Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
10359 results about "Water use" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The water footprint shows the extent of water use in relation to consumption by people. The water footprint of an individual, community or business is defined as the total volume of fresh water used to produce the goods and services consumed by the individual or community or produced by the business. Water use is measured in water volume consumed (evaporated) and/or polluted per unit of time. A water footprint can be calculated for any well-defined group of consumers (e.g., an individual, family, village, city, province, state or nation) or producers (e.g., a public organization, private enterprise or economic sector), for a single process (such as growing rice) or for any product or service.
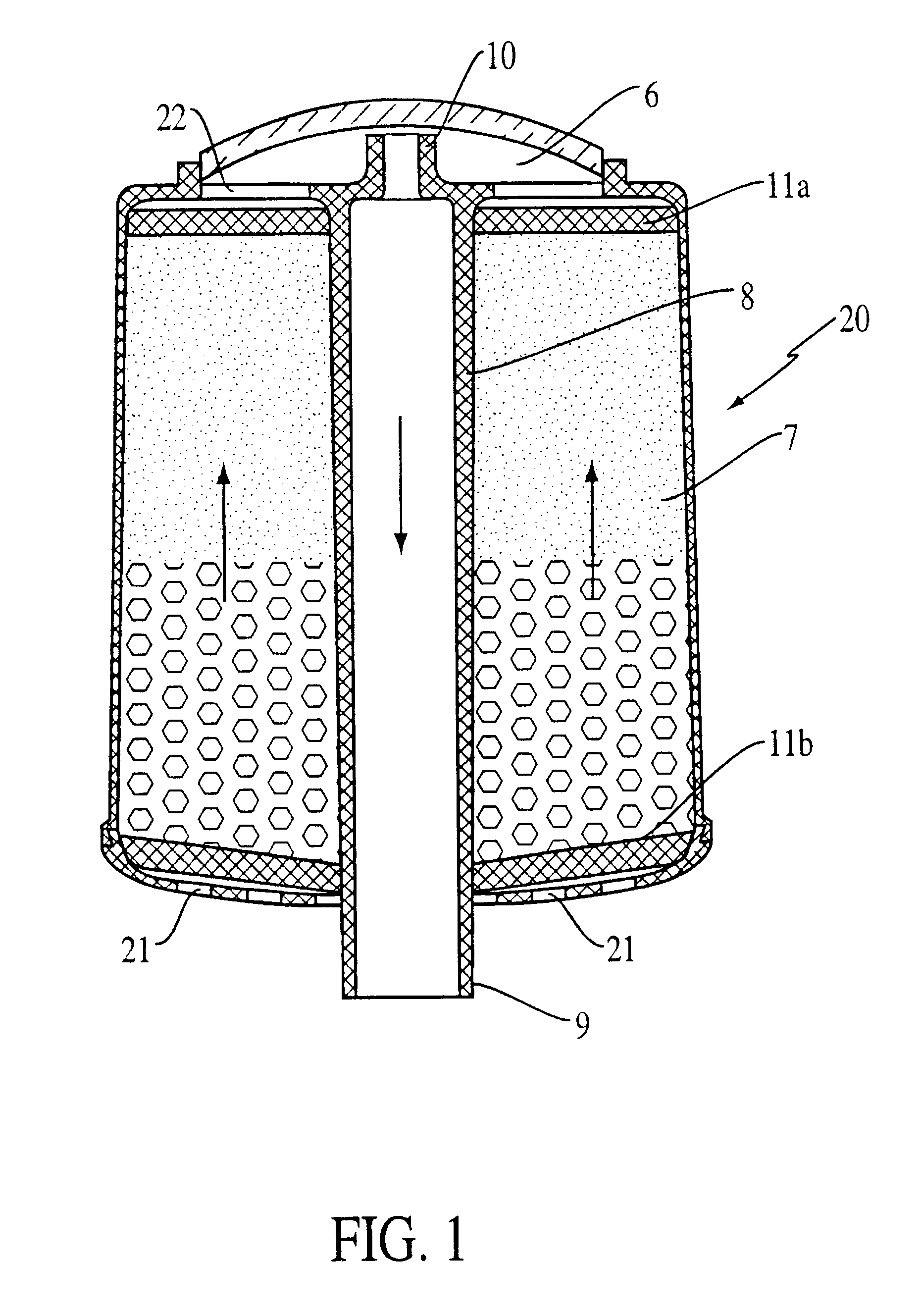
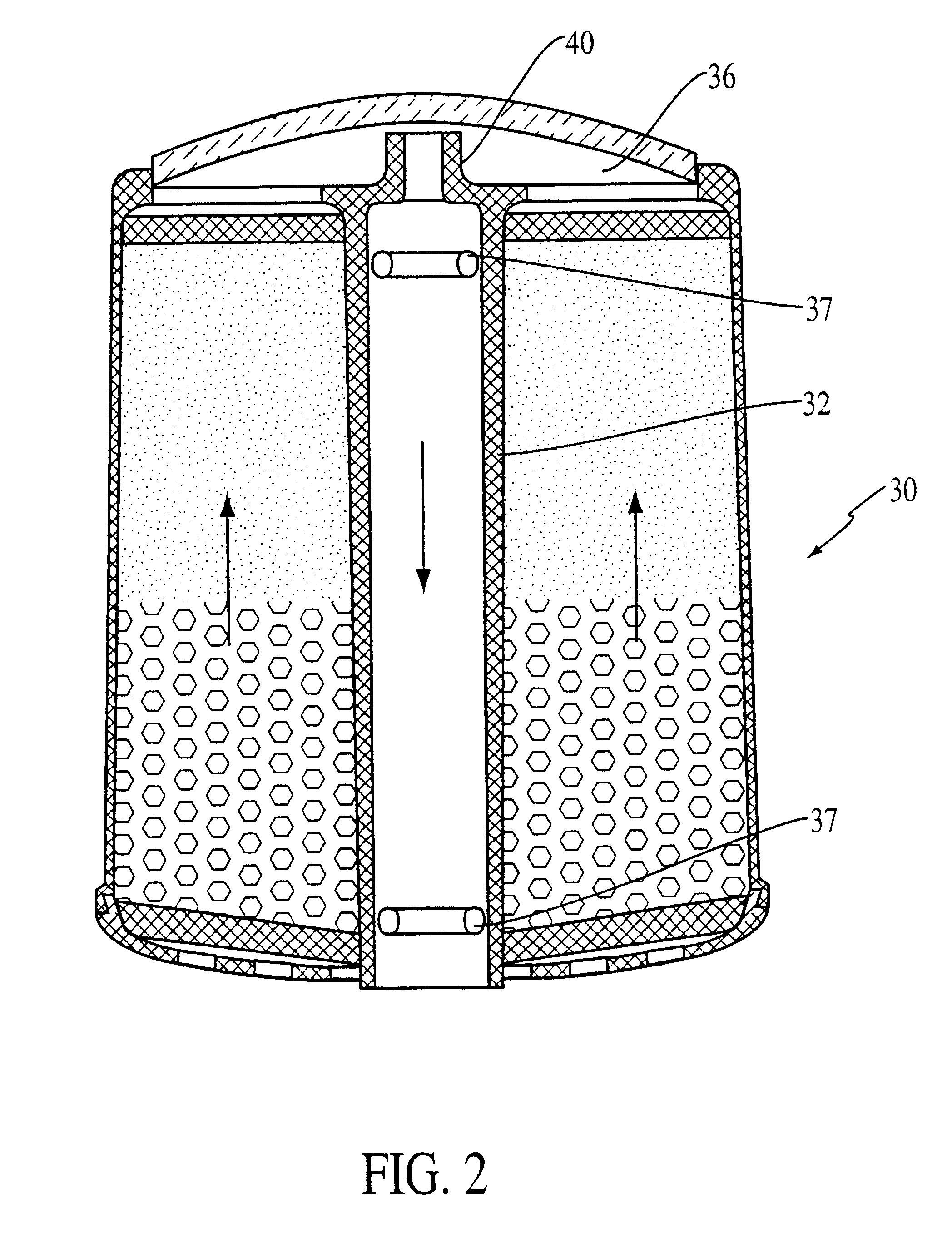
System and method for significant dust detection and enhancement of dust images over land and ocean
InactiveUS20050012035A1Enhanced signalHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansWater useDust detection
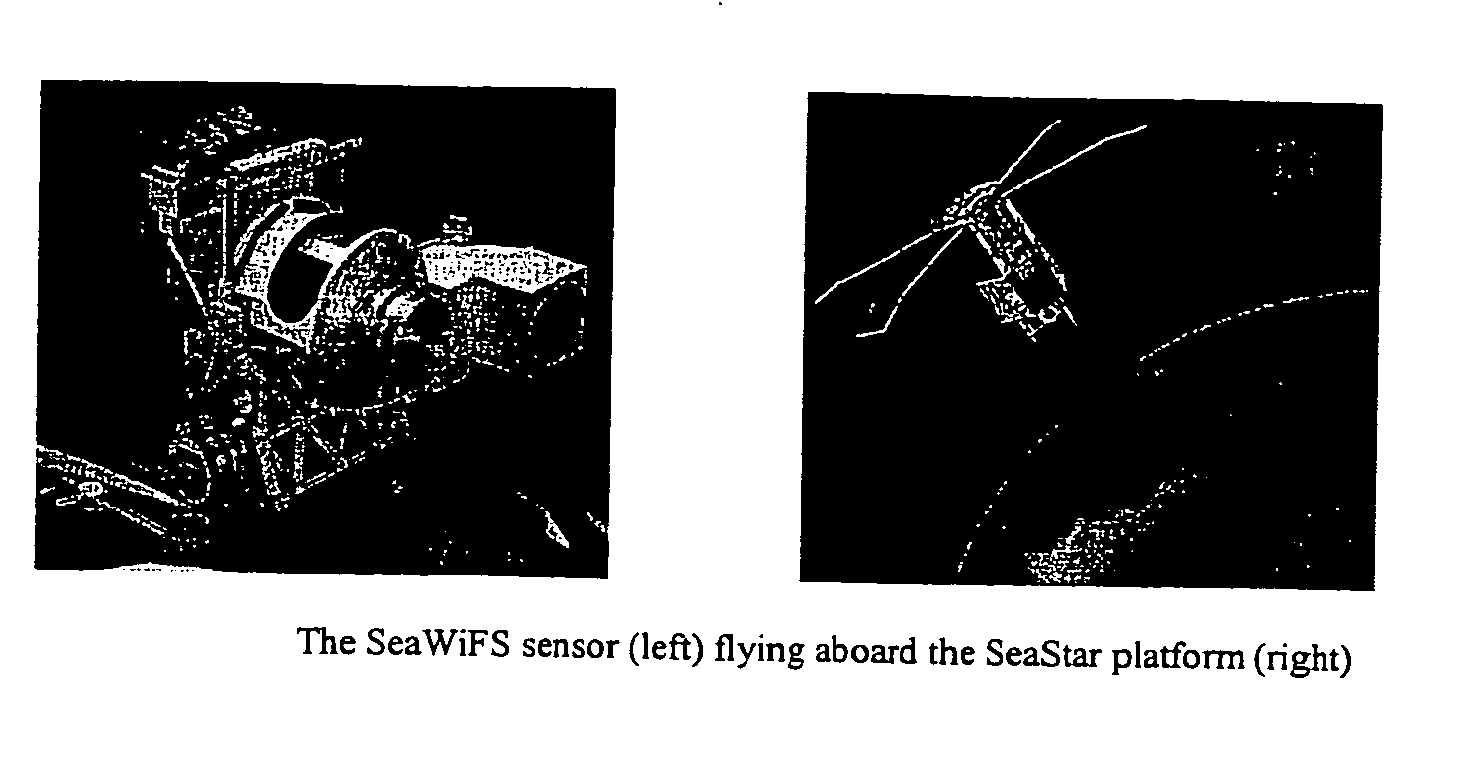
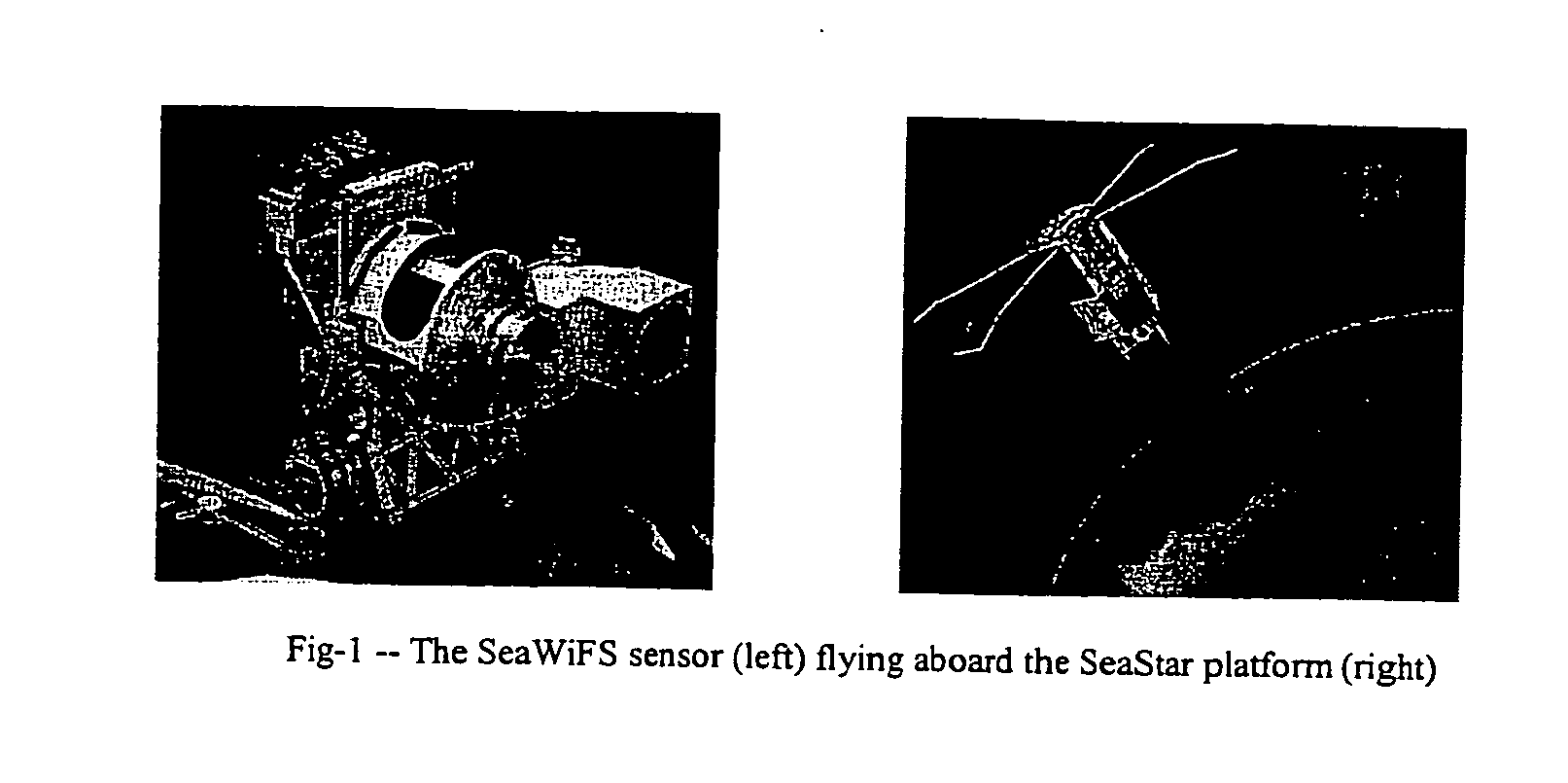
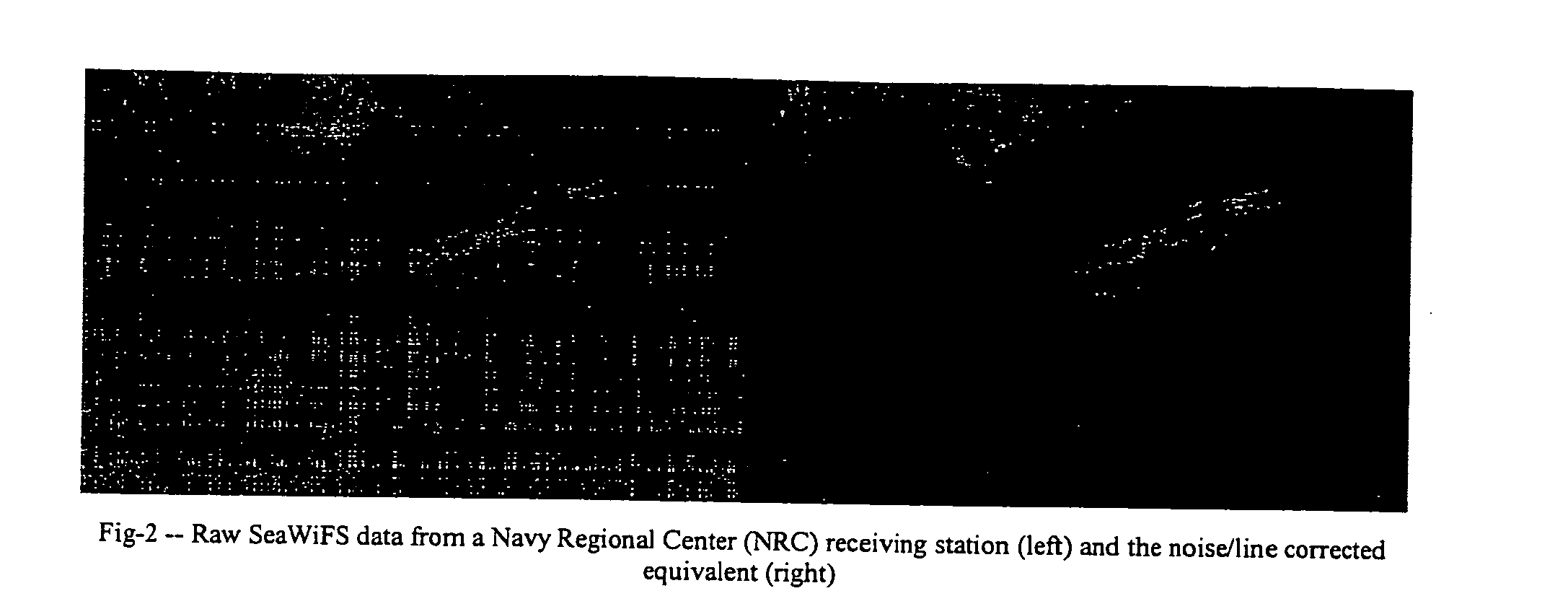
A new processing capability for dust enhancement over land or water using image data from the Sea-viewing Wide Field of View Sensor (SeaWiFS) has been developed for Naval meteorology / oceanography (MetOc) operations support. The data are captured via direct broadcast high-resolution picture transmission (HRPT) at Navy Regional Centers in Rota, Bahrain, and Yokosuka, and processed at the Naval Research Laboratory in Monterey. The raw data are calibrated, corrected for missing lines and clutter, corrected for molecular scatter contamination, and enhanced through multispectral combination to yield value added products. The processing has been automated completely such that products, generated upon receipt of data, are hosted upon a password protected website typically 60 to 90 minutes from time of initial capture. This invention summarizes the SeaWiFS instrument capabilities, the protocol followed for automated near real-time processing, a physical basis for the NRL enhancements, and specific examples of the products with extension to over-land dust enhancement as enabled by MODIS. It closes with a glimpse of the potential utility of these products from the perspective of the warfighter.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Alkaline detergent containing mixed organic and inorganic sequestrants resulting in improved soil removal
InactiveUS6150324ASoften waterImprove organic soil removal propertyInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsNon-ionic surface-active compoundsWater useAlkalinity
Solid block alkaline detergent compositions are disclosed comprising a source of alkalinity, and other detergent additives including sequestrants. The solid block detergents of the invention used a mixed inorganic and organic sequestrant composition that successfully softens service water used in manufacturing aqueous detergents from the composition, but also obtains substantially improved organic soil removal on dishware or flatware. The solid block detergents of the invention comprise large masses of the chemical ingredients having a weight of greater than about 500 grams in a solid block product format that is typically dispensed using a spray on water dispenser that creates an aqueous concentrate that is used in a washing machine.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Composite reverse osmosis membrane having a separation layer with polyvinyl alcohol coating and method of reverse osmotic treatment of water using the same
InactiveUS6177011B1High Salt RejectionPermit practical desalinationGeneral water supply conservationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisZeta potentialWater use
A reverse osmosis composite membrane that has a high salt rejection, a high water permeability, and a high fouling tolerance, and permits practical desalination at a relatively low pressure is provided by coating the surface of a reverse osmosis membrane of aromatic polyamide with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), for example, and controlling the surface zeta potential of the separation layer within±10 mV at pH 6. This reverse osmosis composite membrane is electrically neutral and controls the electrical adsorption of membrane-fouling substances having a charge group present in water. Therefore, a high separation property can be maintained without fouling the membrane even if water containing a surfactant or a transition metal component is supplied as raw water.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
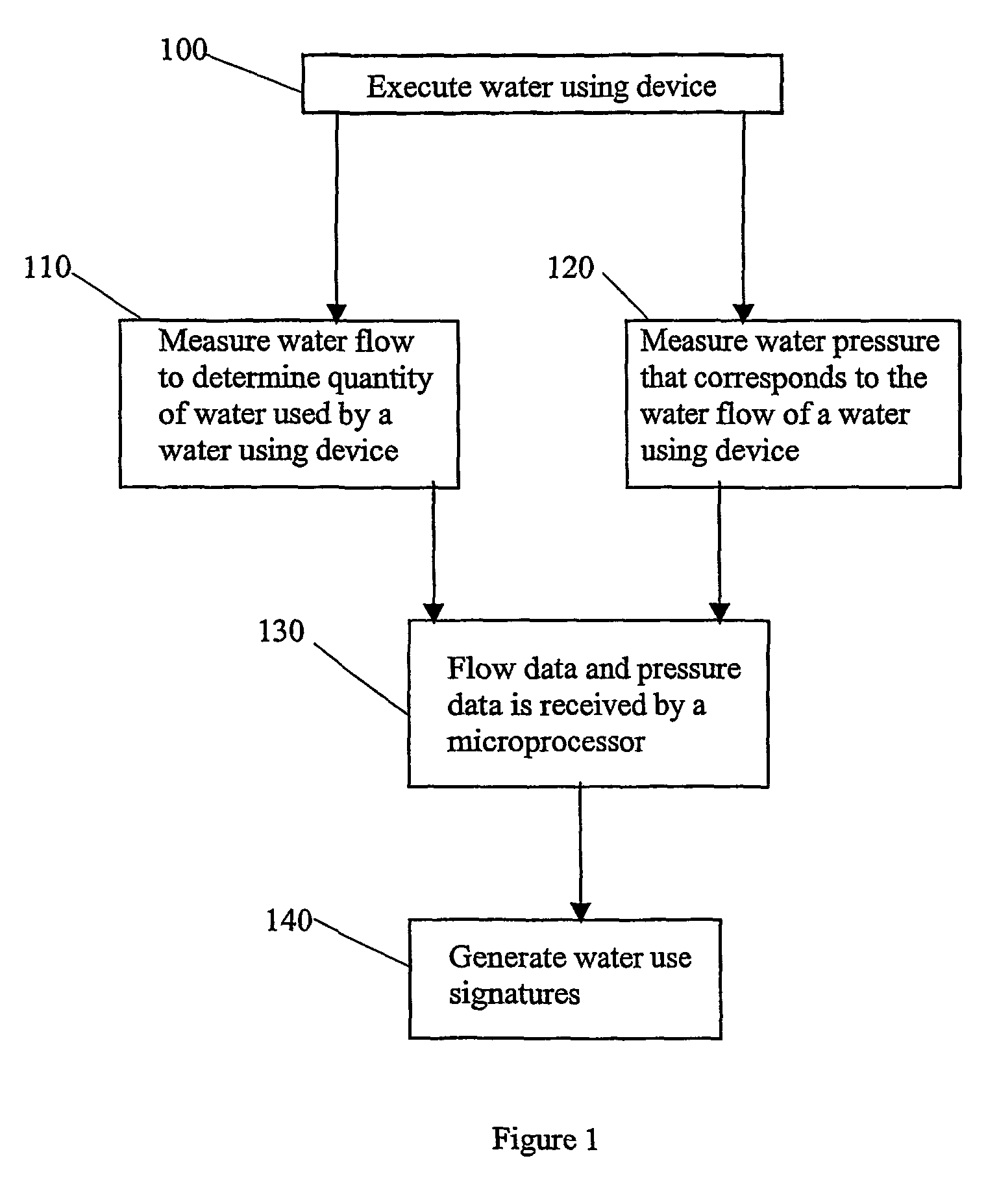
Methods and apparatus for using water use signatures in improving water use efficiency
InactiveUS6963808B1Reduce wasteImprove efficiencyMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateGeneral water supply conservationWater useWater-use efficiency
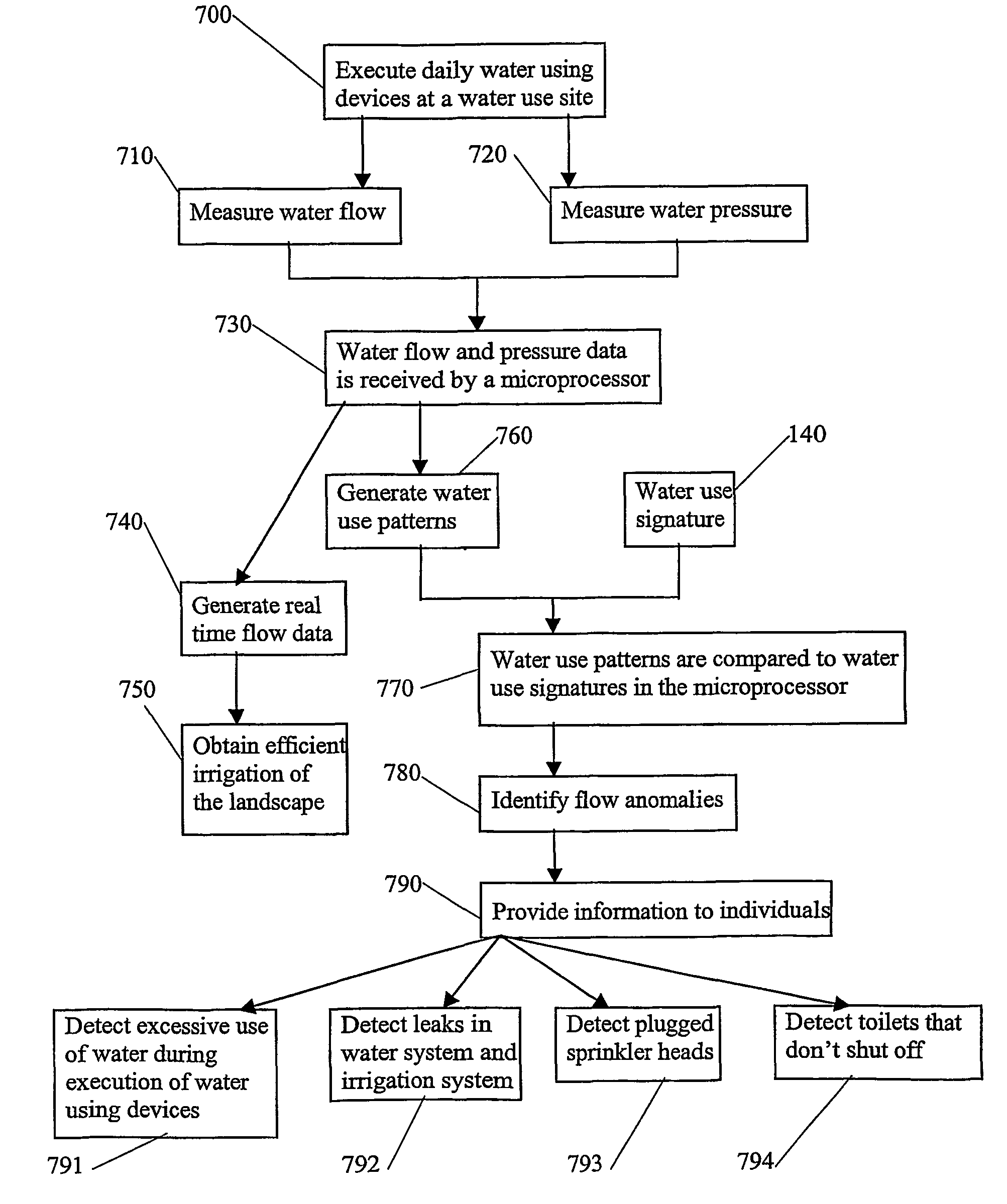
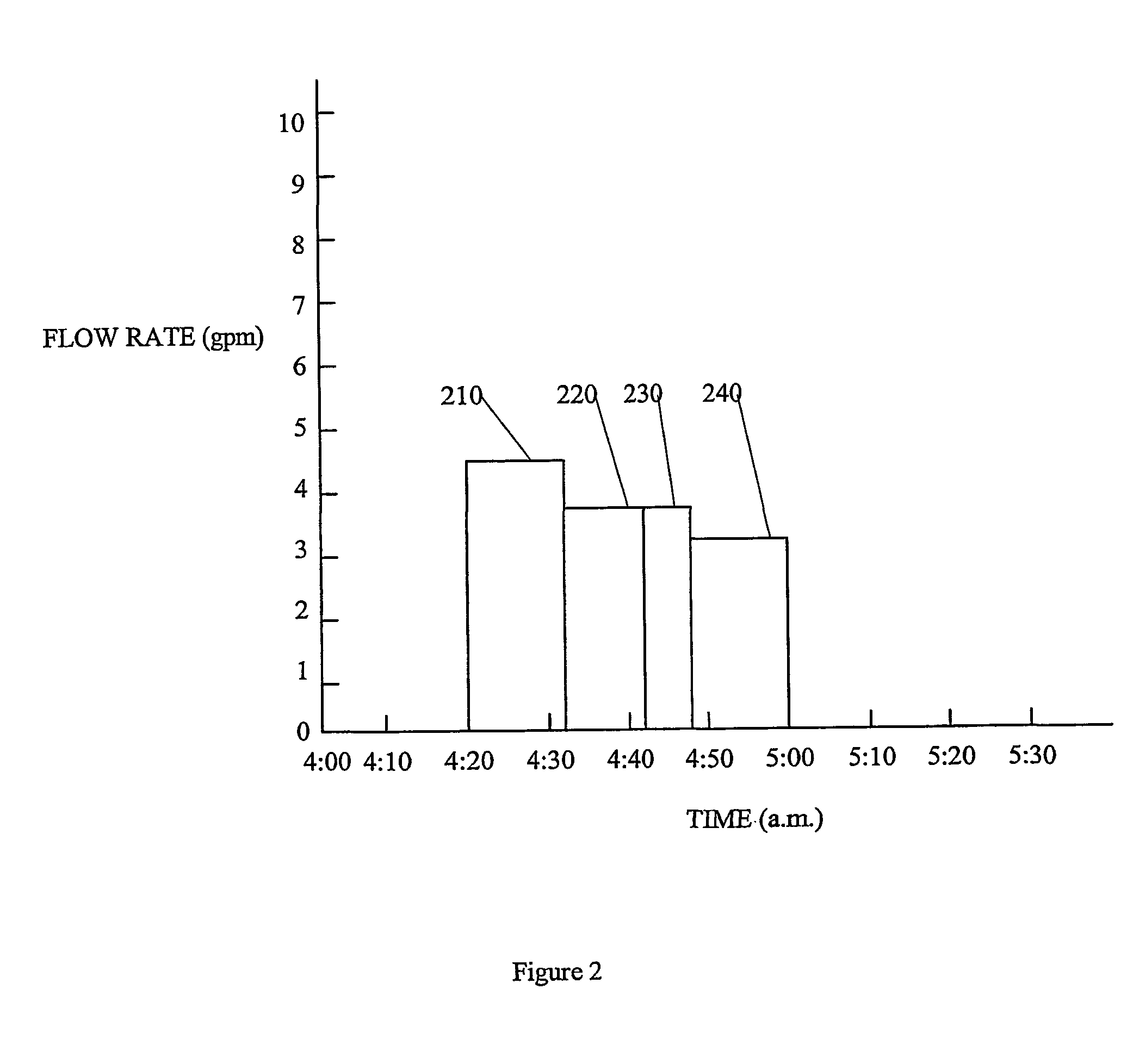
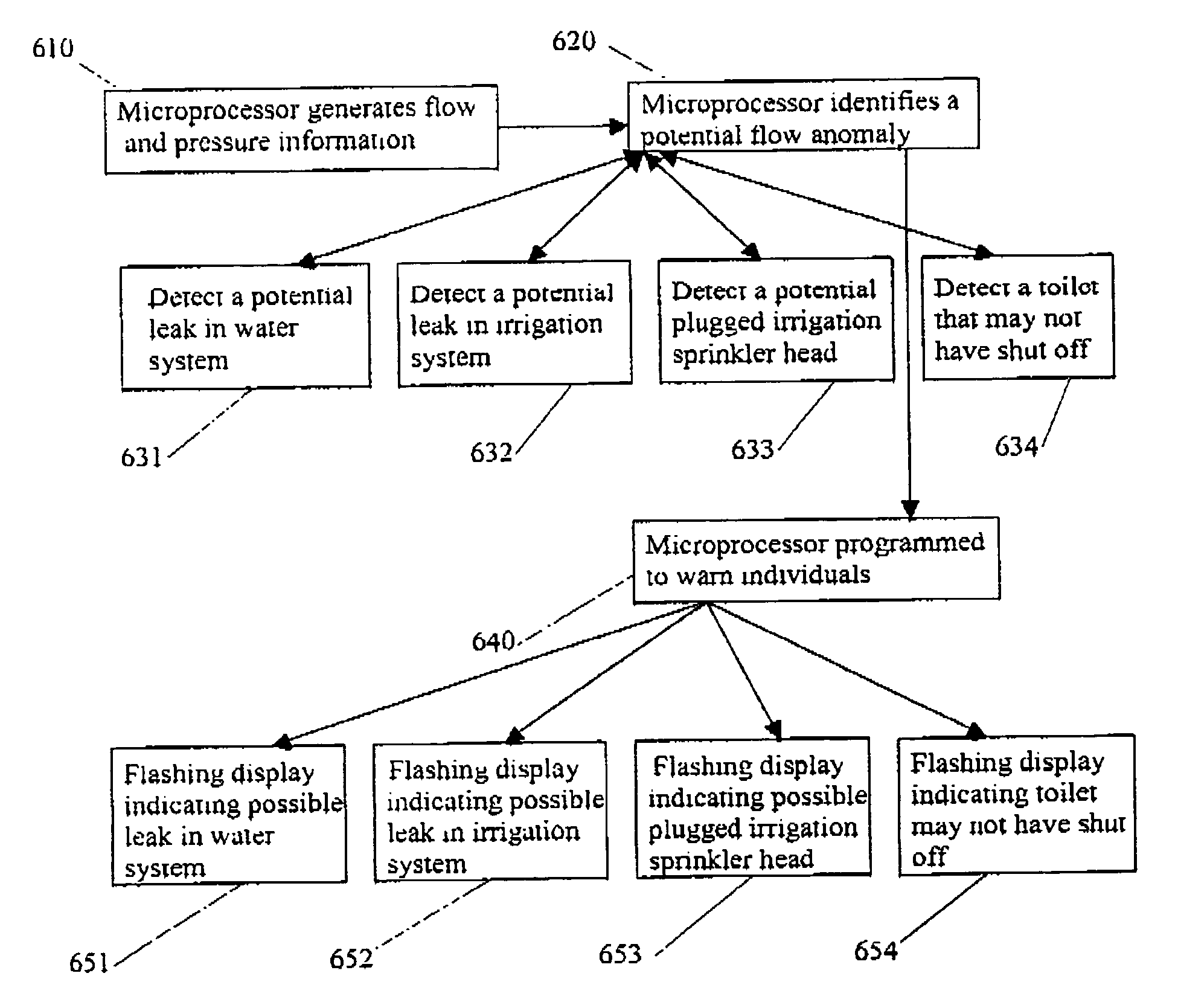
The present invention provides systems and methods that identify a flow anomaly to an operator or other person by: executing a first device of a plurality of water using devices; receiving flow data on a quantity of water used by the first device during a time period required to generate a first water use signature from the first device; comparing a future water use pattern against the first water use signature to identify a flow anomaly with the first device; and providing information regarding the flow anomaly to the person. Identifying anomalies can be useful in numerous ways, including discovering problems that need fixing, reducing waste, and even calculating appropriate irrigation application rates.
