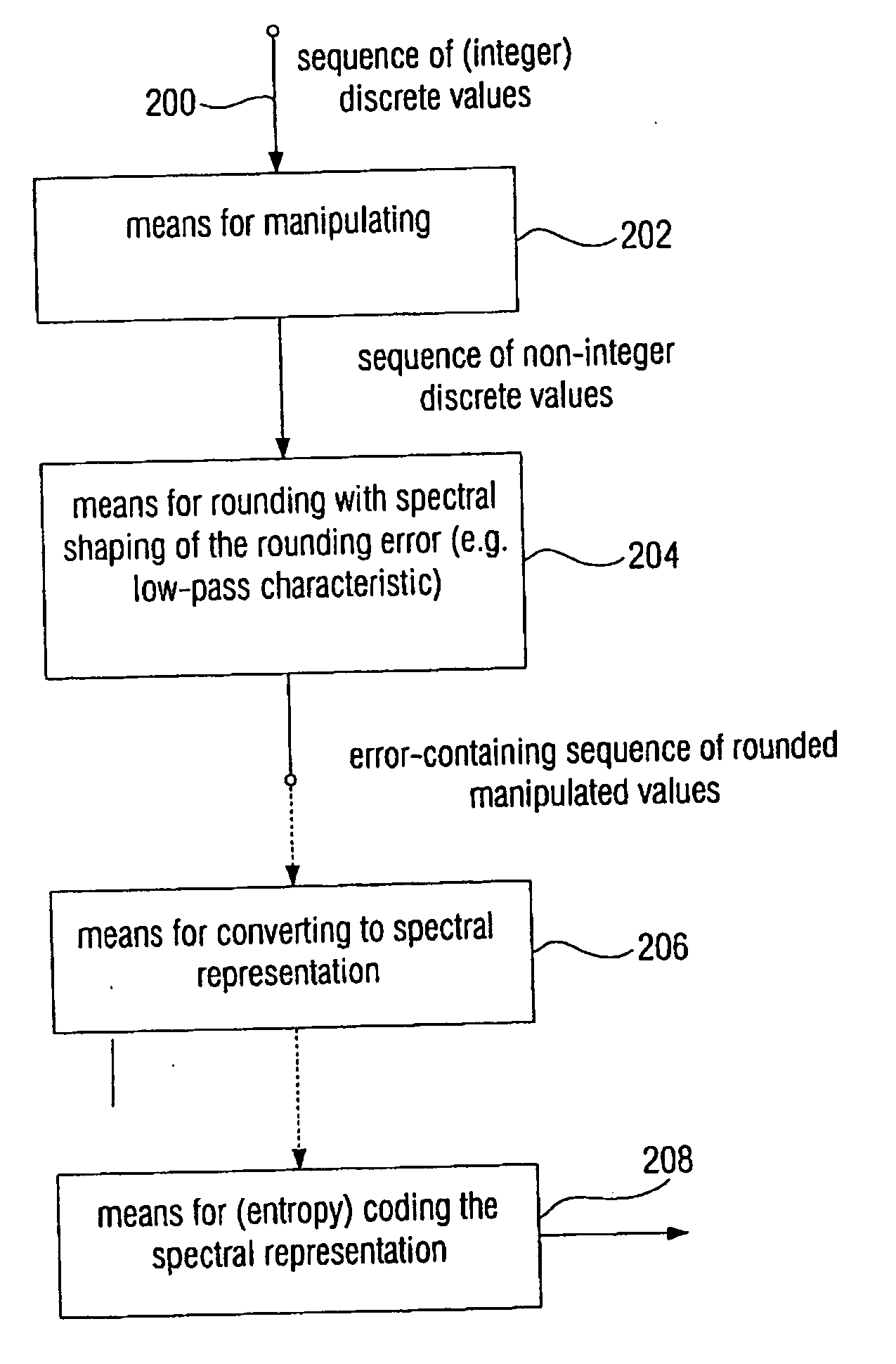
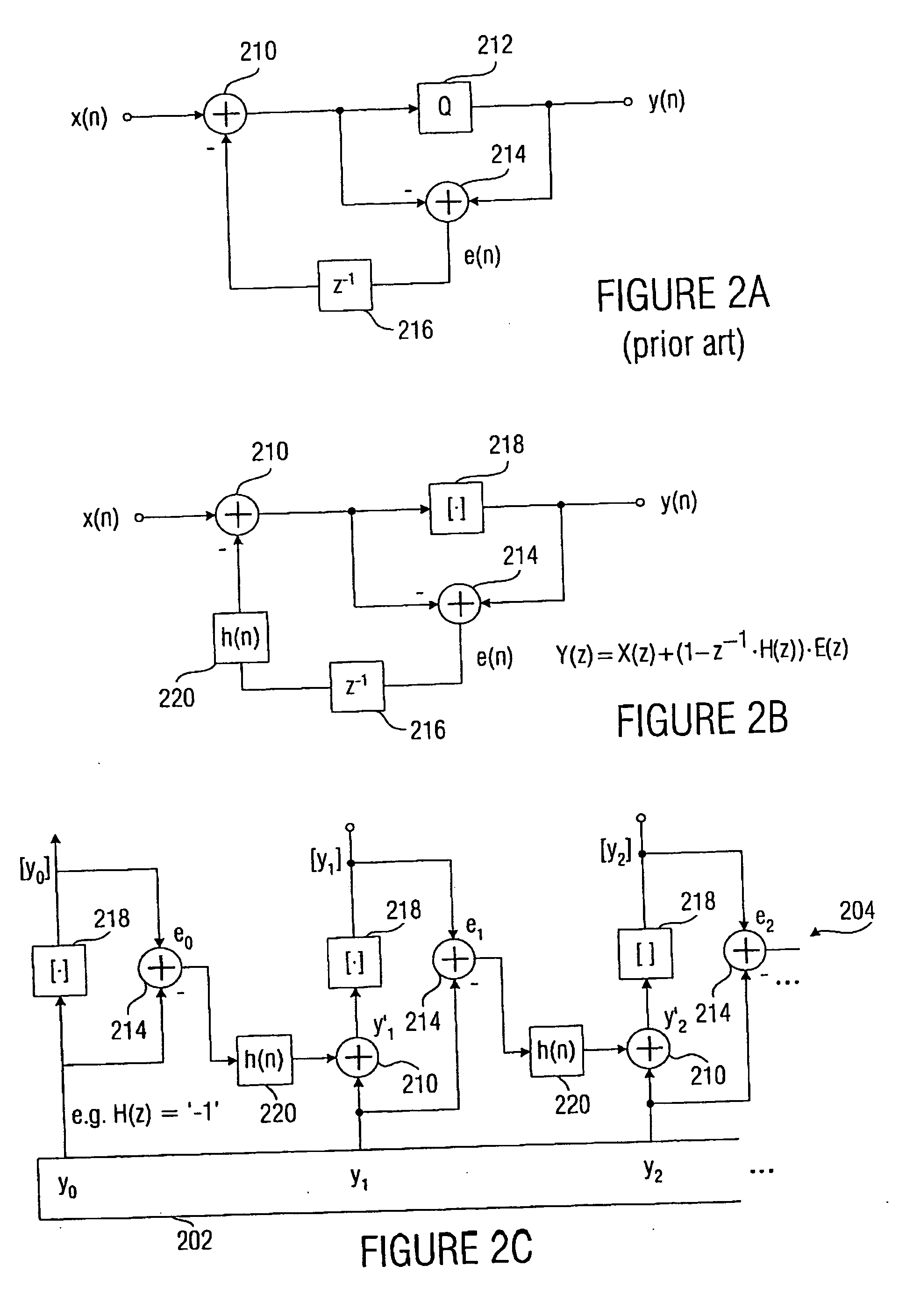
Device and method for processing a signal having a sequence of discrete values
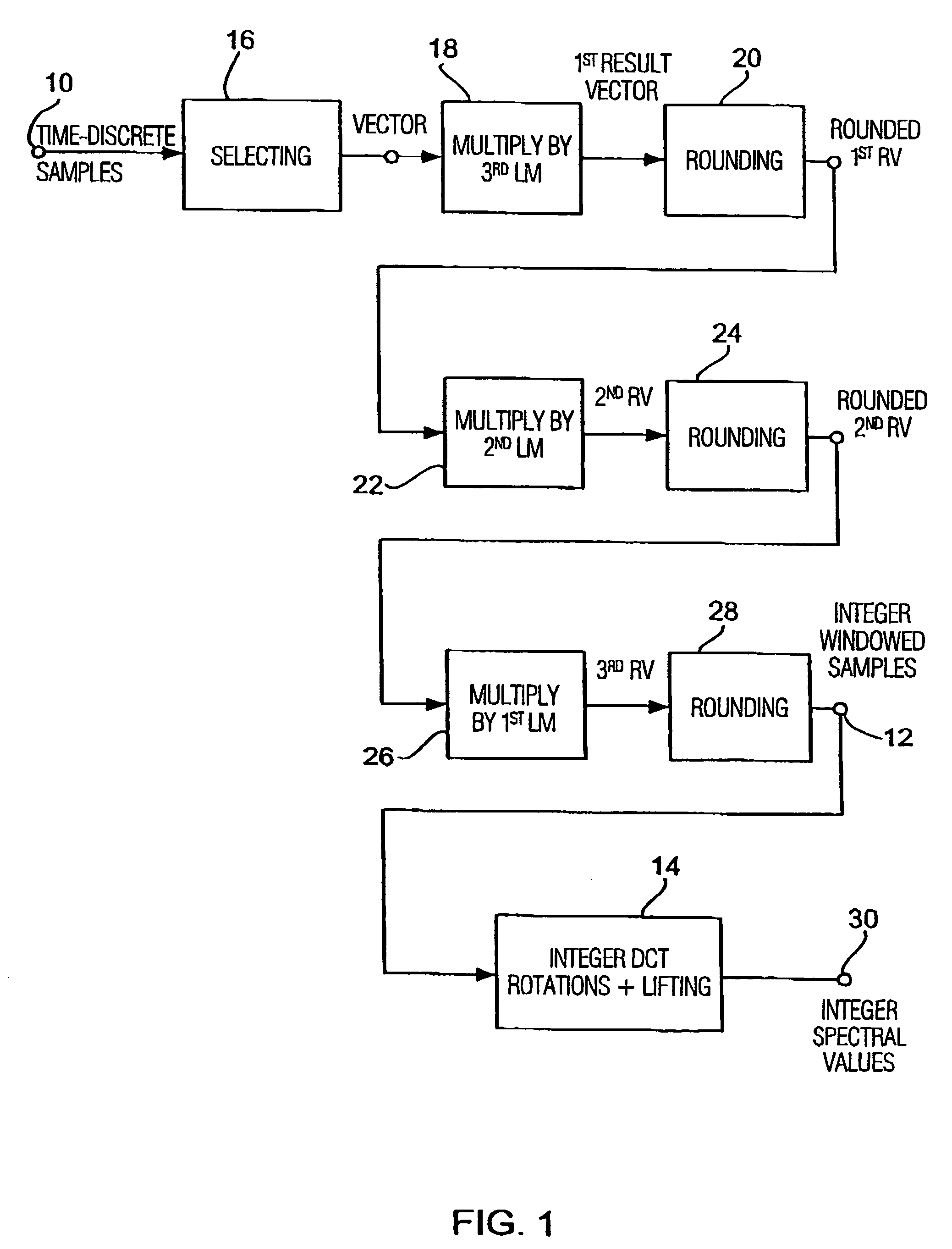
ActiveUS20060210180A1Few rounding errorIncrease the number ofSpeech analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionLossless codingFrequency spectrum
When processing a signal having a sequence of discrete values, wherein there is a first frequency range, in which the signal has a high energy, and wherein there is a second frequency range, in which the signal has a low energy, the sequence of discrete values is first manipulated to obtain a sequence of manipulated values, so that at least one of the manipulated values is non-integer. Then the sequence of manipulated values is rounded to obtain a sequence of manipulated values. The rounding is formed to effect a spectral shaping of a generated rounding error so that a spectrally shaped rounding error has a higher energy in the first frequency range than in the second frequency range. By spectrally shaping the rounding error so that the rounding error does not have any energy either in the storage areas where there is no signal energy, an especially efficient coding is obtained particularly in connection with a lossless coding context.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Image encoding apparatus, image decoding apparatus, control method therefor, computer program, and computer-readable storage medium
InactiveUS20060210176A1Efficiently natural imageNumber of appearance is limitedCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionLossless coding
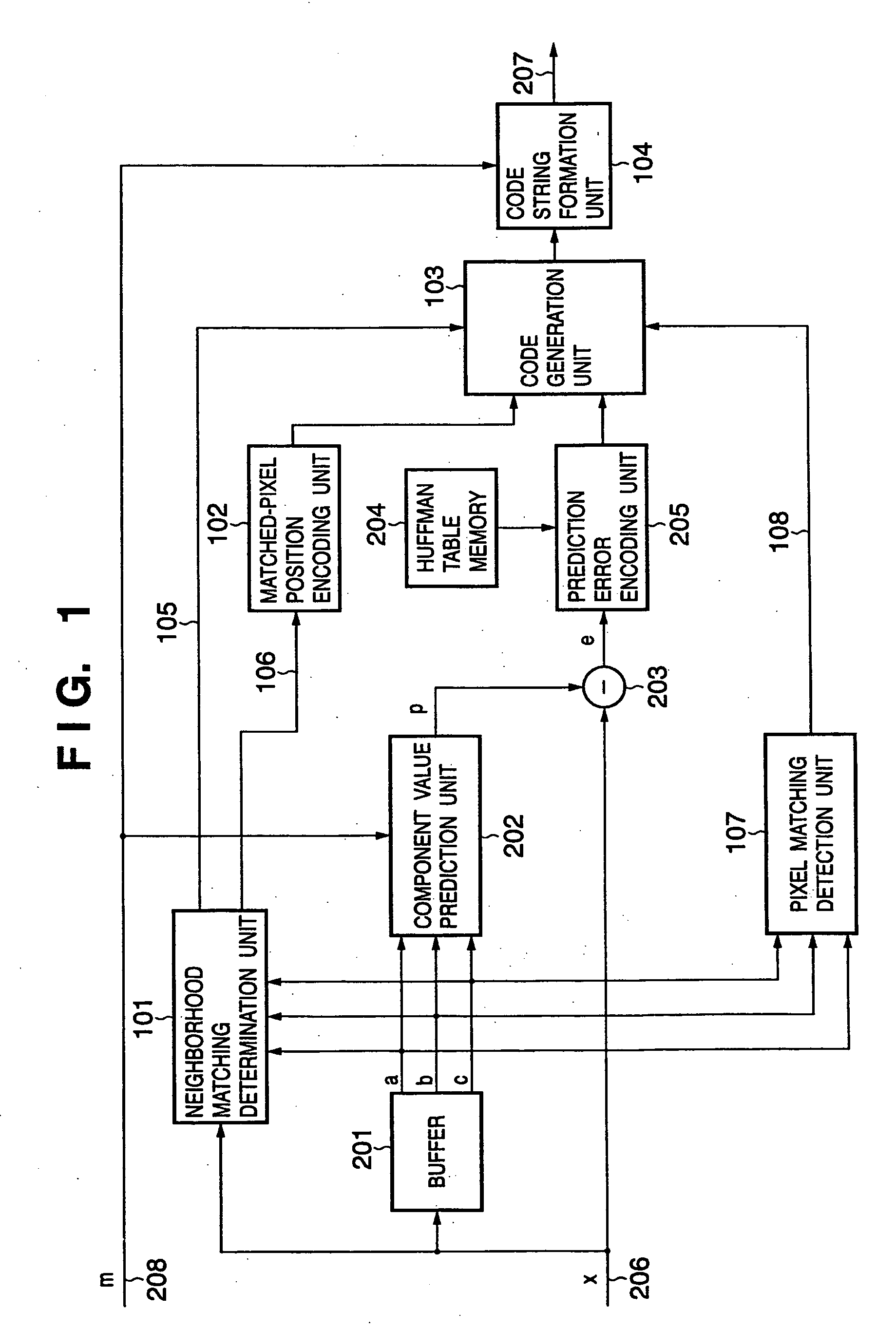
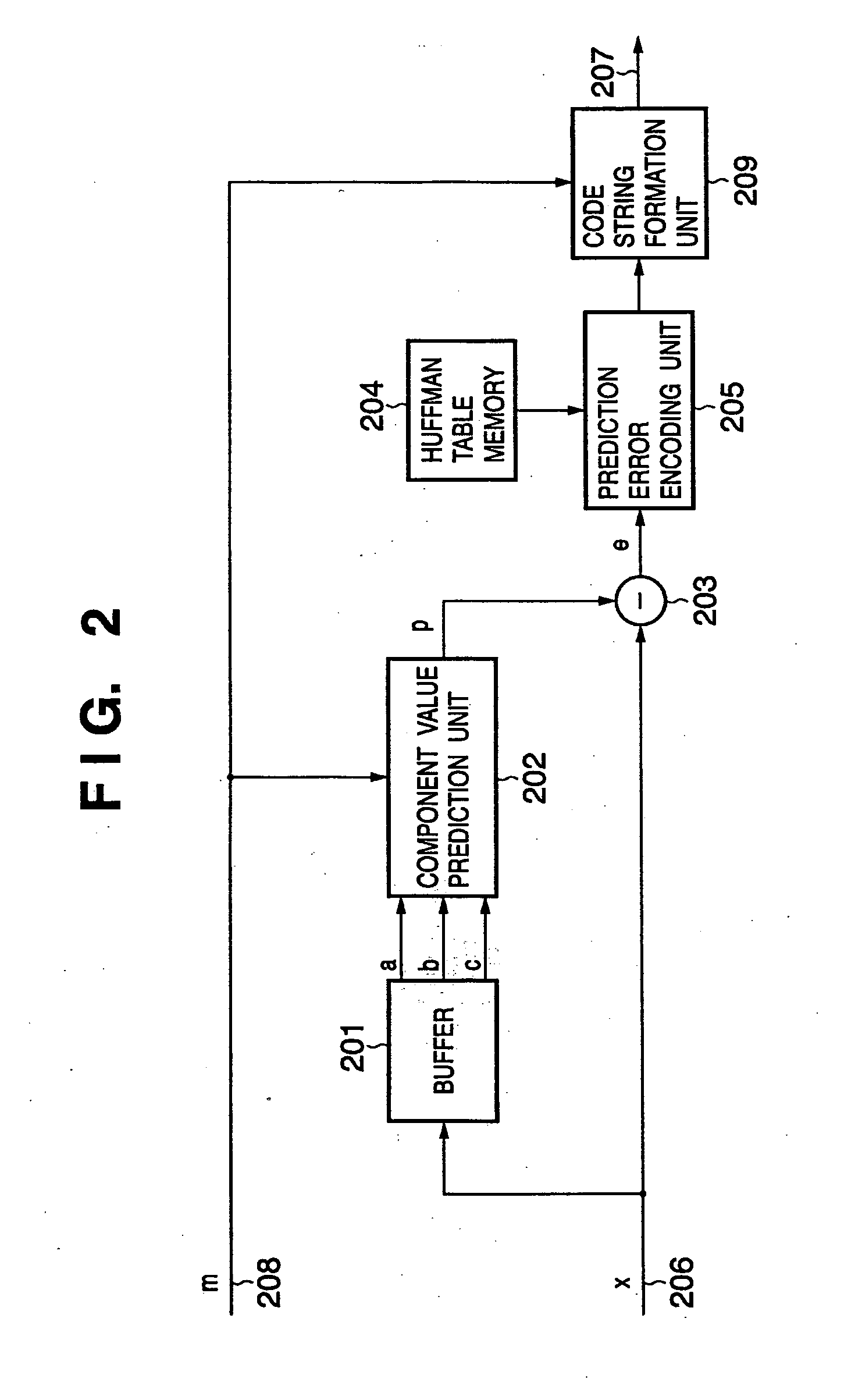
