Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
115 results about "Incident field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
CD metrology analysis using a finite difference method
ActiveUS6919964B2Directly computeSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetrologyDirect evaluation
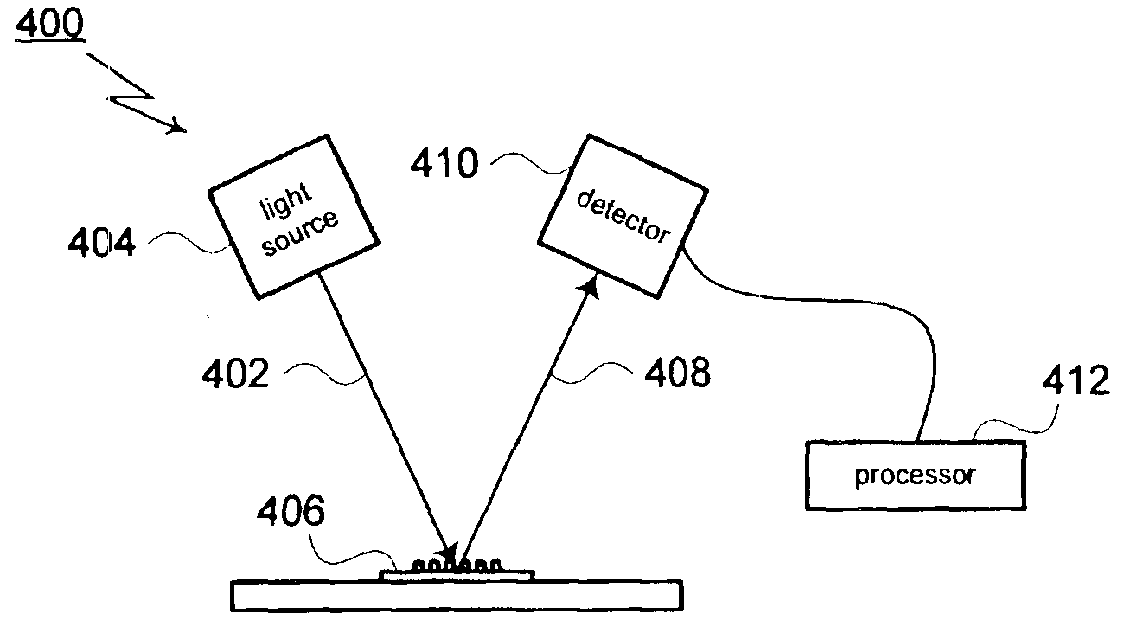
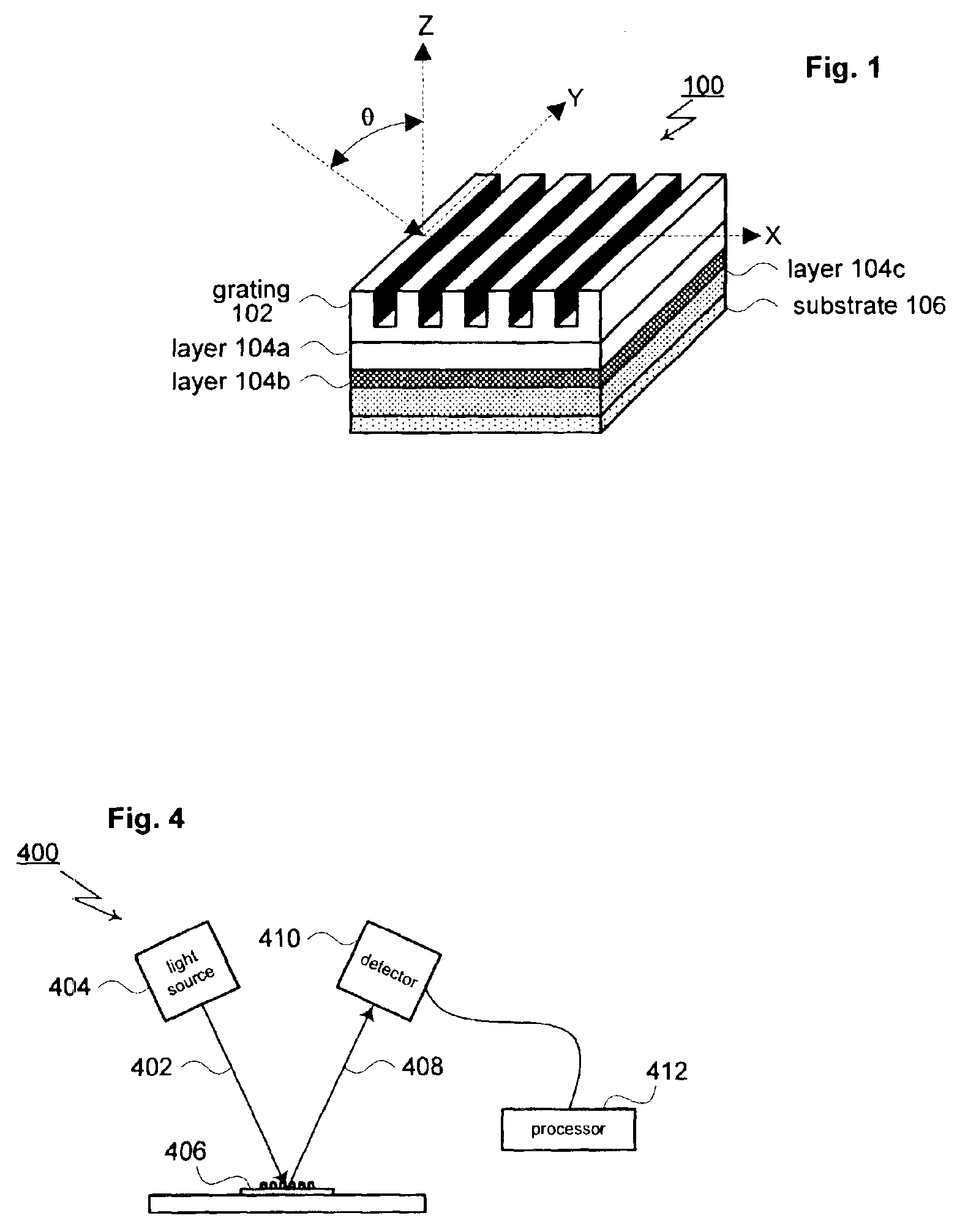
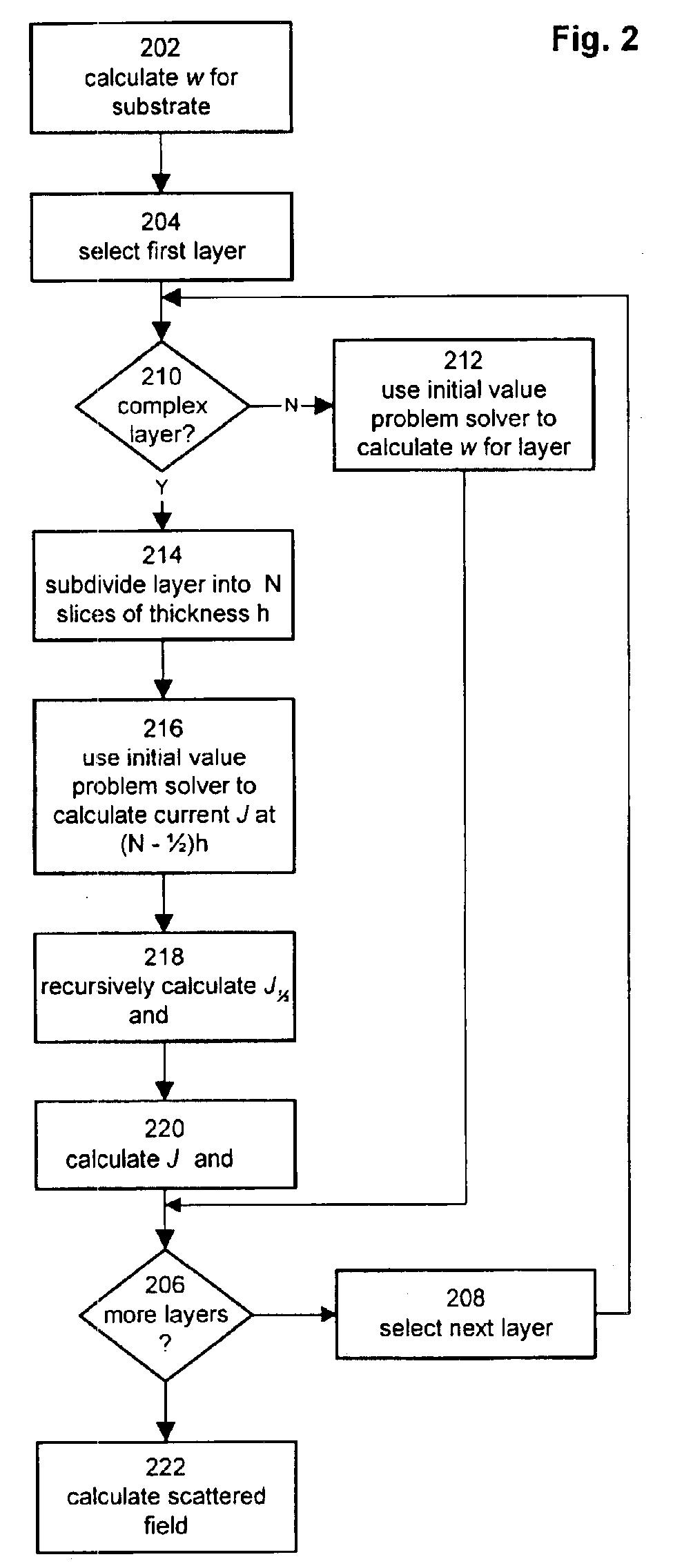
A method for modeling diffraction includes constructing a theoretical model of the subject. A numerical method is then used to predict the output field that is created when an incident field is diffracted by the subject. The numerical method begins by computing the output field at the upper boundary of the substrate and then iterates upward through each of the subject's layers. Structurally simple layers are evaluated directly. More complex layers are discretized into slices. A finite difference scheme is performed for these layers using a recursive expansion of the field-current ratio that starts (or has a base case) at the lowermost slice. The combined evaluation, through all layers, creates a scattering matrix that is evaluated to determine the output field for the subject.
Owner:THERMA WAVE INC
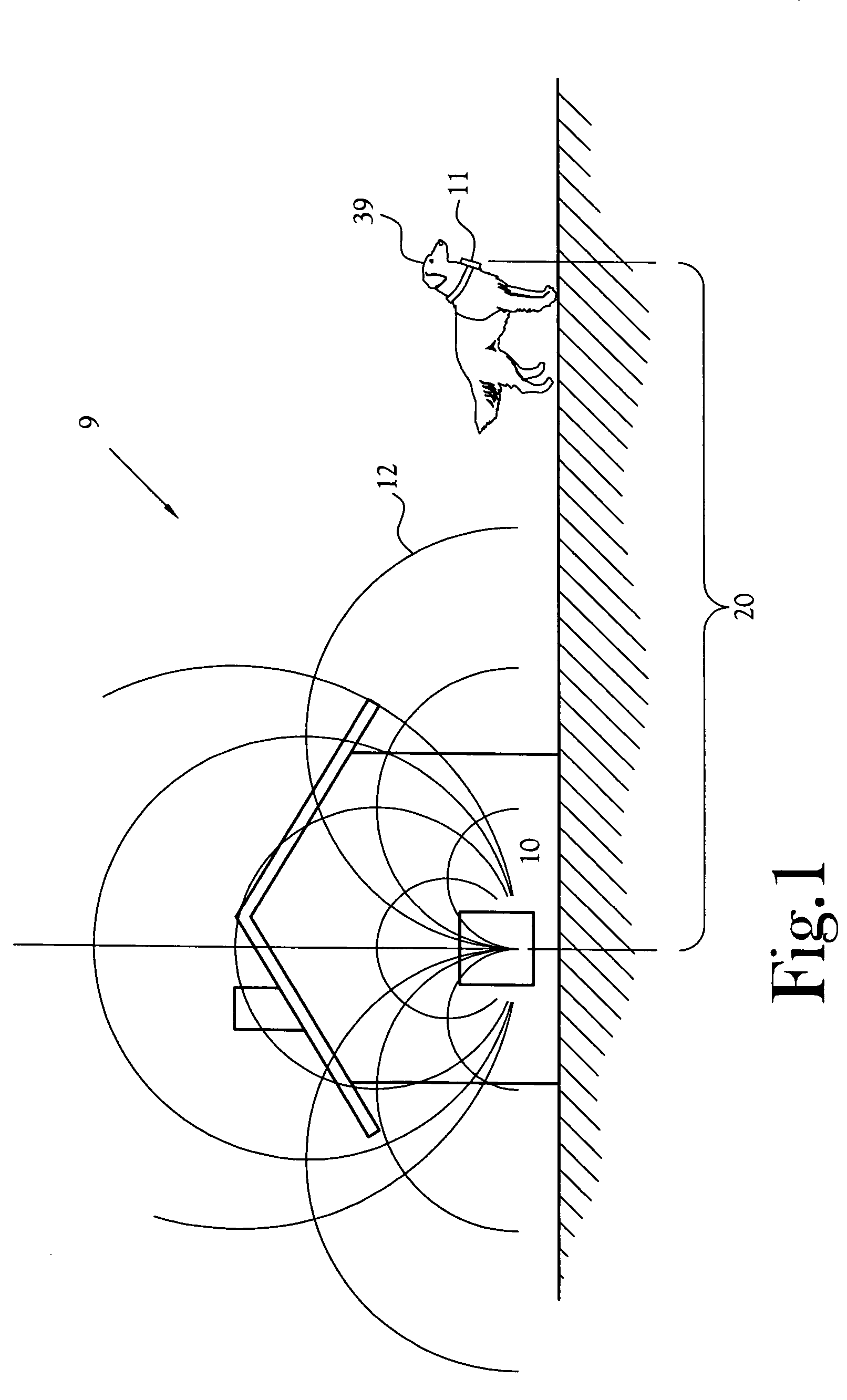
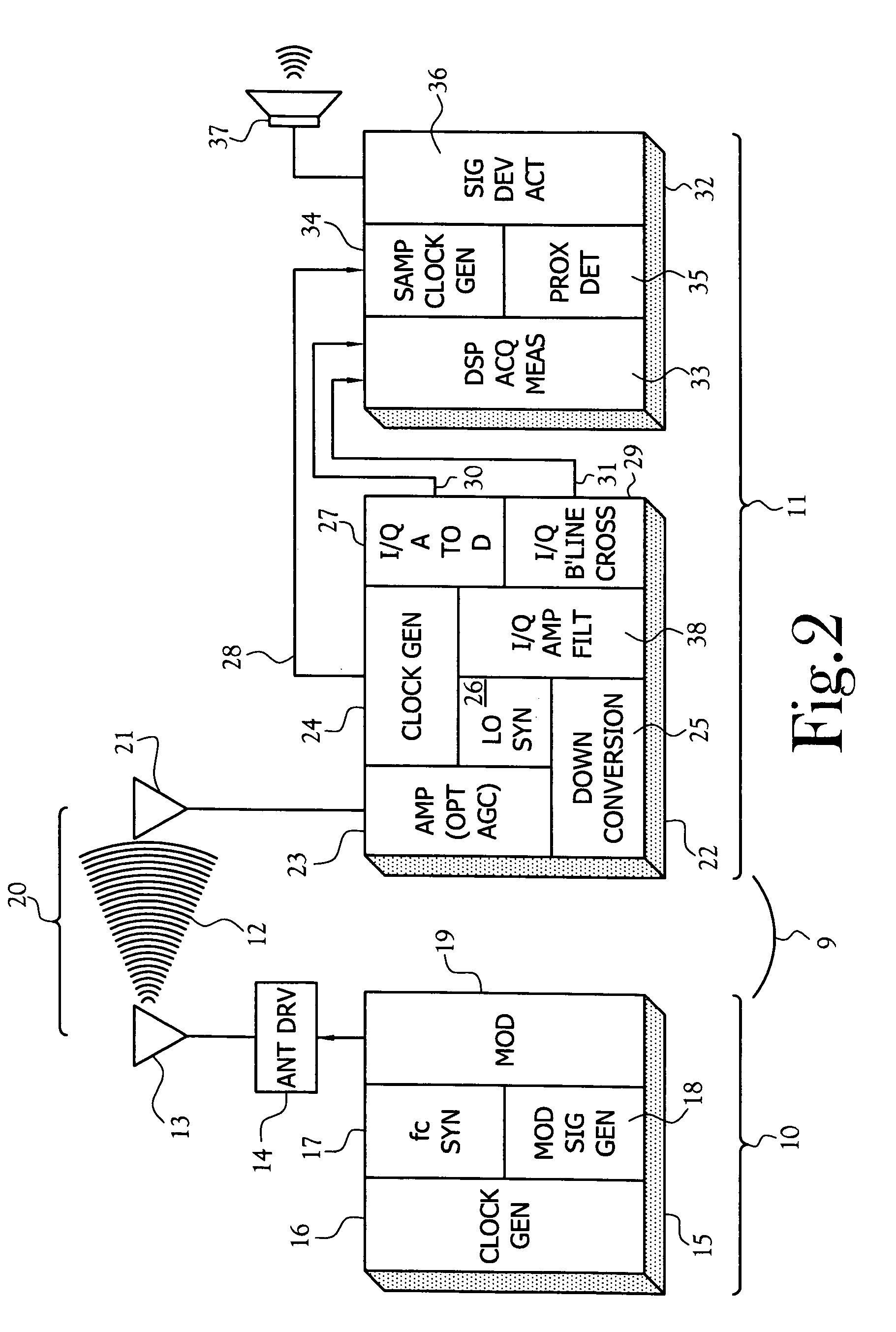
