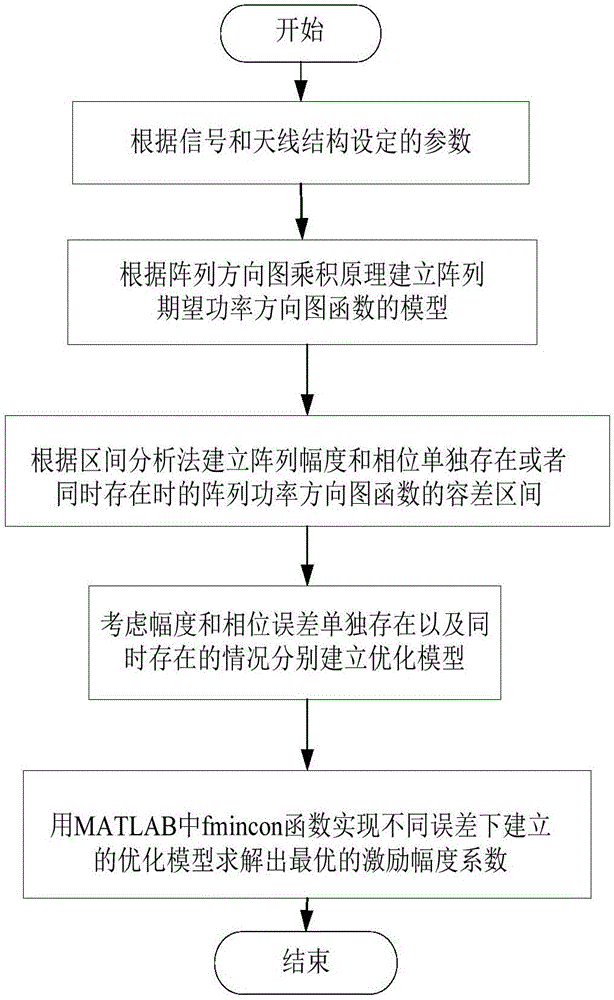
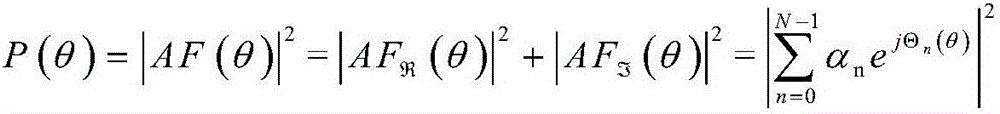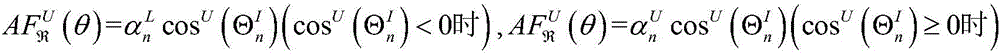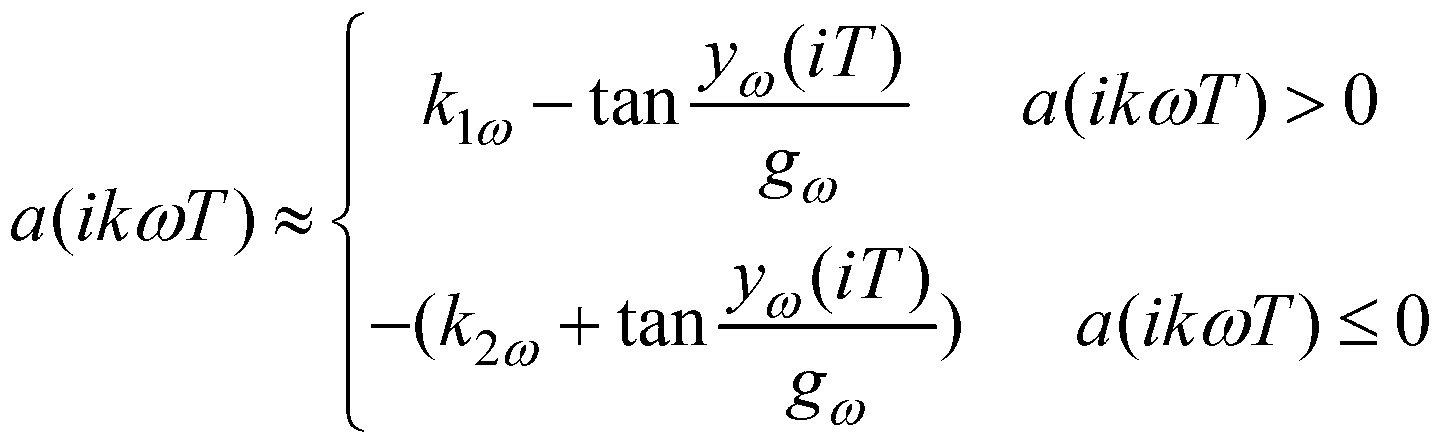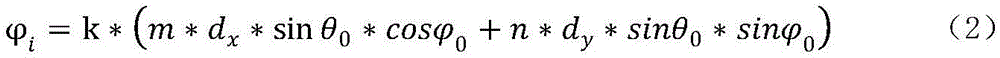Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
172 results about "Excitation amplitude" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
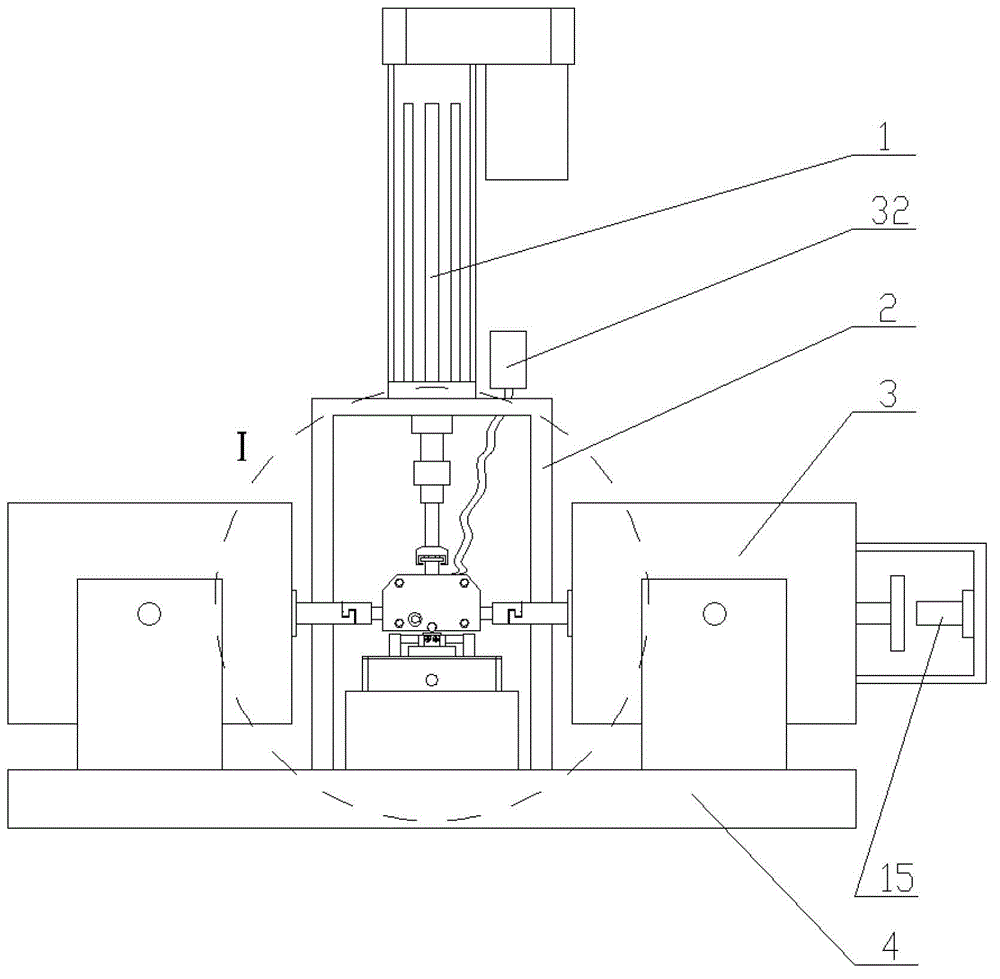
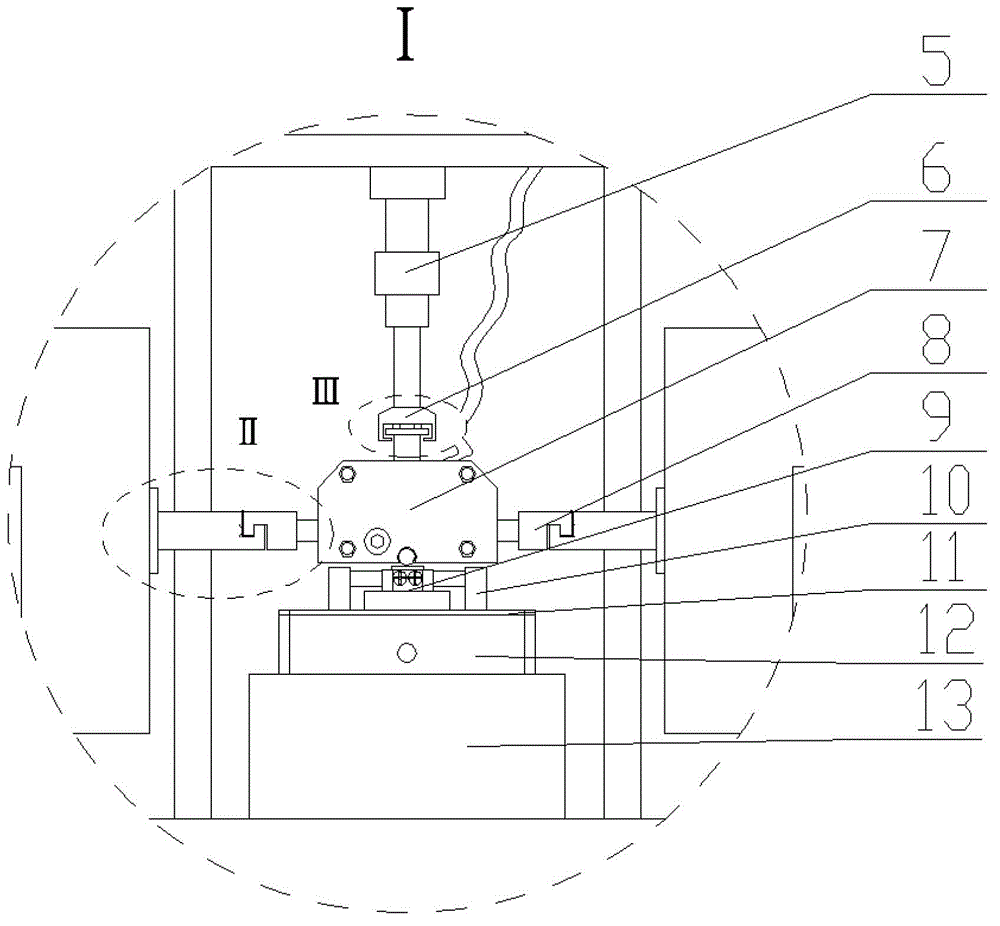
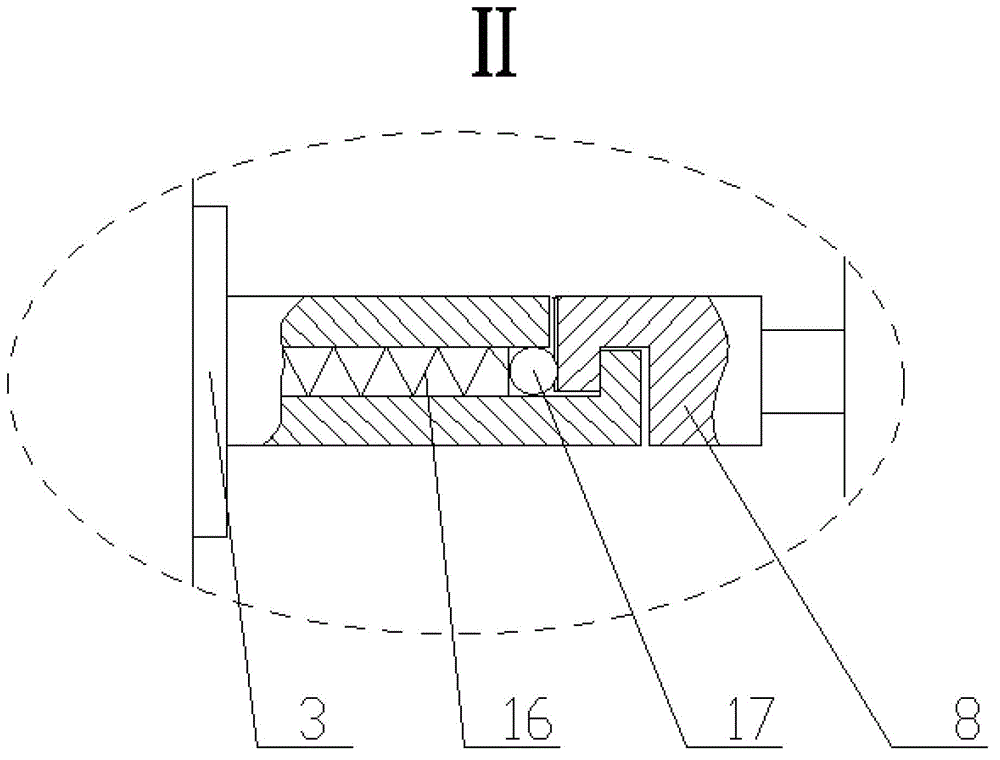
Micro-movement friction and abrasion testing machine
InactiveCN103063530AThe excitation amplitude is adjustableAdjustable vibration modeUsing mechanical meansInvestigating abrasion/wear resistanceClosed loop feedbackEngineering
The invention discloses a micro-movement friction and abrasion testing machine. The micro-movement friction and abrasion testing machine is that two symmetrically arranged electric vibration exciters are adopted and used as excitation sources for generating micro-movement friction between friction pairs; a loading device is adopted and used for applying positive pressure to the friction pairs; a force sensor is adopted and used for collecting a positive pressure signal; a computer data processing device is arranged and produces a closed-loop feedback control together with the acquired positive pressure signal, and the load applied by the loading device is kept constant. In addition, the computer data processing device is used for recording and analyzing the positive pressure signal acquired by the sensor, a micro-movement friction force signal, and a displacement signal, acquired by a displacement sensor, of each electric vibration exciter and then are automatically outputting the signals to generate abrasion performances for a sample A and a sample B of the friction pairs; and therefore, the micro-movement friction and abrasion testing machine has the characteristics of being adjustable in vibration excitation amplitude, variable in vibration mode, convenient to operate and move, high in loading precision, and reproducible in project service condition, the experimental data is high in repeatability and can be used for evaluating the micro-movement friction and abrasion performance of a material.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS +1
Quasi-plane wave generator and generating method based on array antenna
ActiveCN108631046AFlexible changeSimple structureRadiating elements structural formsIndividually energised antenna arraysExcitation amplitudeAntenna feed
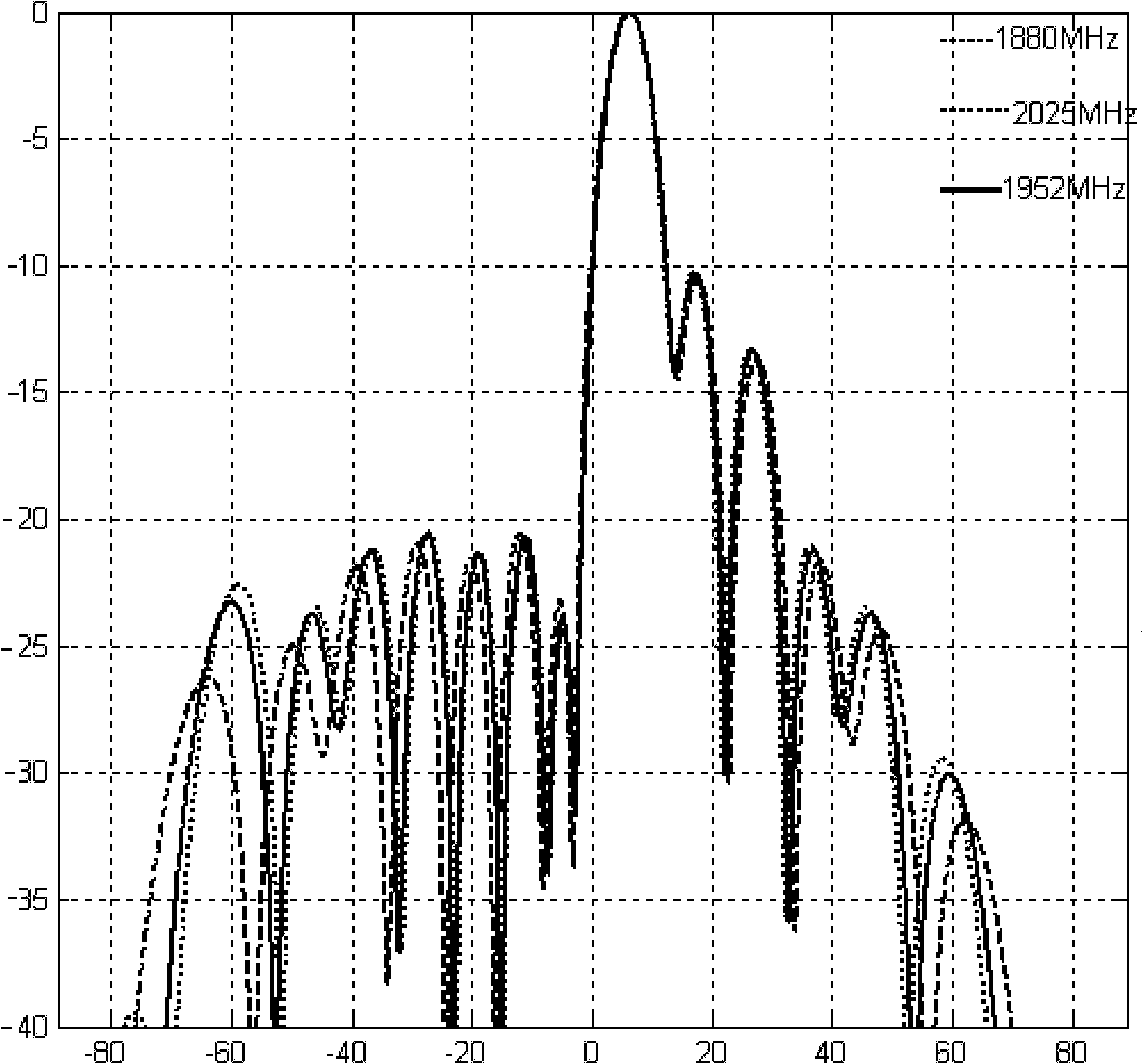
The invention relates to a quasi-plane wave generator and a quasi-plane wave generating method based on an array antenna. The quasi-plane wave generator comprises a two-dimensional array antenna aperture with electrical sizes of length and width exceeding 10 lowest operating frequency wavelengths, an array antenna unit and an array antenna feeding network. The quasi-plane wave generator utilizes aHuygens principle to form a high-quality quasi-plane wave static zone in the vicinity 1.5 times of the aperture size away from the two-dimensional array antenna aperture through performing control over array antenna unit position, excitation amplitude and phases. The quasi-plane wave generator and the generating method based on the array antenna have wide application range, can be applied to directional diagram measurement of an electrical-large antenna and RF index measurement of a system having the electrical-large antenna, and are particularly suitable for base station antenna measurementof 5G mobile communication and measurement of terminal antennas and systems in millimeter wave bands.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Electronic control beam scanning reflection array antenna and beam scanning method thereof
