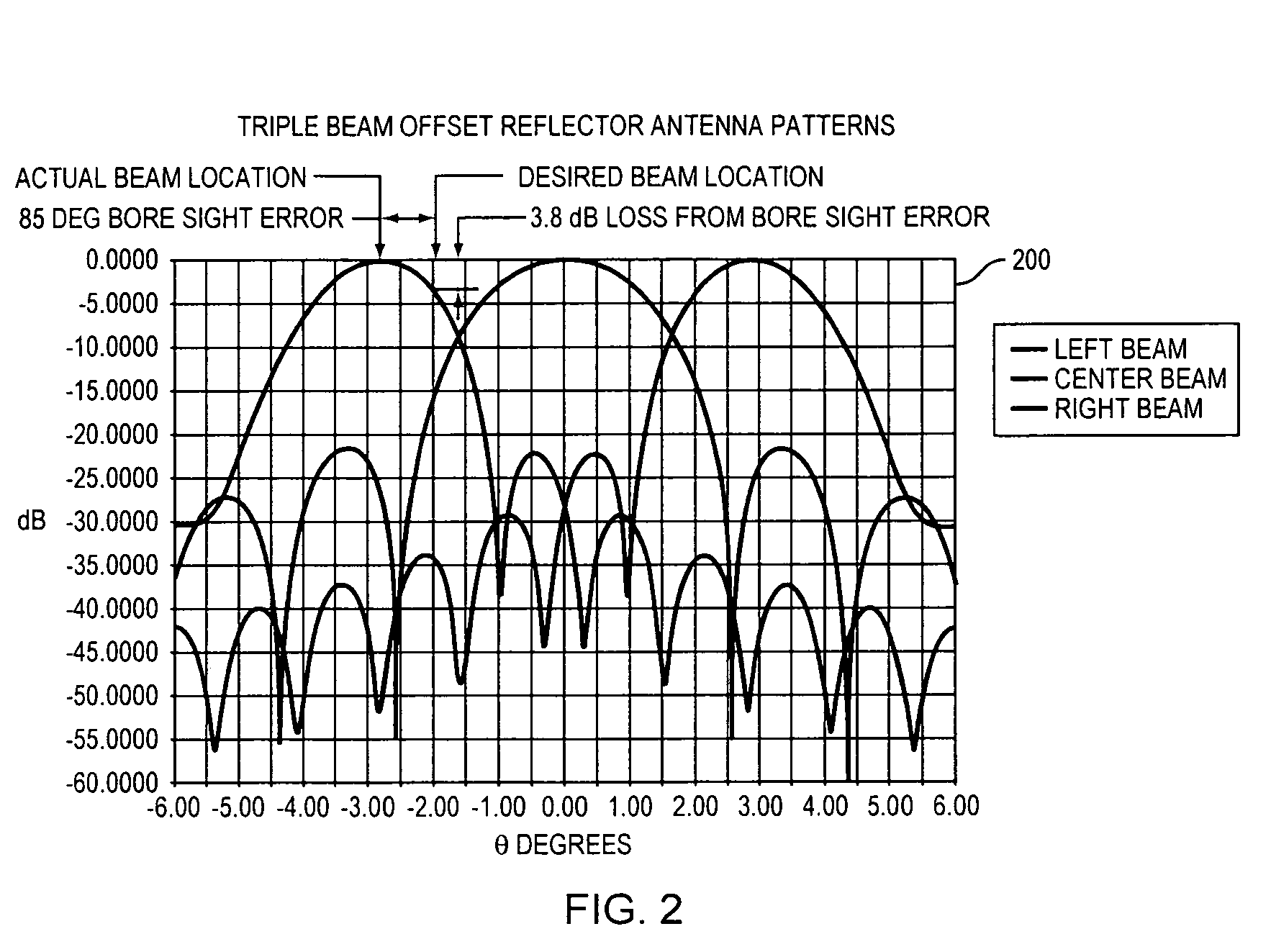
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1223 results about "Antenna design" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
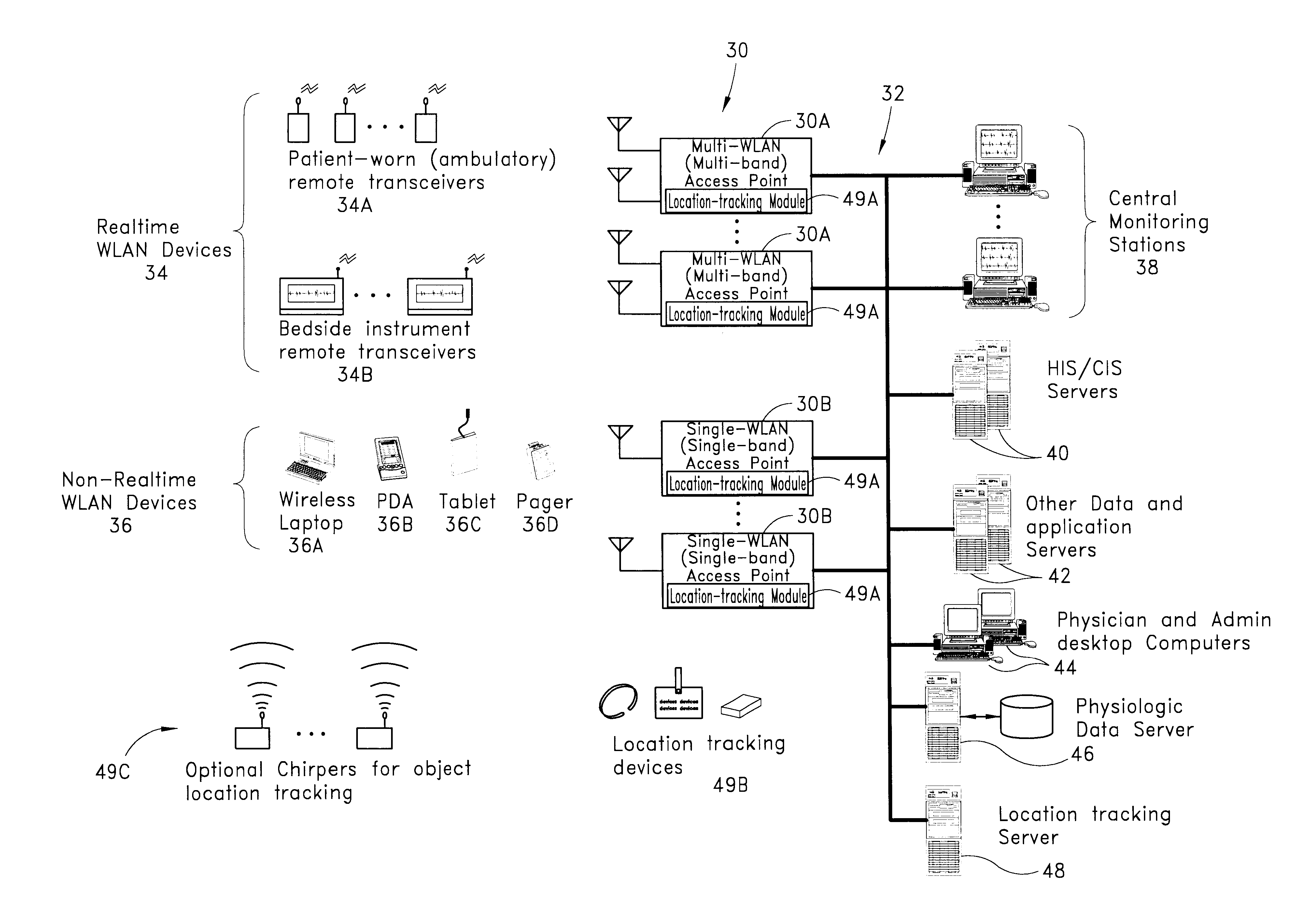
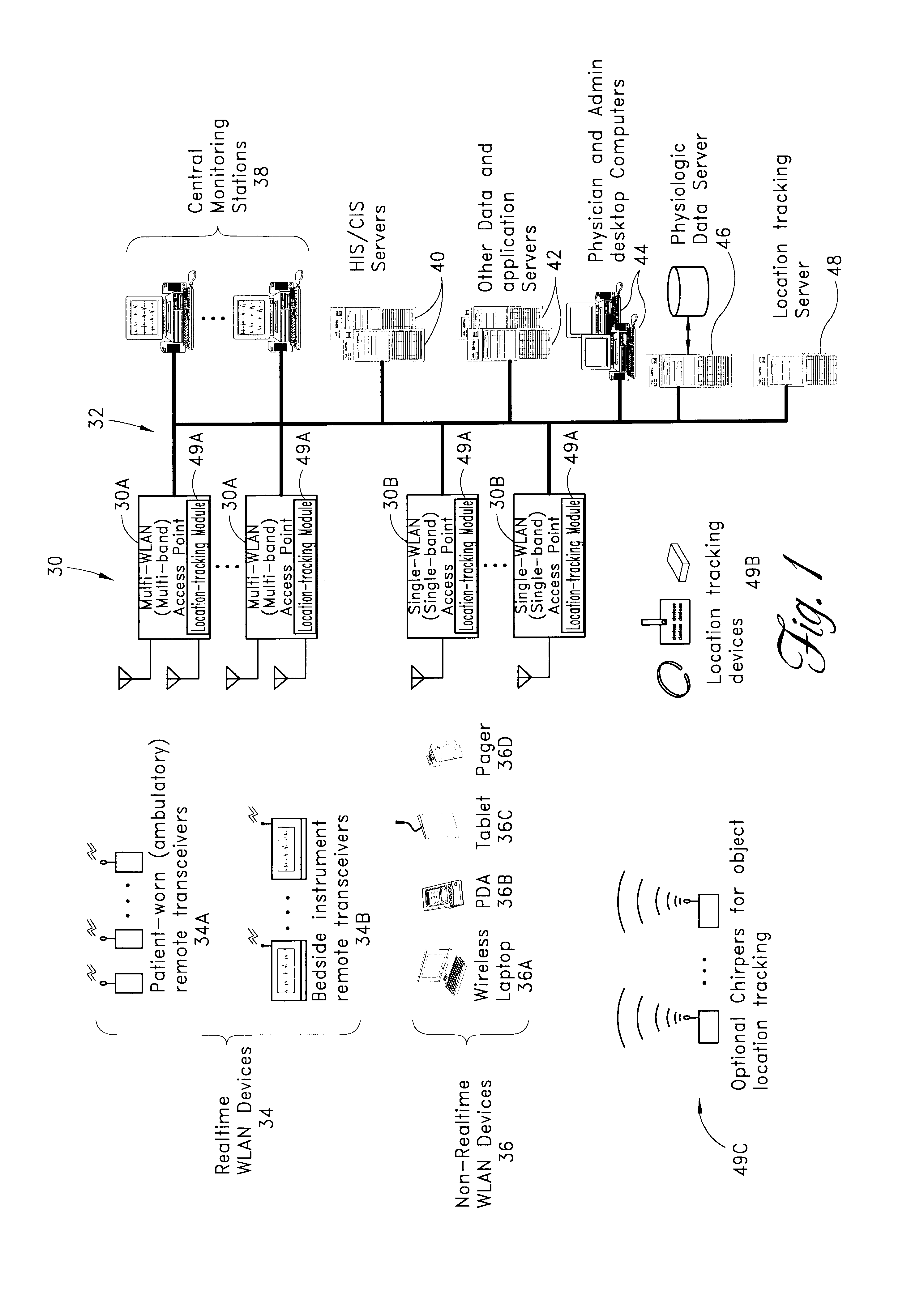
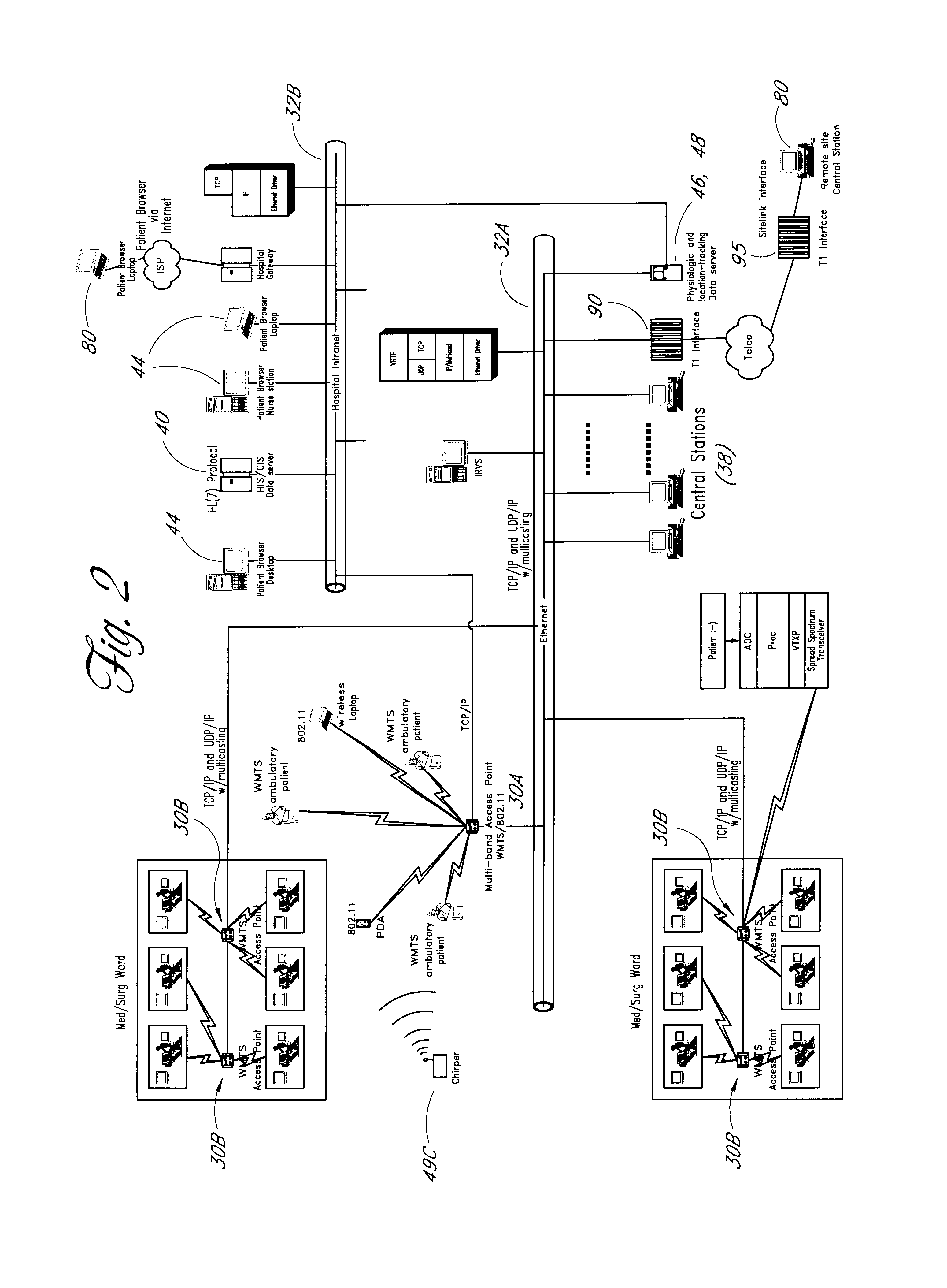
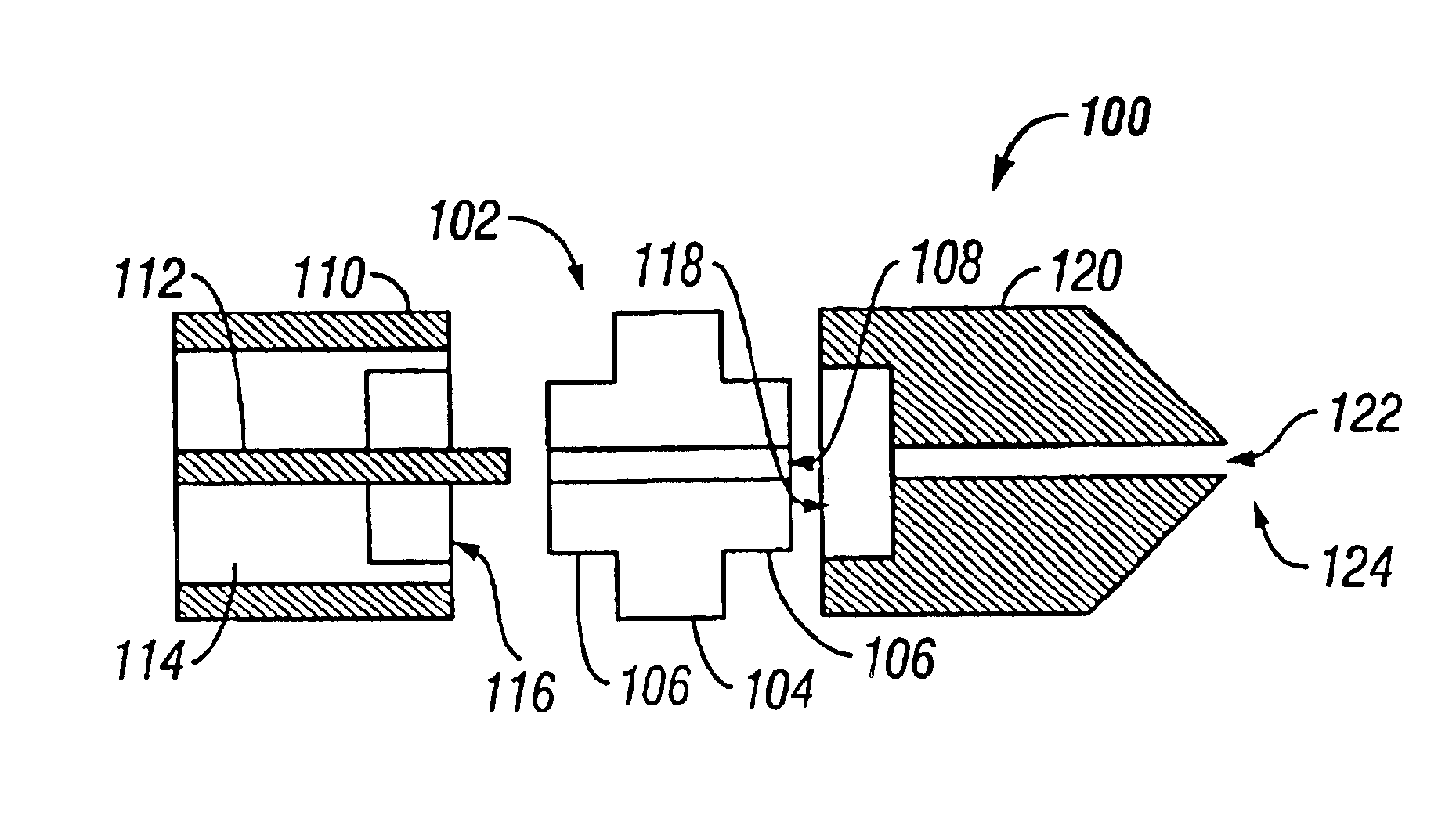
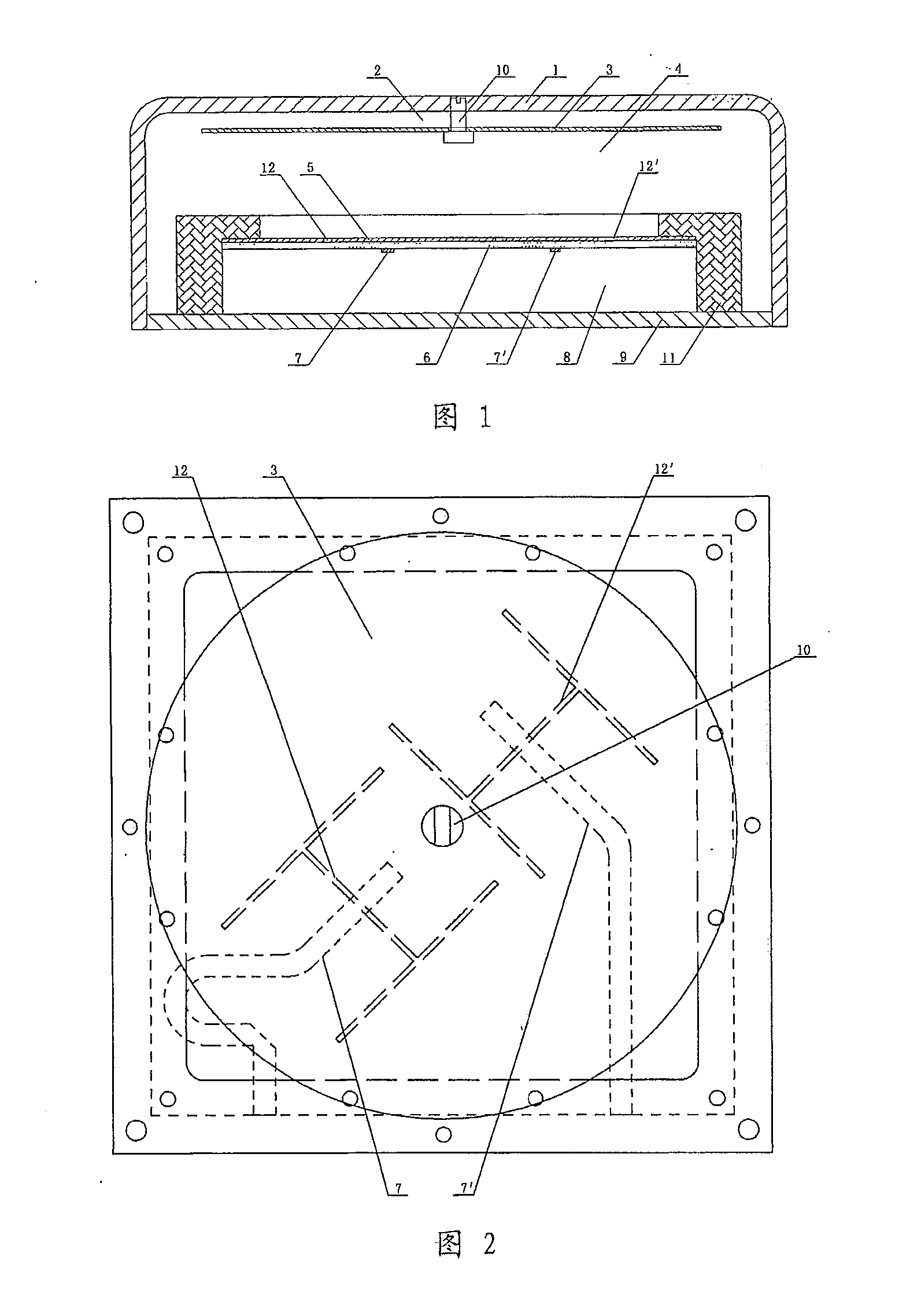
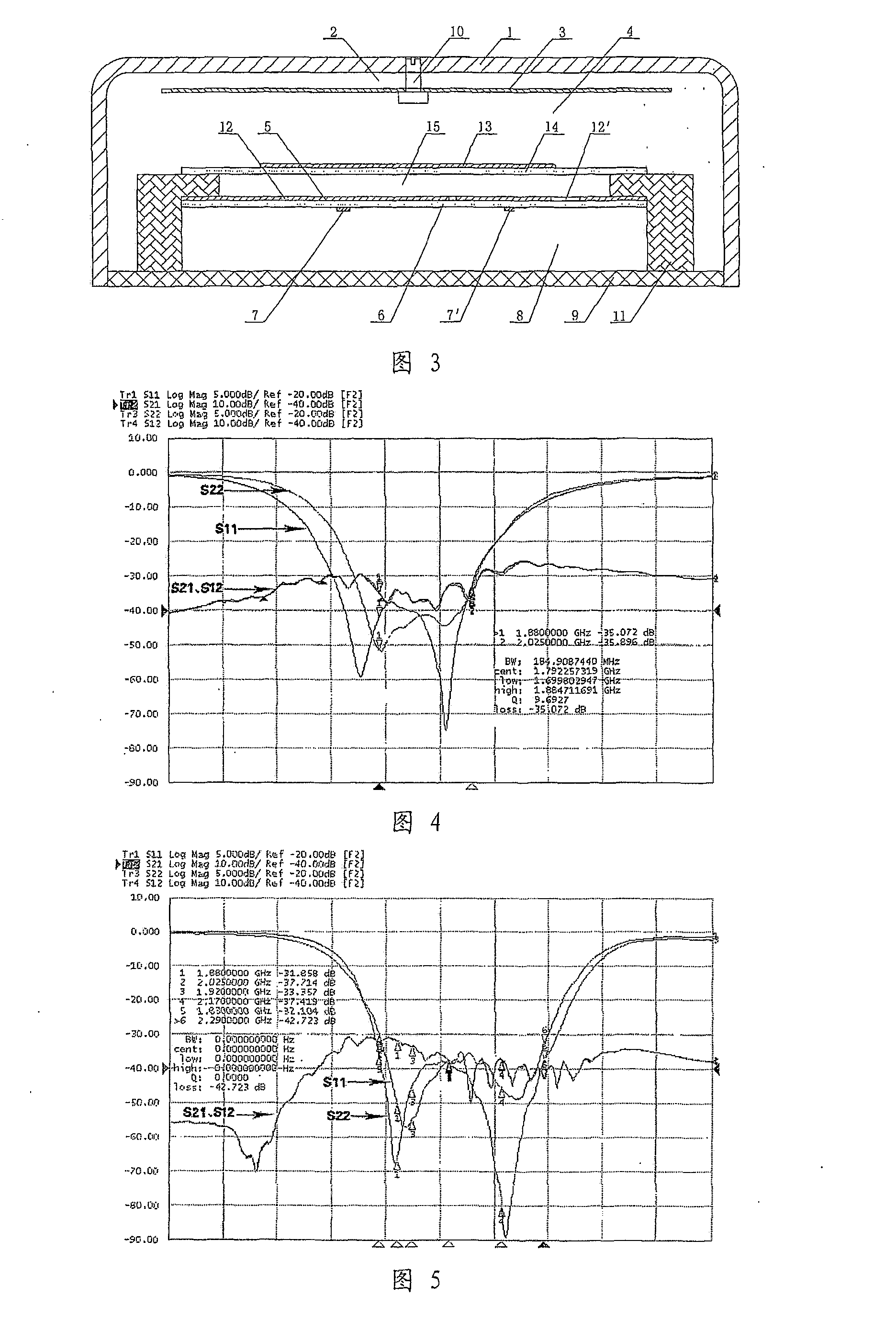
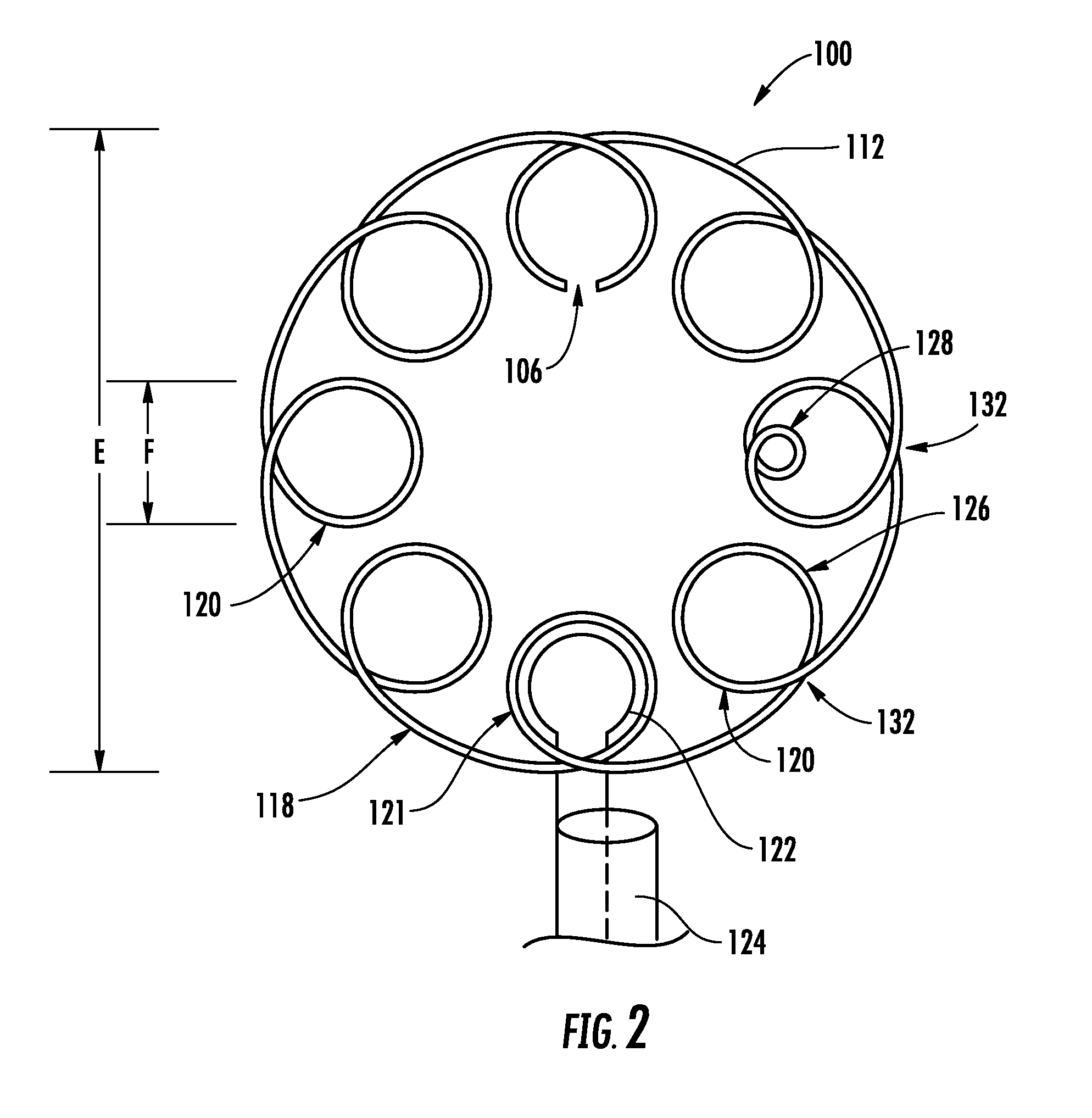
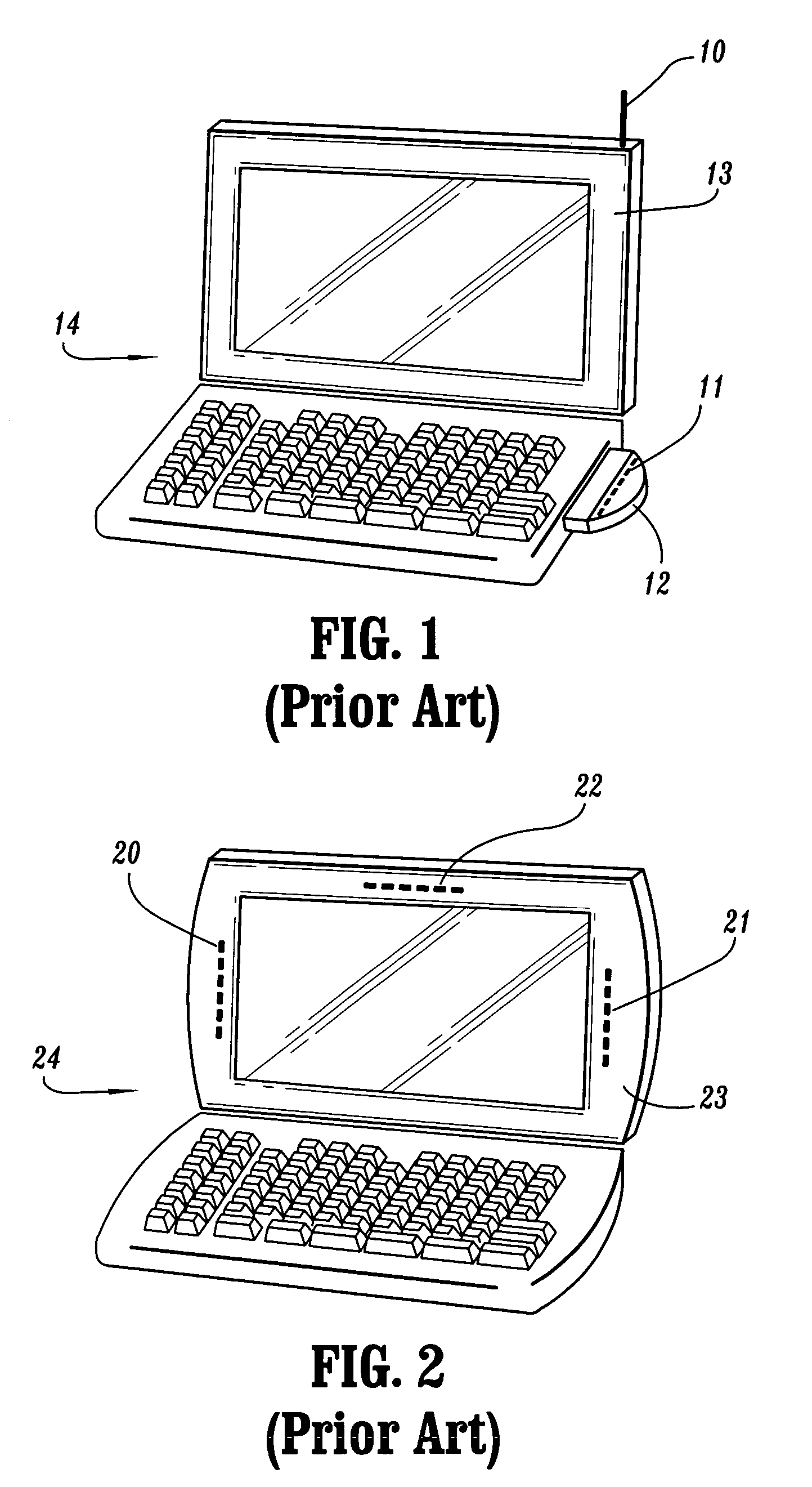
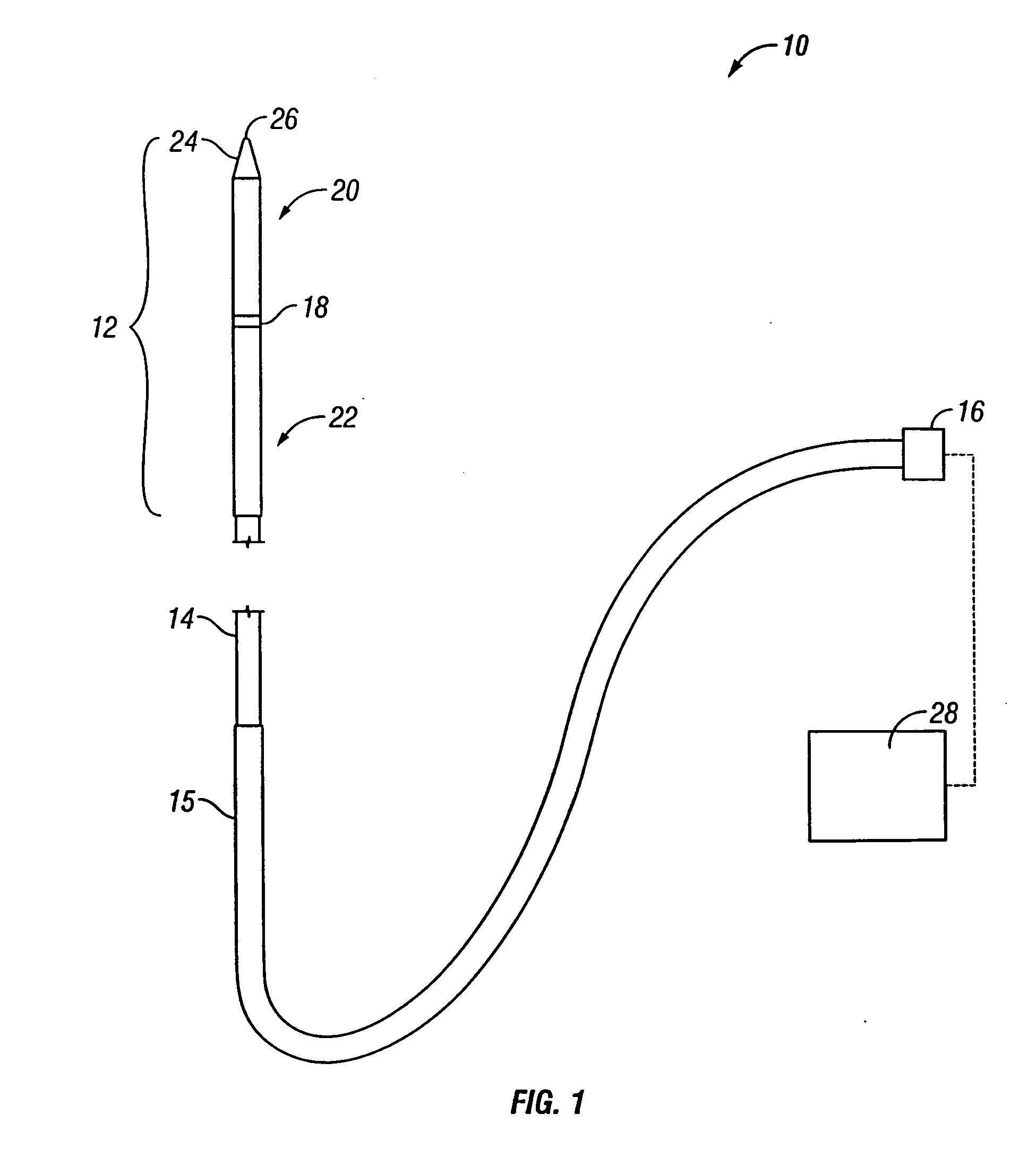
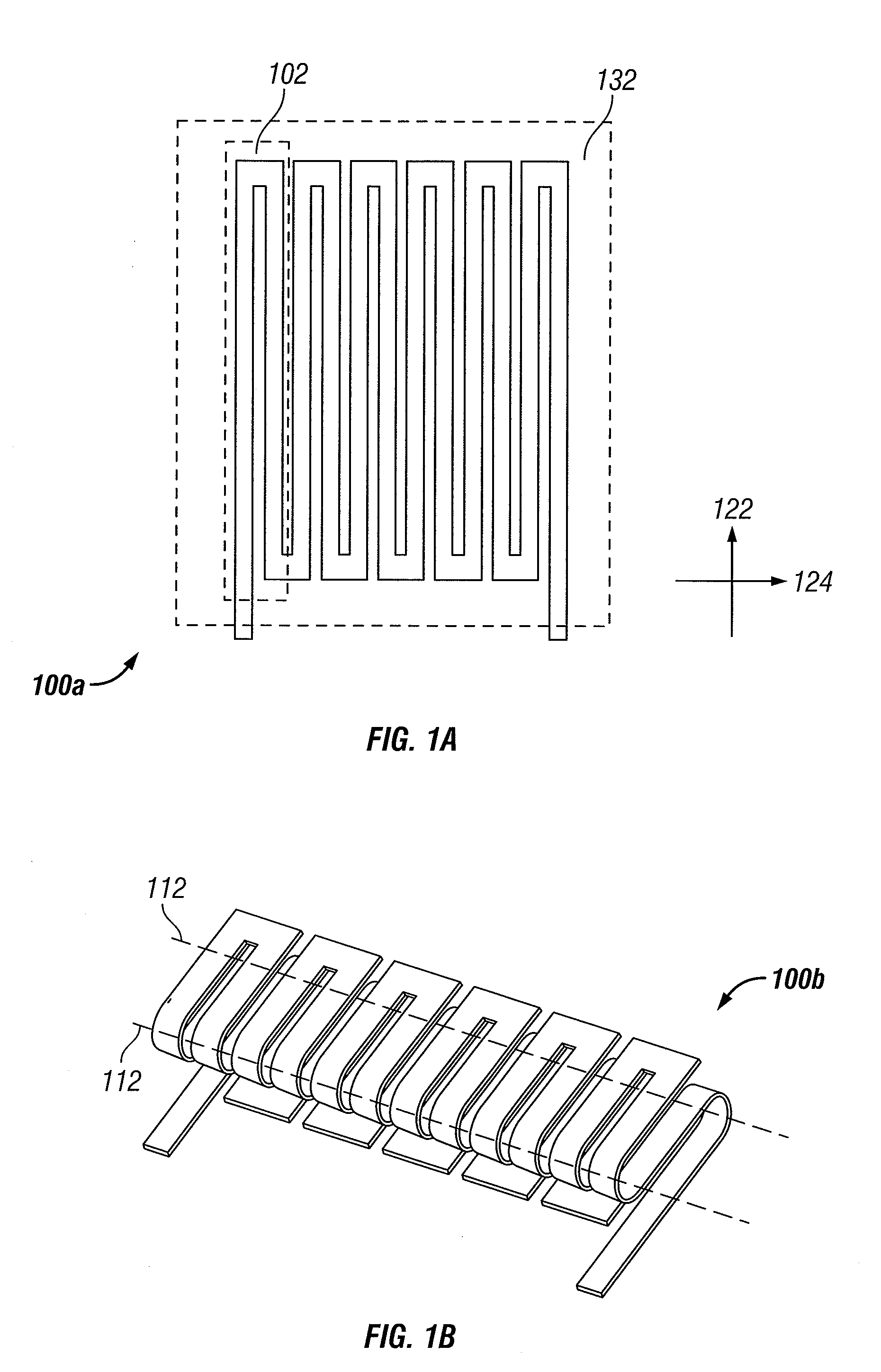
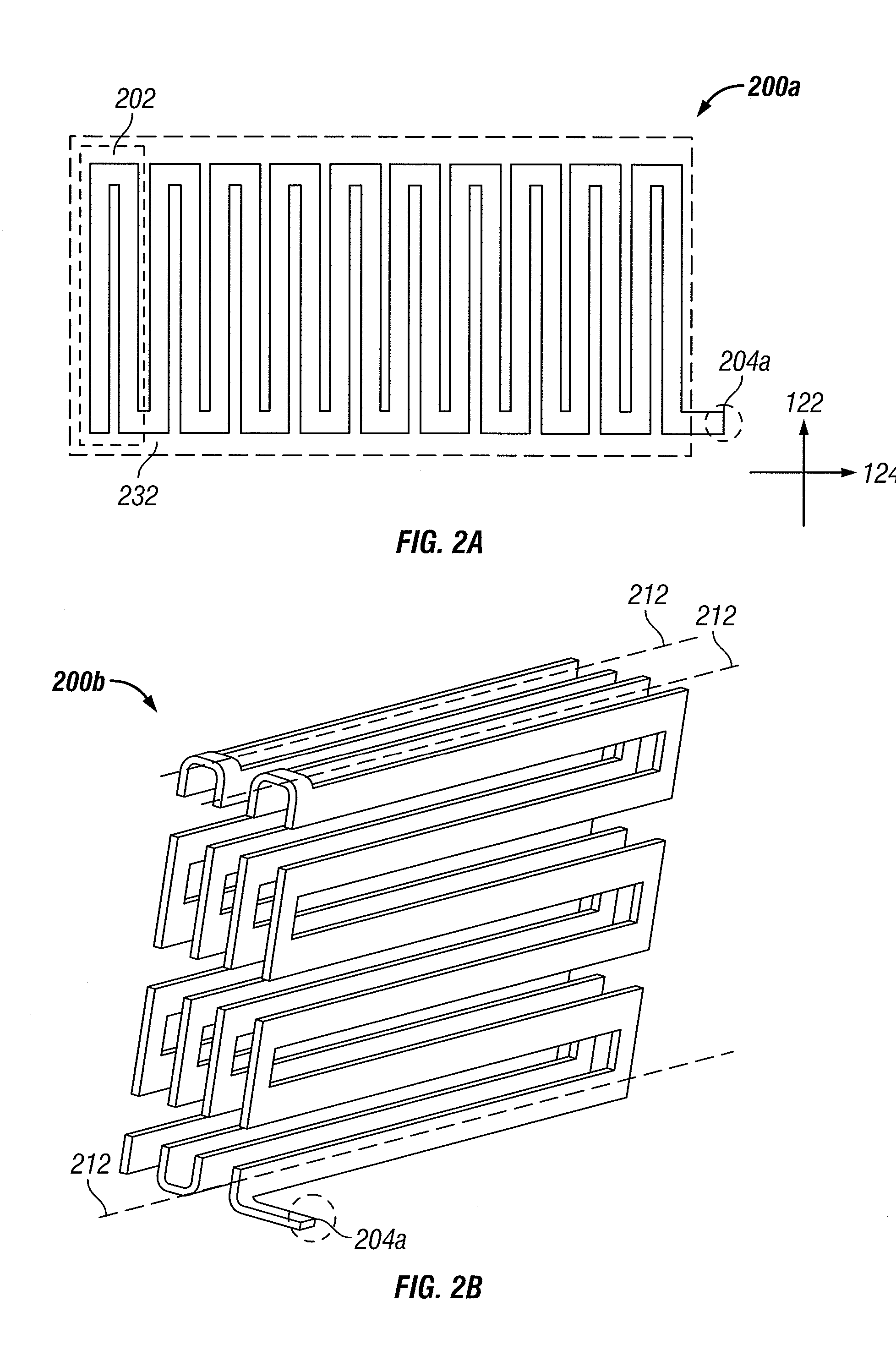
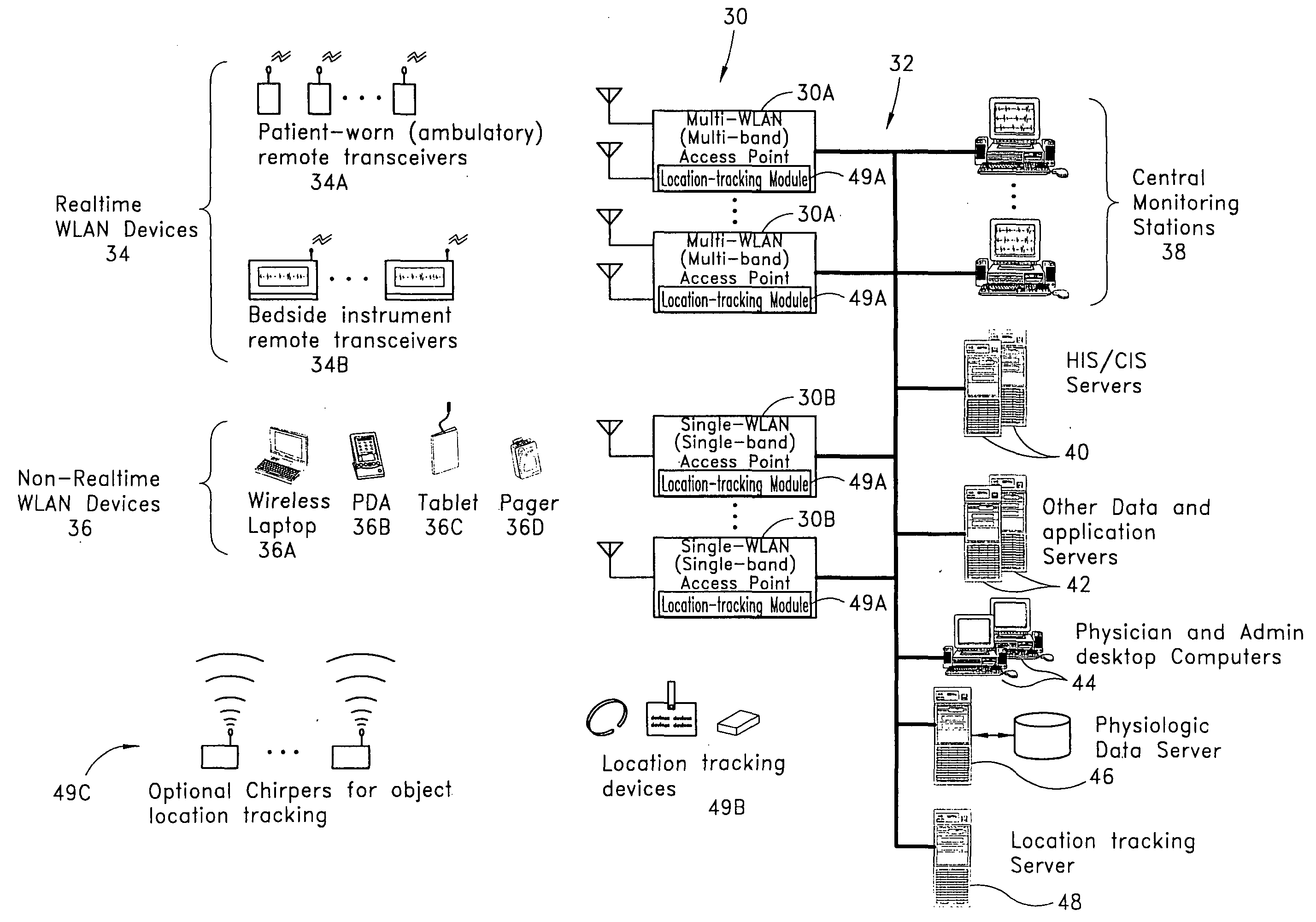
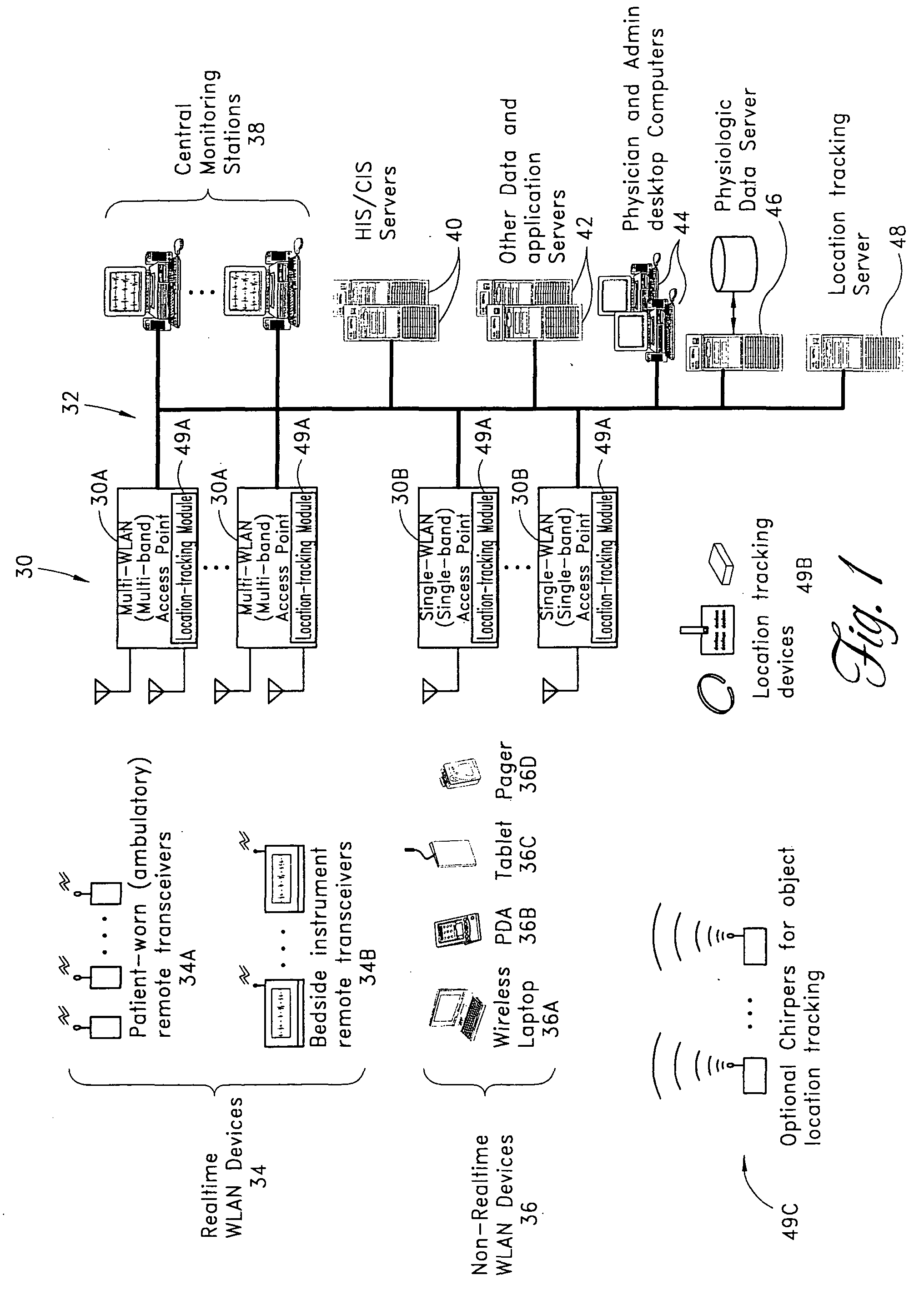
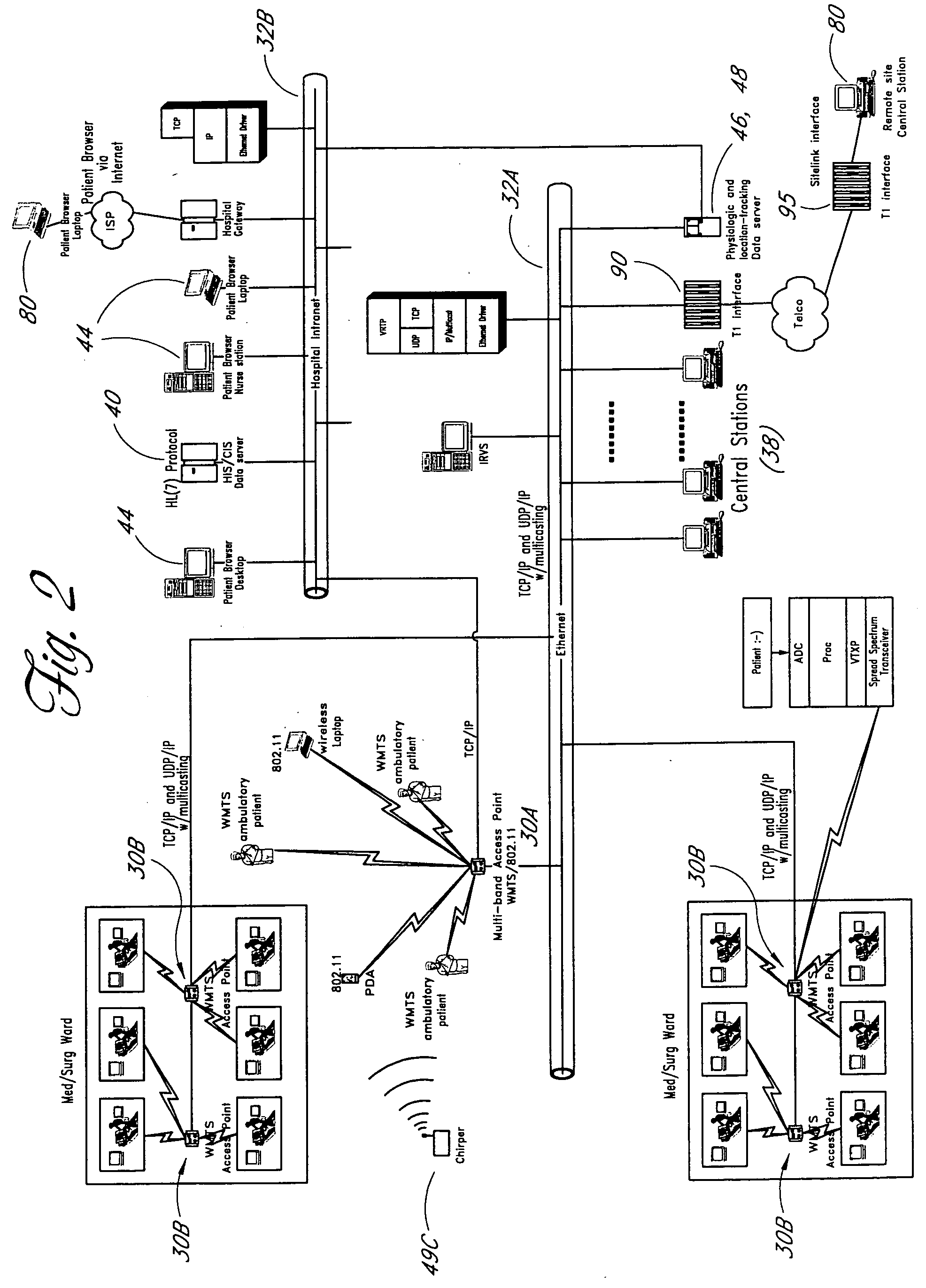
Wireless LAN architecture for integrated time-critical and non-time-critical services within medical facilities
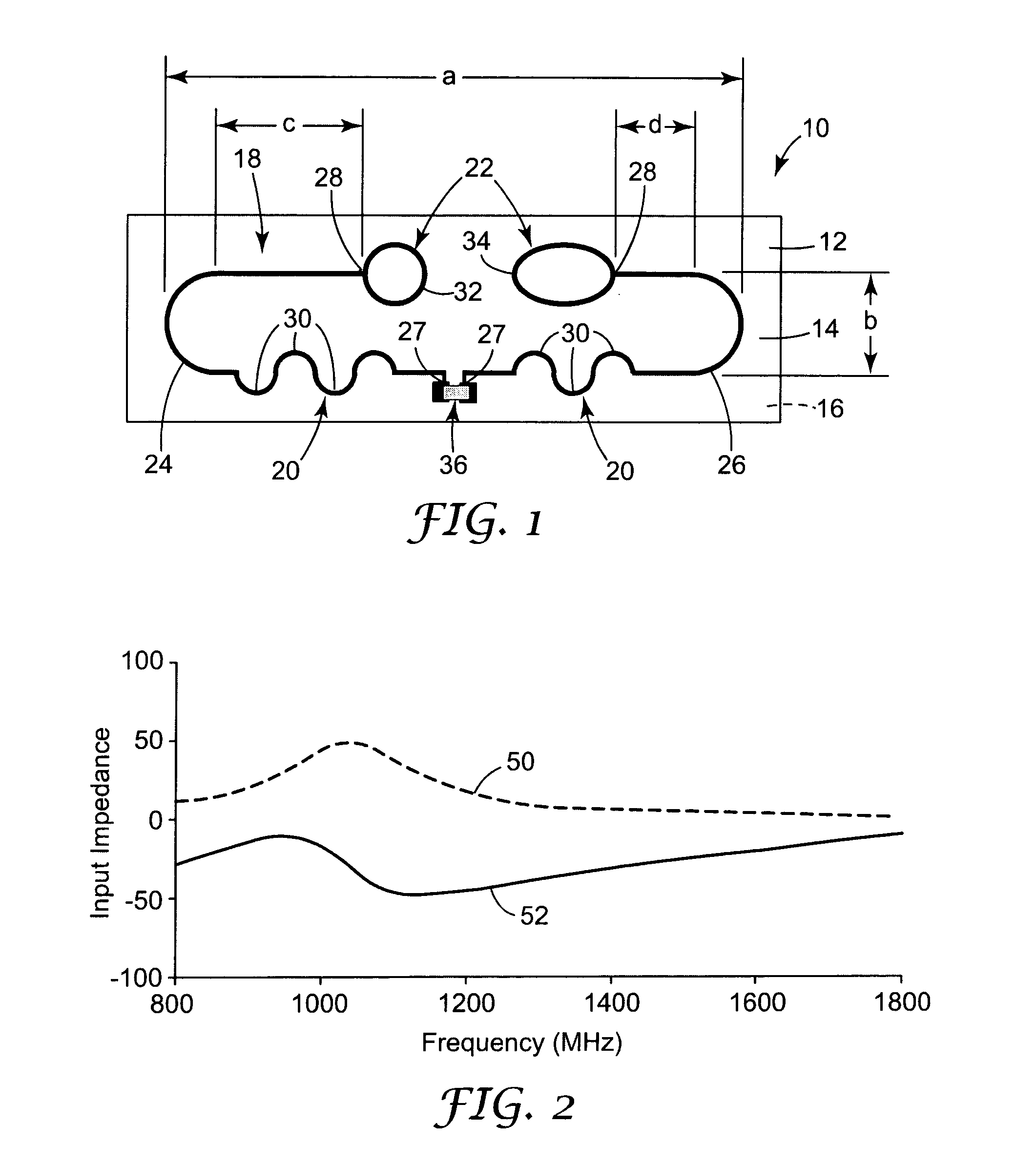
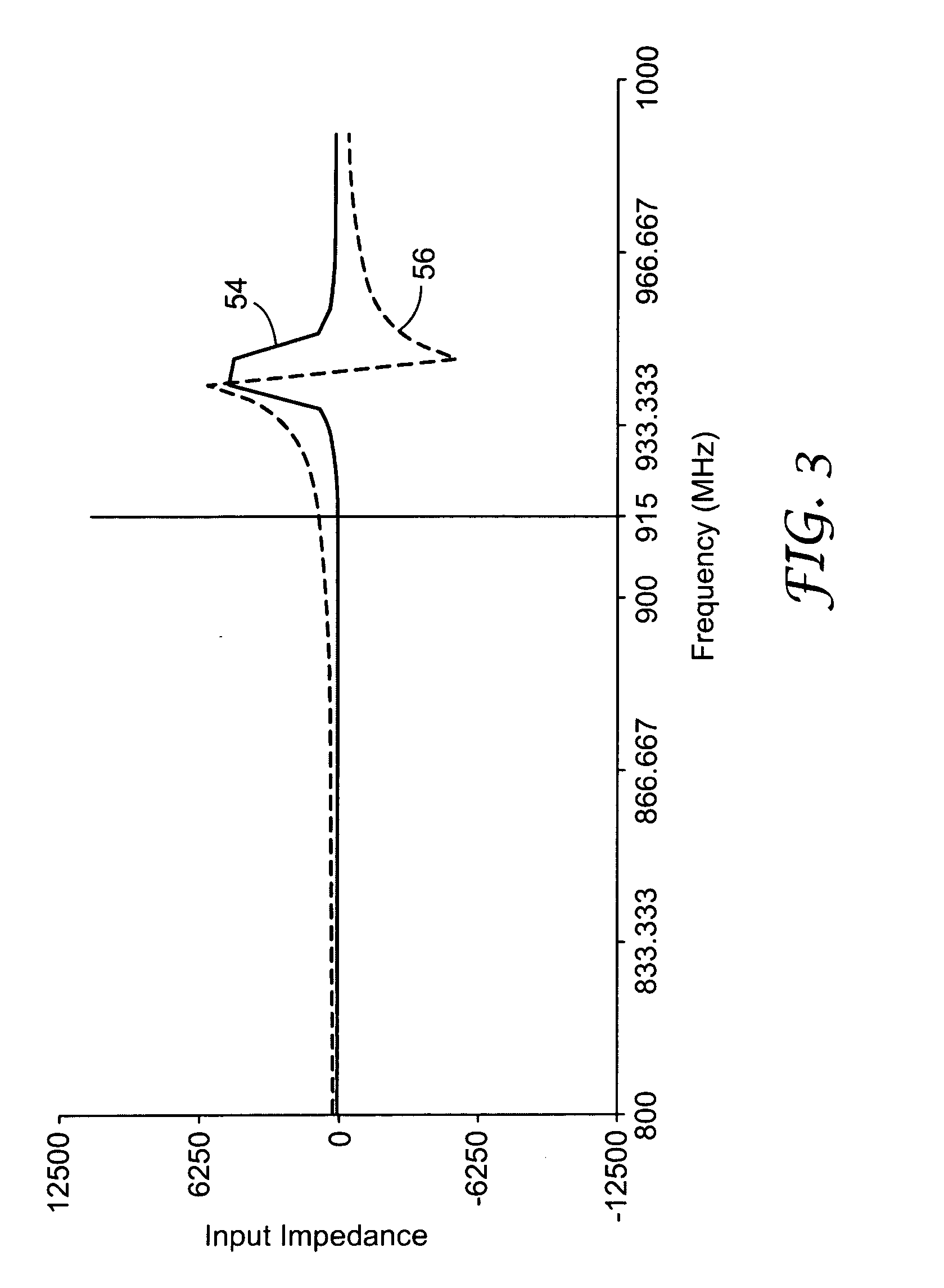
InactiveUS6659947B1Avoiding lockstep interferenceEasy to receiveSurgeryData switching by path configurationAntenna designDevice type
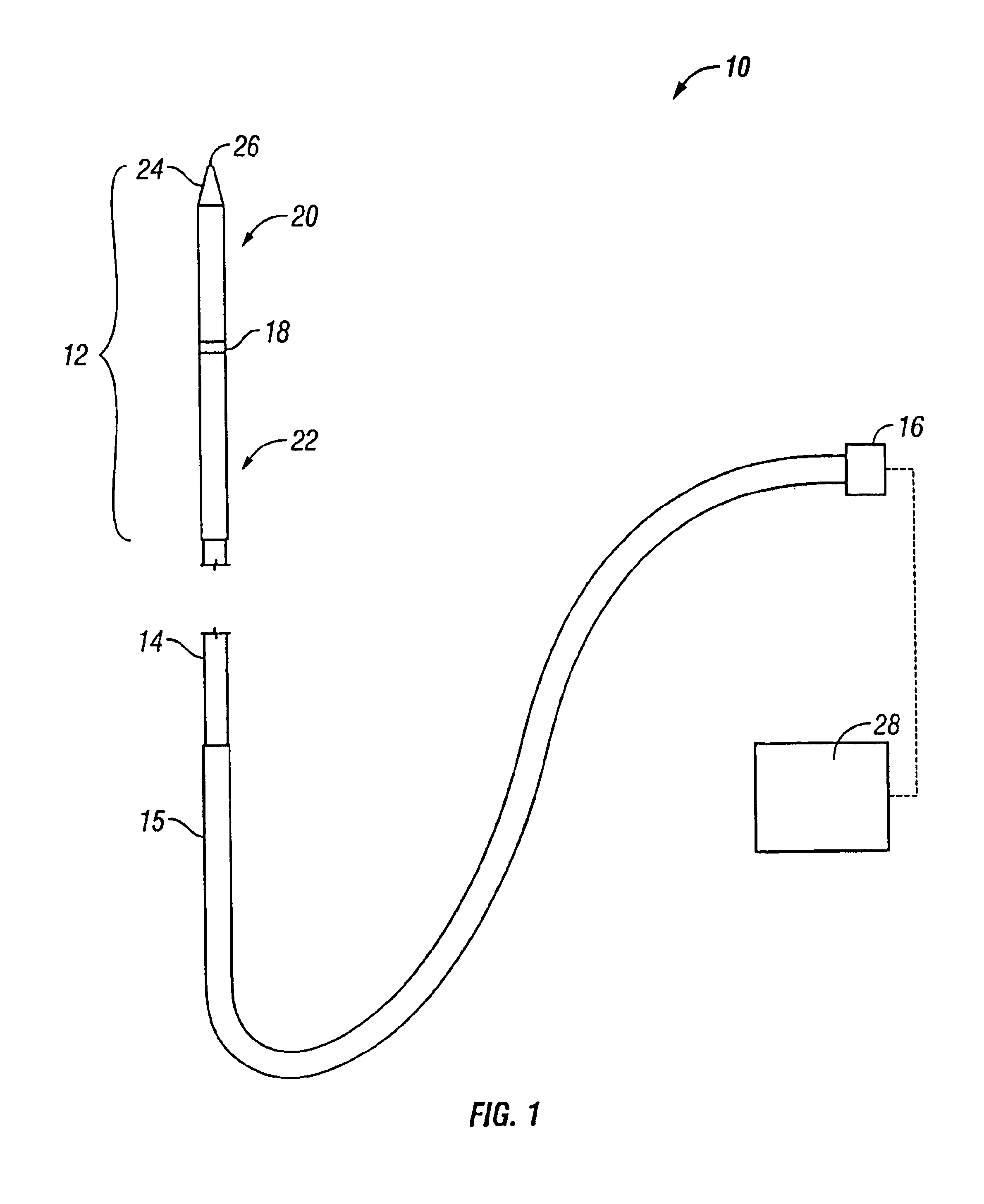
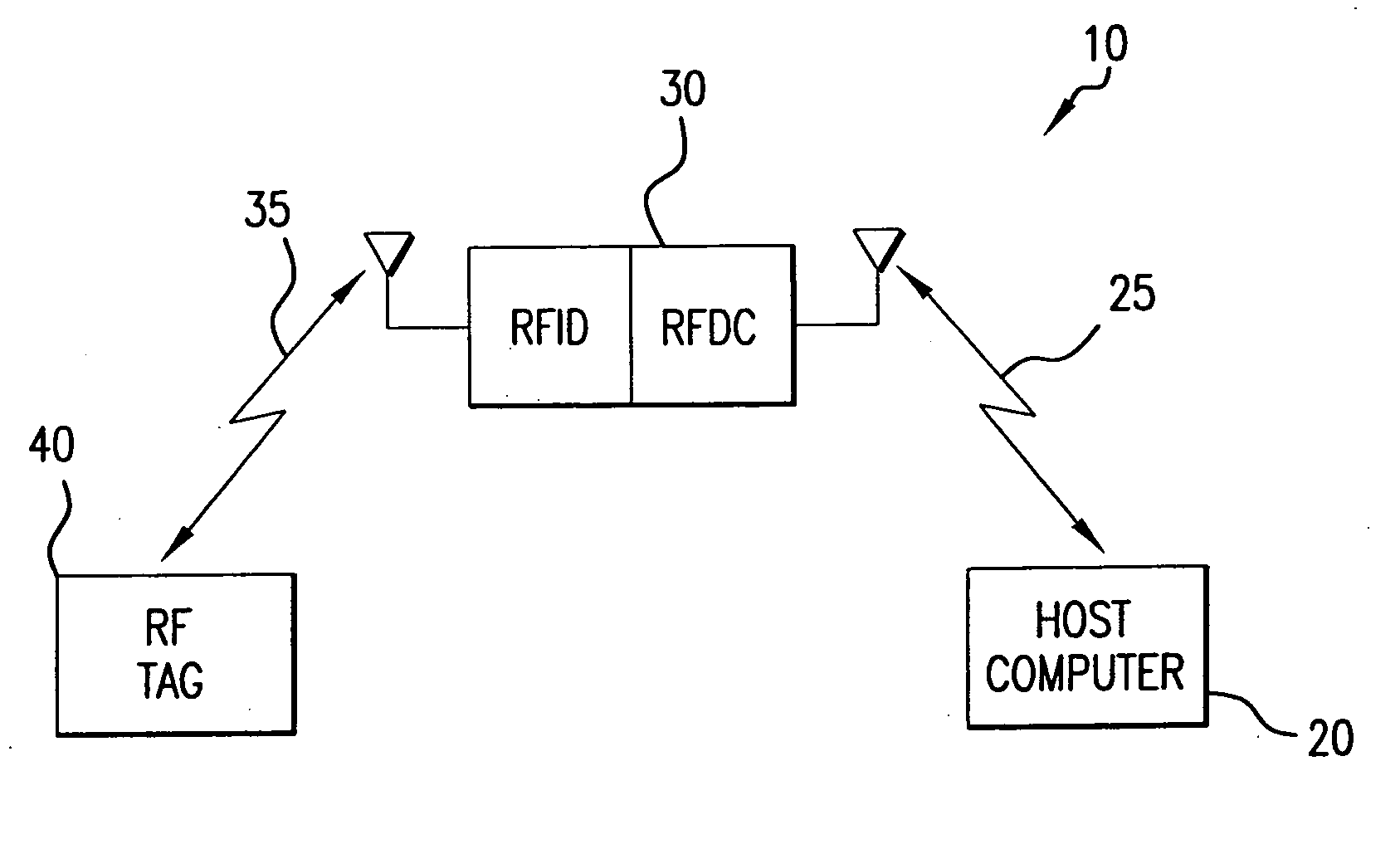
A wireless local area network (WLAN) system comprises multiple access points that are distributed throughout a medical facility to provide wireless access to a hardwired network. The access points implement multiple WLAN protocols, including a realtime protocol for realtime patient monitoring (telemetry) and a standard WLAN protocol (such as IEEE 802.11 within an ISM band) for providing general-purpose wireless access. Some or all of the access points preferably implement both WLAN protocols such that the different WLANs and wireless device types share network access resources. Some or all of the access points may also include RF location-tracking modules which may be used to track locations of patients, hospital personnel, capital equipment, and / or disposable medical supplies. Also disclosed are an antenna design which may be used with the access points to improve reception (particularly for patient monitoring), and a TDMA timeslot rotation method for avoiding lockstep interference between access points that operate on the same channel.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST INFORMATION TECH
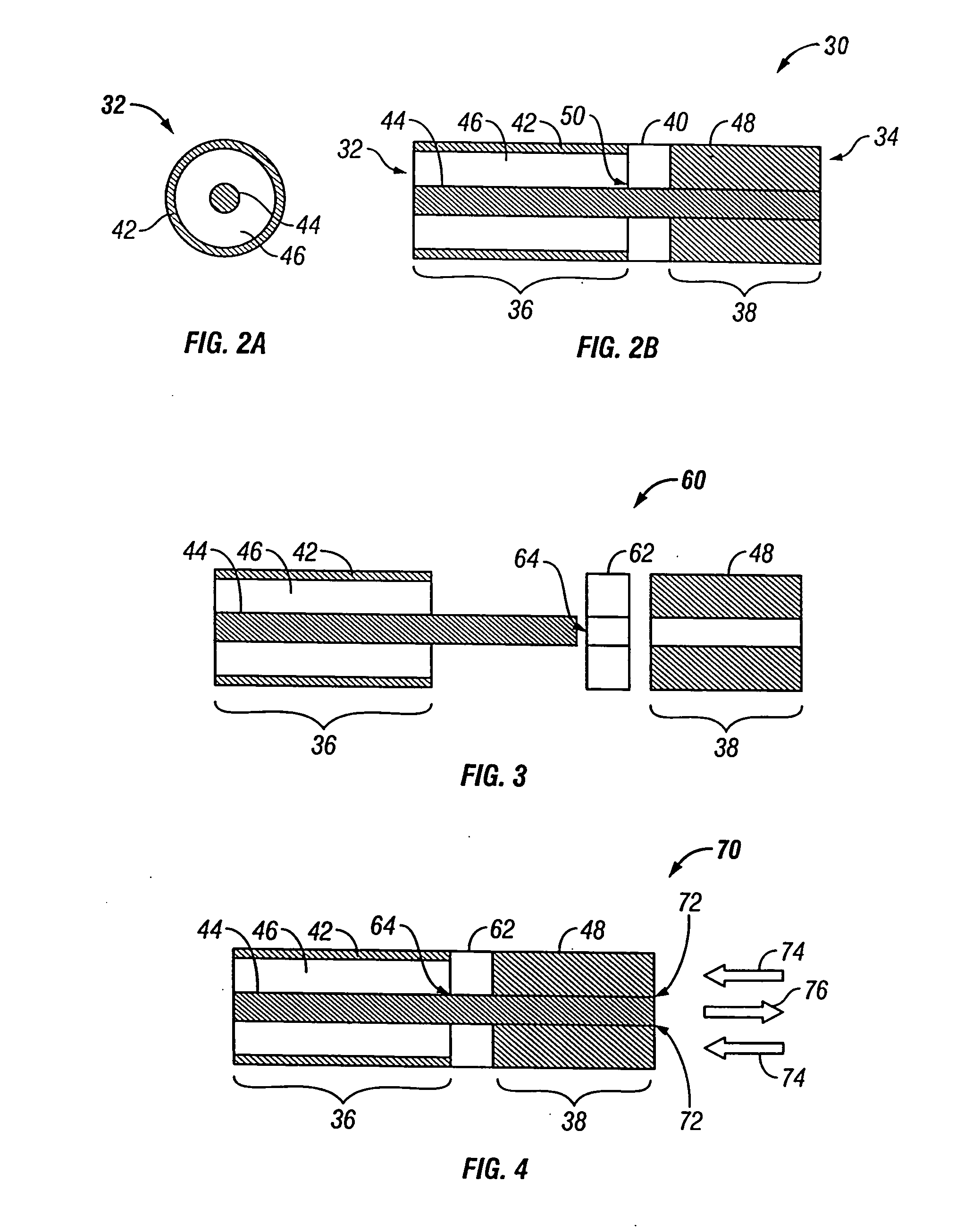
High-strength microwave antenna assemblies
InactiveUS6878147B2Avoid mechanical failureSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingAntenna designElectrical conductor
Various high-strength microwave antenna assemblies are described herein. The microwave antenna has a radiating portion connected by a feedline to a power generating source, e.g., a generator. The antenna is a dipole antenna with the distal end of the radiating portion being tapered and terminating at a tip to allow for direct insertion into tissue. Antenna rigidity comes from placing distal and proximal radiating portions in a pre-stressed state, assembling them via threaded or overlapping joints, or fixedly attaching an inner conductor to the distal portion. The inner conductor is affixed to the distal portion by, e.g., welding, brazing, soldering, or by adhesives. A junction member made from a hard dielectric material, e.g., ceramic, can be placed between the two portions and can have uniform or non-uniform shapes to accommodate varying antenna designs. Electrical chokes may also be used to contain returning currents to the distal end of the antenna.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Ultra-wide band (UWB) artificial magnetic conductor (AMC) metamaterials for electrically thin antennas and arrays
InactiveUS8451189B1Maximize received power transferMinimize reflectionAntenna feed intermediatesAntenna designFractional bandwidth
This disclosure demonstrates a new class of Ultra-Wide Band (UWB) AMC with very large fractional bandwidth (>100%) even at lower frequencies (<1 GHz). This new UWB AMC is enabled by recognizing that any AMC must be an antenna in order to accept the incident radiation into the circuit. Therefore, by using UWB antenna design features, one can make wide band AMCs. Additionally, by manipulation of the UWB AMC element design, a 1 / frequency dependence can be obtained for instantiating the benefits of a quarter wave reflection over a large UWB bandwidth with a single physical thickness.