Wireless boundary proximity determining and animal containment
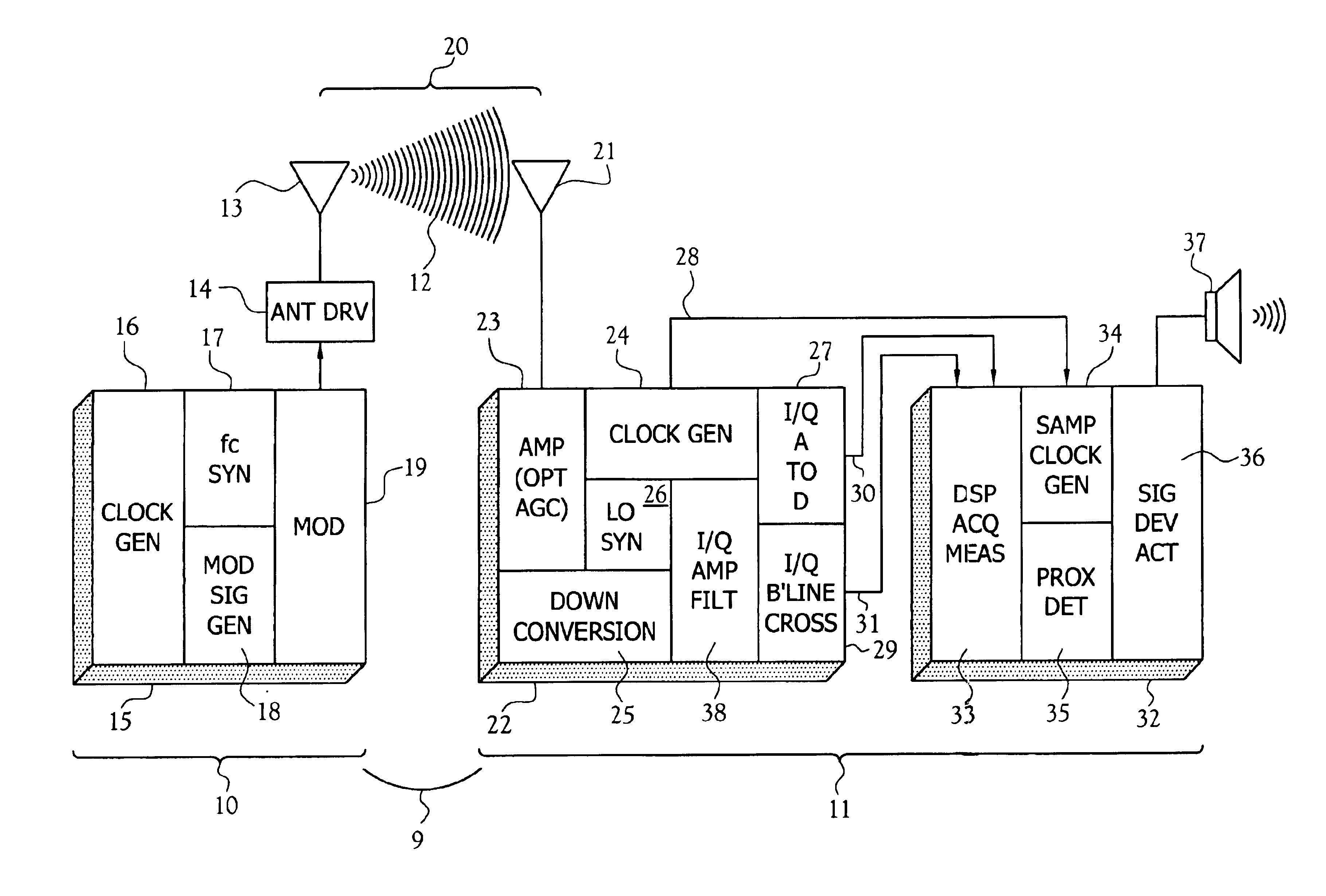
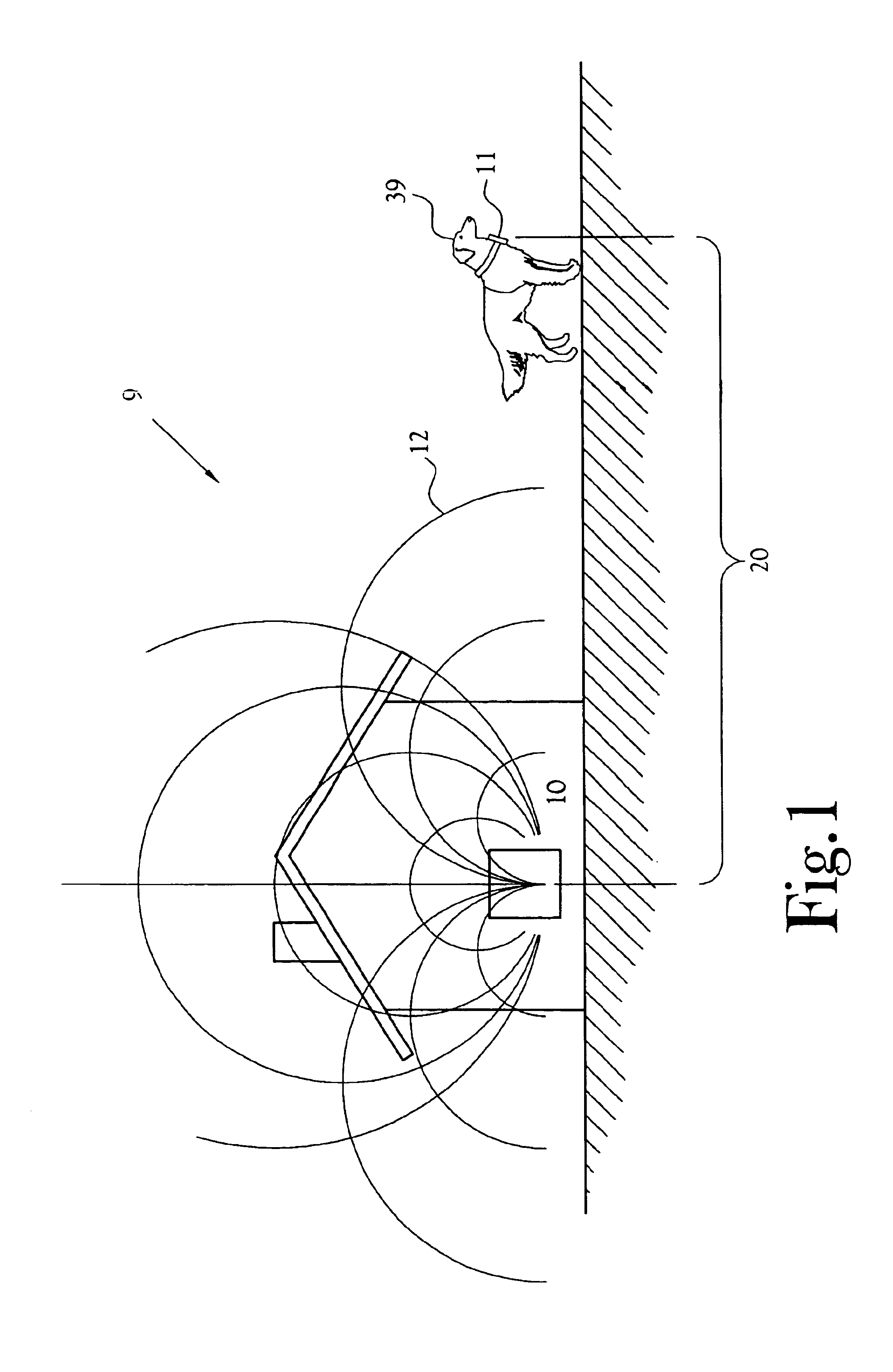
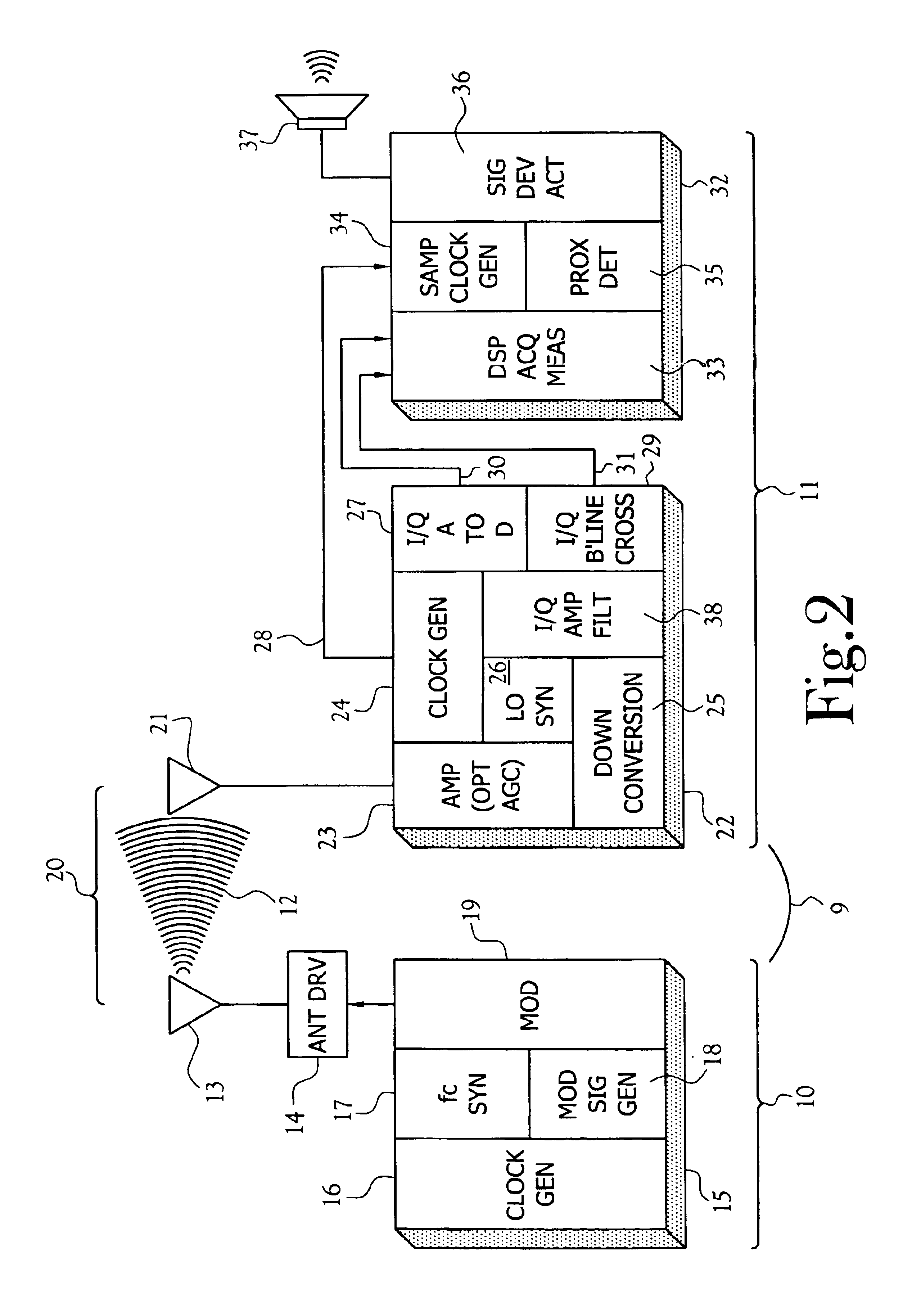
InactiveUS7142167B2Accurate and orientation-independent boundary detectionLow costAlarmsPolarised antenna unit combinationsProximateBroadcasting
Owner:XYZ MICROSYST
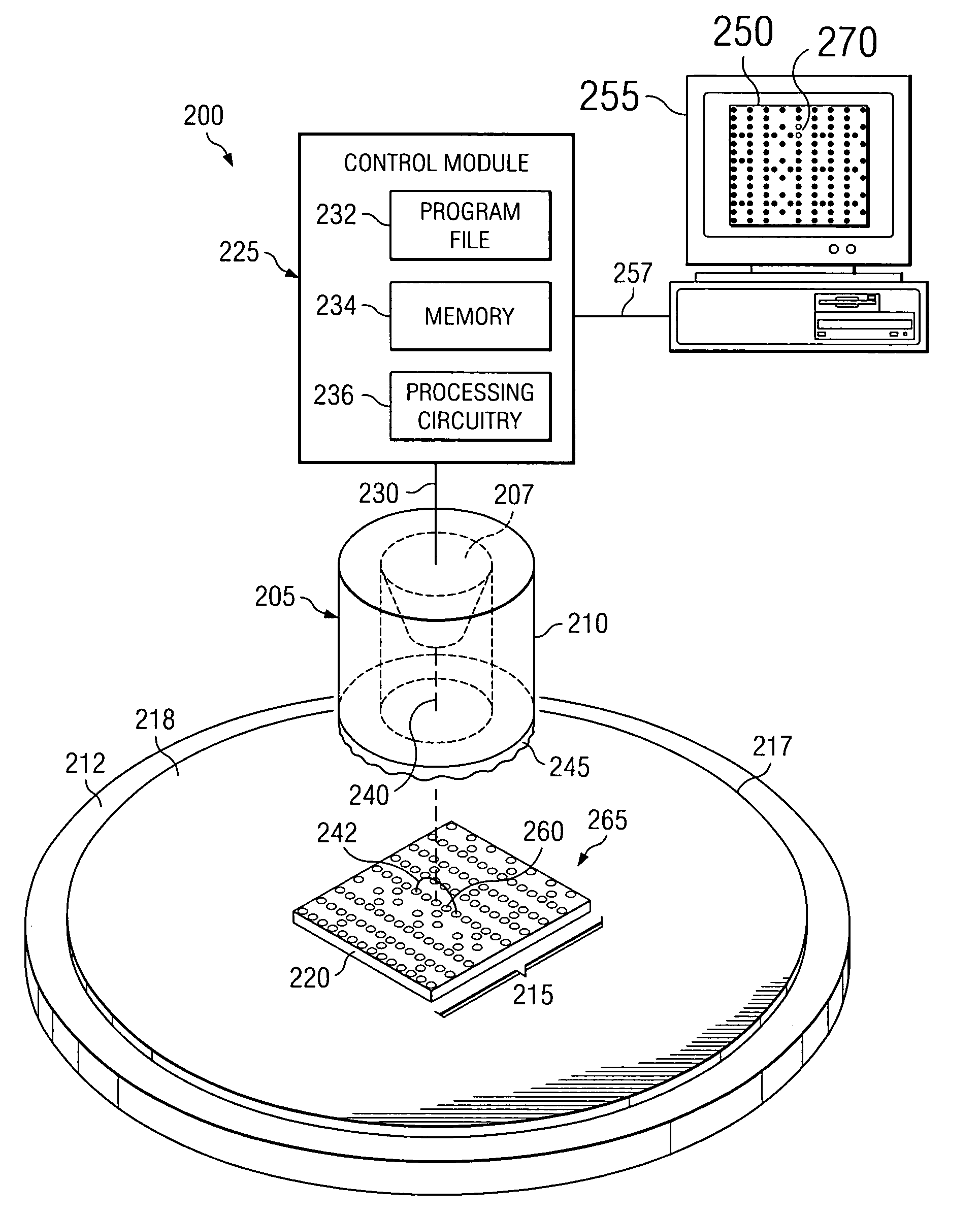
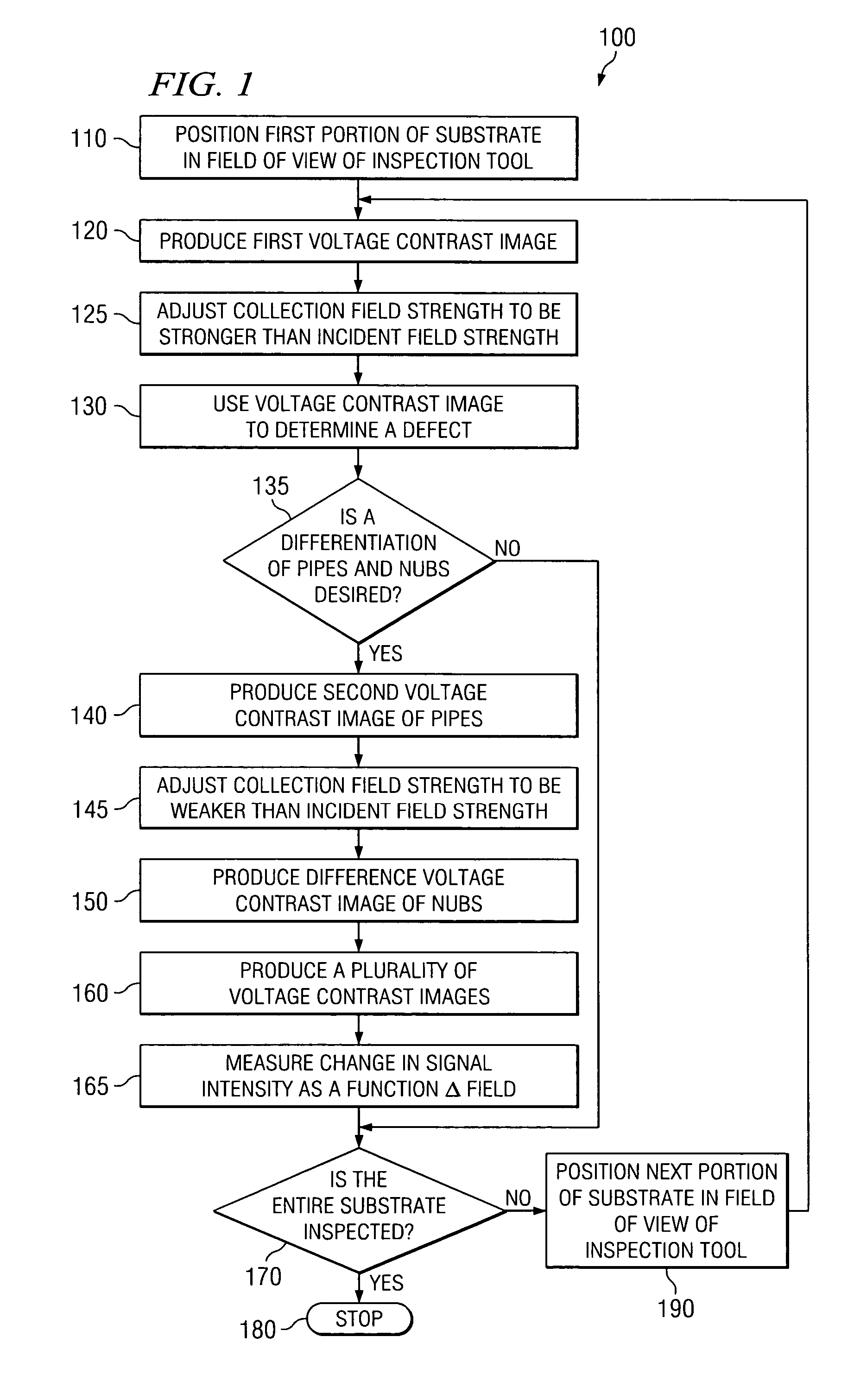
Method to detect and predict metal silicide defects in a microelectronic device during the manufacture of an integrated circuit
ActiveUS7443189B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSalicideMetal silicide
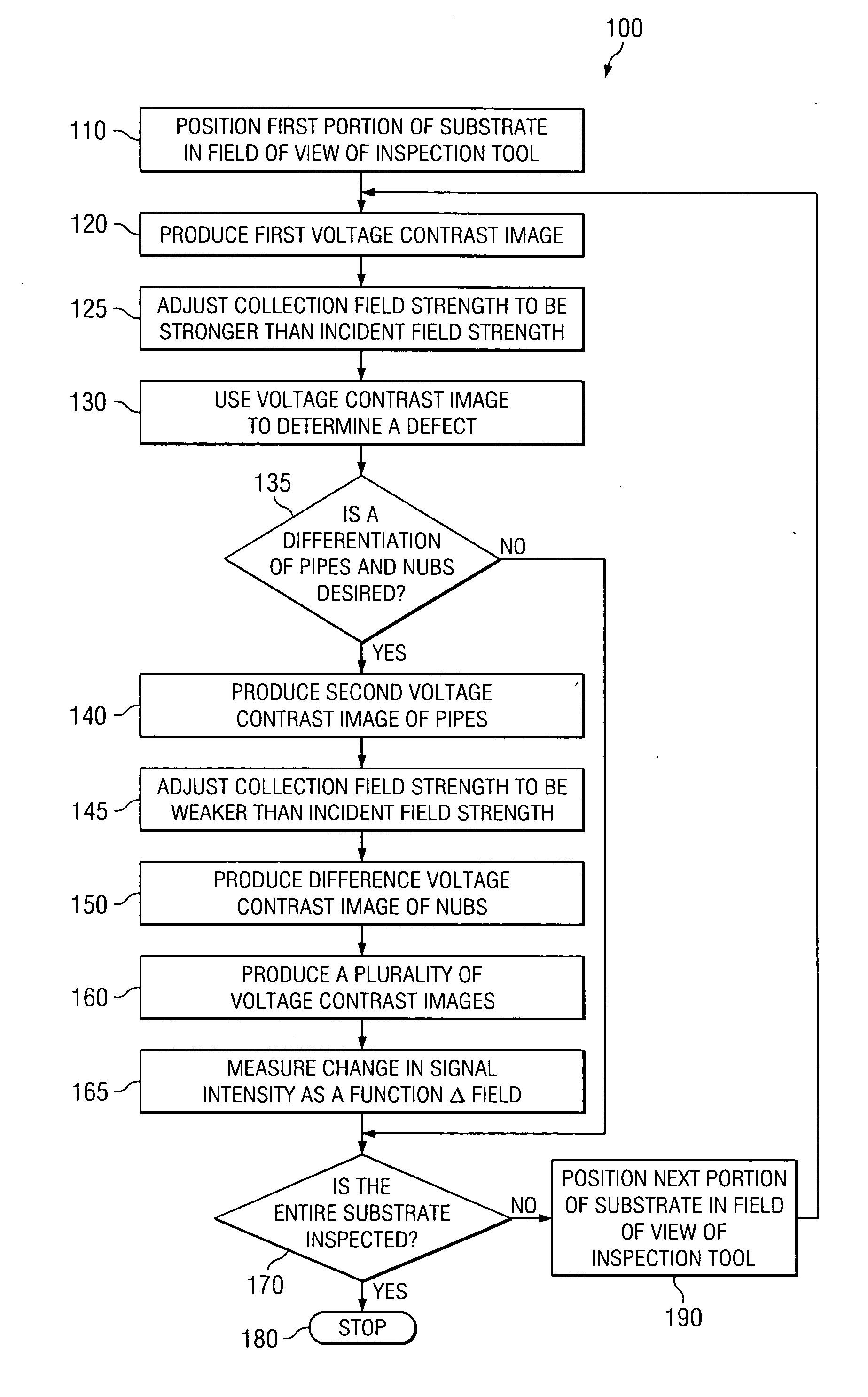
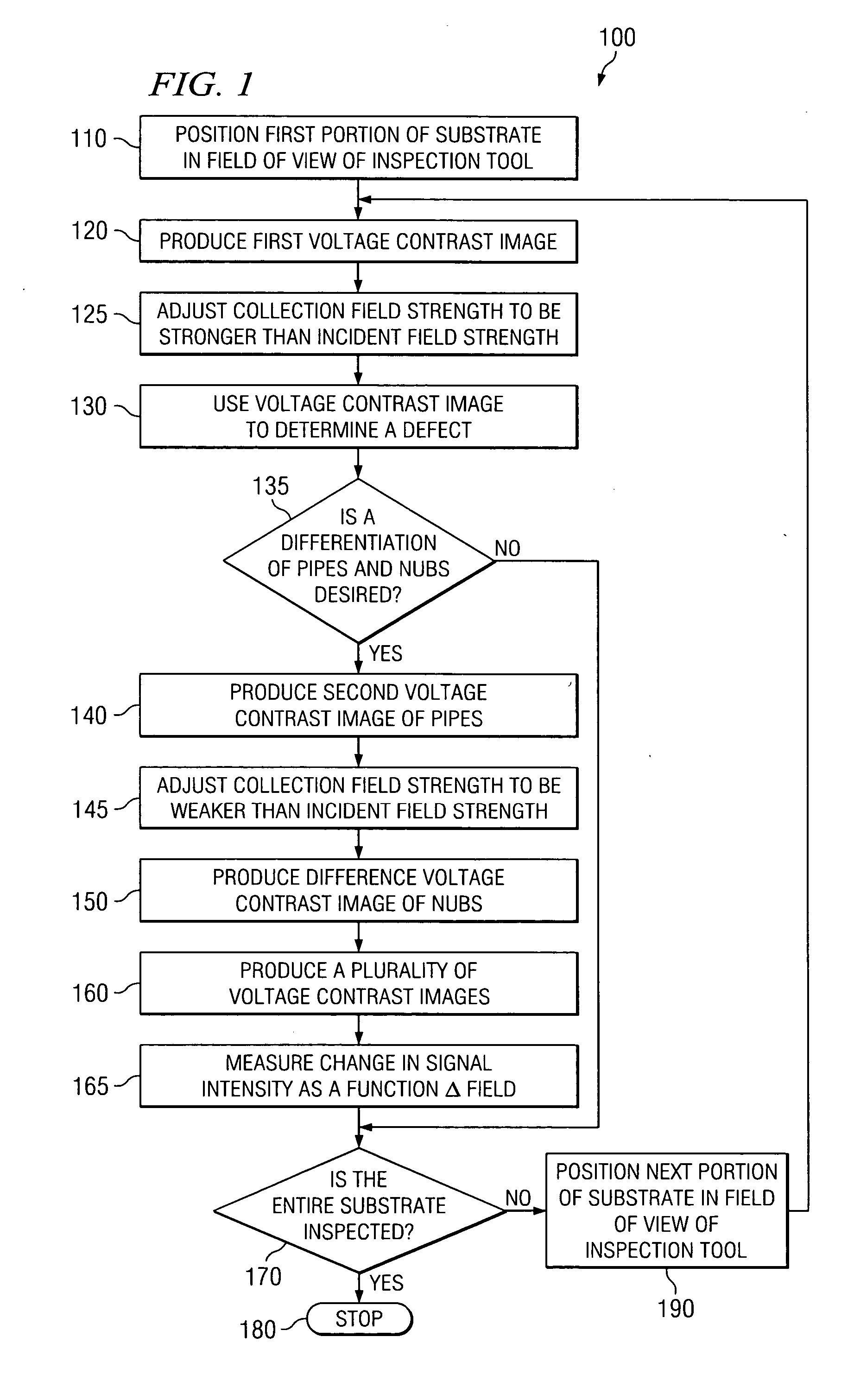
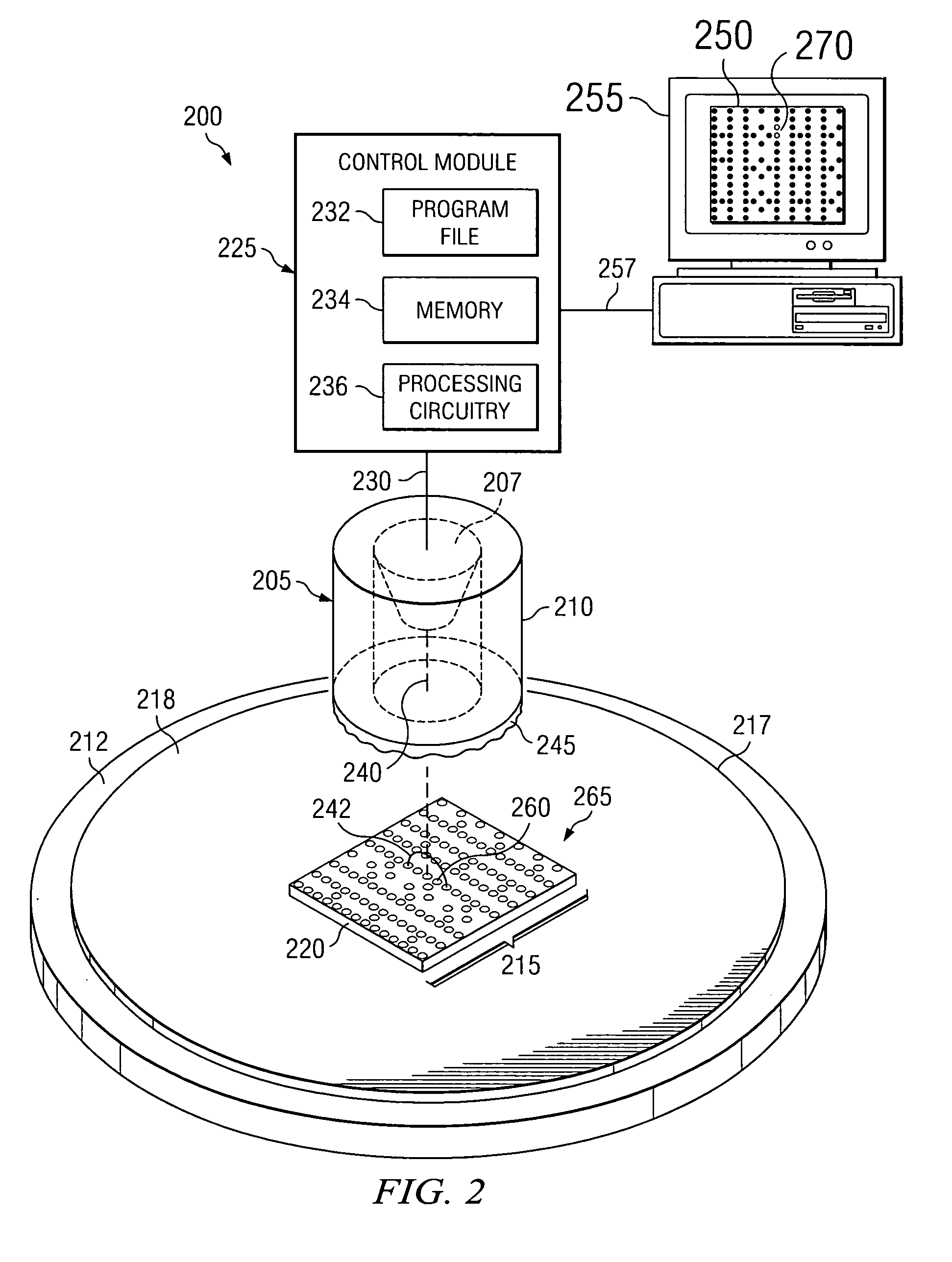
The present teachings provide methods for detection of metal silicide defects in a microelectronic device. In an exemplary embodiment, a portion of a semiconductor substrate may be positioned in a field of view of an inspection tool. The method also includes producing (120) a voltage contrast image of the portion, wherein the image is obtained using a collection field that is stronger than an incident field. The method also includes using (130) the voltage contrast image to determine a metal silicide defect in a microelectronic device. Other embodiments include an inspection system (200) for detecting metal silicide defects and a method of manufacturing an integrated circuit (300).