Owner:AQUA CONSERVATION SYST
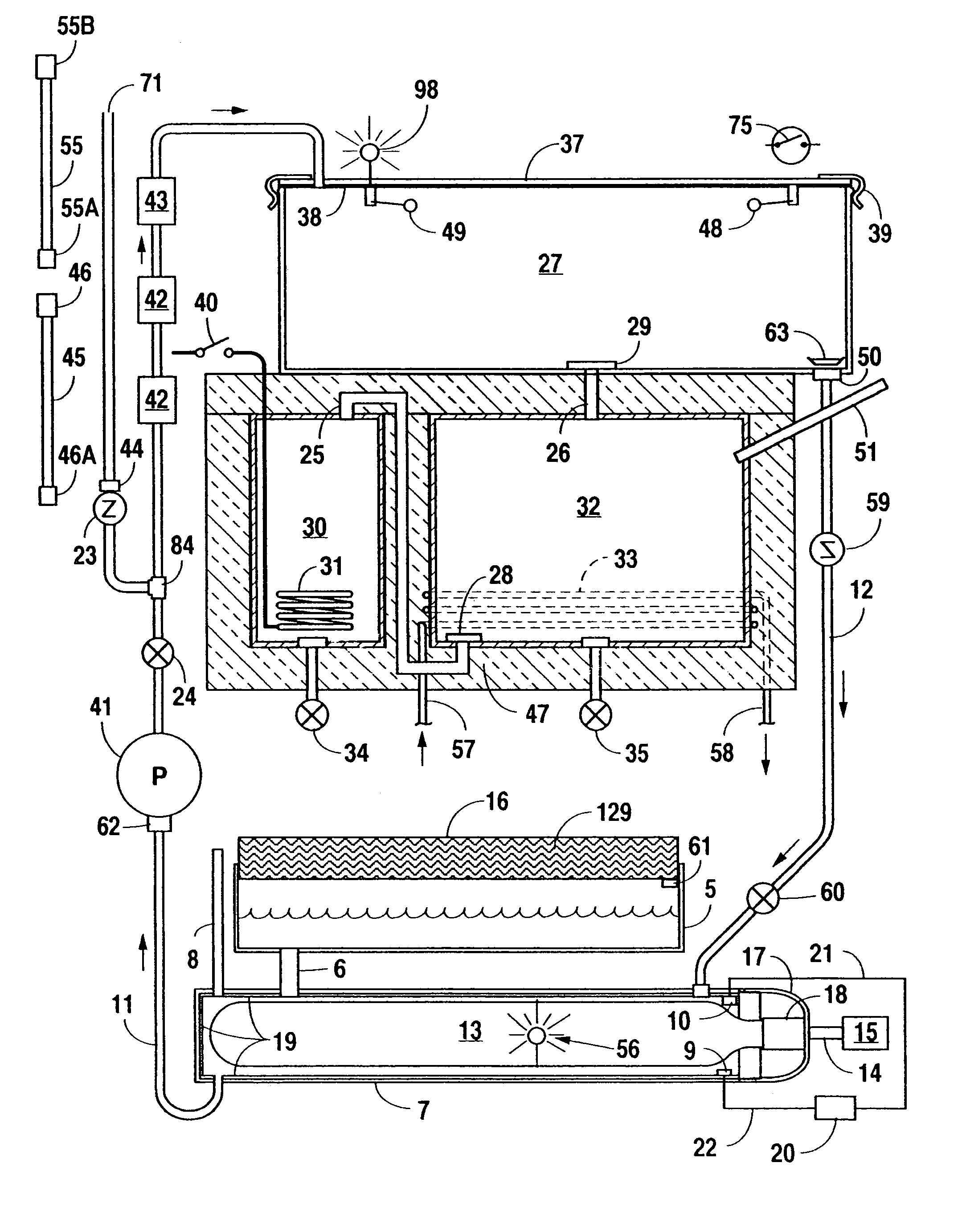
Apparatus for the purification of water and method therefor
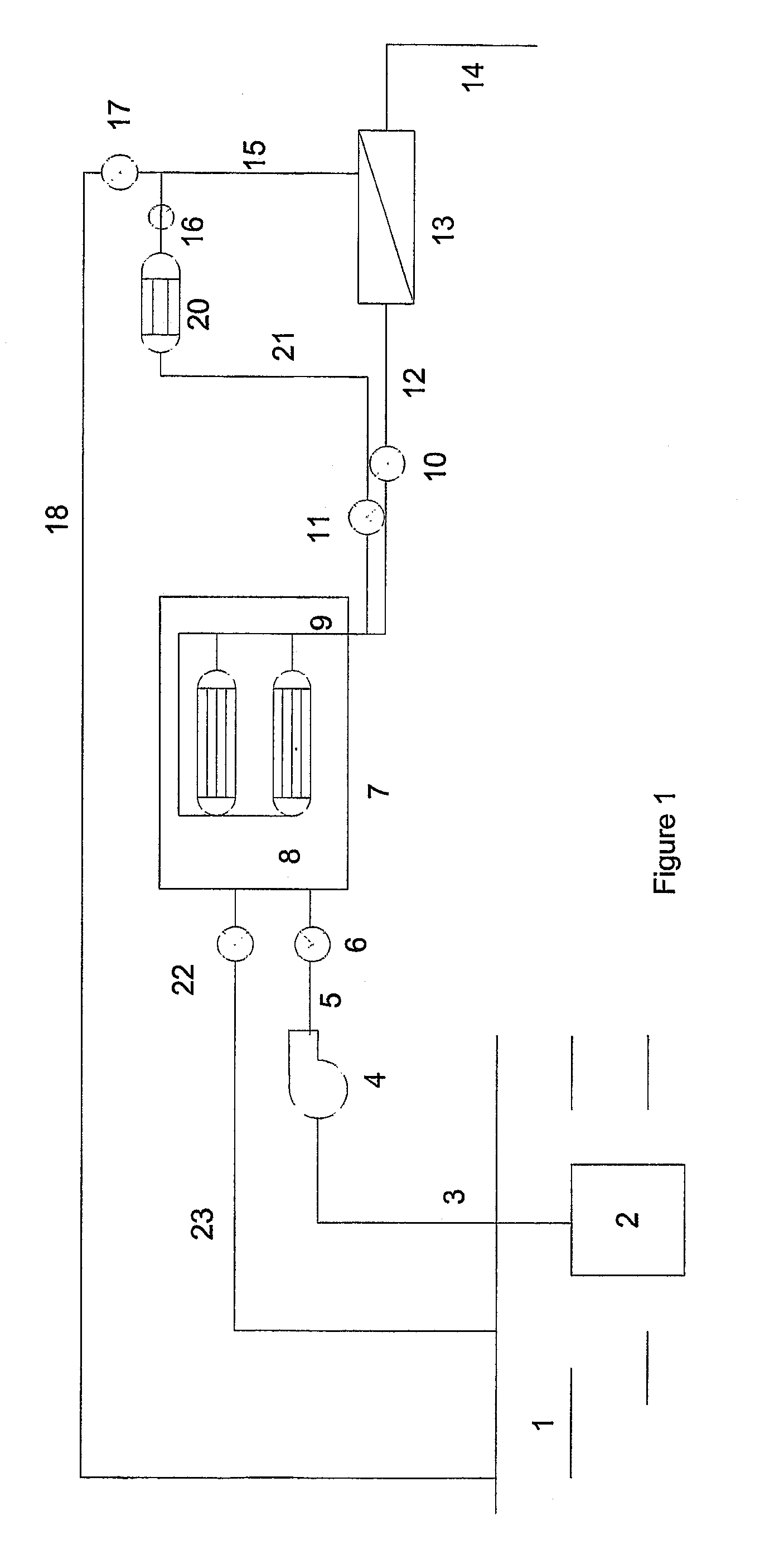
InactiveUS6090294AComprehensive understandingSignificant utilityOther chemical processesIon-exchanger regenerationSolubilityGas phase
An apparatus and method for the purification of contaminated water whereby the contamination level of the wastewater is automatically monitored and treatment self-adjusted and continued until the desired level of purification is reached. Specifically, if upon treatment a pre-set purification level is not obtained a water recycle control means completely precludes the uptake of additional contaminated water and recycles wastewater within the apparatus until the desired level of purification is obtained. The present invention more particularly pertains to an efficient, turn key, economical, movable, automatic and compact apparatus and method for treating a fluid with ozone comprising multiple pressurized contact columns which are arranged in a hybrid parallel and series column configuration, which utilizes a unique water recycle control system and piping arrangement to improve the efficiency of the mass transfer of ozone into the water and increase its solubility by increasing the contact time between the water phase and the gas phase. The apparatus and method of the present invention has the further advantage that it requires minimal installation and may be used to fulfill the clean and safe water needs of any hotel, resort, restaurant, hospital, light industry, commercial business, apartment complex or small city.
Owner:AGRIMOND USA CORP
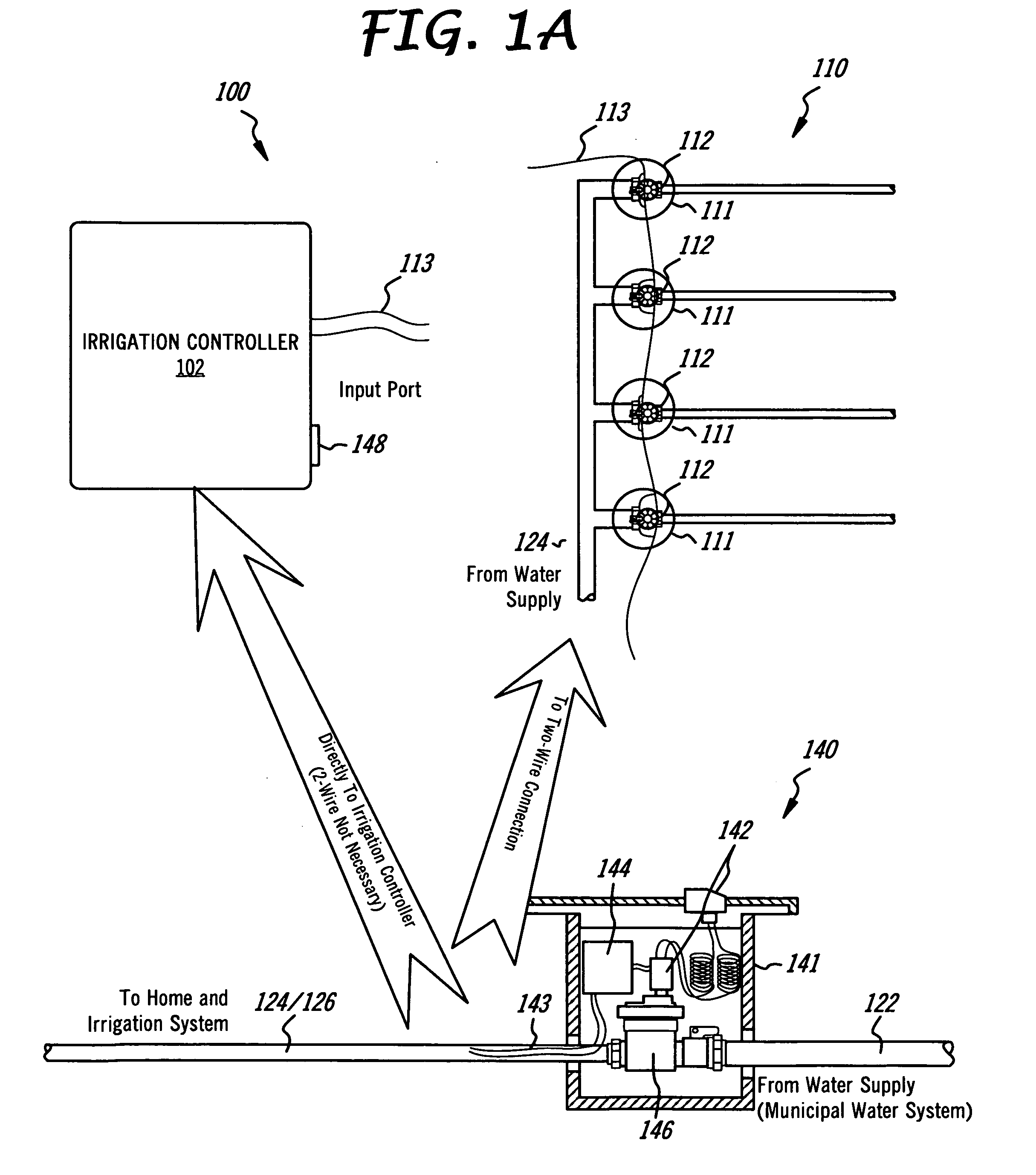
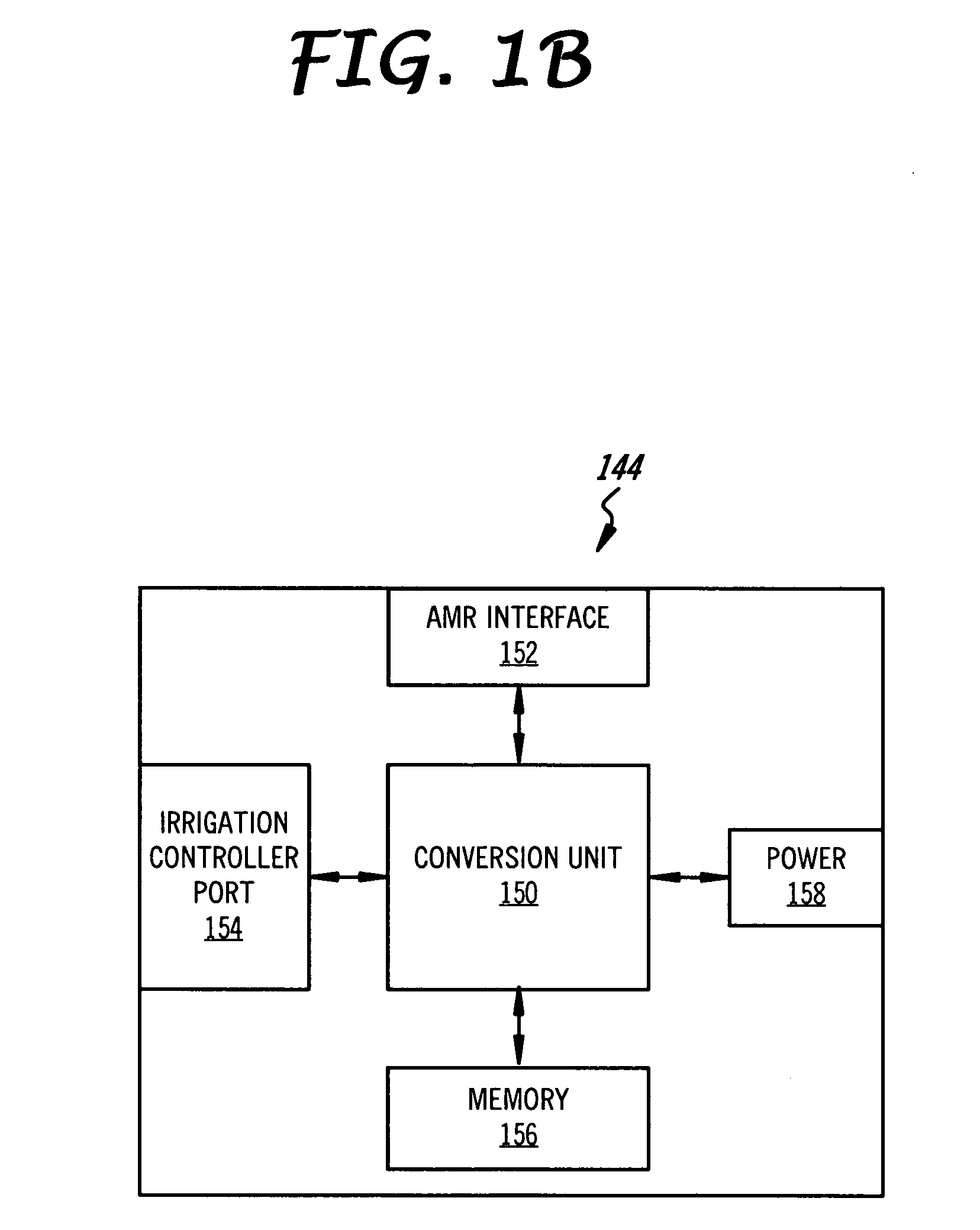
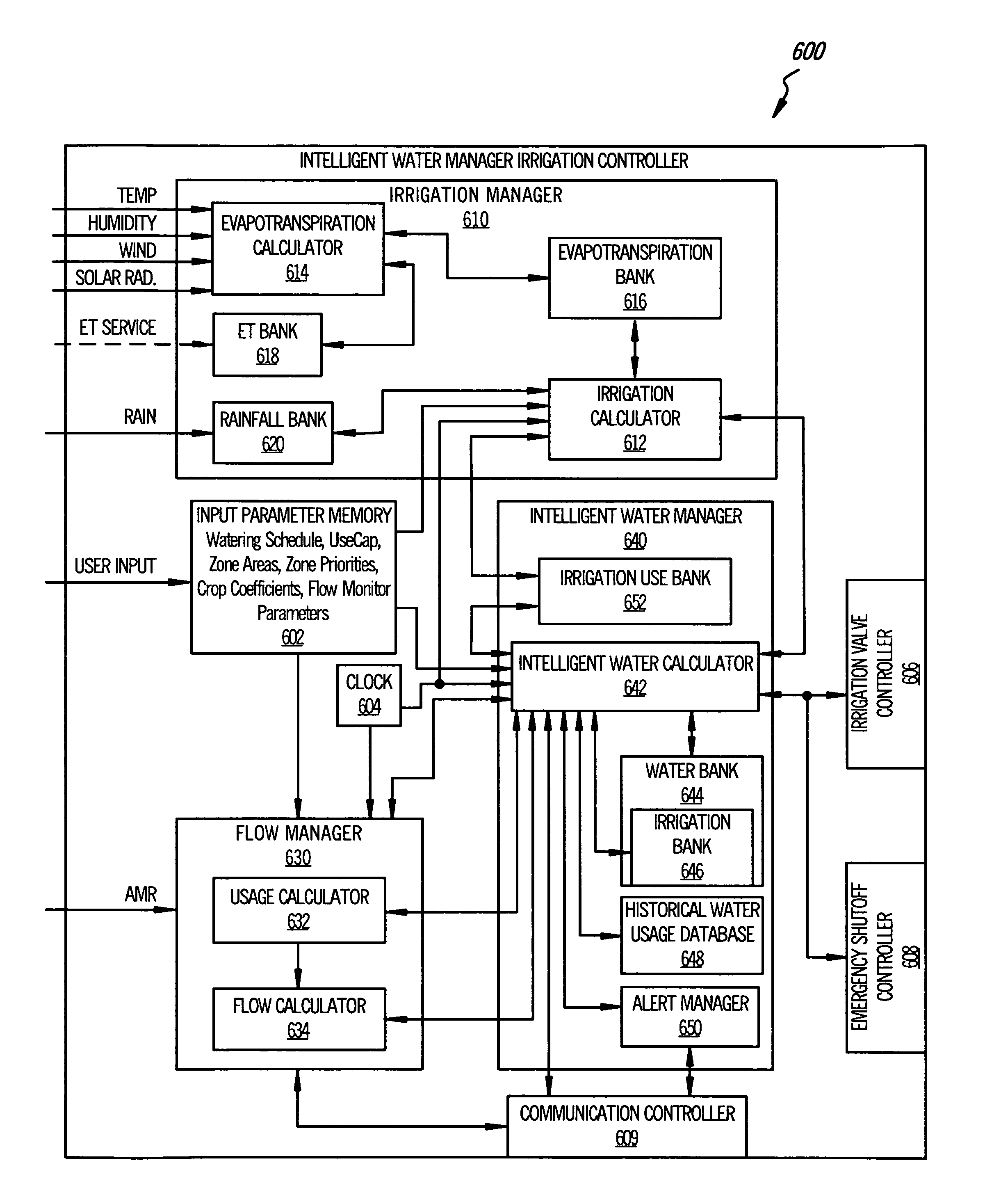
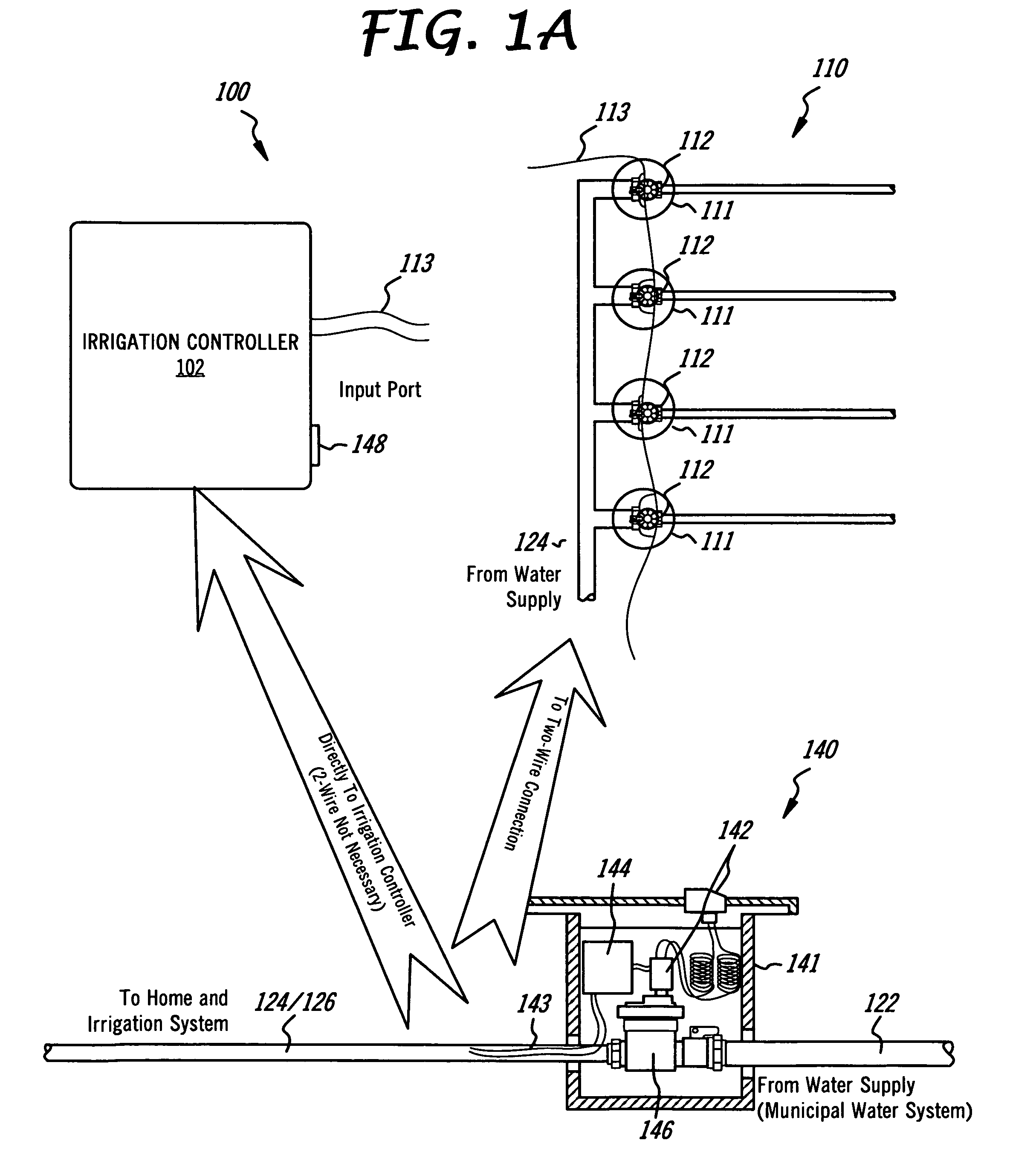
Irrigation flow converter, monitoring system and intelligent water management system
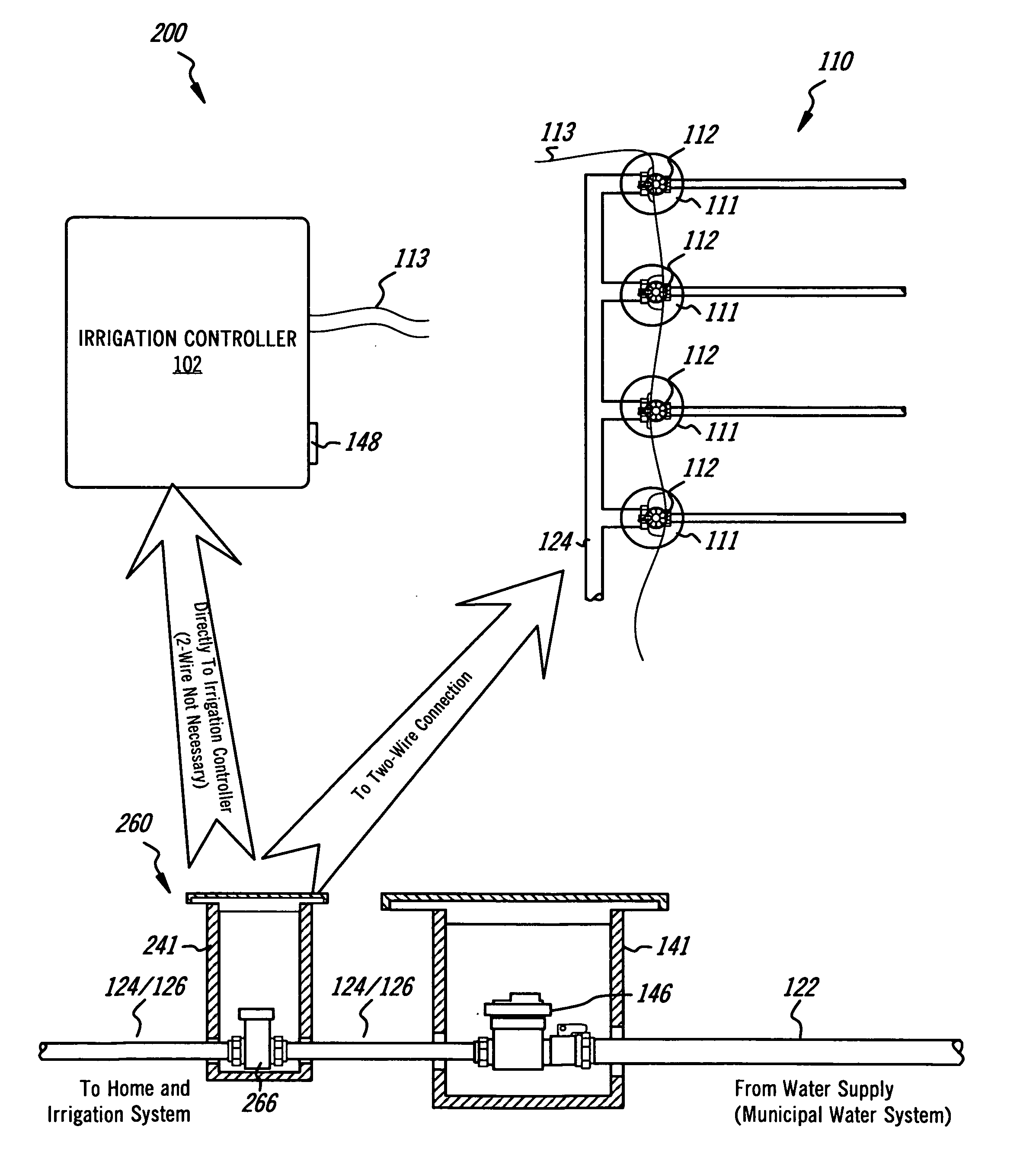
ActiveUS20090271045A1Reduce the amount requiredLess waterOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSelf-acting watering devicesWater useWater management system
The present invention is directed to an intelligent water management irrigation system for monitoring the total water usage for a billing site and preventing cumulative water usage from exceeding a water budget by adjusting the amount of water used for irrigation. Irrigation zone priority values are selected for each irrigation zone that specify a percentage of the full water need that the foliage in the zone can survive and are saved in an intelligent water management irrigation (IWMI) controller. The IWMI controller receives water usage information originating from a property's water meter and compares the measured water usage with the allowable water budget. Water usage is tracked separately for the household use and landscape use (irrigation). Prior to each irrigation cycle, the IWMI controller estimates the amount of water that will be needed by the landscape and for household use during the remainder of a billing cycle; household use is given precedence over landscape use. If the water budget will support both, irrigation can proceed normally. If the budget will not support both, the IWMI controller estimates the amount of water needed for the remainder of the billing cycle if only a priority watering amount is allocated for each landscape zone. If the water budget will support priority irrigation, landscape watering can proceed in priority irrigation mode. If the water budget will not support priority irrigation watering, the irrigation cycle is skipped and the water usage estimations are recalculated prior to the next irrigation cycle.