The invention discloses an electronic control beam scanning reflection array antenna and a beam scanning method thereof. The antenna is low in cost and loss and simple in structure. The antenna is characterized in that two initial feed sources are adopted in the antenna to perform irradiation excitation on a reflective array plane, and the excitation amplitude ratio of the feed source 1 to the feed source 2 is changed to change the phase value distribution of a total incident field in the array plane so that electronic control beam scanning can be achieved. The antenna is simple in structure and does not need extra biasing circuits, so that machining is convenient, and stability is high. High-gain beam scanning can be achieved just through the two initial feed sources without extra T / R modules, so that the manufacturing cost is effectively lowered. The antenna is suitable for microwave or millimeter wave or terahertz frequency bands and can be used in wireless communication and radar systems.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
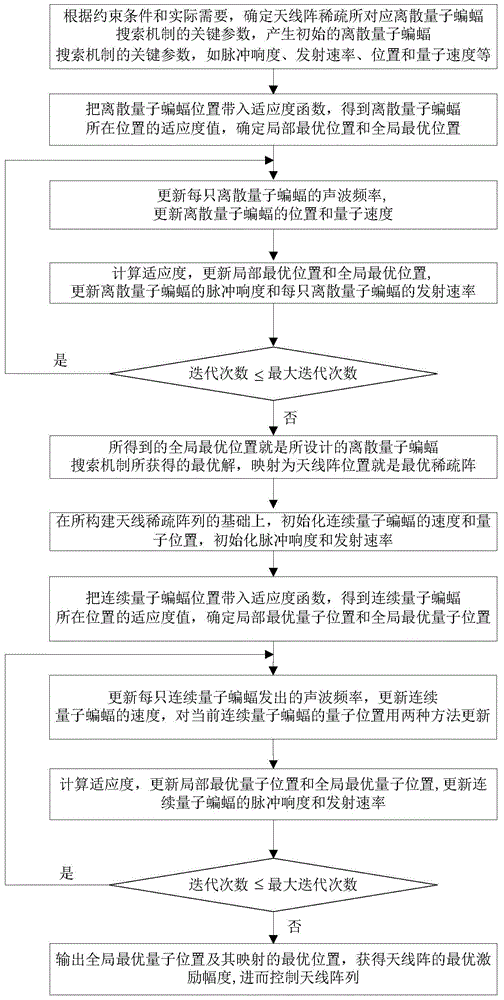
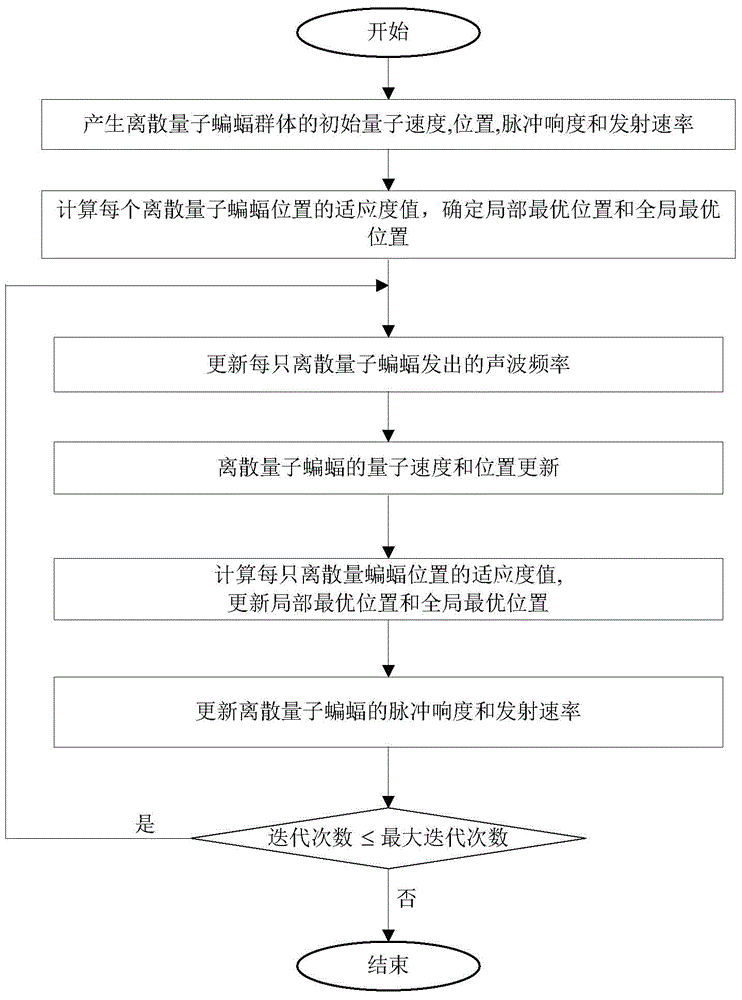
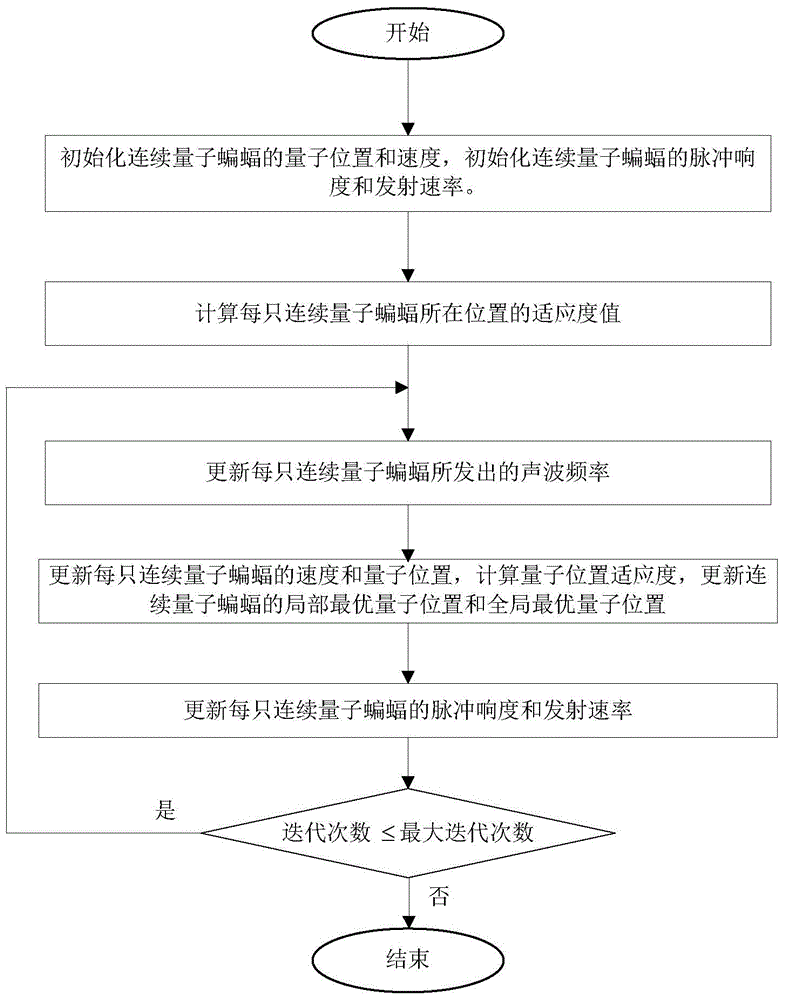
Antenna array sparse construction and directional diagram comprehensive method based on quantum bat searching
ActiveCN104537185ALarge apertureImprove the shortcomings of low convergence speedBiological modelsSpecial data processing applicationsMicrochiropteraQuantum gate
The invention relates to an antenna array sparse construction and a directional diagram comprehensive method based on quantum bat searching. An overall optimal position of a scattered quantum bat group is obtained based on a quantum bat searching mechanism, and the overall optimal position is mapped as a sparse antenna array. On the basis of a constructed sparse antenna array, an overall optimal quantum position and an optimal mapping position of a continuous quantum bat group are obtained based on the quantum bat searching mechanism. Therefore, the optimal excitation amplitude of the antenna array is obtained.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
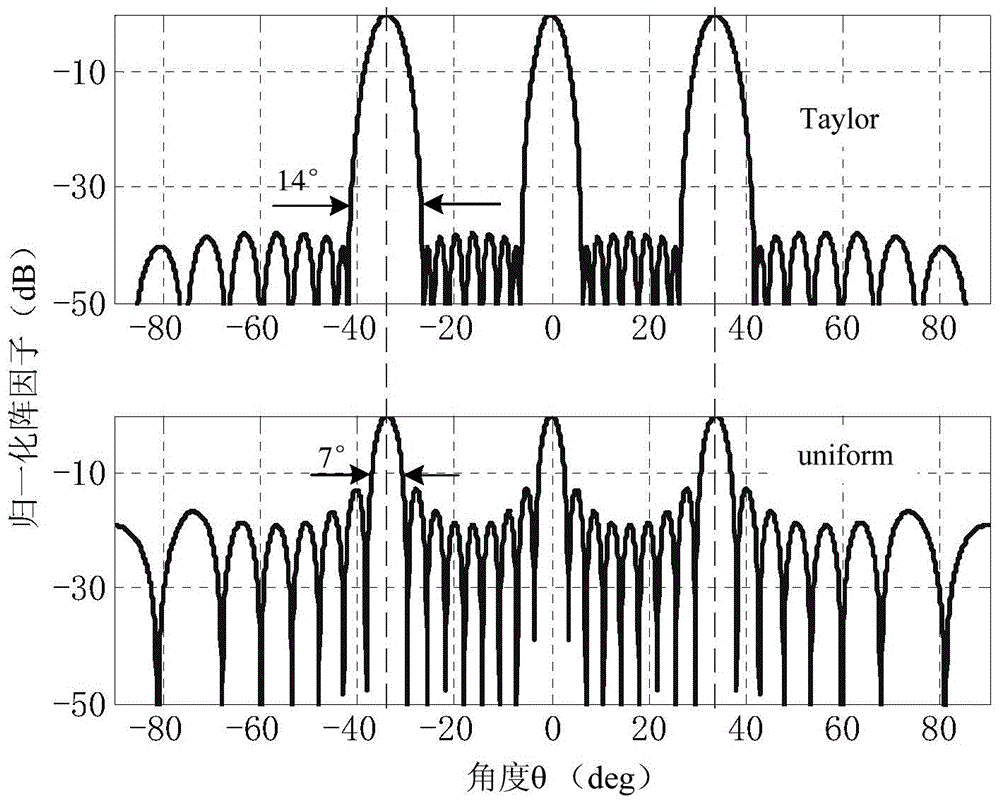
Array antenna Taylor-Schelkunoff polynomial design method
ActiveCN104701639AOffset grating lobesFast convergenceDifferential interacting antenna combinationsRadiation lossEngineering
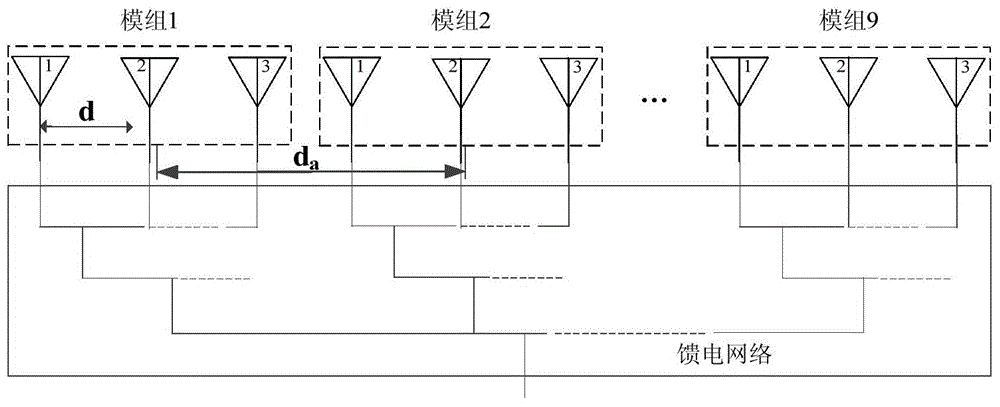
The invention provides an array antenna Taylor-Schelkunoff polynomial design method, and relates to a modular array antenna. The method includes the steps that 1, array antenna parameters are selected; 2, the array antenna is divided into at least two modules; 3, a Taylor synthetic method is selected to calculate an array factor directional diagram of the modules; 4, an SPM synthetic method is selected to obtain a directional diagram with null steering, and the null steering angle is made to correspond to the grating lobe angle of the array factor directional diagram; 5, a directional diagram multiplication principle is adopted, the grating lobe of the array factor directional diagram is offset, the low-minor lobe radiation directional diagram is achieved, and the excitation amplitude of all arrays is controlled through the preset null steering angle; 6, if the obtained low-minor lobe radiation directional diagram cannot meet the design requirement, step 2 is executed, and the array antenna is regrouped. According to the array antenna Taylor-Schelkunoff polynomial design method, the excitation amplitude of all the arrays can be controlled through the preset null steering angle, a modular feed network is achieved through an equipower distributor with the phase and impedance being matched, the radiation loss is reduced, and the design and manufacturing cost is lowered.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
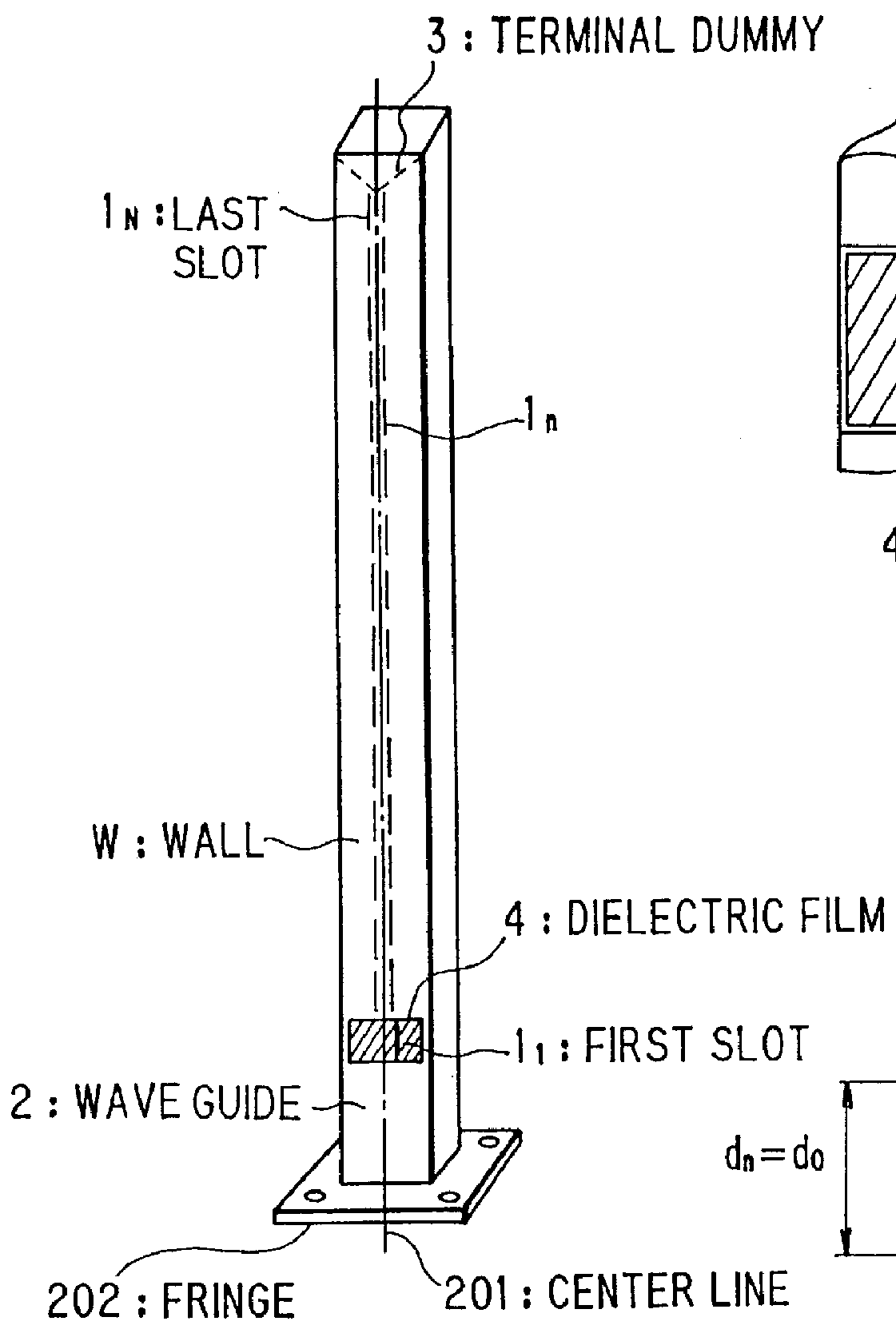
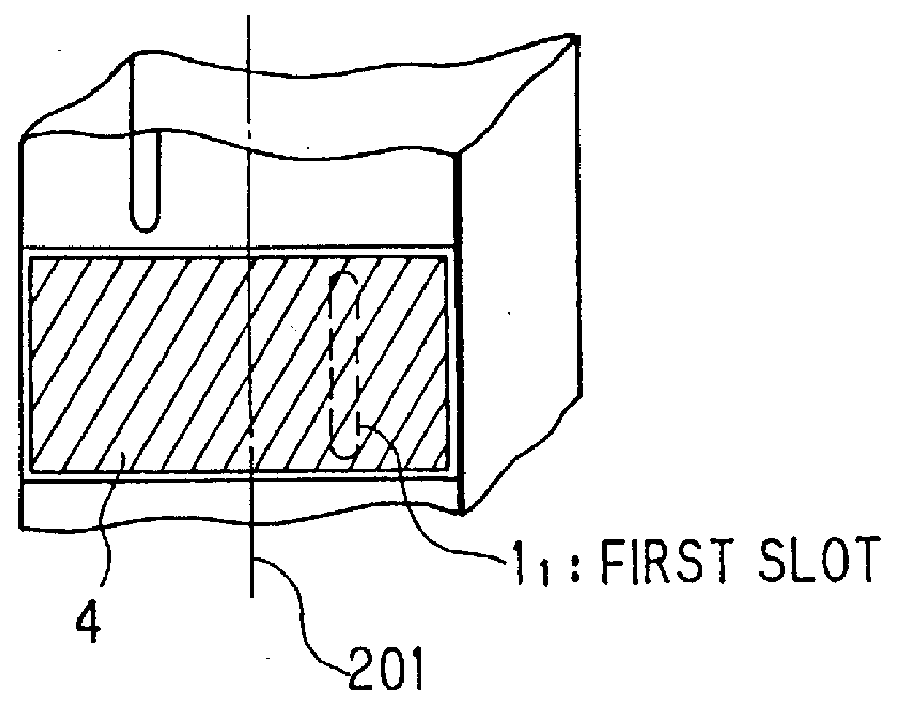
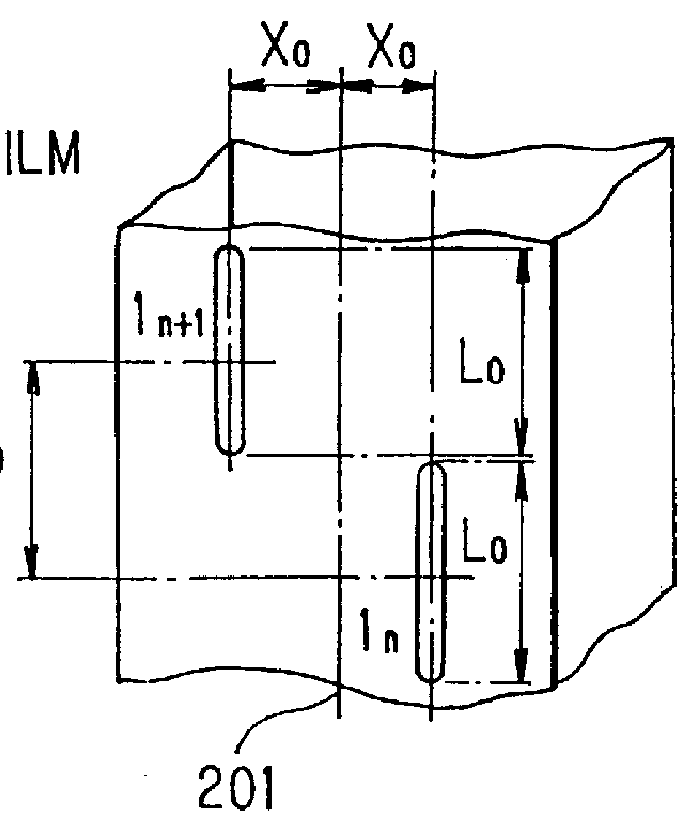
Shaped beam array antenna for generating a cosecant square beam
InactiveUS6107964AEasy to manufactureSimple designSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsShaped beamPhase difference
To simplify designing and fabrication of a shaped beam array antenna for generating a cosecant square beam, slots having the same size are arranged with the same separation on a wall of a wave guide. The slots yield an excitation amplitude distribution wherein the excitation amplitude distribution attenuates exponentially from a feeder side of the wave guide to the terminal side of the wave guide where a terminal dummy is provided. The excitation phase distribution is linear with a slight variation. The first slot nearest to the feeder side is modified to produce an excitation phase difference between the first and the second slot.