According to this invention, while the encoding efficiency of image data (e.g., a natural image) substantially maintains the conventional one, an image (e.g., a CG image or text document) having a small number of appearance colors is losslessly encoded at higher compression ratio. For this purpose, pixel data are input in the raster order and temporarily stored in a buffer. Pixel data at positions having undergone encoding are stored. A neighborhood matching determination unit generates first information representing whether a pixel having the same color as that of the pixel of interest exists in neighboring pixels a, b, and c, and second information for specifying whether a pixel having the same color as that of the pixel of interest exists, and if the pixel having the same color exists, specifying the neighboring pixel. A pixel matching detection unit counts the number of colors contained in the neighboring pixels a, b, and c, and generates information representing whether the number of colors is two or less, or three or less. On the basis of the first information and second information, a code generation unit outputs one or both of encoded data from a matched-pixel position encoding unit and prediction error encoding unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Image processing apparatus and control method thereof
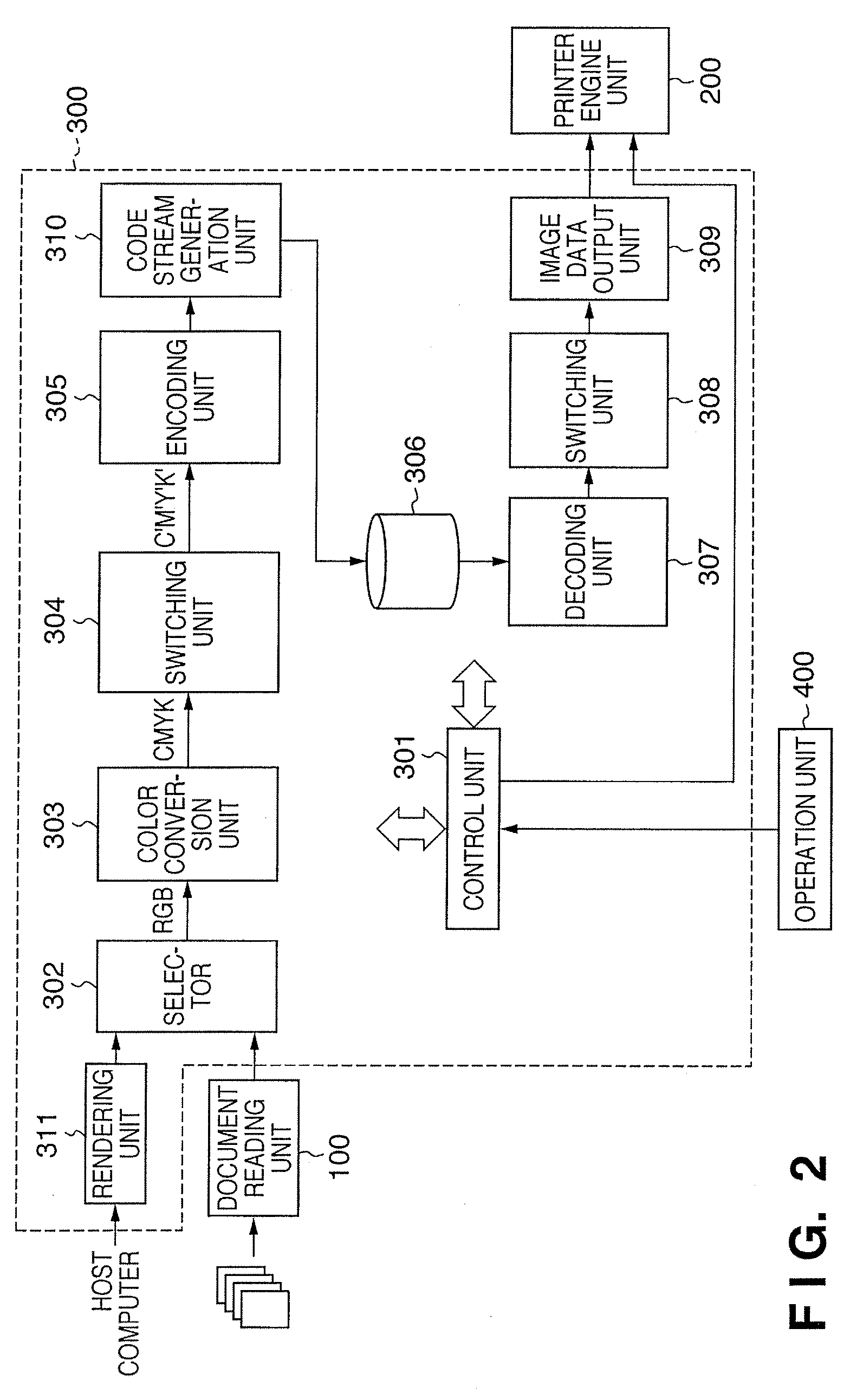
ActiveUS20080037882A1High-speed encodingIncrease speedCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionColor image
In this invention, image data expressed by one component is encoded at a high speed by using a color image lossless encoder. To do this, a color conversion unit converts color image data read by a document reading unit into C, M, Y, and K data. In a color reading mode, a switching unit directly outputs the C, M, Y, and K data to an encoding unit. If the reading mode is a monochrome reading mode, the switching unit neglects the C, M, and Y components of the C, M, Y, and K data. Every time four K components are input, the switching unit supplies the four K components to the encoding unit as pseudo data of C, M, Y, and K color components. The encoding unit lossless-encodes the received C, M, Y, and K component data.