Owner:TELSCO INDS
Irrigation flow converter, monitoring system and intelligent water management system
ActiveUS7930069B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesSelf-acting watering devicesWater useWater management system
The present invention is directed to an intelligent water management irrigation system for monitoring the total water usage for a billing site and preventing cumulative water usage from exceeding a water budget by adjusting the amount of water used for irrigation. Irrigation zone priority values are selected for each irrigation zone that specify a percentage of the full water need that the foliage in the zone can survive and are saved in an intelligent water management irrigation (IWMI) controller. The IWMI controller receives water usage information originating from a property's water meter and compares the measured water usage with the allowable water budget. Water usage is tracked separately for the household use and landscape use (irrigation). Prior to each irrigation cycle, the IWMI controller estimates the amount of water that will be needed by the landscape and for household use during the remainder of a billing cycle; household use is given precedence over landscape use. If the water budget will support both, irrigation can proceed normally. If the budget will not support both, the IWMI controller estimates the amount of water needed for the remainder of the billing cycle if only a priority watering amount is allocated for each landscape zone. If the water budget will support priority irrigation, landscape watering can proceed in priority irrigation mode. If the water budget will not support priority irrigation watering, the irrigation cycle is skipped and the water usage estimations are recalculated prior to the next irrigation cycle.
Owner:TELSCO INDUSTRIES INC
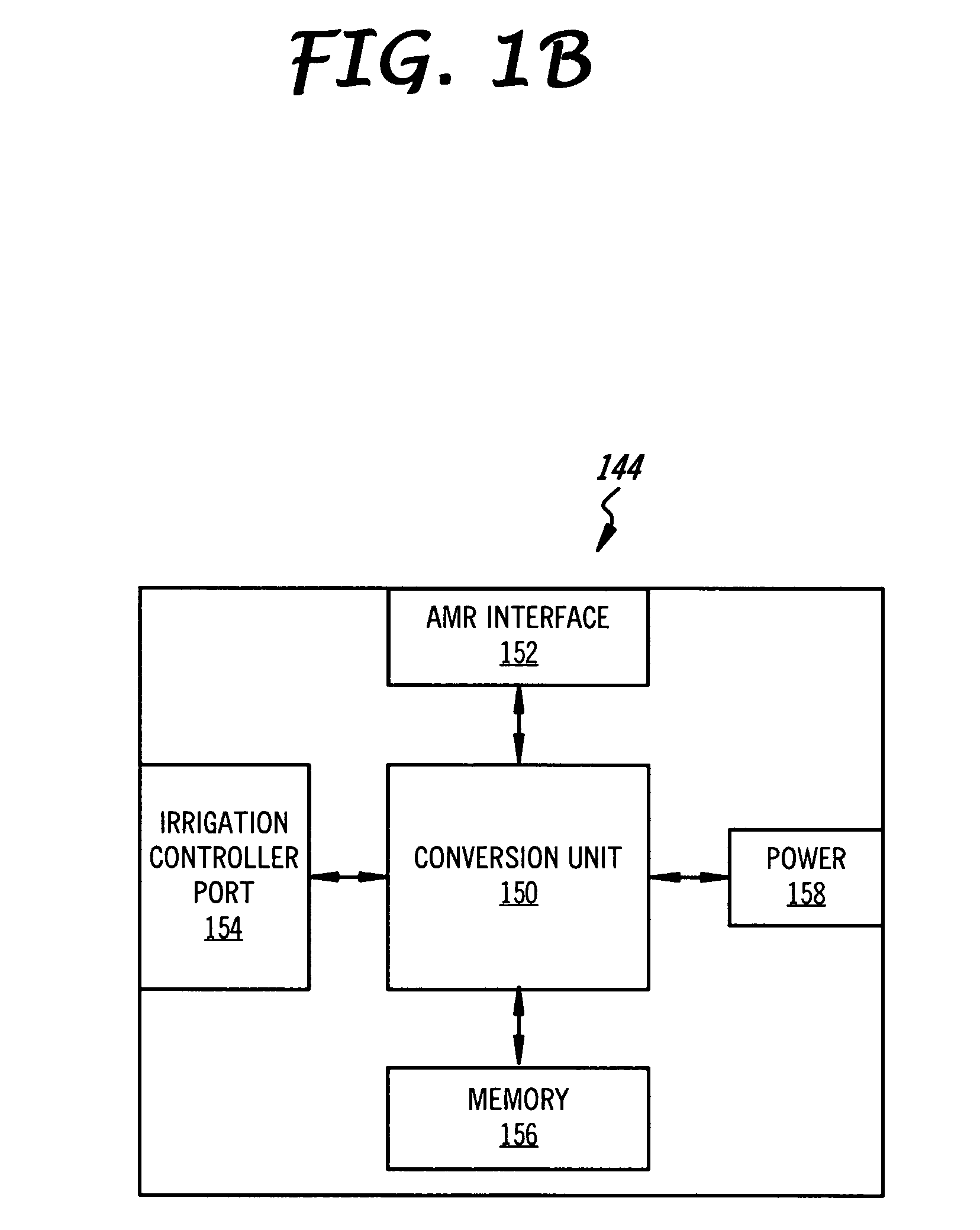
Methods and apparatus for using water use signatures and water pressure in improving water use efficiency
InactiveUS7330796B2Measurement of fluid loss/gain rateGeneral water supply conservationBaseline dataWater use
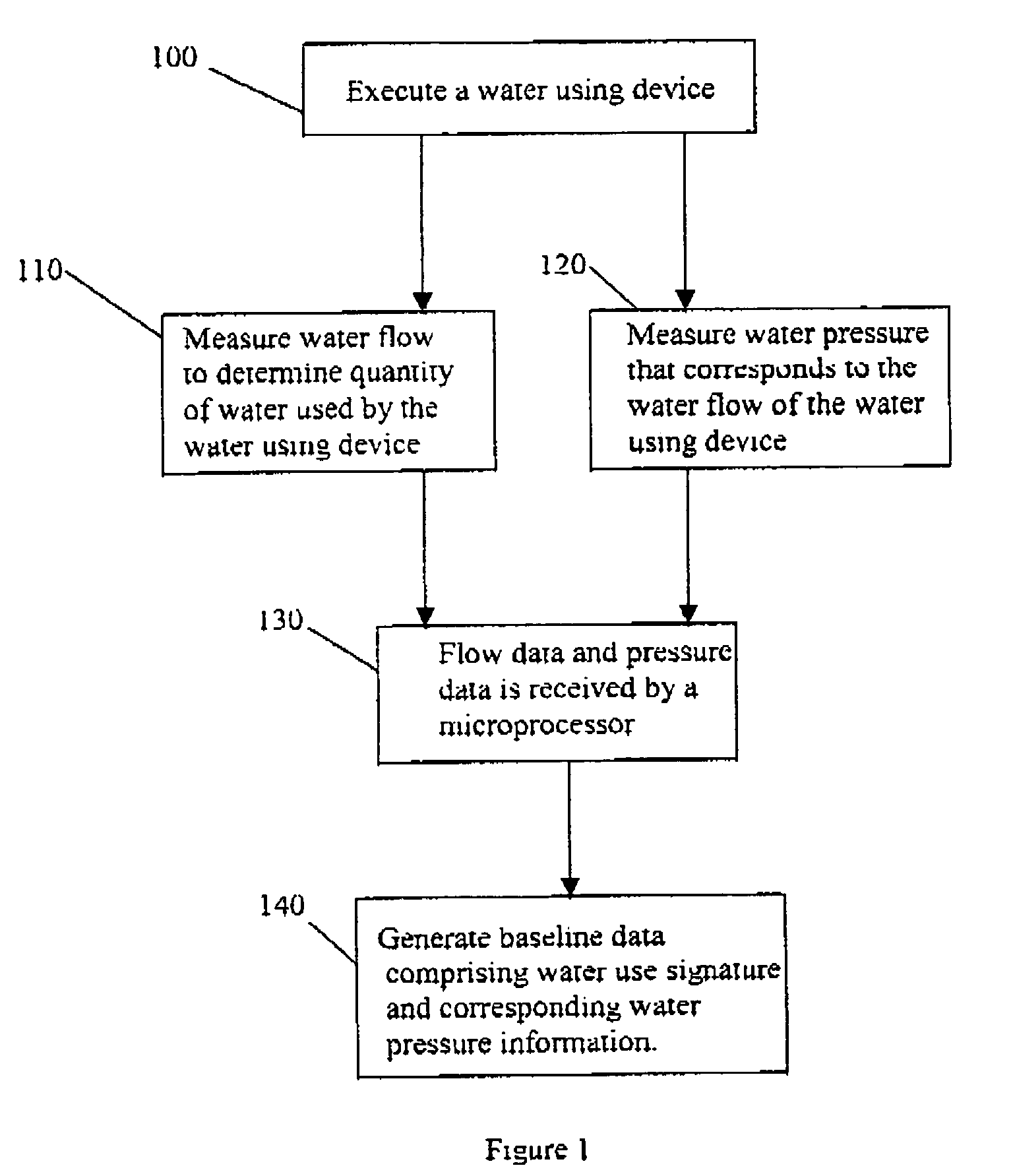
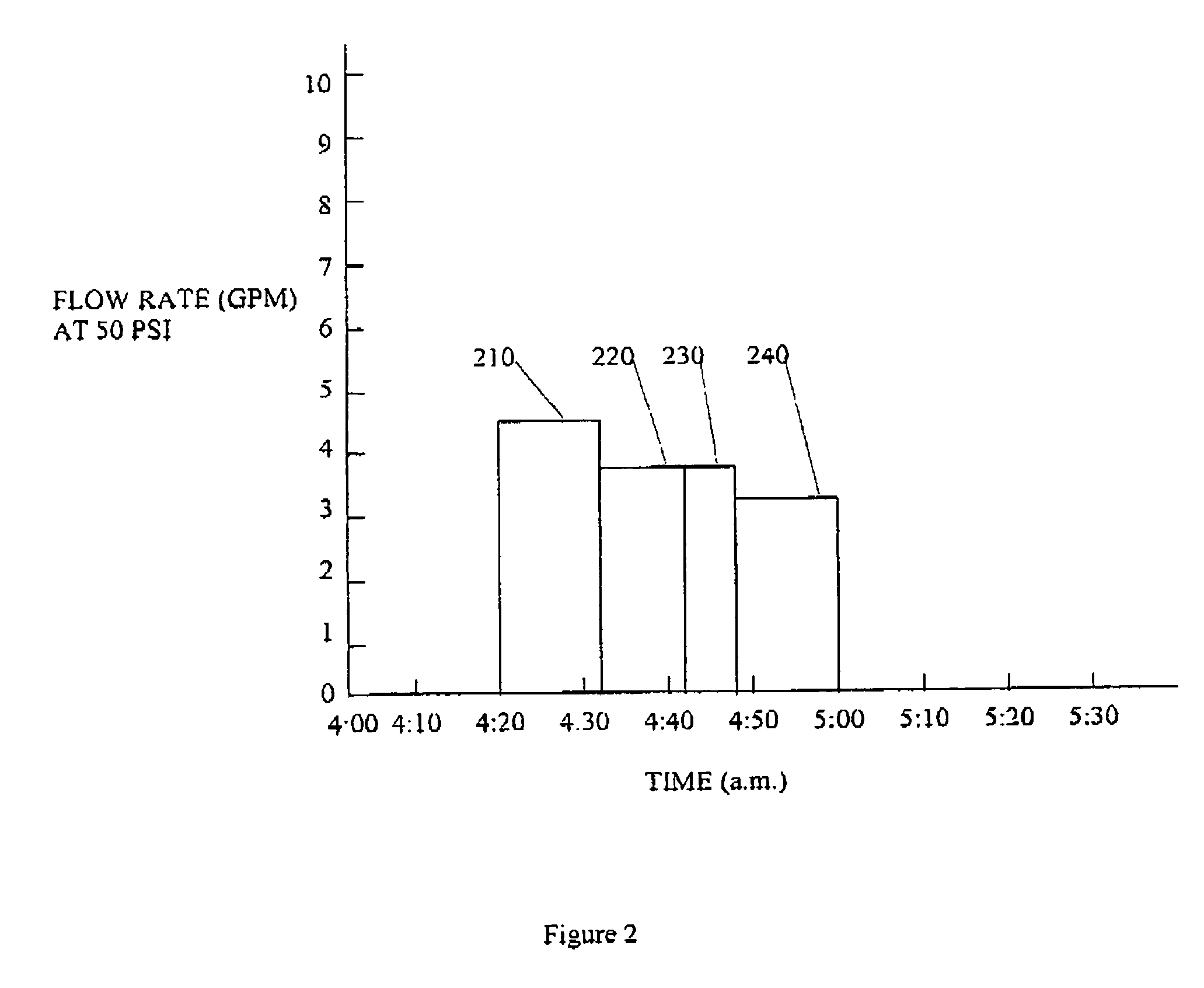
A method to identify a water flow anomaly in a system having first and second water using devices to generate baseline data that preferably has water use signatures and corresponding water pressure information regarding the water using devices; comparing the baseline data with actual water usage signatures and corresponding actual water pressure information to identify a flow anomaly with the water using devices; and providing information on the flow anomaly to an individual. It is especially contemplated that baseline data are generated for multiple devices coupled to a common water supply system, with baseline data from two or more water using devices compared against future water use patterns of the same devices. Apparatus to accomplish these tasks is preferably housed in an irrigation controller, which may be advantageously coupled to a flow meter.
Owner:AQUA CONSERVATION SYST
Process and apparatus for purifying impure water using microfiltration or ultrafiltration in combination with reverse osmosis
InactiveUS20070181496A1Avoid Particulate ContaminationReduces and eliminates amountGeneral water supply conservationUltrafiltrationWater usePotable water
A method of purifying impure water contaminated with a filterable impurity and a dissolved impurity, such as sea-water, comprising the steps of: providing impure water to a primary microfiltration or ultrafiltration unit to remove the filterable impurity and produce impure filtered water contaminated with a dissolved impurity; providing the impure filtered water contaminated with a dissolved impurity to a reverse osmosis unit to produce a potable water stream and a residual reverse osmosis stream; and treating the residual reverse osmosis stream prior to reuse. The treatment may be in the form of passing through a secondary filter (such as another microfiltration or ultrafiltration membrane or a cartridge filter, and the subsequently treated reverse osmosis reject may be used to backwash the microfiltration or ultrafiltration unit.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Desulfurization waste water zero discharging process and system
ActiveCN104843927ASolve pollutionWaste water treatment from gaseous effluentsMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater useHydration reaction
The invention discloses a desulfurization waste water zero discharging process. The process comprises a chemical dosing softening process and a microfiltration membrane treatment process; after incoming water is subjected to two-stage softening, nanofiltration and reverse osmosis separation are performed; sodium sulfate decahydrate with the purity of more than 99% is separated out by utilizing freezing crystallization; a reverse osmosis concentrated water regeneration sodium ion exchange device is utilized; sodium chloride with the purity of more than 98% is separated out by utilizing evaporative crystallization; solids are comprehensively utilized, and no liquid is discharged outside. The invention further provides a desulfurization waste water zero discharging system. According to the desulfurization waste water zero discharging process and the system, water in desulfurization waste water can be separated to be reutilized as domestic and industrial usable water, and other impurities in the desulfurization waste water are separated in solid form, so that pollutants harmful to the natural environment do not generate, and the problem that the desulfurization waste water pollutes the environment can be completely solved.
Owner:华电水务工程有限公司
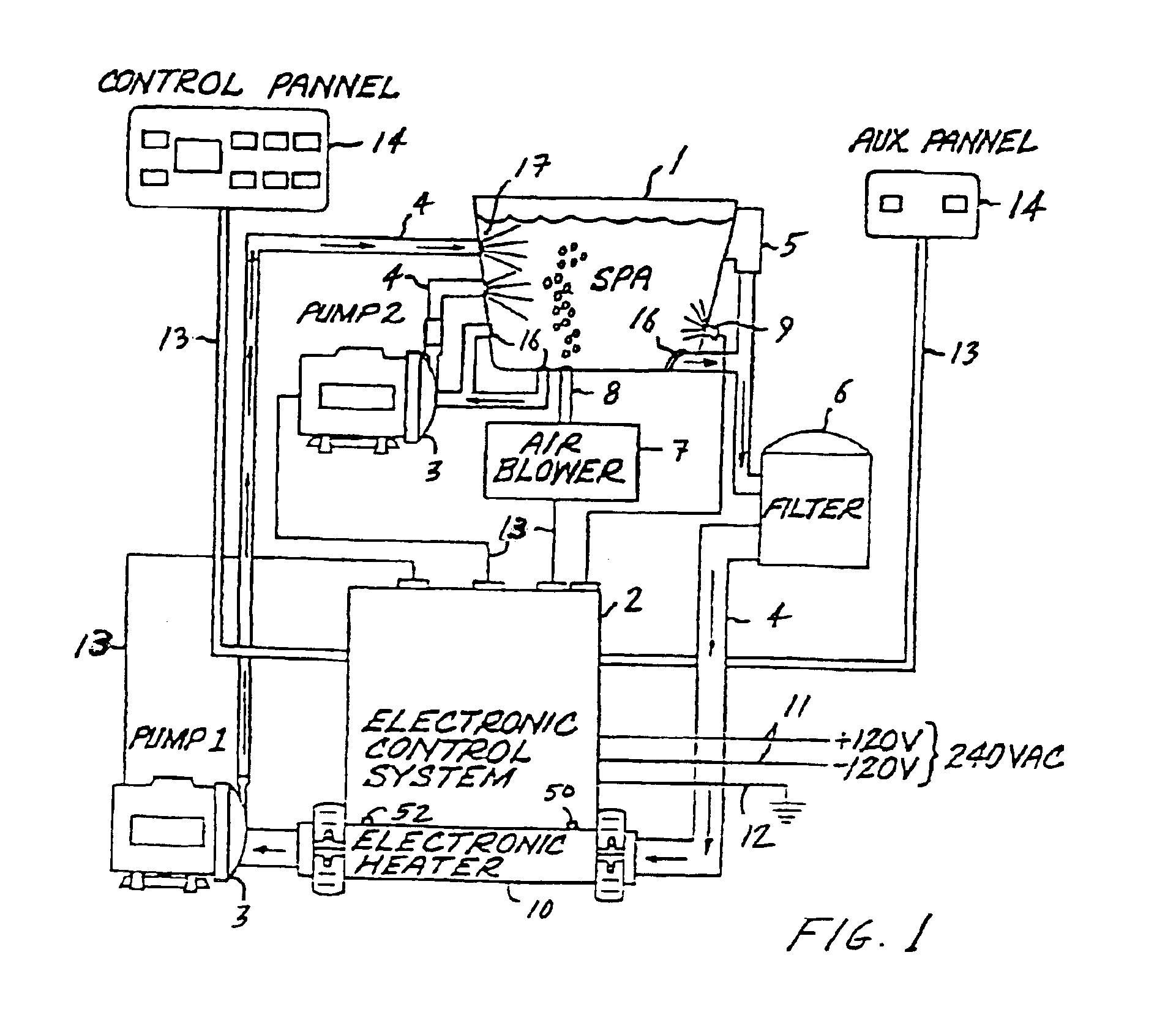
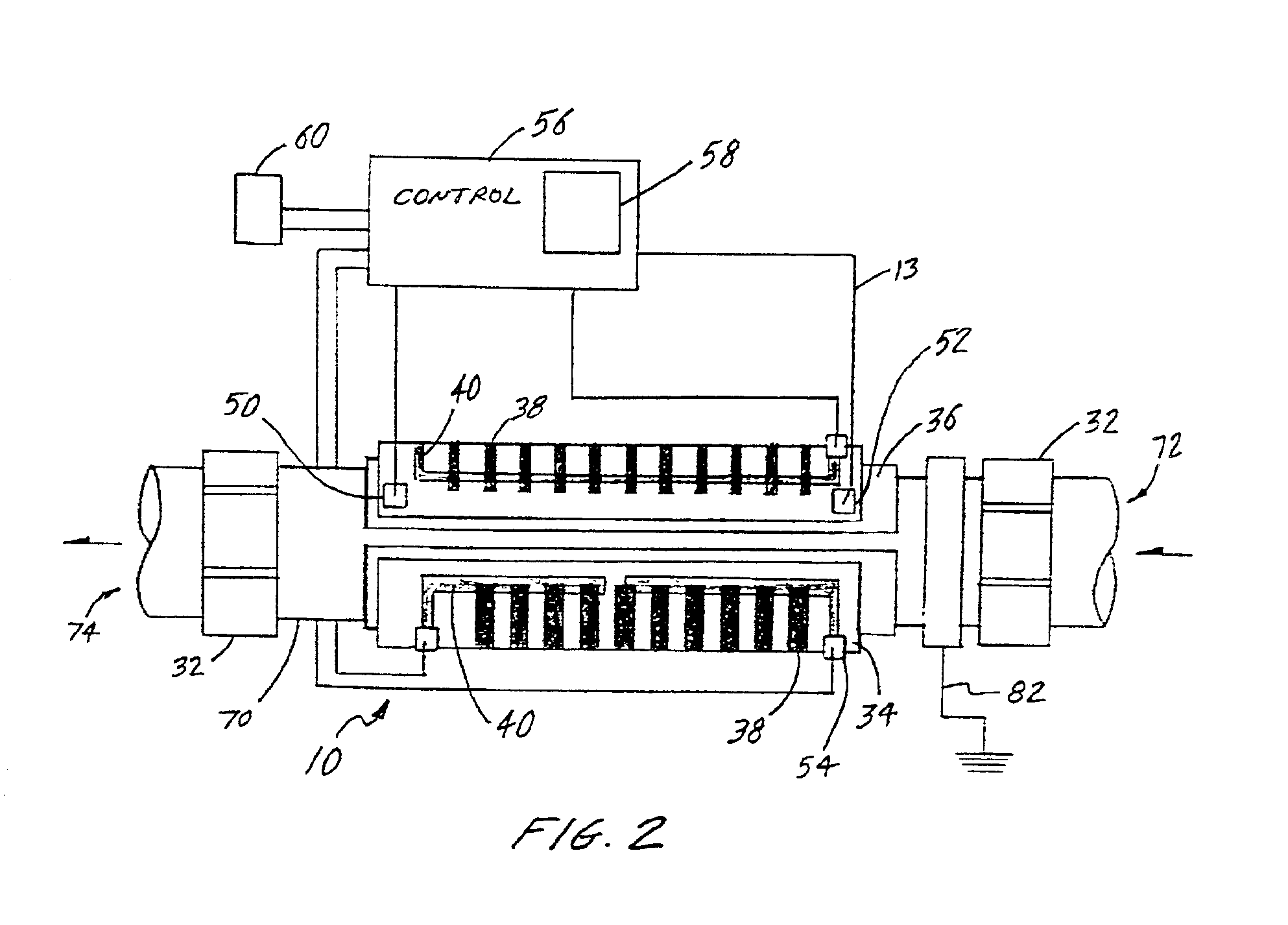
Water heater
InactiveUS6943325B2Eliminate riskEliminate the risk of corrosionBathsDouchesWater useElectronic controller
An improved water heater for use in spas, hot tubs, pools, hydrotherapy pools, bath tubs, and similar bodies of water used indoors, outdoors, or both indoors and outdoors are used for both therapeutic and recreational purposes. The water heater uses heating element technology know as thick film on substrate comprising resistive elements bonded to the outer dry surface of a pipe to heat the pipe which in turn heats the water flowing therethrough. The heater is highly efficient due to the direct contact of the wet heating surface with the water and provides a smooth seamless inner heating surface by eliminating the need to pass electrical leads into the wet region of the heater. This virtually eliminates the risk of leaks in the water heater due to bulkhead fittings. The invention further eliminates the need for a heating element to be contained in the inner wet region of a spa heater, thereby reducing the risk of corrosion. The water heater is used in combination with an electronic controller having a microprocessor to control and regulate the operation of the water heater. The water heater can be used with electrical, electro-mechanical, and mechanical control systems for spas and can be retrofitted into existing spa applications.
Owner:DYMAS FUNDING COMPANY
Catalyst for treatment of waste water, and method for treatment of waste water using the catalyst
InactiveCN102686521AStabilizationImprove purification effectWater contaminantsCatalyst activation/preparationIridiumWater use
Disclosed are: a catalyst which can exhibit an excellent catalytic activity and excellent durability for a long period in the wet oxidation treatment of waste water; a wet oxidation treatment method for waste water using the catalyst; and a novel method for treating waste water containing a nitrogenated compound, in which a catalyst to be used has a lower catalytic cost, the waste water containing the nitrogenated compound can be treated at high purification performance, and the high purification performance can be maintained. The catalyst for use in the treatment of waste water comprises an oxide of at least one element selected from the group consisting of iron, titanium, silicon, aluminum, zirconium and cerium as a component (A) and at least one element selected from the group consisting of silver, gold, platinum, palladium, rhodium, ruthenium and iridium as a component (B), wherein at least 70 mass% of the component (B) is present in a region positioned within 1000 [mu]m from the outer surface of the component (A) (i.e., the oxide), the component (B) has an average particle diameter of 0.5 to 20 nm, and the solid acid content in the component (A) (i.e., the oxide) is 0.20 mmol / g or more. The waste water treatment method uses a catalyst (a pre-catalyst) which is placed on an upstream side of the direction of the flow of the waste water and can convert the nitrogenated compound contained in the waste water into ammoniacal nitrogen in the presence of an oxidizing agent at a temperature of not lower than 100 DEG C and lower than 370 DEG C under a pressure at which the waste water can remain in a liquid state and a downstream-side catalyst (a post-catalyst) which is placed downstream of the direction of the flow of the waste water and can treat the waste water containing ammoniacal nitrogen.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Irrigation flow converter, monitoring system and intelligent water management system
InactiveUS20110190947A1Reduce the amount requiredLess waterControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsWatering devicesWater useMonitoring system
The present invention is directed to an intelligent water management irrigation system for monitoring the total water usage for a billing site and preventing cumulative water usage from exceeding a water budget by adjusting the amount of water used for irrigation. Irrigation zone priority values are selected for each irrigation zone that specify a percentage of the full water need that the foliage in the zone can survive and are saved in an intelligent water management irrigation (IWMI) controller. The IWMI controller receives water usage information originating from a property's water meter and compares the measured water usage with the allowable water budget. Water usage is tracked separately for the household use and landscape use (irrigation). Prior to each irrigation cycle, the IWMI controller estimates the amount of water that will be needed by the landscape and for household use during the remainder of a billing cycle; household use is given precedence over landscape use. If the water budget will support both, irrigation can proceed normally. If the budget will not support both, the IWMI controller estimates the amount of water needed for the remainder of the billing cycle if only a priority watering amount is allocated for each landscape zone. If the water budget will support priority irrigation, landscape watering can proceed in priority irrigation mode. If the water budget will not support priority irrigation watering, the irrigation cycle is skipped and the water usage estimations are recalculated prior to the next irrigation cycle.