Owner:NEC CORP
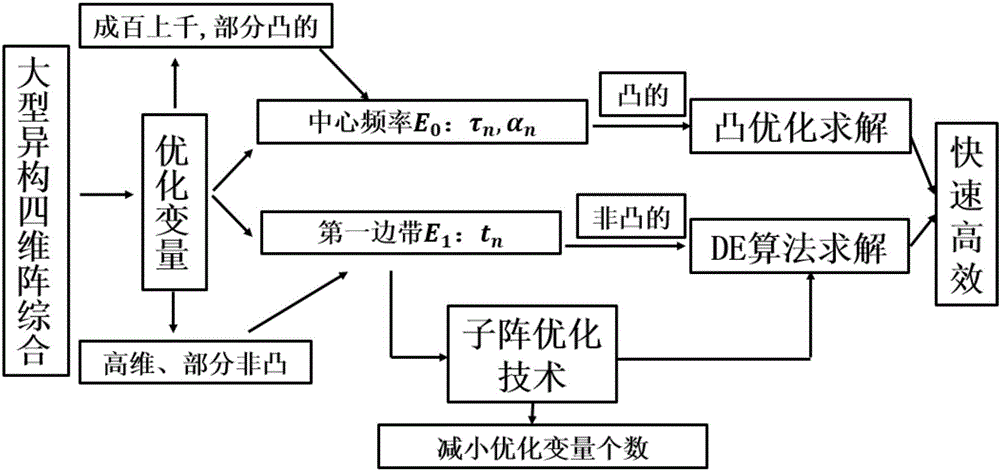
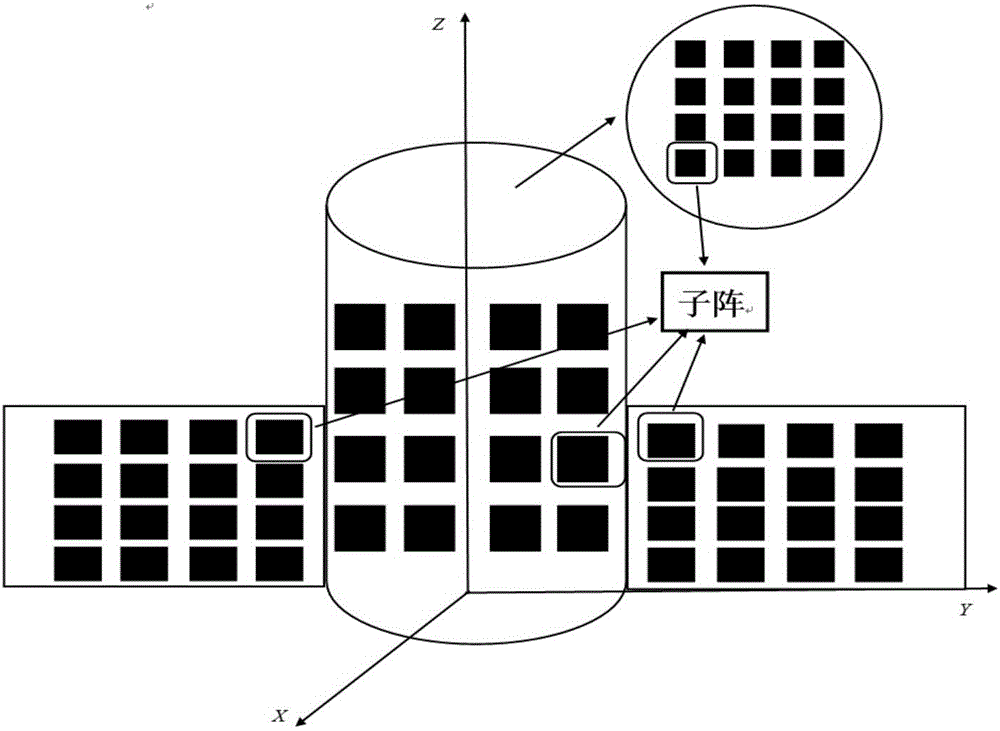
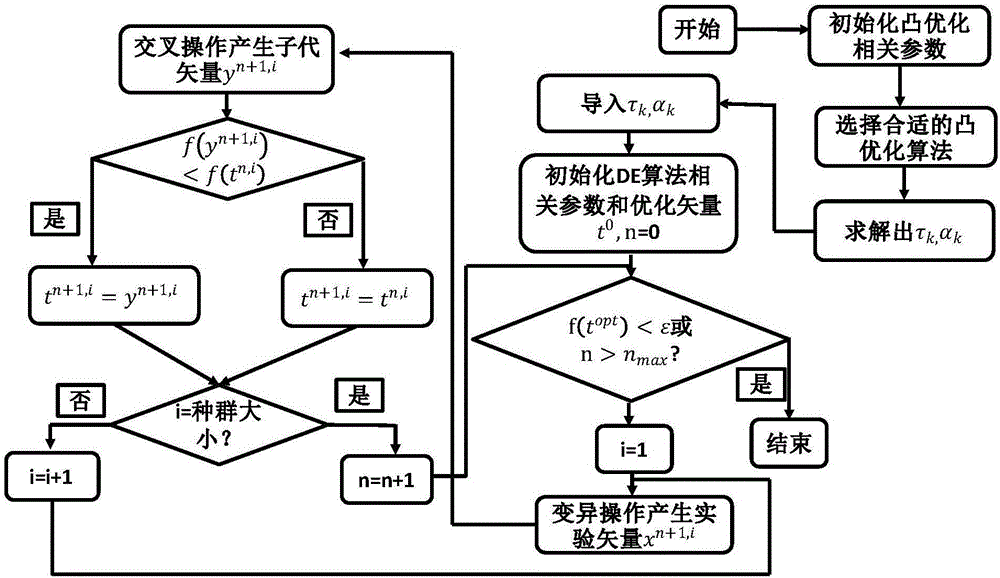
Combined optimization method used for synthesis of large-scale heterogeneous four-dimensional antenna array
ActiveCN106329153AReduce difficultyHigh speedAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesAntenna arrays manufacturePhase shiftedCombined method
The invention discloses a combined optimization method used for synthesizing a large-scale heterogeneous four-dimensional antenna array which employs a pulse phase shift sequence. According to the combined method, a part of convexity of an original synthesis problem is fully utilized, and the original complicated synthesis problem is divided into two sub-problems; and then optimization is performed by two steps: step 1, rapidly optimizing an equivalent excitation amplitude (switch switch-on duration) and a static excitation phase with high efficiency according to constraint of a field at a center frequency by employing a convex optimization algorithm; and step 2, optimizing a switch switch-on initial time with the combination of a subarray optimization technology by employing a differential evolution algorithm according to the requirement of a directional diagram by a sideband so that the whole optimization problem can be rapidly solved with high efficiency. According to the method, the biggest innovation is the discovery of the essential characteristic of the original optimization problem, optimization is performed with the combination of the convex optimization algorithm and the differential evolution algorithm, the speed and the efficiency of the whole optimization process are greatly increased, and the effect of getting double the result with half the effort is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Damage detection using laser vibrometry
InactiveUS20110314915A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResonant frequencyData setLaser vibrometry
Methods and apparatus for exciting a structure and determining its structural integrity. In particular, methods of nonlinear analysis are used to compare first and second response datasets, each dataset resulting from a different excitation amplitude that the other dataset.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Synthesis method of array antenna shaped beam with controllable excitation amplitude dynamic range
ActiveCN106650097AUniversalHigh utility valueAntenna arraysDesign optimisation/simulationShaped beamMathematical model
The invention discloses a synthesis method of an array antenna shaped beam with a controllable excitation amplitude dynamic range, and relates to array antennae. The method comprises the following steps: expressing an array antenna shaped power pattern synthesis problem with the controllable excitation amplitude dynamic range into a mathematical model; introducing an auxiliary variable zeta, performing equality conversion on the constraint of an array excitation amplitude dynamic range ratio, so as to ensure that the constraint of the array excitation amplitude dynamic range ratio is equivalent to the constraint of a square mode on each array element excitation; respectively converting power constraint conditions of a main lobe and a side lobe of a shaped beam into the mode of a trace of a matrix Tr (.), and meanwhile further expressing the DRR constraint of the array element excitation into a constraint mode of a trace of a matrix. As the synthesis problem belongs to a typical nonlinear and nonconvex problem, certain nonconvex constraints are loosened, and meanwhile the looseness is controlled through certain other measures, the nonconvex problem is converted into a convex problem, further a characteristic value decomposition method can be utilized for solving, and finally excitation amplitude distribution meeting requirements is finally obtained.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
Optimizing method for processing signal errors of different array antennas
ActiveCN106788799AOptimal Array Excitation ParametersImprove robustnessTransmitters monitoringAntenna designProcess error
The invention discloses an optimizing method for processing signal errors of different array antennas, and relates to the signal processing field of the antenna arrays, especially to an optimized design method for processing errors of the different arrays. According to measured amplitude array and array element phase error of reception signals of an array, an IA algorithm is used to determine an array factor model, an accurate change boundary of a power directional diagram is calculated, a convex optimization model of an array excitation amplitude is established, and a power directional diagram satisfying the performance requirement is obtained in an integrated way according to an obtained optimization excitation weight. Compared with an IA-PSO algorithm in a global random searching manner, the method of the invention can be used to obtain a better array excitation parameter under the same error, and the amplitude error of the array is kept relatively stable. Important parameters including the sidelobe level, the main lobe width and the array direction coefficient can be controlled effectively in antenna design.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
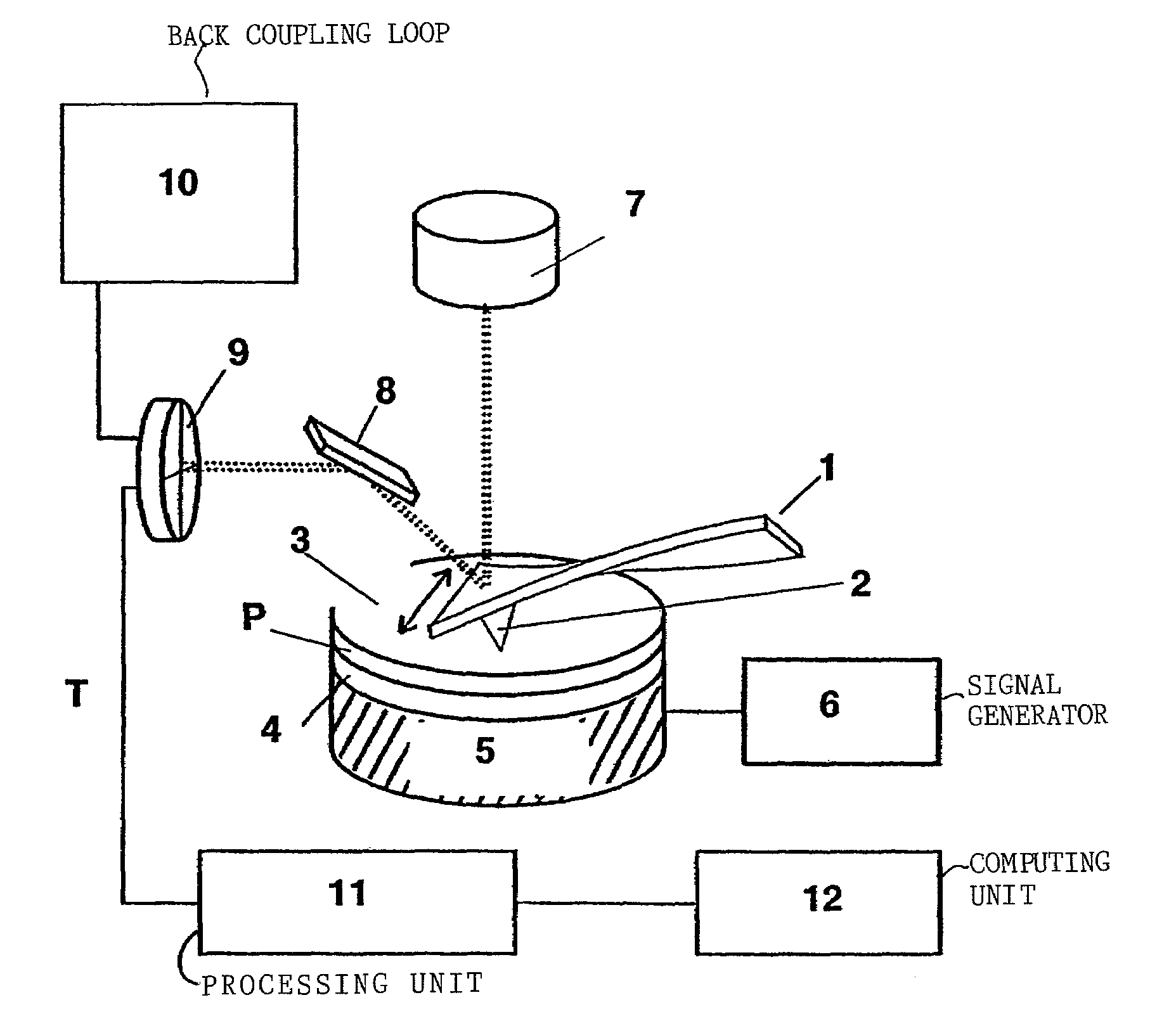
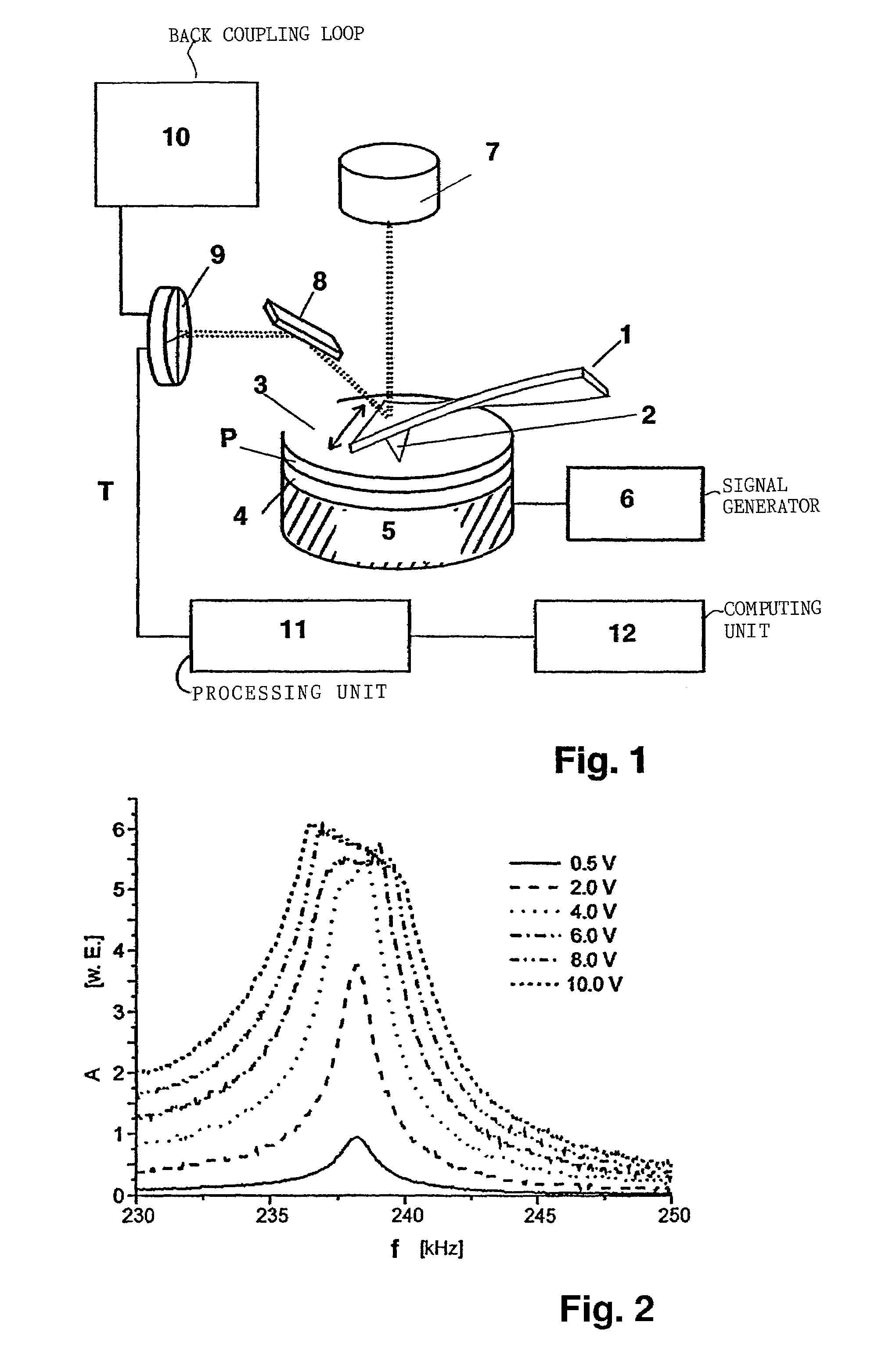
Method for determining tribological properties of a sample surface using a scanning microscope (sem) and associated scanning microscope
InactiveUS20060150719A1High locally resolved determinationInformation obtainedVibration measurement in fluidUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationHarmonic vibrationTorsional vibration