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Multipath resolving correlation interferometer direction finding
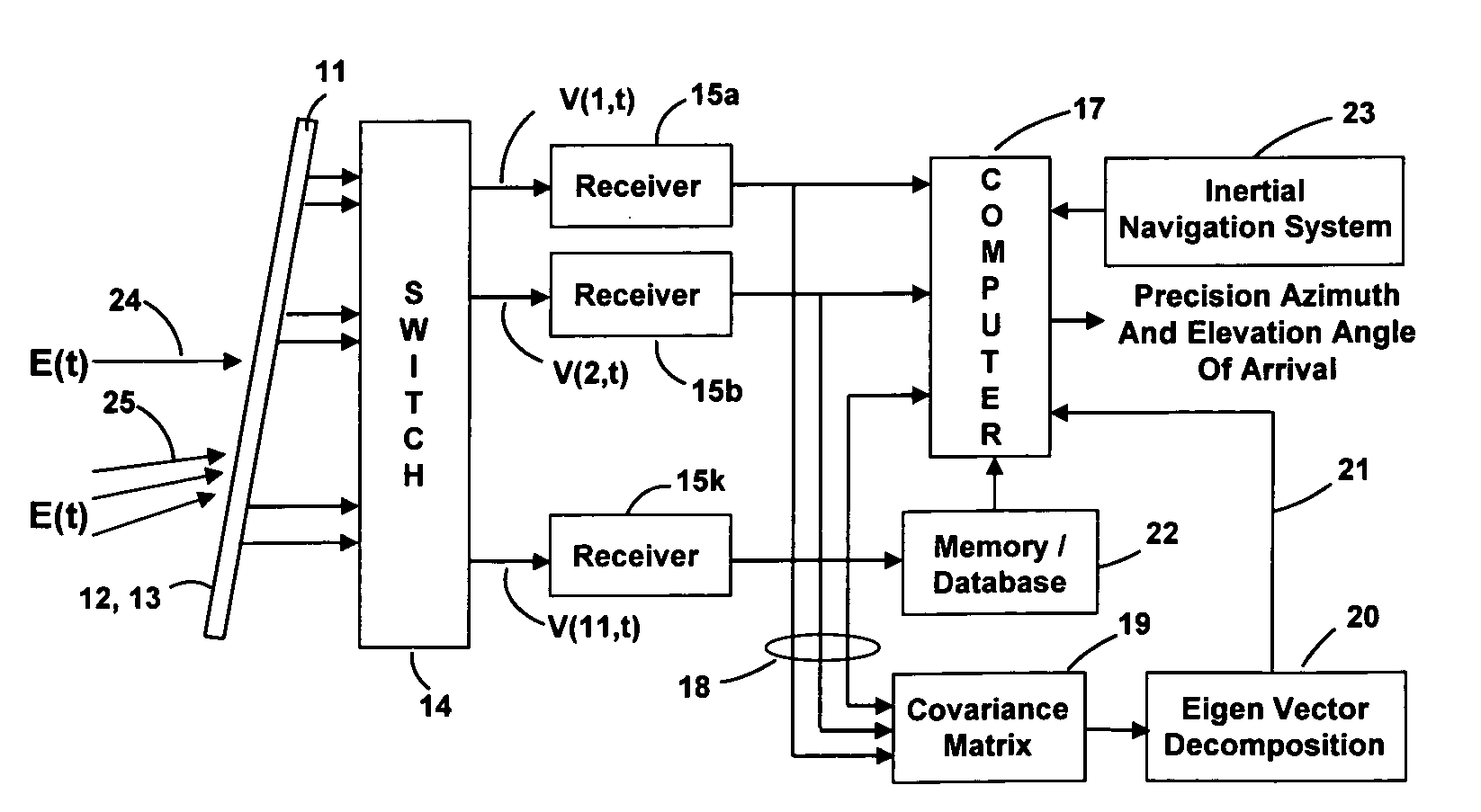
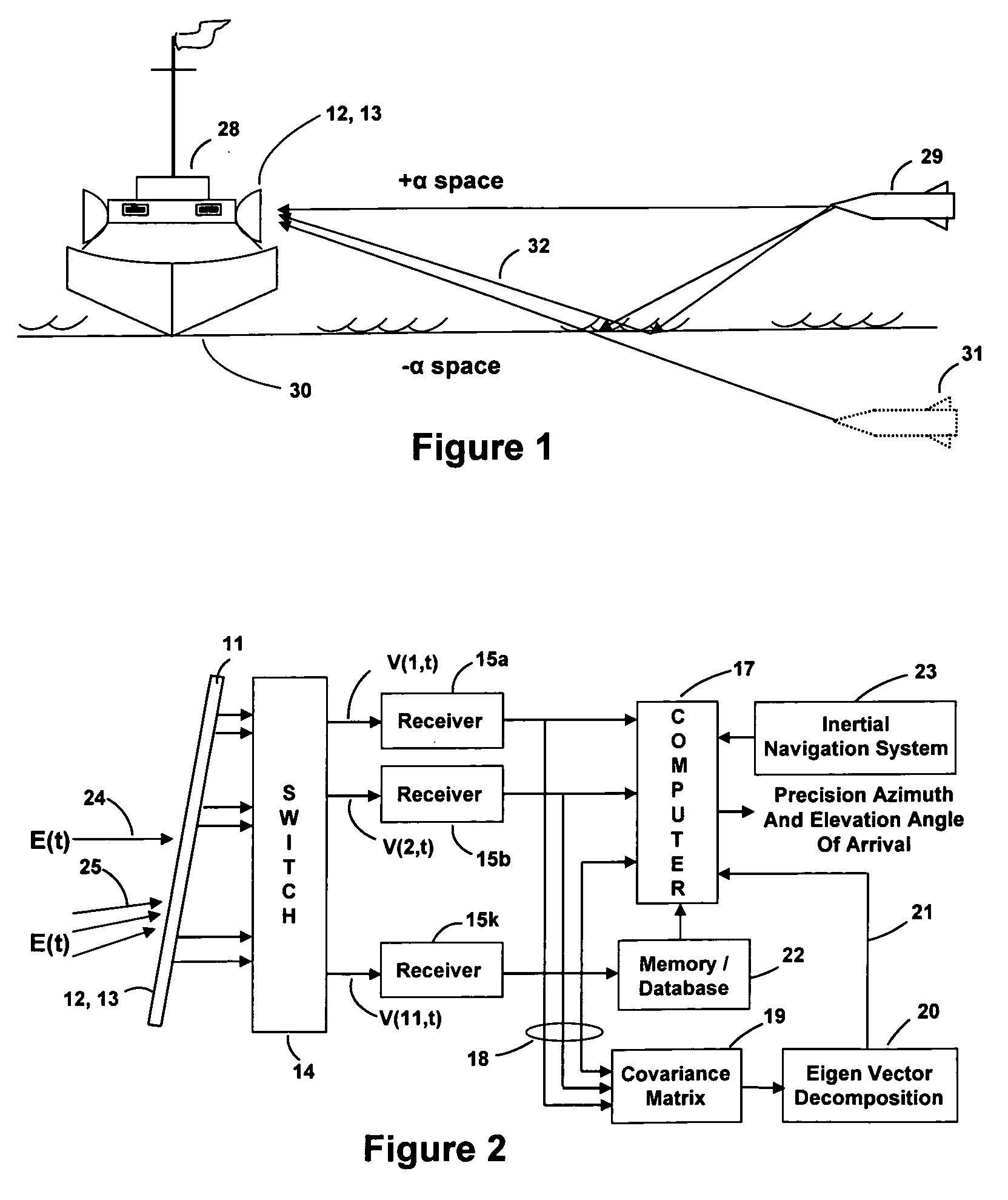
ActiveUS20070273576A1Improve accuracyRobust and accurateMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionWater useCovariance
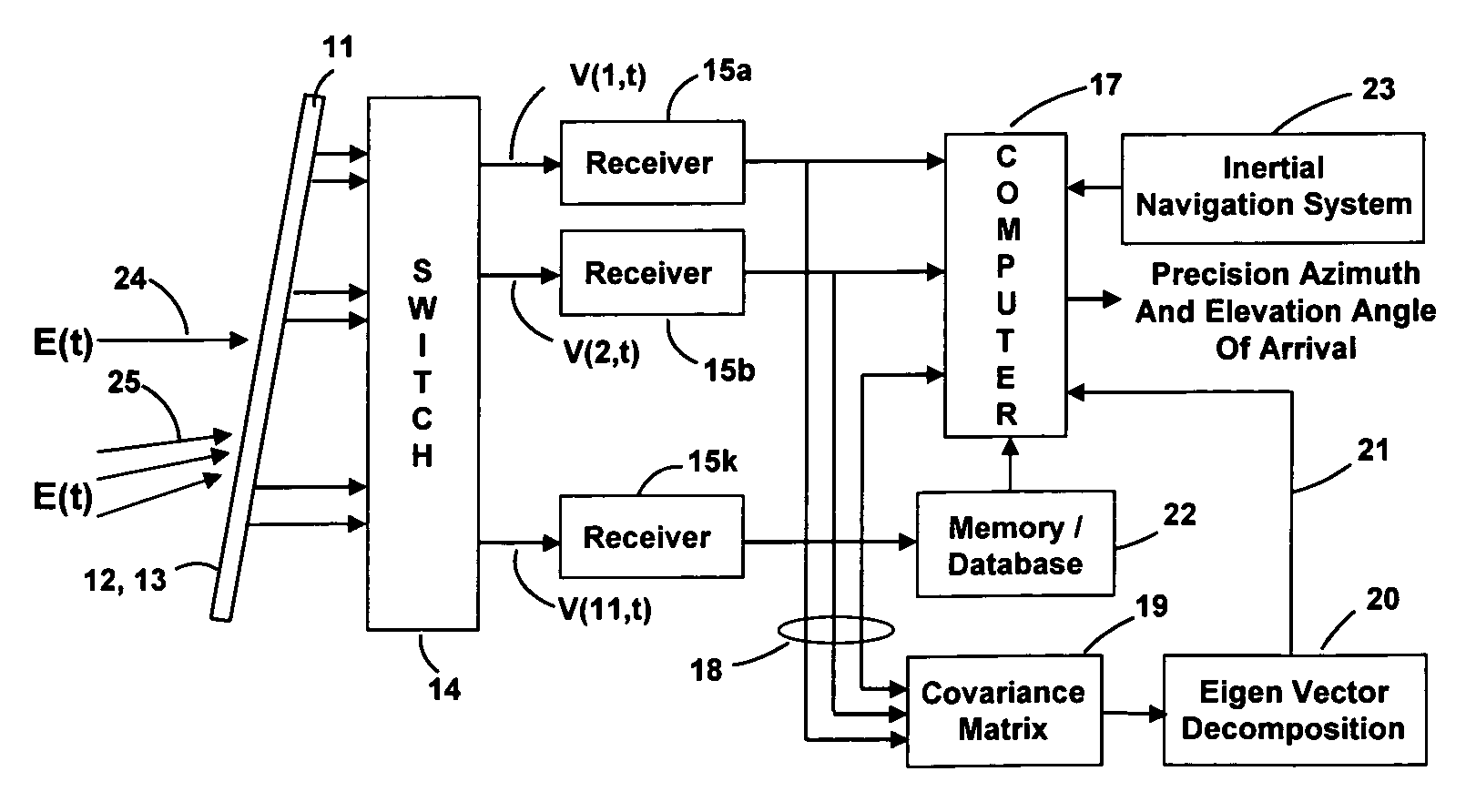
Apparatus and a method utilizing correlation interferometer direction finding for determining the azimuth and elevation to an aircraft at long range and flying at low altitudes above water with a transmitting radar while resolving multipath signals. The signals from the radar are received both directly and reflected from the surface of the water using horizontally polarized and vertically polarized antenna arrays, are digitized and are stored in separate covariant matrices. Eigenvalues for the eigenvectors of the matrices processed on signal samples recorded on horizontally polarized X arrays are compared to the eigenvalues for the eigenvectors of the covariance matrices processed on signal samples recorded on vertically polarized X arrays. Incident field polarization is associated with the antenna array measurements that yield the strongest eigenvalue. The eigenvector and eigenvalues for the strongest signal are selected and used for subsequent signal processing. An initial global search assuming mirror sea-state reflection conditions using the signal eigenvector having the strongest eigenvalue is performed to yield an approximate elevation α and azimuth β to the aircraft. The approximate values are then used as the starting point for a subsequent conjugate gradient search to determine accurate elevation α and azimuth β to the aircraft.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Wireless boundary proximity determining and animal containment system and method
InactiveUS6879300B2Exact rangeLow costPolarised antenna unit combinationsBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalProximateBroadcasting
A proximity detection system for determining when a single channel receiver becomes proximate to any point on a wireless closed boundary continuously generated by a transmitter. The transmitter includes a magnetic field generator broadcasting a composite, modulated, time-varying magnetic field signal of a particular carrier frequency. The receiver forms a measure of the broadcast magnetic field intensity incident to the location of the receiver or a measure of the power or energy of incident field.