Owner:TELSCO INDS
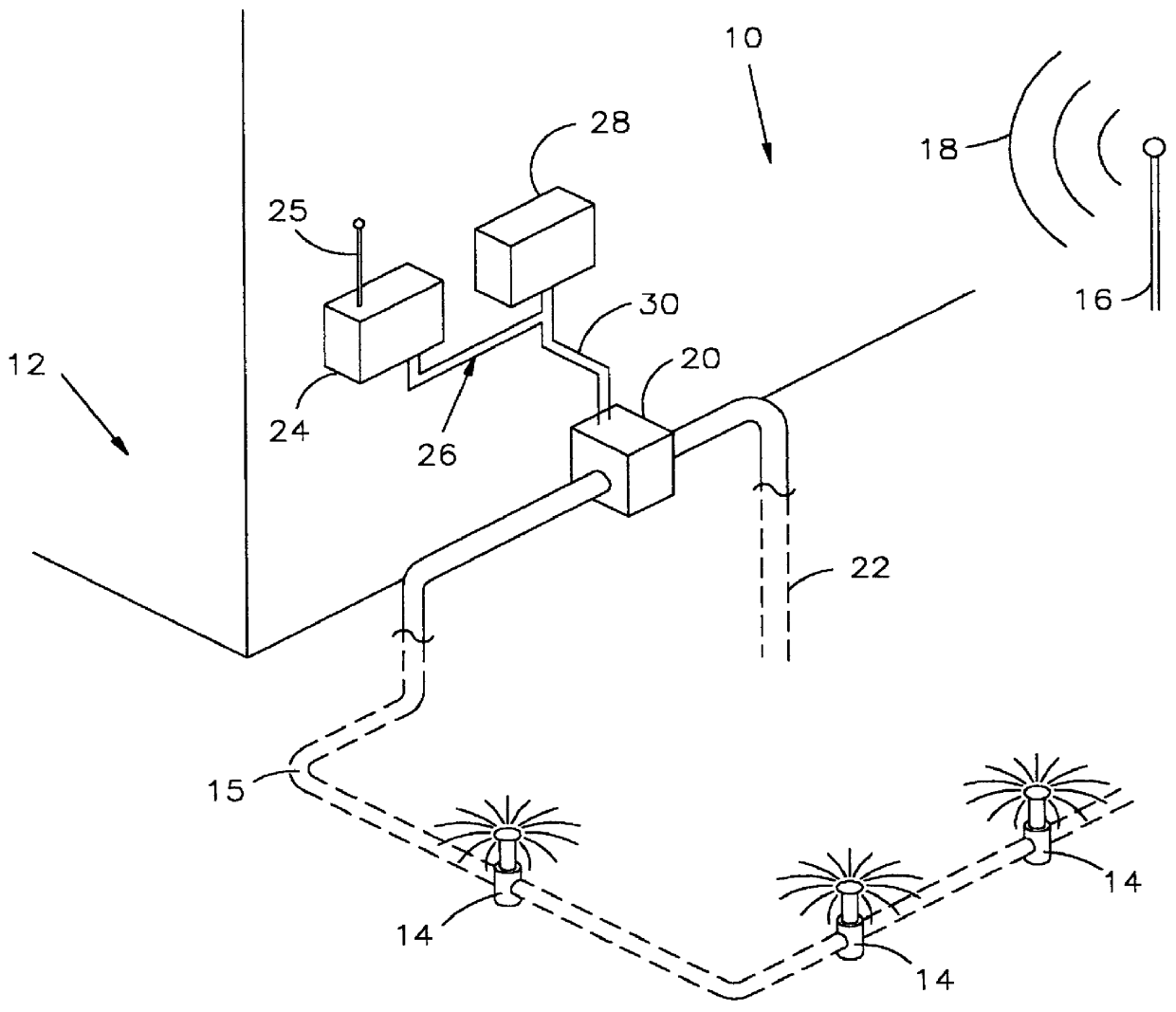
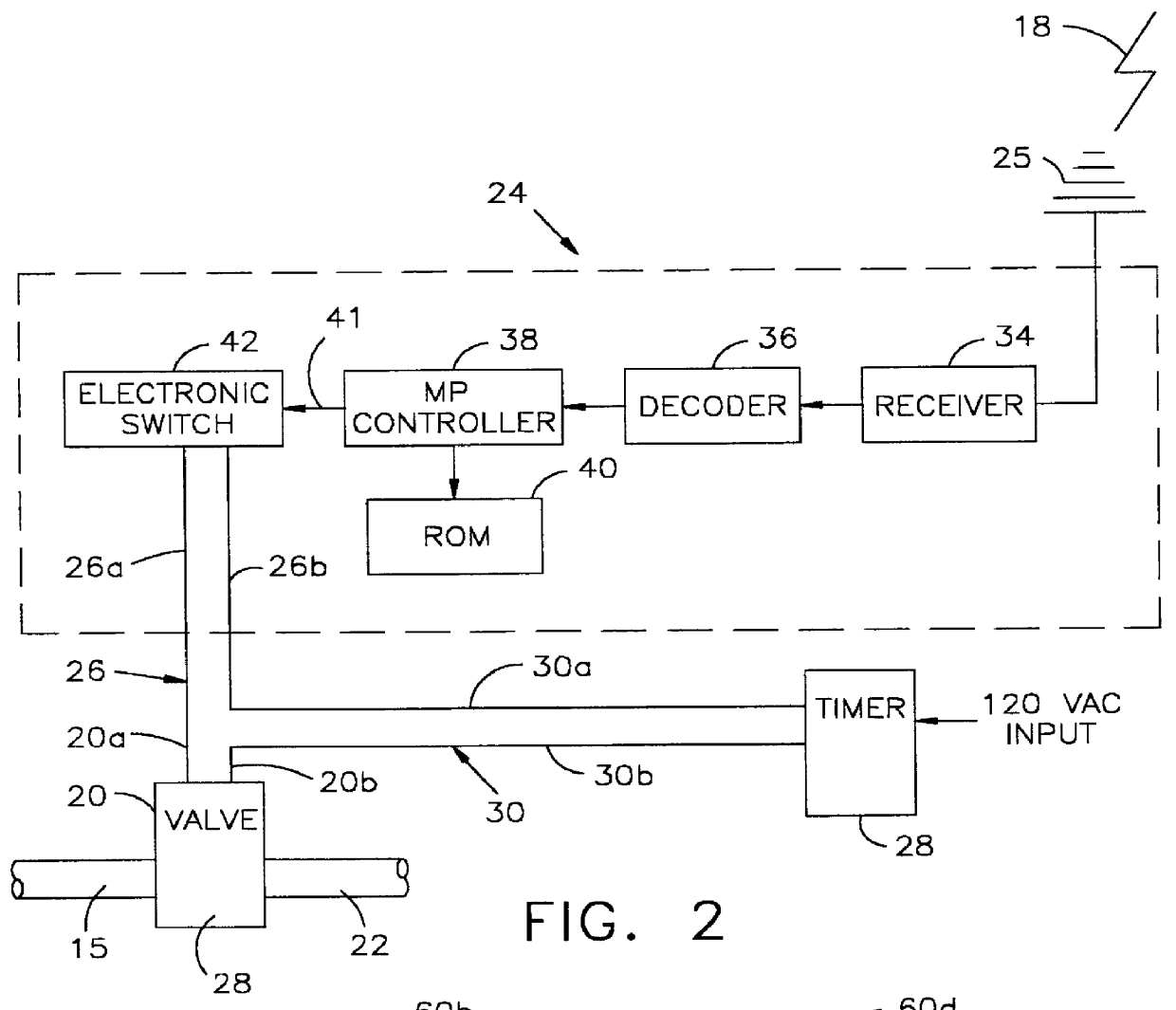
Master control system for conserving water by sprinkler systems within a geographical region
InactiveUS6098898AEasy constructionEconomical to useSelf-acting watering devicesWatering devicesWater useSprinkler system
A master control system for conserving water used by sprinkler systems within a predetermined geographical region includes a plurality of sprinkler systems each of which is assigned an identifying indicia. A transmitting station is arranged for transmitting control signals receivable at any location within the geographical region. A valve connects each sprinkler system to a water source for selectively feeding water to an associated sprinkler system when the valve is open and for precluding water from being fed to the associated sprinkler system when the valve is closed. A receiver is provided for each sprinkler system within the region connected to an associated valve for receiving the control signals and generating a disabling signal for causing only said valves for the sprinkler systems assigned said identifying indicia to open independently of their status. In this manner, said transmitting station can control and override the operation of selected sprinkler systems assigned said identifying indicia to regulate the extent to which water may be used within said geographical region in accordance with protocols established for the consumption of water by such sprinkler systems within said geographical region.
Owner:SFLASHLIGHT PAUL
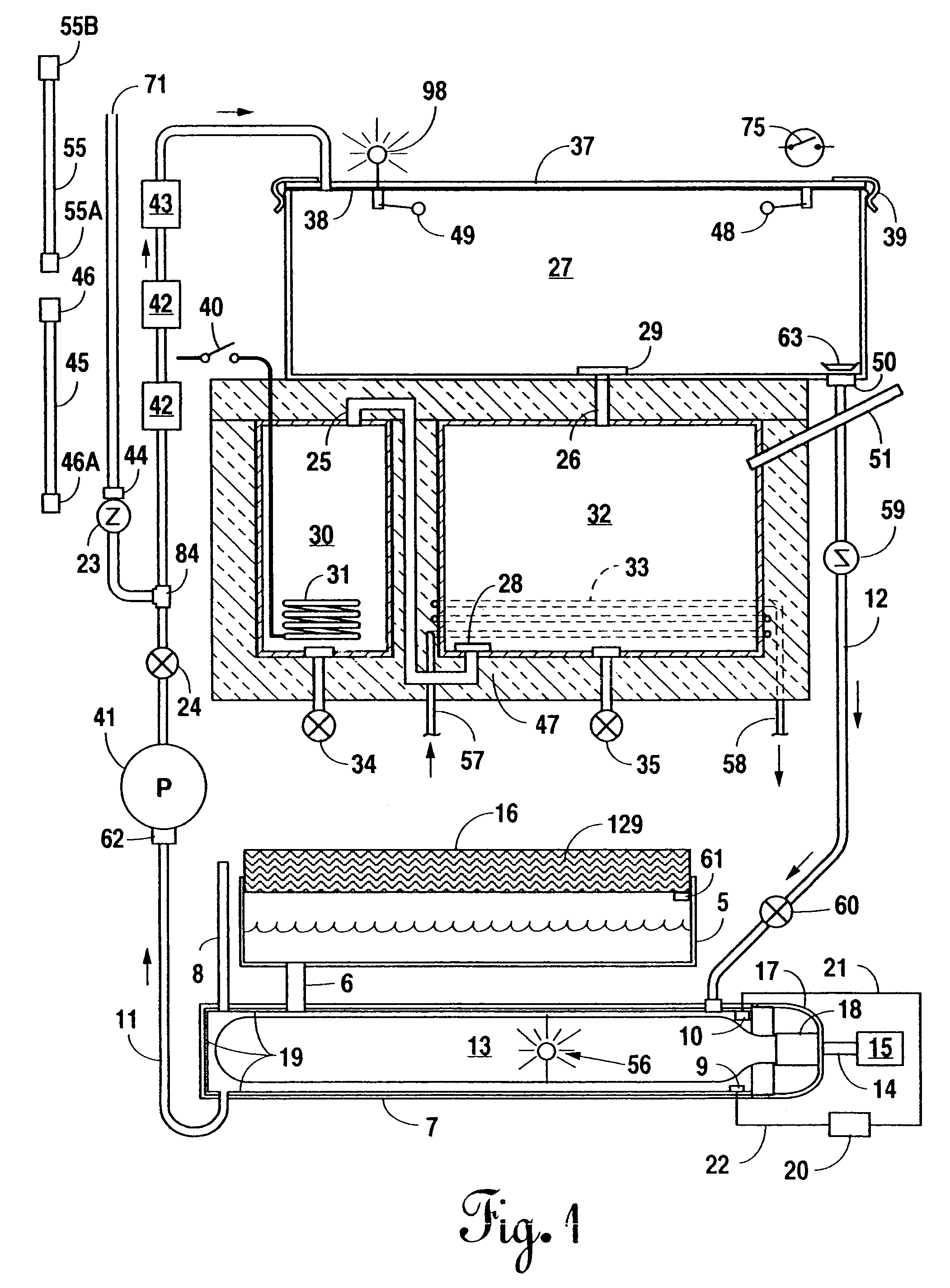
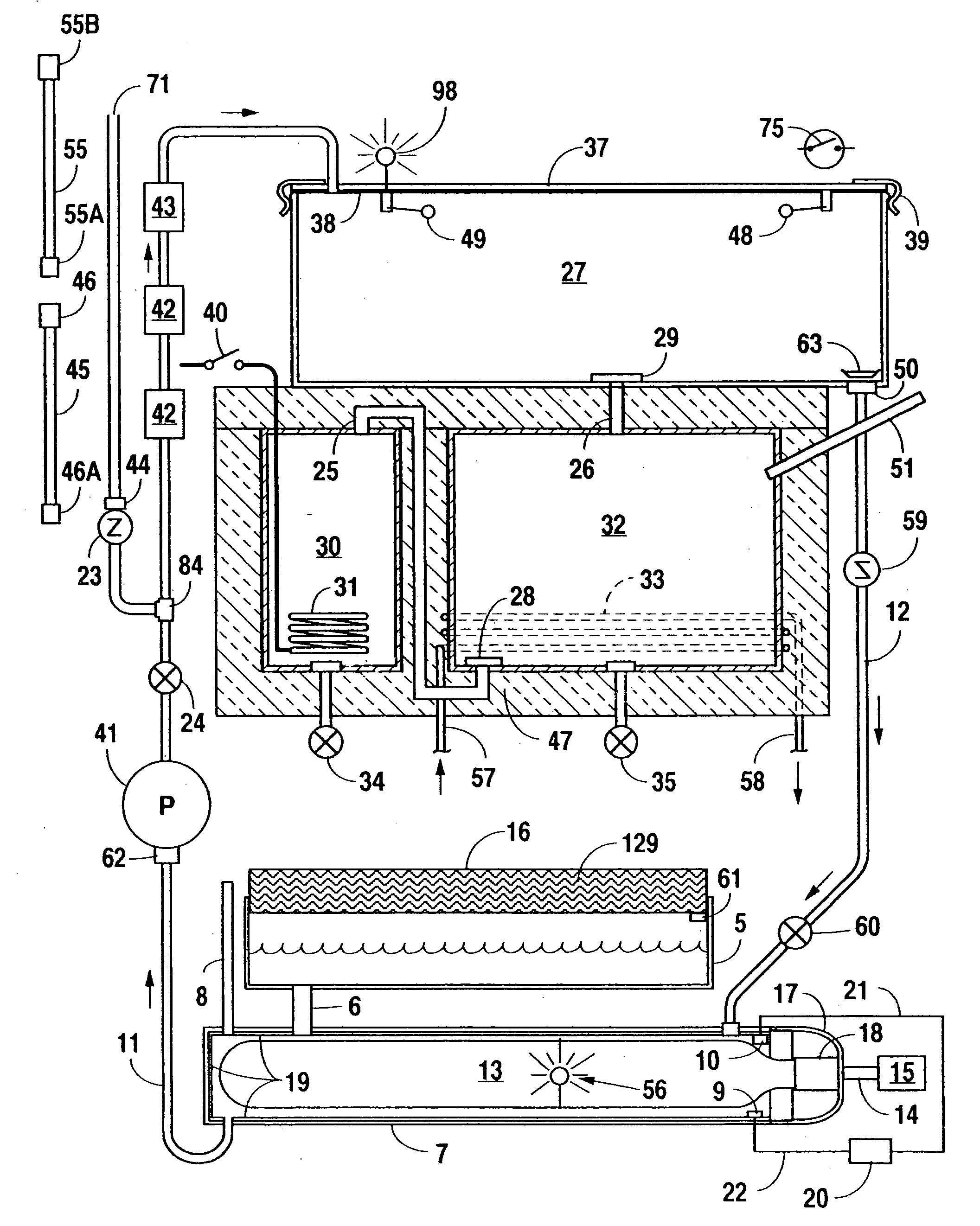
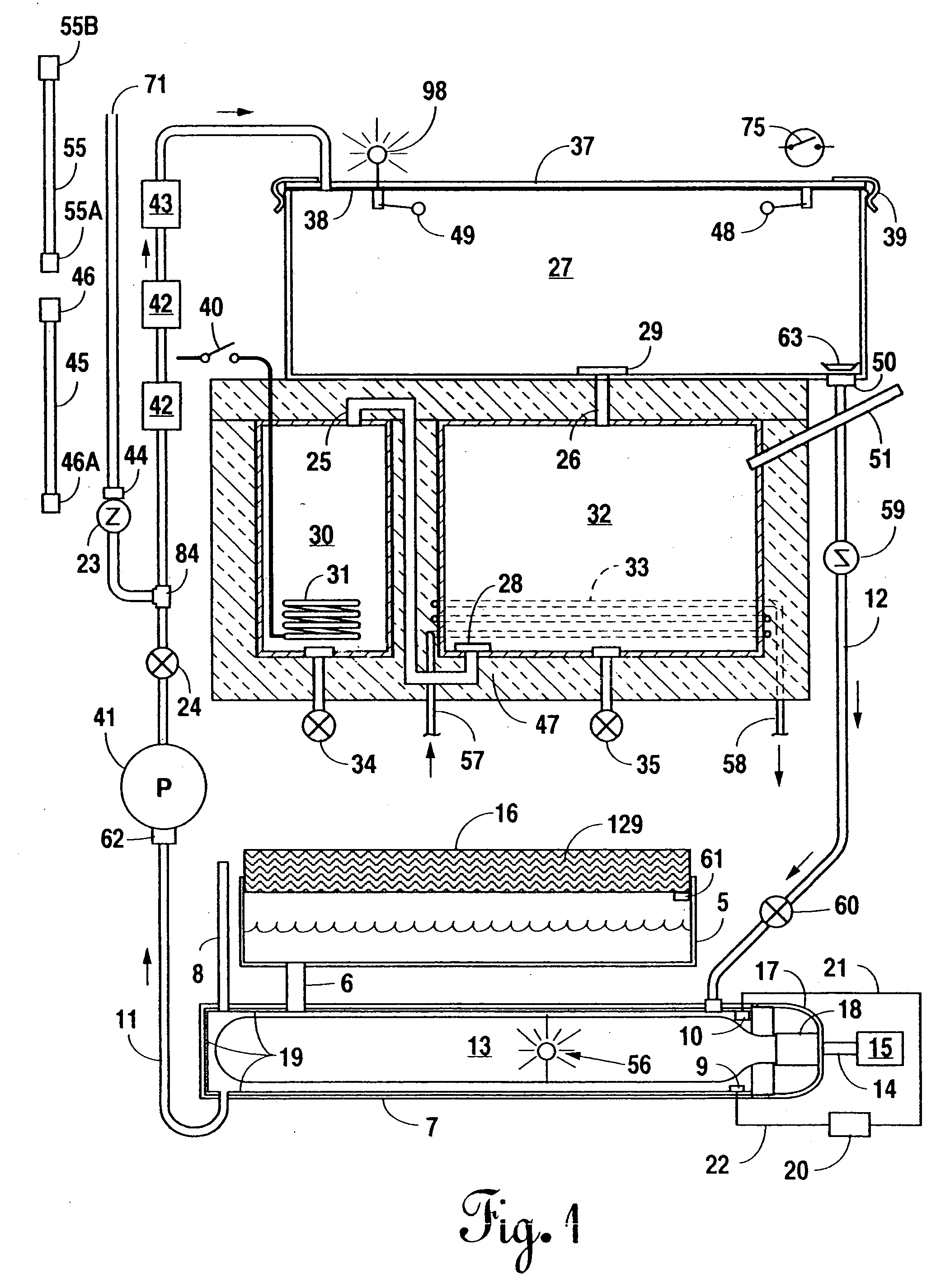
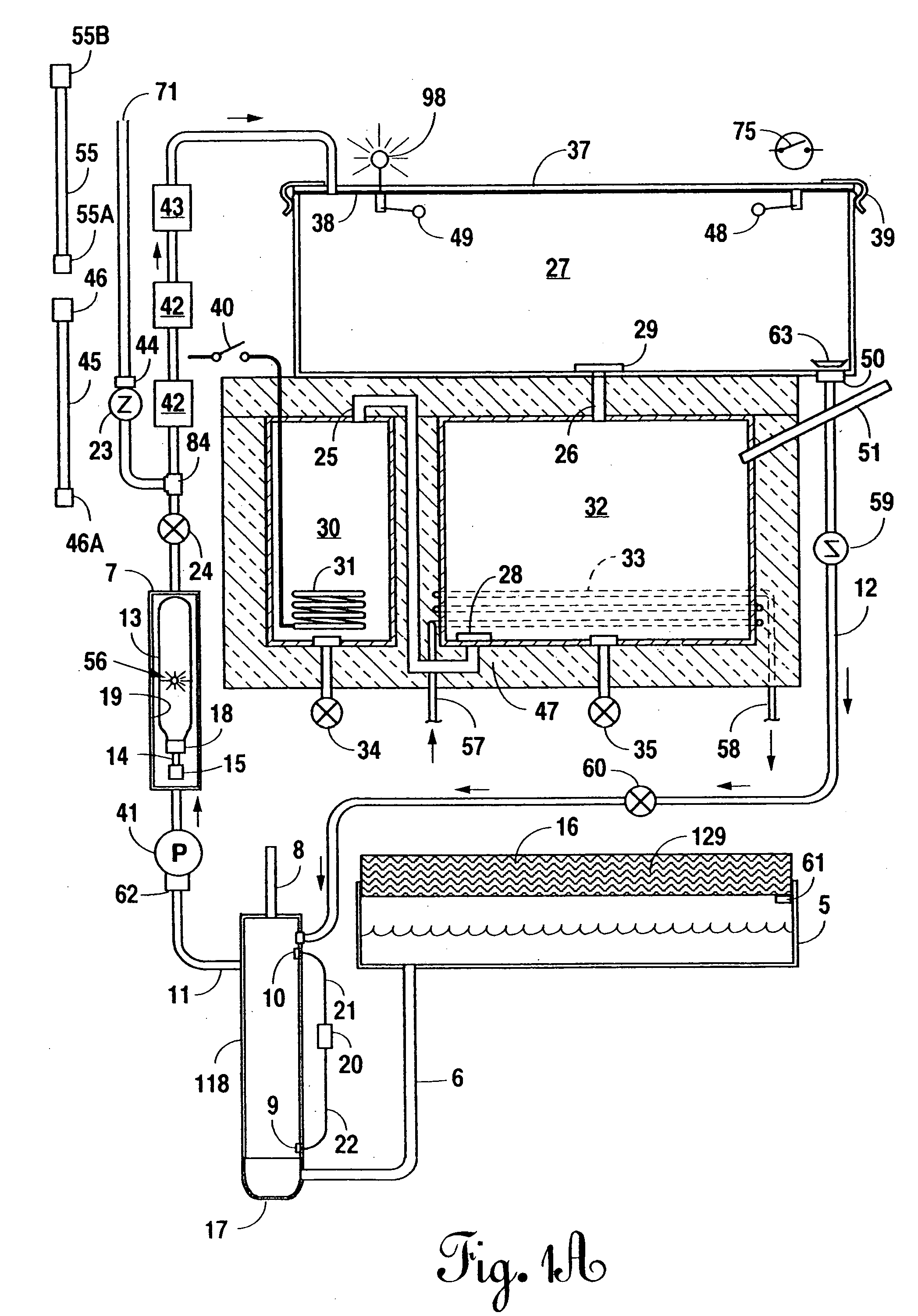
Portable, potable water recovery and dispensing apparatus
InactiveUS7089763B2Maximum efficiencyMaximum productionLiquefactionSpace heating and ventilationParticulatesBiological body
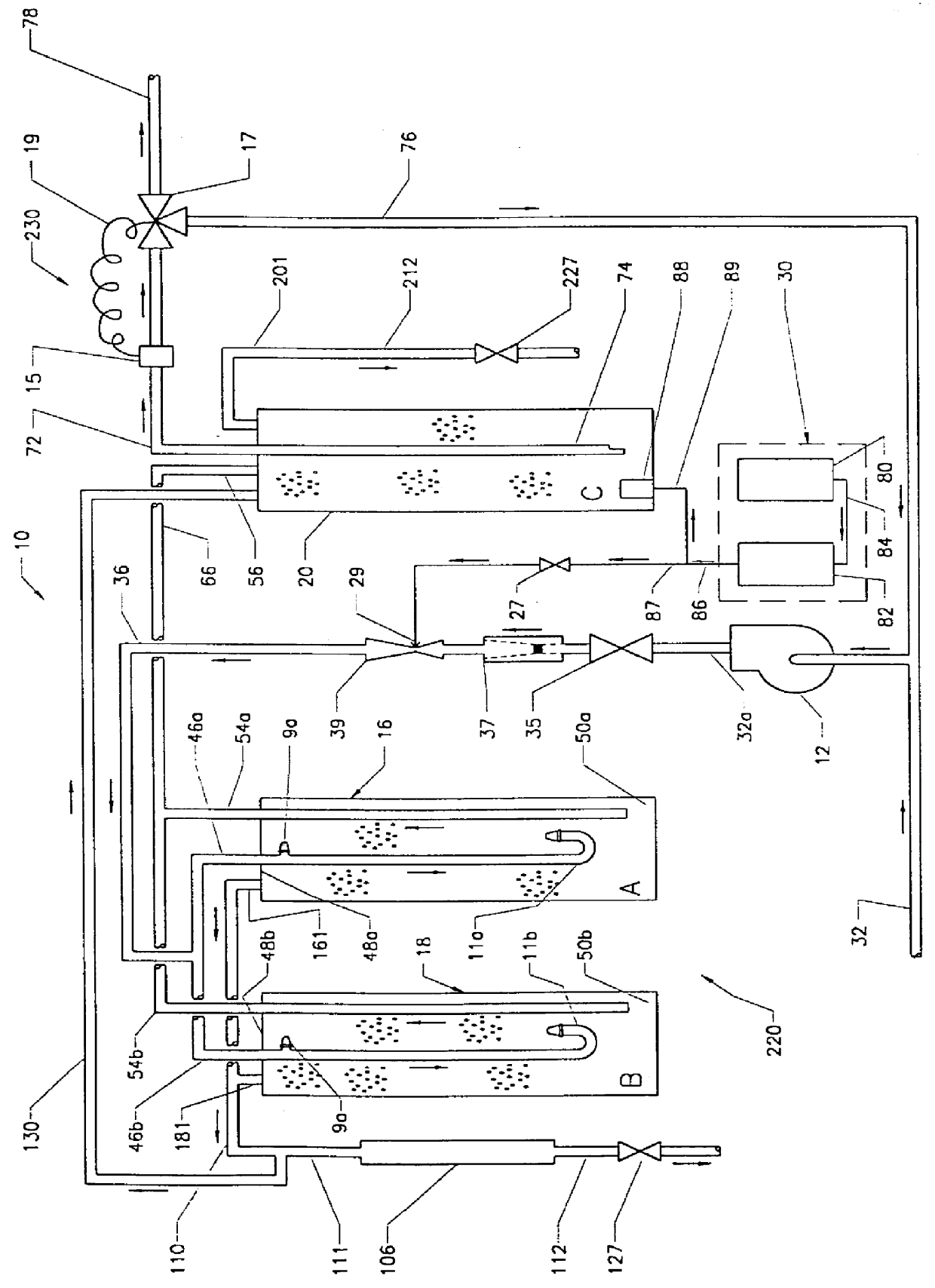
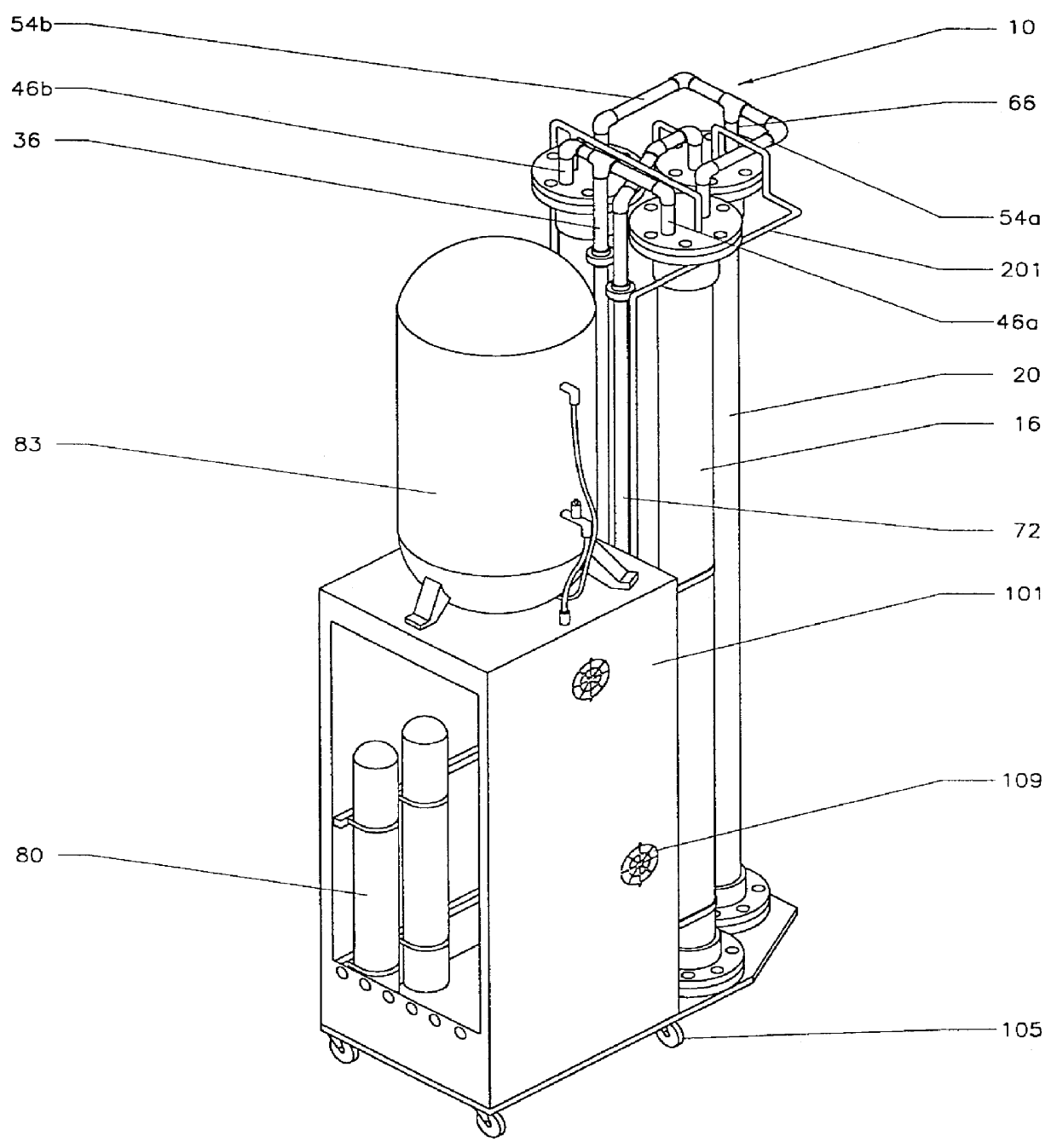
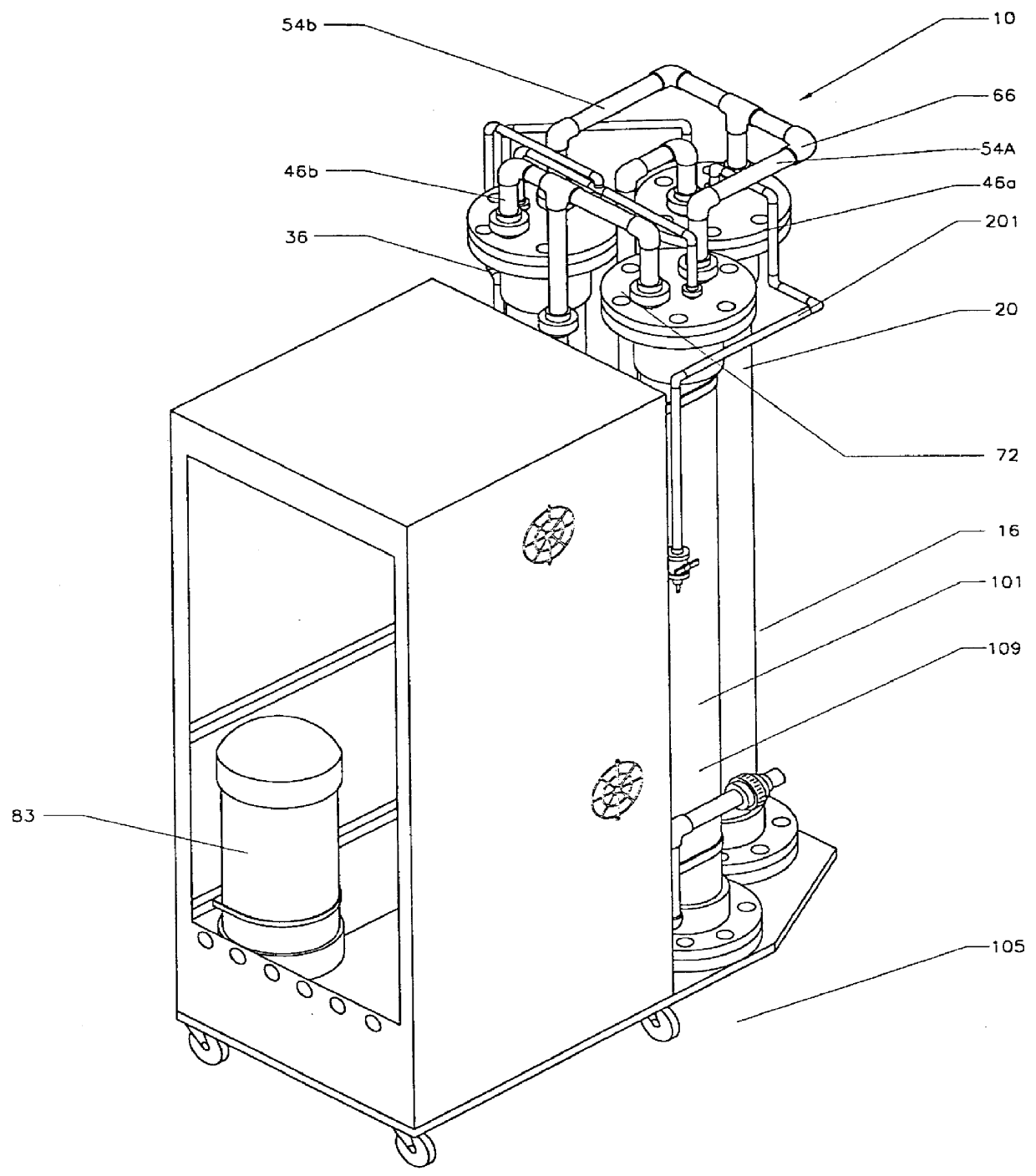
A portable, potable-water generator for producing high-purity liquid water by condensation of water vapor from ambient air. The generator (125) employs an air filter (119) to remove particulates and aerosols from the incoming air. An enclosed heat absorber cools the filtered air to its dew point and collects droplets of condensate into a condensate collector (5). Before discharge, the collected dew is treated in a bacteriostat loop to destroy adventitious living organisms and to filter out undesirable and dangerous contaminants. A recirculation loop provides the ability to recirculate stored condensate, including during periods of inactivity. Further, quick disconnect fittings (55b) and variable length flexible tubing allows use of the invention to serve remote dispensers and / or appliances and allow use of municipal water treated through the apparatus in low condensate situations.