Described is a method for examining a surface of a sample using an atomic force scanning microscope (AFM) comprising a cantilever with a longitudinal extension along which a measuring tip is disposed, which is selectively arranged relative to said sample surface by a driver means and whose spatial position is detected using a sensor unit, and said microscope is provided with at least one ultrasound generator, which initiates vibration excitation at a given excitation frequency between said sample surface and said cantilever, the measuring tip of which is brought into contact with said sample surface in such a manner that said measuring tip is excited to vibrations which are oriented lateral to said sample surface and perpendicular to said longitudinal extension of said cantilever and that the torsional vibrations induced in said cantilever are detected and analyzed by means of an evaluation unit. The invention is distinguished in that the vibration excitation occurs in such a manner that the oscillations executed by the measuring tip have higher harmonic vibration parts relative to the excitation frequency, that vibration excitation is conducted at excitation amplitudes which lead inside the cantilever to torsional amplitudes, the maximum values of which form a largely constant plateau value despite increasing excitation amplitudes and the resonance spectra of which undergo, in the range of the maximum values of the torsional amplitudes, a widening of the resonance spectrum which is determinable by a plateau width, and that used for examining the sample surface are the resonance spectra, preferably the plateau value, the plateau width and / or the gradient of the respective resonance spectra.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method for determining tribological properties of a sample surface using a scanning microscope (sem) and associated scanning microscope
InactiveUS7360404B2High locally resolved determinationInformation obtainedVibration measurement in fluidUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationScanning electron microscopeResonance spectrum
A method for examining a surface of a sample is described using an atomic force scanning microscope (AFM) comprising a cantilever with a longitudinal extension along which a measuring tip is disposed, which is selectively arranged relative to the sample surface by a means for driving and whose spatial position is detected using a sensor unit. Vibration excitation is conducted at excitation amplitudes which produce inside the cantilever torsional amplitudes with maximum values which form a largely (substantively) constant plateau value despite increasing excitation amplitudes and the resonance spectra, in a range of maximum values of the torsional amplitudes, a widening of the resonance spectrum which is determinable by a plateau width. The resonance spectra, preferably the plateau value, the plateau width and / or the gradient of the respective resonance spectra are used for examining the sample.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method for optimizing linear array antenna radiation pattern
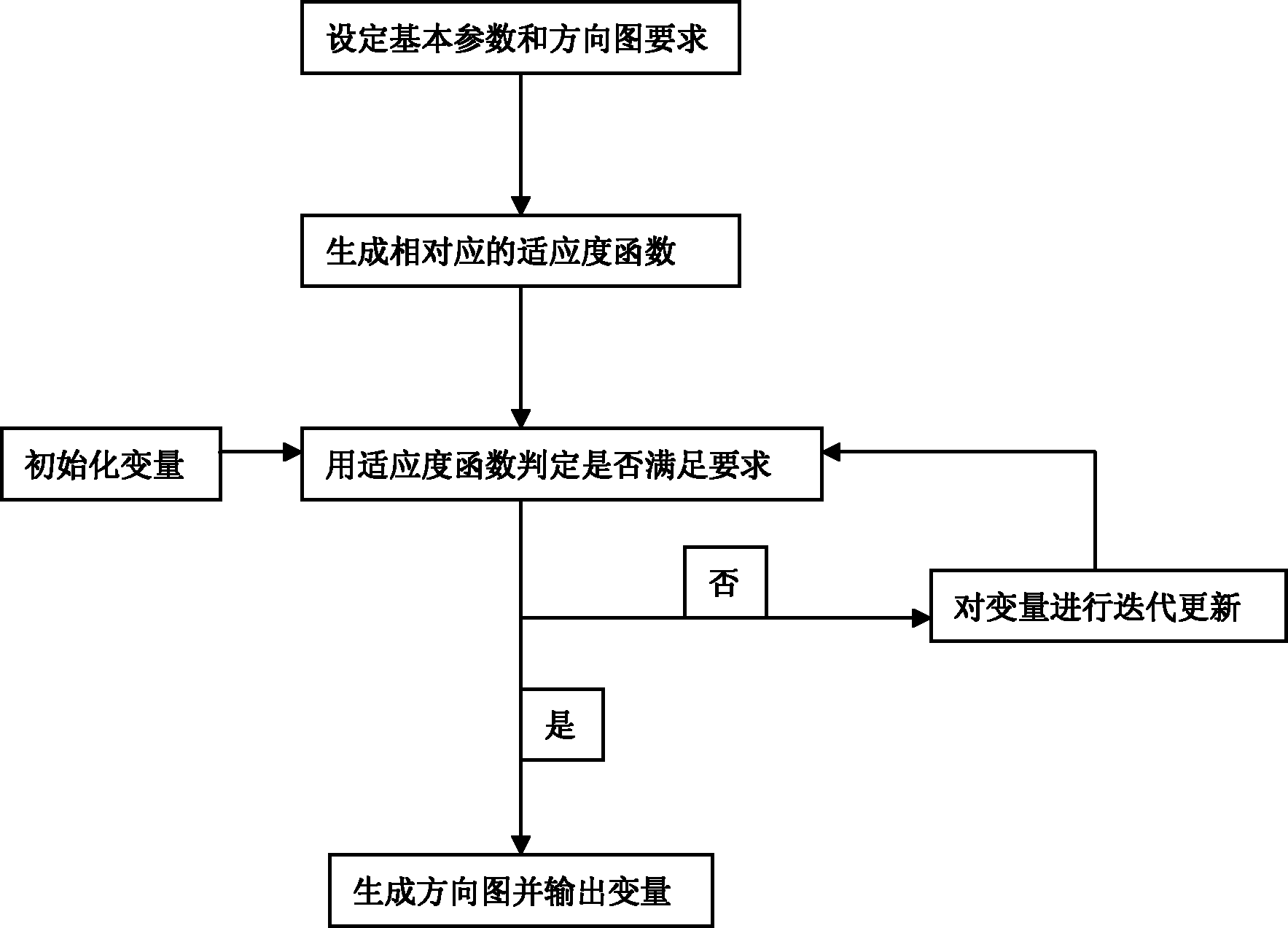
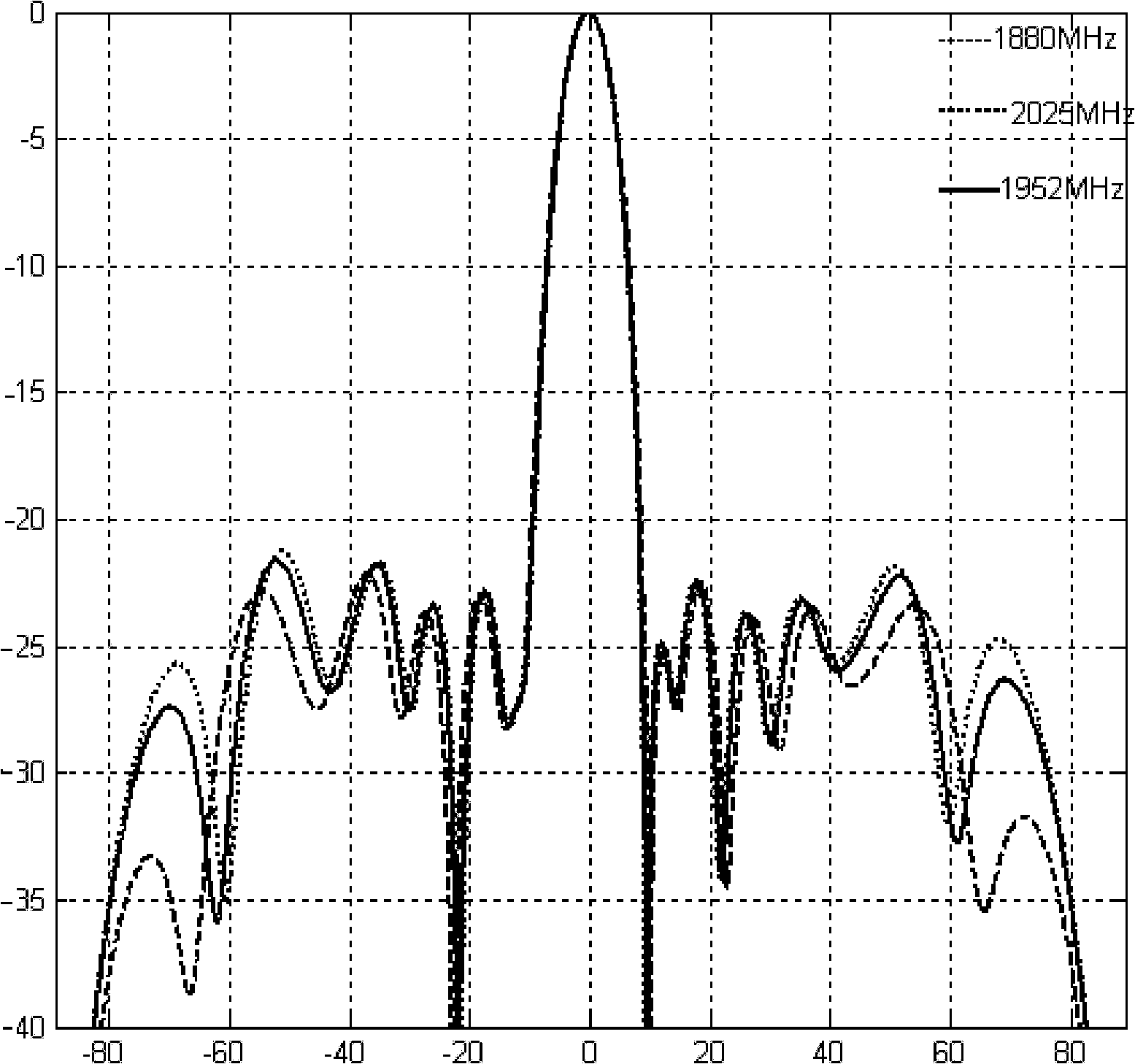
InactiveCN102122765AImprove computing efficiencySlow convergenceBiological modelsAntennasSystem requirementsExcitation amplitude
The invention discloses a method for optimizing a linear array antenna radiation pattern, which mainly solves the problems of low shaping and optimizing speed, low accuracy and low flexibility of the conventional antenna radiation pattern. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) setting parameters given by a system and a radiation pattern level value required by the system; (2) generating a level restraining fitness function, a level filling fitness function and a lower inclination angle fitness function according to the radiation pattern level value required by the system; (3) initializing excitation amplitude, an excitation phase and a unit distance parameter, and performing iterative optimization according to an optimizing formula until the requirement that the sum of values of the three fitness functions is equal to zero can be met; and (4) generating an antenna radiation pattern from the optimized excitation amplitude and / or the optimized excitation phase and / or the unit distance according to the theory of the array antenna radiation pattern so as to finish optimization on the radiation pattern. The method has advantages of high calculation speed, high accuracy and strong flexibility, and the optimized design, meeting the various system requirements, of the linear array antenna radiation pattern can be achieved.
Owner:西安新海天通信有限公司
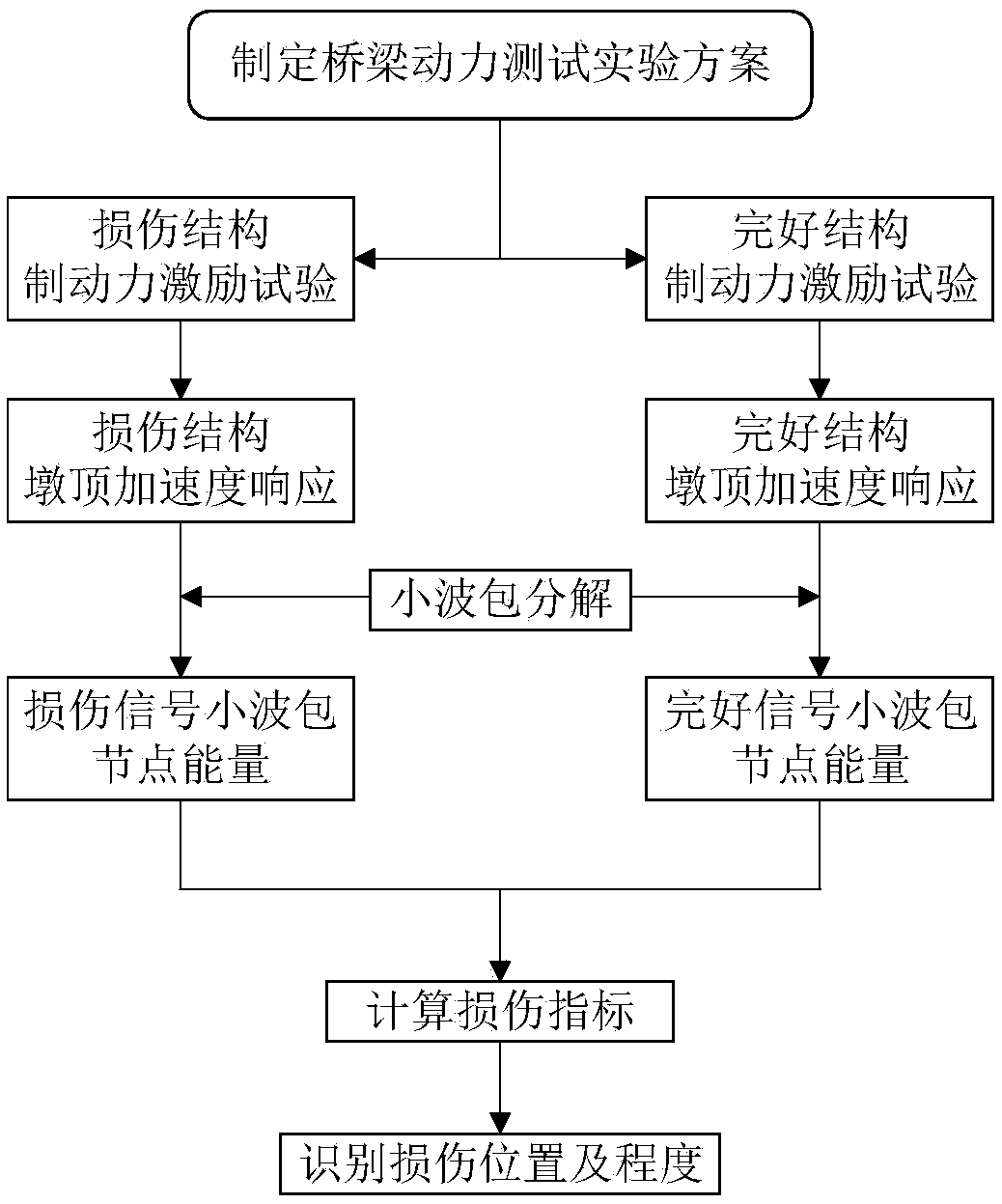
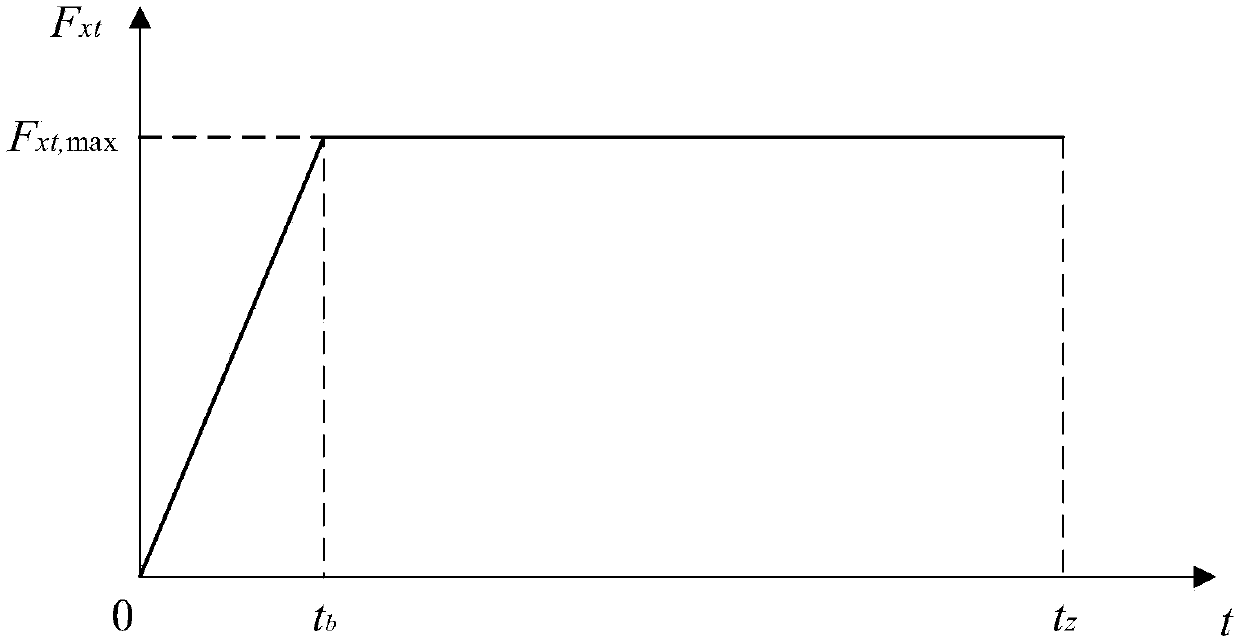
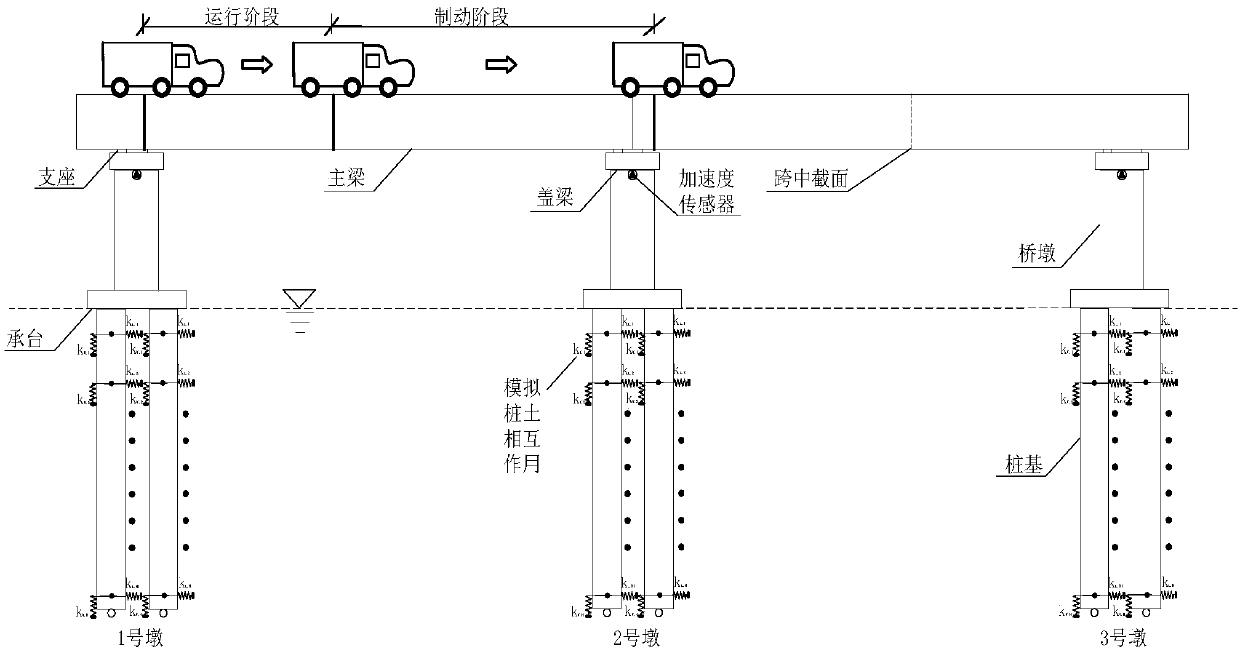
A method of bridge foundation erosion identification based on vehicle braking impact
ActiveCN109002673AFully reflect the dynamic characteristicsTimely and detailed health status informationGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationObservational errorEngineering
The invention relates to a method of bridge foundation erosion identification based on vehicle braking impact, belonging to the technical field of bridge pile foundation erosion damage identification.The invention aims at solving the problem that the sensor is easily disturbed by hydrological conditions when placed under water in the existing bridge pier scour monitoring method, and the measurement error is relatively large, and the sensor is liable to be limited by actual environment and climate when installed. The method comprises the steps of: with brake force of the vehicle being used asan exciting source, exciting the acceleration response of the pier in the direction of the bridge, and arranging an acceleration sensor at the top of each pier, taking the acceleration signal collected from the pier top as the analysis signal, obtaining the wavelet packet energy variance of the intact bridge structure and the damaged bridge structure by wavelet packet decomposition and reconstruction, and comparing the wavelet packet energy variance change rate of the intact bridge structure and the damaged bridge structure to determine the damage location and degree. The structural damage identification excitation mode of the invention increases the excitation amplitude, improves the processing precision, and has the advantages of strong real-time performance, simplicity and easy operation, etc.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