Owner:FLUHLER HERBERT U
Microstrip antenna for RFID device
InactiveUS20070164868A1Low costEliminate needSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMicrostrip patch antennaAntenna design
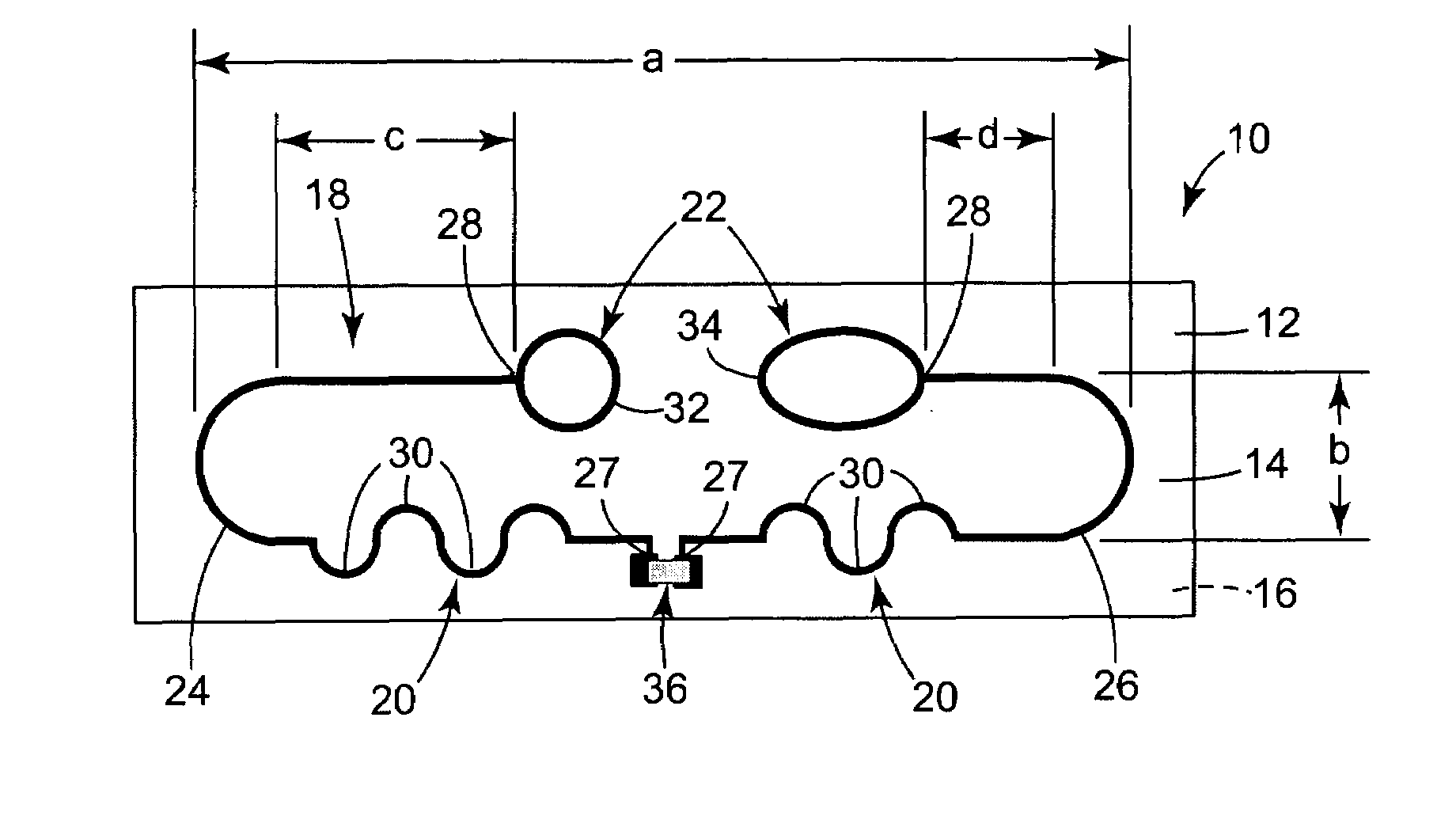
Microstrip patch antenna (46), feed structure (48), and matching circuit (50) designs for an RFID tag (10). A balanced feed design using balanced feeds coupled by a shorting stub (56) to create a virtual short between the two feeds so as to eliminate the need for physically connecting substrate to the ground plane. A dual feed structure design using a four-terminal IC can be connected to two antennas (46a,46b) resonating at different frequencies so as to provide directional and polarization diversity. A combined near / field-far / field design using a microstrip antenna providing electromagnetic coupling for far-field operation, and a looping matching circuit providing inductive coupling for near-field operation. A dual-antenna design using first and second microstrip antennas providing directional diversity when affixed to a cylindrical or conical object, and a protective superstrate (66). An annual antenna (46c) design for application to the top of a metal cylinder around a stem.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
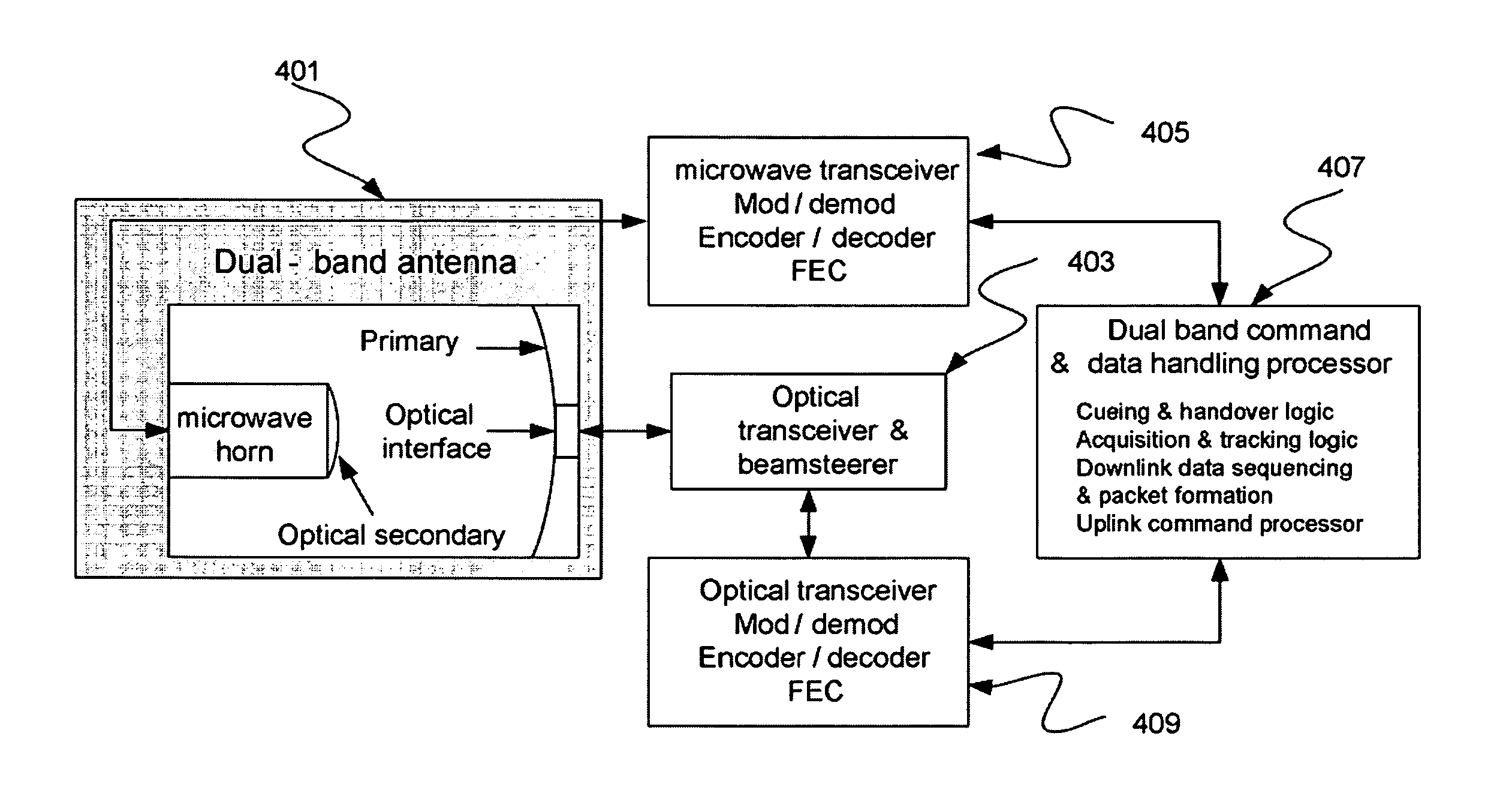
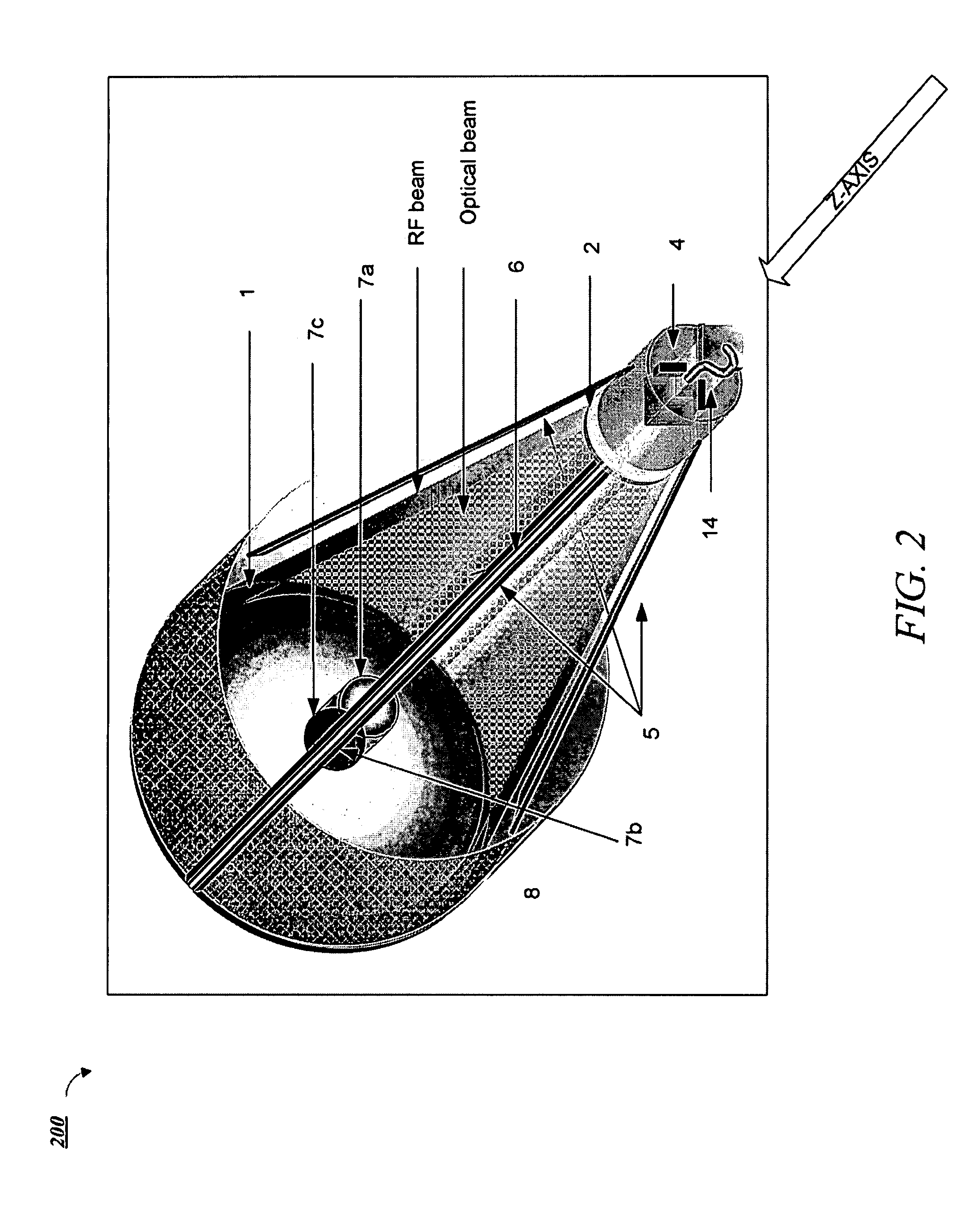
Dual band radio frequency (RF) and optical communications antenna and terminal design methodology and implementation
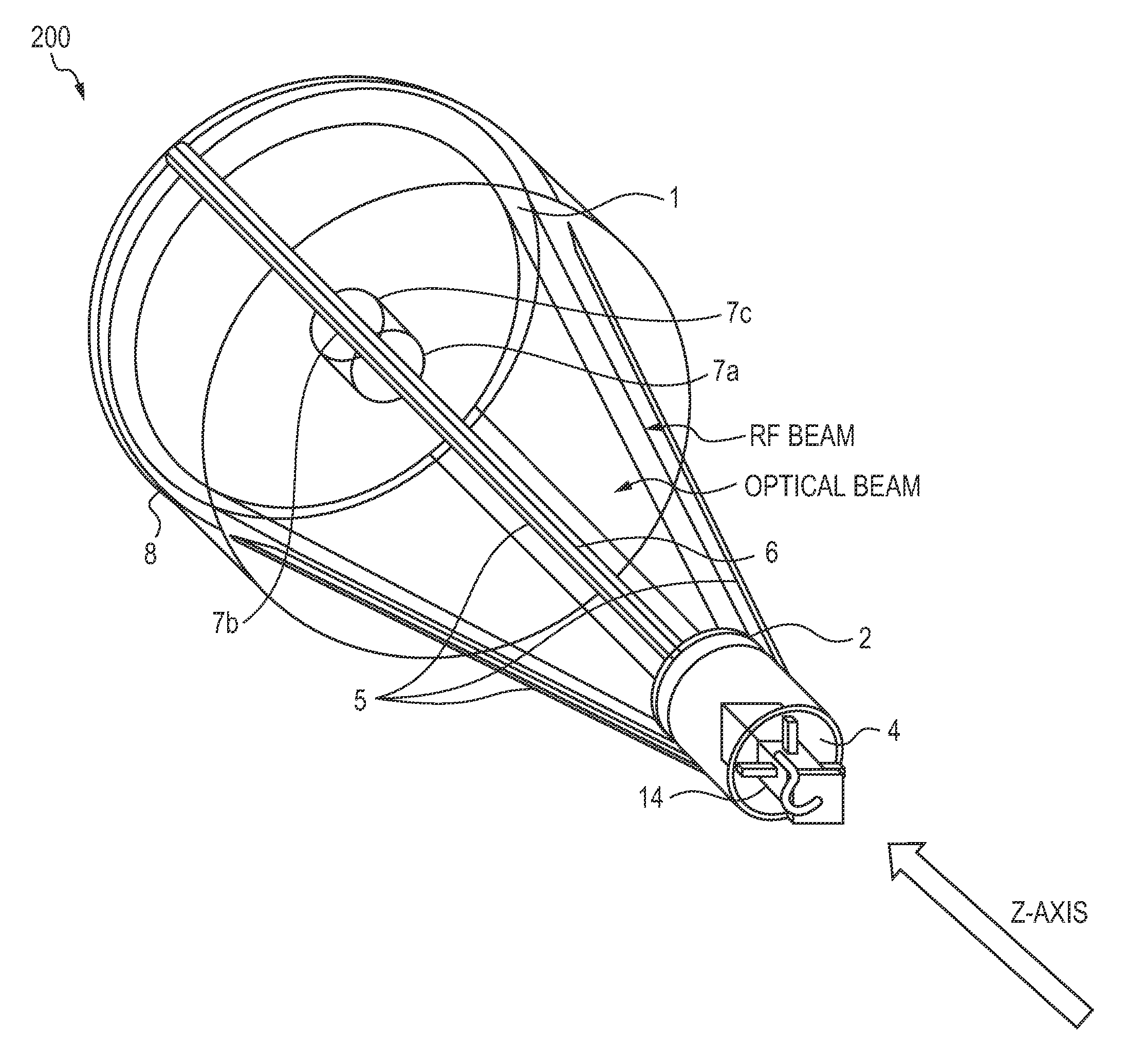
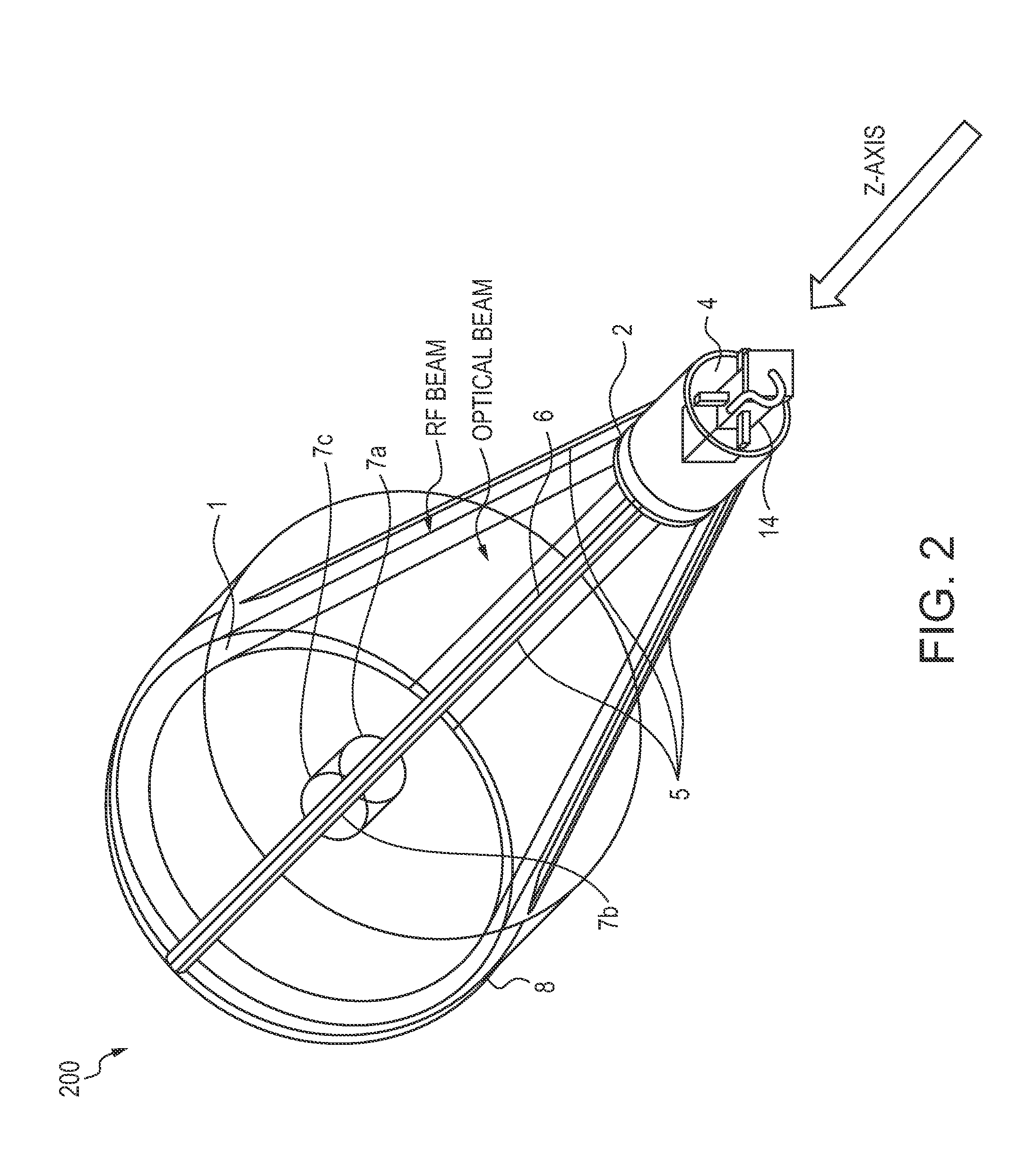
ActiveUS8094081B1High bandwidthMinimized massAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna designTransceiver
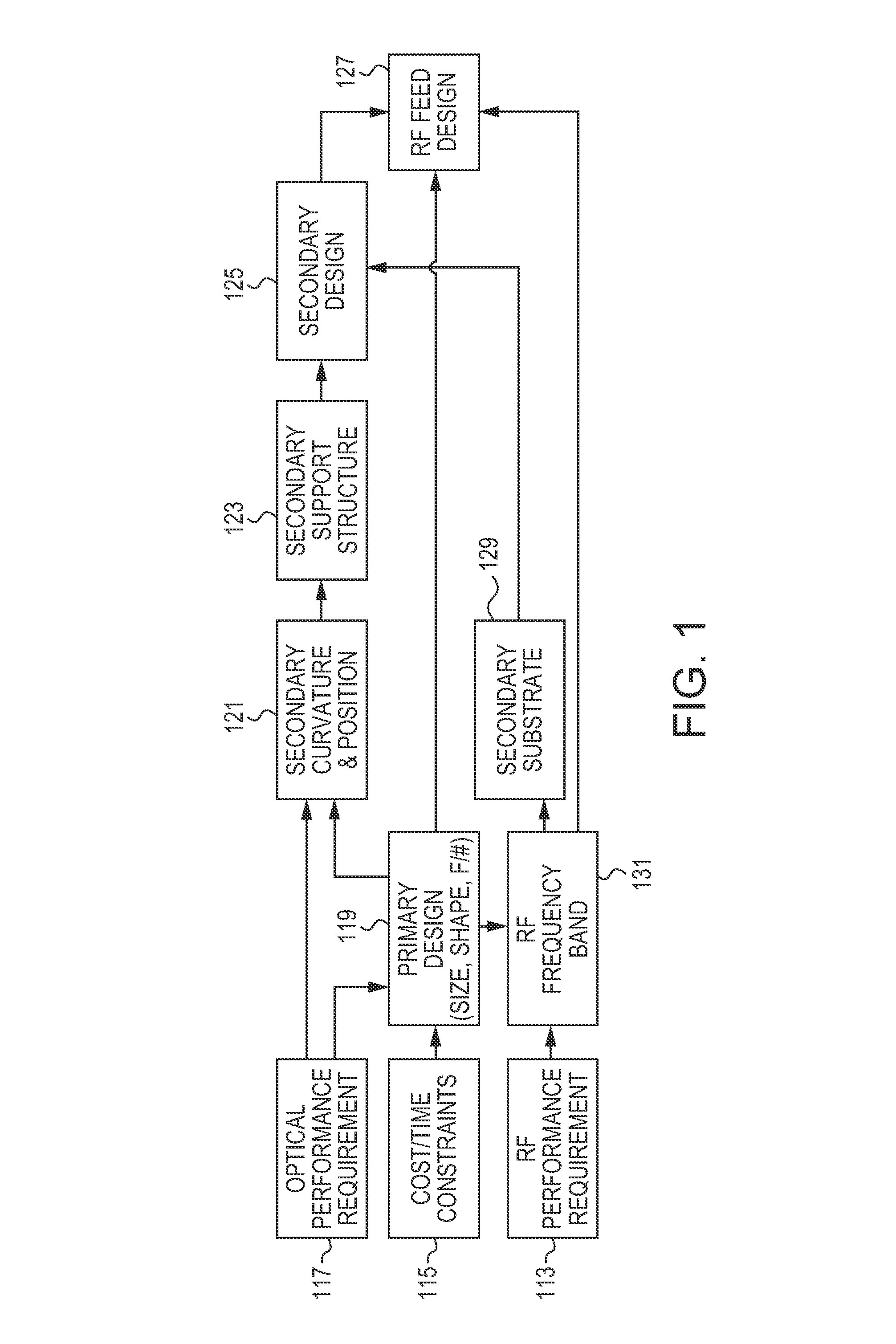
A dual-band antenna is provided that combines two normally disparate communications modes into a single compact aperture minimizing overall mass and volume, while maintaining high performance efficiency and reciprocity of each individual mode. The antenna is compatible with both optical (near-IR / visible) and RF (microwave / millimeter-wave) transceiver subsystems for high bandwidth communications, applicable primarily to long- to extremely long-range (space-to-ground) link distances. The optical link provides high bandwidth while the RF provides a lower data-rate weather backup, accommodation for traditional navigation techniques, and assistance in cueing the extremely tight optical beam by matching the RF beamwidth to an optical fine-steering mechanism field-of-regard. The configuration is built around a near-diffraction-limited high performance primary mirror shared by both a direct-fed RF antenna design and a Cassegrain optical telescope. Material properties are exploited to combine the optical secondary mirror with the RF feed structure, providing a collimated optical beam interface at the antenna vertex.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Small ultra wideband antenna having unidirectional radiation pattern
ActiveUS7589686B2Enhancing the electromagnetic waves radiatingAntenna arraysElectrically short antennasUltra-widebandAntenna design
A small ultra wideband (UWB) antenna designed to have a unidirectional radiation pattern is disclosed. The UWB antenna includes a substrate; a power feeding part, provided on an upper surface of the substrate, for receiving a supply of an external electromagnetic energy; a dipole radiator excited by the electromagnetic energy fed through the power feeding part and radiating electromagnetic waves in one and the other directions of the substrate; and an active loop radiator excited by the electromagnetic energy fed through the power feeding part, respectively enhancing and canceling the electromagnetic fields produced in one or the other directions of the substrate by the dipole radiator.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Small wave-guide radiators for closely spaced feeds on multi-beam antennas
Owner:PRO BRAND INT
Dual band radio frequency (RF) & optical communications antenna and terminal design methodology and implementation
ActiveUS20120002973A1Increase system capacityLink robustnessWaveguide hornsAntenna arraysAntenna designTransceiver
A dual-band antenna is provided that combines two normally disparate communications modes into a single compact aperture minimizing overall mass and volume, while maintaining high performance efficiency and reciprocity of each individual mode. The antenna is compatible with both optical (near-IR / visible) and RF (microwave / millimeter-wave) transceiver subsystems for high bandwidth communications, applicable primarily to long- to extremely long-range (space-to-ground) link distances. The optical link provides high bandwidth while the RF provides a lower data-rate weather backup, accommodation for traditional navigation techniques, and assistance in cueing the extremely tight optical beam by matching the RF beamwidth to an optical fine-steering mechanism field-of-regard. The configuration is built around a near-diffraction-limited high performance primary mirror shared by both a direct-fed RF antenna design and a Cassegrain optical telescope. Material properties are exploited to combine the optical secondary mirror with the RF feed structure, providing a collimated optical beam interface at the antenna vertex.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Wireless locating and tracking systems