Owner:WORLDWIDE WATER INC
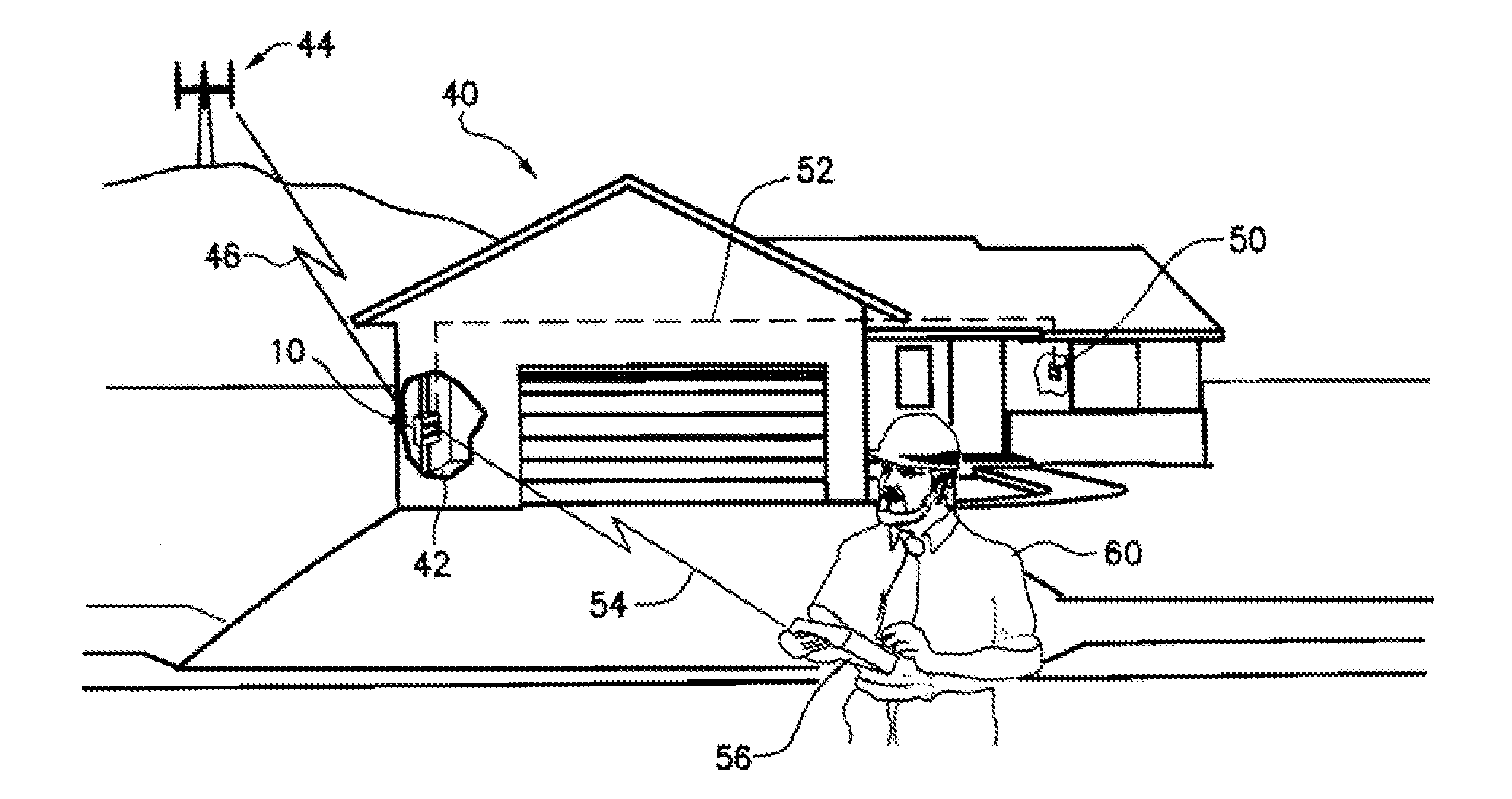
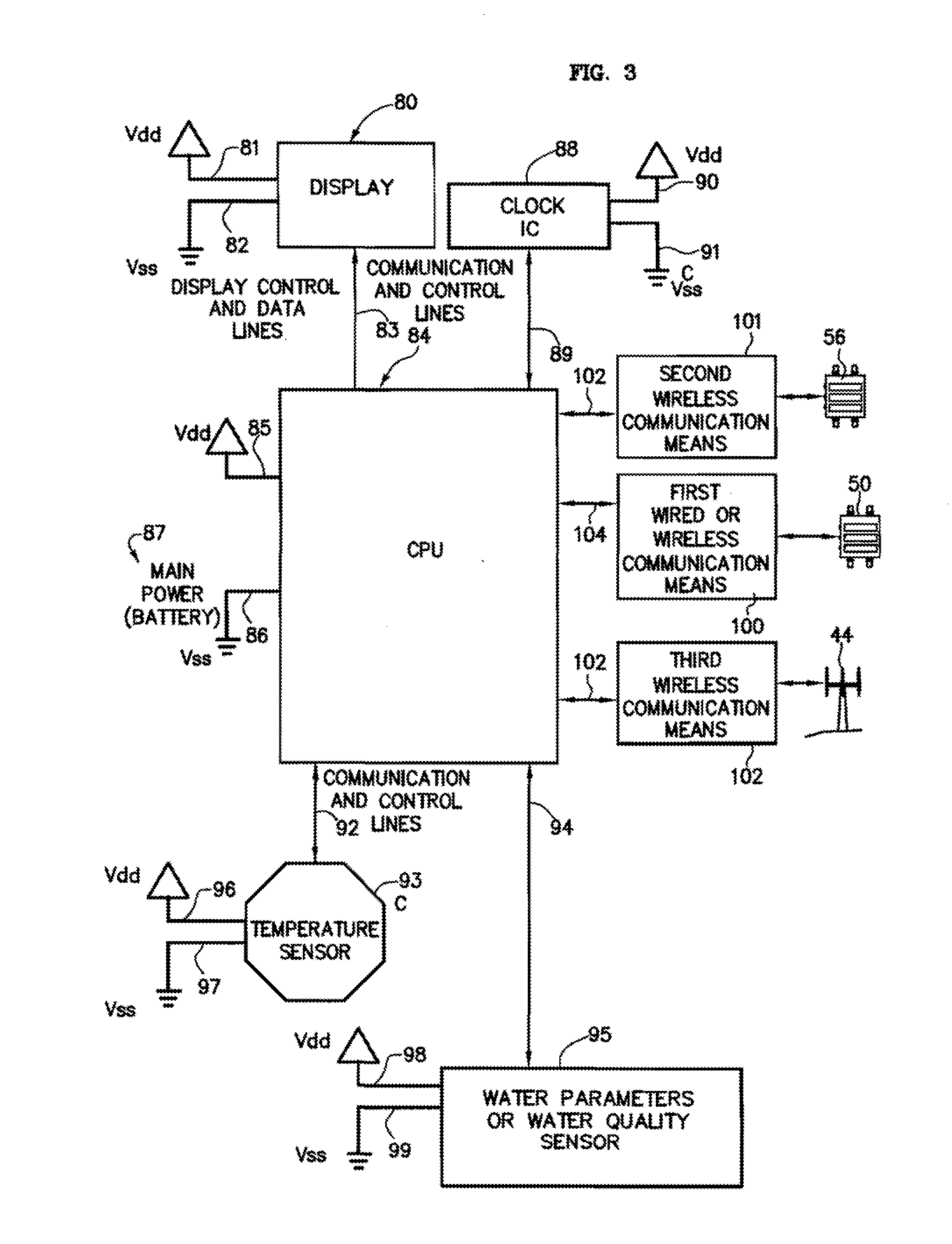
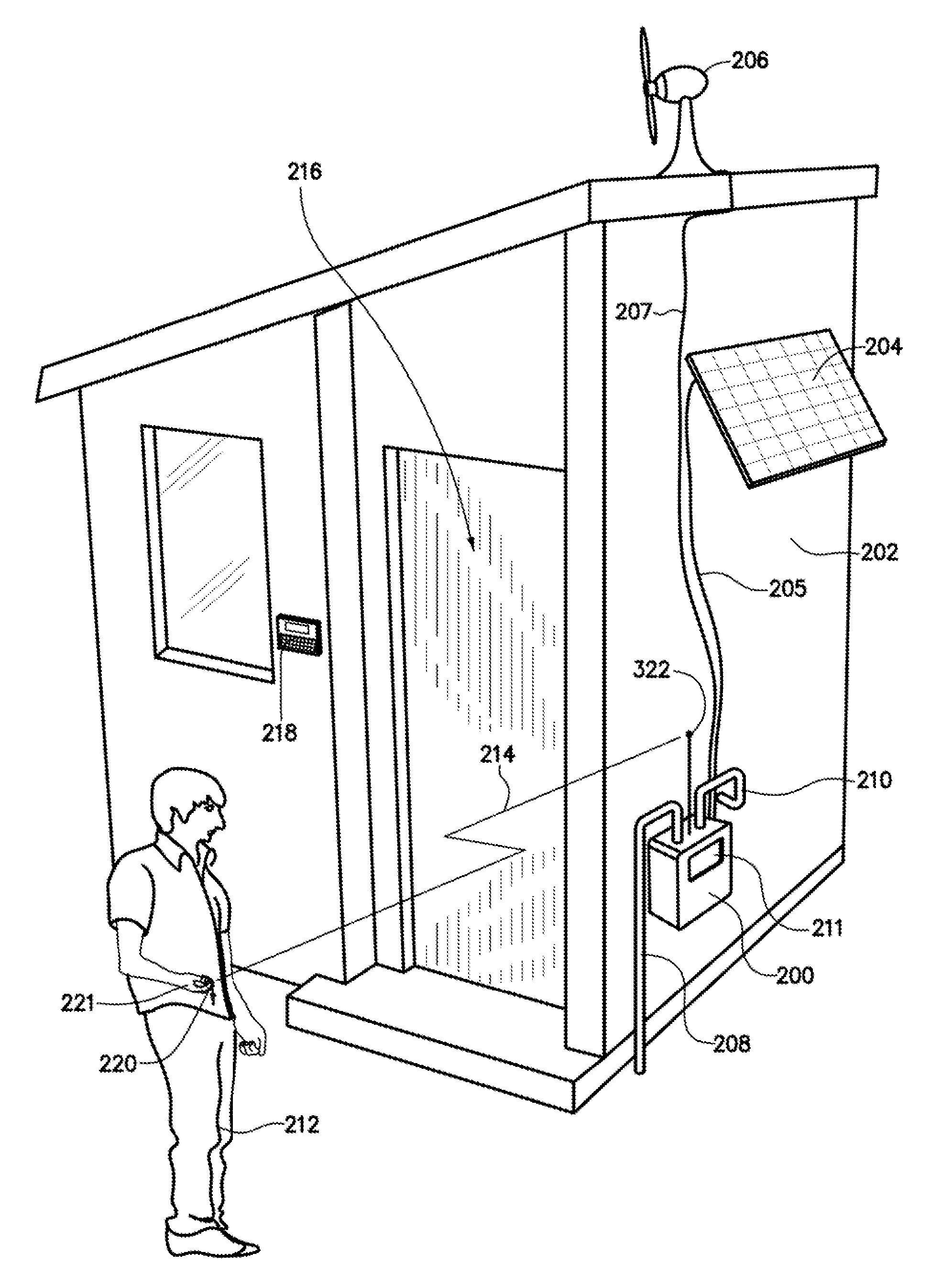
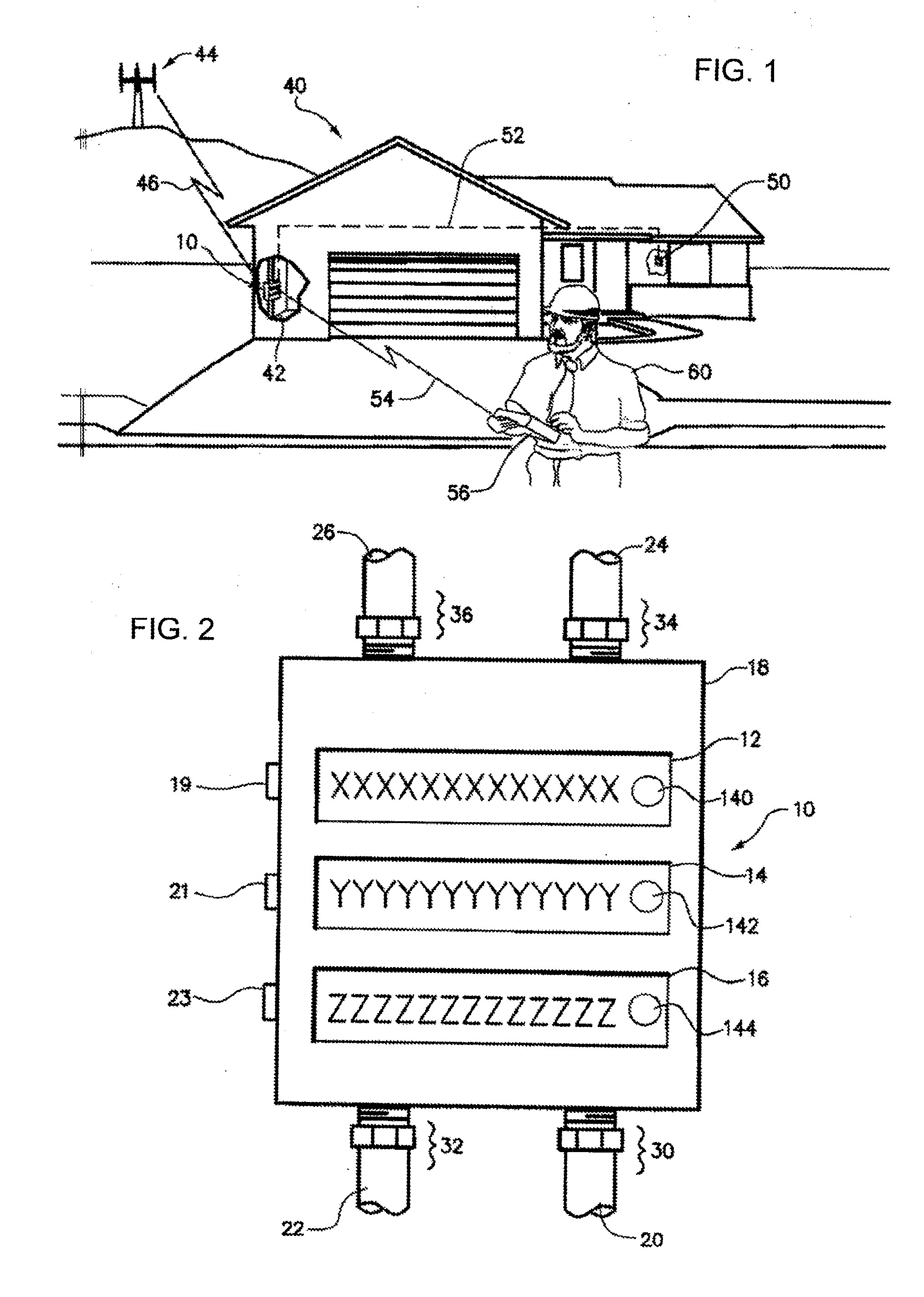
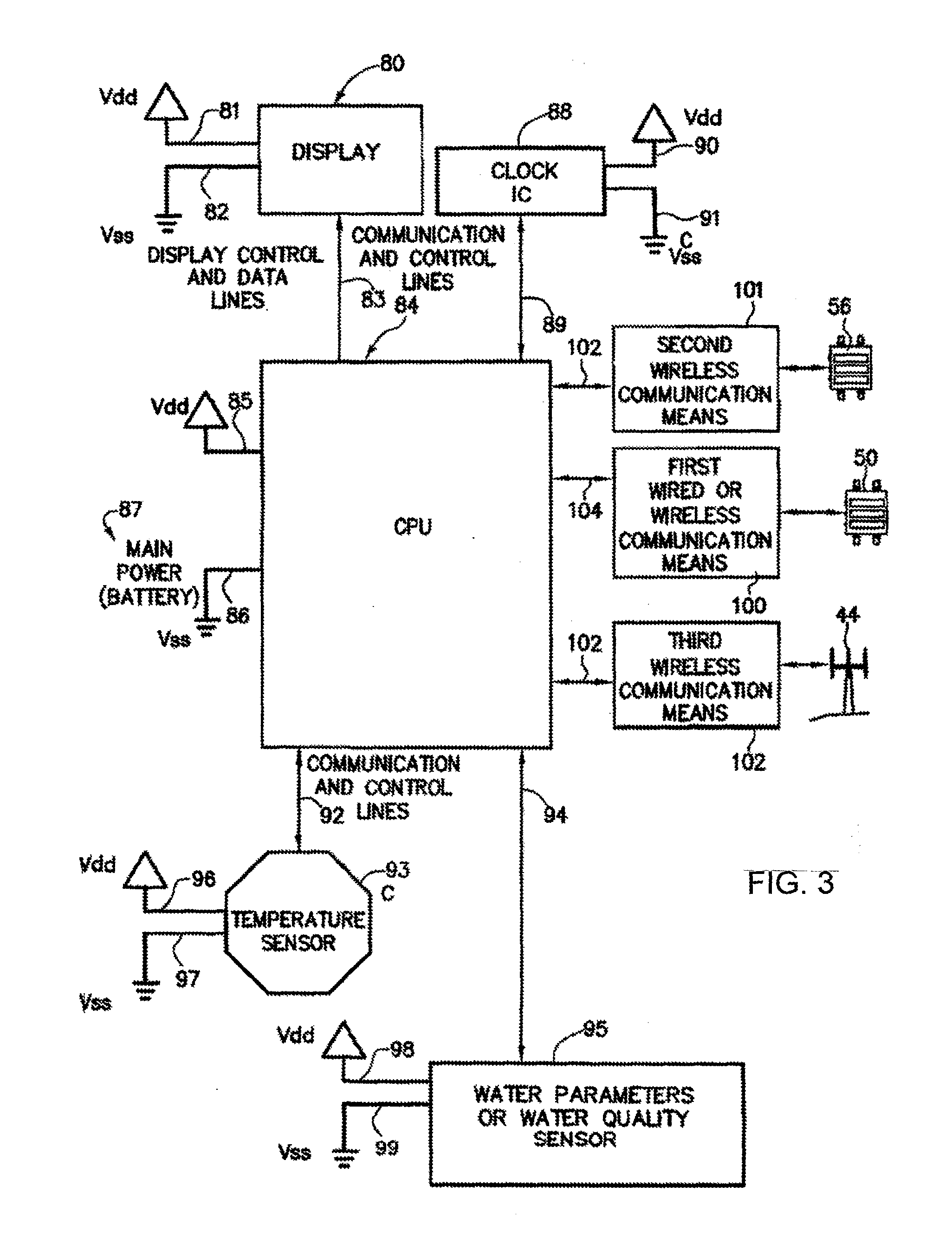
Water Use Monitoring Apparatus
The present invention is a water use and / or a water energy use monitoring apparatus that is affixed to the hot and cold water supply piping for continuously (or on demand) monitoring displaying the water and water energy (hot vs. ambient) use within a residential or commercial building. A first wire or wireless means is incorporated to communicate with a remote display for viewing by the owner of a commercial building or occupier / resident of a home. A second optional wire or wireless means can be incorporated that can be monitored by civil, commercial, governmental or municipal operators or agencies, using a remote display and / or recorder means or by a secure wire or wireless communication network (e.g. cell phone technology communication means). A third wireless means communicates water parameter data utilizing typical cell tower technology and / or mesh network technology. The water use monitor apparatus includes a power generation, a microprocessor, temperature and water flow sensors, optional water quality sensors, timing circuits, wireless circuitry, and a display means. A first wired or wireless means is designed to electronically communicate water use and water energy use information to a remotely located display for convenient observation by a commercial operator or occupier, or resident. An optional second wireless means is designed to electronically communicate water and / or water energy use information to governmental or municipal operators or agencies.
Owner:REIN TECH INC
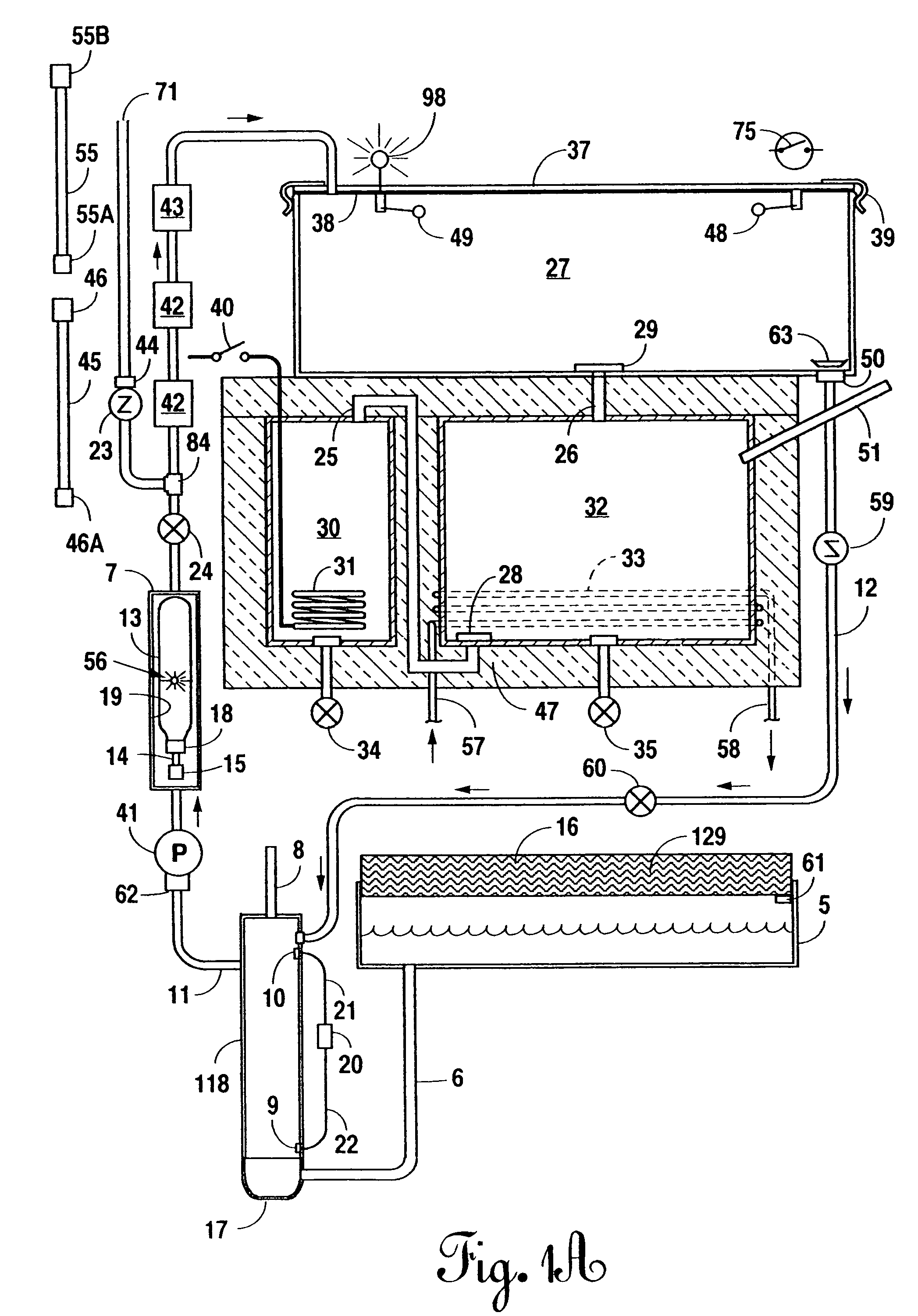
Portable, potable water recovery and dispensing apparatus
InactiveUS20050139552A1Maximum productionMaximum efficiencyLiquefactionSpace heating and ventilationParticulatesBiological body
A portable, potable-water generator for producing high-purity liquid water by condensation of water vapor from ambient air. The generator (125) employs an air filter (119) to remove particulates and aerosols from the incoming air. An enclosed heat absorber cools the filtered air to its dew point and collects droplets of condensate into a condensate collector (5). Before discharge, the collected dew is treated in a bacteriostat loop to destroy adventitious living organisms and to filter out undesirable and dangerous contaminants. A recirculation loop provides the ability to recirculate stored condensate, including during periods of inactivity. Further, quick disconnect fittings (55b) and variable length flexible tubing allows use of the invention to serve remote dispensers and / or appliances and allow use of municipal water treated through the apparatus in low condensate situations.
Owner:WORLDWIDE WATER INC
Water use monitoring apparatus and water damage prevention system
ActiveUS9297150B2Avoid flowAvoid failureOperating means/releasing devices for valvesGeneral water supply conservationWater useWired communication
The present invention is a water damage prevention system that has a residential or industrial / commercial facility water supply interruption system. The system is comprised of a remotely controllable base station with shut-off / on mechanism that is in wireless or wired communication with a convenient controller. The base station with shut-off / on mechanism is interposed within a water line from a water main to the living or operating quarters portion of a residential or a industrial / commercial facility or building, such that activation of the base station with shut-off / on valve operates to prevent flow of water from the water main to the living quarters when the residential home or industrial / commercial facility or building is vacated or unsupervised. In this manner, damage to the living quarters or the industrial / commercial facility or building from failure of water pipes running through the living or working quarters is prevented during times that the shut-off mechanism is activated.