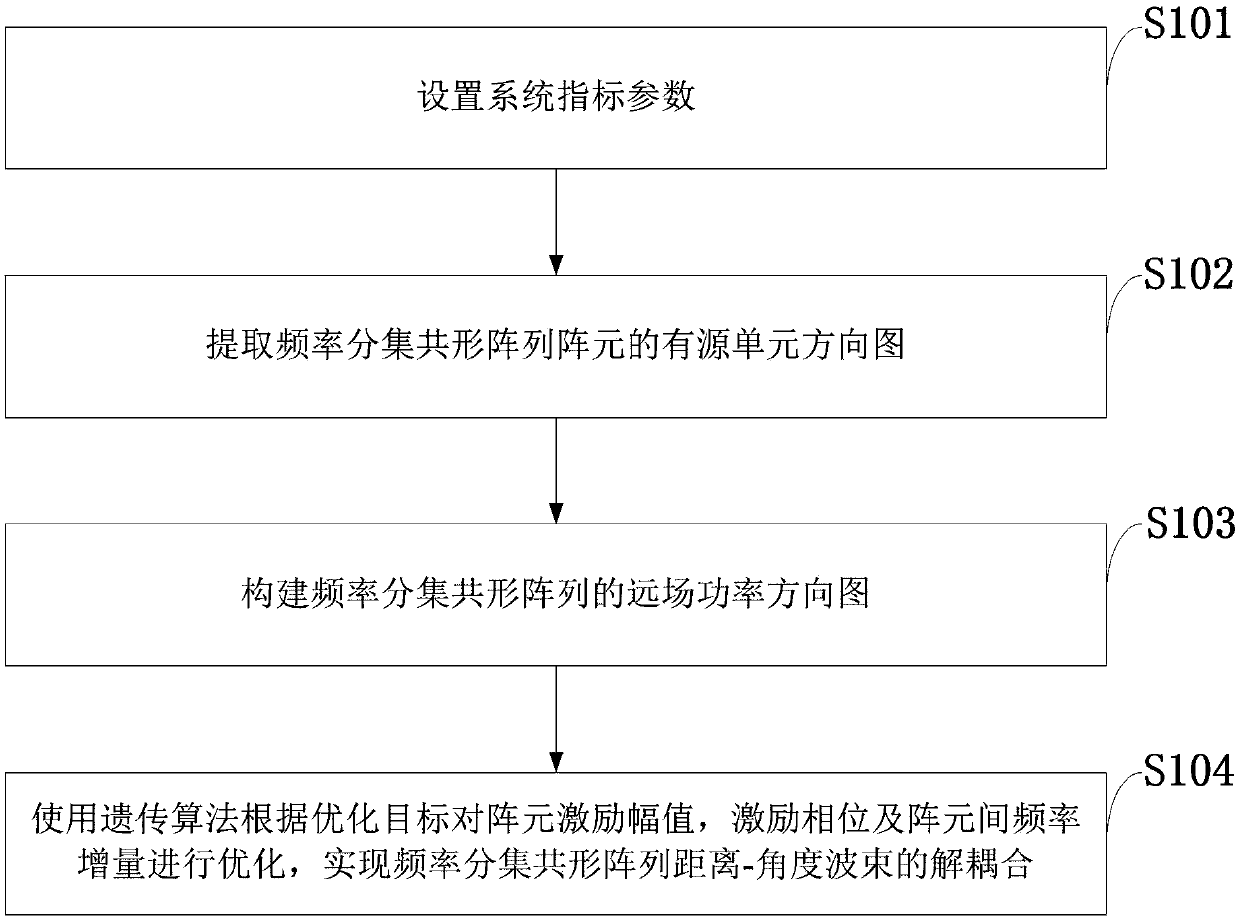
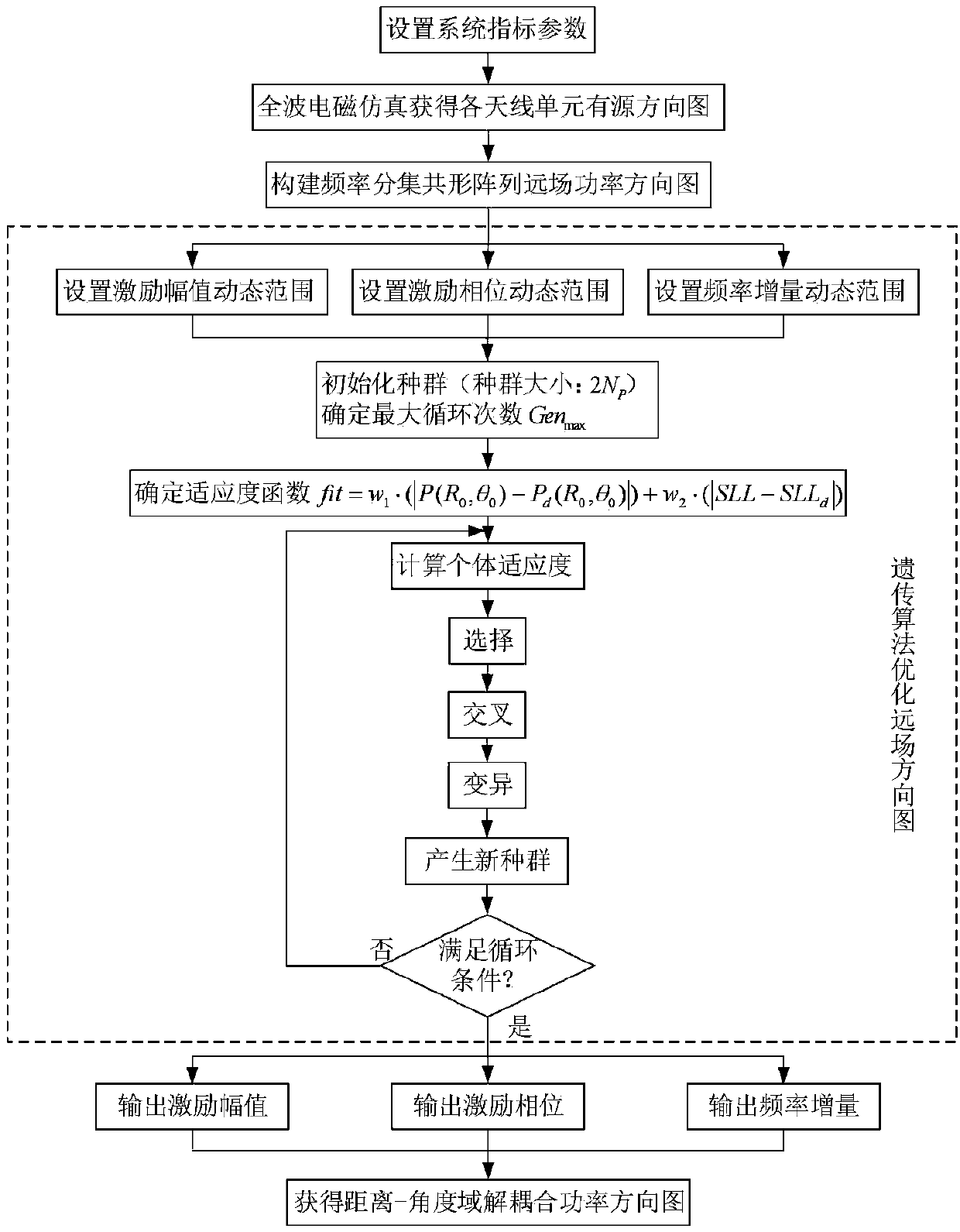
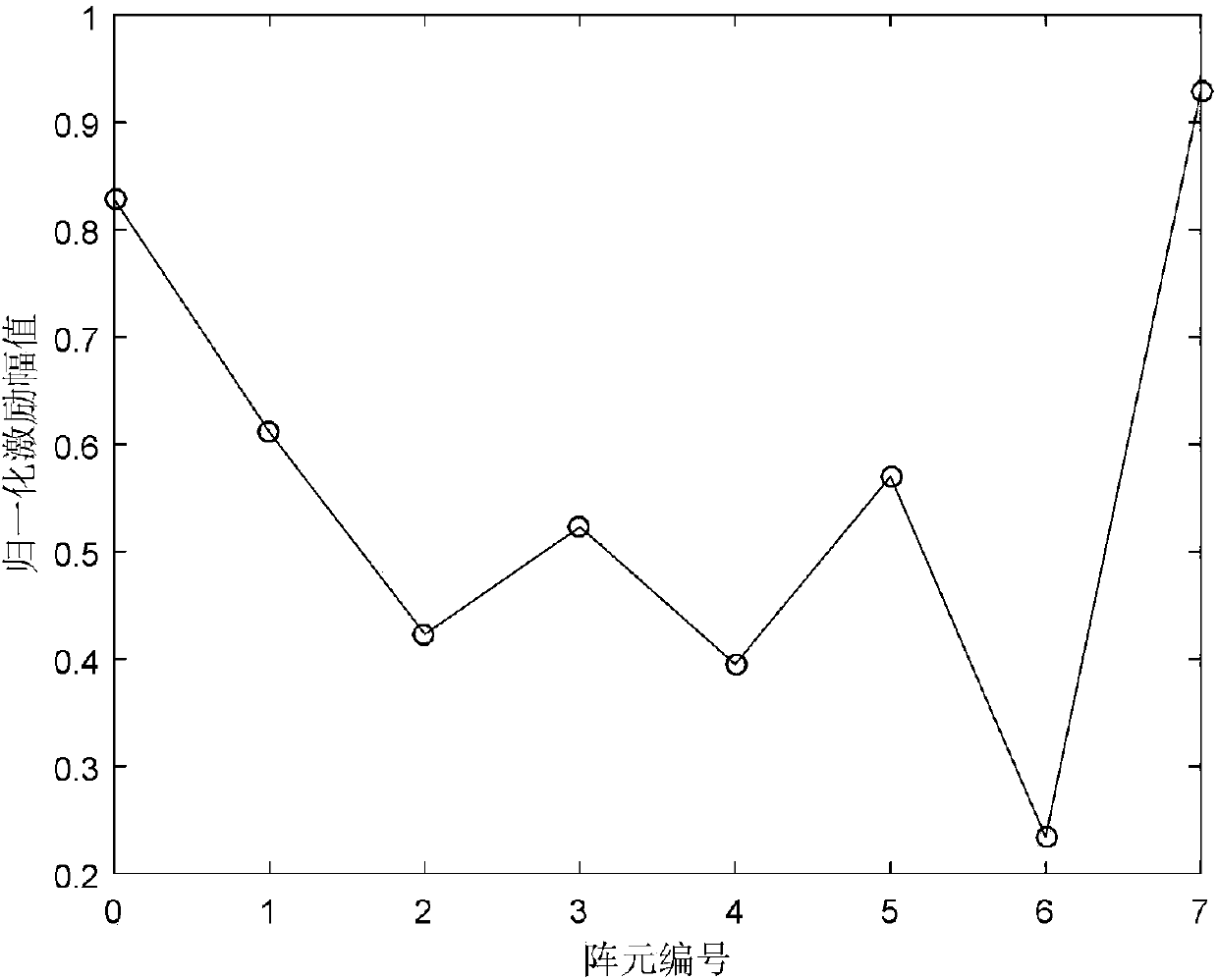
Decoupling method based on genetic algorithm for frequency diversity conformal array beam and antenna
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar antennas, and discloses a decoupling method based on a genetic algorithm for a frequency diversity conformal array distance-angle beam and an antenna. An active element pattern of a frequency diversity conformal array antenna element is extracted through full-wave electromagnetic simulation software, and a frequency diversity conformal array far-field power radiation pattern is constructed to optimize the excitation amplitude, the excitation phase and the inter-array-element frequency increment of an array element by the genetic algorithm,so that a main lobe of a frequency diversity conformal array radiation pattern is concentrated in a desired distance-angle area, and decoupling of the frequency diversity conformal array distance-angle beam is finished. Through adoption of the decoupling method, the main lobe is formed in the desired distance-angle area of the radiation pattern, and a decoupled beam of the distance-angle area is formed. The decoupling method can be used for detecting a target of the distance-angle area, and restraining interference associated with a distance.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
Method of making disc brake pads
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL PROD US LLC
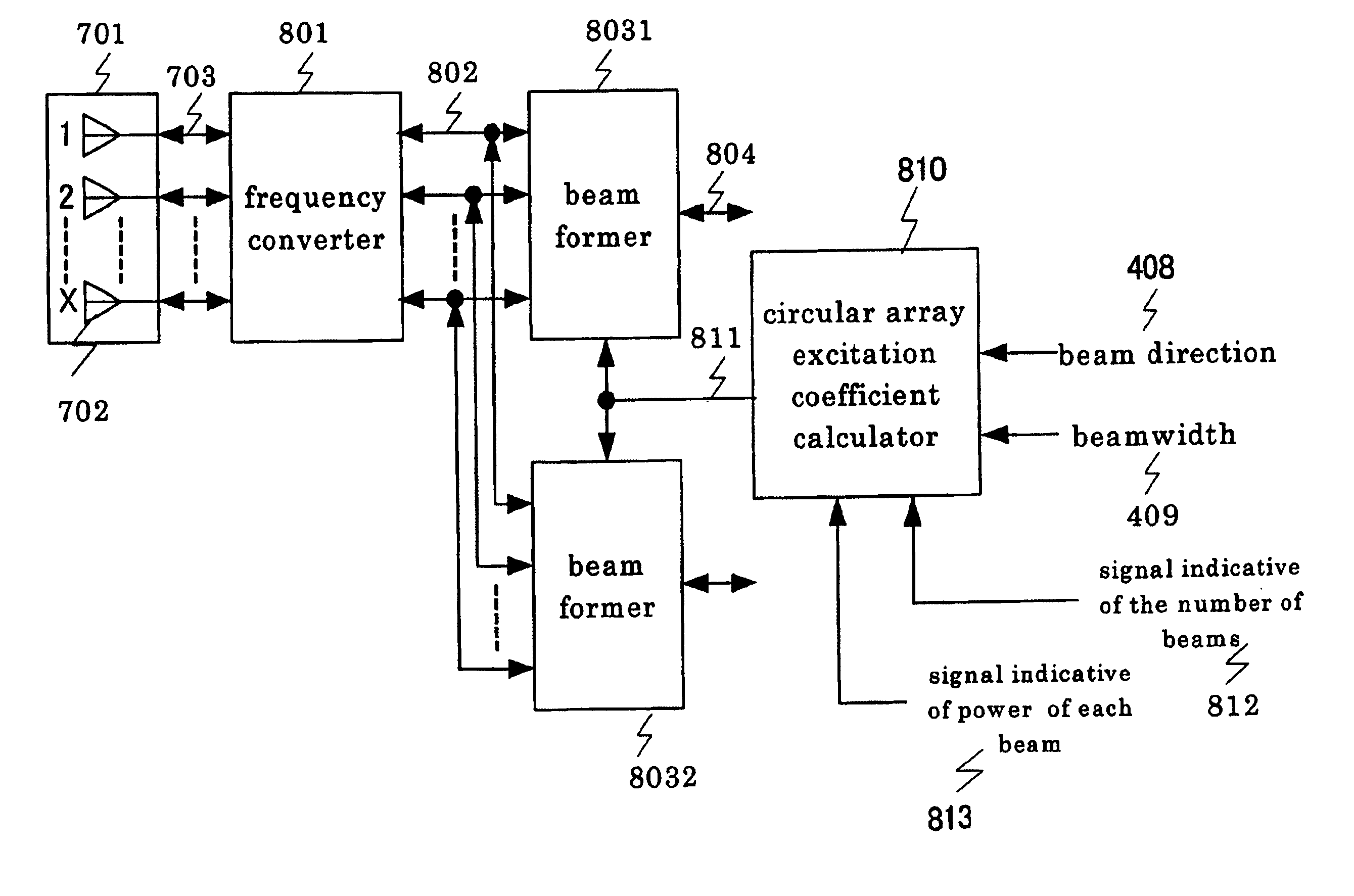
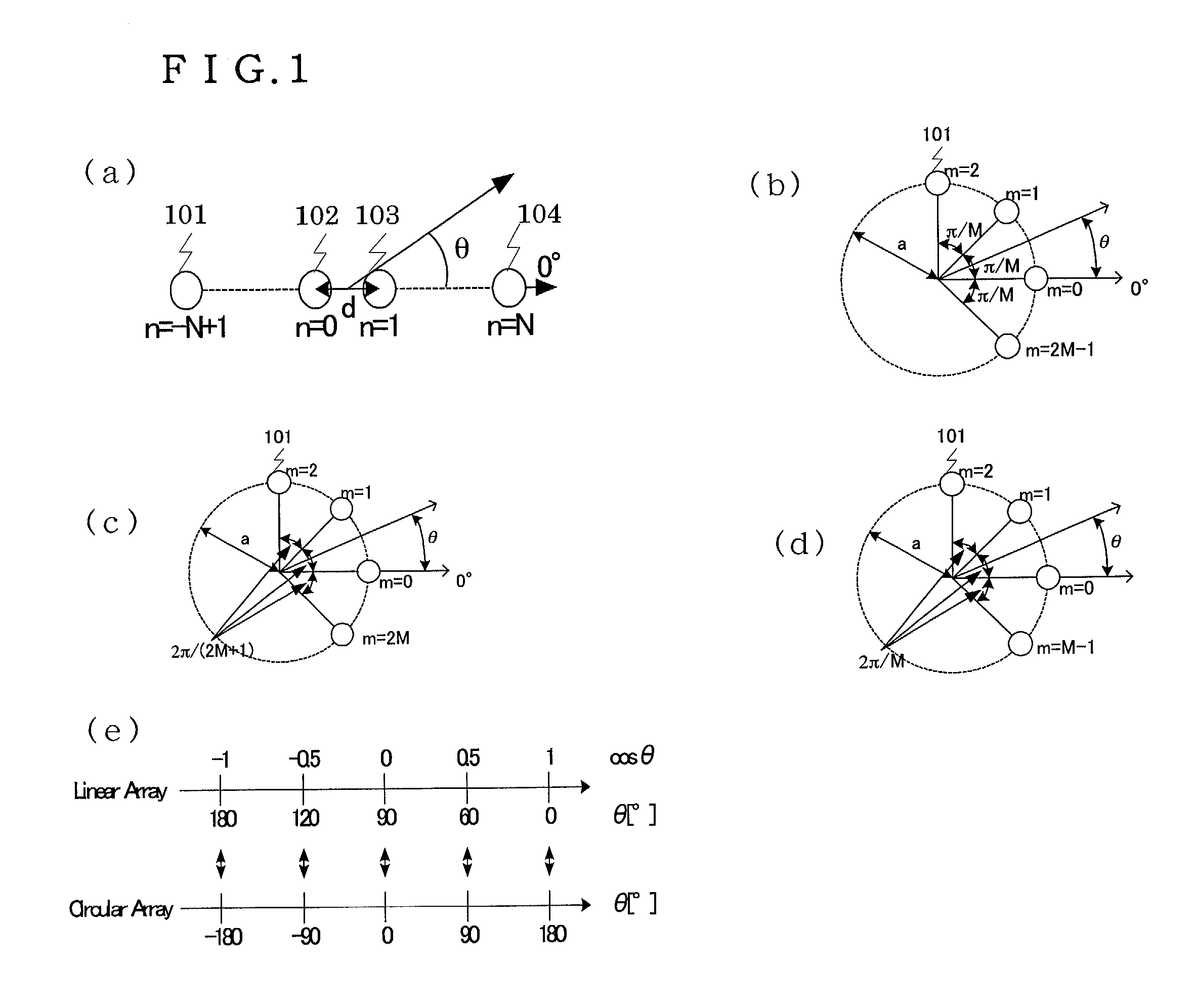
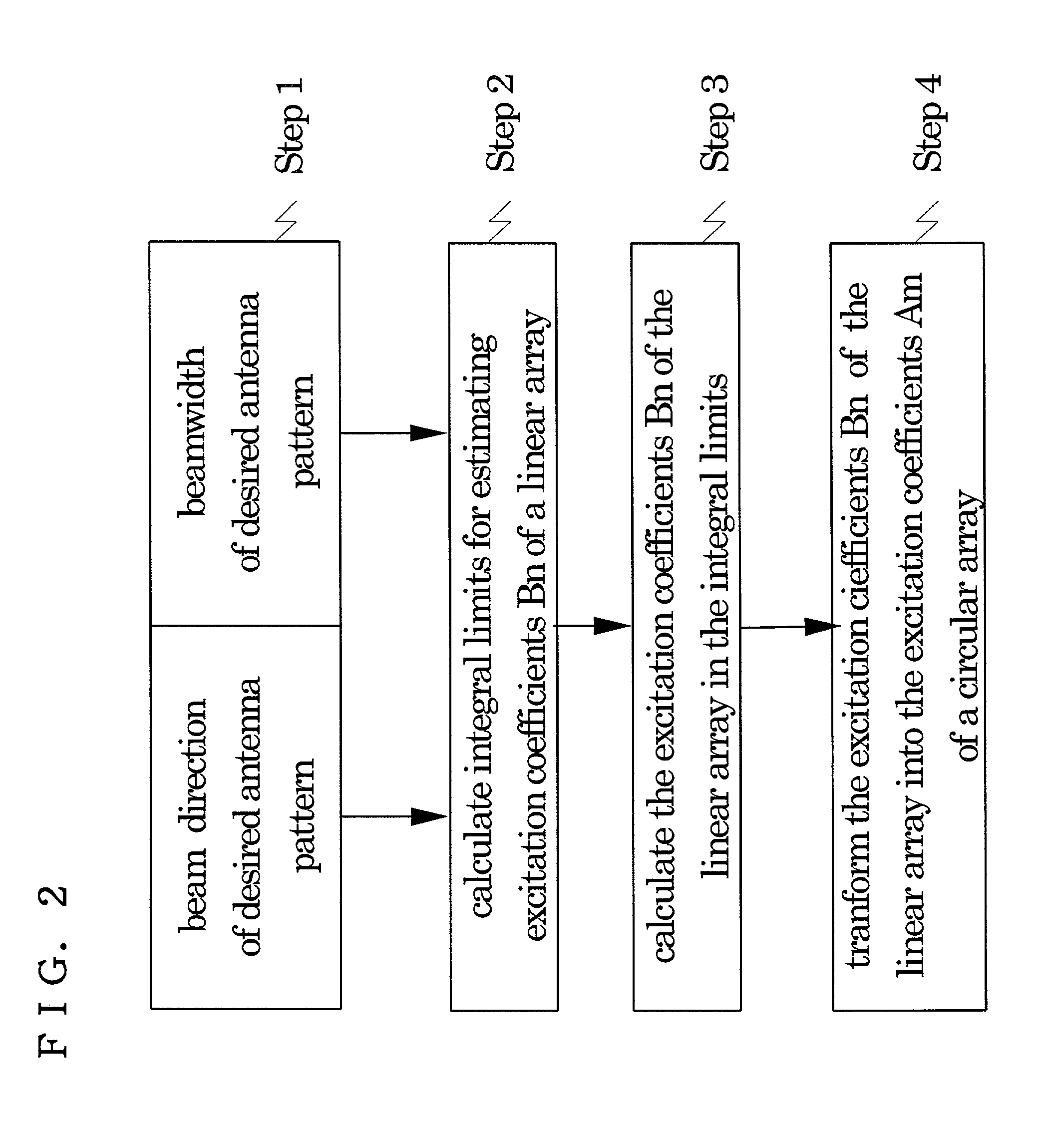
Method of calculating exciting coefficients for circular array antenna and radio unit utilizing the same
InactiveUS7031719B2Polarisation/directional diversityAntenna supports/mountingsSeries expansionExcitation amplitude
A method of calculating coefficients determining excitation amplitudes and phases for obtaining a desired antenna pattern of a circular array antenna comprising a plurality of antenna elements disposed circularly. Coefficients for a linear array antenna having the same number of antenna elements as the circular array antenna are determined by a Fourier series expansion in integral limits calculated from a beam direction and a beam width that are estimated from incoming radio waves and then are transformed into the coefficients for the circular array antenna. With this method, the beam direction and the beam width of the antenna pattern of the circular array antenna can be set at will. Consequently, this method enables adaptive control of sectored beams of sectored antennas at a base station or the like used for a mobile communication system, thus enhancing efficiency of the use of the antennas.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Installation error compensation method for harmonic oscillator and external base of hemispherical resonant gyroscope (HRG)
The invention provides an installation error compensation method for a harmonic oscillator and an external base of a hemispherical resonant gyroscope (HRG) and relates to the technical field of inertia. The invention aims to improve the output precision of the hemispherical resonant gyroscope. The method comprises the following steps: calculating an installation error vector according to the installation error between the harmonic oscillator and the external base; calculating the variable quantity of an excitation capacitance between the harmonic oscillator and the external base according to the vibration displacement relationship and the installation error vector of the harmonic oscillator; calculating an excitation coefficient and an excitation amplitude after change according to a relational expression between the variable quantity of the excitation capacitance and the excitation coefficient; according to a gyroscope output error model, calculating the gyroscope output error and performing error compensation. By the application of the installation error compensation method provided by the invention, the influence of the installation error between the harmonic oscillator and theexternal base on the gyroscope output accuracy can be quantitatively analyzed; according to the gyroscope output accuracy, the output of the hemispherical resonant gyroscope is compensated, so that the output accuracy of the hemispherical resonant gyroscope is improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
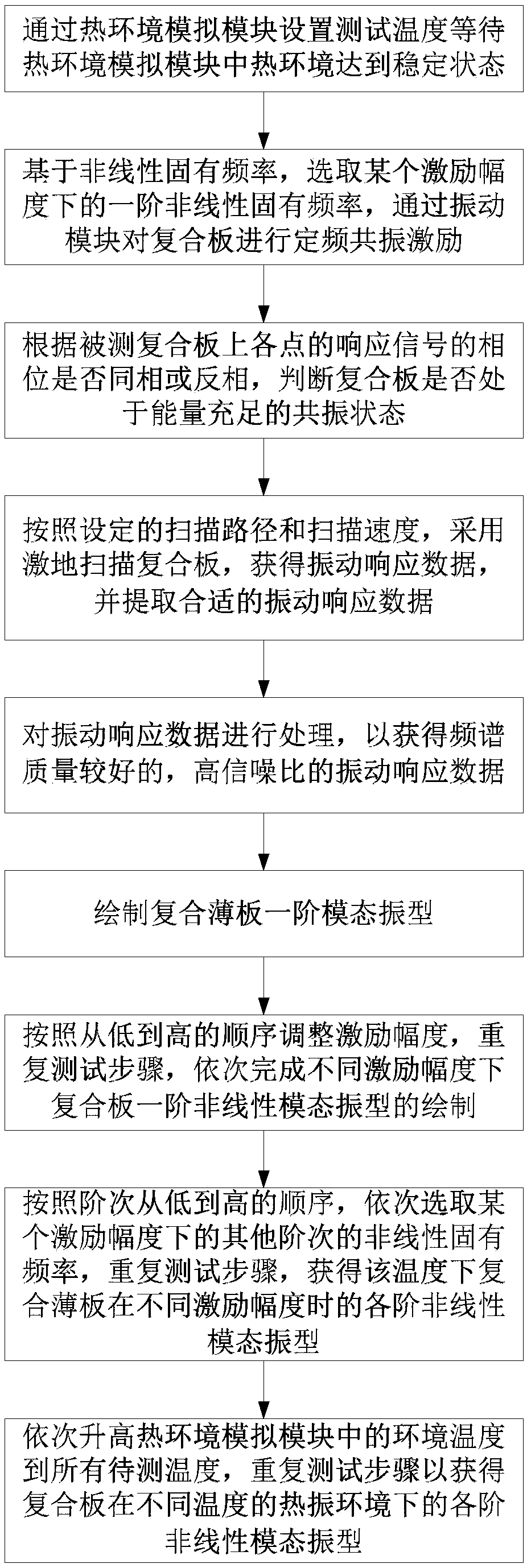
Non-linear dynamic parameter testing method and system of fiber composite board in thermal-shock environment
InactiveCN107818222AAccurate acquisition of nonlinear dynamic parametersImplement testGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsVibration measurementFiber
The invention provides a non-linear dynamic parameter testing method and system of a fiber composite board in a thermal-vibration environment. The method comprises the steps that the thermal-vibrationtesting environment is built, the fiber composite board is fixed to an installation platform of a vibration module through an installation clamp, the installation platform stretches into a thermal-insulated box of a thermal environment simulation module, and then the thermal-insulated box is sealed with a soft rubber strip; a laser scanning vibration measurement module is arranged above the thermal-insulated box, and during testing, laser penetrates through high-temperature-resistant optical glass on the top surface of the thermal-insulated box to scan the fiber composite board; the non-linear inherent frequencies of various orders, the non-linear modal shapes of various orders and the non-linear damping of the fiber composite board at different excitation amplitudes in the thermal-vibration environment are tested in sequence. The testing method and system are perfect and effectively, and the non-linear dynamic parameters including the non-linear inherent frequencies, the non-linear modal shapes of various orders and the non-linear damping can be accurately obtained.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