Owner:XYZ MICROSYST
Method to detect and predict metal silicide defects in a microelectronic device during the manufacture of an integrated circuit
ActiveUS20060172443A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal silicideEngineering
The present invention provides a method detecting metal silicide defects in a microelectronic device. The method comprises positioning (110) a portion of a semiconductor substrate in a field of view of an inspection tool. The method also comprises producing (120) a voltage contrast image of the portion, wherein the image is obtained using a collection field that is stronger than an incident field. The method further comprises using (130) the voltage contrast image to determine a metal silicide defect in a microelectronic device. Other aspects of the present invention include an inspection system (200) for detecting metal silicide defects and a method of manufacturing an integrated circuit (300).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Photonic signal frequency up and down-conversion using a photonic band gap structure
InactiveUS6744552B2Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotonic bandgapMid infrared
A photonic band gap (PBG) device is provided for frequency up and / or down-converting first and second photonic signals incident on the device to produce a down-converted output photonic signal. When the first and second incident photonic signals have respective first and second frequencies omega3 and omega2, the down-converted photonic signal has a third frequency omega1=omega3-omega2. When the first incident field has a frequency omega1, the first up-converted photonic signal has a second frequency omega2. The second up-converted photonic signal has a third frequency omega3=omega1+omega2. Thus, the PBG device can be used to generate coherent near- and mid-IR signals by frequency down-converting photonic signals from readily available photonic signal sources, or red, blue, and ultraviolet signals by up-converting the same readily available photonic signal sources.
Owner:SCALORA MICHAEL +3
Multipath resolving correlation interferometer direction finding
ActiveUS7358891B2Improve accuracyRobust and accurateMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionWater useCovariance
Apparatus and a method utilizing correlation interferometer direction finding for determining the azimuth and elevation to an aircraft at long range and flying at low altitudes above water with a transmitting radar while resolving multipath signals. The signals from the radar are received both directly and reflected from the surface of the water using horizontally polarized and vertically polarized antenna arrays, are digitized and are stored in separate covariant matrices. Eigenvalues for the eigenvectors of the matrices processed on signal samples recorded on horizontally polarized X arrays are compared to the eigenvalues for the eigenvectors of the covariance matrices processed on signal samples recorded on vertically polarized X arrays. Incident field polarization is associated with the antenna array measurements that yield the strongest eigenvalue. The eigenvector and eigenvalues for the strongest signal are selected and used for subsequent signal processing. An initial global search assuming mirror sea-state reflection conditions using the signal eigenvector having the strongest eigenvalue is performed to yield an approximate elevation α and azimuth β to the aircraft. The approximate values are then used as the starting point for a subsequent conjugate gradient search to determine accurate elevation α and azimuth β to the aircraft.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Electronic control beam scanning reflection array antenna and beam scanning method thereof
The invention discloses an electronic control beam scanning reflection array antenna and a beam scanning method thereof. The antenna is low in cost and loss and simple in structure. The antenna is characterized in that two initial feed sources are adopted in the antenna to perform irradiation excitation on a reflective array plane, and the excitation amplitude ratio of the feed source 1 to the feed source 2 is changed to change the phase value distribution of a total incident field in the array plane so that electronic control beam scanning can be achieved. The antenna is simple in structure and does not need extra biasing circuits, so that machining is convenient, and stability is high. High-gain beam scanning can be achieved just through the two initial feed sources without extra T / R modules, so that the manufacturing cost is effectively lowered. The antenna is suitable for microwave or millimeter wave or terahertz frequency bands and can be used in wireless communication and radar systems.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Rapid and accurate computation method for large-scale MIMO array antenna far-field radiation field
ActiveCN104992001AFast analysisImprove synthesis accuracySpecial data processing applicationsFull waveRadiation field
The present invention belongs to the field of electromagnetic value computing, and particularly relates to a rapid and accurate analysis method for large-scale MIMO array antenna far-field radiation. The method comprises: determining a structural parameter of an M*N-element plane array antenna; computing a relationship between an incident field and a scattered field of an element antenna; according to mutual coupling characteristics among element antennas, selecting a sub-array form and size of an extraction unit on an array environment condition; for an antenna sub-array of the extraction unit, computing a unit far-field radiation pattern of the sub-array; and according to the unit far-field radiation patterns of the array and a superposition principle, computing an array antenna far-field radiation pattern. According to the invention, by utilizing the accuracy of mutual coupling computation, the problems that the use of such methods as the moment method, the finite element method and the finite difference time domain (FDTD) method are limited by computing capacity of a single computer, and when the scale of the array antenna is too large, rapid and accurate computation of the antenna radiation field cannot be implemented with a full wave simulation method because of large consumption of memory and computing time, are effectively solved. The method provided by the invention is capable of analyzing the radiation pattern of a large and conformal array antenna, and has higher synthesizing accuracy and higher analysis speed.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
Method for calculating radar cross section of corner reflector
InactiveCN103530469AQuick calculationImprove computing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsReflected wavesClassical mechanics
The invention provides a method for calculating the radar cross section (RCS) of a corner reflector. RCS calculation is conducted through GO and the Gordan surface element integral method. Firstly, radial tracing is conducted on incident waves and reflected waves according to GO, so that an incident field generated every time and a corresponding lighting zone of the incident field are determined; then, a scattered field of each lighting zone is obtained through the Gordan surface element integral method and the scattered fields are accumulated, so that the total RCS is obtained. The method for calculating the RCS of the corner reflector is capable of greatly improving the calculation effect of the RCS of the corner reflector and shortening the calculation time and high in practicality.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
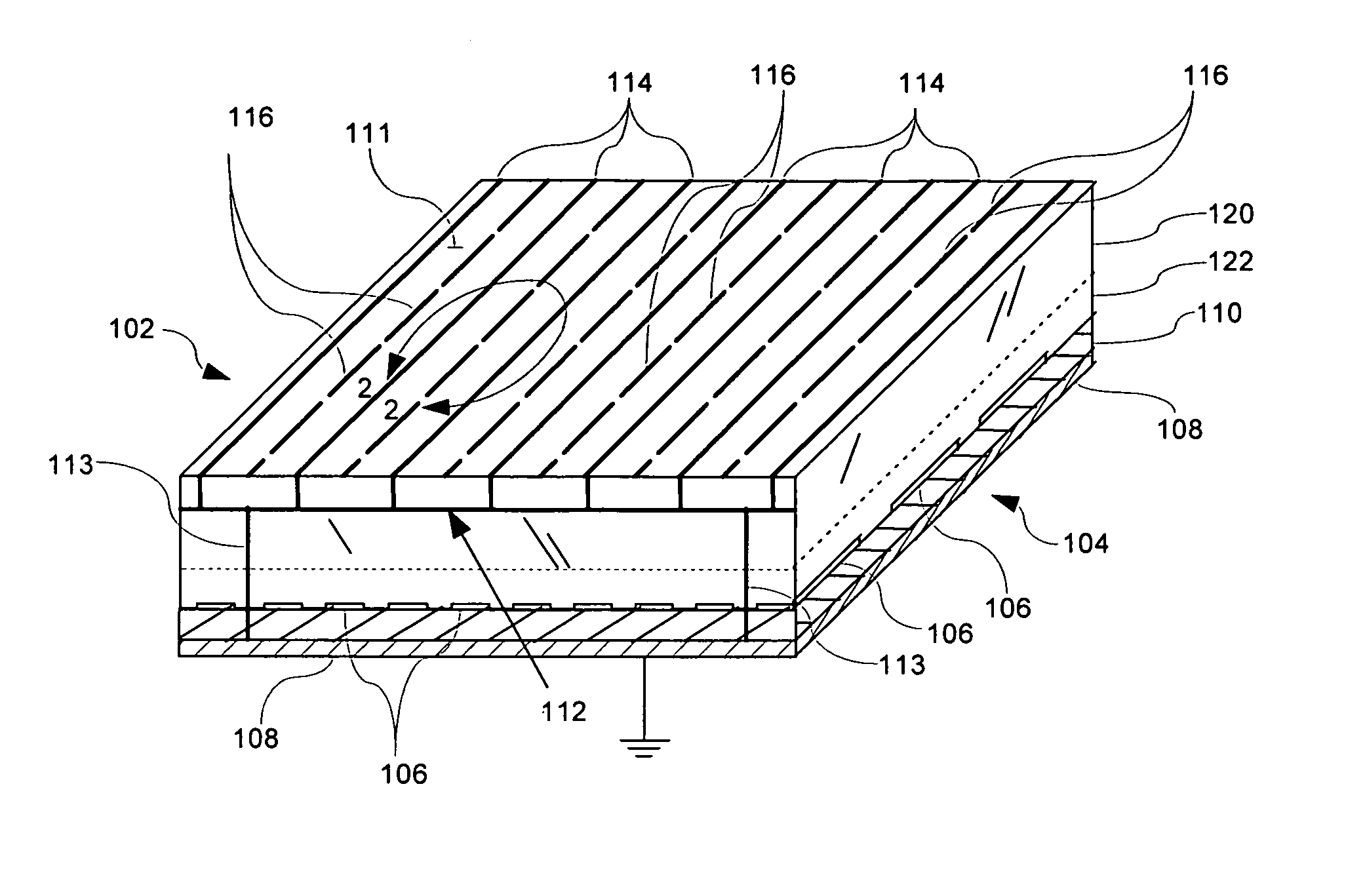
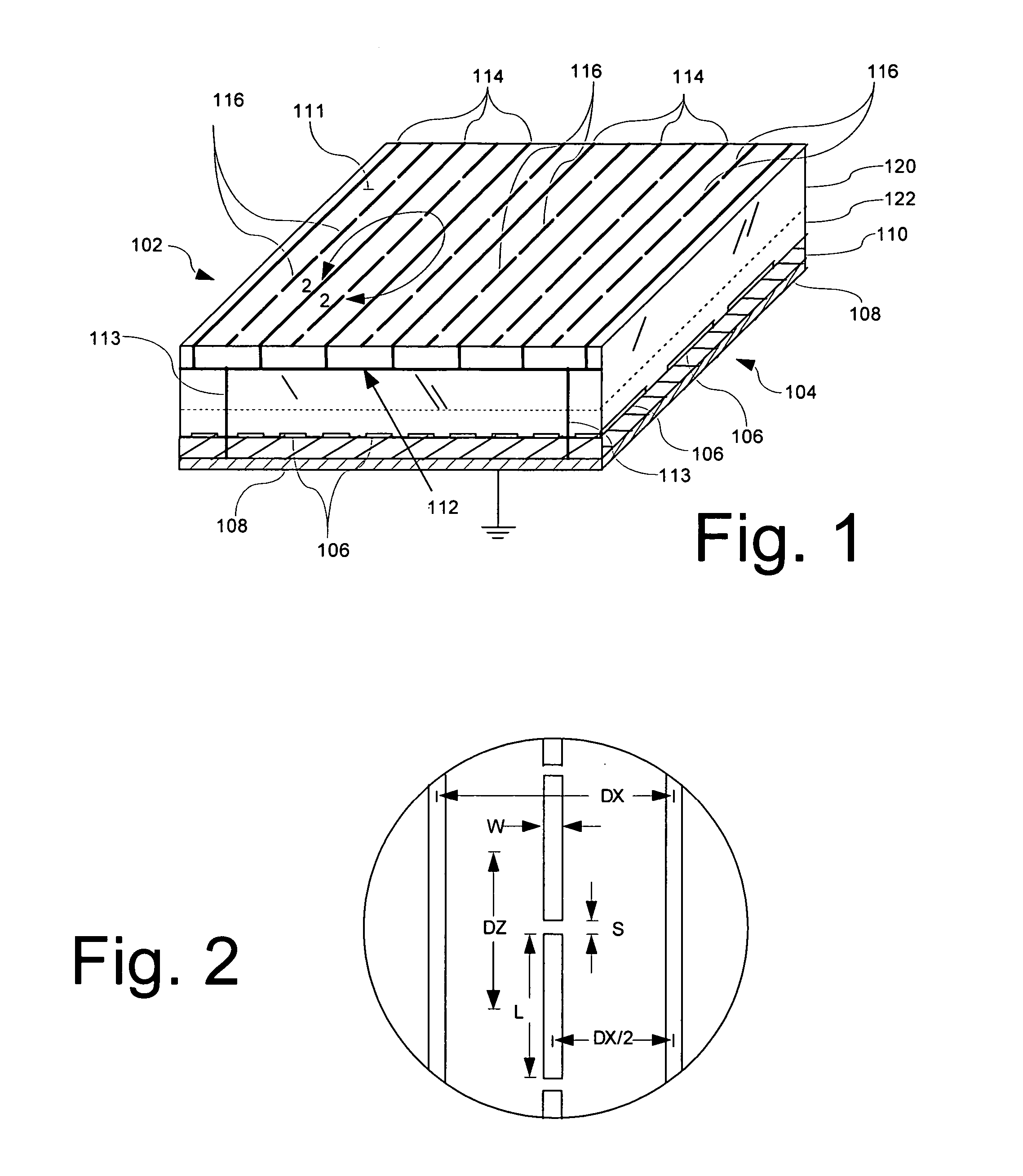
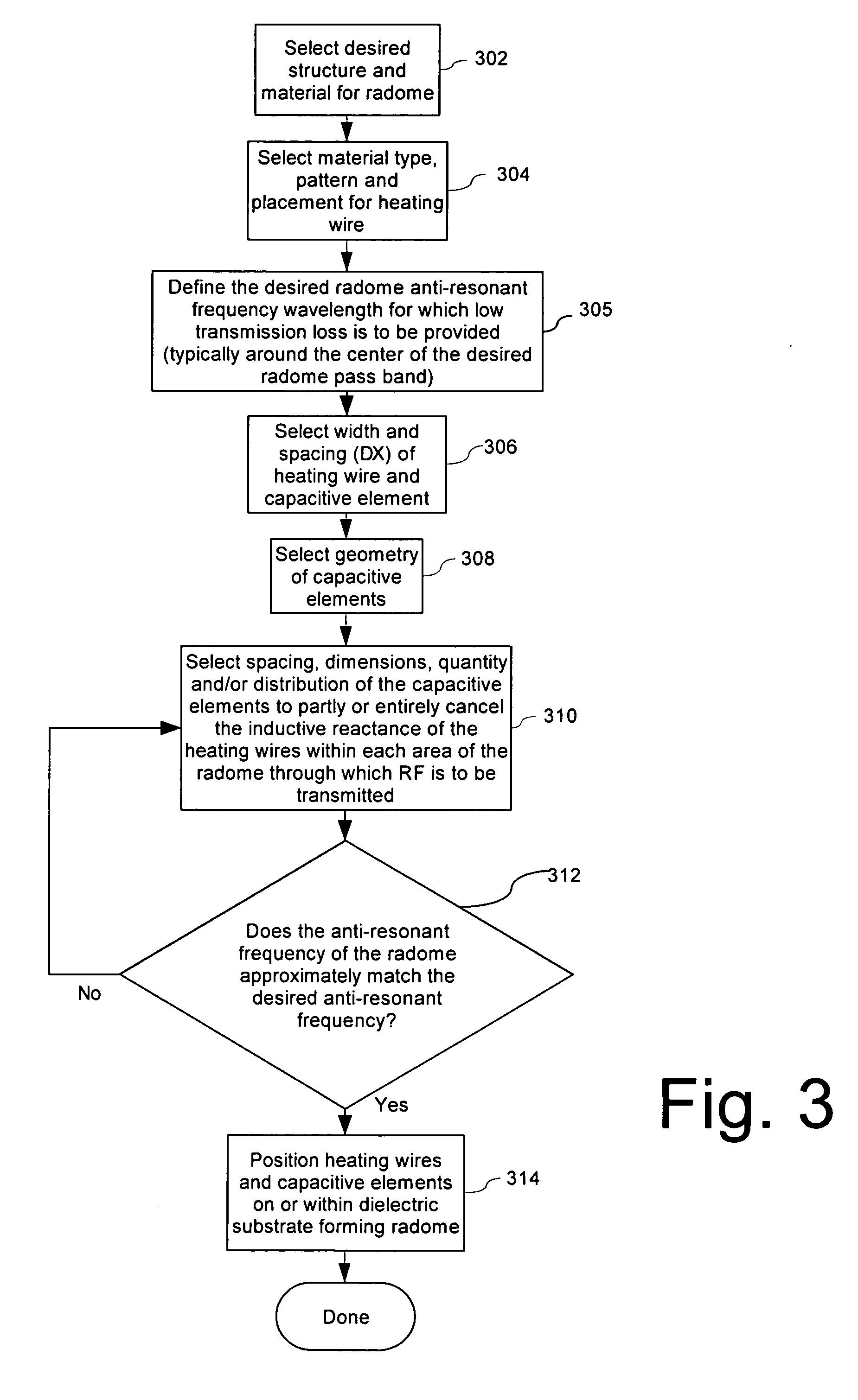
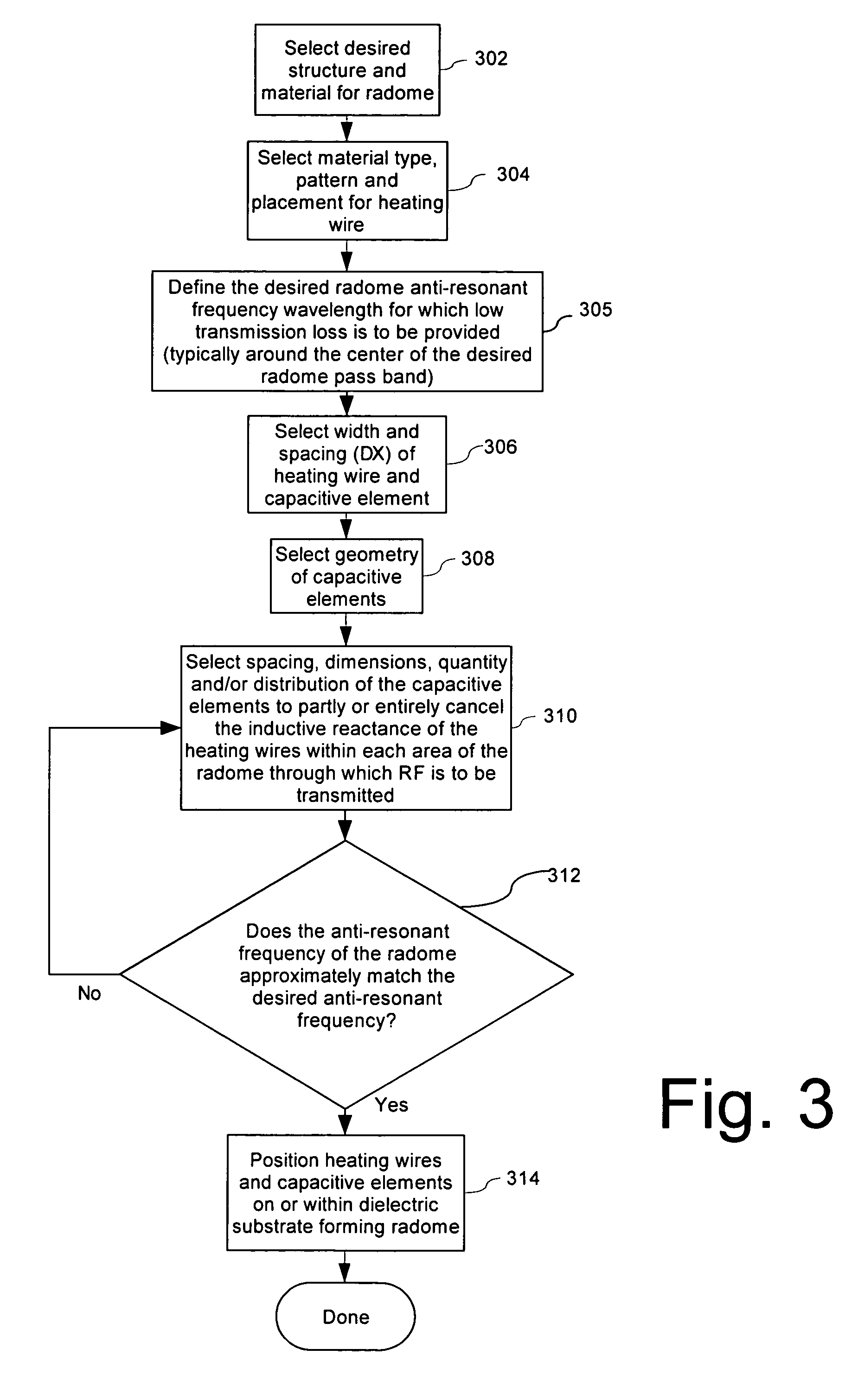
Radome with detuned elements and continuous wires
InactiveUS20070252775A1Improve light protectionImprove protection anti-staticRadiating element housingsDe-icing/drying-out arrangementsCapacitanceElectricity
A radome uses traditional continuous heating wires mixed with detuned dipoles between heating wires and can be placed at any chosen distance from an array antenna or FSS. The continuous heating wires add a reactive component to the incident field phase, which is effectively cancelled out by the detuned dipoles which provide a capacitive component. The orthogonal components of the incident field are transmitted with very small losses over a wide number of scan angles. These heating and detuned dipoles can be printed on low loss dielectric materials. In addition, the printed elements of this radome can be scaled to operate over a chosen frequency band.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Multi-band antenna system