Owner:REIN TECH INC
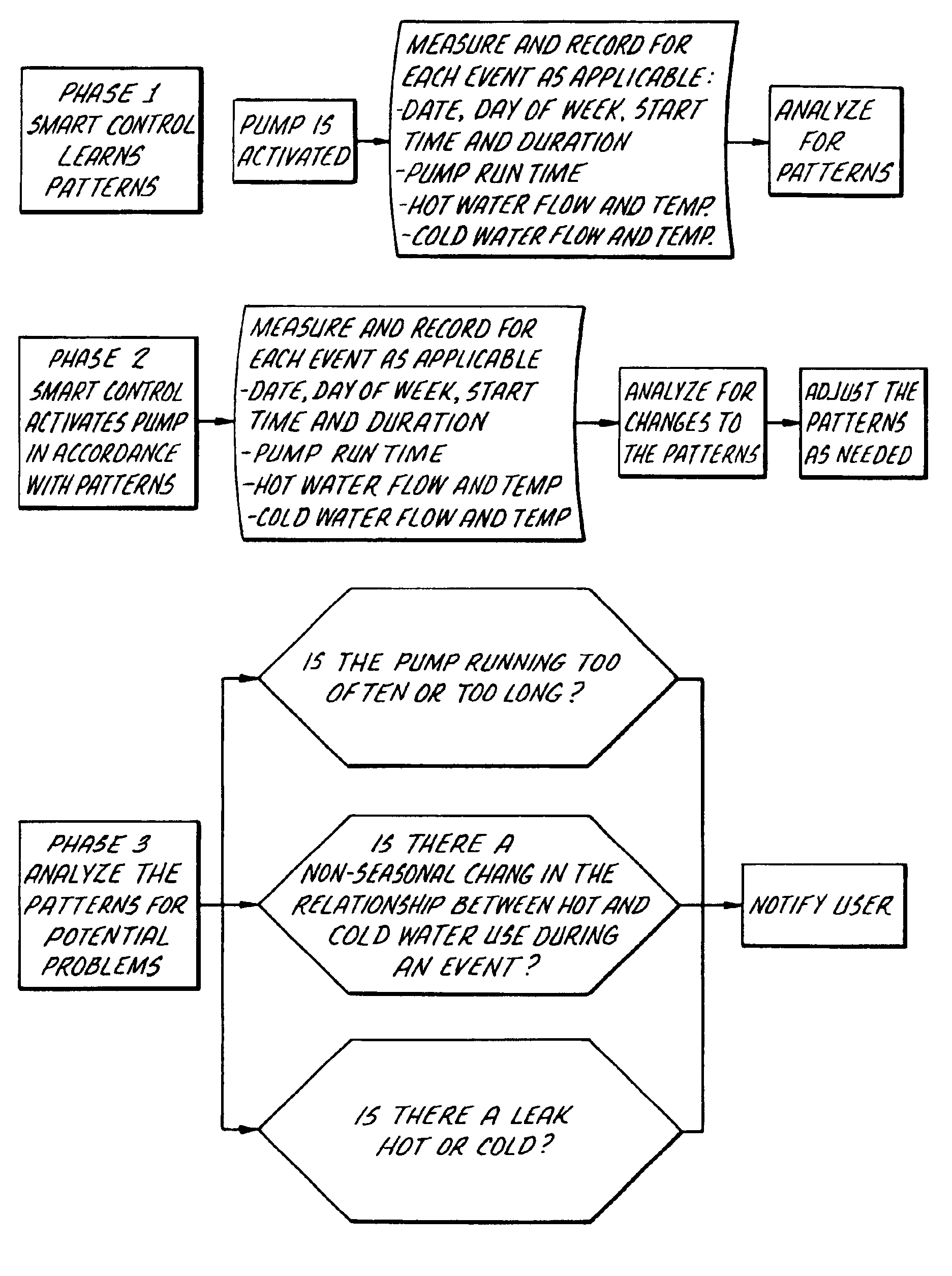
Method for operating a multi family/commercial plumbing system
InactiveUS6962162B2Water loss is reducedDelay water lossLighting and heating apparatusPipe heating/coolingWater useStart time
A method for operating a multi-family / commercial plumbing system includes sensing an event and recording for each sensed event at least one parameter selected from the group consisting of date, day of the week, start time, duration of the event, water flow, water temperature, and humidity. The parameters are analyzed to determine a pattern and thereafter water flow, circulation, water temperature, and water use are controlled in accordance with the determined pattern.
Owner:ADVANCED CONSERVATION TECH DISTRIBUTION INC
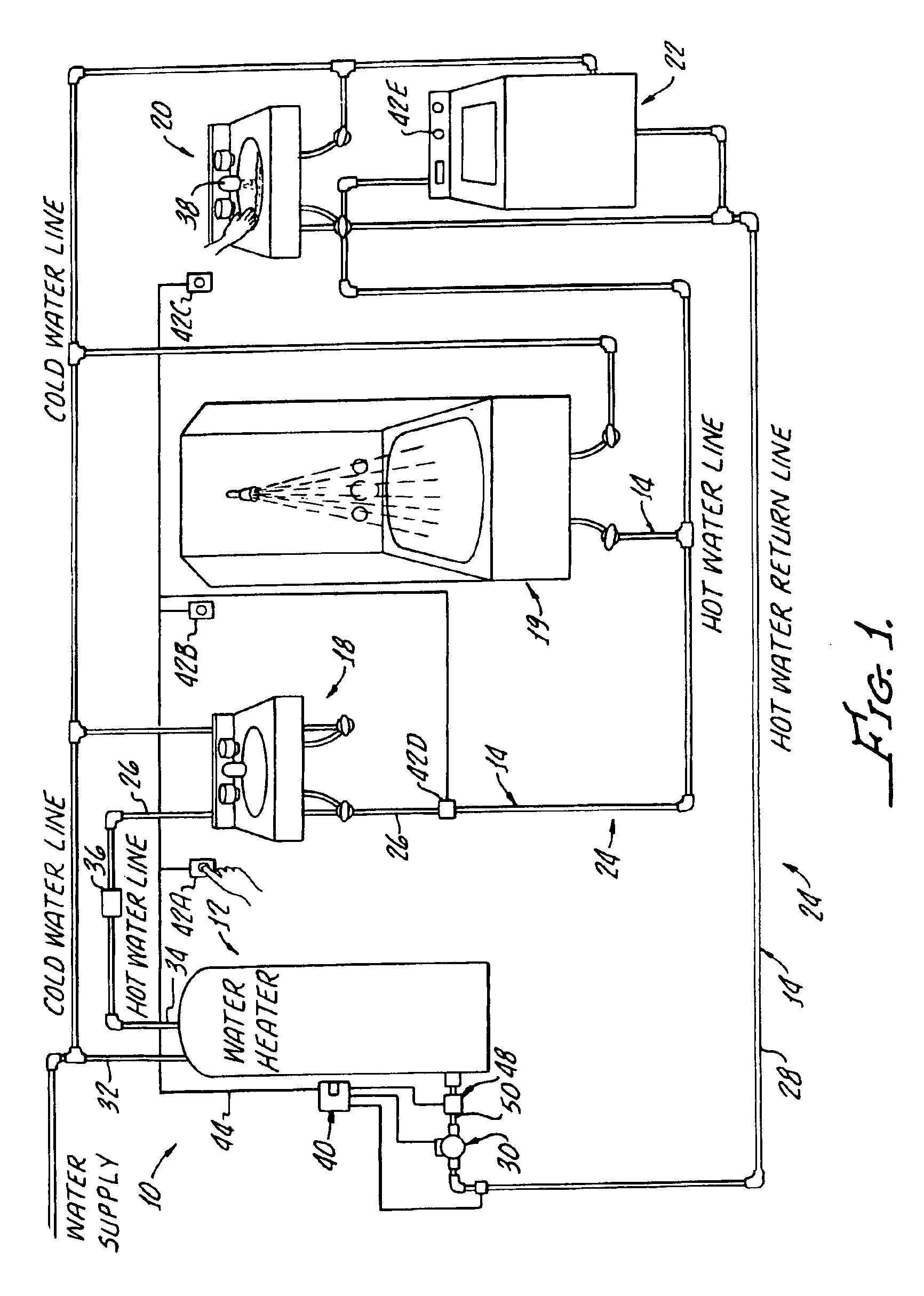
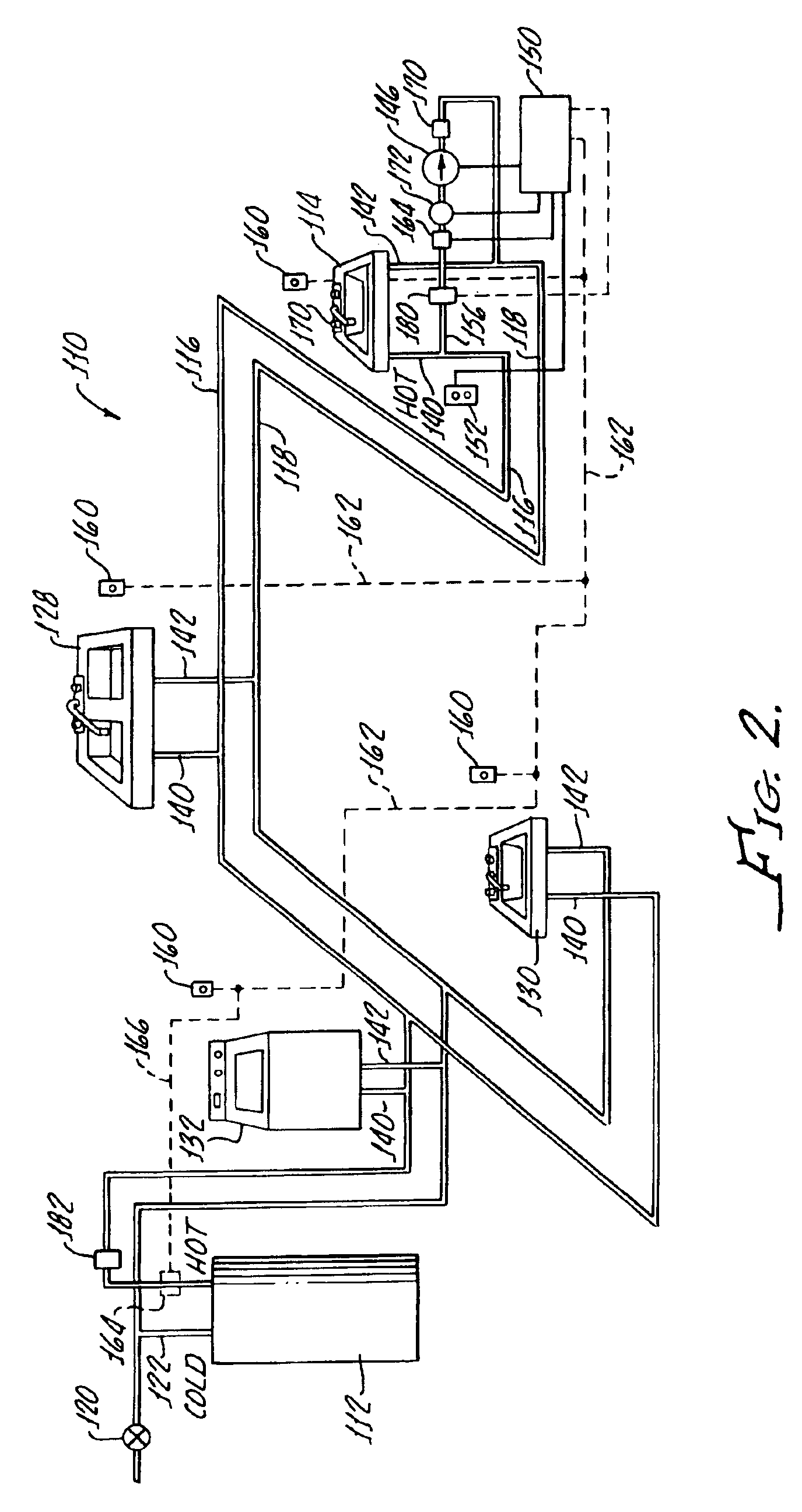
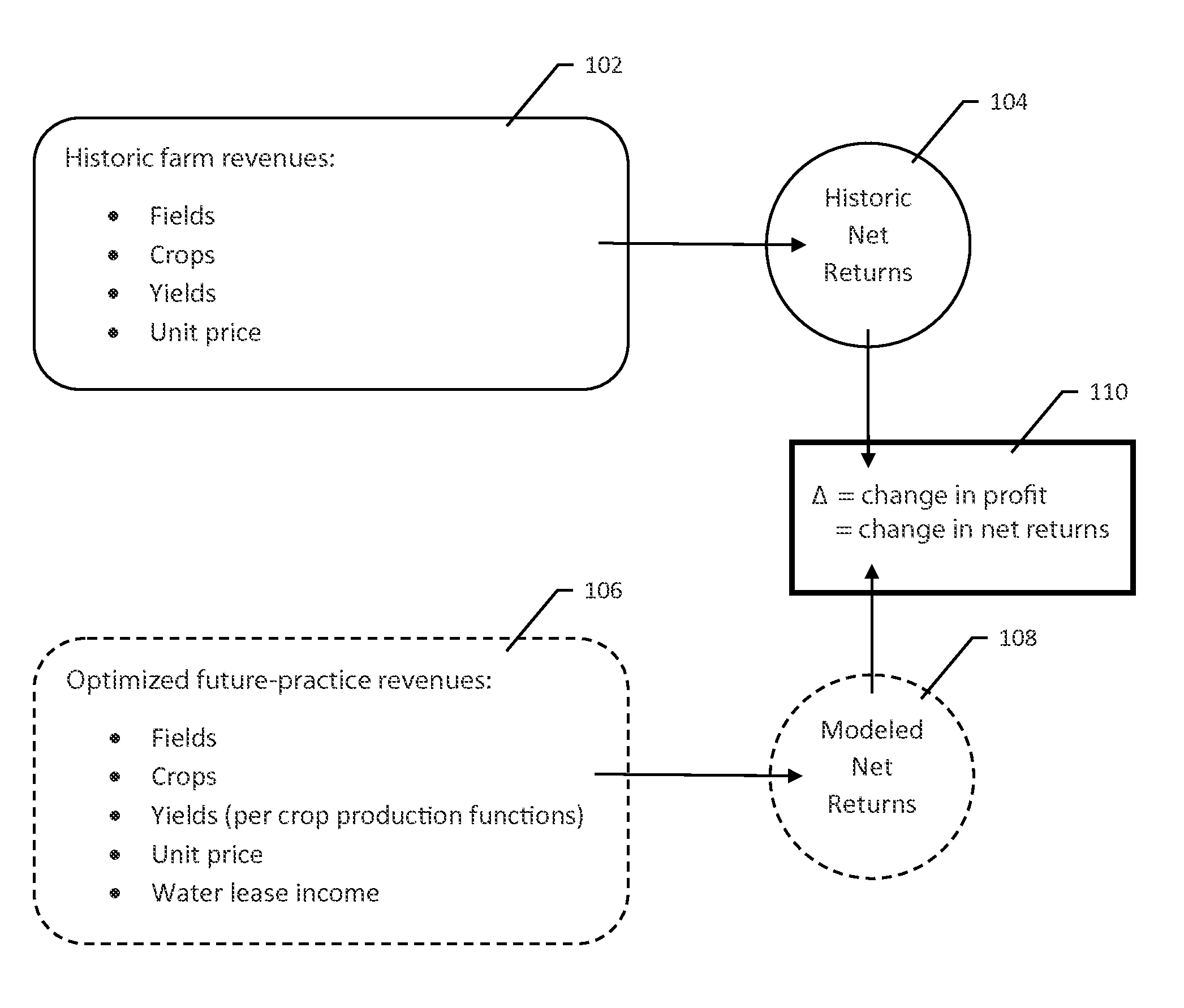
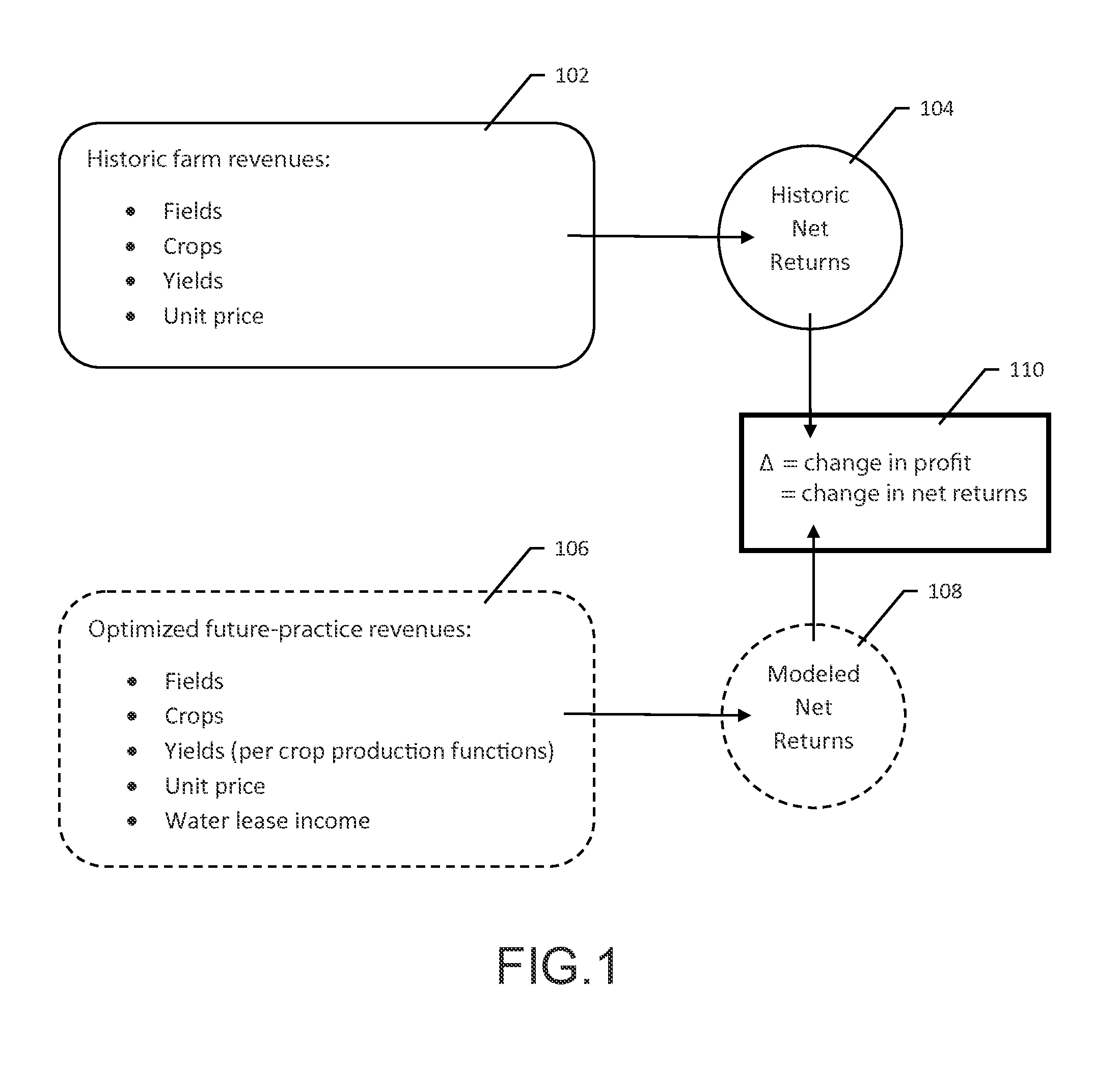
System and method for conserving water and optimizing land and water use
ActiveUS9202252B1Easy to save energyFacilitate water conservationDesign optimisation/simulationLevel indicatorsWater useNet return
Software, databases, computer models, and a series of monitoring devices are provided that are used collectively to optimize farming operations for the purpose of efficiently utilizing the water right associated with the land while recognizing the potential to transfer a proportional amount of the water right in a lease or sale arrangement to other water users. The contemplated system encourages water conservation by allowing those owning water rights to determine the feasibility of changed farming practices intended to maximize net returns and profitability of their overall farming operations.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
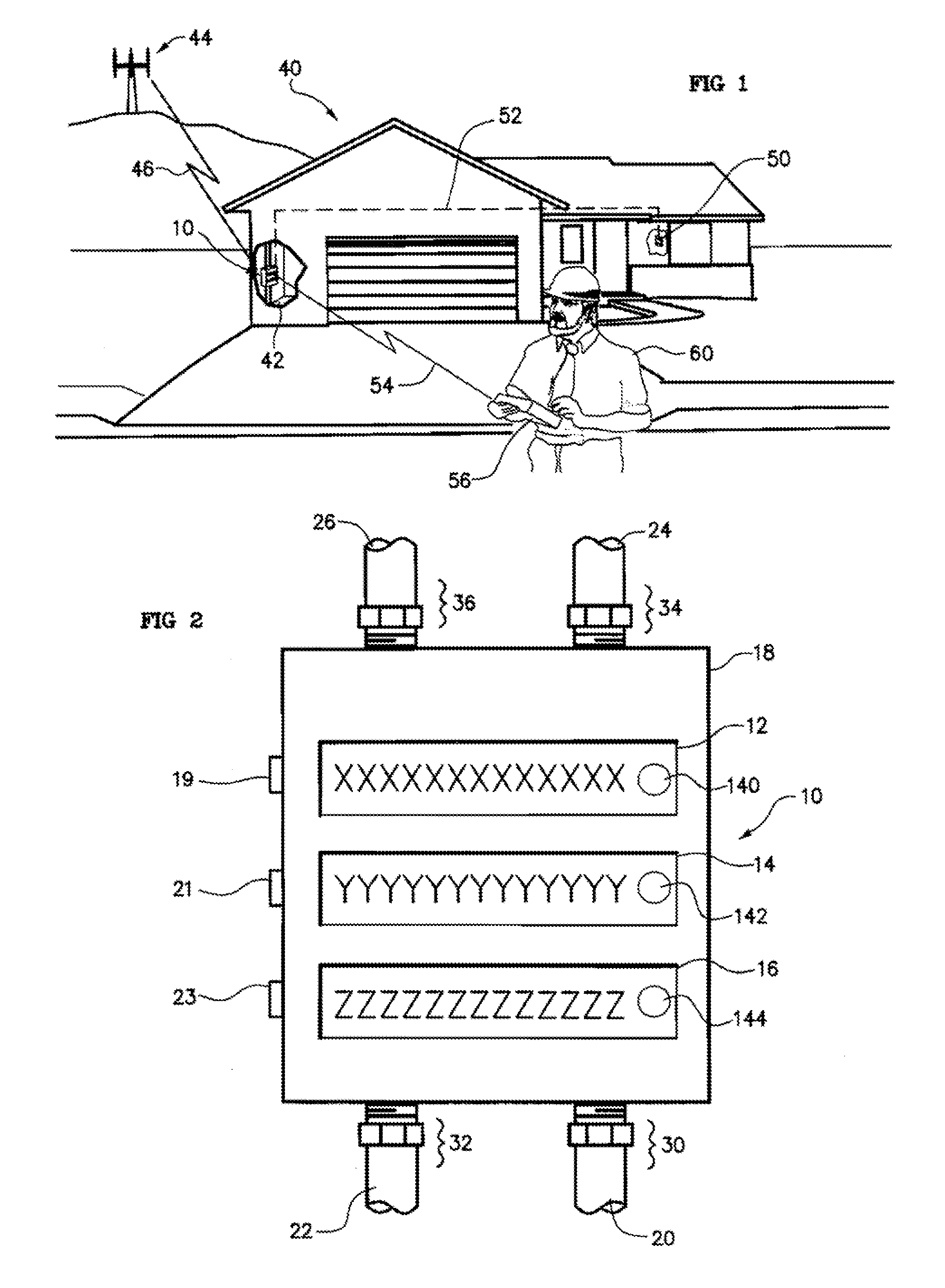
Water Use Monitoring Apparatus
ActiveUS20160076909A1Easy to observeGeneral water supply conservationVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsWater useTechnology communication
The present invention is a water use and / or a water energy use monitoring apparatus that is affixed to the hot and cold water supply piping for continuously (or on demand) monitoring displaying the water and water energy (hot vs. ambient) use within a residential or commercial building. A first wire or wireless means is incorporated to communicate with a remote display for viewing by the owner of a commercial building or occupier / resident of a home. A second optional wire or wireless means can be incorporated that can be monitored by civil, commercial, governmental or municipal operators or agencies, using a remote display and / or recorder means or by a secure wire or wireless communication network (e.g. cell phone, smart phone or other similar technology communication means). A third wireless means communicates water parameter data utilizing typical cell tower technology and / or mesh network technology. The water use monitor apparatus includes a power generation, a microprocessor, temperature and water flow sensors, optional water quality sensors, timing circuits, wireless circuitry, and a display means. A wired or wireless means is designed to electronically communicate water use, water energy use and / or water quality information to a remotely located display apparatus or typical cell phone, smart phones, or similar apparatus for convenient observation by a commercial, operator or occupier, resident, municipal or government agency.
Owner:REIN TECH INC
Beverage dispenser
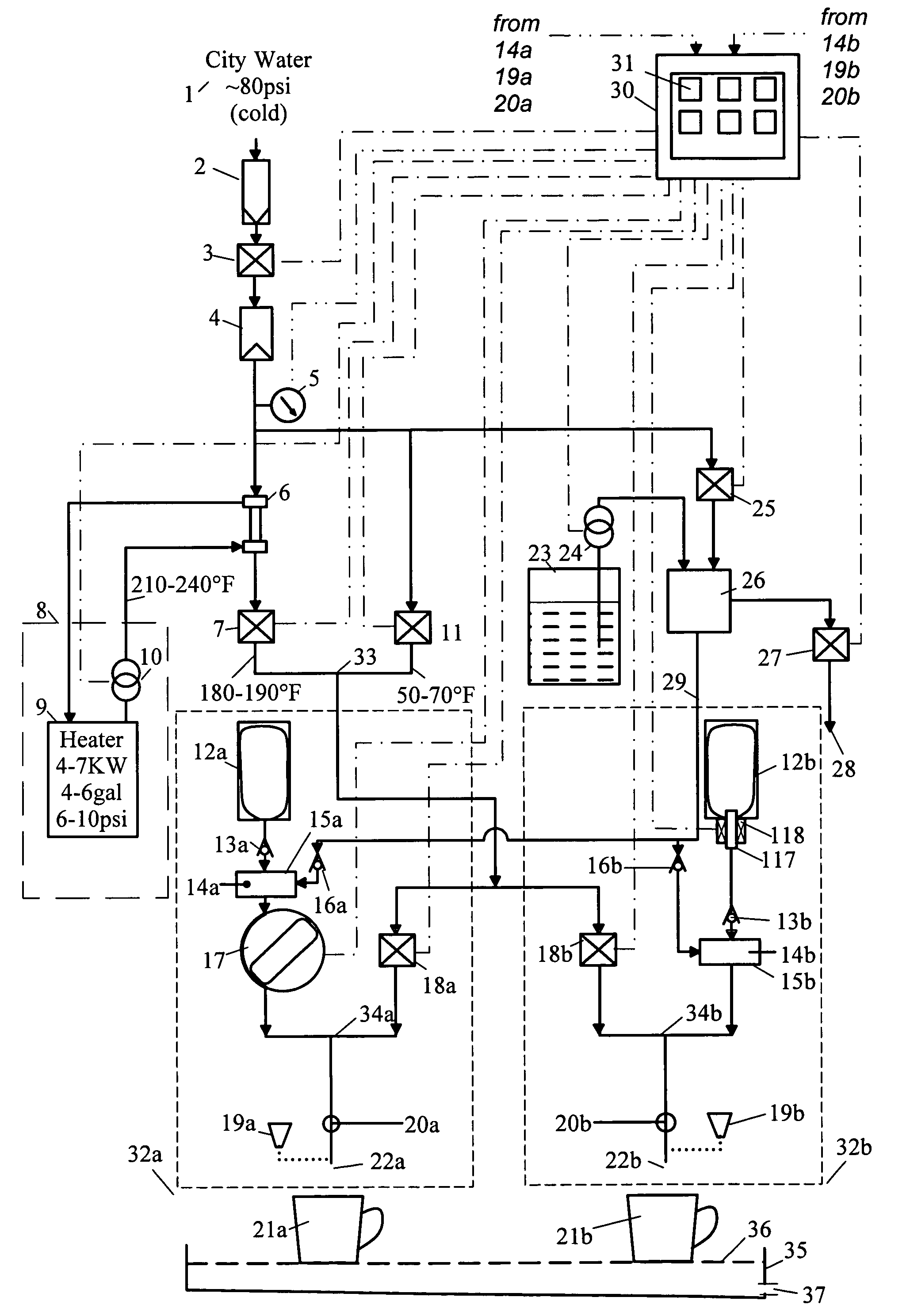
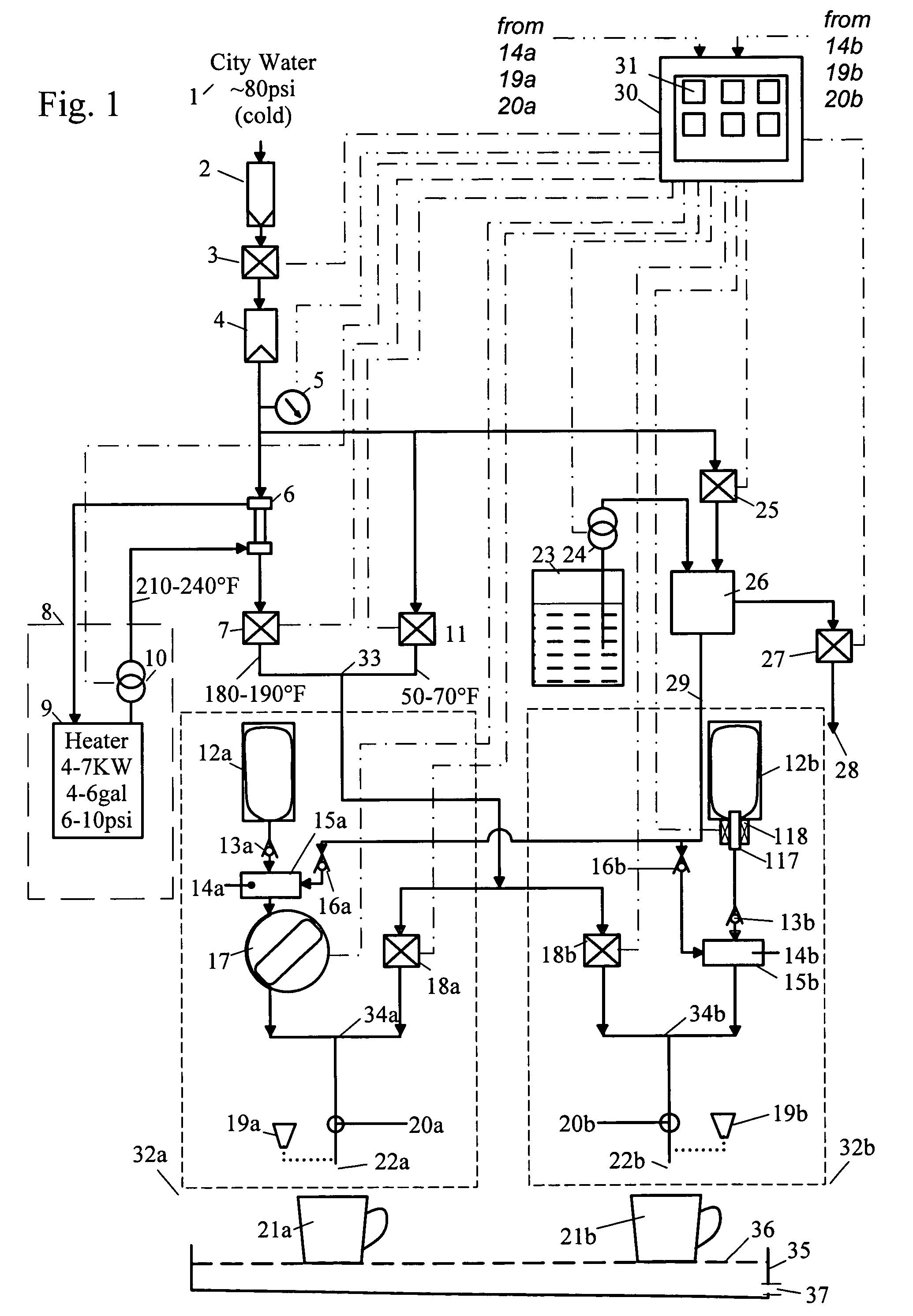
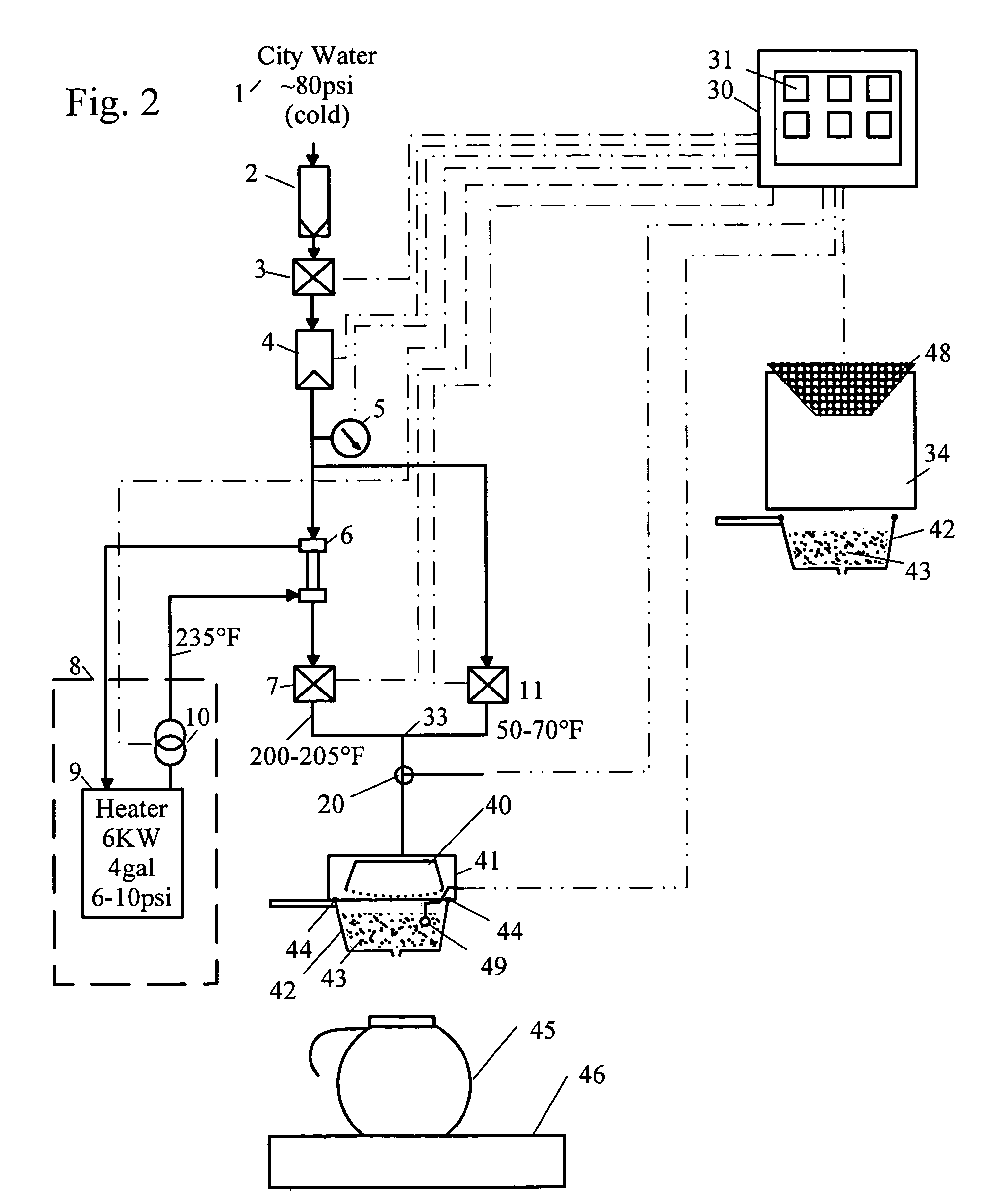
InactiveUS7654191B2Improves aroma and look and tasteEffectively sanitizedBeverage vesselsLiquid transferring devicesWater useEngineering
A beverage dispenser and method of operation, in which incoming water for beverage preparation is heated by a liquid-to-liquid heat exchanger. The heated water may be mixed with cold water using controlled valves, to generate a selected temperature stream. This controlled-temperature stream may be mixed with beverage concentrate or sprayed over coffee grounds to brew fresh coffee.