Owner:CANON KK
Matrix improvements to lossless encoding and decoding
InactiveUS7193538B2Signal can be recoveredPrevent overloadTelevision system detailsStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsLossless coding24-bit
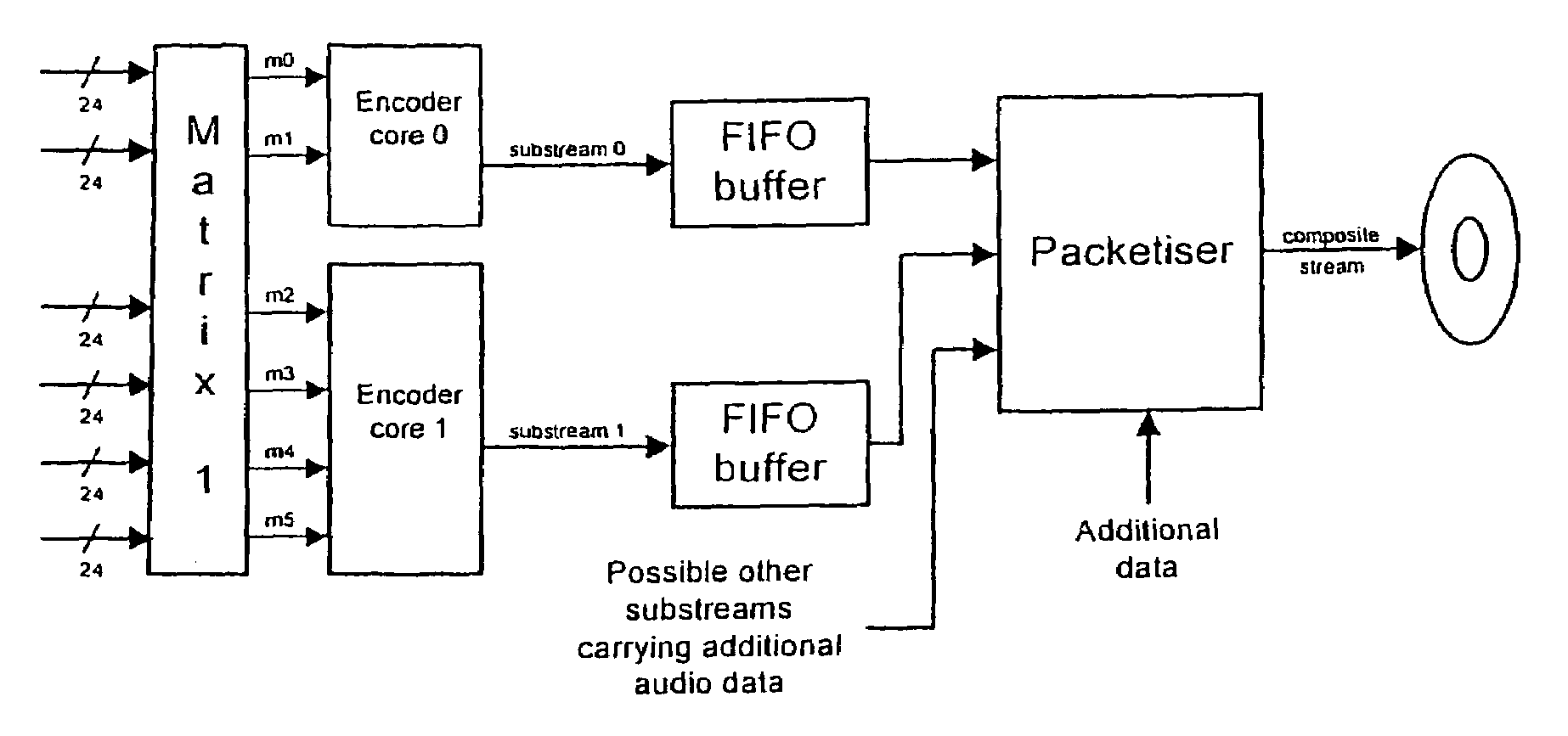
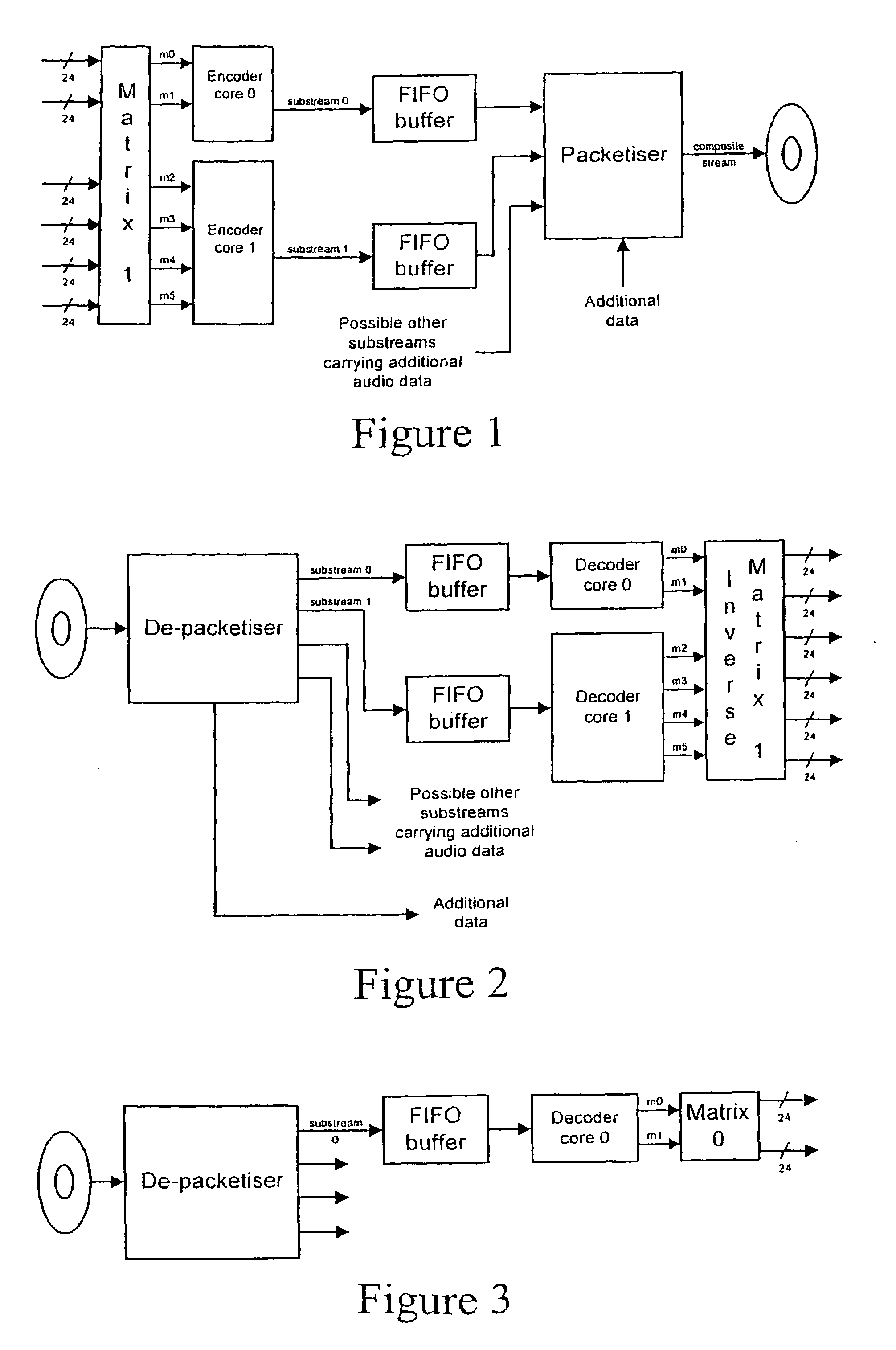
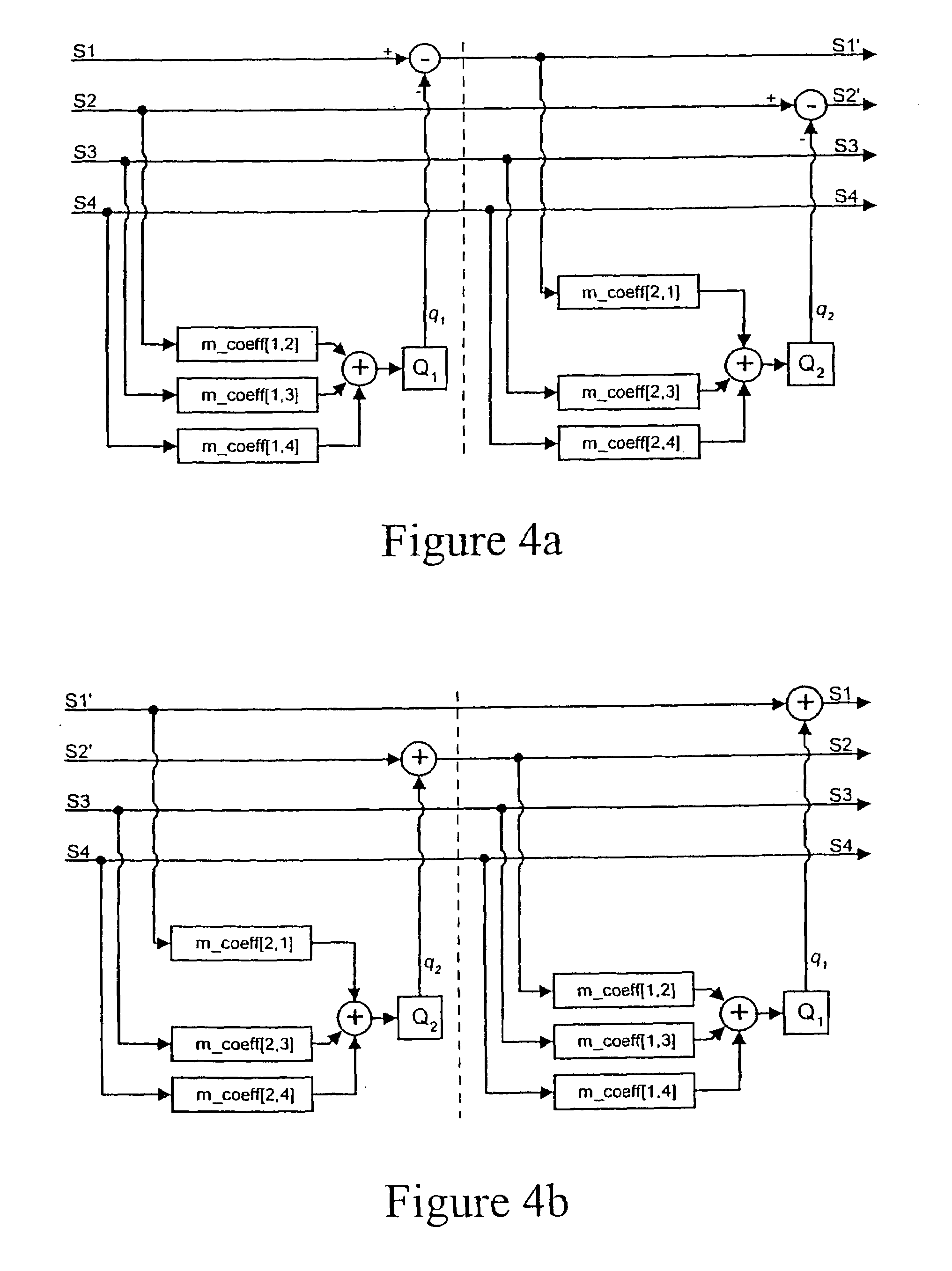
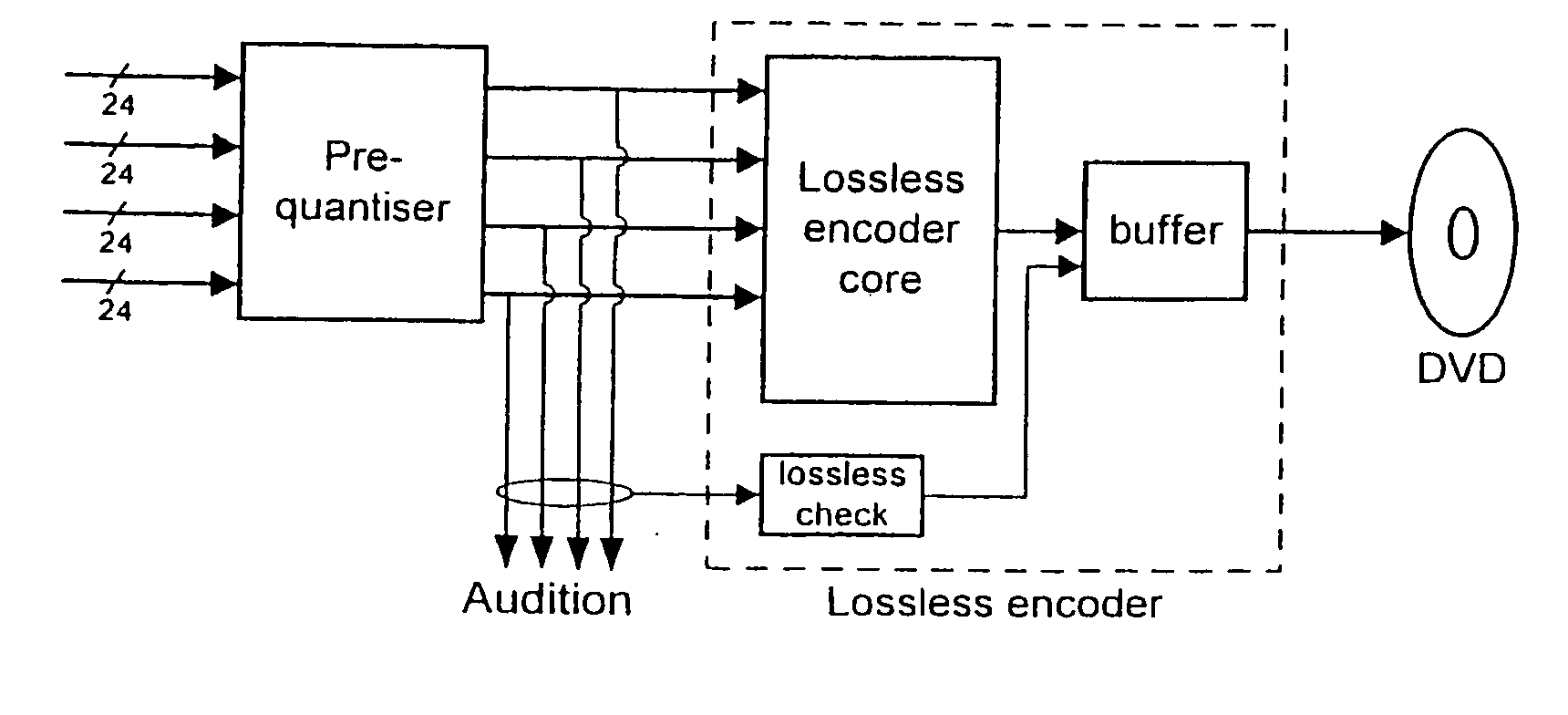
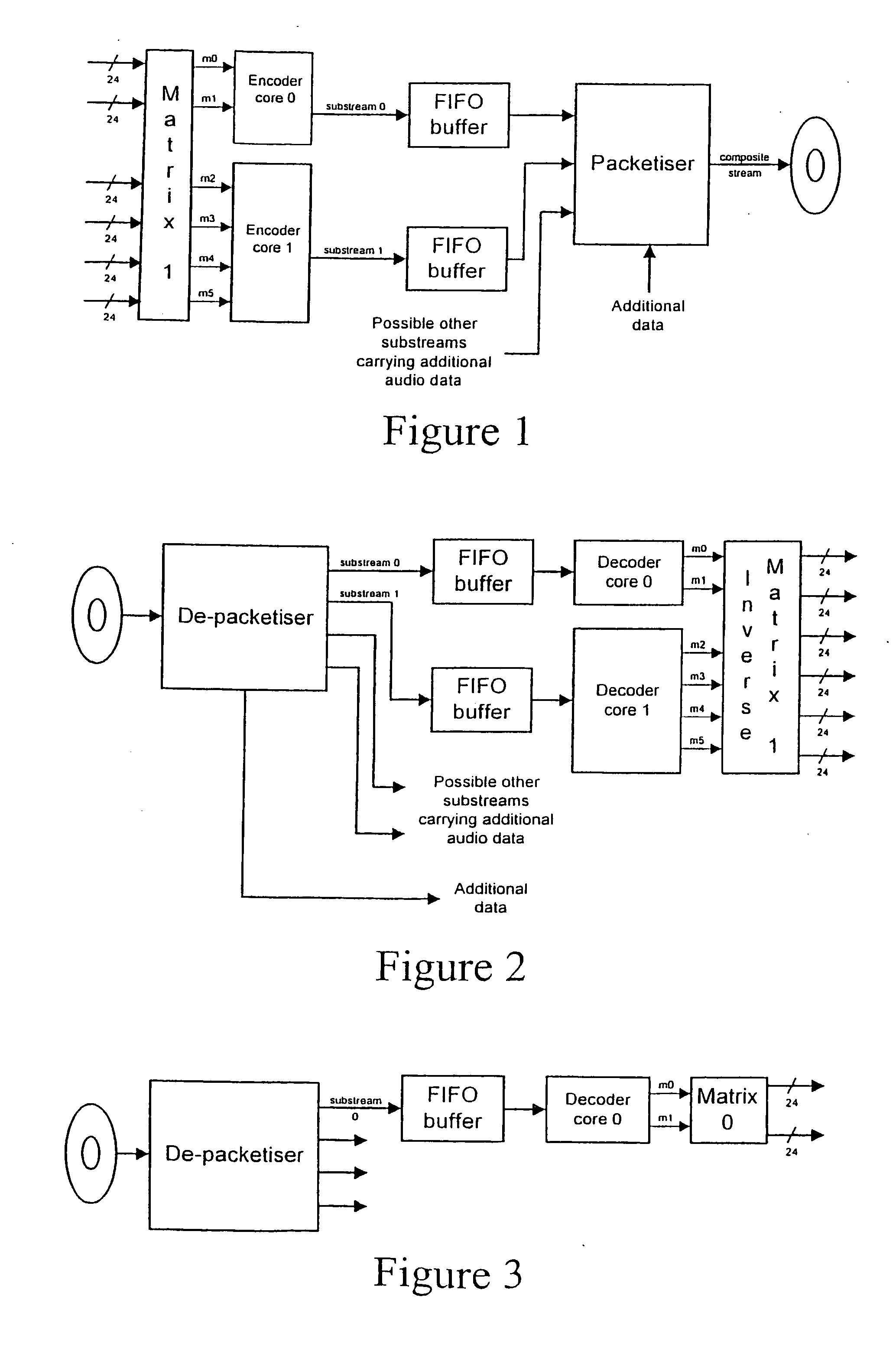
A lossless encoder and decoder are provided for transmitting a multichannel signal on a medium such as DVD-Audio. The encoder accepts additionally a downmix specification and splits the encoded stream into two substreams, such that a two-channel decoder of meagre computational power can implement the downmix specification by decoding one substream, while a multichannel decoder can decode the original multichannel signal losslessly using both substreams. Further features provide for efficient implementation on 24-bit processors, for confirmation of lossless reproduction to the user, and for benign behaviour in the case of downmix specifications that result in overload. The principle is also extended to mixed-rate signals, where for example some input channels are sampled at 48 kHz and some are sampled at 96 kHz.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Hybrid text and image based encoding
A configuration for encoding and decoding the data is disclosed herein. A server retrieves webpage content to filter and extract text and image data. The text data is encoded using a lossless encoder, whereas the image data is downsampled to a lower resolution and encoded using a lossy encoder. The encoded text and image data is transmitted over a network. Once the encoded data is received on the client device, the text and image data is decoded using an inverse encoding algorithm and resized at a resolution appropriate to the native resolution of the display device.