The present invention is an improved antenna system. In an embodiment of the invention, the antenna system of the present invention may be a high-gain, low-profile wide-band antenna. Advantageously, the antenna system of the present invention may include a plate with reflecting elements to form a reflectarray antenna suitable for mounting on an aircraft. The reflectarray antenna of the present invention may be formed from a planar array of waveguides which may operate as a low loss, wide-band reflecting elements. Individual waveguides may be designed to scatter an incident field while impressing appropriate phase shifts in order to form a plane wavefront at the array aperture to produce a desired output signal. Waveguides may include ridges to employ vertical and horizontal polarization across a wide bandwidth operable at a high frequency, such as 10 GHz to 30 GHz.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
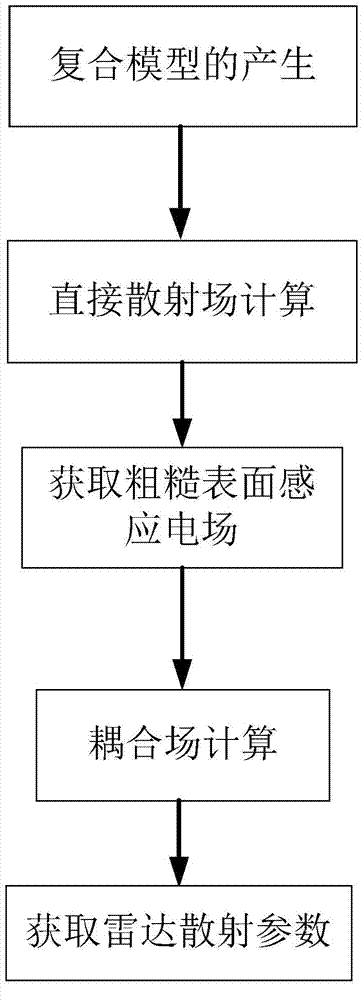
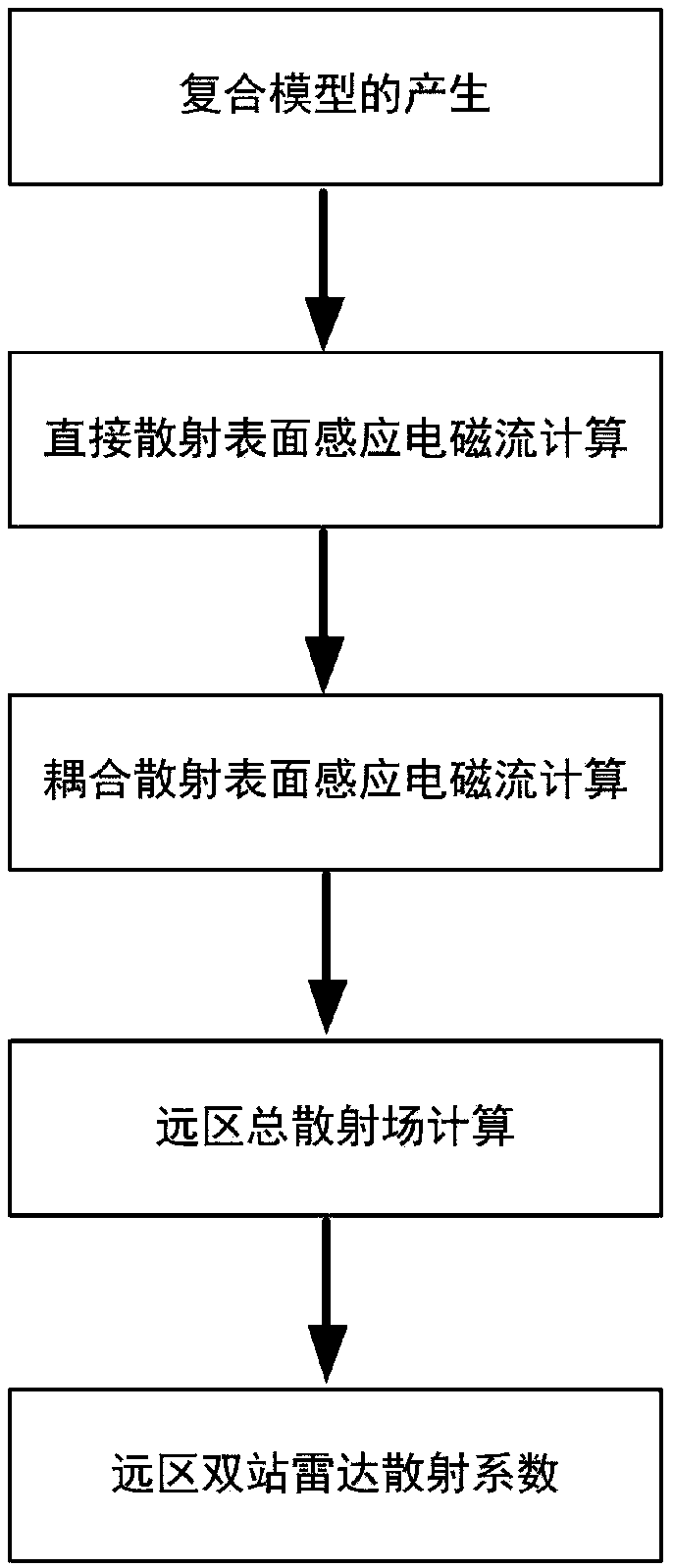
Rough surface and target composite electromagnetic scattering simulation method based on reciprocity principle
ActiveCN103593510AAvoid artificial reflexesImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsState of artRadar
The invention discloses a rough surface and target composite electromagnetic scattering simulation method based on the reciprocity principle, mainly solving problems of low simulation efficiency, poor simulation universality and high memory requirements in the prior art. The rough surface and target composite electromagnetic scattering simulation method based on the reciprocity principle is implemented by the steps of (1) generating the rough surface by the Monte Carlo method according to the power spectrum density function of the rough surface, (2) performing geometric modeling to the target according the size and shape requirements of the target, (3) adding the geometric model of the target into a rough surface model to generate a composite model, (4) calculating a direct scattered field by means of Kirchhoff approximation, (5) acquiring a coupling field between the rough surface and the target according to the reciprocity principle, (6) calculating the total scatted field of the composite model according the direct scatted field and the coupling field, and (7) acquiring monostatic radar scatted parameter of the composite model according the total scattered field and an incident field of the composite model. The rough surface and target composite electromagnetic scattering simulation method based on the reciprocity principle has the advantages of high simulation speed, simulation precision and universality, and can be applied to target detection in the background of the rough surface.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Three-dimensional anisotropic radio frequency magneto telluric adaptive finite element forward modeling method
ActiveCN110058315AHigh precisionImprove efficiencyElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationPhase responseEarth surface
The invention discloses a three-dimensional anisotropic radio frequency magneto telluric adaptive finite element forward modeling method. The three-dimensional anisotropic radio frequency magneto telluric adaptive finite element forward modeling method comprises the steps that a three-dimensional geoelectric geometric model representing a solution region is constructed, and control parameters of different regions are acquired; the three-dimensional geoelectric geometric model is divided into a plurality of mutually disjoint tetrahedral elements; the integration weak form corresponding to the three-dimensional anisotropic radio frequency magneto telluric is acquired, sparse linear equation sets are constructed, then incident fields with two different polarization directions are introduced to the earth surface so as to obtain different right-end items in the two sparse linear equation sets, and the two sparse linear equation sets are solved to obtain approximate electric field tangentialcomponent on each edge in the two polarization directions; based on the approximate electric field tangential component on each edge in the two polarization directions, and a combination of parameters of one or more of an electric field, a magnetic field, impedance tensor, magnetic inclination sub vector, apparent resistivity, and phase response at a measuring point is acquired. According to thethree-dimensional anisotropic radio frequency magneto telluric adaptive finite element forward modeling method, 3D RMT anisotropic forward modeling simulation is realized based on an adaptive finite element method.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Terahertz magnetic radiation source
InactiveCN105742141AReduce the starting current densityImprove coupling strengthTubes with velocity/density modulated electron streamTransit-tube coupling devicesWave structurePower flow
The invention provides a terahertz magnetic radiation source. The terahertz magnetic radiation source comprises an electron gun, an electron beam collection pole, a first slow wave structure, a drift segment and a second slow wave structure, wherein the first slow wave structure is arranged between the electron gun and the electron beam collection pole, an electron beam and the first slow wave structure jointly act to generate a cluster, the first slow wave structure is used for modulating the travelling speed and the density of the electron beam to form an initial electron string, the drift segment is arranged between the first slow wave structure and the electron beam collection pole and is used for clustering the initial electron string to form a modulated electro string, the second slow wave structure is arranged between the drift segment and the electron beam collection pole, the modulated electron string and the second slow wave structure jointly act to generate electromagnetic oscillation, and the frequency of the electromagnetic oscillation is an integer multiple of the modulation frequency during modulation of the electron beam by the first slow wave structure. The coupling strength between a coherent incident field of the modulated electron string and a high-frequency field in the second slow wave structure is higher than that between a non-coherent incident field of the continuous electron beam and the high-frequency field, and thus, the starting oscillation current density of the terahertz source is reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
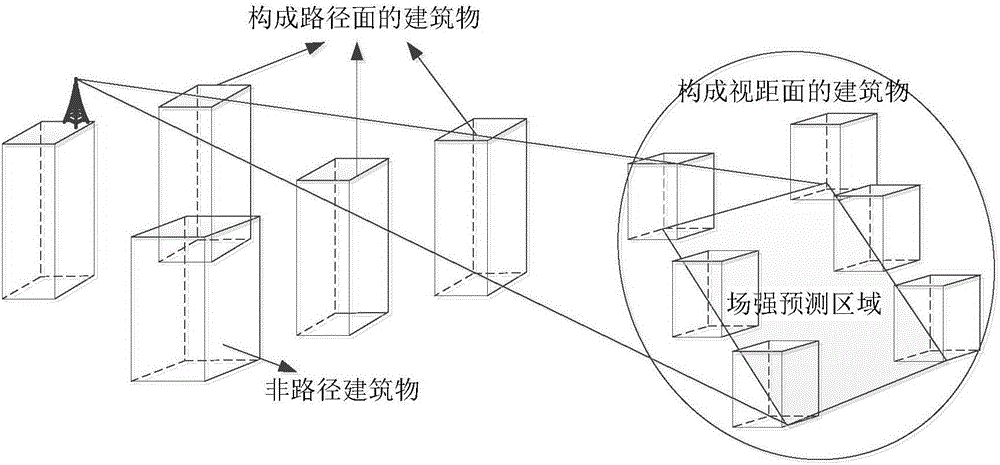
Method for predicting 5G millimeter wave network signal strength spatial distribution situation
The invention discloses a method for predicting a 5G millimeter wave network signal strength spatial distribution situation. The method comprises the steps of carrying out inversion to obtain dielectric parameters on surfaces of building materials in a prediction area; establishing a path plane model and a sight distance plane model, giving a maximum multipath distribution result for a special transceiving end location and selecting valid reflection multipaths; and carrying out direct wave consistent area division on the prediction area, measuring direct wave field intensity amplitudes and phases of direct wave consistent areas, predicting field intensity of certain receiving point, judging the direct wave consistent area to which the certain receiving point belongs, calculating a direct reflection field of the receiving point according to a field intensity measuring value of the direct wave consistent area, judging the direct wave consistent area to which a reflection point belongs according to reflection point locations of the valid reflection multipaths, calculating a reflection field by taking a transmission field amplitude of the direct wave consistent area to which the reflection point belongs as an incident field amplitude of a reflection wave, overlapping the direct field and all reflection multipath fields, determining an electric field vector of the receiving point, and summarizing the receiving field of each point in the prediction area. Electromagnetism situation distribution is predicted.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
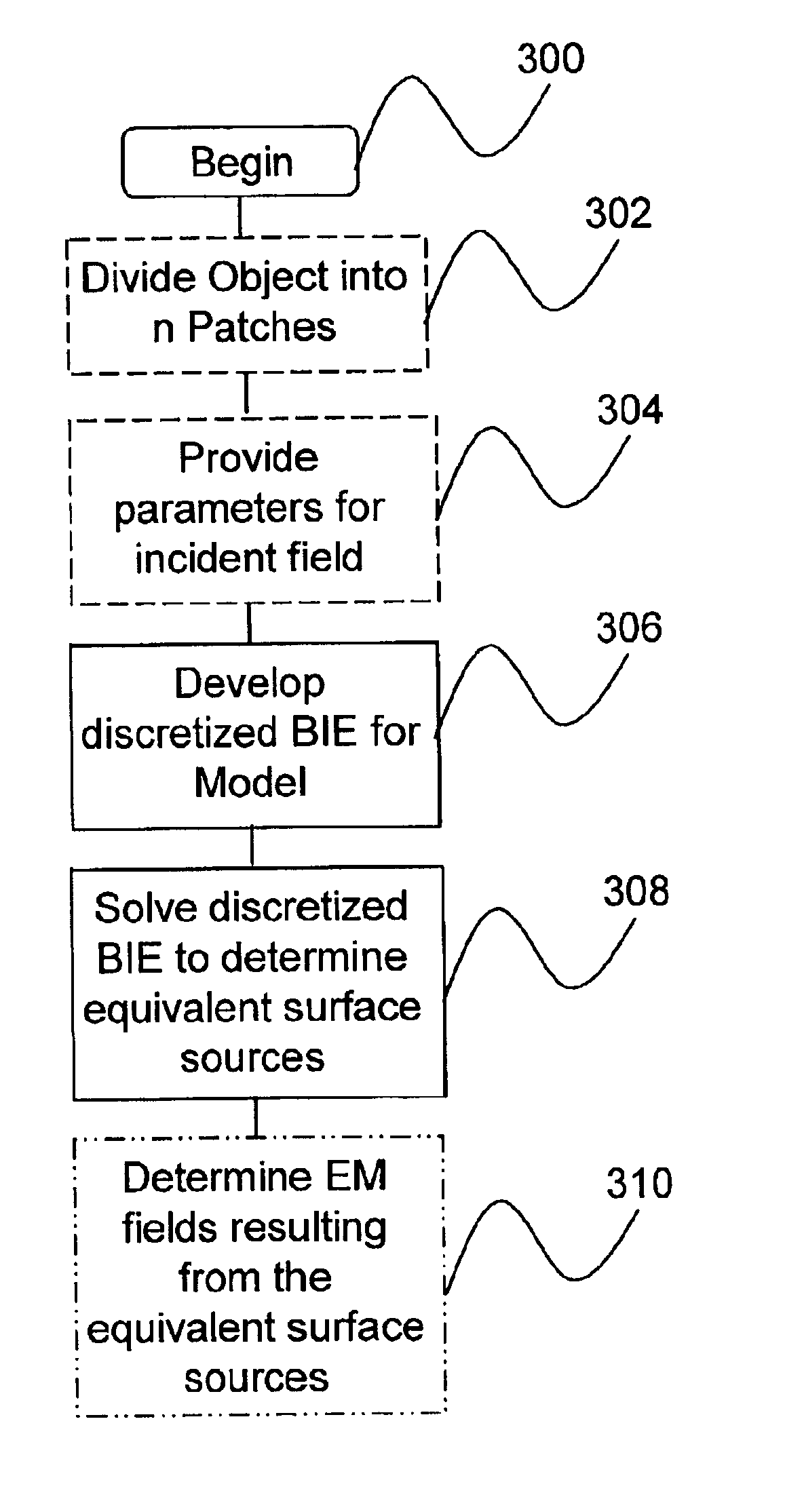
Method and apparatus for modeling three-dimensional electromagnetic scattering from arbitrarily shaped three-dimensional objects