InactiveUS7005968B1Antenna supports/mountingsCo-operative working arrangementsAntenna designEngineering
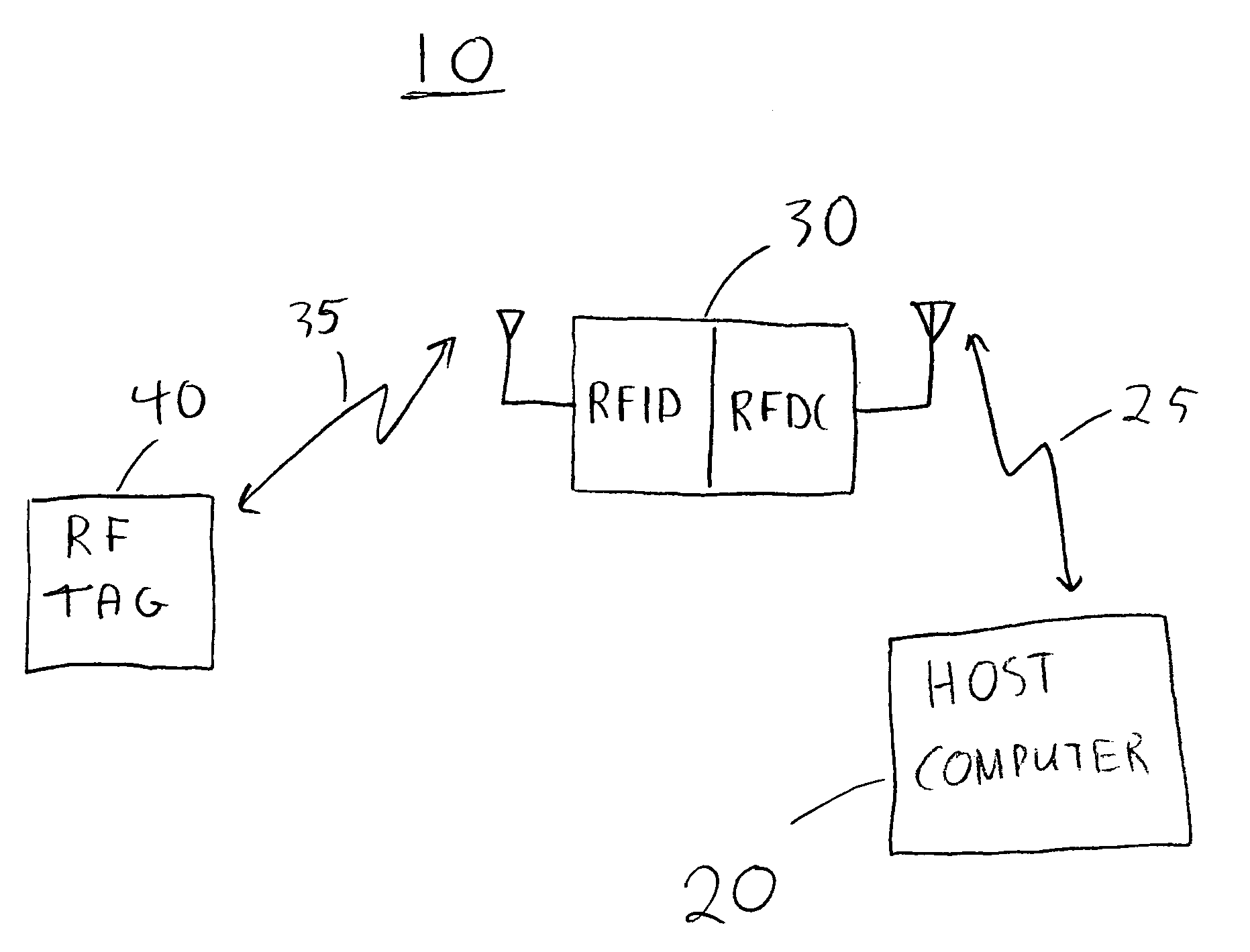
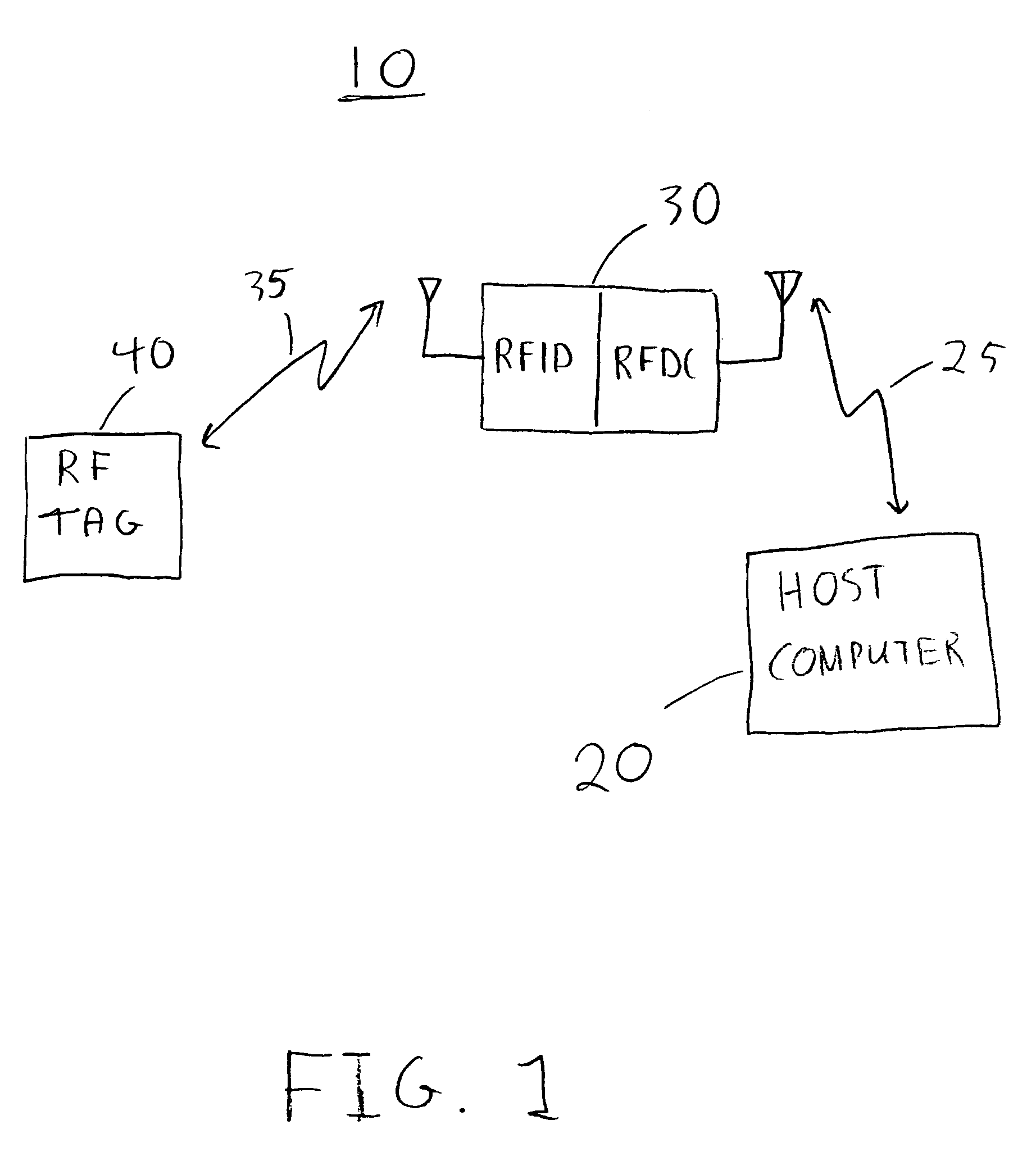
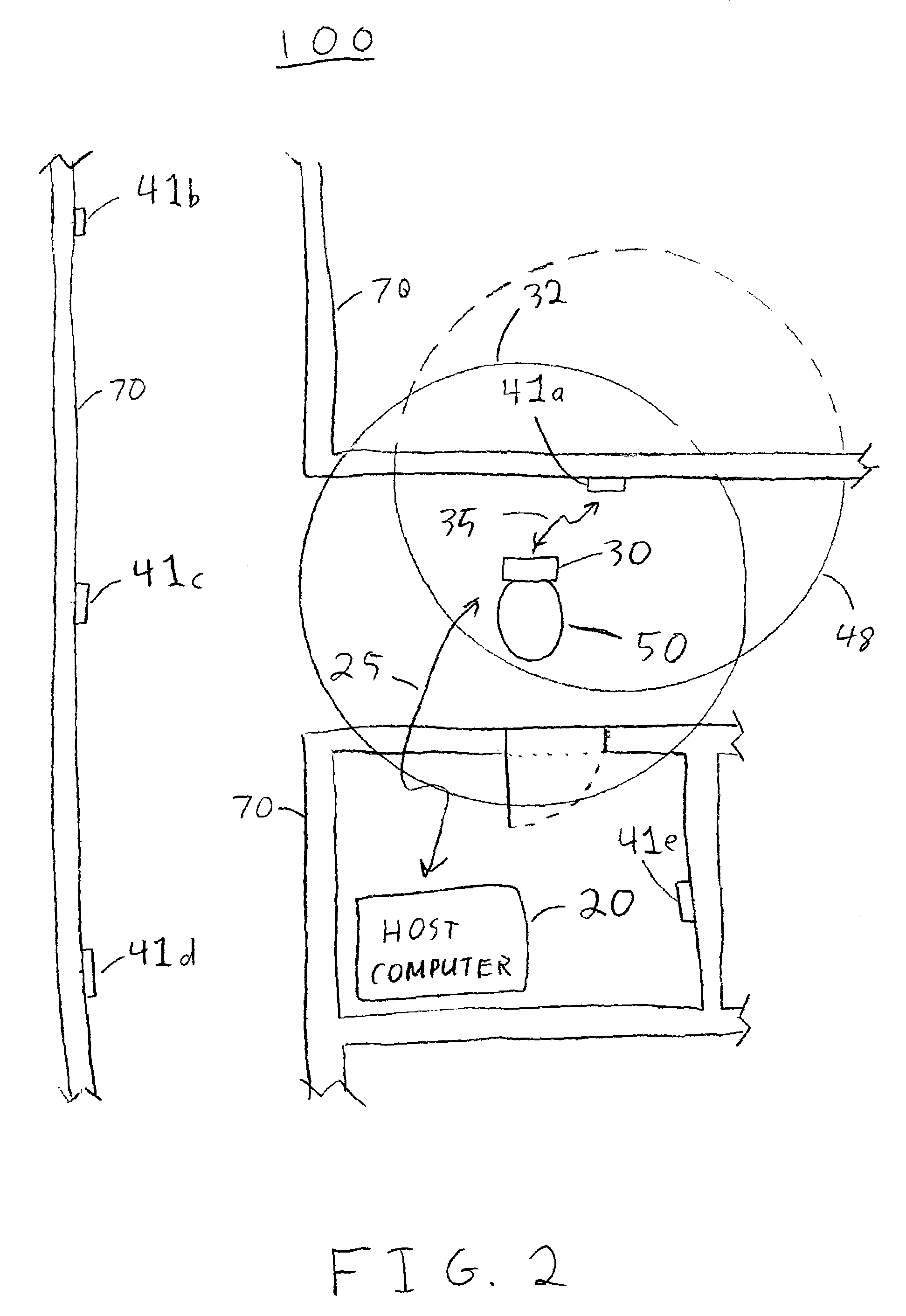
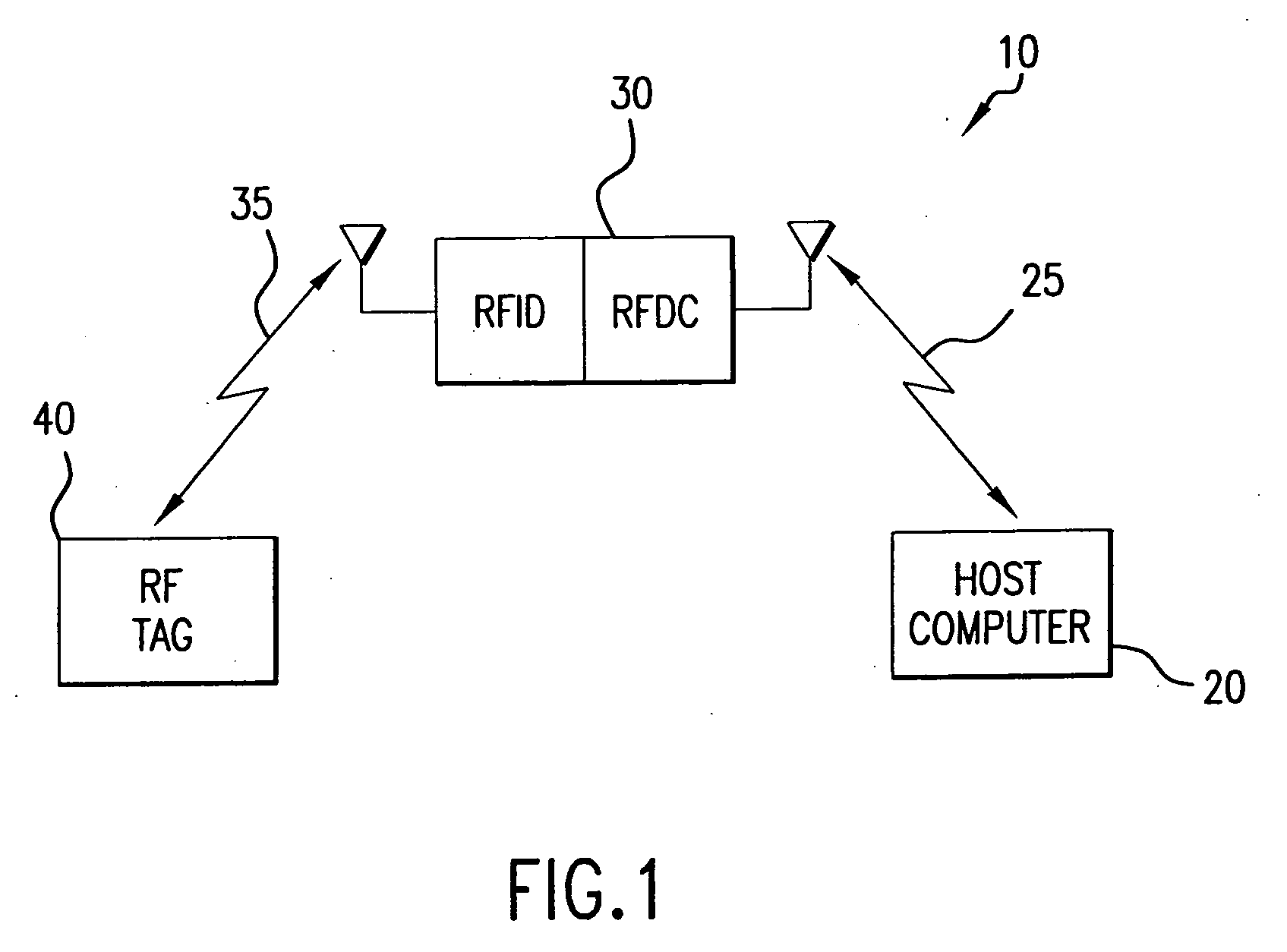
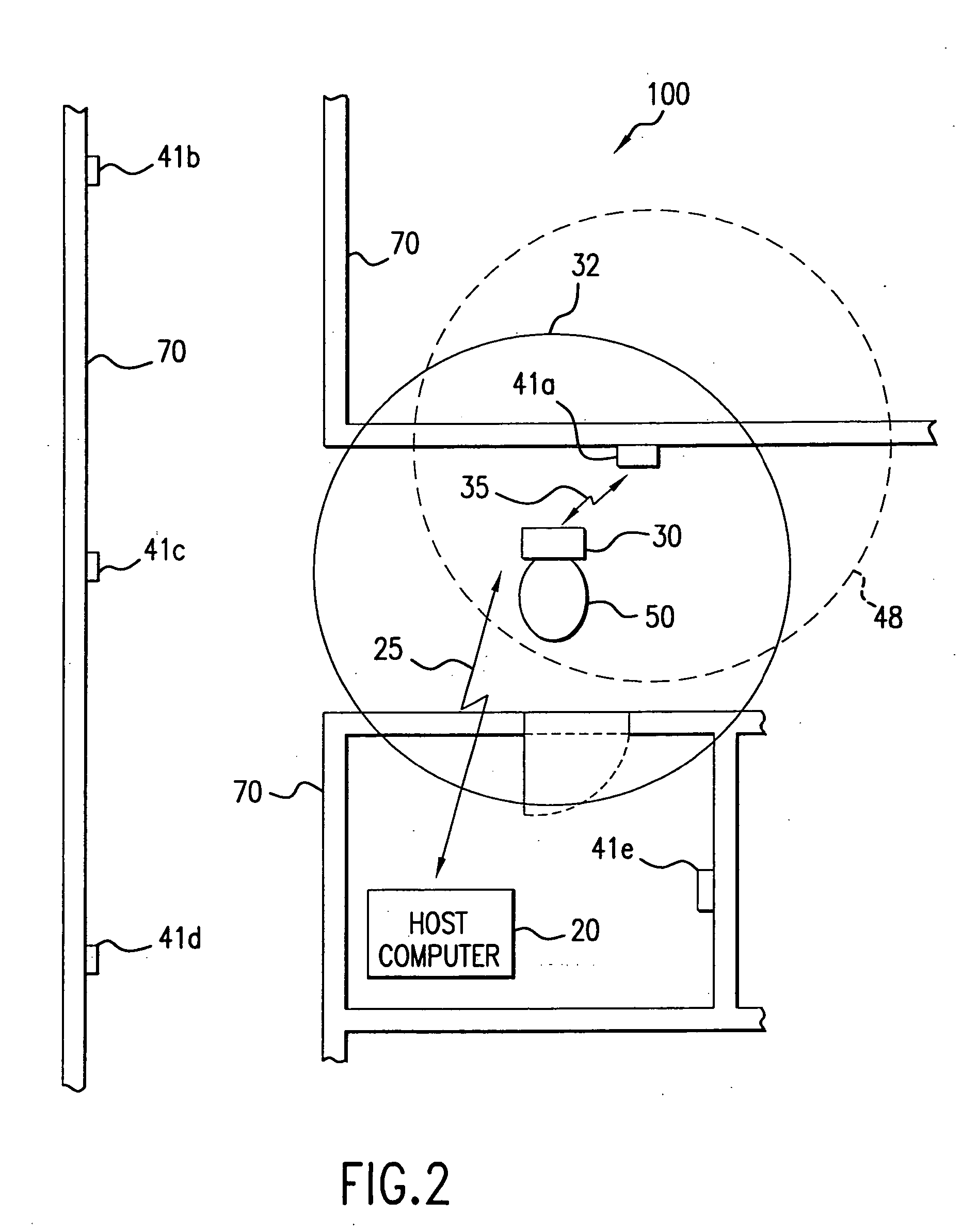
A locating and tracking system is provided in which the assets desired to be located and tracked are associated with either radio frequency (RF) tags or radio frequency identification and radio frequency data communication (RFID / RFDC) devices. Depending on which device is attached to the asset, the other device is located at known locations. The RFID / RFDC devices interrogate and receive signals from the RF tags. The received information is sent to a host computer. With the location of either the RF tags or RFID / RFDC devices known, the assets may be located and tracked. An improved RF tag antenna design is also provided by using a switching mechanism connected to at least two antennas.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
Dual-Polarized Microstrip Antenna
InactiveUS20130044035A1Excellent polarization isolationReduce areaAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna designDielectric layer
A dual-polarized microstrip antenna includes: at least one metal radiating patch, i.e. a first metal radiating patch; at least one ground metal layer whereon excitation micro-slots are etched; at least one dielectric layer, i.e. a first dielectric layer it is preferred that the dielectric layer is a resonant dielectric layer such as a resonant dielectric layer of air or other layers of optimization resonant materials; at least one set of bipolar excitation microstrip lines; the dielectric layer is between the first metal radiating patch and the ground metal layer. The dual-polarized microstrip antenna of multi-layer radiation structure is designed in a relatively small volume, which effectively saves the cost of antenna installation and maintenance, and is widely applied in the fields of mobile communication and internet technology.
Owner:ZHUANG KUNJIE
Antenna having a reflector for improved efficiency, gain, and directivity
InactiveUS20160181701A1Improve radiation efficiencySimultaneous aerial operationsResonant antennasAntenna designConductive materials
An antenna having at least one reflector for improving radiation efficiency, gain, and directivity is disclosed. The antenna may be formed on a substrate or be a standalone conductive material that is designed to operate in at least one band of frequency. The antenna includes a reflector for each band of frequency the antenna is designed to operate in. The reflector is positioned relative to the antenna to redirect electromagnetic radiation of the antenna away from surrounding materials or objects that affect, i.e., reflect, refract, diffract, absorb and scatter the antenna's electromagnetic radiation.
Owner:SANGARAN PRAGASH +1
Ultra high frequency radio frequency identification tag
An antenna design for radio frequency identification (“RFID”) tags. More particularly, the present invention relates to design for RFID tags particularly operating in the ultra high frequency (“UHF”) operating band.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Wireless locating and tracking systems
InactiveUS20060033609A1Large rangeMaximum omni-directionalityAntenna supports/mountingsCo-operative working arrangementsAntenna designEngineering
A locating and tracking system is provided in which the assets are desired to be located and tracked are associated with either radio frequency (RF) tags or radio frequency identification and radio frequency data communication (RFID / RFDC) devices. Depending on which device is attached to the asset, the other device is located at known locations. The RFID / RFDC devices interrogate and receive signals from the RF tags. The received information is sent to the host computer. With the location of either the RF tags or the RFID / RFDC devices known, the assets may be located and tracked. An improved RF tag antenna design is also provided by using a switching mechanism connected to at least two antennas.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
Ultra high frequency radio frequency identification tag
InactiveUS6999028B2Antenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna designRadio-frequency identification
An antenna design for radio frequency identification (“RFID”) tags. More particularly, the present invention relates to design for RFID tags particularly operating in the ultra high frequency (“UHF”) operating band.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
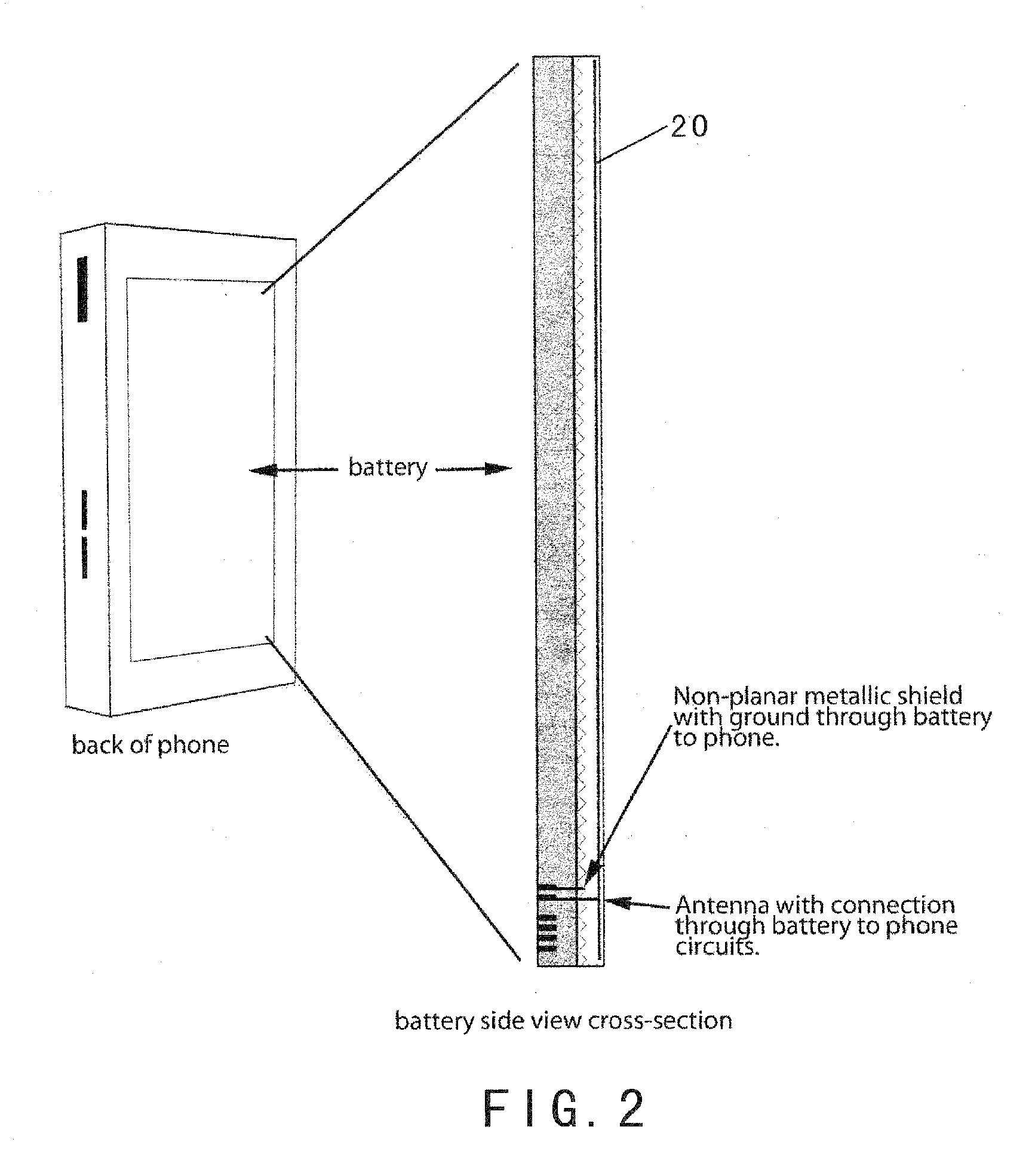
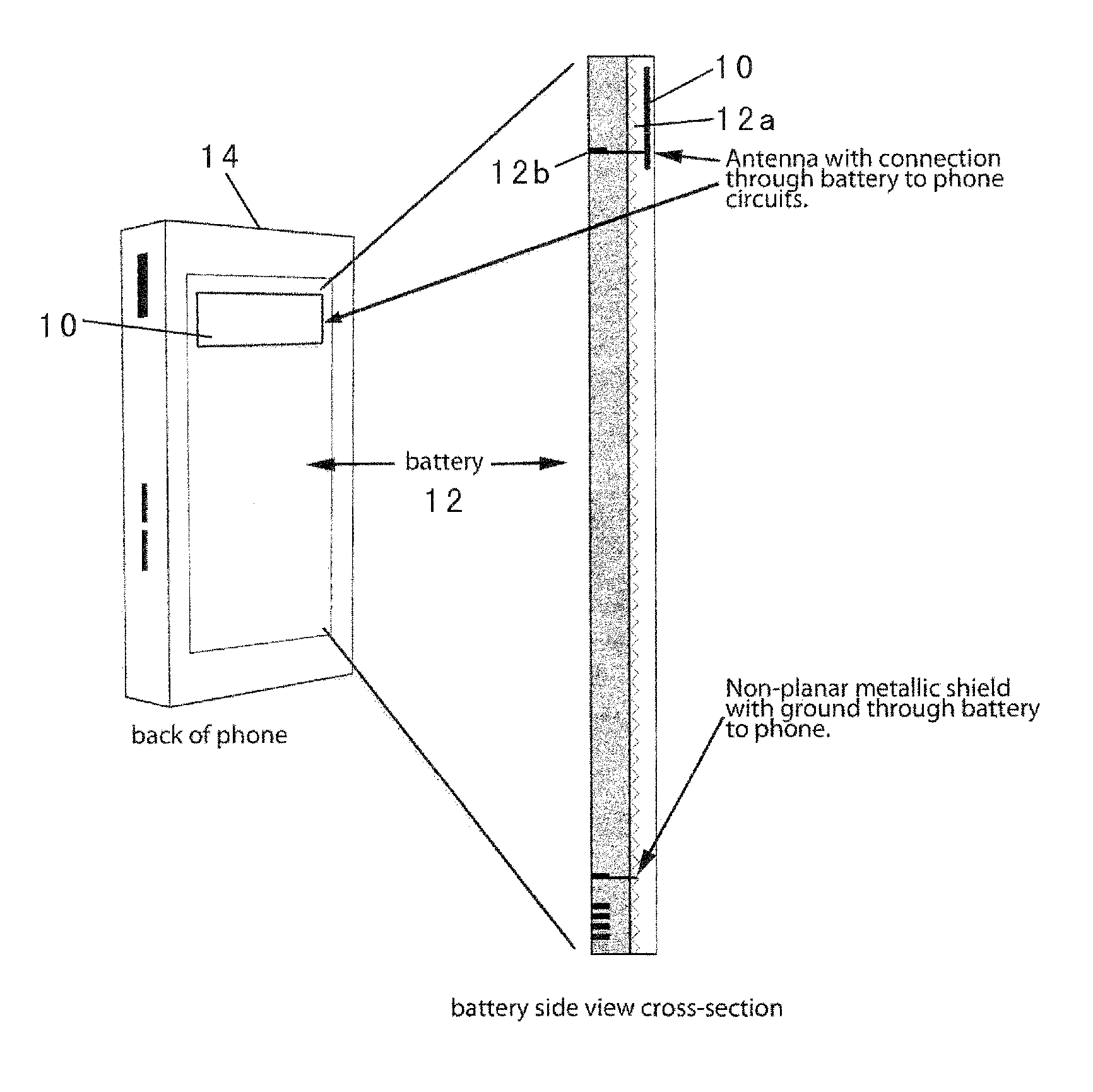
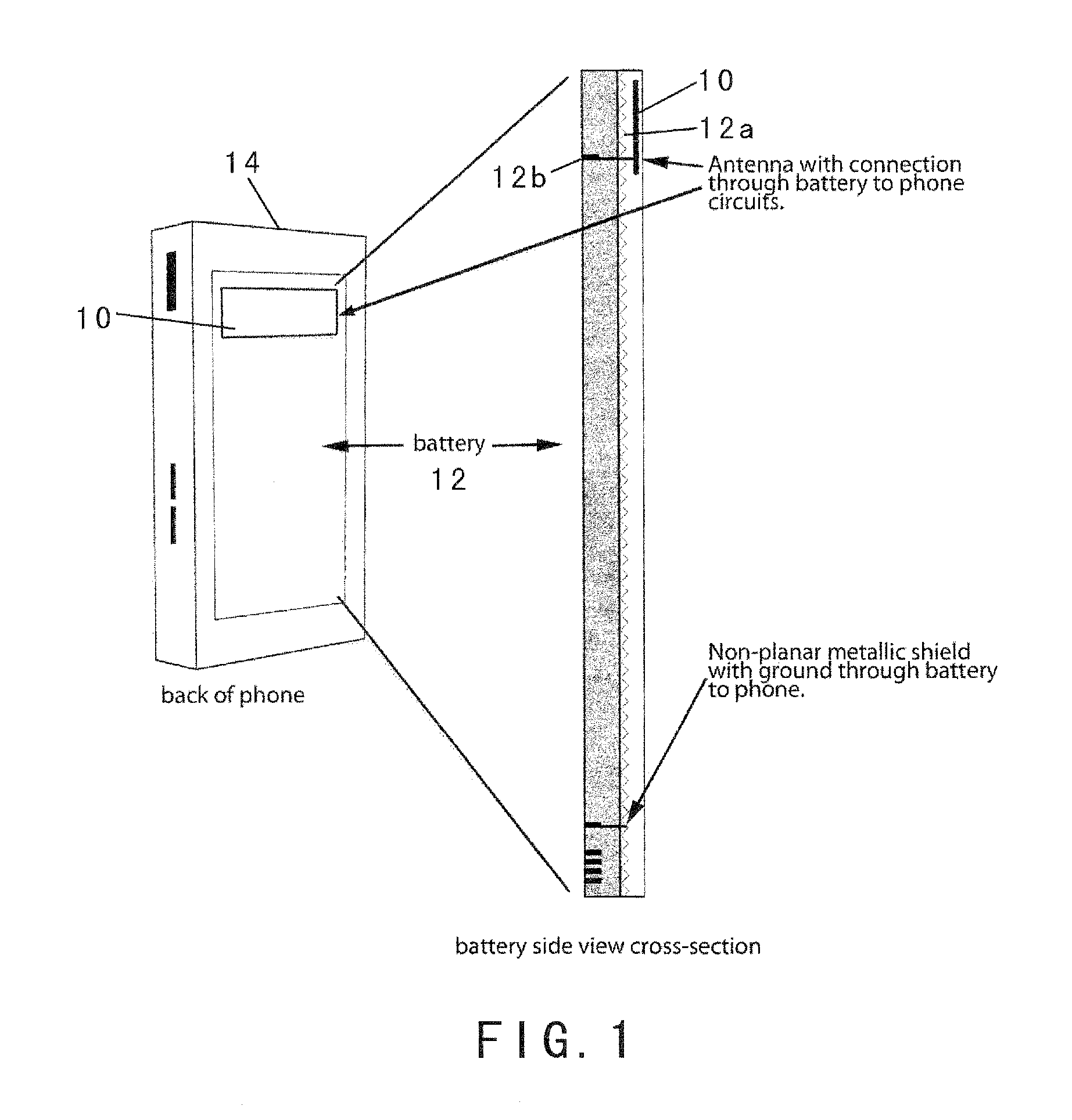
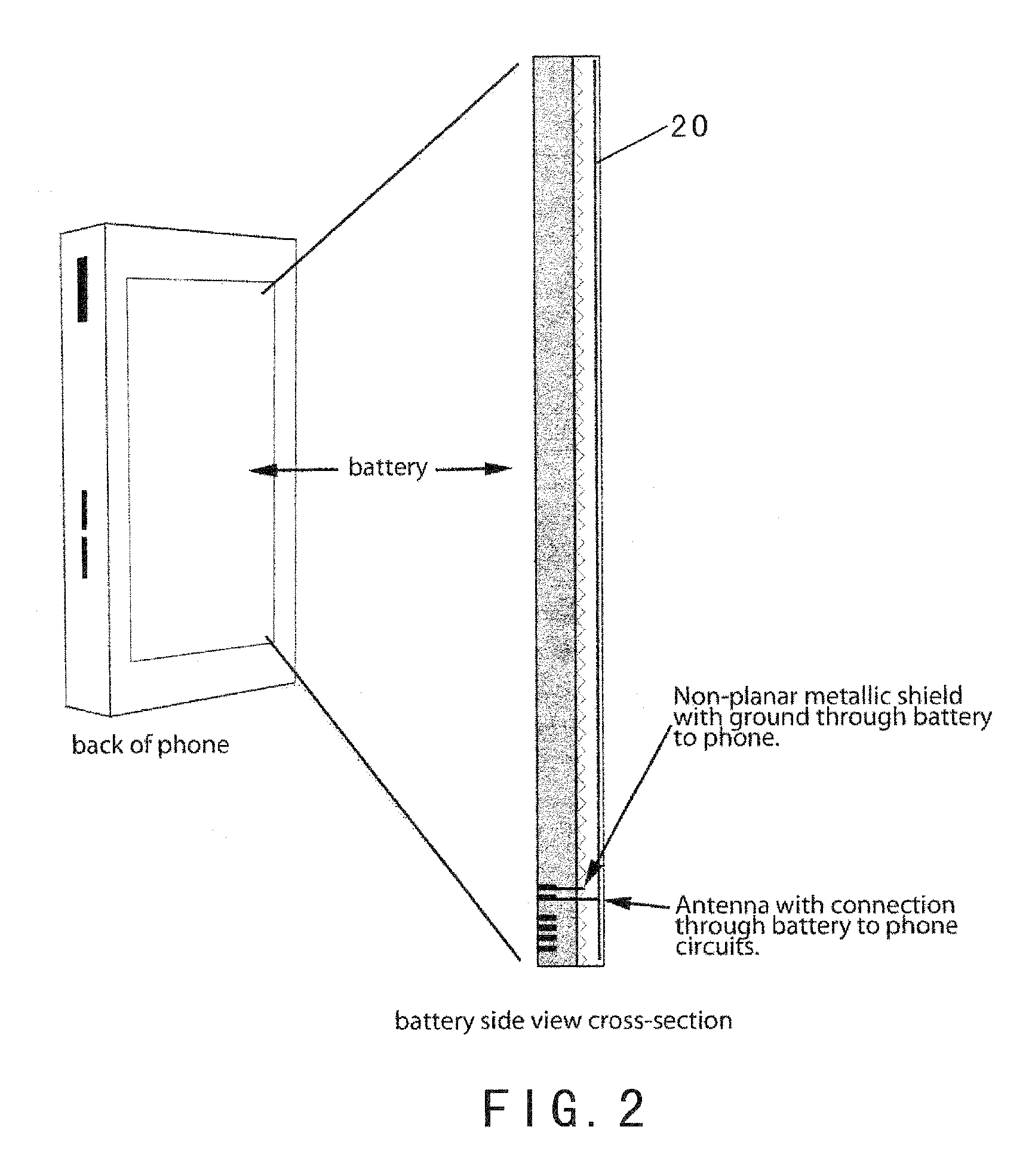
Radiation Redirecting External Case For Portable Communication Device and Antenna Embedded In Battery of Portable Communication Device
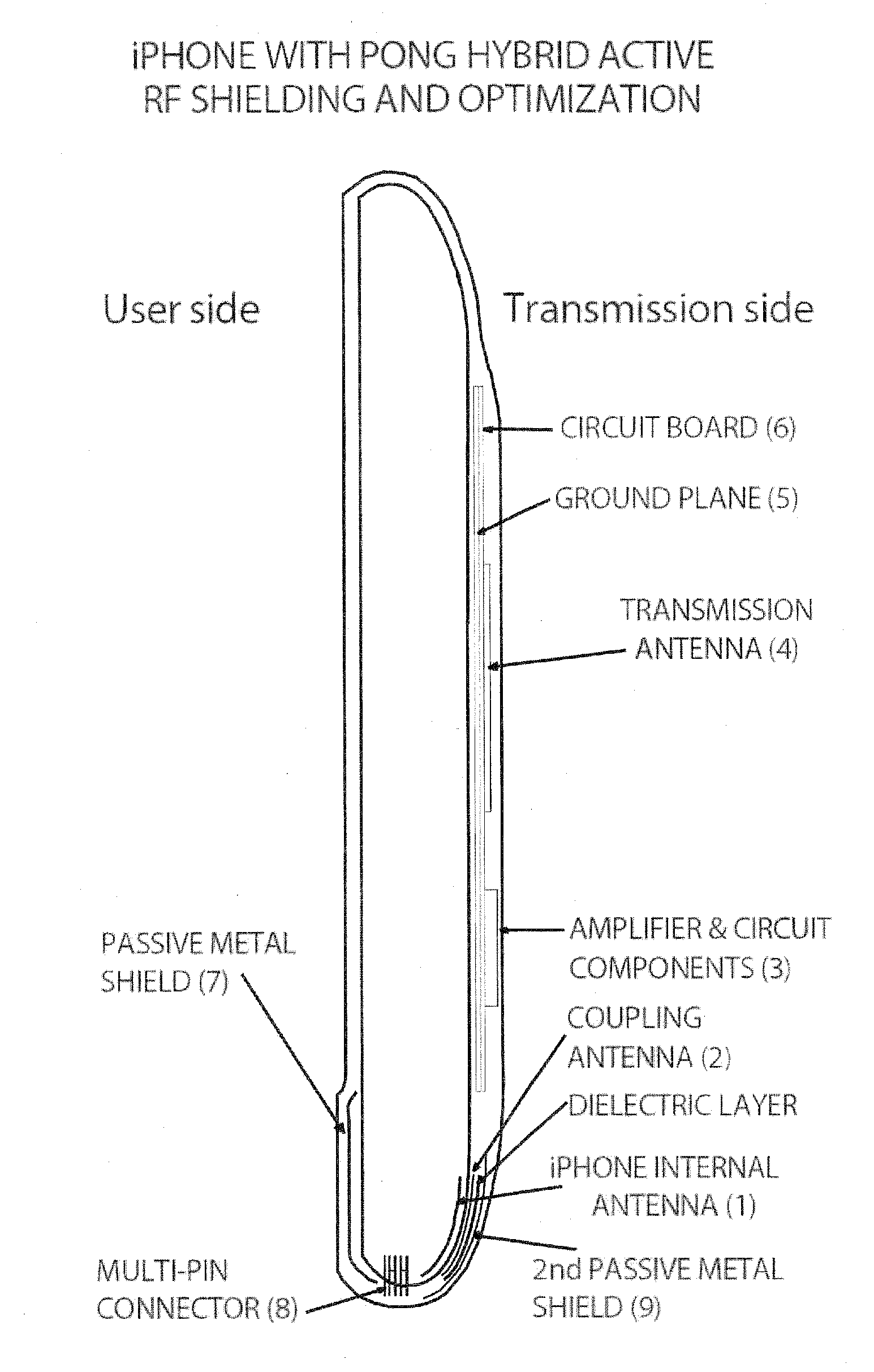
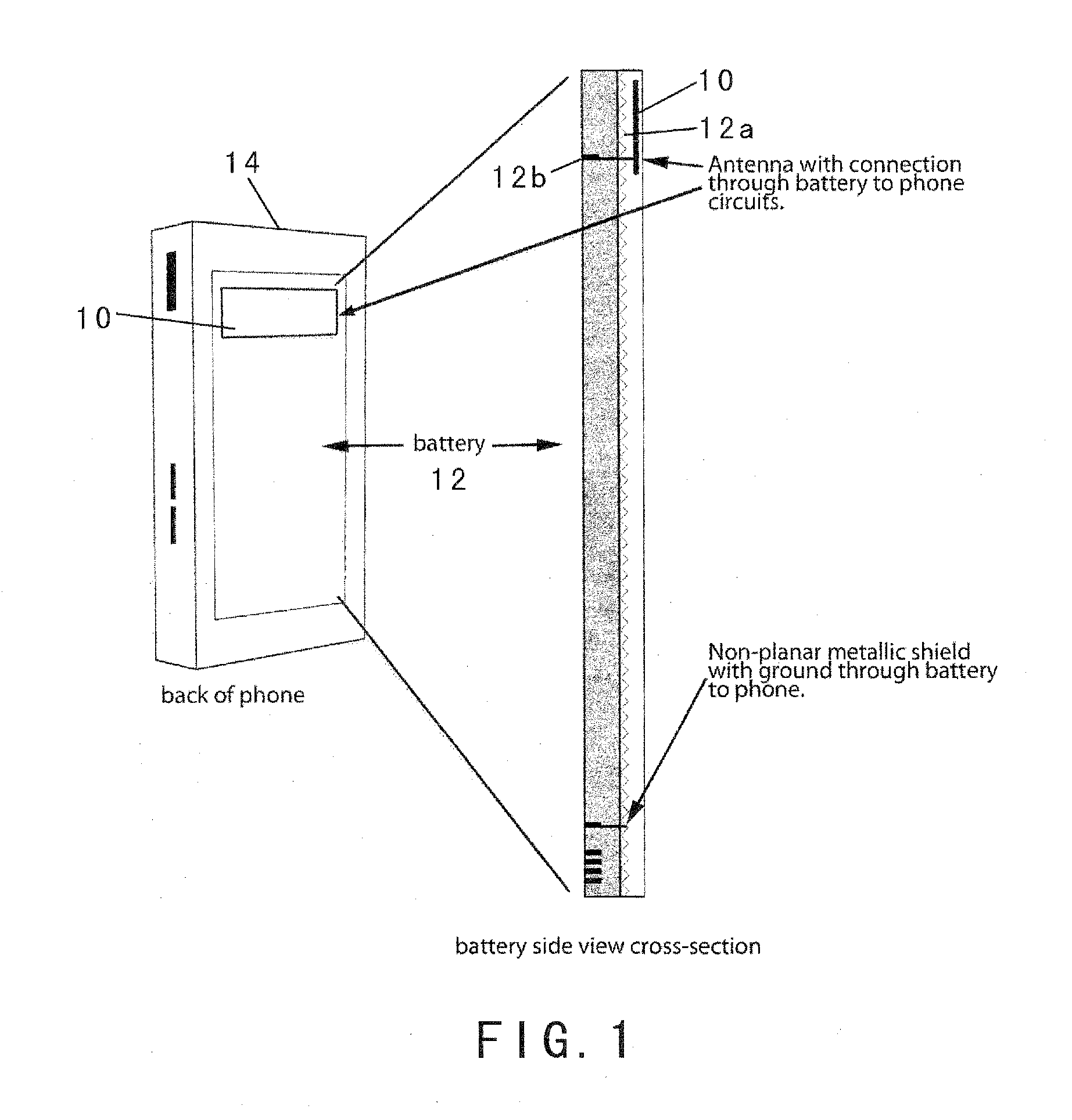