Owner:OTELLO CORP ASA
Method and apparatus for encoding mixed content image sequences
InactiveUS8965140B1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionLossless coding
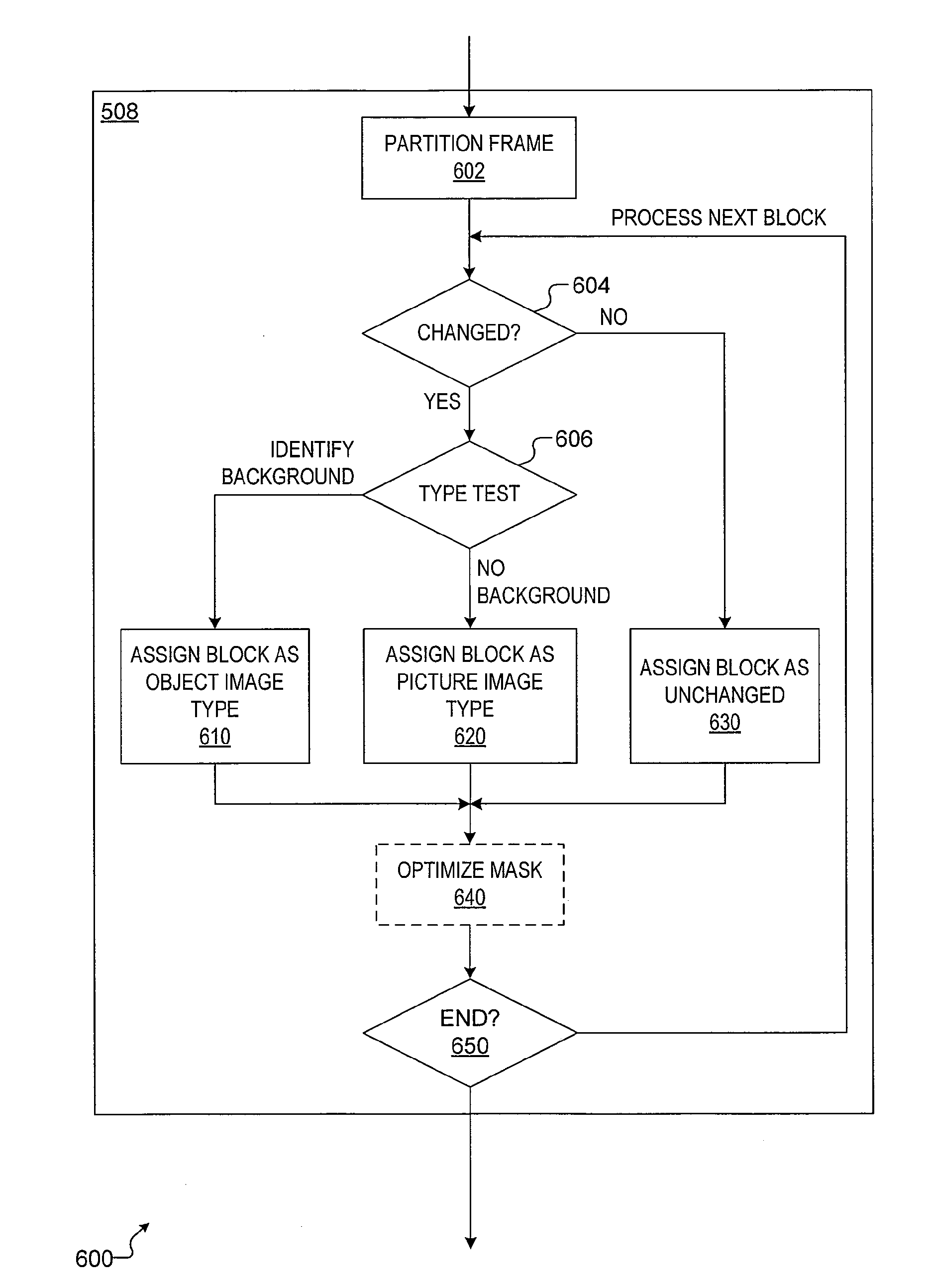
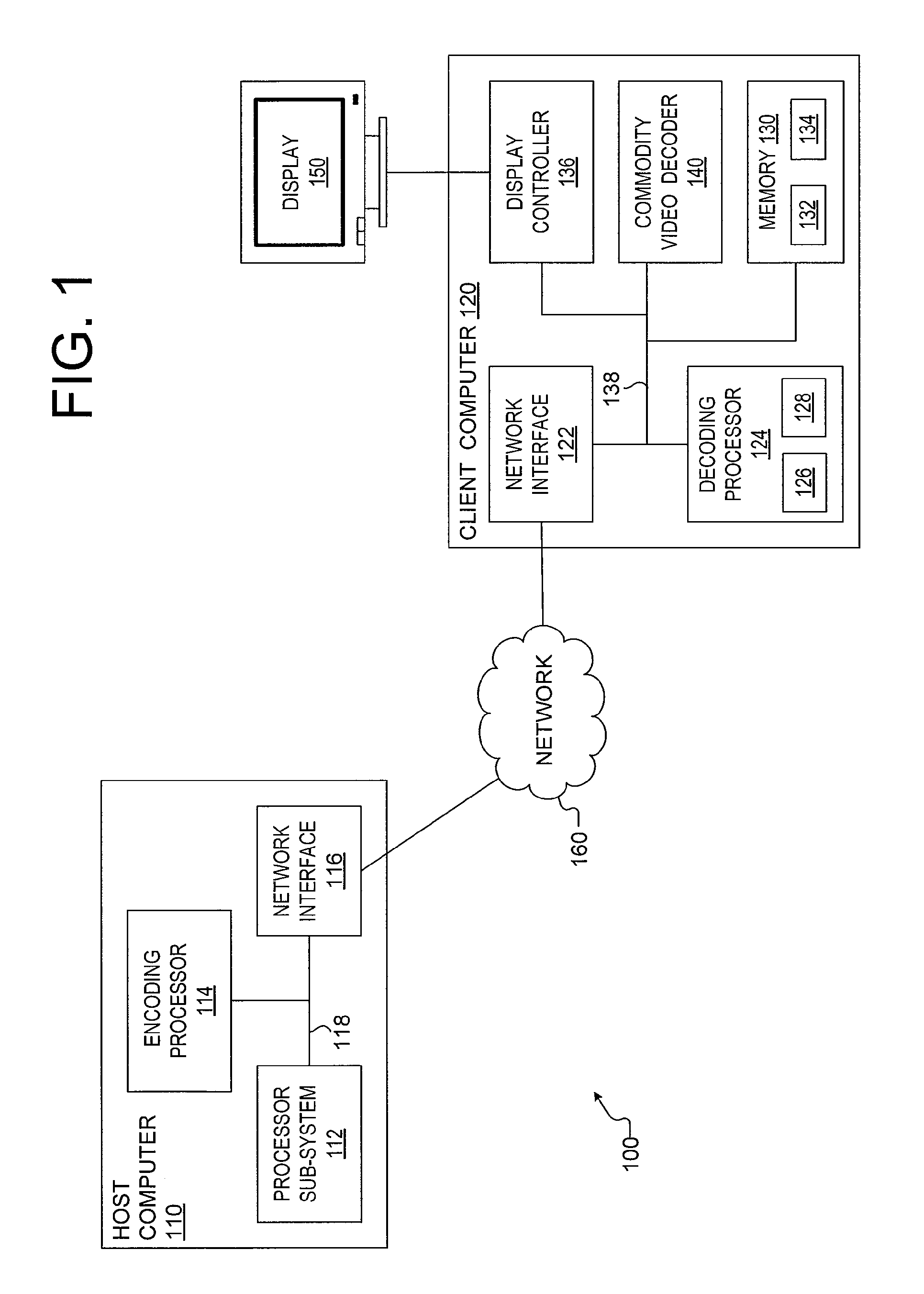
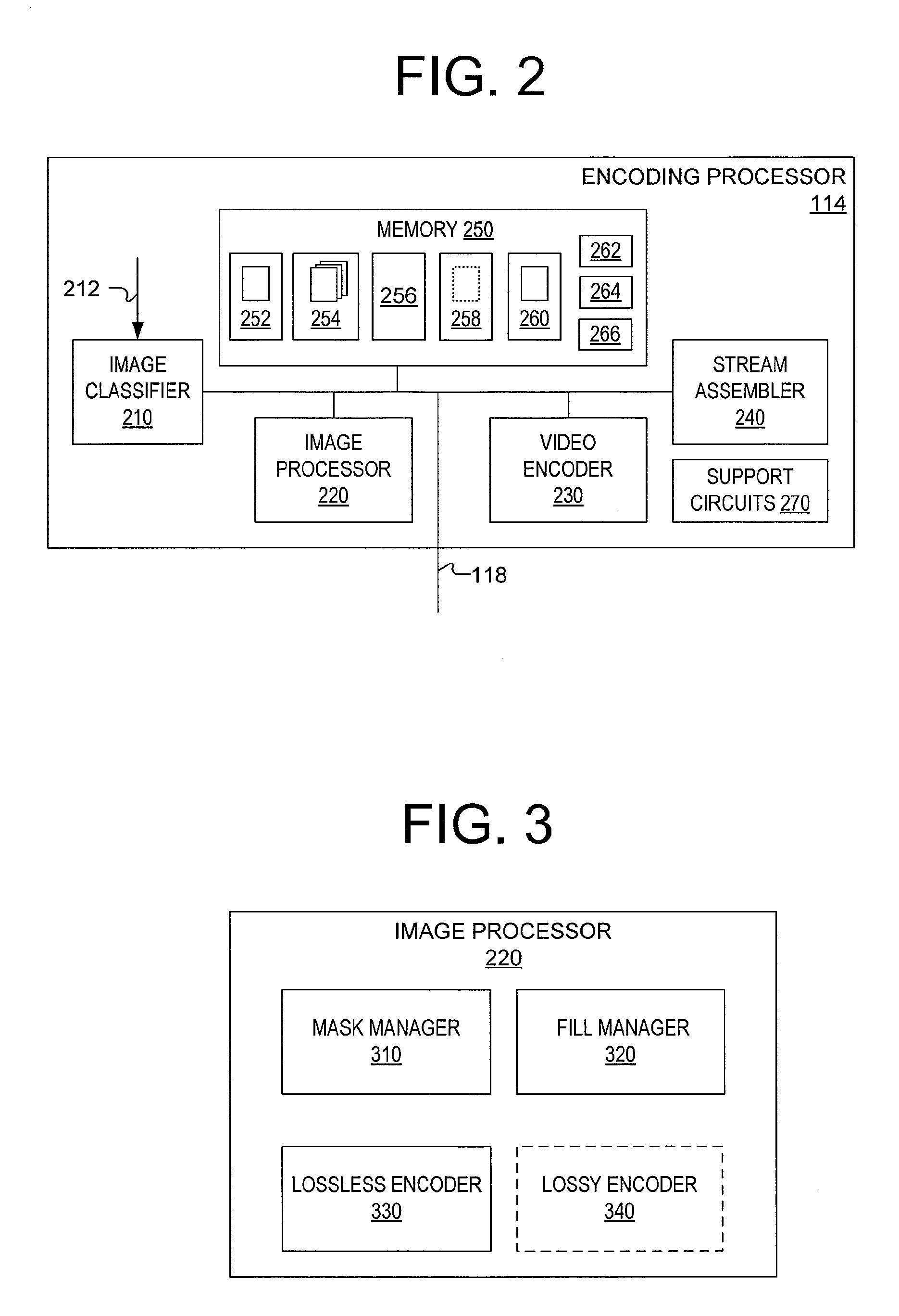
A method and apparatus for encoding a frame from a mixed content image sequence. In one embodiment, the method, executed under the control of a processor configured with computer executable instructions, comprises (i) generating, by an encoding processor, an image type mask that divides the frame into an unchanged portion, an object portion and a picture portion; (ii) producing lossless encoded content, by the encoding processor, from the object portion and the image type mask; (iii) generating, by the encoding processor, a filtered facsimile from the frame, the filtered facsimile generated by retaining the picture portion and filling the unchanged portion and the object portion with neutral image data; and (iv) producing, by the encoding processor, lossy encoded content from the filtered facsimile.
Owner:TERADICI CORP
Matrix improvements to lossless encoding and decoding
InactiveUS20050007262A1Prevent overloadSignal can be recoveredTelevision system detailsStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsLossless coding24-bit
A lossless encoder and decoder are provided for transmitting a multichannel signal on a medium such as DVD-Audio. The encoder accepts additionally a downmix specification and splits the encoded stream into two substreams, such that a two-channel decoder of meagre computational power can implement the downmix specification by decoding one substream, while a multichannel decoder can decode the original multichannel signal losslessly using both substreams. Further features provide for efficient implementation on 24-bit processors, for confirmation of lossless reproduction to the user, and for benign behaviour in the case of downmix specifications that result in overload. The principle is also extended to mixed-rate signals, where for example some input channels are sampled at 48 kHz and some are sampled at 96 kHz
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
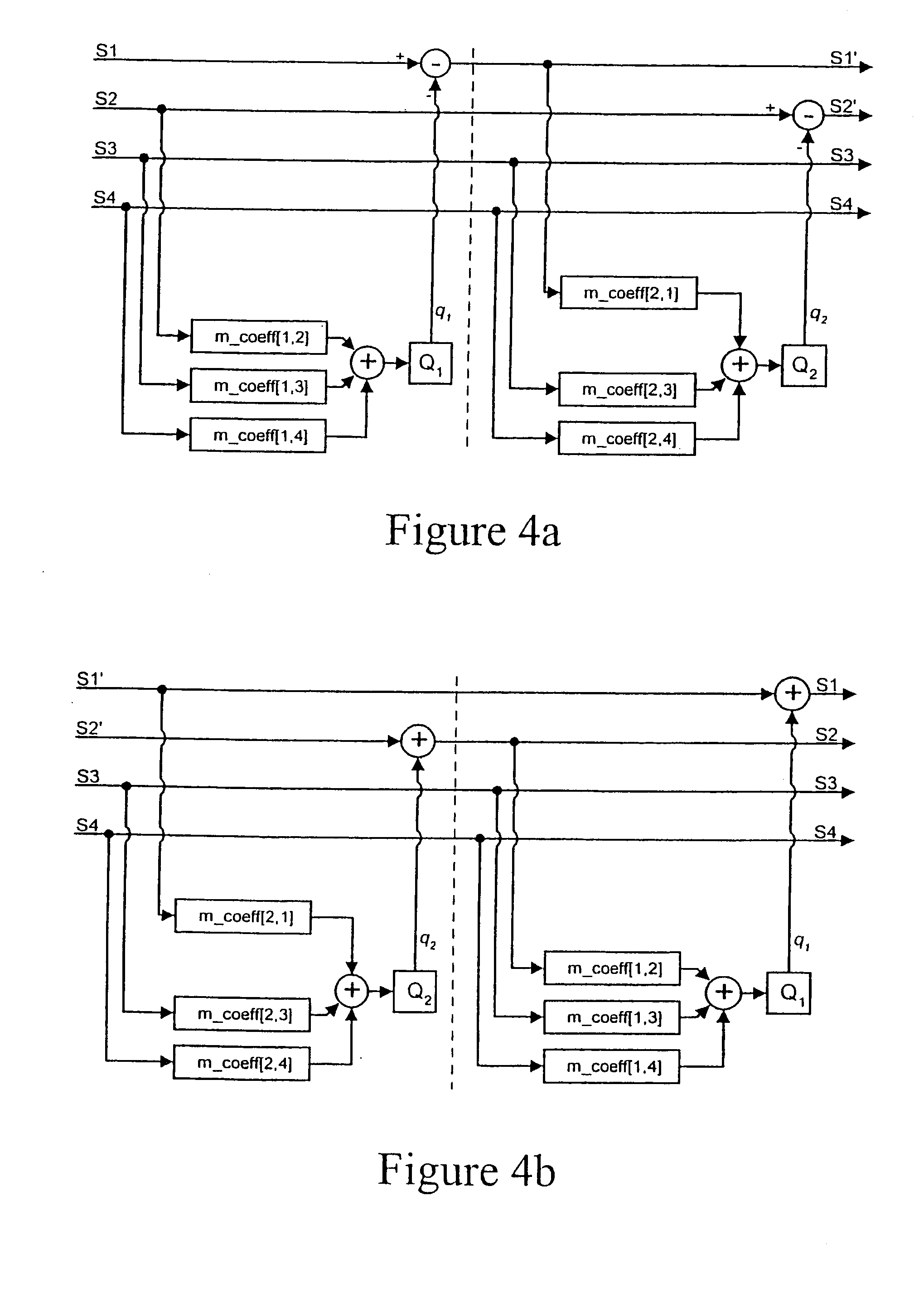
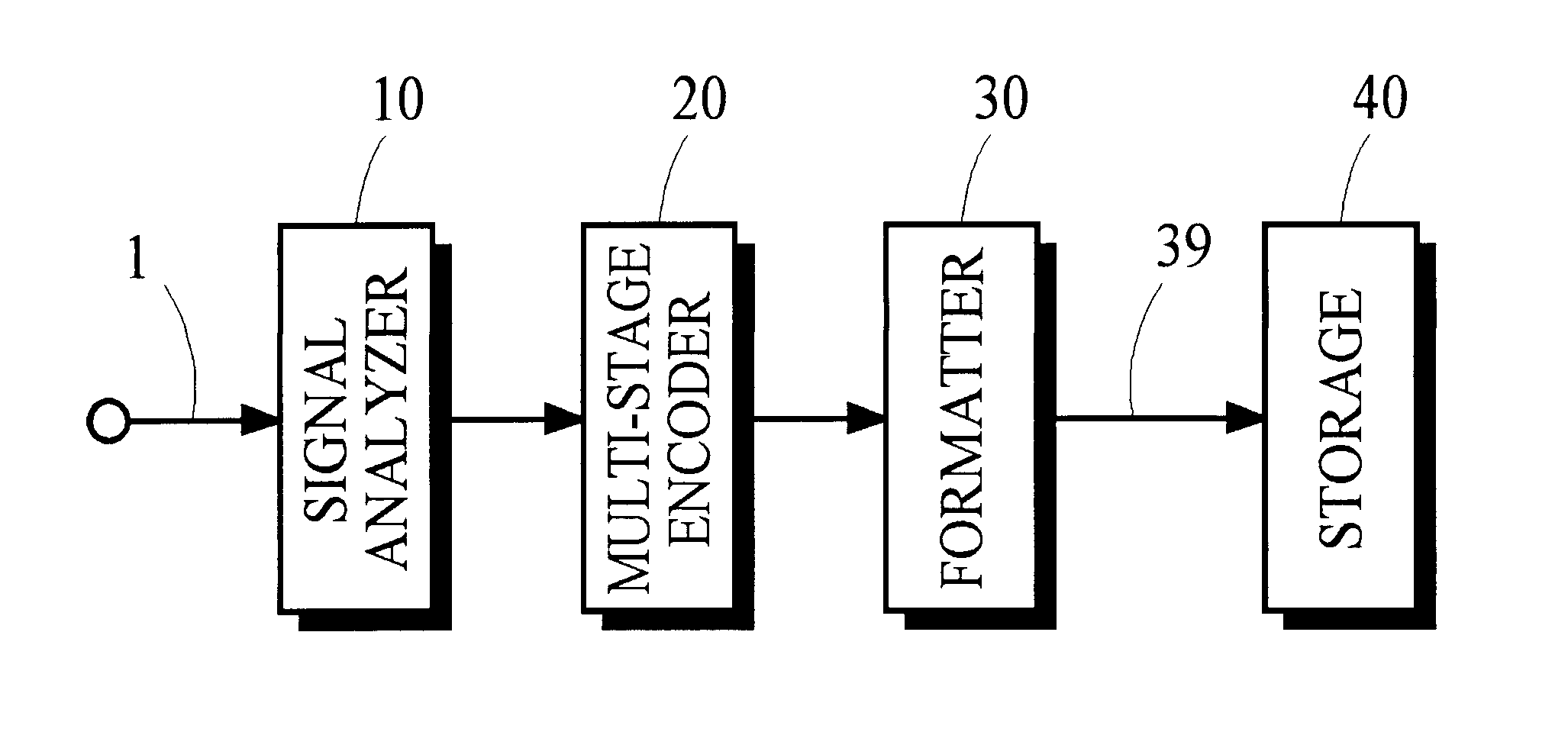
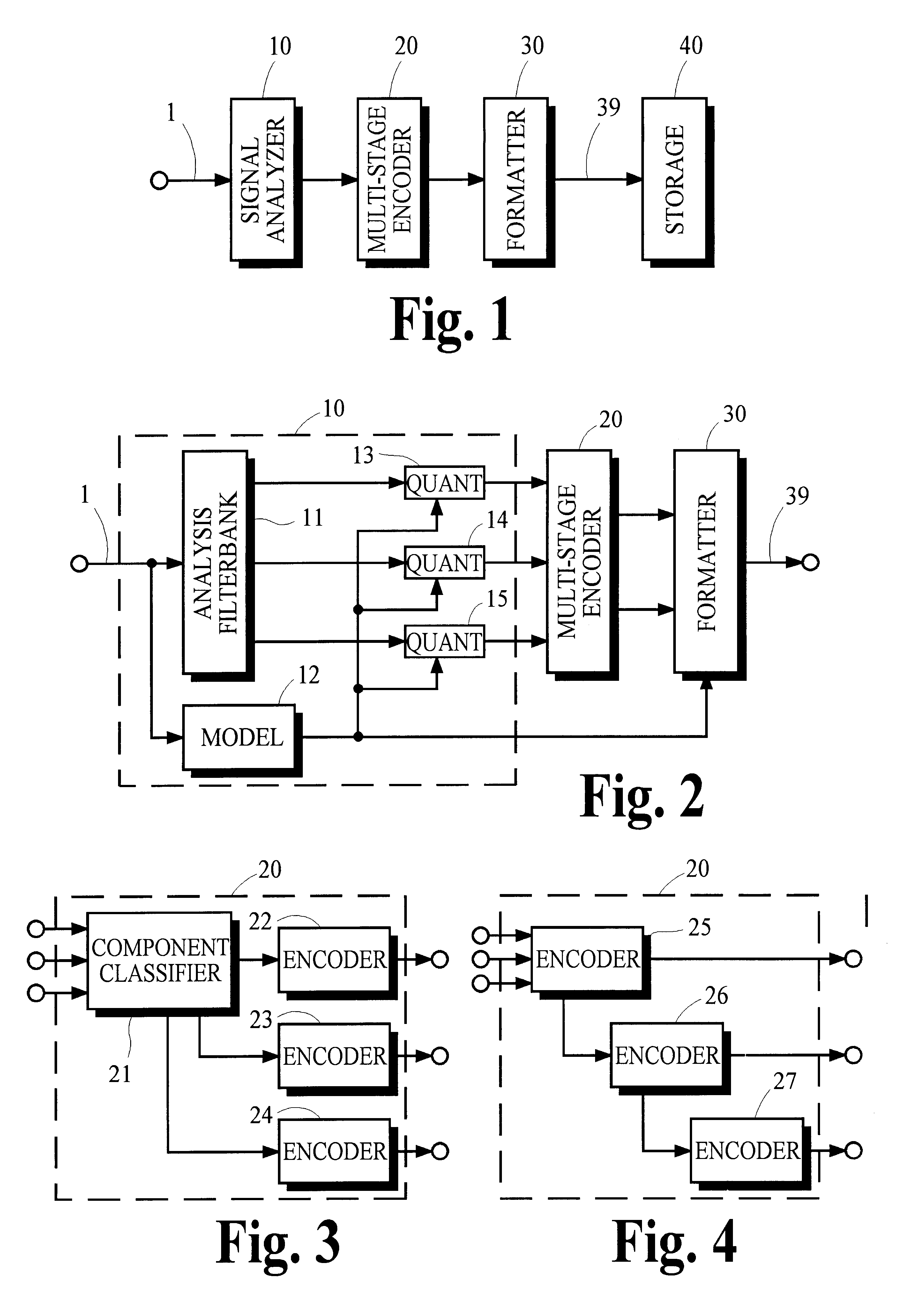
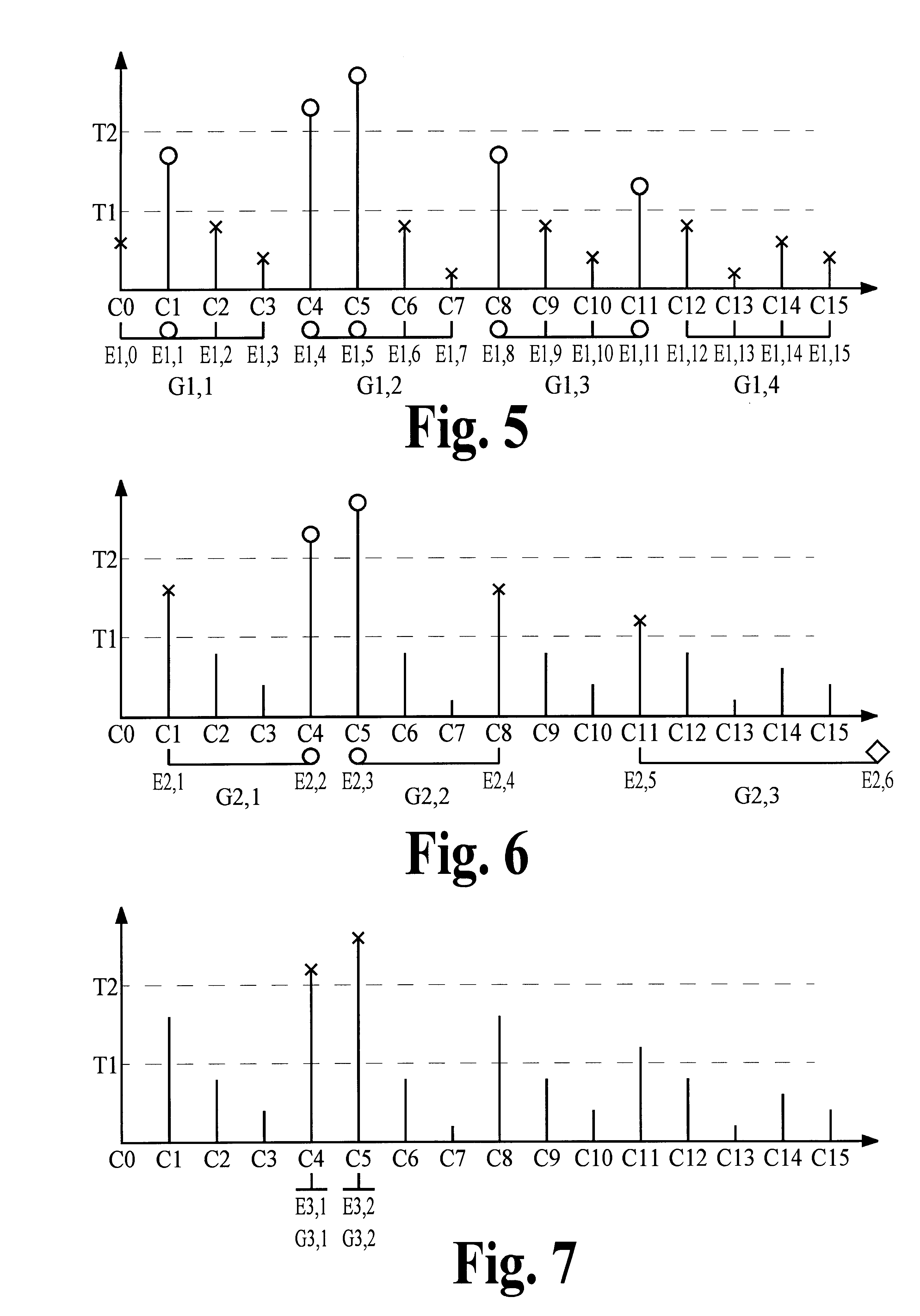