InactiveUS6847925B2High degreeImprove computing efficiencyGeometric CADWave based measurement systemsRadarHarmonic
A computer program product, an apparatus, and a method for modeling equivalent surface sources on a closed, arbitrarily shaped object that result from the imposition of an arbitrary time-harmonic incident field (e.g., a radar wave) are provided. An object divided into by a plurality of patches 302 and parameters for the incident field and the properties of the object 304 are provided to the system. Next, the system produces a discretized representation of a well-conditioned boundary integral equation in the form of a well-conditioned matrix equation, modeling the interaction between the incident field and the object 306. The well-conditioned linear system is solved numerically to determine equivalent surface sources on the object 308. The equivalent sources may then be used to determine electromagnetic fields resulting therefrom 310. The invention provides improved computational efficiency as well as increased modeling accuracy by effectively reducing the numerical precision necessary.
Owner:HRL LAB
Method for generating rotatable optical focal field on basis of radiation field of rotating field antenna
The invention provides a method for generating a rotatable optical focal field on the basis of a radiation field of a rotating field antenna. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: S1, placing a virtual rotating field antenna composed of two dipoles which are perpendicular to each other and have a phase difference of 90 degrees at the center of a focal plane of a 4Pi focusing system, so that an electromagnetic field radiated by the virtual rotating field antenna is completely converged by two opposite high numerical aperture lenses and collimated onto a pupil plane; andS2, focusing two incident fields different for 180 degrees onto the optical focal plane of the two opposite high numerical aperture lenses by virtue of the two opposite high numerical aperture lenses. Intensity distribution of an '8'-shaped optical focal field generated by the method provided by the invention rotates at a circular frequency omega around an optical axis on the focal plane along with time. The rotatable optical focal field has important application value in the aspects of particle rotation, particle acceleration and near-field scanning optical microscopes.
Owner:QUANZHOU NORMAL UNIV
Electromagnetic imaging system and method employing oblique incident wave
InactiveCN105929395AOvercome occlusionFlexible layoutRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMicrowaveCoupling
The invention discloses an electromagnetic imaging system and method employing an oblique incident wave. A scatterer is fixed on a rotating platform, and the periphery of the scatterer is uniformly provided with a plurality of receiving antennas at intervals. All receiving antennas are connected to a microwave switching network, and the needed receiving antennas are selected to be connected for operation through the microwave switching network. The microwave switching network is connected with a vector network analyzer, and the vector network analyzer is connected with a transmitting antenna through a radio frequency power amplifier. The incident field data and the total field data after each rotation are obtained firstly, and then the subtraction of the incident field data and the total field data is carried out to obtain the scattering field data of each measurement. An imaging region is equally divided to obtain a Green function, and a target function is built. An optimization algorithm is employed for solving the minimum value of the target function, and the distribution of dielectric constants is obtained. The system and method solve a problem of shading and cross coupling of receiving and transmitting antennas in an electromagnetic imaging system employing normal incident waves. The receiving and transmitting antennas can be flexibly arranged, and the proper incident angles can be freely selected according to the actual conditions.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Rapid analysis method of MIMO antenna mutual-coupling characteristic
ActiveCN104993881AReduce the number of subdivisionsEasy to implement modularlyTransmitters monitoringSpatial transmit diversityCouplingMimo antenna
The invention belongs to the field of antenna electromagnetic analyses, and specifically relates to a rapid analysis method of an MIMO antenna mutual-coupling characteristic. The method comprises expanding fields of unit antennas according to a vector wave function, building a relational expression representing a scattering field coefficient and an incident field coefficient, determining a relationship between scattering field coefficients of the different unit antennas after iteration by utilizing an iteration scattering algorithm, respectively performing excitation on antenna units in an array, and determining an S parameter, i.e., a mutual-coupling characteristic parameter between the different units according to an iteration rule of the scattering fields between the antennas. The problem that an existing method cannot rapidly analyze the MIMO array mutual-coupling characteristic is solved, the rapid analysis method is suitable for a condition that the array antenna units are placed in parallel or have the same radiation direction, a mutual influence between the antennas is analyzed by utilizing the iteration scattering algorithm, and the mutual-coupling characteristic between the array antennas can be directly calculated; and the fields of the antenna units and an iteration mutual-coupling field are calculated separately, modularization of the algorithm is convenient to achieve, and calculating precision is improved.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
Method for generating two-dimensional identical-focal spot array by using radiation field of planar array antenna
ActiveCN109188687AQuantity is easy to controlOptical elementsHigh numerical apertureElectromagnetic field
The invention relates to a method for generating a two-dimensional identical-focal spot array by using the radiation field of a planar array antenna. The method comprises the steps of firstly adoptinga 4[pai] focusing system composed of two high numerical aperture lenses; then arranging a virtual planar antenna array in the center of the focal plane of the 4[pai] focusing system composed of the two high numerical aperture lenses, wherein the electromagnetic field radiated by the antenna array is outwards propagated to the lens on the image space side, and completely collected by the two highnumerical aperture lenses, and then continuously propagated to the pupil planes of the two lenses, and thus field distribution on the pupil planes is achieved; and at last, regarding the field distribution on the pupil planes to be incident fields and reversely transmitting the incident fields to a focal region, so as to generate the two-dimensional identical-focal spot array with specific characteristics on the focal plane of the high numerical aperture lenses. According to the method provided by the invention, the two-dimensional identical-focal spot array having the specific quantity, separation distances and positions is generated by using the method with no need to optimize.
Owner:QUANZHOU NORMAL UNIV
A microwaveband microwave absorbing device and method based on a phase-adjustable supersurface
The invention provides a microband microwave absorbing device and a method based on a phase-adjustable supersurface, comprising at least one unit structure. The unit structure comprises a metal structure, a dielectric substrate, a first via, a second via, a ground substrate, a varactor diode, a first via, a second via penetrating the dielectric substrate and the ground substrate, and one end of the first via hole is connected to the metal structure, and the varactor diode is connected between symmetrical metal structures of the metal structure. The control unit adjusts the phase response distribution of the cell structure by providing a reverse bias voltage to the cell structure and adjusting the varactor diode. By applying the bias voltage to the sub-wavelength cell to change the electromagnetic state, the independent phase of the super-surface cell structure can be adjusted, and then the reflected phase of the incident field in the super-surface cell structure can be arbitrarily changed, which has the characteristics of simple design, easy processing, flexible application and so on.