ActiveUS20100113111A1Increase effective spaceEffective redirectingSimultaneous aerial operationsMagnetic/electric field screeningAntenna designMulti band
An advanced antenna or set of antennae for a wireless device is provided by embedding the antennae into the battery case or generally the largest surface area of a wireless phone. The antenna connections are made through the battery's connections to the wireless device. The antenna design can be compact and located in any area of the battery. The antenna design can be thin and flat, located at the back surface of the battery or the large rear surface of a wireless phone, facing away from the user. An RF shielding device can be embedded into the battery and configured in relation to the antenna such that the RF field intensity and the consequent specific absorption rate for the user is lowered while the outgoing signals of the wireless device remain fully adequate for the function of the wireless device. This feature is preserved for a multi-band operation because a digital phase shifter is used between two radiating antennae. An external case is used as a complement to the wireless phone to provide additional antennae, power and capability.
Owner:PENUMBRA BRANDS LLC
Miniature sub-resonant multi-band vhf-uhf antenna
InactiveUS20080305750A1Low costSmall sizeAntenna supports/mountingsModulation with suppressed carrierMulti bandAntenna design
A novel antenna system for receiving transmissions in the VHF and UHF frequency bands particularly suitable as a miniaturized antenna for UHF reception, such as of digital video broadcasting transmissions. The antenna system utilizes a combination of three techniques including (1) the use of dialect loading using a high dielectric constant ceramic substrate; (2) an antenna dielectrically loaded and tuned to a significantly higher frequency than desired; and (3) use of a tuning circuit to compensate for the frequency offset of the antenna thereby shifting the resonant frequency to cover the entire band. The antenna is intentionally designed to be too small to radiate at the frequency of interest. The antenna element is then ‘forced’ to be tuned to the desired lower frequency using passive (or active) reactive components as part of a tuning circuit. Multi-band operation is achieved by providing a bypass switch to connect the antenna element either to (1) a first receiver without the tuning circuit (i.e. high frequency tuning) or (2) a second receiver with the tuning circuit (i.e. low frequency tuning).
Owner:VISHAY INTERTECHNOLOGY INC
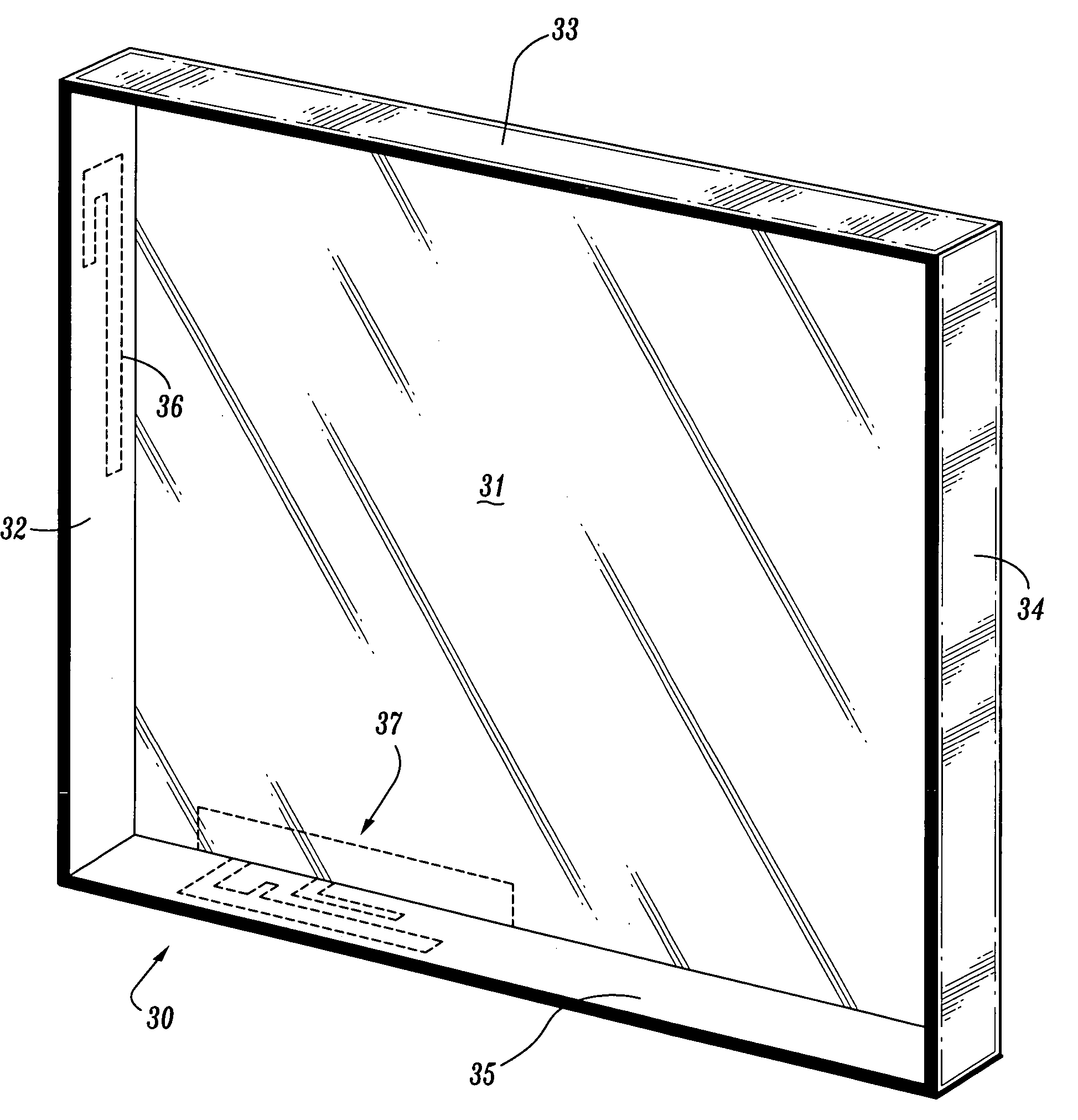
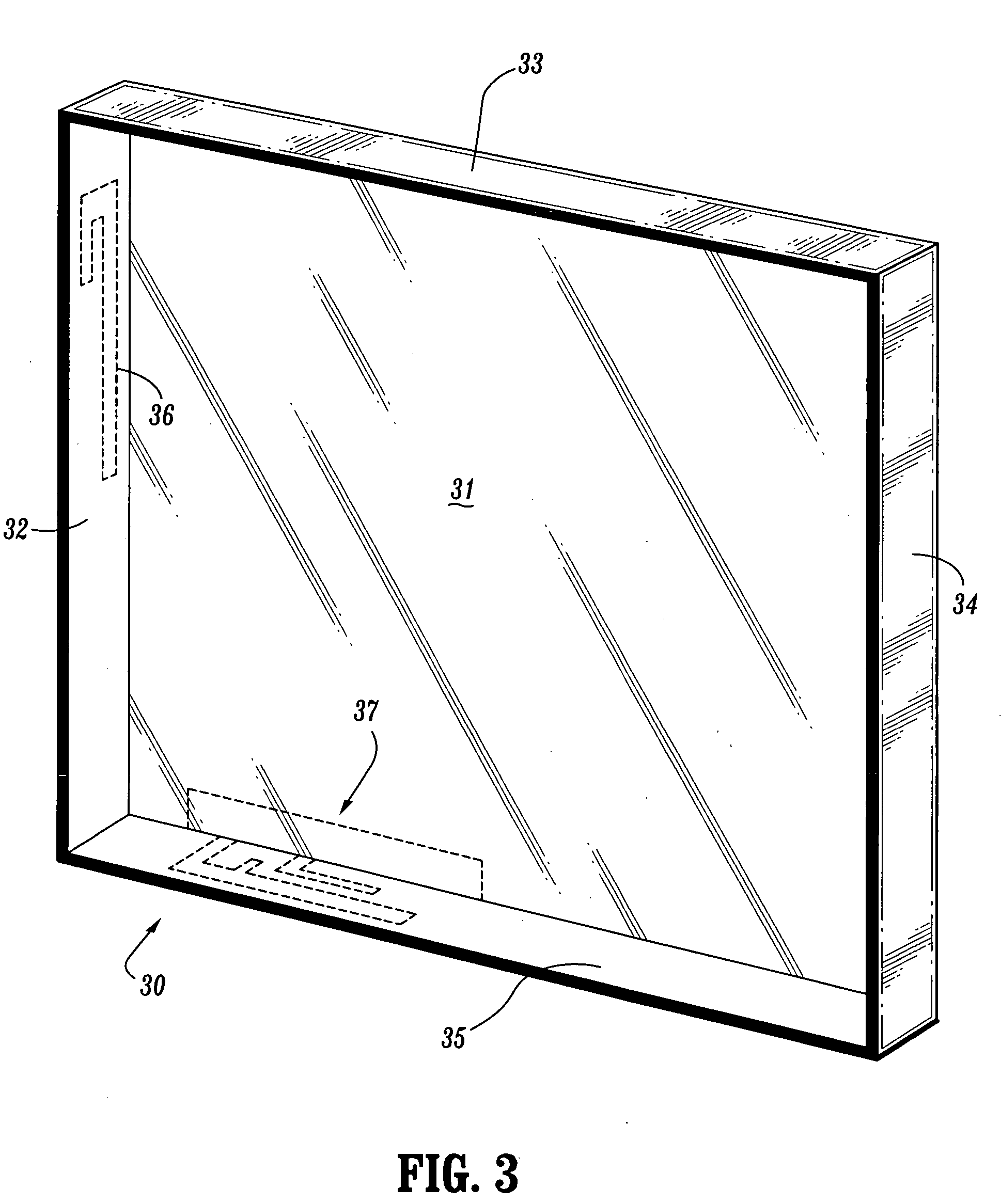
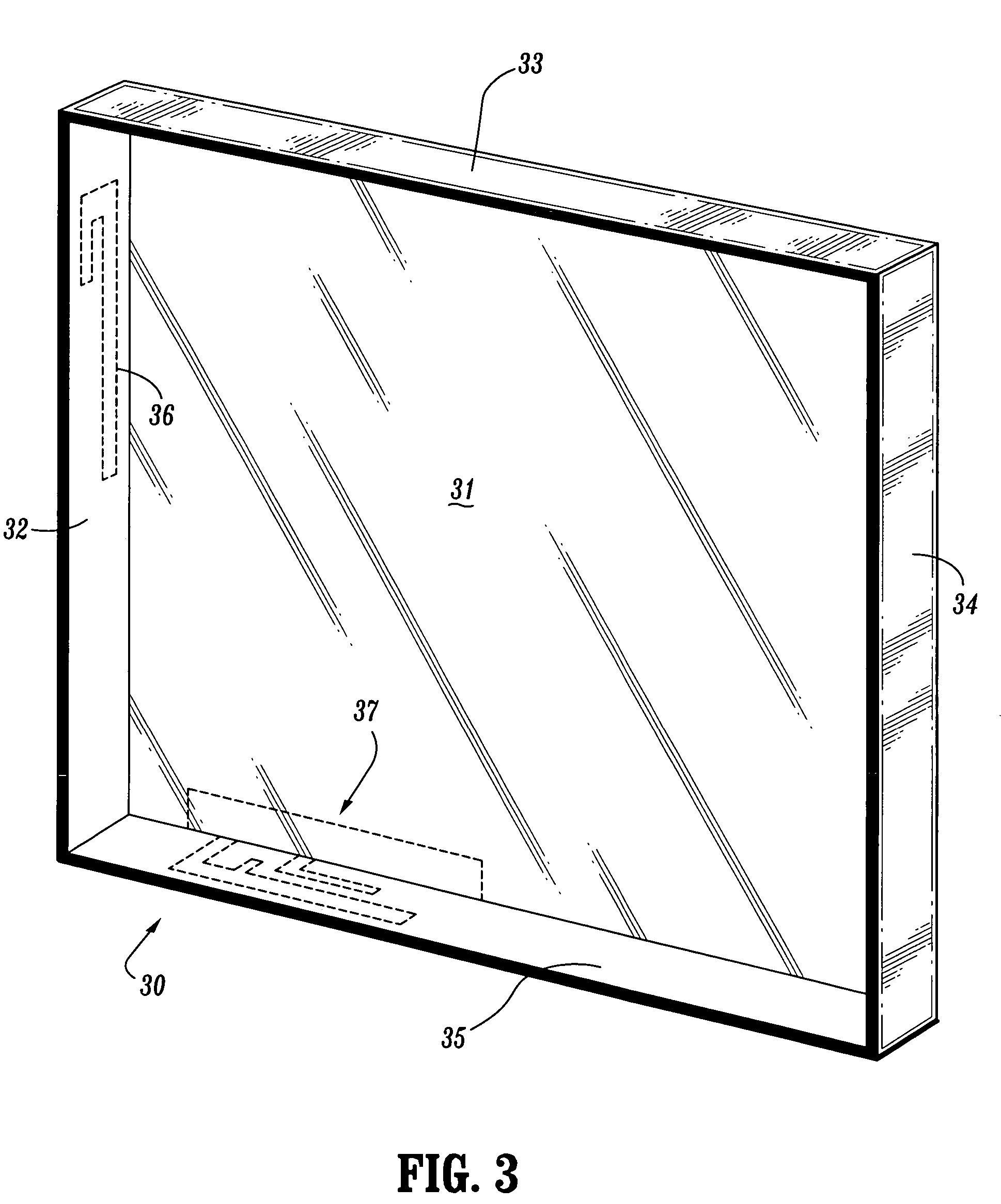
Antennas encapsulated within plastic display covers of computing devices
ActiveUS20060061512A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna designDisplay device
Antenna devices are provided comprising antenna structures encapsulated or molded into plastic covers of computing devices to enable wireless communication. For example, one or more antenna structures can be encasulated within, or molded into, a plastic display cover of a portable laptop computer. Embedded antenna designs can include various antenna types that are built using one or more wires or thin metallic strips encapsulated into plastic device covers. Insert / injection molding methods can be used to encapsulate antenna structures in plastic device covers during fabrication of the plastic device covers.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
Low cost antenna design for wireless communications
ActiveUS20080284661A1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsAntenna designGround plane
A low cost and multi-featured antenna is disclosed. The antenna employs a radiating element mounted to a ground plane and having first and second branches spaced above the ground plane forming a generally L shaped planar radiating structure. The antenna can be either linear or circular polarization, and can be either single band or dual band, and only one feeding port is needed to obtain circular polarization. The antenna can be easily applied to various frequency bands.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Planar communications antenna having an epicyclic structure and isotropic radiation, and associated methods
ActiveUS20110121822A1Frequency stabilitySufficient gainLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna designElectrical conductor
The antenna device includes an electrical conductor extending on a substrate and having at least one gap therein, and with an outer ring portion to define a radiating antenna element, and at least one inner ring portion to define a feed coupler and connected in series with the outer ring portion and extending within the outer ring portion. A coupling feed element is adjacent the at least one inner ring portion, and a feed structure is connected to the coupling feed element to feed the outer ring portion. A plurality of inner ring portions may be provided with the coupling feed element being adjacent a selected one of the plurality of inner ring portions. The plurality of inner ring portions may have a common size and be symmetrically spaced within the outer ring portion. The radiation pattern may be sufficiently isotropic to eliminate the need for antenna aiming. An epicyclic geometry radiating element provides for a compound antenna design.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