Owner:GREENWALD TECH
Filtration device for liquid purification
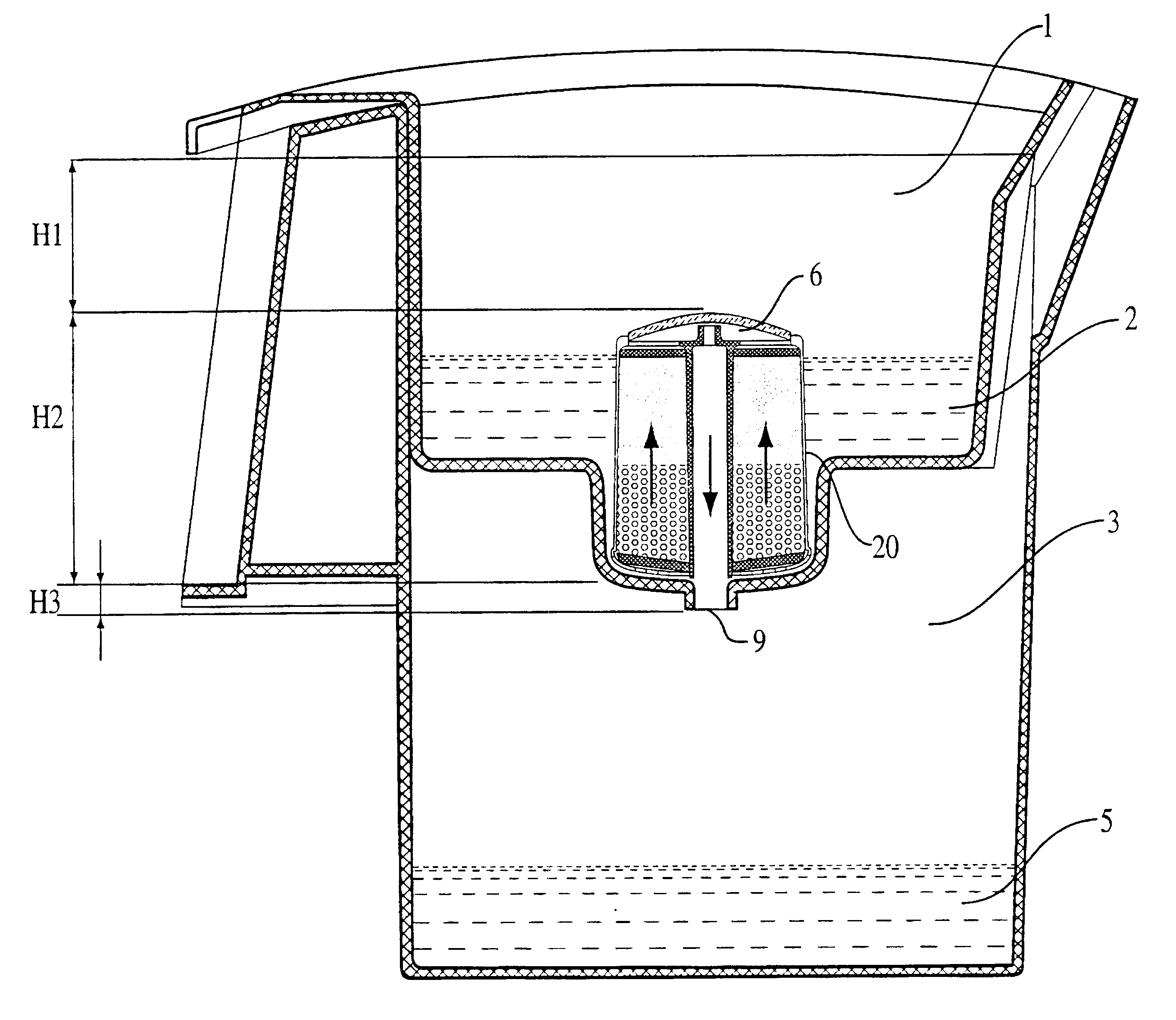
InactiveUS6387260B1Confirm its effectivenessIon-exchange column/bed processesTreatment involving filtrationInternal pressureWater use
The invention is directed to purification of liquids, such as drinking water using filters, wherein filtration is effected while the liquid flows upwardly. The invention includes both the method and a device enabling the method to be carried out. The device is constructed to intake impure liquid at the bottom of the filter and initially to effect flow by filling liquid to above the filter outlet near the top, and maintaining flow thereafter by virtue of the presence of a low internal pressure that develops as the liquid passes through the system.
Owner:ELECTROPHOR INC
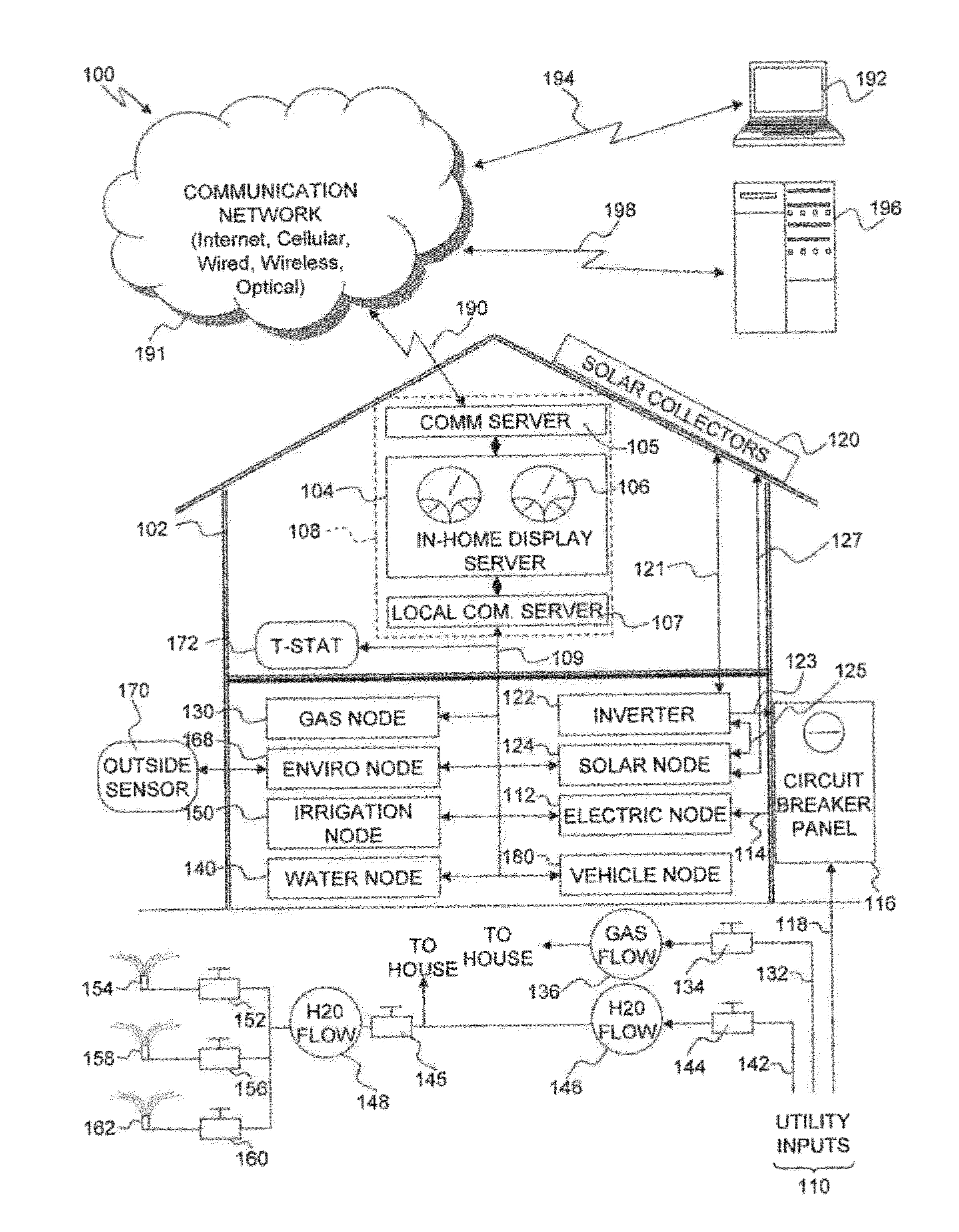
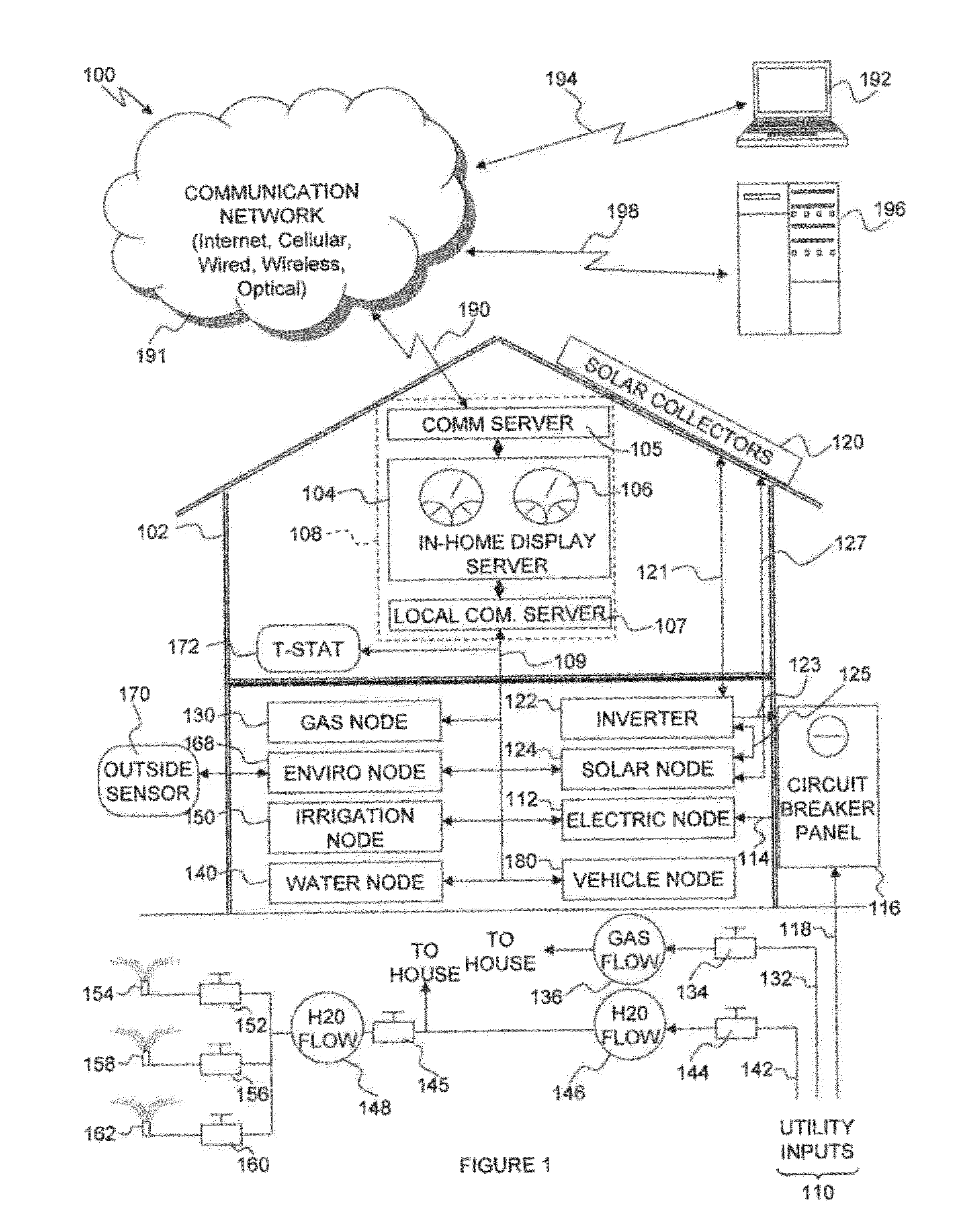
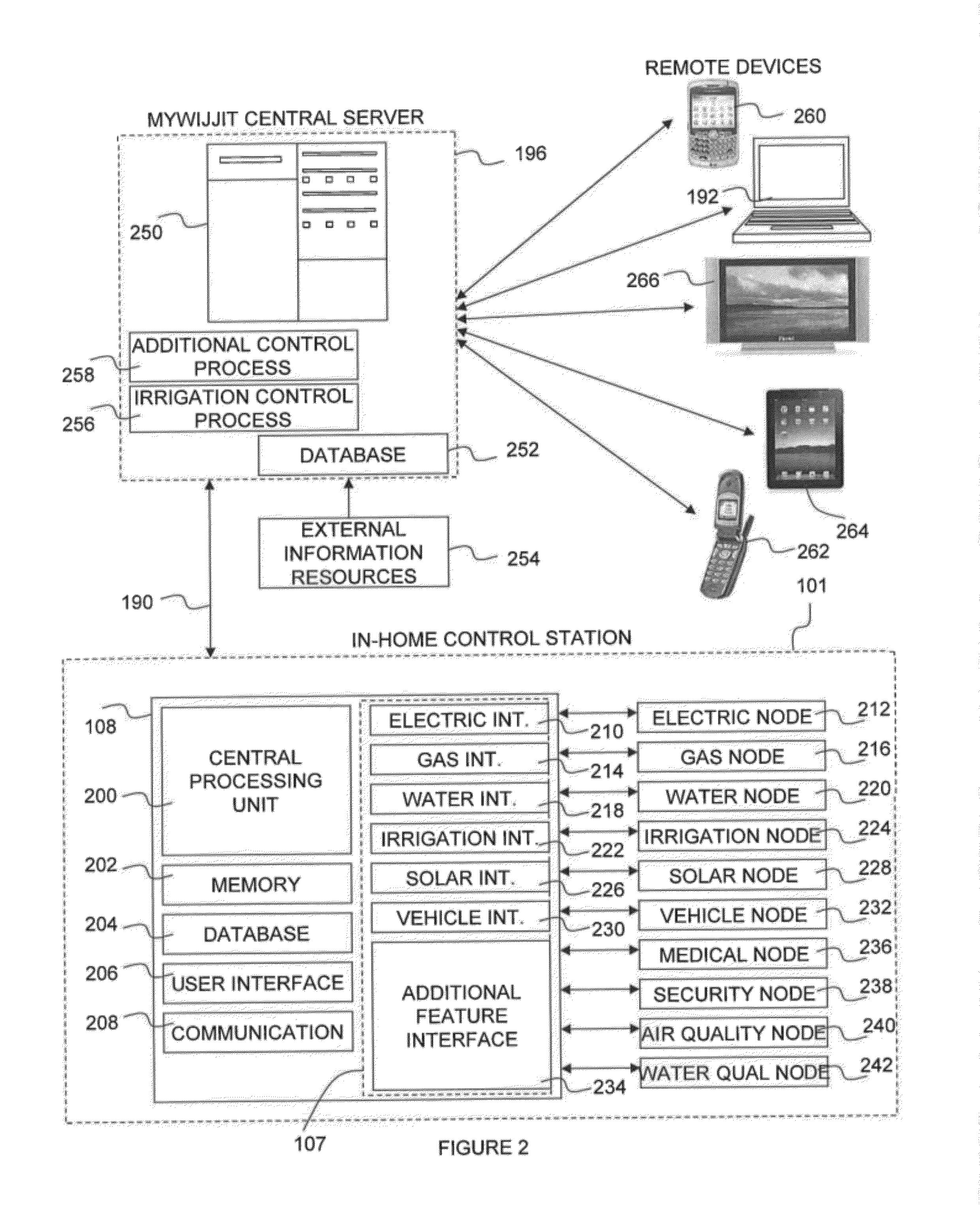
Resource management and control system
InactiveUS20120054125A1Easy to useSave effortProgramme controlData processing applicationsWater useService-level agreement
A resource management and control system includes real-time visibility to energy and water consumption. The resource management platform is flexible and allows users to create a system to suit their individual needs, and to make changes to that platform as their needs change and new needs arise. The resource management and control system monitors electricity and gas consumption, solar production, and water use in real time. The control system includes a number of wireless access nodes for interfacing with the various systems within a property, and also includes monitoring, diagnostic and alerting capabilities. Billing system integration provides historical data for the cost of resource usage and production relative to time, geography and consumer service level agreements and allows the user the ability to directly correlate consumption behaviors with cost implications. Autonomously operating control processes are incorporated to automatically configure and control devices for optimal resource consumption and application.