Multi-stage encoding of signal components that are classified according to component value
InactiveUS6735339B1Improve the level ofHigh complexitySpeech analysisCode conversionLossless codingMulti dimensional
A high degree of compression can be achieved in audio and image coding systems by using a multiple-stage lossless encoding process having low computational cost that does not require high-accuracy pre-defined probability distribution functions of the information to be compressed. The multiple-stage encoding process classifies the signal components to be compressed into one of several classifications according to signal component value. Signal components placed into higher-level classifications are represented by tokens in the lower-level classifications. Each stage of the encoding process forms groups of signal components and tokens and applies a multi-dimensional encoding process to the groups. The dimension of the coding process is equal to the size of the group to which it is applied, and is chosen to balance computational requirements of the encoding process against compression performance.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
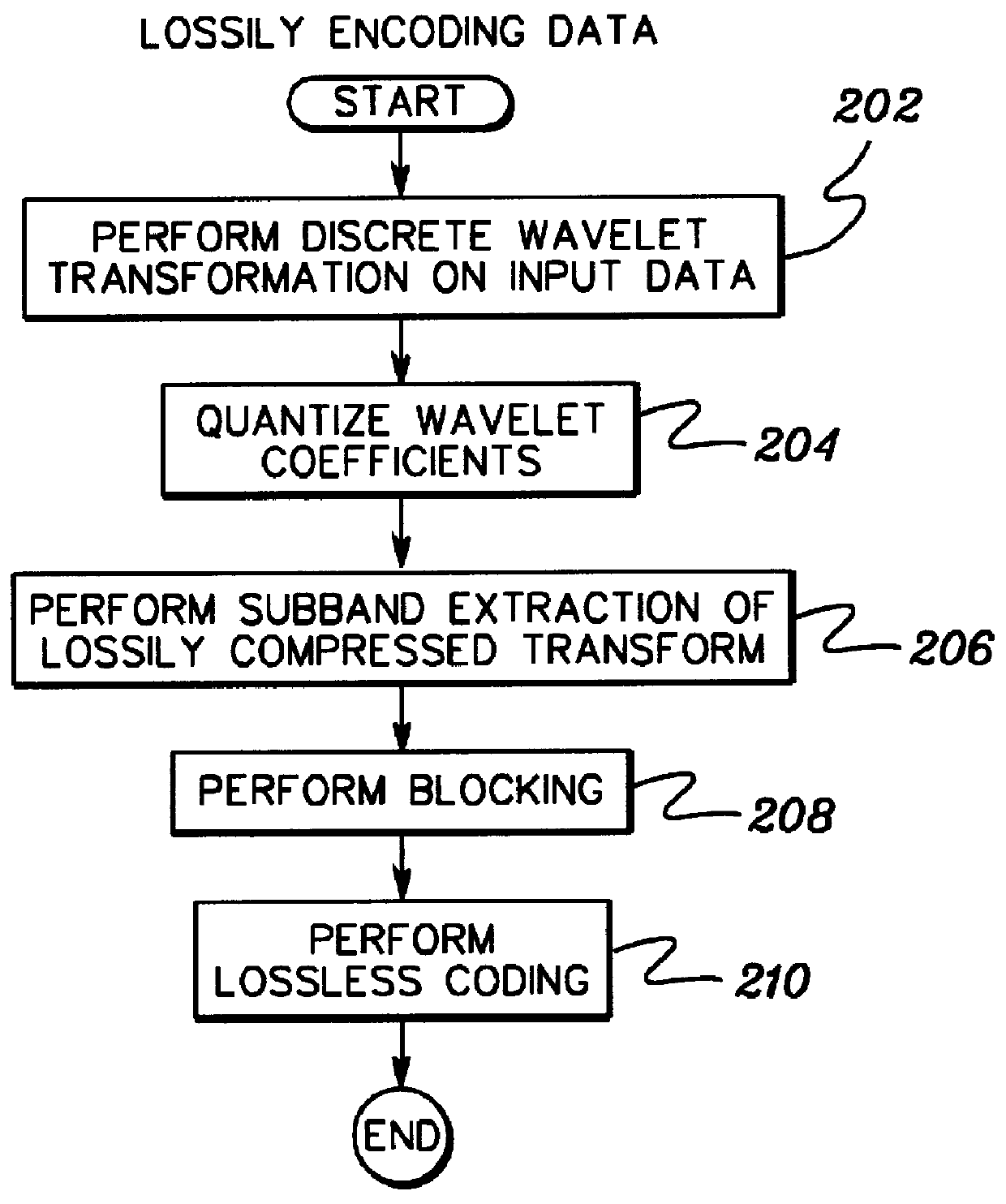
Method for image coding by rate-distortion adaptive zerotree-based residual vector quantization and system for effecting same
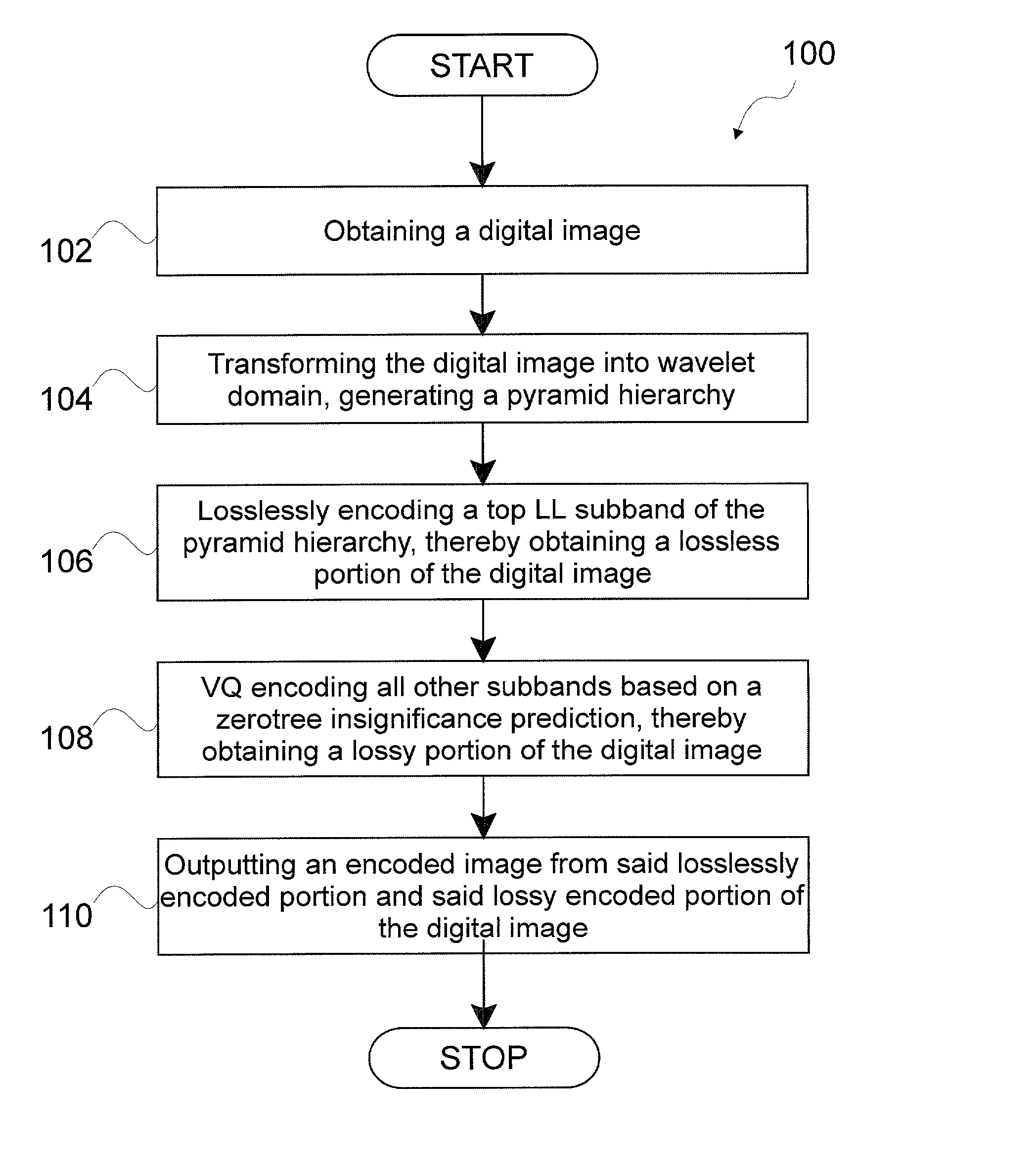
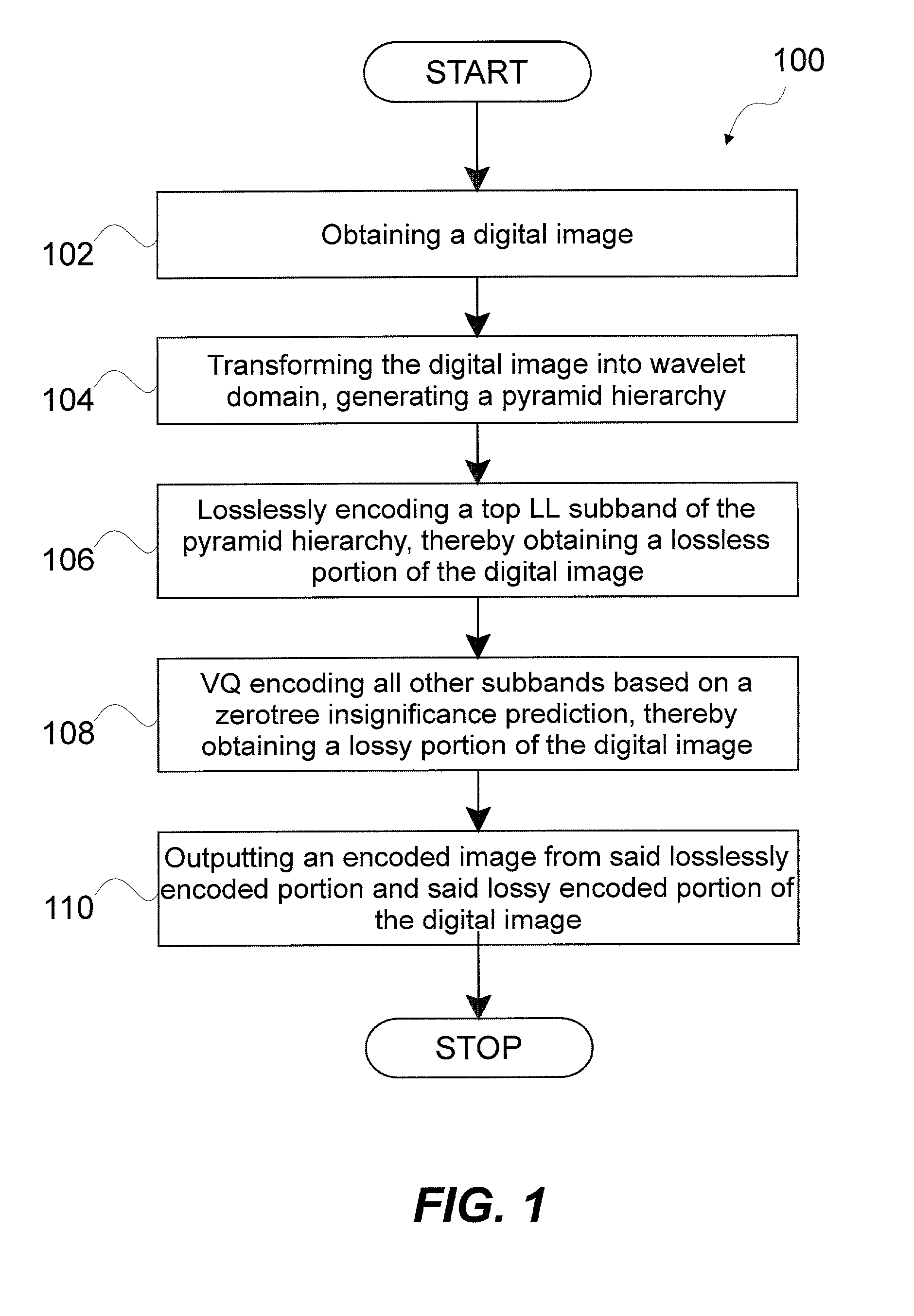
Methods and systems for encoding, transmitting and decoding digital images by rate-distortion adaptive zerotree-based residual vector quantization are disclosed. A method of the invention includes receiving a digital image, transforming the digital image into the wavelet domain generating a pyramid hierarchy, losslessly encoding a top LL subband from the pyramid hierarchy, encoding other subbands by vector quantization based on a zerotree insignificance prediction, generating an encoded image from the lossless encoding and vector quantization encoding, transmitting the encoded image along a communications channel, receiving the encoded image transmitted along the communications channel, reconstructing a zerotree from the encoded image, vector quantization decoding subbands from the encoded image other than a top LL subband, losslessly decoding the top LL subband from the encoded image, reverse wavelet transforming the top LL subband and the vector quantization decoded subbands and outputting a decoded image.