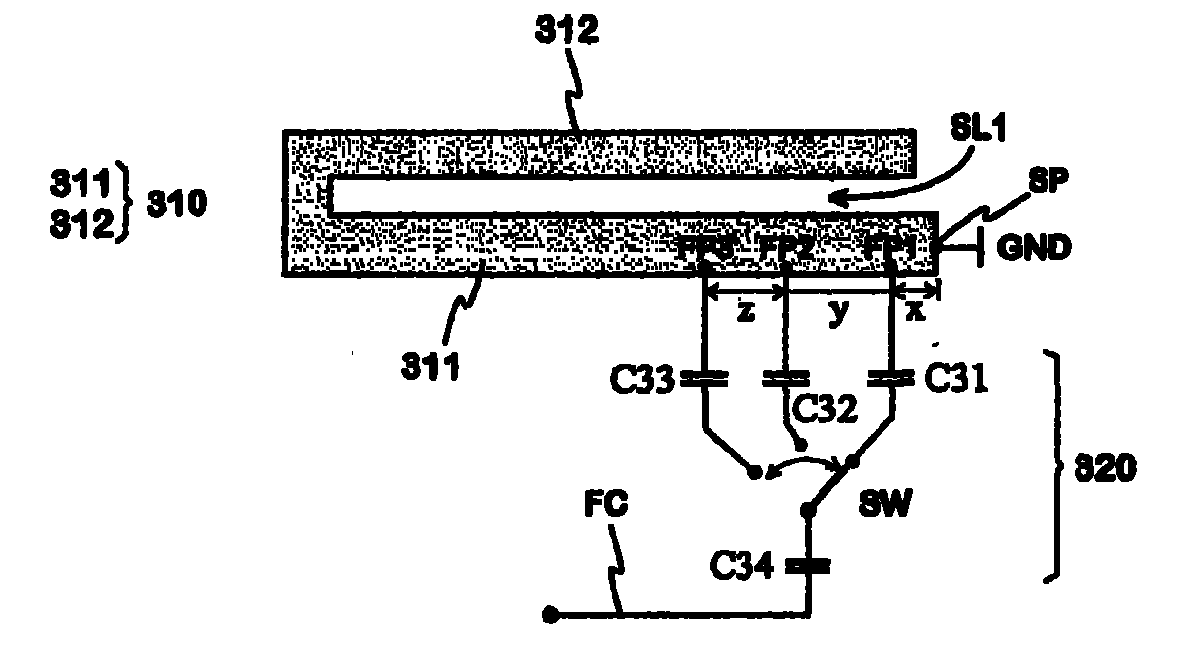
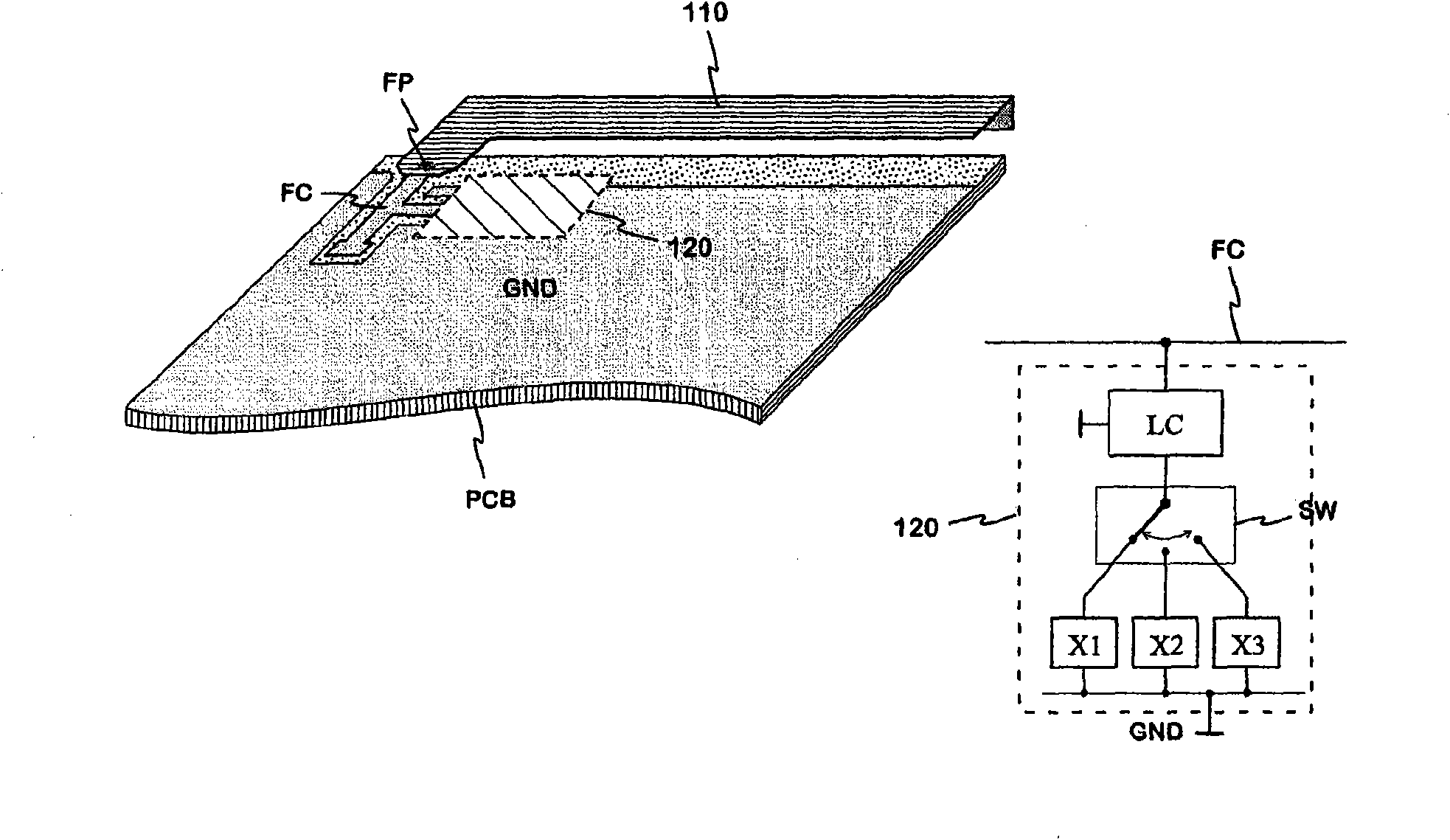
Adjustable multiband antenna
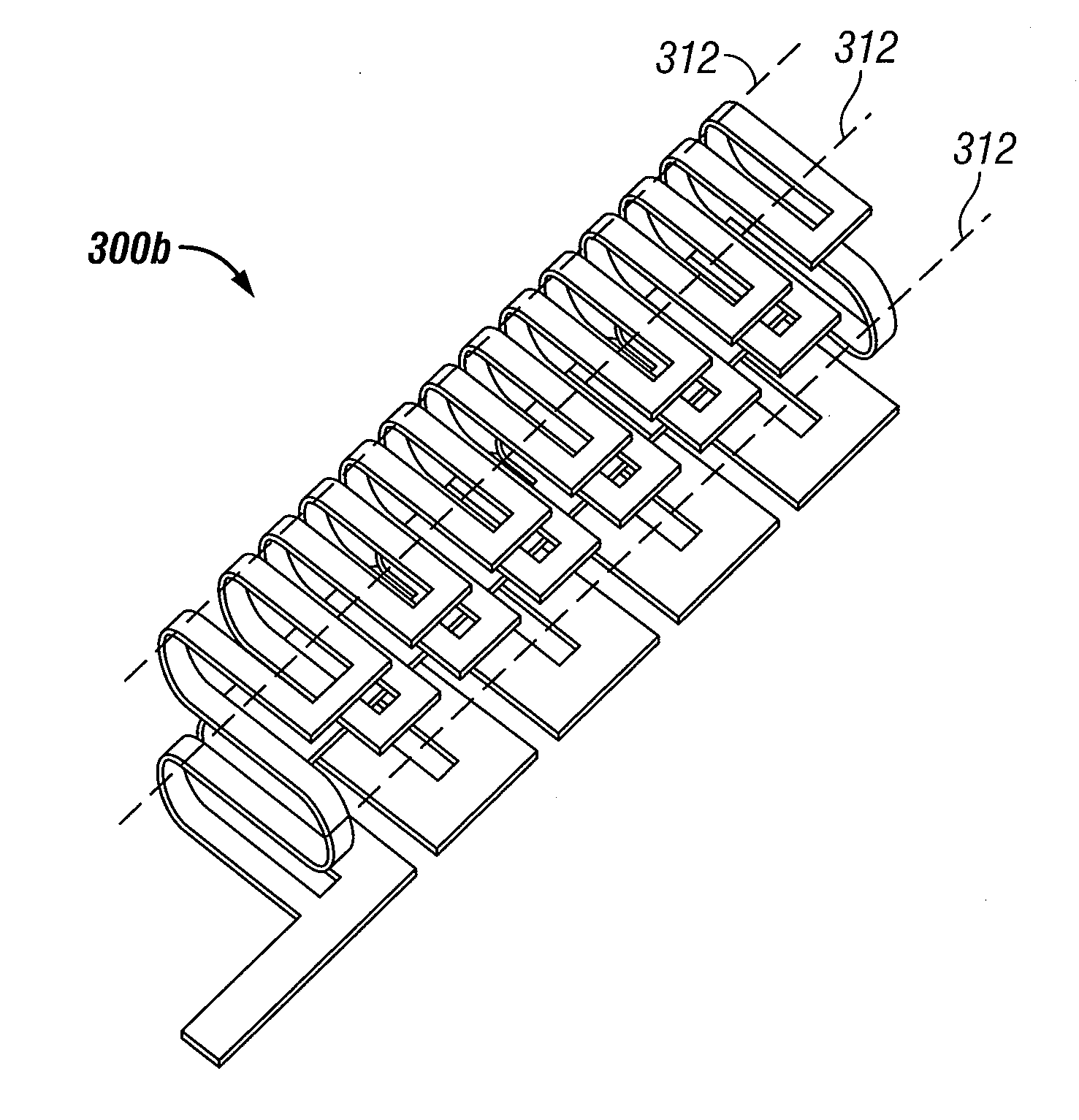
ActiveCN101809813AImprove efficiencySave spaceSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsBasic dimensionCapacitance
An adjustable multi-band planar antenna especially applicable in mobile terminals. The feed of the antenna can be connected by a multiple-way switch (SW) to at least two alternative points (FP1, FP2, FP3) in the radiator (310). When the feed point is changed, the resonance frequencies and thus the operating bands of the antenna change. Besides the basic dimensions of the antenna, the distance (x, y, z) of each feed point to other feed points and possible short-circuit point in the radiator, the value of the series capacitance (C31; C32; C33) belonging to a reactive circuit between the feed point and switch and the distance of the ground plane (GND) from the radiator are variables in the antenna design.
Owner:PULSE FINLAND
Antennas encapsulated within plastic display covers of computing devices
ActiveUS7271769B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna designDisplay device
Antenna devices are provided comprising antenna structures encapsulated or molded into plastic covers of computing devices to enable wireless communication. For example, one or more antenna structures can be encasulated within, or molded into, a plastic display cover of a portable laptop computer. Embedded antenna designs can include various antenna types that are built using one or more wires or thin metallic strips encapsulated into plastic device covers. Insert / injection molding methods can be used to encapsulate antenna structures in plastic device covers during fabrication of the plastic device covers.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
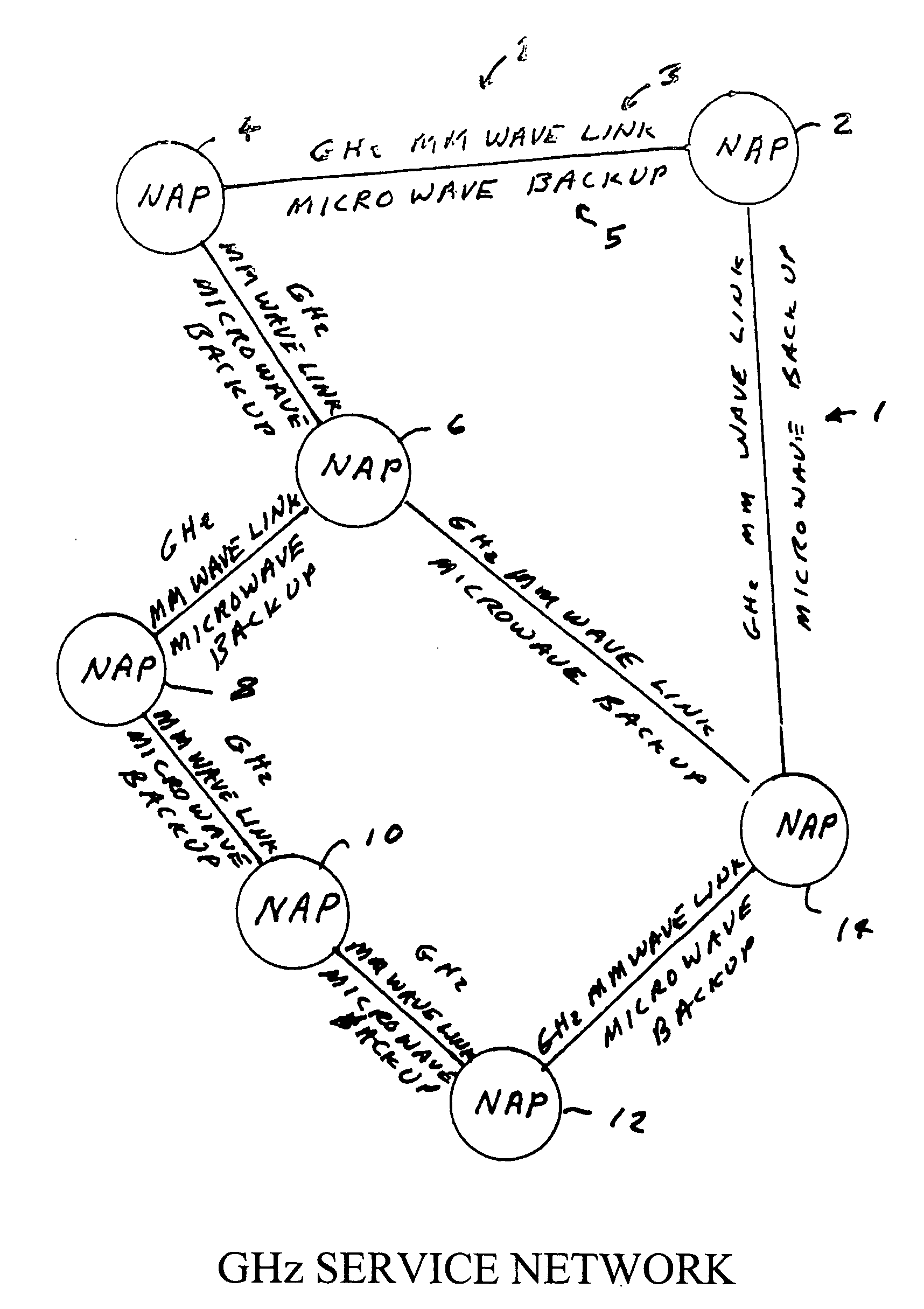
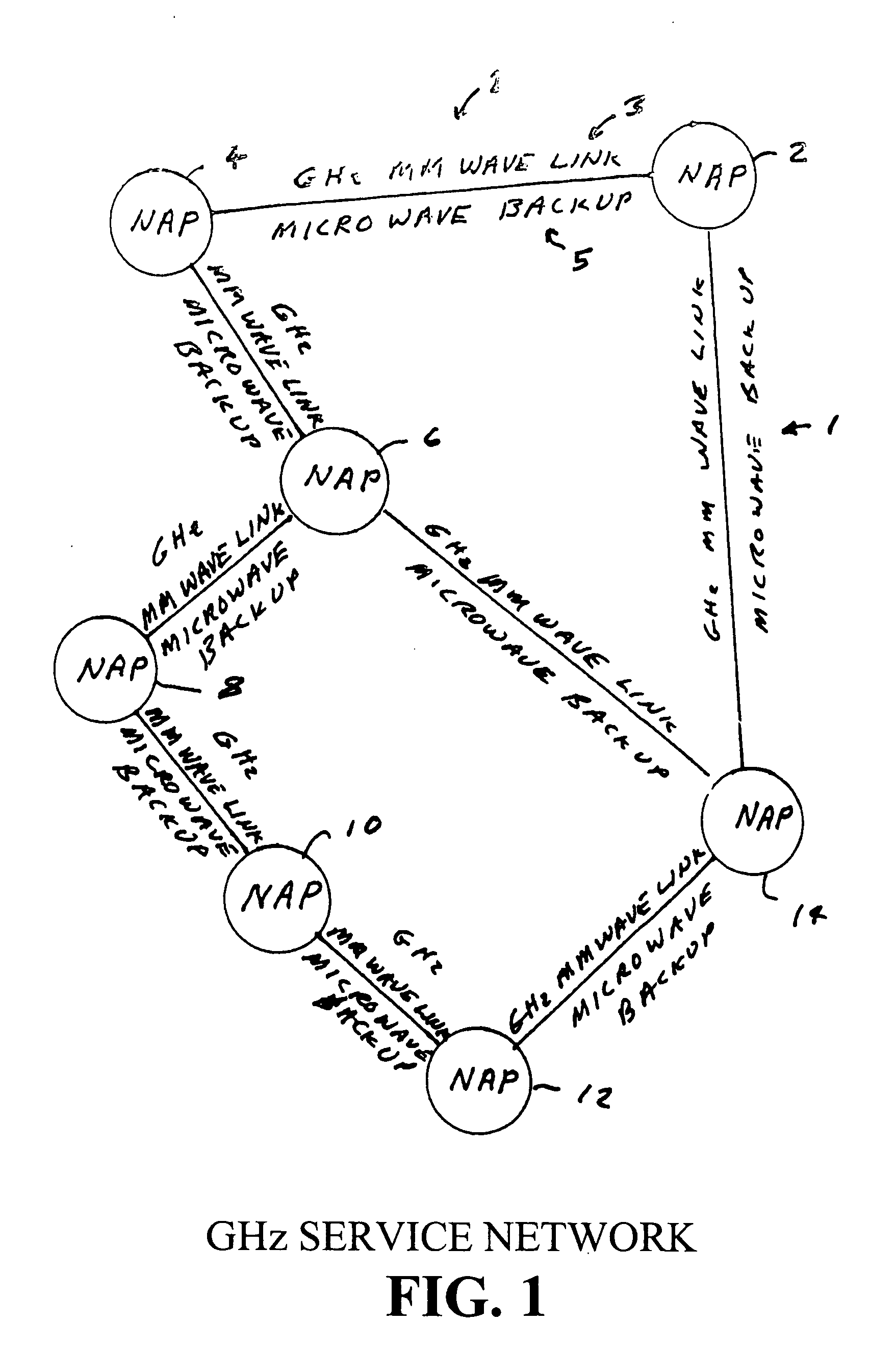
Circuit switched millimeter wave communication network
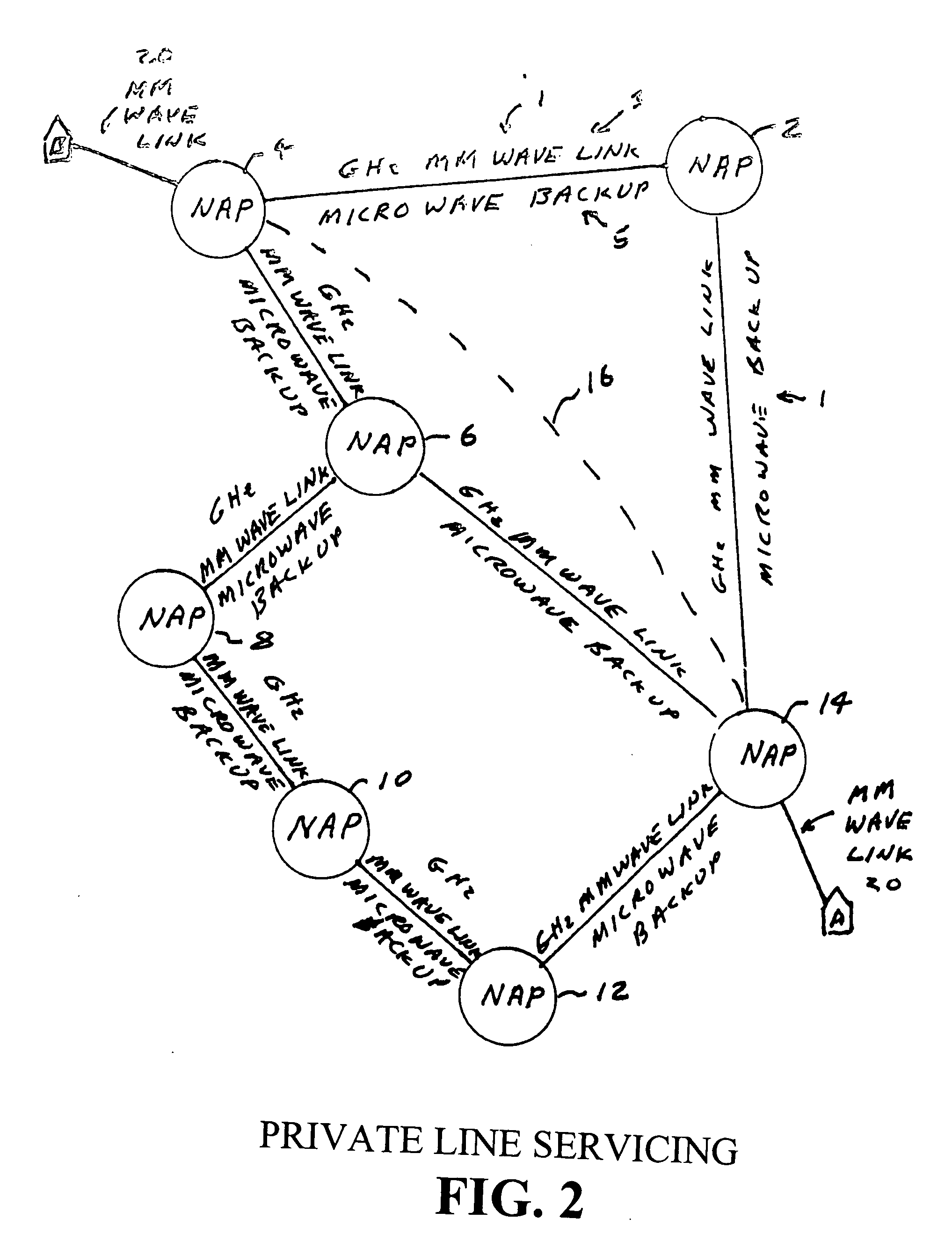
InactiveUS20120135724A1High bandwidthLower latencyRadio transmissionWireless commuication servicesAntenna designHigh bandwidth
A high bandwidth, low latency middle-mile core communications network providing low-cost and high-speed communications among the users of the network. Embodiments of the invention include a number of network access points located at a number of spaced apart sites. At least some of these network access points in the network are in communication with each other via millimeter radio links with microwave backup links. In preferred embodiments the millimeter radio links include two millimeter radios, one transmitting in the frequency range of 71-76 GHz and receiving in the frequency range if 81 to 86 GHz and the other radio transmitting in the frequency range of 81-86 GHz and receiving in the frequency range if 71 to 76 GHz. In these preferred embodiments each millimeter wave radio is equipped with an antenna designed to produce a millimeter wave beam with an angular spread of less than two degrees. A high-speed switch is located at each network access point. The switches include a plurality of ports through which a plurality of network users transmits information through the network. Preferred embodiments utilize Ethernet switches programmed to encapsulate and tag incoming packets with a special set of tags which allow the tagging switch and other Ethernet switches in the network to direct the packets to one or more output ports of itself and / or one or more of the output ports of other Ethernet switches at one or more distant network access points, without a need for any of the network equipment to read any MAC or IP address information contained in the packets.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Radiation redirecting external case for portable communication device and antenna embedded in battery of portable communication device
ActiveUS8208980B2Increase effective spaceAvailable spaceSimultaneous aerial operationsMagnetic/electric field screeningAntenna designMulti band
An advanced antenna or set of antennae for a wireless device is provided by embedding the antennae into the battery case or generally the largest surface area of a wireless phone. The antenna connections are made through the battery's connections to the wireless device. The antenna design can be compact and located in any area of the battery. The antenna design can be thin and flat, located at the back surface of the battery or the large rear surface of a wireless phone, facing away from the user. An RF shielding device can be embedded into the battery and configured in relation to the antenna such that the RF field intensity and the consequent specific absorption rate for the user is lowered while the outgoing signals of the wireless device remain fully adequate for the function of the wireless device. This feature is preserved for a multi-band operation because a digital phase shifter is used between two radiating antennae. An external case is used as a complement to the wireless phone to provide additional antennae, power and capability.