Owner:CELEVATORON ERIC DOUGLASS +1
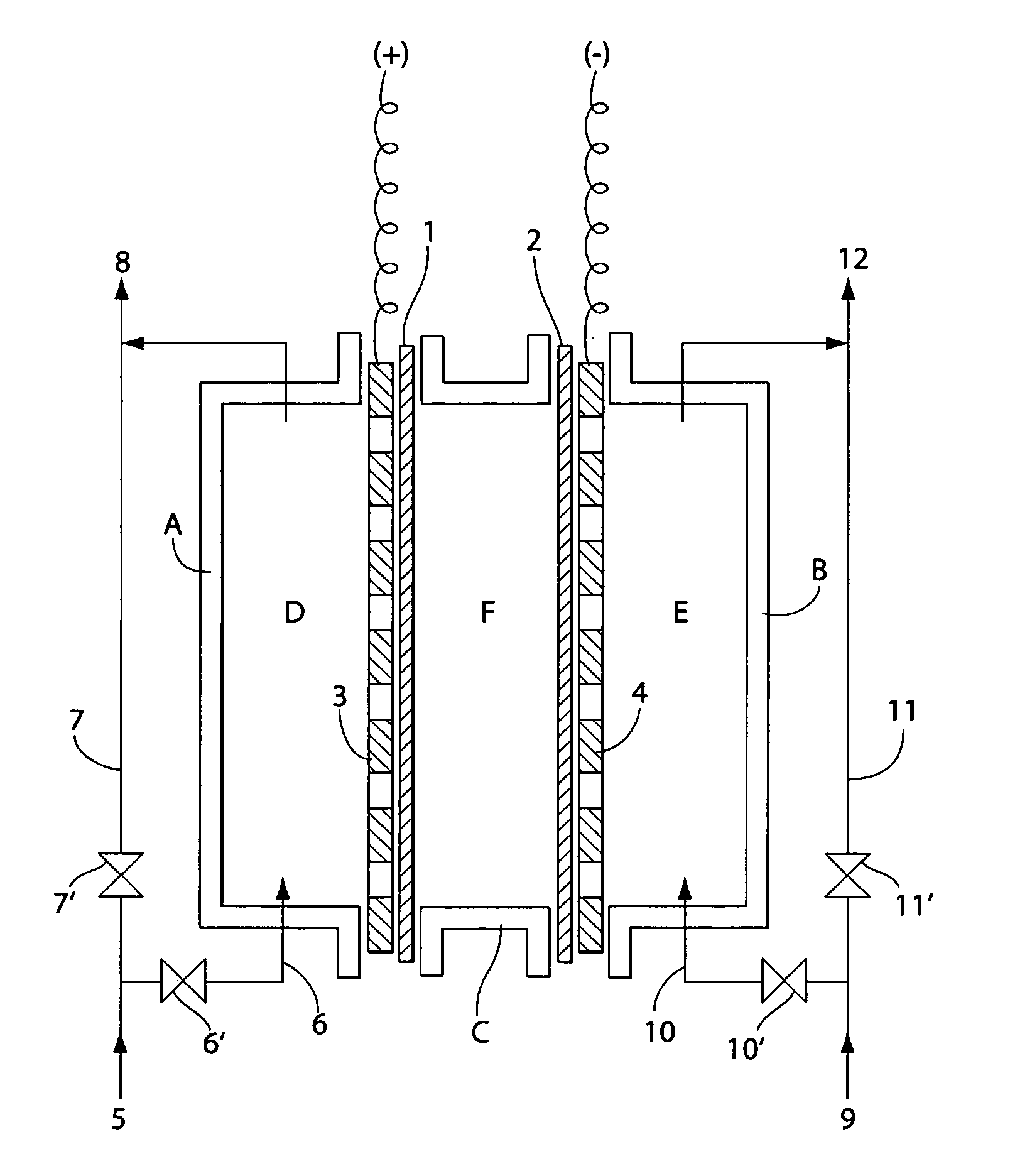
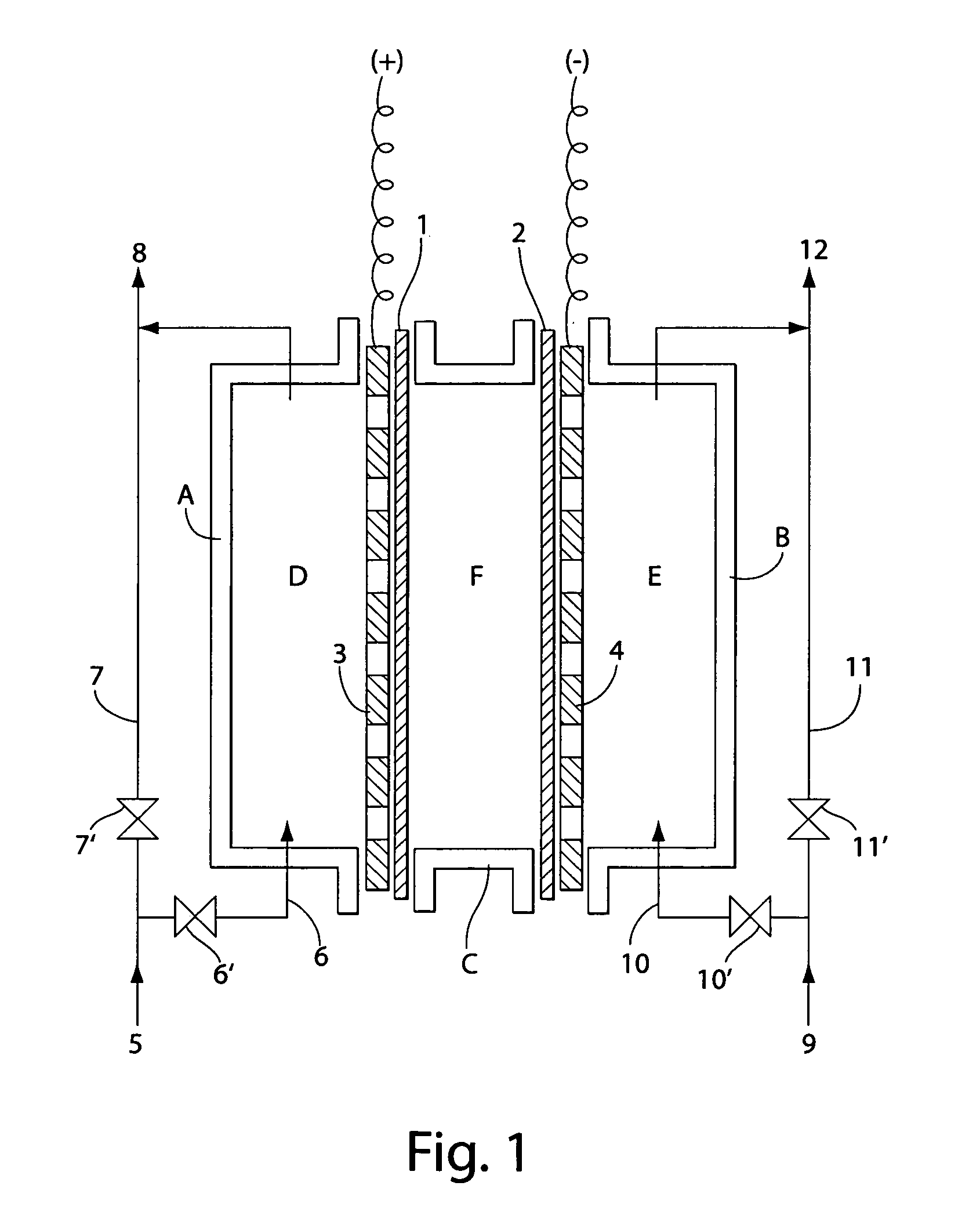
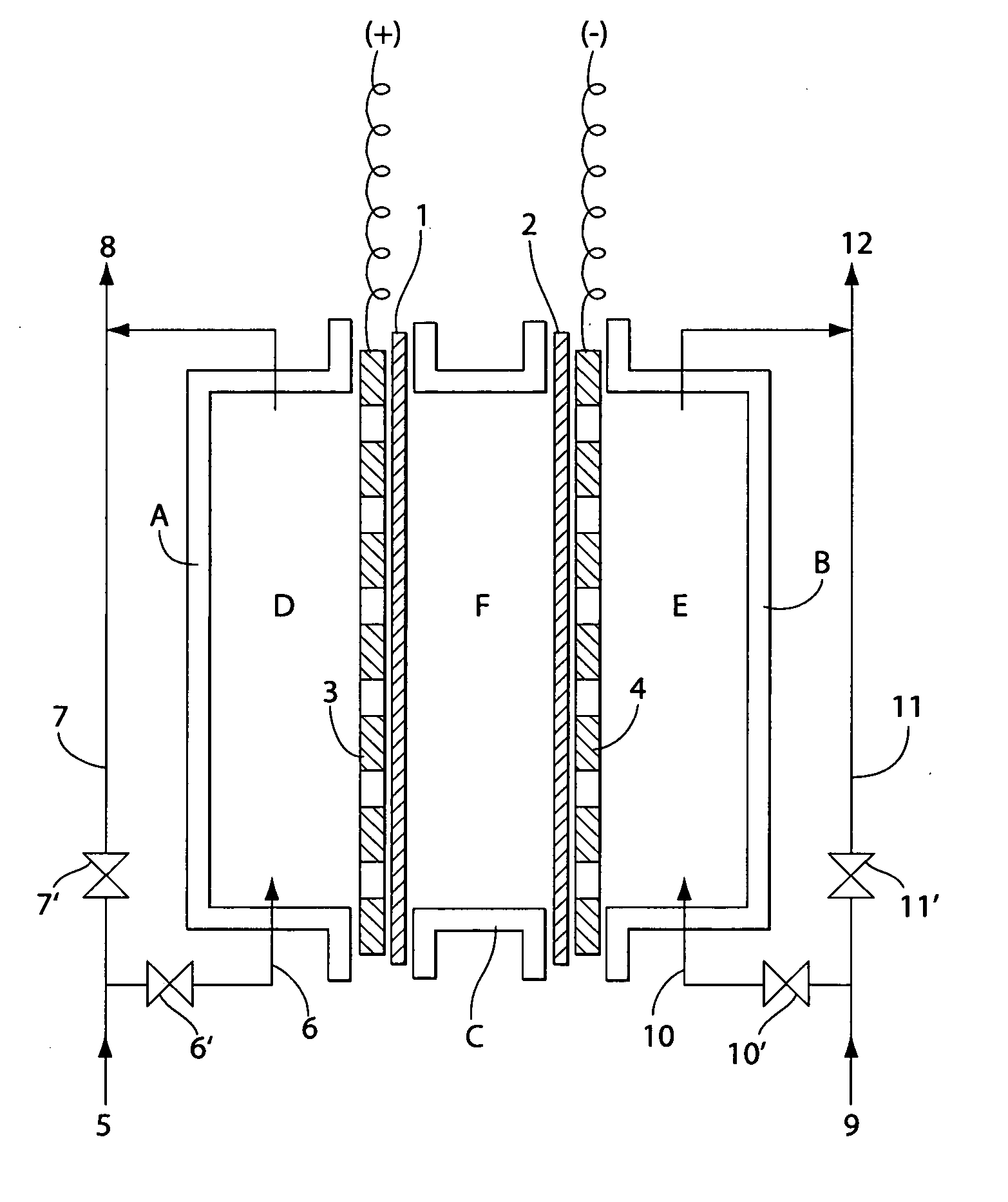
Production of electrolytic water
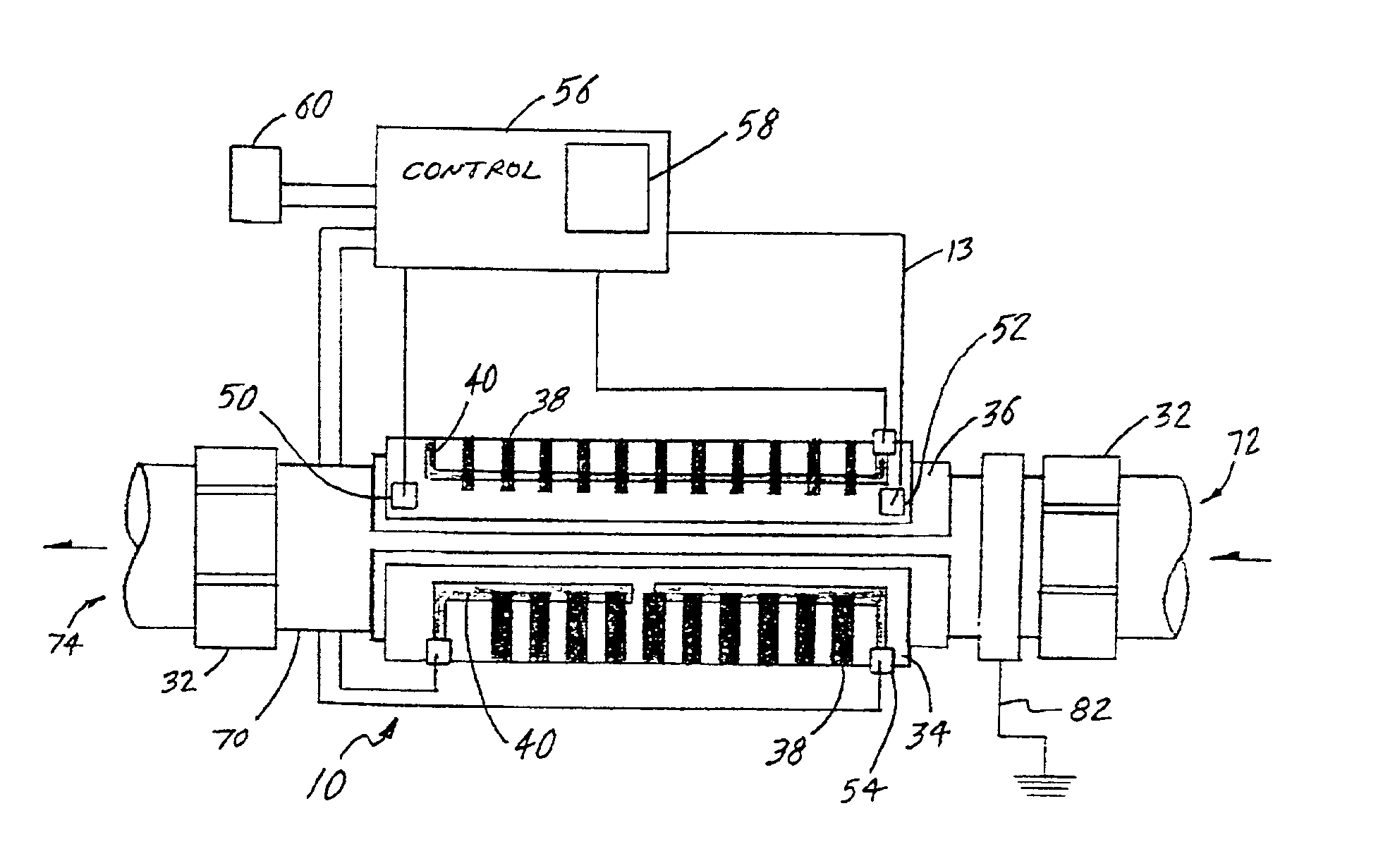
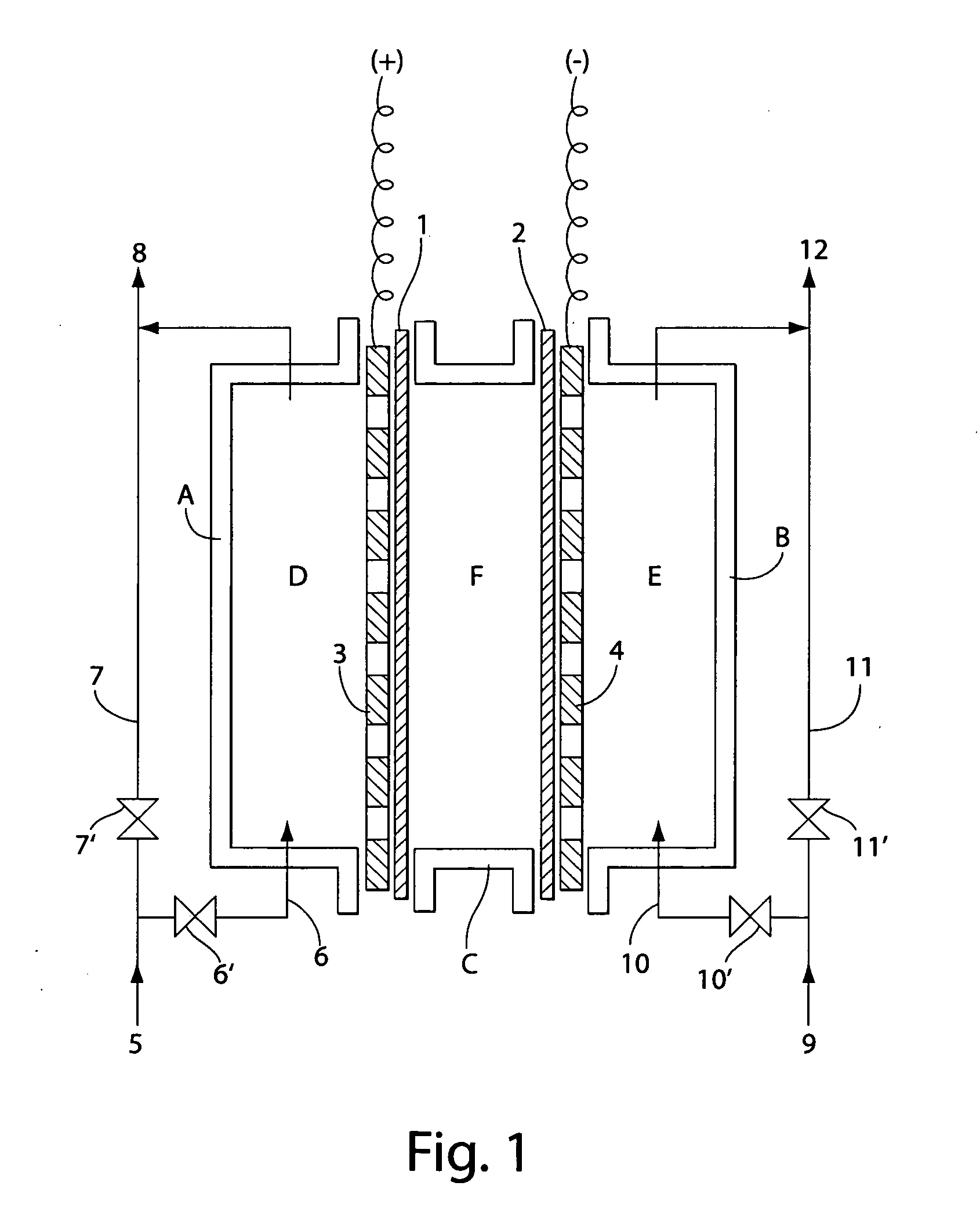
InactiveUS7238272B2Prevent adhesionIncrease productivityCellsLiquid separation by electricityWater useElectrolysed water
Apparatus and methods are provided for producing electrolytic water using three chambers, rigid plates and ion exchange membranes. Benefits include reduced scale production and increased long-term bactericidal effects of the water produced.
Owner:ELECTROLYZER
Systems and methods for water harvesting and recycling
ActiveUS20110174706A1Reduce sunken and uneven surface areaReduce water billsWater treatment parameter controlWater cleaningWater useSprinkler system
This disclosure describes a system for recycling and reusing water from sprinkler systems to water or irrigate a yard or an area of land. The system includes a water reclamation tank that stores water captured from beneath the area of land. When it is time to water the area of land, the sprinkler system draws water from the water reclamation tank. A portion of this water is then recaptured and supplied back to the water reclamation tank for further storage until the next time the sprinkler system is activated. This cyclical process occurs repeatedly and enables a significant reduction in the amount of freshly supplied water used to maintain the area of land.
Owner:RUSSELL AUSTIN
Methods for removing heavy metals from water using chemical precipitation and field separation methods
InactiveUS6896815B2Small sizeChemical cost reductionSolid sorbent liquid separationGold compoundsWater useSludge
A two-step chemical precipitation process involving hydroxide precipitation and sulfide precipitation combined with “field separation” technology such as magnetic separation, dissolved air flotation, vortex separation or expanded plastics flotation, effectively removes chelated and non-chelated heavy metal precipitates and other fine particles from water. In the first-step, the non-chelated heavy metals are precipitated as hydroxides and removed from the water by a conventional liquid / solids separator such as an inclined plate clarifier to remove a large percentage of the dissolved heavy metals. The cleaned water is then treated in a second precipitation step to remove the residual heavy metals to meet discharge limits. In the second precipitation step, any metal precipitant more effective than hydroxide for metal precipitation can be used. The invention improves metal removal, lowers cost because fewer chemicals are used, produces less sludge, and reduces the discharge of toxic metals and metal precipitants to the environment.
Owner:CORT STEVEN L
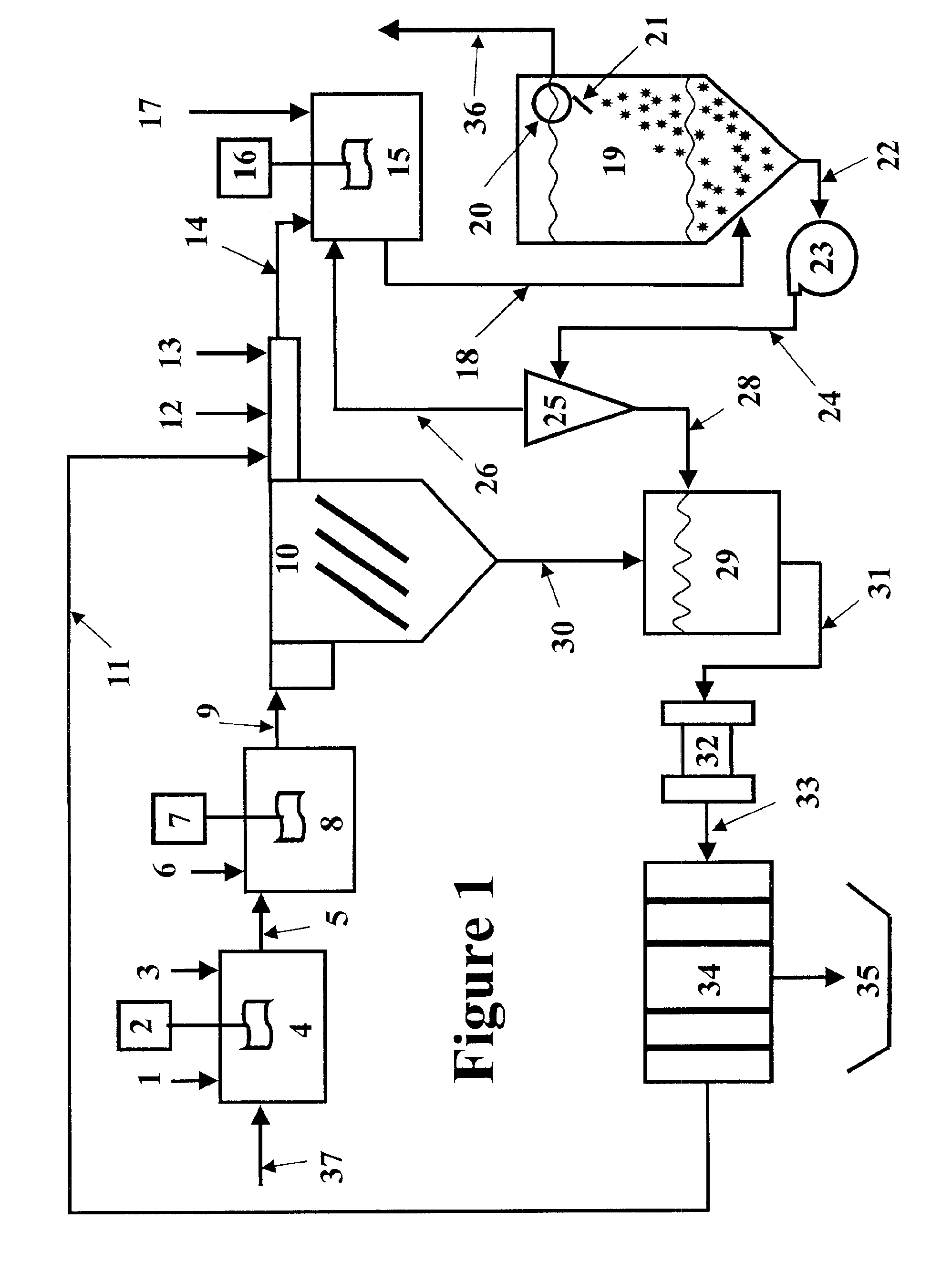
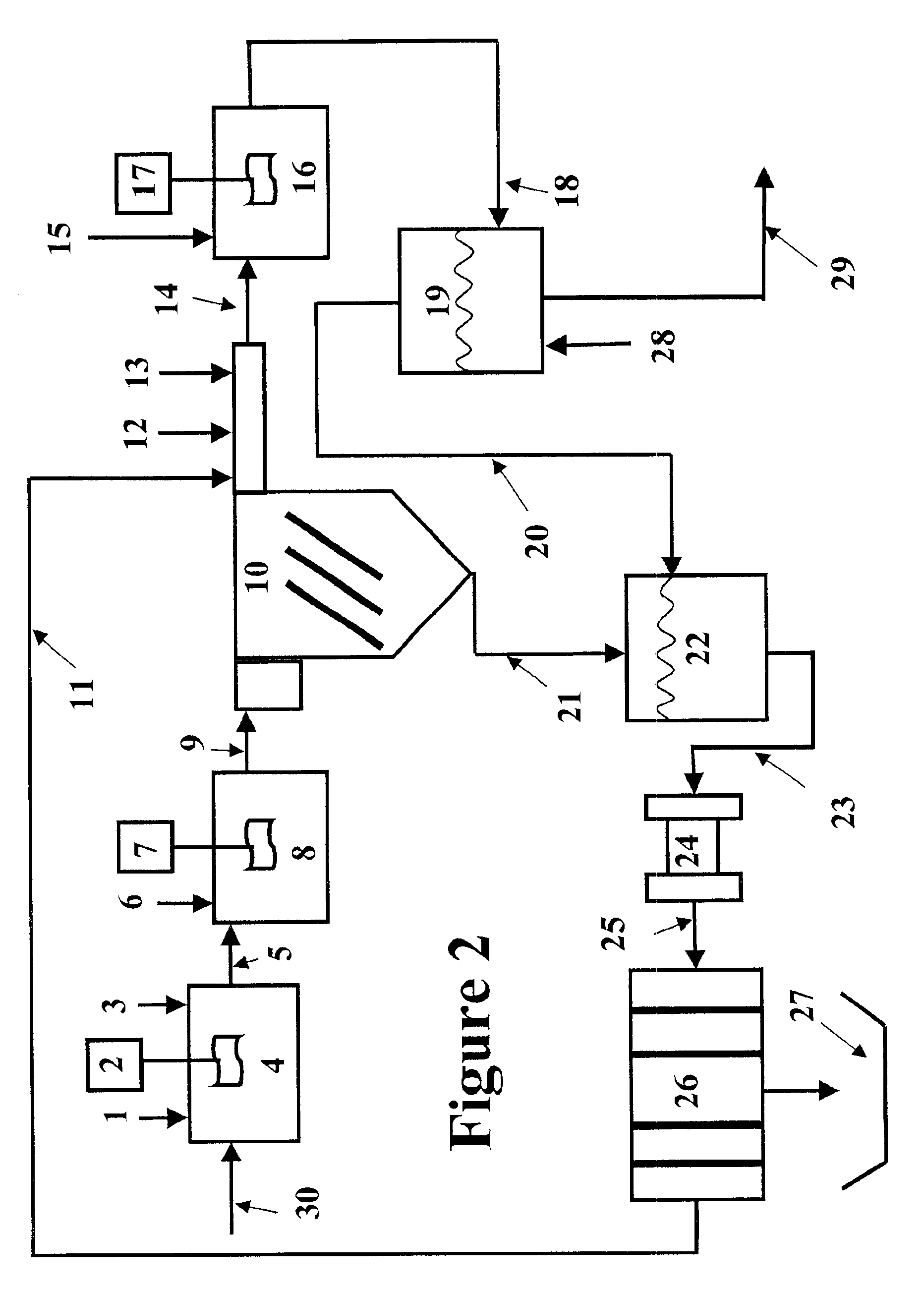
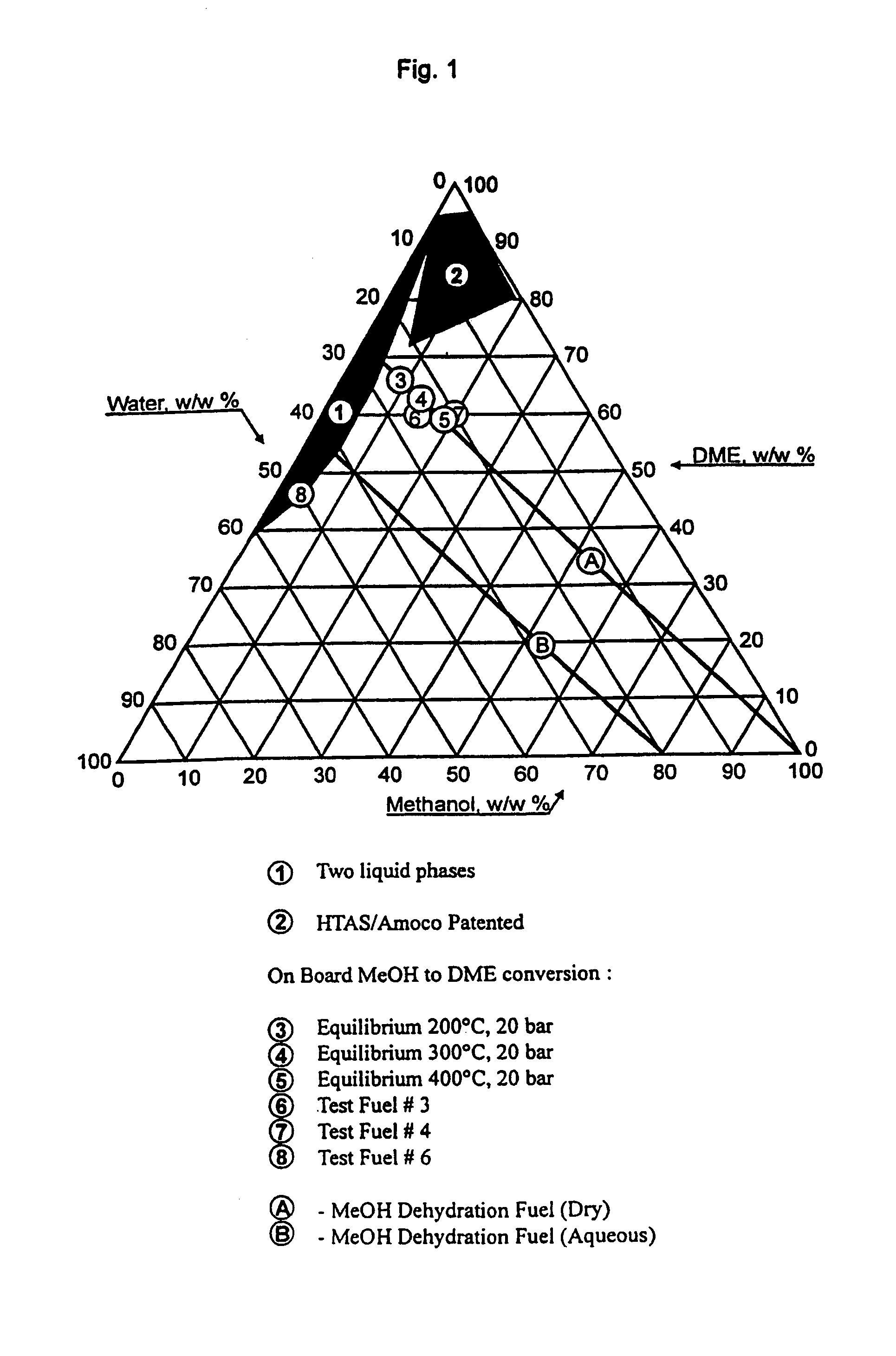
Continuous dehydration of alcohol to ether and water used as fuel for diesel engines
InactiveUS7449034B1Improve fuel efficiencyEmission reductionDomestic stoves or rangesExhaust apparatusWater useCombustion
The present invention relates to an oxygenated fuel composition suitable for use in compression ignition internal combustion engines, equipped with inlet air heater and catalytic alcohol dehydration equipment suitable for chemical equilibrium conversion of methanol and higher alcohol to their associated ether plus water.
Owner:HALDOR TOPSOE AS
Production of electrolytic water
InactiveUS20050189237A1Increase free chlorine production efficiencyPrevent adhesion of scaleCellsLiquid separation by electricityWater useElectrolysed water
Apparatus and methods are provided for producing electrolytic water using three chambers, rigid plates and ion exchange membranes. Benefits include reduced scale production and increased long-term bactericidal effects of the water produced.
Owner:ELECTROLYZER
Air energy water heater and control method and device for same
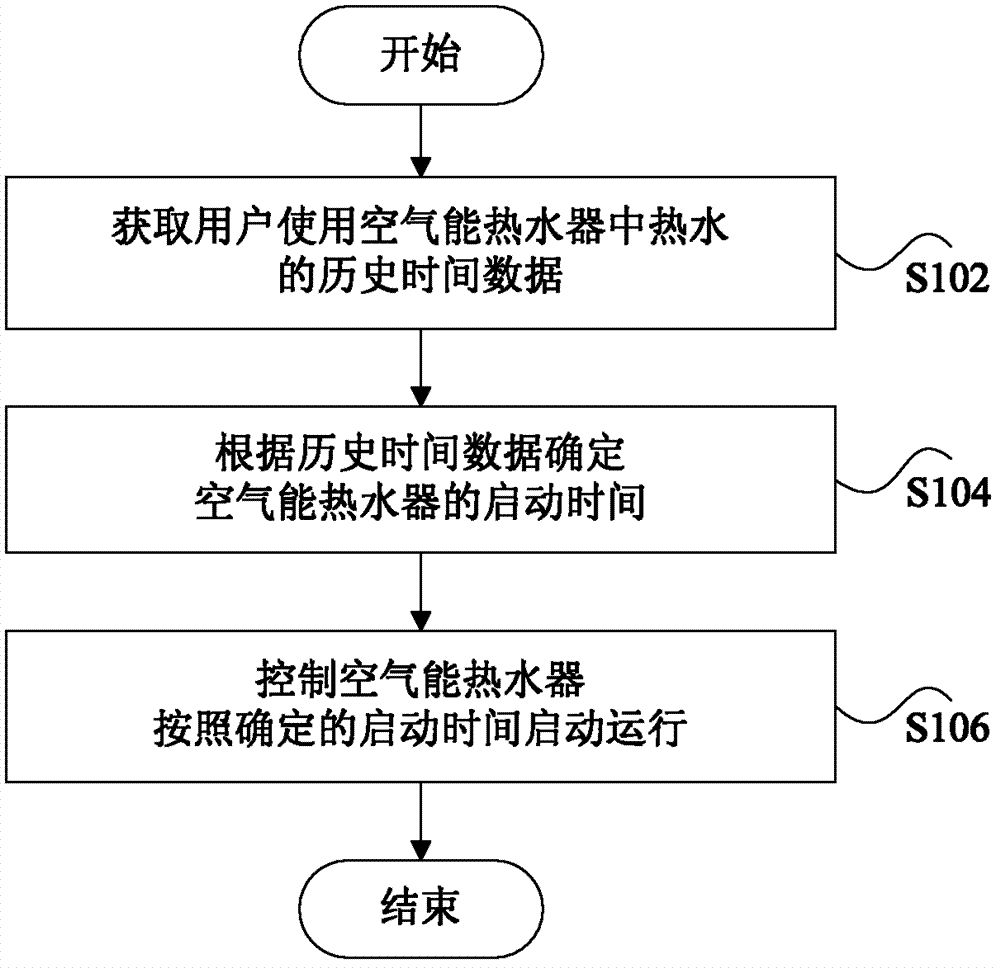
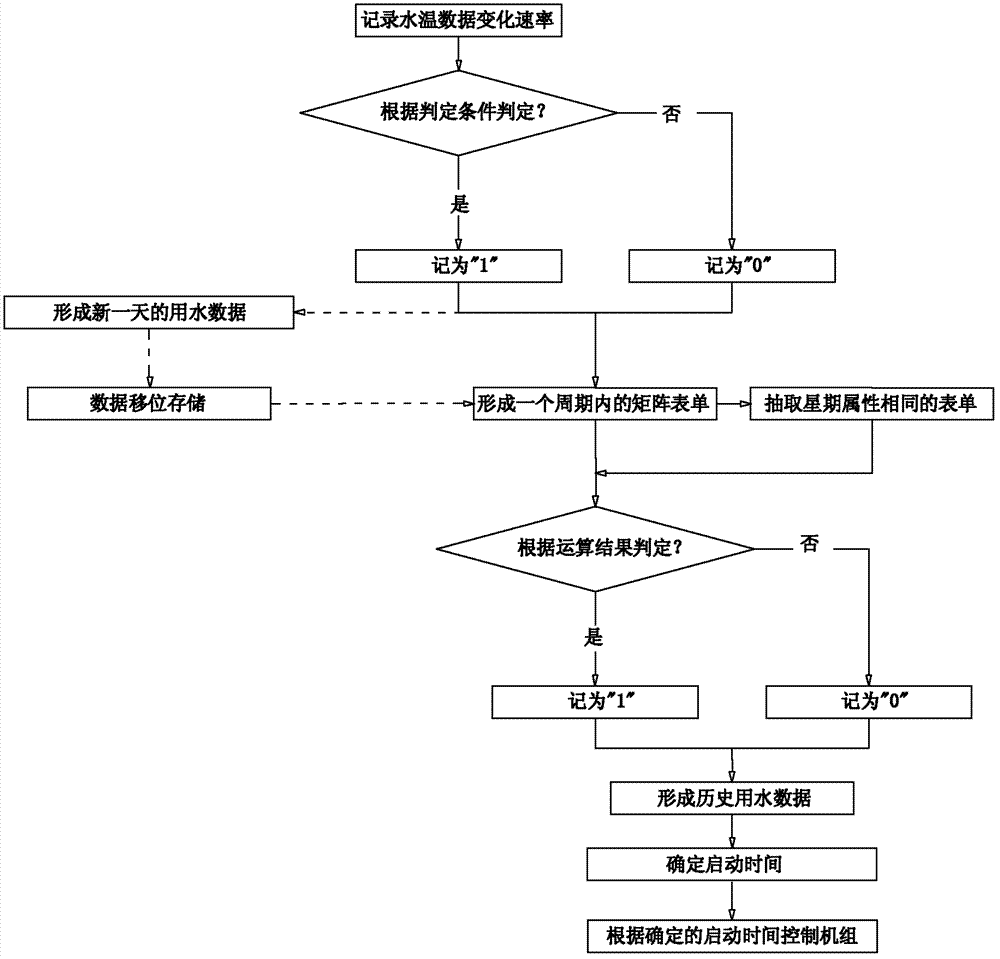
ActiveCN103363670ASolve the problem of high energy consumptionRealize energy-saving controlFluid heatersStart timeEngineering
The invention provides an air energy water heater and a control method and device for the same. The control method comprises obtaining historical time data of utilization of hot water in the air energy water heater by users; determining starting time of the air energy water heater according to the historical time data; controlling the air energy water heater to be started to operate according to the determined starting time. By means of the air energy water heater and the control method and device for the same, the air energy water heater can be controlled to be started to operate according to user own water consumption habits, so that hot water can be provided as user required, frequent heating is not required, and energy-saving control is effectively achieved.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com