Owner:余姚市万邦电机有限公司 +1
Light conduction and separation method and device based on reflective waveguide coupler
InactiveCN107643559AReduce in quantityImprove experienceOptical light guidesAcute angleImaging quality
The invention provides a light conduction and separation method and device based on a reflective waveguide coupler. The method includes the steps of obtaining a set incident field angle of the waveguide coupler and a refraction angle range of incident light on a light guide plate surface; and adjusting the refraction angle in the refraction angle range, and adjusting an acute-angle included anglebetween a reflecting cell in the waveguide coupler and the light guide plate surface, so that the acute-angle included angle and the refraction angle meet preset conditions, incident light corresponding to the incident field angle is led out from an emergent end of the waveguide coupler, and information light used for forming an image is separated from emergent light of the waveguide coupler. Thusstray light entering human eyes can be greatly reduced, thereby improving image quality formed in the human eyes, and improving user experience.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Calculation method for steel rail potential current distribution influences
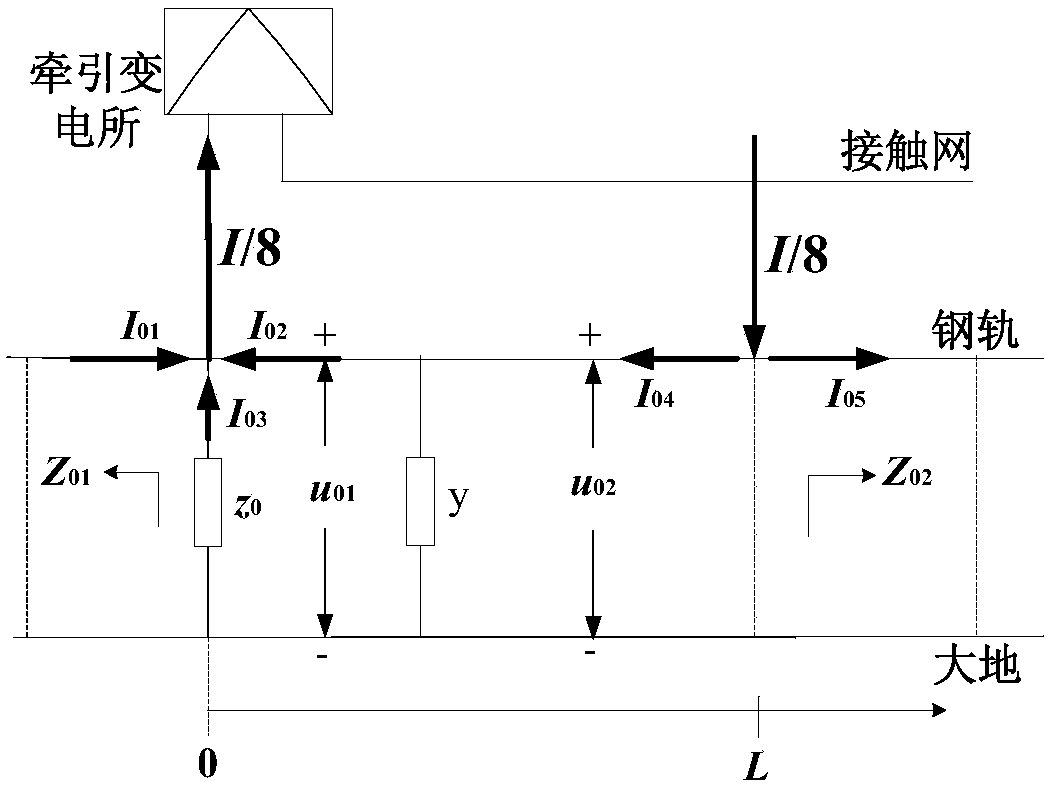
InactiveCN108153708AGuaranteed uptimeDesign optimisation/simulationPower railsMetallurgyCurrent distribution
The invention discloses a calculation method for steel rail potential current distribution influences. The method comprises the steps that on the basis of the injection rate of each return current ona steel rail, the return current collected at a traction substation is resolved, and according to the injection position of each sub-return current on the steel rail, a power supply arm road section is divided into different sections; according to each sub-return current injected on the steel rail, by writing a steel rail potential and steel rail current differential equation, excitation source response and sensibility interference incident field excitation response steel rail potential and steel rail current calculation formulas are adopted when each sub-return current is injected into (flowsout of) a steel rail-ground return, and then according to the boundary conditions, steel rail potential and current distribution is obtained; finally, the steel rail potential and current caused by all injected sub-return currents involved inside the sections are overlaid, and the steel rail potential and current distribution affected by the multi-workshop interval and grounding technology insidethe same power supply arm can be obtained precisely. The good basis is provided for steel rail protection in a traction power supply system.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Rough surface and multi-target composite scattering simulation method based on iterative physical optics
ActiveCN109100692AAvoid artificial reflexesImprove accuracyWave based measurement systemsICT adaptationPhysical opticsSimulation
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar electromagnetic simulation, and discloses a rough surface and multi-target composite scattering simulation method based on iterative physical optics. The method comprises the following steps: inputting a rough surface power spectral density function and a roughness parameter, obtaining a rough surface geometric contour by the Monte Carlo method; using the simulation software FEKO to geometrically model the targets; adding the geometric models of the targets to the rough surface model to generate a composite model; using the physical opticsmethod to calculate the surface induced electromagnetic current directly scattered by the rough surface and each target; calculating the surface-induced electromagnetic current between the rough surface and the targets and between the targets according to the iterative strategy and Huygens principle; obtaining a far-field total scattering field of the composite model by the Huygens principle; andobtaining a two-station radar scattering coefficient of the composite model based on the total scattering field and the incident field of the composite model. The rough surface and multi-target composite scattering simulation method based on iterative physical optics has the advantages such as low memory requirement, high simulation efficiency and strong versatility of the simulation method.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for improving linearity of microwave imaging by using compressed sensing
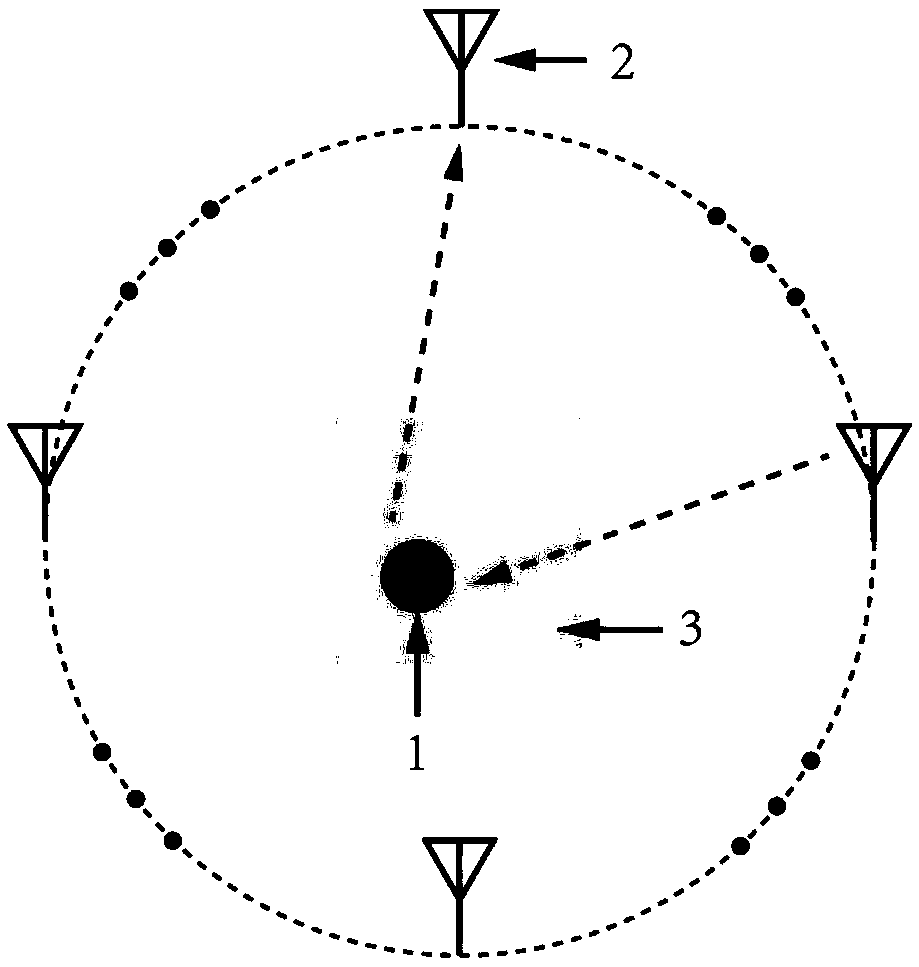
InactiveCN109283530ALower equivalent dielectric constantImproving Imaging LinearityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging algorithmLinearity
The invention discloses a method for improving the linearity of microwave imaging by using compressed sensing, which comprises the steps of setting up a microwave imaging system, wherein a plurality of transmitting and receiving antennas are uniformly distributed at intervals in a circle around a target to be measured with a large dielectric constant, one of the transmitting and receiving antennasserves as a transmitting antenna to emit electromagnetic waves to the target to be measured so as to form an incident field, the incident field forms a scattering field around the target to be measured, the rest of the transmitting and receiving antennas serve as receiving antennas to uniformly receive the scattering field; establishing a preliminary imaging area according to the approximate position range of the target to be measured, enabling the target to be measured to be located in the preliminary imaging area, increasing the space sparsity characteristics between the target to be measured and the imaging area, and carrying out processing and imaging on received scattering field signals by adopting a compressed sensing method, wherein the imaging effect is ideal along the increase inlinearity of an imaging algorithm. The method disclosed by the invention can effectively improve the nonlinearity of the traditional microwave imaging algorithm when imaging a target with a large dielectric constant, and has the characteristics of simple and convenient implementation, fast calculation and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for recording subsurface structure and directly imaging by utilizing micro-earthquake
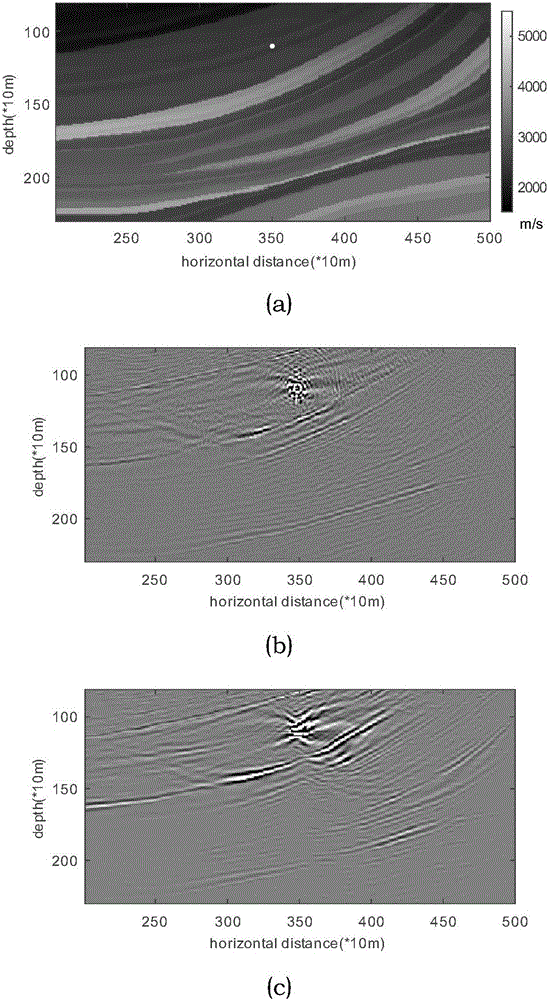
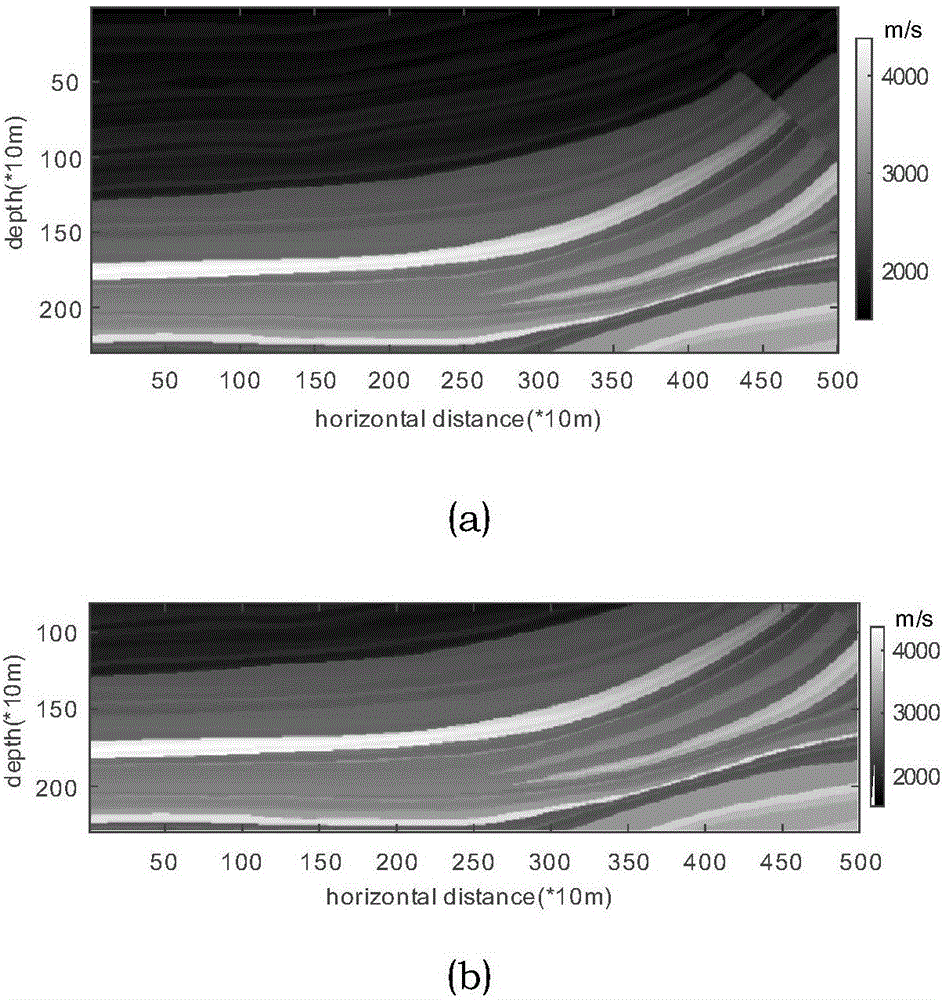
InactiveCN107179551AImproved incident field accuracyImprove imaging effectSeismic signal processingReverse timeImaging condition
The invention relates to a method for recording subsurface structure and directly imaging by utilizing micro-earthquake, micro-earthquake position and a wavelet are assumed to be known, reverse time migration is directly used, cross-correlation imaging conditions are adopted, a micro-earthquake event is served as a boundary condition for incident field reconstruction, a timeline-inversed micro-earthquake record is served as a boundary condition for scattered field reconstruction, and imaging is performed on a subsurface structure. According to the invention, the micro-earthquake event is served as the boundary condition for incident field reconstruction, the incident field precision of deep medium is effectively improved, and the deep medium imaging effect from the direct imaging method is effectively improved. Scattered micro-earthquake event can image without requirements of properties such as amount, density, distribution and the like of micro-earthquake; the micro-earthquake event is adopted to reconstruct the incident field, so that the incident field below a seismic source is more precise; a method for up and down wave separation and left and right wave separation is used for depressing high-frequency and low-frequency noises, solving wavelet shape is avoided, and plenty of calculation time is saved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Radome with detuned elements and continuous wires
InactiveUS7554499B2Prevent freezingReduce buildRadiating element housingsDe-icing/drying-out arrangementsCapacitanceScan angle
A radome uses traditional continuous heating wires mixed with detuned dipoles between heating wires and can be placed at any chosen distance from an array antenna or FSS. The continuous heating wires add a reactive component to the incident field phase, which is effectively cancelled out by the detuned dipoles which provide a capacitive component. The orthogonal components of the incident field are transmitted with very small losses over a wide number of scan angles. These heating and detuned dipoles can be printed on low loss dielectric materials. In addition, the printed elements of this radome can be scaled to operate over a chosen frequency band.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
ISAR imaging simulation method based on time domain shooting bouncing ray quick near-field calculation
ActiveCN106556833ACalculation speedImprove calculation accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPatch modelDelay calculation
The invention relates to an ISAR imaging simulation method based on time domain shooting bouncing ray-method quick near-field calculation. The method comprises steps of (S1) setting a target triangular patch model and transient incident field capable of being any time domain waveform, (S2) employing a time domain shooting bouncing ray quick near-field calculation method to calculate a transient near-field scattering echo illuminated on the target triangular patch model by time domain plane waves, (S3) unifying the target transient near-field scattering echo in a frequency domain according to an incident signal, and (S4) repeatedly executing step 2 and 3 according to angle width and sampling density required by ISAR imaging definition to achieve echo data of a selected angle sample, and then conducting azimuth focusing to achieve a target ISAR image. Real narrow pulse broadband radar close range imaging detection can be simulated; quick calculation speed, high calculation precision and wide application range can be achieved; and pre-estimating data can be provided for target near-field scattering image diagnosis, so cost can be reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com