Owner:UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY
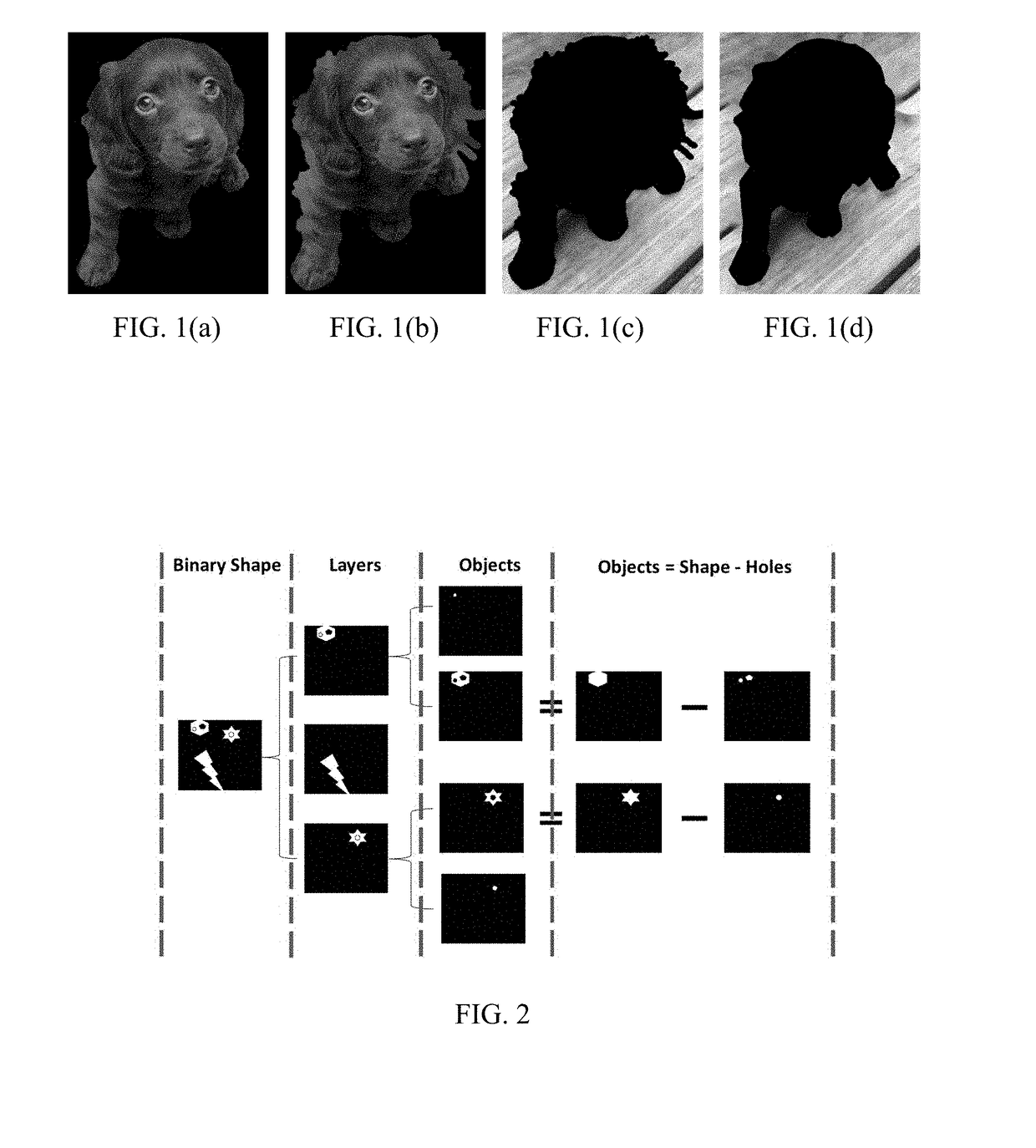
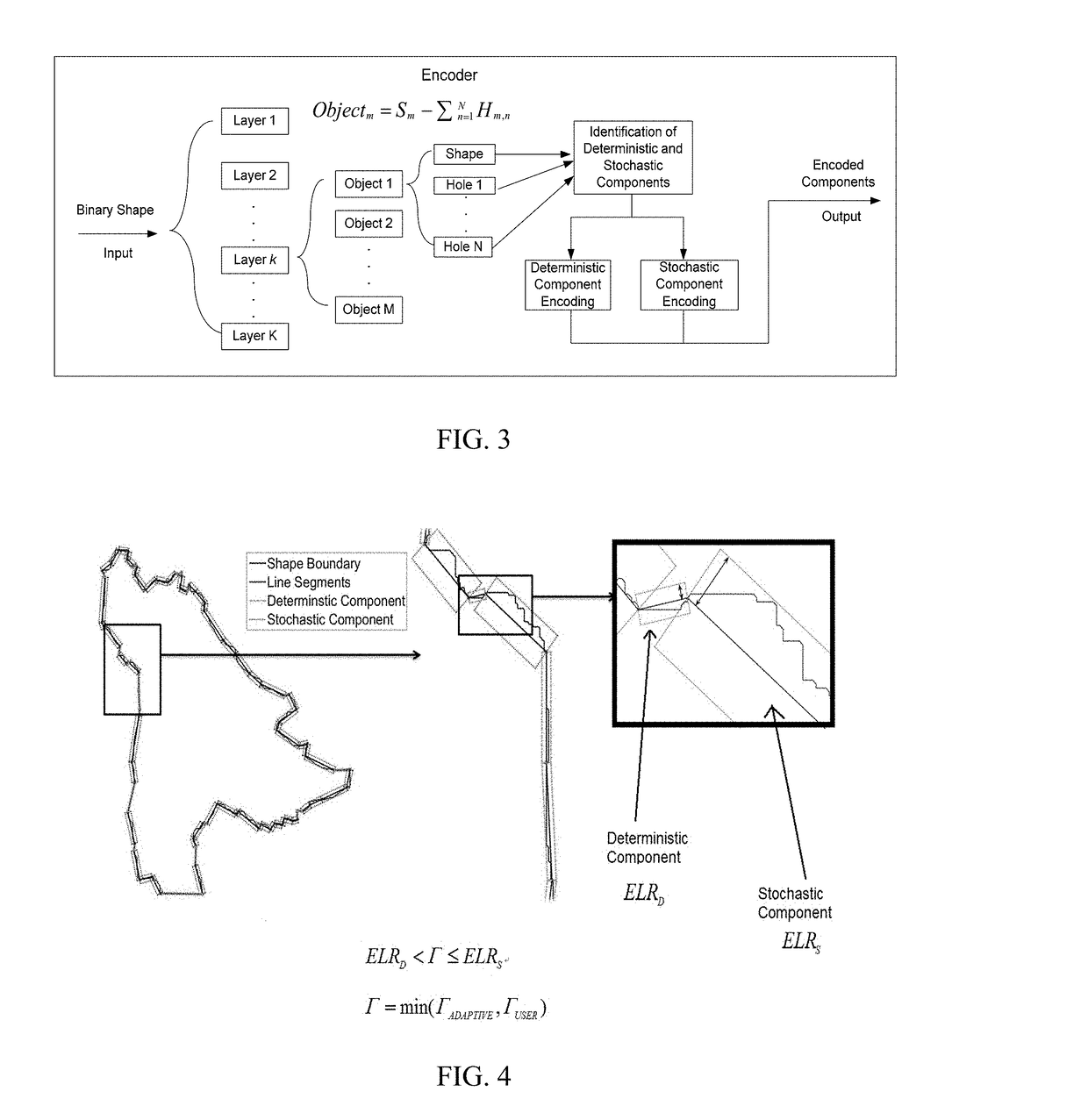
Shape-adaptive model-based codec for lossy and lossless compression of images
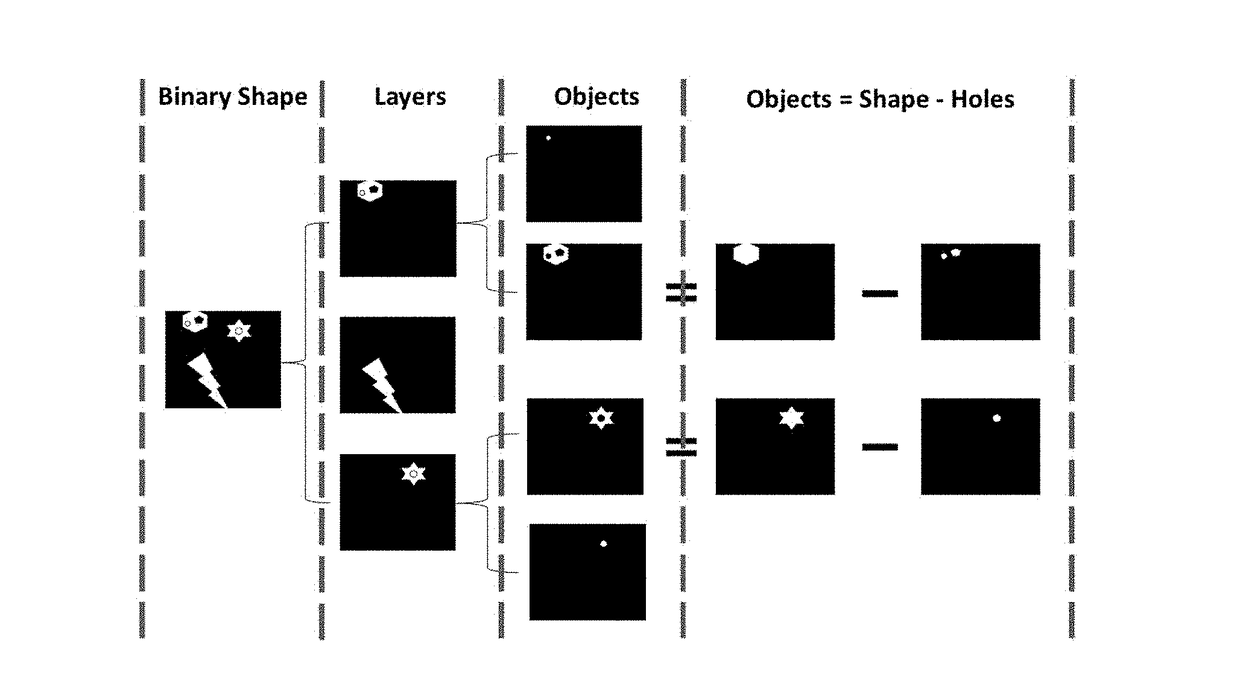
ActiveUS20170251214A1Increase the compression ratioReduce in quantityImage codingDigital video signal modificationLossless codingPattern recognition
The present invention relate to methods and codecs for image and video compression. Embodiments of the present invention include a novel shape-adaptive model-based codec (SAM) that supports binary shapes as well as matte and soft segmentation image compression by decomposing input shapes into deterministic and stochastic components for flexible lossy and lossless coding. The present invention can provide inter / intra prediction and flexibly adapts between lossy and lossless modes with various parameters for compression quality control. The compression module can also be adapted with numerous other compression techniques.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
Image encoding apparatus and method
InactiveUS20070206867A1Fast dataPreventing any sense of discomfortImage codingCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer hardwareLossless coding
This invention is to generate encoded data within a target amount. A first encoding unit generates lossy encoded data of each pixel block by using a quantization matrix Qi specified by a parameter i. A second encoding unit generates lossless encoded data of each pixel block. Let Lx be the lossless encoded data length, and Ly be the lossy encoded data length. A control unit determines, using a nonlinear boundary function fi,j( ) specified by the parameters i and j, whether condition: Ly<fi,j(Lx) is satisfied and stores the determination result as history information in a history memory unit. One of the two encoded data is stored in a memory based on the determination result. If the encoded data amount stored in the memory has exceeded the target amount, the control unit updates at least one of the encoding parameters i and j on the basis of the history information.