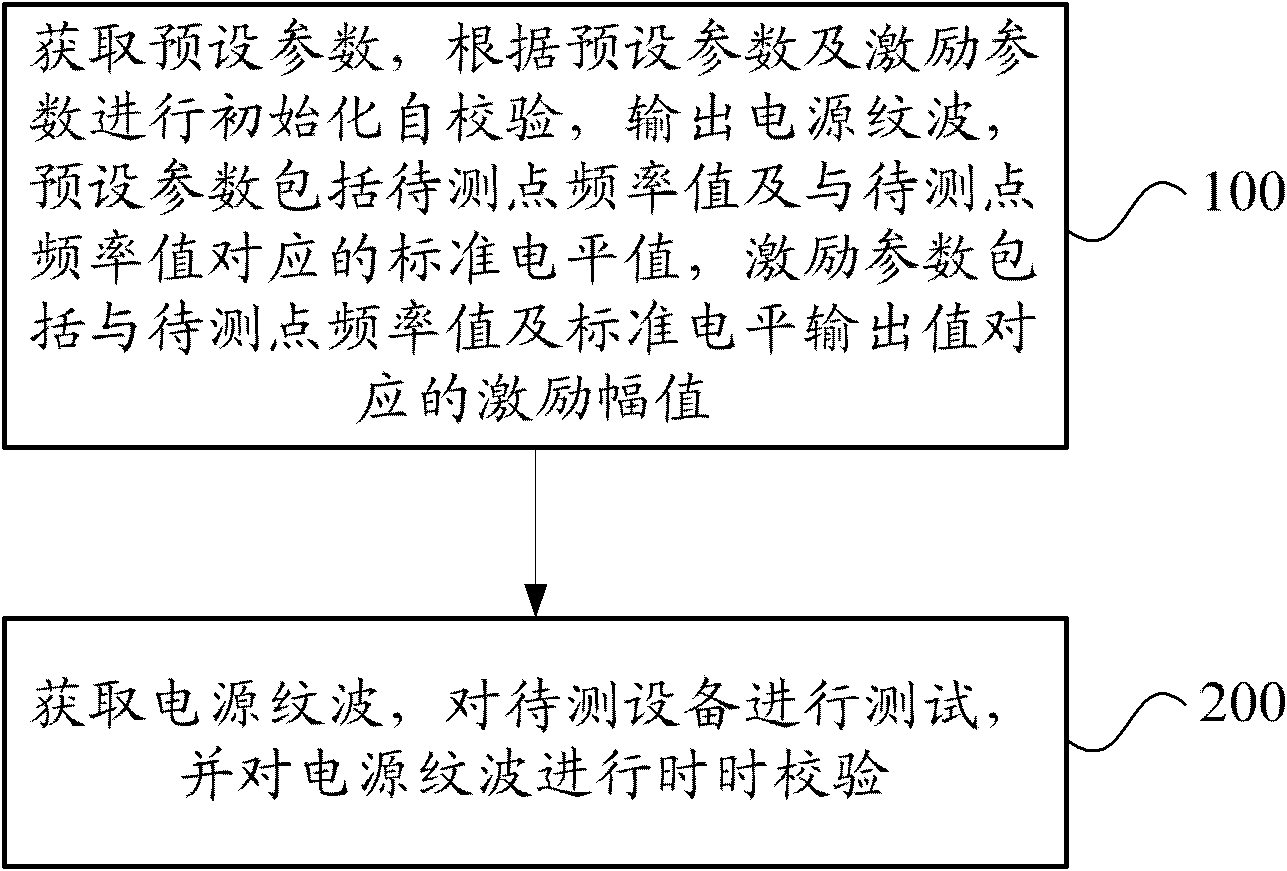
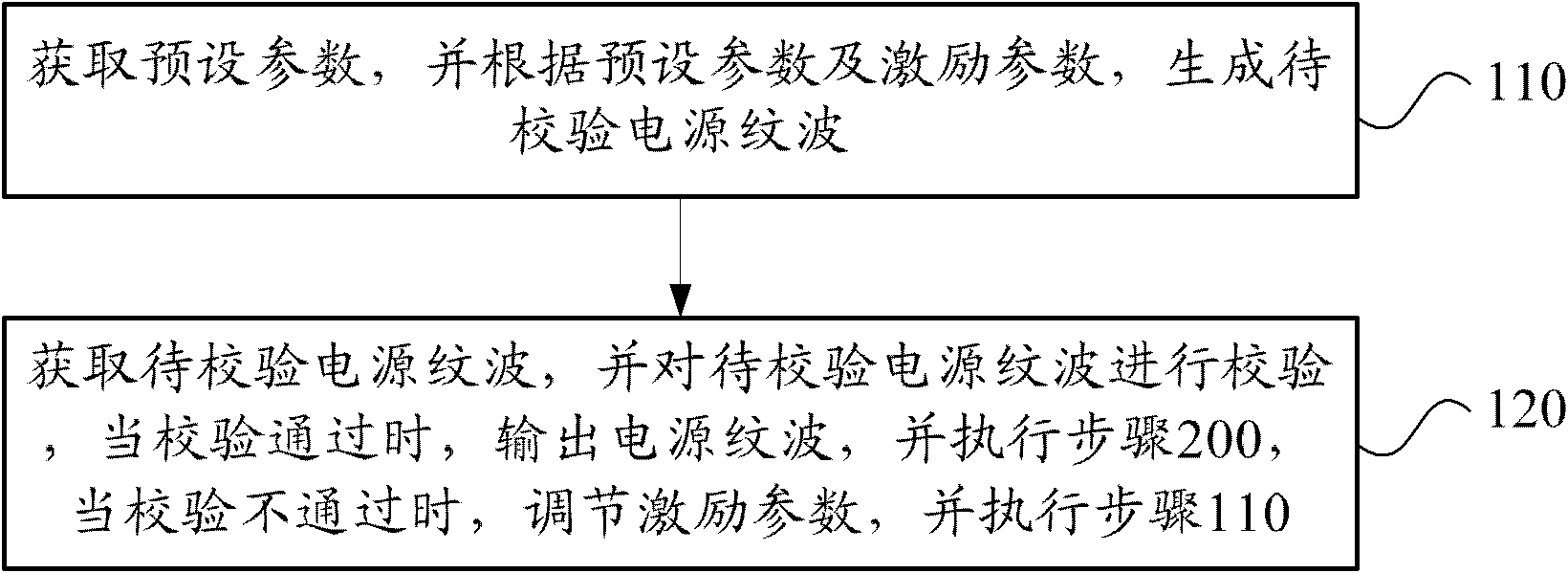
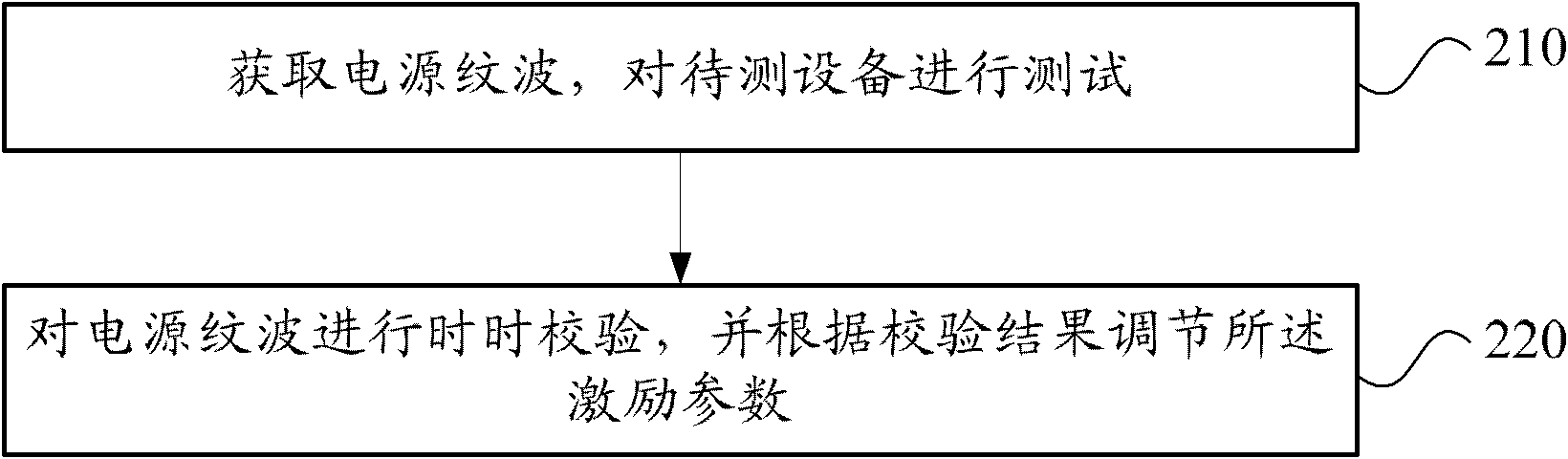
Power supply ripple interference test method and system
ActiveCN102830296AReduce manual operationsImprove test efficiencyElectrical testingTest efficiencyExcitation amplitude
The invention provides a power supply ripple interference test method and system. The method comprises the steps of: obtaining preset parameters, carrying out initialization self-checking according to the preset parameters and an excitation parameter and outputting a power supply ripple, wherein the preset parameters comprise a frequency value of the point to be tested and a standard level value corresponding to the frequency value of the point to be tested, and the excitation parameter comprises an excitation amplitude value corresponding to the frequency value of the point to be tested and the standard level output value; and testing the equipment to be tested, and carrying out real-time verification on the power supply ripple. The system comprises an initialization self-checking module and a real-time verification and test module, wherein the initialization self-checking module is used for obtaining the preset parameters, carrying out initialization self-checking according to the preset parameters and the excitation parameter and outputting the power supply ripple; and the real-time verification and test module is used for obtaining the power supply ripple, testing the equipment to be tested, and carrying out real-time verification on the power supply ripple. By adopting the method and system, the testing efficiency and measurement accuracy are effectively improved, therefore, the efficiency and accuracy requirements in a power supply ripple interference test process of automobile electronic equipment are met.
Owner:INTERTEK TESTING SERVICES
RFID reader wave beam switching type array antenna
The invention relates to an RFID reader wave beam switching type array antenna and belongs to the radio frequency identification technology and antenna technology field. The RFID reader wave beam switching type array antenna comprises four antenna radiation units, an electrical control phase shifter, a power divider and an attenuator, wherein the antenna radiation units employ a microstrip antenna mode to realize miniaturization of reader antennas, a radiation paster is provided with a groove, a dielectric layer is an air layer, a grounding face is a flat bonded copper, a coaxial line feeding mode is utilized, phase control on an output signal can be realized by the electrical control phase shifter through a main chip, so the wave beam switching function is realized; the power divider is a quartering power divider formed by microstrip lines, the power divider is independently designed, the structure is simple, mounting is convenient, debugging is easy, amplitude attenuation for a signal current can be carried out through an attenuator, so the excitation amplitude proportion is satisfied. According to the RFID reader wave beam switching type array antenna, area scanning for labels can be carried out through a reader, the identification area of the reader is expanded, and guidance meaning is exerted on the RFID system.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Environmental noise variable-excitation amplitude modulation and frequency modulation detecting and estimating method
ActiveCN103308153AExpand the scope of detectionSolve the real problemSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing electrical meansEnvironmental noiseHysteresis
The invention provides an environmental noise variable-excitation amplitude modulation and frequency modulation detecting and estimating method in order to overcome the technical defect that different types of noise sensors are needed for different environmental noises and to solve the magnetic saturation problem. The method has the advantages that by a common excitation mode of winding a coil on a soft magnetic core prior to powering on, size and direction of electric excitation of the coil are controlled by means of PWM (pulse width modulation) so as to form magnetic fields and hysteresis loops in different intensities, so that frequency and amplitude of received acoustical signalsare changed, and detection range of a sensor is enlarged; detected signals are subjected to frequency reduction, then noise intensity is computed, and the problem that existing moving-coil noise sensors require different types and magnetic saturation for different environmental noises is solved.
Owner:XIAN FEISIDA AUTOMATION ENG
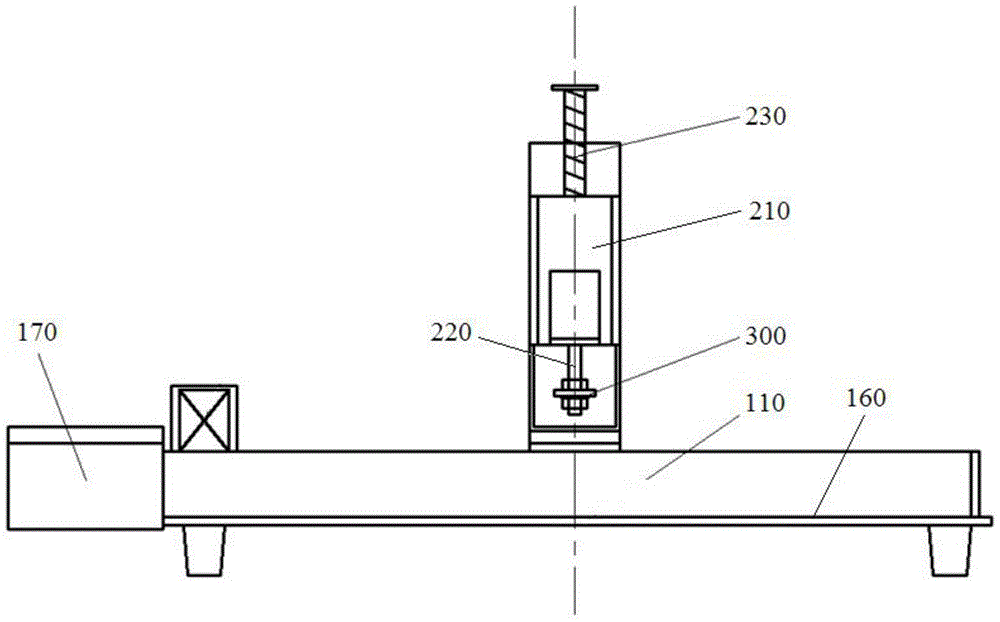
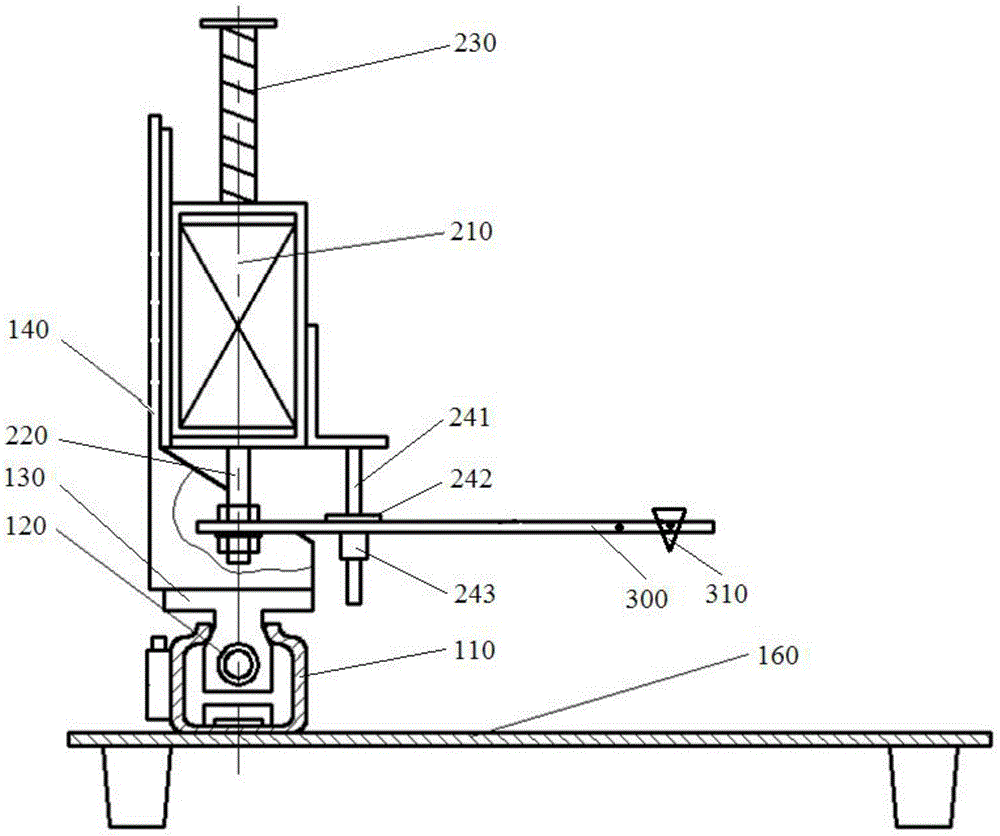
Modal test device
The invention relates to a modal test device. The modal test device comprises a base, a translation mechanism installed on the base, and an excitation mechanism installed on the translation mechanism, wherein the excitation mechanism comprises a vibration exciter and a hammer handle butted with the vibration exciter, the hammer handle is provided with a hammer head, and the hammer head itself is a force sensing element or the hammer head is provided with a force sensing element. The vibration exciter and an elastic reset member control the lifting and falling of the hammer handle so as to control the hammer head to knock a structure or the hammer head to leave the structure. In a plurality of tests, the excitation amplitude generated by the hammer head to the structure is certain, and the repeatability is good. The excitation mechanism is installed on the translation mechanism, the translation mechanism drives the excitation mechanism to move horizontally relative to the base, and the hammering test can be carried out on a plurality of points on the structure by one time of positioning, so that the test is convenient and rapid, and the efficiency is high.