Owner:PENUMBRA BRANDS LLC
Contactless radiofrequency device featuring several antennas and related antenna selection circuit
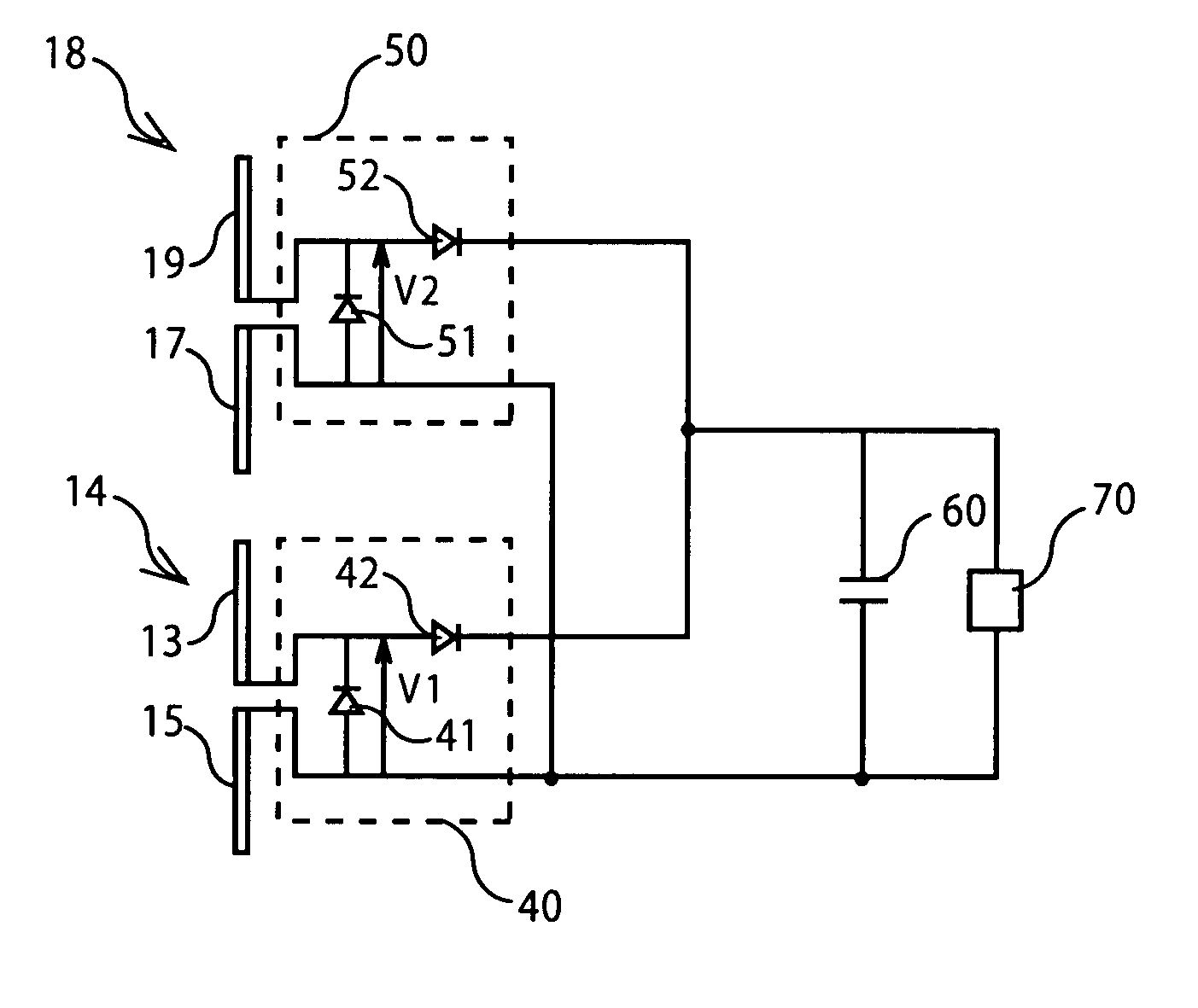
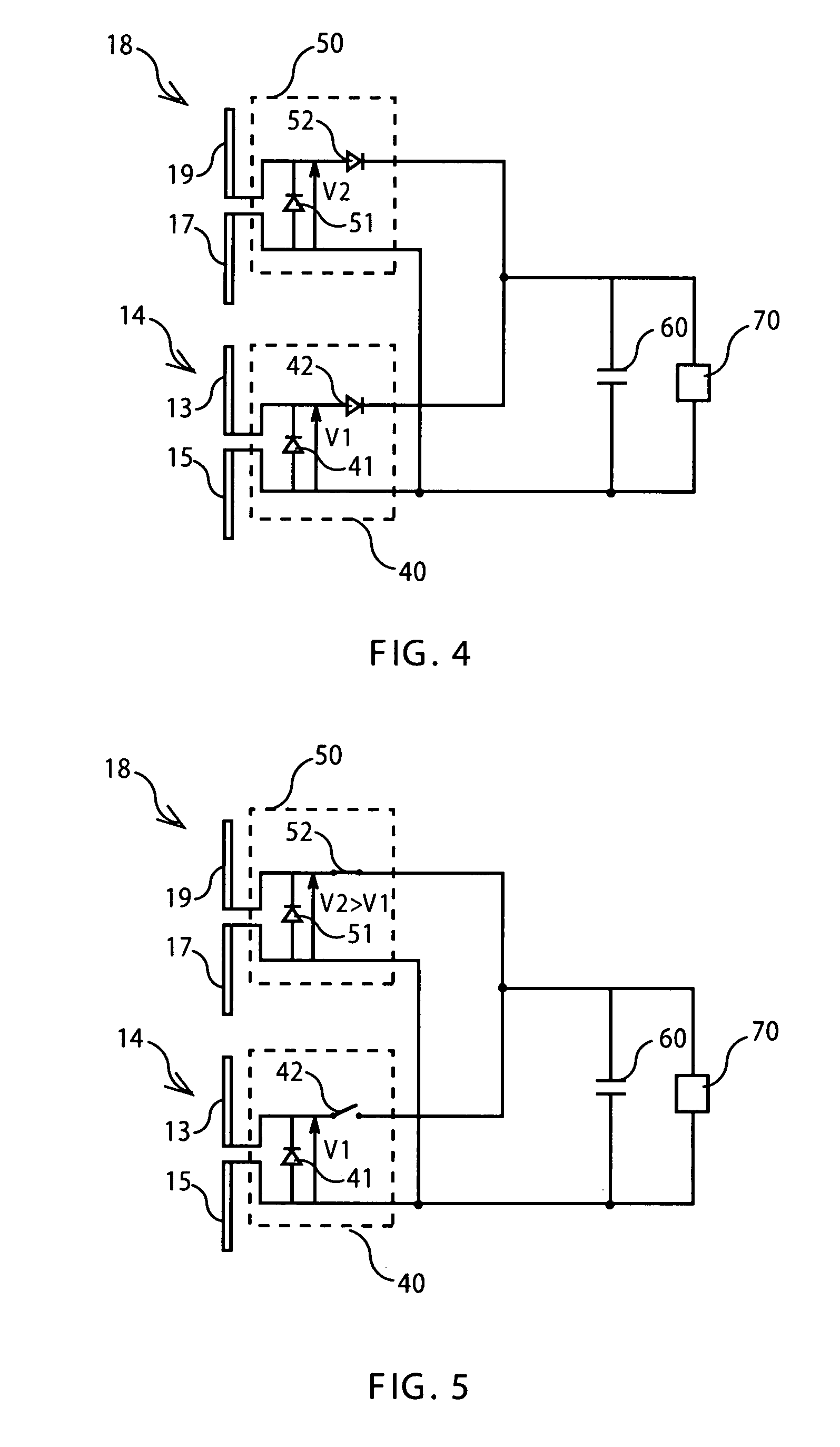
InactiveUS20080068132A1Enhanced radiationSpatial transmit diversityNear-field in RFIDAntenna designEngineering
The invention relates to an integrated circuit for contactless radiofrequency device connected to a first antenna and to a second antenna designed to receive a radiofrequency signal coming from a reader. According to a main characteristic, the integrated circuit includes a first rectifier circuit and a second rectifier circuit to rectify each radiofrequency signal received from the first antenna and the second antenna, respectively, so as to produce two positive output voltages V1 and V2, the rectifier circuits being mounted in parallel in order to select an output voltage value that corresponds to the maximum voltage value between V1 and V2.
Owner:ASK SA (FR)
High-strength microwave antenna assemblies
InactiveUS20050062666A1High strengthAvoid mechanical failureSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingAntenna designElectrical conductor
Various high-strength microwave antenna assemblies are described herein. The microwave antenna has a radiating portion connected by a feedline to a power generating source, e.g., a generator. The antenna is a dipole antenna with the distal end of the radiating portion being tapered and terminating at a tip to allow for direct insertion into tissue. Antenna rigidity comes from placing distal and proximal radiating portions in a pre-stressed state, assembling them via threaded or overlapping joints, or fixedly attaching an inner conductor to the distal portion. The inner conductor is affixed to the distal portion by, e.g., welding, brazing, soldering, or by adhesives. A junction member made from a hard dielectric material, e.g., ceramic, can be placed between the two portions and can have uniform or non-uniform shapes to accommodate varying antenna designs. Electrical chokes may also be used to contain returning currents to the distal end of the antenna.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
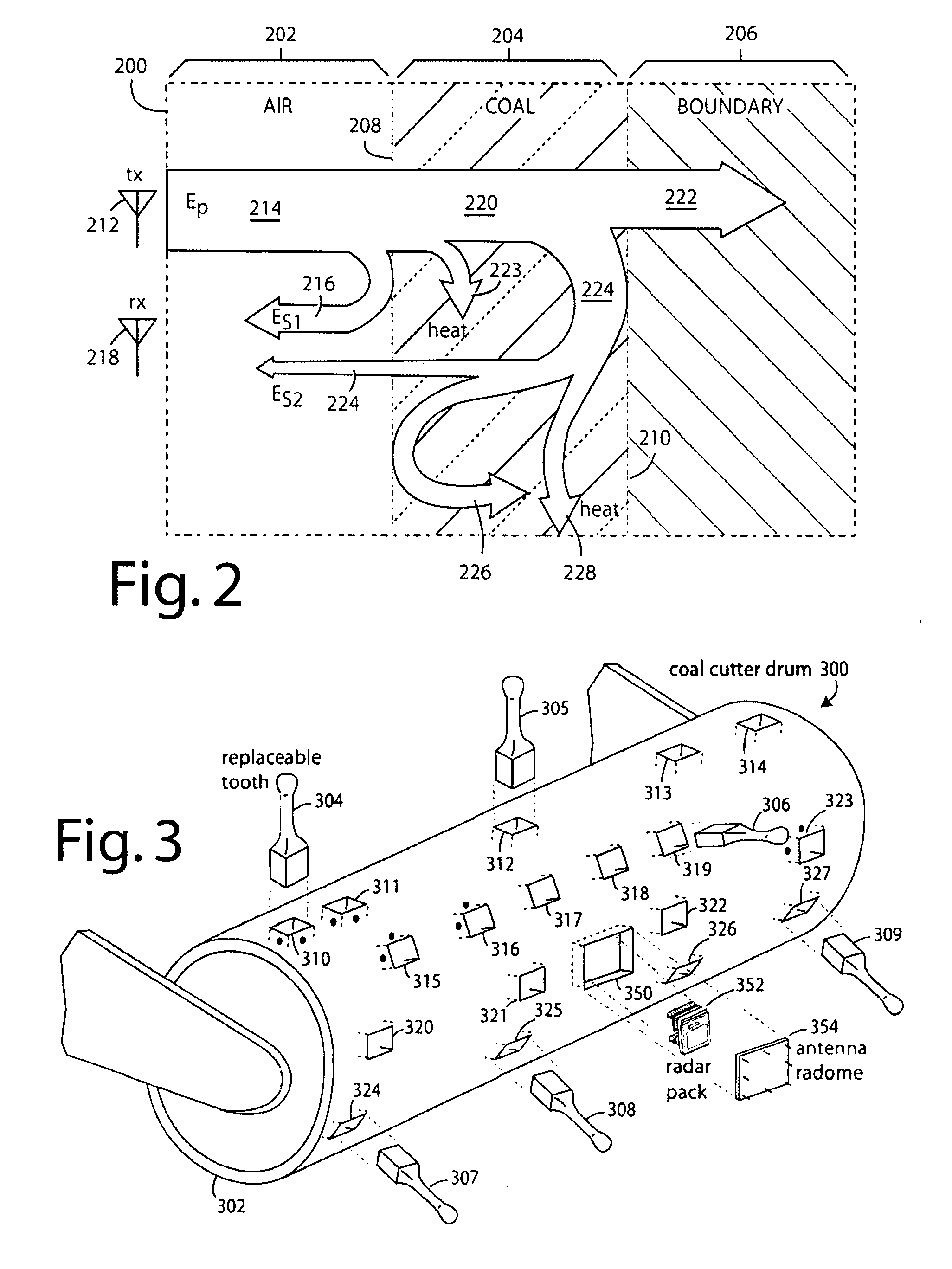
Double-sideband suppressed-carrier radar to null near-field reflections from a first interface between media layers
InactiveUS20080218400A1Increase reflectionSlitting machinesDetection using electromagnetic wavesMicrostrip patch antennaAntenna design
A ground-penetrating radar comprises a software-definable transmitter for launching pairs of widely separated and coherent continuous waves. Each pair is separated by a constant or variable different amount double-sideband suppressed carrier modulation such as 10 MHz, 20 MHz, and 30 MHz Processing suppresses the larger first interface reflection and emphasizes the smaller second, third, etc. reflections. Processing determines the electrical parameter of the natural medium adjacent to the antenna.The modulation process may be the variable or constant frequency difference between pairs of frequencies. If a variable frequency is used in modulation, pairs of tunable resonant microstrip patch antennas (resonant microstrip patch antenna) can be used in the antenna design. If a constant frequency difference is used in the software-defined transceiver, a wide-bandwidth antenna design is used featuring a swept or stepped-frequency continuous-wave (SFCW) radar design.The received modulation signal has a phase range that starts at 0-degrees at the transmitter antenna, which is near the first interface surface. After coherent demodulation, the first reflection is suppressed. The pair of antennas may increase suppression. Then the modulation signal phase is changed by 90-degrees and the first interface signal is measured to determine the in situ electrical parameters of the natural medium.Deep reflections at 90-degrees and 270-degrees create maximum reflection and will be illuminated with modulation signal peaks. Quadrature detection, mixing, and down-conversion result in 0-degree and 180-degree reflections effectively dropping out in demodulation.
Owner:STOLAR
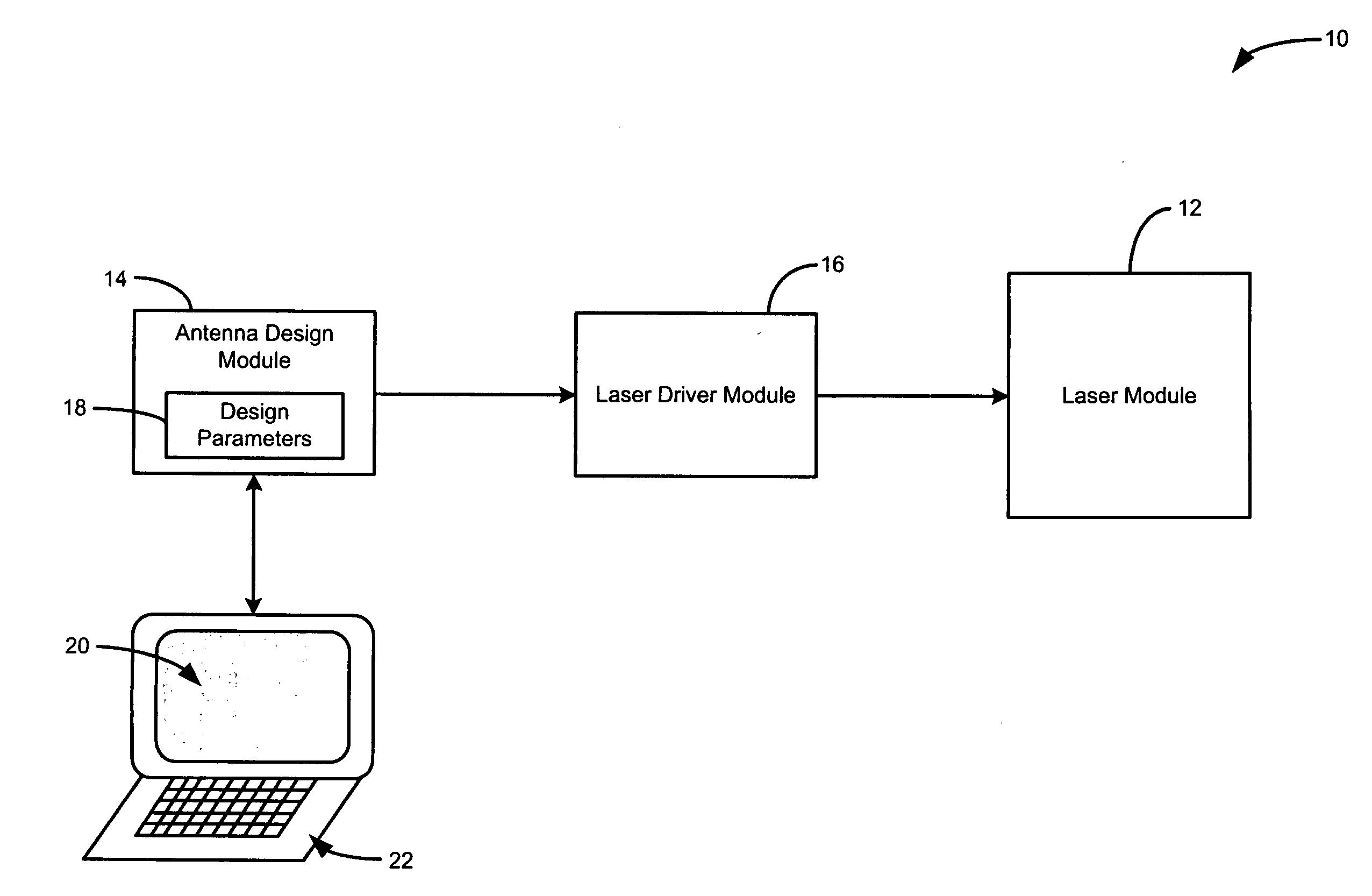
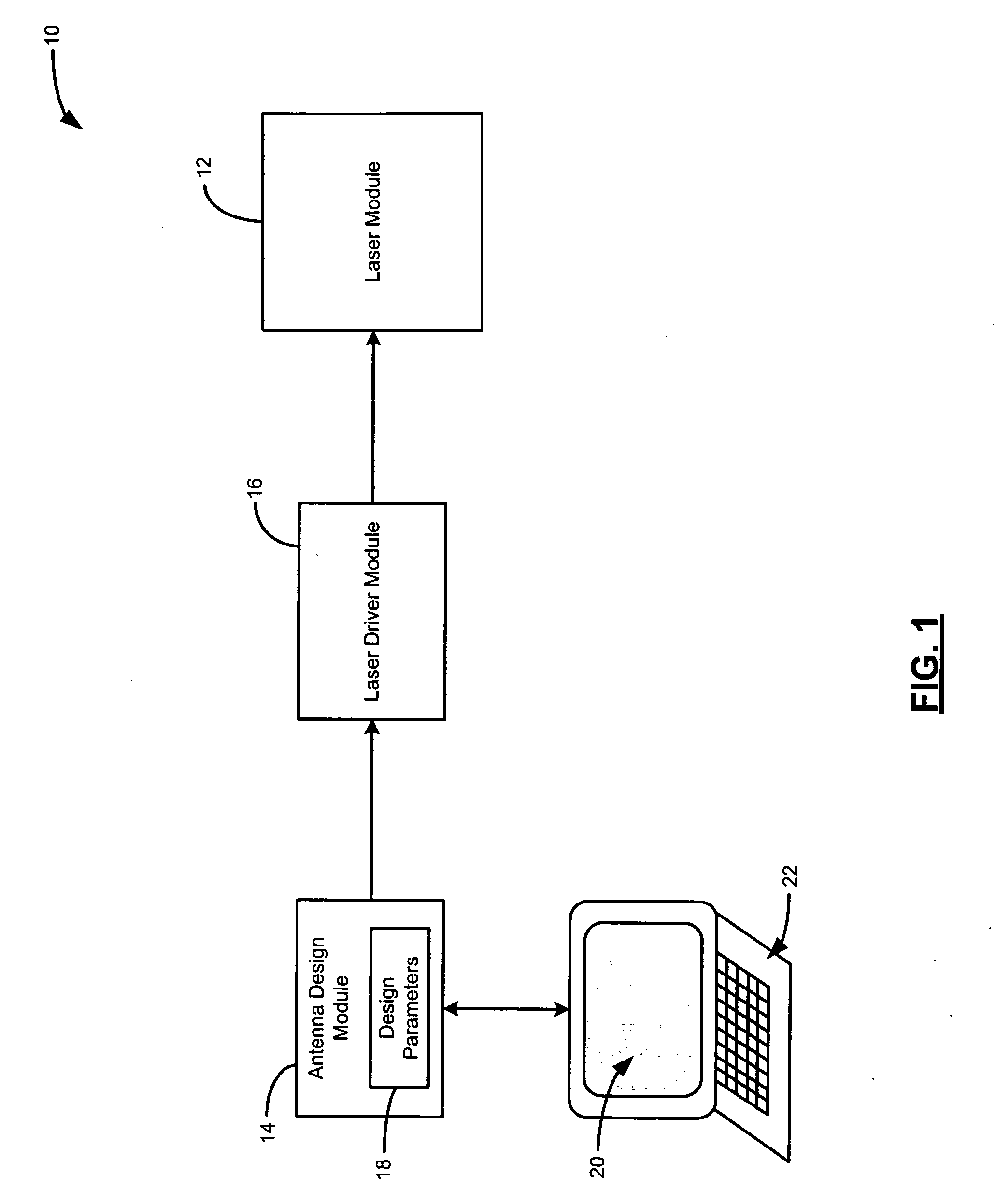
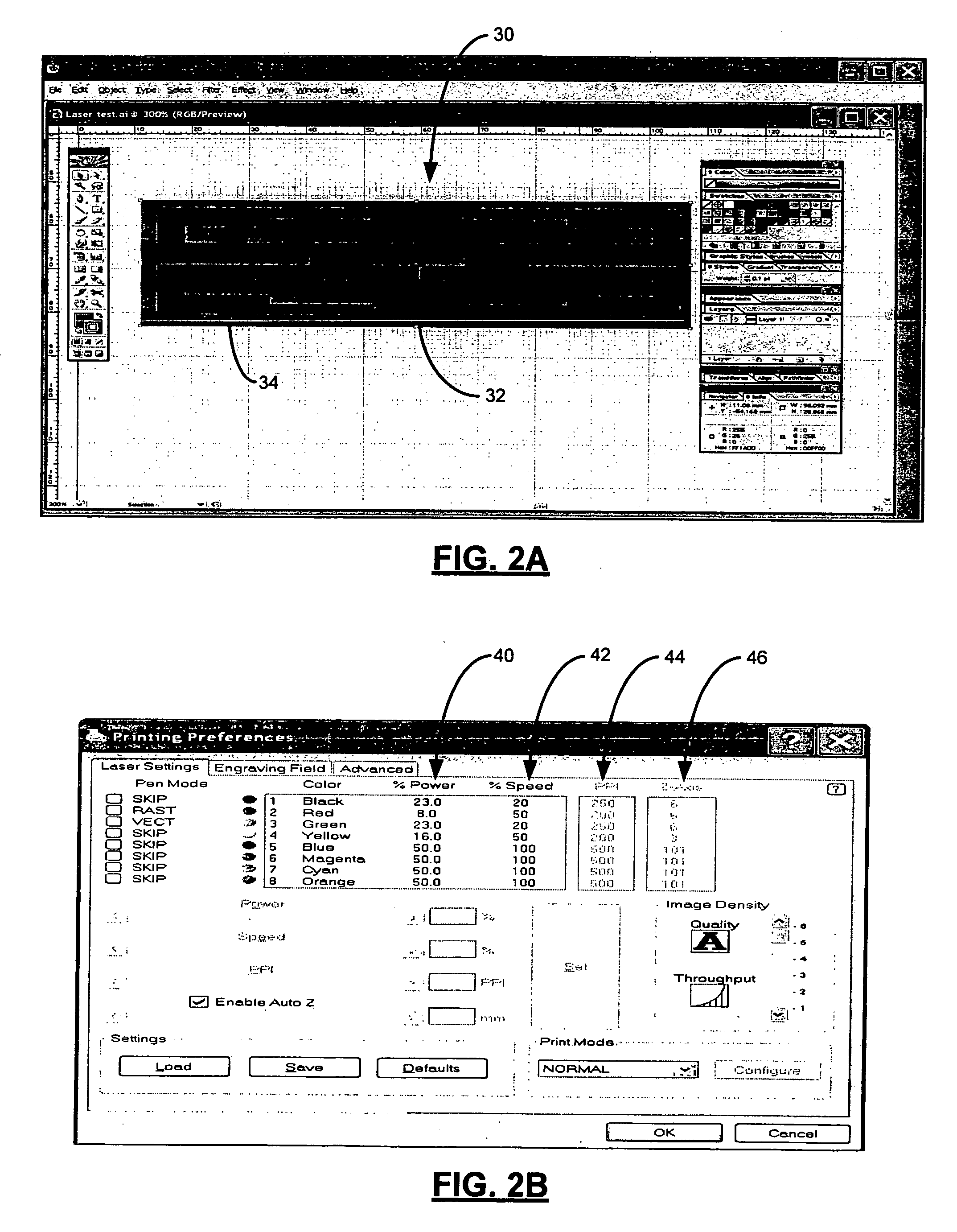
Laser ablation prototyping of RFID antennas
InactiveUS20070130754A1Less powerRecord carriers used with machinesBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalAntenna designEngineering
A laser ablation radio frequency identification (RFID) antenna prototyping system includes an antenna design module, an ablation laser, and a laser driver. The antenna design module includes design parameters for an RFID antenna prototype. The laser driver communicates with the antenna design module and the ablation laser. The laser driver uses the design parameters to direct the ablation laser to heat a portion of a conductive ink layer that is formed on a substrate.
Owner:ZIH CORP
Mobile phone terminal antenna
InactiveCN103390796ASolve unibody designAesthetically pleasingAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsMulti bandAntenna design
The invention provides a mobile phone terminal antenna. The antenna comprises a metal casing, as well as a main antenna and an auxiliary antenna which are connected with the metal casing through insulating medium, wherein the main antenna is used for receiving and emitting wireless signals; the auxiliary antenna, as a diversity antenna, is used for emitting and receiving signals of GPS / WIFI frequency band; the main antenna is arranged at the lower end of the metal casing and comprises a main antenna radiation body, a first feeding part, an inductor and a second circuit part, the first feeding part and the inductor are positioned at an upper end surface of the connecting part of the main antenna radiation body and the metal casing, and the second circuit part is positioned at a lower end surface of the connecting part of the main antenna radiation body and the metal casing; a switch is arranged in the second circuit part and controls the second circuit part to be grounded or not so as to realize different working frequencies. According to the antenna, the metal casing and the antenna part are integrally formed through injection moulding and other processes. Besides, the switch and the inductor are also arranged, the working states of two frequency bands are realized to meet multi-band communication; the antenna design can be conveniently adjusted.
Owner:SHANGHAI AMPHENOL AIRWAVE COMM ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Chip Antenna
InactiveUS20070240297A1Low freedomLong costAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsAntenna designPolymer
A chip antenna has an antenna body and a package. The antenna body has multiple meandered metal lines and is encapsulated with the package. The material of the package is a dielectric composite formed with polymers and ceramic powders, which has a dielectric constant designed for the antenna. The characteristics of the chip antenna are determined by the structures of the antenna body and the dielectric constant of the package. Thus, a requirement for tiny structures in antenna applications can be satisfied.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Wireless LAN architecture for integrated time-critical and non-time-critical services within medical facilities
InactiveUS20040109429A1Avoiding lockstep interferenceEasy to receiveSurgeryData switching by path configurationAntenna designDevice type
A wireless local area network (WLAN) system comprises multiple access points that are distributed throughout a medical facility to provide wireless access to a hardwired network. The access points implement multiple WLAN protocols, including a realtime protocol for realtime patient monitoring (telemetry) and a standard WLAN protocol (such as IEEE 802.11 within an ISM band) for providing general-purpose wireless access. Some or all of the access points preferably implement both WLAN protocols such that the different WLANs and wireless device types share network access resources. Some or all of the access points may also include RF location-tracking modules which may be used to track locations of patients, hospital personnel, capital equipment, and / or disposable medical supplies. Also disclosed are an antenna design which may be used with the access points to improve-reception (particularly for patient monitoring), and a TDMA timeslot rotation method for avoiding lockstep interference between access points that operate on the same channel.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST INFORMATION TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com