Owner:CANON KK
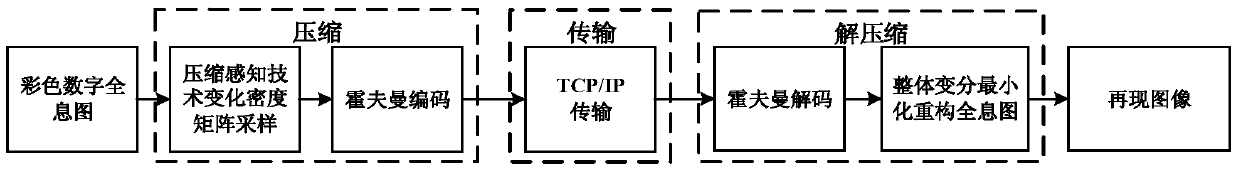
Digital hologram coding transmission method employing compressed sensing
ActiveCN105451024AIncrease the compression ratioReduce system complexityDigital video signal modificationLossless codingSpatial light modulator
The invention discloses a digital hologram coding transmission method employing compressed sensing. The method carries out the compression, transmission and decoding of a digital hologram based on the compressed sensing, carries out targeted reconstruction of the digital hologram in a wavelet domain through a total variation method, and improves the quality of image reproduction. The method specifically comprises the steps: carrying out the downsampling of the digital hologram at a sampling rate lower than the sampling rate of the Nyquist law through employing a variable density sampling matrix, so as to reduce the data amount for subsequent coding and transmission; further carrying out the compression and coding of the sample data through a Hoffman lossless coding method, wherein the iteration and reconstruction is multi-level partitioned iteration and reconstruction. Compared with a common method for reducing a measurement value for a measurement matrix, the method further improves the compression rate, reduces the calculation amount of a transmission end and the system complexity, improves the quality of image reproduction, reconstructs the digital hologram after decompression, and can be used for three-dimensional display in a space light modulator and other optical systems.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
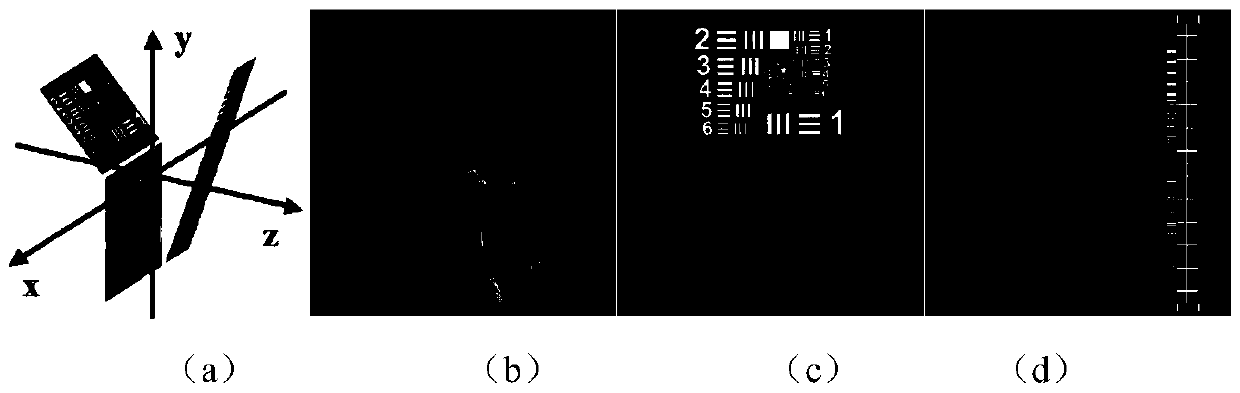
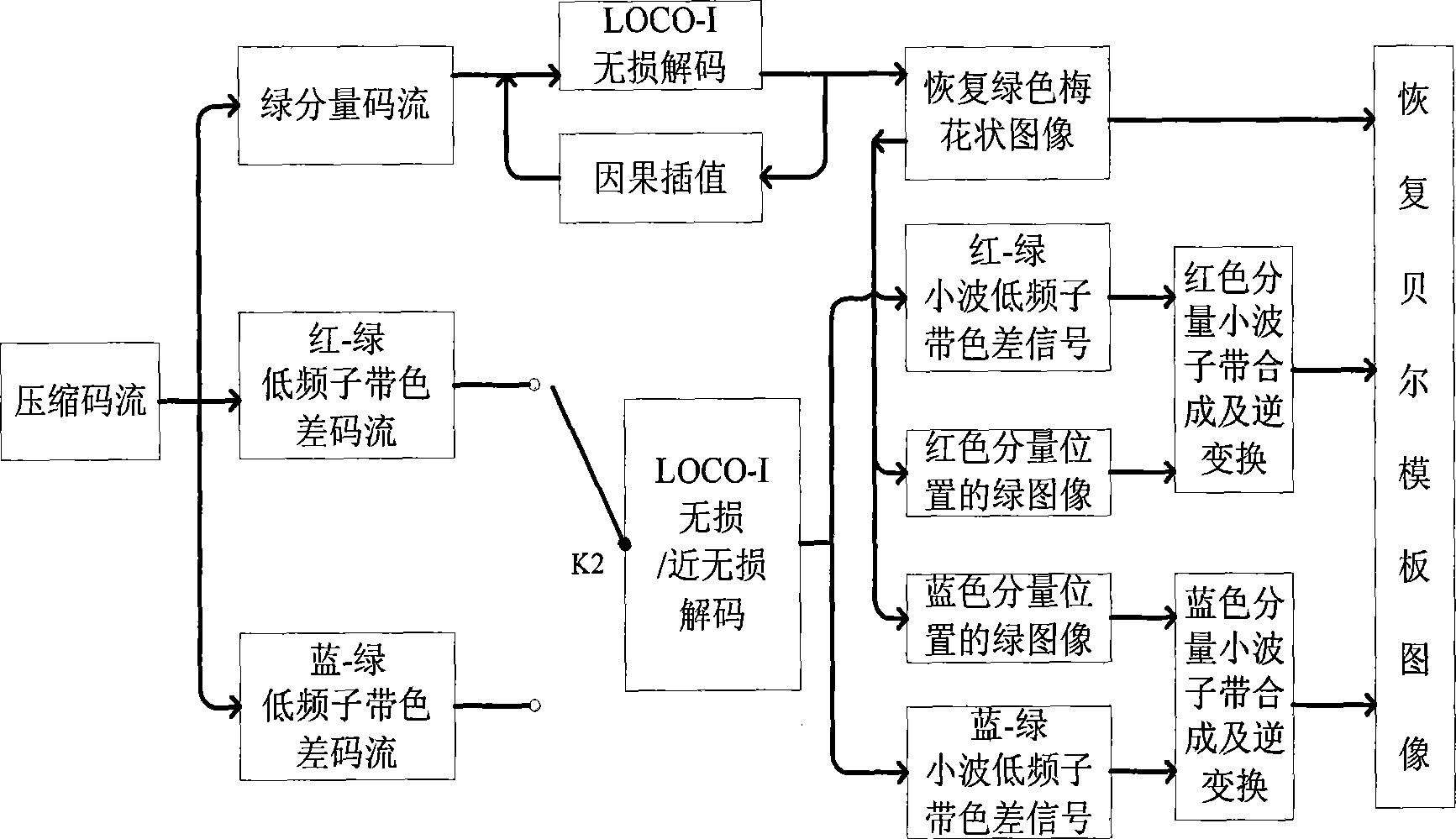
Method for encoding and decoding Bell formwork image
InactiveCN101442673AReduce complexitySimple structureColor television with bandwidth reductionTelevision systemsColor imageDigital image compression
The invention relates to digital image compression technology, in particular to a method for encoding and decoding Bayer patter images, and aims to solve the problem of the difficult establishment of good balance between compression ratio, quality and complexity of restructured color images in the prior method which compresses Bayer pattern image data directly. The invention uses LOCO-I technology to perform lossless encoding for a green component; and through estimation of the green component on the site of a red-blue component by a gradient interpolation method, a color difference signal between the small-wave low-frequency subband of the red-blue component and the low-frequency subband of the estimated green component can be acquired, and can undergo lossless or nearly lossless compression by the LOCO-I technology. At the decoding end, the lossless green component should be obtained firstly, then the green component on the site of the red-blue component is estimated through an process identical to the encoding process; the small-wave high-frequency subband of the estimated green component can replace the corresponding small-wave high-frequency subband of the red-blue component, and the rest part is a reverse process of encoding. The method is characterized by high efficiency and low complexity.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for data compression and inference