Owner:FIFTH ELECTRONICS RES INST OF MINIST OF IND & INFORMATION TECH
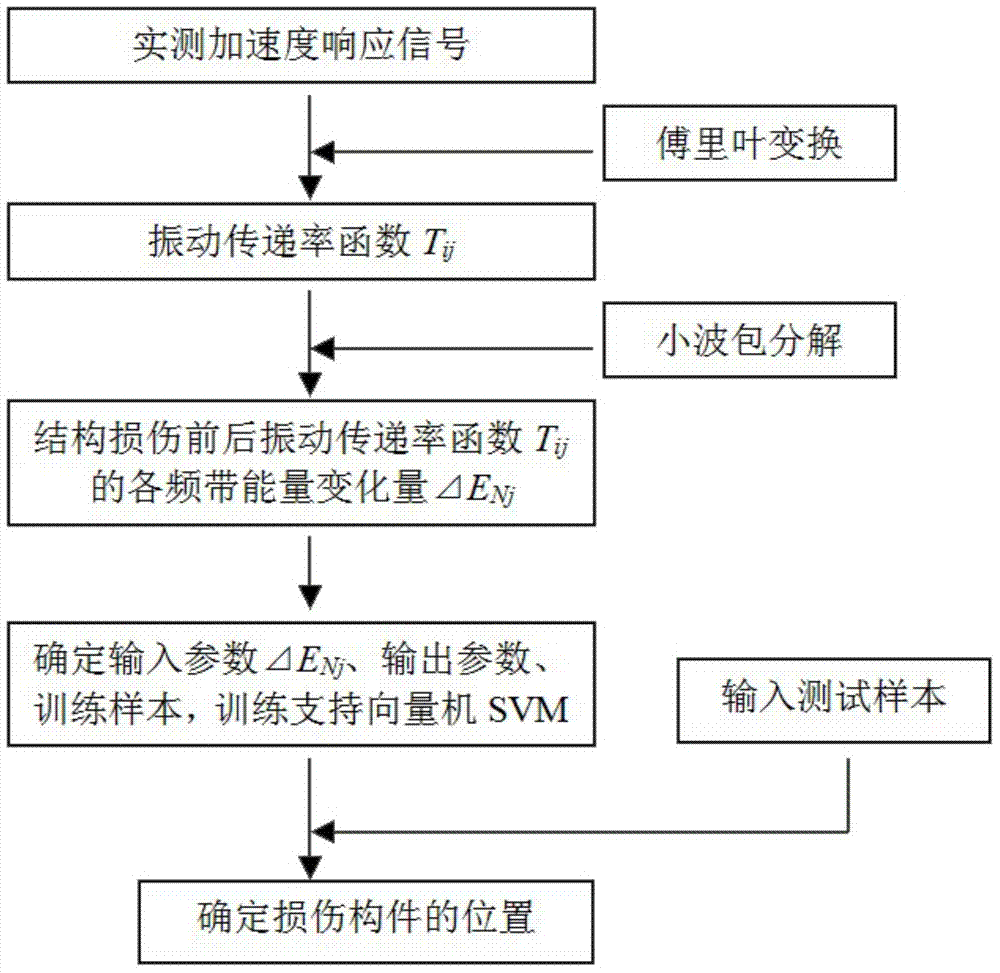
Method for identifying structural damage based on vibration transmissibility function and support vector machine
ActiveCN103543026AAvoid hard to determineAvoid problems prone to local minimaStructural/machines measurementSupport vector machineNetwork structure
The invention relates to the field of structural damage identification, in particular to a method for identifying structural damage based on a vibration transmissibility function and a support vector machine. The vibration transmissibility function is constructed through an accelerated speed response, the amplitude value of the vibration transmissibility function is used as an analysis signal, all frequency band signals are obtained through wavelet packet decomposition and reconstruction, the energy ENj of all the frequency band signals is obtained through calculation, the variable quantity delta ENj of the energy of the front and rear frequency band signals of the structural damage is used as damage characteristic indexes, and the mode identification function of the support vector machine is used for identifying the structural damage. The method for identifying the structural damage is not influenced by the excitation amplitude value, meanwhile, a structural damage identification method with the problems that a neural network structure is hard to determine and prone to being in local minimization is avoided, operability is strong, processing precision is improved, and the damage identification process is simplified.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
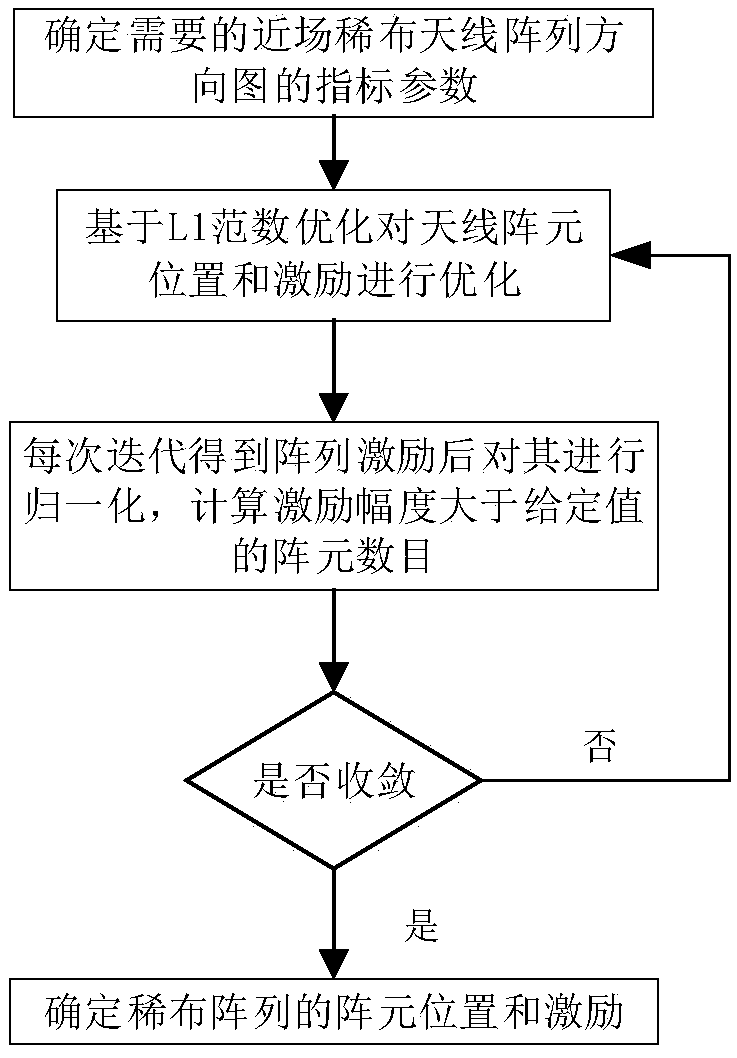
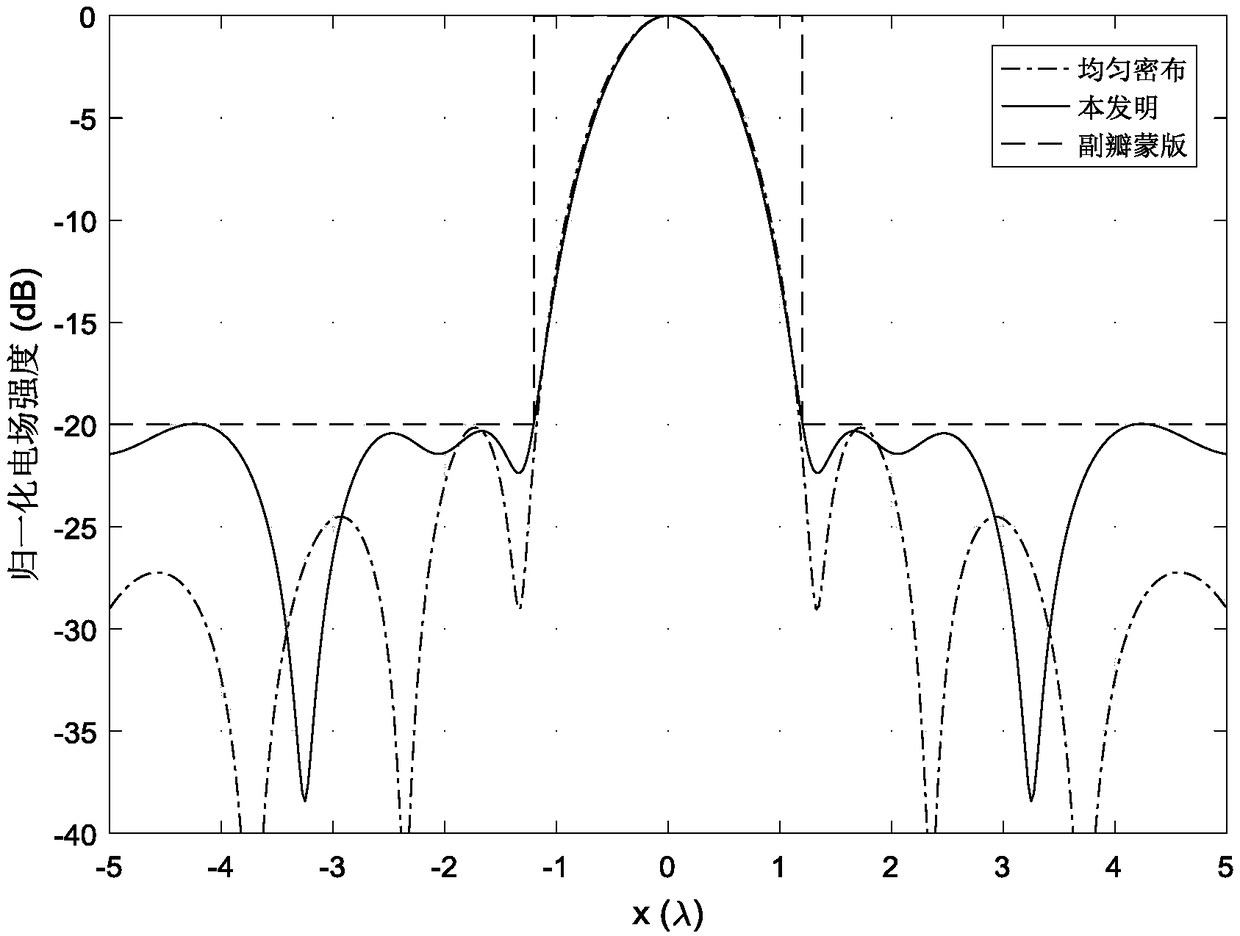
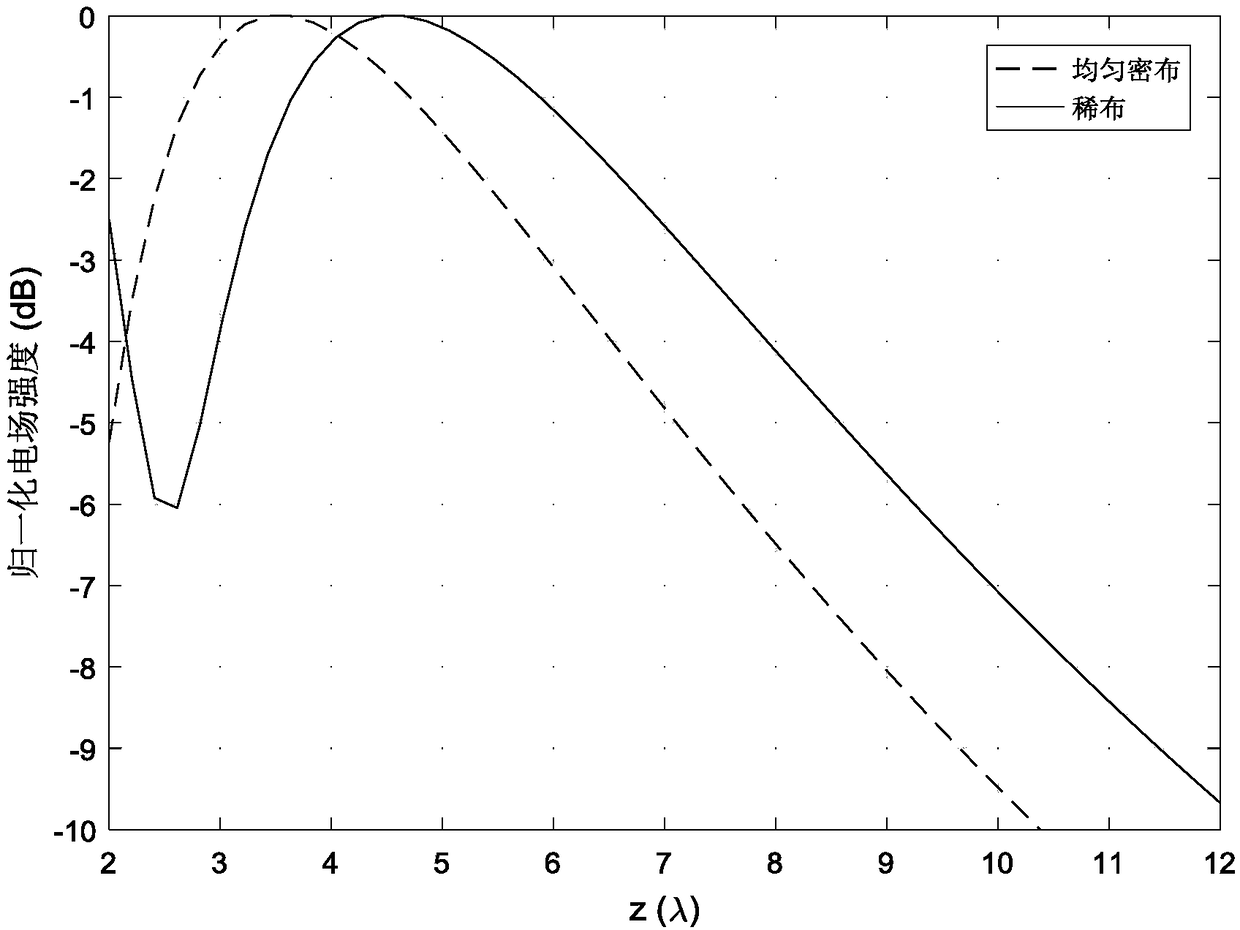
Near-field sparse antenna array optimization method based on L1 norm constraint
ActiveCN109033647ALevel controllableSolve the focus shift problemDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithm convergenceArray element
The invention provides a near-field sparse antenna array optimization method based on L1 norm constraint, which comprises the following steps: 1. determining the index parameters of the needed near-field sparse antenna array pattern; 2. determining the index parameters of the near-field sparse antenna array pattern. 2, using the L1 norm constraint theory to carry out iterative solution on the array element position and corresponding excitation; 3, normalizing the array excitation obtained by each iteration, and calculating the number of array elements whose excitation amplitude is greater thana given value; 4, judging whether that numb of units of three successive iterations is equal, if equal, the algorithm converges to obtain the final array topology and corresponding excitation. The invention obtains the sparse near-field antenna array topology and corresponding excitation based on the L1 norm minimization. Compared with the traditional method, the sidelobe level is controllable, and the problem of focus shift in the near-field focusing technology is solved at the same time.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
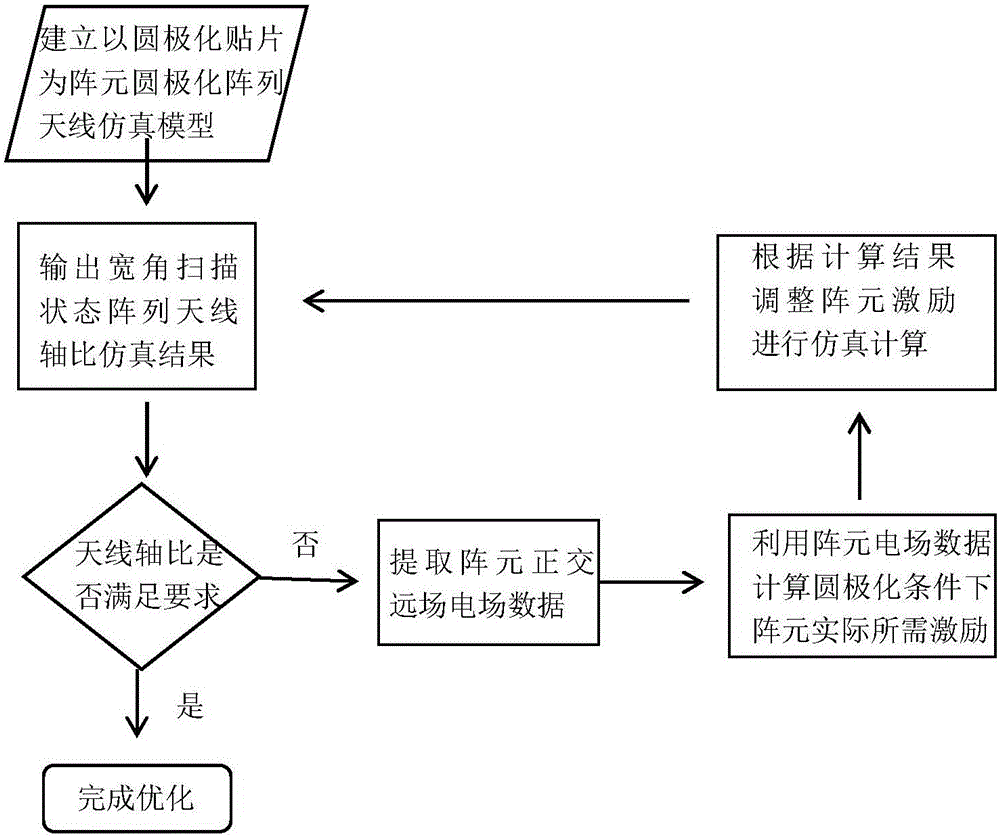
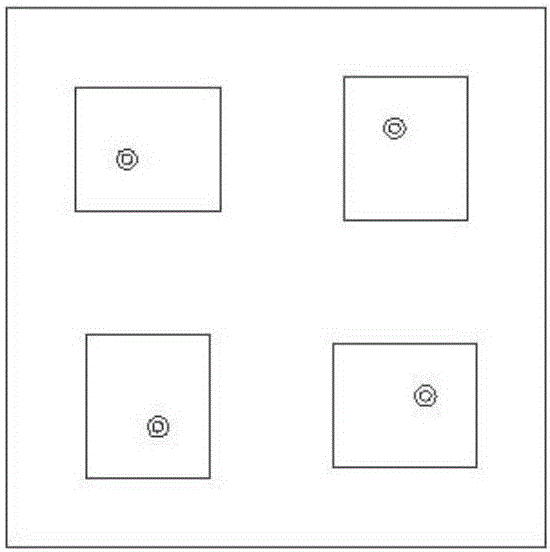
Axial ratio optimization method of rotating circular polarization microstrip array antenna in wide-angle scanning state
InactiveCN106096160ASave time and costAchieve axle ratio optimizationSpecial data processing applicationsMicrostrip array antennaAxial ratio
The invention provides an axial ratio optimization method of a rotating circular polarization microstrip array antenna in a wide-angle scanning state. By means of the method, the axial ratio of the rotating circular polarization microstrip array antenna in the wide-angle scanning state can be remarkably improved, and a high antenna gain and back lobe level can be achieved. The method includes the steps that an array antenna simulation model is established in simulation software, namely, an HFSS (High Frequency Structure Simulator); simulation calculation is conducted on the array antenna in the wide-angle scanning state, and targeted to any beam pointing, orthogonal electric field data of all array elements in all units is stored and output through a VBscript program; then, a 2*2 sub-array serves as a calculation unit, array element electric field data serves as the basis, and the excitation amplitude and the excitation phase actually required by all the array elements in all the units meeting the circular polarization condition are calculated through a MATLAB (matrix laboratory) program; an HFSS simulation data processing module directly loads the excitation amplitude and the excitation phase actually required by all the units and stored and output by the MATLAB to conduct simulation calculation again, and axial ratio optimization is achieved.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Methods for fragmenting ions in a linear ion trap
ActiveUS20090194686A1Reduce lossesIsotope separationSpecific reaction combinationsIon trap mass spectrometryPhysical chemistry