InactiveUS20140132429A1Competitive compression performanceSmooth transitOther decoding techniquesCode conversionData compressionLossless coding
Lossless and lossy codes are combined for data compression. In one embodiment, the most significant bits of each value are losslessly coded along with a lossy version of the original data. Upon decompression, the lossless reduced-precision values establish absolute bounds for the lossy code. Another embodiment losslessly codes the leading bits while trailing bits undergo lossy coding. Upon decompression, the two codes are summed. The method preserves edges and other sharp transitions for superior lossy compression. Additionally, the method enables description-length inference using noisy data.
Owner:SCOVILLE JOHN CONANT
Audio encoding device, decoding device, method, circuit, and program
InactiveUS20110268279A1Avoid sound qualityImprove coding efficiencySpeech analysisStereophonic arrangmentsLossless codingAbsolute pitch
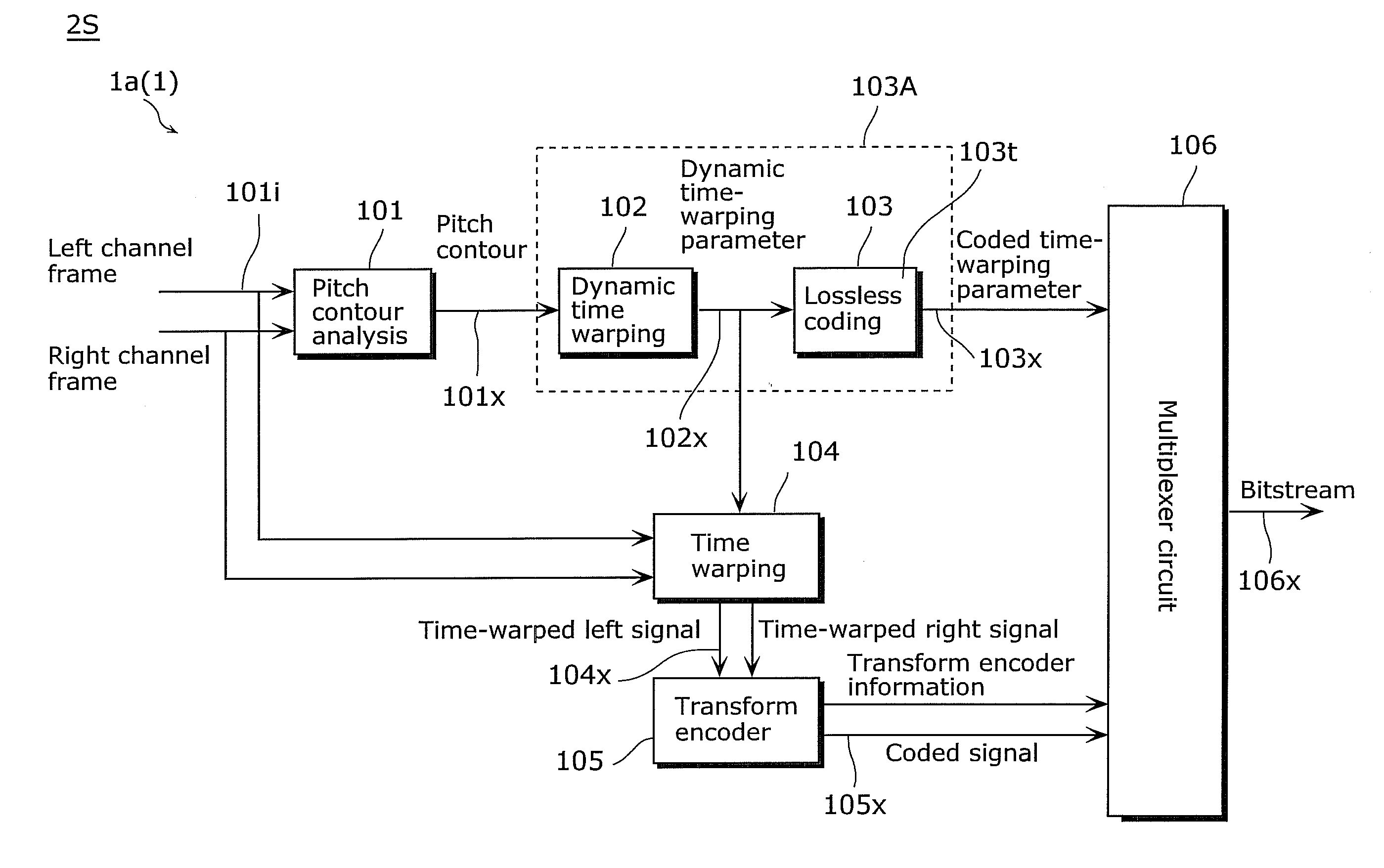
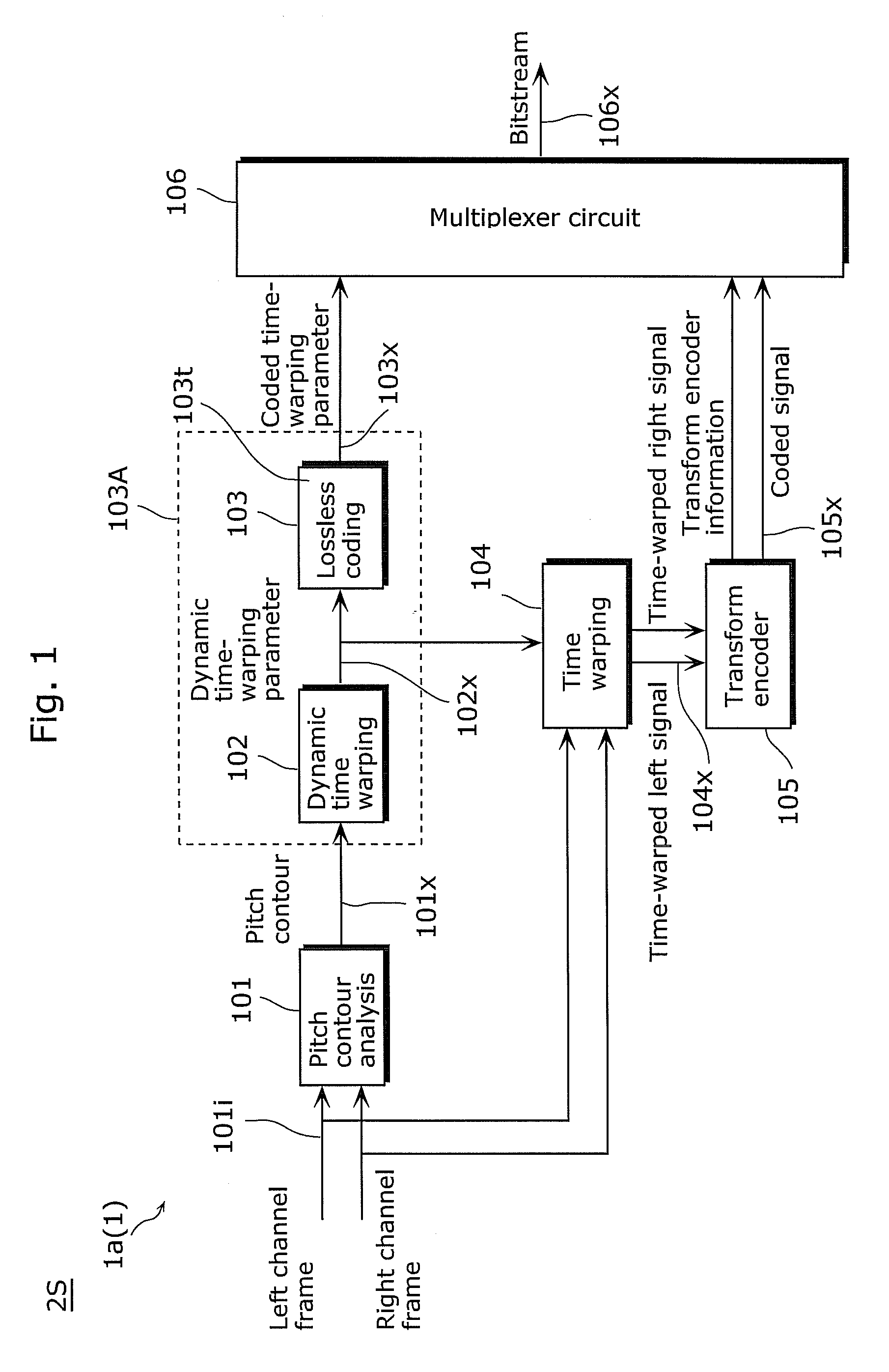
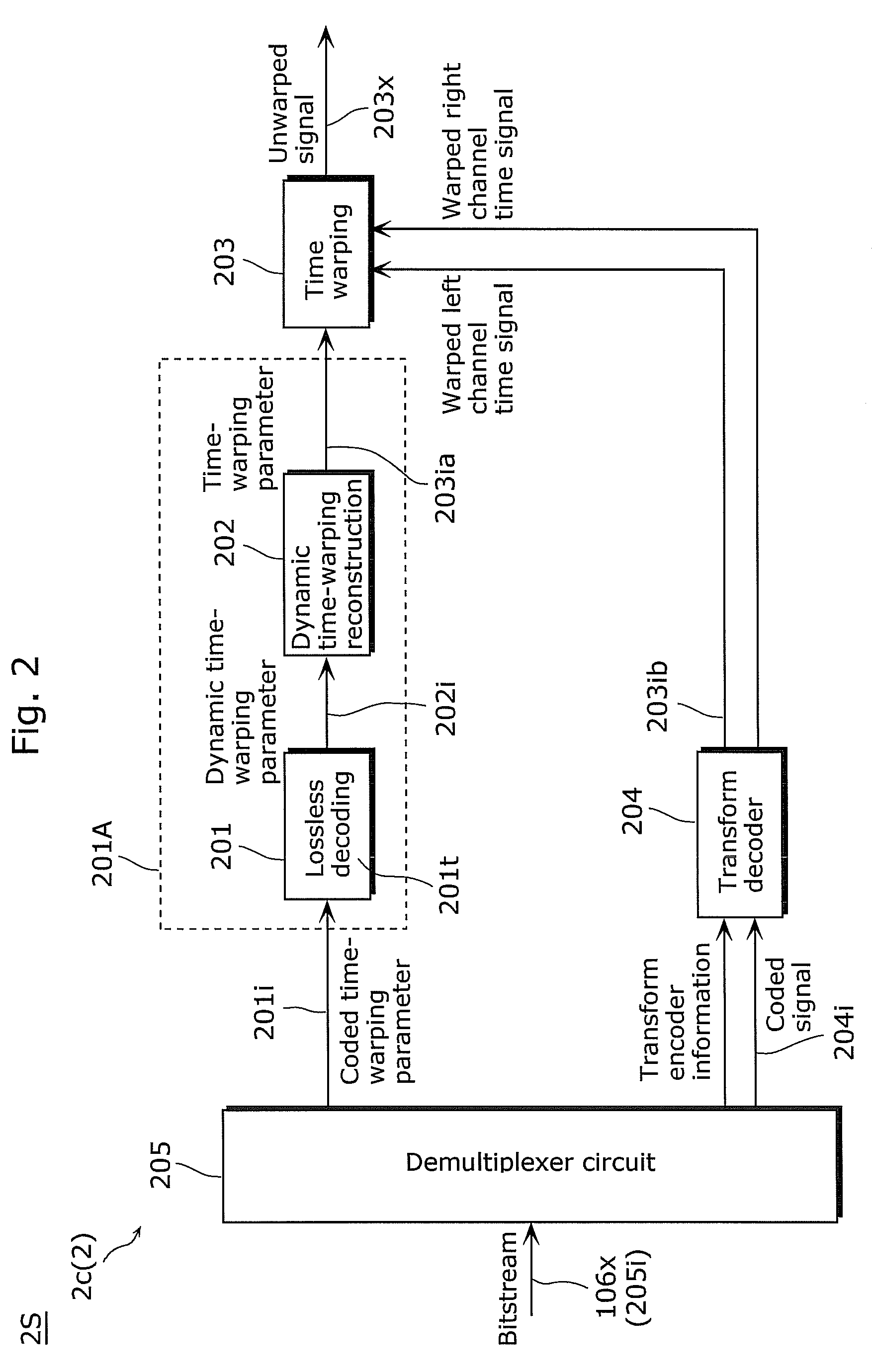
Provided is an encoding device (1) including: a pitch contour analysis unit (101) which detects information, a dynamic time-warping unit (102) which generates, based on the information, pitch change ratios (Tw_ratio in FIG. 18) within a range (86) including a range (86a) of the pitch change ratios corresponding to absolute pitch differences of 42 cents or larger; a first lossless coding unit (103) which codes the generated pitch parameters (102x); a time-warping unit (104) which shifts a pitch of a signal according to the information; and a second encoding unit which codes a signal (104x) obtained by the shifting.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and apparatus for enhancing performance of entropy coding, and video coding method and apparatus using the entropy coding performance enhancing method
InactiveUS7348903B2Improve performanceCode conversionDigital video signal modificationLossless codingComputer architecture
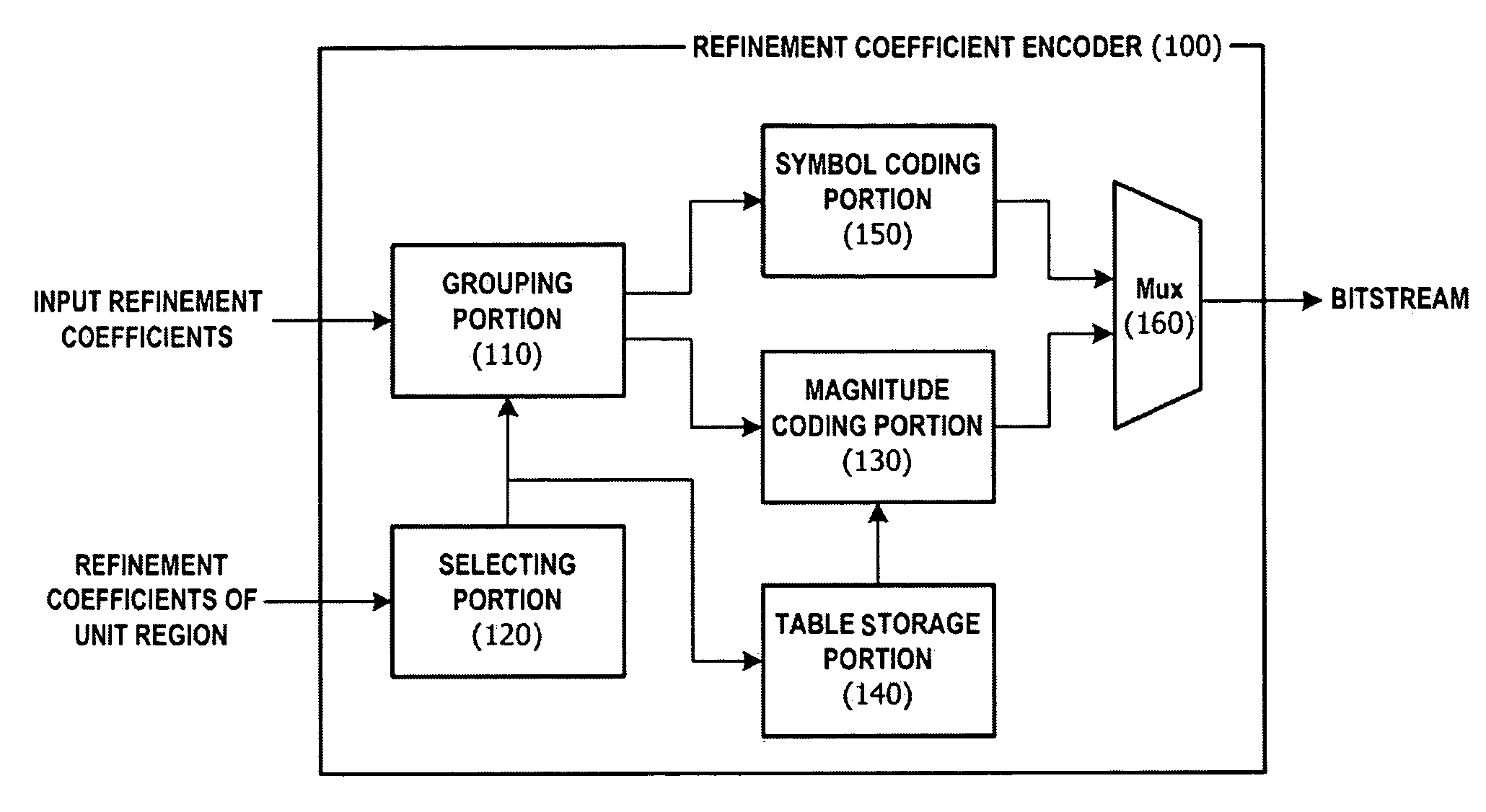
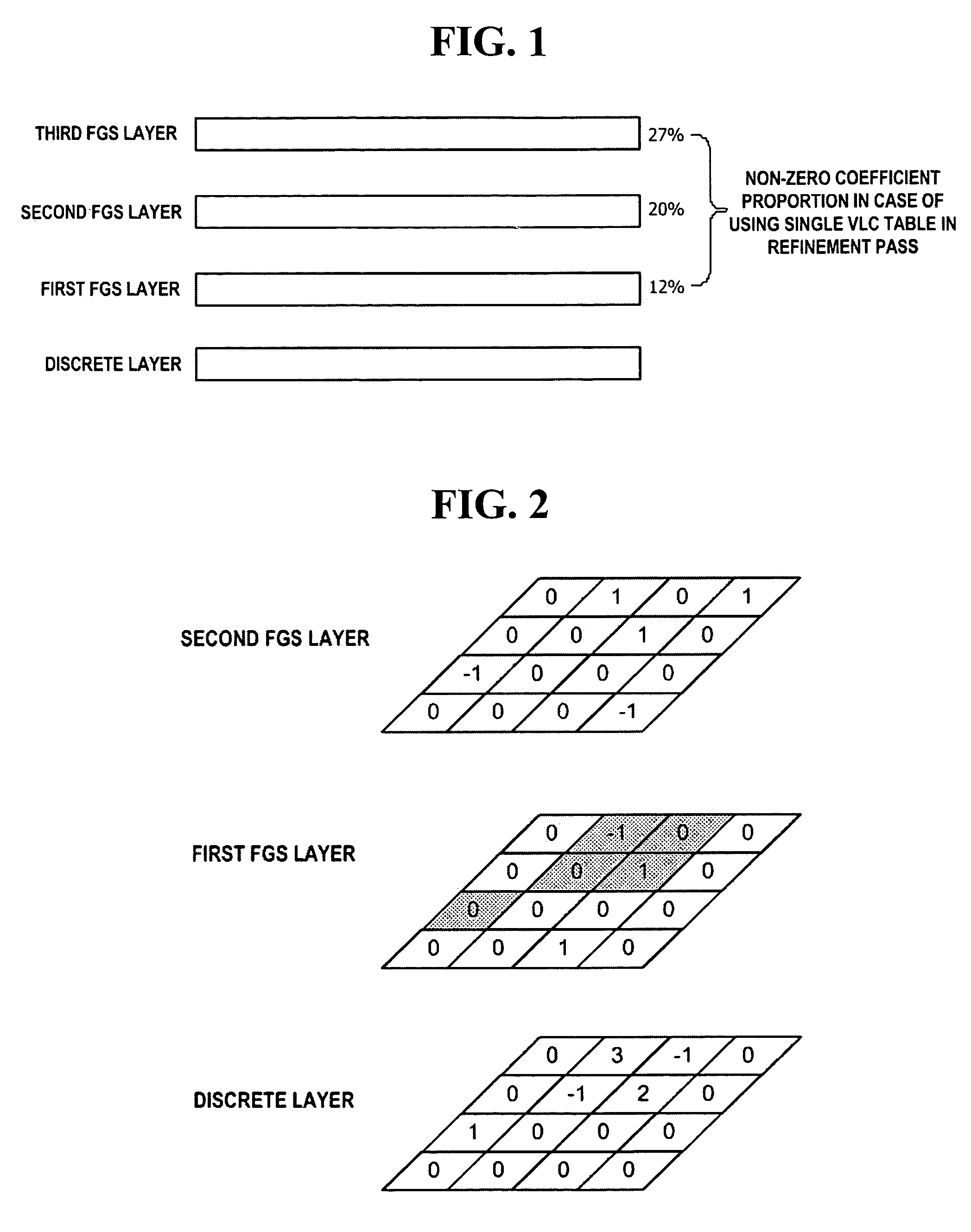
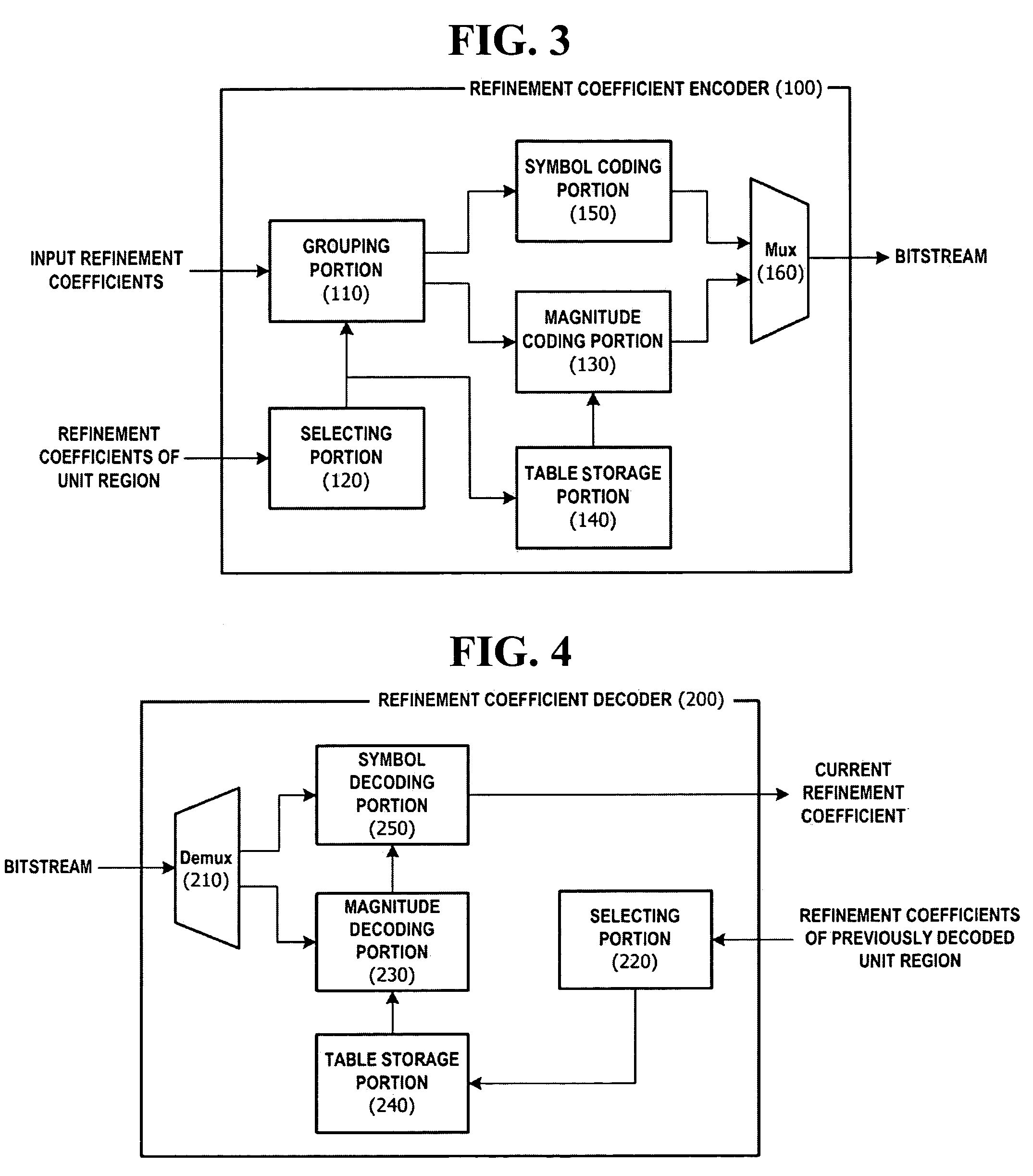
A method and apparatus for enhancing the performance of entropy coding in a multilayer-based codec system are provided. In a variable length coding method for lossless-coding first coefficients among coefficients of a discrete layer and one or more fine granular scalability (FGS) layers, the variable length coding method includes determining a proportion of zeros included in a predetermined unit region to which the first coefficients belong, selecting one of a plurality of grouping units depending on whether or not the proportion exceeds a predetermined threshold, grouping absolute values of the first coefficients using the selected grouping unit, and transforming the grouped absolute values into a code word mapped thereto by referring to a VLC table corresponding to the selected group unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com