Methods for fragmenting ions retained in an ion trap are described. In various embodiments, a non-steady-state pressure of a neutral collision gas of less than about 5×10−4 Torr and an excitation amplitude of less than about 500 mV (peak to ground) is used to fragment ions with greater than about 80% fragmentation efficiency. In various embodiments, duration of ion excitation is greater than about 25 ms.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
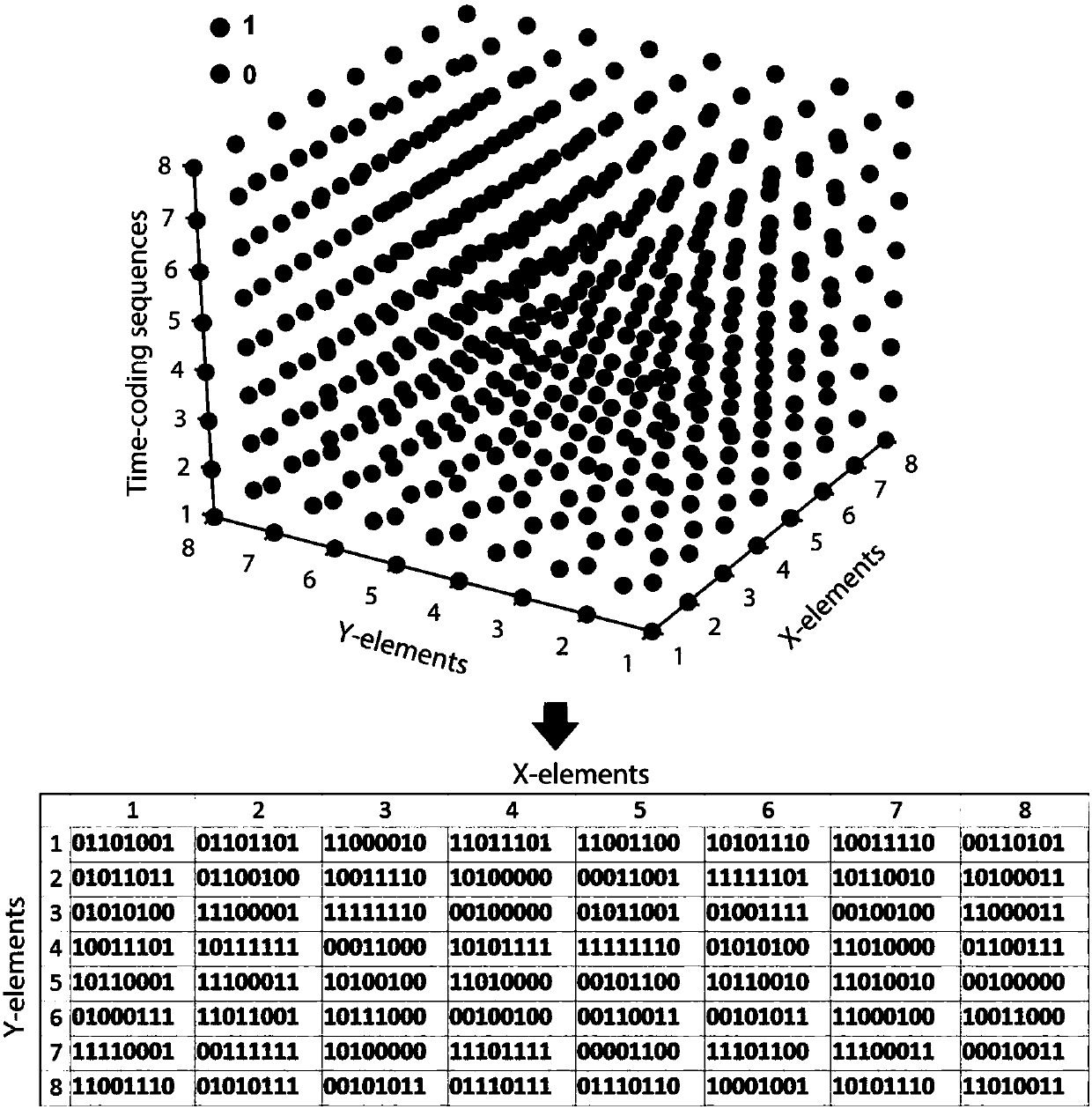
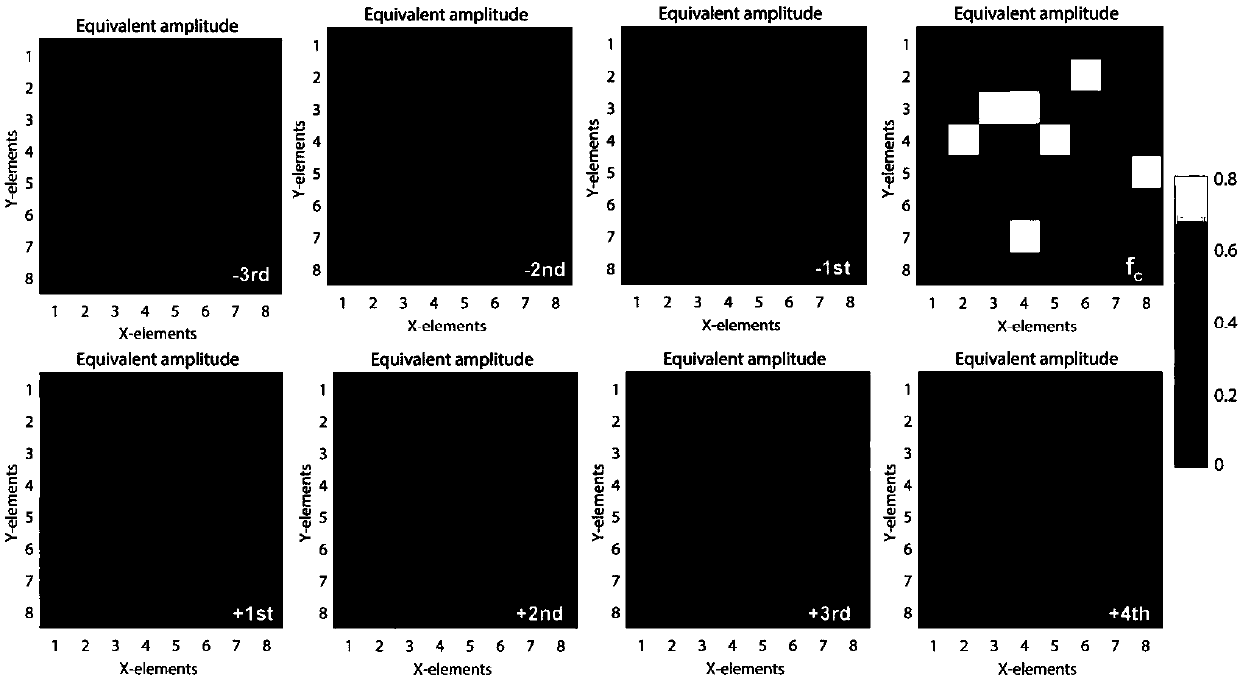
Random bit programmable meta-material design method based on space-time coding
ActiveCN108511915AAvoid difficultiesSimplify the control circuitAntennasMaterial DesignElectromagnetic response
The invention discloses a random bit programmable meta-material design method based on space-time coding; the method comprises the specific steps: 1, designing a coding unit with a low bit, arrangingin a spatial period to form a two dimension programmable meta-material, wherein each unit structure is integrated with one or more active device, and the unit can present different electromagnetic responses under a digital control module; 2, giving a set of independent time coding sequence to each unit, and periodically cycling to form an equivalent excitation amplitude and phase, thus realizing random high bit responses; 3, designing a corresponding space-time three dimensional coding matrix, and calculating the space scattering energy of the meta-material at different harmonic frequencies, thus satisfying specific application demands. The method can solve the problems that a conventional programmable meta-material is hard to realize high bit designs, thus simplifying a control circuit and a feed network, and saving active devices.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
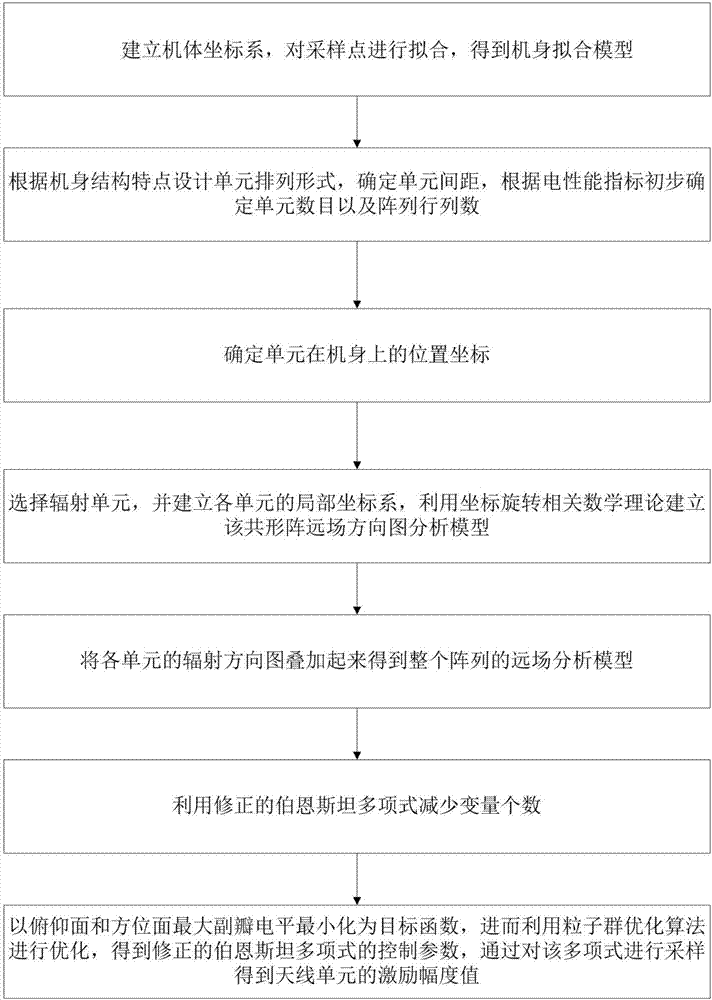
Unit layout and electromagnetic design method of fuselage conformal array antenna
InactiveCN107017468ASolving Dynamics ProblemsImprove the defect of small beam scanning rangeAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesDesign optimisation/simulationEngineeringField analysis
The invention relates to a unit layout and electromagnetic design method of a fuselage conformal array antenna. The method includes: (1) establishing a body coordinate system; (2) designing a unit arrangement form according to a fuselage structural characteristic, determining a unit spacing, and preliminarily determining a unit number and an array row number according to an electrical performance index; (3) determining position coordinates of the units on a fuselage; (4) selecting a radiation unit, establishing a local coordinate system shown in the description of each unit, and establishing a far-field pattern analysis model of a conformal array by employing a mathematical theory related to coordinate rotation; (5) superposing radiation patterns of the units to obtain a far-field analysis model of the whole array; (6) reducing the number of variables by employing a corrected Bernstein polynomial; and (7) regarding a pitching plane maximum side-lobe level and an azimuth plane maximum side-lobe level as a target function, performing optimization by employing a particle swarm optimization algorithm to obtain a control parameter of the corrected Bernstein polynomial, and sampling the polynomial to obtain an excitation amplitude value of an antenna unit.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
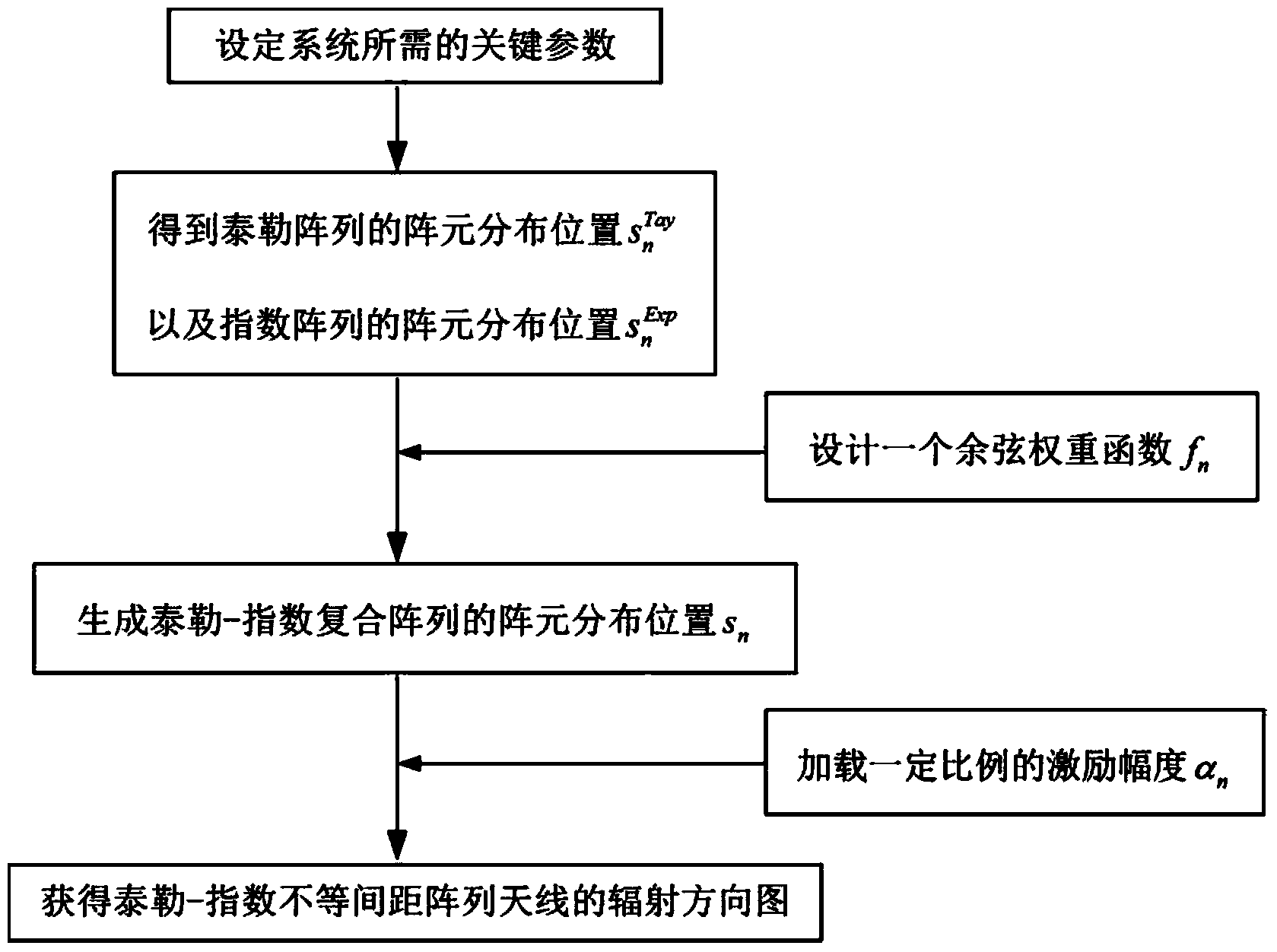
Method for designing Taylor-index composite non-equidistant modular array antenna
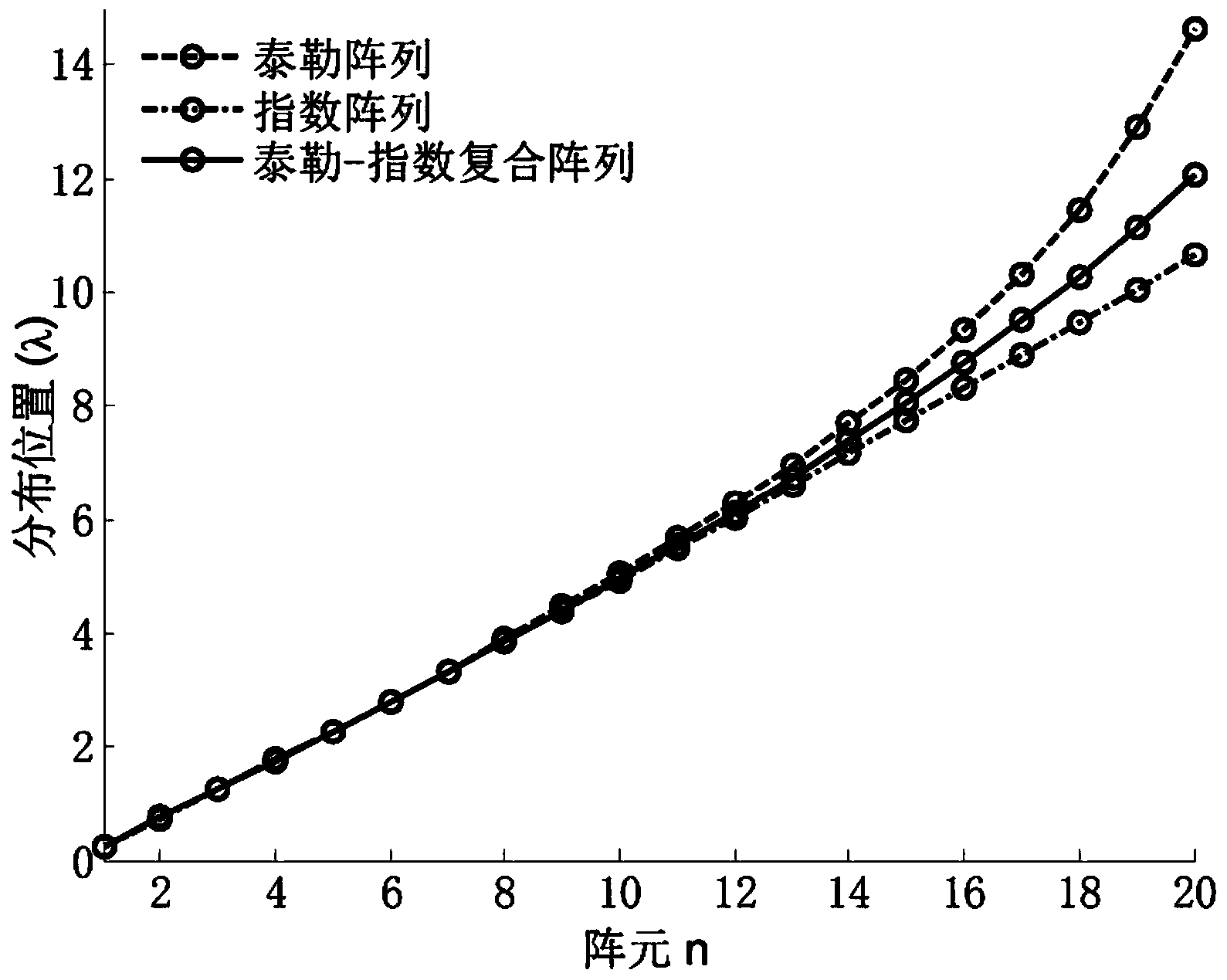
InactiveCN103715518AReduce radiation lossReduce design costAntenna arraysEngineeringExcitation amplitude
The invention discloses a method for designing a Taylor-index composite non-equidistant modular array antenna, and relates to a non-equidistant array antenna. The method comprises the following steps: setting parameters required by a system according to an integrated gain requirement, and respectively substituting a non-equidistant Taylor array and an index array to obtain the distribution positions of two groups of array elements; designing a cosine weighting function, and combining the distribution positions of the two groups of array elements to generate an array element distribution position configuration of a Taylor-index composite array; dividing an array antenna into eight modules in a proportion of 4:3:2:1 according to the total quantity of the array elements, and loading an excitation amplitude in the same proportion for the array elements in the modules to obtain the Taylor-index composite non-equidistant modular array antenna. By selecting an appropriate cosine weighting function, the minor lobe level of a radiation pattern can be controlled as required; a modular feed network can be realized by using a phase-impedance matched proportional power divider, so that a simple feed network is maintained, the radiation loss is reduced, and the design cost and the manufacturing cost are reduced; pattern integration can be flexibly regulated as required.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com